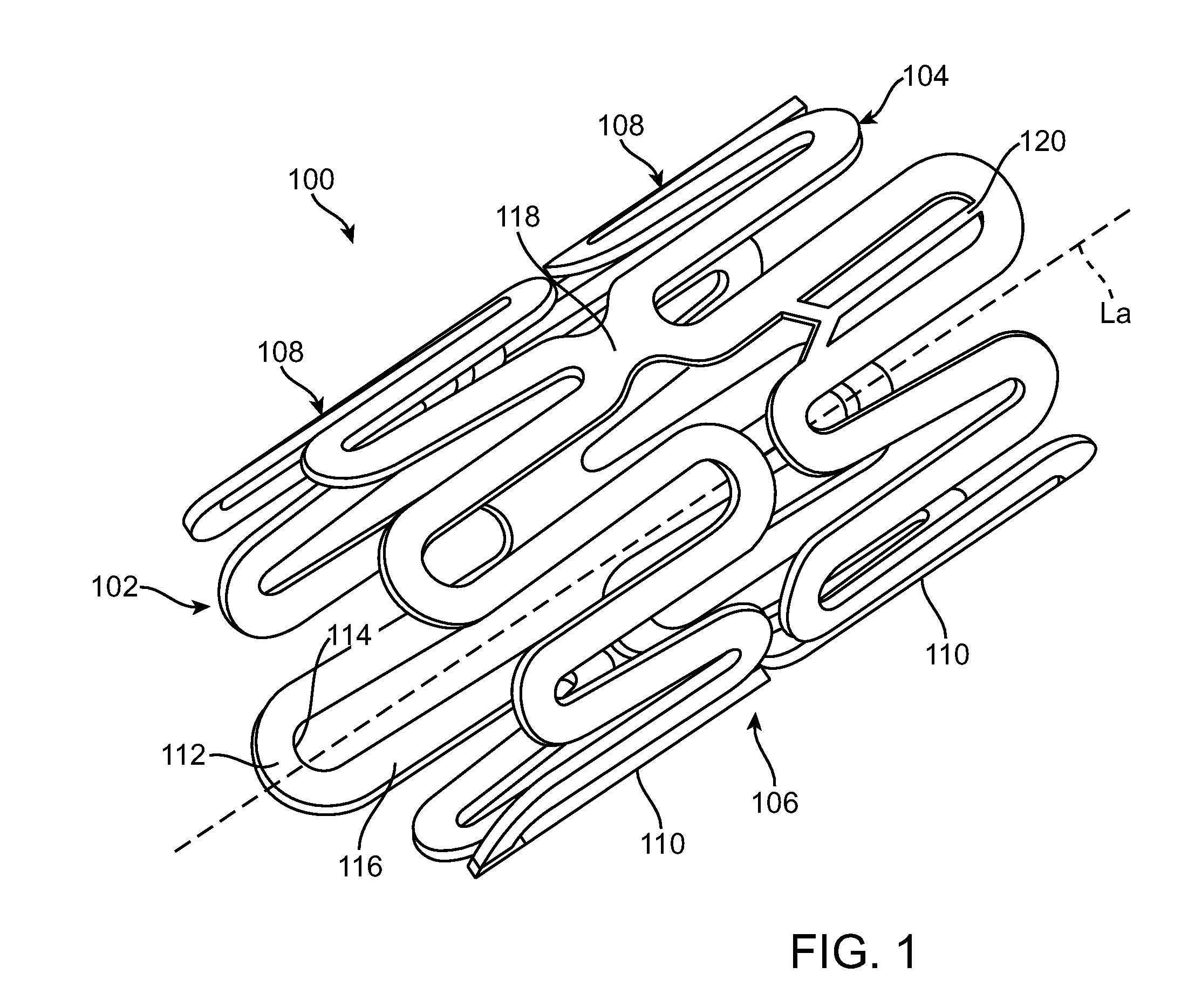
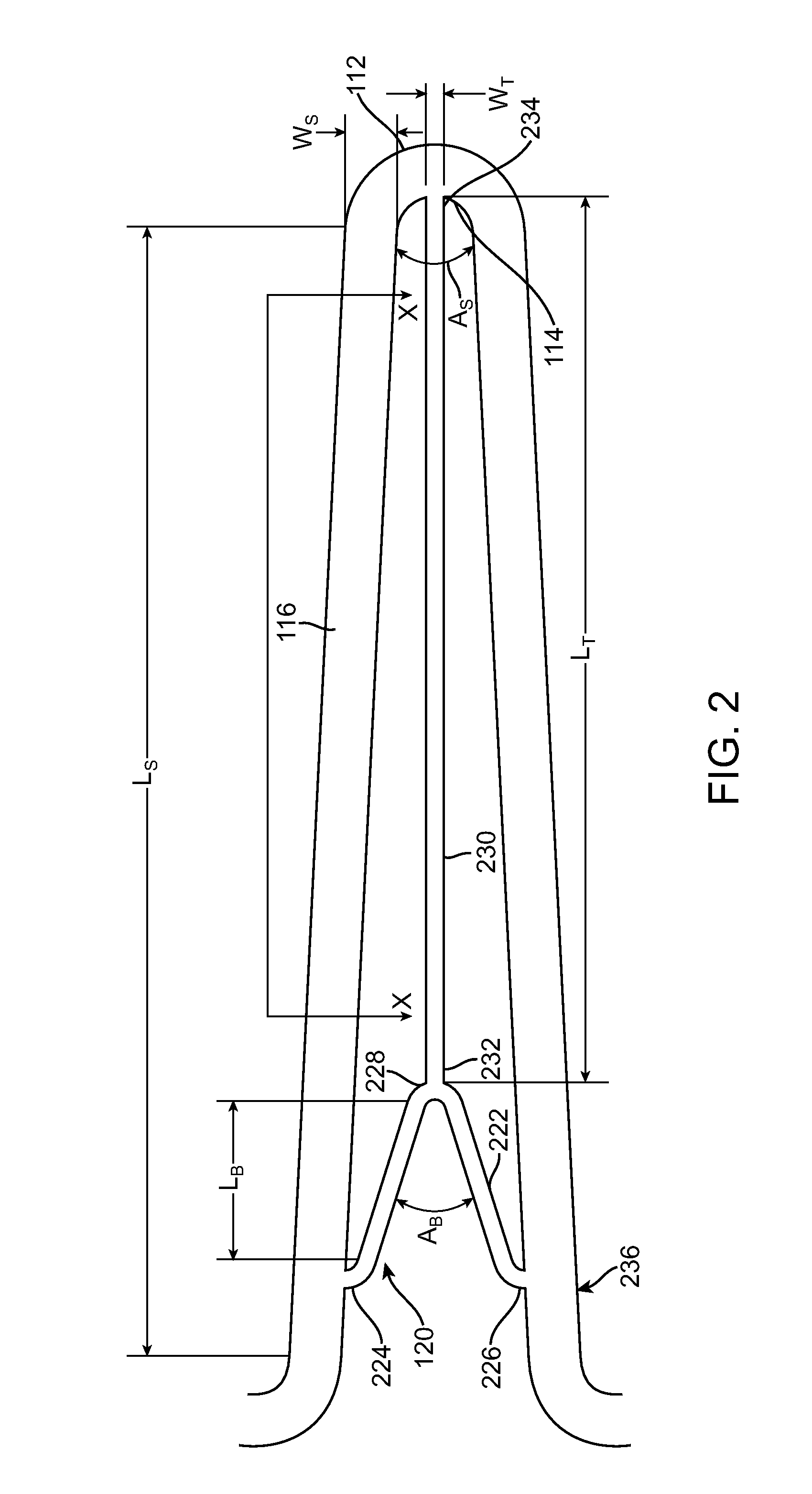
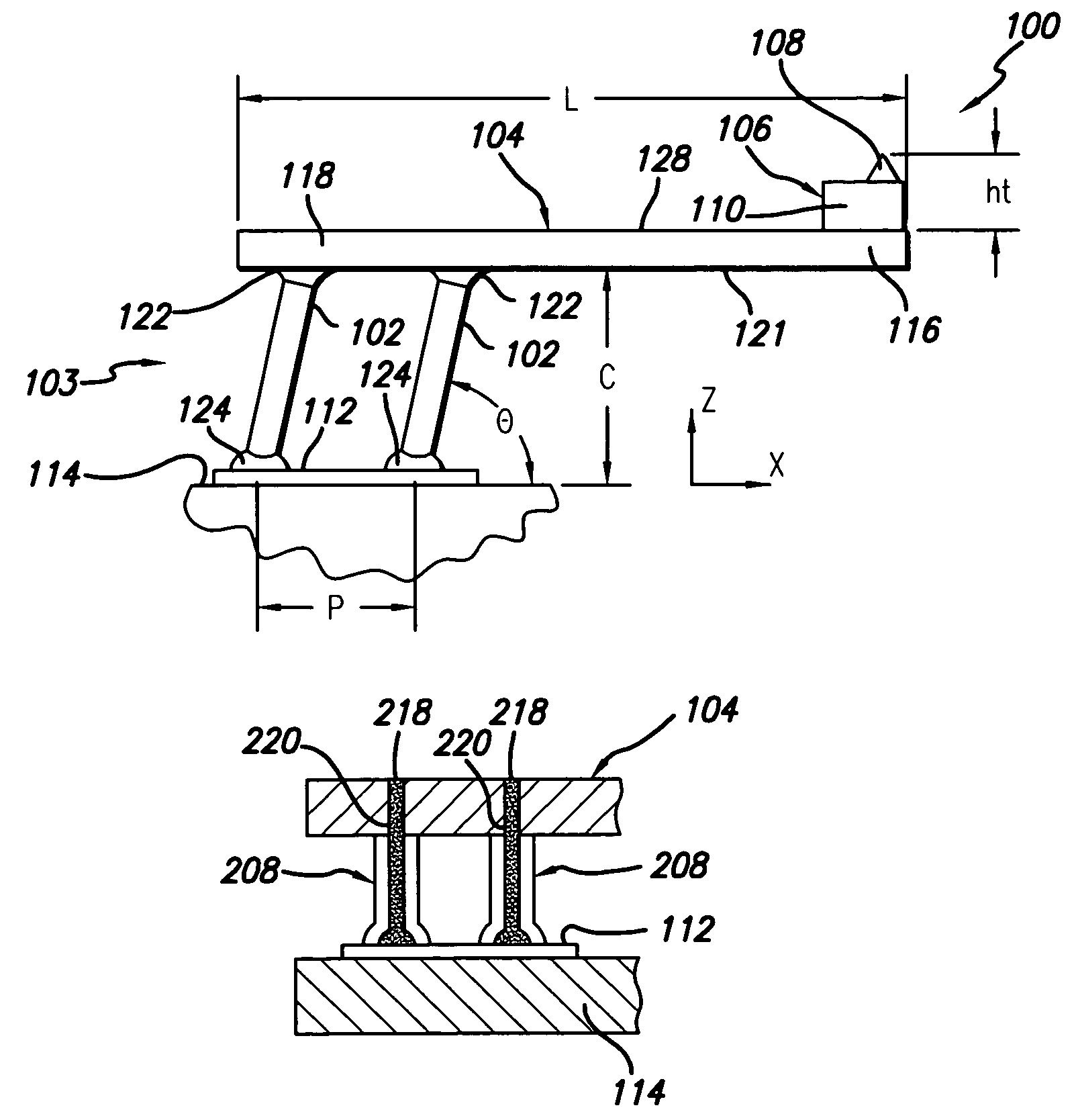
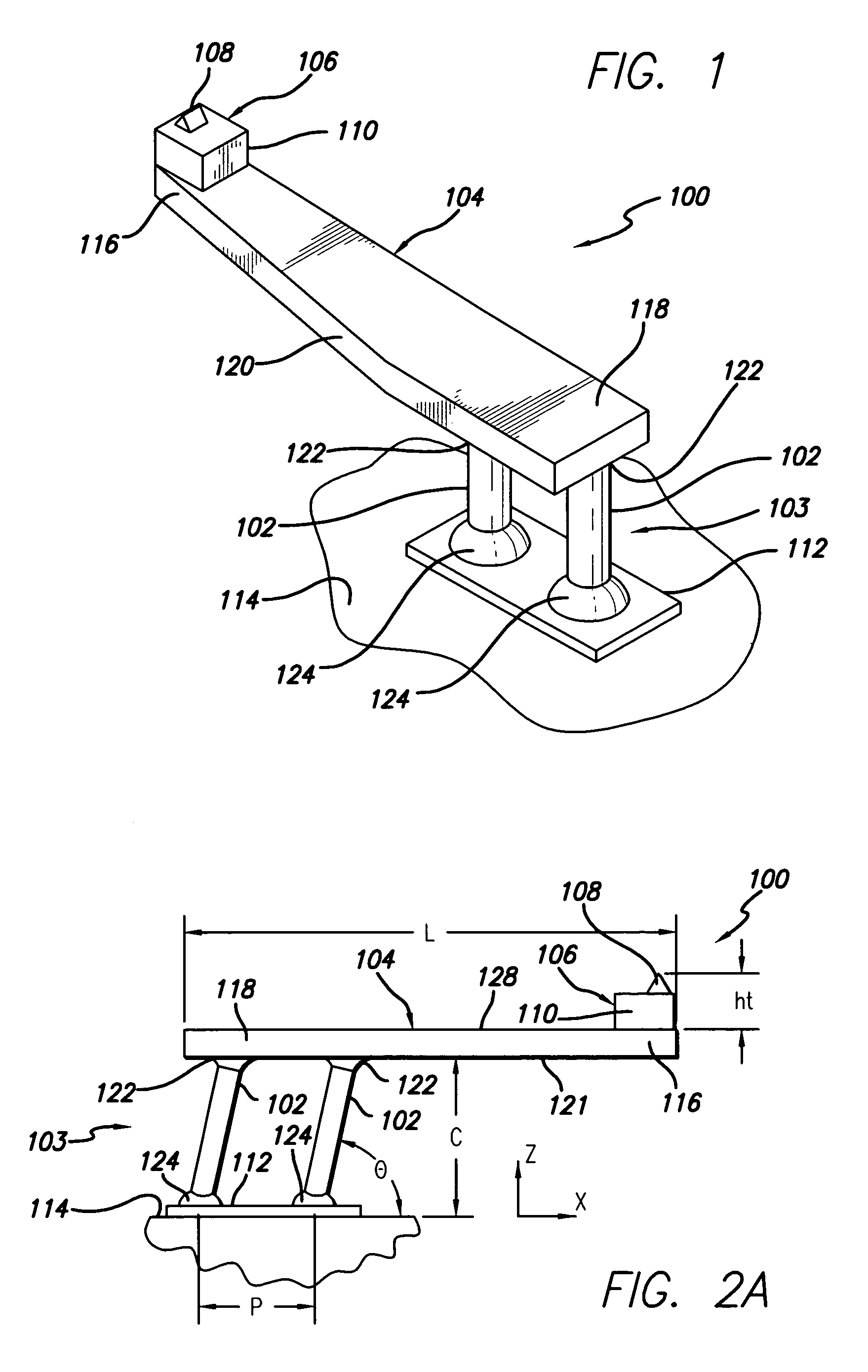
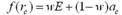Patents
Literature
697 results about "Straight segment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
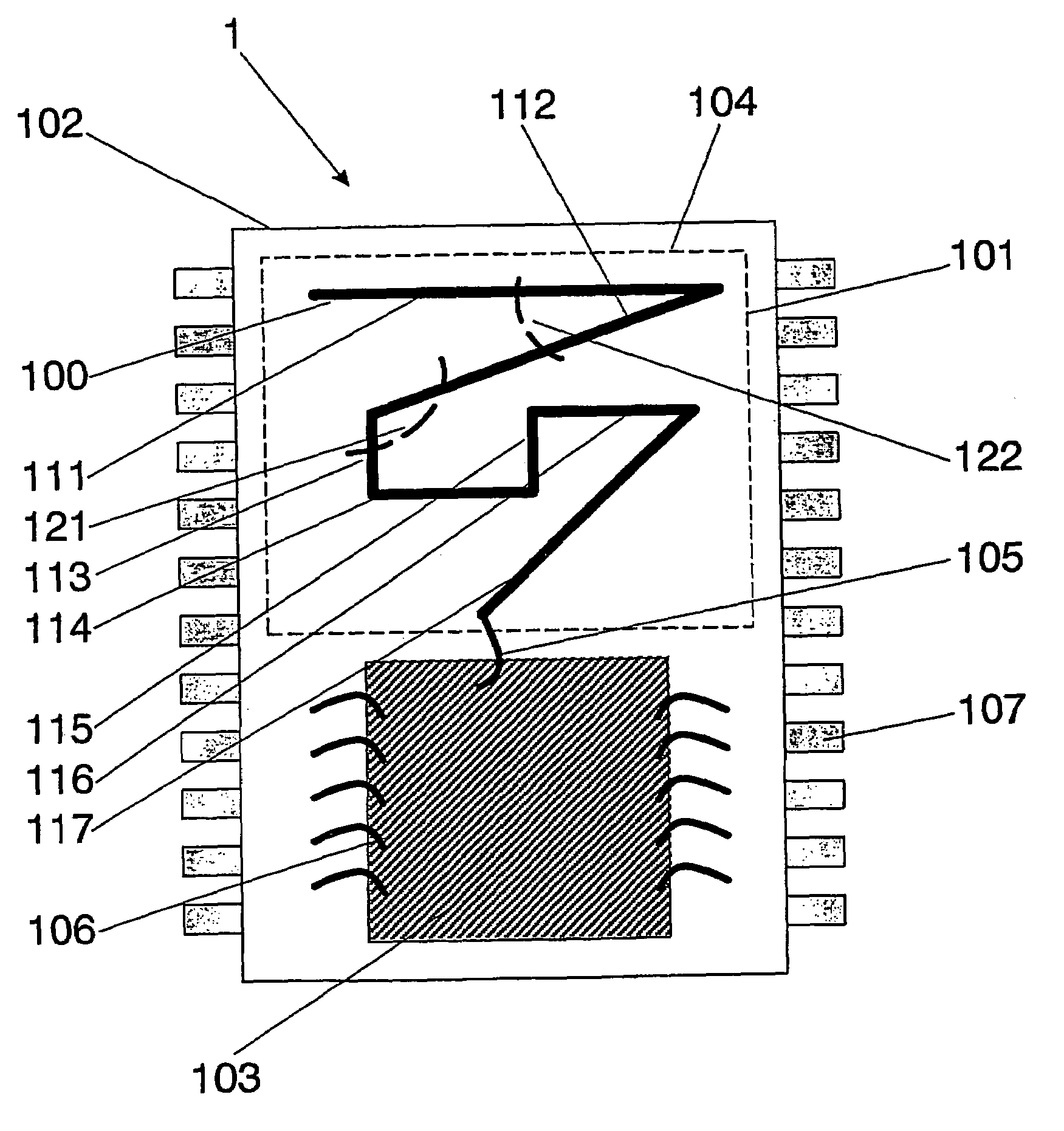
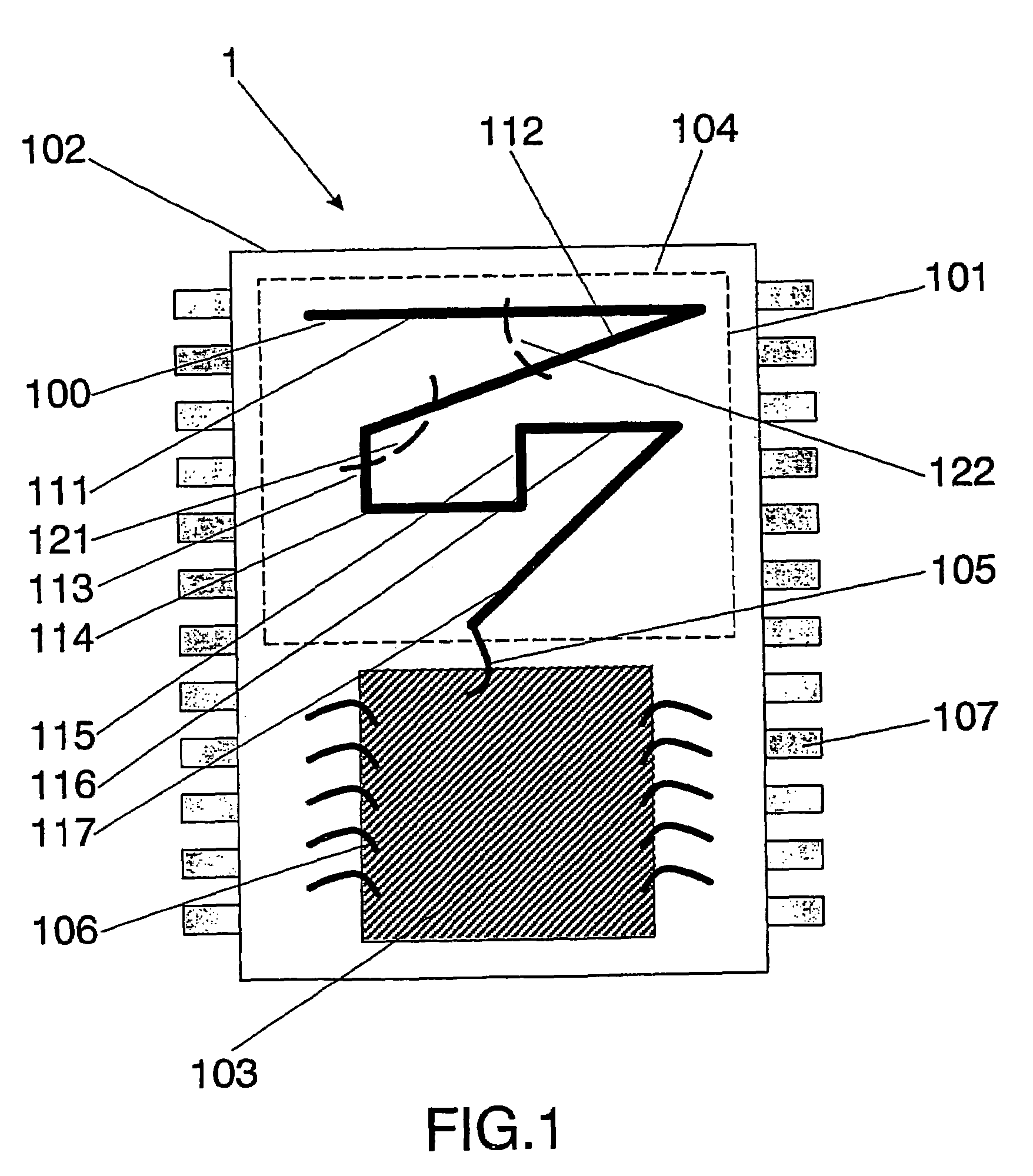
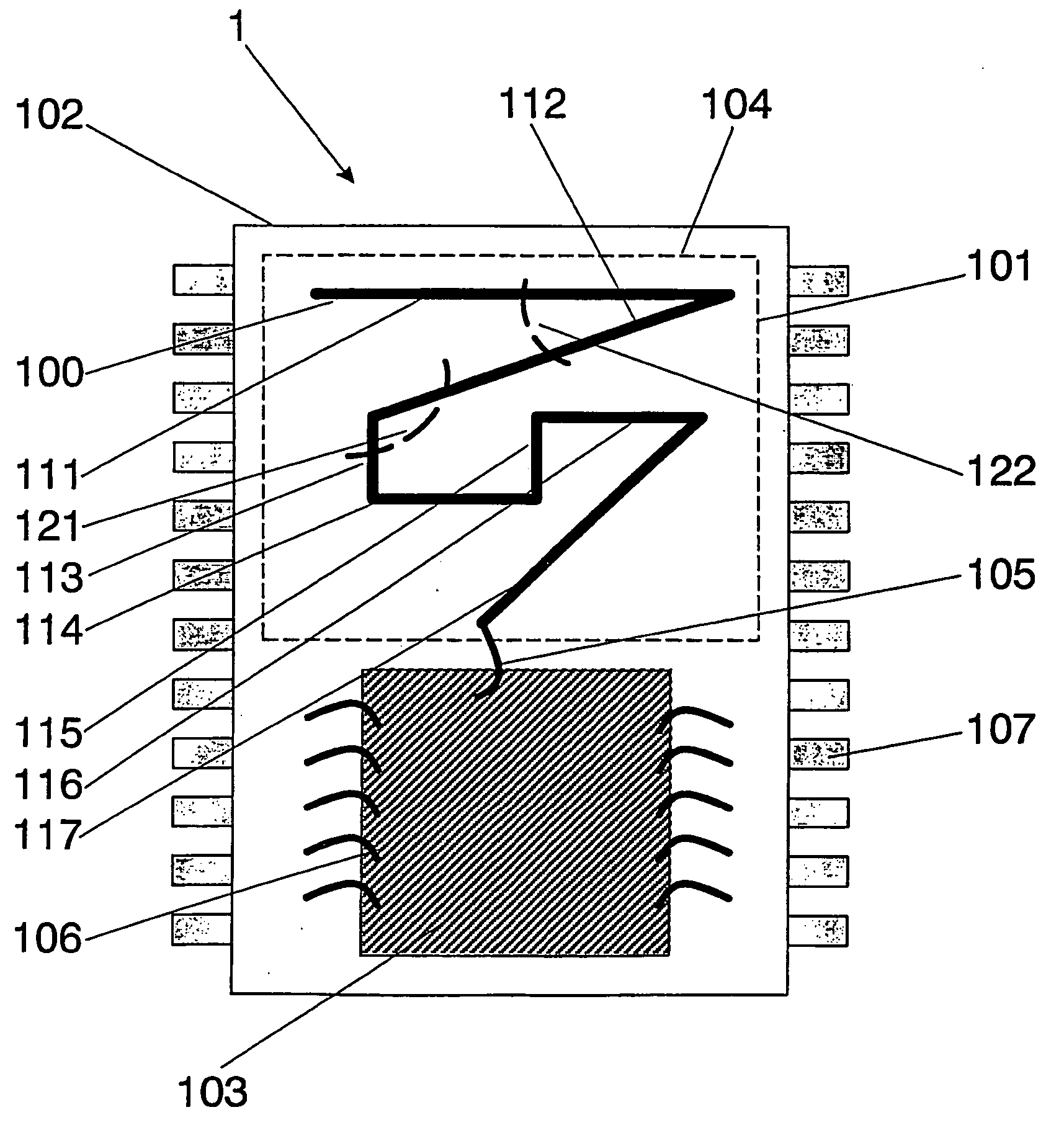
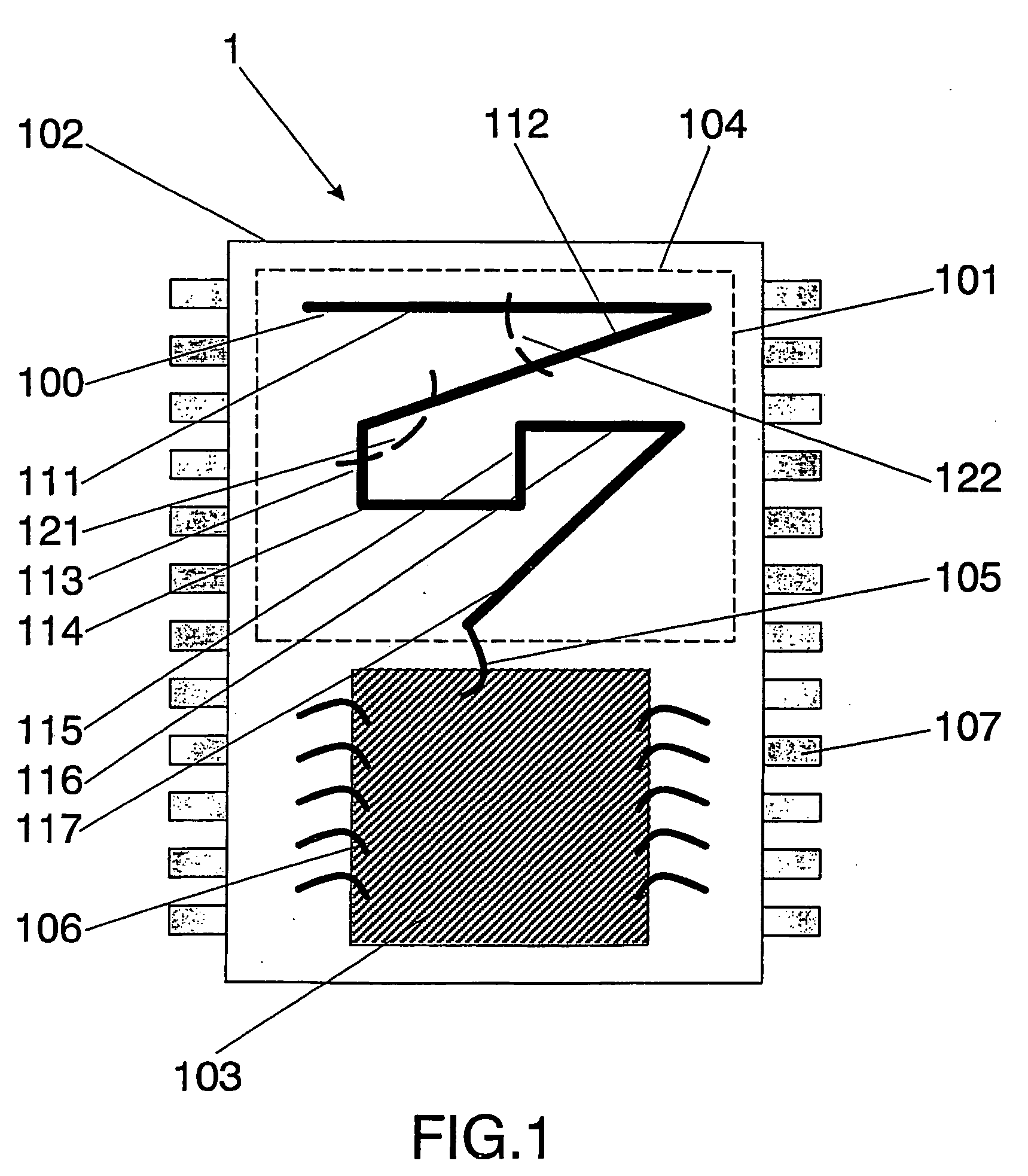
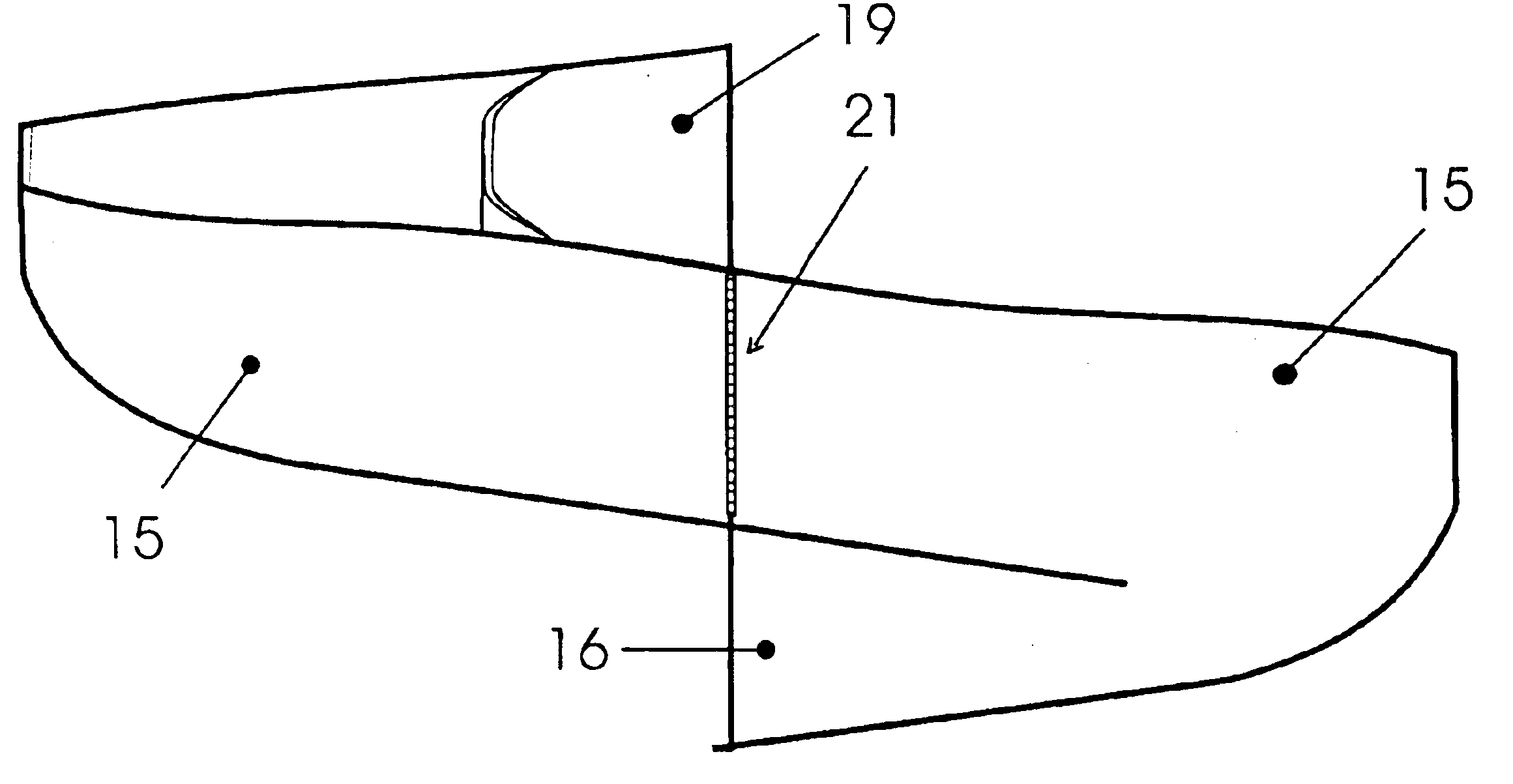
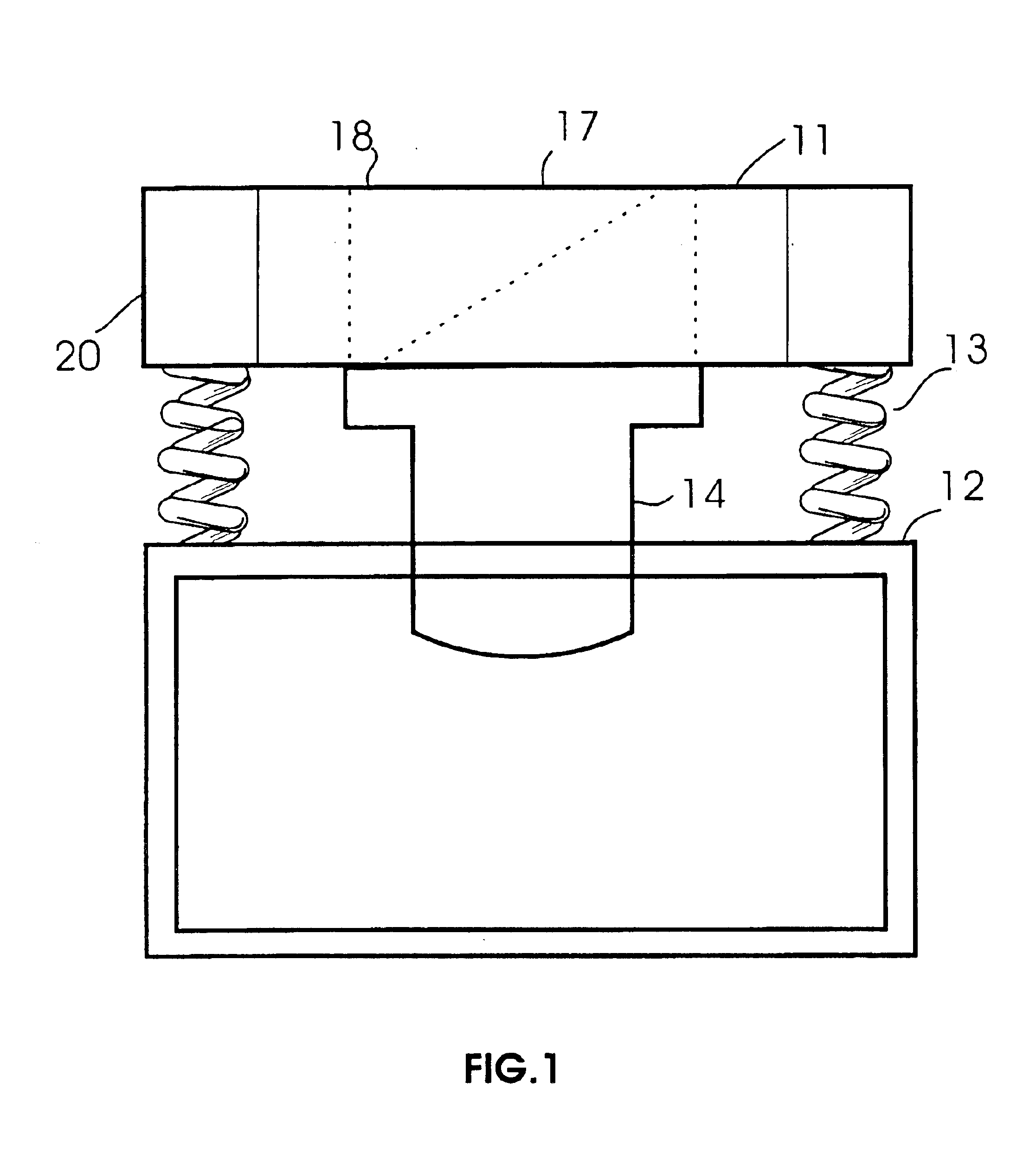
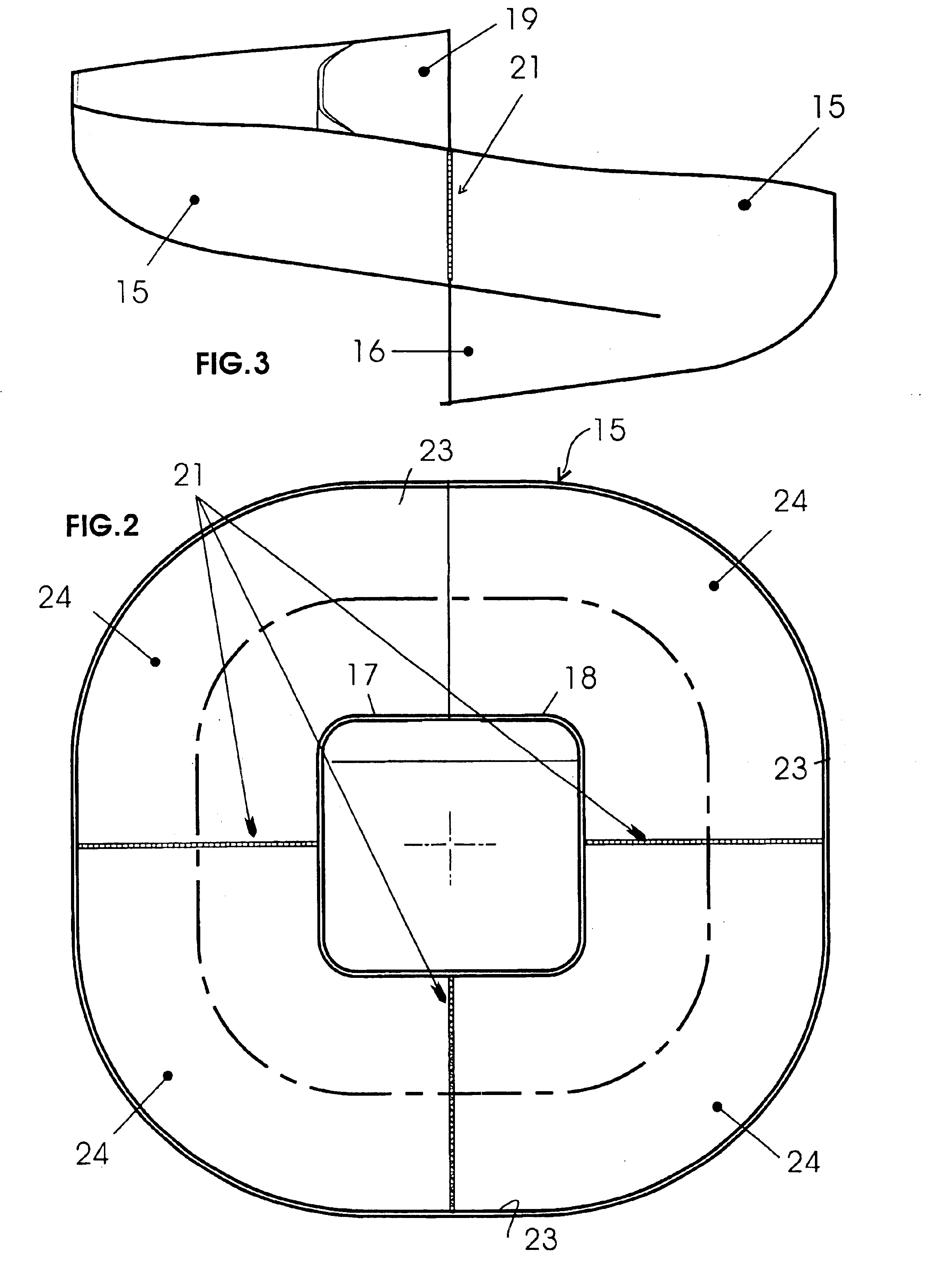
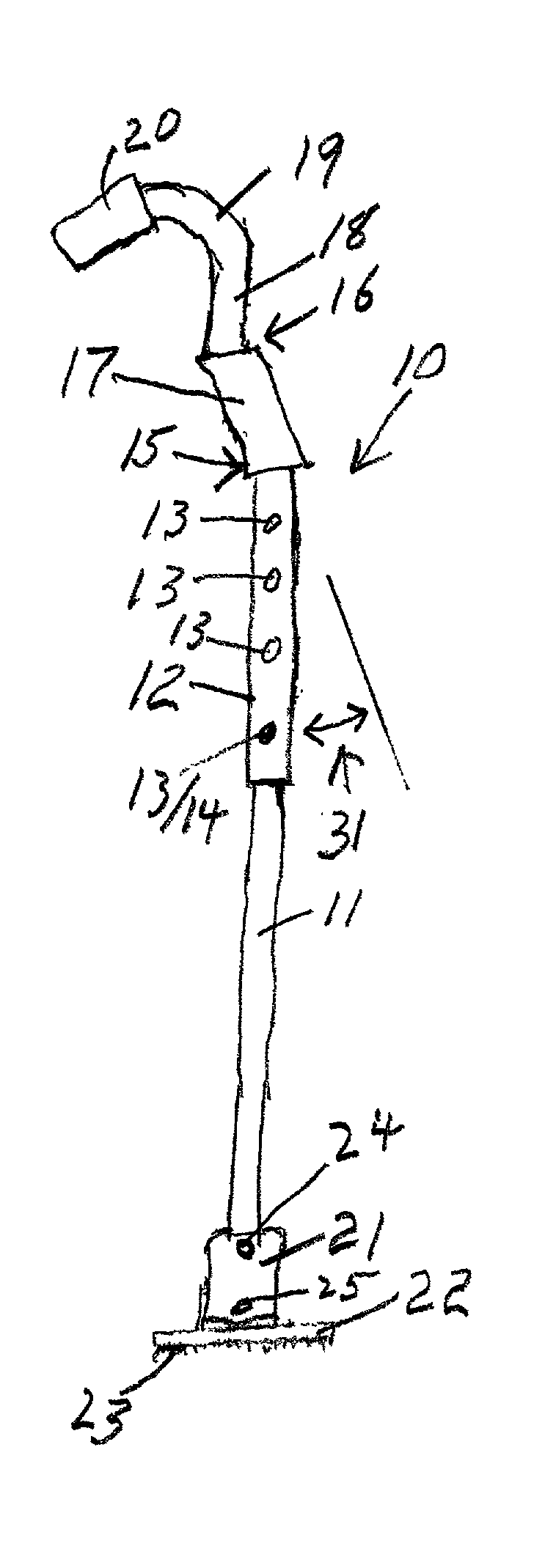
Integrated circuit package including miniature antenna
InactiveUS7095372B2Minimize coiling effectEfficient integrationResonant long antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsSemiconductor chipEngineering
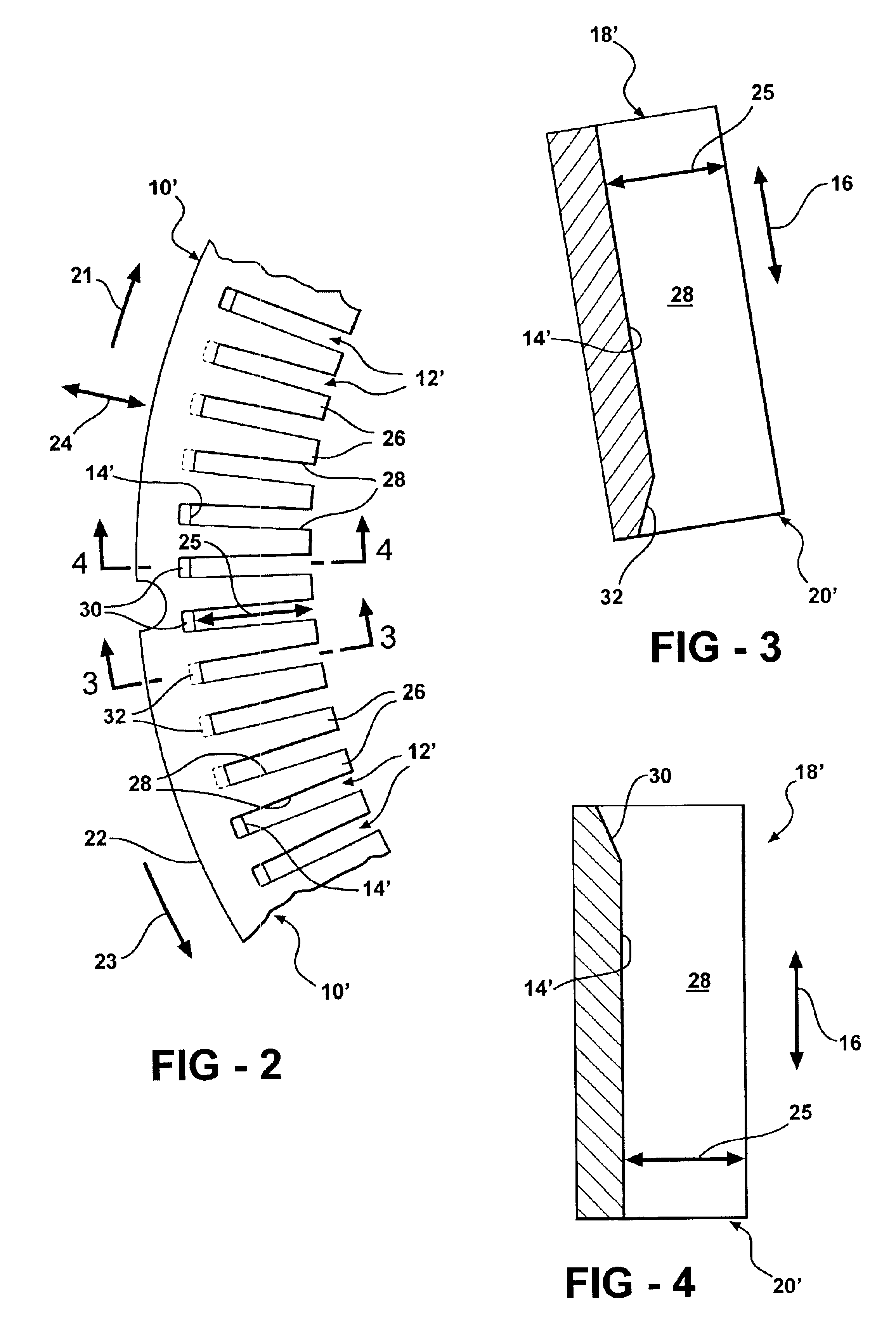
The present invention relates to an integrated circuit package comprising at least one substrate, each substrate including at least one layer, at least one semiconductor die, at least one terminal, and an antenna located in the integrated circuit package, but not on said at least one semiconductor die. The conducting pattern comprises a curve having at least five sections or segments, at least three of the sections or segments being shorter than one-tenth of the longest free-space operating wavelength of the antenna, each of the five sections or segments forming a pair of angles with each adjacent segment or section, wherein the smaller angle of each of the four pairs of angles between sections or segments is less than 180° (i.e., no pair of sections or segments define a longer straight segment), wherein at least two of the angles are less than 115°, wherein at least two of the angles are not equal, and wherein the curve fits inside a rectangular area the longest edge of which is shorter than one-fifth of the longest free-space operating wavelength of the antenna.
Owner:FRACTUS
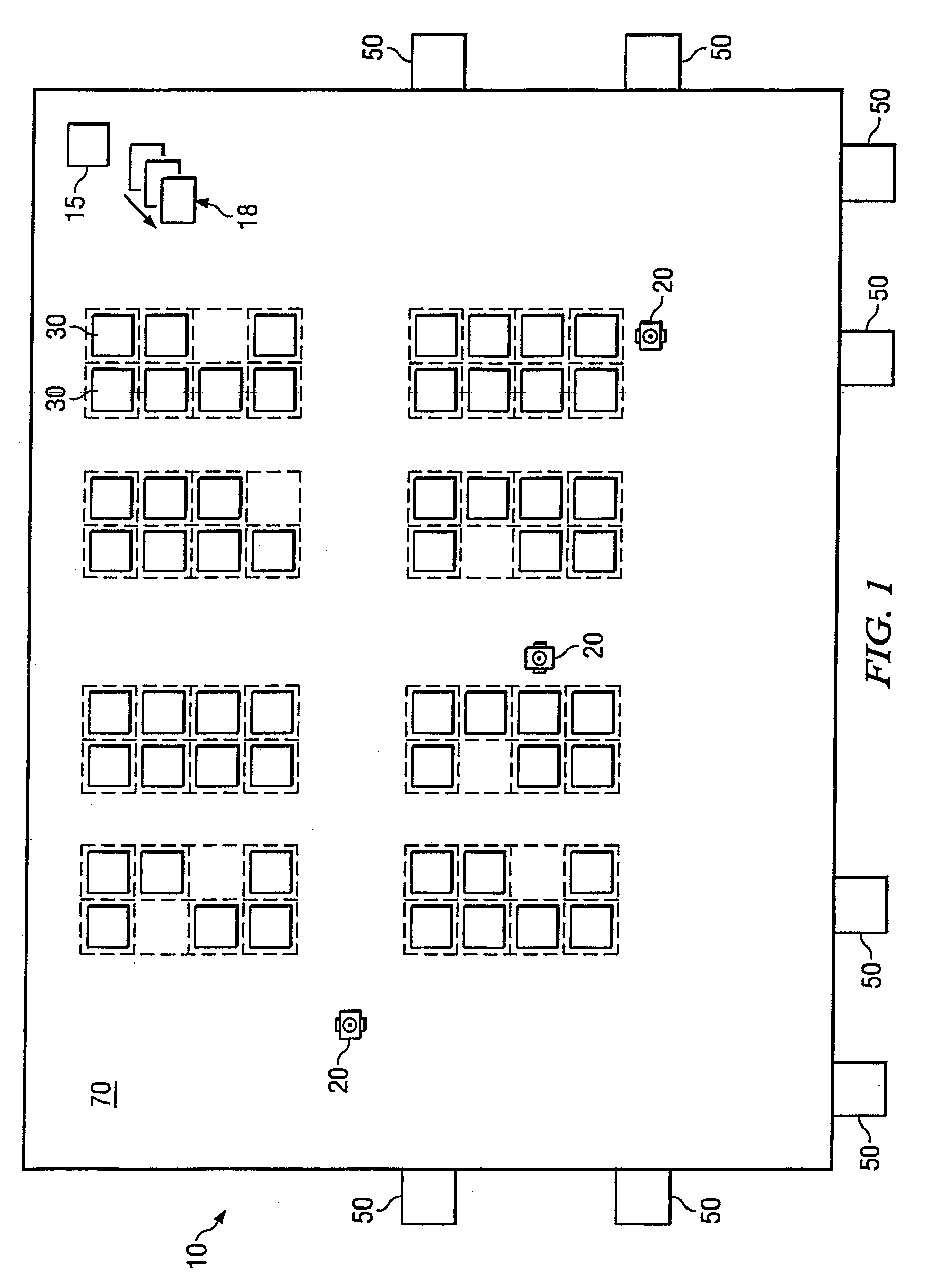
System and method for maneuvering a mobile drive unit
ActiveUS20070290040A1Disadvantages and reduced eliminatedInventory reduced eliminatedVehicle position/course/altitude controlCommerceWorkspaceEngineering
A method of rotating an inventory holder includes moving an inventory holder towards a rotation area along a straight segment of a path with a first face of the inventory holder facing a first direction. The rotation area includes a portion of a workspace designated for rotation of inventory holders. The method further includes moving the inventory holder into the rotation area along a first arced segment with an orientation of the first face perpendicular to the first arced segment. The method additionally includes executing a rotation maneuver within the rotation area and moving the inventory holder out of the rotation area along a second arced segment with a second face facing the first direction.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
