Patents
Literature
1345results about How to "Lower threshold voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
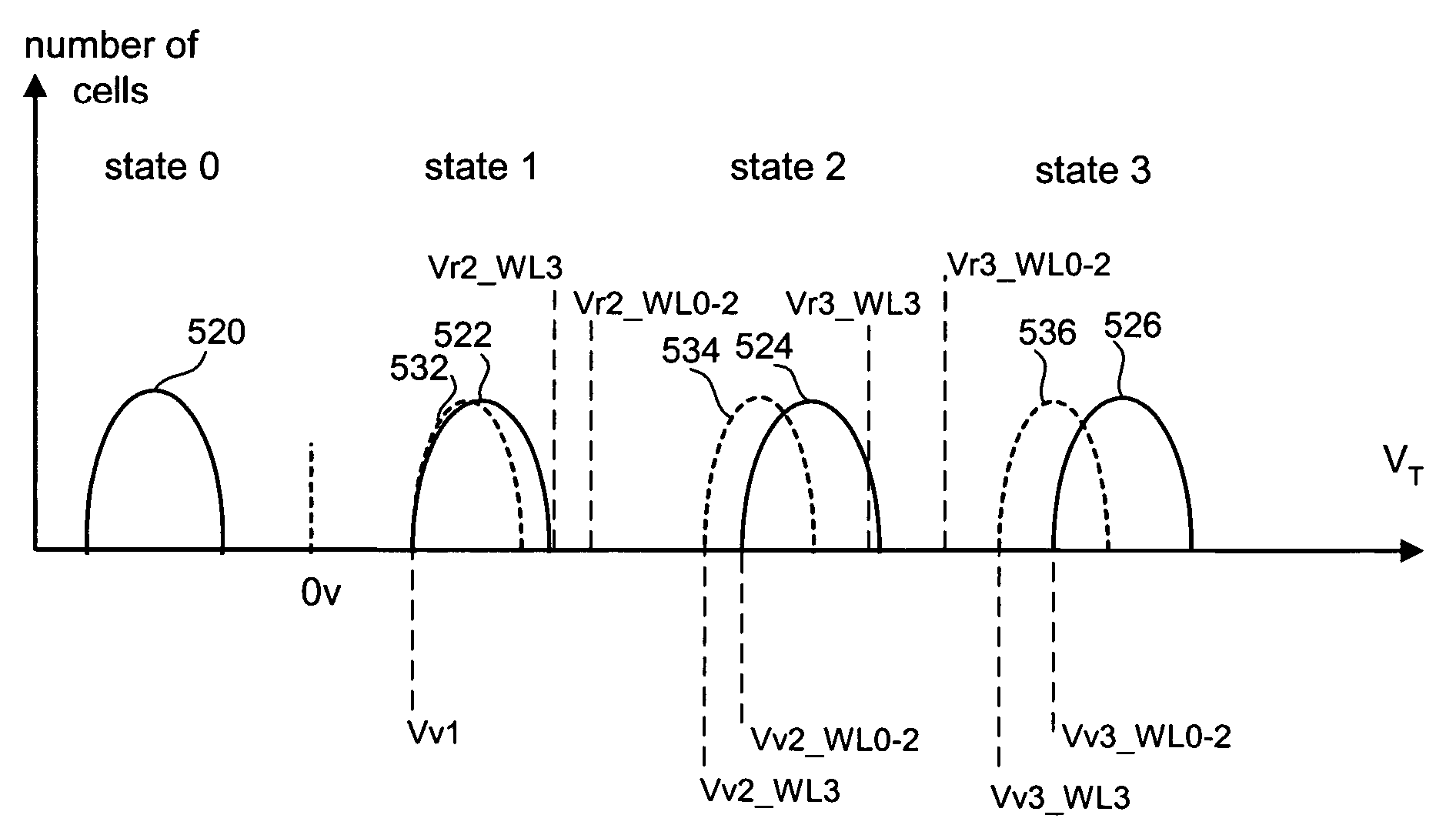
Variable programming of non-volatile memory
ActiveUS7020017B2Improve data retentionDecreased program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storageReading levelNon-volatile memory
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments can provide for reduced program disturb in non-volatile semiconductor memory. In one embodiment, select memory cells such as those connected to a last word line of a NAND string are programmed using one or more program verify levels or voltages that are different than a corresponding level used to program other cells or word lines. One exemplary embodiment includes using a lower threshold voltage verify level for select physical states when programming the last word line to be programmed for a string during a program operation. Another embodiment includes applying a lower program voltage to program memory cells of the last word line to select physical states. Additional read levels are established for reading the states programmed using lower verify levels in some exemplary implementations. A second program voltage step size that is larger than a nominal step size is used in one embodiment when programming select memory cells or word lines, such as the last word line to be programmed for a NAND string.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
CMOS devices with a single work function gate electrode and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20070090416A1Lower threshold voltageEasy to manufactureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSDevice form
Described herein are a device utilizing a gate electrode material with a single work function for both the pMOS and nMOS transistors where the magnitude of the transistor threshold voltages is modified by semiconductor band engineering and article made thereby. Further described herein are methods of fabricating a device formed of complementary (pMOS and nMOS) transistors having semiconductor channel regions which have been band gap engineered to achieve a low threshold voltage.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
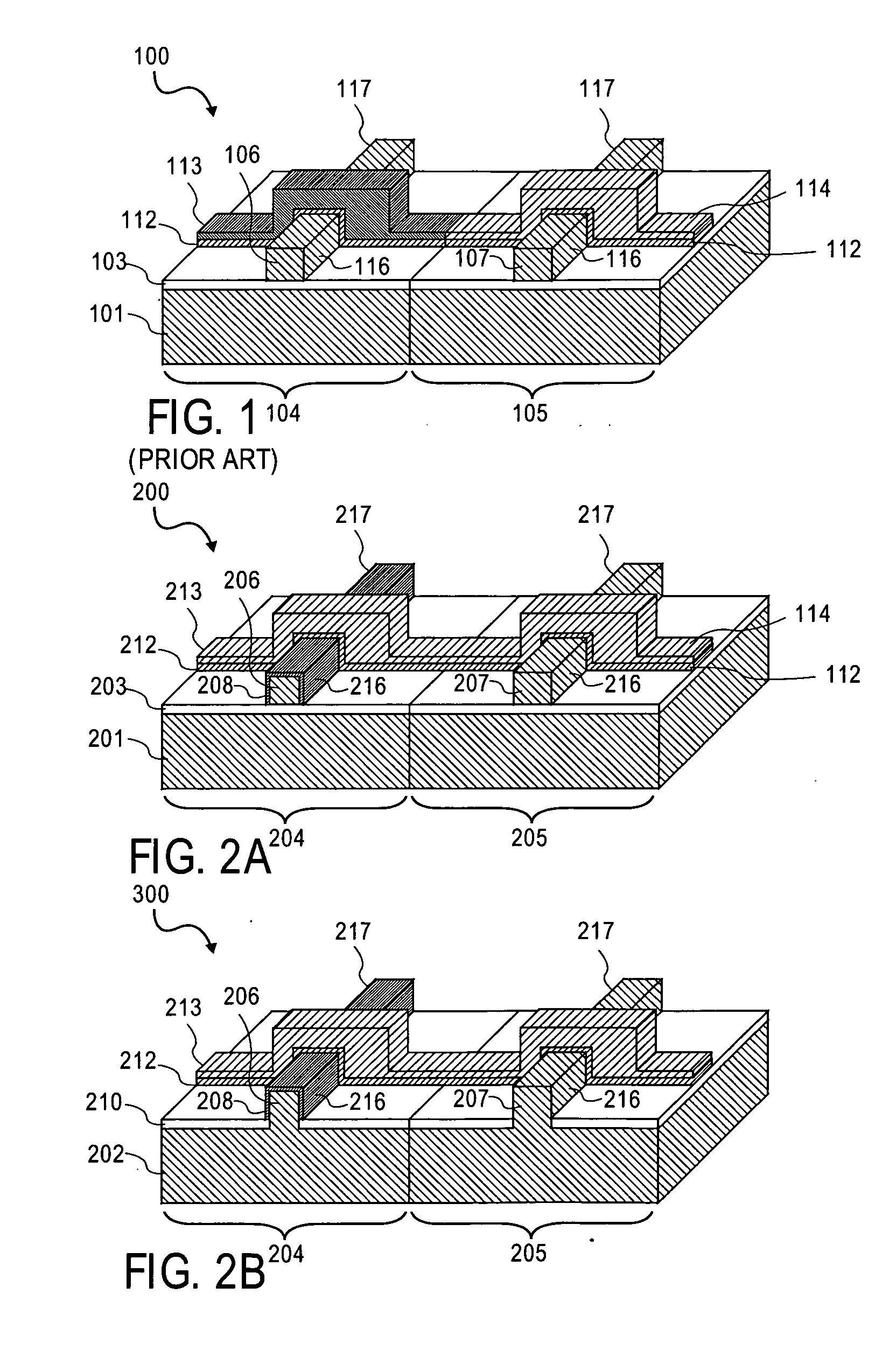
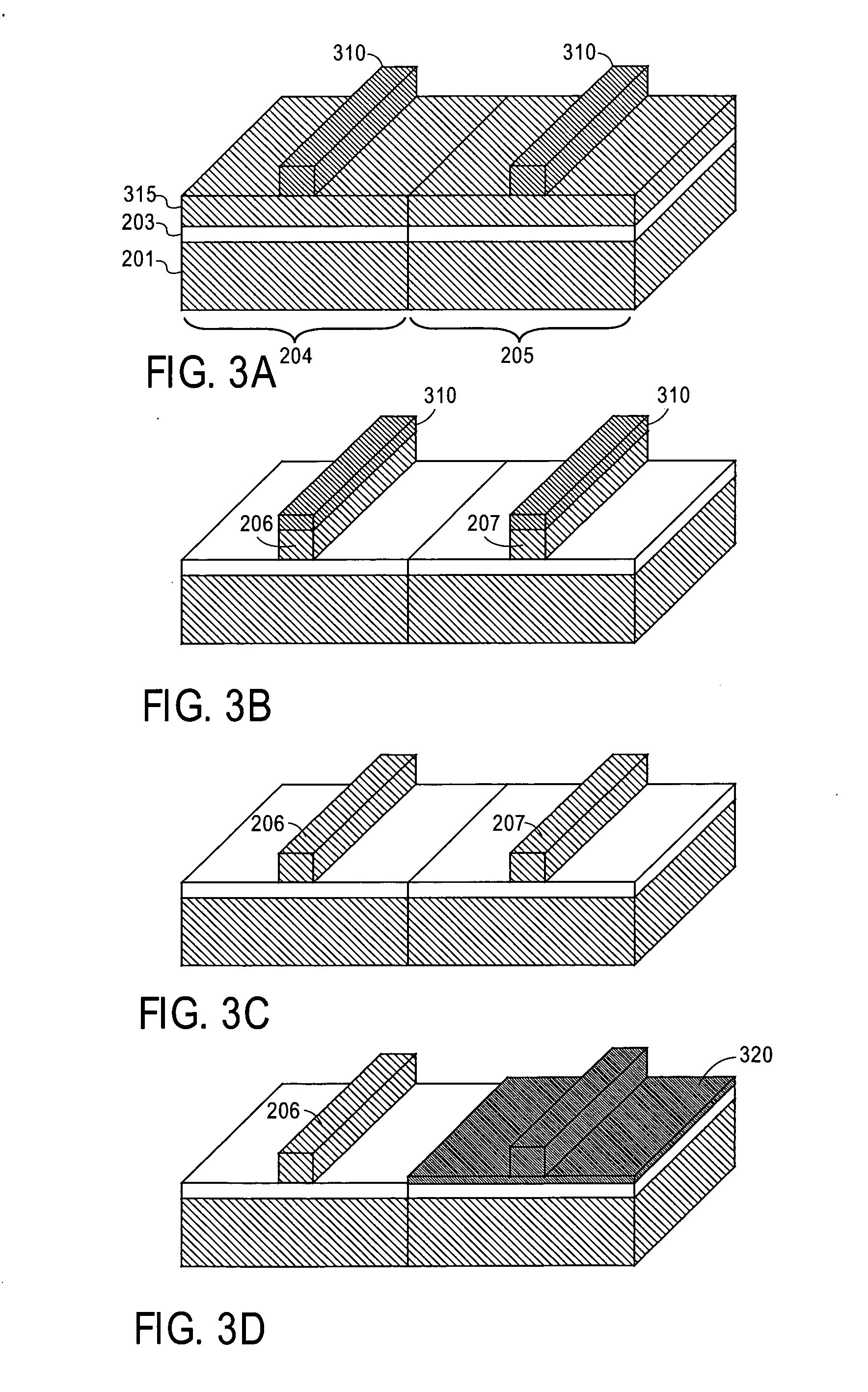
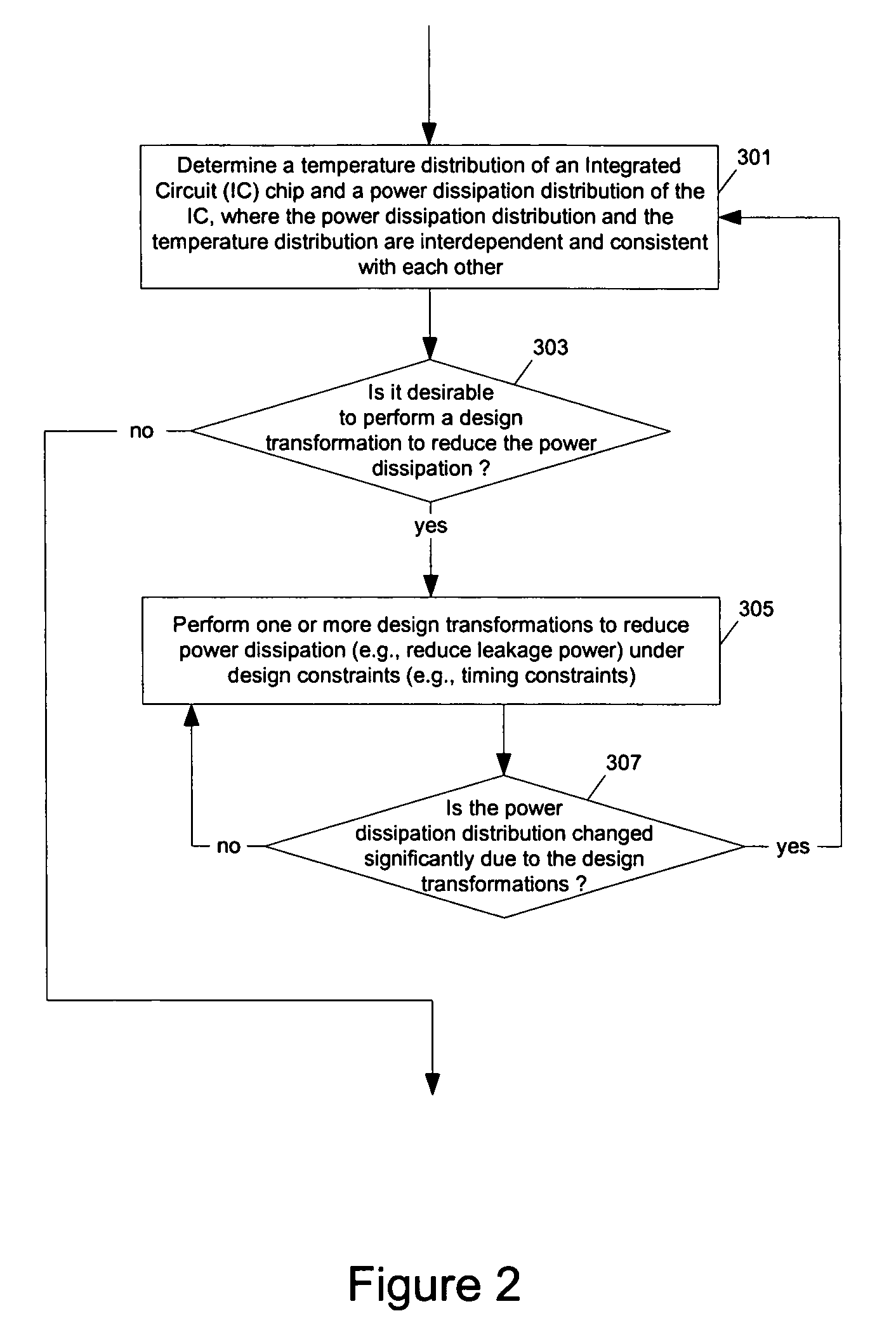
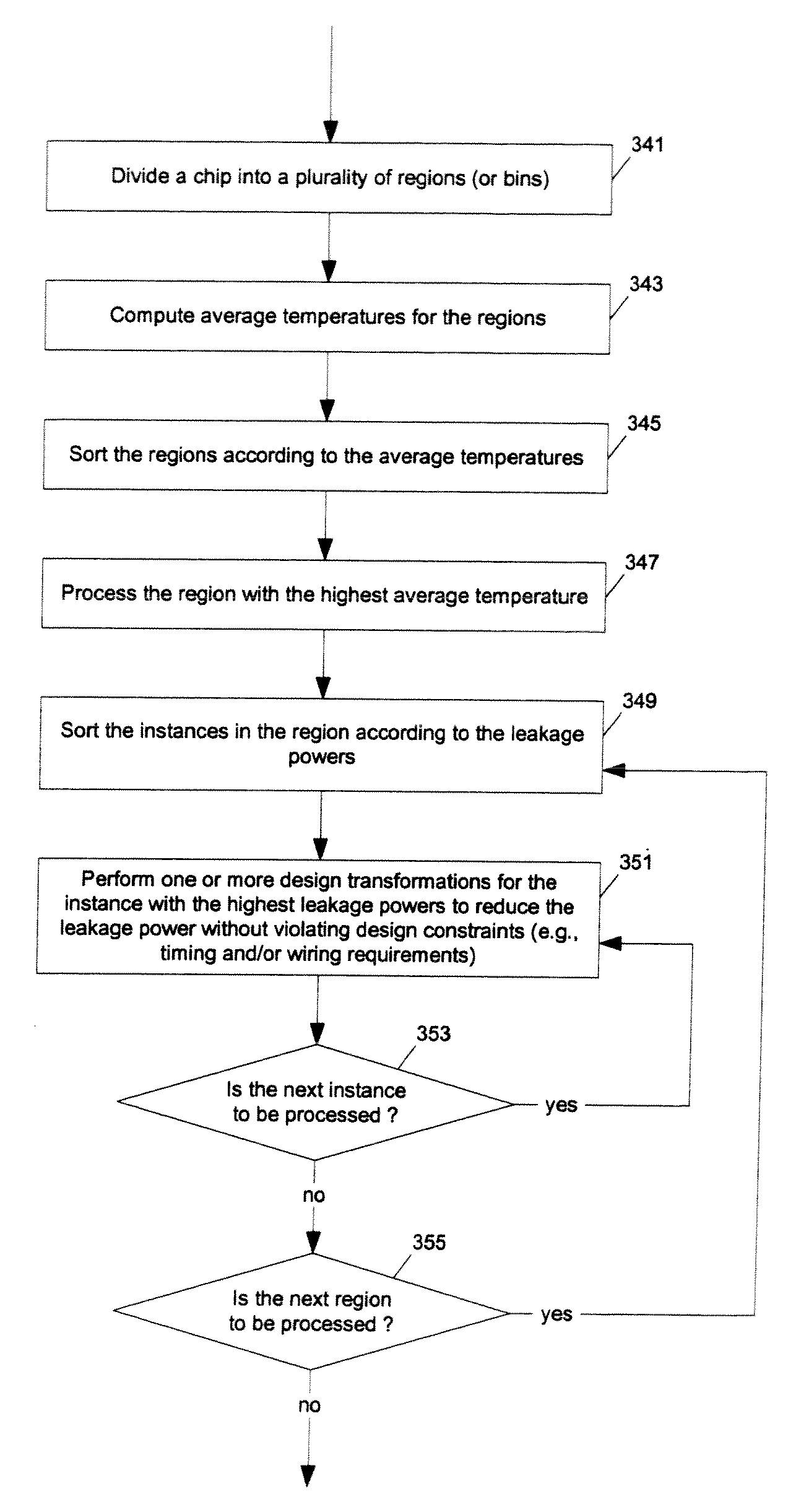
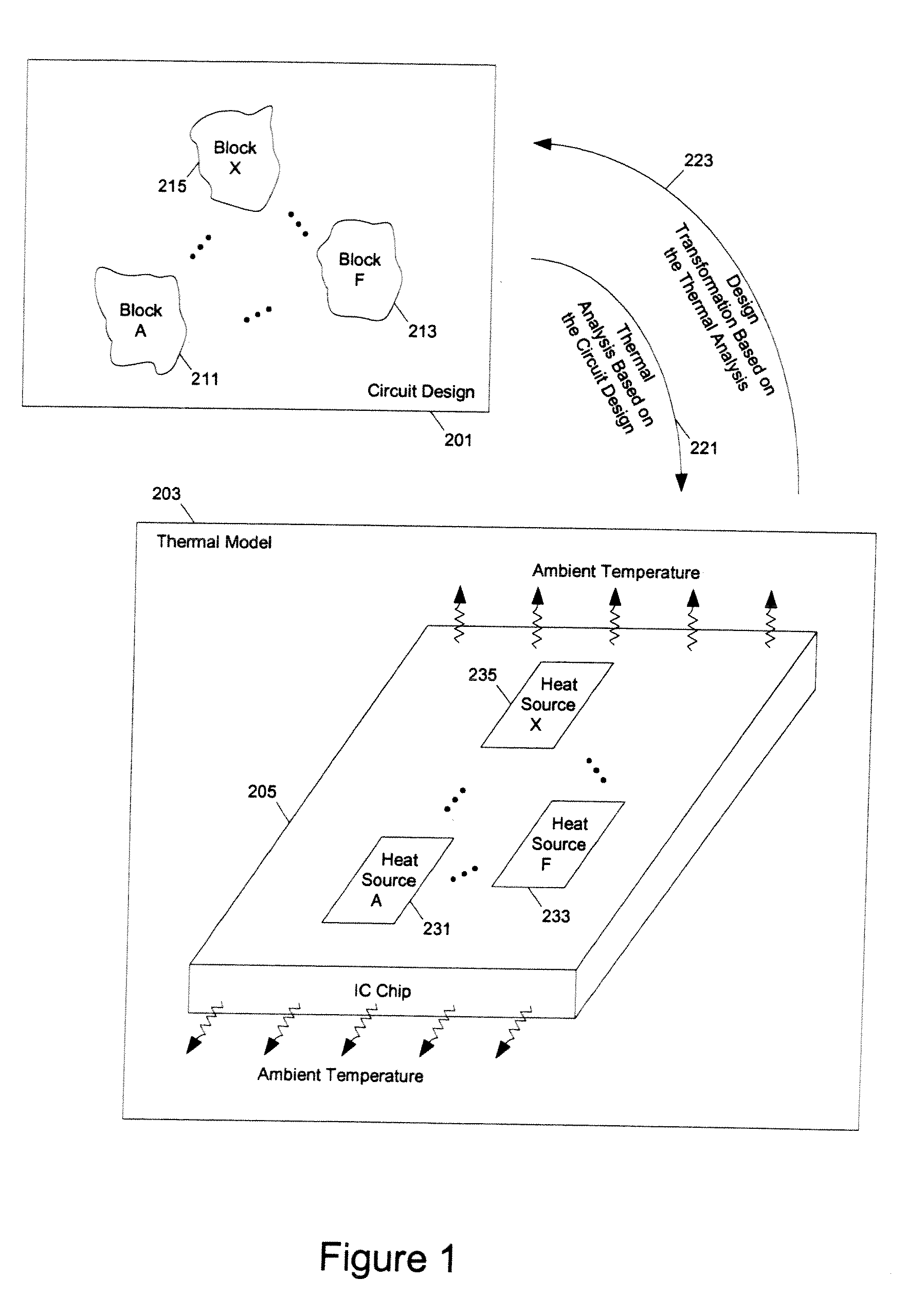
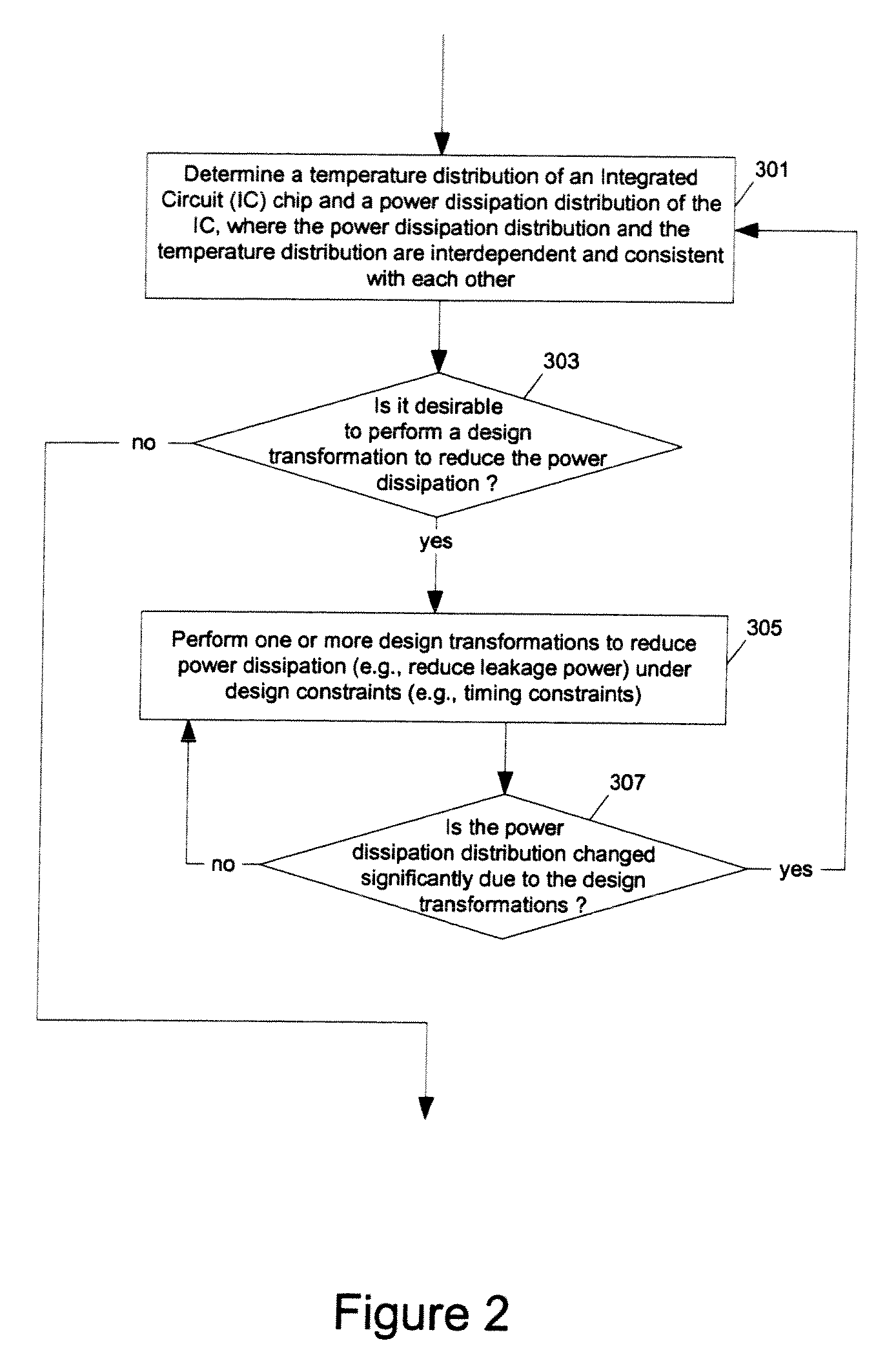
Methods and apparatuses for thermal analysis based circuit design
ActiveUS7366997B1Reduce power consumptionExtension of timeSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsPower usageTransition time
