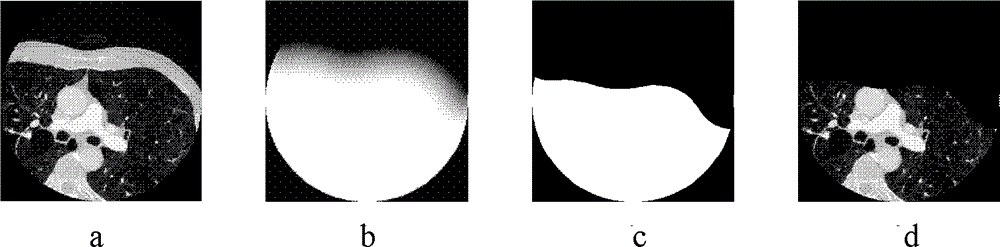Patents
Literature
97 results about "Descending aorta" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
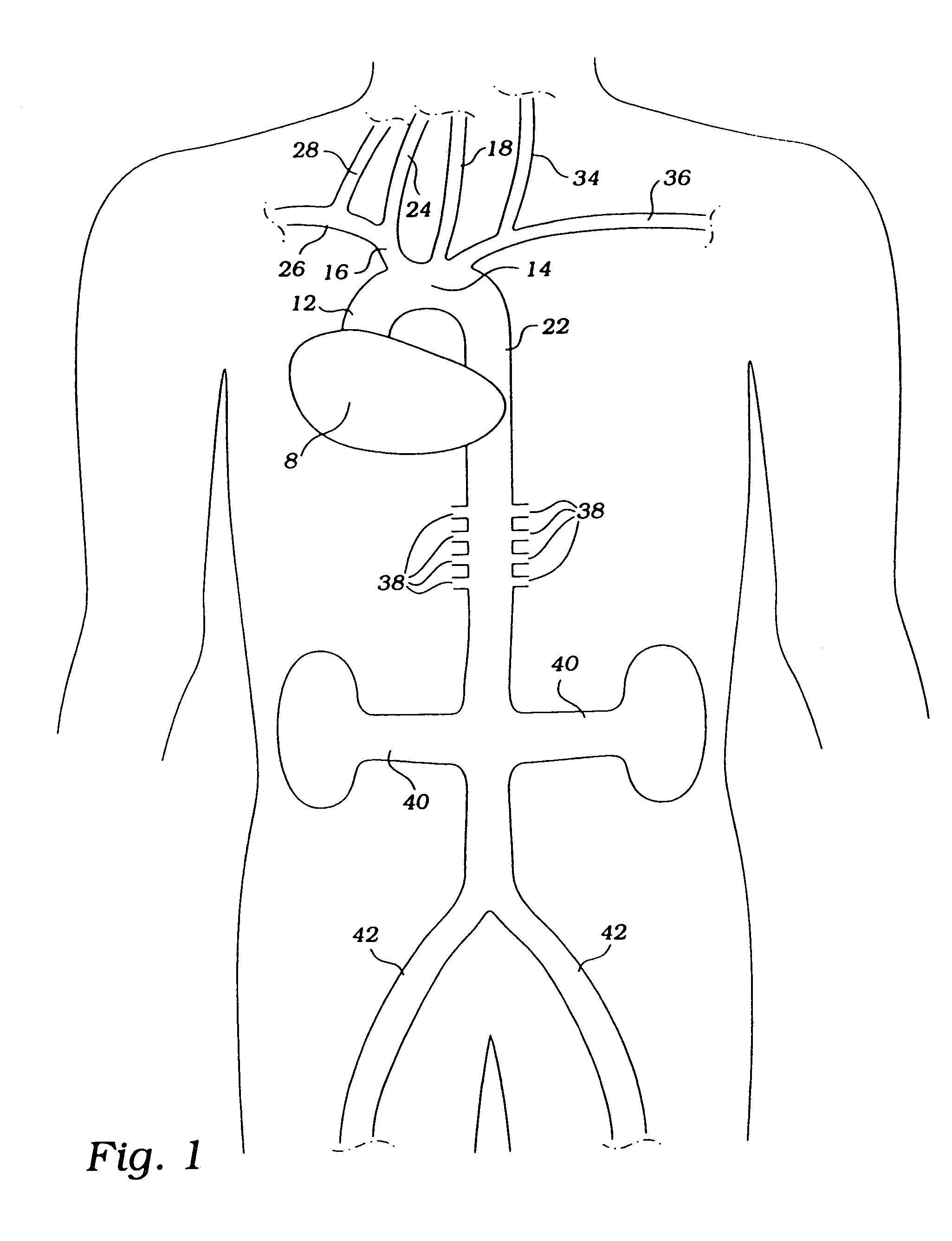
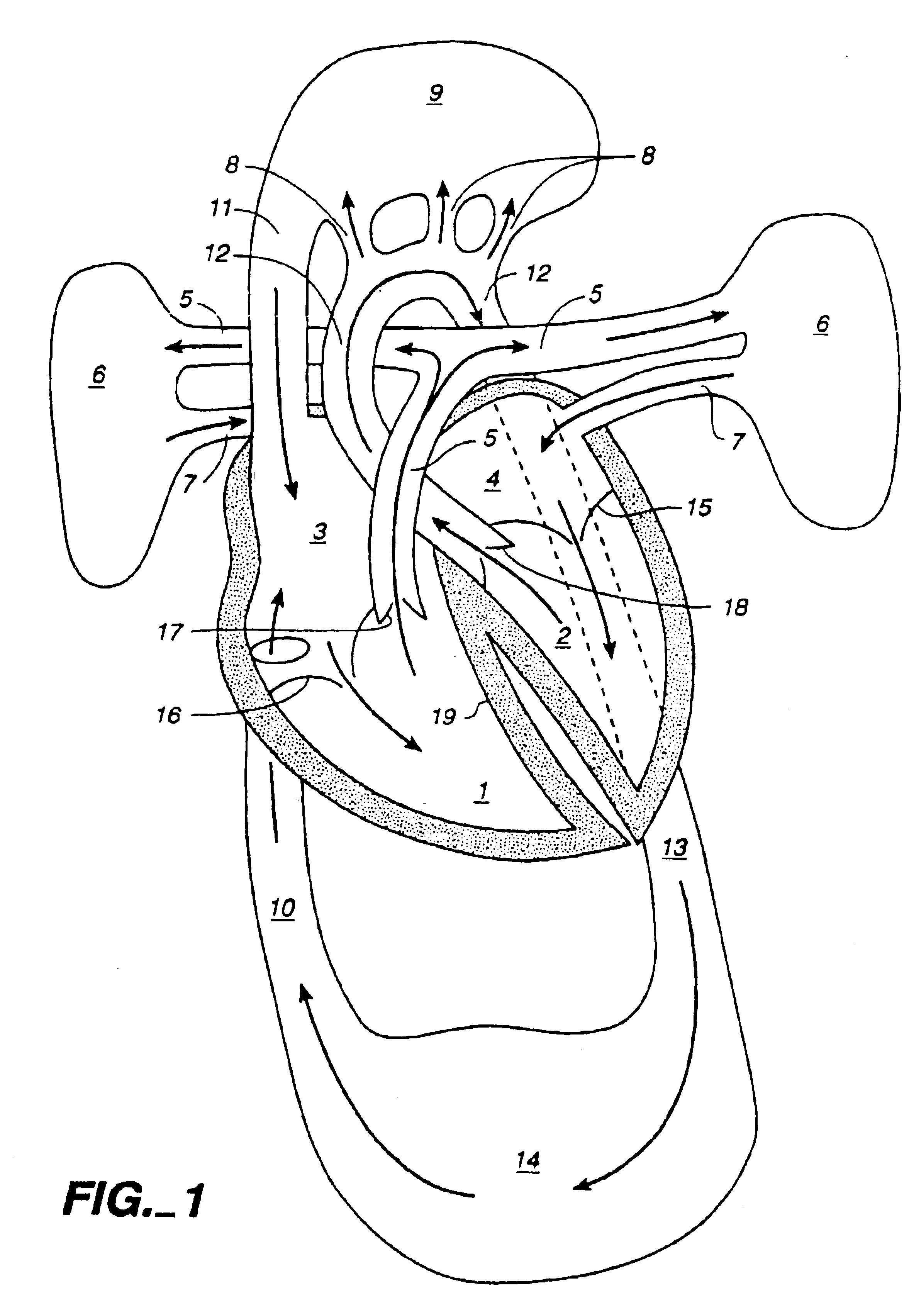
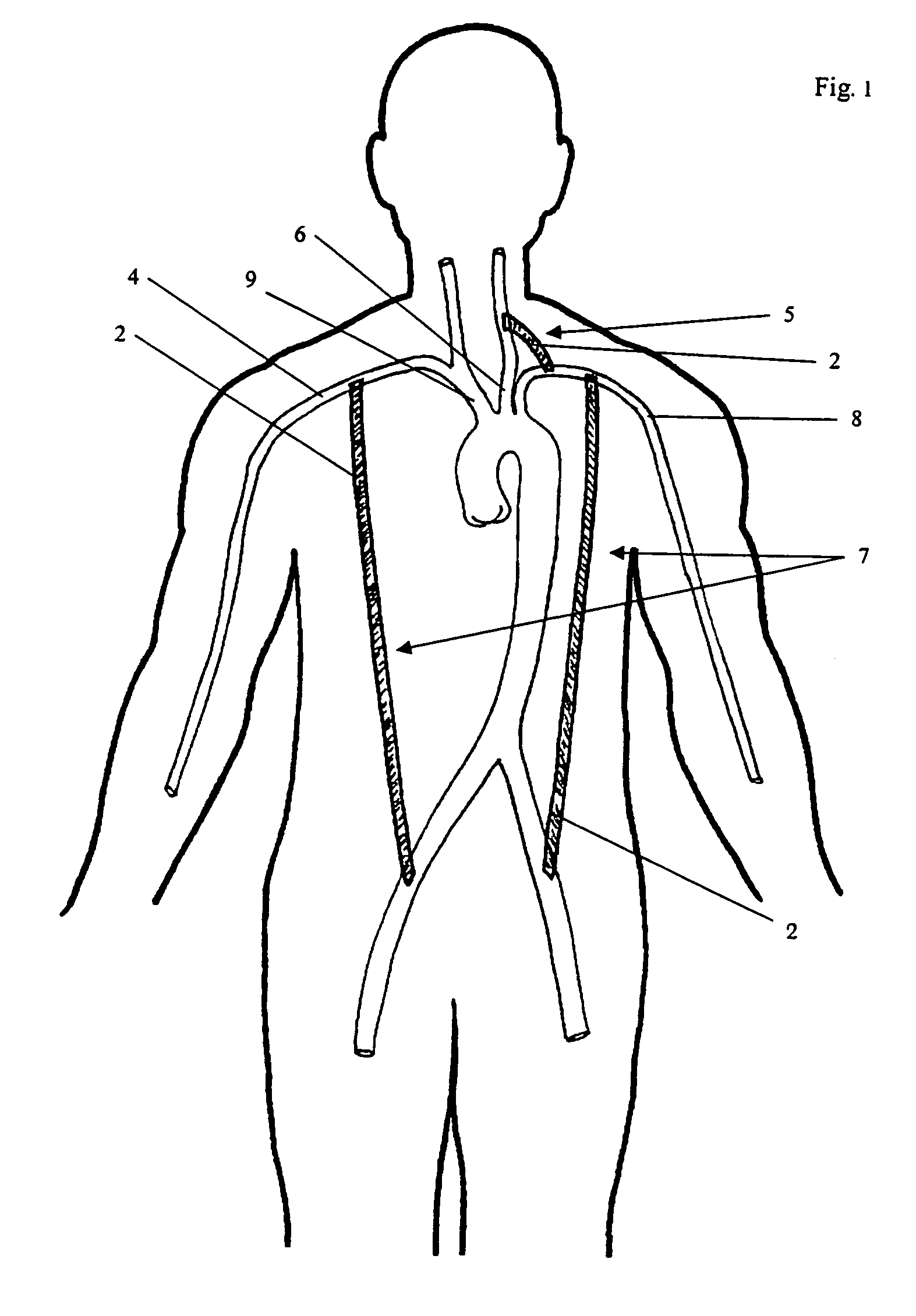
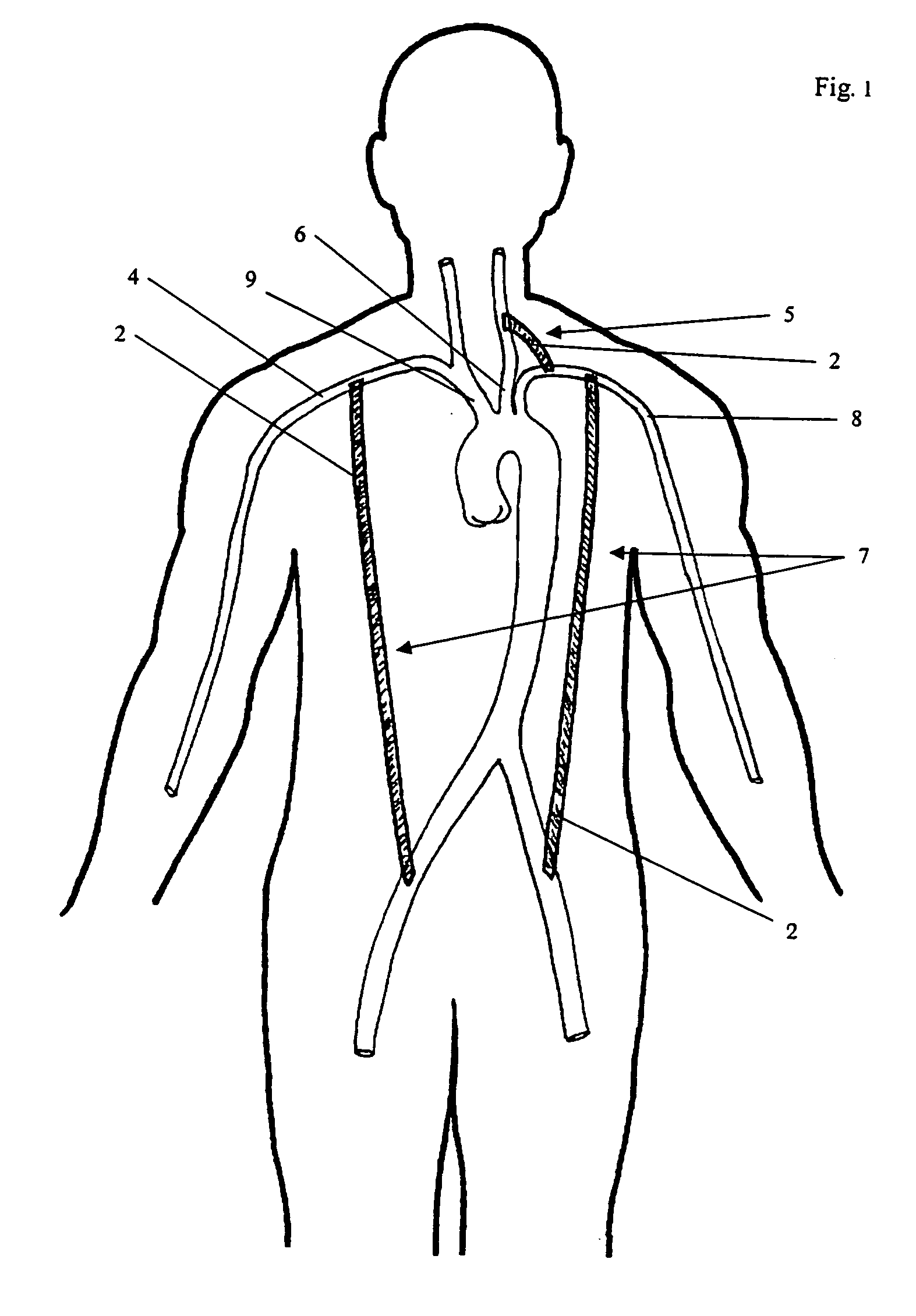
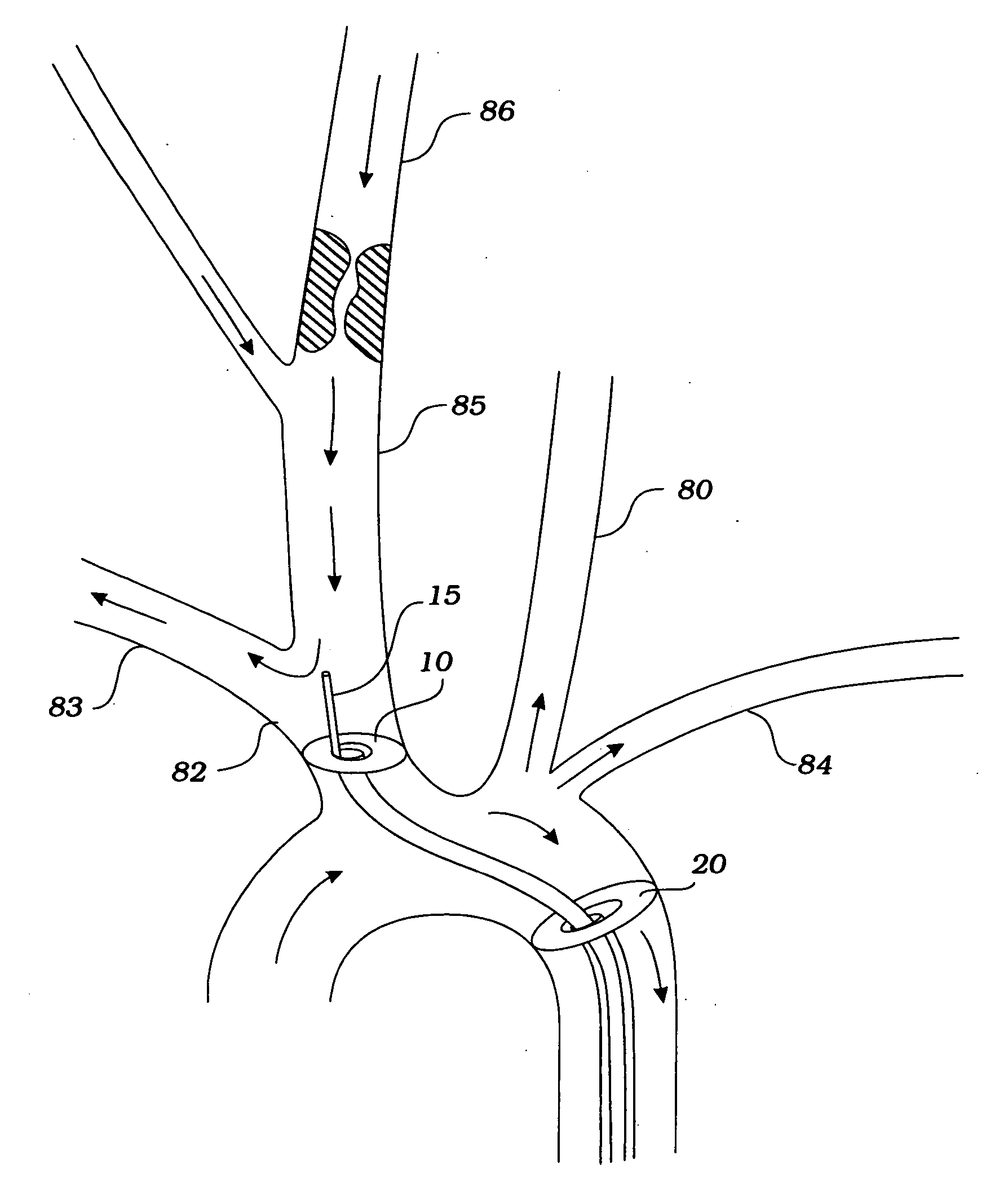
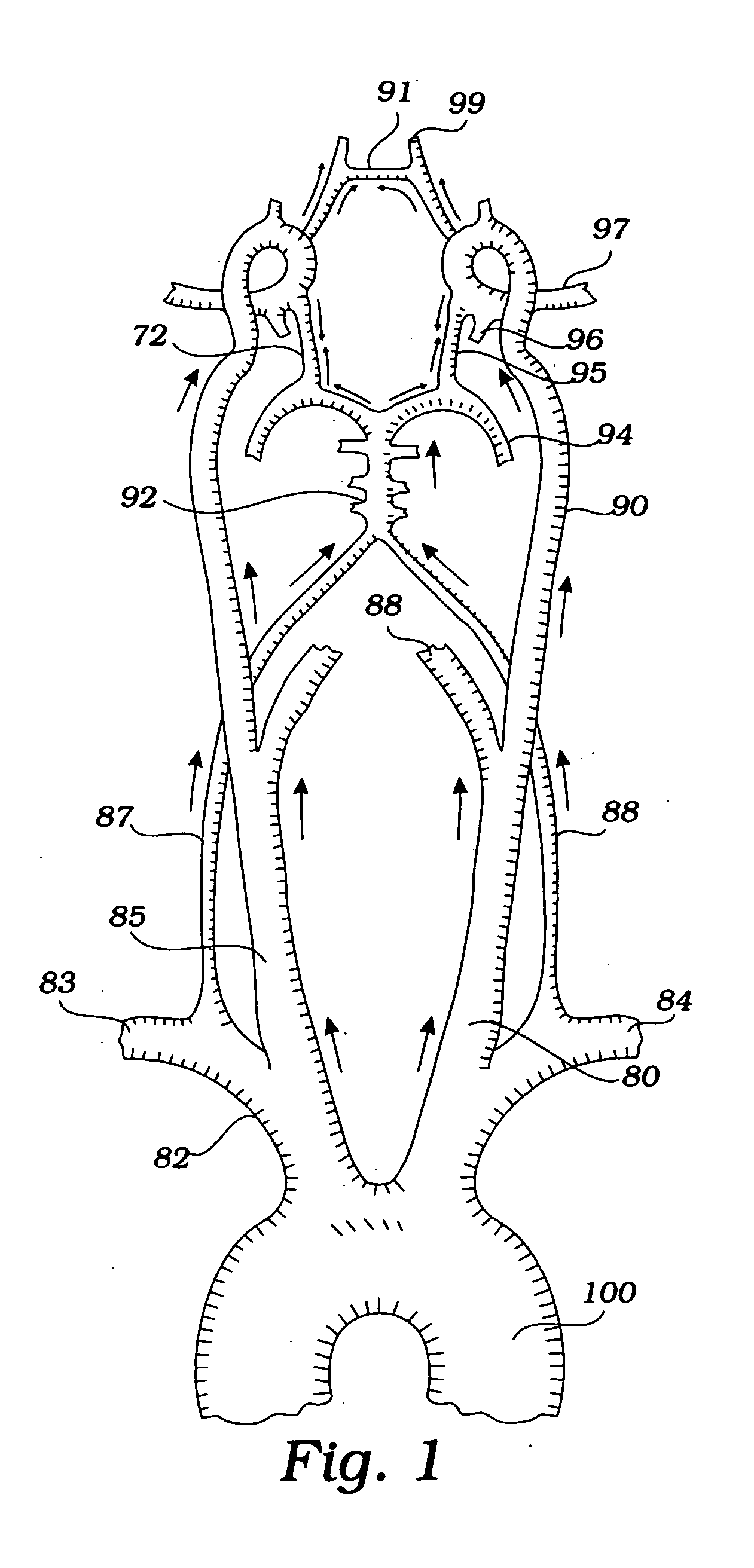
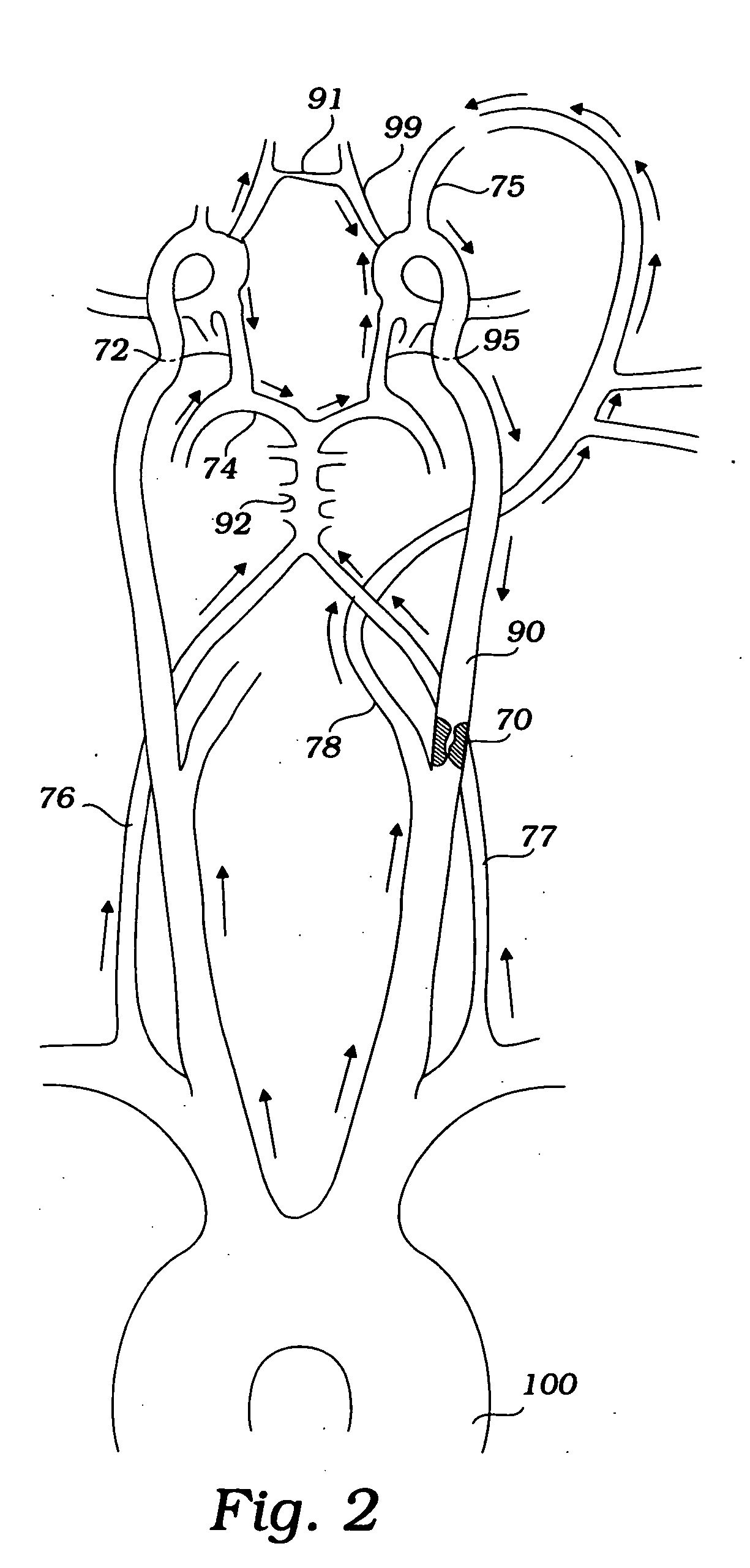
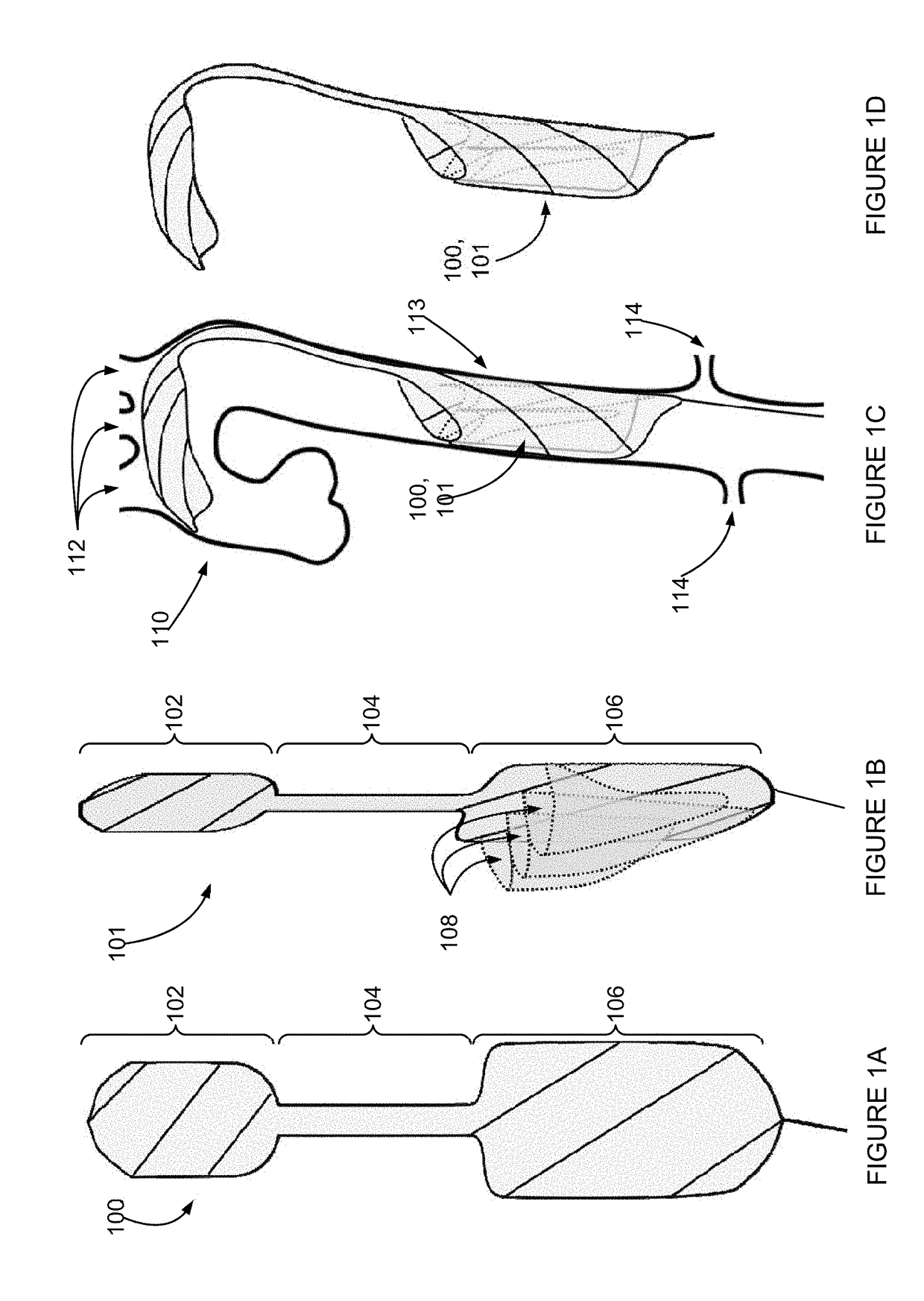
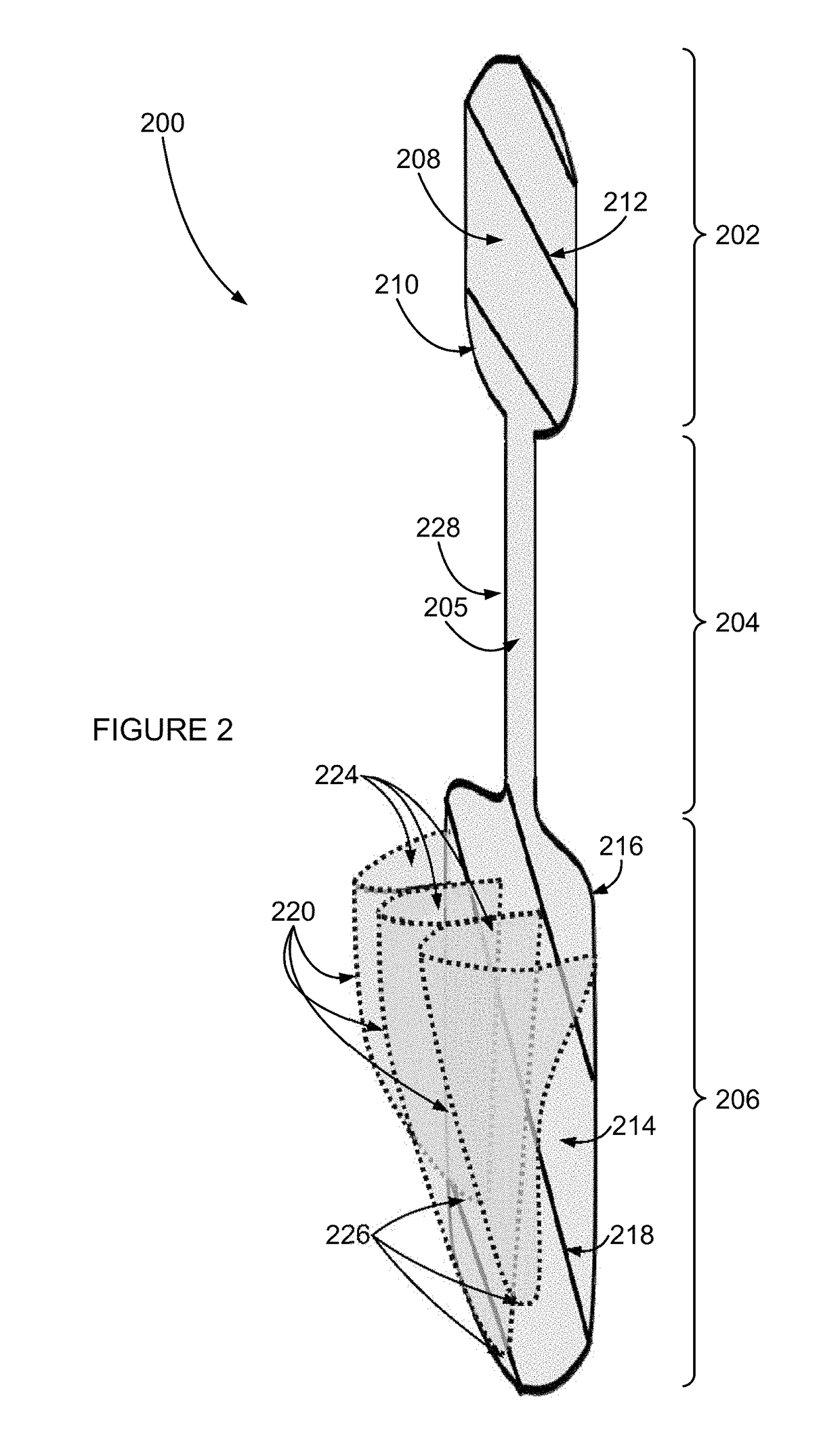
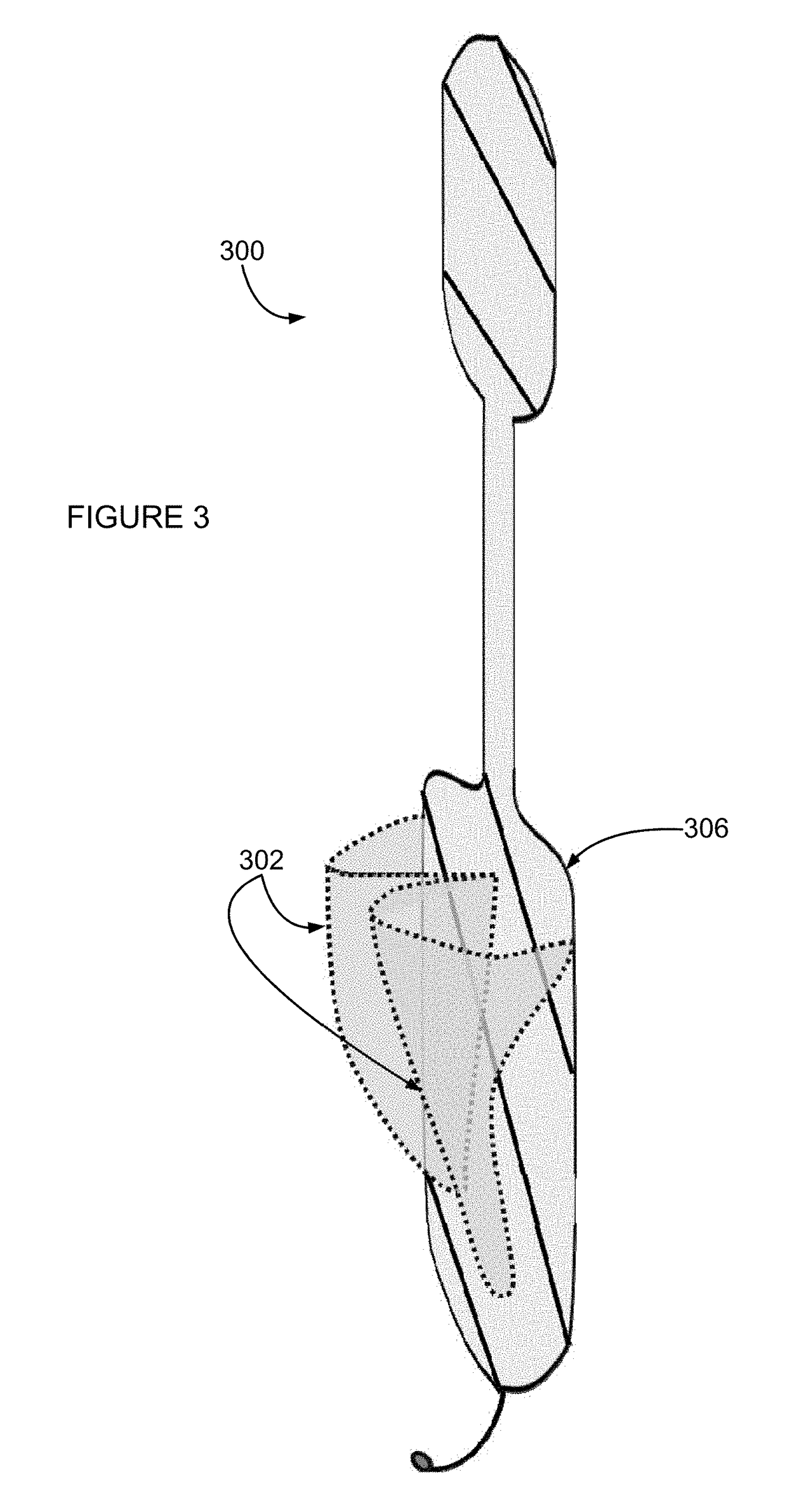
The descending aorta is part of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The descending aorta begins at the aortic arch and runs down through the chest and abdomen. The descending aorta anatomically consists of two portions or segments, the thoracic and the abdominal aorta, in correspondence with the two great cavities of the trunk in which it is situated. Within the abdomen, the descending aorta branches into the two common iliac arteries which serve the pelvis and eventually legs.
