Patents
Literature
277 results about "Third aortic arch" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
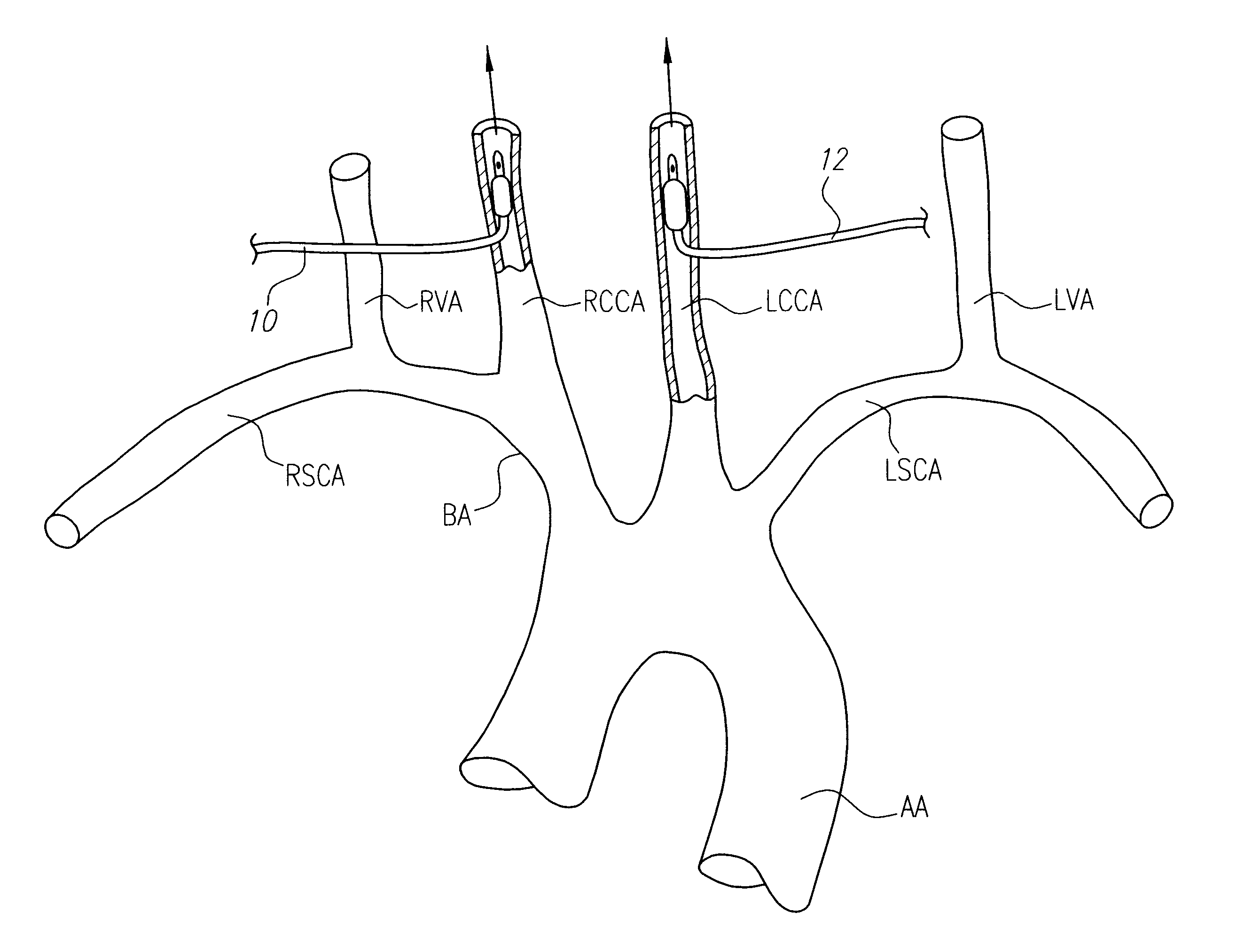
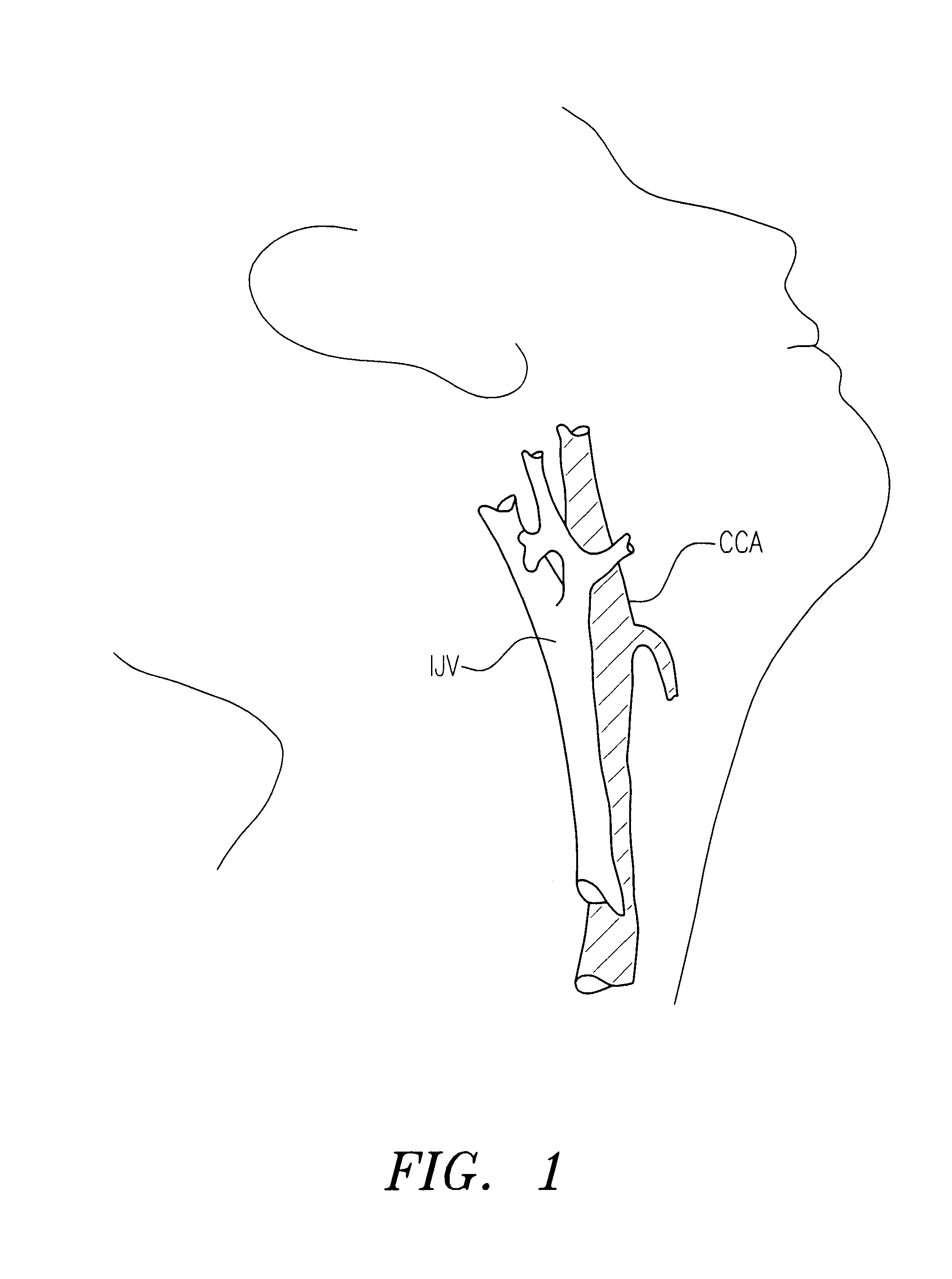
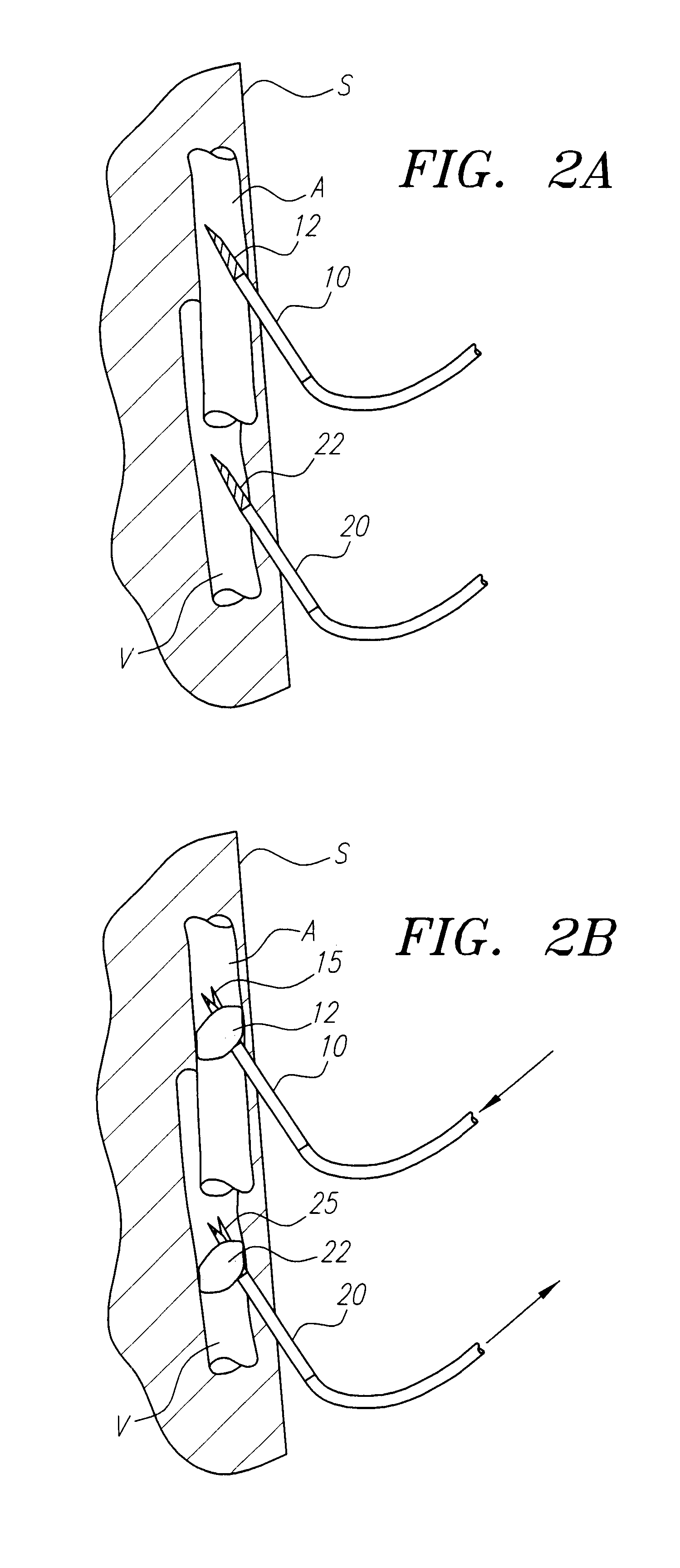
The third aortic arch constitutes the commencement of the internal carotid artery, and is therefore named the carotid arch. It contributes to the common carotid artery and the proximal portion of the internal carotid artery.
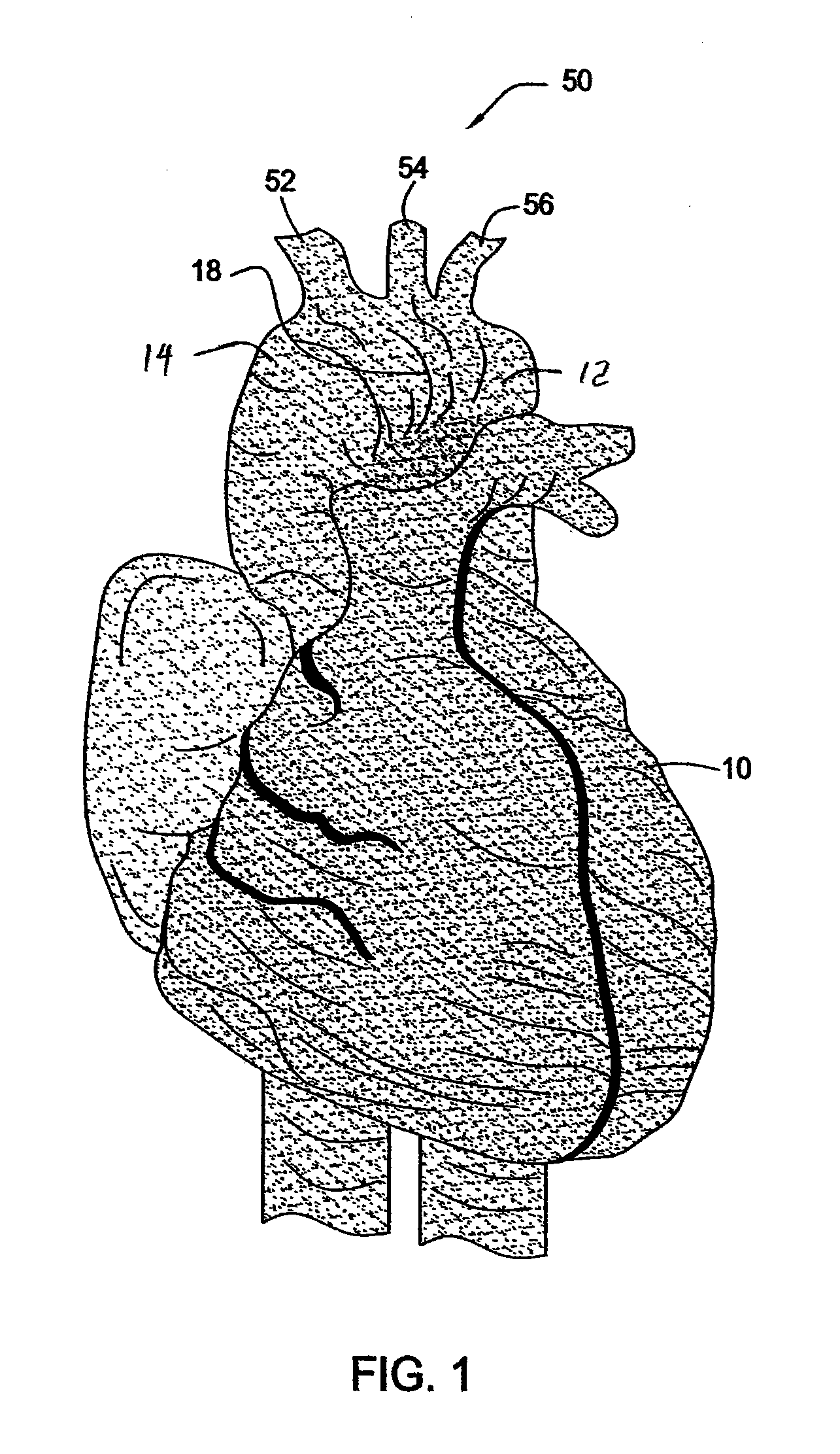
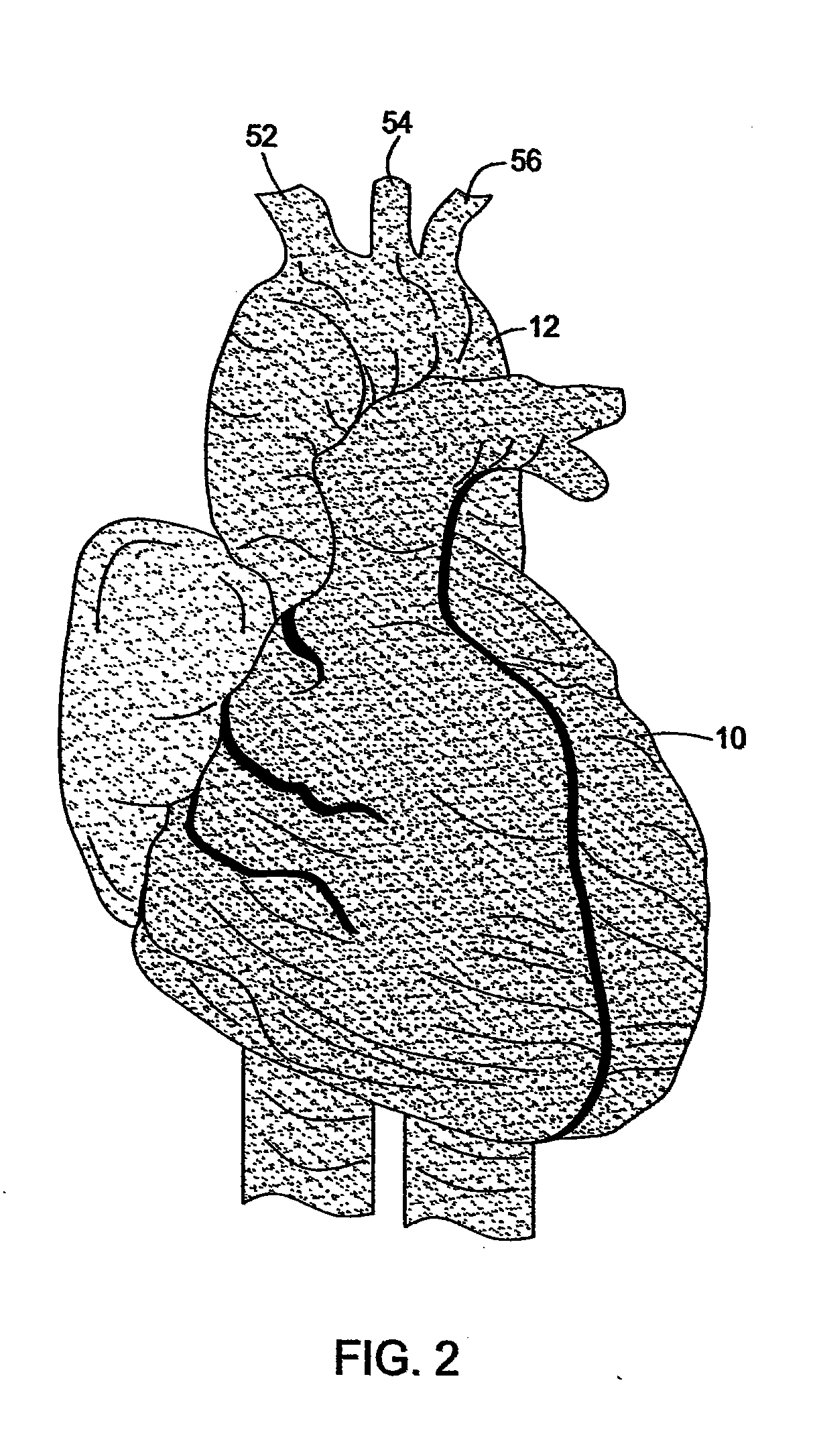
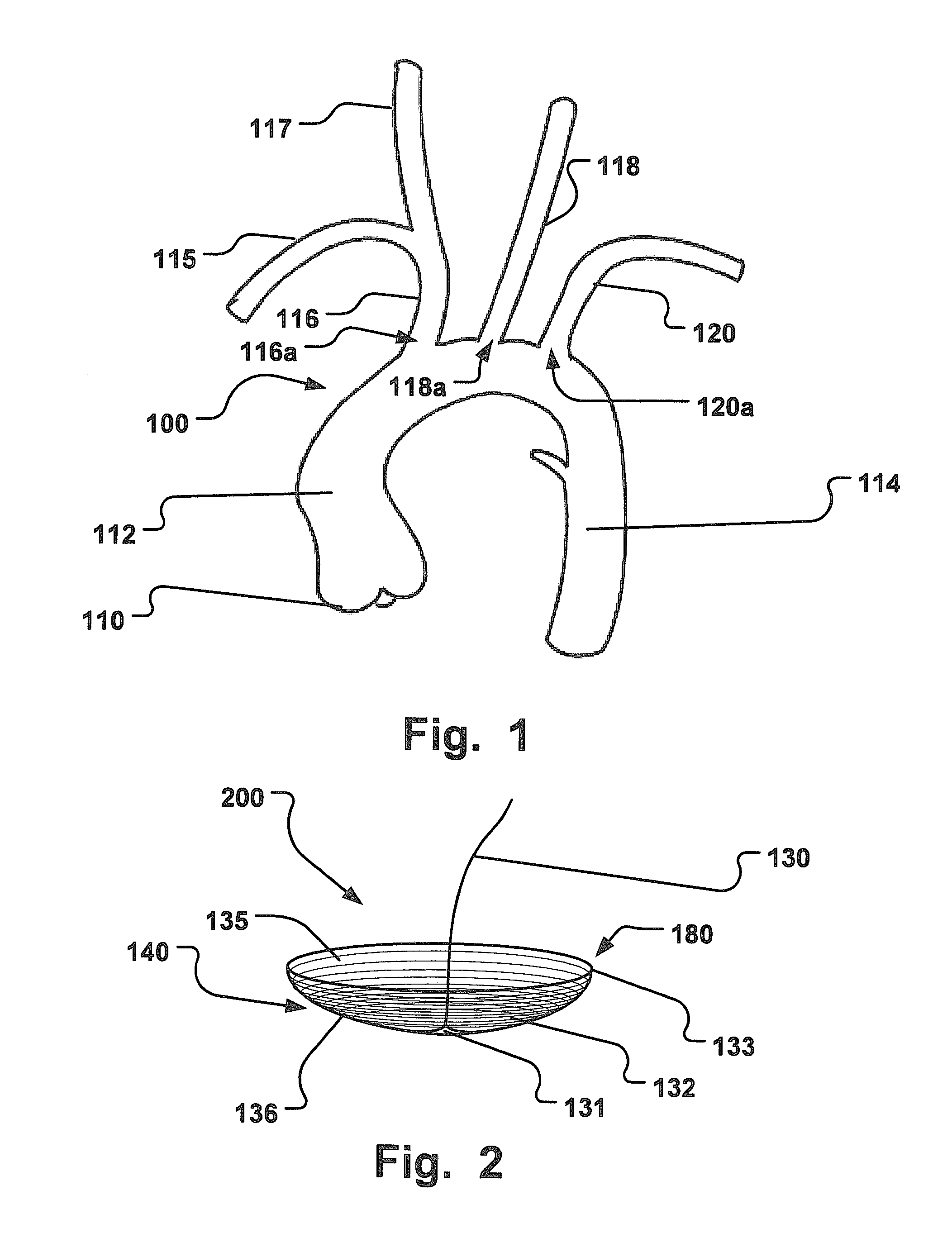
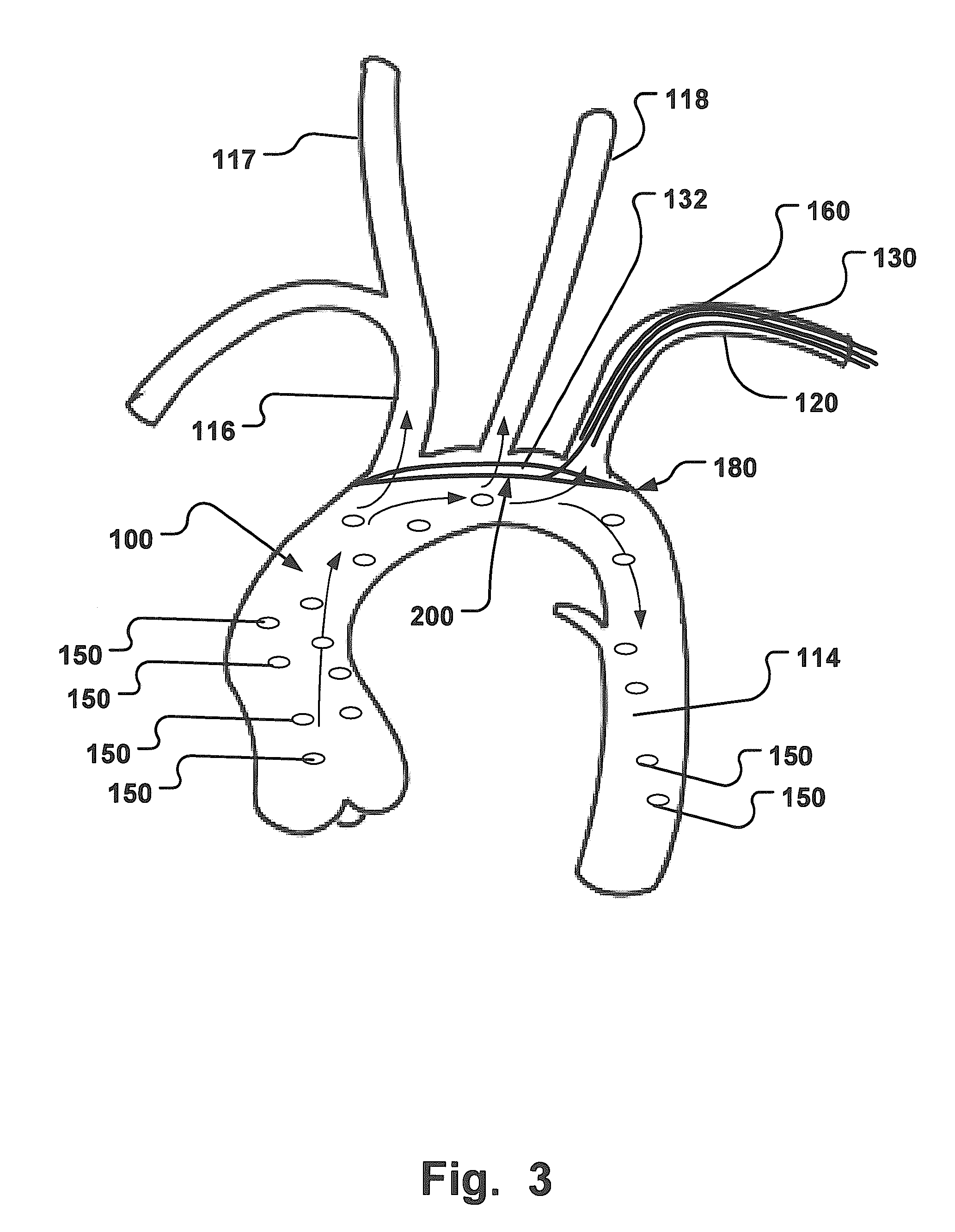
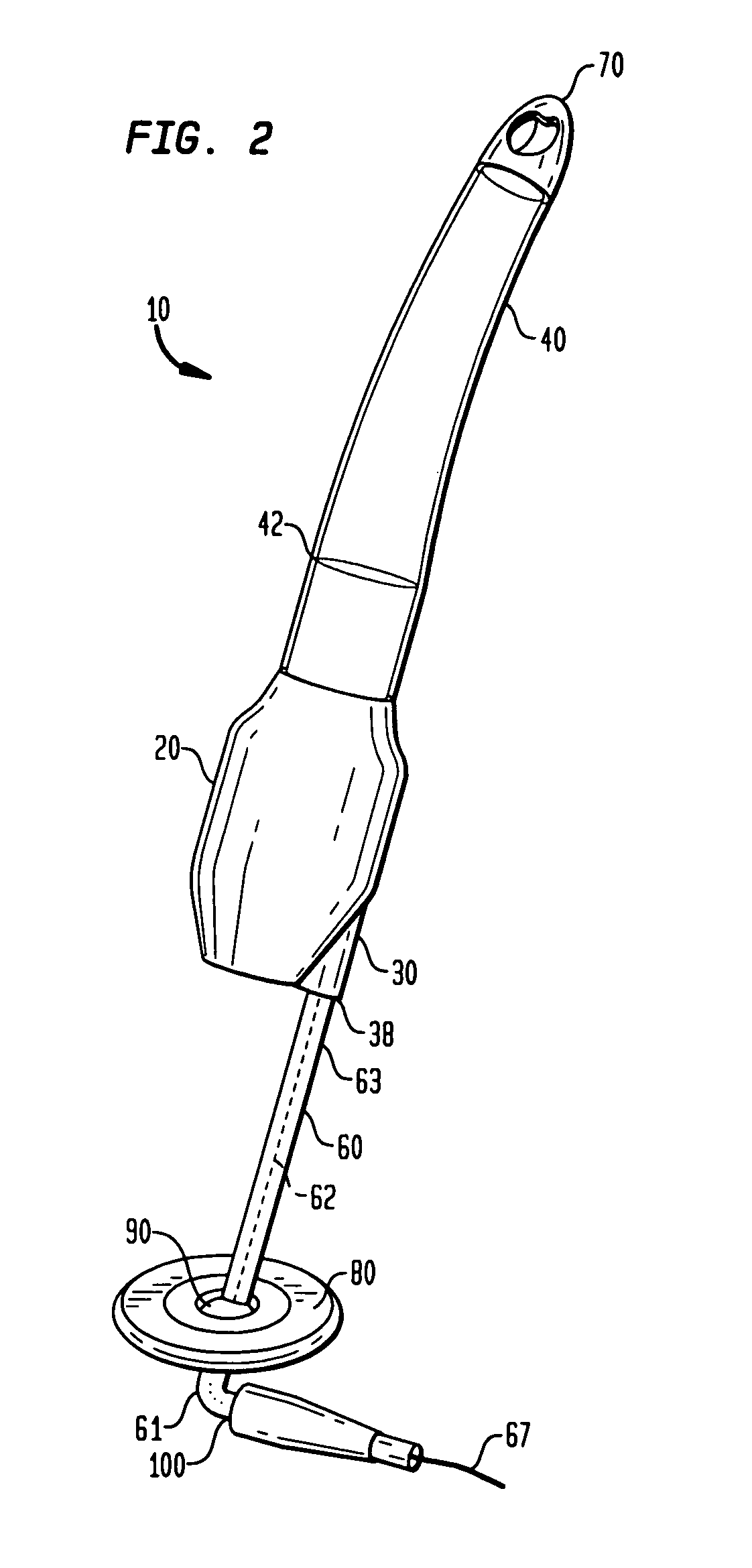
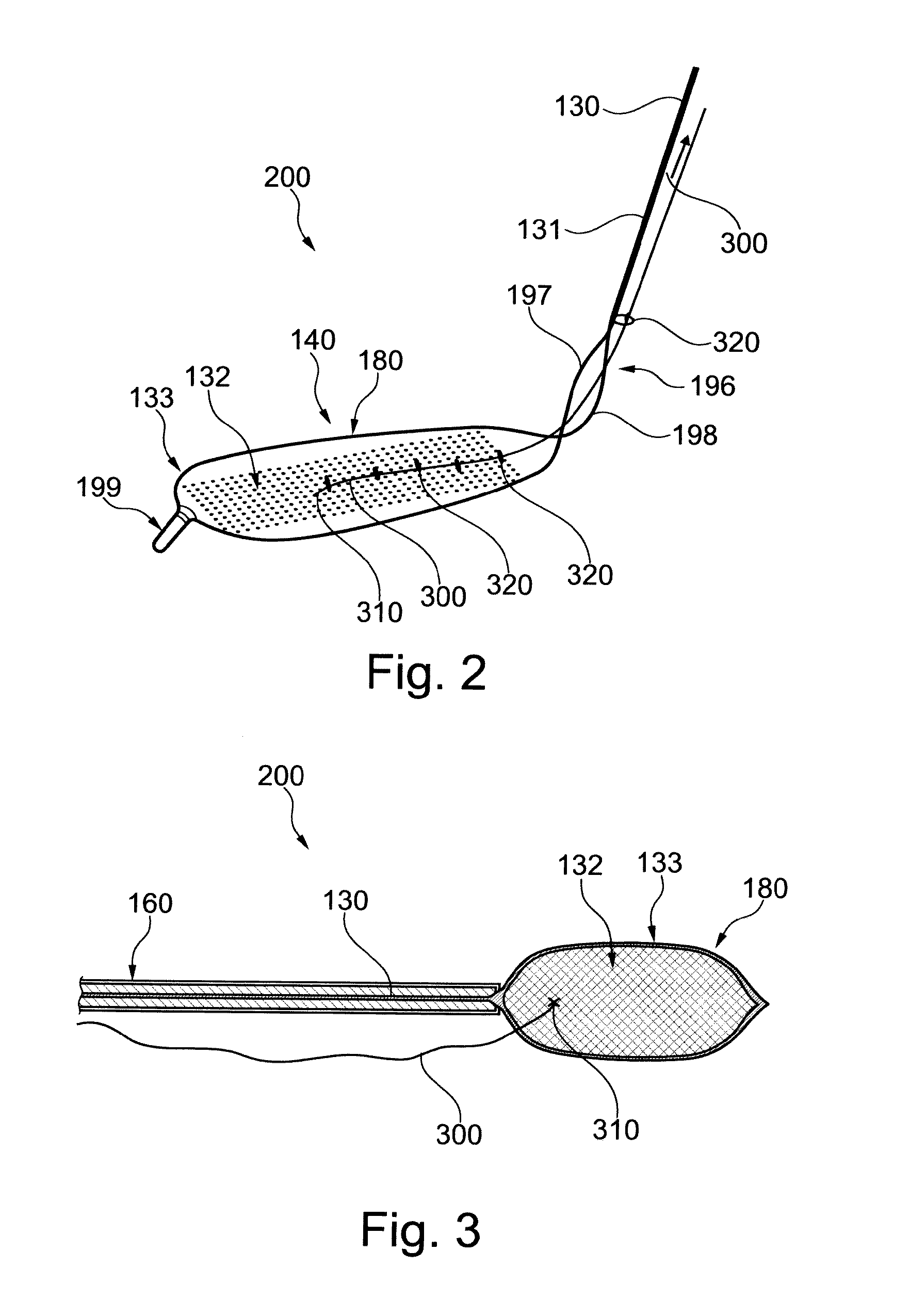
System for cardiac procedures
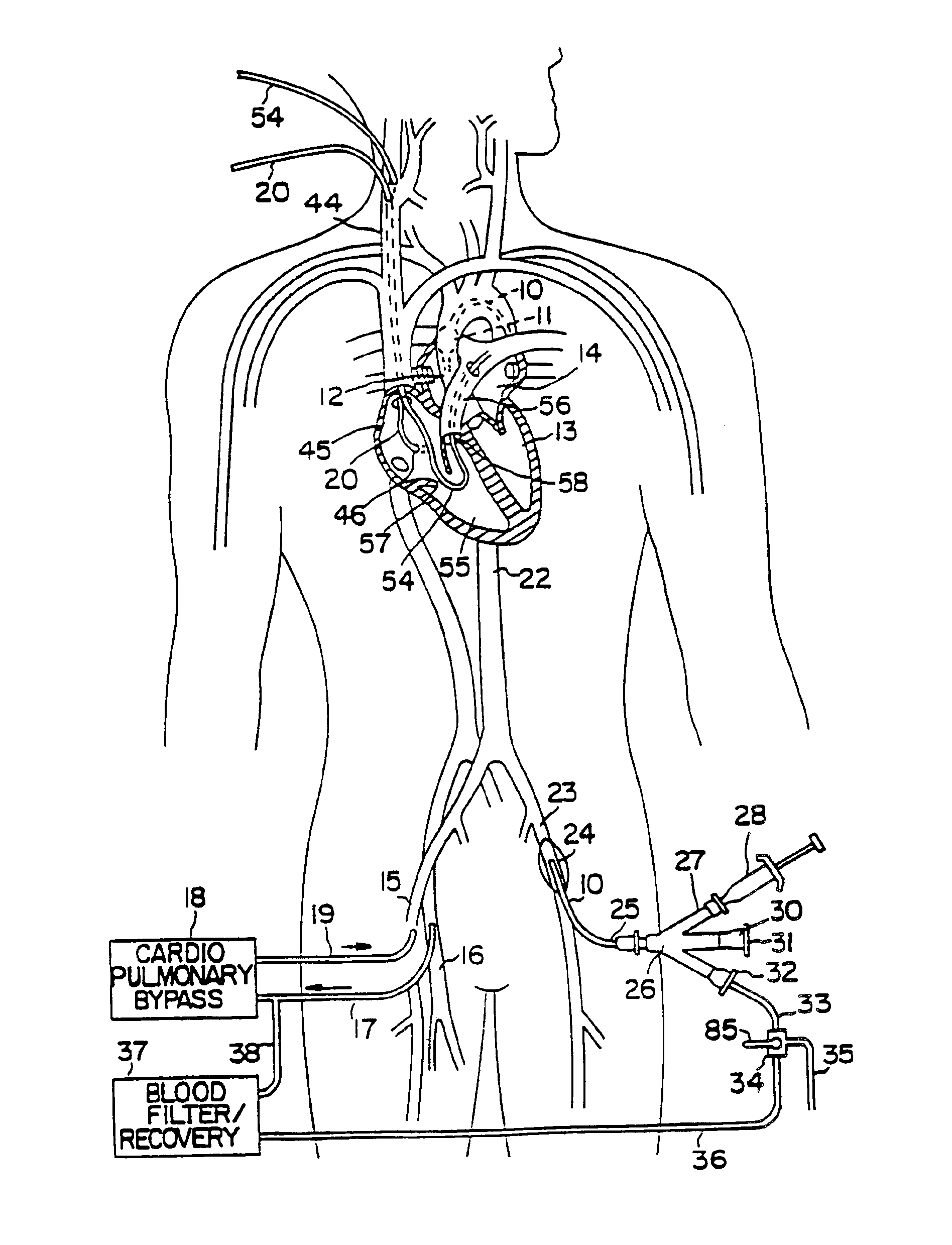
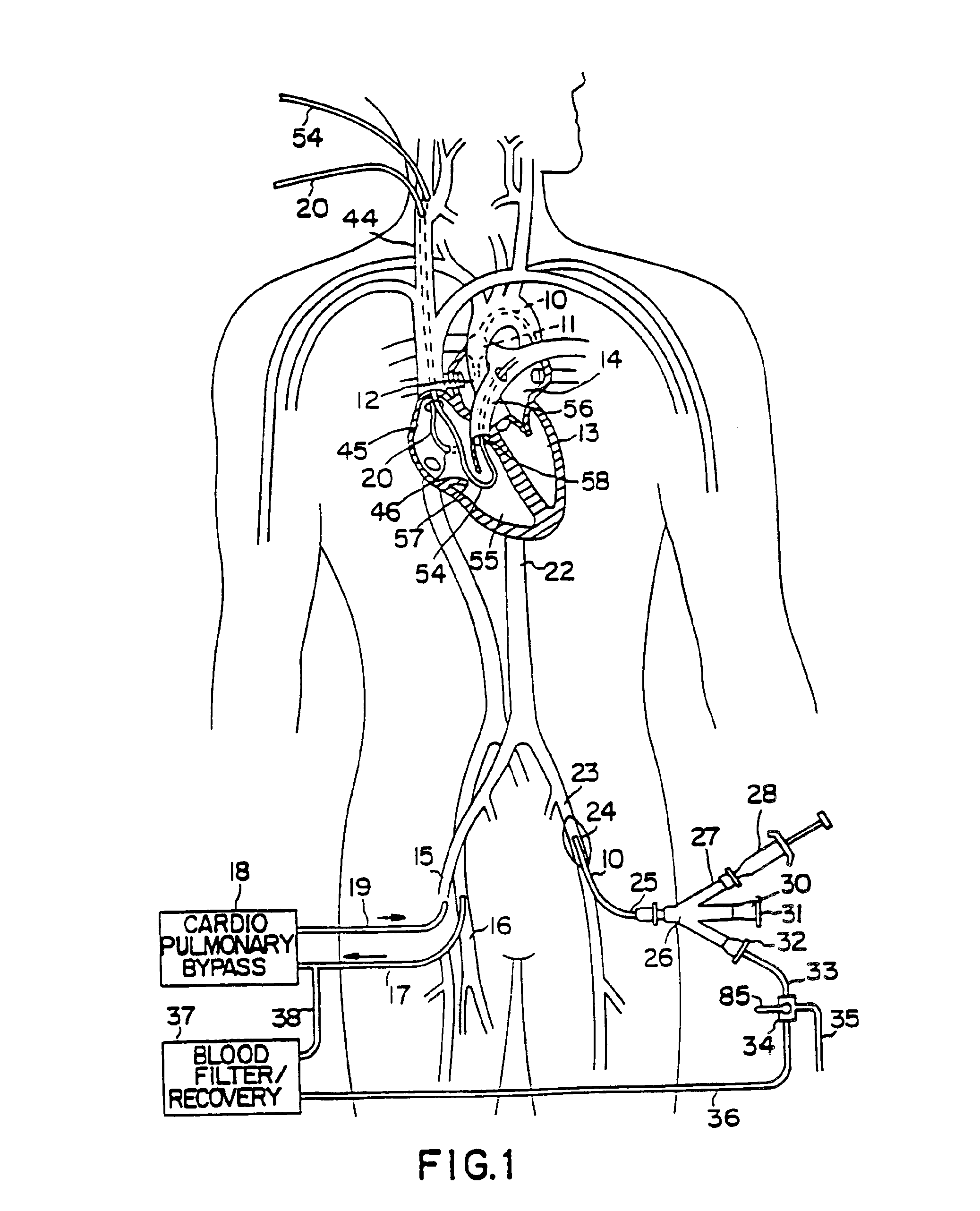
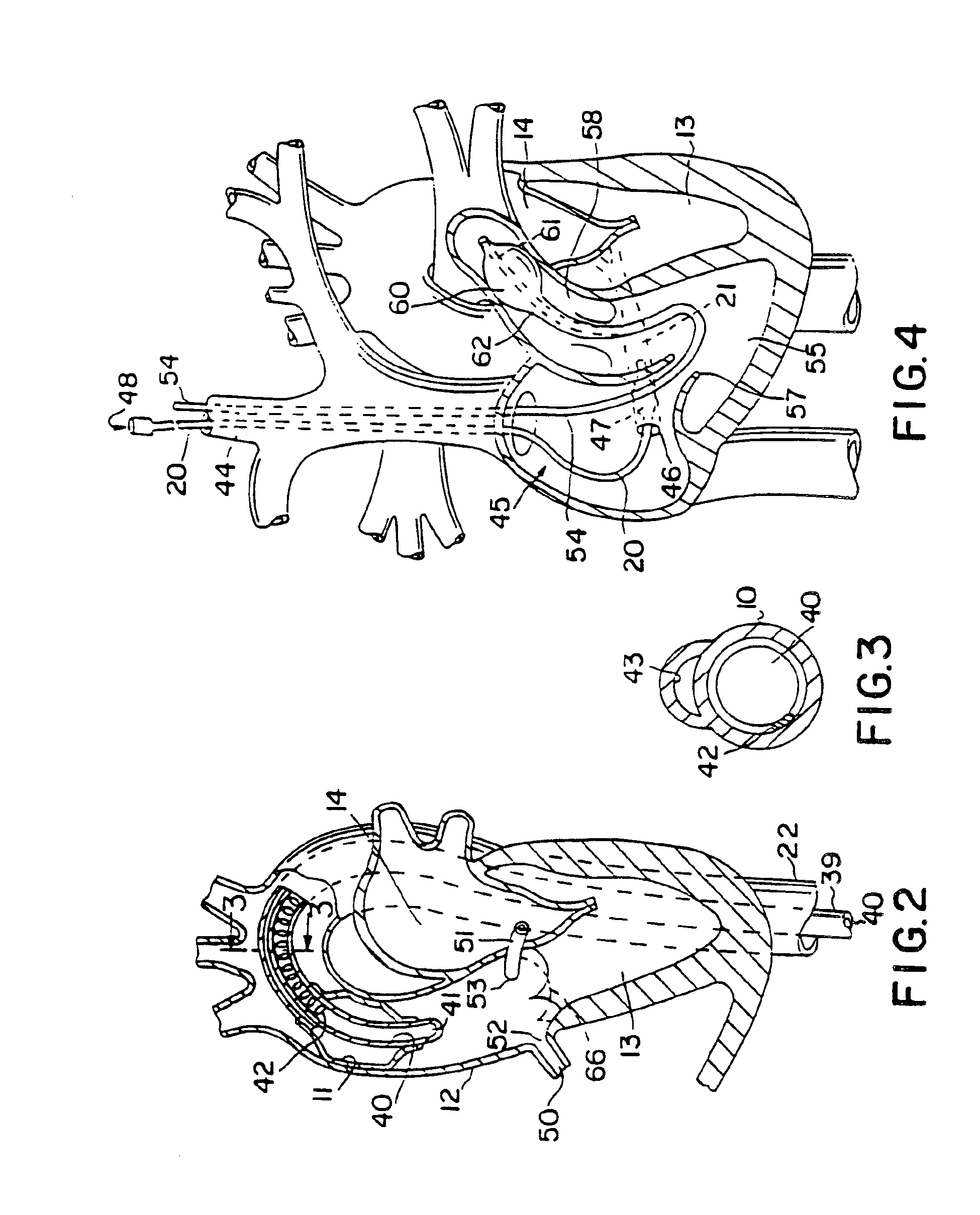
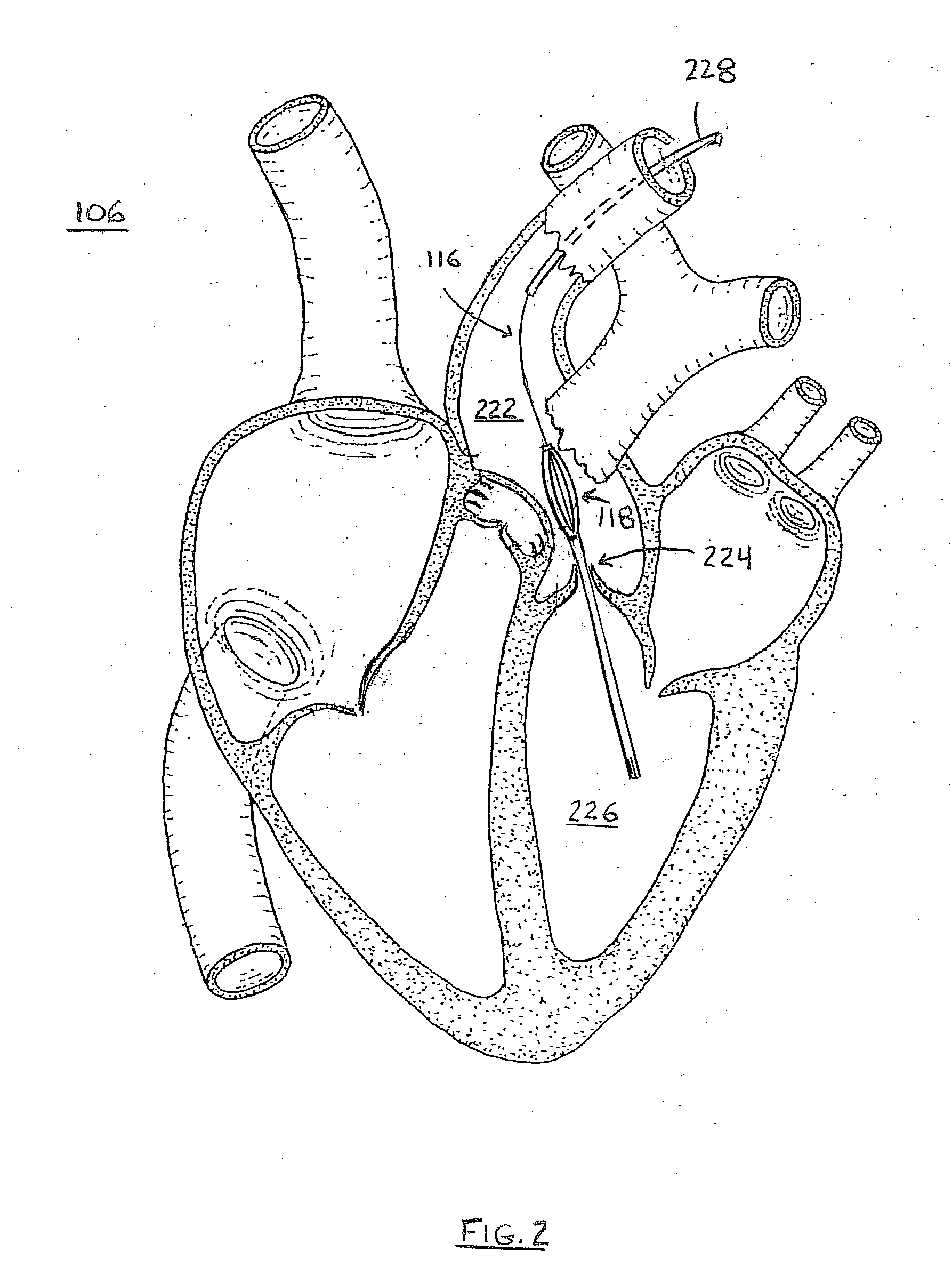
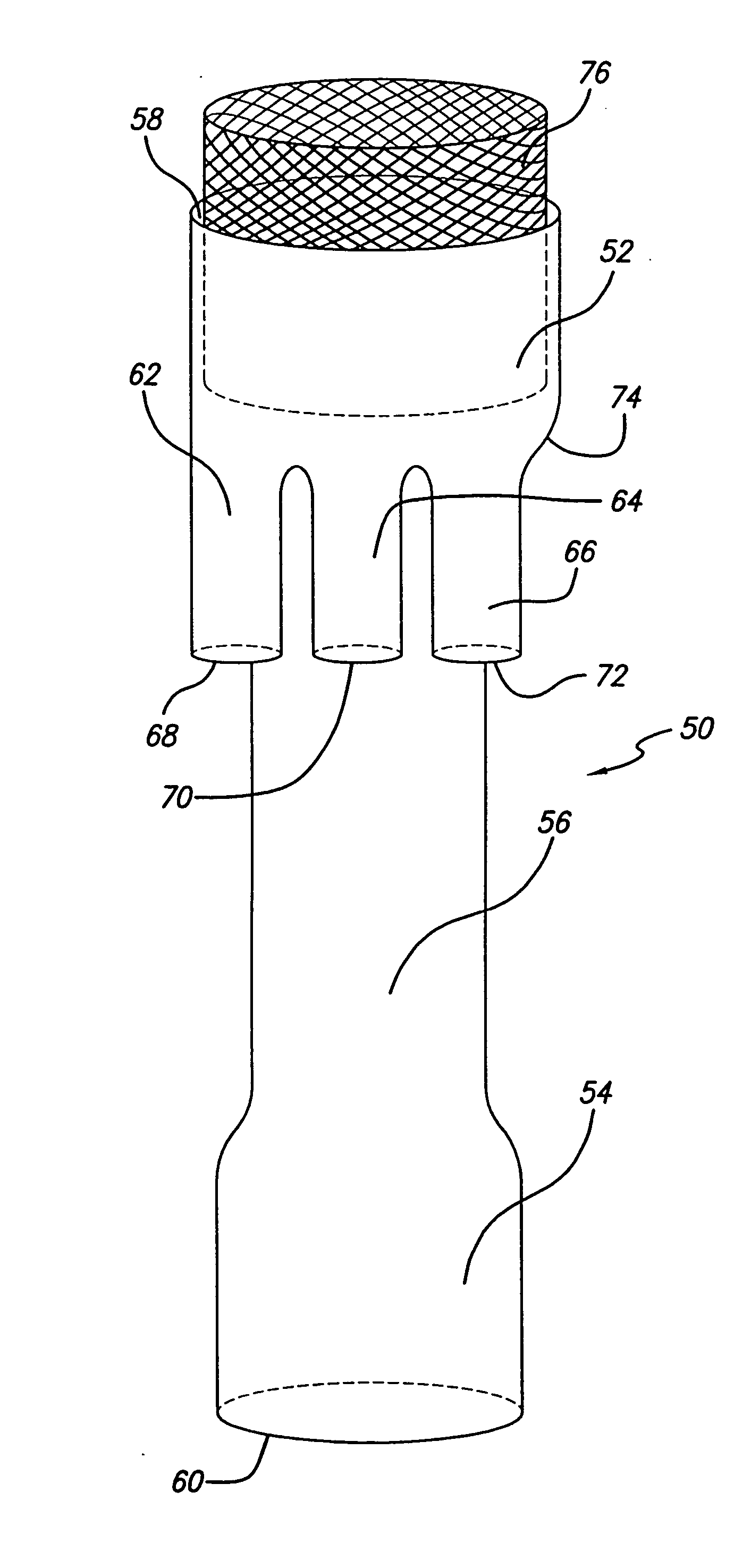
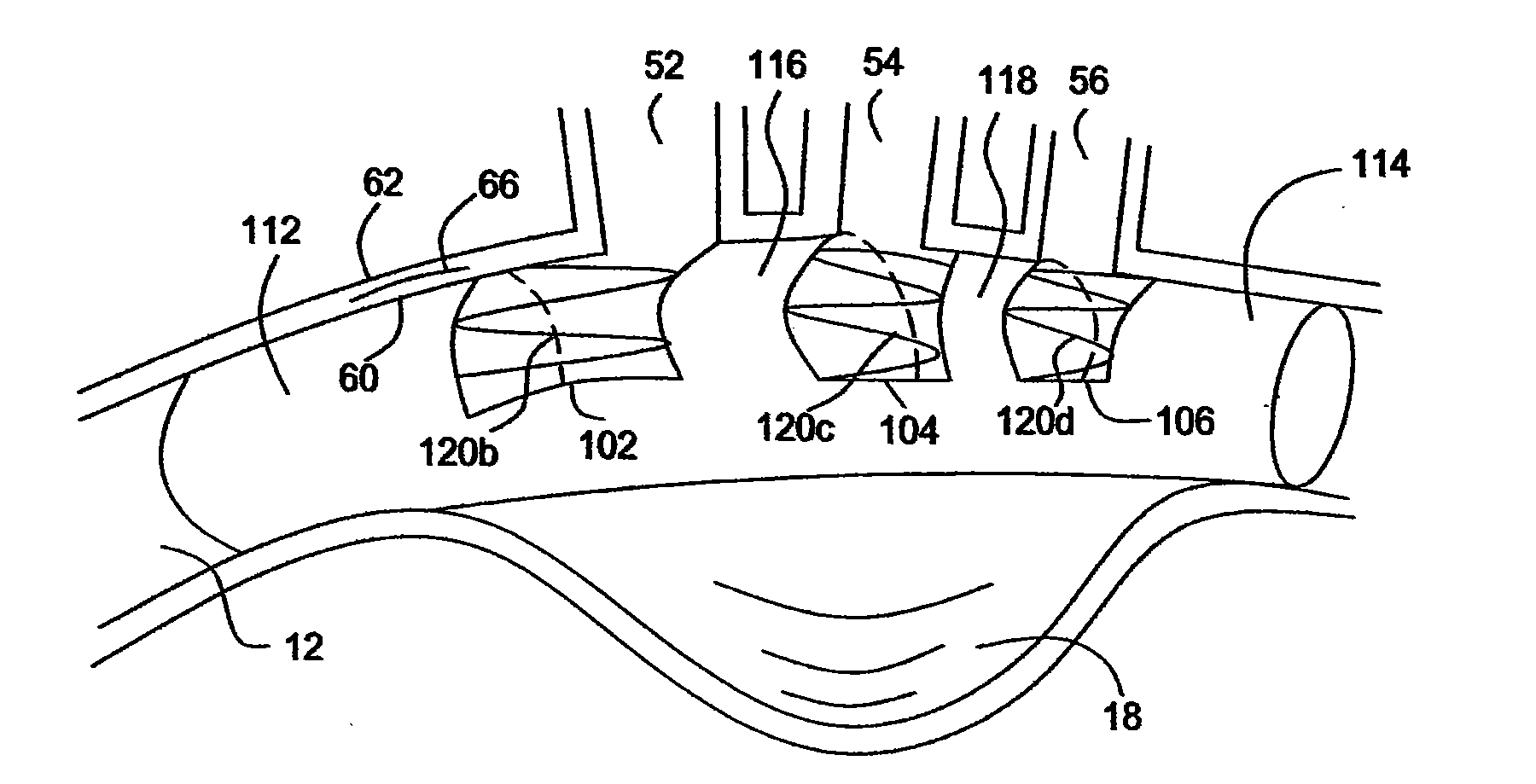
A system for accessing a patient's cardiac anatomy which includes an endovascular aortic partitioning device that separates the coronary arteries and the heart from the rest of the patient's arterial system. The endovascular device for partitioning a patient's ascending aorta comprises a flexible shaft having a distal end, a proximal end, and a