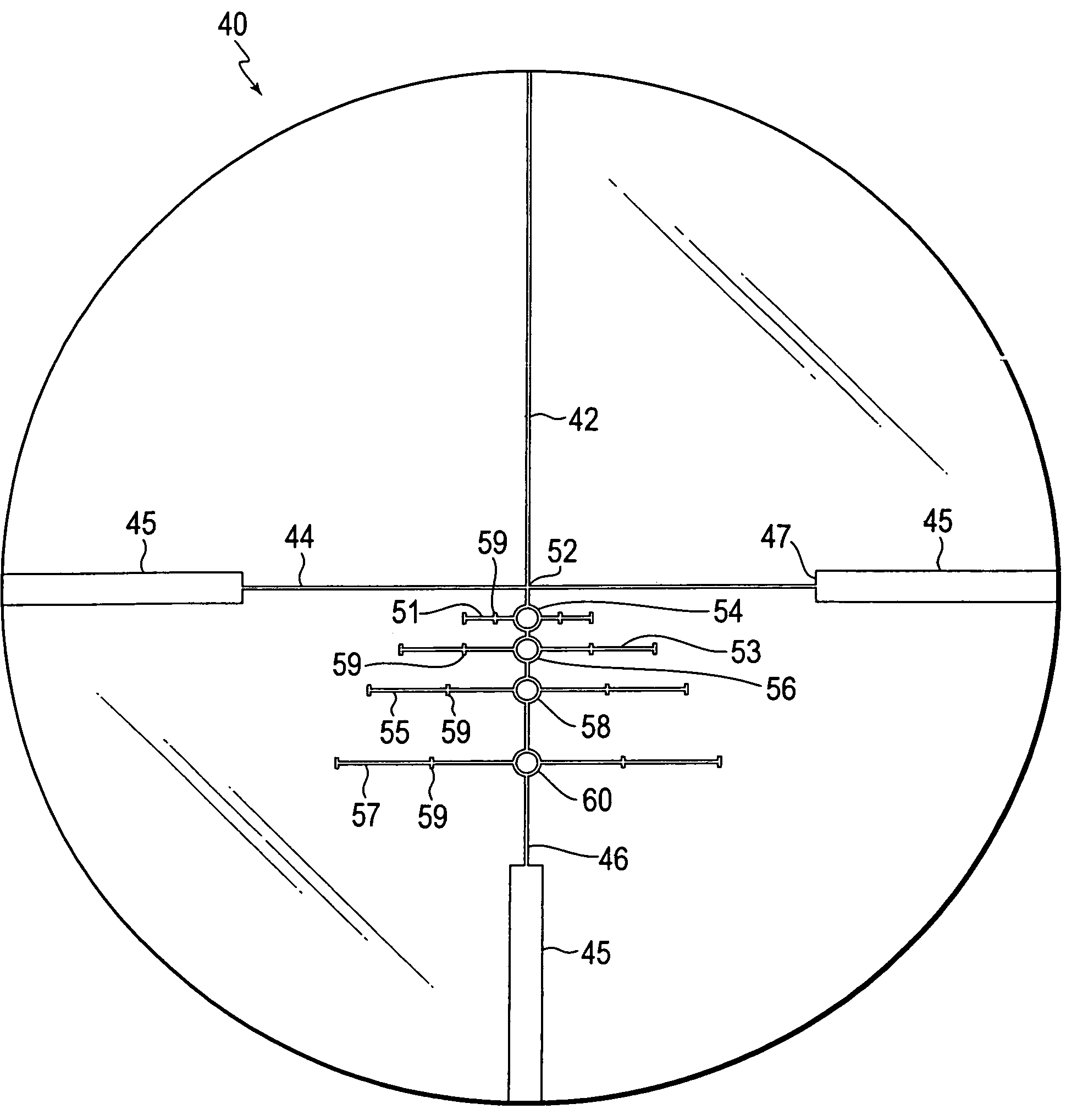
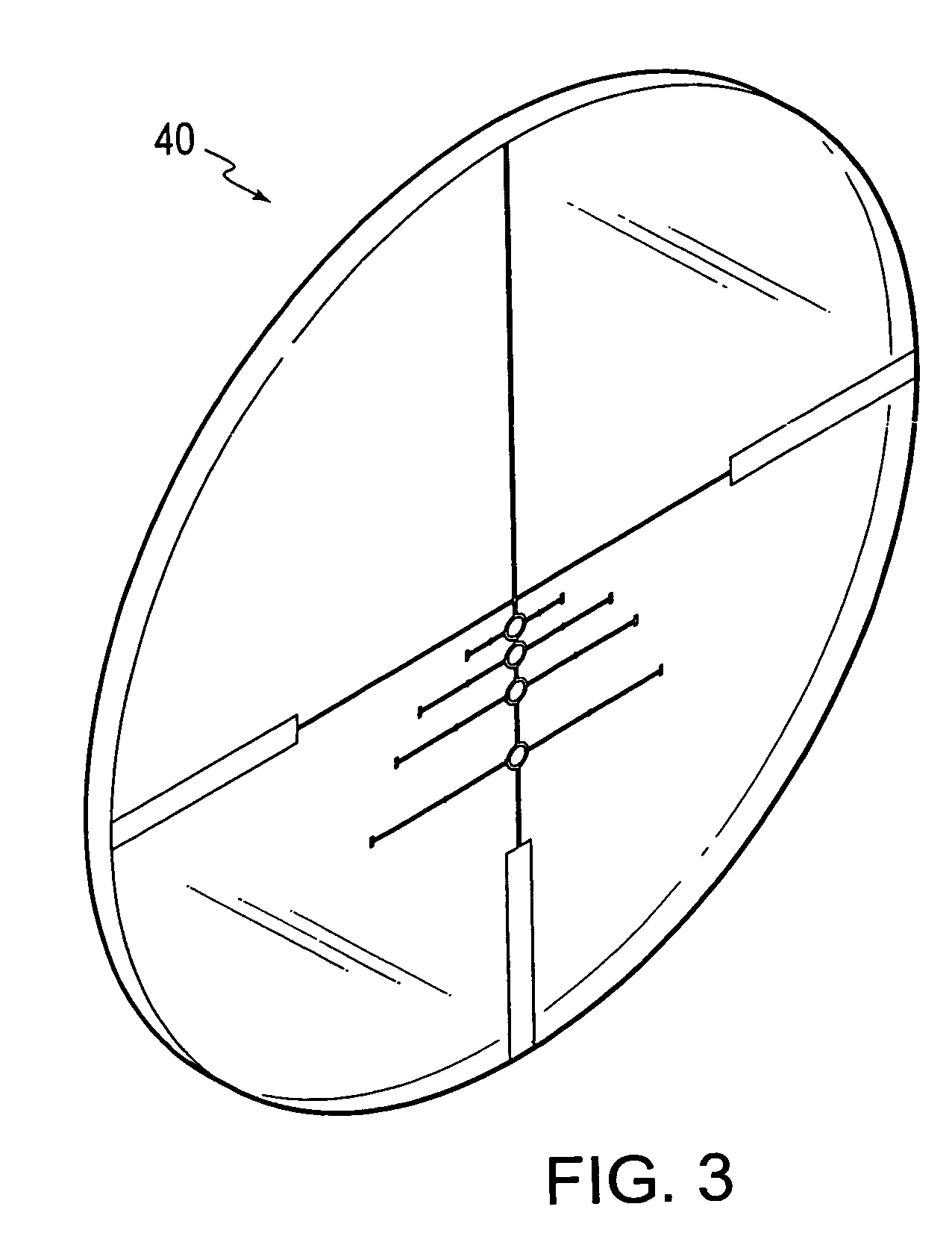
Gun sight reticle having open sighting areas for bullet drop compensation
A gun sight reticle that has orthogonally intersecting center horizontal and center vertical straight hairlines is designed such that at least a portion of the vertical hairline located on a first side of the horizontal hairline is discontinuous such that discontinuities are disposed between straight segments of the vertical hairline. Sighting areas are disposed in at least some of the vertical hairline discontinuities, and the sighting areas are circumscribed by indicia that encloses the sighting area. In one example, the sighting areas are circular, and the indicia for each of the circumscribed sighting areas forms a circle.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL CO INC
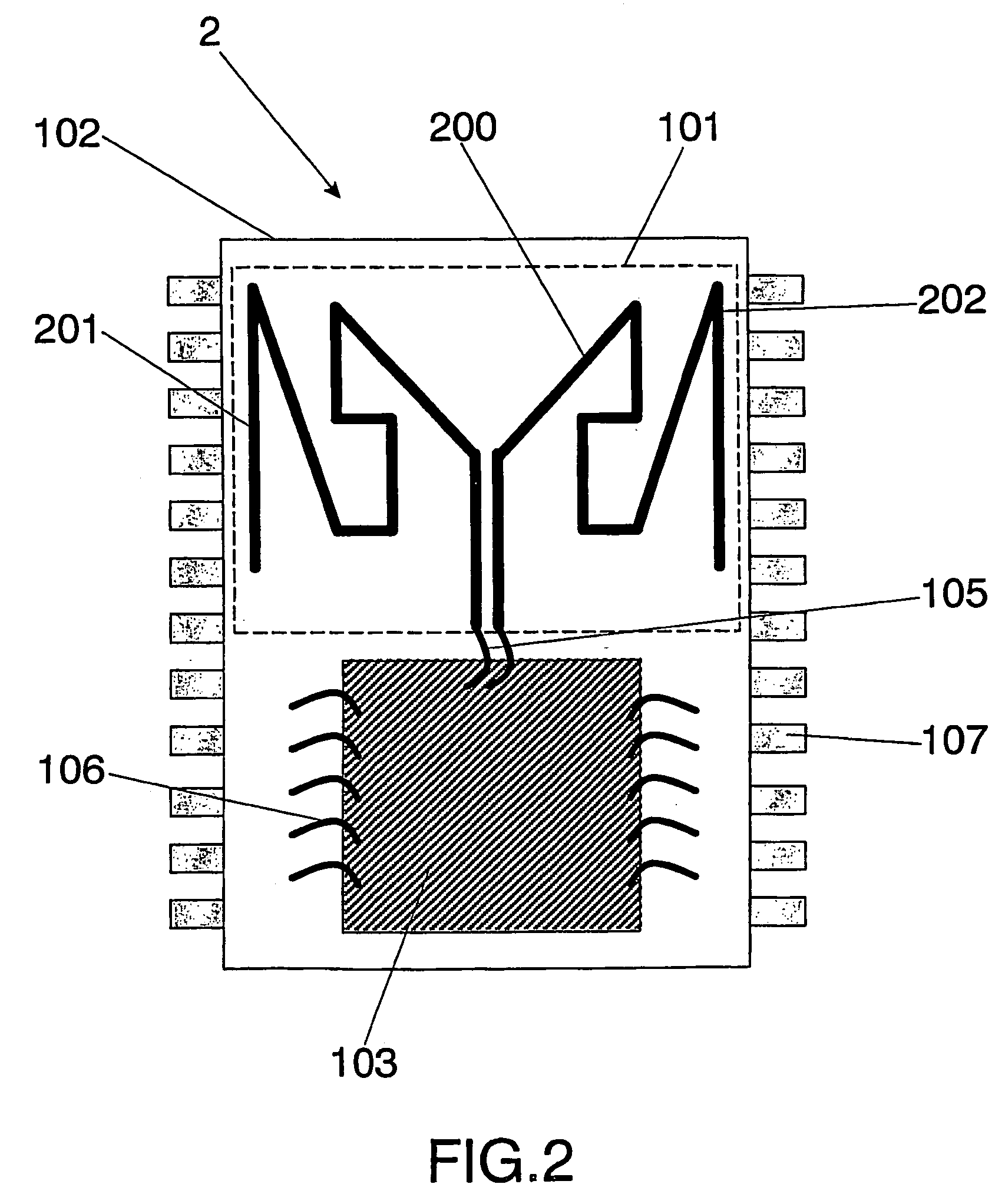
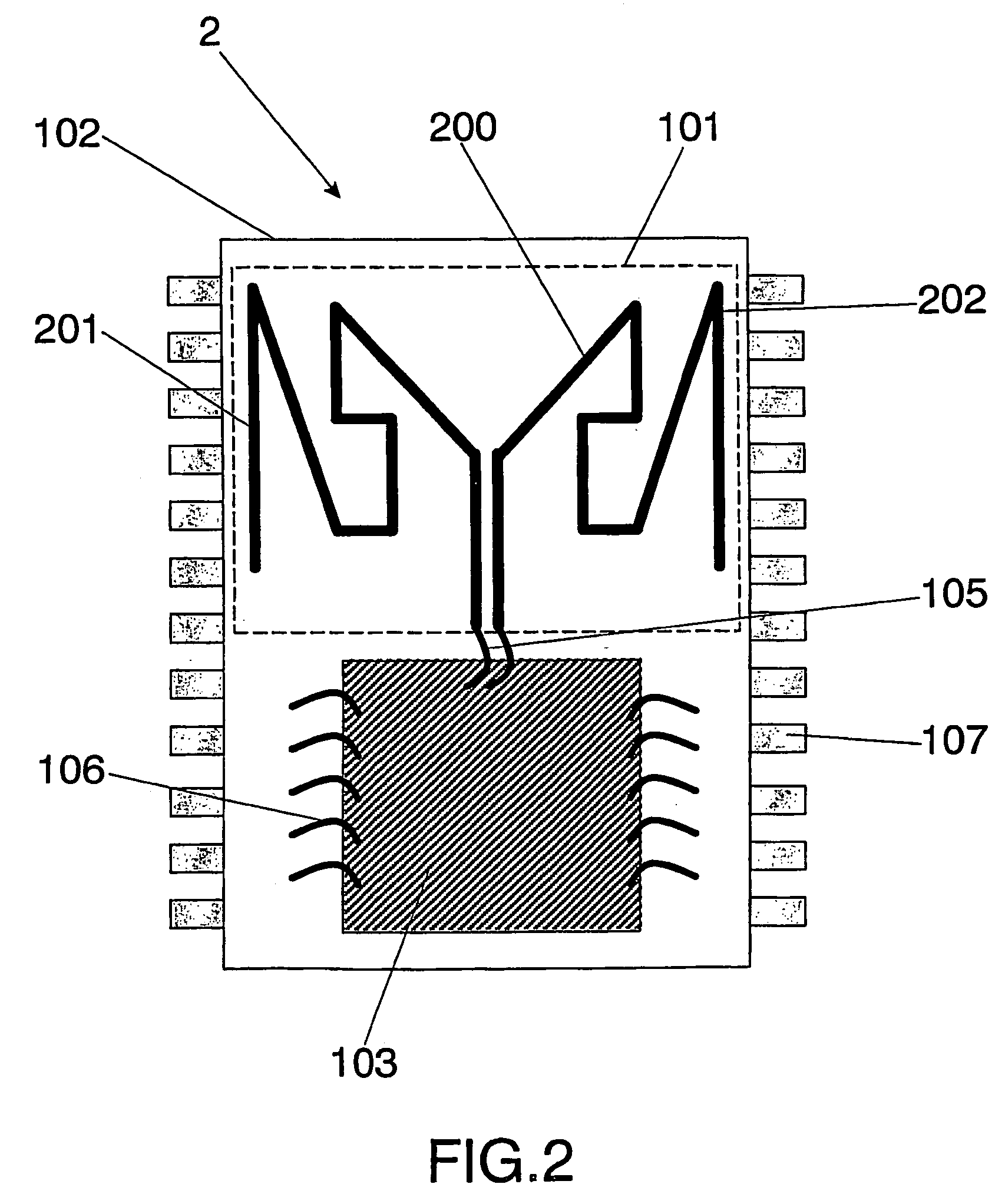
Integrated circuit package including miniature antenna
InactiveUS20060033664A1Small sizeMinimize coiling effectResonant long antennasSimultaneous aerial operationsSemiconductor chipEngineering
The present invention relates to an integrated circuit package comprising at least one substrate, each substrate including at least one layer, at least one semiconductor die, at least one terminal, and an antenna located in the integrated circuit package, but not on said at least one semiconductor die. The conducting pattern comprises a curve having at least five sections or segments, at least three of the sections or segments being shorter than one-tenth of the longest free-space operating wavelength of the antenna, each of the five sections or segments forming a pair of angles with each adjacent segment or section, wherein the smaller angle of each of the four pairs of angles between sections or segments is less than 180° (i.e., no pair of sections or segments define a longer straight segment), wherein at least two of the angles are less than 115°, wherein at least two of the angles are not equal, and wherein the curve fits inside a rectangular area the longest edge of which is shorter than one-fifth of the longest free-space operating wavelength of the antenna.
Owner:FRACTUS
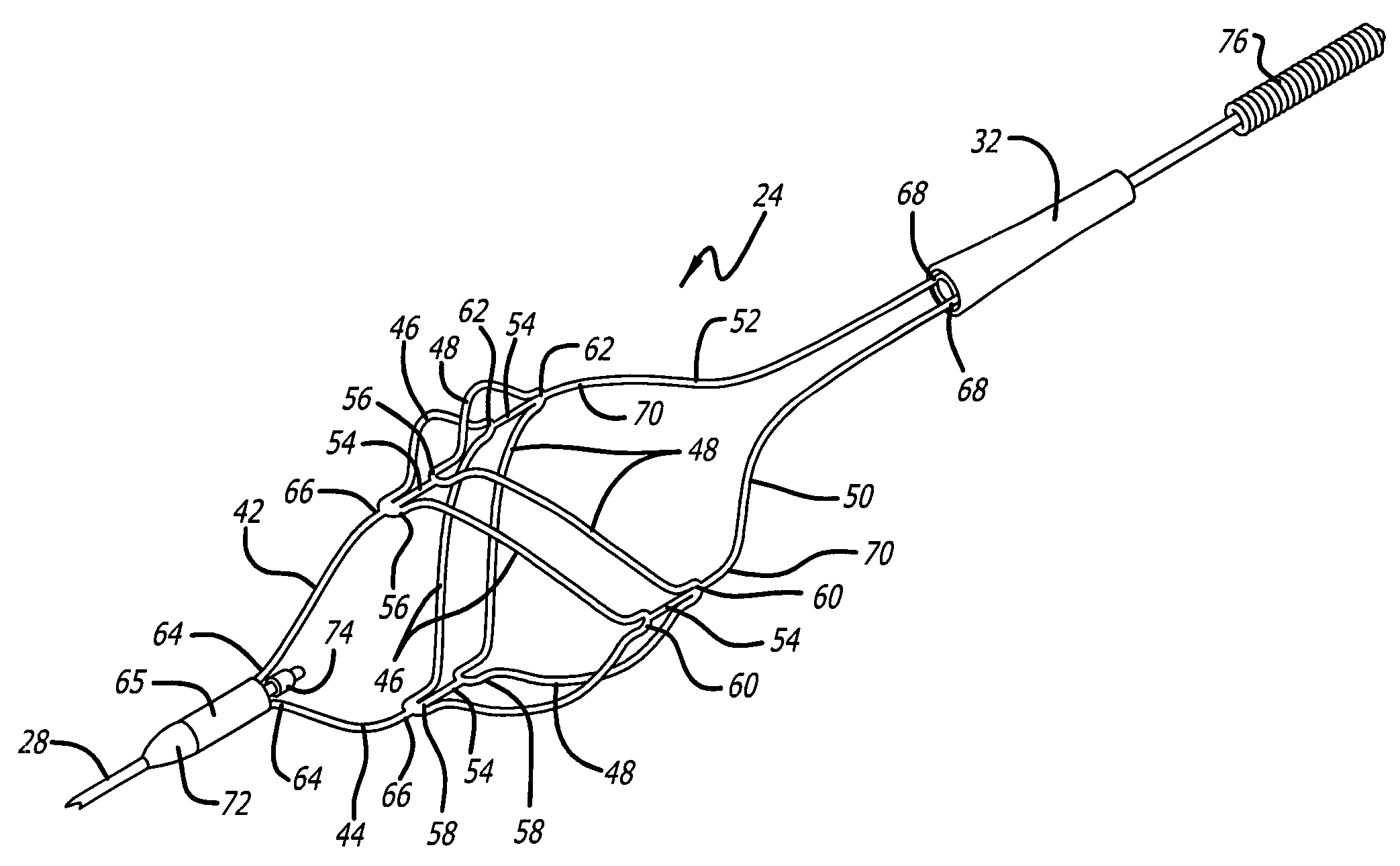
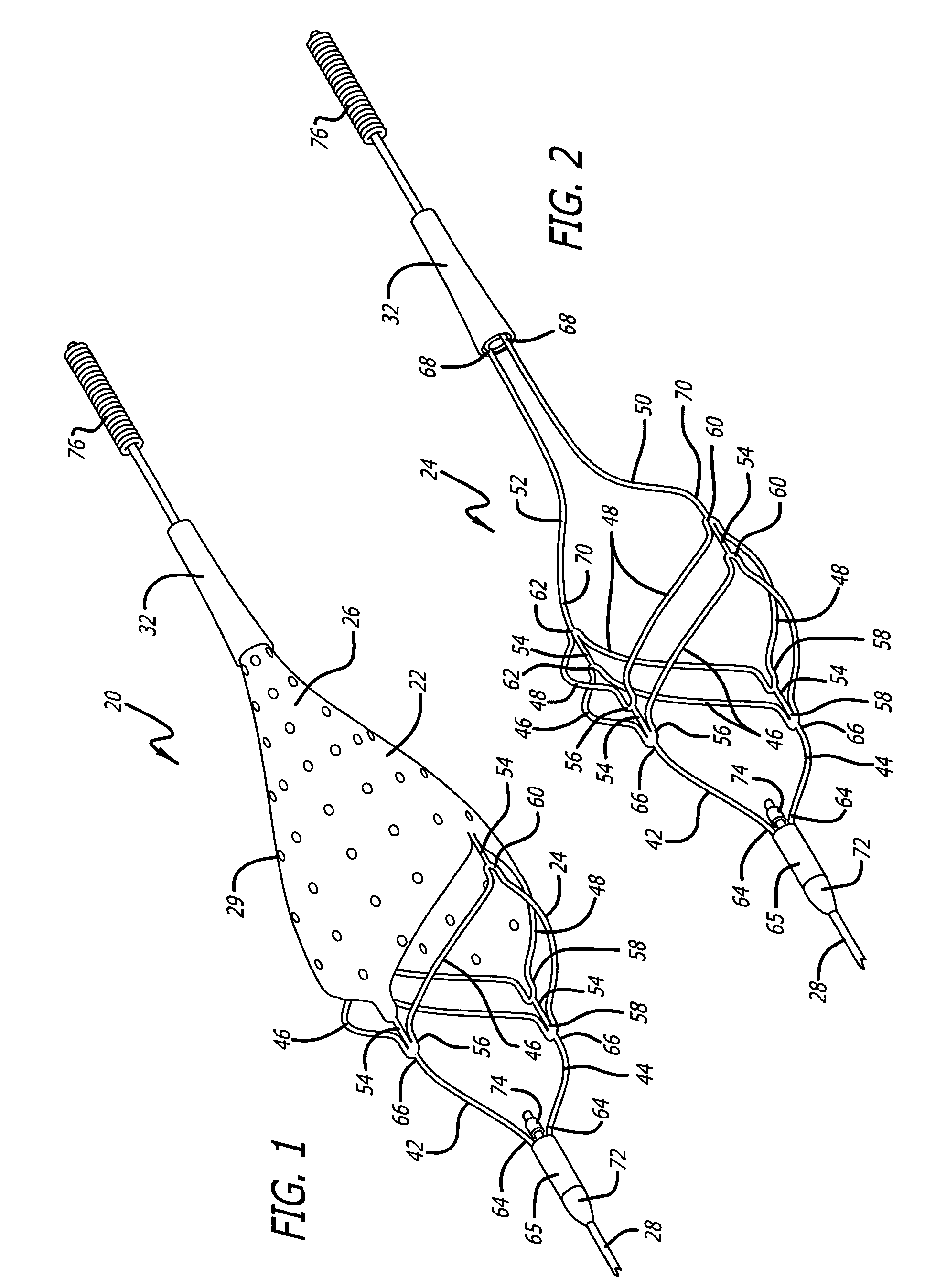
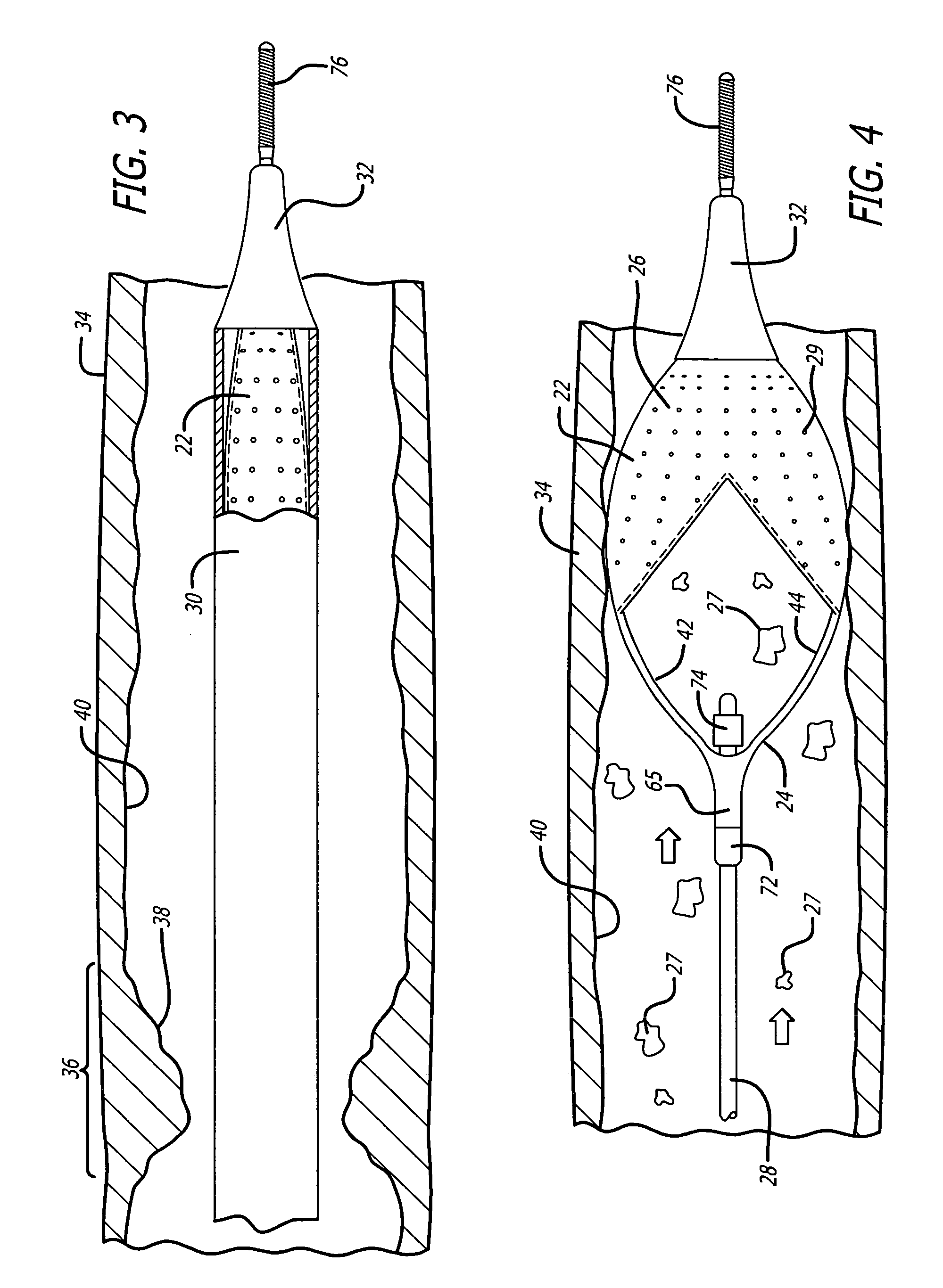
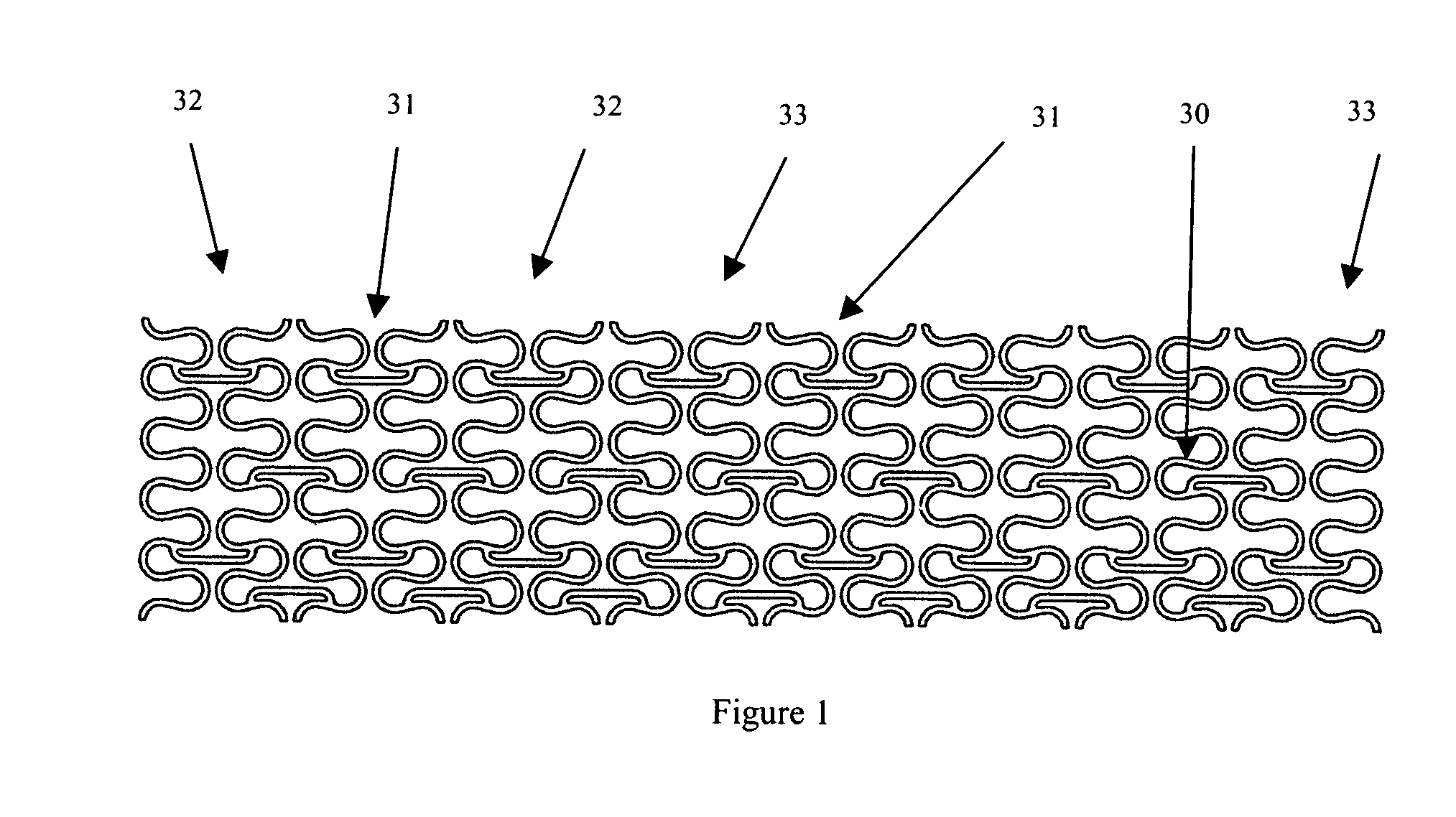
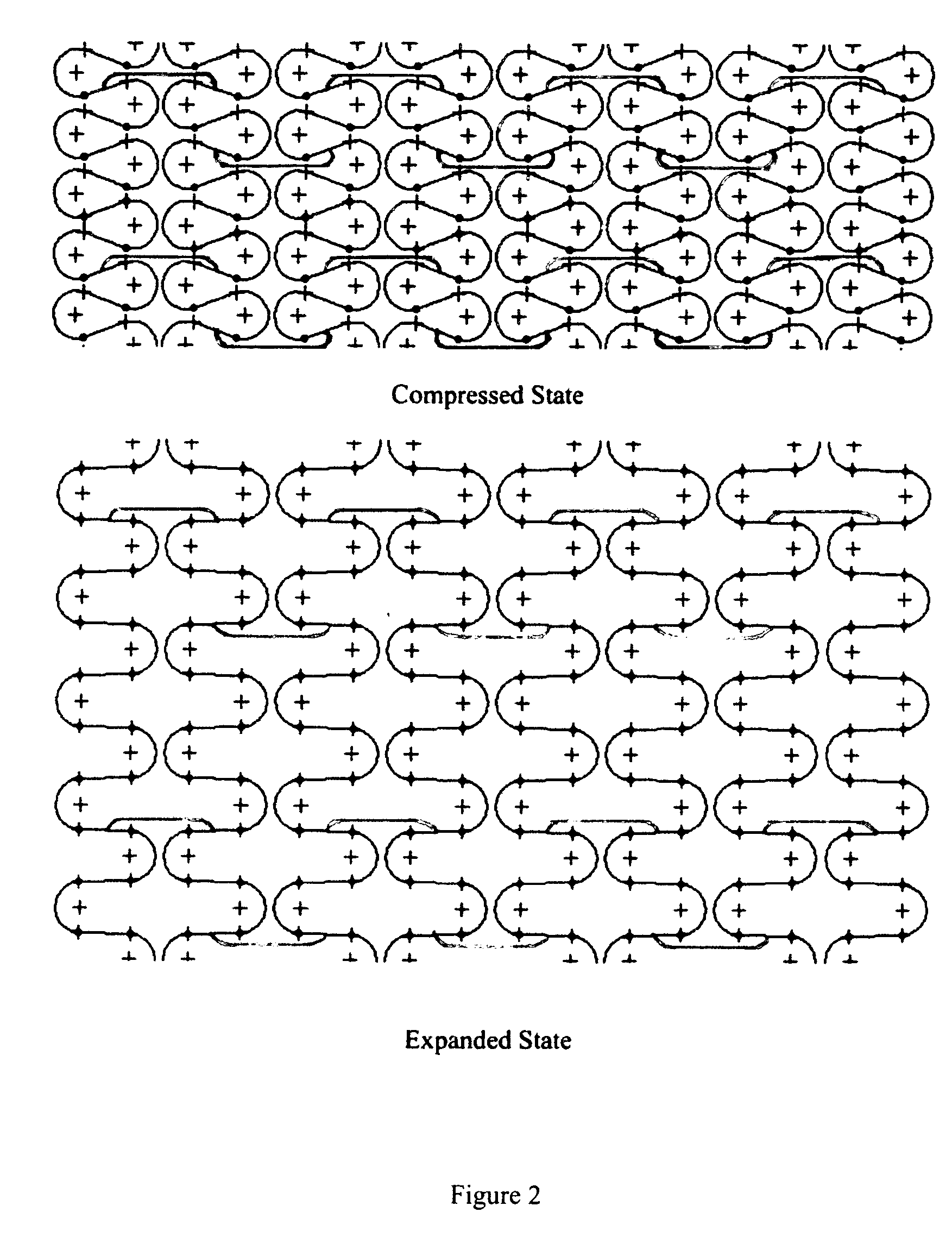
