Patents
Literature
411results about How to "Improve data retention" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
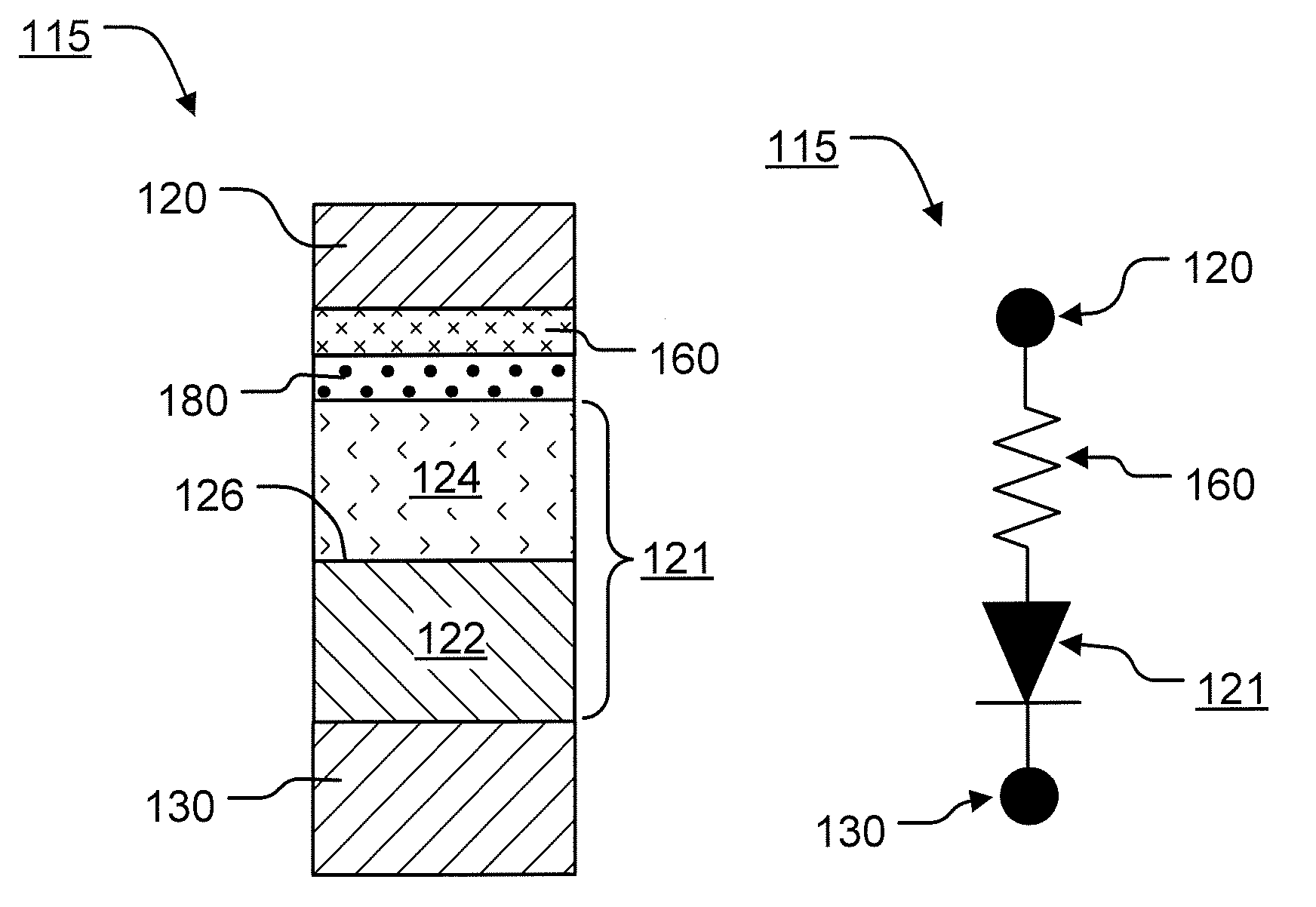
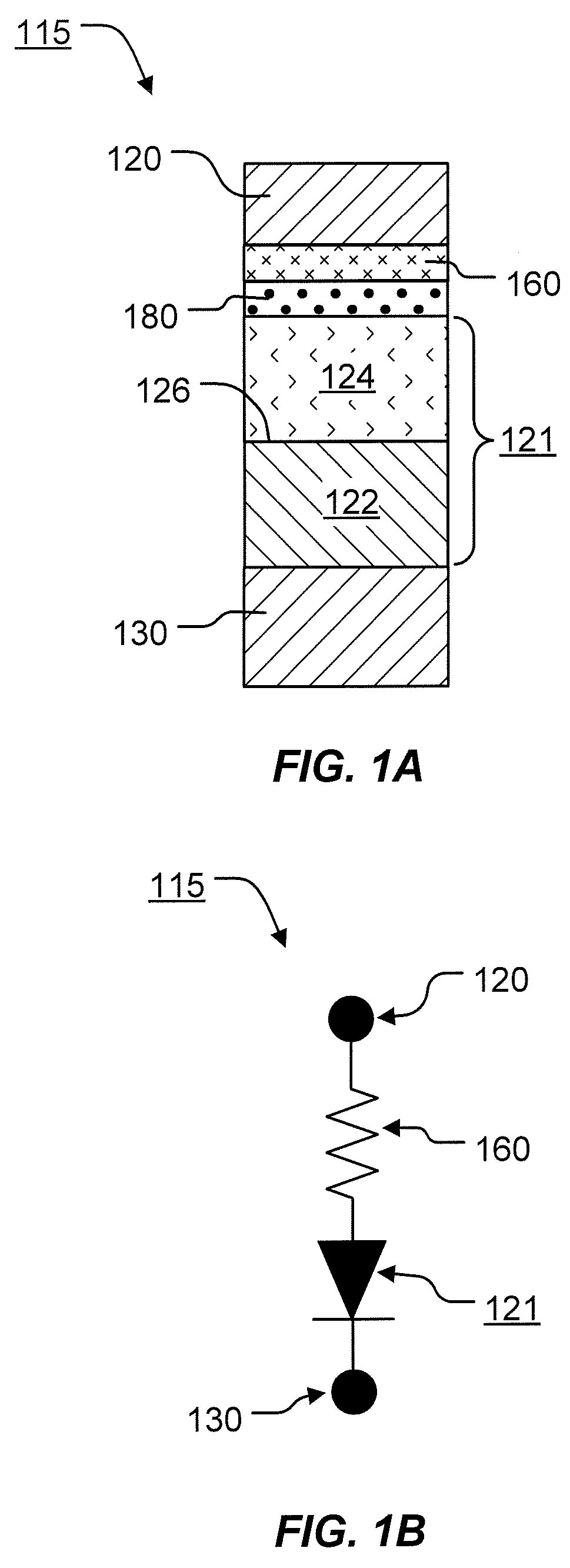
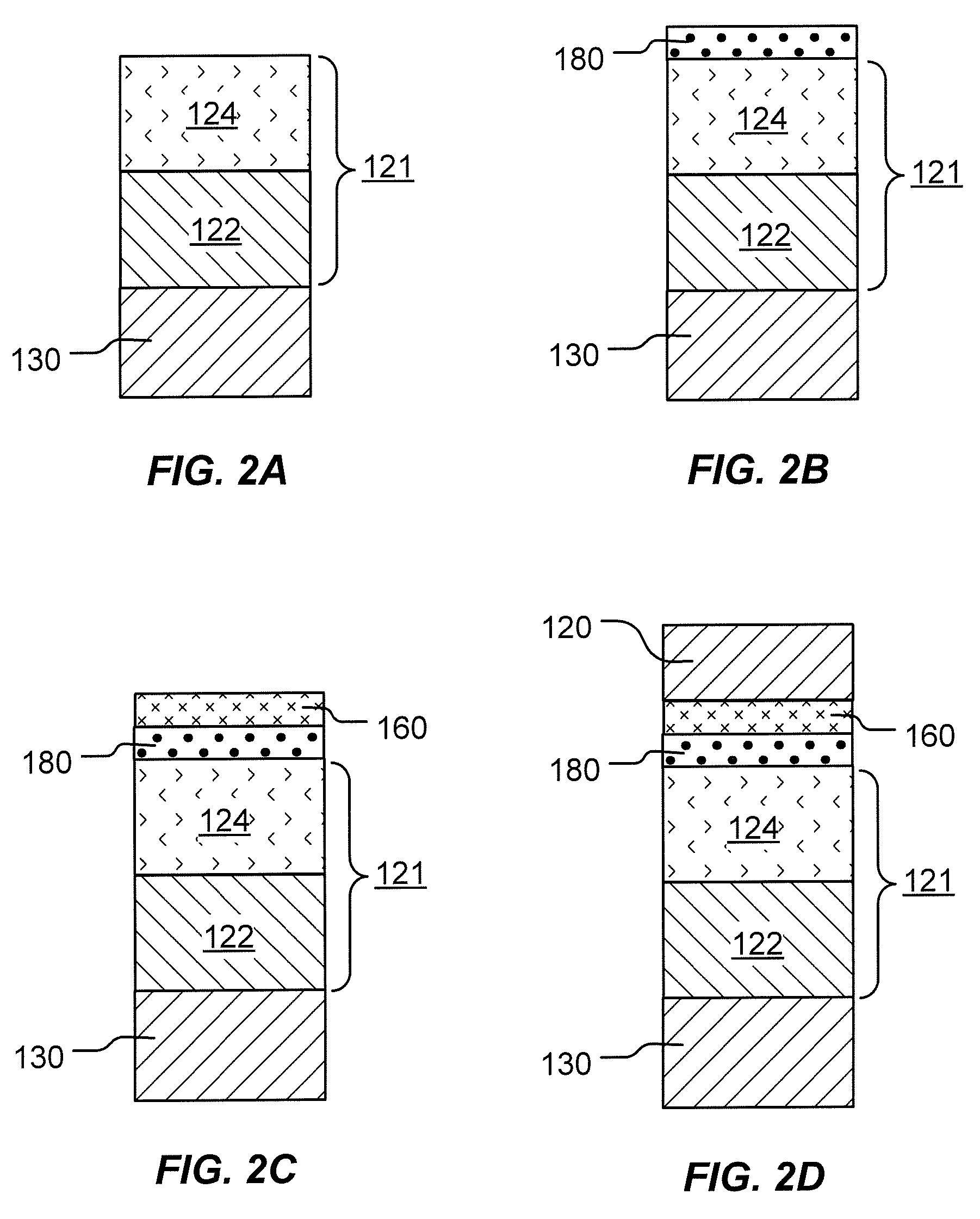
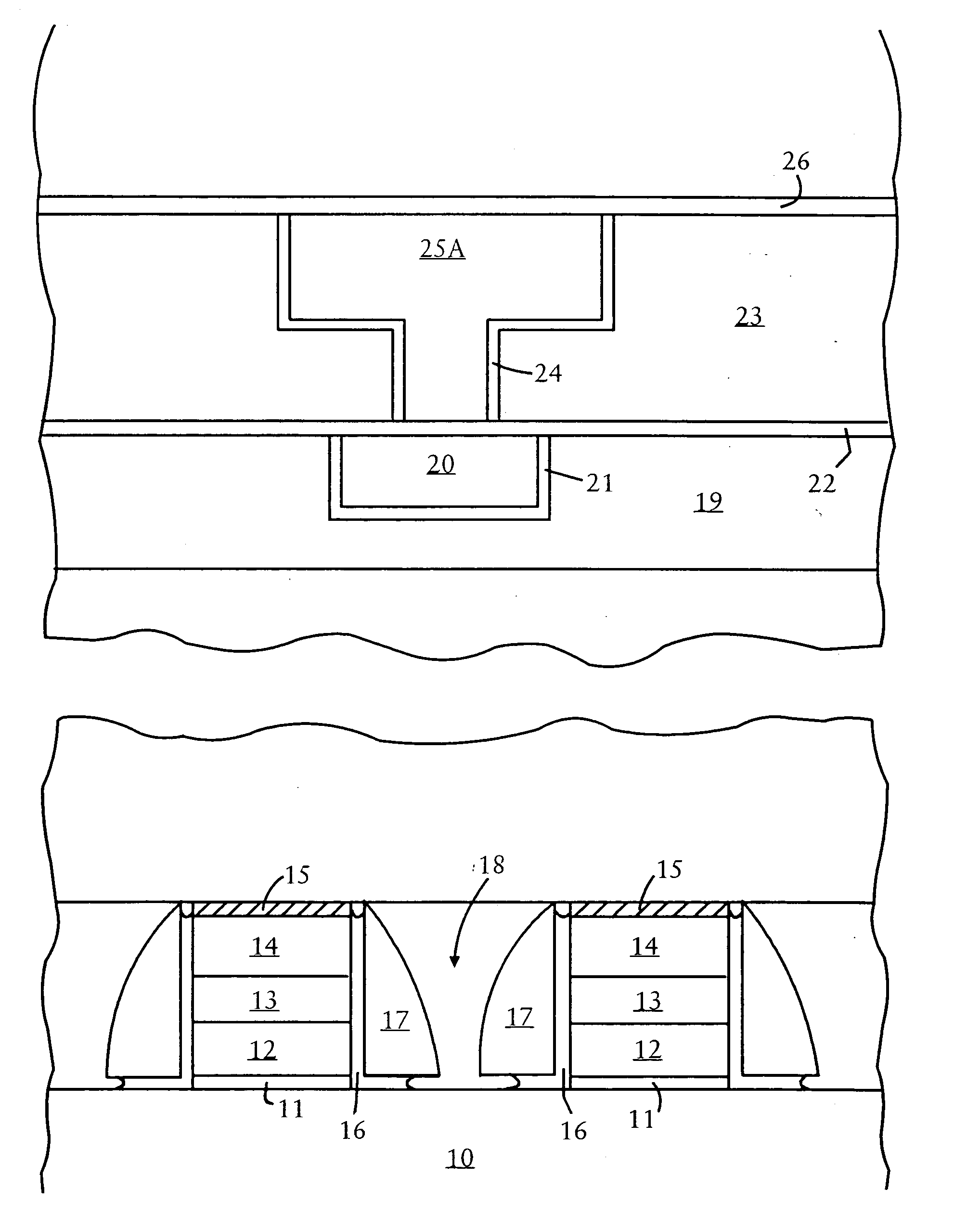
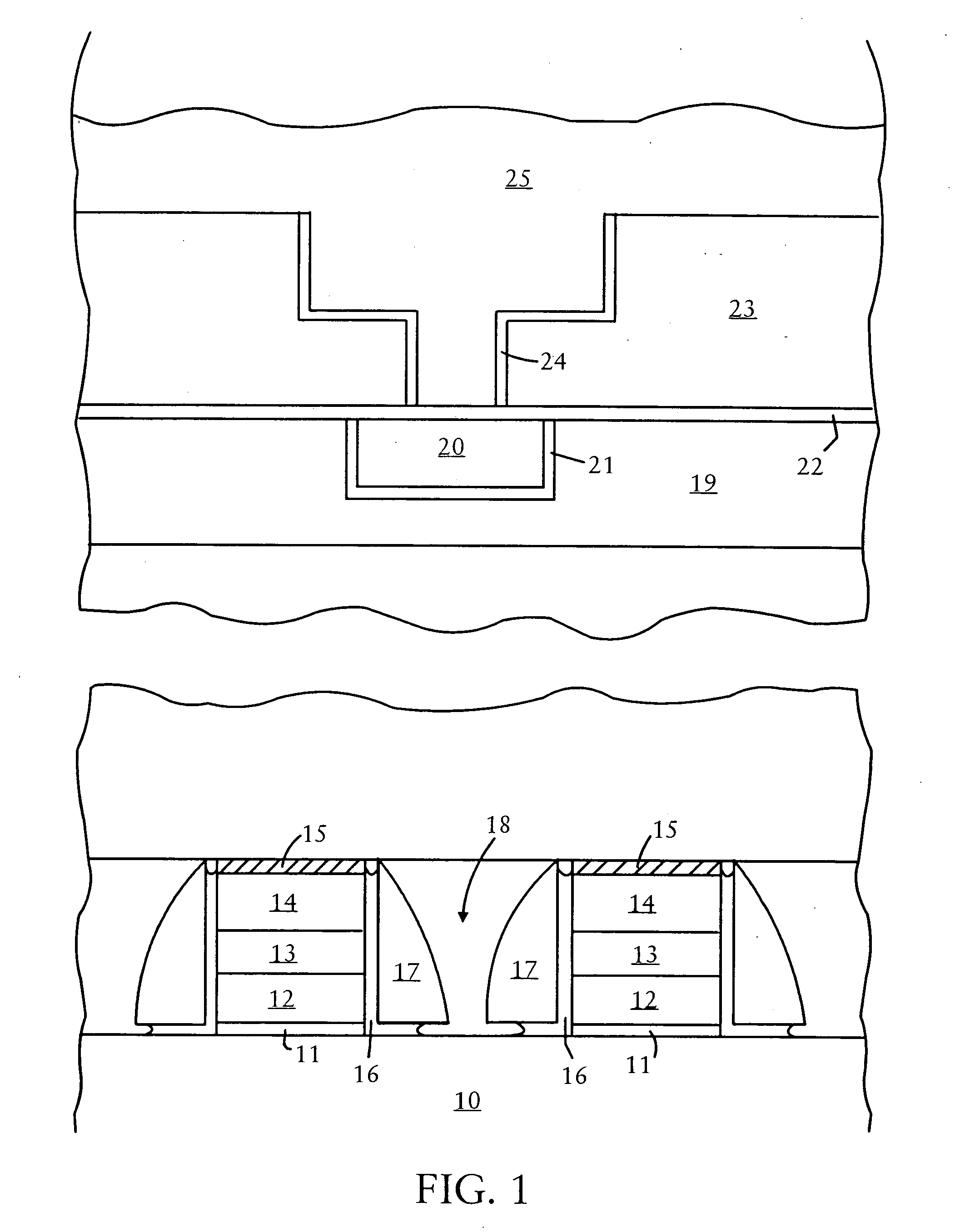
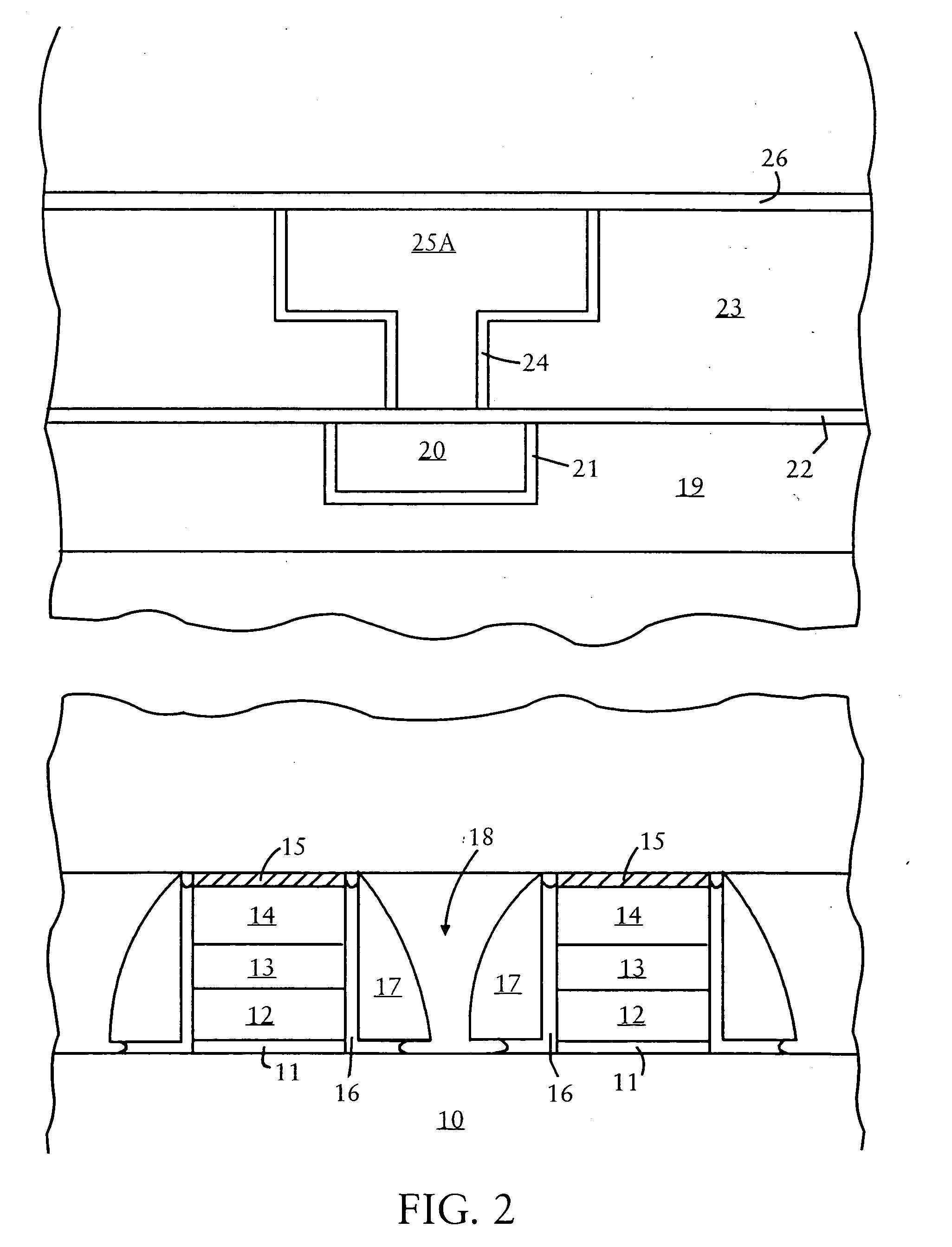
Variable programming of non-volatile memory
ActiveUS7020017B2Improve data retentionDecreased program disturbRead-only memoriesDigital storageReading levelNon-volatile memory
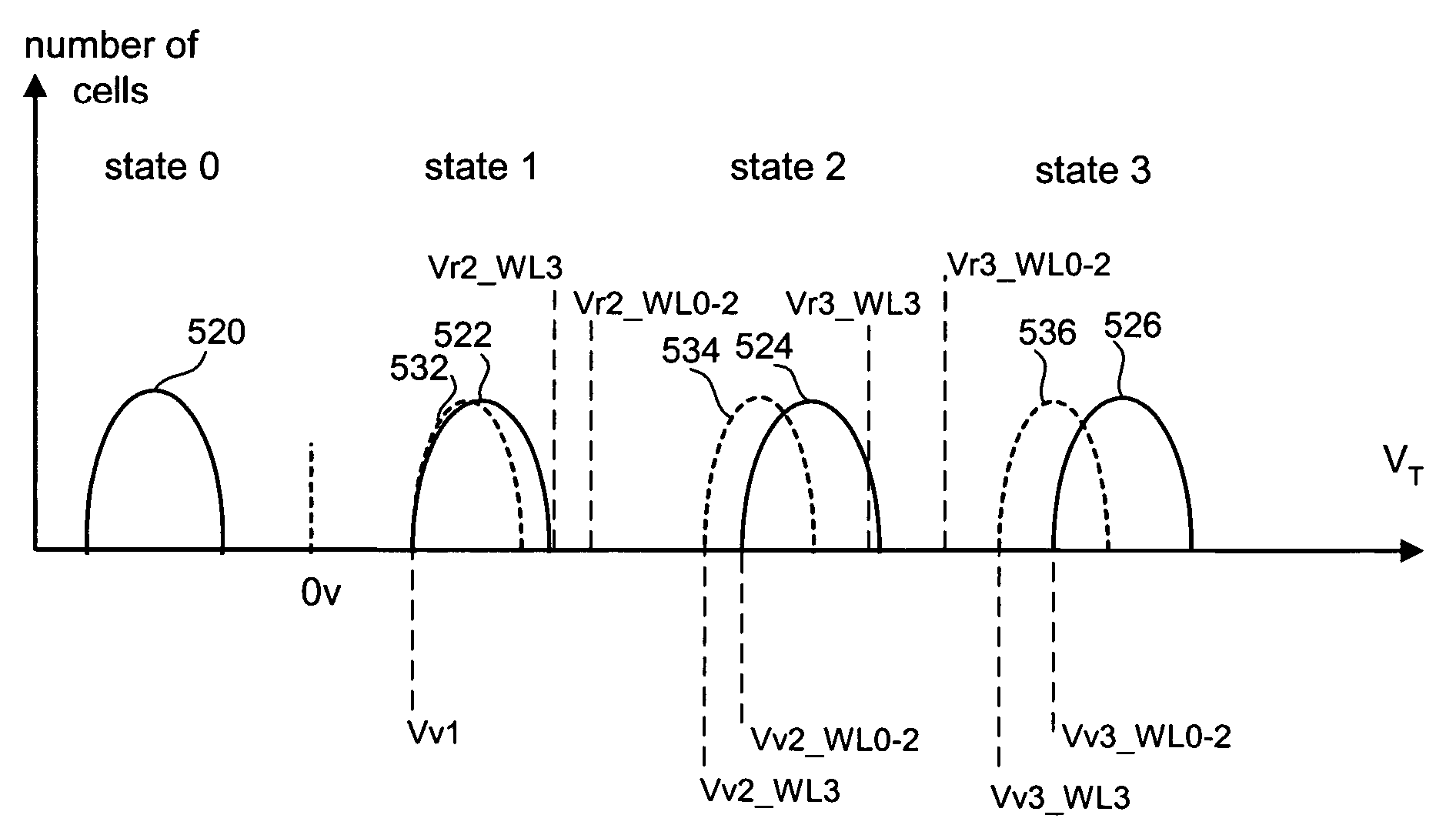
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments can provide for reduced program disturb in non-volatile semiconductor memory. In one embodiment, select memory cells such as those connected to a last word line of a NAND string are programmed using one or more program verify levels or voltages that are different than a corresponding level used to program other cells or word lines. One exemplary embodiment includes using a lower threshold voltage verify level for select physical states when programming the last word line to be programmed for a string during a program operation. Another embodiment includes applying a lower program voltage to program memory cells of the last word line to select physical states. Additional read levels are established for reading the states programmed using lower verify levels in some exemplary implementations. A second program voltage step size that is larger than a nominal step size is used in one embodiment when programming select memory cells or word lines, such as the last word line to be programmed for a NAND string.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Use of high-K dielectric material for ONO and tunnel oxide to improve floating gate flash memory coupling
InactiveUS6617639B1Enhanced couplingReduce equivalent oxide thicknessTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCouplingDielectric layer
A floating gate flash memory device including a substrate comprising a source region, a drain region, and a channel region positioned therebetween; a floating gate electrode positioned above the channel region and separated from the channel region by a tunnel dielectric material layer; and a control gate electrode positioned above the floating gate electrode and separated from the floating gate electrode by an interpoly dielectric layer, the interpoly dielectric layer comprising a modified ONO structure having a bottom dielectric material layer adjacent to the floating gate electrode, a top dielectric material layer adjacent to the control gate electrode, and a center layer comprising a nitride and positioned between the bottom dielectric material layer and the top dielectric material layer, in which the tunnel dielectric material layer, and at least one of the bottom dielectric material layer and the top dielectric material layer, comprise a high-K dielectric material.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
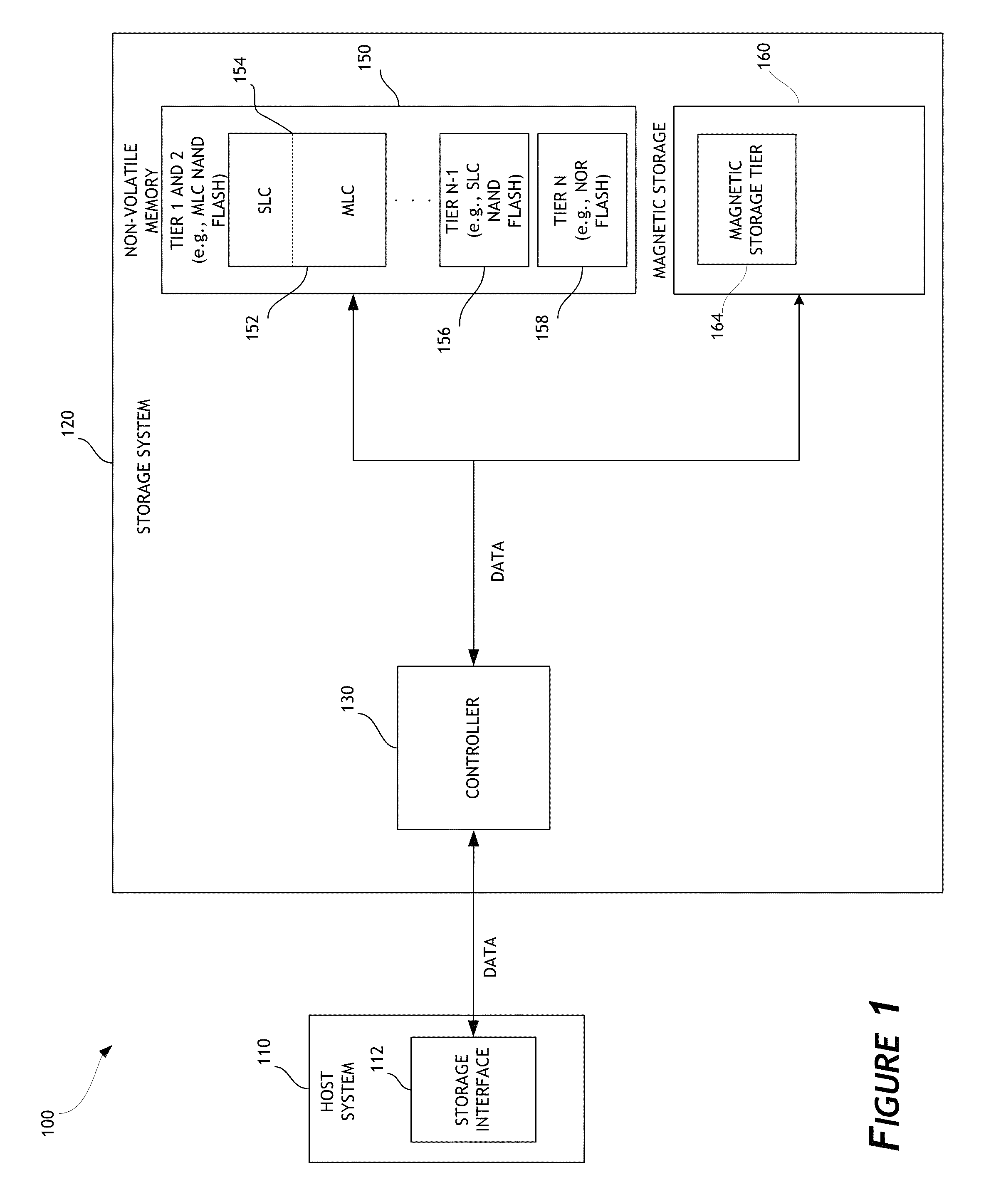
Disk drive data caching using a multi-tiered memory
