Patents
Literature
253 results about "Charge loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
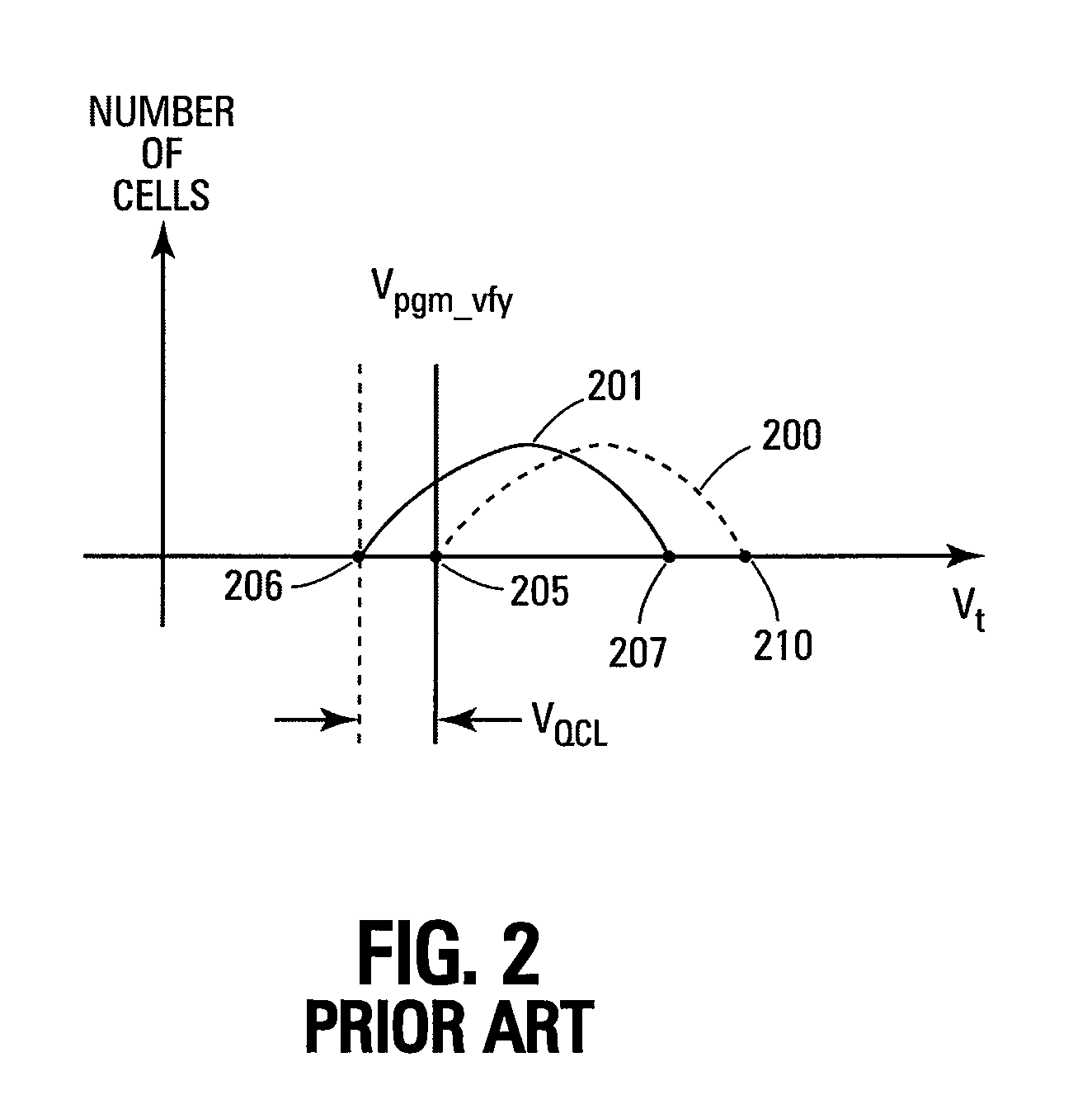
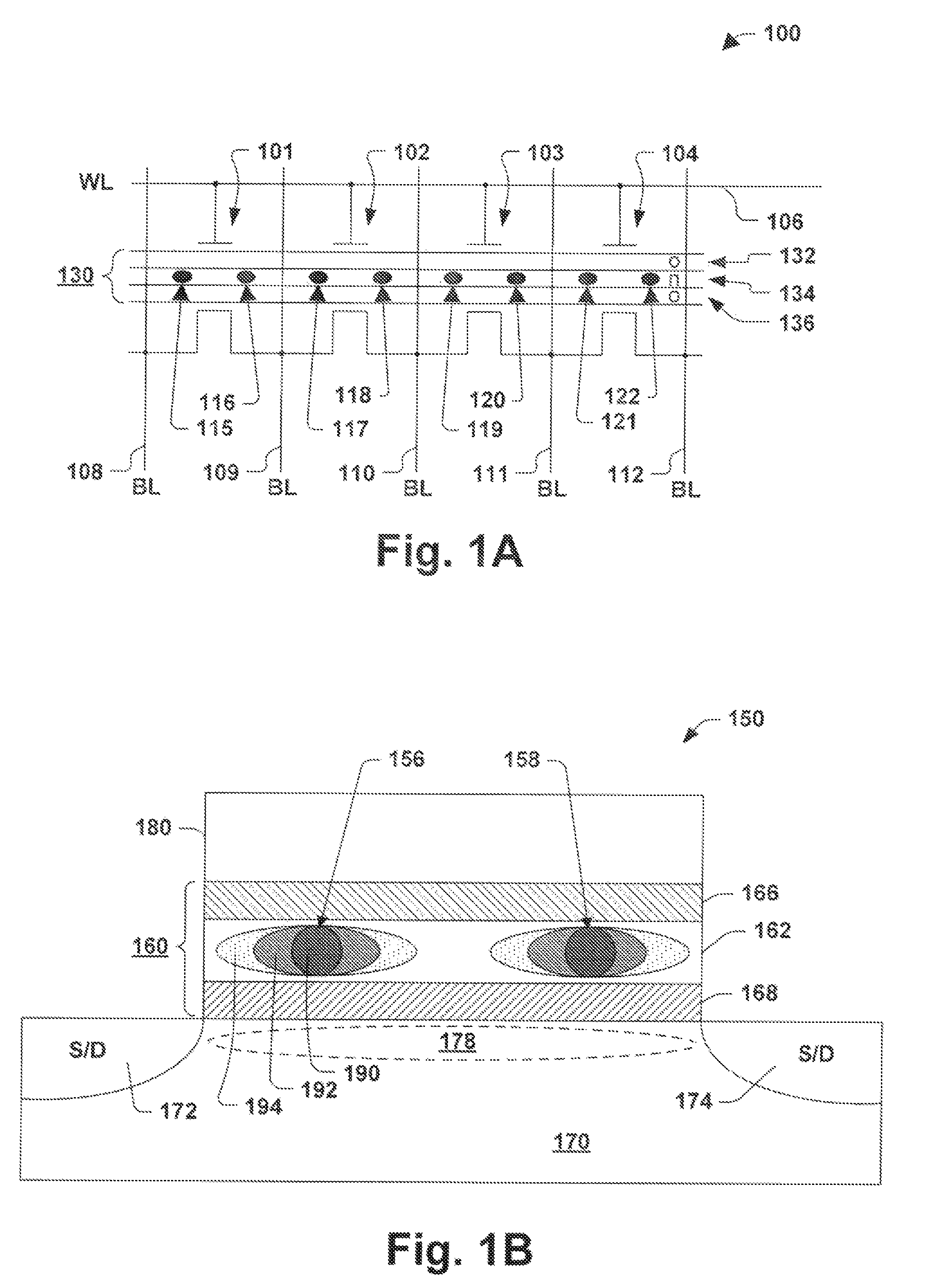
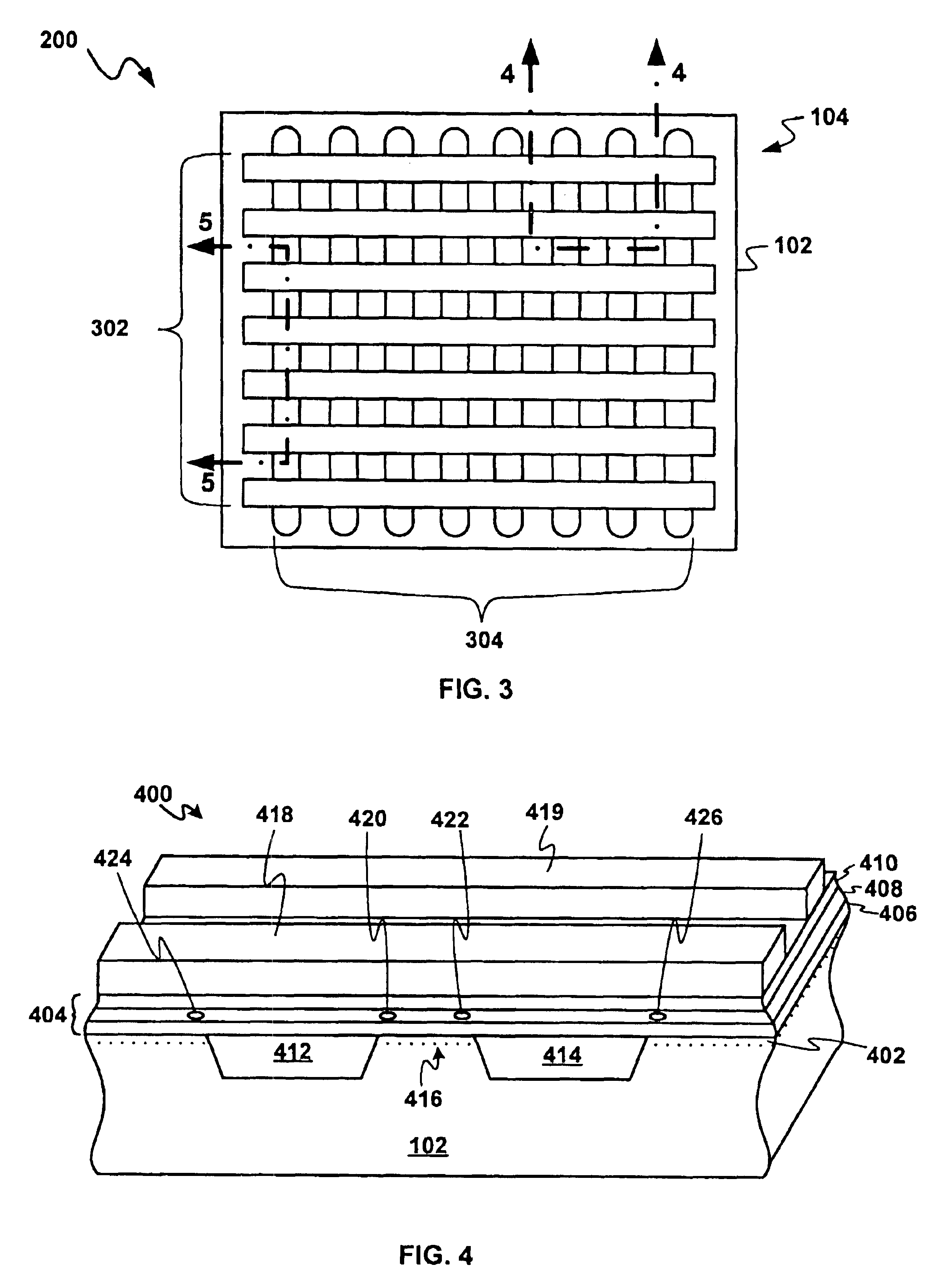
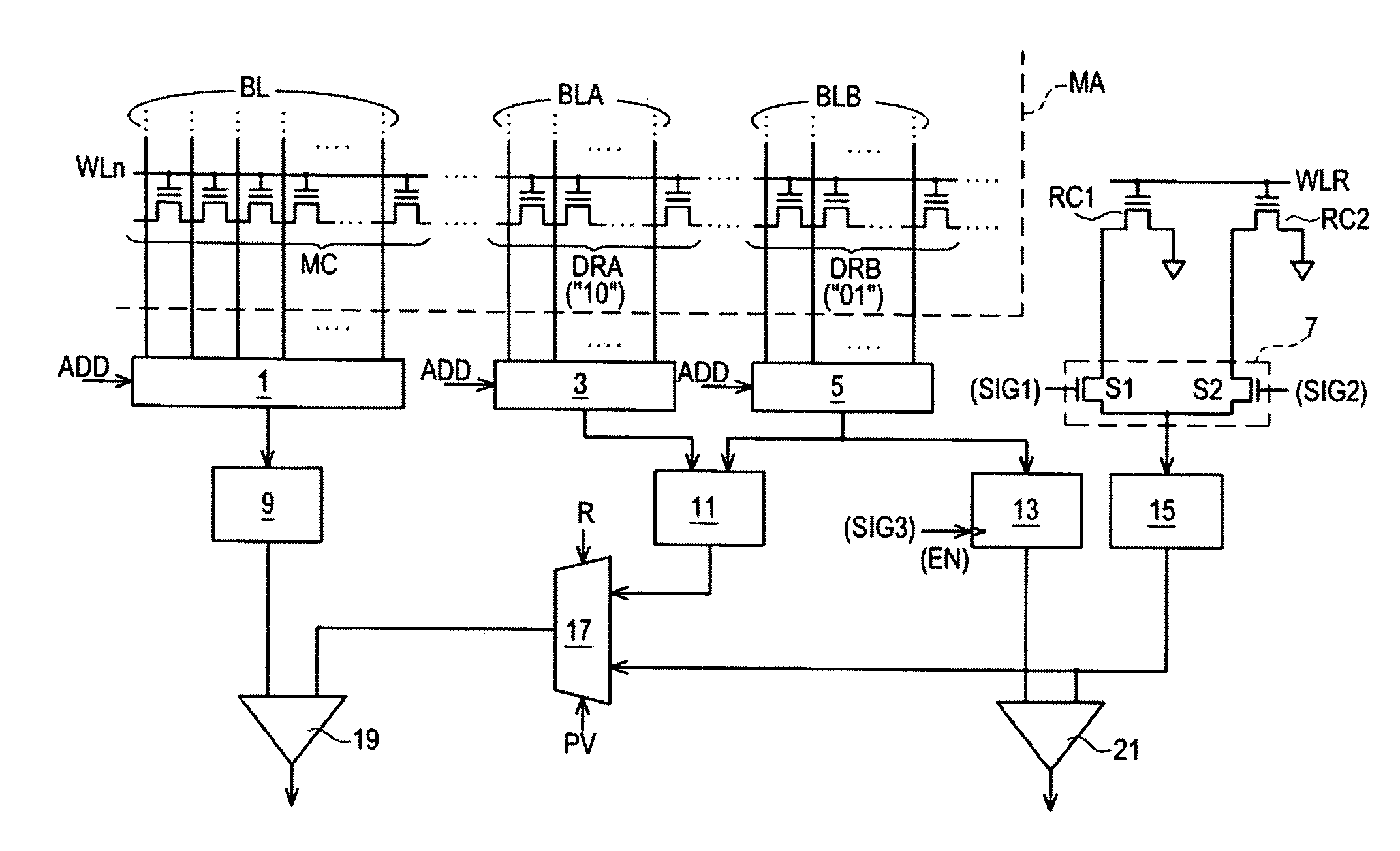
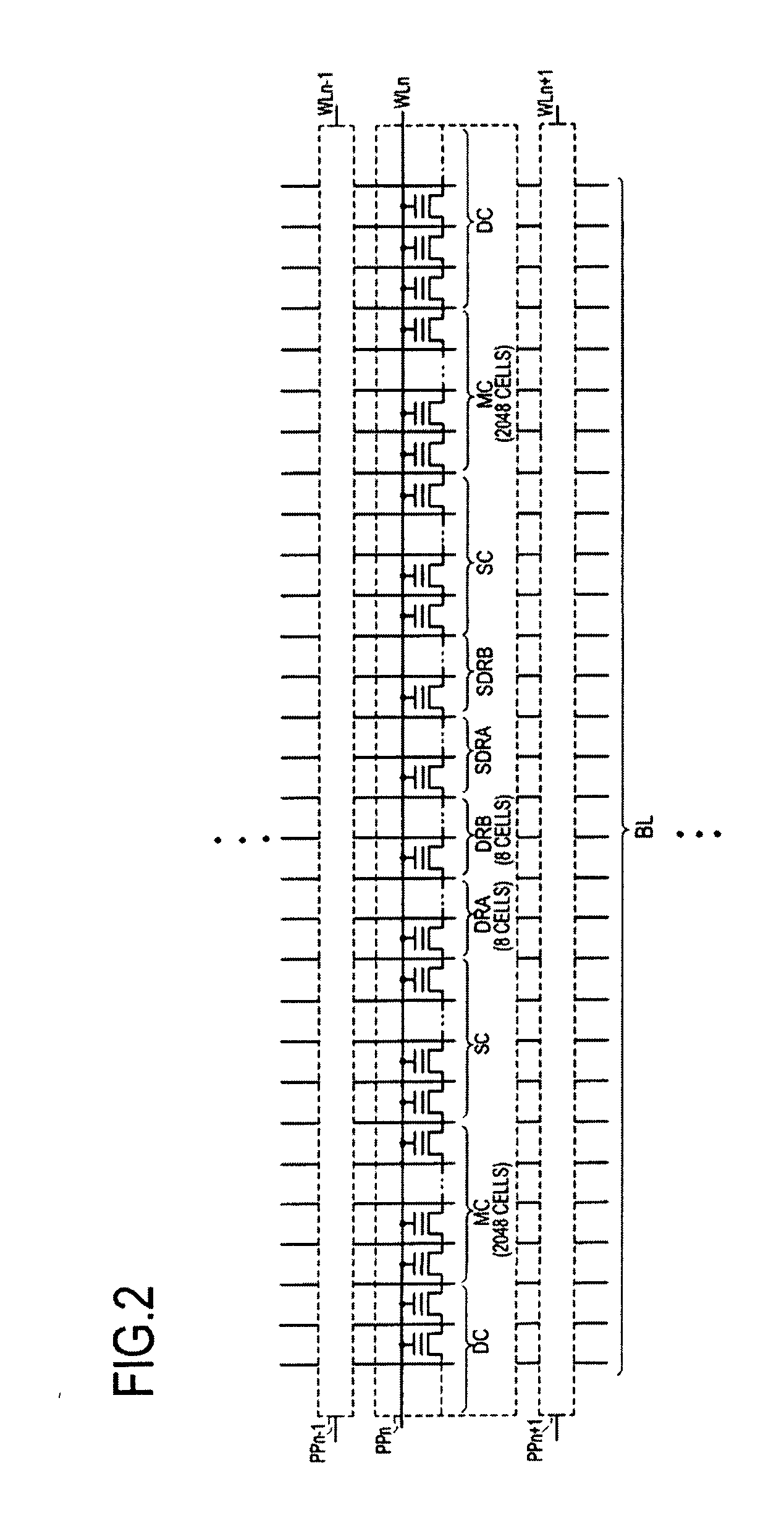
Program method of flash memory capable of compensating read margin reduced due to charge loss
The present invention provides a program method of a flash memory device including a plurality of memory cells for storing multi-bit data indicating one of a plurality of states. The memory cells are subjected to a primary program operation. Those memory cells arranged within a specific region of respective states are subjected to a secondary program operation to have a threshold voltage equivalent to or higher than a verify voltage used in the primary program operation. Thus, although a threshold voltage distribution is widened due to an electric field coupling / F-poly coupling and HTS, a read margin between adjacent states may be sufficiently secured using the program method.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
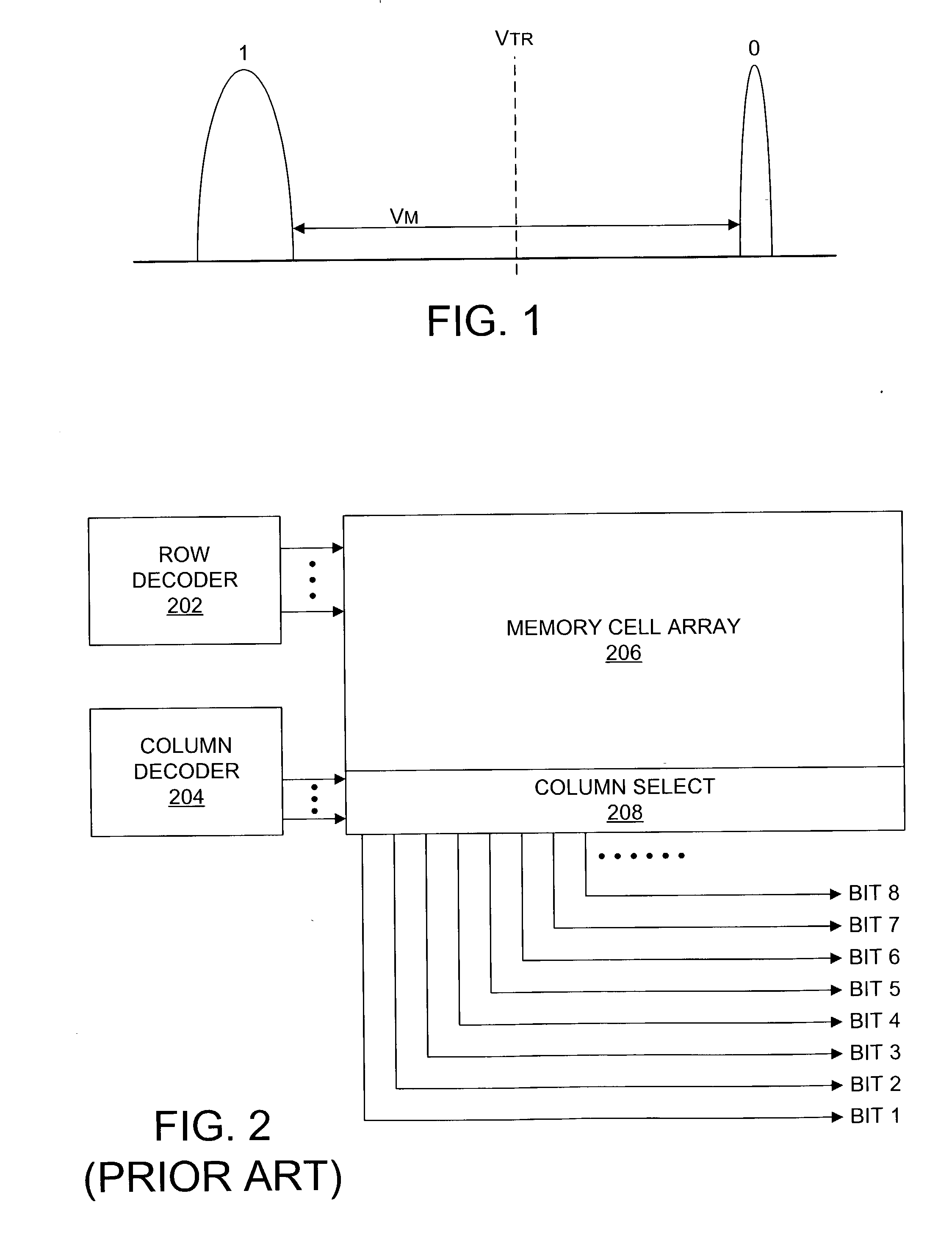
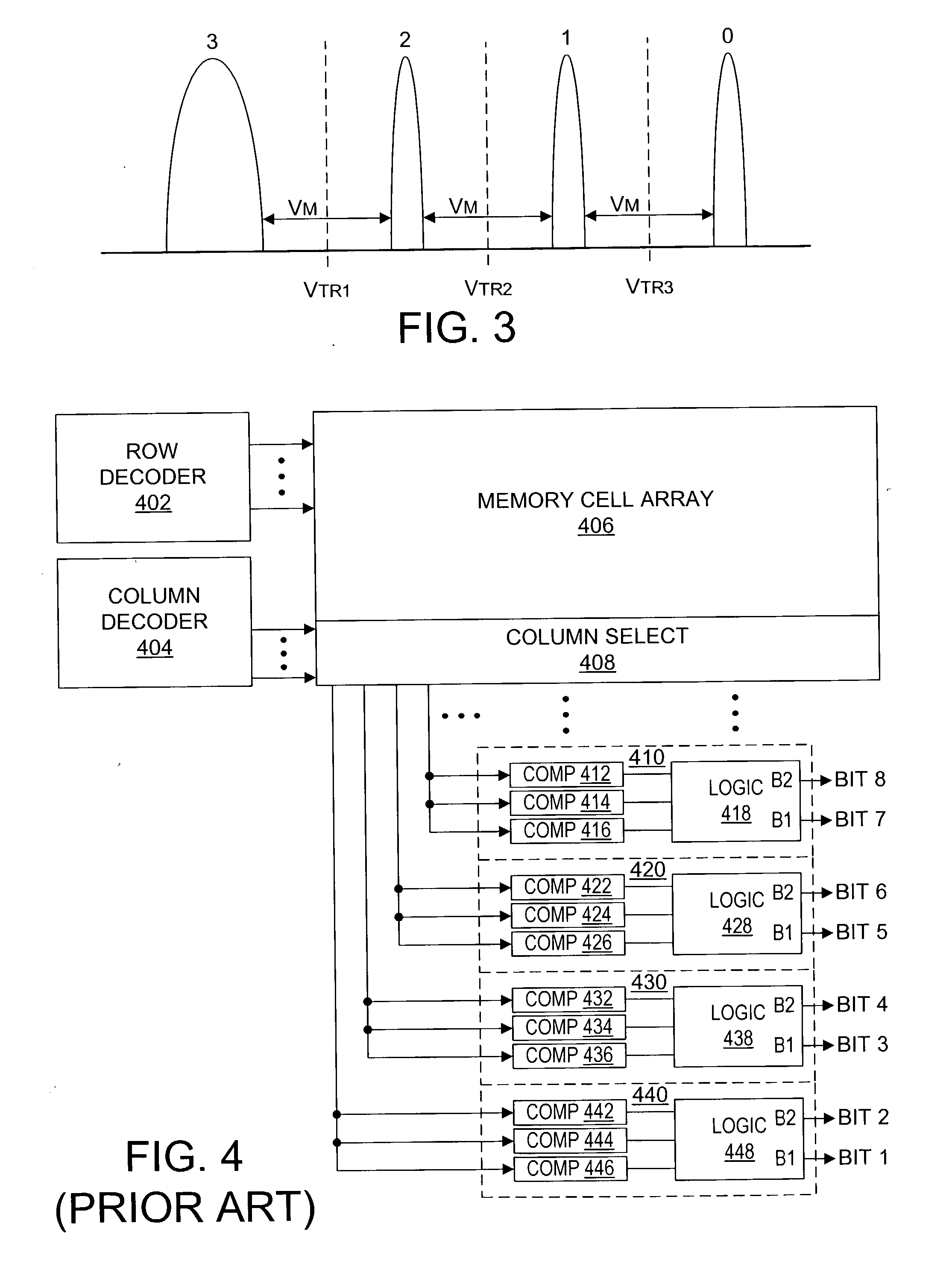
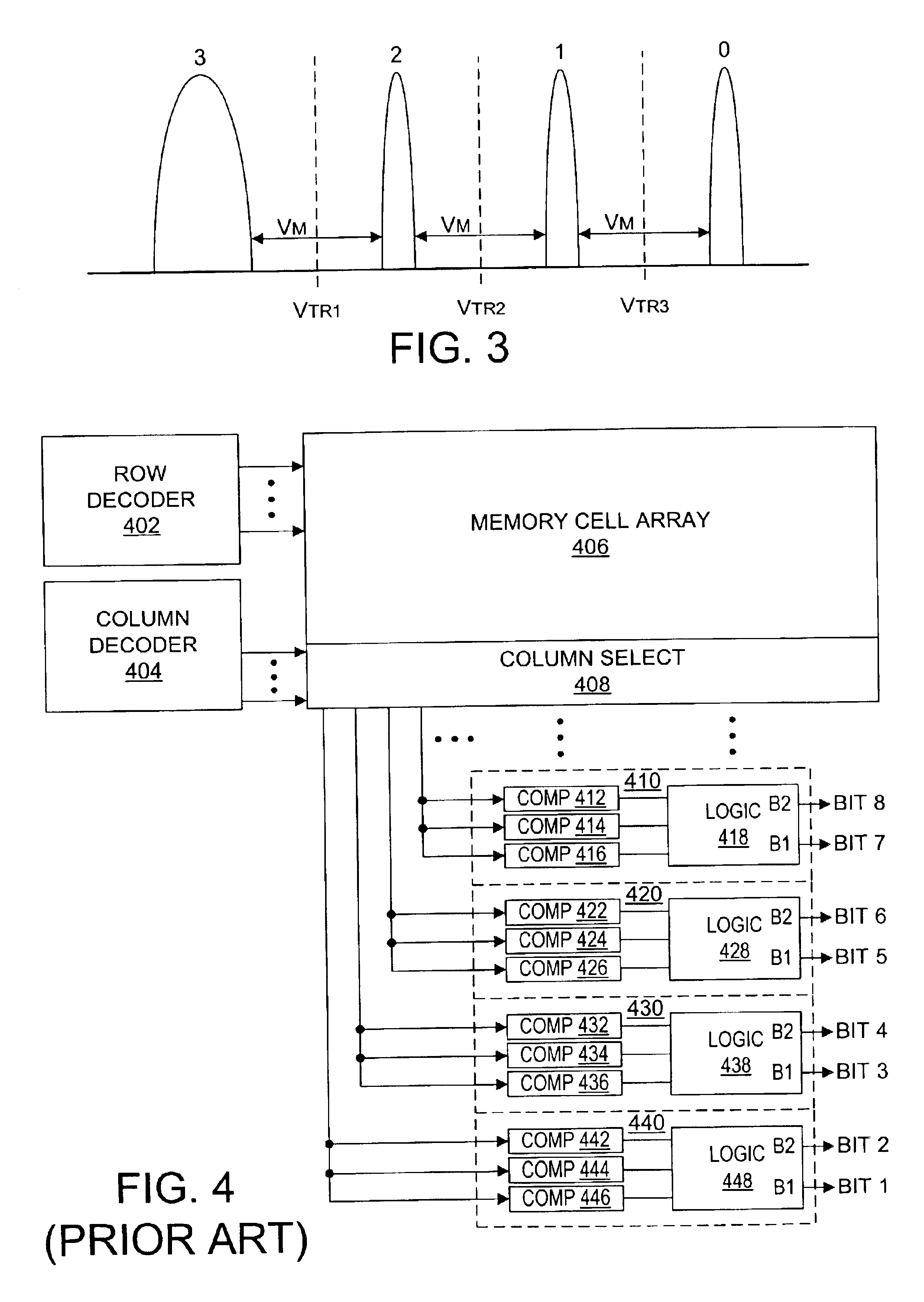
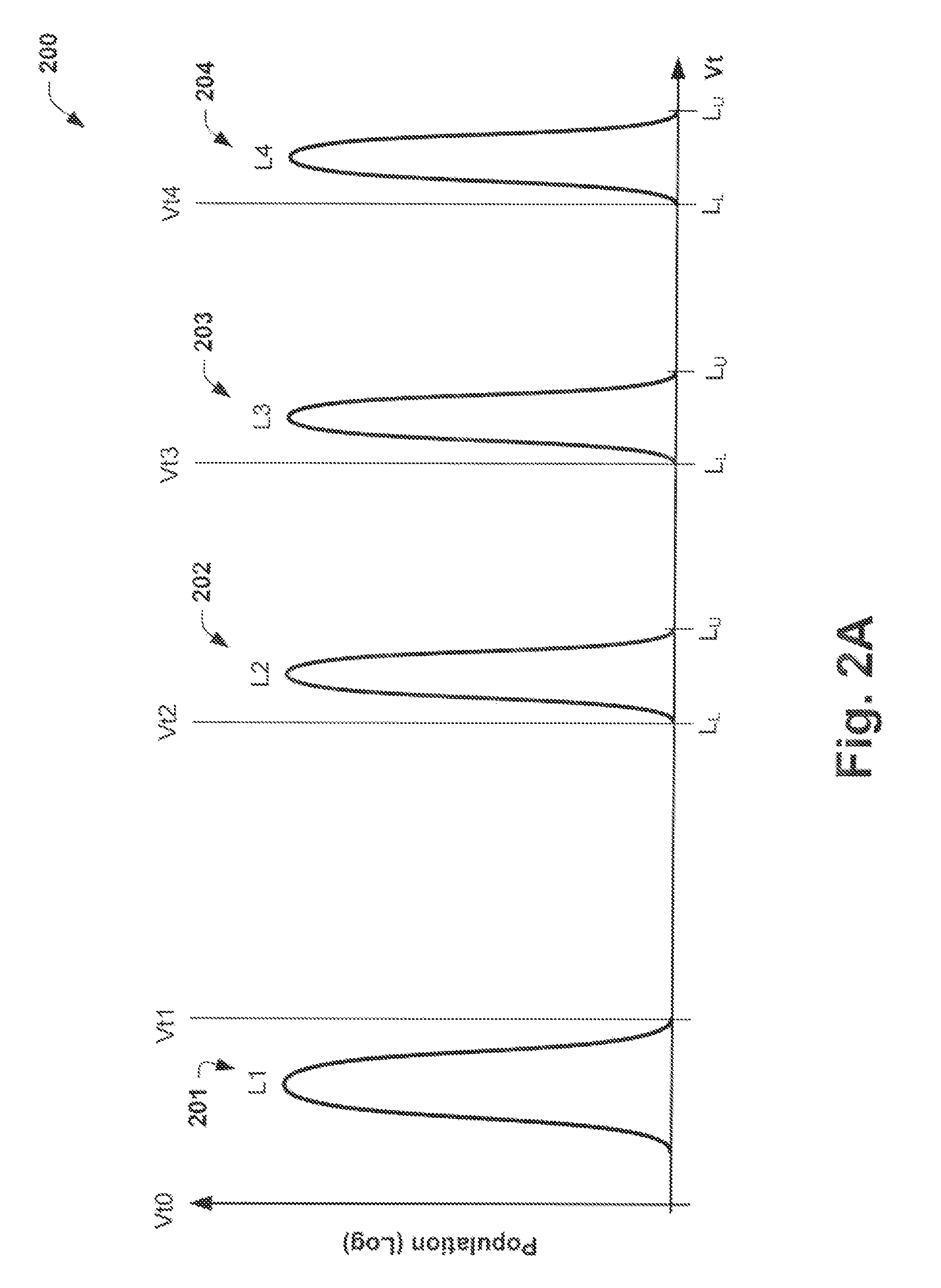
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory having three-level memory cells and program and read mapping circuits therefor
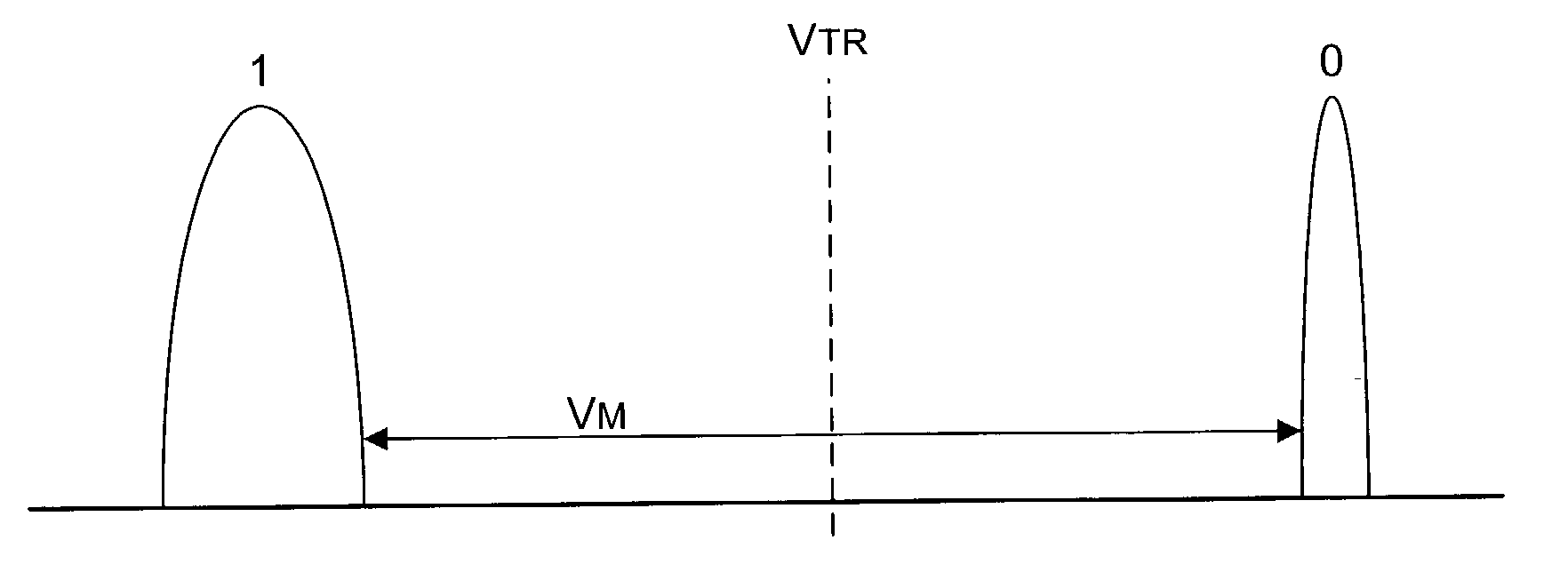
A memory uses multiple threshold levels in a memory cell that are not a power of two, and further uses a cell mapping technique wherein the read mapping is only a partial function The domain of read states for a single three-level memory cell, for example, has three states, but only two of them can be uniquely mapped to a bit. The domain of read states for two three-level memory cell, for example, has nine states, but only eight of them can be uniquely mapped to three bits. Although the read mapping is only partial, the voltage margin for the three-level memory cells is larger that the voltage margin available in the commonly used four-level memory cells. This increased voltage margin facilitates memory cell threshold voltage sensing, thereby increasing the reliability of the memory. Memory reliability may be further improved by increasing the voltage margin between the memory cell 0 state and the 1 state relative to the voltage margin between the 1 state and the 2 state, which more effectively accommodates charge loss from the 0 state through electron leakage. Asymmetrical read and program mapping may also be used to improve read reliability in the presence of ground noise or VCC noise.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
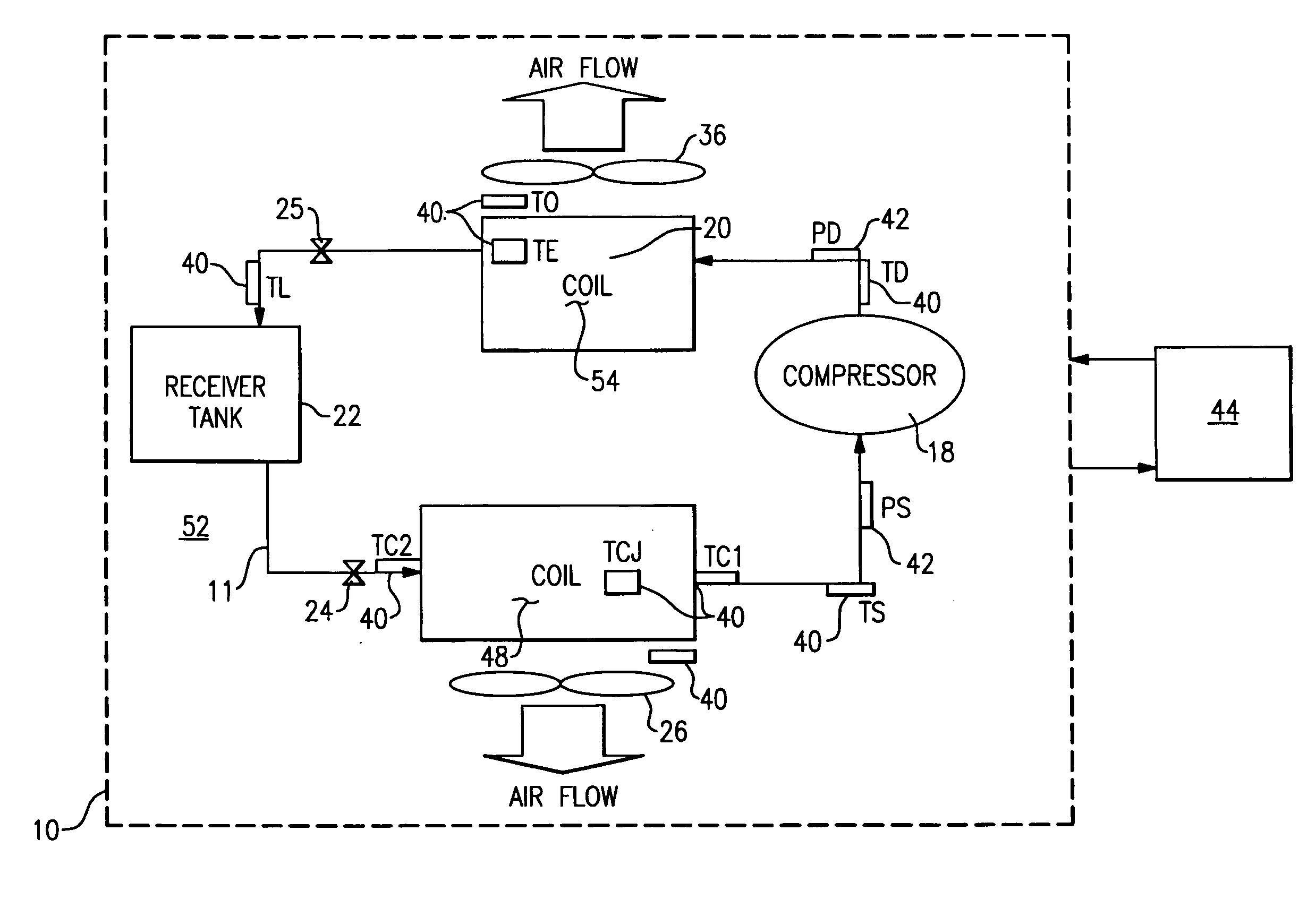
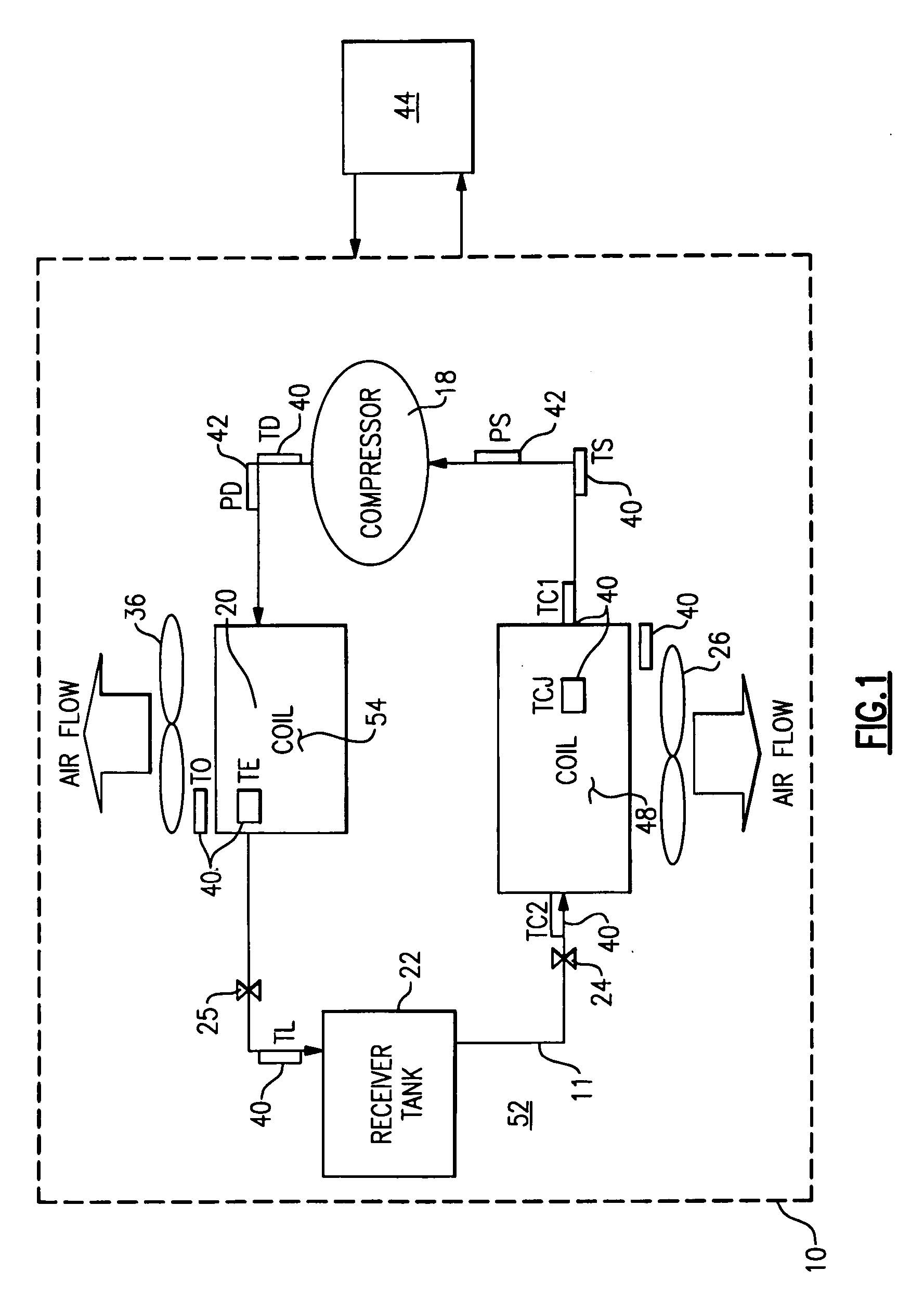
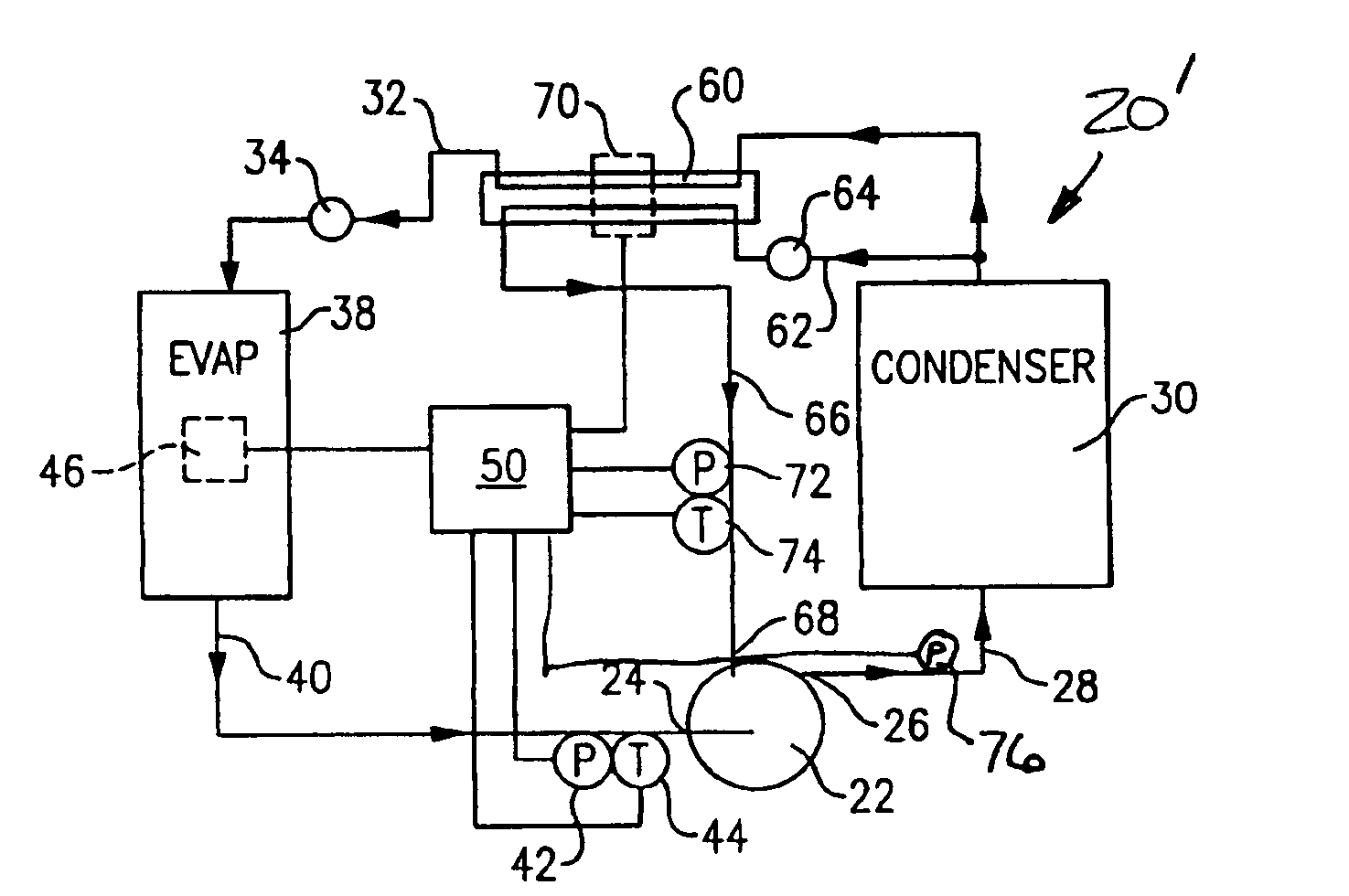
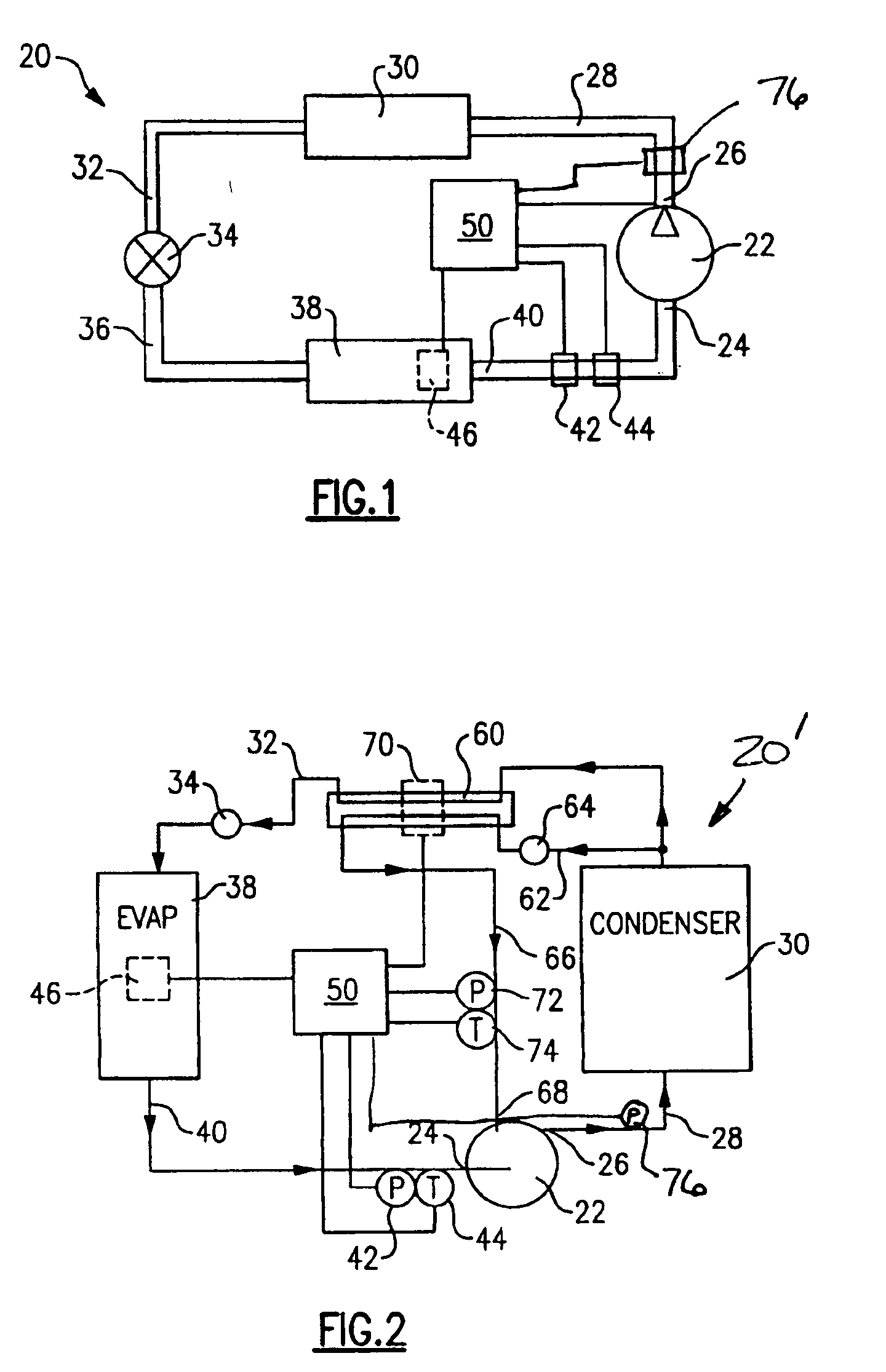
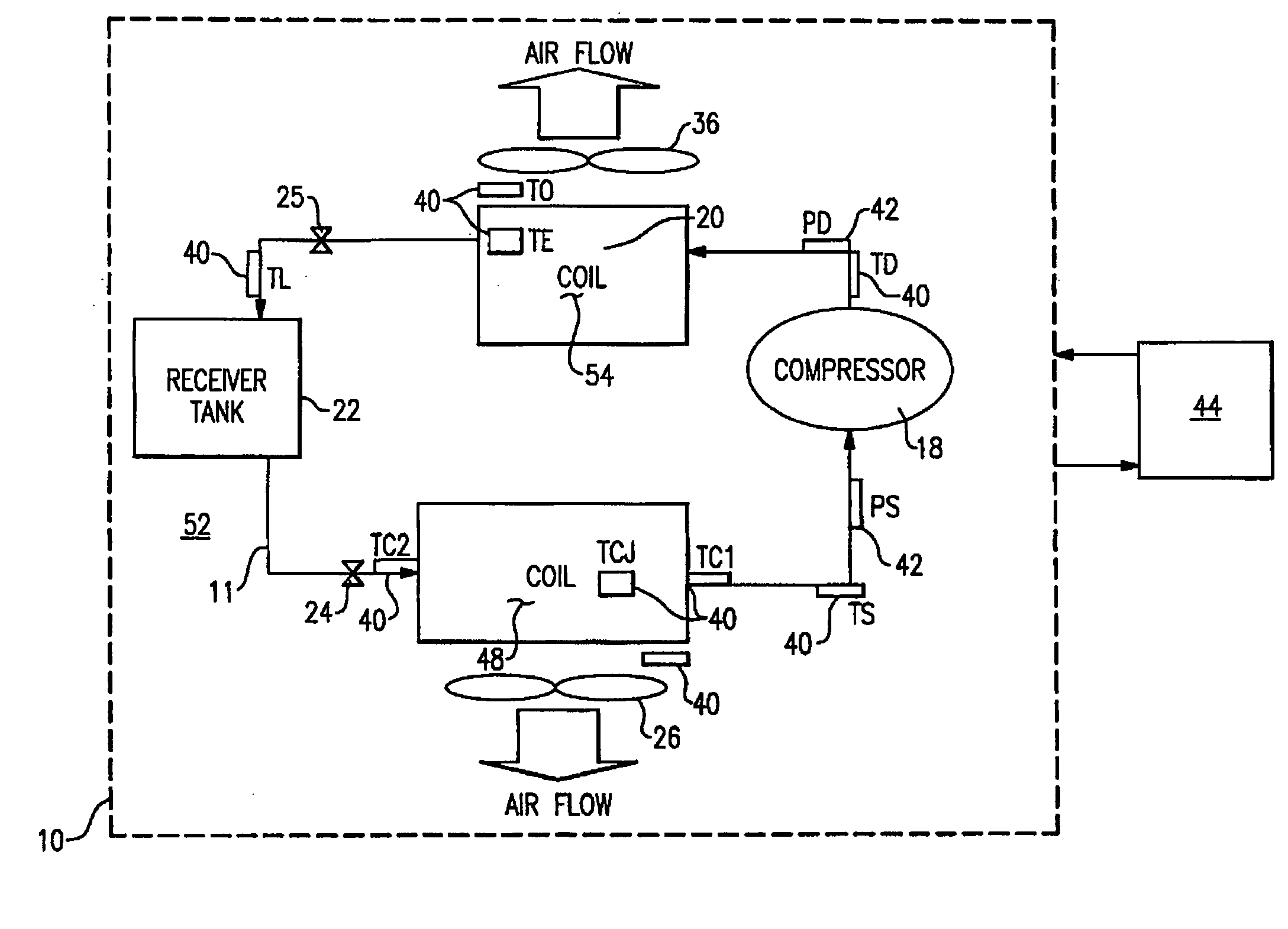
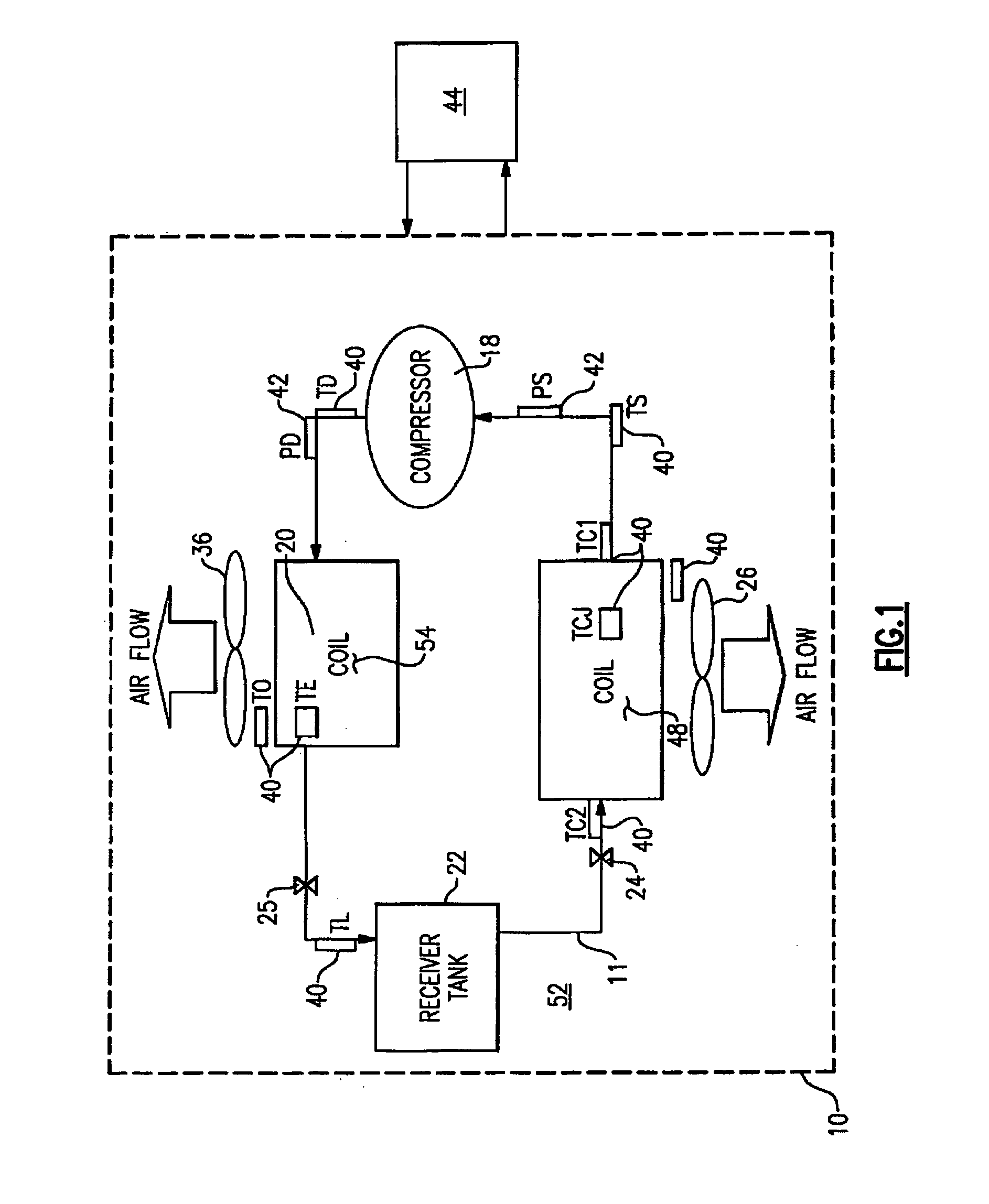
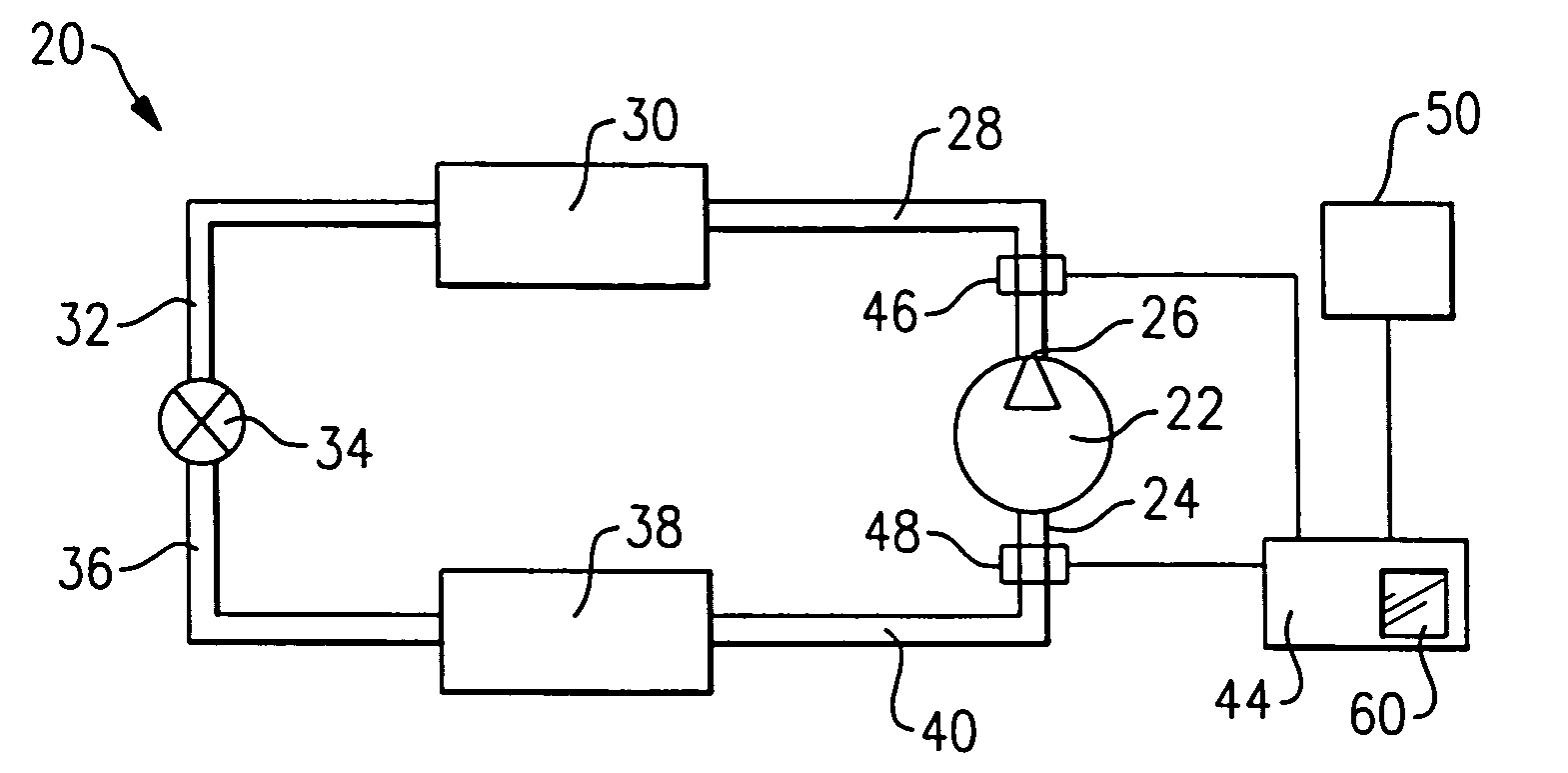
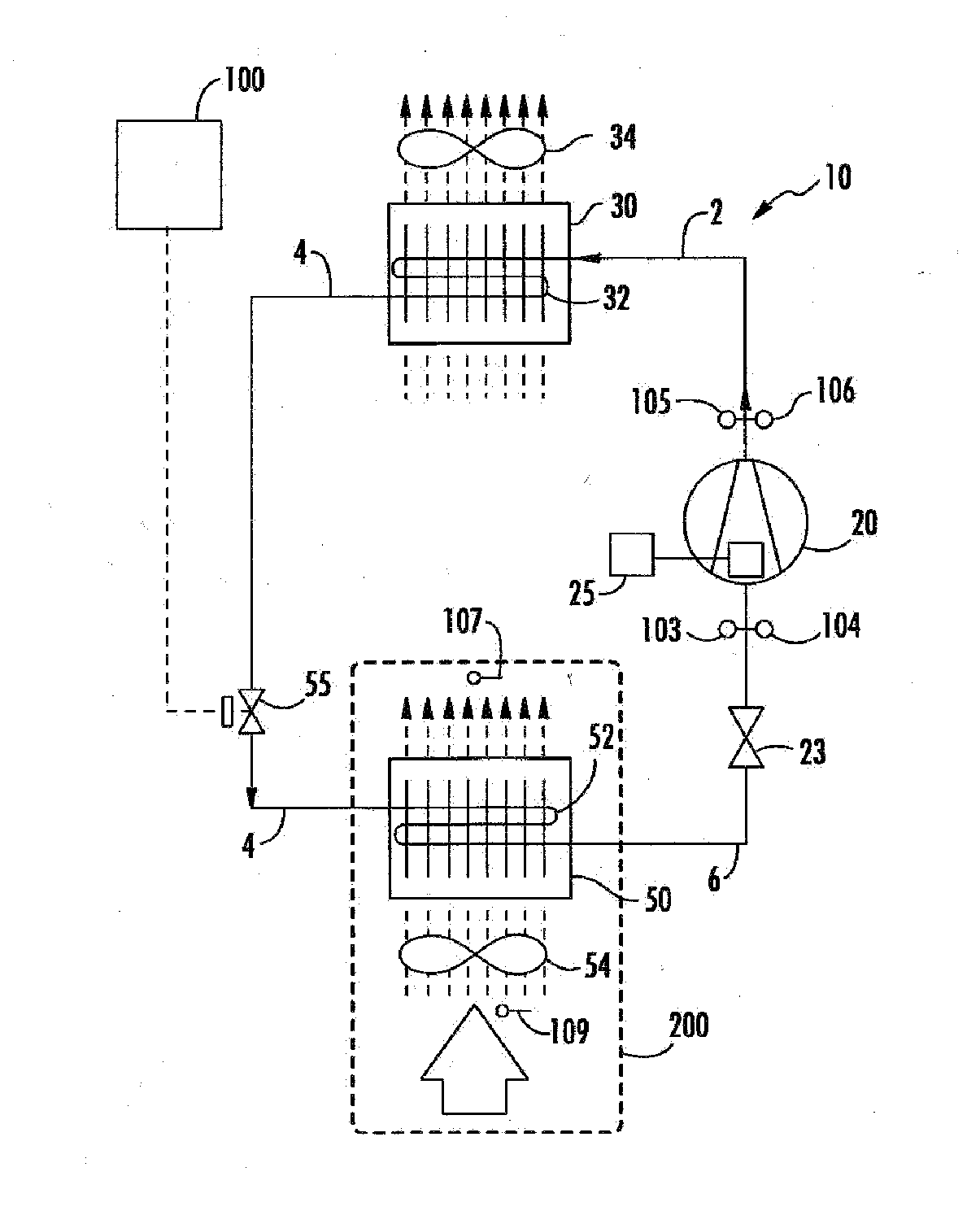
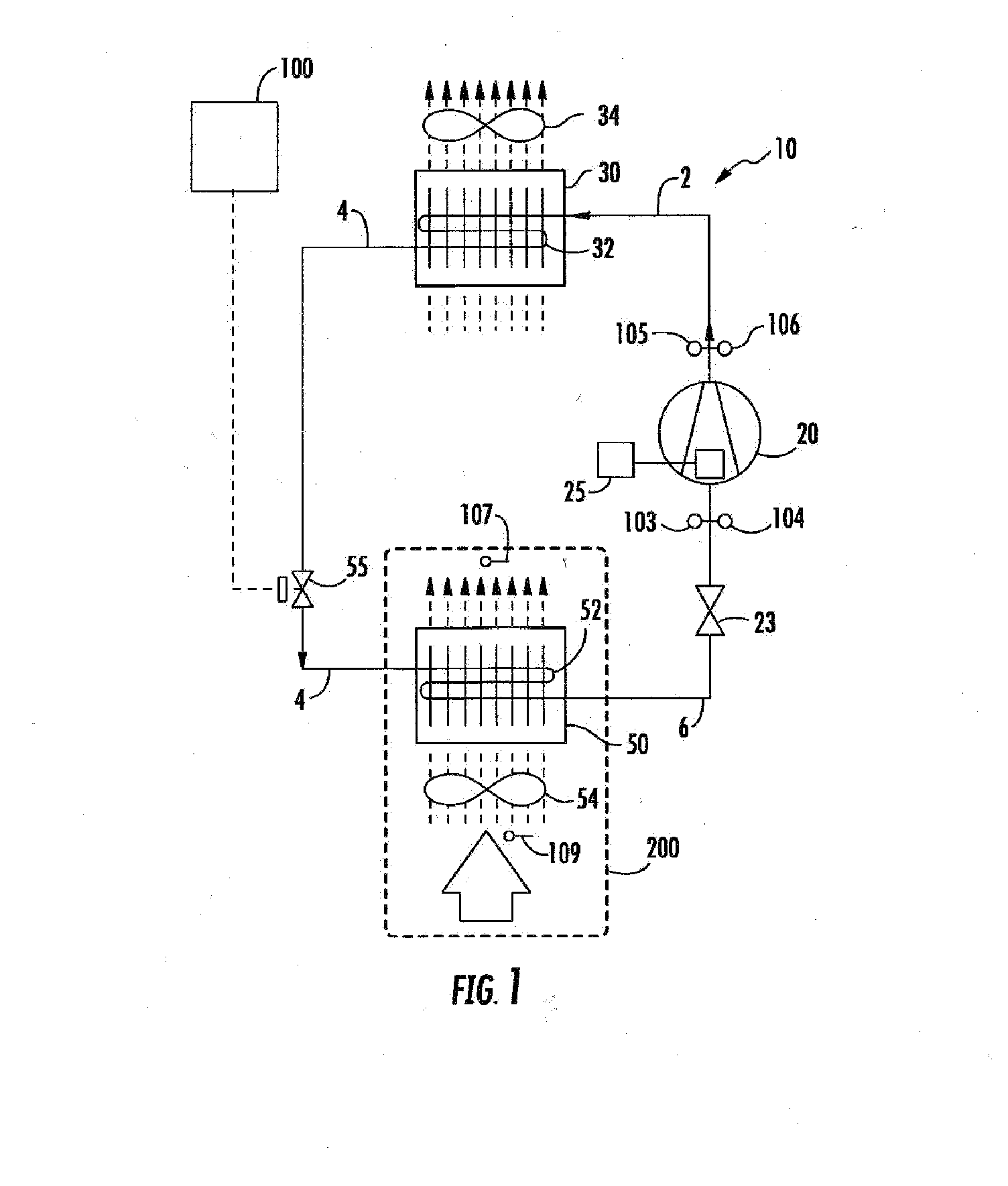
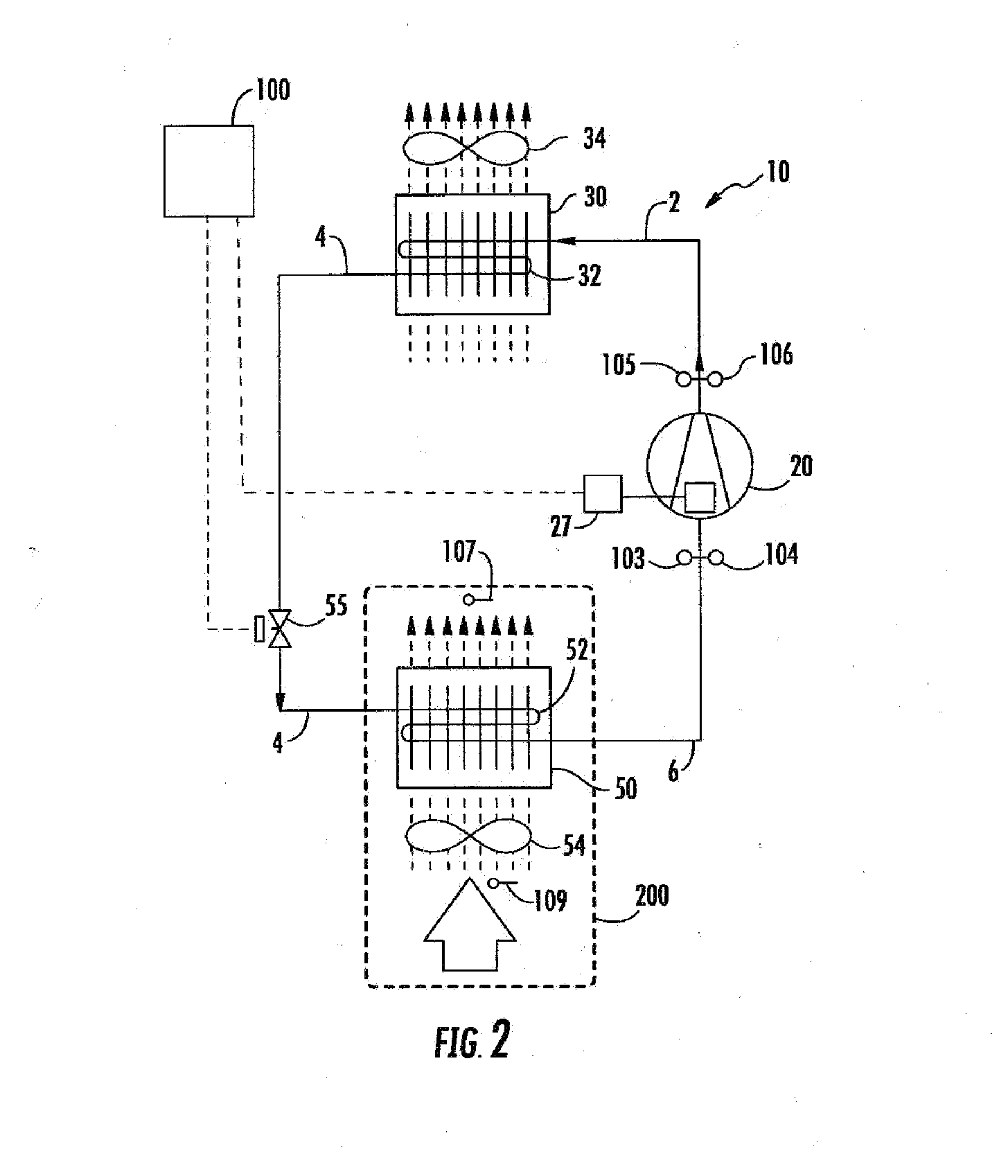