Flexible and conformable embolic filtering devices
InactiveUS7241304B2Increase flexibilityImprove bendabilitySurgeryDilatorsExpandable cageCombined use
A self-expanding cage for use in conjunction with an embolic filtering device includes one or more circumferential members adapted to expand from an unexpanded position to a expanded position within the patient's body vessel. At least one proximal strut and at least one distal strut are attached to the circumferential member to form the basket. The circumferential member may include a plurality of bending regions which enhance the ability of the circumferential member to move between the unexpanded and expanded positions. The proximal and distal struts can be attached to one of the bending regions. When two or more circumferential members are utilized, each member may be connected by a connecting strut which may be connected at a bending region. The connecting strut can be a straight segment or may have a non-linear shape to provide additional flexibility. The expandable cage can be mounted to a elongated member, such as a guide wire, and can be either permanently mounted or rotatably mounted thereto.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
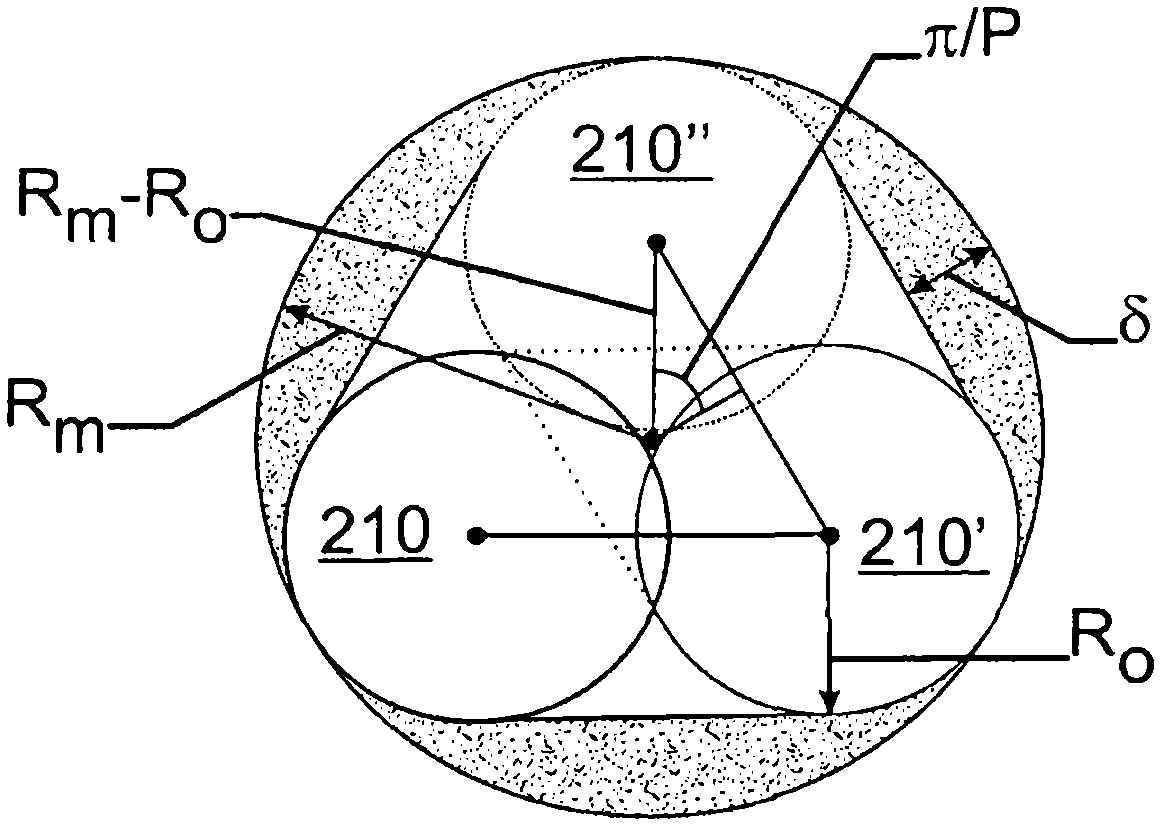
Method for Determining the Horizontal Profile of a Flight Plan Complying with a Prescribed Vertical Flight Profile
ActiveUS20080306680A1Reduce computing costReduce calculationInstruments for road network navigationRoad vehicles traffic controlCheck pointStraight segment
The present invention relates to the definition, in a flight plan, of the horizontal profile of an air route with vertical flight and speed profile prescribed on departure and / or on arrival, by a stringing together of check-points and / or turn points associated with local flight constraints and called “D-Fix” because they are not listed in a published navigation database like those called “Waypoints”. It consists in charting, on curvilinear distance maps, a direct curvilinear path joining the departure point to the destination point of the air route while complying with vertical flight and speed profiles prescribed on departure and / or on arrival and while guaranteeing a circumnavigation of the surrounding reliefs and compliance with regulated overfly zones, then in approximating the series of points of the direct curvilinear path by a sequence of straight segments complying with an arbitrary maximum deviation threshold relative to the points of the series and an arbitrary minimum lateral deviation threshold relative to the set of obstacles to be circumnavigated and in adopting as “D-Fix” points the points of the intermediate intersections of the rectilinear segments.
