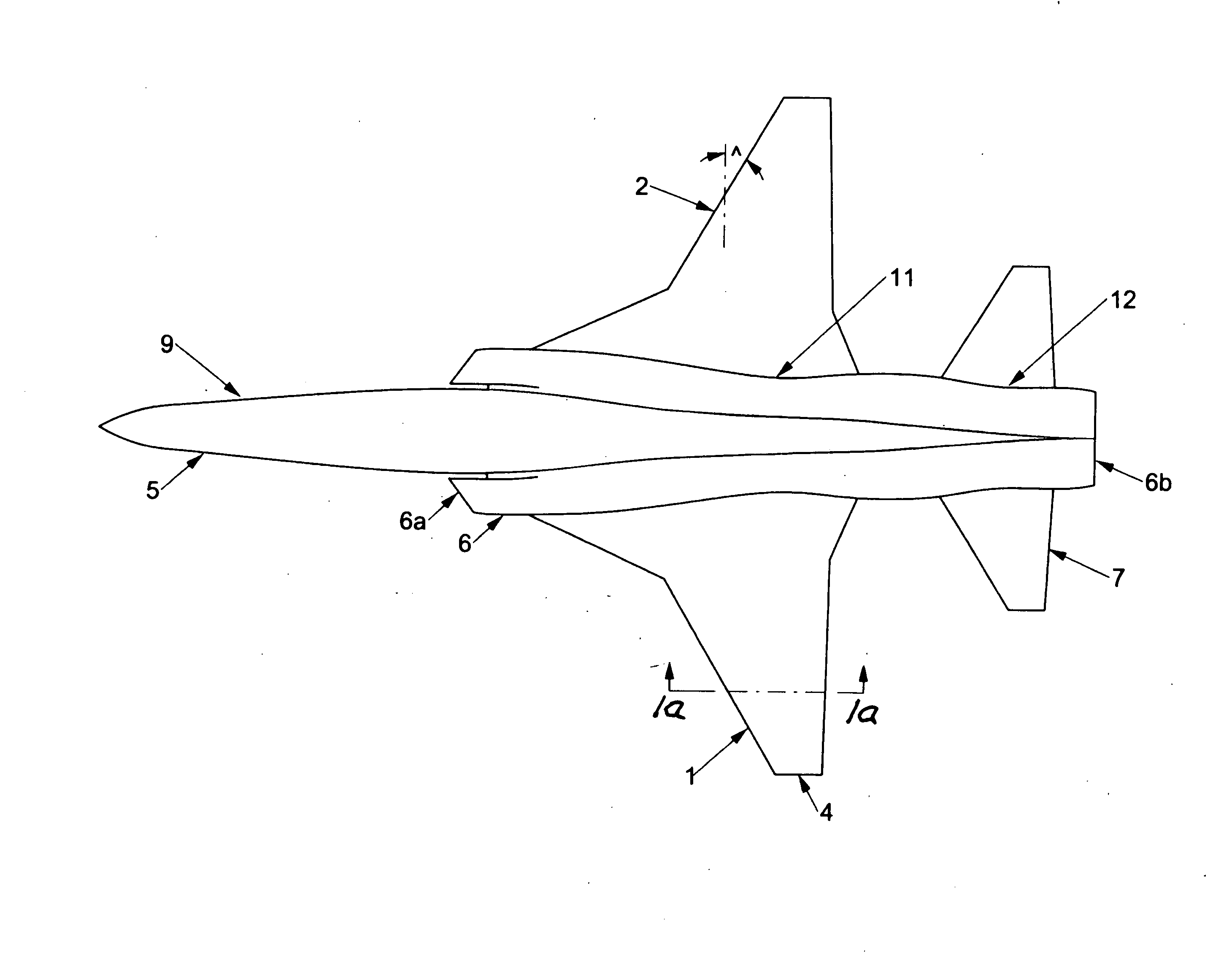
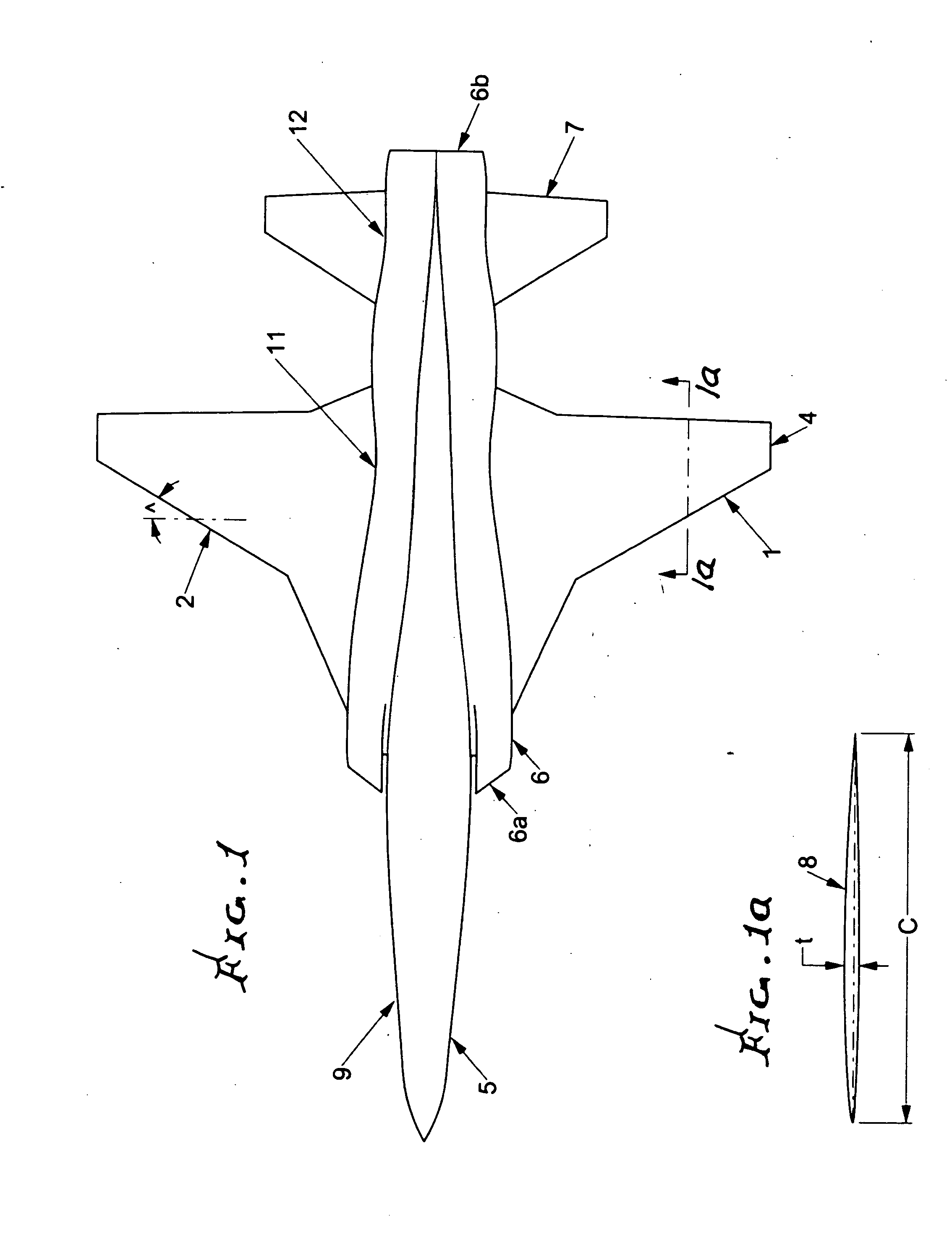
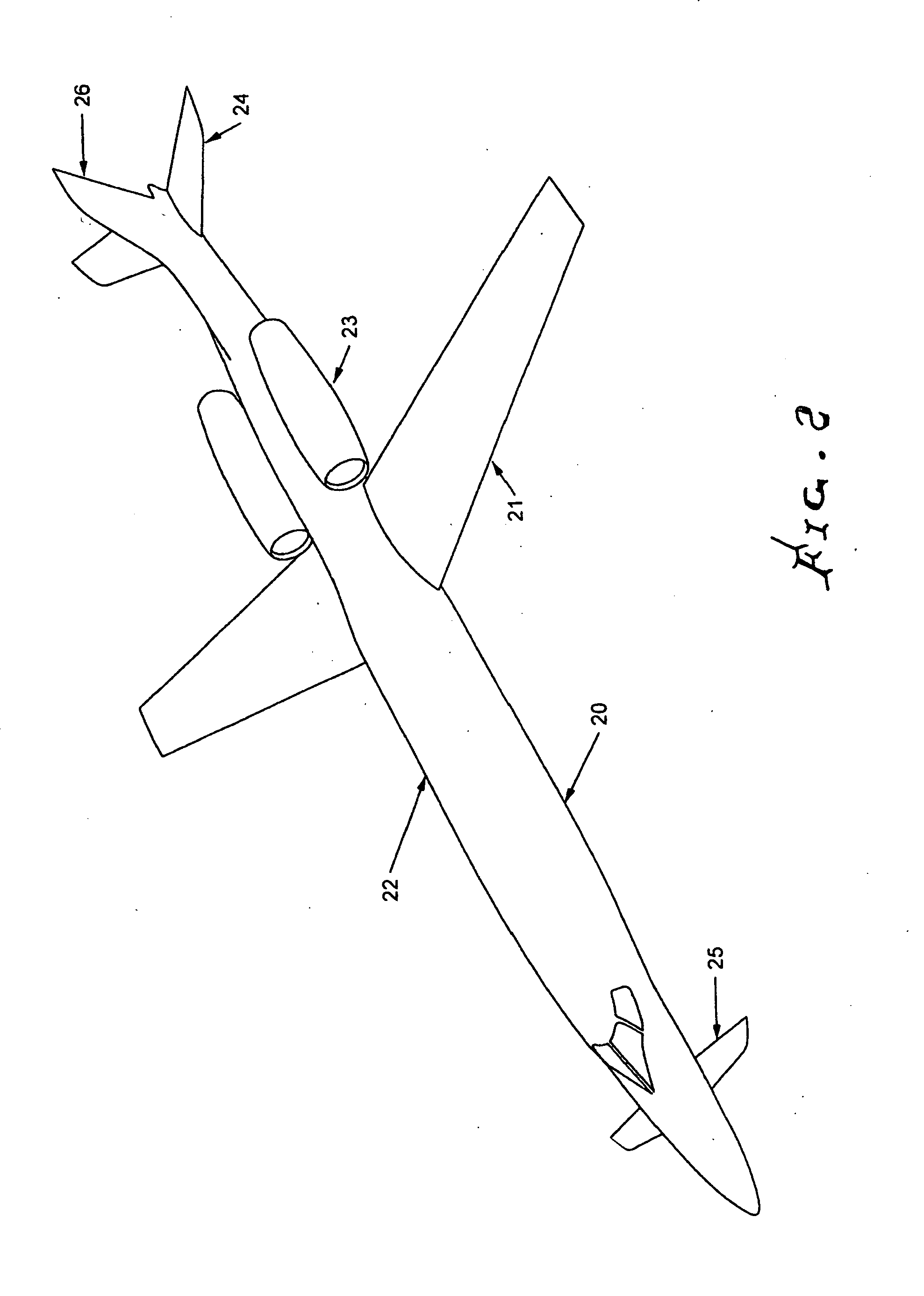
Patents
Literature
154 results about "Transonic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In aeronautics, transonic (or transsonic) flight is flying at or near the speed of sound 343 meters per second (1,235 km/h; 1,125 ft/s; 767 mph; 667 kn, at sea level under average conditions), relative to the air through which the vehicle is traveling. A typical convention used is to define transonic flight as speeds in the range of Mach 0.72 to 1.0 (965–1,235 km/h (600–767 mph) at sea level).
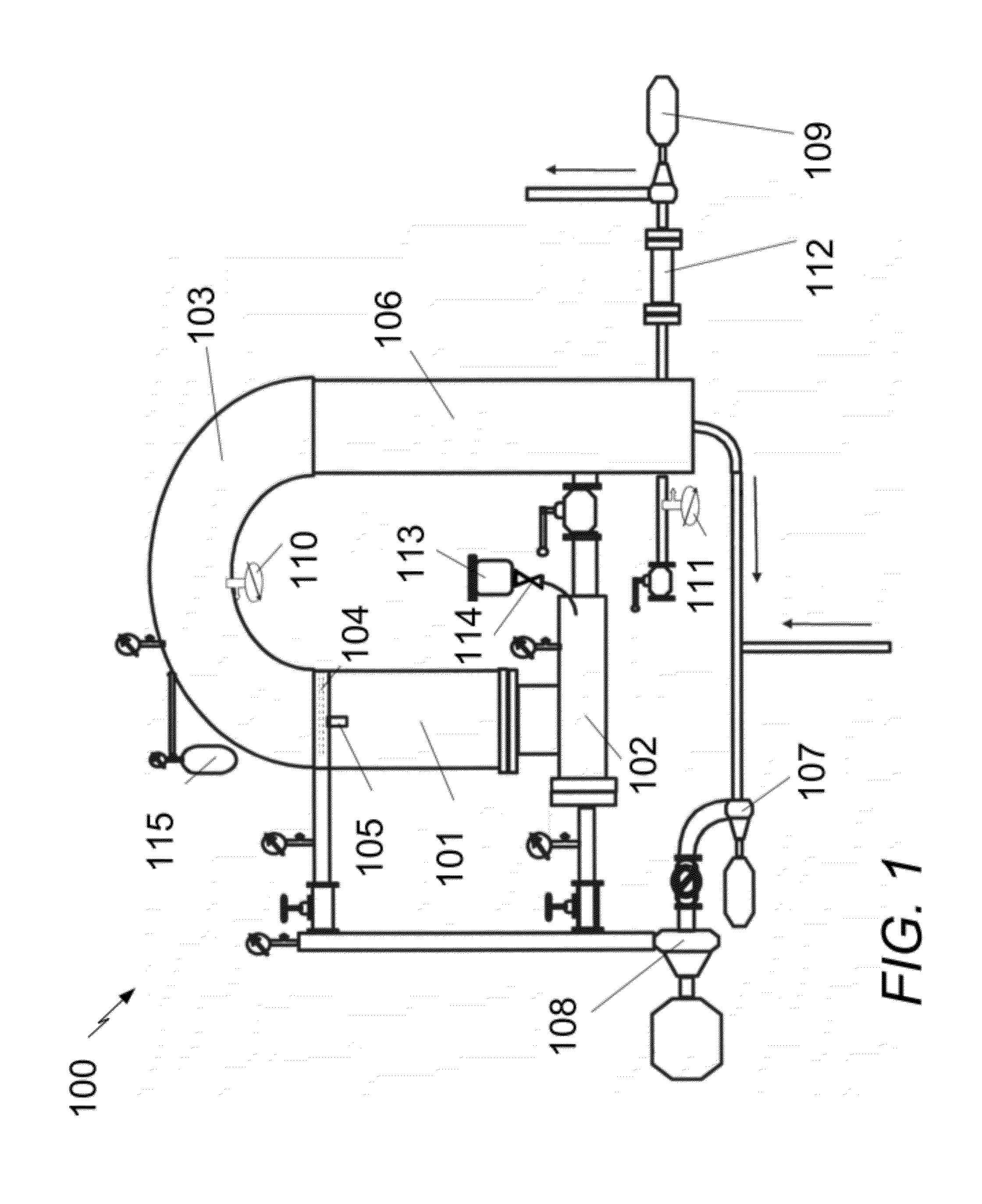
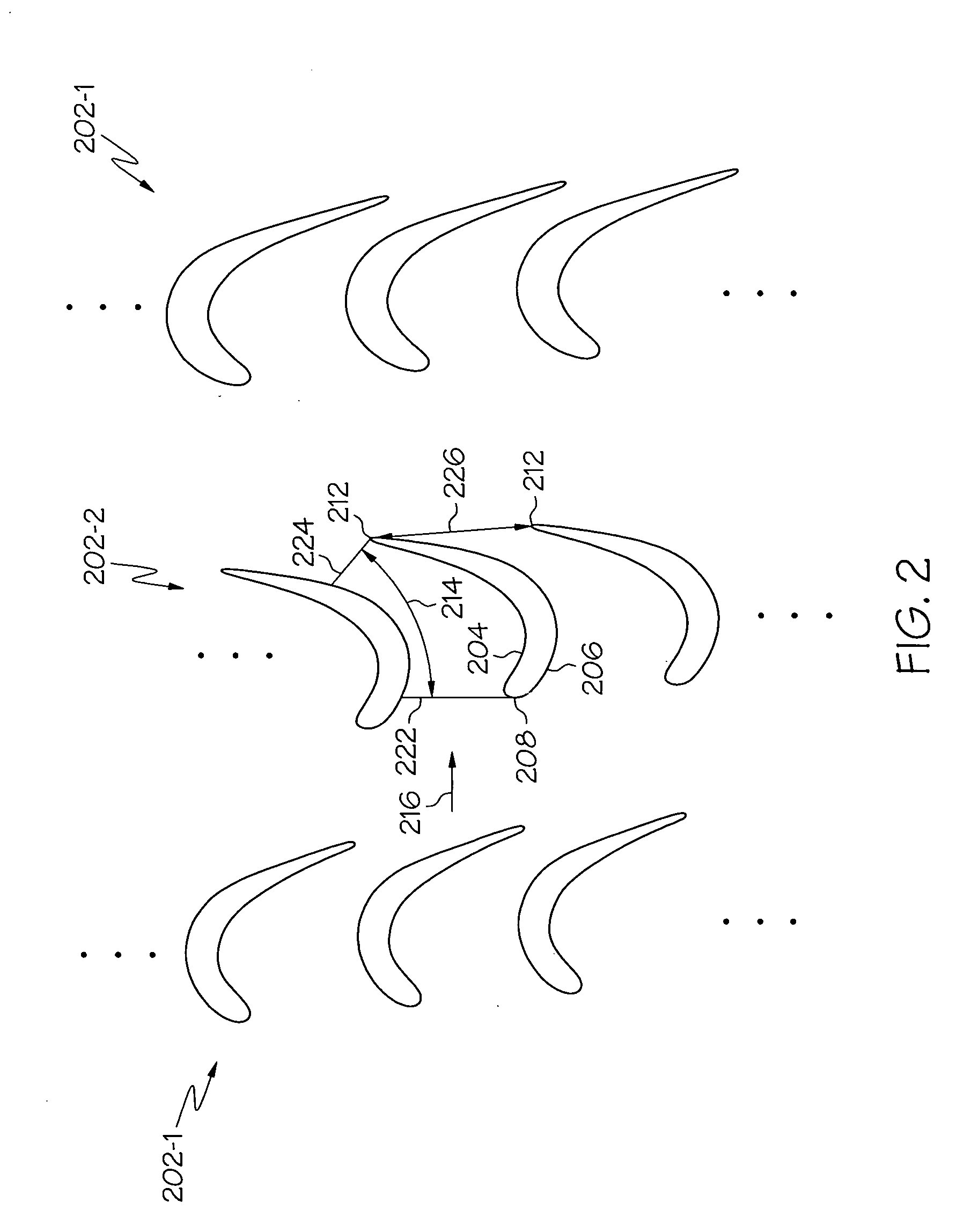
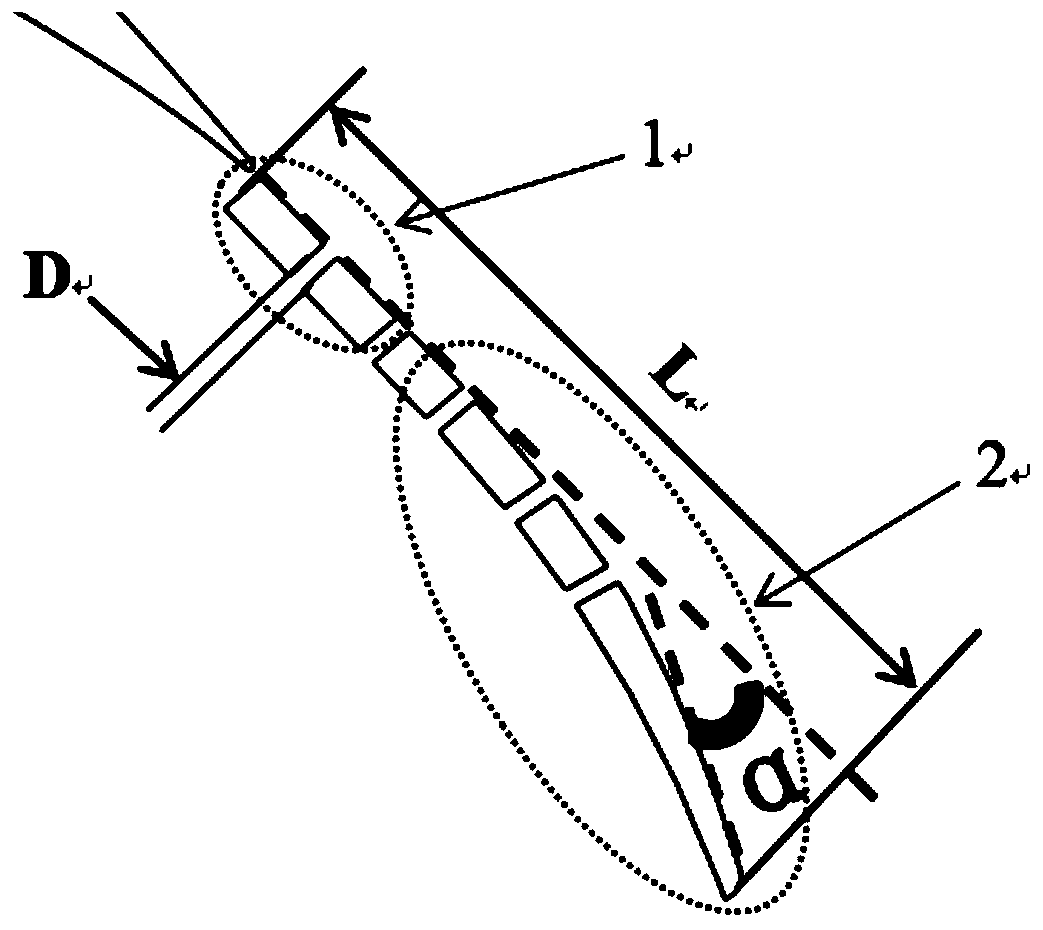
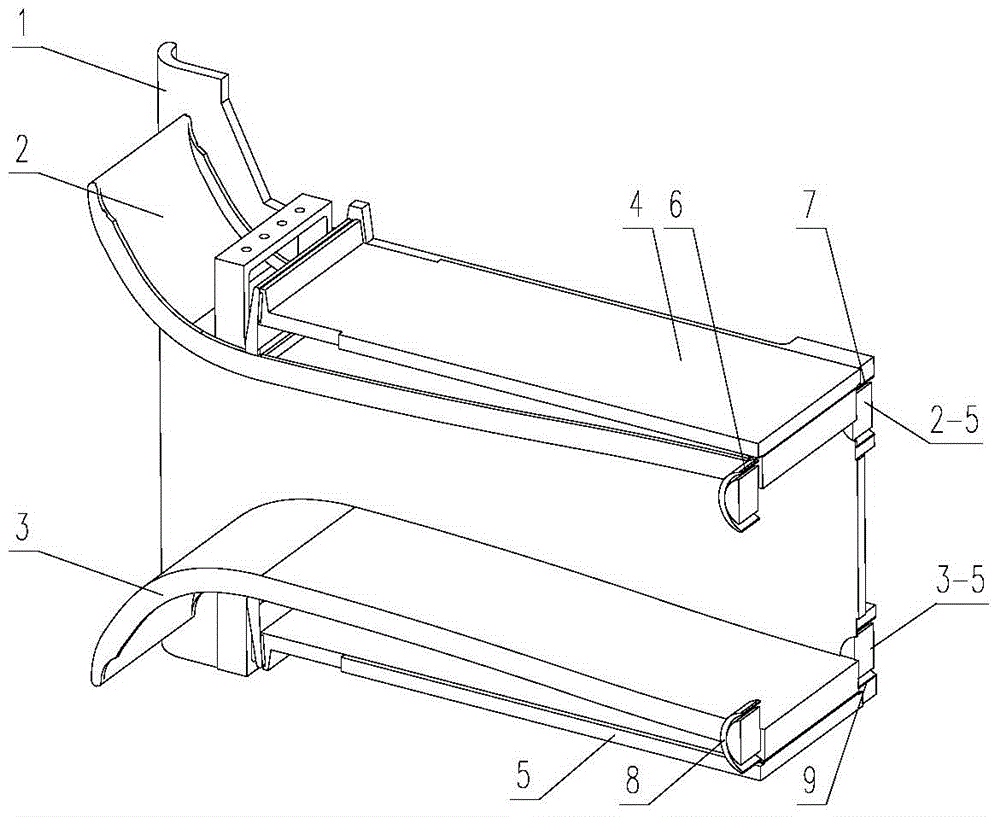
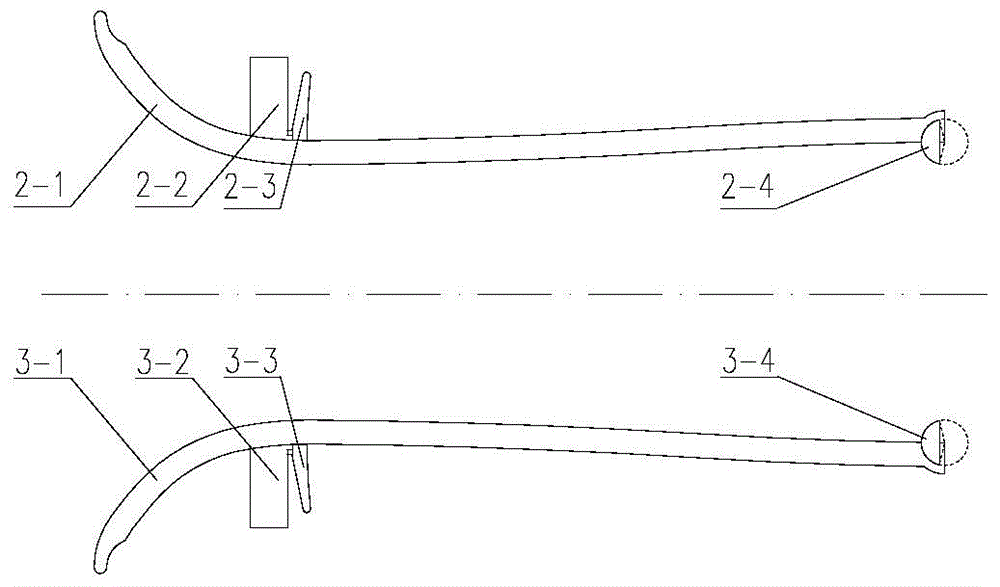
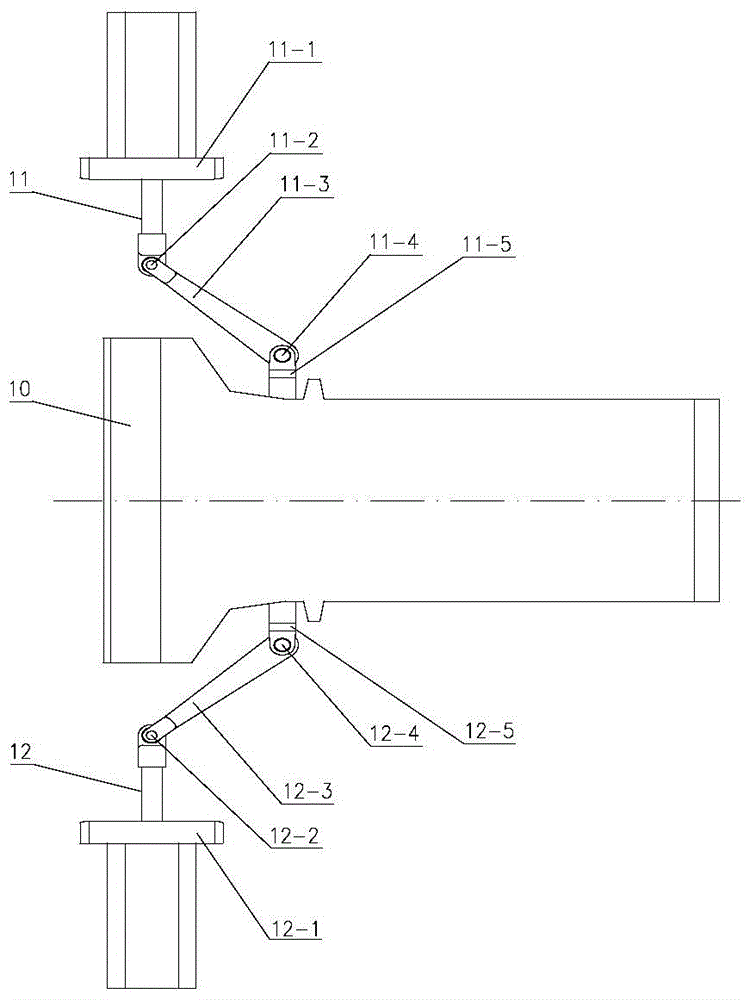
Three-hole transonic speed pressure probe
ActiveCN105716788AReduce resistanceNot easy to bendFluid pressure measurementTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesShock waveEngineering
The invention discloses a three-hole transonic speed pressure probe. As a pneumatic technology develops, a transonic speed air flow appears more and more frequently, for instance, many air flows in an aeroengine reach a transonic speed state, so these transonic speed flow fields need to be measured and analyzed during development of engine components. Conventionally, the transonic speed flow fields are measured respectively by use of a total pressure probe and a direction probe so that total pressure and air flow directions can be obtained. When a flow speed reaches a transonic speed, the probes are under great resistance, and the probes are blown bent easily. When the flow speed reaches an ultrasonic speed, due to the existence of shock waves, there is large total pressure loss, and the influences exerted by the probes on the flow fields are quite large. Though these conventional probes can be used in an ultrasonic air flow, the influences exerted by the probes on the flow fields cannot be neglected, and the requirement for the strength of the probes is quite high. The novel three-hole transonic speed pressure probe provided by the invention is used for measuring the transonic speed flow fields. By use of the probe provided by the invention, the intensity of the shock waves in front of the probe can be weakened during measurement, the influences exerted by the probe on the flow fields are reduced, air-flow total pressure, static pressure, a Mach number and an air-flow deflection angle can be measured simultaneously, the resistance acting on the probe can be effectively reduced, and the firmness and reliability of the probe are guaranteed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
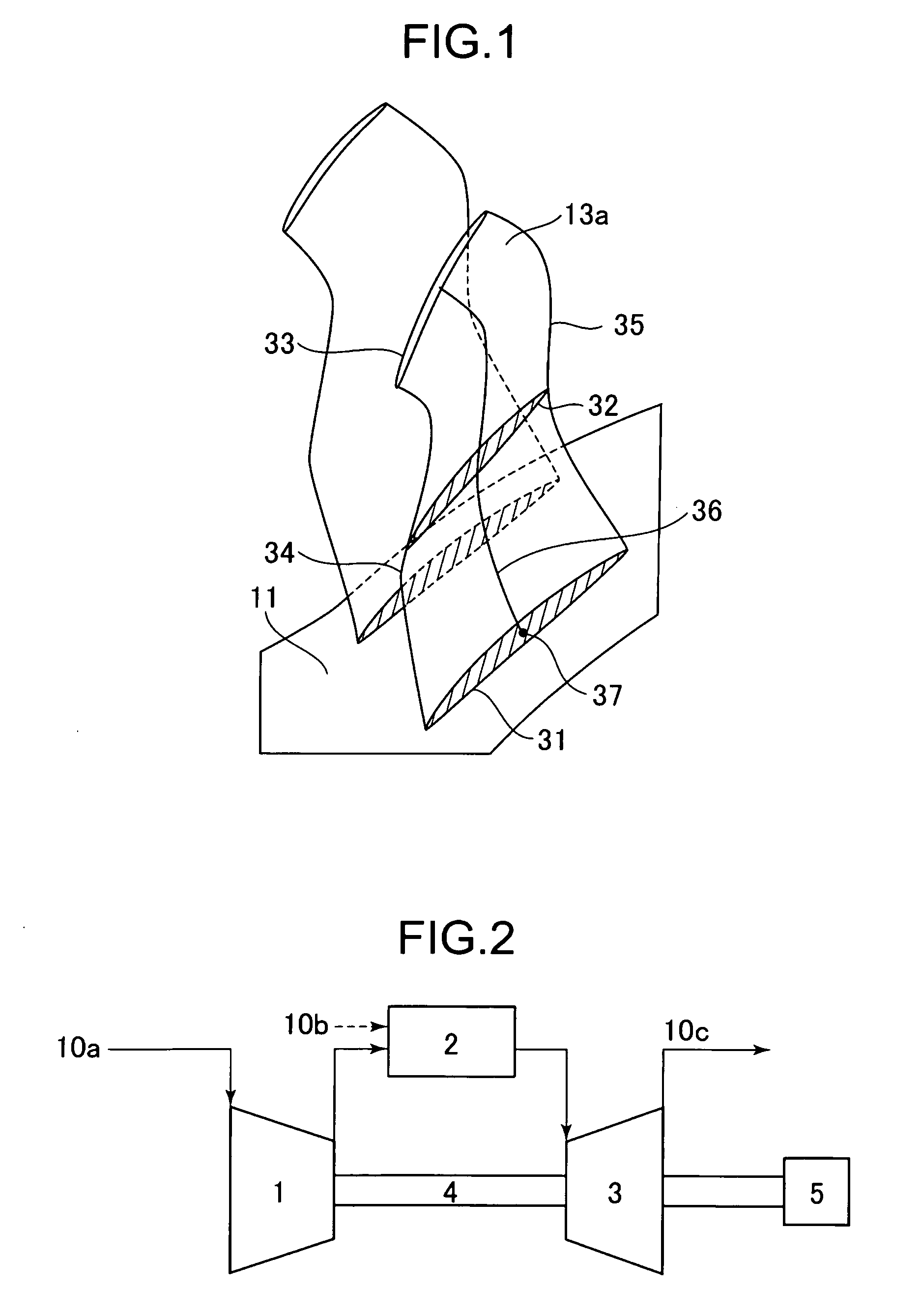
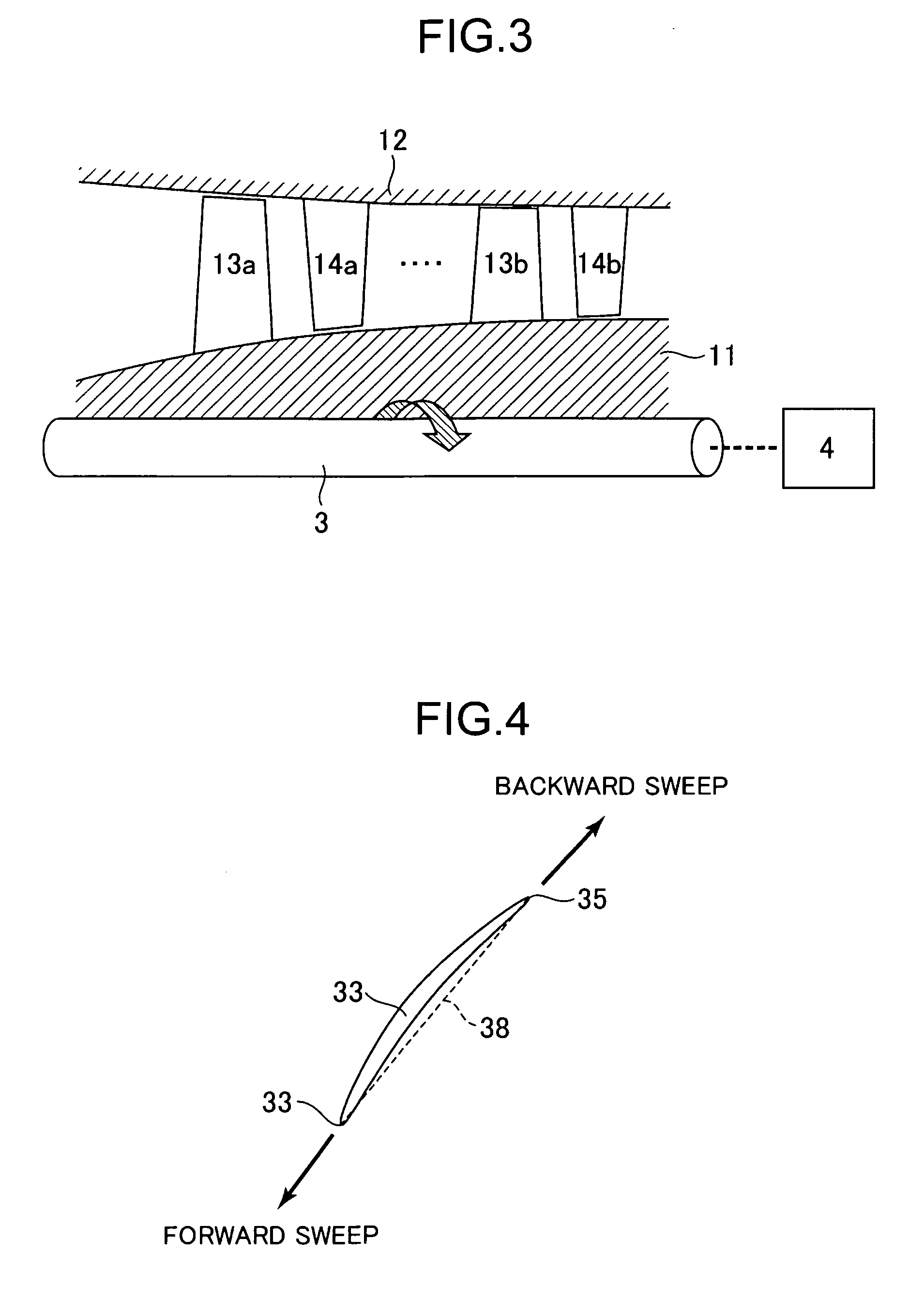
Transonic blade
ActiveUS20100215503A1Reduce various lossesImprove local stressPropellersReaction enginesLeading edgeWorking fluid
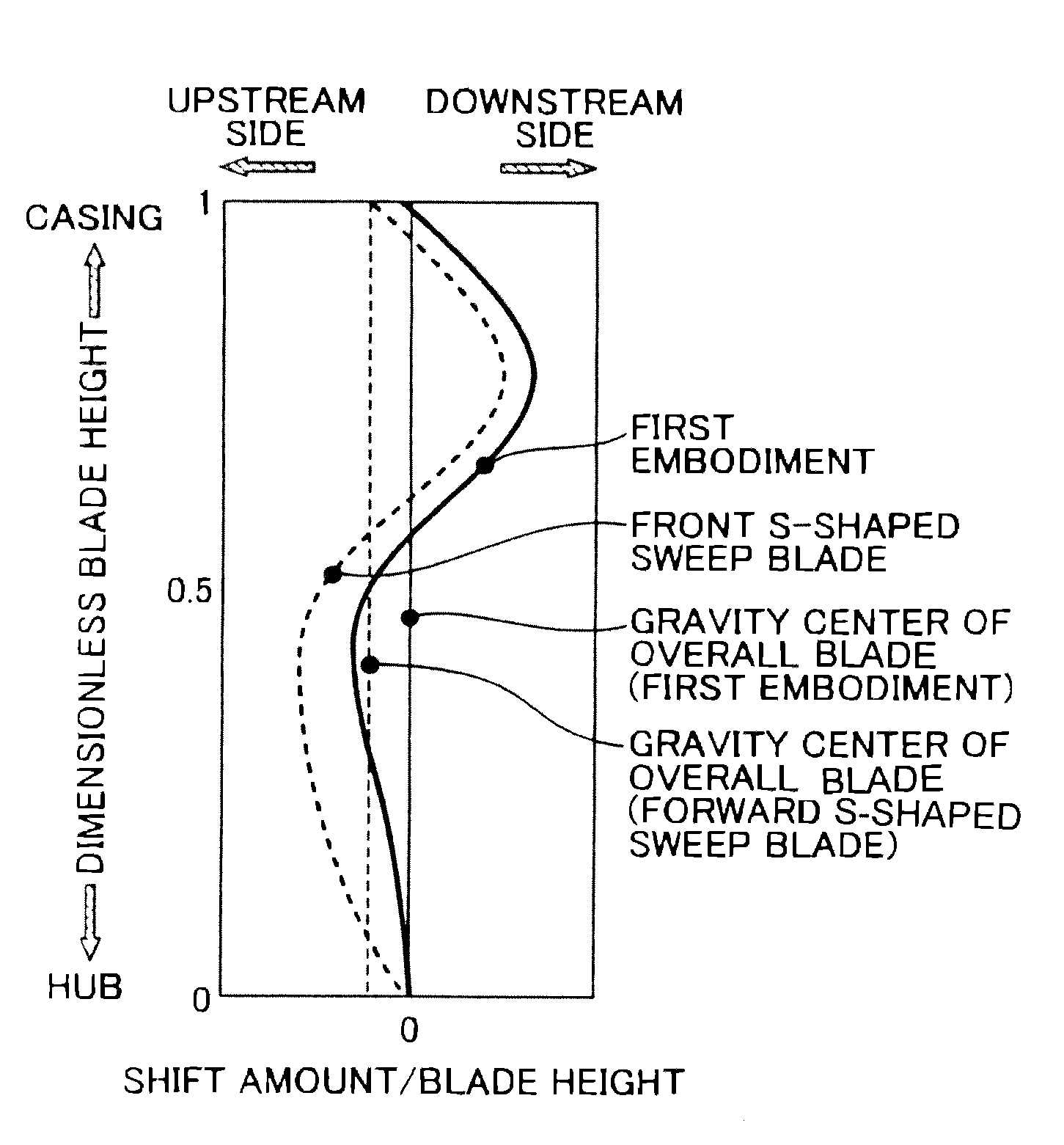
A transonic blade is provided that operates in a flow field where flow has a transonic speed or higher in an axial-flow rotating machine and that concurrently achieves a reduction in shock loss and in the local stress of the blade.The transonic blade includes a hub cross-sectional surface joined to a rotating shaft or an outer circumferential side casing of a rotating machine; a tip cross-sectional surface located furthest from the hub cross-sectional surface in a spanwise direction which is a vertical direction of the rotating shaft; a leading edge located on an upstream side; and a trailing edge located on a downstream side. At least a part of a passing working fluid flow has a transonic speed or higher. A portion of a stacking line which is a line connecting together respective gravity centers of cross-sectional surfaces located from the hub cross-sectional surface to the tip cross-sectional surface is located on a downstream side of a stacking center in a flow direction of a working fluid main flow.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Method and system for a quick calculation of aerodynamic forces on an aircraft in transonic conditions