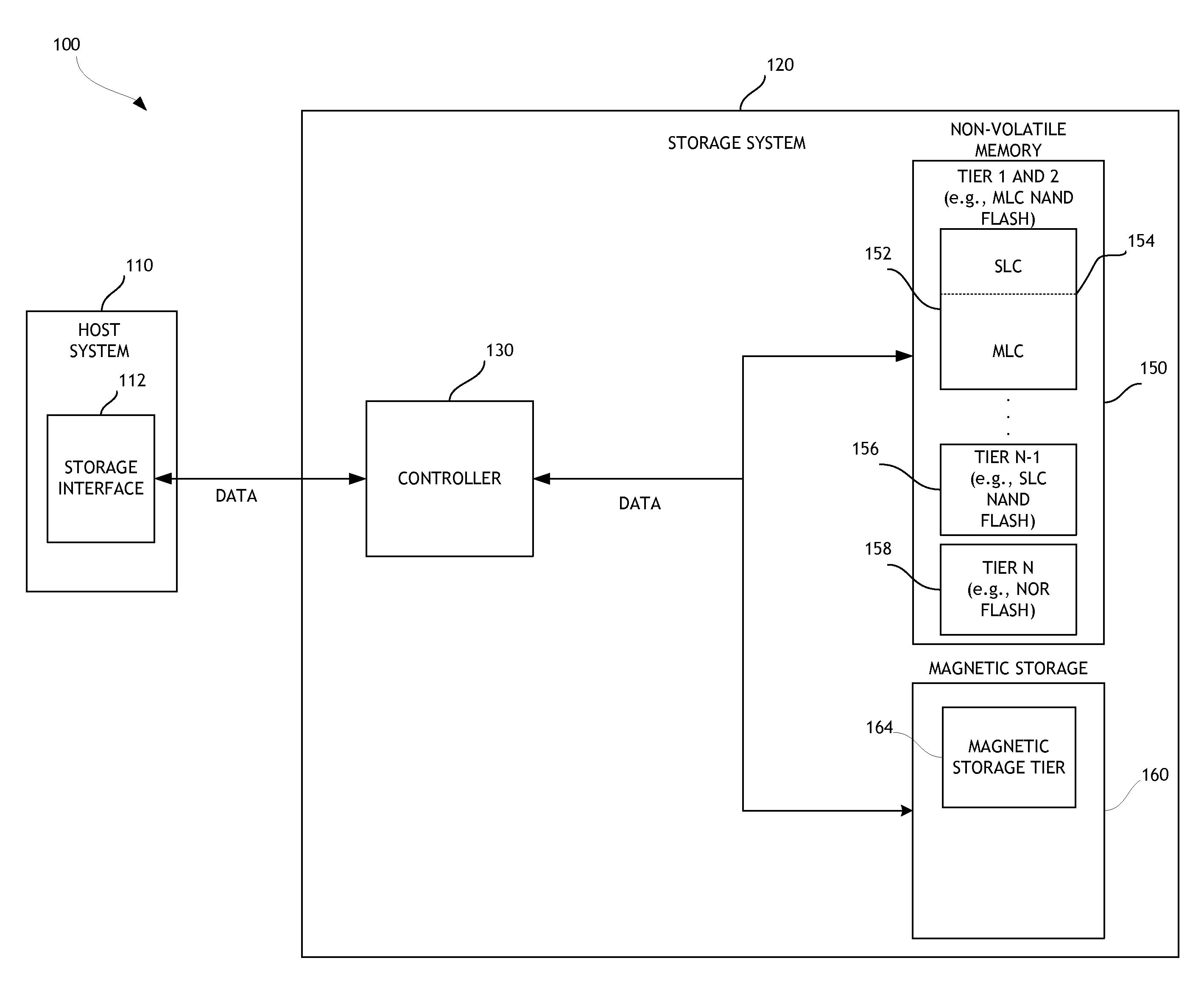
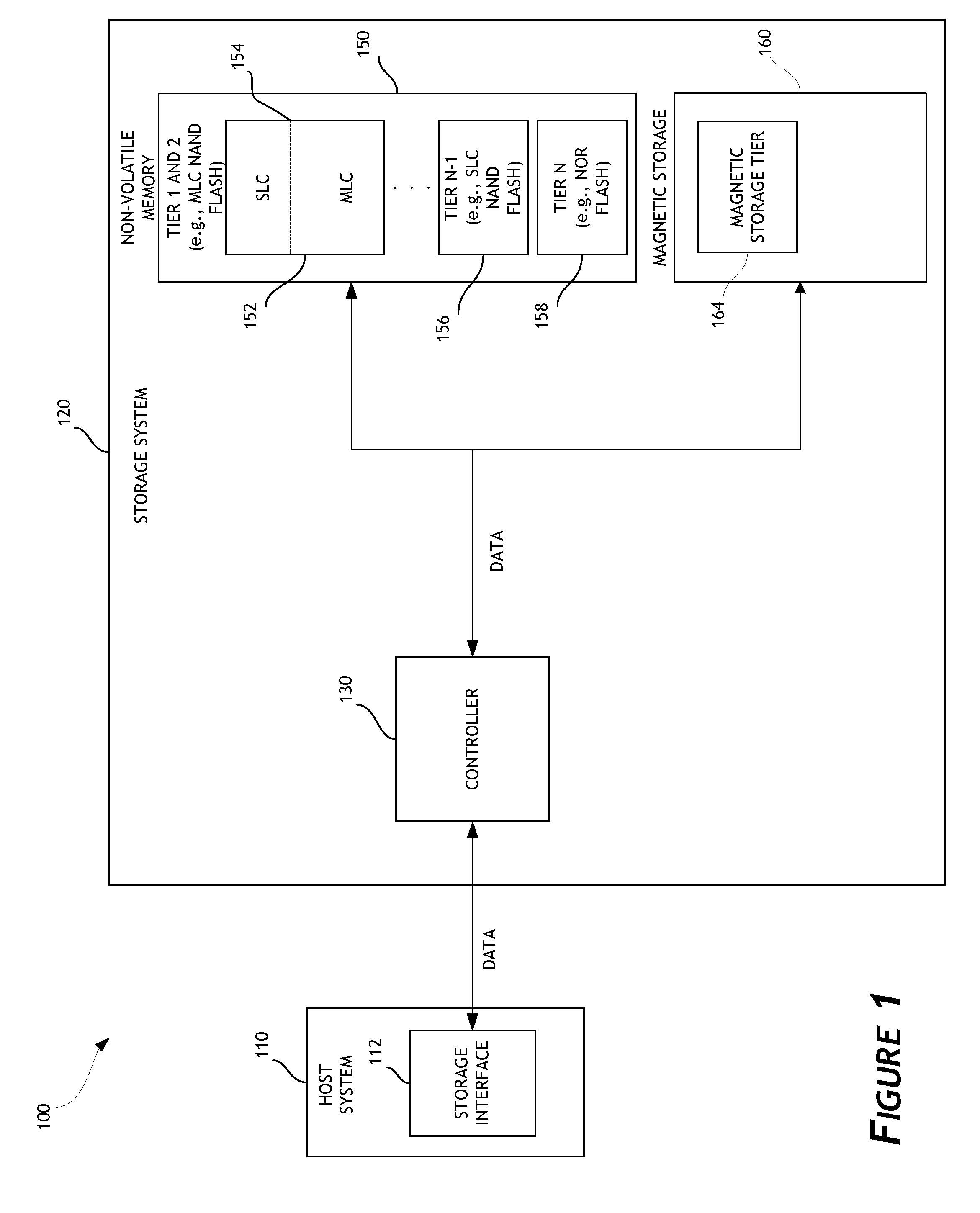
ActiveUS20130132638A1Limit usable lifeReduce dataMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTSingle levelComputer science
A disk drive is disclosed that utilizes multi-tiered solid state memory for caching data received from a host. Data can be stored in a memory tier that can provide the required performance at a low cost. For example, multi-level cell (MLC) memory can be used to store data that is frequently read but infrequently written. As another example, single-level cell (SLC) memory can be used to store data that is frequently written. Improved performance, reduced costs, and improved power consumption can thereby be attained.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Integrated code and data flash memory
ActiveUS7158411B2Easy to manufactureLow costTransistorSolid-state devicesMemory architectureNon-volatile memory
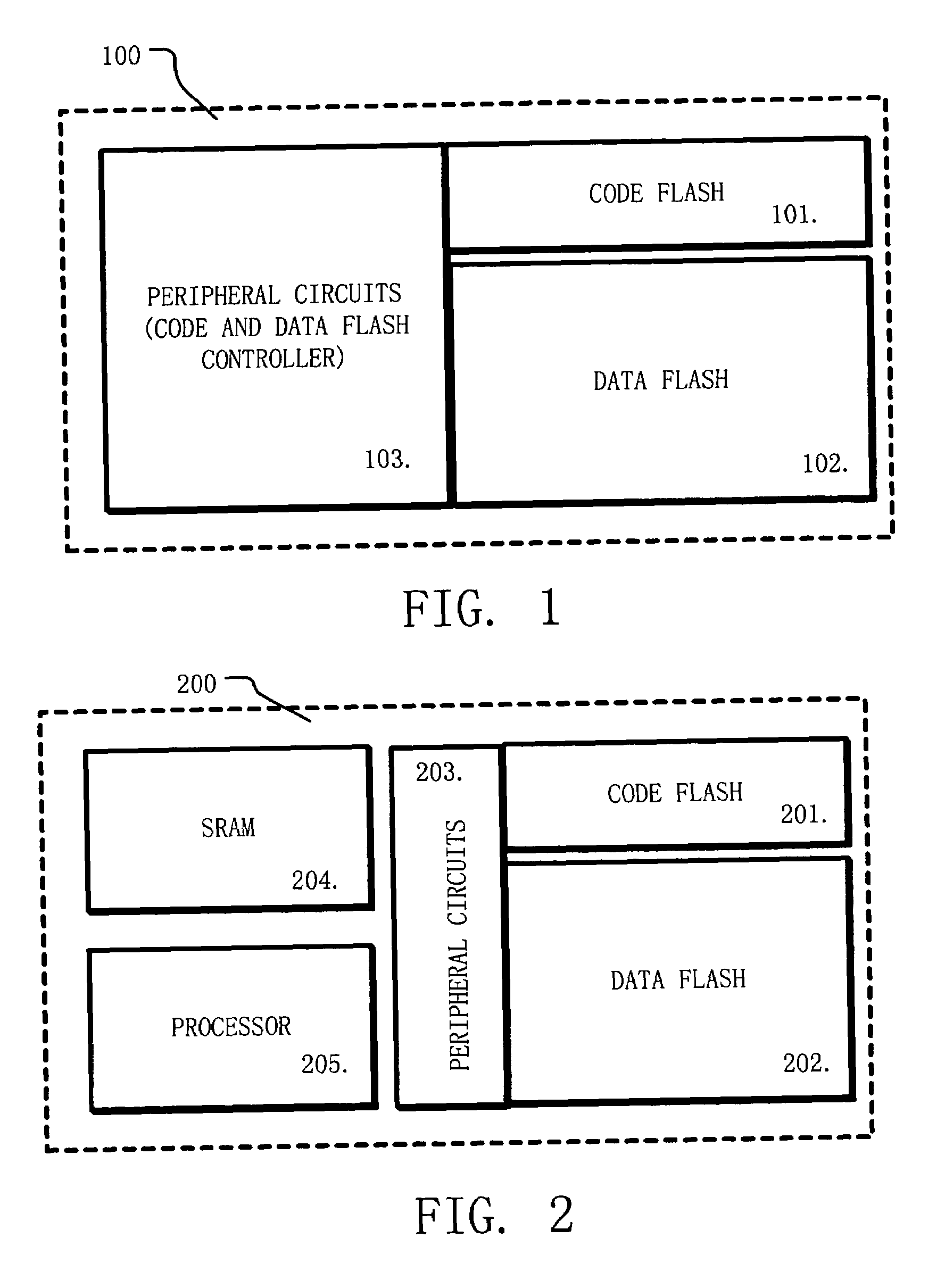
A memory architecture for an integrated circuit comprises a first memory array configured to store data for one pattern of data usage and a second memory array configured to store data for another pattern of data usage. The first and second memory arrays comprise charge storage based nonvolatile memory cells having substantially the same structure in both arrays. A first operation algorithm adapted for example for data flash applications is used for programming, erasing and reading data in the first memory array. A second operation algorithm adapted for example for code flash applications is used for programming, erasing and reading data in the second memory array, wherein the second operation algorithm is different than the first operation algorithm. Thus, one die with memory for both code flash and data flash applications can be easily manufactured using a simple process, at low cost and high yield.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Aluminum copper oxide based memory devices and methods for manufacture
ActiveUS8067815B2Reduce voltageBig ratioTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectricityCopper oxide
Memory devices are described along with methods for manufacturing. A memory device as described herein includes a first electrode and a second electrode. The memory device further includes a diode and an anti-fuse metal-oxide memory element comprising aluminum oxide and copper oxide. The diode and the metal-oxide memory element are arranged in electrical series between the first electrode and the second electrode.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Programmable resistive memory cell with sacrificial metal
ActiveUS8097874B2Improve data retentionLow resistance stateBulk negative resistance effect devicesElectrical conductorStandard electrode potential