Cerebral perfusion augmentation
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
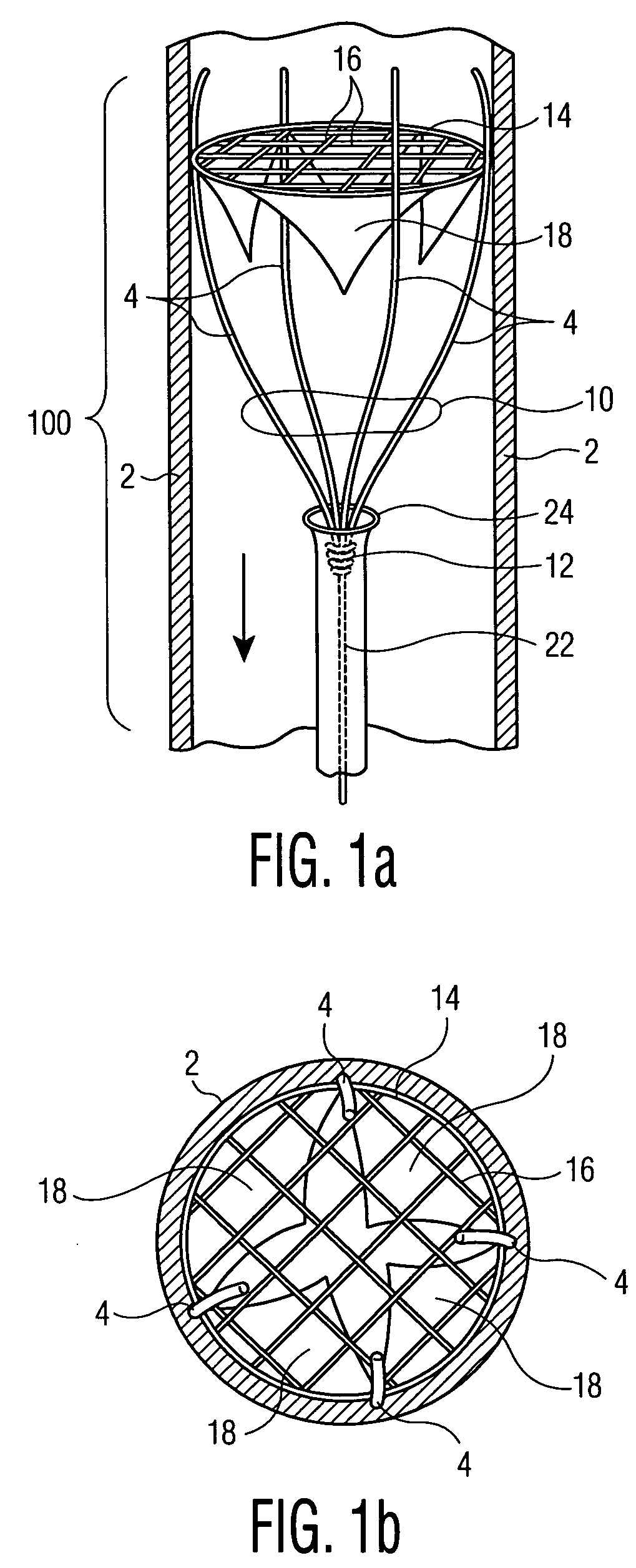
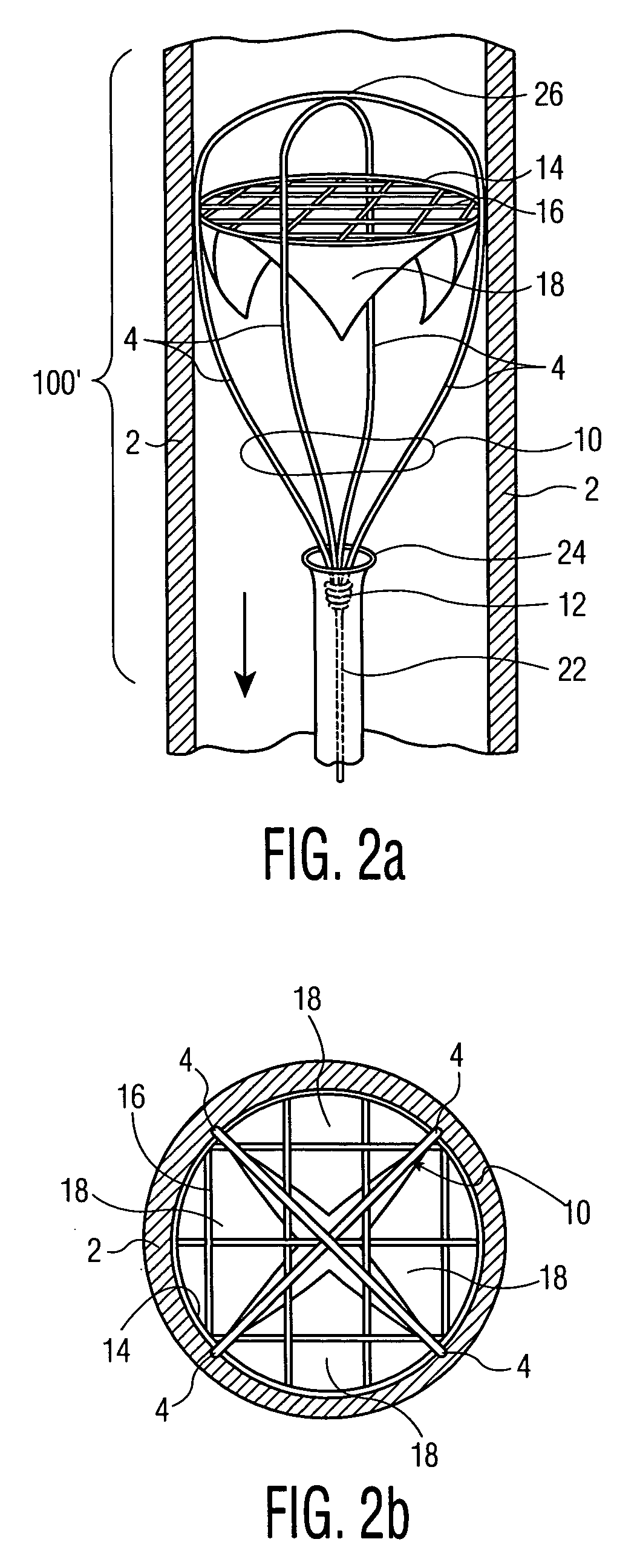
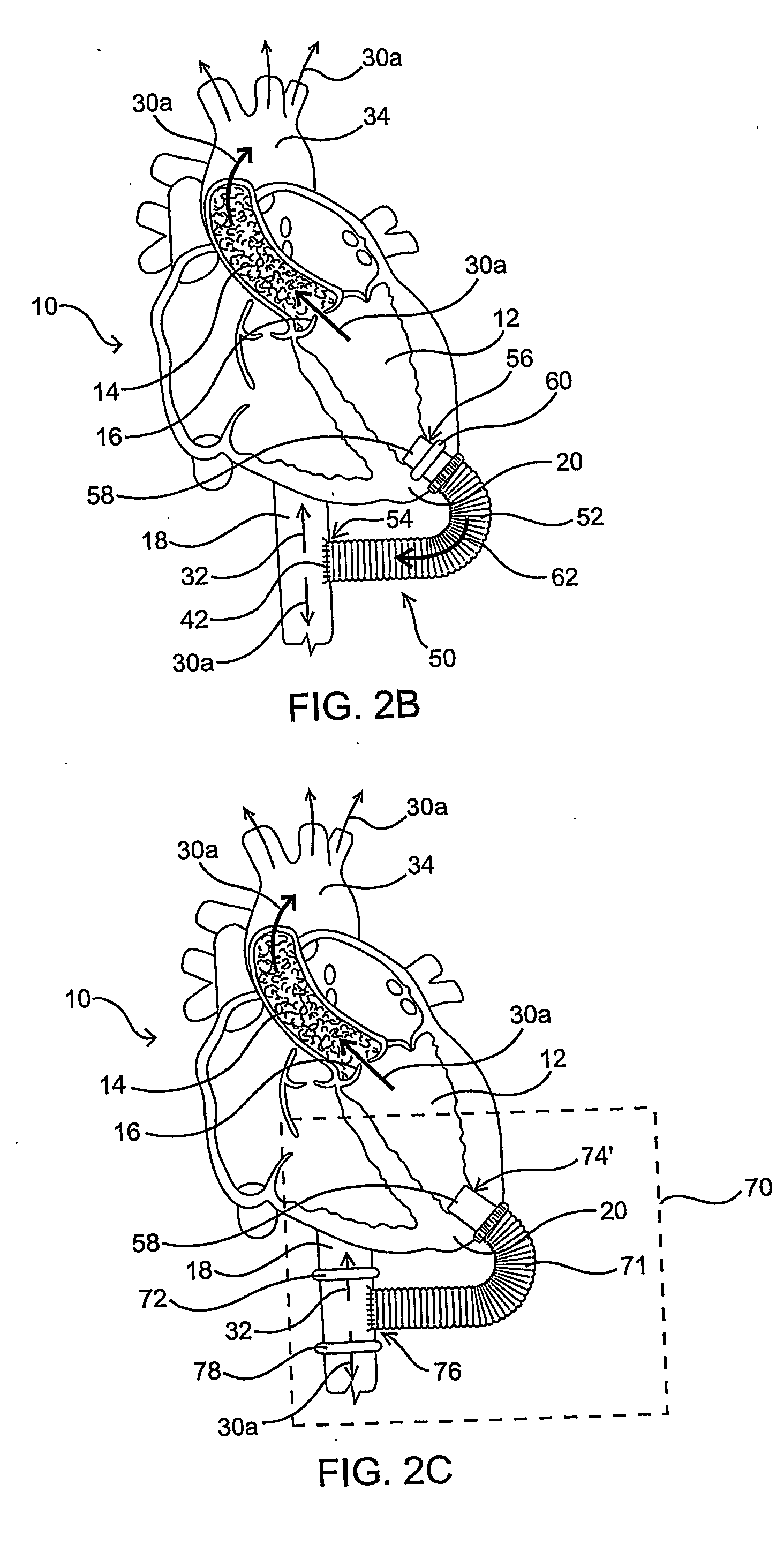
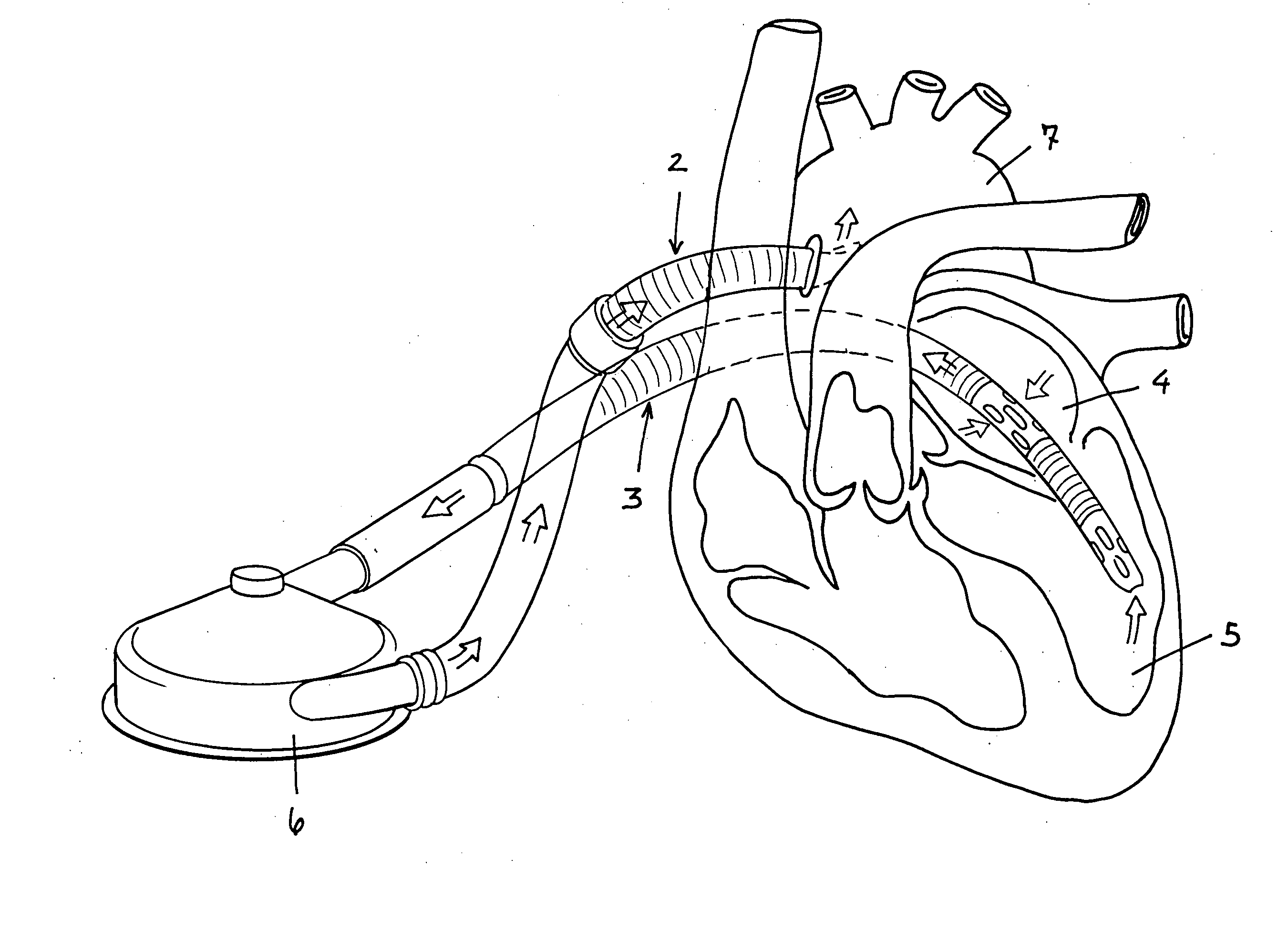
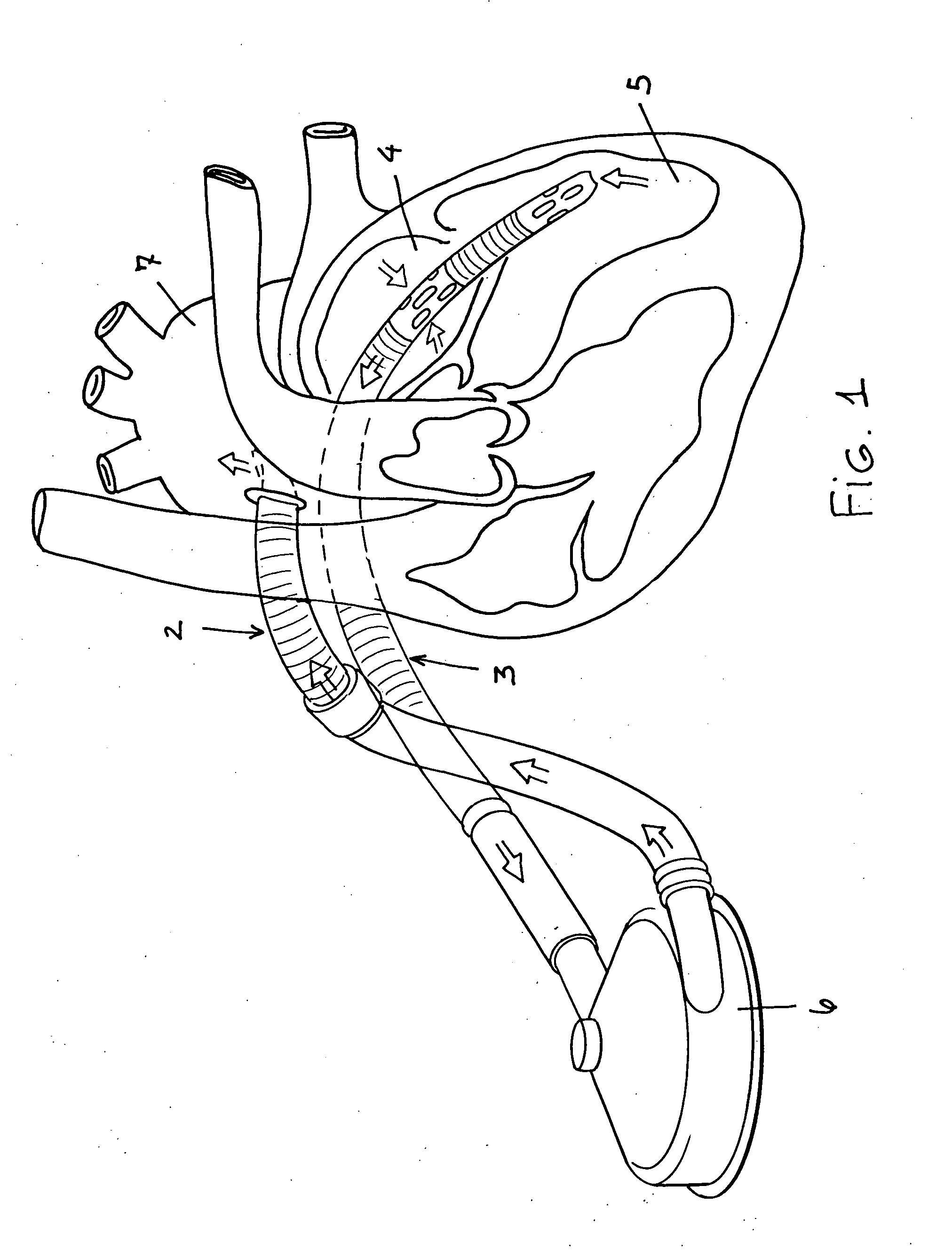
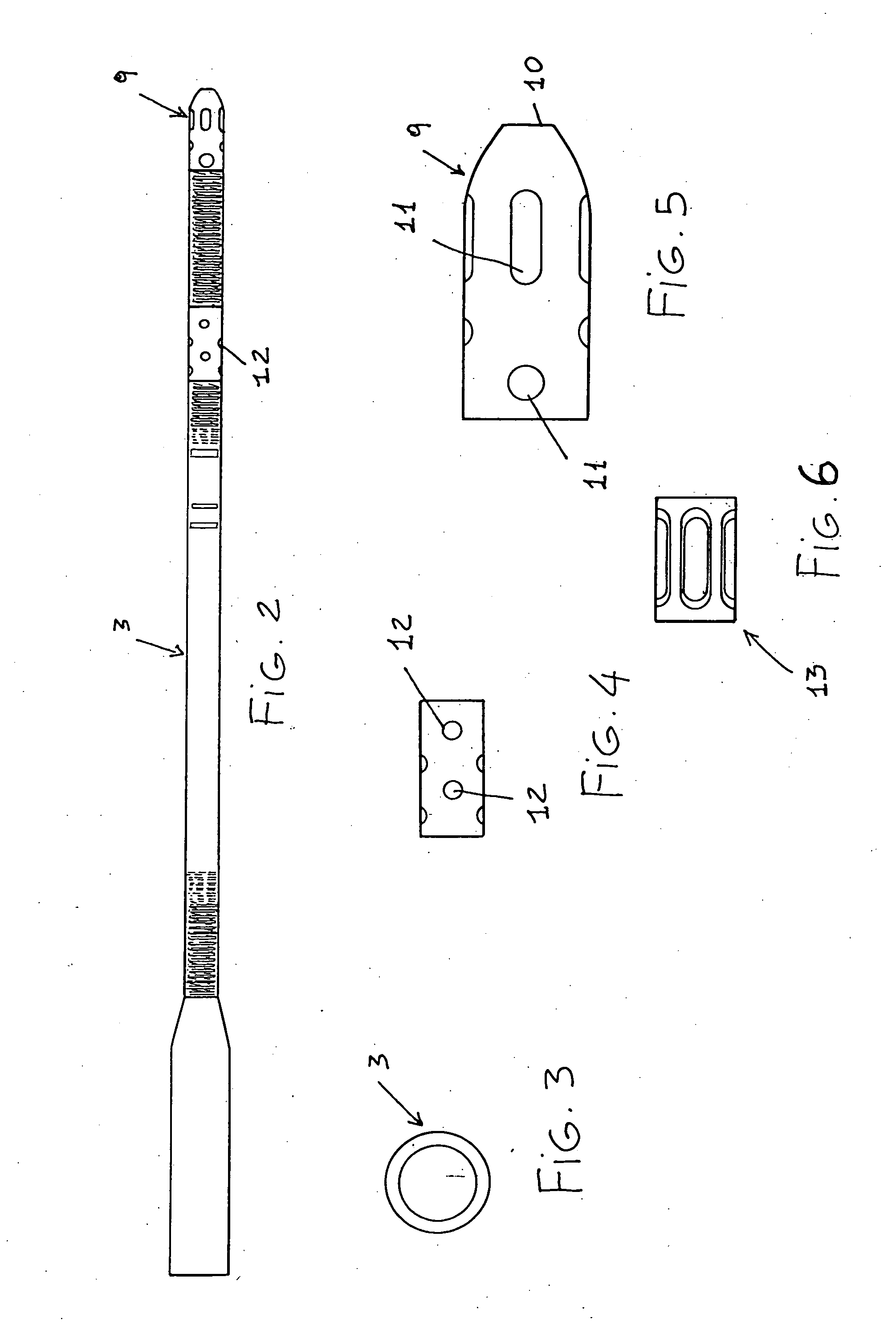
Methods and devices for improving cardiac output
InactiveUS7077801B2Facilitate cardiac output functionEliminate the problemExcision instrumentsIntravenous devicesProsthesisCatheter
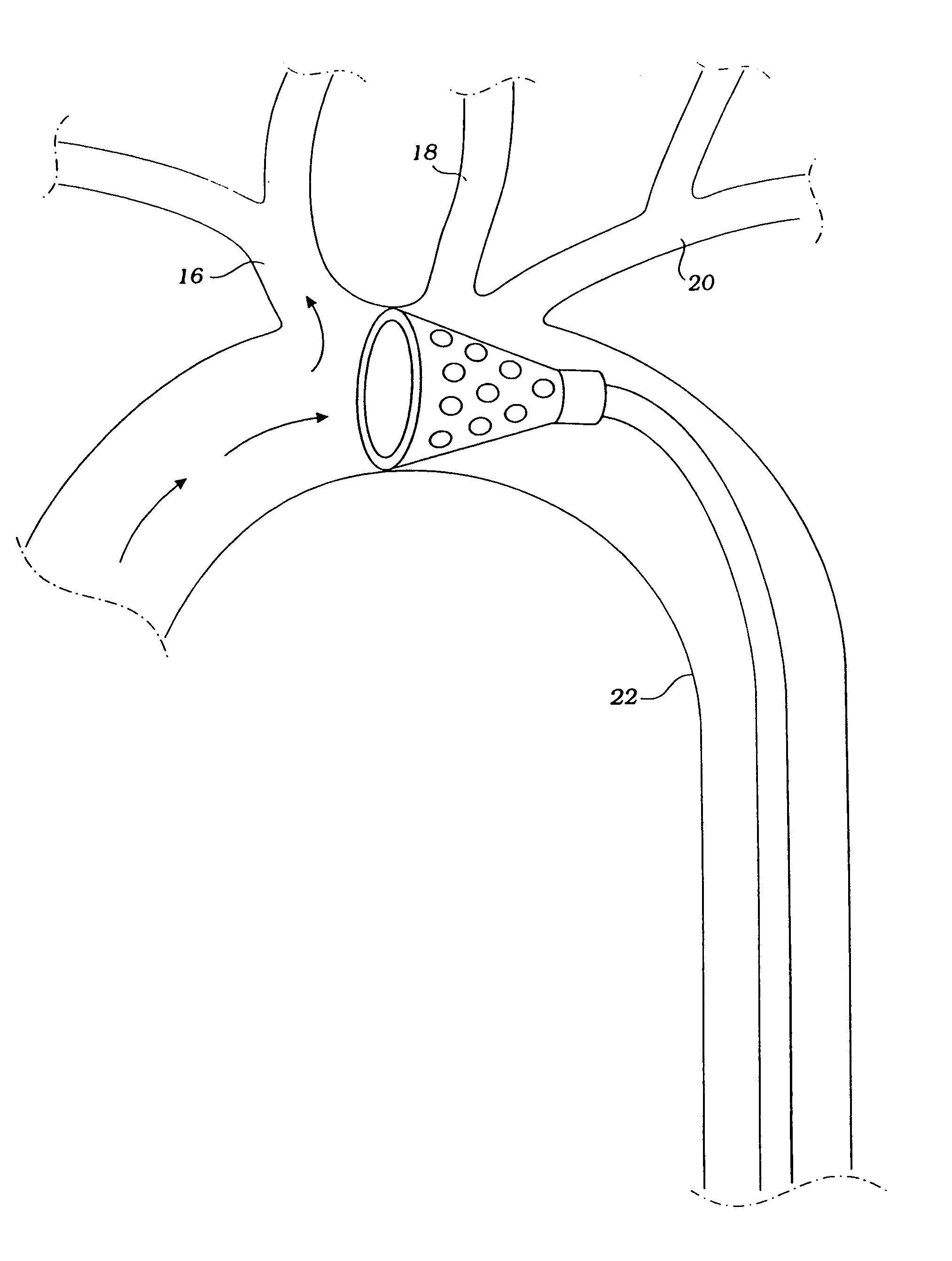
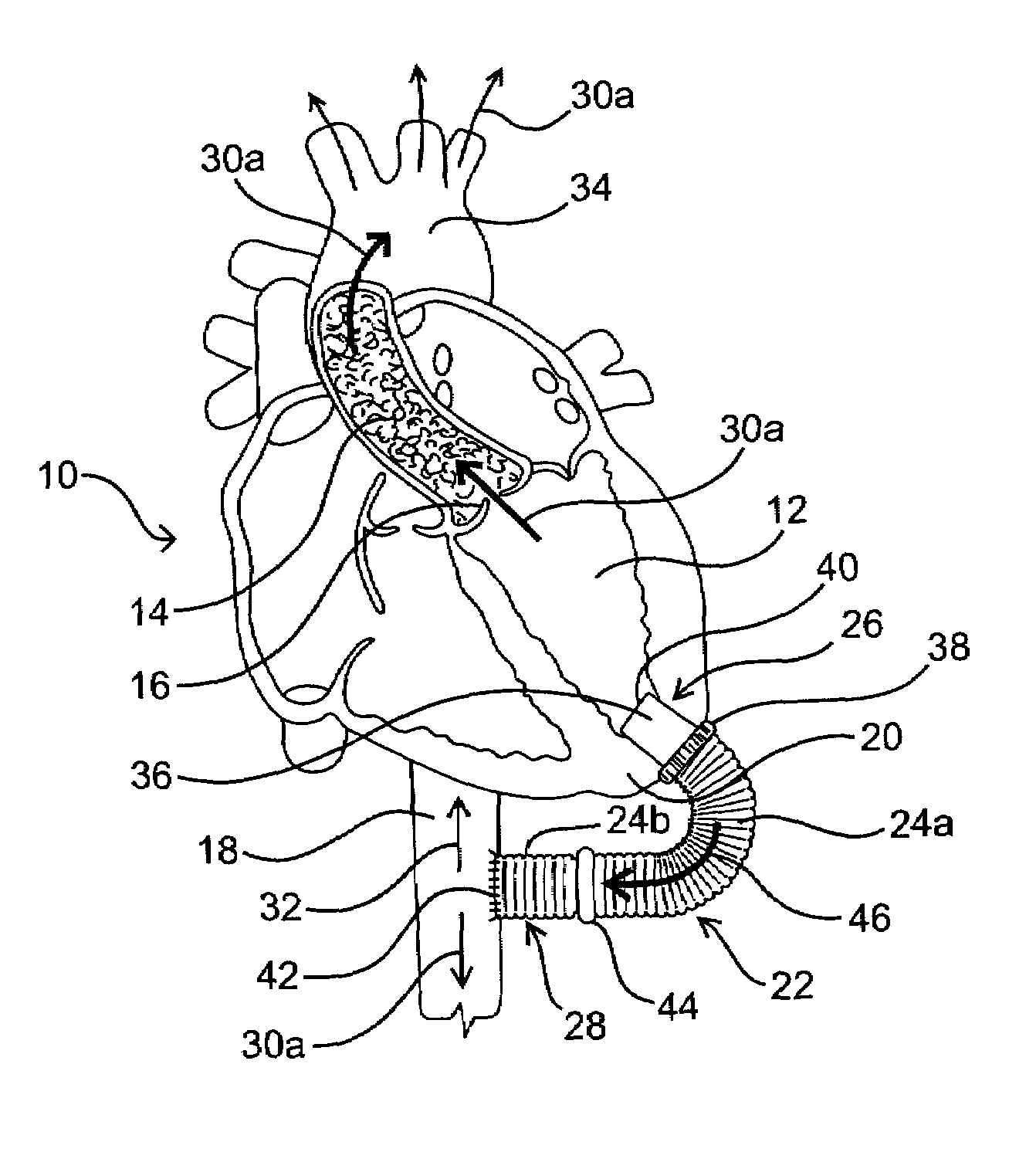
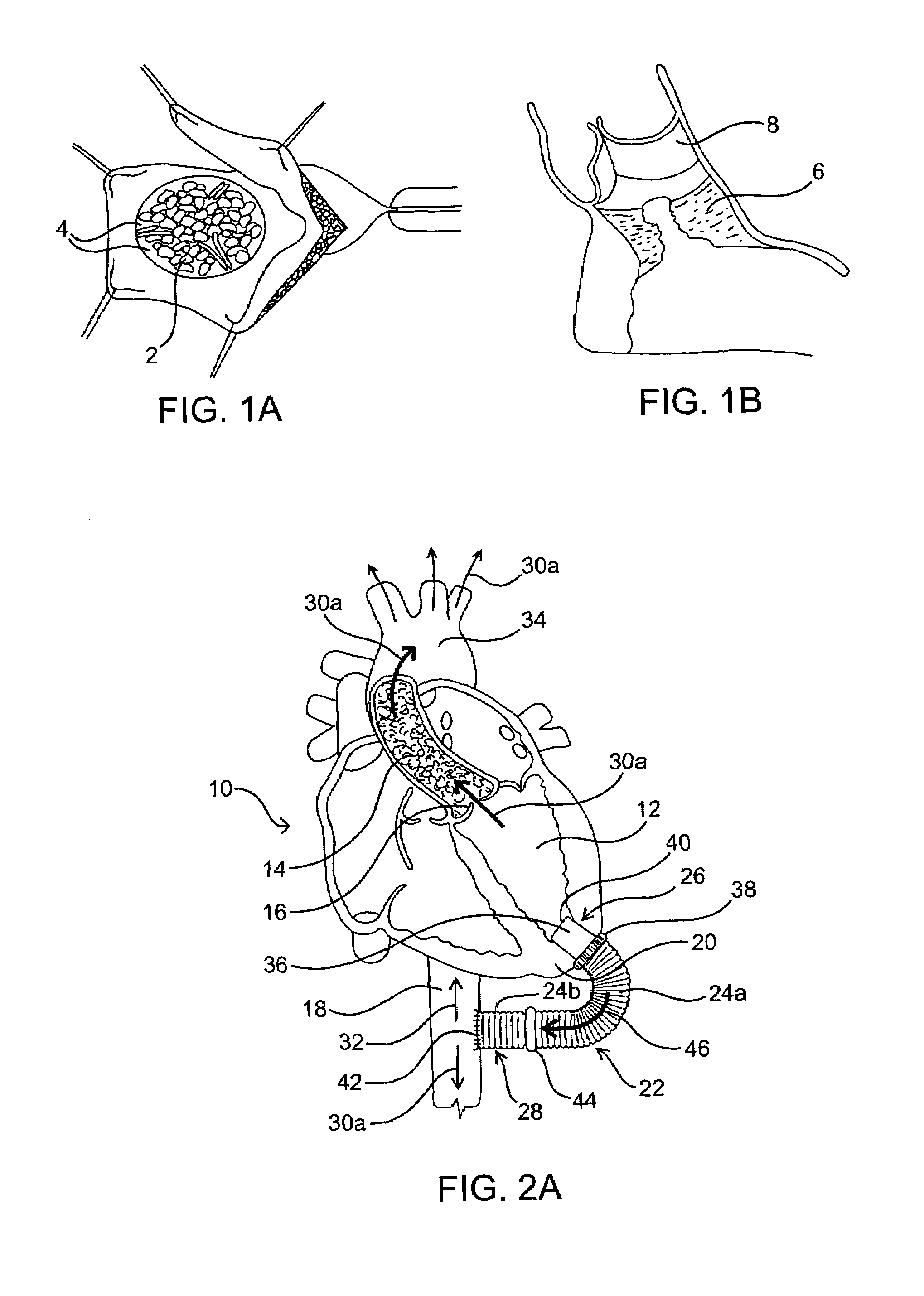
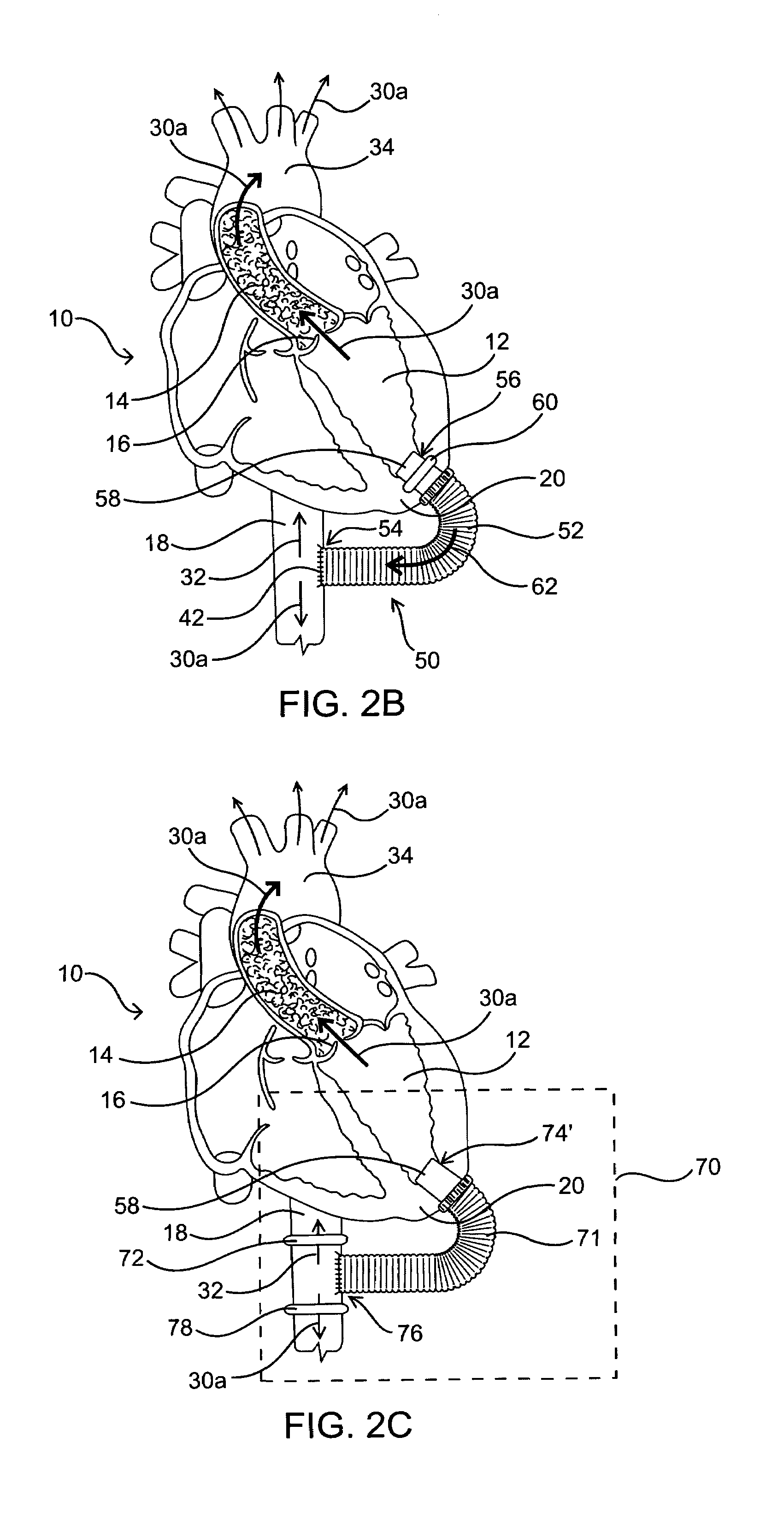
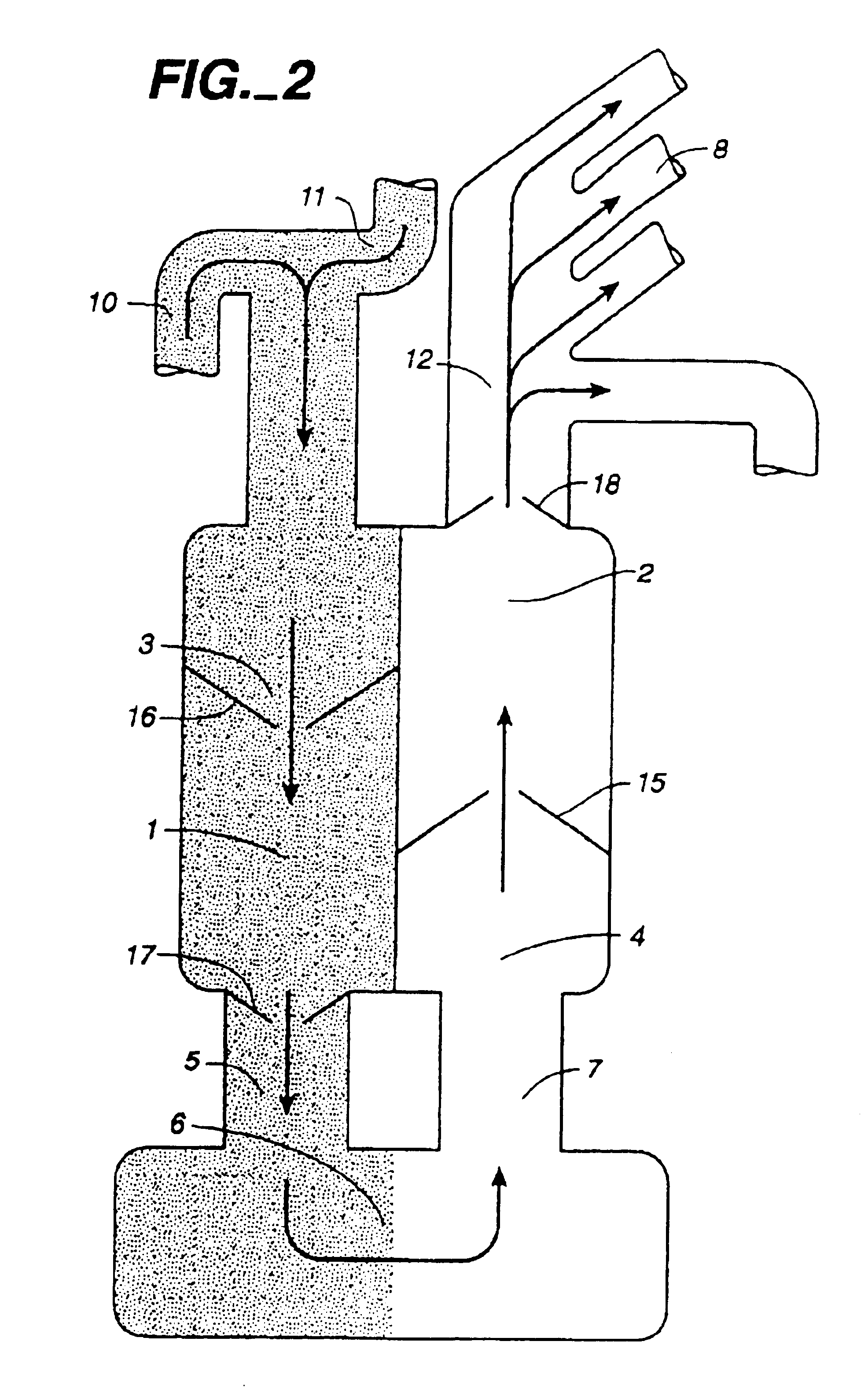
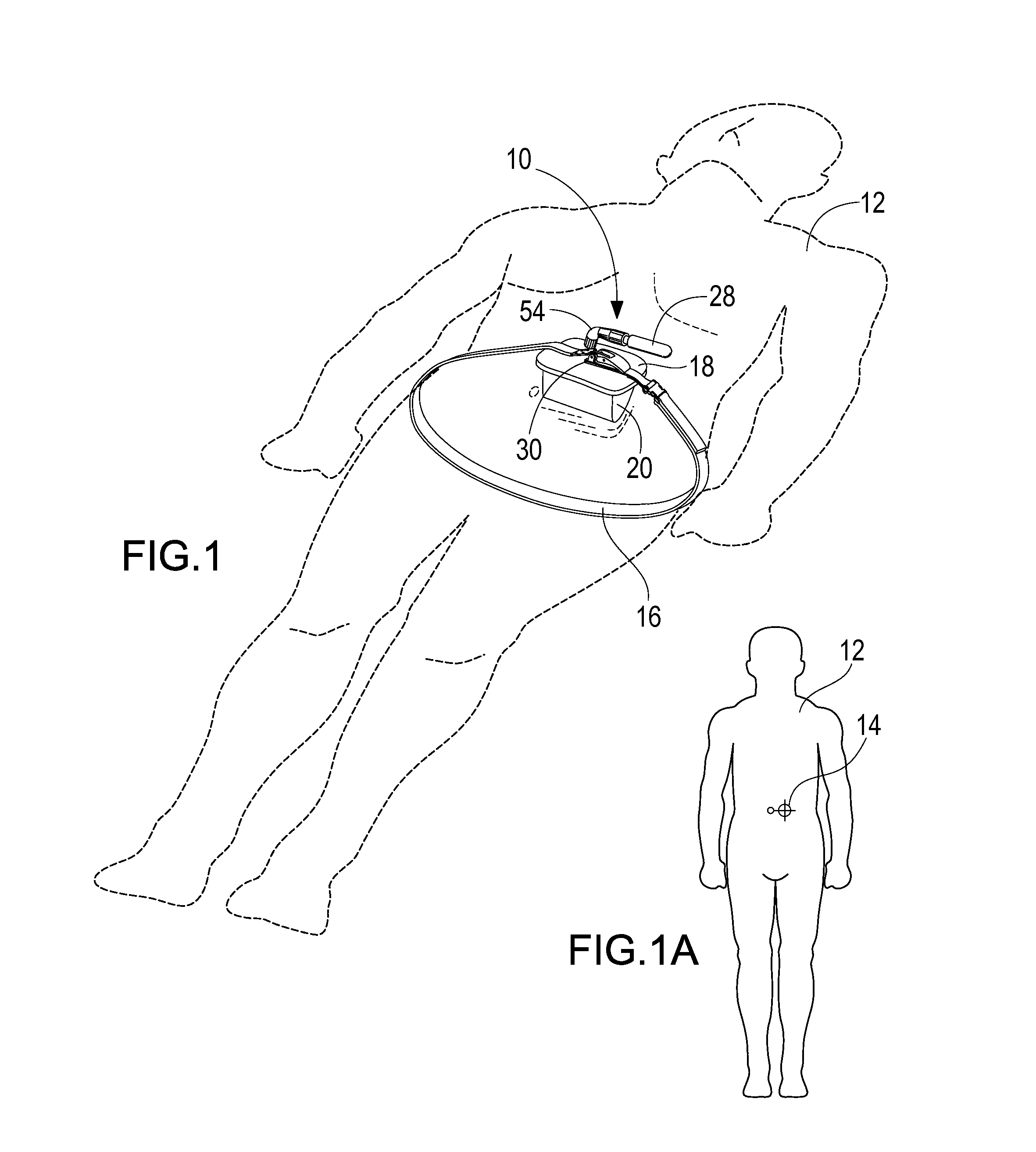
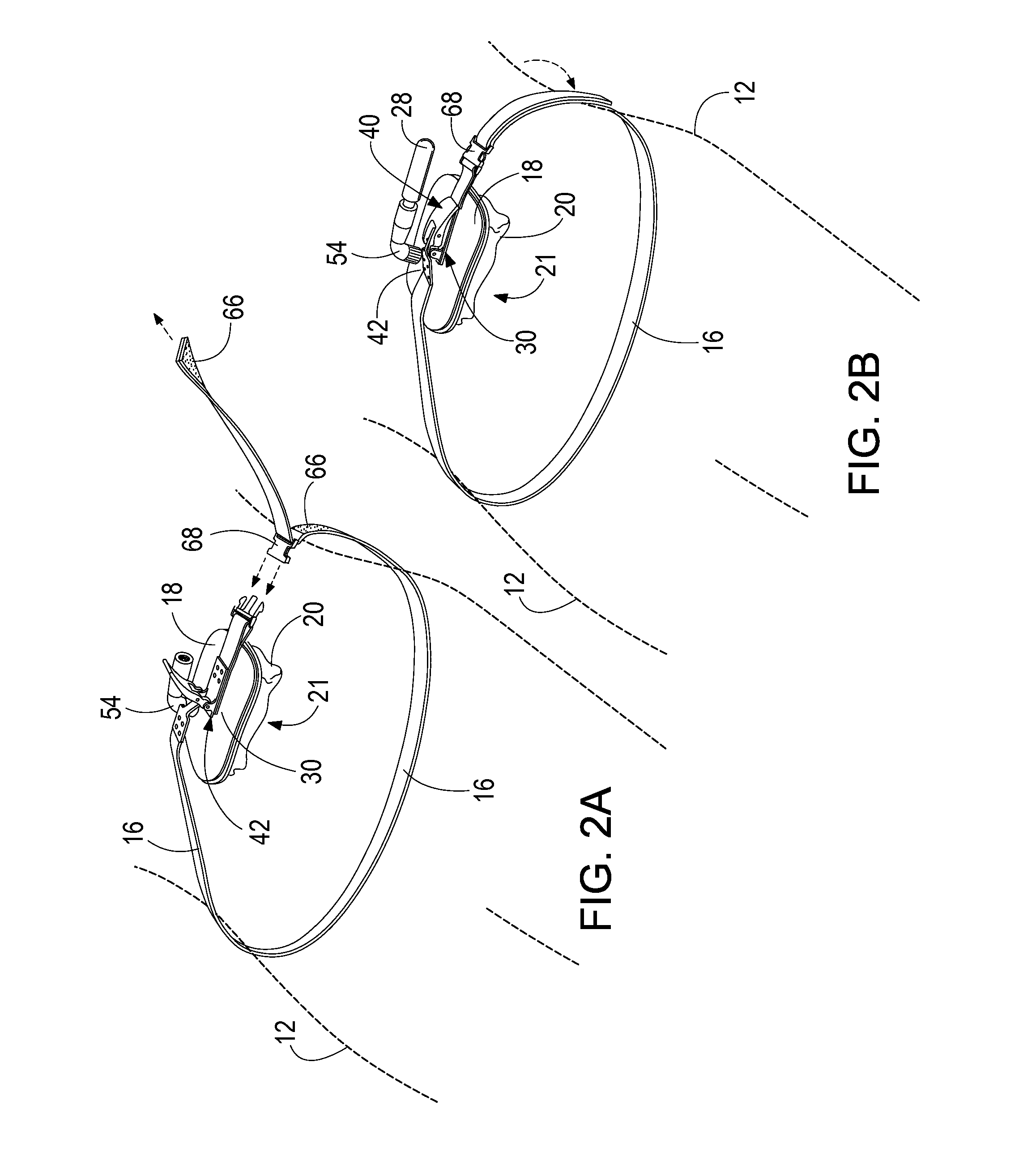
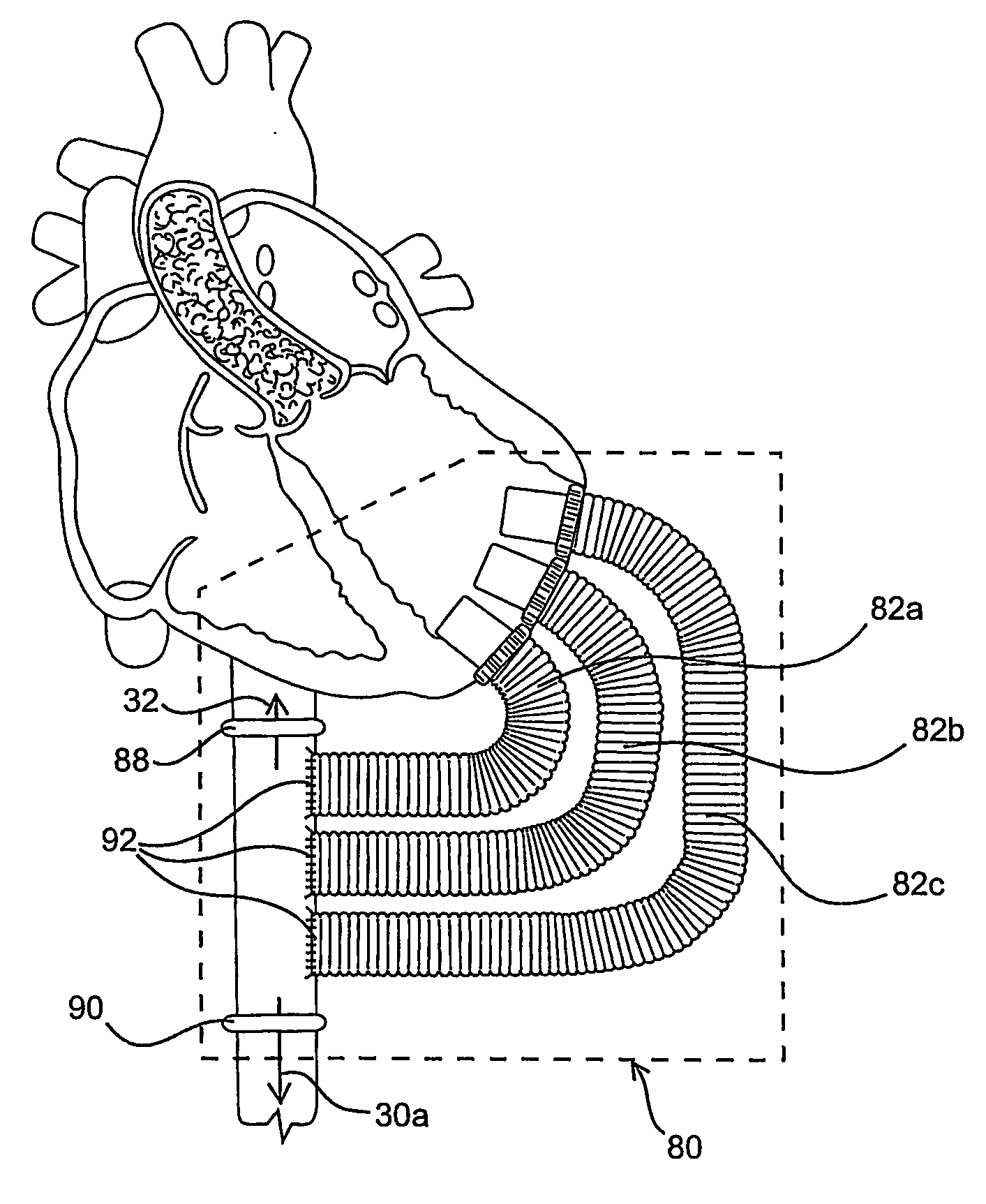
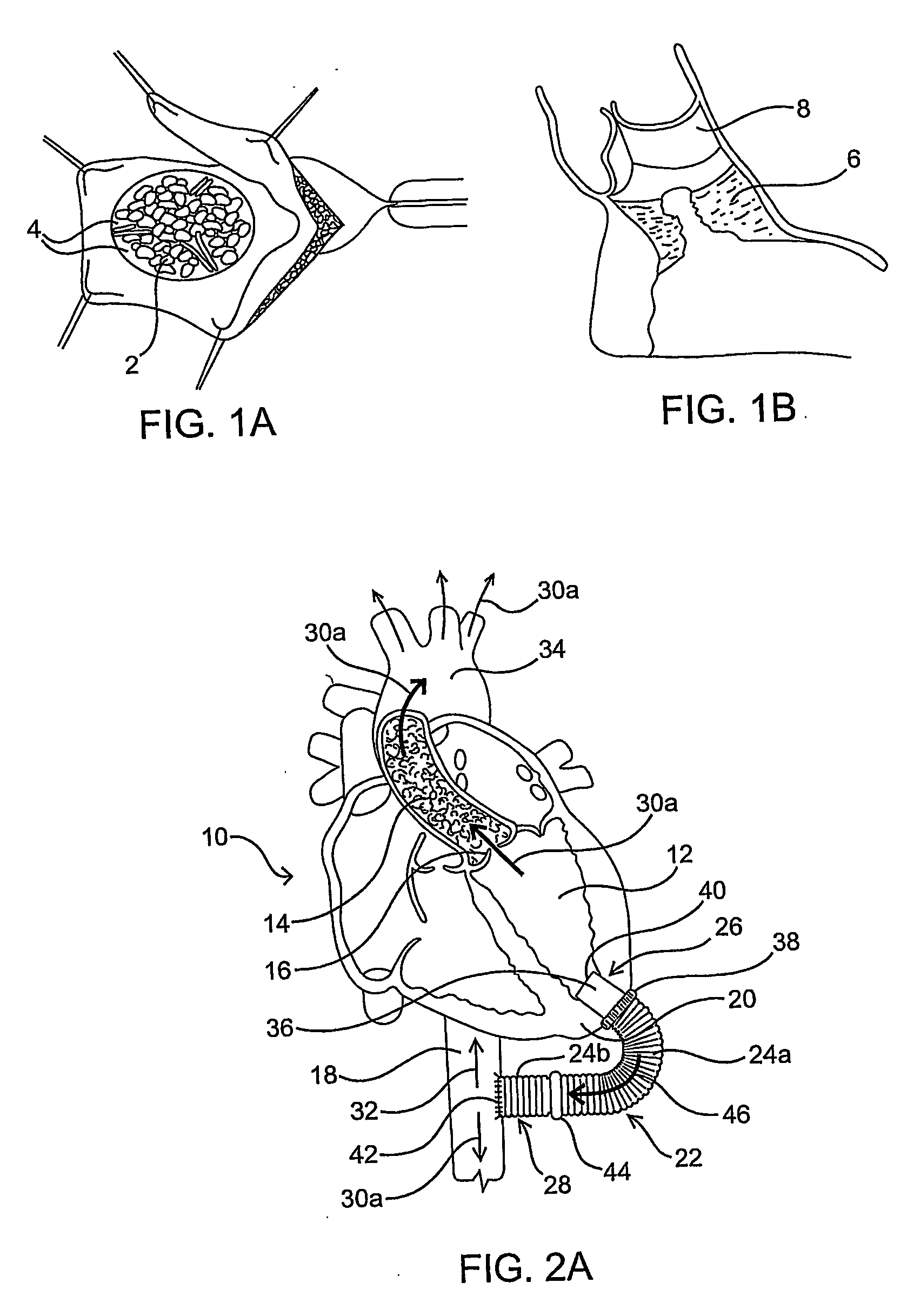
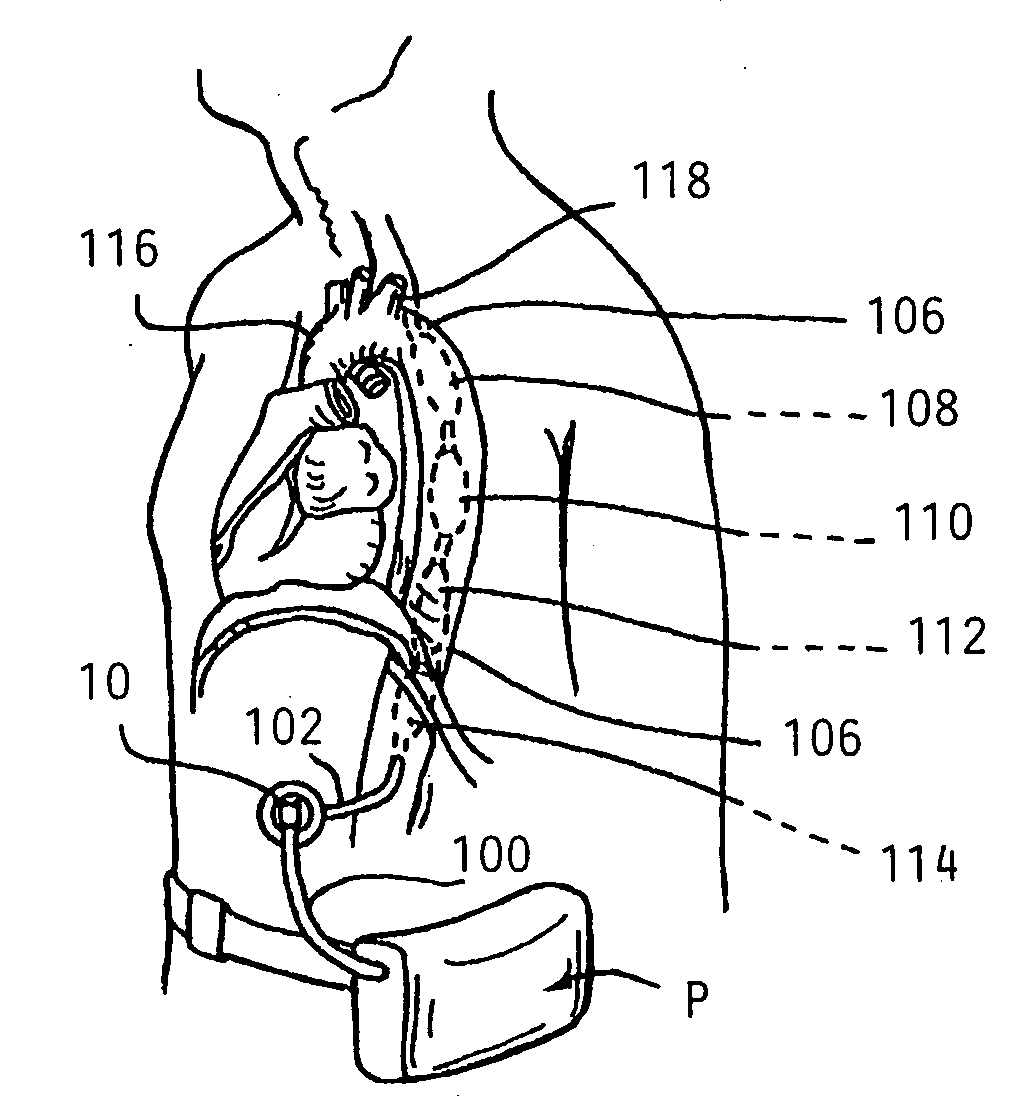
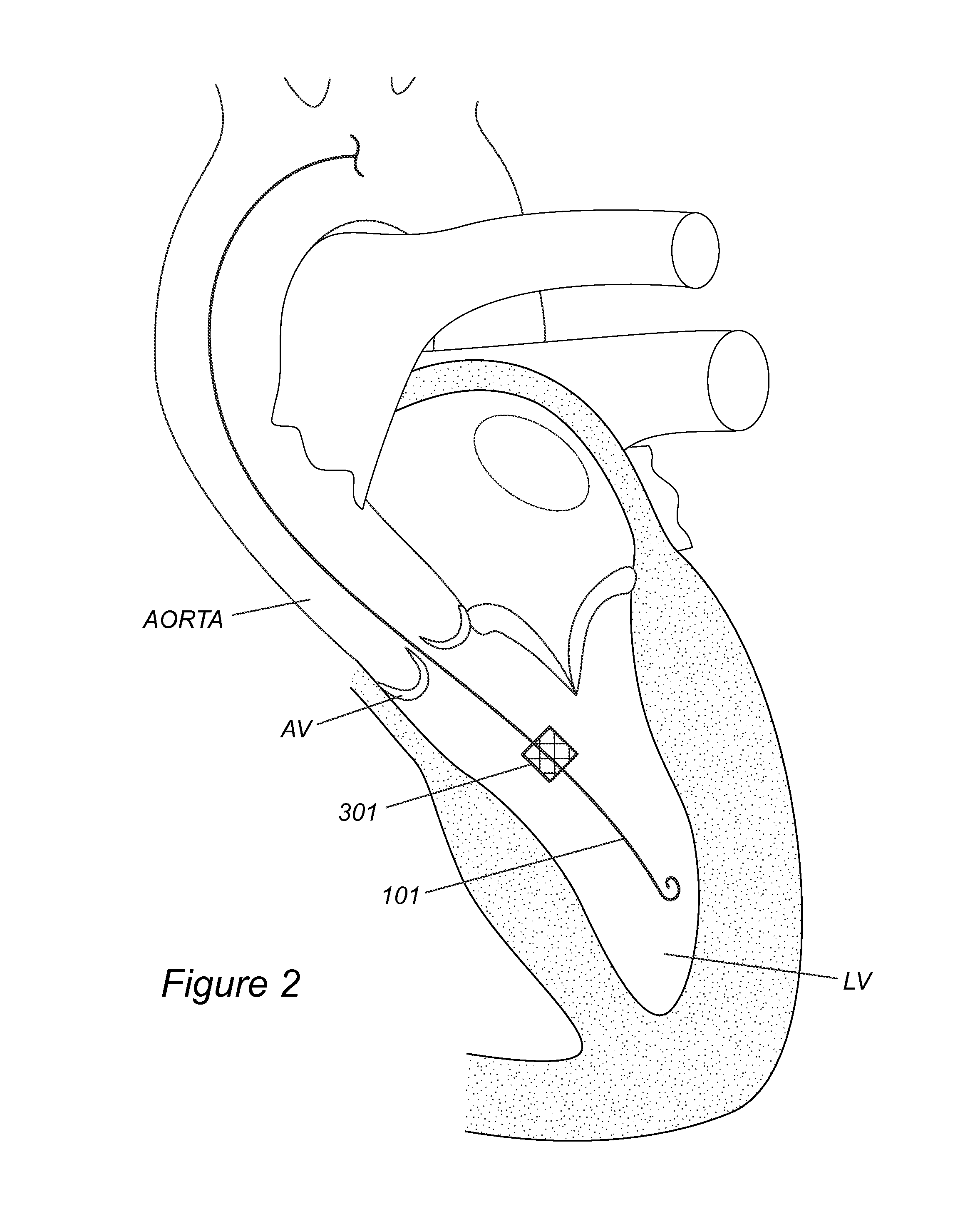
Methods and devices are provided for improving cardiac output. The methods involve establishing a fluid communication pathway between the left ventricle and another natural or prosthetic structure. In one method, a conduit is implanted between the left ventricle and the descending aorta where ventricular blood flows from the left ventricle directly into the descending aorta and bypassing the aortic valve. The devices include such conduits and valves for forming the fluid communication pathways.
Owner:CORLIFE GBR
Endoscopic arterial pumps for treatment of cardiac insufficiency and venous pumps for right-sided cardiac support
Methods for using blood pumps to treat heart failure are disclosed. The pump is mounted on an interior of a stent, and the stent is releasably mounted on a distal end of a catheter. The distal end of the catheter is inserted into a peripheral artery and advanced to position at a region of interest within the descending aorta, the ascending aorta, or the left ventricle. The stent and the pump are released from the catheter, and the pump is activated to increase blood flow downstream of the pump. The pump can also be positioned in the vena cava or used to treat right-sided heart failure following the insertion of an LVAD, or to improve venous return in patients with varicose veins. Non-stent pumps are described for insertion between the pulmonary vein and aorta, and between the vena cava and pulmonary artery designed for use during cardiac surgery.