first inner lumen therebetween with an opening at the distal end. The shaft may have a preshaped distal portion with a curvature generally corresponding to the curvature of the patient's aortic arch. An expandable means, e.g. a balloon, is disposed near the distal end of the shaft proximal to the opening in the first inner lumen for occluding the ascending aorta so as to block substantially all blood flow therethrough for a plurality of cardiac cycles, while the patient is supported by cardiopulmonary bypass. The endovascular aortic partitioning device may be coupled to an arterial bypass cannula for delivering oxygenated blood to the patient's arterial system. The heart muscle or myocardium is paralyzed by the retrograde delivery of a cardioplegic fluid to the myocardium through patient's coronary sinus and coronary veins, or by antegrade delivery of cardioplegic fluid through a lumen in the endovascular aortic partitioning device to infuse cardioplegic fluid into the coronary arteries. The pulmonary trunk may be vented by withdrawing liquid from the trunk through an inner lumen of an elongated catheter. The cardiac accessing system is particularly suitable for removing the aortic valve and replacing the removed valve with a prosthetic valve.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
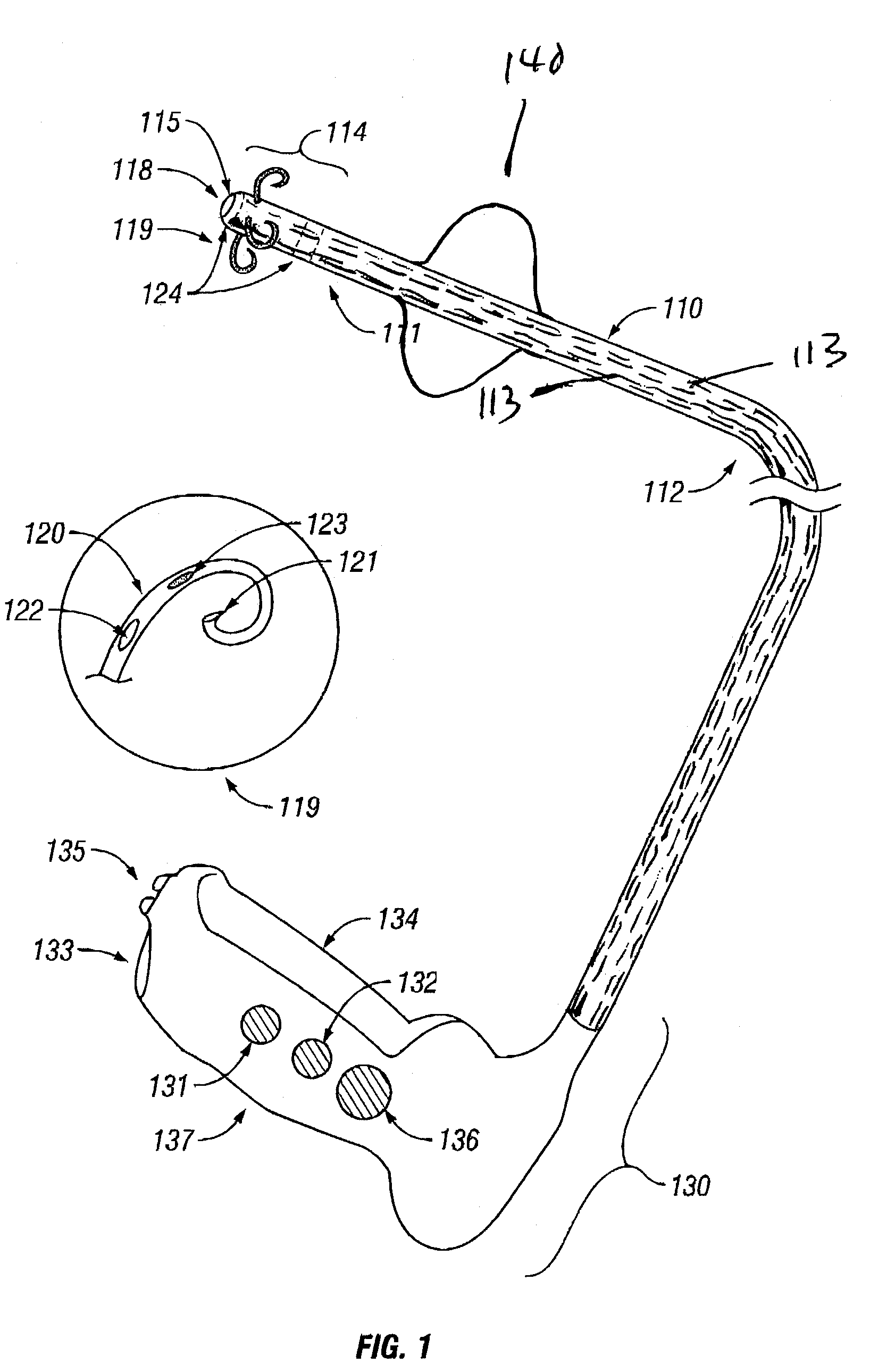
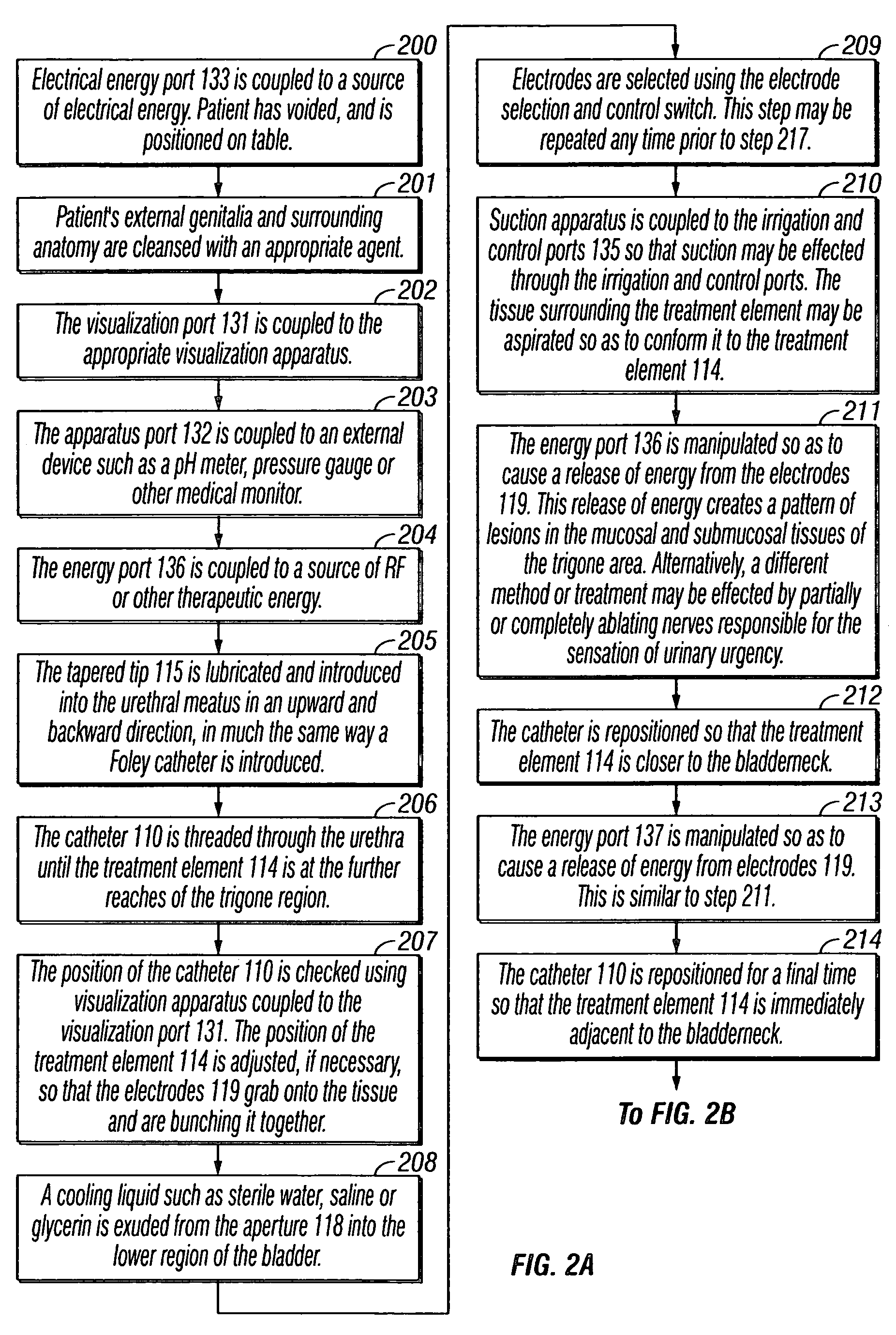
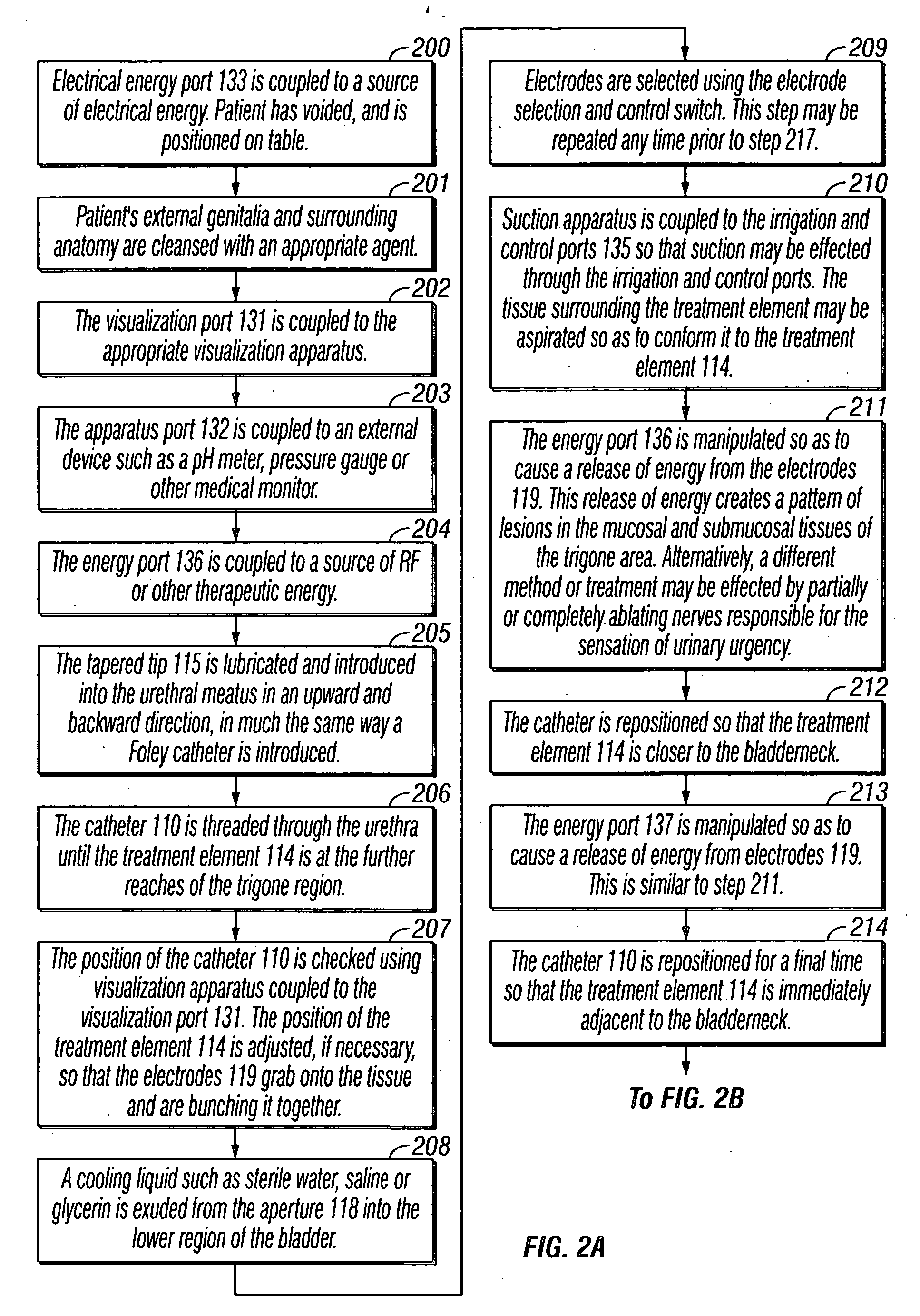
Treatment of urinary incontinence and other disorders by application of energy and drugs
The invention provides a method and system for treating disorders in parts of the body. A particular treatment can include on or more of, or some combination of: ablation, nerve modulation, three-dimensional tissue shaping, drug delivery, mapping stimulating, shrinking and reducing strain on structures by altering the geometry thereof and providing bulk to particularly defined regions. The particular body structures or tissues can include one or more of or some combination of region, including: the bladder, esophagus, vagina, penis, larynx, pharynx, aortic arch, abdominal aorta, thoracic, aorta, large intestine, sinus, auditory canal, uterus, vas deferens, trachea, and all associated sphincters. Types of energy that can be applied include radiofrequency, laser, microwave, infrared waves, ultrasound, or some combination thereof. Types of substances that can be applied include pharmaceutical agents such as analgesics, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs, bulking agents such as biologically non-reactive particles, cooling fluids, or dessicants such as liquid nitrogen for use in cryo-based treatments.
