Patents
Literature
148 results about "Ground noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
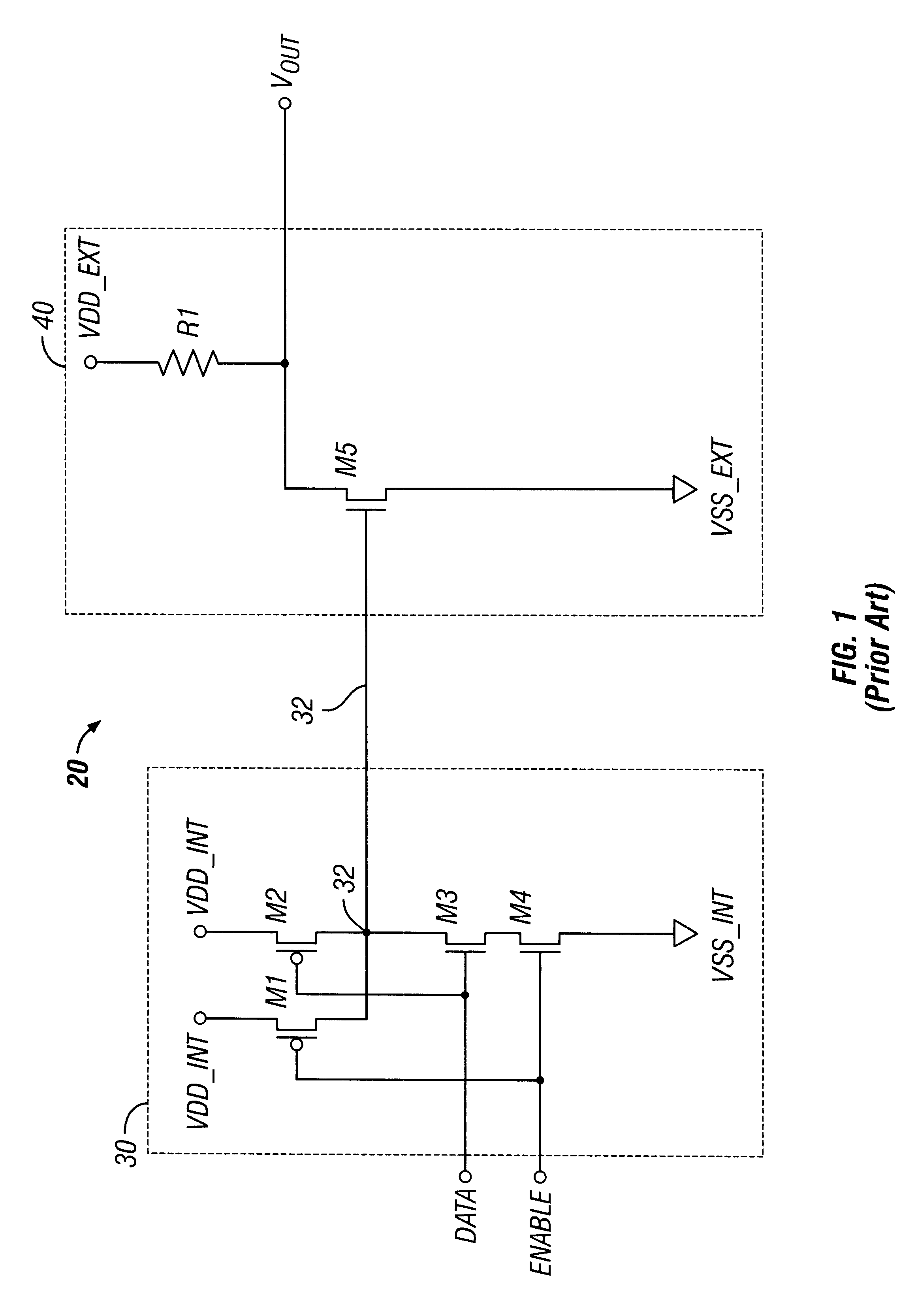
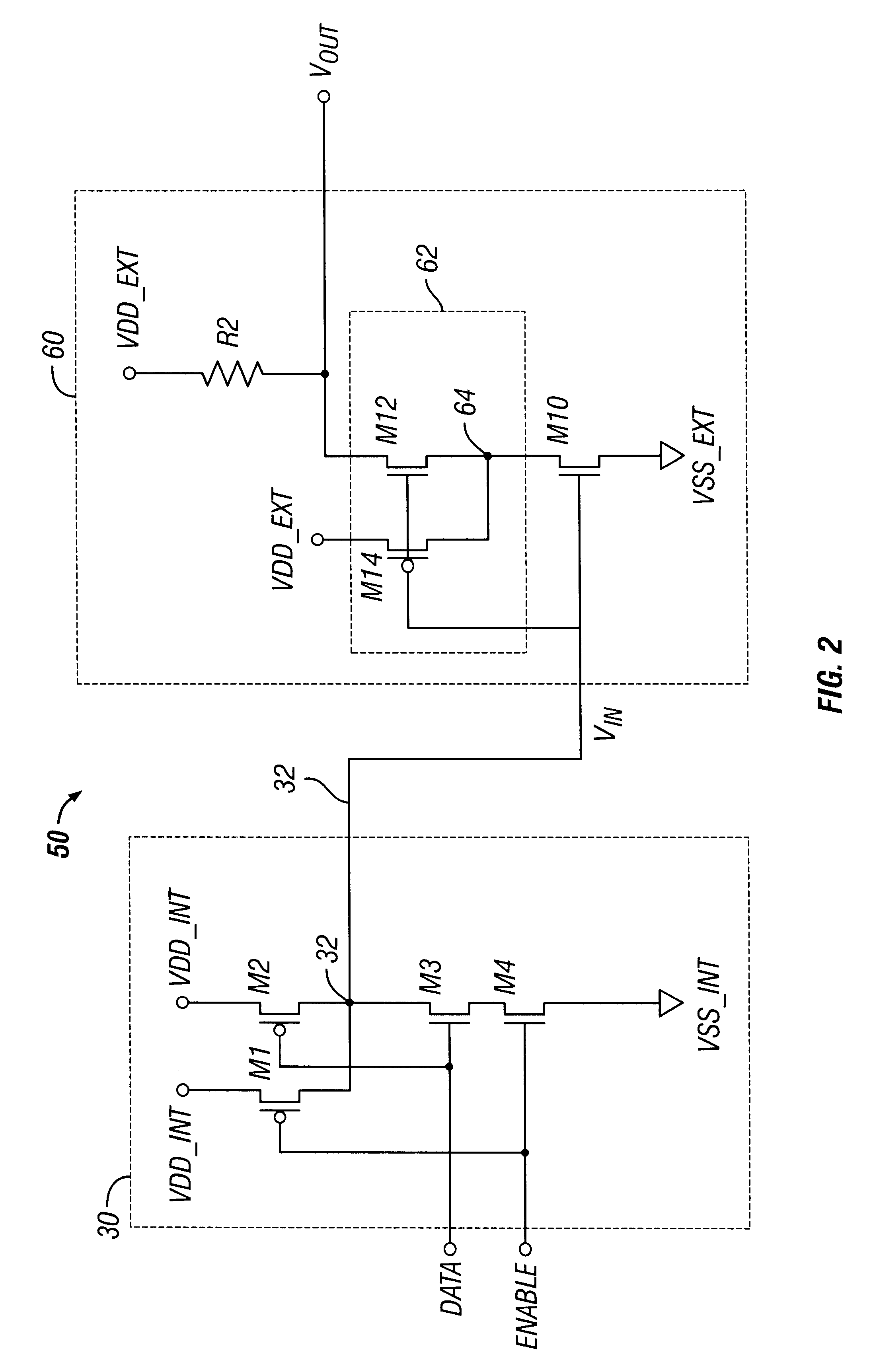
In electronics, ground noise is electronic noise on the ground wires or busses of an electronic circuit. In audio, radio, and digital equipment it represents an undesirable condition since the noise can get into the signal path of the device, appearing as interference in the output. Like other types of electronic noise it can manifest in audio equipment as a hum, hiss, distortion or other unwanted sound in the speakers, in analog video equipment as "snow" on the screen, and in digital circuits and control systems as erratic or faulty operation or computer "crashes". A major source of ground noise is ground loops created by improper interconnection of audio, video or computer components.
Motor controller incorporating an electronic circuit for protection against inrush currents
InactiveUS7050278B2Minimize the numberConveniently activatedSingle-phase induction motor startersAC motor controlElectrical resistance and conductanceFiltration
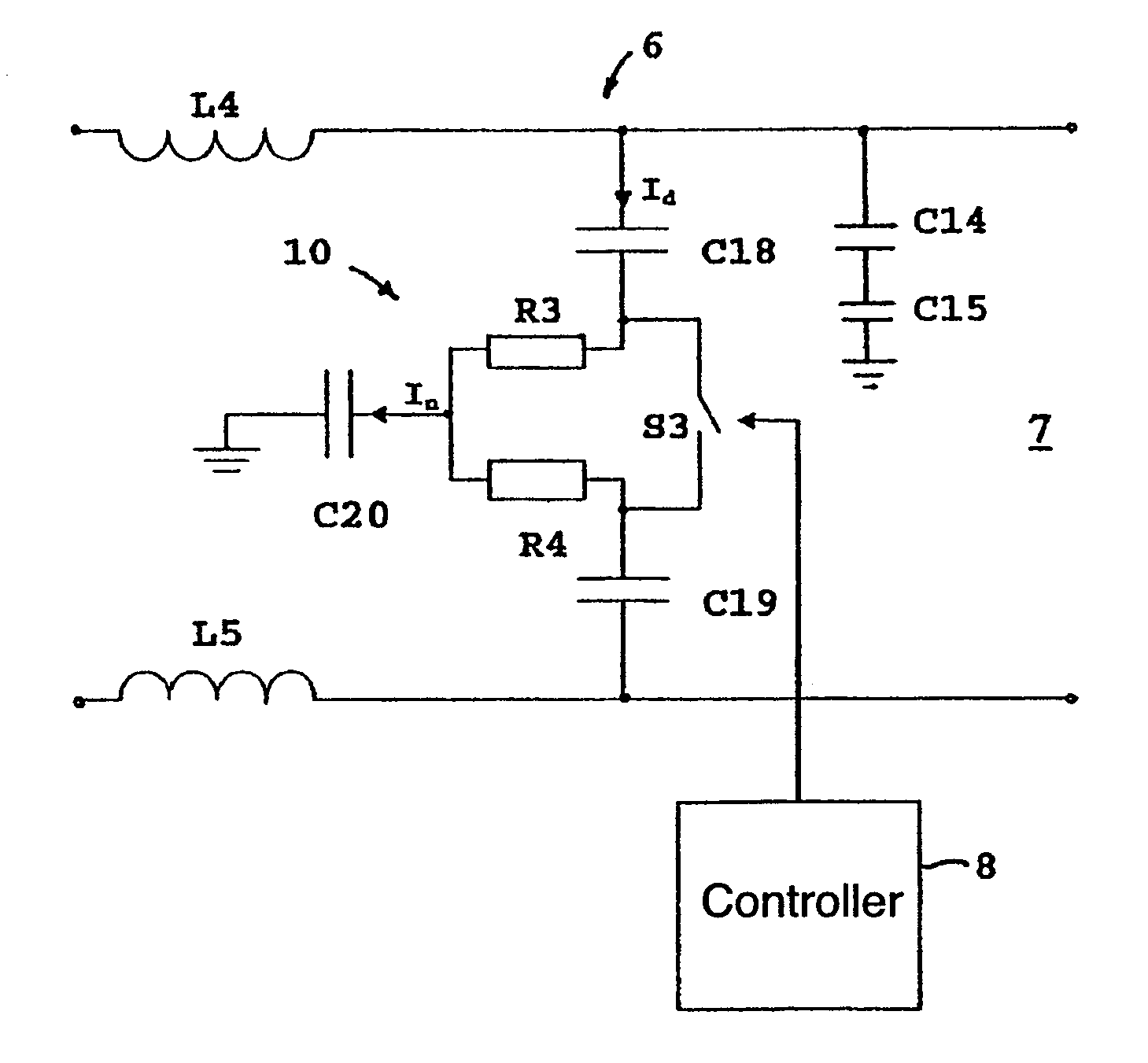
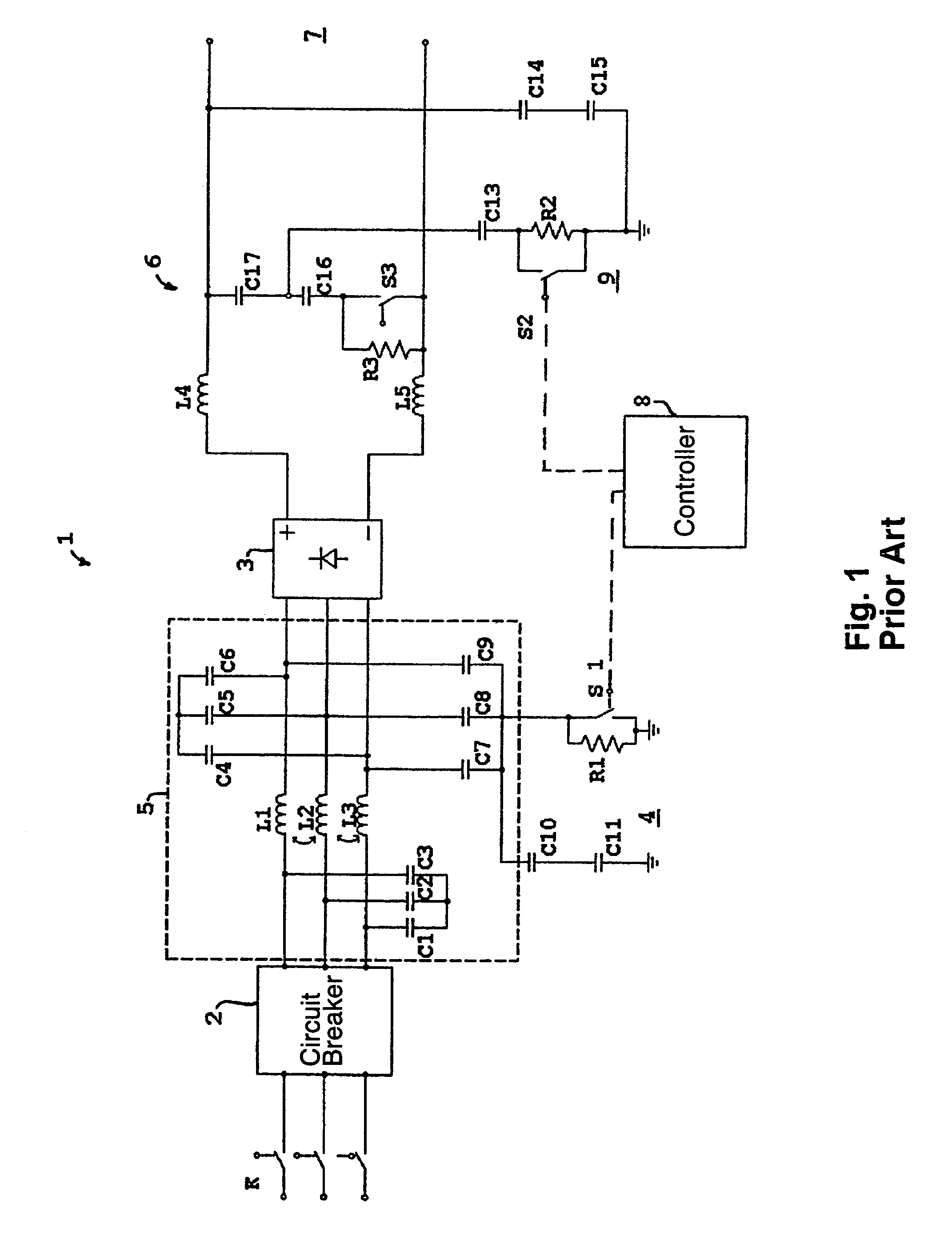
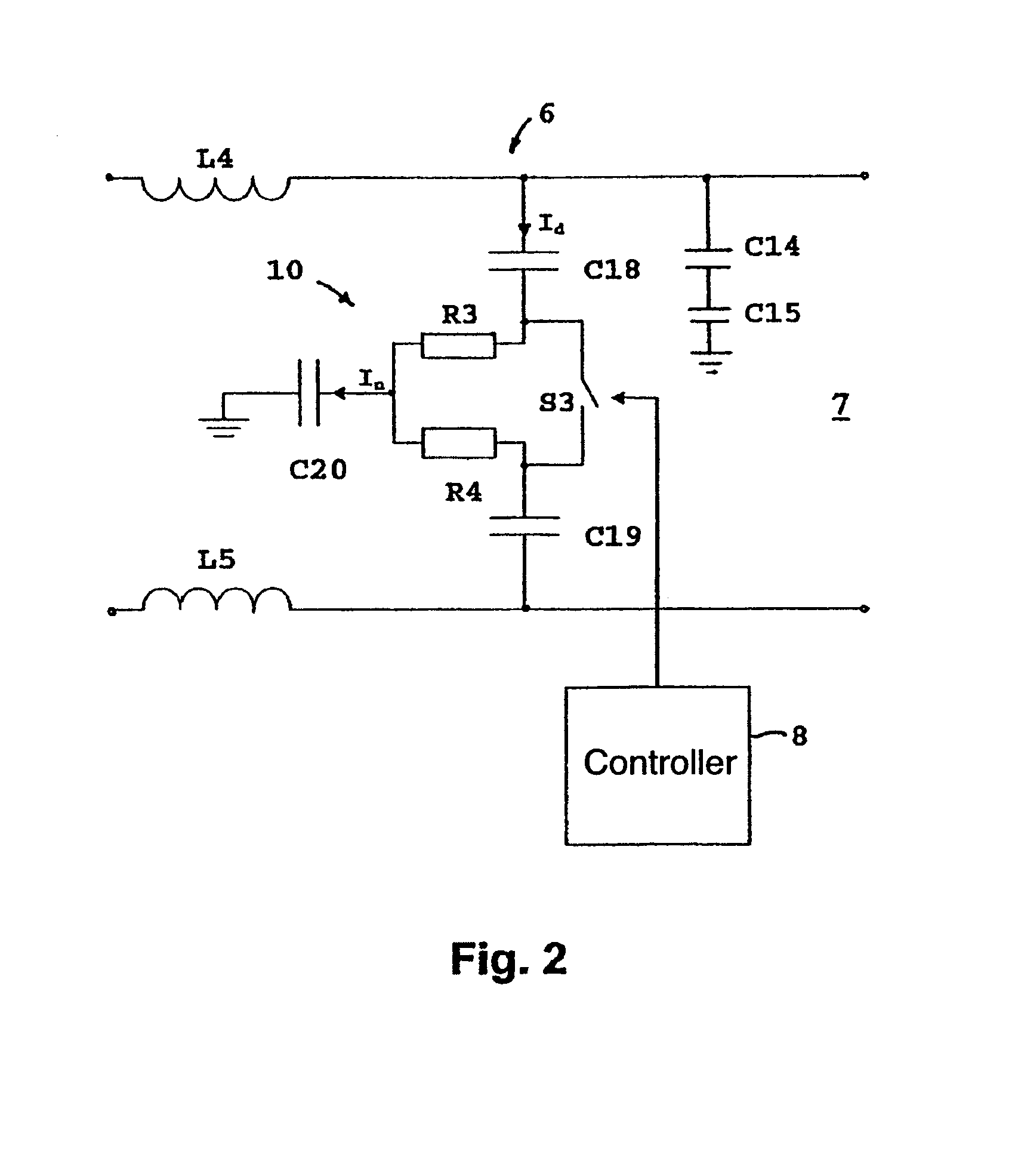
Inrush currents in the dc intermediate circuit of a motor controller necessitate the incorporation of protection circuits. These circuits usually take the form of a resistor inserted in series with the intermediate circuit, and the resistor is short-circuited after completion of inrush by a switch positioned in parallel with the resistor. To reduce cable-transmitted electrical noise an earthed noise-decoupling capacitor is added to the intermediate circuit, but it also requires protection against inrush currents. To minimise the number of components, a protection circuit is described which combines noise filtration and inrush protection. According to the invention, the inrush resistor has the form of a resistor network and is connected to a switch which via a controller alters the resistance of the resistor network, so that when the switch is open, the resistance to a differential current is greater than the resistance to a common mode current, and when the switch is closed, there is greater resistance to a common mode current than to the differential current.
Owner:DANFOSS DRIVES
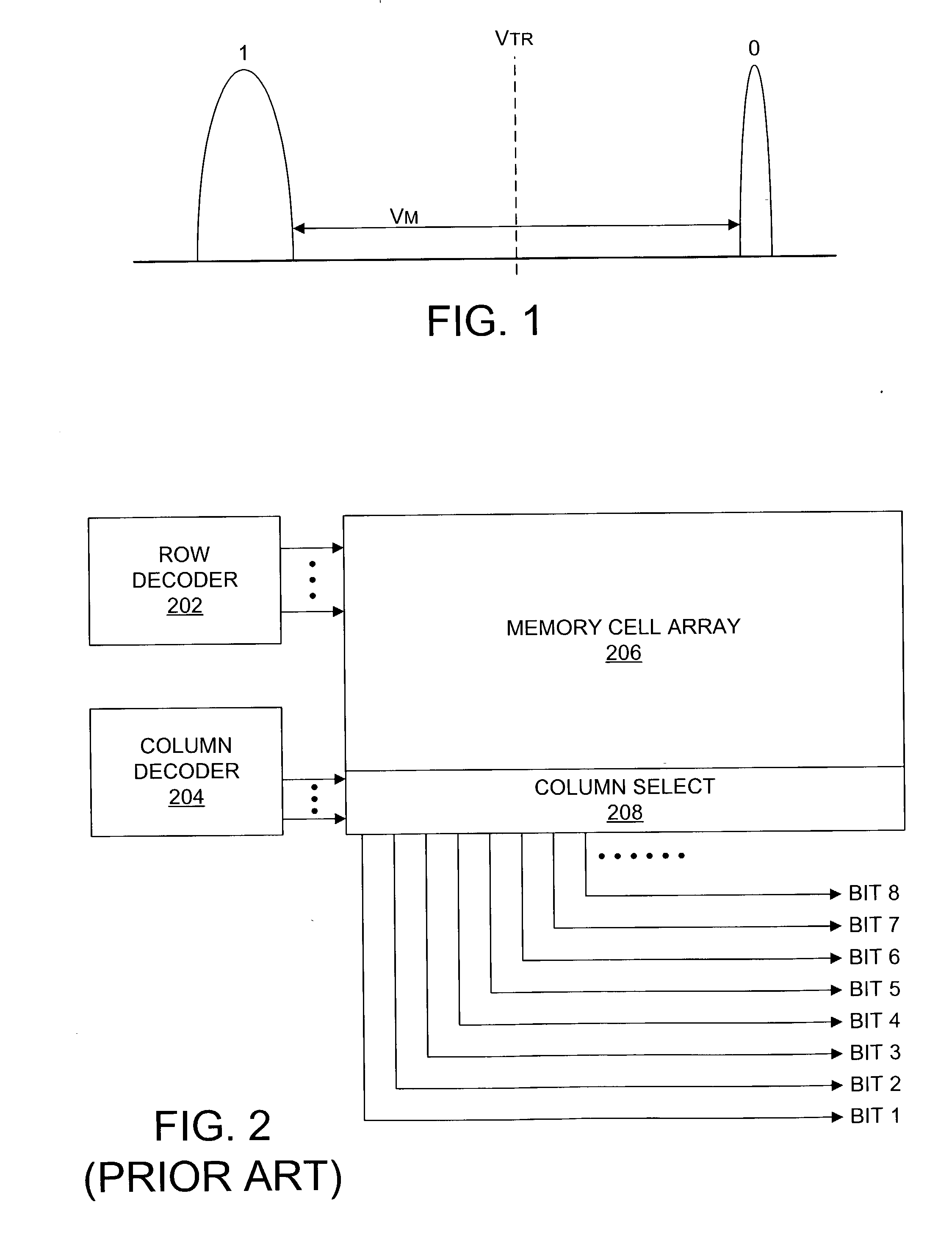
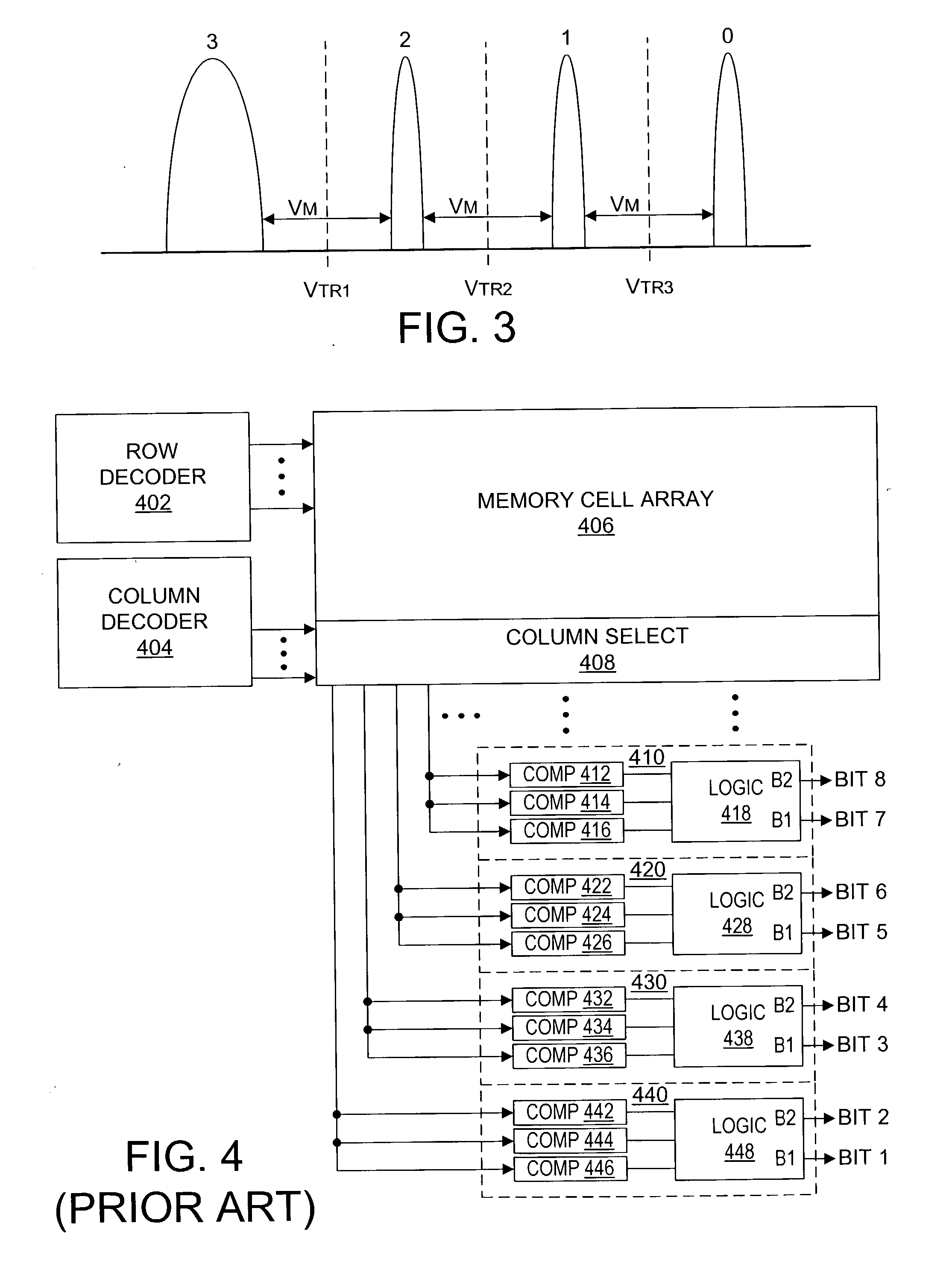
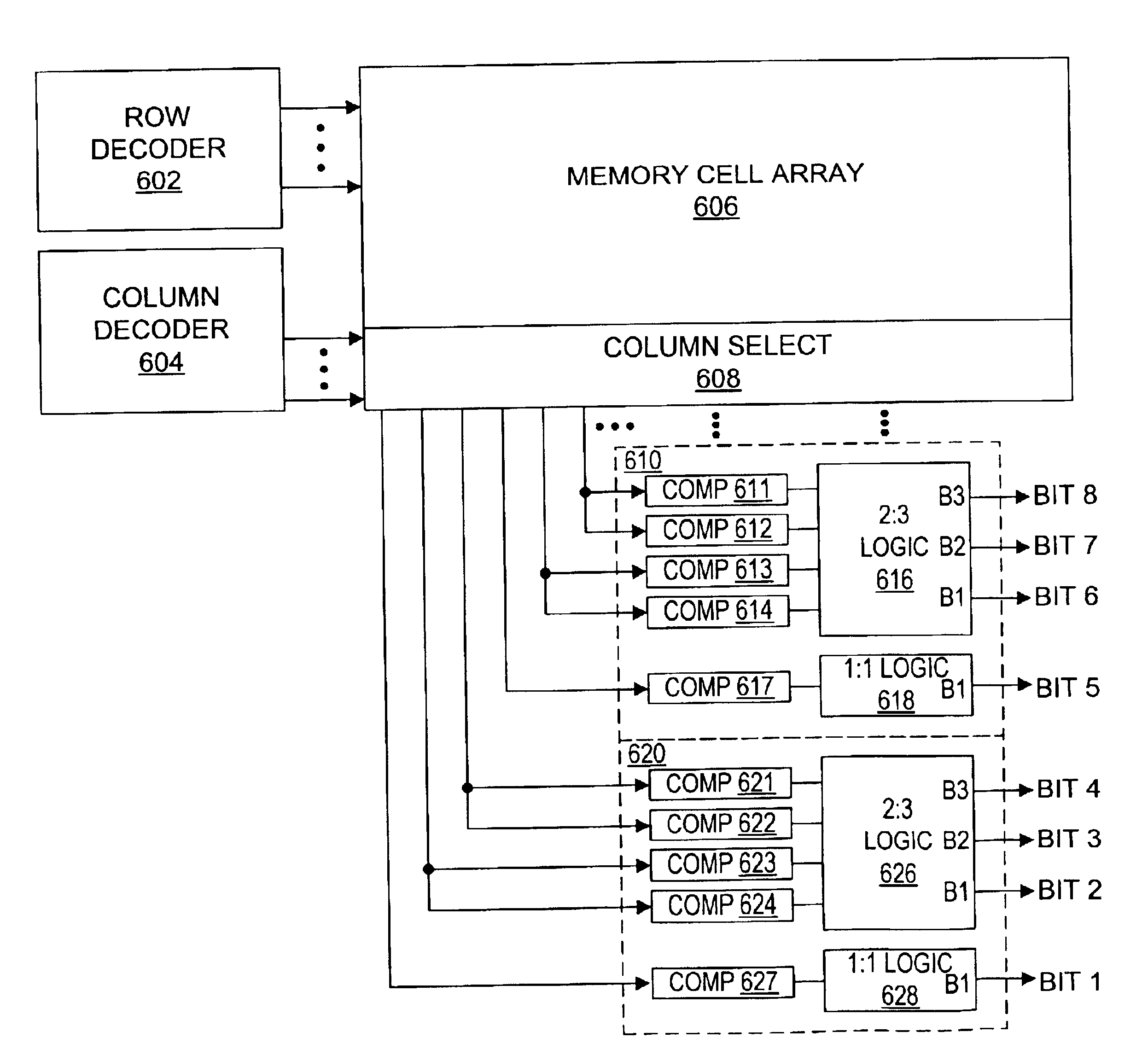
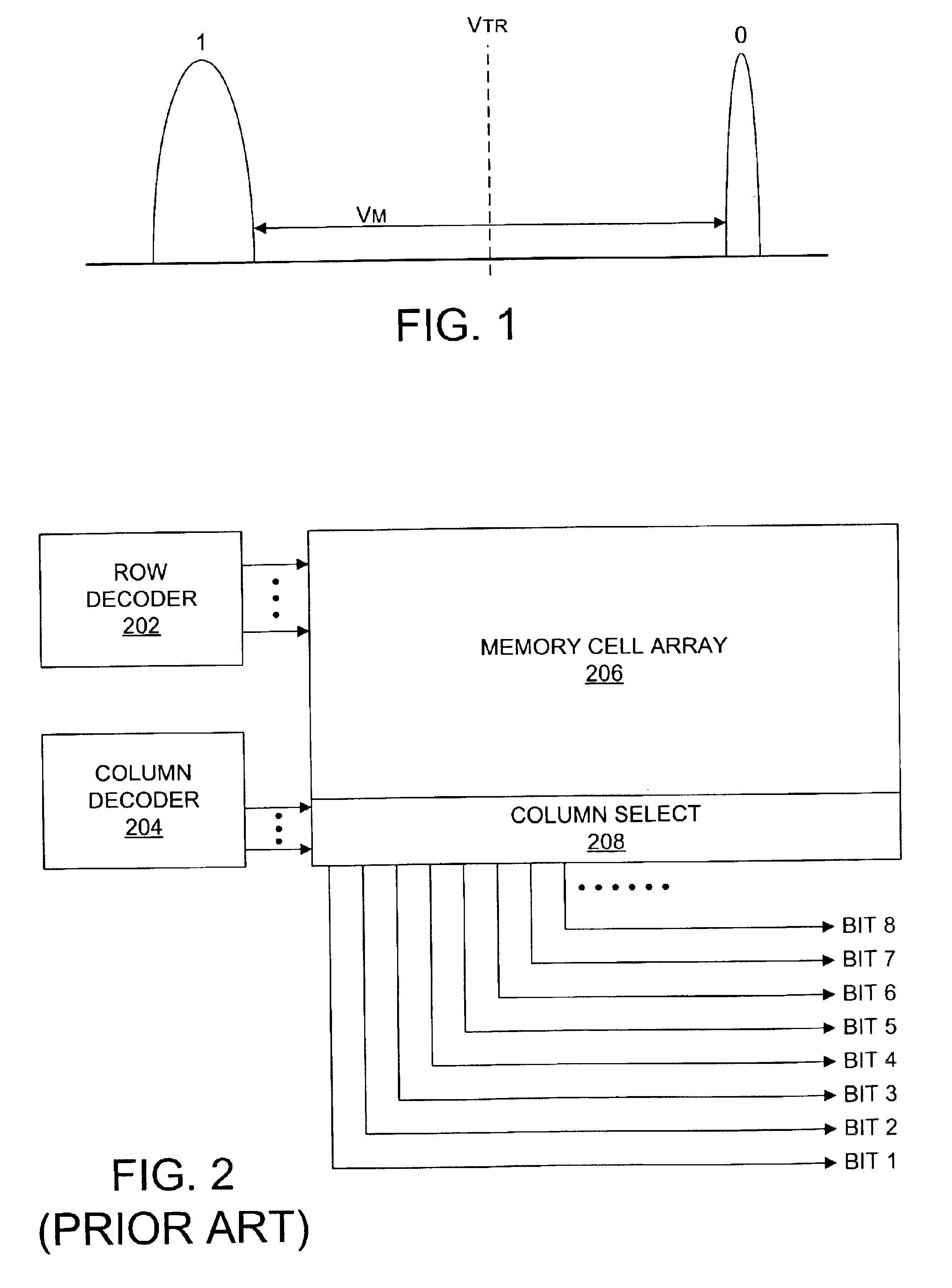
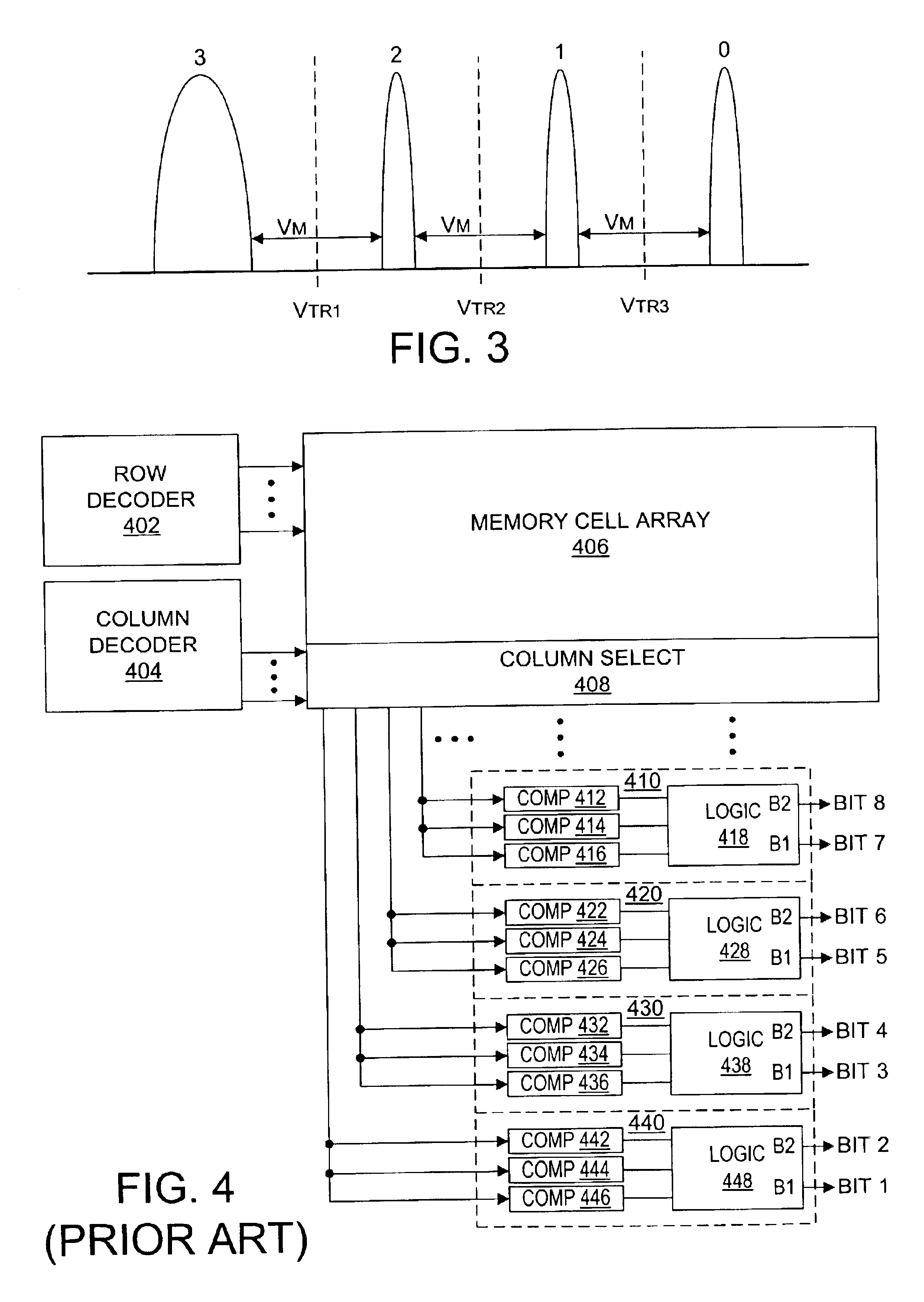
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory having three-level memory cells and program and read mapping circuits therefor
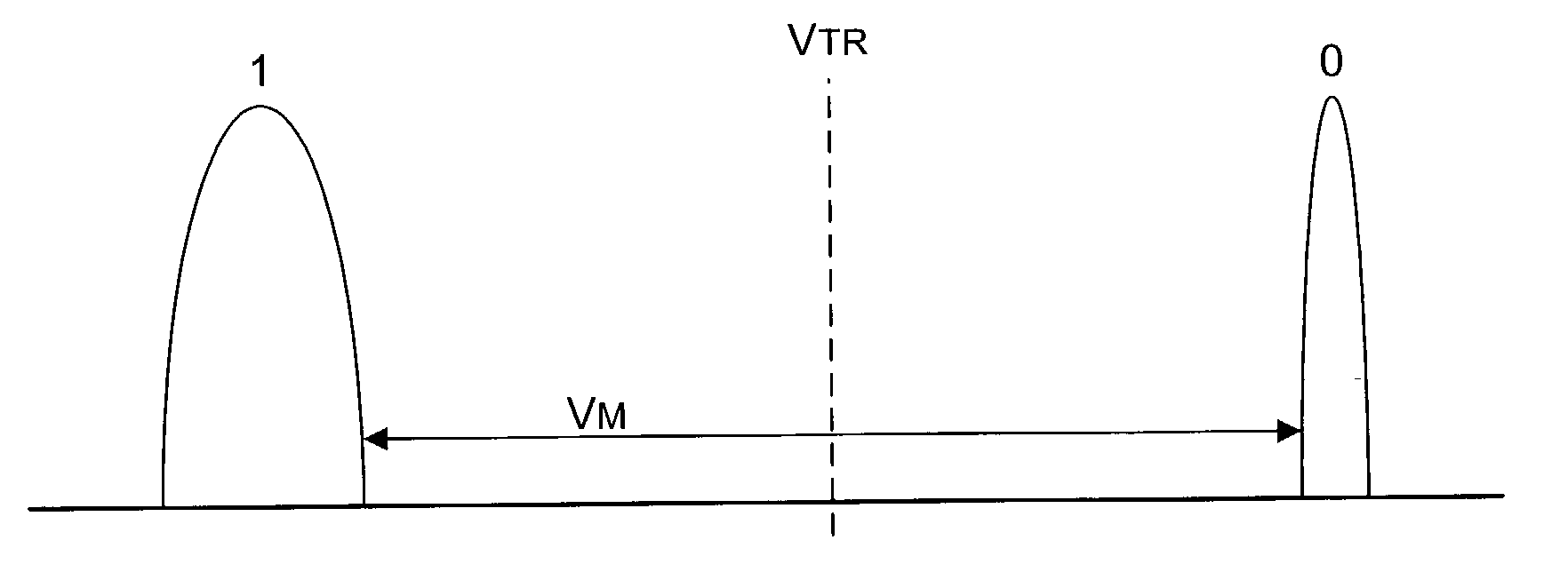
A memory uses multiple threshold levels in a memory cell that are not a power of two, and further uses a cell mapping technique wherein the read mapping is only a partial function The domain of read states for a single three-level memory cell, for example, has three states, but only two of them can be uniquely mapped to a bit. The domain of read states for two three-level memory cell, for example, has nine states, but only eight of them can be uniquely mapped to three bits. Although the read mapping is only partial, the voltage margin for the three-level memory cells is larger that the voltage margin available in the commonly used four-level memory cells. This increased voltage margin facilitates memory cell threshold voltage sensing, thereby increasing the reliability of the memory. Memory reliability may be further improved by increasing the voltage margin between the memory cell 0 state and the 1 state relative to the voltage margin between the 1 state and the 2 state, which more effectively accommodates charge loss from the 0 state through electron leakage. Asymmetrical read and program mapping may also be used to improve read reliability in the presence of ground noise or VCC noise.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory having three-level memory cells and program and read mapping circuits therefor
InactiveUS6847550B2Improve reliabilityHigh voltageRead-only memoriesDigital storageThree levelNon symmetric
A memory uses multiple threshold levels in a memory cell that are not a power of two, and further uses a cell mapping technique wherein the read mapping is only a partial function The domain of read states for a single three-level memory cell, for example, has three states, but only two of them can be uniquely mapped to a bit. The domain of read states for two three-level memory cell, for example, has nine states, but only eight of them can be uniquely mapped to three bits. Although the read mapping is only partial, the voltage margin for the three-level memory cells is larger that the voltage margin available in the commonly used four-level memory cells. This increased voltage margin facilitates memory cell threshold voltage sensing, thereby increasing the reliability of the memory. Memory reliability may be further improved by increasing the voltage margin between the memory cell 0 state and the 1 state relative to the voltage margin between the 1 state and the 2 state, which more effectively accommodates charge loss from the 0 state through electron leakage. Asymmetrical read and program mapping may also be used to improve read reliability in the presence of ground noise or VCC noise.