Charge loss detection and prognostics for multi-modular split systems
InactiveUS20060021362A1Compression machines with non-reversible cycleFluid circulation arrangementCharge lossPrognostics
A method for detecting and predicting refrigerant level includes the steps of determining an estimated value for a parameter indicative of refrigerant level and comparing that estimated value to an actual value. The difference between the actual and estimated value provides a refrigerant charge indicator value. The charge indicator value is indicative of the amount of refrigerant contained within the system. A change value is combined with the charge indicator value to provide a prediction for the future value of the charge indicator value. This future value is determined based on a rate of change and charge indicator value over a selected period of time.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
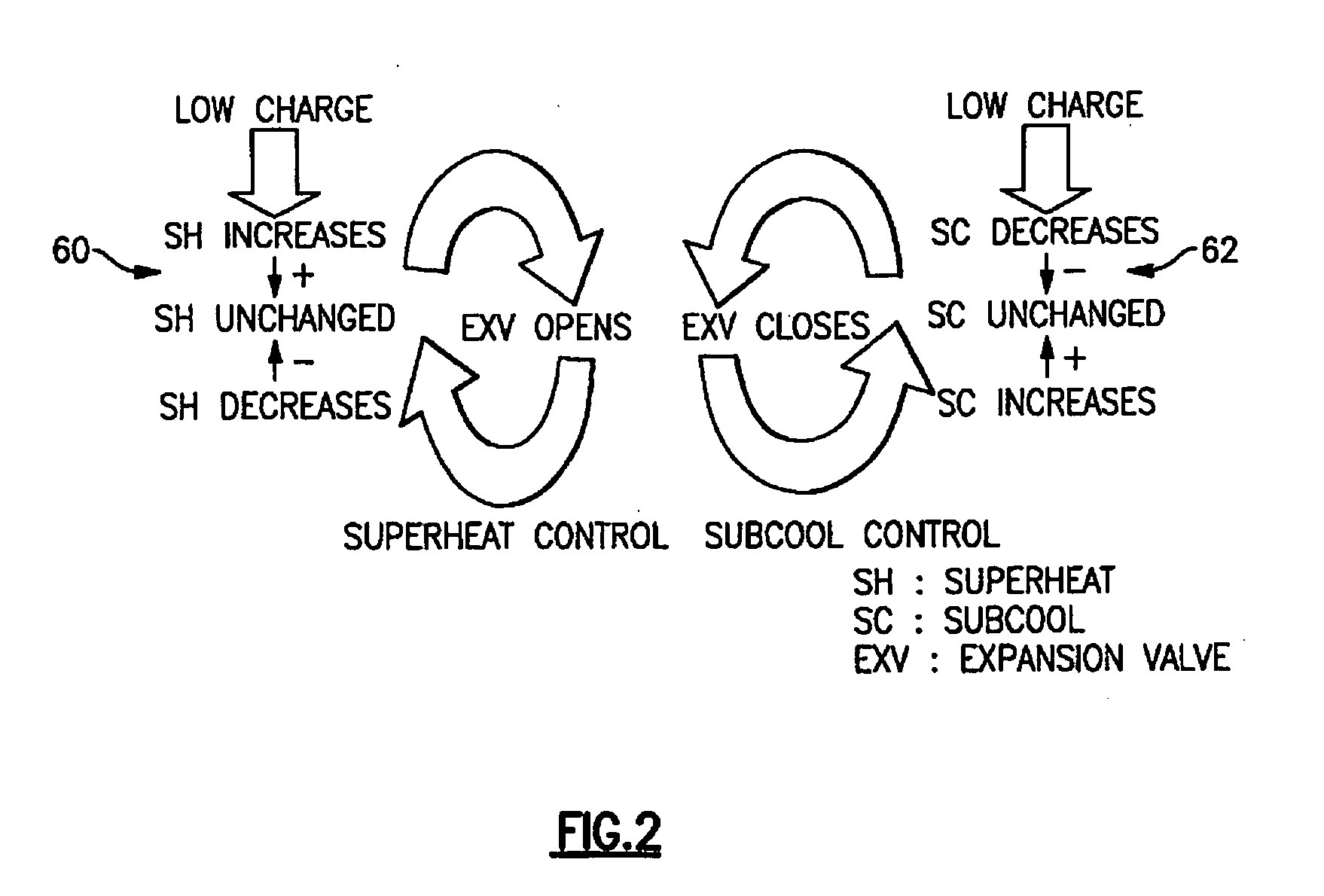
Loss of refrigerant charge and expansion valve malfunction detection
InactiveUS20050126190A1Thermometer applicationsRefrigeration safety arrangementEngineeringCharge loss
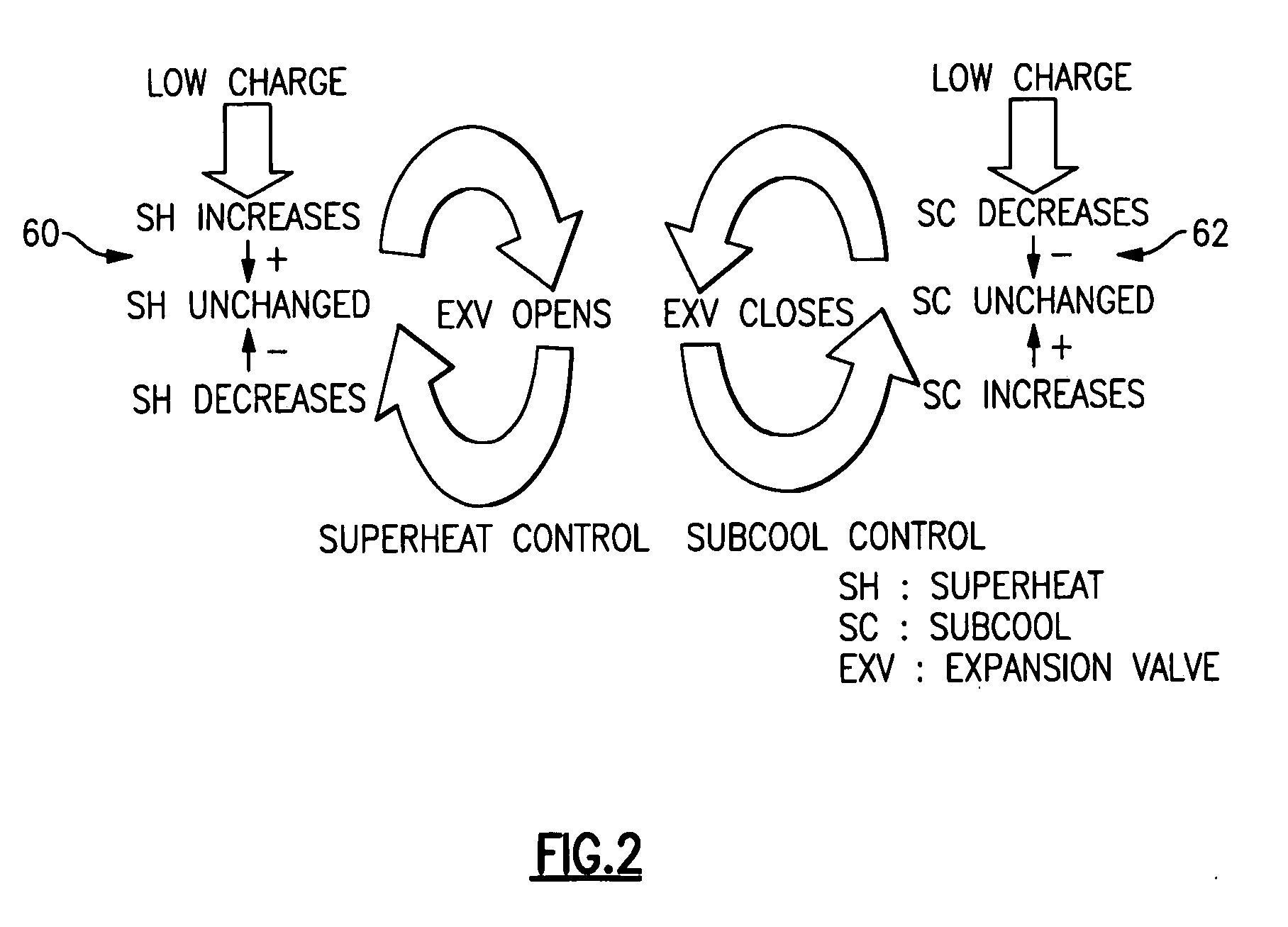
An actual superheat value in a refrigerant system is compared to an expected superheat level. If the actual superheat valve exceeds a certain predetermined value, this is an indication of refrigerant charge loss or a malfunctioning expansion device. In one example, the superheat valve is determined by comparing a difference between a saturated vapor temperature and an actual operating vapor temperature. The superheat determination can be made either at evaporator exit, economizer heat exchange exit or near the compressor discharge port.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
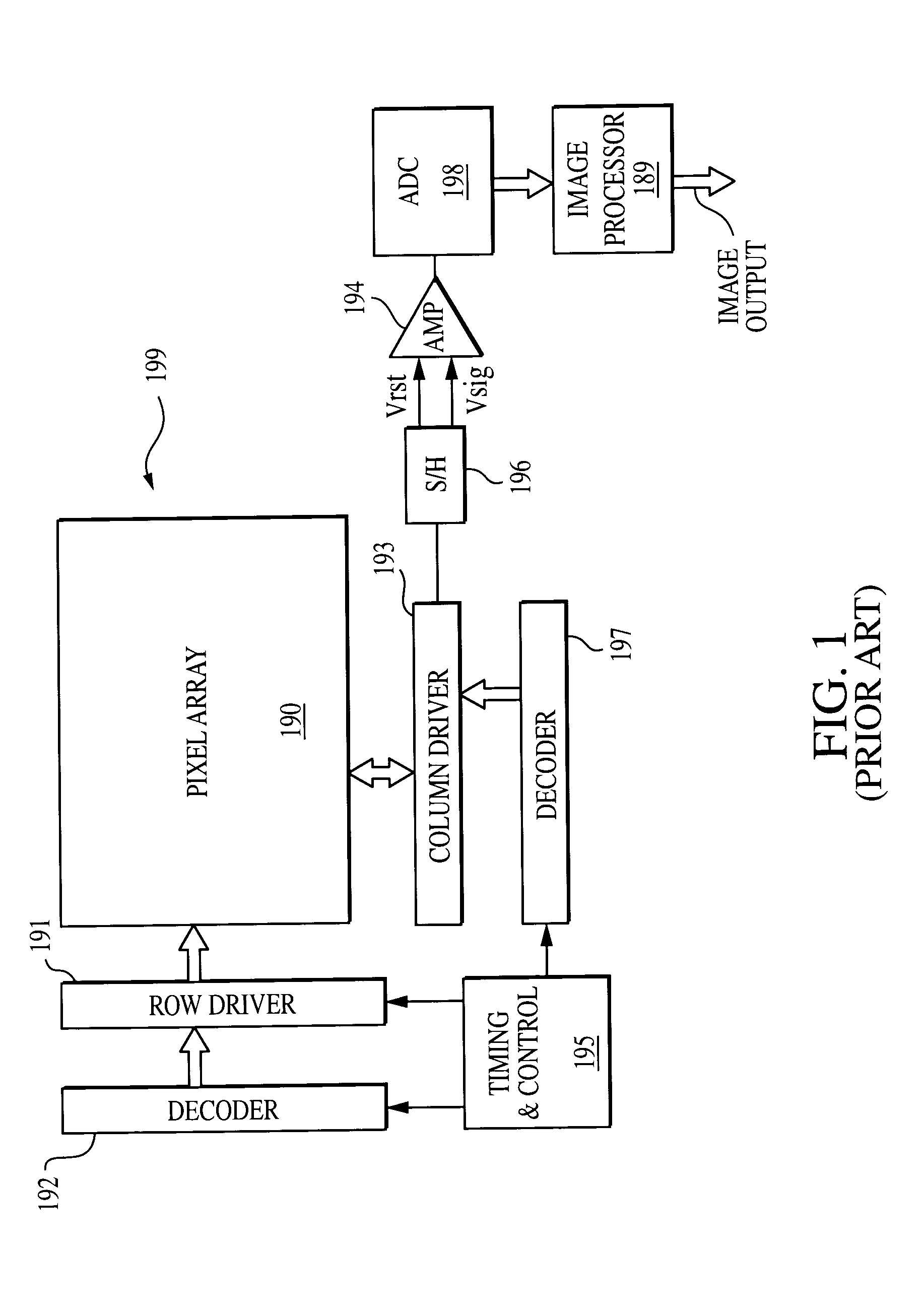
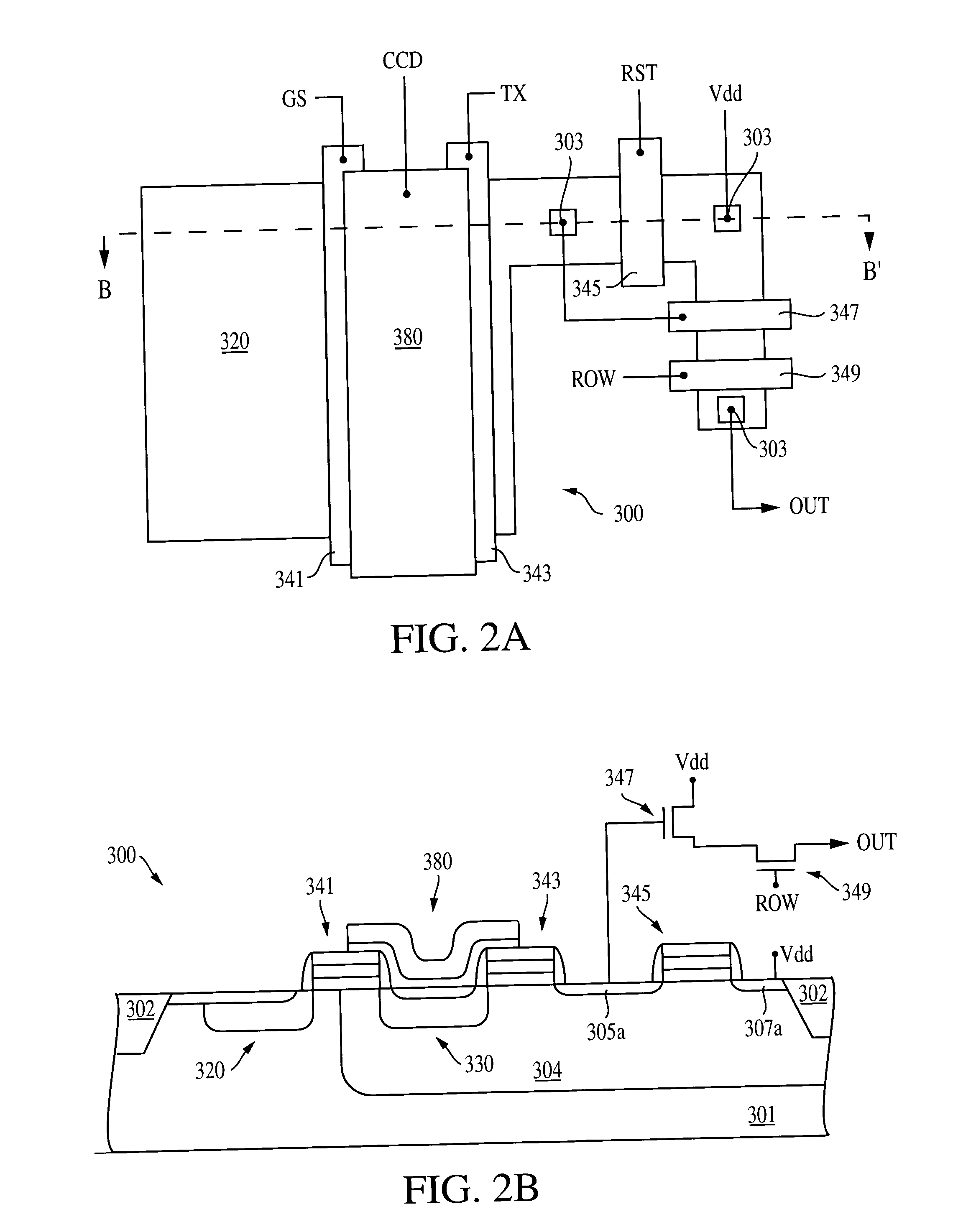
Imaging with gate controlled charge storage
InactiveUS20050040393A1Improve charge transfer efficiencyReduce charge lossSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringCharge loss
A pixel cell comprises a photo-conversion device for generating charge and a gate controlled charge storage region for storing photo-generated charge under control of a control gate. The charge storage region can be a single CCD stage having a buried channel to obtain efficient charge transfer and low charge loss. The charge storage region is adjacent to a gate of a transistor. The transistor gate is adjacent to the photo-conversion device and, in conjunction with the control gate, transfers photo-generated charge from the photo-conversion device to the charge storage region.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory having three-level memory cells and program and read mapping circuits therefor
InactiveUS6847550B2Improve reliabilityHigh voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageThree levelNon symmetric