Programmable metallization memory cells include an electrochemically active electrode and an inert electrode and an ion conductor solid electrolyte material between the electrochemically active electrode and the inert electrode. A sacrificial metal is disposed between the electrochemically active electrode and the inert electrode. The sacrificial metal has a more negative standard electrode potential than the filament forming metal.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Gain cell type non-volatile memory having charge accumulating region charges or discharged by channel current from a thin film channel path
InactiveUS20050205921A1Write performanceImprove data retentionTransistorSolid-state devicesDrain currentSemiconductor
Owner:HITACHI LTD
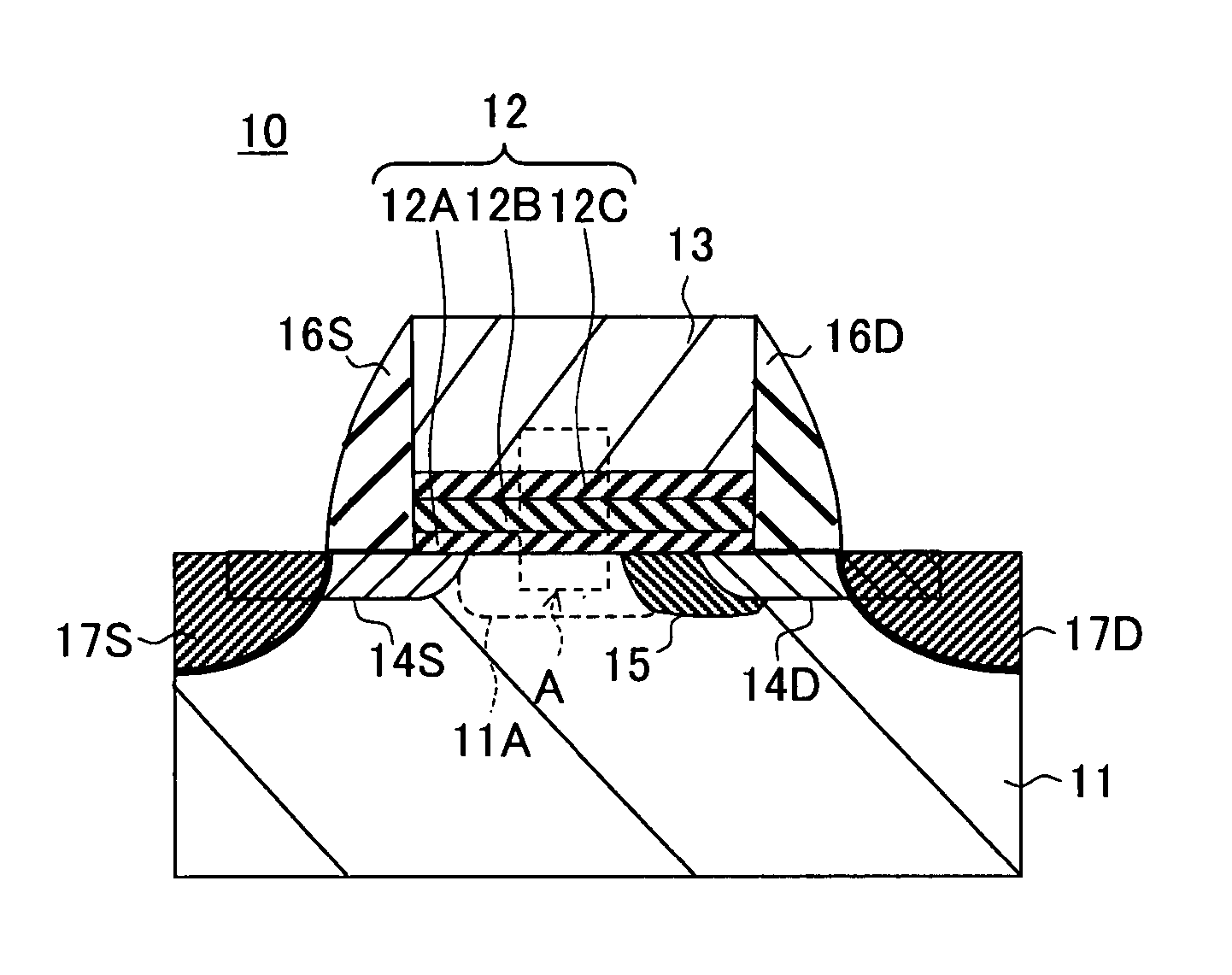
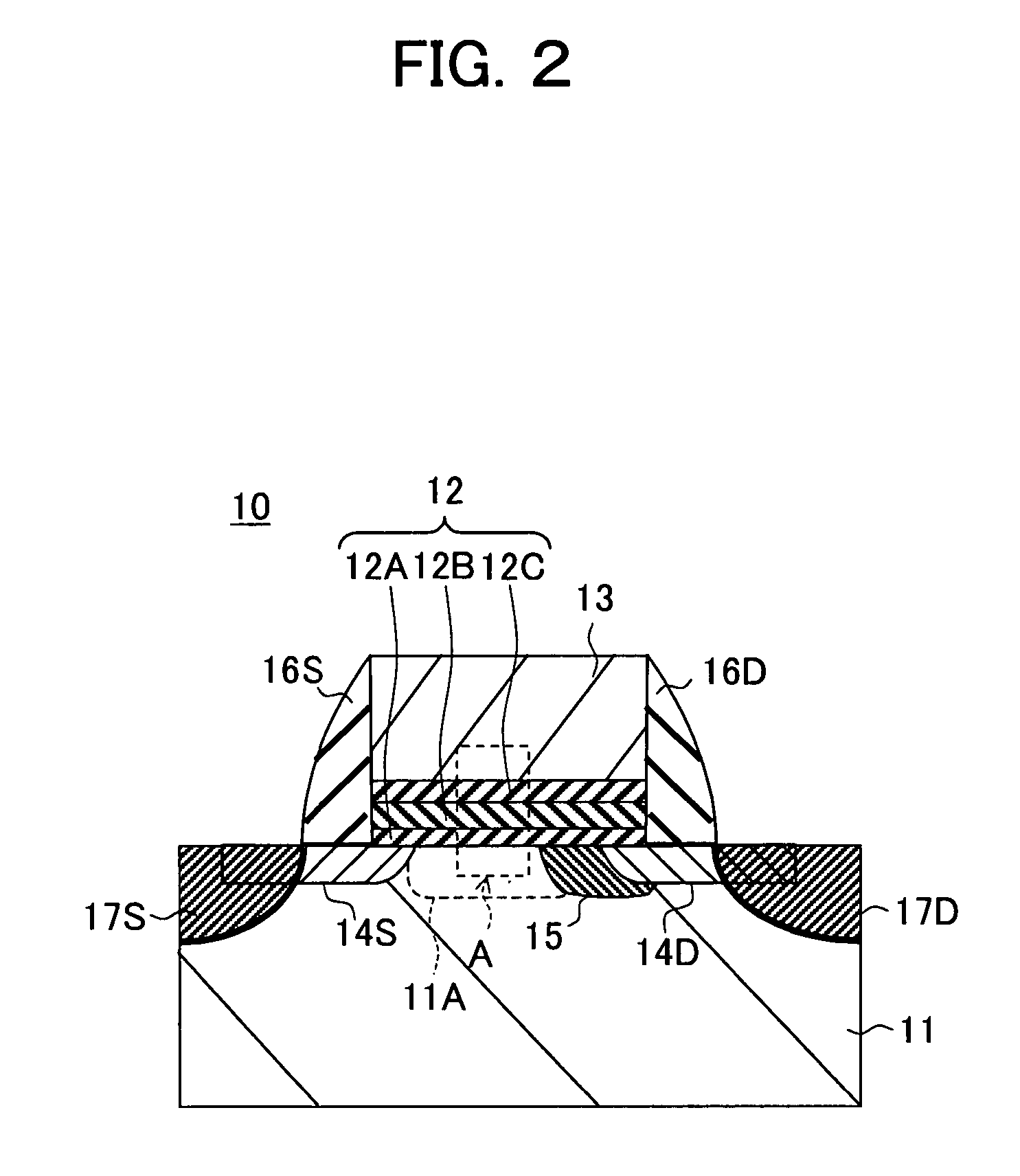
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and programming or erasing method therefor
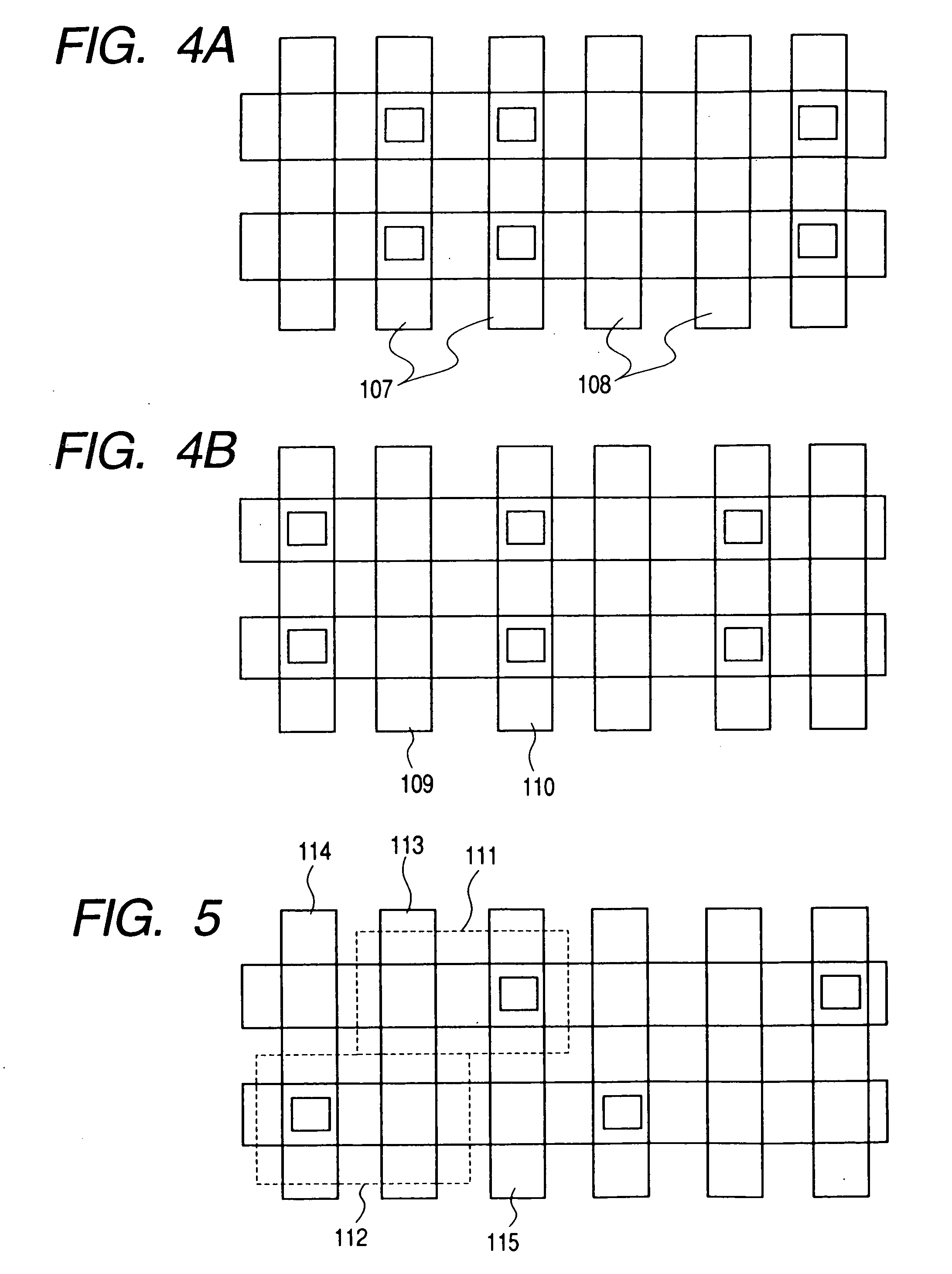
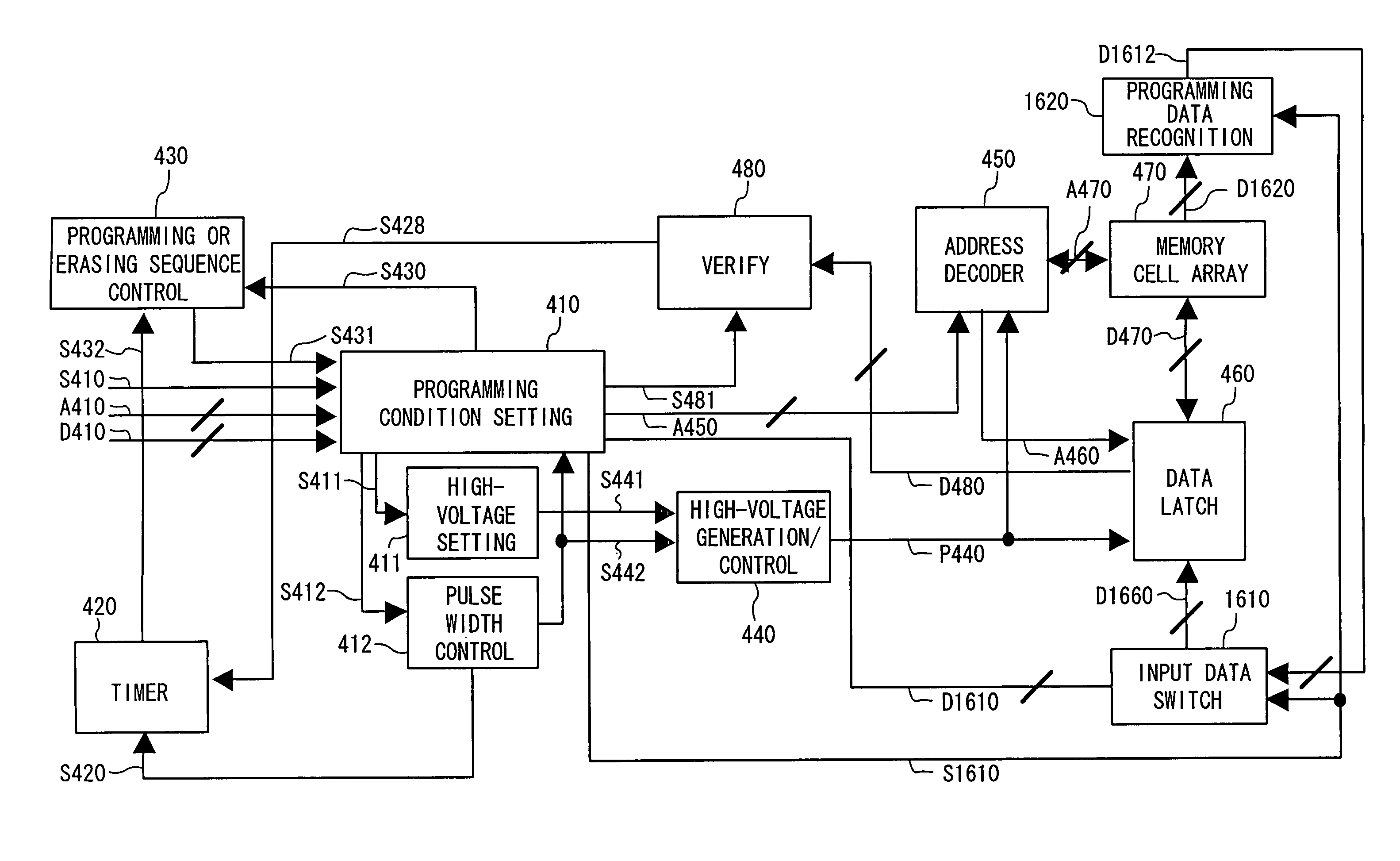
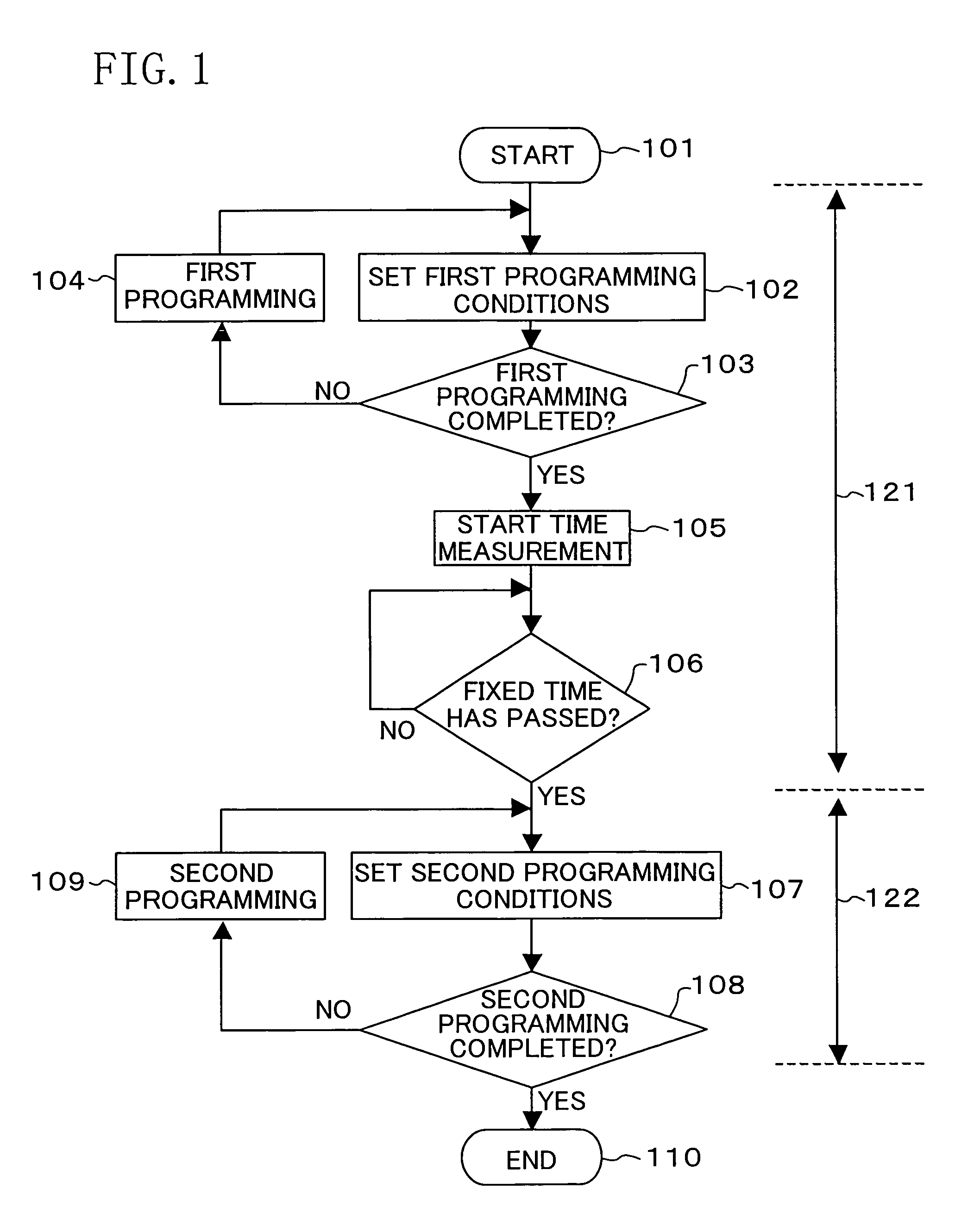
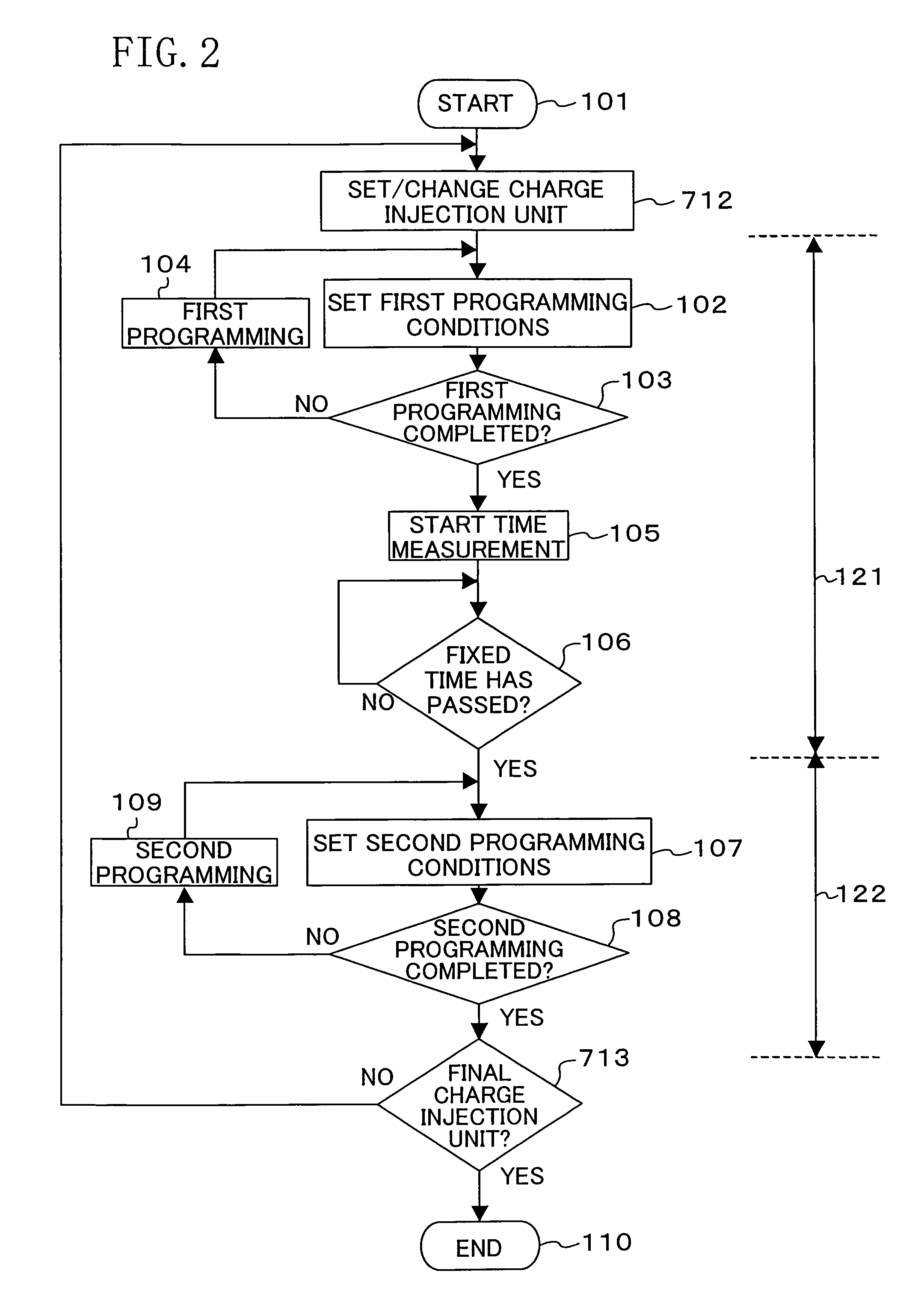
ActiveUS7460410B2Inhibit deteriorationData retentionRead-only memoriesDigital storageCharge injectionCharge loss
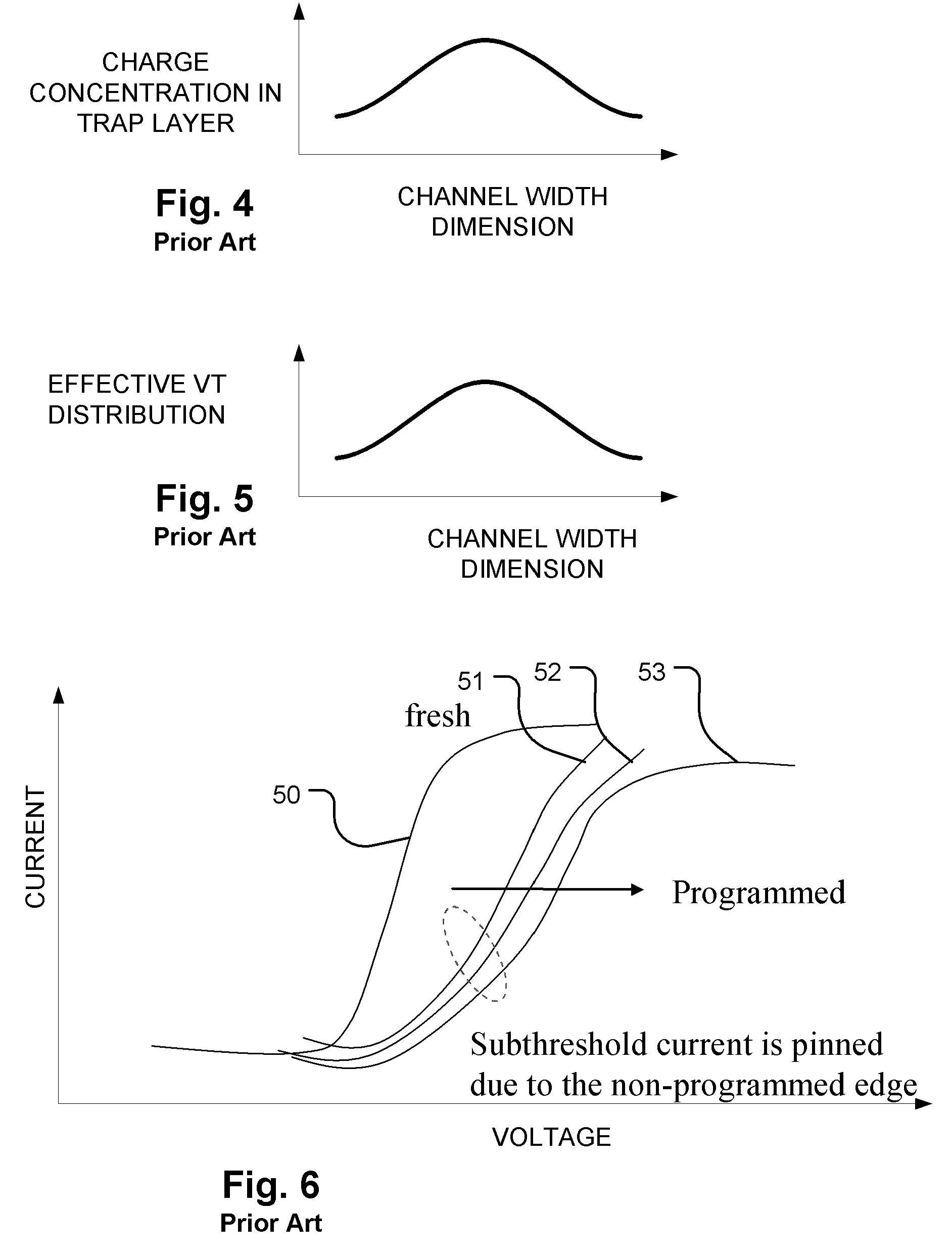
In a nonvolatile memory cell having a trap layer, programming or erasing is made in a sequence of first charge injection with a given wait time being secured and second charge injection executed after the first charge injection. Surrounding charge that deteriorates the data retention characteristic is reduced by use of initial variation occurring immediately after programming (charge loss phenomenon due to binding of injected charge with the surrounding charge in an extremely short time), and then the charge loss due to the initial variation is compensated, to thereby improve the data retention characteristic.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Tool for synchronization of business information
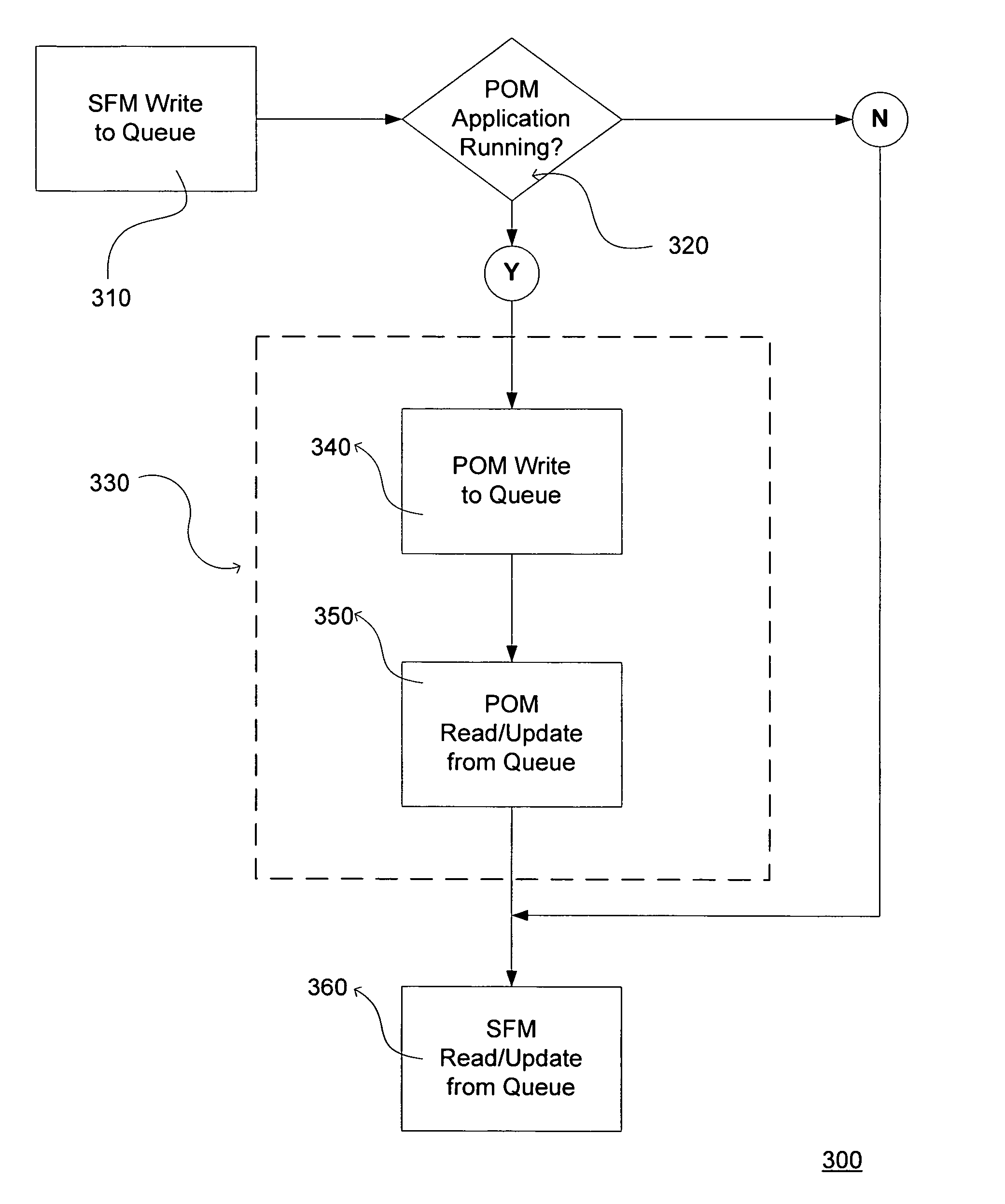
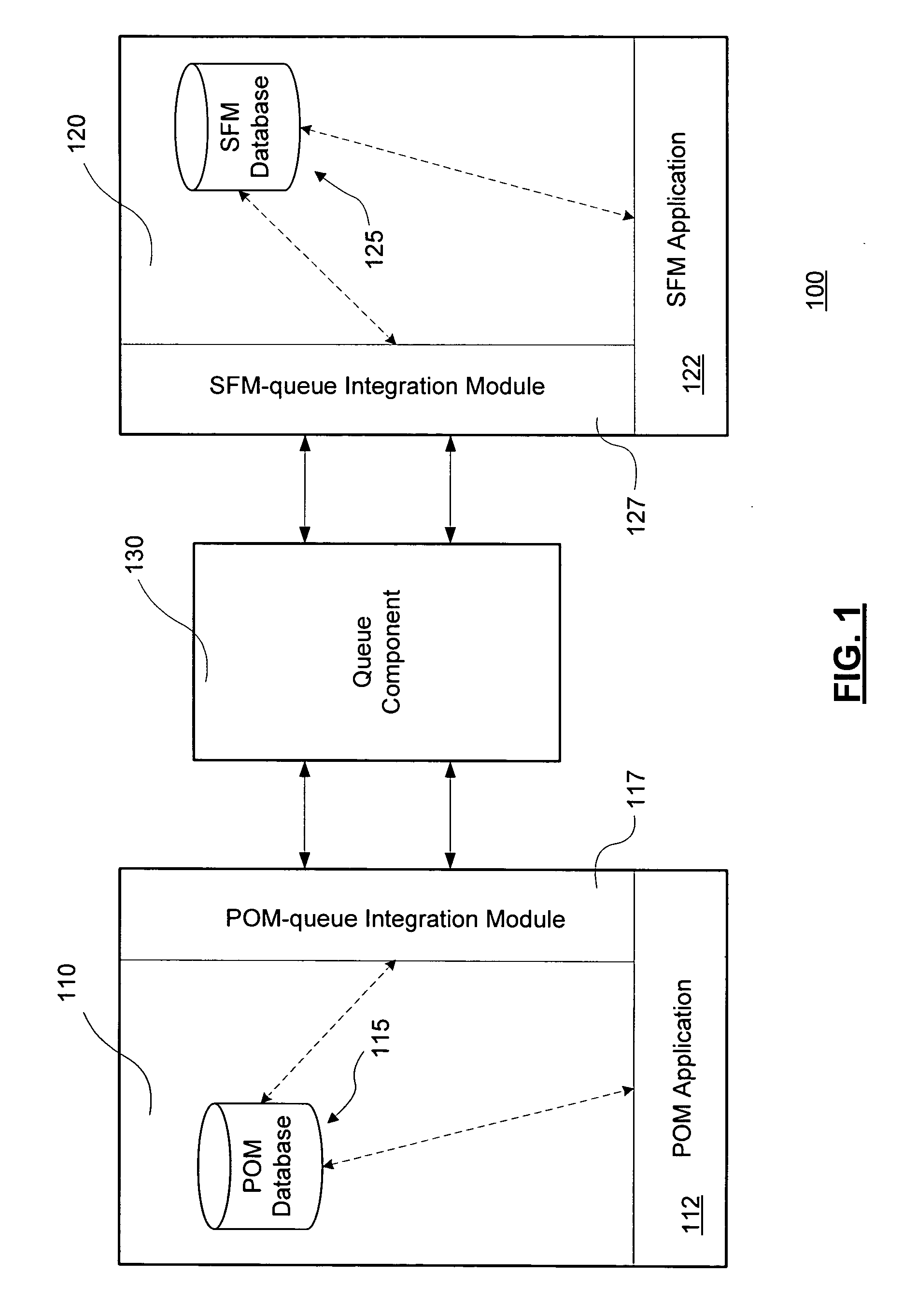
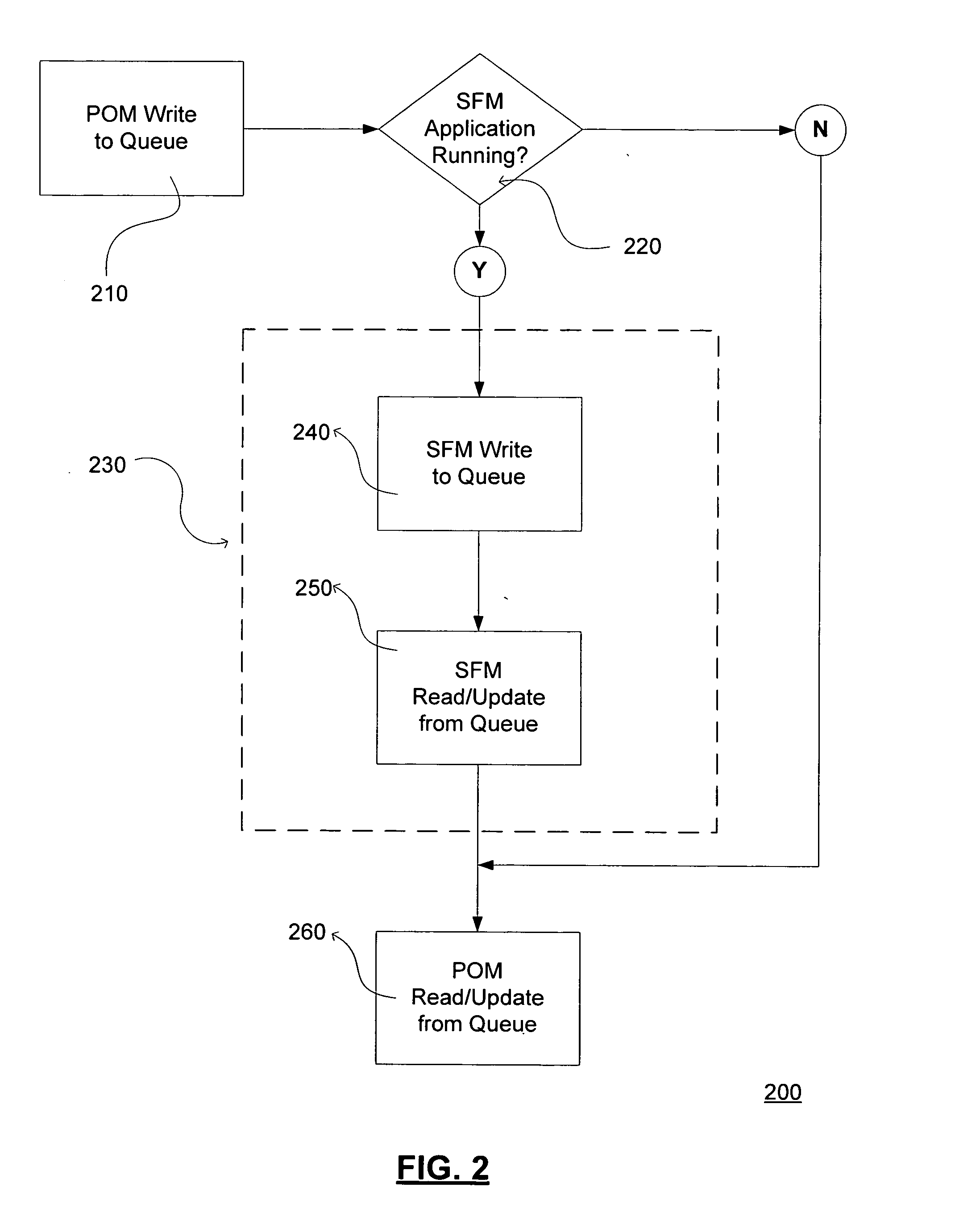
InactiveUS20050198085A1Frequent useImprove data retentionDigital computer detailsDatabase distribution/replicationBusiness ruleProgram management
Disclosed herein are systems, electronic tools and related methods for integrating the business rules, processes, and technology necessary to enable collaboration between personal office management applications, which are used by individuals on a daily basis to organize personal contacts, appointment calendars, and tasks, with sales force management applications, which are used to manage client and account contact information and coordinate the pursuit of business opportunities across an organization. Users of both applications can have their data electronically synchronized to share specifically designated information automatically within the applications. The information designated for synchronization can be of three types having different rules regarding their sharing among the applications, wherein the types include business contacts, sales force activities, and opportunity tasks. Users can thereby manage a large synchronized base of business contacts via both their personal office management application and a sales force management application, synchronize sales force activities from their personal office management application into the sales force management application, and assign client or account opportunity action items to other users in the organization via the sales force management application, and then have those action items automatically appear to the assigned user in that assigned user's personal office management application as a task.