ActiveUS20100250205A1Quick calculationGeometric CADSustainable transportationShock waveFlight vehicle
A computer-aided method suitable for assisting in the design of an aircraft by providing relevant dimensioning values corresponding to an aircraft component in transonic conditions inside a predefined parameter space by means of a reconstruction of the CFD computations for an initial group of points in the parameter space using a POD reduced-order model, comprising the following steps: a) Decomposing for each flow variable the complete flow field into a smooth field and a shock wave field in each of said computations; b) Obtaining the POD modes associated with the smooth field and the shock wave field considering all said computations; c) Obtaining the POD coefficients using a genetic algorithm (GA) that minimizes a fitness function; d) Calculating said dimensioning values for whatever combination of values of said parameters using the reduced-order model. The invention also refers to a system able to perform the method.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS SL +1
Transonic Blade
ActiveUS20130259668A1Increase stall marginReduce lossesSupersonic fluid pumpsPump componentsLeading edgeEngineering
The present invention provides a transonic blade that concurrently achieves reduction in shock loss at a design point and improvement in stall margin in blades operating in a flow field of transonic speed or higher in an axial-flow rotating machine. A cross-sectional surface at each of spanwise positions of the blade is shifted parallel to a stagger line connecting a leading edge with a trailing edge of the blade. A stacking line is shifted toward an upstream side of working fluid. The stacking line connects together respective gravity center positions of blade cross-sectional surfaces at spanwise positions in a range from a hub cross-sectional surface joined to a rotating shaft or an outer circumferential side casing of a rotating machine to a tip cross-sectional surface lying at a position most remote from the hub cross-sectional surface in a spanwise direction.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
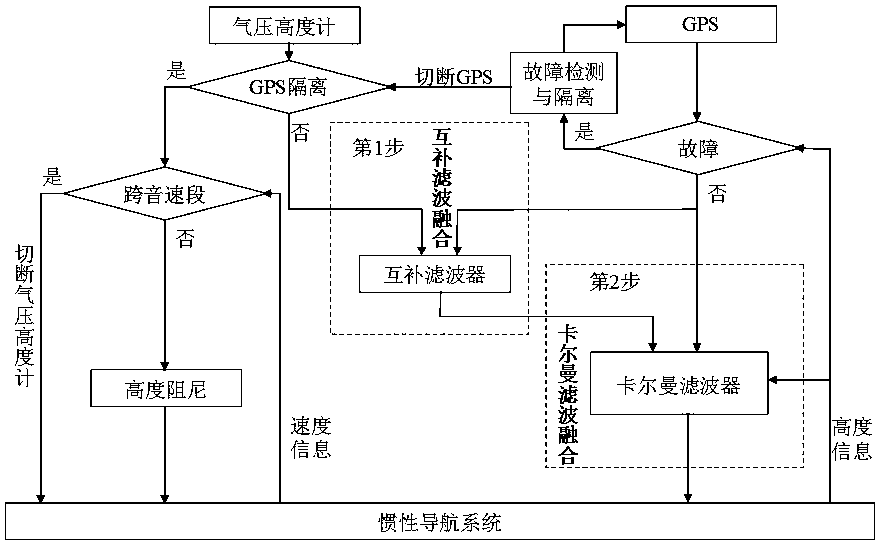
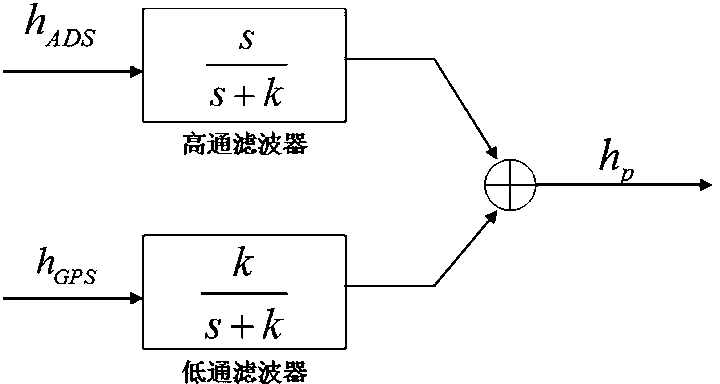
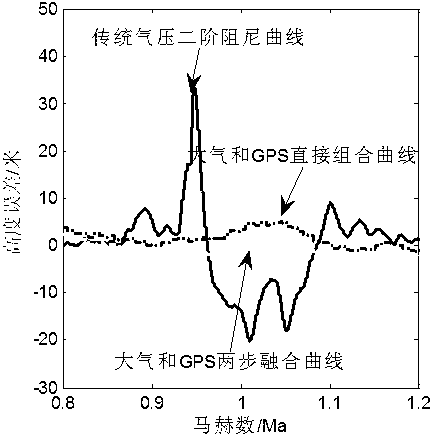
Transonic segment barometric altimeter and GPS information two-step fusion method in inertial navigation system
ActiveCN102937449ADrastic change eliminationSmooth changeNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsSatellite radio beaconingTwo stepNavigation system
The invention discloses a transonic segment barometric altimeter and GPS information two-step fusion method used in an inertial navigation system. The method comprises complementary filtering and Kalman filtering. Atmosphere / GPS altitude channel complementary fusion filtering is adopted in complementary filtering, such that barometric altitude value drastic change is eliminated. In Kalman filtering, a barometric altimeter / GPS / inertial navigation system composite navigation system state equation and measurement equation are established, and state optimal estimation of inertial altitude channel can be finally obtained through two-step fusion. According to the invention, the barometric altimeter and GPS form a high redundance and fault detection isolation system, such that the precision of transonic stage altitude value in flight process can be effectively improved, and good conditions are provided for precise navigation and flight control.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