A memory uses multiple threshold levels in a memory cell that are not a power of two, and further uses a cell mapping technique wherein the read mapping is only a partial function The domain of read states for a single three-level memory cell, for example, has three states, but only two of them can be uniquely mapped to a bit. The domain of read states for two three-level memory cell, for example, has nine states, but only eight of them can be uniquely mapped to three bits. Although the read mapping is only partial, the voltage margin for the three-level memory cells is larger that the voltage margin available in the commonly used four-level memory cells. This increased voltage margin facilitates memory cell threshold voltage sensing, thereby increasing the reliability of the memory. Memory reliability may be further improved by increasing the voltage margin between the memory cell 0 state and the 1 state relative to the voltage margin between the 1 state and the 2 state, which more effectively accommodates charge loss from the 0 state through electron leakage. Asymmetrical read and program mapping may also be used to improve read reliability in the presence of ground noise or VCC noise.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
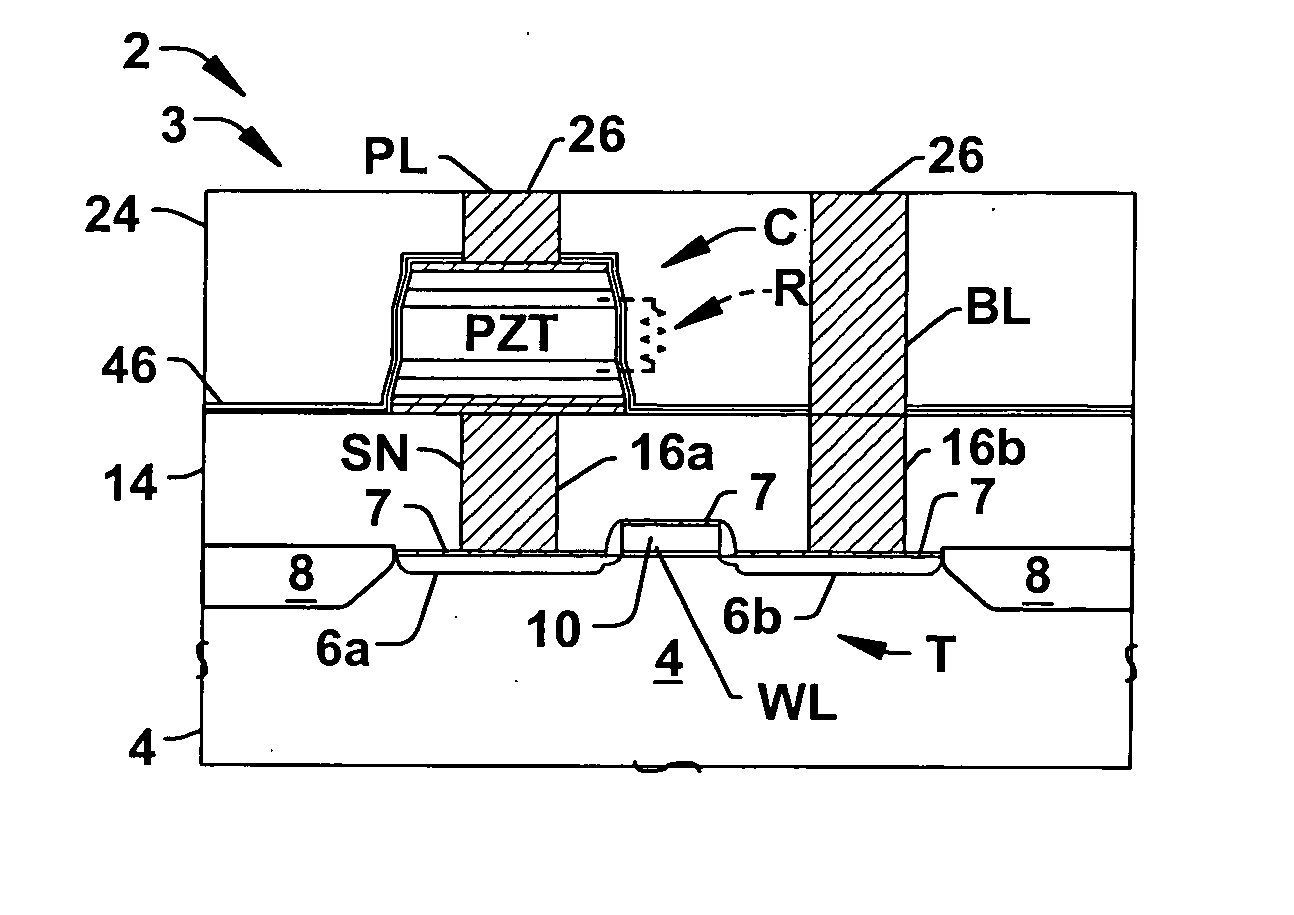
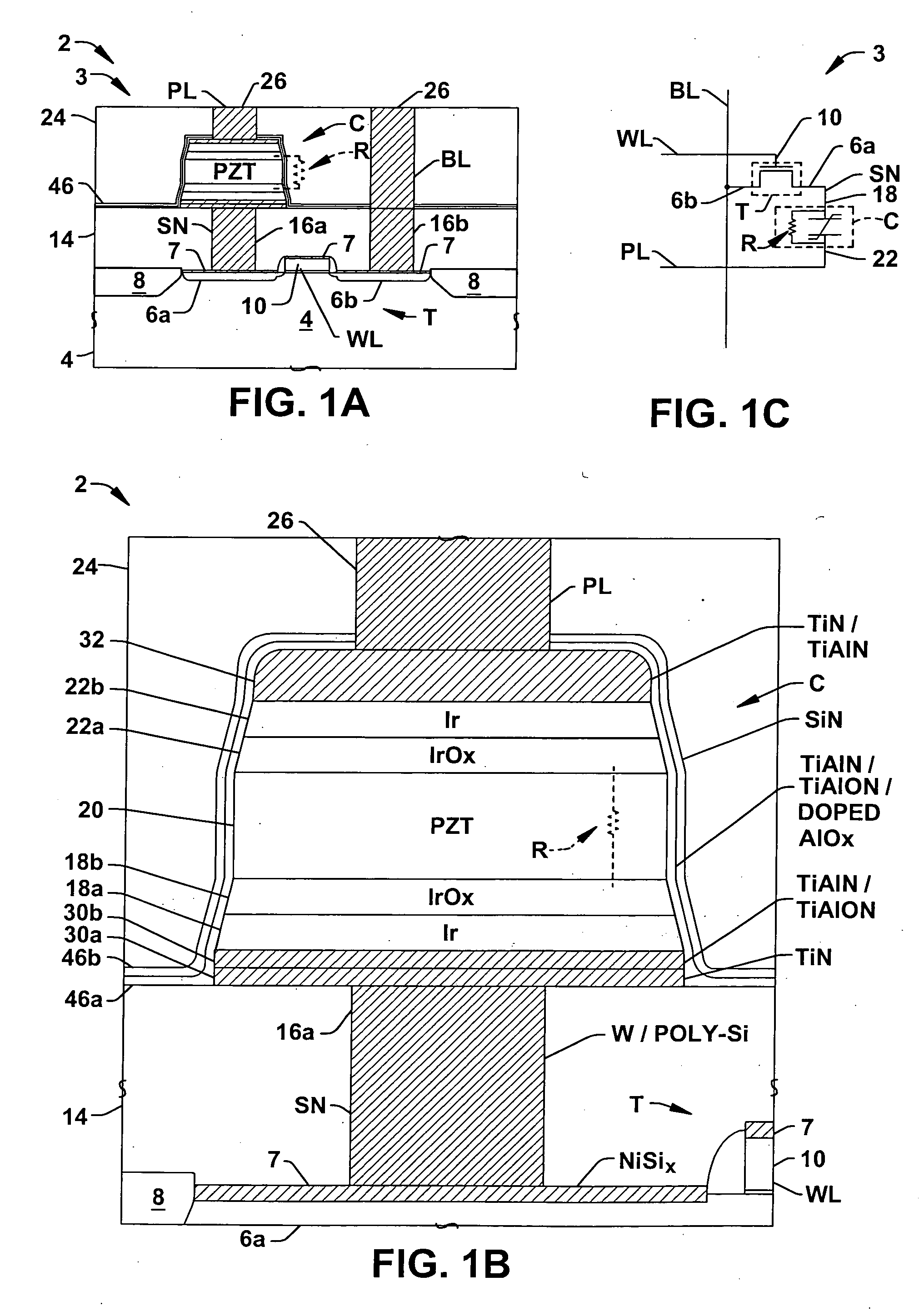
Ferroelectric capacitor with parallel resistance for ferroelectric memory
ActiveUS20060118841A1Avoid charge accumulationInhibits charge charge lossSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringCharge loss
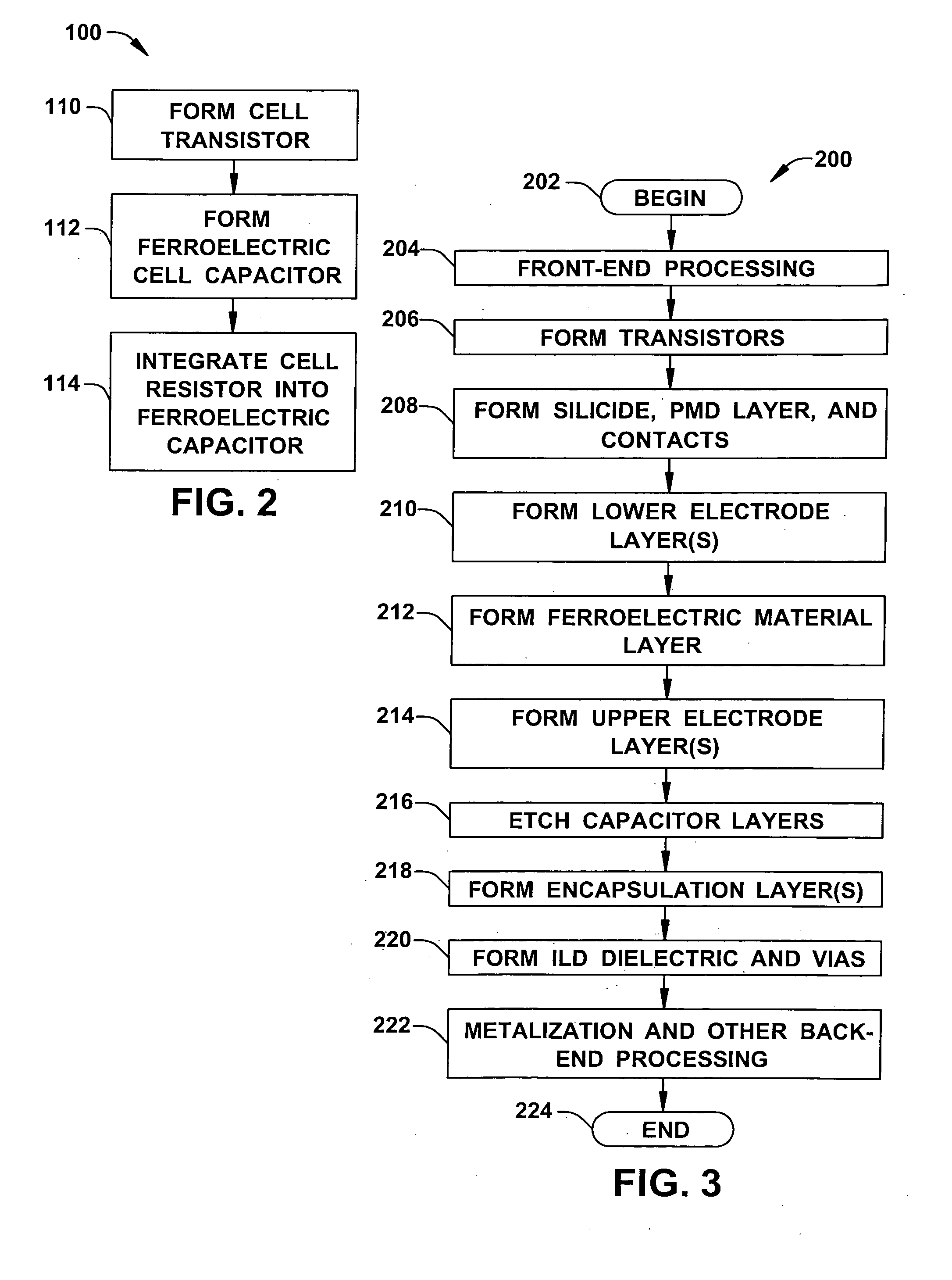
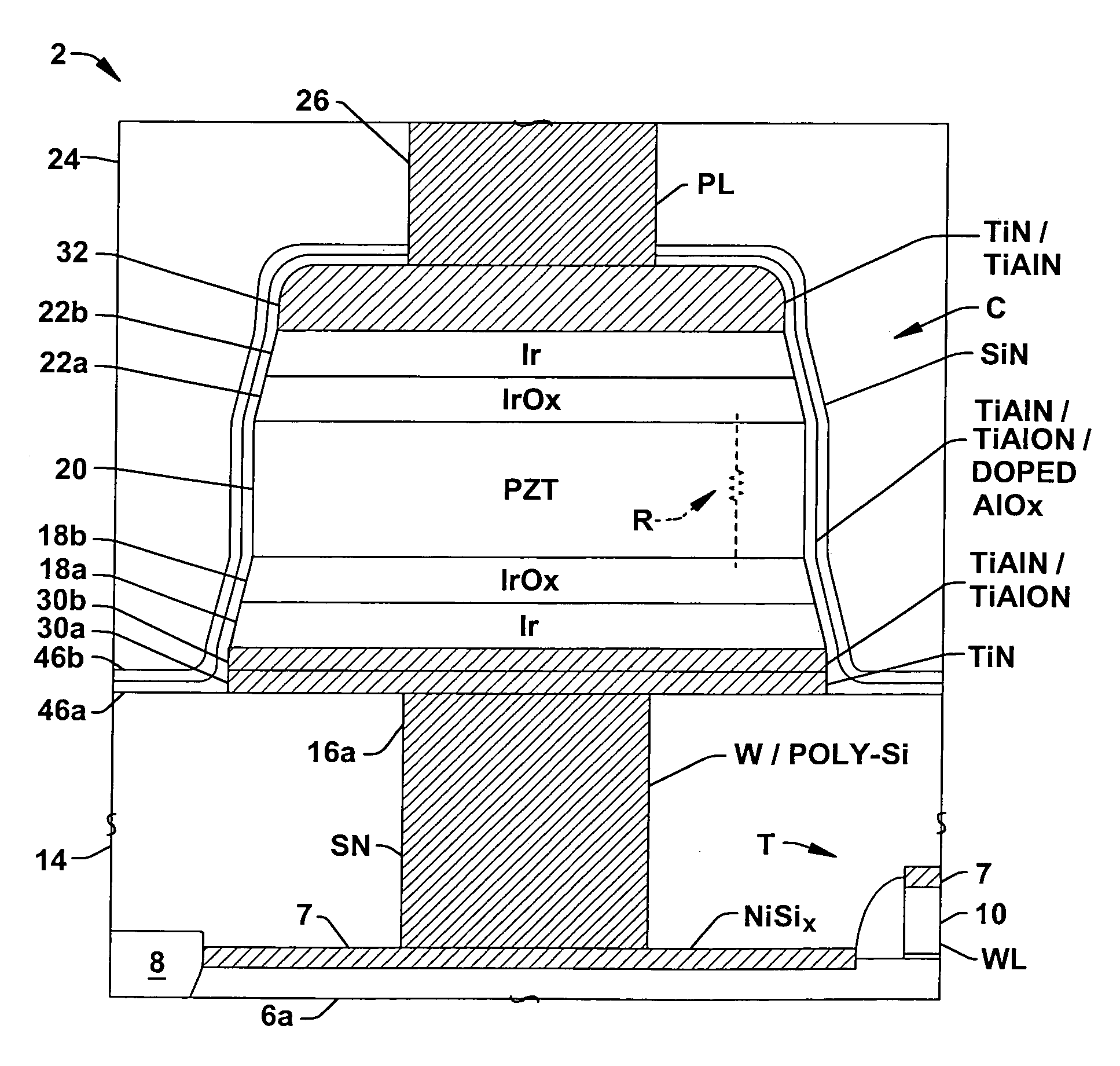
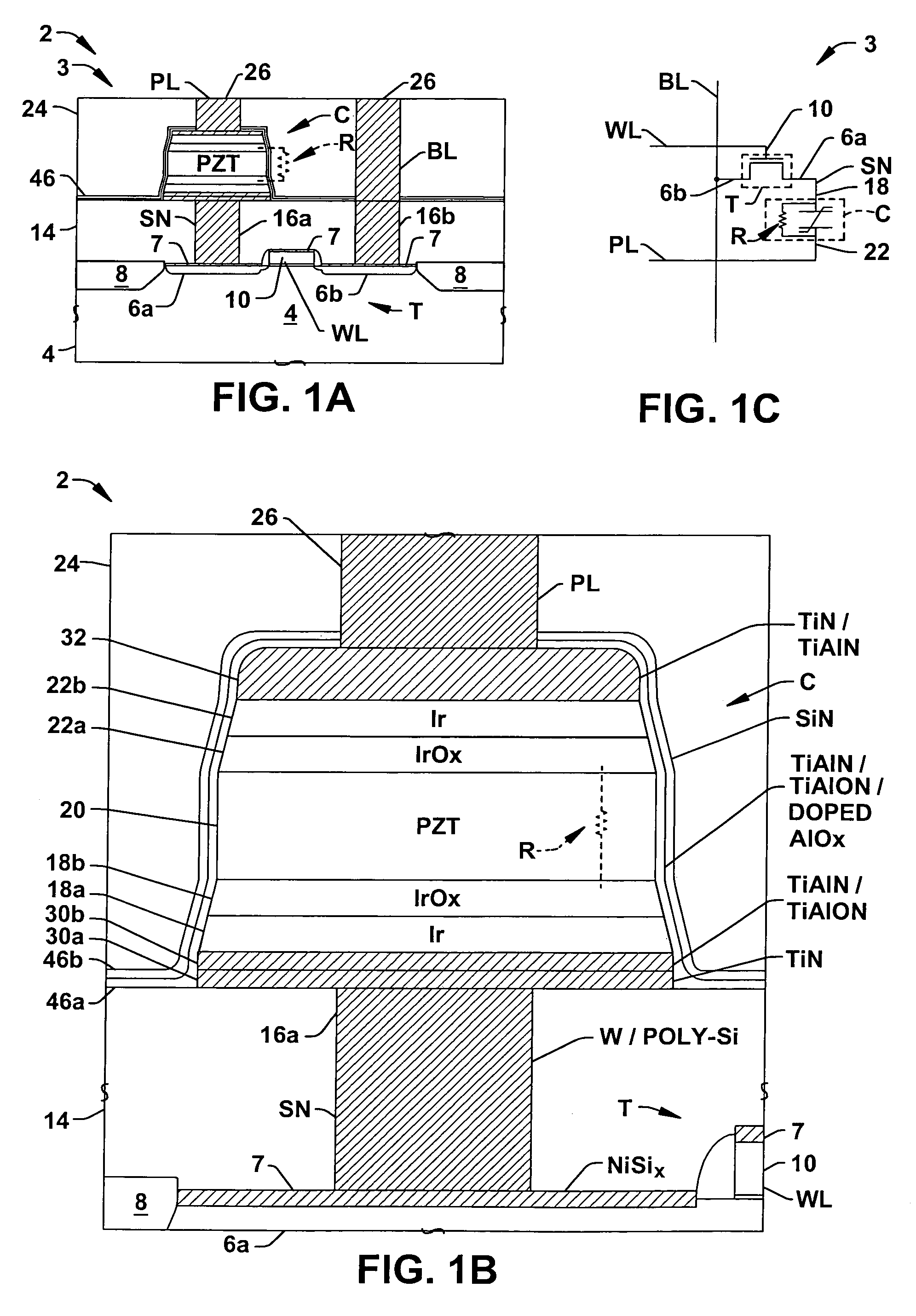
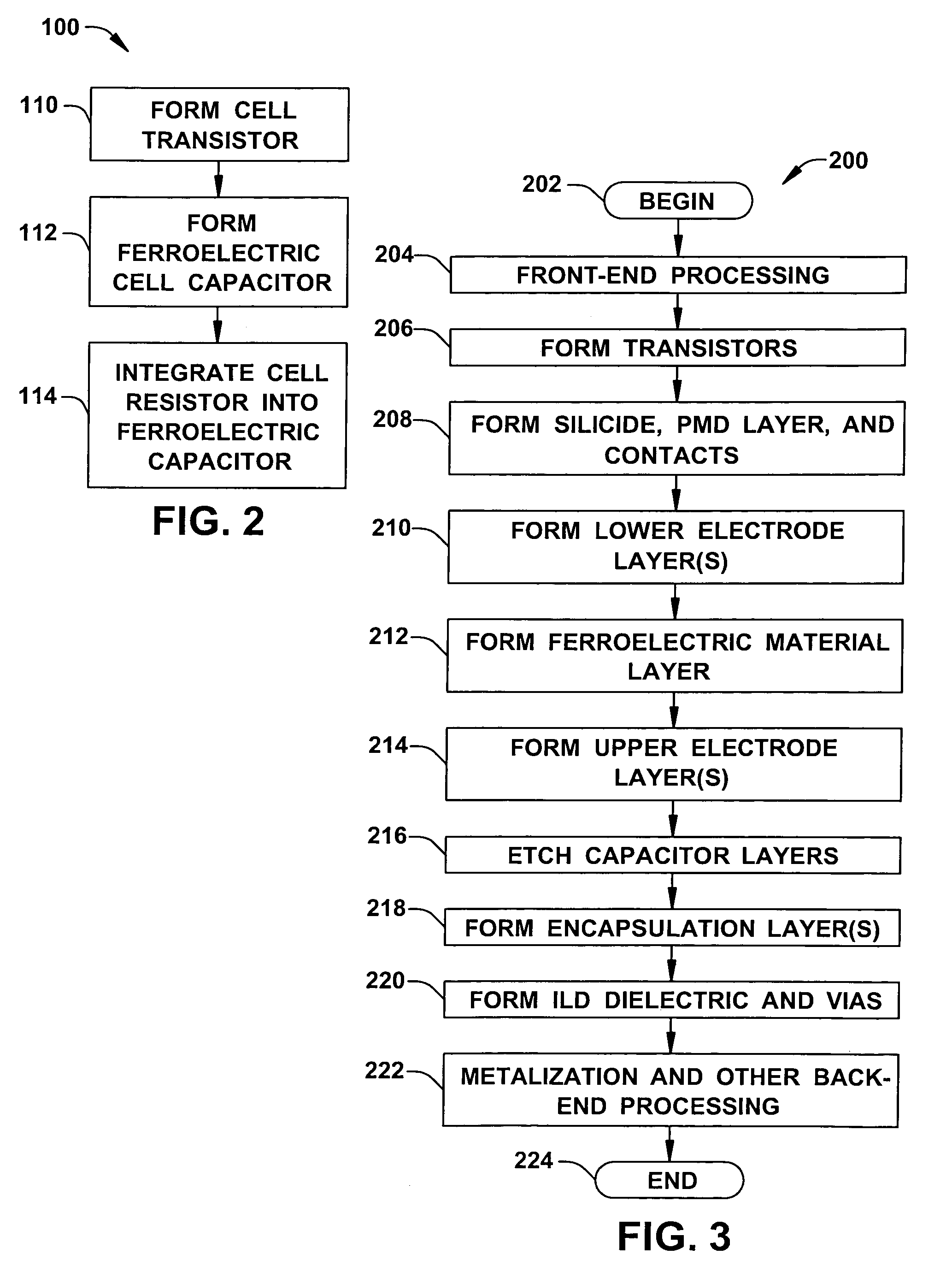
Ferroelectric memory cells (3) are presented, in which a cell resistor (R) is integrated into the cell capacitor (C) to inhibit charge accumulation or charge loss at the cell storage node (SN) when the cell (3) is not being accessed while avoiding significant disruption of memory cell access operations. Methods (100, 200) are provided for fabricating ferroelectric memory cells (3) and ferroelectric capacitors (C), in which a parallel resistance (R) is integrated in the capacitor ferroelectric material (20) or in an encapsulation layer (46) formed over the patterned capacitor structure (C).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
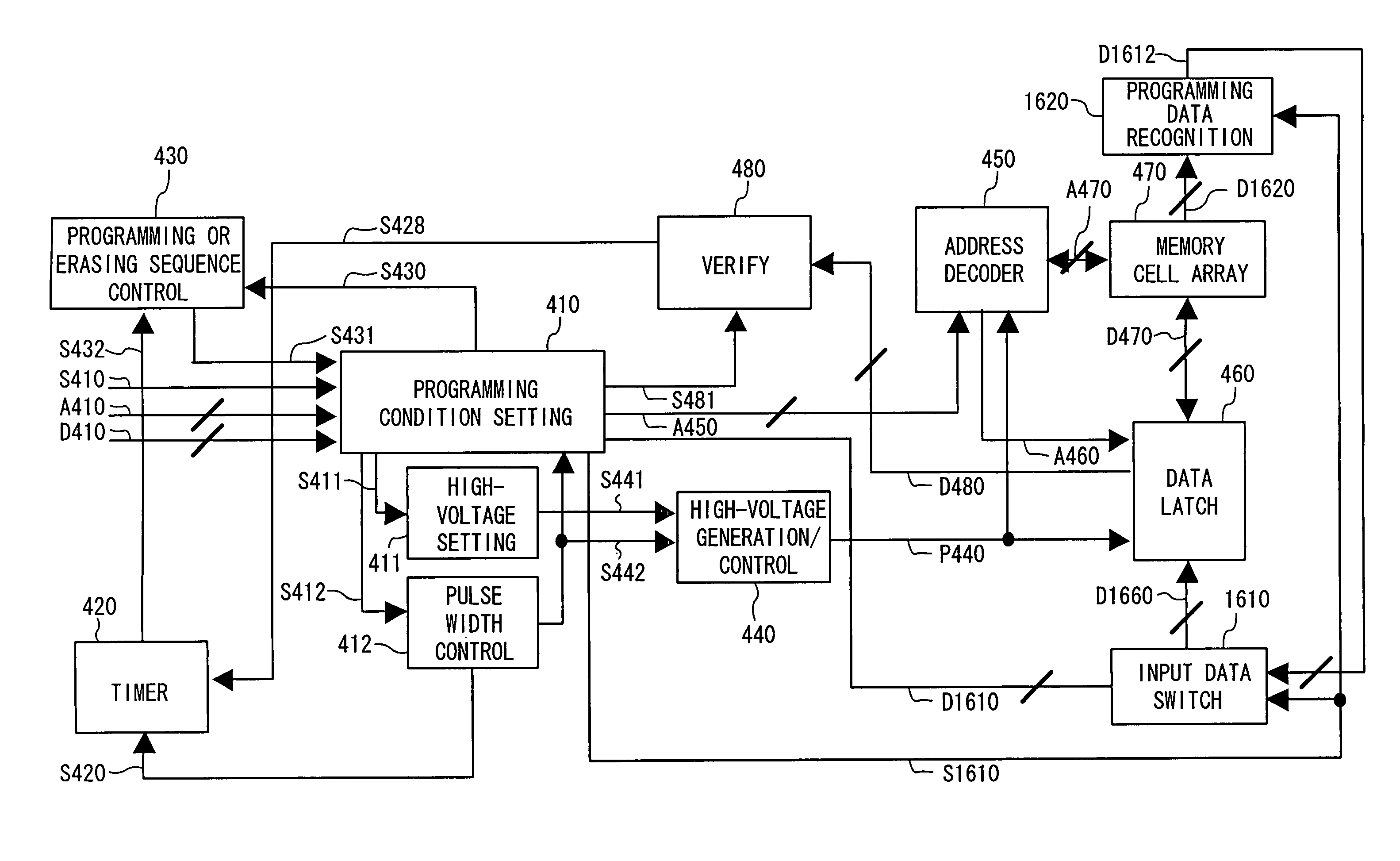
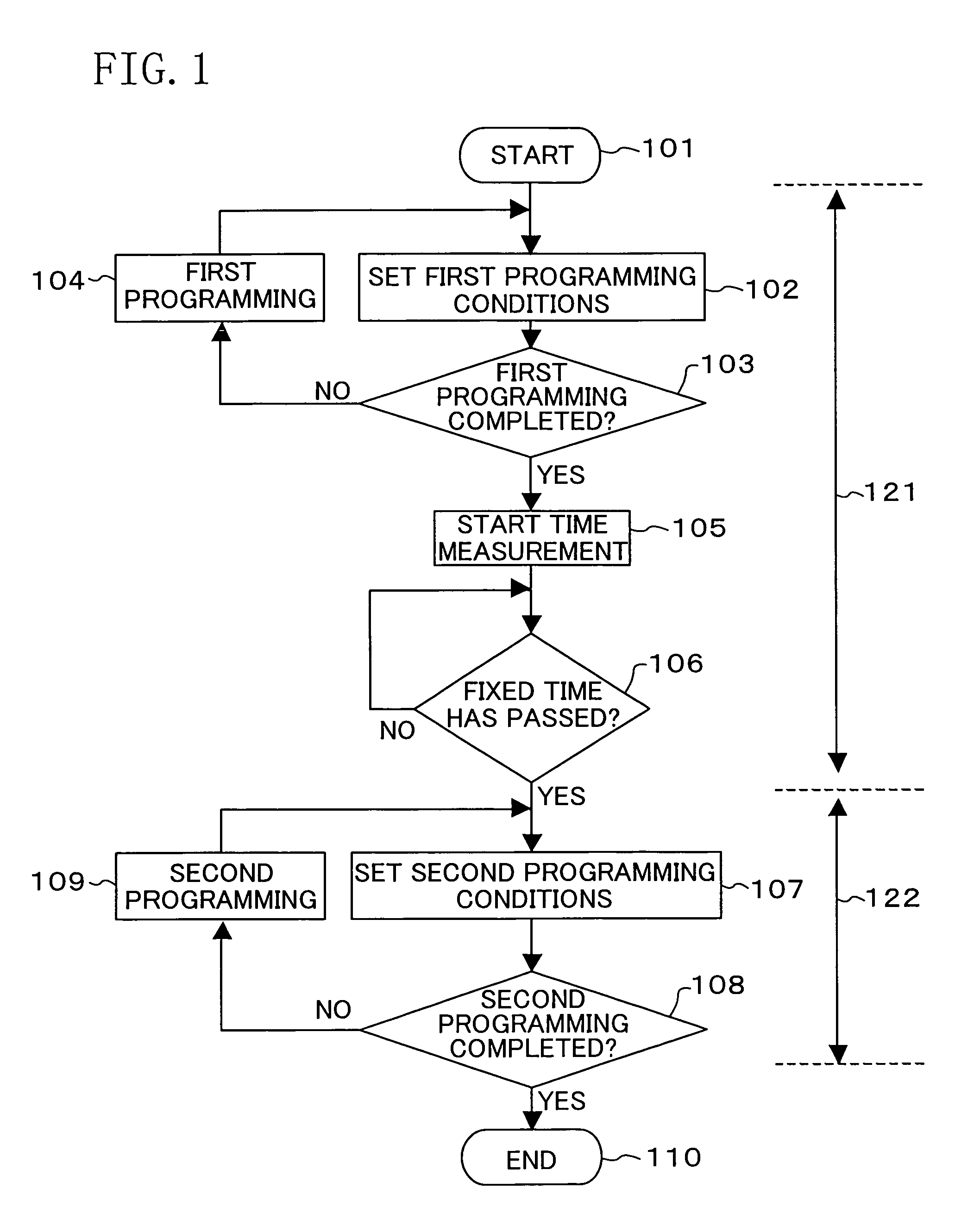
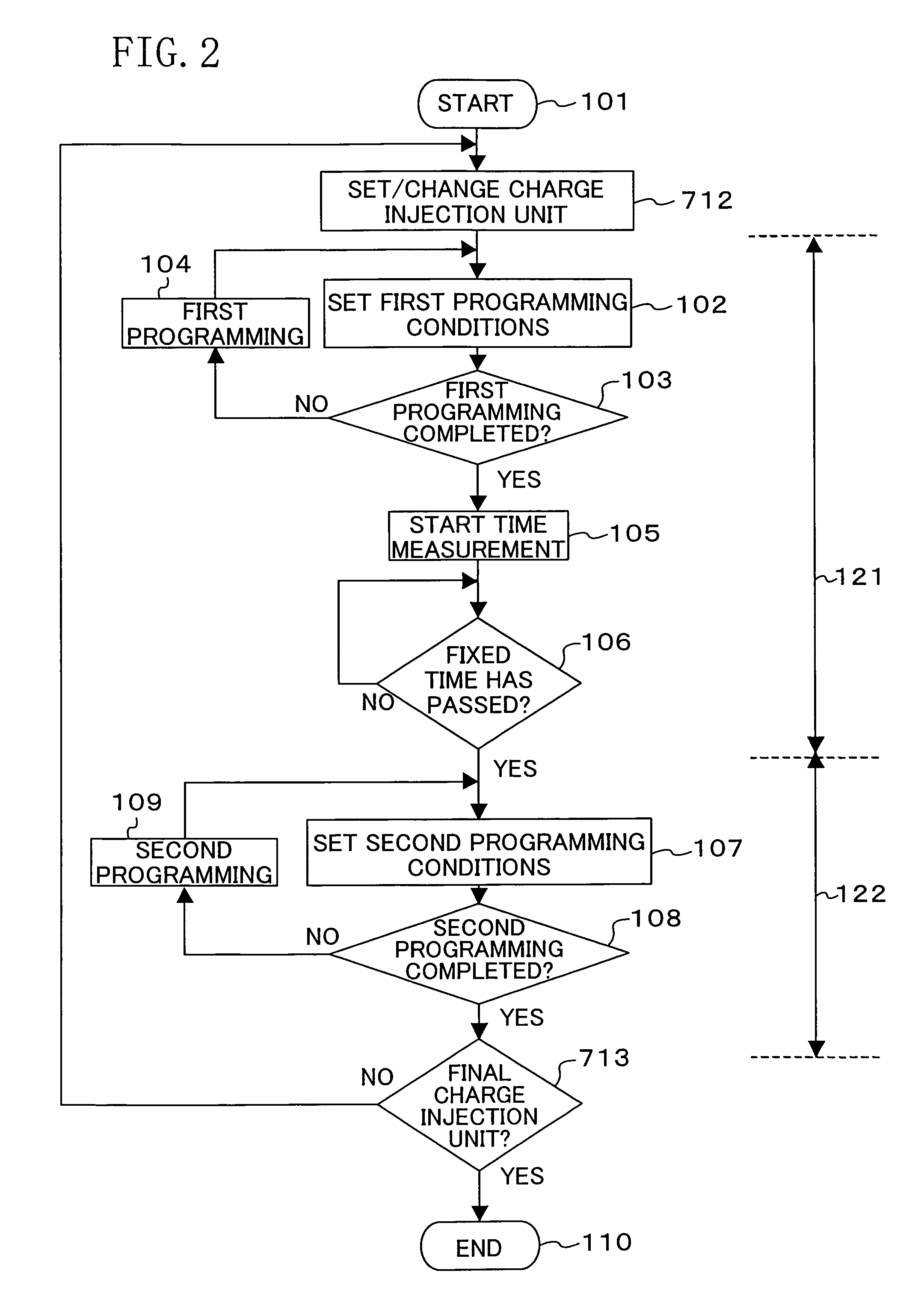
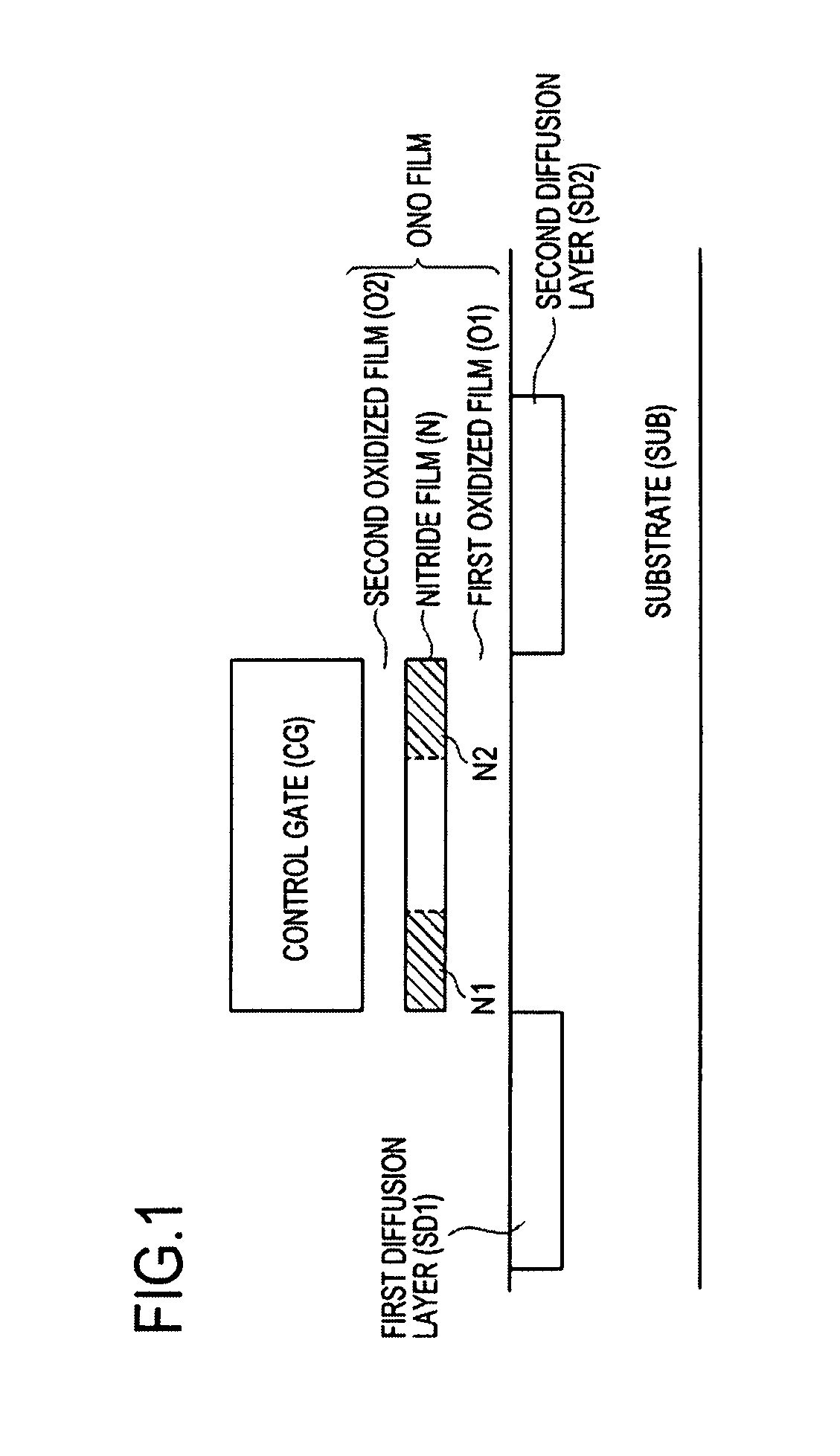
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and programming or erasing method therefor
ActiveUS7460410B2Inhibit deteriorationData retentionRead-only memoriesDigital storageCharge injectionCharge loss
In a nonvolatile memory cell having a trap layer, programming or erasing is made in a sequence of first charge injection with a given wait time being secured and second charge injection executed after the first charge injection. Surrounding charge that deteriorates the data retention characteristic is reduced by use of initial variation occurring immediately after programming (charge loss phenomenon due to binding of injected charge with the surrounding charge in an extremely short time), and then the charge loss due to the initial variation is compensated, to thereby improve the data retention characteristic.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Charge loss detection and prognostics for multi-modular split systems
