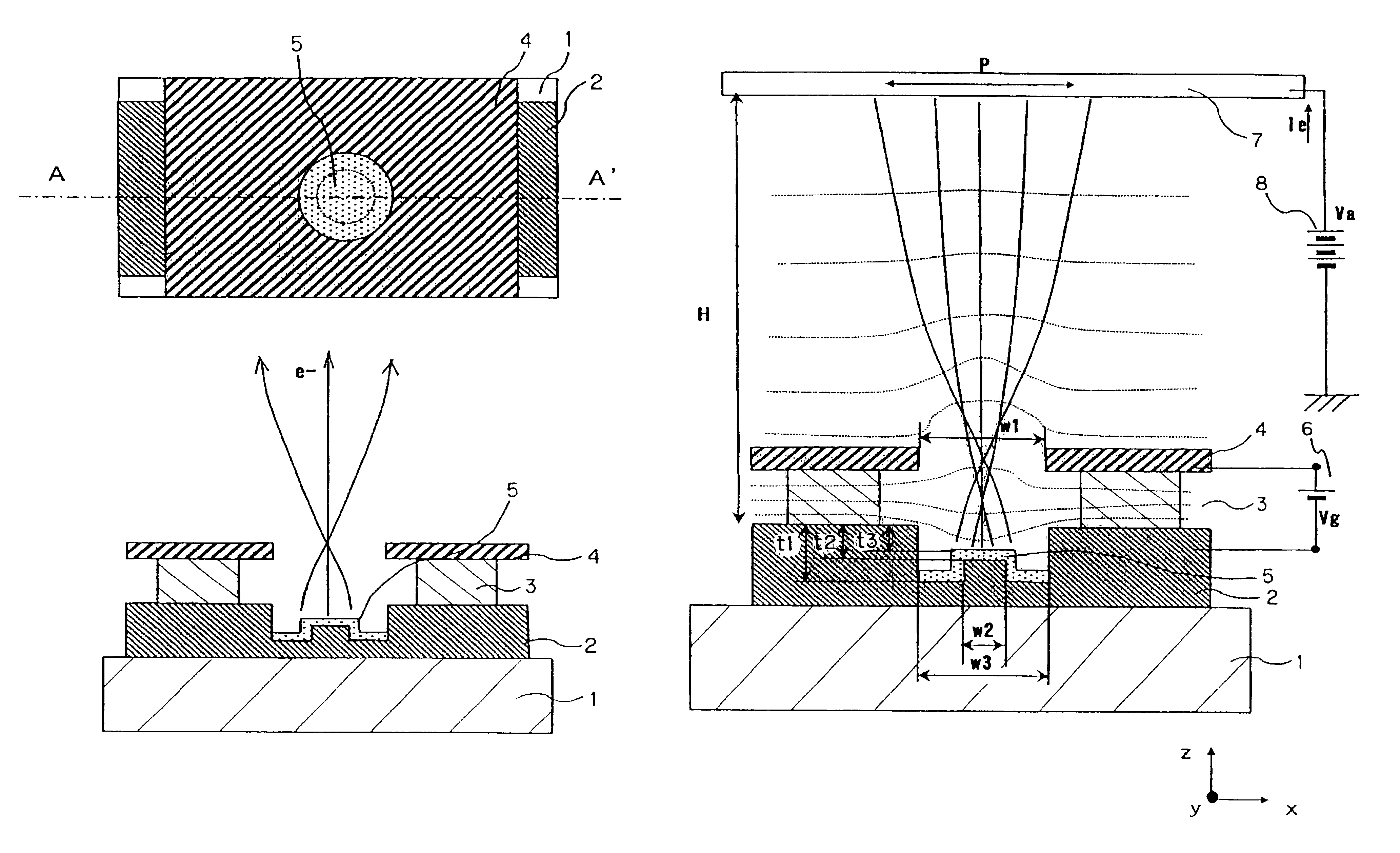
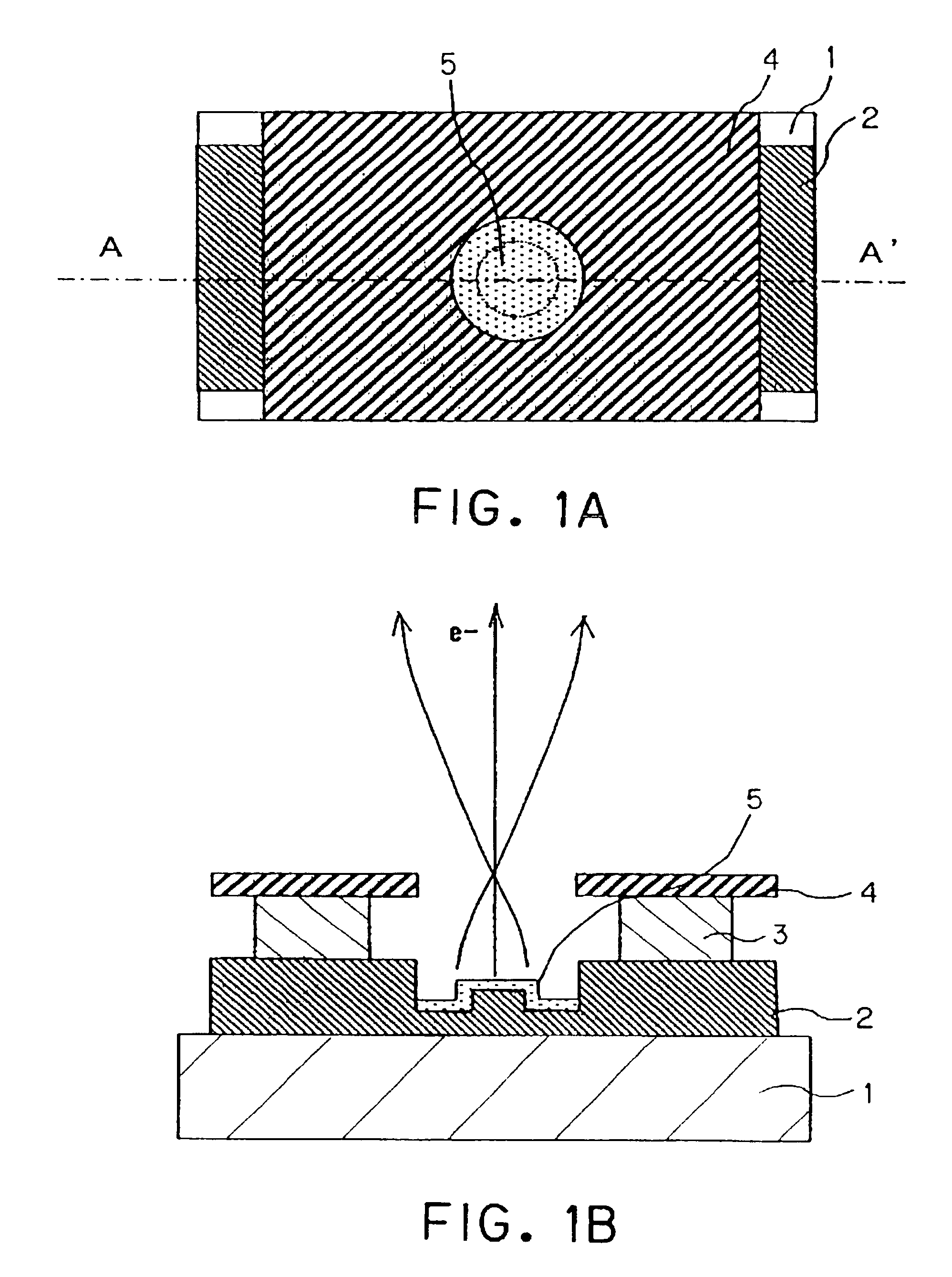
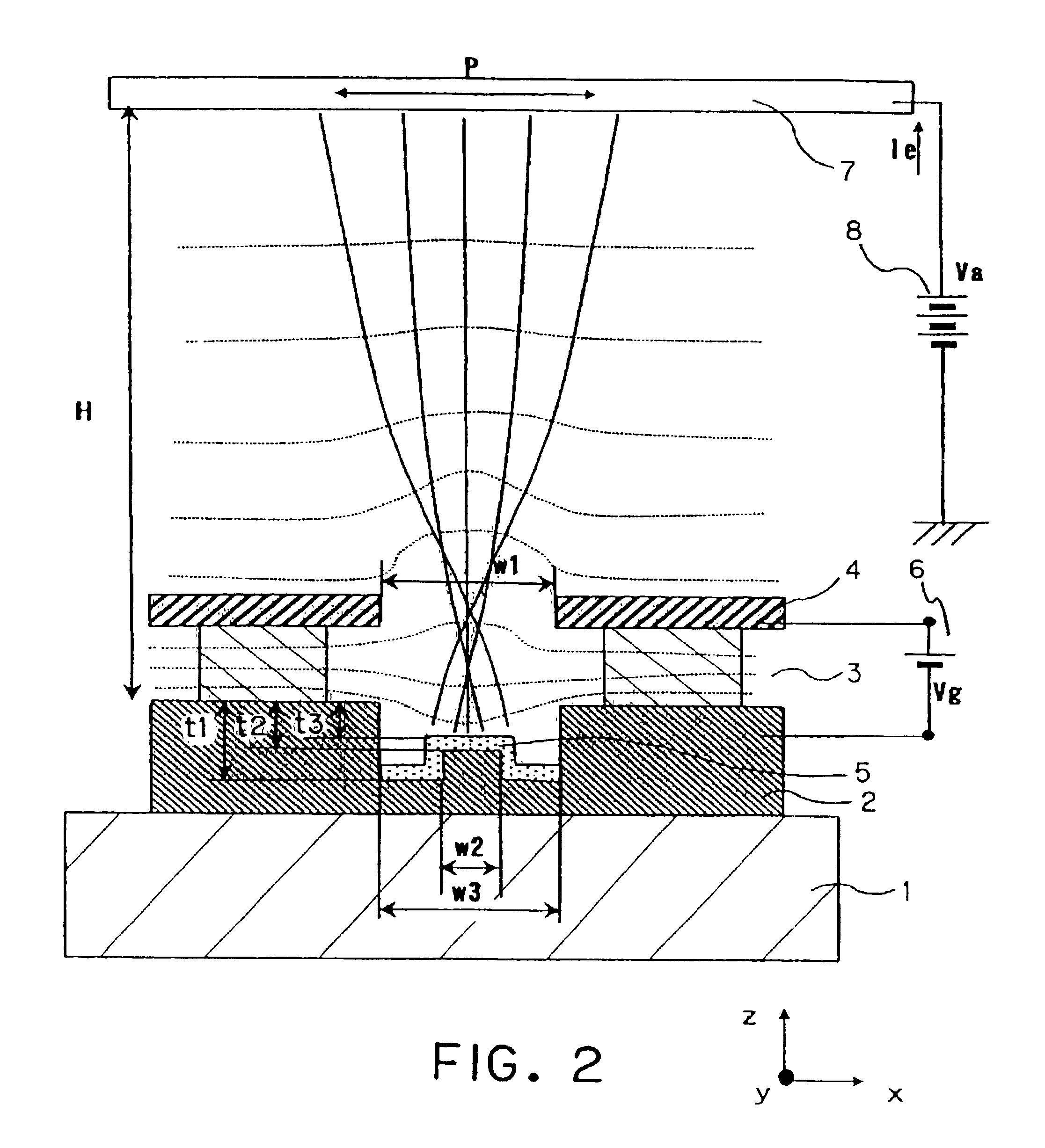
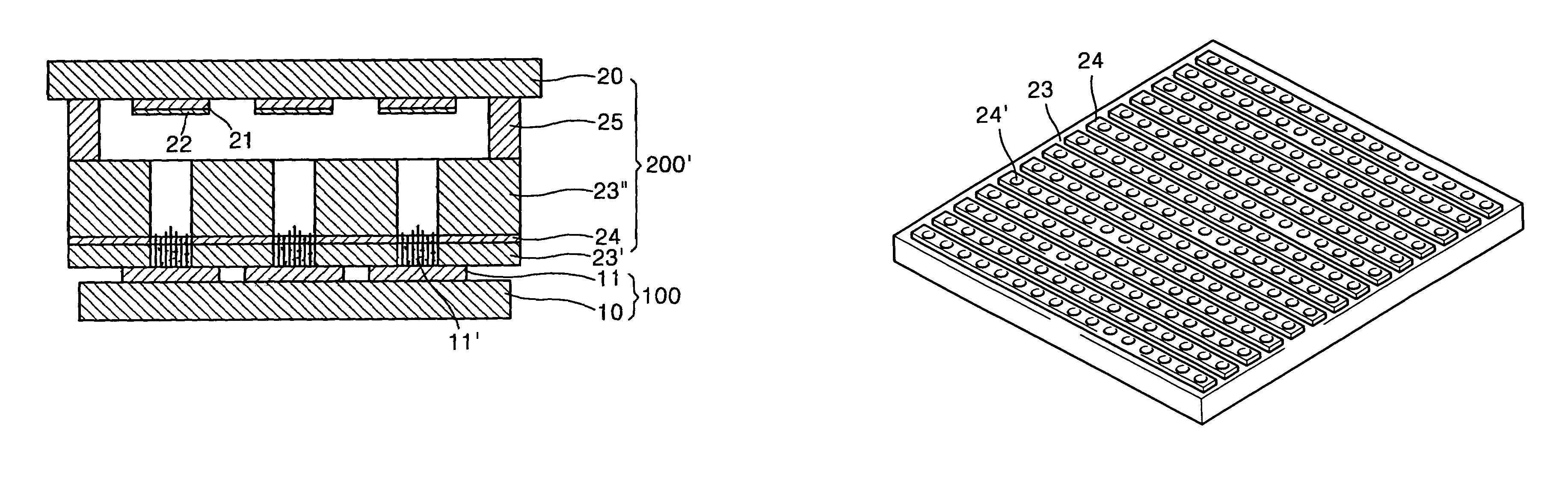
Patents
Literature
1122results about "Discharge tube cold cathodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
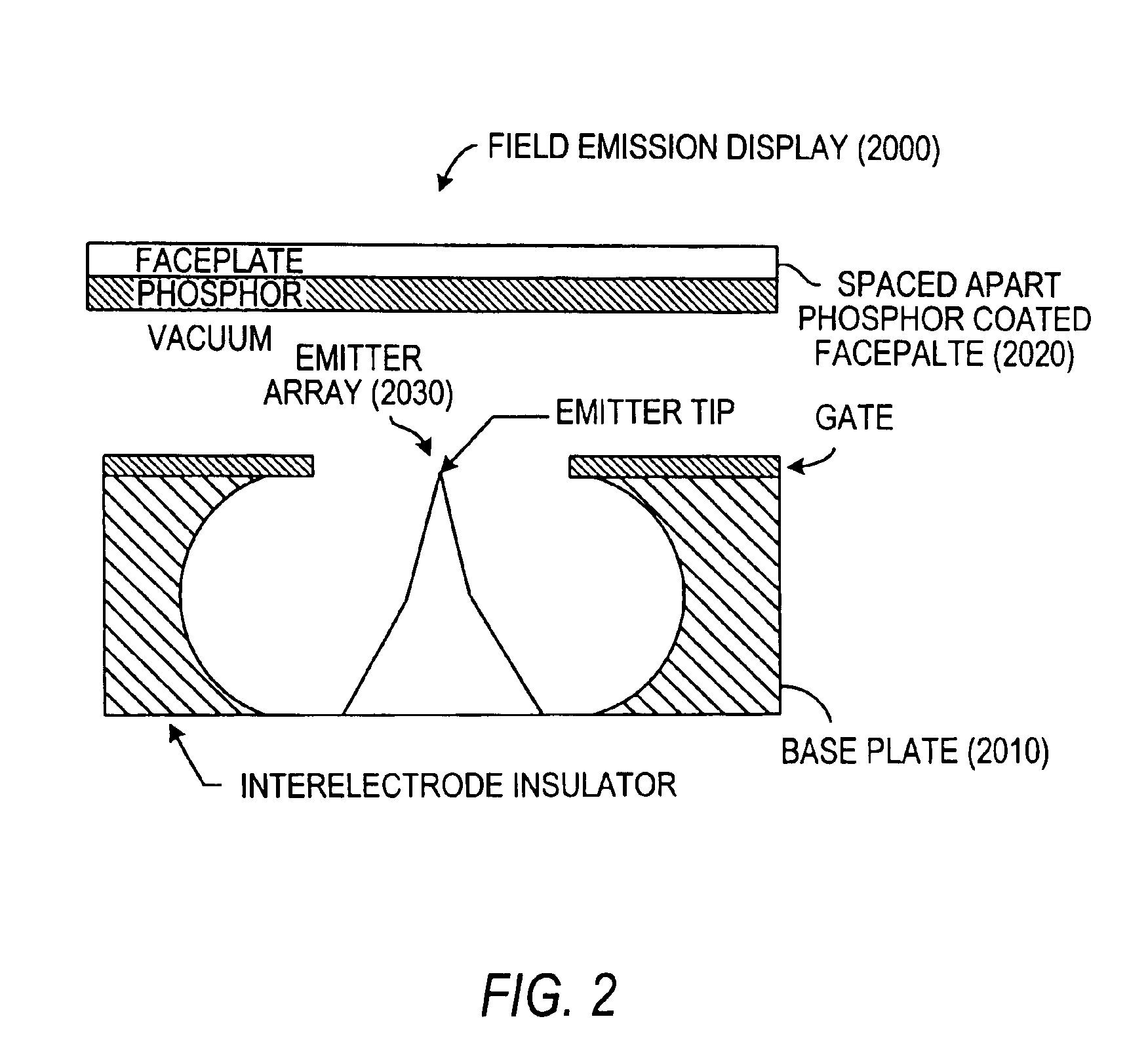
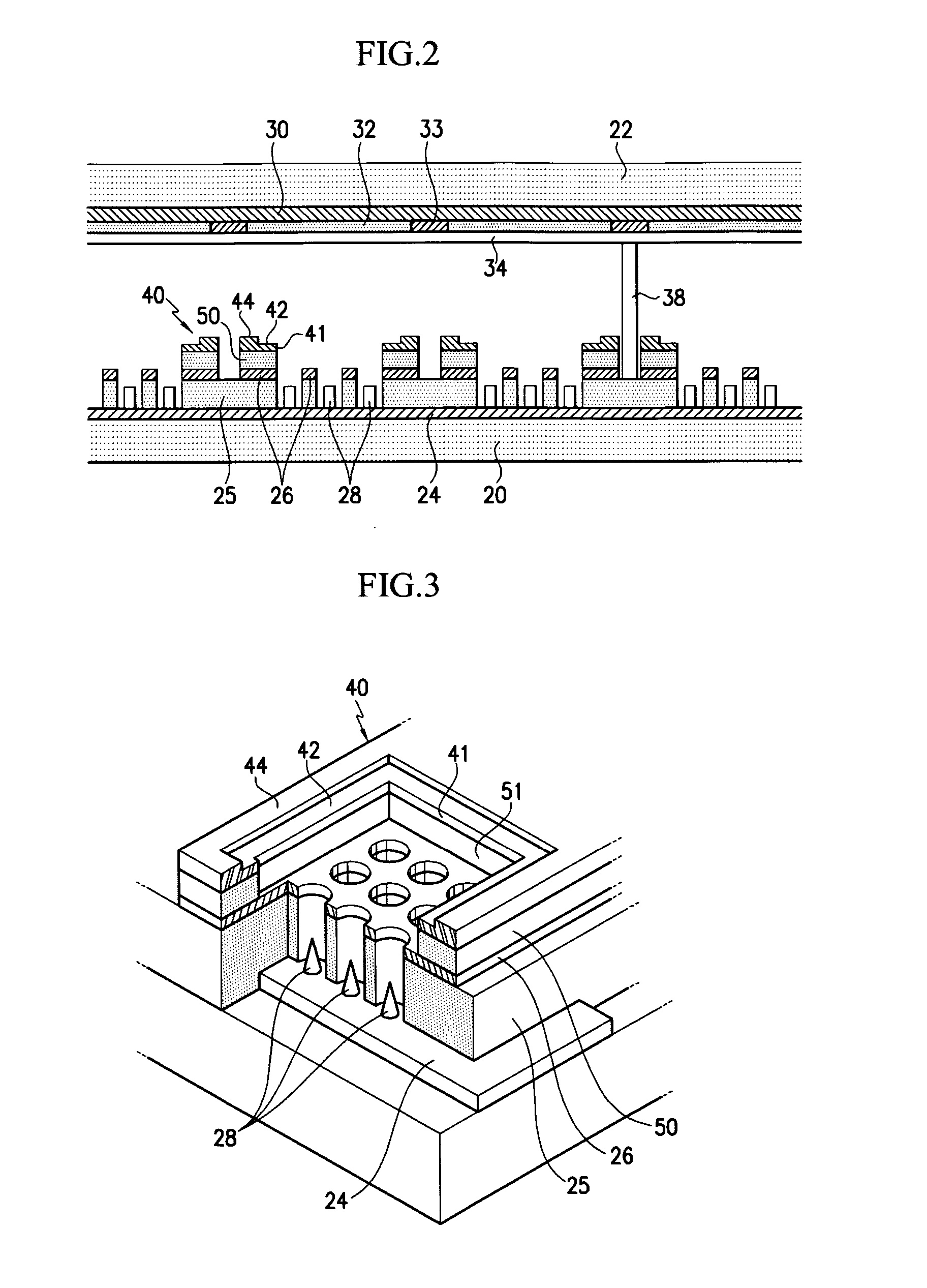
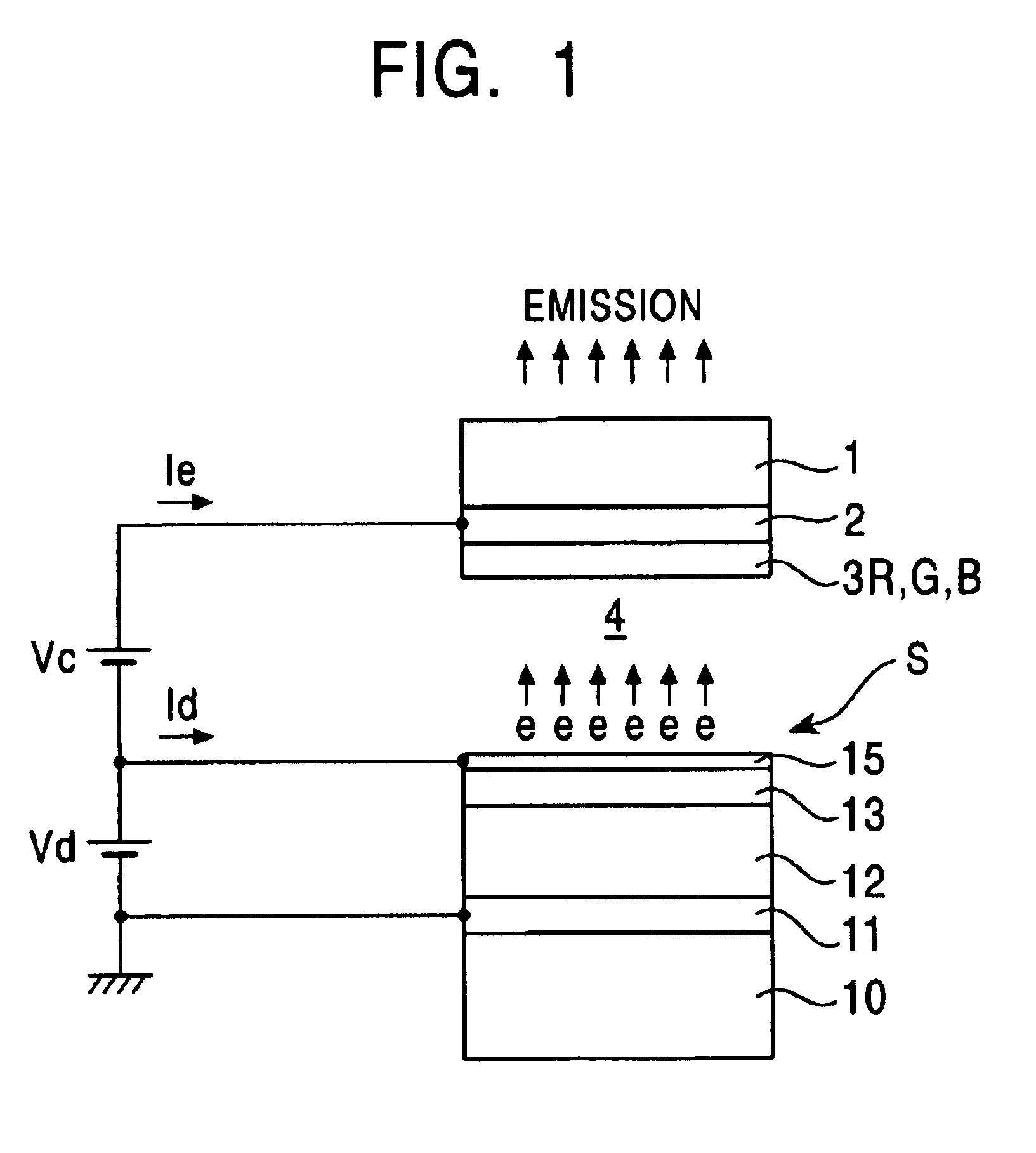
Field emission electron source
InactiveUS6057637AStable and reproducible current-voltage characteristicStraightforward and commercially feasibleElectric discharge tubesLayered productsElectron currentElectron source
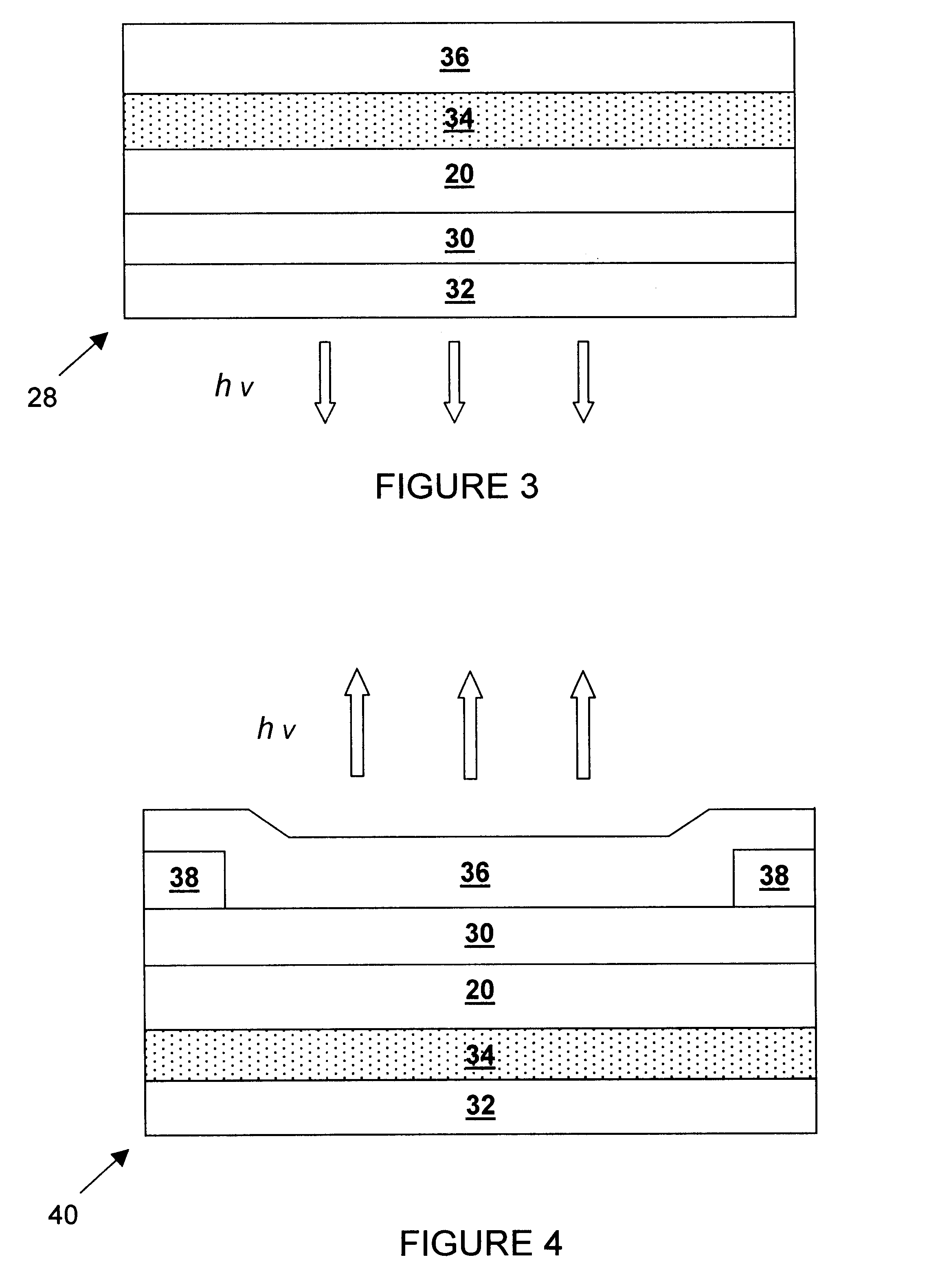
A novel field emitter material, field emission electron source, and commercially feasible fabrication method is described. The inventive field emission electron source produces reliable electron currents of up to 400 mA / cm2 at 200 volts. The emitter is robust and the current it produces is not sensitive to variability of vacuum or the distance between the emitter tip and the cathode. The novel emitter has a sharp turn-on near 100 volts.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
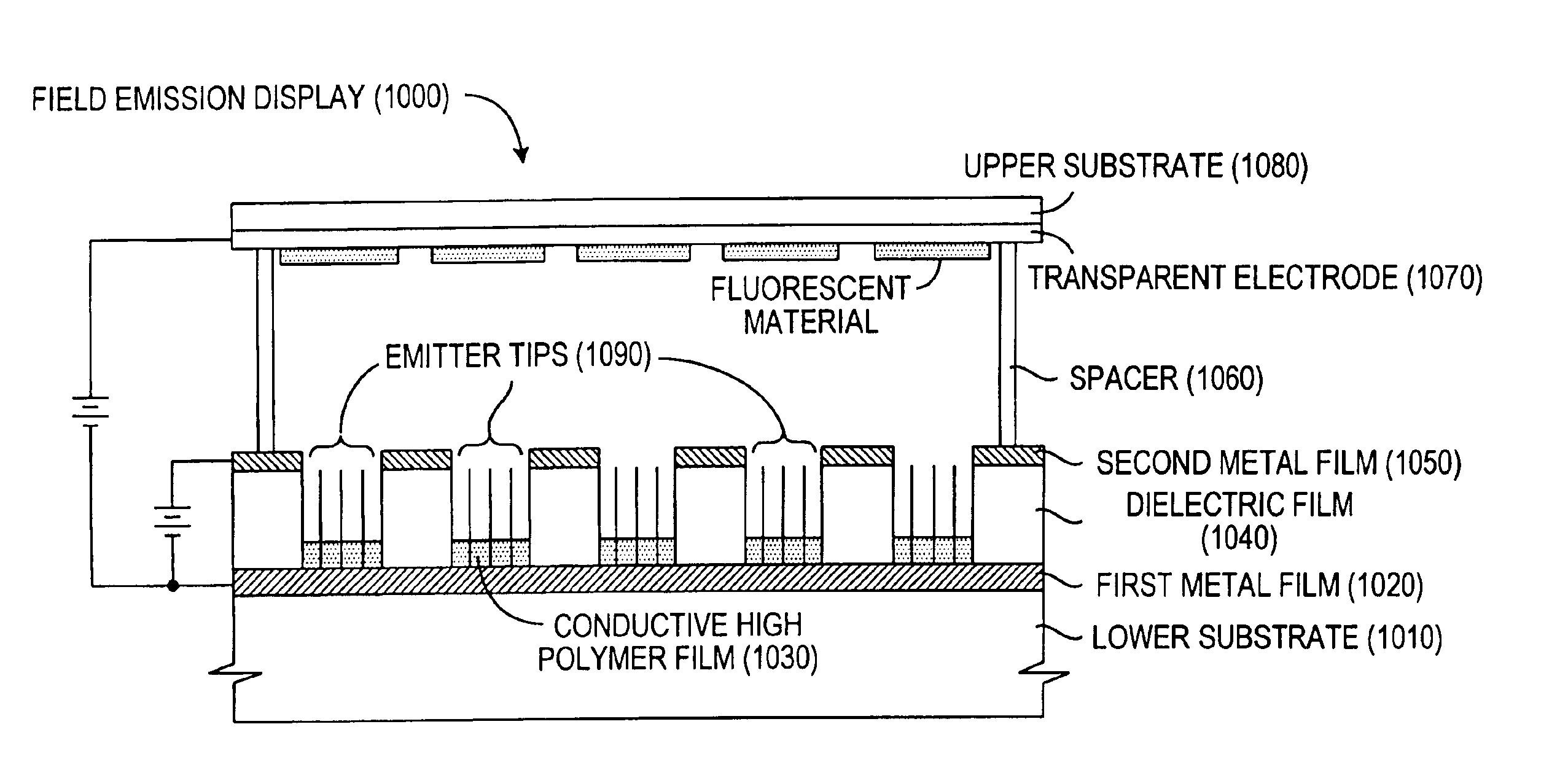
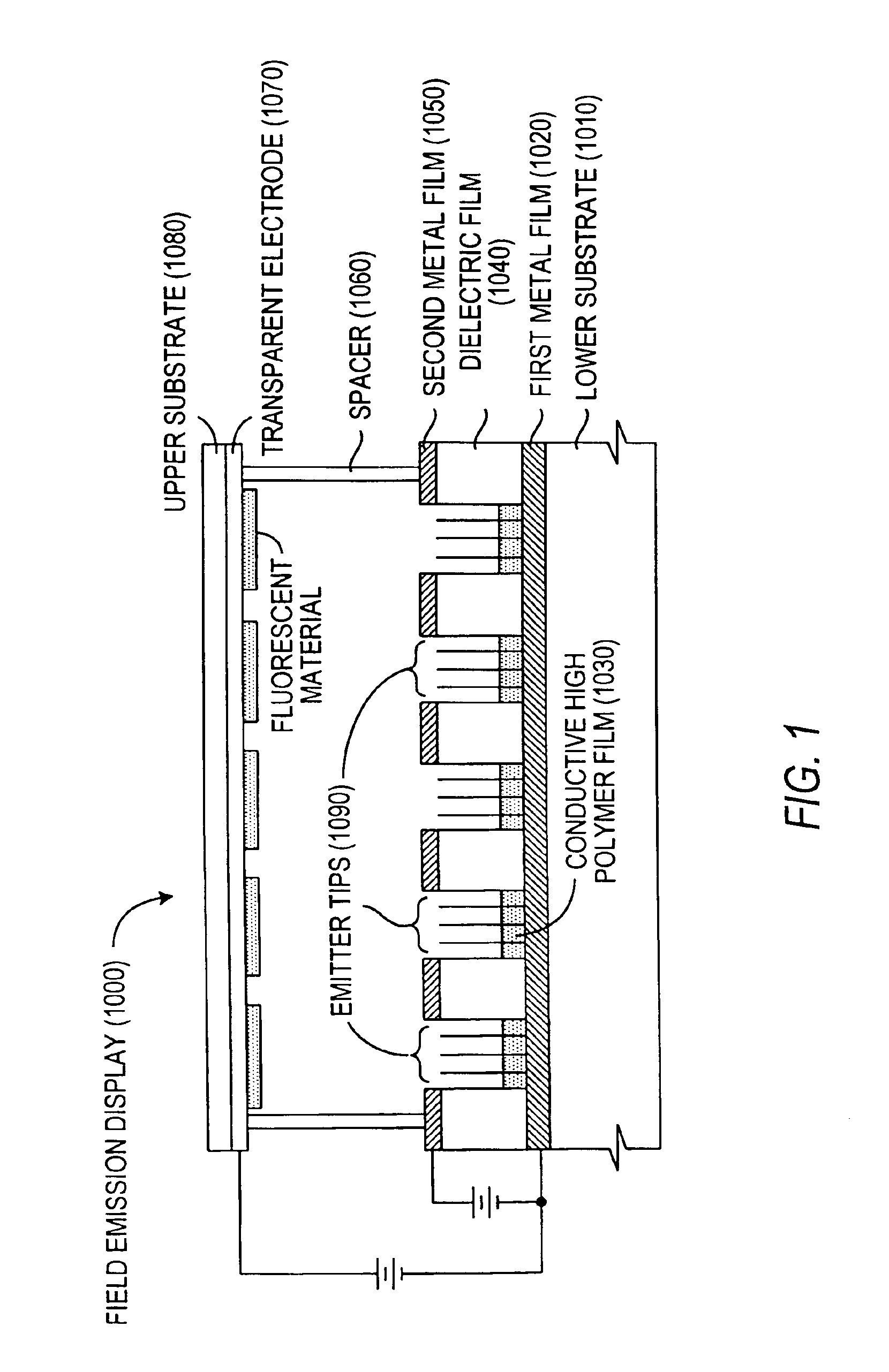
Field emission display and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20010004979A1Stable driving voltageUniform characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLow voltageCarbon nanotube
Field emission display and method for fabricating the same, the field emission display including a cathode array having a cathode electrode formed on a substrate, insulating layers and carbon nanotube films for use as emitter electrodes formed alternately on the cathode electrode, and a gate electrode formed on the insulating layer, thereby permitting fabrication of a large sized cathode plate at a low cost because the film is formed by screen printing and exposure, which can reduce the cumbersome steps in fabrication of the related art Spindt emitter tip, and both a low voltage and a high voltage FEDs because the carbon nanotube film used as the emitter has a low work function, with an easy and stable electron emission capability.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Electron-emitting device provided with pores that have carbon deposited therein
