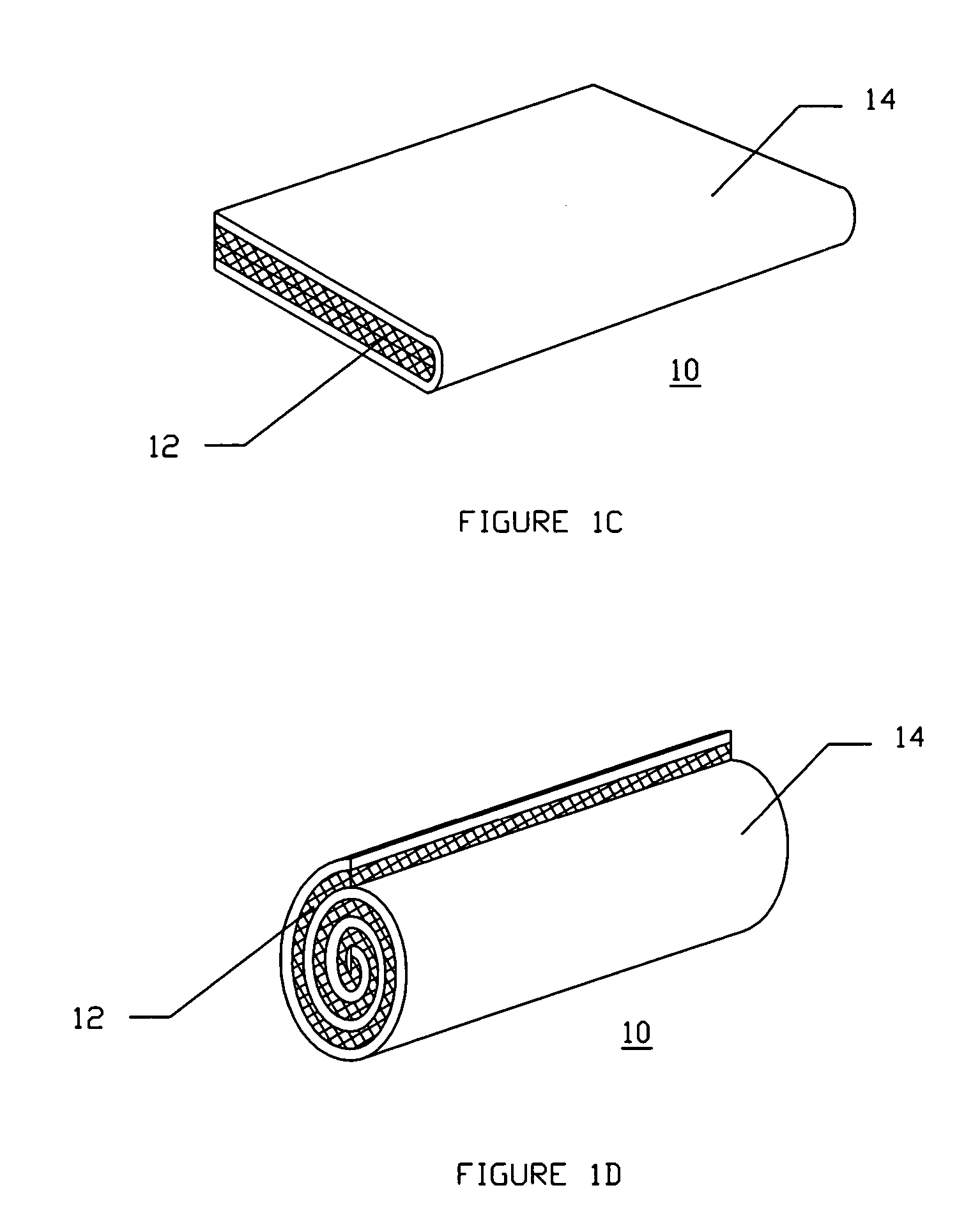
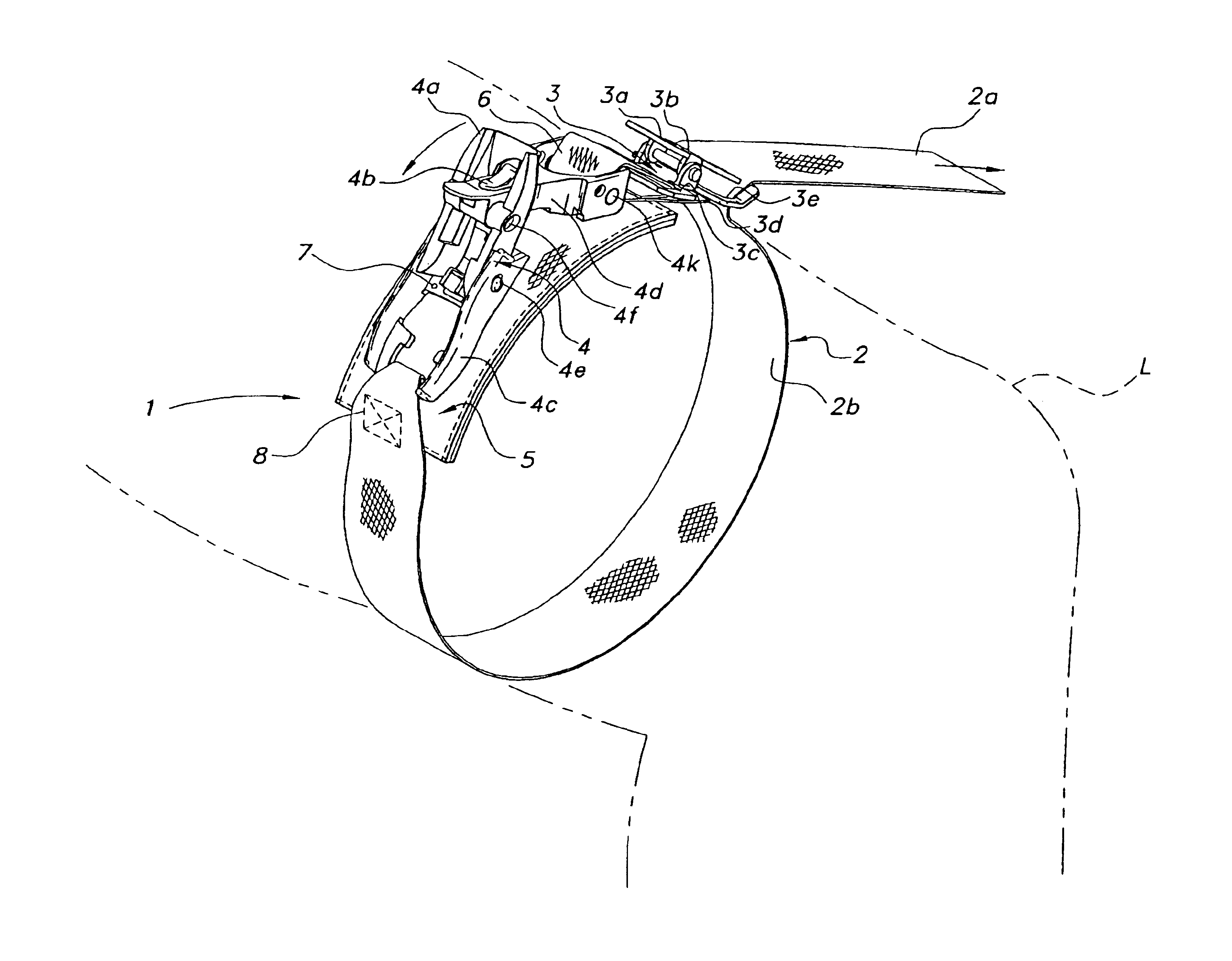
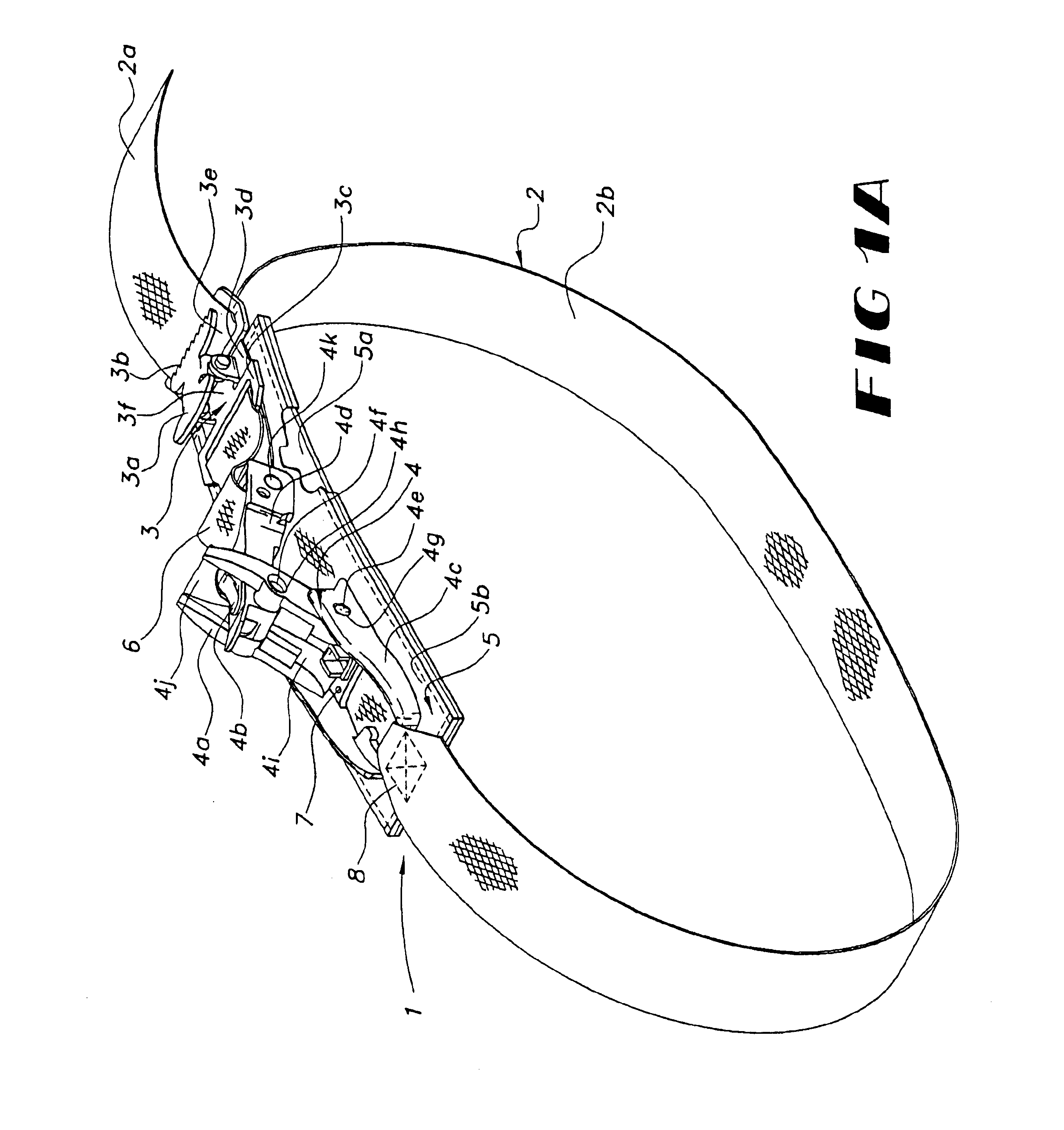
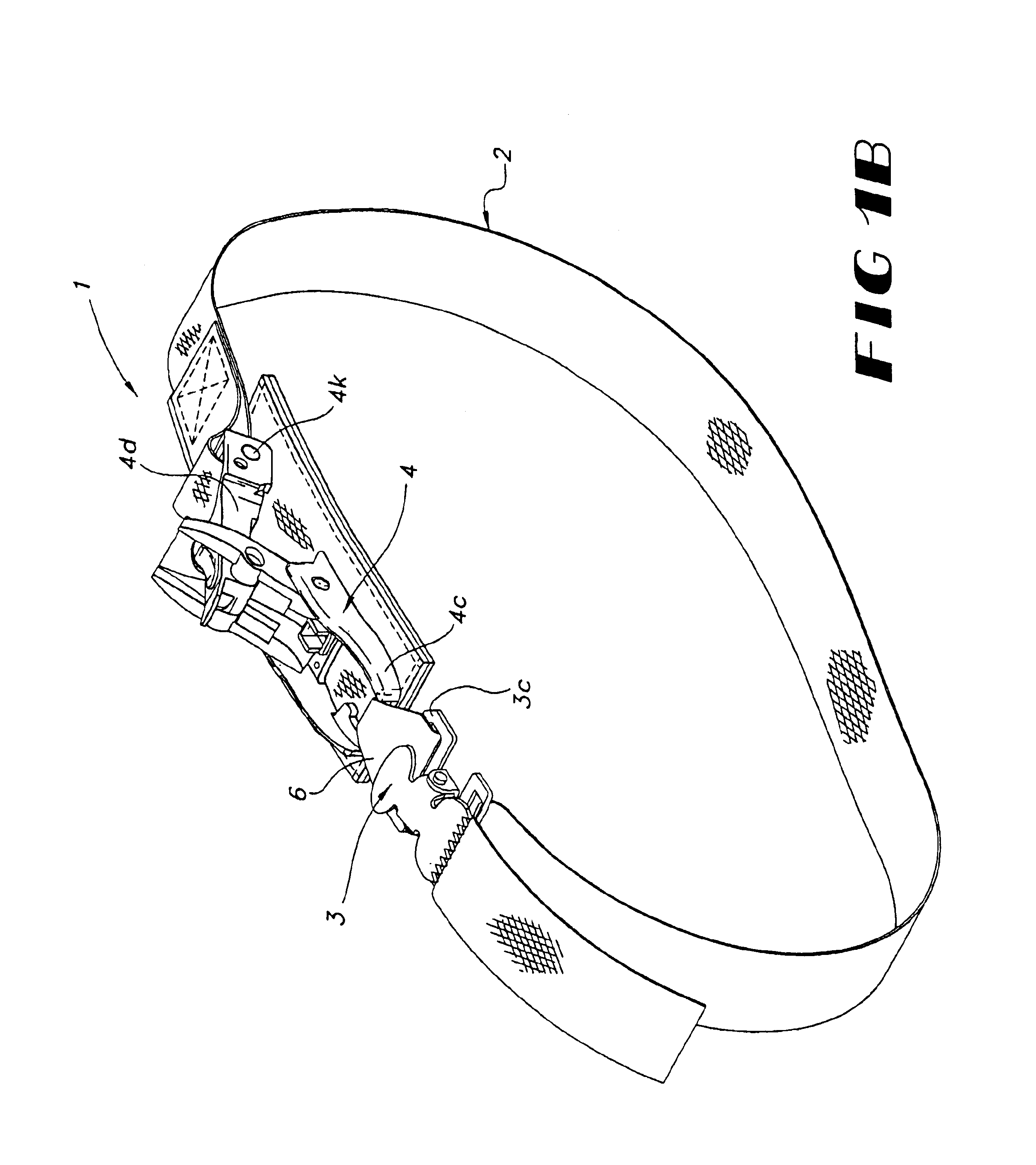
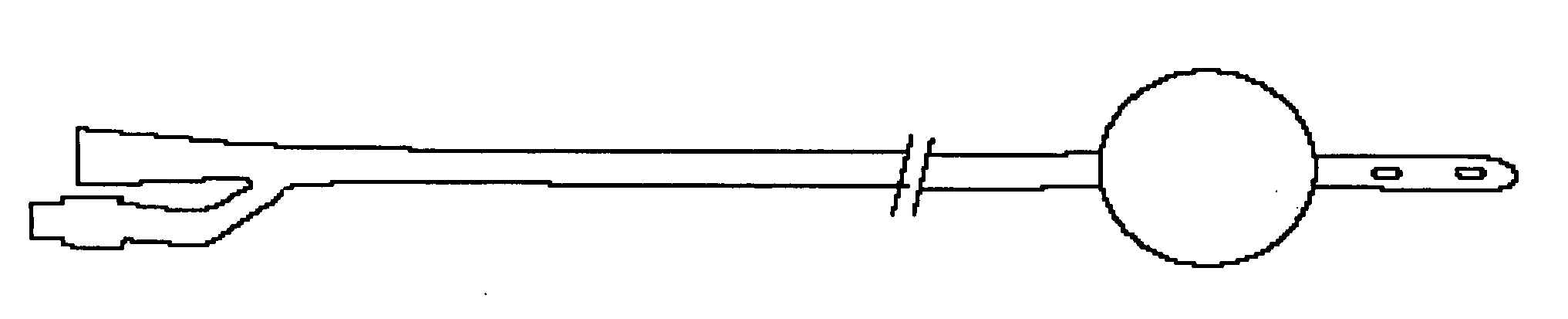Patents
Literature
457 results about "Tourniquet time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A tourniquet can be defined as a constricting or compressing device used to control arterial and venous blood flow to a portion of an extremity for a period of time.