InactiveUS7159408B2Compression machines with non-reversible cycleFluid circulation arrangementTime segmentCharge loss
Owner:CARRIER CORP
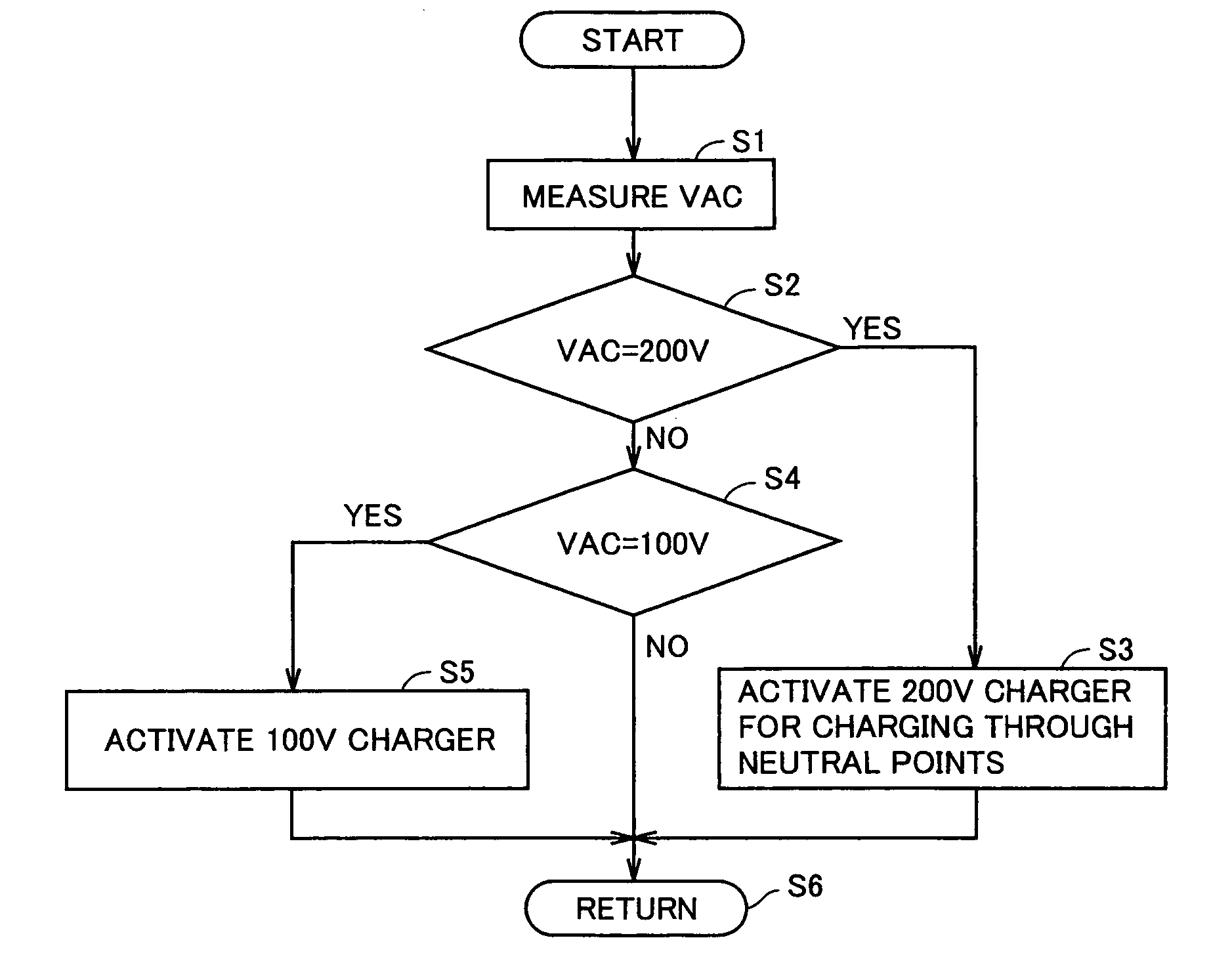
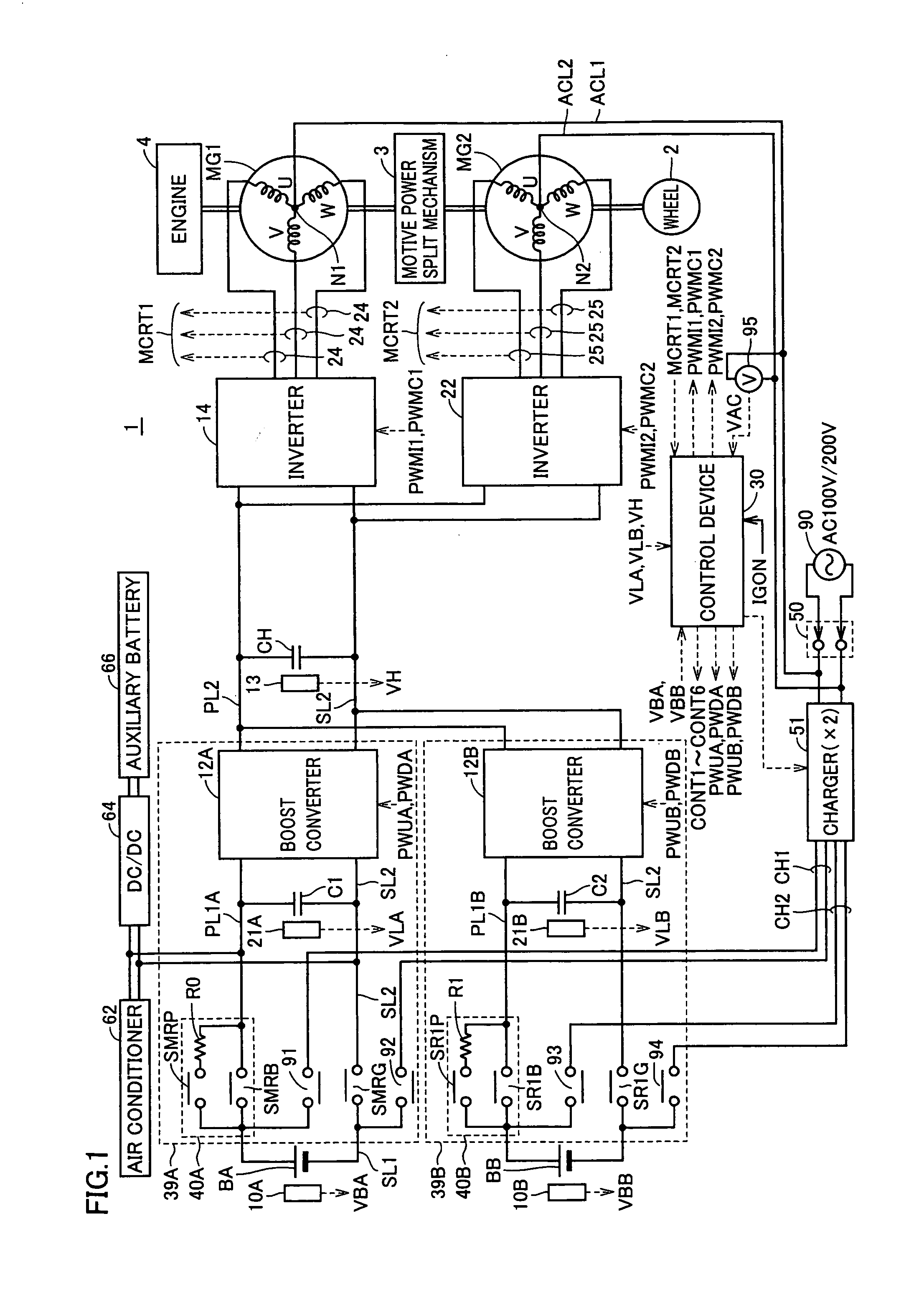
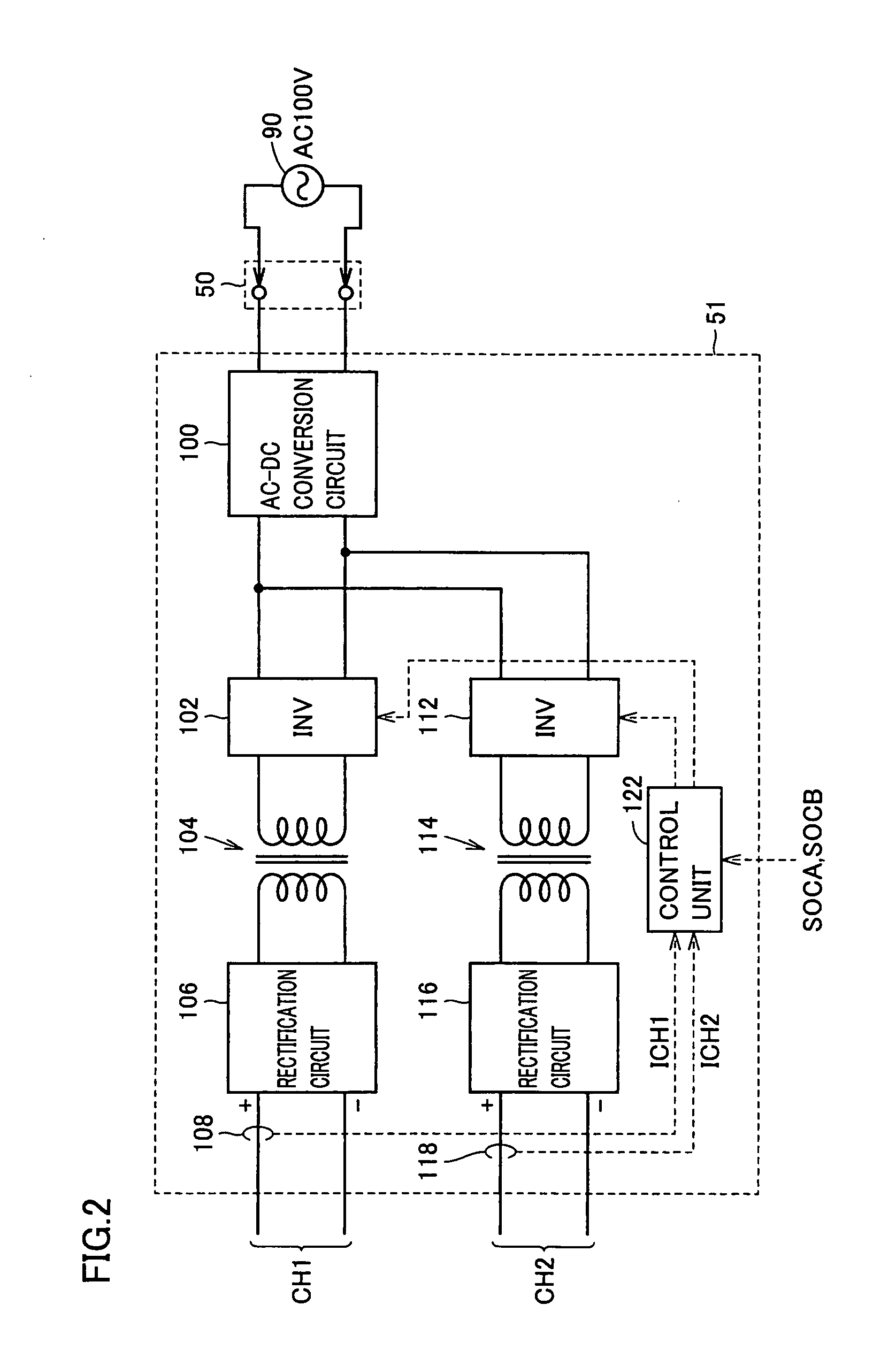
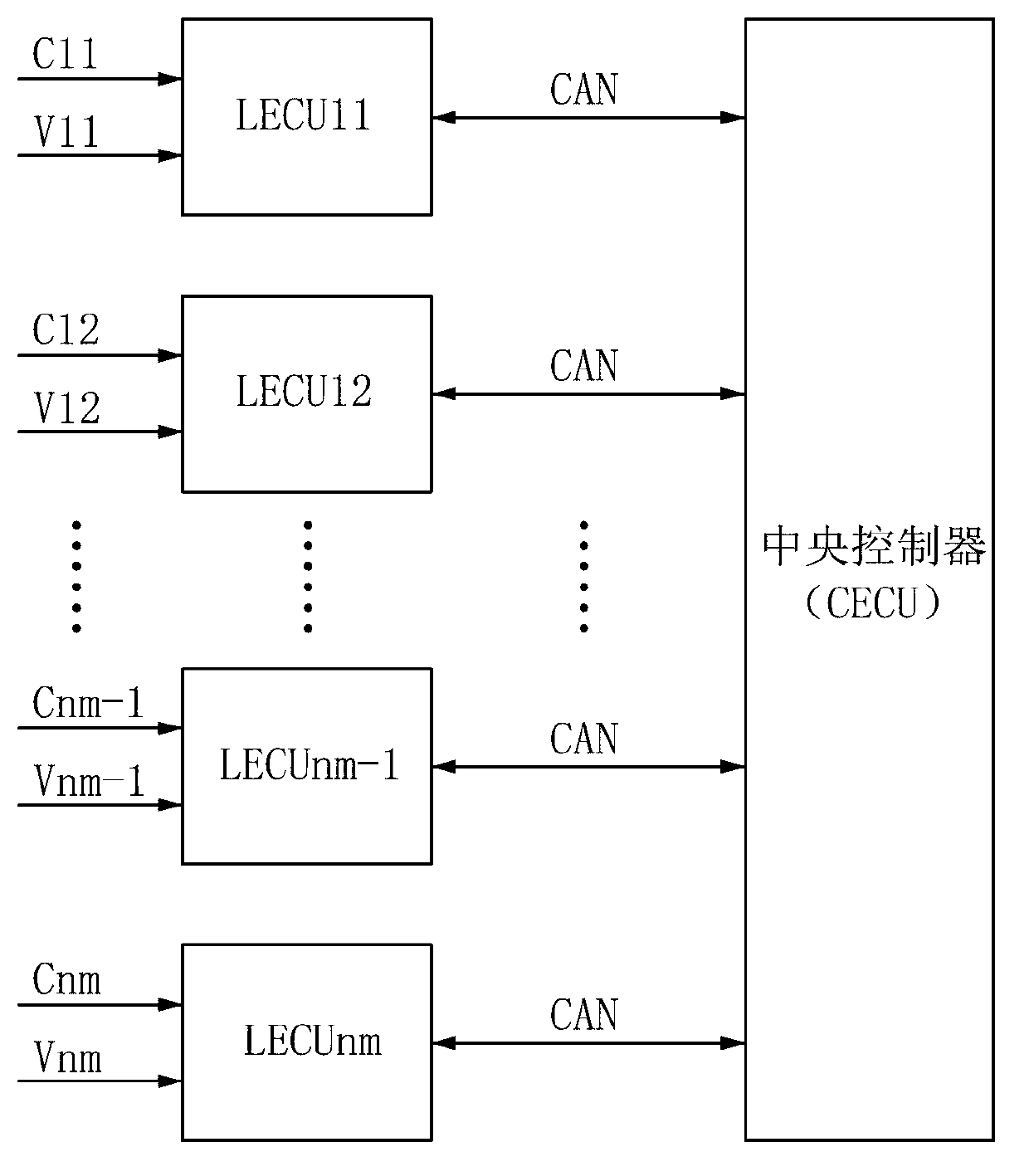
Power supply system for vehicle
ActiveUS20090115375A1Reduce charging lossEfficient chargingBatteries circuit arrangementsCharging stationsElectric power systemElectrical battery
A power supply system for a vehicle includes: batteries; motor generators operating as rotating electrical machines driven by electric power in the batteries when the vehicle is running, and constituting a first charger when the batteries are charged by electric power received from a source external to the vehicle and; an inlet receiving the electric power supplied from the external source; a second charger receiving the electric power supplied from the external source and charging the batteries; and a control device selecting one of the first and second chargers and performing control for converting the electric power supplied from the external source to the inlet into charging electric power using the selected charger. Thus, a power supply system for a vehicle that is chargeable from various power supplies at the time of charging and has reduced charge loss can be provided.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
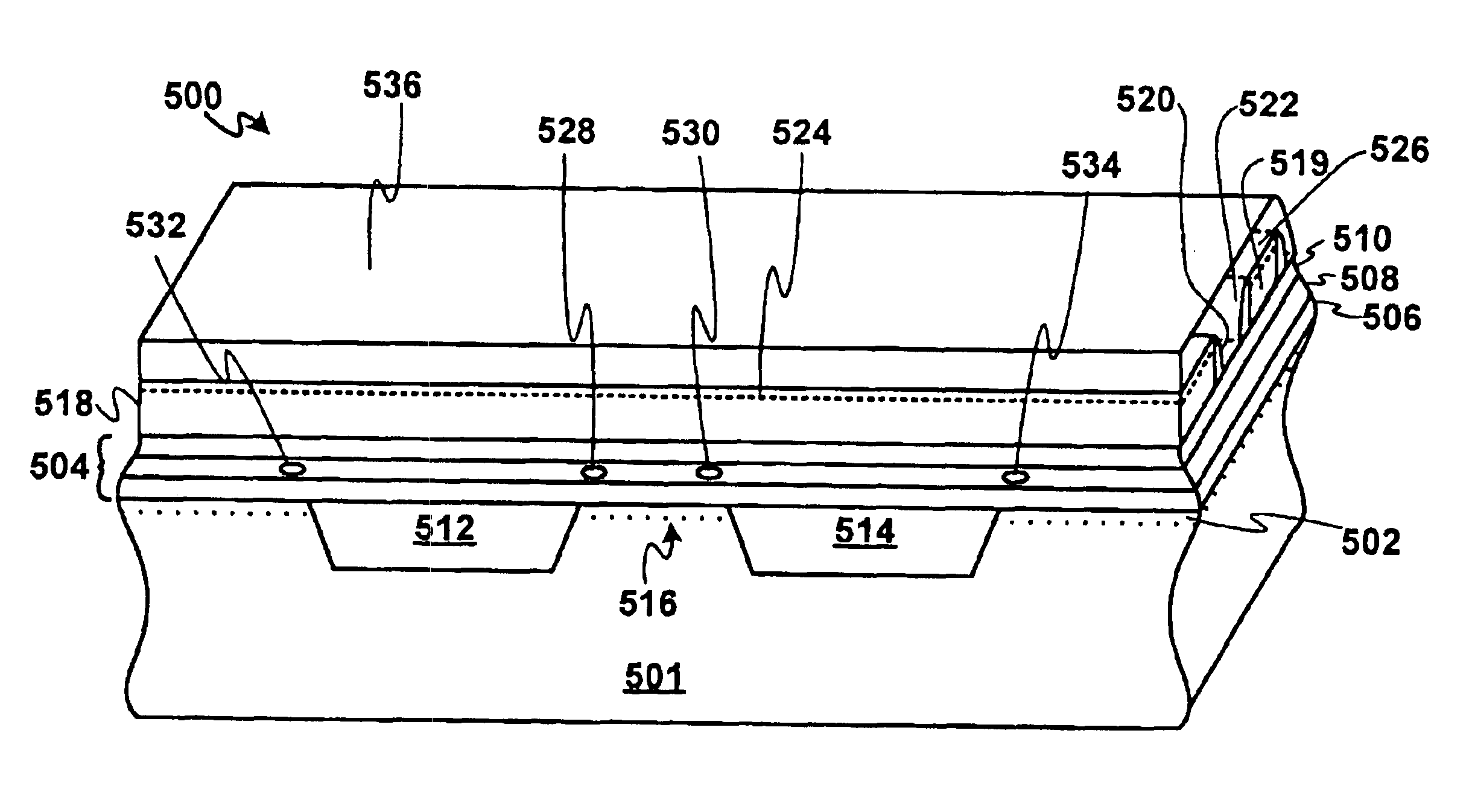
Charge trap flash memory device and memory card and system including the same
ActiveUS20080246078A1Increased charge storage capacityAvoid lossNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanodotCharge loss
A charge trap flash memory device and method of making same are provided. The device includes: a tunnel insulating layer, a charge trap layer; a blocking insulating layer; and a gate electrode sequentially formed on a substrate. The charge trap layer includes: plural trap layers comprising a first material having a first band gap energy level; spaced apart nanodots, each nanodot being at least partially surrounded by at least one of the trap layers, wherein the nanodots comprise a second material having a second band gap energy level that is lower than the first band gap energy level; and an intermediate blocking layer comprising a third material having a third band gap energy level that is higher than the first band gap energy level, formed between at least two of the trap layers. This structure prevents loss of charges from the charge trap layer and improves charge storage capacity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
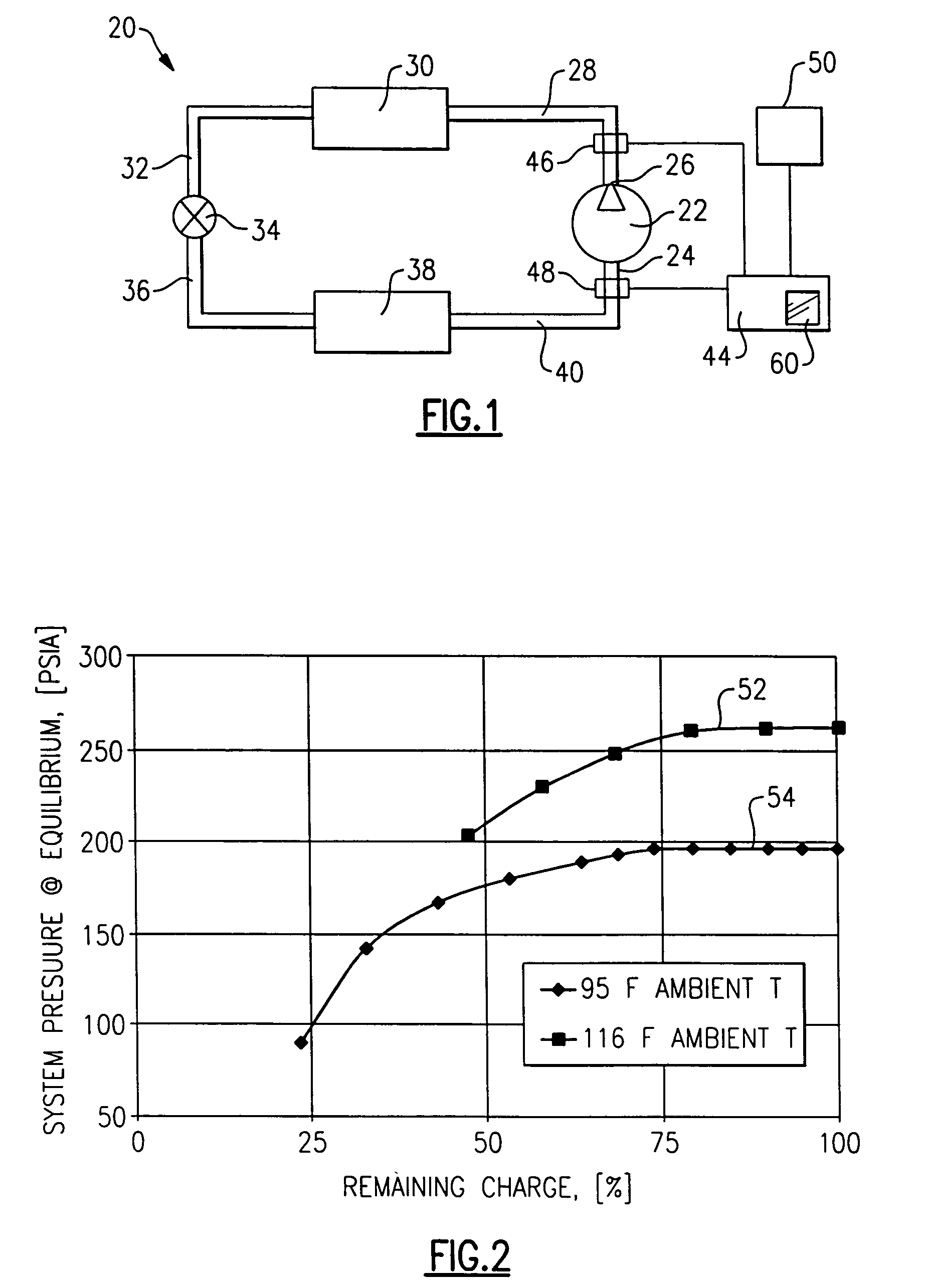
Diagnosing a loss of refrigerant charge in a refrigerant system
InactiveUS7343750B2Thermometer applicationsRefrigeration safety arrangementCharge lossControl theory