Methods and apparatuses for circuit design to reduce power usage, such as reducing temperature dependent power usage, and / or to improve timing, such as reducing temperature dependent delay or transition time. At least one embodiment of the present invention reduces the power dissipation and improves the timing of an integrated circuit to optimize the design. A thermal analysis is used to determine the temperature dependent power dissipation of a circuit and the temperature distribution of the circuit resulting from dissipating the heat created by the temperature dependent power dissipation. Then, the components of the design are selectively transformed to reduce the power dissipation and to improve timing based on the temperature solution. The transformation may include placement changes and netlist changes, such as the change of transistor threshold voltages for cells or for blocks of the circuit chip.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Erase and Program Method of Flash Memory Device for Increasing Program Speed of Flash Memory Device
ActiveUS20070058446A1Fail occurrence ratioImproved Threshold Voltage DistributionRead-only memoriesDigital storageVoltage rangeThreshold voltage
The present invention relates to erase and program methods of a flash memory device including MLCs for increasing the program speed. In the erase method according to the present invention, MLCs are pre-programmed so that a voltage range in which threshold voltages of MLCs are distributed can be reduced. Therefore, a fail occurrence ratio can be reduced when erasing MLCs, the threshold voltage distribution of MLCs can be improved and an overall program time can be shortened in a subsequent program operation.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
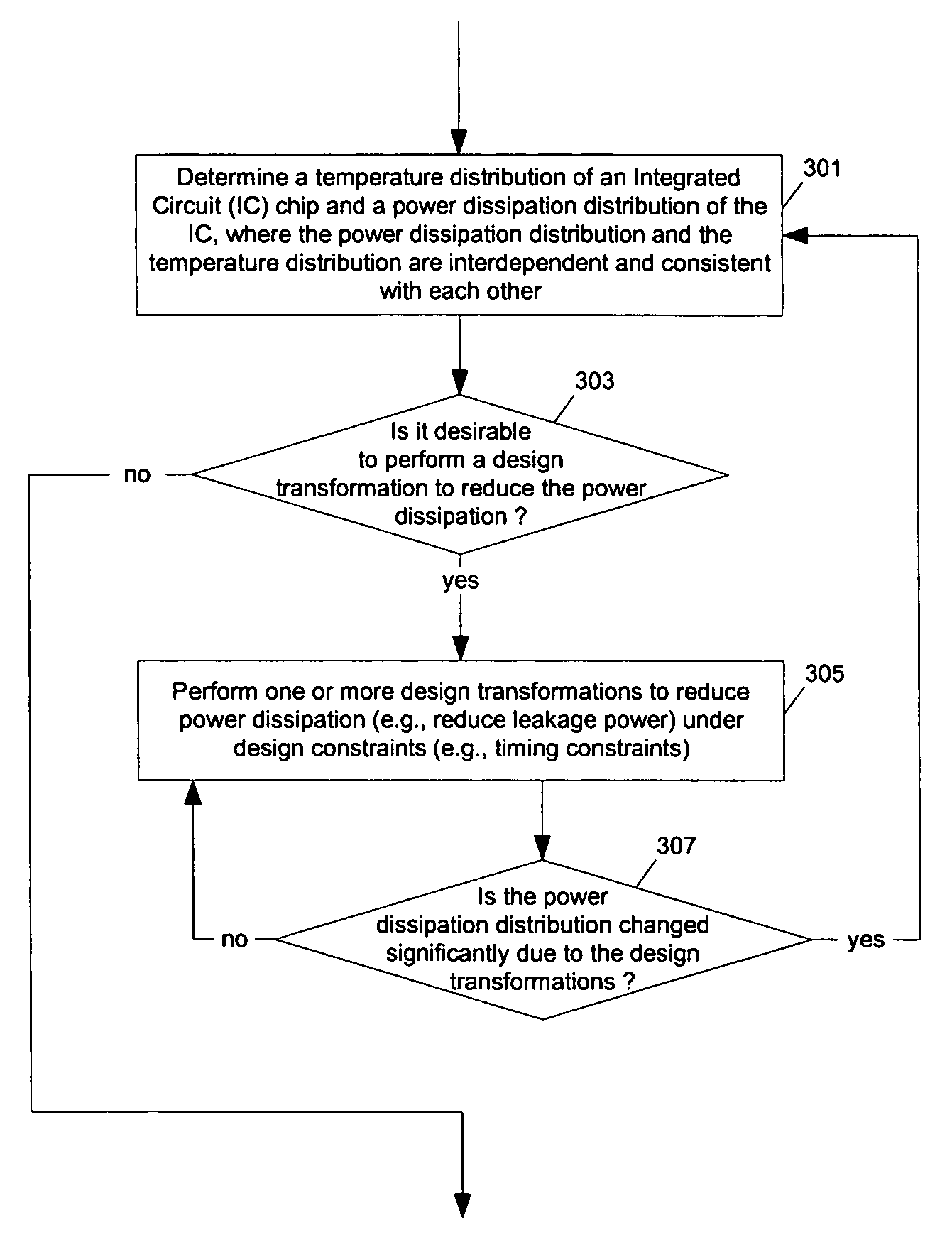
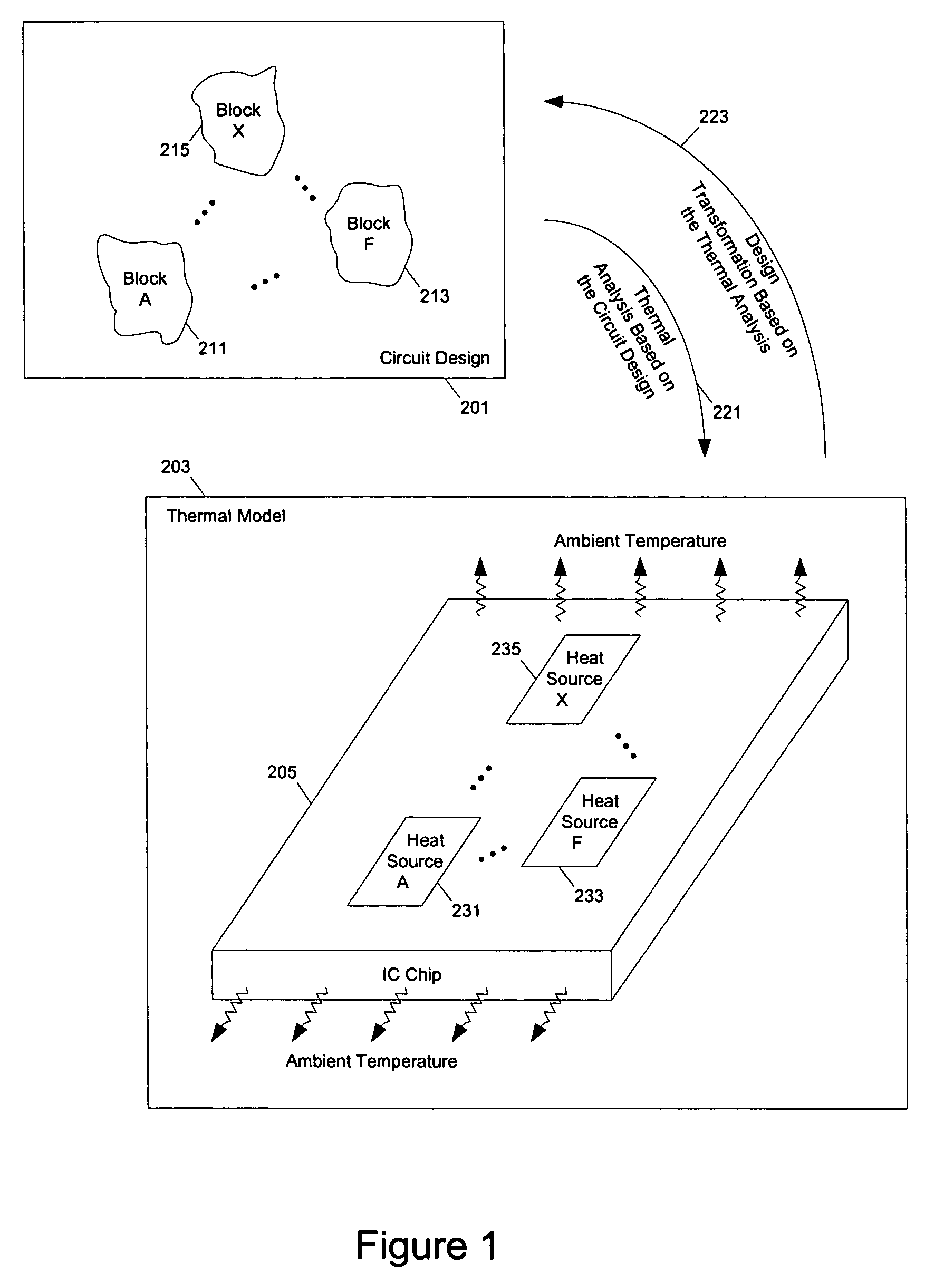
Methods and apparatuses for thermal analysis based circuit design
ActiveUS20080168406A1Reduce power consumptionExtension of timeSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringPower usage
Methods and apparatuses for circuit design to reduce power usage, such as reducing temperature dependent power usage, and / or to improve timing, such as reducing temperature dependent delay or transition time. At least one embodiment of the present invention reduces the power dissipation and improves the timing of an integrated circuit to optimize the design. A thermal analysis is used to determine the temperature dependent power dissipation of a circuit and the temperature distribution of the circuit resulting from dissipating the heat created by the temperature dependent power dissipation. Then, the components of the design are selectively transformed to reduce the power dissipation and to improve timing based on the temperature solution. The transformation may include placement changes and netlist changes, such as the change of transistor threshold voltages for cells or for blocks of the circuit chip.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Mosfet and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20130099315A1Adjustment of threshold voltageRaise the threshold voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETWafering
The present disclosure discloses a MOSFET and a method for manufacturing the same, wherein the MOSFET comprises: an SOI wafer which comprises a semiconductor substrate, a buried insulating layer, and a semiconductor layer, the buried insulating layer being on the semiconductor substrate, and the semiconductor layer being on the buried insulating layer; a gate stack on the semiconductor layer; a source region and a drain region, which are in the semiconductor layer and on opposite sides of the gate stack; and a channel region, which is in the semiconductor layer and sandwiched by the source region and the drain region, wherein the MOSFET further comprises a back gate, the back gate being located in the semiconductor substrate and having a first doped region in a lower portion of the back gate and a second doped region in an upper portion of the back gate. The MOSFET can adjust the threshold voltage by changing the doping type and doping concentration of the anti-doped region.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Increasing doping of well compensating dopant region
InactiveUS20060154428A1More compensation dopingIncreasing gate-lengthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDopantEngineering
Methods and resulting structure of implementing a compensating implant that creates more compensation doping as the gate length is increased are disclosed. In particular, the invention performs an angled compensation implant through a gate opening during the damascene process such that the compensating dopant concentration increases as the gate length increases. In this fashion, the threshold voltage of a longer device is reduced much more than the threshold voltage of a shorter device, thereby reducing the threshold voltage of the longer device to acceptable levels without affecting the threshold voltage of the shorter device. The invention is especially advantageous relative to super-steep retrograde wells.
Owner:IBM CORP
Thin-film field-effect transistor with organic semiconductor requiring low operating voltages
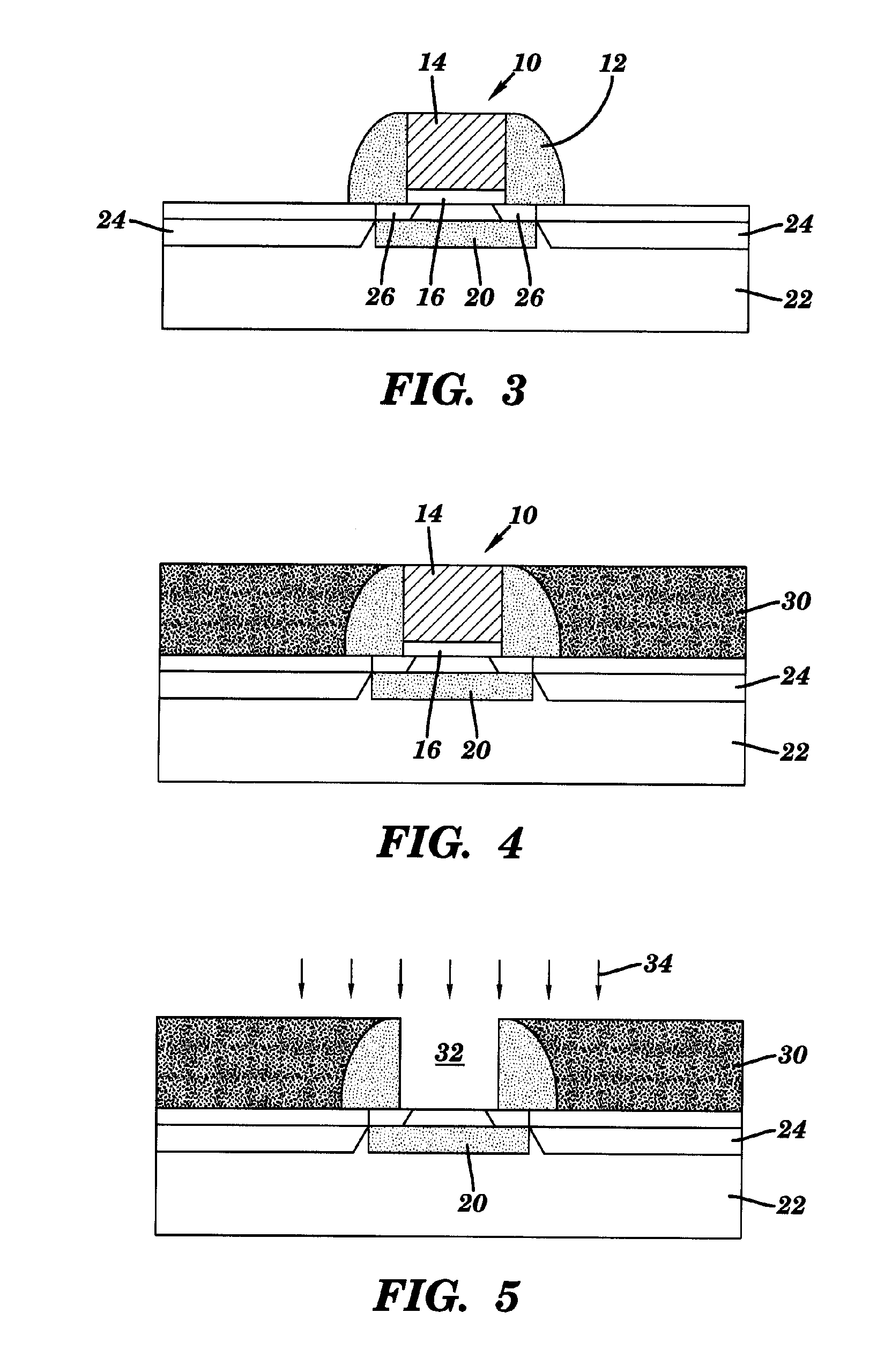
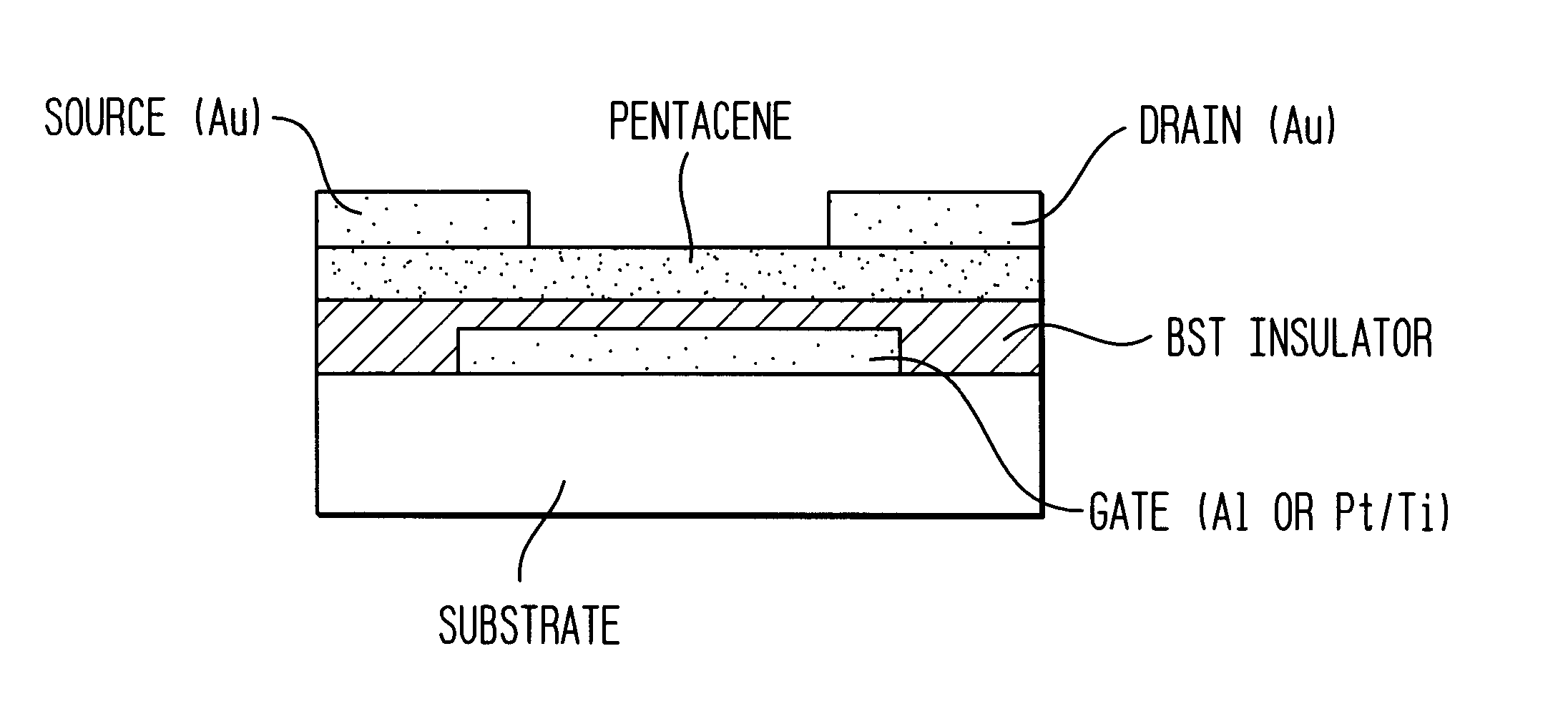
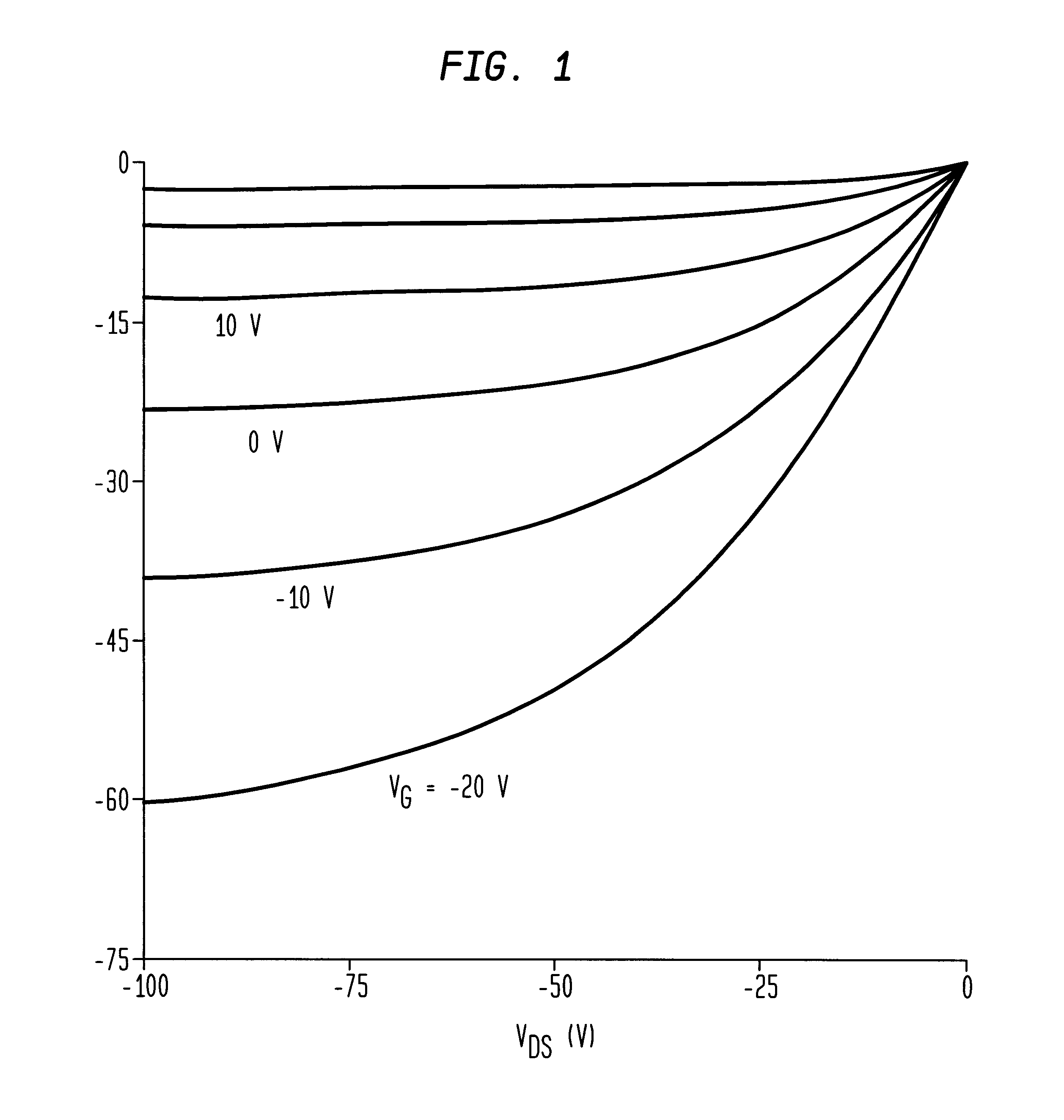
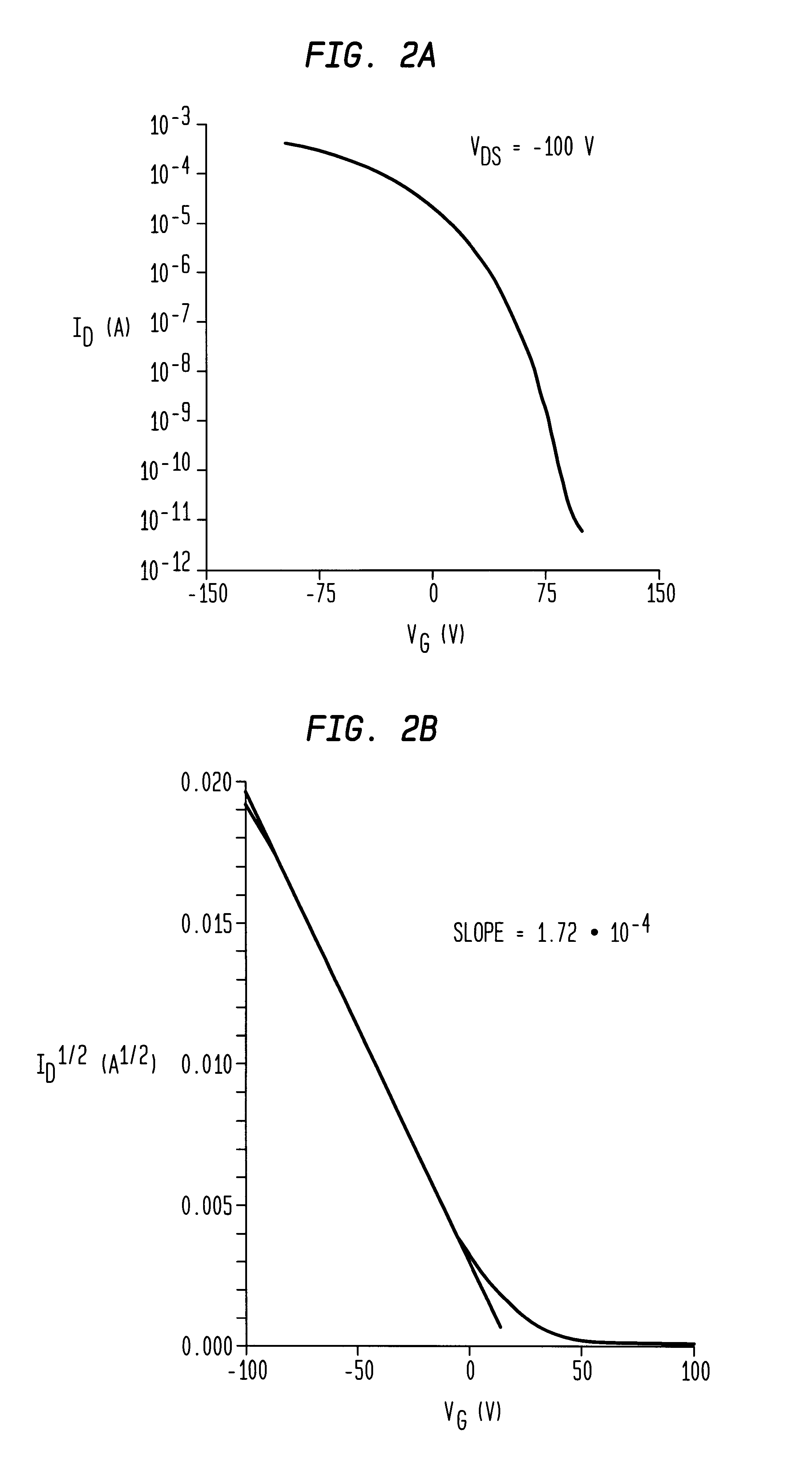
InactiveUS6344660B1Reduce thicknessImprove mobilityTransistorSolid-state devicesDisplay deviceFlat panel display
A thin film transistor (TFT) device structure based on an organic semiconductor material, that exhibits a high field effect mobility, high current modulation and a low sub-threshold slope at lower operating voltages than the current state of the art organic TFT devices. The structure comprises a suitable substrate disposed with he following sequence of features: a set of conducting gate electrodes covered with a high dielectric constant insulator, a layer of the organic semiconductor, sets of electrically conducting source and drain electrodes corresponding to each of the gate lines, and an optional passivation layer that can overcoat and protect the device structure. Use of high dielectric constant gate insulators exploits the unexpected gate voltage dependence of the organic semiconductor to achieve high field effect mobility levels at very low operating voltages. Judicious combinations of the choice of this insulator material and the means to integrate it into the TFT structure are taught that would enable easy fabrication on glass or plastic substrates and the use of such devices in flat panel display applications.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Vertical FET with nanowire channels and a silicided bottom contact
