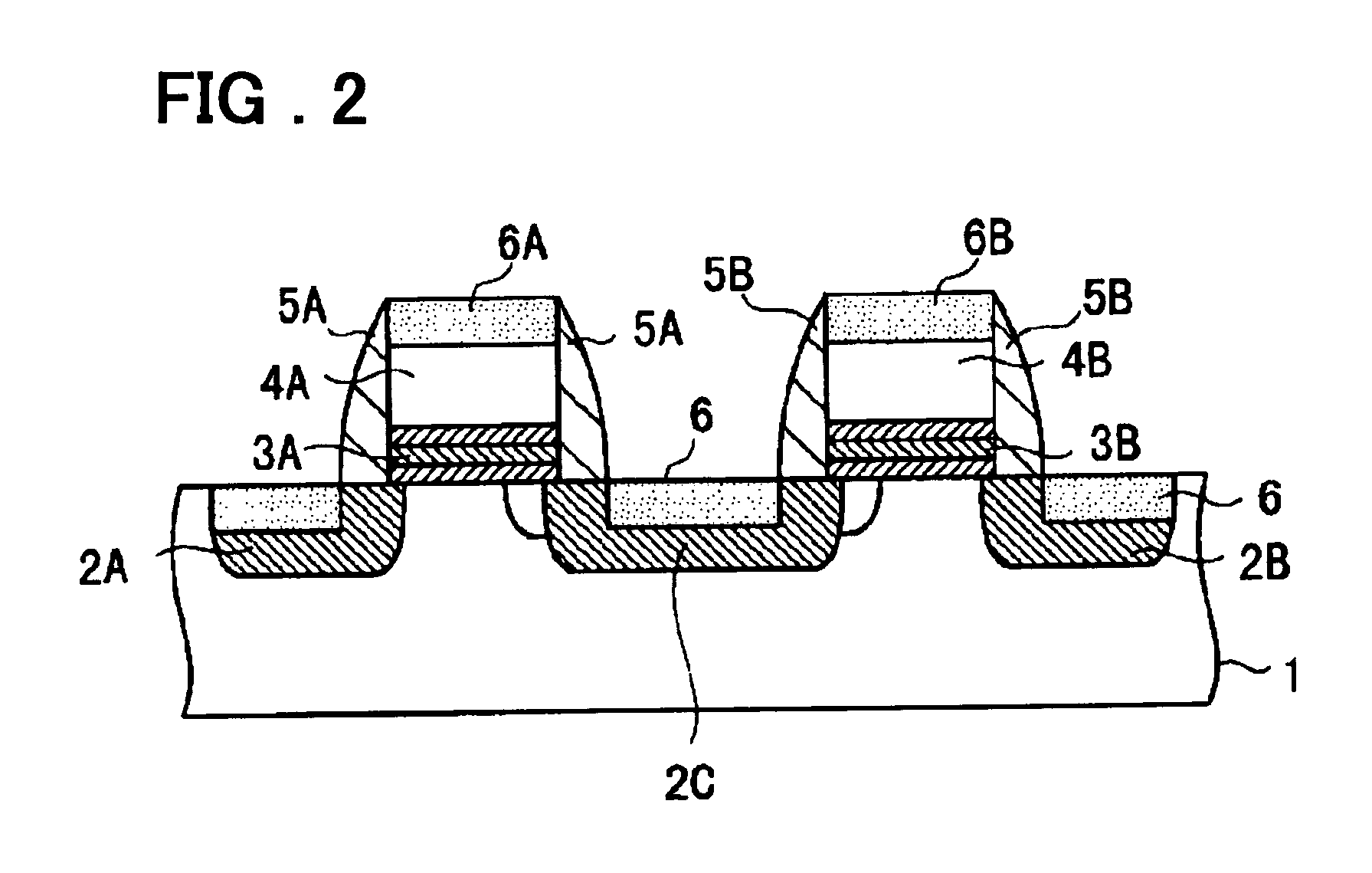
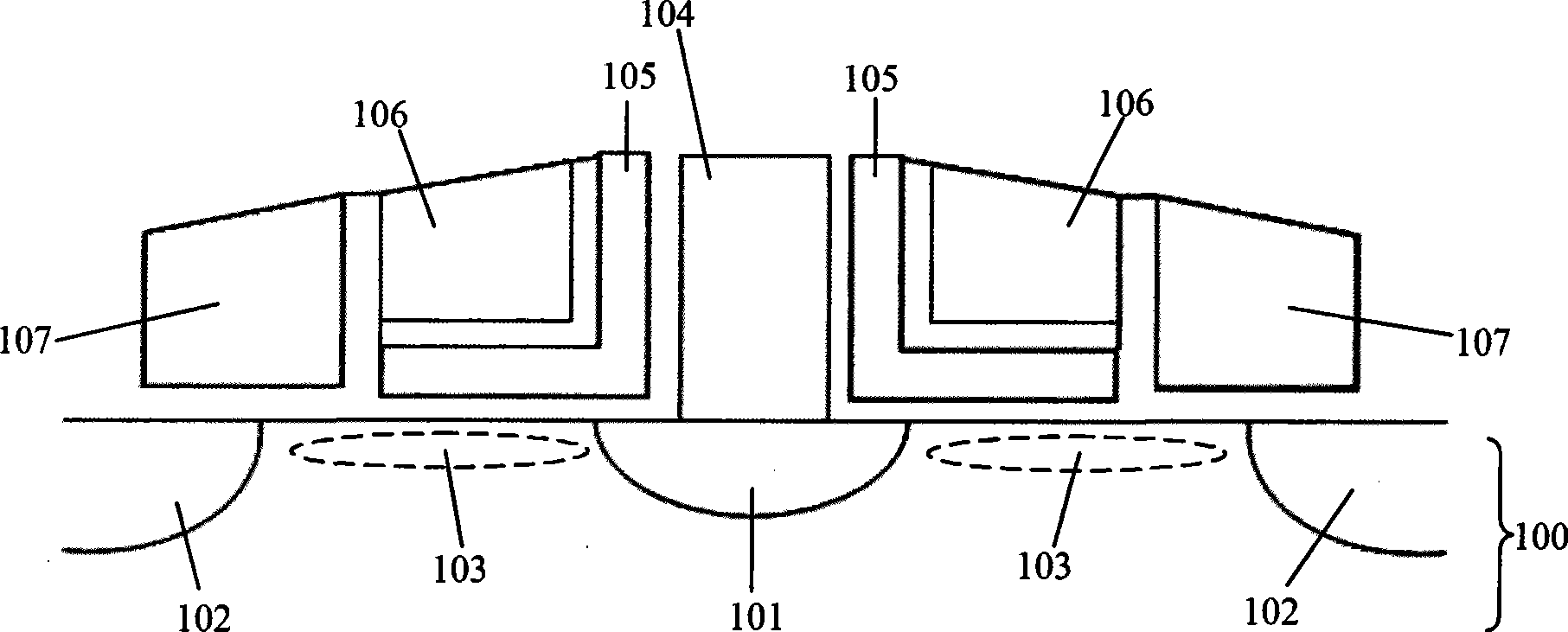
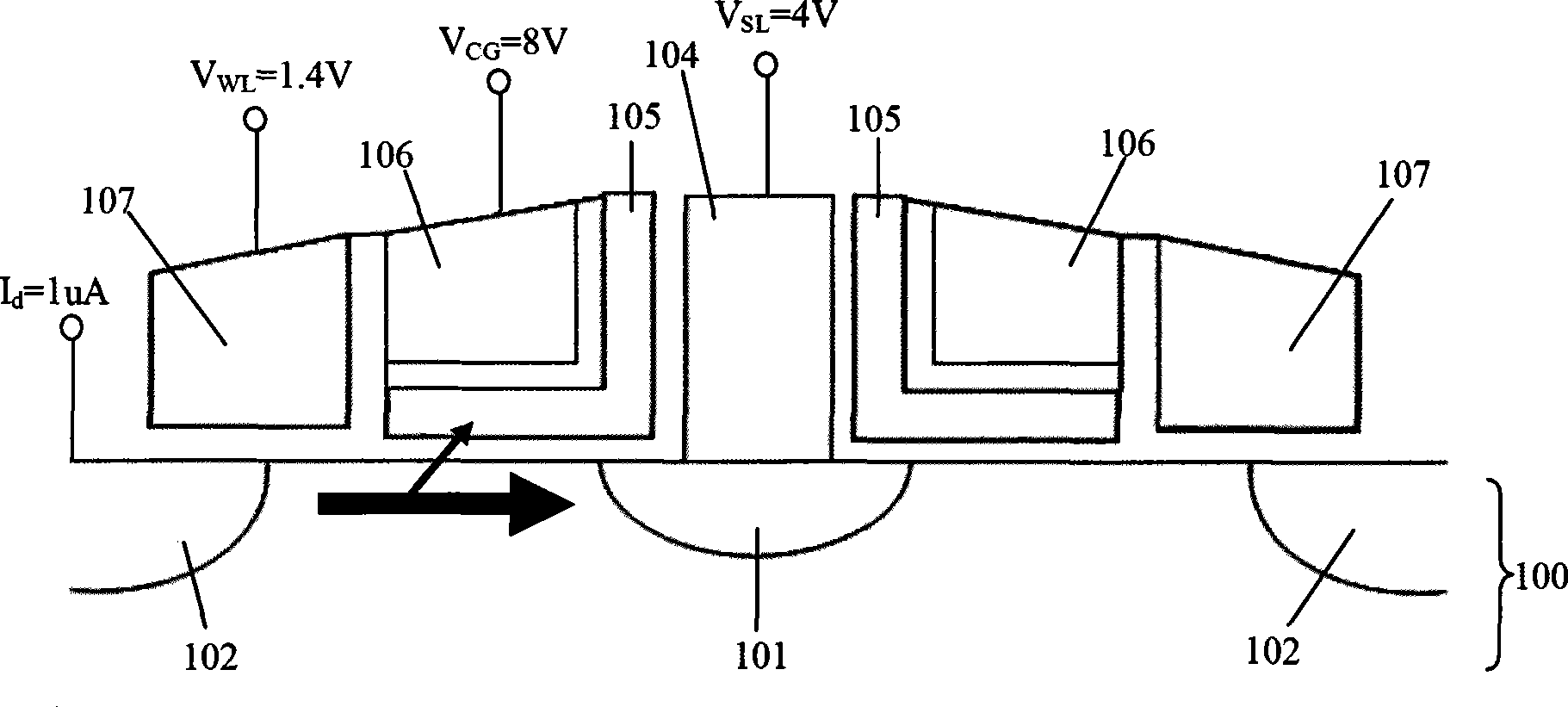
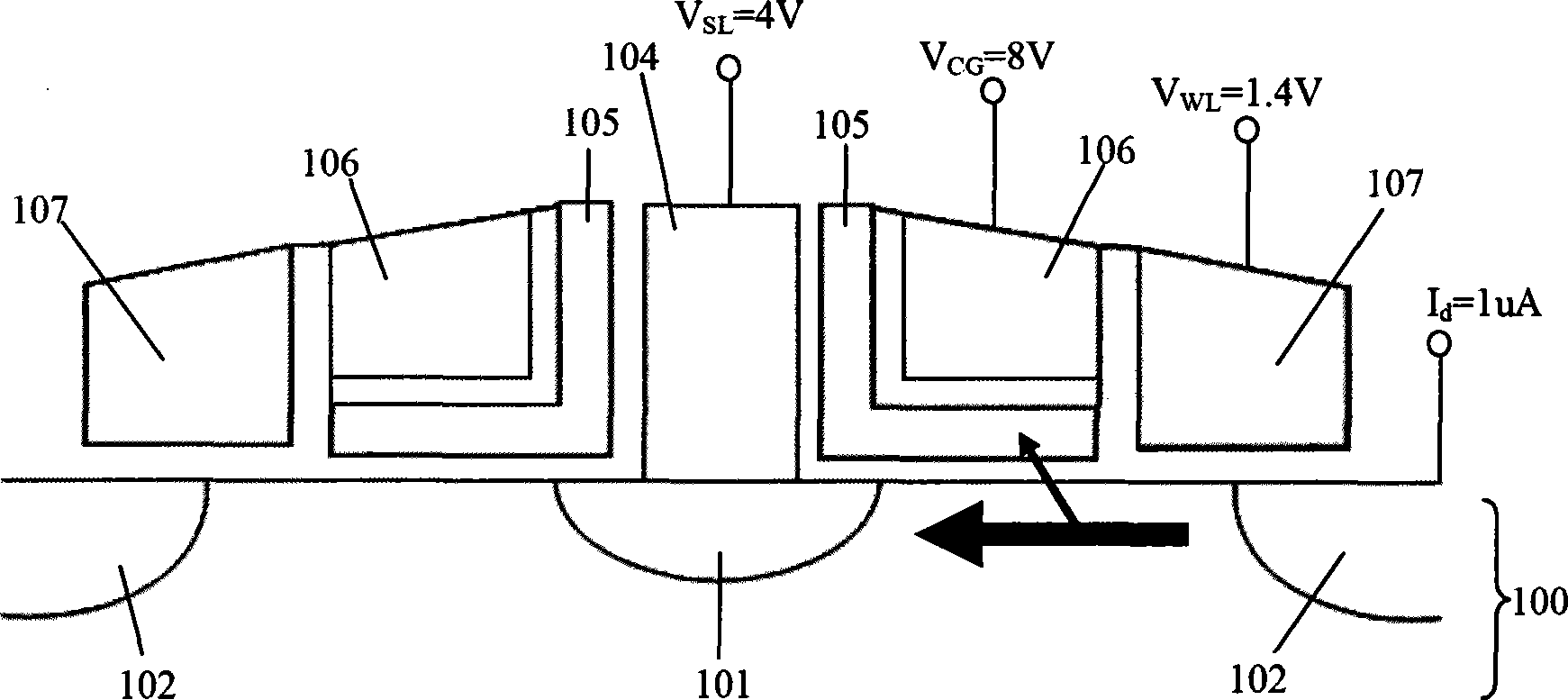
Patents
Literature
88results about How to "Lower programming voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
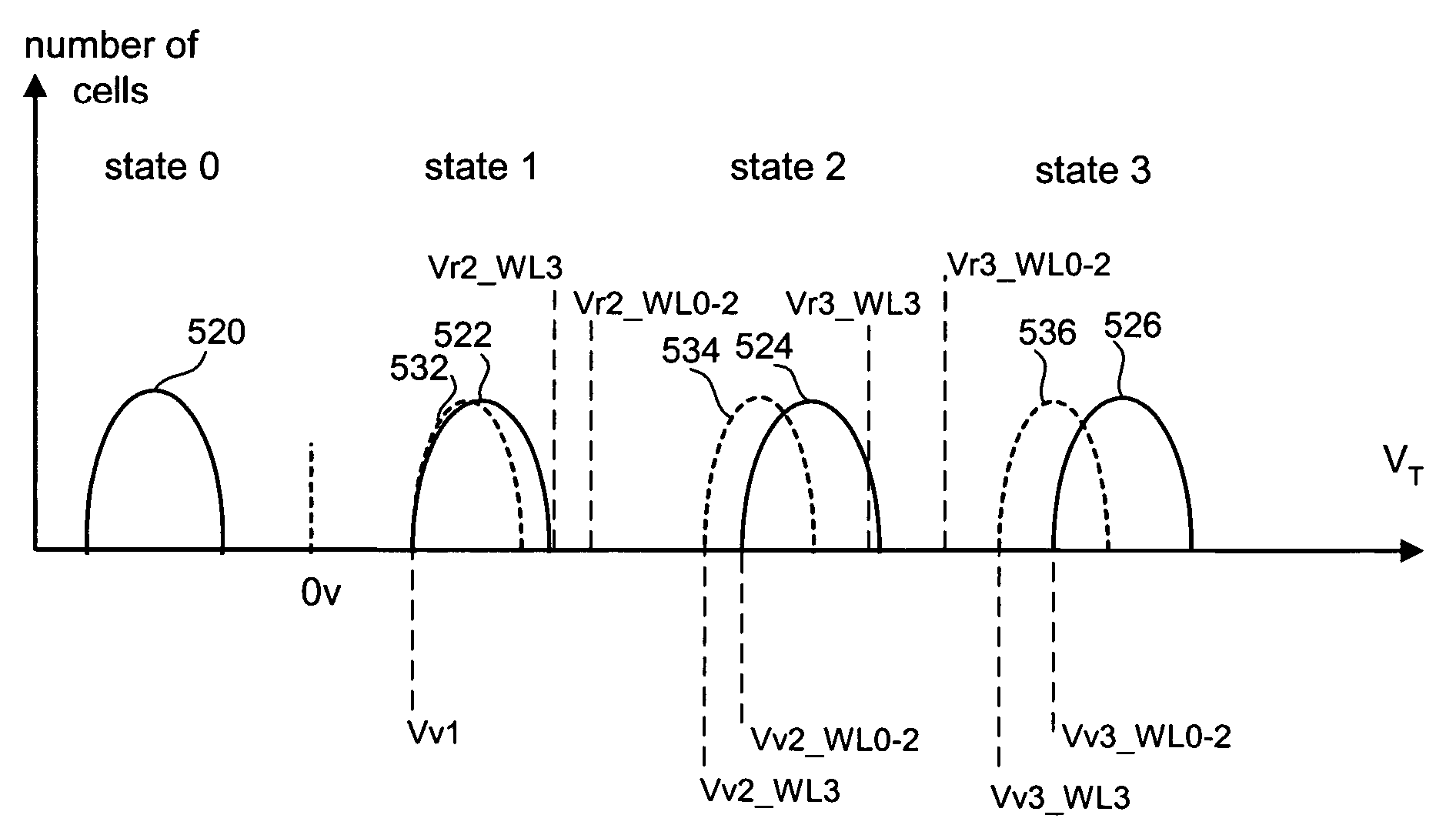
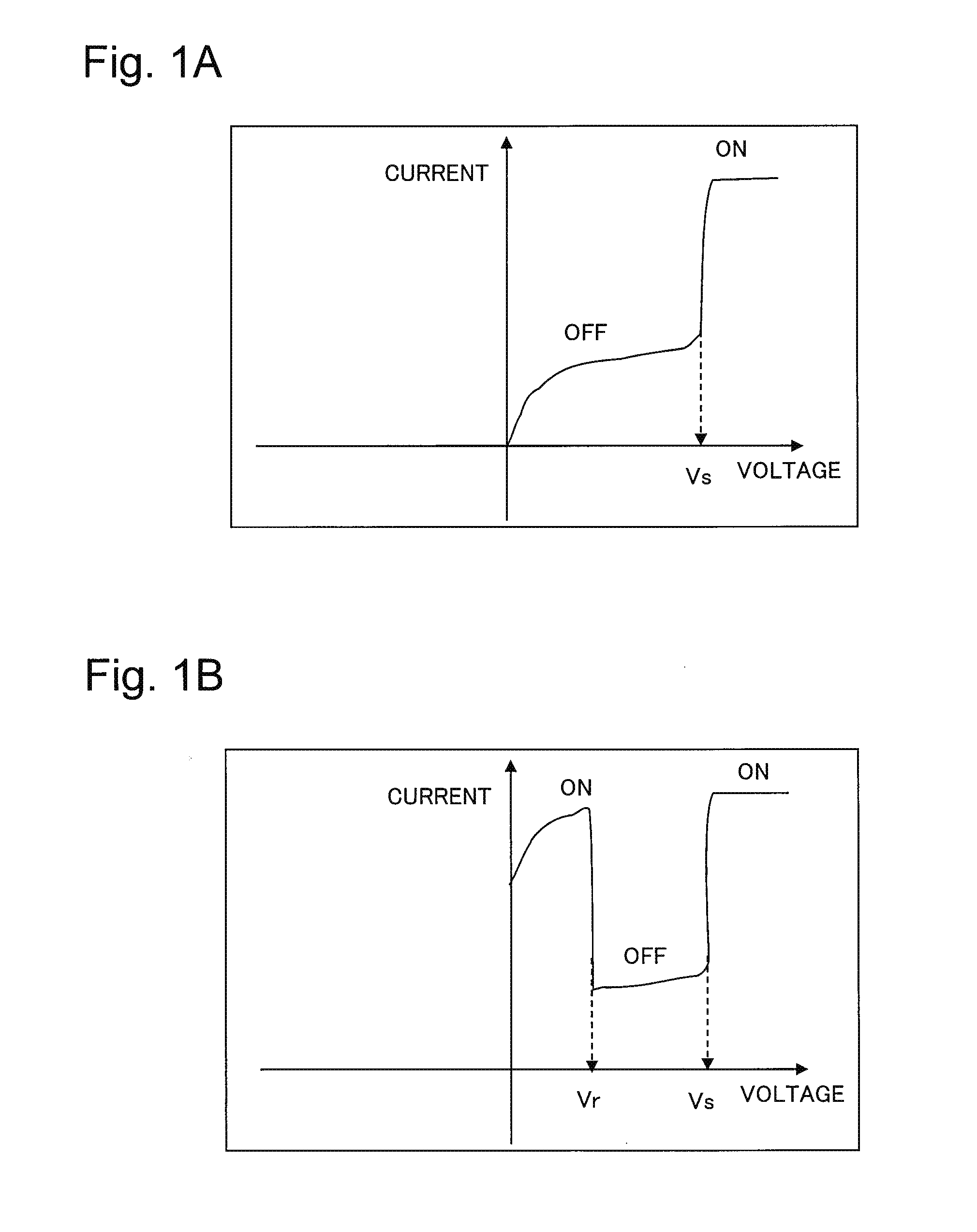
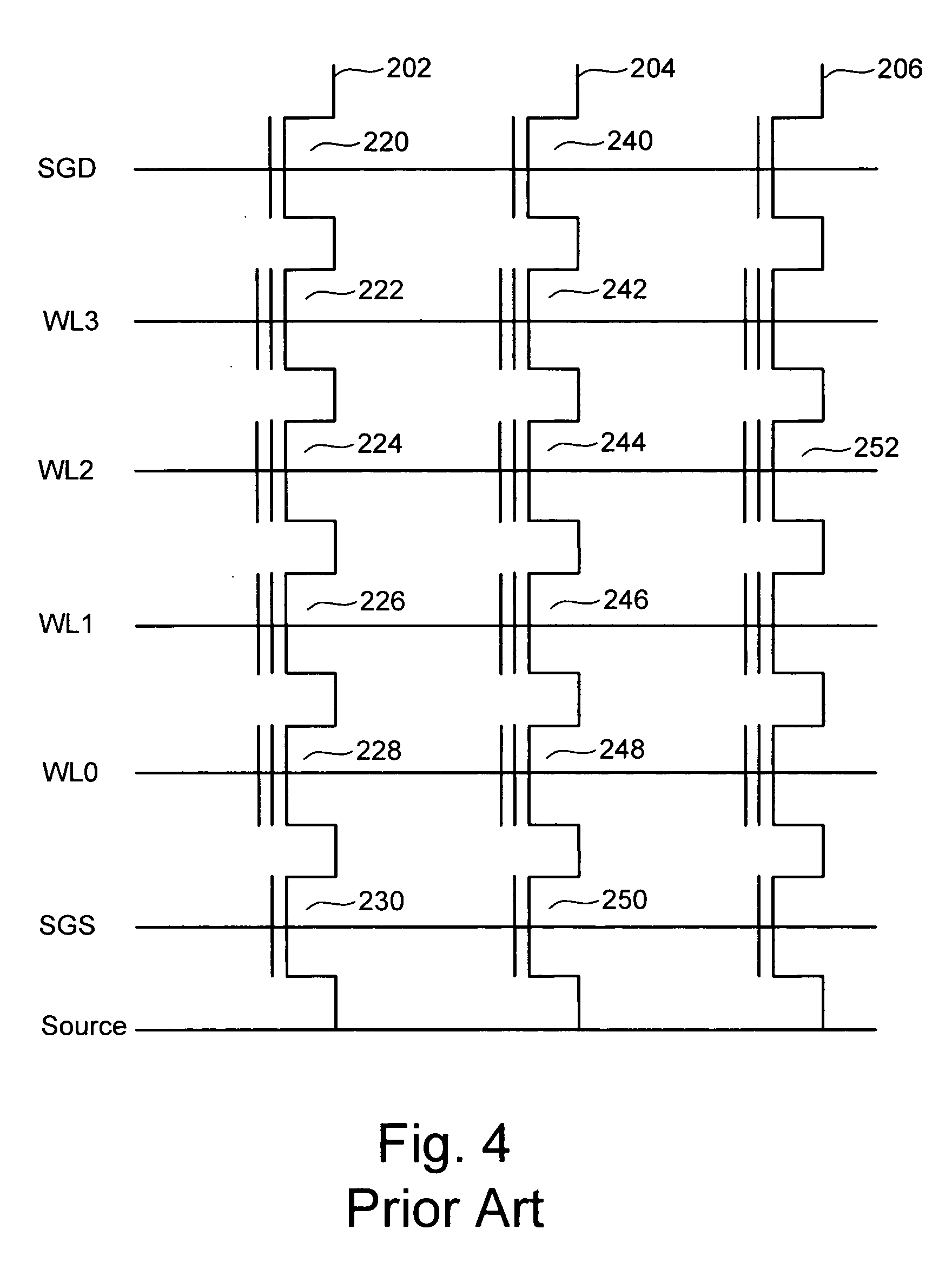
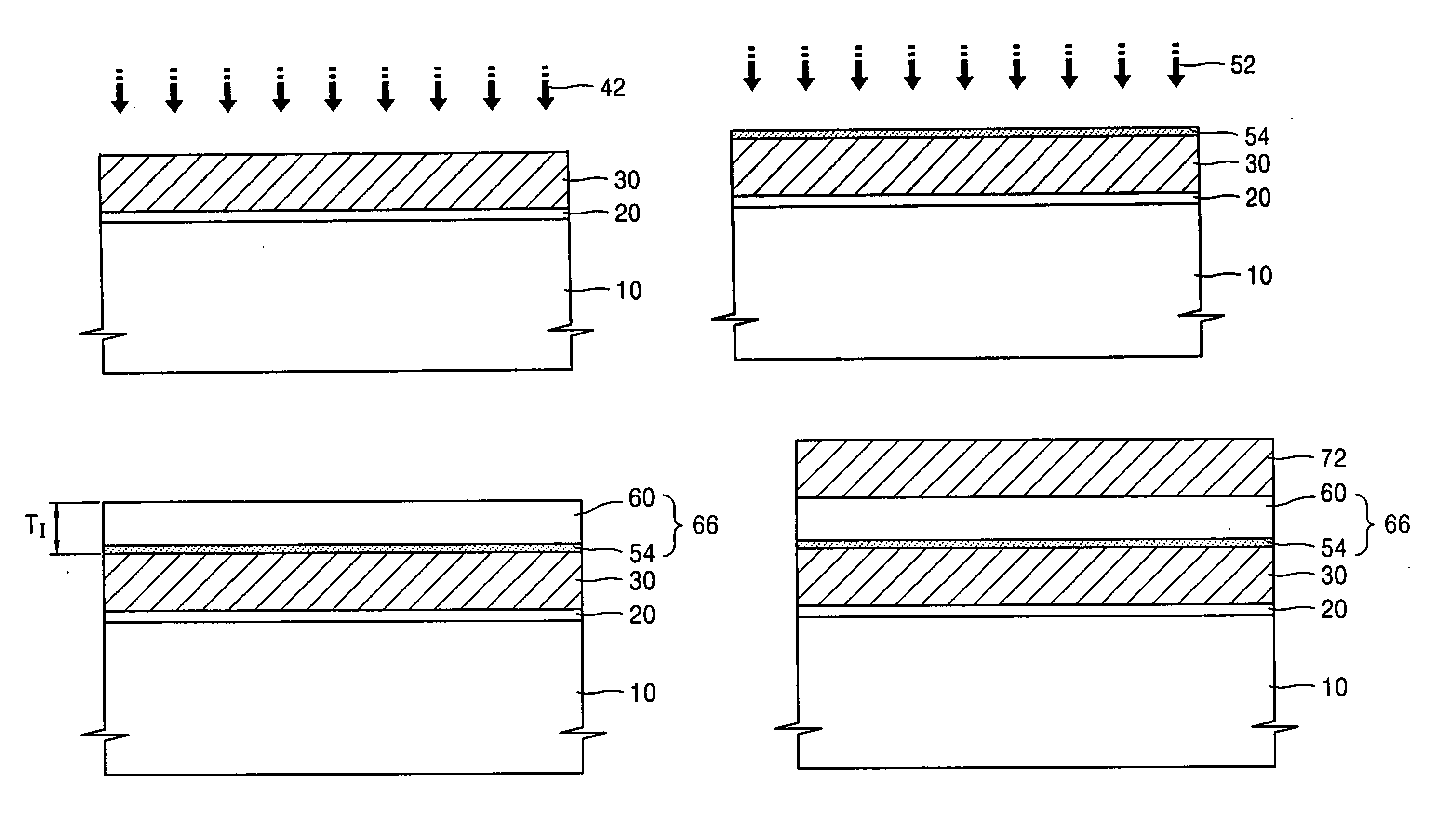
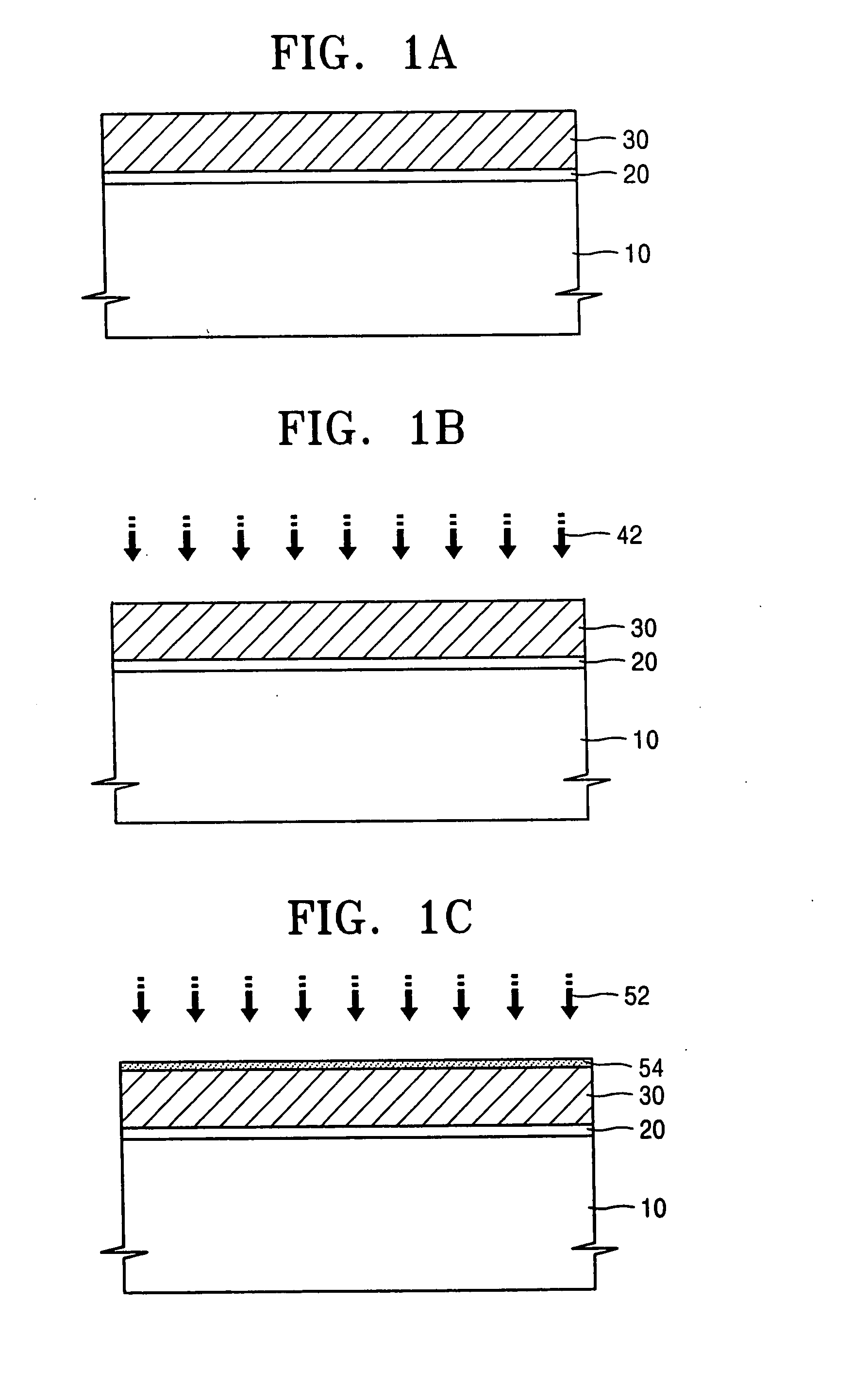
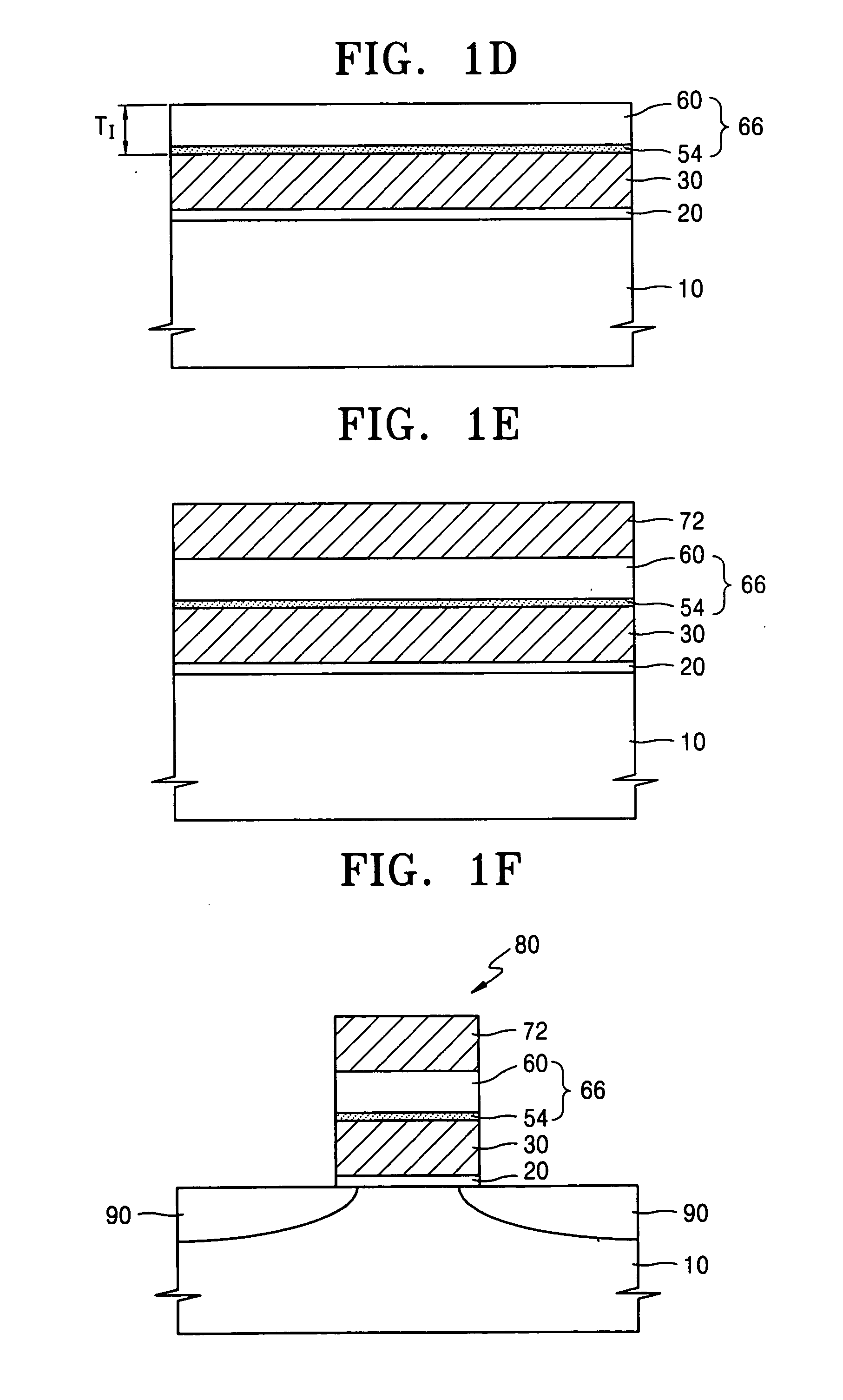
Variable programming of non-volatile memory
ActiveUS7020017B2Improve data retentionDecreased program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storageReading levelNon-volatile memory
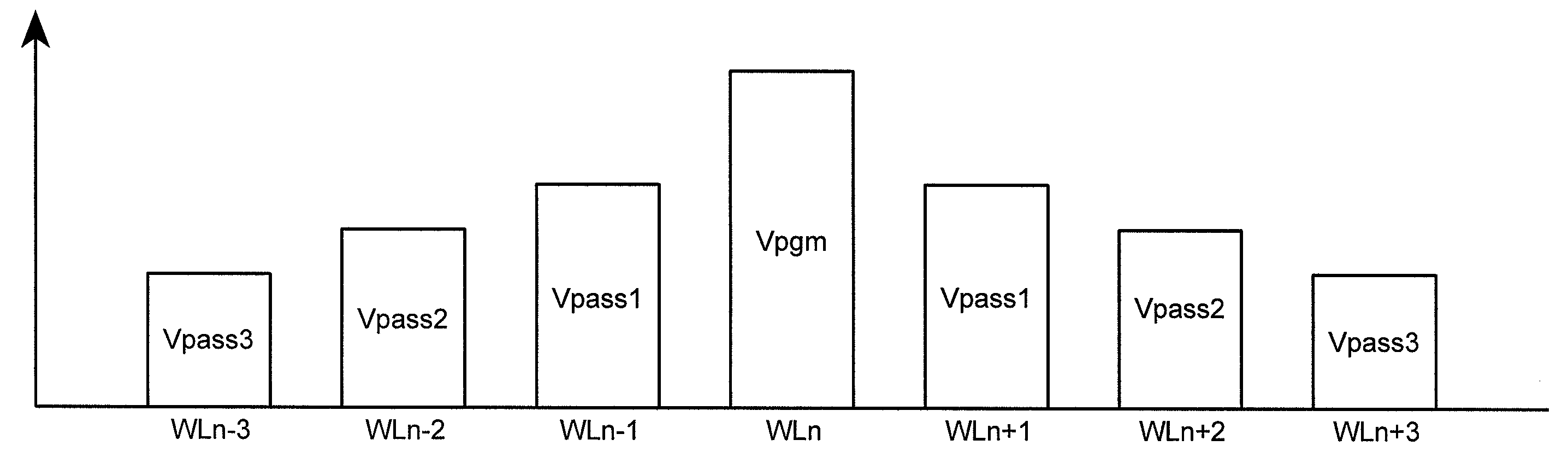
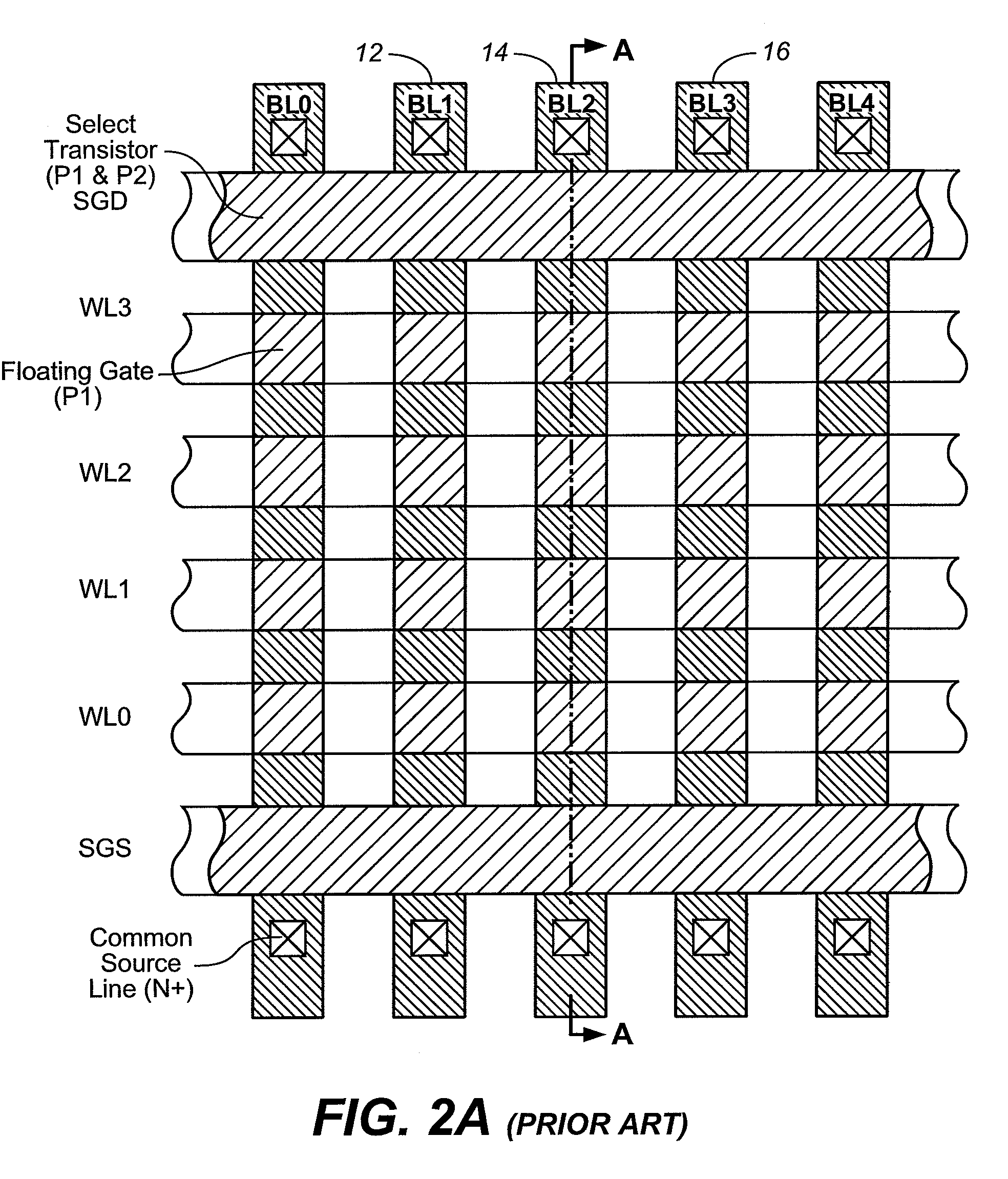
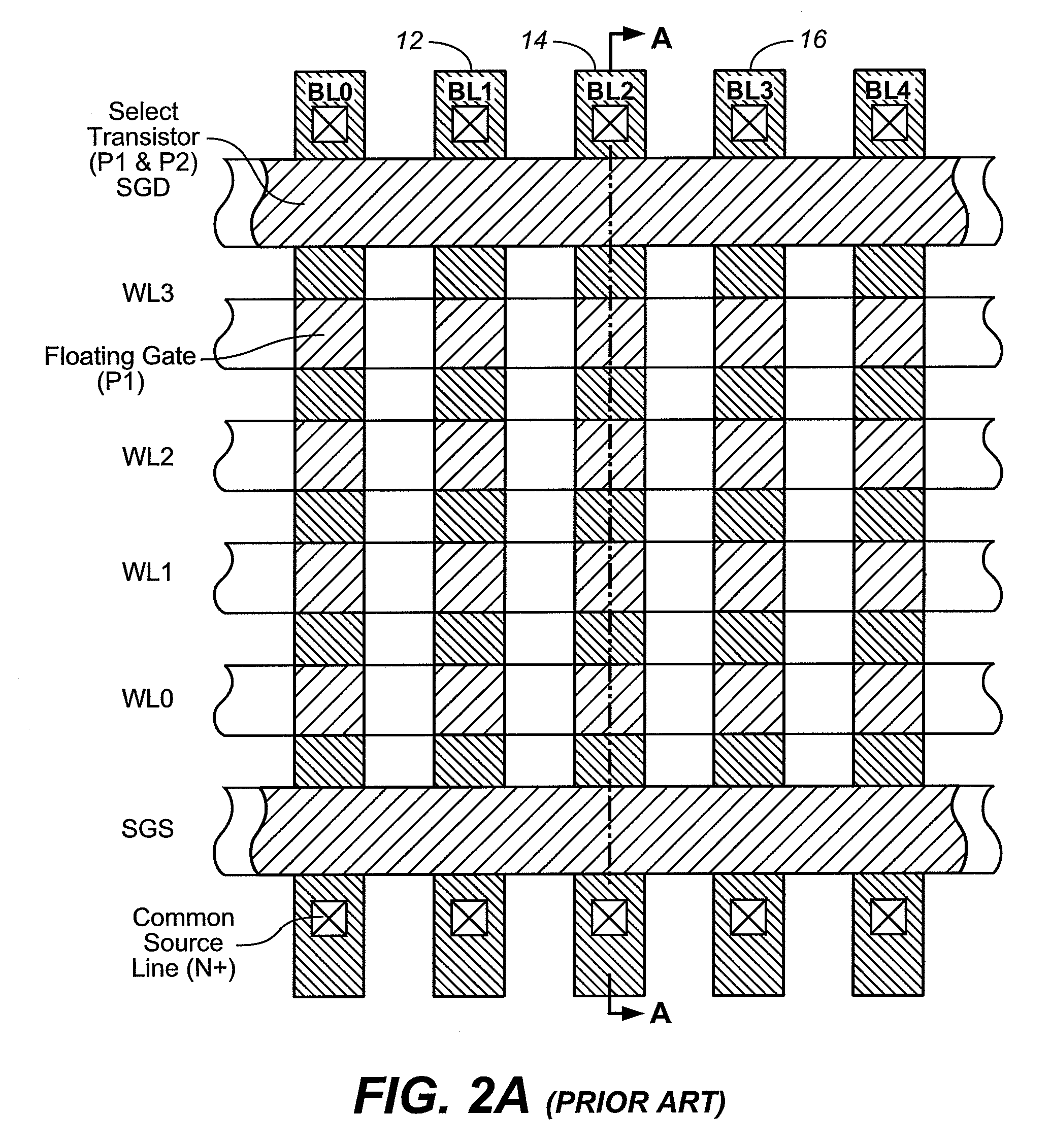
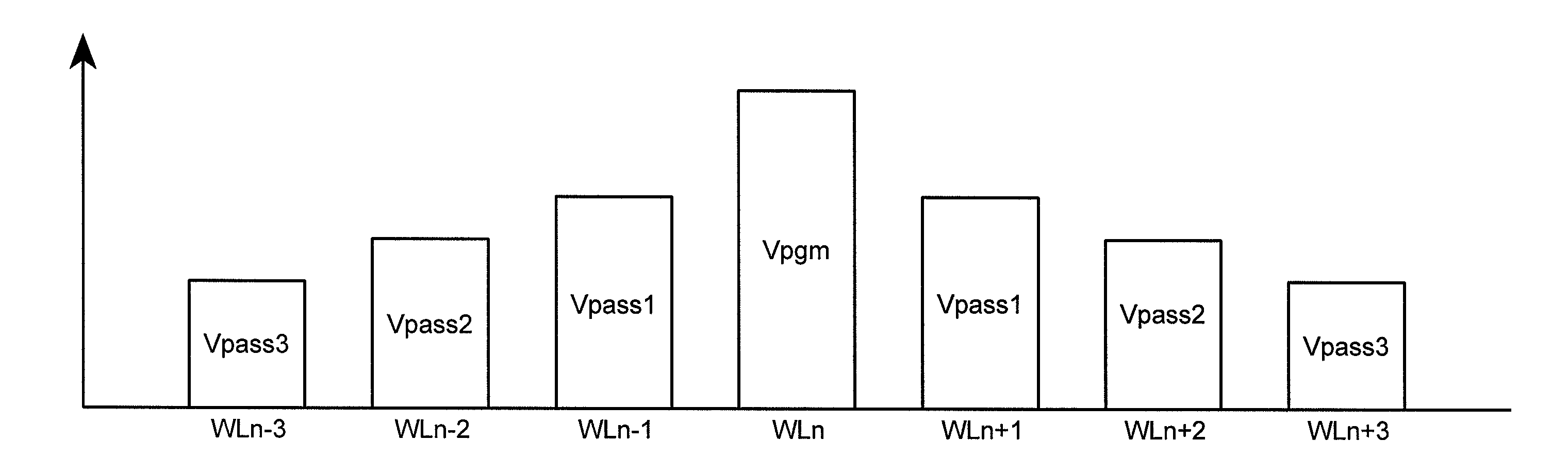
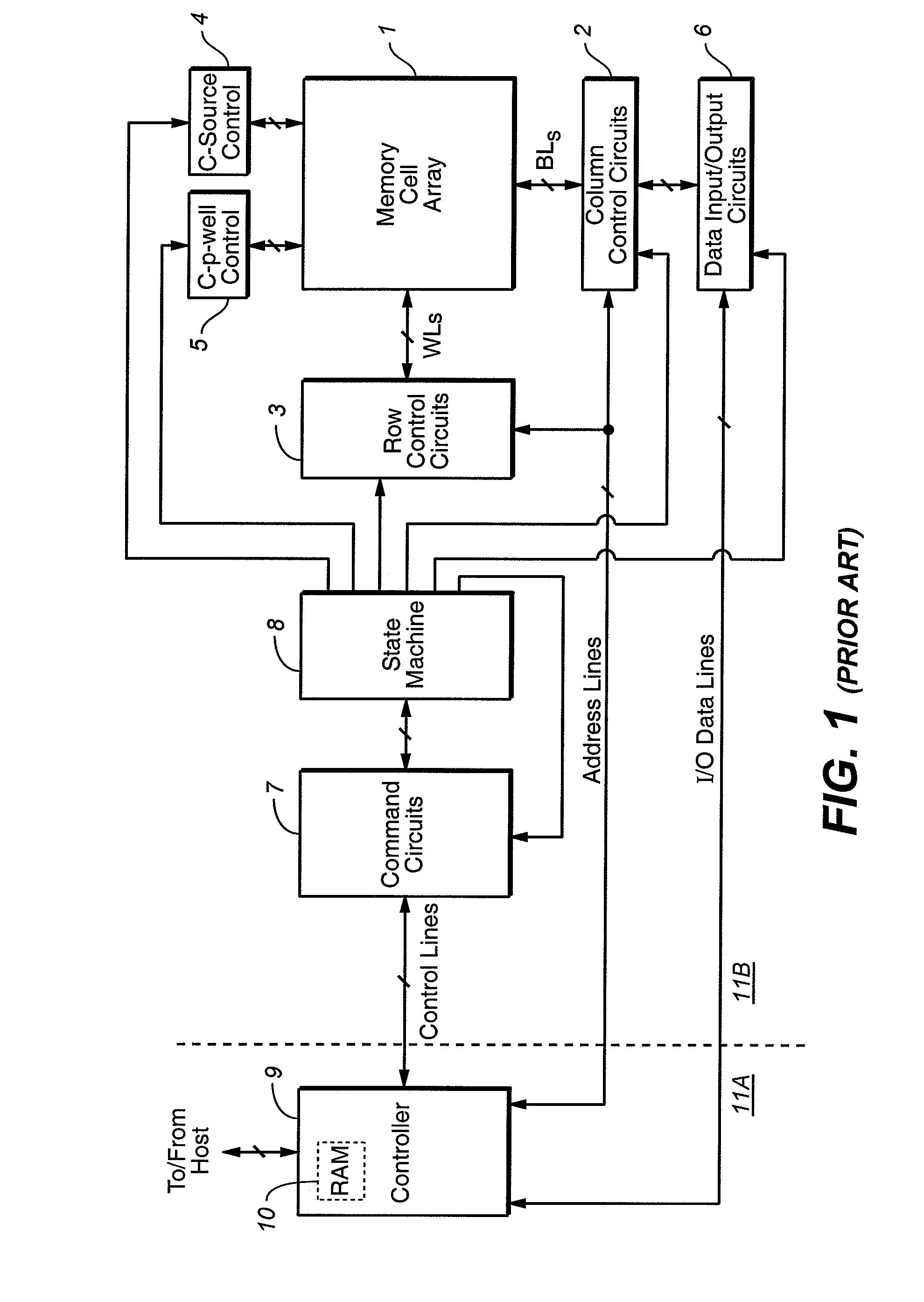
