Patents
Literature
88 results about "Carotid imt" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
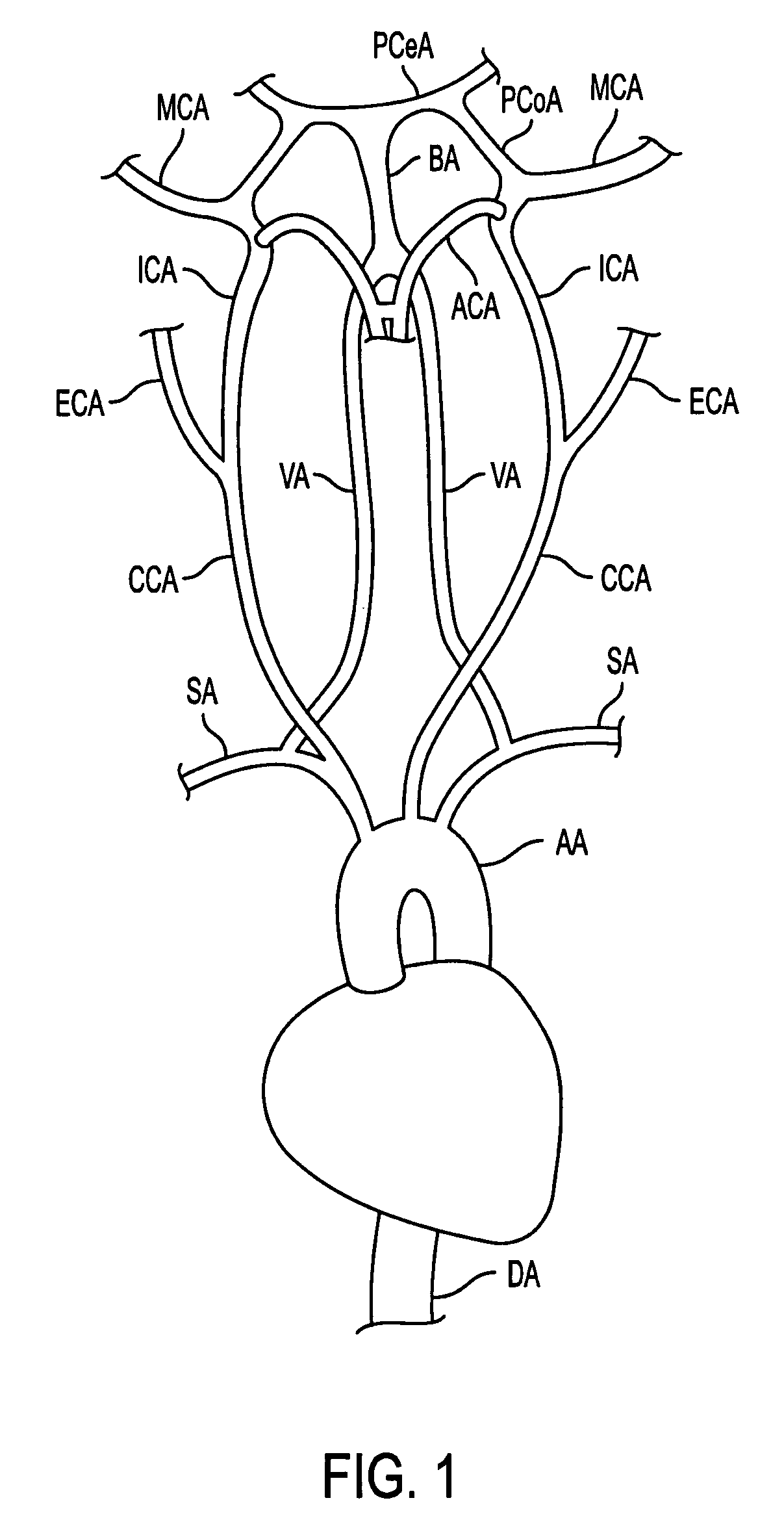
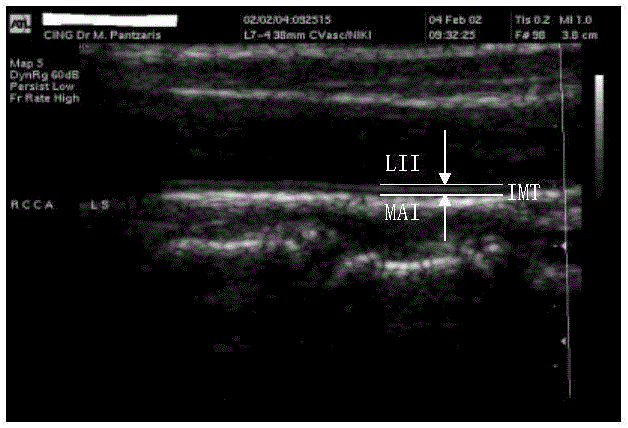
The carotid intima-media thickness test (CIMT) is a measure used to diagnose the extent of carotid atherosclerotic vascular disease. The test measures the thickness of the inner two layers of the carotid artery—the intima and media—and alerts physicians to any thickening when patients are still asymptomatic.
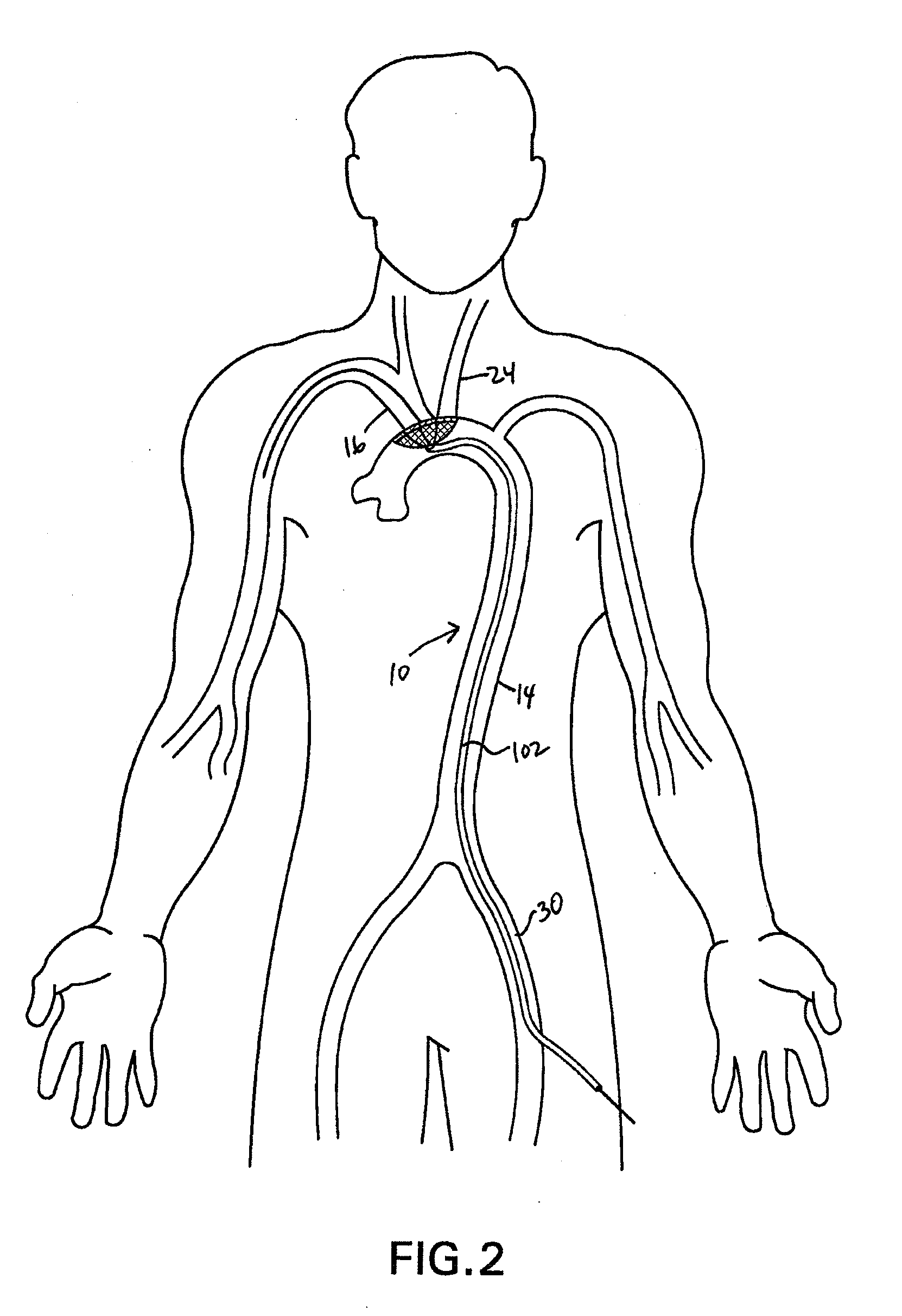
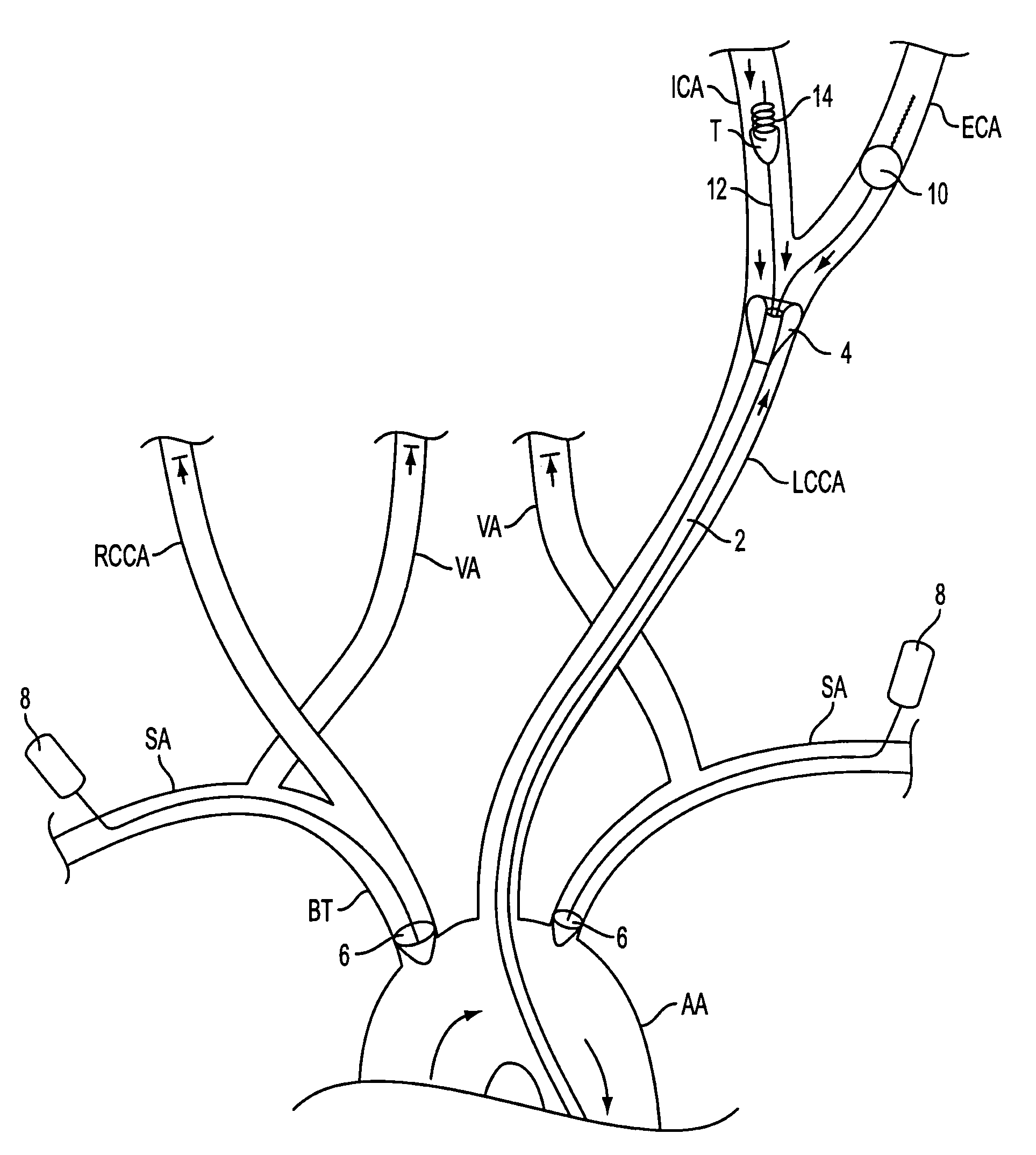
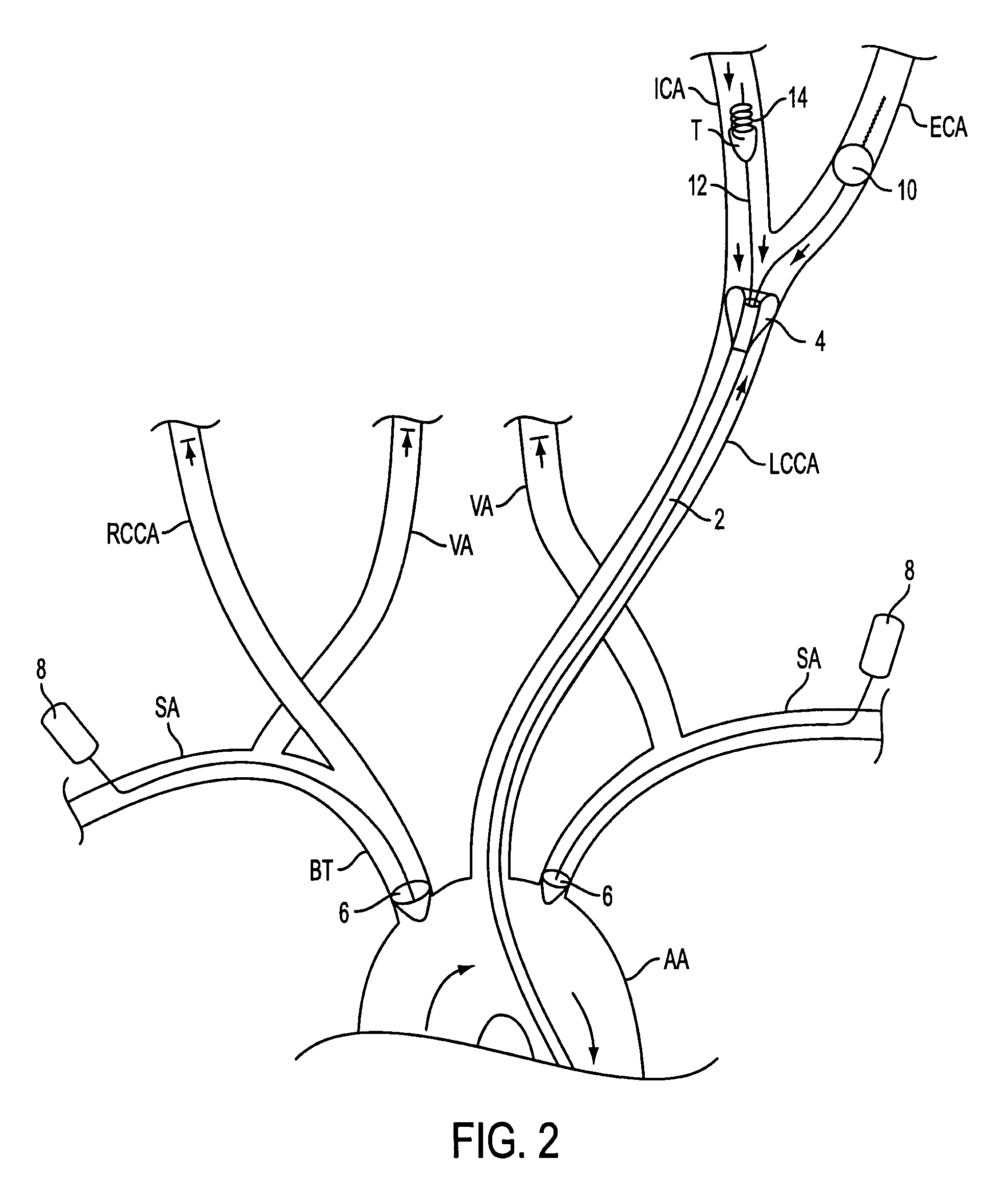
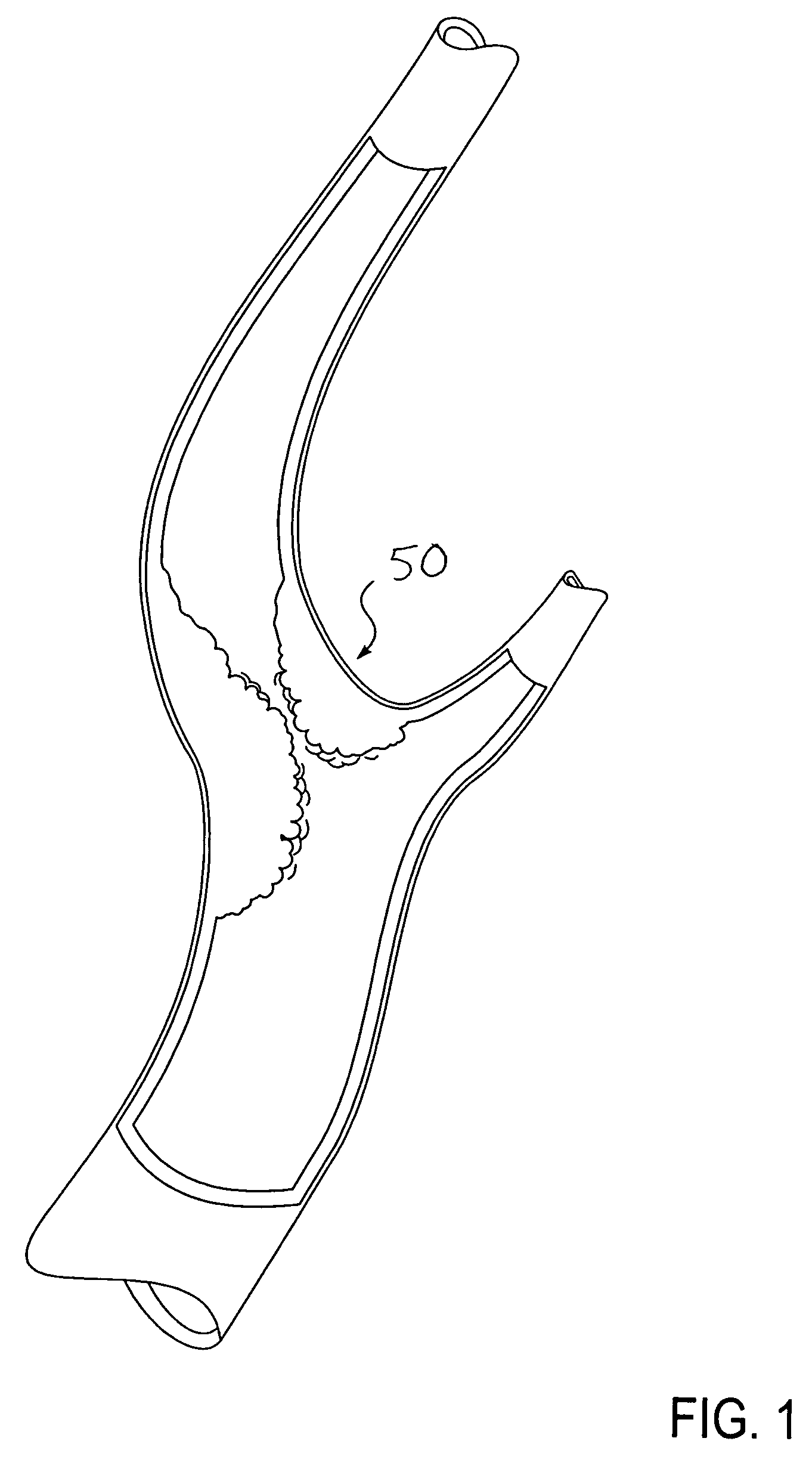
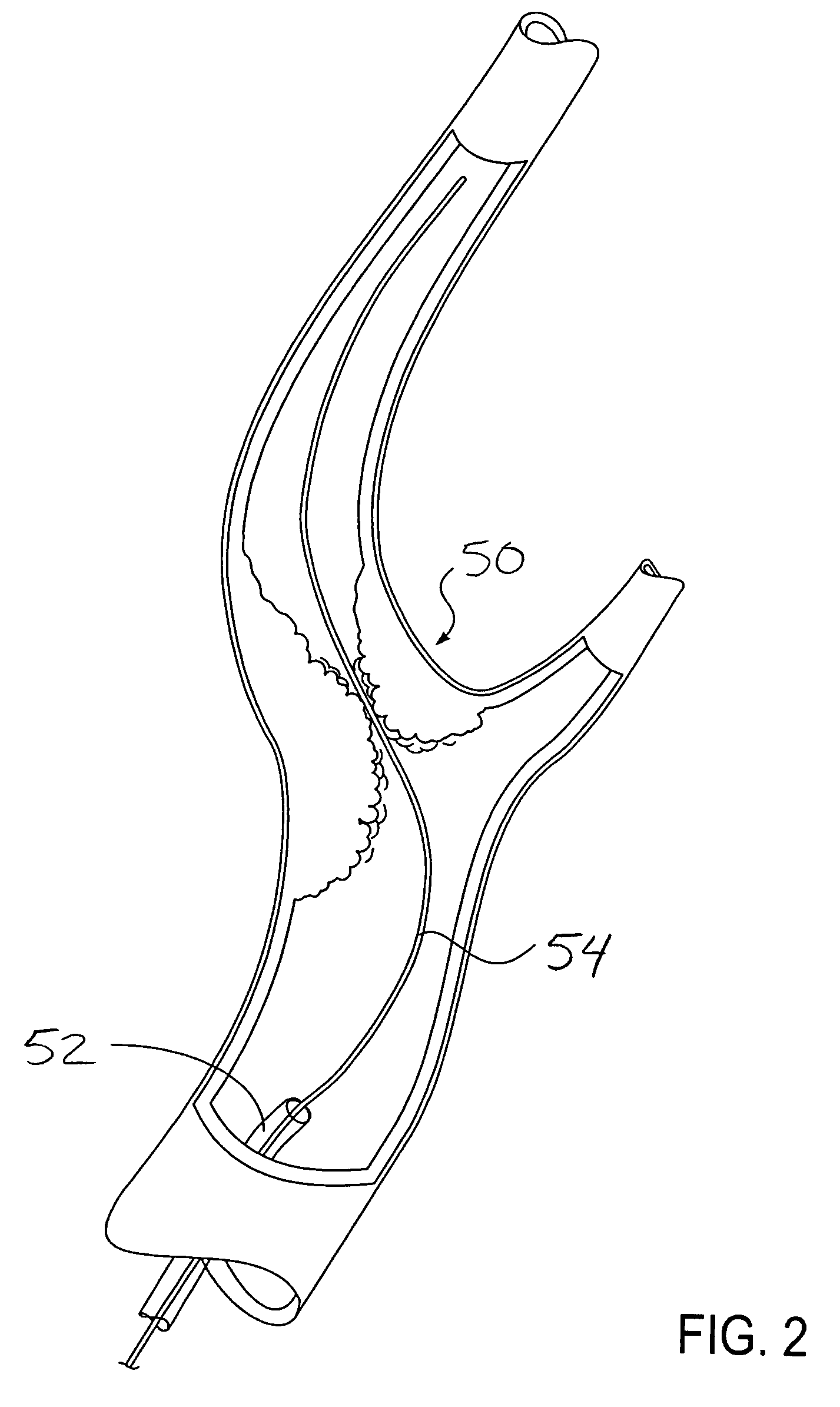
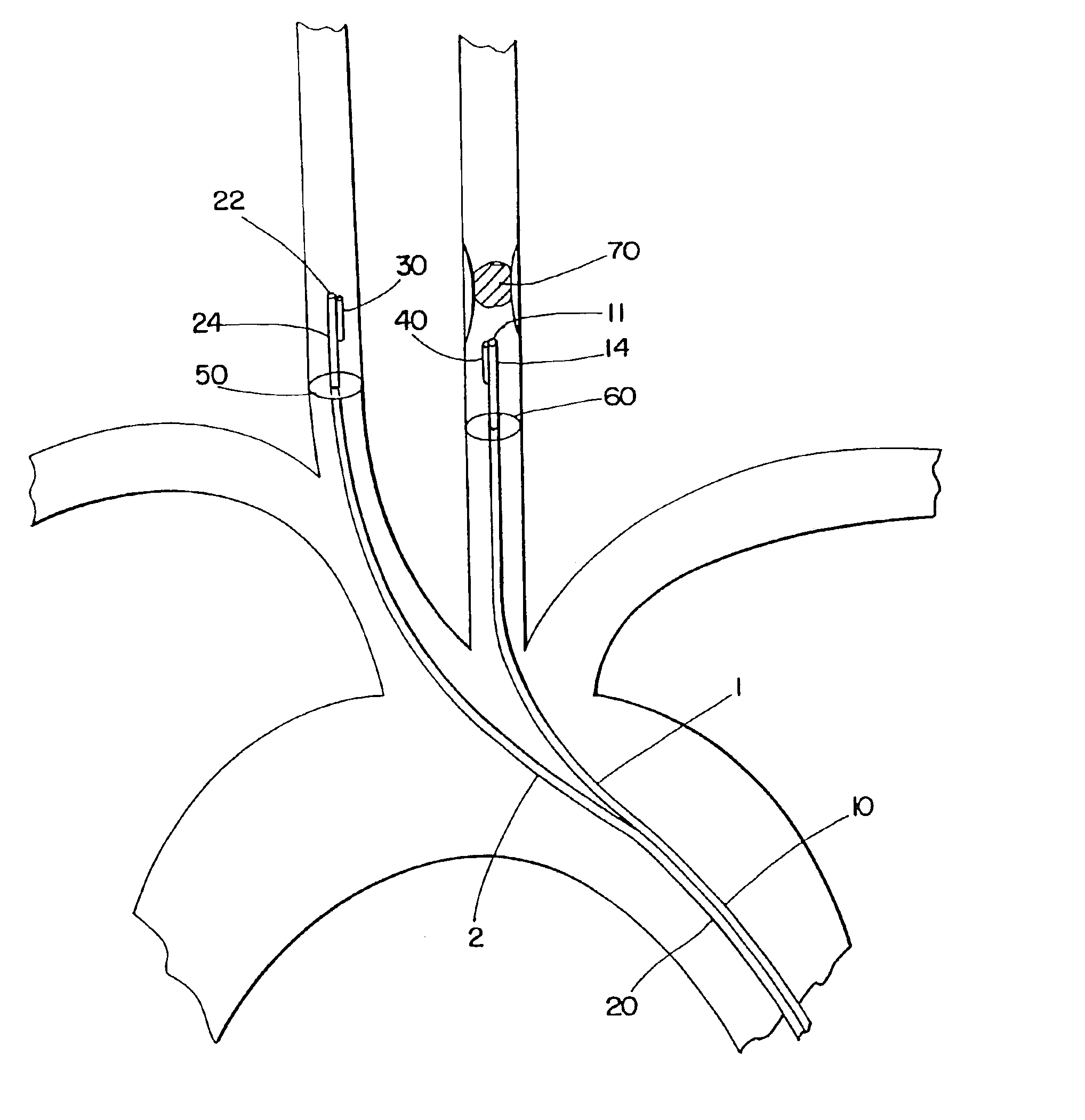
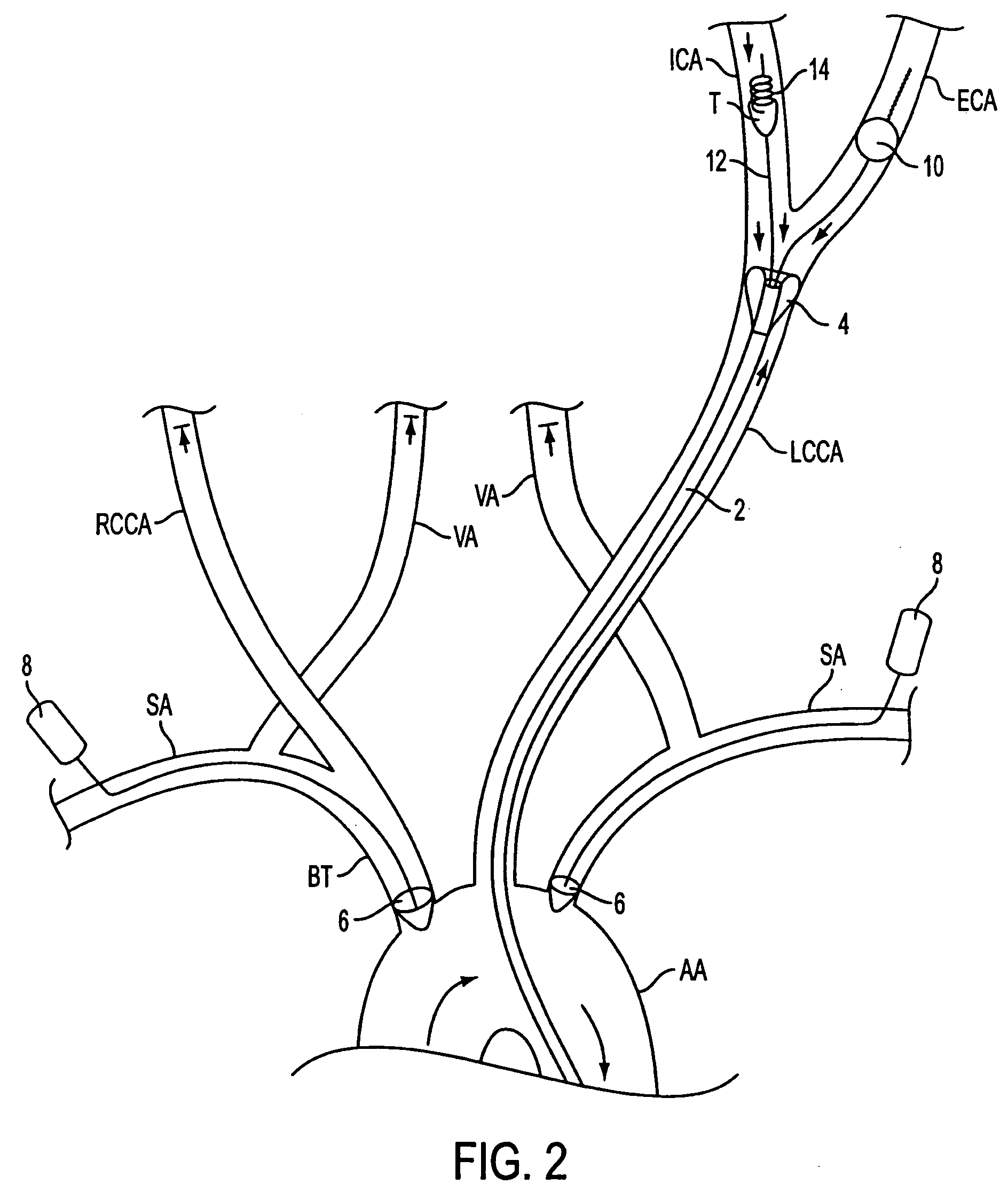
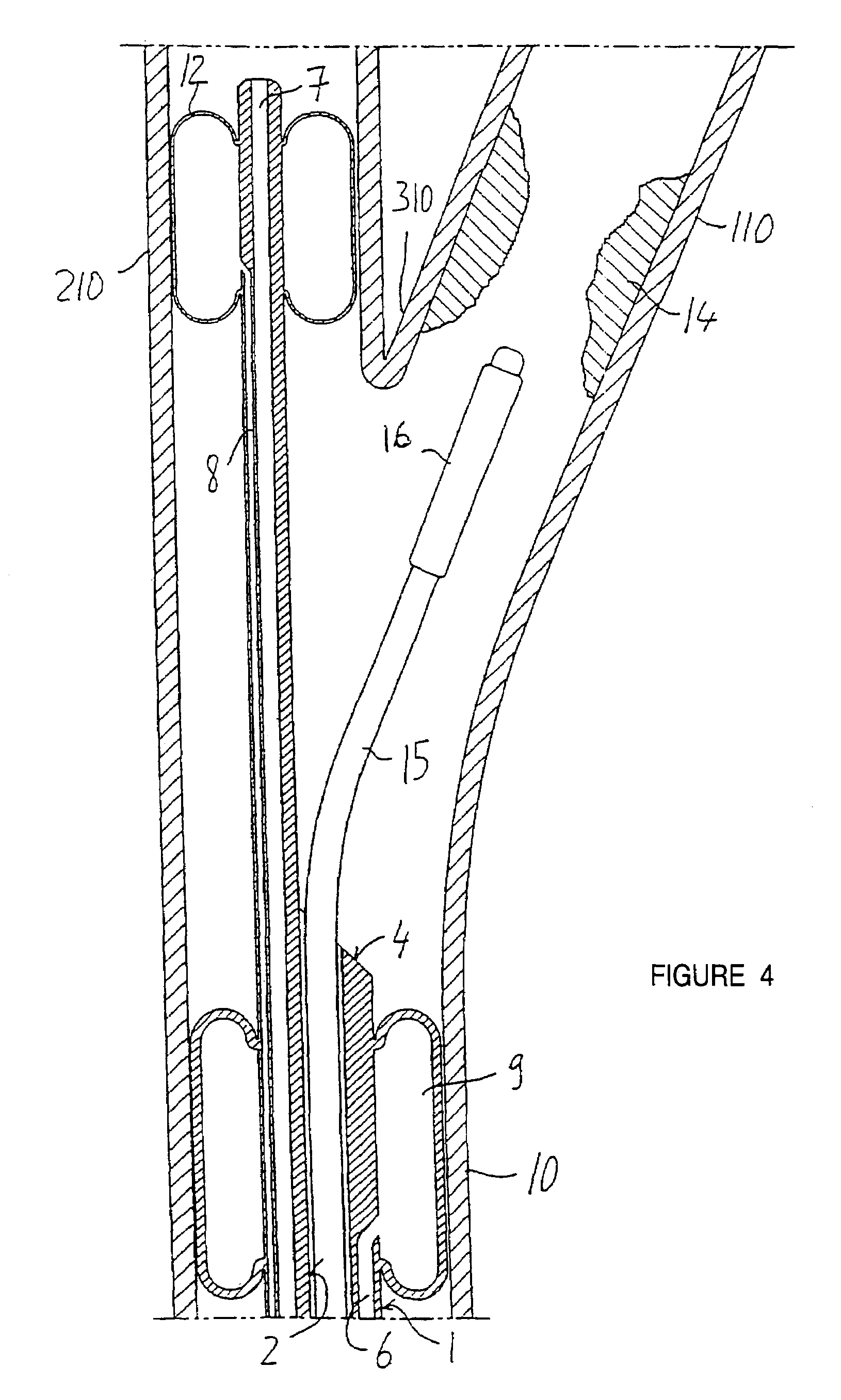
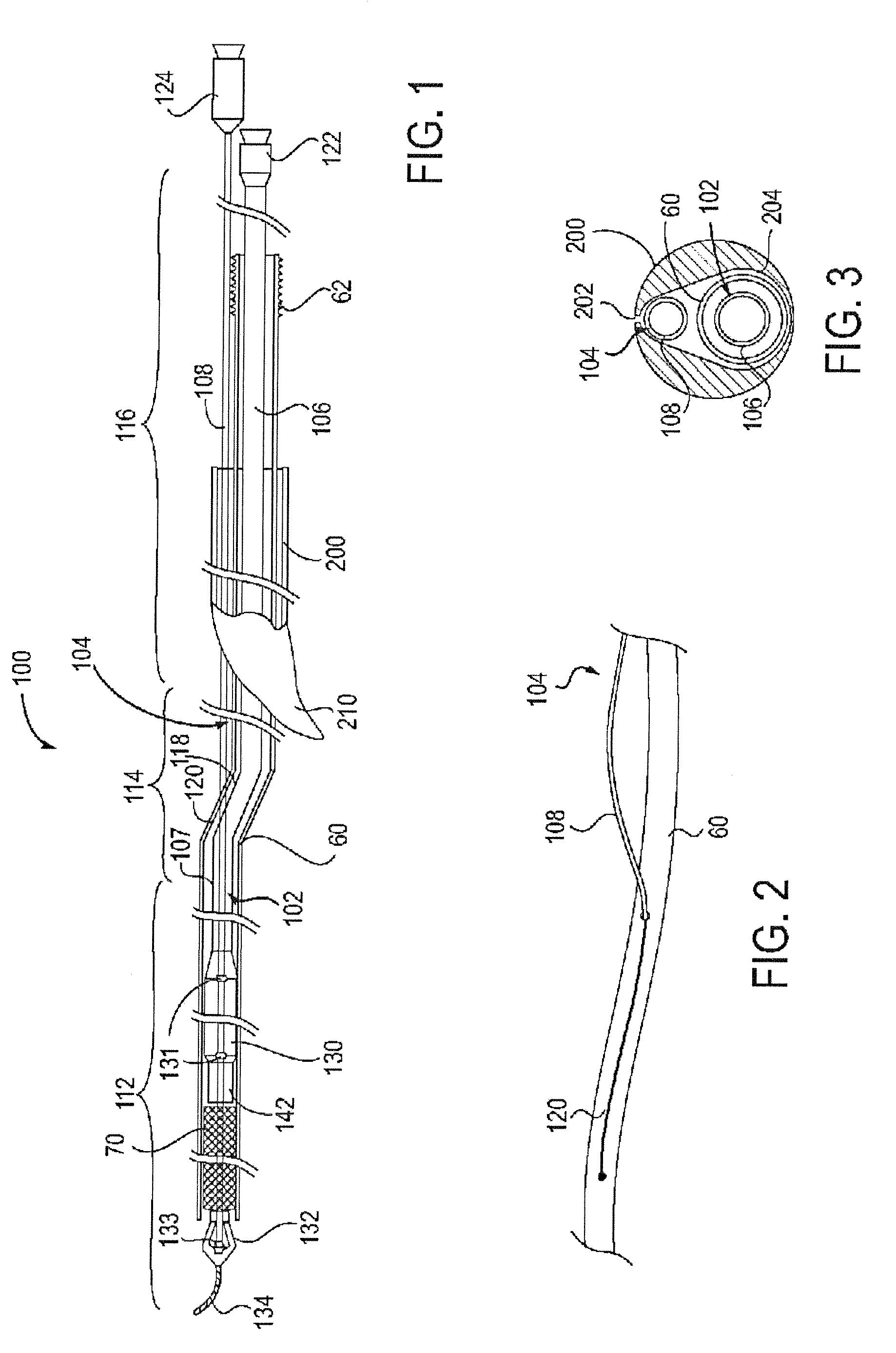
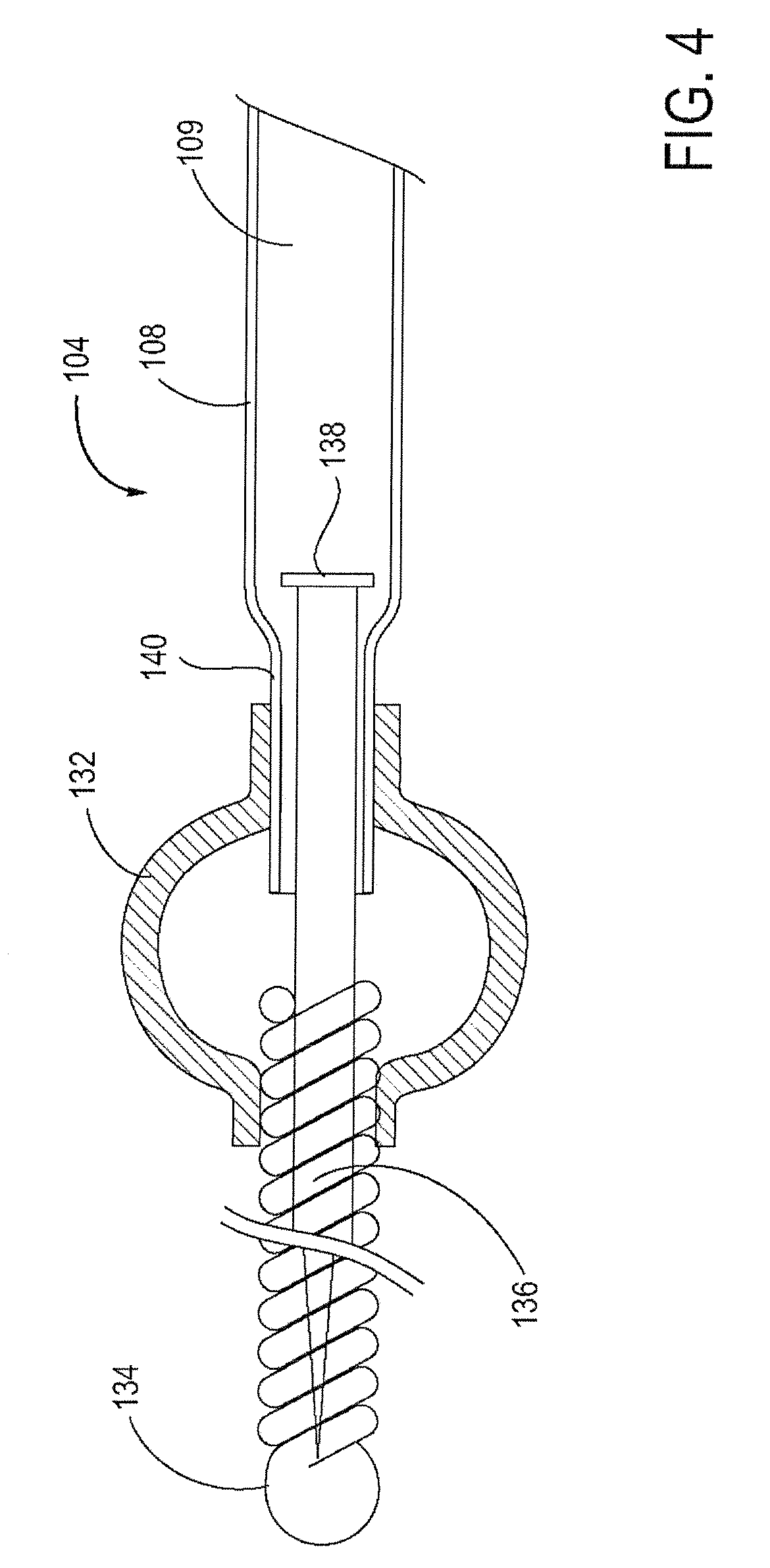
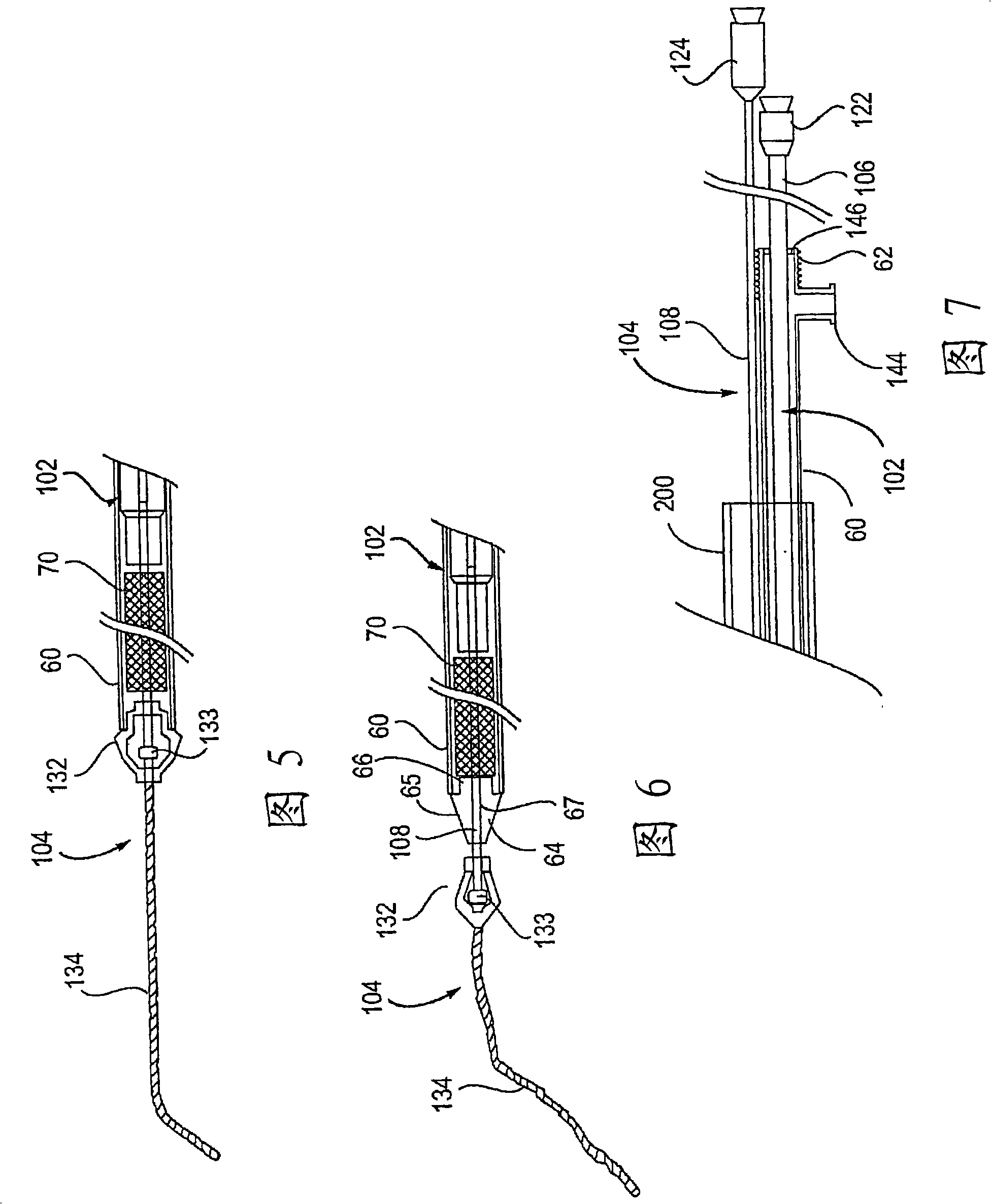
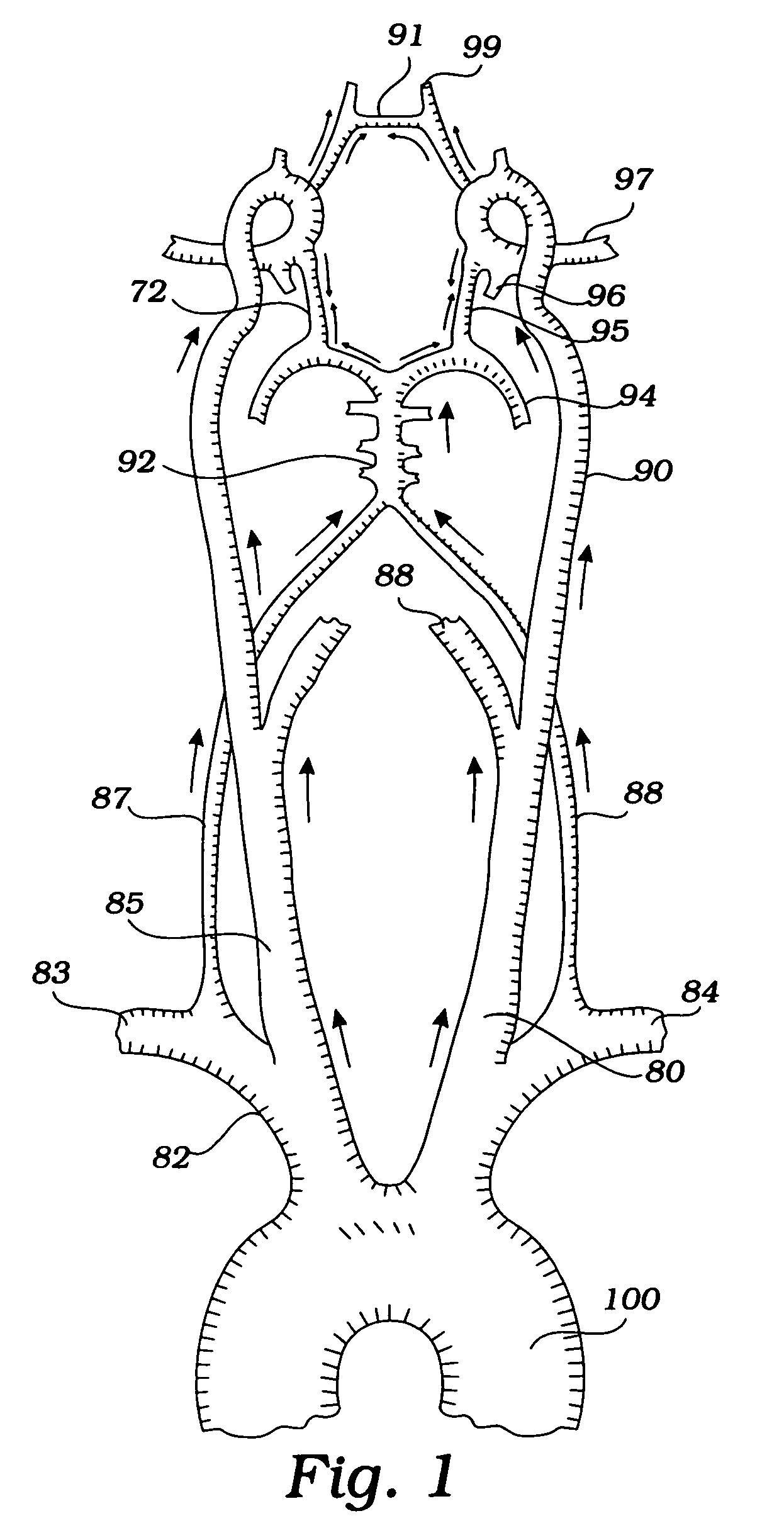