Owner:WINBOND ELECTRONICS CORP
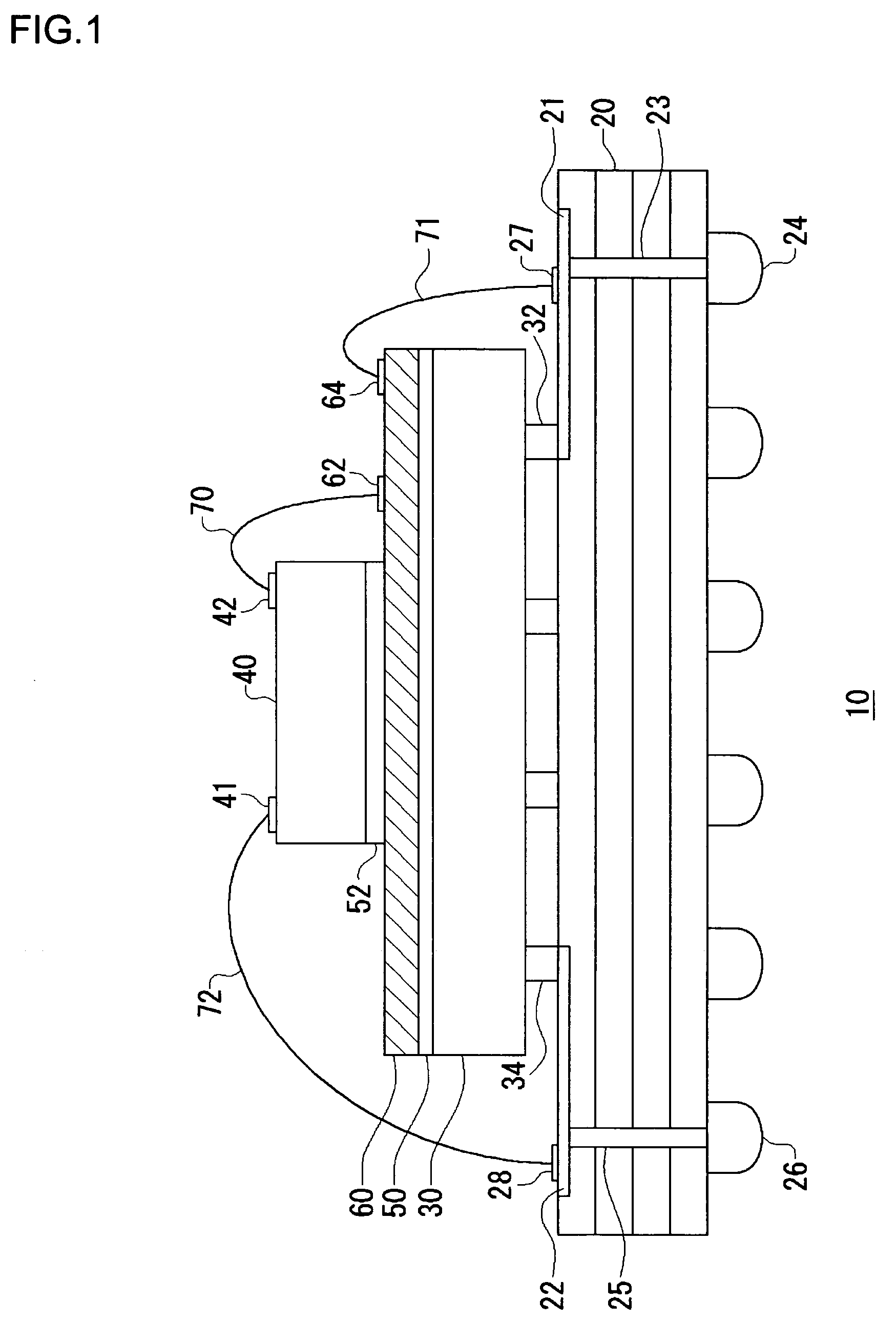
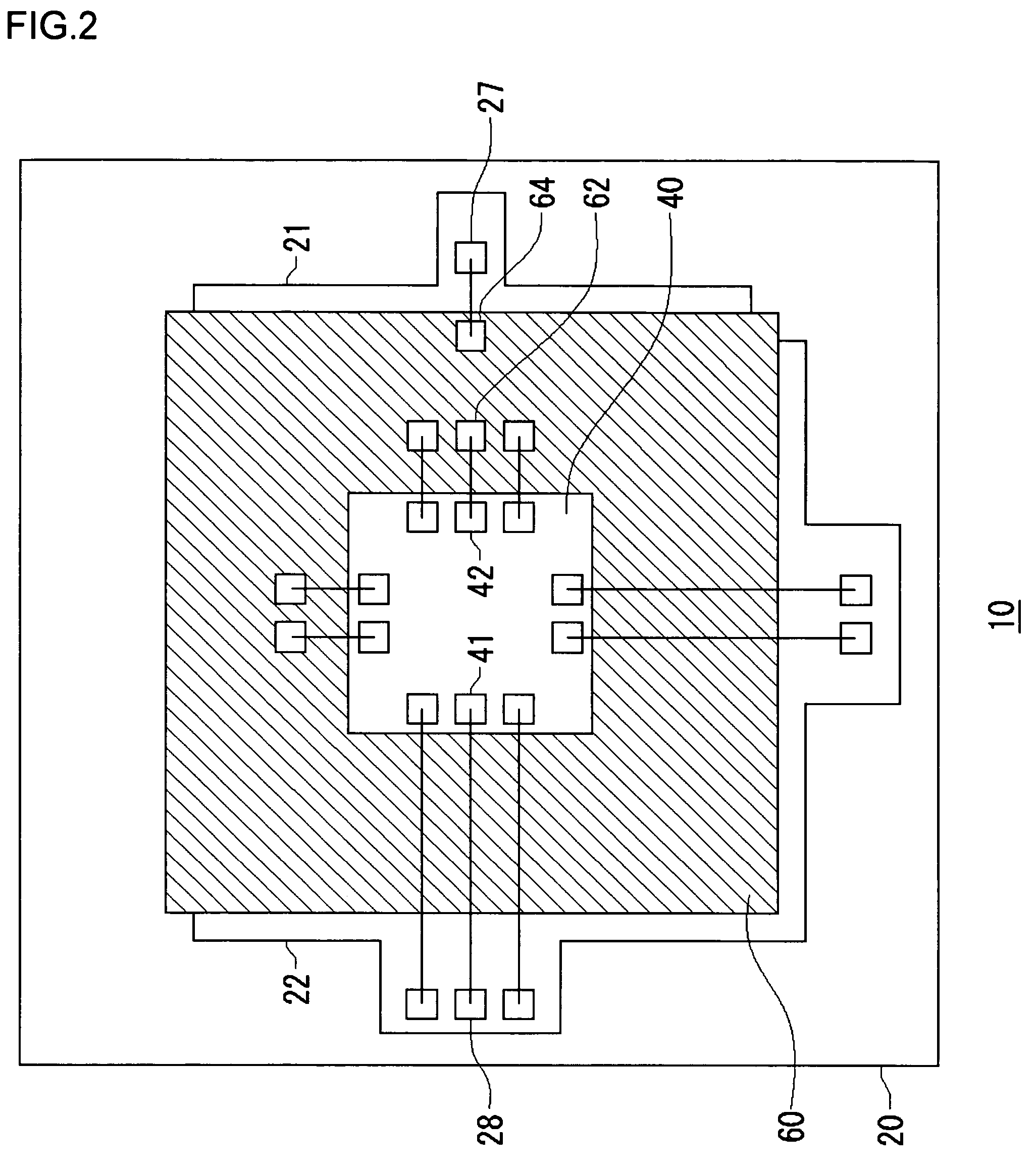
Probe card
InactiveUS6909297B2Reduce noiseSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectrical measurement instrument detailsProbe cardGround noise
A probe card is provided which includes a plurality of stacked signal printed circuit boards for transmitting signals, and a plurality of ground printed circuit boards respectively interposed between the signal printed circuit boards. To reduce ground noise, each of the ground printed circuit boards includes a plurality of conductive ground regions which are insulated from each other.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Point cloud data partitioning method based on three-dimensional laser radar
ActiveCN103226833AImprove efficiencyGuaranteed real-timeImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingPoint cloud
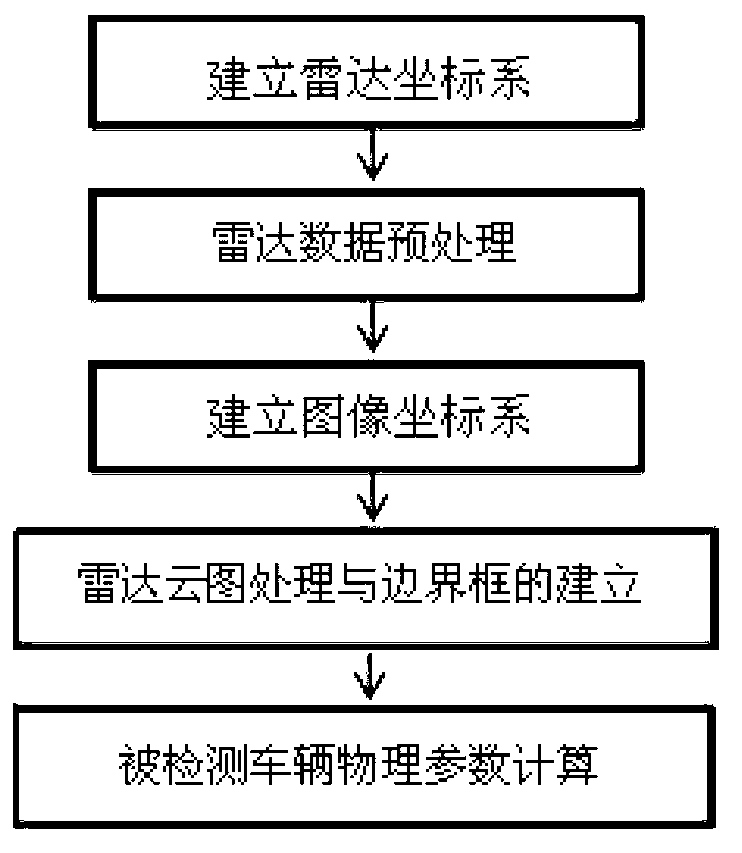
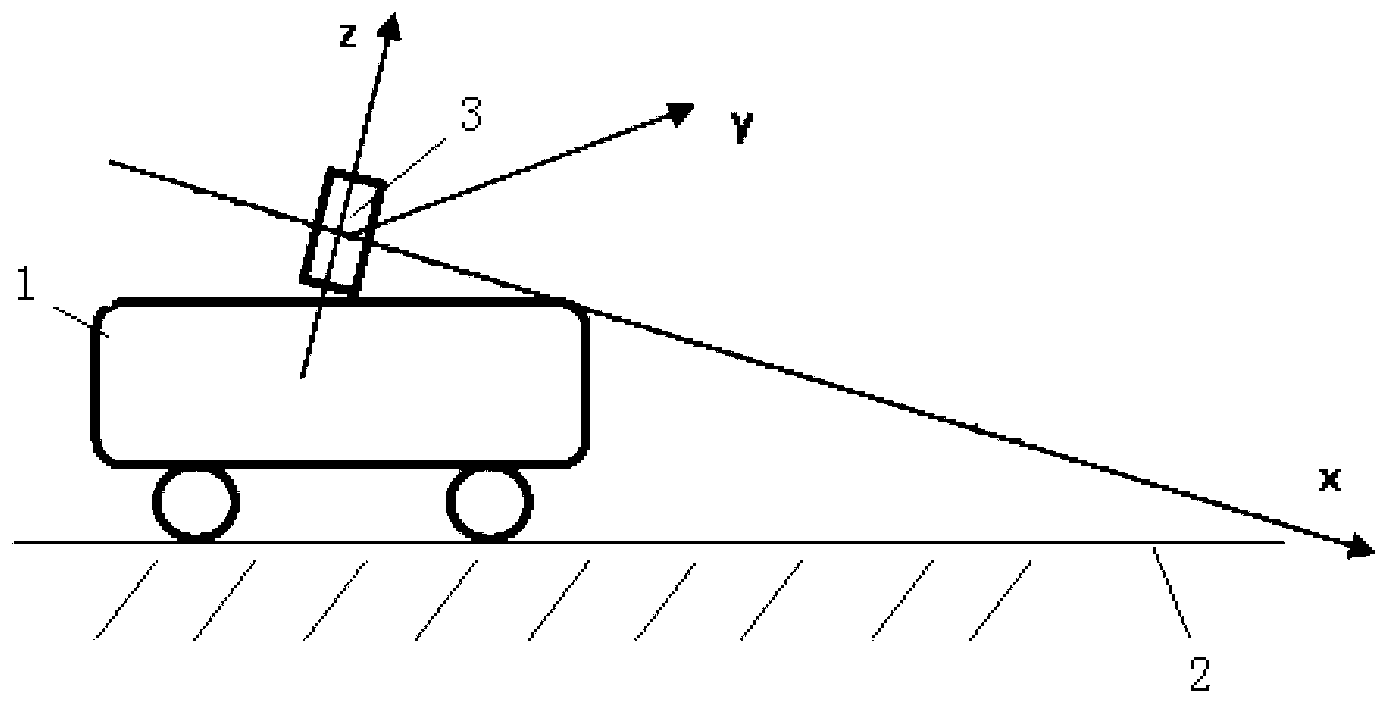
The invention relates to a point cloud data partitioning method based on three-dimensional laser radar. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) establishing a radar coordinate system oxyz of tested vehicles; (2) preprocessing the radar data acquired by the laser radar, establishing a region of interest under the radar coordinate system oxyz and filtering out ground noise; (3) establishing an image coordinate system o'uv, and defining the mapping relation between the radar coordinate system oxyz and the image coordinate system o'uv; (4) testing vehicles on a radar cloud picture directly by using an image processing algorithm, and characterizing all tested vehicles (except the testing vehicles) in the region of interest by using a bounding box so as to obtain four vertex coordinates of the bounding box of the tested vehicles under the image coordinate system o'uv; and (5) mapping the four vertex coordinates of the bounding box under the image coordinate system o'uv in step (4) to the radar coordinate system oxyz according to the coordinate mapping model so as to obtain the shape vector parameters of the tested vehicles according to the position vector parameter of the tested vehicles. The method is high in operation efficiency, test precision and reliability, and can be widely applied to the technical field of vehicle environment sensing.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Bit line setup and discharge circuit for programming non-volatile memory
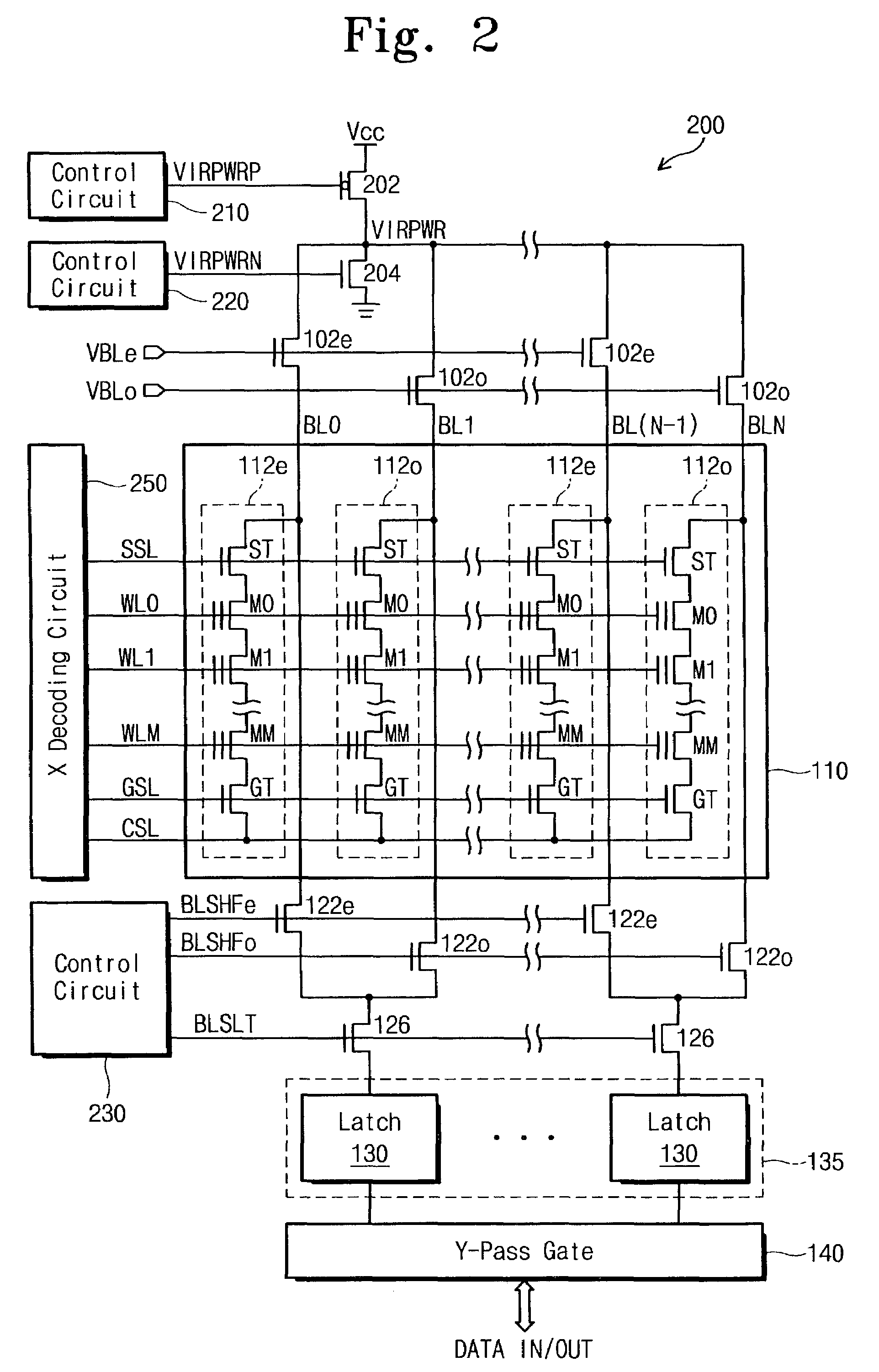
InactiveUS7453729B2Reduce ground noiseReduce Power NoiseRead-only memoriesDigital storagePre-chargeHemt circuits
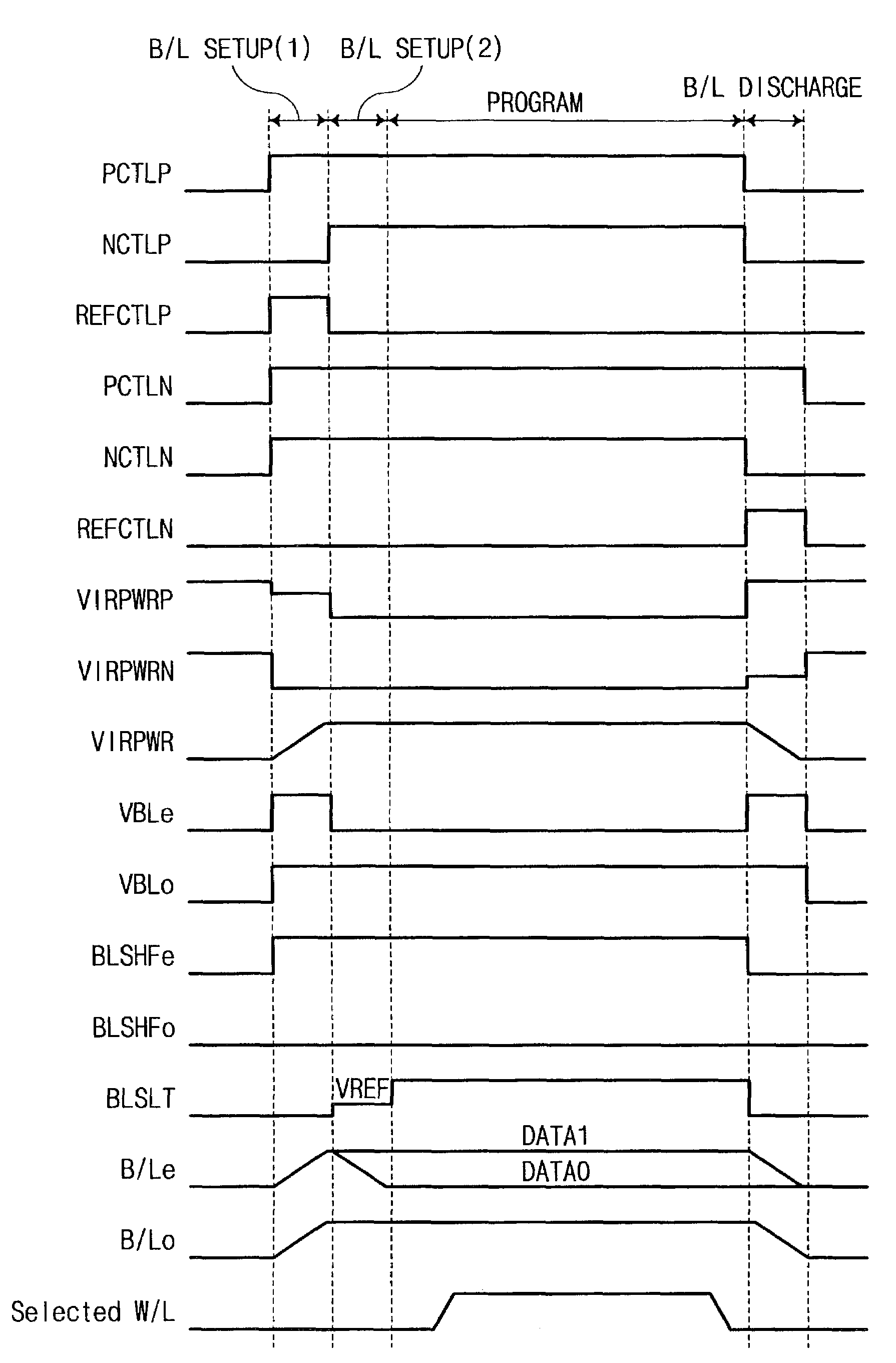
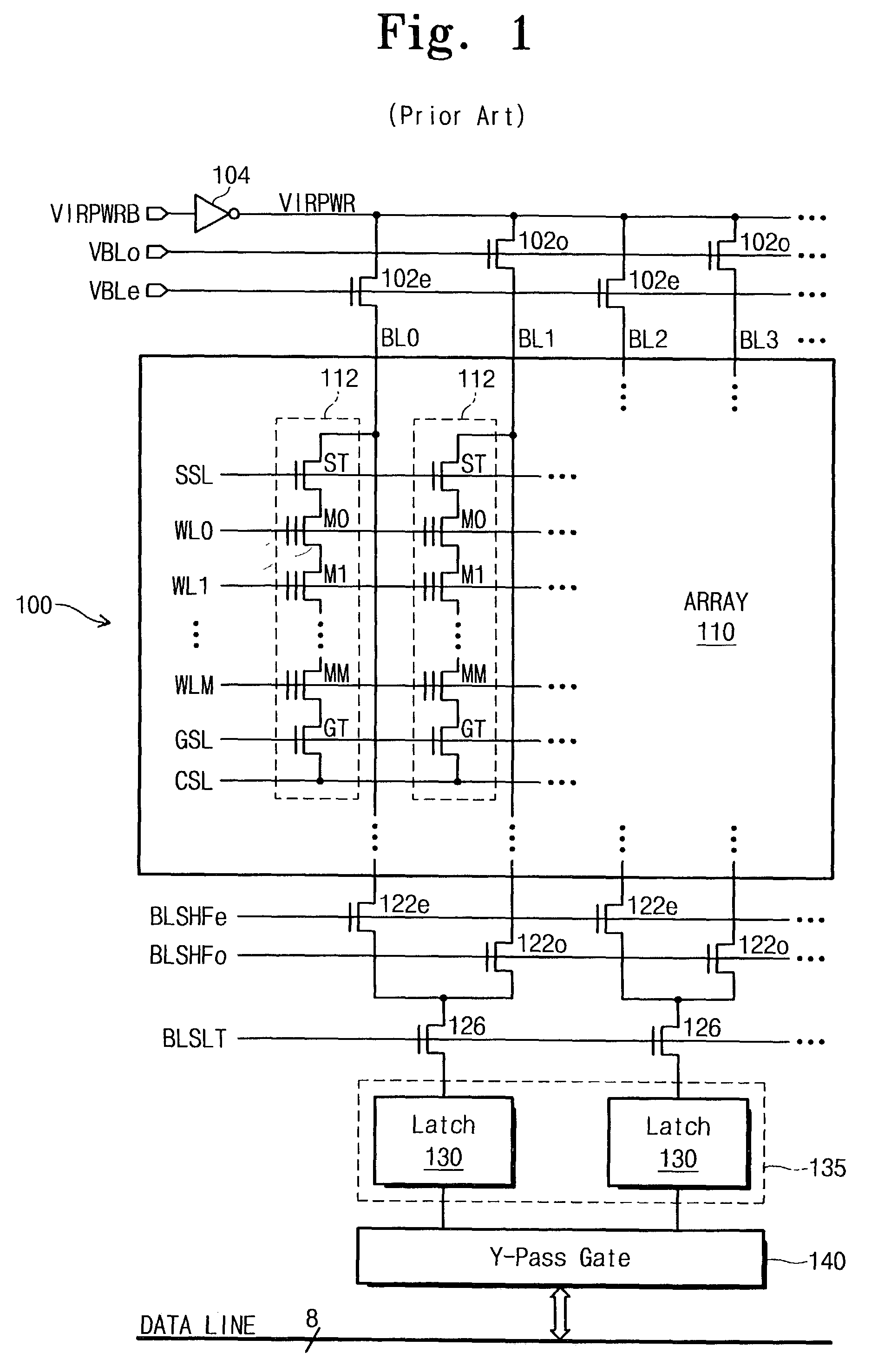