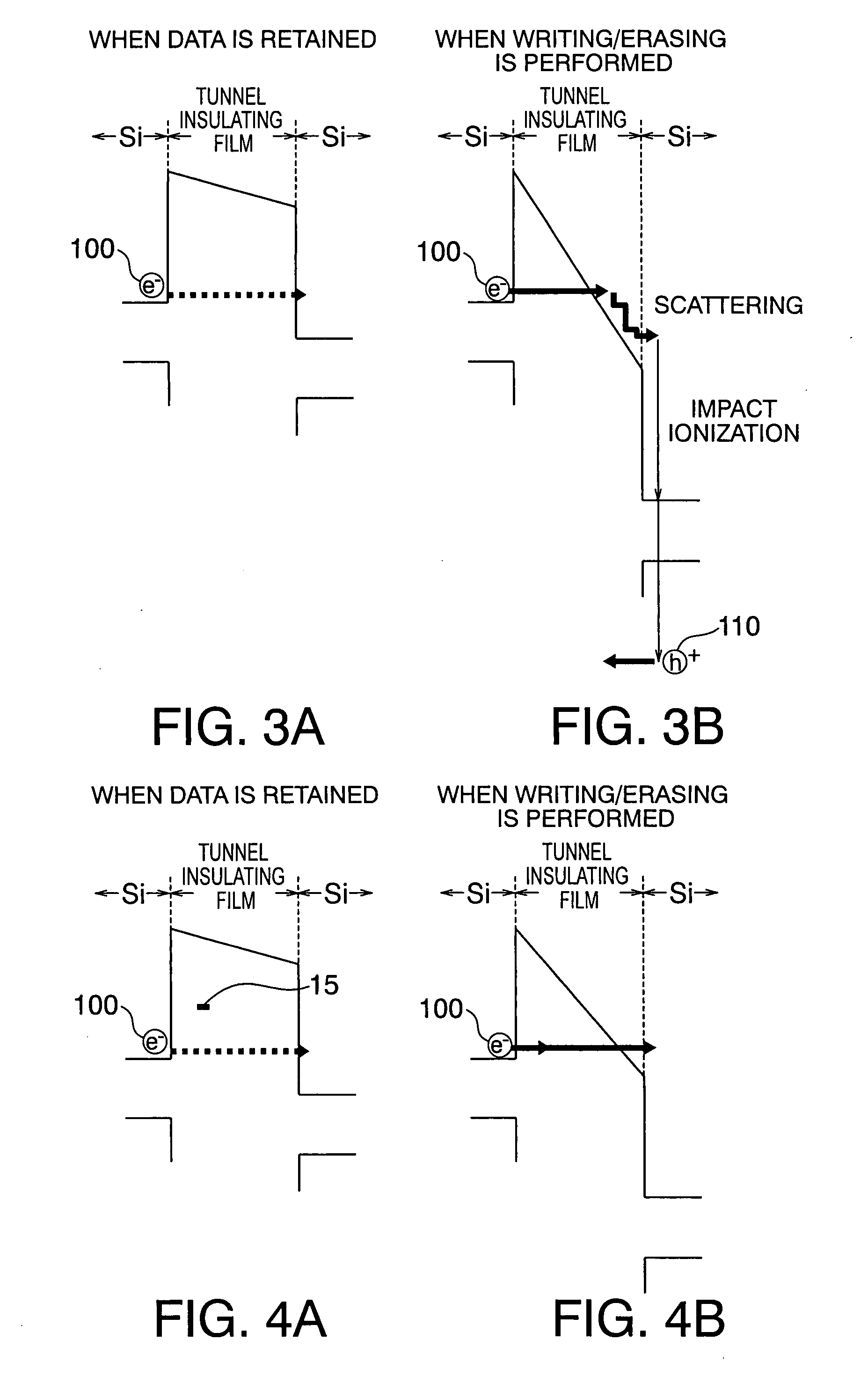
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments can provide for reduced program disturb in non-volatile semiconductor memory. In one embodiment, select memory cells such as those connected to a last word line of a NAND string are programmed using one or more program verify levels or voltages that are different than a corresponding level used to program other cells or word lines. One exemplary embodiment includes using a lower threshold voltage verify level for select physical states when programming the last word line to be programmed for a string during a program operation. Another embodiment includes applying a lower program voltage to program memory cells of the last word line to select physical states. Additional read levels are established for reading the states programmed using lower verify levels in some exemplary implementations. A second program voltage step size that is