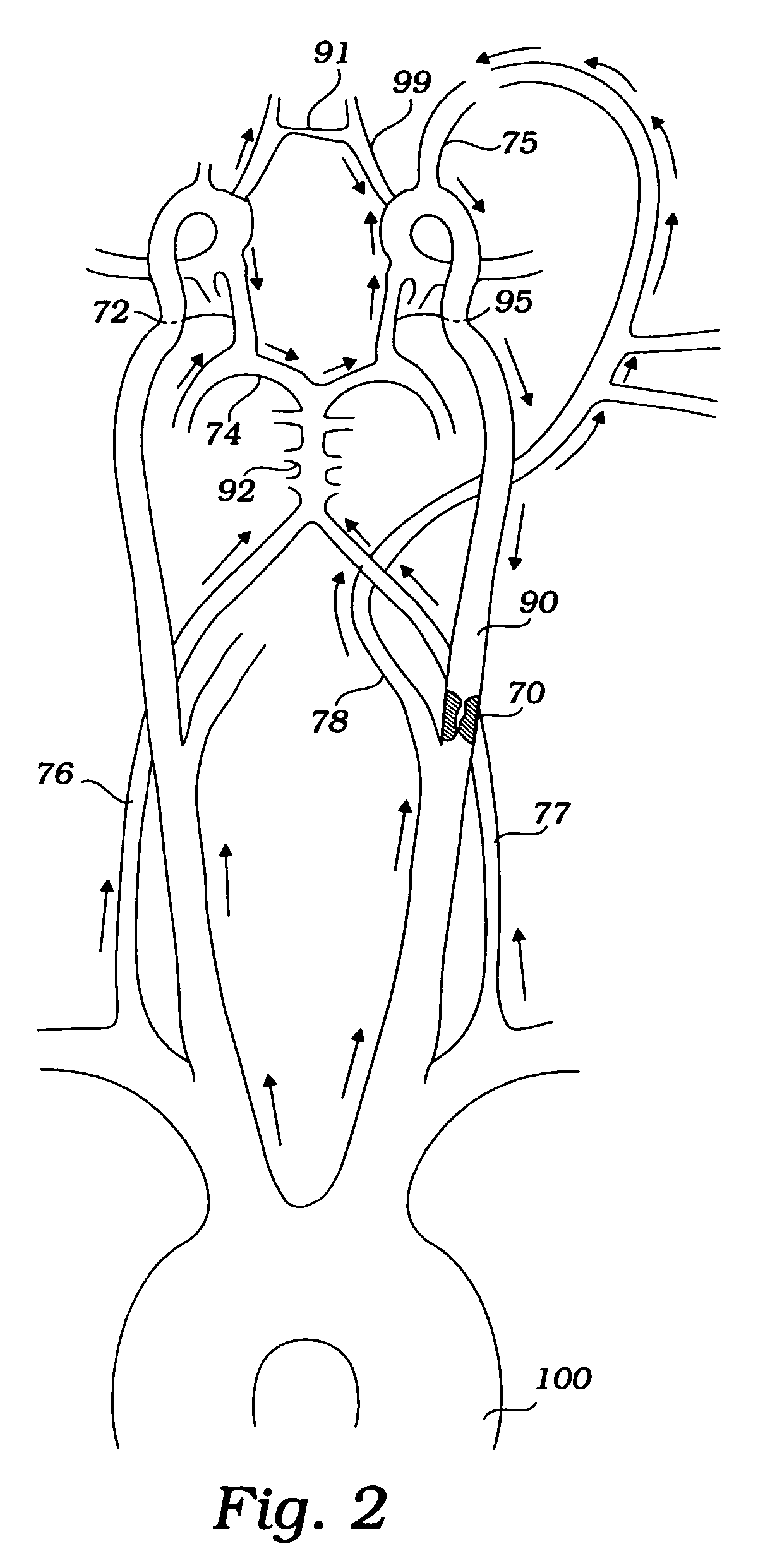
Apparatus and methods for treating stroke and controlling cerebral flow characteristics
InactiveUS6902540B2Quickly and efficiently treat cerebral occlusionEfficient removalStentsBalloon catheterCarotid imtEmbolus
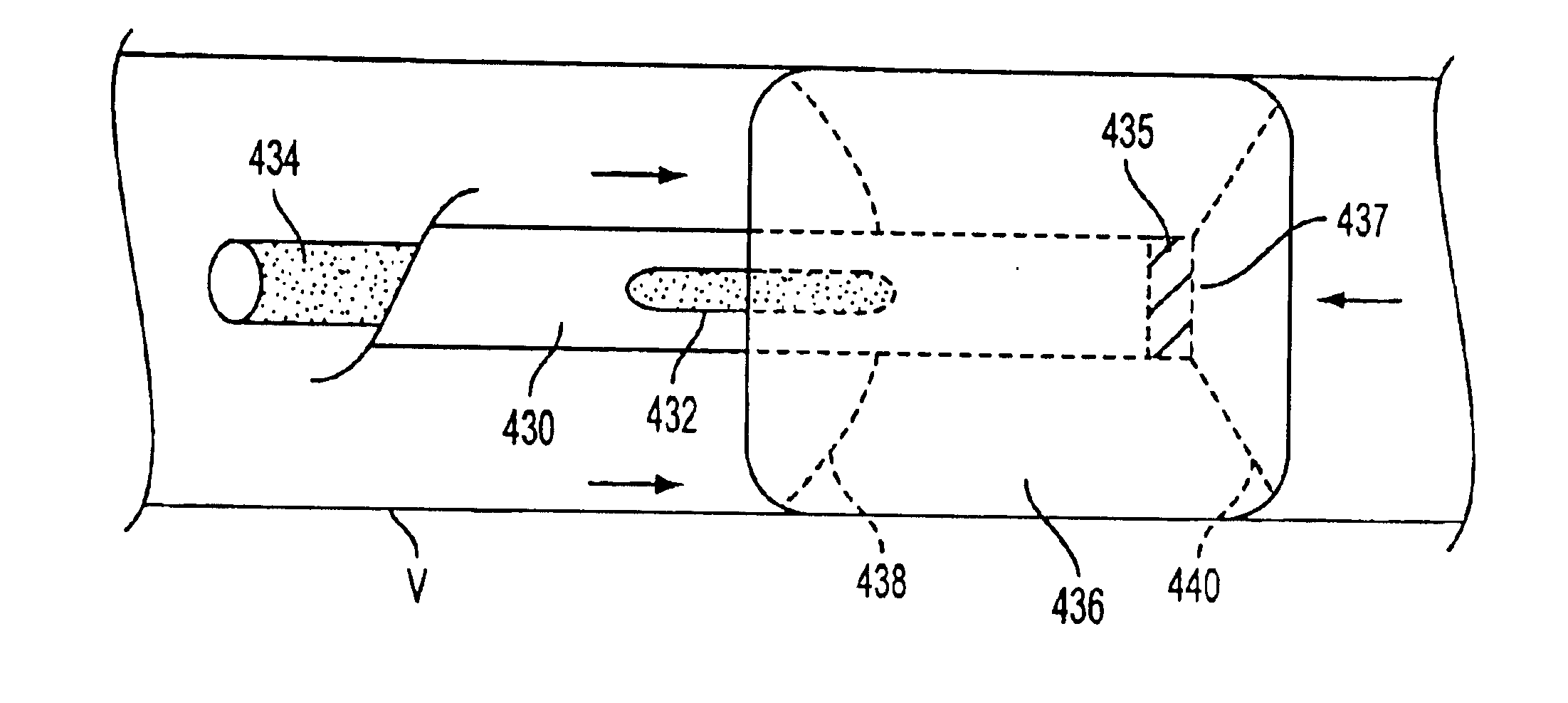
Apparatus and methods for treatment of stroke are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention disposes at least one catheter having a distal occlusive member in either the common carotid artery (CCA) or both the vertebral artery (VA) and the CCA on the hemisphere of the cerebral occlusion. Blood flow in the opposing carotid and / or vertebral arteries may be inhibited. Retrograde or antegrade flow may be provided through either catheter independently to effectively control cerebral flow characteristics. Under such controlled flow conditions, a thrombectomy device may be used to treat the occlusion, and any emboli generated are directed into the catheter(s).