An electron-emitting device disclosed has stable electron emission characteristics with little variation, in high electron emission efficiency, in high definition, and at low driving voltage. The electron-emitting device disclosed is constructed in such structure that on a substrate there are a lower electrode, an insulating layer having pores, and an upper electrode stacked in this order, the insulating layer is an anodic oxide layer, and a carbon deposit is formed in the pores.
Owner:CANON KK
Method of manufacturing a light filament from carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6957993B2Large specific surface areaIncreased durabilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotube yarnCarbon nanotube fet
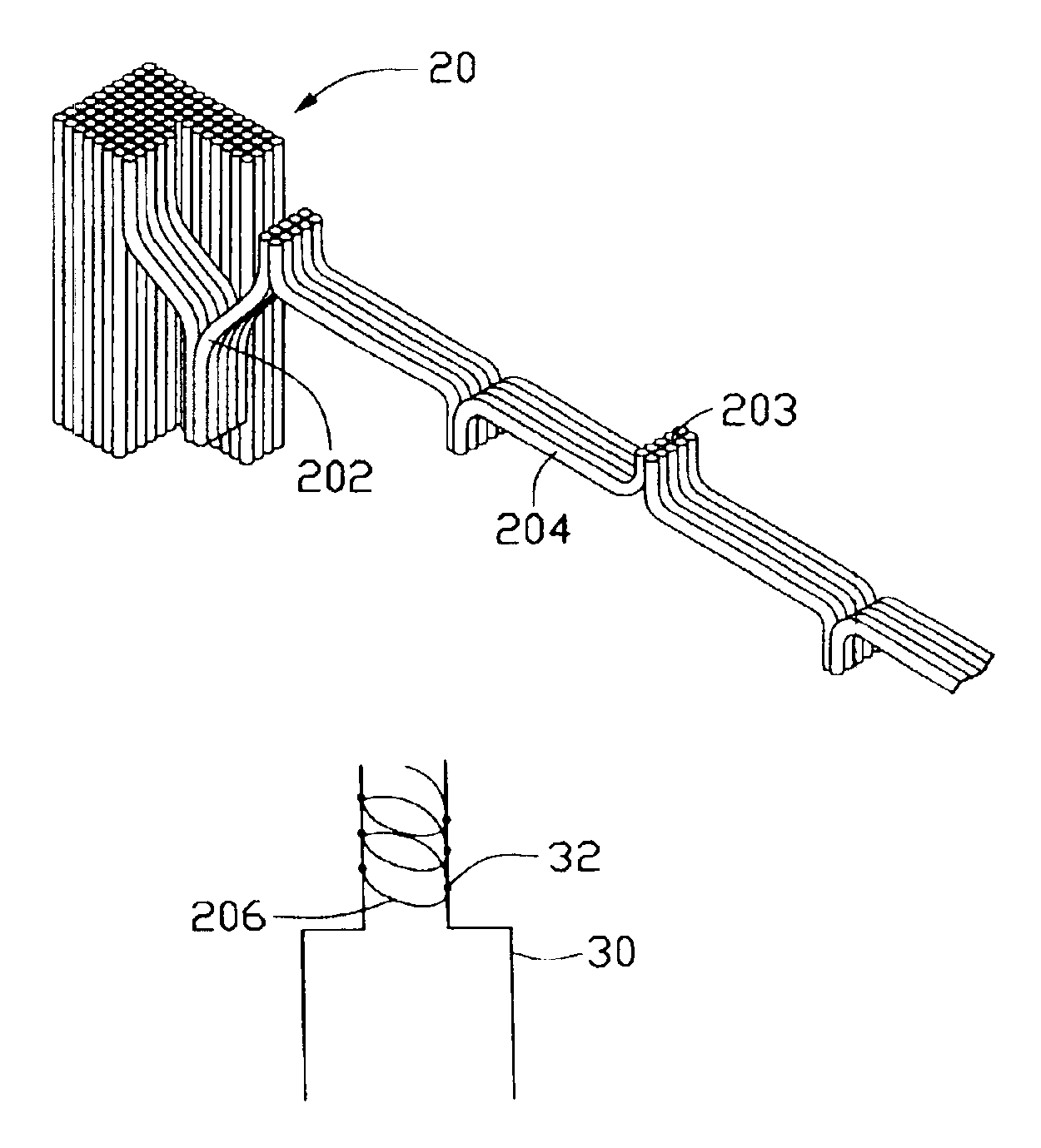
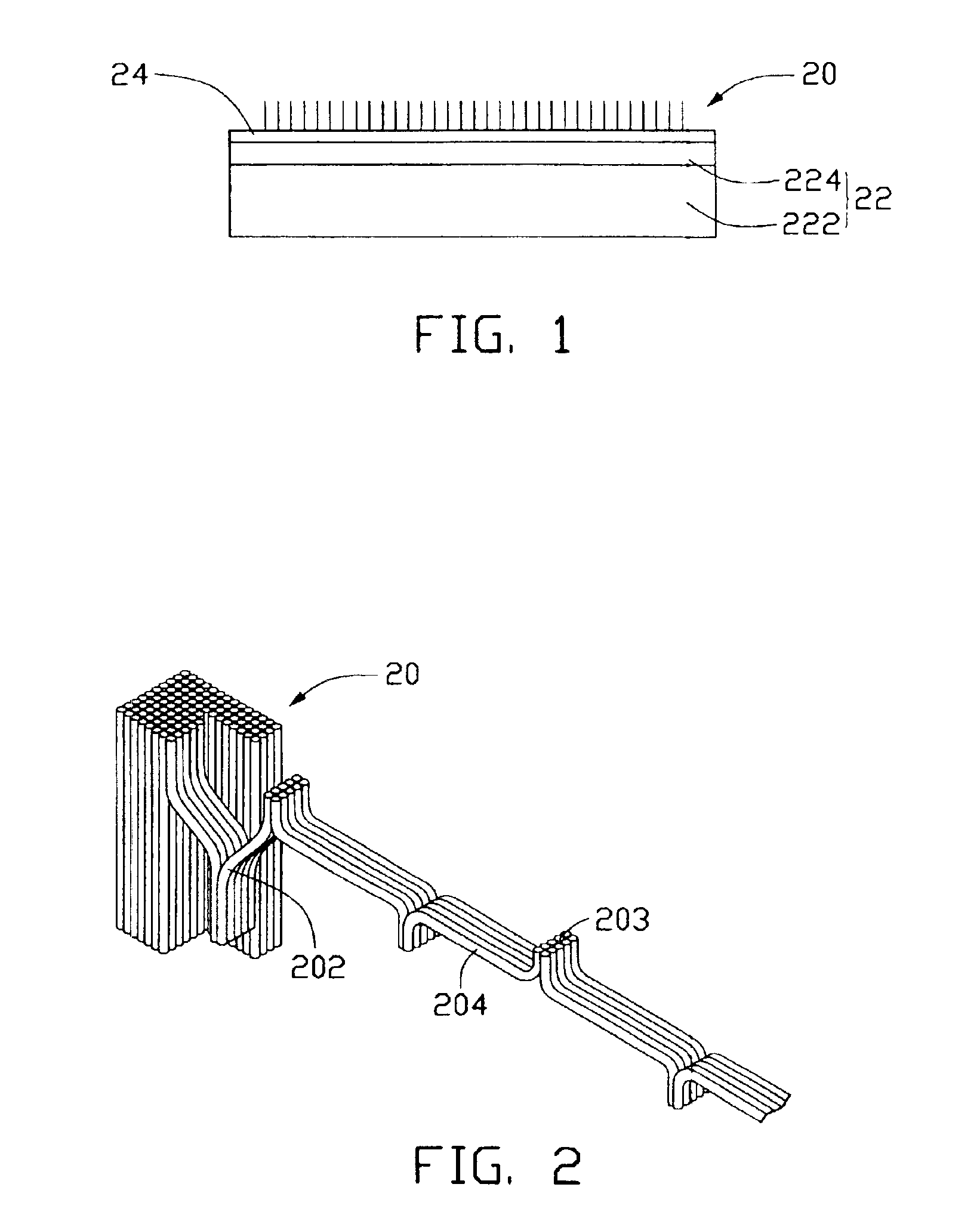
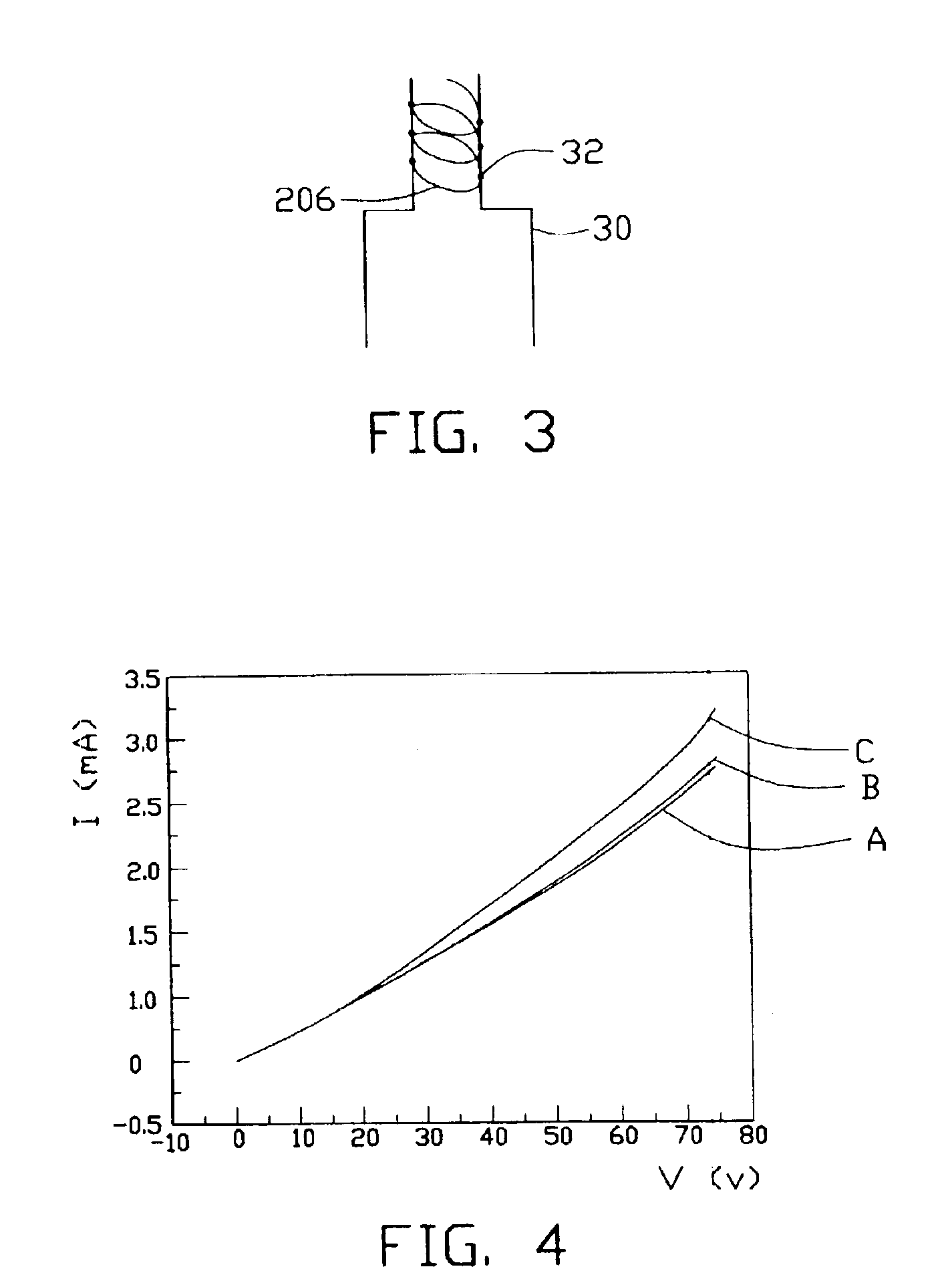
A light filament (206) formed from carbon nanotubes is characterized by high mechanical strength and durability at elevated temperatures, a high surface area to volume ratio, and high emissivity. Additionally, electrical resistance of the light filament does not increase with increasing temperature as much as electrical resistance of metallic light filaments. Accordingly, power consumption of the light filament is low at incandescent operating temperatures. A method for making a light filament made of carbon nanotubes includes the steps of: forming an array of carbon nanotubes (20); pulling out carbon nanotube yarn (204) from the carbon nanotube array; and winding the yarn between two leads (30) functioning as electrodes to form the light filament.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD +1
Micro-component for use in a light-emitting panel
InactiveUS6762566B1Sufficient resolutionManufactured very thinMechanical apparatusVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsEngineeringImproved method
An improved light-emitting panel having a plurality of micro-components sandwiched between two substrates is disclosed. Each micro-component contains a gas or gas-mixture capable of ionization when a sufficiently large voltage is supplied across the micro-component via at least two electrodes. Several improved methods of forming micro-components are also disclosed.