Owner:BARBUT DENISE R +2
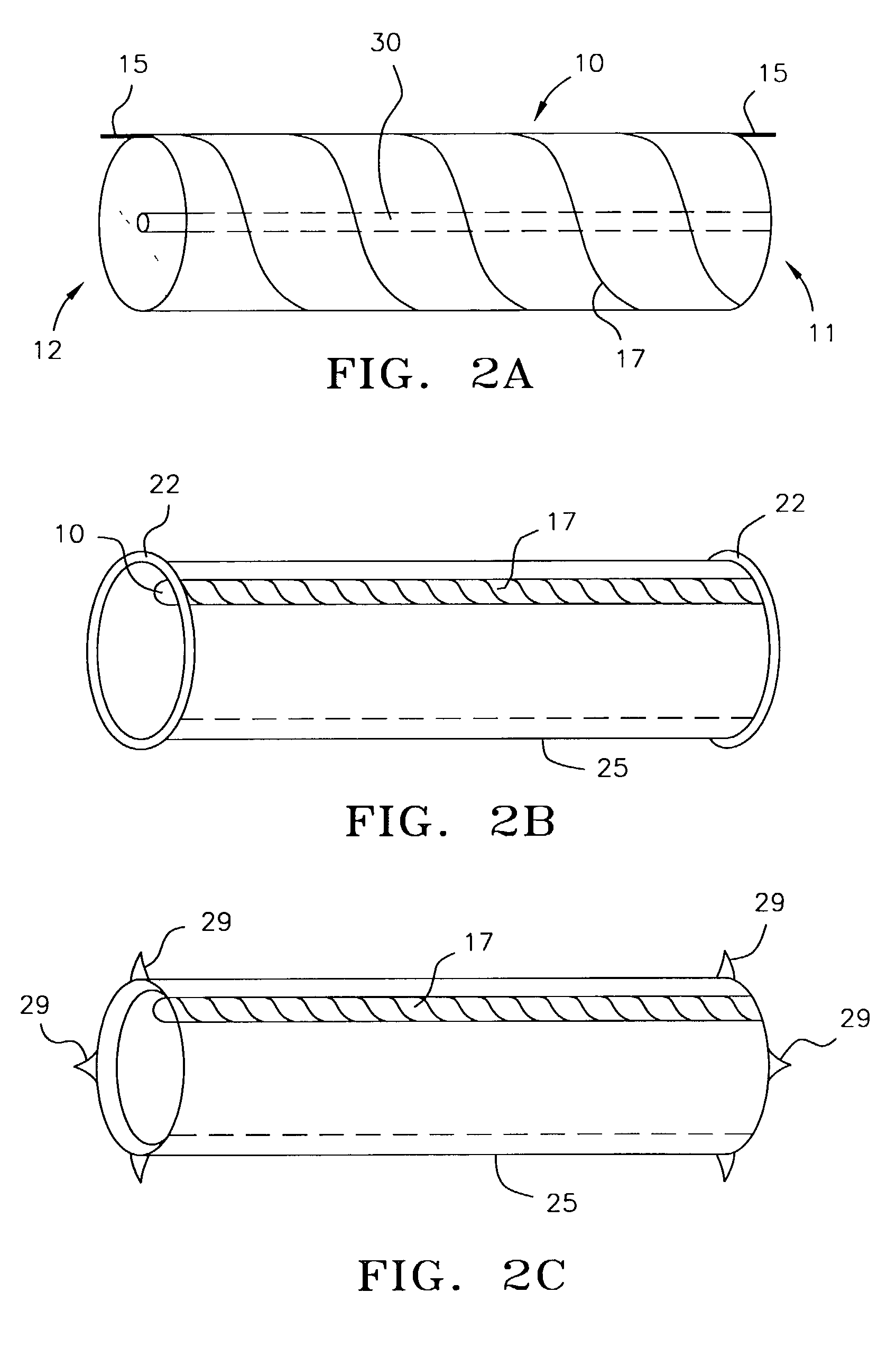
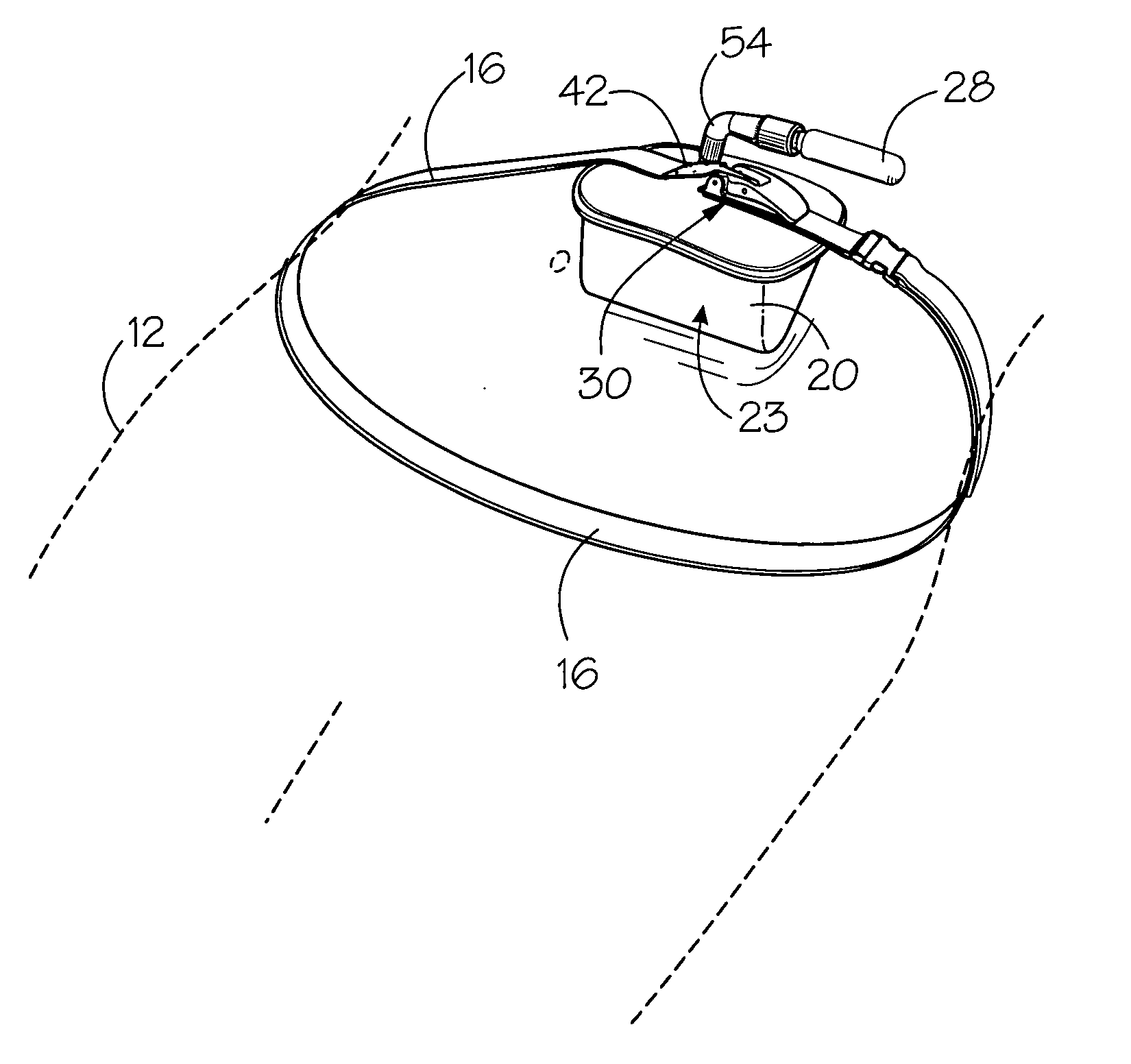
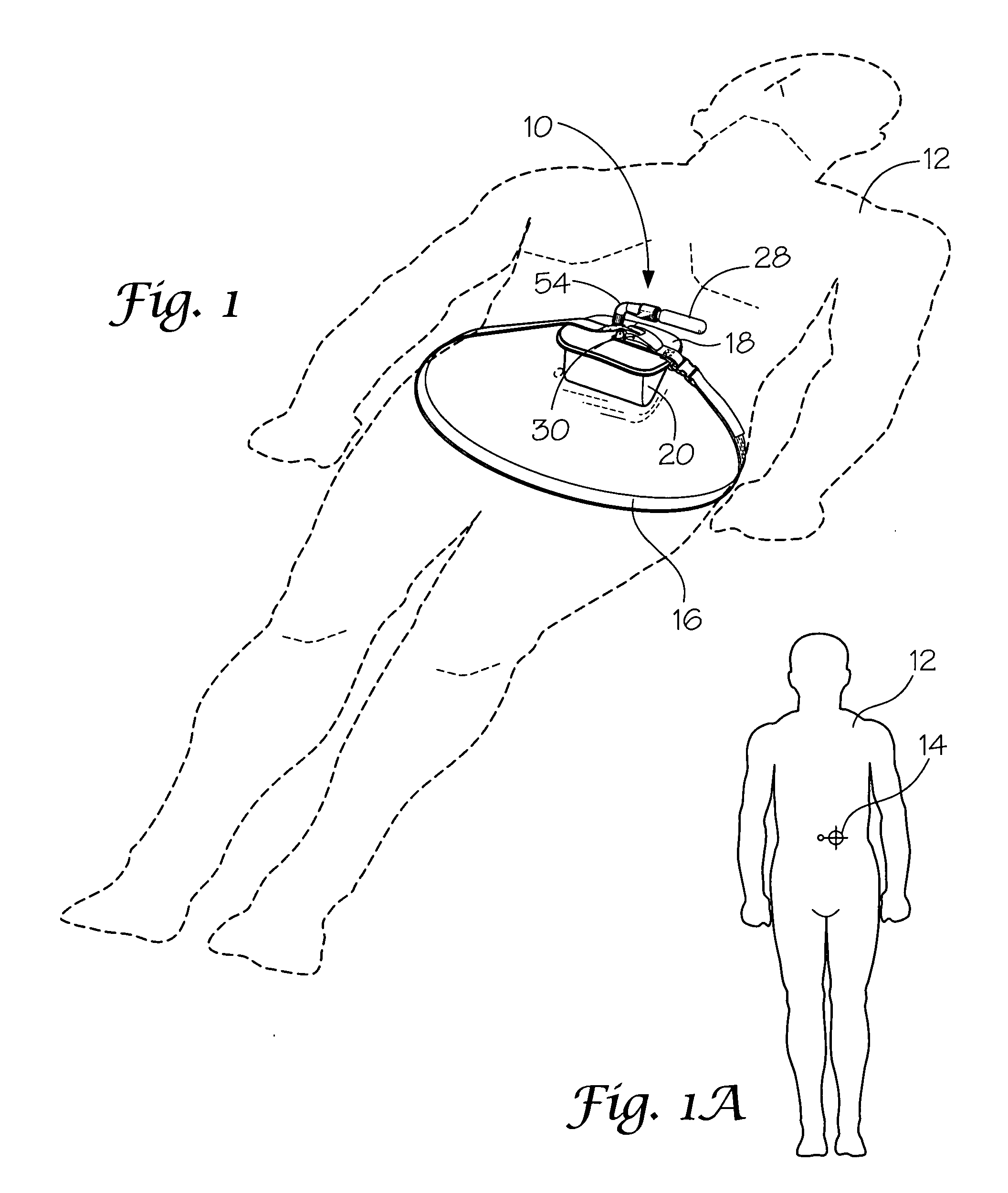
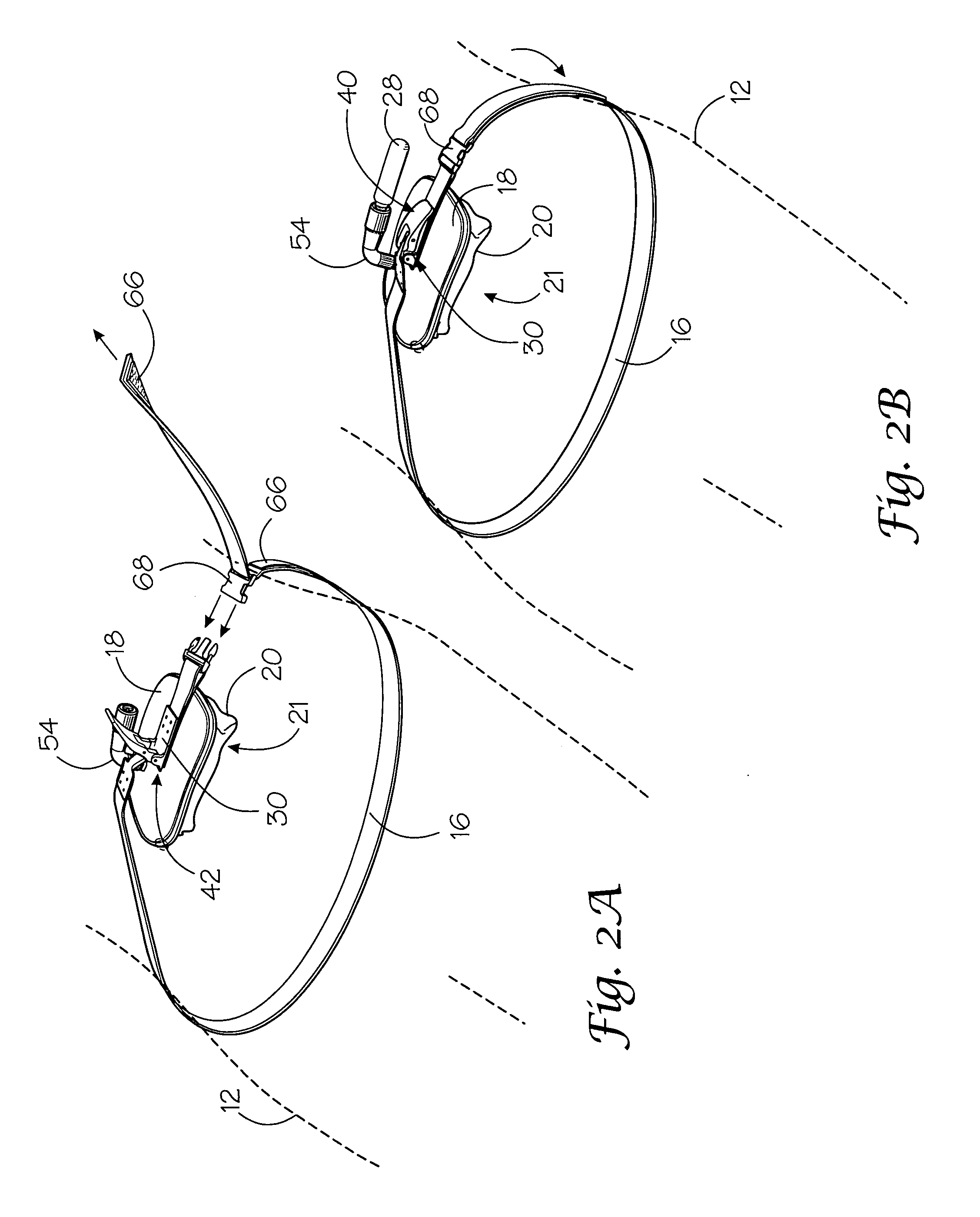
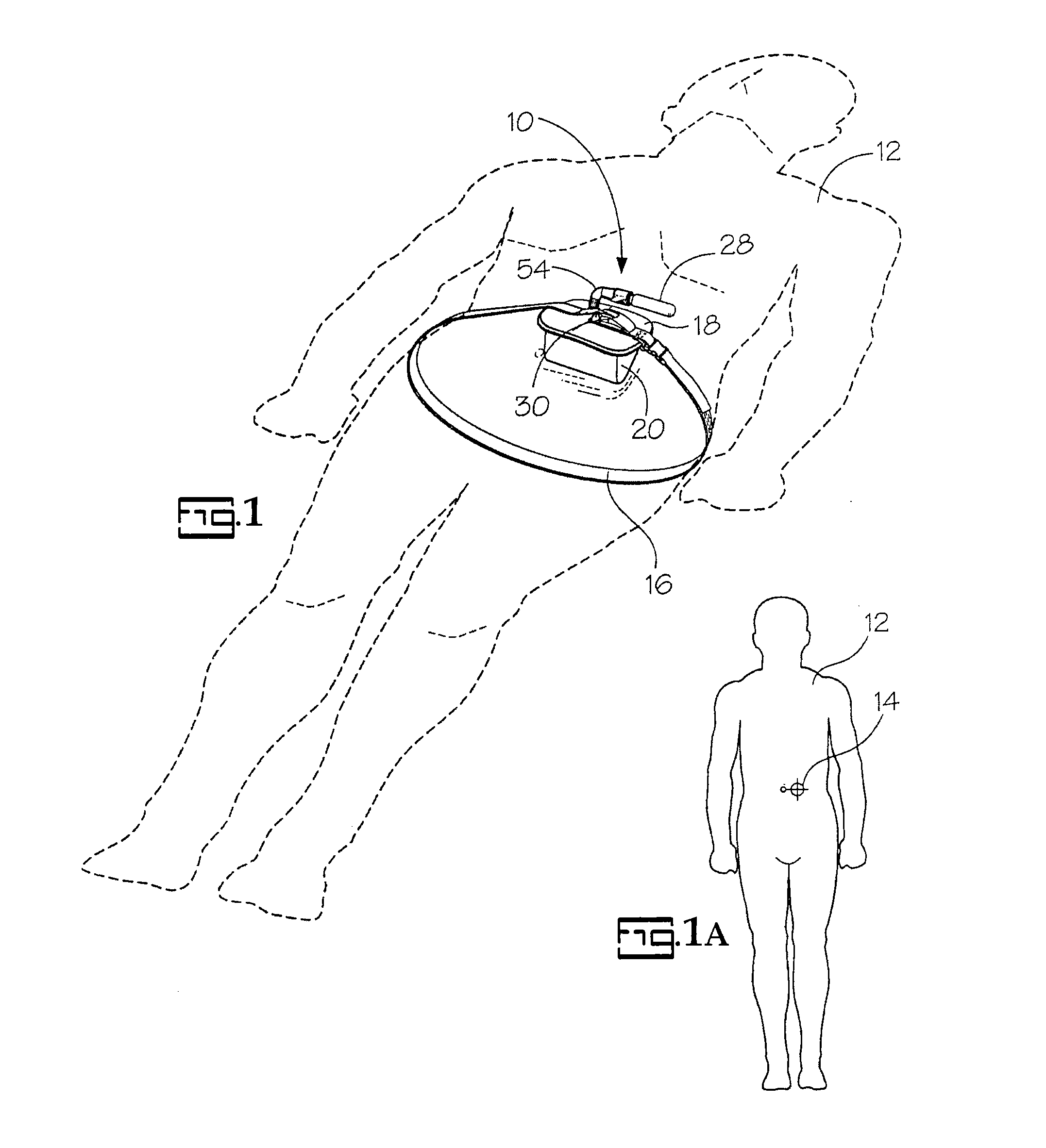
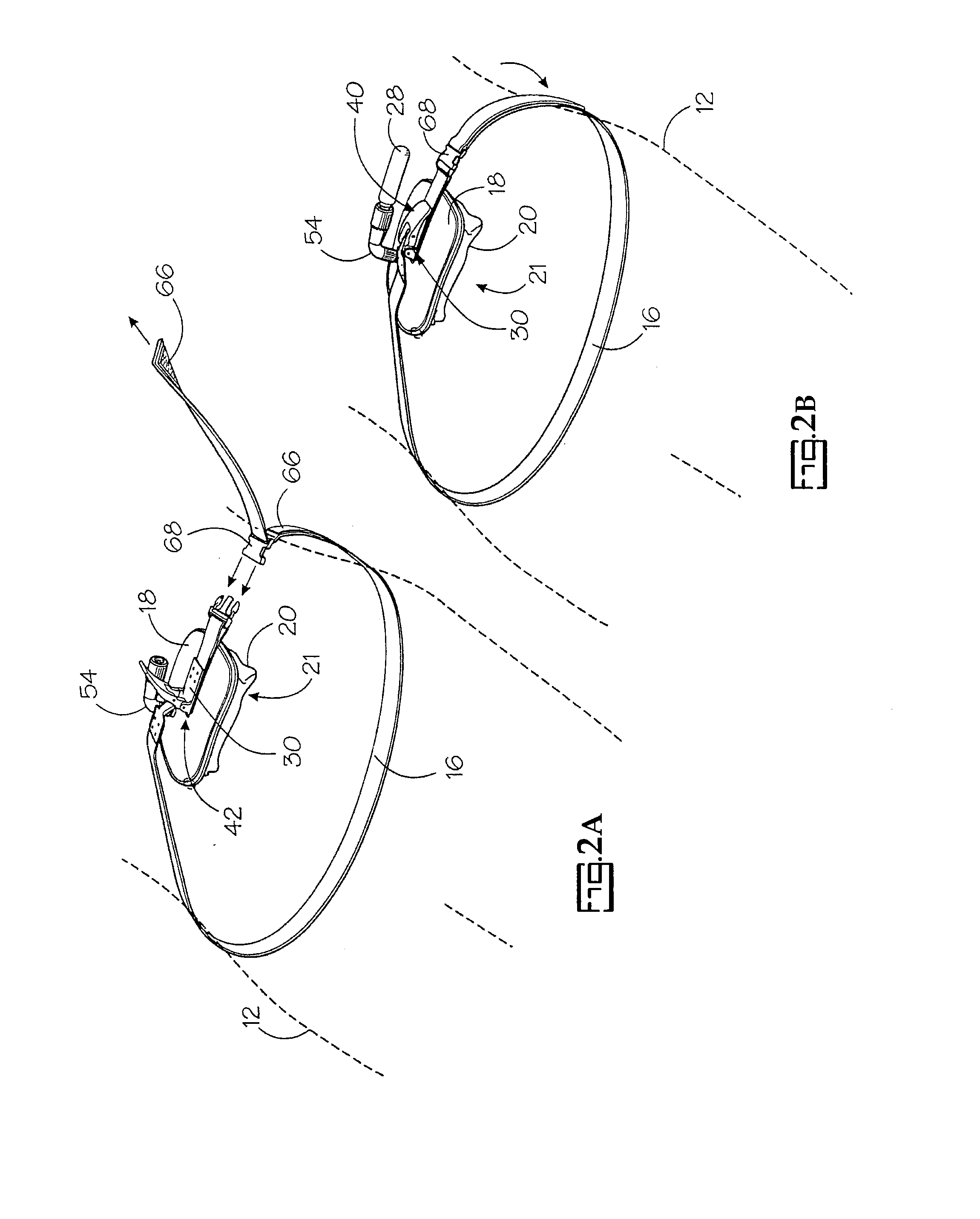
Portable pneumatic abdominal aortic tourniquet
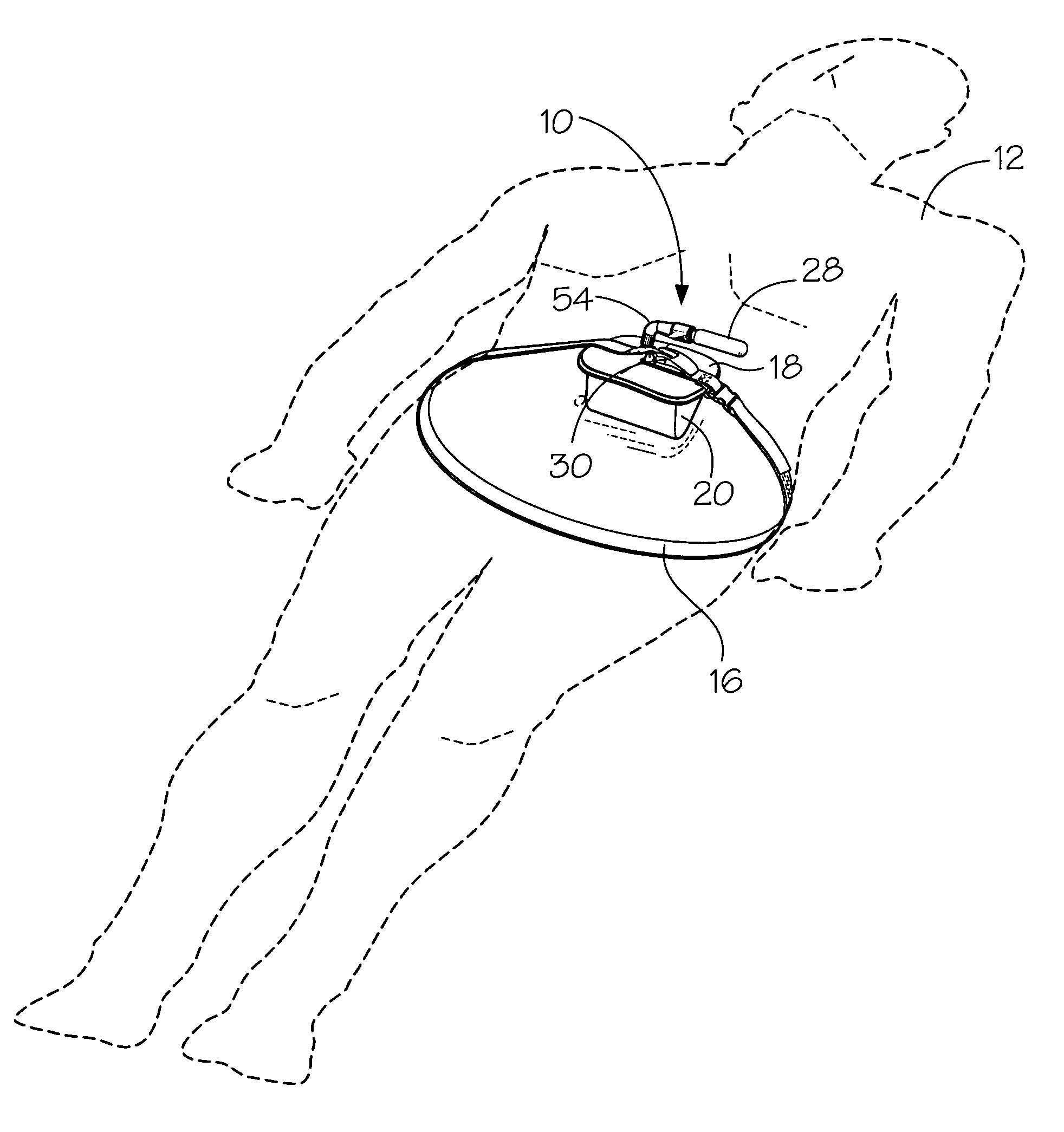
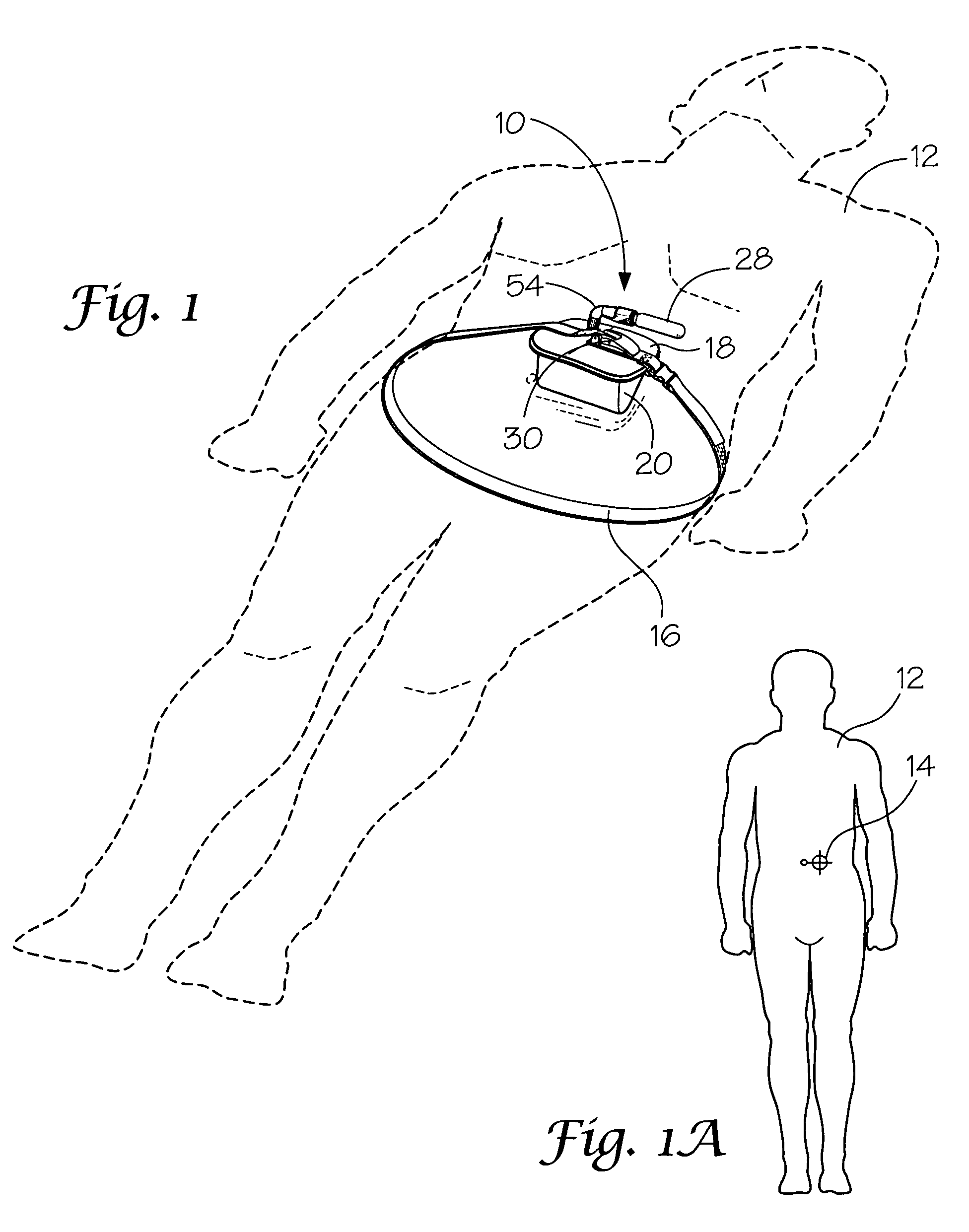
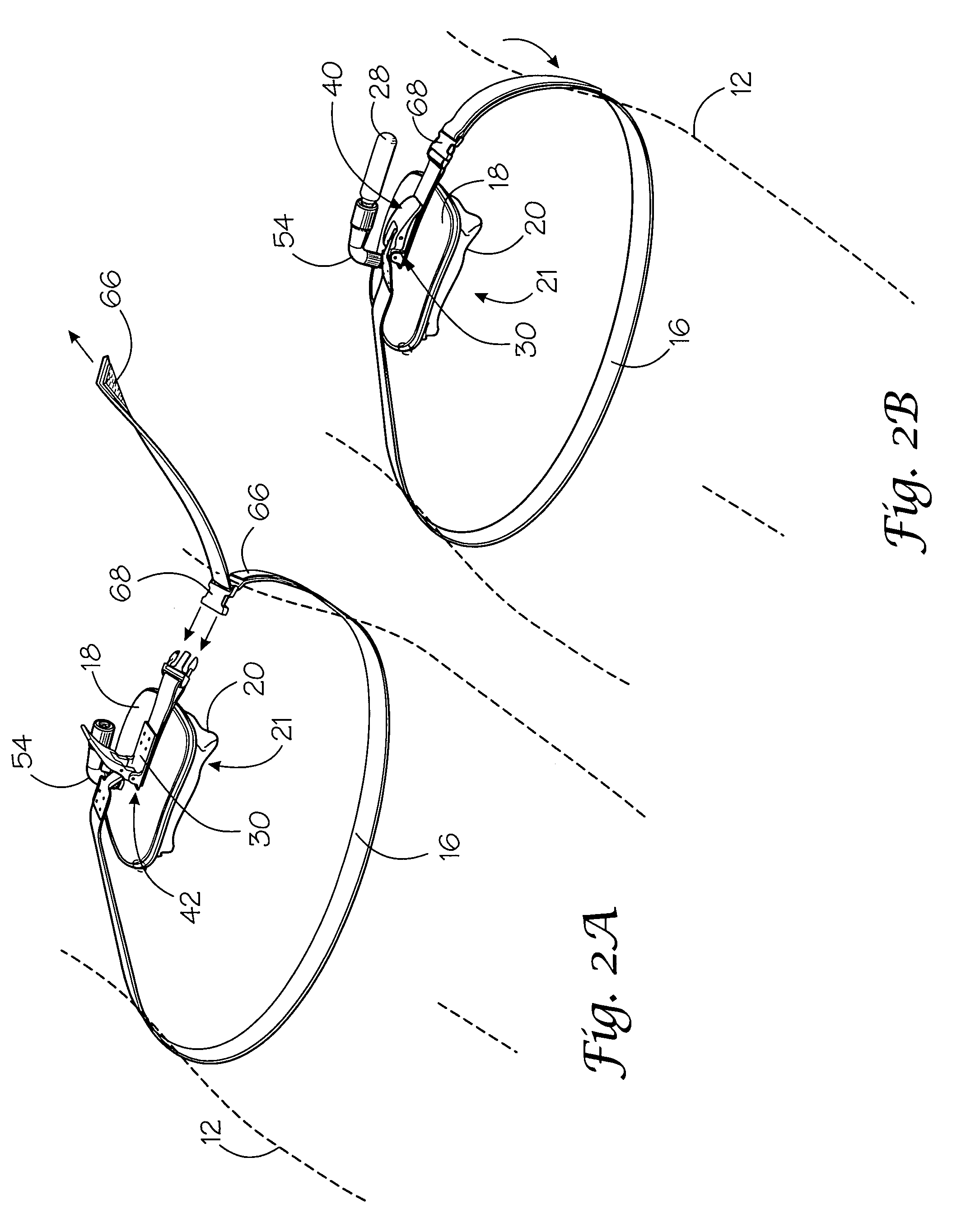
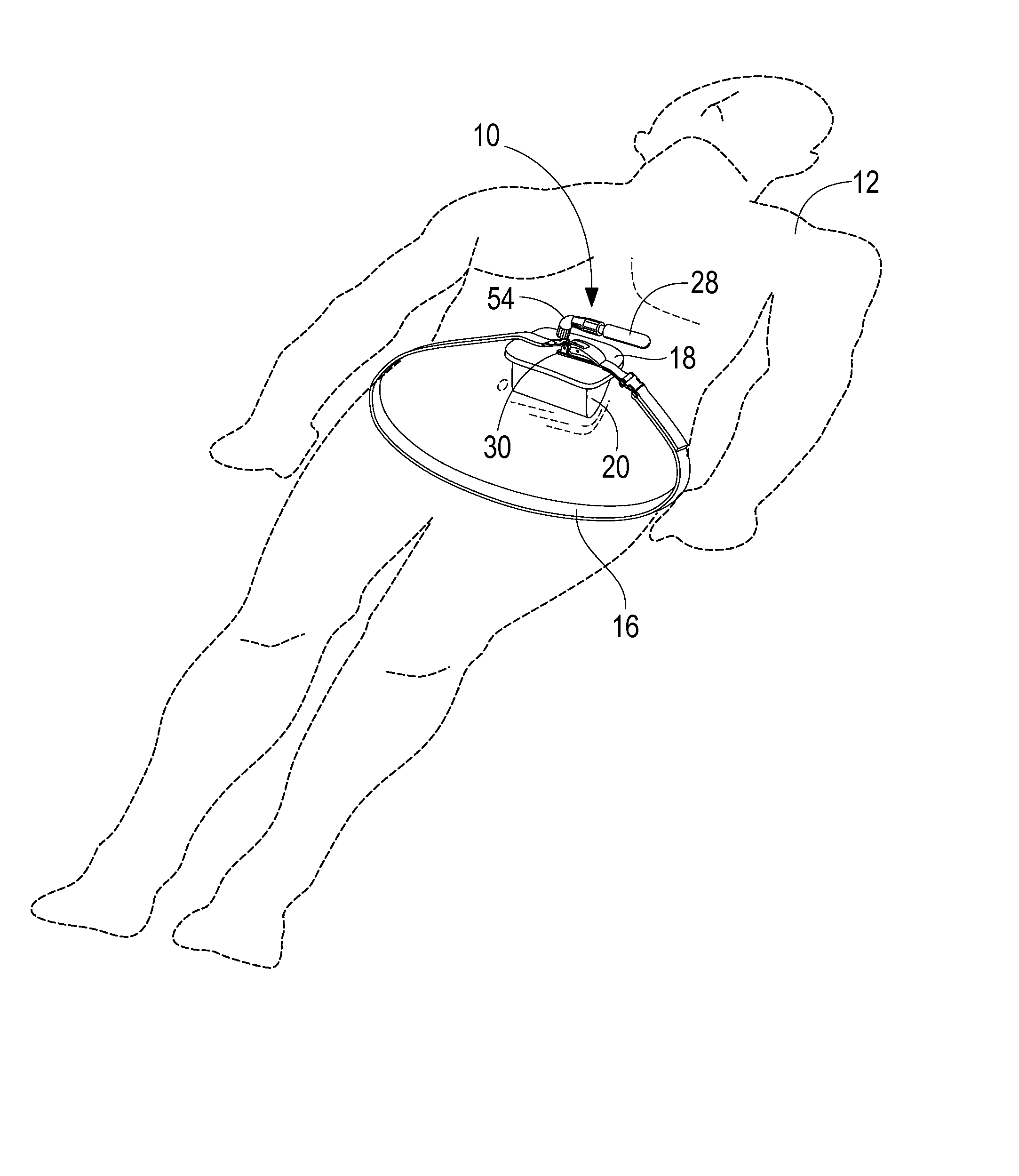
A portable pneumatic abdominal aortic tourniquet for occlusion of the abdominal descending aorta to restrict blood supply to a non-compressible arterial hemorrhage in the abdominal region. The tourniquet comprising an adjustable waist strap for securing around an abdomen; a directed air bladder mounted to the waist strap having a generally “V” shaped construction operable between a deflated condition wherein the directed air bladder is collapsed, and an inflated condition wherein the directed air bladder is expanded for exerting pressure against the abdomen; and, an air source connected to the directed air bladder for operating the directed air bladder between the deflated condition and the inflated condition.