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Intravascular methods and apparatus for isolation and selective cooling of the cerebral vasculature during surgical procedures
InactiveUS6555057B1Reduce riskIncrease perfusionOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesRisk strokeSurgical department
Patients having diminished circulation in the cerebral vasculature as a result of stroke or from other causes such as cardiac arrest, shock or head trauma, or aneurysm surgery or aortic surgery, are treated by flowing an oxygenated medium through an arterial access site into the cerebral vasculature and collecting the medium through an access site in the venous site of the cerebral vasculature. Usually, the cold oxygenated medium will comprise autologous blood, and the blood will be recirculated for a time sufficient to permit treatment of the underlying cause of diminished circulation. In addition to oxygenation, the recirculating blood will also be cooled to hypothermically treat and preserve brain tissue. Isolation and cooling of cerebral vasculature in patients undergoing aortic and other procedures is achieved by internally occluding at least the right common carotid artery above the aortic arch. Blood or other oxygenated medium is perfused through the occluded common carotid artery(ies) and into the arterial cerebral vasculature. Usually, oxygen depleted blood or other medium leaving the cerebral vasculature is collected, oxygenated, and cooled in an extracorporeal circuit so that it may be returned to the patient. Occlusion of the carotid artery(ies) is preferably accomplished using expansible occluders, such as balloon-tipped cannula, catheters, or similar access devices. Access to the occlusion site(s) may be open surgical, percutaneous, or intravascular.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE +3
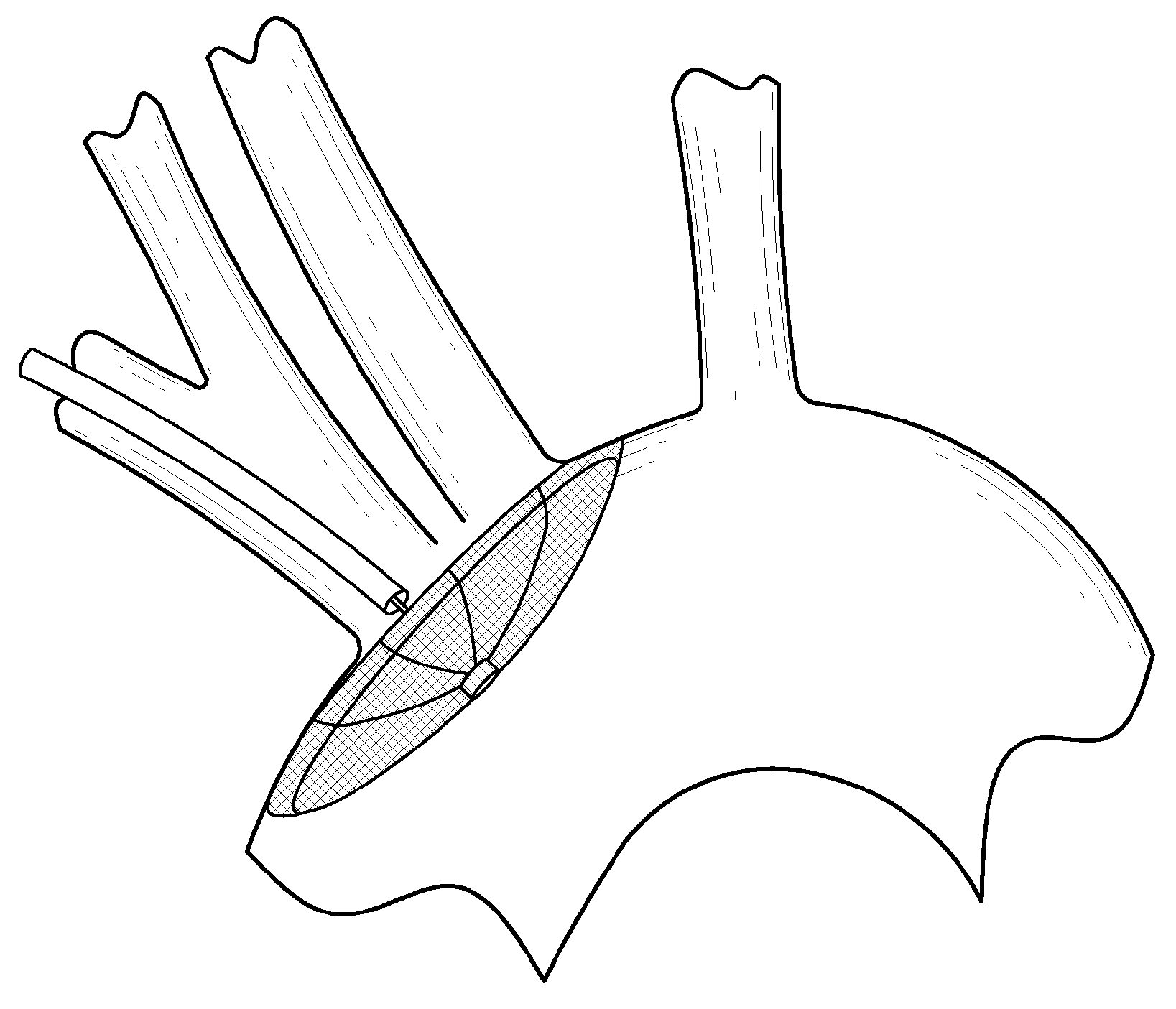
Methods of deploying and retrieving an embolic diversion device
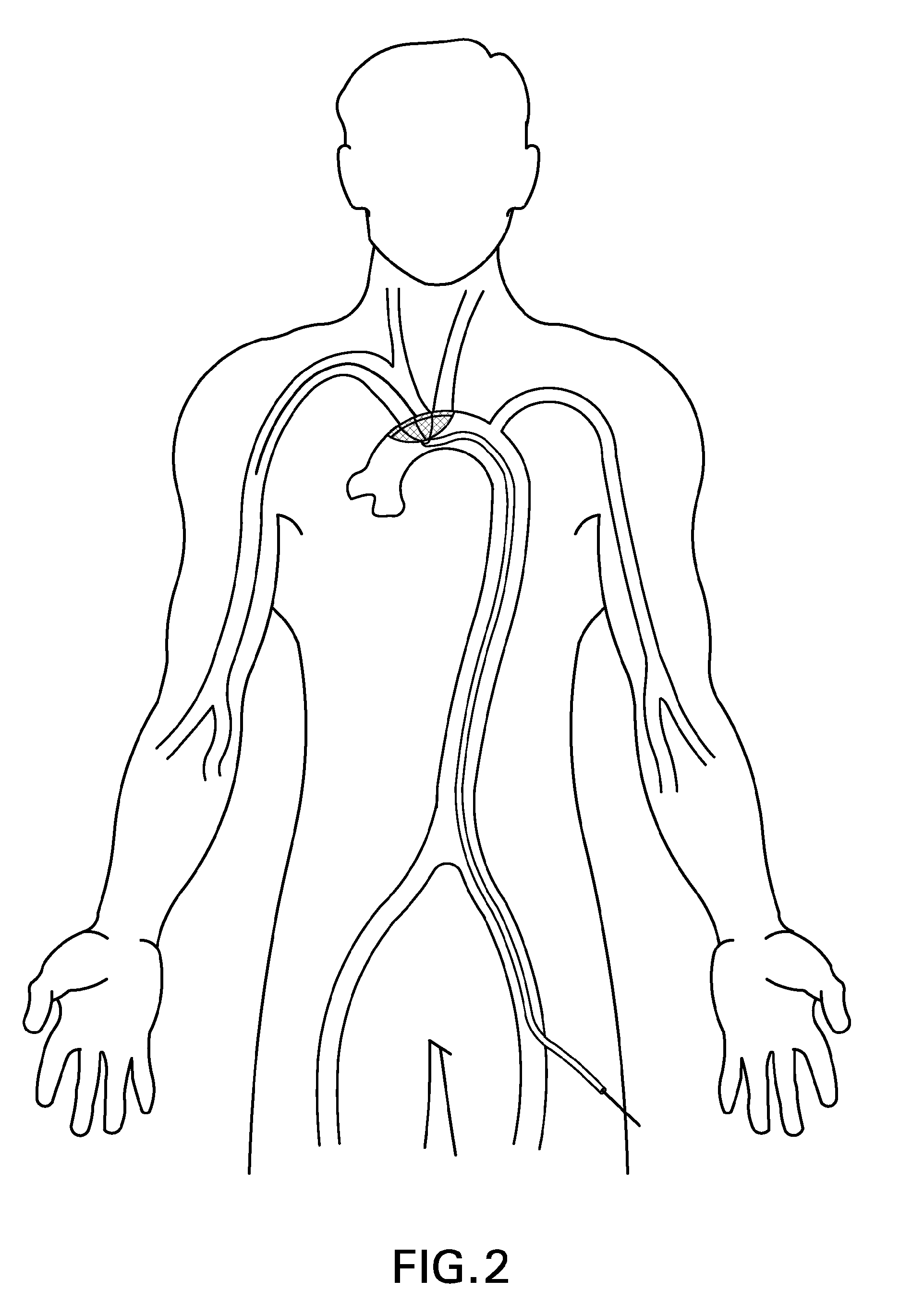
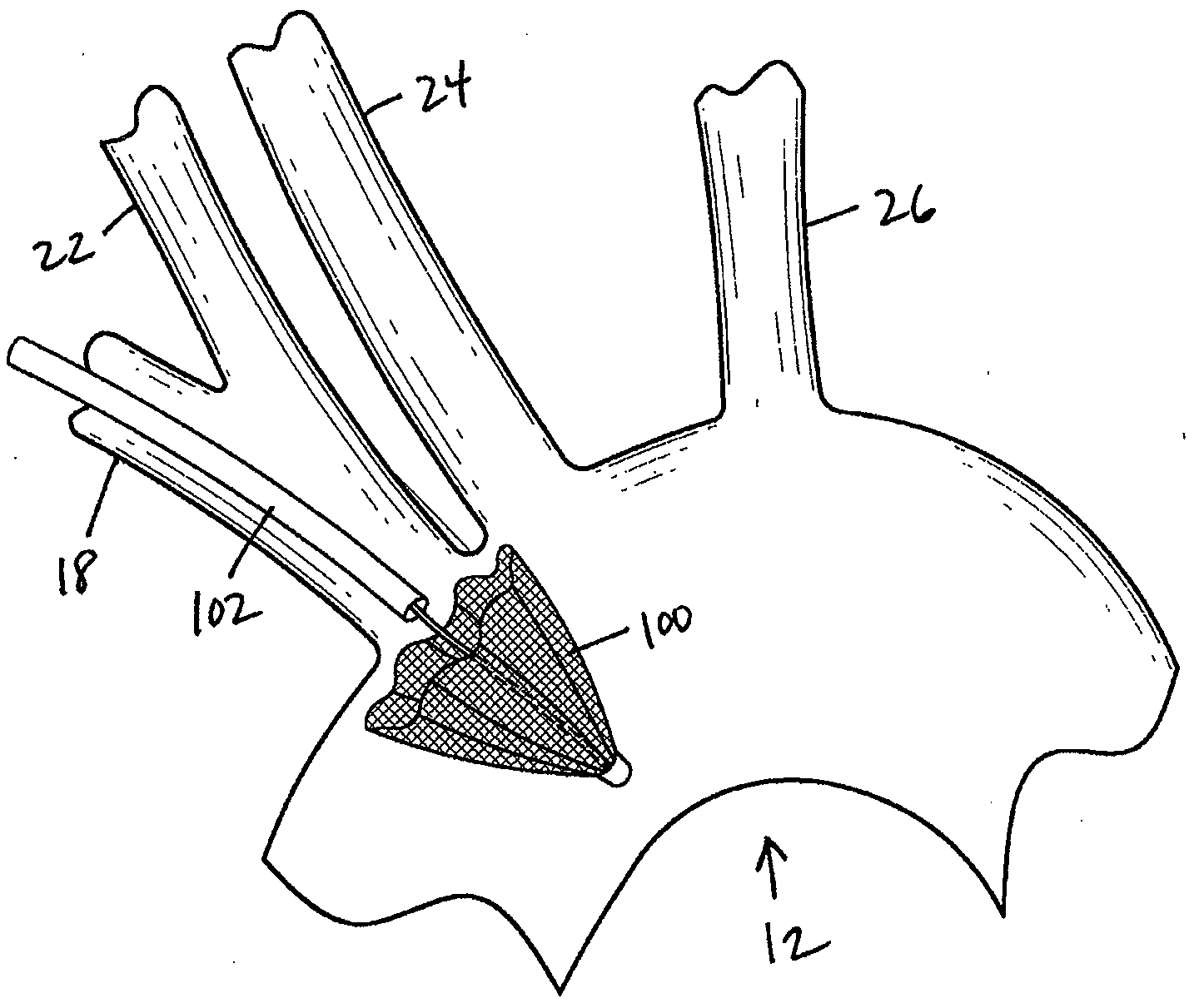
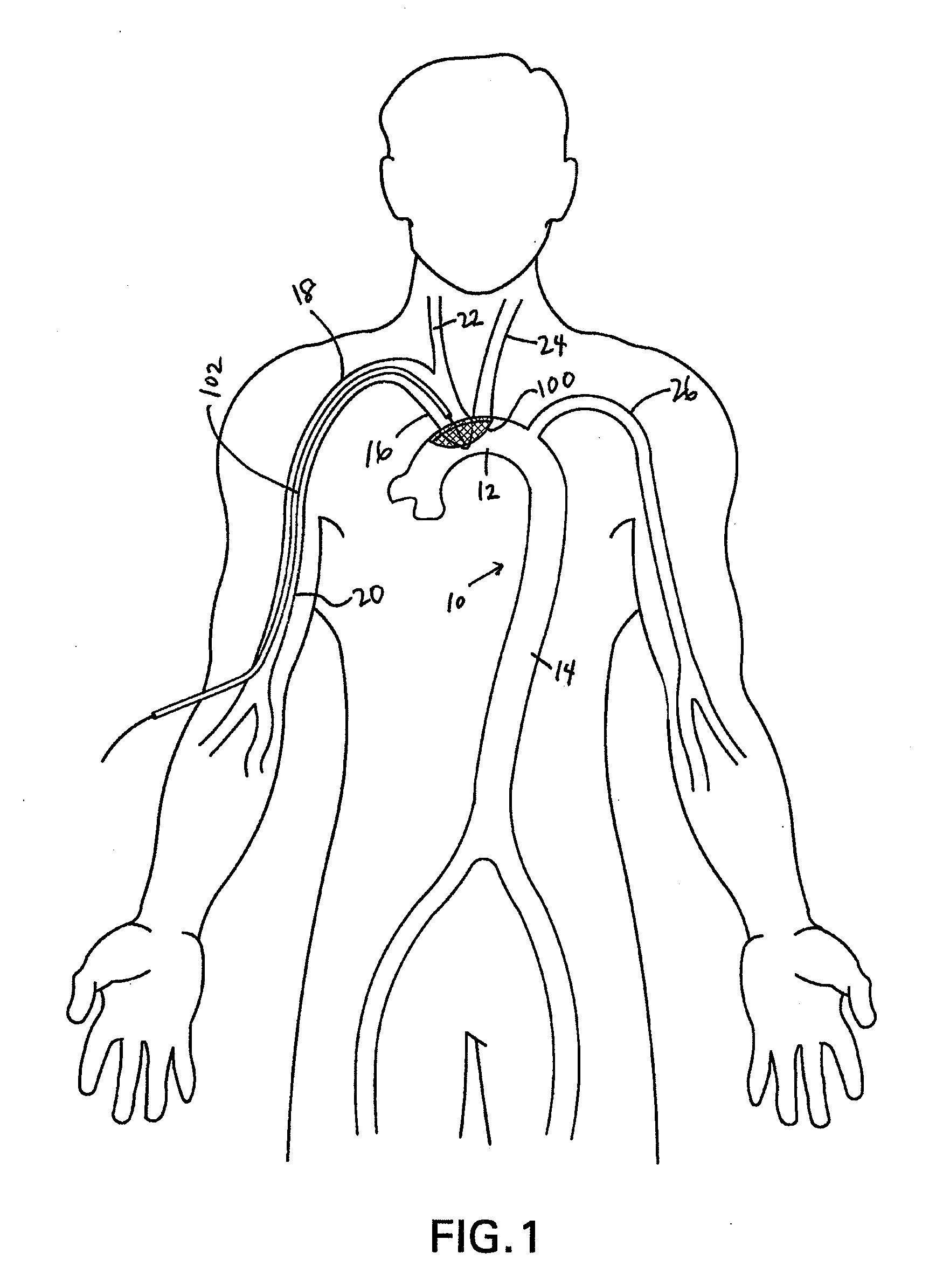
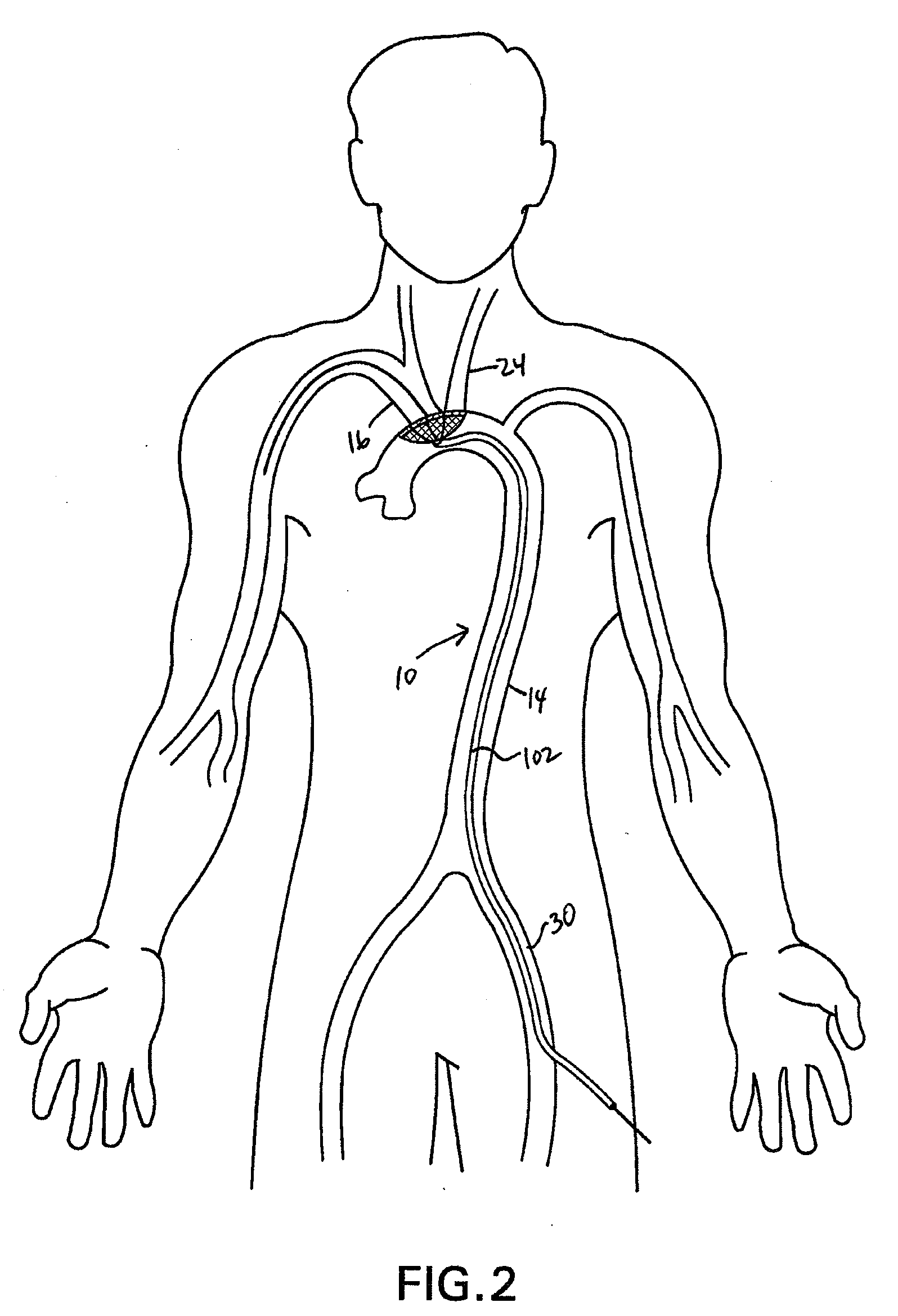
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (such as greater than 100 microns) from entering either the right or left common carotid arteries, and / or the right or left vertebral arteries by deflecting emboli downstream of these vessels. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The deflector has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
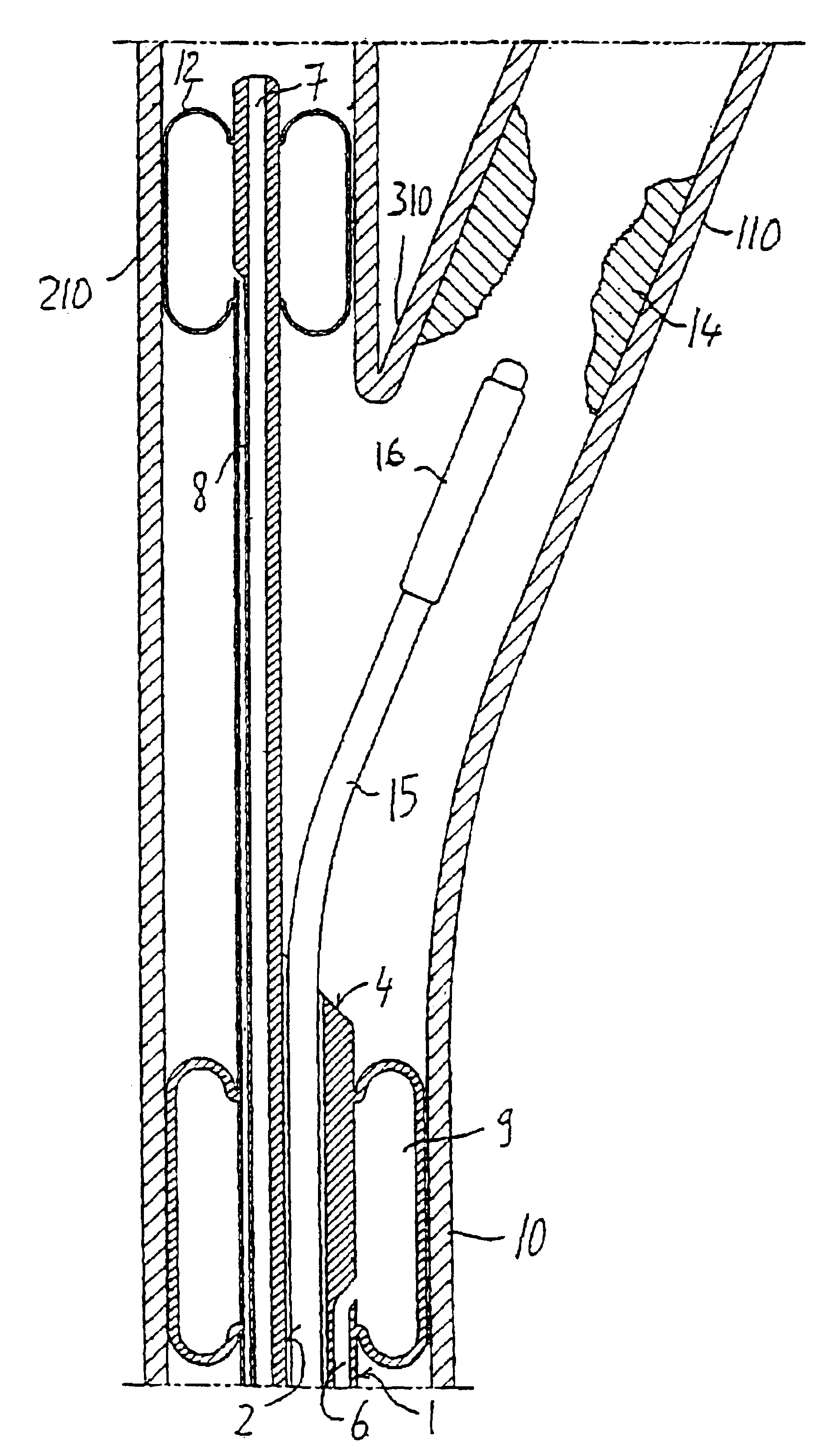
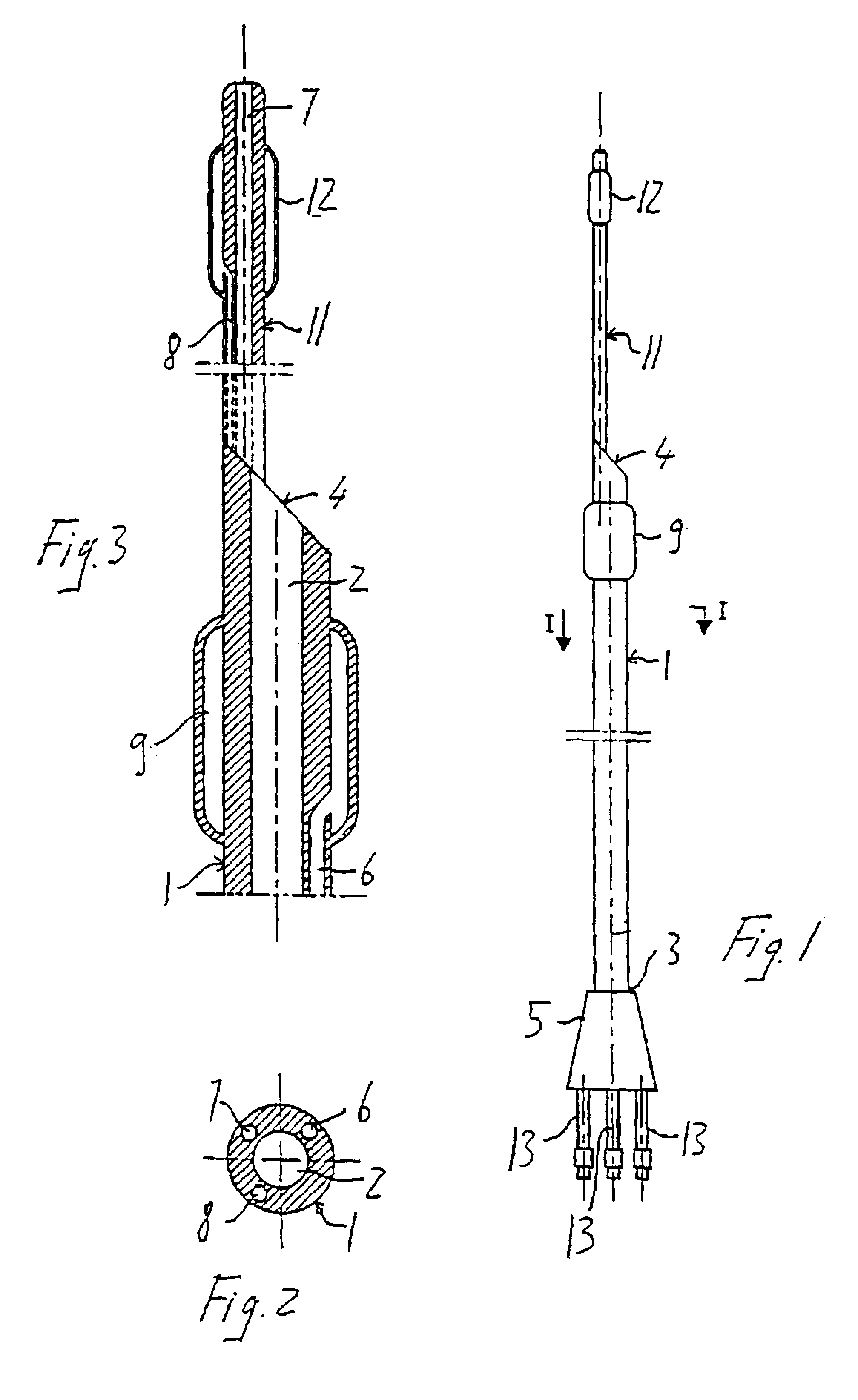
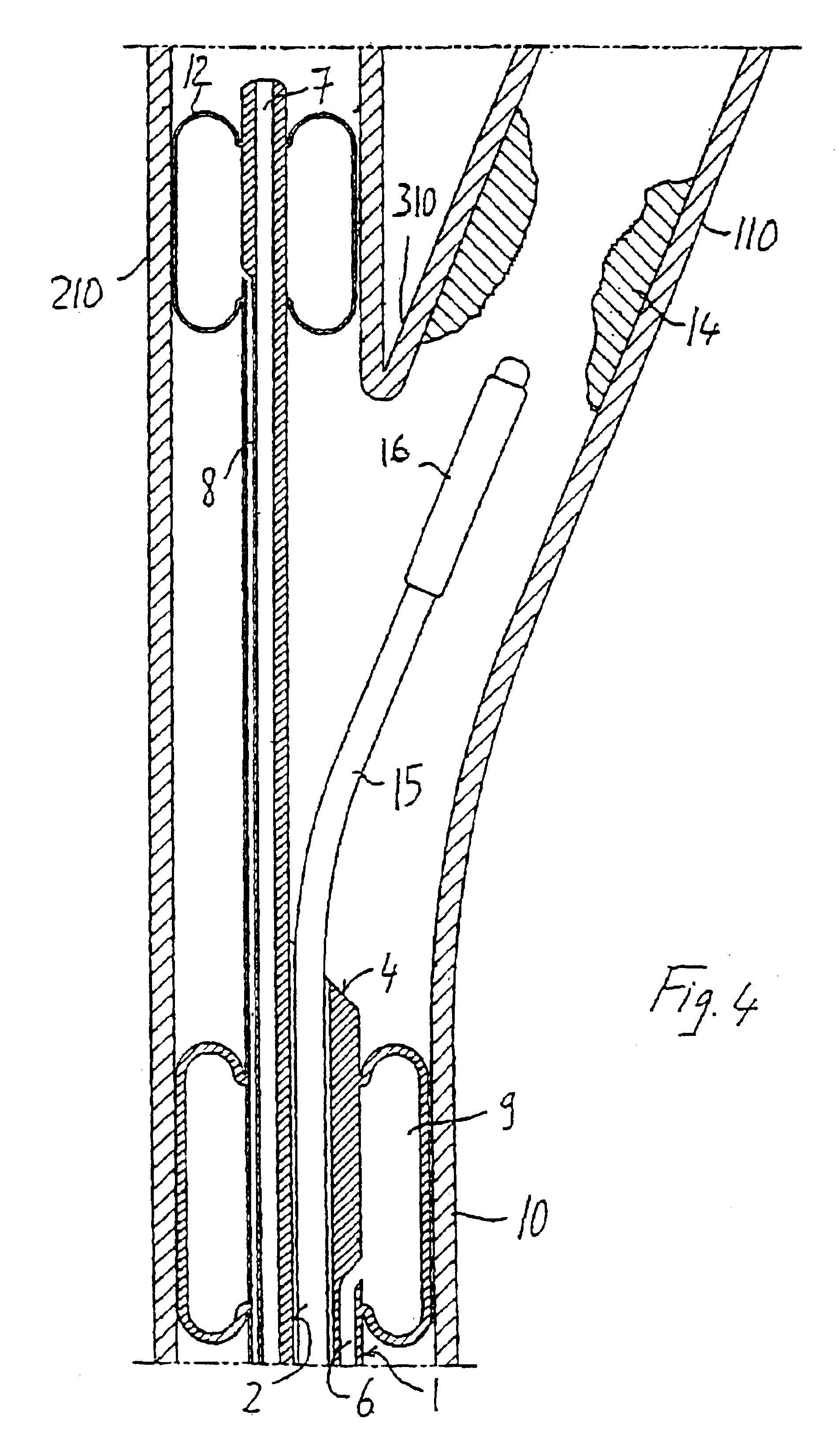
Endovascular system for the treatment of stenoses of the carotid and catheter for this system
A catheter, in particular for endovascular applications, including a long and flexible, hollow, tubular body having an insertion end and a connection end intended to remain outside the body. The catheter includes in the insertion end at least two elements which are expandable / contractible by means of external operations. Those elements are located at a distance from each other, one upstream and the other downstream of a given section of a vessel. With the catheter it is possible to operate in the section between the two expandable elements and, if necessary, in the intermediate arterial branch which, on account of the two elements upstream and downstream, will have a zero flow.
Owner:INVATEC +3
Apparatus and methods for treating stroke and controlling cerebral flow characteristics
InactiveUS7063714B2Quickly and efficiently treat cerebral occlusionEfficient removalStentsBalloon catheterLeft vertebral arteryThrombus
Apparatus and methods for treatment of stroke are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention disposes at least one catheter having a distal occlusive member in either the common carotid artery (CCA) or both the vertebral artery (VA) and the CCA on the hemisphere of the cerebral occlusion. Blood flow in the opposing carotid and / or vertebral arteries may be inhibited. Retrograde or antegrade flow may be provided through either catheter independently to effectively control cerebral flow characteristics. Under such controlled flow conditions, a thrombectomy device may be used to treat the occlusion, and any emboli generated are directed into the catheter(s).