A refrigerant system has a controller associated with it that determines an equilibrium pressure when the system is inactive. The controller determines if the equilibrium pressure differs from an expected equilibrium pressure corresponding to a current ambient temperature and the selected refrigerant type. When the difference exceeds a selected threshold, the controller determines that the amount of refrigerant within the circuit is below a desired level. In one example, the controller provides an indication of a low charge amount. The disclosed technique allows early detection of refrigerant charge loss and differentiation between loss-of-charge and other failure modes. Consequently, system performance is enhanced, component damage is prevented, service interruptions and maintenance are reduced, exhaustive troubleshooting is avoided and potential exposure to refrigerant substances is minimized.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
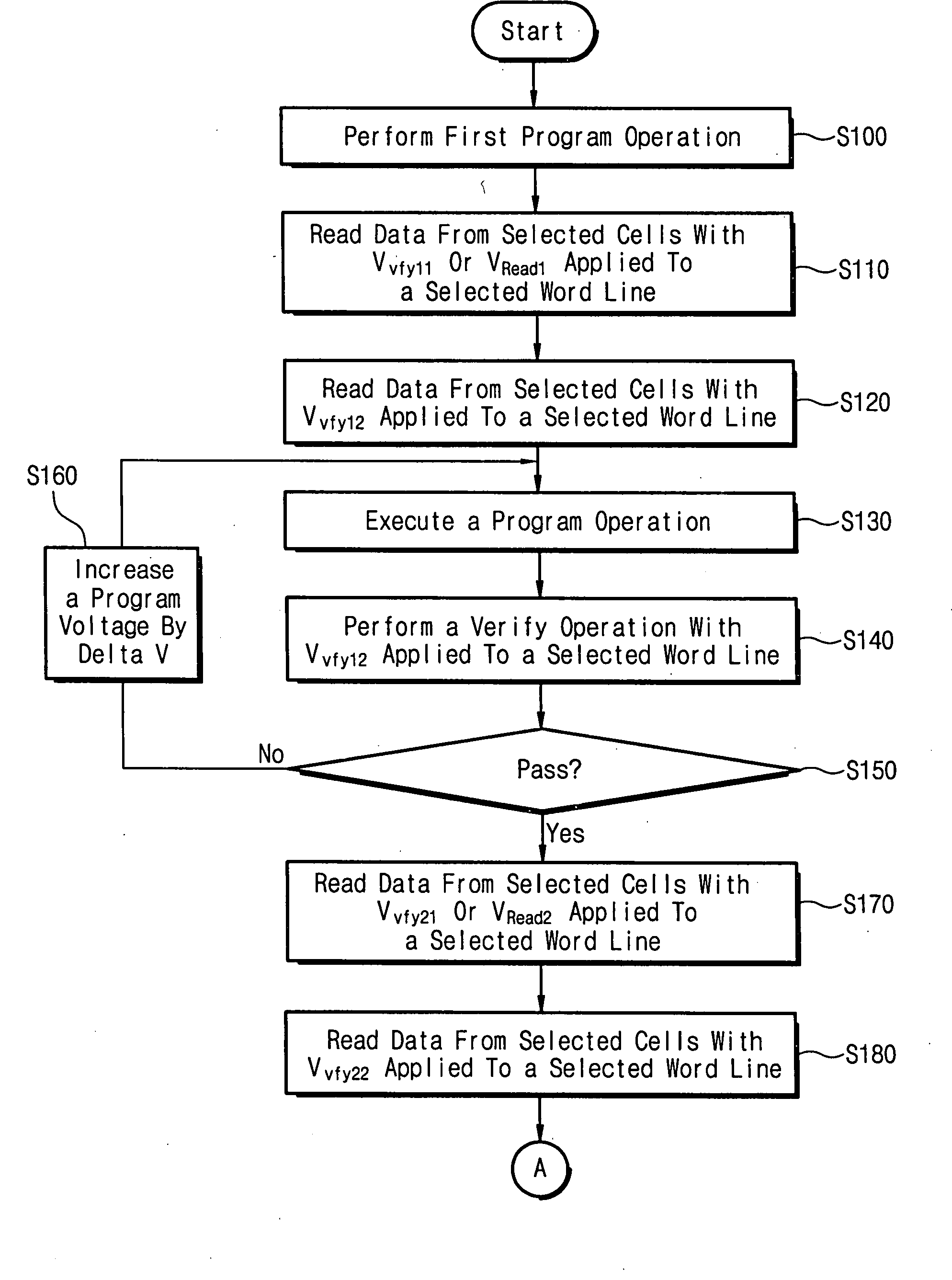
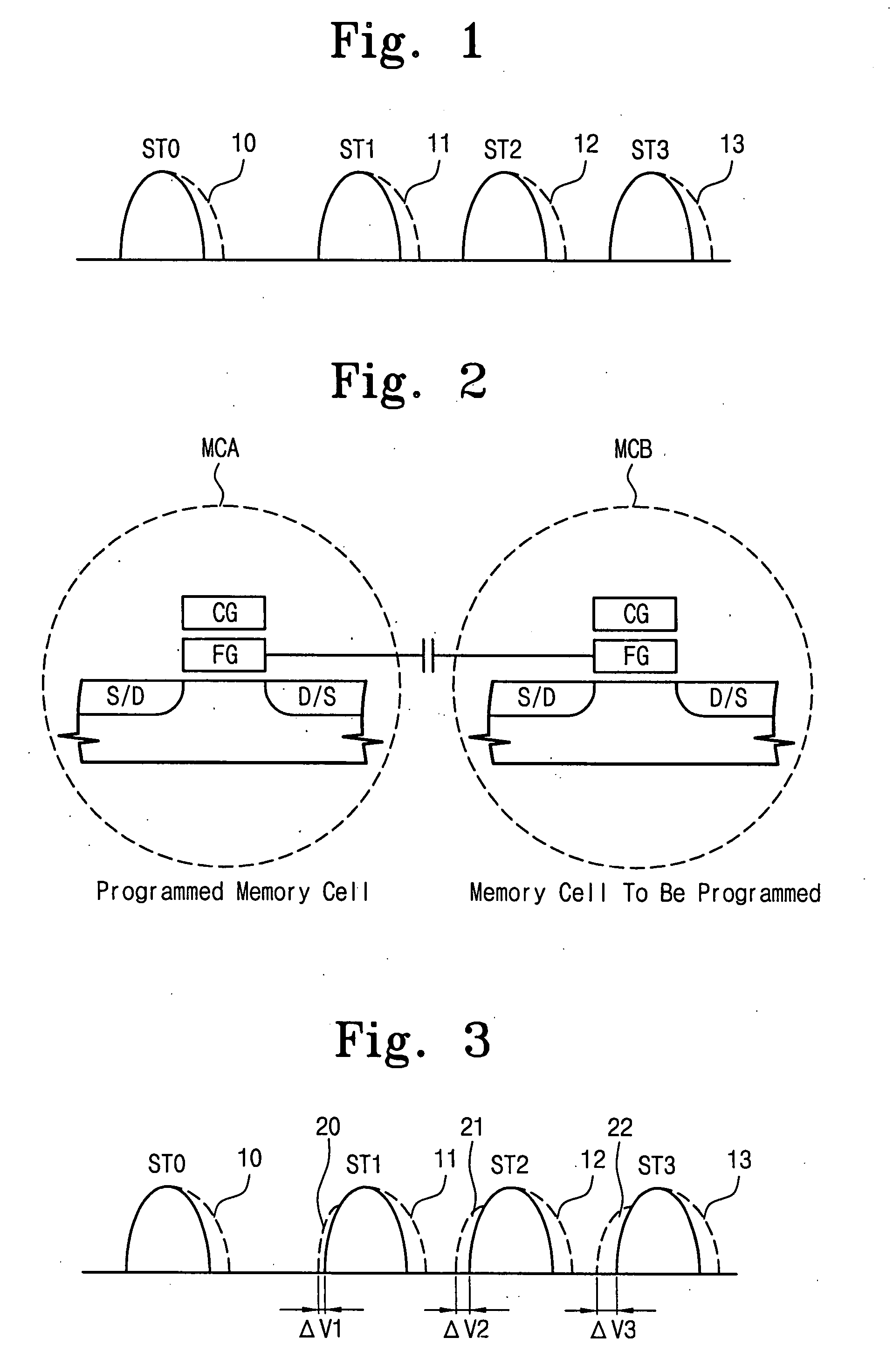
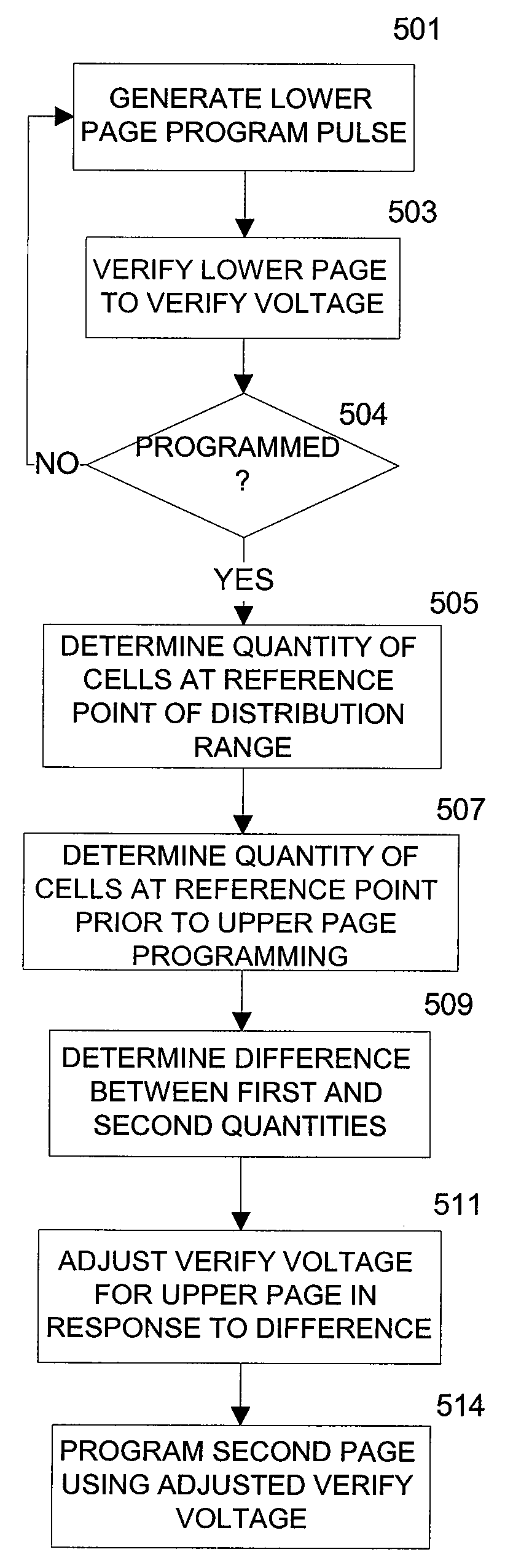
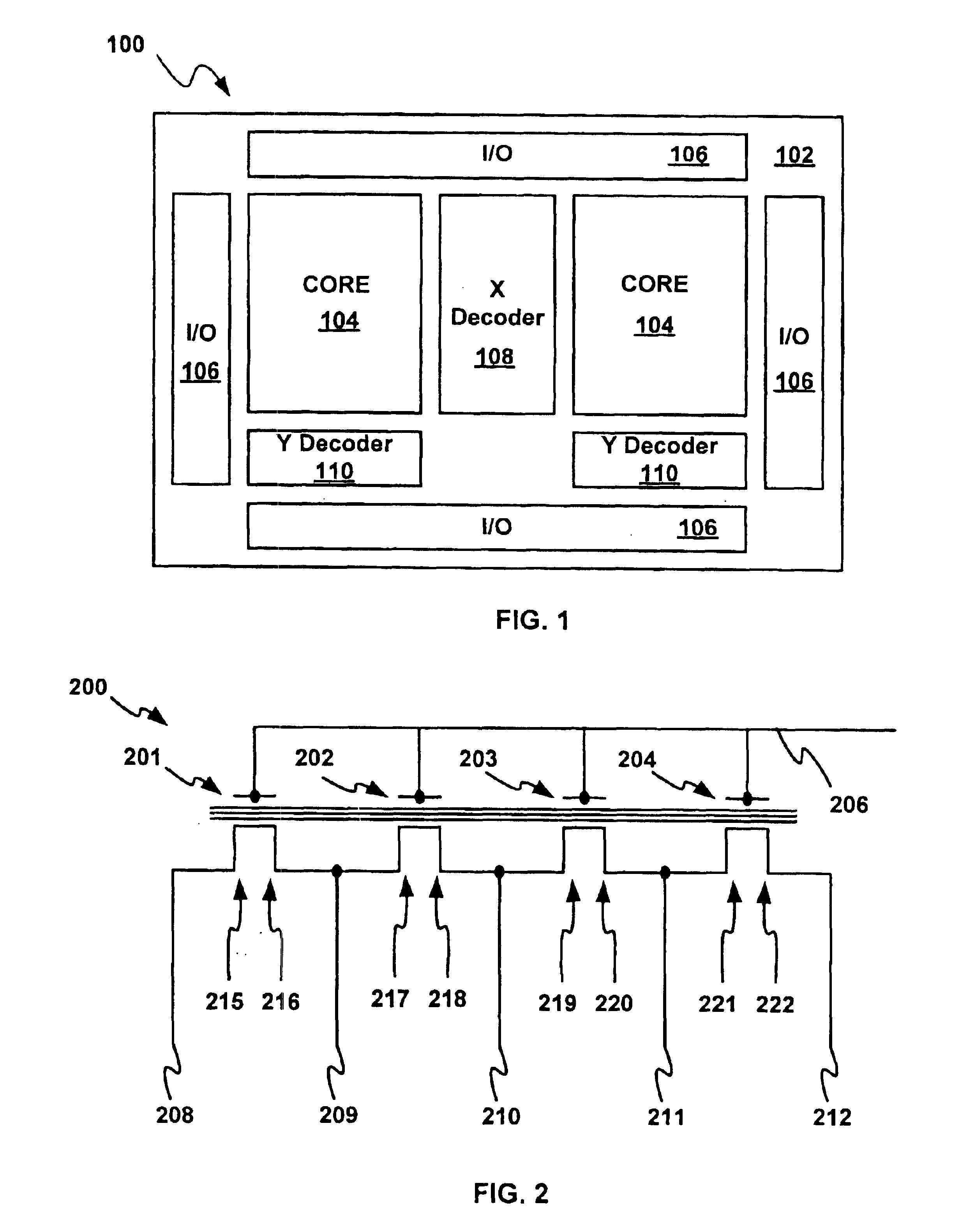
Charge loss compensation during programming of a memory device
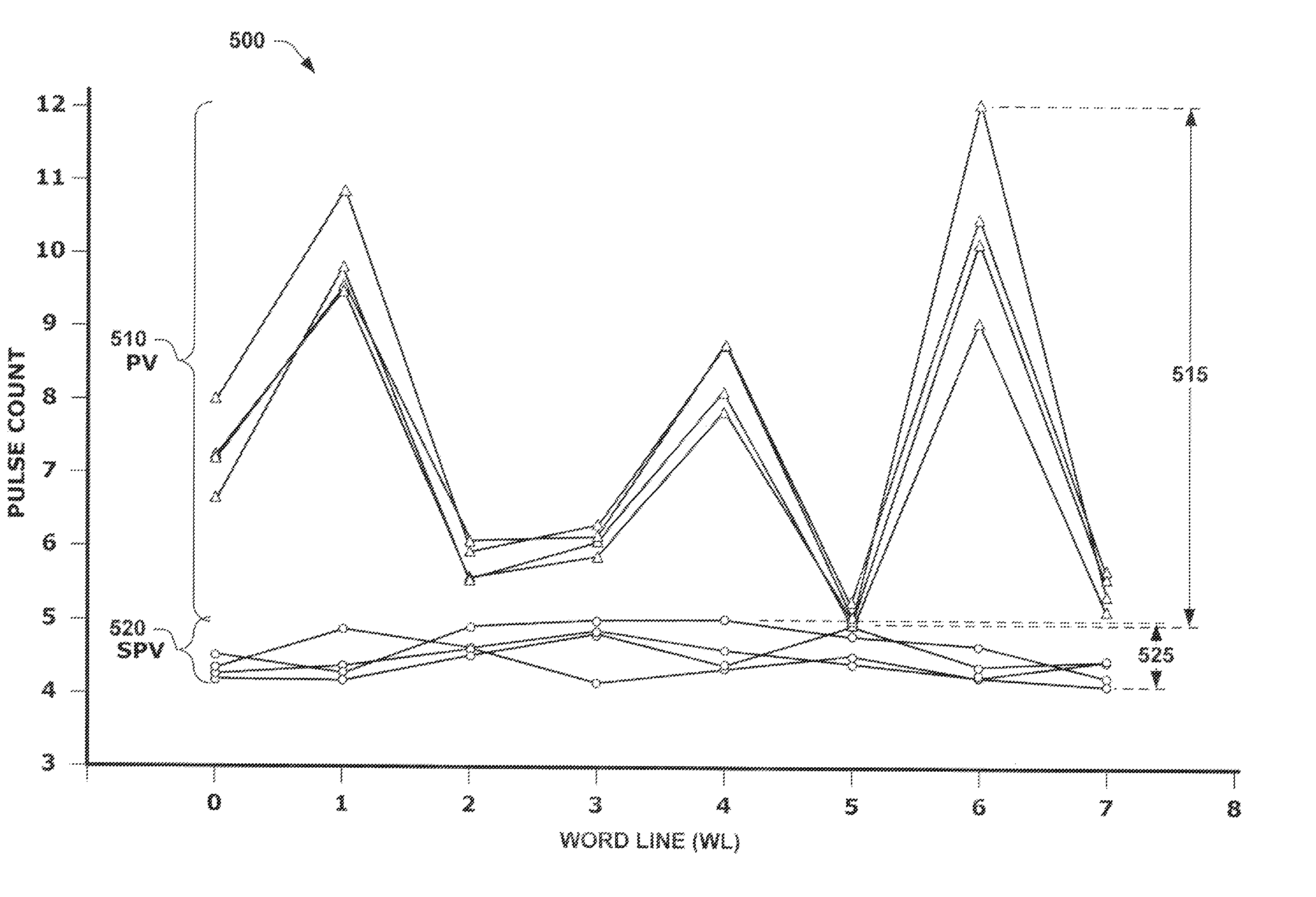
In programming a selected word line of memory cells, a first program verify or read operation is performed, after one page of a selected word line is programmed, in order to determine a first quantity of memory cells that have been programmed to a predetermined reference point in the programmed first page distribution. Prior to programming the second page of the selected word line, a second program verify or read operation is performed to determine a second quantity of cells that are still at the reference point. The difference between the first and second quantities is an indication of the quantity of cells that experienced quick charge loss. The difference is used to determine an adjustment voltage for the second page verification operation after programming of the second page.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Method for analysing amino acids, peptides and proteins
The invention provides methods, reagents and kits for amino acid, peptide and protein identification, differential quantitation and for the analysis of post translational modification and cross-linking status, comprising: derivatizing a mixture of amino acids peptides or proteins, to form at least one amino acid peptide or protein containing a fixed-charge ion, other than at the C-terminal or N-terminal end thereof; introducing the mixture of amino acids peptides or proteins containing the fixed charge derivatized amino acid peptide or protein to a mass spectrometer; passing the mixture of amino acids peptides or proteins containing the fixed charge derivatized amino acid peptide or protein through a first mass resolving spectrometer to select precursor protein or peptide ions having a first desired mass-to-charge ratio; subjecting the precursor ions of the first mass to charge ratio to dissociation to form a product ion having a second mass-to-charge ratio that is characteristic of a fragmentation occurring at a site adjacent to the fixed charge; and detecting the product ions having the second mass-to-charge ratio. The product ion having the second mass-to-charge ratio may be either a product ion formed by neutral loss of the fixed charge from the precursor ion, or a product ion formed by charged loss of the fixed charge from the precursor ion.