A NAND EEPROM having a shielded bit line architecture reduces supply voltage and ground noise resulting from charging or discharging bit lines. The EEPROM has a PMOS pull-up transistor and an NMOS pull down transistor connected to a virtual power node. A control circuit for charging or discharging bit lines controls the gate voltage of the PMOS or NMOS transistor to limit peak current when charging or discharging bit lines via the virtual power node. In particular, the control circuit operates the PMOS or NMOS transistor in a non-saturation mode to limit current. One such control circuit creates a current mirror or applies a reference voltage to control gate voltages. A programming method sets up bit lines by pre-charging unselected bit lines via the PMOS pull-up transistor having controlled gate voltage while latches in the programming circuitry charge or discharge selected bit lines according to respective data bits being stored. Another bit line setup includes two stages. A first stage pre-charges all bit lines via PMOS pull-up, and the second stage uses the latches to discharge or leave charged the selected bit lines depending on respective data bits being stored. The gate voltages of NMOS transistors in the programming circuitry can be controlled to reduce noise caused by discharging selected bit lines through the latches.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
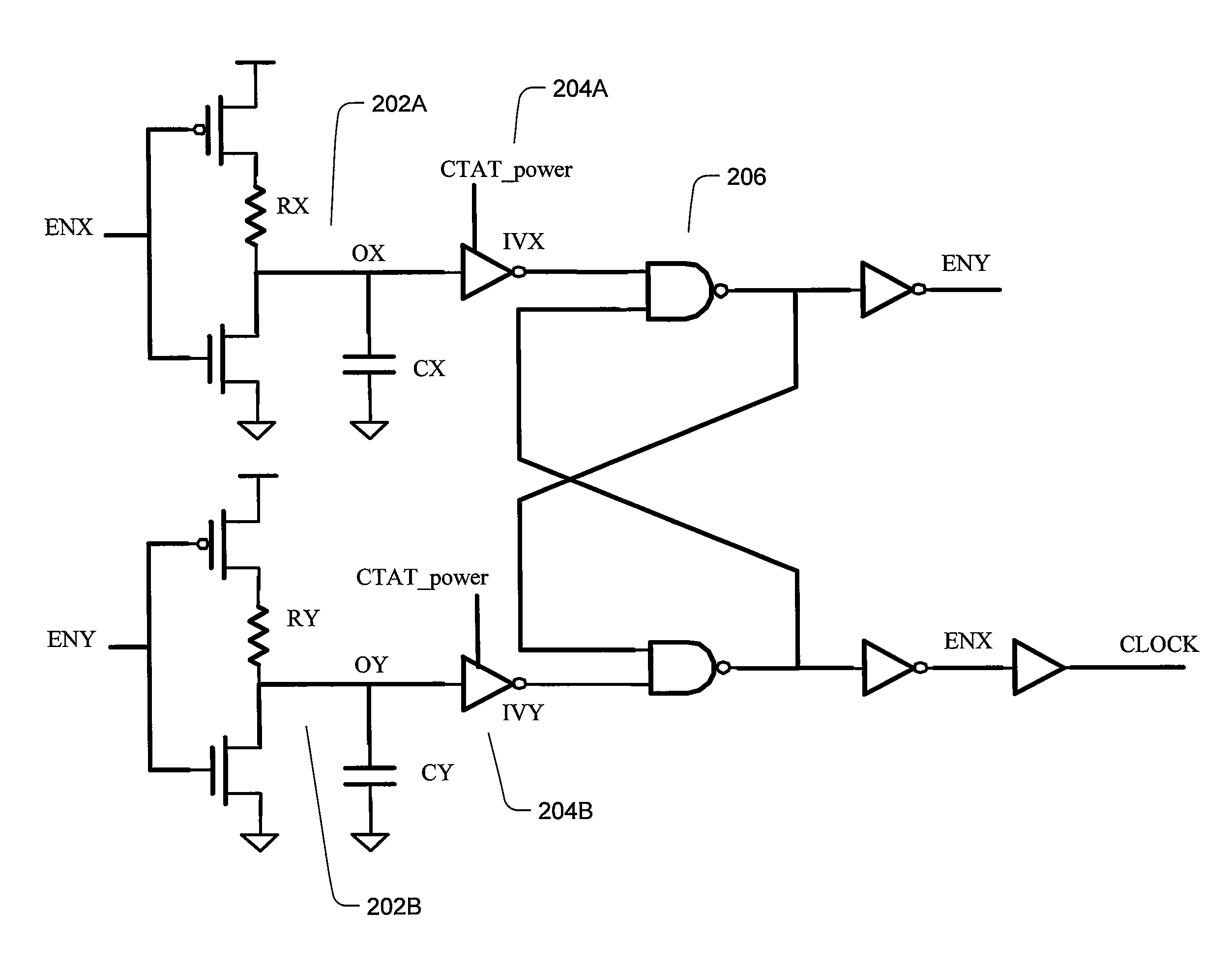
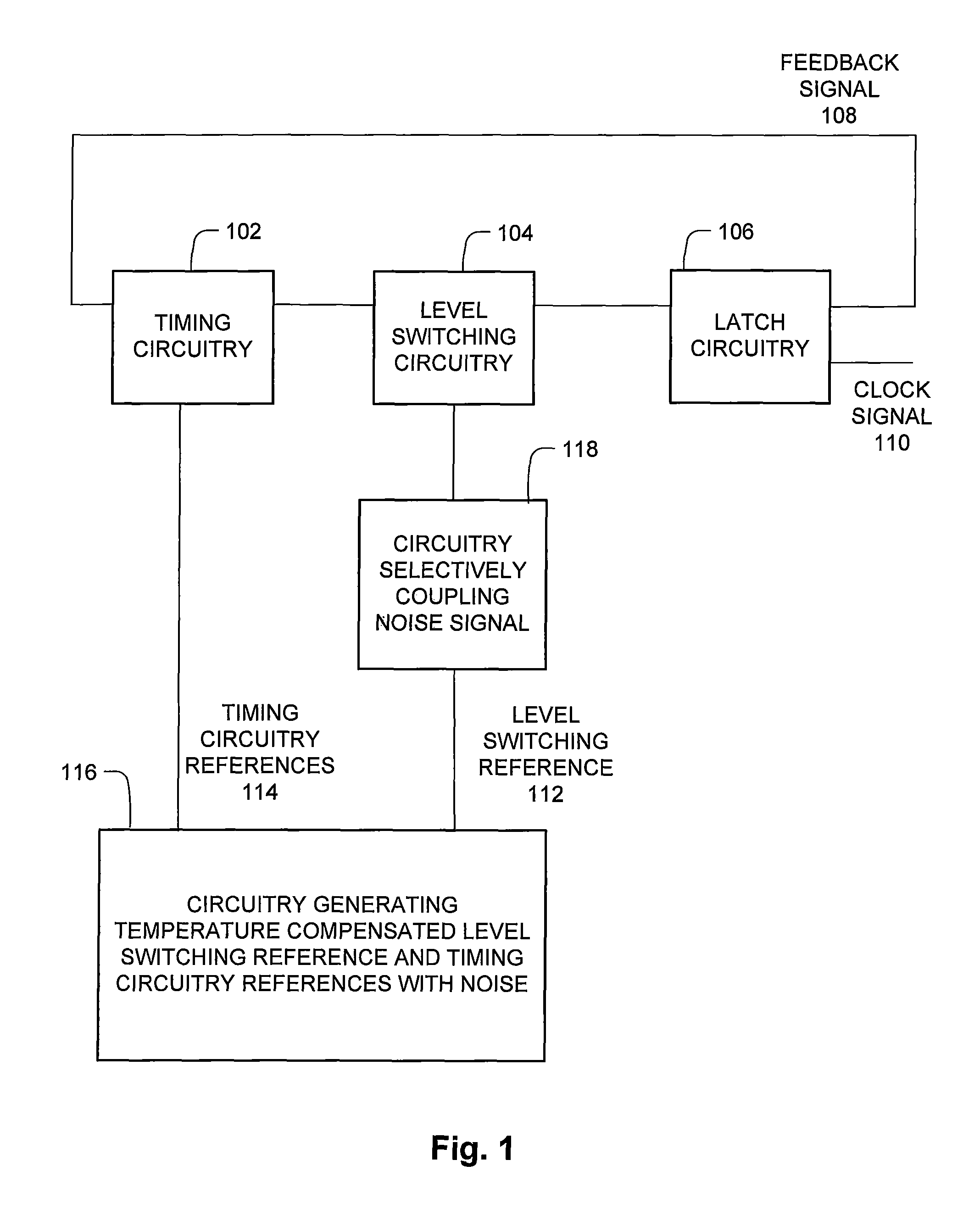
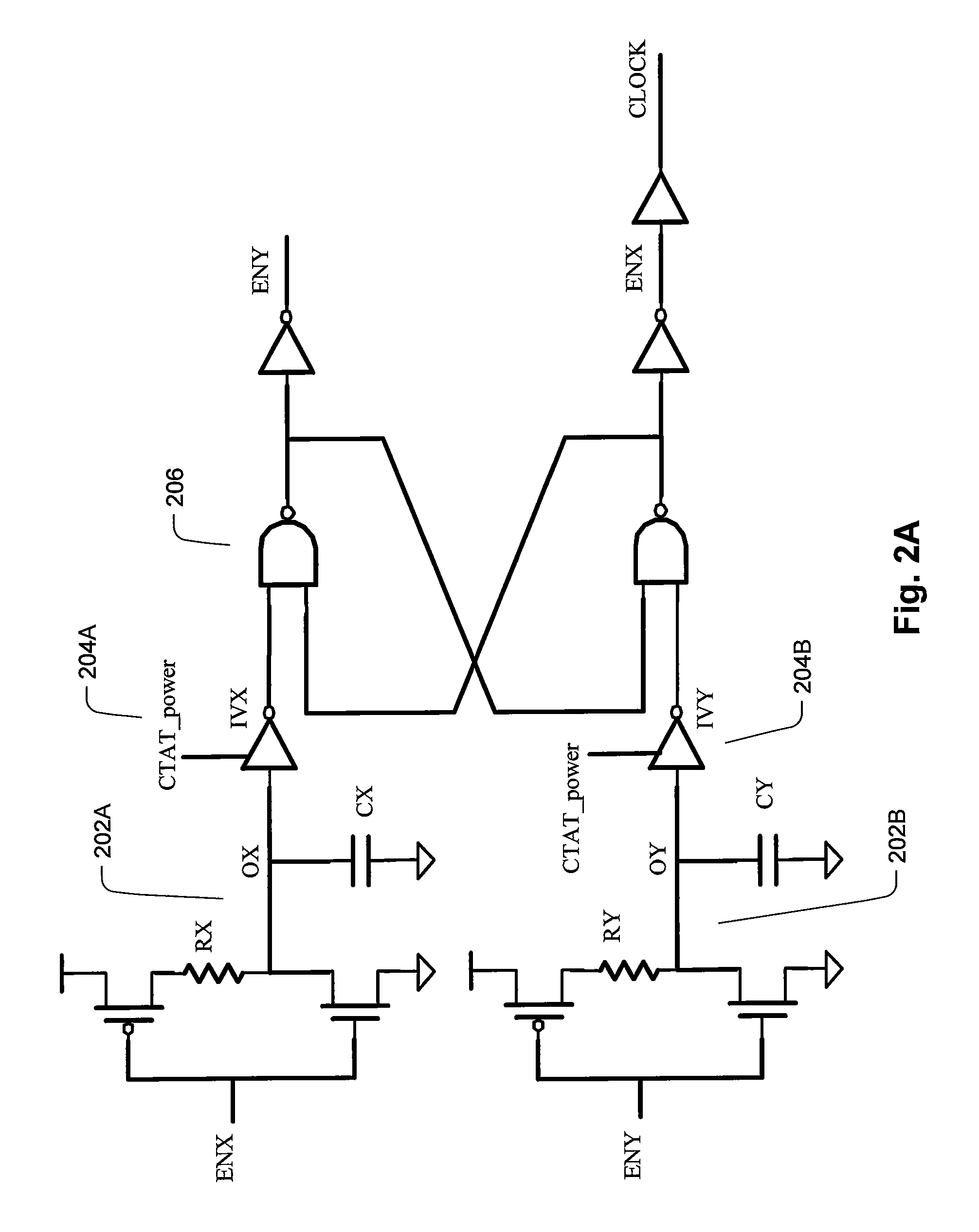
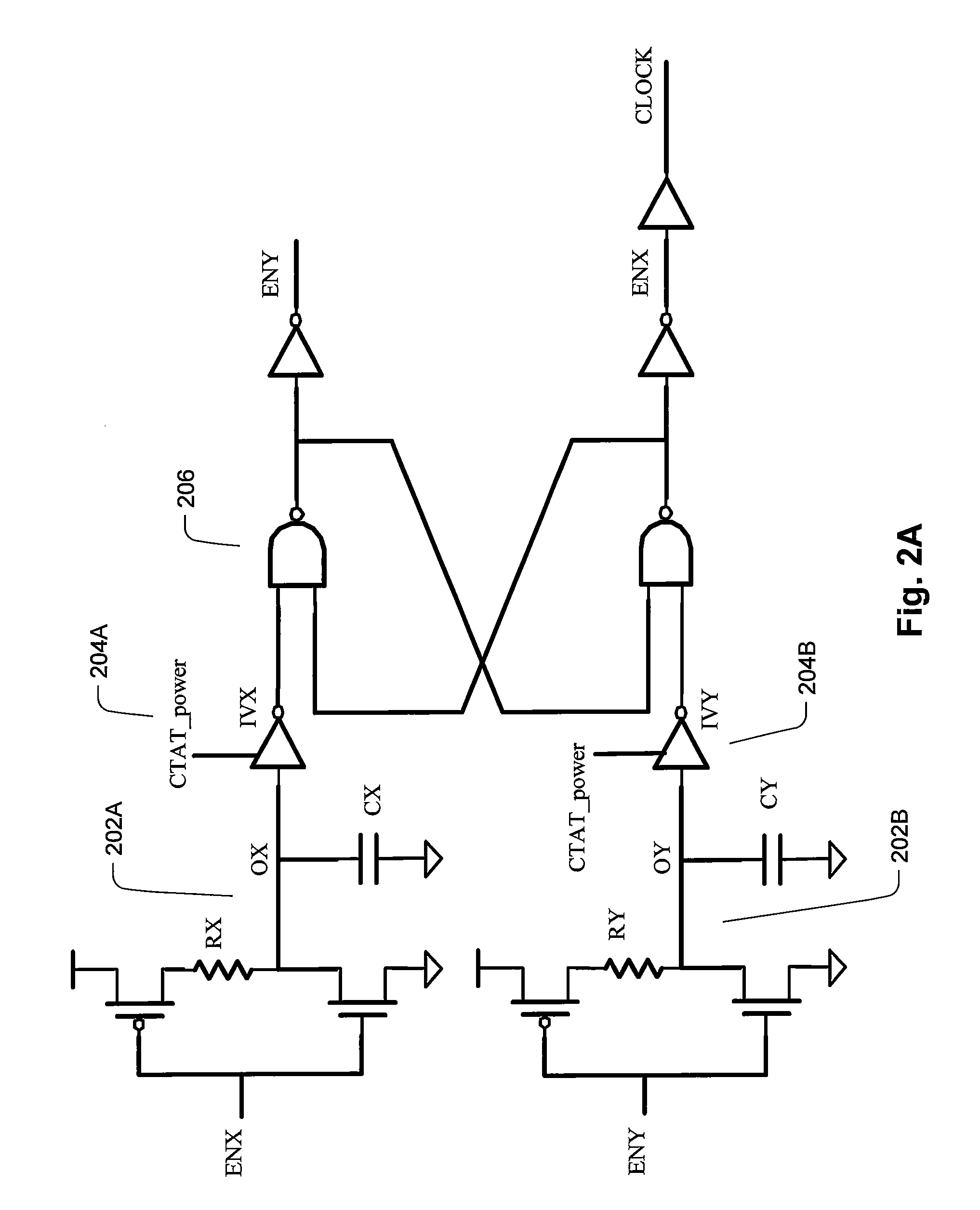
Clock integrated circuit
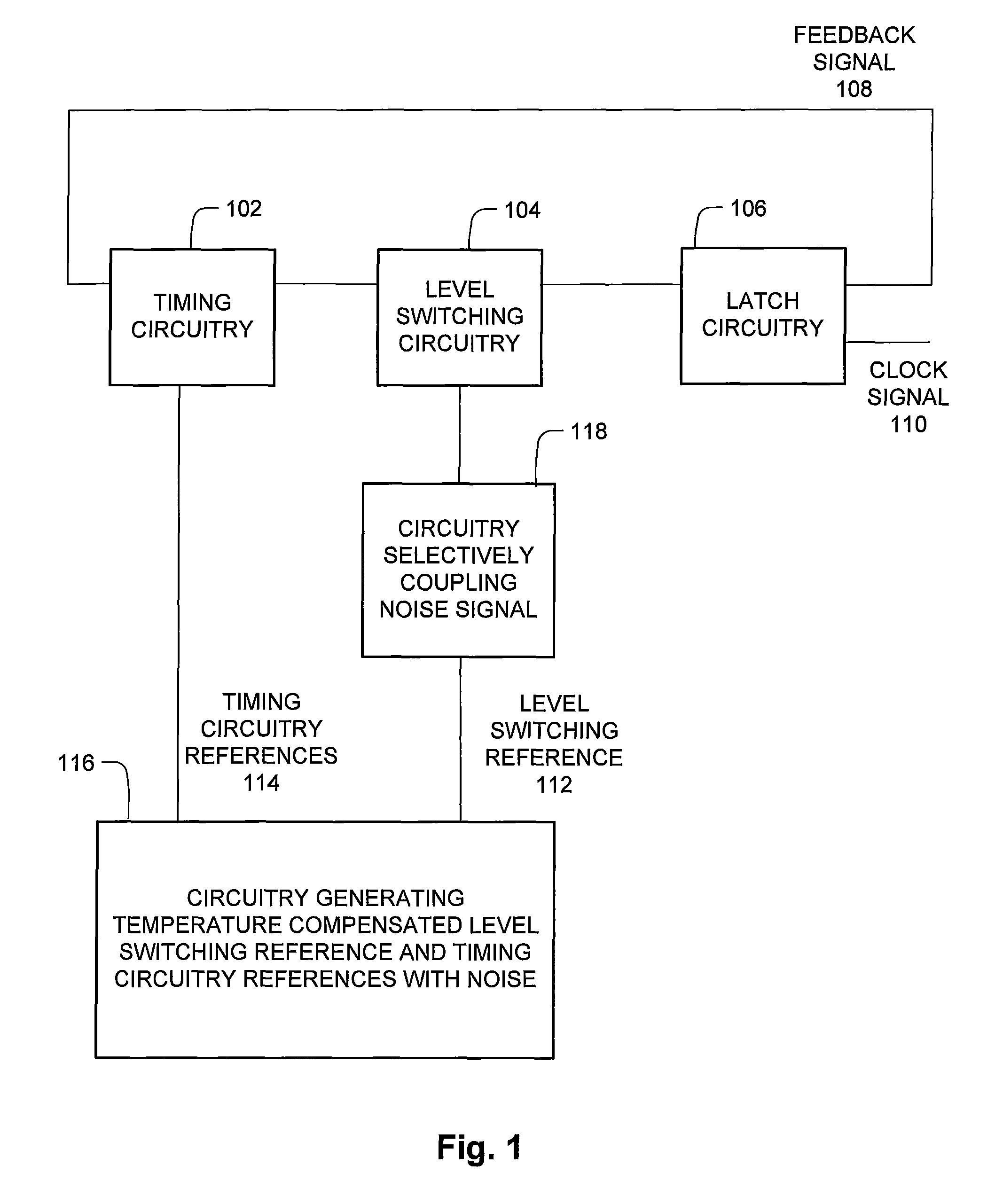
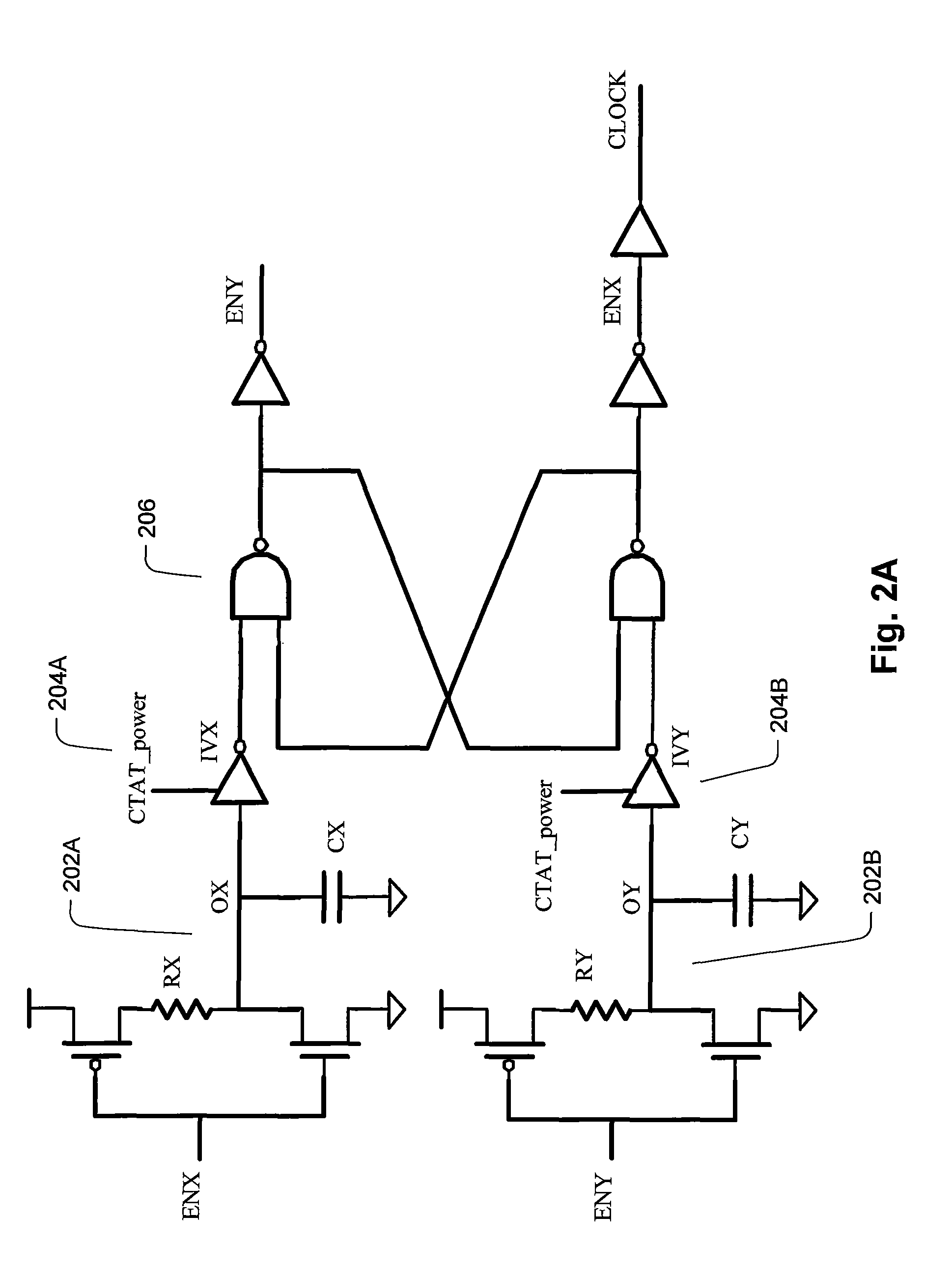
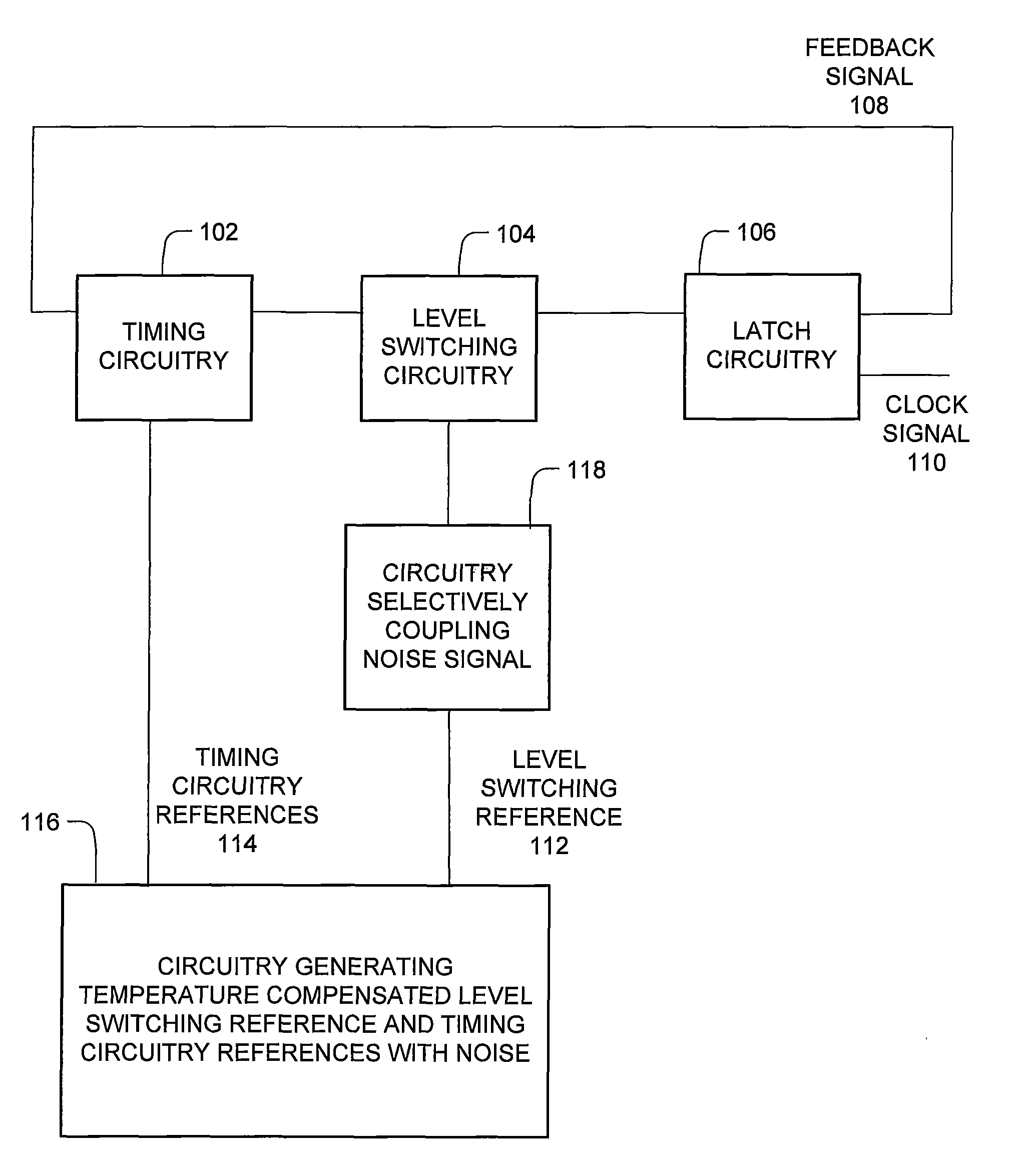
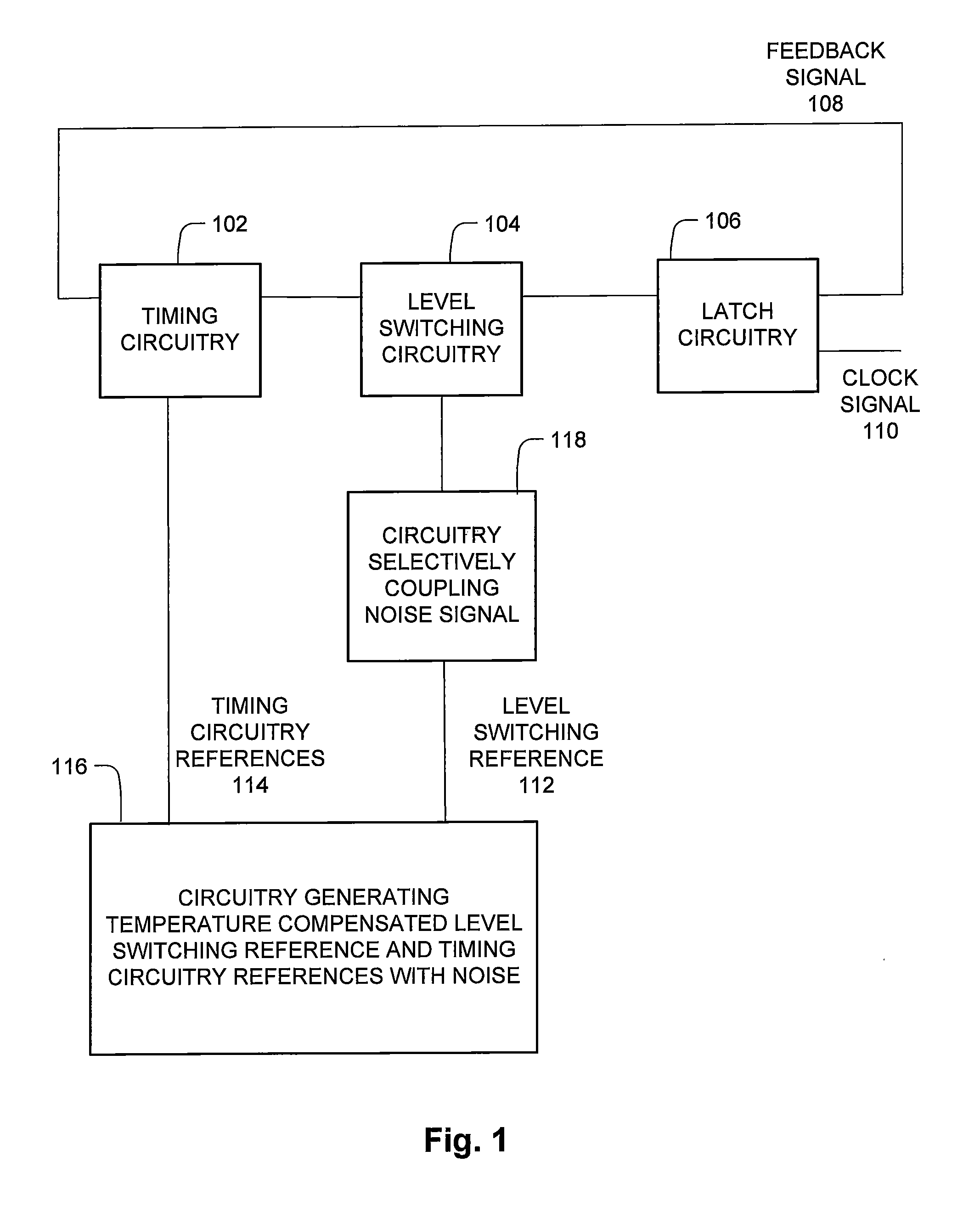
The clock circuit of an integrated circuit operates with variations such as temperature, ground noise, and power noise. Various aspects of an improved clock integrated circuit address one or more of the variations in temperature, ground noise, and power noise.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
System and method for weighing items such as mailpieces in the presence of external vibration
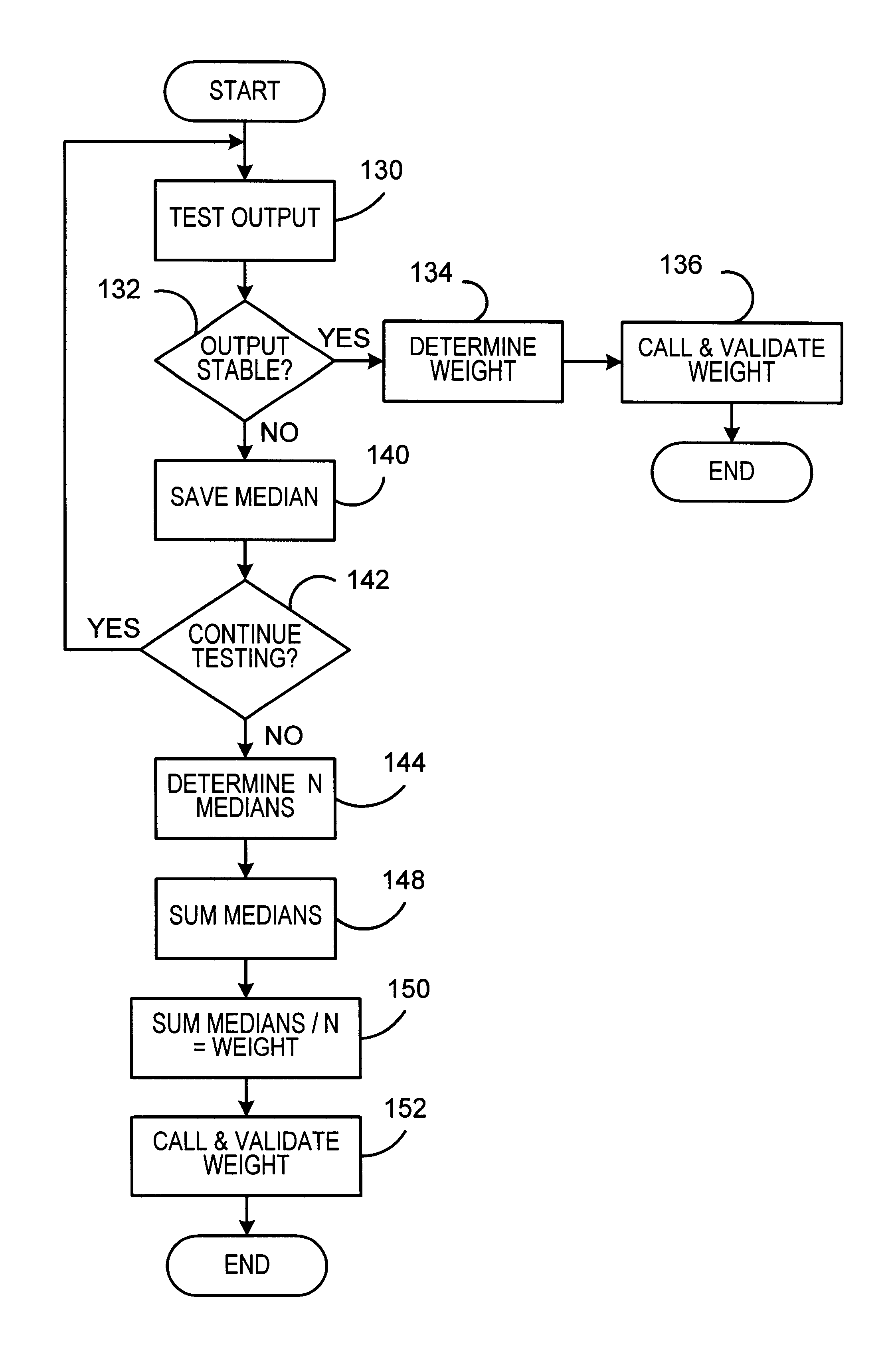
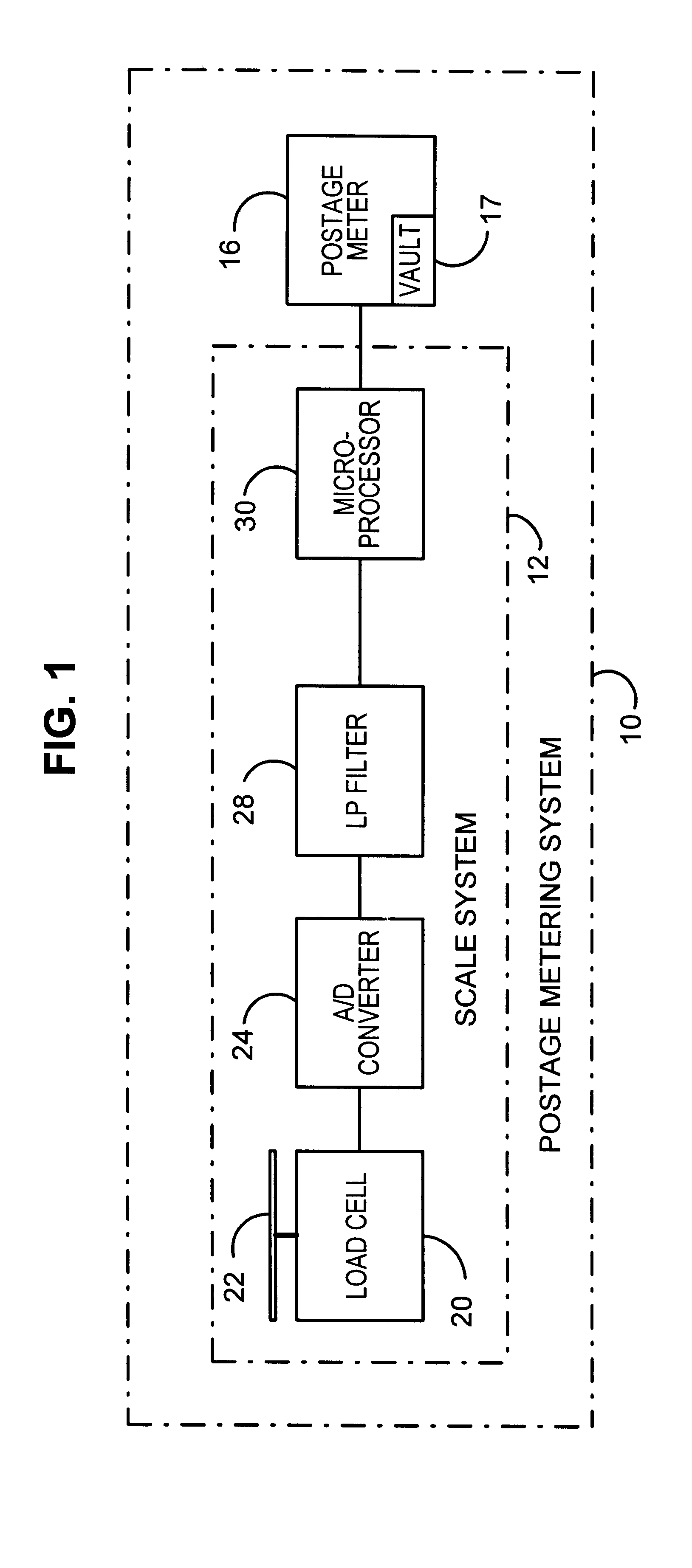
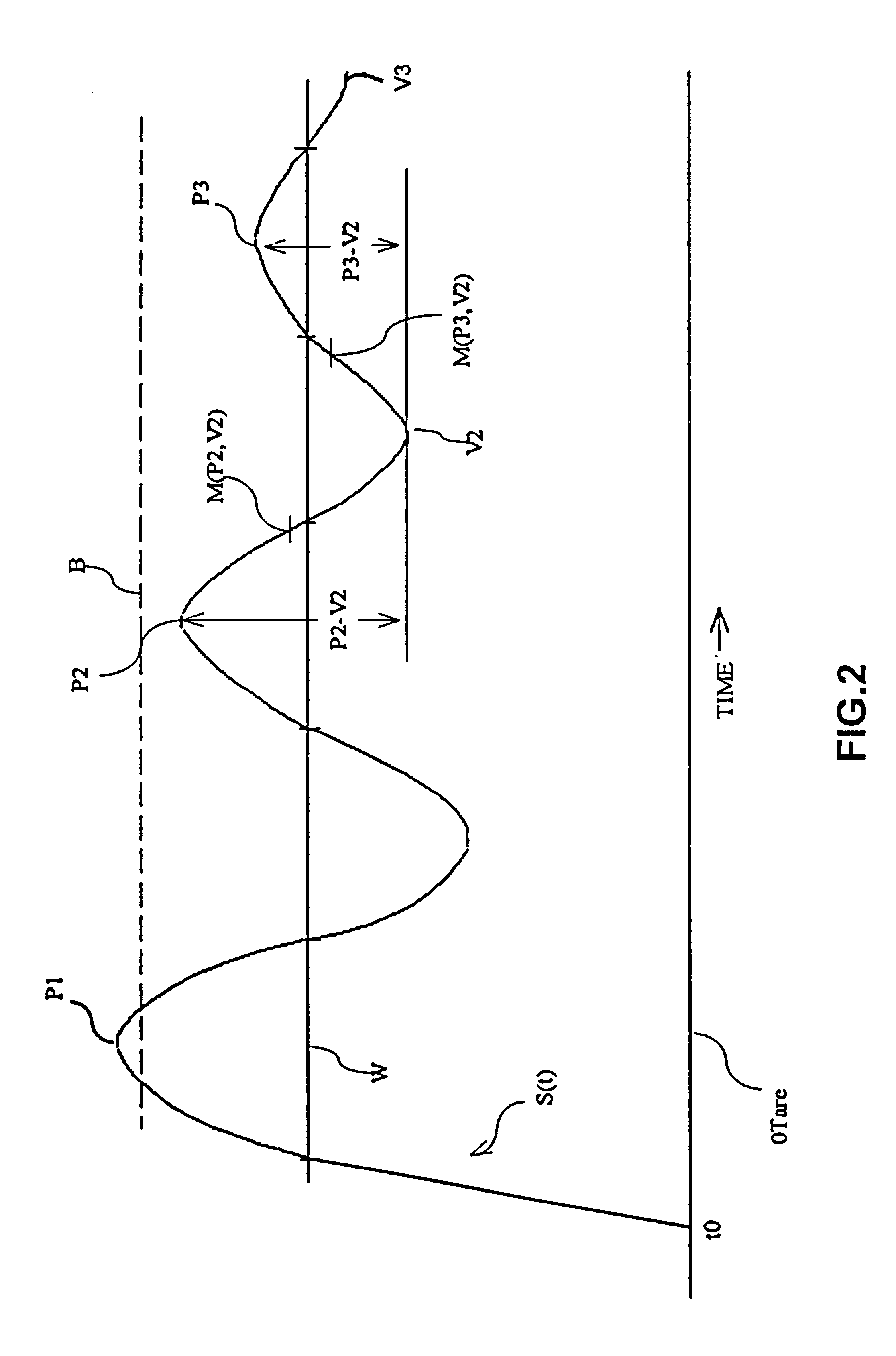
A system and method for weighing of items such as mailpieces in the presence of external vibration such as ground noise. The system includes a scale system having a platform connected to a load cell, which provides an output signal to an analog-to-digital converter. The resulting digital output signal is processed by a low pass filter and analyzed by a microprocessor to determine weights of items on the platform. The microprocessor also determines postage amounts as functions of the weights and outputs these postage amounts to a postage meter. The microprocessor determines the weights as the median of the peak to valley difference of the digital output signal when the digital output signal peak to valley difference is less than a predetermined value. The microprocessor identifies peaks and valleys of the digital output signal by determining when the derivative of the signal changes sign. The microprocessor estimates the weight as an average of a sum of medians for N preceding cycles if the digital output signal does not converge.