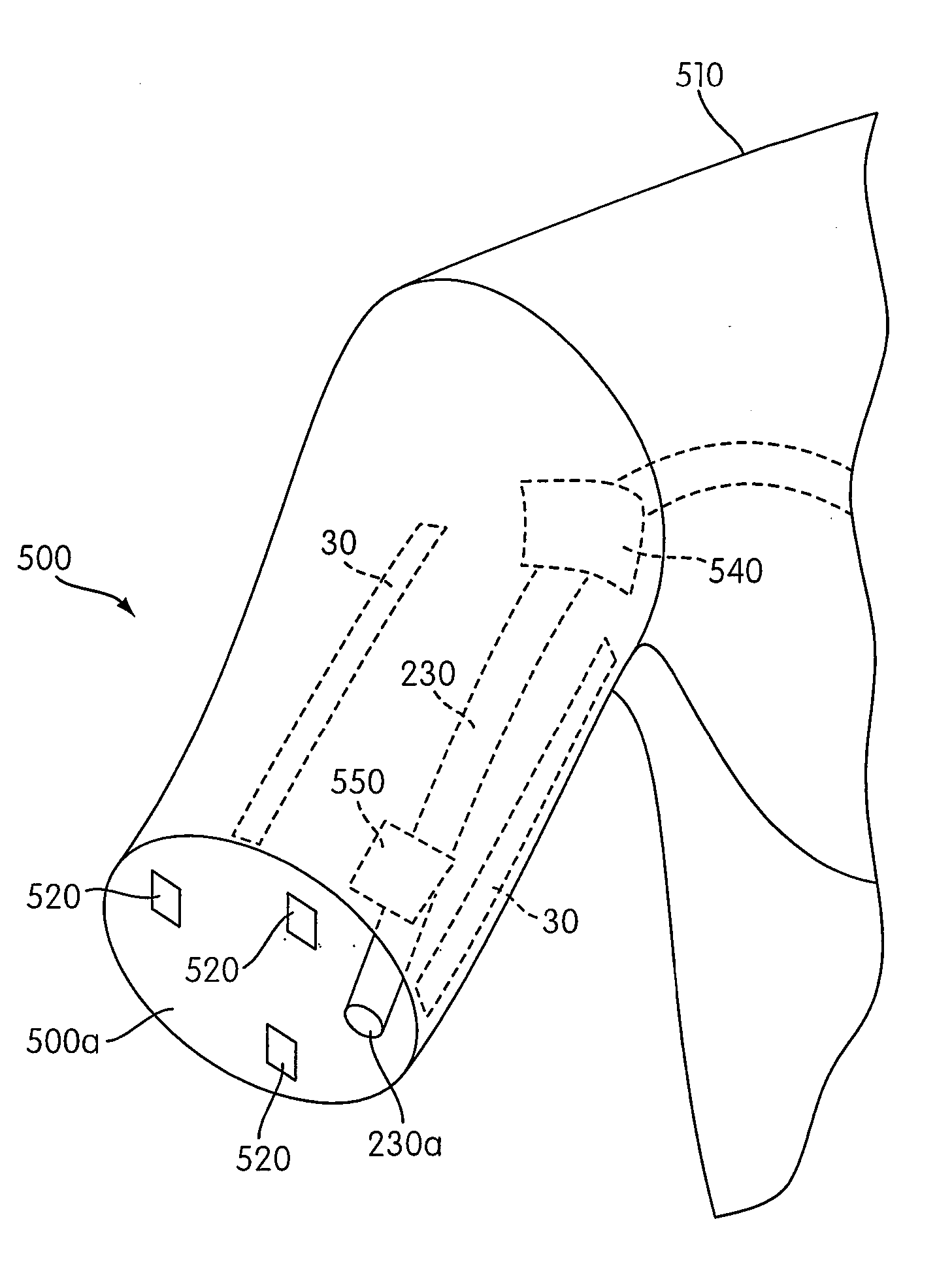
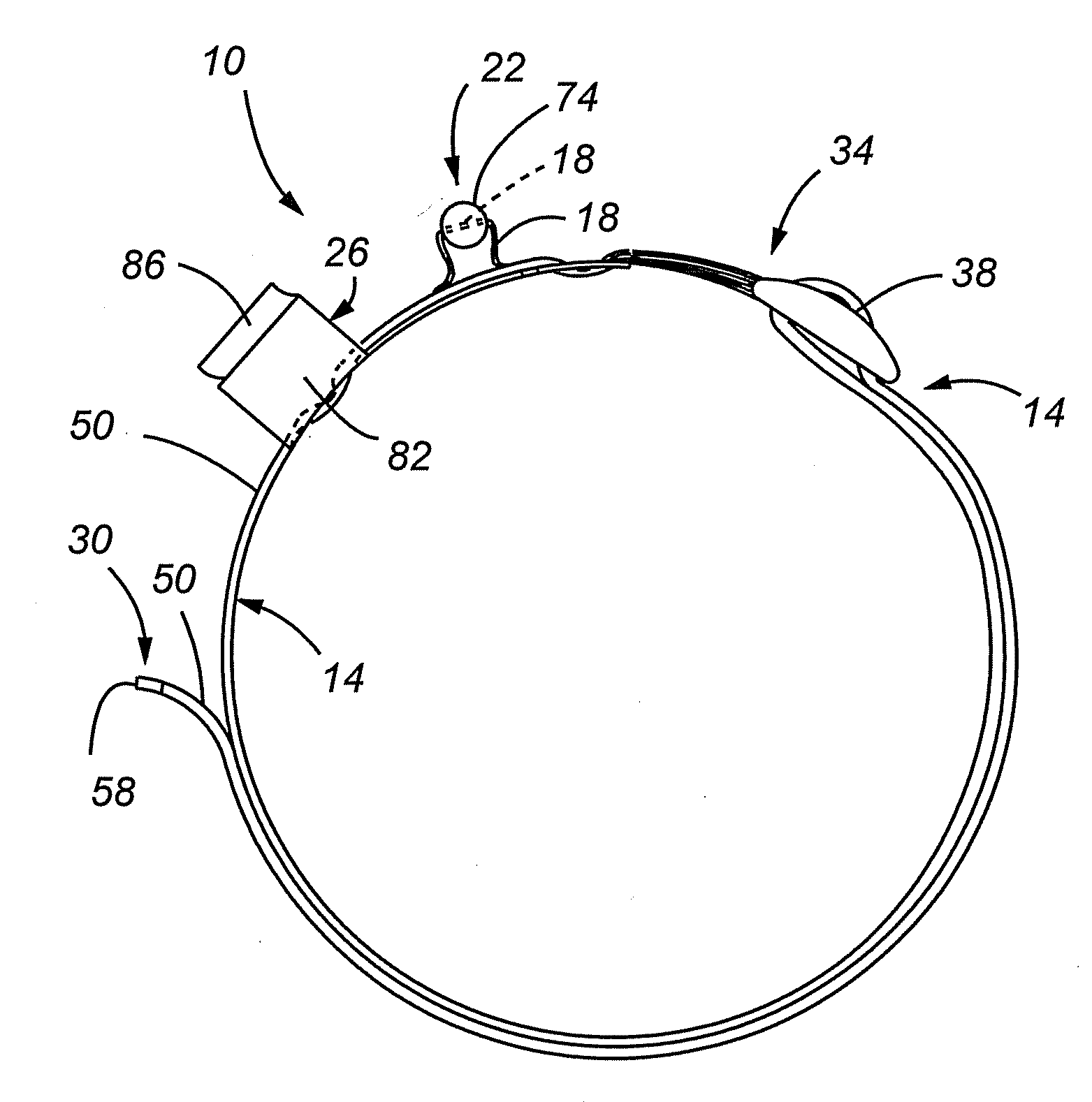
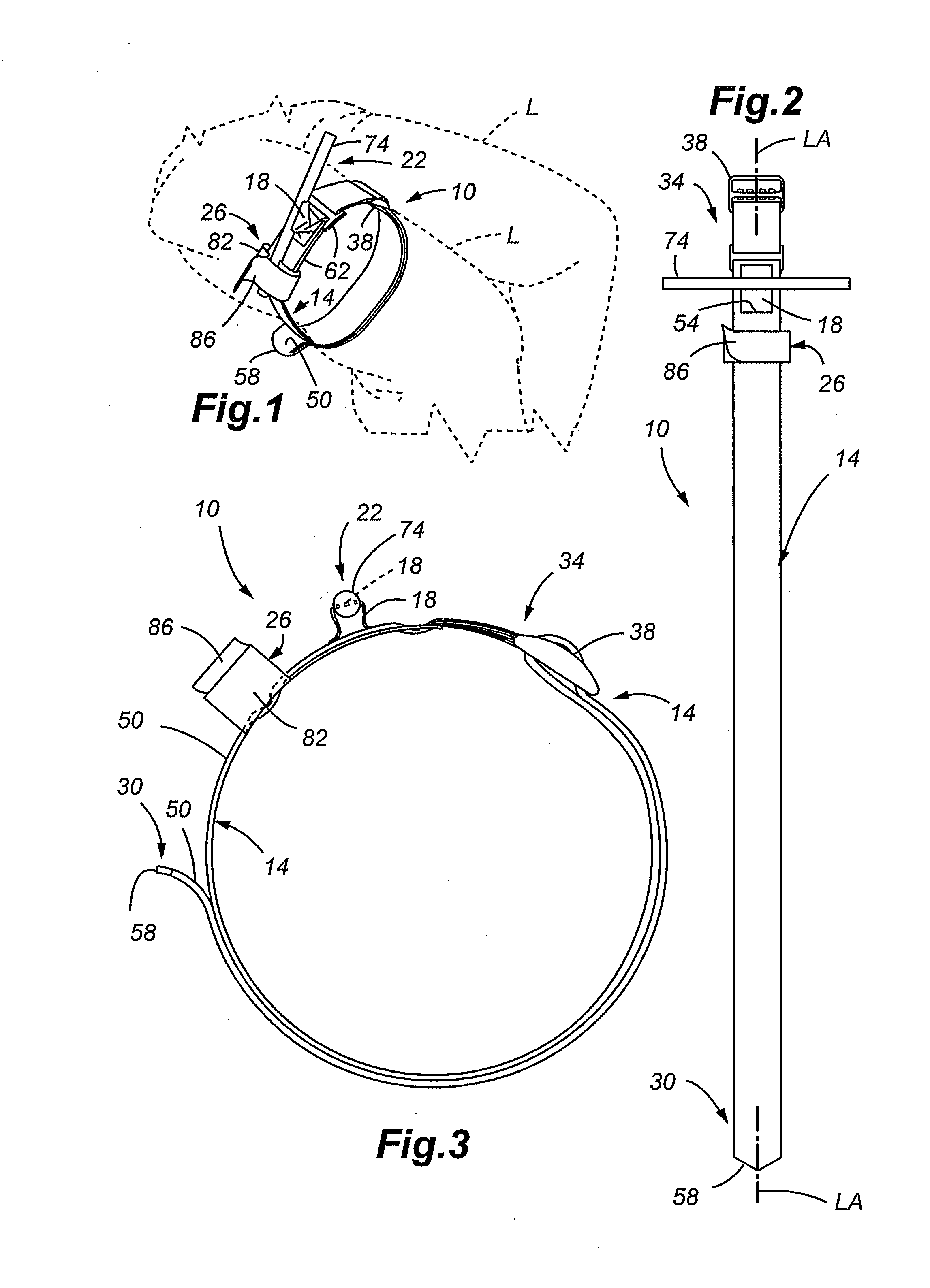
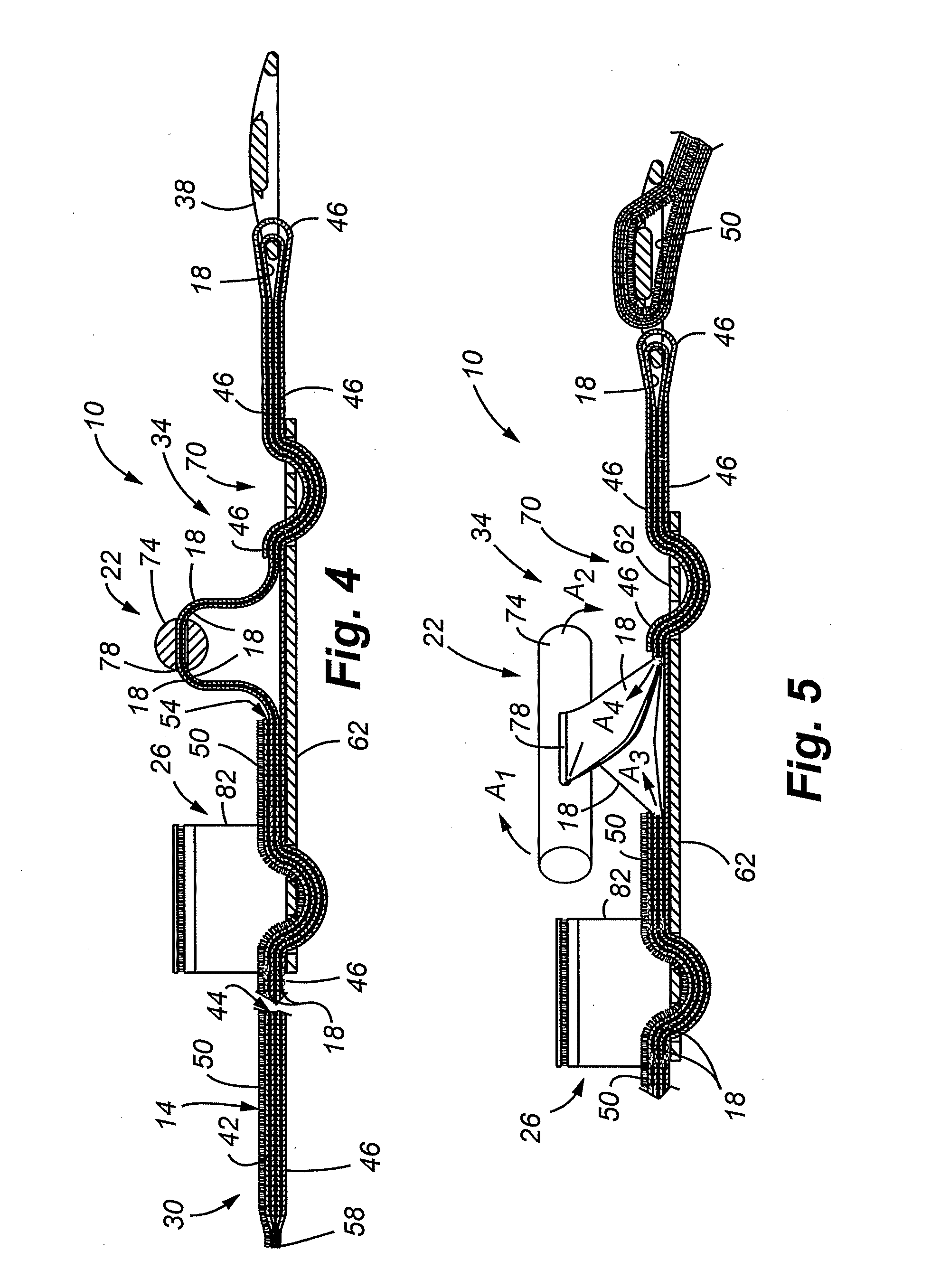
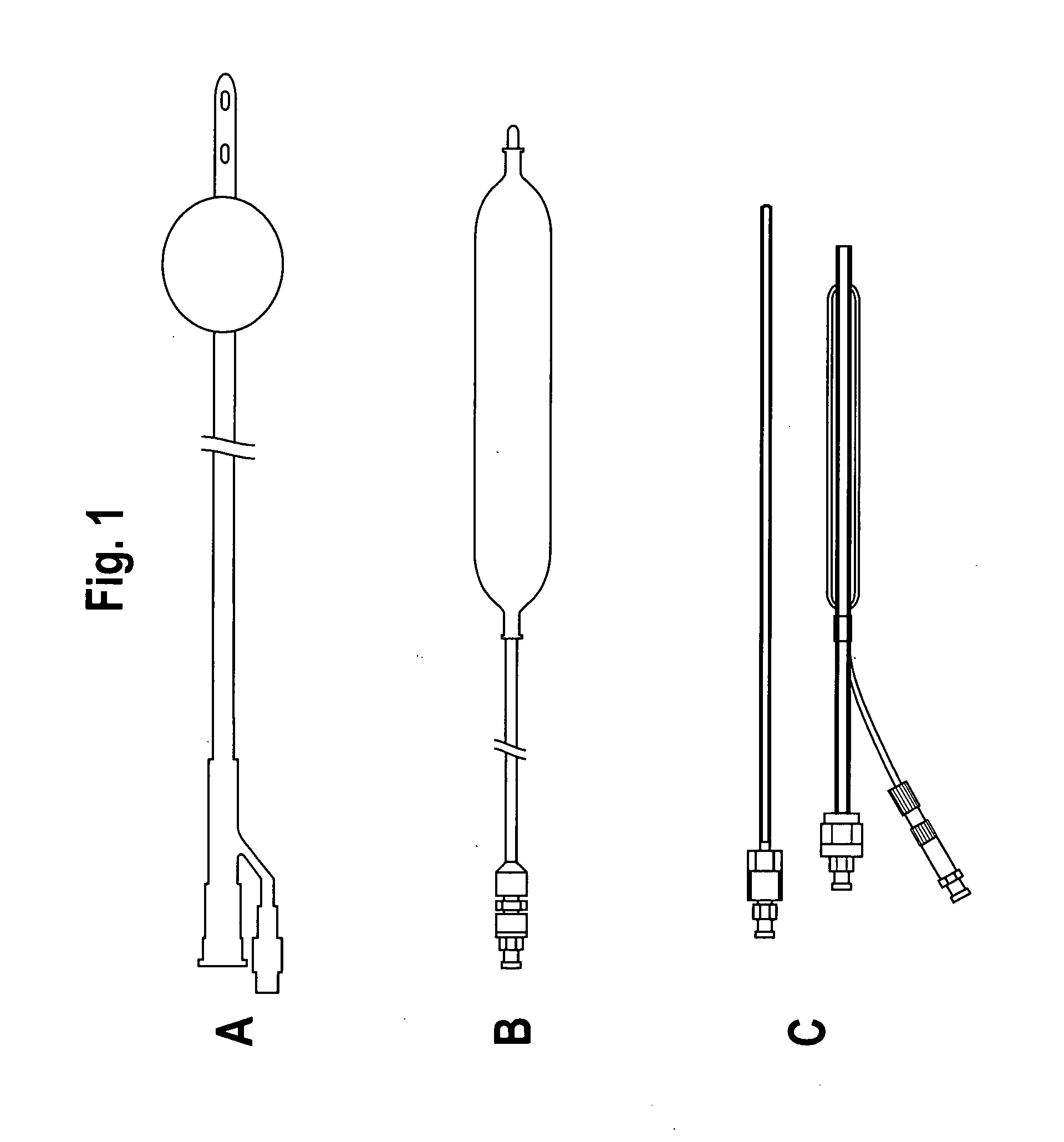
Internal compression tourniquet catheter system and method for wound track navigation and hemorrhage control
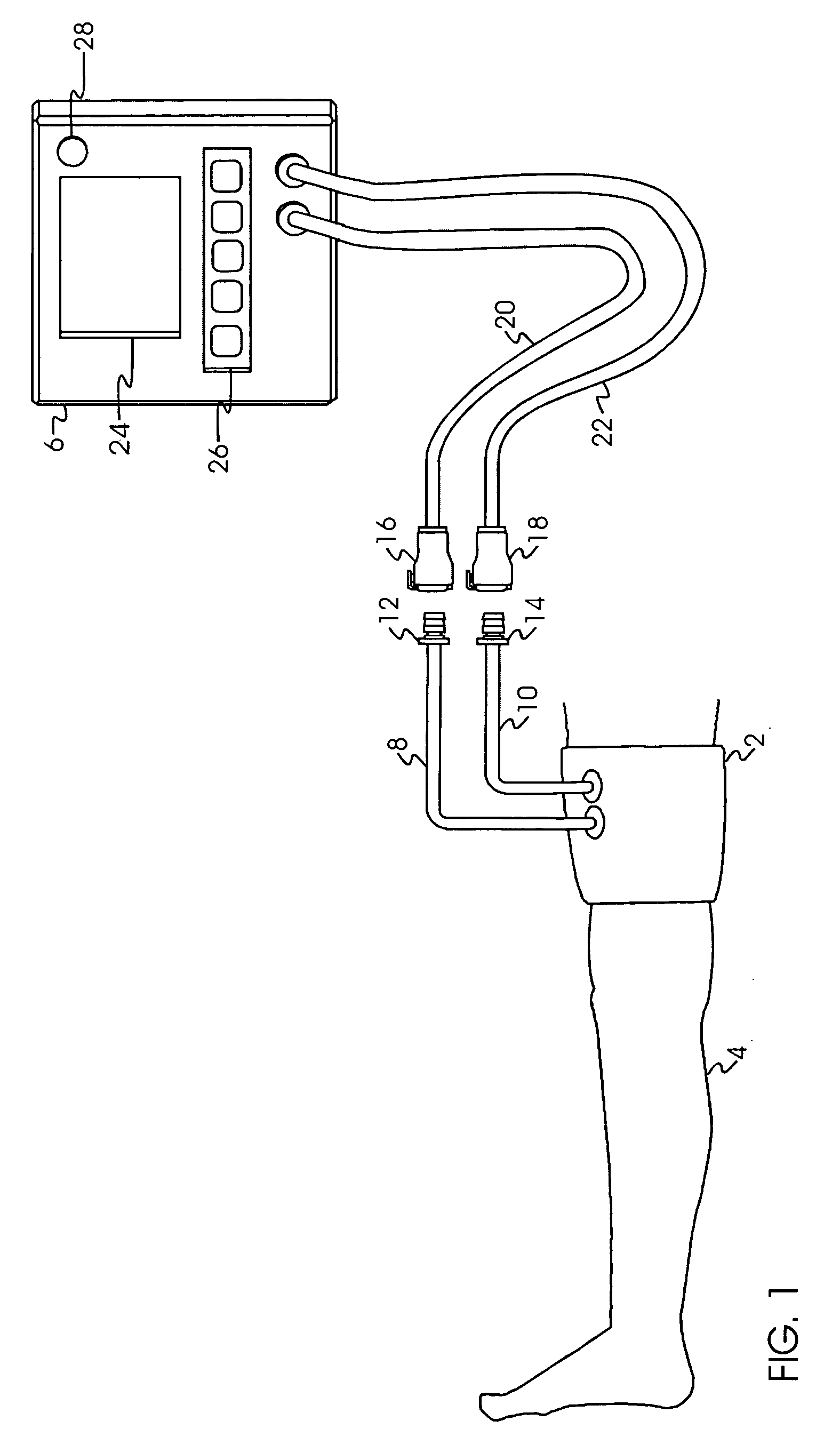
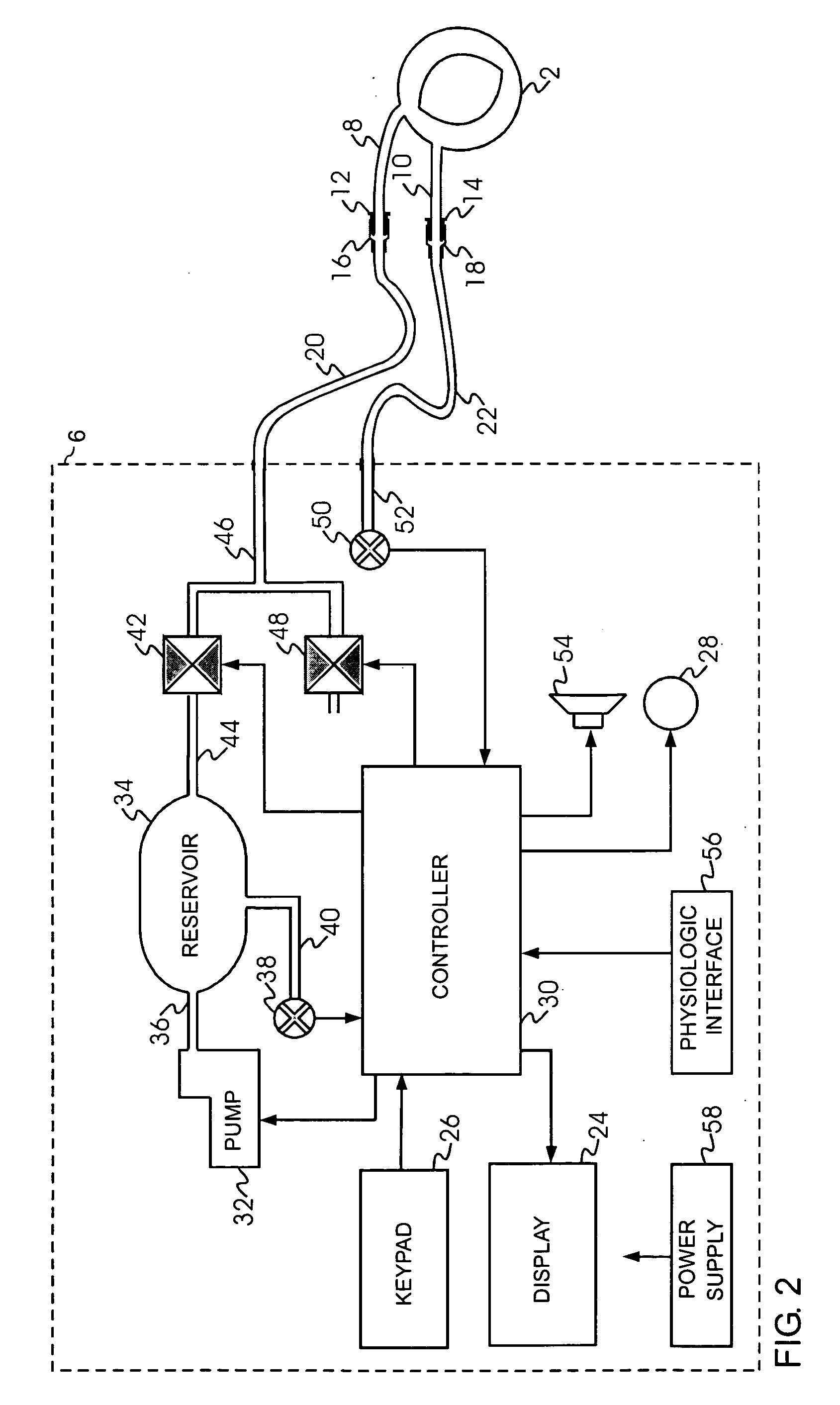
An internal compression tourniquet catheter system and method for controlling hemorrhage from wounds, particularly penetrating wounds. Its construction includes an inflatable member constructed of very thin, flexible, biocompatible, and nonelastic and puncture resistant material such that when deflated it lies flat and can be wrapped around the catheter shaft, which passes within and has a lumen to inflate it, to minimize overall diameter when deflated for insertion into the tissue track created by the wounding agent. The inflatable member is of large potential volume enabling full inflation with near zero internal pressure when unconstrained externally. When positioned within a wound track and inflated, the gas or liquid injected into the balloon lumen creates pressure because its expansion is constrained by the tissues of the wound, and that pressure is transmitted directly to the surrounding tissue of the wound track. The pressure exerted on the tissue can be precisely measured and controlled, automatically if appropriate, such that sufficient pressure is applied to tamponade bleeding, but not damage tissue. Since the balloon is of large potential volume, it can easily expand to fill and compress small, large, and irregular wound tracks and can successfully tamponade wounds that smaller, elastic balloon catheters would be unable to tamponade. The catheter system includes means to assist insertion into the wound track, including a rounded or bulbous exploring tip and an internal stylet with an external orientable handle. The distal end of the catheter-stylet assembly can be bent slightly to allow following a curved or irregular wound track, such wound track navigation further assisted by twisting the stylet handle to orient the bent catheter tip within the wound track.