Owner:COMPRESSION WORKS
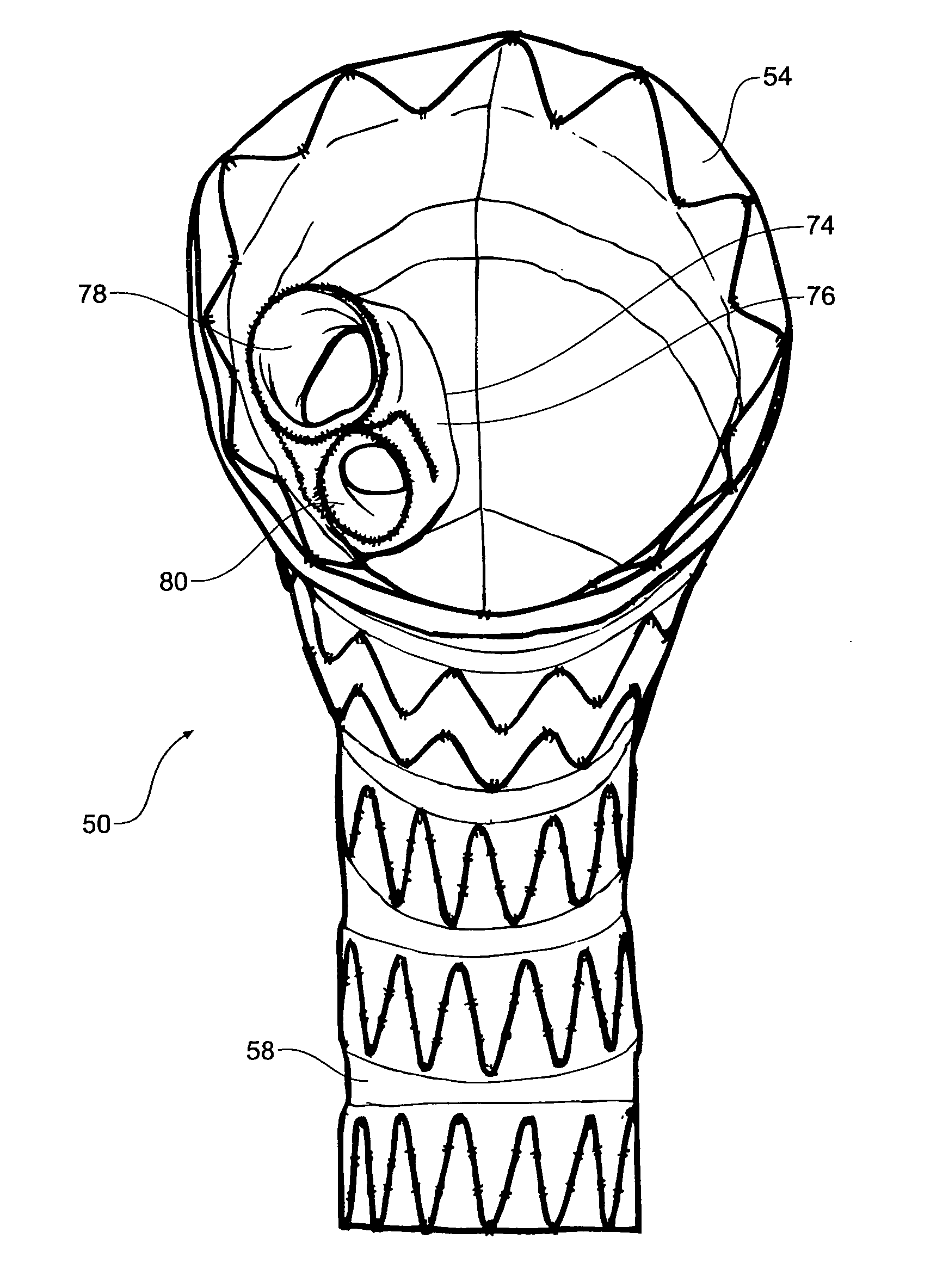
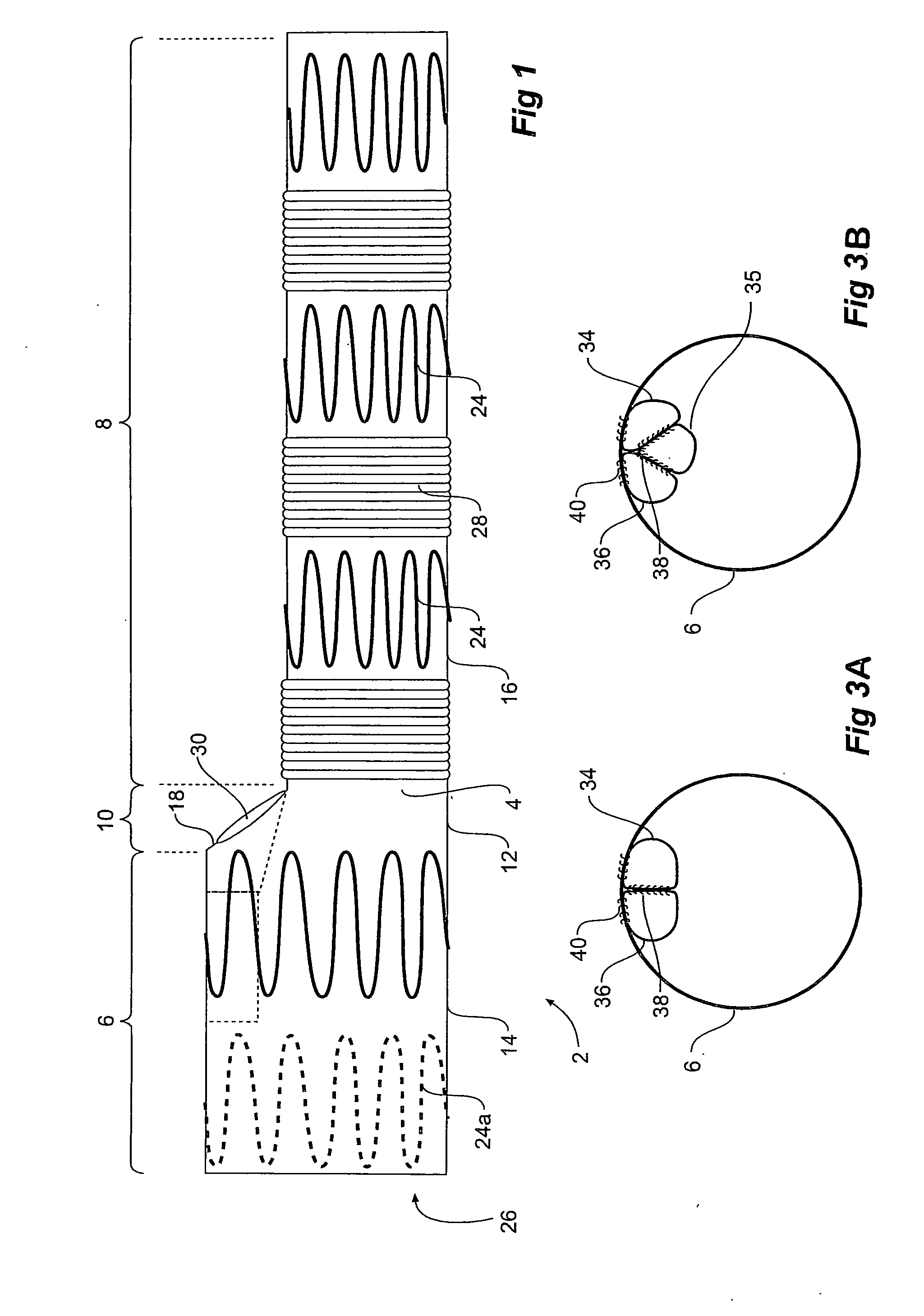
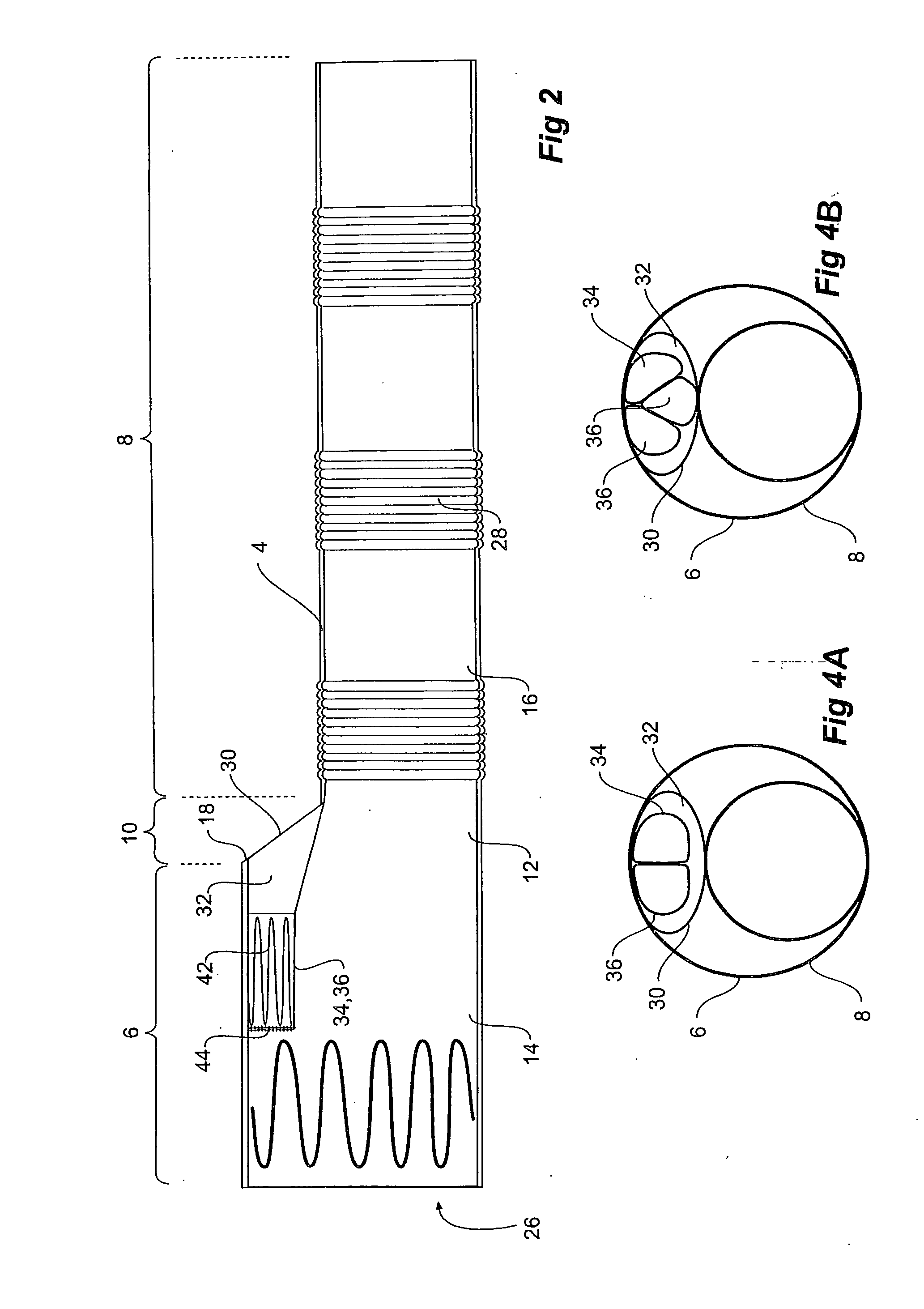
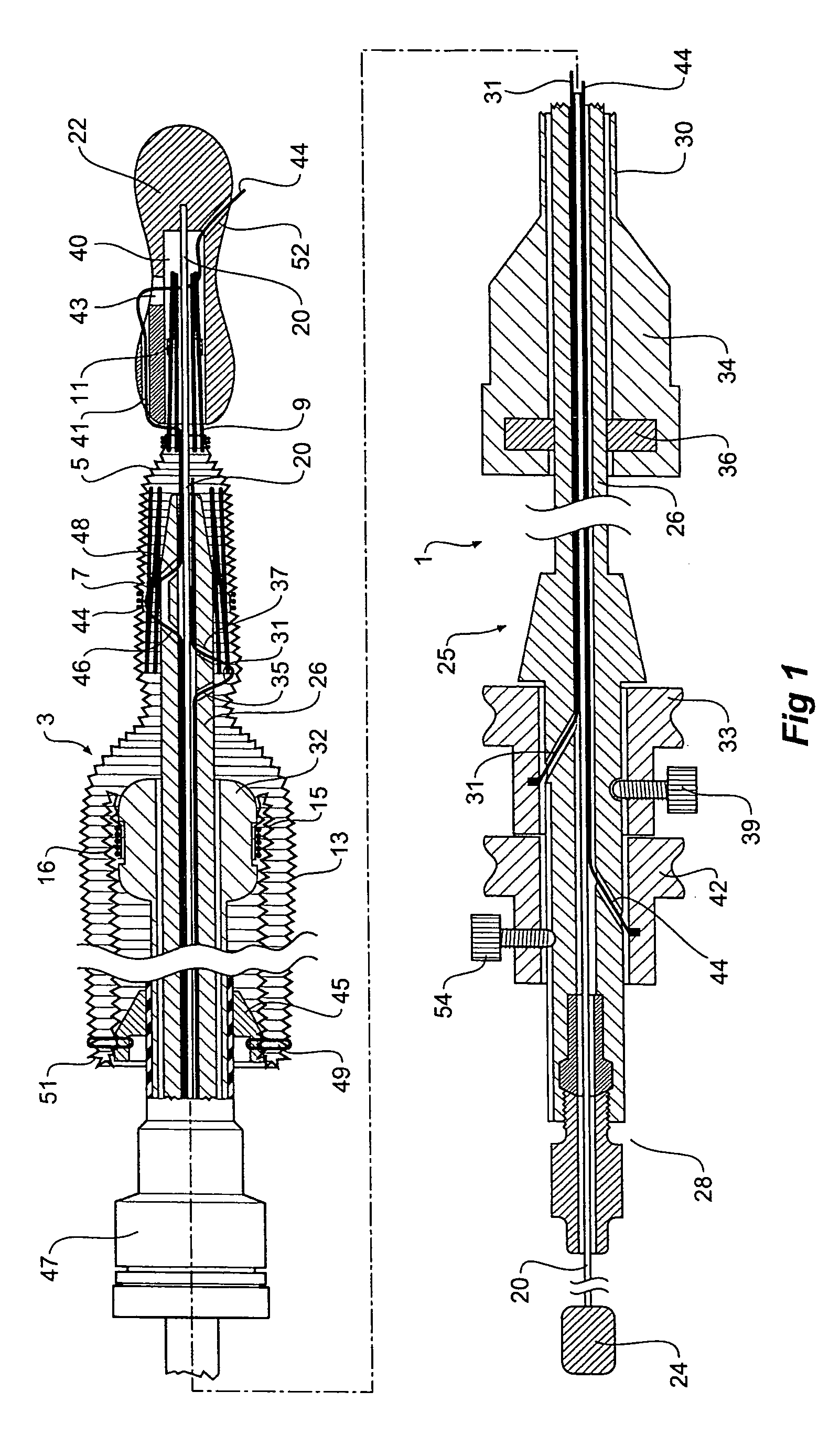
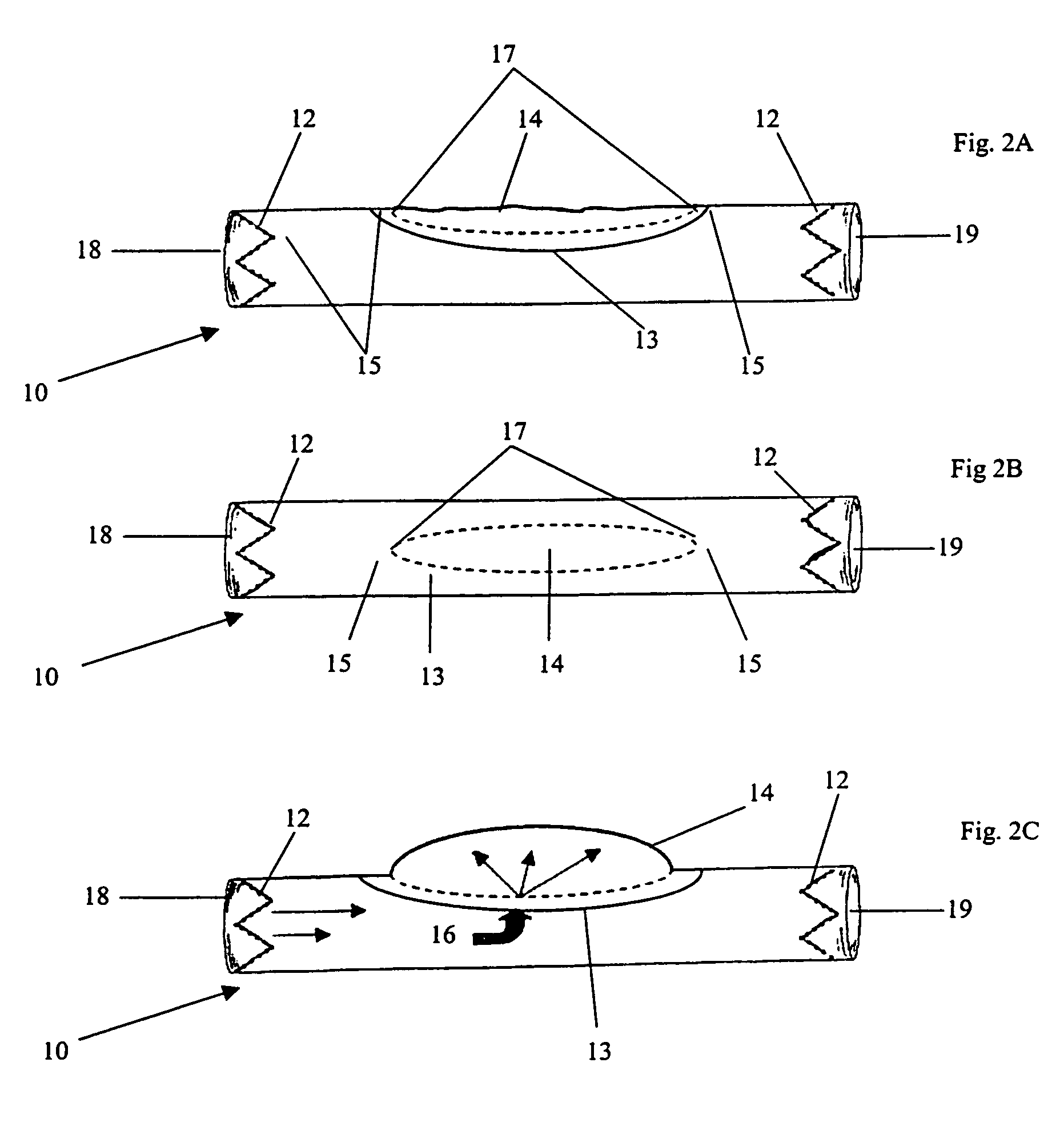
Thoracic aorta stent graft with access region
ActiveUS20110257731A1Allow for flexibility of stentAllow flexibilityStentsBlood vesselsAscending aortaThoracic aorta
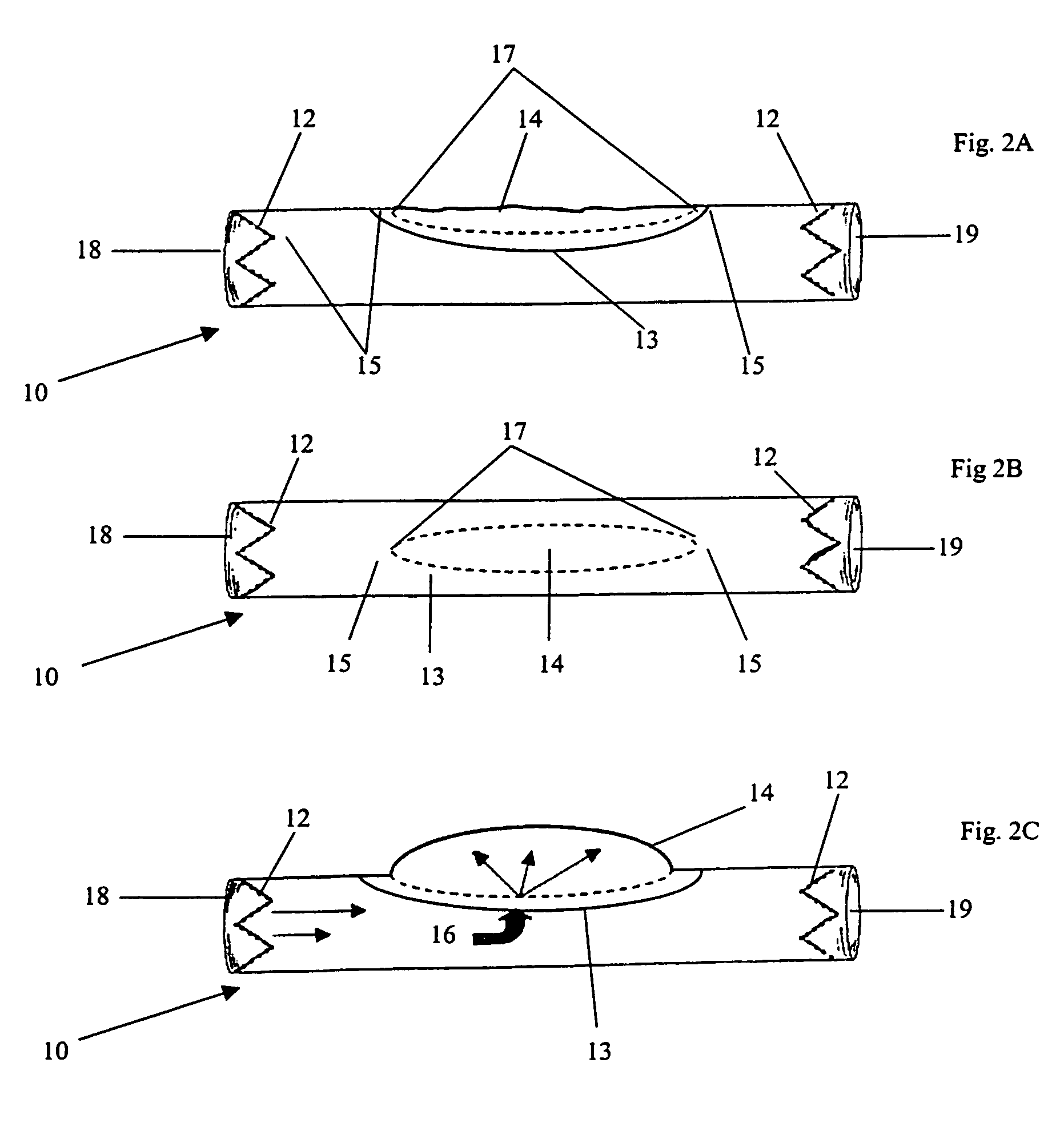
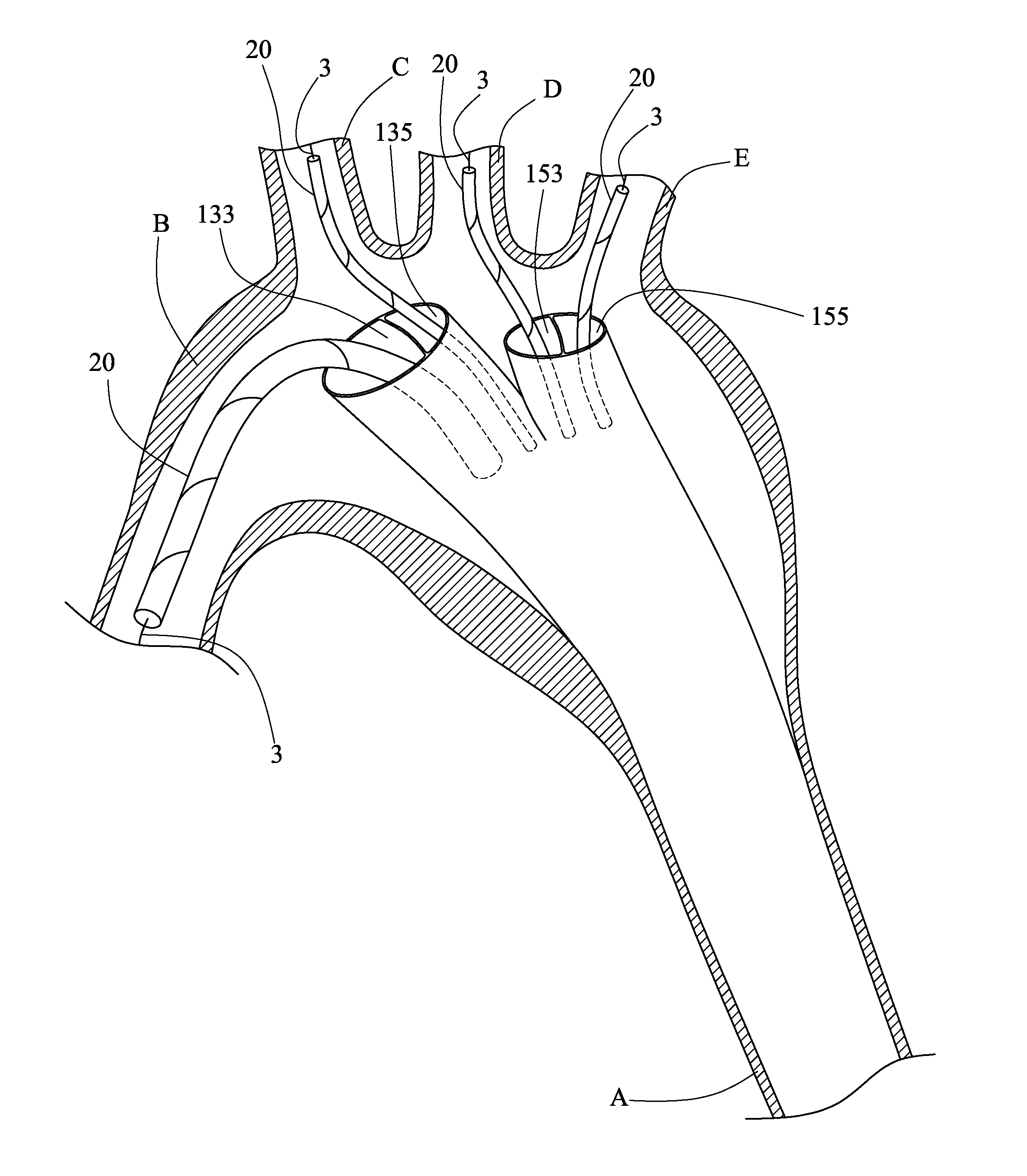
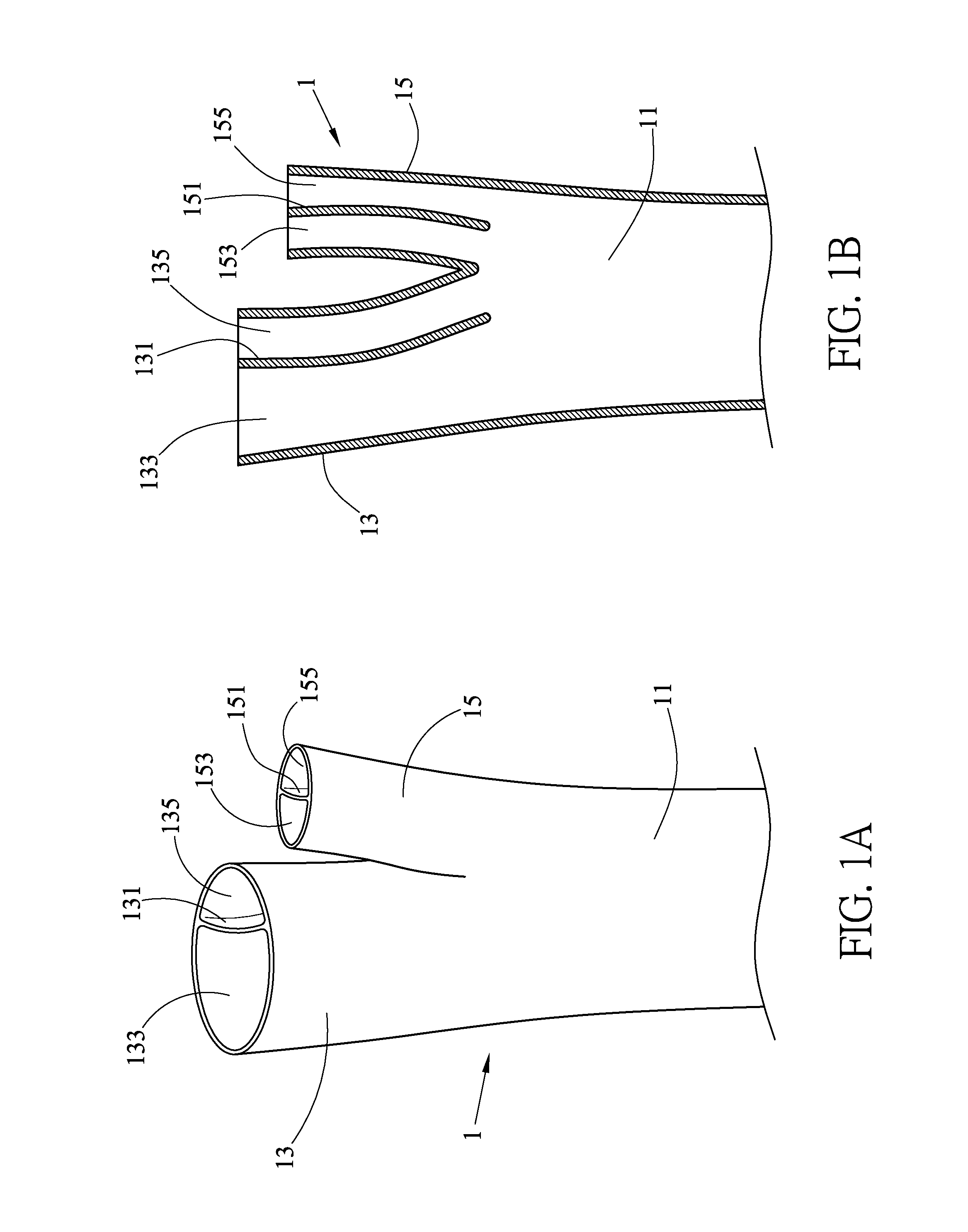
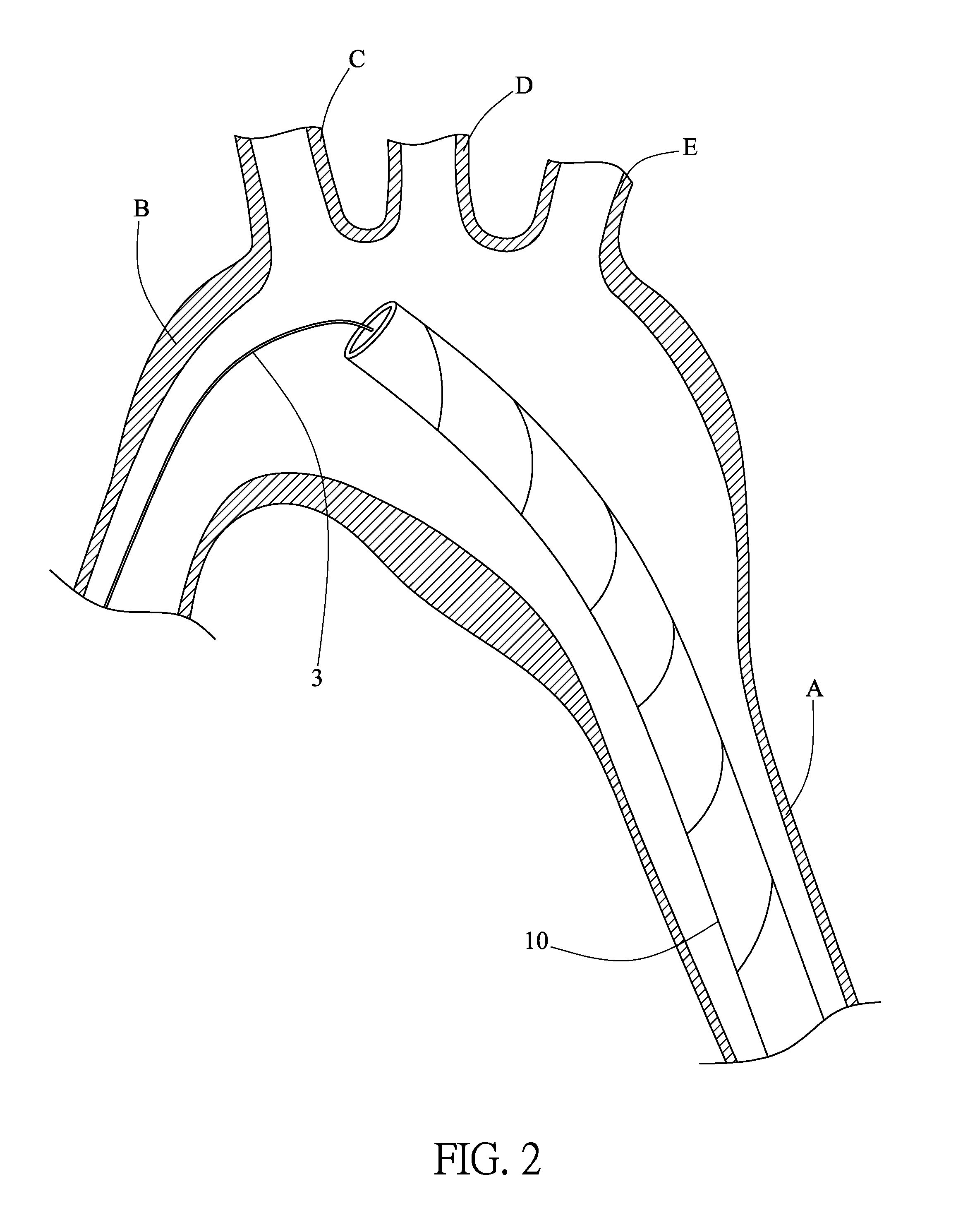
A stent graft (2) for placement in the thoracic arch of a patient has a first tubular body portion (6) with a first lumen therein for placement in the ascending aorta of a patient and a second tubular body portion (8) to extend along the thoracic arch and down the descending aorta. The second tubular body portion is of a lesser diameter than the first tubular body portion. There is a step portion (10) between the first body portion and the second body portion. The step portion is joined to and continuous with the first portion and the second portion. A first side of each of the first body portion, the step portion and the second body portion are substantially aligned so that there is a step (18) defined on a second side opposite to the first side of the body portion. There is an aperture (30) in the step portion and an internal tube (32) extending from the aperture towards the first body portion. The internal tube is divided along part of its length into at least two smaller internal tubes (34, 36) with the smaller internal tubes opening into the first lumen.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +1
Method of treatment and devices for the treatment of left ventricular failure
InactiveUS20060074483A1Improve performanceDecrease in heart rateSurgeryDilatorsLeft ventricular sizeLeft ventricular wall
The effects of acute left ventricular heart failure are mitigated by temporary support of the cardiac function through use of either one or both of an expendable temporary one-way valve positioned in the aorta, having a collapsible frame that is expanded upon deployment, and / or a temporary dilation device positioned in the descending aorta for expanding upon deployment to increase the diameter of the associated portion of the aorta. When used together, the dilation device is positioned distal to the temporary one-way valve.