larger than a nominal step size is used in one embodiment when programming select memory cells or word lines, such as the last word line to be programmed for a NAND string.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
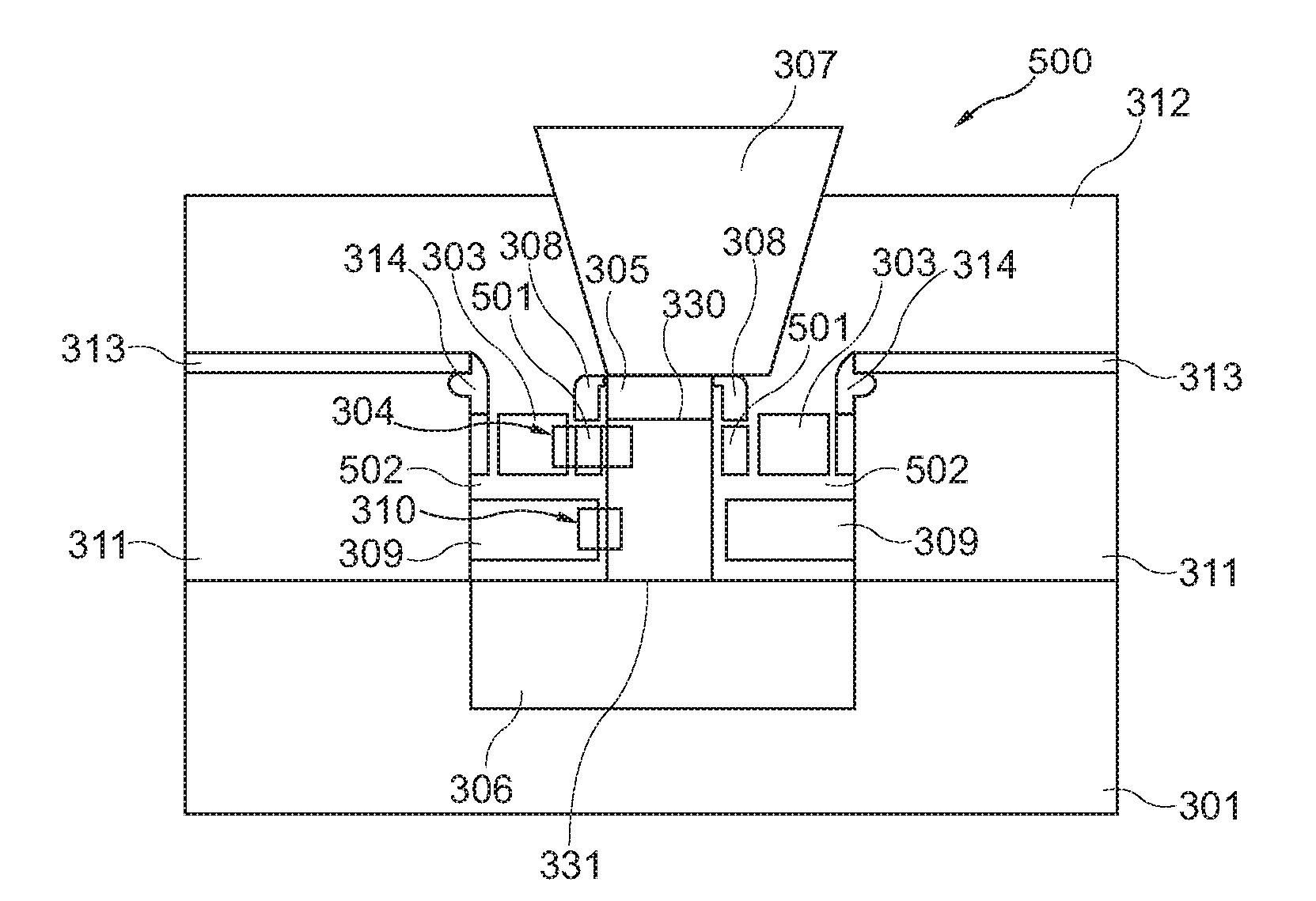
Nonvolatile memory cell comprising a nonwire and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20100117138A1Easy to controlScale upNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesNanowireNon-volatile memory
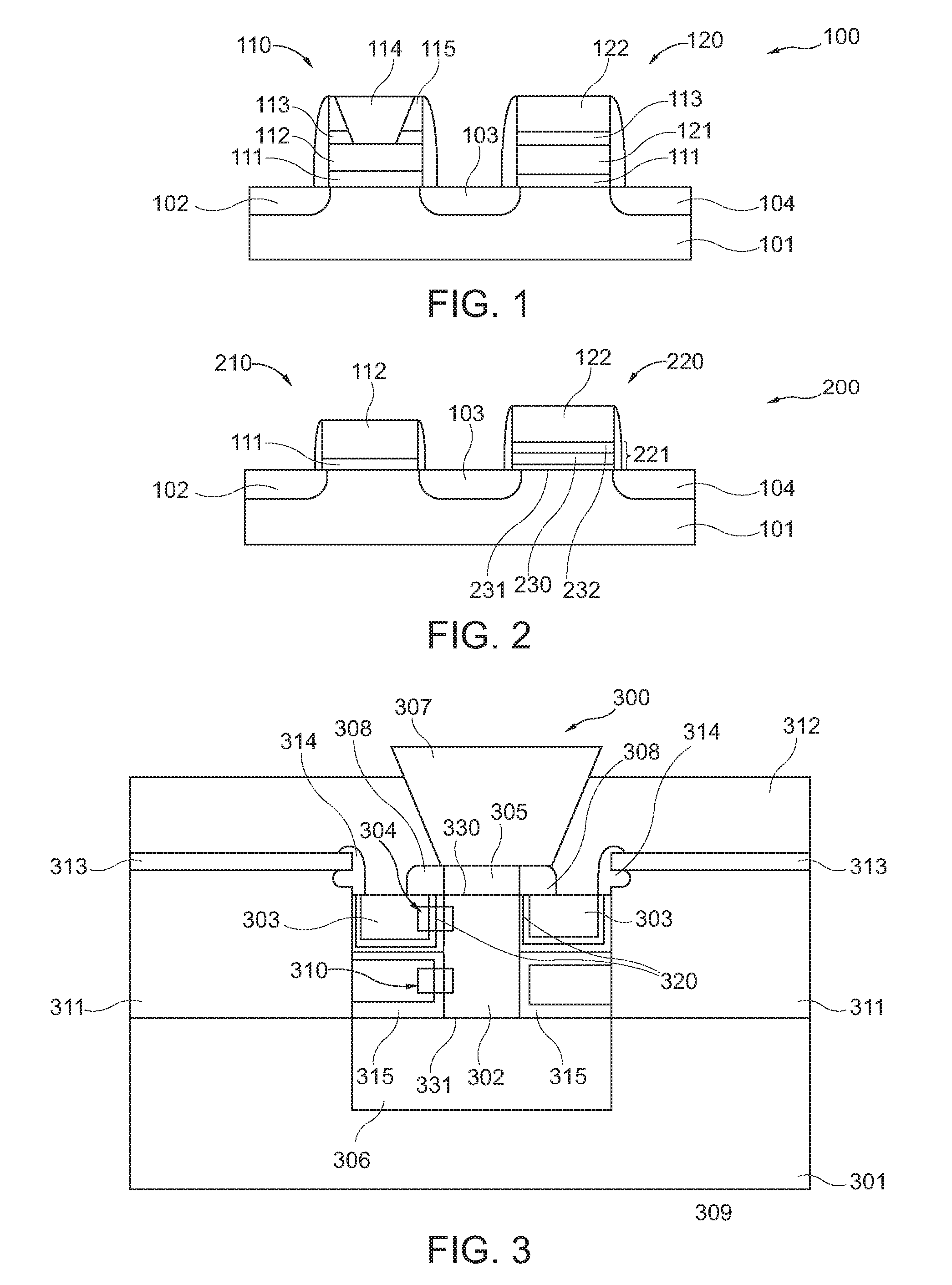
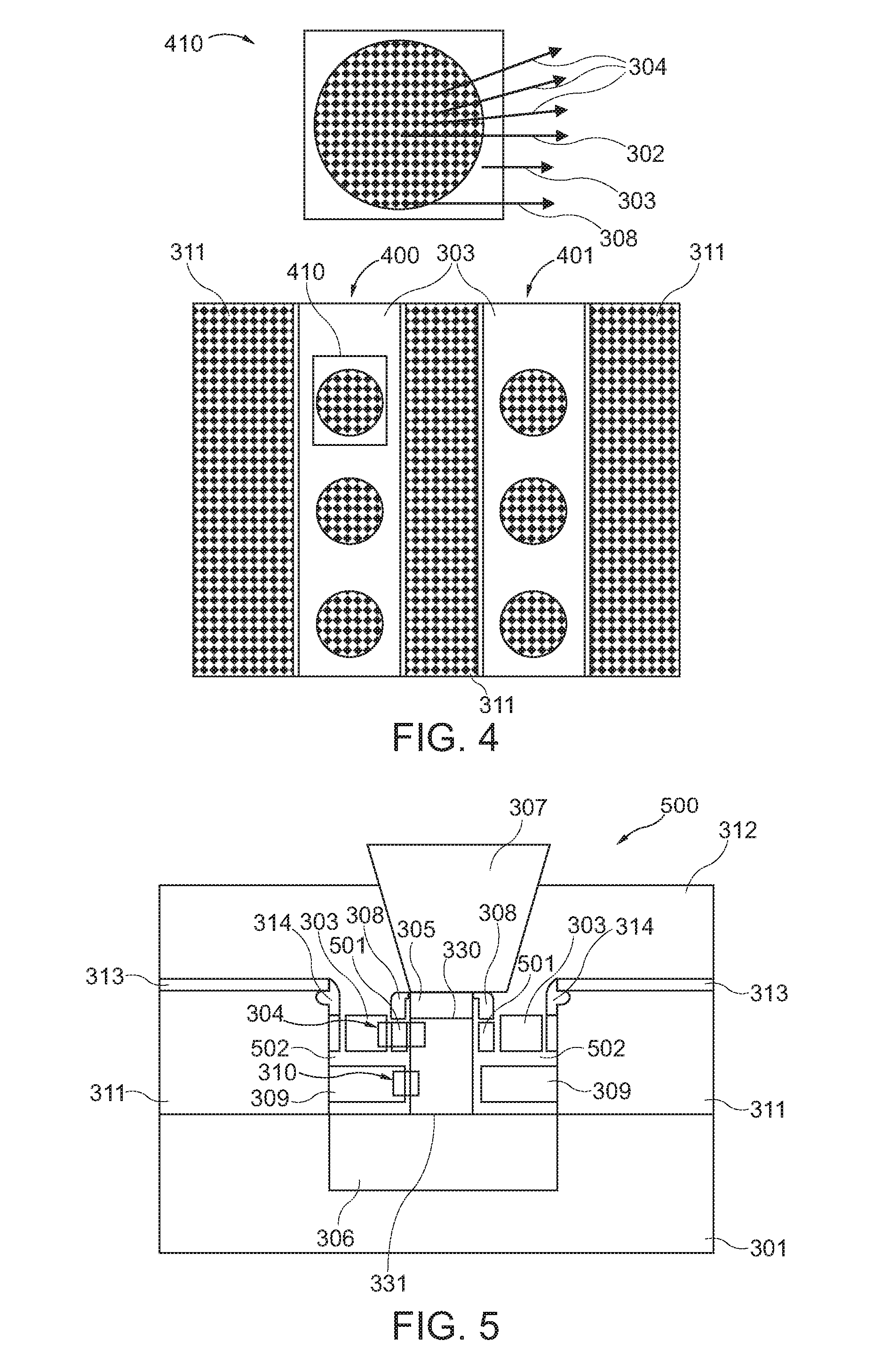
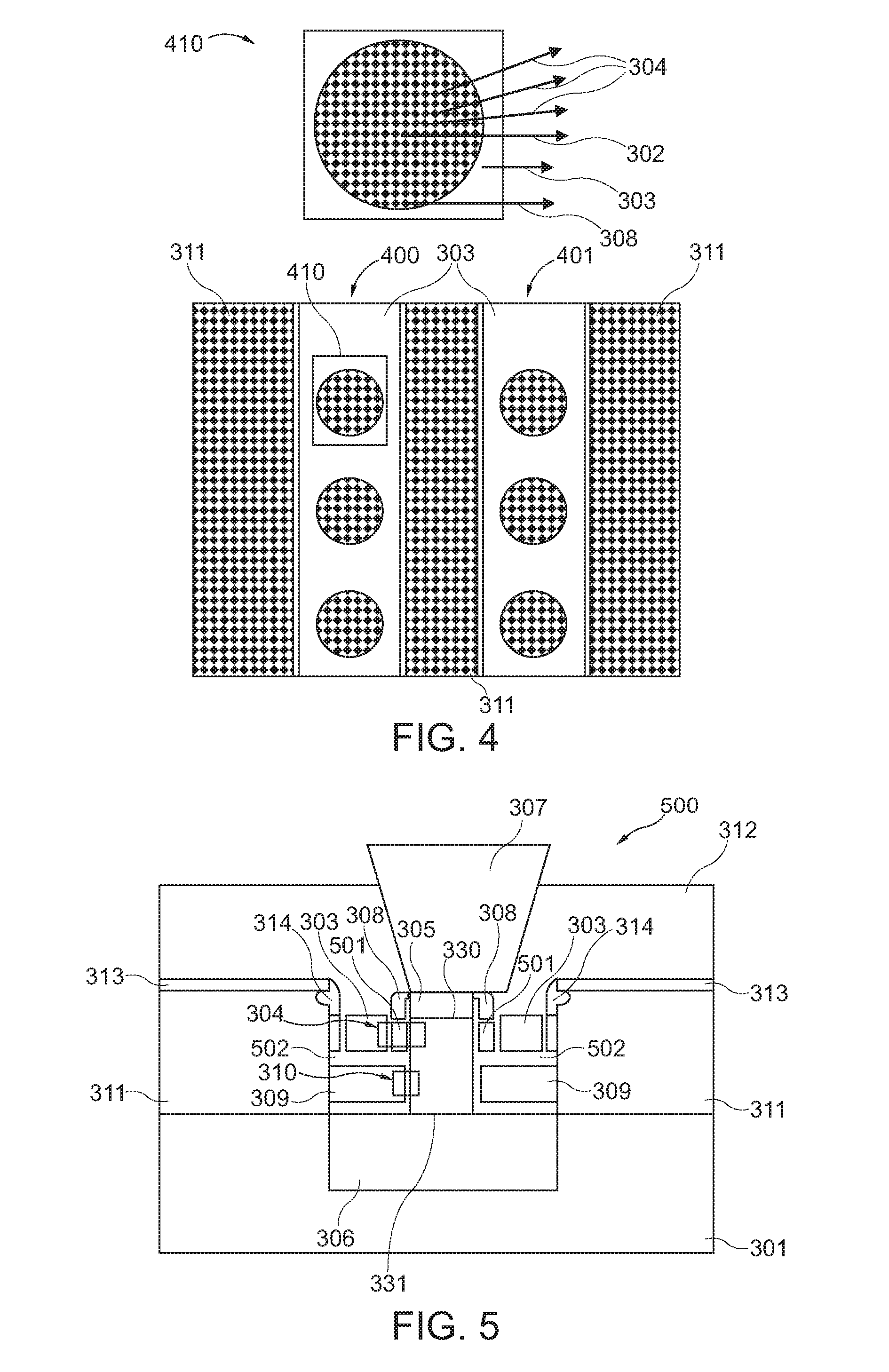
A memory cell (300, 500), the memory cell (300, 500) comprising a substrate (301), a nanowire (302) extending along a vertical trench formed in the substrate (301), a control gate (303) surrounding the nanowire (302), and a charge storage structure (320, 501) formed between the control gate (303) and the nanowire (302).