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
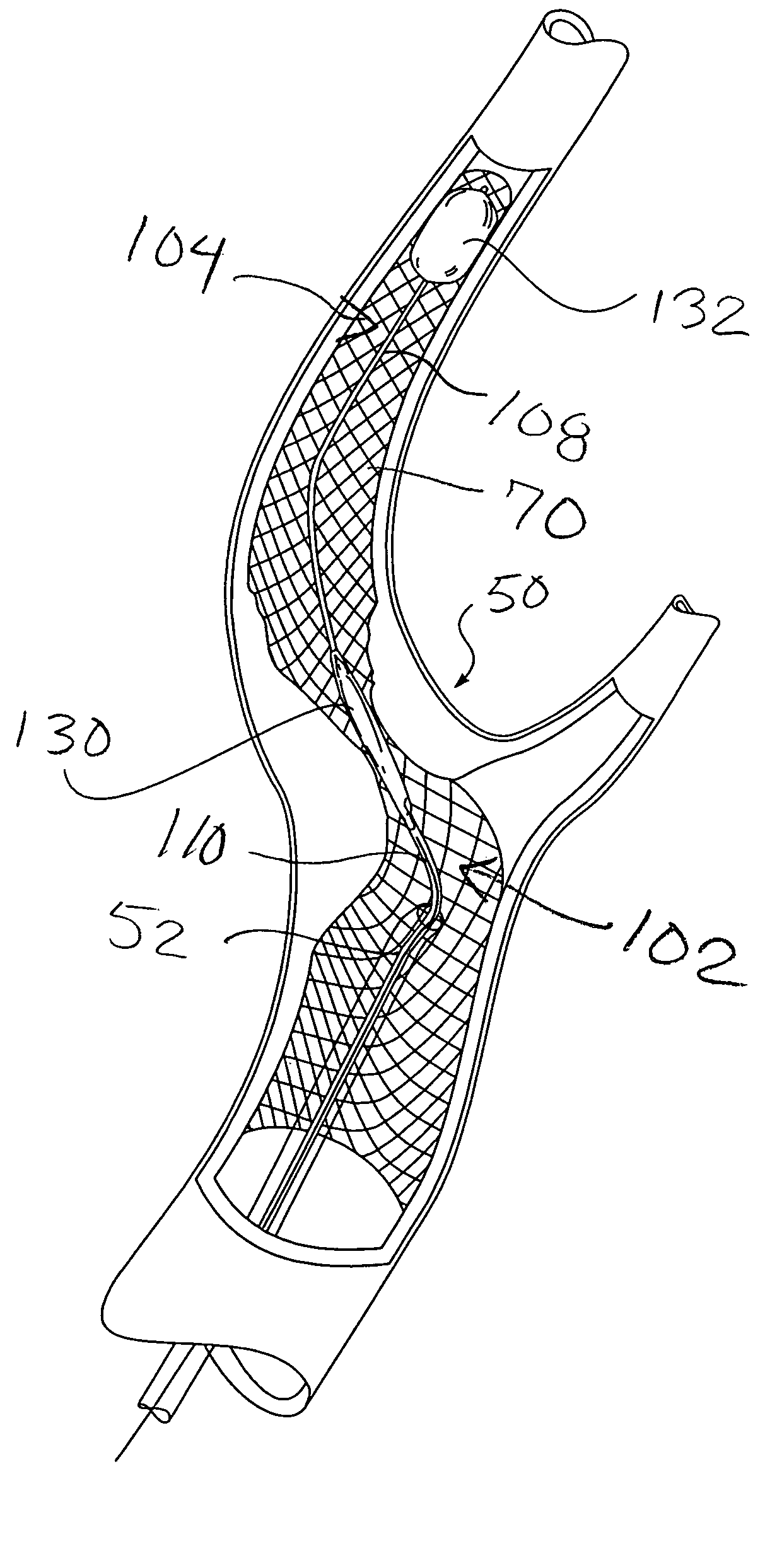
Method of performing protected angioplasty and stenting at a carotid bifurcation
ActiveUS7172621B2Avoid complicationsGood curative effectStentsDilatorsAngioplasty balloonPercutaneous angioplasty
A method is described for performing protected angioplasty and stenting of a patient's carotid bifurcation. A self-expanding stent is deployed across a stenosis in the patient's carotid artery. A catheter system that includes a rapid exchange balloon angioplasty catheter with an occlusion balloon catheter positioned through the guidewire lumen is advanced through the guiding catheter and into the distal end of the stent. The occlusion balloon is inflated within the lumen of the stent to occlude the carotid artery and to prevent any embolic debris from traveling downstream from the treatment site. The angioplasty balloon is inflated to dilate the stenosis and to complete the expansion of the self-expanding stent. The angioplasty catheter is withdrawn and any potential embolic debris is aspirated out through the lumen of the guiding catheter. The occlusion balloon is deflated and the catheter system is withdrawn.
Owner:THERON LAURENCE
Embolic Protection Device and Method of Use
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (greater than 100 microns in the preferred embodiment) from entering either the right or left carotid arteries by deflecting emboli downstream in the blood flow. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The device has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the device.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG +1
Methods of diverting embolic debris away from the cerebral circulation
There is disclosed a porous emboli deflector for preventing cerebral emboli while maintaining cerebral blood flow during an endovascular or open surgical procedure. The device prevents the entrance of emboli of a size able to cause stroke (such as greater than 100 microns) from entering either the right or left common carotid arteries, and / or the right or left vertebral arteries by deflecting emboli downstream of these vessels. The device can be placed prior to any manipulation of the heart or aorta allowing maximal protection of the brain during the index procedure. The deflector has a low profile within the aorta which allows sheaths, catheters, or wires used in the index procedure to pass. Also disclosed are methods for insertion and removal of the deflector.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Methods for flow augmentation in patients with occlusive cerebrovascular disease
InactiveUS6878140B2Enhanced reversal of blood flowControl flowStentsBalloon catheterDiseasePercutaneous angioplasty
The invention provides a method for augmenting circulation in a patient having carotid stenosis. An elongate tubular member is provided having a lumen communicating with a port at a distal end. The tubular member is inserted into a peripheral artery and the distal port is advanced into a first carotid artery substantially free of a lesion where the patient possesses a second carotid artery substantially occluded by a lesion. Blood is perfused into the first carotid artery through the tubular member. Contralateral flow is augmented to improve perfusion to an ischemic region distal to the carotid stenosis. Angioplasty and stenting can be used to open the lesion in the second carotid artery.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
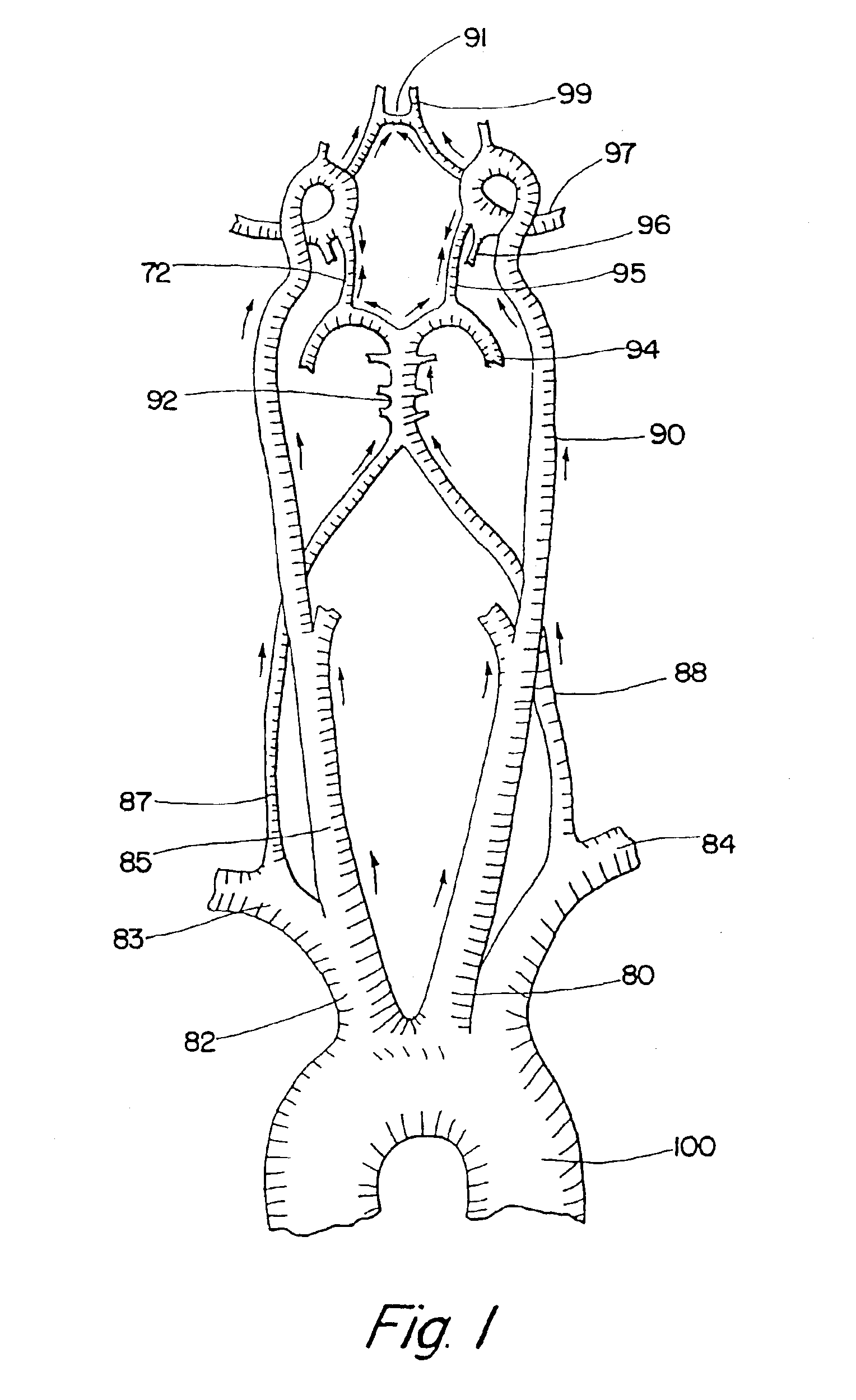
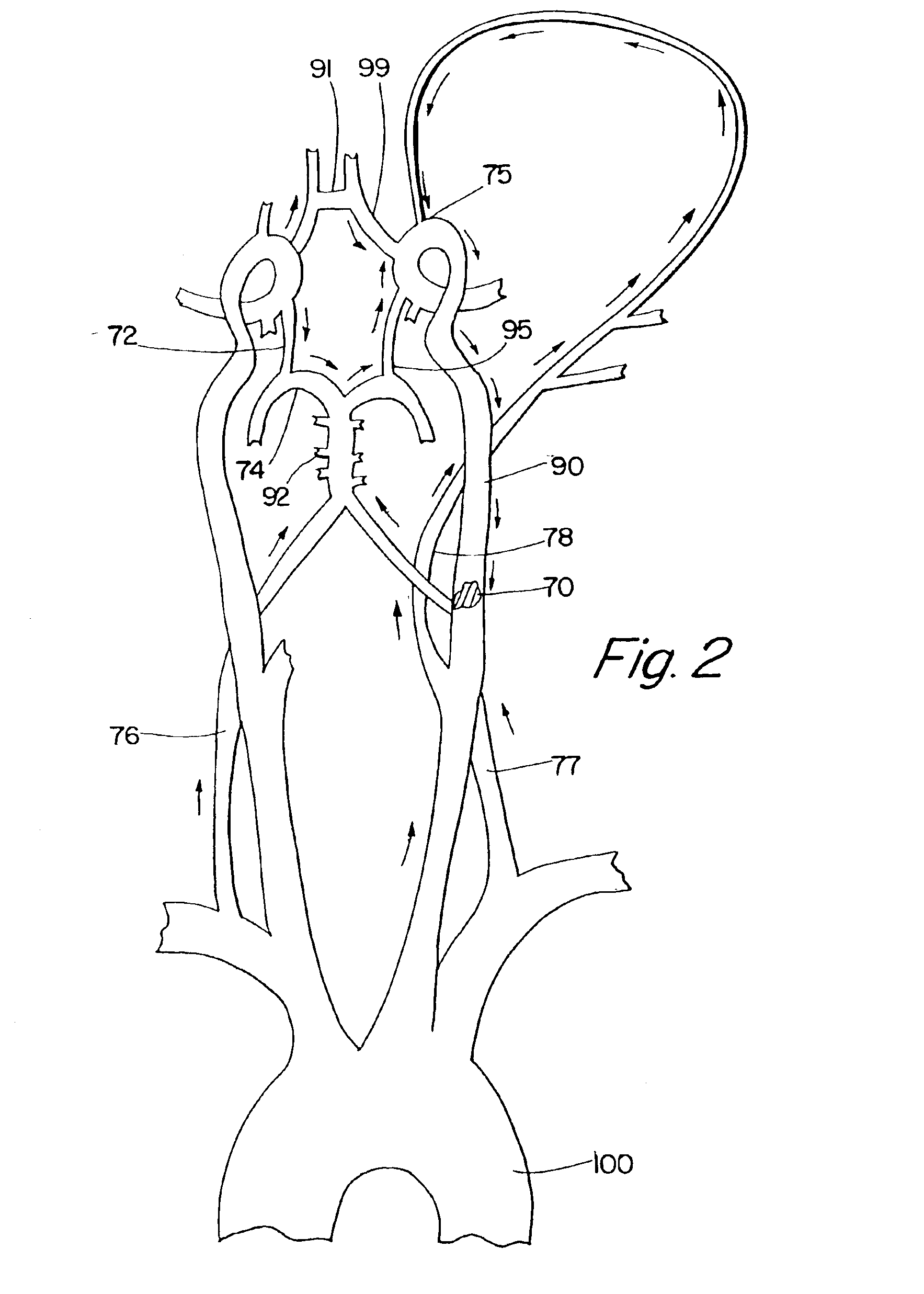
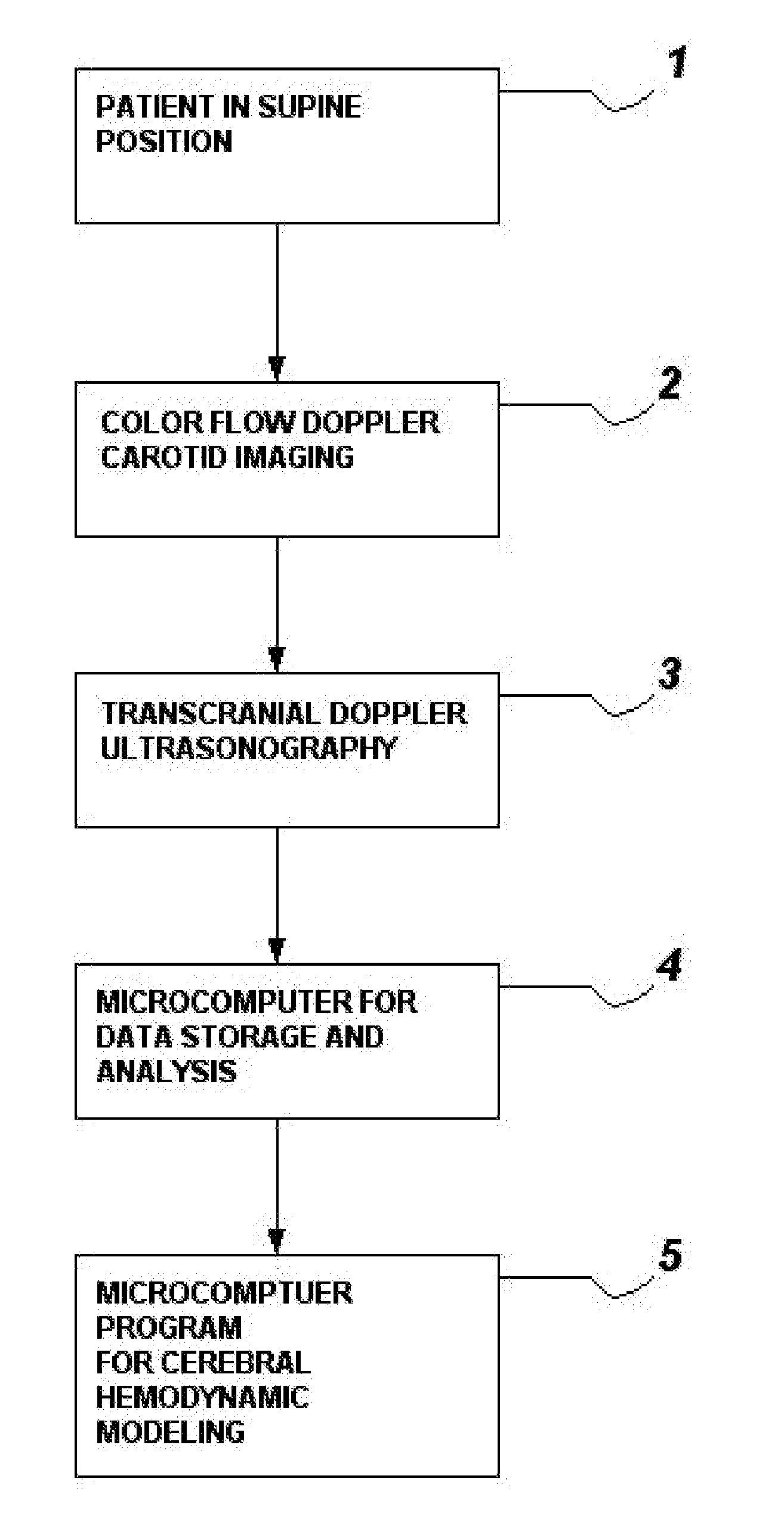
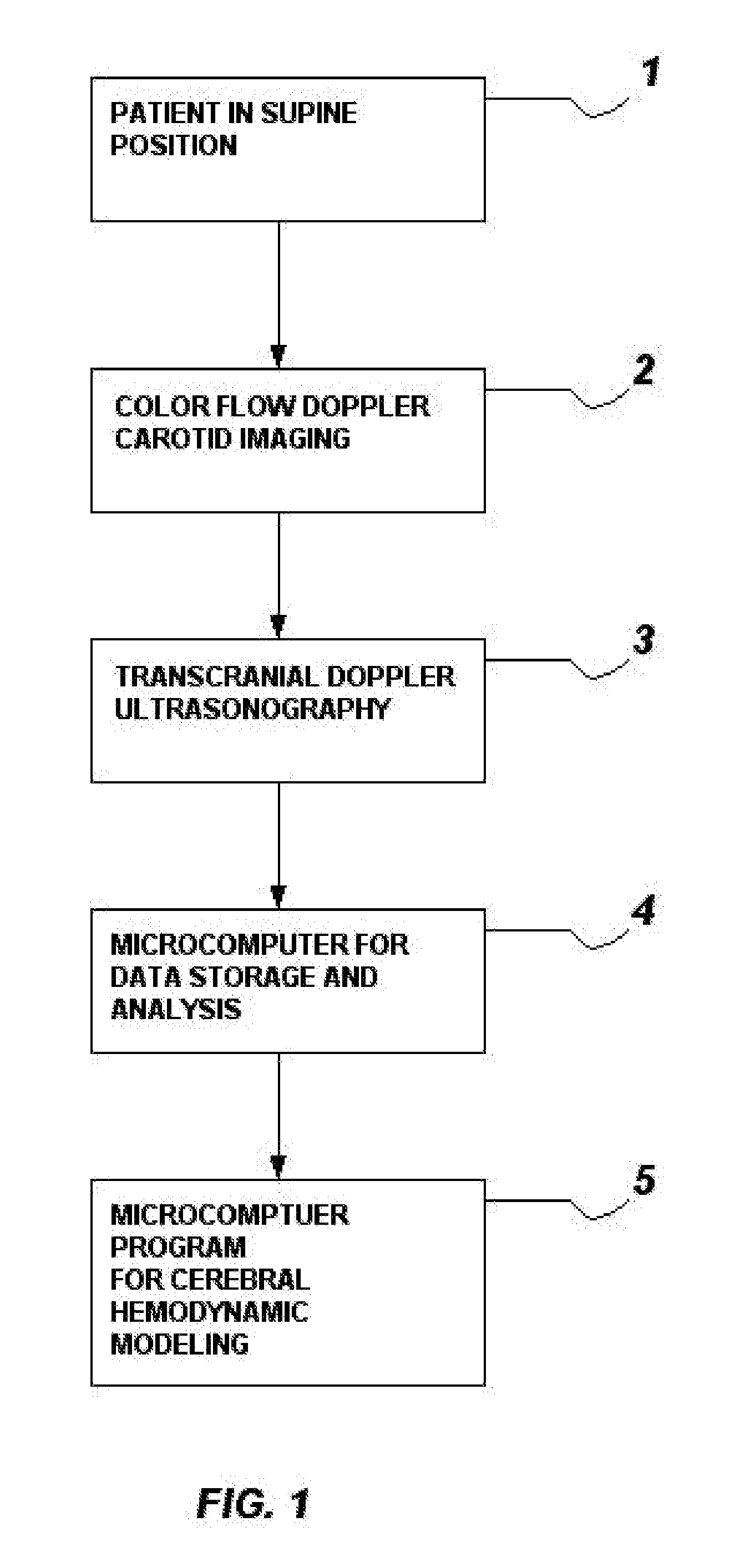
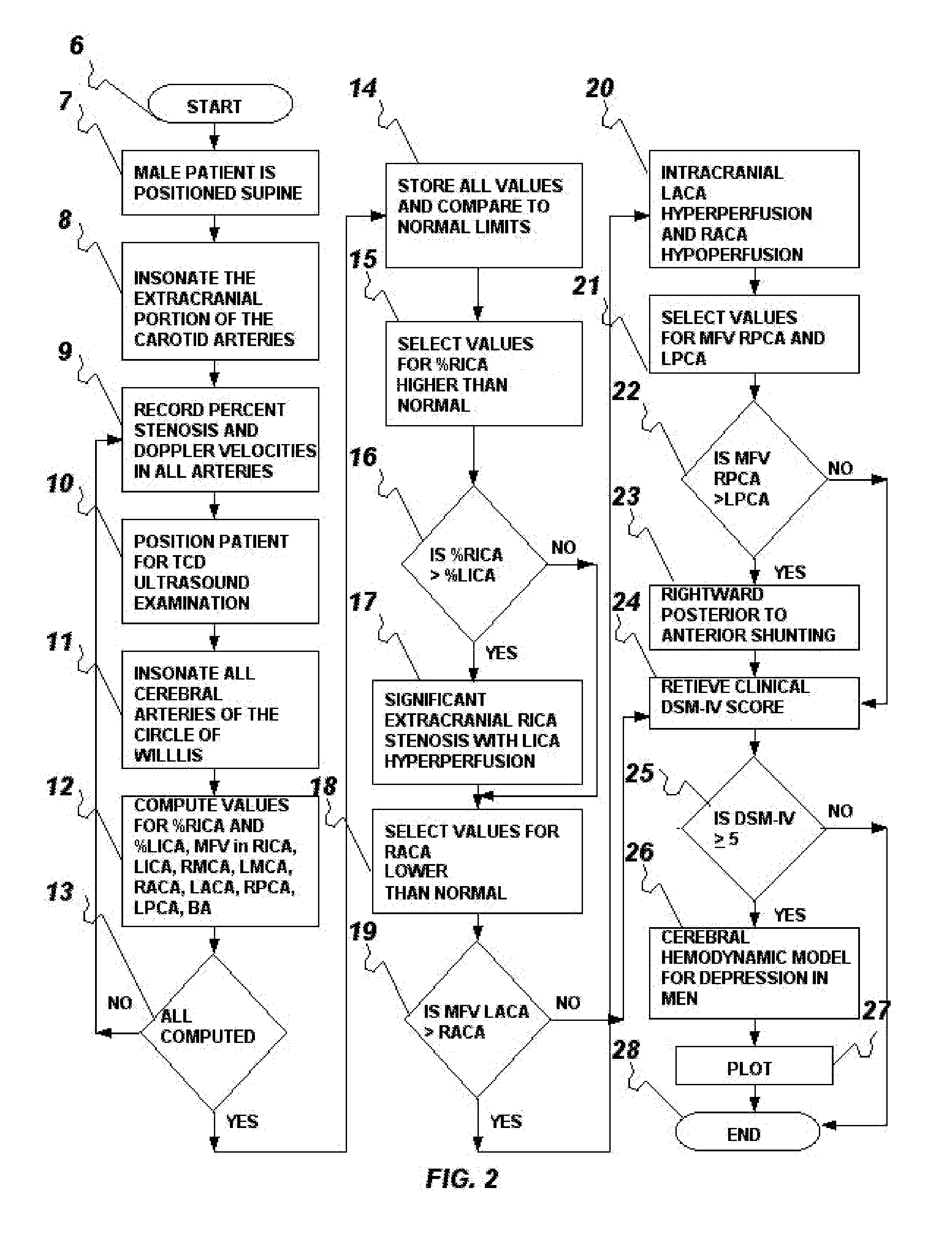
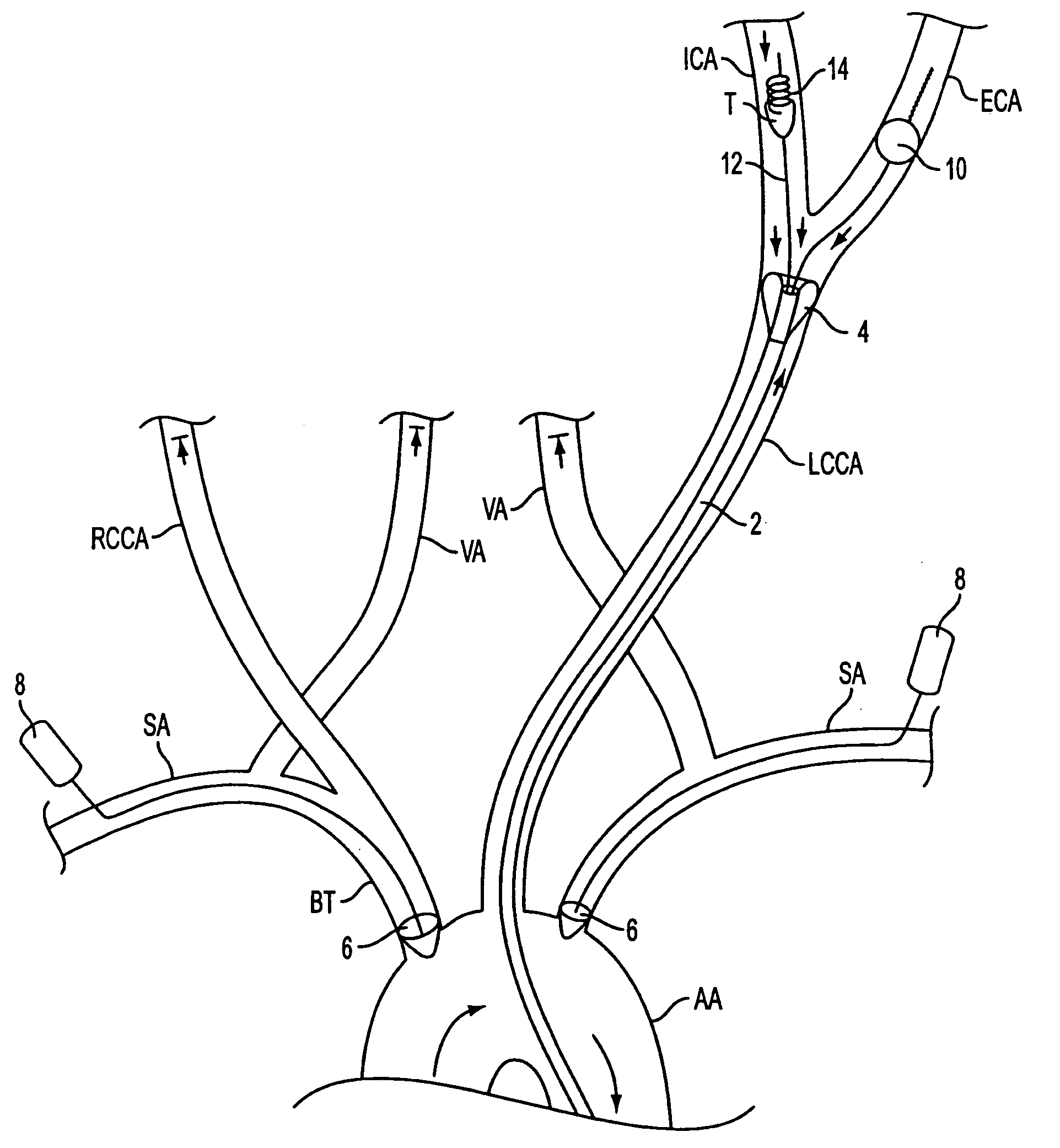
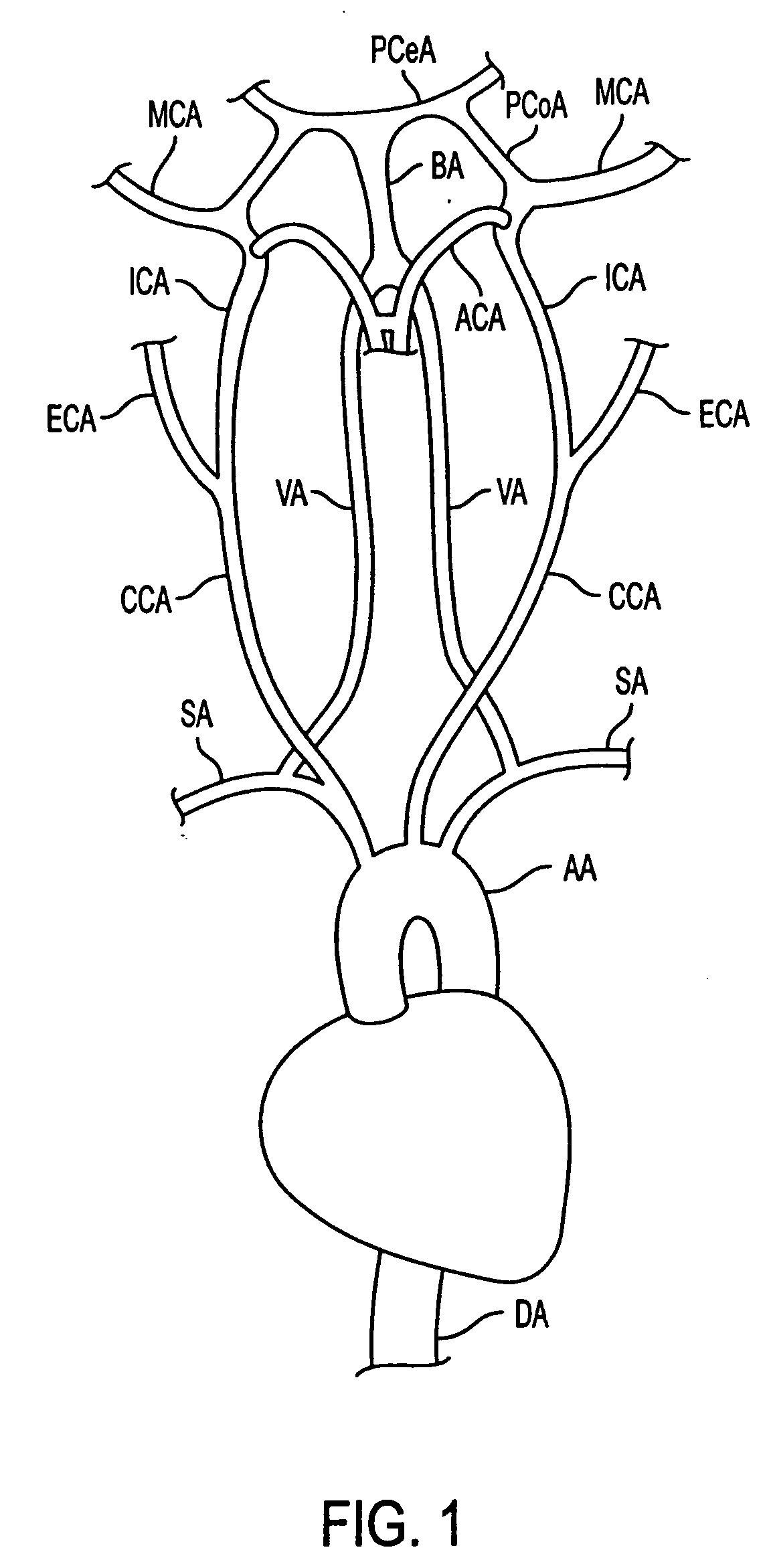
Method and system for evaluation of the hemodynamic model in depression for diagnosis and treatment
InactiveUS20090054774A1Less computation timeLow costBlood flow measurement devicesInfrasonic diagnosticsLeft posterior cerebral arteryLeft posterior
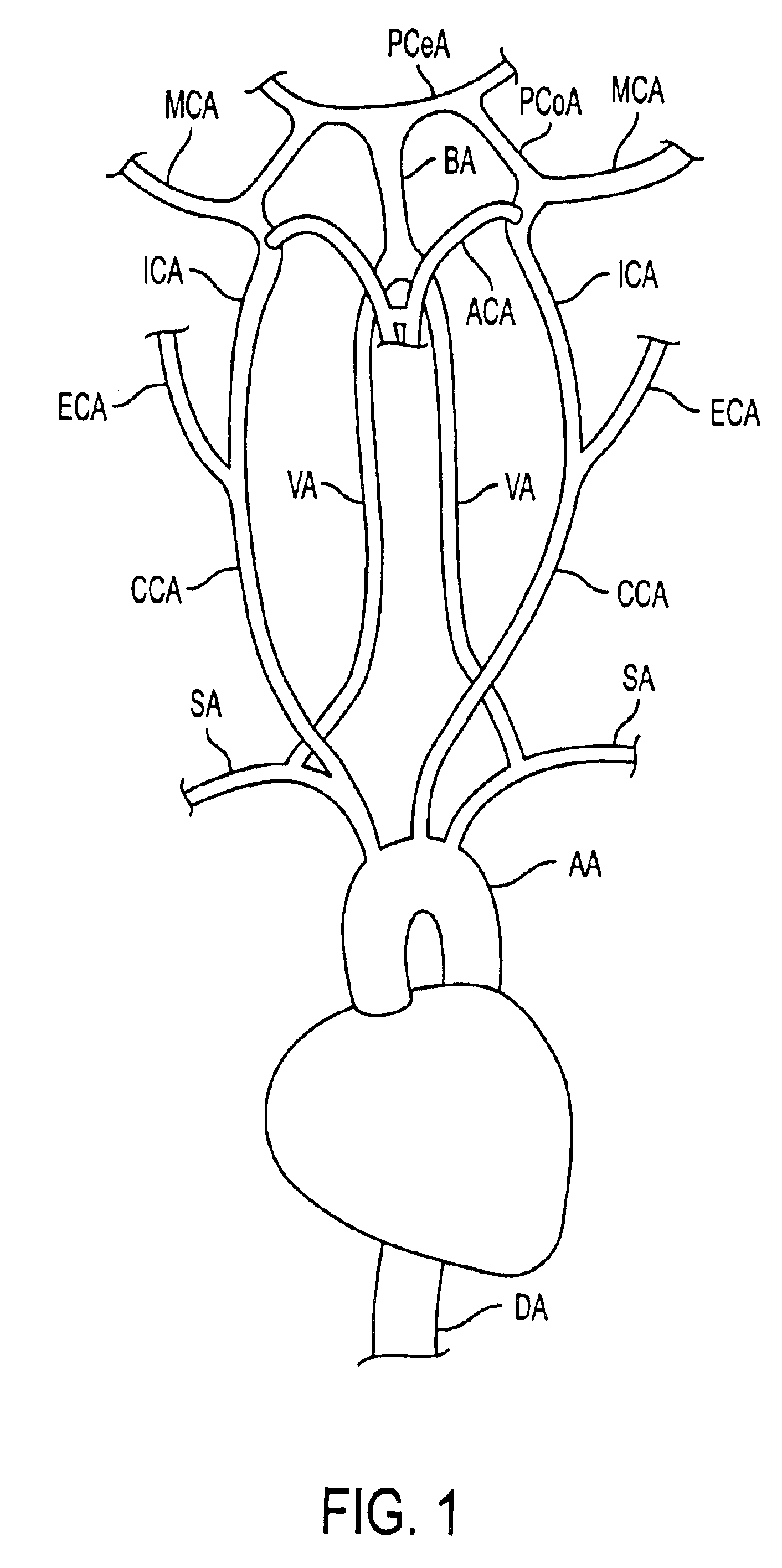
The present invention provides a method and system for determining the cerebral hemodynamic model for depression, using carotid duplex ultrasound to establish percent stenosis of the extracranial right and left internal carotid arteries and transcranial Doppler ultrasound instrument to measure mean flow velocity within the cerebral including the right and left internal carotid arteries, right and left middle cerebral arteries, right and left anterior cerebral arteries, right and left posterior cerebral arteries, and basilar artery. The percent carotid stenosis and the mean flow velocity values in cerebral arteries are used to determine the cerebral hemodynamic model associated with depression in men and women, respectively.