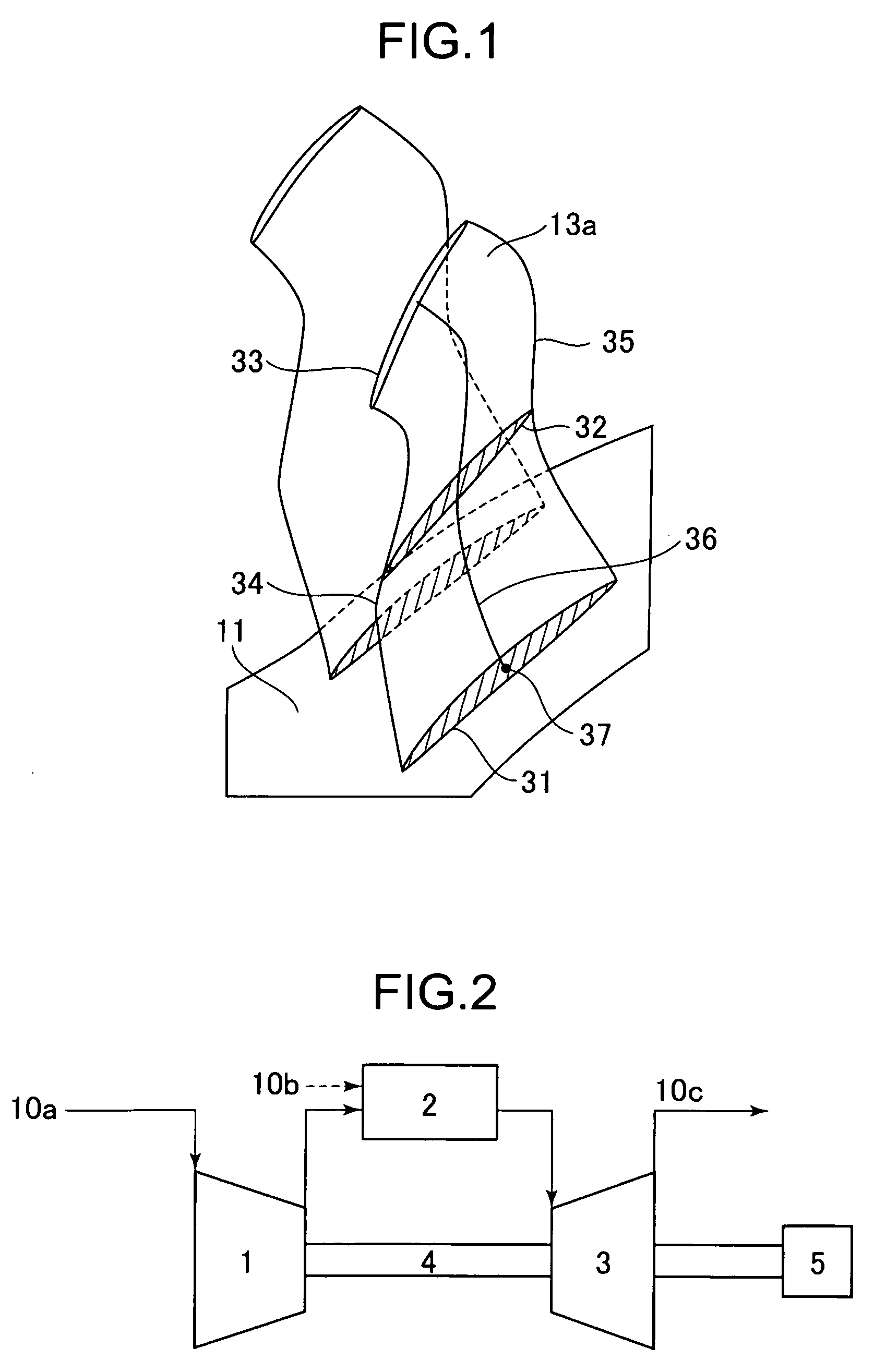
High lift transonic turbine blade
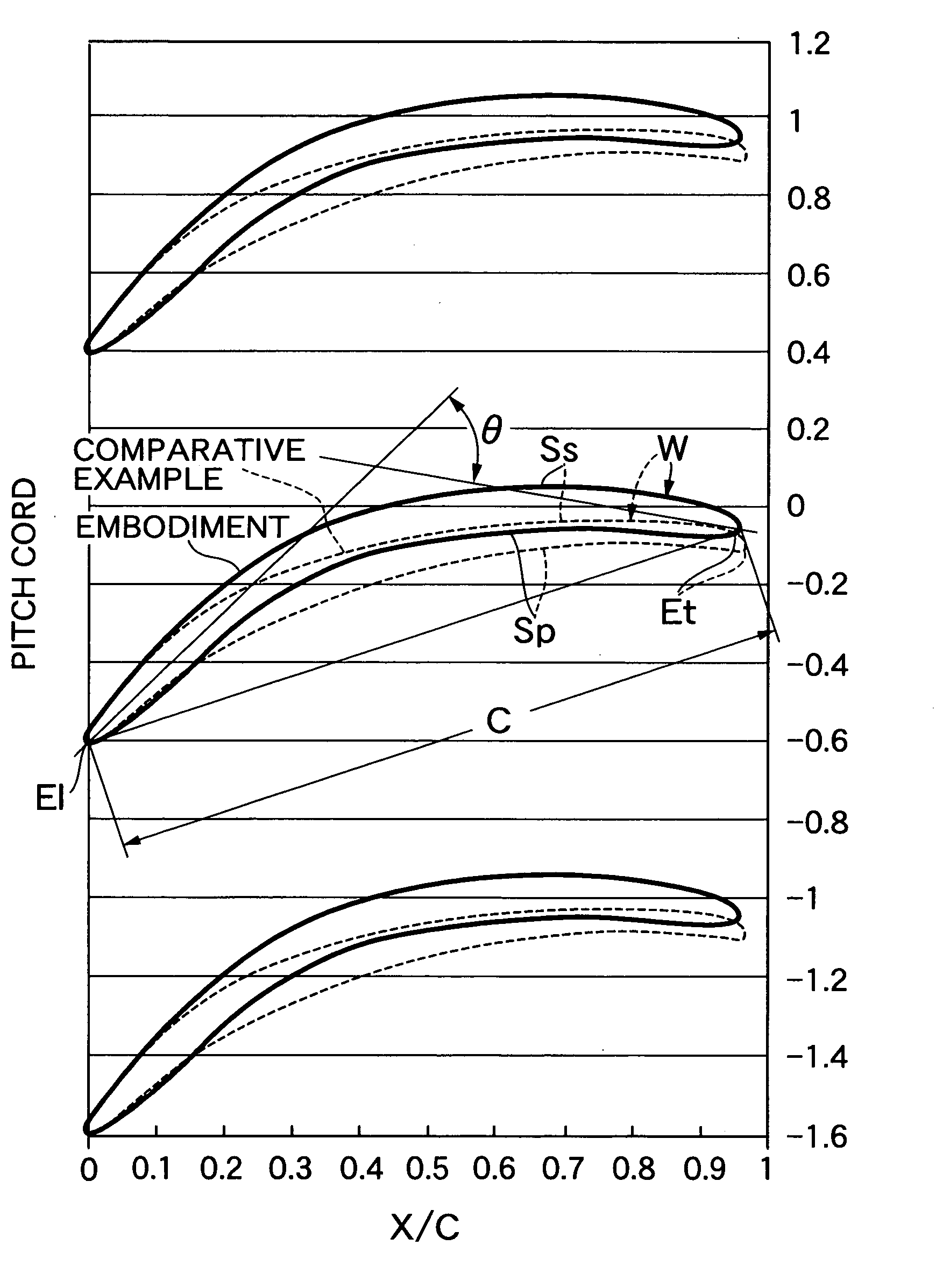
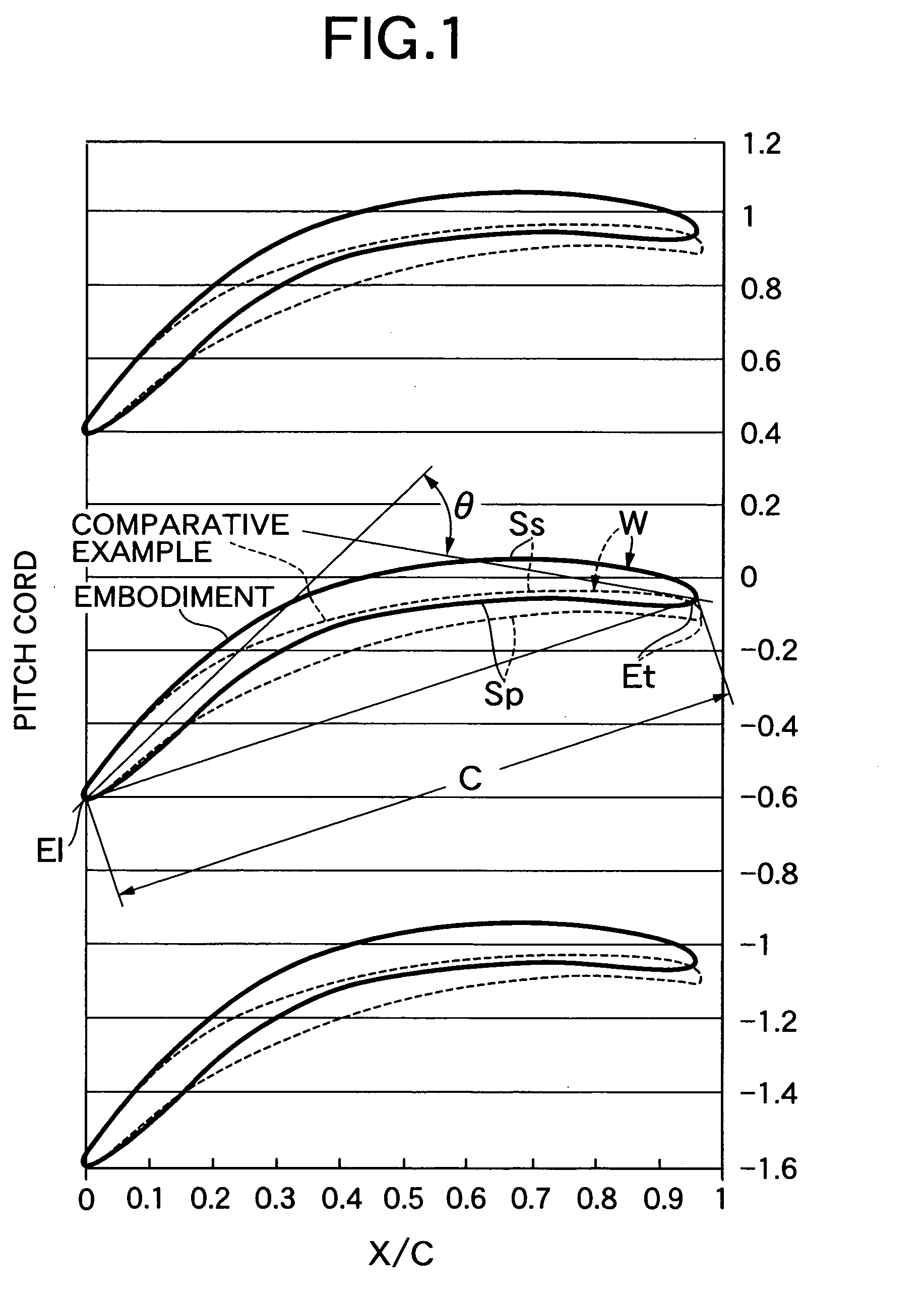
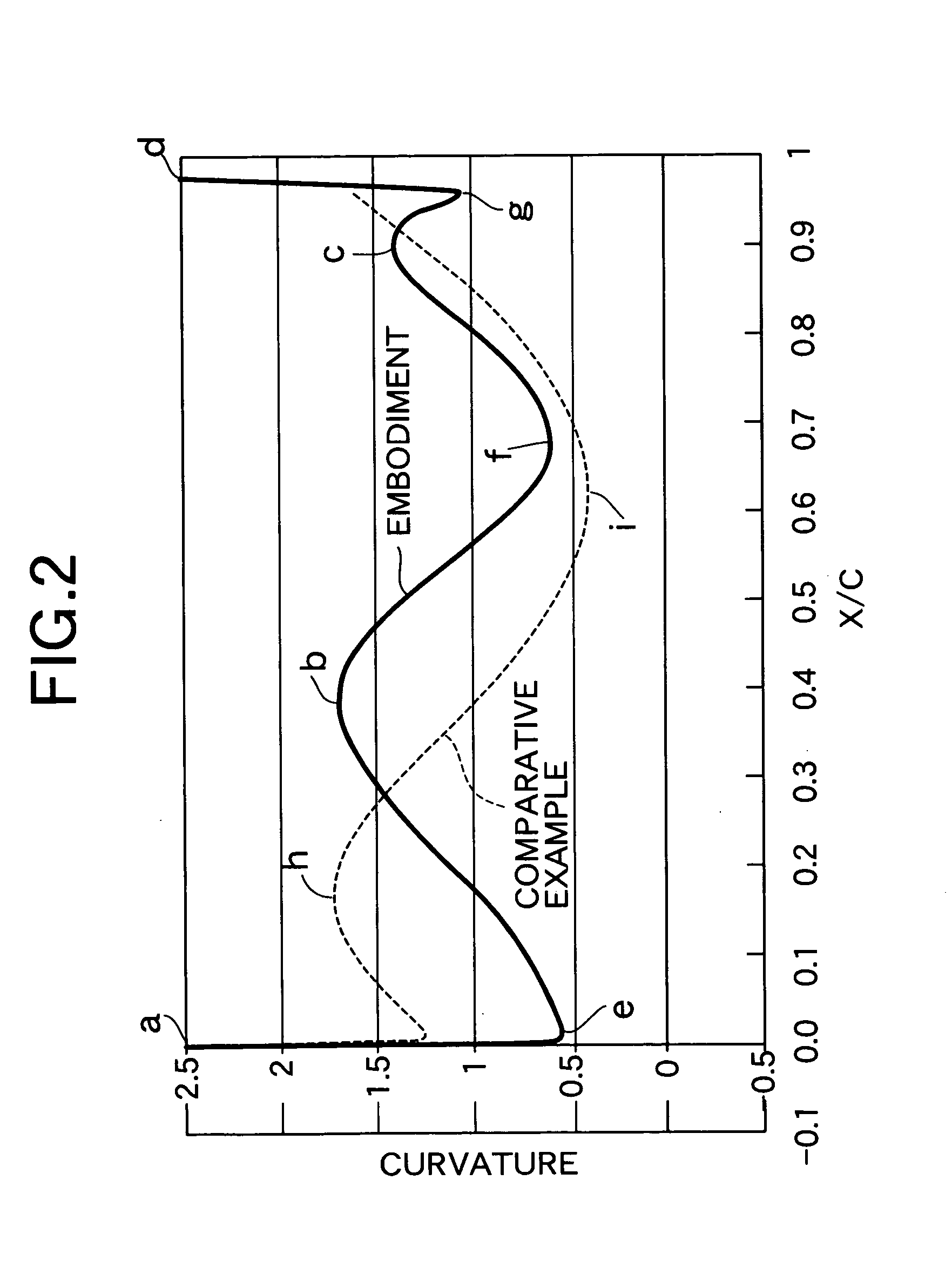
A turbine blade system including a blade airfoil having an airfoil shape with the blade airfoil having a nominal profile substantially in accordance with normalized Cartesian coordinate values Z set forth in a table 1 below and which values are dimensionless values that are convertible to corresponding absolute distance values that define nominal airfoil profile sections and which, when joined smoothly with adjacent ones thereof, form a complete nominal airfoil shape that is substantially matched by the airfoil shape of the blade airfoil. This blade airfoil can be supported on a ring platform having a support surface with a support surface shape in the vicinity of the location at which that blade airfoil is supported thereon formed in a similar manner.
Owner:RTX CORP
Method for estimating reverse twisting process of fan blade of gas turbine
InactiveCN102799730AImprove calculation accuracyOptimizing Manufacturing AirfoilsSpecial data processing applicationsThermal stateEngineering
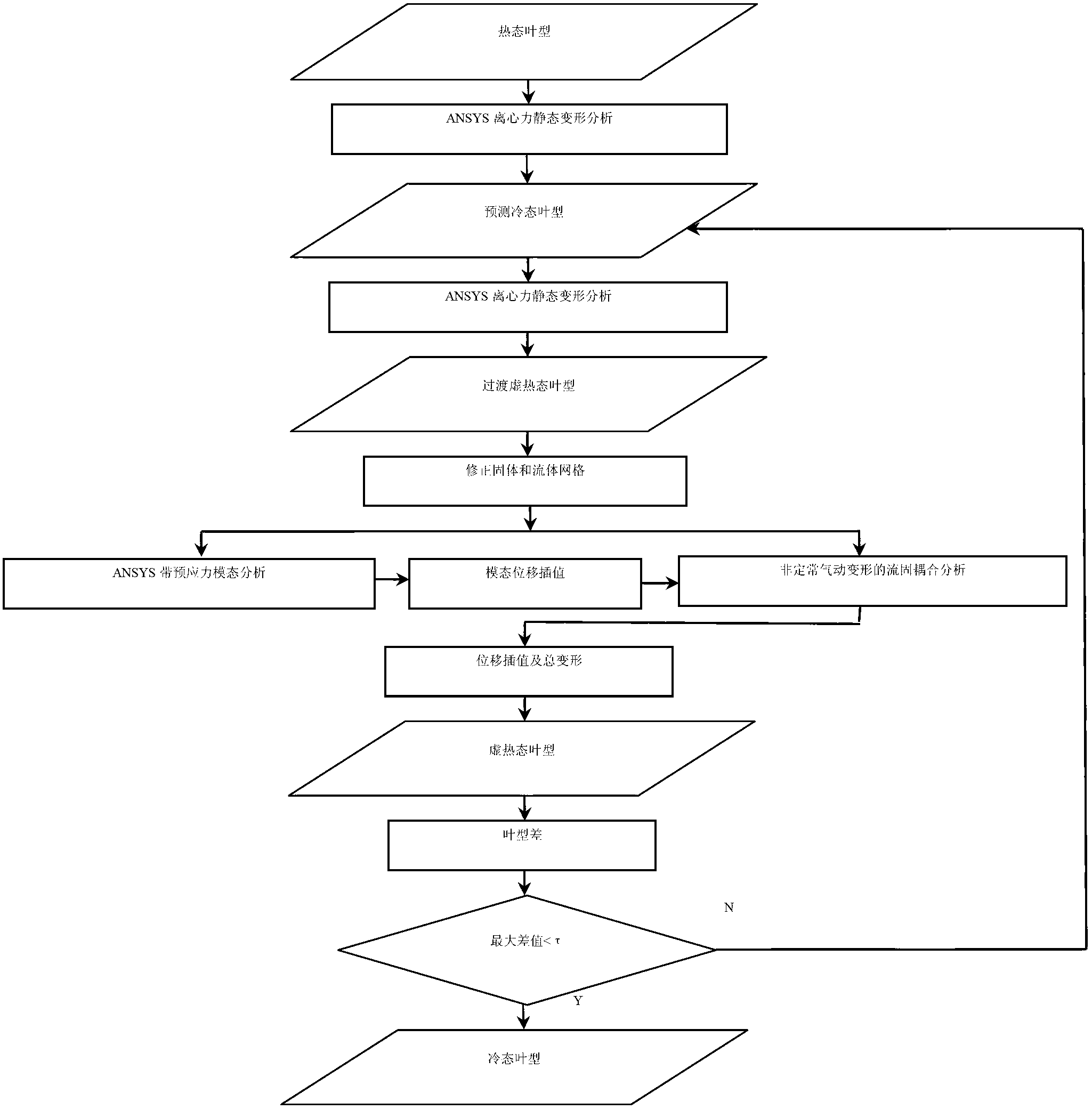
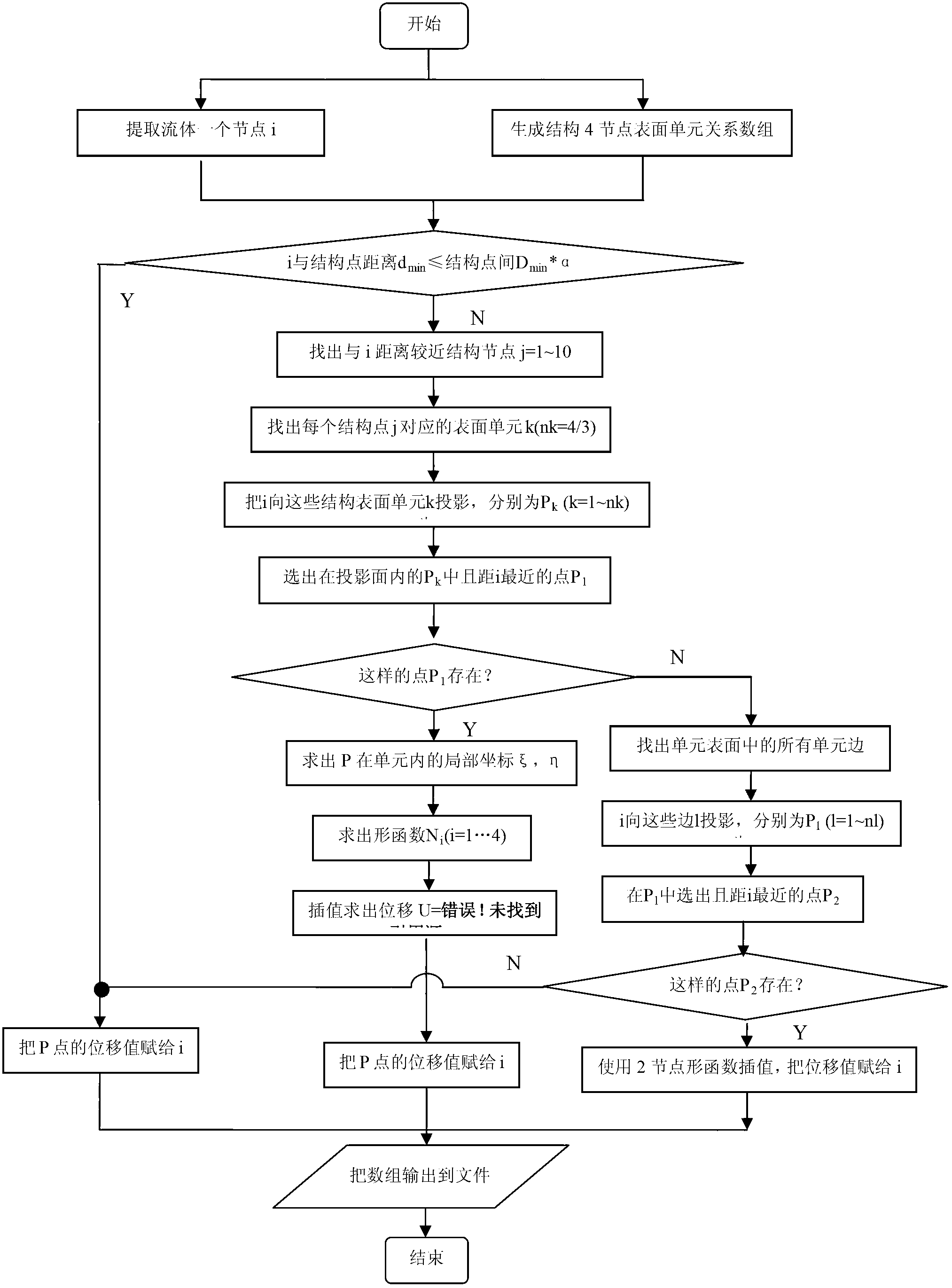
The invention provides a method for estimating a reverse twisting process of a fan blade of a gas turbine, and aims to solve the problem that the conventional gas turbine fan blade reverse twisting design method is incomplete. According to the method, a cold state blade profile can be finally obtained by steps of performing analysis software (ANSYS) centrifugal force static deformation analysis on a thermal state blade profile, forecasting the cold state blade profile, then performing ANSYS centrifugal force static deformation analysis on the forecast cold state blade profile, transitioning a virtual thermal state blade profile, correcting a solid and liquid grid, performing aerodynamic force deformation fluid-solid coupling analysis and the like. The method has great significance for implementing consistency between the forecast thermal state blade profile and an actual working state blade profile of the blade under each pneumatic working condition and researching a method for precisely estimating the reverse twisting process of the fan blade of the gas turbine; and particularly, the method has important engineering application value in developing transonic speed fans with large bypass ratios.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
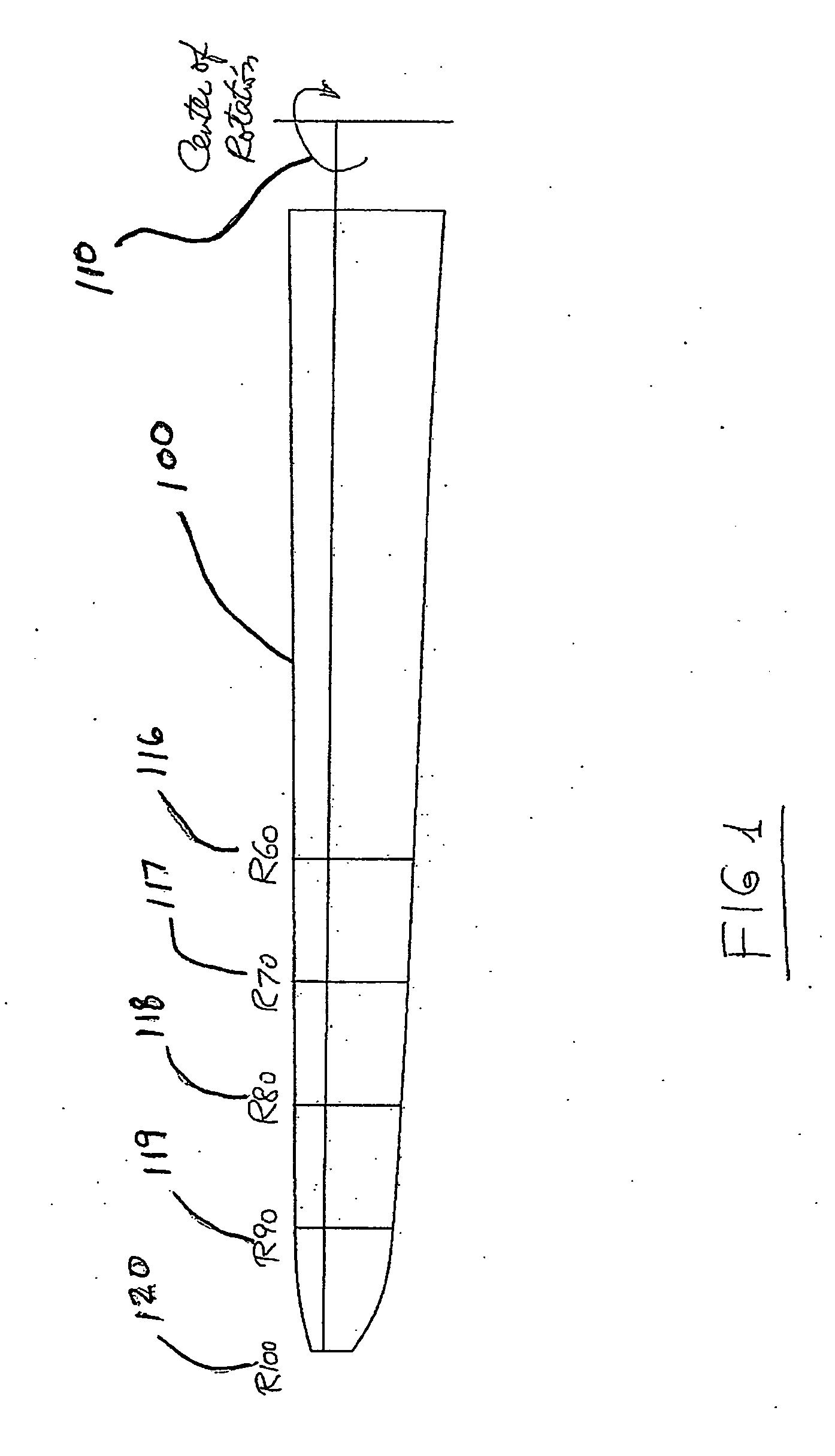
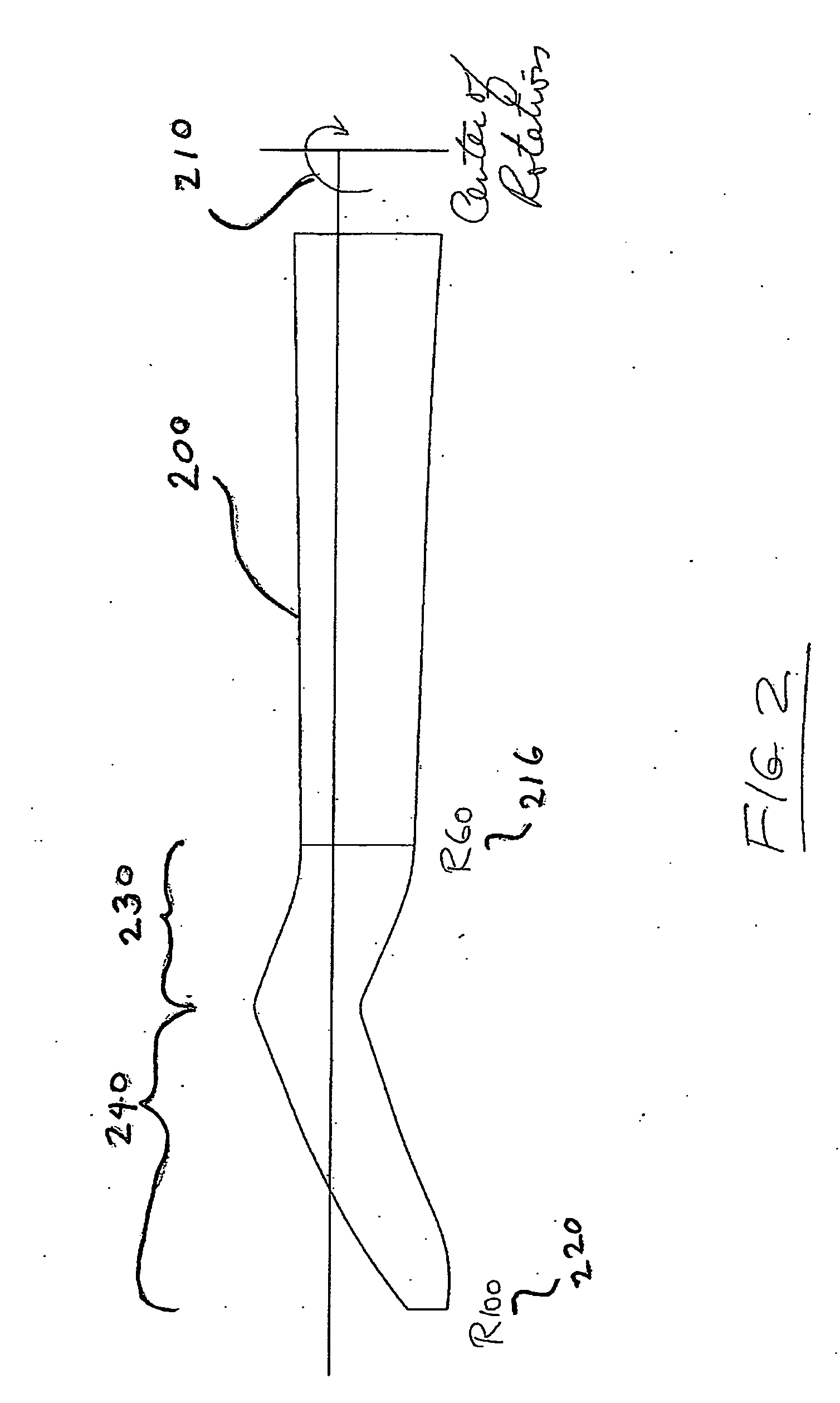
High performance outboard section for rotor blades
ActiveUS20100272576A1Increased maximum take-off weightReduced rotor loadPropellersPump componentsLow noiseRotary wing
Blades for rotorcraft are designed and / or implemented with rotor blades having a swept portion that occupies at least 20-40% of a length of the blade. Forward and aft sweeps are contemplated, with up to 20° or more of sweep. The swept portion preferably has a thickness ration of at least 10-20% at R80, and can have a tapered planform with a relatively outboard section having a smaller chord than a relatively inboard section. Contemplated design methods include optimizing or otherwise designing the rotor blade planform and lift distribution along the blade for efficiency in various flight conditions without taking into account the detrimental effects of high Mach numbers, and then using sweep angle, airfoil thickness and transonic airfoil shaping to maintain the lift distribution, low drag and low noise level at real Mach numbers at the various blade stations at the various flight conditions.