Owner:THALES SA
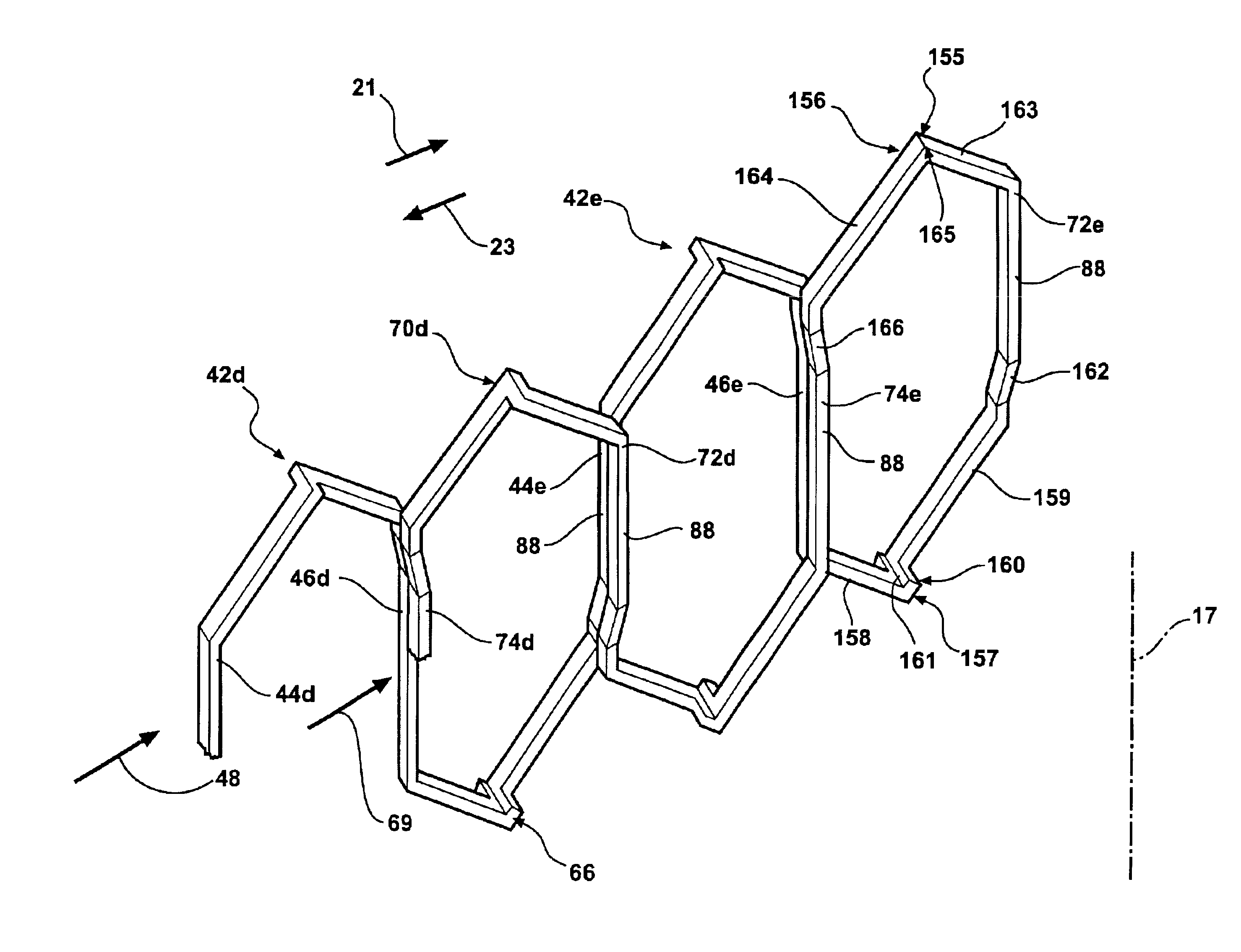
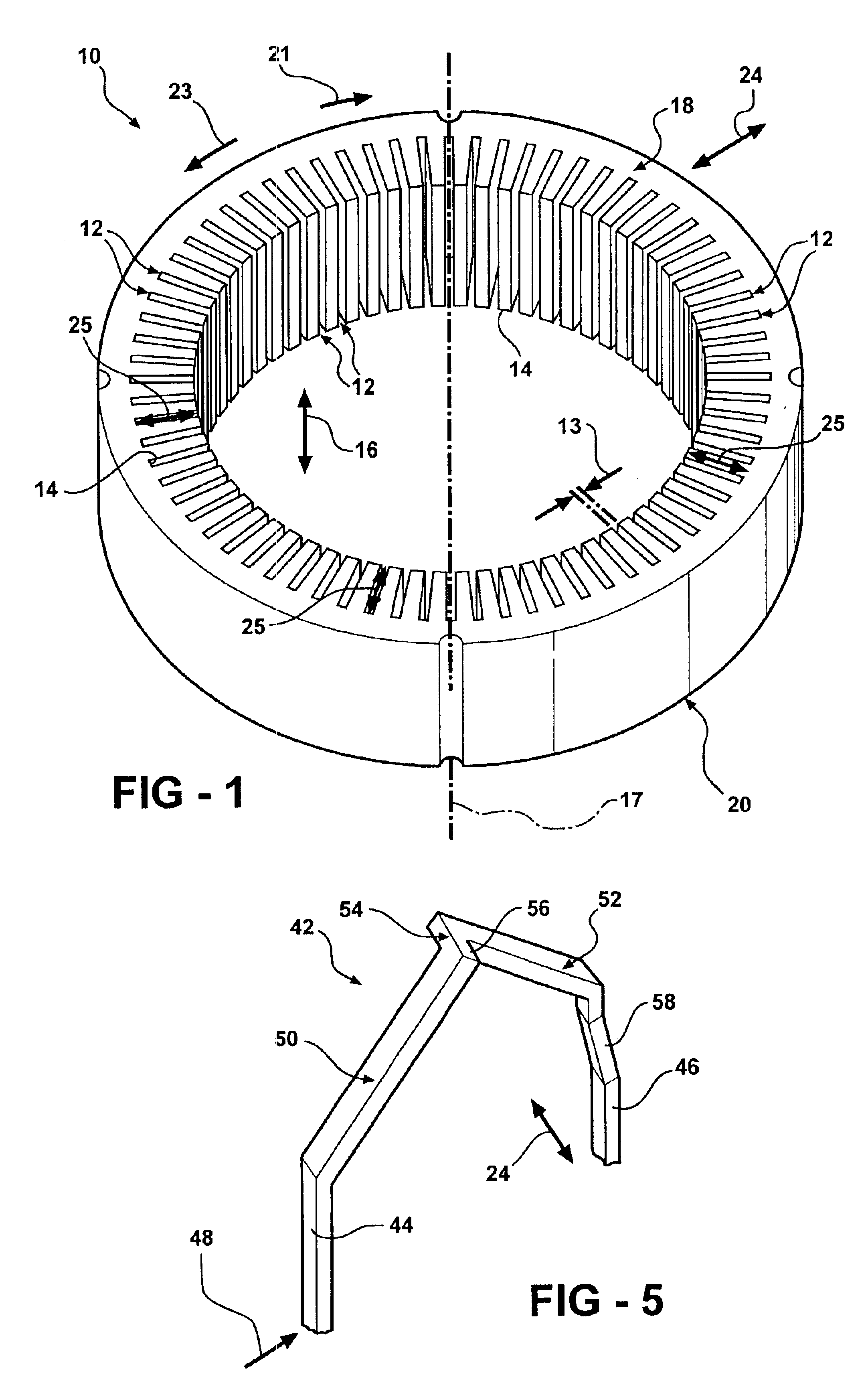
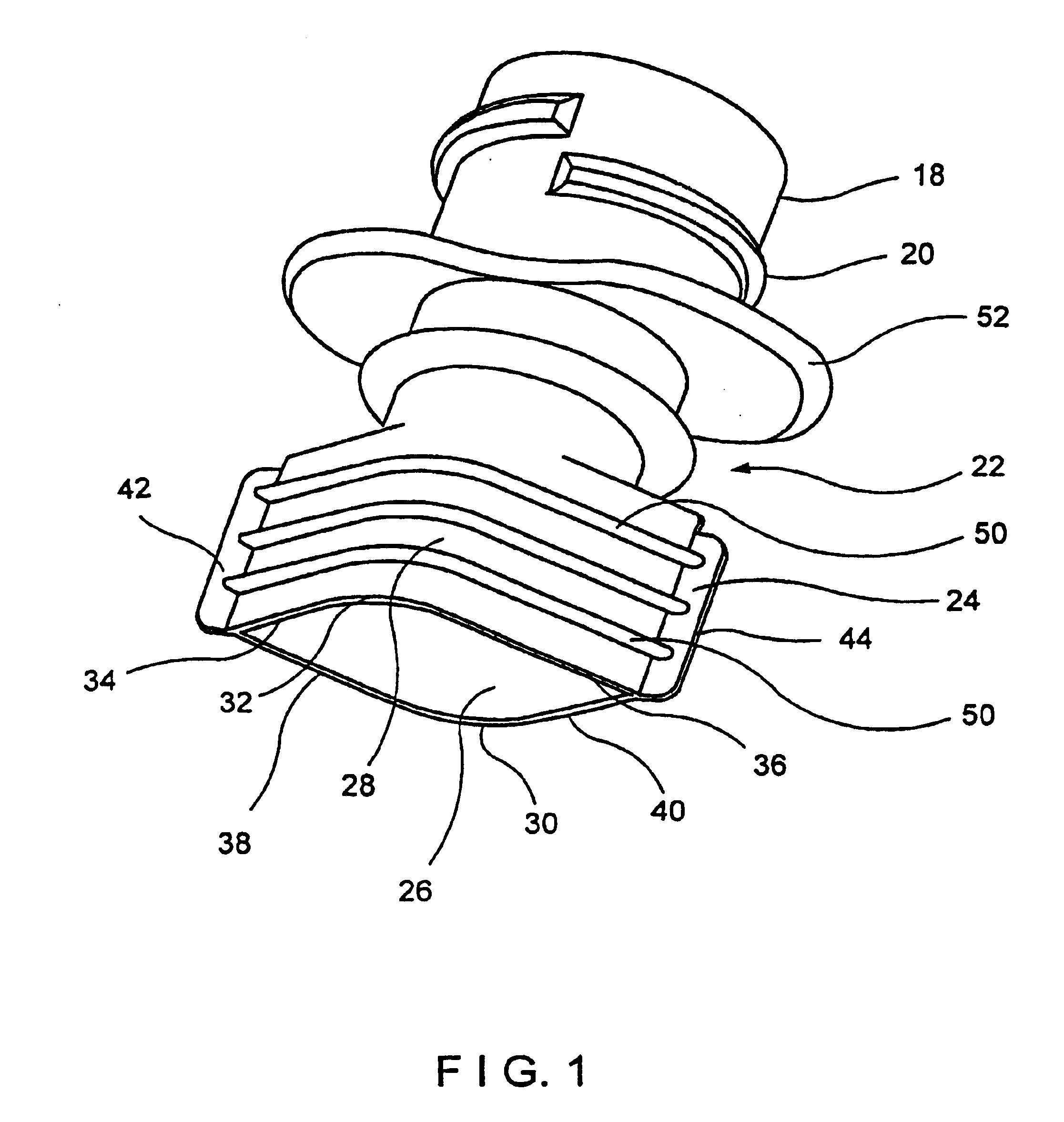
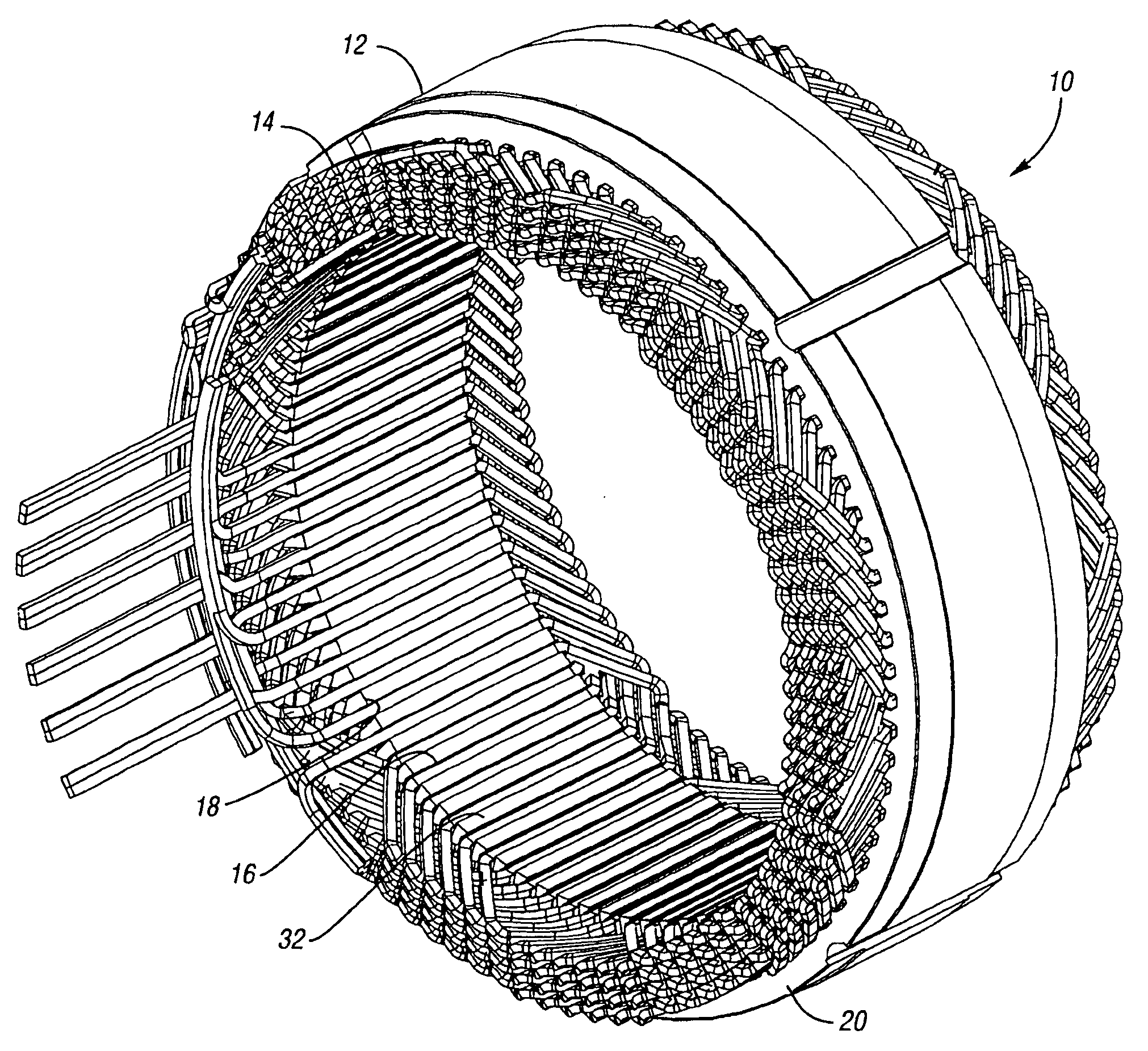
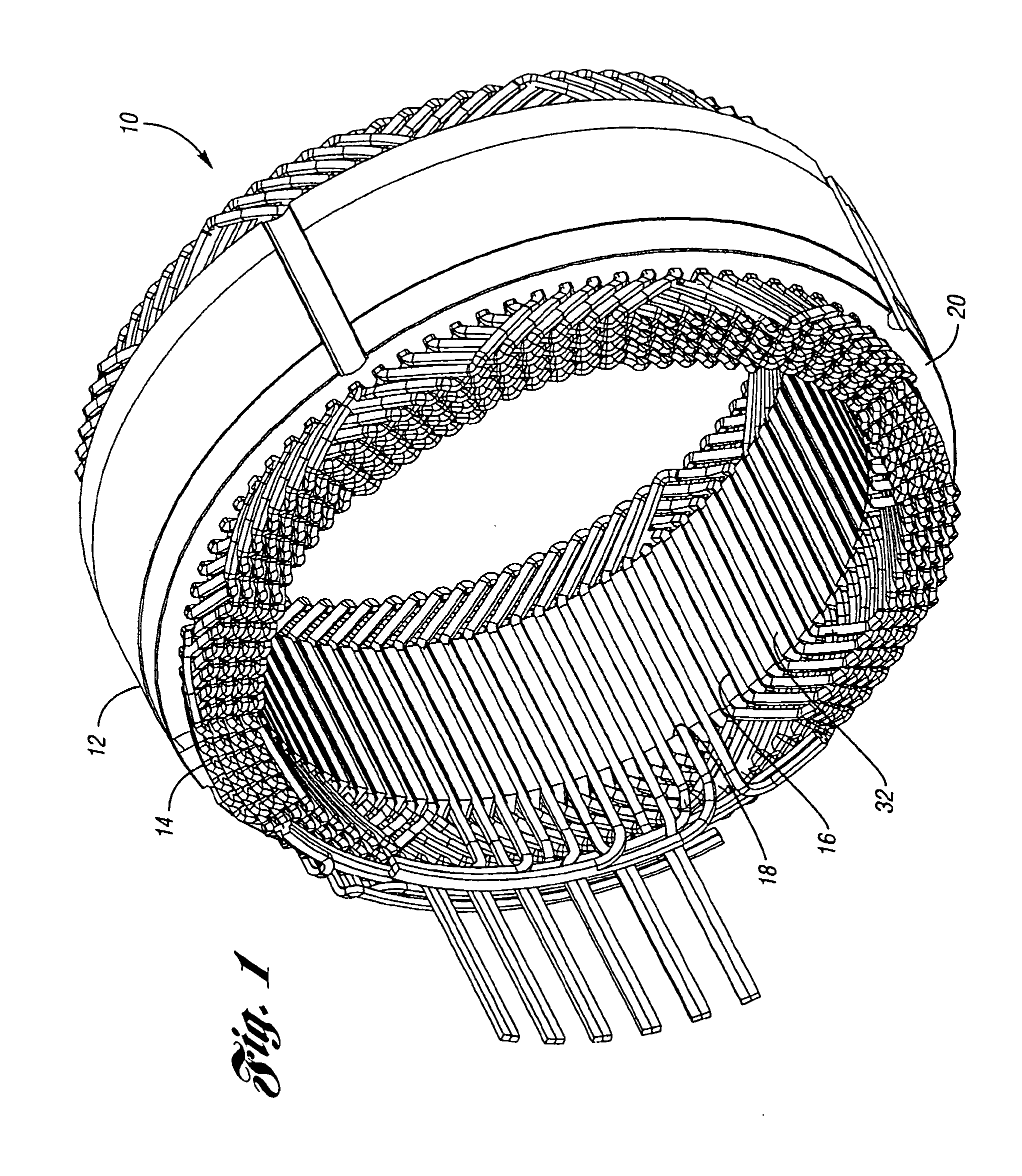
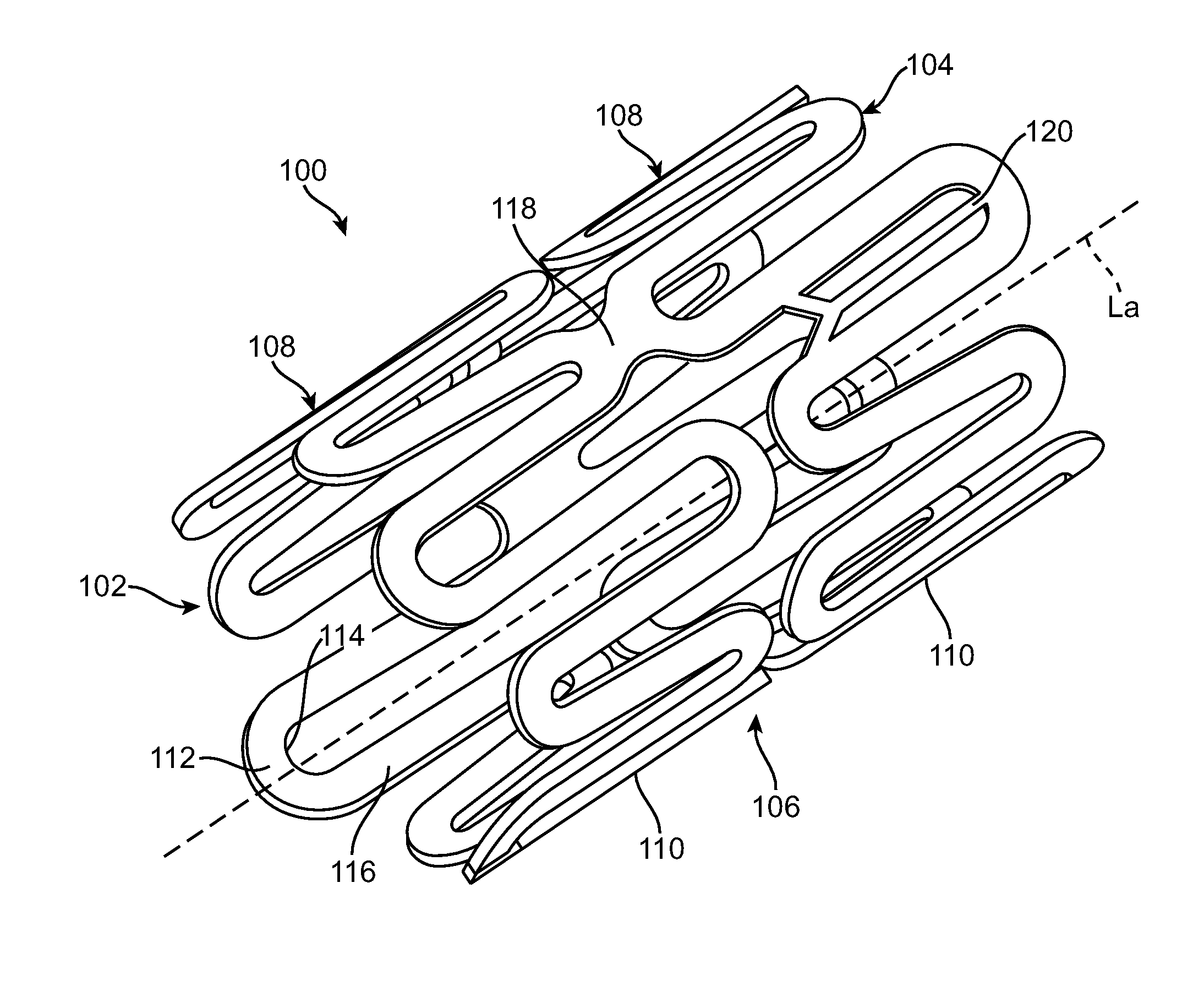
Stator winding having cascaded end loops
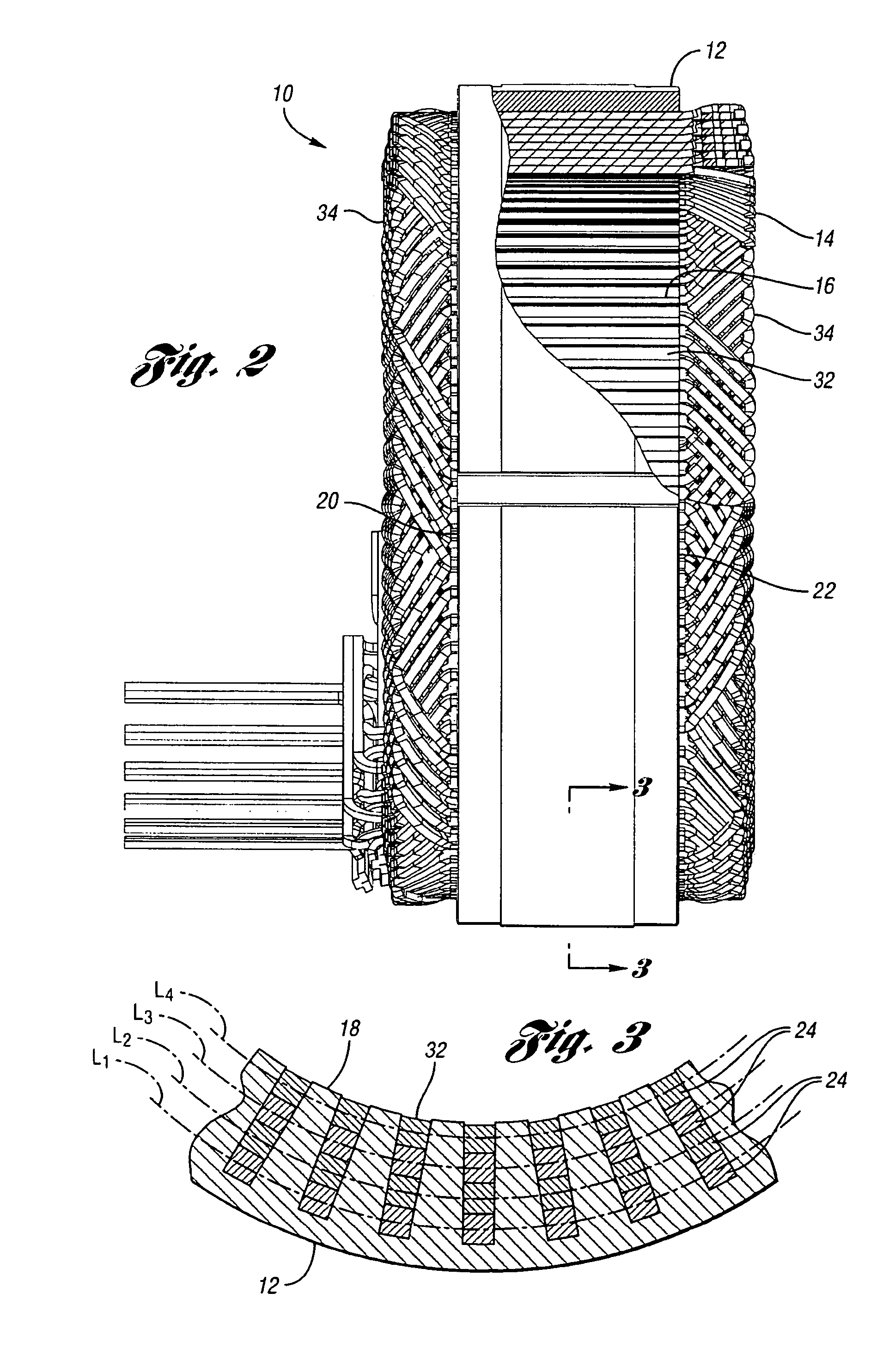
An alternator stator having cascaded end loop segments includes a multi-phase stator winding that is adapted to be placed in a plurality of circumferentially spaced axially-extending core slots in a surface of a stator core. The stator winding includes a plurality of straight segments alternately connected at the first and second ends of the stator core by a plurality of end loop segments to form the winding. The end loop segments include first and second sloped portions meeting at an apex portion. Each of the end loop segments includes a radial outward adjustment and a radial inward adjustment and forms a cascaded winding pattern.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Compact microchannel system
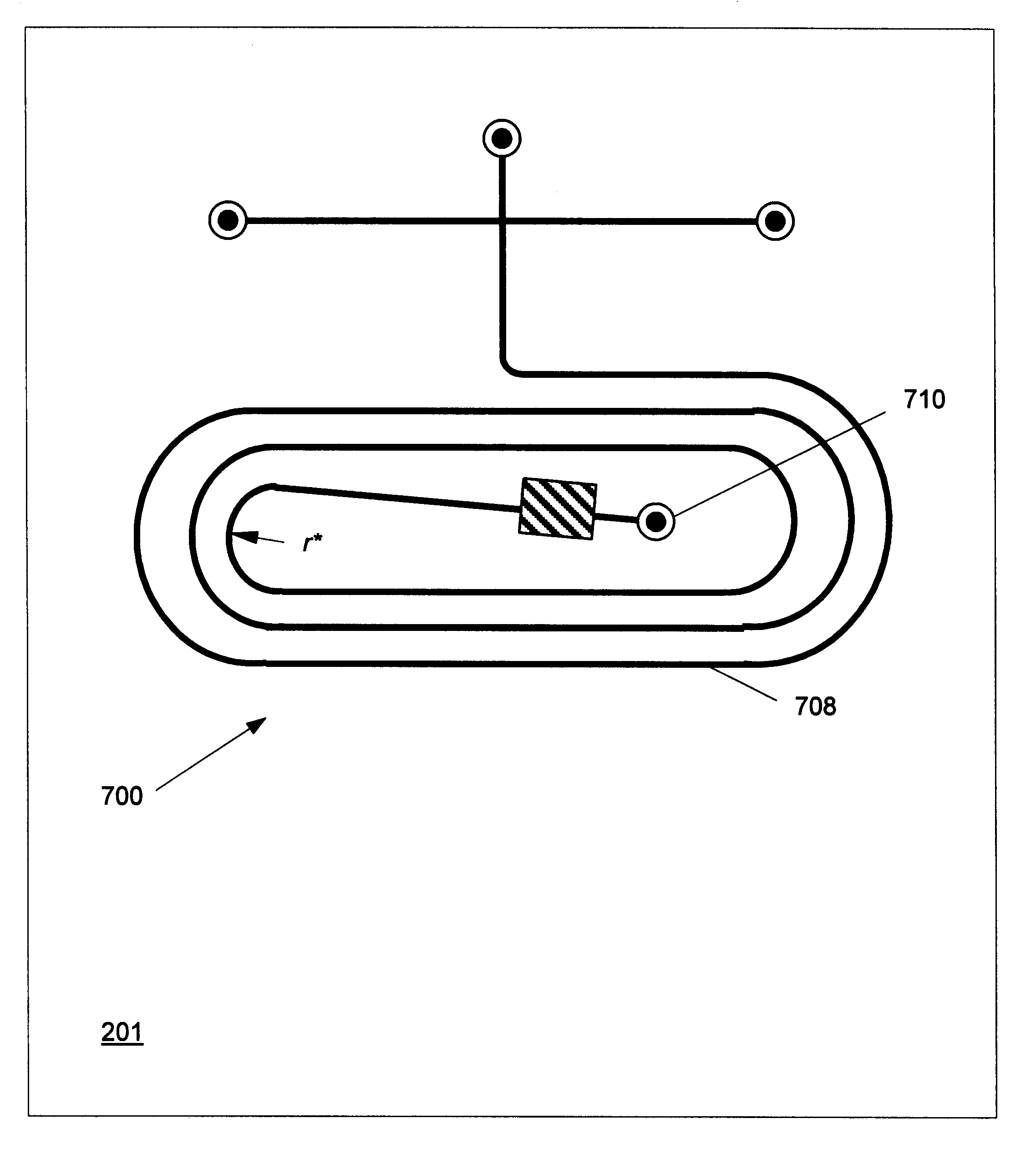
InactiveUS6627076B2Reduces the minimum turn radiusReduction in the minimum radiusIon-exchange process apparatusCellsEngineeringStraight segment
The present invention provides compact geometries for the layout of microchannel columns through the use of turns and straight channel segments. These compact geometries permit the use of long separation or reaction columns on a small microchannel substrate or, equivalently, permit columns of a fixed length to occupy a smaller substrate area. The new geometries are based in part on mathematical analyses that provide the minimum turn radius for which column performance in not degraded. In particular, we find that straight channel segments of sufficient length reduce the required minimum turn radius, enabling compact channel layout when turns and straight segments are combined. The compact geometries are obtained by using turns and straight segments in overlapped or nested arrangements to form pleated or coiled columns.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Iso-truss structure
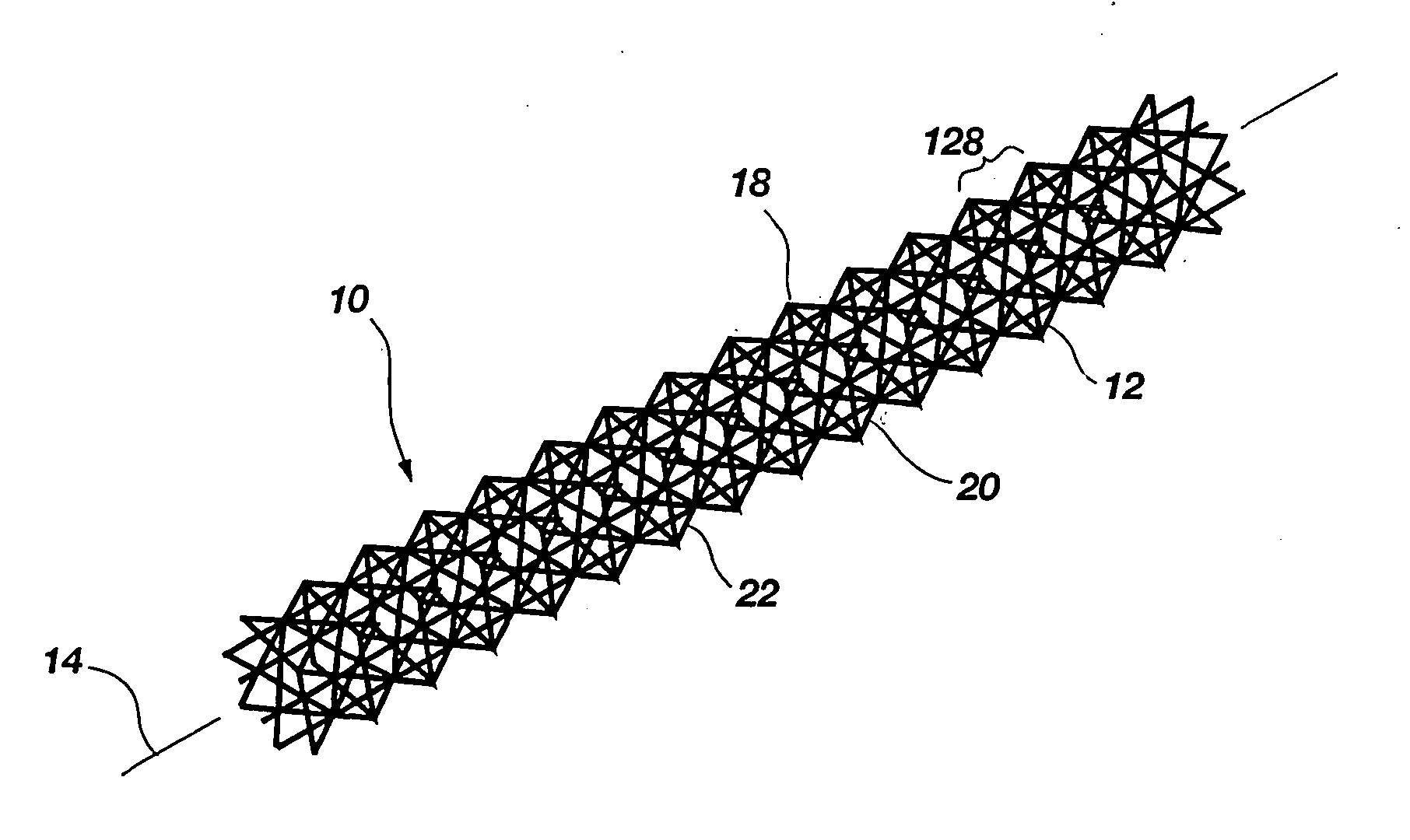
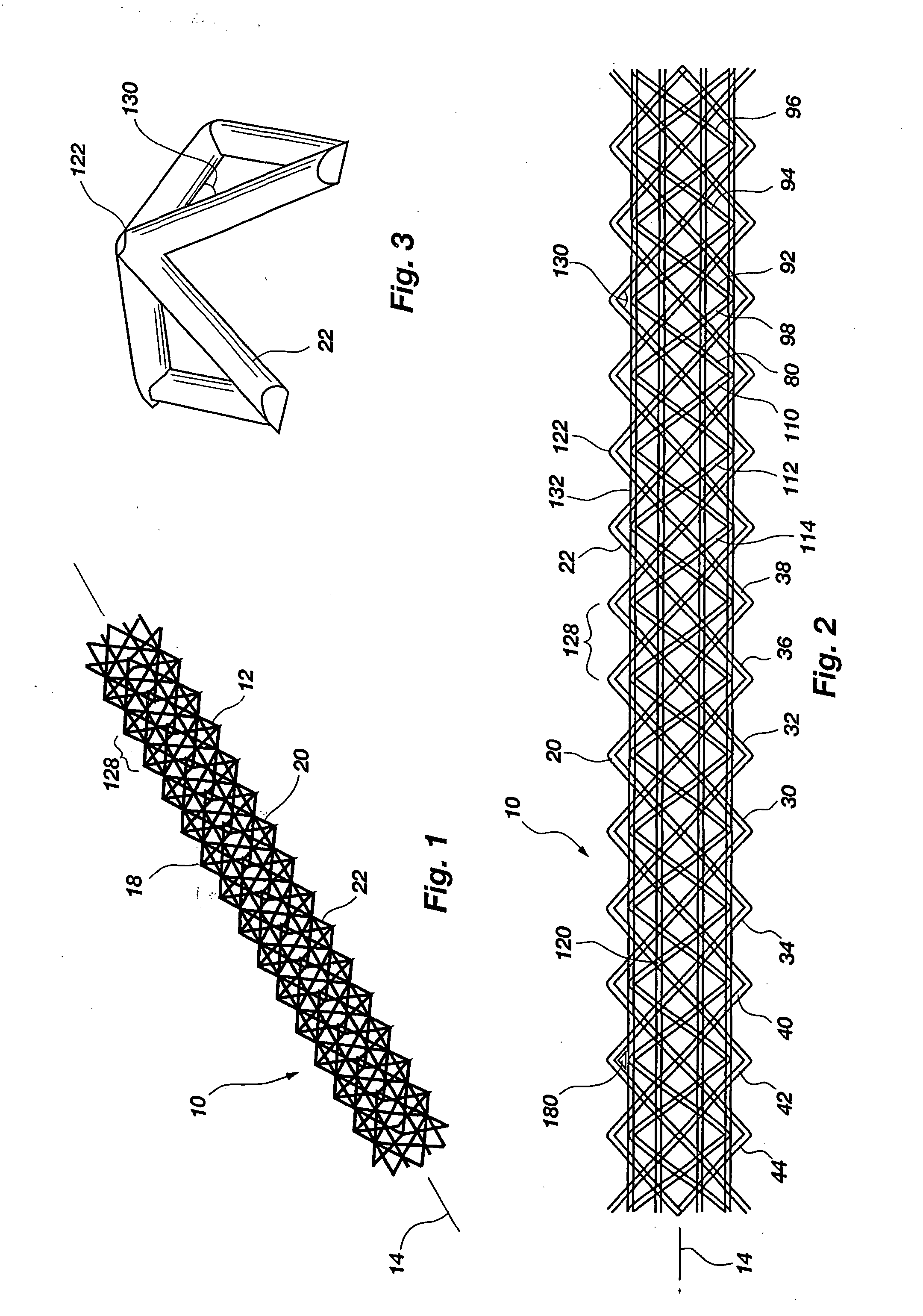
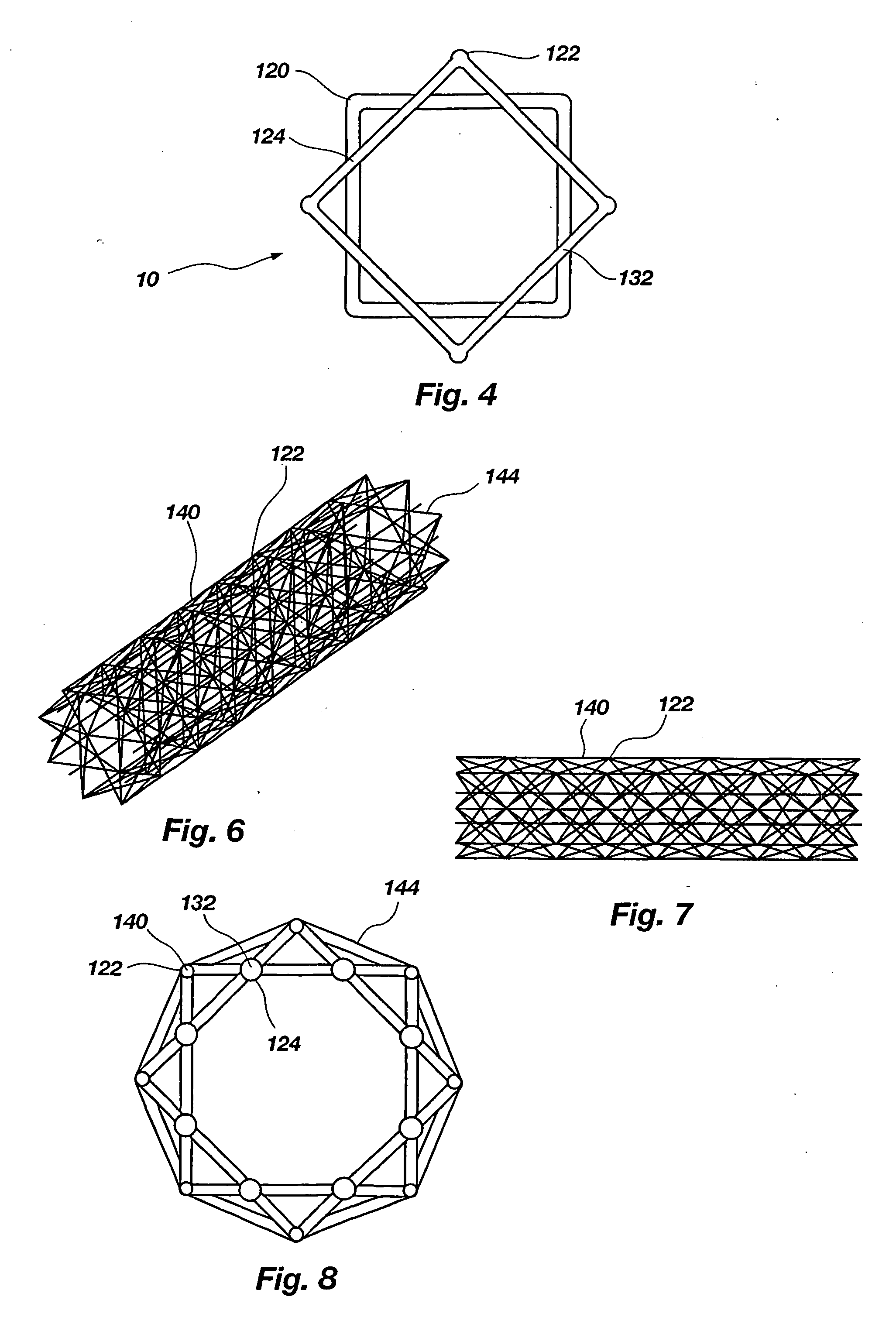
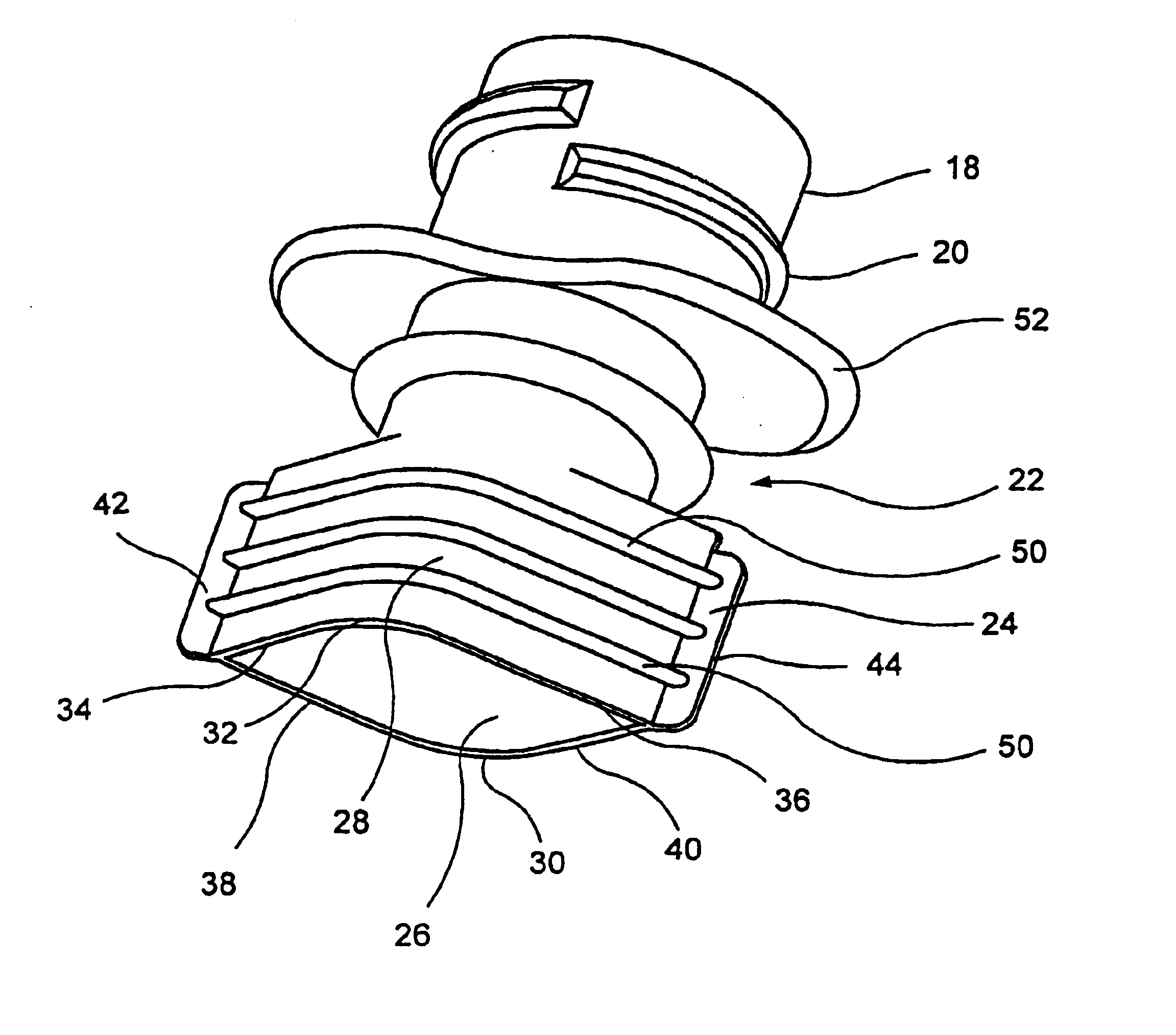
InactiveUS20050115186A1Improved performance characteristicsReduced strengthTravelling sacksTruss-type bridgeSquare cross sectionAngular orientation
An iso-truss structure (10) includes at least two helical components (30, 32) and at least one reverse helical component (34) attached thereto with opposing angular orientations. Each helical and reverse helical component preferably includes at least four elongate, straight segments (22) rigidly connected end to end in a helical configuration forming a single, substantially complete rotation about a common axis (14) forming a first square cross section. The structure may further include at least two rotated helical components (80, 92) and at least one rotated reverse helical component (98) which are rotated with respect to the helical and reverse helical components forming a second square cross section, rotated with respect to the first. The structure may be straight, curved, flexible, or form angles.
Owner:ISOTRUSS IND LLC
Flexible pouch fitment structure
InactiveUS6860406B2Increase speedFacilitate and enhance sealingEnvelopes/bags making machineryBag making operationsEngineeringStraight segment
A flexible plastic fitment for providing spouts for pouches formed of sheet material. The fitment includes a pair of opposed side walls each having a center portion formed from diametrically opposed segments of a common cylinder and straight segments that blend respectively into the cylindrical segments on opposite sides of the common cylinder. The side walls are joined together at both ends thereof to form a canoe shape. A cover, which provides the only support for the side walls joins the top edges of the canoe shape and extends at both ends of the canoe shape between the cylindrical segments and the joined ends. A thin fin extends from each end of the joined side walls. A method of and apparatus for attaching the fitment by distending the side walls outwardly while urging the sheet material toward the side walls is also disclosed.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Energy dissipation type buckling constraint support with symmetrical initial imperfection unit at end