Owner:LEIDOS
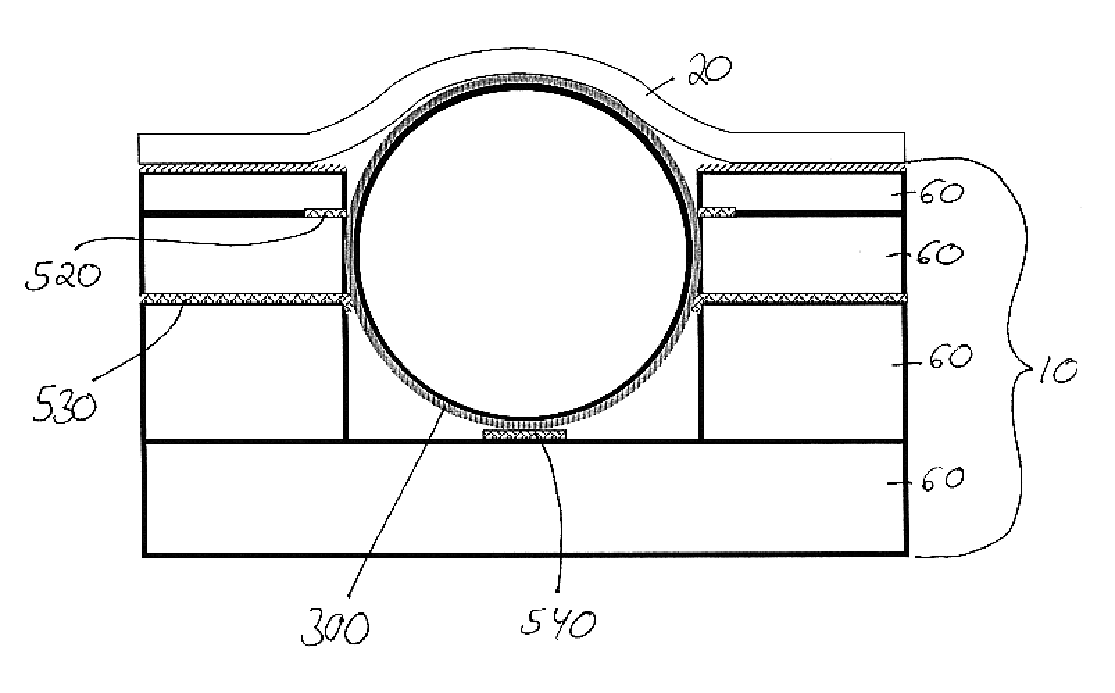
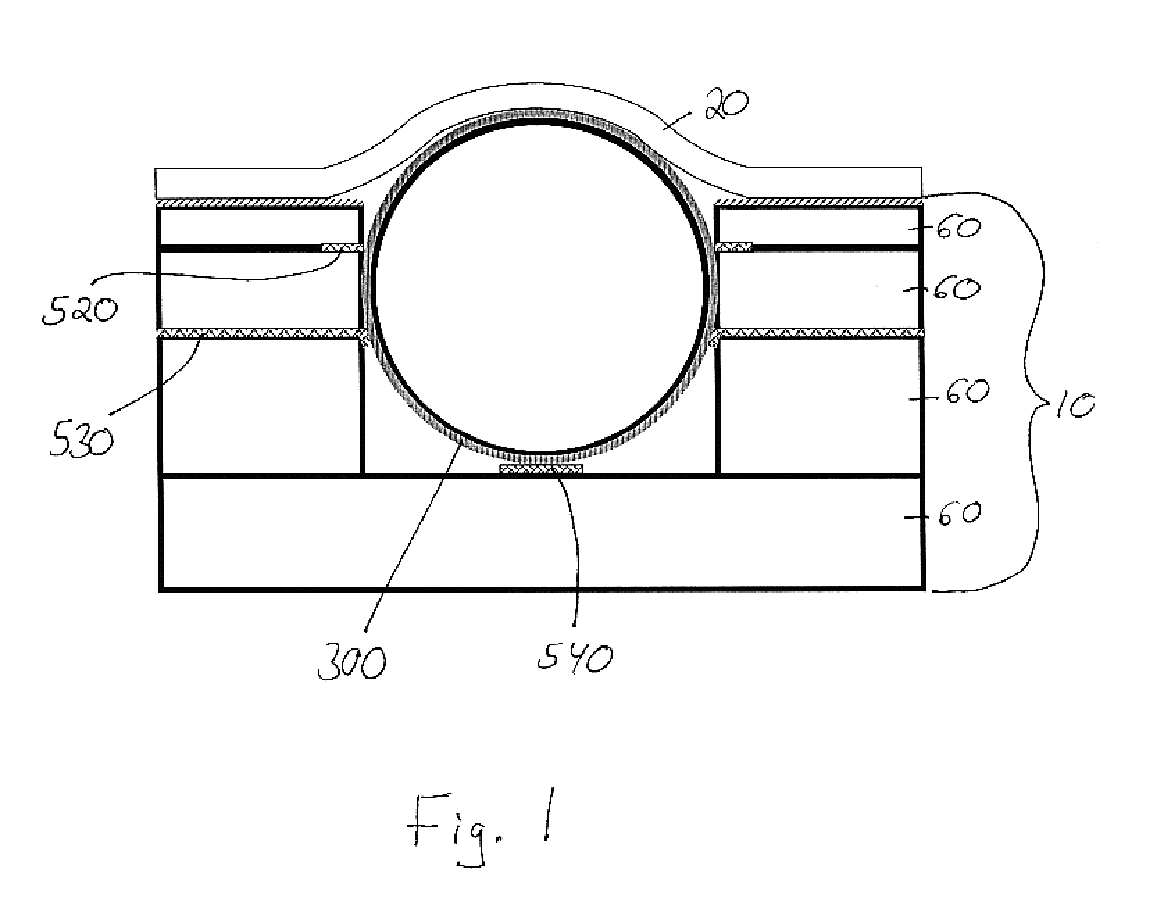
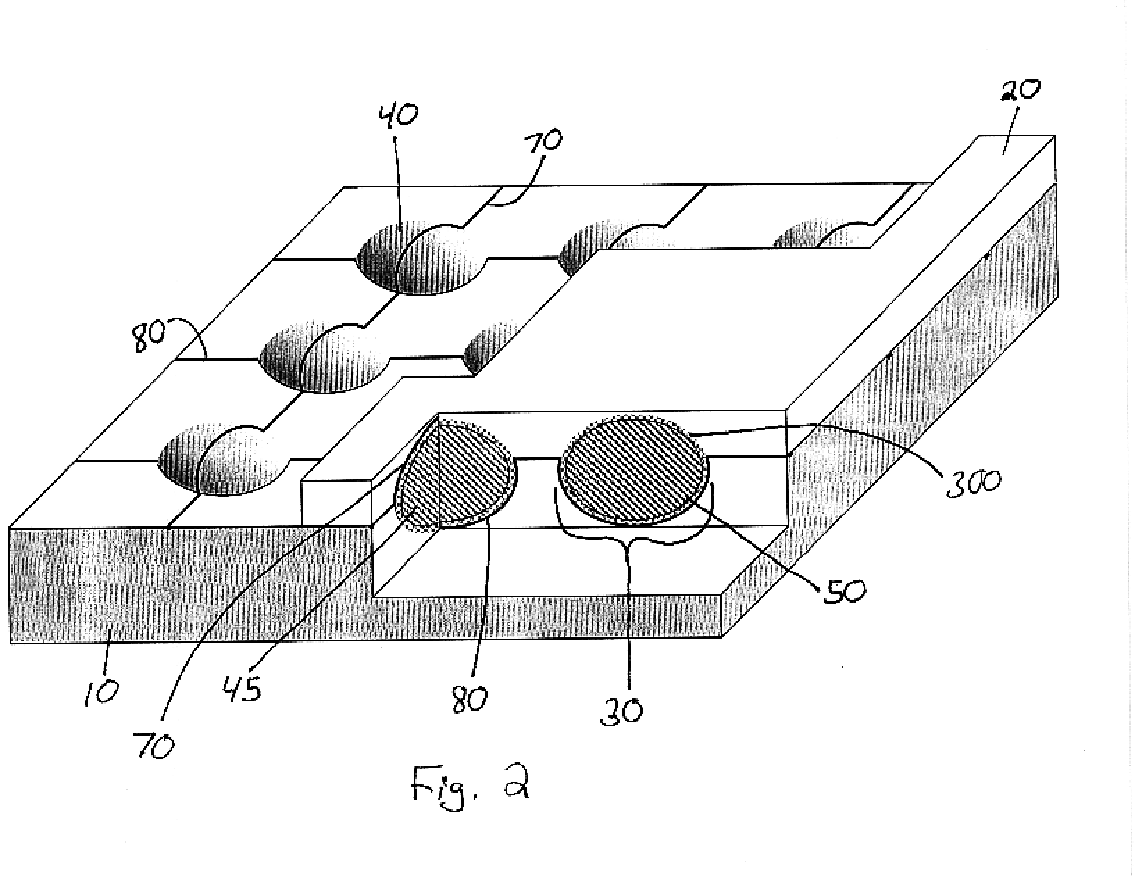
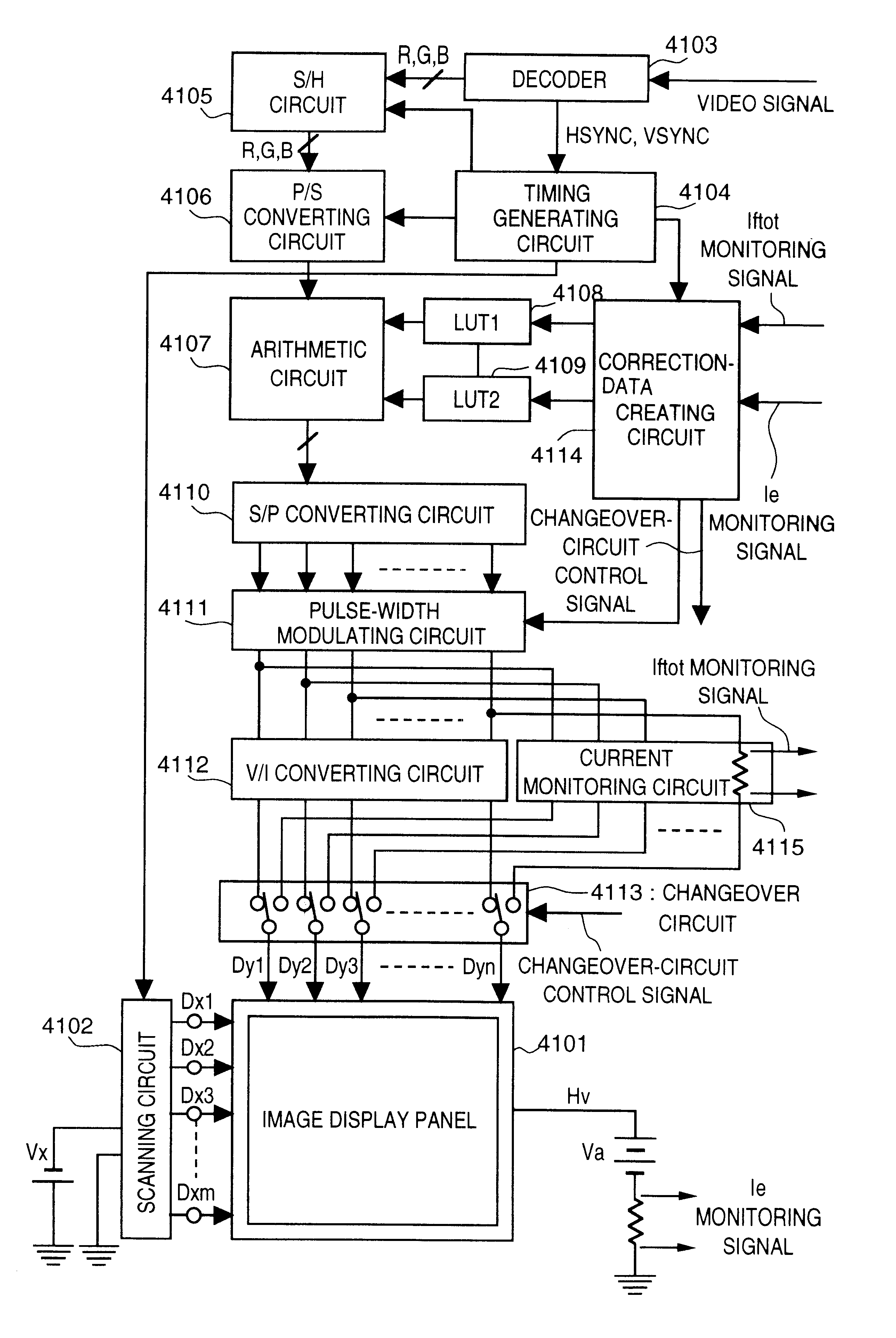
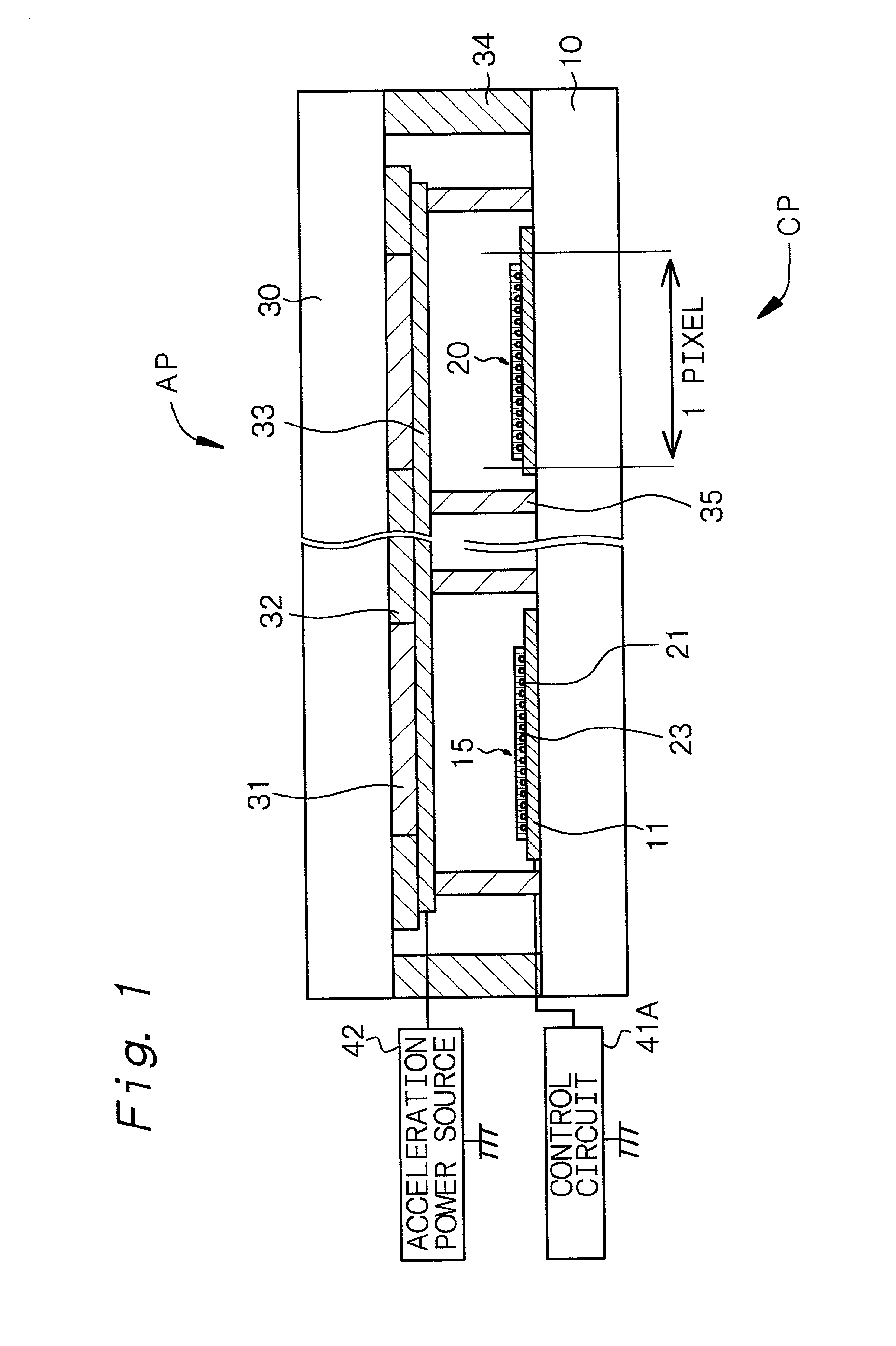
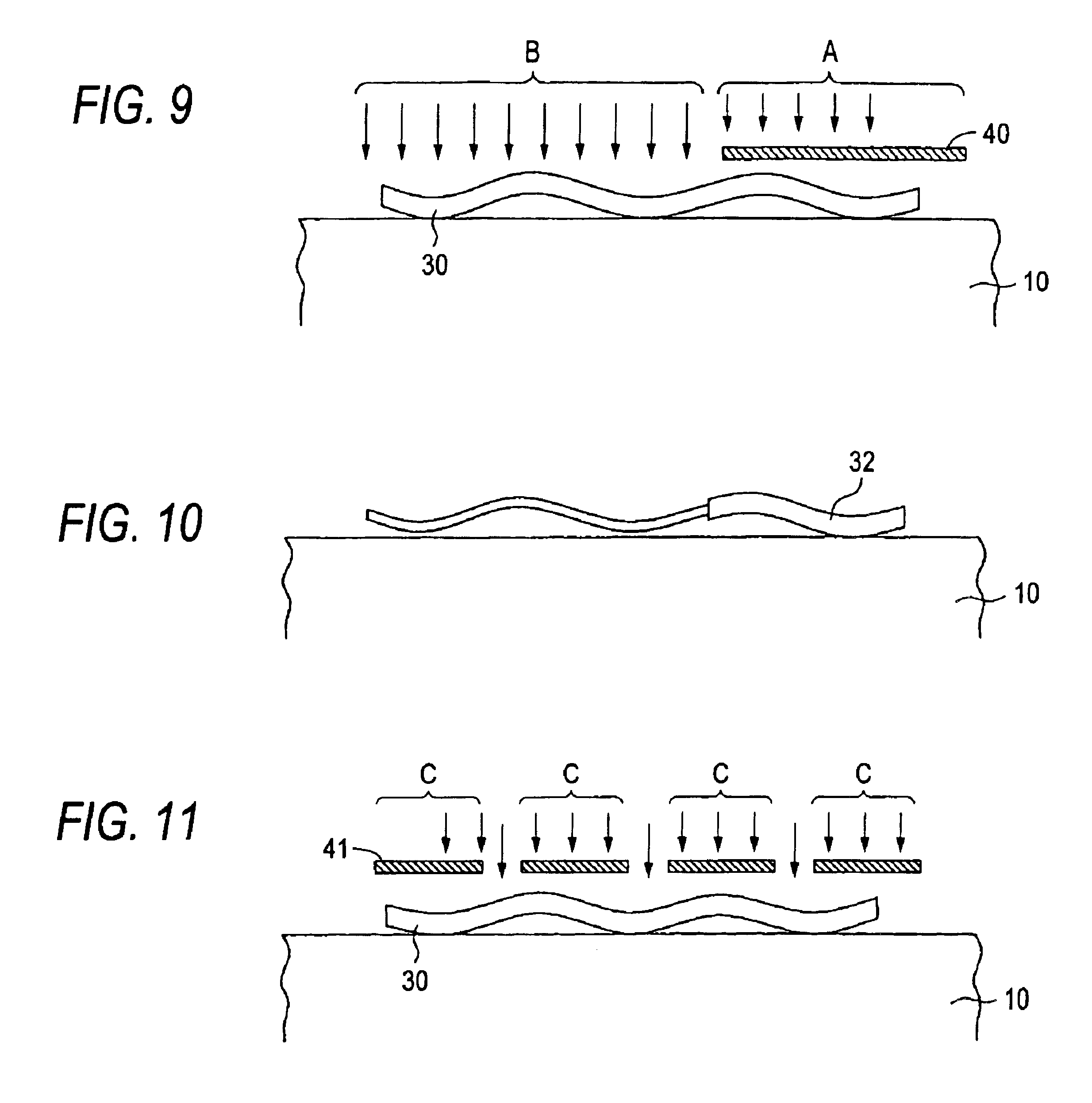
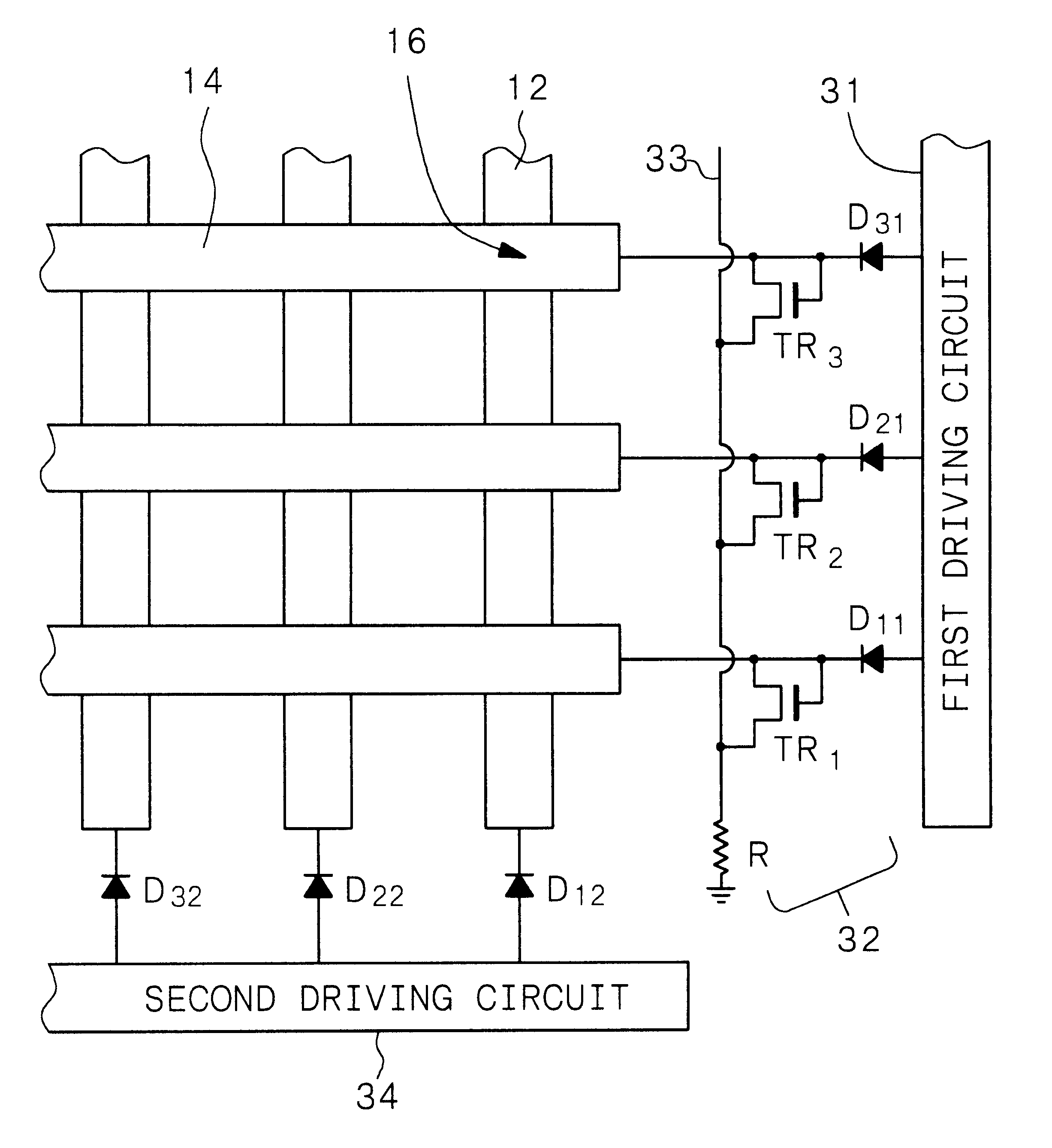
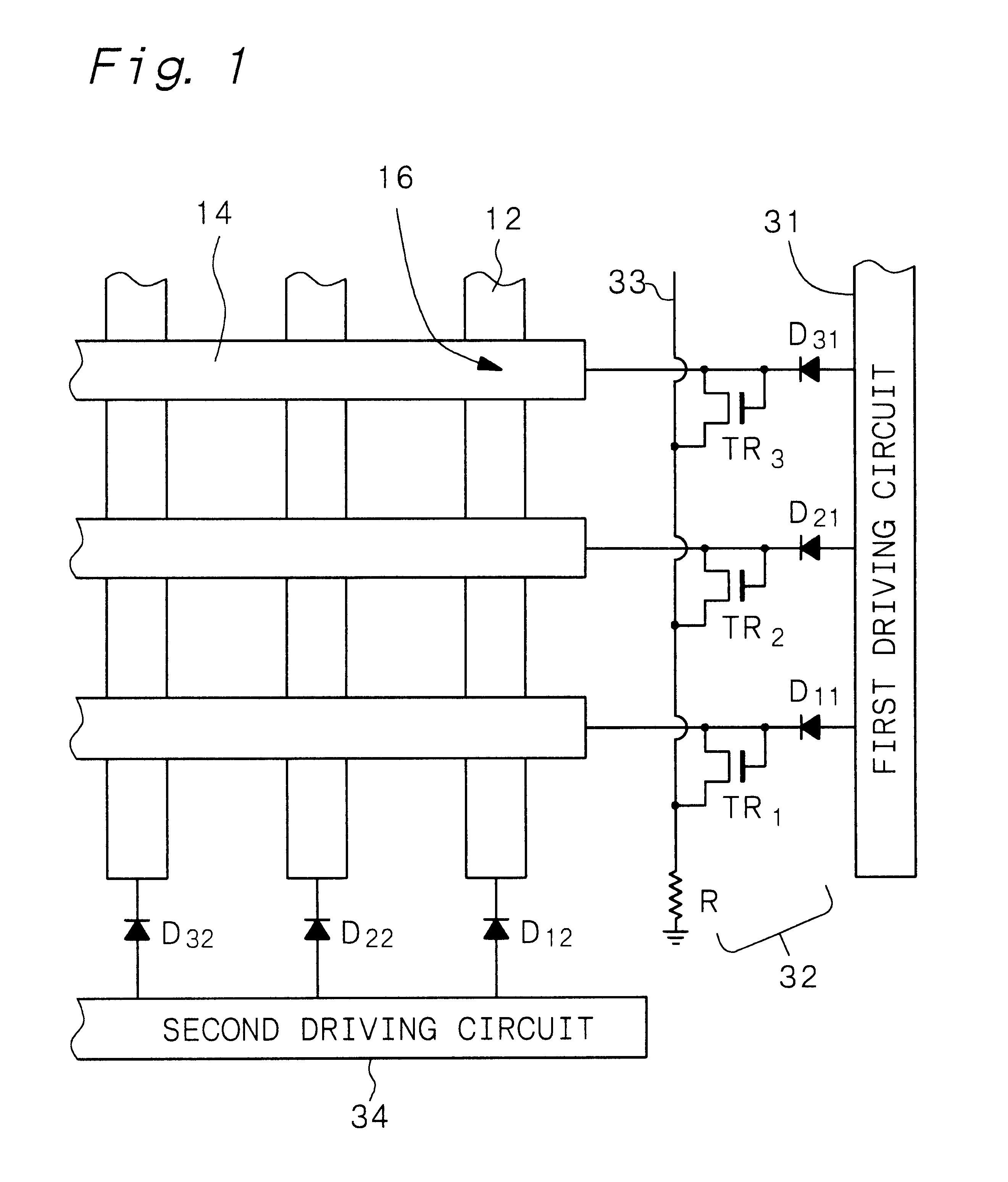
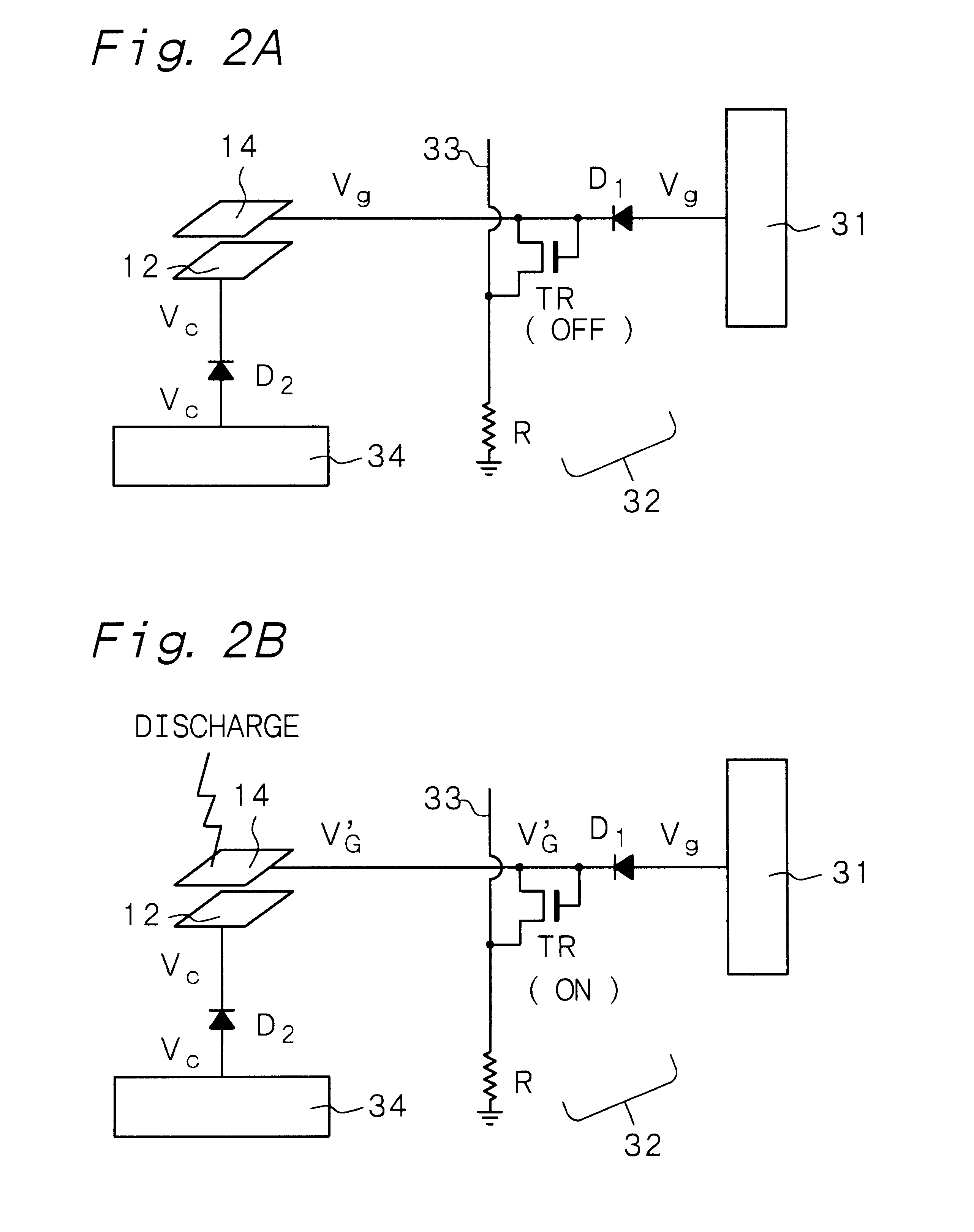
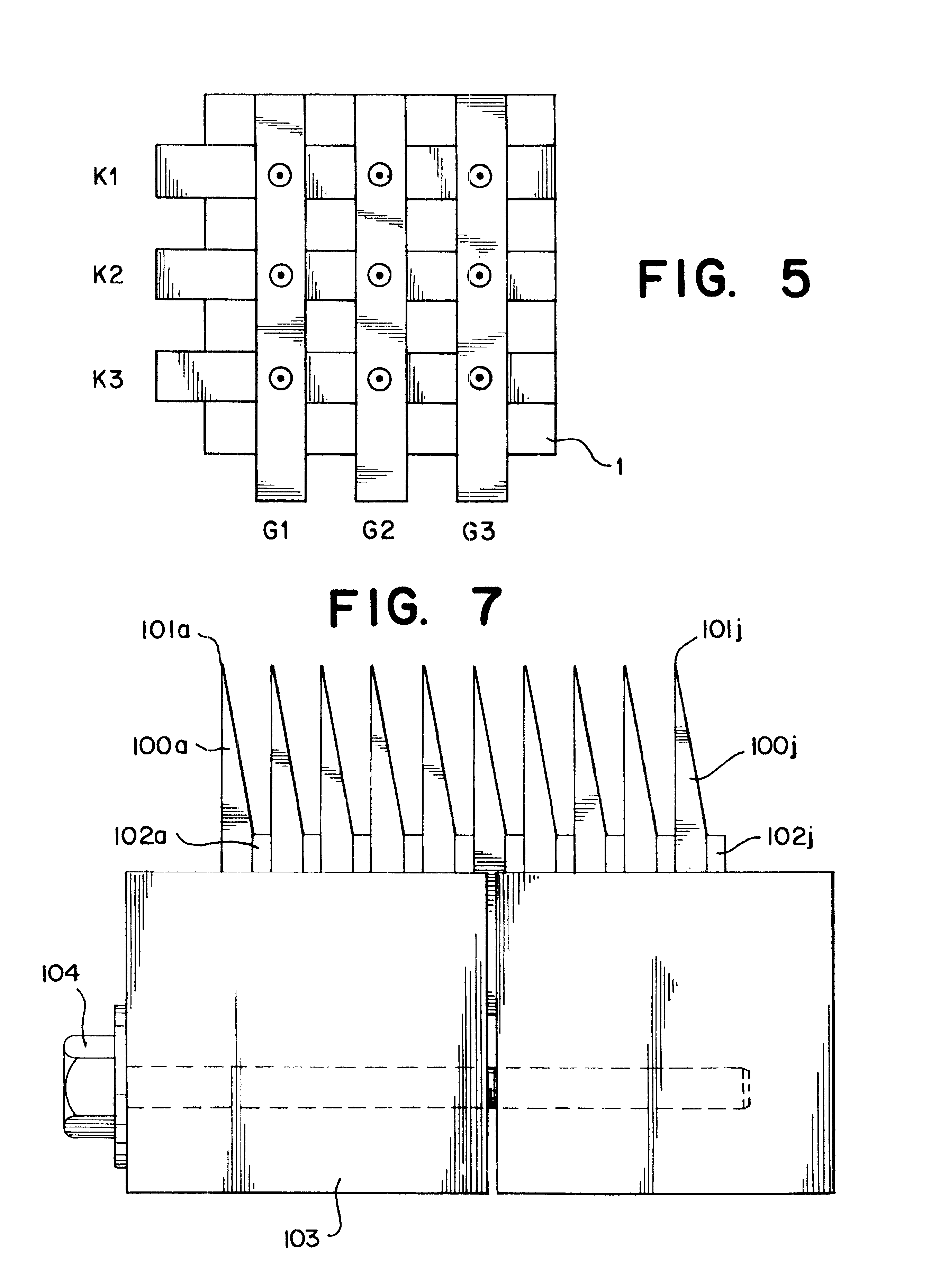
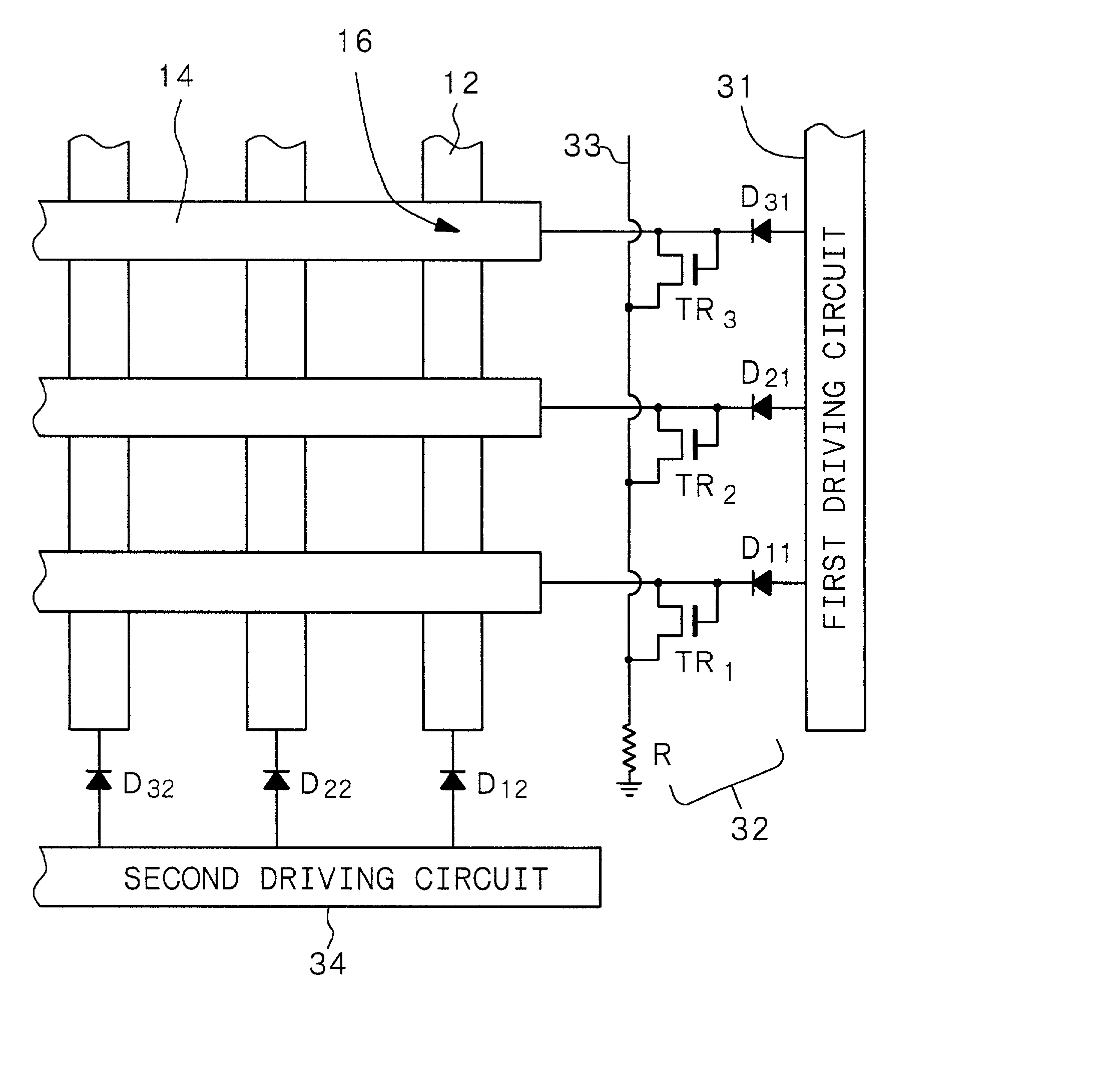
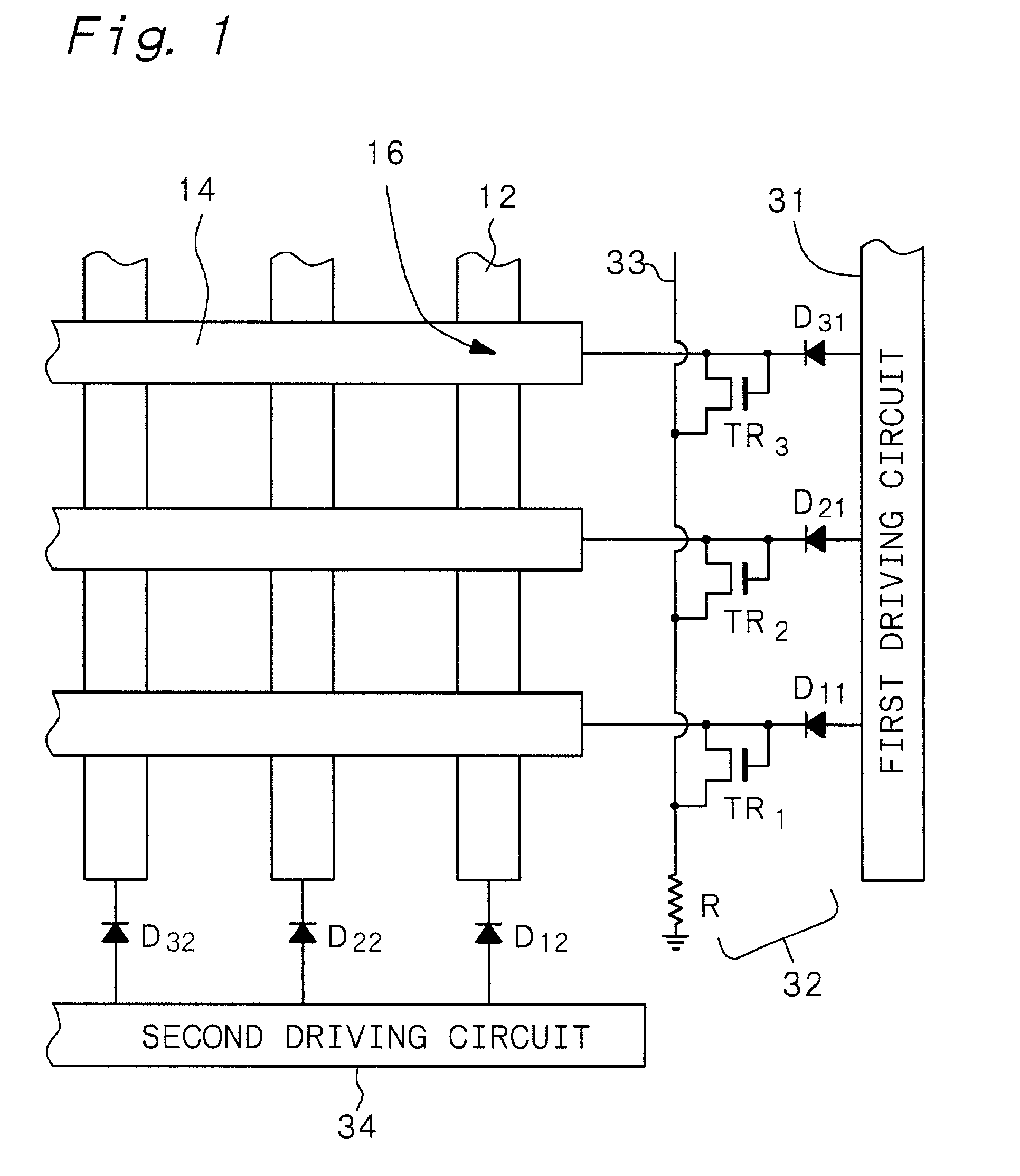
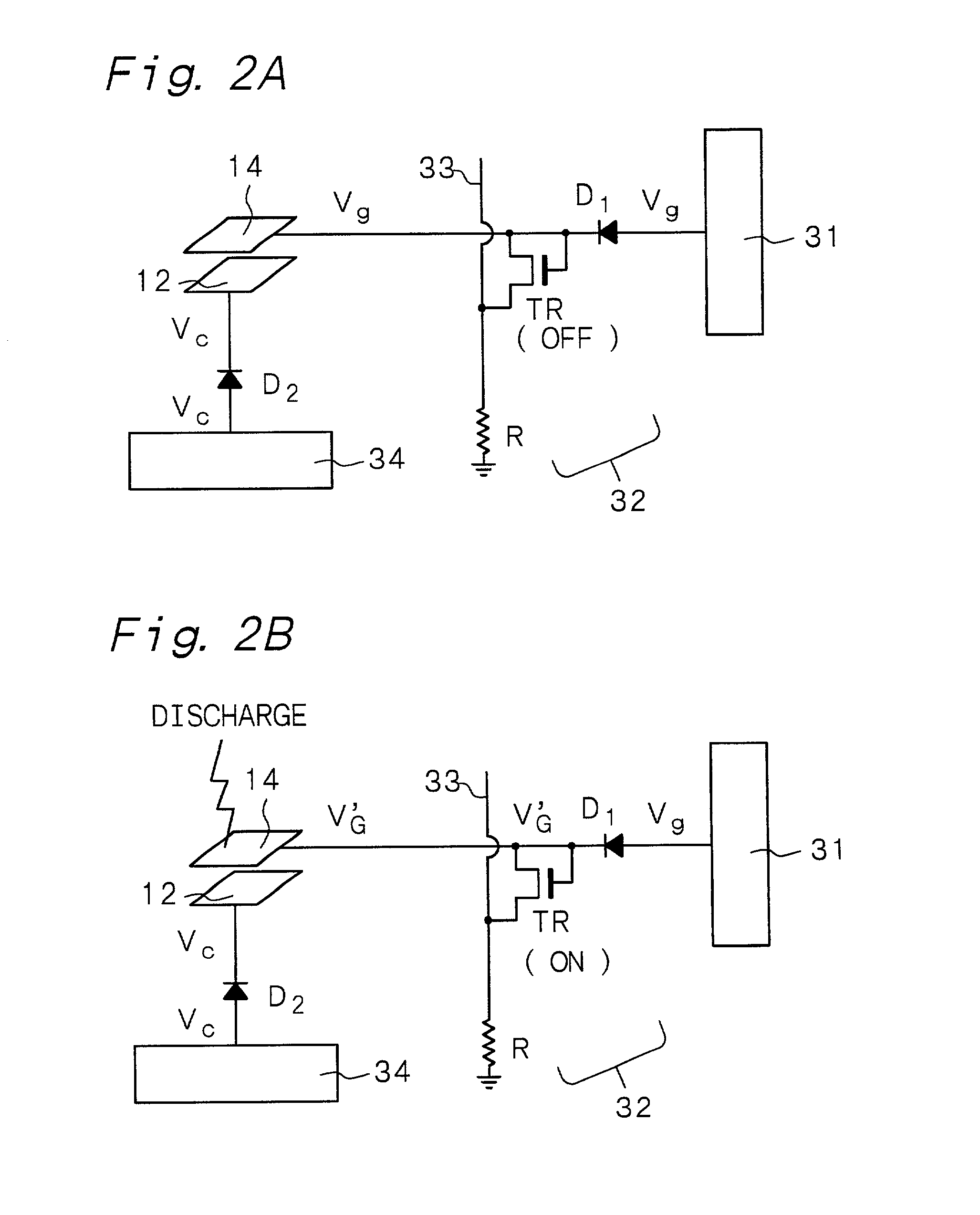
Electron-beam generating device having a plurality of cold cathode elements, method of driving said device and image forming apparatus applying same
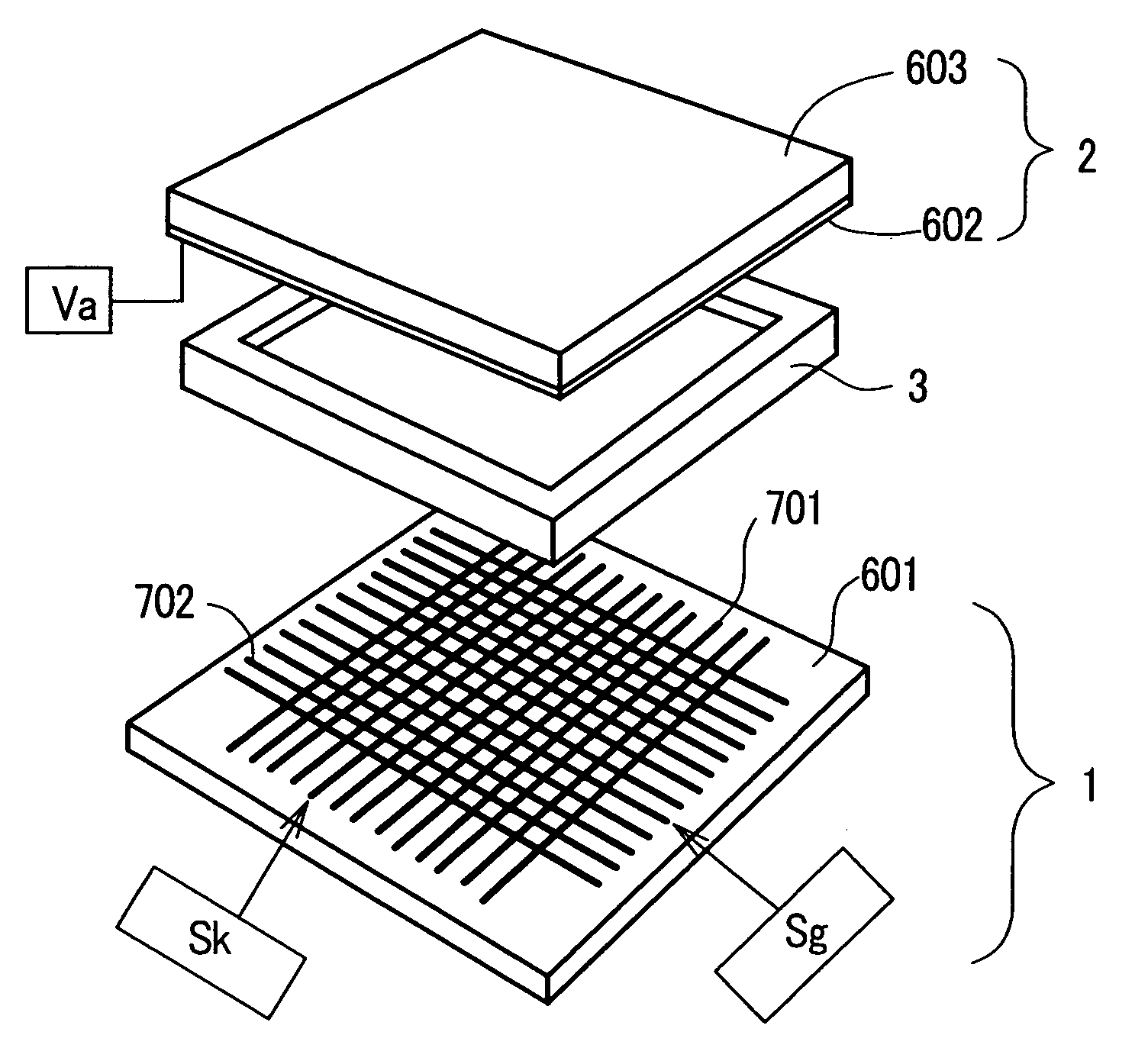
A method and apparatus for driving an electron source in which a high-quality image display is presented by correcting a non-uniform effective current distribution caused in cold cathode elements by leakage current. A digital video signal enters a shift register where a serial-to-parallel conversion is made for each line of an image based upon a shift clock signal. One line of the image data that has been subjected to the serial-to-parallel conversion is latched in a latch circuit and then applied to a voltage modulating circuit. The latter voltage-modulates the input data and sends the modulated signal to a voltage / current converting circuit. The latter converts the voltage quantity to a current quantity, which is applied to each of the cold cathode elements of a display panel through respective column terminals. A voltage V1 is applied to the selected row wire, and a voltage V2 (V2<> V1) is applied to all other row wires, for controlling the leakage current.
Owner:CANON KK
Electronic light emissive displays incorporating transparent and conductive zinc oxide thin film
InactiveUS6541908B1Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesDisplay deviceOxide cathode
The present invention provides co-doped zinc oxide to flat panel, light emissive display devices and vacuum microelectronic devices to improve their efficiency and lifetime. This material has a low growth temperature and is compatible with metal oxide semiconductor (MOS) processing technology. It is tranparent, chemically stable and has a low work function, which result in many advantages when being used as the cathode for the aforementioned devices. In one embodiment of the emissive display device, an organic light diode (OLED) display has a high work function metal anode, such as platinum (Pt), gold (Au) or nickel (Ni) and a low work function co-doped zinc oxide cathode. Because of the energy level alignment provided by these two materials, the potential energy barriers to injection of electrons from the cathode and holes from the anode into the organic emissive medium are minimized so the display device operates more efficiently.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Emissive flat panel display having electron sources with high current density and low electric field strength