Owner:CARDIOCOMMAND
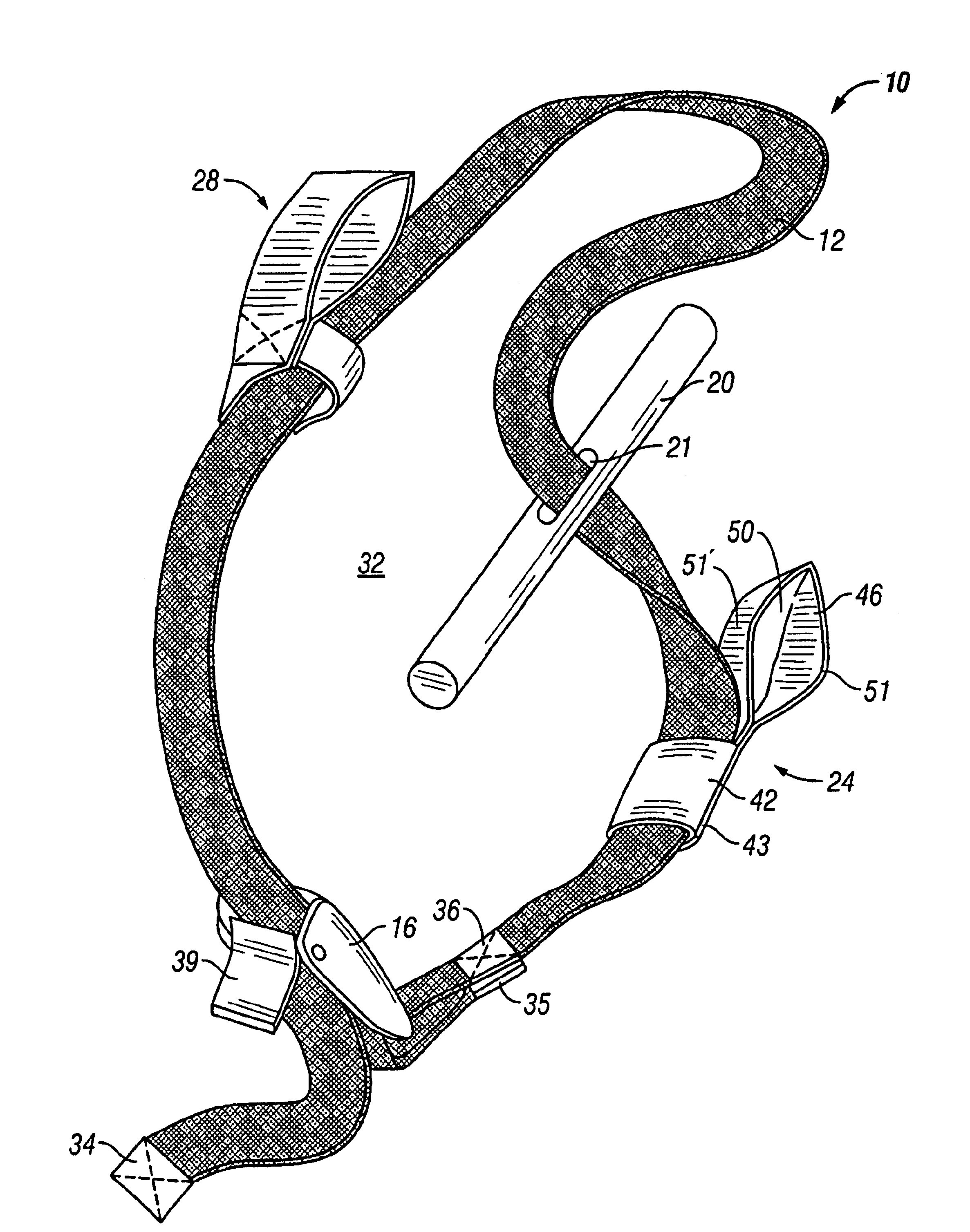
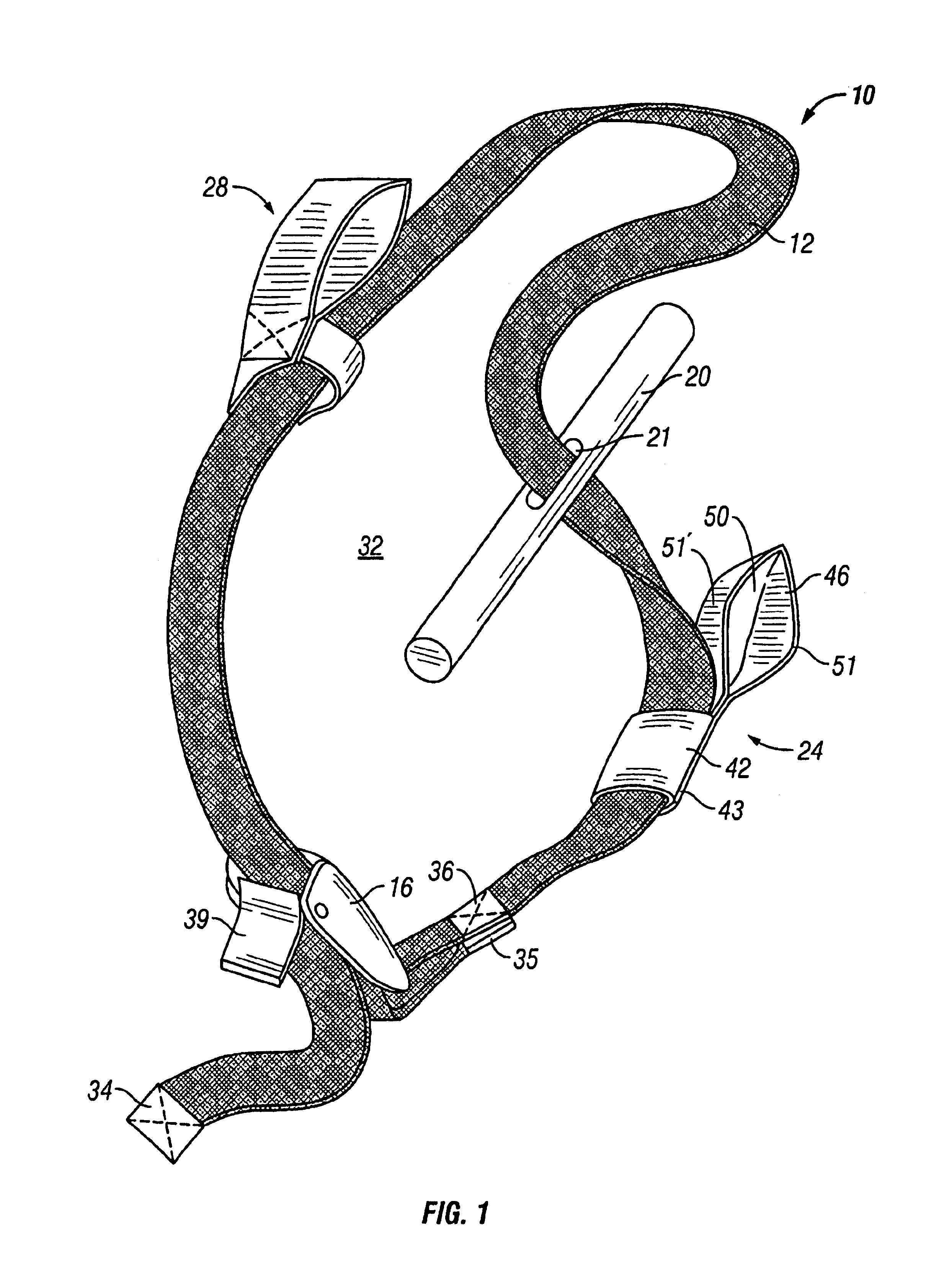
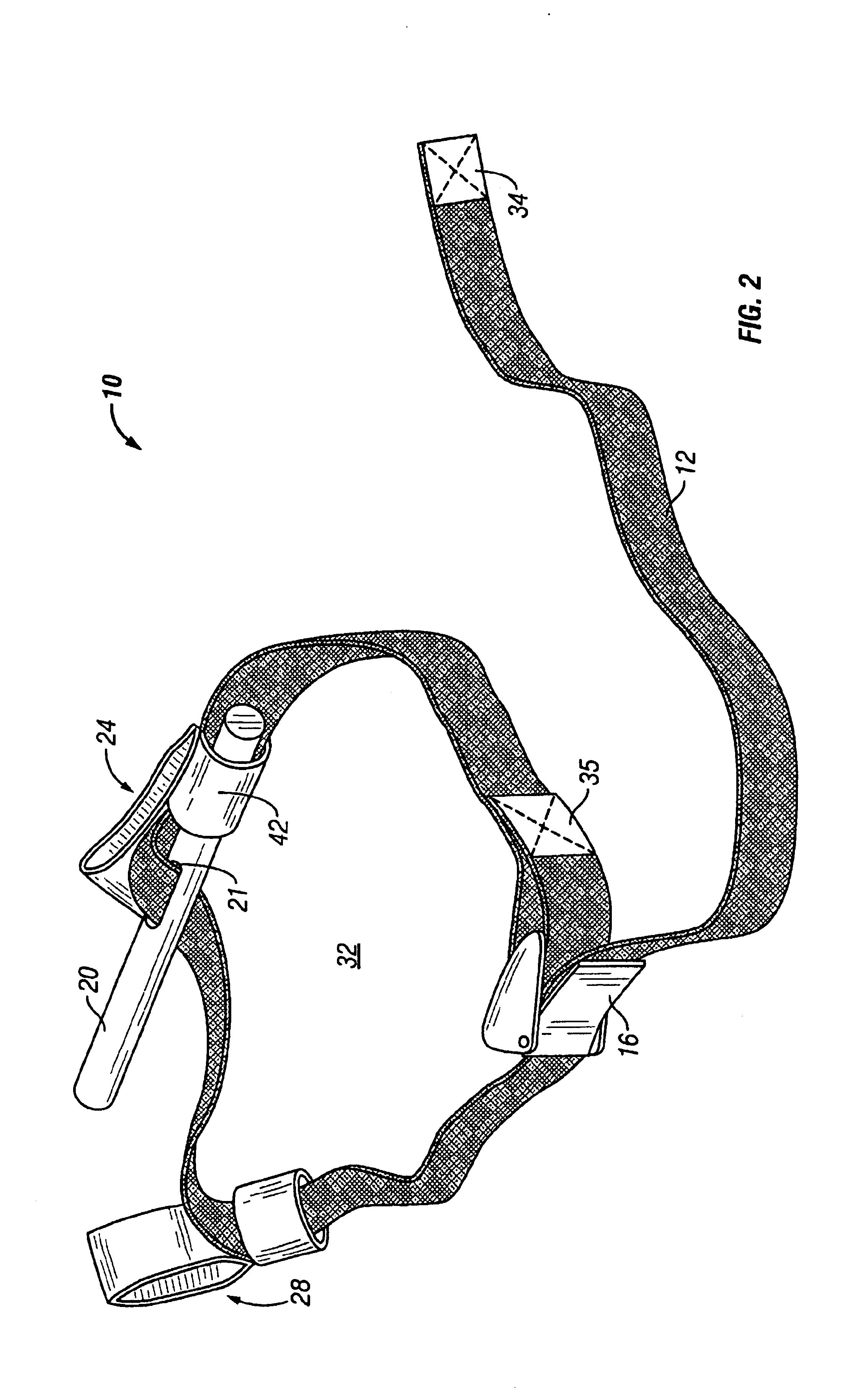
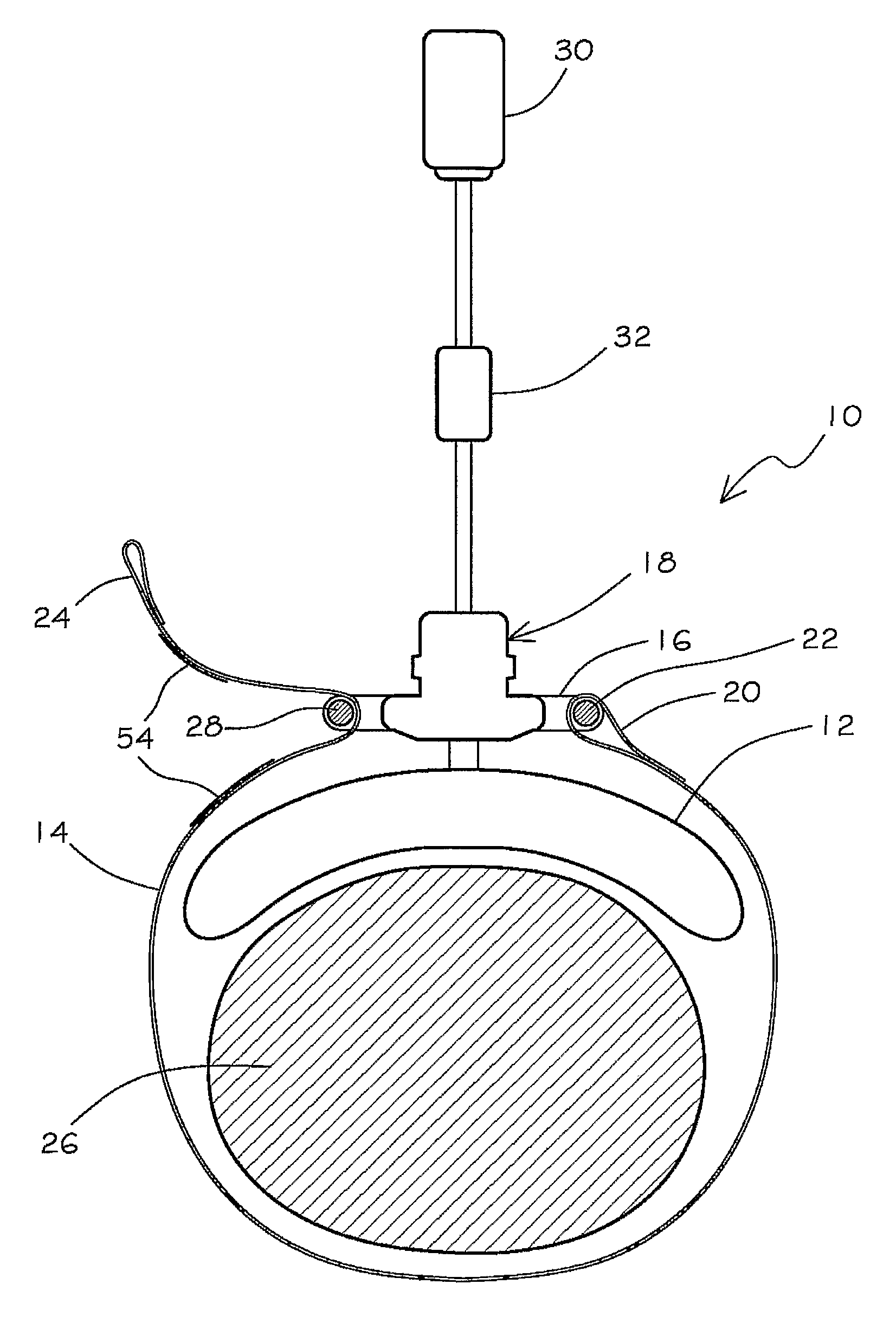
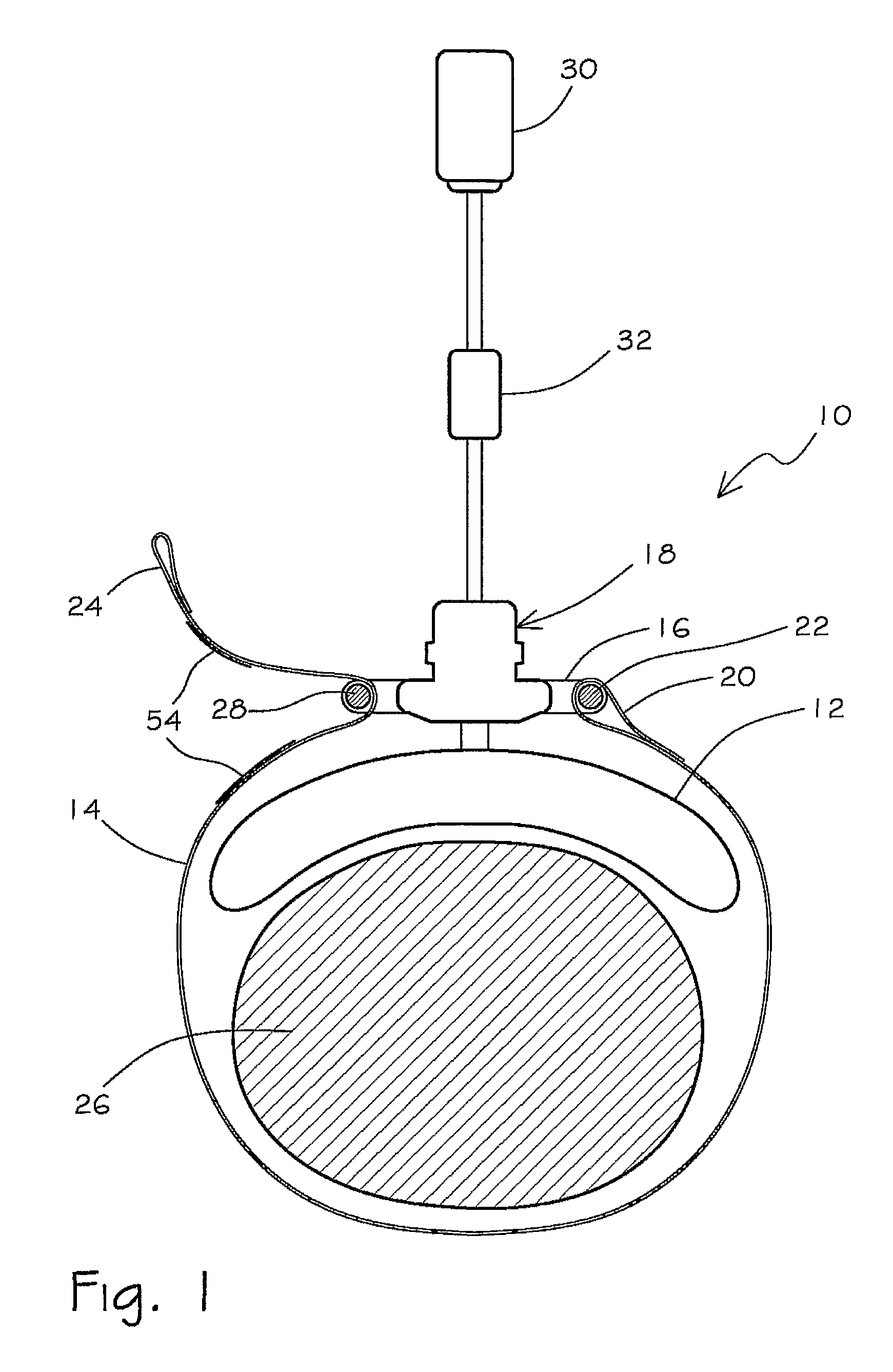
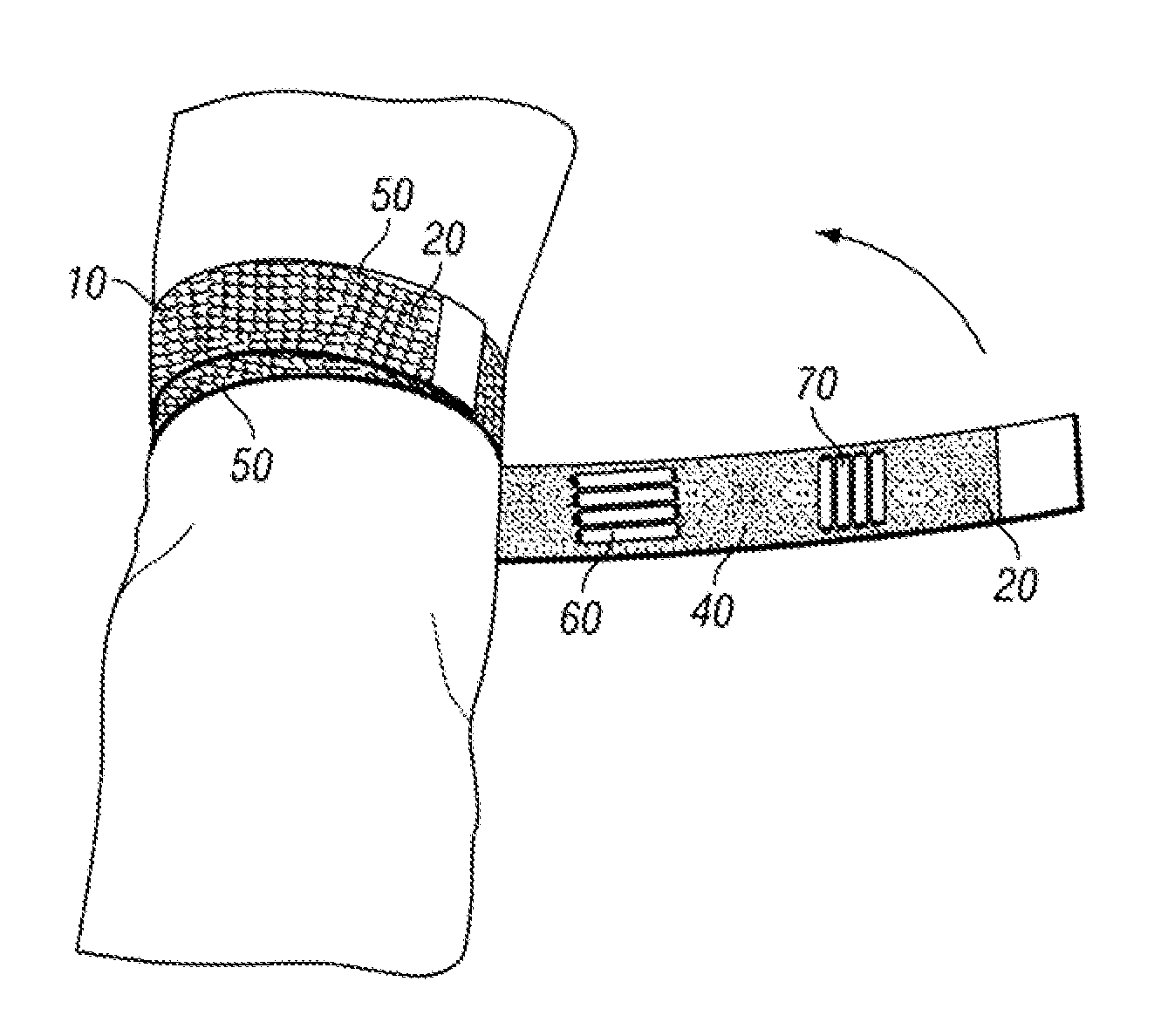