ActiveCN105971356AOptimize layoutFlexible layoutProtective buildings/sheltersShock proofingManufacturing technologyBuckling-restrained brace
The invention discloses an energy dissipation type buckling constraint support with a symmetrical initial imperfection unit at the end. The energy dissipation type buckling constraint support is characterized in that the support is composed of an end constraint segment, an energy dissipation segment and a support straight segment; and the two ends are connected with beams or column components or nodes to form a whole through bolt connection so as to achieve the purpose of improving of the resistant-lateral rigidity of components. The energy dissipation type buckling constraint support with the symmetrical initial imperfection unit at the end is adopted, and thus under the action of a small earthquake, the buckling constraint support keeps elasticity; and under the action of a medium earthquake or a severe earthquake, the buckling constraint support enters a yield stage, and the effect of a damper can further be achieved through the good hysteretic energy dissipation performance of the buckling constraint support. Compared with traditional buckling constraint supports, according to a manufacturing technology of the energy dissipation type buckling constraint support, the processes of adding a sleeve outside a core energy dissipation component, grouting and the like in the traditional manufacturing process are avoided in the manufacturing technology, so that manufacturing is convenient. The energy dissipation type buckling constraint support can be prefabricated and formed in a factory, the quality of the components is ensured, the workload of site operation is reduced, and energy conservation and environment protection are achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Syringe and method of using
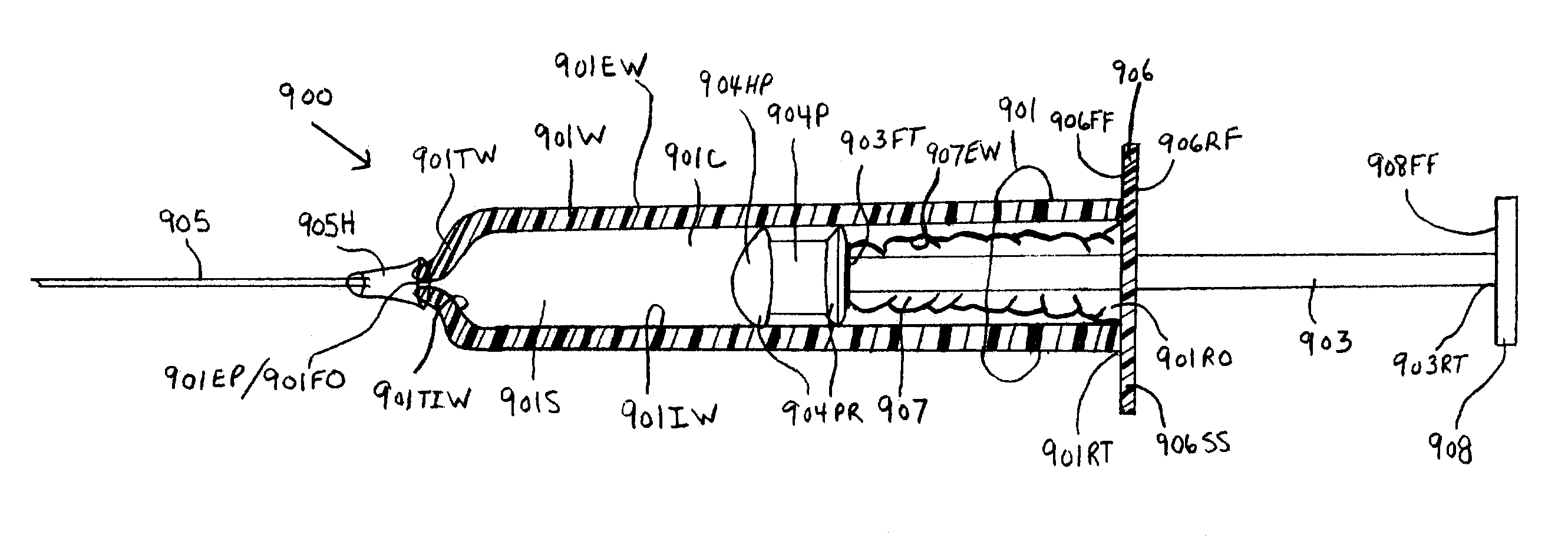
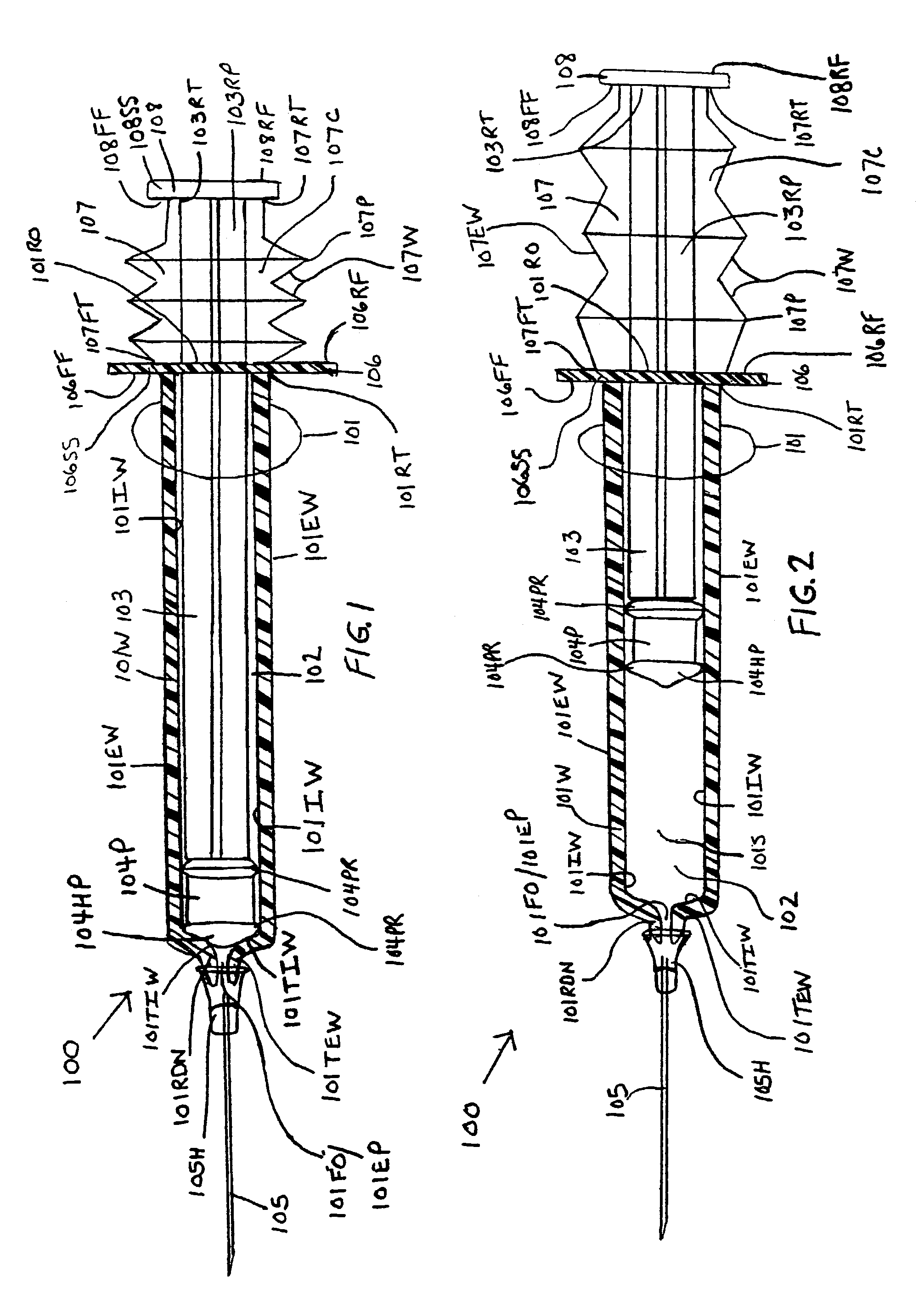
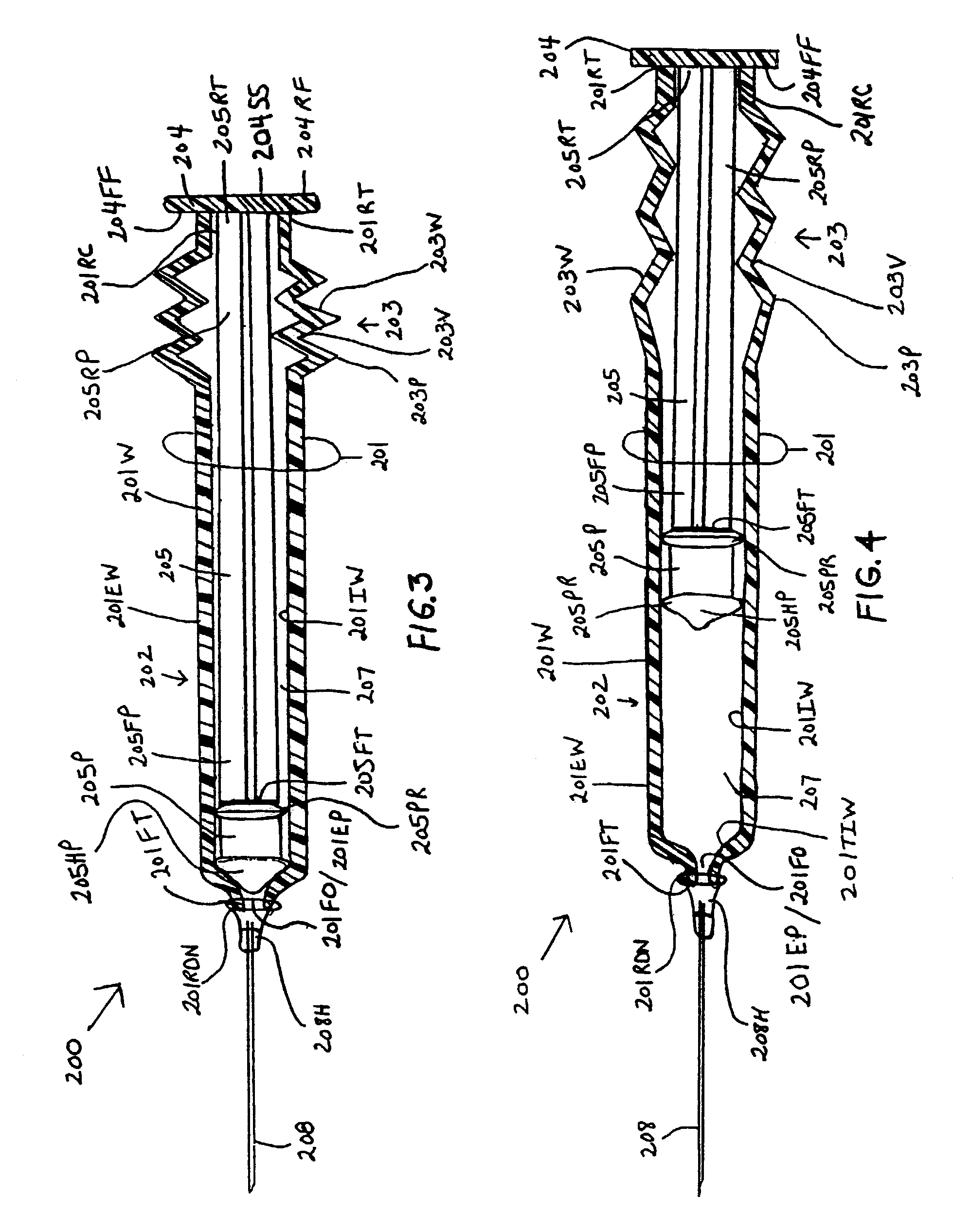
InactiveUS7077826B1Avoid accidental separationGuaranteed stable workInfusion syringesIntravenous devicesStraight segmentBiomedical engineering
Syringes and methods of using are described which protect the syringe barrel cavity from contaminants. A first syringe is formed with a corrugated sheath or non-corrugated sheath which is positioned internal or external to the syringe barrel cavity. A second syringe is formed with a syringe barrel having a straight segment and a corrugated segment having the forward face of the plunger handle member molded to the rearward terminus of the corrugated segment of the syringe barrel. A third syringe is formed from mating syringe barrel and plunger member walls. The walls of the mating syringe barrel and plunger member are concentric and slide relative to each other while maintaining an enclosure around the plunger shaft. A fourth syringe is formed from inner and outer concentric syringe barrel walls mating with the walls of a plunger member. The mating walls are concentric and slide relative to each other while maintaining an enclosure around the plunger shaft. A fifth syringe is formed with an end cap contaminant shield having an extension wall that is mated with the inner wall surfaces of the syringe barrel cavity, or outer wall surfaces of the syringe barrel. Alternatively, the end cap contaminant shield can be provided with a flat design without the extending wall and is bonded or molded to the rearward end terminus of the syringe barrel. The end cap contaminant shield designs are provided with an opening defining the shape of the cross-section of the plunger shaft.