Owner:SCHRAYER HOWARD L
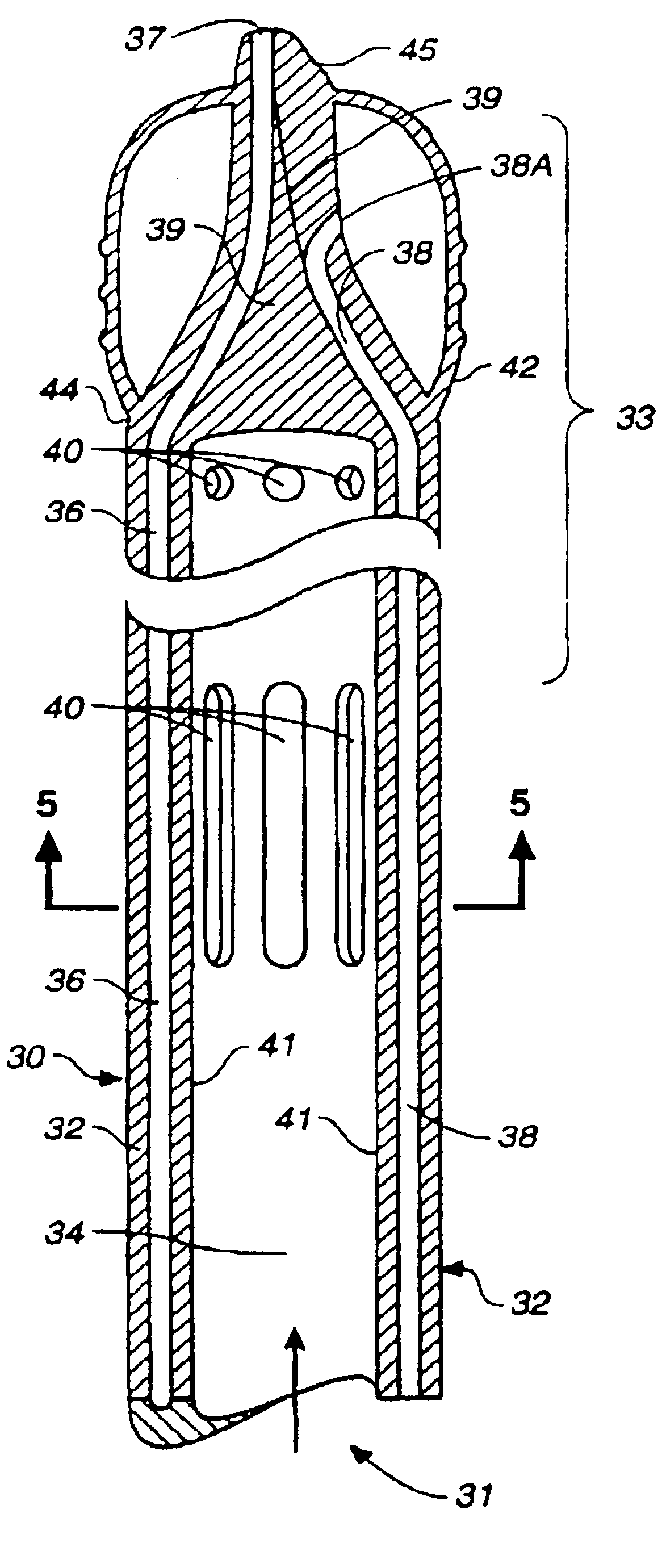
Multichannel catheter
InactiveUS6902545B2Easy to manageImprove treatmentSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisExtracorporeal circulationAscending aorta
A single, multichannel catheter is useful for extracorporeal circulation of blood to a patient undergoing cardiovascular treatments or surgery. The catheter has three independent channels and an expandable balloon at one end of the catheter. The first channel is largest and allows for delivery of blood to a patient in an amount sufficient to maintain the patient's metabolism and perfusion throughout the treatment or surgery. The second and third channels are smaller and integrated into the wall of the first channel. The second channel is for delivering a biologically active fluid to the heart and / or venting the left heart. The third channel is for delivering a fluid to the balloon for its expansion when positioned in the ascending aorta to occlude the flow of blood to the heart. One or more perfusion openings may be located in the descending aorta.
Owner:SORIN GRP USA INC
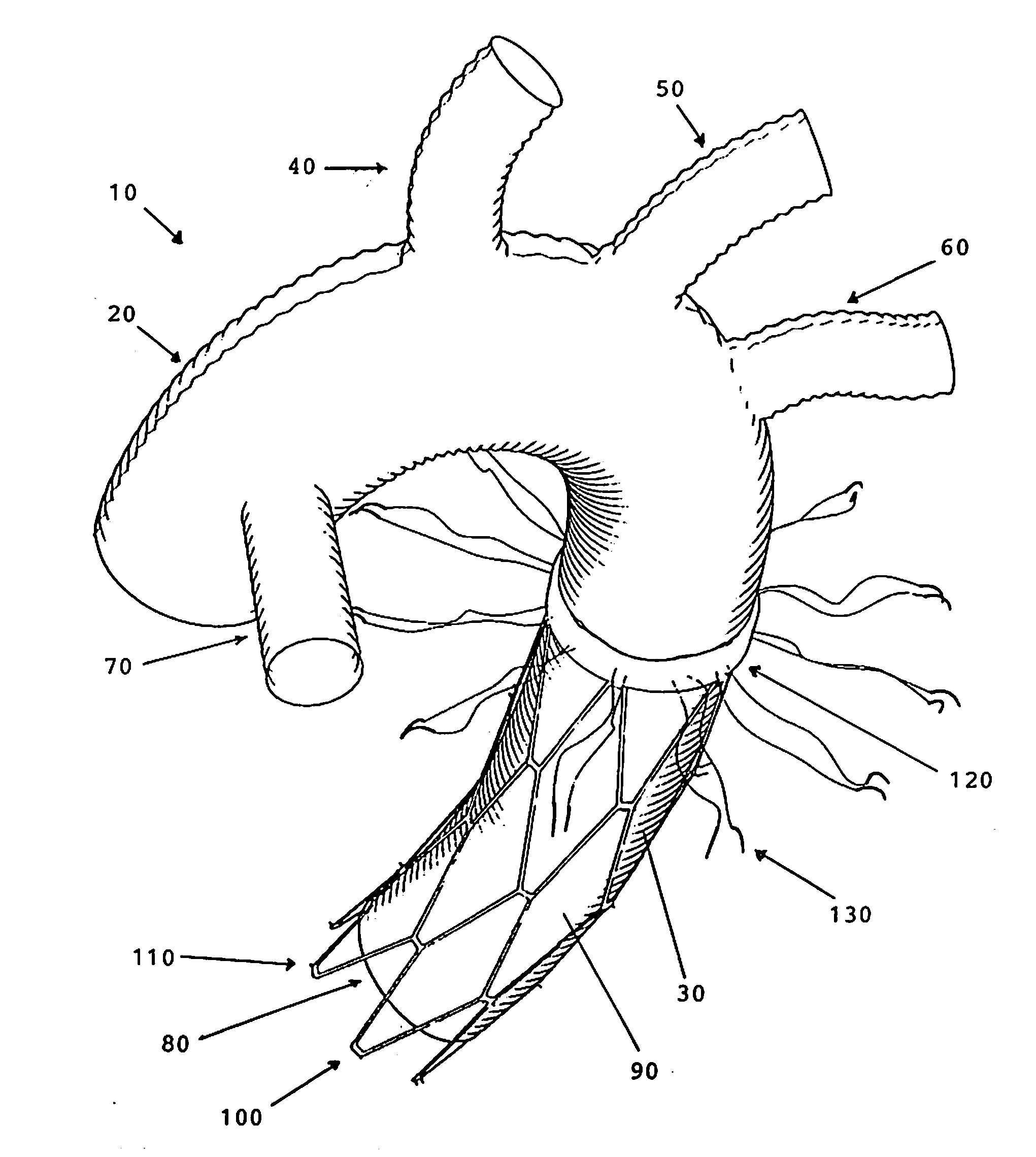
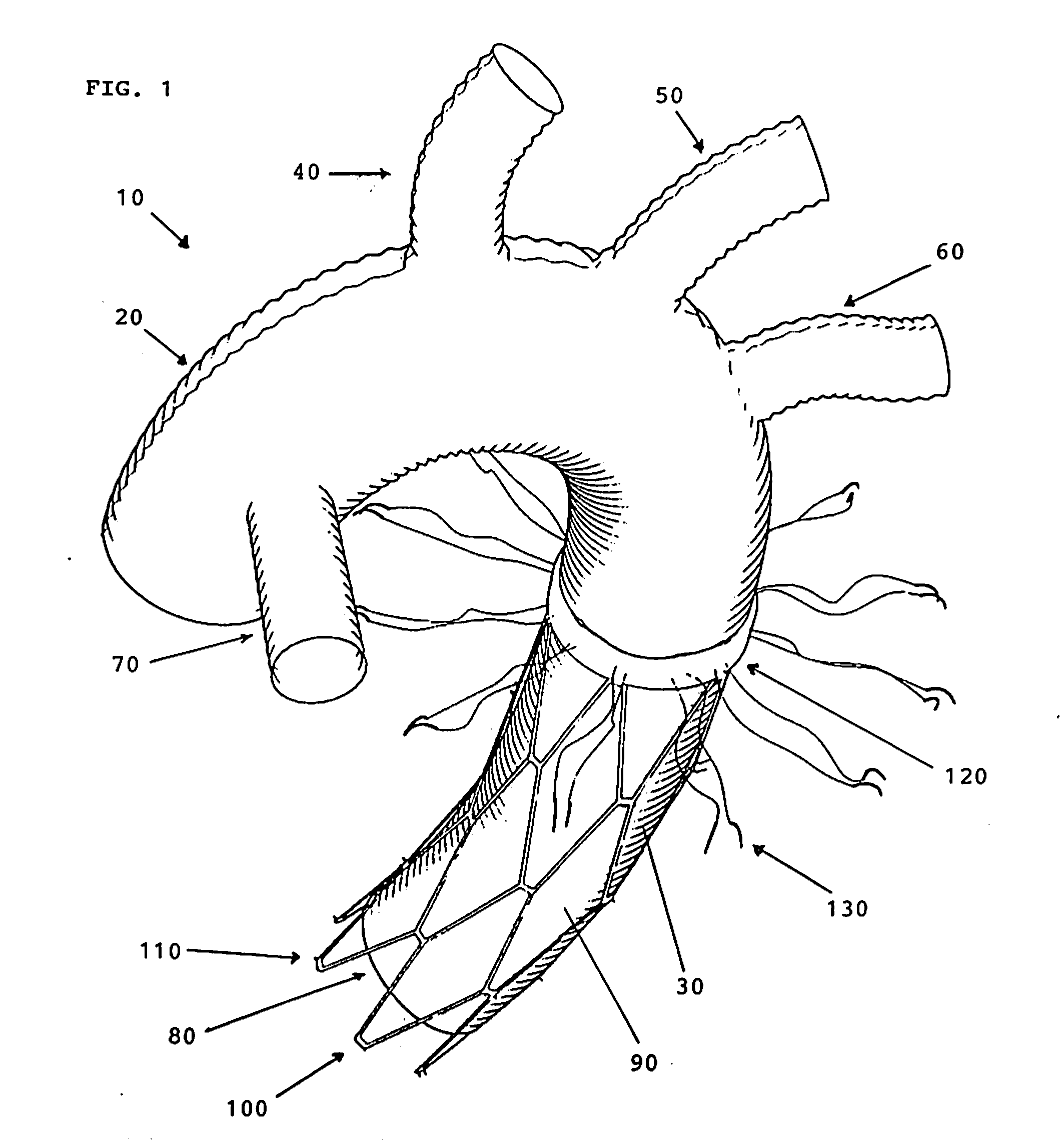
Implantation device for an aorta in an aortic arch
InactiveUS20030097170A1Simple and rapid simultaneous treatmentSpend less timeStentsBlood vesselsAortic arch aneurysmImplanted device
A stent made of a self-expandable or balloon-expandable metal mesh fabric that can be widened to a diameter larger than that of the descending aorta. The stent has a flexible lining of vessel-replacing material, wherein the lining covers it at least partly in longitudinal direction and forms a tubular segment which projects beyond the end of the stent at least at one end and which functions as the vascular prosthesis. Such implantable arrangements (1) make it possible to achieve short surgical times, especially during the treatment of aortic arch aneurysms involving the cephalic arteries.
Owner:CURATIVE
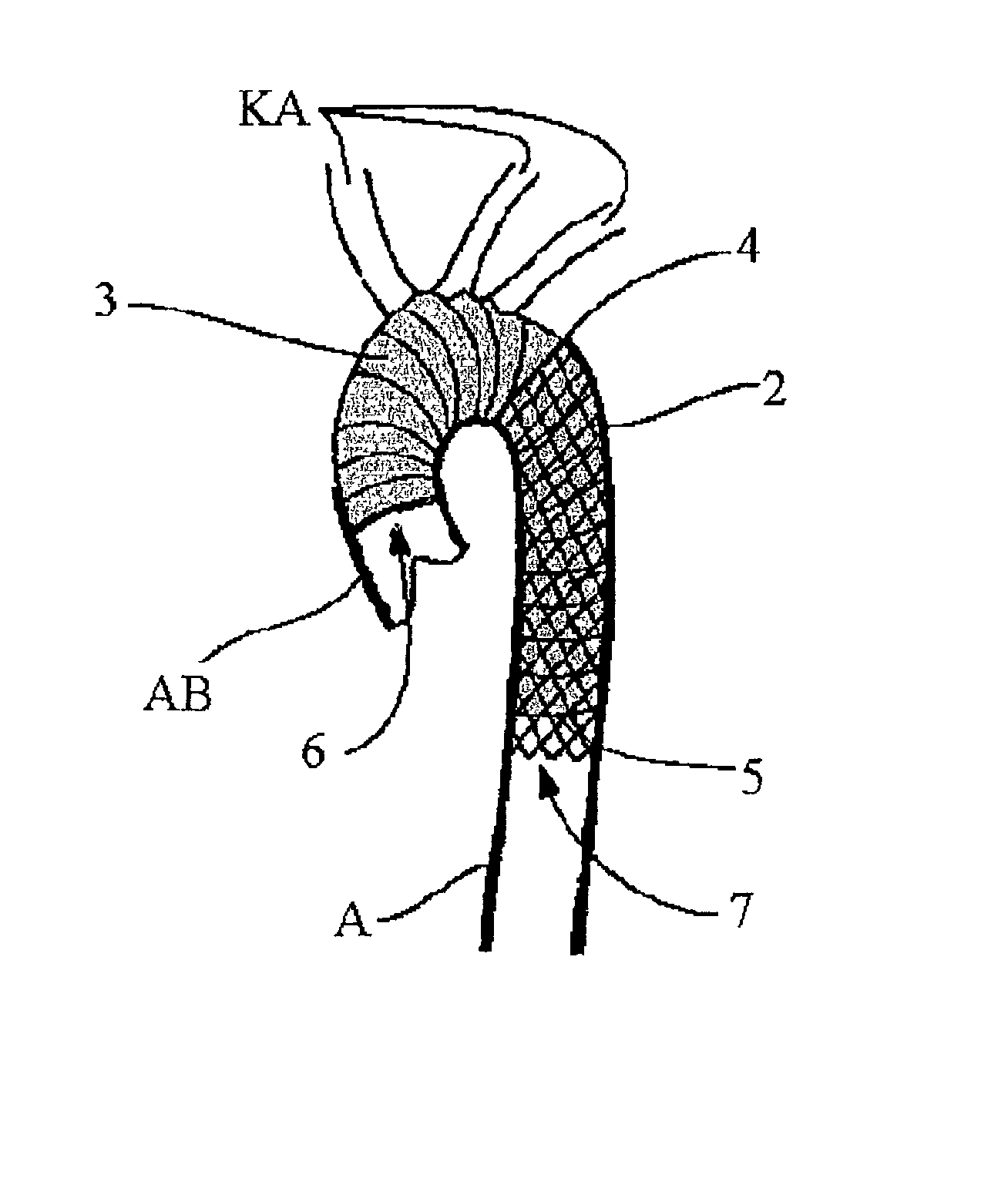
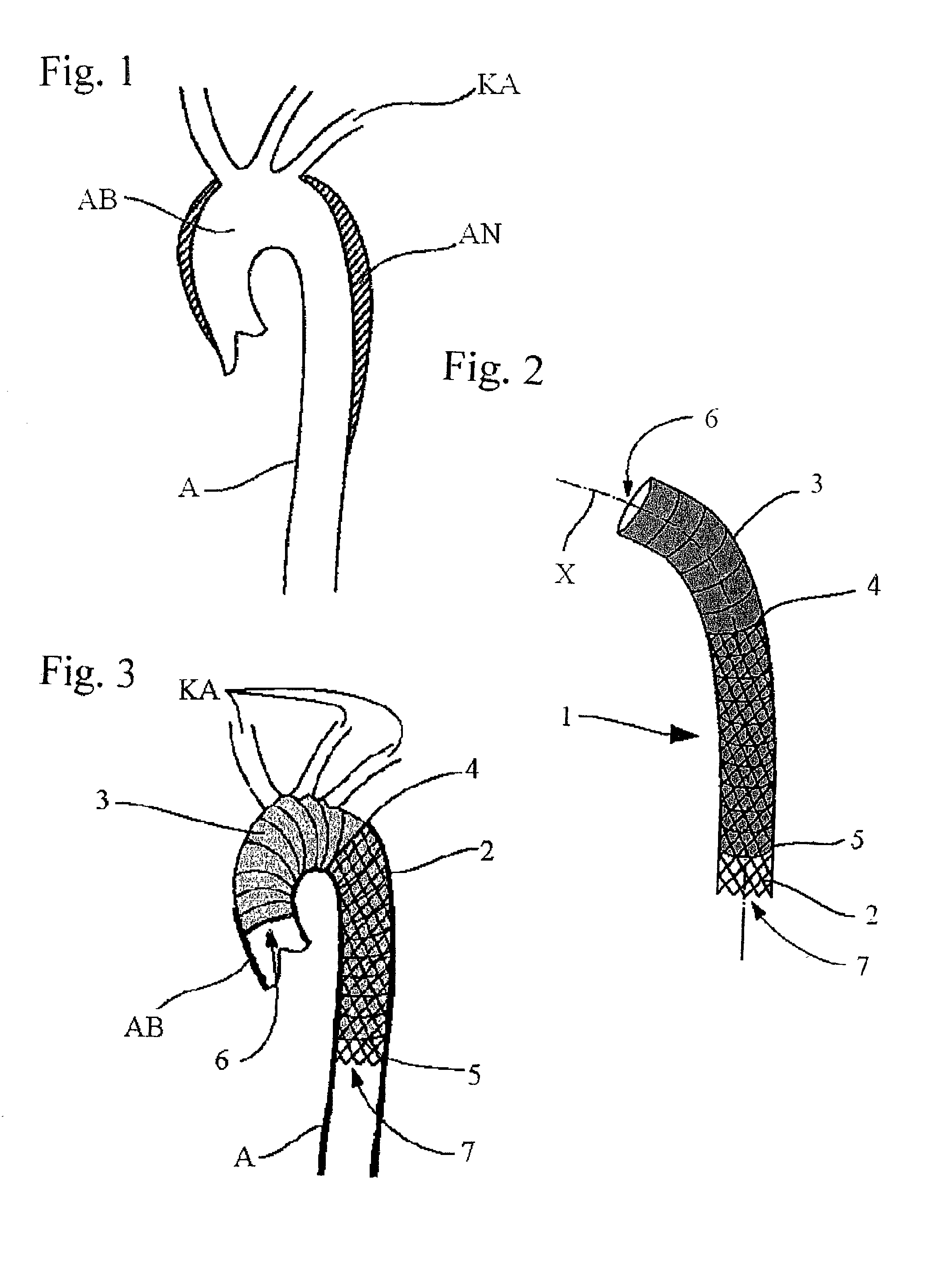
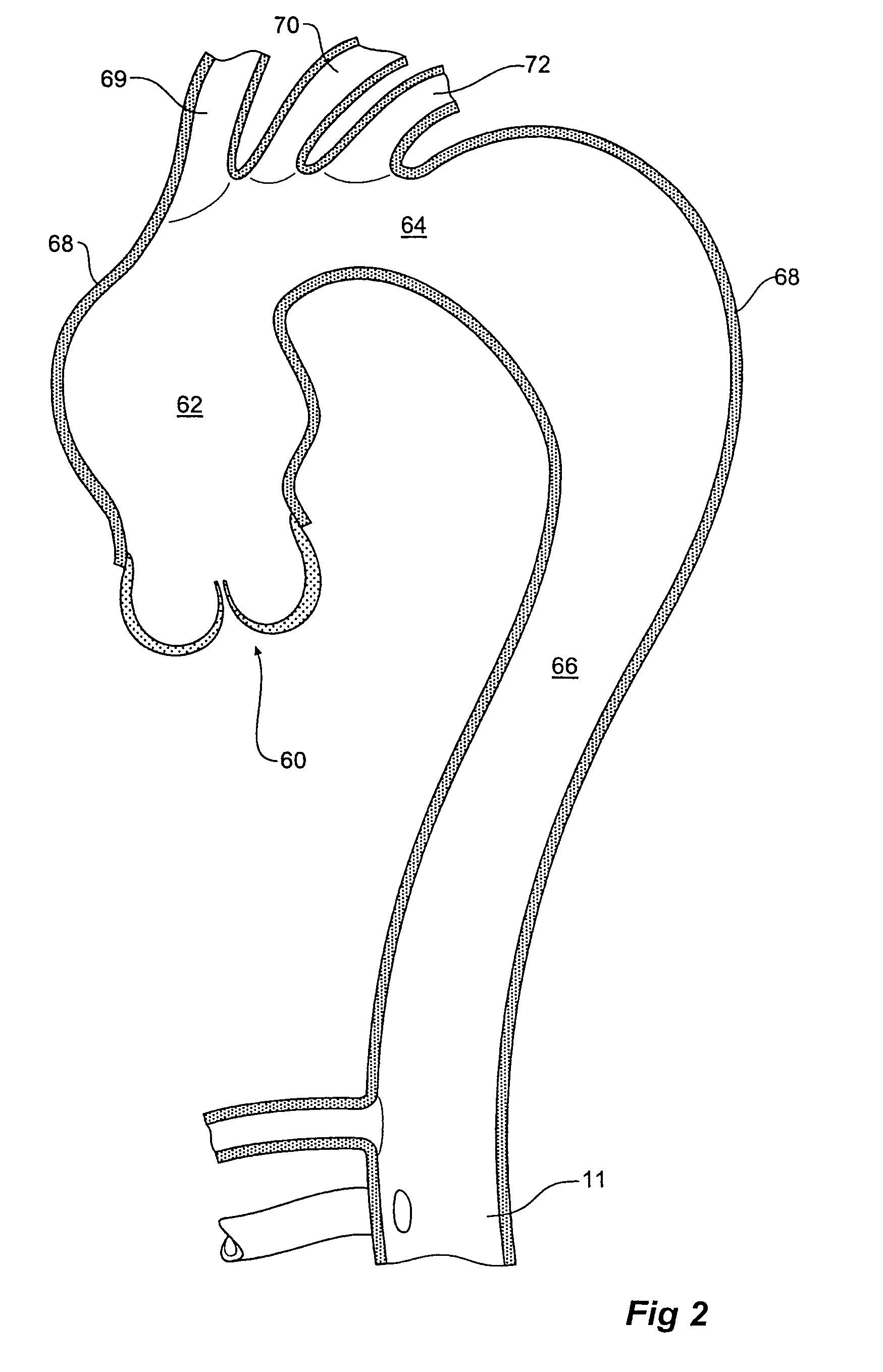
Device and method for treating thoracic aorta
A prosthesis, introducer device and a method for repair of an aortic aneurysm which is positioned at least partially in the ascending aorta (62). The prosthesis (3) has a proximal end (15) and a distal end (5) and is formed from a biocompatible material, the proximal end is adapted to be surgically fastened adjacent and around the aortic heart valve (60) of a patient and the distal end is adapted to extend into the descending aorta (66). The distal end has a distally extending exposed self-expanding stent (9). The introducer device can be deployed through an incision (75) in the thoracic arch (64) and extend down the descending aorta to place the distal end of the prosthesis first and then removed so that the proximal end of the prosthesis can be sutured in place around the aortic heart valve (60).
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +2
Exclusion of ascending/descending aorta and/or aortic arch aneurysm
Owner:TAHERI SYDE A
Thoracic aorta stent graft with access region
A stent graft (2) for placement in the thoracic arch of a patient has a first tubular body portion (6) with a first lumen therein for placement in the ascending aorta of a patient and a second tubular body portion (8) to extend along the thoracic arch and down the descending aorta. The second tubular body portion is of a lesser diameter than the first tubular body portion. There is a step portion (10) between the first body portion and the second body portion. The step portion is joined to and continuous with the first portion and the second portion. A first side of each of the first body portion, the step portion and the second body portion are substantially aligned so that there is a step (18) defined on a second side opposite to the first side of the body portion. There is an aperture (30) in the step portion and an internal tube (32) extending from the aperture towards the first body portion. The internal tube is divided along part of its length into at least two smaller internal tubes (34, 36) with the smaller internal tubes opening into the first lumen.