InactiveUS7196463B2Reduce voltageNo coarsenessDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsHigh current densityLow voltage
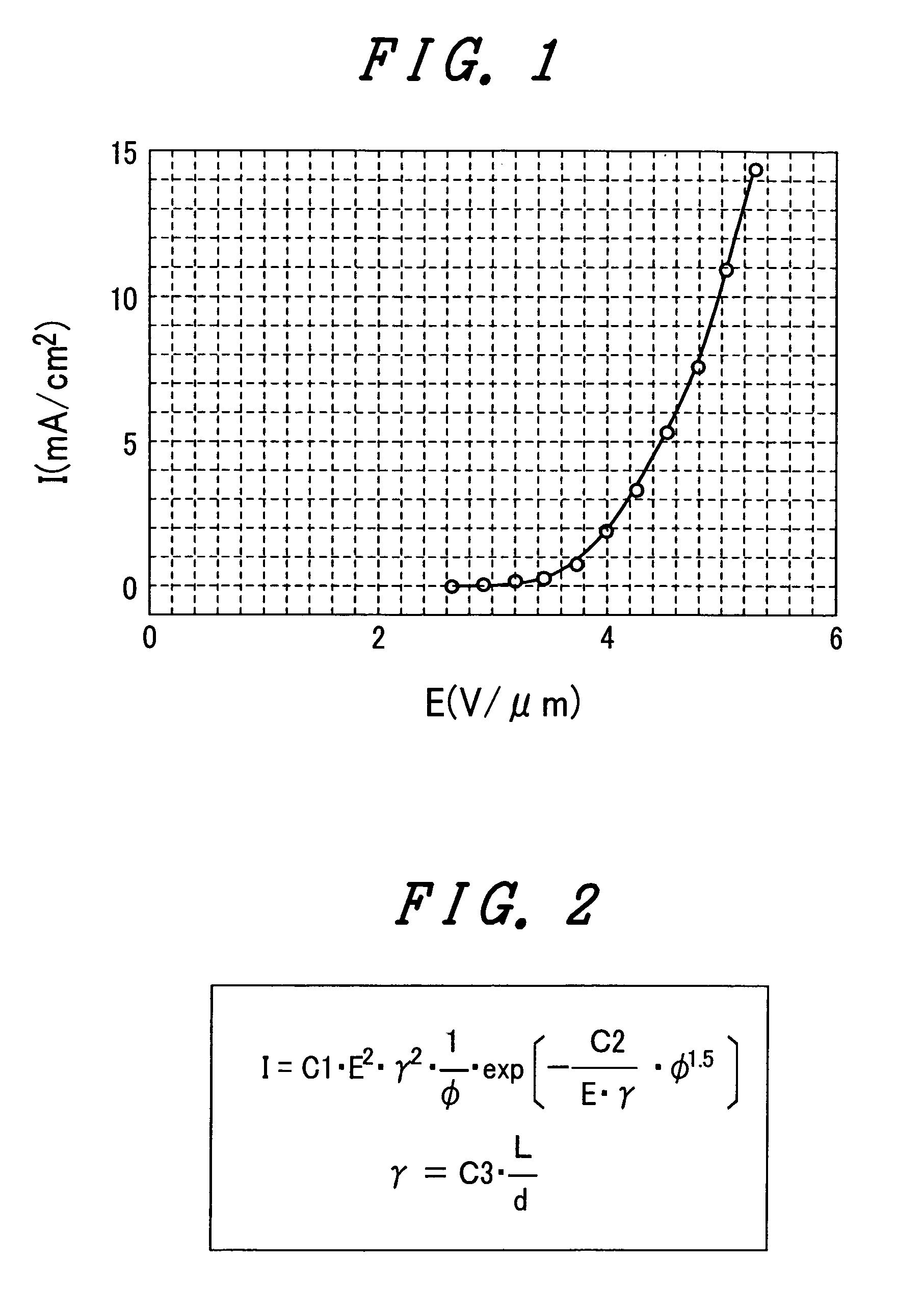
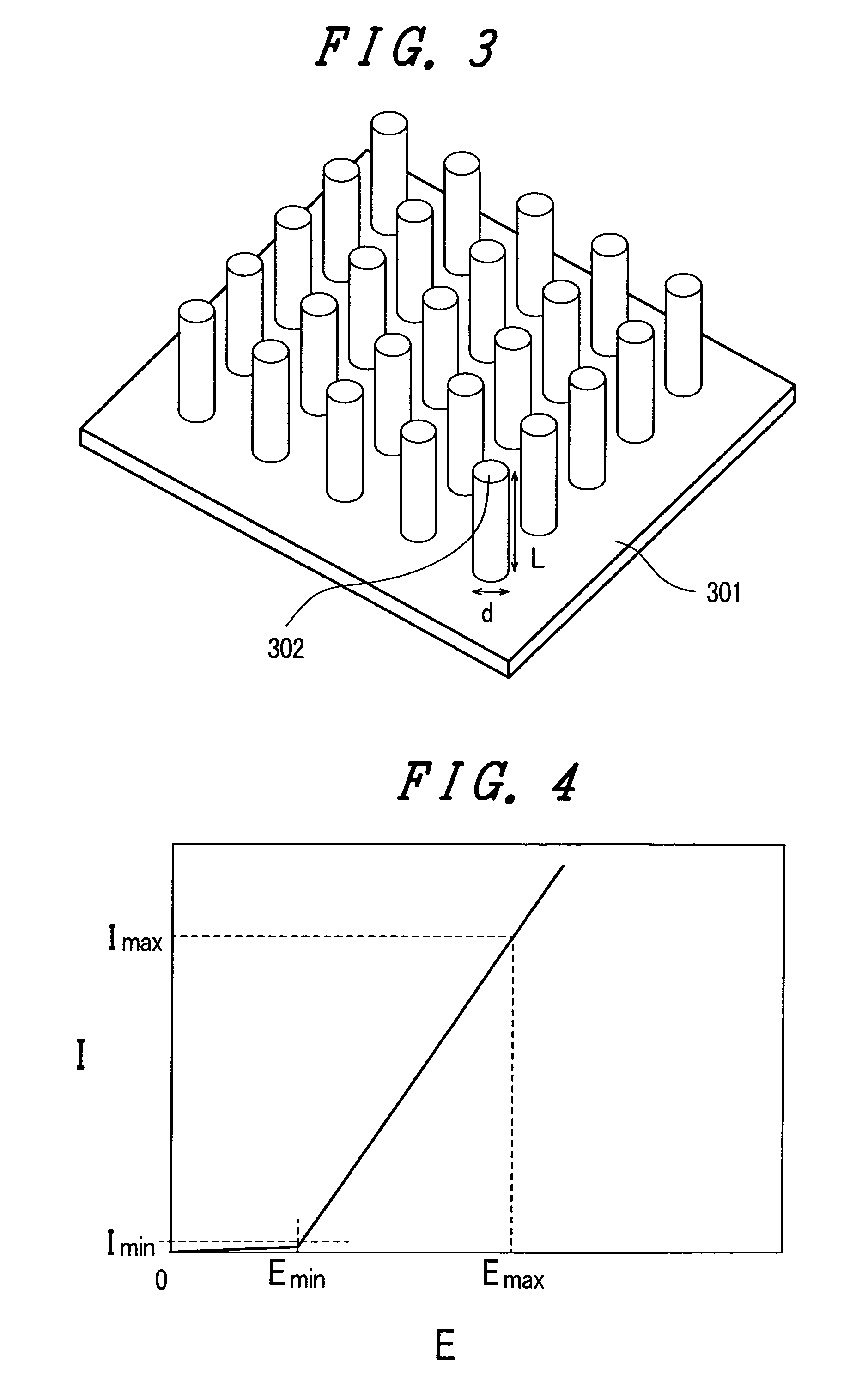
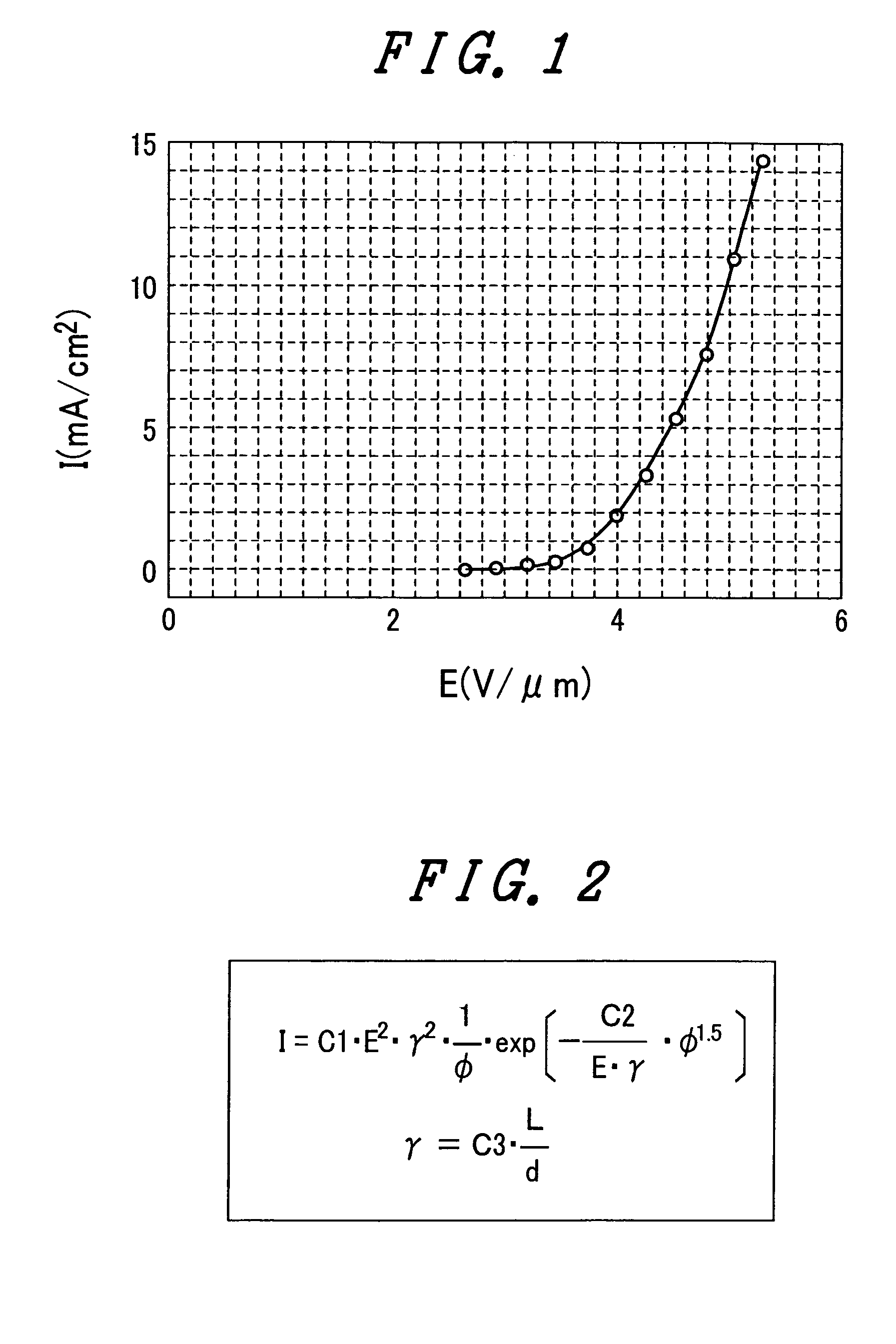
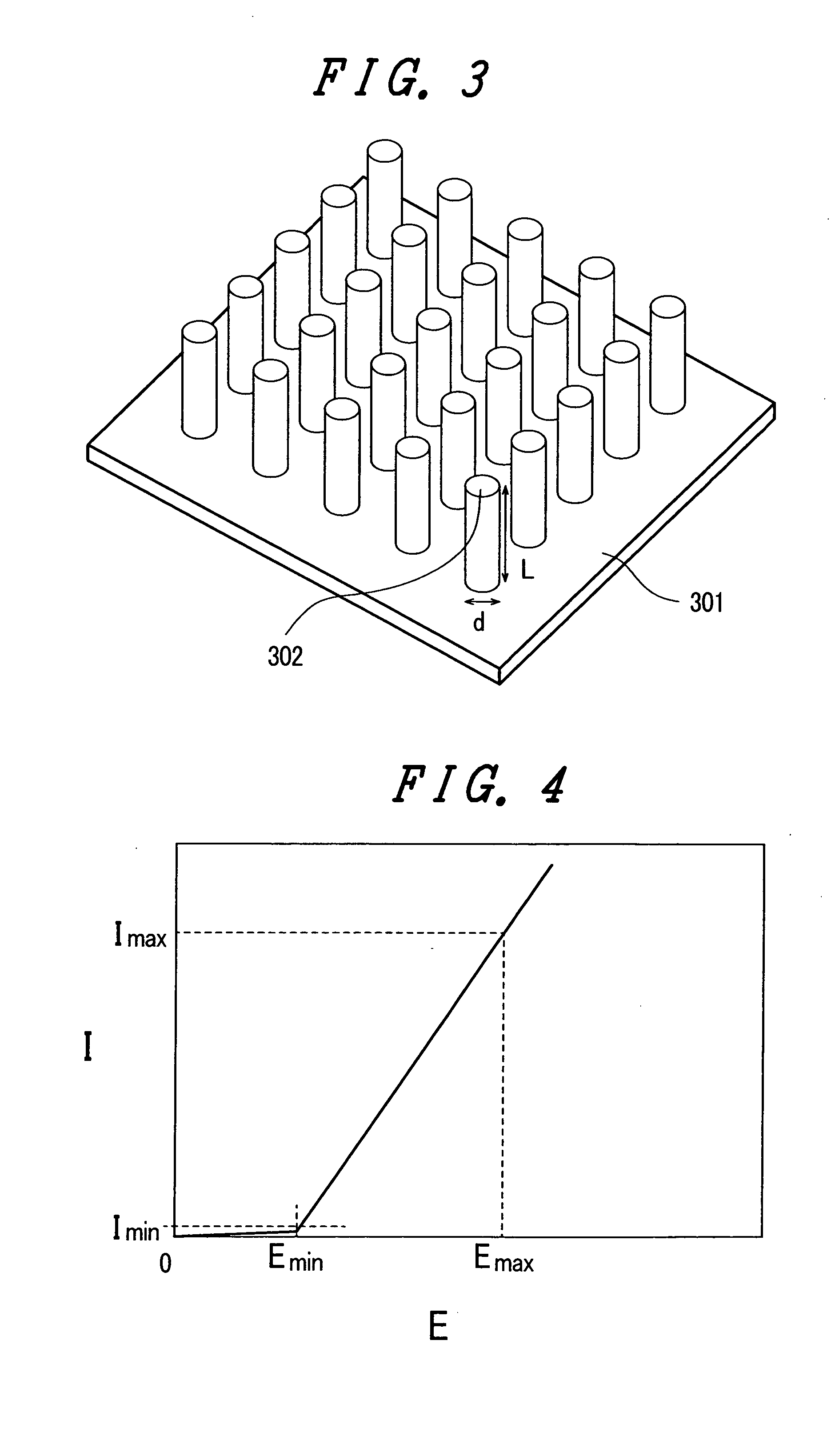
The present invention provides an emissive flat panel display device which is capable of performing a gate operation at a relatively low voltage of several V to several tens V using gate electrodes. In the emissive flat panel display device which includes a back panel which is constituted of a back substrate on which cathode electrodes having electron sources formed of carbon nanotubes and gate electrodes are formed, a face panel which forms phosphors and anode electrodes thereon, and a sealing frame which seals the back panel and the face panel, the difference between an electric field strength Emax for allowing the electron sources to obtain the required maximum emission current density and an electric field strength Emin which becomes the minimum emission current density is set to 1V / μm or less, and preferably 0.5V / μm or less.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS
Field emission devices using ion bombarded carbon nanotubes
InactiveUS6911767B2Reduce voltageAccelerate emissionsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesNanoinformaticsField emission deviceOxygen
The present invention relates to a field emission device comprising an anode and a cathode, wherein said cathode includes carbon nanotubes which have been treated with an ion beam. The ion beam may be any ions, including gallium, hydrogen, helium, argon, carbon, oxygen, and xenon ions. The present invention also relates to a field emission cathode comprising carbon nanotubes, wherein the nanotubes have been treated with an ion beam. A method for treating the carbon nanotubes and for creating a field emission cathode is also disclosed. A field emission display device containing carbon nanotube which have been treated with an ion beam is further disclosed.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
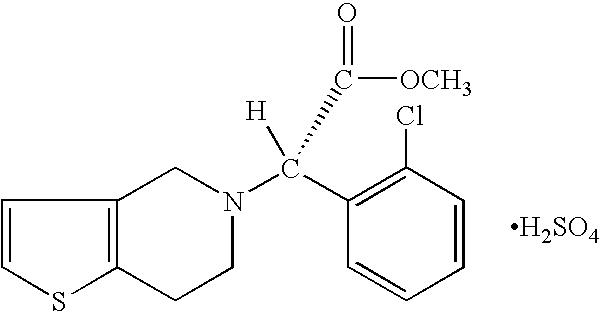
Nanoparticulate clopidogrel and aspirin combination formulations
InactiveUS20070003615A1Reduced bioavailabilityHigh dissolution ratePowder deliveryBiocideControl releasePharmaceutical drug
The present invention is directed to compositions comprising a nanoparticulate clopidogrel and aspirin combination, or salts or derivatives thereof, having improved clopidogrel bioavailability. The nanoparticulate clopidogrel particles, and optionally the nanoparticulate aspirin particles, of the composition have an effective average particle size of less than about 2000 nm and are useful in the prevention and treatment of pathologies induced by platelet aggregation. The clopidogrel and aspirin particles may also be formulated as a controlled release polymeric coating or matrix drug delivery system.