Owner:GRAY ROBIN SCOTT
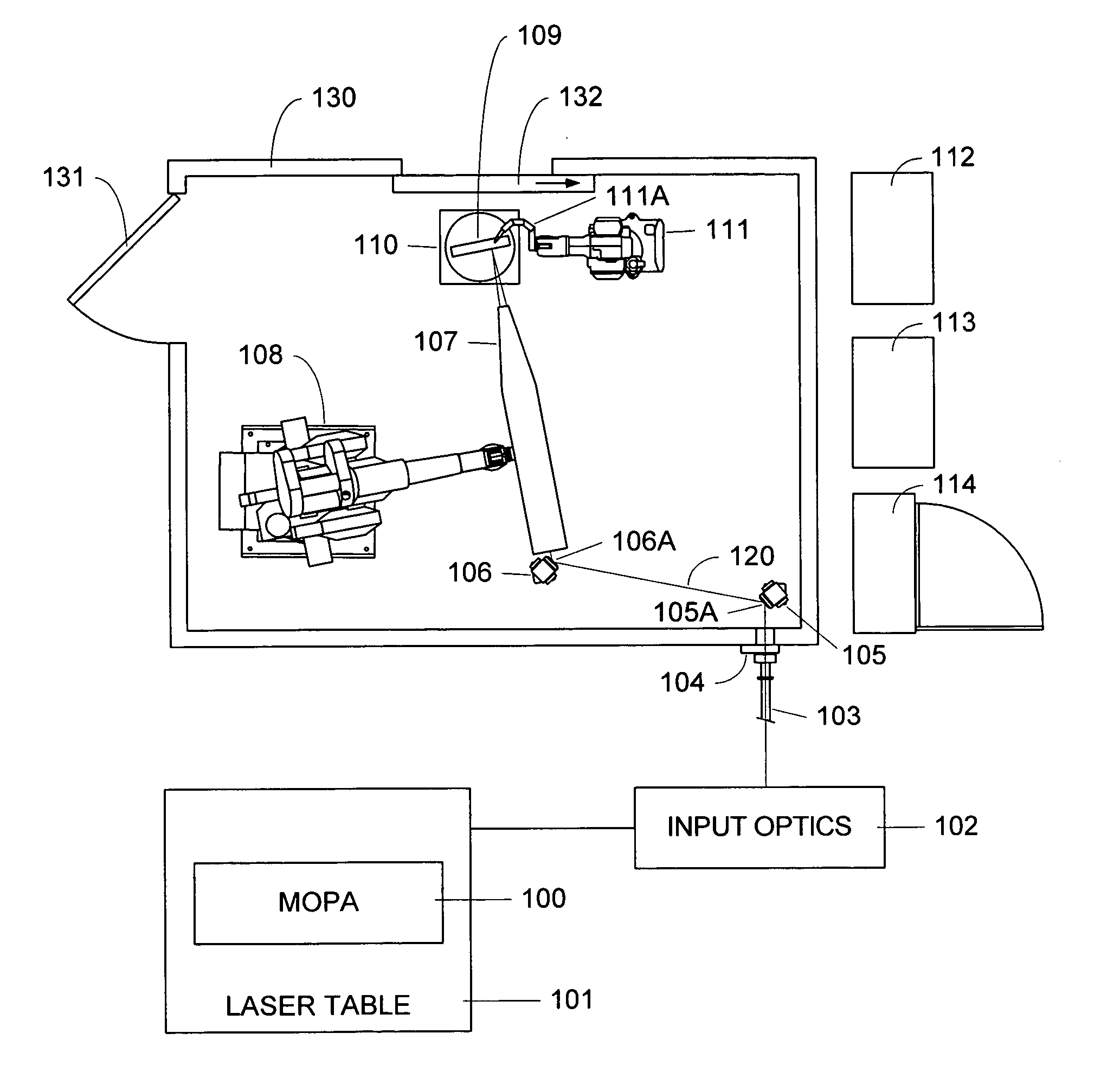
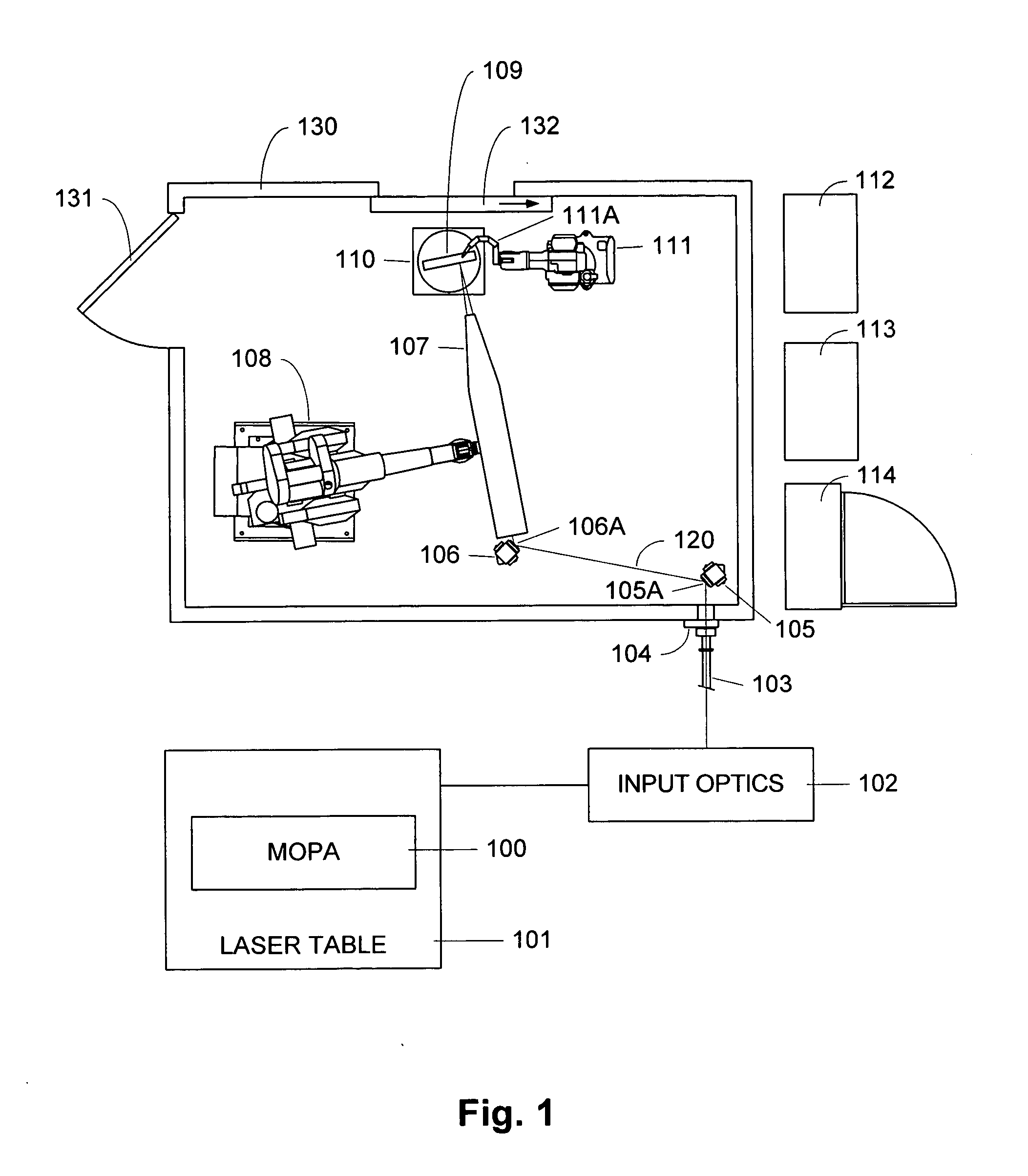
Active beam delivery system for laser peening and laser peening method
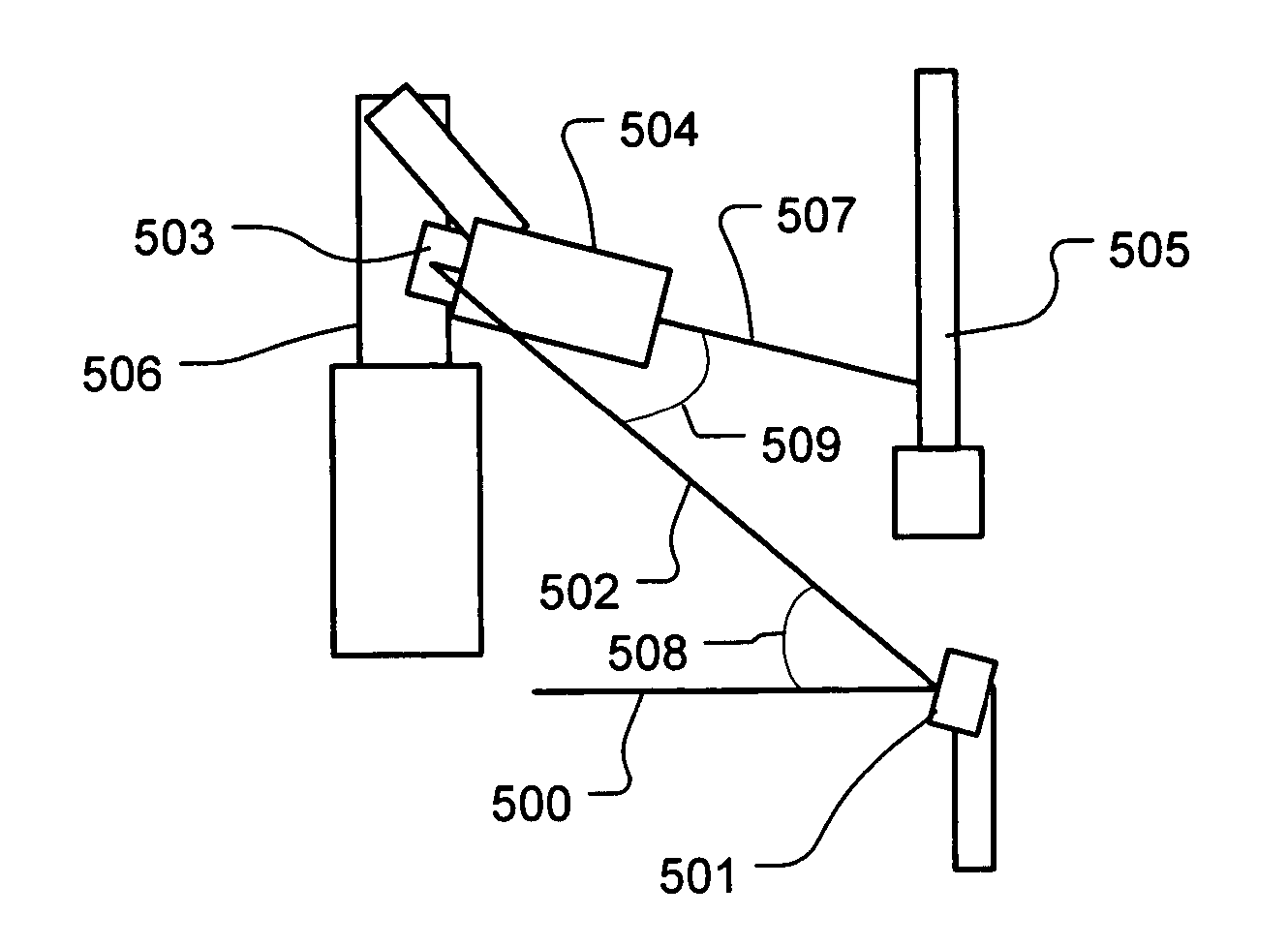
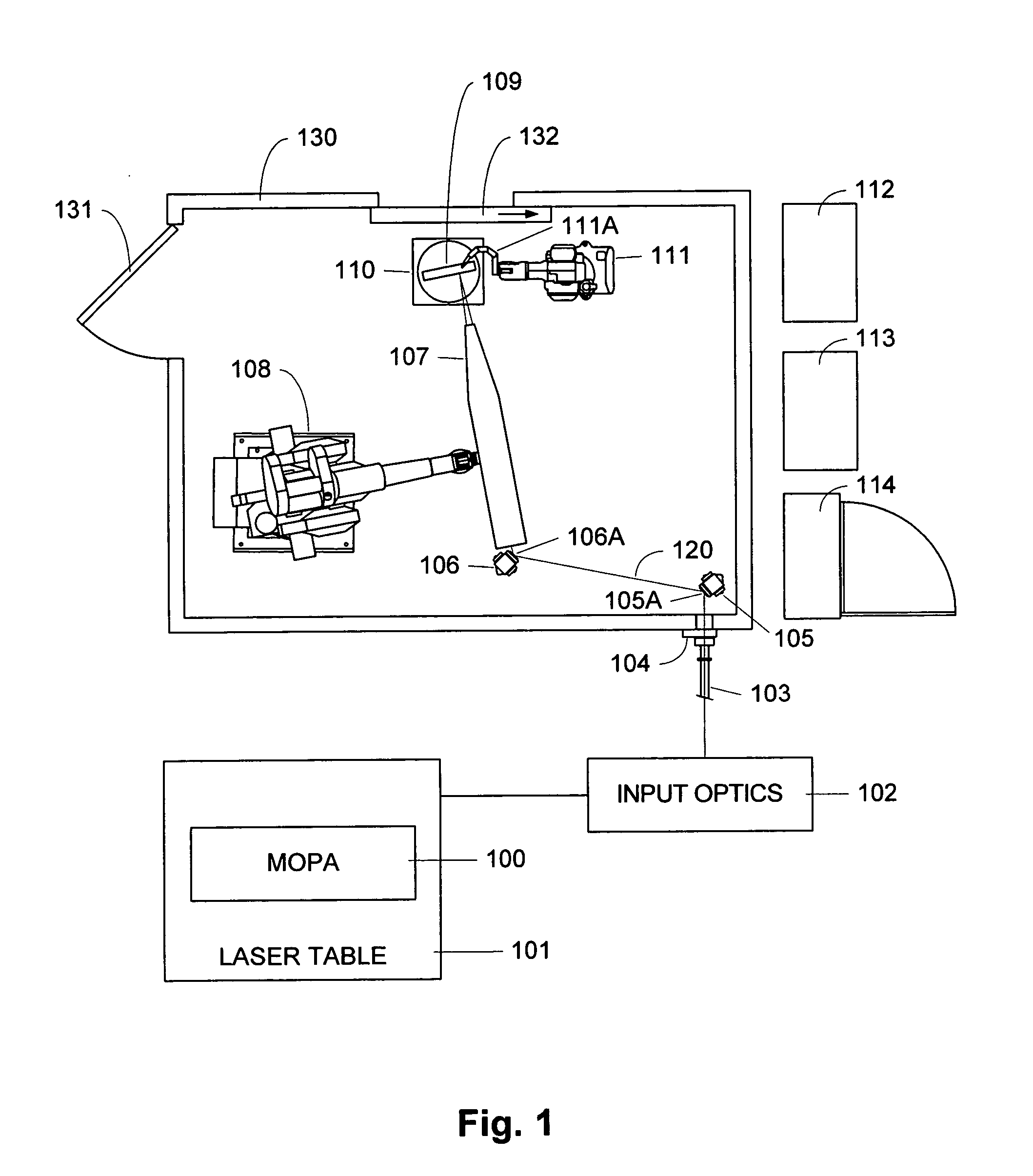
ActiveUS20060102609A1Minimizes holding fixtureMinimizes work piece moving complexityWelding/cutting auxillary devicesAuxillary welding devicesAngle of incidenceVariable length
A laser peening method and system allows the work piece to be fixed, while moving and directing the laser beam. A laser energy delivery system includes a relay imaging system. Input optics arranged to receive the laser energy, a transmitting mirror having adjustable angle of incidence relative to the input optics, and a robot mounted processing head including an optical assembly are configured to direct laser energy toward the movable target image plane. The laser energy follows an optical path including an essentially straight segment from the transmitting mirror to the receiving mirror, having a variable length and a variable angle relative to the input optics. Diagnostics on the processing head facilitate operation.
Owner:METAL IMPROVEMENT CO INC
Expandable endovascular stent
InactiveUS20050080479A1Minimize amount of materialSubstantial longitudinal flexibility longitudinalStentsBlood vesselsStress concentrationPercent Diameter Stenosis
Disclosed herein is a tubular endovascular stent comprising a plurality of annular segments connected by one or more bridging elements. Each annular segment takes forms of periodic wavelets with a plurality of alternating symmetric peaks and valleys, preferably consisting of circular arc segments of large radii connected tangentially with straight segments to minimize stress concentration when the stent undergoes radial deformation, transverse to the longitudinal axis of the stent. The points of connection between the bridging elements and adjacent annular segments are so designed that deformations of the bridging elements remain negligible as the stent deforms radially, namely, the longitudinal dimension of the stent does not vary during the radial expansion or contraction of the stent. Hence, the radial strength and the longitudinal flexibility of the stent made according to the principles disclosed by the present invention can be independently controlled by the design parameters for the annular segments and bridging elements, without compromising the longitudinal dimensional stability of the stent. Since stress concentration and deformation in the stent can lead to restenosis, stent made from the invention disclosed here can reduce the probability of restenosis.
Owner:FENG JAMES Q +1
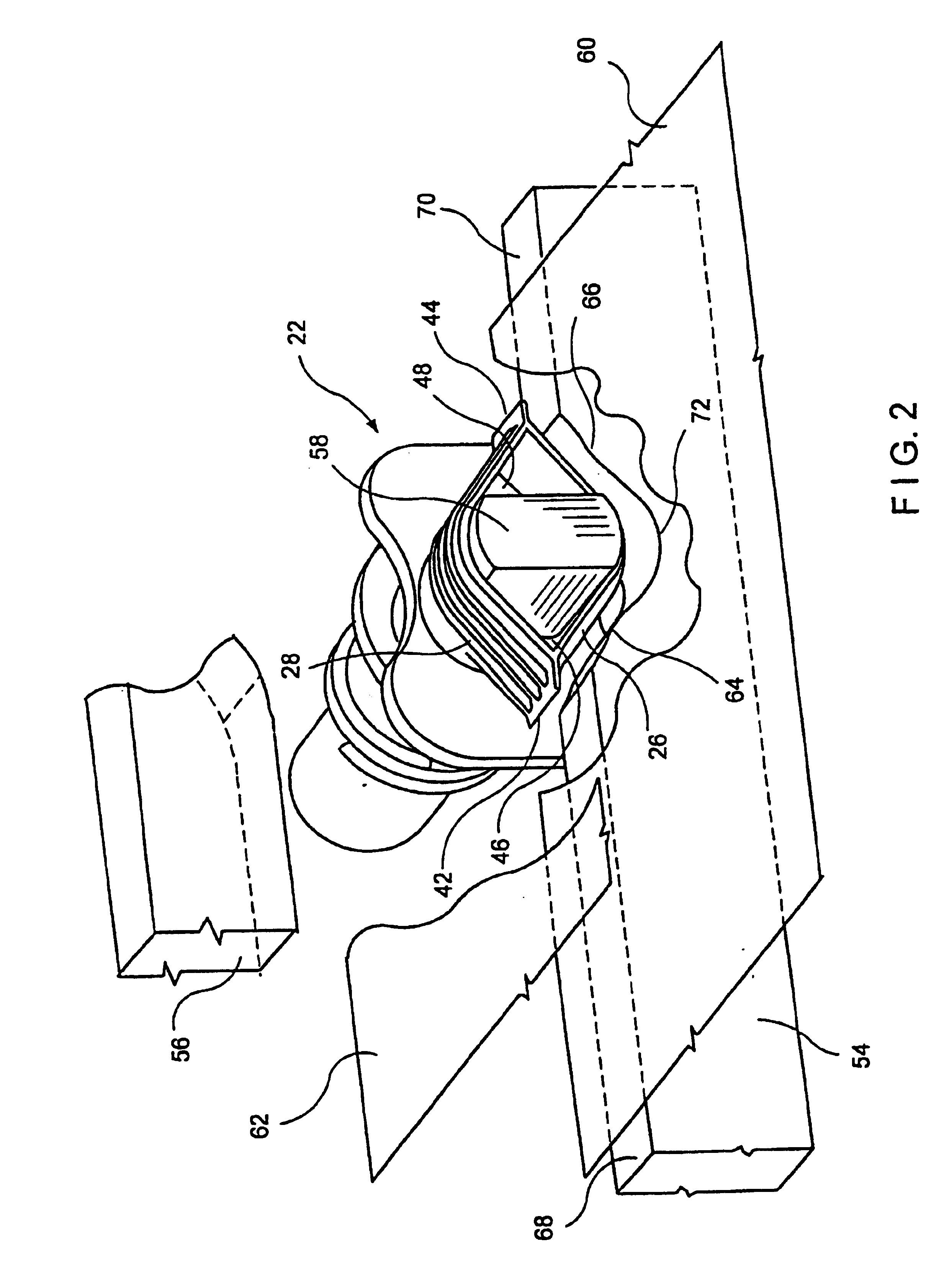
Method of making cascaded multilayer stator winding with interleaved transitions
A method for making a stator assembly includes forming several continuous conductors with generally-coplanar parallel-spaced straight segments interconnected by end loop segments, as by winding each of several conductors on a peg board, and then pressing the conductors to form either one, two, or three generally-orthogonal “jogs” in a given end loop segment. The conductors are interpositioned with their straight segments staggered and with a first leg of each subsequent conductor's end loop segments generally overlying a second leg of the immediately-prior conductor's end loop segments, except for the two end loop segments following the first conductor's “nth” straight segment, and multiples thereof, where the stacking order is reversed (“n” being equal to the number of stator core slots divided by the number of conductors that will form a given winding layer). The resulting preform is inserted into the core slots over multiple revolutions to thereby obtain a multilayer cascaded stator winding with interleaved transitions.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
System and method for maneuvering a mobile drive unit
ActiveUS8649899B2Disadvantages and reduced eliminatedInventory reduced eliminatedDigital data processing detailsVehicle position/course/altitude controlWorkspaceEngineering
A method of rotating an inventory holder includes moving an inventory holder towards a rotation area along a straight segment of a path with a first face of the inventory holder facing a first direction. The rotation area includes a portion of a workspace designated for rotation of inventory holders. The method further includes moving the inventory holder into the rotation area along a first arced segment with an orientation of the first face perpendicular to the first arced segment. The method additionally includes executing a rotation maneuver within the rotation area and moving the inventory holder out of the rotation area along a second arced segment with a second face facing the first direction.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
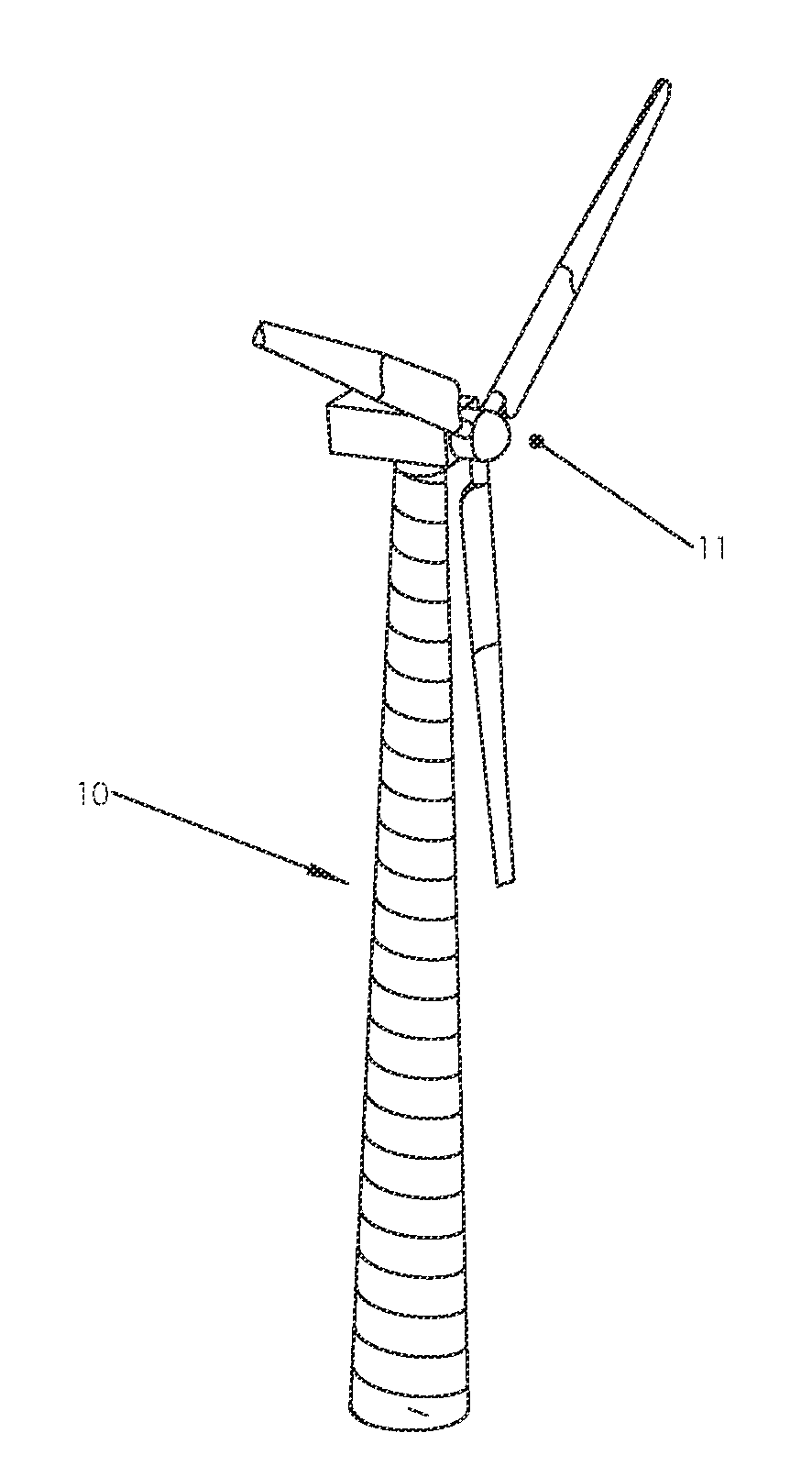
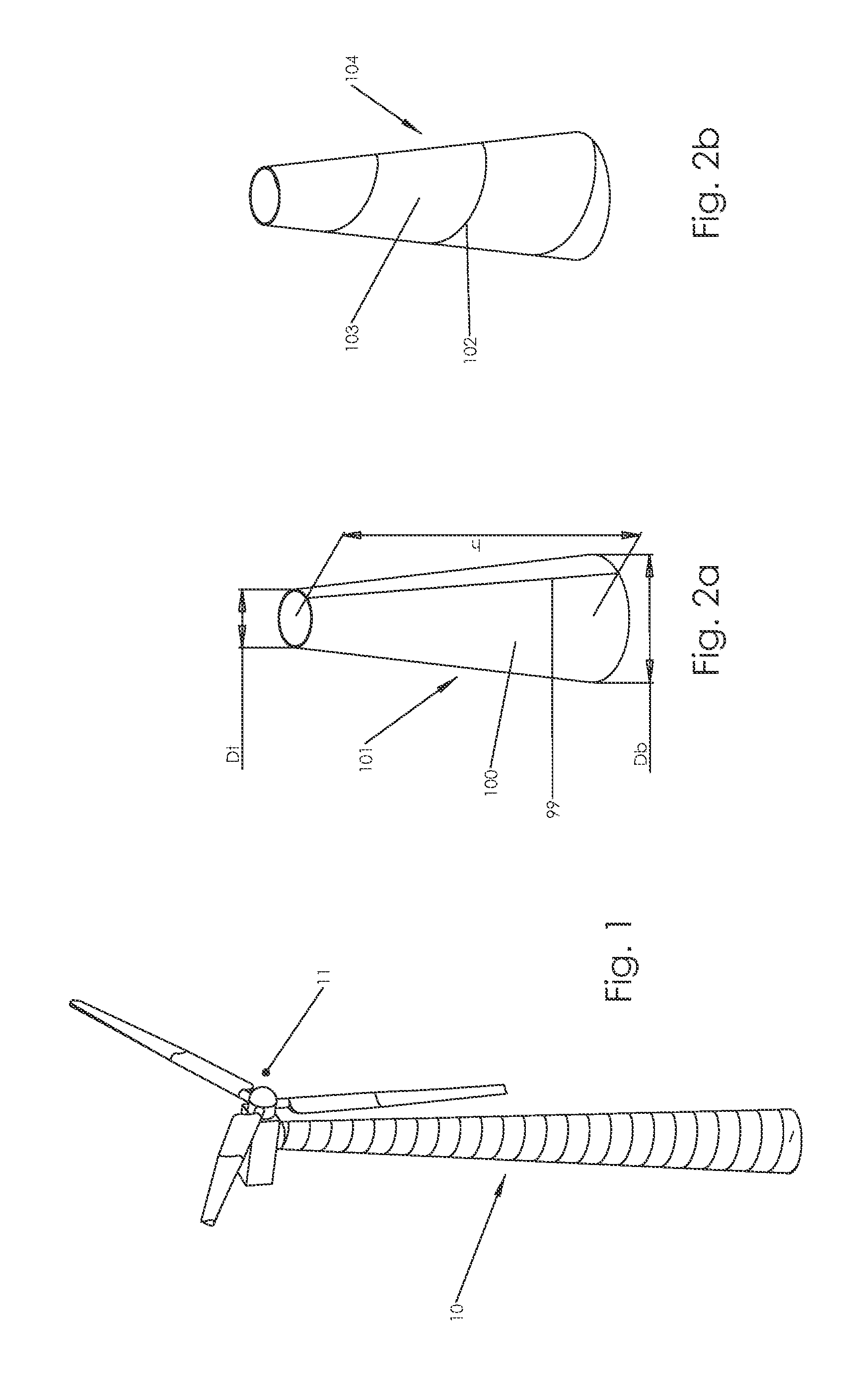
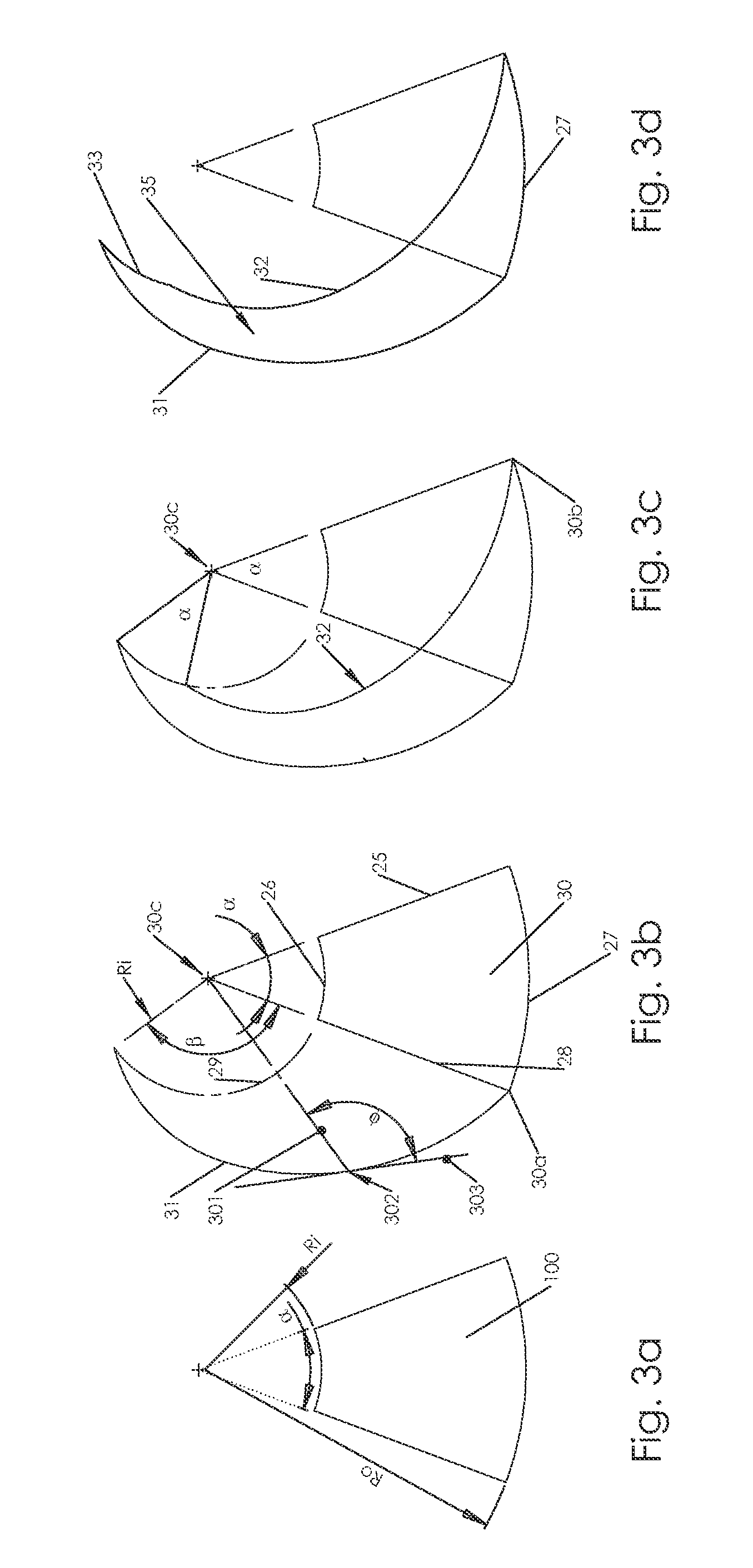
Tapered Spiral Welded Structure
Owner:KEYSTONE TOWER SYST
Stent prosthesis having select flared crowns
A generally tubular, cylindrical stent prosthesis has an unexpanded delivery configuration and an expanded configuration for contacting the vessel wall. The stent prosthesis has a plurality of adjacent stent struts, each stent strut having a wavelike or sinusoidal pattern of straight segments and crowns. A Y-shaped member is attached to one or more crowns to cause the crowns to flare outwardly at an angle from the cylindrical stent body when the stent is expanded. Upon expansion of the stent, the crown(s) having Y-shaped members attached thereto are angled with respect to the longitudinal axis and radially flare from the cylindrical stent body. The flared crowns anchor the stent within the vessel by protruding into the vessel wall and / or seating the stent within an ostium.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Composite microelectronic spring structure and method for making same
InactiveUS7063541B2Eliminate needLess timePrinted circuit assemblingElectronic circuit testingProbe cardInterposer
An improved microelectronic spring structure, and method of making the same, are disclosed. The improvement comprises, in a spring contact of the type comprising a beam attached to a post, of replacing the post with a plurality of column elements. The beam component is thus provided with one or more column elements which both structurally support and electrically connect one end of the beam to an electronic component. The column elements are preferably comprised of relatively straight segments of wire elements that are ball-bonded to a substrate and are over-coated with suitable structural and / or conducting materials. In the alternative, the improvement comprises a single column element comprised of a relatively straight segment of wire that is ball-bonded to a substrate and over-coated with suitable structural and conducting materials, wherein the column element is essentially rigid. The improved spring structures are especially useful for use as spring contacts on substrates such as probe cards, interposers, semiconductor devices, and other electronic components.