Owner:ACCENTURE GLOBAL SERVICES LTD
Gain cell type non-volatile memory having charge accumulating region charged or discharged by channel current from a thin film channel path
InactiveUS6876023B2Reduce leakage currentWrite performanceTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringLow power dissipation
A semiconductor memory element subject to a threshold voltage controlling method other than those based on low leak currents or on the implantation of impurities. Such semiconductor elements are used to form semiconductor memory elements that are employed in scaled-down structures and are conducive to high-speed write operations thanks to a sufficiently prolonged refresh cycle. These semiconductor memory elements are in turn used to constitute a semiconductor memory device. A very thin semiconductor film is used as channels so that leak currents are reduced by the quantum-mechanical containment effect in the direction of film thickness. An amount of electrical charges in each charge accumulating region is used to change conductance between a source and a drain region of each read transistor structure, the conductance change being utilized for data storage. A channel of a transistor for electrically charging or discharging each charge accumulating region is made of a semiconductor film 5 nm thick at most. The arrangement affords both high-speed data write performance and an extended data retention time. The invention provides a high-speed, power-saving semiconductor device of high integration particularly advantageous for producing a small-scale system of low-power dissipation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
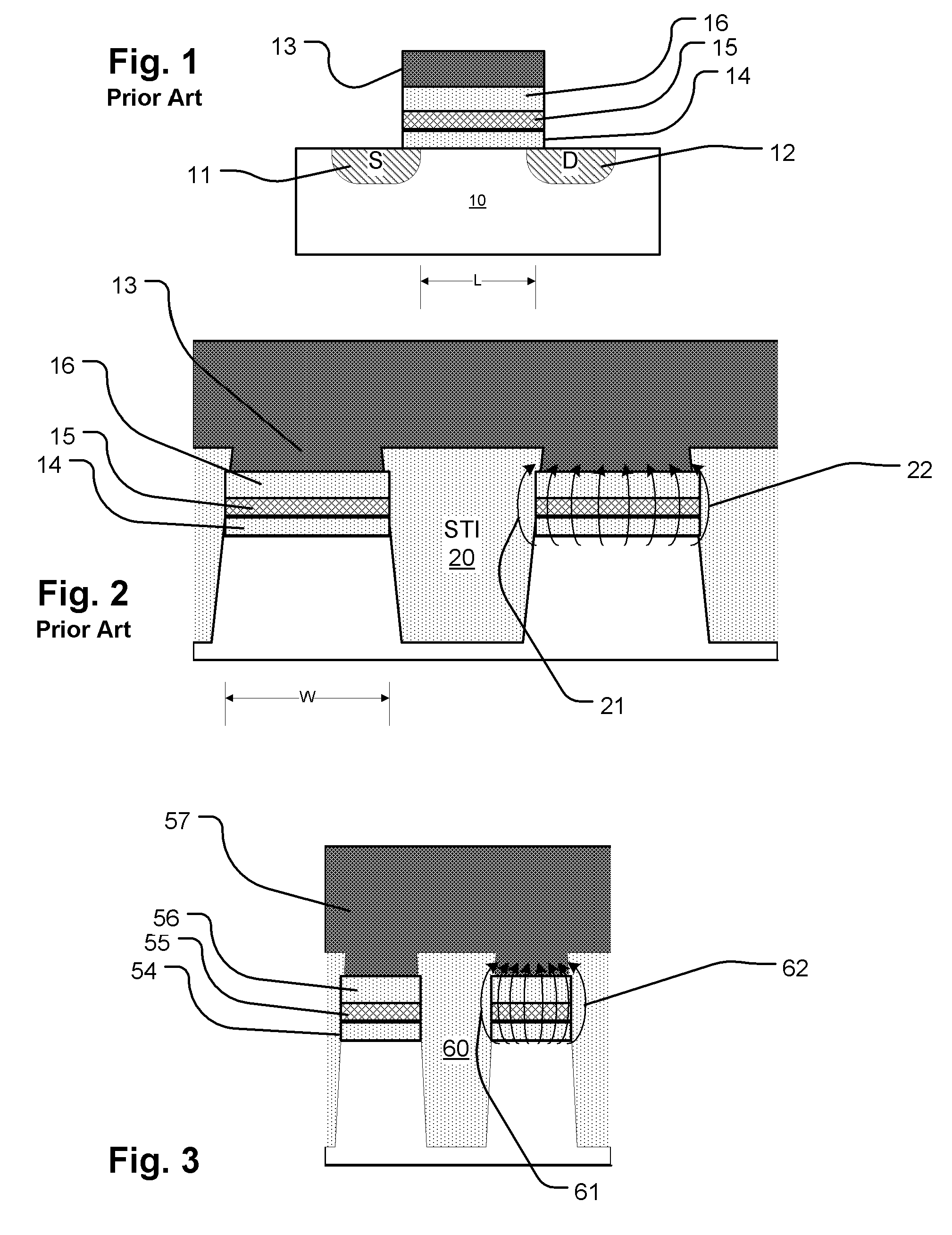
Methods for fabricating an improved floating gate memory cell
Methods for fabricating improved floating gate memory cells are provided. A substrate and a first insulating layer are fabricated, where the first insulating layer is formed on the substrate. A shallow trench isolation (STI) region is fabricated having walls that form edges in the substrate and edges to a first conducting layer where the edges of the first conducting layer are aligned with the edges of the substrate. A second insulating layer is formed on the first conducting layer and a second conducting layer formed on the first insulating layer. The invention also includes a method that capitalizes on a single step process for defining the STI region and the floating gate for a memory cell that aligns edges formed in the substrate by the walls of the STI region with the edges of the floating gate formed by the walls of the STI region.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
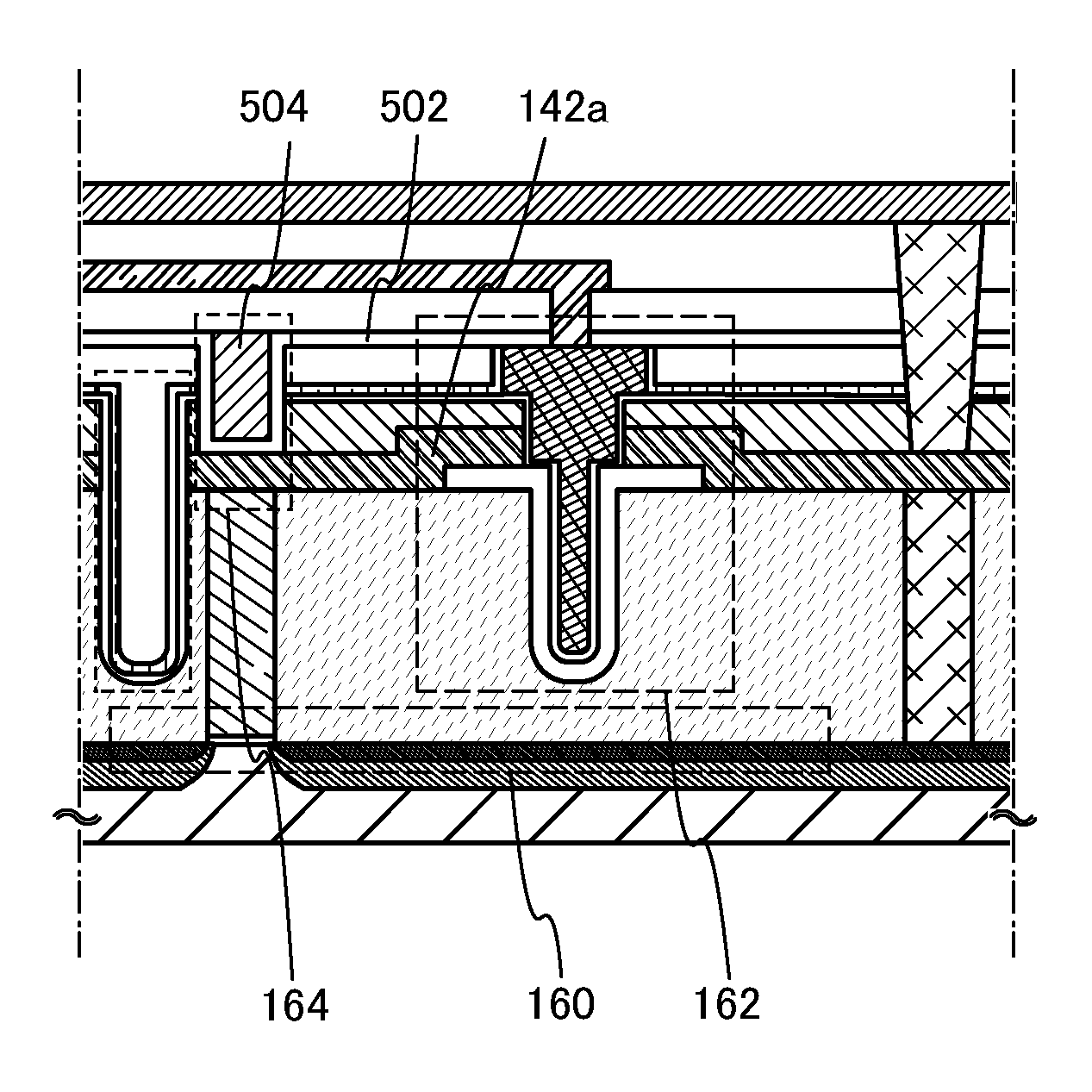