Owner:ELAN PHRMA INT LTD
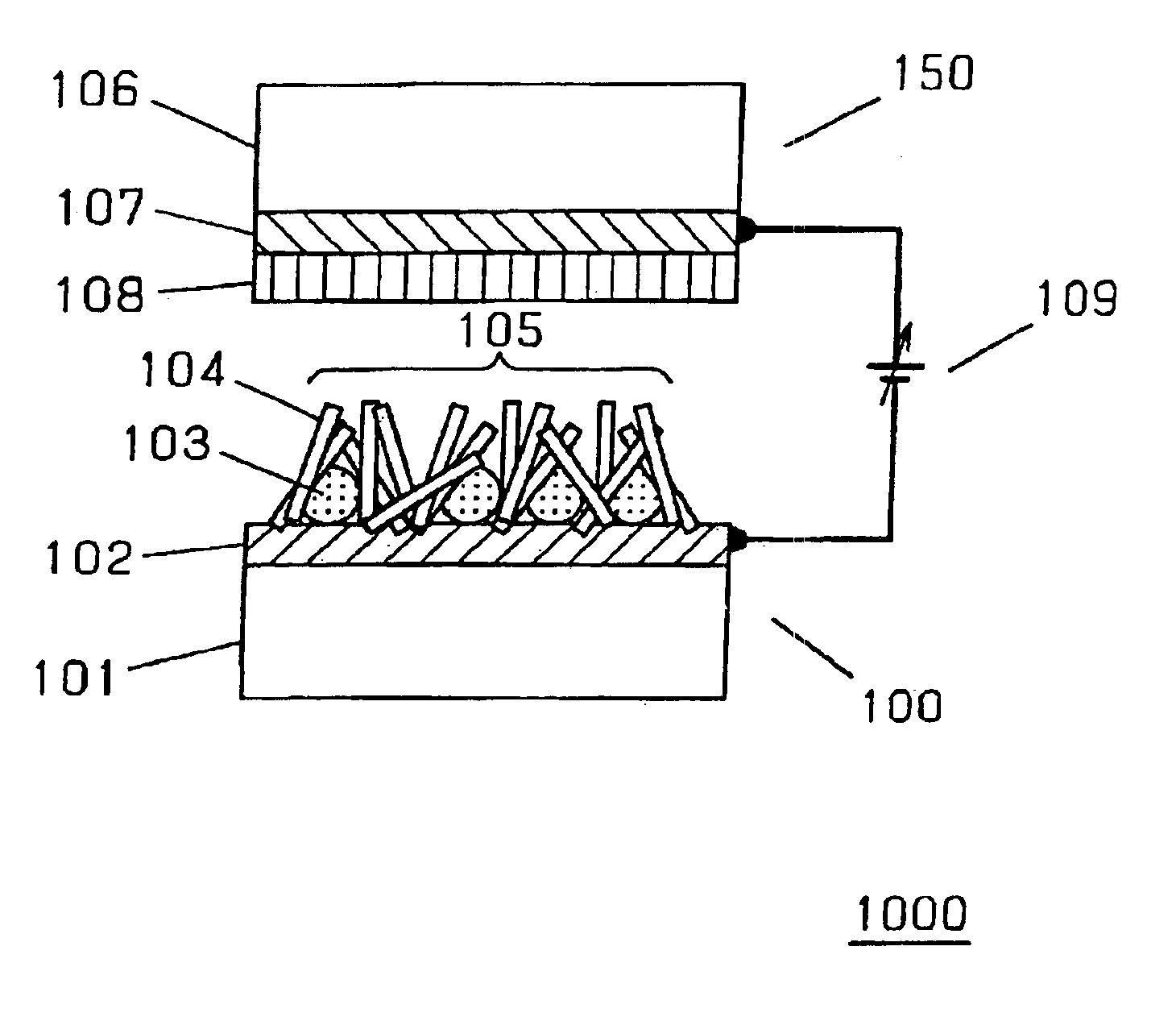
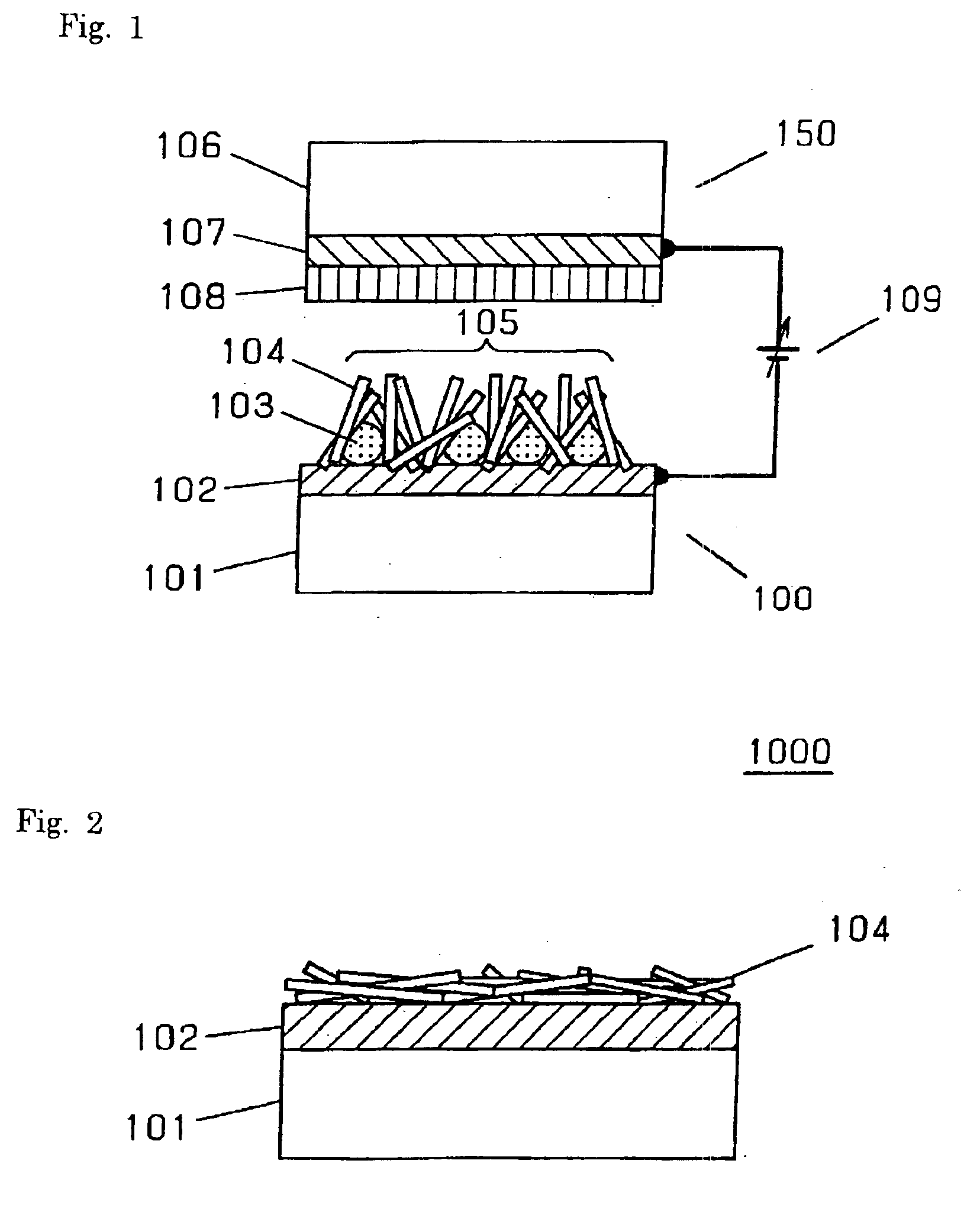
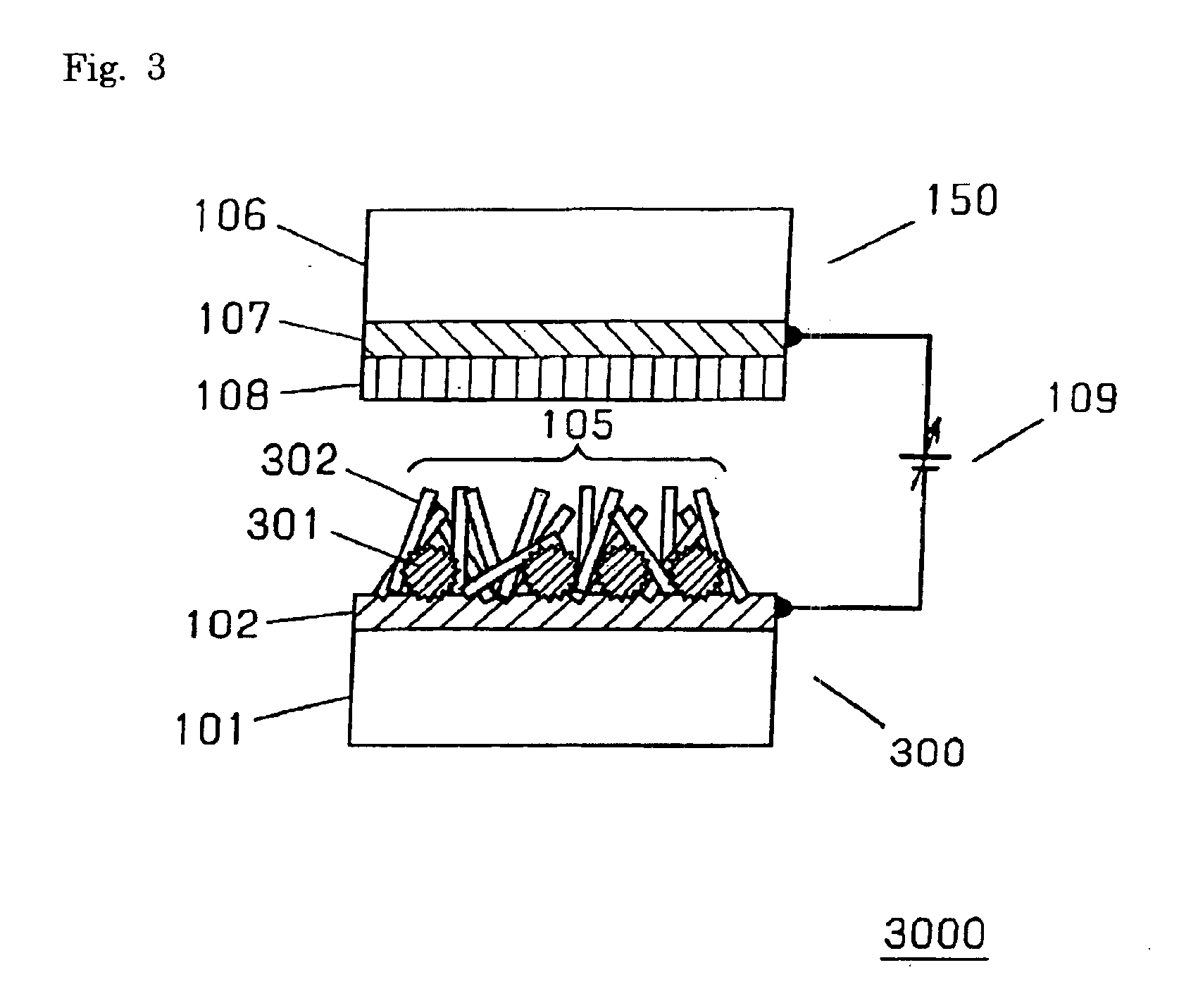
Electron-emitting element and electron source, field emission image display device, and fluorescent lamp utilizing the same and methods of fabricating the same
Disclosed are an electron-emitting element having a large operating current at a low operating voltage and excellent operation stability, and an electron source, an image display device and the like utilizing such an electron-emitting element, and further a method of fabricating such an element with few process steps at low cost. A cold cathode member is configured utilizing hybrid particle of a first particle serving to emit electrons into the space and a second particle being in the vicinity of the first particle and serving to control the position of the first particle. In this configuration, it is preferable that the first particle have a higher electron emission efficiency than the second particle and that the second particle be conductive.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Automatically sharp field emission cathodes
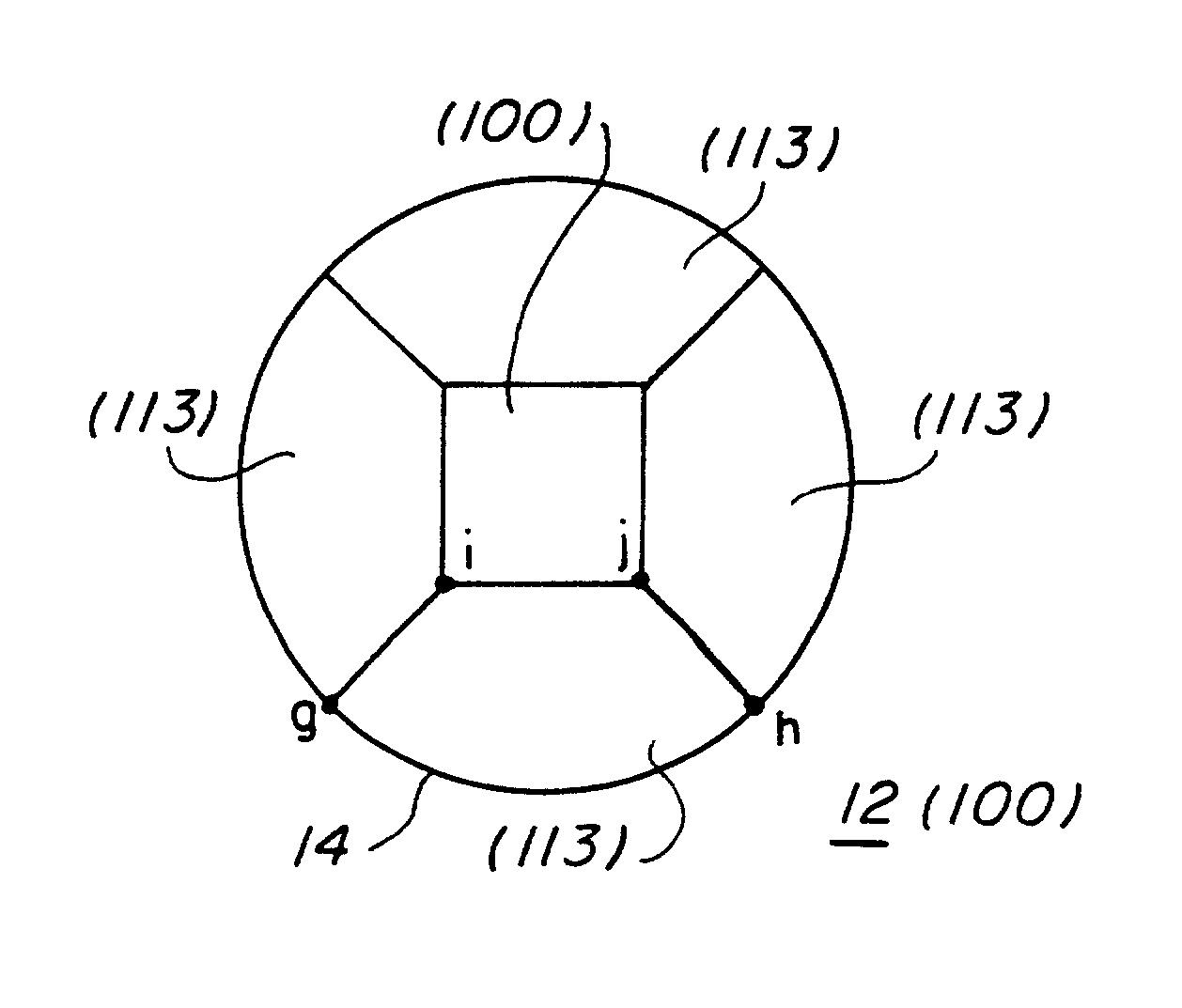
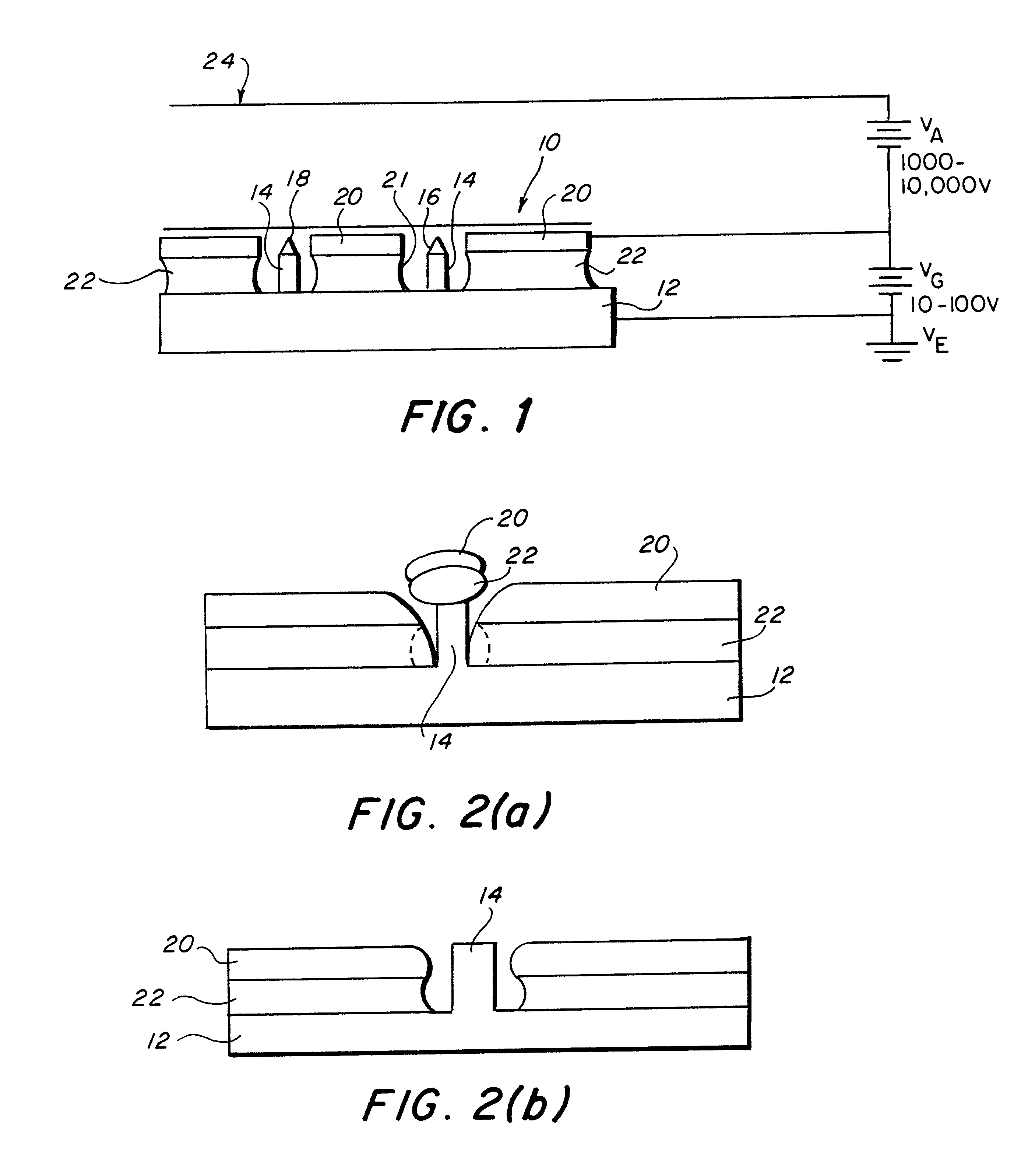
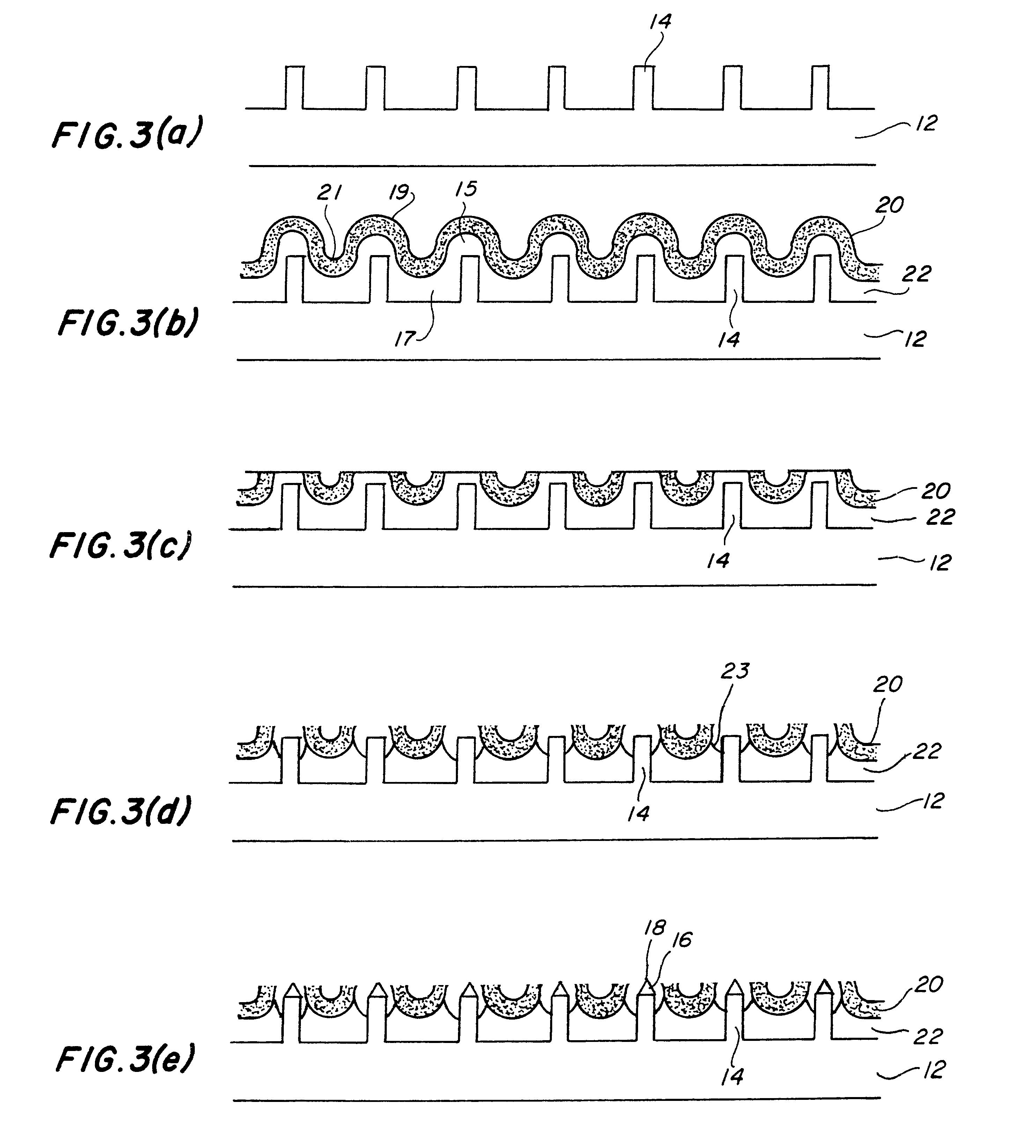
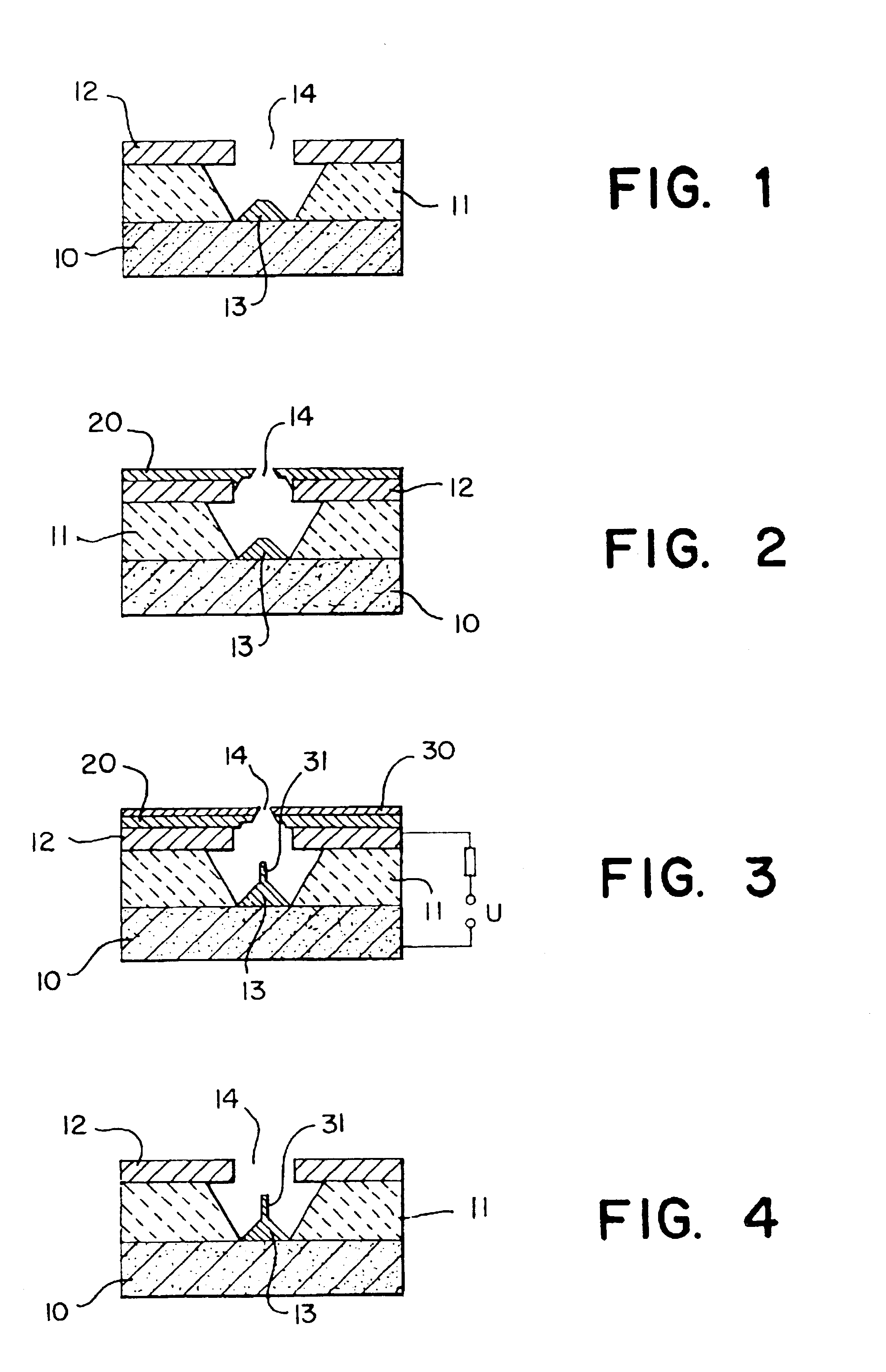
InactiveUS6201342B1Clarity is not affectedImprove uniformityThermionic cathodesDischarge tube cold cathodesSingle crystalSelf assembling
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Electron emission device, cold cathode field emission device and method for the production thereof, and cold cathode field emission display and method for the production thereof
InactiveUS20020036452A1Improve image qualityReduce power consumptionImage/pattern display tubesDischarge tube cold cathodesPhysicsCarbon film
A cold cathode field emission device comprising (a) a cathode electrode formed on a supporting substrate, and (b) a gate electrode which is formed above the cathode electrode and has an opening portion, and further comprising (c) an electron emitting portion composed of a carbon film formed on a surface of a portion of the cathode electrode which portion is positioned in a bottom portion of the opening portion.