Owner:PITNEY BOWES INC
Circuit device
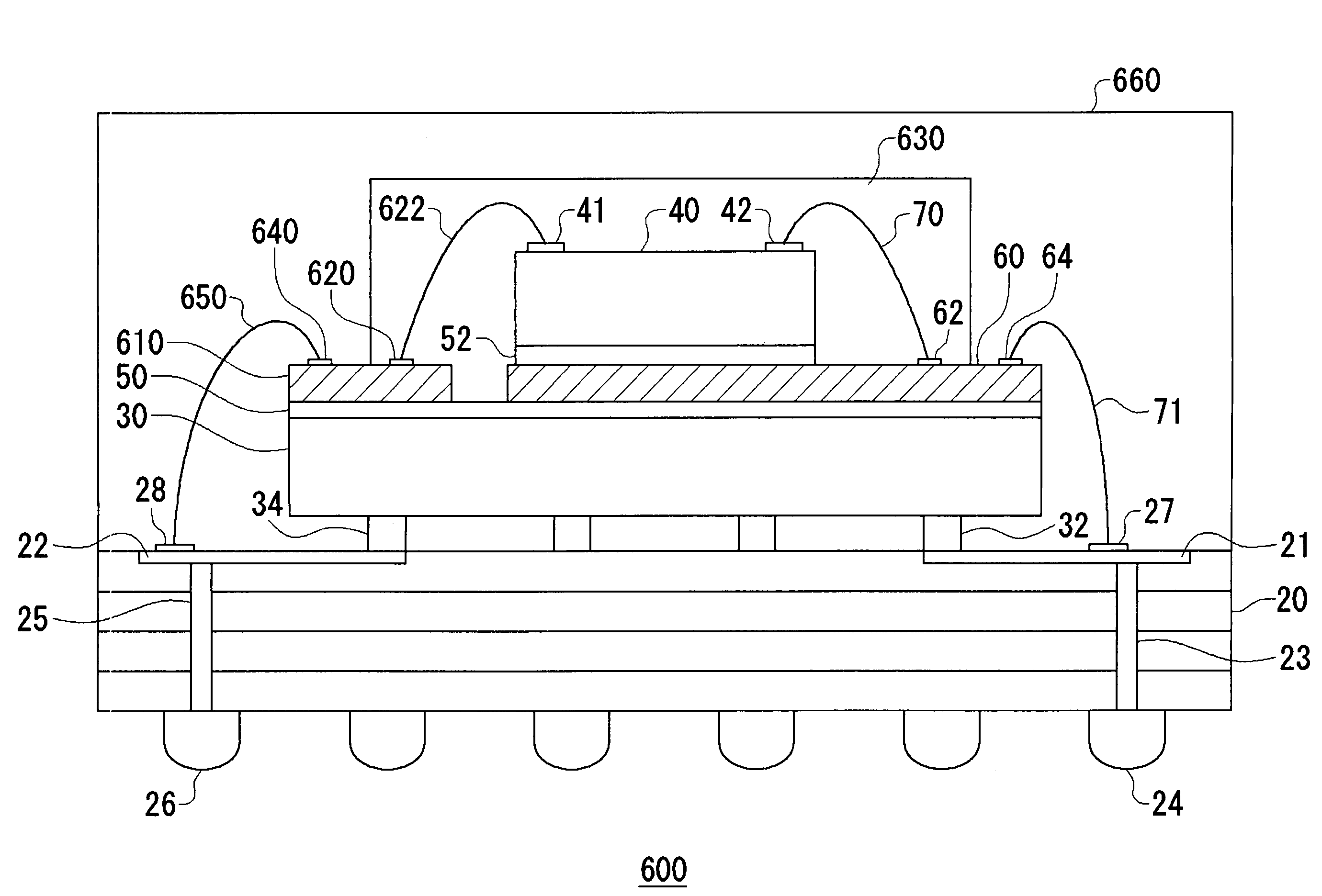
ActiveUS7453153B2Reduced ground noise propagatingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceGround noise
The ground noise is reduced which propagates between circuit elements in a circuit device having a multiple stack structure. A grounding bonding pad provided on the surface of a second circuit element is connected to a bonding wire provided on the surface of a conduction layer via a grounding wire such as gold. A bonding pad provided on the surface of the conductive layer is connected to a lead provided on a ground wire via a grounding wire such as gold. This structure creates a capacitance between the second circuit element and the conduction layer so as to prevent the propagation of noise circuit from element to the ground wiring.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC +1
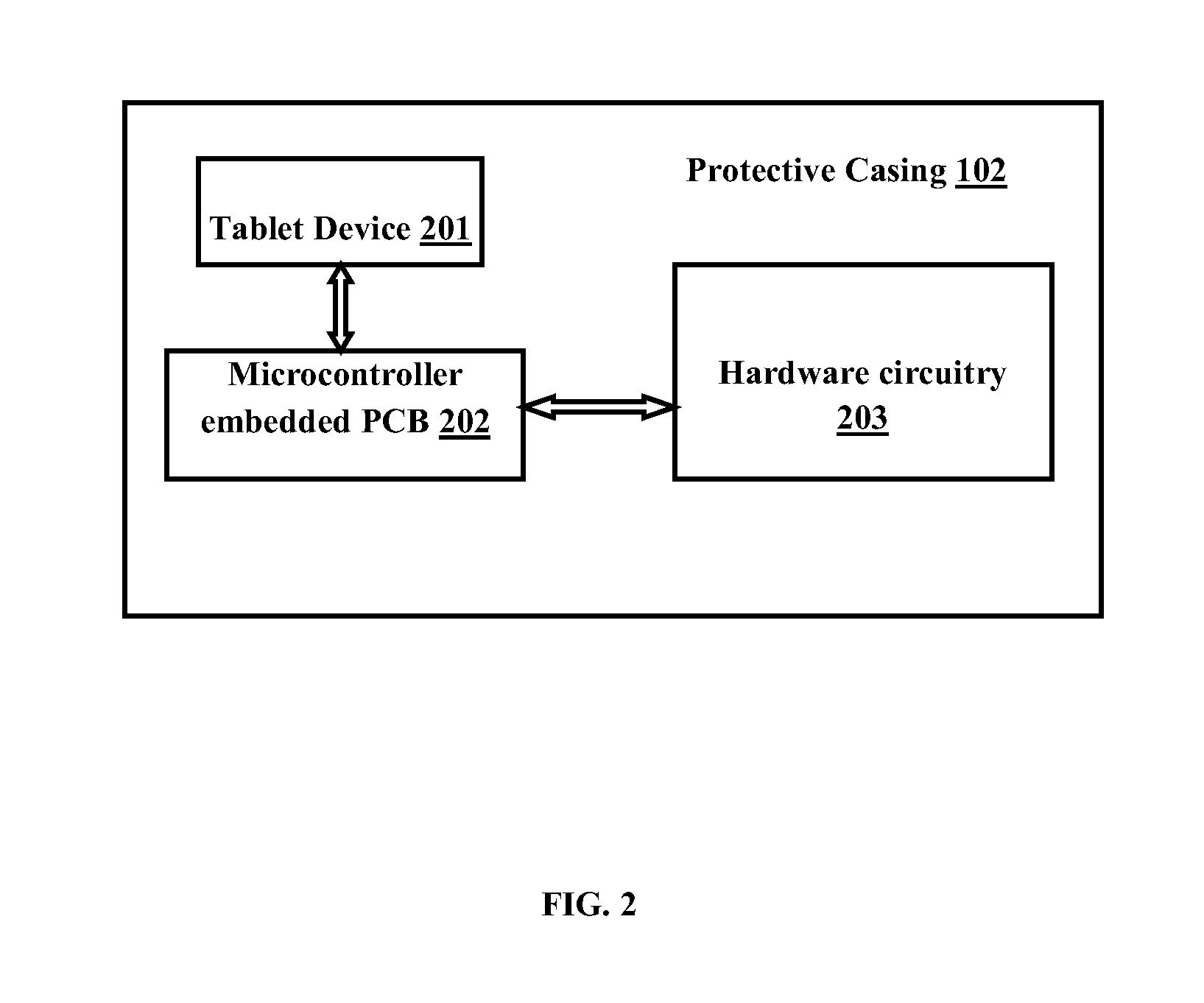
Intelligent casing for smart devices
InactiveUS20130077235A1Provide compatibilityDigital data processing detailsElectrical apparatus contructional detailsMicrocontrollerGround noise
The various embodiments herein provide an intelligent protective casing for smart devices. The casing comprises a frame to releasably engage and hold a tablet device. The frame comprises an opening provided on the center for exposing a display panel of the tablet device, a printed circuit board (PCB), a microcontroller embedded in the PCB and a hardware circuitry interface for providing functional compatibility between the tablet device and the frame. The hardware circuitry includes a plurality of user configurable hardware features which are enabled according to user preferences. The user configurable hardware features comprises a fingerprint scanner, a thermal printer, one or more smart card readers, a magnetic swipe card reader, high amplitude speakers, a barcode scanner, an iris scanner, a projector, a solar panel, a back ground noise cancellation circuit, one or more noise cancellation microphones and at least one swappable battery to drive the circuitry.
Owner:BEWO TECH PVT
Circuit for detecting and measuring noise in semiconductor integrated circuit
InactiveUS20060221531A1No deterioration of detect characteristicImprove noiseNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementDigital signal processingLoad circuit
A noise measuring circuit and a noise measuring circuit of the present invention can figure out power supply noise waveforms, ground level noise waveforms, and a spatial distribution of noise occurring positions by being embedded into distributed arrangement positions in said semiconductor integrated circuit comprising plural circuit block for performing a digital signal processing, and the noise measuring circuit and the noise measuring circuit is manufactured by the manufacturing process of the CMOS semiconductor integrated circuit. The power supply noise measuring circuit and the ground level noise measuring circuit comprise a source follower, a select read out switch, and source-grounded amplifier. These noise measuring circuits can be configured by several (about 6) MOS transistors, so the layout for the measuring circuit can be small and be achieved by the same size as that of a standard cell type logic gate circuit. As for the output of the noise measuring circuits, the output current of said source-grounded amplifier is connected to the current bus line, the outputted current is amplified and the amplified current is read by driving the external resistance load circuit. Plural noise measuring circuits can be connected parallel to the current bus line, and the multiple points noise measuring in the main integrated circuit can be achieved by reading out the output current.
Owner:THE NEW IND RES ORG
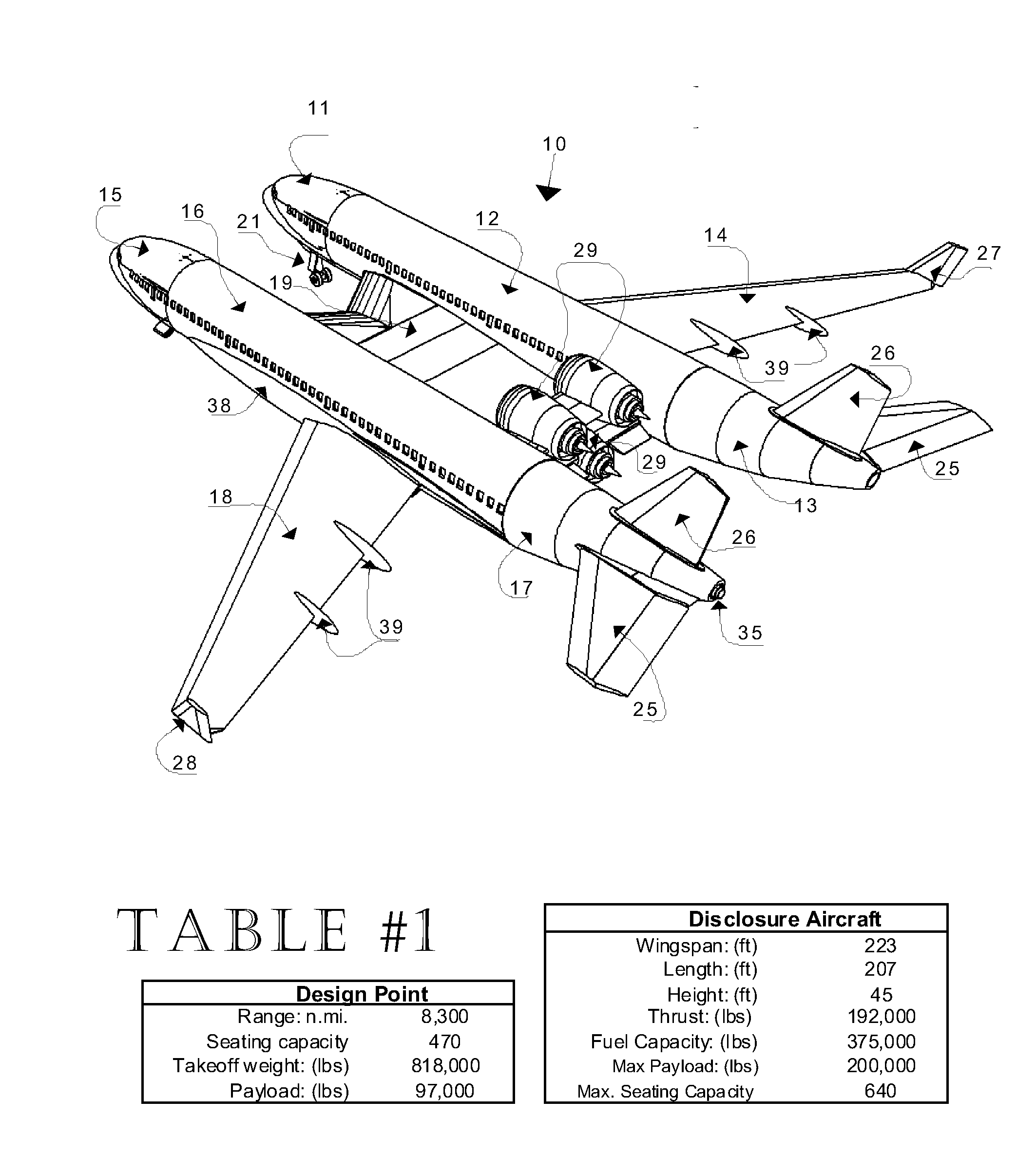
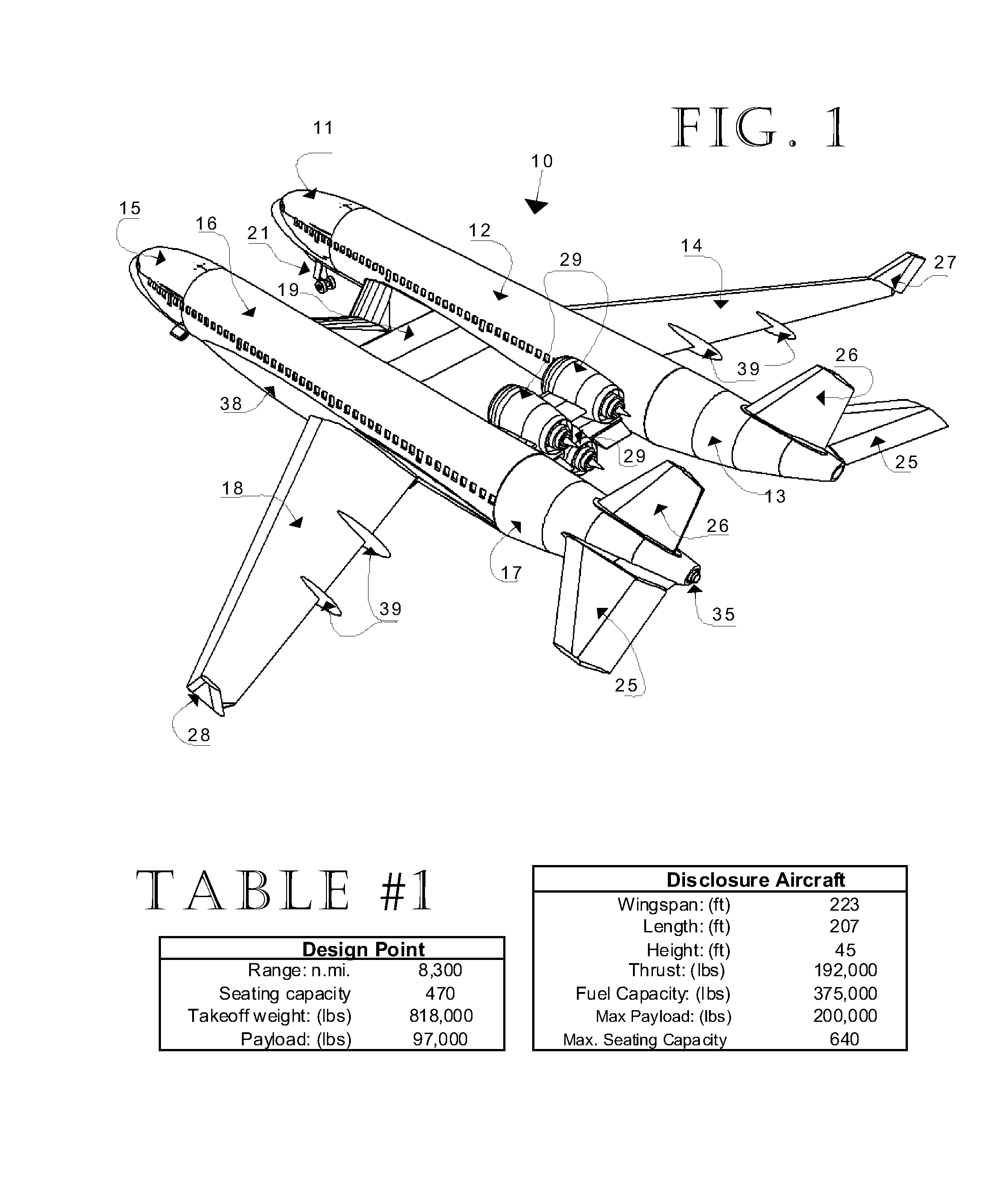
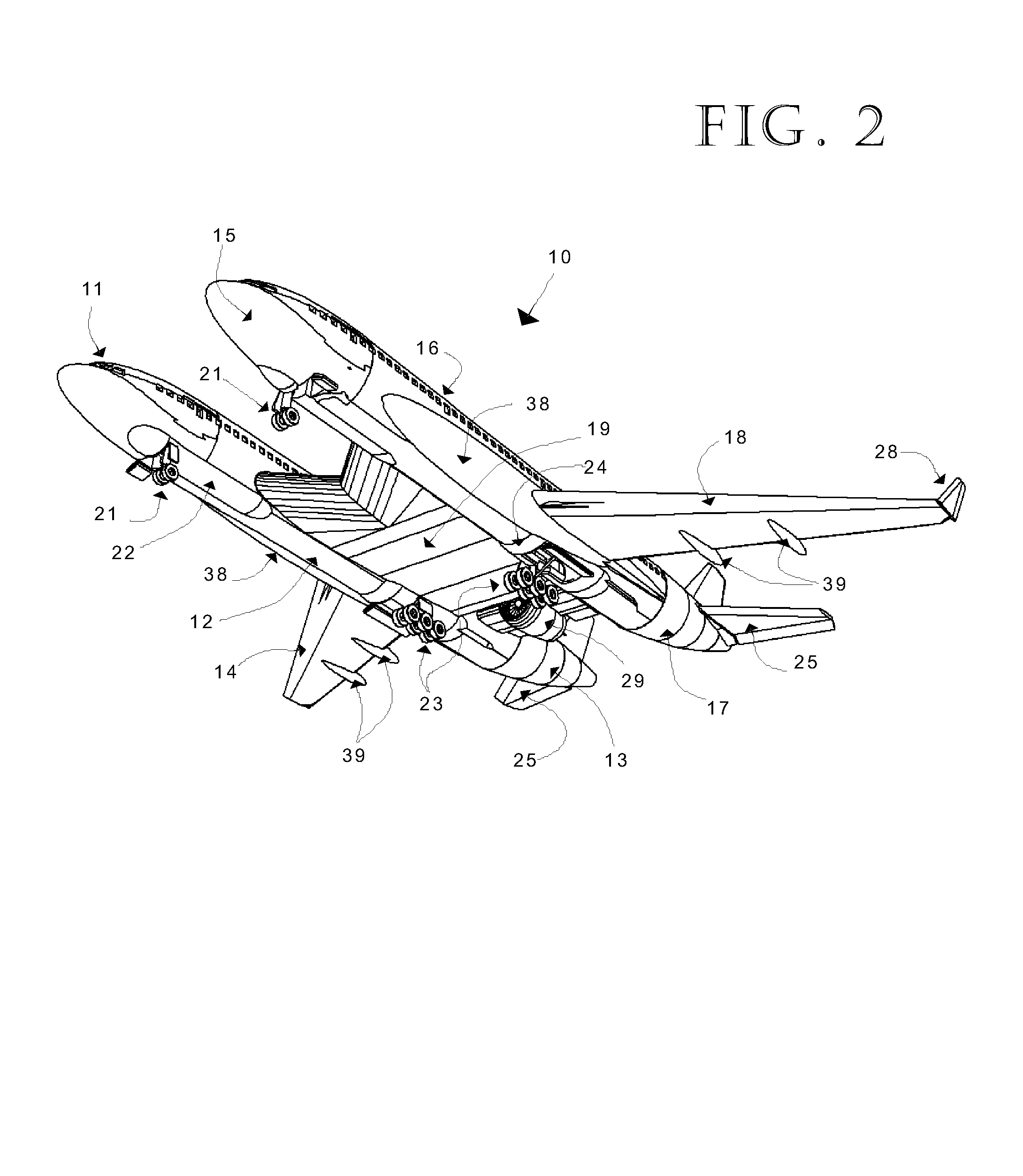
Cross-wing Twin-Fuselage Aircraft
InactiveUS20140263831A1Reduction factorEfficiency advantageGas turbine type power plantsWeight reductionGround noiseAppendage
A dimensionally size-efficient aircraft being of a twin-fuselage configuration that addresses long-range high-capacity passenger commercial or military application needs, unique in that propelling engines (two, three, or four engine arrangements) are centrally mounted aft of a central cross-wing section, that section addressing the structural requirements of fuselage attachment with a means of passage between fuselages, the outer main wings being free from hanging appendages, thereby enabling efficient aerodynamic-lift wing design, the configuration using a split stabilizer and a split vertical tail for stable aerodynamic control. Engine locations are biased high and aft with the central and outer wings providing ground noise abatement while in flight, passenger cabin noise low due to aft engine locations.Efficiencies of operation derive from: 1) a low overall weight / revenue seat ratio, 2) large and adaptable passenger floor plans, 3) compatibility with existing ground terminal facilities, 4) multiple engine configuration selections enabled by this aircraft layout, both turbo-fan and turbo-prop, and 5) opportunities of growth within this configuration. It is a low wave-drag configuration that better approaches the cross-sectional frontal-area shape ideal for minimum drag at near transonic speeds. This disclosure represents a general design concept and not a specific point design.