Owner:VERATHON
Method for Deployment of a Medical Device
InactiveUS20080132748A1Reduce bending loadMinimizing contact pressureControl devicesBlood pumpsAortic archMedical device
A method for deploying a cardiac-assist device is disclosed. In accordance with the illustrative embodiment, an introducing tube, such as a catheter, sheath, or the like is inserted into the vascular system and advanced beyond the aortic arch. The cardiac-assist device is then inserted into the tube, advanced through it, and deployed from its distal end. In some embodiments, the diameter of the cardiac-assist device expands when it deploys from the distal end of the tube.
Owner:MEDICAL VALUE PARTNERS
Aspiration catheter
InactiveUS6849068B1Fast and efficient aspirationEasy to useStentsBalloon catheterThird aortic archSaphenous veins
Aspiration catheters suitable for use in the treatment of an occlusion in a blood vessel are disclosed. These catheters are especially useful in the removal of occlusions from saphenous vein grafts, the coronary and carotid arteries, arteries above the aortic arch and even smaller vessels. The catheters of the present invention are provided in either over-the-wire or in single operator form. Radiopaque markers are preferably incorporated into distal ends of the catheters to facilitate their positioning within the body. The catheters are provided with varying flexibility along the length of the shaft, such that they are soft and flexible enough to be navigated through the vasculature of a patient without causing damage, but are stiff enough to sustain the axial push required to position the catheter properly and to sustain the aspiration pressures.
Owner:MEDTRONIC AVE
Aspiration method
InactiveUS20030009146A1Fast and efficient aspirationReduce amountBalloon catheterGuide wiresSaphenous veinsSaphenous vein graft
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Ventricular assist device for intraventricular placement
A ventricular assist device includes a pump such as an axial flow pump, an outflow cannula connected to the outlet of the pump, and an anchor element. The anchor element is physically connected to the pump, as by an elongate element. The pump is implanted within the left ventricle with the outflow cannula projecting through the aortic valve but desirably terminating short of the aortic arch. The anchor element is fixed to the wall of the heart near the apex of the heart so that the anchor element holds the pump and outflow cannula in position.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
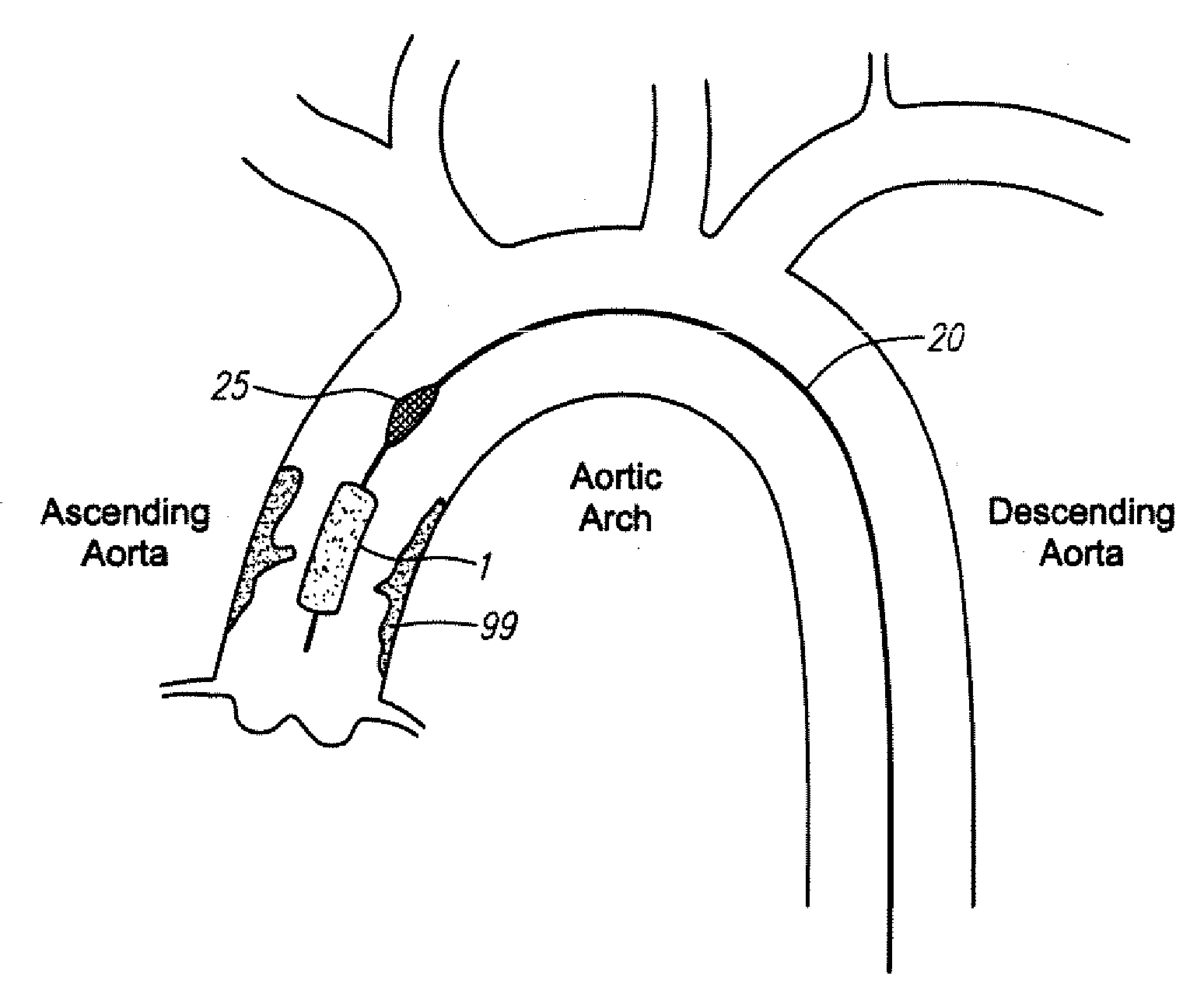
Methods and devices for treating aortic atheroma
InactiveUS20060161241A1Precise positioningAvoid obstructionStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryAortic atheroma
A method for treating both sessile and mobile aortic atheroma is described. A radially expanding device, such as a stent or compliant cast, comprising a generally cylindrical member expandable between a compressed state and an enlarged state is provided. The cylindrical member has a proximal opening, a distal opening, a lumen therebetween, and at least one side opening in the wall of the generally cylindrical member. The methods comprise imaging the aorta to identify position and extent of atheroma. The stent is then advanced into the aortic arch and positioned so that the at least one side-opening is aligned with the takeoff of one or more of the right brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery, or the left subclavian artery. The stent is expanded into contact with the endoluminal surface of the aorta and atheroma is trapped between the stent and the endoluminal surface of the aorta.
Owner:SAGE MEDICAL TECH
Guide catheter having selected flexural modulus segments
InactiveUS6858024B1Prevent guide catheter back-outIncreasing back-out resistanceGuide needlesFlexible pipesFlexural modulusAortic arch
A guiding catheter for use in coronary angioplasty and other cardiovascular interventions which incorporates a plurality of segment of selected flexural modulus in the shaft of the device. The segments which have a different flexibility than the sections immediately proximal and distal to them, creating zones in the catheter shaft which are either more or less flexible than other zones of the shaft. The flexibility and length of the shaft in a given zone is then matched to its clinical function and role. A mid-shaft zone is significantly softer than a proximal shaft or distal secondary curve to better traverse the aortic arch shape without storing too much energy. A secondary zone section is designed to have maximum stiffness to provide optimum backup support and stability.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Intravascular methods and apparatus for isolation and selective cooling of the cerebral vasculature during surgical procedures
InactiveUS6555057B1Reduce riskIncrease perfusionOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesRisk strokeSurgical department
Patients having diminished circulation in the cerebral vasculature as a result of stroke or from other causes such as cardiac arrest, shock or head trauma, or aneurysm surgery or aortic surgery, are treated by flowing an oxygenated medium through an arterial access site into the cerebral vasculature and collecting the medium through an access site in the venous site of the cerebral vasculature. Usually, the cold oxygenated medium will comprise autologous blood, and the blood will be recirculated for a time sufficient to permit treatment of the underlying cause of diminished circulation. In addition to oxygenation, the recirculating blood will also be cooled to hypothermically treat and preserve brain tissue. Isolation and cooling of cerebral vasculature in patients undergoing aortic and other procedures is achieved by internally occluding at least the right common carotid artery above the aortic arch. Blood or other oxygenated medium is perfused through the occluded common carotid artery(ies) and into the arterial cerebral vasculature. Usually, oxygen depleted blood or other medium leaving the cerebral vasculature is collected, oxygenated, and cooled in an extracorporeal circuit so that it may be returned to the patient. Occlusion of the carotid artery(ies) is preferably accomplished using expansible occluders, such as balloon-tipped cannula, catheters, or similar access devices. Access to the occlusion site(s) may be open surgical, percutaneous, or intravascular.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE +3
Modular stent-graft for endovascular repair of aortic arch aneurysms and dissections
InactiveUS20050010277A1Avoid complex processMinimally invasiveStentsHeart valvesAortic arch aneurysmStent grafting