Owner:SONY CORP
Hollow graphene sheet structure, electrode structure, process for the production thereof, and device thus produced
InactiveUS6869581B2Partially decomposePigmenting treatmentElectric discharge tubesGrapheneMaterials science
A hollow graphene sheet structure has at least one pair of hollow graphene sheet materials disposed in a continuous form, in which the adjacent ends of the pair of hollow graphene sheet materials are opposed to each other with a gap.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Flat-type display
InactiveUS6580223B2Reliably inhibitedAvoid dischargeDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceIrradiation
A flat-type display comprising a first panel having electron-emitting portions; a second panel having an electron irradiation surface; and an electron-emitting-portion driving circuit for driving the electron-emitting portions, wherein an electron-emitting-portion cutoff circuit is provided between the electron-emitting portions and the electron-emitting-portion driving circuit for preventing a discharge between the electron-emitting portions and the electron irradiation surface.
Owner:SONY CORP
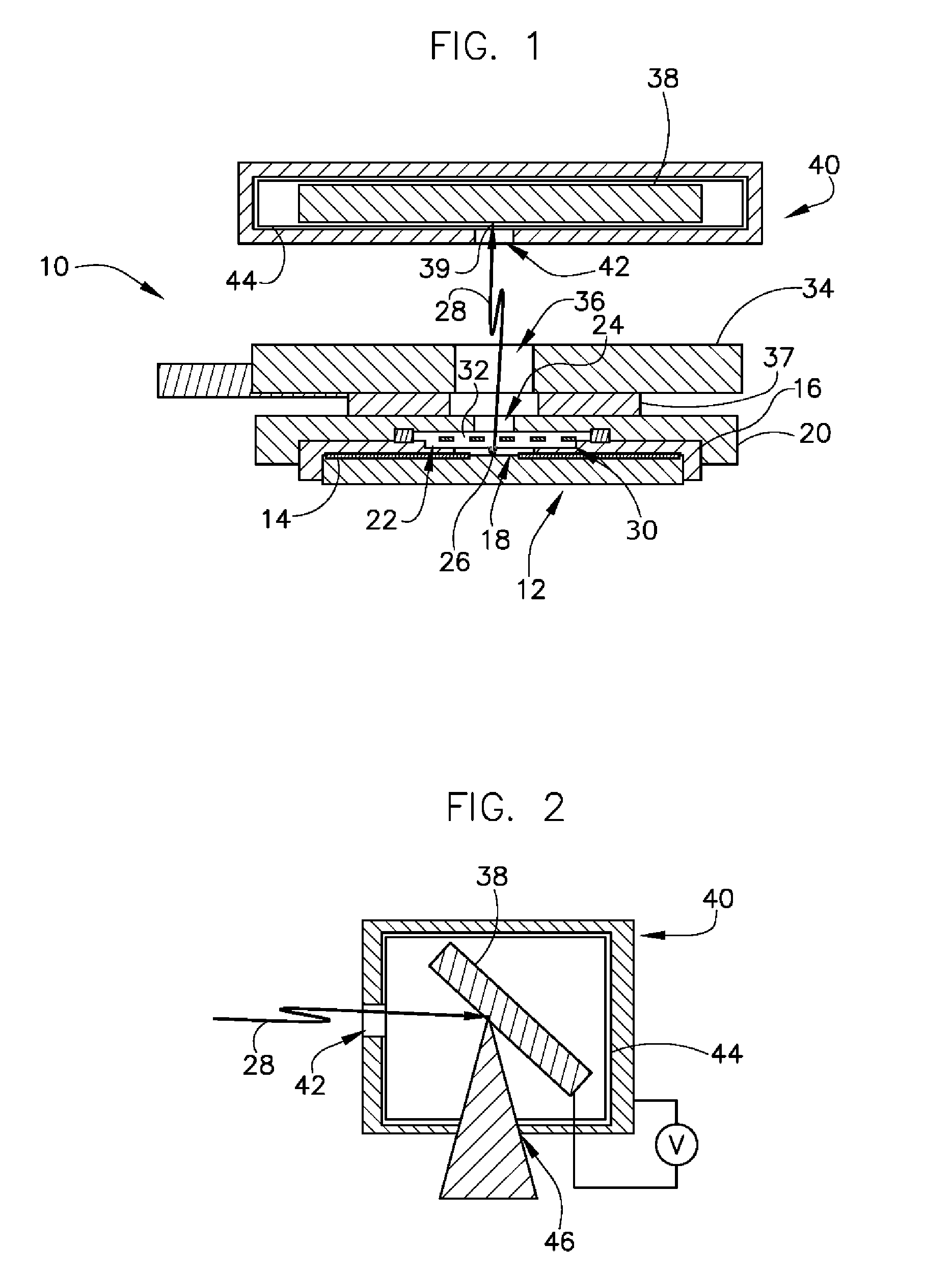
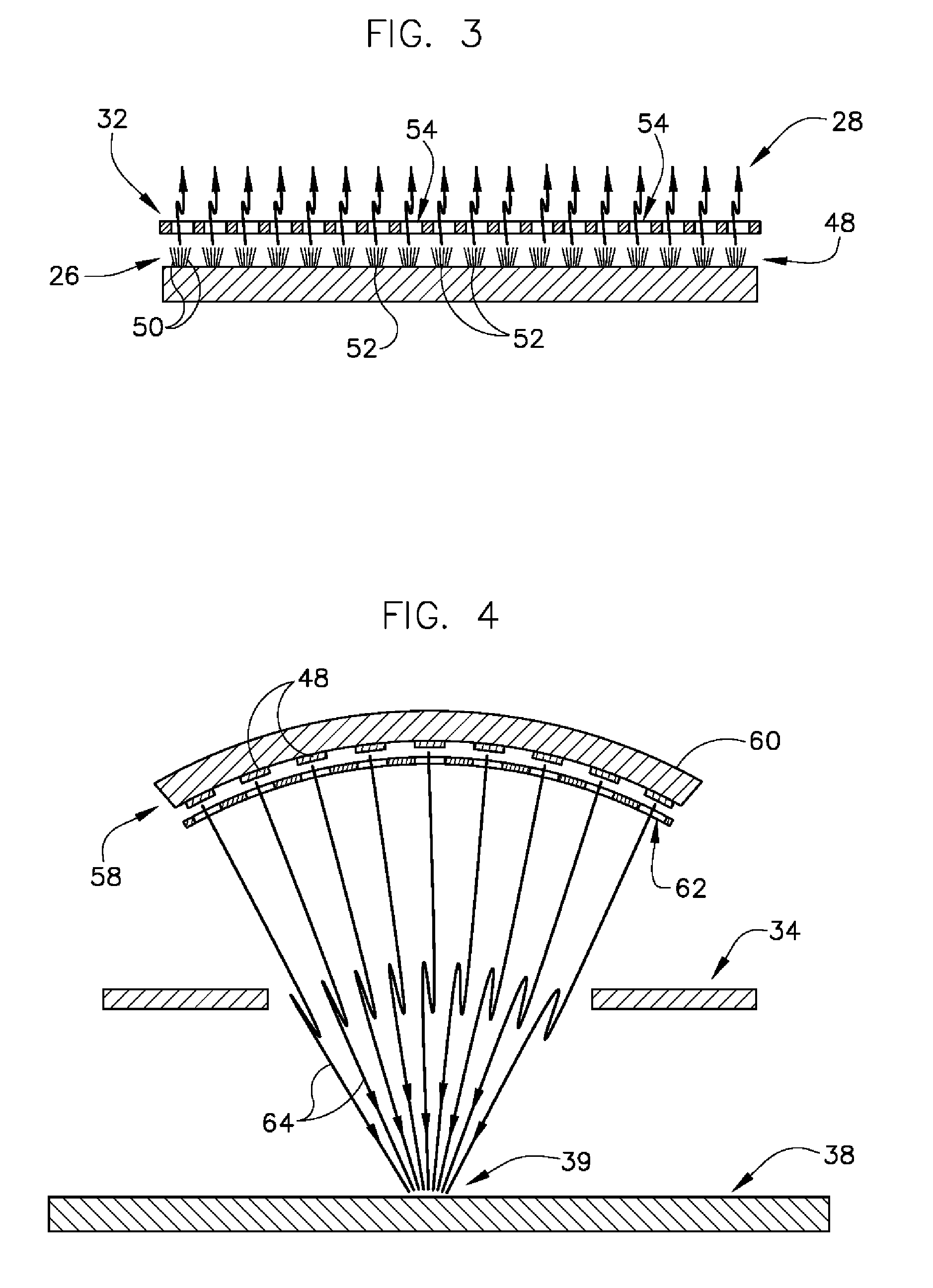
Apparatus for producing electron source
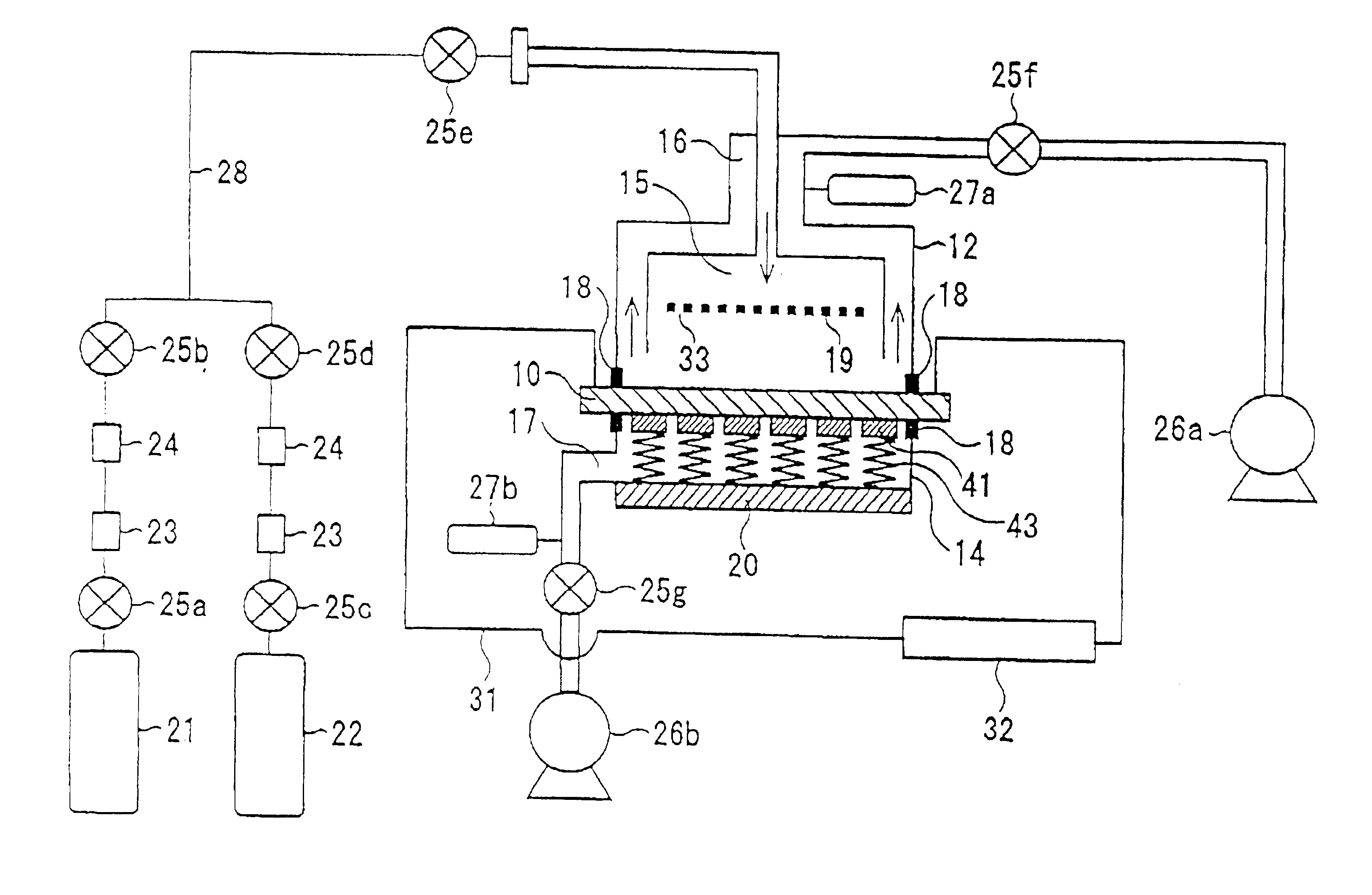
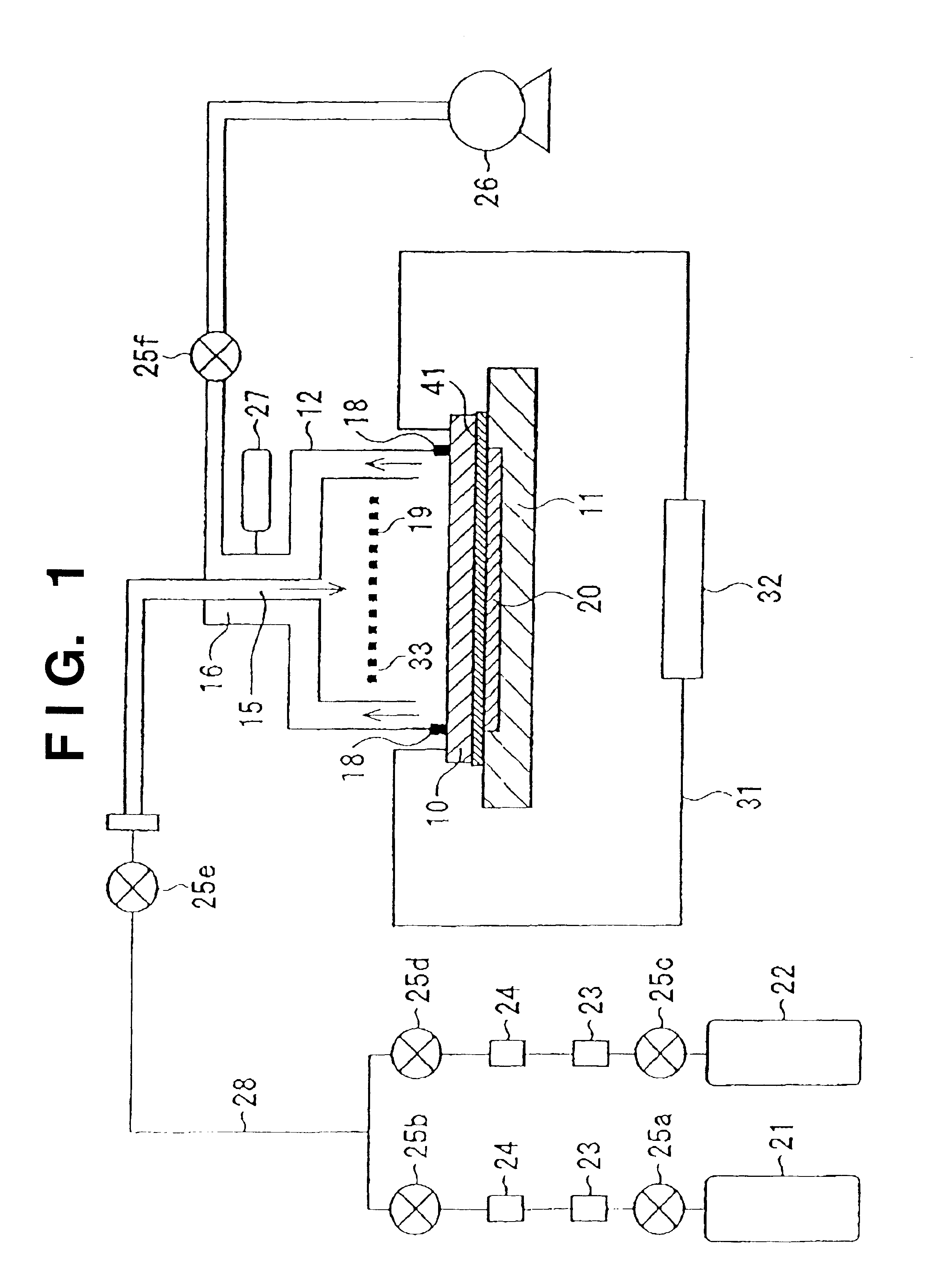
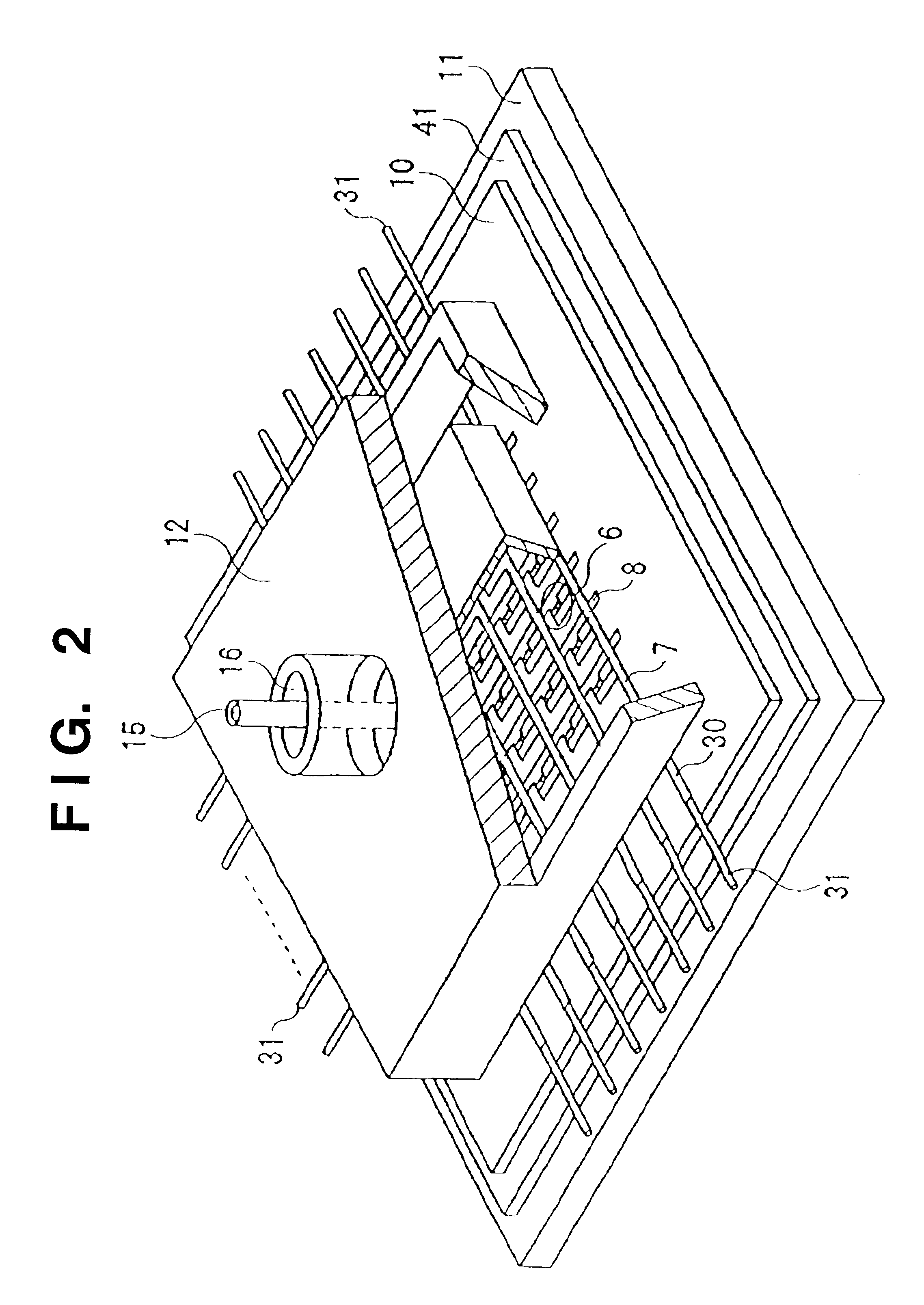
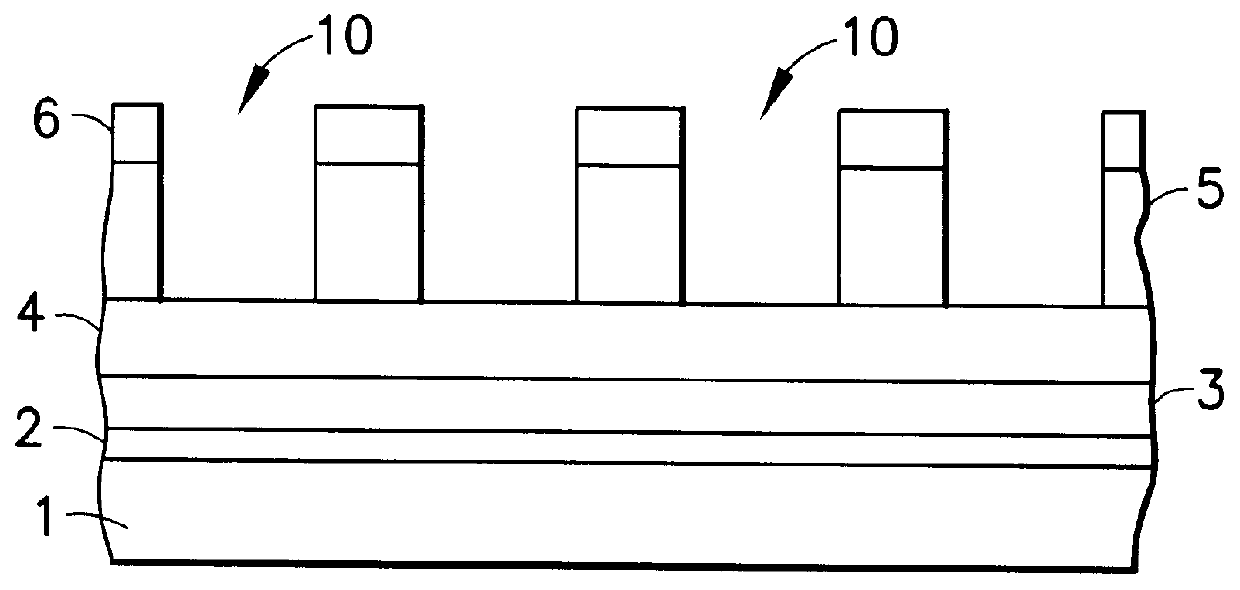
InactiveUS6726520B2Easy to operateAvoid damageElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorElectron source
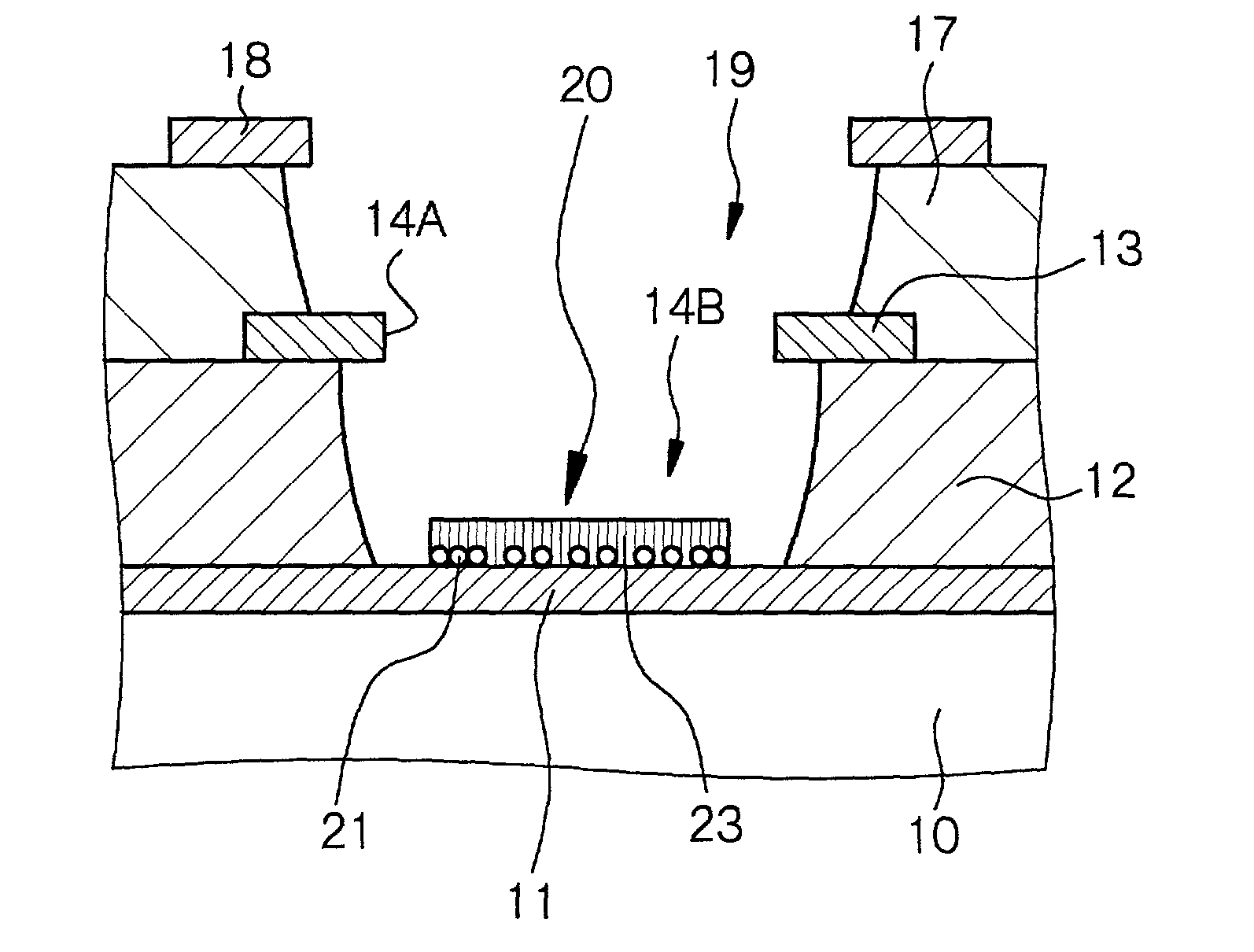
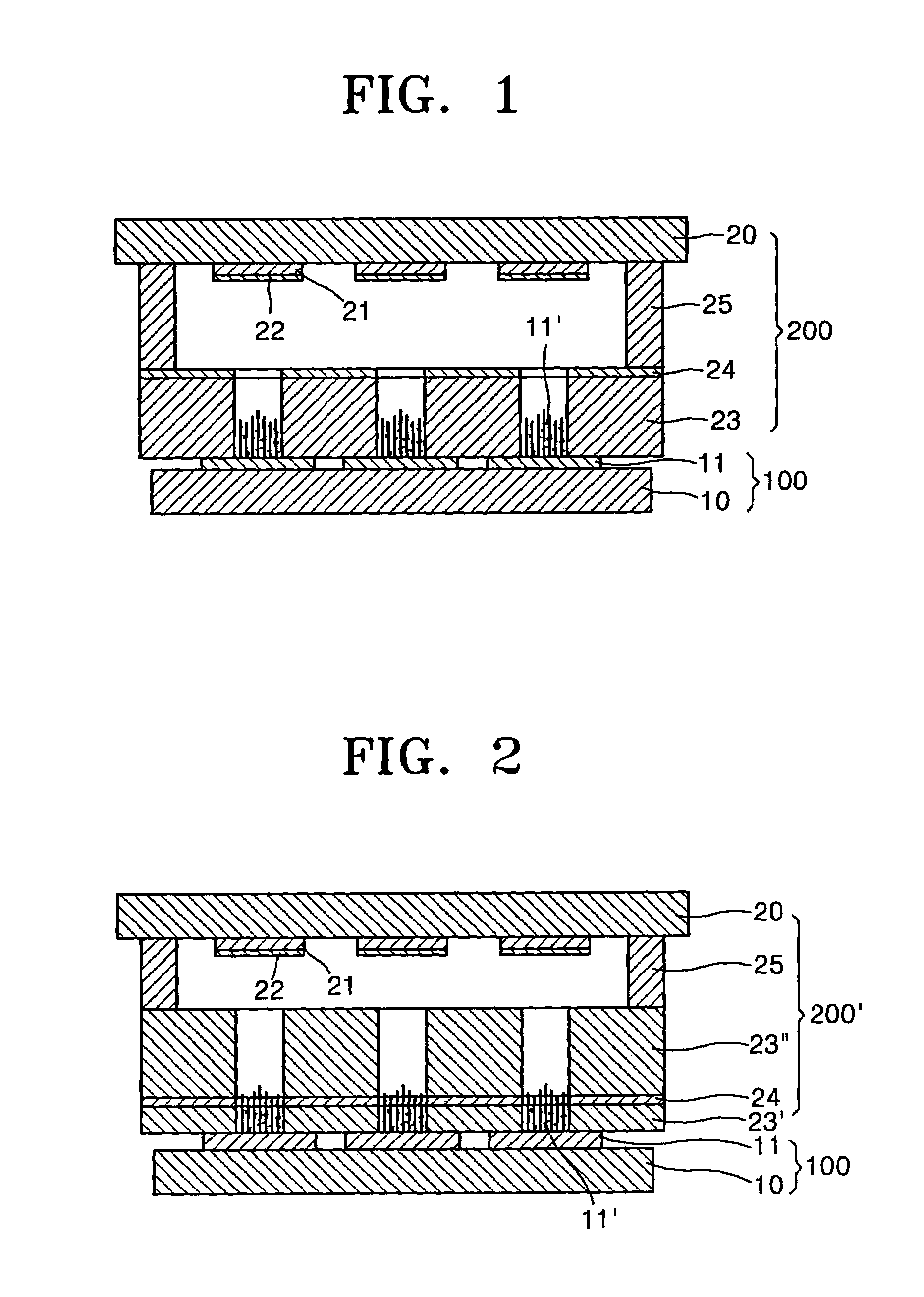
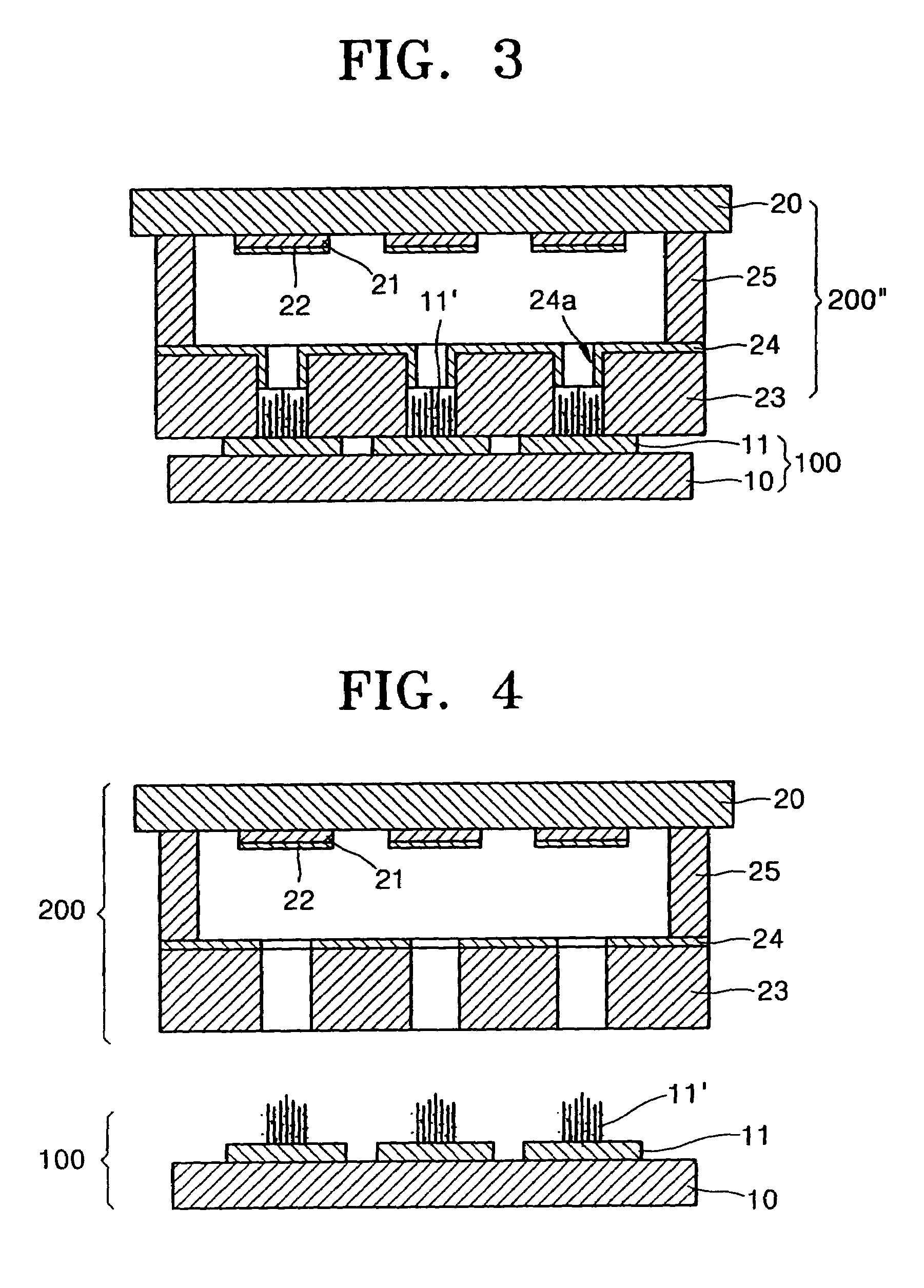
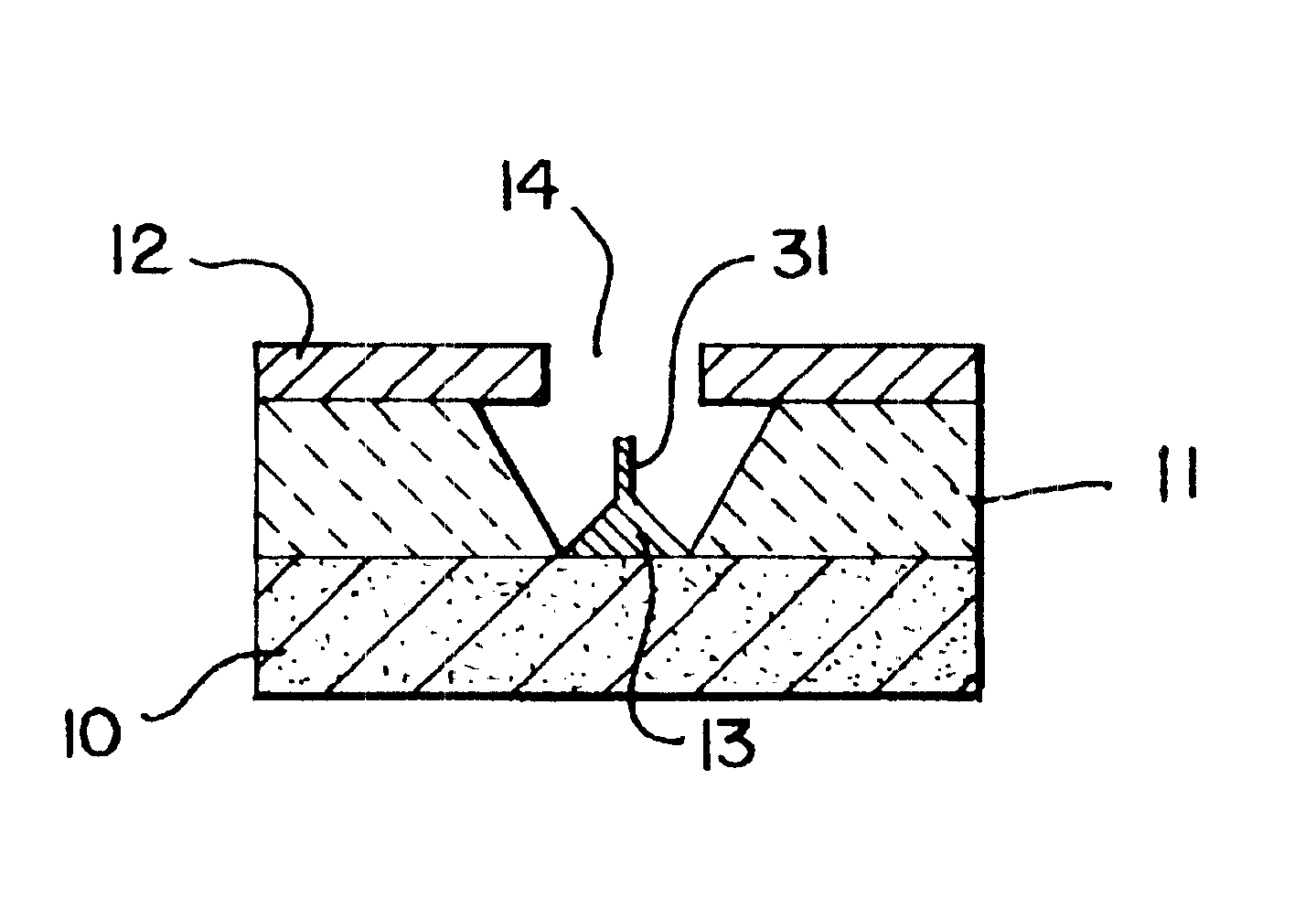
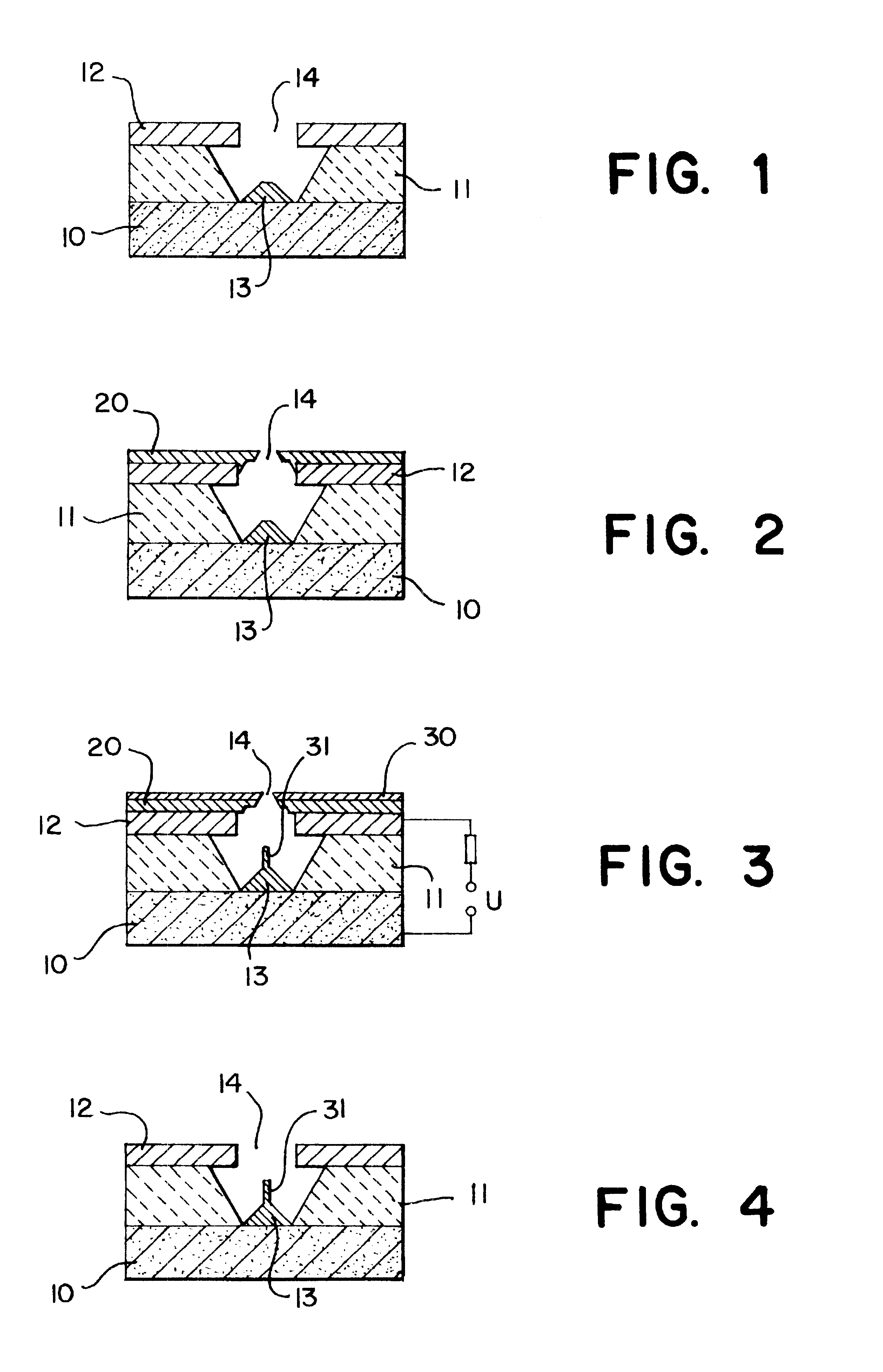
This invention provides an electron source manufacturing apparatus which can be easily downsized and operated. The electron source manufacturing apparatus includes a support member for supporting a substrate (10) having a conductor (11), a vessel (12) which has a gas inlet port (15) and a gas exhaust port (16) and covers a partial region of the surface of the substrate (10); a gas inlet unit (24) connected to the gas inlet port (15) to introduce gas into the vessel, an exhaust unit (26) connected to the gas exhaust port to evacuate the interior of the vessel, and a voltage application unit (32) for applying a voltage to the conductor.