Owner:MITCHELL JR LAWRENCE C
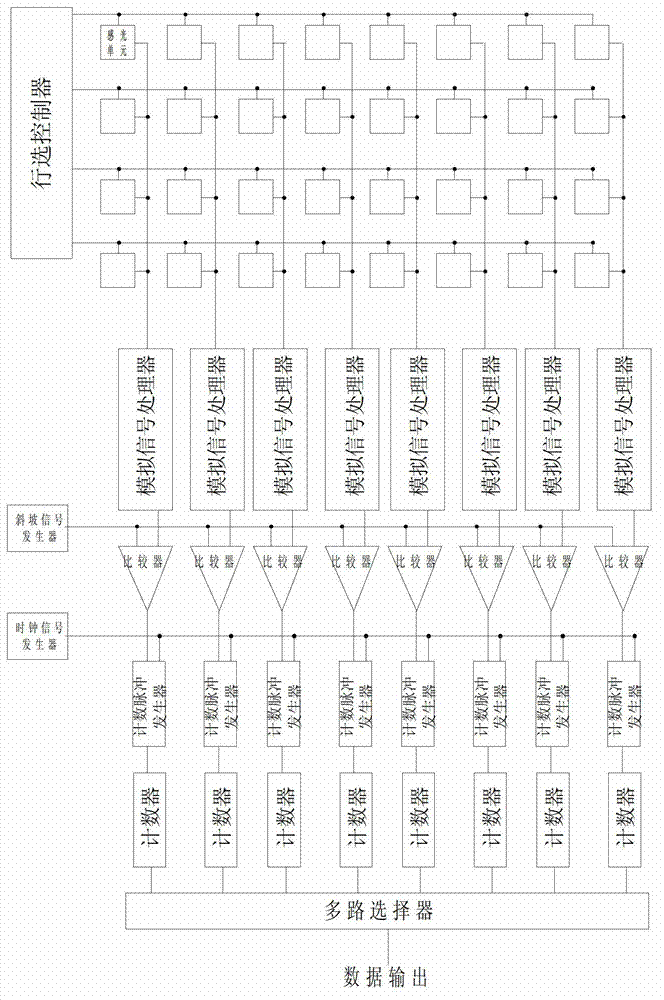
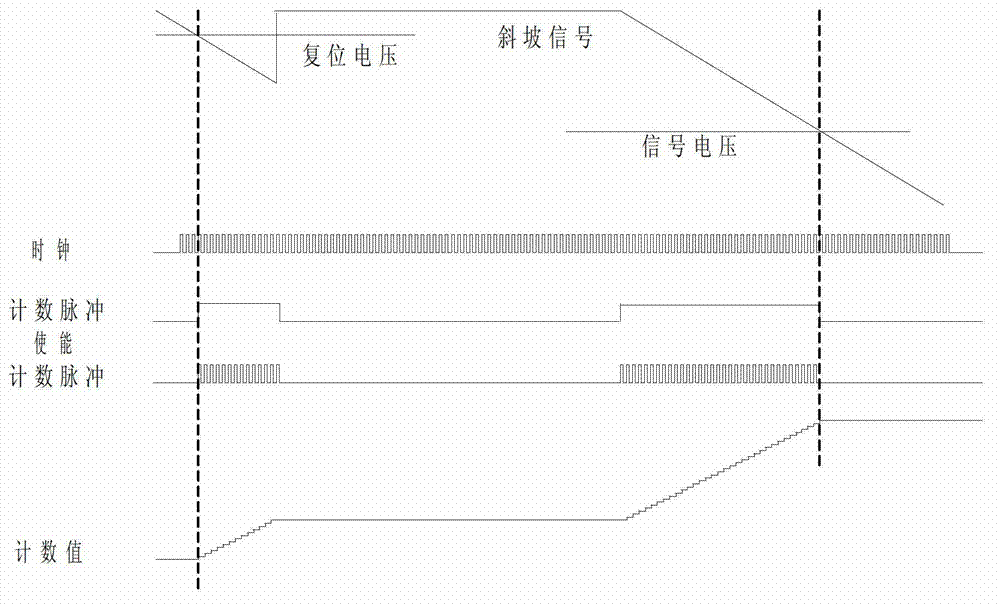
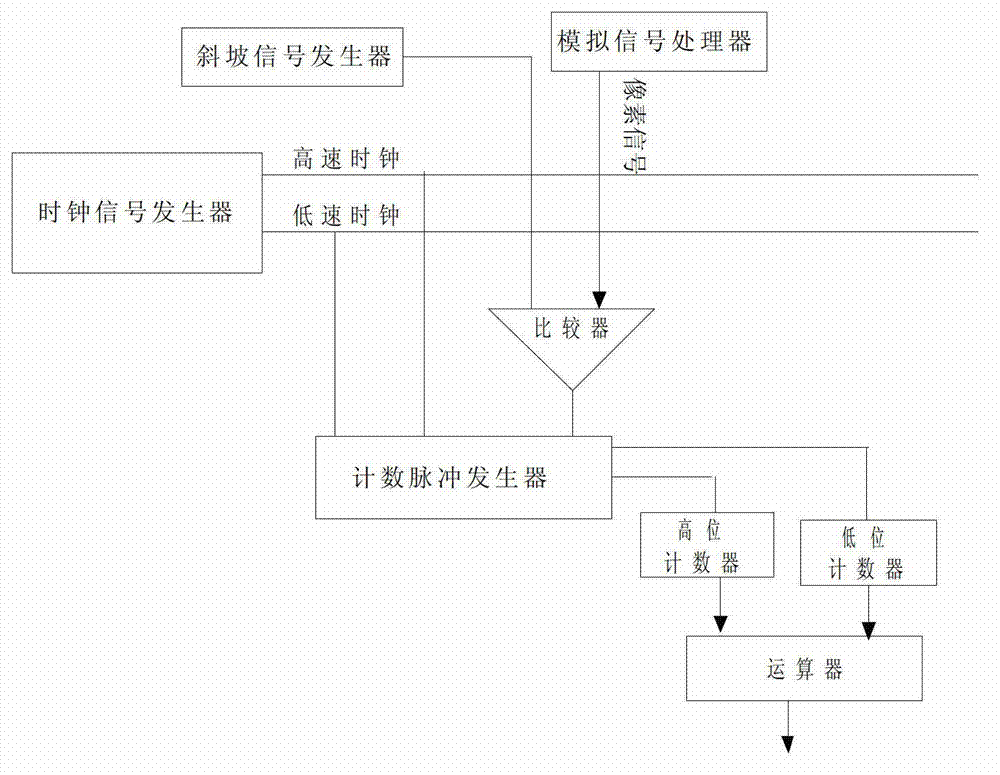
Image data analogue-digital conversion method and image sensor
ActiveCN103051848ACount downReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsGround noiseImage sensor
The invention relates to an image data analogue-digital conversion method and an image sensor. A row selection controller of the image sensor is connected with light sensing unit arrays; each light sensing unit array is connected with a corresponding analogue signal processor through an array bus; each analogue signal processor is connected with a corresponding image data analogue-digital conversion device; and an arithmetic device of each image data analogue-digital conversion device is connected to a multi-path controller. The image data analogue-digital conversion devices adopt the image data analogue-digital conversion method disclosed by the invention to respectively carry out high-level and low-level counting through a low-speed clock pulse and a high-speed clock pulse, and finally obtain quantized pixel image data through operation treatment. The quantized pixel image data is read out of the image sensor array by array by the multi-path controller in a horizontal direction. According to the image data analogue-digital conversion method and the image sensor disclosed by the invention, power consumption of a sensor digital module and ground noises are greatly reduced; and meanwhile, the power consumption of the sensor is not changed along the light intensity so that the image quality of the sensor is further guaranteed.
Owner:长春长光辰芯微电子股份有限公司
Semiconductor device
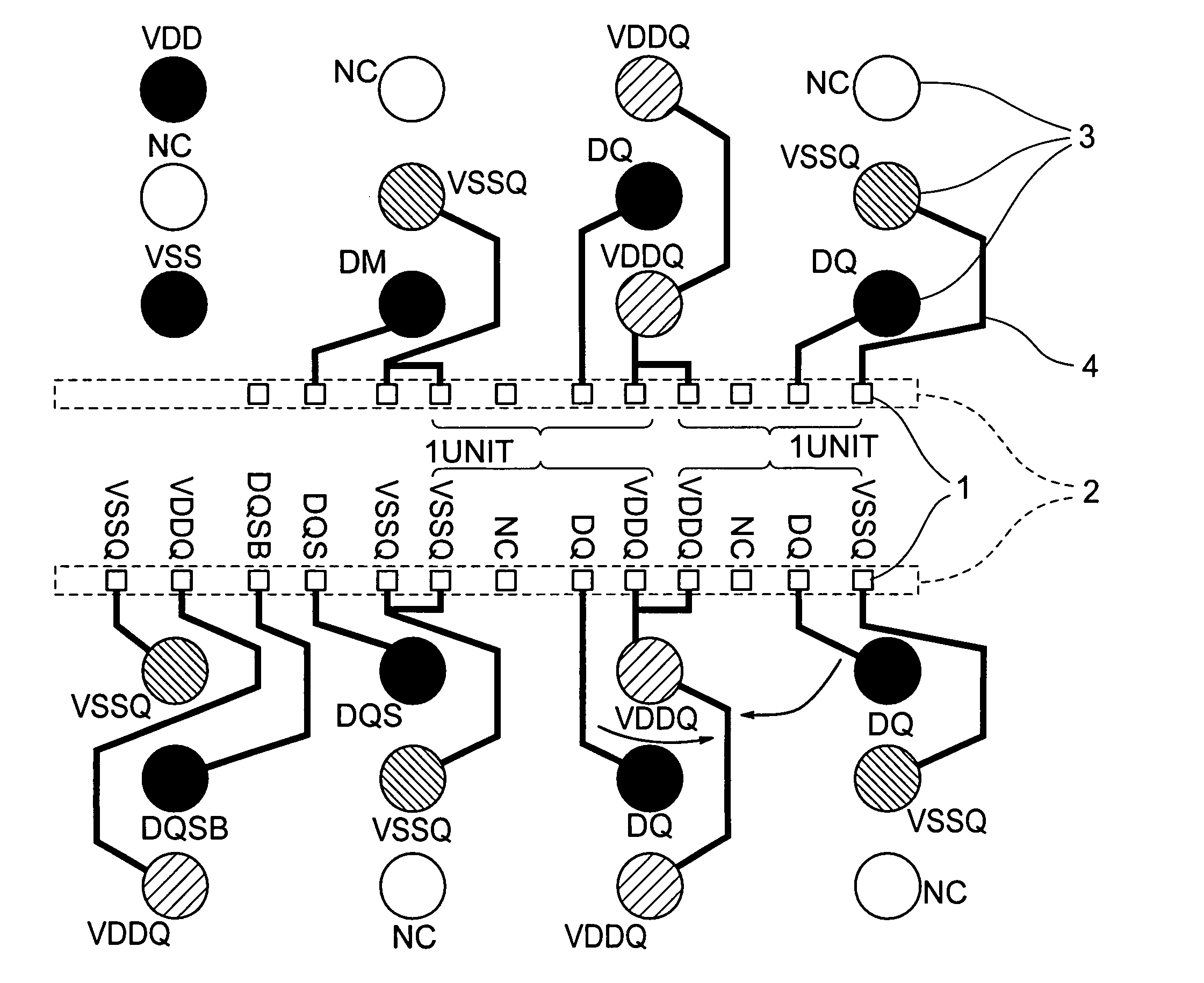
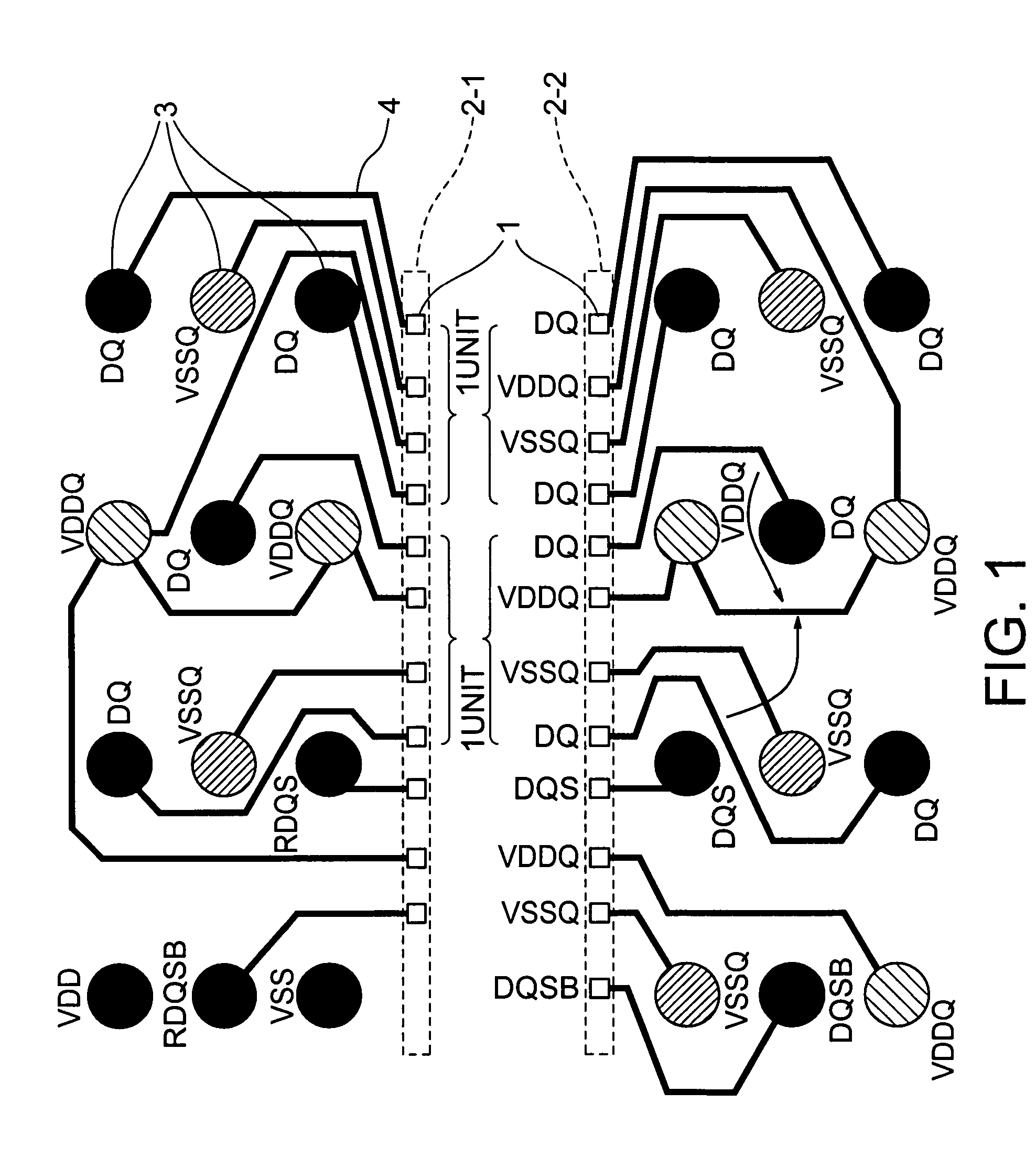
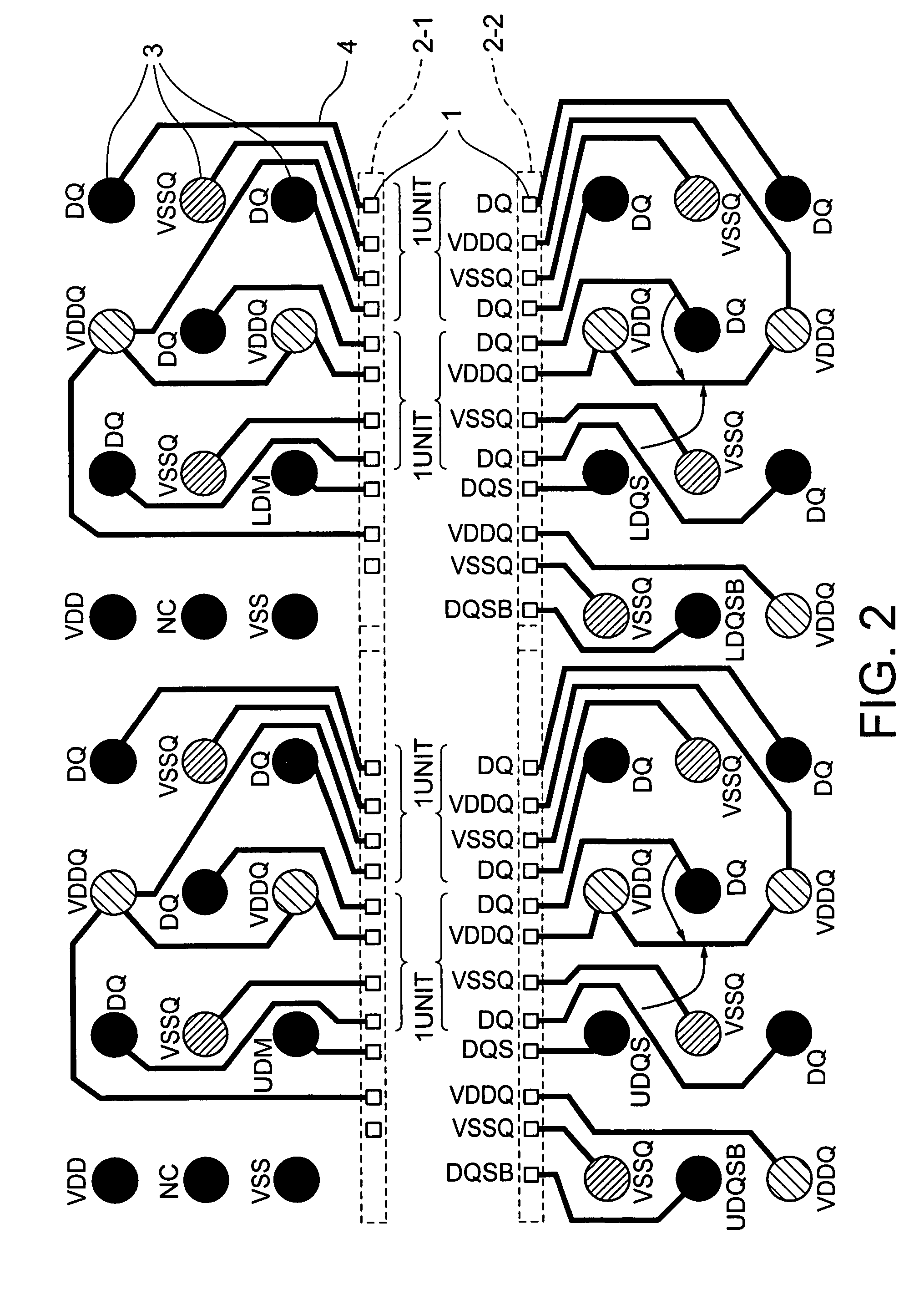
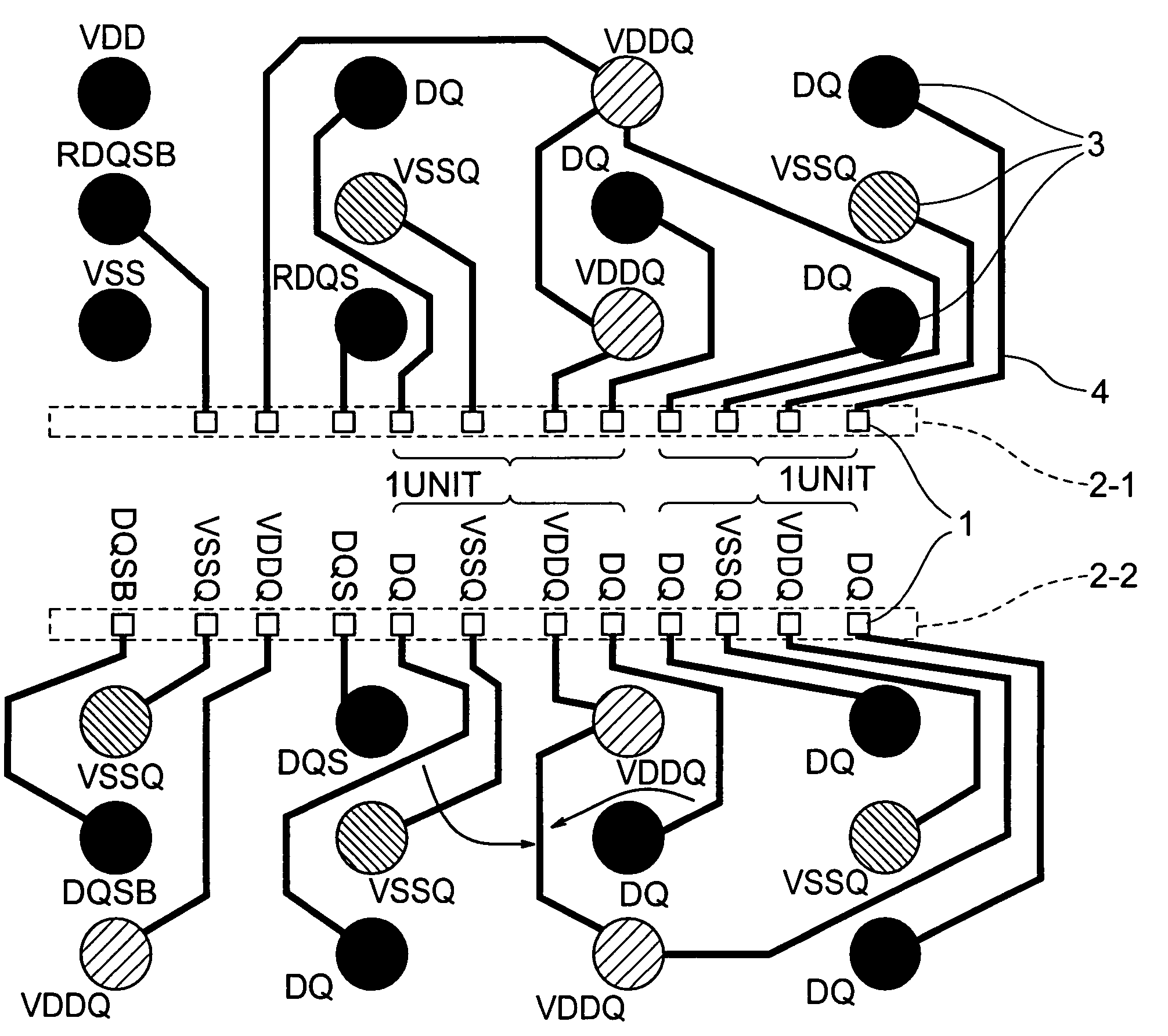
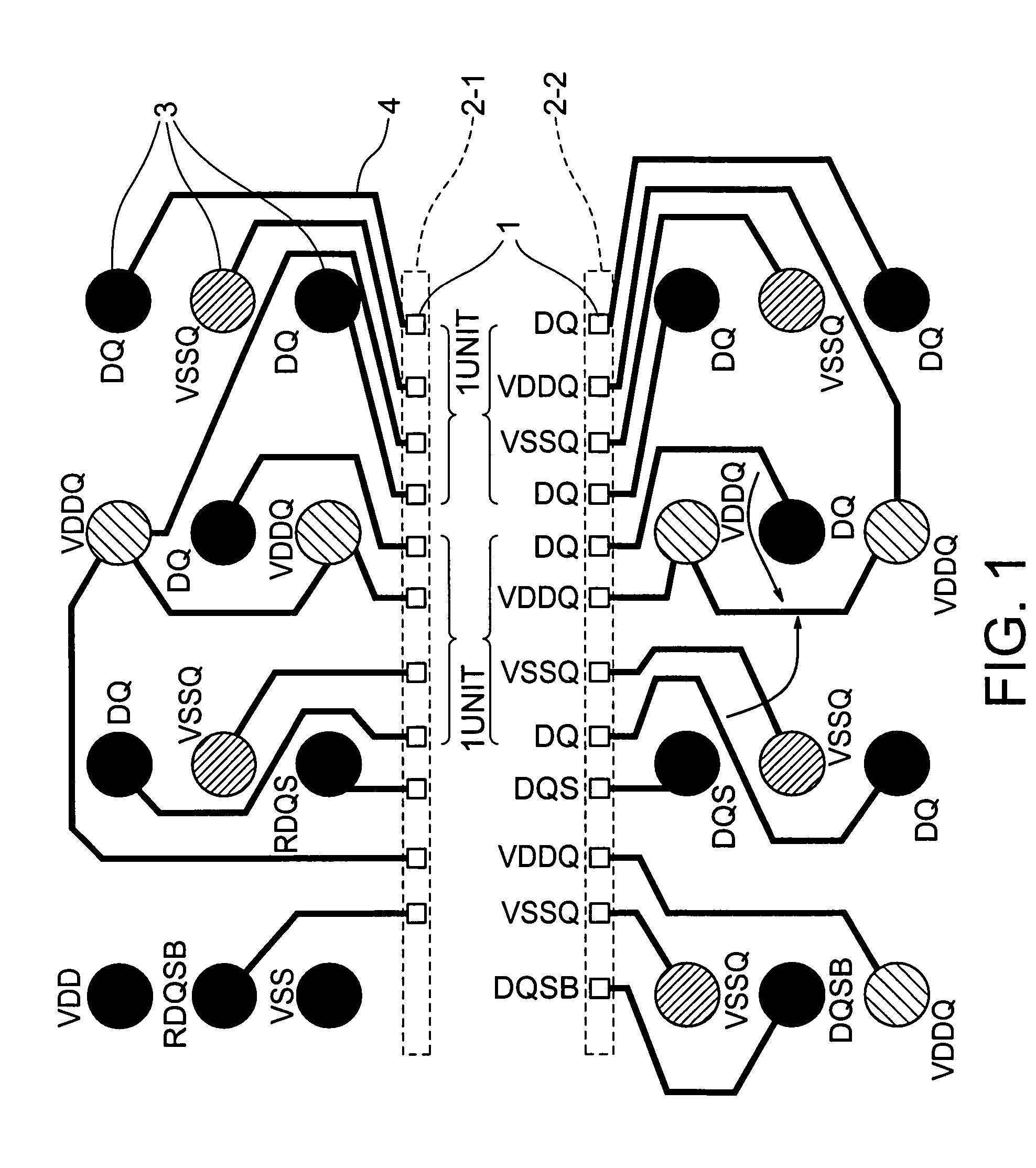
ActiveUS20060249842A1Reduce inductanceHigh speed data transmissionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialGround noise
A semiconductor device is disclosed including a data family pad layout wherein an effort is made to contrive layouts of a power lead wire and a ground lead wire to minimize effective inductance in priority to a length of a lead wire between a pad and a solder ball land of a semiconductor chip. Pad layouts are arrayed in two rows and one unit of the pad layout is configured such that a data power source and ground are adjacent to each other or one data is inserted between the data power source and the ground. Such configurations decrease mutual inductance between the data power sources and increase mutual inductance between the data power source and the ground causing reduction in effective inductance between the data power source and the ground with the resultant minimization of power and ground noises.
Owner:SEMICON PATENT
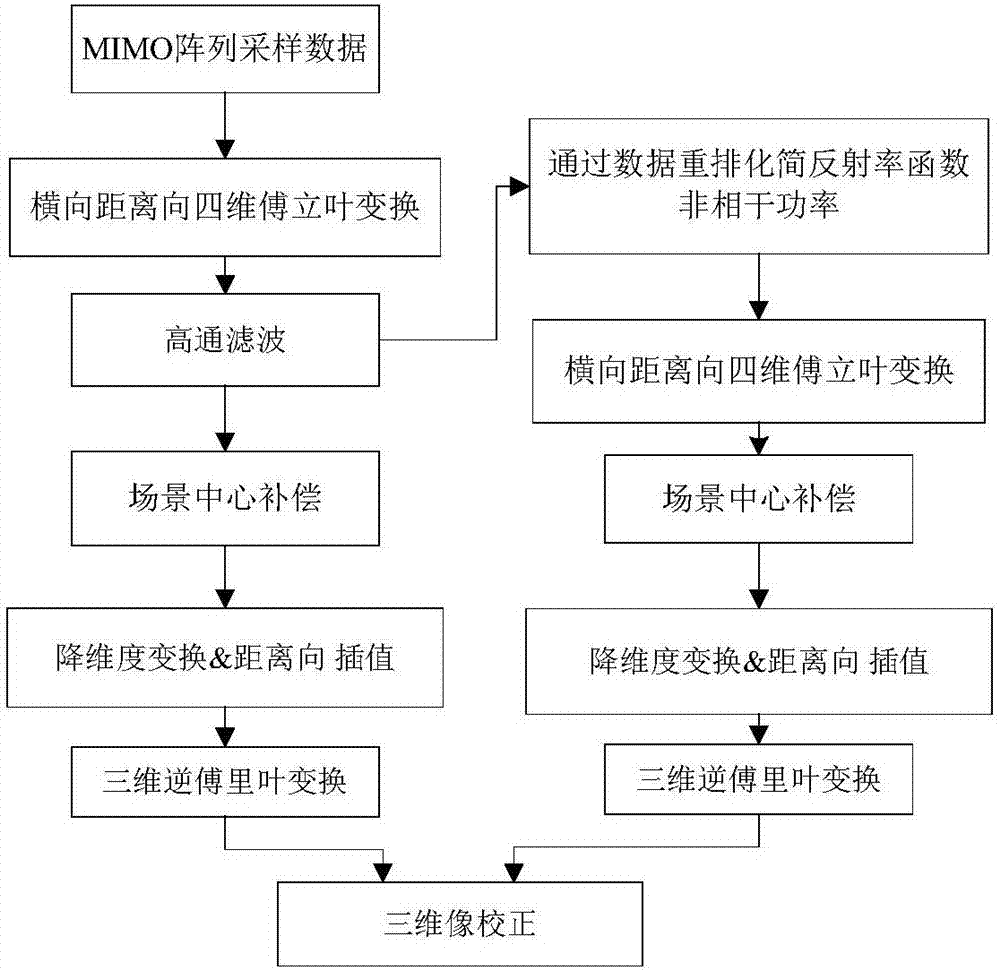
High-seed super-resolution MIMO (multi input multi output) array imaging method
ActiveCN107390215ACalculation speedGuaranteed real-timeRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti inputParallel algorithm
The present invention discloses a high-seed super-resolution MIMO (multi input multi output) array imaging method. The method includes the following steps that: step 1, data sampling is performed on an MIMO array; step 2, an MIMO-RMA (range migration algorithm) is utilized to complete three-dimensional reflectivity image reconstruction; step 3, the acceleration of the MIMO-RMA is utilized to calculate a coherence factor; and step 4, the coherence factor corrects a reflectivity three-dimensional image. According to the imaging algorithm of the invention, reflectivity incoherent power is simplified by rearranging echo data, the acceleration of the MIMO-RMA is utilized to calculate the coherence factor, and the calculation speed of the coherence factor is greatly increased in combination with a parallel algorithm; super-resolution performance is balanced through controlling parameters alpha and beta according to a defect that the coherent factor suppresses weak scattering points, and at the same time, the stability of the algorithm is not affected; and the coherence factor is utilized to correct the reconstructed three-dimensional image, so that sidelobe and ground noises can be effectively suppressed, and higher resolution can be achieved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Dynamic calibration method and method for infrared proximity transducer
InactiveCN106973163AAvoid not being able to turn on the screenAvoid the situationSubstation equipmentGeological measurementsProximity sensorTarget signal
The invention discloses a dynamic calibration method and method for an infrared proximity transducer. The method comprises the following steps of calling a calibration function module of a mobile terminal to calibrate a ground noise value of the infrared proximity transducer to a target signal value To when no shelter exists; presetting an initial proximity threshold value Hi, an initial distant threshold value Lo and an oil contamination threshold Max-N of the infrared proximity transducer; obtaining a real-time infrared signal S of the infrared proximity transducer and comparing the real-time infrared signal S with the oil contamination threshold Max-N when the shelter exists; when the real-time infrared signal S is not smaller than the oil contamination threshold Max-N, judging that the oil contamination exists and computing to obtain a corrected distant threshold value Lo+Od; and comparing the real-time infrared signal S with the corrected distant threshold value Lo+Od, when the real-time infrared signal S is smaller than the corrected distant threshold value Lo+Od, calibrating the target signal value To to the real-time infrared signal S. The invention aims at solving the technical problem that the existing infrared proximity transducer is easily affected by the oil contamination to cause change of intensity of the infrared signal due.