Owner:FORMFACTOR INC
Camera guide for video pipe inspection system
InactiveUS6862945B2Convenient travelPipe elementsStructural/machines measurementCoil springEngineering
A guide for a video pipe inspection system that includes a camera head and a tubular coil spring having a central axis. A guide member with radially extending fins is configured to surround the tubular spring. At least one pin is removably engageable with the guide member and the tubular coil spring to retain the guide member in position with respect to the tubular coil spring. The straight segments of a pair of opposing U-shaped pins can be inserted into grooves in the guide member so that they extend between adjacent coils of the tubular coil spring. In alternate form, the guide member may include an inner capture ring assembly that receives the pins. An outer yoke assembly surrounds, and is freely rotatable about, the inner capture ring assembly and includes a pair of axles for rotatably supporting a pair of wheels that engage an interior wall of the pipe.
Owner:SEEK TECH
Machine for drying, polishing and burnishing cutlery and metal tableware
InactiveUS6814654B2Improve effectivenessImprove efficiencyEdge grinding machinesPolishing machinesStraight segmentMechanical engineering
This invention concerns a machine for the drying, polishing and burnishing cutlery and other metal tableware. It consists of a tank suspended upon a base and moved by a vibrating device, having a treatment channel (15) designed to receive a drying material and the articles for treatment. The treatment channel (15) rises in a spiral from an entrance chute at the loading mouth to an exit passage or chute for the articles and has, in a transverse cross-section, a U-shaped bottom (22) defined by a substantially cylindrical concave surface and, lengthways, by a series of straight segments (23) which alternate with and are joined to curved segments (24), without sharp edges or corners. Ideally, the channel has a steeper gradient towards the exit.
Owner:HYPPOCAMPUS
Dust mop handle method and apparatus
This is a dust mop handle and method in which the handle has a plurality of arcuate and straight segments including means to attach a dust mop to one end; unique hand holding means providing for bi-planar holding and movement of the dust mop handle in such manner that the effective force being applied to the dust mop is multiplied and enhanced and strain on the user is reduced.
Owner:BIGGS BLYTH S
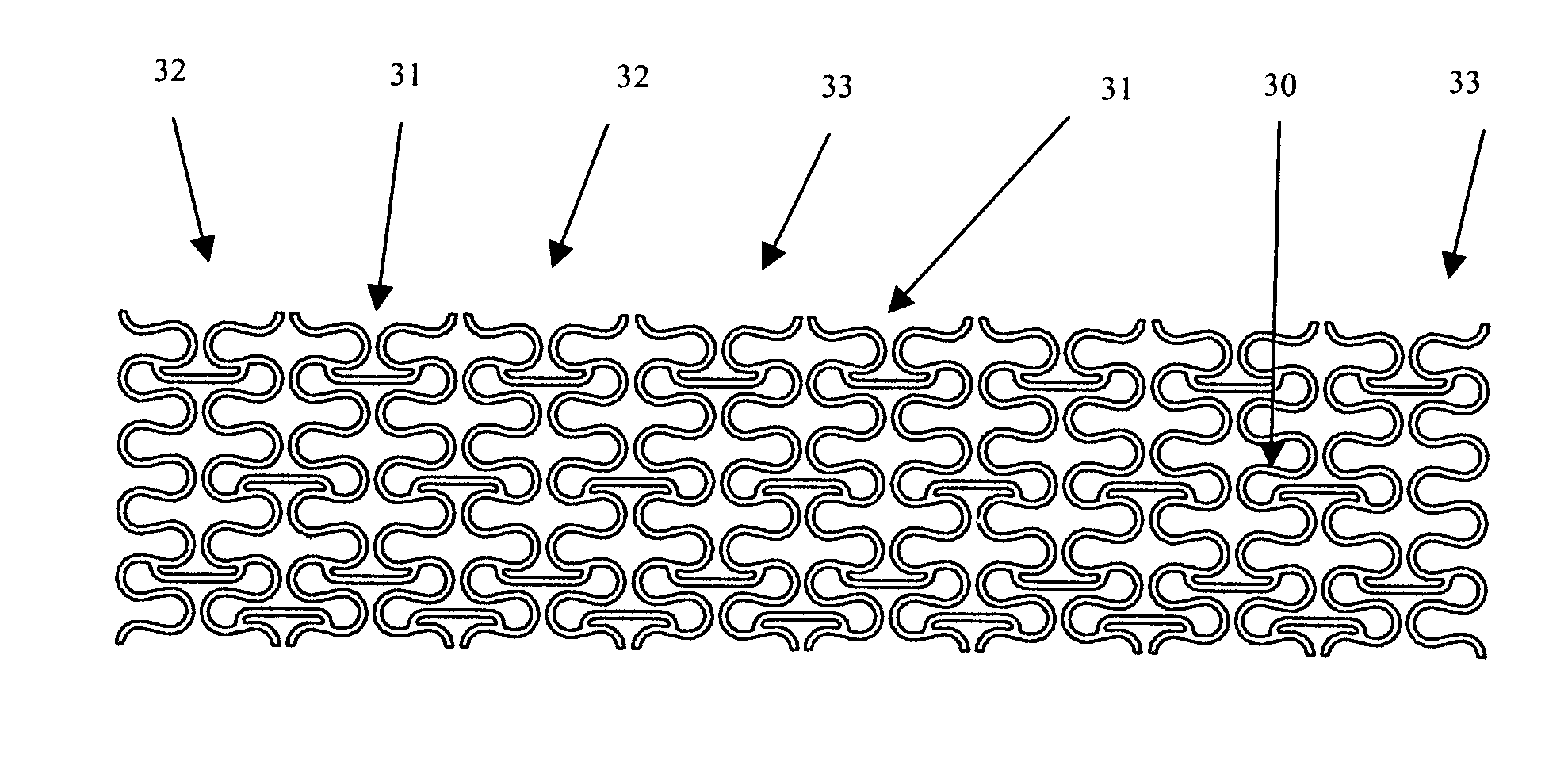
A structured sawing wire
A steel sawing wire (302) with a helicoidal shape, wherein straight segments alternate with outwardly oriented bends is described. The shape of the sawing wire (302) is configured so as to have a good cooperation with the abrasive particles the wire is used with in the following way: when the wire (302) is used gaps form at the segments between the bends and the circumscribed semi-cylinder formed by the workpiece that is being cut. The gaps have a maximum gapsize that is from 0.25 to 2 times the median diameter of the abrasive particles used. In this way at the gaps active, large particles are pushed against the workpiece while worn abrasive debris escapes through the gaps. Additionally several manufacturing methods are described which result in such kind of wire (302).
Owner:BEKAERT BINJIANG STEEL CORD CO LTD
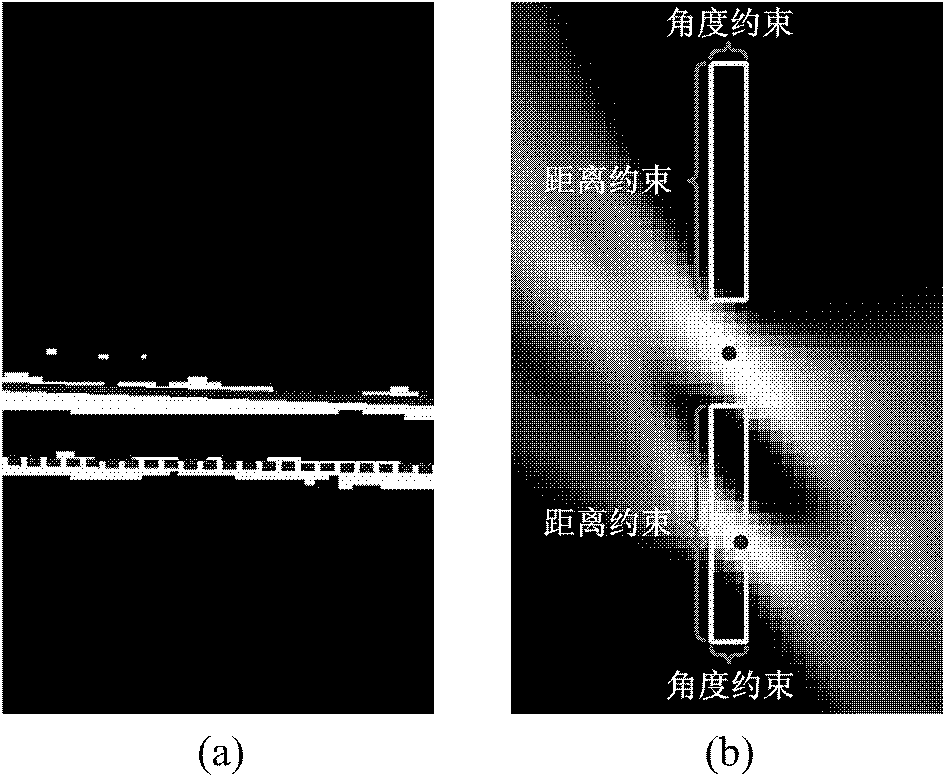
Method for automatic computerized segmentation and analysis on thickness uniformity of intima media of carotid artery blood wall in sonographic image
InactiveCN102163326ANot susceptible to image noiseOvercoming the Effect of Boundary Discontinuities on MeasurementsImage enhancementOrgan movement/changes detectionStraight segmentCarotid imt
The invention belongs to the field of intersection of computer technologies and medical images, and particularly relates to a method for automatic computerized segmentation and analysis on the thickness uniformity of an intima media of a carotid artery blood wall in a sonographic image. The method comprises the following steps of: loading an original blood wall sonographic image; selecting a rectangular region of interest (ROI) containing carotid artery intima media of a far side blood wall; artificially defining or automatically detecting an original contour line by a computer; calculating aone-way edge map; performing binarization and segmentation; detecting two straight segments PLi and SLi serving as partial and correction connection of a lumen intima interface (LII) and a media adventitia interface (MAI) on a sub-image through Hough transformation; obtaining an intima media boundary contour line by adopting double-Snake model evolution; and calculating the thickness uniformity on the basis of two boundaries obtained from segmentation. By the method, problems of noise and discontinuous boundaries in the images can be effectively solved, the purpose of accurate segmentation ofthe intima media boundary is fulfilled and workloads of a doctor can be reduced. Moreover, thickness uniformity parameters obtained on the basis of the method can provide more information for early analysis on atherosclerosis.
Owner:武汉上上智科技发展有限公司
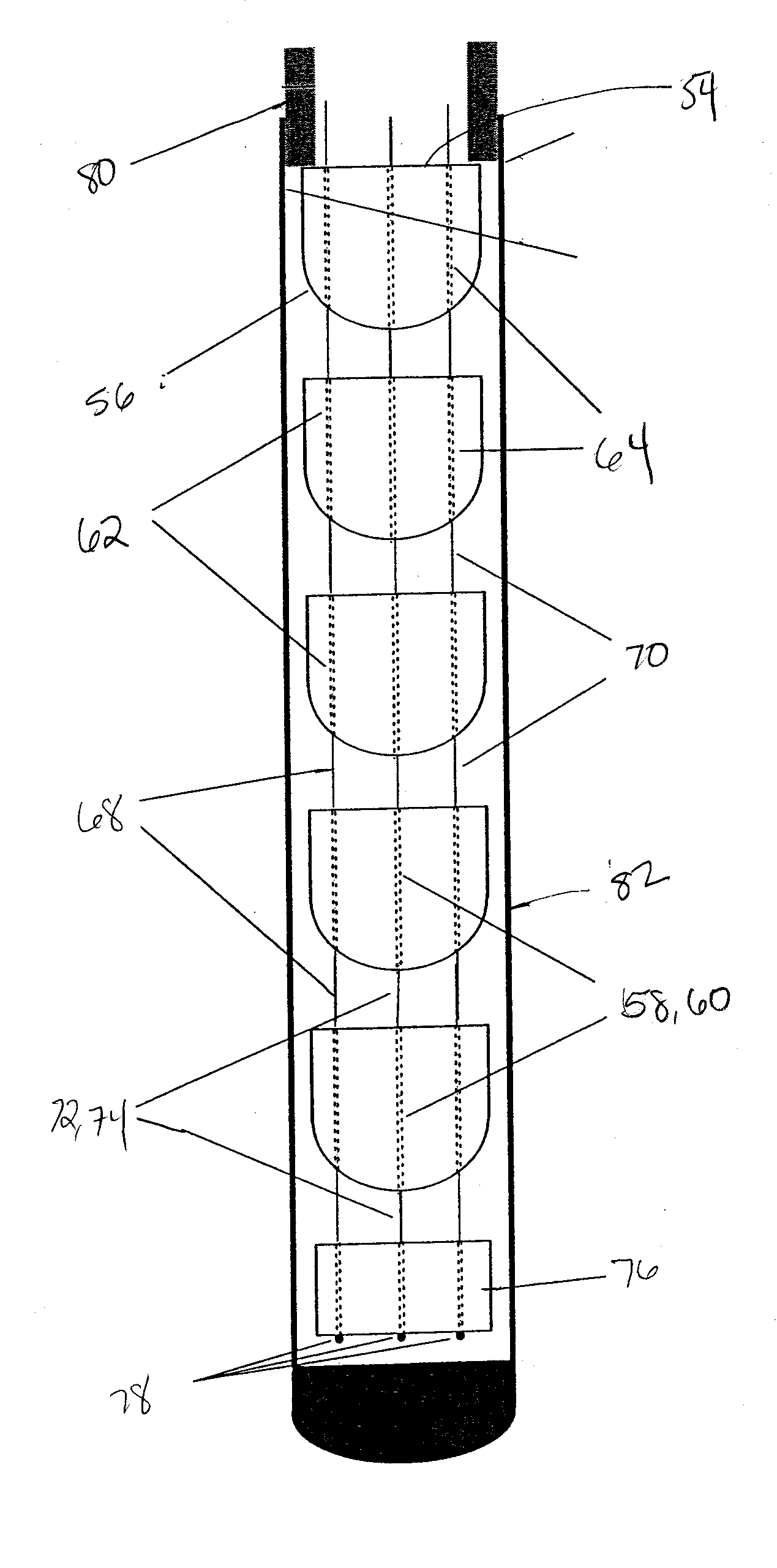
System and method for influencing an anatomical structure
A relocation system for influencing an anatomical structure in relation to an internal surgical site. The system is composed of an elongated member constructed and arranged for insertion into a patient. The elongated member is composed of a plurality of segments interconnected by a plurality of control lines. The plurality of segments having one or more straight segments, one or more deflection segments, which are used to shape and steer the elongated member upon manipulation of at least one of the control lines. This causes the elongated member to deform into any desired shape capable of influencing the anatomical structure.
Owner:MILLER STEVEN
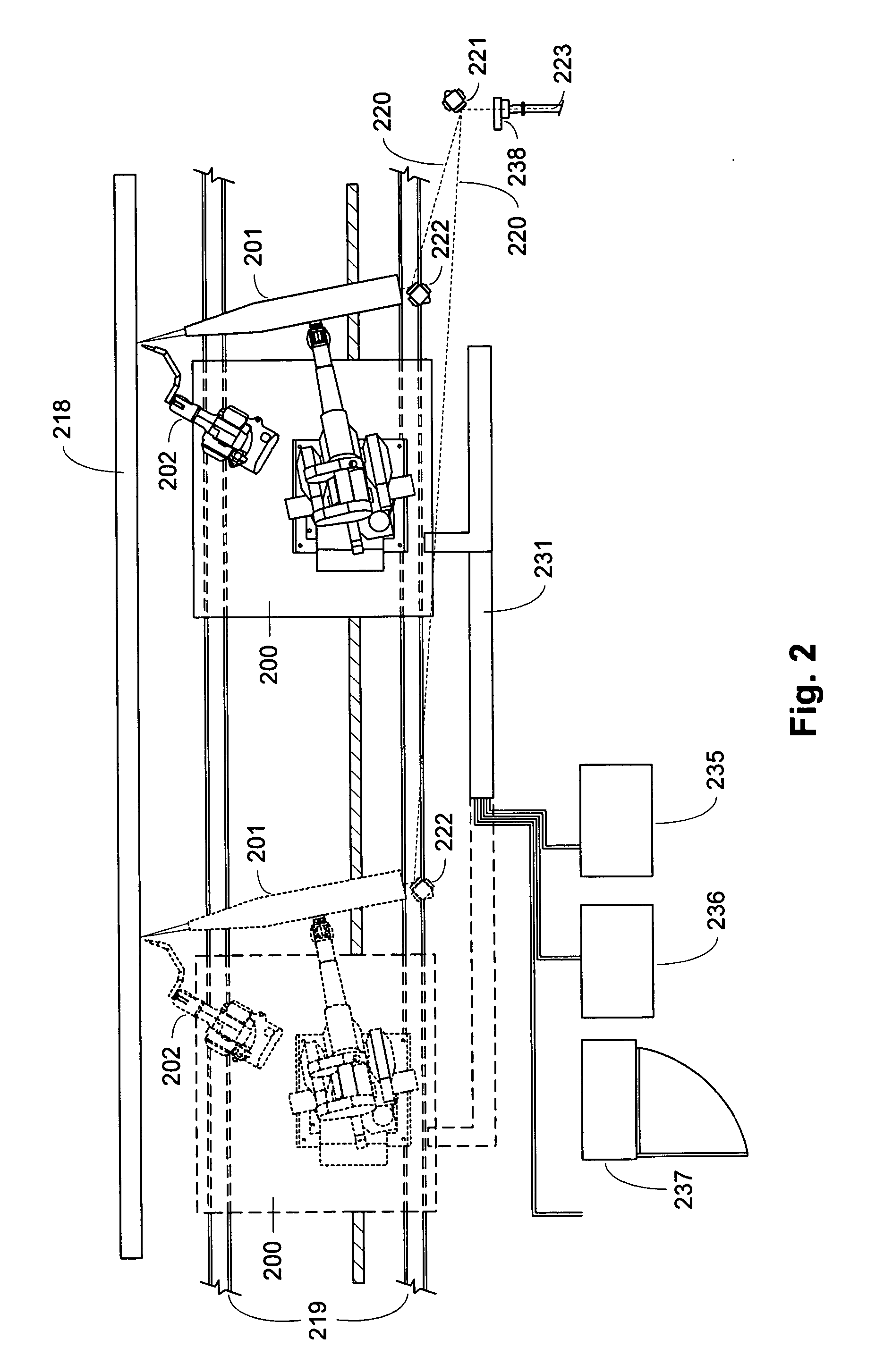
Active beam delivery system with image relay
ActiveUS20060102604A1Minimizes holding fixtureMinimizes work piece moving complexityLaser beam welding apparatusAngle of incidenceVariable length
An active laser energy delivery system includes a relay imaging system. Input optics arranged to receive the laser energy, a transmitting mirror having adjustable angle of incidence relative to the input optics, and a robot mounted processing head including an optical assembly are configured to direct laser energy toward the movable target image plane. The laser energy follows an optical path including an essentially straight segment from the transmitting mirror to the receiving mirror, having a variable length and a variable angle relative to the input optics. Diagnostics on the processing head facilitate operation.