Owner:CANON KK
Integrated circuit devices and methods employing amorphous silicon carbide resistor materials
InactiveUS6031250AReduce the temperatureLow implementation costSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingField emission deviceOxygen
Integrated circuits, including field emission devices, have a resistor element of amorphous SixC1-x wherein 0<x<1, and wherein the SixC1-x incorporates at least one impurity selected from the group consisting of hydrogen, halogens, nitrogen, oxygen, sulphur, selenium, transition metals, boron, aluminum, phosphorus, gallium, arsenic, lithium, beryllium, sodium and magnesium.
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC +1
Electron-emitting device, electron source, image-forming apparatus, and method for producing electron-emitting device and image forming apparatus
InactiveUS6848962B2Reduce the differenceUniform and stableSparking plugsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesFiberElectron source
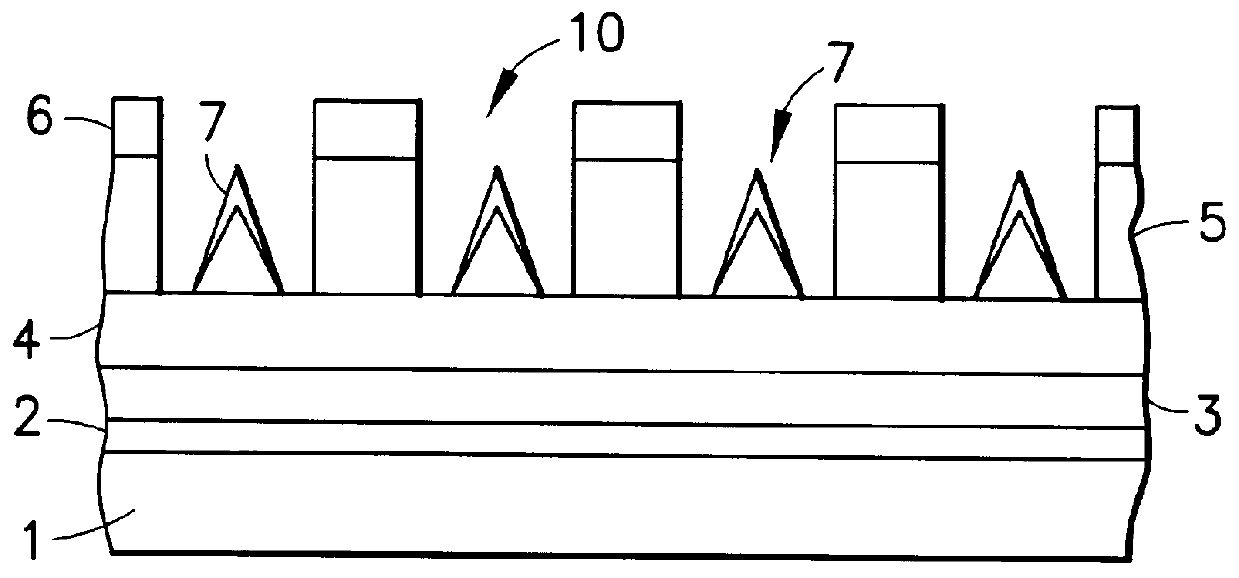
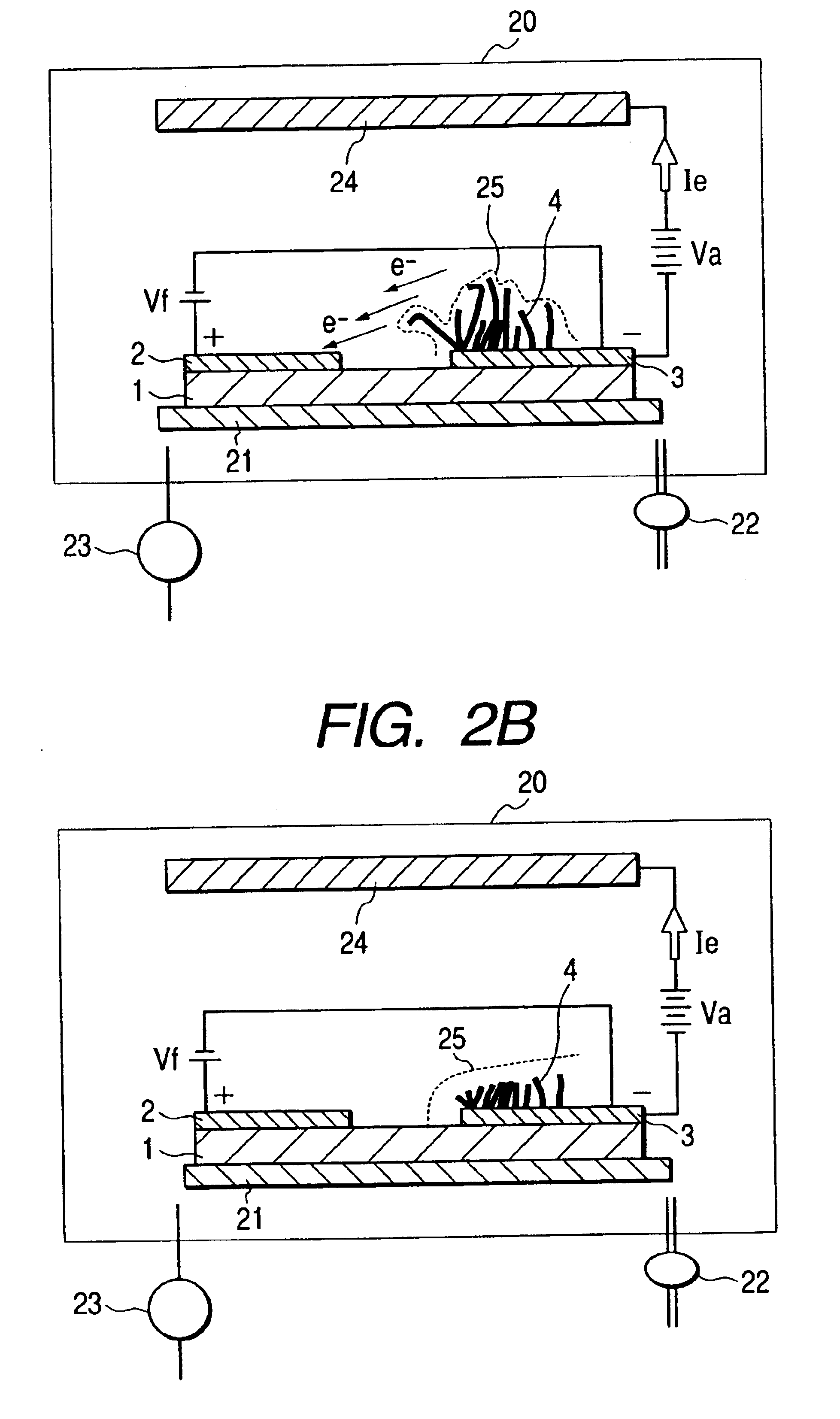
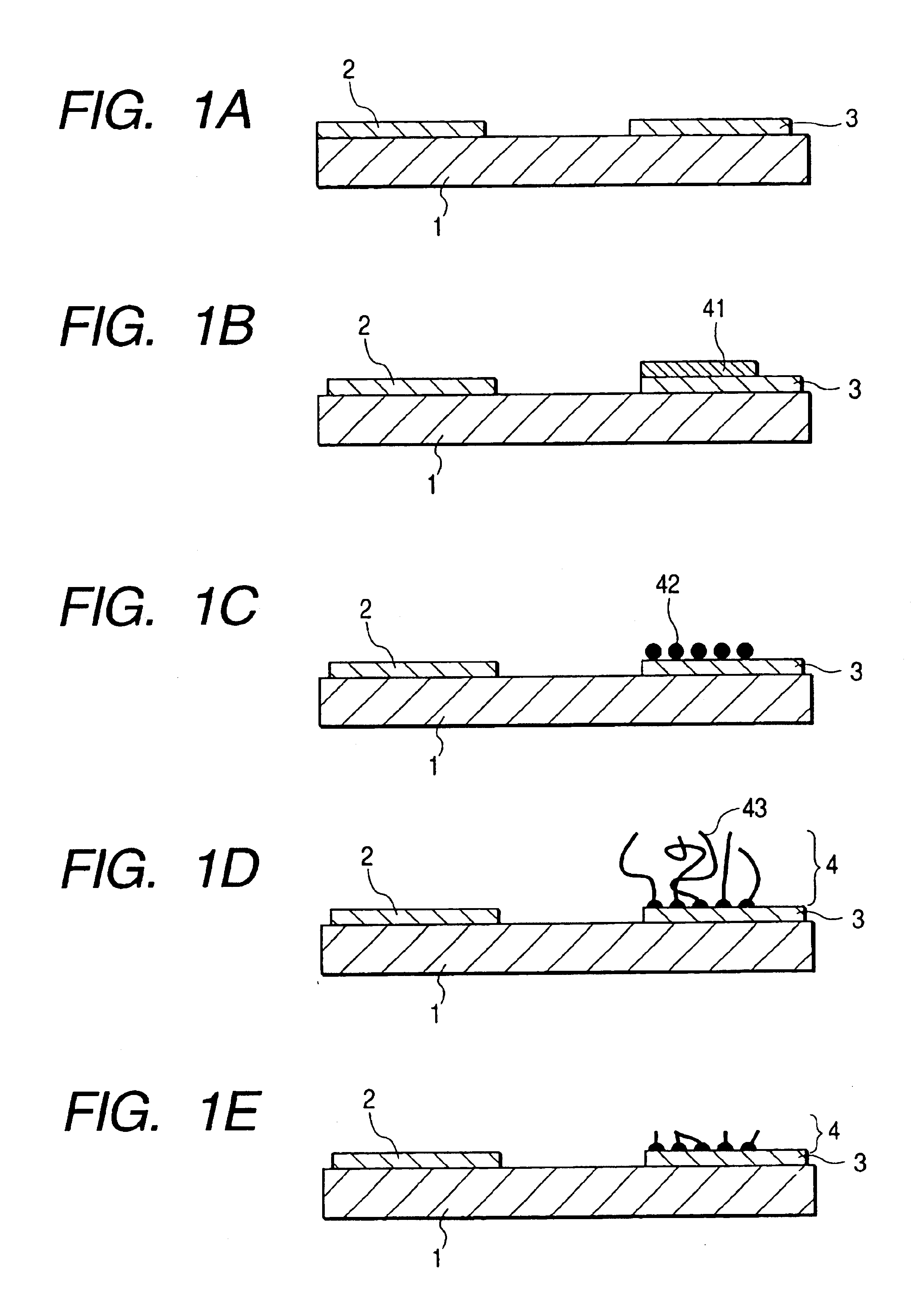
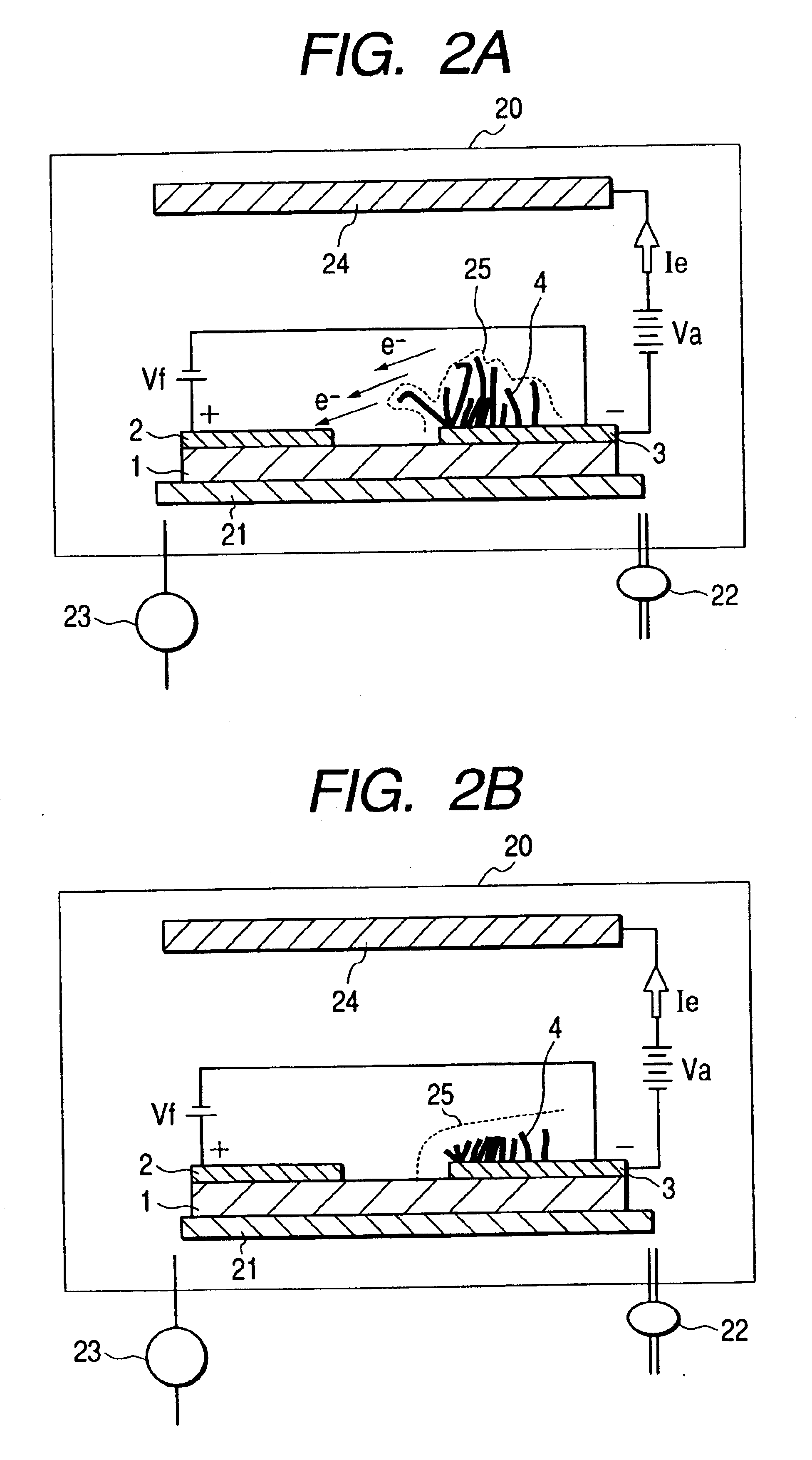
A method for producing a durable electron-emitting device having a uniform electron emission characteristic, an electron source, and an image-forming apparatus having a uniform display characteristic for a long period are provided. The method for producing an electron-emitting device according to the present invention includes the steps of: disposing a cathode electrode on a surface of a substrate; providing an electrode opposite the cathode electrode; disposing plural pieces of fiber containing carbon as a main component on the cathode electrode; and applying potential higher than potential applied to the cathode electrode under depressurized condition to an electrode opposite the cathode electrode.