Owner:深圳市君利信达科技有限公司
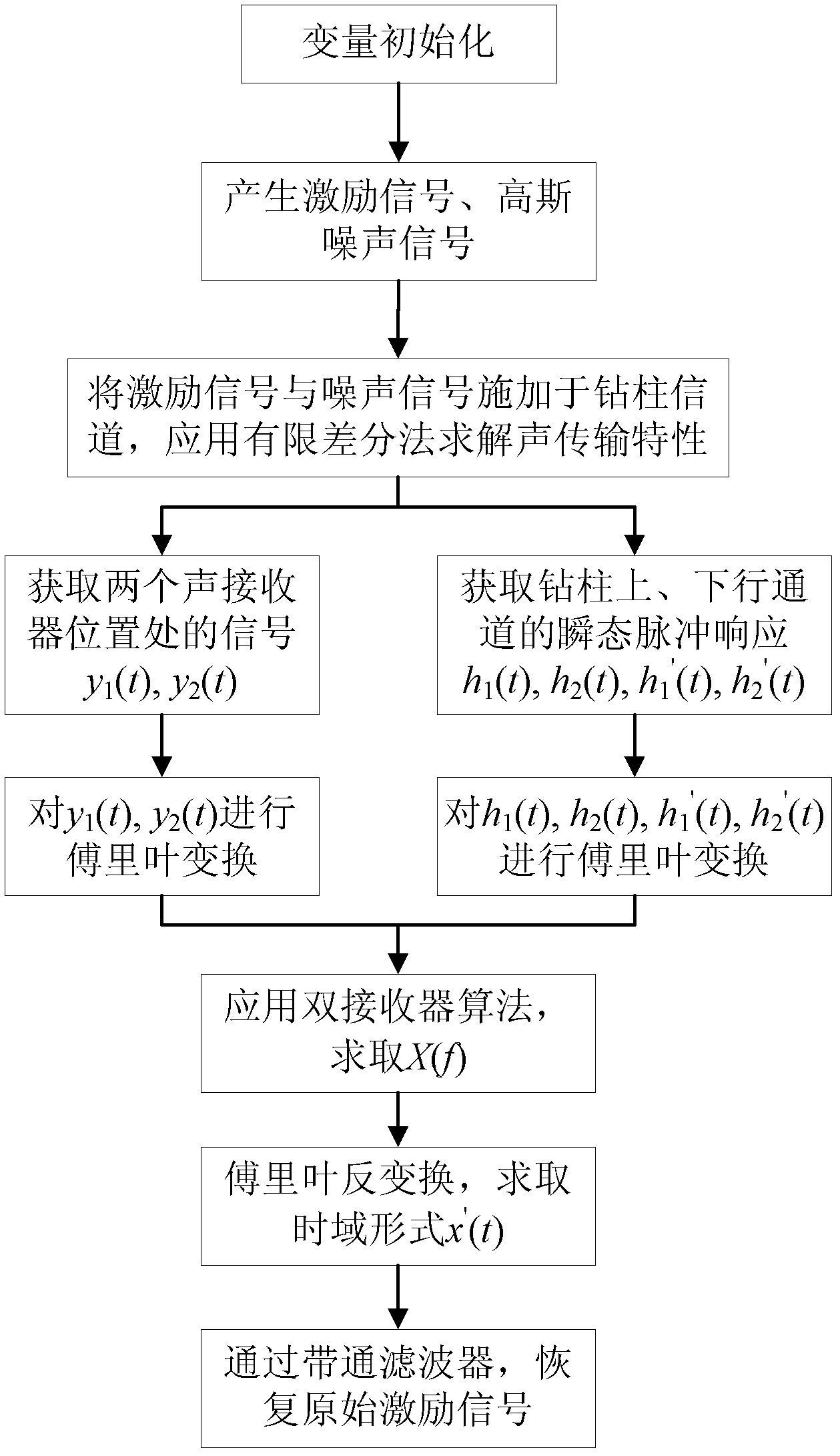
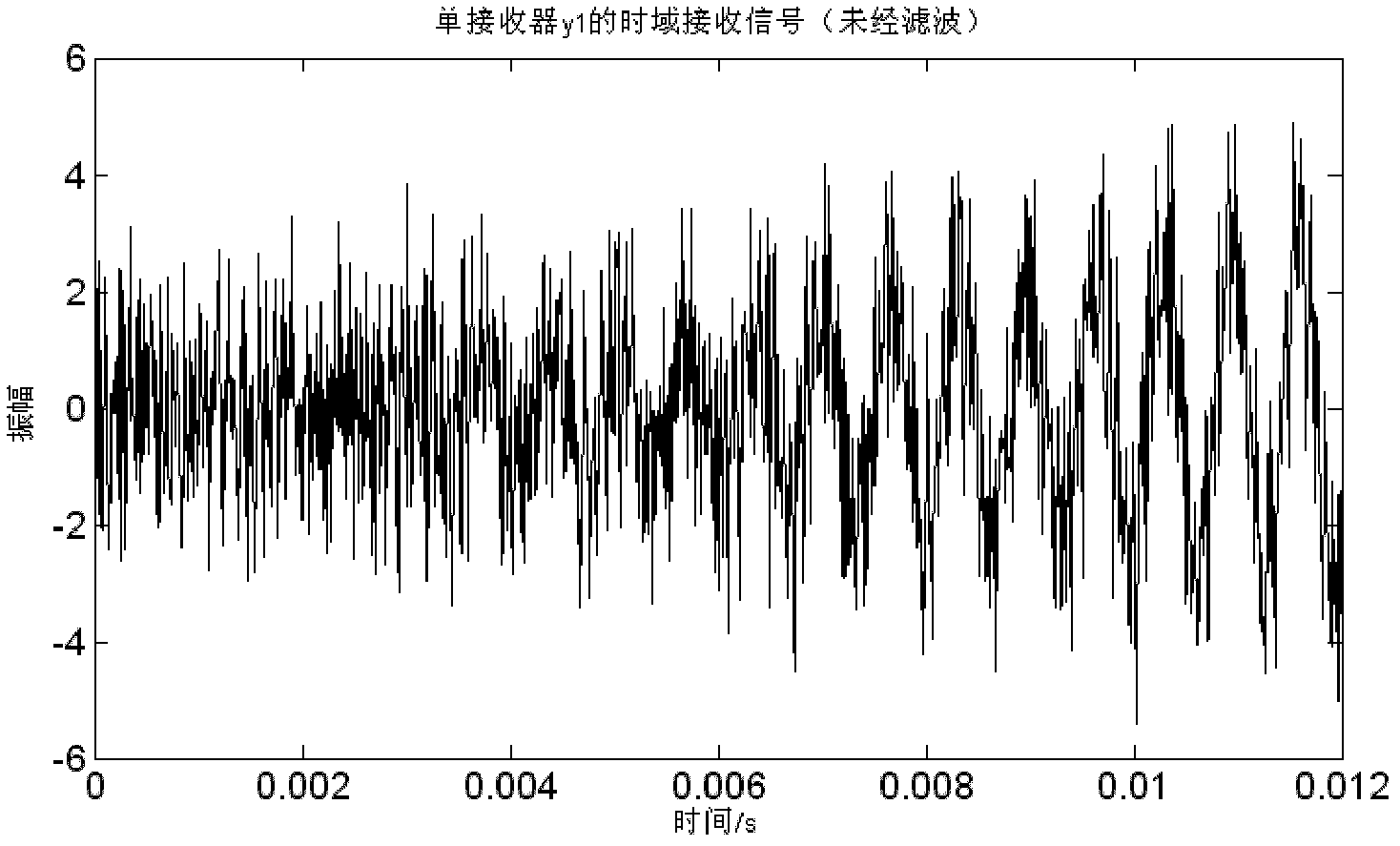
Unidirectional echo and noise suppression method used in drill string acoustic transmission technology
InactiveCN102354501AEcho noise suppressionSimple structureSurveySpeech analysisGround noiseSignal-to-quantization-noise ratio
The invention relates to a unidirectional echo and noise suppression method used in a drill string acoustic transmission technology, and belongs to the technical field of downhole data transmission during the well drilling process. In order to solve the problem that the transmission performance of an acoustic signal in a drill string is reduced due to echo and noise resulting from factors such as ground noise, a discontinuous structure of the drill string and the like in the prior art, by virtue of transient pulse response of uplink and downlink channels of the drill string, an improved echo and noise suppression modeling method is adopted so as to achieve the purpose of suppressing the downhole echo and noise by a receiving mode based on double sound receivers. Therefore, the unidirectional echo and noise suppression method has the beneficial effects of improving the signal-to-noise ratio of a receiving signal, increasing the transmission rate, shortening the logging period and saving the well drilling cost; and the method is characterized in that the adopted structure is simple.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS7391113B2Reduce inductanceHigh speed data transmissionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesGround noiseSolder ball
A semiconductor device is disclosed including a data family pad layout wherein an effort is made to contrive layouts of a power lead wire and a ground lead wire to minimize effective inductance in priority to a length of a lead wire between a pad and a solder ball land of a semiconductor chip. Pad layouts are arrayed in two rows and one unit of the pad layout is configured such that a data power source and ground are adjacent to each other or one data is inserted between the data power source and the ground. Such configurations decrease mutual inductance between the data power sources and increase mutual inductance between the data power source and the ground causing reduction in effective inductance between the data power source and the ground with the resultant minimization of power and ground noises.
Owner:SEMICON PATENT
Self-adapting ringing unit cooperate with chord ring
InactiveCN1446013AOvercoming the drawbacks of being prone to missed callsEasy to adjust and effectiveCalling susbscriber number recording/indicationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsInternal memoryGround noise
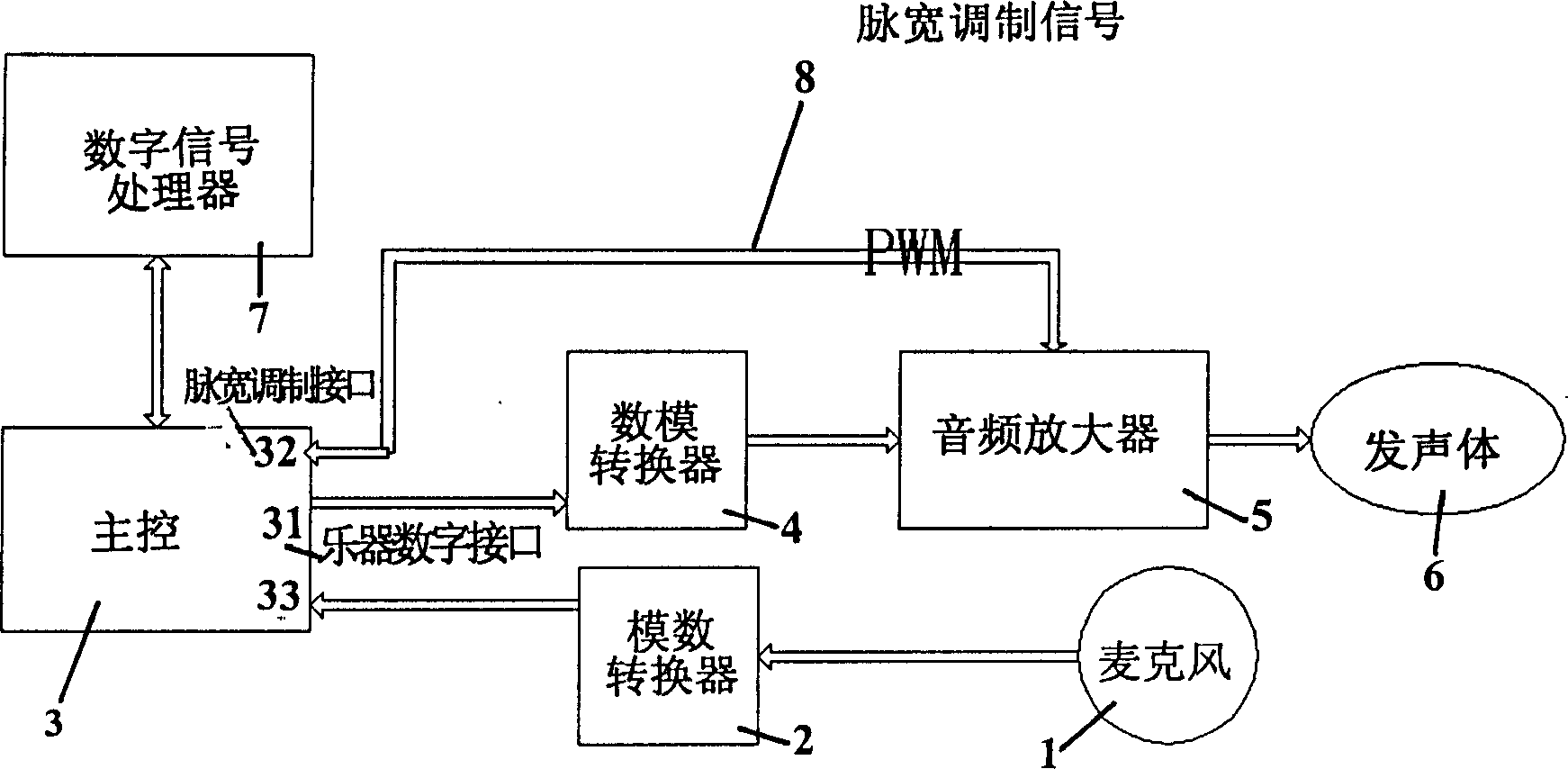
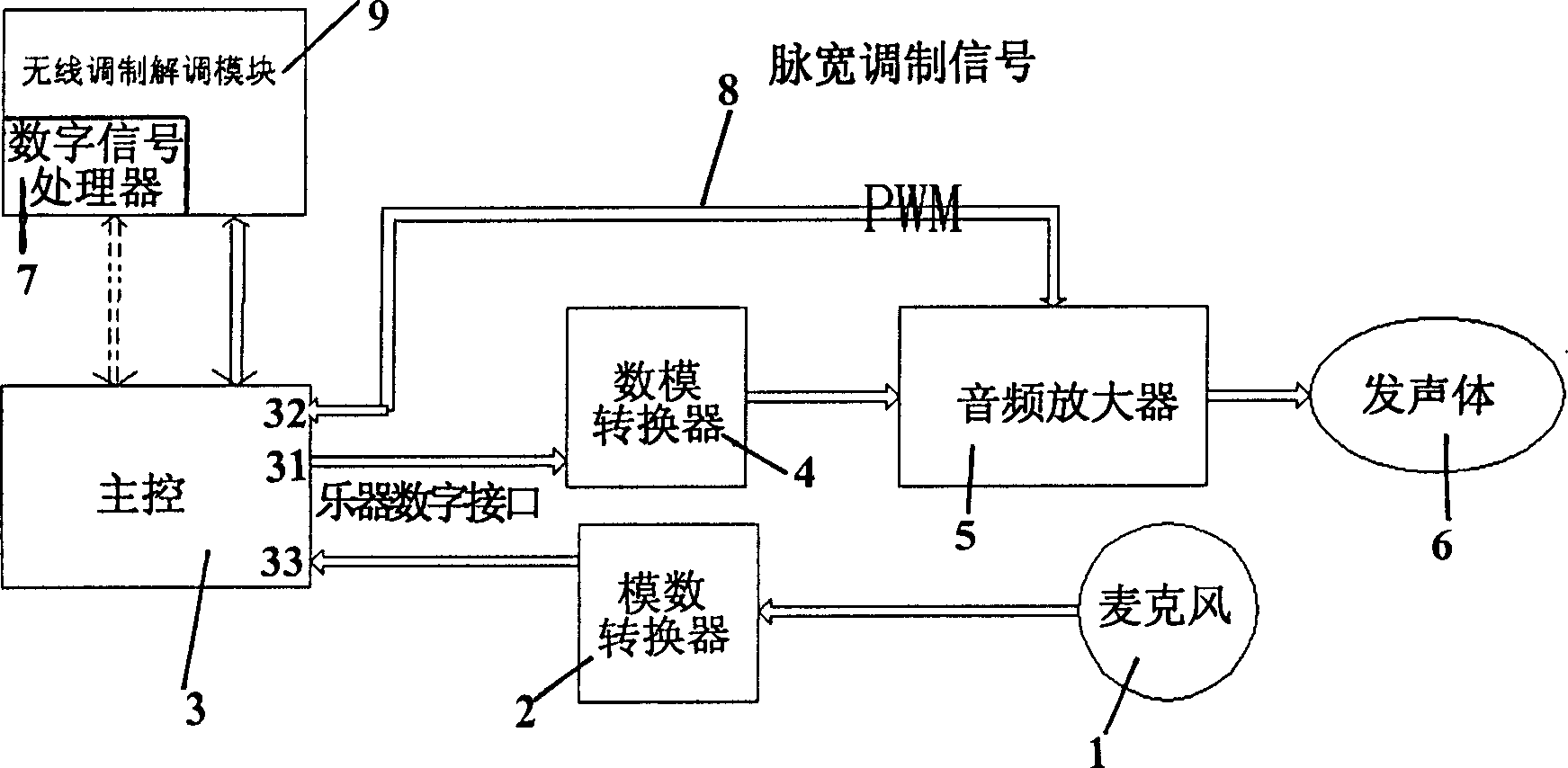
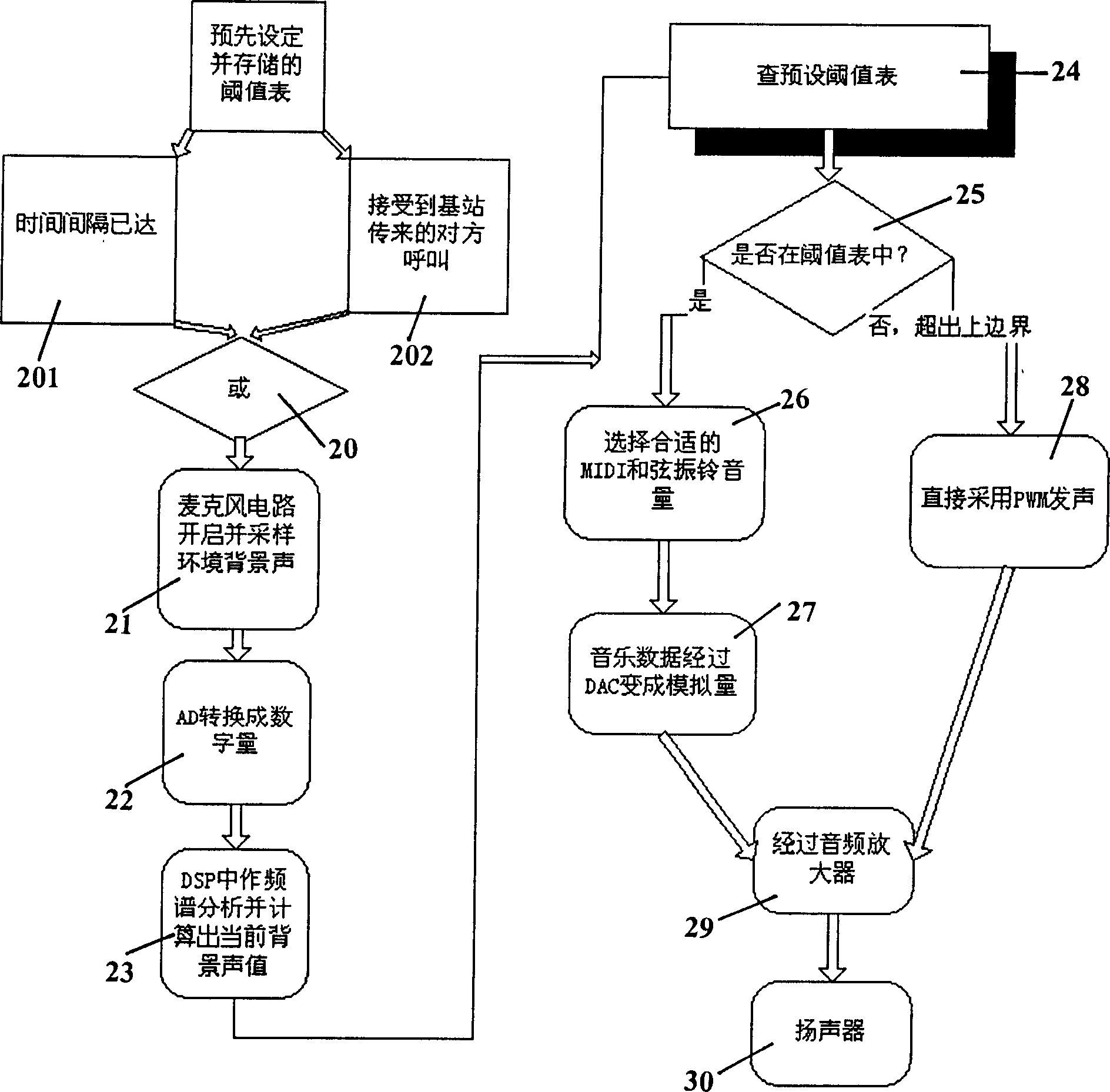
An adaptive ringing device includes connecting in sequence of microphone, A / D converter, main controller, D / A converter, audio amplifier and sound with circuit connection as well as digital signal precessor being circuit-connected with the main controller in two-way connection and it have a music instrument digit output to send musical instrument digit signal to D / A converter. Its features are: a. A controllable circuit formed by an output outlet of pulsewidth modulation signal in the said main controller and audio amplifier can send plusewidth modulation signal to audio amplifier as required; b) an adaptive control program for cooperating with chard ringing sound is stored in the nonvolatile internal memory of communication terminal; and c) a back ground noise threshold table is preset and stored in the program storage area of nonvolatile internal memory and it can be called by the adaptive control program.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) LTD
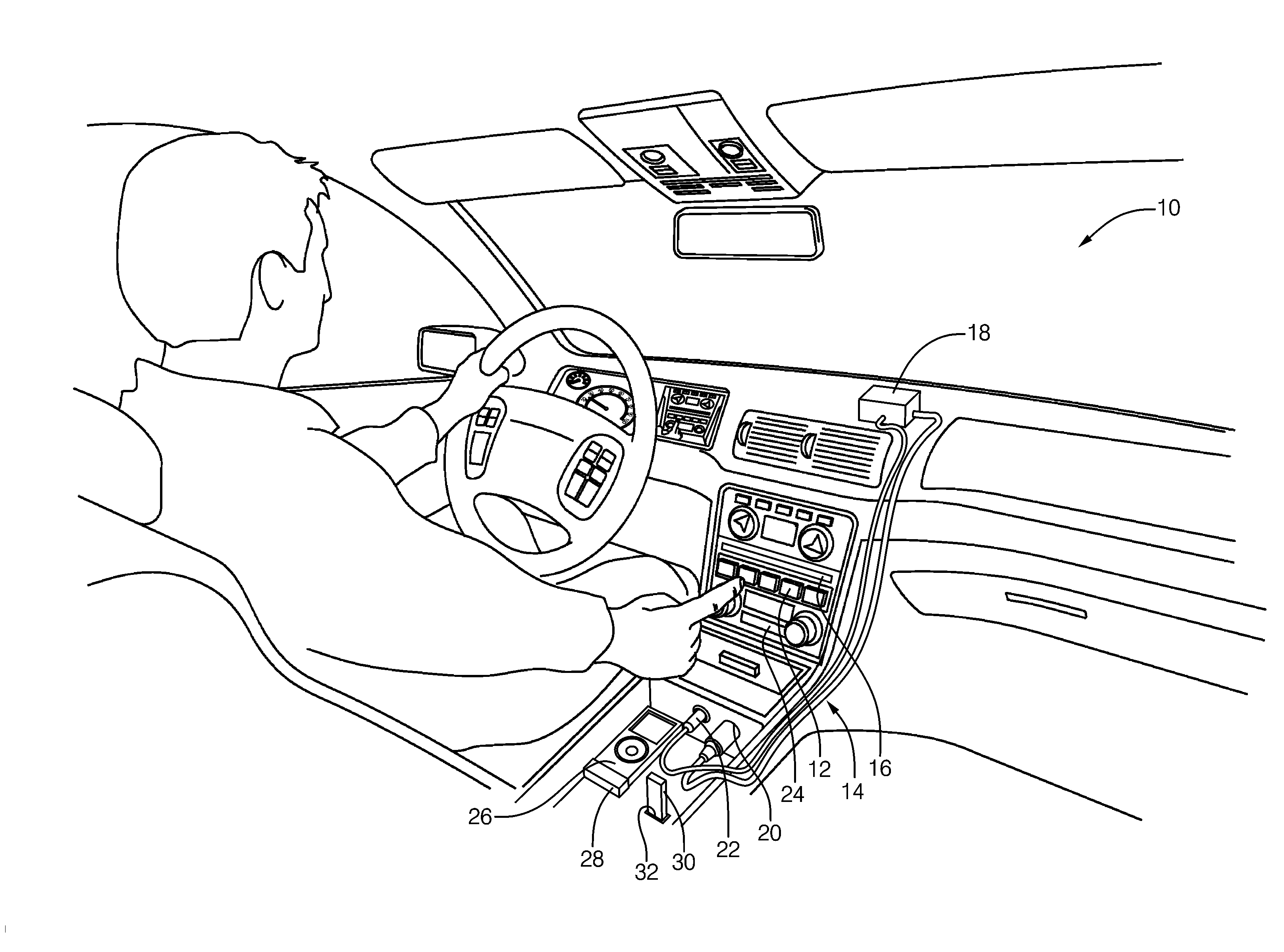
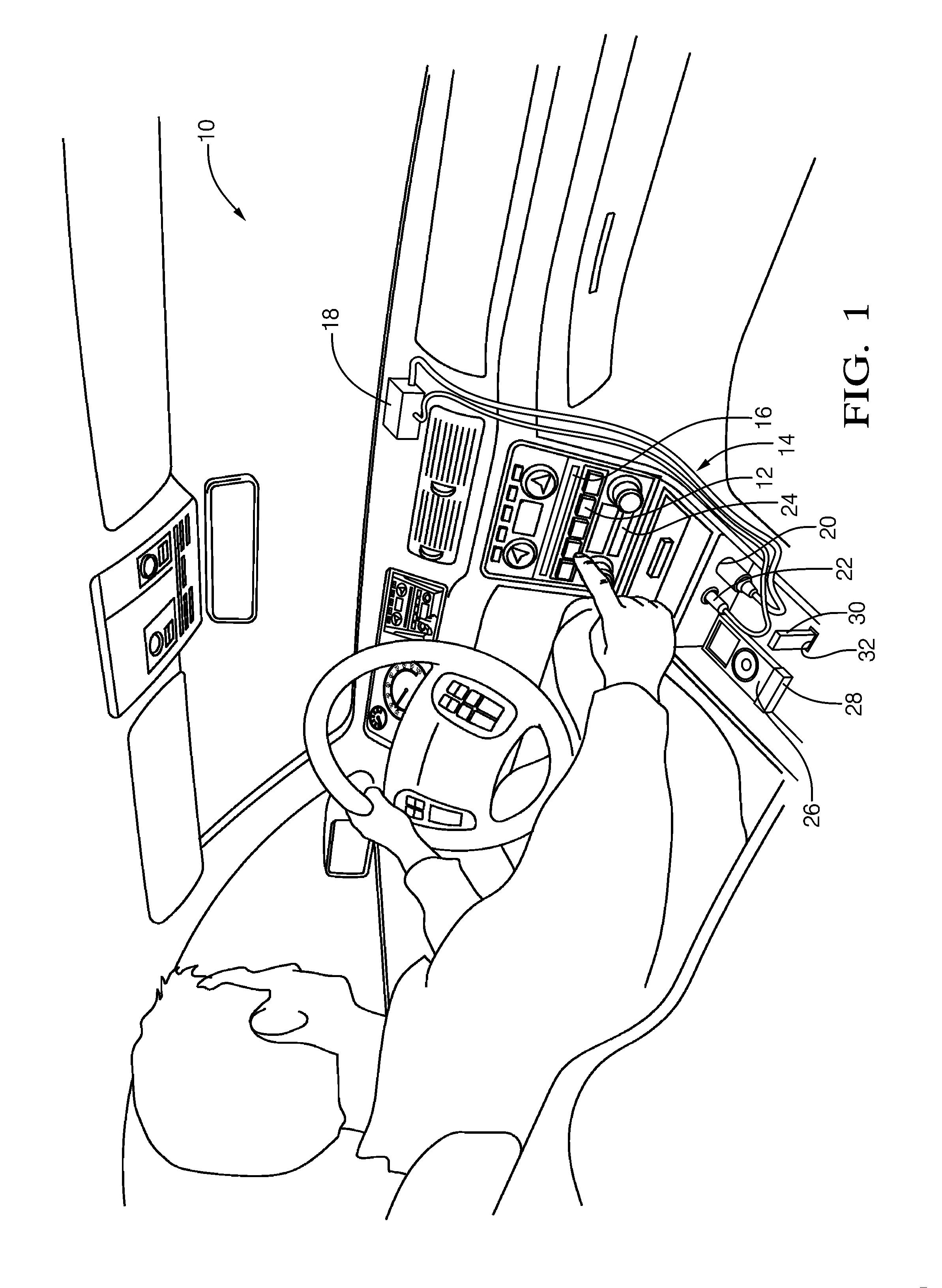
Vehicle entertainment system having ground noise reduction and method of operating the same
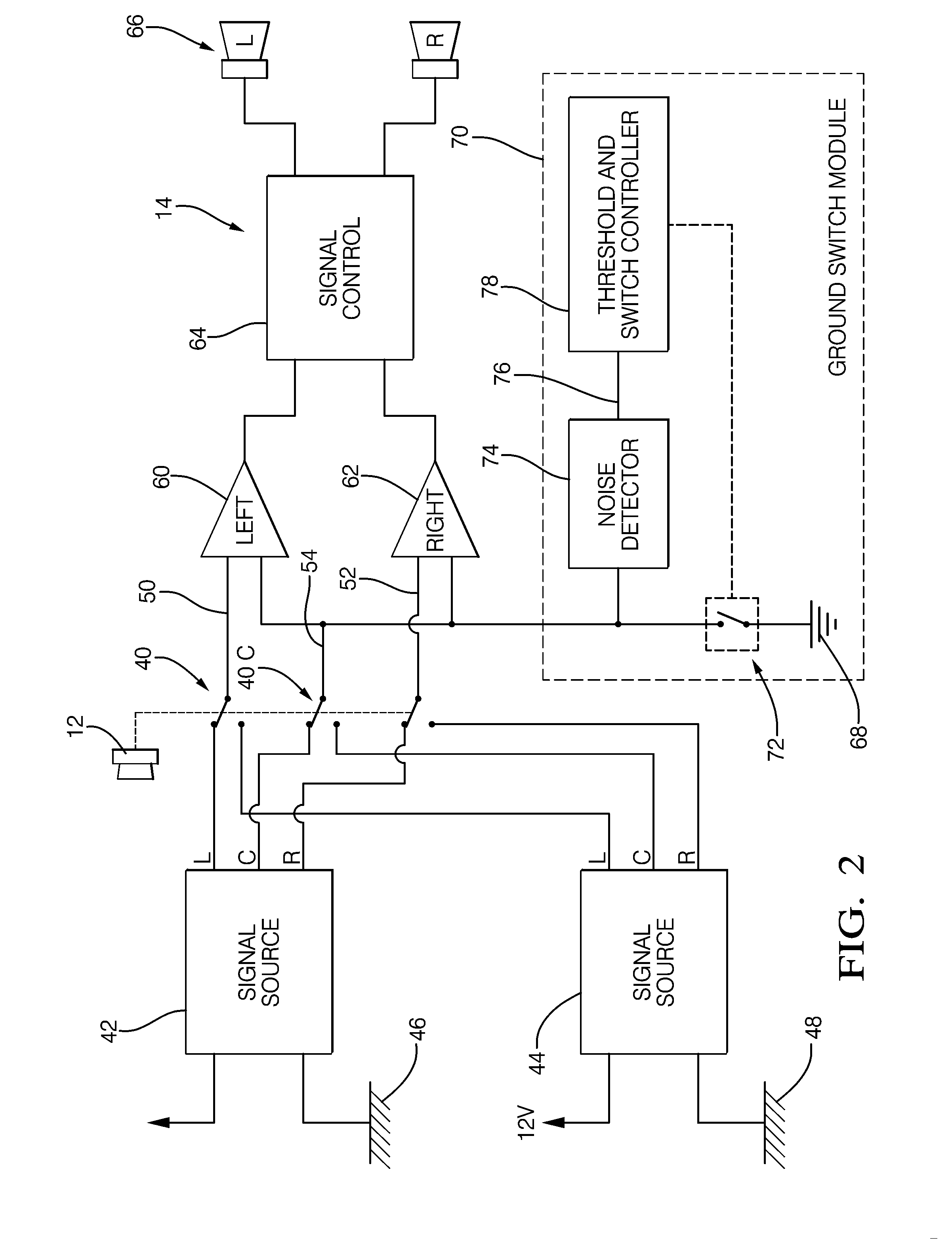
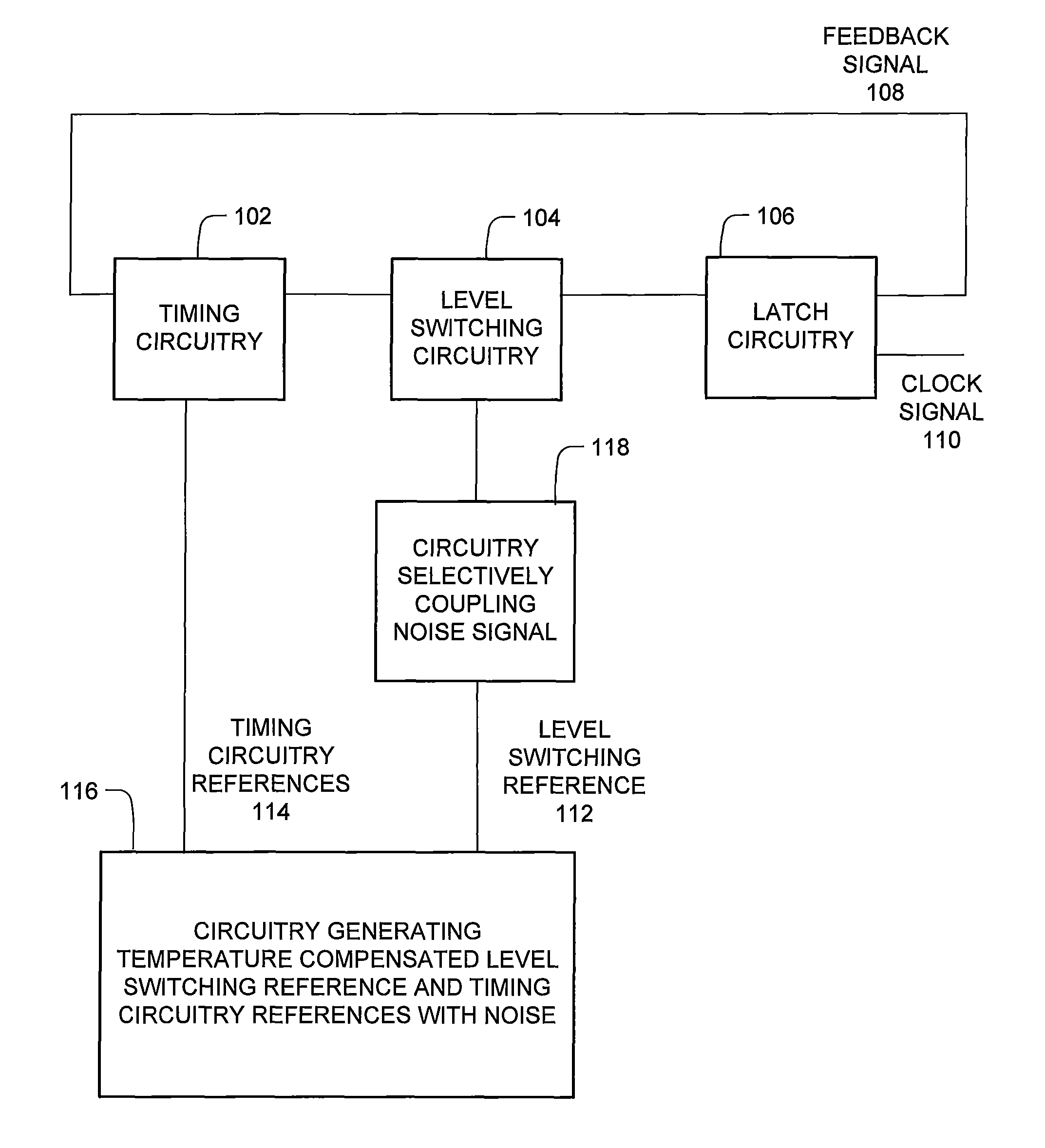
ActiveUS20110206208A1Ground noise reductionTransmission noise suppressionTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsGround noiseEngineering
A vehicle entertainment system and method that alternately configures an input of the entertainment system as a differential input that is decoupled from a ground point, or as ground referenced input that is coupled to a ground point. A noise detector determines a noise signal value for a ground switch module that alternately changes a switch state between a coupled state that couples the common channel connection to the ground point, and a decoupled state that decouples the common channel connection from the ground point, based upon the noise signal value being greater than a threshold.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
Clock integrated circuit
The clock circuit of an integrated circuit operates with variations such as temperature, ground noise, and power noise. Various aspects of an improved clock integrated circuit address one or more of the variations in temperature, ground noise, and power noise.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Clock integrated circuit