A system and method for treating and repairing complex anatomy characterized by a plurality of vessel portions oriented at various angles relative to each other. The system including a graft device that is capable of being assembled in situ and has associated therewith a method that avoids the cessation of blood flow to vital organs. A delivery catheter system and various graft supporting, mating and anchoring structures are additionally included.
Owner:LIFESHIELD SCI
Treatment of urinary incontinence and other disorders by application of energy and drugs
The invention provides a method and system for treating disorders in parts of the body. A particular treatment can include on or more of, or some combination of: ablation, nerve modulation, three-dimensional tissue shaping, drug delivery, mapping stimulating, shrinking and reducing strain on structures by altering the geometry thereof and providing bulk to particularly defined regions. The particular body structures or tissues can include one or more of or some combination of region, including: the bladder, esophagus, vagina, penis, larynx, pharynx, aortic arch, abdominal aorta, thoracic, aorta, large intestine, sinus, auditory canal, uterus, vas deferens, trachea, and all associated sphincters. Types of energy that can be applied include radiofrequency, laser, microwave, infrared waves, ultrasound, or some combination thereof. Types of substances that can be applied include pharmaceutical agents such as analgesics, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs, bulking agents such as biologically non-reactive particles, cooling fluids, or dessicants such as liquid nitrogen for use in cryo-based treatments.
Owner:VERATHON
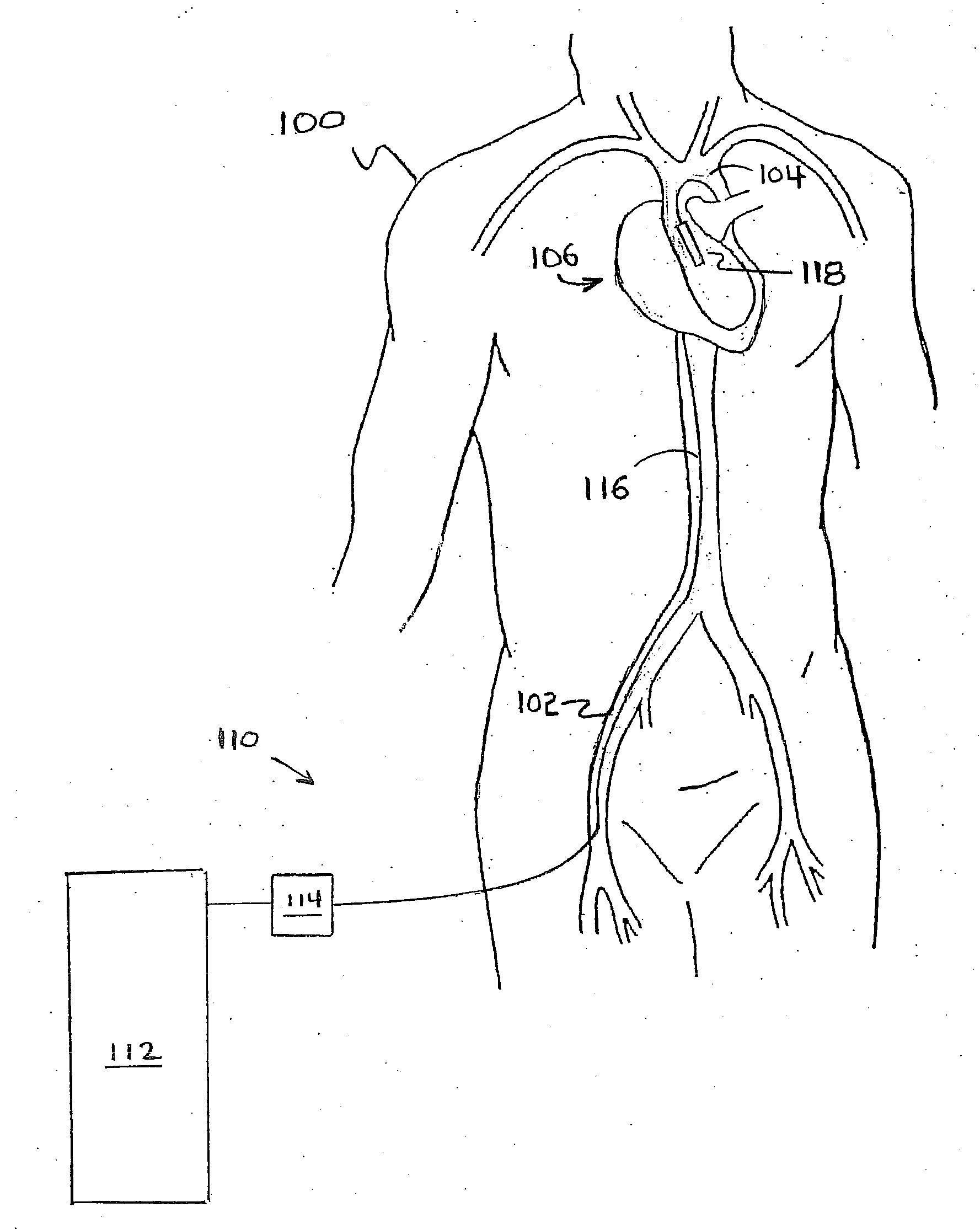
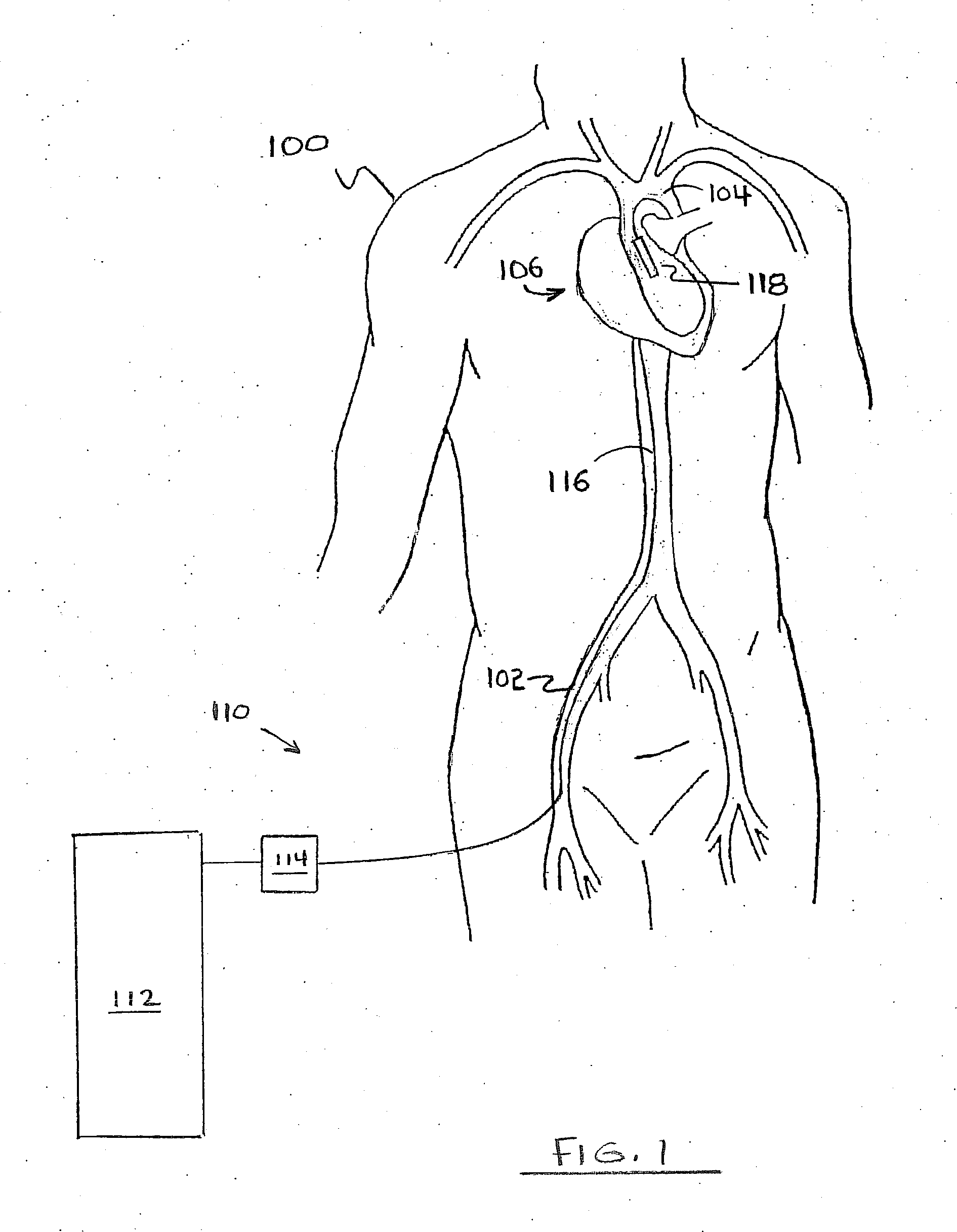
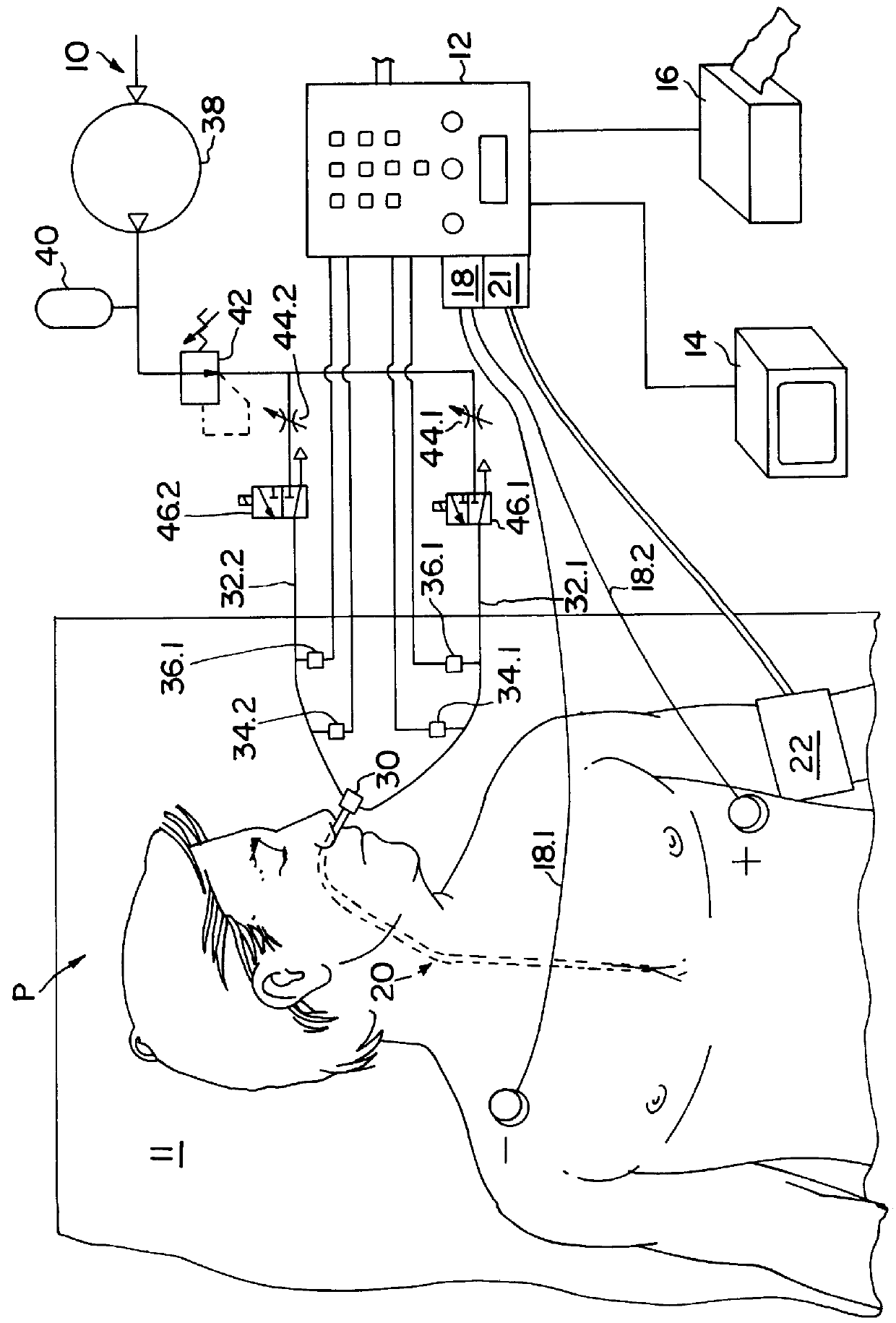
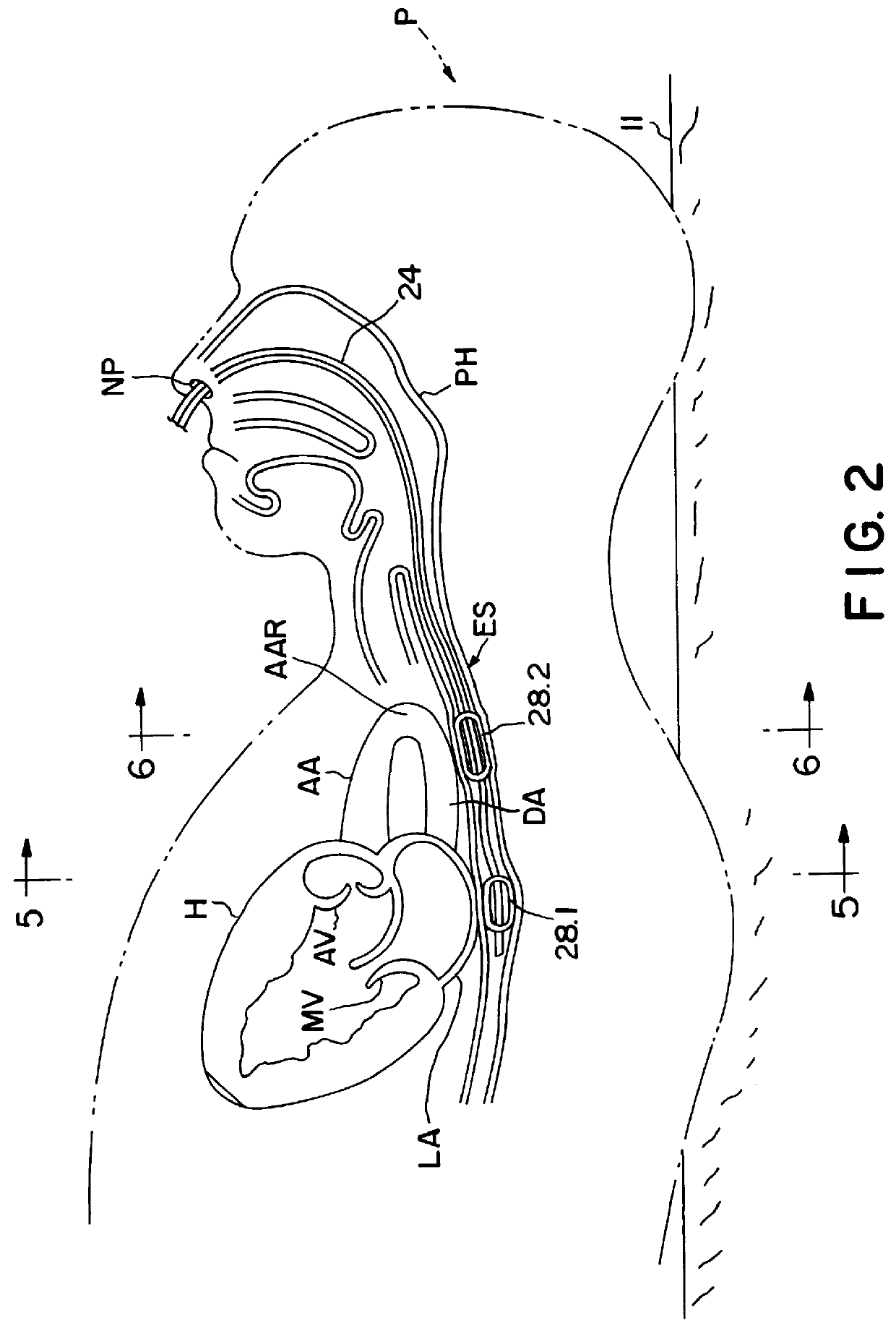
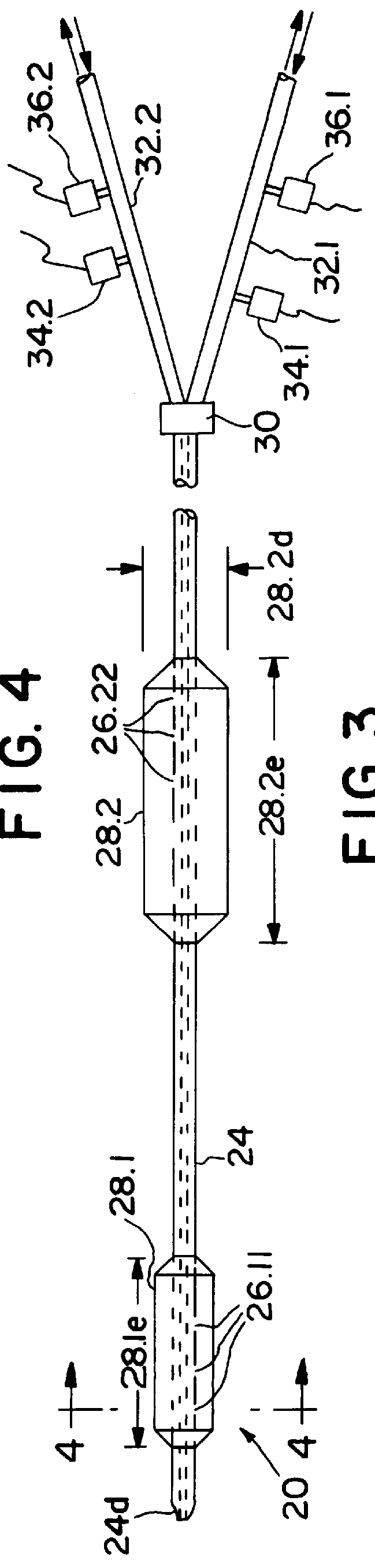
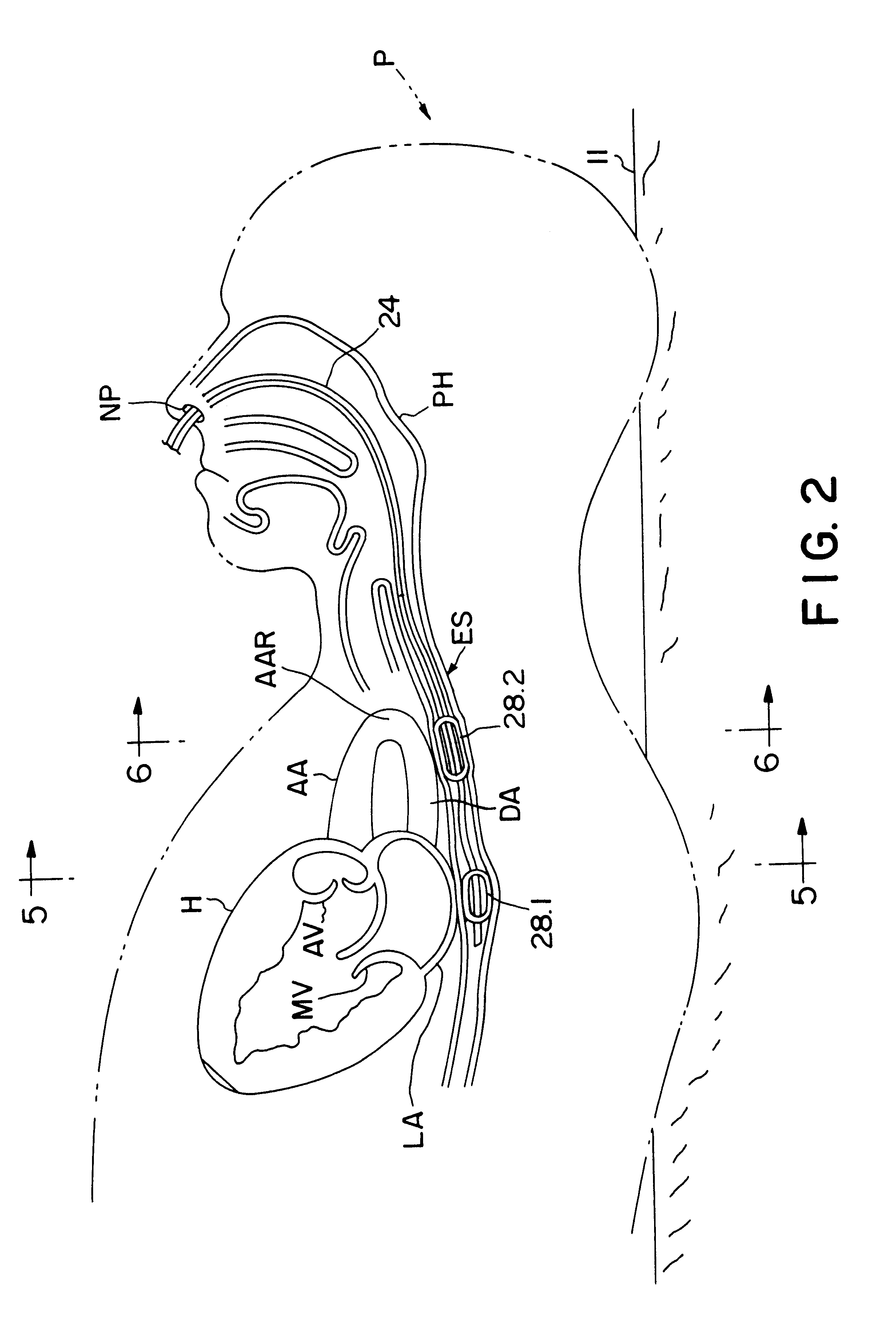
Method and apparatus for noninvasive determination of cardiac performance parameters
InactiveUS6120442AInexpensive and reliableEasy to usePerson identificationCatheterSystoleLeft atrial pressure
Apparatus and method for noninvasively determining cardiac performance parameters including 1) lengths of systolic time intervals, (2) contractility index, (3) pulse amplitude ratios while performing the Valsalva maneuver, (4) cardiac output index, and (5) a pulse wave velocity index. A catheter having at least one balloon is inserted into the esophagus and pressurized and positioned adjacent the aortic arch to sense aortic pressure. The effects of aortic pressure on the balloon are utilized to determine at least one of the cardiac performance parameters. The catheter may include a second balloon which is spaced from the aortic balloon a distance such that when the second balloon is in a position adjacent the left atrium to sense left atrial pressure the aortic balloon is in a position adjacent the aortic arch to sense aortic pressure, this distance being related to the distance between the left atrium and aortic arch in most adult persons.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Transcatheter Heart Valve Delivery System With Reduced Area Moment of Inertia
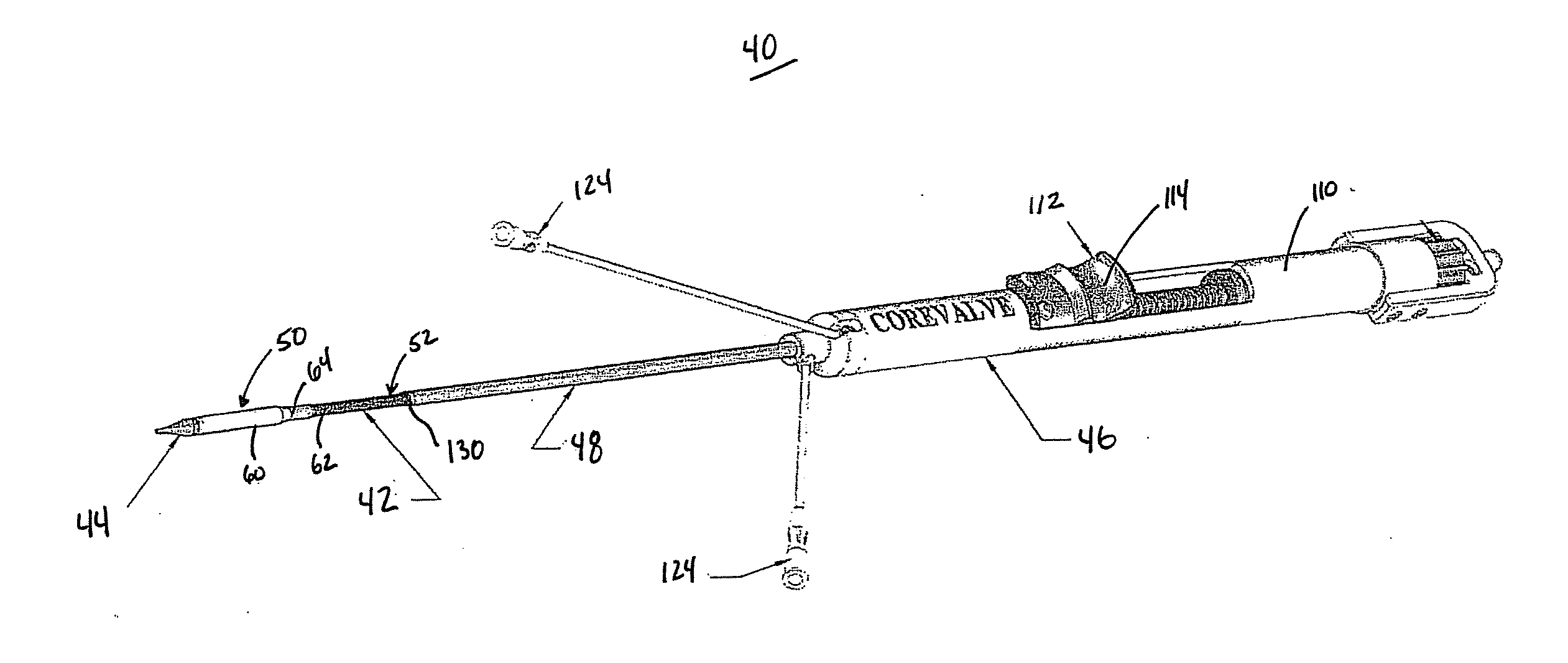
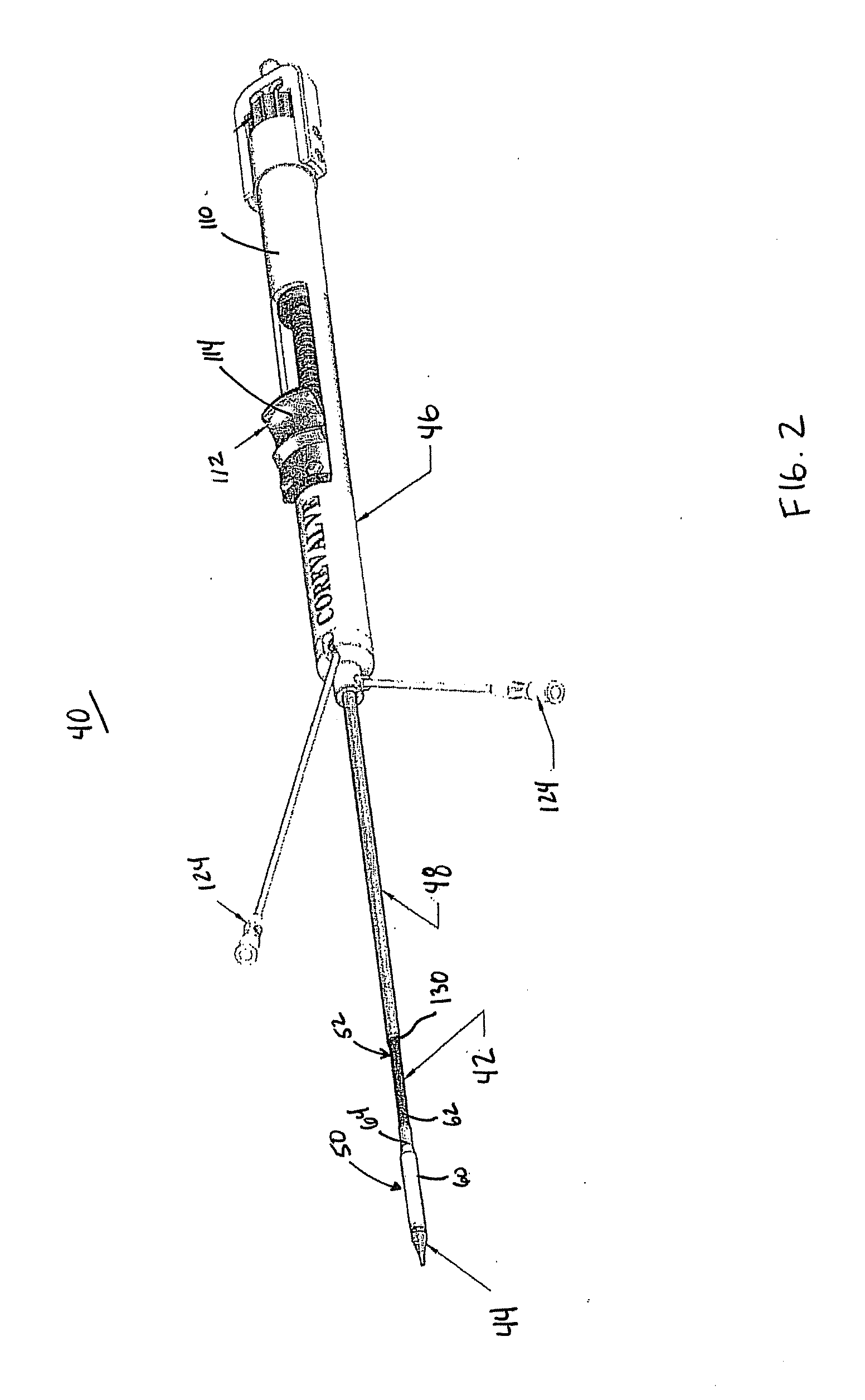
ActiveUS20110251680A1Maintain consistencyLow area momentHeart valvesBlood vesselsProsthetic heartThird aortic arch
A device for percutaneously repairing a heart valve of a patient including a self-expanding, stented prosthetic heart valve and a delivery system. The delivery system includes delivery sheath slidably receiving an inner shaft forming a coupling structure. A capsule of the delivery sheath includes a distal segment and a proximal segment. An outer diameter of the distal segment is greater than that of the proximal segment. An area moment of inertia of the distal segment can be greater than an area moment of inertia of the proximal segment. Regardless, an axial length of the distal segment is less than the axial length of the prosthesis. In a loaded state, the prosthesis engages the coupling structure and is compressively retained within the capsule. The capsule is unlikely to kink when traversing the patient's vasculature, such as when tracking around the aortic arch, promoting recapturing of the prosthesis.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and system for selective or isolated integrate cerebral perfusion and cooling
InactiveUS6736790B2Reduce riskImproving cerebral perfuisionBronchoscopesLaryngoscopesOxygenPerfusion
Patients having diminished circulation in the cerebral vasculature as a result of cardiac arrest or from other causes are treated by flowing an oxygenated medium through an arterial access site into the cerebral vasculature and collecting the medium through an access site in the venous site of the cerebral vasculature. In addition to oxygenation, the recirculating blood may also be cooled to hypothermically treat and preserve brain tissue. Isolation and cooling of cerebral vasculature in patients undergoing aortic and other procedures is achieved by internally occluding at least the right common carotid artery above the aortic arch. Blood or other oxygenated medium is perfused through the occluded common carotid artery(ies) and into the arterial cerebral vasculature. Usually, oxygen depleted blood or other medium leaving the cerebral vasculature is collected, oxygenated, and cooled in an extracorporeal circuit so that it may be returned to the patient.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE & PATTERSON RUSSEL +1
Method and apparatus for noninvasive determination of cardiac performance parameters
InactiveUS6238349B1Inexpensive and reliableEasy to usePerson identificationCatheterSystoleLeft atrial pressure
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Methods and devices for treatging aortic atheroma
InactiveUS20080004687A1Avoid obstructionPrecise positioningStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryAortic atheroma
A method for treating both sessile and mobile aortic atheroma is described. A radially expanding device, such as a stent or compliant cast, comprising a generally cylindrical member expandable between a compressed state and an enlarged state is provided. The cylindrical member has a proximal opening, a distal opening, a lumen therebetween, and at least one side opening in the wall of the generally cylindrical member. The methods comprise imaging the aorta to identify position and extent of atheroma. The stent is then advanced into the aortic arch and positioned so that the at least one side-opening is aligned with the takeoff of one or more of the right brachiocephalic artery, the left common carotid artery, or the left subclavian artery. The stent is expanded into contact with the endoluminal surface of the aorta and atheroma is trapped between the stent and the endoluminal surface of the aorta.