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
Boosting methods for NAND flash memory
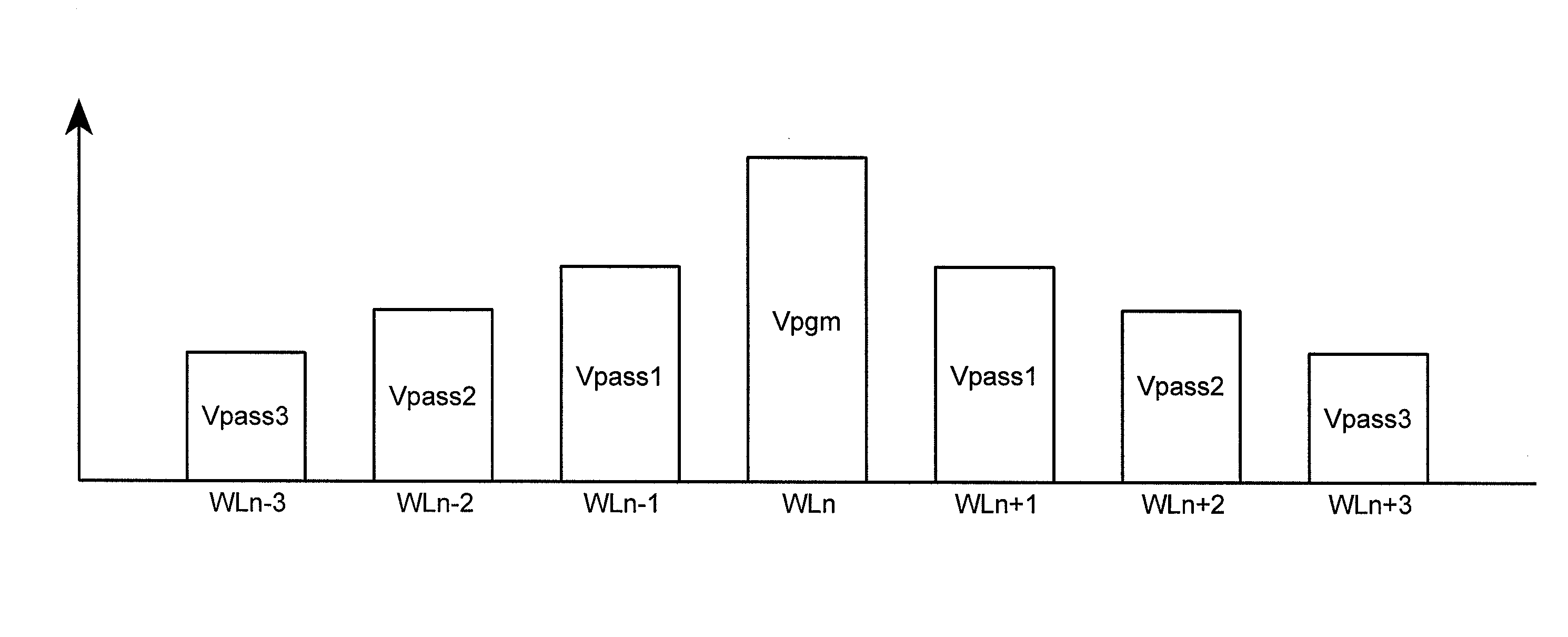
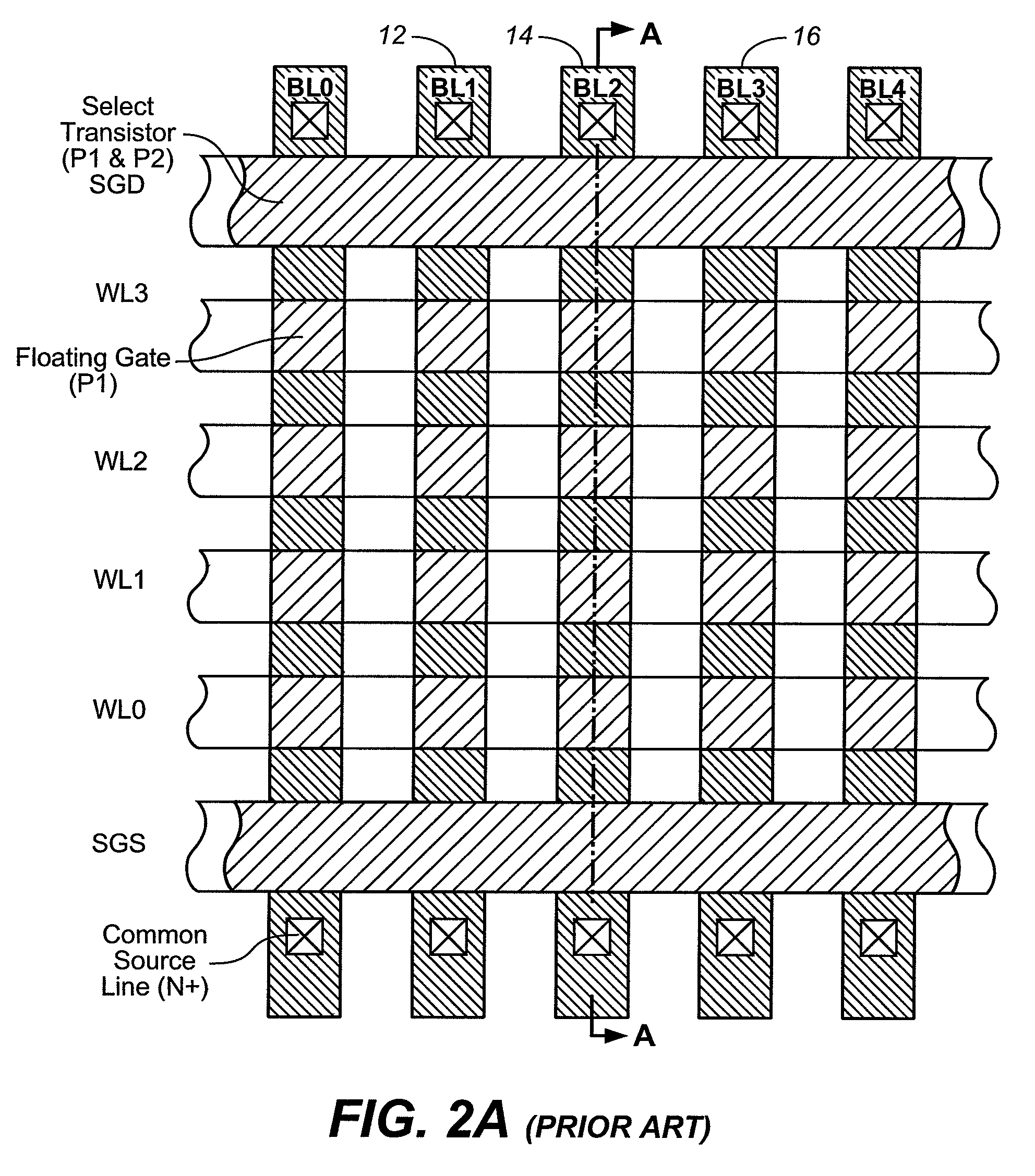
InactiveUS7286408B1Reducing Vpgm-disturbsHigh boosting voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsEngineering
A floating gate memory array includes row control circuits that provide a programming voltage to a selected word line and provide a stair-like pattern of boosting voltages to unselected word lines. Boosting voltages descend with increased distance from the selected word line. Boosting voltages are increased in small increments up to their final values.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Boosting methods for NAND flash memory
InactiveUS20070258286A1High voltageLower programming voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageControl circuitVoltage
A floating gate memory array includes row control circuits that provide a programming voltage to a selected word line and provide a stair-like pattern of boosting voltages to unselected word lines. Boosting voltages descend with increased distance from the selected word line. Boosting voltages are increased in small increments up to their final values.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Nonvolatile memory device
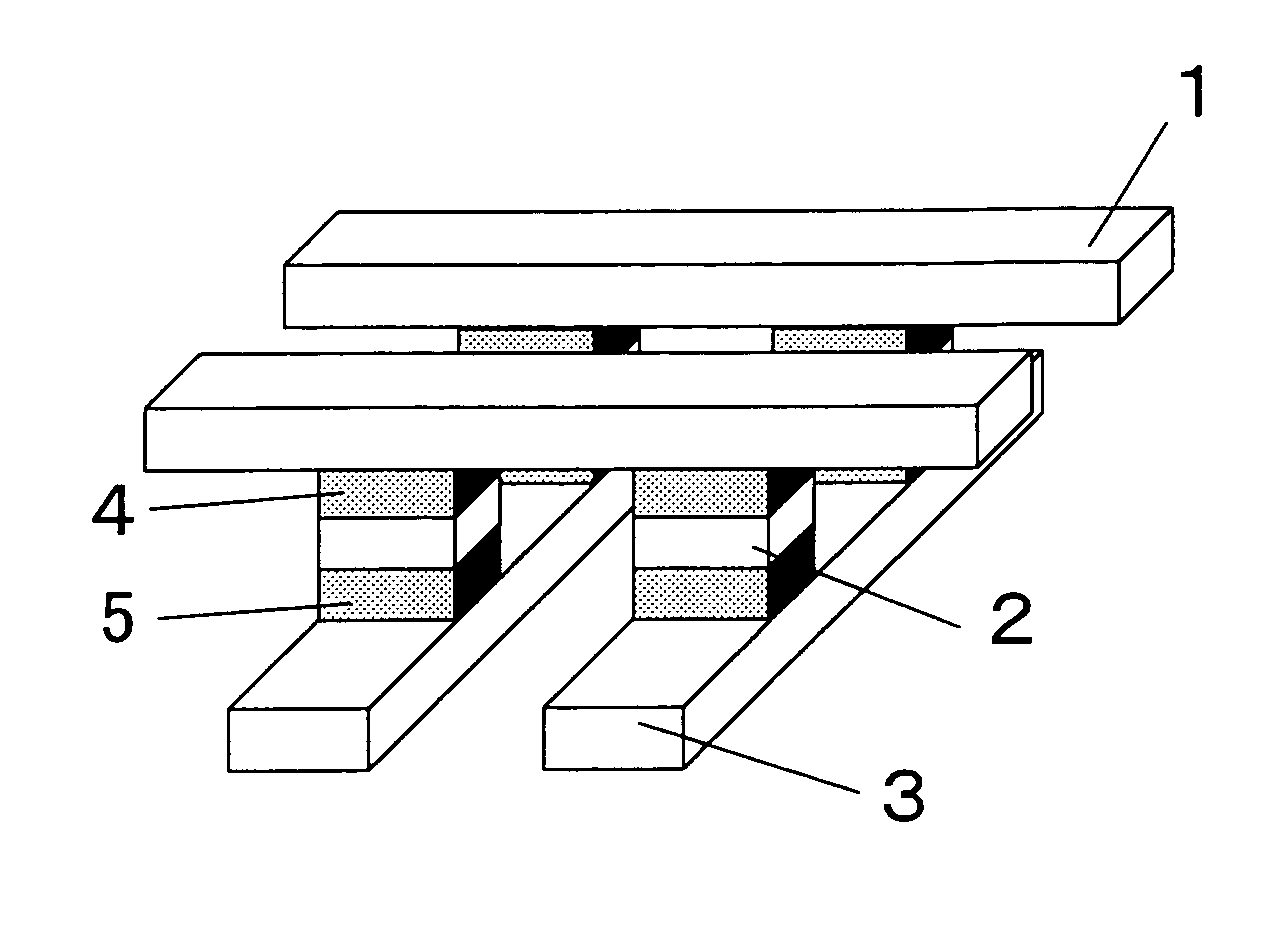
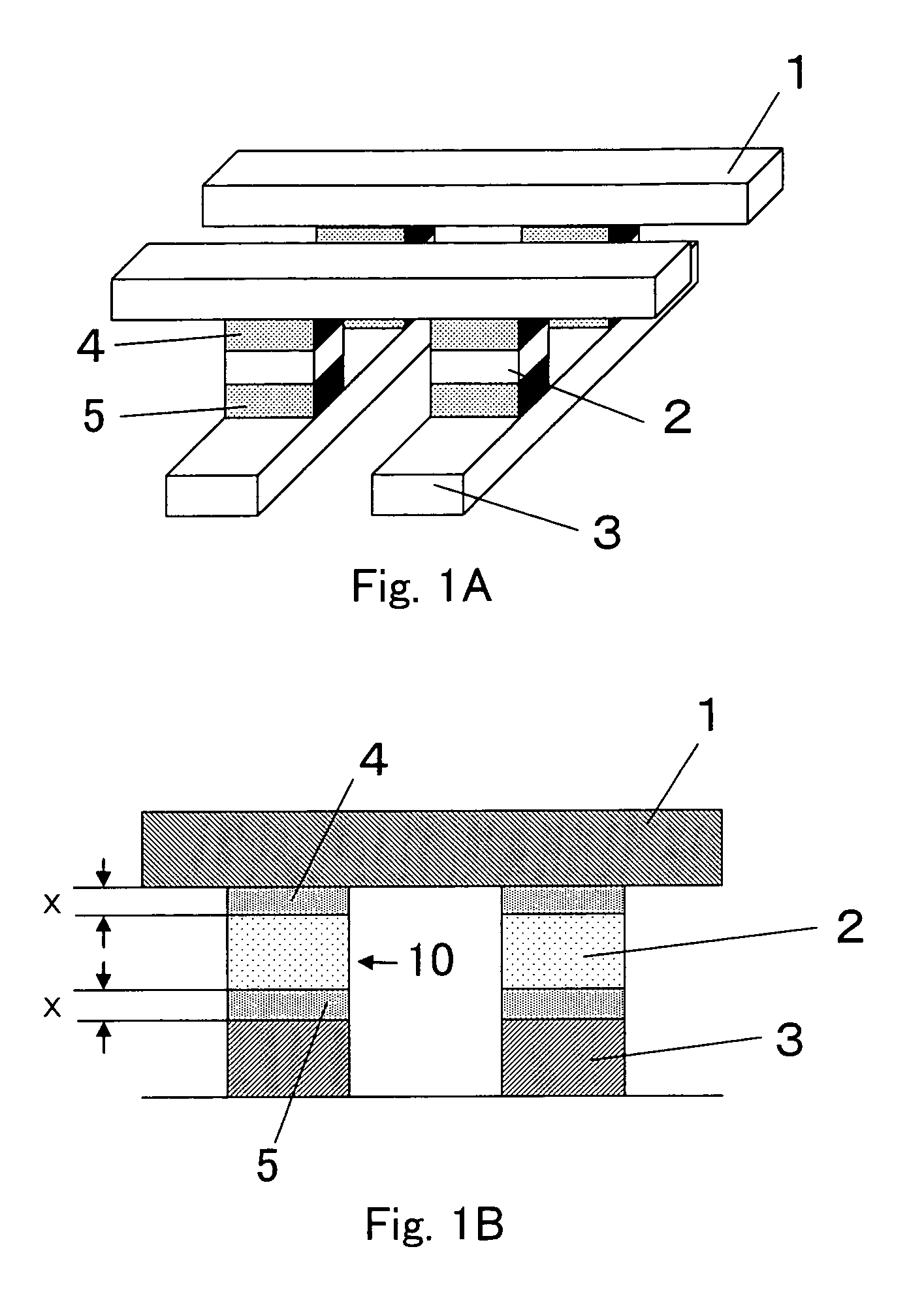
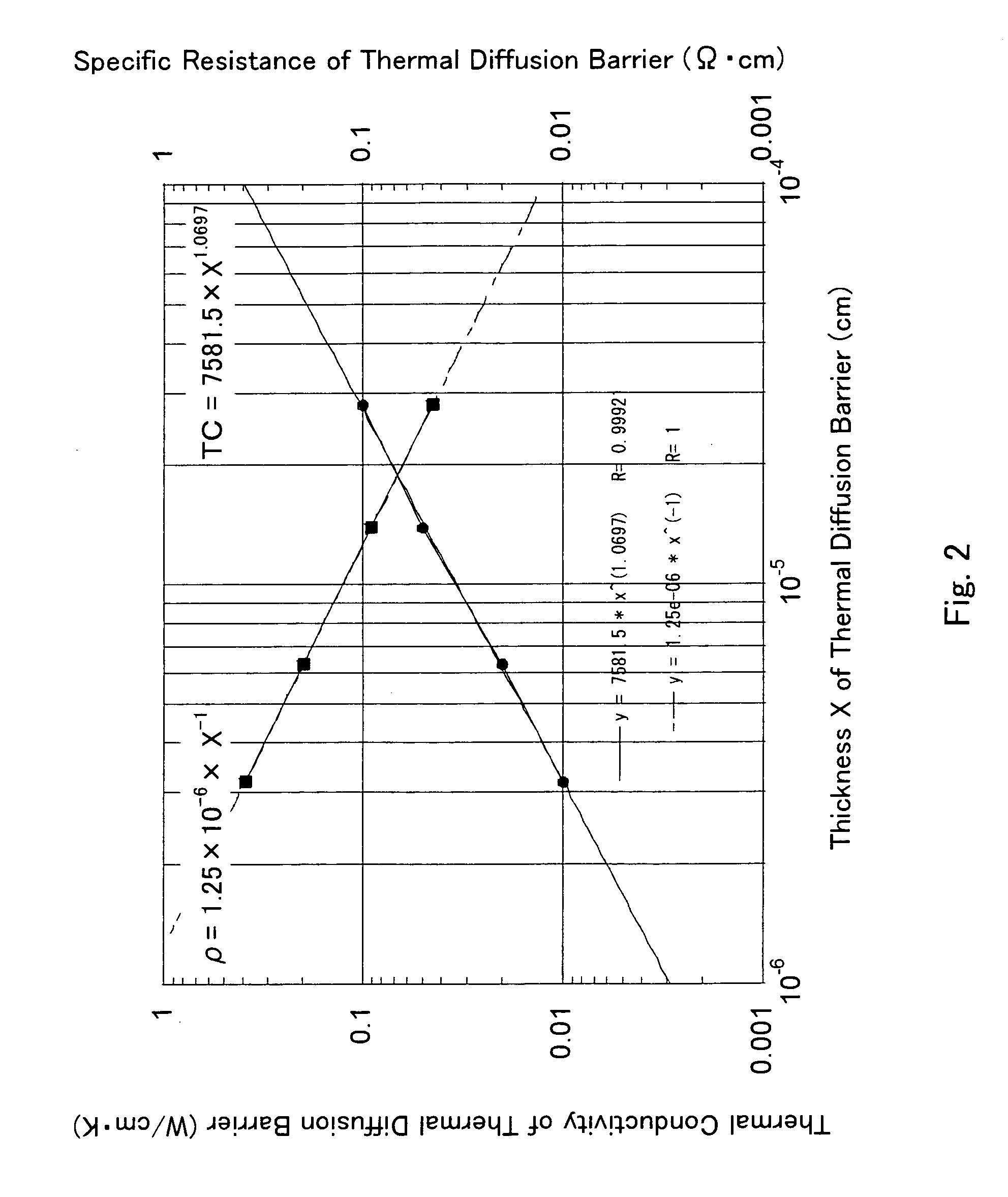
InactiveUS7863598B2Avoid heatSuppress DiffuseSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A nonvolatile memory device comprises memory cells, each including a variable resistor element for storing data in accordance with a change in electrical resistance due to application of electrical stress, and a thermal diffusion barrier on a thermal diffusion path, wherein the thermal diffusion barrier is capable of suppressing a change in resistance of the variable resistor element due to heat diffusion from one of two adjacent memory cells separated by an electrical insulator from each other where heat is generated by applying the electrical stress for changing the electrical resistance of the variable resistor element to the other memory cell via the thermal diffusion path including an electrically conductive wiring material higher in thermal conductivity than that of the electrical insulator.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
NAND flash memory with boosting
ActiveUS7436709B2High voltageLower programming voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageHemt circuitsEngineering
A floating gate memory array includes row control circuits that provide a programming voltage to a selected word line and provide a stair-like pattern of boosting voltages to unselected word lines. Boosting voltages descend with increased distance from the selected word line. Boosting voltages are increased in small increments up to their final values.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
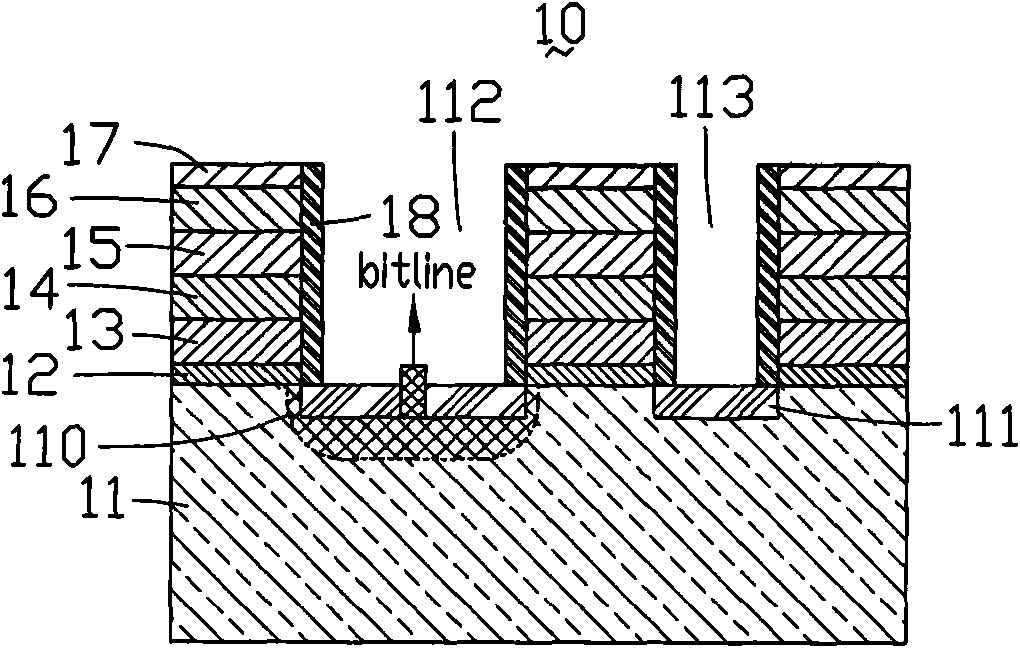
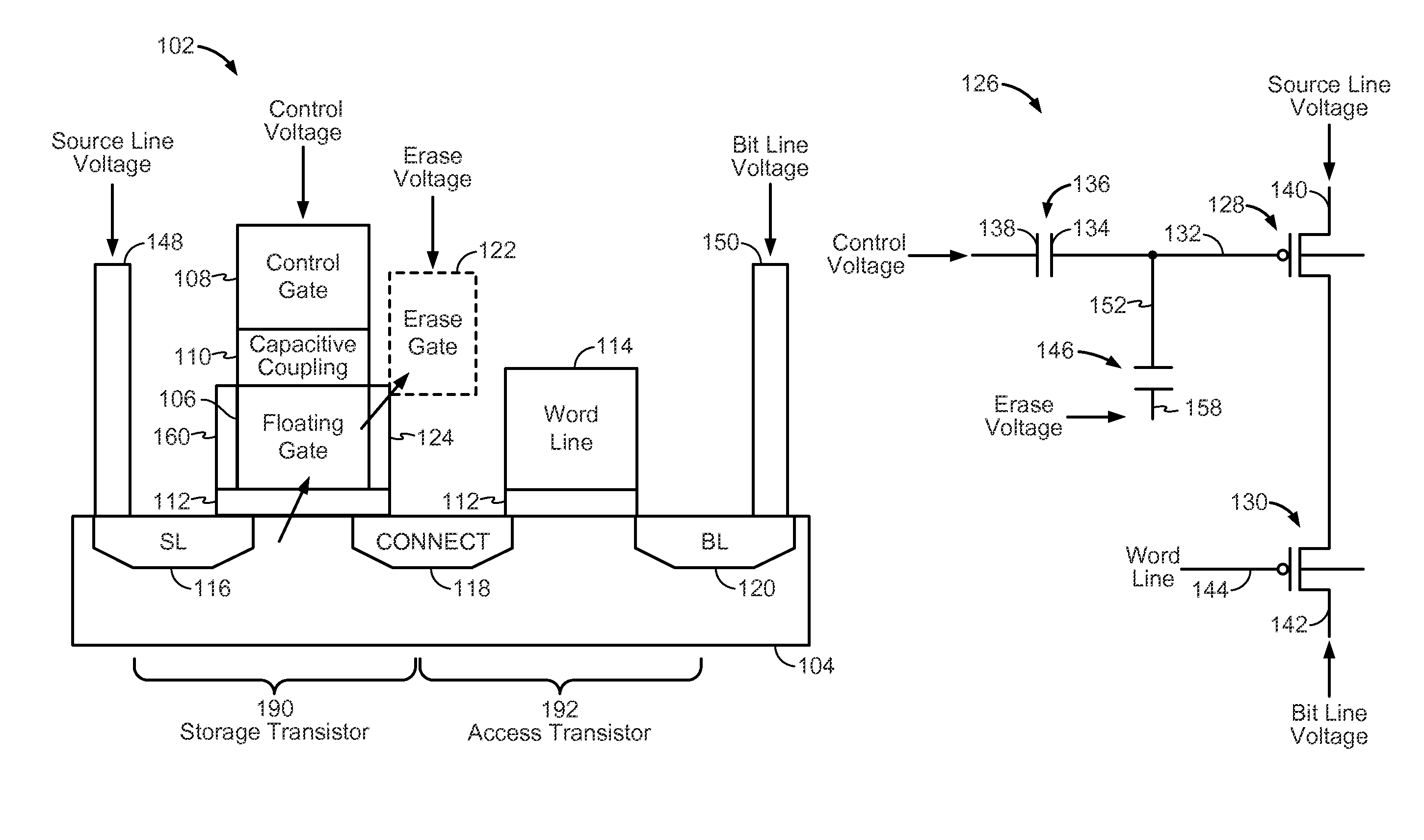
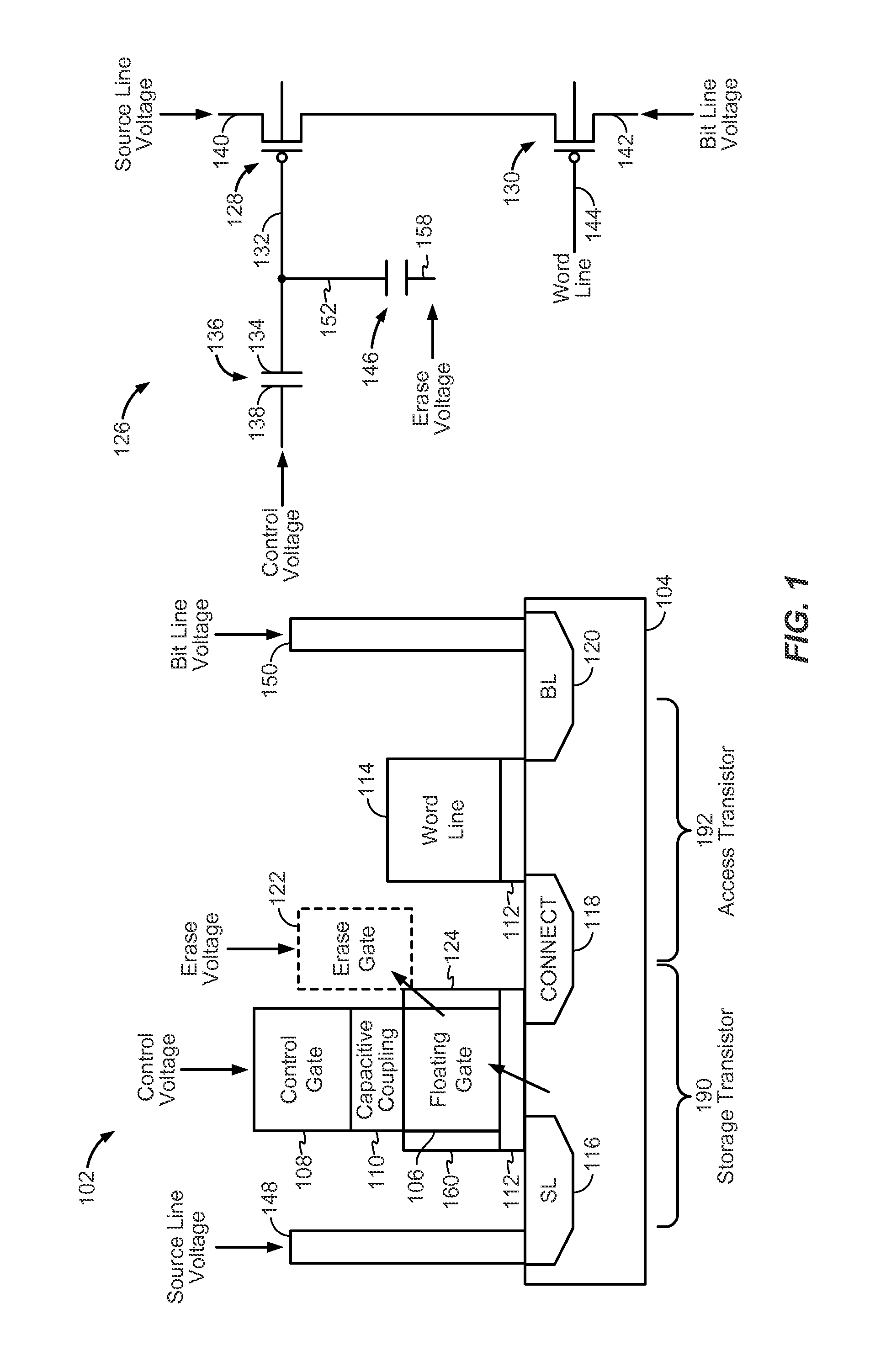
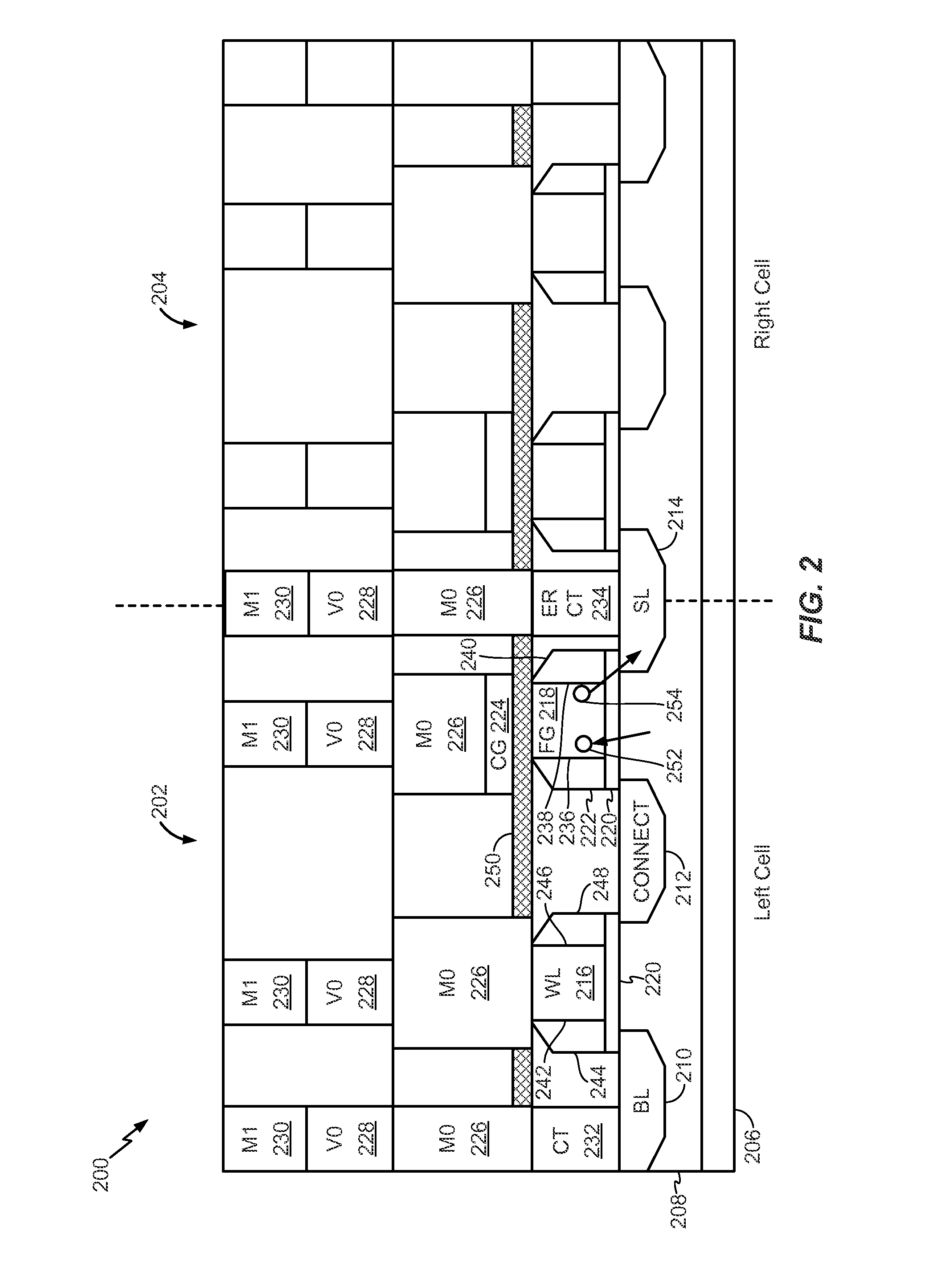
Flash memory cell with capacitive coupling between a metal floating gate and a metal control gate
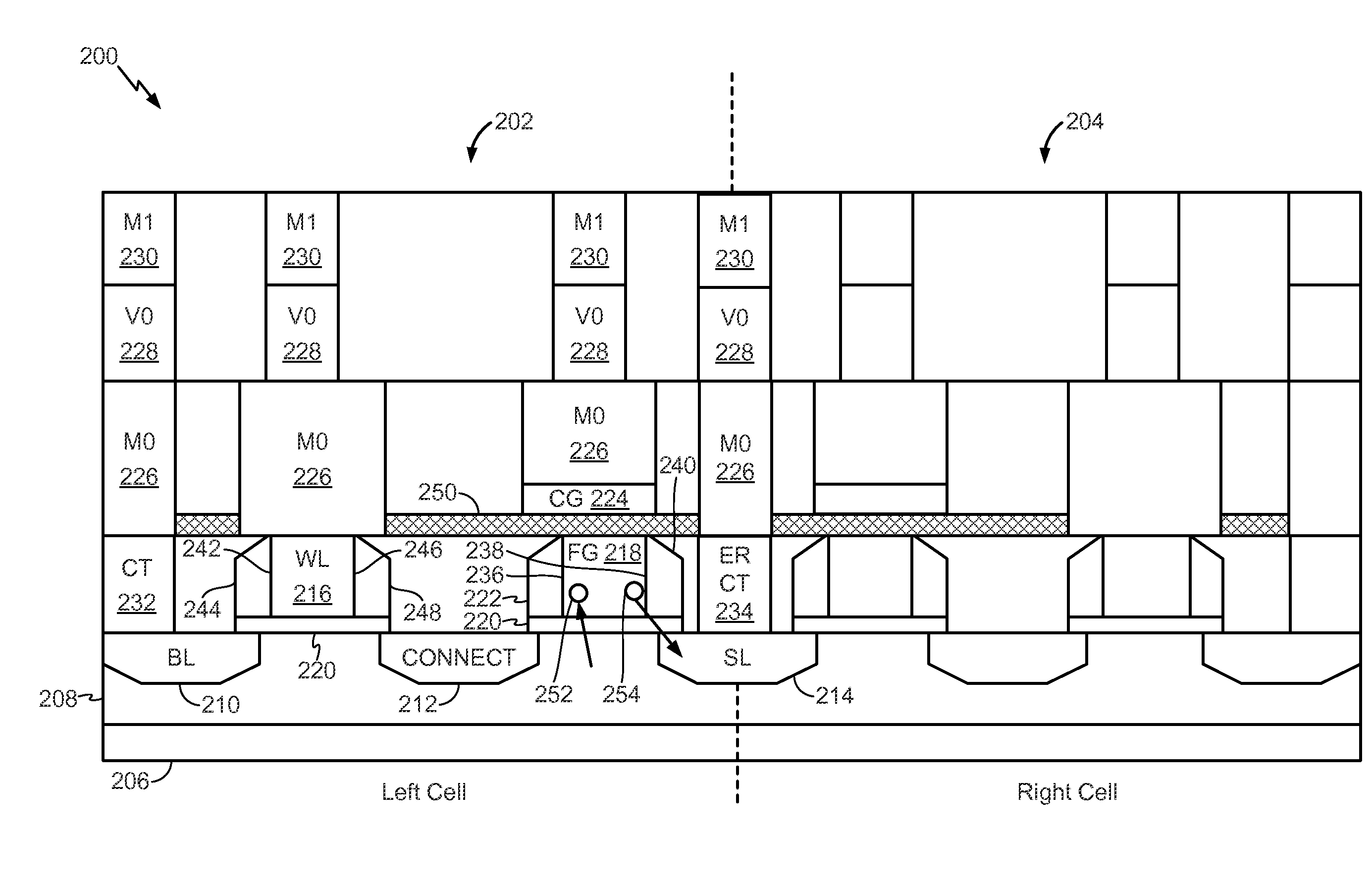
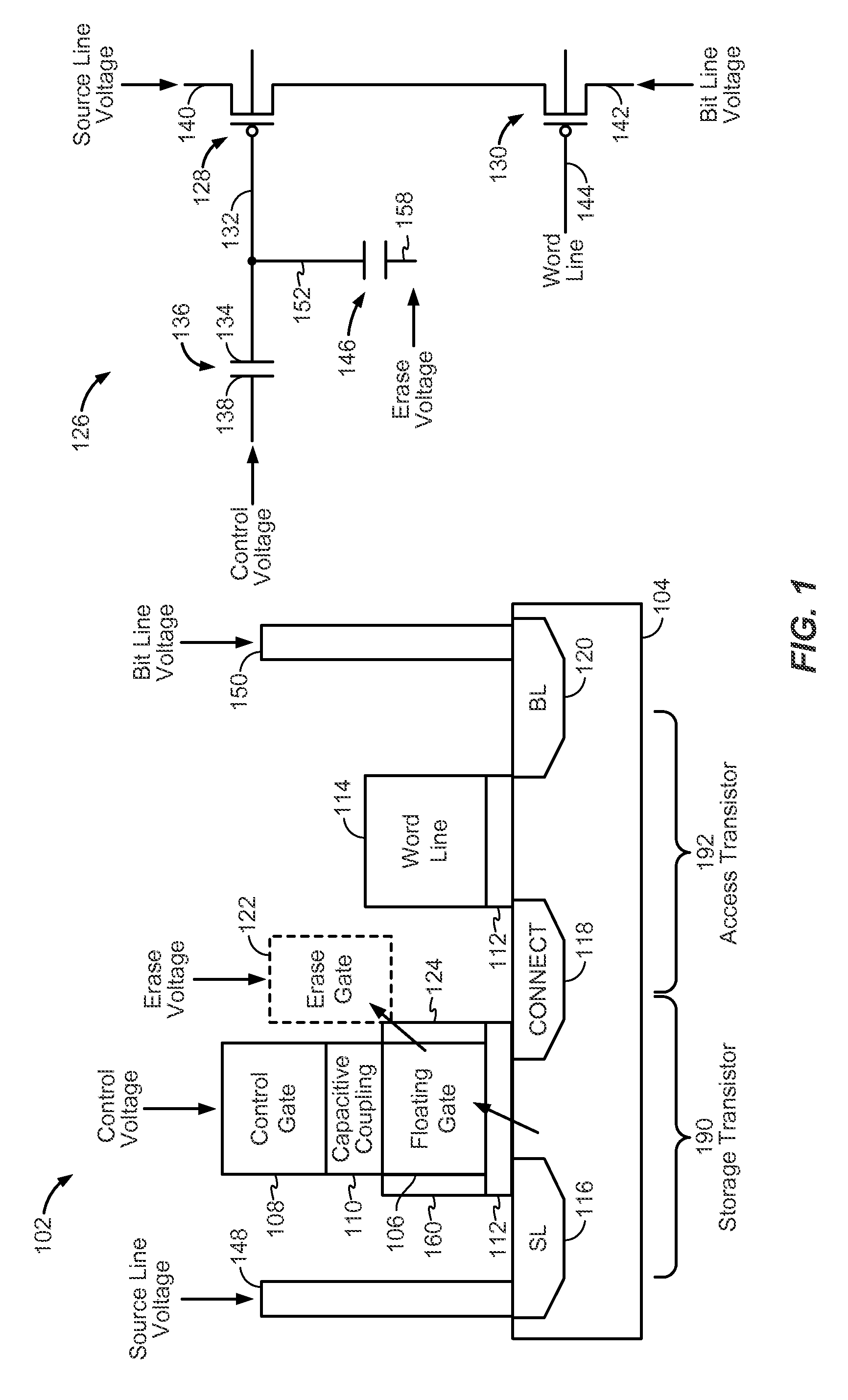
ActiveUS20150036437A1Enhance capacitive couplingProgramming voltage be reduceRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitive couplingCapacitance
An apparatus includes a storage transistor. The storage transistor includes a floating gate configured to store electrical charge and a control gate. The floating gate is coupled to the control gate via capacitive coupling. The floating gate and the control gate are metal. The apparatus also includes an access transistor coupled to the storage transistor. A gate of the access transistor is coupled to a word line. The storage transistor and the access transistor are serially coupled between a bit line and a source line.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
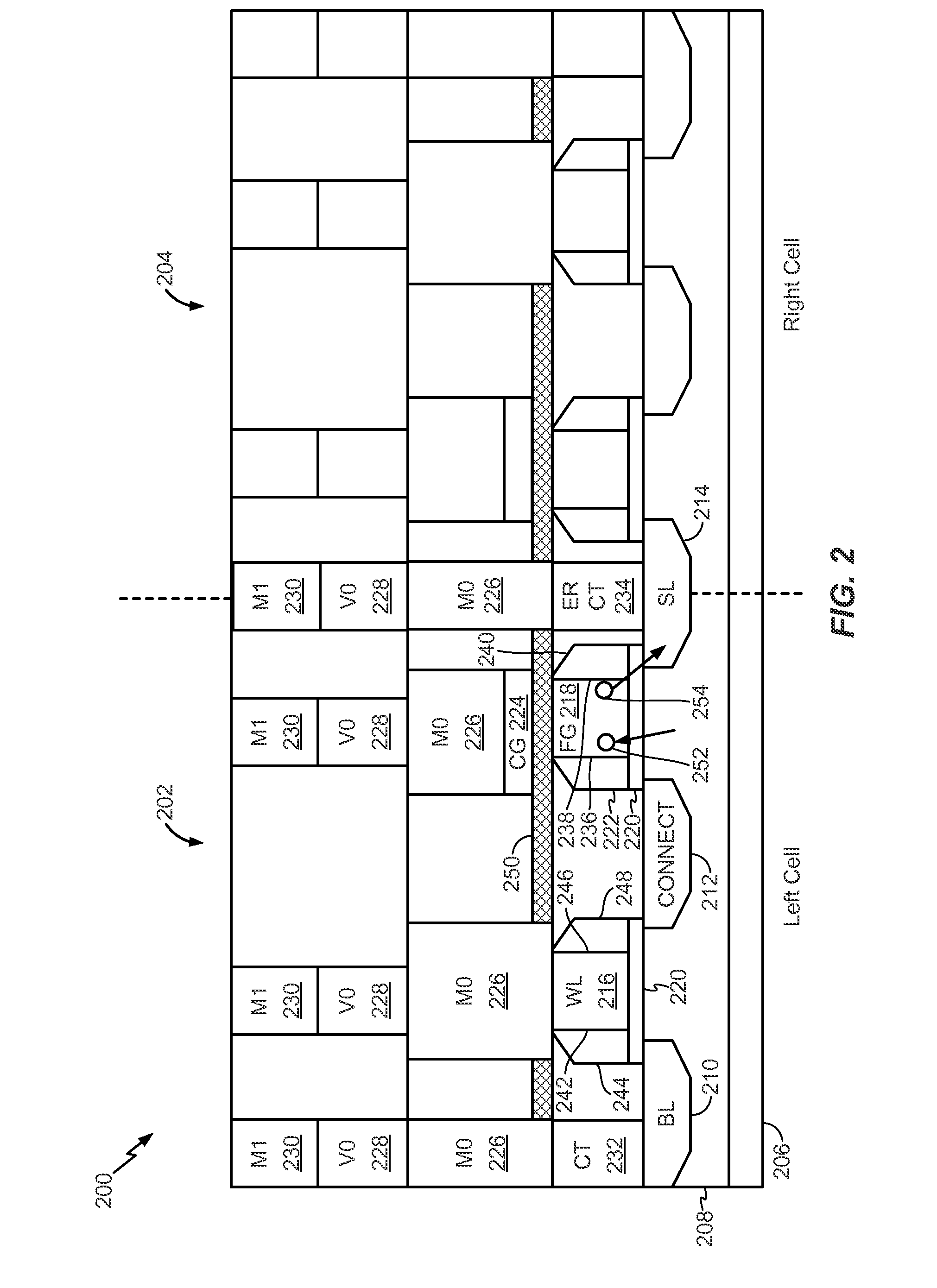
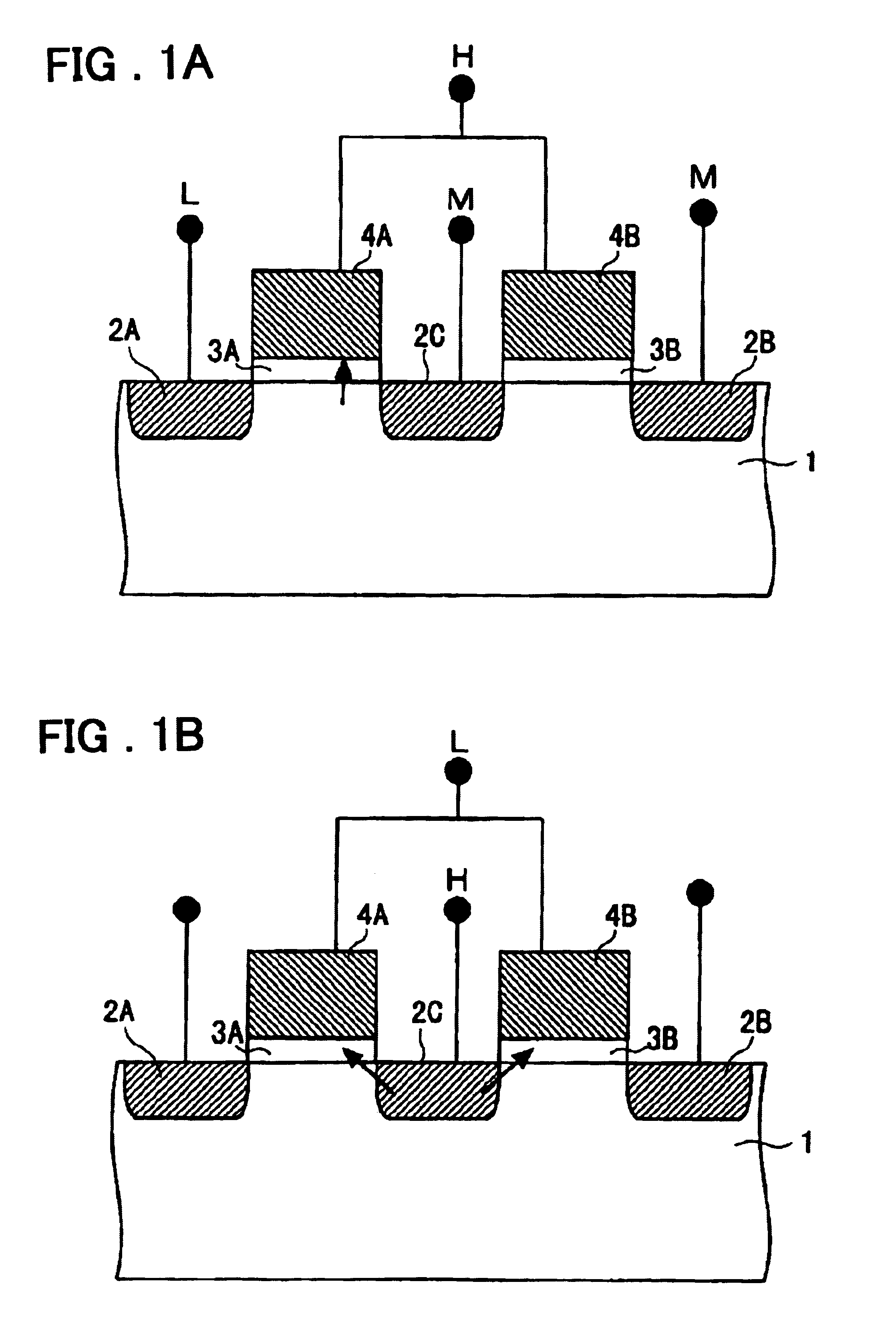
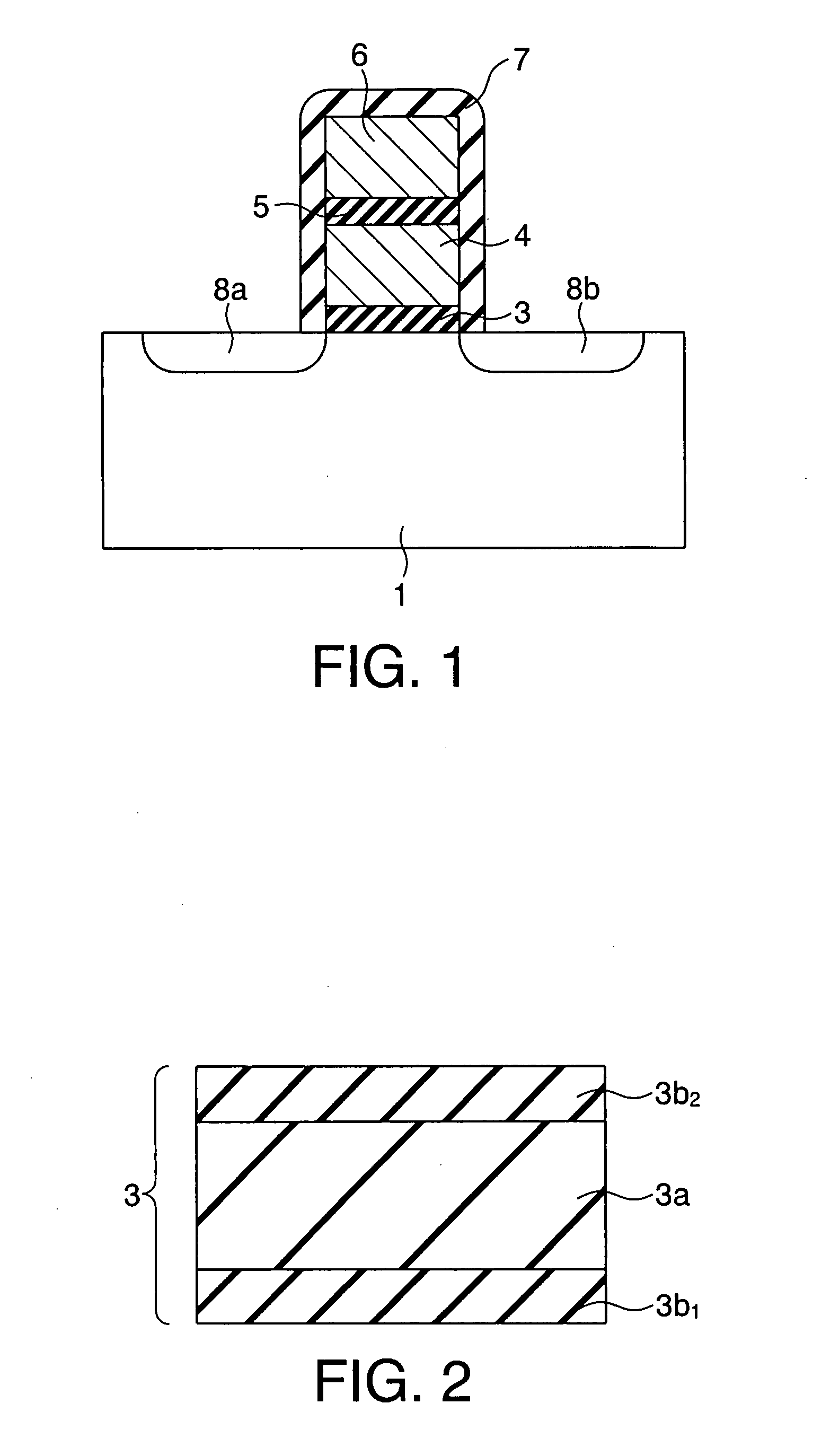