The clock circuit of an integrated circuit operates with variations such as temperature, ground noise, and power noise. Various aspects of an improved clock integrated circuit address one or more of the variations in temperature, ground noise, and power noise.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
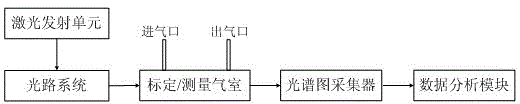
Marking method for background noise difference removal in laser Raman gas analysis system
The invention relates to a marking method for background noise difference removal in a laser Raman gas analysis system. The marking method is based on a Raman scattering spectrogram of marked gases and an intermediate carrier gas and comprises the steps that firstly, the influence of ground noise of the system is eliminated, so that a Raman scattering spectrogram of the marked gases and the intermediate carrier gas without background noise is obtained; a marking constant is obtained through data processing on information obtained from the spectrogram, and according to the physical characteristics of the gas, the marking constant is not influenced by the temperature, the pressure, the environment and other factors; in this way, all known gases can be marked relative to the intermediate carrier gas, and a marking database of all the gases relative to the intermediate carrier gas is established. The marking method is used for marking in the laser Raman gas analysis system, effective Raman information can be effectively extracted from complicated background noise, the marking precision is greatly improved, and therefore the measuring precision of the system is improved; besides, the marking method is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:WUHAN CUBIC OPTOELECTRONICS
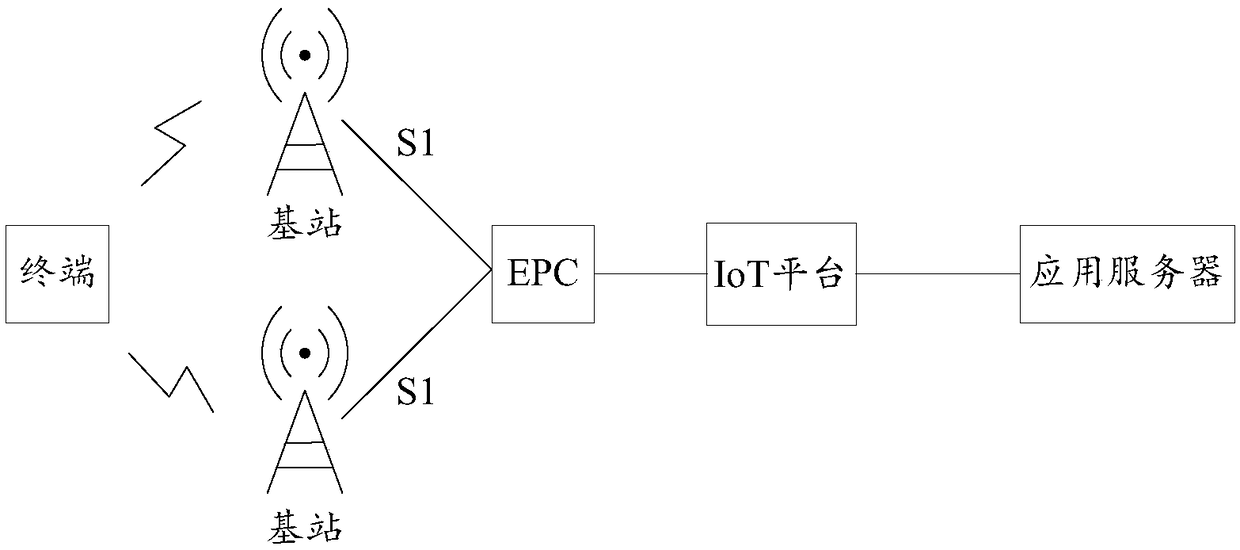
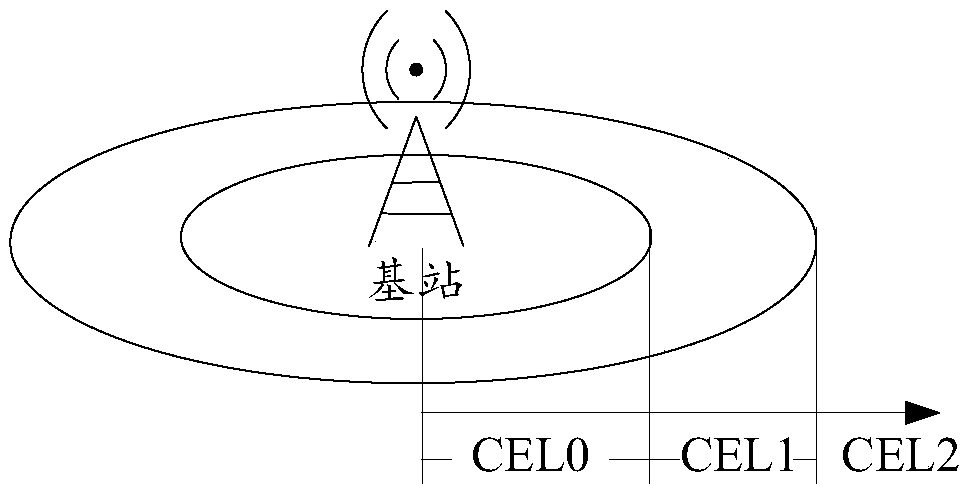
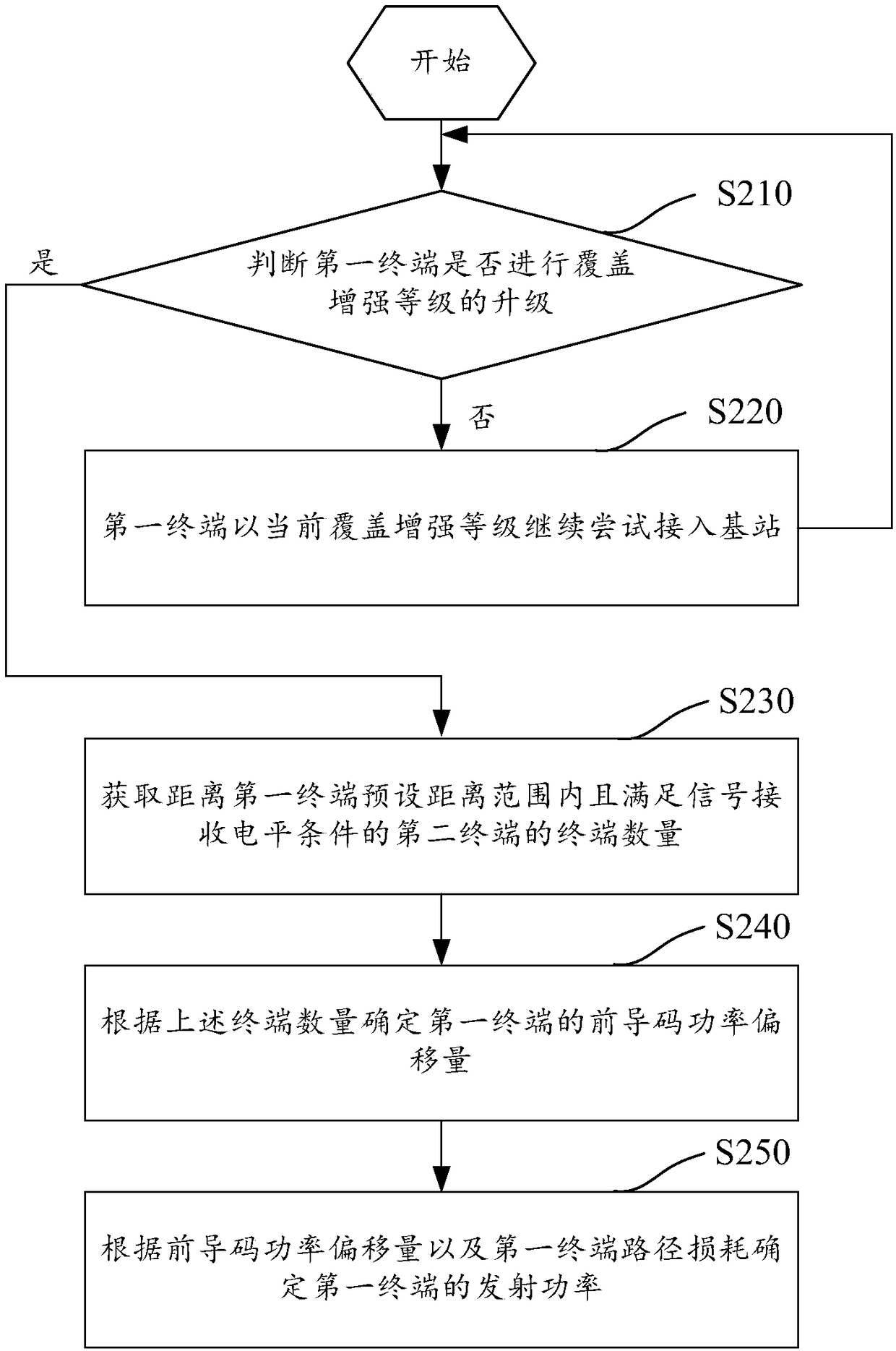
Terminal transmission power control method and device based on NB-IoT system
The embodiment of the invention discloses a terminal transmission power control method and device based on an NB-IoT system, relates to the technical field of communication, and is used for solving atechnical problem that the uplink interference of the NB-IoT system is excessively high due to the excessive rise of the transmission power of the terminal in the prior art. The method includes the steps: judging whether a first terminal performs the upgrading of a coverage enhancement level or not; acquiring the number of the second terminals that are within a preset distance range from the firstterminal and meet a signal receiving level condition if the determination result is yes; determining a lead code power offset of the first terminal according to the number of terminals; and determining the transmitting power of the first terminal according to the lead code power offset. The method is used for reducing uplink interference of the NB-IoT system and effectively suppresses the rise ofthe ground noise of a base station.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
Ring oscillator with constant 50% duty cycle and ground-noise insensitive
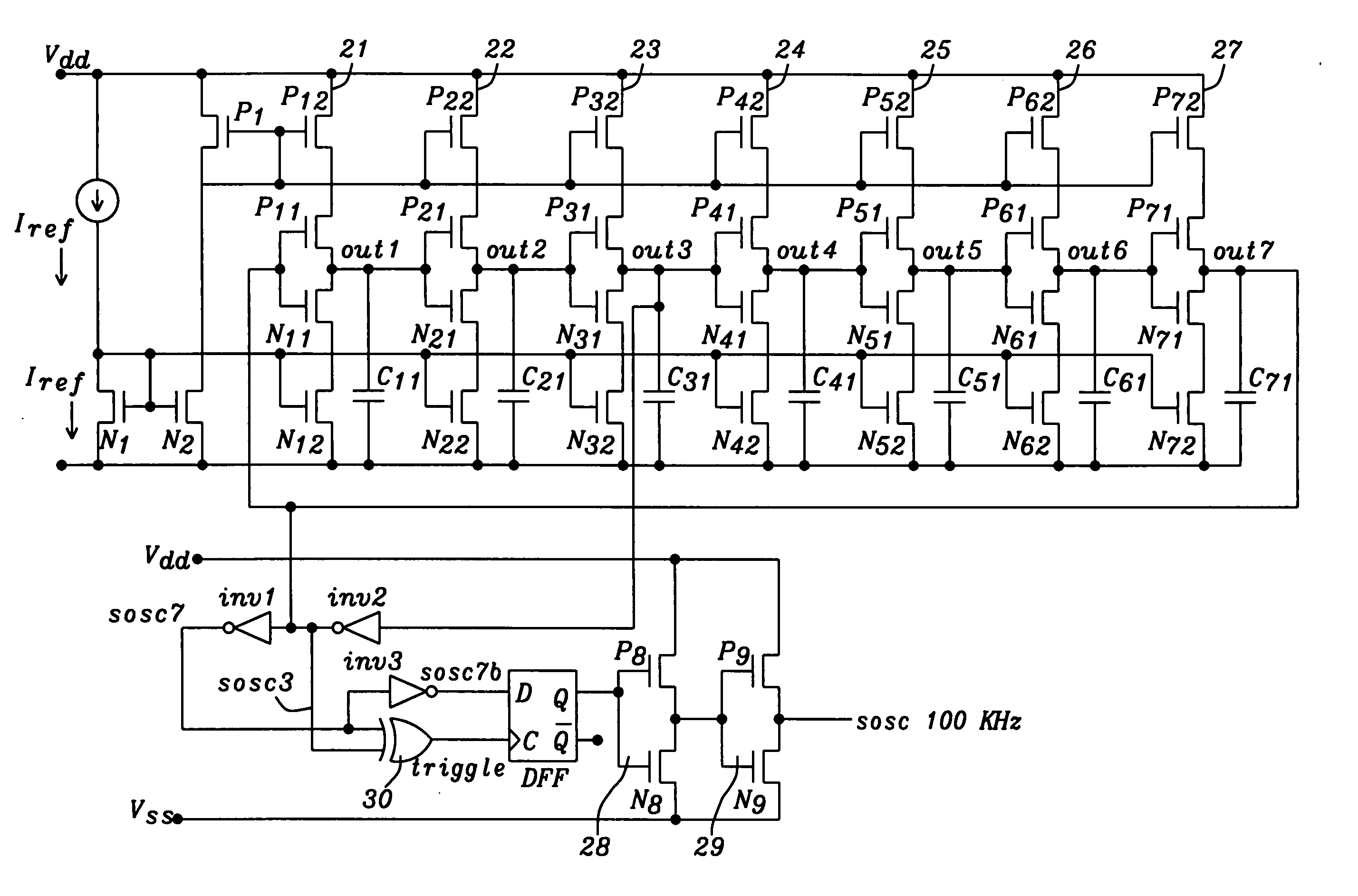
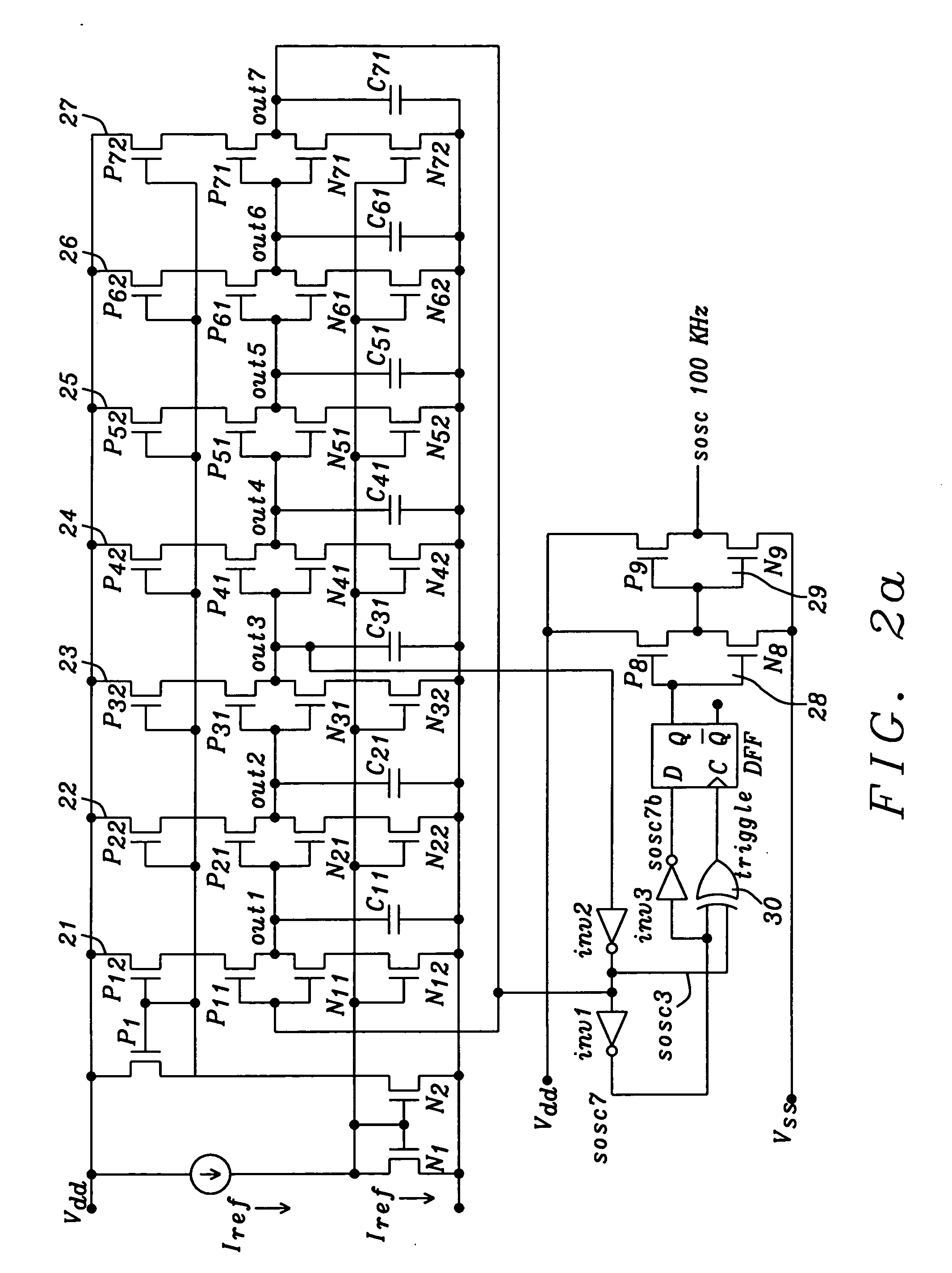
ActiveUS20070013454A1Cancel noiseStabilize duty cycleGenerator stabilizationPulse generation by logic circuitsPhase shiftedGround noise
Methods and circuits for chain ring oscillators having a constant duty cycle and being insensitive to ground noise have been disclosed. The ring oscillator generates n outputs with 360° / n phase shift and each stage is delayed by T2×n.The output of a suitable stage is selected so that a digital XOR-gate, using the output of a selected stage and the output of the nth stage, eliminates variations of the duty cycle caused by temperature and process variations. In case a 50% duty cycle is desired the stage number N of the selected stage can be calculated using the equation N=(n−1) / 2. The duty cycle can be varied by selecting the output of another gate. A D-flipflop, clocked by the output of the XOR-gate removes noise from the clock pulses.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR
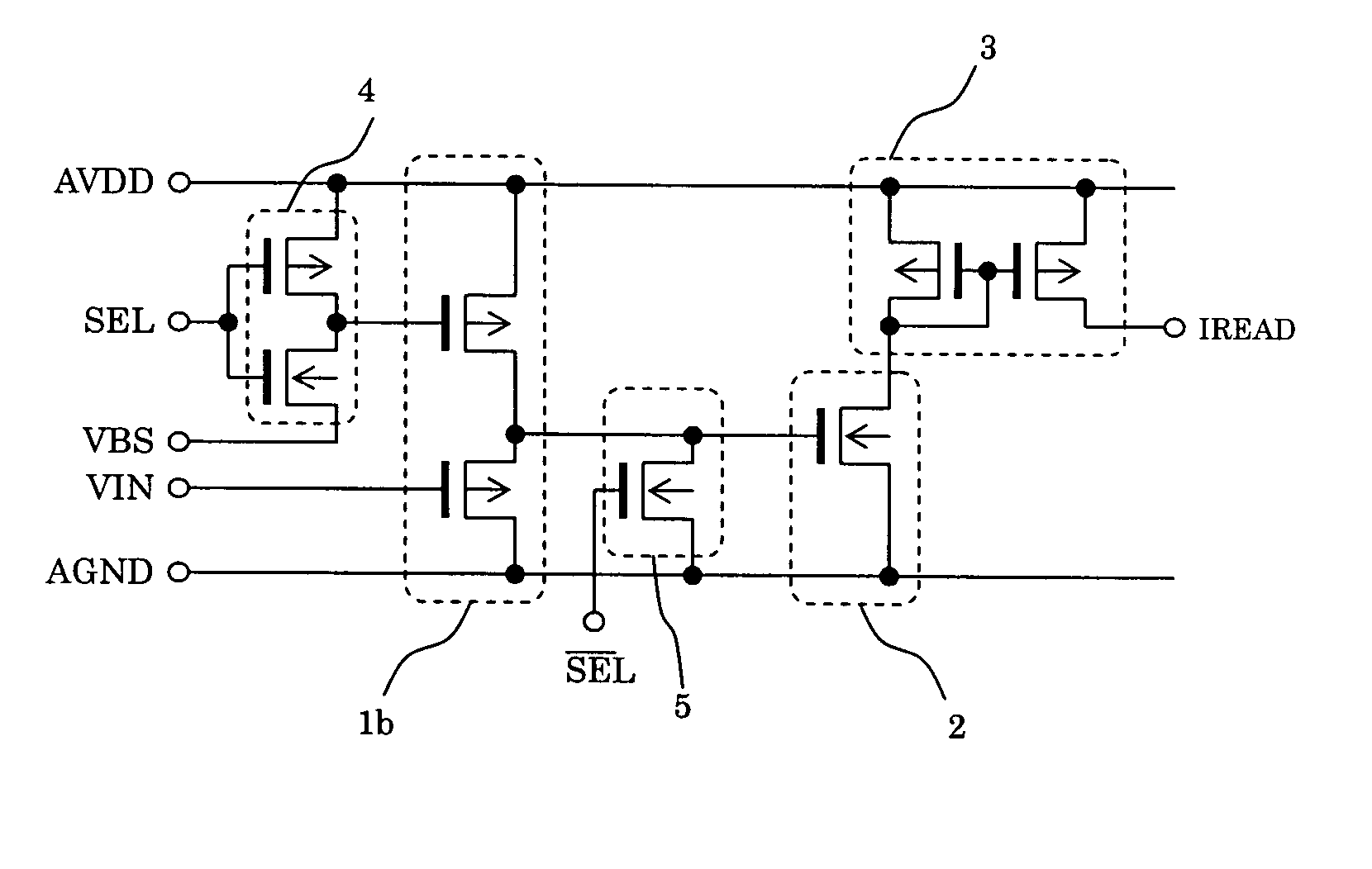
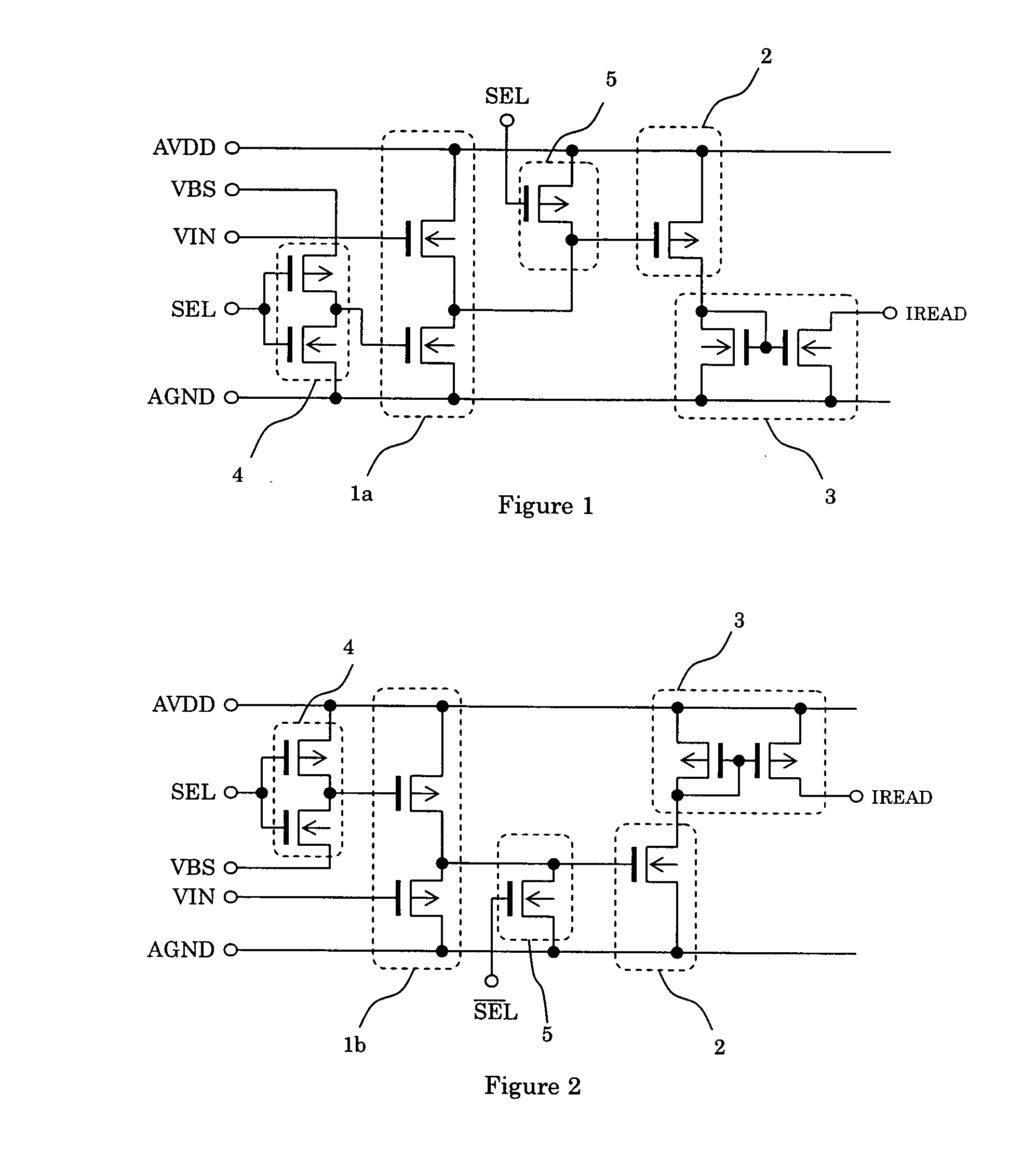
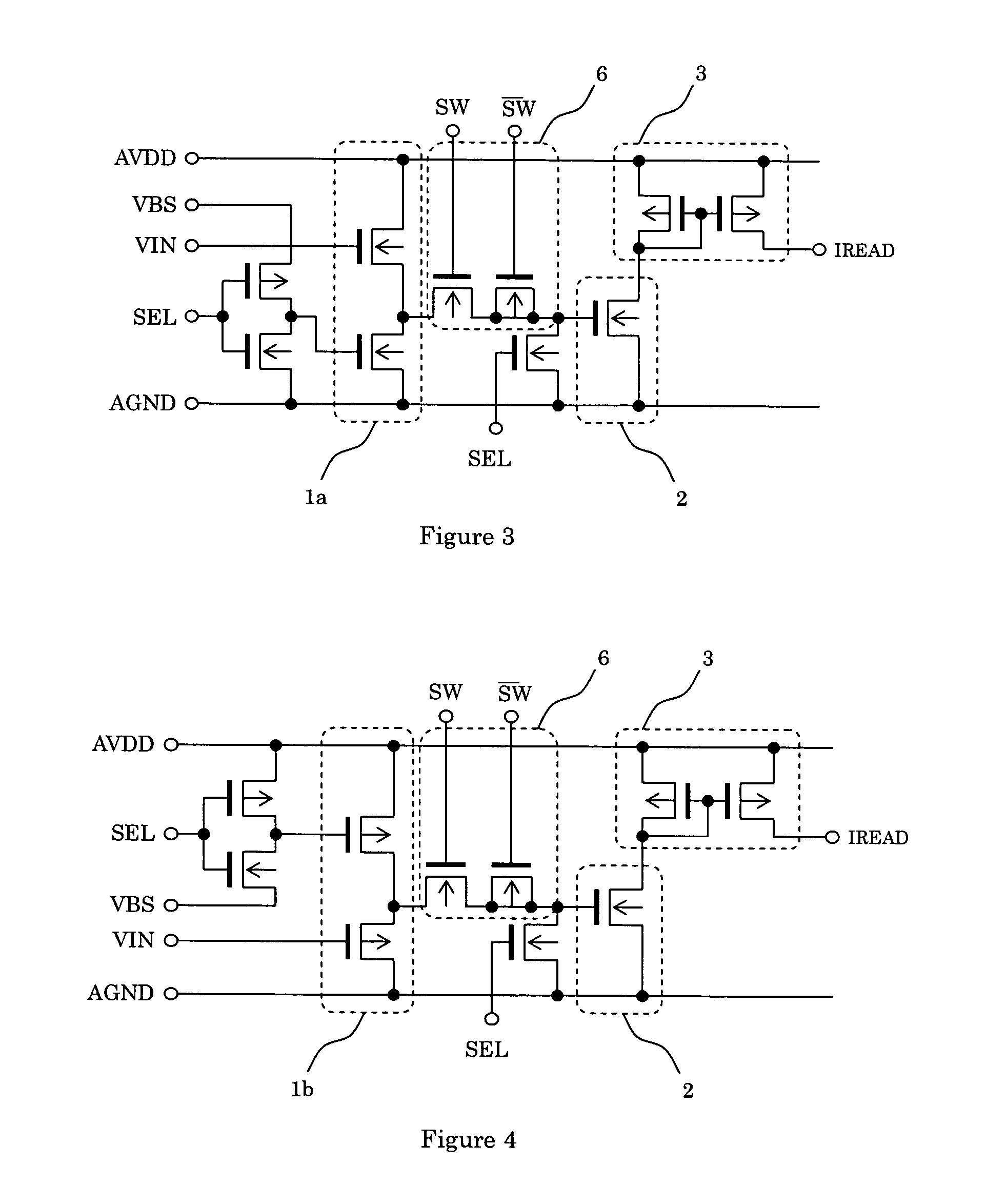
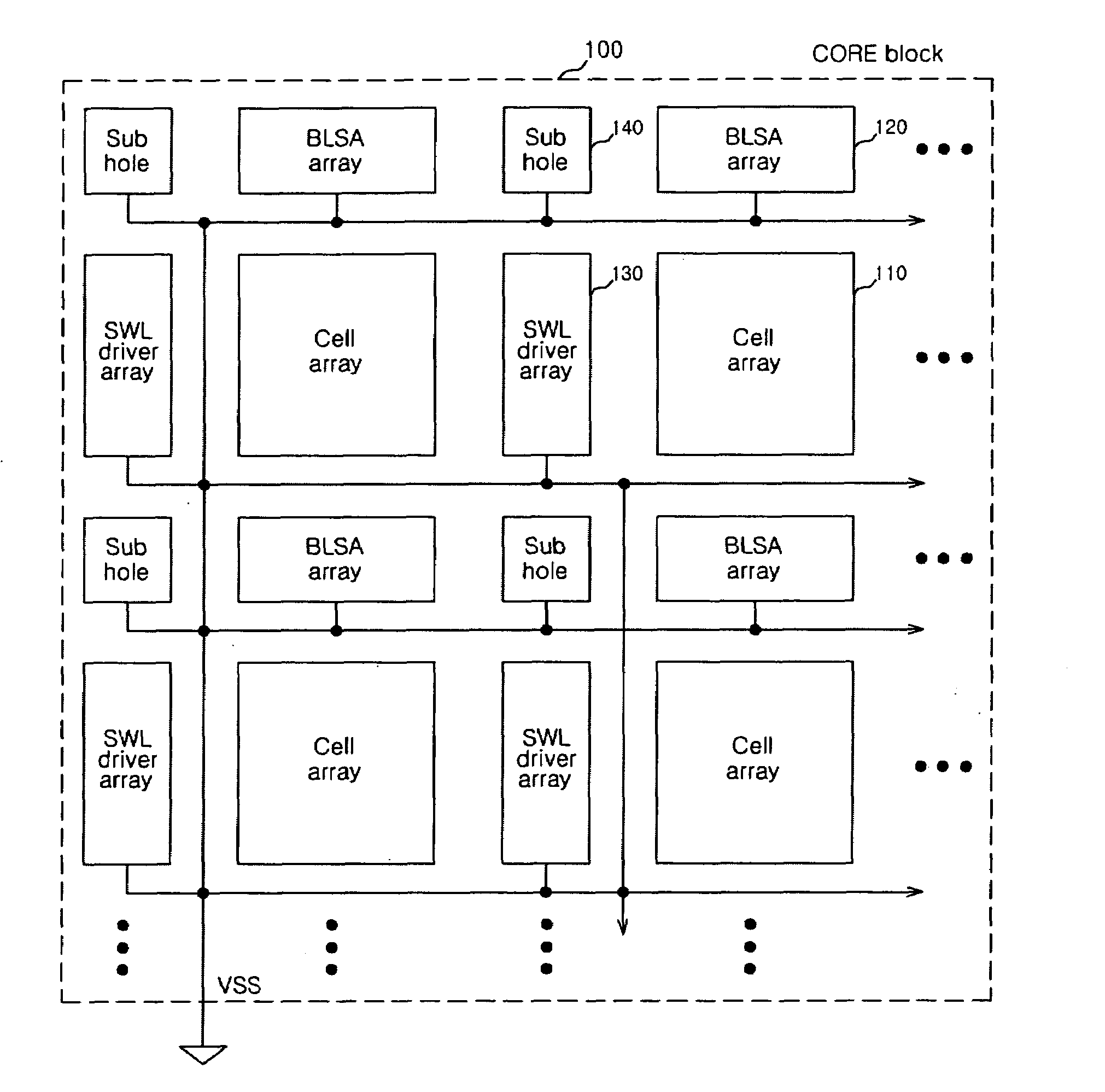
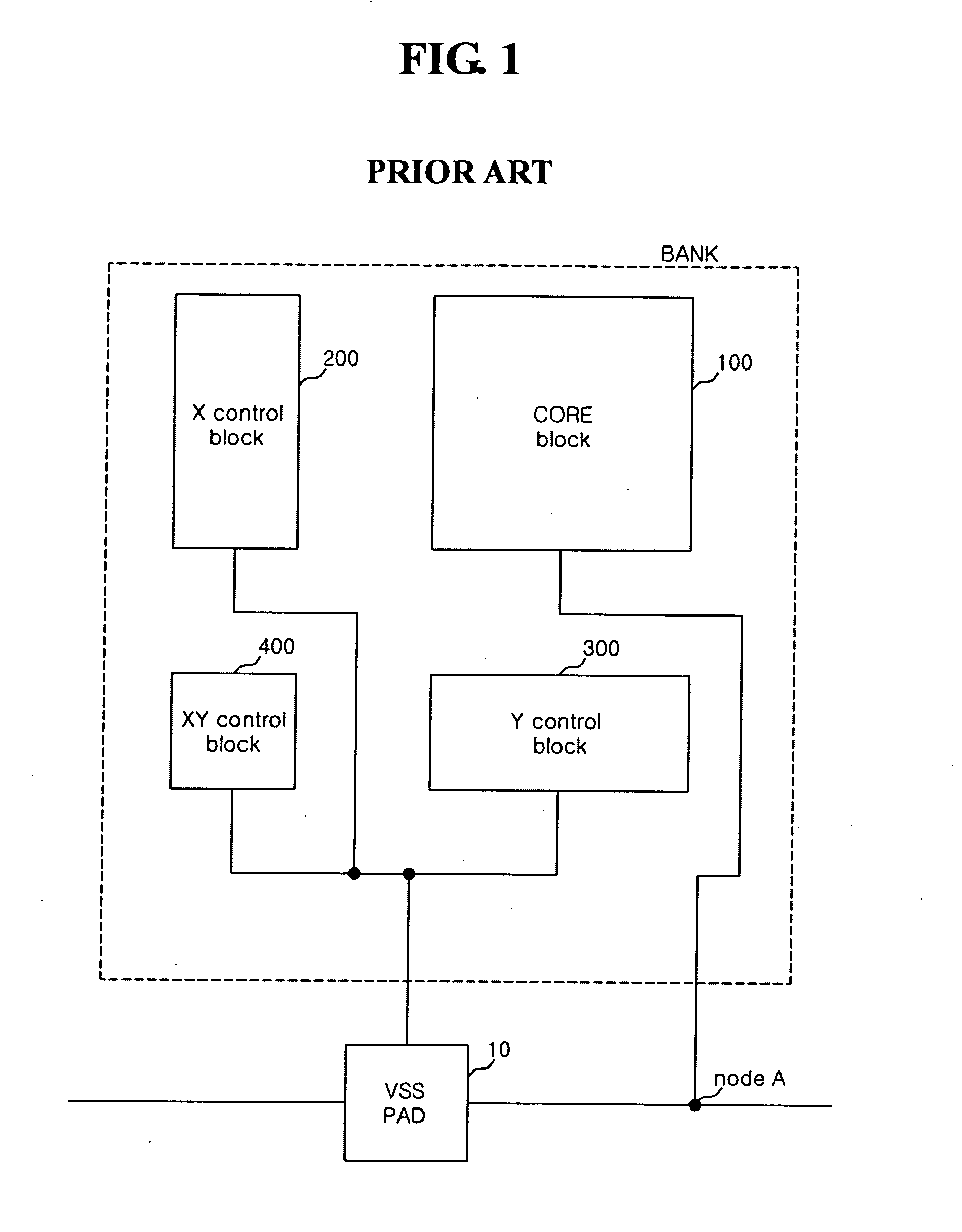
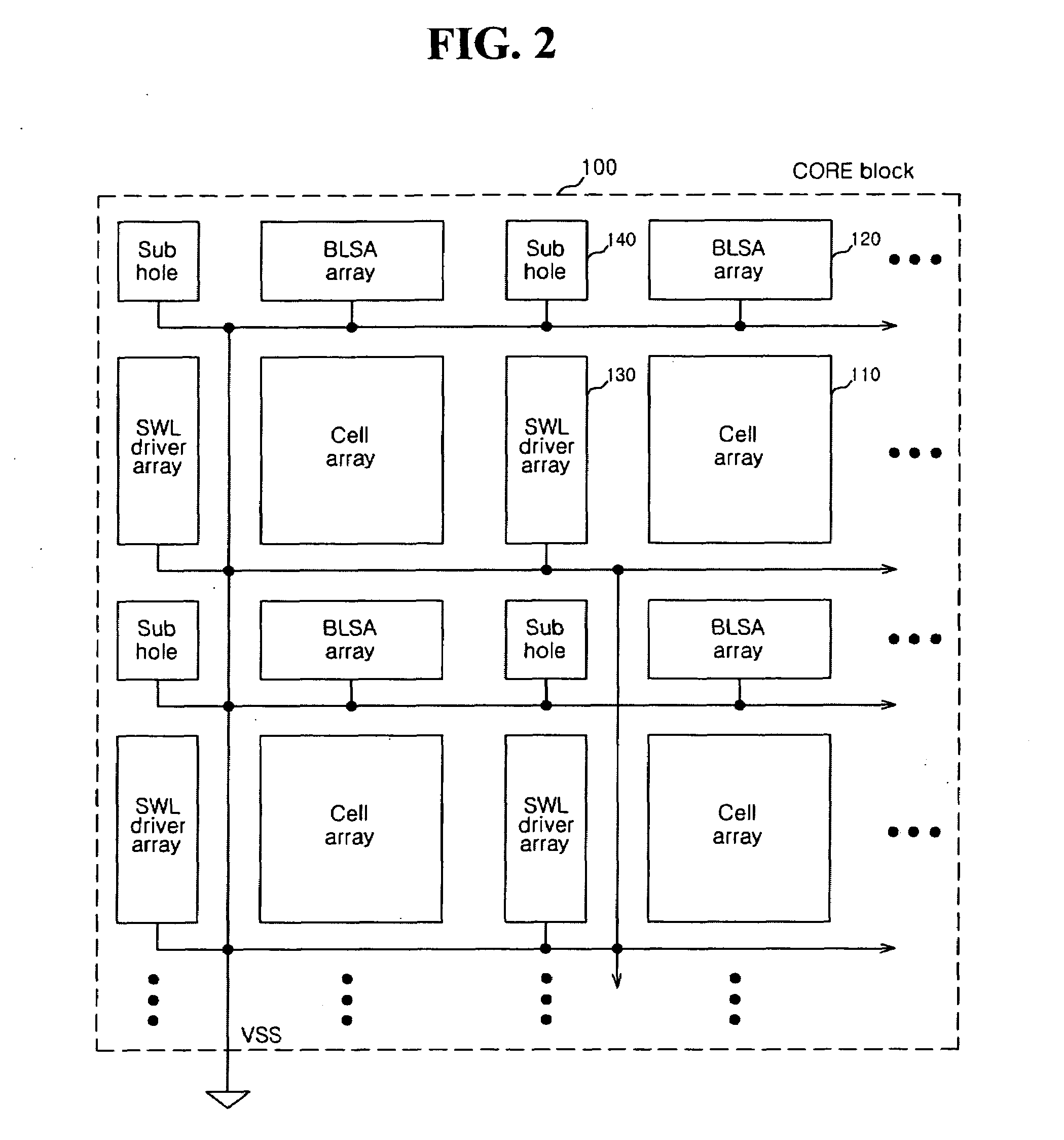
Semiconductor memory apparatus capable of reducing ground noise
A semiconductor memory apparatus includes a bank that includes a core block where a memory cell array is disposed and a control block to drive the memory cell array, a ground power supply pad that is supplied with a ground power through a ground line, a switch that connects the ground line and the core block, and a block control unit that controls an on / off operation of the switch.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Open drain driver having enhanced immunity to I/O ground noise