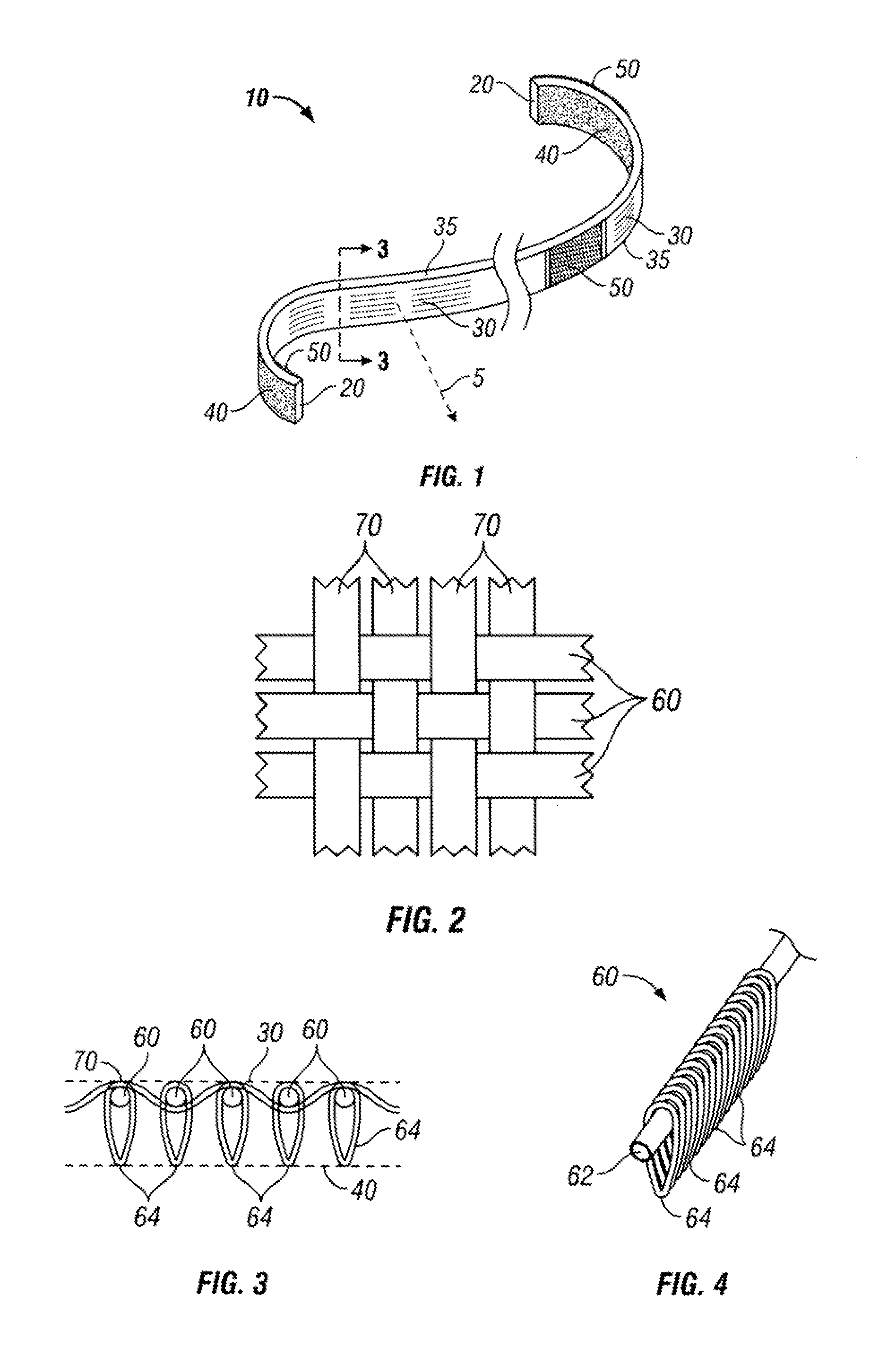
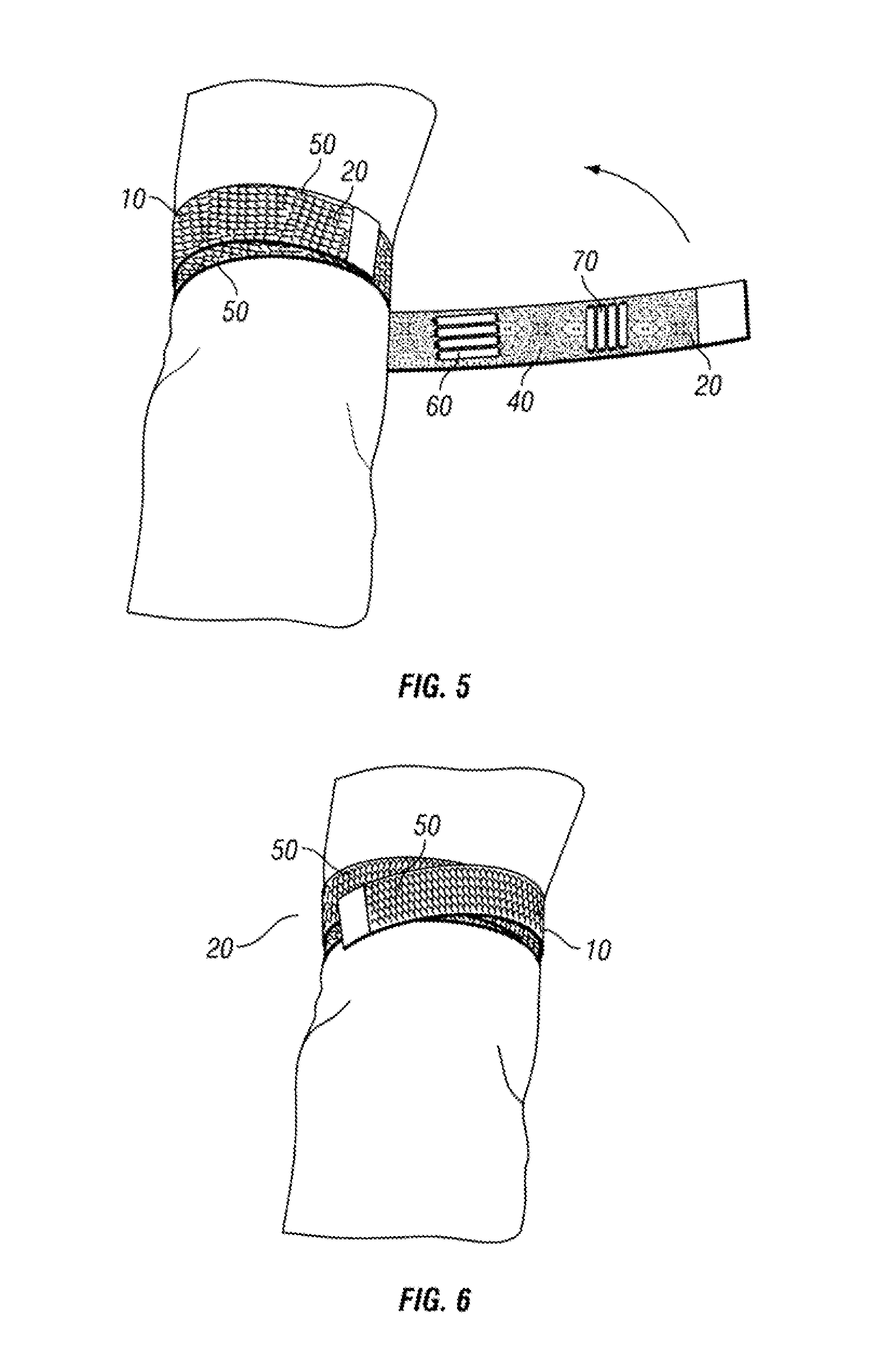
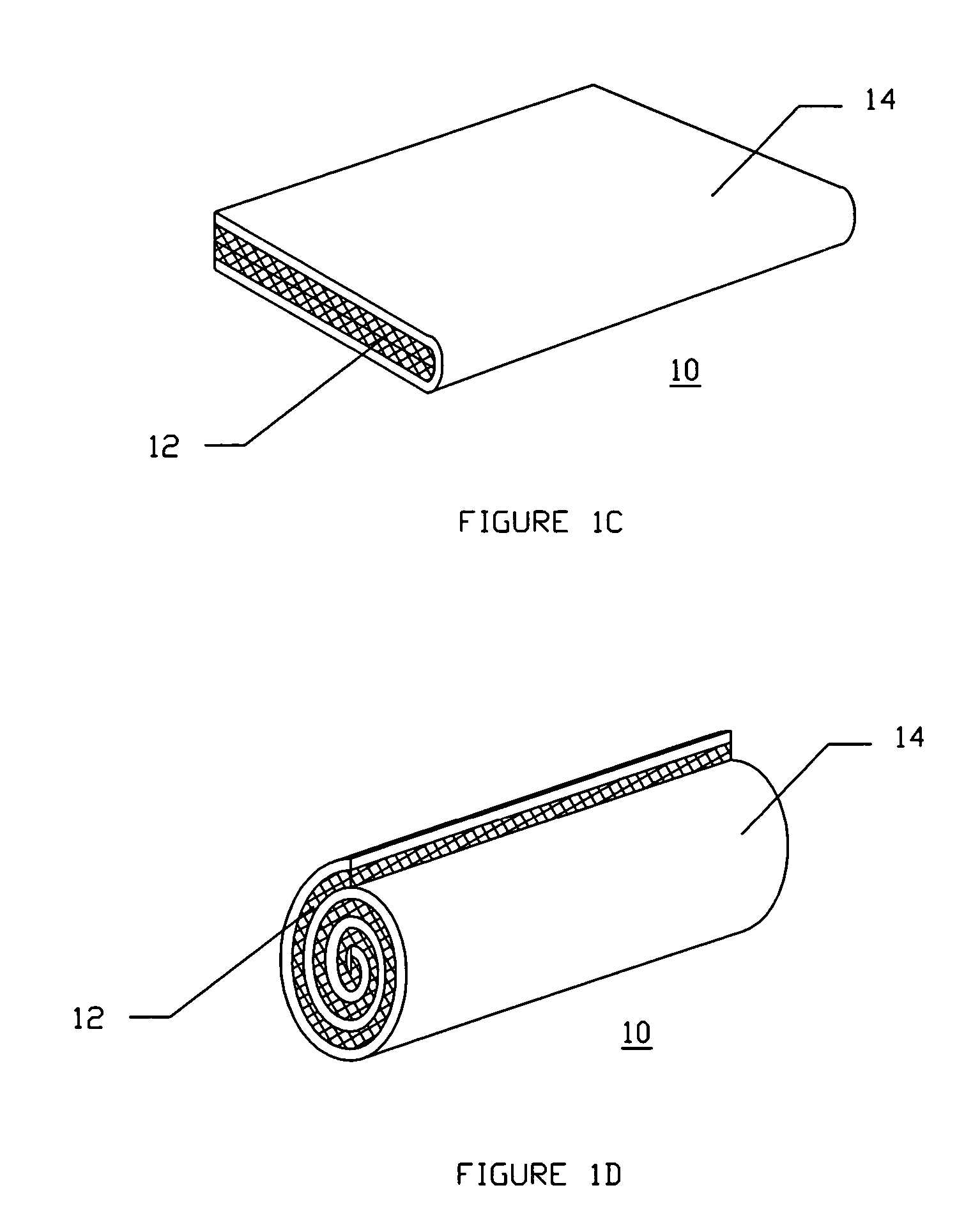
Tourniquet
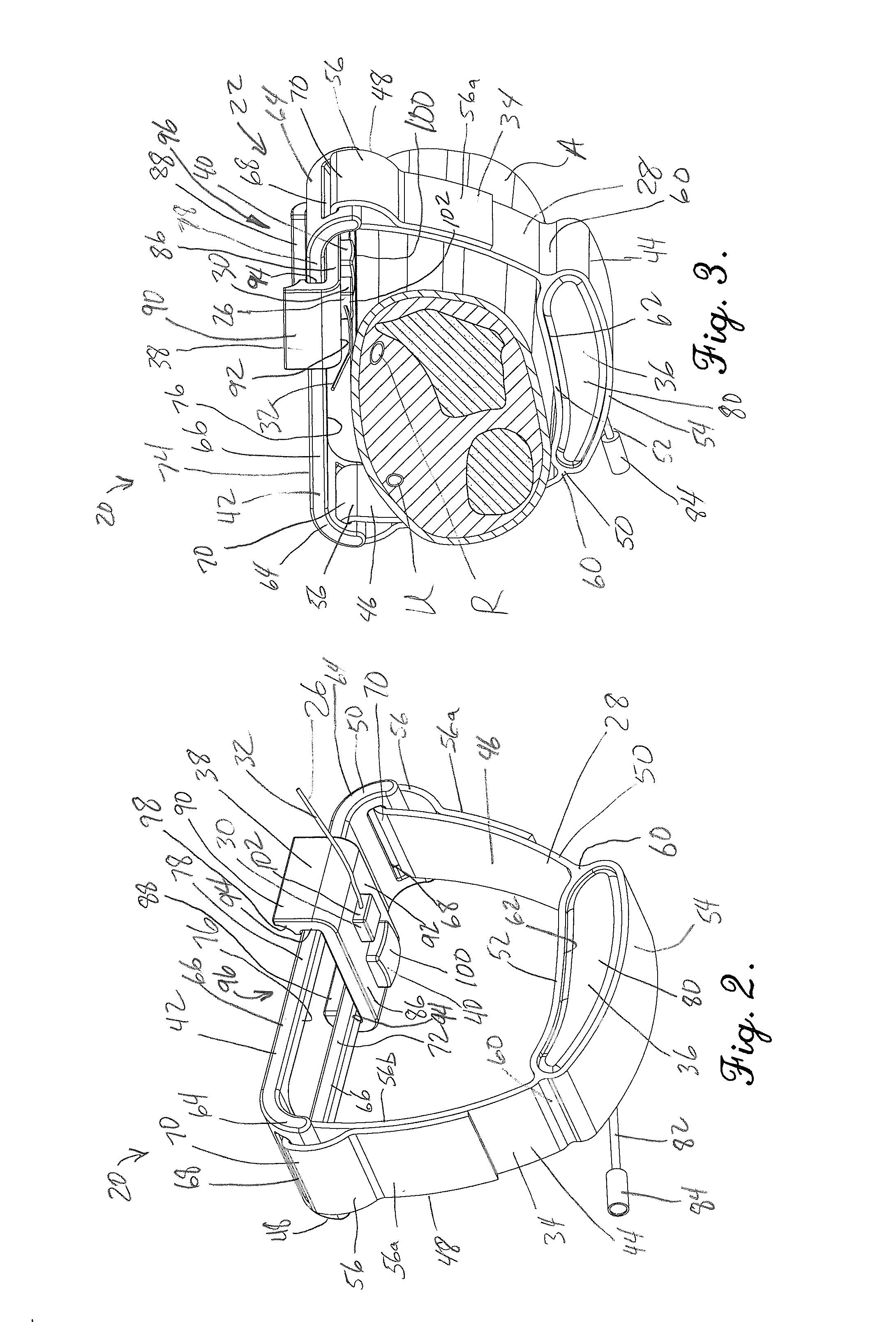
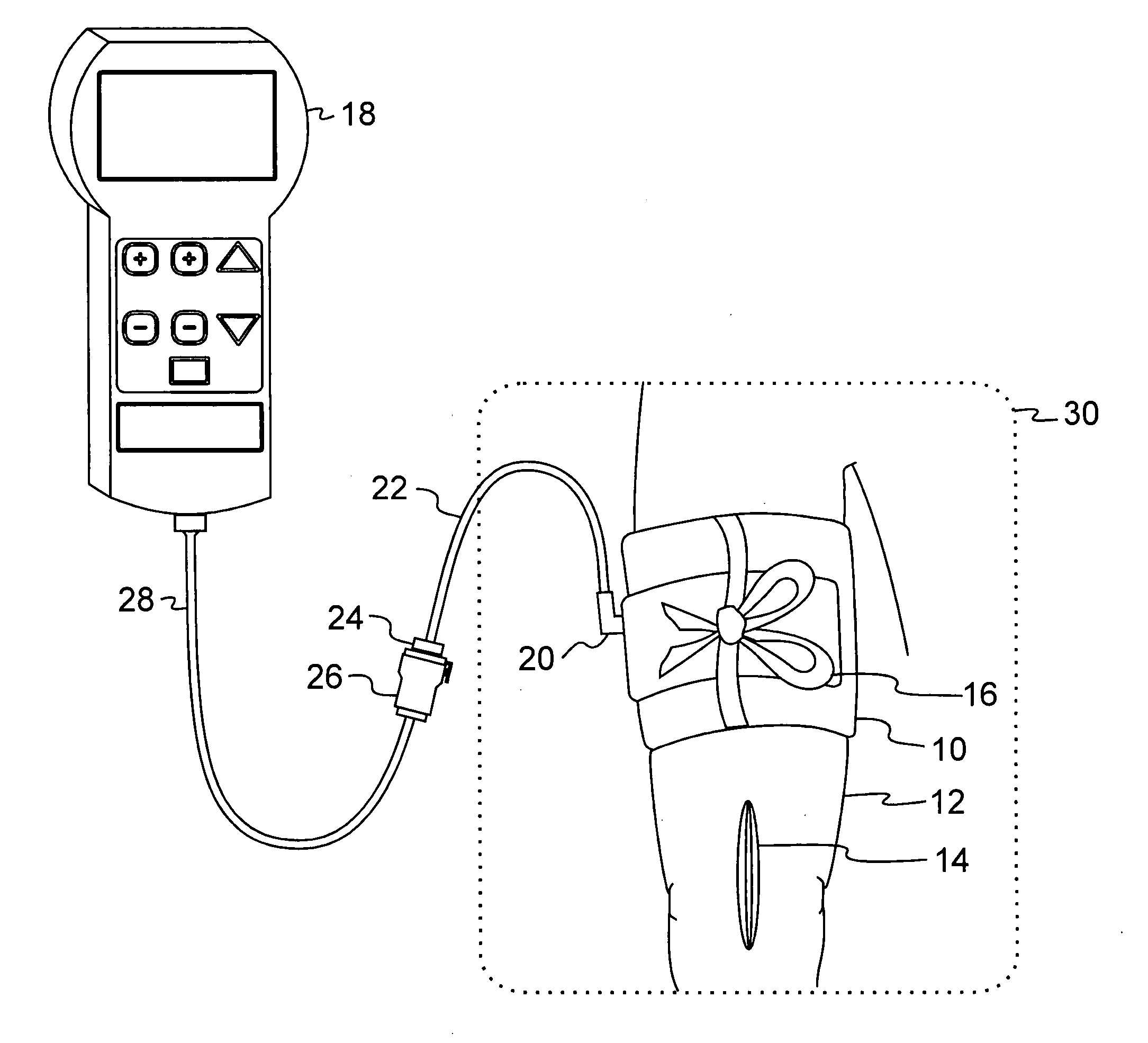
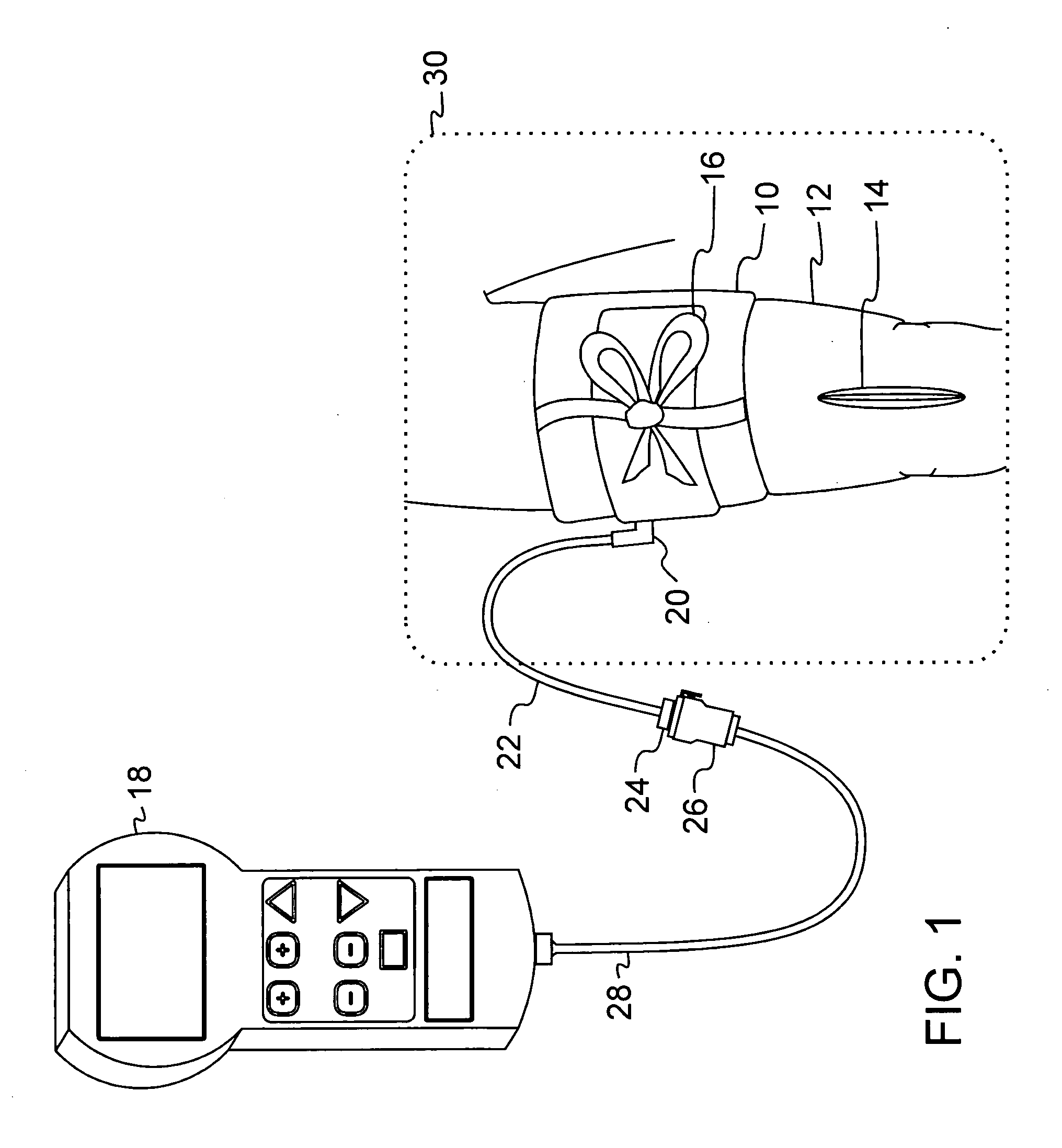