Owner:LUDWIG INST FOR CANCER RES
Industrial vapour generator for the deposition of an alloy coating onto a metal strip
ActiveUS20110000431A1Improve evennessEasy to superviseLiquid surface applicatorsVacuum evaporation coatingMetal stripsMetal coating
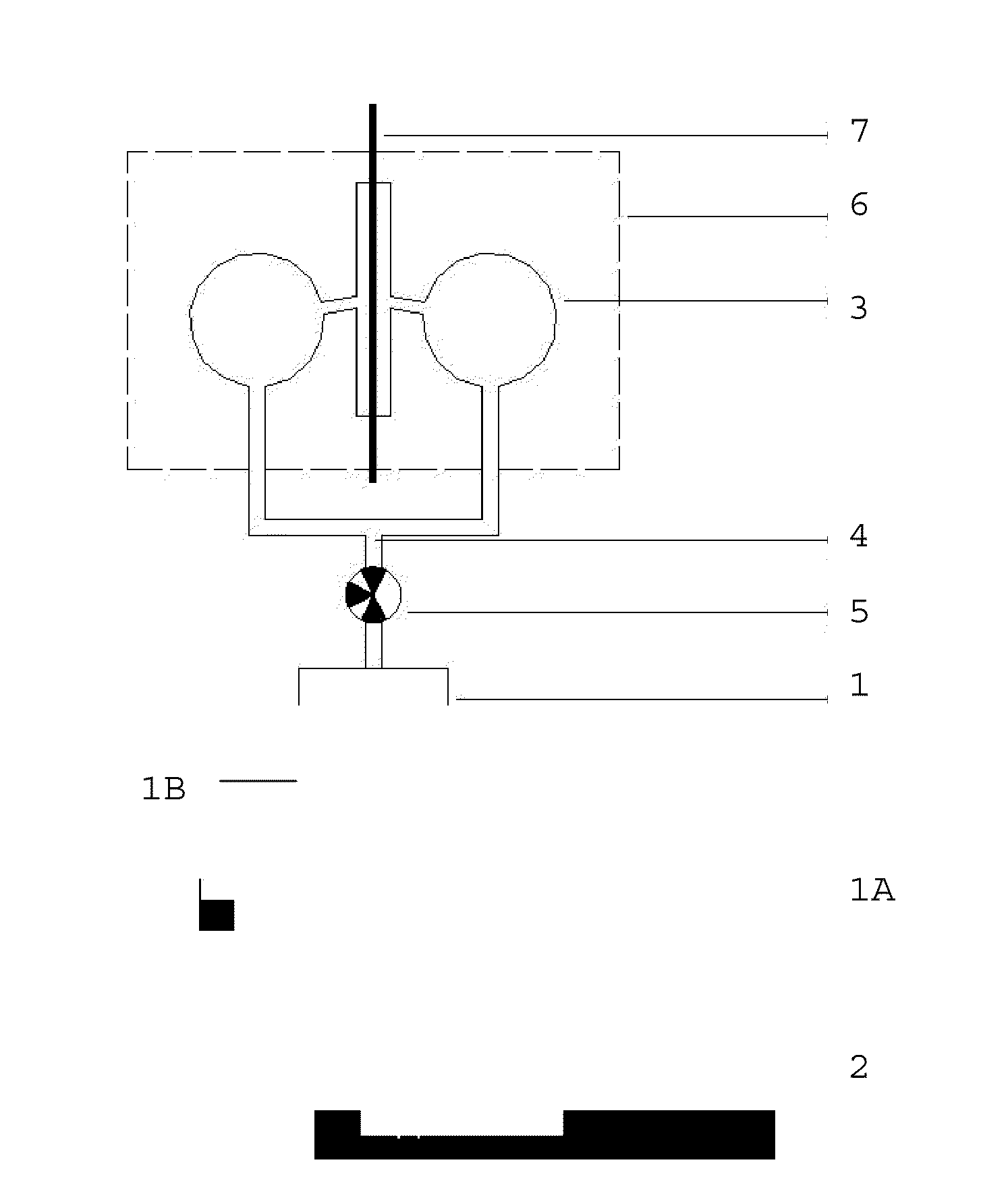
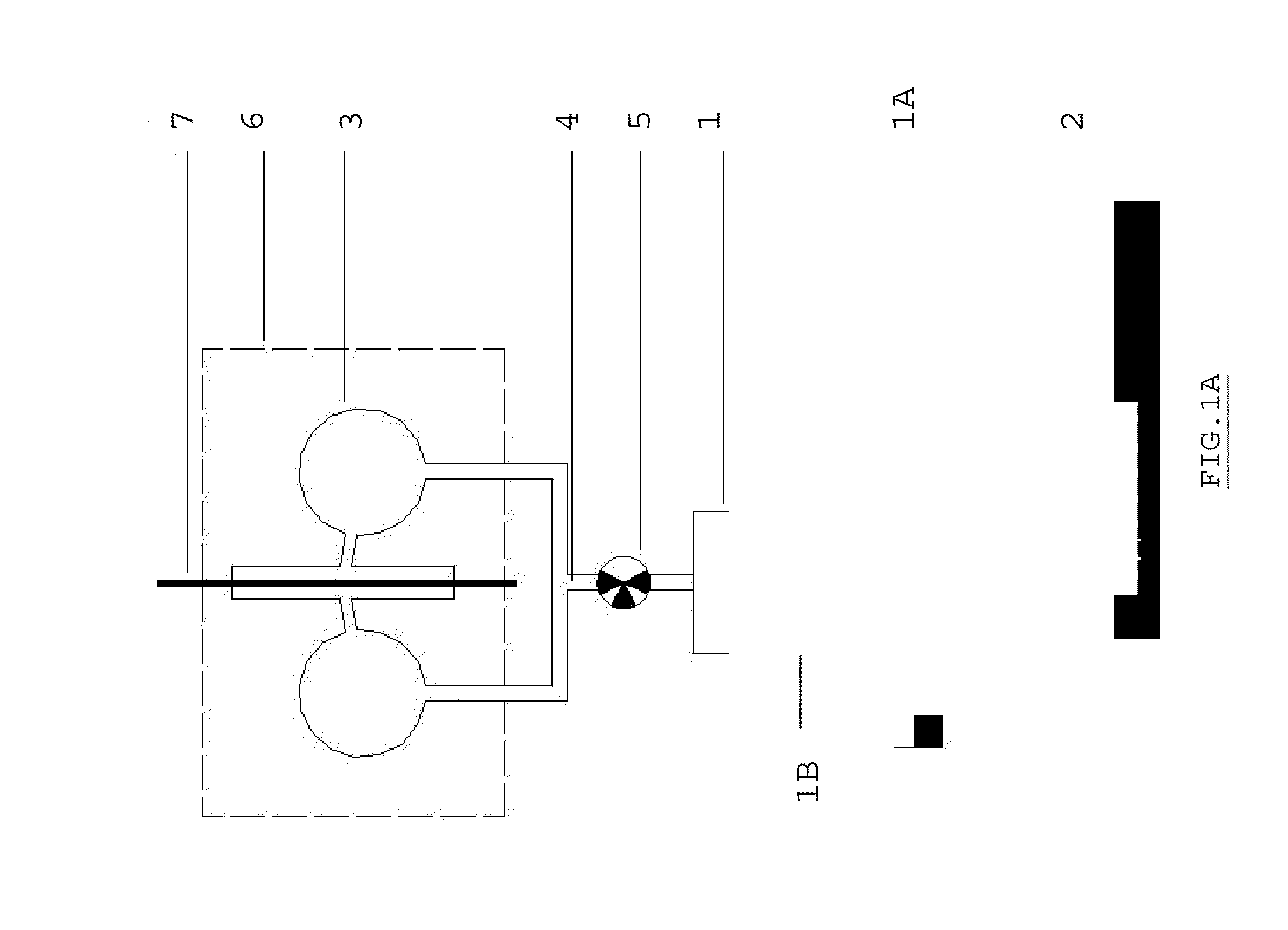
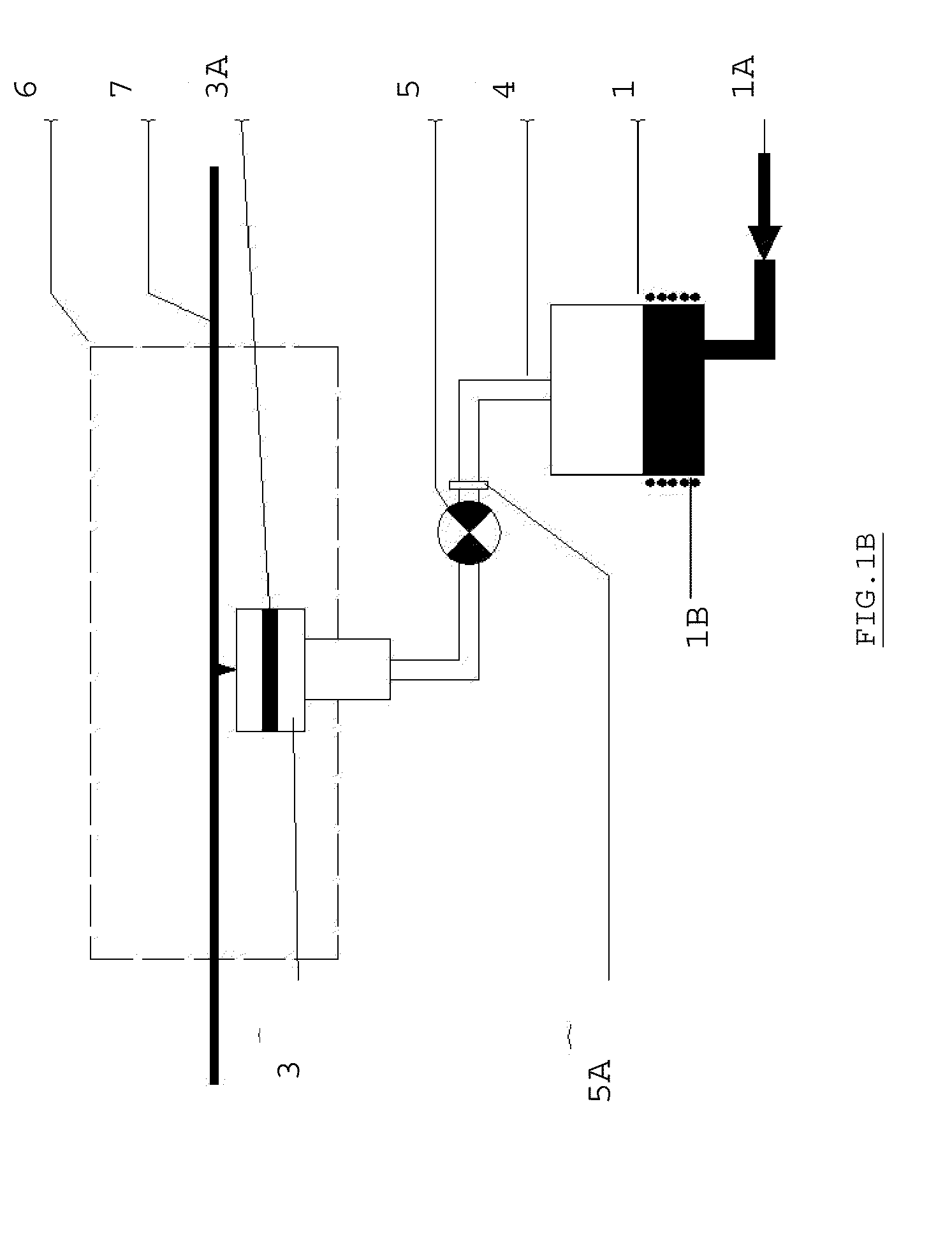
The invention relates to a vapour generator for the deposition of a metal coating onto a substrate (7), preferably a steel strip, that comprises a vacuum chamber (6) in the form of a housing including a vapour deposition head or ejector (3) in tight communication via a supply duct (4) with at least one crucible (1) containing the coating metal in a liquid form and located outside the vacuum chamber (6), characterised in that the ejector (3) includes a longitudinal slot for the vapour outlet acting as a sonic throat and extending on the entire width of the substrate (7), a filtration medium or a charge loss member (3A) made of a sintered material being provided in the ejector immediately before said slot on the vapour path in order to equalise the flow speed of the vapour exiting the ejector (3) through the sonic throat.
Owner:ARCELORMITTAL INVESTIGACION Y DESARROLLO SL
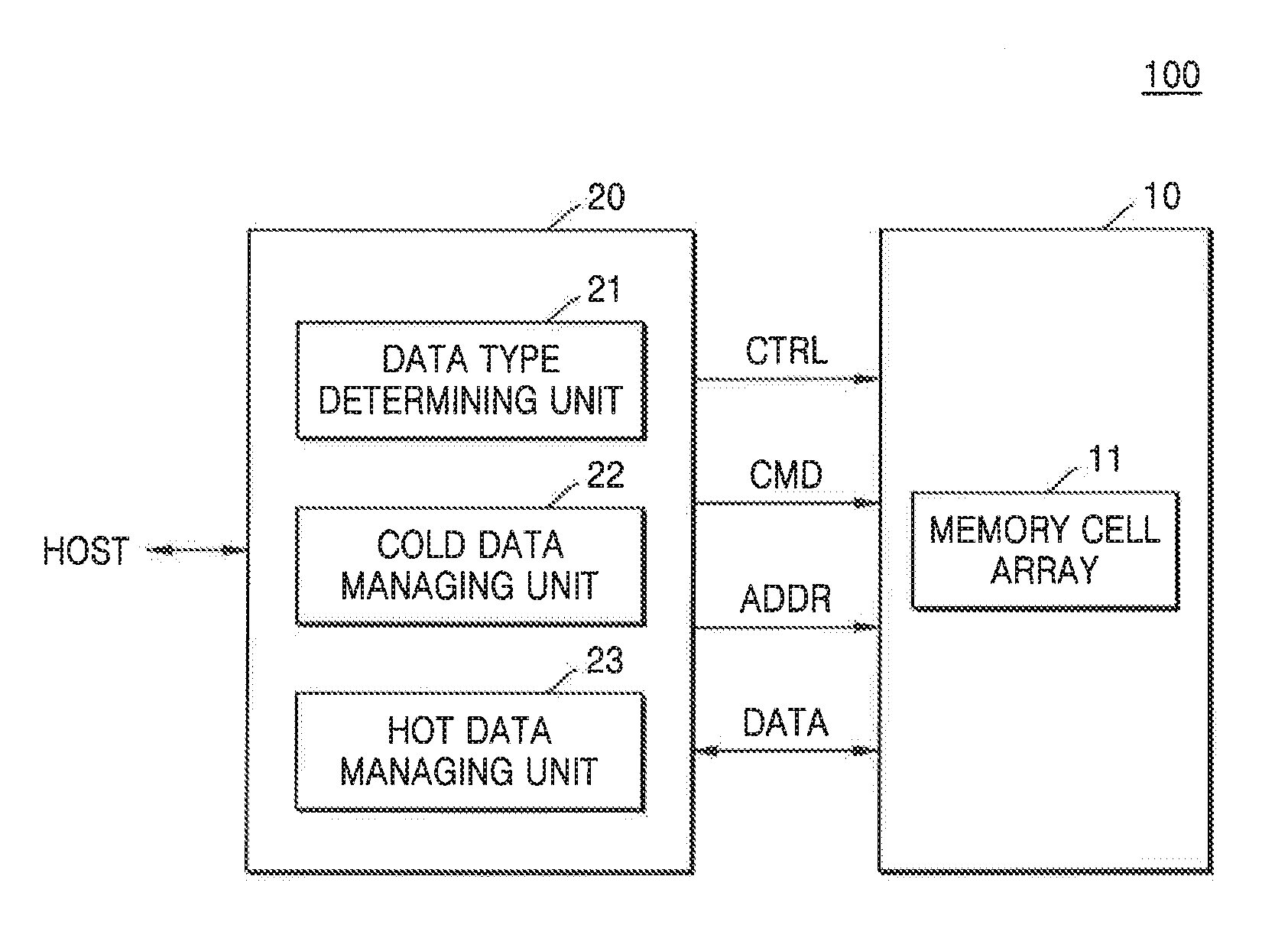
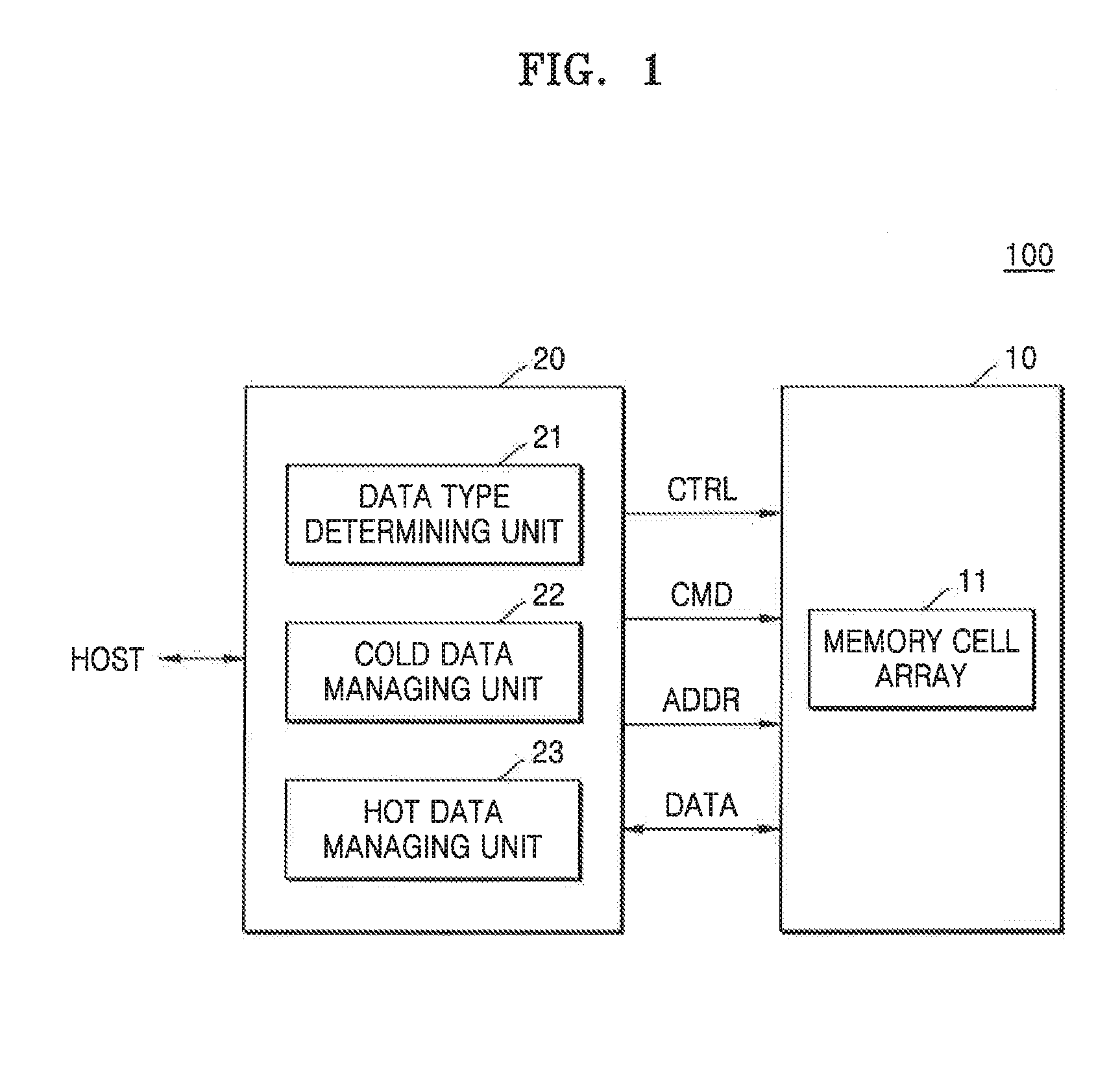
Storage medium, memory system, and method of managing storage area in memory system
InactiveUS20160011971A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCharge lossComputer science
A method of managing a storage area of a memory device in a memory system is provided. A first data is received. The first data has a logical address to be written to the memory device having a plurality of memory blocks. The first data is classified into one of a hot data and a cold data based on an update frequency of the first data. A memory block is defined into a first storage area and a second storage area based on an amount of charge loss of a memory cell in the memory block. A memory cell of the first storage area has charge loss greater than a memory cell of the second storage area. The logical address of the first data is converted to a physical address of the memory device according to a result of the classifying of the first data. The first data is written to a memory cell having the physical address of the memory device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
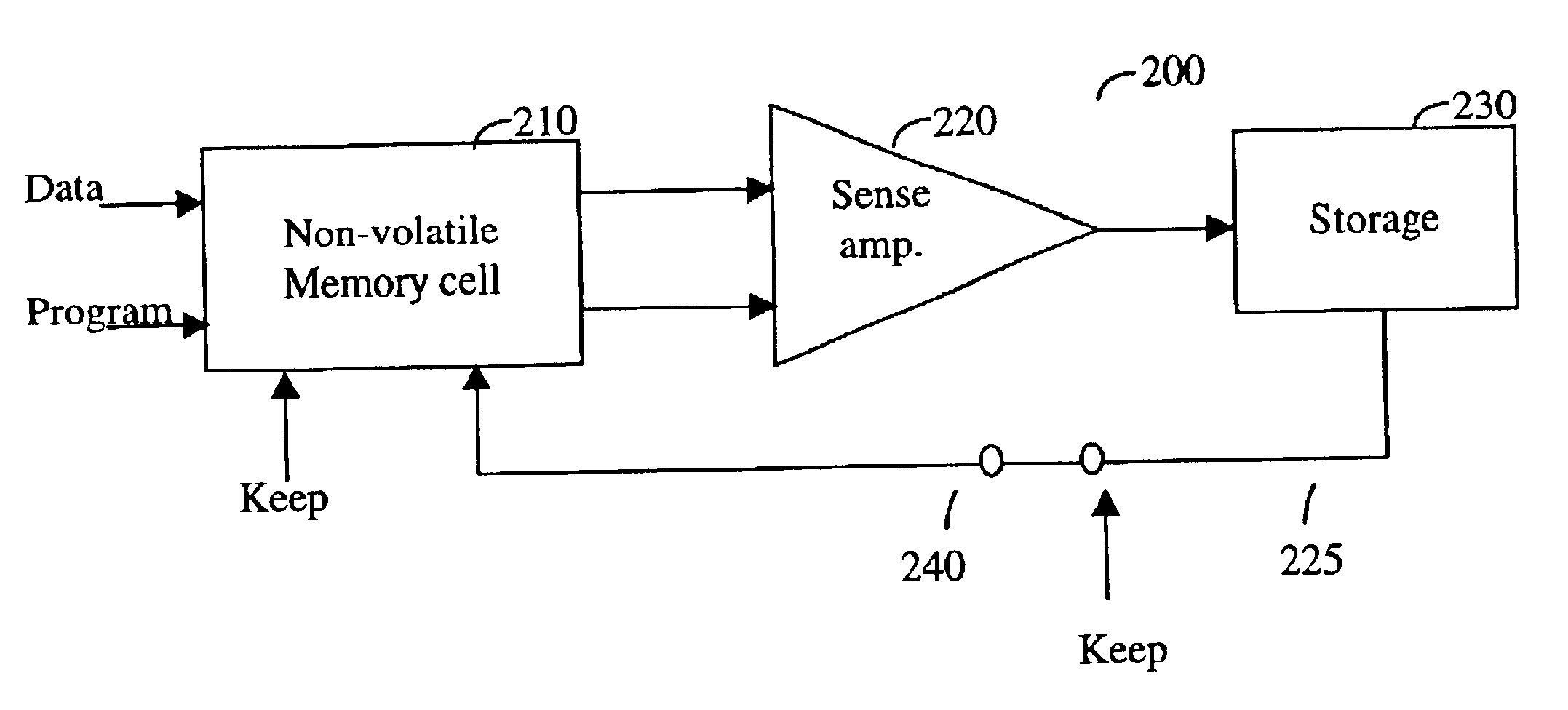
Methods and apparatuses for maintaining information stored in a non-volatile memory cell
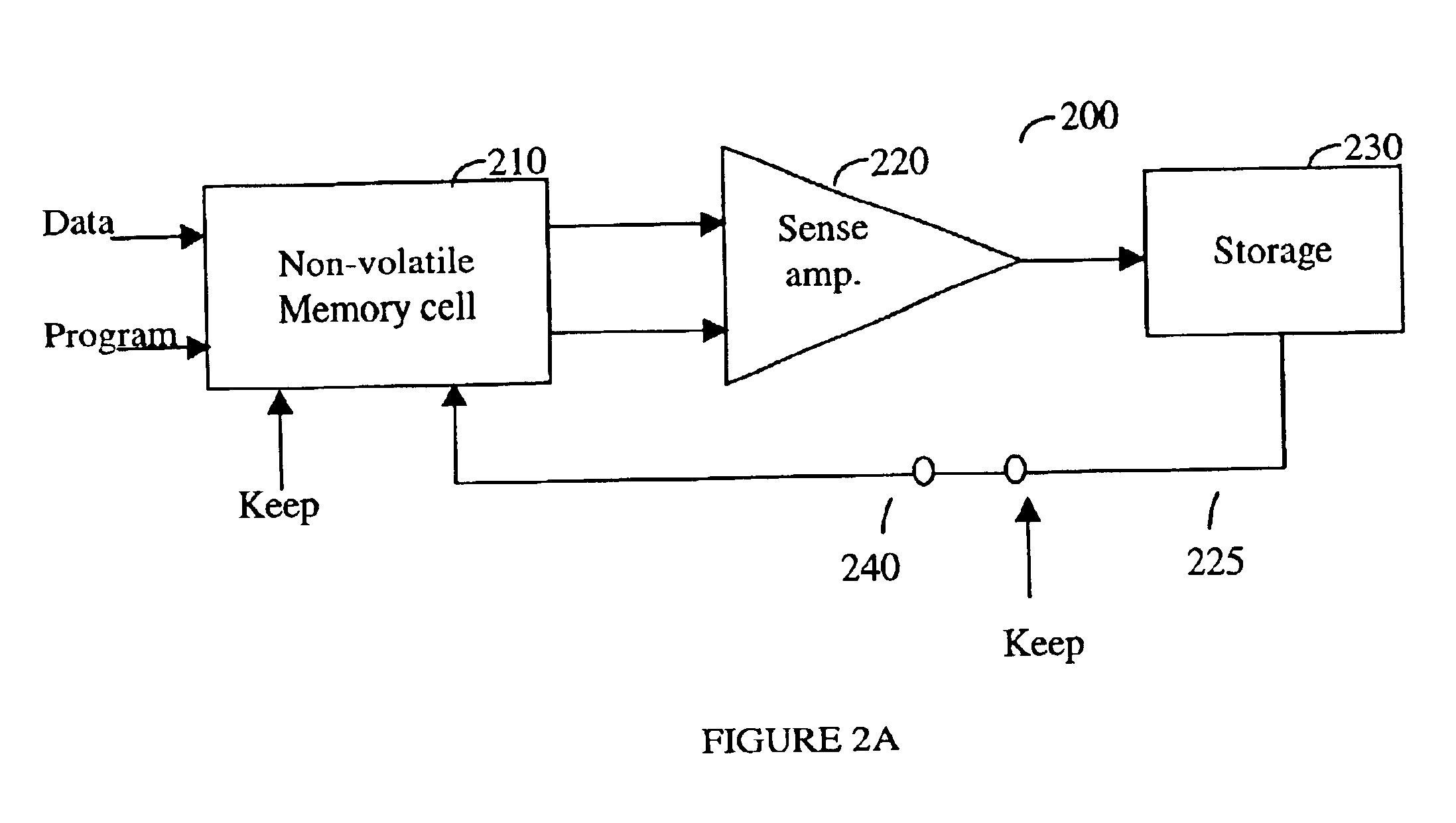
Various apparatuses and methods in which an integrated circuit includes a non-volatile memory cell and a keep mode circuit. The non-volatile memory cell has a charge storage component. The keep mode circuit has a storage device and a keep mode switch. The storage device receives information stored in the non-volatile memory cell. The keep mode switch connects the storage device to the non-volatile memory cell in order to apply a static bias voltage across the charge storage component to restrict charge-loss to a predetermined level.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
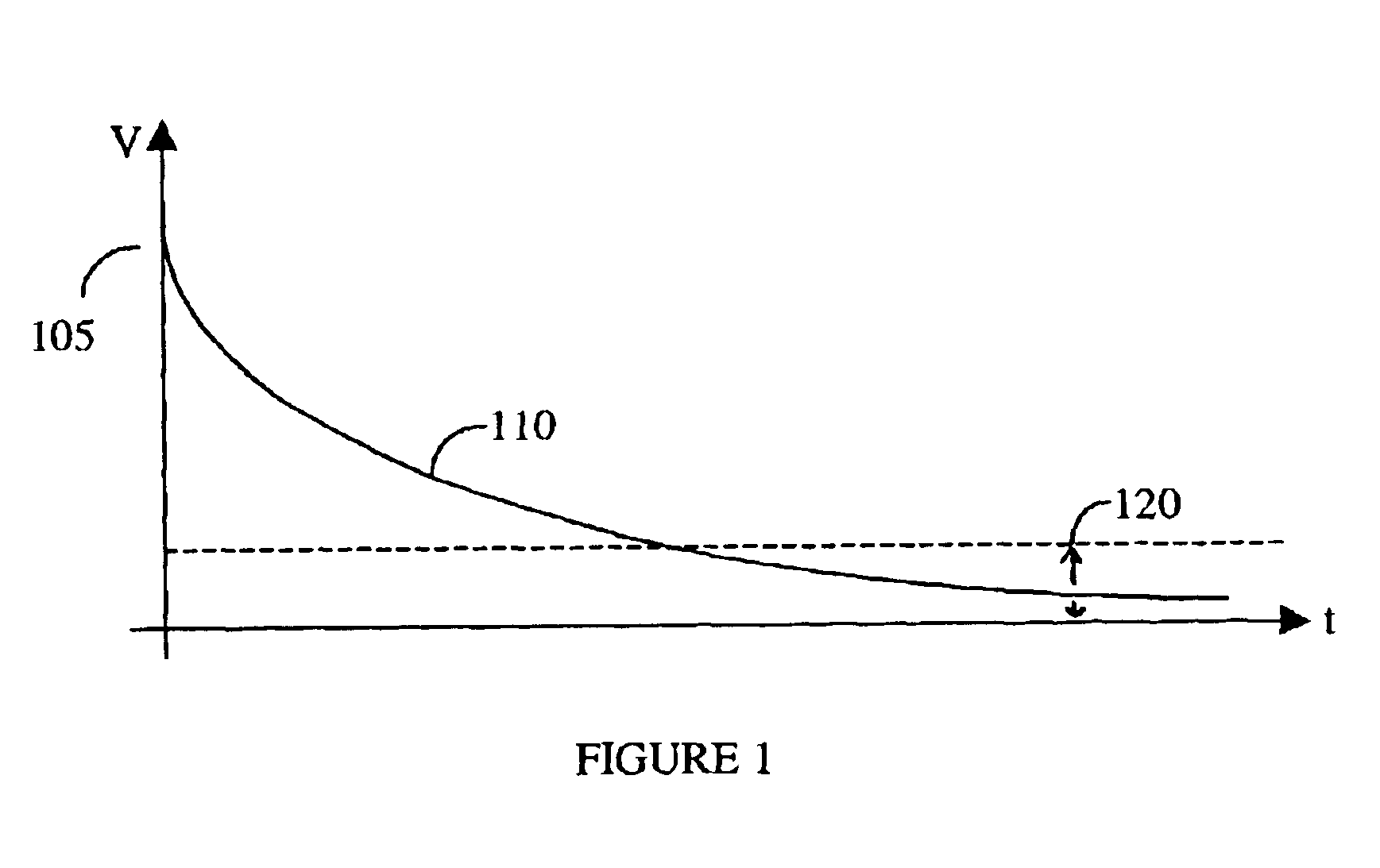
Method and apparatus for maintaining energy storage in an electrical storage device
A method and an apparatus for performing maintaining a charge in an electrical energy storing device, such as a capacitor. A set-point voltage for the electrical energy storage device is used during an initial device charging process to charge the storage device to the set-point voltage. A charge maintenance process is also performed that offsets charge loss due to leakage currents, polarization currents and the like. The charge maintenance process involves providing a charge maintenance current to the storage device until the storage device is therapeutically discharged (e.g., during cardiac defibrillation therapy delivery).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Ferroelectric capacitor with parallel resistance for ferroelectric memory
ActiveUS7180141B2Easy dischargeReduce areaSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringCharge loss
Ferroelectric memory cells (3) are presented, in which a cell resistor (R) is integrated into the cell capacitor (C) to inhibit charge accumulation or charge loss at the cell storage node (SN) when the cell (3) is not being accessed while avoiding significant disruption of memory cell access operations. Methods (100, 200) are provided for fabricating ferroelectric memory cells (3) and ferroelectric capacitors (C), in which a parallel resistance (R) is integrated in the capacitor ferroelectric material (20) or in an encapsulation layer (46) formed over the patterned capacitor structure (C).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Algorithm for charge loss reduction and Vt distribution improvement
InactiveUS7619932B2Reduce charging lossHigh data reliabilityRead-only memoriesDigital storageCharge lossData reliability
Methods and systems for accurately programming or erasing one or more memory cells on a selected wordline of a memory device are provided. In one embodiment, the memory device comprises a memory array, a threshold voltage measuring component configured to measure a threshold voltage of each memory cell on the selected wordline of the memory array, and an average threshold voltage determining component configured to determine an average threshold voltage result uniquely associated with the selected wordline, based on the measured threshold voltages. The memory device is configured to program one or more of the memory cells to a predefined program level relative to the determined average threshold voltage, or to erase memory cells of the selected wordline to the determined average threshold voltage. The method is particularly useful for multi-level flash memory cells to reduce charge loss while improving data reliability and Vt distributions of the programmed element states.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor memory with deuterated materials