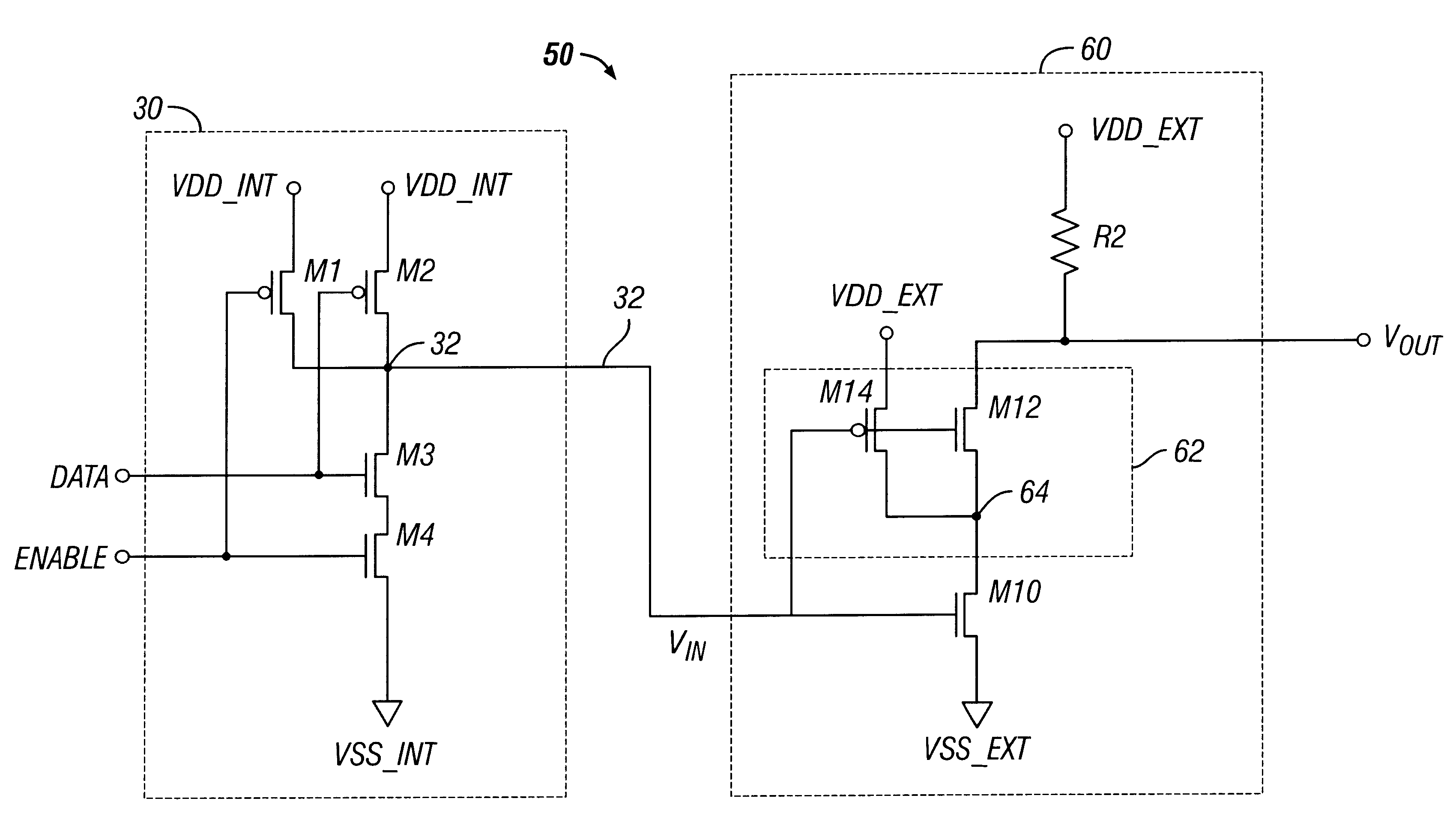
InactiveUS6472906B2Electronic switchingVoltage/current interference eliminationGround noiseEngineering
An open drain I / O driver includes an input node, an output node, a first reference node, a first transistor, and noise immunity circuitry. The first transistor has its gate coupled to the input node and its conducting path coupled in series with the output node and the first reference node. The first transistor operates to uncouple the output node from the first reference node in response to an input voltage applied to the input node. The noise immunity circuitry keeps the output node uncoupled from the first reference node during undershoot noise in a first reference voltage that causes the first transistor to change from an off state to an on state. The noise immunity circuitry includes second and third transistors. The second transistor has its gate coupled to the input node and its conducting path coupled in series with the conducting path of the first transistor. The third transistor is configured to keep the second transistor in an off state during the undershoot noise.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Active noise reduction earphone ground noise reducing method and device
InactiveCN106601225AGood noise reduction experienceActive Noise Cancellation ExcellentSound producing devicesEarpiece/earphone noise reductionAudio power amplifierGround noise
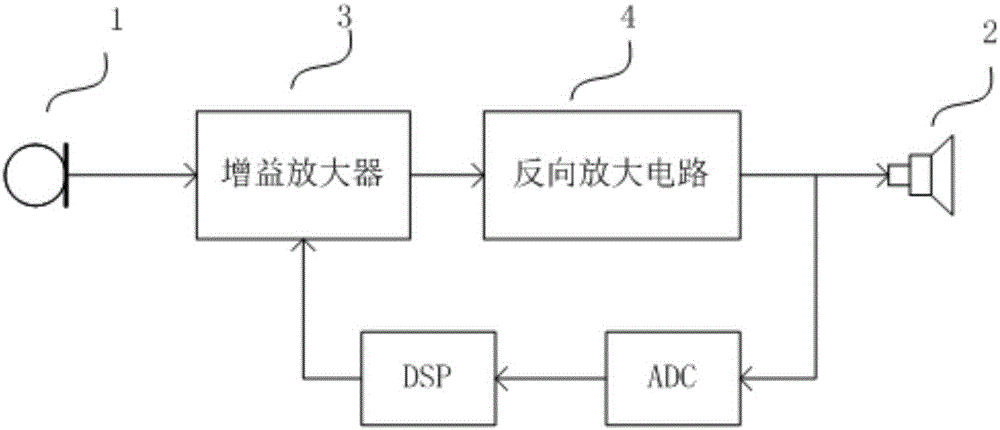
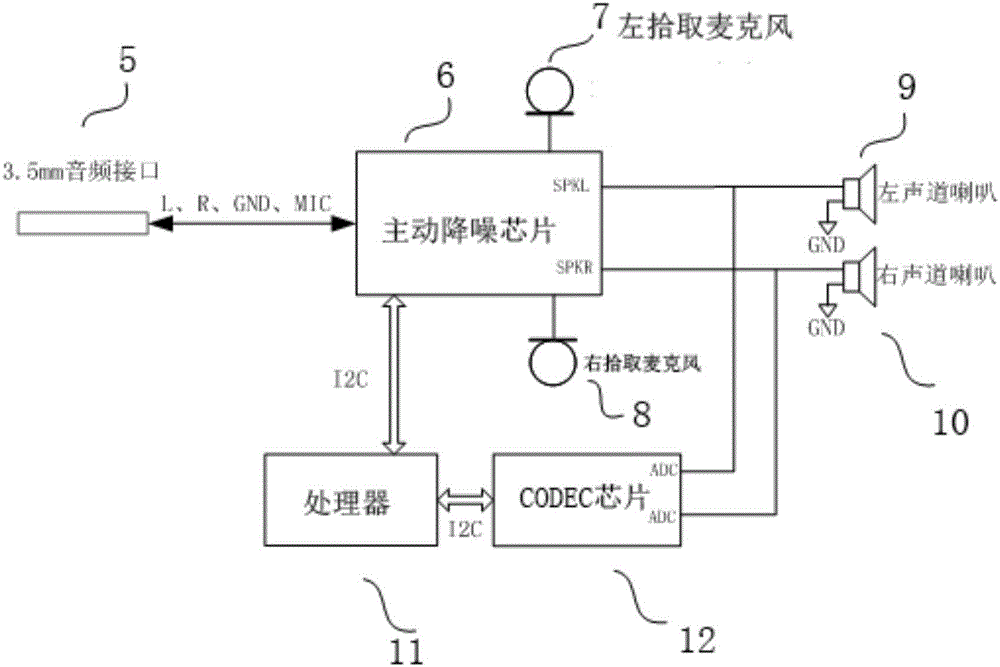
The invention discloses an active noise reduction earphone ground noise reducing method and device. The method comprises the following steps: a noise reduction microphone (1) collects ambient noise and is connected with a gain amplifier (3) to form a ground noise control and feedback circuit; an input sound signal of the loudspeaker is collected and analyzed to obtain a stable noise signal in the signal; and through the amplitude of the signal, active noise reduction microphone gain value is adjusted to obtain an active noise reduction and ground noise optimum effect, thereby providing a better noise reduction experience for a user.
Owner:SHENZHEN SHENGYUAN TECH LTD
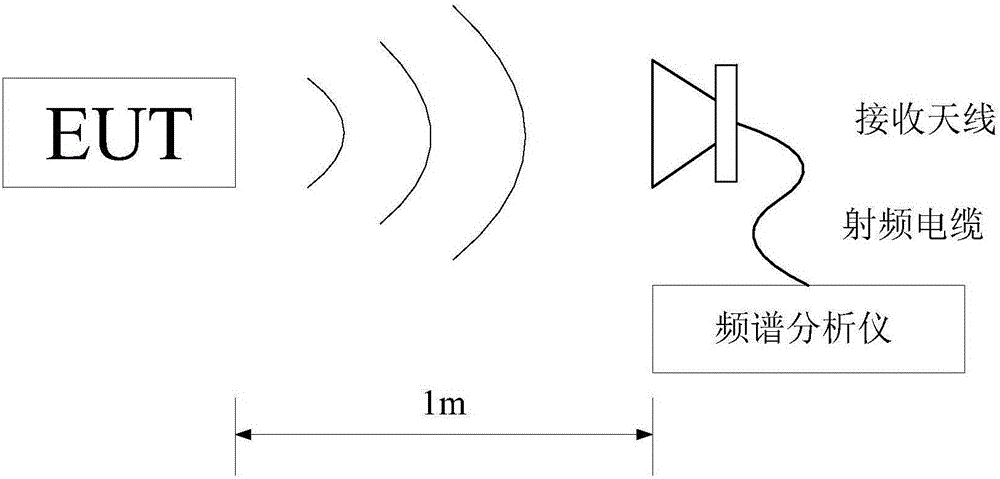
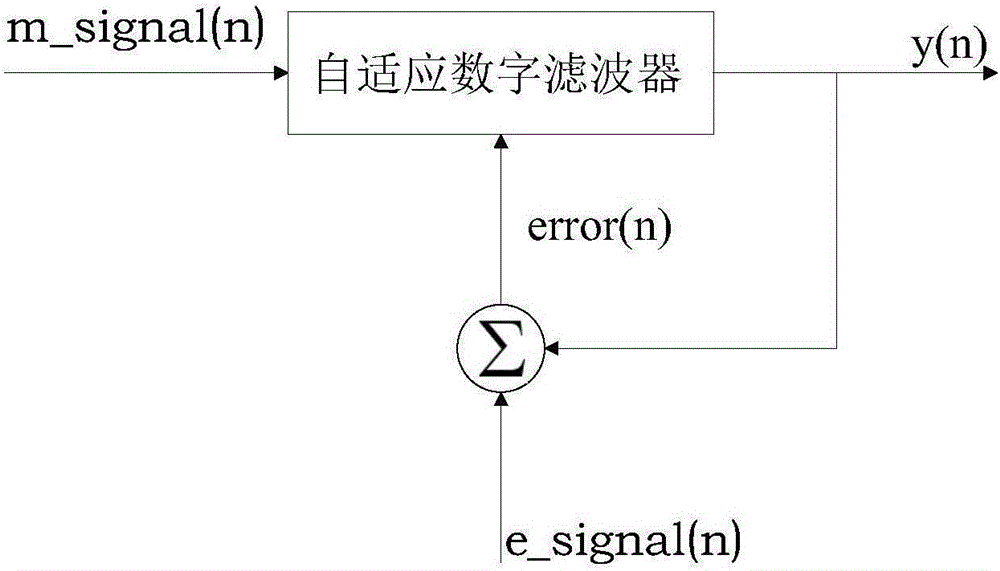
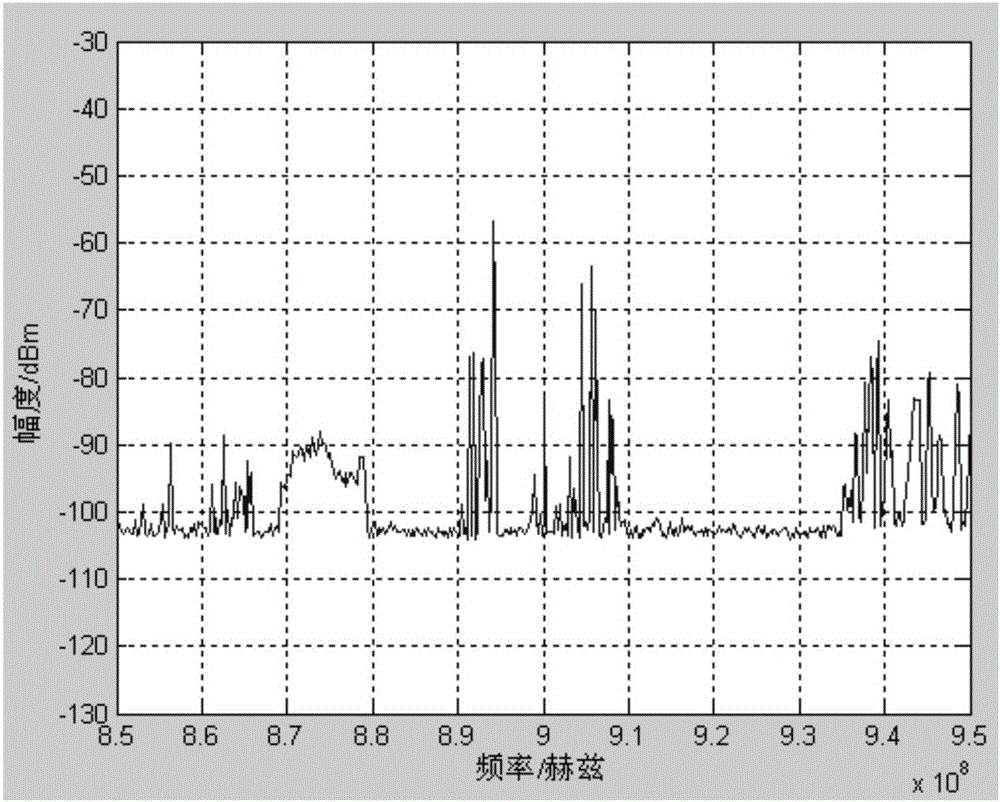
Background signal eliminating method suitable for on-site electromagnetic interference detection
ActiveCN105842561AReduce the impact of background noise instabilityAmplitude EliminationMeasuring interference from external sourcesFrequency spectrumSpectrum analyzer
The invention discloses a background signal eliminating method suitable for on-site electromagnetic interference detection. The detection can be completed with simple devices including a portable frequency spectrograph and an antenna, background noise in a period of time is acquired with a maximal retaining mode, EUT electromagnetic emission and environment mixed signals are acquired when a device to be detected is powered on, and the EUT electromagnetic emission is obtained through a frequency domain adaptive filtering algorithm. The background noise, mixed signals and other frequency spectrum data are acquired in the maximal retaining mode, so that the influence caused by unstable background noise can be minimized. After the mixed signals and background noise are inputted into an adaptive digital filter, the EUT electromagnetic emission frequency points are obtained from the output signals, and the amplitude value of each EUT electromagnetic emission frequency point is obtained from the mixed signals. Other frequency point uses the ground noise of the frequency spectrum analyzer as the amplitude value after eliminating background signals.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
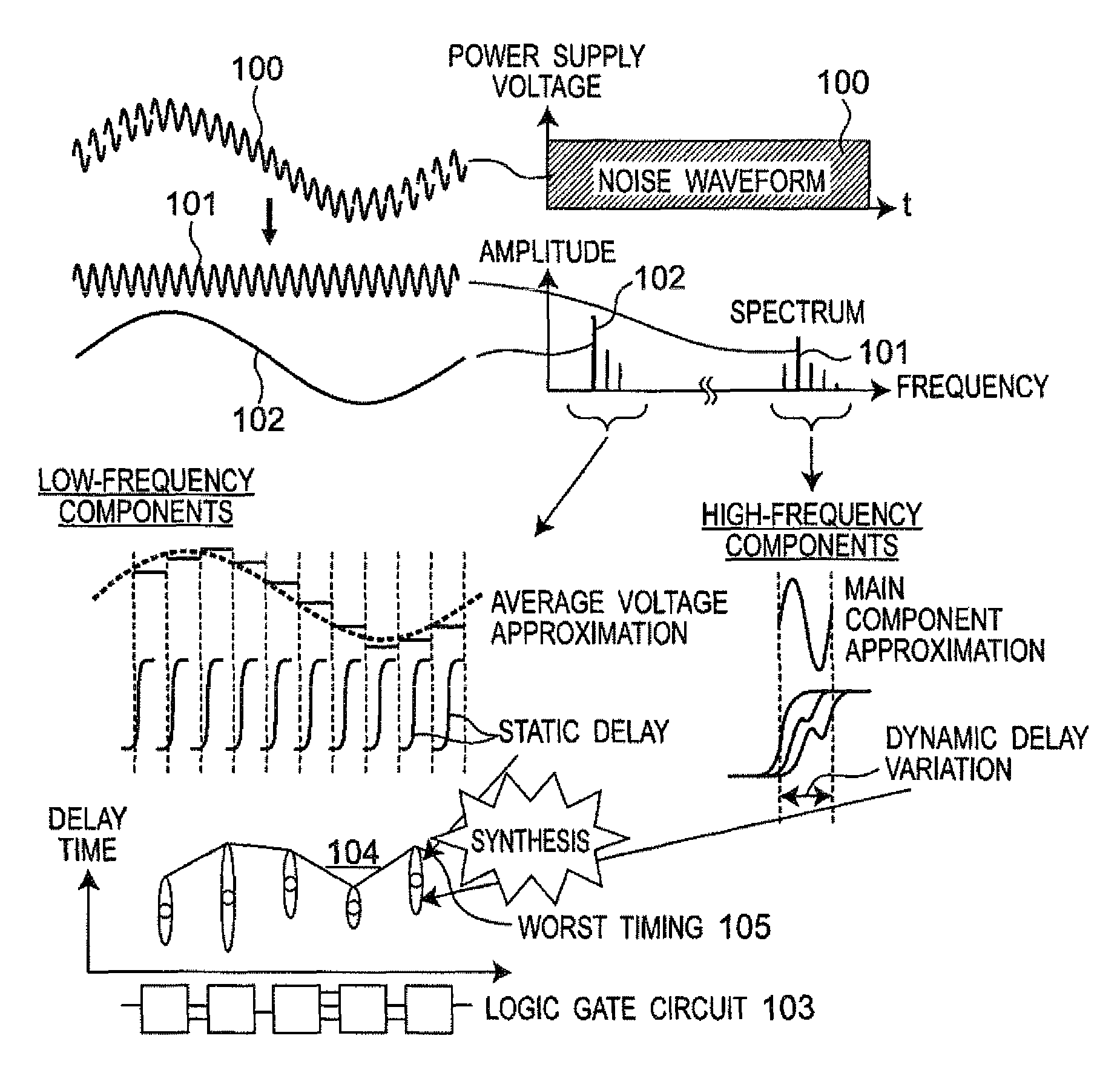
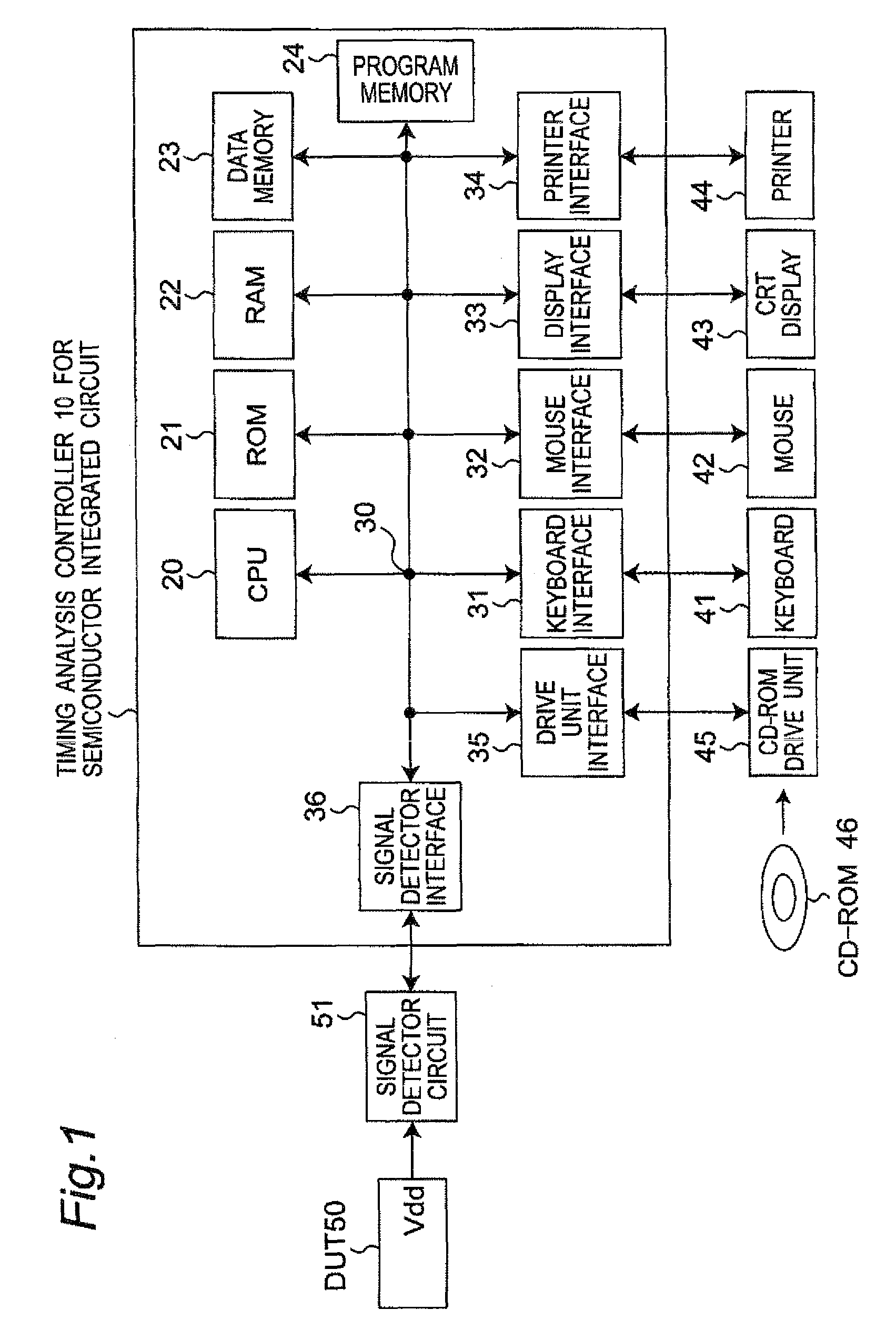
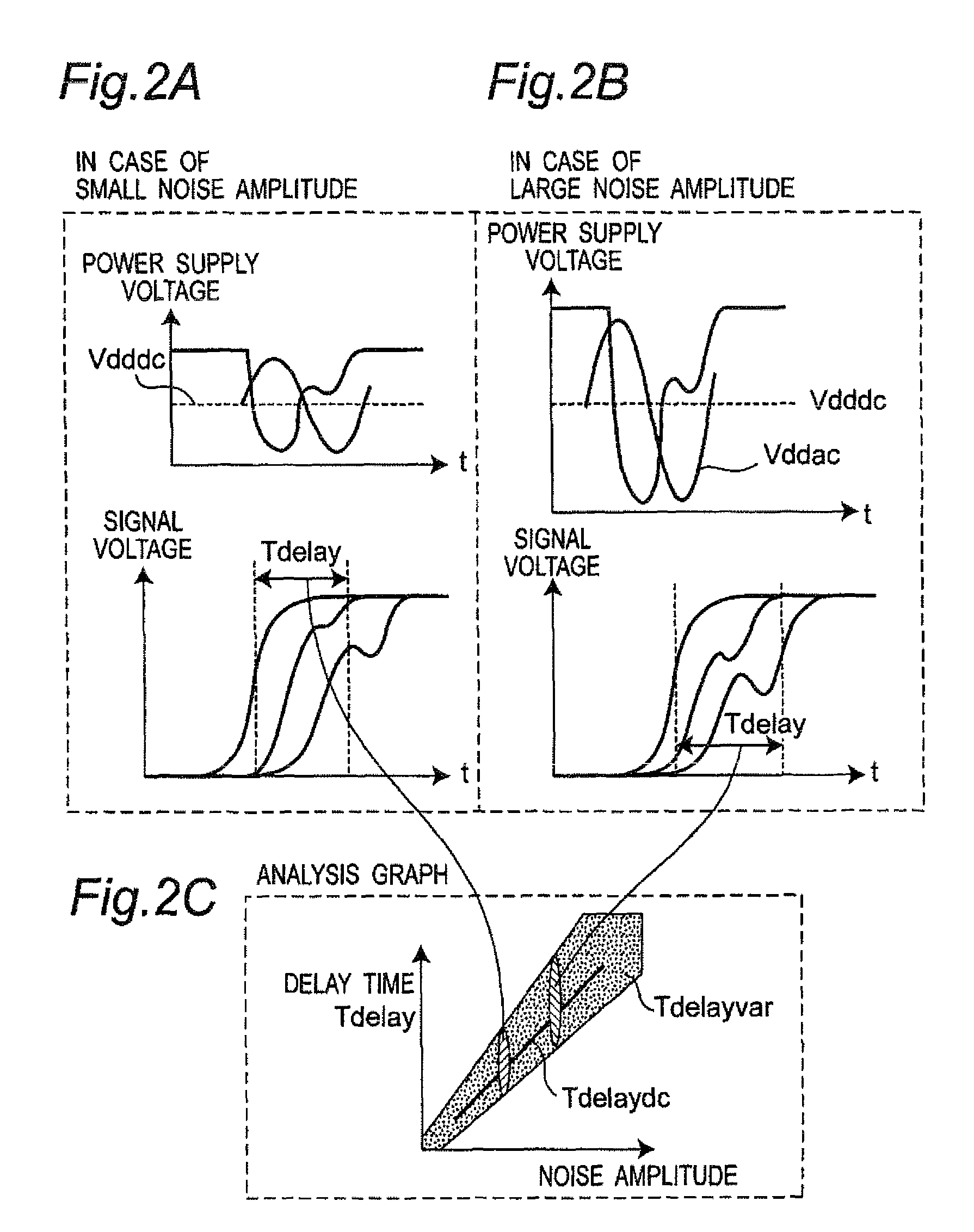
Timing analysis apparatus and method for semiconductor integrated circuit in consideration of power supply and ground noises
InactiveUS8020130B2Improve accuracySignificant calculationMultiple-port networksFrequency-division multiplex detailsGround noiseEngineering
In a timing analysis apparatus for use in a semiconductor integrated circuit, which analyzes operation timing of a semiconductor integrated circuit having a logic gate circuit including a plurality of logic gates, a controller detects at least one of a power supply voltage and a ground voltage of a power supply, decomposes the noise waveform into frequency components, classifies the frequency components into low-frequency components lower than a predetermined threshold frequency and high-frequency components higher than the threshold frequency, calculates a static delay time of each of the logic gates due to the low-frequency components, calculates a dynamic delay time of each of the logic gates due to the high-frequency components, and determines a delay time of each of the logic gates by synthesizing the calculated respective delay times.
Owner:SEMICON TECH ACADEMIC RES CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com