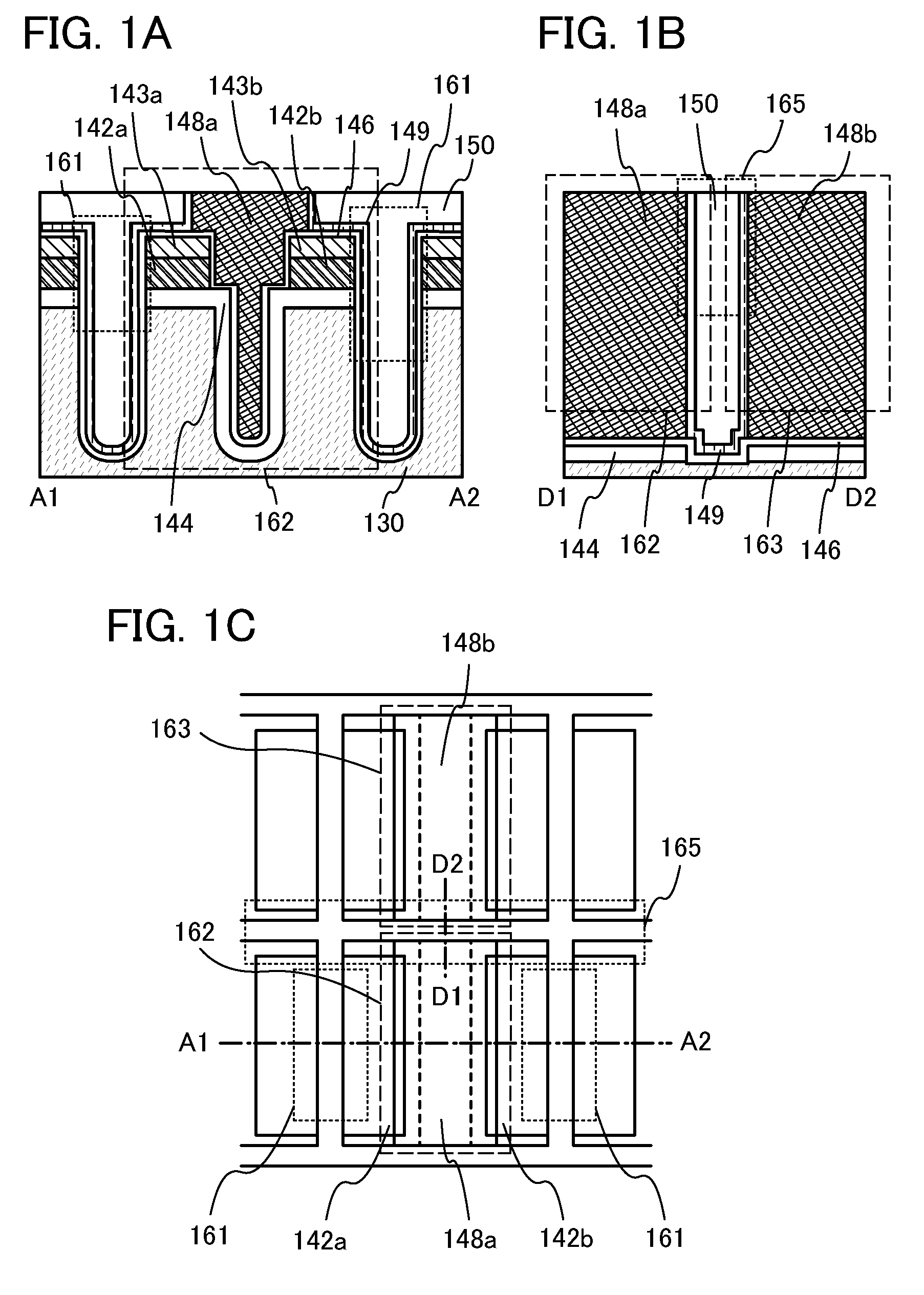
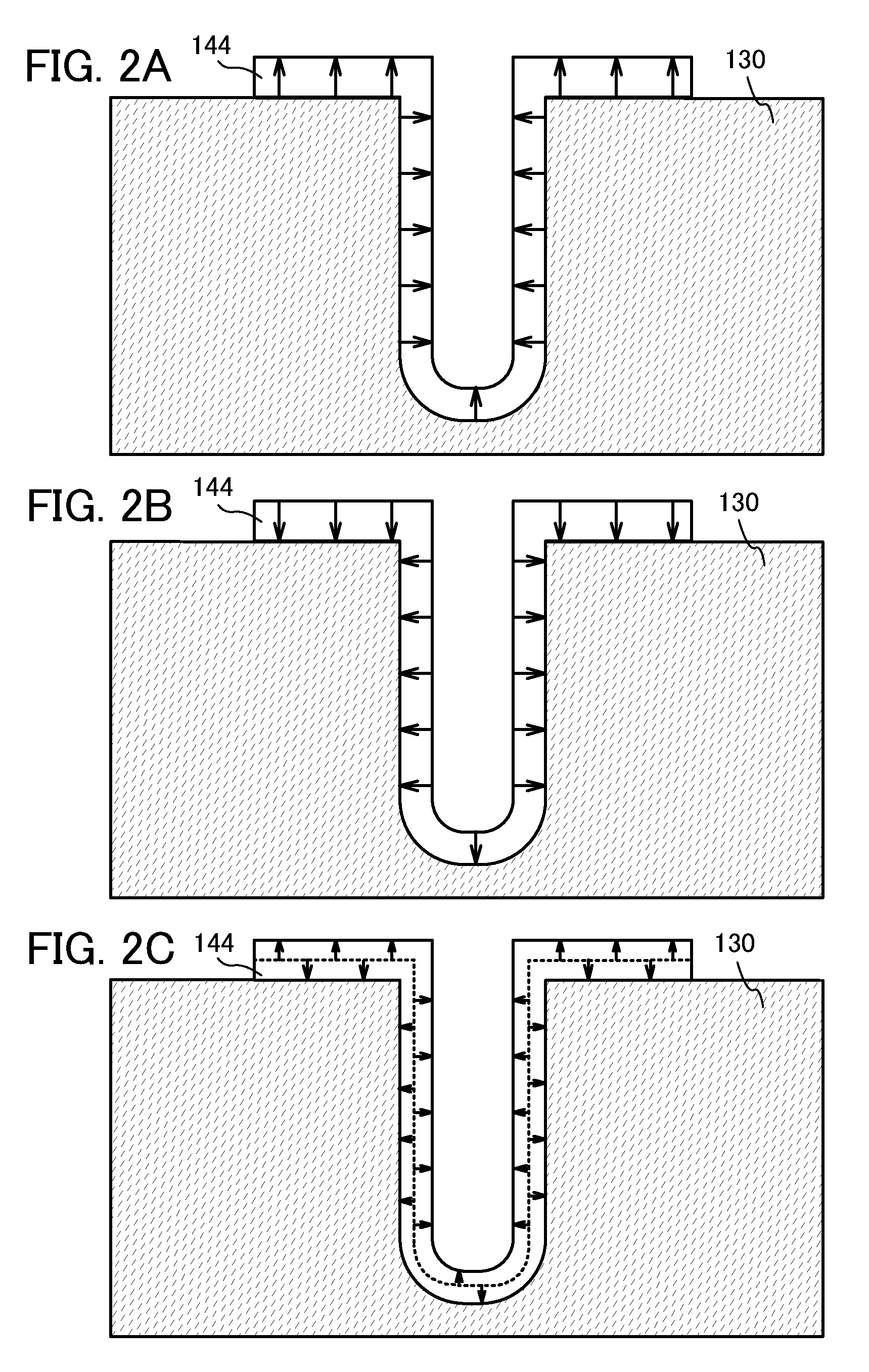
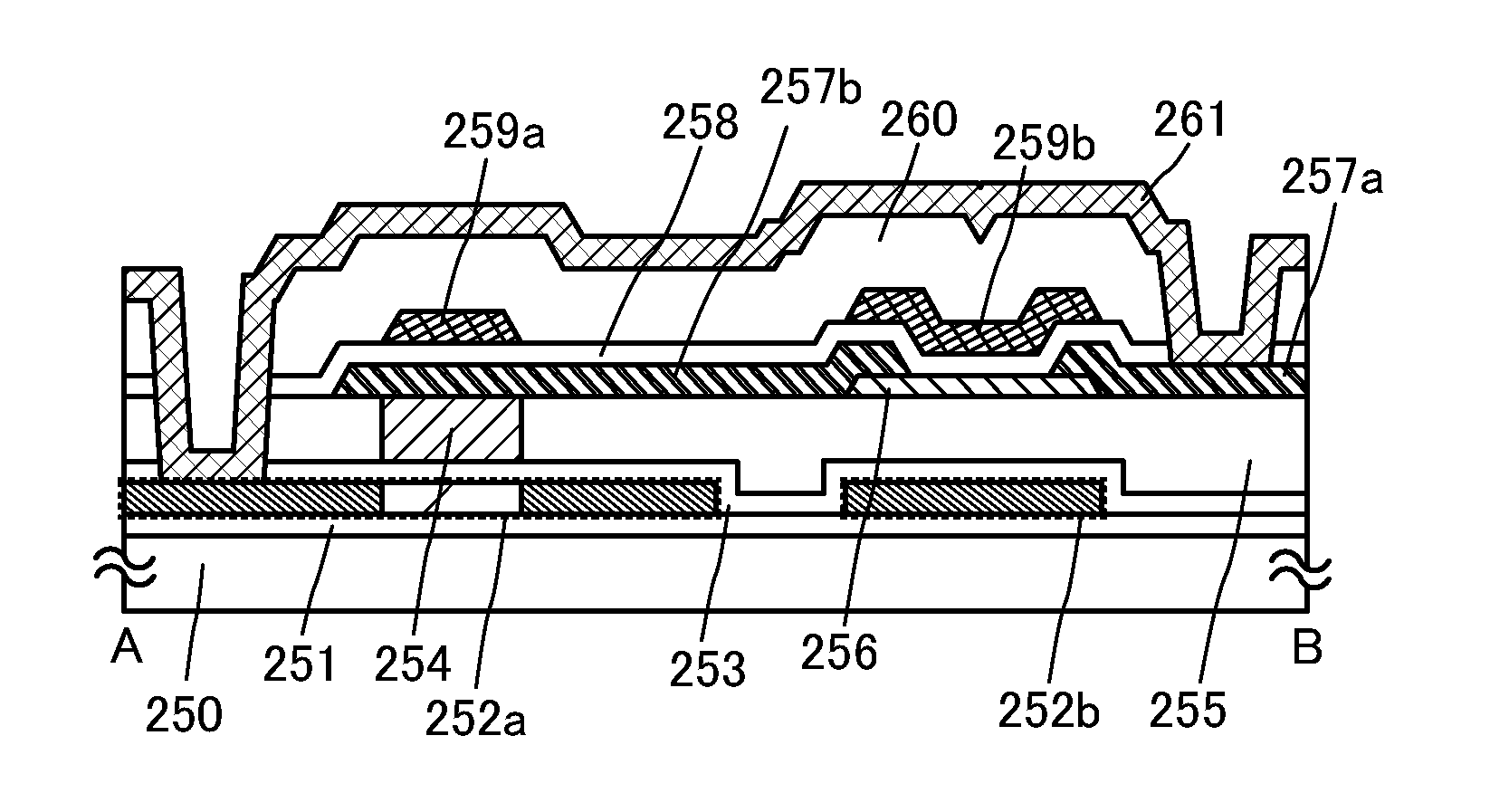
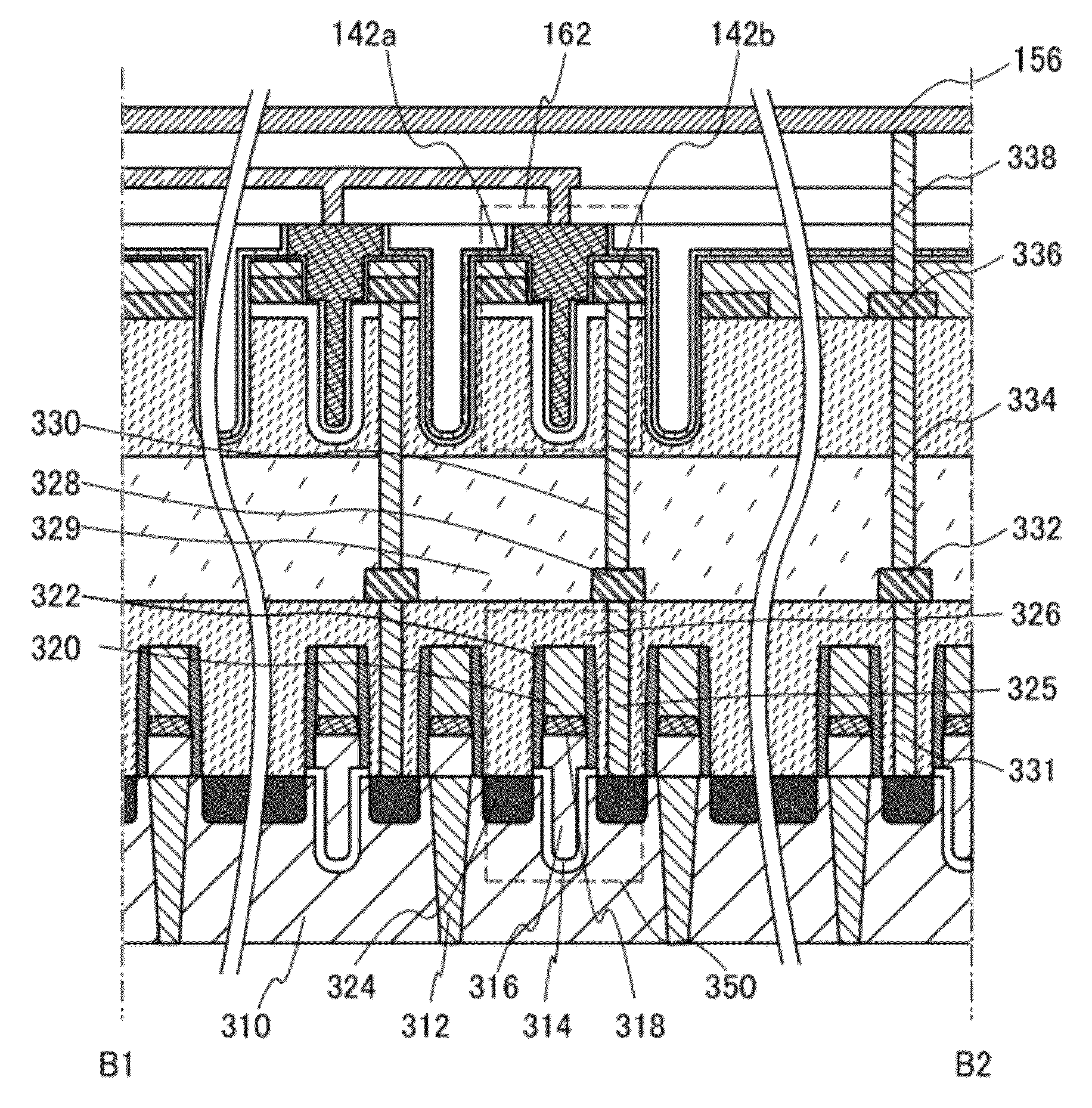
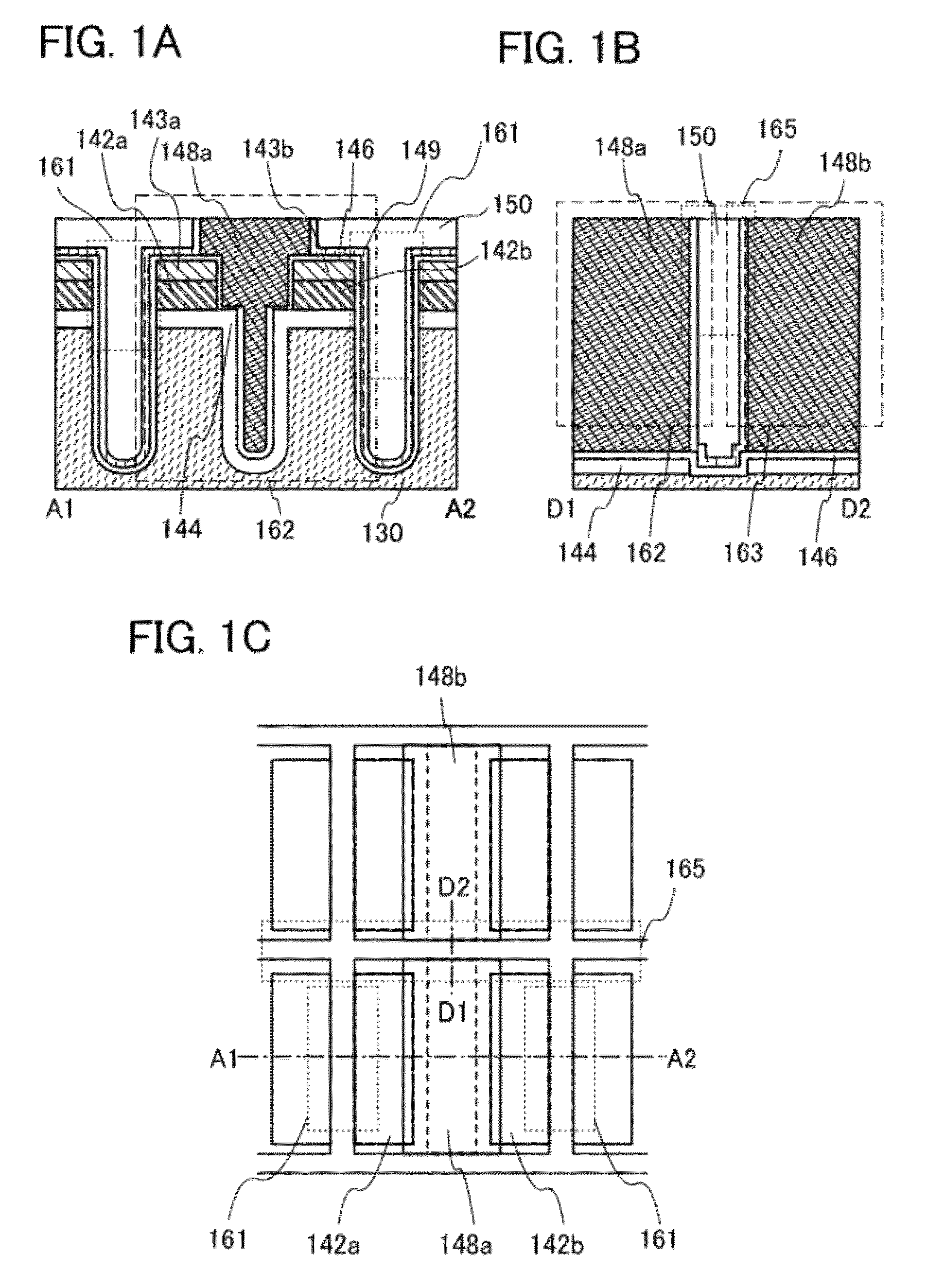
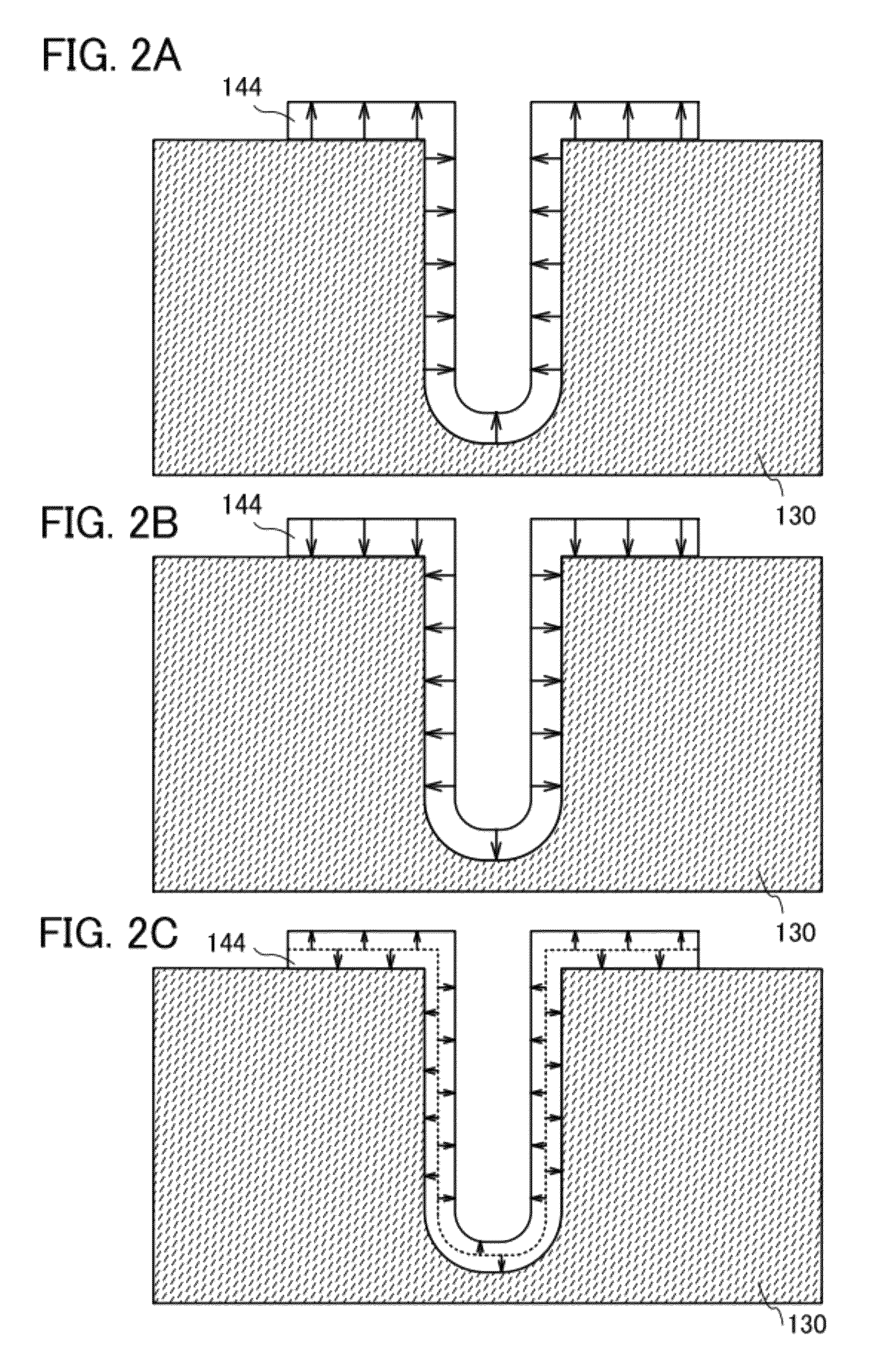
ActiveUS20120187410A1Improve data retentionReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialMiniaturization
A conventional DRAM needs to be refreshed at an interval of several tens of milliseconds to hold data, which results in large power consumption. In addition, a transistor therein is frequently turned on and off; thus, deterioration of the transistor is also a problem. These problems become significant as the memory capacity increases and transistor miniaturization advances. A transistor is provided which includes an oxide semiconductor and has a trench structure including a trench for a gate electrode and a trench for element isolation. Even when the distance between a source electrode and a drain electrode is decreased, the occurrence of a short-channel effect can be suppressed by setting the depth of the trench for the gate electrode as appropriate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Cu annealing for improved data retention in flash memory devices
ActiveUS20080108193A1Improve data retentionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrogenMetallurgy
Data retention in flash memory devices, such as mirrorbit devices, is improved by reducing the generation and / or diffusion of hydrogen ions during back end processing, such as annealing inlaid Cu. Embodiments include annealing inlaid Cu in an N2 atmosphere containing low H2 or no H2, and at temperatures less than 200° C., e.g., 100° C. to 150° C.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Variable resistance element, its manufacturing method and semiconductor memory device comprising the same
InactiveUS20090097300A1Stable switching operationFavorable data retention characteristicCurrent responsive resistorsSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage pulse
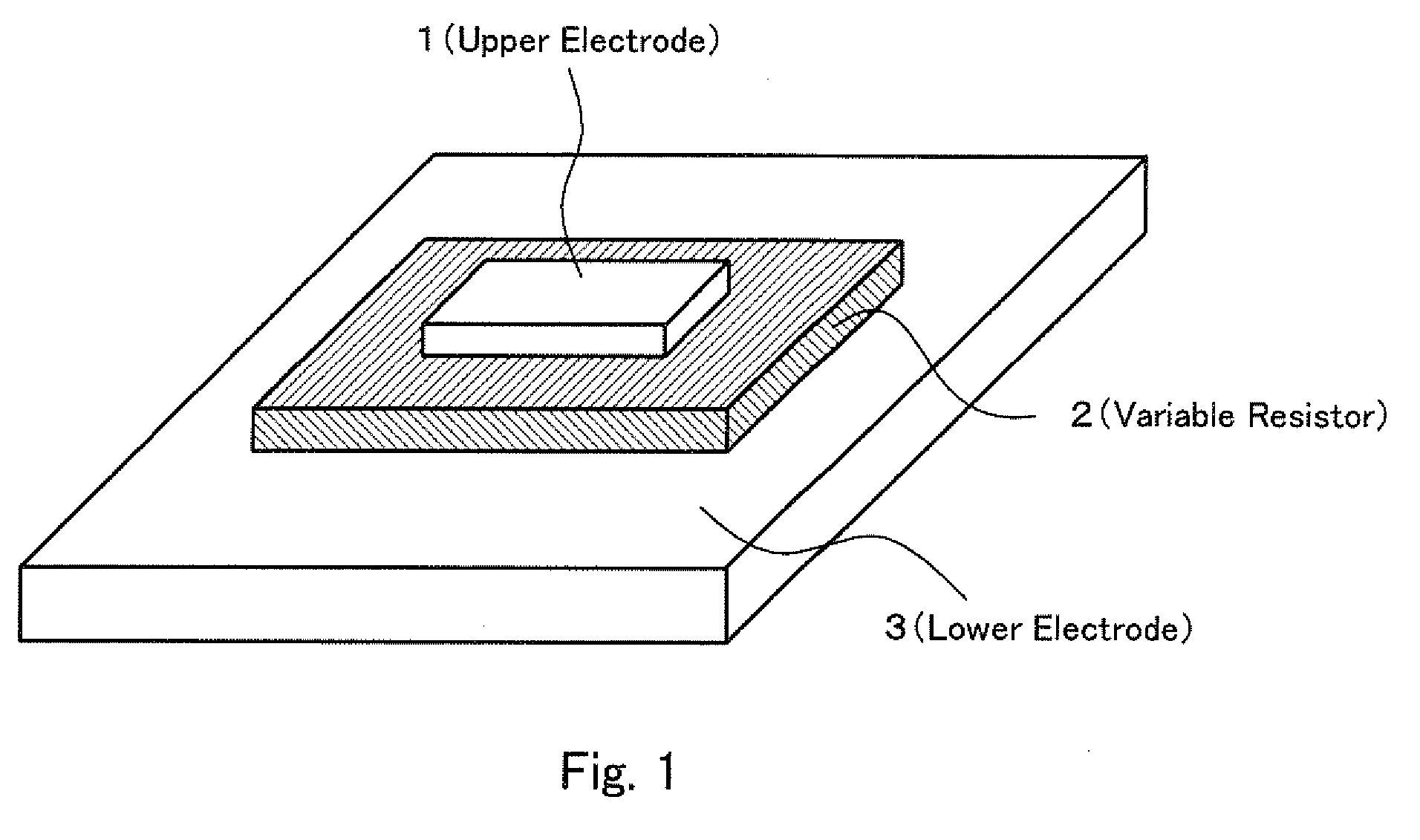
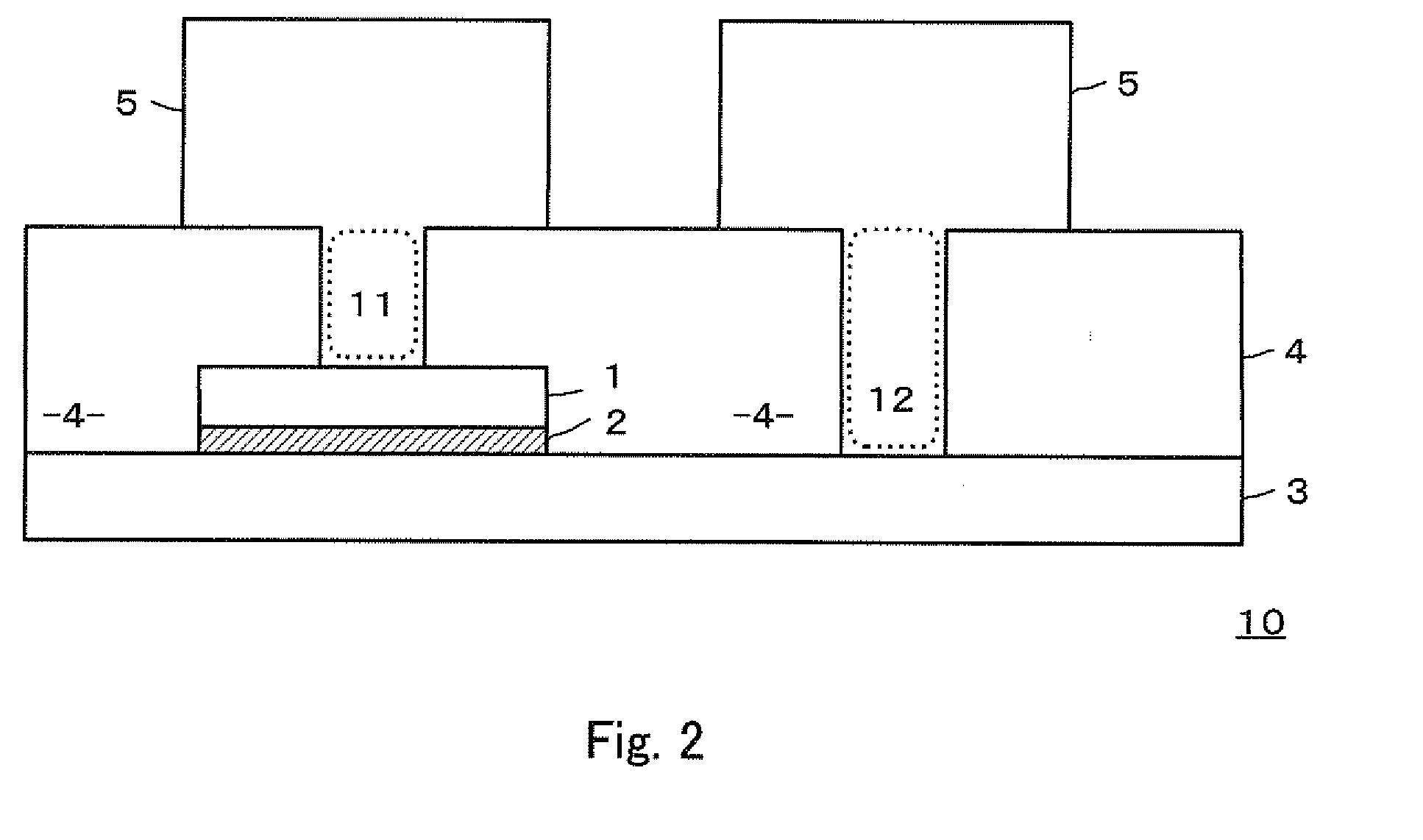
Provided is a variable resistance element capable of performing a stable resistance switching operation and having a favorable resistance value retention characteristics, comprising a variable resistor 2 sandwiched between a upper electrode 1 and lower electrode 3 and formed of titanium oxide or titanium oxynitride having a crystal grain diameter of 30 nm or less. When the variable resistance 2 is formed under the substrate temperature of 150° C. to 500° C., an anatase-type crystal having a crystal grain diameter of 30 nm or less is formed. Since the crystalline state of the variable resistor changes by applying a voltage pulse and the resistance value changes, no forming process is required. Moreover, it is possible to perform a stable resistance switching operation and obtain an excellent effect that the resistance fluctuation is small even if the switching is repeated, or the variable resistance element is stored for a long time under a high temperature.