Owner:SAGE MEDICAL TECH
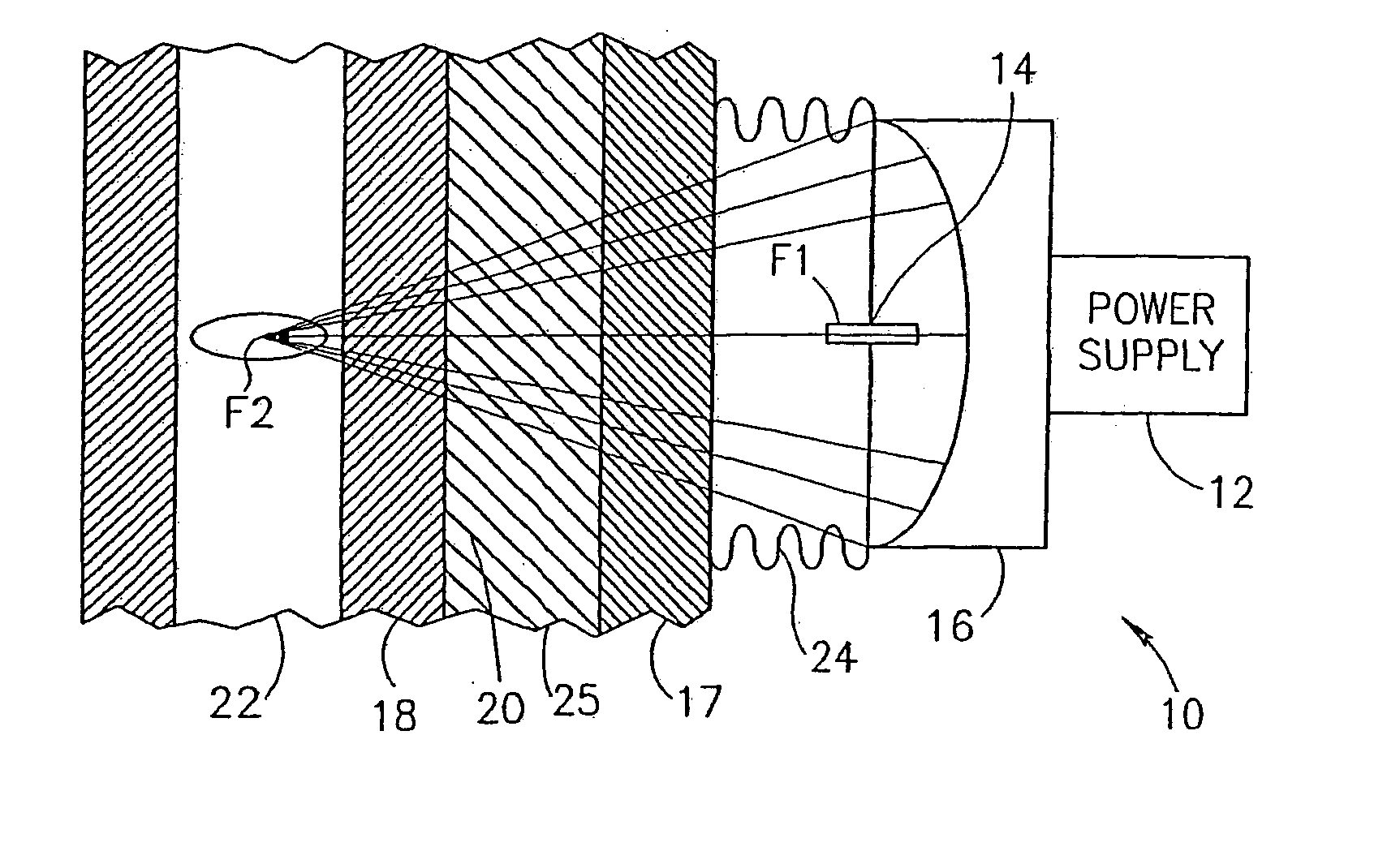
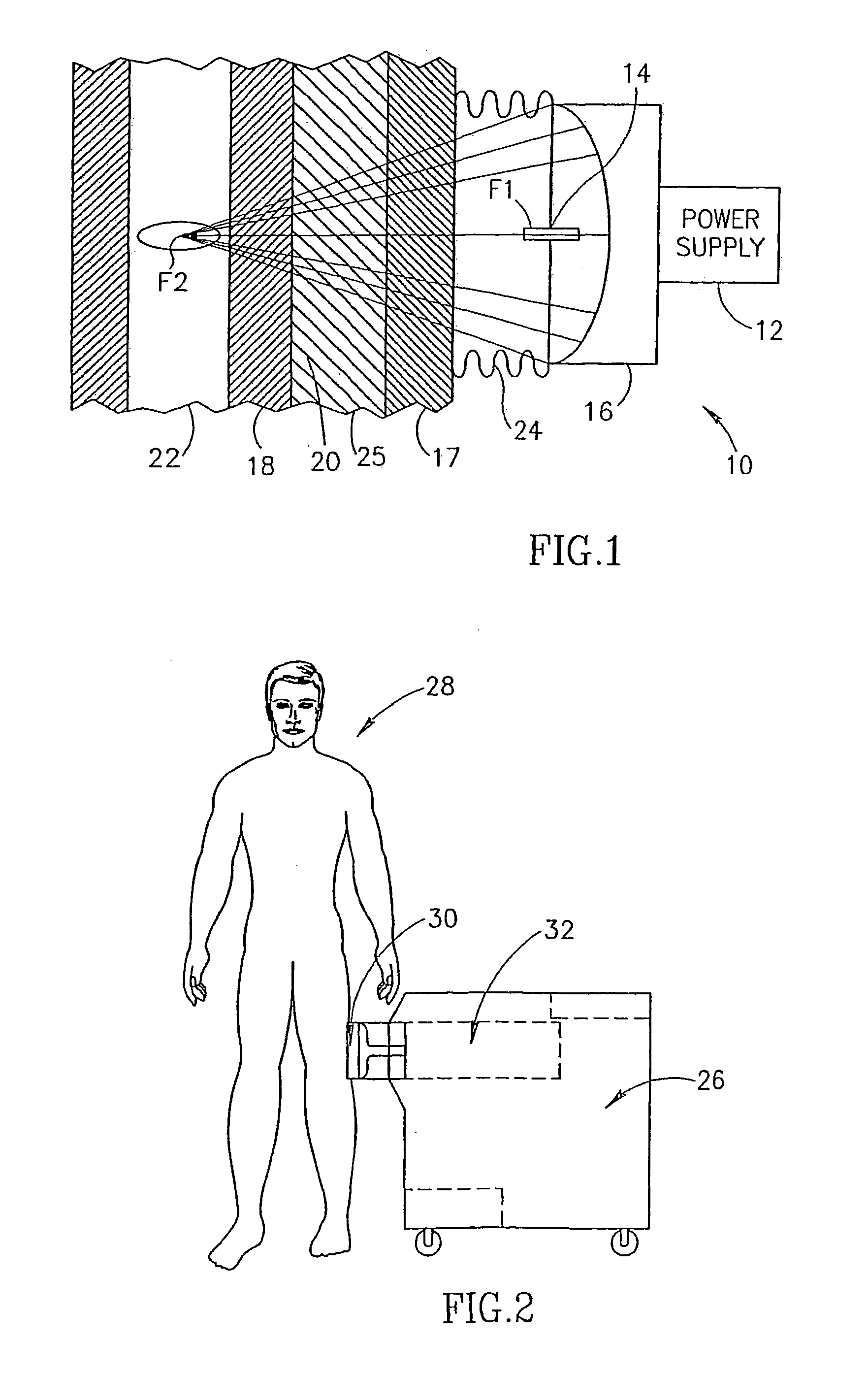
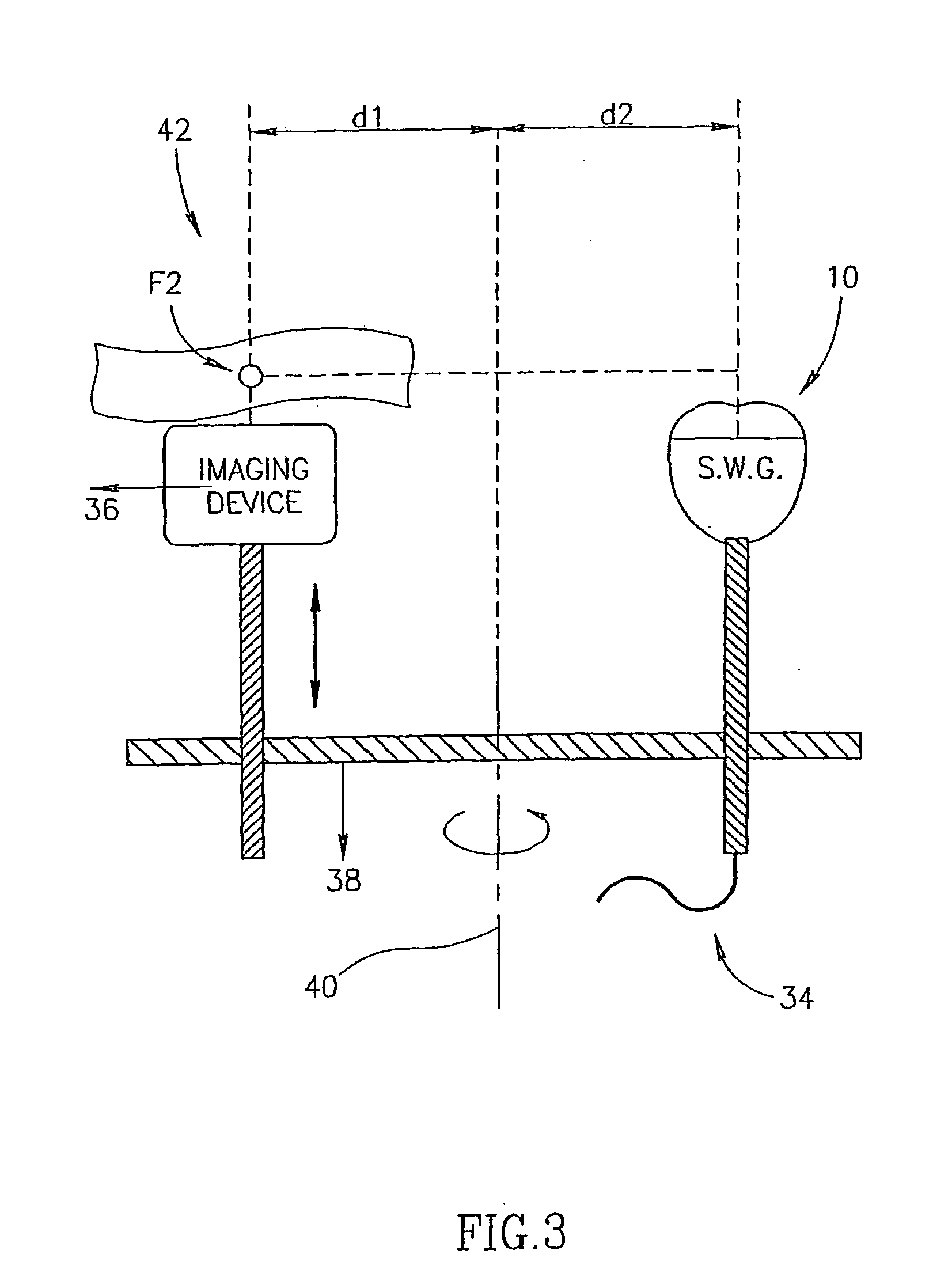
Pressure-pulse therapy device for treatment of deposits
A device, system and method for the generation of therapeutic acoustic shock waves for at least partially separating a deposit from a vascular structure. The shock waves may optionally be generated according to any mechanism which is known in the art, including but not limited to, spark gap technology, electromagnetic shock wave generation and piezoelectric technology for generating therapeutic pressure pulses. Examples of deposits which may be treated with the present invention include, but are not limited to, atherosclerotic plaques, any type of clot, and any type of thrombus or embolus. The vascular structure itself may be any such structure for conducting blood flow, including but not limited to arteries, veins and the aortic arch.
Owner:MEDISPEC LTD
Aortic arch prosthetic graft
An implantable textile prosthesis includes a first woven section having a tubular branch wall defining a fluid passageway therethrough. The tubular branch wall includes an elongate tubular extent and an asymptotically flared tubular extent, which is asymptotic with respect to the tubular branch wall. The asymptotically flared tubular extent includes a weaving pattern having a plurality of warp yarns and fill yarns and incorporating a gradual change in the number of warp yarns with respect to the fill yarns to provide a seamless and substantially fluid-tight transition region along said flared tubular extent. The tubular branch wall may be sutured to an elongate tubular main wall to provide an implantable tubular textile prosthesis particularly useful in branched end-to-side anastomoses. The tubular main wall may be heat-settably arched to resemble the natural arch of the aorta.
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOVASCULAR LLC
Device For Delivery Of Medical Devices To A Cardiac Valve
ActiveUS20140228942A1Reduce riskBlood flow is minimalStentsBalloon catheterAortic archMedical device
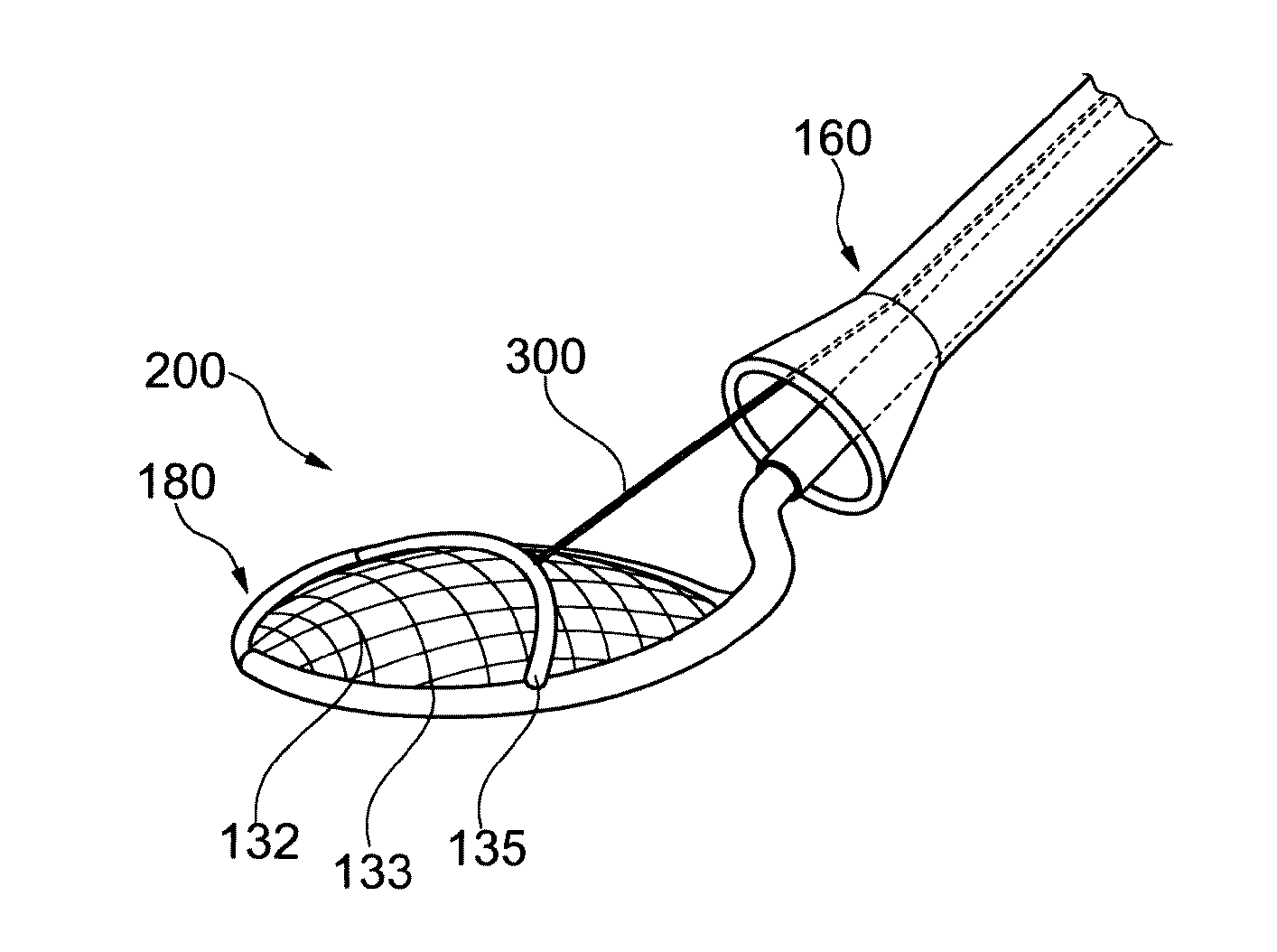
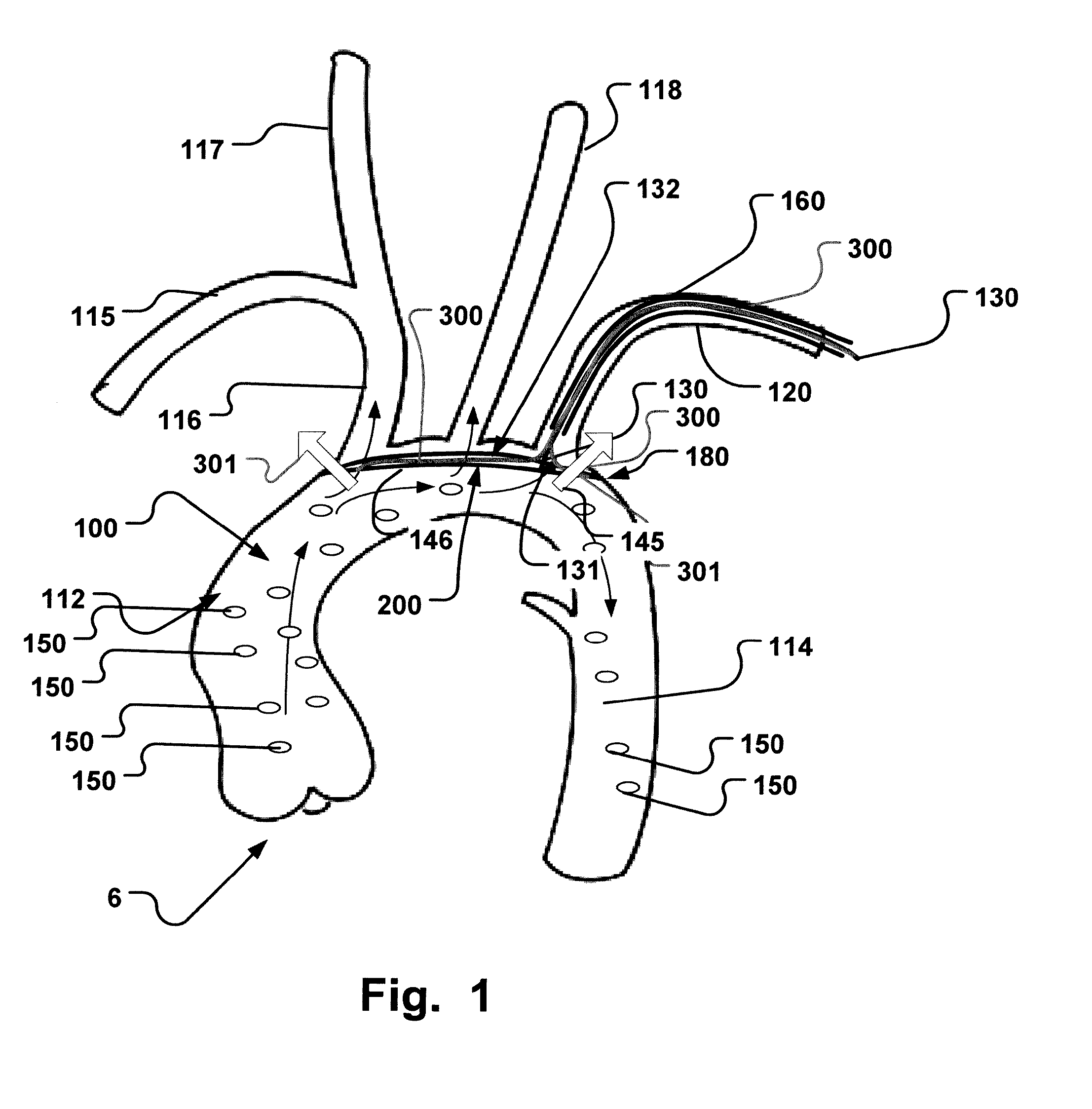
A catheter device (1) is disclosed for transvascular delivery of a medical device to a cardiac valve region of a patient. The catheter device comprises an elongate sheath (2) with a lumen and a distal end (3) for positioning at a heart valve (6), and a second channel (7) that extends parallel to, or in, said elongate sheath, an expandable embolic protection unit (8), such as a filter, wherein at least a portion of the expandable embolic protection unit is arranged to extend from an orifice of the second channel, wherein the embolic protection unit is non-tubular, extending substantially planar in the expanded state for covering ostia of the side branch vessels in the aortic arch.