ActiveUS20060273389A1Reduce access series resistanceReduce overlap capacitanceNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceAND gate
A vertical FET structure with nanowire forming the FET channels is disclosed. The nanowires are formed over a conductive silicide layer. The nanowires are gated by a surrounding gate. Top and bottom insulator plugs function as gate spacers and reduce the gate-source and gate-drain capacitance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Vertical FET with nanowire channels and a silicided bottom contact
ActiveUS7230286B2Reduce resistanceGood short channel characteristicsTransistorNanoinformaticsCapacitanceNanowire
A vertical FET structure with nanowire forming the FET channels is disclosed. The nanowires are formed over a conductive silicide layer. The nanowires are gated by a surrounding gate. Top and bottom insulator plugs function as gate spacers and reduce the gate-source and gate-drain capacitance.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
Method of fabricating CMOS devices having a single work function gate electrode by band gap engineering and article made thereby
InactiveUS20070069302A1Lower threshold voltageEasy to manufactureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSWork function
A method utilizing a common gate electrode material with a single work function for both the pMOS and nMOS transistors where the magnitude of the transistor threshold voltages is modified by semiconductor band engineering and article made thereby.
Owner:INTEL CORP
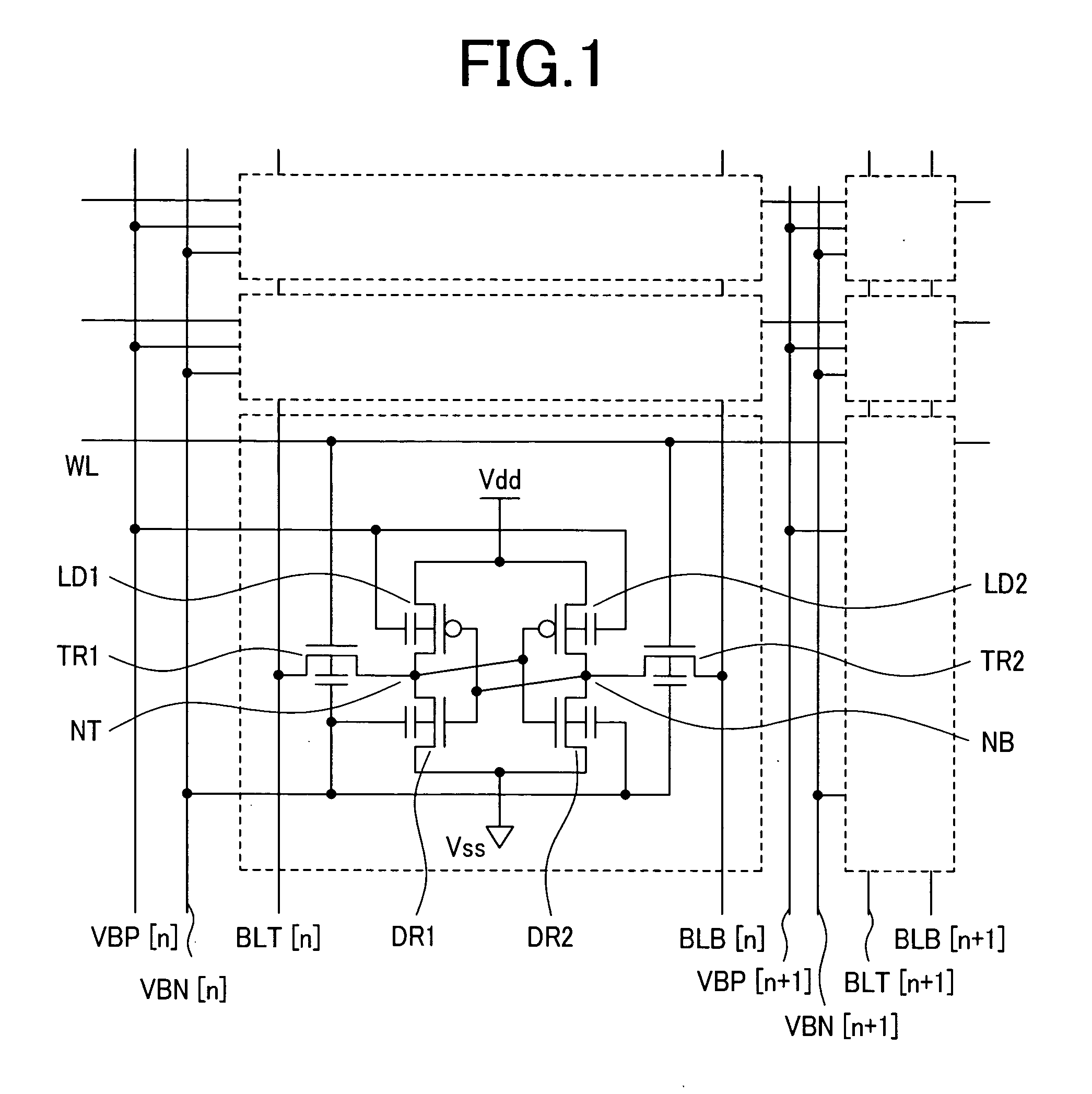
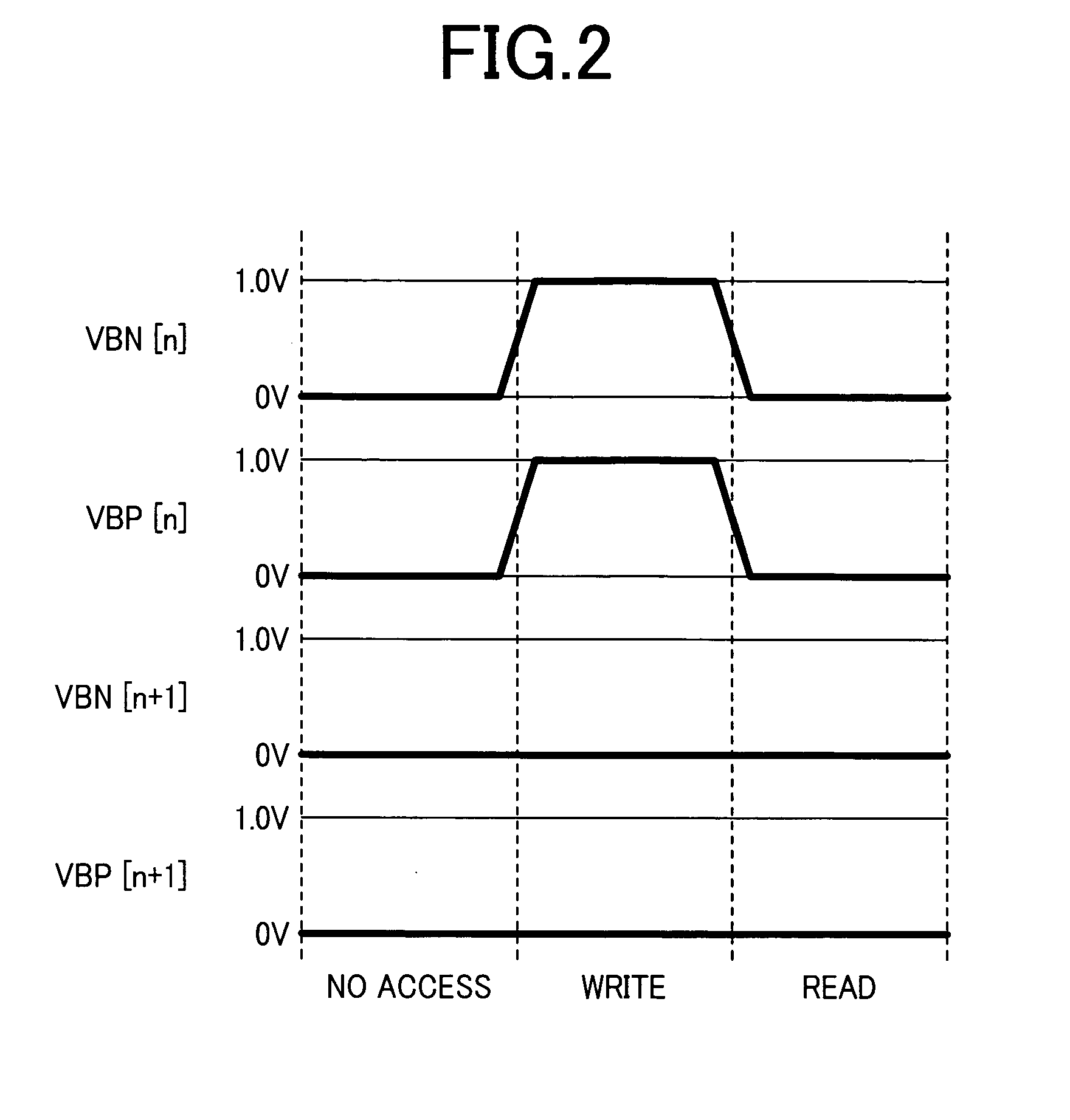
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory circuit utilizing a mis transistor as a memory cell
ActiveUS20090316477A1Lower threshold voltagePotential differenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHemt circuitsMemory circuits
A memory circuit includes a latch having a first node and a second node to store data such that a logic level of the first node is an inverse of a logic level of the second node, a MIS transistor having a gate node, a first source / drain node, and a second source / drain node, the first source / drain node coupled to the first node of the latch, and a control circuit configured to control the gate node and second source / drain node of the MIS transistor in a first operation such that a lingering change is created in transistor characteristics of the MIS transistor in response to the data stored in the latch, wherein the MIS transistor includes a highly-doped substrate layer, a lightly-doped substrate layer disposed on the highly-doped substrate layer, diffusion regions formed in the lightly-doped substrate layer, a gate electrode, sidewalls, and an insulating film.