Owner:KAREM ABE
High lift transonic turbine blade
A turbine blade system including a blade airfoil having an airfoil shape with the blade airfoil having a nominal profile substantially in accordance with normalized Cartesian coordinate values Z set forth in a table 1 below and which values are dimensionless values that are convertible to corresponding absolute distance values that define nominal airfoil profile sections and which, when joined smoothly with adjacent ones thereof, form a complete nominal airfoil shape that is substantially matched by the airfoil shape of the blade airfoil. This blade airfoil can be supported on a ring platform having a support surface with a support surface shape in the vicinity of the location at which that blade airfoil is supported thereon formed in a similar manner.
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Shockwave-induced boundary layer bleed
An apparatus and method is provided for improving efficiency of a transonic gas turbine engine compressor by bleeding off a shockwave-induced boundary layer from the gas flow passage of the compressor using an array of bleed holes having a downstream edge aligned with a foot of an oblique shock wave which originates on the leading edge of an adjacent transonic rotor blade tip.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Dynamic bumps for drag reduction at transonic-supersonic speeds
A system for reducing overall drag of a mobile platform includes a surface on which an airflow forms a boundary layer and a generally normal shockwave. The airflow is at a first velocity that is one of transonic and supersonic. An oscillating jet injects and extracts a jet flow through the surface. The jet flow is at a second velocity that is substantially less than the first velocity. A recirculation region is upstream of the normal shockwave and is disposed at least partially in the boundary layer. The recirculation region is established at least by the oscillating jet. A generally oblique wave is established by the recirculation region and weakens the normal shockwave to reduce the overall drag experienced by the surface.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Hybrid transonic-subsonic aerofoils
ActiveUS20060226283A1Improve performanceLoss of performanceAircraft stabilisationWing shapesEngineeringTransonic
Owner:ISRAEL AEROSPACE IND
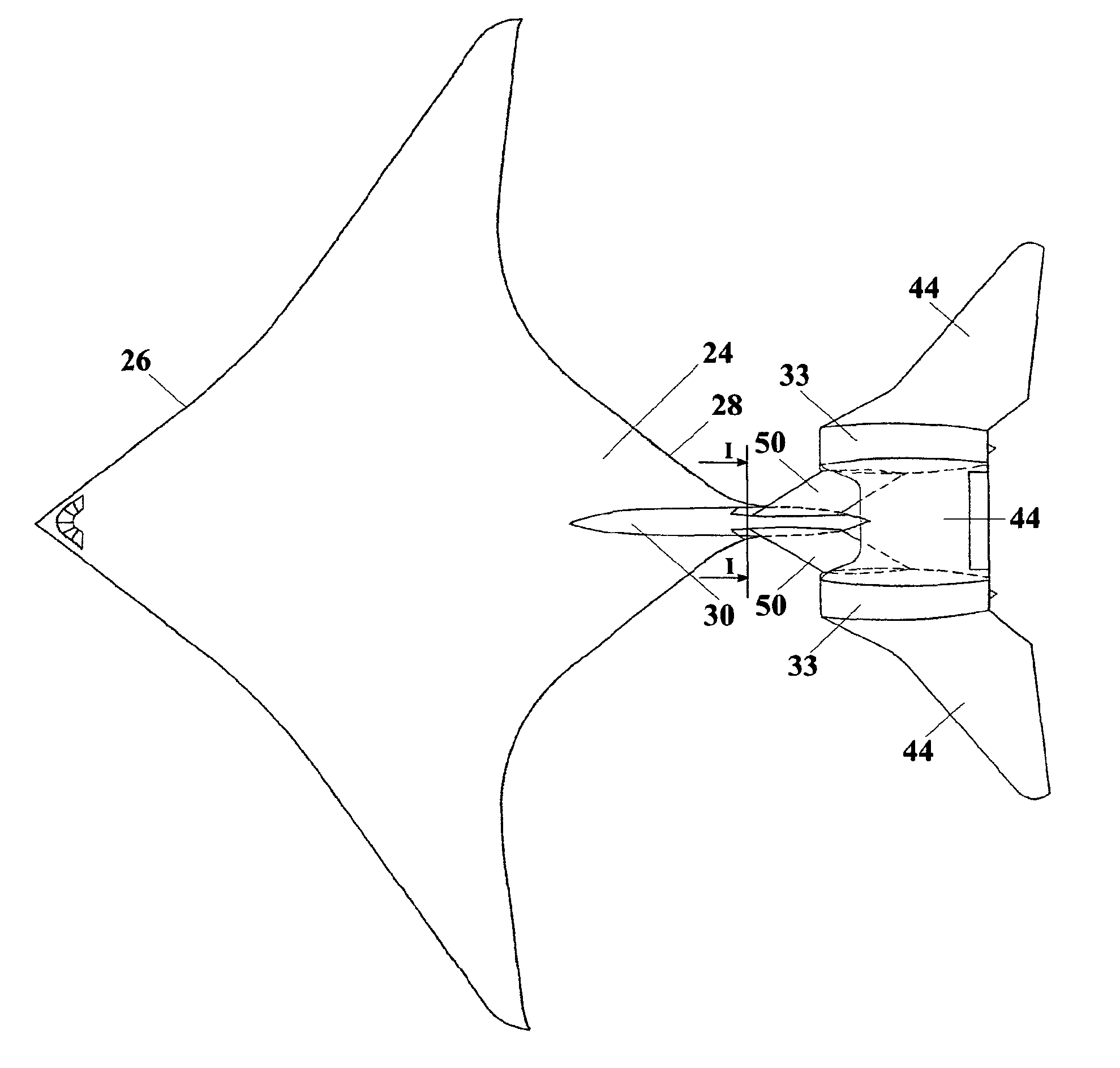
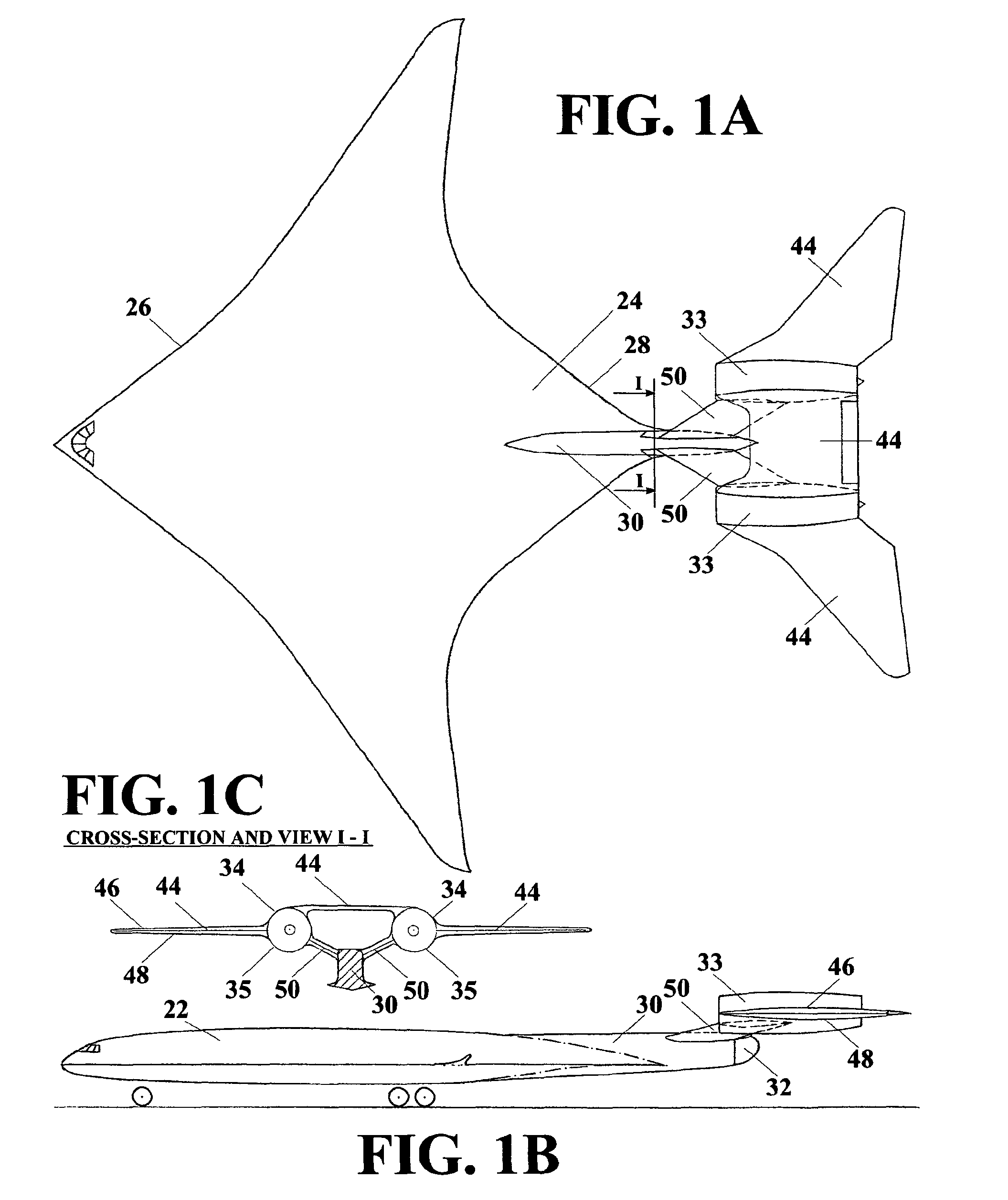
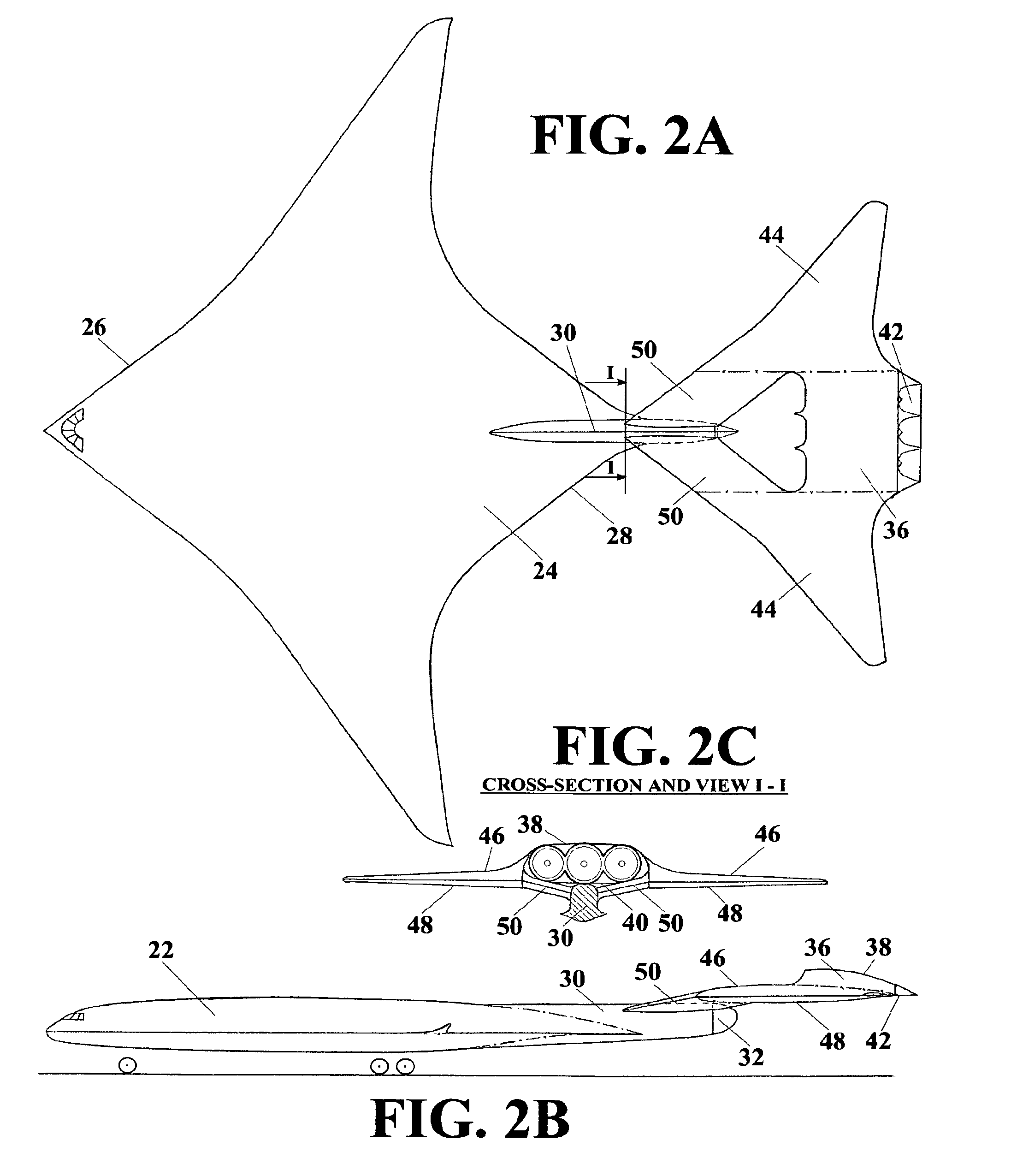
Longitudinal flying wing aircraft
ActiveUS8056852B1Produce significantAircraft stabilisationGas turbine type power plantsLifting capacityHigh lift
The Longitudinal Flying Wing aircraft idea provides for design of large cargo and passenger aircraft in range from low to high subsonic and transonic speed. Such aircraft would have up to twice lower fuel consumption per unit of payload, higher lift capacity, and a significantly longer range, while having a significantly lower level of noise inside passenger cabin and cockpit relative to classical concept aircraft. This idea is further providing for efficient, reliable, and simple flight controls, hence it may be successfully applied for design of all-size, long range, high-lift-capacity unmanned aircraft throughout the entire range of subsonic speeds.