Owner:SHARP KK
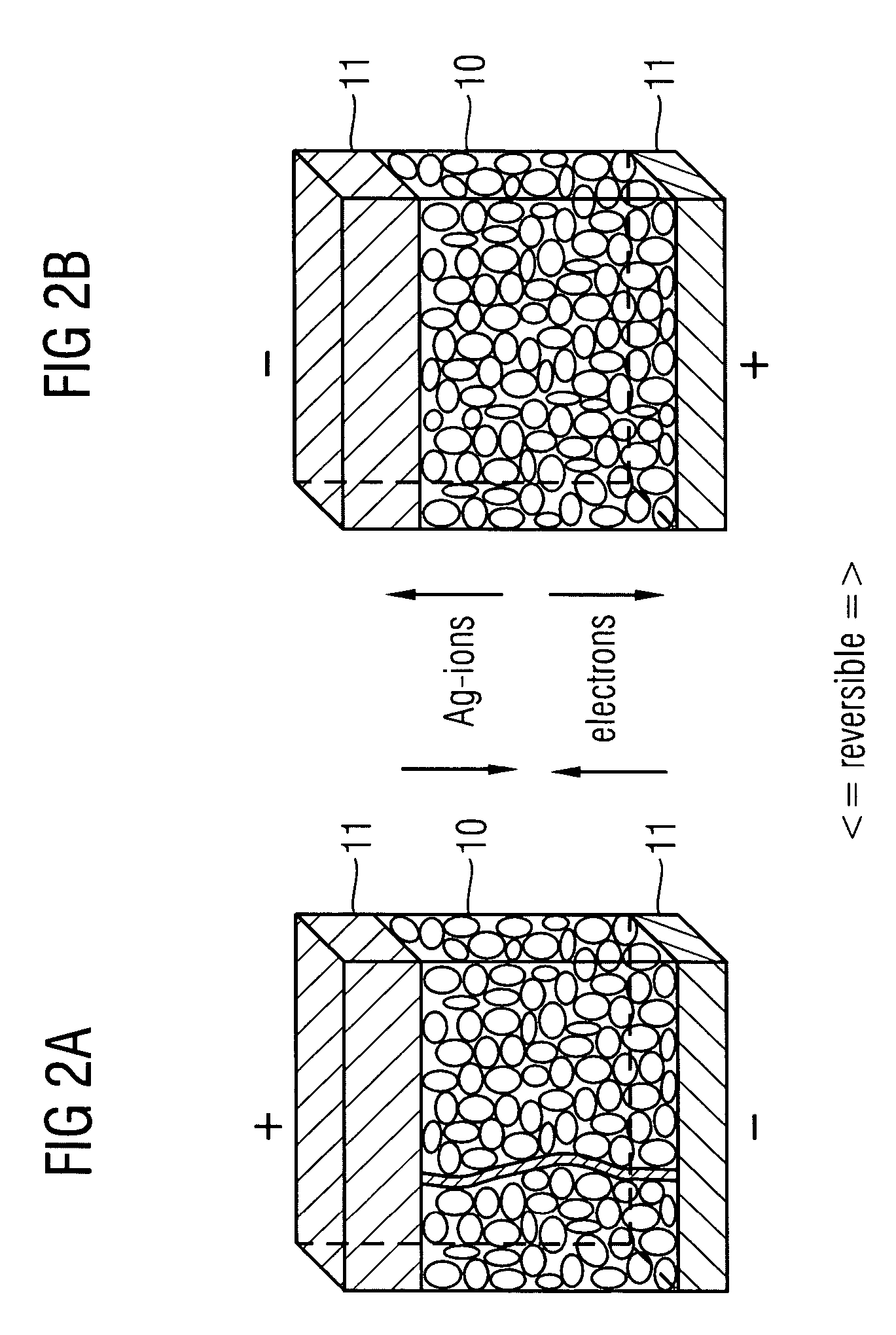
Method for operating a PMC memory cell and CBRAM memory circuit
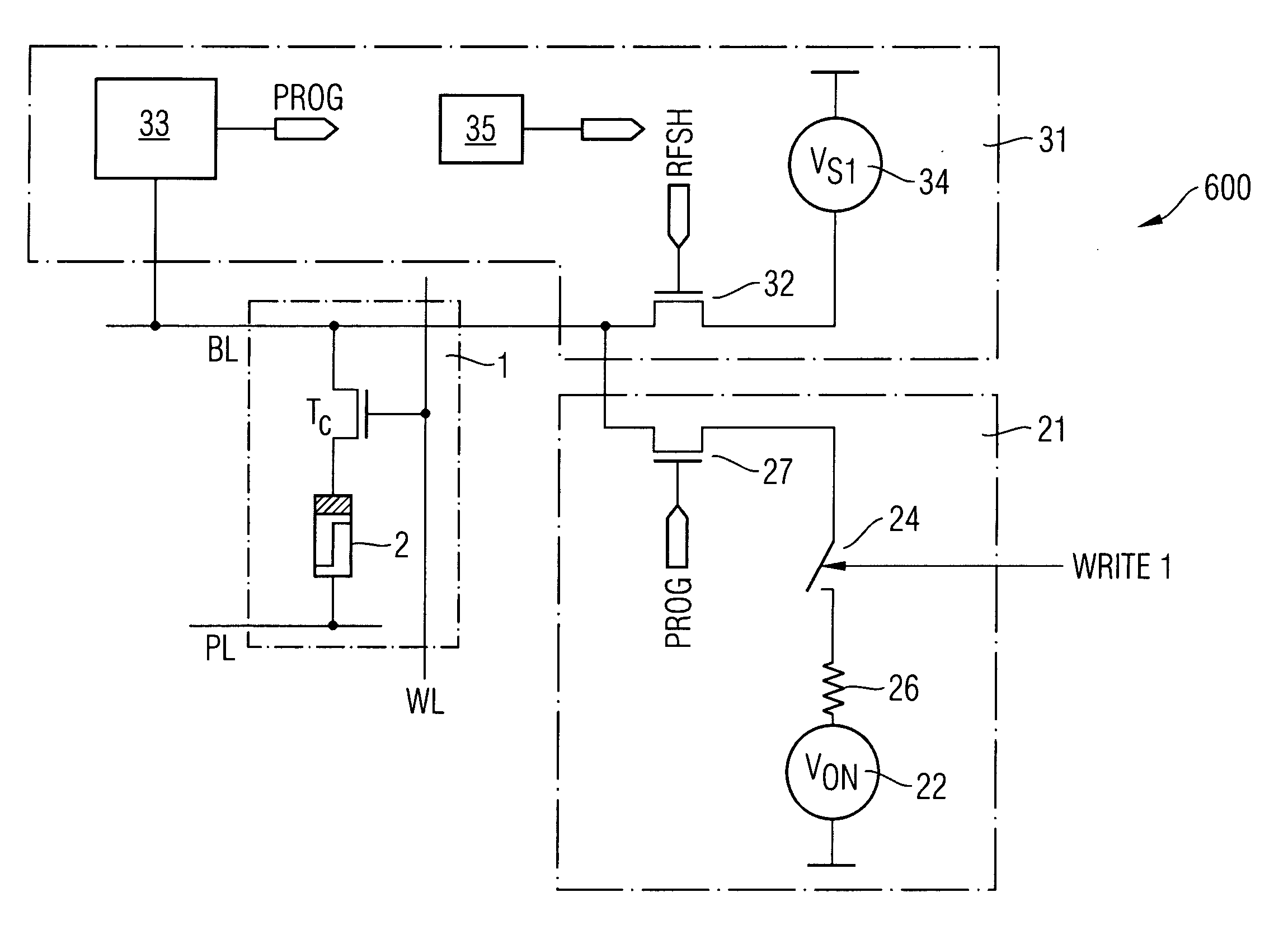
ActiveUS20060265548A1Avoid programmingReduce developmentRead-only memoriesDigital storageMemory circuitsComputer science
The present invention relates to a method for operating a PMC memory cell for use in a CBRAM memory array, wherein the PMC memory cell includes a solid electrolyte which is adapted to selectively develop and diminish a conductive path depending on an applied electrical field. The PMC memory cell is programmed to change to a programmed state by applying a programming voltage, and the PMC memory cell is erased to change to an erased state by applying an erase voltage. A refresh voltage is applied to the PMC memory cell at a predetermined time to stabilize the programmed state of the PMC memory cell, wherein the refresh voltage is selected such as that, while applying the refresh voltage, a programming of the PMC memory cell in the erased state to a programmed state is prevented, and that, by applying the refresh voltage, a stabilizing of the programmed state of the PMC memory cell is performed.
Owner:ADESTO TECH +1
Nonvolatile memory device and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20060065919A1Reduce voltageImprove data retentionTransistorSolid-state devicesExtinctionPeak value
To provide a nonvolatile memory device suppressing a reduction of a data retention characteristic even if charges injected and stored into a local area of a nitride film is redistributed to achieve a reduction of voltage, the nonvolatile memory device in which hot electrons are injected into the local area of the nitride film at one or both of source•drain regions side to store data in a memory transistor is satisfied with a standard for evaluating a film quality of the nitride film, the standard being defined by one of the followings: a density of the bond group of silicon and hydrogen being under 1×1021 cm−3; an extinction coefficient in an ultraviolet region at a wavelength of 240 nm being under 0.10 or the extinction coefficient in 230 nm being under 0.14; an optical energy, a peak wavelength of an luminance spectrum, or a peak energy thereof.
Owner:SONY CORP
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120187417A1Improve reliabilityAvoid changeTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialHemt circuits
A conventional DRAM needs to be refreshed at an interval of several tens of milliseconds to hold data, which results in large power consumption. In addition, a transistor therein is frequently turned on and off; thus, deterioration of the transistor is also a problem. These problems become significant as the memory capacity increases and transistor miniaturization advances. Another problem is that an increase in memory capacity leads to an increase in the area, despite an attempt at integration through advancement of transistor miniaturization. A transistor is provided which includes an oxide semiconductor and has a trench structure including a trench for a gate electrode and a trench for element isolation. In addition, a plurality of memory elements each including the transistor having a trench structure and including an oxide semiconductor is stacked in a semiconductor device, whereby the circuit area of the semiconductor device can be reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor memory
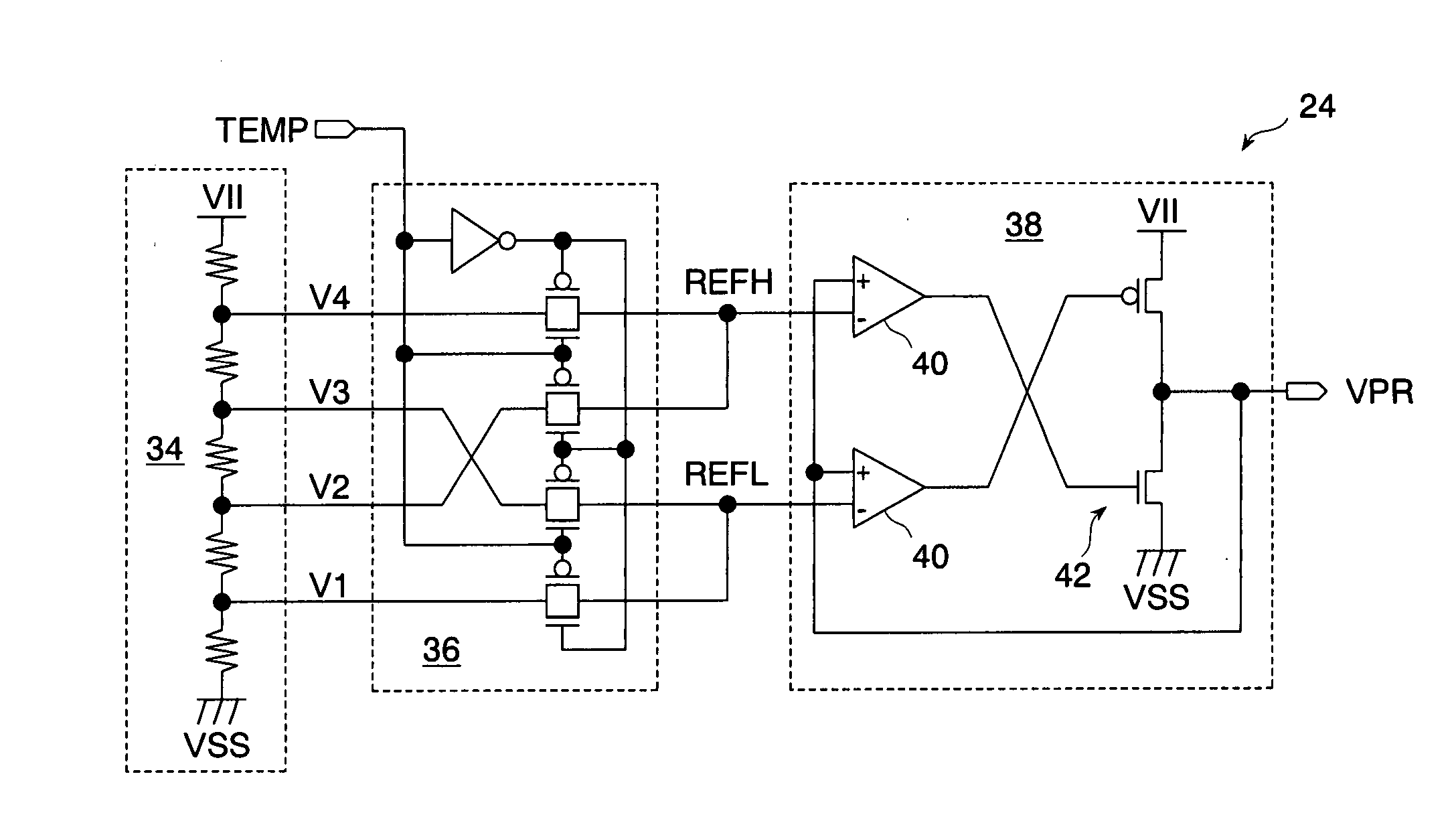
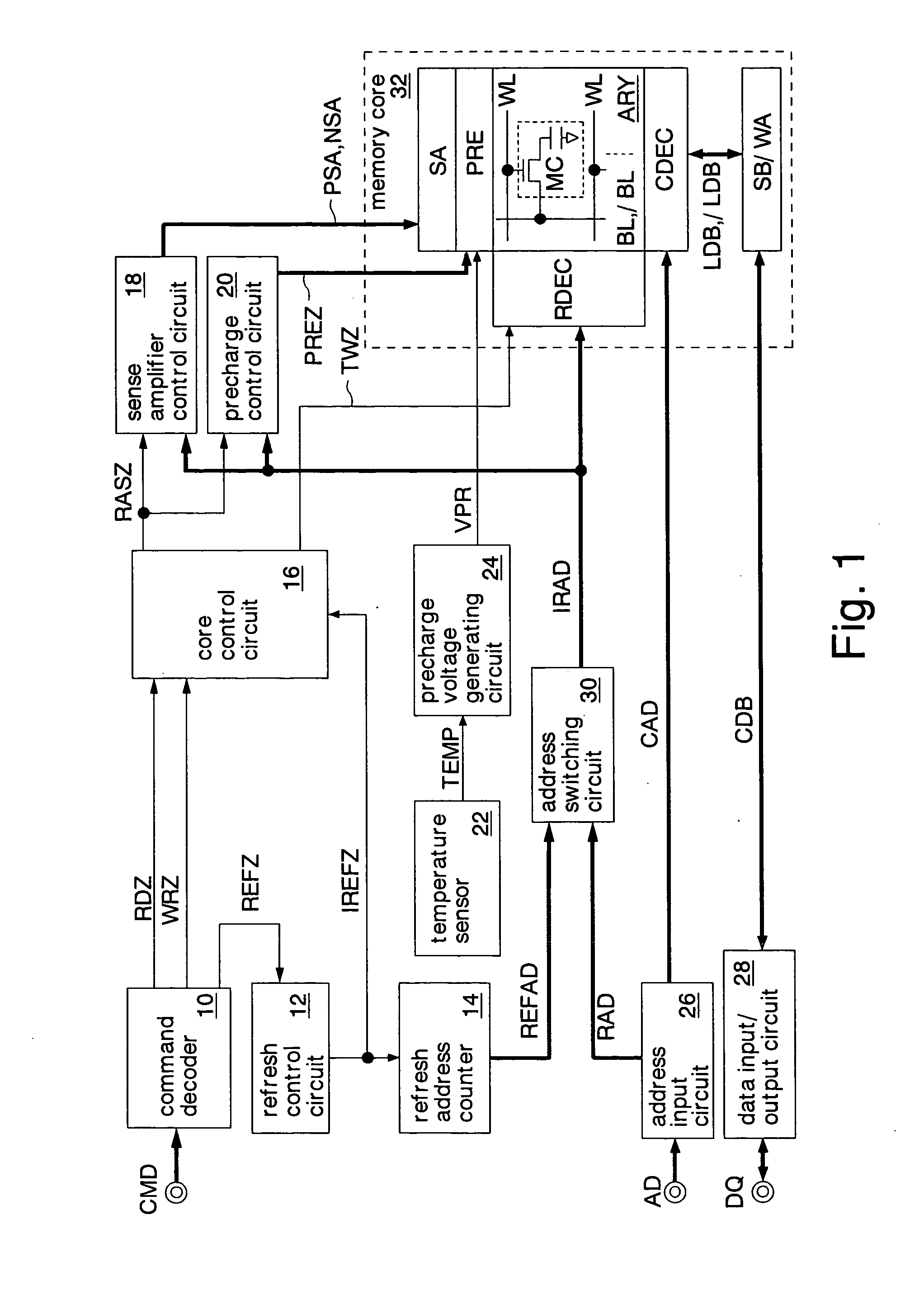
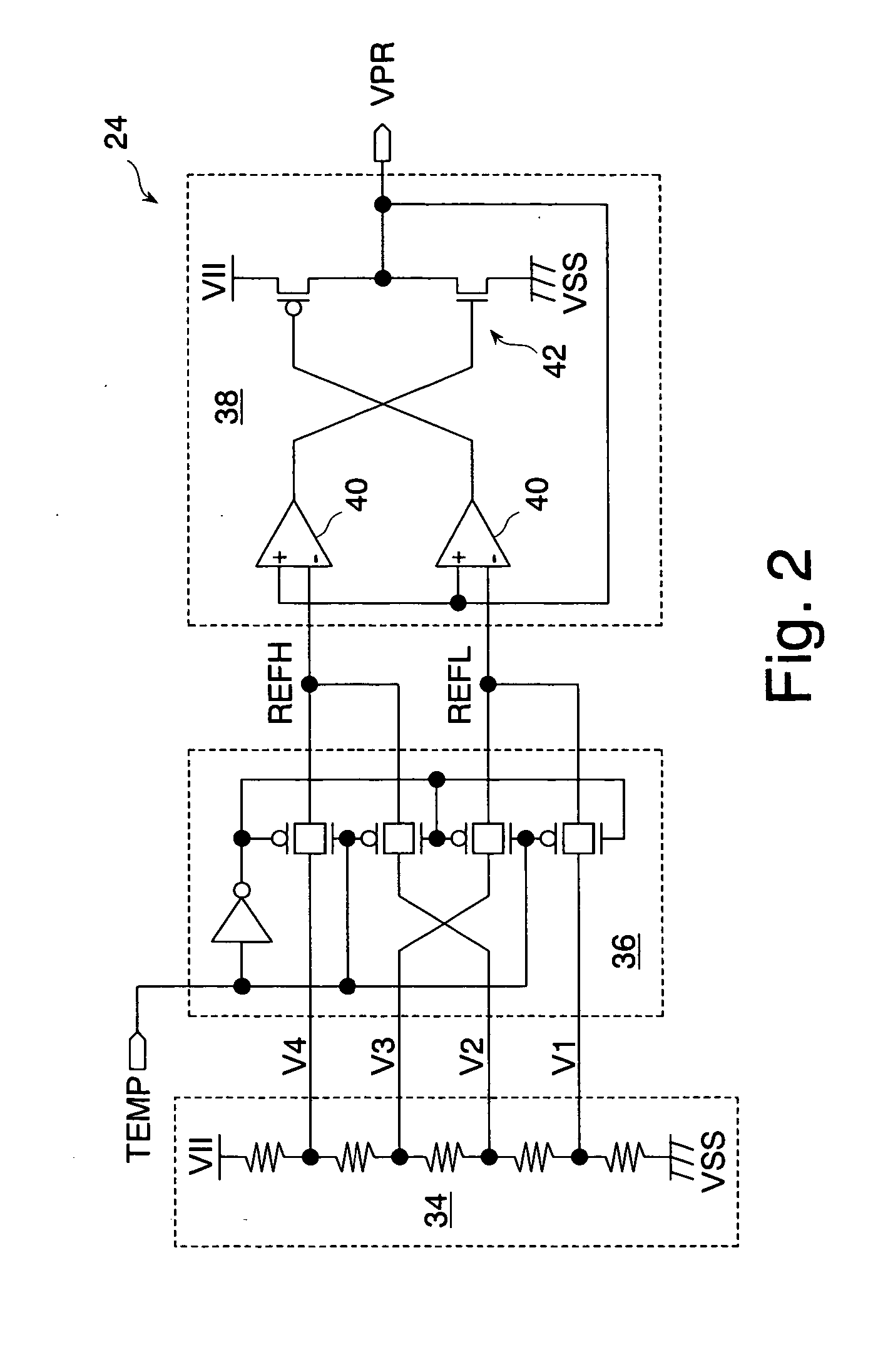
ActiveUS20070091703A1Easy switch controlPrevent circuit scaleDigital storageBit lineAudio power amplifier
A precharge voltage generating circuit outputs any of a plurality of kinds of precharge voltages in accordance with an ambient temperature. A precharge circuit supplies the precharge voltage to a bit line during the nonaccess of a dynamic memory cell. A sense amplifier amplifies a difference between the voltage of a data signal read from the dynamic memory cell onto the bit line and the supplied precharge voltage. The precharge voltage is altered in accordance with the ambient temperature, whereby the read margin of the sense amplifier can be changed, and the worst value of the data retaining time of the memory cell can be improved. As a result, the frequency of refreshing of the memory cell can be lowered, reducing power consumption and a standby current.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
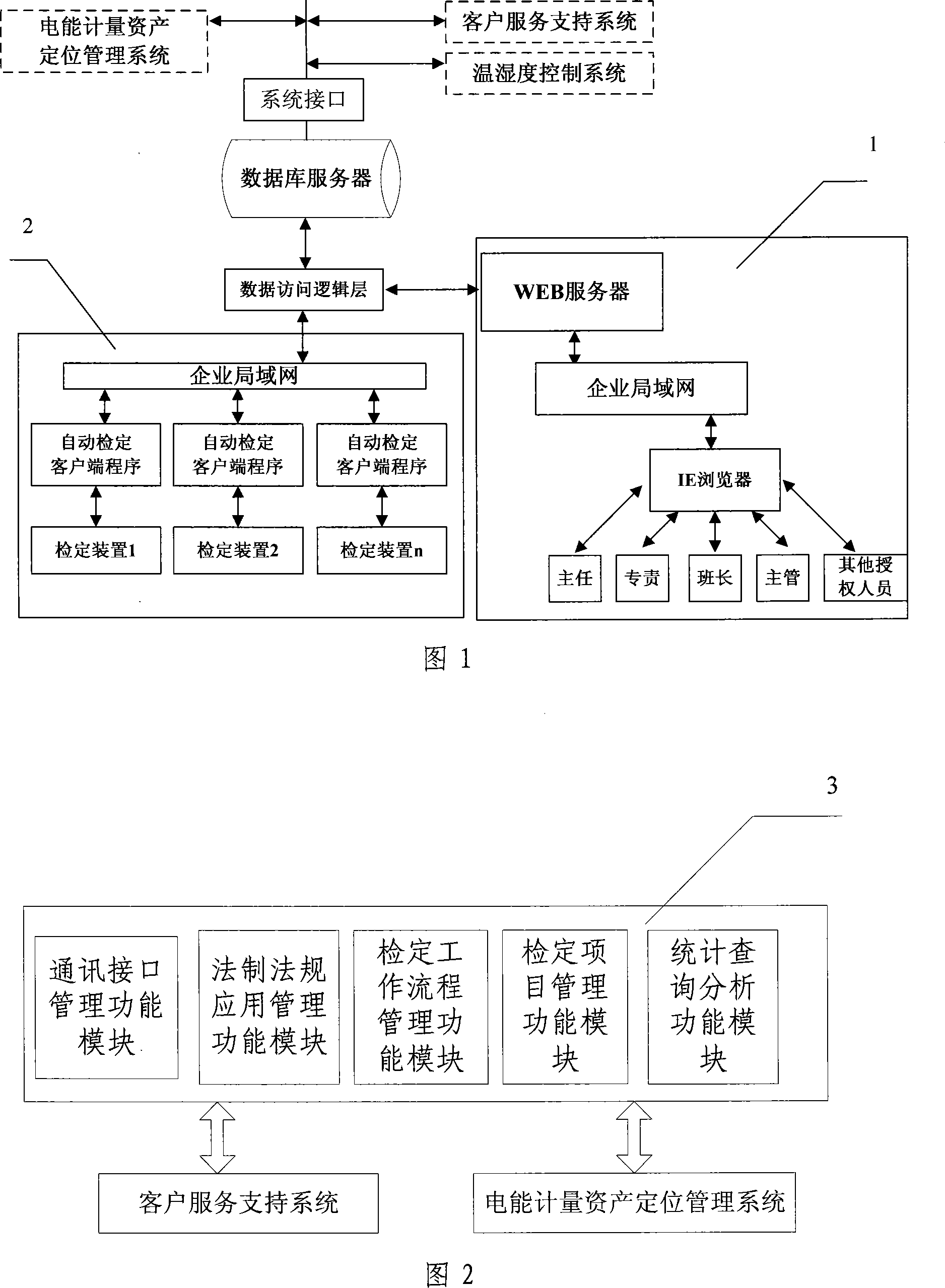
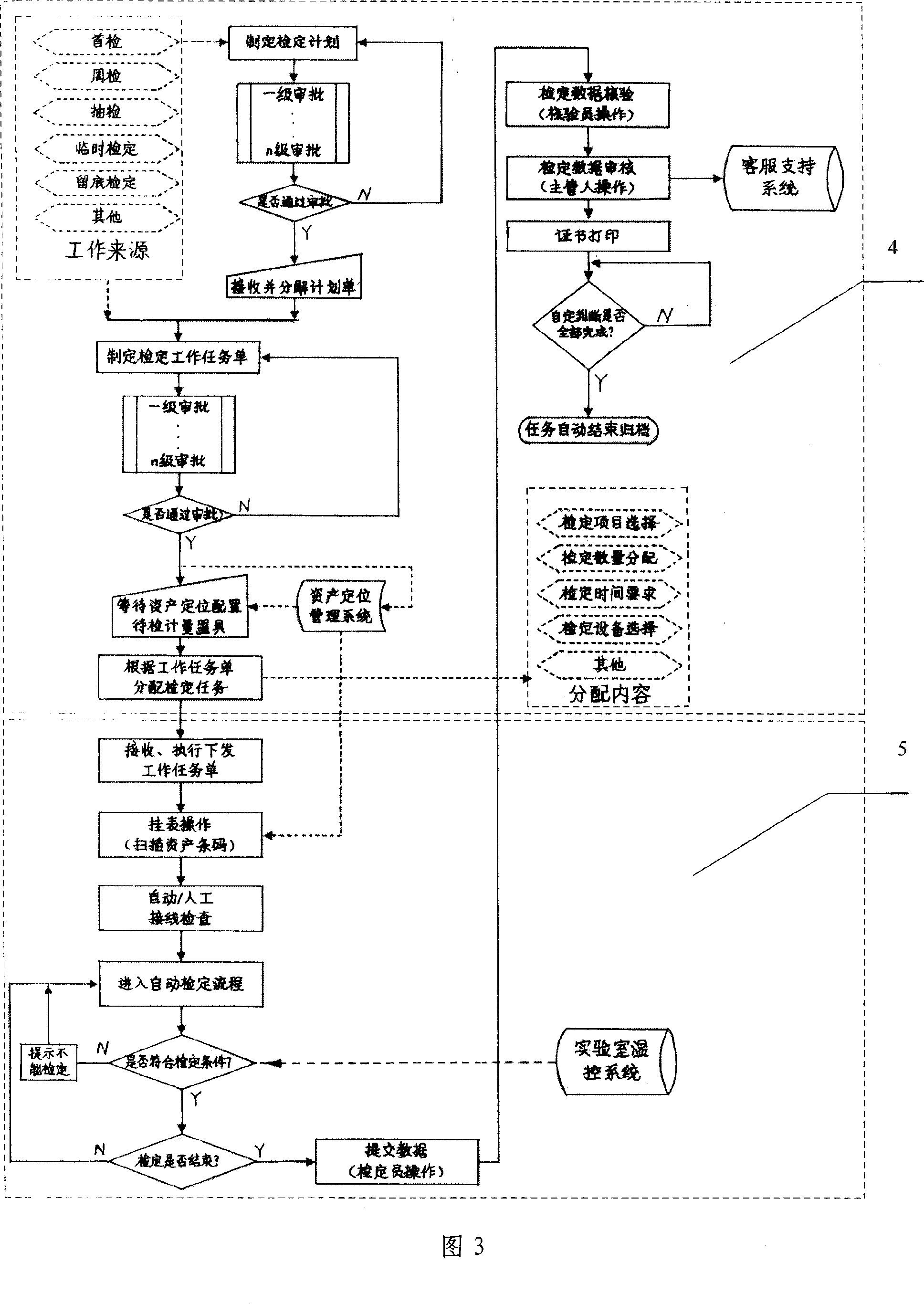
Electrical energy metering automatic verification integrative management platform system