Owner:NSCORE
Method for preparing graphene oxide films and fibers
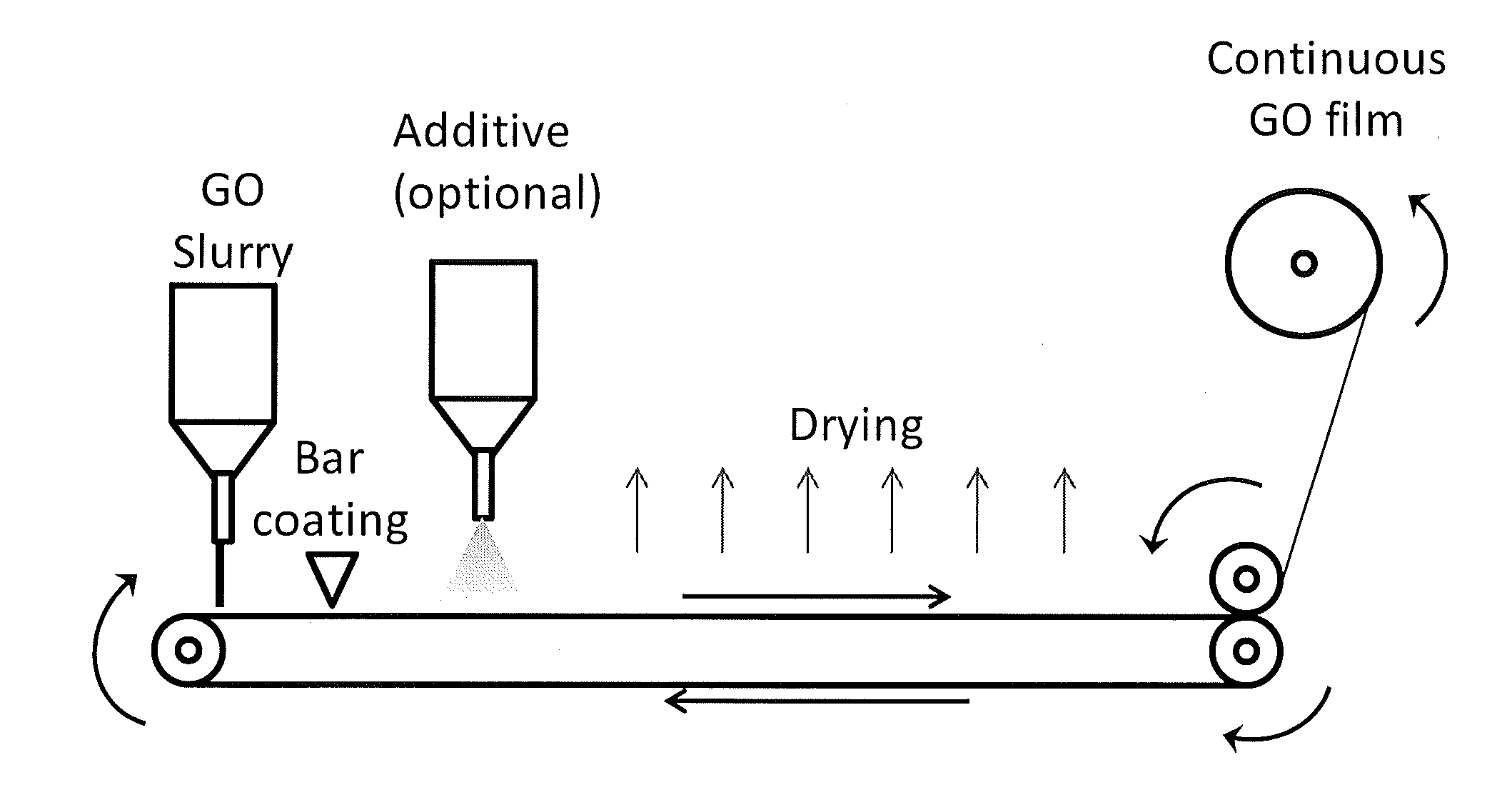
ActiveUS20150111449A1Improve conductivityHigh densityCarbon compoundsFilament/thread formingFiberSolid content
We report a method of preparation of highly elastic graphene oxide films, and their transformation into graphene oxide fibers and electrically conductive graphene fibers by spinning. Methods typically include: 1) oxidation of graphite to graphene oxide, 2) preparation of graphene oxide slurry with high solid contents and residues of sulfuric acid impurities. 3) preparation of large area films by bar-coating or dropcasting the graphene oxide dispersion and drying at low temperature. 4) spinning the graphene oxide film into a fiber, and 5) thermal or chemical reduction of the graphene oxide fiber into an electrically conductive graphene fiber. The resulting films and fiber have excellent mechanical properties, improved morphology as compared with current graphene oxide fibers, high electrical conductivity upon thermal reduction, and improved field emission properties.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND +1
Methods of hyperdoping semiconductor materials and hyperdoped semiconductor materials and devices
InactiveUS20030121468A1Avoiding and mitigating formationEasy to operateTransistorPolycrystalline material growthSide effectSemiconductor materials
Methods are disclosed for producing highly doped semiconductor materials. Using the invention, one can achieve doping densities that exceed traditional, established carrier saturation limits without deleterious side effects. Additionally, highly doped semiconductor materials are disclosed, as well as improved electronic and optoelectronic devices / components using said materials. The innovative materials and processes enabled by the invention yield significant performance improvements and / or cost reductions for a wide variety of semiconductor-based microelectronic and optoelectronic devices / systems. Materials are grown in an anion-rich environment, which, in the preferred embodiment, are produced by moderate substrate temperatures during growth in an oxygen-poor environment. The materials exhibit fewer non-radiative recombination centers at higher doping concentrations than prior art materials, and the highly doped state of matter can exhibit a minority carrier lifetime dominated by radiative recombination at higher doping levels and higher majority carrier concentrations than achieved in prior art materials. Important applications enabled by these novel materials include high performance electronic or optoelectronic devices, which can be smaller and faster, yet still capture or emit light efficiently, and high performance electronics, such as transistors, which can be smaller and faster, yet cooler.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Active matrix organic light emitting diode display panel circuit
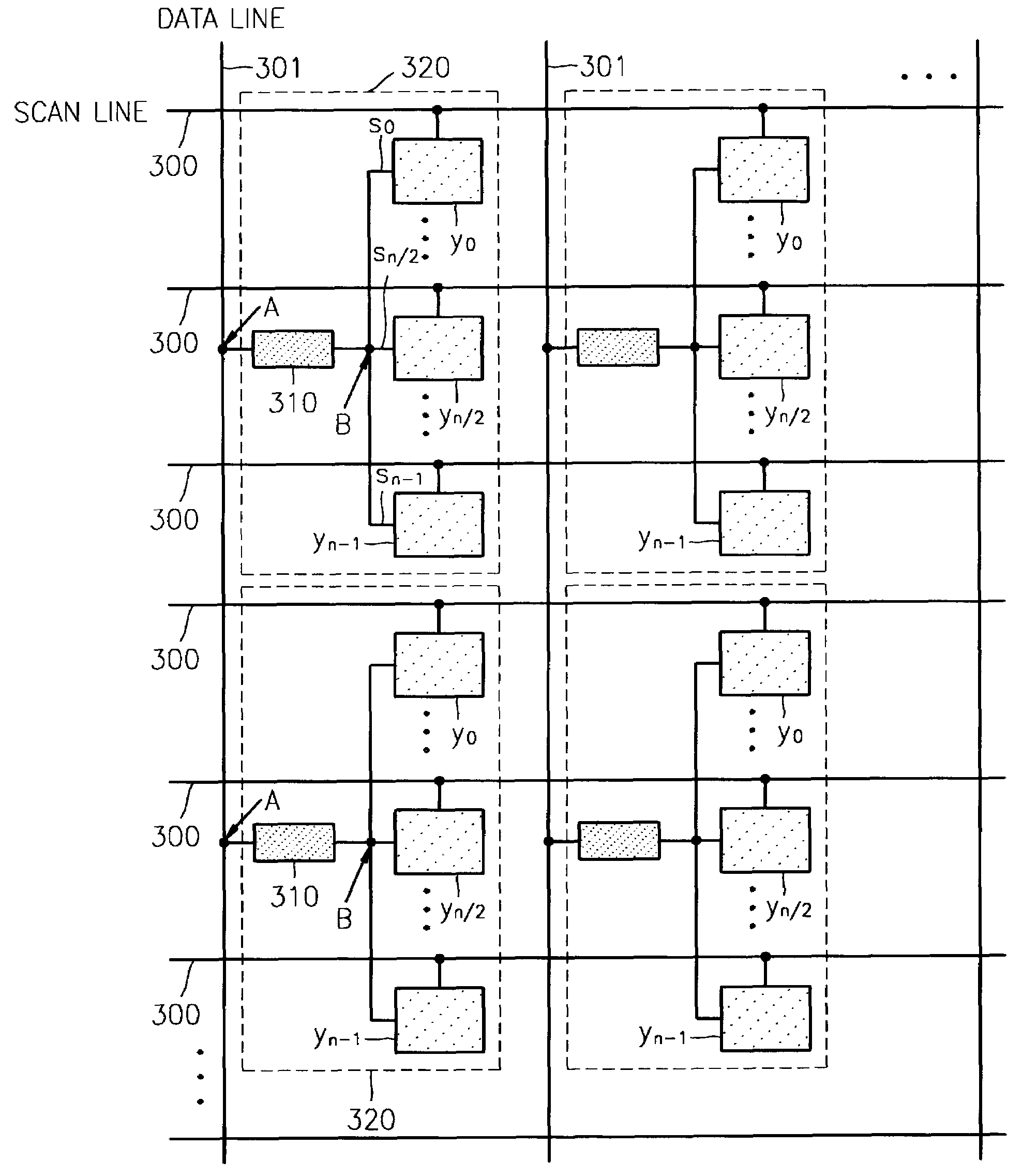
InactiveUS6970149B2Increase in sizeLower threshold voltageCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingActive matrixDisplay device
An active matrix organic light emitting diode display panel circuit capable of reducing current and brightness nonuniformities between pixels by including a threshold voltage compensation circuit block between a data line and the pixels is provided. The threshold voltage of a video signal loaded in a data line is compensated for while the video signal passes through the threshold voltage compensation circuit block and then provided to a driving transistor of the pixels. One threshold voltage compensation circuit block is connected commonly to a plurality of pixels, rather than be connected to every pixel, so that threshold voltage compensation can be achieved for high-quality, large-sized displays, without increasing the number of transistors for the pixels.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Semiconductor device and semiconductor device manufacturing method
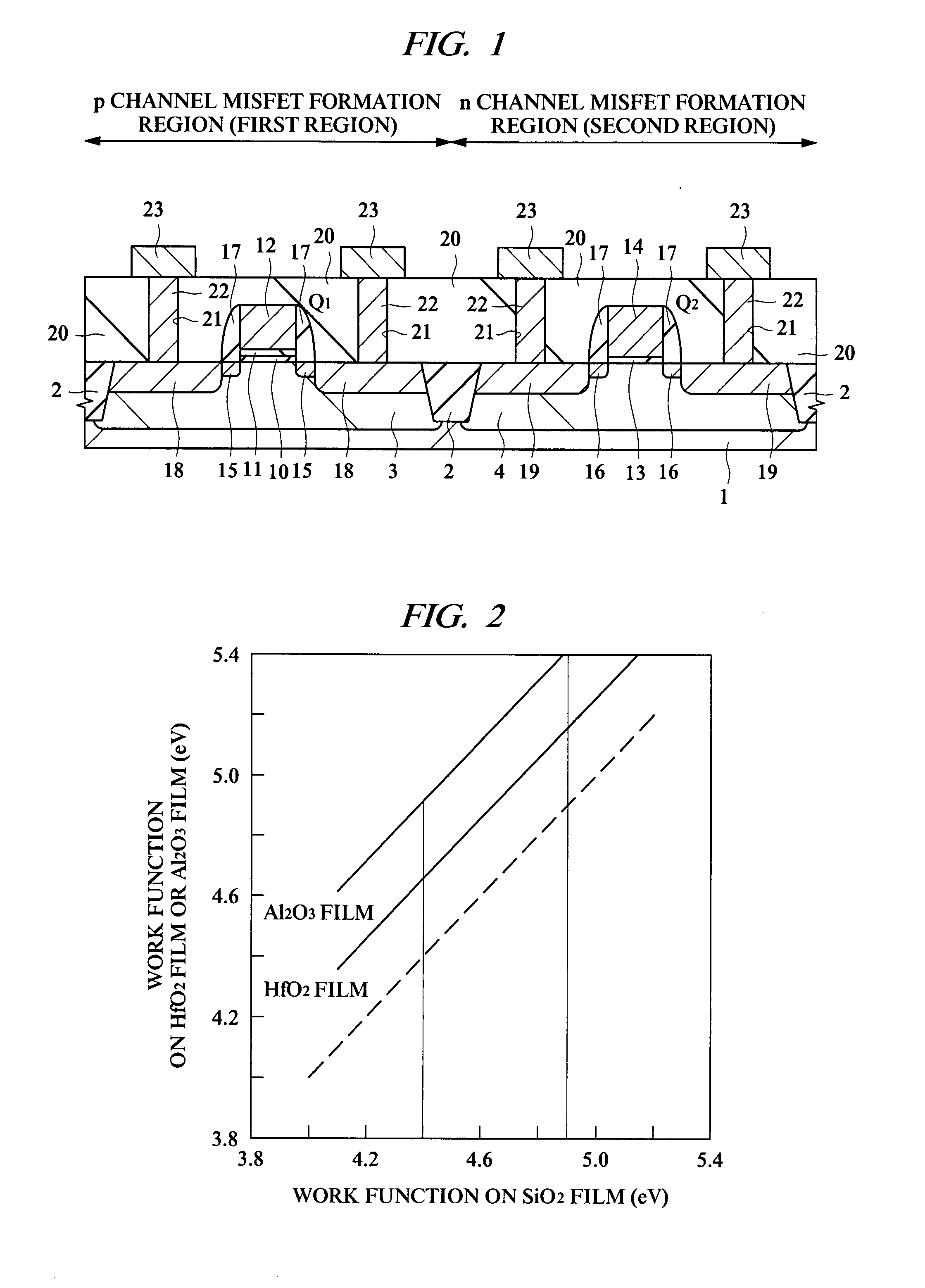
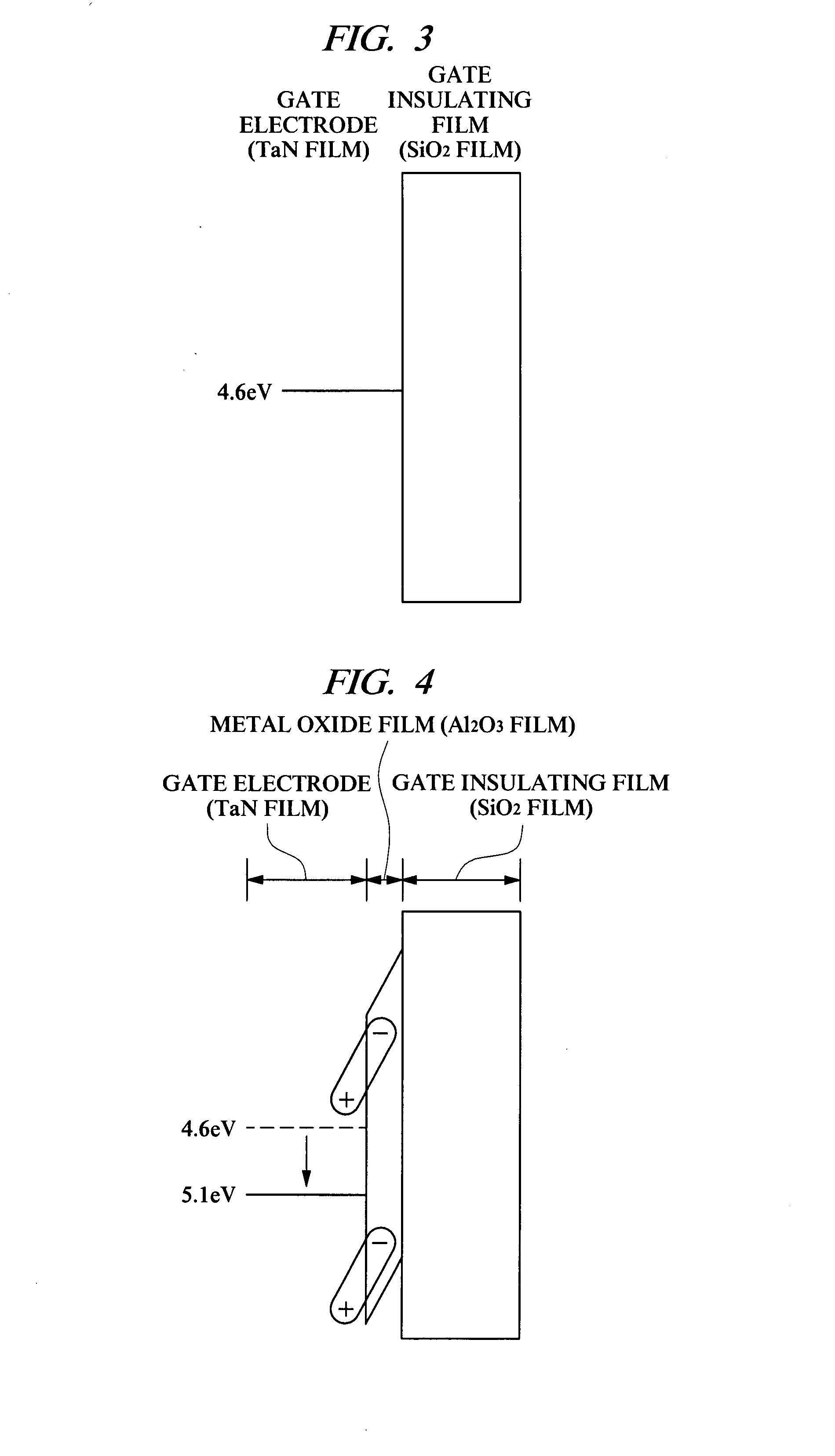
InactiveUS20070210354A1Increased physical film thicknessReduce leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringSilicon oxide
Provided is a technology capable of improving the productivity of a p channel MISFET using a high dielectric-constant film as a gate insulating film and a conductive film containing metal as a gate electrode. In this technology, a threshold voltage of the p channel MISFET can be decreased even if a work function value of the conductive film containing metal at the time of contacting a silicon oxide film is away from a value near a valence band of silicon. A p channel MISFET formed on a semiconductor substrate has a gate insulating film formed of a hafnium oxide film, a metal oxide film formed of an aluminum oxide film on this gate insulating film, and a gate electrode formed of a tantalum nitride film on this metal oxide film. The metal oxide film has a function to shift a work function value of the gate electrode.
Owner:RENESAS TECH CORP
Nano mosfet with trench bottom oxide shielded and third dimensional p-body contact
A semiconductor power device may include a lightly doped layer formed on a heavily doped layer. One or more devices are formed in the lightly doped layer. Each device may include a body region, a source region, and one or more gate electrodes formed in corresponding trenches in the lightly doped region. Each of the trenches has a depth in a first dimension, a width in a second dimension and a length in a third dimension. The body region is of opposite conductivity type to the lightly and heavily doped layers. The source region is formed proximate the upper surface. One or more deep contacts are formed at one or more locations along the third dimension proximate one or more of the trenches. The contacts extend in the first direction from the upper surface into the lightly doped layer and are in electrical contact with the source region.