Owner:DIZDAREVIC FARUK +1
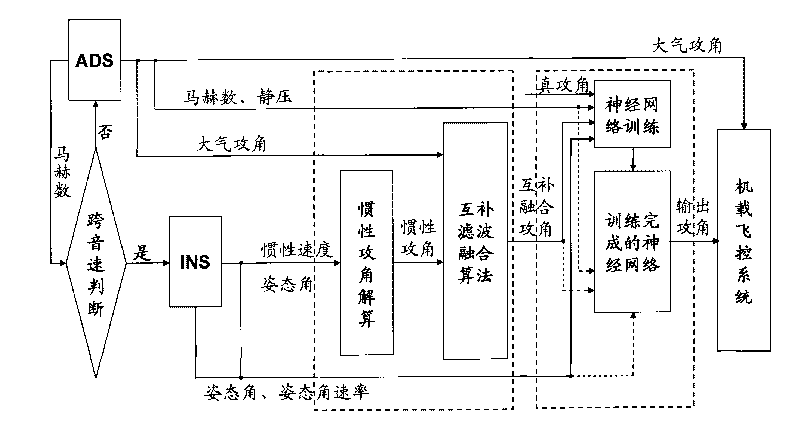
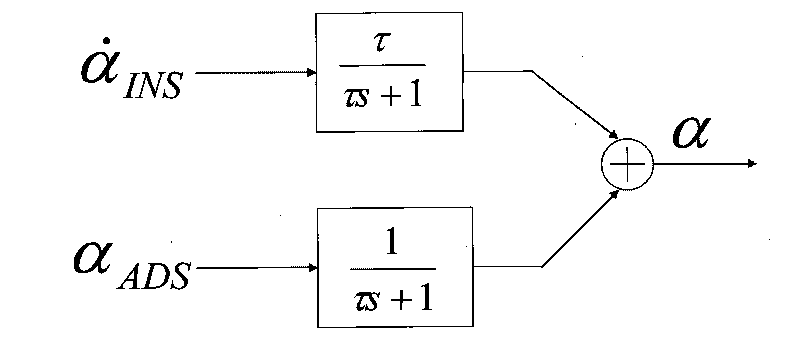
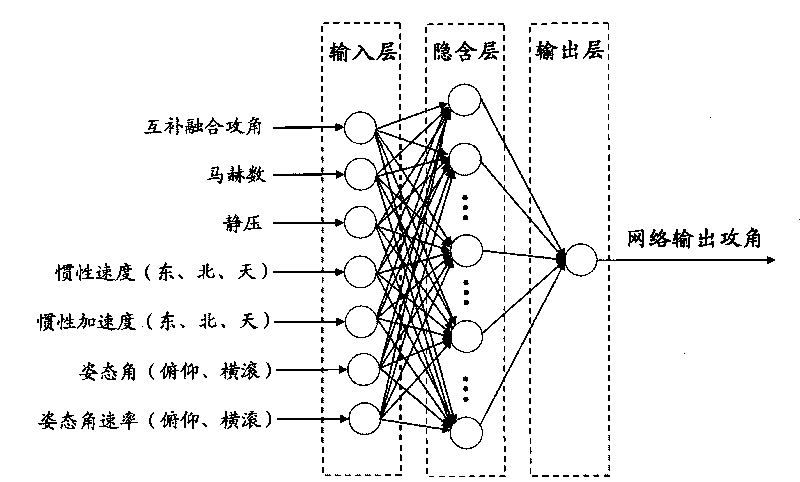
Fusing method of atmospheric attack angle and inertia attack angle in transonic flight stage
InactiveCN101713654AHigh precisionImprove reliabilityNavigation instrumentsShock waveNonlinear approximation
The invention discloses a fusing method of an atmospheric attack angle and an inertia attack angle in transonic flight stage. The fusing method comprises the following steps of: firstly, data acquisition; secondly, transonic flight stage judgment; thirdly, inertia attack angle solution; fourthly, complementary filtering fusing; and fifthly, BP neural network correction. Through a complementary filter, the method inhibits impact wave interference fluctuation of the atmospheric attack angle, and enables complementary fused attack angles to eliminate fierce fluctuation and become stable. Further, by utilizing a favorable learning ability and a non-linear approximation property of the neural network, the method ensures a better anastomosis degree between a real attack angle and a final fused modified attack angle which is treated by the neural network, and enables whole precision and reliability of the attack angle to be improved further. By replacing a primary atmospheric attack angle in the transonic flight stage with the fused modified attack angle, the invention can effectively improve whole precision of the attack angle during flight, and provides a beneficial foundation of accurate navigation and flight control.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
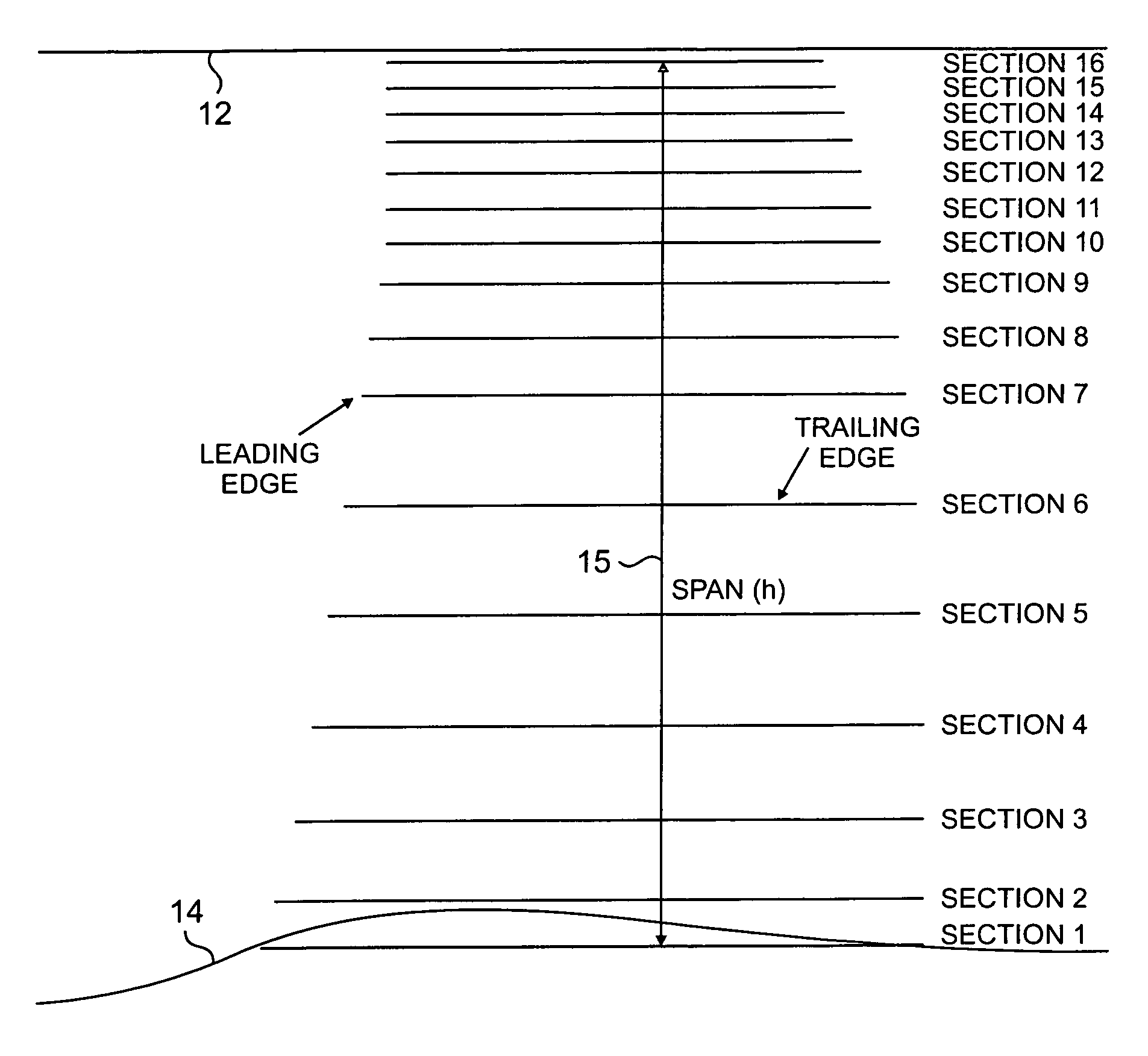
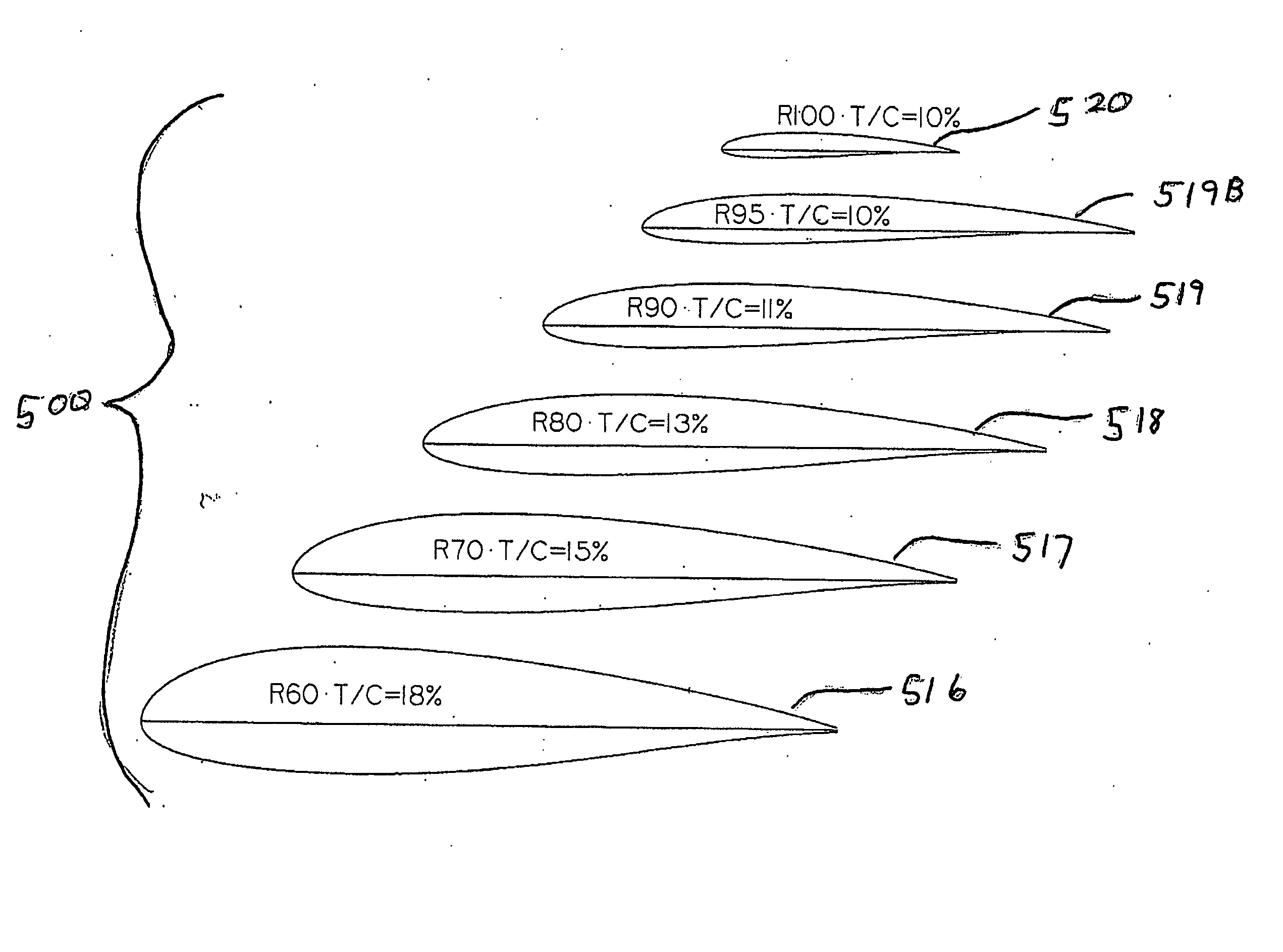
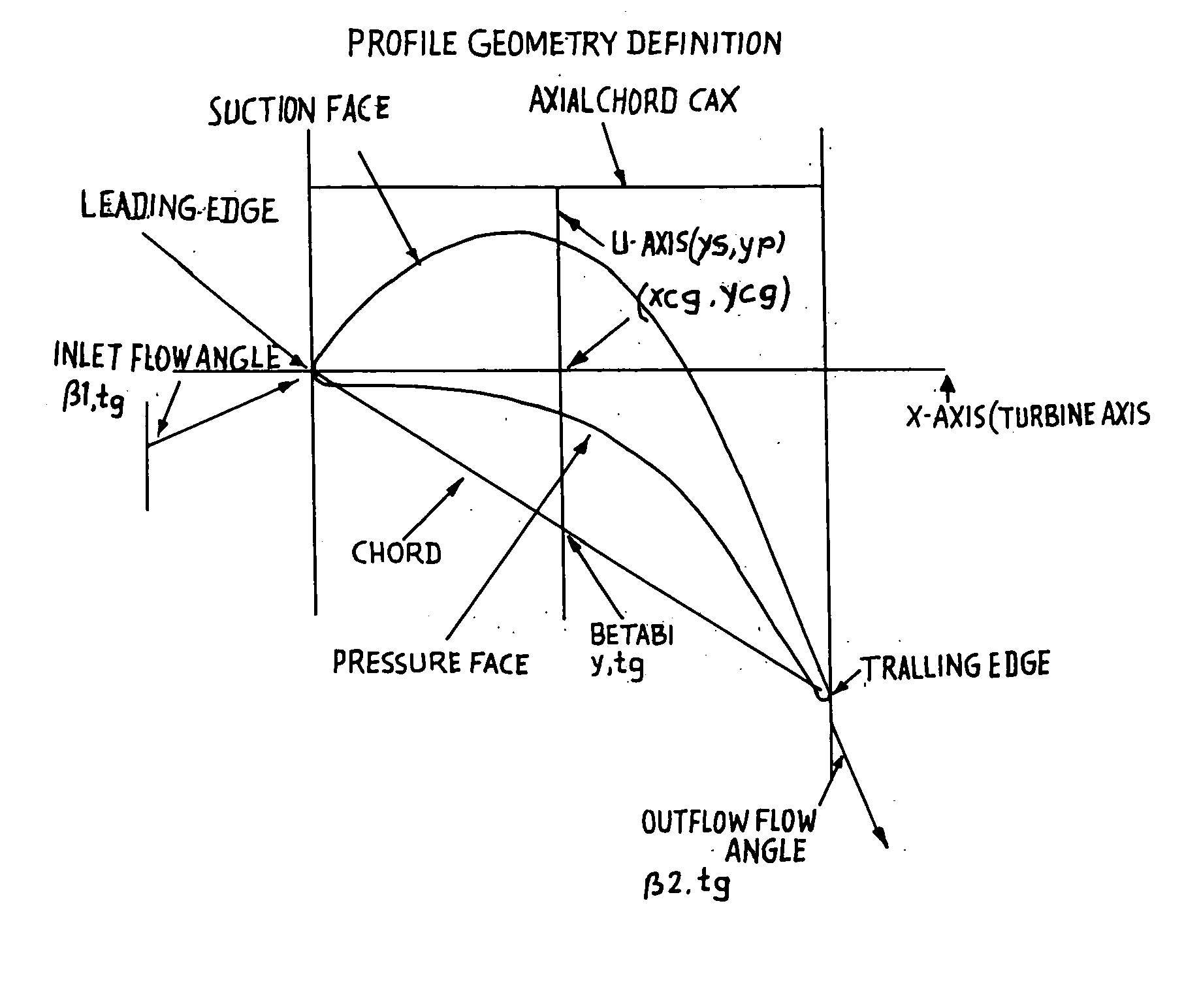
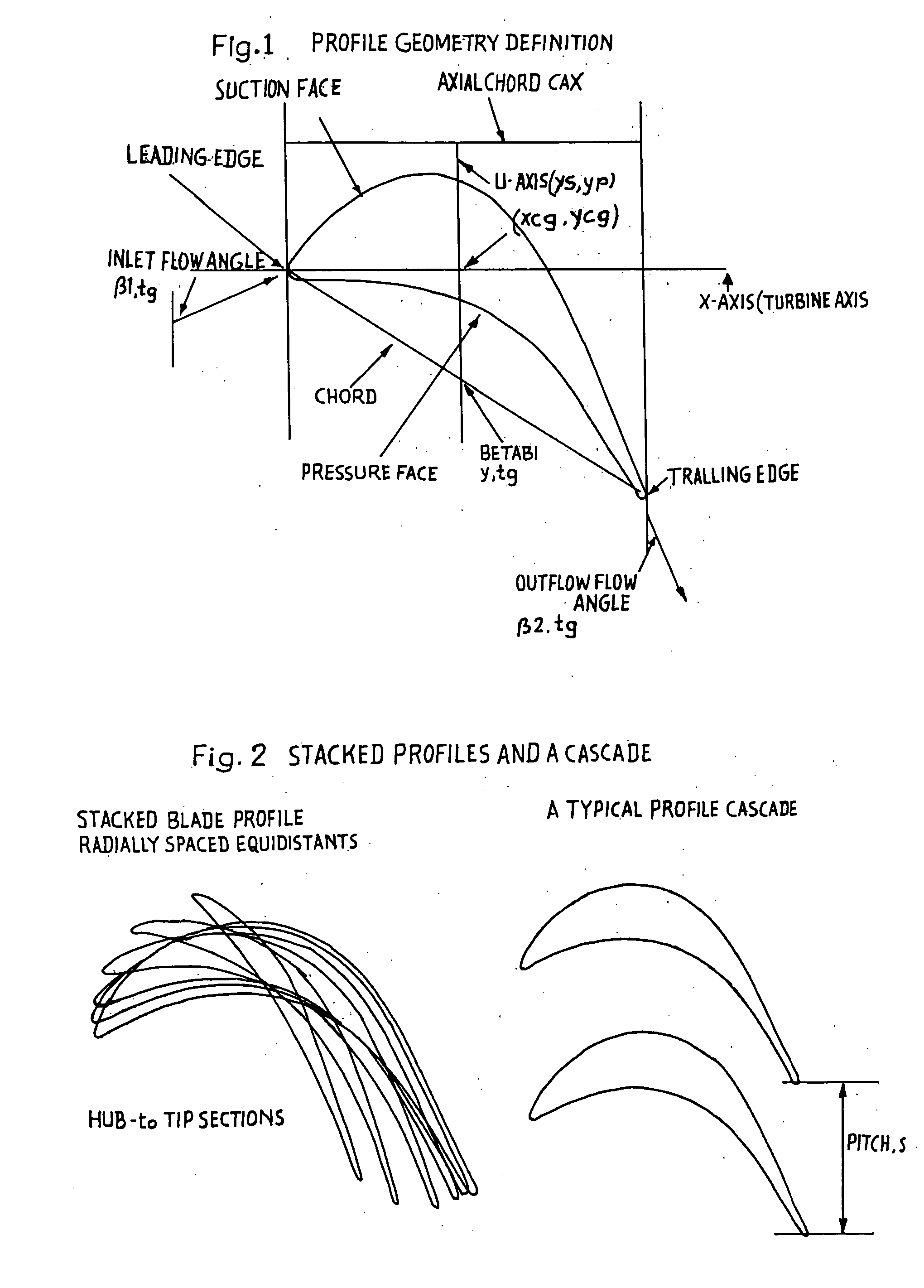
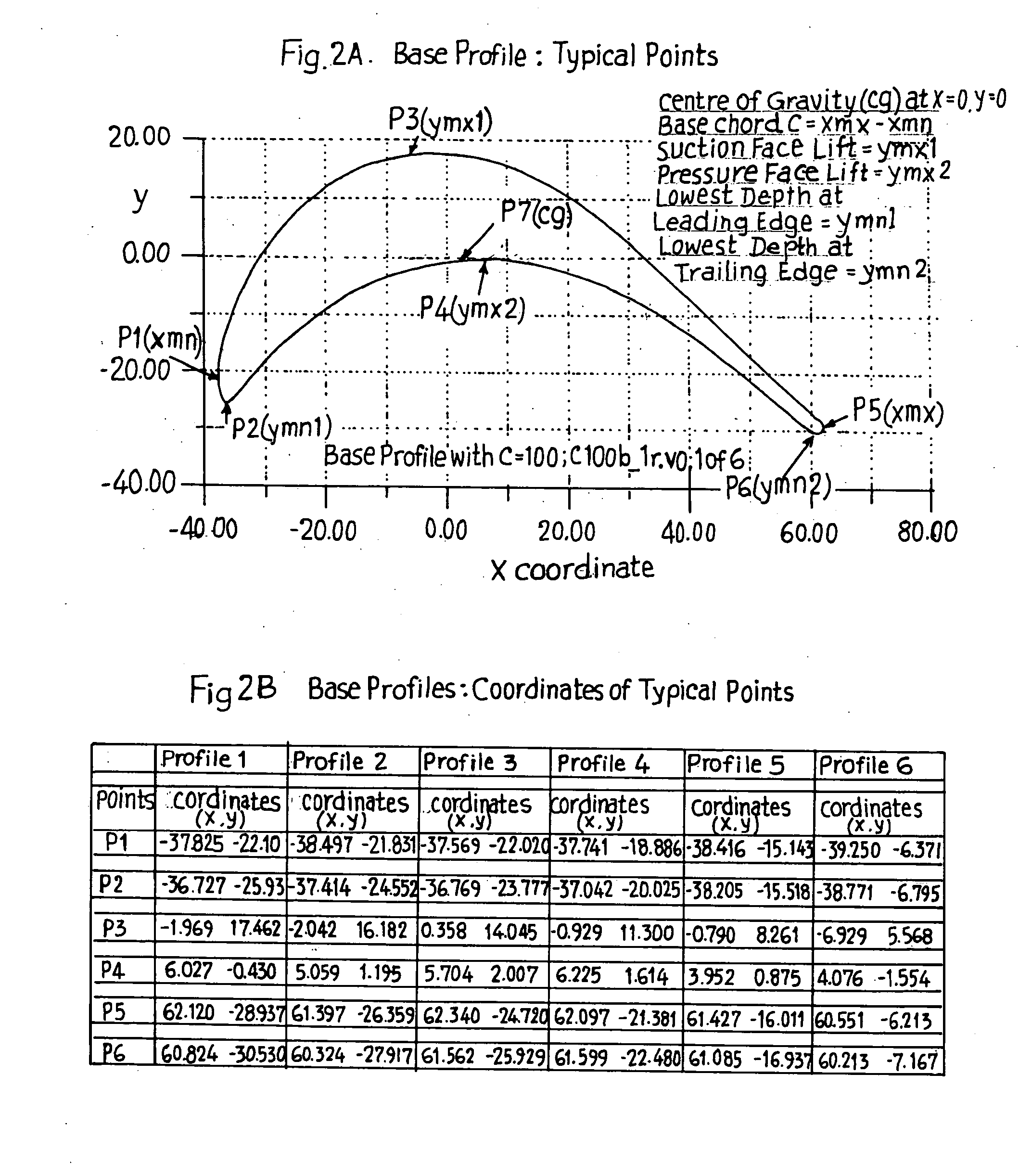
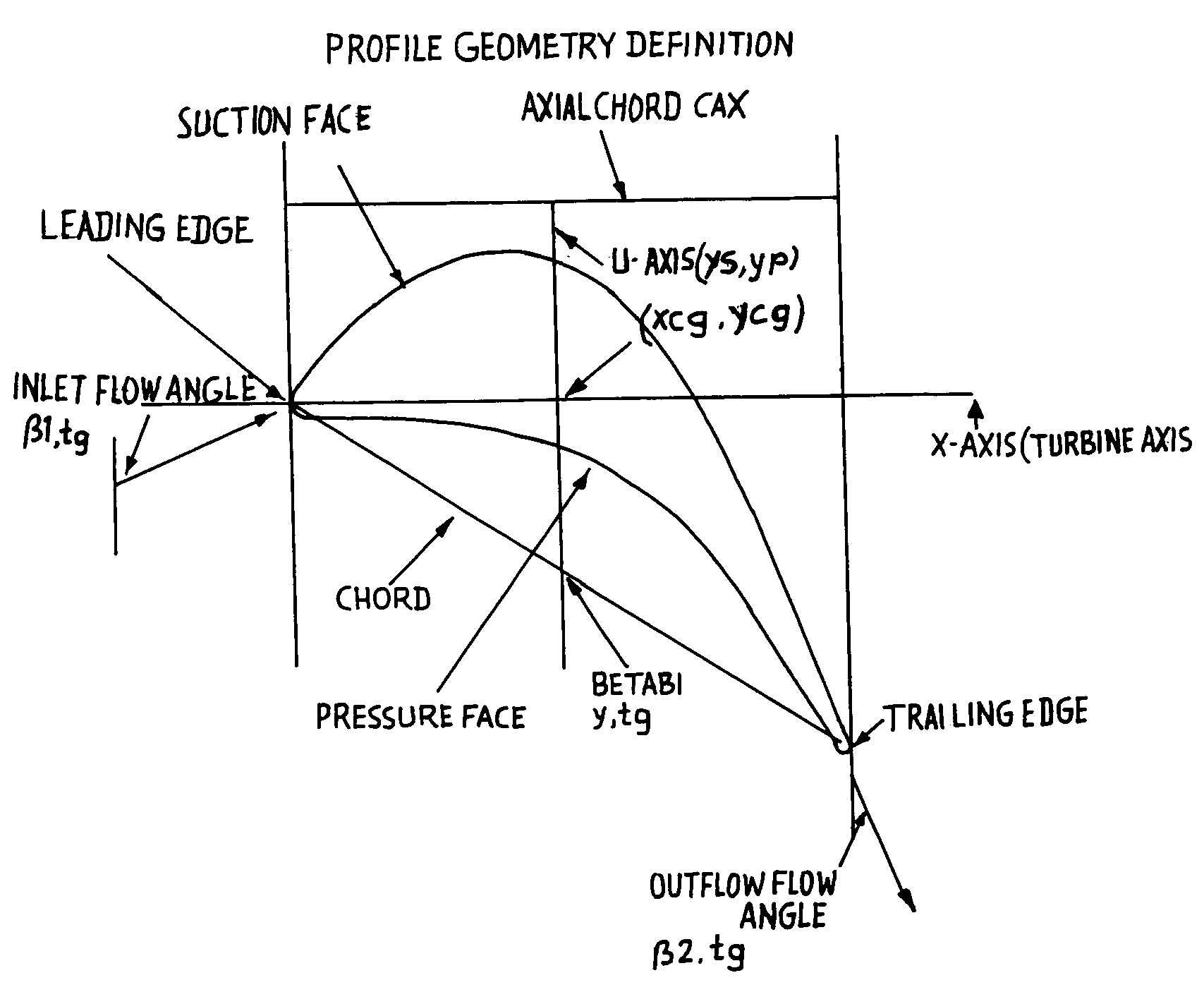
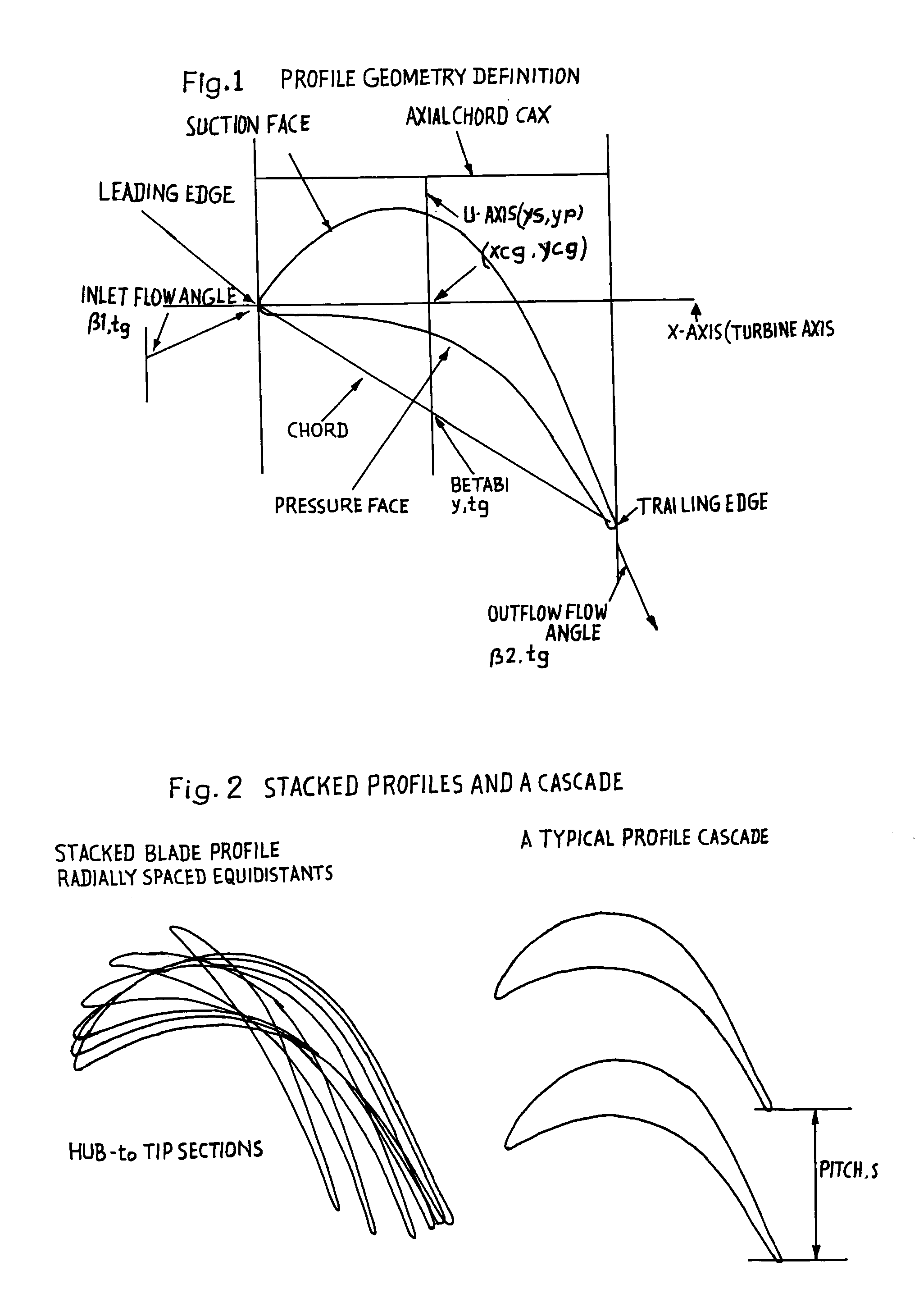
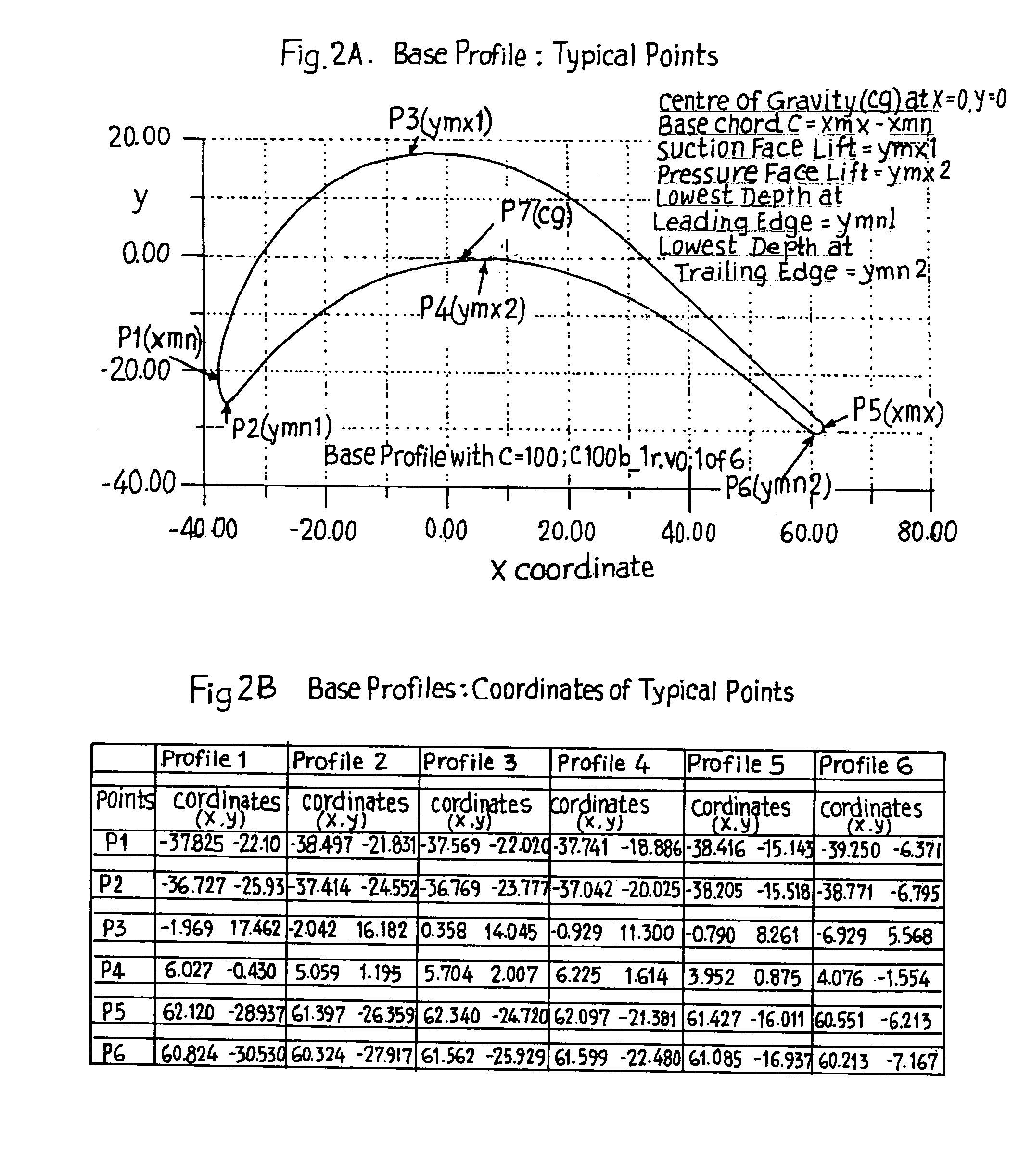
Transonic blade profiles
InactiveUS20050220625A1Taller in heightHigh aspect ratioEngine manufactureOther chemical processesEngineeringNomogram
The present invention relates to the aerodynamic design of moving blades, pertaining to later stages of axial steam turbines where the inlet flow is non-uniform over the blade height. The claim made herein is a set of six invented transonic blade profiles which can be used to develop various type of 3D twisted blades for axial steam turbine. The aerodynamic characteristics of these 6 base profiles are evaluated herein as a function of stagger angle and pitch / chord ratios. The aerodynamic characteristics invented herein is for a group of six base profiles which are to be used for creation of three dimensional blades made of varying cross-sections and twisted over the blade height while ensuring the centers of gravity of these sections lie in a radial line. Each of the blades, sections from hub to tip is twisted differently from desired outlet angle. Thus the nomograms can be used to develop quickly a first level design of a 3D blade making use of 2D base profiles whose performance is shown in the form of nomograms.