InactiveUS6884681B1Improve data retentionReduce charging lossTransistorSolid-state devicesHydrogenInter layer
A method for manufacturing a MirrorBit® Flash memory includes providing a semiconductor substrate and successively depositing a first insulating layer, a charge-trapping layer, and a second insulating layer. First and second bitlines are implanted and wordlines are formed before completing the memory. Spacers are formed between the wordlines and an inter-layer dielectric layer is formed over the wordlines. One or more of the second insulating layer, wordlines, spacers, and inter-layer dielectric layers are deuterated, replacing hydrogen bonds with deuterium, thus improving data retention and substantially reducing charge loss.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
Method For Detection Of Loss Of Refrigerant
A method is provided for detecting in real-time a refrigerant charge loss in a refrigerant vapor compression system. If both a sensed evaporator outlet superheat exceeds a target evaporator outlet superheat by at least a preset amount of superheat and a sensed degree of openness of an electronic expansion valve exceeds a preset degree of openness for a preset time of period, and a sensed air temperature of either a flow of supply air having traversed the evaporator or a flow of return air returning to the evaporator is changing at a rate less than preset air temperature rate of change, a service alarm is generated indicating a loss of charge warning.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
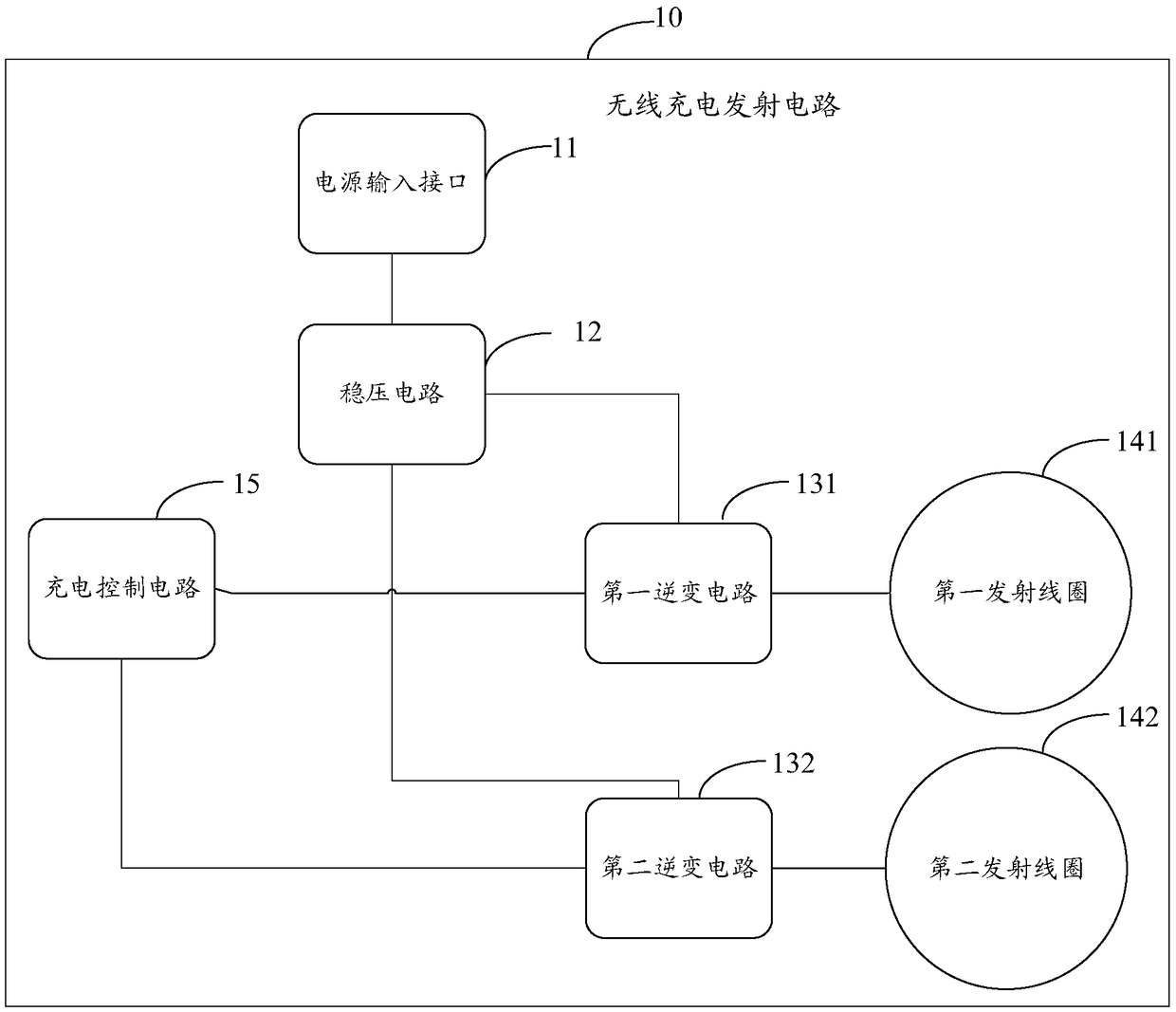
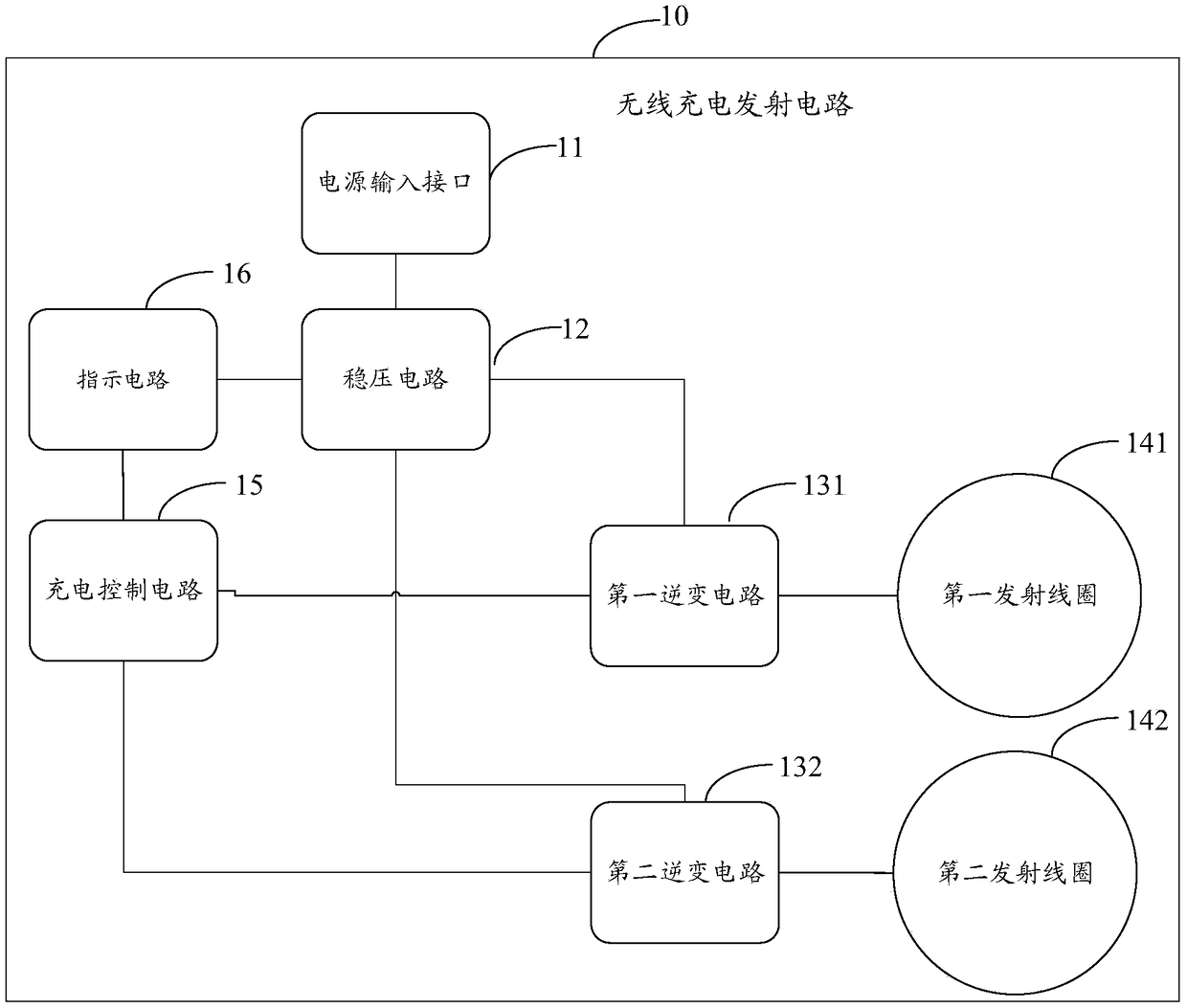
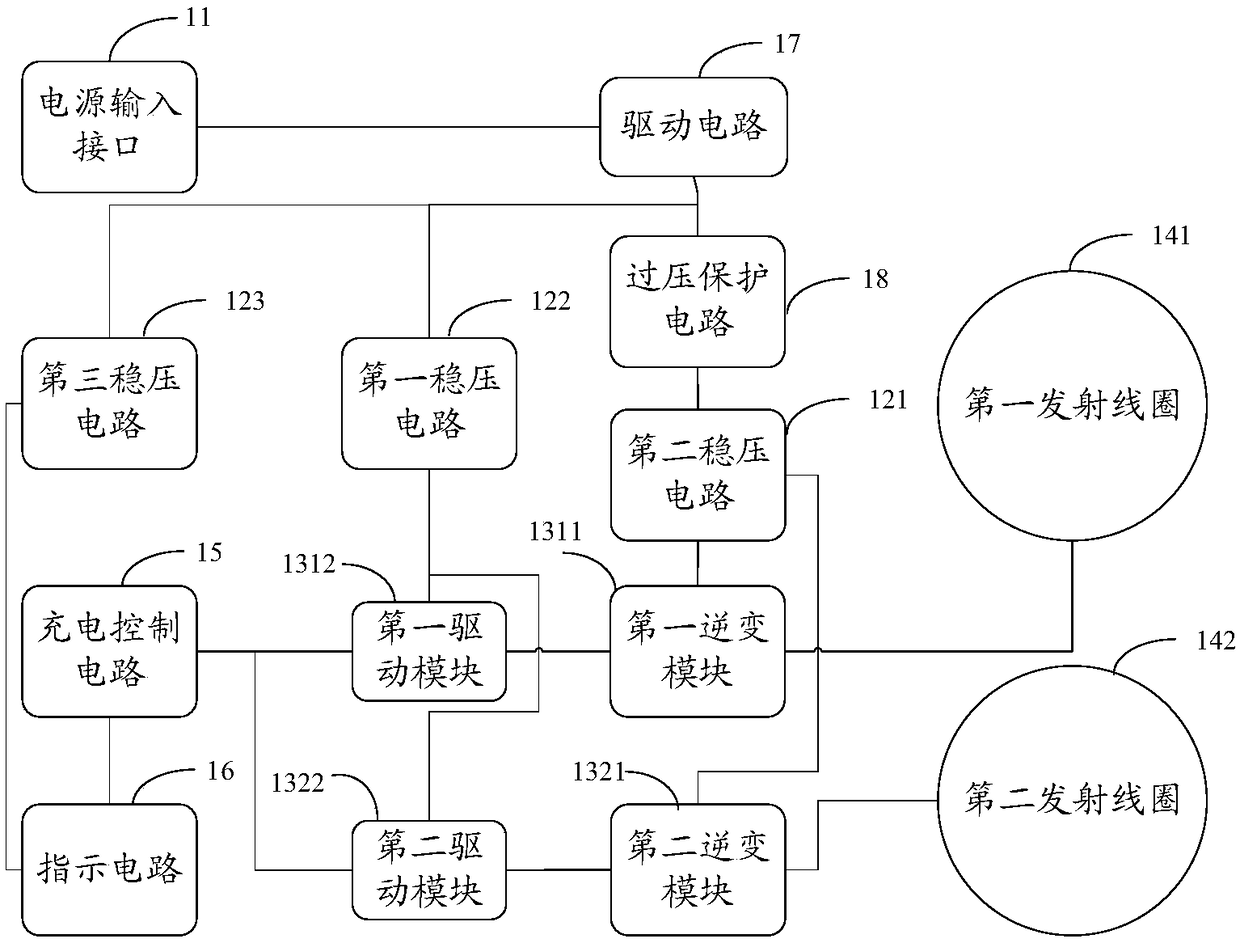
Wireless charging transmitting circuit, and wireless charging receiving circuit and method
ActiveCN108923509AReduce temperature riseBatteries circuit arrangementsTransformersCharge controlCharge loss
The invention provides a wireless charging transmitting circuit, and a wireless charging receiving circuit and method. The circuit comprises a power supply input interface, a voltage stabilizing circuit, a first transmitting coil, a second transmitting coil and a charging control circuit, wherein one end of the voltage stabilizing circuit is connected with the power supply input interface, and theother end is connected with the first input end of a first inverter circuit and the first input end of a second inverter circuit separately; the first transmitting coil is connected with the output end of the first inverter circuit; the second transmitting coil is connected with the output end of the second inverter circuit; and the charging control circuit is used for controlling the first transmitting coil and the second transmitting coil to charge synchronously or controlling the first transmitting coil and the second transmitting coil to charge alternately when the receiving coil exists in both of the charging ranges of the first transmitting coil and the second transmitting coil. By virtue of the wireless charging transmitting circuit provided by the invention, the temperature rise and the charging loss in the wireless charging process can be reduced.
Owner:VIVO MOBILE COMM CO LTD
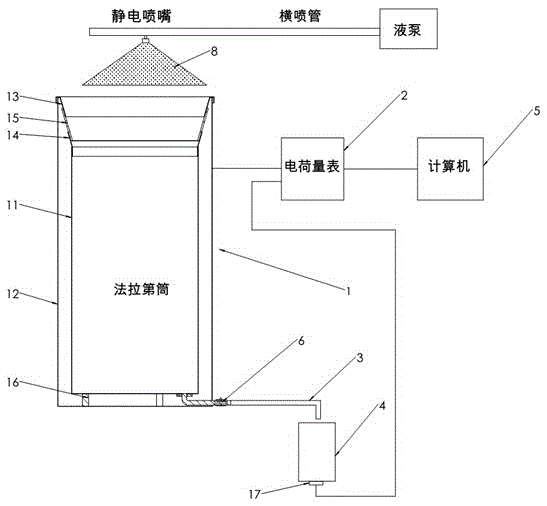
Device for measuring droplet charge-mass ratio of electrostatic spraying droplets
InactiveCN105676010AReduce churnPrevent sprayingElectrical measurementsMass ratioMovement measurement
The invention relates to the field of agriculture and forestry plant protection technology, and more particularly relates to a device for measuring the droplet charge-mass ratio of electrostatic spraying droplets. The device is characterized by comprising a faraday cylinder (1), a coulometer (2), a water outlet pipe (3), a liquid collecting barrel (4) and a computer (5). The faraday cylinder (1) and the coulometer (2) are connected. The coulometer (2) and the computer (5) are connected. The water outlet pipe (3) is communicated with the bottom of the faraday cylinder (1). The bottom of the liquid collecting barrel (4) is provided with a weight sensor (17). The weight sensor (17) and the coulometer (2) are connected. The liquid collecting barrel (4) is used for collecting the liquid that flows out of the water outlet pipe (3). Compared with the prior art, the technical effects of small charge loss between sealed inner and outer cylinders, easy operation, good measurement real-time performance, high accuracy, high cost performance, convenient movement measurement and the like are realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
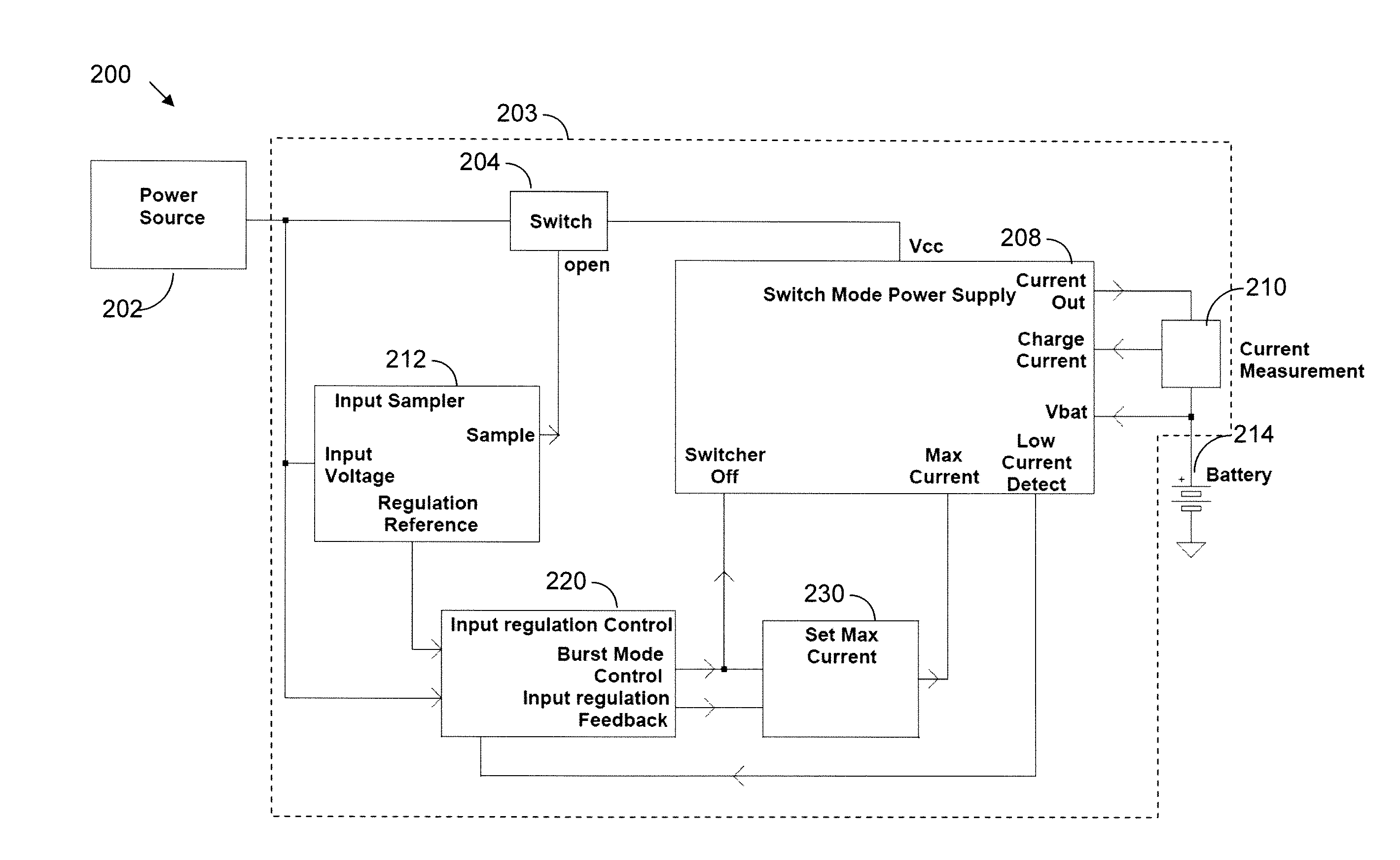
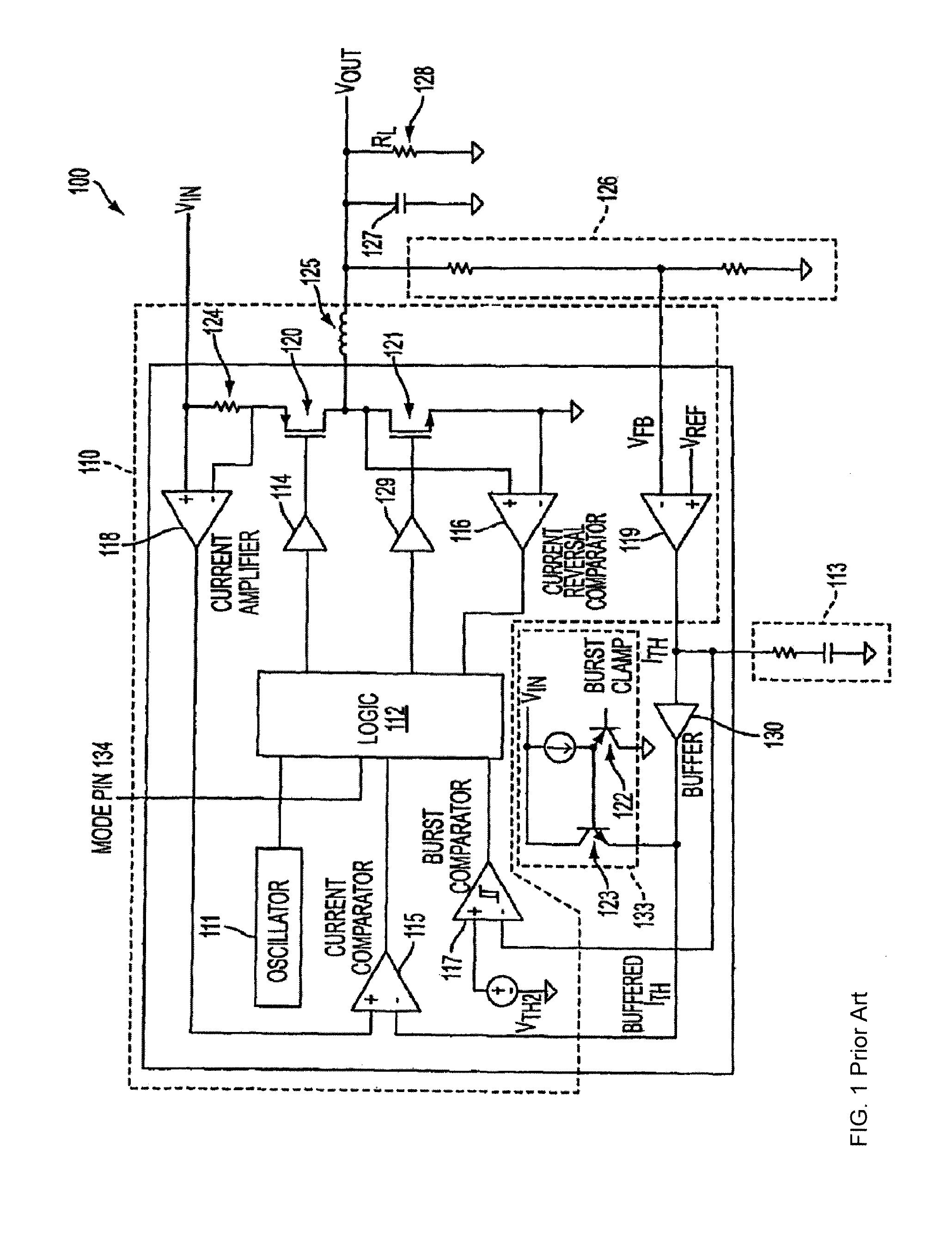
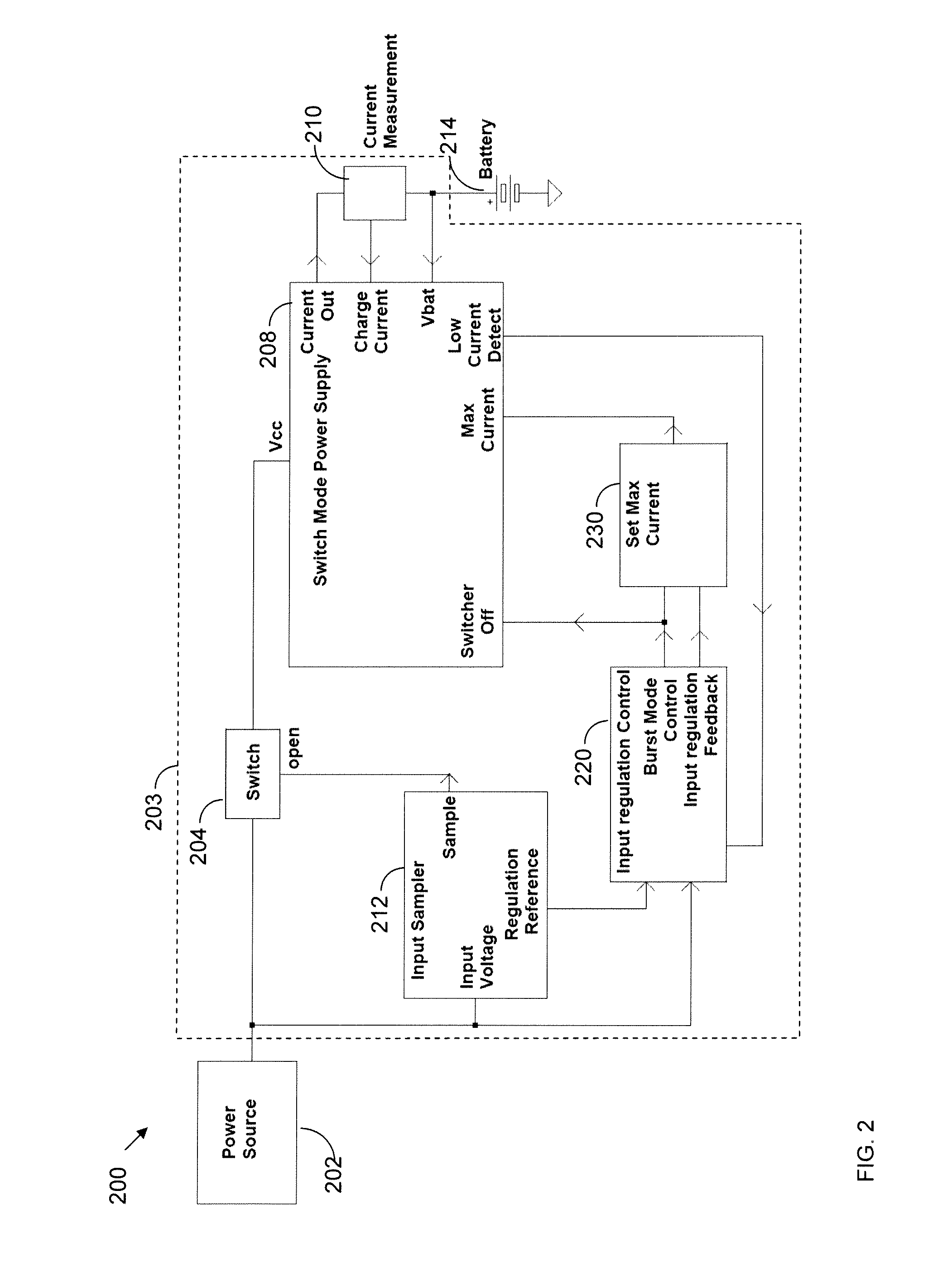
System and method for input voltage regulation of switch mode supplies implementing burst mode operation
ActiveUS20140097814A1Batteries circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionCurrent thresholdVoltage regulation
Switching regulator methods and systems are provided for supplying output current at a regulated voltage level to a load. Upon determining that the output current is not below a predetermined current threshold, the regulator is operated in a continuous mode. The input voltage is monitored. If the input voltage is not below a first input threshold level, the system remains in continuous mode. Otherwise, the system enters a burst mode in which the switch mode power supply is turned OFF, thereby reducing transistor gate charge losses.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
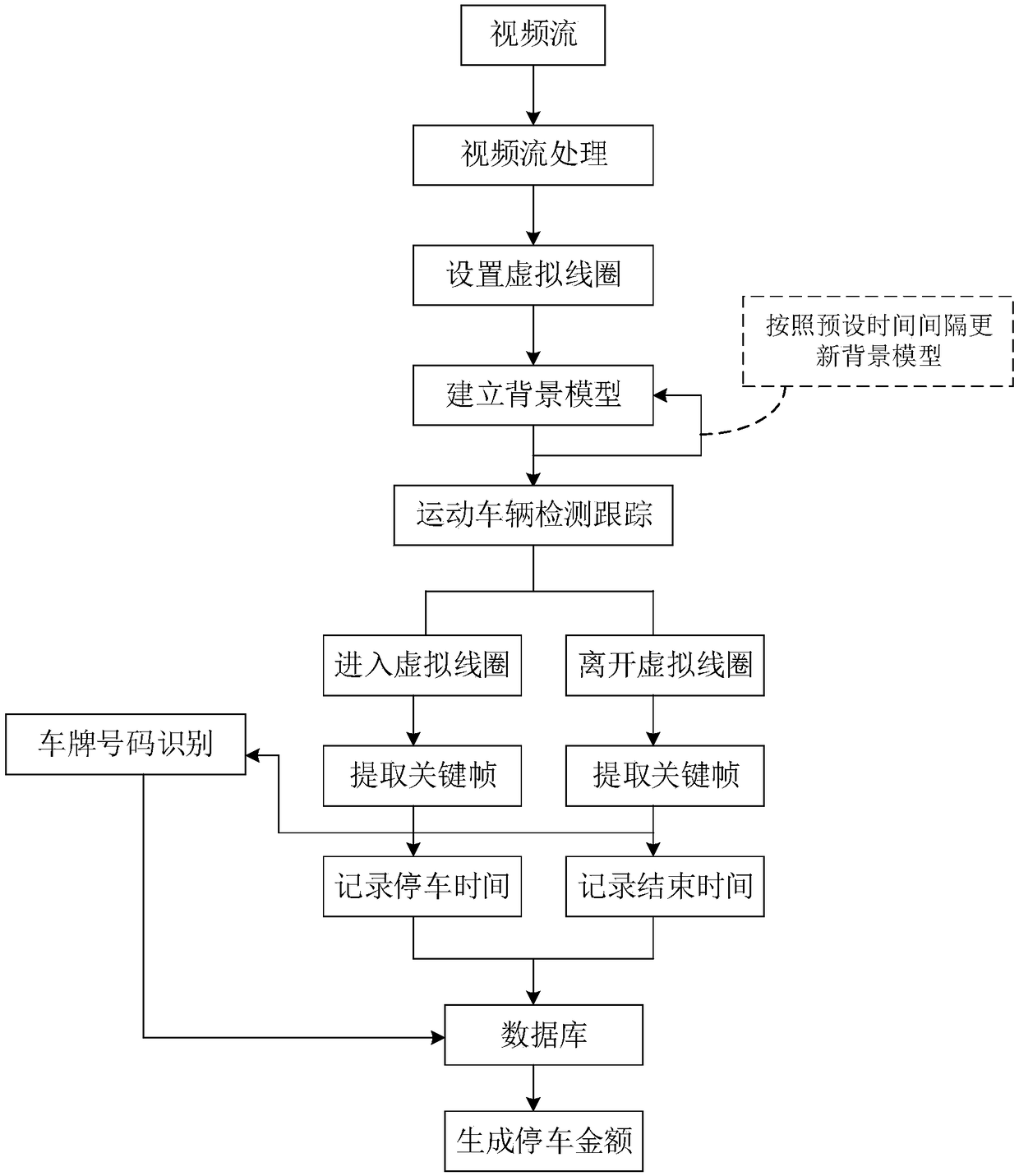
Video analysis technology-based side parking charging management method
InactiveCN108921956AImprove management efficiencySolve churnTicket-issuing apparatusRoad vehicles traffic controlSurveillance cameraParking space