Owner:ALPHA & OMEGA SEMICON INC
Semiconductor device with high-k gate dielectric and quasi-metal gate, and method of forming thereof
ActiveUS20060017112A1Lower threshold voltageTransistorSolid-state devicesGate dielectricDevice material
A process and apparatus for a semiconductor device is provided. A device comprises a first transistor having a first charge carrier type. The first transistor comprises a high-k gate dielectric and a first doped electrode. The first charge carrier type comprises one of p-type and n-type and the first doped electrode comprises the other of p-type and n-type. The device further comprises a second transistor having a charge carrier type opposite the first charge carrier type. The second transistor comprises the high-k gate dielectric, and a second doped electrode, wherein the second doped electrode comprises the other of p-type and n-type.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Electron emission device, cold cathode field emission device and method for the production thereof, and cold cathode field emission display and method for the production thereof
InactiveUS20020036452A1Improve image qualityReduce power consumptionImage/pattern display tubesDischarge tube cold cathodesPhysicsCarbon film
A cold cathode field emission device comprising (a) a cathode electrode formed on a supporting substrate, and (b) a gate electrode which is formed above the cathode electrode and has an opening portion, and further comprising (c) an electron emitting portion composed of a carbon film formed on a surface of a portion of the cathode electrode which portion is positioned in a bottom portion of the opening portion.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20070076467A1Reduce consumptionSmall sizeDigital storageSubthreshold leakage currentHemt circuits
An object of the present invention is to provide a technique of reducing the power consumption of an entire low power consumption SRAM LSI circuit employing scaled-down transistors and of increasing the stability of read and write operations on the memory cells by reducing the subthreshold leakage current and the leakage current flowing from the drain electrode to the substrate electrode. Another object of the present invention is to provide a technique of preventing an increase in the number of transistors in a memory cell and thereby preventing an increase in the cell area. Still another object of the present invention is to provide a technique of ensuring stable operation of an SRAM memory cell made up of SOI or FD-SOI transistors having a BOX layer by controlling the potentials of the wells under the BOX layers of the drive transistors.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
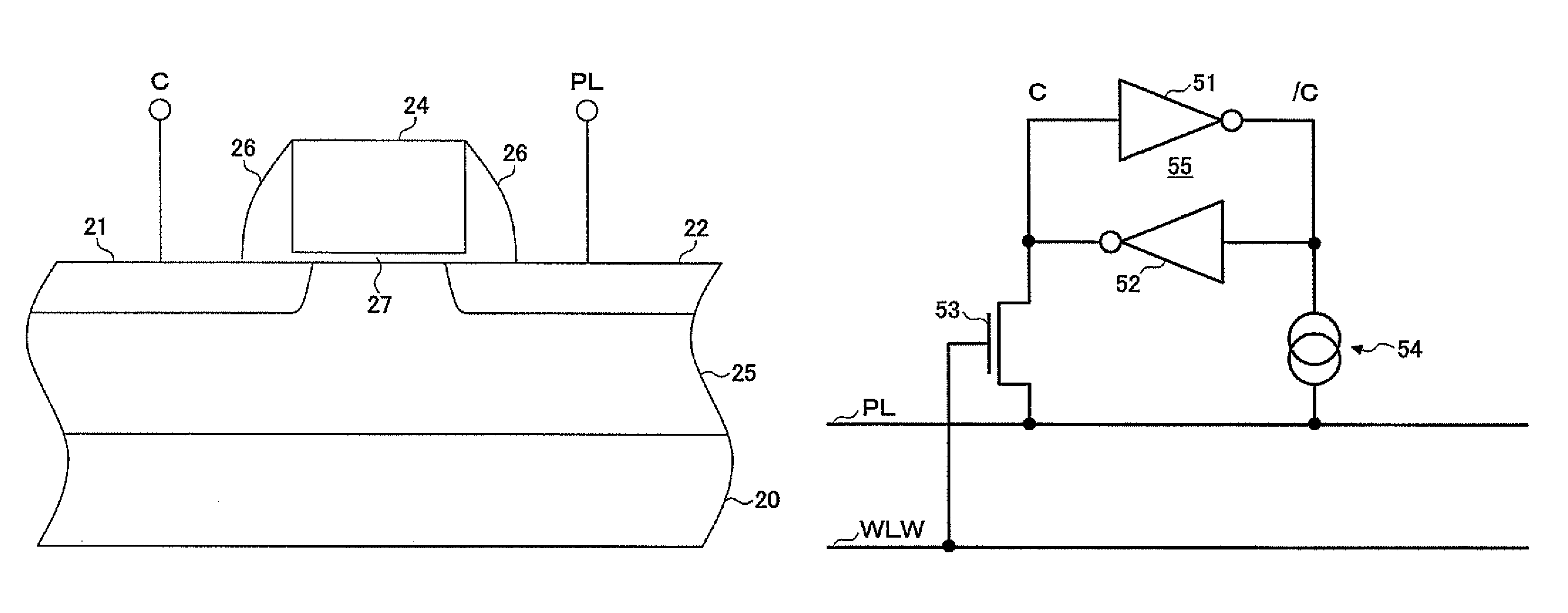
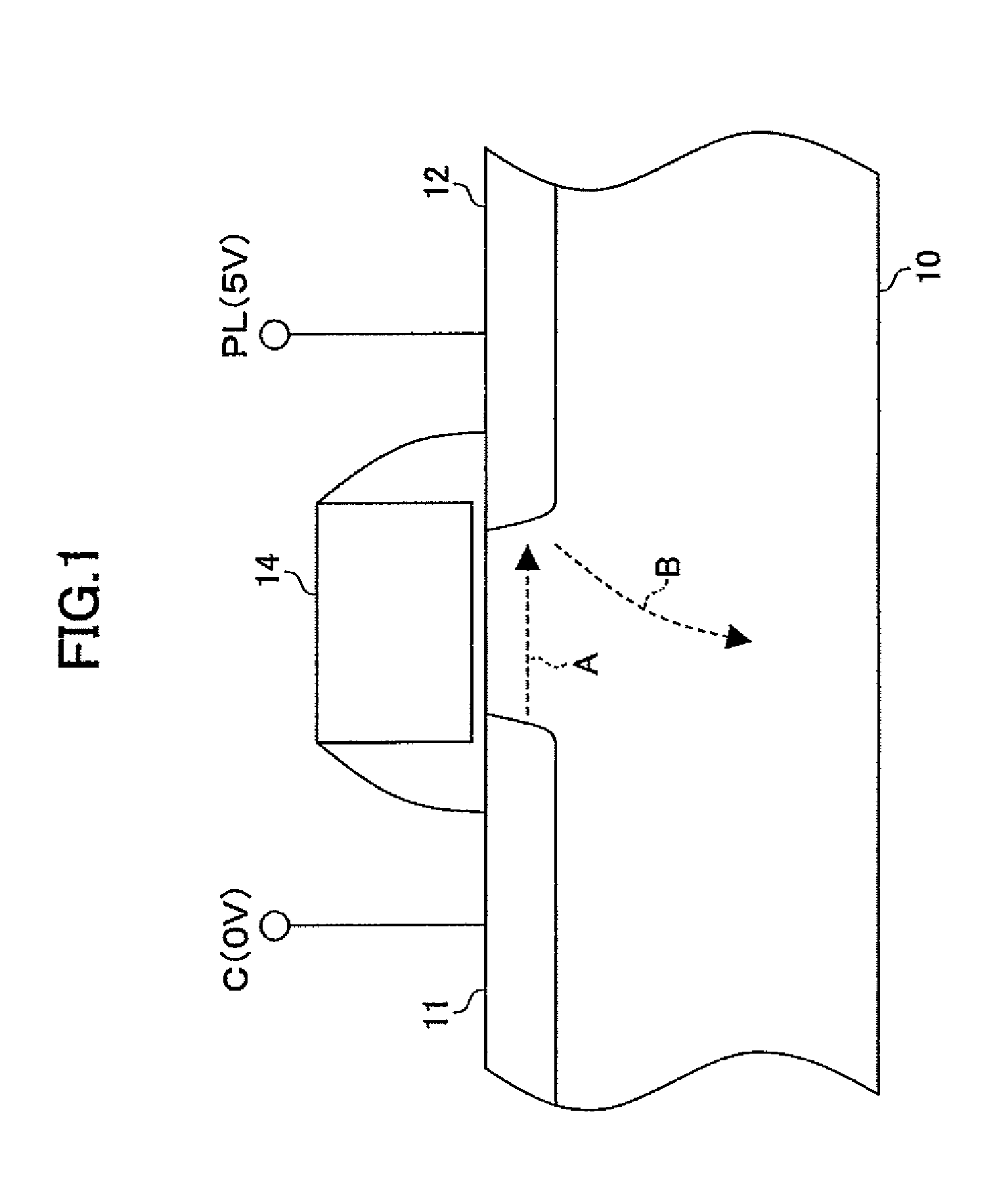
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory circuit utilizing a MIS transistor as a memory cell
ActiveUS7821806B2Many problemReduce adverse effectsSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesHemt circuitsMemory circuits
A memory circuit includes a latch having a first node and a second node to store data such that a logic level of the first node is an inverse of a logic level of the second node, a MIS transistor having a gate node, a first source / drain node, and a second source / drain node, the first source / drain node coupled to the first node of the latch, and a control circuit configured to control the gate node and second source / drain node of the MIS transistor in a first operation such that a lingering change is created in transistor characteristics of the MIS transistor in response to the data stored in the latch, wherein the MIS transistor includes a highly-doped substrate layer, a lightly-doped substrate layer disposed on the highly-doped substrate layer, diffusion regions formed in the lightly-doped substrate layer, a gate electrode, sidewalls, and an insulating film.
Owner:NSCORE
CMOS Devices with a single work function gate electrode and method of fabrication
InactiveUS20070111419A1Lower threshold voltageEasy to manufactureThyristorSolid-state devicesCMOSDevice form
Described herein are a device utilizing a gate electrode material with a single work function for both the pMOS and nMOS transistors where the magnitude of the transistor threshold voltages is modified by semiconductor band engineering and article made thereby. Further described herein are methods of fabricating a device formed of complementary (pMOS and nMOS) transistors having semiconductor channel regions which have been band gap engineered to achieve a low threshold voltage.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Perylene-imide semiconductor polymers
ActiveUS20100283047A1Excellent charge transport propertiesLarge solubilityConductive materialSolid-state devicesImideSemiconductor materials
Disclosed are new semiconductor materials prepared from perylene-imide copolymers. Such polymers can exhibit high n-type carrier mobility and / or good current modulation characteristics. In addition, the compounds of the present teachings can possess certain processing advantages such as solution-processability and / or good stability at ambient conditions.
Owner:RAYNERGY TEK INC +1
Organic TFT and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050285102A1Lower threshold voltageReduce leakage currentSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate insulatorOrganic semiconductor