Owner:BHARAT HEAVY ELECTRICALS LIMITED
Transonic blade profiles
The present invention relates to the aerodynamic design of moving blades, pertaining to later stages of axial steam turbines where the inlet flow is non-uniform over the blade height. The claim made herein is a set of six invented transonic blade profiles which can be used to develop various type of 3D twisted blades for axial steam turbine. The aerodynamic characteristics of these 6 base profiles are evaluated herein as a function of stagger angle and pitch / chord ratios.
Owner:BHARAT HEAVY ELECTRICALS LIMITED
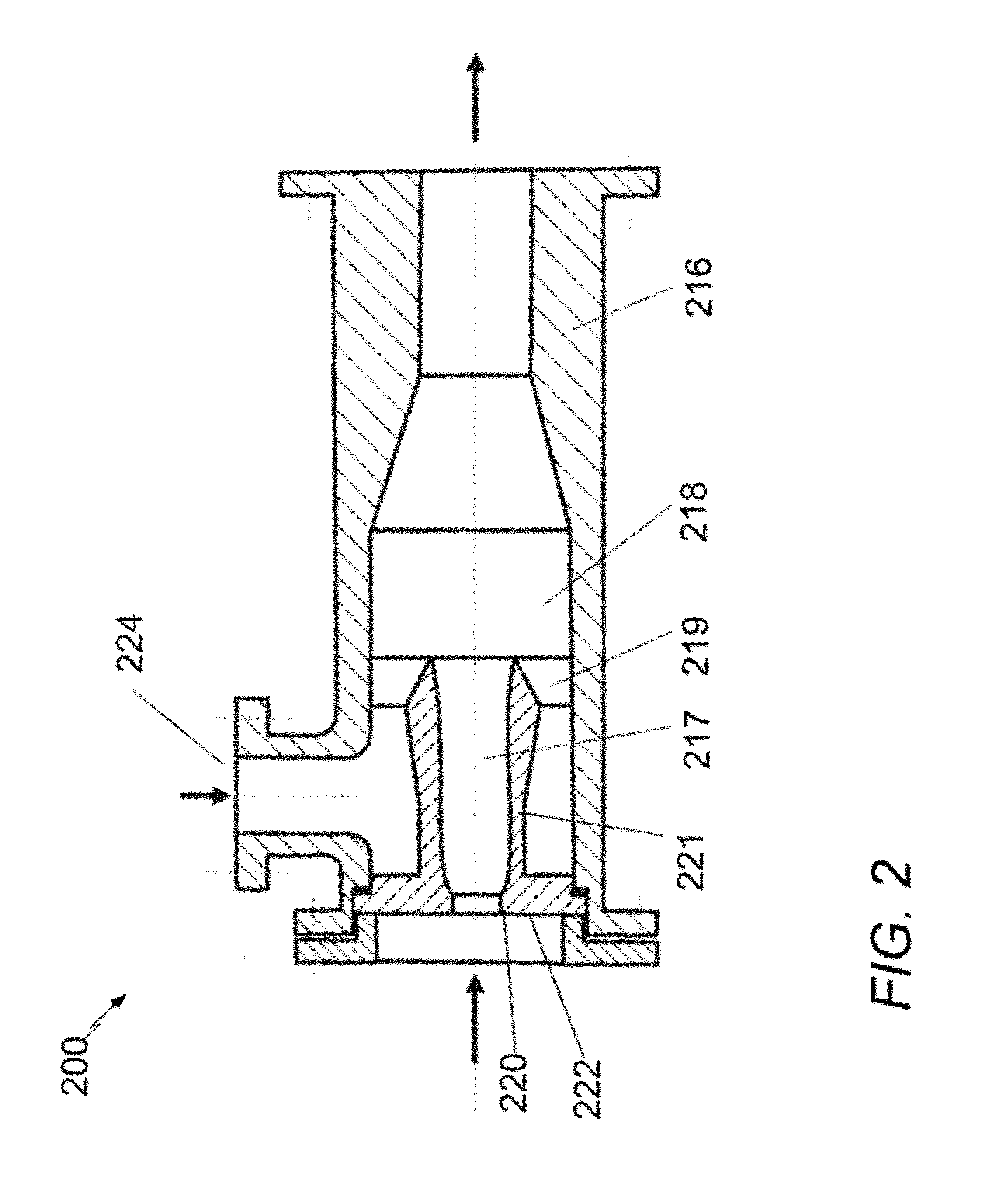
Supersonic/hypersonic aerocraft engine overexpansion nozzle bypass type device
The invention discloses a supersonic / hypersonic aerocraft engine overexpansion nozzle bypass type device. The device comprises a nozzle contracting segment, a nozzle expanding segment, an air-bleeding bypass and a control device for controlling the air-bleeding bypass to be opened and closed, the air-bleeding bypass is an internal flowing passage communicating the nozzle contracting segment and the nozzle expanding segment, and an internal flow field is established by the aid of natural pressure difference between an air inlet of the nozzle contracting segment and an air outlet of the nozzle expanding segment. When the aerocraft works in the transonic and over-expanding state, the bypass is opened, high-pressure air of the nozzle contracting segment is bled to the nozzle expanding segment to form secondary flow injecting effect, and thrust coefficient of the nozzle is increased; and when the aerocraft in the normal working state, the air-bleeding bypass passage is closed, and nozzle design point performances cannot be affected. The supersonic / hypersonic aerocraft engine overexpansion nozzle bypass type device is simple in structure, needs no extra air bleeding sources and is free of additional weight, and thrust performances of the nozzle are improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Apparatus for combustion products utilization and heat generation
InactiveUS20120145050A1Reduce specific fuel consumptionMinimizing carbon dioxideLiquid degasificationUsing liquid separation agentVapor–liquid separatorCombustion
A method and apparatus for heating a fluid and treating a combustion products waste stream includes two or more nozzles discharging into a mixing chamber, and an outlet of the mixing chamber discharging to a gas-liquid separator. A liquid output of the gas-liquid separator may be treated to remove carbonaceous or other impurities. The nozzles may include an annular nozzle, Fisenko nozzle, and / or Laval nozzle arranged in a transonic jet module. A heated input liquid may be accelerated to sonic velocity in a main nozzle, causing boiling due to pressure drop prior to mixing with a combustion product stream in the mixing chamber. Heat may be recovered from a mixture discharged from the mixing chamber. Carbonic, sulfuric, or other combustion impurities may be captured by dissolving in water or other solvent in the transonic jet module and then recovered or otherwise used in a liquid stream from the separator.
Owner:FISONIC HLDG
Transonic blade
ActiveUS8425185B2Reduce various lossesImprove local stressPropellersReaction enginesLeading edgeWorking fluid
A transonic blade is provided that operates in a flow field where flow has a transonic speed or higher in an axial-flow rotating machine and that concurrently achieves a reduction in shock loss and in the local stress of the blade. The transonic blade includes a hub cross-sectional surface joined to a rotating shaft or an outer circumferential side casing of a rotating machine; a tip cross-sectional surface located furthest from the hub cross-sectional surface in a spanwise direction which is a vertical direction of the rotating shaft; a leading edge located on an upstream side; and a trailing edge located on a downstream side. At least a part of a passing working fluid flow has a transonic speed or higher. A portion of a stacking line which is a line connecting together respective gravity centers of cross-sectional surfaces located from the hub cross-sectional surface to the tip cross-sectional surface is located on a downstream side of a stacking center in a flow direction of a working fluid main flow.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Transonic airfoil and axial flow rotary machine
ActiveUS8133012B2Improve efficiencyLow efficiencySupersonic fluid pumpsPropellersEngineeringMechanical engineering
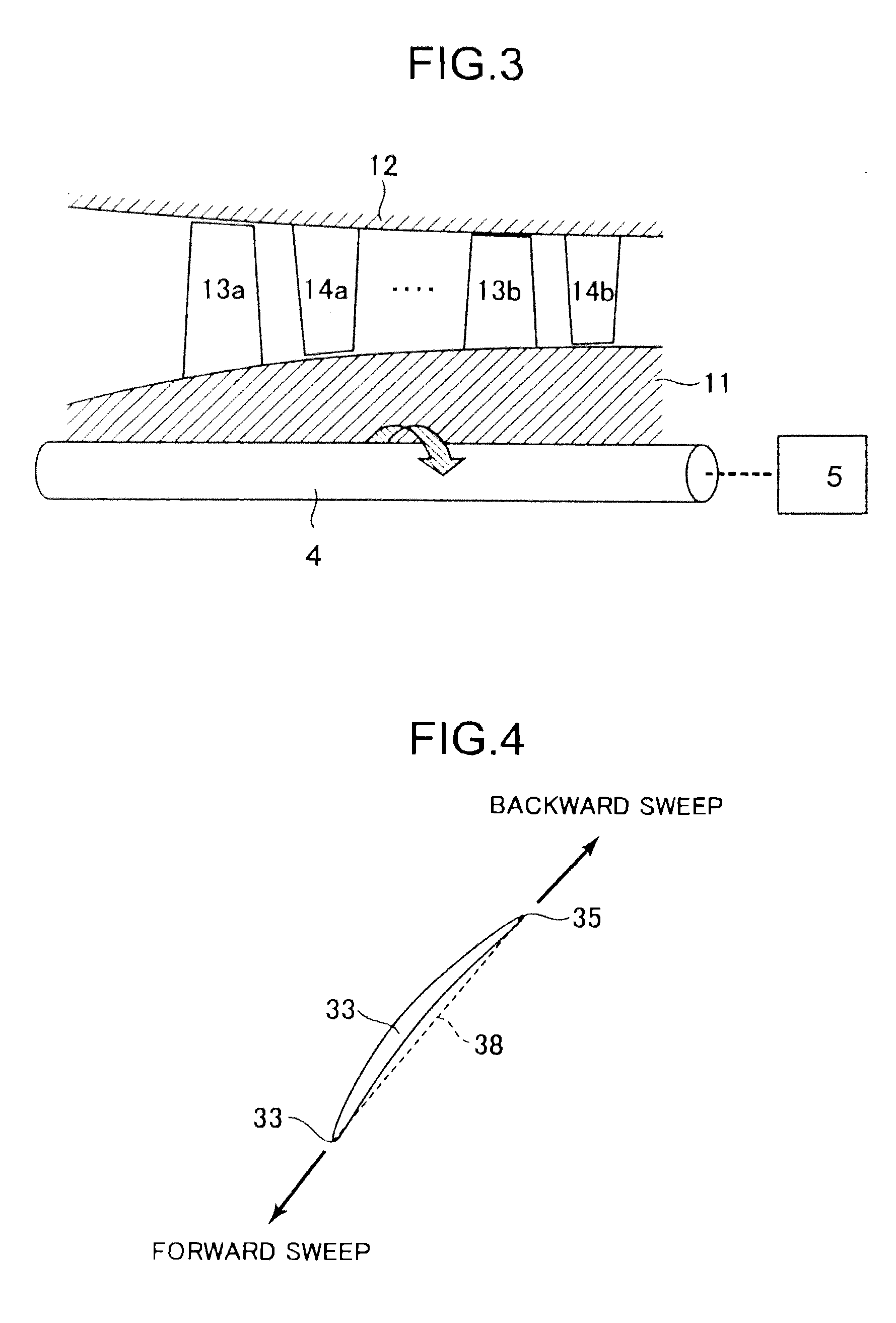
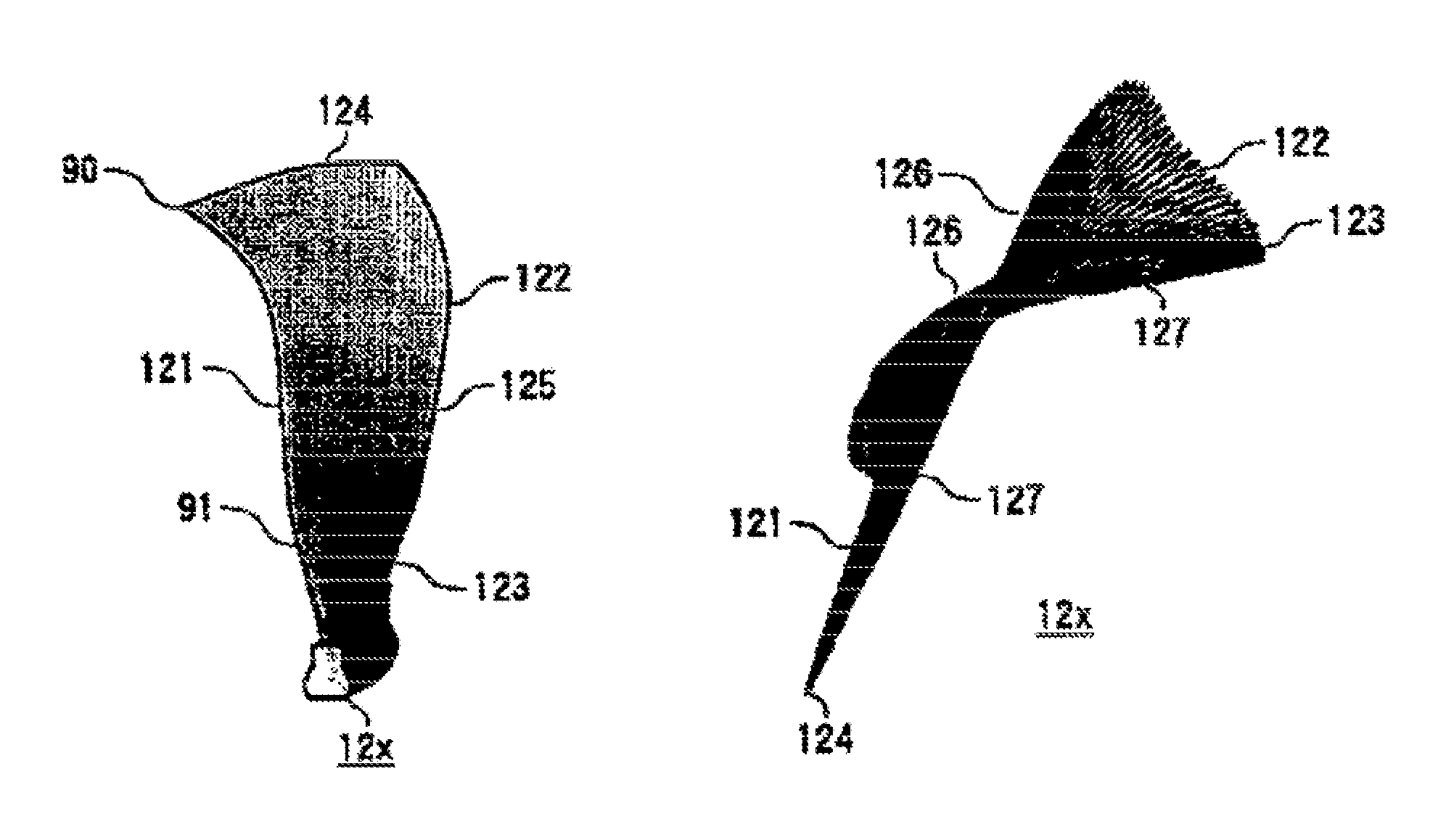
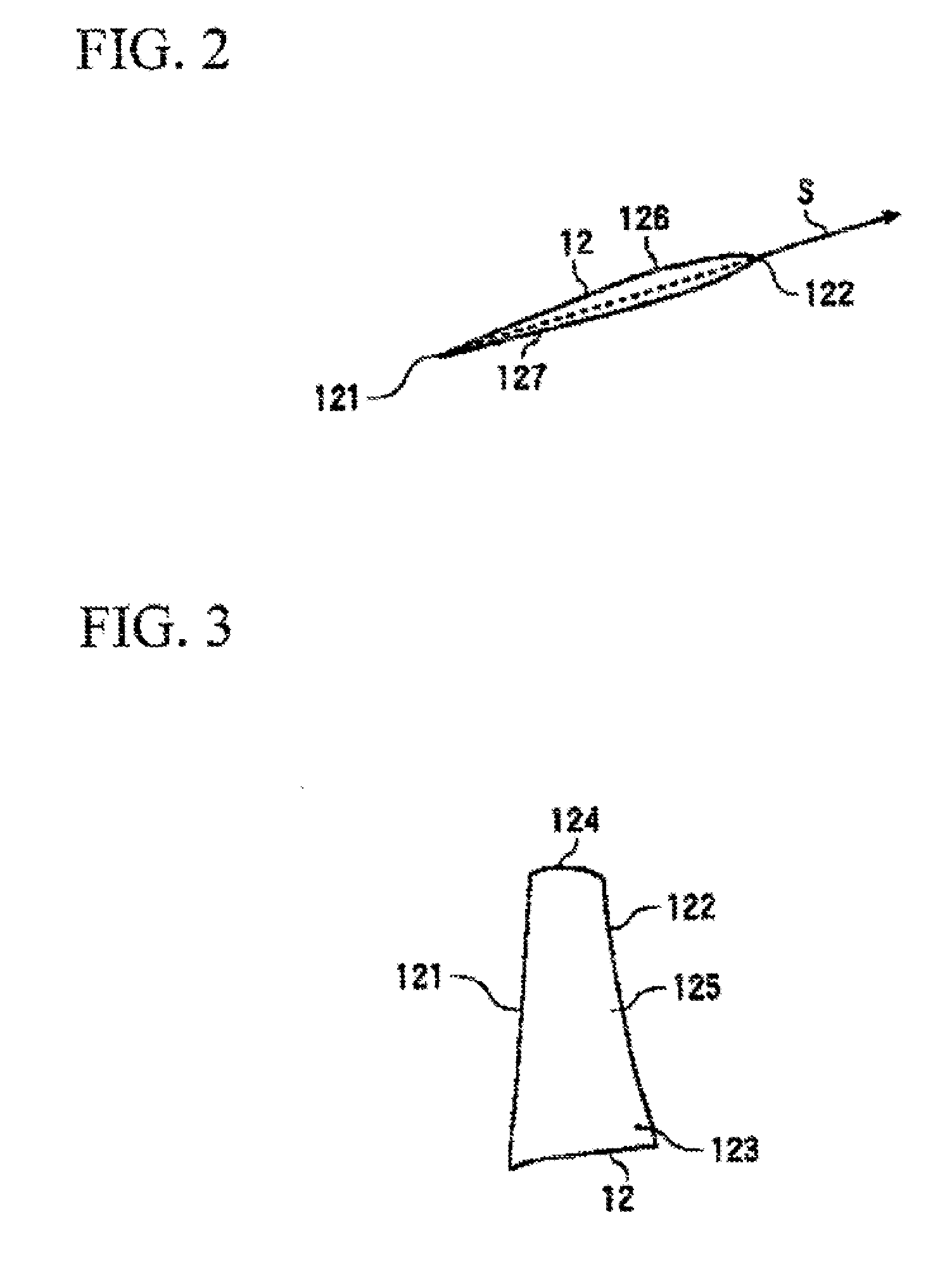
Sectional profiles close to a tip 124 and a part between a midportion 125 and a hub 123 are shifted to the upstream of an operating fluid flow in a sweep direction. Accordingly, an S shape is formed in which the tip 124 and the part between the midportion 125 and the hub 123 protrude. As a result, it is possible reduce various losses due to shook, waves, thereby forming a transonic airfoil having an excellent aerodynamic characteristic.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
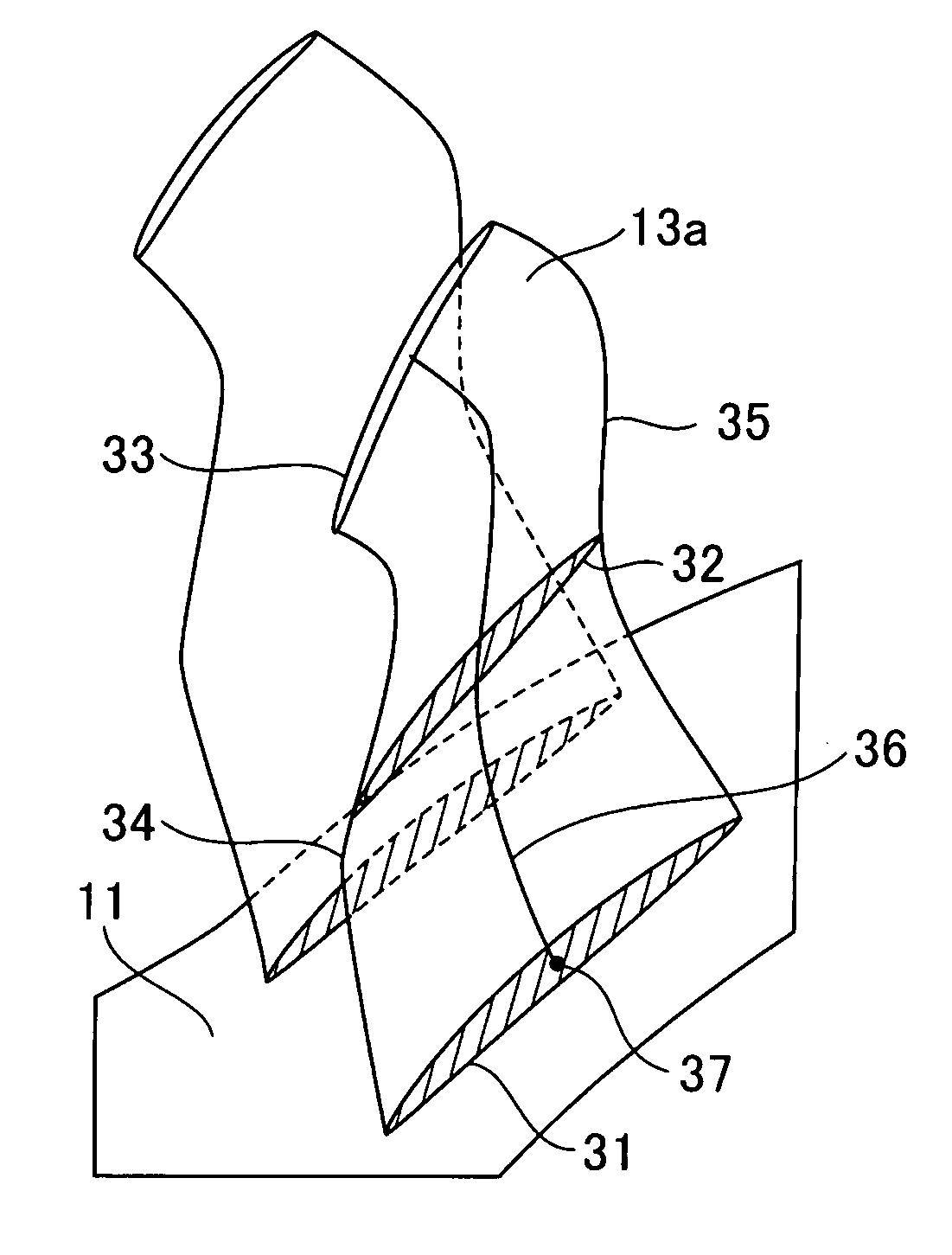
High-turning and high-transonic blade
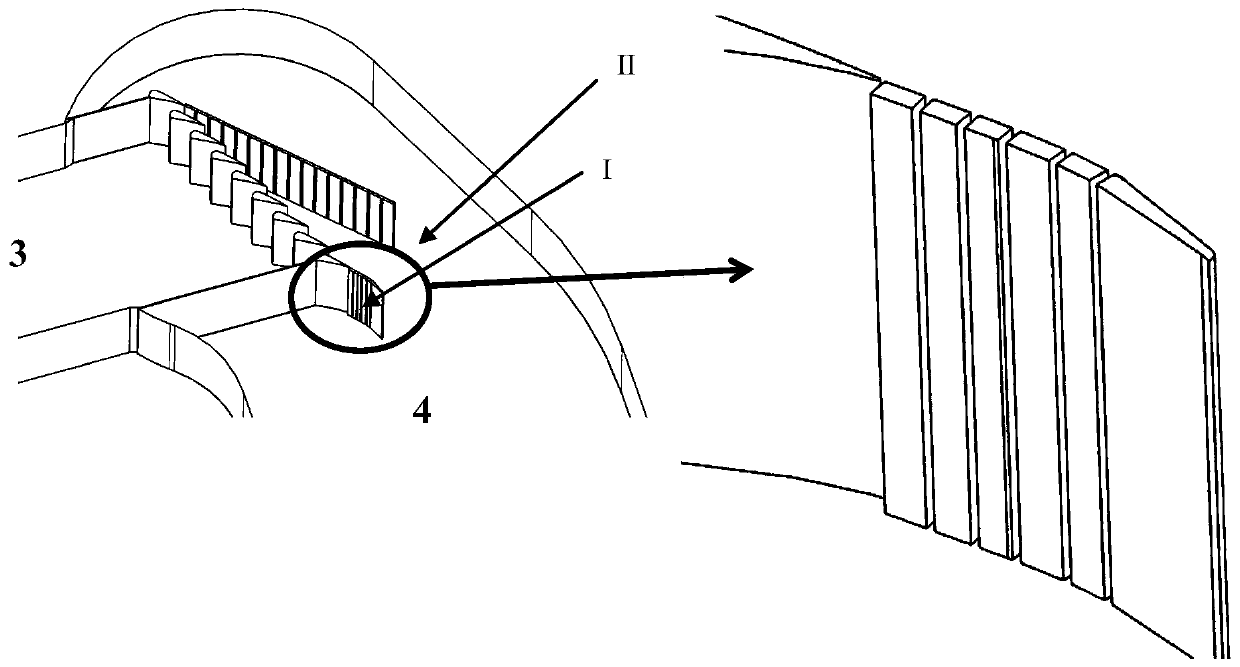
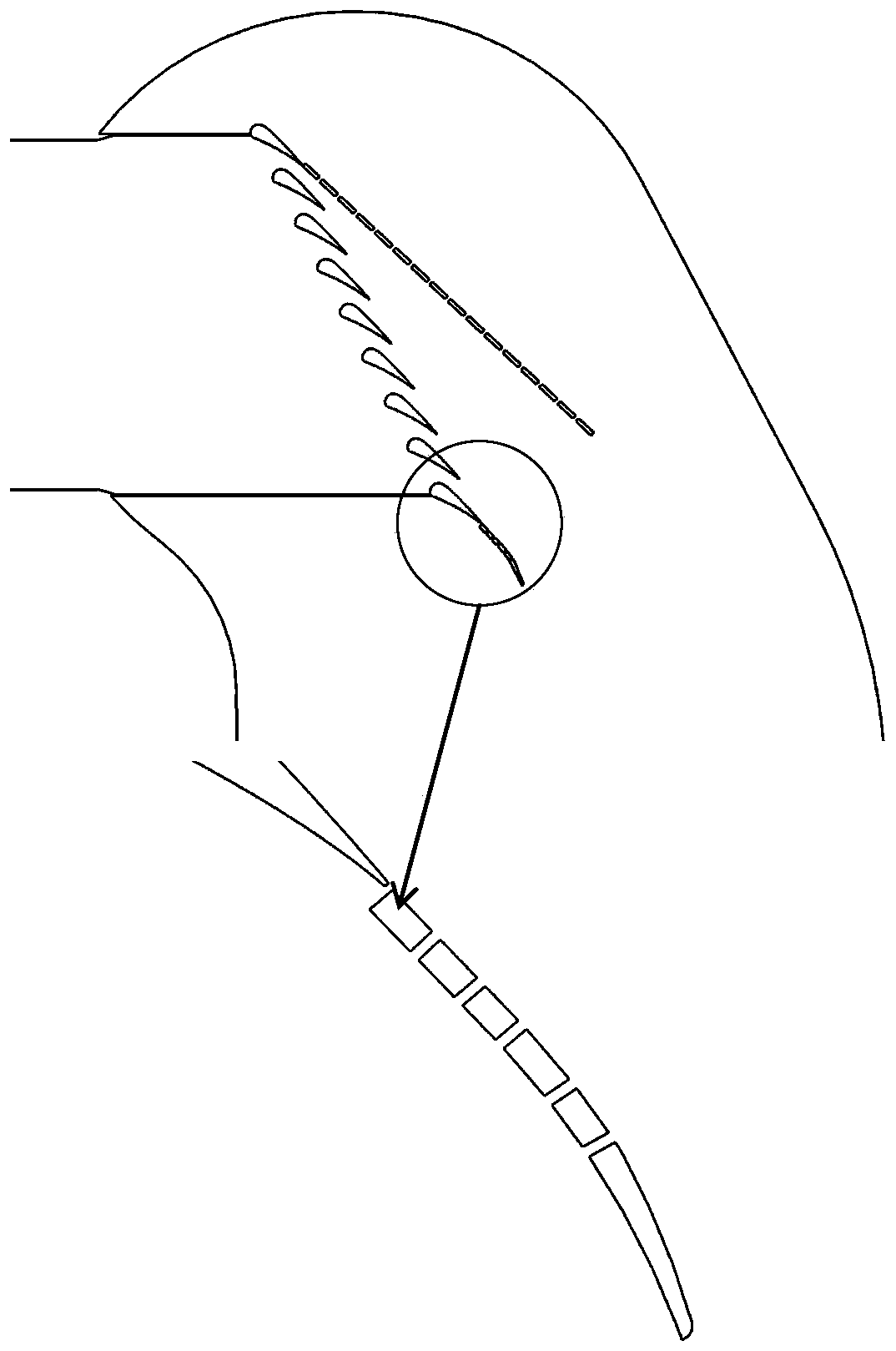