Semiconductor memory device and control method and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS6979856B2Lower levelFacilitate salicidationTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A semiconductor memory device includes a first insulating film provided on a semiconductor substrate between first and second diffusion regions, a first gate electrode provided on the first insulating film, a second insulating film provided on the semiconductor substrate between the second diffusion region and a third diffusion region, and a second gate electrode provided on the second insulating film. The first and second diffusion regions, first insulating film, and first gate electrode constitute a first memory cell, while the second and third diffusion regions, second insulating film, and second gate electrode constitute a second memory cell. The first and second gate electrodes are connected in common to form a word line electrode. The first and third diffusion regions are connected to first and second read bit lines. The second diffusion region is connected to a program and erase bit line.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
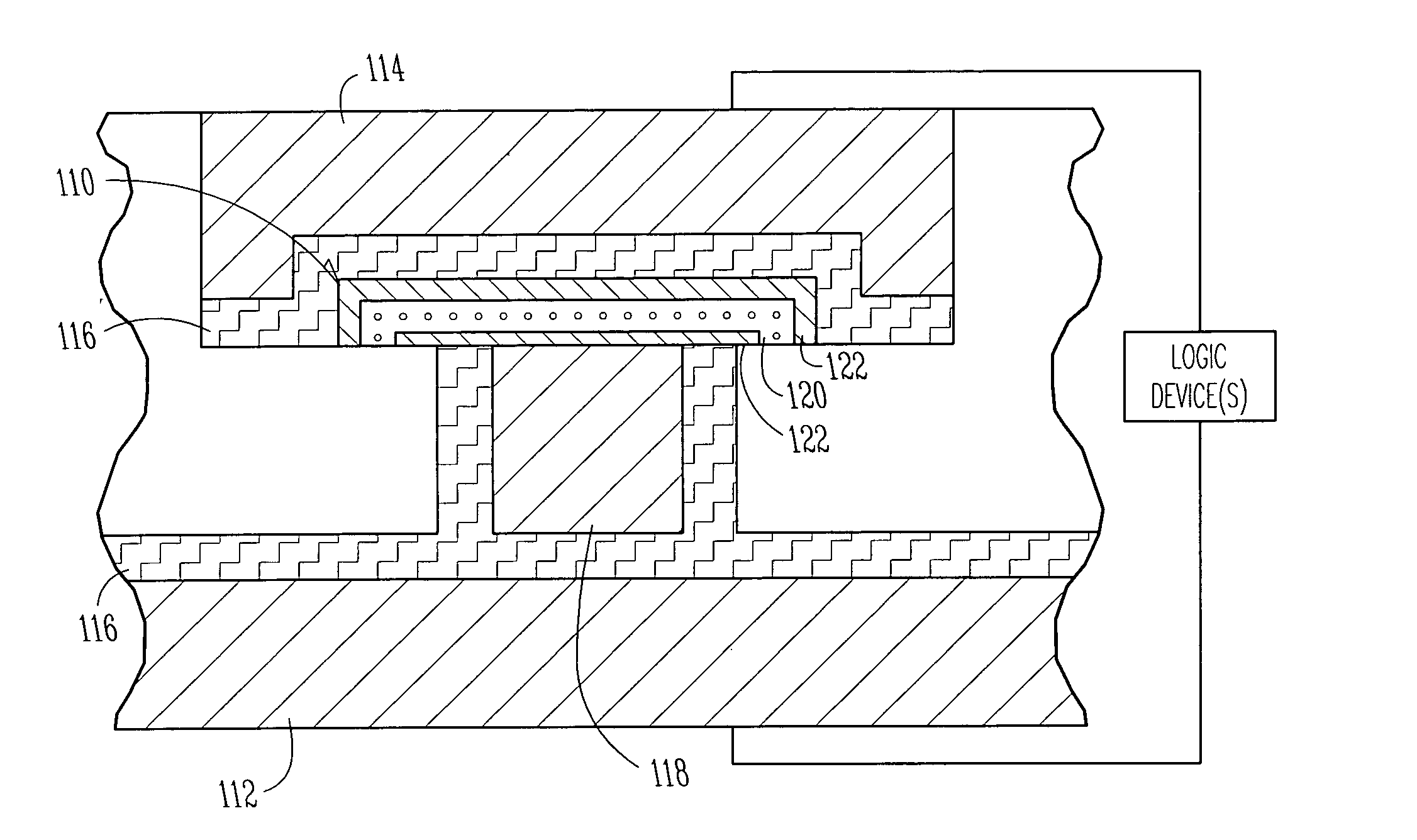
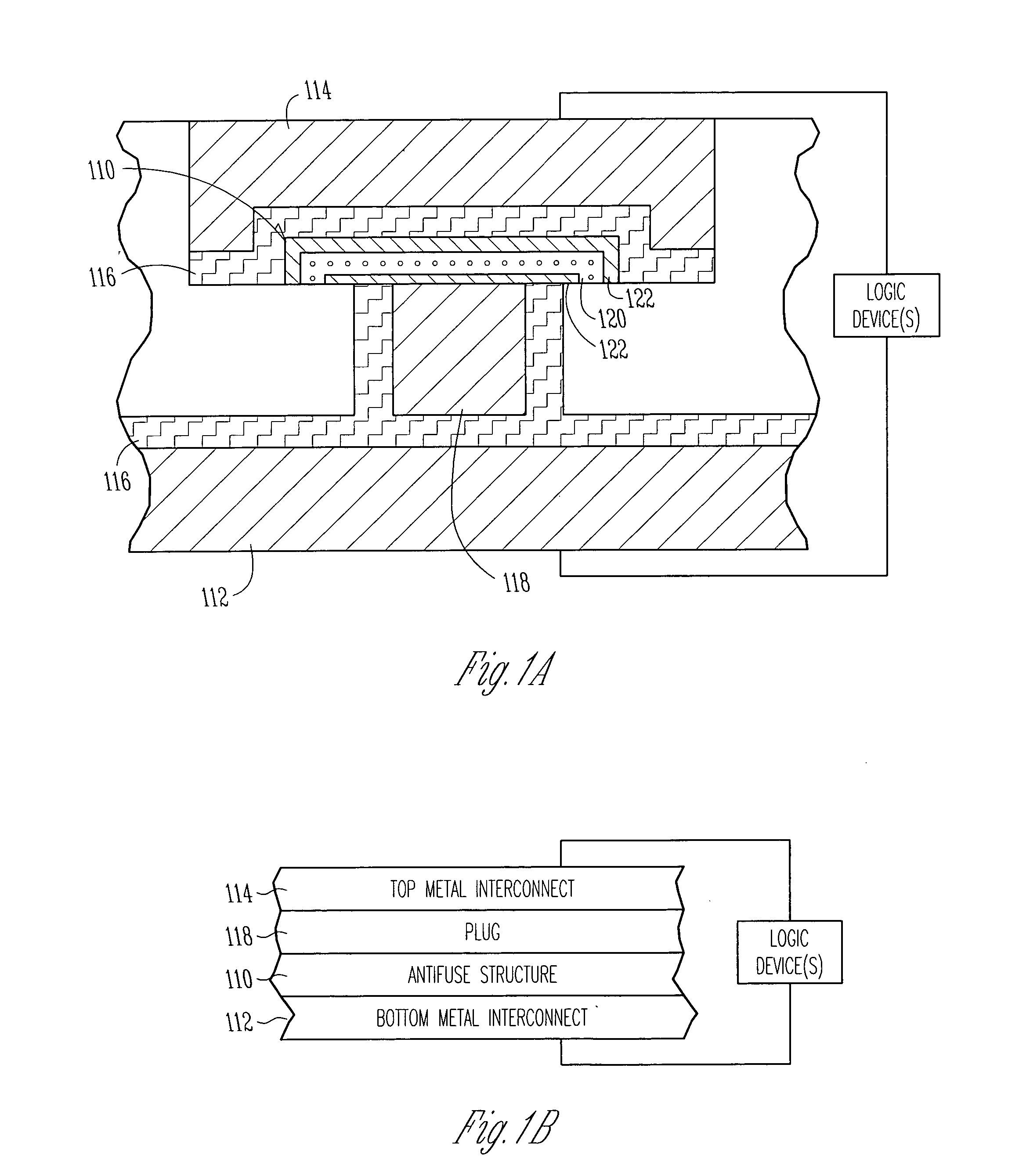
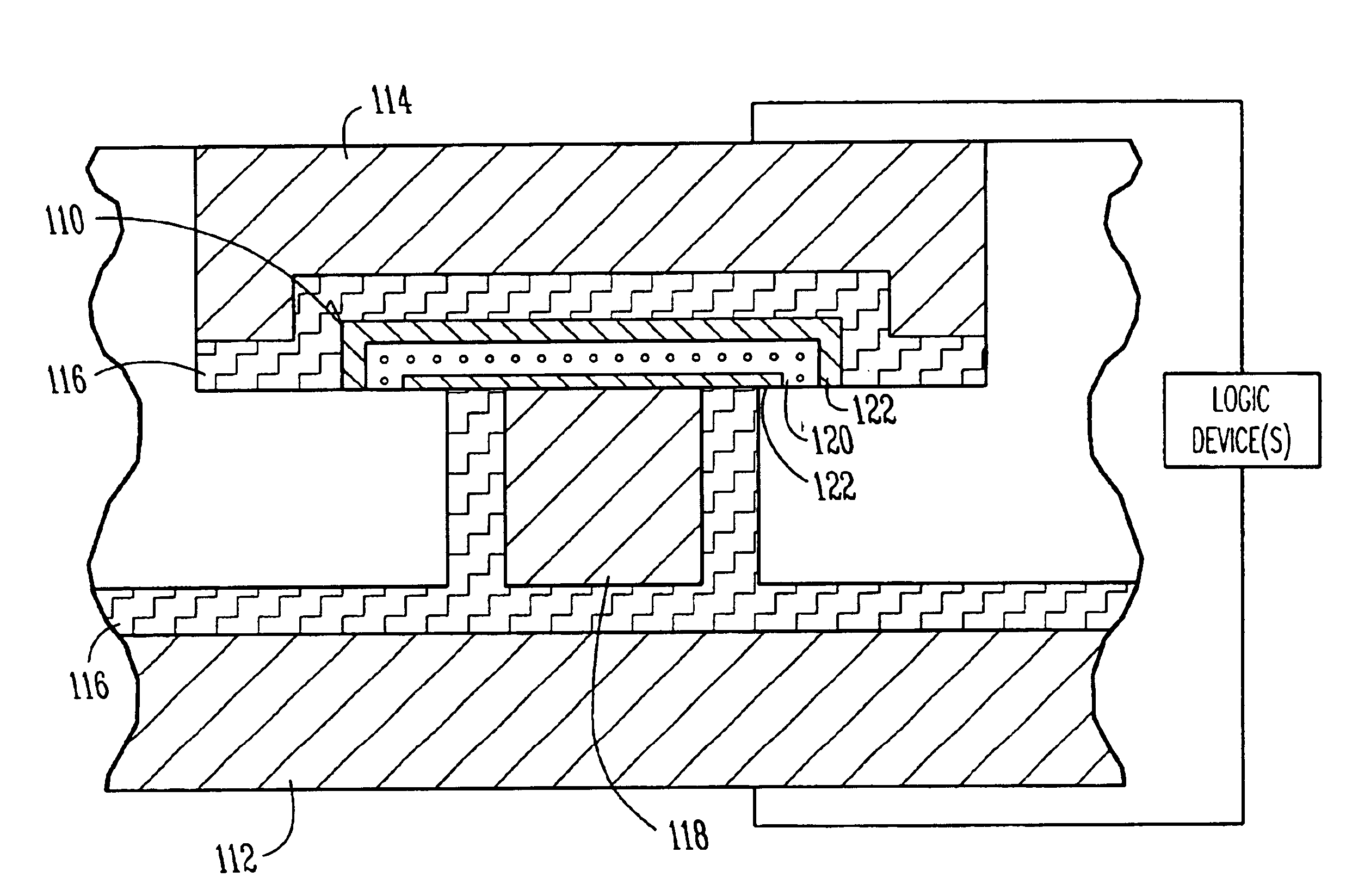
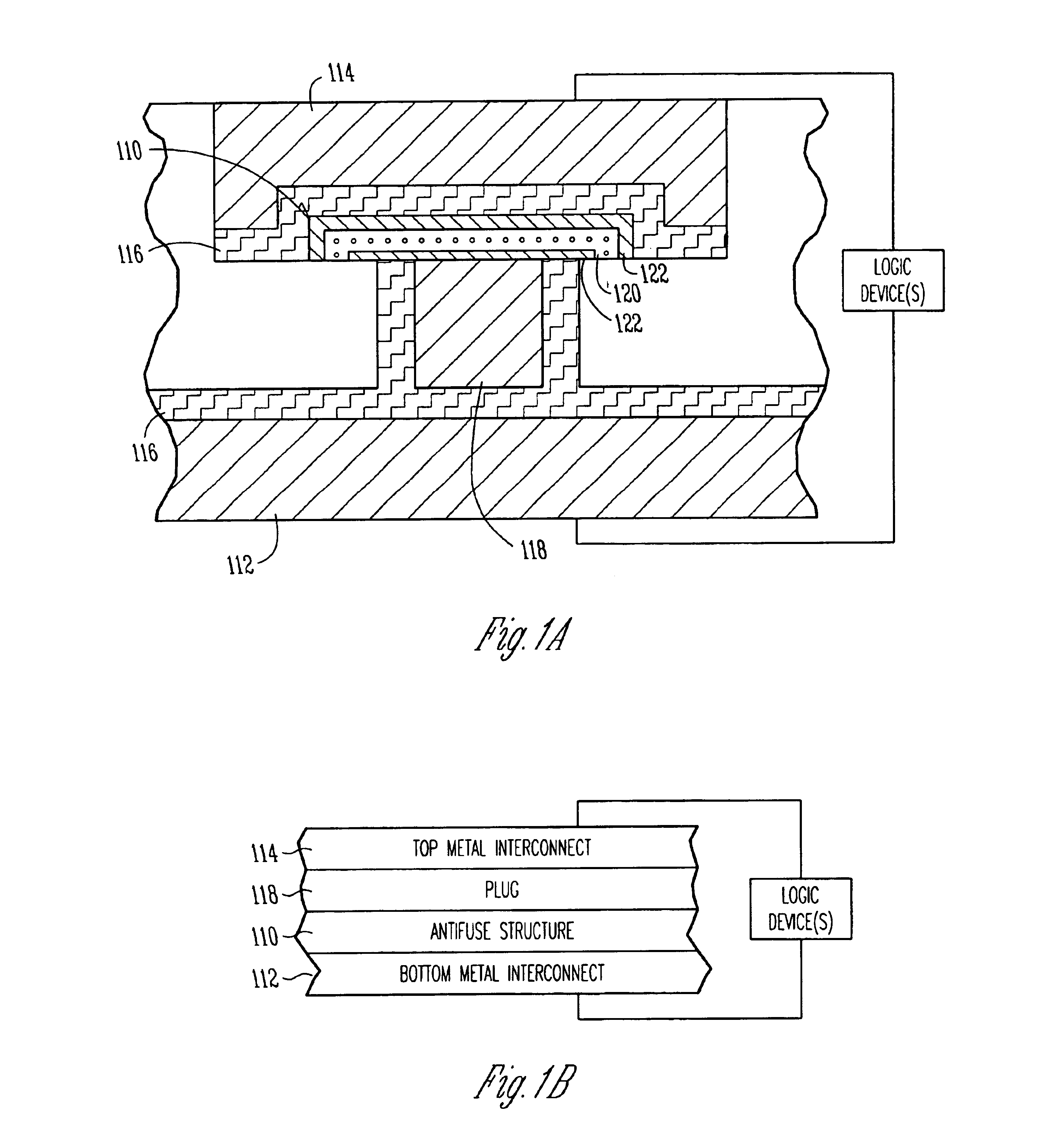
Scalable high performance antifuse structure and process
InactiveUS20050023638A1Improve performanceReduce capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesProcess systemsSubject matter
Systems and methods are provided for a scalable high-performance antifuse structure and process that has a low RC component, a uniform dielectric breakdown, and a very low, effective dielectric constant (keff) such that a programming pulse voltage is scalable with Vdd. One aspect of the present subject matter is an antifuse device that is positioned or coupled between a first metal level and a second metal level. One embodiment of the antifuse device includes a porous antifuse dielectric layer, and at least one injector Silicon-Rich-Insulator (SRI) layer in contact with the porous antifuse dielectric layer. In one embodiment, the porous antifuse dielectric layer includes SiO2 formed with air-filled voids. In one embodiment, the at least one injector SRI layer includes two injector Silicon-Rich-Nitride layers that sandwich the porous antifuse dielectric layer. Other aspects are provided herein.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20080135922A1Lower programming voltageReducing stress-induced leakage currentSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesConduction bandSemiconductor
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes: a memory element, the memory element including: a semiconductor substrate; a first insulating film formed on a region in the semiconductor substrate located between a source region and a drain region, and having a stack structure formed with a first insulating layer, a second insulating layer, and a third insulating layer in this order, the first insulating layer including an electron trapping site, the second insulating layer not including the electron trapping site, and the third insulating layer including the electron trapping site, and the electron trapping site being located in a position lower than conduction band minimum of the first through third insulating layers while being located in a position higher than conduction band minimum of a material forming the semiconductor substrate; a charge storage film formed on the first insulating film; a second insulating film formed on the charge storage film; and a control gate electrode formed on the second insulating film.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
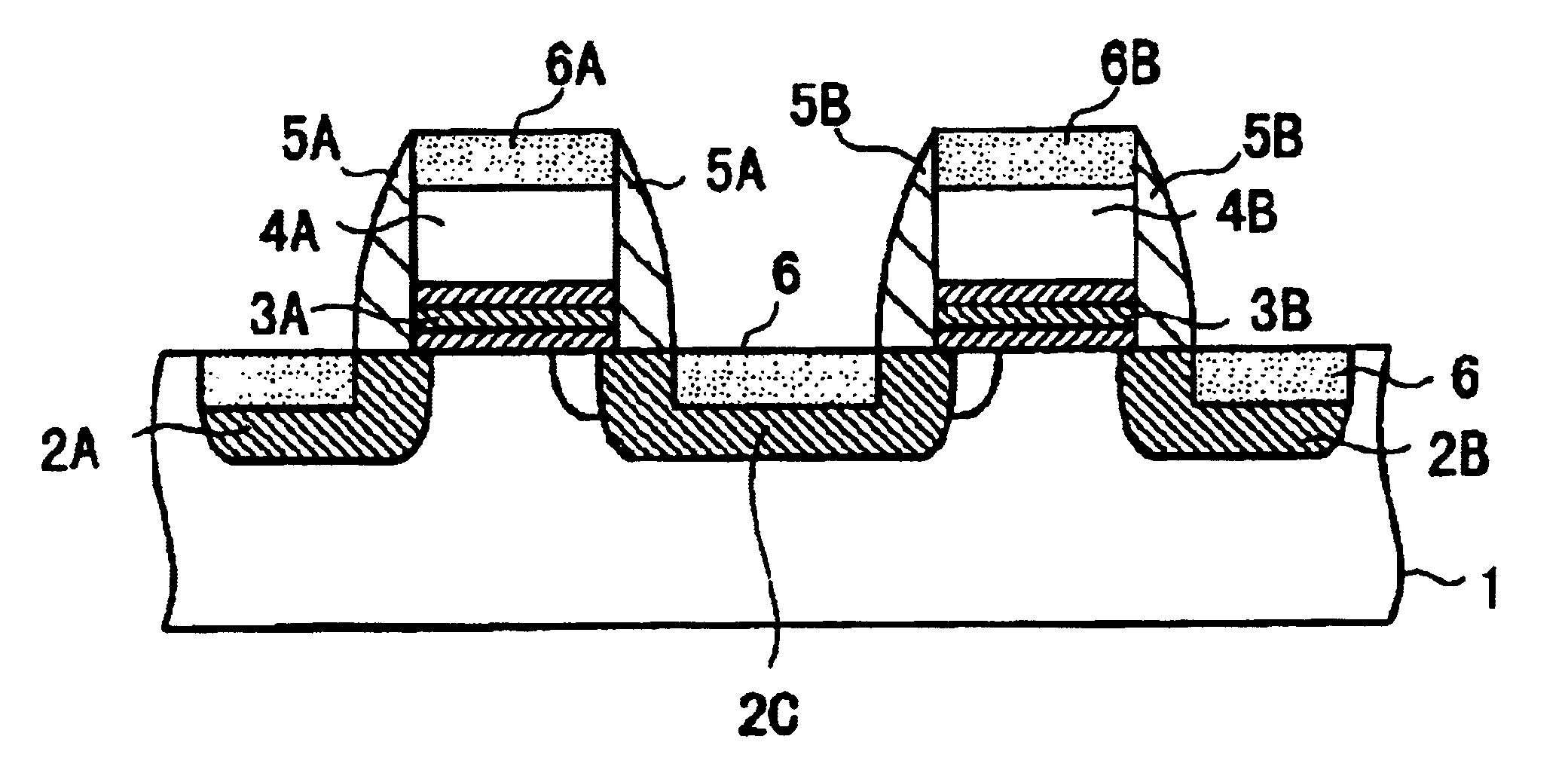
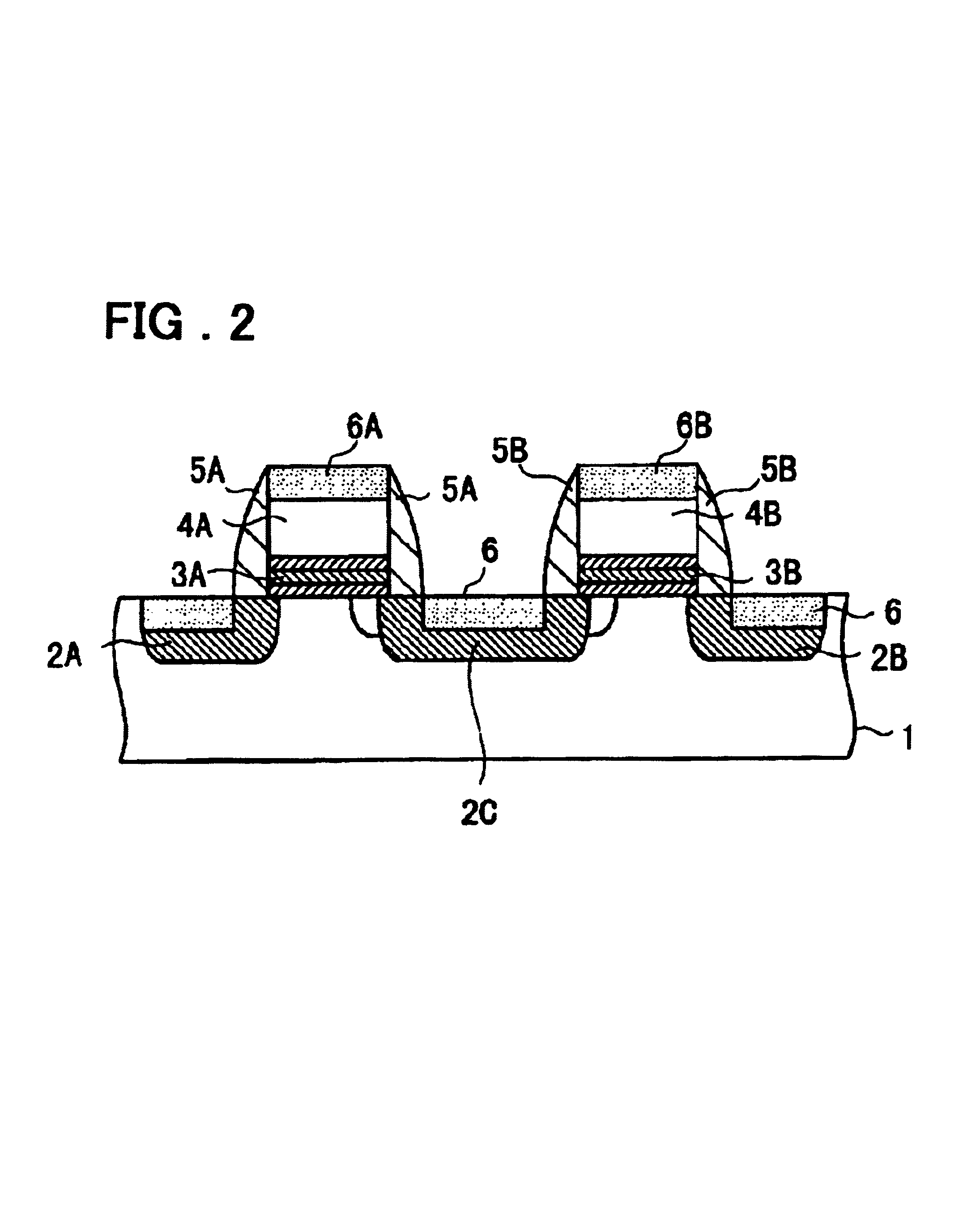
Semiconductor memory device and control method and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20040071011A1Lower levelFacilitate salicidationTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A semiconductor memory device includes a first insulating film provided on a semiconductor substrate between first and second diffusion regions, a first gate electrode provided on the first insulating film, a second insulating film provided on the semiconductor substrate between the second diffusion region and a third diffusion region, and a second gate electrode provided on the second insulating film are included, wherein the first and second diffusion regions, first insulating film, and first gate electrode constitute a first memory cell, while the second and third diffusion regions, second insulating film, and second gate electrode constitute a second memory cell. The first and second gate electrodes are connected in common to form a word line electrode. The first and third diffusion regions are connected to first and second read bit lines disposed on a layer overlying the semiconductor substrate. The second diffusion region is connected to a program and erase bit line disposed on a layer overlying the semiconductor substrate. Programming is performed to a selected memory cell transistor by hot electron injection, while erasing from the selected memory cell is performed by the hot hole injection.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