The present invention provides a comprehensive managing platform system for automatically rating the electric energy measurement, and consists of a database server, a data accessing logic layer, an automatic rating user end, a WEB server, and a system interface part. The system adopts a C / S and B / S configuration coexisting net combining method, adopts a device communication unified interface design, and connects the technologies which are irrelevant to the device with different measuring devices. The present invention can realize the standardization, the unification, and the standardization of the electric energy measuring task by five function modules of the communication interface managing function, the legal system and law application managing function, the rating work flow managing function, the rating item managing function, and the statistic searching and analyzing function, thereby ensuring the multi-machine work by one person justly and rightly according to the law.
Owner:SHANXI YINXING POWER ELECTRONICS TECH
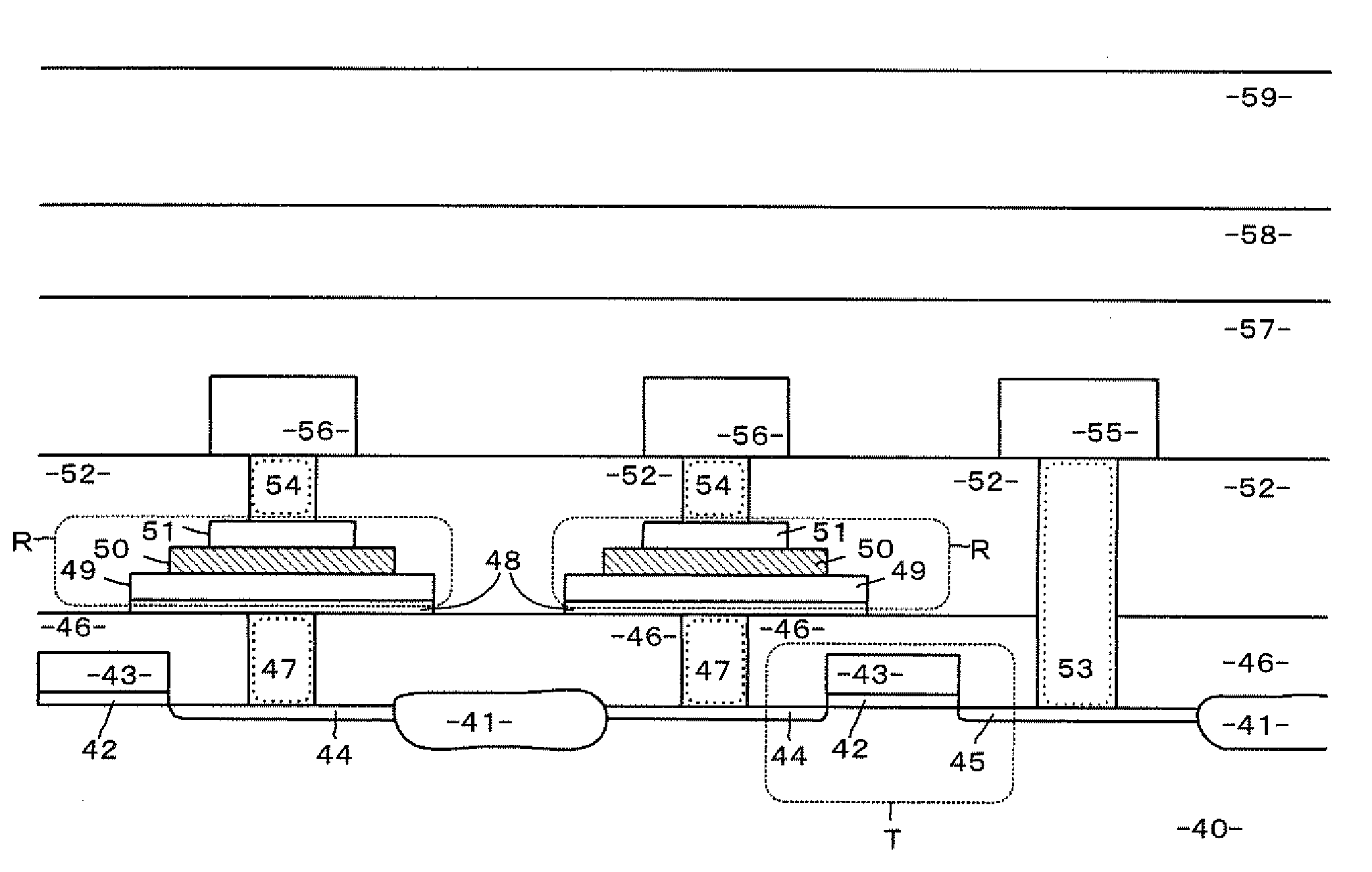
Semiconductor nonvolatile memory transistor and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS6133605AImprove reliabilityWrite speedTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenSilicon oxide
A MONOS nonvatile memory transistor includes a semiconductor substrate, a memory insulator film on the semiconductor substrate composed of a tunnel insulator film, a memory nitride film and a top oxide film, and a memory gate electrode on the memory insulator film. The tunnel insulator film is constituted of a silicon nitrided oxide film containing oxygen and nitrogen and an oxygen-rich silicon nitrided oxide film or a silicon oxide film to make the nitrogen content of the tunnel insulator film in the vicinity of its interface with the semiconductor substrate greater than its nitrogen content in the vicinity of its interface with the memory nitride film. By this, the barrier height of the tunnel insulator film to holes in the semiconductor substrate is lowered without lowering the barrier height thereof to holes captured on the memory nitride film side.
Owner:CITIZEN WATCH CO LTD
Oxide-nitride-oxide stack containing a plurality of oxynitrides layers
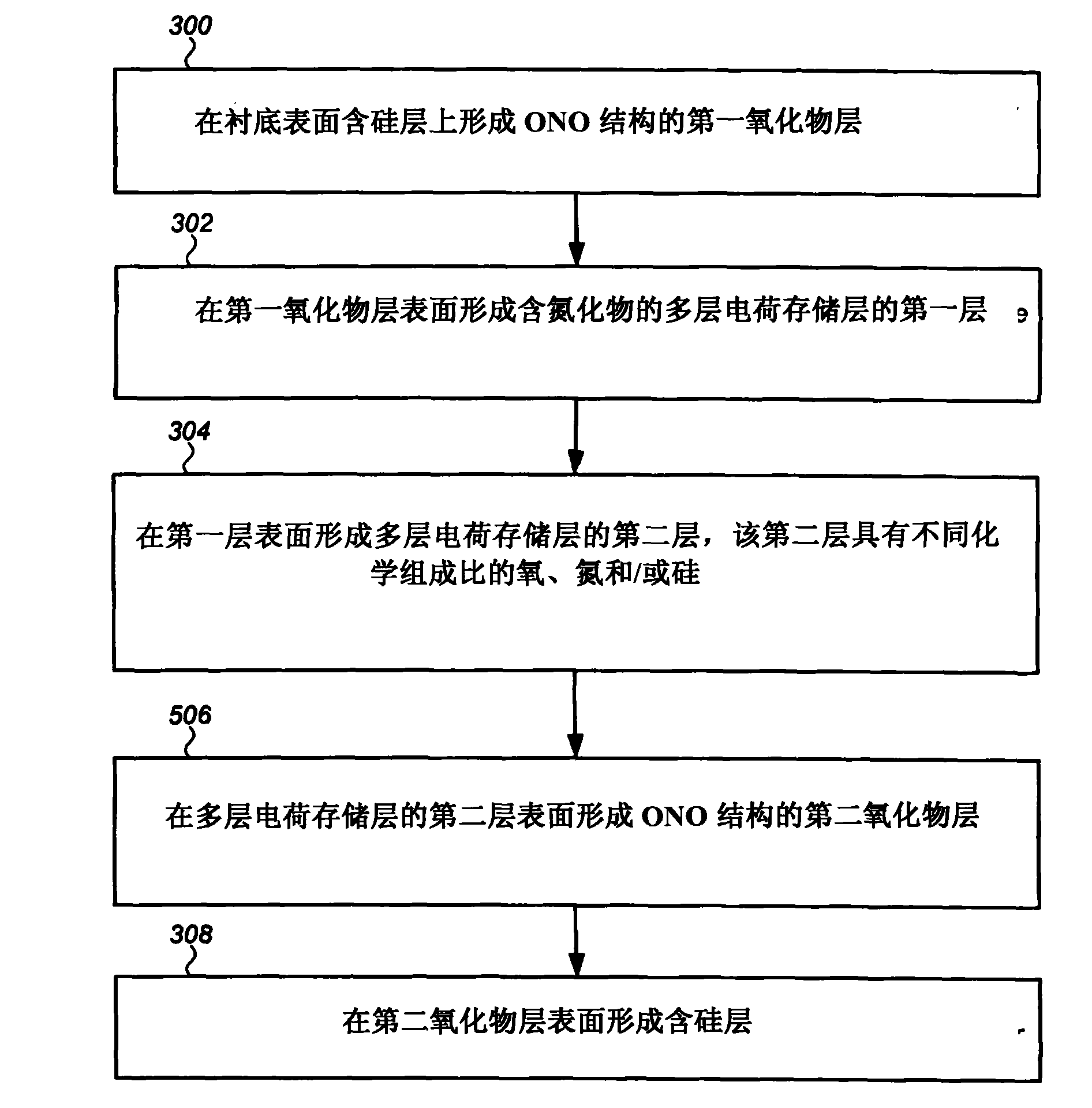
ActiveCN101859702AImprove data retentionHigh speedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingNitrogenSilicon oxide
The invention discloses a semiconductor device of an oxide-nitride-oxide (ONO) stack containing a plurality of charge storage layers and a forming method thereof. Generally, the method comprises the following steps of: firstly, forming a first oxide layer on an ONO structure; secondly, forming the plurality of charge storage layers containing nitride on the first oxide layer; and thirdly, forming a second oxide layer in the ONO structure on the plurality of charge storage layers. Preferably, each charge storage layer comprises at least two silicon oxynitride layers with two chemical constitutional ratios of oxygen, nitrogen and / or silicon. More preferably, the ONO structure is a part of a silicon-oxide-nitride-oxide-silicon (SONOS) structure, and the semiconductor device is an SONOS memory transistor.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120112191A1Increase in number of manufacturing step can be suppressedExtended maintenance periodSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesElectrical conductorMemory circuits
A data retention period in a semiconductor device or a semiconductor memory device is lengthened. The semiconductor device or the semiconductor memory includes a memory circuit including a first transistor including a first semiconductor layer and a first gate and a second transistor including a second semiconductor layer, a second gate, and a third gate The first semiconductor layer is formed at the same time as a layer including the second gate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
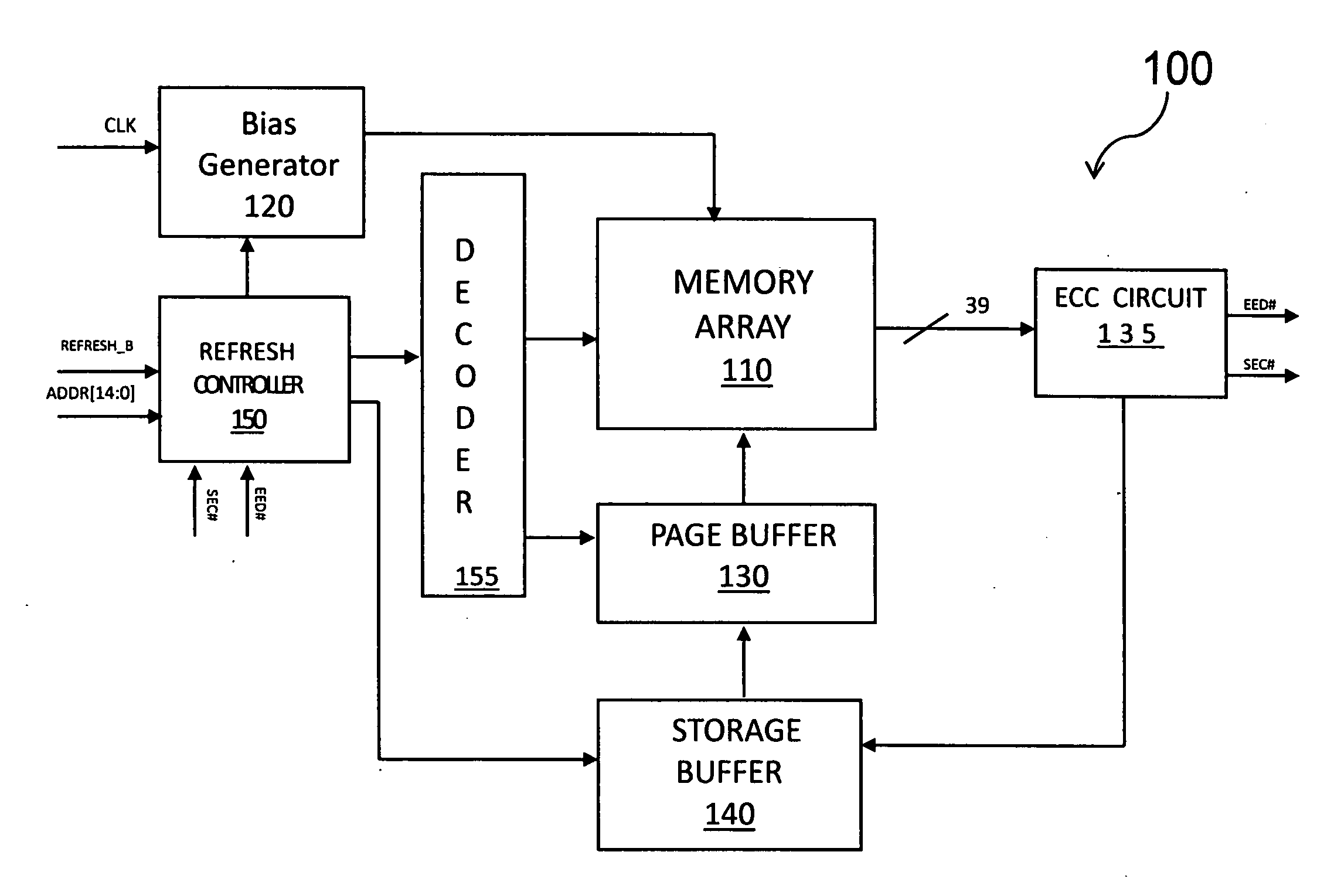
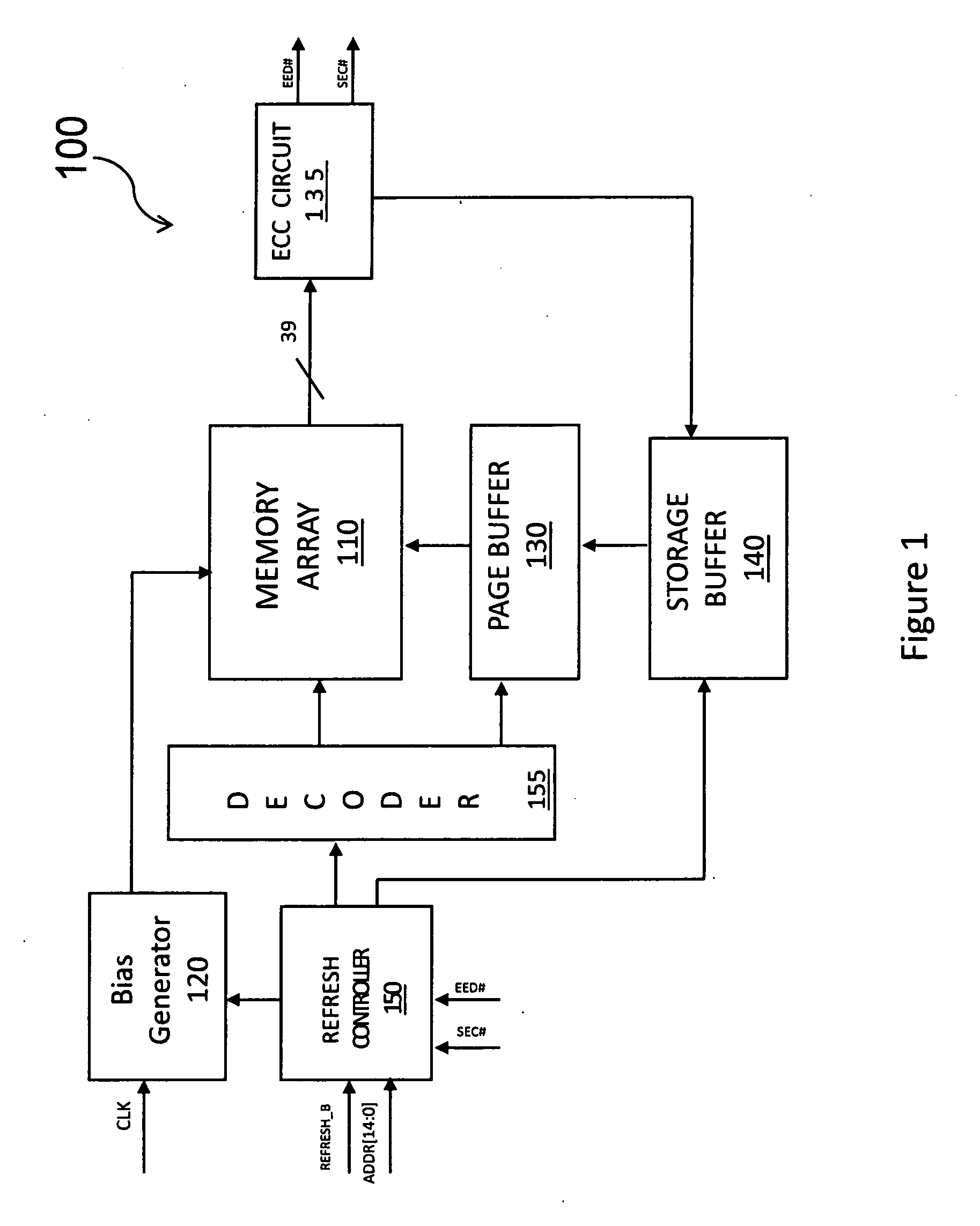
Automatic refresh for improving data retention and endurance characteristics of an embedded non-volatile memory in a standard CMOS logic process
ActiveUS20100205504A1Improve data retentionMinimizes refresh timeRead-only memoriesCode conversionCMOSData retention
A method for selectively refreshing data in a nonvolatile memory array based on failure type detected by an error correction code. If the page is determined to be error-free, no refresh operation takes place. Otherwise, if single-error words on a page contain erased and programmed bit errors, then a refresh operation, consisting of an erase and program, takes place. The erase operation is skipped if single-error words on a page solely contain a program failure.