A high-turning and high-transonic blade for use in a blade cascade of an axial-flow compressor, wherein a distribution of flow speed on an extrados at a leading edge of the blade has a supersonic region of a substantially constant flow speed in the rear of a first large value of the flow speed and inside a position corresponding to 15% of a chord length from the leading edge. The supersonic region is established so that a value obtained by the division of a difference between Mach numbers at front and rear ends of the supersonic region by a chord-wise length of the supersonic region is smaller than 1, and the maximum Mach number in the supersonic region is smaller than 1.4. A first large shock wave is positively generated at a position where the flow speed assumes a first maximum value, whereby a second shock wave generated in the supersonic region of the substantially constant flow speed in the rear of such a position can be weakened. Thus, boundary layer separation due to the second shock wave can be suppressed, to thereby remarkably reduce the pressure loss of a following flow on the blade.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
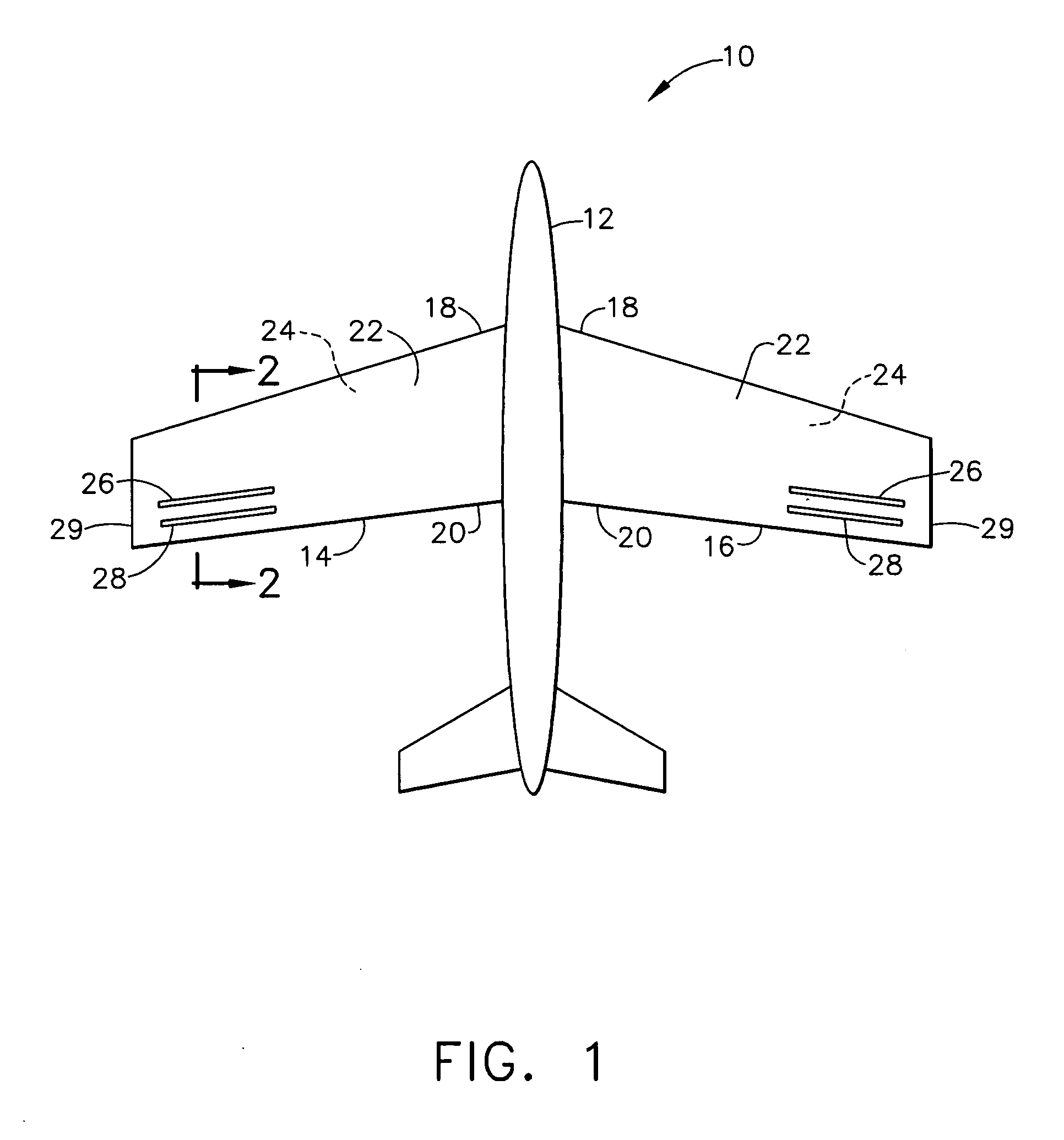
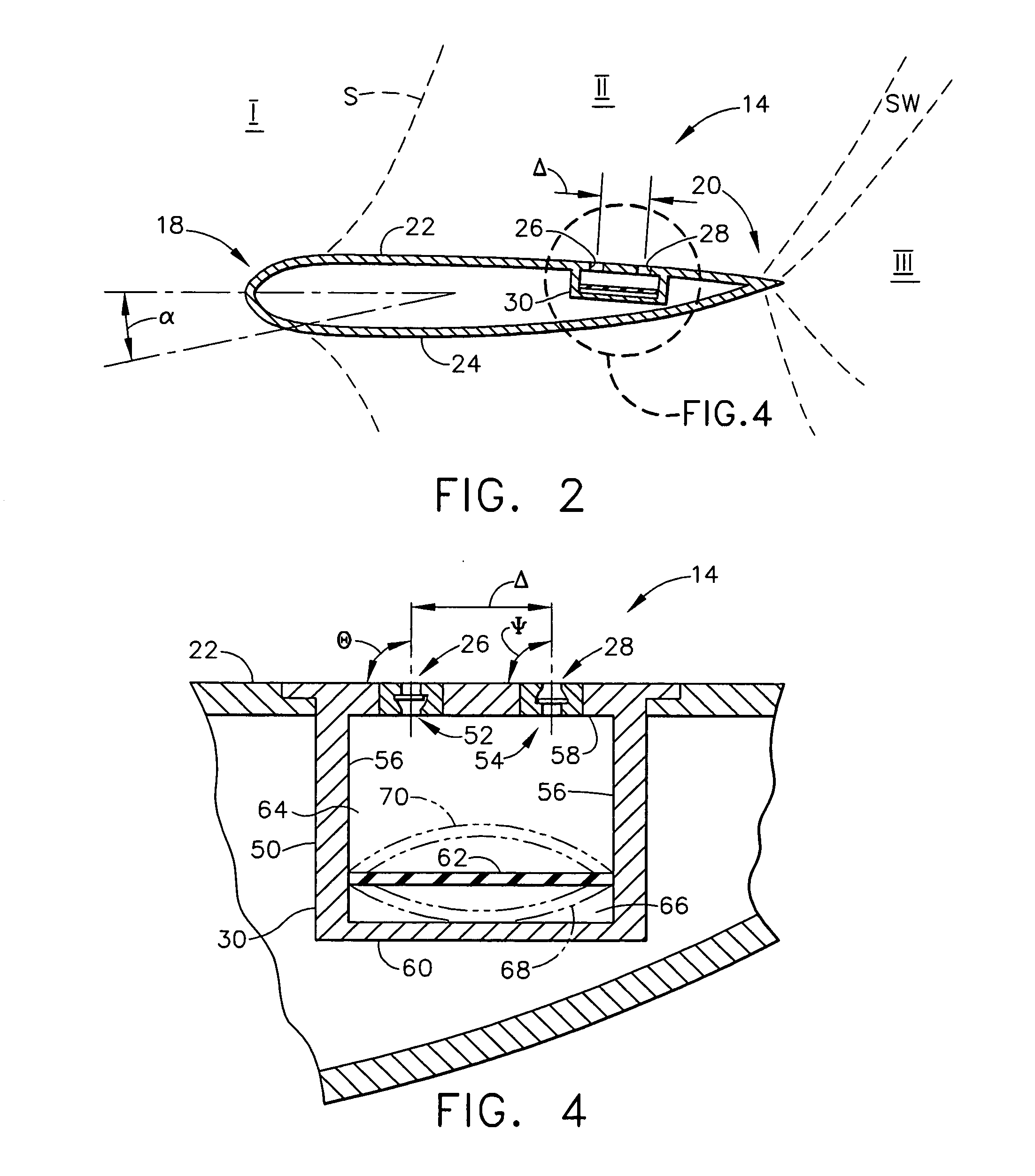
Dual point active flow control system for controlling air vehicle attitude during transonic flight
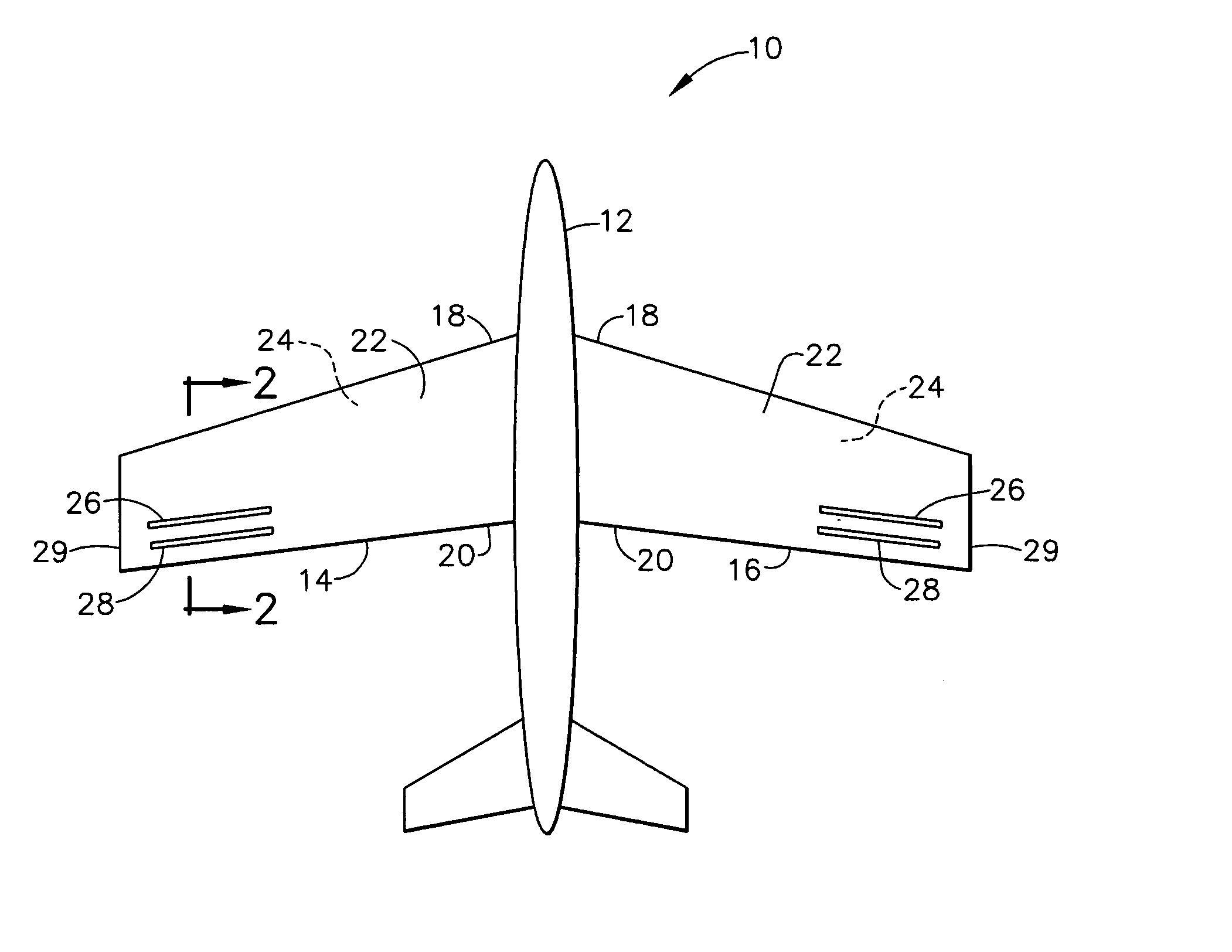
An air vehicle having a fuselage and two wings extending laterally therefrom and having a first surface between leading and trailing edges and an opposite second surface. The vehicle includes adjacent upstream and downstream orifices positioned on at least one first surface. Each upstream orifice is closer to the leading edge than the downstream orifice. Each second surface is substantially free of orifices. The vehicle includes an actuator within each wing having orifices. Each actuator is connected to corresponding upstream and downstream orifices for creating a negative pressure differential at the upstream orifice and a positive pressure differential at the downstream orifice so air is drawn into the upstream orifice and air is pushed away form the downstream orifice. The orifice is configured so air is drawn into and directed out of the upstream and downstream orifices, respectively, at an angle of about 90% with respect to the first surface.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Process to minimize turbine airfoil downstream shock induced flowfield disturbance
InactiveUS20070033802A1Minimize downstream shockVariation in flowPropellersReaction enginesProcess engineeringTrailing edge
A process of designing a transonic airfoil that results in an exit deviation angle that is optimized to minimize downstream shock induced flowfield disturbances. Specifically, a design process of a transonic airfoil minimizes pitchwise variation in downstream static pressure that includes determining an airfoil exit deviation angle and downstream turning for reduced shock from a trailing edge of the transonic airfoil.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
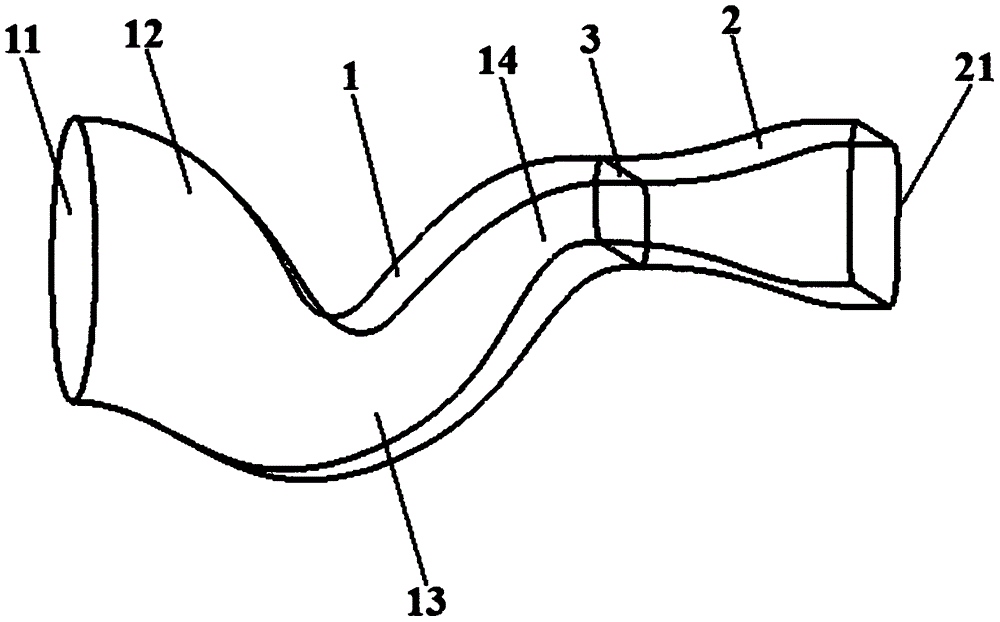
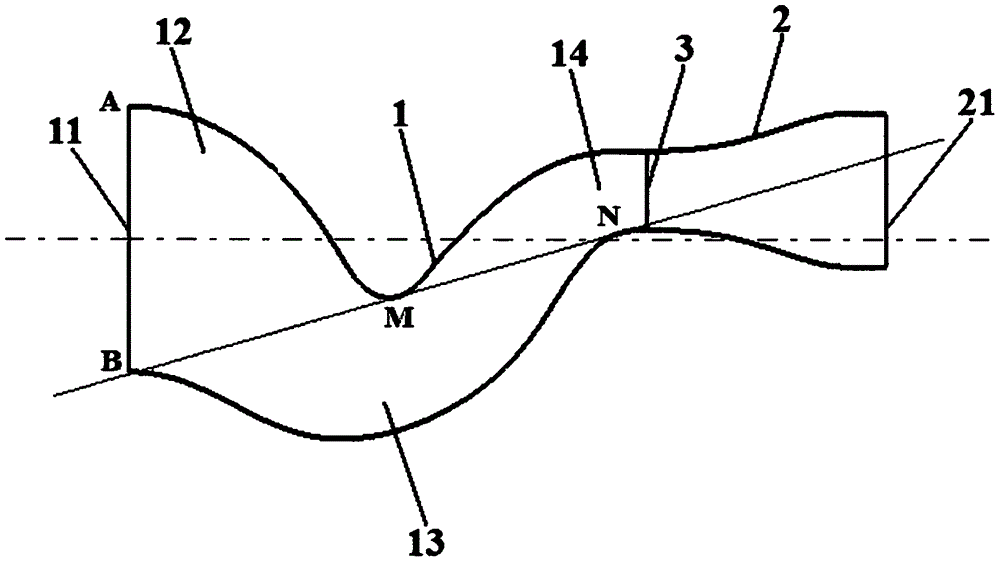
S-shaped bent shrinking-expanding spray pipe structure
InactiveCN106438103ASolve the inability to meet the needs of fighter aircraft coverageSolve the problem of trans and supersonic flightJet propulsion plantsThroatEngineering
The invention discloses an S-shaped bent shrinking-expanding spray pipe structure which comprises a shrinking section and an expanding section; the shrinking section is equipped with a gas inlet which is connected with a high-temperature turbine outlet of an engine; the expanding section is connected to the tail part of the shrinking section and is equipped with a gas outlet; and a spray pipe throat is formed on a transition part of the shrinking section and the expanding section. According to the S-shaped bent shrinking-expanding spray pipe structure which adopts the technical scheme, gas flow from the high-temperature turbine outlet of the engine is expanded and accelerated during shrinking and expanding, and is accelerated to sound speed at the spray pipe throat; and the gas flow which reaches sound speed is further accelerated to ultrasonic sound speed at the expanding section after passing through the spray pipe throat. The S-shaped bent shrinking-expanding spray pipe structure disclosed by the invention solves the problem that a shrinking type engine tail spray pipe adopted by a warplane in the prior art cannot meet the needs of covering infrasound speed flight, transonic sped flight and ultrasonic sound speed flight of the warplane.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
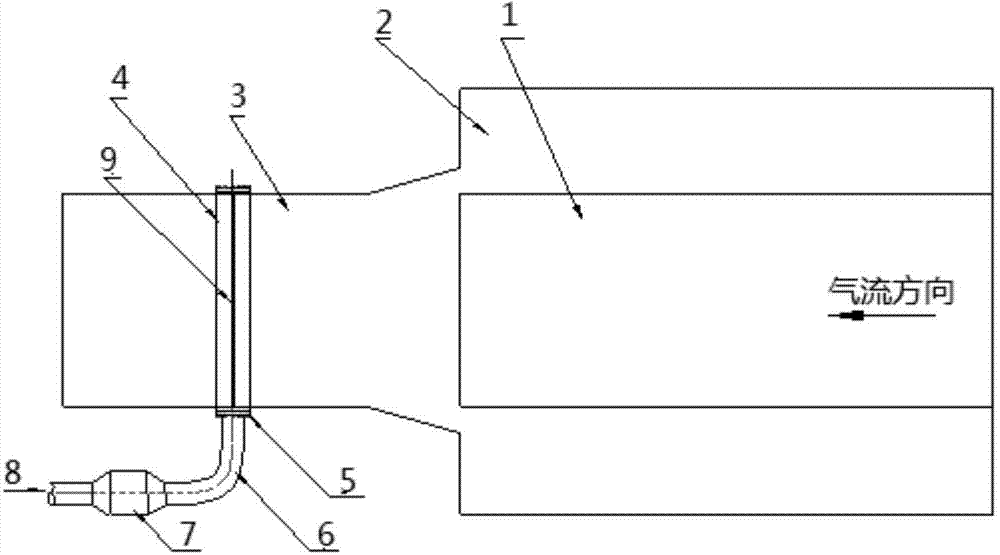
Auxiliary jet-flow system for controlling high speed wind tunnel transonic flow field
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF AEROSPACE AERODYNAMICS
Cascade bent tail plate with hole groove structure for suction type transonic velocity plane cascade turbine test bed
ActiveCN110186688AIdeal flow field periodicityAvoid destructionMachine part testingGas-turbine engine testingStraight segmentTurbine