Owner:COOK MEDICAL TECH LLC +1
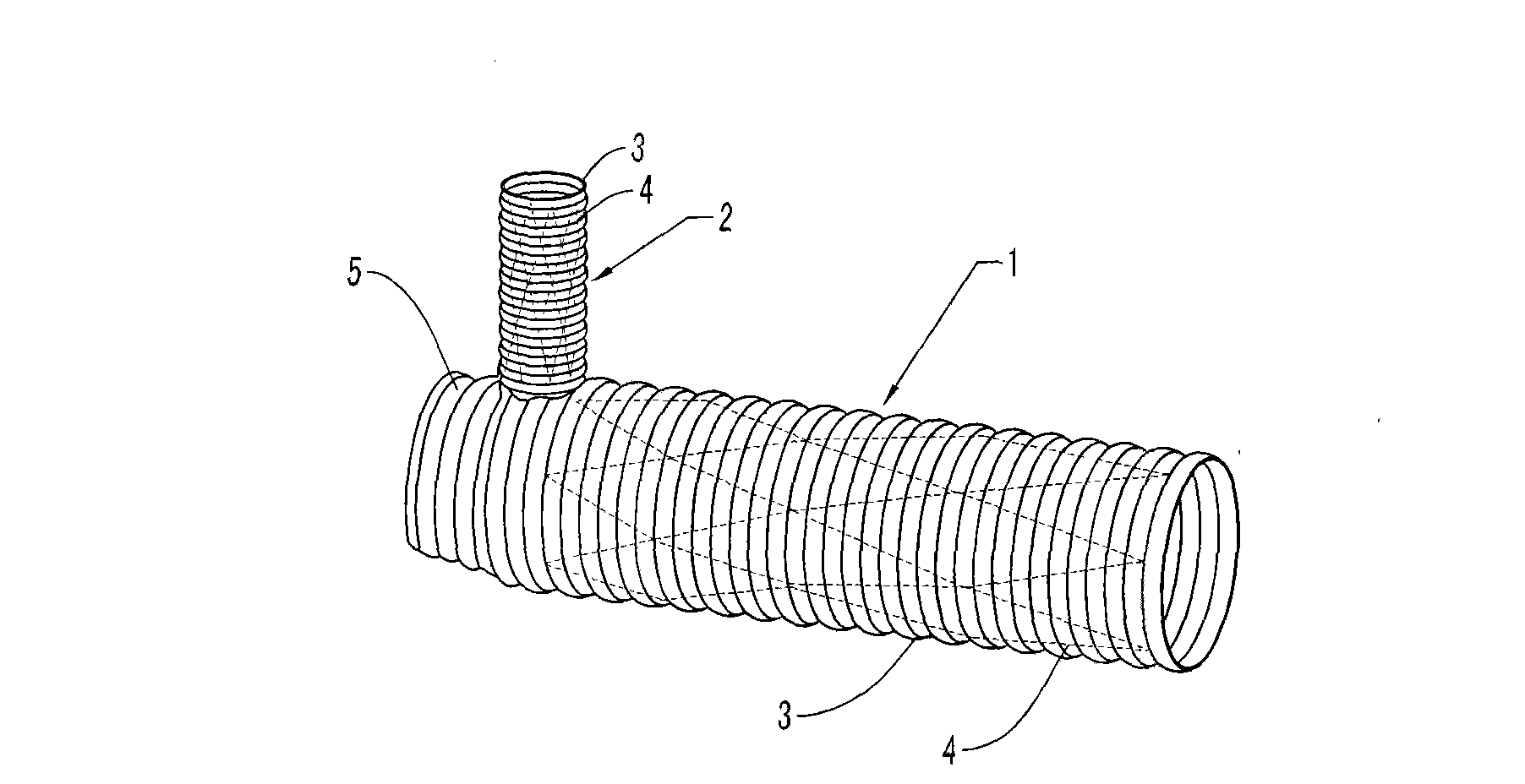
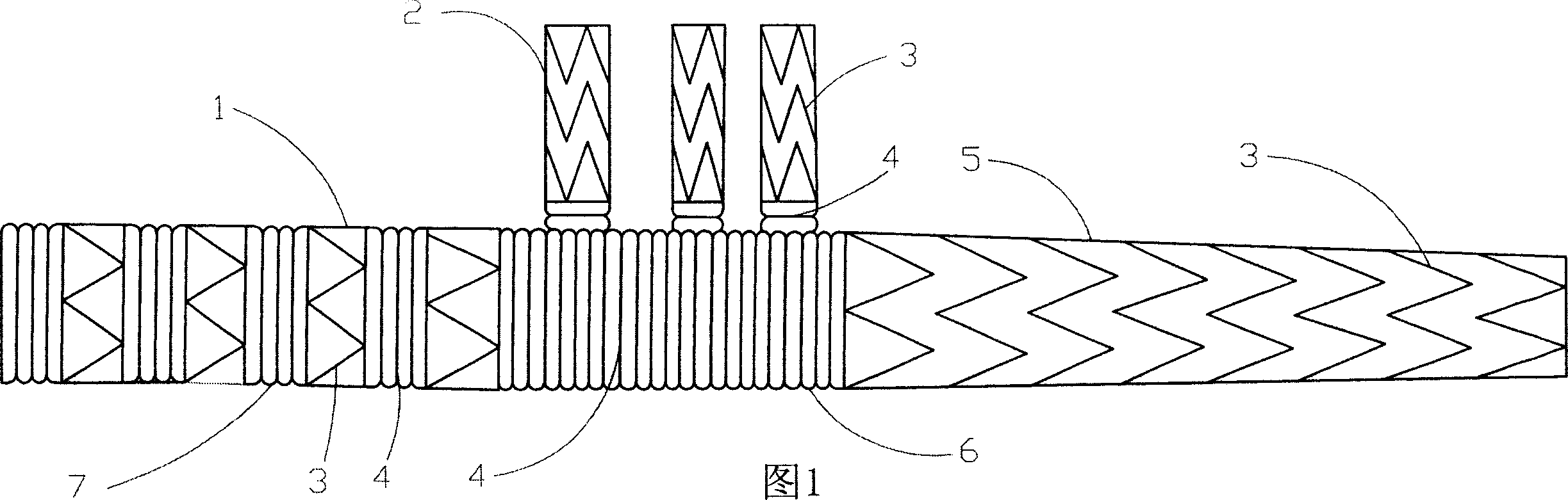
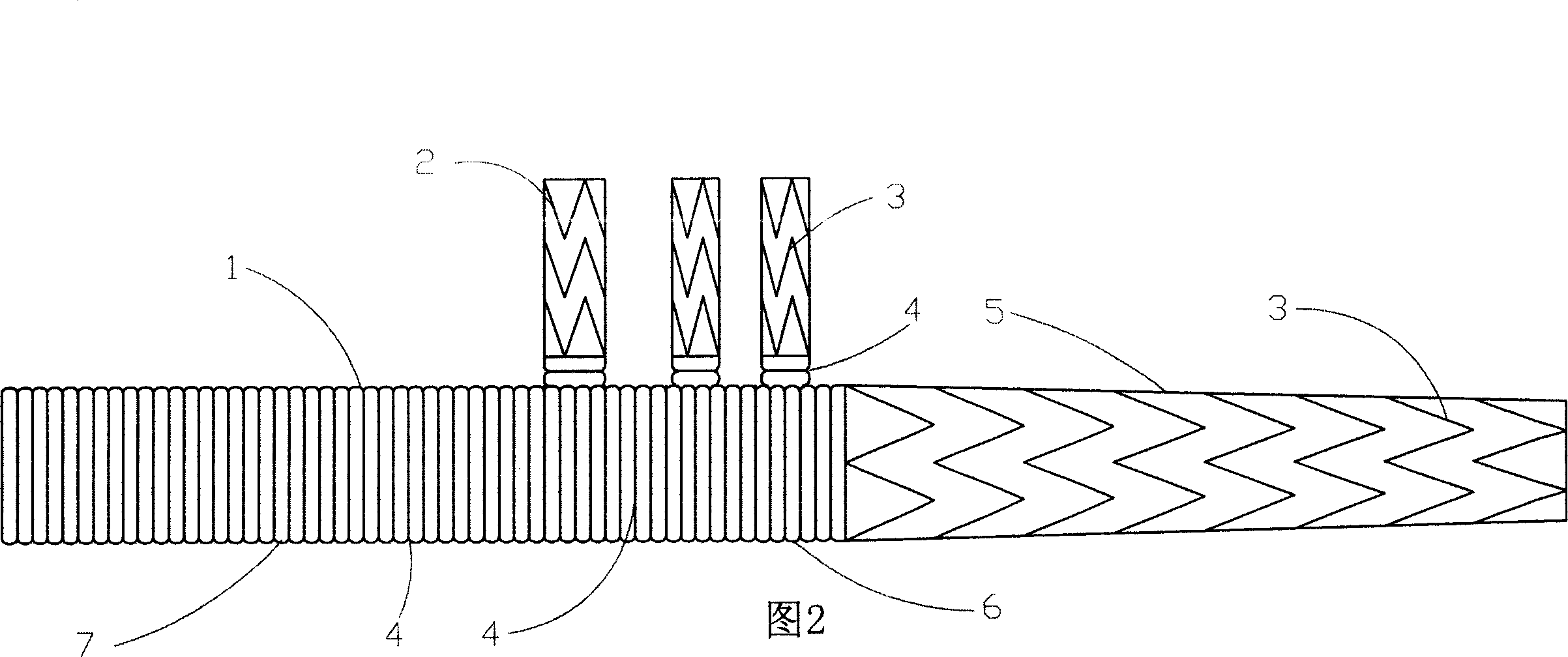
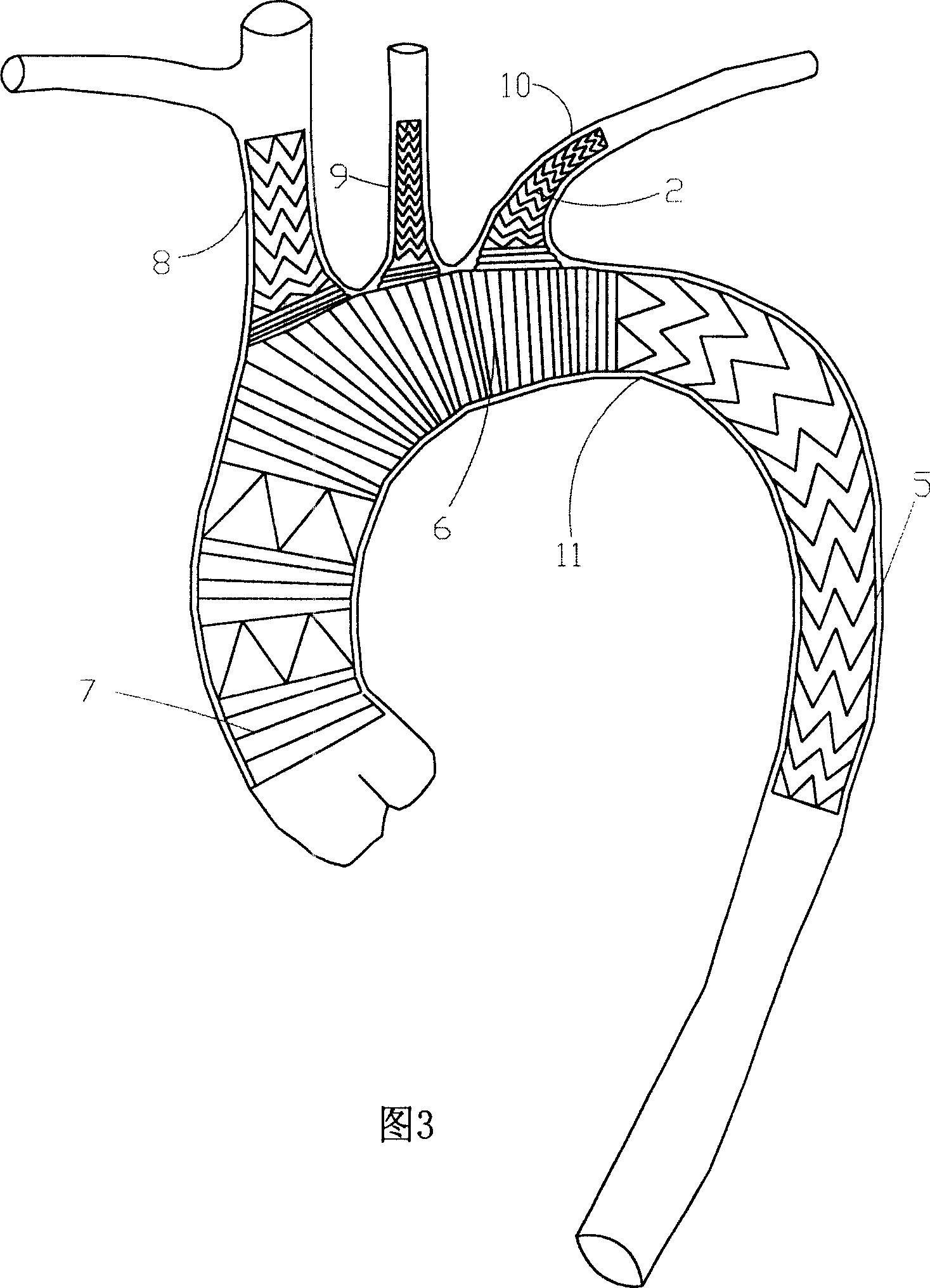
Branch artificial blood vessel bracket applied in surgery
The invention relates to a branch artificial blood vessel bracket applied in surgery, which is provided with a terylene fabric blood vessel and a large bracket lined with a harder memory alloy wire; an artificial blood vessel of 1cm long without alloy wires is arranged at the near end and taken as a sewing ring; the branch artificial blood vessel bracket is characterized in that the near end of the large bracket is sewed by a small bracket; and the small bracket consists of the terylene fabric blood vessel and the lined soft memory alloy wire. The branch artificial blood vessel bracket creatively adds a branch bracket used for supporting the true lumen of left subclavian artery so as to keep smooth and complete left subclavian artery and the distal end of thoracic descending aorta, overcome the defects of the current surgery and avoid the coincidence of the left subclavian artery; and the distal end coincident hole is arranged between the innominate artery and the left common carotid artery, thus solving the most difficult point of the technique.
Owner:陈良万 +2
Three-collateral bracket vascellum for arcus aortae
InactiveCN101152109AReduce the incidence of injuryReduce the chance of bleedingStentsBlood vesselsLeft subclavian arteryBlood vessel
The present invention relates to aortic arch three collateral support blood vessels comprising an aorta support vascular that comprises an aorta ascenden section, an aortic arch section and an aorta section; the aorta support vascular also comprises three collateral artery support vasculars which are fixed respectively on an aortic arch section arc surface of the aorta support vascular and are formed into an five-way type. The three collateral artery support vasculars are corresponding respectively to an arteria anonyma, a left common carotid artery and a left subclavian artery. The invention is capable of greatly simplifying an operation process and greatly shortens the time of a deep hypothermia and a circulation arrest, which is characterized by not only omitting an inosculation between an artificial vascular graft and three branches of the aortic arch but also reducing bleeding rate and operation risk. In an operation, the invention changes an operation method from a partial blood vessel replacement plus partial endovascular repair to a complete endovascular repair.
Owner:黄方炯
Exclusion of ascending/descending aorta and/or aortic arch aneurysm
A system and method for exclusion of an aneurysm of an aortic arch region using a graft delivery system capable of maneuvering around an aortic arch, an aortic arch graft, and an occluder system for isolating an aneurysm while occluding one or more corresponding arteries, and with bypass of those arteries being performed using one or more selected bypass grafts. The graft may be branched or branchless. The graft delivery system has a flexible sheath that is manipulated manually with the aid of a guidance system. A hoist delivery system may also be provided. The occluder system may comprise independent occluders with one or more anchor members adjacent to one end. Alternatively, the occluders can be provided as part of the aortic arch graft, either as a built-in singular self-deploying occluder or as built-in multiple occluders. A kit is also provided containing a graft, stents, occluders, and optional delivery system.
Owner:TAHERI SYDE A
Portable pneumatic abdominal aortic tourniquet
Owner:COMPRESSION WORKS
Portable pneumatic abdominal aortic tourniquet with supplemental tensioning means
ActiveUS20150032149A1Facilitating effective aorta occlusionEffective occlusionTourniquetsArterial hemorrhageTourniquet time
A portable pneumatic abdominal aortic tourniquet for occlusion of the abdominal descending aorta to restrict blood supply to a non-compressible arterial hemorrhage in or below the inguinal region is presented. The tourniquet includes an adjustable waist strap for securing it around the abdomen of a patient and a windlass rod connected to the waist strap to selectively tighten the strap as needed to tightly secure it to patient. A directed air bladder is mounted to the waist strap having a generally “V” shaped construction and is expanded for exerting directed pressure against the abdomen. Upon inflation of the air bladder and adjustment of the windlass, occlusion or restriction of blood flow through the abdominal descending aorta will occur which will achieve cessation of hemorrhage in or below the inguinal area or achieve other therapeutic effects like elevated blood pressure to enhance CPR or blood flow control to the lower extremities.
Owner:COMPRESSION WORKS
Methods and devices for improving cardiac output
InactiveUS20060241544A1Facilitate cardiac output functionEliminate the problemExcision instrumentsIntravenous devicesProsthesisCatheter
Owner:CORLIFE GBR
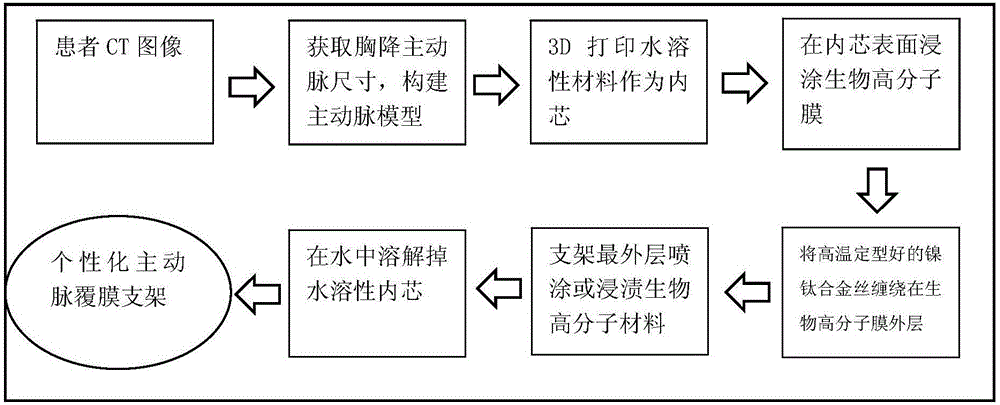
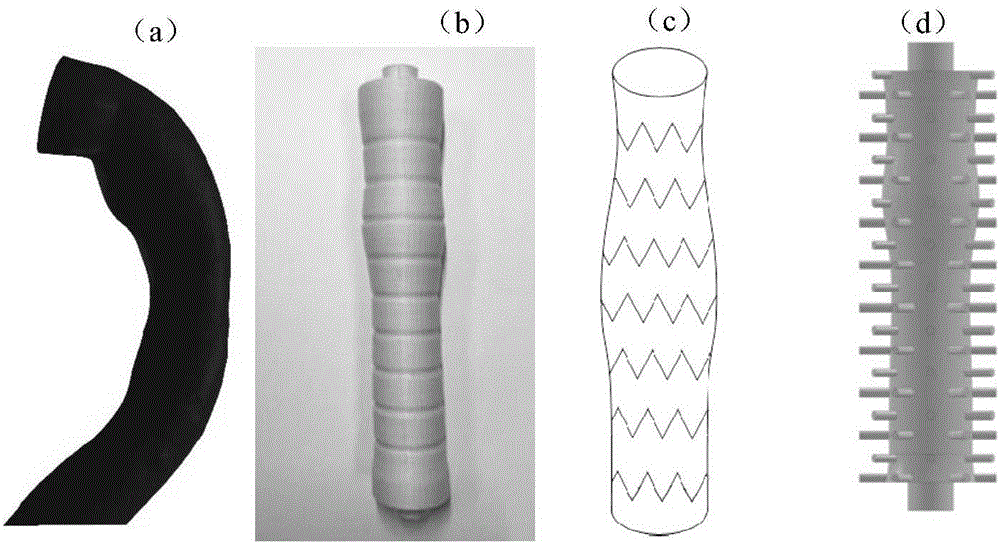
Method for forming aortic stent graft
InactiveCN106491241AEfficient preparationMade preciselyStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusAorta partDip-coating
The invention discloses a method for forming an aortic stent graft. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an image of aorta, and extracting a three-dimensional (3D) model of the aorta according to the image; extracting diameter characteristics of the aorta in the axial direction of the aorta of the 3D model; reconstructing an aortic vascular model according to the extracted diameter characteristics; 3D-printing a water-soluble vascular inner core according to the aortic vascular model; dip-coating a polymer film on a surface of the water-soluble vascular inner core; spirally weaving a metal mesh outside the treated water-soluble vascular inner core as a metal stent; bonding the polymer film and the metal stent, and then removing the water-soluble vascular inner core to obtain the aortic stent graft. The method provided by the invention can efficiently and accurately manufacture a vascular stent graft according to the actual size of a thoracic descending aorta of a patient based on a 3D printing technology, can effectively solve a detect that an existing equal-diameter vascular stent does not match a true vascular size of the patient, provides an effective medical means for treatment of acute vascular aneurysm, and has important clinical value.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Method of implanting an aortic stent
A method of implanting an aortic stent comprising steps of: putting a main tube on a metal guide wire; moving the main tube along the metal guide wire to the descending aorta, the main tube is constrained by a first cover, and first and second tube bifurcations are branched from the main section; removing the first cover; inserting a second and third metal guide wire through the first tube bifurcation into the ascending aorta and branchiocephalic artery respectively; a first and a second tube branch moving into the ascending aorta and the branchiocephalic artery respectively; inserting a fourth and fifth metal guide wire through the first tube bifurcation into the ascending aorta and branchiocephalic artery respectively; a third and a fourth tube branch moving into left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery respectively; removing a second cover constraining said tube branches.
Owner:VICTOR ACTION LTD
Portable pneumatic abdominal aortic compression system
InactiveUS20130310872A1Reduce and occlude flowSufficient forceTourniquetsArterial hemorrhageTourniquet time
A portable pneumatic abdominal aortic tourniquet for occlusion of the abdominal descending aorta to restrict blood supply to a non-compressible arterial hemorrhage in the abdominal region. The tourniquet comprising an adjustable waist strap for securing around an abdomen; a directed air bladder mounted to the waist strap having a generally “V” shaped construction operable between a deflated condition wherein the directed air bladder is collapsed, and an inflated condition wherein the directed air bladder is expanded for exerting pressure against the abdomen; and, an air source connected to the directed air bladder for operating the directed air bladder between the deflated condition and the inflated condition.
Owner:COMPRESSION WORKS
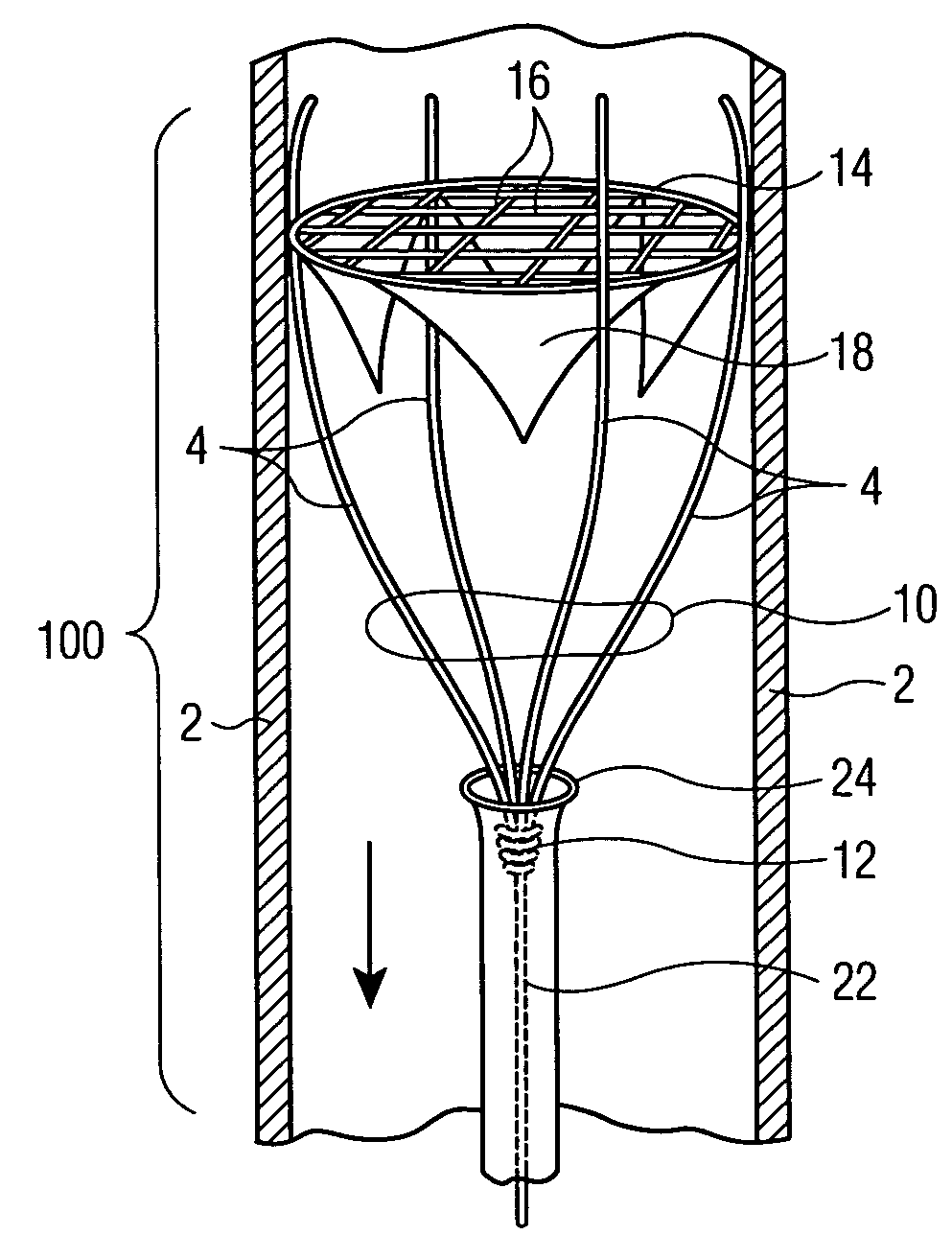
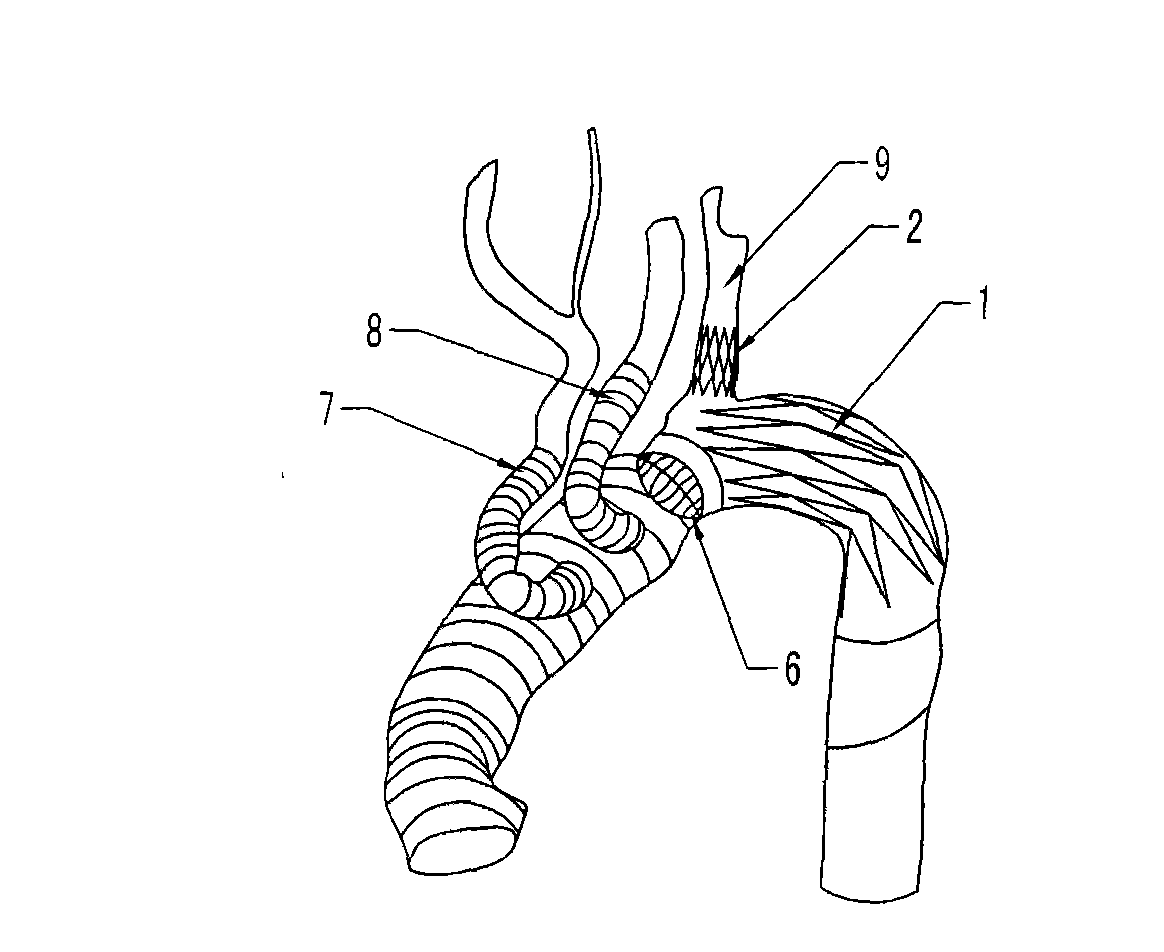
Total aortic arch reconstruction graft
A total aortic arch reconstruction graft, includinga) a first, hollow cylindrical segment in the shape of an aortic arch and adapted to be joined to a patient's ascending aorta, and including three side hollow cylindrical branches in communication therewith and adapted to be joined to a patient's left subclavian artery, left common carotid artery and innominate artery, respectively, and a fourth hollow cylindrical branch adapted to be joined to a heart-lung machine;b) a second, hollow cylindrical segment having a first end being joined to the second end of the first segment, and a second end adapted to be inserted into the descending aorta of a patient, the second segment having an expandable outer wall covered with an expandable open-mesh stent having means for attaching the second segment to an internal surface of a patient's descending aorta,c) a collar having a diameter slightly larger than the diameter of said first segment, the collar located at a juncture where the first end of the second segment is joined to the second end of the first segment, with the collar having means for attachment to the open end of a patient's descending aorta. A surgical procedure for total replacement of the aortic arch of a patient is also disclosed.
Owner:SHERIF HISHAM M F
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal and perfusion augmentation within the cerebral vasculature
InactiveUS20050090854A1Prevention of distal embolizationMinimizing blood lossBalloon catheterSurgeryAtherectomyBlood flow
A medical device having a catheter and one or more expandable constricting / occluding members. The catheter is adapted for use with therapeutic or diagnostic devices, including an angioplasty / stent catheter and an atherectomy catheter. A first constrictor / occluder mounted at the distal end of the catheter is adapted for placement in a brachiocephalic or subclavian artery. A second constrictor mounted proximal to the first constrictor / occluder is adapted for placement in the descending aorta. Pressure measuring devices may be included, and filters may be used to capture embolic debris. Methods of using the devices for preventing distal embolization during extracranial or intracranial carotid procedures or vertebral artery procedures by augmenting collateral cerebral circulation by coarctation of the aorta to enhance reversal of blood flow in an internal carotid artery, an external carotid artery, and / or a common carotid artery toward the subclavian artery are disclosed.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
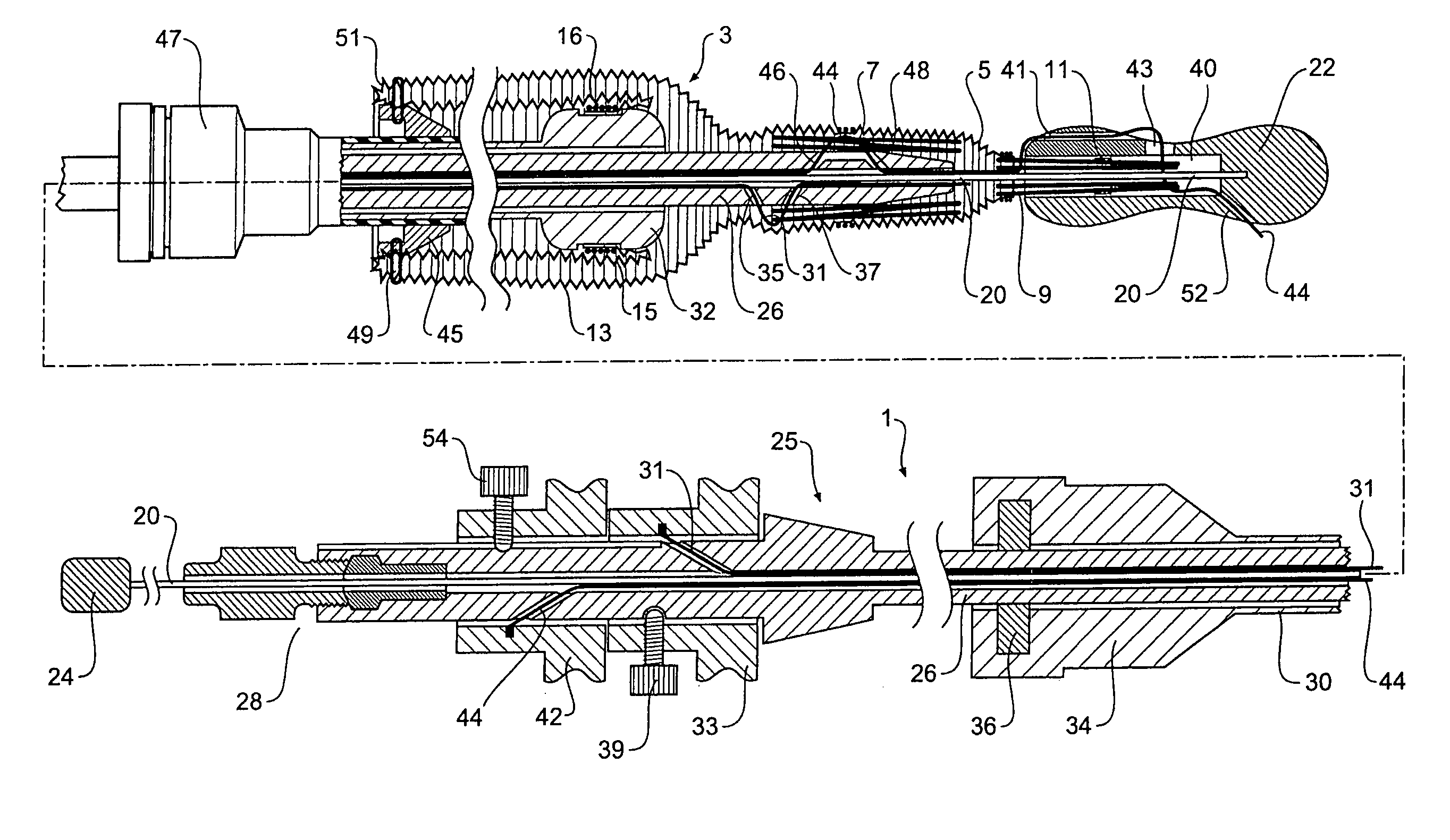
Long term ambulatory intro-aortic balloon pump with percutaneous access device
ActiveUS20080281147A1Assist cardiac functionReduce the overall diameterElectrocardiographyTransvascular endocardial electrodesAmbulatoryAortic balloon pump
Disclosed herein are embodiments of long-term ambulatory intra-aortic balloon pump systems for providing left ventricular cardiac assistance to a patient. The systems can comprise an external drive system for supplying a compressed fluid, the drive system operating in accordance with a control program stored in memory, an intra-luminal balloon pump having an elongate inflatable chamber positionable to be lying completely within a descending aorta of the patient, and a percutaneous access device. The percutaneous access device can be a biocompatible implantable portal comprising a communicative passage through an interior bore and an exterior having a neck region adapted to promote autologous cell growth thereon in an implantable region, the neck region having a plurality of channels extending about the neck region.