High-efficient erasing and writing flash memory in grating
ActiveCN101419972AImprove coupling coefficientHigh densityTransistorSolid-state devicesGratingDielectric layer
The invention provides an efficiently erasable and writable split-gate flash memory. The split-gate flash memory comprises a semiconductor substrate which has a source electrode area and two drain electrode areas which are positioned at the two sides of the source electrode area and separated by a channel area; source electrode wires which are positioned above the source electrode area and interconnected; two floating gates which are arranged at two sides of the source electrode wires as memory cells, are in L-shaped symmetrical distribution, are separated by an insulating dielectric layer, and side edges of which are respectively adjacent to the source electrode wires, part of the source electrode area and part of the channel area; two control gates which are respectively adjacent to thetwo L-shaped floating gates and separated by the insulating dielectric layer; and two word lines which are respectively adjacent to the two control gates, the side edges of the two L-shaped floating gates, part of the channel area and part of the two drain electrode areas, and are separated from each other by the insulating dielectric layer. In the efficiently erasable and writable split-gate flash memory, the programming voltage thereof can be further reduced, thus improving the device density.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Scalable high performance antifuse structure and process
InactiveUS6943065B2Improve performanceReduce capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesProcess systemsSubject matter
Systems and methods are provided for a scalable high-performance antifuse structure and process that has a low RC component, a uniform dielectric breakdown, and a very low, effective dielectric constant (keff) such that a programming pulse voltage is scalable with Vdd. One aspect of the present subject matter is an antifuse device that is positioned or coupled between a first metal level and a second metal level. One embodiment of the antifuse device includes a porous antifuse dielectric layer, and at least one injector Silicon-Rich-Insulator (SRI) layer in contact with the porous antifuse dielectric layer. In one embodiment, the porous antifuse dielectric layer includes SiO2 formed with air-filled voids. In one embodiment, the at least one injector SRI layer includes two injector Silicon-Rich-Nitride layers that sandwich the porous antifuse dielectric layer. Other aspects are provided herein.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Variable resistance element, semiconductor device having variable resistance element, semiconductor device manufacturing method, and programming method using variable resistance element
ActiveUS20150103583A1Variation can be suppressedLower programming voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialEngineering
This variable resistance element is provided with a variable resistance film, a first electrode, which is disposed in contact with one surface of the variable resistance film, and a second electrode, which is disposed in contact with the other surface of the variable resistance film. The first and the second electrodes have corner portions, respectively, and the distance between the corner portions of the first and the second electrodes is set equal to the shortest distance between the first and the second electrodes. Furthermore, the variable resistance element has a third electrode, which is disposed on the one surface of the variable resistance film.
Owner:NANOBRIDGE SEMICON INC
Nonvolatile memory cell comprising a nanowire and manufacturing method thereof
A memory cell, the memory cell comprising a substrate, a nanowire extending along a vertical trench formed in the substrate, a control gate surrounding the nanowire, and a charge storage structure formed between the control gate and the nanowire.