The present invention provides an organic thin film transistor and method for fabricating the same. The organic thin film transistor has a substrate and a gate electrode that is positioned on the substrate. A gate insulator has a stacked structure comprising an inorganic gate insulator and an organic gate insulator that are positioned on the gate electrode. An organic semiconductor layer is positioned on the gate insulator to overlap the gate electrode. Accordingly, an organic thin film transistor that has flexibility, decreased leakage current, and a low threshold is formed.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Field emission device
InactiveUS20040095050A1Lower threshold voltageMaterial nanotechnologyElectric discharge tubesField emission deviceMicrometer
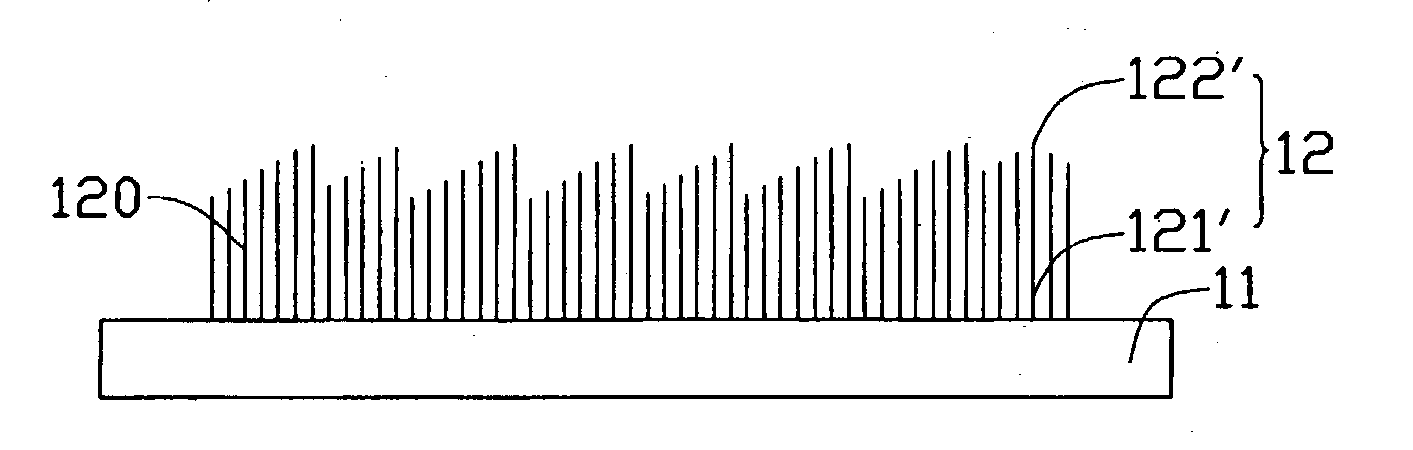
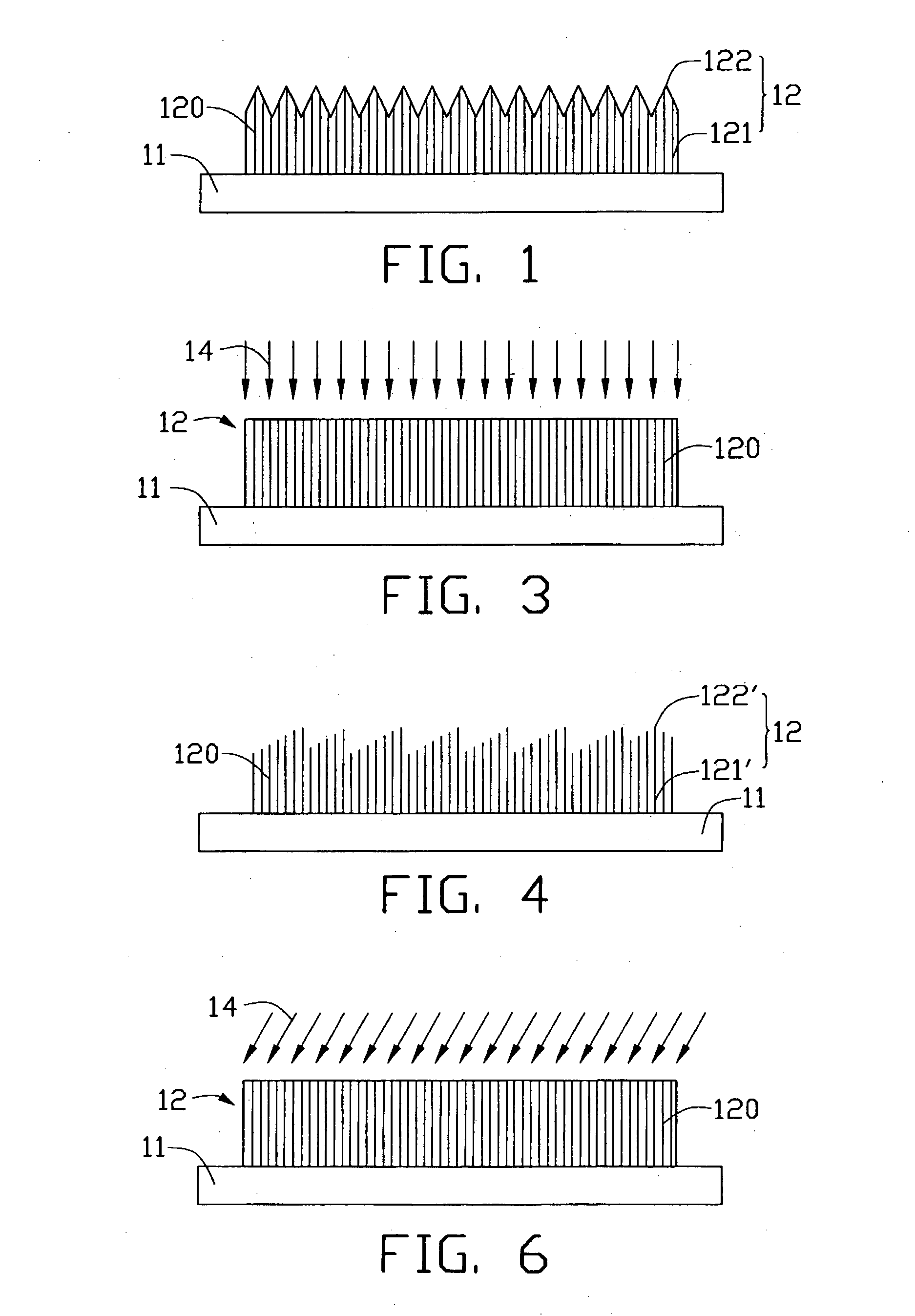
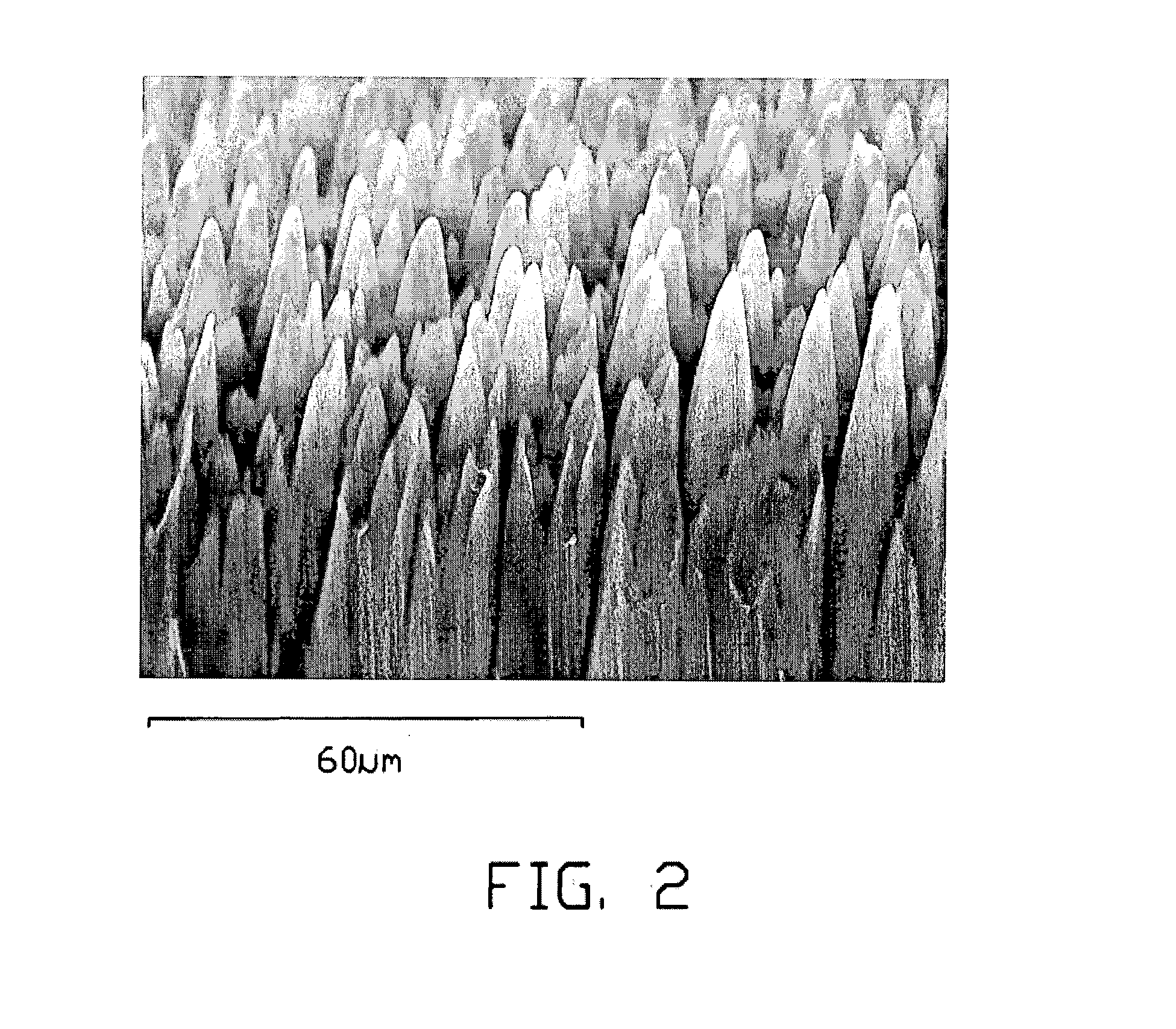
A field emission device includes a substrate (11) and a carbon nanotube array (12) formed thereon. Carbon nanotubes (120) of the carbon nanotube array are parallel to each other and cooperatively form a plurality of substantially rod-shaped lower portions (121, 121') and a plurality of corresponding tapered tips (122, 122') above the lower portions. Each lower portion and tapered tips have a plurality of carbon nanotubes. Distances between adjacent tips are approximately uniform, and are more than one micrometer. Preferably, the distance is in the range from 1 to 30 micrometers. The field emission device with this structure has reduced shielding between adjacent carbon nanotubes and has decreased threshold voltage required for field emission by the carbon nanotubes. The field emission device also contributes to an improved field emission concentration and efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Five-ring liquid crystal compound having cyclohexane ring, liquid crystal composition, and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20090302273A1High clearing pointSmall viscosityLiquid crystal compositionsIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationCrystallographyLiquid-crystal display
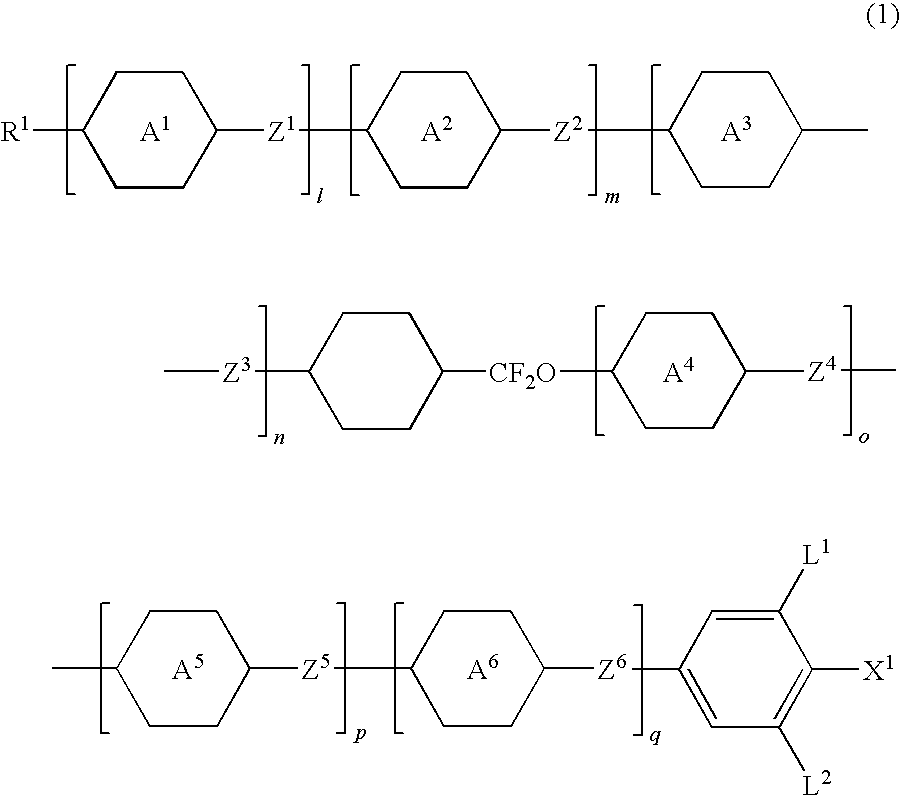
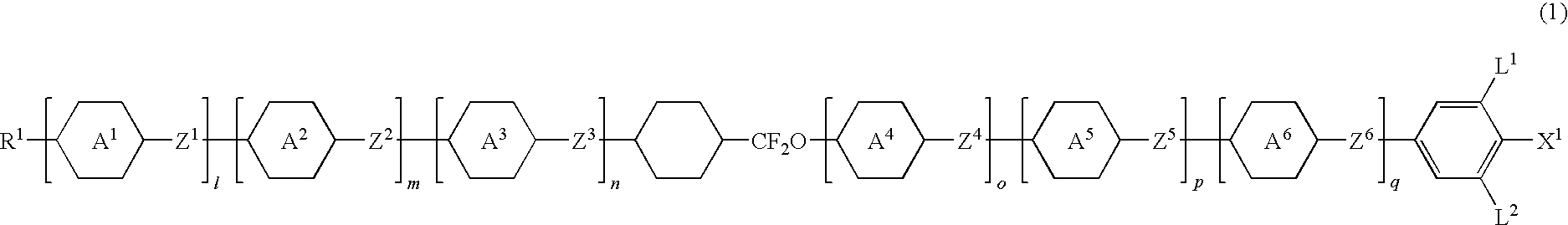
A liquid crystal compound represented by formula (1), a liquid crystal composition comprising the compound, and a liquid crystal display device comprising the composition:For example, R1 is alkyl having 1 to 20; ring A1, ring A2, ring A3, ring A4, ring A5, and ring A6 are 1,4-cyclohexylene or 1,4-phenylene; Z1, Z2, Z3, Z4, Z5, and Z6 is a single bond; X1 is hydrogen or halogen; l, m, n, o, p, and q are 0 or 1, and l+m+n+o+p+q is 3.
Owner:JNC CORP +1
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110180796A1Run at high speedReduce power consumptionSemiconductor devicesMiniaturizationSemiconductor
An object is to provide a semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor, which maintains favorable characteristics and achieves miniaturization. The semiconductor device includes an oxide semiconductor layer, a source electrode and a drain electrode in contact with the oxide semiconductor layer, a gate electrode overlapping with the oxide semiconductor layer, and a gate insulating layer provided between the oxide semiconductor layer and the gate electrode, in which the source electrode and the drain electrode each include a first conductive layer, and a second conductive layer having a region which extends in a channel length direction from an end portion of the first conductive layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method
InactiveUS20100044752A1Mitigates reduction in threshold voltageReduce voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMetal insulatorElectron mobility
A metal-insulator-semiconductor high electron mobility transistor (MIS-HEMT) has a substrate in which an electron supply layer is interposed between an electron channel layer and the surface of the substrate. A pair of main electrodes are formed on the surface of the substrate. A recess is formed in the surface of the substrate between the main electrodes. A gate insulation film is formed on the surface of the substrate, at least between the first and second main electrodes, covering the inside walls and floor of the recess. A gate electrode is formed on the gate insulation film, filling in the recess. The gate insulation film has a crystal density of at least 2.9 g / cm3, which mitigates the reduction in threshold voltage caused by the recess.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
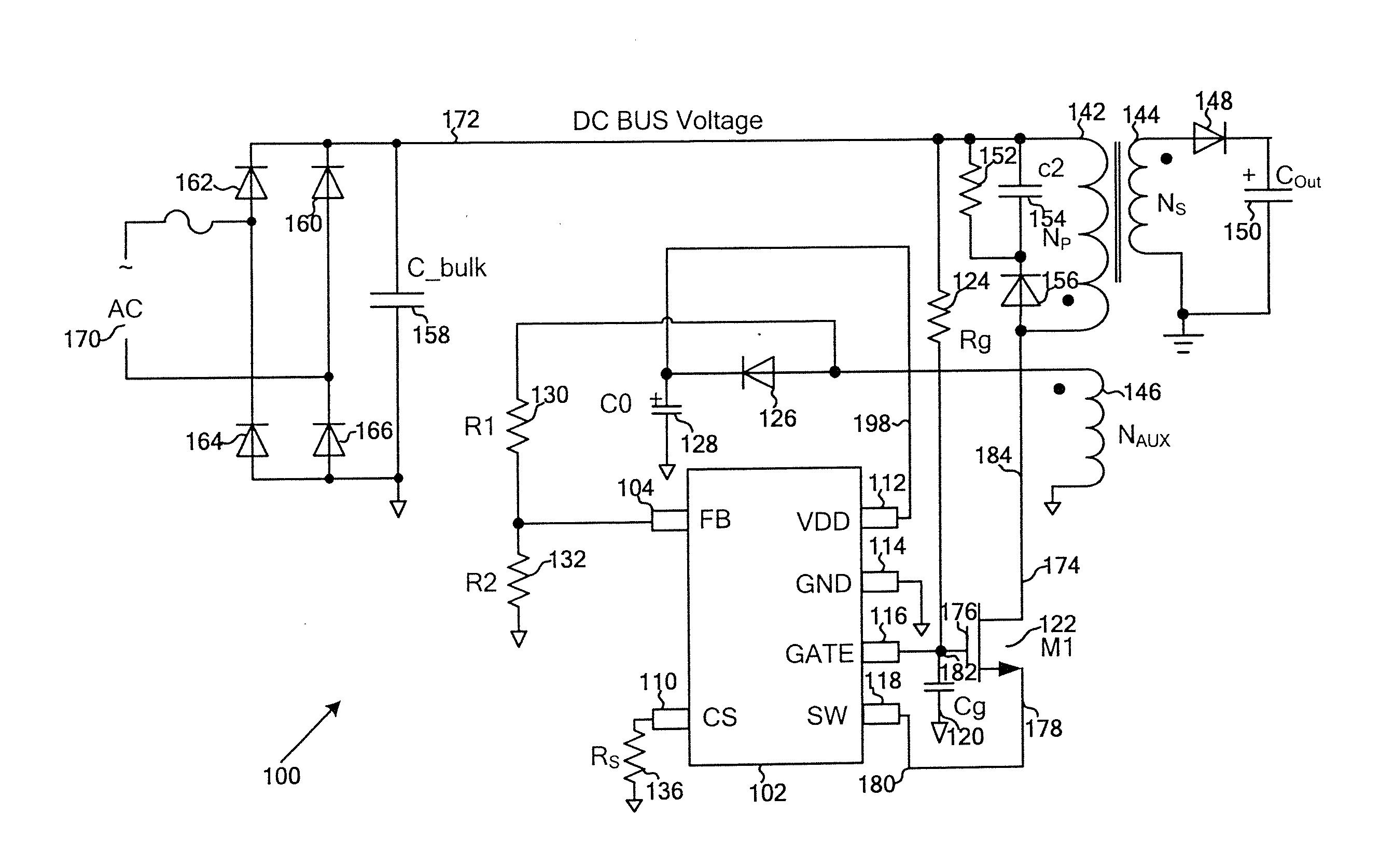
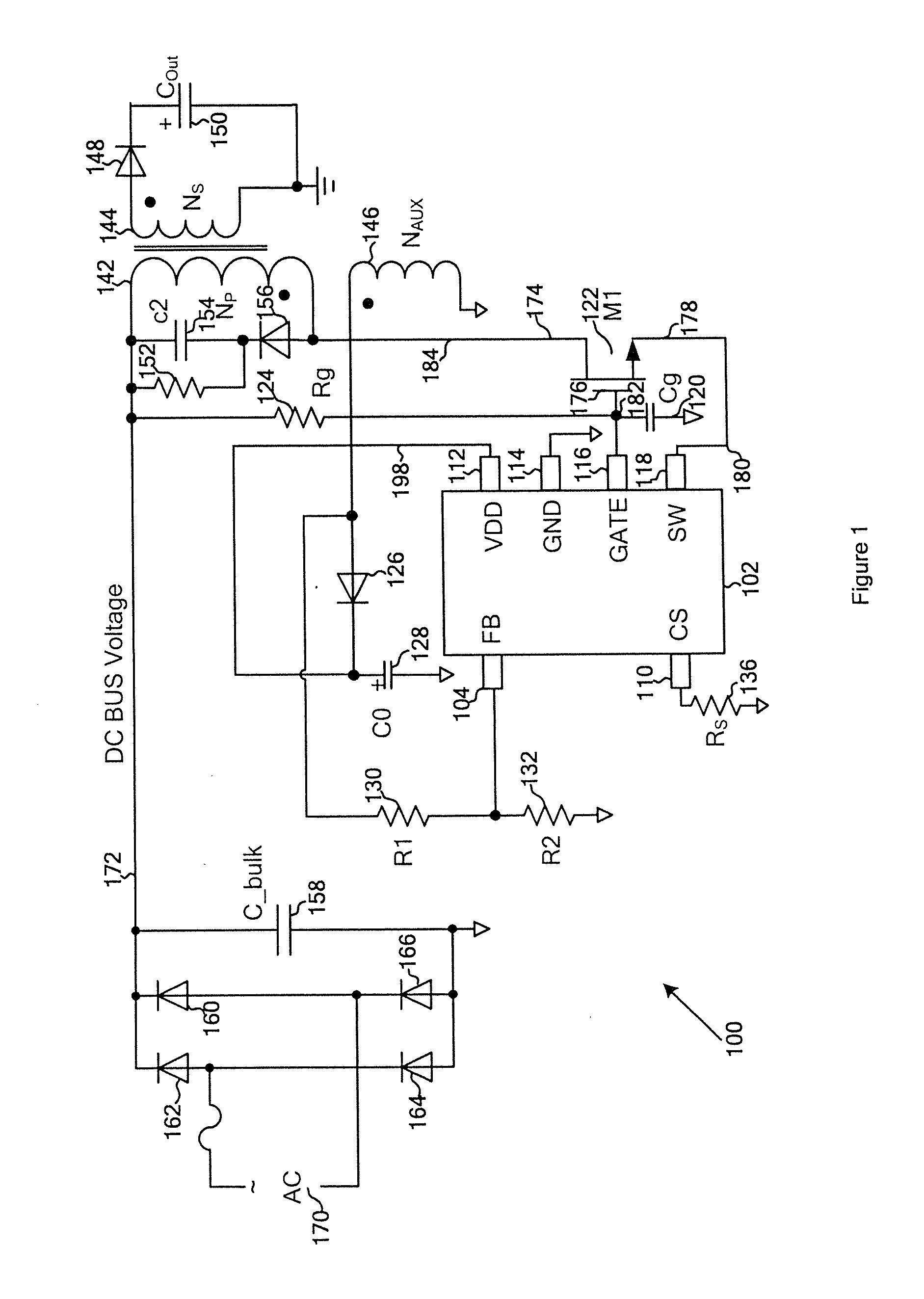
Systems and methods for source switching and voltage generation
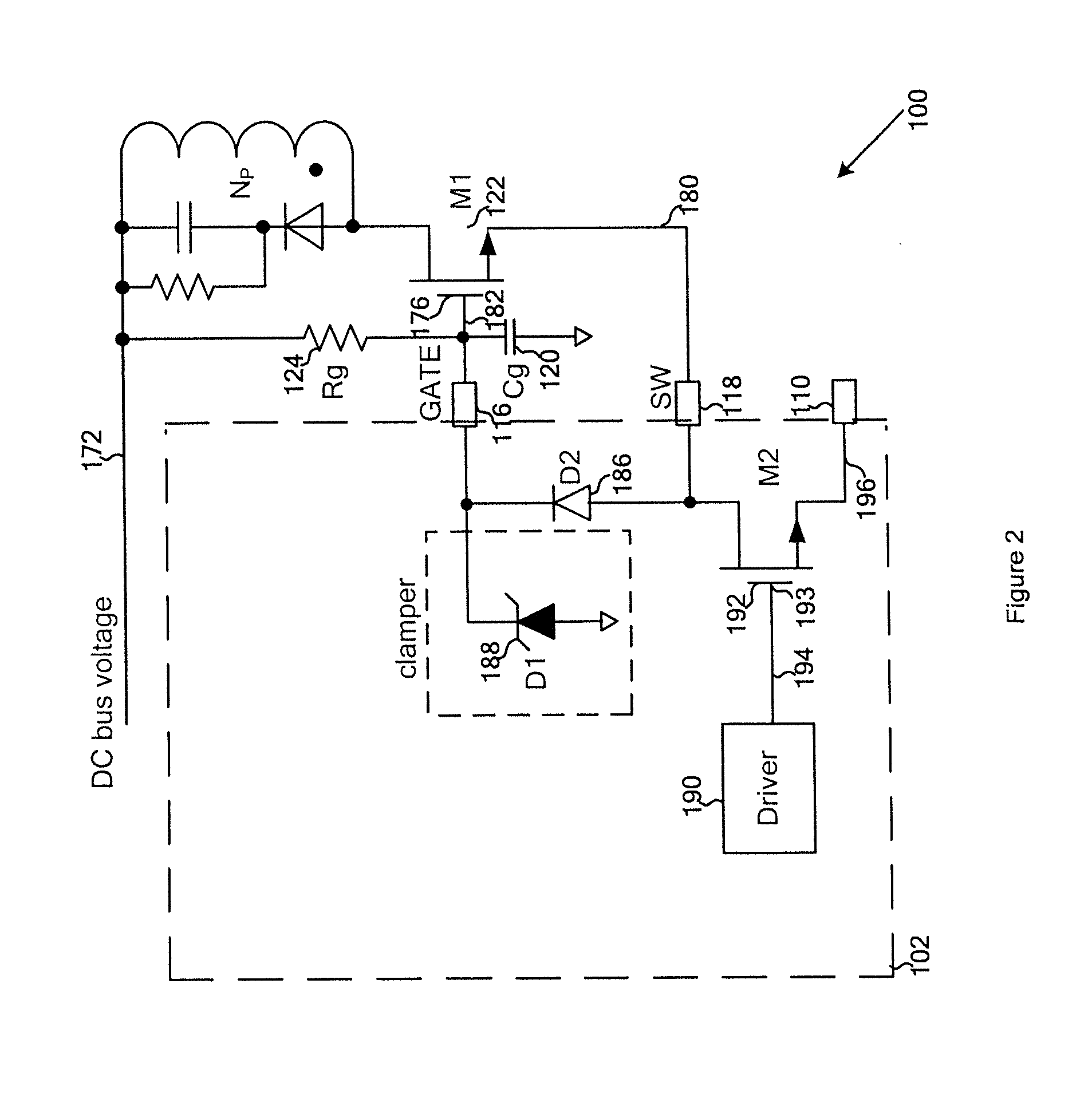
ActiveUS20140177280A1Reduce threshold voltageQuickly chargeDc network circuit arrangementsApparatus with intermediate ac conversionConductor CoilControl theory
System and method for regulating a power conversion system. An example system controller for regulating a power conversion system includes a first controller terminal associated with a first controller voltage and coupled to a first transistor terminal of a first transistor, the first transistor further including a second transistor terminal and a third transistor terminal, the second transistor terminal being coupled to a primary winding of a power conversion system, a second controller terminal associated with a second controller voltage and coupled to the third transistor terminal, and a third controller terminal associated with a third controller voltage. The first controller voltage is equal to a sum of the third controller voltage and a first voltage difference. The second controller voltage is equal to a sum of the third controller voltage and a second voltage difference.