Owner:MOSYS INC
Disk drive data caching using a multi-tiered memory
ActiveUS8977803B2Limit usable lifeReduce dataMemory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTEngineeringTerm memory
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor memory with deuterated materials
InactiveUS6884681B1Improve data retentionReduce charging lossTransistorSolid-state devicesHydrogenInter layer
A method for manufacturing a MirrorBit® Flash memory includes providing a semiconductor substrate and successively depositing a first insulating layer, a charge-trapping layer, and a second insulating layer. First and second bitlines are implanted and wordlines are formed before completing the memory. Spacers are formed between the wordlines and an inter-layer dielectric layer is formed over the wordlines. One or more of the second insulating layer, wordlines, spacers, and inter-layer dielectric layers are deuterated, replacing hydrogen bonds with deuterium, thus improving data retention and substantially reducing charge loss.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
Low Power Retention Random Access Memory with Error Correction on Wake-Up
ActiveUS20120324314A1Reduce power consumptionAverage power consumptionCode conversionSingle error correctionRandom access memoryOperation mode
Solid-state random access memory including error correction capability applied to memory arrays entering and exiting a data retention mode. Error correction coding of the data to be retained is performed upon determining that a portion of the memory is to enter data retention mode; the parity bits (i.e., bits in addition to those required for storage of the payload) are stored in available memory cells within or external to the retention domain. Upon exit from retention mode, the code words are decoded to correct any errors, and the payload data are returned to the original cells. Error correction encoding and decoding is not performed in the normal operating mode.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
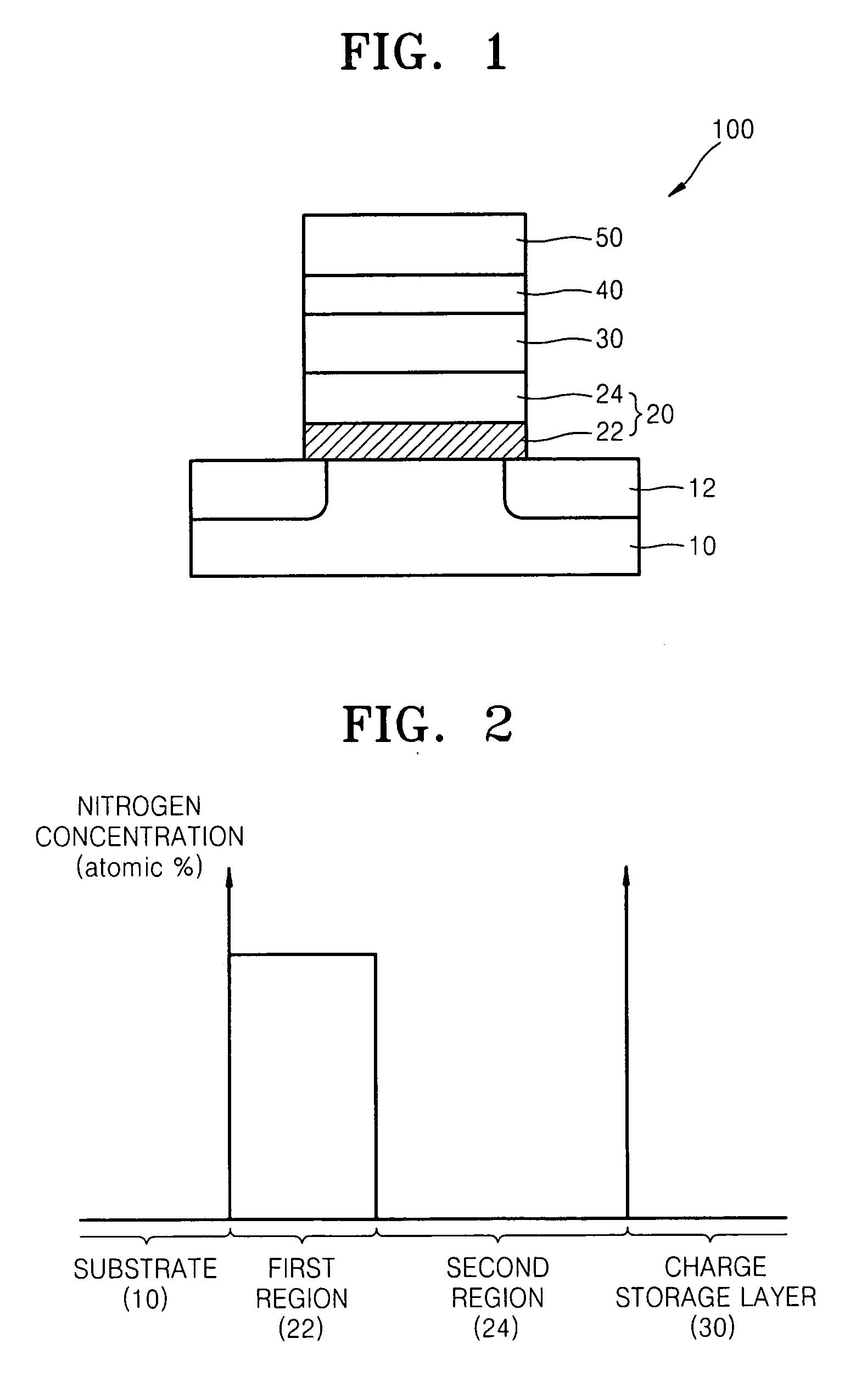
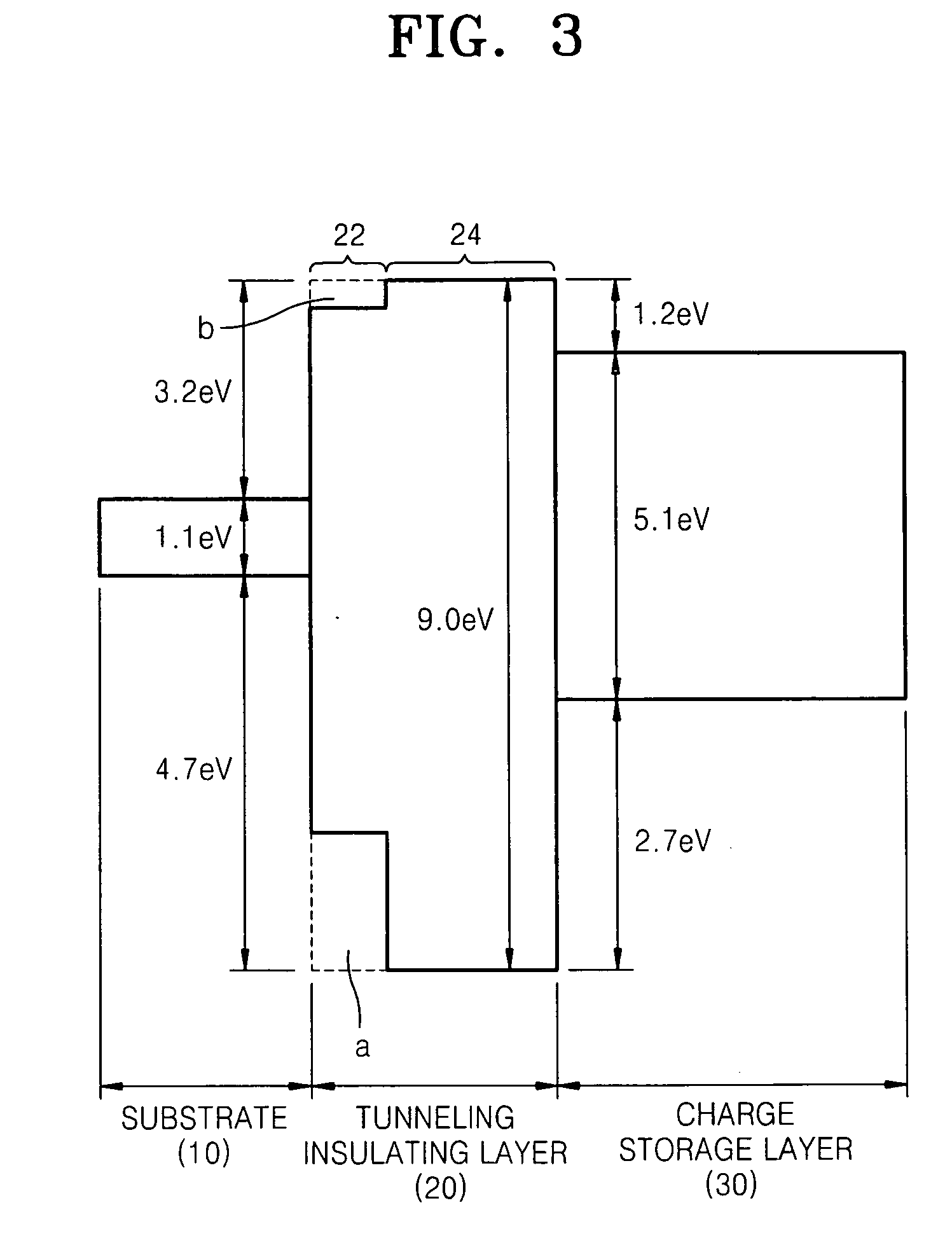
Tunneling insulating layer, flash memory device including the same, memory card and system including the flash memory device, and methods of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090134450A1High speedImprove data retentionTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInsulation layerNitrogen
Provided is a tunneling insulating layer, a flash memory device including the same that increases a program / erase operation speed of the flash memory device and has improved data retention in order to increase reliability of the flash memory device, a memory card and system including the flash memory device, and methods of manufacturing the same. A tunneling insulating layer may include a first region and a second region on the first region, wherein the first region has a first nitrogen atomic percent, the second region has a second nitrogen atomic percent, and the second nitrogen atomic percent is less than the first nitrogen atomic percent. The flash memory device according to example embodiments may include a substrate including source and drain regions and a channel region between the source and drain regions, the tunneling insulating layer on the channel region, a charge storage layer on the tunneling insulating layer, a blocking insulation layer on the charge storage layer, and a gate electrode on the blocking insulation layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
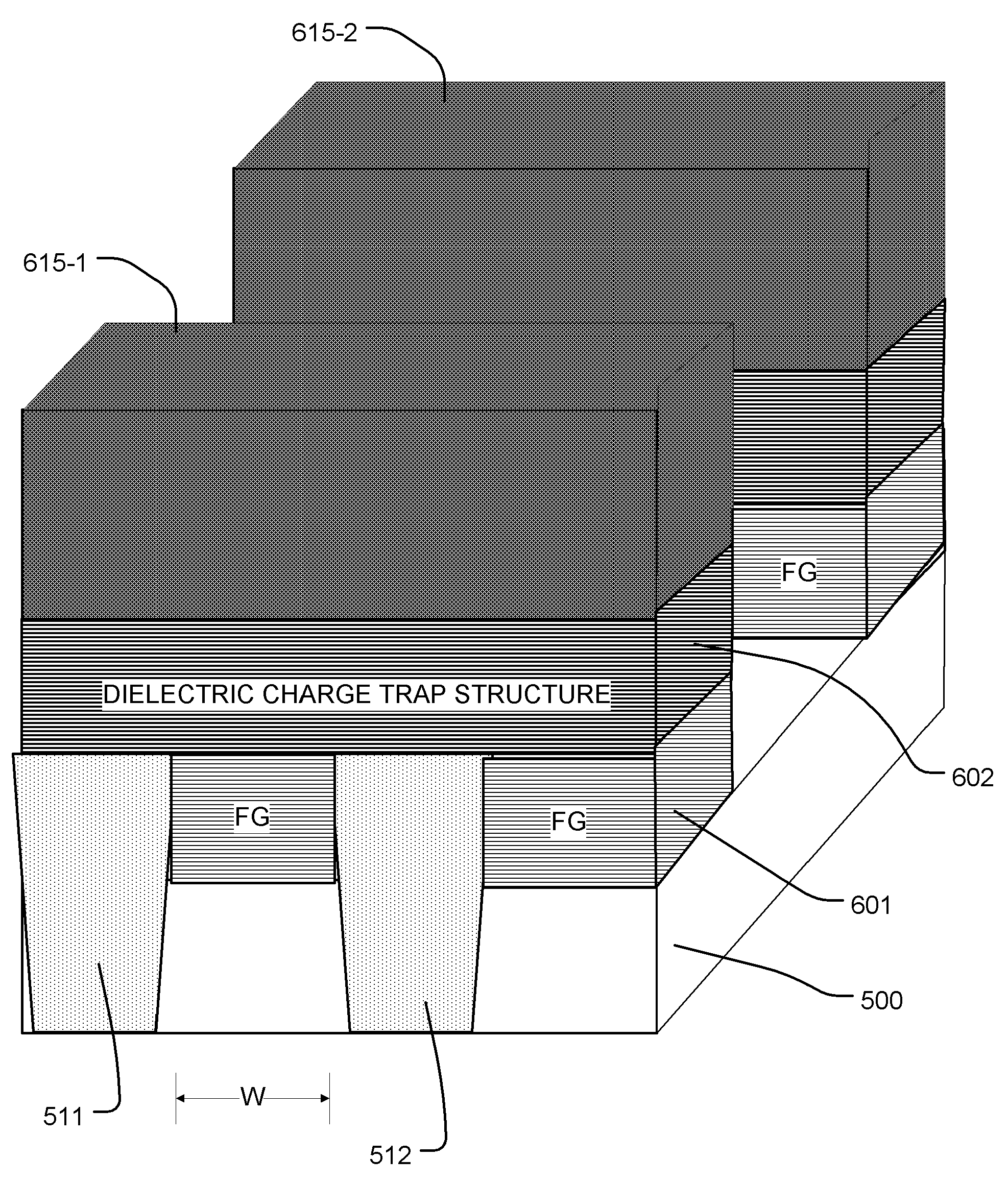
Floating gate memory device with interpoly charge trapping structure
ActiveUS8068370B2Reduce distractionsImprove data retentionTransistorSolid-state devicesPower flowElectrical conductor
A charge trapping floating gate is described with asymmetric tunneling barriers. The memory cell includes a source region and a drain region separated by a channel region. A first tunneling barrier structure is disposed above the channel region. A floating gate is disposed above the first tunneling barrier structure covering the channel region. A second tunneling barrier is disposed above the floating gate. A dielectric charge trapping structure disposed above the second tunneling barrier and a blocking dielectric structure is disposed above the charge trapping structure. A top conductive layer disposed above the top dielectric structure acts as a gate. The second tunneling barrier is a more efficient conductor of tunneling current, under bias conditions applied for programming and erasing the memory cell, than the first tunneling barrier structure.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Methods of fabricating ferroelectric devices
ActiveUS20080020489A1Improved ferroelectricImprove electrical characteristicsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptoelectronicsImpurity
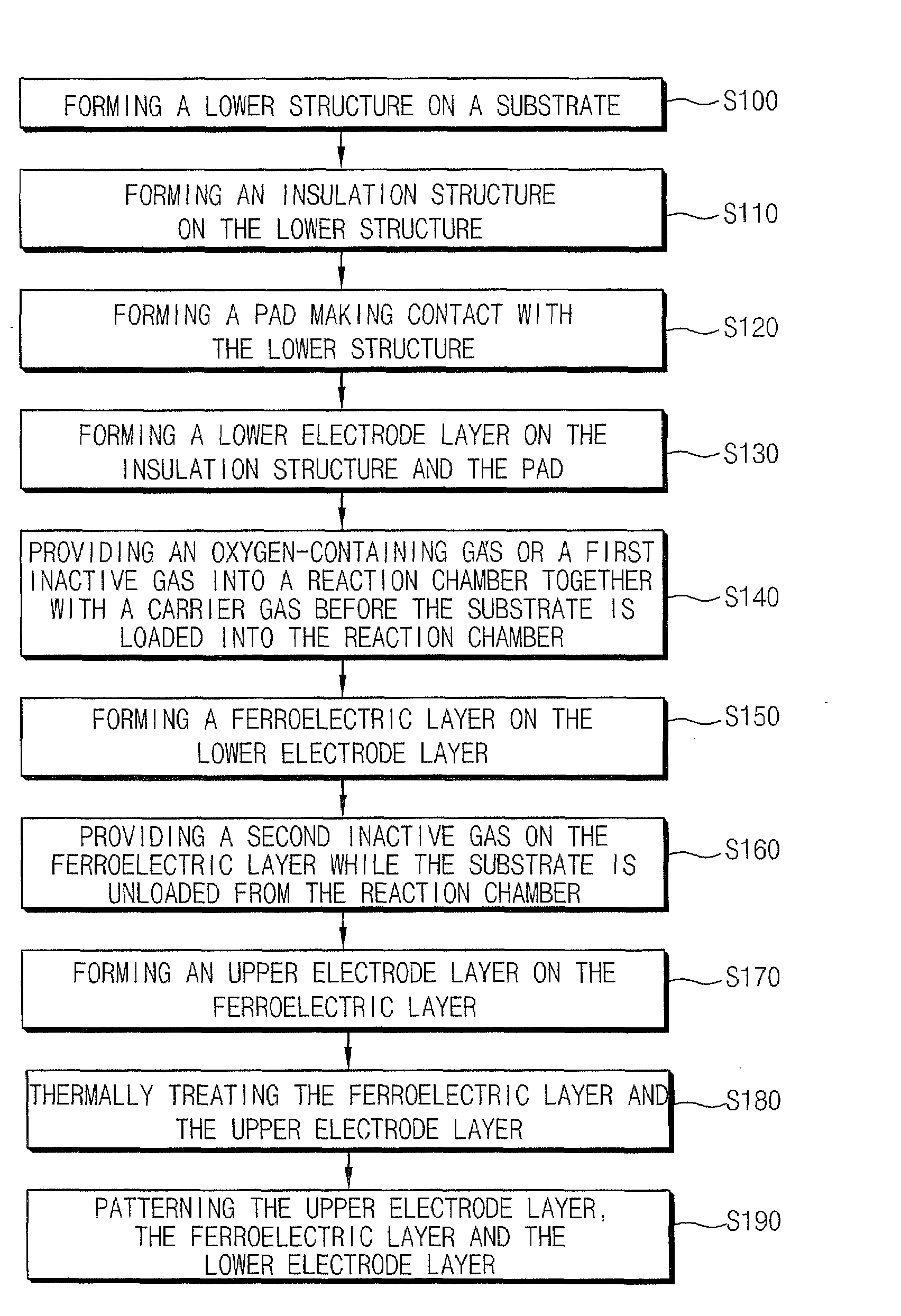
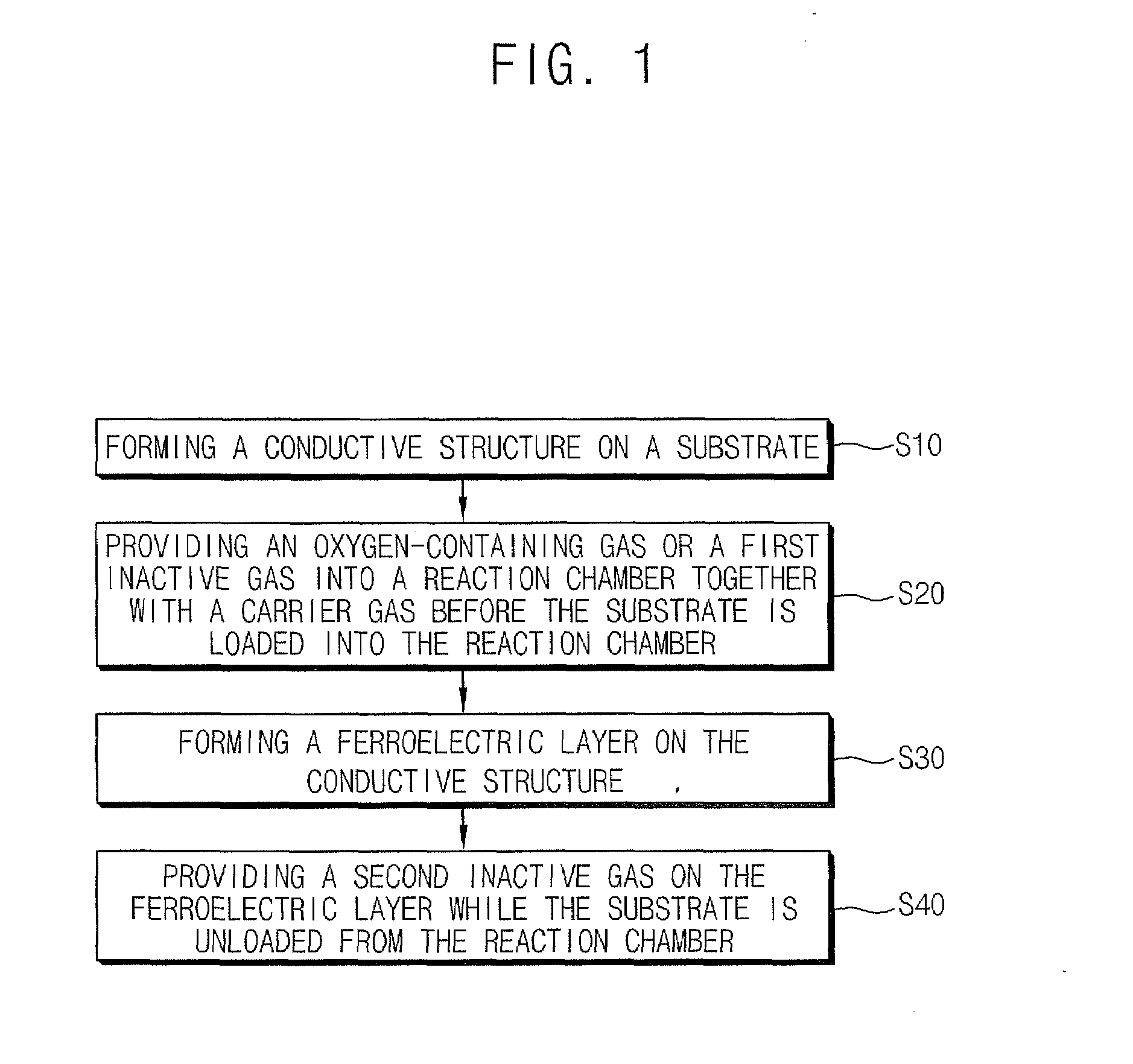
A method of fabricating a ferroelectric device includes forming a ferroelectric layer on a substrate in a reaction chamber. An inactive gas is provided into the reaction chamber while unloading the substrate therefrom to thereby substantially inhibit formation of an impurity layer on the ferroelectric layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS8779432B2Improve data retentionReduce power consumptionTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceMiniaturization
A conventional DRAM needs to be refreshed at an interval of several tens of milliseconds to hold data, which results in large power consumption. In addition, a transistor therein is frequently turned on and off; thus, deterioration of the transistor is also a problem. These problems become significant as the memory capacity increases and transistor miniaturization advances. A transistor is provided which includes an oxide semiconductor and has a trench structure including a trench for a gate electrode and a trench for element isolation. Even when the distance between a source electrode and a drain electrode is decreased, the occurrence of a short-channel effect can be suppressed by setting the depth of the trench for the gate electrode as appropriate.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com