Owner:MARLIN SEMICON LTD
Non-Volatile Memory Device and Method of Fabricating the Same
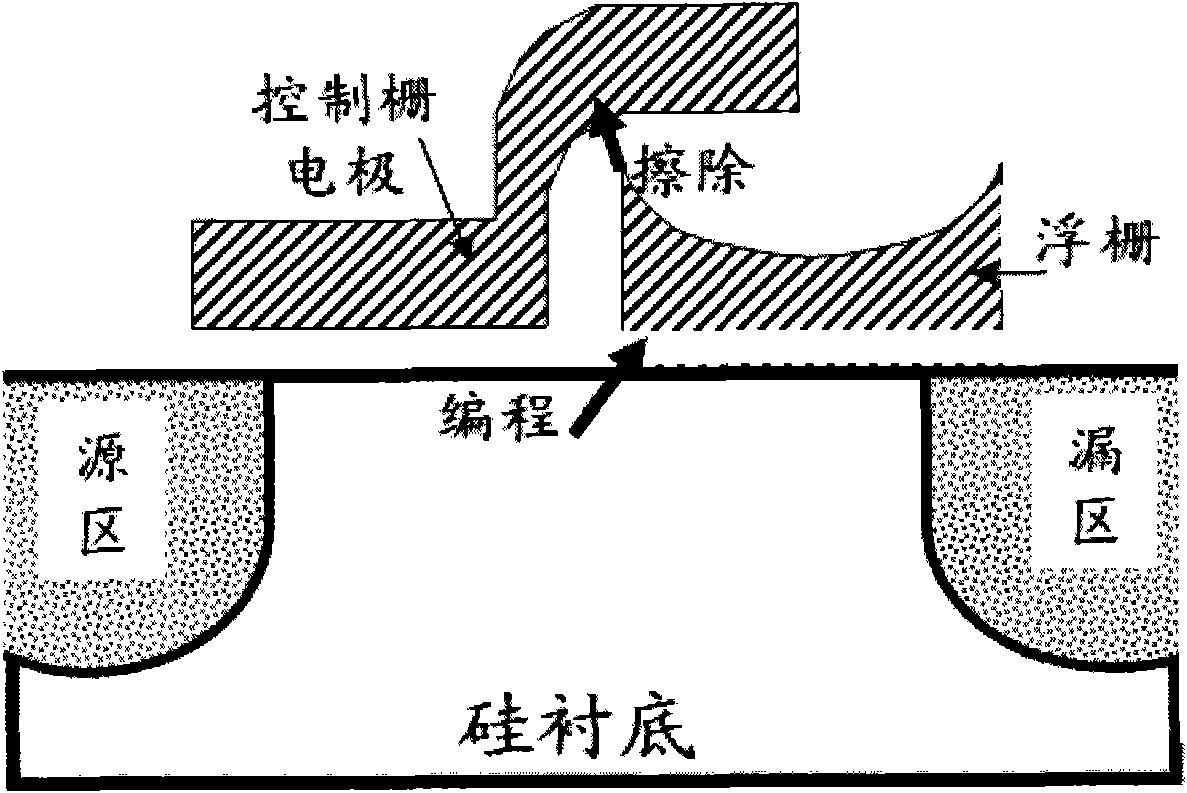
Provided are a non-volatile memory device and a method of fabricating the same. The non-volatile memory device comprises: a control gate region formed by doping a semiconductor substrate with second impurities; an electron injection region formed by doping the semiconductor substrate with first impurities, where a top surface of the electron injection region includes a tip portion at an edge; a floating gate electrode covering at least a portion of the control gate region and the tip portion of the electron injection region; a first tunnel oxide layer interposed between the floating gate electrode and the control gate region; a second tunnel oxide layer interposed between the floating gate electrode and the electron injection region; a trench surrounding the electron injection region in the semiconductor substrate; and a device isolation layer pattern filled in the trench.
Owner:COLUMBA TECH INC
High-reliability split-gate nonvolatile memory structure with high-speed low-voltage operation function
ActiveCN102339833AImprove programming efficiencyEvenly distributedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesCMOSLow voltage
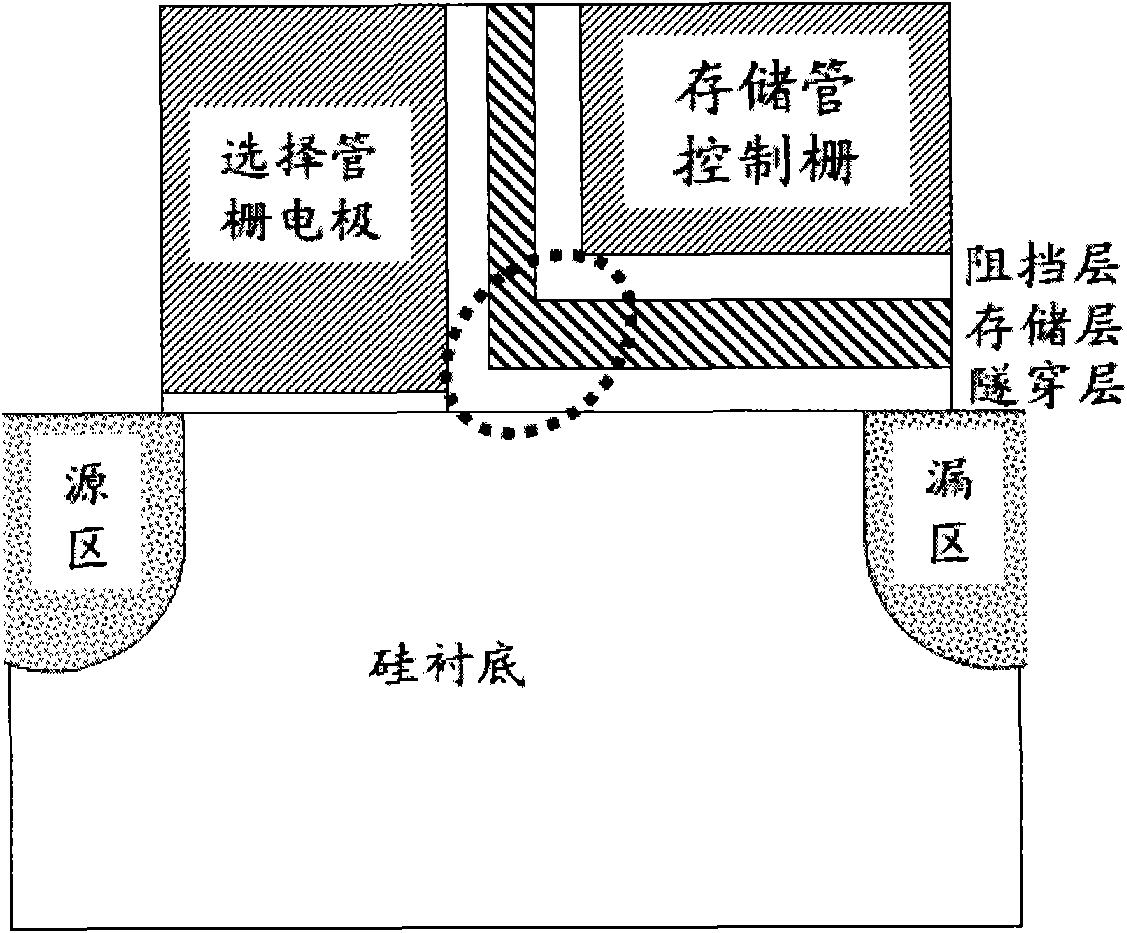
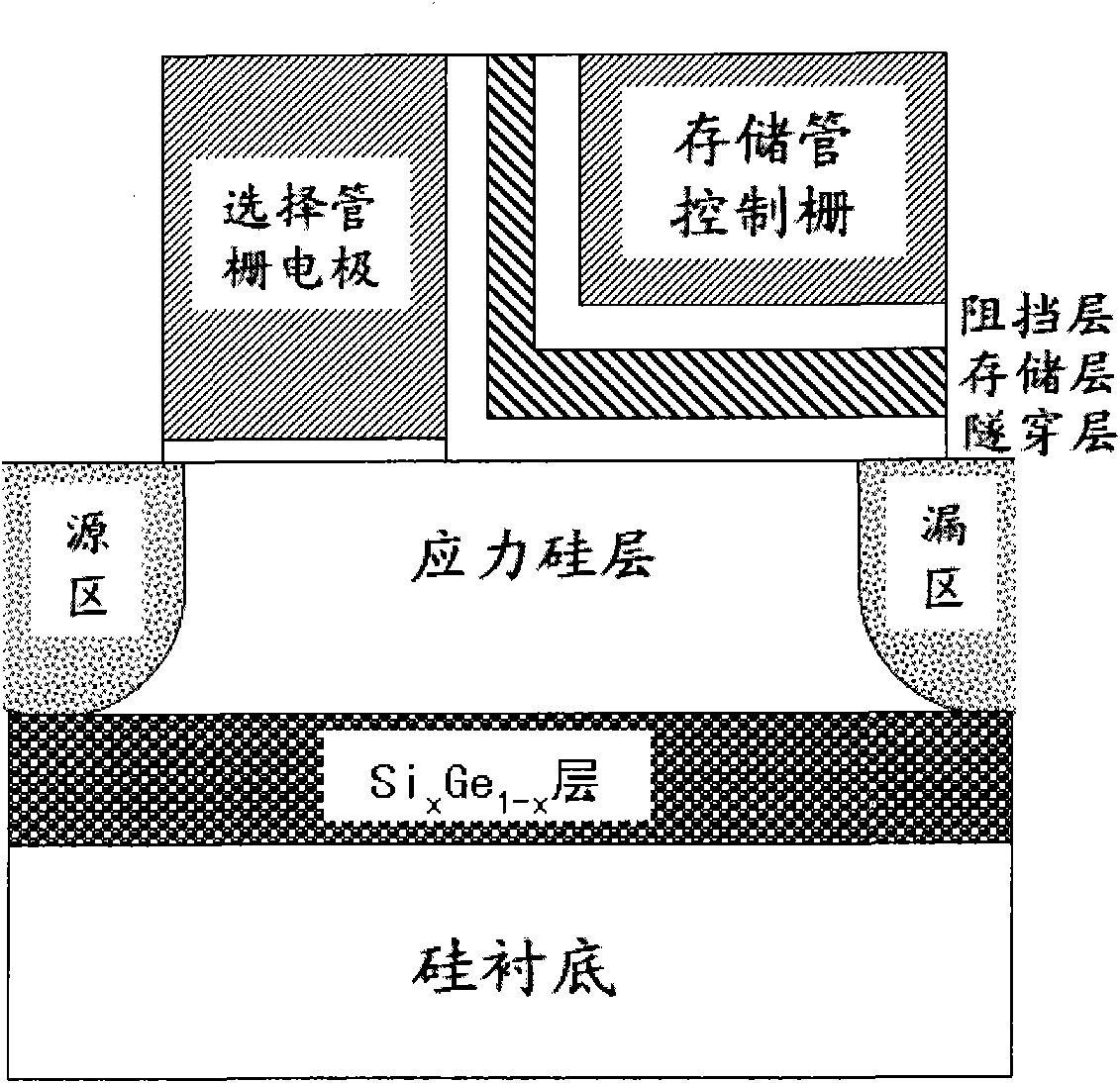
The invention discloses a high-reliability split-gate nonvolatile memory structure with a high-speed low-voltage operation function, which is characterized in that the structure comprises a selection transistor and a memory transistor, the selection transistor and the memory transistor share a substrate region and a source / drain doped region, the memory transistor is provided with a stack structure and information is stored in a charge storage layer below a grid region. By adopting a dual-layer or multilayer substrate made of stress silicon / germanium-silicon and by comprehensively utilizing high collision ionization rate brought by primary collision ionization of the channels of the stress silicon, high collision ionization rate brought by the introduction of a SixGel-x layer and wider transverse electron distribution produced resultantly, the programming efficiency of a split-gate structure can be greatly improved, the programming voltage is reduced, the data hold characteristic of adevice is improved and the high-reliability operation of the device is facilitated. Since the charge-trap-type split-gate memory preparation process disclosed by the invention is compatible with the traditional silicon planar complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) process, the wide application is facilitated.
Owner:宁夏储芯科技有限公司
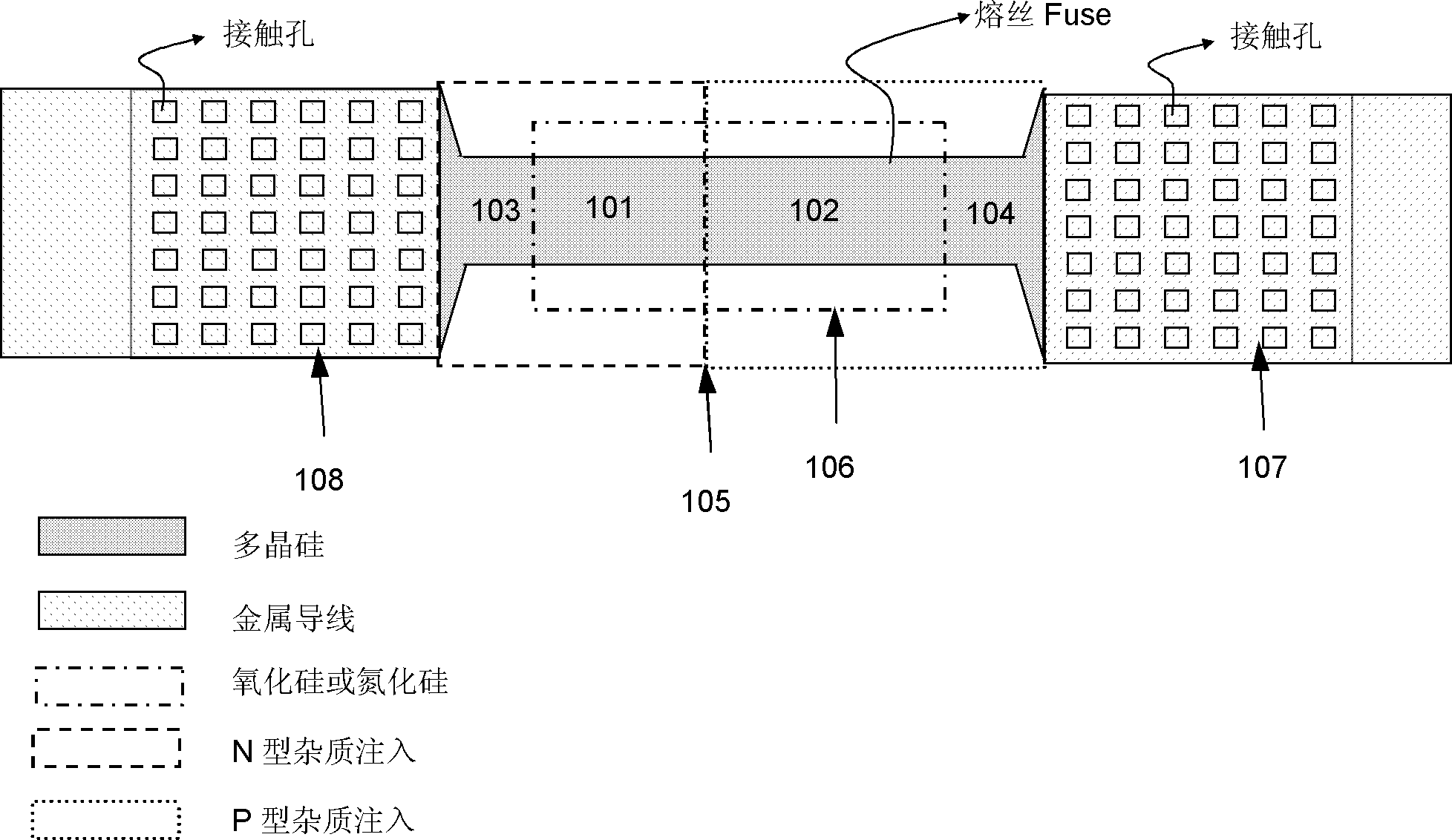
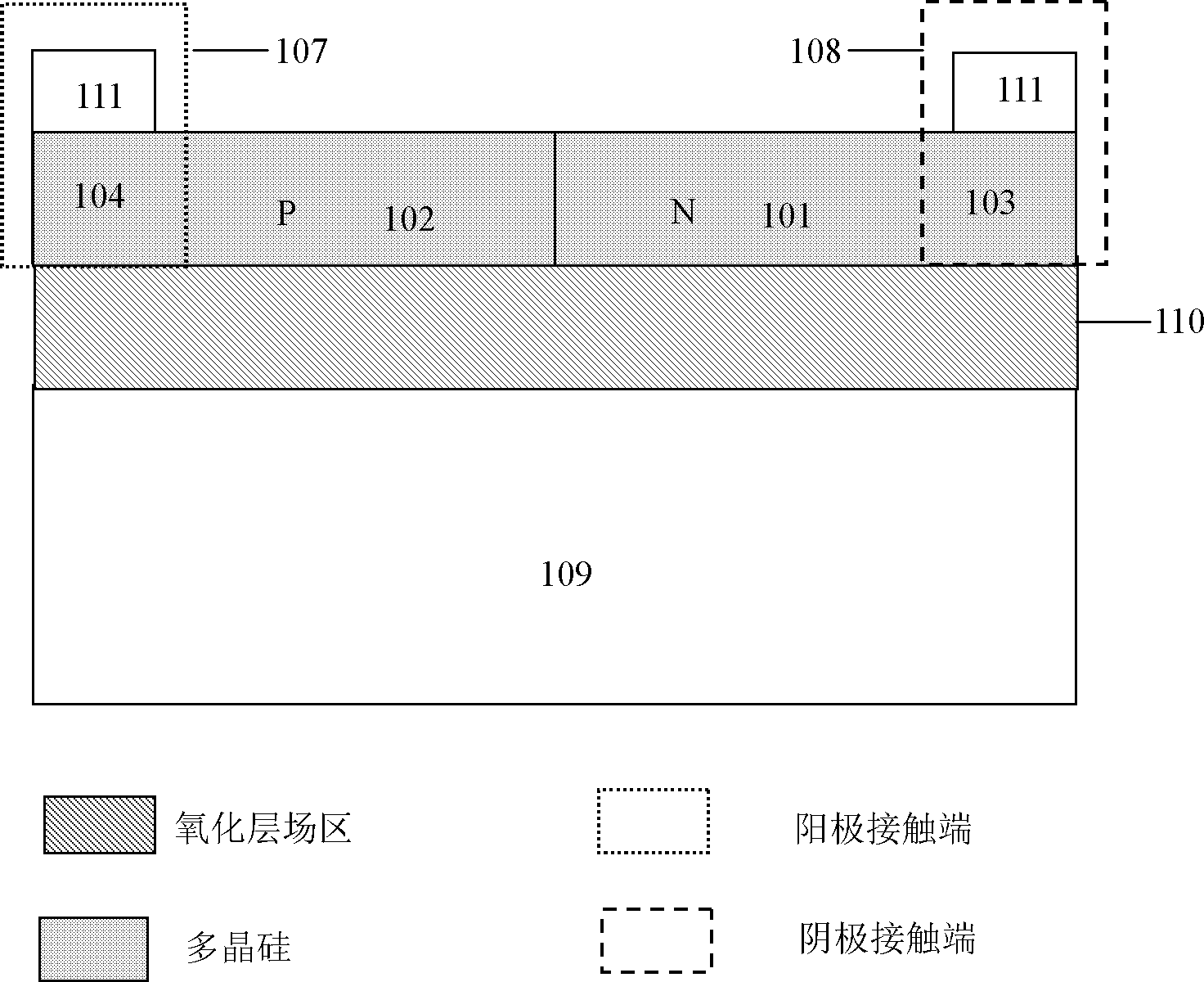
Programmable polycrystalline silicon fuse device structure and realizing method of technology of programmable polycrystalline silicon fuse device structure
InactiveCN103107159ALower programming voltageReduce heatSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh resistanceSalicide
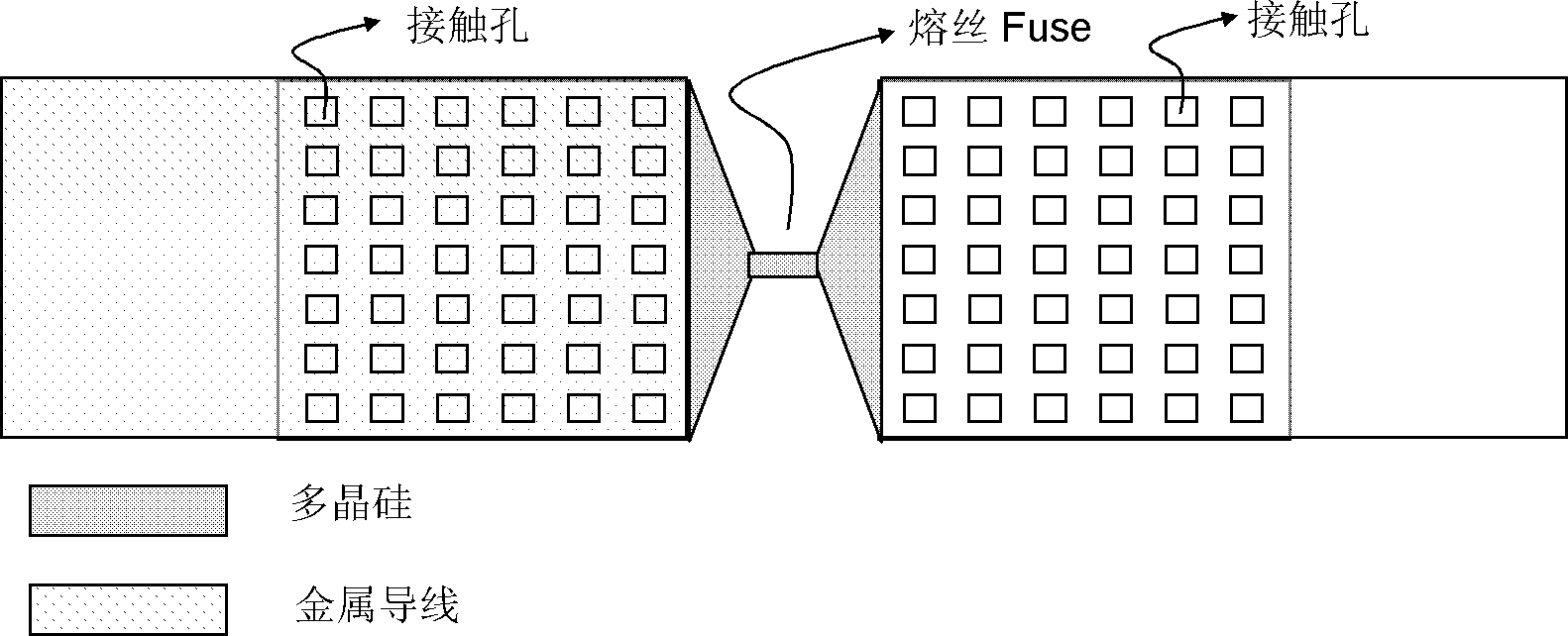
The invention discloses a programmable polycrystalline silicon fuse device structure and a realizing method of the technology of the programmable polycrystalline silicon fuse device structure. The programmable polycrystalline silicon fuse device structure comprises an N type high-resistance polycrystalline silicon resistor, a P type high-resistance polycrystalline silicon resistor an NP diode, a negative electrode contact end and a positive electrode contact end. The method comprises the steps that an oxide layer field area is formed on a P type substrate, a polycrystalline silicon area is formed on the oxide layer field area, P type polycrystalline silicon is formed on one side of the polycrystalline silicon area and N type polycrystalline silicon is formed on the other side of the polycrystalline silicon area, the NP diode is formed in a junction position of the N type polycrystalline silicon and the P type polycrystalline silicon, silicon oxide or silicon nitride is produced in a P,N type high-resistance polycrystalline silicon resistor area to prevent formation of metal silicide, the metal silicide is formed in a P type low-resistance polycrystalline silicon resistor area on the polycrystalline silicon and in an type type low-resistance polycrystalline silicon resistor area on the polycrystalline silicon, a through hole is formed, metal wire connection is achieved, and the negative electrode end and the positive electrode end of a polycrystalline silicon fuse device are led out. The programmable polycrystalline silicon fuse device structure and the realizing method of the technology of the programmable polycrystalline silicon fuse device structure can be applied to various technologies, reliability is guaranteed, the yield of a device is well guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Variable programming of non-volatile memory
InactiveUS20060098483A1Improve data retentionDecreased program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storageReading levelNon-volatile memory
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments can provide for reduced program disturb in non-volatile semiconductor memory. In one embodiment, select memory cells such as those connected to a last word line of a NAND string are programmed using one or more program verify levels or voltages that are different than a corresponding level used to program other cells or word lines. One exemplary embodiment includes using a lower threshold voltage verify level for select physical states when programming the last word line to be programmed for a string during a program operation. Another embodiment includes applying a lower program voltage to program memory cells of the last word line to select physical states. Additional read levels are established for reading the states programmed using lower verify levels in some exemplary implementations. A second program voltage step size that is larger than a nominal step size is used in one embodiment when programming select memory cells or word lines, such as the last word line to be programmed for a NAND string.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
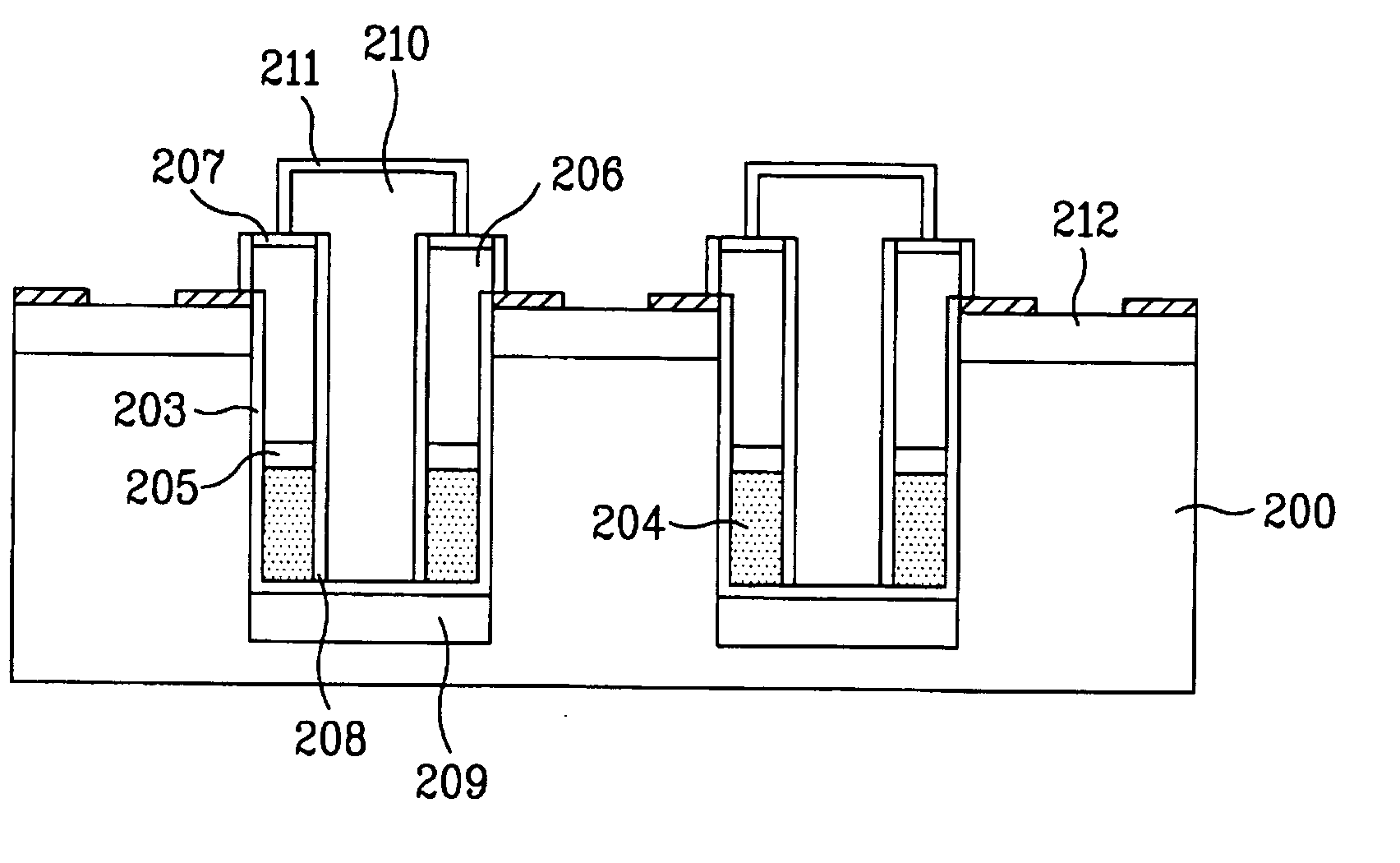
Memory device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20060146640A1Minimize cell sizeImprove the coupling ratioSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling ratioDielectric layer
A split gate (flash) EEPROM cell and a method for manufacturing the same is disclosed, in which a control gate and a floating gate are formed in a vertical structure, to minimize a size of the cell, to obtain a high coupling ratio, and to lower a programming voltage. The split gate EEPROM cell includes a semiconductor substrate having a trench; a tunneling oxide layer at sidewalls of the trench; a floating gate, a dielectric layer and a control gate in sequence on the tunneling oxide layer; a buffer dielectric layer at sidewalls of the floating gate and the control gate; a source junction in the semiconductor substrate at the bottom surface of the trench; a source electrode in the trench between opposing buffer dielectric layers, electrically connected to the source junction; and a drain junction on the surface of the semiconductor substrate outside the trench.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
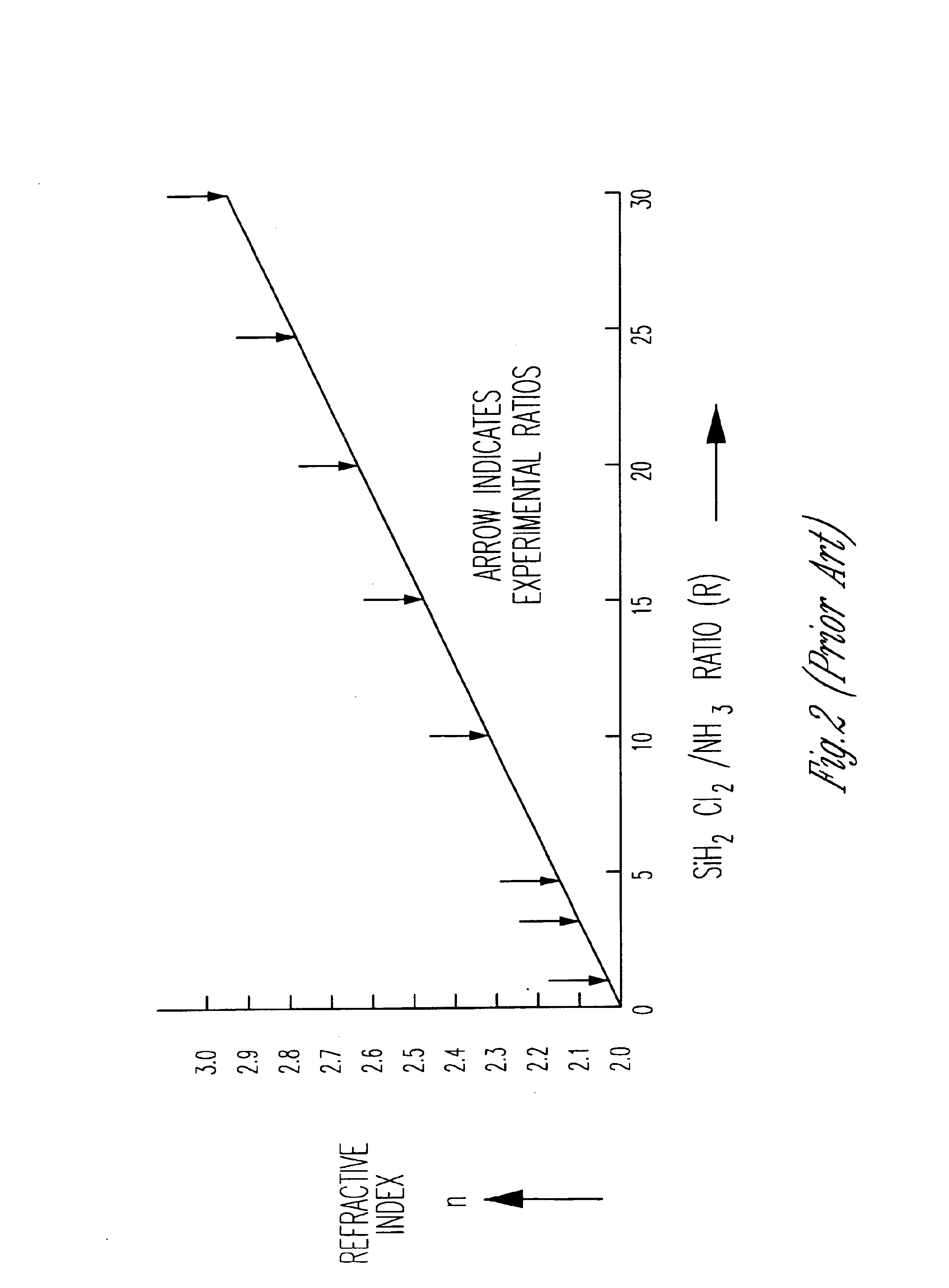
Method of manufacturing a thin dielectric layer using a heat treatment and a semiconductor device formed using the method
ActiveUS20050106897A1Enhancing Capacitive CouplingLower programming voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceGate dielectric
In a method for forming a semiconductor device and a semiconductor device formed in accordance with the method, a thin dielectric layer is provided between a lower conductive layer and an upper conductive layer. In one embodiment, the thin dielectric layer comprises an inter-gate dielectric layer, the lower conductive layer comprises a floating gate and the upper dielectric layer comprises a control gate of a transistor, for example, a non-volatile memory cell transistor. The thin dielectric layer is formed using a heat treating process that results in reduction of surface roughness of the underlying floating gate, and results in a thin silicon oxy-nitride layer being formed on the floating gate. In this manner, the thin dielectric layer provides for increased capacitive coupling between the lower floating gate and the upper control gate. This also leads to a lowered programming voltage, erasing voltage and read voltage for the transistor, while maintaining the threshold voltage in a desired range. In addition, the size of the transistor and resulting storage cell can be minimized and the need for a high-voltage region in the circuit is mitigated, since, assuming a lowered programming voltage, pumping circuitry is not required.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
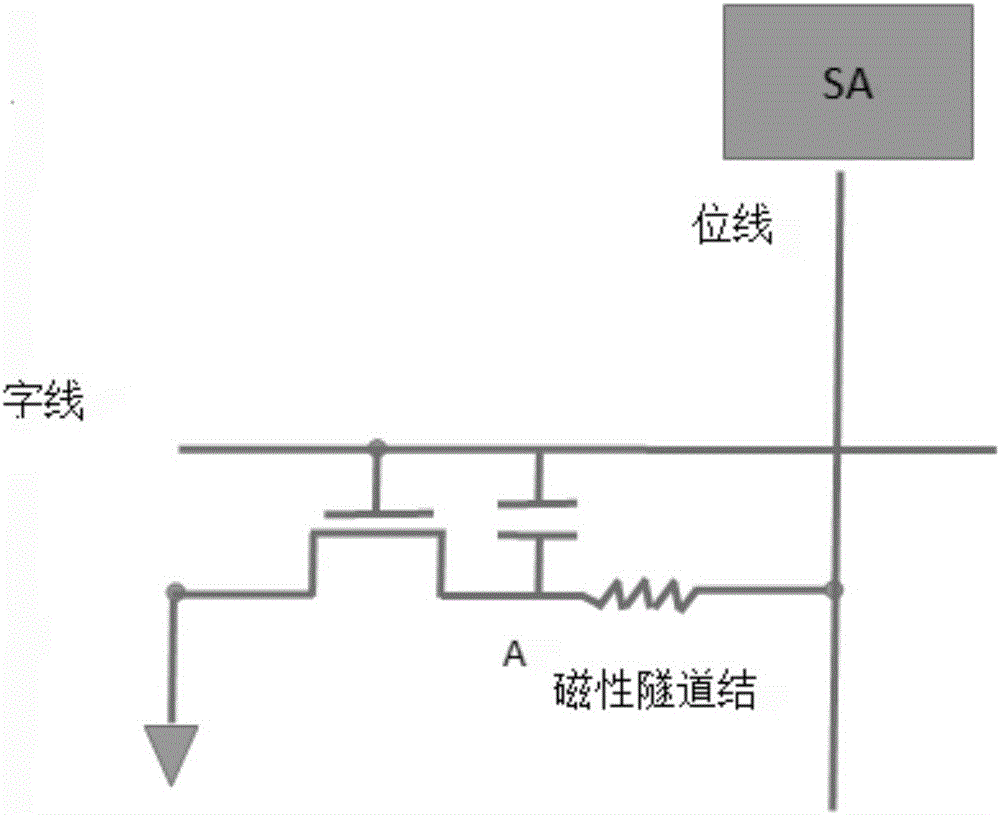
Capacitor mechanism-based one-time programmable device and programming realization method
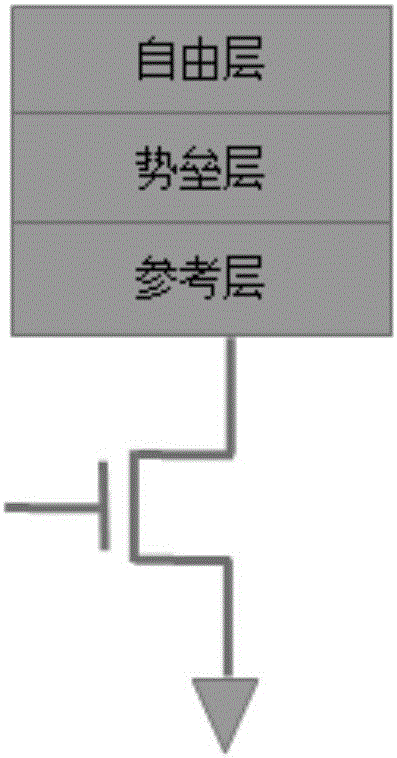
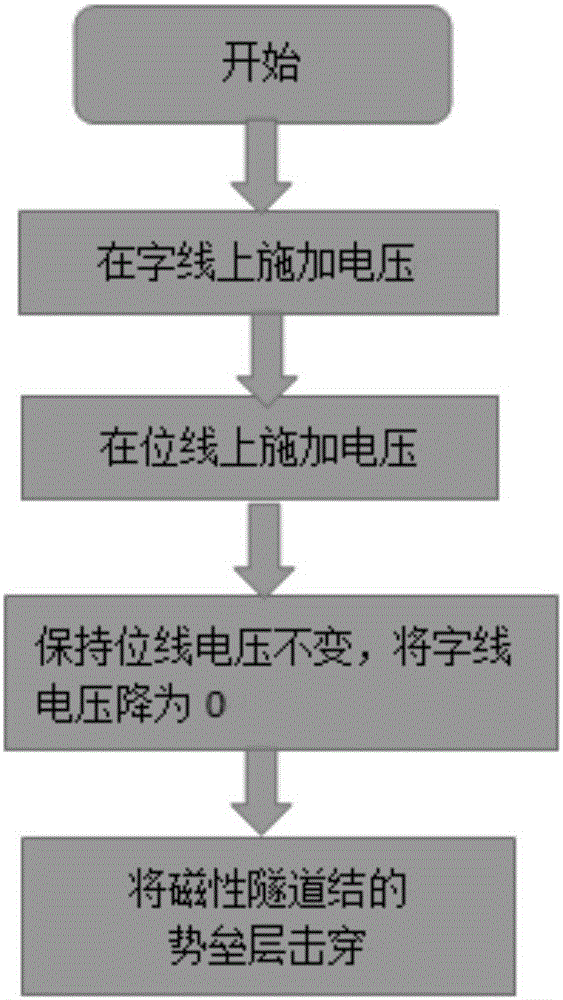
InactiveCN106128496ASmall footprintReduce power consumptionRead-only memoriesDigital storageCapacitanceInductive programming