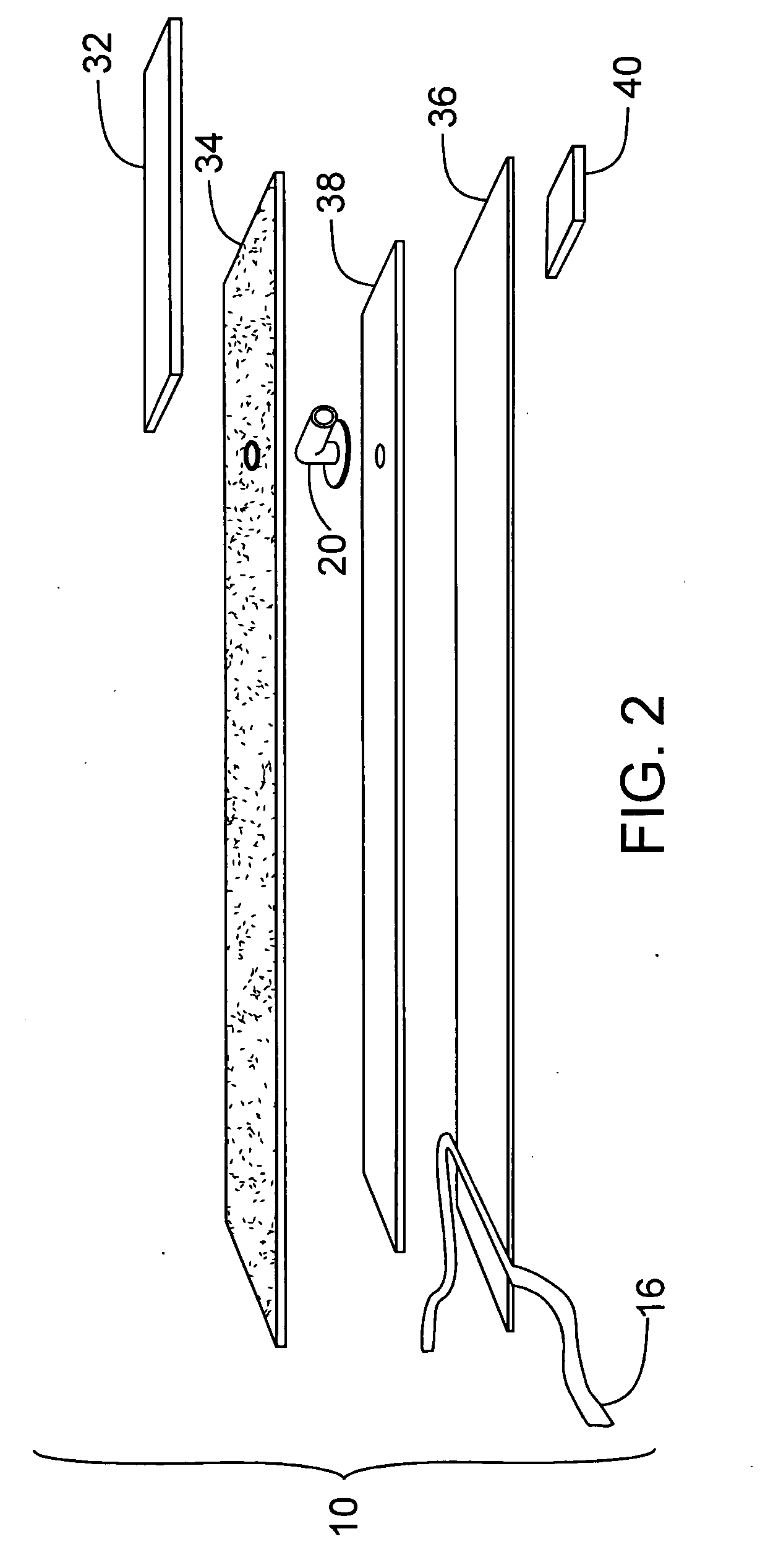
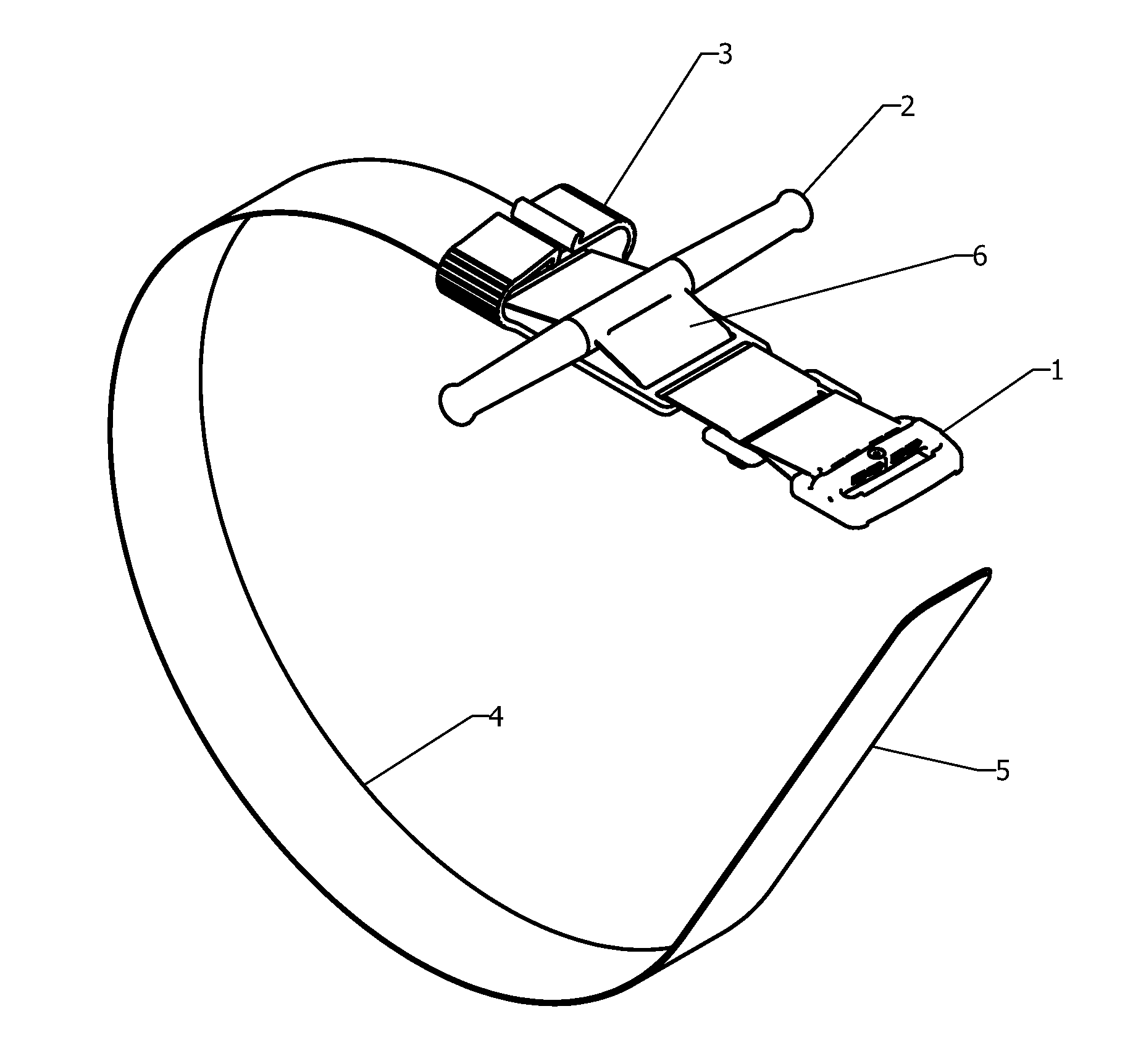
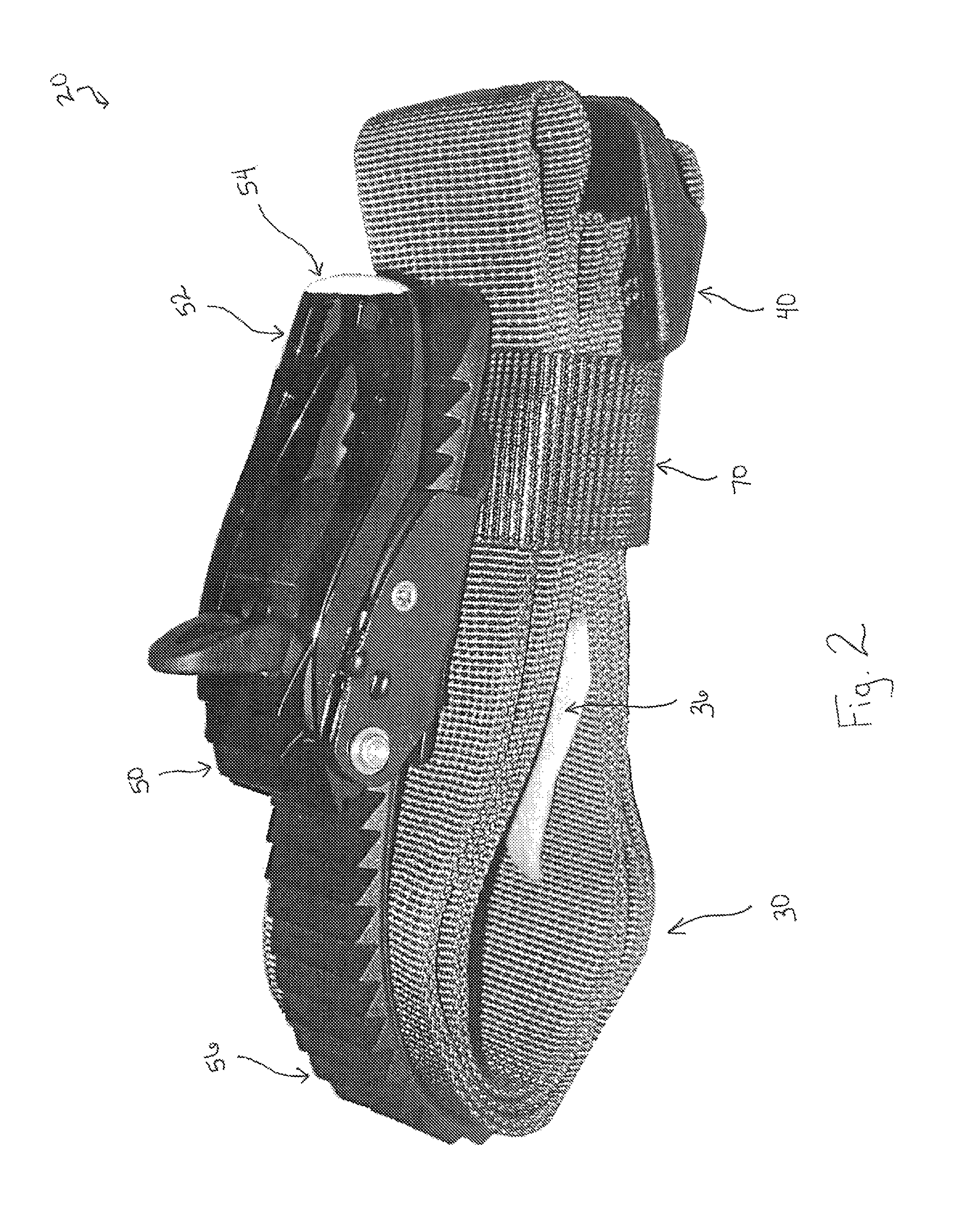
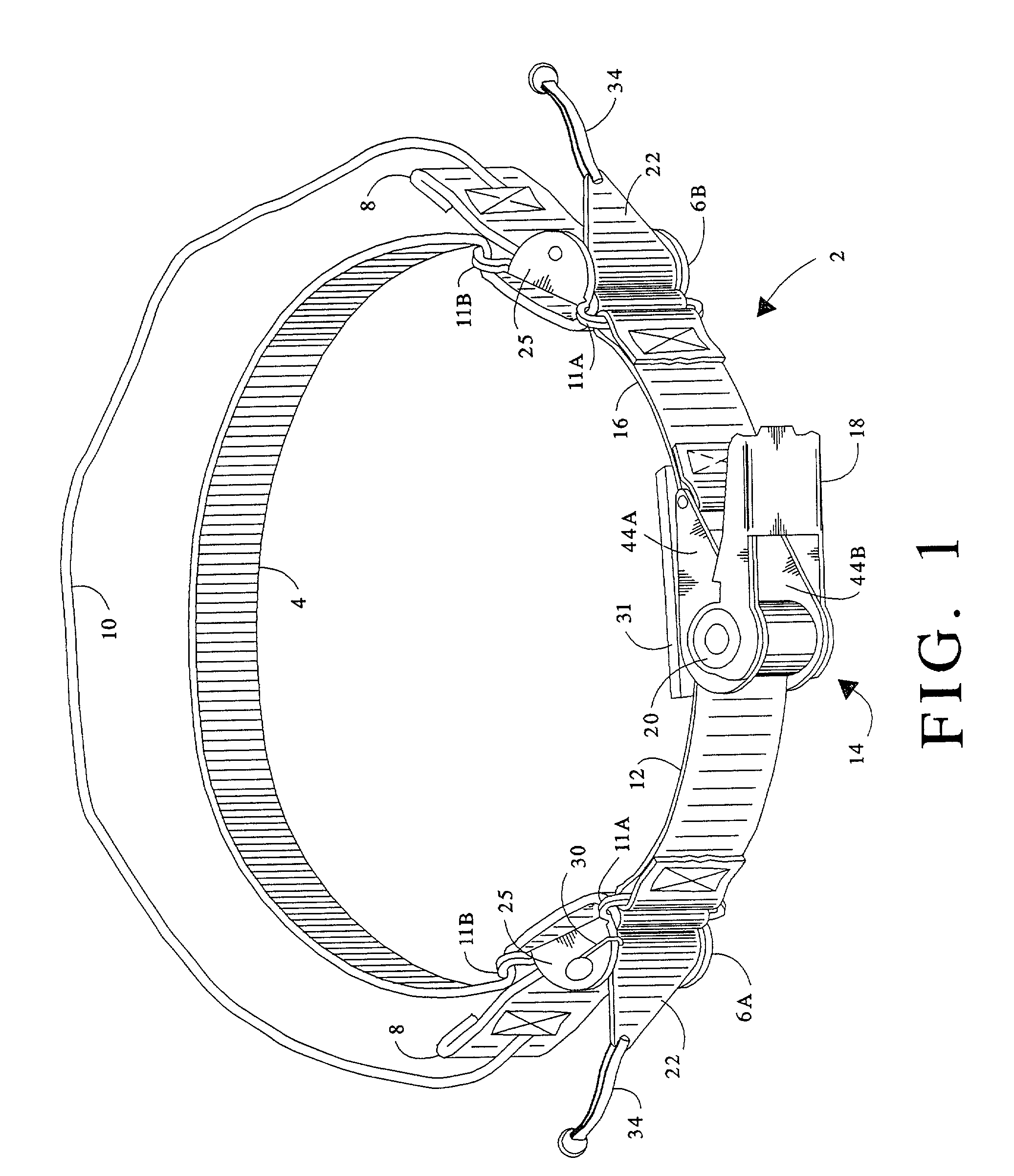
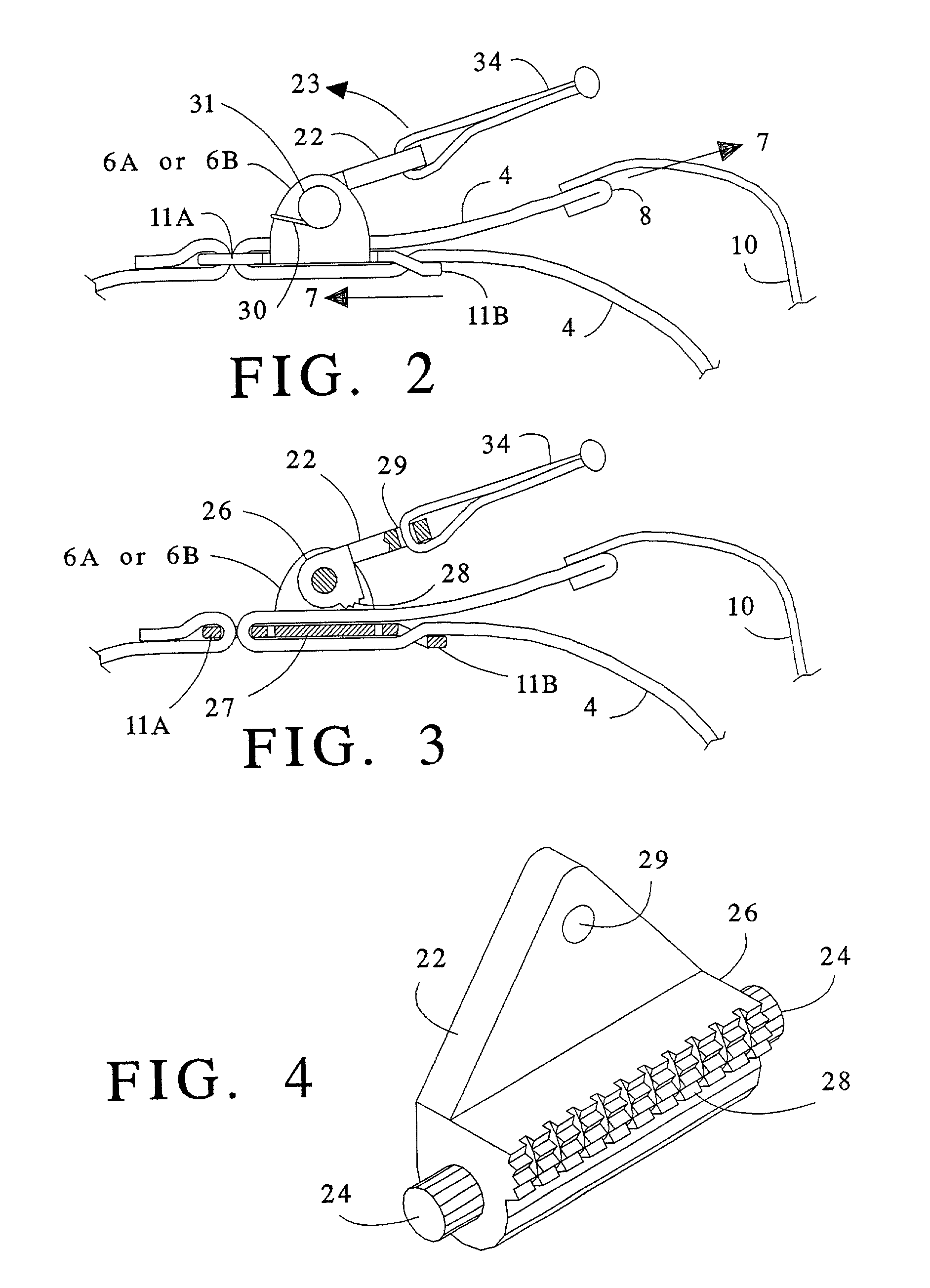
A tourniquet for use in constricting blood flow to limbs. The tourniquet comprises a strap with integral pocket-assemblies, a rod, and a cam-type buckle for fixing an initial circumference. The pocket assemblies receive the ends of the rod to hold the strap in a twisted configuration after tightening with the rod.