Owner:CANON KK
Electron-emitting device and image-forming apparatus
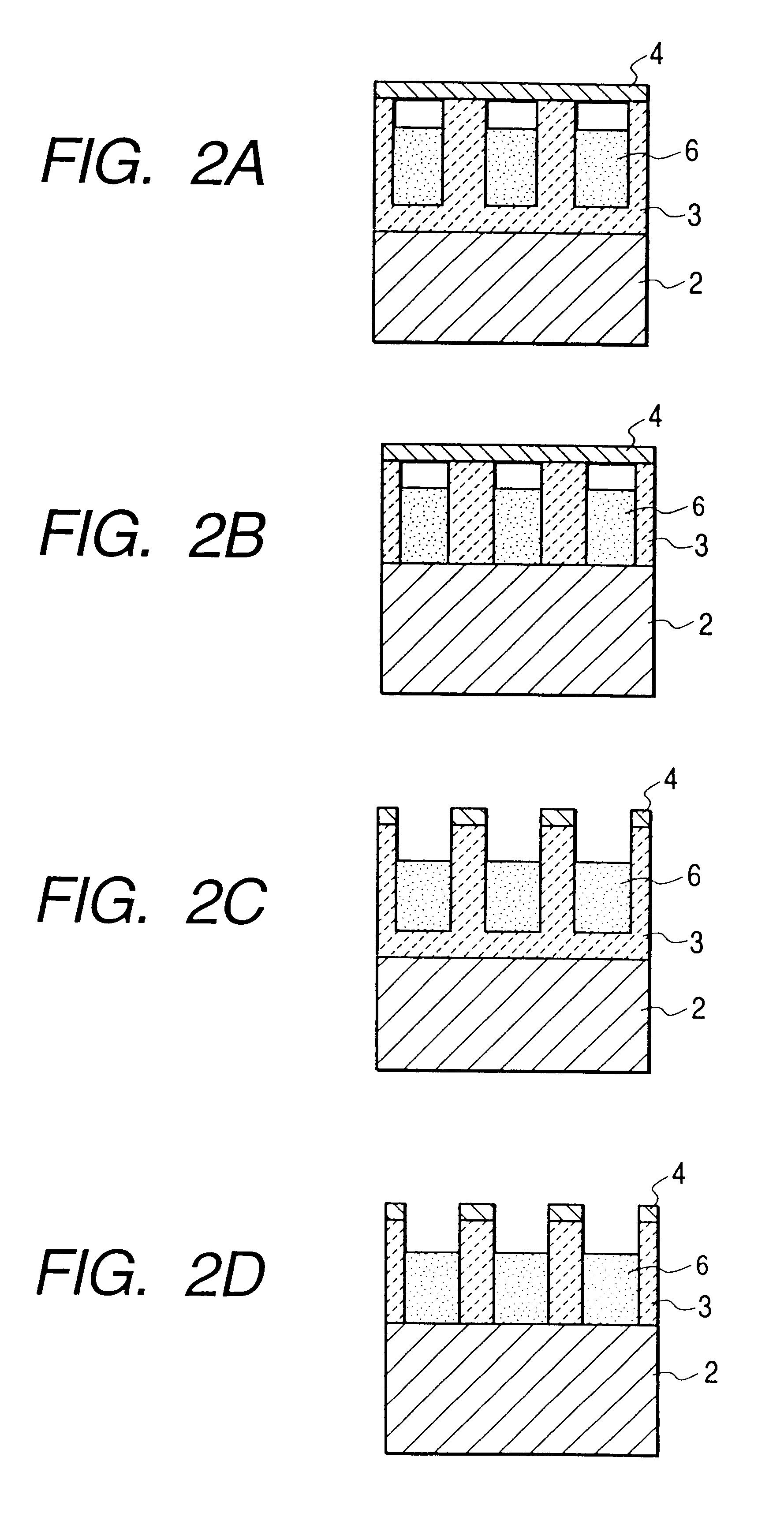
An electron-emitting device having a small electron beam size is proposed. In order to provide a high definition image display device having high image quality by utilizing this type of electron-emitting device and an electron source, a cathode electrode (2) has an opening which is trenched in a portion thereof, and further, the depth at which the opening is trenched is deep at a peripheral portion of the opening bottom face, and shallow at a central portion of the opening bottom face. A surface of an electron-emitting material is formed in a portion deeper than a boundary surface between the cathode electrode and an insulating layer.
Owner:CANON KK
Field emission array with carbon nanotubes and method for fabricating the field emission array
InactiveUS6976897B2Simple film formationTube/lamp screens manufactureCathode-ray/electron-beam tube vessels/containersPhosphorCarbon nanotube
A field emission array adopting carbon nanotubes as an electron emitter source, wherein the array includes a rear substrate assembly including cathodes formed as stripes over a rear substrate and carbon nanotubes; a front substrate assembly including anodes formed as stripes over a front substrate with phosphors being deposited on the anodes, a plurality of openings separated by a distance corresponding to the distance between the anodes in a nonconductive plate, and gates formed as stripes perpendicular to the stripes of anodes on the nonconductive plate with a plurality of emitter openings corresponding to the plurality of openings. The nonconductive plate is supported and separated from the front substrate using spacers. The rear substrate assembly is combined with the front substrate assembly such that the carbon nanotubes on the cathodes project through the emitter openings.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Field emission cathode having an electrically conducting material shaped of a narrow rod or knife edge
InactiveUSRE38223E1Improve emission qualityLong lastingNanoinformaticsThermionic cathodesConfocalConductive materials
A field emission cathode device consisting of an electrically conducting material and with a narrow, rod-shaped geometry or a knife edge, to achieve a high amplification of the electric field strength is characterized in that the electron-emitting part of the field emission cathode at least partly has preferred cylindrical host molecules and / or compounds with host compounds and / or cylindrical atomic networks, possibly with end caps with diameters measuring in the nanometer range.
Owner:KEESMANN TILL
Flat-type display
InactiveUS20020011777A1Avoid dischargeReliably inhibitedDischarge tube luminescnet screensStatic indicating devicesDisplay deviceIrradiation
A flat-type display comprising a first panel having electron-emitting portions; a second panel having an electron irradiation surface; and an electron-emitting-portion driving circuit for driving the electron-emitting portions, wherein an electron-emitting-portion cutoff circuit is provided between the electron-emitting portions and the electron-emitting-portion driving circuit for preventing a discharge between the electron-emitting portions and the electron irradiation surface.
Owner:SONY CORP
Emissive flat panel display device
InactiveUS20050029924A1Reduce voltageNo coarsenessDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsElectron sourceLow voltage
The present invention provides an emissive flat panel display device which is capable of performing a gate operation at a relatively low voltage of several V to several tens V using gate electrodes. In the emissive flat panel display device which includes a back panel which is constituted of a back substrate on which cathode electrodes having electron sources formed of carbon nanotubes and gate electrodes are formed, a face panel which forms phosphors and anode electrodes thereon, and a sealing frame which seals the back panel and the face panel, the difference between an electric field strength Emax for allowing the electron sources to obtain the required maximum emission current density and an electric field strength Emin which becomes the minimum emission current density is set to 1V / μm or less, and preferably 0.5V / μm or less.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS
Field emission cathode
InactiveUSRE38561E1Long life-timeImprove emission qualityDischarge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsConfocalConductive materials
A field emission cathode device consisting of an electrically conducting material and with a narrow, rod-shaped geometry or a knife edge, to achieve a high amplification of the electric field strength is characterized in that the electron-emitting part of the field emission cathode at least partly has preferred cylindrical host molecules and / or compounds with host compounds and / or cylindrical atomic networks, possibly with end caps with diameters measuring in the nanometer range.
Owner:KEESMANN TILL
Electron emission device
InactiveUS20050184647A1Simple structureSufficient beam focusing capacityDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectrode and associated part arrangementsLight beamThin layer
An electron emission device is provided comprising first and second substrates facing each other and separated from each other by a predetermined distance. An electron emission unit is disposed on the first substrate, and an image display unit is disposed on the second substrate. A focusing electrode comprising a plurality of beam-guide holes is disposed between the first and second substrates. The portion of the focusing electrode located near a beam-guide hole comprises a thin layer. The remainder of the focusing electrode comprises a thick layer having a thickness larger than the thickness of the thin layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
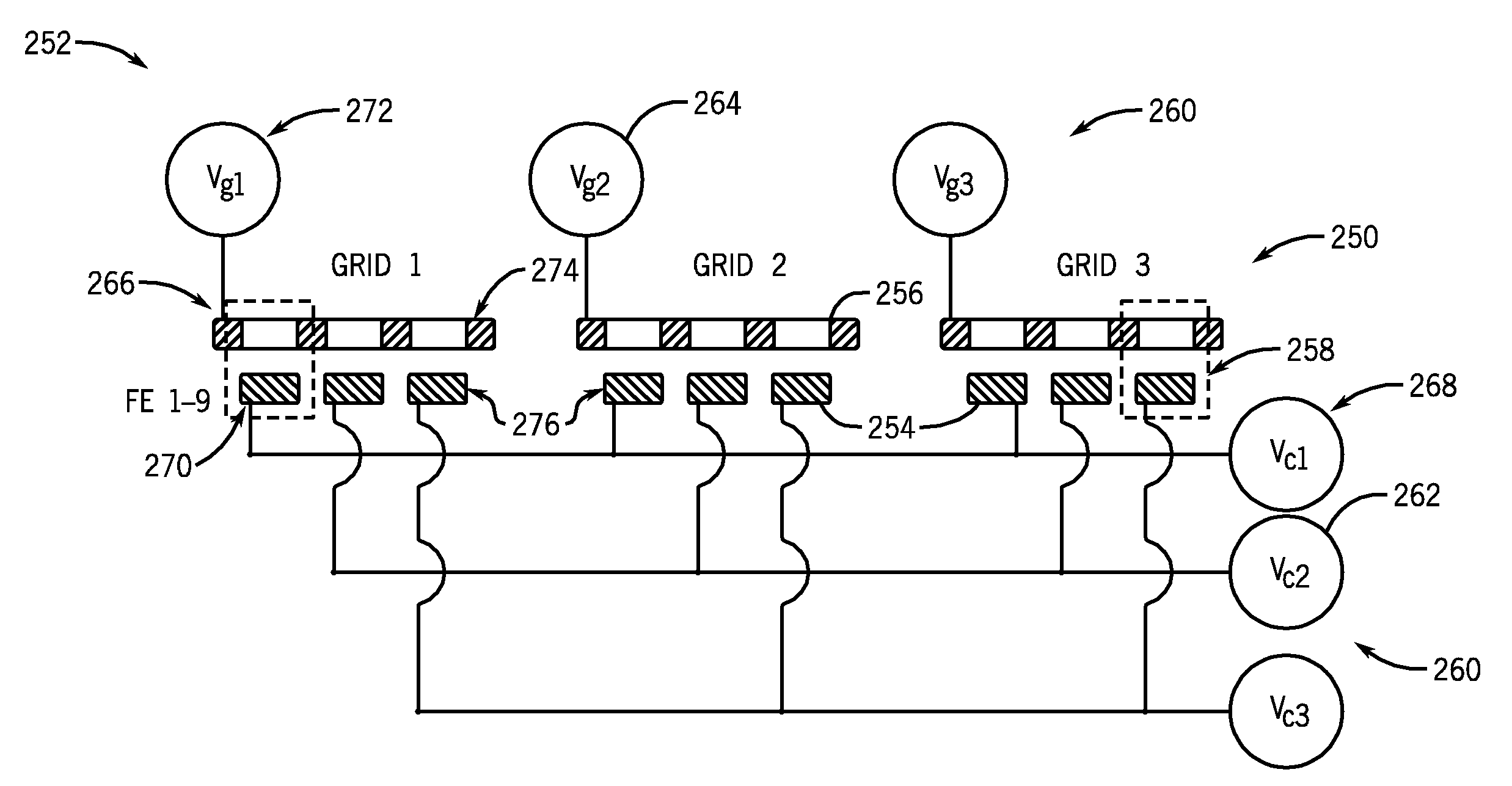
Virtual matrix control scheme for multiple spot X-ray source
ActiveUS7826594B2Minimal numberMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayVoltage control
A system and method for addressing individual electron emitters in an emitter array is disclosed. The system includes an emitter array comprising a plurality of emitter elements arranged in a non-rectangular layout and configured to generate at least one electron beam and a plurality of extraction grids positioned adjacent to the emitter array, each extraction grid being associated with at least one emitter element to extract the at least one electron beam therefrom. The field emitter array system also includes a plurality of voltage control channels connected to the plurality of emitter elements and the plurality of extraction grids such that each of the emitter elements and each of the extraction grids is individually addressable. In the field emitter array system, the number of voltage control channels is equal to the sum of a pair of integers closest in value whose product equals the number of emitter elements.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Luminescence display panel and method for fabricating the same
A luminescence display panel, which can be manufactured without any damage to an organic layer thereof, and a method for fabricating the same are disclosed. According to one of the embodiments in the present invention, the luminescence display panel includes a first electrode formed on a lower substrate, an organic layer formed on the first electrode, the organic layer including a luminescence layer, a second electrode formed on the organic layer, the second electrode having a thin film structure, and an auxiliary electrode formed on an upper substrate and facing the lower substrate, the auxiliary electrode being connected to the second electrode. The second electrode is thinner than at least one of the first electrode and the auxiliary electrode.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
Display device of flat panel structure with emission devices of matrix array
InactiveUS6787992B2Avoid shortingUniform electric fieldCathode-ray/electron-beam tube electrical connectionNanoinformaticsDisplay deviceOptoelectronics
A display device has an emitting region constituted by a plurality of first electrodes provided on a substrate and extending in parallel, a plurality of second electrodes provided on the first electrodes and extending substantially perpendicularly to the first electrodes, and a plurality of emission sites for emitting electrons or light respectively connected to a plurality of intersections between the first and second electrodes and arranged on the substrate and has a peripheral region surrounding the emitting region on the substrate. In this display device, first and second groups of external repeating terminals for the first and second electrodes are collectively provided side by side in a part of the peripheral region.
Owner:PIONEER CORP
Electron emission source composition for field emission display device and field emission display device fabricated using same
Disclosed is an electron emission source composition for a field emission display device including 1 to 20% by weight of carbon nano tubes; glass frit; an organic binder resin comprising ethyl cellulose and acrylate resin and / or acryl resin; and an organic solvent, wherein the glass frit is present in an amount of 1 to 500 parts by weight with respect to 100 parts by weight of the carbon nano tubes.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Flat surface emitter for use in field emission display devices
InactiveUS6011356AImprove efficiencyExcellent optical propertiesElectric discharge tubesStatic indicating devicesSecondary electronsVoltage source
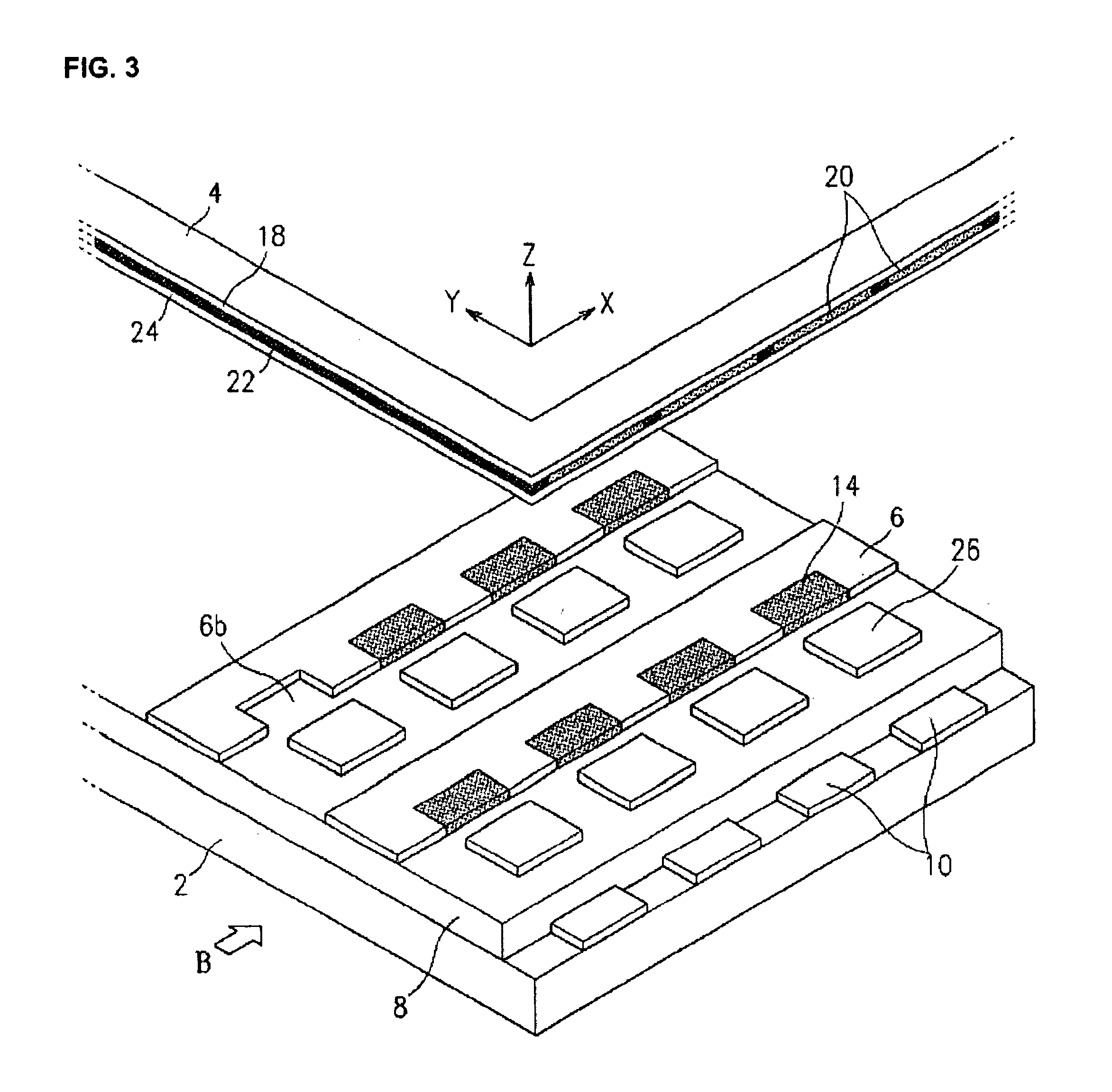
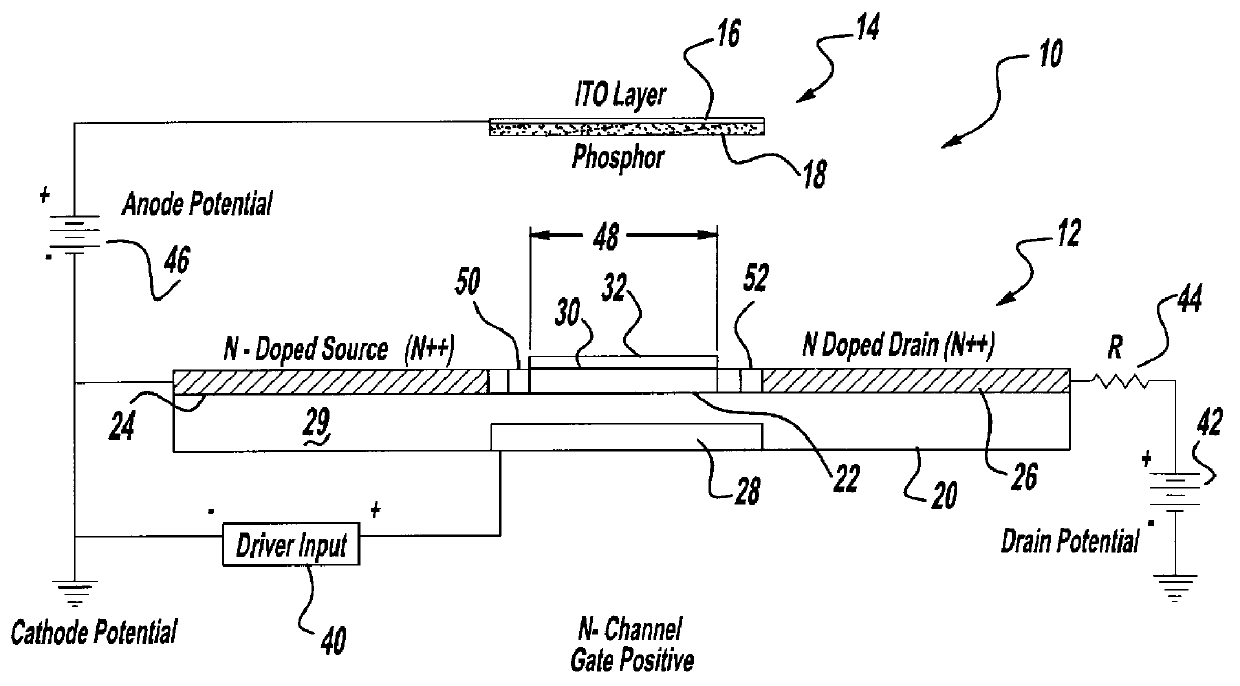
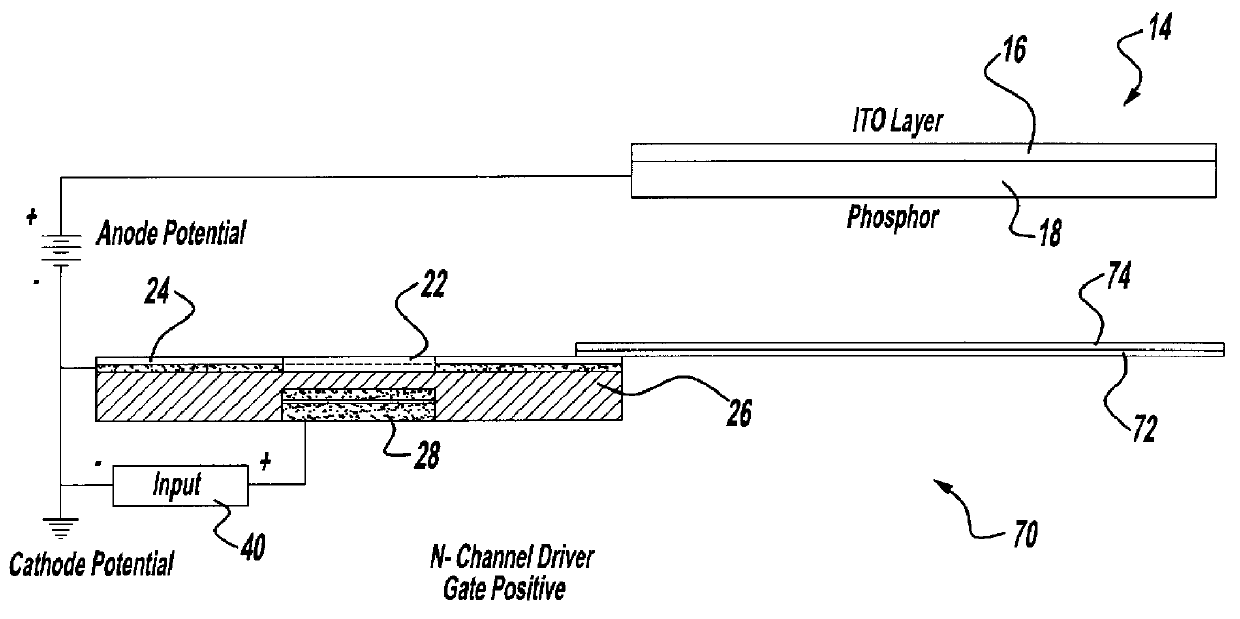
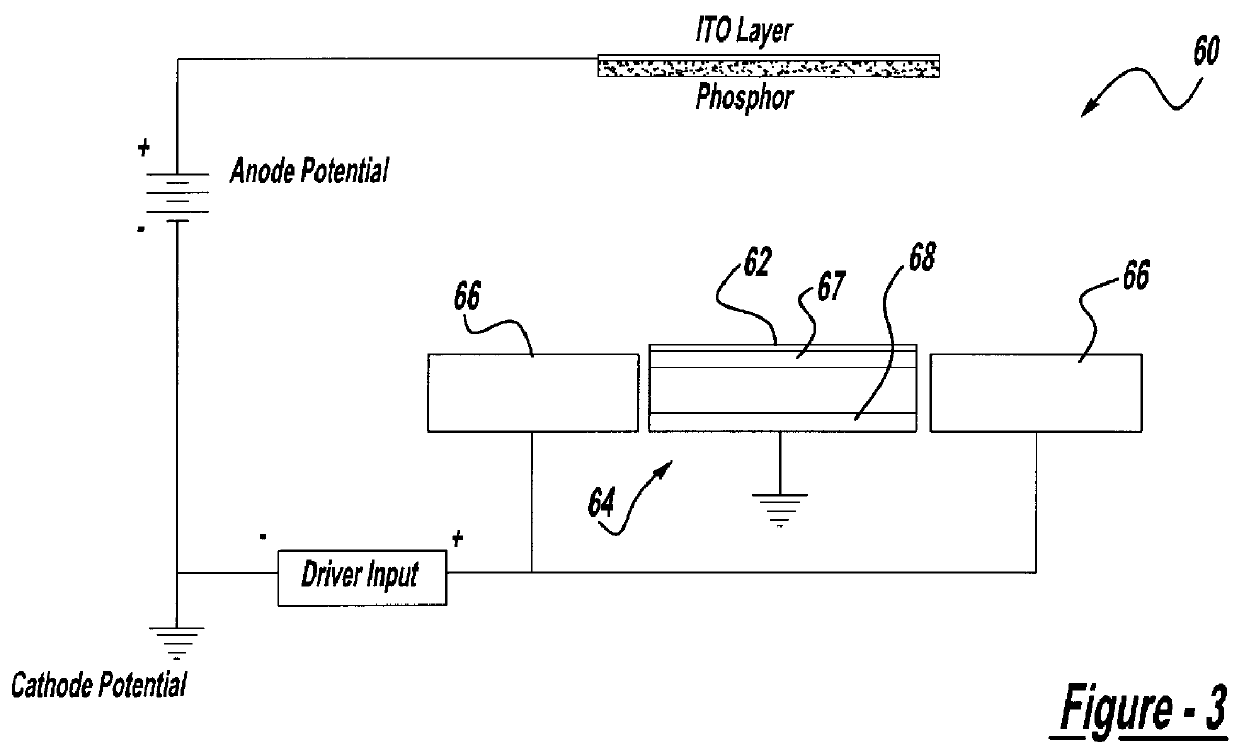
For use in cathodoluminescent field emission display devices, a cathode emitter can comprise an inverted field effect transistor having a diamond film or other low effective work function material deposited onto the channel layer of the transistor, such that the diamond film provides a source of primary electron emissions. A variable voltage source is applied to the gate of the transistor creating an electric field that controls the conductivity of the channel layer, thereby activating or deactivating electron emissions from this cathode emitter structure. In addition, electron blocking junctions can be incorporated into the emitter structure to inhibit current flow through the device during a deactivated state. In a variation, the transistor of the cathode emitter has the diamond film being deposited onto an electrically conductive pad that is electrically connected to, and extending outwardly from, the transistor. Alternatively, a sideways laterally gated transistor structure can be used with the emitter surface being applied to the transistor's drain. A near mono-molecular oxide film of high secondary electron emission material can also be included on the emitter surface for enhanced electron emissions.
Owner:ST CLAIR INTPROP CONSULTANTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com