Owner:METAL IMPROVEMENT
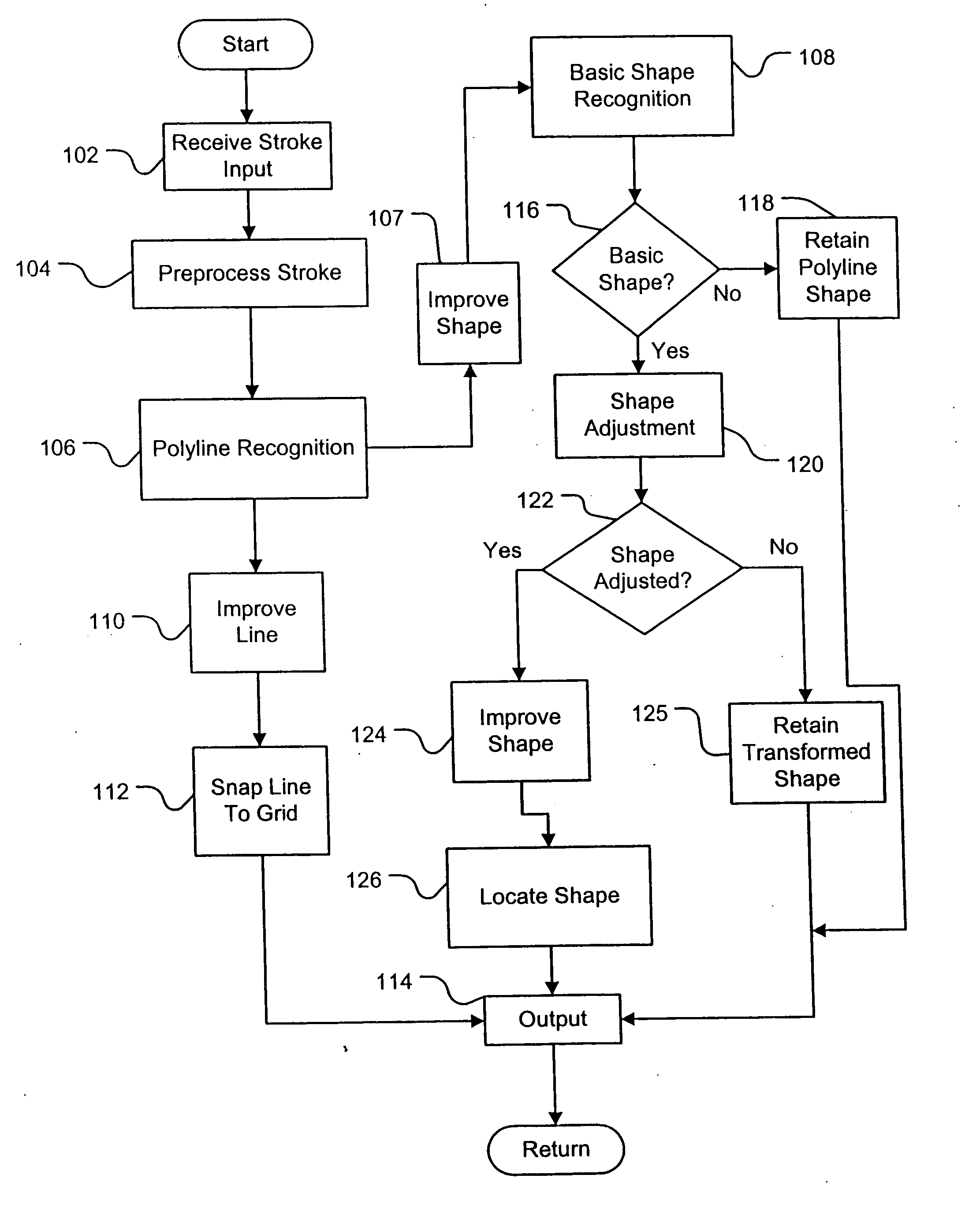
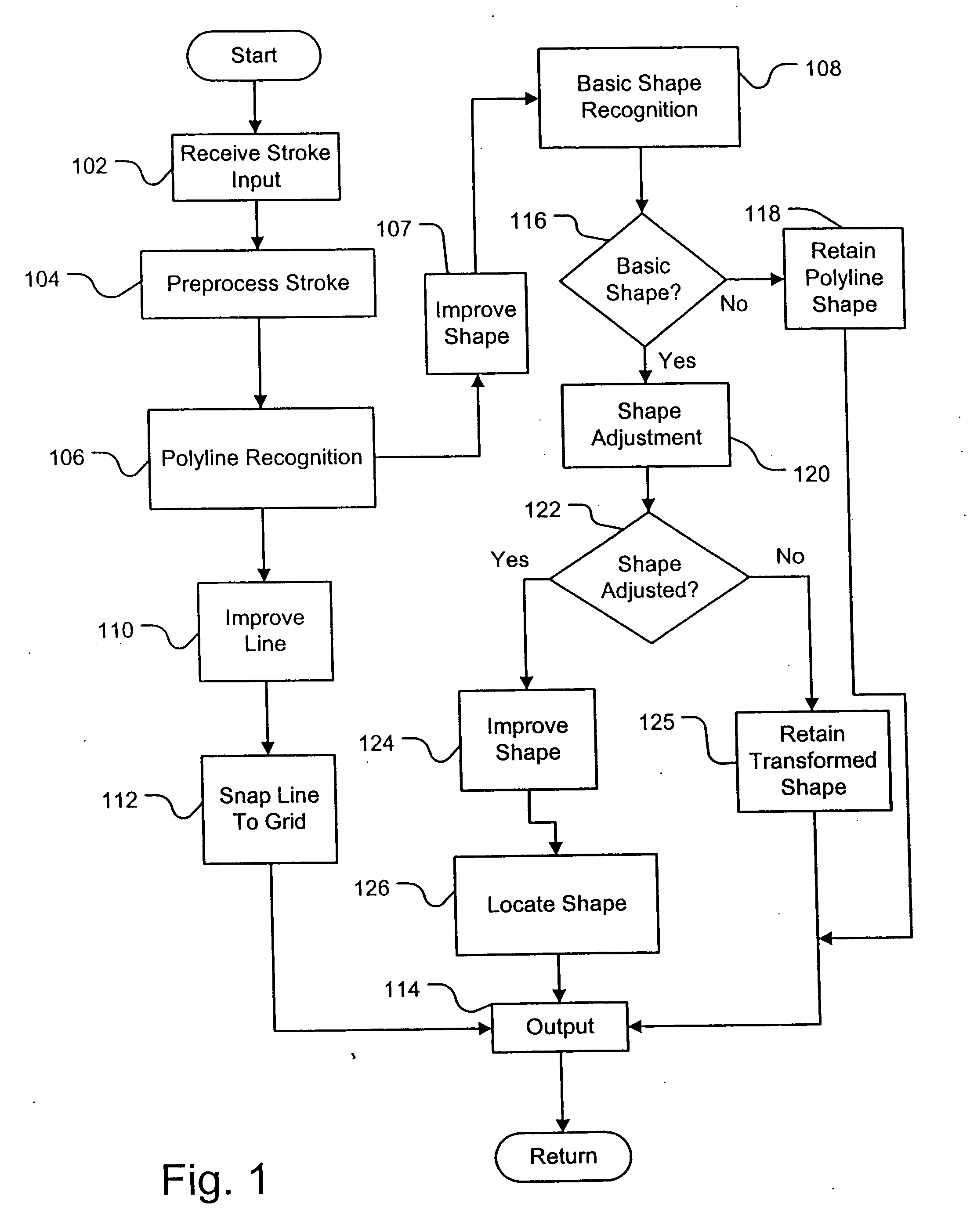
Reshaping freehand drawn lines and shapes in an electronic document
InactiveUS20050244058A1Drawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionElectronic documentComputer graphics (images)
The invention improves the appearance of freehand drawn lines and shapes in an electronic document by first recognizing freehand drawn lines and shapes and generating a line made up of sequential straight line segments for the freehand drawn line when the line does not form a closed line and generating a multiple straight-line-segment shape when the line forms a closed line. If a multiple segment shape is being reshaped, a basic shape is selected from reference ideal shapes as the basic shape of the multiple segment shape. The basic shape is adjusted to provide a specific shape as an improved shape for the freehand drawn shape. The recognition of the freehand drawn lines and shapes is accomplished by comparing source segments of a source freehand drawn line to a straight line and substituting a straight line segment for a source segment if the deviation between the source segment and the straight line is below a predetermined value. Sequential source segments of a source freehand drawn line are evaluated to determine if they are an angle segment. A segment pair of sequential source line segments are defined as an angle segment having two straight line segments intersecting at a common end point if both source segments of the segment pair are within a predetermined deviation value from a straight line. The straight line segments and angle segments are combined to form a multiple segment line if the line does not close on itself and a multiple segment shape if the line does close on itself.
Owner:EVERNOTE +1
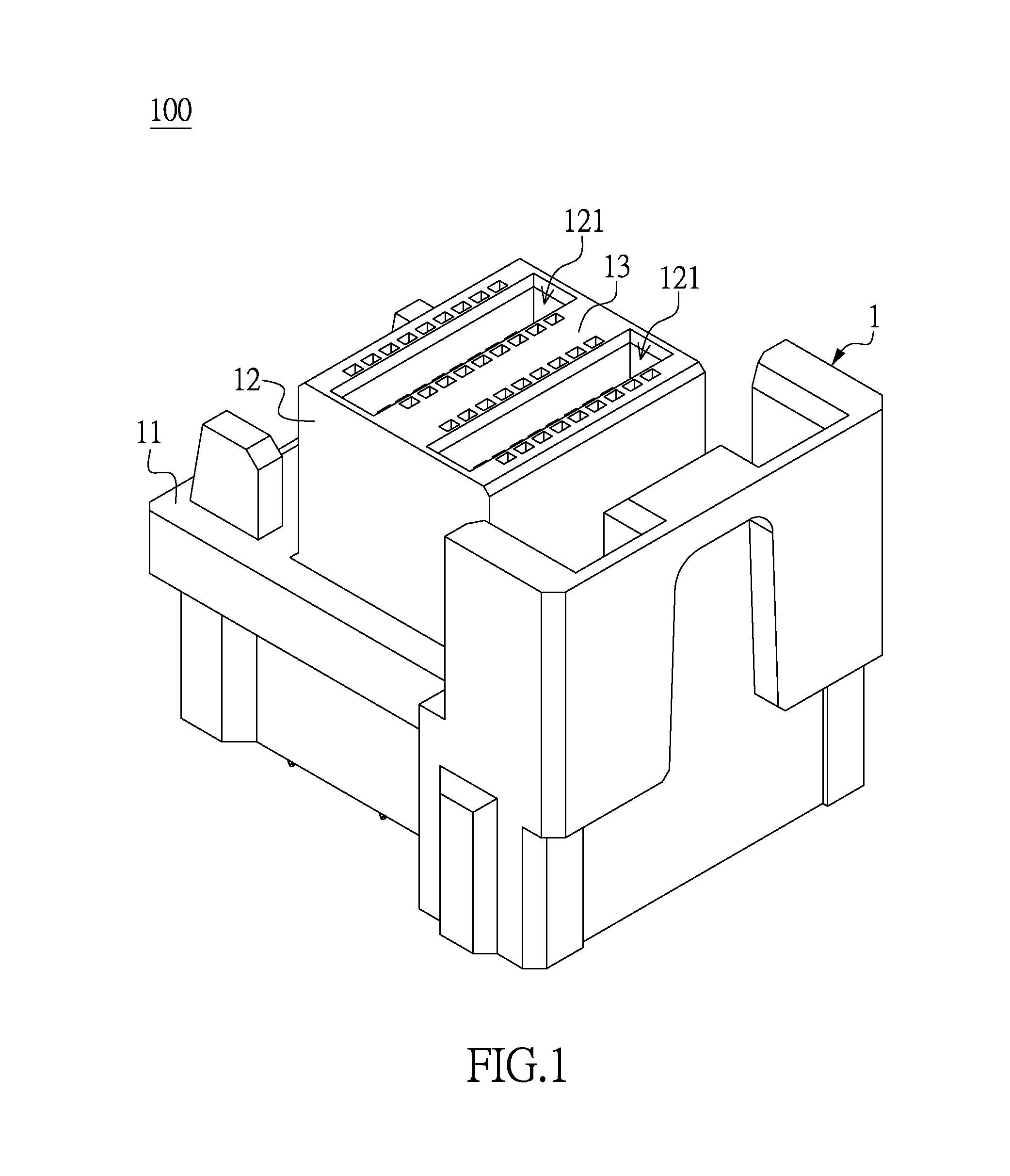
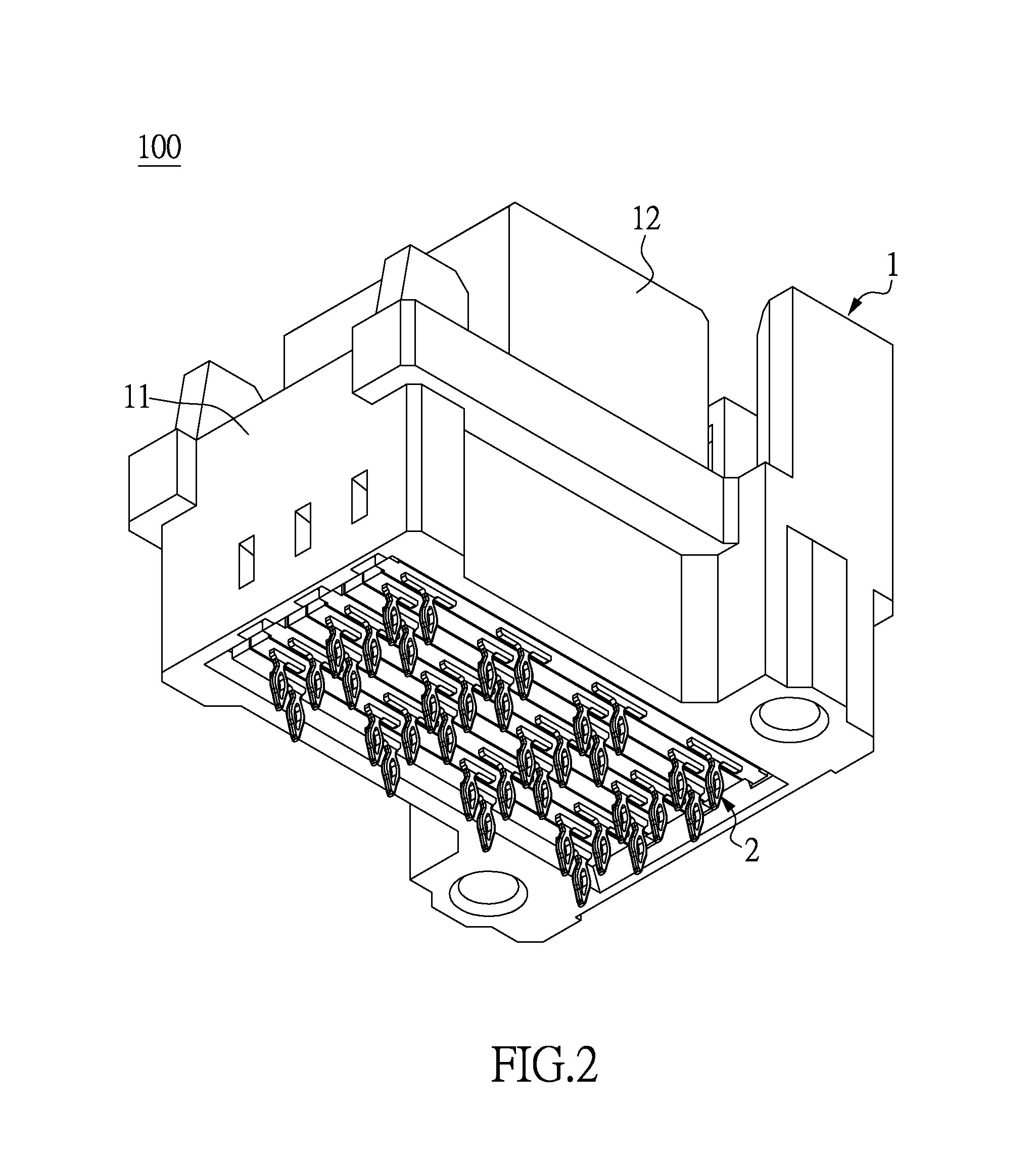
Communication connector and transmission wafer thereof
ActiveUS9160123B1Easy to produceEasy alignmentTwo-part coupling devicesCoupling protective earth/shielding arrangementsMating connectionAcute angle
A communication connector includes an outer casing and a plurality of transmission wafers inserted into the outer casing. The transmission wafers are provided for receiving a mating connector along an inserting direction. Each communication wafer includes at least two terminals in coplanar arrangement, and each terminal has a straight segment. The straight segments of the terminals are respectively arranged in a first acute angle and a second acute angle with respective to the inserting direction, in which the first acute angle is smaller than the second acute angle. Two virtual lines, which are respectively defined by extending from the straight segments along the longitudinal directions thereof, are intersecting to form an angle. The angle is the difference of the first and second acute angles. Thus, the communication connector provided by the instant disclosure is produced easily.
Owner:SUZHOU CHIEF HSIN ELECTRONICS CO LTD
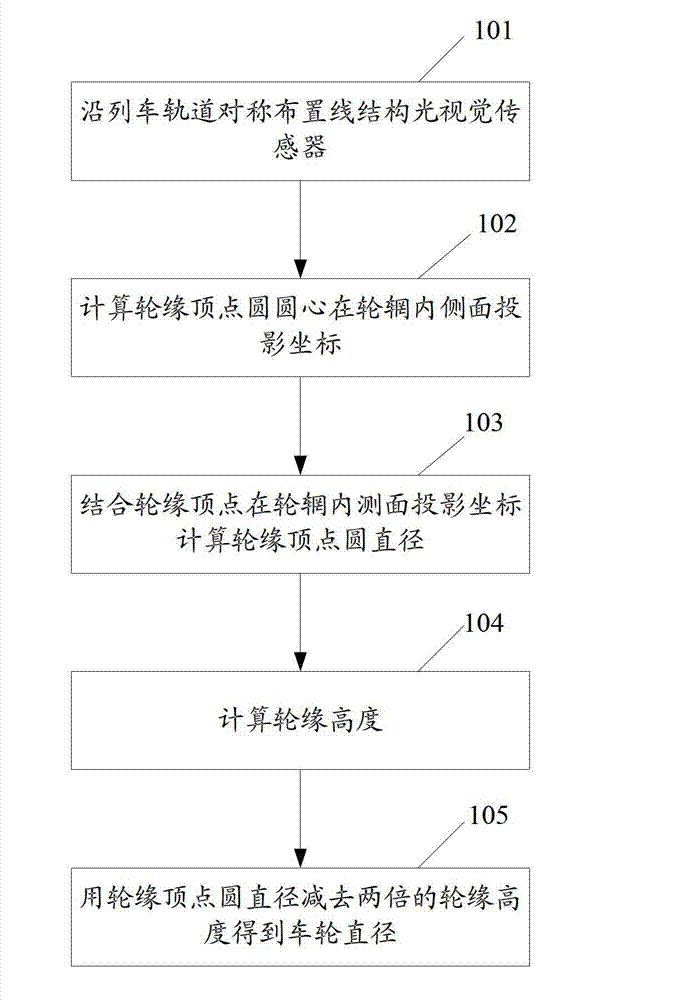
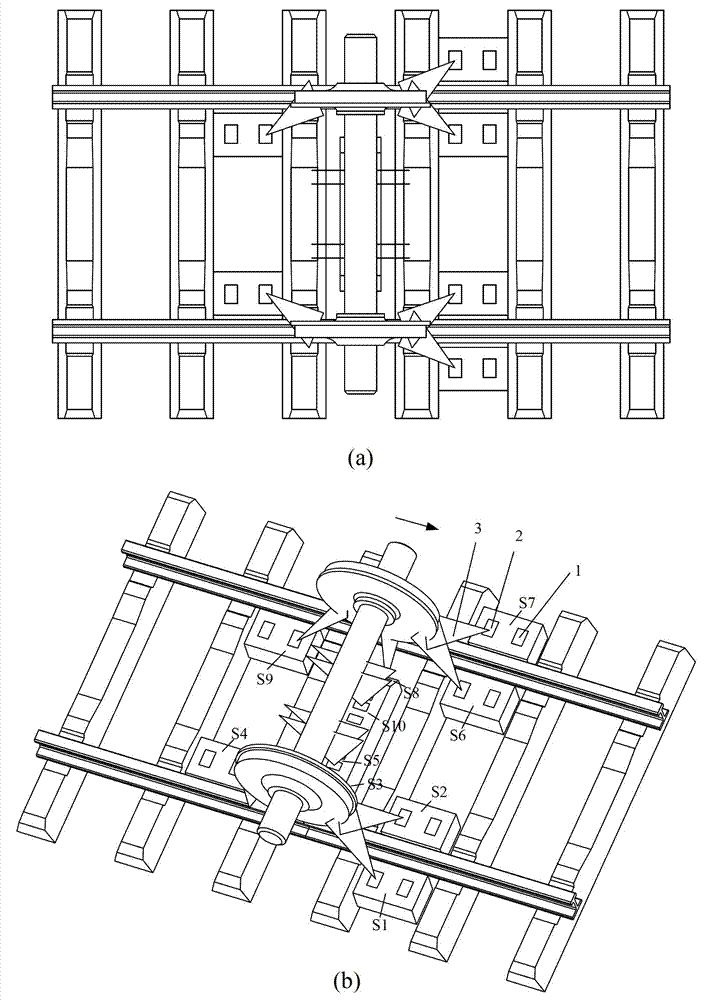
Dynamic measurement method and system for train wheel diameter
ActiveCN102901457AReduce processing costsLow on-site installation requirementsUsing optical meansContact highStraight segment
The invention discloses a dynamic measurement method for train wheel diameter. The dynamic measurement method comprises the following steps of: symmetrically arranging line-structured light vision sensors along a train track and acquiring light bar images of fracture surface contours of a train wheel and an axle; determining an inner side surface equation of a rim through the light bar of the fracture surface contour of the wheel and a straight segment corresponding to the inner side of the rim, determining an axis equation of the axle through the light bar of the fracture surface contour of the axle, and calculating projection coordinates of the inner side surface of the center of a vertex circle of a wheel flange through the intersection of the axis and the inner side surface of the rim; calculating the diameter of the vertex circle of the wheel flange through projection coordinates of the center of the vertex circle of the wheel flange and the vertex of the wheel flange in the inner side surface of the rim; recovering complete fracture surface contour of the wheel through the light bars of the local contours of the inner side and the outer side of fracture surface of the wheel, and calculating the height of the wheel flange; and subtracting the height of the wheel flange twice from the diameter of the vertex circle of the wheel flange to obtain the diameter of the wheel. The invention discloses a dynamic measurement system for the train wheel diameter simultaneously. The dynamic measurement method and the dynamic measurement system provided by the invention can be adopted for non-contact high-precision dynamic measurement of the train wheel diameter.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
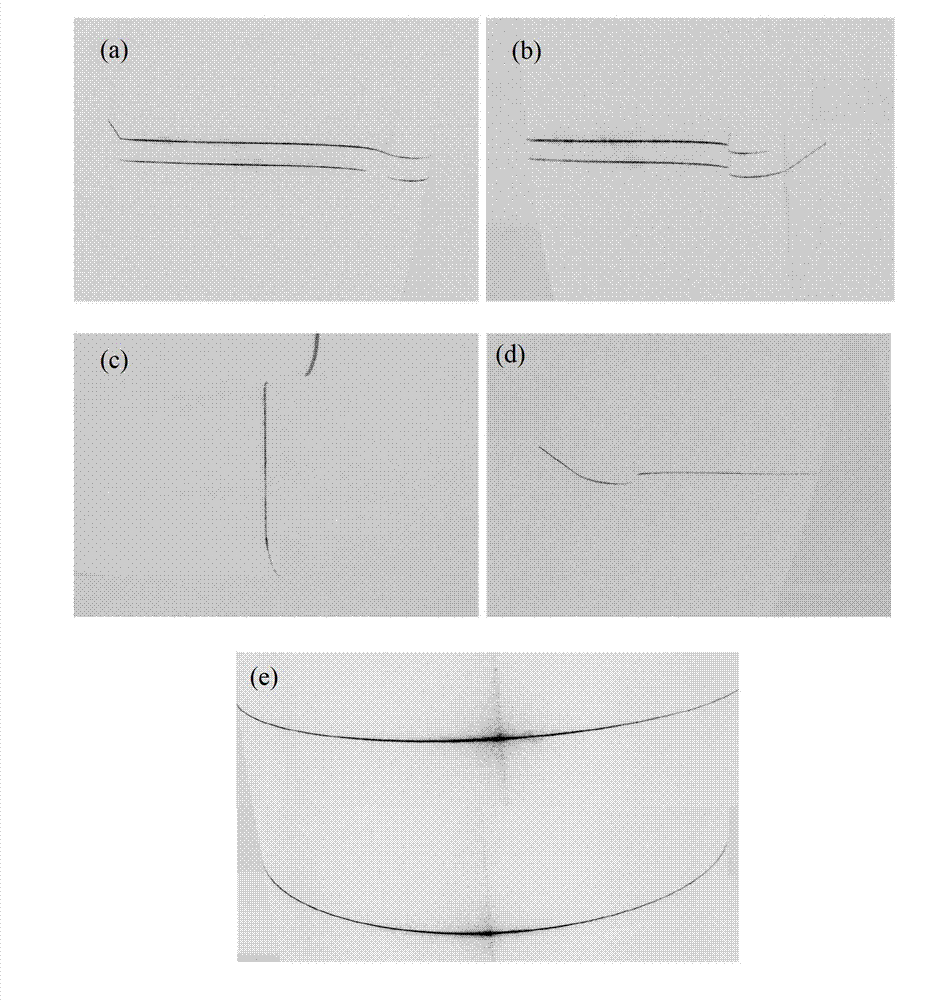
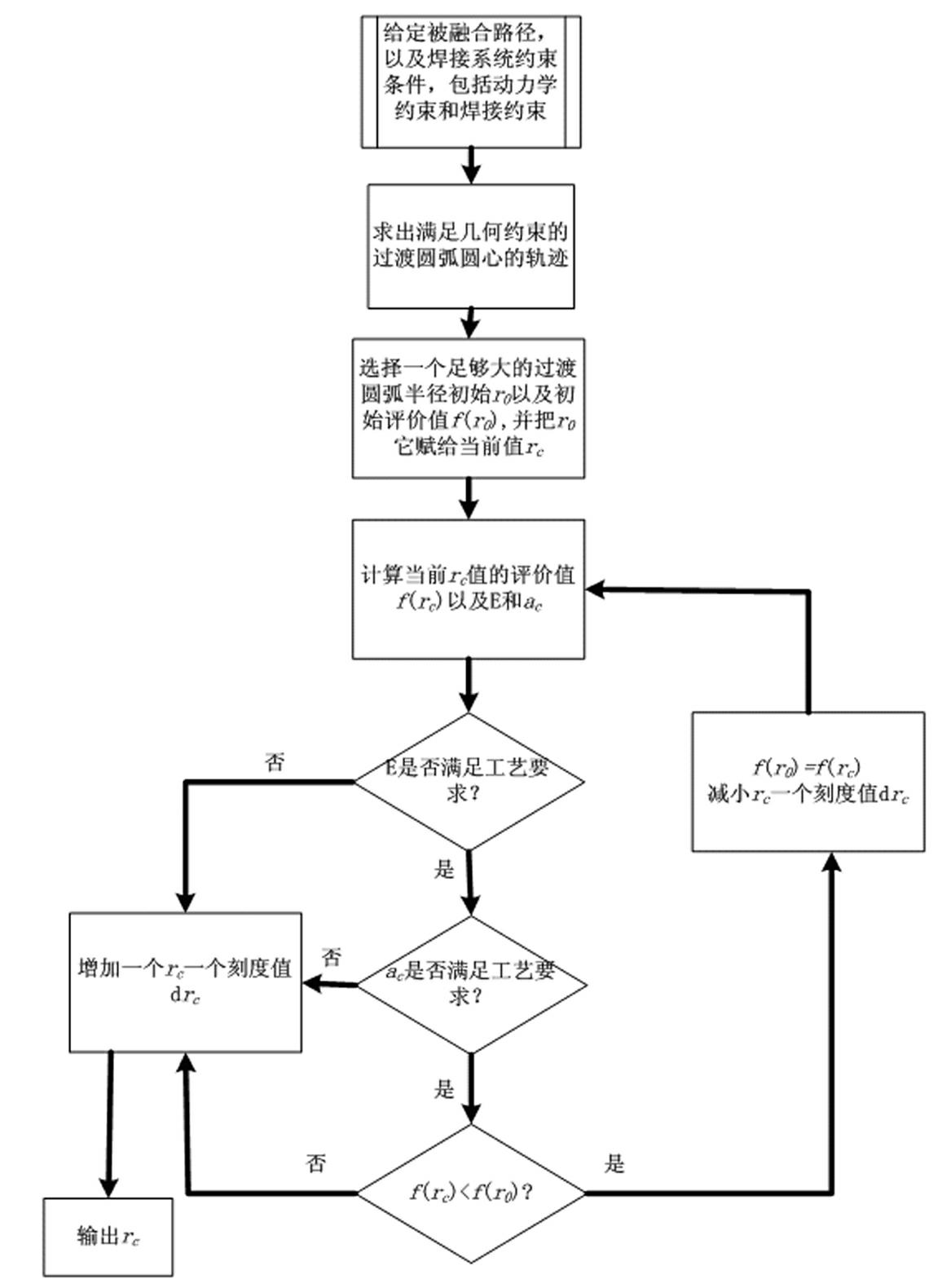
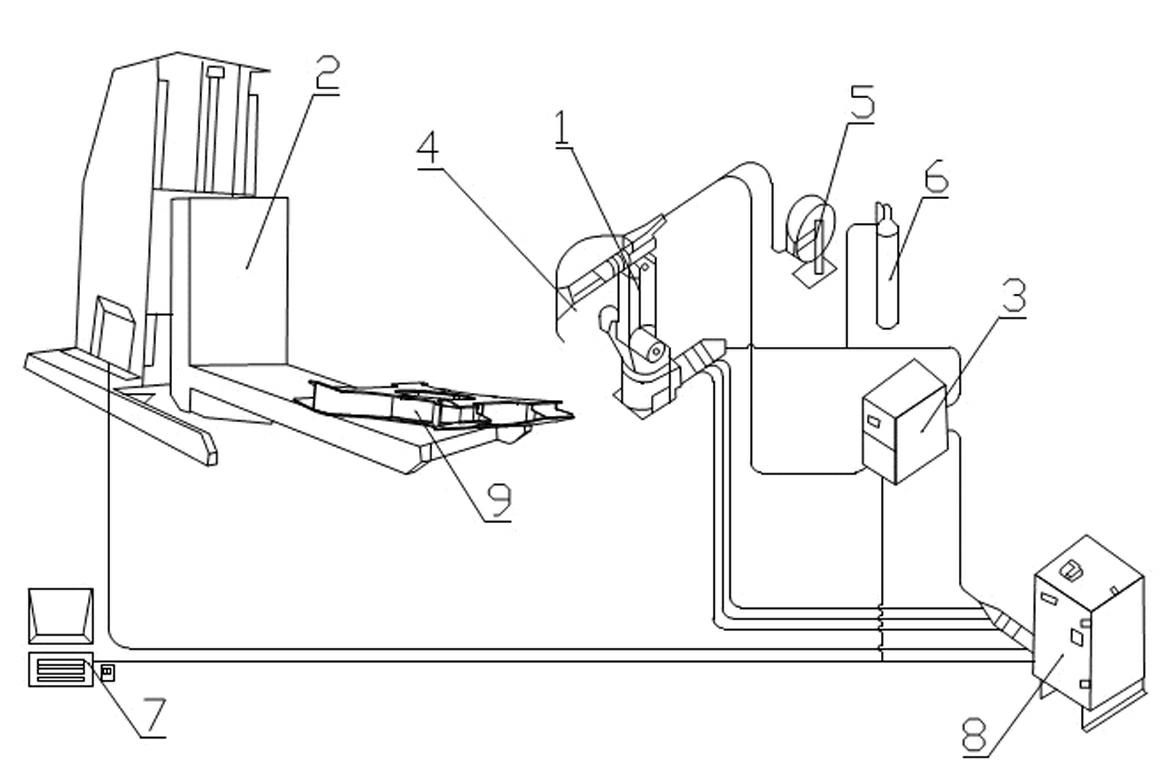
Transitional track planning method for welding robot
InactiveCN102091879AExecution time minimizationFacet joint torque fluctuationsWelding apparatusSimulationStraight segment
The invention discloses a transitional track planning method for a welding robot. The transitional track is used for fusing a straight segment welding line and an arc segment welding line, geometric constraint conditions of adjacent fused straight segment welding line and fused arc segment welding line of a workpiece to be welded are imported into a robot path planning module to generate a transitional segment arc welding line track, and by controlling the arc radius of the transitional segment track, welding constraint conditions and robot welding system dynamic constraint conditions are metwhen the robot welds the transitional segment. The track planning method is suitable for switching different segments of tracks and planning transitional tracks, and solves the problem of smoothness of transiting from the straight segment welding line to the arc segment welding line when the robot performs arc welding.
Owner:CHANGSHA HONGDIAN AUTOMATION TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com