Owner:NJEMANZE PHILIP CHIDI
Apparatus and methods for treating stroke and controlling cerebral flow characteristics
InactiveUS20050124973A1Enhance flow manipulationEasy to disassembleStentsBalloon catheterLeft vertebral arteryThrombus
Apparatus and methods for treatment of stroke are provided. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention disposes at least one catheter having a distal occlusive member in either the common carotid artery (CCA) or both the vertebral artery (VA) and the CCA on the hemisphere of the cerebral occlusion. Blood flow in the opposing carotid and / or vertebral arteries may be inhibited. Retrograde or antegrade flow may be provided through either catheter independently to effectively control cerebral flow characteristics. Under such controlled flow conditions, a thrombectomy device may be used to treat the occlusion, and any emboli generated are directed into the catheter(s).
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Aortic arch filtration system for carotid artery protection
Filtration systems with integrated filter element(s) forming portions of the wall of the filtration catheter are disclosed. The filtration catheters disclosed herein are designed to be used alone or in conjunction with another filter device to provide embolic protection of both carotid arteries. Occlusive element such as balloon is placed on the exterior of the filtration catheter to redirect blood flow in the vessels during the filtration process as well as to help anchor the filtration catheter inside the vessel. The integrated filter element(s) does not require collapsing thus significantly reduces the complexity of the filtration system retrieval process and the chances of releasing emboli back into the blood stream. The compact design of the filtration systems makes them particularly suitable for embolic protection during endovascular procedures on or close to the heart.
Owner:LUMEN BIOMEDICAL
Non-invasive intracranial pressure sensor
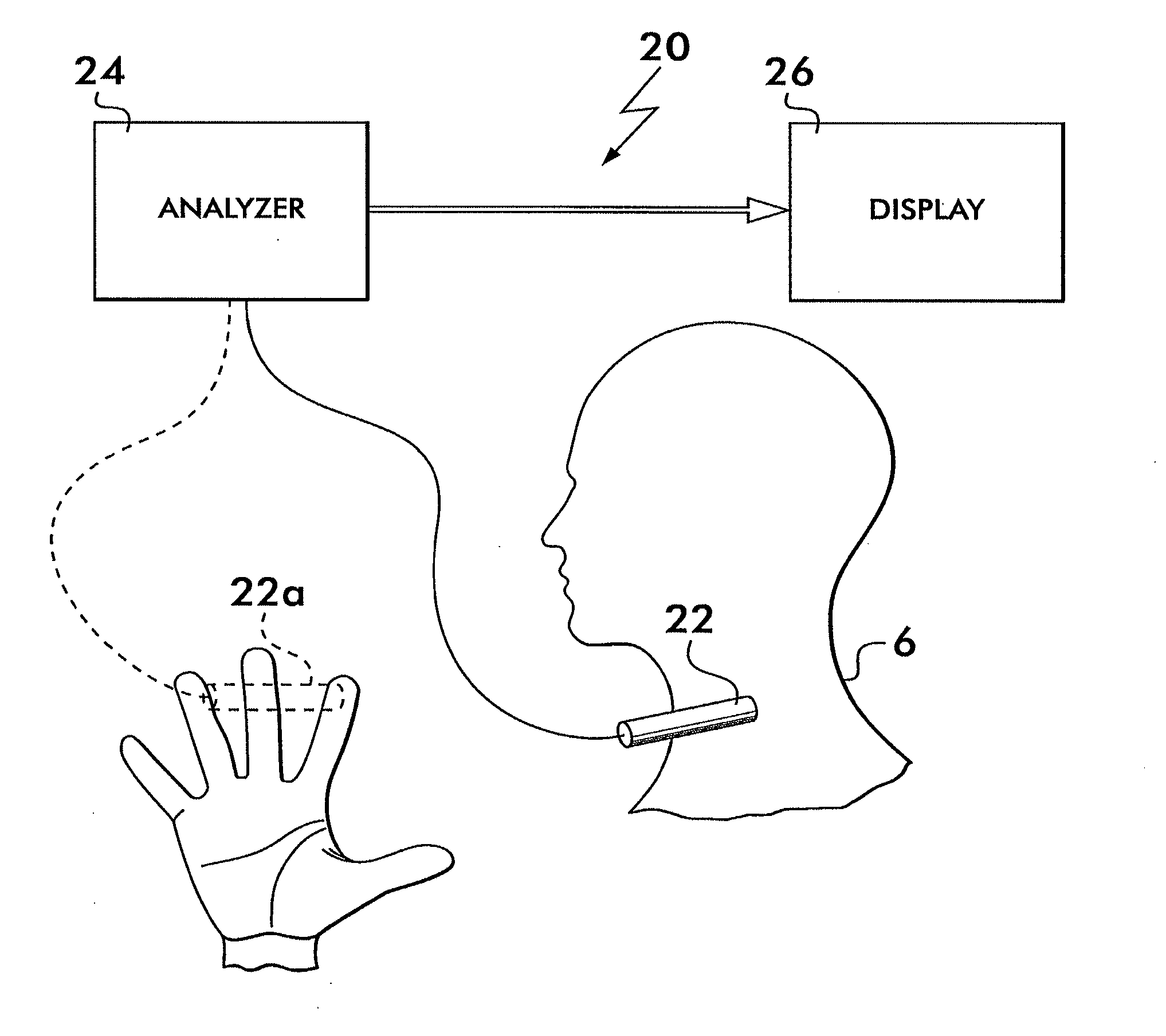
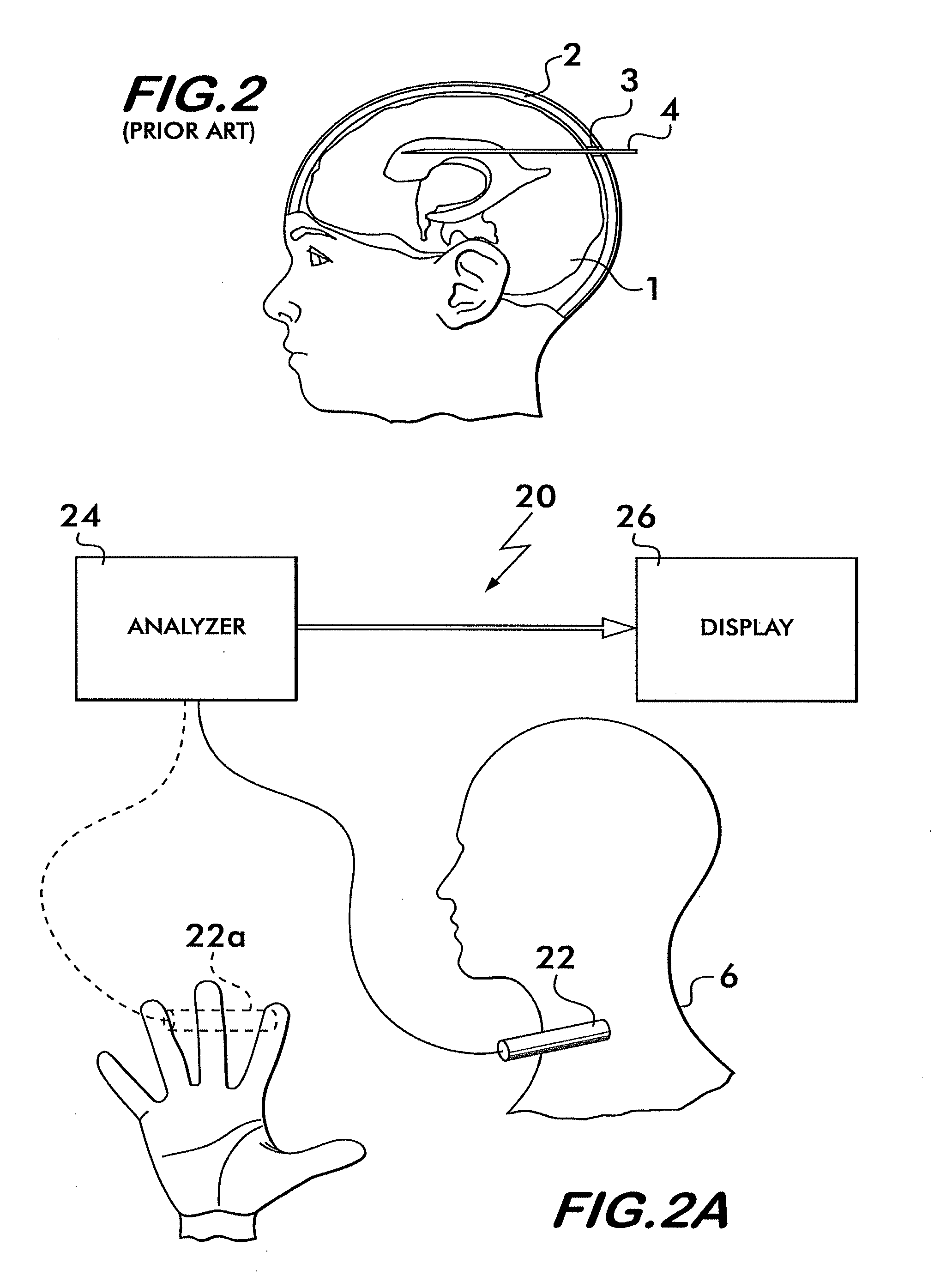
A system and method for non-invasively detecting intracranial pressure (ICP) of a living being by detecting impedance mismatches between carotid arteries and cerebral vessels via a reflection of the carotid pressure waveform using a pressure sensor positioned against the palpable carotid artery, as well as analyzing the reflection and comparing the analysis with known cerebral vasculature data, to calculate ICP non-invasively. A remote blood pressure waveform can also be used to compensate for blood system impedance.
Owner:NEURODX DEV
Coronary Artery Disease Prediction using Automated IMT
InactiveUS20120177275A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementCoronary artery diseaseX-ray
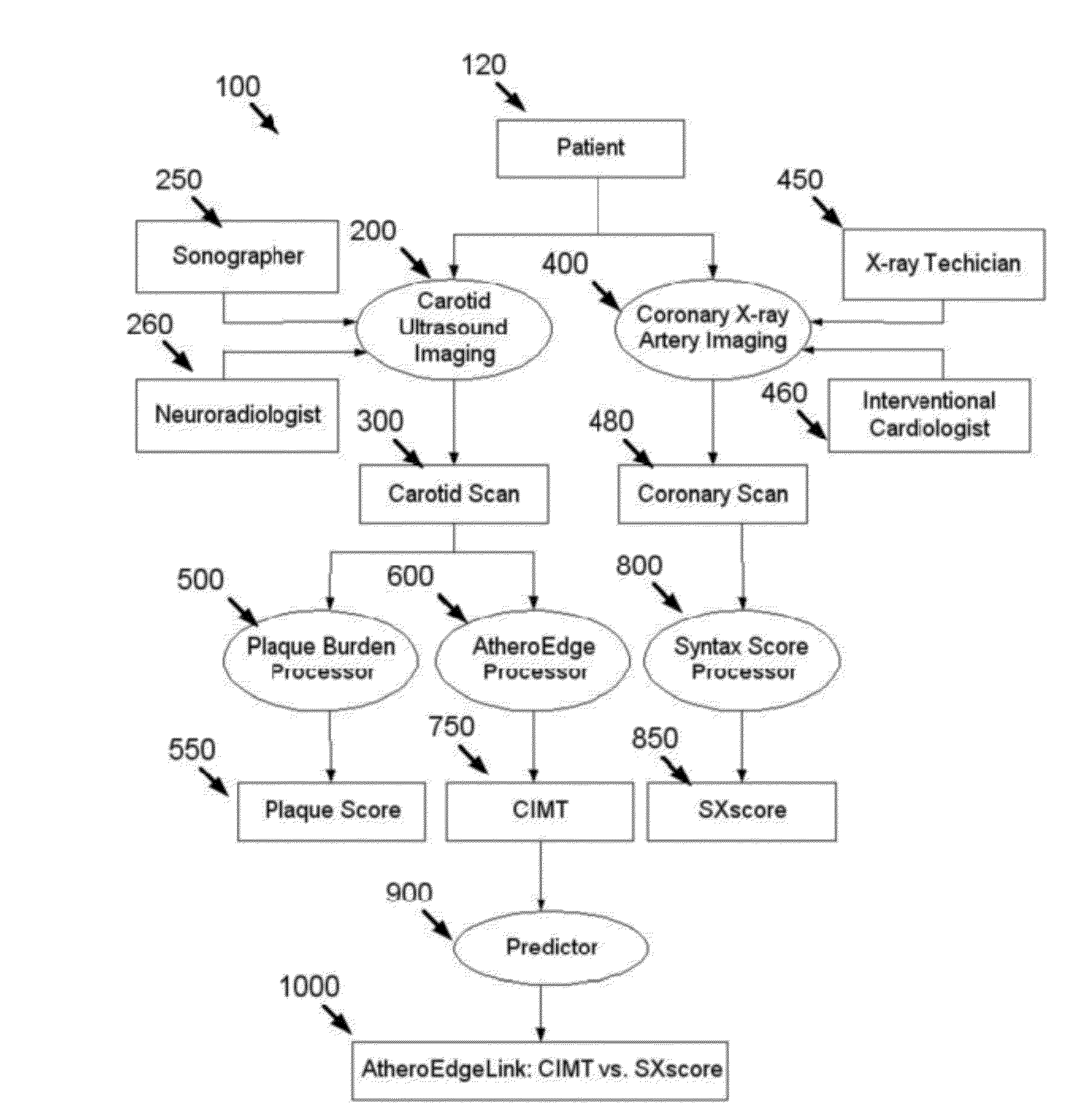
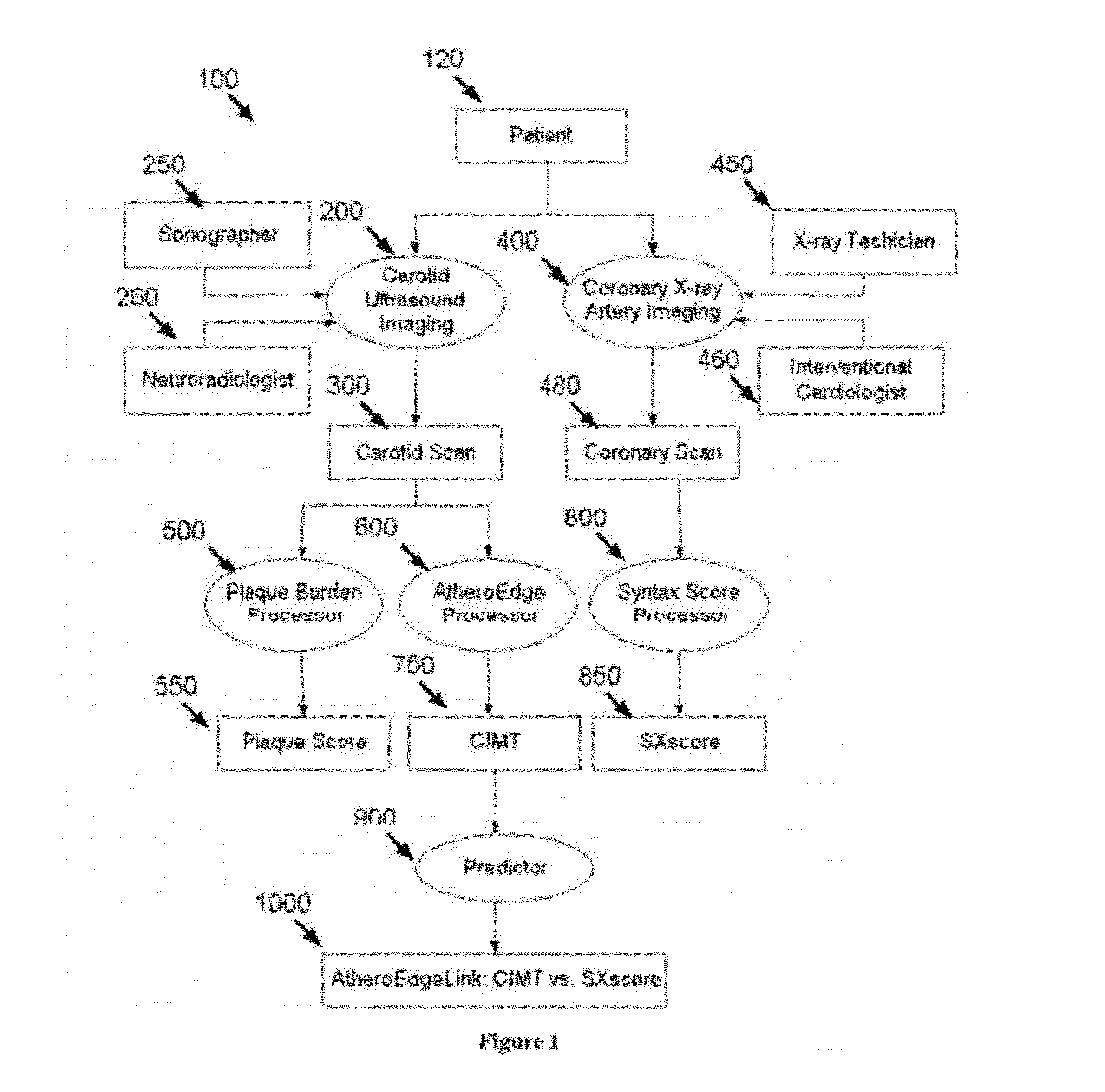
A system (AtheroEdgeLink™) that links and predicts the Syntax Score for Coronary Artery Disease Patients using carotid IMT in Ultrasound. Ultrasound is acquired for the carotids and CIMT is estimated using AtheroEdge™. For the same images, plaque burden or plaque score is estimated. Syntax score is estimated from cardiac X-ray angiograms. The AtheroEdgeLink™ technique correlates between CIMT computed using AtheroEdge™ and Syntax Score. The system AtheroEdgeLink™ can help compute the ROC area under the curve (Az) between CIMT and Syntax Score for Coronary Artery Disease patients. Such a system can also help to find the specificity of finding the threshold on CIMT for associating the presence of Coronary Artery Disease.
Owner:SURI JASJIT S
Endovascular system for the treatment of stenoses of the carotid and catheter for this system
A catheter, in particular for endovascular applications, including a long and flexible, hollow, tubular body having an insertion end and a connection end intended to remain outside the body. The catheter includes in the insertion end at least two elements which are expandable / contractible by means of external operations. Those elements are located at a distance from each other, one upstream and the other downstream of a given section of a vessel. With the catheter it is possible to operate in the section between the two expandable elements and, if necessary, in the intermediate arterial branch which, on account of the two elements upstream and downstream, will have a zero flow.
Owner:INVATEC
Method of performing protected angioplasty and stenting at a carotid bifurcation
ActiveUS20060074474A1Good curative effectSmall volumeStentsDilatorsAngioplasty balloonPercutaneous angioplasty
A method is described for performing protected angioplasty and stenting of a patient's carotid bifurcation. A self-expanding stent is deployed across a stenosis in the patient's carotid artery. A catheter system that includes a rapid exchange balloon angioplasty catheter with an occlusion balloon catheter positioned through the guidewire lumen is advanced through the guiding catheter and into the distal end of the stent. The occlusion balloon is inflated within the lumen of the stent to occlude the carotid artery and to prevent any embolic debris from traveling downstream from the treatment site. The angioplasty balloon is inflated to dilate the stenosis and to complete the expansion of the self-expanding stent. The angioplasty catheter is withdrawn and any potential embolic debris is aspirated out through the lumen of the guiding catheter. The occlusion balloon is deflated and the catheter system is withdrawn.
Owner:THERON LAURENCE
Automatic dividing method of ultrasound carotid artery plaque
ActiveCN102800088AGuaranteed reasonablenessOvercome limitationsImage analysisOrgan movement/changes detectionCurve fittingTherapeutic effect
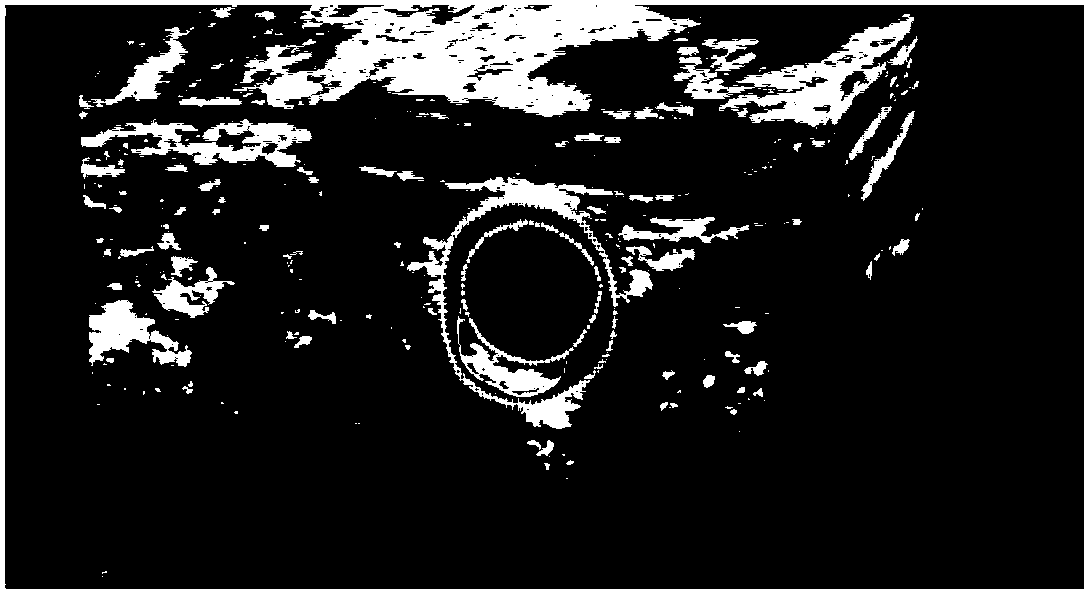
The invention belongs to the field of intersection of a computer technology and medical images, and in particular relates to a dividing method of plaque in the cross section direction of carotid artery blood vessel in an ultrasound image. The method specifically comprises the following steps of: selecting the current frame image; dividing to obtain profiles of internal and external membranes of the blood vessel; extracting the plaque and dividing the interested area; detecting an initial plaque external boundary: carrying out curve fitting on each column of pixel point gray value between the internal and external membrane profiles on a polar coordinate image obtained through conversion in the interested area, and detecting the pixel point with the minimum gray value and nearest to the external membrane profile as the initial plaque external boundary point; carrying out level set evolution to obtain the final plaque external boundary; and using the area between the final external boundary and the internal membrane profile as the plaque area. By adopting the dividing method of ultrasound carotid artery plaque, plaque can be accurately divided, the workload of doctors can be greatly reduced, and the plaque size and area calculated on the basis of the division result can help doctors analyze the lesion degree and treatment effect.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for automatic computerized segmentation and analysis on thickness uniformity of intima media of carotid artery blood wall in sonographic image
InactiveCN102163326ANot susceptible to image noiseOvercoming the Effect of Boundary Discontinuities on MeasurementsImage enhancementOrgan movement/changes detectionStraight segmentCarotid imt
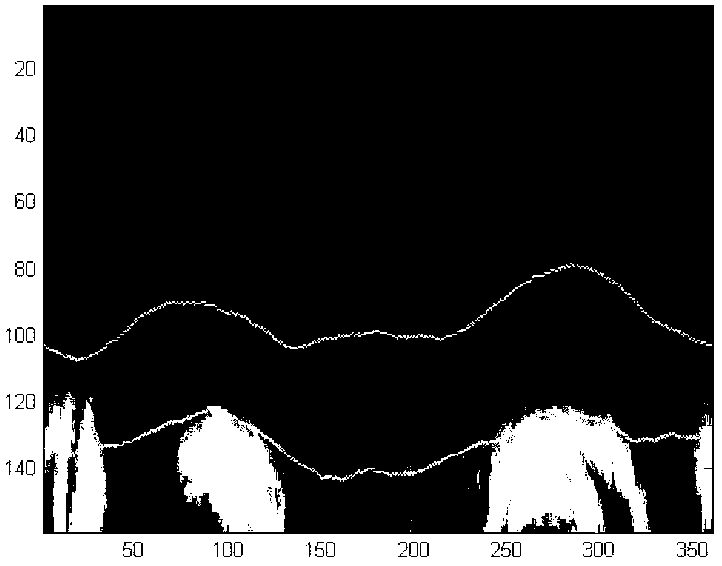
The invention belongs to the field of intersection of computer technologies and medical images, and particularly relates to a method for automatic computerized segmentation and analysis on the thickness uniformity of an intima media of a carotid artery blood wall in a sonographic image. The method comprises the following steps of: loading an original blood wall sonographic image; selecting a rectangular region of interest (ROI) containing carotid artery intima media of a far side blood wall; artificially defining or automatically detecting an original contour line by a computer; calculating aone-way edge map; performing binarization and segmentation; detecting two straight segments PLi and SLi serving as partial and correction connection of a lumen intima interface (LII) and a media adventitia interface (MAI) on a sub-image through Hough transformation; obtaining an intima media boundary contour line by adopting double-Snake model evolution; and calculating the thickness uniformity on the basis of two boundaries obtained from segmentation. By the method, problems of noise and discontinuous boundaries in the images can be effectively solved, the purpose of accurate segmentation ofthe intima media boundary is fulfilled and workloads of a doctor can be reduced. Moreover, thickness uniformity parameters obtained on the basis of the method can provide more information for early analysis on atherosclerosis.