The invention relates to a capacitor mechanism-based one-time programmable device and a programming realization method. The capacitance mechanism-based one-time programmable device comprises a switch MOS tube, an MTJ (magnetic tunnel junction) and a capacitor. Through the capacitor which is rechargeable, when the voltage is relatively low, a manner of charging the capacitor to generate a voltage higher than a normal programming voltage of the MTJ is used to carry out one-time writing on an OTP device, and a barrier layer in the MTJ is punched through, so that the effect of one-time programming is achieved. According to the method, a manner of supercharging through internal capacitor charging is utilized to reduce the externally required programming voltage, so that compared with the traditional OTP structure, the capacitor mechanism-based one-time programmable device is small in floor space, easy to realize and simple to operate, and can be used for reducing the power consumption of one-time programming and saving the manufacturing cost.
Owner:CETHIK GRP
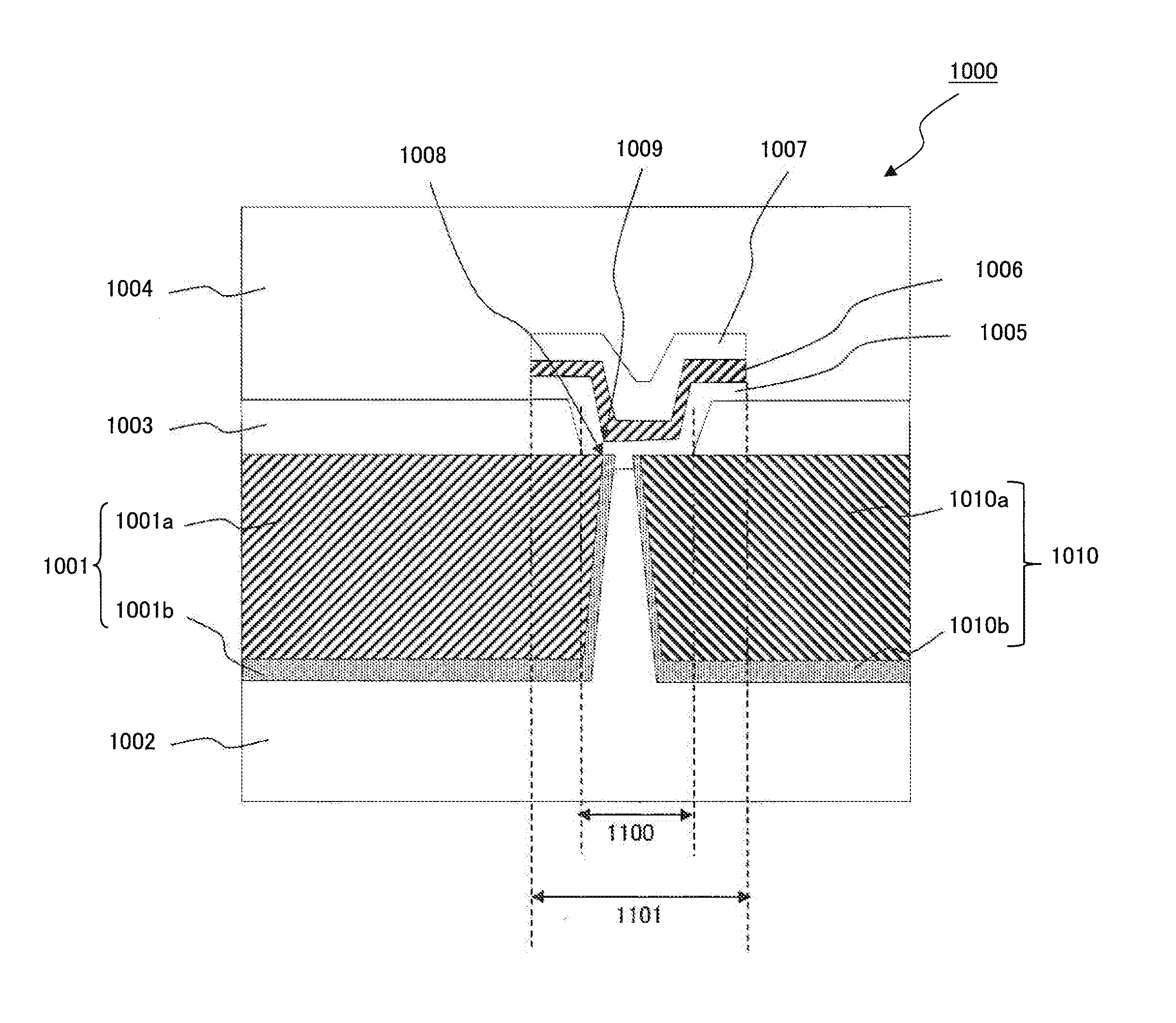
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN105720050ALower programming voltageTurn easilySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectric fieldEngineering
The application discloses a semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof. The semiconductor device includes: a substrate including a first region and a second region; a recess disposed on a surface of the second region; a functional part disposed on the first region; and an antifuse structure disposed on the second region , wherein the antifuse structure includes a conductive component and an insulating component, and the insulating component covers the recess and part of the second region. In this semiconductor device, since the insulating member covers the recessed portion, the lower surface of the insulating member has a raised portion corresponding to the recessed portion, and when a voltage is applied to the antifuse structure, a high electric field is generated near the raised portion. The strong electric field makes the insulating part break down at a lower voltage, which reduces the programming voltage of the antifuse structure, so that the antifuse structure in the semiconductor device is easier to conduct under the working voltage.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Anti-fuse structure and method for forming the same
ActiveCN104103624ALower programming voltageNo increase in process costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesInterconnectionEngineering
An anti-fuse structure and a method for forming the same. The anti-fuse structure includes: a semiconductor substrate including an anti-fuse area and an interconnection area; a shallow trench isolation structure located inside the semiconductor substrate and isolating the anti-fuse area into at least one active area; a gate oxide located on an entire surface of the active area, the thickness of a gate oxide on an edge position of the active area is smaller than that of a gate oxide in a middle position; a gate electrode located on a surface of the gate oxide and a surface of part of the shallow trench isolation structure; and a first electrode located on a surface of the interconnection area of the semiconductor substrate, the first electrode being electrically connected with the active area. Since a thinner gate oxide is formed on an edge part of the whole active area, the area of the thinner gate oxide becomes larger, and thus a programming voltage for programming of gate oxide anti-fuse is reduced.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Non-volatile memory device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20090321815A1Lower programming voltageBreakdown voltage is limitedTransistorSolid-state devicesPhysicsNon-volatile memory
A non-volatile memory device, including a substrate of a first conductivity type, the substrate including a plurality of wells of a second conductivity type, a plurality of memory cells in one of the plurality of wells of the second conductivity type, and a peripheral circuit including at least one first transistor of the second conductivity type on the substrate, and at least one second transistor of the first conductivity type in another one of the plurality of wells of the second conductivity type.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
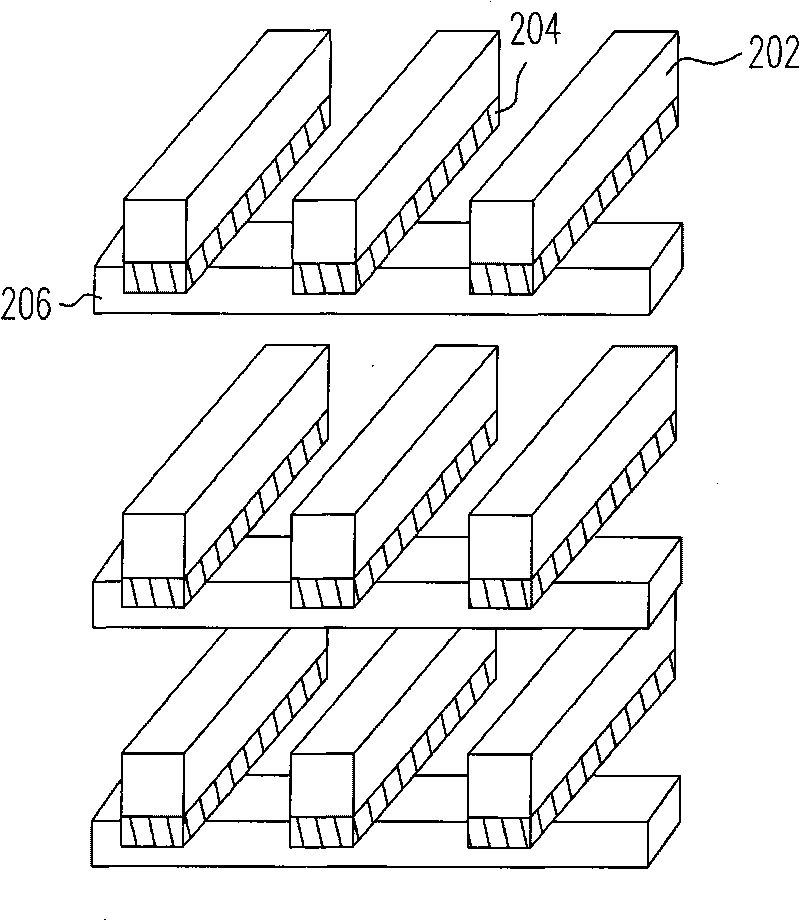
3D memory and operation method thereof
A 3D memory constituted by multiple layer memories. Each layer of memory includes m word lines, n bit lines and a plurality of initial switch layers, where m, n are natural numbers. The initial switch layer consists of Chalcogenide material. Two initial switches C[i, j +1] and C[i +1, j] are provided in a region surrounded by the word line i, the word line i +1 and the bit line j, the bit line j +1; and no initial switch is provided in a region surrounded by the word line i +1, the word line i +2 and the bit line j, and the bit line j +1, wherein i is odd and 1<=i<=m-1; j is a natural number and j is in a range from 1 to n-1, the initial switch layer C[i, j +1] denotes an initial switch connecting the word line i and the bit line j +1, and the initial switch layer C[i +1, j] denotes an initial switch connecting the word line i +1 and the bit line j. Each initial switch constitutes a memory core along with the connected word line and the connected bit line.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
High speed nano two-end nonvolatile storage and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103824937AImprove yieldEasy to prepareElectrical apparatusNanoinformaticsRetention timeVolumetric Mass Density
The invention discloses a high speed nano two-end nonvolatile storage and a manufacturing method thereof. The high speed nano two-end nonvolatile storage is characterized in that p-type doping one-dimensional nanomaterials, a graphene electrode and a metal electrode are distributed on an insulating substrate, and the graphene electrode is communicated with the metal electrode through the p-type doping one-dimensional nanomaterials; the p-type doping one-dimensional nanomaterials are p-type doping ZnS one-dimensional nanomaterials or p-type doping ZnSe one-dimensional nanomaterials; the metal electrode is a Cu electrode or a Ag electrode. The manufacturing method of the high speed nano two-end nonvolatile storage is simple, easy to control, high in rate of finished products and capable of being applied to large-scale integration conveniently. The manufactured storage has the excellent characteristics of being low in programming voltage, high in reading / writing speed, long in retention time and the like, thereby having a potential application prospect in development of a low-power dissipation, high speed and high integration density storage.
Owner:合肥庐阳科技创新集团有限公司
Electric charge capture non-volatile semiconductor storage unit and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN101800251ALower programming voltageReduce power consumptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorEngineering
The invention provides an electric charge capture non-volatile semiconductor storage unit and a manufacture method thereof. The electric charge capture non-volatile semiconductor storage unit comprises a semiconductor substrate, a source region, a drain region and a tunnel insulating layer, and an electric charge capture layer, a barrier insulating layer and a gate electrode layer which are formed on the semiconductor substrate in sequence, wherein the drain region comprises a P-N junction, and the source region comprises a metal semiconductor junction formed by any one of titanium, cobalt, nickel and platinum or a mixture thereof with the semiconductor substrate. The electric charge capture non-volatile semiconductor storage unit has low programming voltage, low programming speed, lower power consumption and higher reliability.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Flash memory cell with capacitive coupling between a metal floating gate and a metal control gate
ActiveUS9047960B2Reduce complexityReduce power consumptionRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceBit line
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
One-Time Programmable Memory Cell, Memory and Manufacturing Method Thereof
InactiveUS20130163306A1Low programming voltageReduce voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsOptoelectronicsMedia layer
The present invention pertains to the technical field of one-time programmable memory (OTP), and in particular to a one-time programmable memory unit, OTP, and method of fabricating the same. The OTP unit comprises a lower electrode, an upper electrode and a storage medium layer placed between the upper electrode and the lower electrode, the storage medium layer comprises a first metal oxide layer and a second metal oxide layer, wherein an adjoining area for programming is formed between the first metal oxide layer and the second metal oxide layer. The OTP comprises a plurality of the above-described one-time programmable memory units arranged in rows and columns. The OTP unit and the OTP have such characteristics as low programming voltage, small unit area, being able to integrate into a back-end structure of integrated circuit, great process flexibility, and the method of fabricating the OTP unit and the OTP is relatively simple and low in cost.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com