Owner:L VAD TECH
Devices and methods for preventing distal embolization using flow reversal and perfusion augmentation within the cerebral vasculature
InactiveUS7635376B2Preventing ischemic strokeStroke preventionBalloon catheterSurgeryAtherectomyCoarctation of the aorta
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
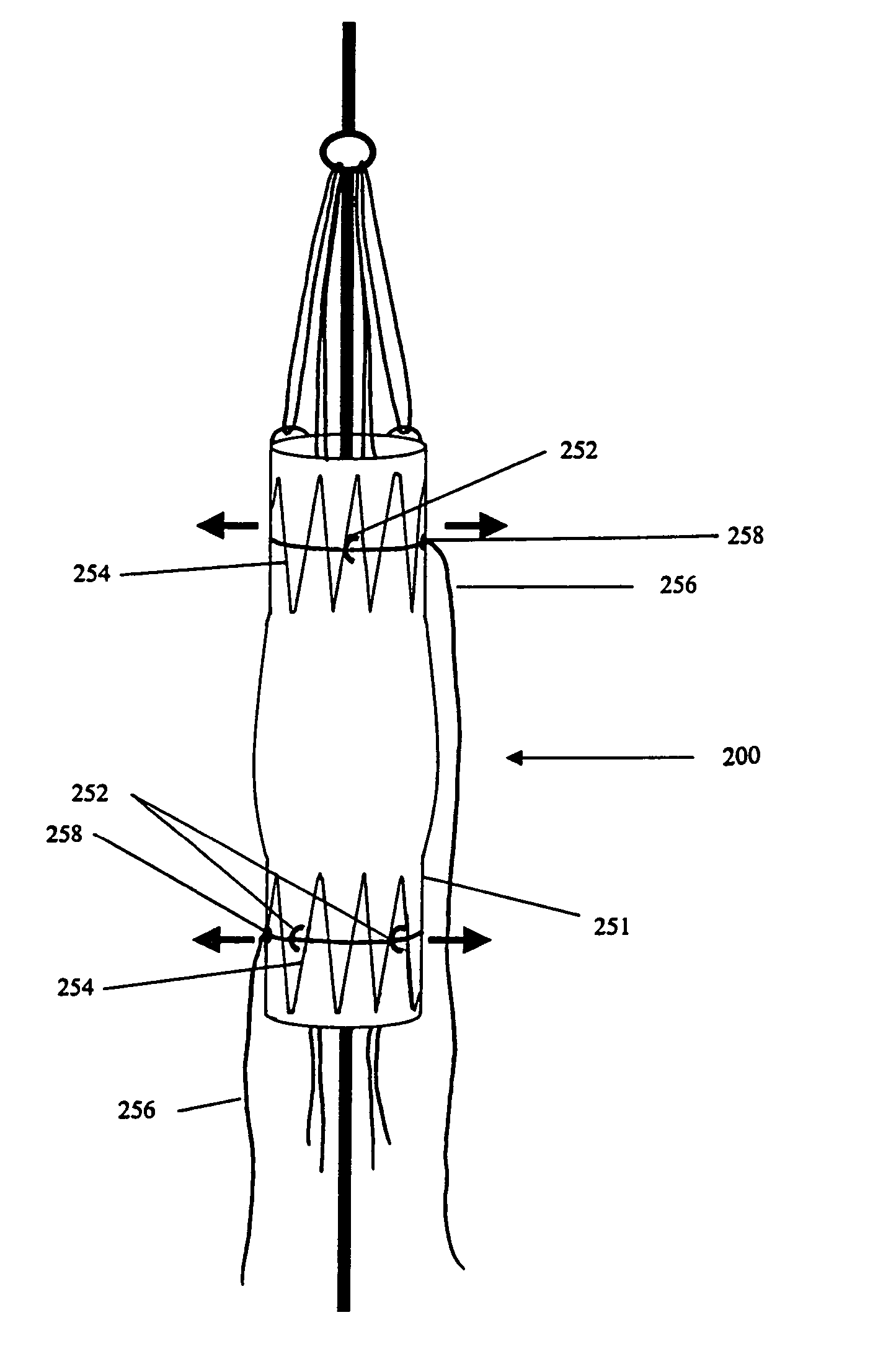
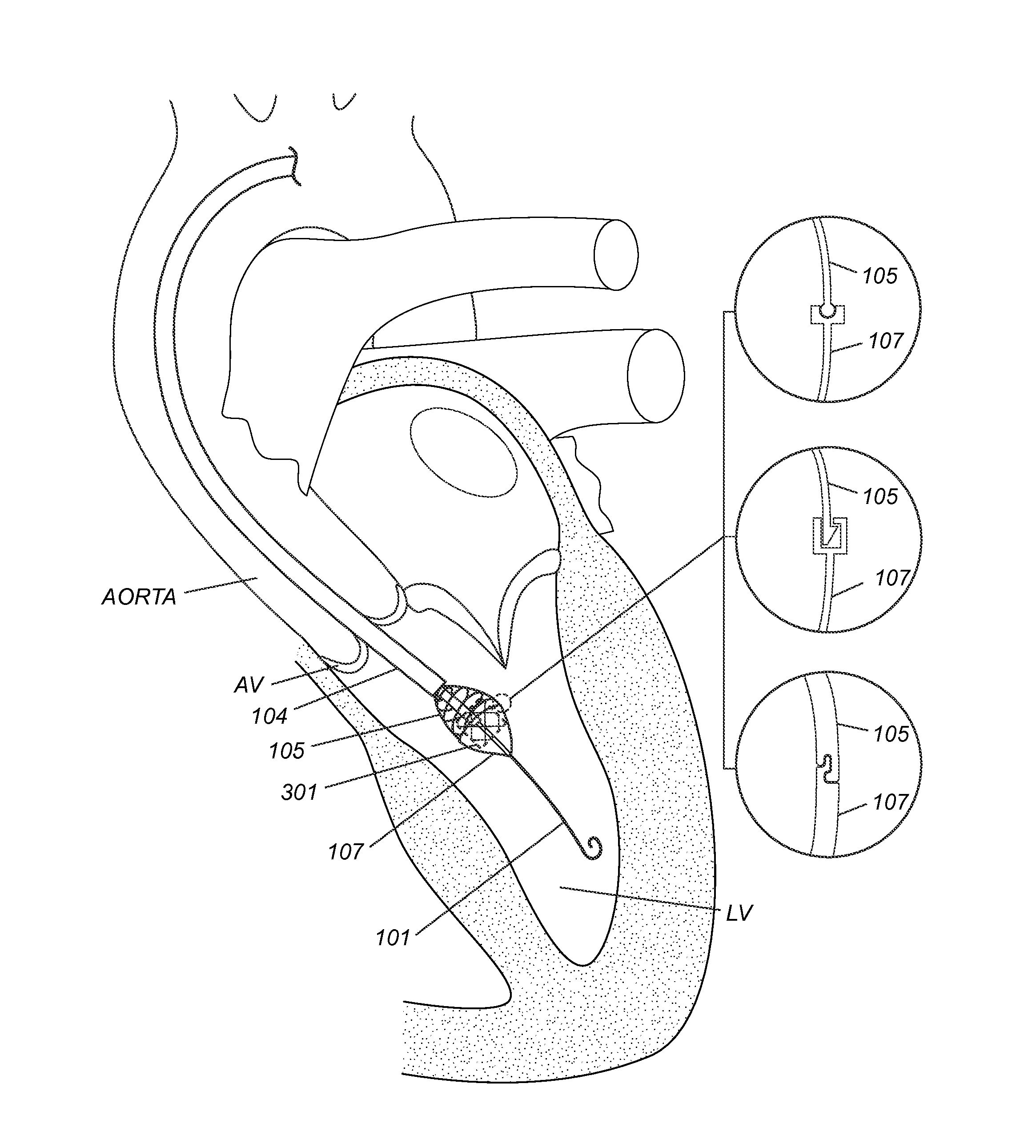
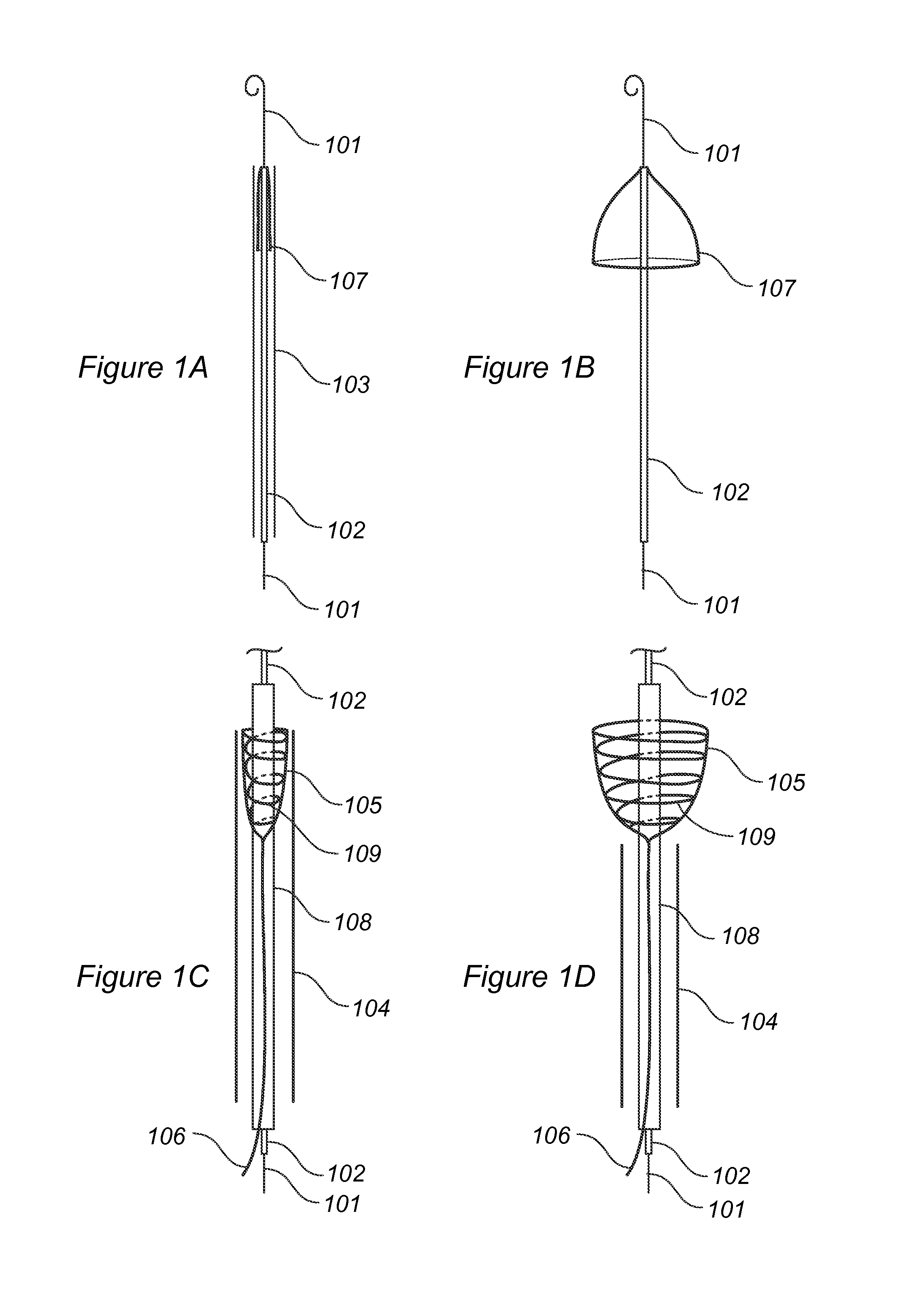
Improved embolic protection device and method
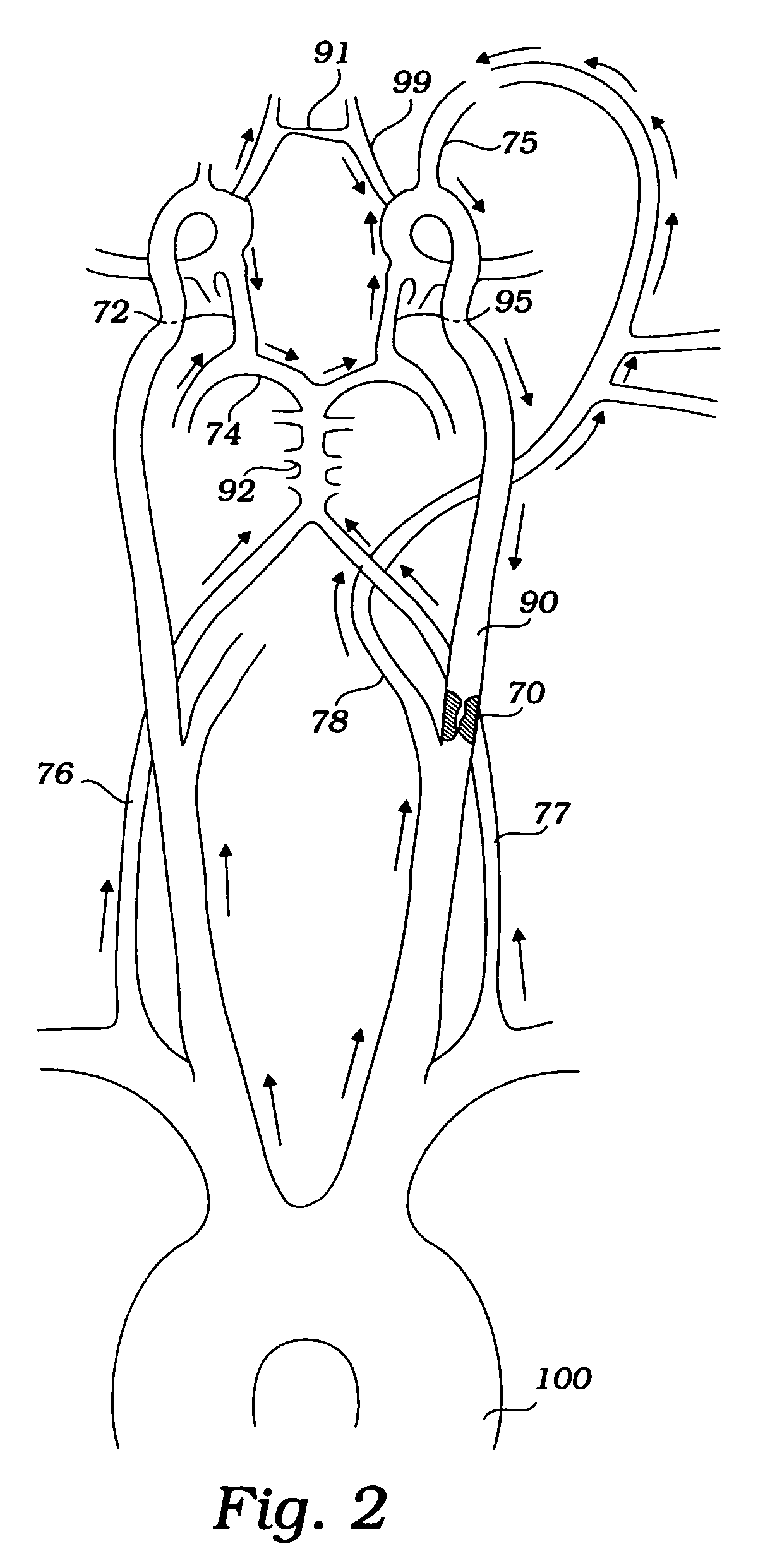
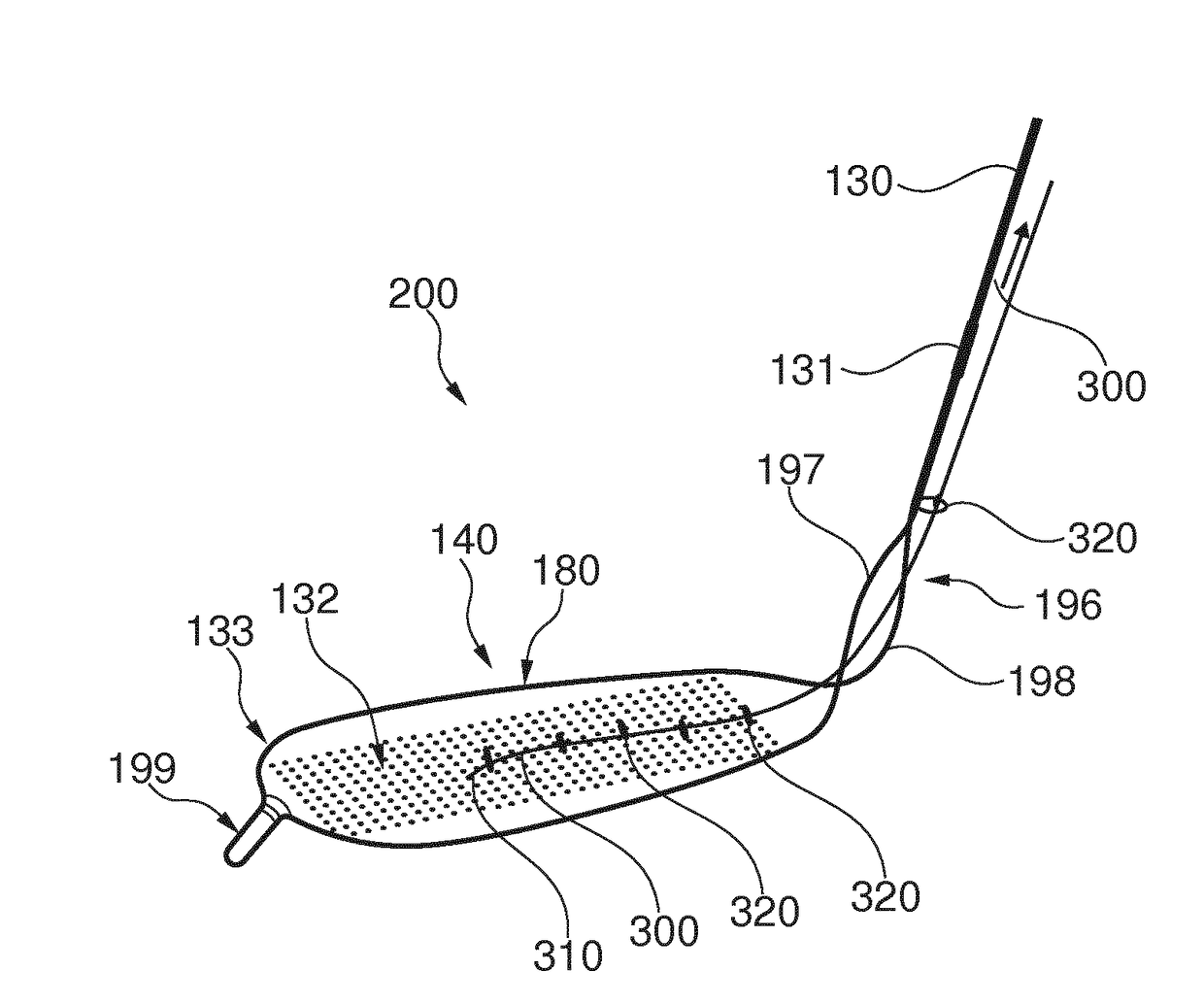
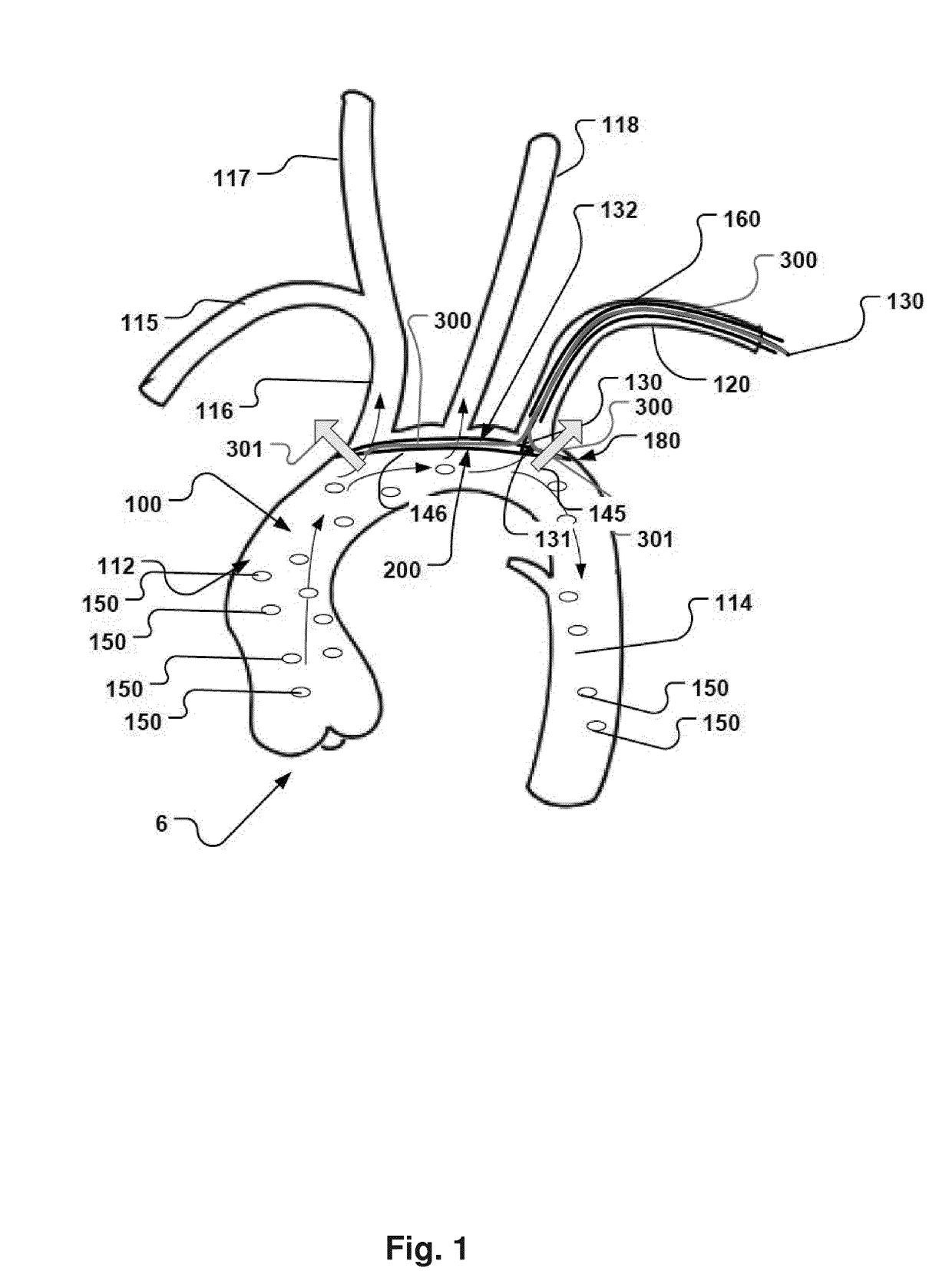
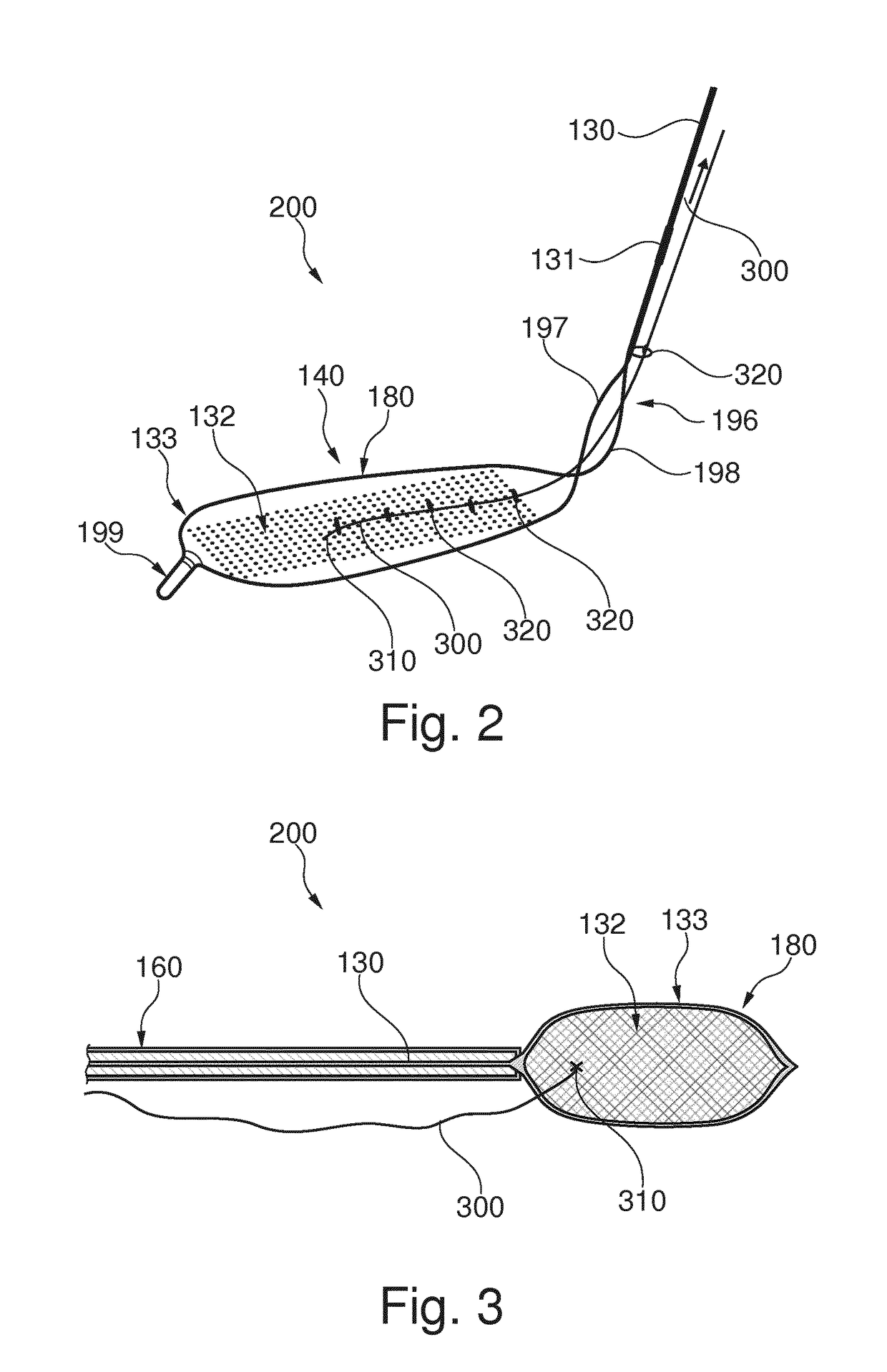
ActiveUS20170189160A1Mitigate, alleviate or eliminate one or more deficiencies, disadvantages or issuesGuide needlesBalloon catheterAscending aortaEmbolic Protection Devices
A catheter device is disclosed comprising; an elongate sheath (503) with a lumen and a distal end for positioning at a heart valve (6), an embolic protection device (200) for temporarily positioning in the aortic arch for deflection of embolic debris from the ascending aorta to the descending aorta, said embolic protection device is connectable to a transluminal delivery unit (130) extending proximally from a connection point (131), and having: a frame with a periphery, a blood permeable unit within said periphery for preventing embolic particles from passing therethrough with a blood flow downstream an aortic valve into side vessels of said aortic arch to the brain of a patient, and at least one tissue apposition sustaining unit (300, 350) extending from said catheter, into said aortic arch, and being attached to said embolic protection device at a sustaining point (502), for application of a stabilization force offset to said connection point at said embolic protection device, such as at said periphery, and for providing said stabilization force towards an inner wall of said aortic arch, away from said heart, and in a direction perpendicular to a longitudinal extension of said periphery, when said catheter device is positioned in said aortic arch, such that tissue apposition of said periphery to an inner wall of said aortic arch is supported by said force for improving stability and peripheral sealing. In addition related methods are disclosed.
Owner:SWAT MEDICAL AB
Intra-aortic emboli protection filter device
ActiveUS20190000604A1More freedomBlood vesselsBlood vessel filtersEmbolic Protection DevicesEngineering
An embolic protection device including a porous deflector screen including a filter, arranged to expand and to conform to a wall of the aortic arch covering entrances to arteries branching from an aorta, an emboli collector including a cylinder arranged to expand and to lie along walls of a descending aorta, pushing against walls of the descending aorta and anchoring the porous deflector screen, and a connecting portion for connecting the porous deflector screen and the emboli collector, arranged to push the porous deflector screen against a wall of the aortic arch while anchoring against the emboli collector. Related apparatus and methods are also described.
Owner:FILTERLEX MEDICAL LTD
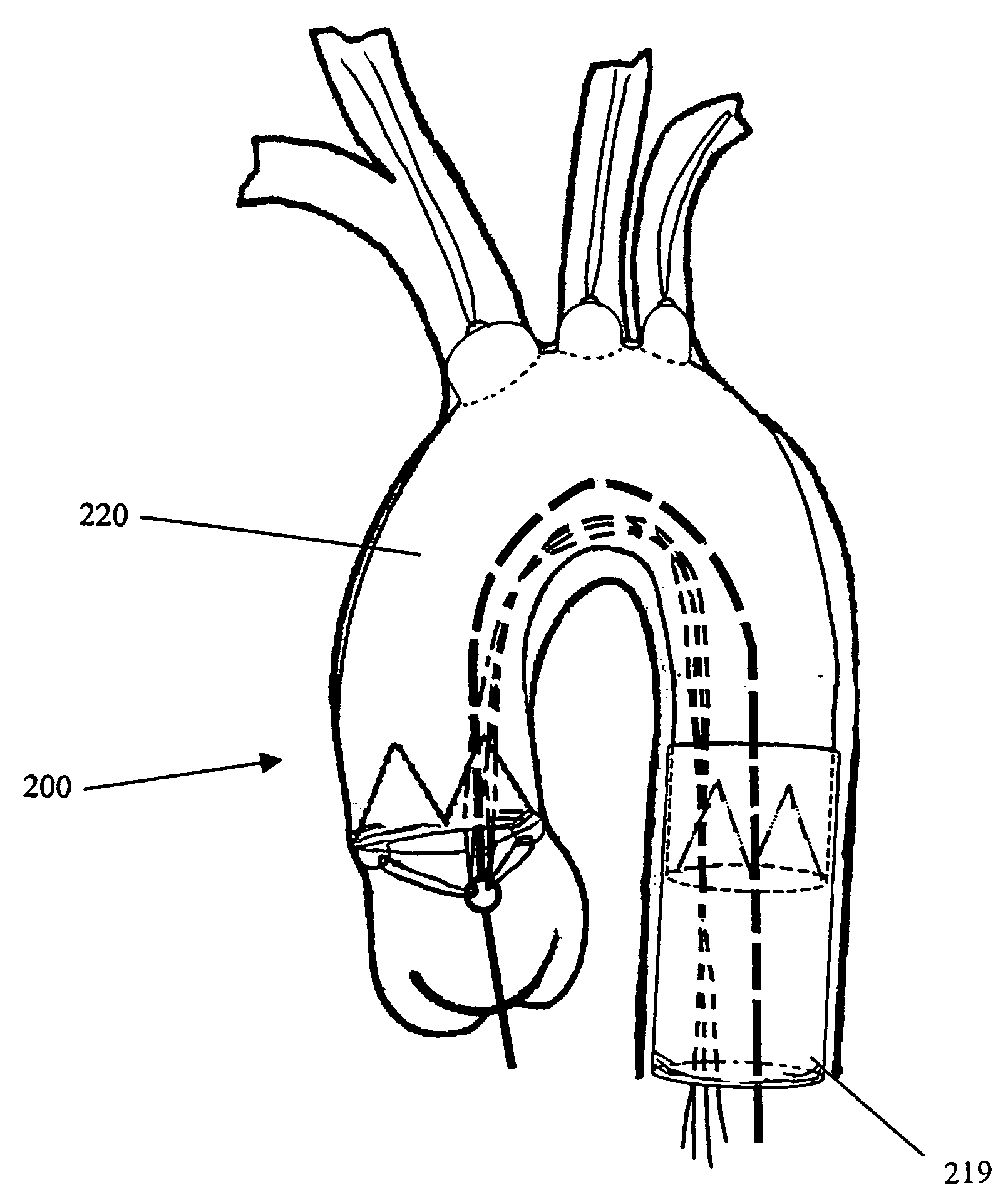
Apparatus for performing myocardial revascularization in a beating heart and left ventricular assistance condition
InactiveUS20070282243A1Reduce riskReduce expensesBlood pumpsMedical devicesExtracorporeal circulationLeft ventricular size
An apparatus for performing myocardial revascularization in a beating heart and left ventricular assistance condition comprises an arterial cannula, of a per se known type, arranged in the descending aorta, a novel arterial draining cannula, of a two cannula stage type, so arranged that the draining occurs from the left auricle and left ventricle, and a centrifugal pump allowing blood flow from the left ventricle to the aorta. The apparatus allow the patients to be operated on with the safety of a conventional extra-corporeal circulation and with a risk and cost reduction due to the off-pump technique.
Owner:N G C MEDICAL
Device to percutaneously treat heart valve embolization
The present invention provides devices and methods for percutaneously retrieving an embolized or malpositioned heart valve or foreign bodies from a patient's body. Several of these devices may include a catheter system with expandable and retractable baskets attached to a catheter and guidewire system. The guidewire may be inserted through the lumen of the embolized or malpositioned heart valve, capturing the valve in the baskets, and deploying a mechanism to crush the valve within the baskets. Then the crushed baskets and valve may be retrieved either from the body or to a safer location such as but not limited to the descending aorta. This system is advantageous because it does not require open surgery to retrieve the valve or embolized material.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Ultrasonic diagnostic system
InactiveUS20120215109A1Improve accuracyGood reproducibilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHealth-index calculationMedicineContact position
When an amount of visceral fat is measured using ultrasonic waves during medical examination of metabolic syndrome, three contact positions are defined on the surface of the abdominal region, and three distances inside the living body are measured by bringing a probe into contact with the surface of the abdominal region at the contact positions. Specifically, three measurement paths having a starting point at the center of the descending aorta are set, and the distances from the center to a surface of the fat layer adjacent to the surface of the body (inner surface of the subcutaneous layer) in the measurement paths are observed. An approximate area of a visceral fat region can be determined from the three distances and two angles defined by the three measurement paths, and an index value is calculated on the basis of the area. A probe holder having three holding portions is desirably used.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Whole heart extracting method based on heart CT image
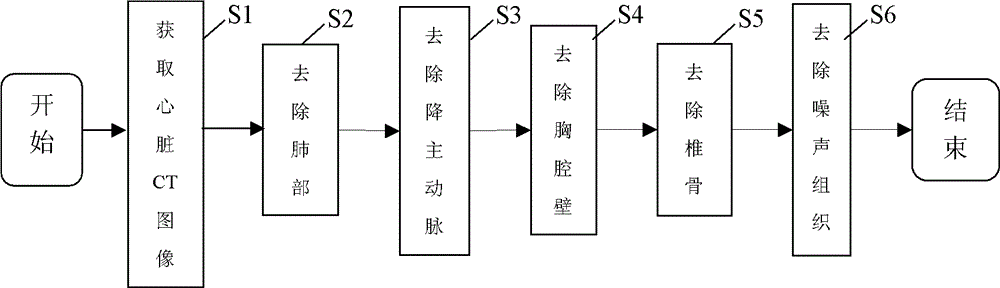
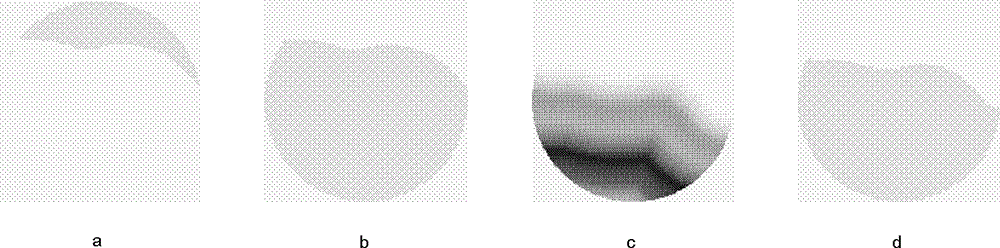
InactiveCN103985122ARealize remote auxiliary diagnosisAdaptableImage enhancementImage analysisThoracic structureThoracic cavity
A whole heart extracting method based on a heart CT image comprises the steps of obtaining the heart CT image, removing the lung part, the descending aorta part, the thoracic cavity wall part and the vertebra part of the heart CT image to obtain a middle image, and removing the noise part in the middle image. The whole heart extracting method based on the heart CT image gradually removes the non-heart parts such as the thoracic cavity wall, the lung, the vertebra and the descending aorta in an reverse angle mode to achieve the purpose of extracting the whole heart, has the advantages of being high in self-adaptation performance, high in operation efficiency, accurate in extraction effect and the like, can be rapidly embedded in an existing medical network, and achieves remote auxiliary diagnosis.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com