The invention provides a video analysis technology-based side parking charging management method. The method comprises video flow processing and vehicle license plate recognition. According to the method, video flows acquired by road segment cameras are processed by utilizing a video analysis technology, and vehicles entering and exiting from parking spots are analyzed by a method for previously setting virtual coils at parking spot areas, so as to extract key frame static images of the vehicles entering and exiting the parking spots and record the time when the vehicles enter and exit the parking spot areas; the vehicle license plate numbers of the parking vehicles are recognized by taking the extracted key frame static images of the vehicles as inputs of the vehicle license plate recognition part; and vehicle parking amounts are generated by utilizing obtained information. According to the method, a side parking-automatic and unattended charging management manner is realized via lowcost and high efficiency by utilizing the advanced video analysis technology on the basis of video flows acquired by monitor cameras in intelligent traffic fields, so that the side parking managementefficiency is improved, the manpower and material resources are saved, and the problem of parking charge loss caused by long-term backward toll collection manners of side parking is solved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
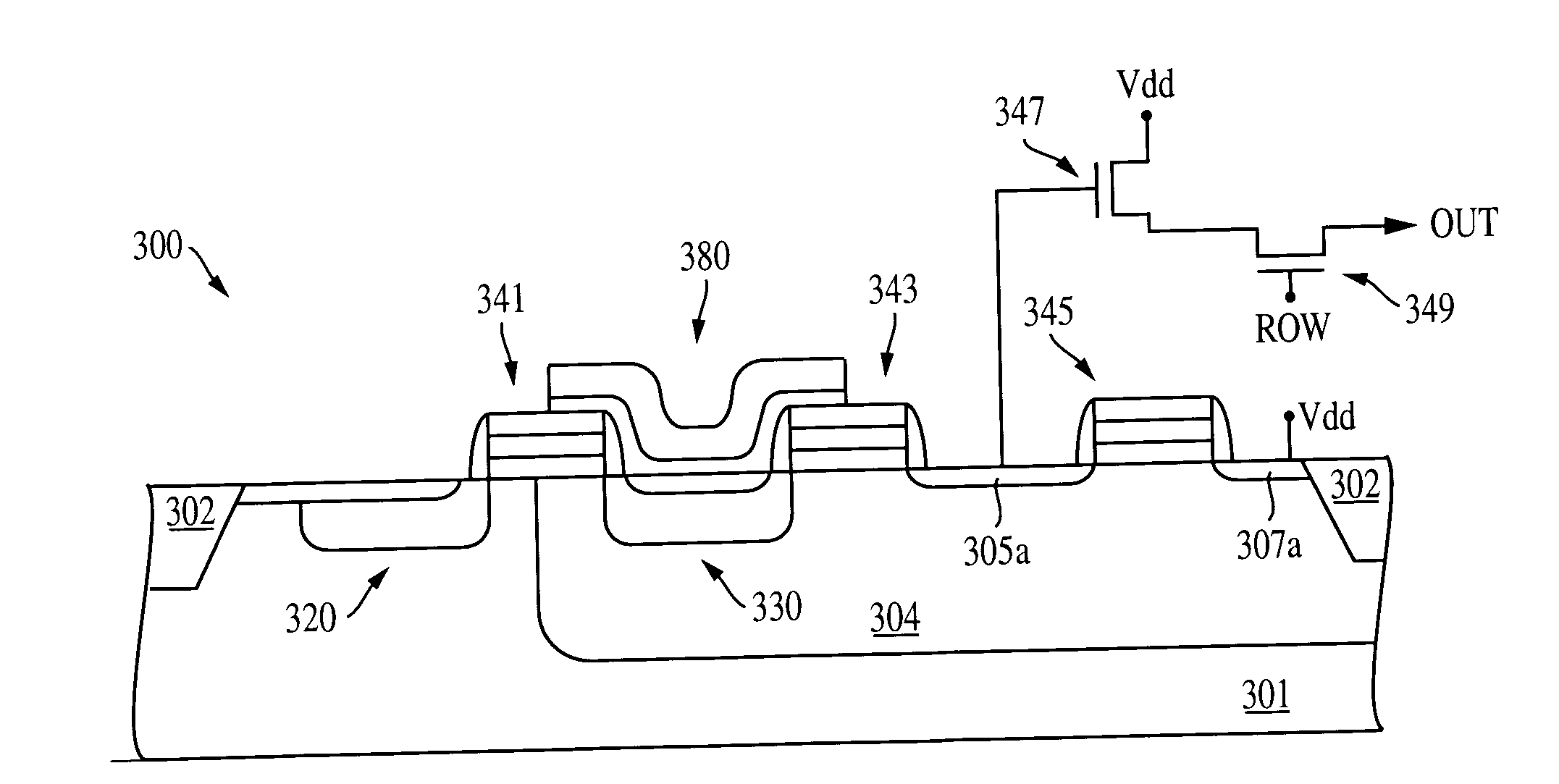
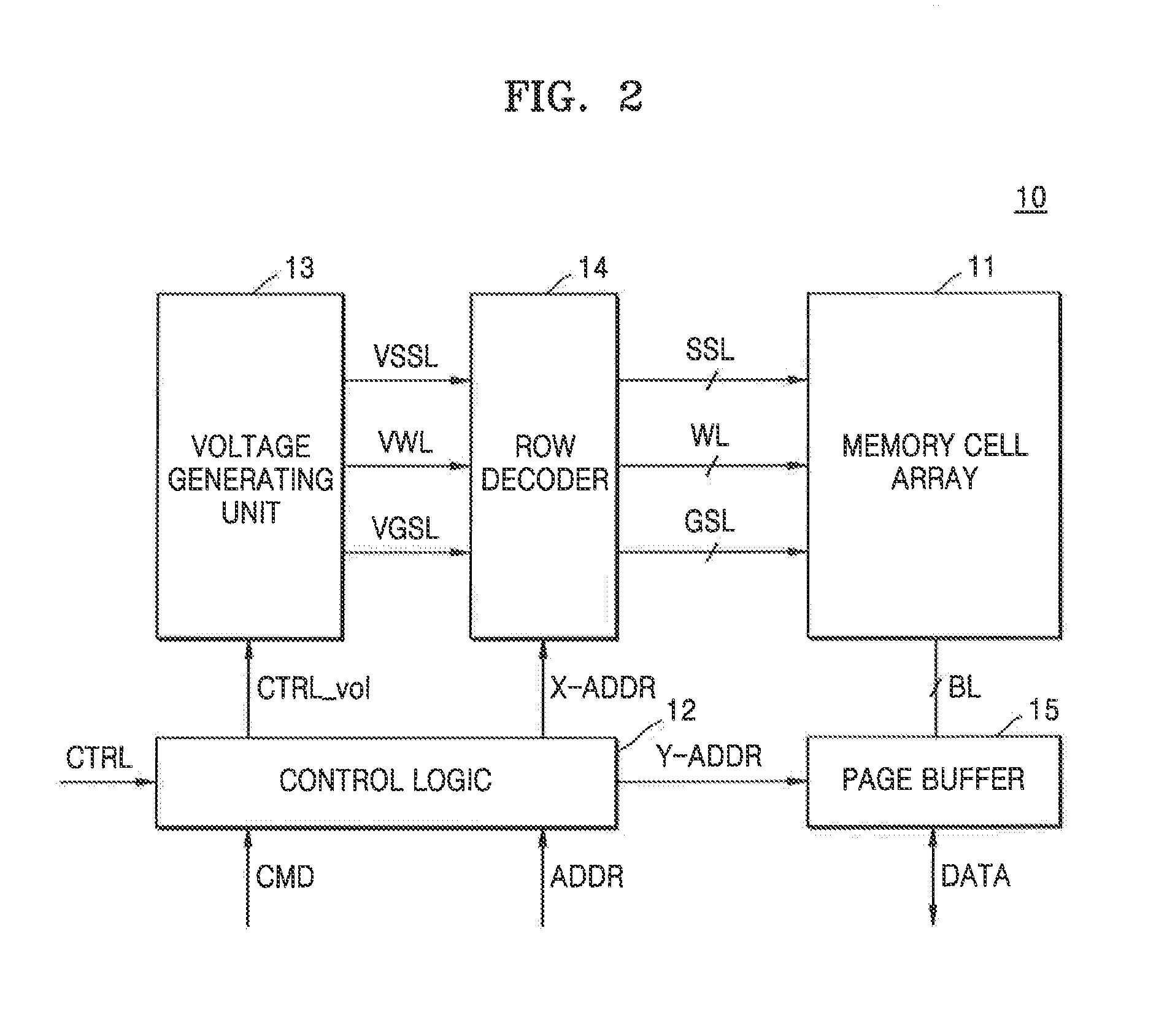
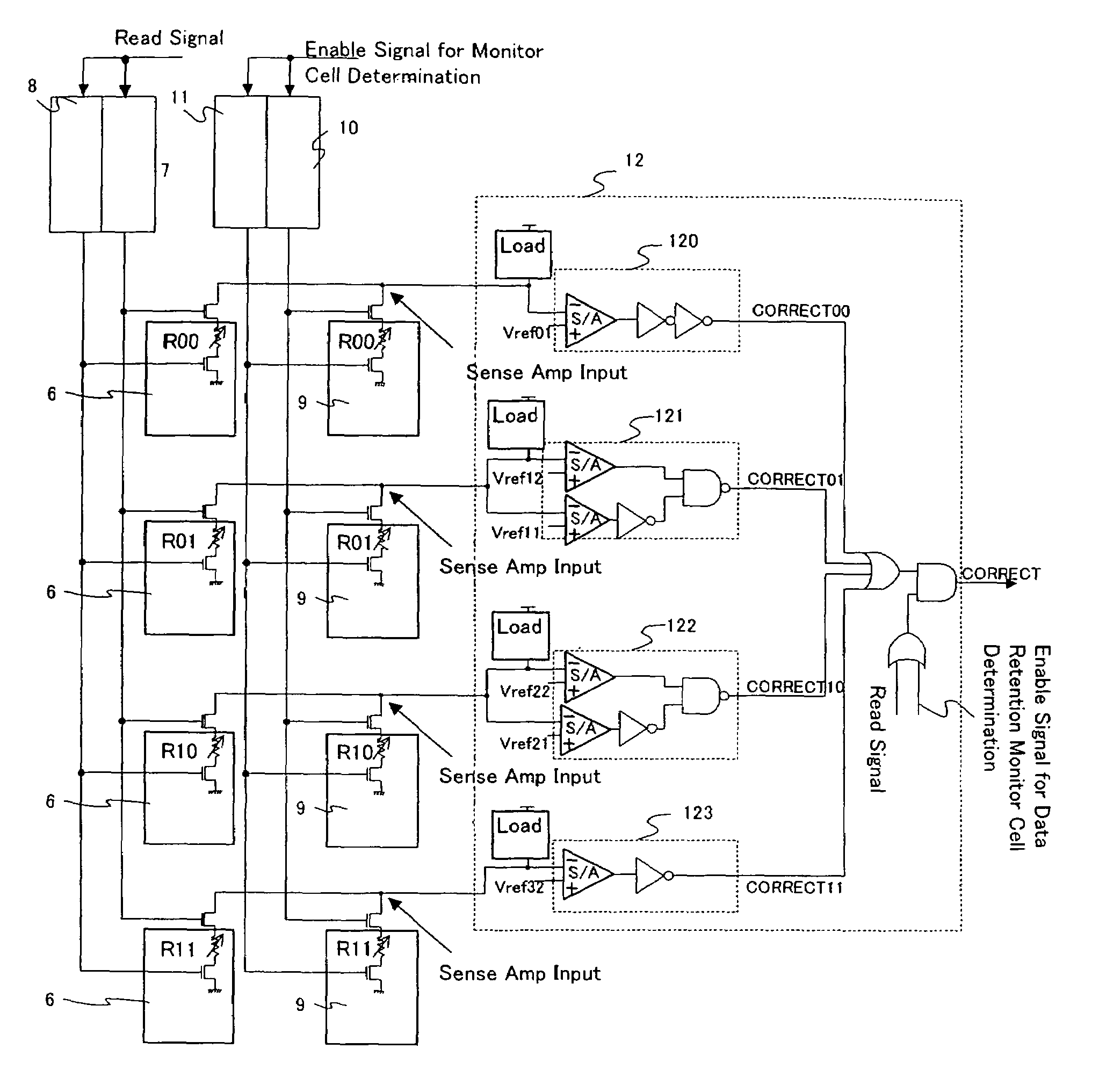
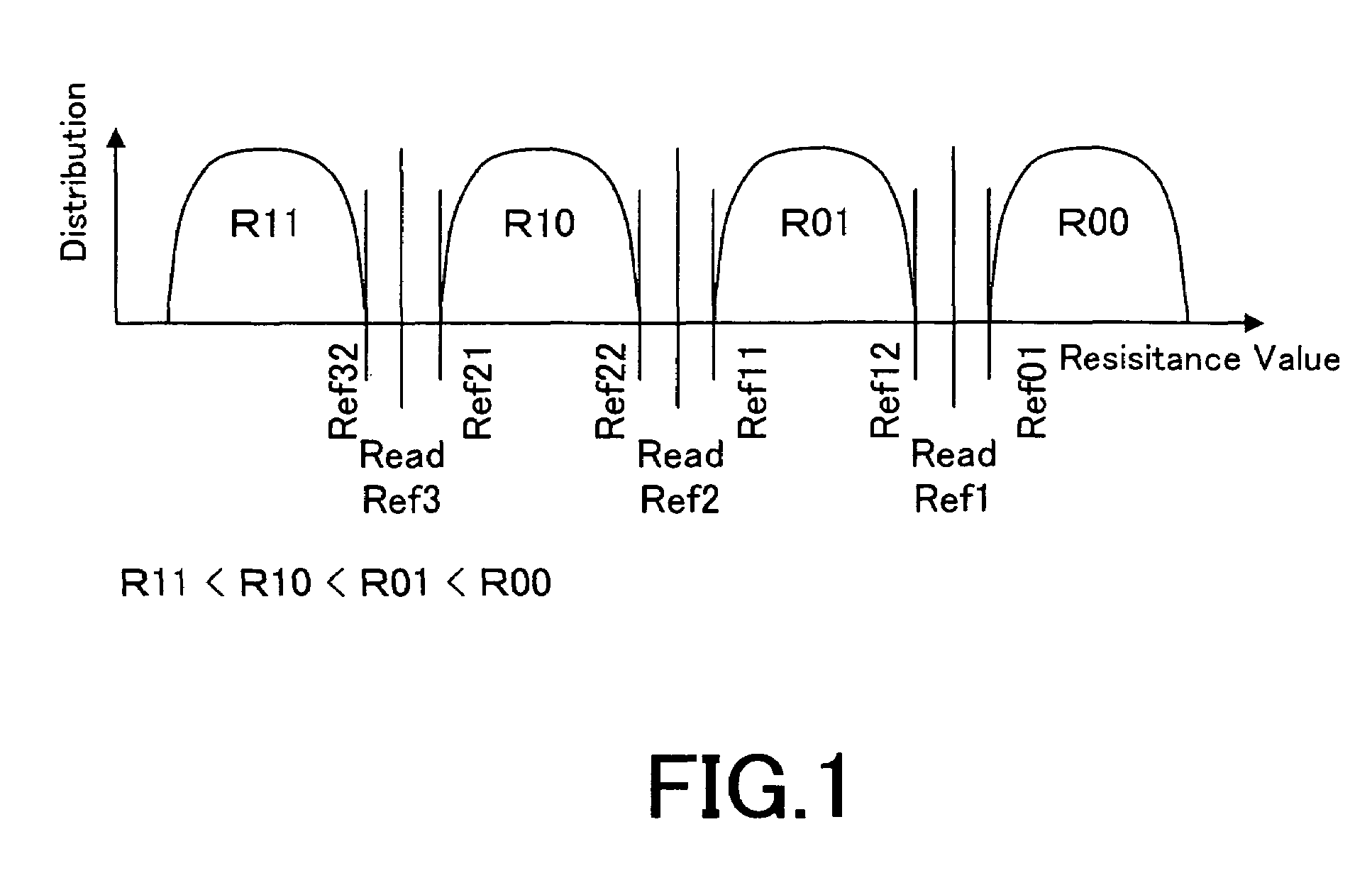
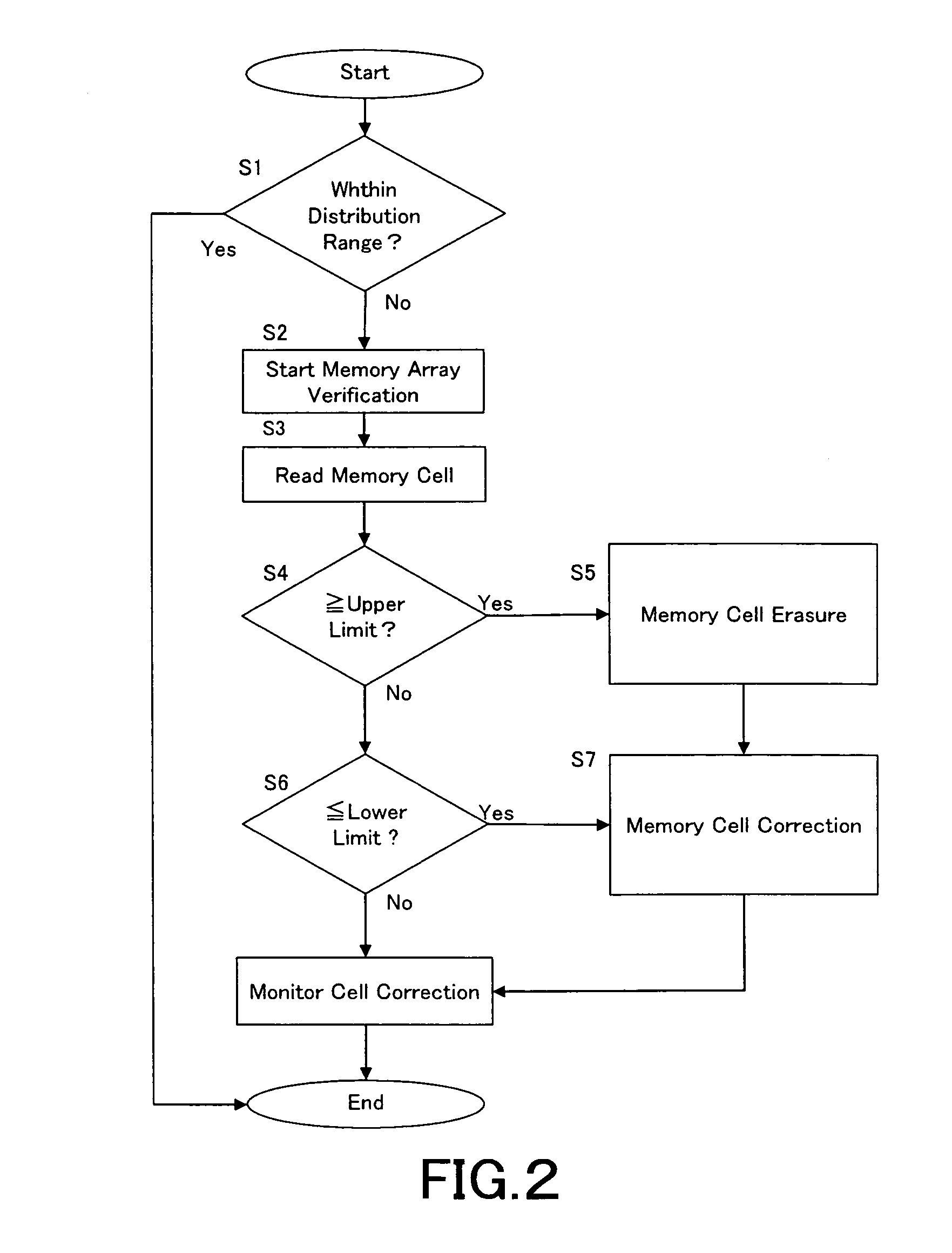
Semiconductor memory device and method for correcting memory cell data
ActiveUS6967867B2Reduce power consumptionUnnecessary stressRead-only memoriesDigital storageCharge lossLevel data
A semiconductor memory device comprises a plurality of memory cells, each of which is capable of storing N-level data and being reprogrammed; and a plurality of monitor cells that separately store individual data values of the N-level data by using the same scheme as that used for the memory cells. Sensing means senses whether a physical quantity of the monitor cell which corresponds to the data value stored in the monitor cell is within a preset range; verification means verifies whether the physical quantity of the memory cell which corresponds to the data value stored in the memory cell is within the preset range when the sensing means has sensed that the physical quantity of the monitor cell is out of the preset range; correction means corrects the physical quantity. Consequently, a physical quantity variation can be efficiently detected without overstressing memory cells, and correction can be implemented for not only a downward variation due to charge loss and / or the like but also a variation in an upward physical quantity variation due to charge gain and / or the like in a specified range.
Owner:III HLDG 12 LLC
Nonvolatile storage device and control method thereof
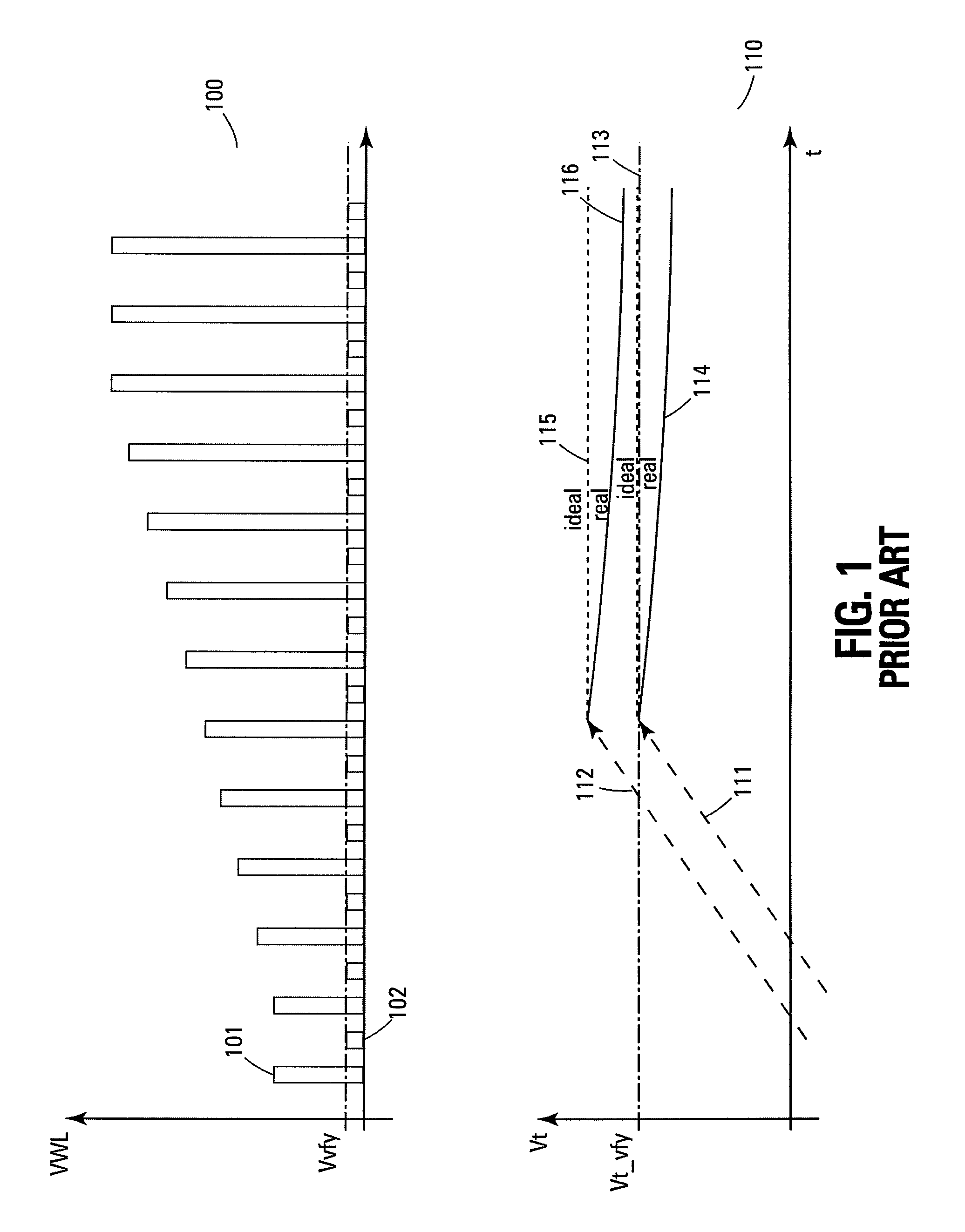
ActiveUS20080144388A1Shorten the timeLittle interruptionRead-only memoriesDigital storageCharge lossComputer science
A nonvolatile memory device that responds to a decrease in electric charge stored in memory cells attributed to the charge loss phenomenon occurring during program operation by adjusting the level of a program verify operation according to the degree of the charge loss so that the program operation can be performed with little (if any) interruption.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
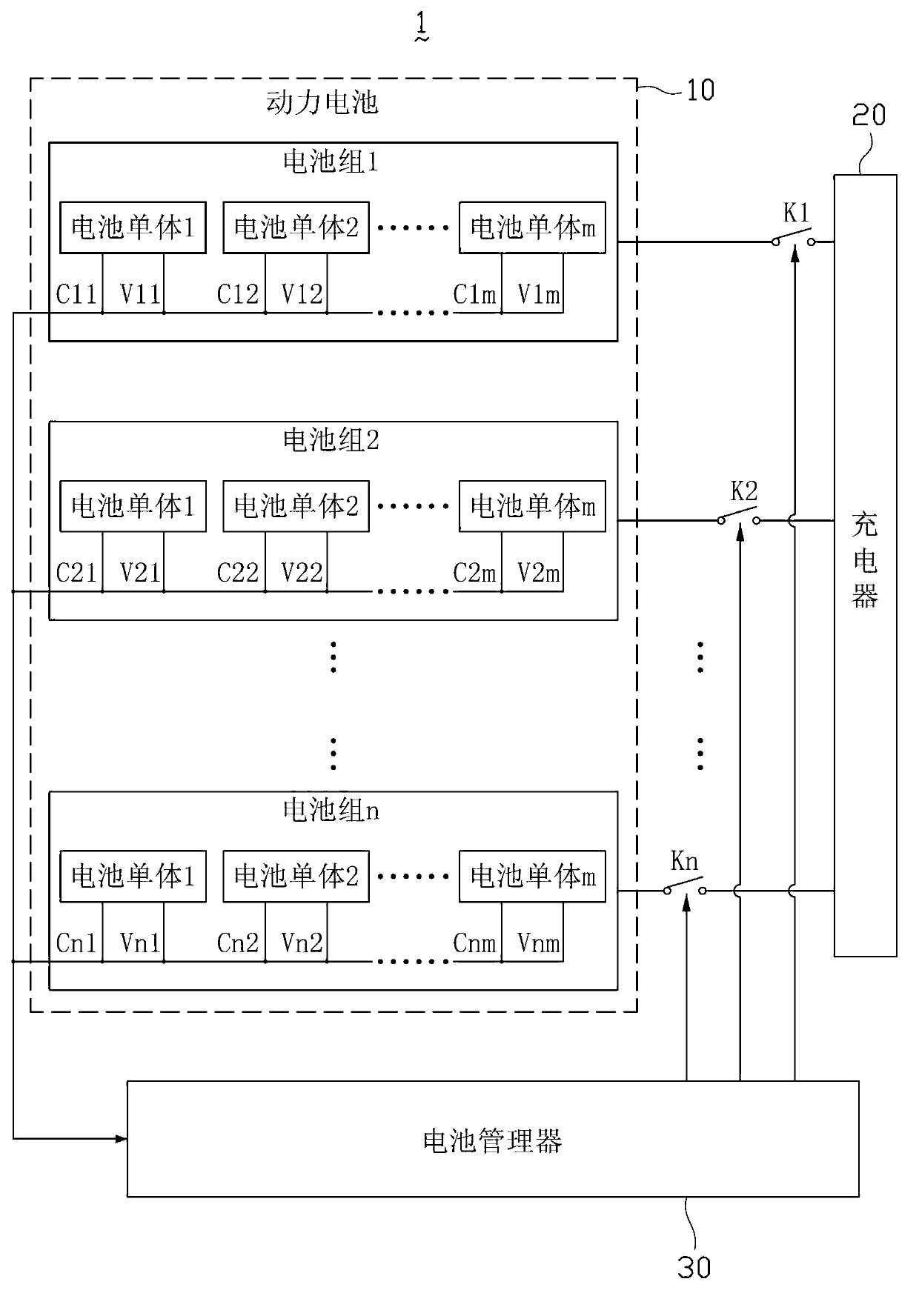
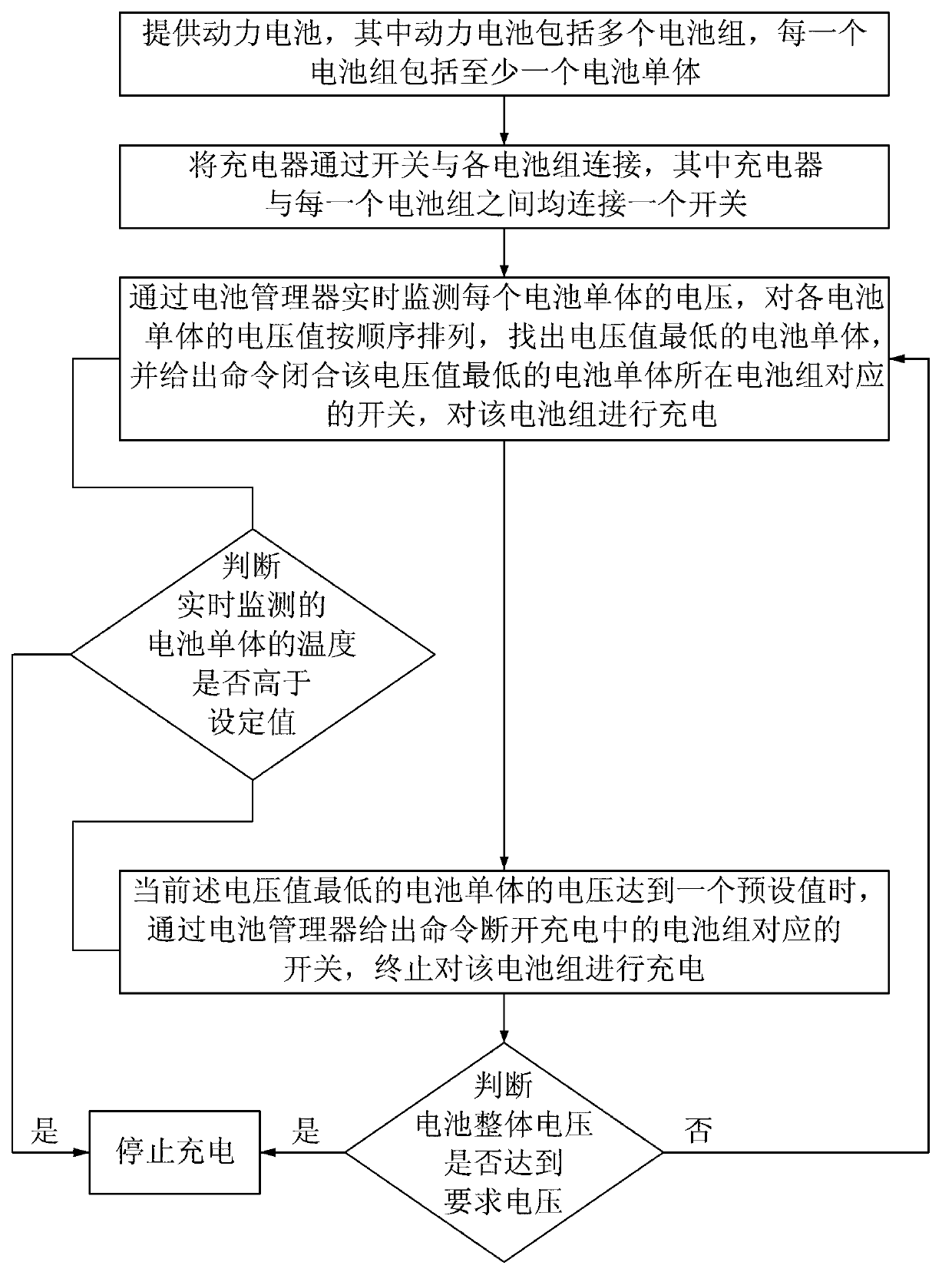
Charging system and charging method for automobile power battery
ActiveCN103280854ALower loop currentBalanced chargingBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerPower batteryPower flow
The invention discloses a safety charging system and a charging method for an automobile power battery. The safety charging system for the automobile power battery comprises a power battery, a charger and a battery manager, wherein the power battery comprises a plurality of battery packs; each battery pack comprises at least one battery monomer; each battery pack and the charger construct a charging circuit; a switch is connected between each battery pack and the charger; and the battery manager is used for acquiring the voltage parameters and temperature parameters of each battery monomer in real time, processing these parameters, and controlling the switch-on / off of each switch according a processing result to charge a selected battery pack or stop charging, namely, charge the battery packs in sequence. Due to the adoption of the charging system and the charging method, the circuit current of system hardware can be lowered, the effects of balancing charging and reducing charging loss are achieved, and the safety is enhanced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GEELY AUTOMOBILE RES INST CO LTD +1
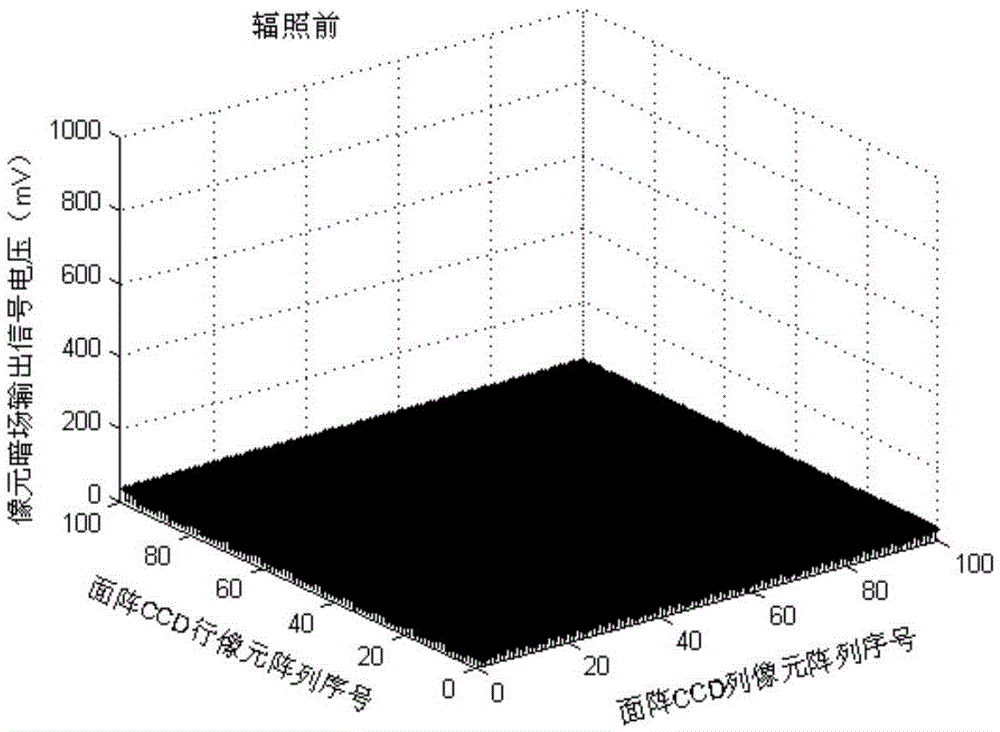
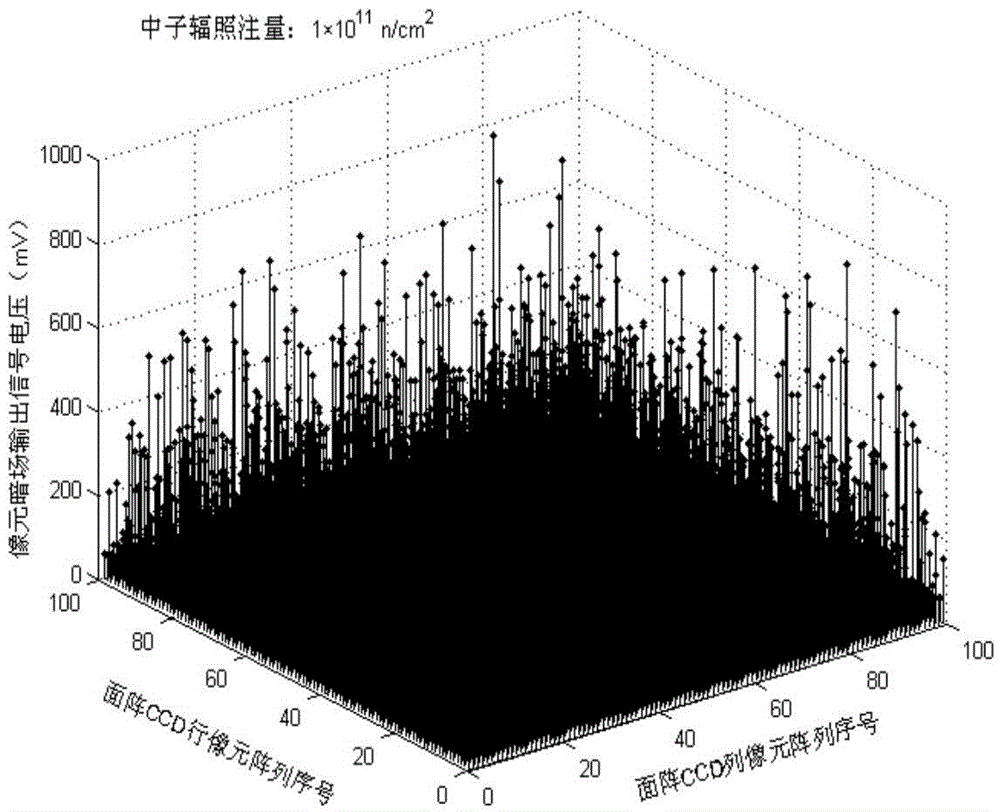
Charge transfer efficiency test method of post-neutron irradiation charge coupled device
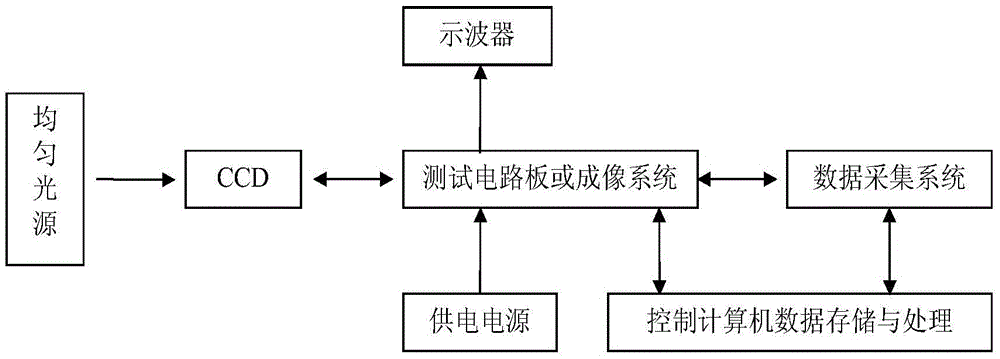
ActiveCN105572486ABig impact on degradationSaturated output has little effectElectromagentic field characteristicsNeutron irradiationCharge loss
The invention provides a charge transfer efficiency test method of a post-neutron irradiation charge coupled device. According to the method, when the readout of CCD signal charges occur, an overscanning pixel output unit is additionally adopted; defects which are generated due to the induction of neutron irradiation are made to capture CCD signal charges; captured CCD signal charges are collected in the overscanning pixel output unit; signal charge loss generated by the induction of neutron irradiation can be displayed intuitively through image output; saturated illumination is adopted to eliminate the influence of dark signal peaks on signal charge packets in a process in which the signal charge packets are sequentially transferred between CCD transfer channels; and requirements for the consistency of the size of the signal charge packets in a charge transfer efficiency test (CTE) after different neutron fluence irradiation can be satisfied. With the method adopted, the problem that a CTE test is inaccurate or even if cannot be performed existing on the post-neutron irradiation charge coupled device can be solved.
Owner:NORTHWEST INST OF NUCLEAR TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com