Owner:SWAT MEDICAL AB
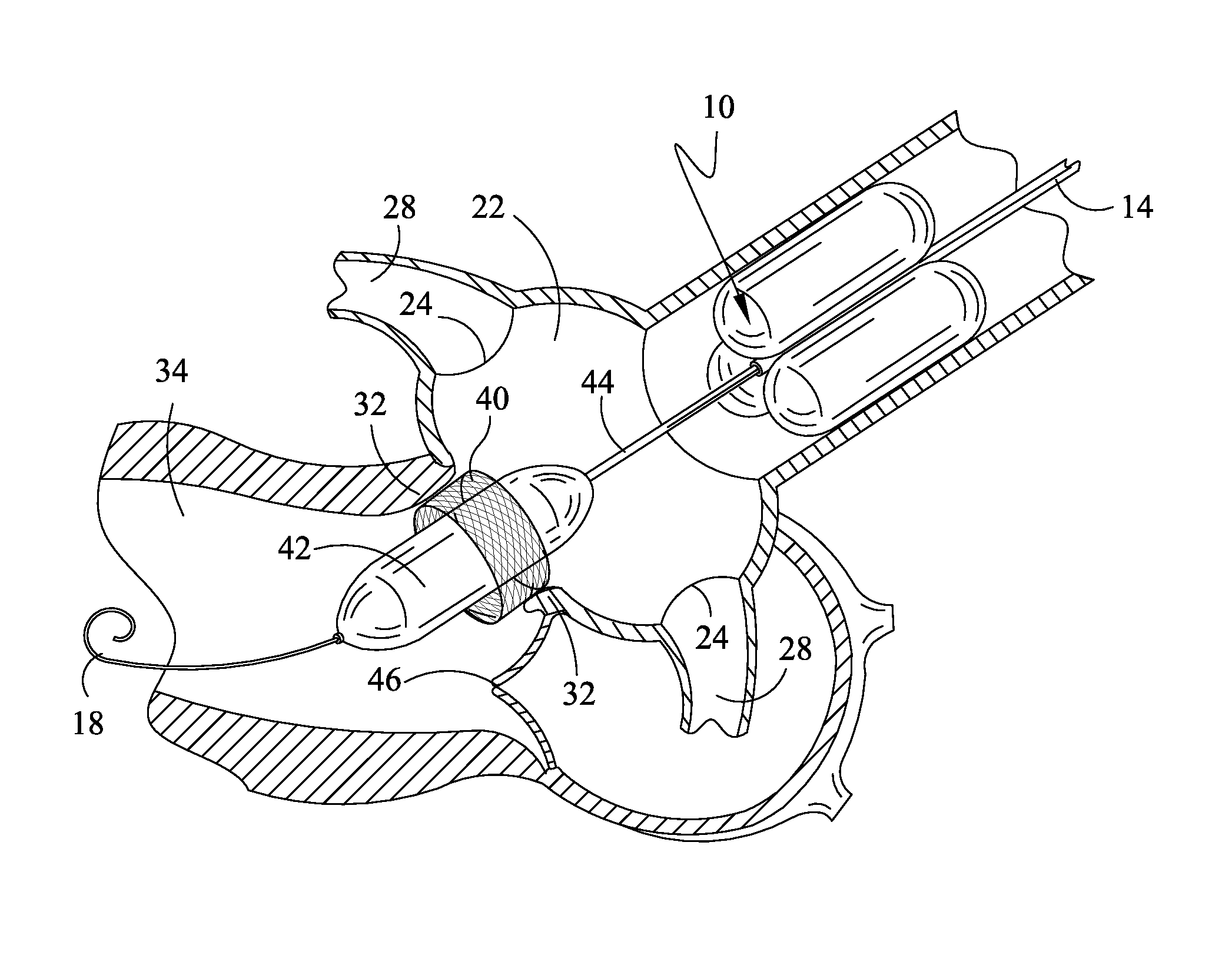
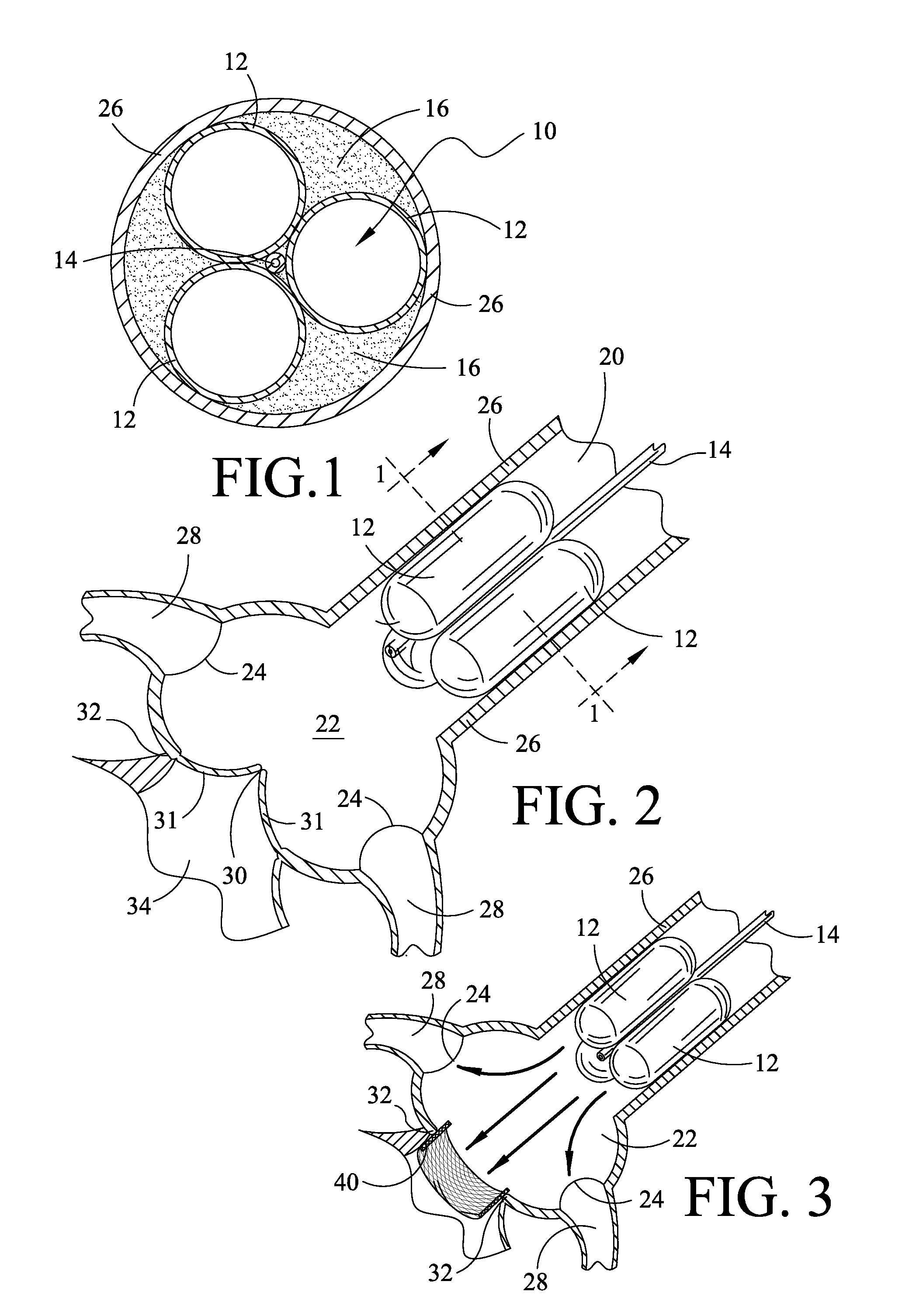
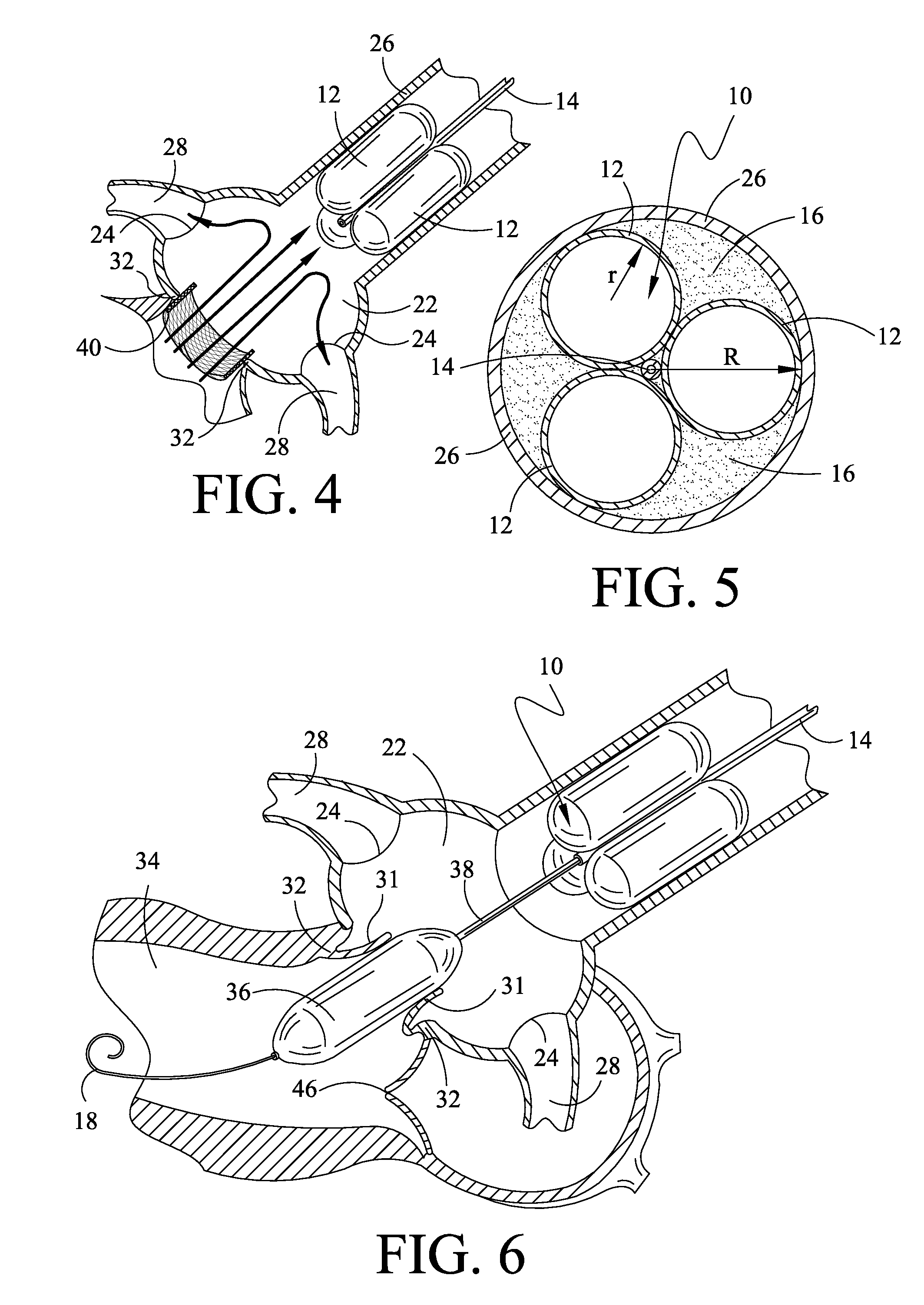
Aortic arch filtration system for carotid artery protection
Filtration systems with integrated filter element(s) forming portions of the wall of the filtration catheter are disclosed. The filtration catheters disclosed herein are designed to be used alone or in conjunction with another filter device to provide embolic protection of both carotid arteries. Occlusive element such as balloon is placed on the exterior of the filtration catheter to redirect blood flow in the vessels during the filtration process as well as to help anchor the filtration catheter inside the vessel. The integrated filter element(s) does not require collapsing thus significantly reduces the complexity of the filtration system retrieval process and the chances of releasing emboli back into the blood stream. The compact design of the filtration systems makes them particularly suitable for embolic protection during endovascular procedures on or close to the heart.
Owner:LUMEN BIOMEDICAL
Methods and Apparatus for Treatment of Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms
Methods and apparatus for aiding in support and repair of a thoracic aneurysm of the aortic arch. A stent graft provides a window therein, which enables blood to flow freely into branch vessels which would otherwise be occluded by the stent graft. Additionally, the stent portions of the stent graft are configured to minimize the risk of overexpansion, wherein stents are provided in the window portion.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Temporary Embolic Protection Device And Medical Procedure For Delivery Thereof
ActiveUS20110295304A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one or more deficiencies, disadvantages or issuesDilatorsOcculdersEmbolic Protection DevicesAortic arch
An embolic protection device and medical procedure for positioning the device in the aortic arch is disclosed. The device and method effectively prevent material from entering with blood flow into side branch vessels of the aortic arch. The device is a collapsible embolic protection device devised for temporary transvascular delivery to an aortic arch of a patient, wherein the device has a protection unit that comprises a selectively permeable unit adapted to prevent embolic material from passage with a blood flow into a plurality of aortic side branch vessels at the aortic arch. The protection unit is permanently attached to a transvascular delivery unit at a connection point provided at the selectively permeable unit, and a first support member for the protection unit that is at least partly arranged at a periphery of the selectively permeable unit. In an expanded state of the device, the connection point is enclosed by the first support member or arranged at said support member.
Owner:SWAT MEDICAL AB
Implantation device for an aorta in an aortic arch
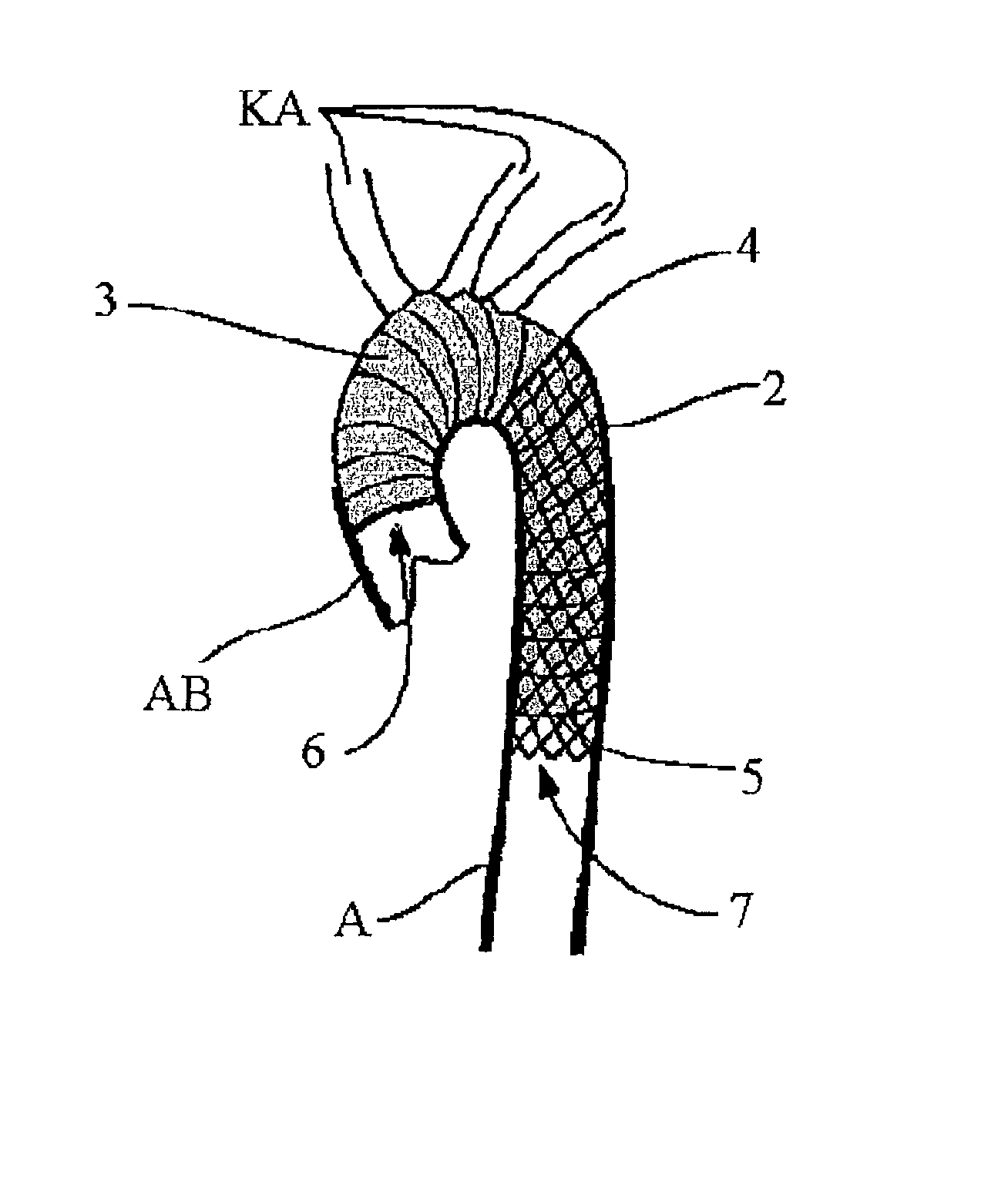
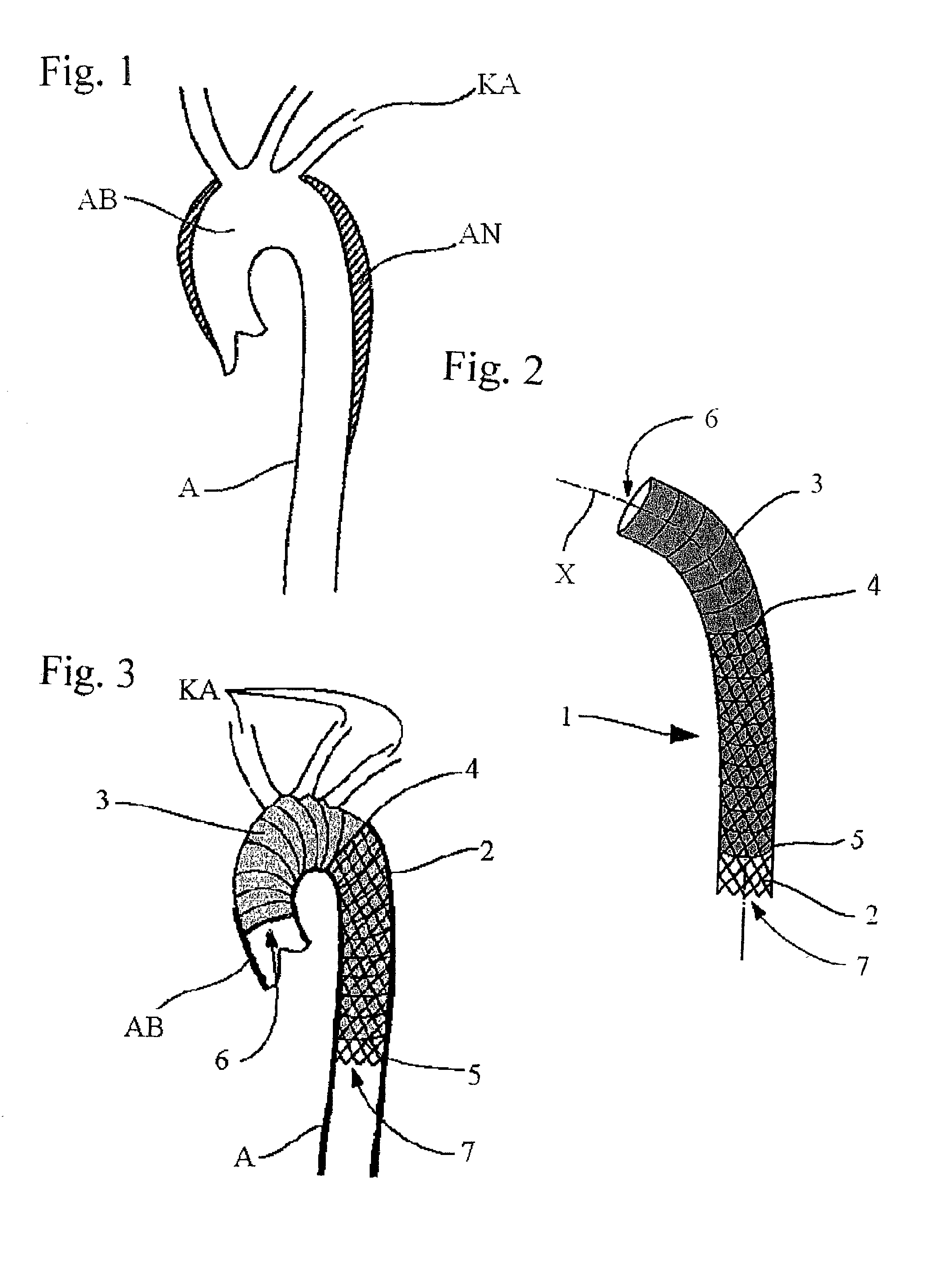
InactiveUS20030097170A1Simple and rapid simultaneous treatmentSpend less timeStentsBlood vesselsAortic arch aneurysmImplanted device
A stent made of a self-expandable or balloon-expandable metal mesh fabric that can be widened to a diameter larger than that of the descending aorta. The stent has a flexible lining of vessel-replacing material, wherein the lining covers it at least partly in longitudinal direction and forms a tubular segment which projects beyond the end of the stent at least at one end and which functions as the vascular prosthesis. Such implantable arrangements (1) make it possible to achieve short surgical times, especially during the treatment of aortic arch aneurysms involving the cephalic arteries.
Owner:CURATIVE
System and method for autonomic blood pressure regulation
InactiveUS20140067003A1Improve complianceReduce cardiovascular riskSpinal electrodesCatheterCervical vertebral bodyEfferent
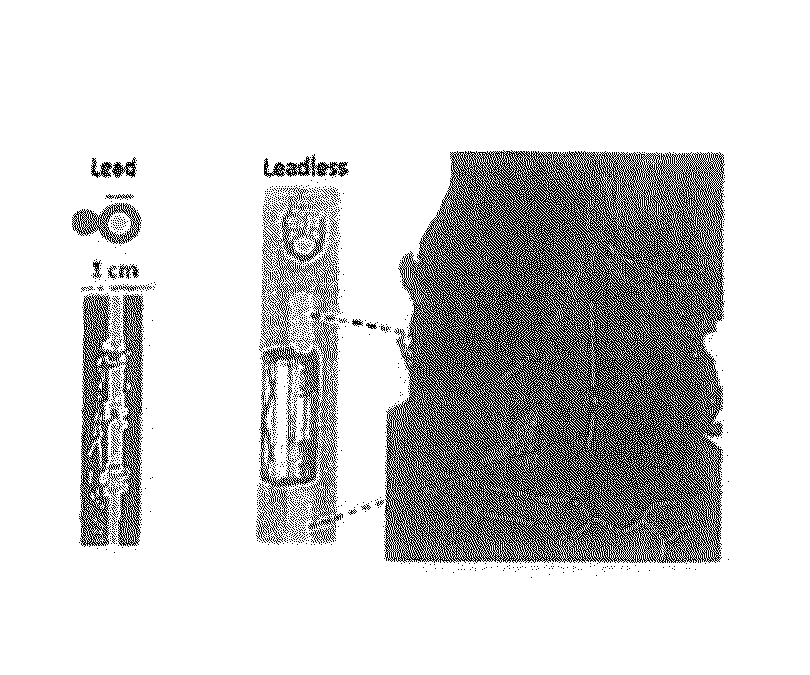
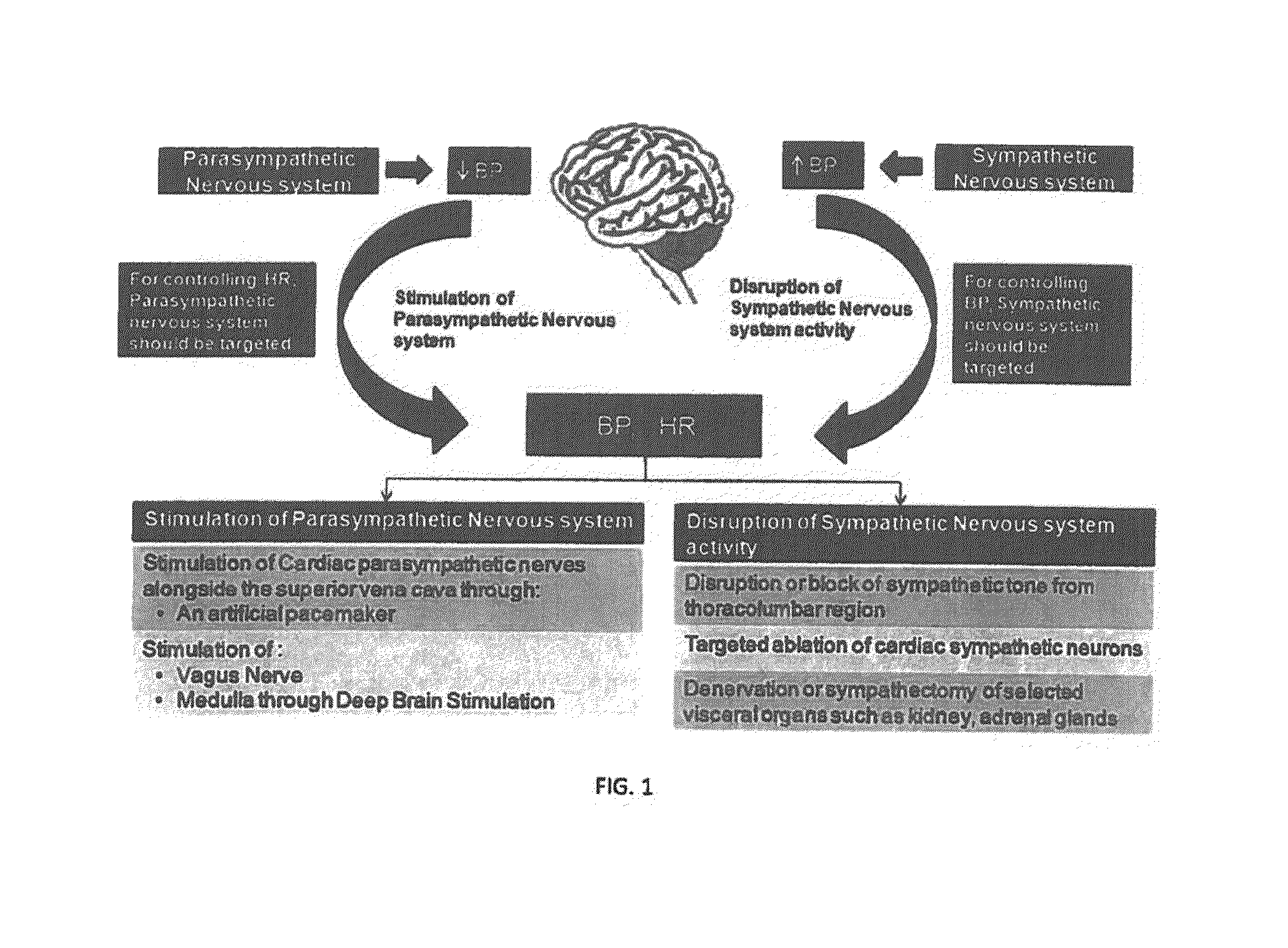
A system for regulating blood pressure by stimulating an afferent pathway to the brain which produces an efferent output in kidneys includes a electrode device adapted for implantation in the cervical region, a stimulator generator, a cable connecting the electrode device and the stimulator generator, wherein the cervical region is generally located between a pair of common carotid arteries, above an aortic arch and in front of cervical vertebrae C2 and C3. A method of implantation includes placing the electrode device in the cervical region, selectively energizing the device in accordance with a stimulation scheme, assessing any changes in the patient's blood pressure, selectively energizing the device in accordance with another stimulation scheme, and assessing any changes in the patient's blood, for determining an optical stimulation scheme, wherein stimulation scheme involves parameters including, for example, position, placement and configuration of the electrode device in relation to surrounding tissue and / or organs, selection of electrodes energized, width, frequency and amplitude of stimulation current.