Owner:武汉上上智科技发展有限公司
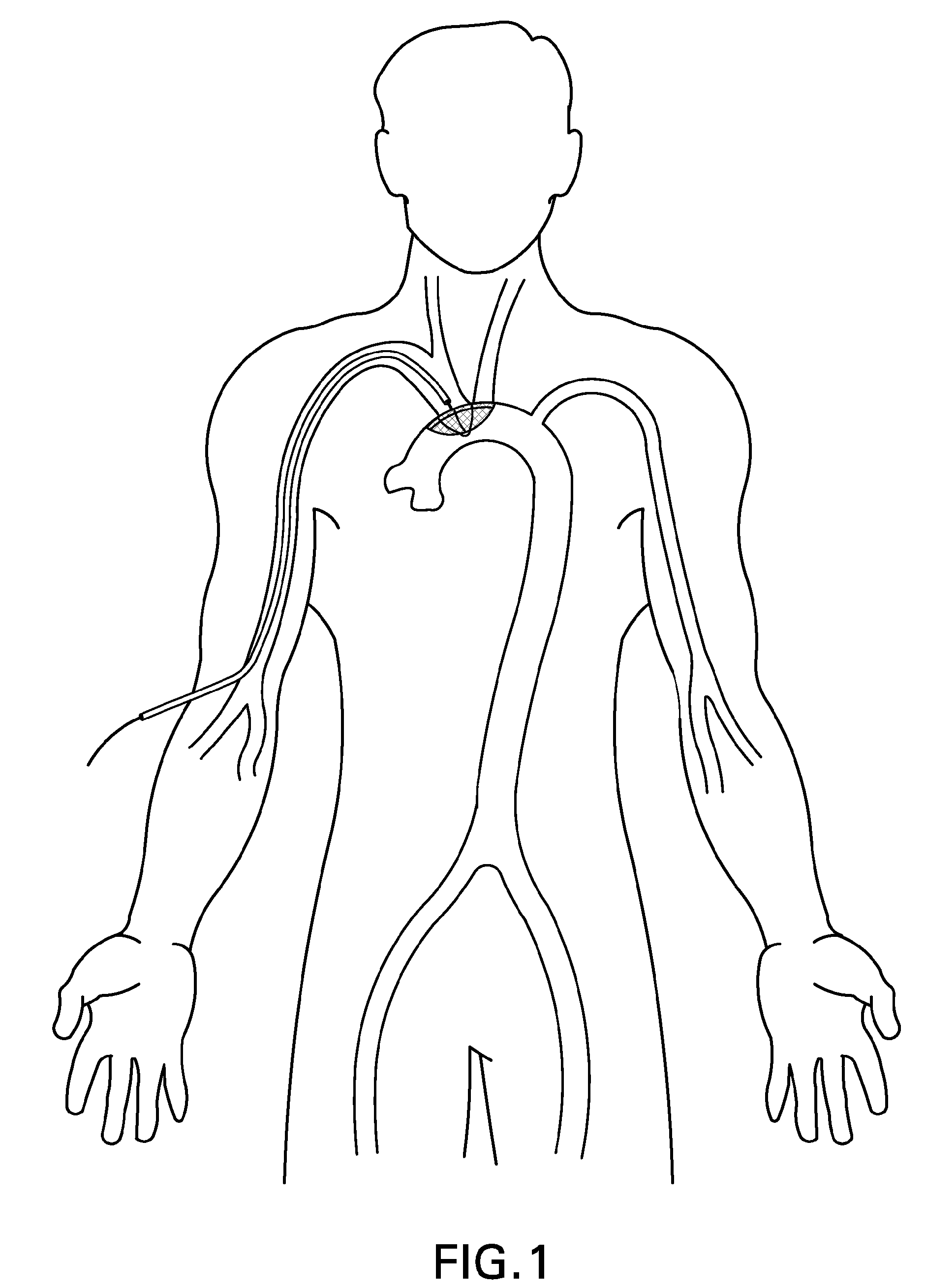
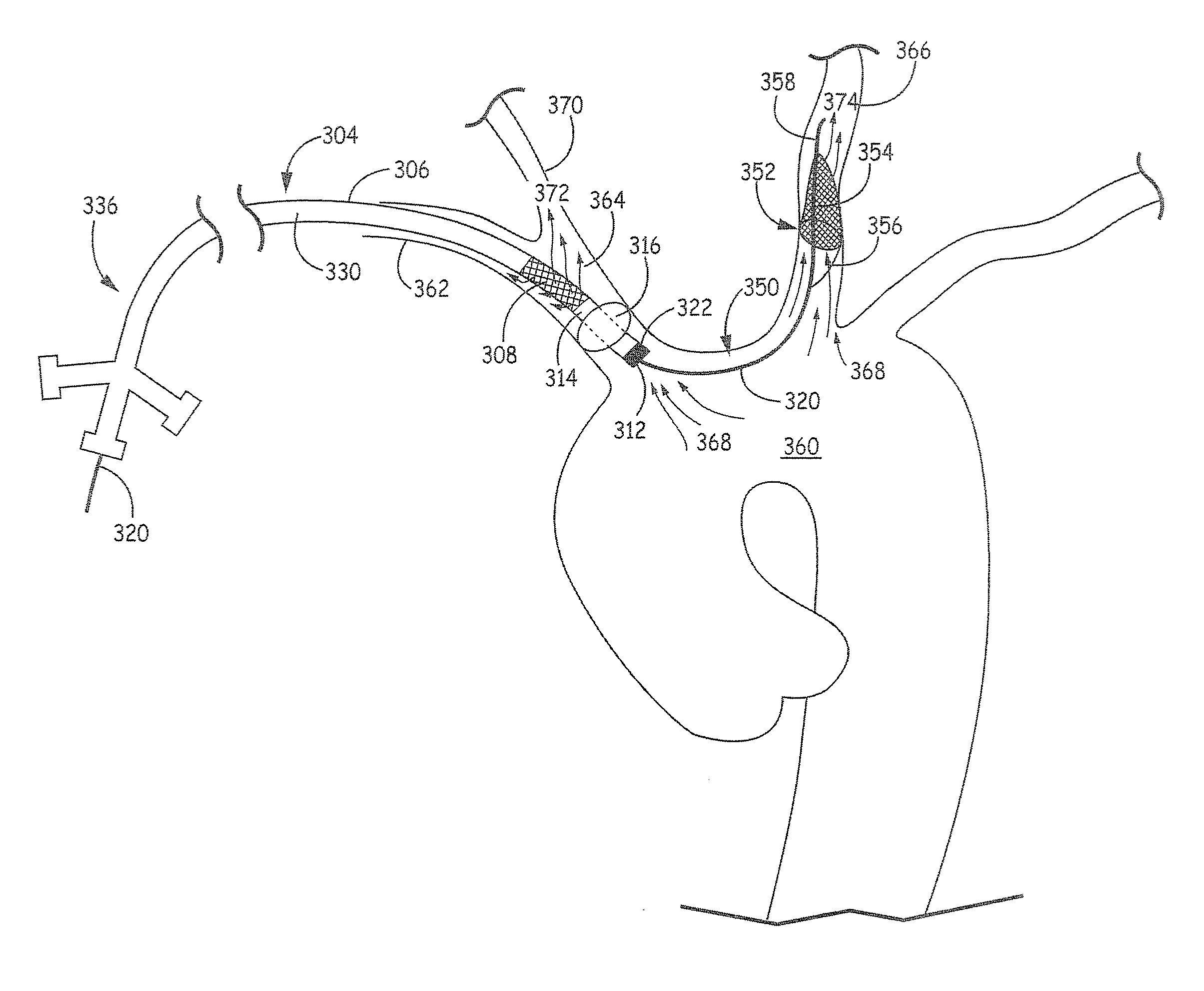
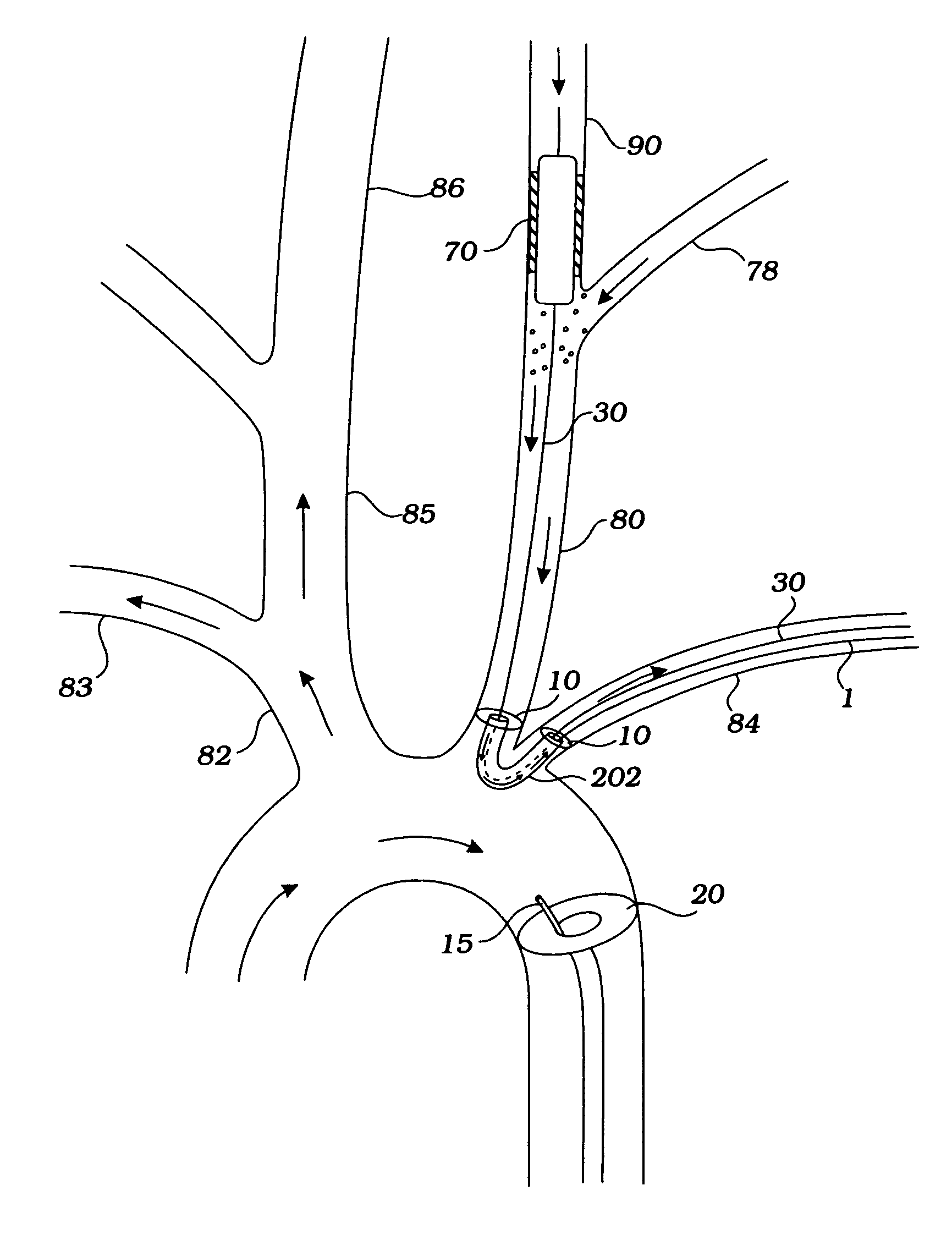
Methods and systems for establishing retrograde carotid arterial blood flow
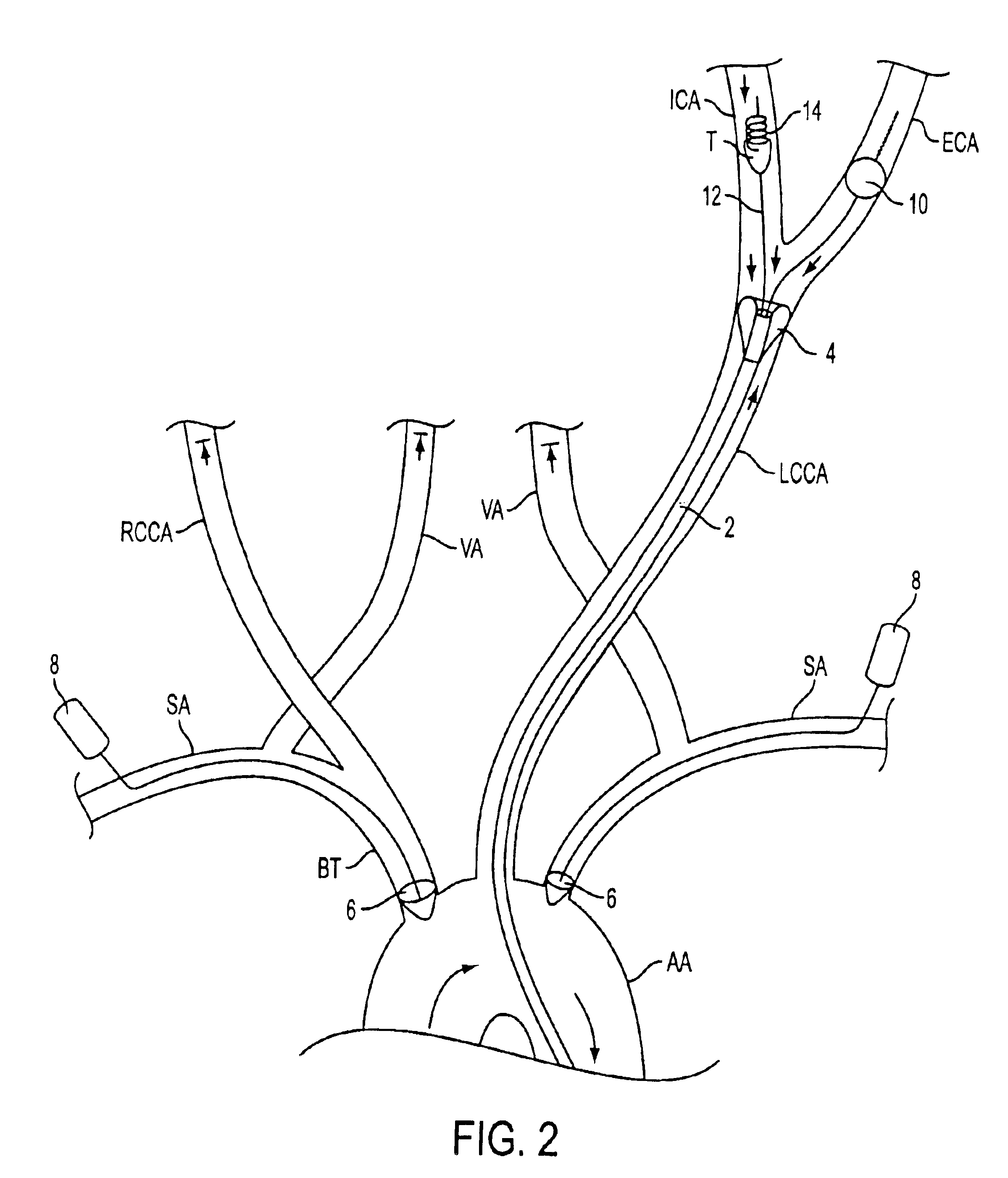
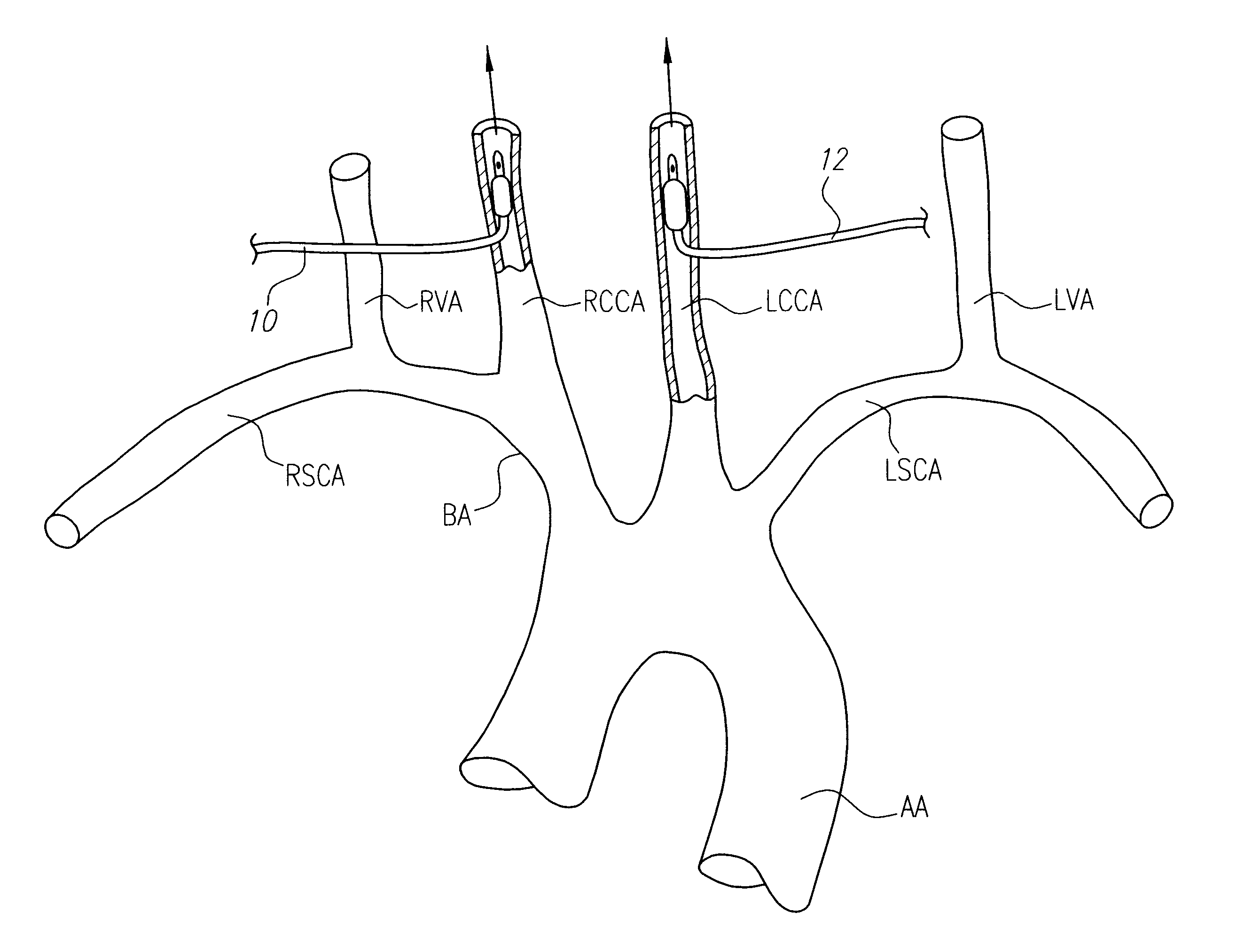
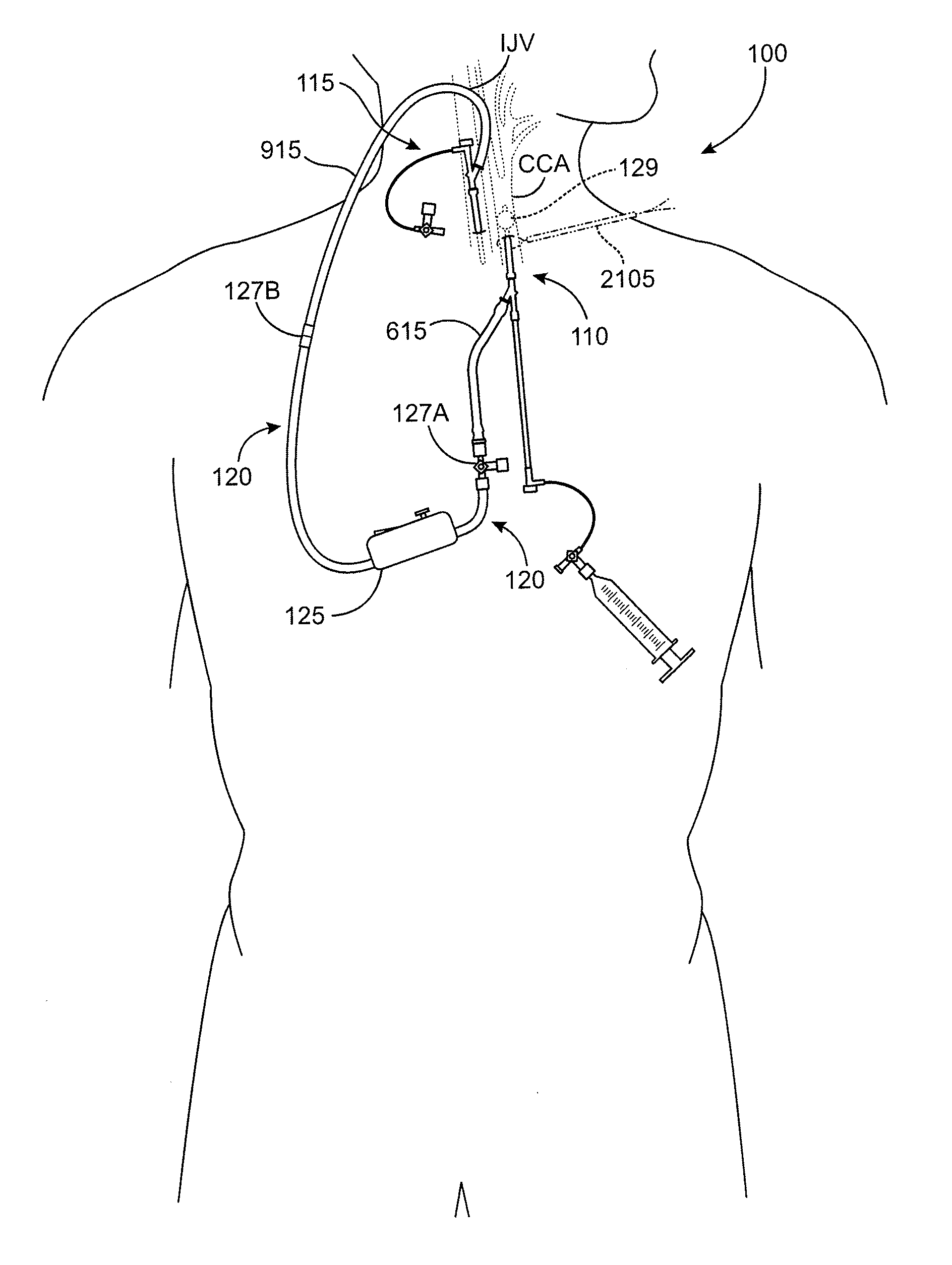
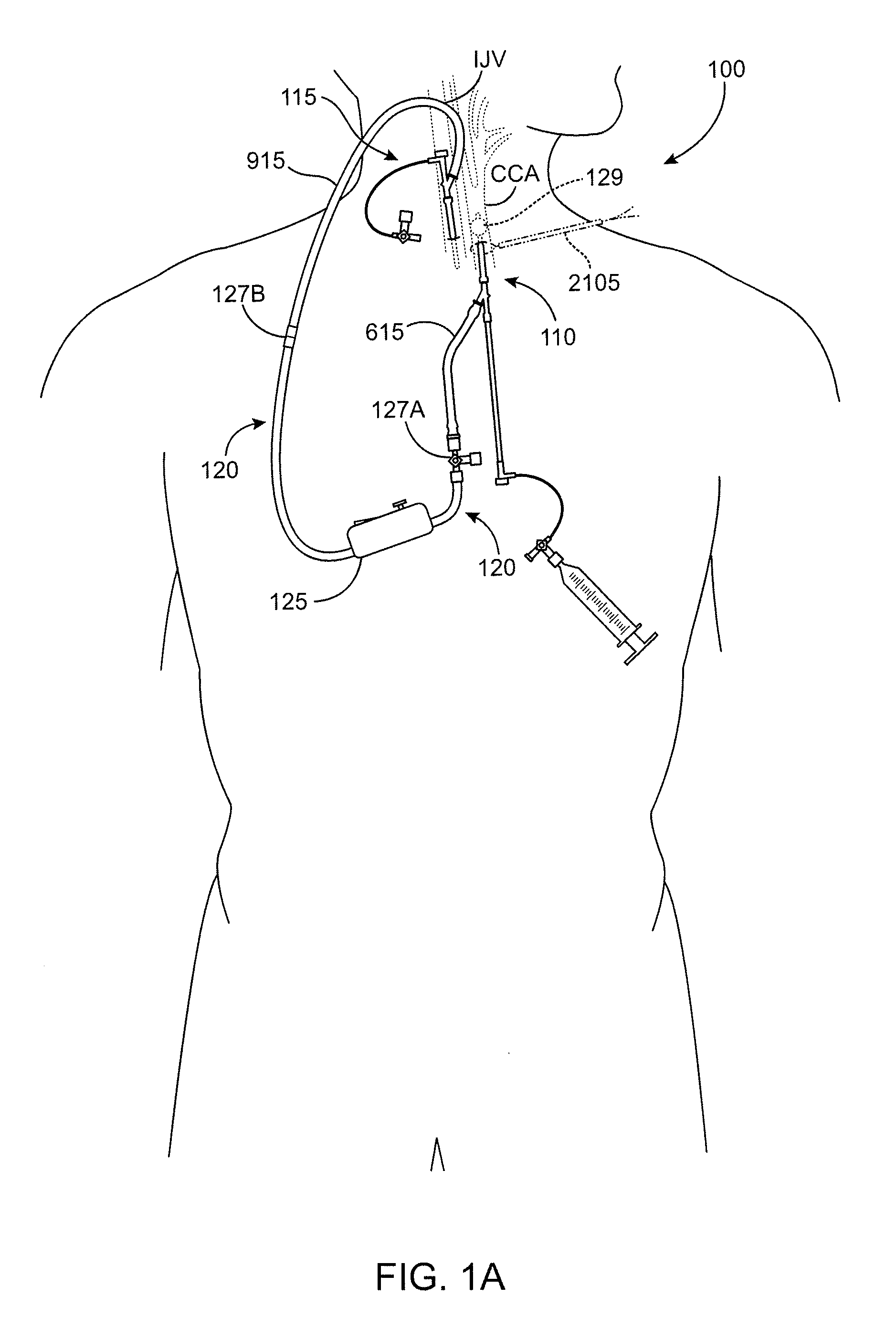
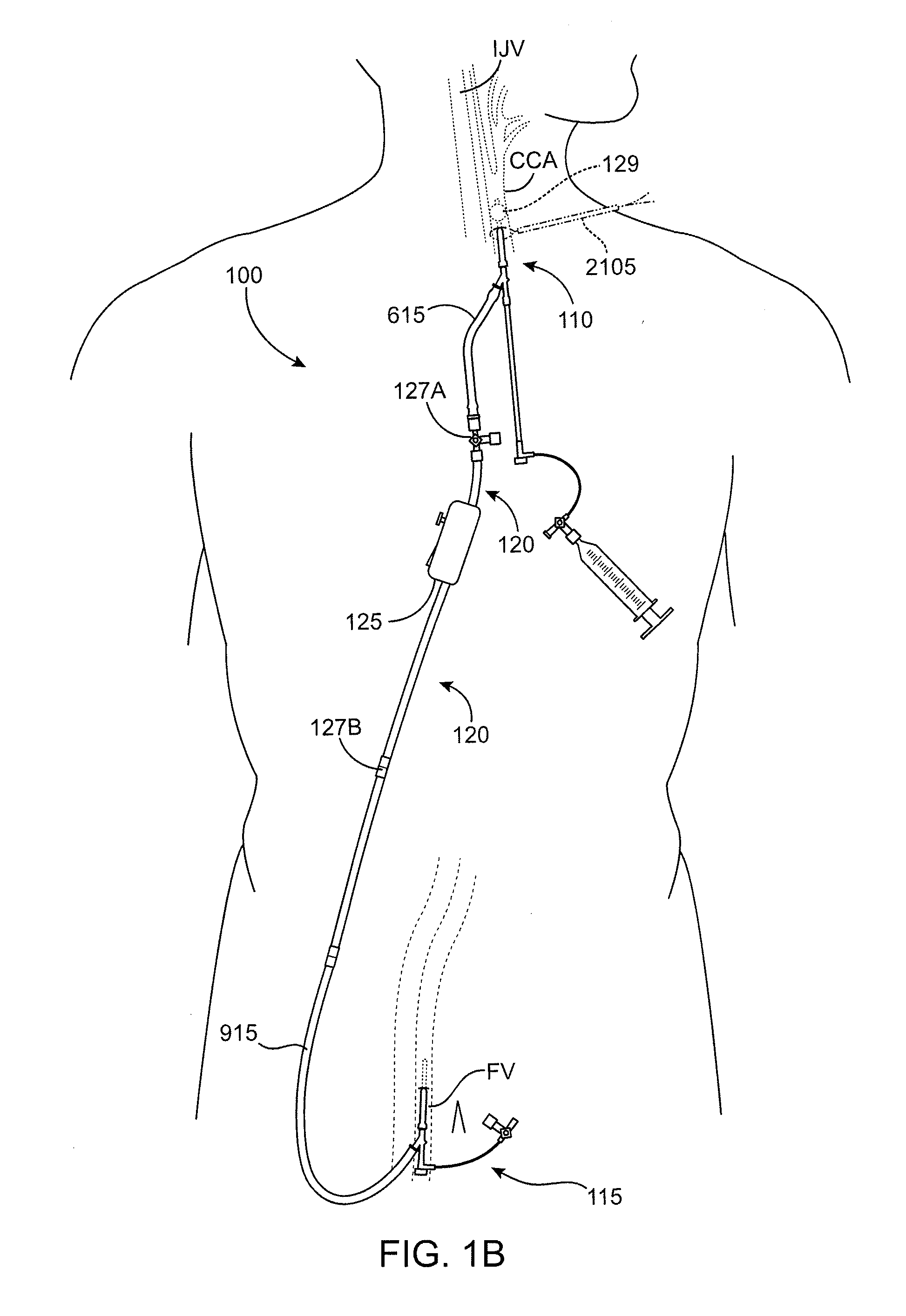
Interventional procedures on the carotid arteries are performed through a transcervical access while retrograde blood flow is established from the internal carotid artery to a venous or external location. A system for use in accessing and treating a carotid artery includes an arterial access device, a shunt fluidly connected to the arterial access device, and a flow control assembly coupled to the shunt and adapted to regulate blood flow through the shunt between at least a first blood flow state and at least a second blood flow state. The flow control assembly includes one or more components that interact with the blood flow through the shunt.