The invention provides a cascade bent tail plate with a hole groove structure for a suction type transonic velocity plane cascade turbine test bed, which is used for improving a cascade wake flow field of the suction type transonic velocity plane cascade turbine test bed. The tail plate is mainly composed of an inner side curved type tail plate and a hole-shaped or groove-shaped hollow structure on the tail plate, wherein the inner side curved type tail plate comprises two-part geometric structures including a straight segment and a quadratic curve segment, and the tail plate is provided withthe hole-shaped or groove-shaped hollow structure. Under a working condition of a high Mach number large negative attack angle test, usage of a curved shape surface of the tail plate and the hole-shaped or groove-shaped hollow structure on the tail plate can prevent a wake from being over-expanded when the wake disengaging the tail plate to enter a suction channel. The two structures make the pressure of the wake rise to the suction pipeline pressure approaching an outlet at an end section of the tail plate, the over-expansion phenomenon is avoided when the tail plate is disengaged, thereby avoiding damage of turbine plane blade cascade periodicity, and at the same time, it finds through calculation that usage of the bent tail plate have no deterioration in working conditions at differentattack angles of other Mach numbers.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
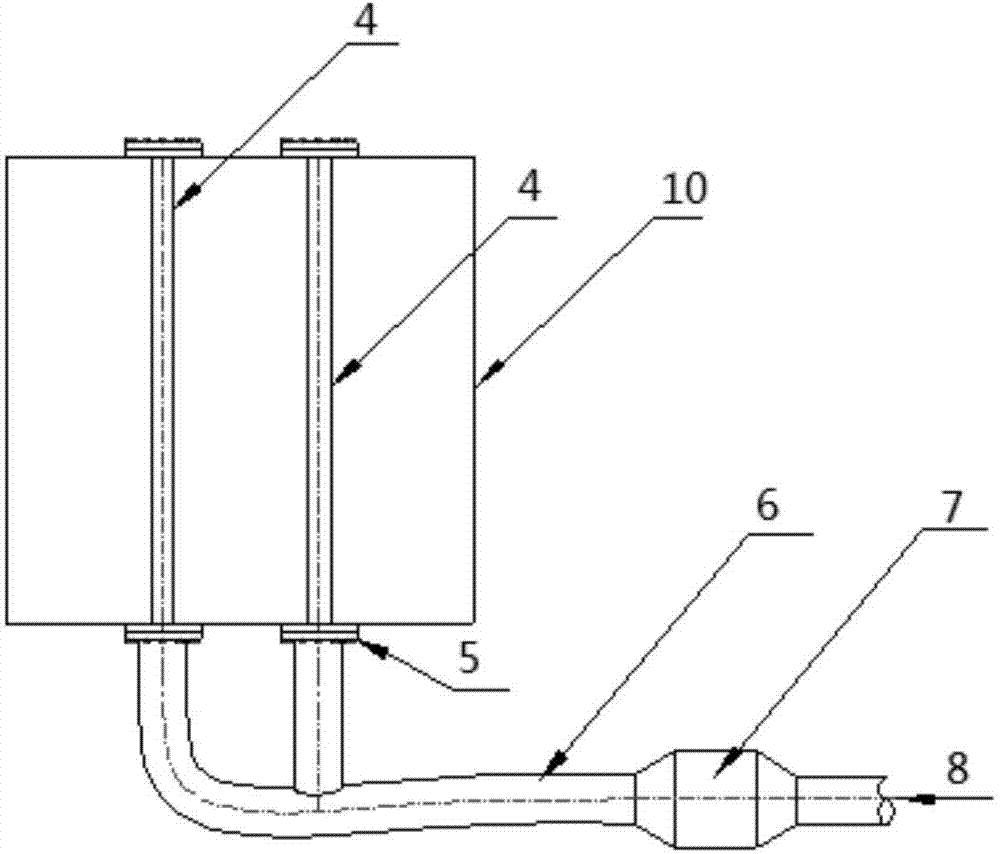
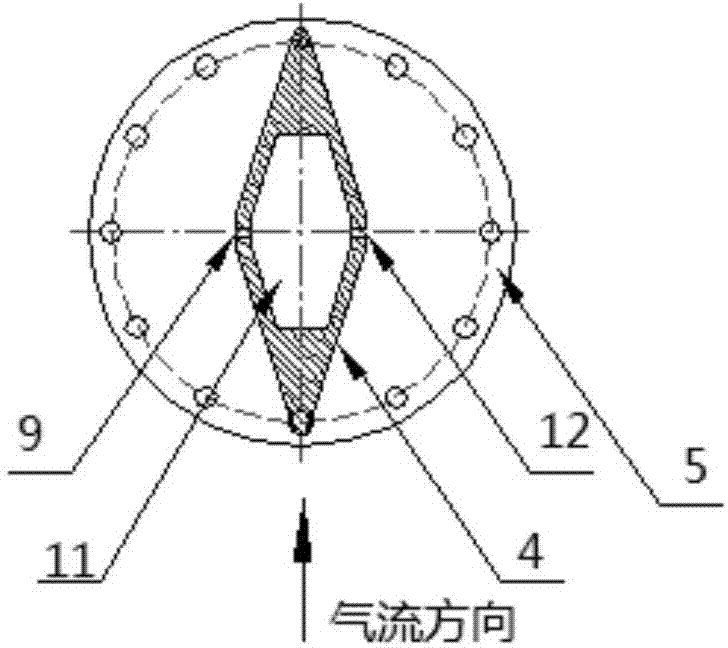
Variable mach number transonic rigid free jet nozzle
The invention relates to a variable mach number transonic rigid free jet nozzle which comprises a left sidewall (1), a right sidewall (10), an upper support plate (4) and a lower support plate (5), wherein the left sidewall (1) and the right sidewall (10) are bilaterally symmetric, and are fixed and connected into an open nozzle frame in a supporting way by virtue of the upper support plate (4) and the lower support plate (5), which are symmetrically arranged; an upper molded surface mechanism (2) and a lower molded surface mechanism (3) are longitudinally and symmetrically arranged in the nozzle frame. The variable mach number transonic rigid free jet nozzle is characterized by also comprising an upper right semicircular bearing (6) and an upper left semicircular bearing (7). According to the variable mach number transonic rigid free jet nozzle, the pneumatic flow field is good, and a design method is reasonable; a semicircular shaft design is adopted for the tail end of a rigid molded surface, so that the area of an outlet of the open nozzle is kept constant, and an airflow field at the outlet of the nozzle is uniform and regular; an obvious uniform test area can be formed at the outlet of the nozzle, so that test requirements are met, and good effects are achieved in a high-altitude stand air blowing test.
Owner:CHINA GAS TURBINE ESTAB
Laminar flow wing optimized for transonic cruise aircraft
ActiveUS20120043430A1Extensive laminar flowEasy to liftWing shapesAll-wing aircraftLeading edgeCruise speed
On an aircraft designed for maximum efficient cruise speed in the range from about Mach 0.8 to about Mach 1.2, and having fuselage and wings with: (a) less than about 25 degrees of leading edge sweep, in combination with airfoil thickness to chord ratios between about 3% and about 8%, as an average along the wing semi-span outboard from the zone of substantial fuselage influence, and (b) wing leading edge sweep between about 20 degrees and about 35 degrees, in combination with airfoil thickness to chord ratios equal to or below about 3% as an average along the semi-span outboard from the zone of substantial fuselage influence to the wing tip.
Owner:AERION INTPROP MANAGEMENT CORP
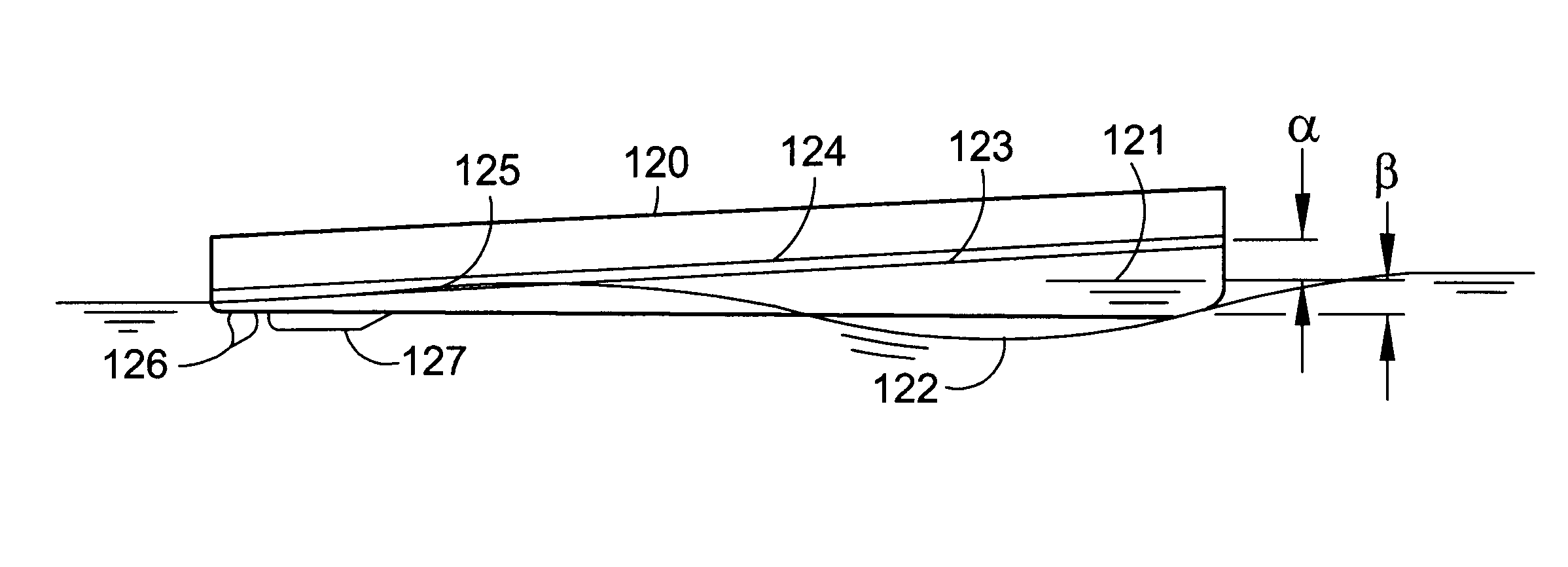
Transonic hull and hydrofield (part III)
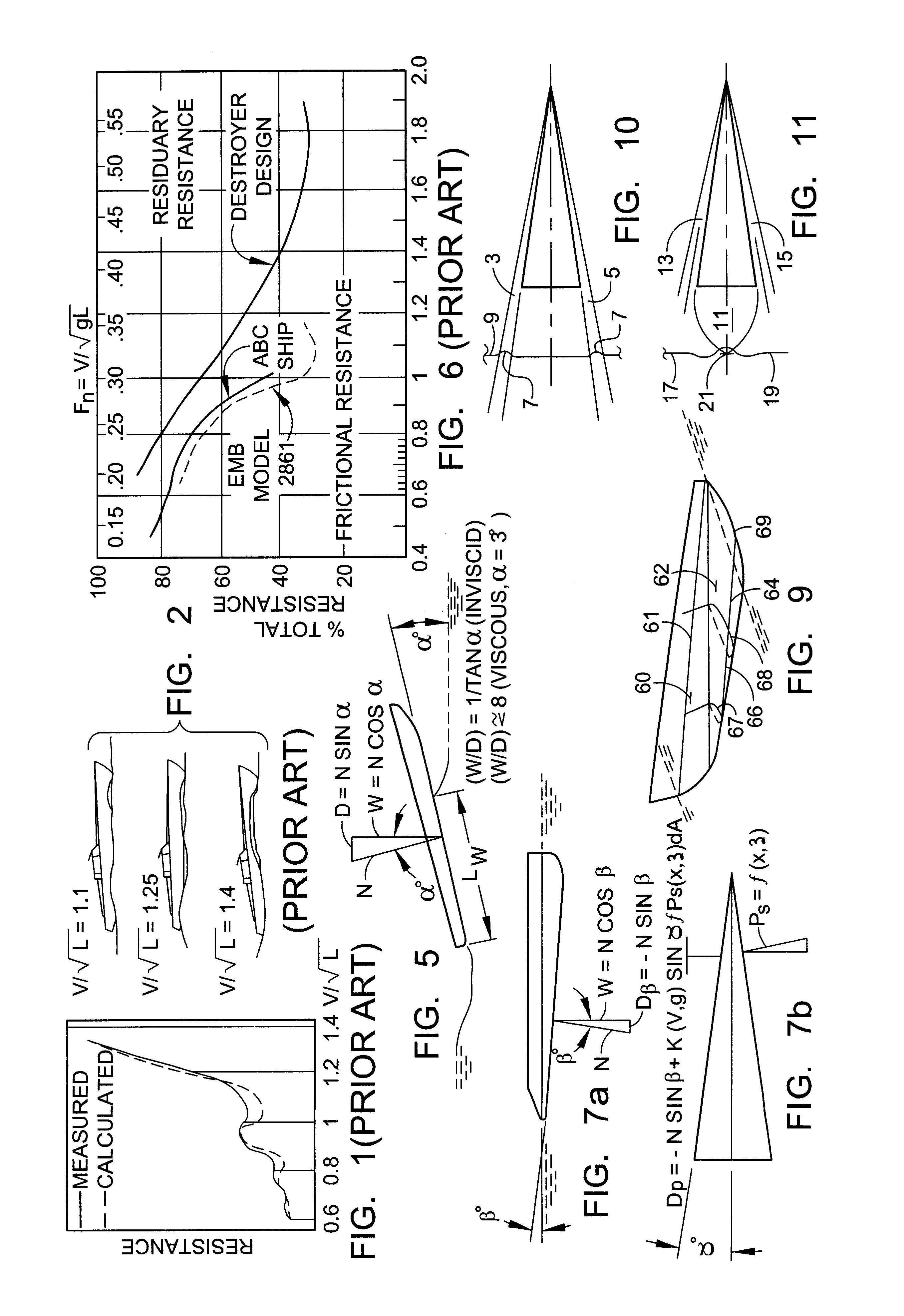
InactiveUS6843193B1Improve efficiencyExpand the scope ofVessel movement reduction by foilsMovement controllersSternPart iii
A transonic hull having a bow, a stern, a longitudinal length therebetween, side surfaces extending from the bow to outboard portions of the stern, a lower surface extending between the side surfaces, the transonic hull having a submerged volume with an approximately triangular shape in planview with apex adjacent the bow and a base adjacent the stern, and an approximately triangular shape in side view when in motion with a base adjacent the bow and an apex adjacent the stern.
Owner:ALVAREZ CALDERON F ALBERTO
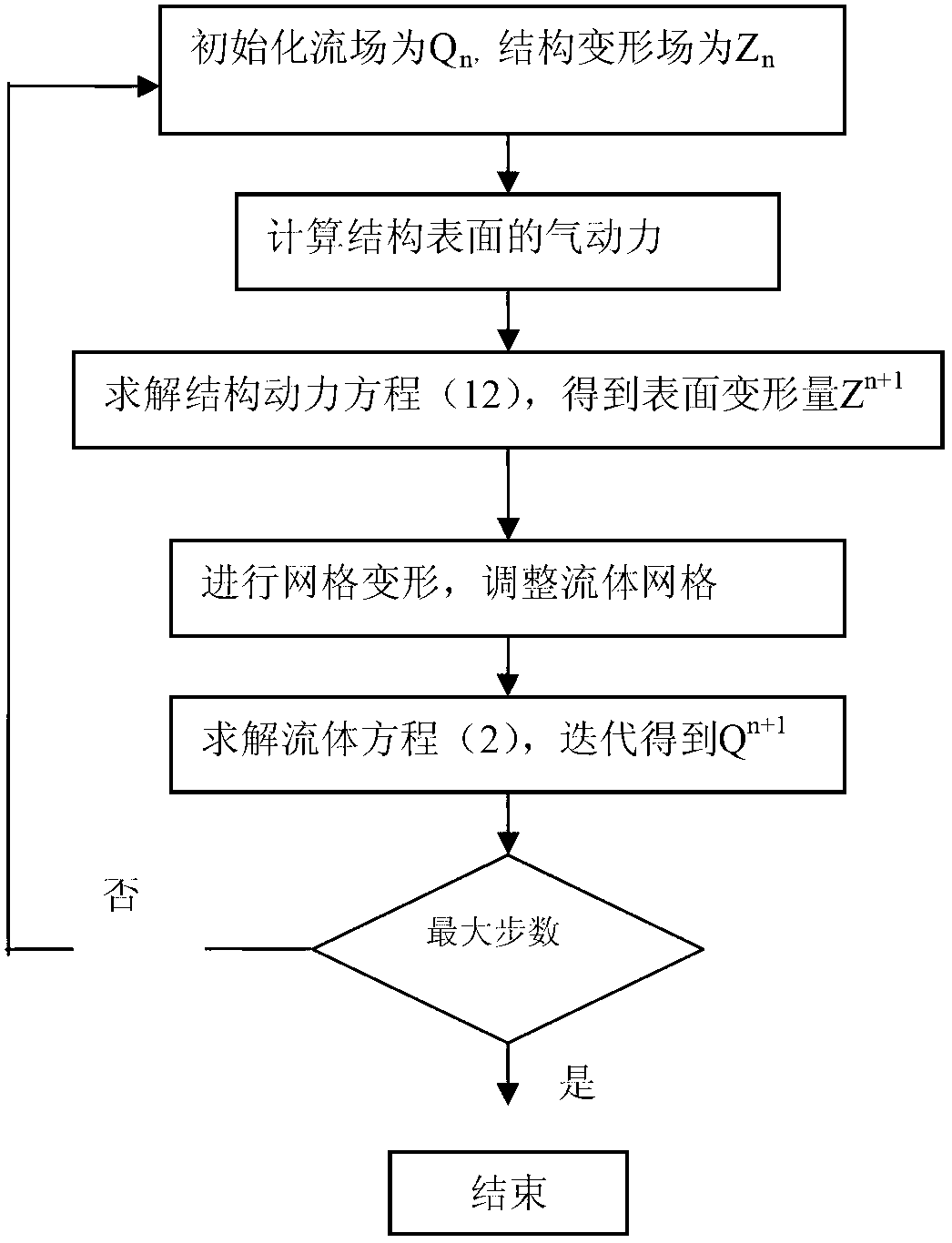
Transonic limit cycle flutter analysis method
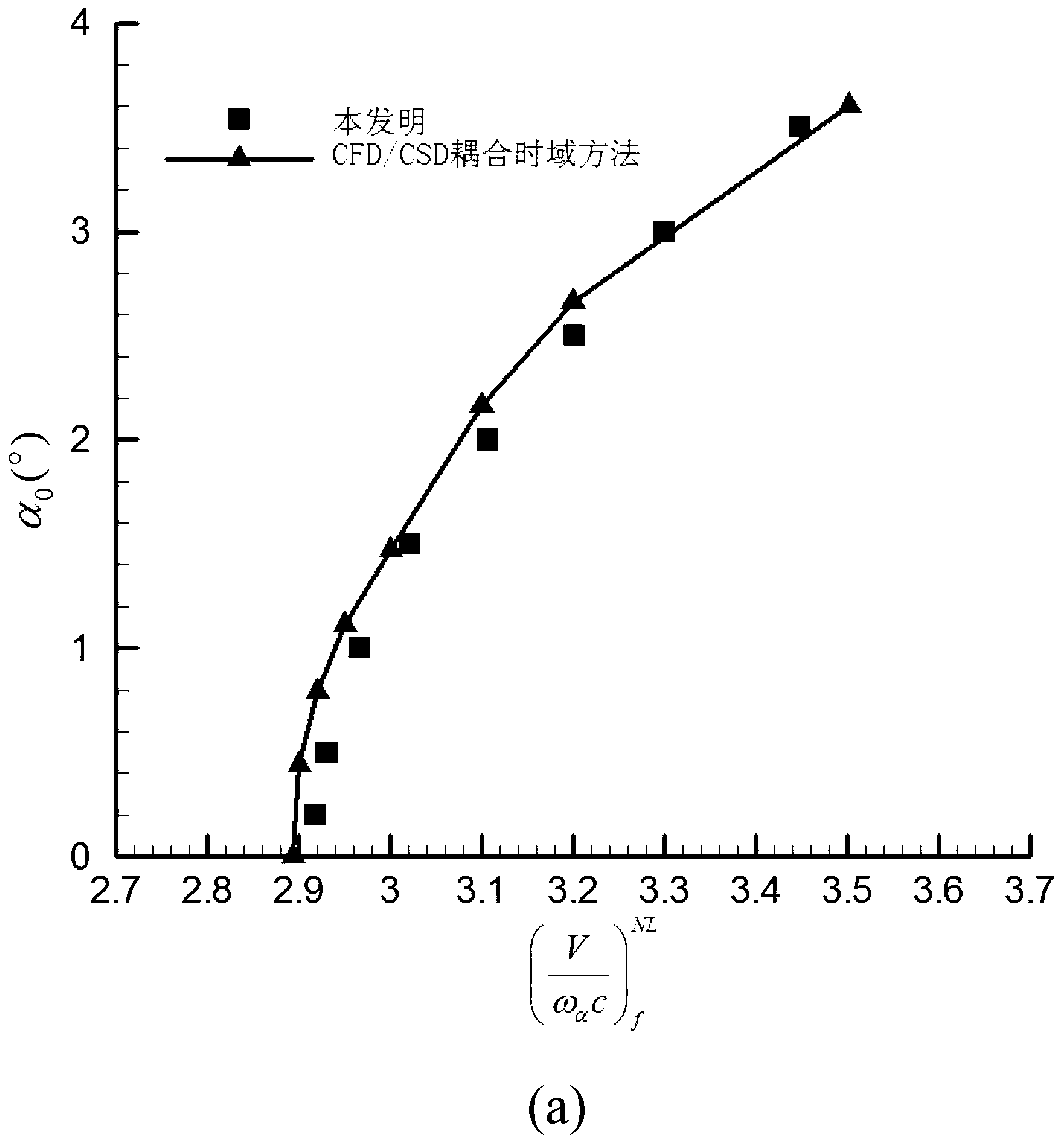
InactiveCN103310060AModerate amount of calculationEasy to masterSustainable transportationSpecial data processing applicationsEquivalent linearizationAnalysis method
The invention provides a transonic limit cycle flutter analysis method. The transonic limit cycle flutter analysis method comprises the following steps: through equivalent linearization of a describing function, processing nonlinear characteristics of a transonic aerodynamic force; substituting a frequency-domain aerodynamic coefficient after the equivalent linearization into a flutter equation; obtaining a flutter speed and a flutter frequency by a frequency-domain flutter solving method; and for different limit cycle amplitudes, calculating to obtain different flutter speeds and flutter frequencies to form limit cycle characteristics of a transonic nonlinear flutter. The equivalent linearization is performed on the nonlinear characteristics of the transonic aerodynamic force through the aerodynamic describing function, the flutter equation is solved within a frequency domain, so that the flutter speed and the flutter frequency at a given limit cycle amplitude can be accurately predicted; and the transonic limit cycle flutter analysis method is moderate in computation amount, easy to master and very good in robustness.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com