Owner:VASE ABHI +1
Ventricular assist device for intraventricular placement
A ventricular assist device includes a pump such as an axial flow pump, an outflow cannula connected to the outlet of the pump, and an anchor element. The anchor element is physically connected to the pump, as by an elongate element. The pump is implanted within the left ventricle with the outflow cannula projecting through the aortic valve but desirably terminating short of the aortic arch. The anchor element is fixed to the wall of the heart near the apex of the heart so that the anchor element holds the pump and outflow cannula in position.
Owner:HEARTWARE INC
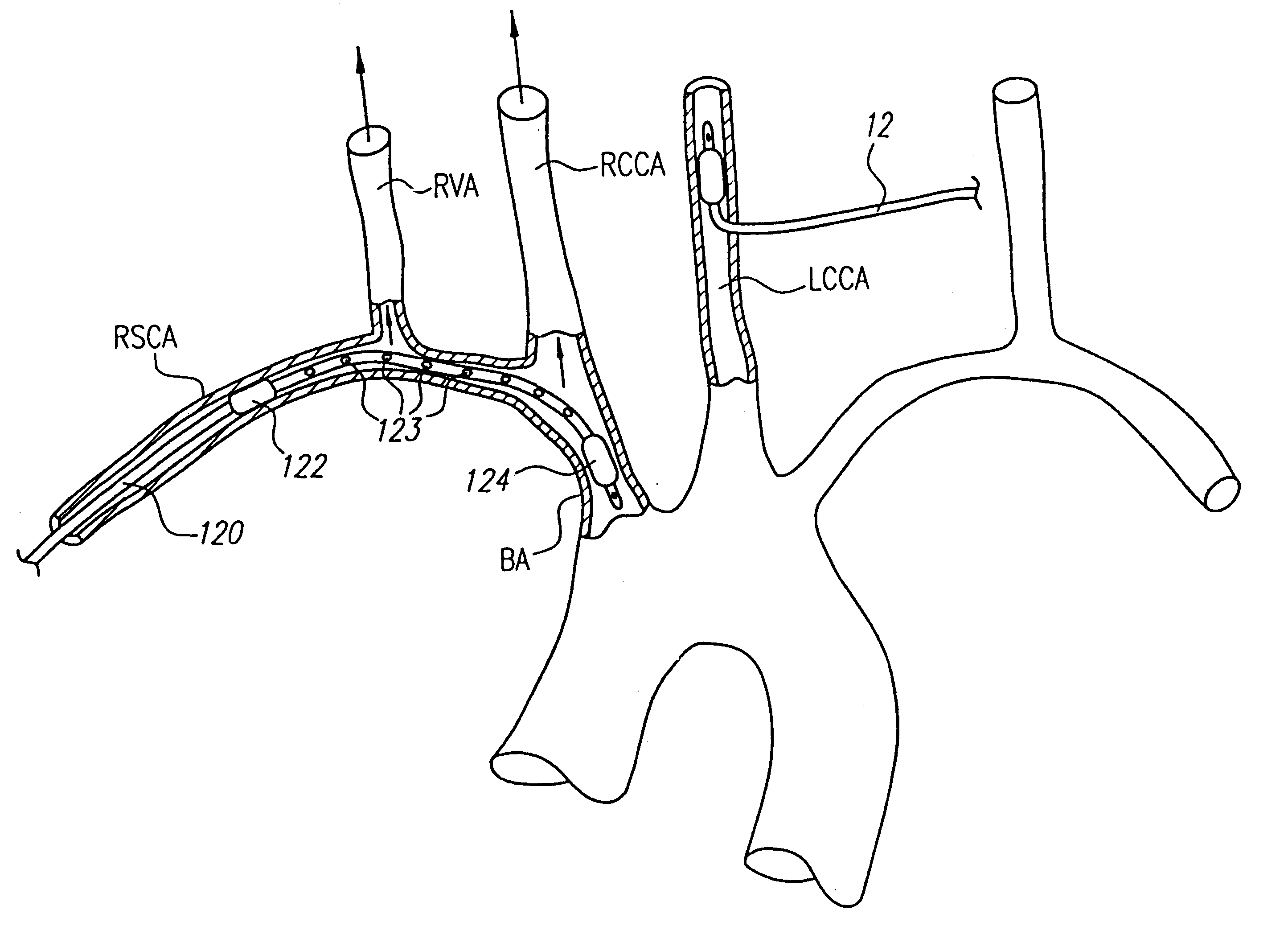
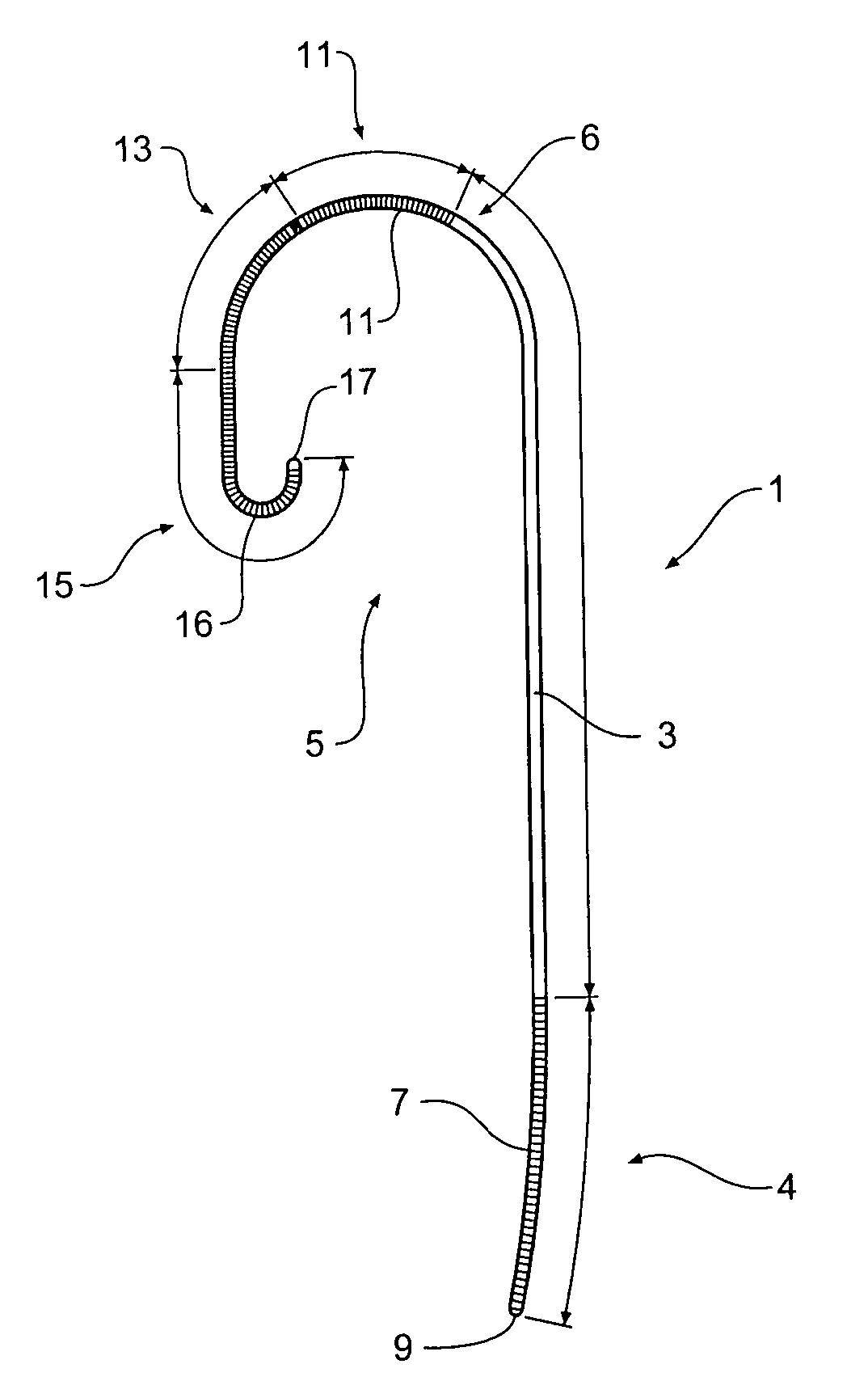
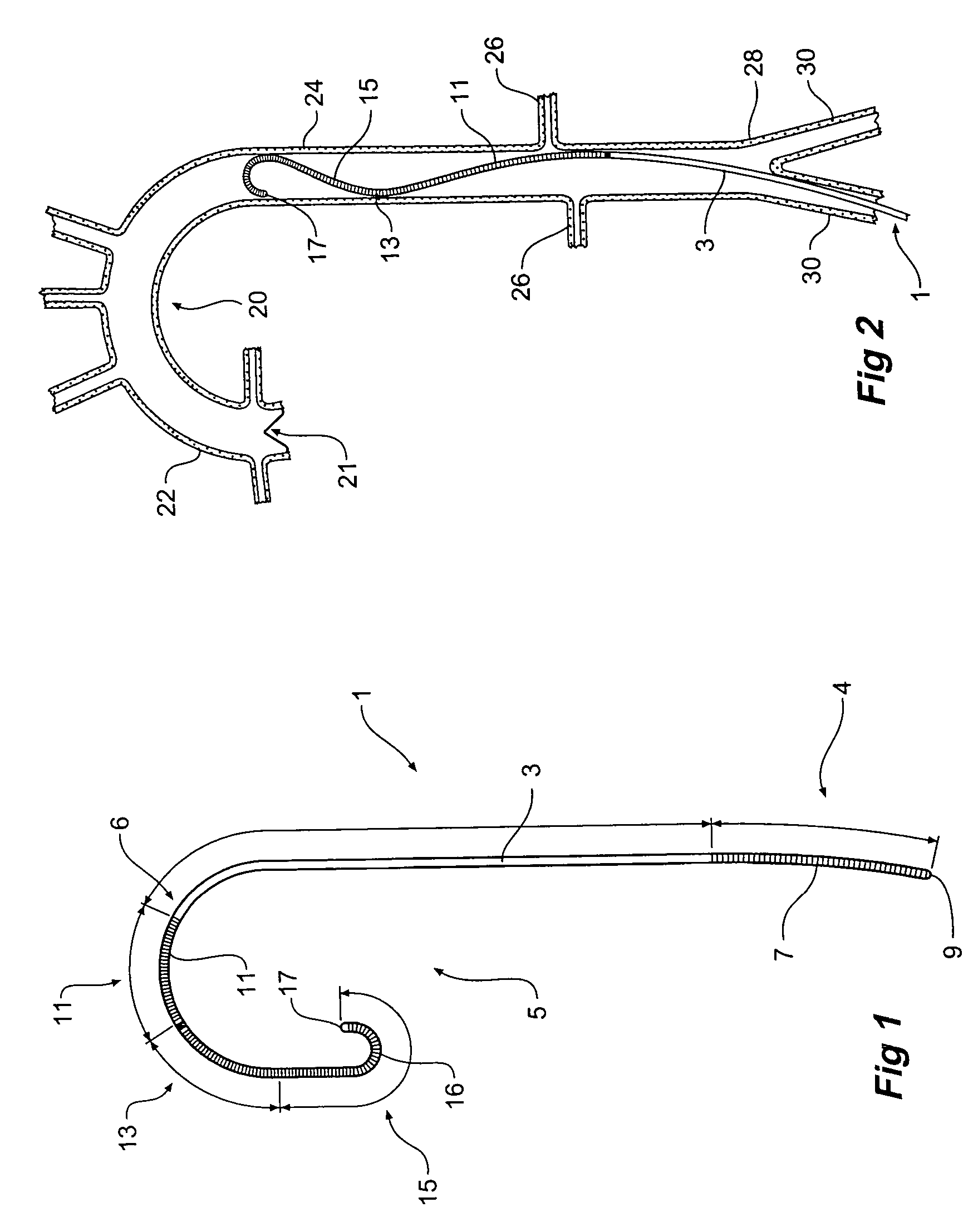
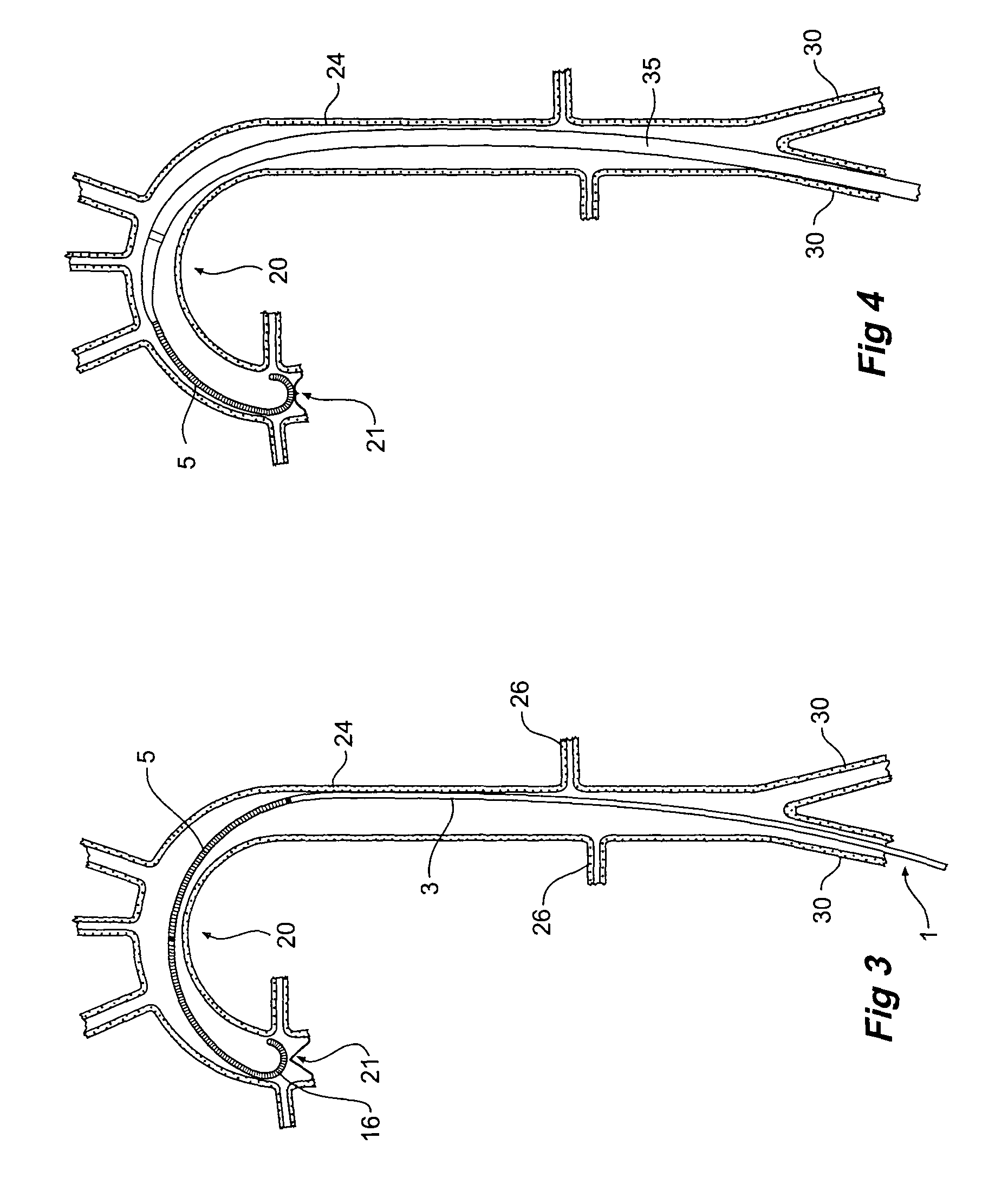
Guide wire
ActiveUS7715903B2Provide strengthIncrease flexibilityGuide wiresInfusion syringesHigh stiffnessAortic arch
A guide wire (1) to assist percutaneous endovascular deployment which has zones of varying stiffness. An elongate central zone (3) of high stiffness, a proximal zone (4) of transition from high stiffness to semi-stiffness and a distal zone (5) of transition from high stiffness to being relatively flexible. The distal zone (5) has three zones, a semi stiff zone (11) adjacent the central zone, a transition zone (13) being of flexibility of from semi-stiff extending to flexible and a tip zone (15) being of high flexibility. The distal tip has a small J curve (16) to ensure that it is atraumatic in vessels and to prevent damage to the aortic heart valve. The distal zone (5) can also have a large curve to assist with anchoring the guide wire into the aortic arch.
Owner:WILLIAM A COOK AUSTRALIA +1
Branching type aortal vascular stent system
ActiveCN102641164AWon't blockAvoid the risk of ischemiaStentsBlood vesselsAscending aortaAortic arch
The invention discloses a branching type aortal vascular stent system comprising an aortal vascular stent and three branch arterial vascular stents, wherein a concave part is formed in the middle section of the aortal vascular stent, and provided with three side holes; and the three branch arterial vascular stents are separately mounted in the three side holes. The branching type aortal vascular stent system is capable of isolating aortal lesion involving the aortic arch and the ascending aorta, reestablishing the blood flow of the branch artery and avoiding the customization of the stent; and the branching type aortal vascular stent system is suitable for batch production and can be used for emergency operations.
Owner:舒畅 +1
Guide catheter having selected flexural modulus segments
InactiveUS7674411B2Increase flexibilityPrevent guide catheter back-outGuide needlesLamination ancillary operationsFlexural modulusPliability
A guiding catheter for use in coronary angioplasty and other cardiovascular interventions which incorporates a plurality of segment of selected flexural modulus in the shaft of the device. The segments which have a different flexibility than the sections immediately proximal and distal to them, creating zones in the catheter shaft which are either more or less flexible than other zones of the shaft. The flexibility and length of the shaft in a given zone is then matched to its clinical function and role. A mid-shaft zone is significantly softer than a proximal shaft or distal secondary curve to better traverse the aortic arch shape without storing too much energy. A secondary zone section is designed to have maximum stiffness to provide optimum backup support and stability.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Improved Embolic Protection Device And Method
ActiveUS20150313701A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one or more deficiencies, disadvantages or issuesSuture equipmentsLigamentsEmbolic Protection DevicesAortic arch
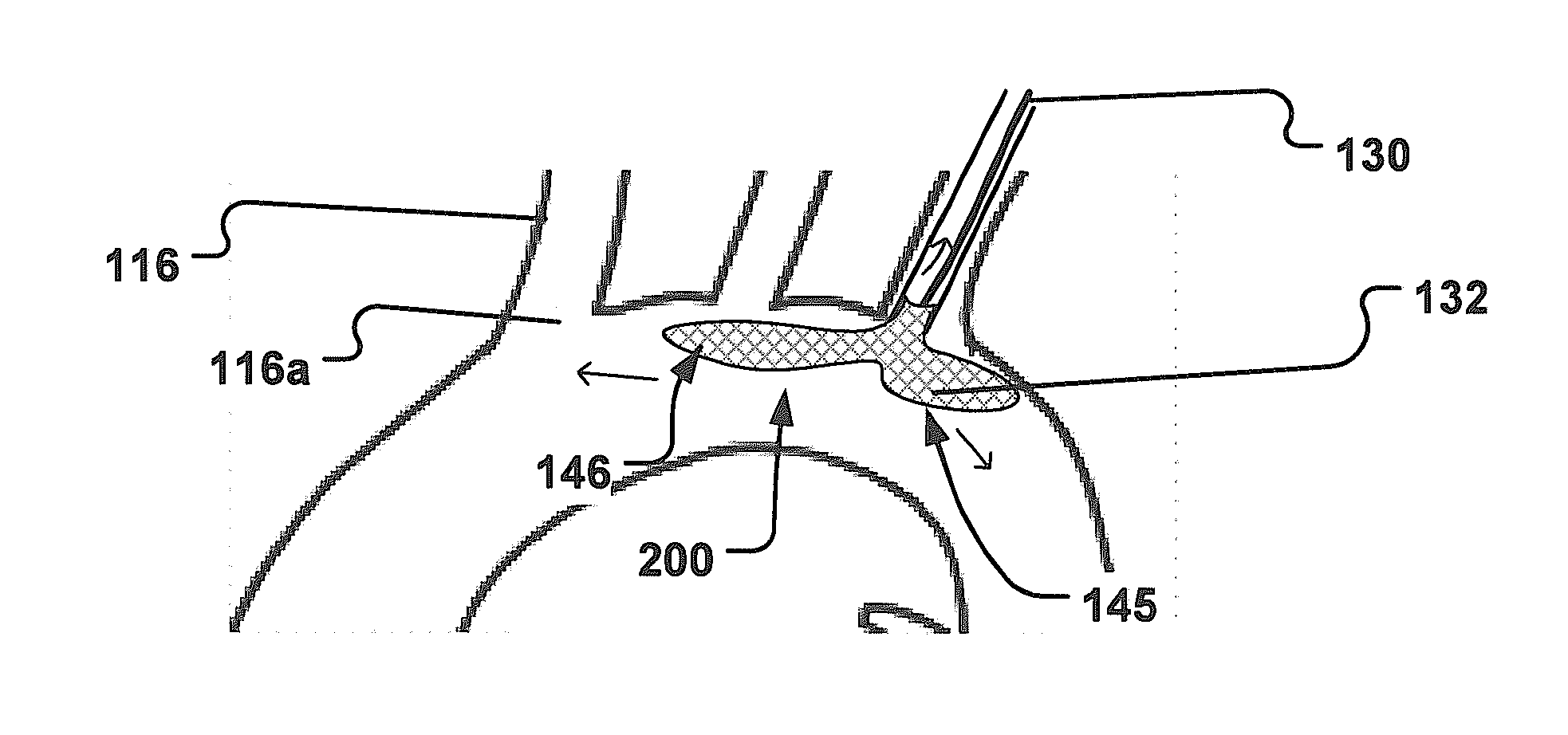
A collapsible, transluminally deliverable embolic protection device (200) for temporarily positioning in the aortic arch is disclosed. The device is connectable to a transluminal delivery unit (130) extending proximally from a connection point (131). The device has a frame with a periphery, and a blood permeable unit within said periphery for preventing embolic particles from passing therethrough into side vessels of said aortic arch to the brain of a patient. Further, the device has at least one tissue apposition sustaining unit, not being a delivery shaft of said device, for application of a force offset to said connection point at said device, such as at said periphery, towards an inner wall of said aortic arch when said device is positioned in said aortic arch, such that tissue apposition of said periphery to an inner wall of said aortic arch is supported by said force. In addition related methods are disclosed.
Owner:SWAT MEDICAL AB
Method and apparatus for percutaneous aortic valve replacement
ActiveUS8663318B2Stable environmentImplant stabilityBalloon catheterHeart valvesAscending aortaCoronary artery ostium
A catheter adapted for placement in the ascending aorta comprises a central catheter mechanism and a balloon structure or other occluding structure at its distal end. The catheter may be placed over the aortic arch such that the balloon structure is placed in the ascending aorta just above the Sinus of Valsalva and coronary ostia. Once in place, the balloon structure is inflated to control blood flow through the aorta during aortic valve ablation and replacement protocols.
Owner:HOCOR CARDIOVASCULAR TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com