Owner:SILK ROAD MEDICAL
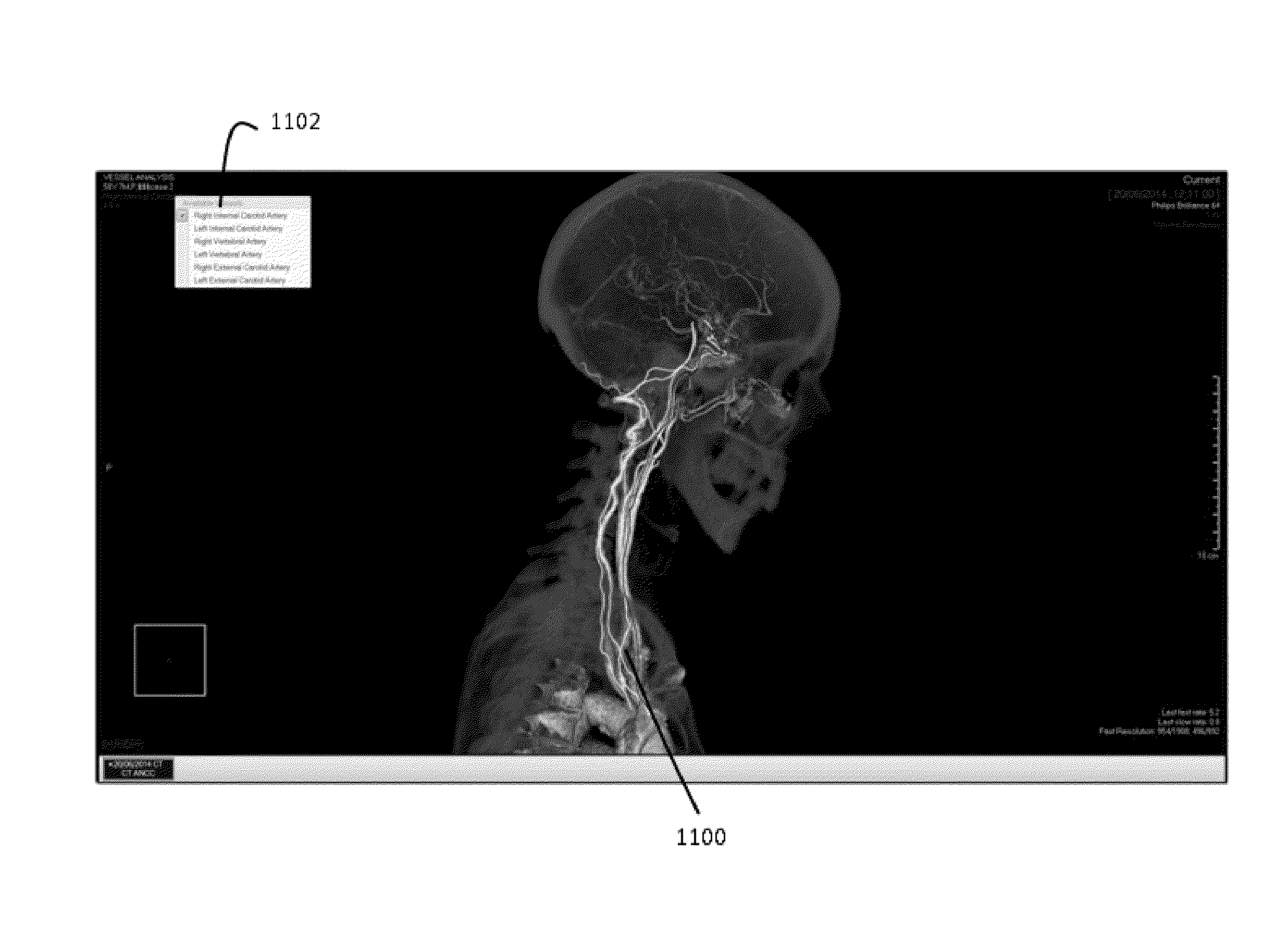
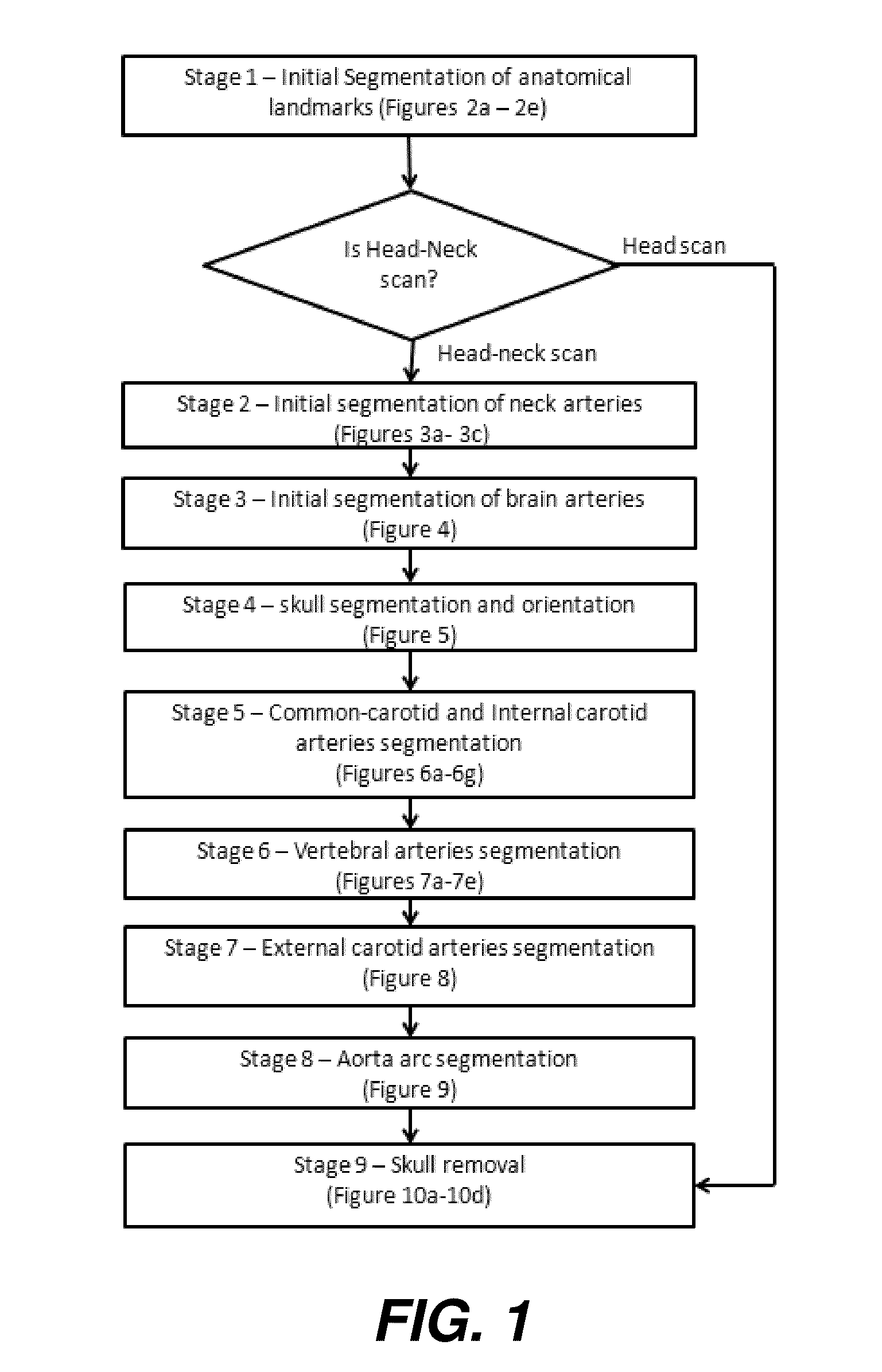
Method for segmentation of the head-neck arteries, brain and skull in medical images
ActiveUS20160125595A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionAnatomical landmarkHead and neck
A method for automated segmentation of a blood vessel of a head and neck of a subject in a medical image, the method comprising: identifying the location of anatomical landmarks in the medical image; identifying regions of interest in the medical image based on the landmarks; segmenting segments of blood vessels in the medical image; classifying at least one of the segments as defining the blood vessel based on its position relative to the landmarks within the regions of interest to create a classified blood vessel; identifying a starting seed for the blood vessel from the classified blood vessel; identifying an ending seed for the blood vessel from the classified blood vessel; segmenting the blood vessel between the starting seed and the ending seed; and defining a path between the starting seed and the ending seed.
Owner:PHILIPS MEDICAL SYST TECH
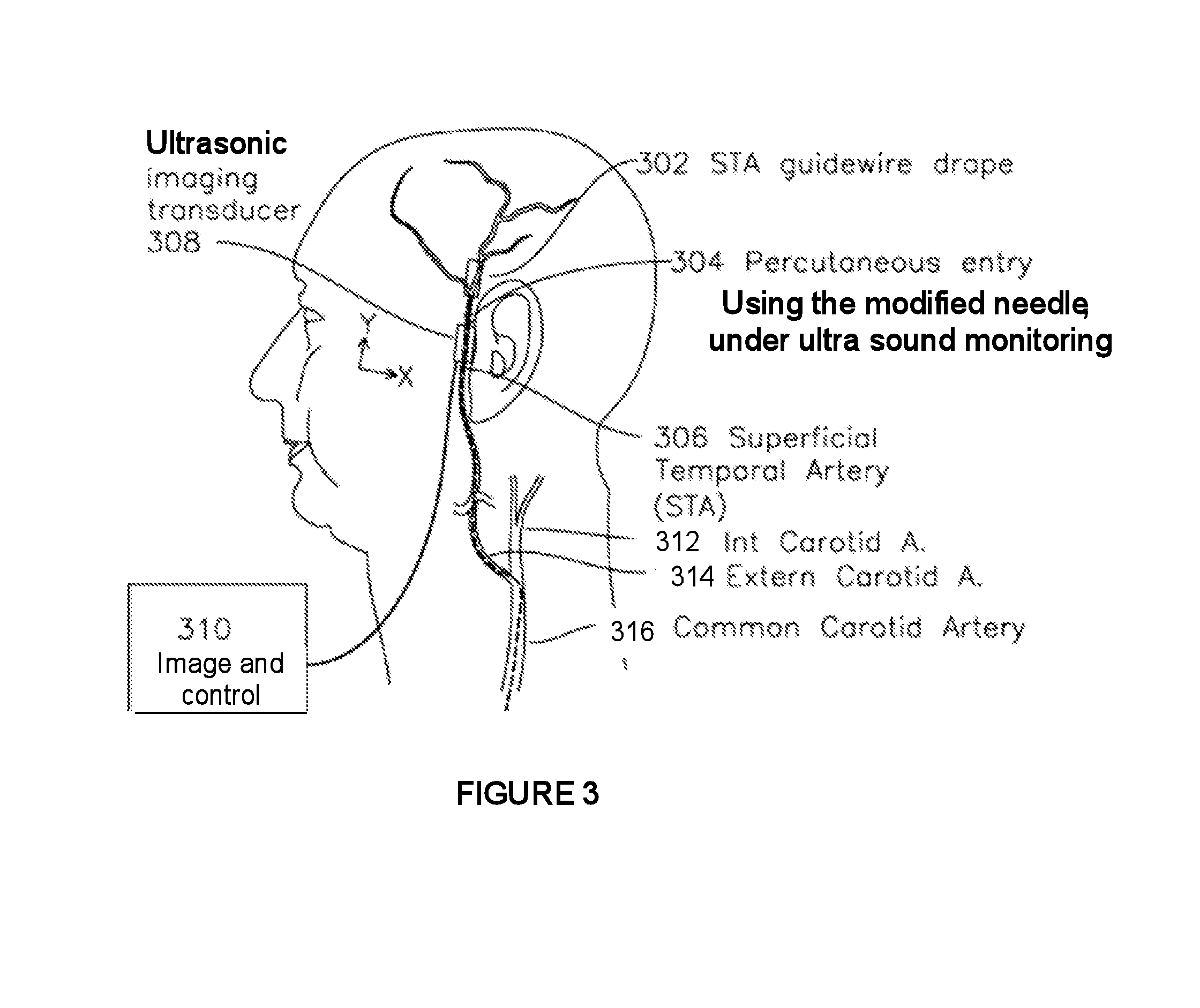
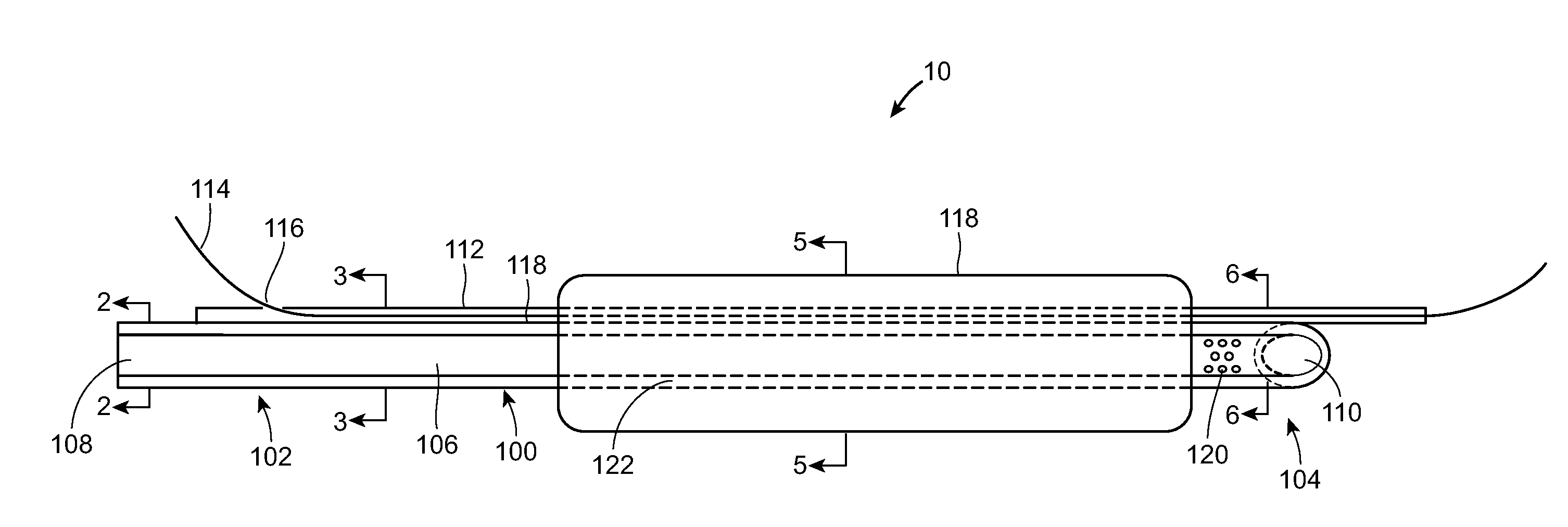
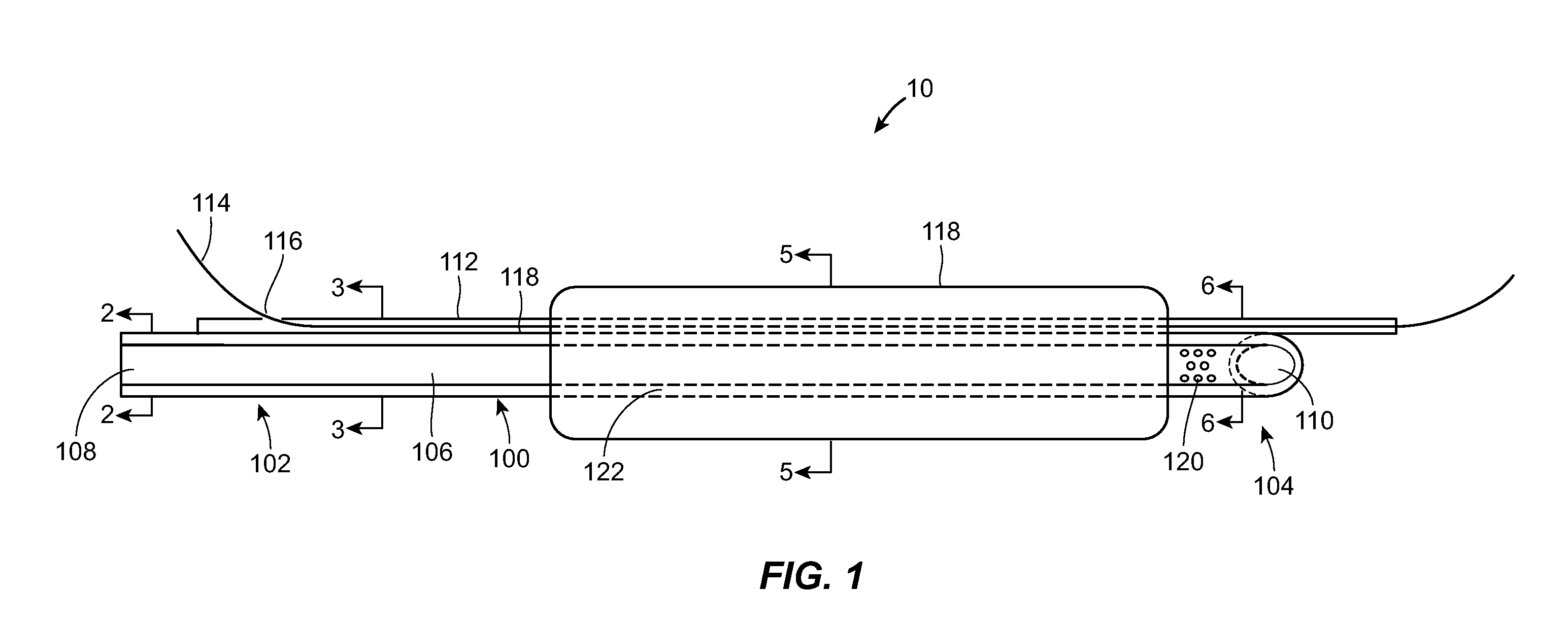
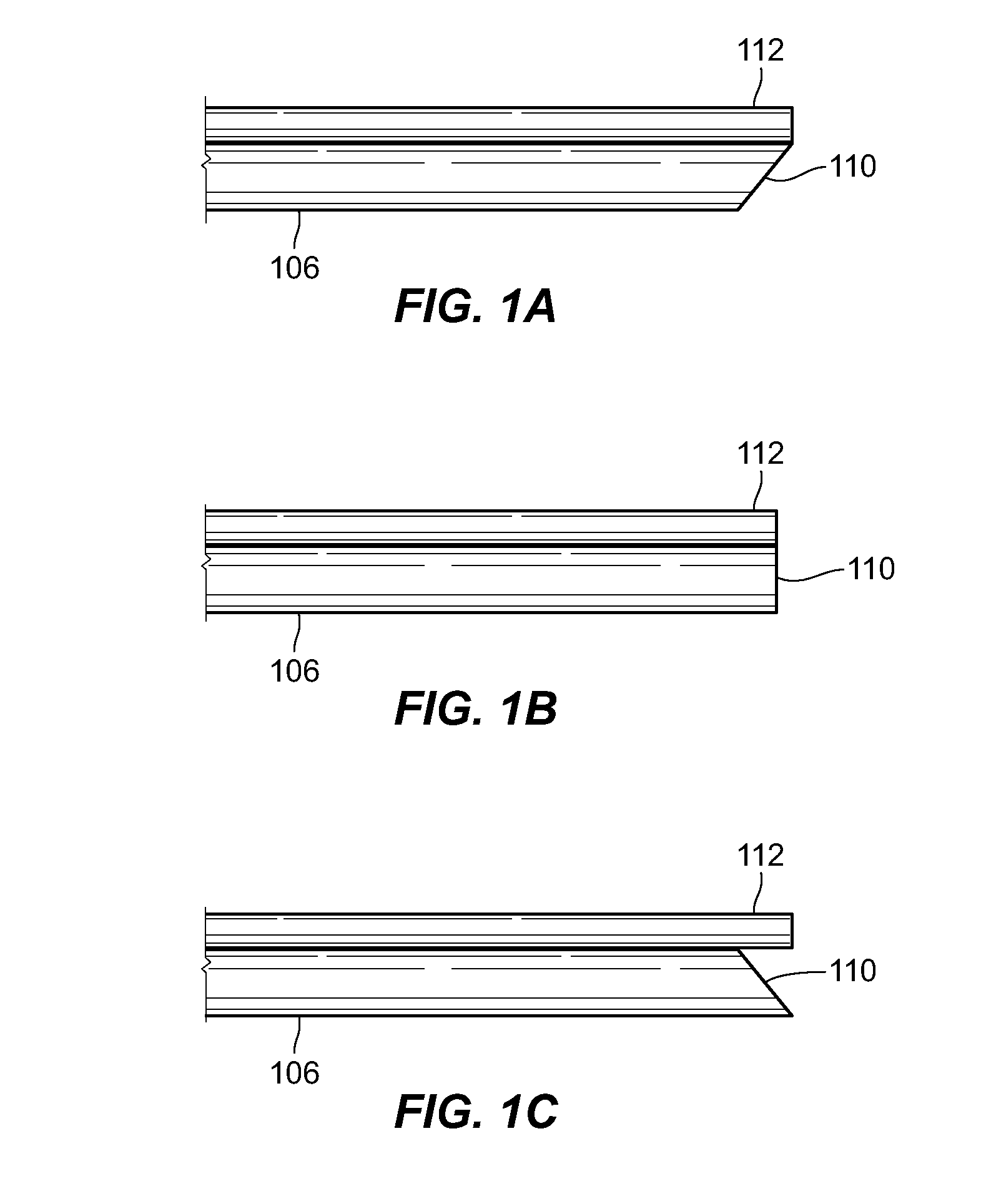
Hypodermic needle with enhanced ultrasound signature for carotid artery stenting
A hypodermic needle outer surface deflects ultrasound signals hitting the surface. The reflected signals depend on the surface which the ultrasound signal hits. According to the invention the outer surface of the needle, beginning at the tip or cutting edge of the needle featuring any one or more of: a) dimples having one or more distinct patterns; b) pits, randomly scattered; and, c) double helix, i.e., two grooves starting at an angle apart, preferably 180 degrees, and spiraling backwards in a helical fashion from the tip. By periodically repeating different pattern(s) for a predetermined length of the needle the position of the needle can be accurately identified using ultrasound imaging. The needle, in different lengths and gauges, can be used to facilitate stenting of the carotid artery as well as other ultrasound guided procedures such as biopsies, drainages / aspirations, solid organ tumor ablations and vascular access in general.
Owner:SYED MUBIN I
Angioplasty Balloon with Therapeutic/Aspiration Channel
An angioplasty balloon catheter with an added channel for delivering medication or removing body fluids distal to the site of angioplasty is disclosed. The balloons are especially useful in the treatment of occlusions in saphenous vein grafts, the coronary and carotid arteries, arteries arising from the aorta and branches thereof and in veins flowing to the heart or their tributaries and sub tributaries thereof.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Apparatus and methods for protected angioplasty and stenting at a carotid bifurcation
InactiveUS20090157160A1Good curative effectSmall volumeStentsSurgeryEmbolic Protection DevicesPercutaneous angioplasty
Apparatus and methods are described for performing protected angioplasty and stenting of a patient's carotid bifurcation. An integrated catheter system can be configured in a rapid-exchange version or in an over-the-wire version. The catheter system includes a self-expanding stent, a stent delivery sheath, a combination angioplasty balloon catheter and stent pusher catheter, an embolic protection device and, in the rapid-exchange version, an auto-releasing sheath. The method includes: inserting a guiding catheter to the carotid bifurcation; inserting the catheter system through the guiding catheter; advancing the embolic protection device beyond the lesion; positioning the stent and balloon segment of the catheter system at the lesion; releasing the self-expanding stent; pulling the stent delivery sheath back into the guiding catheter; positioning and deploying the protection member; advancing the combination angioplasty balloon catheter and stent pusher catheter and inflating the angioplasty balloon within the lesion; deflating the angioplasty balloon and withdrawing the combination angioplasty balloon catheter and stent pusher catheter and stent delivery sheath together; and aspirating potential emboli through the guiding catheter.
Owner:MINVASYS SA
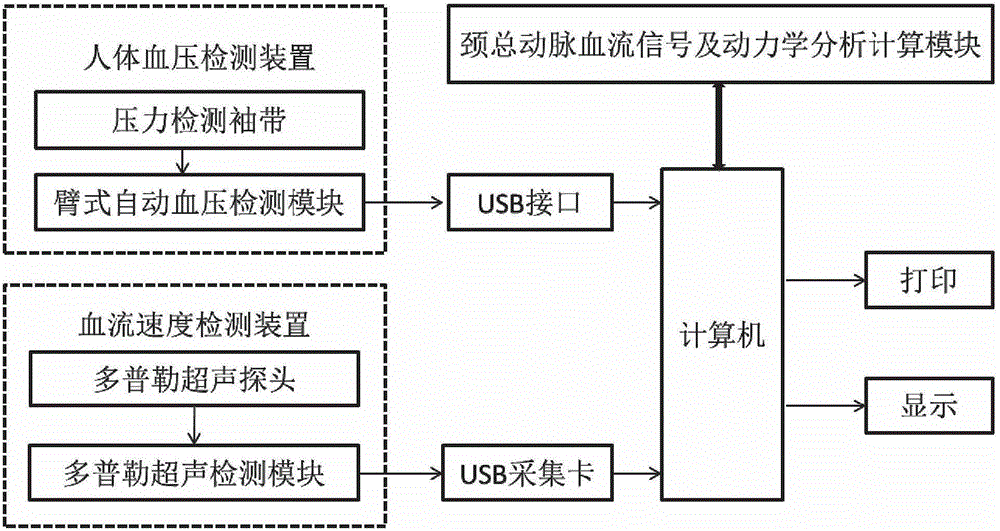
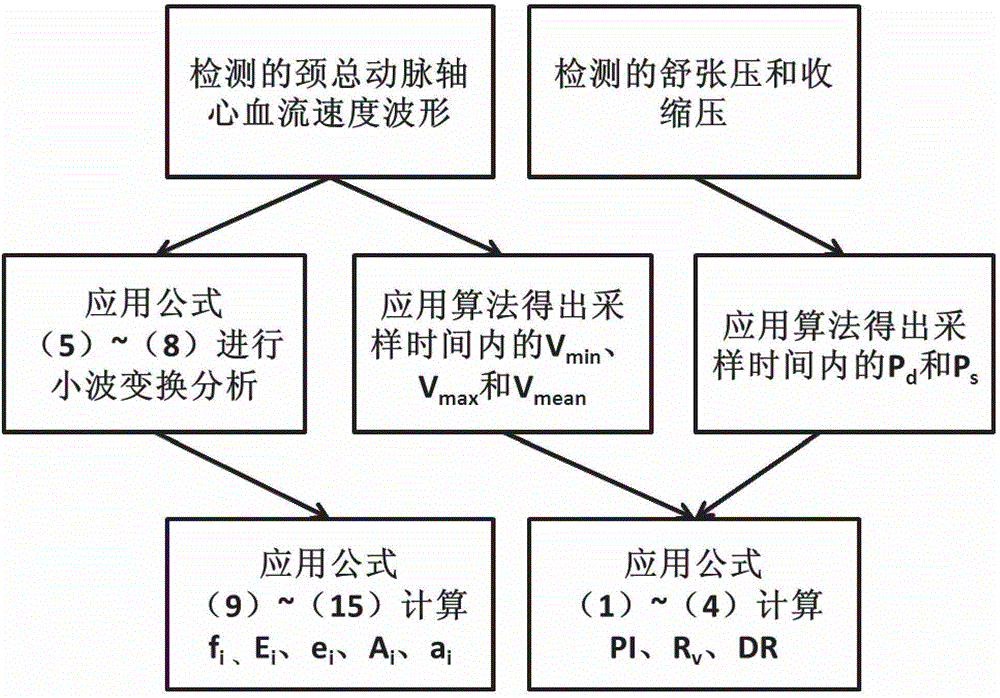
Hemodynamics and signal analysis system and method of carotid arterial system
The invention provides a simple and convenient method and a simple and convenient system for evaluating hemodynamic indexes and characteristic parameters of a blood signal of a carotid arterial system through non-invasive detection on blood pressure of brachial arteries and an axial blood velocity signal of a common carotid artery. The method comprises the following steps: detecting the waveform and a numerical value of an axial blood velocity of the common carotid artery by using a continuous Doppler blood velocity waveform detecting module, detecting diastolic pressure and systolic pressure of a human body by using an arm-type electronic blood pressure detecting module, and then calculating hemodynamic parameters of the carotid arterial system by a simplified method; and selecting Morlet mother wavelet for wavelet analysis on the waveform of the blood velocity of the common carotid artery, and calculating the characteristic parameters of the blood signal. The method is an analysis method which combines the hemodynamic principle and wavelet transformation; compared with the method adopted by the conventional cerebral hemodynamic analysis device, the signal acquisition and analysis method is simpler; and to a great extent, the defects that the conventional analysis device is complicated in structure, huge in volume, complex in operation, high in price and the like are overcome.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH +1
Non-invasive intracranial pressure sensor
A system and method for non-invasively detecting intracranial pressure (ICP) of a living being by detecting impedance mismatches between carotid arteries and cerebral vessels via a reflection of the carotid pressure waveform using a pressure sensor positioned against the palpable carotid artery, as well as analyzing the reflection and comparing the analysis with known cerebral vasculature data, to calculate ICP non-invasively. A remote blood pressure waveform can also be used to compensate for blood system impedance.