Owner:ON BRIGHT ELECTRONICS SHANGHAI
Polarization control in VCSELs using photonics crystals
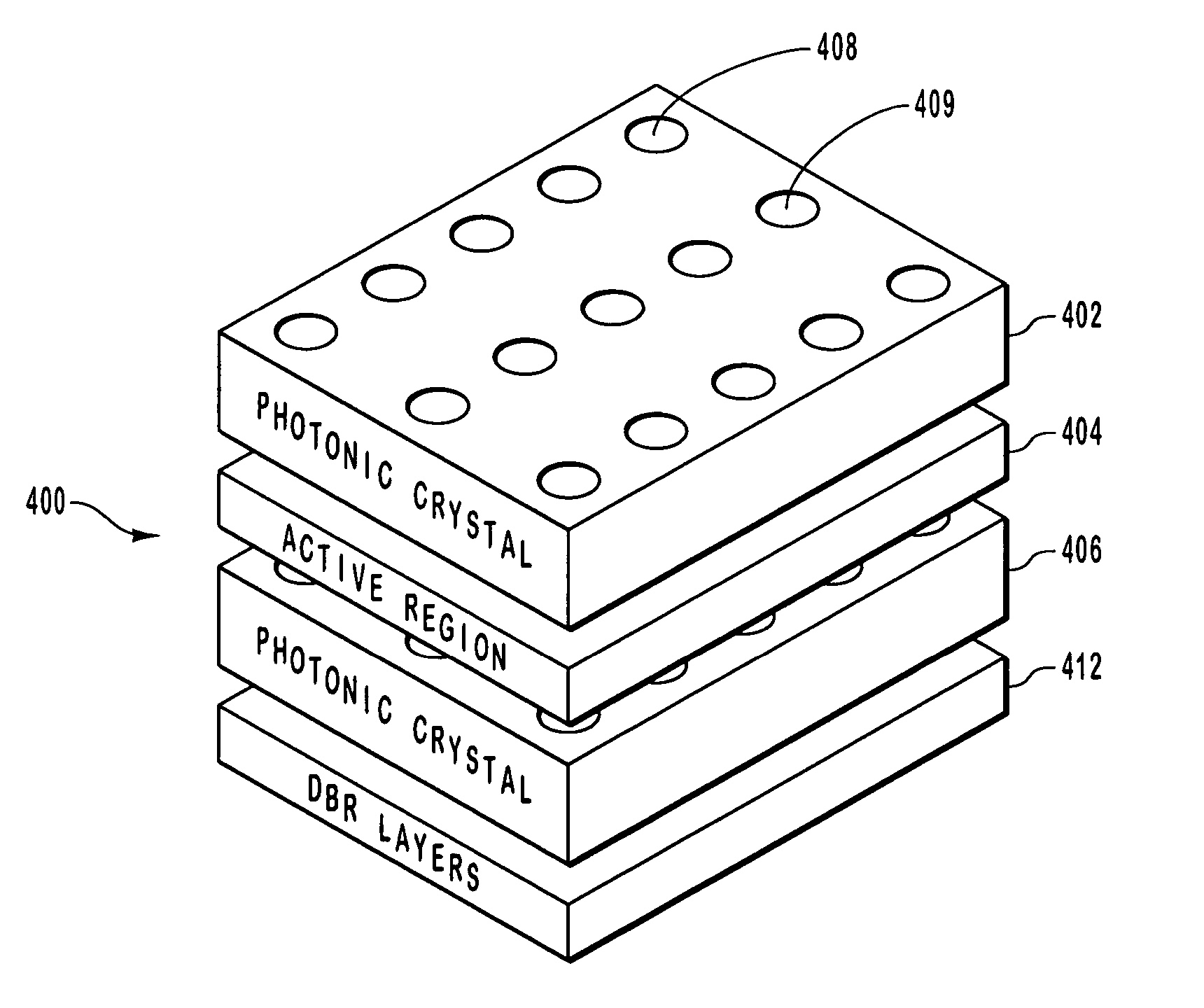
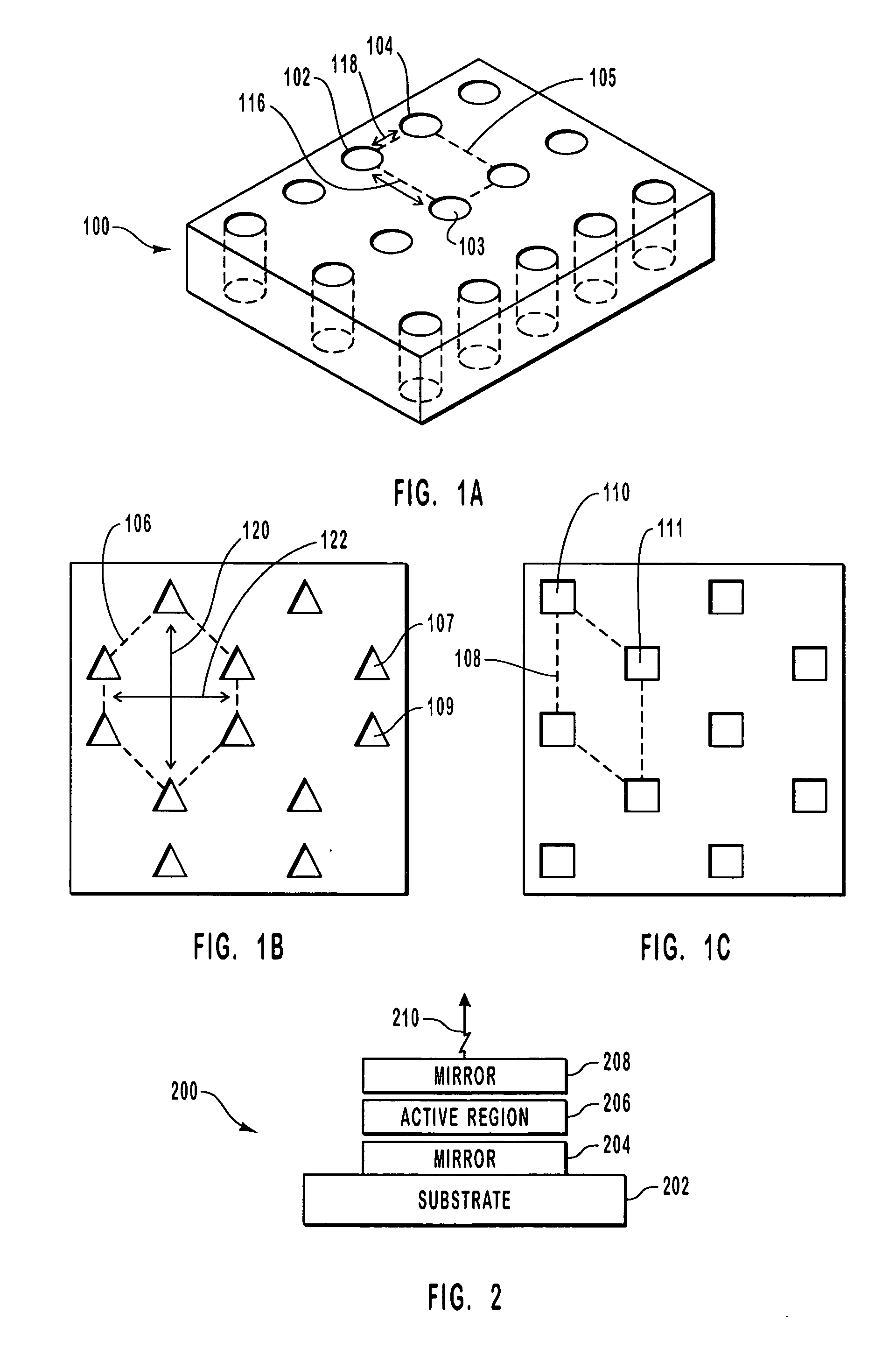
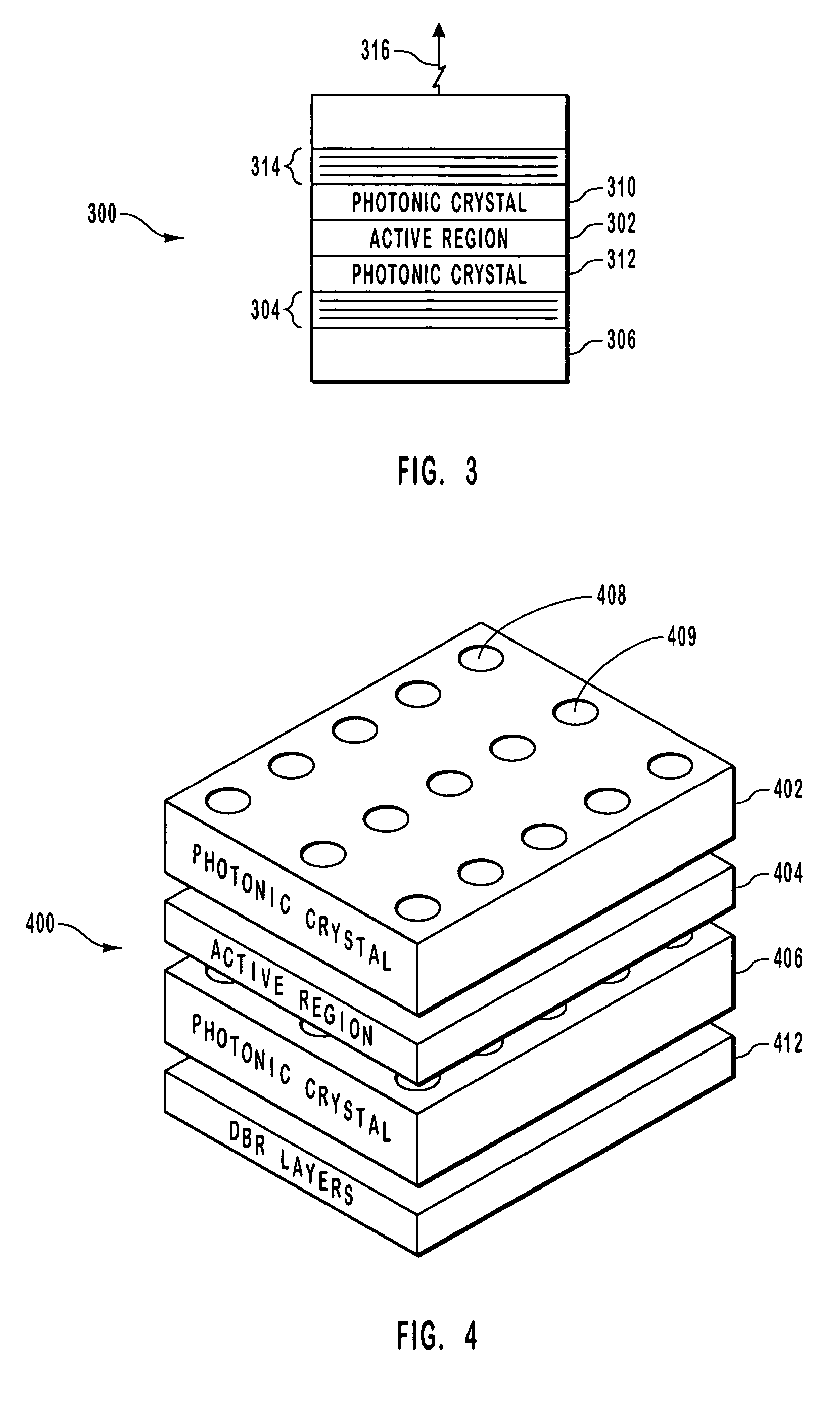
InactiveUS20070030873A1Lower threshold voltageOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserPhotonic crystal
An optical device including a polarization control photonic crystal. The optical device includes a vertical cavity surface emitting laser. The optical device further includes a lower mirror formed on a substrate. The optical device also includes an upper mirror. An active region is between the lower mirror and the upper mirror. Photons generated in the active region are reflected between the upper mirror and the lower mirror through the active region. An asymmetrical photonic crystal including cavities is optically coupled in the optical device such that one polarization of light is better reflected by the asymmetrical photonic crystal than a competing polarization of light.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com