Owner:ICPCHECK
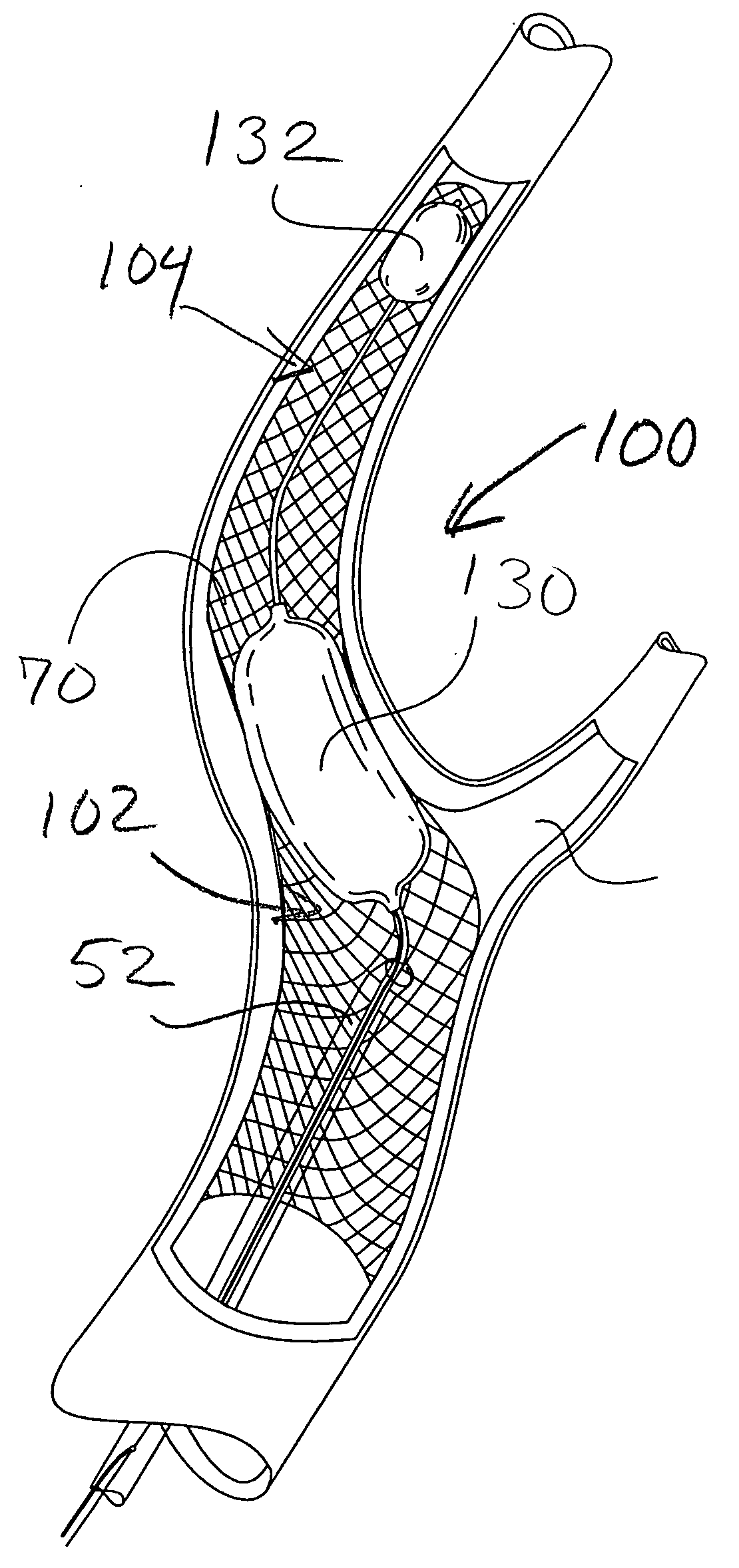
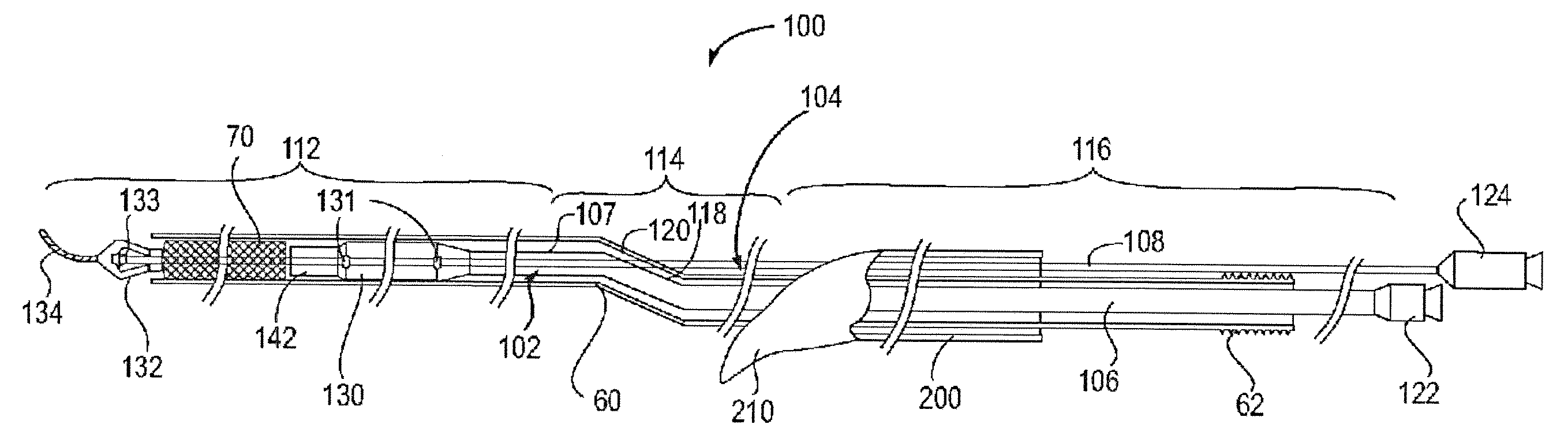
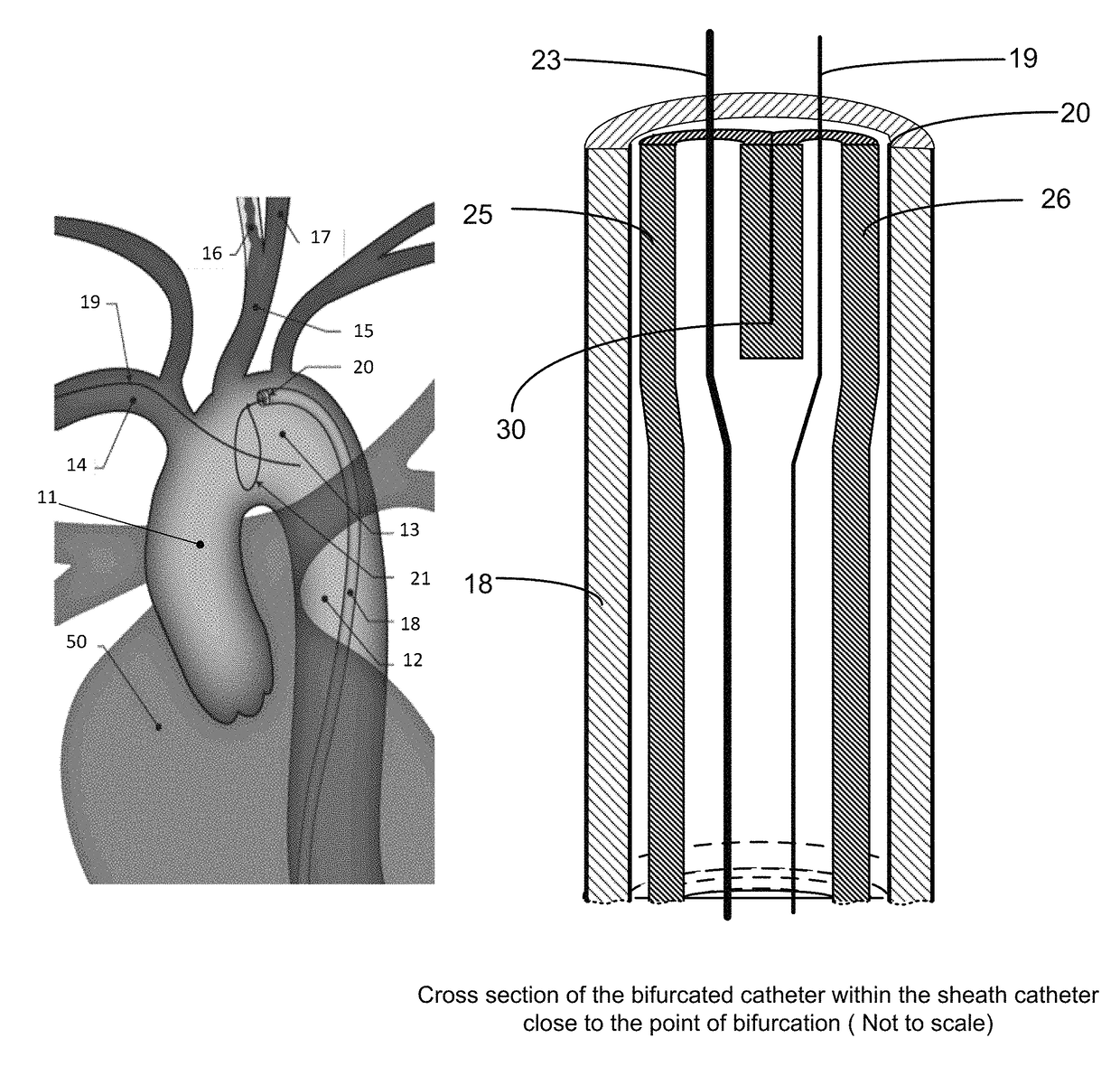
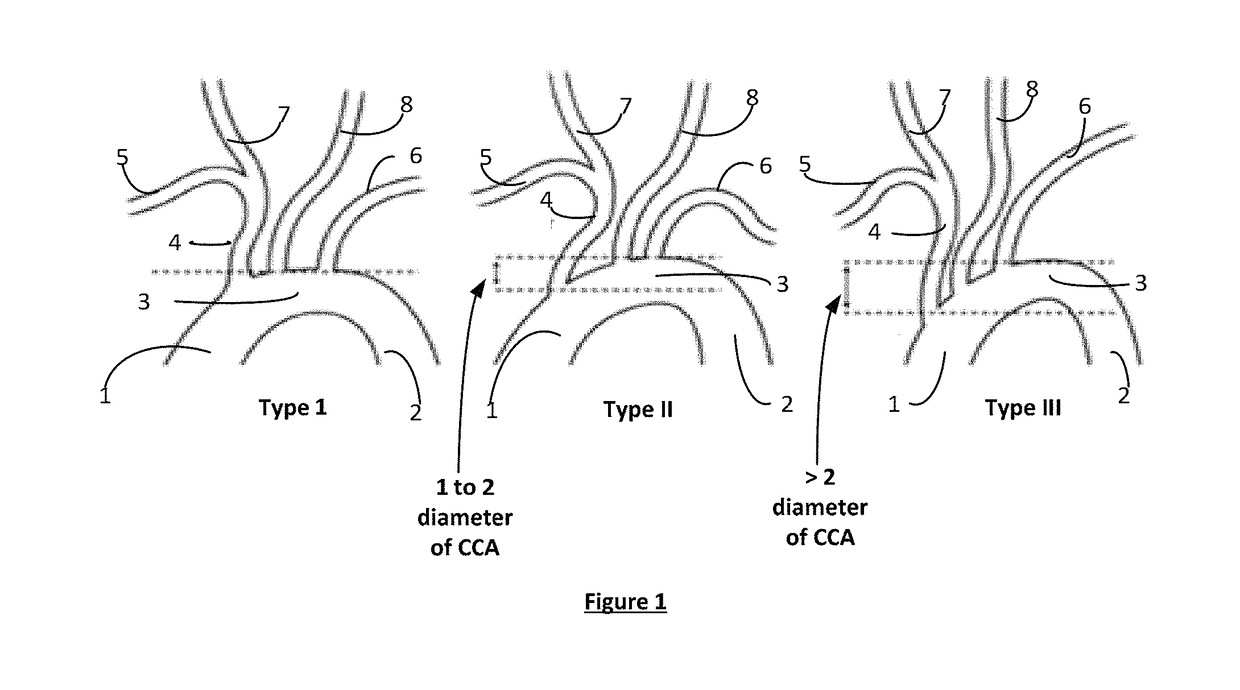
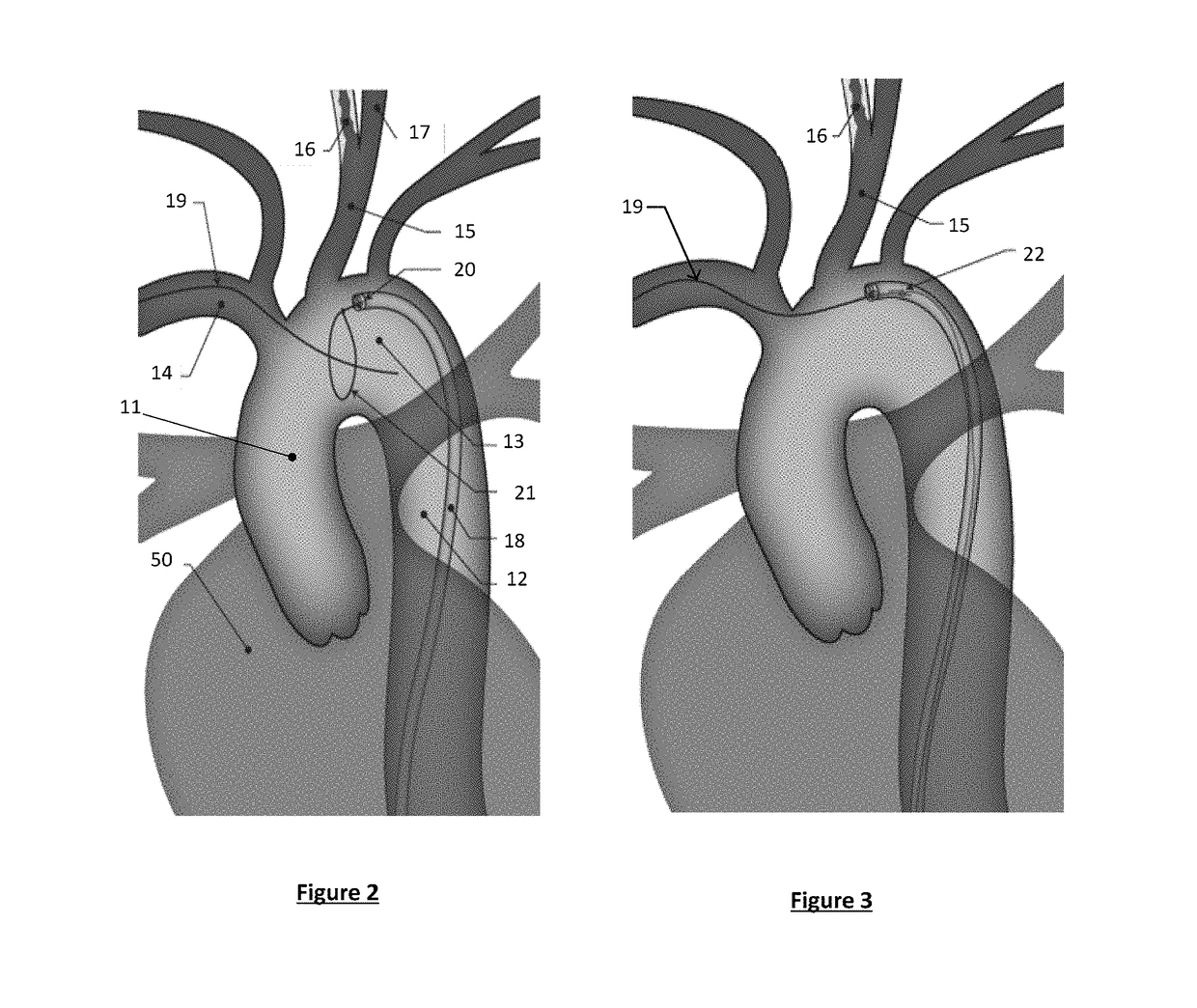
Apparatus and method for a bifurcated catheter for use in hostile aortic arches
Systems and methods for addressing the percutaneous intervention related trauma to the vessels that arise from type-III hostile aortic arches, from uncontrolled prolapse of sheaths, embolic protection devices and stent delivery systems, by stabilizing the systems while stenting of the left and right carotid arteries. Guide wires to stabilize catheters used to access the left or right carotid arteries (CA) for carotid percutaneous intervention of the vessels originating from a tortuous aortic arch are disclosed. A bifurcated catheter for stabilizing the catheters is also disclosed. The bifurcated catheter has a main catheter that divides into two separate catheters forming a “Y” shape. One leg of the catheter has a smaller diameter with a smaller working lumen (inner diameter) to carry the stabilizing wire and the other leg of the catheter has a larger working lumen for arterial stenting operations.
Owner:RAM MEDICAL INNOVATIONS INC
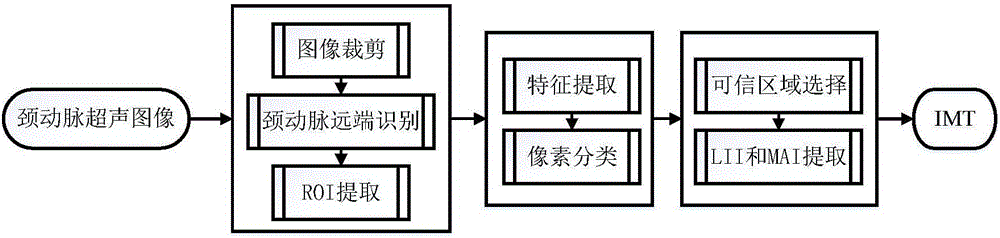
Ultrasonic carotid artery intima media thickness measurement device and method based on deep learning
InactiveCN106408017APoor resolutionFully automaticCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesMeasurement deviceSonification
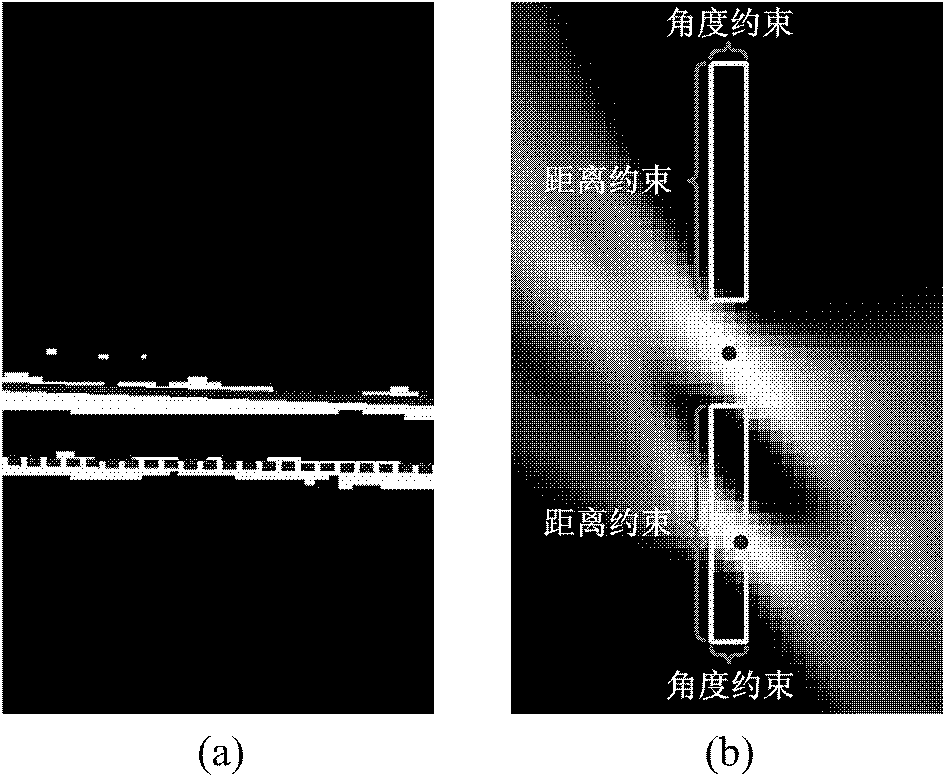
The invention relates to medical image processing, and provides an IMT (Intima Media Thickness) measurement algorithm with good overall performance. By using the method, there is no need for artificial participation, the time complexity is relatively low, the result of automatic measurement and the result of manual measurement by experts are highly consistent, and a satisfactory measurement result can be obtained for intima media of different morphological structures. An ultrasonic carotid artery intima media thickness measurement method based on deep learning of the invention comprises the following steps: (1) ROI (Region of Internet) acquisition; automatically identifying the far end of an ultrasonic carotid artery by use of a convolution neural network (CNN), and extracting an ROI; (2) pixel classification: performing more advanced feature extraction, and after feature extraction, building a pattern classifier by use of a stacked auto-encoder and a logistic regression classification layer to complete image pixel classification; and (3) boundary extraction: selecting a classification region based on the area information and location of a target classification region, and performing polynomial curve fitting on the classification boundary. The method is mainly applied in medical image processing.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Apparatus and methods for protected angioplasty and stenting at a carotid bifurcation
Apparatus and methods are described for performing protected angioplasty and stenting of a patient's carotid bifurcation. An integrated catheter system can be configured in a rapid- exchange version or in an over-the-wire version. The catheter system includes a self- expanding stent, a stent delivery sheath, a combination angioplasty balloon catheter and stent pusher catheter, an embolic protection device and, in the rapid-exchange version, an auto-releasing sheath. The method includes: inserting a guiding catheter to the carotid bifurcation; inserting the catheter system through the guiding catheter; advancing the embolic protection device beyond the lesion; positioning the stent and balloon segment of the catheter system at the lesion; releasing the self-expanding stent; pulling the stent delivery sheath back into the guiding catheter; positioning and deploying the protection member; advancing the combination angioplasty balloon catheter and stent pusher catheter and inflating the angioplasty balloon within the lesion; deflating the angioplasty balloon and withdrawing the combination angioplasty balloon catheter and stent pusher catheter and stent delivery sheath together; and aspirating potential emboli through the guiding catheter.
Owner:MINVASYS SA
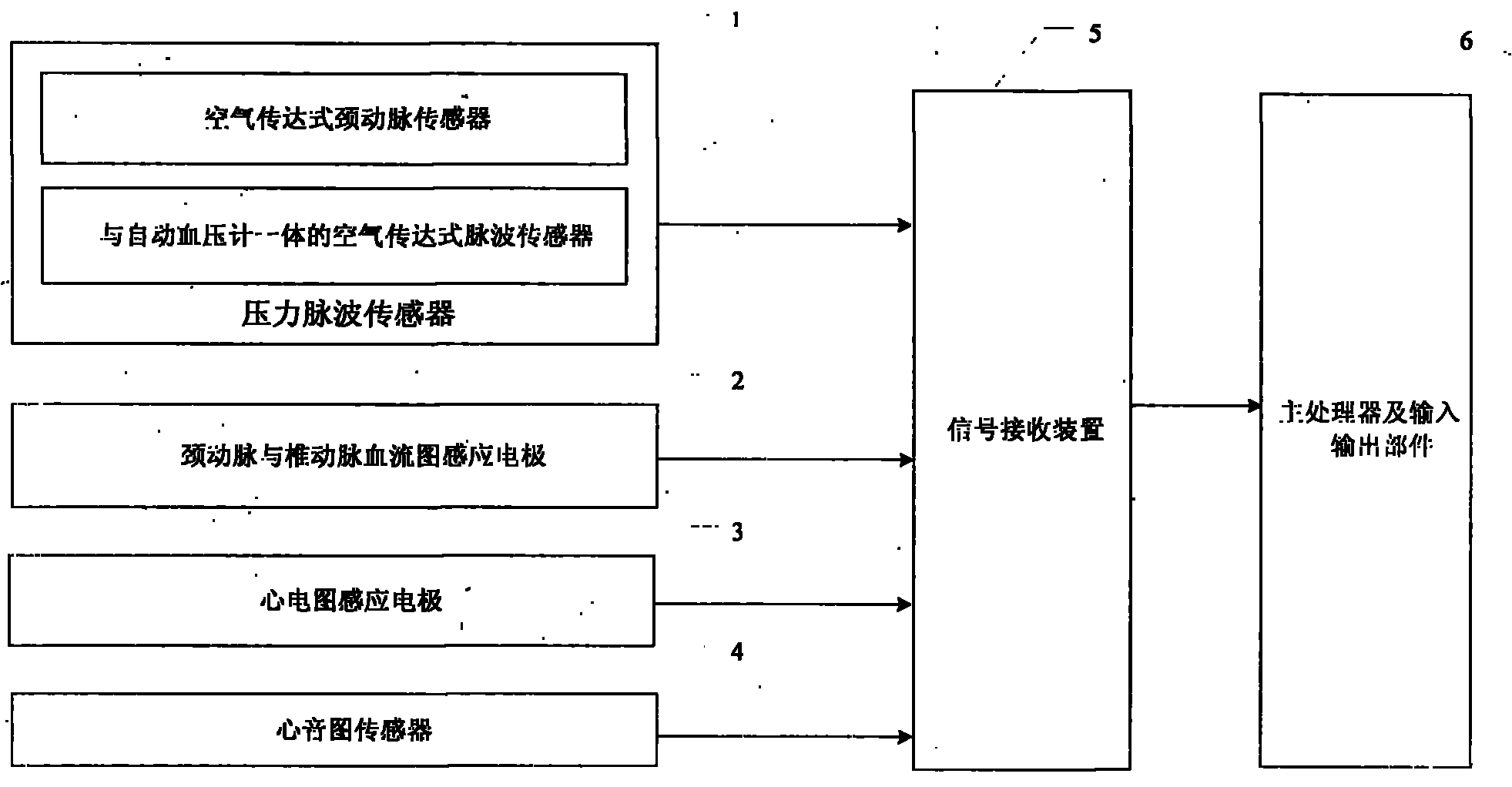
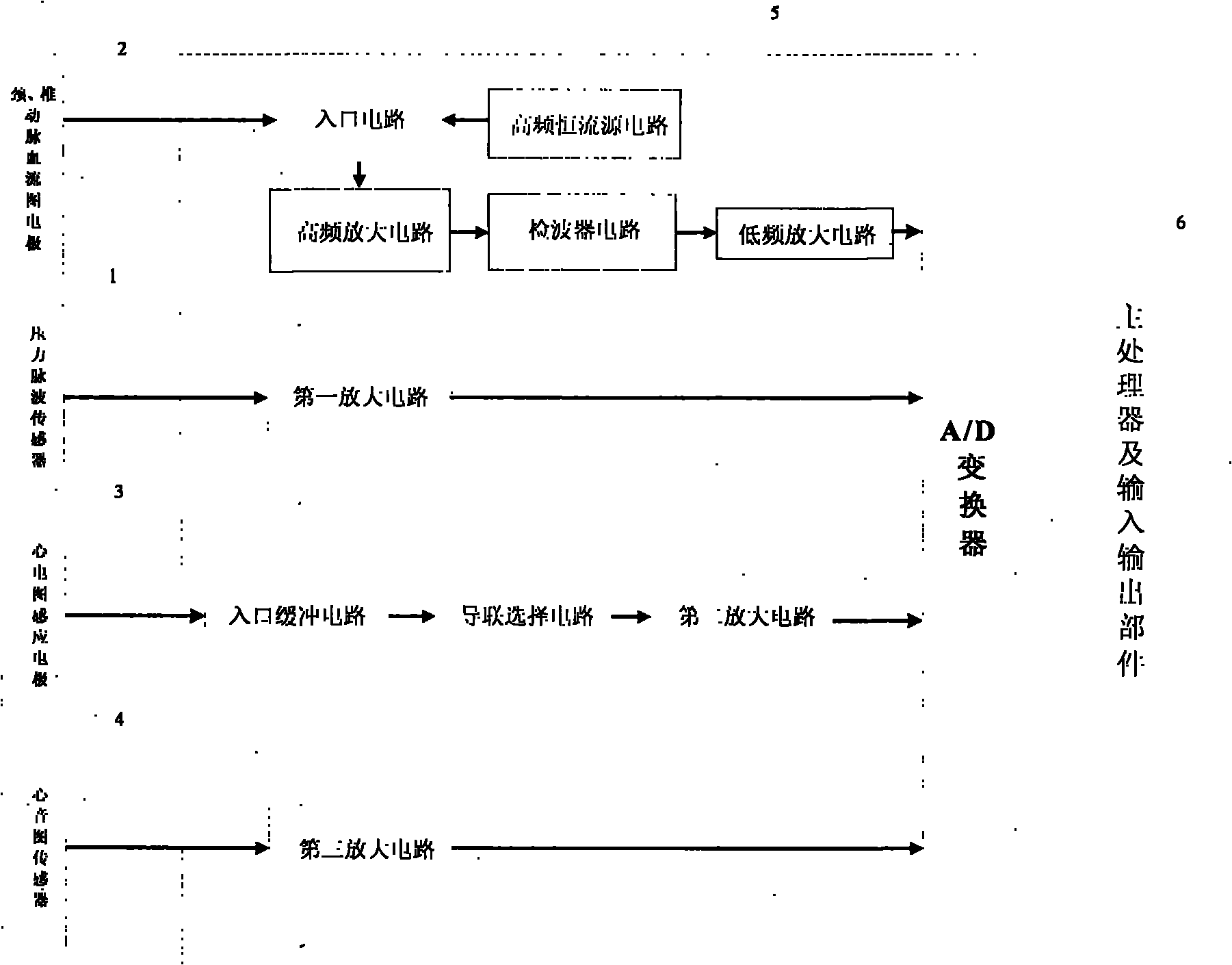
Device for analyzing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular characteristics and blood characteristics and detecting method
The invention provides a device for analyzing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular characteristics and blood characteristics and a detecting method, belonging to the field of medical equipment. The device comprises a pressure pulse wave sensor, a carotid artery and vertebral artery rheogram inductance electrode, an electrocardiogram inductance electrode, a cardiophonogram sensor, a signal receiver, a main processor and an in-out part. The device can realize the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular noninvasive detection, and biomechanically analyzes each branched blood vessel of the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular system by measuring the blood pressure and the blood flow volume of a left cervical vertebra artery, a right cervical vertebra artery, a cerebrum front artery, a cerebrum middle artery, a cerebrum back artery, a left coronary artery and a right coronary artery, obtains biomechanics indexes such as the elasticity coefficient, the compliance, the blood resistance, the blood flow volume and the like of each branched blood vessel of the cardial blood vessel and the brain blood vessel, has an important significance for the early diagnosis of the myocardial infarction and the cerebral thrombosis by taking as equipment for the cardiography, the magnatic resonance imaging MRI, the CT and the like and supplementary equipment between the TCD and the ECG.
Owner:沈阳恒德医疗器械研发有限公司
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal and perfusion augmentation within the cerebral vasculature
InactiveUS7635376B2Preventing ischemic strokeStroke preventionBalloon catheterSurgeryAtherectomyCoarctation of the aorta
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com