Owner:MCMILLAN DIANE C
Tourniquet and method of using same
A tourniquet includes a tensioning mechanism configured to provide a continuous range of adjustment of tension applied by the tourniquet. The tensioning mechanism includes a housing, an arbor coupled to the housing, the arbor being connected to the strap, and a crank assembly coupled to the arbor. The crank assembly includes a crank, and at least one gear mechanism coupled to the crank and to the arbor. In one embodiment, the at least one gear mechanism includes a worm shaft and a worm wheel. In another embodiment, the crank is movable between a use position and a stowed position. A method of restricting blood flow to a portion of a limb is further disclosed.
Owner:TIAX LLC
Limb hemorrhage trauma simulator
A limb hemorrhage trauma simulator provides didactic and hands-on training for the prehospital treatment of a limb trauma victim. The simulator realistically simulates a wounded limb, providing simulated pulse and hemorrhage blood flow. The simulator provides a simulated scenario in which the wound occurred. The student then responds to the scenario by treating the limb via direct pressure, tourniquet, and / or wound analysis. The simulator modifies hemorrhage blood flow and pulse in response to direct or tourniquet pressure applied to the limb. The simulator records the student's actions to provide feedback and grade the student's response.
Owner:SIMQUEST
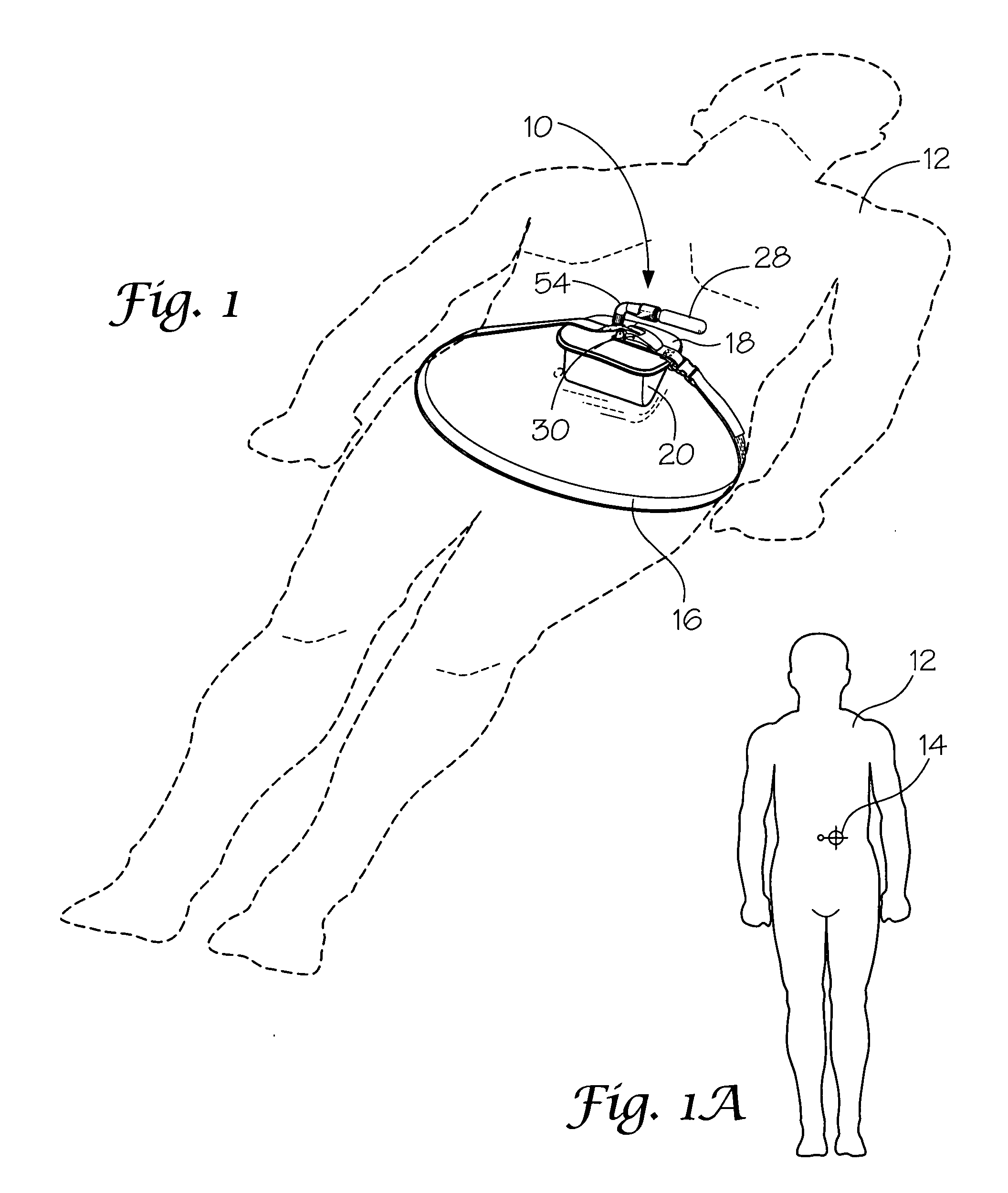
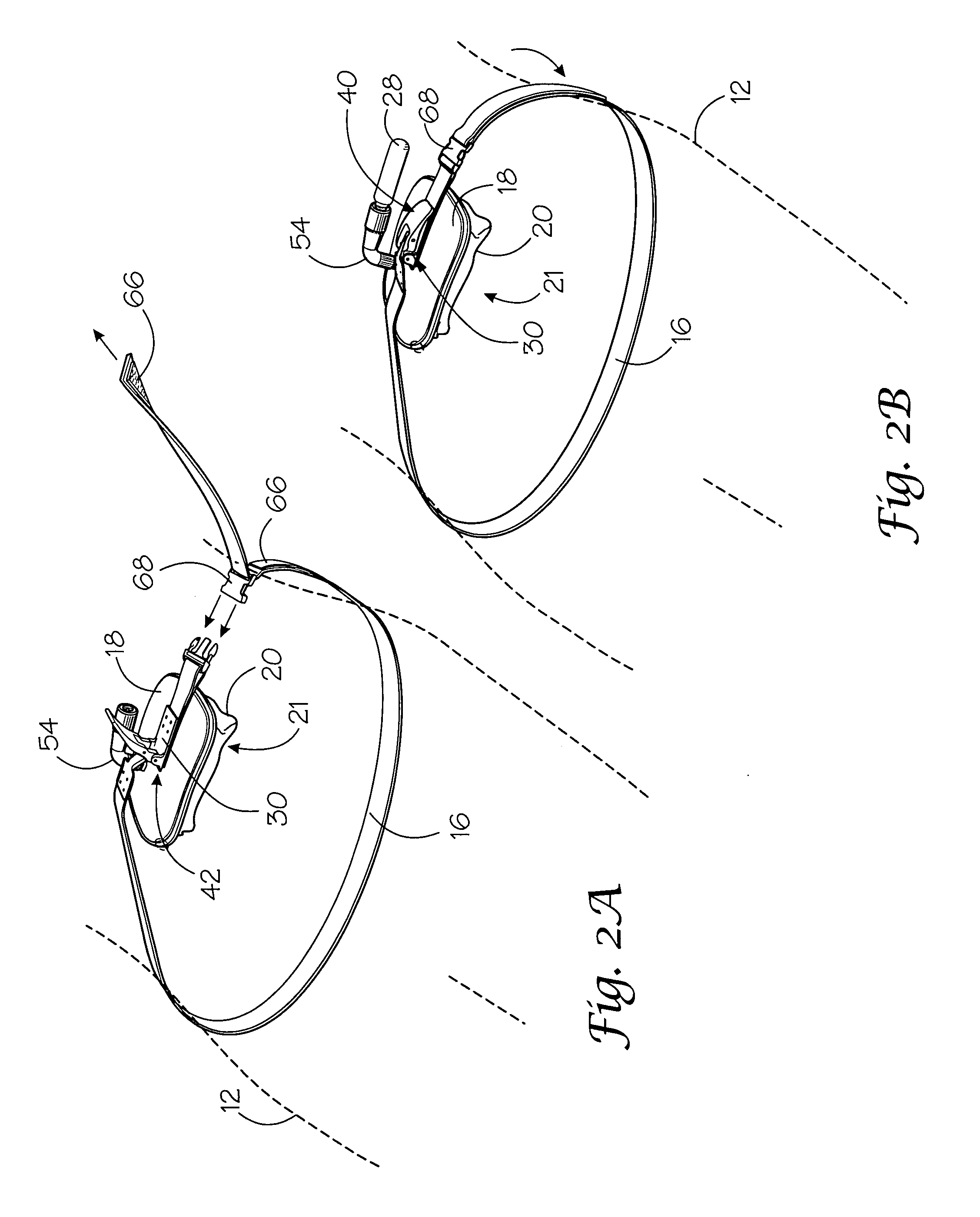
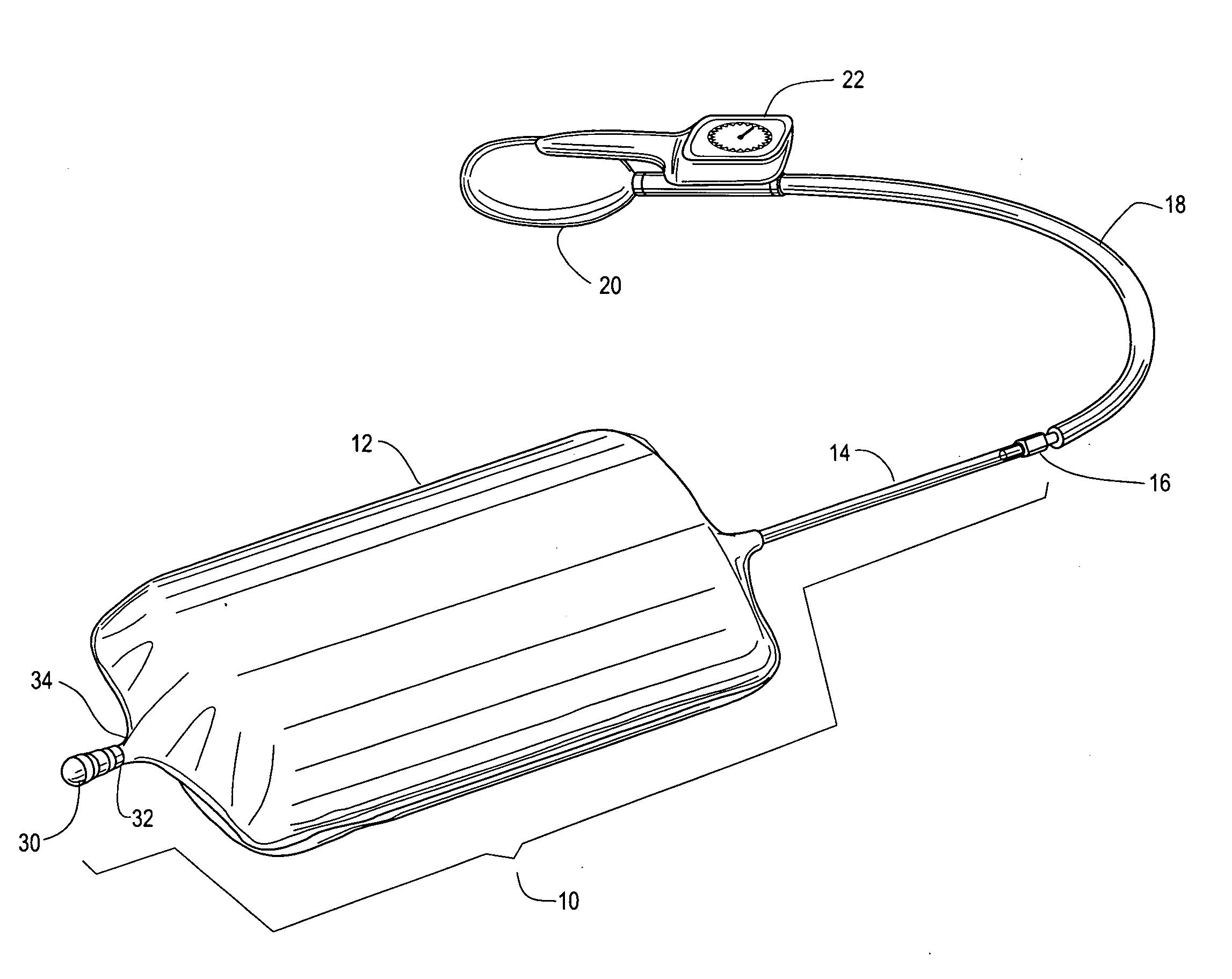
Portable pneumatic abdominal aortic tourniquet
A portable pneumatic abdominal aortic tourniquet for occlusion of the abdominal descending aorta to restrict blood supply to a non-compressible arterial hemorrhage in the abdominal region. The tourniquet comprising an adjustable waist strap for securing around an abdomen; a directed air bladder mounted to the waist strap having a generally “V” shaped construction operable between a deflated condition wherein the directed air bladder is collapsed, and an inflated condition wherein the directed air bladder is expanded for exerting pressure against the abdomen; and, an air source connected to the directed air bladder for operating the directed air bladder between the deflated condition and the inflated condition.
Owner:COMPRESSION WORKS
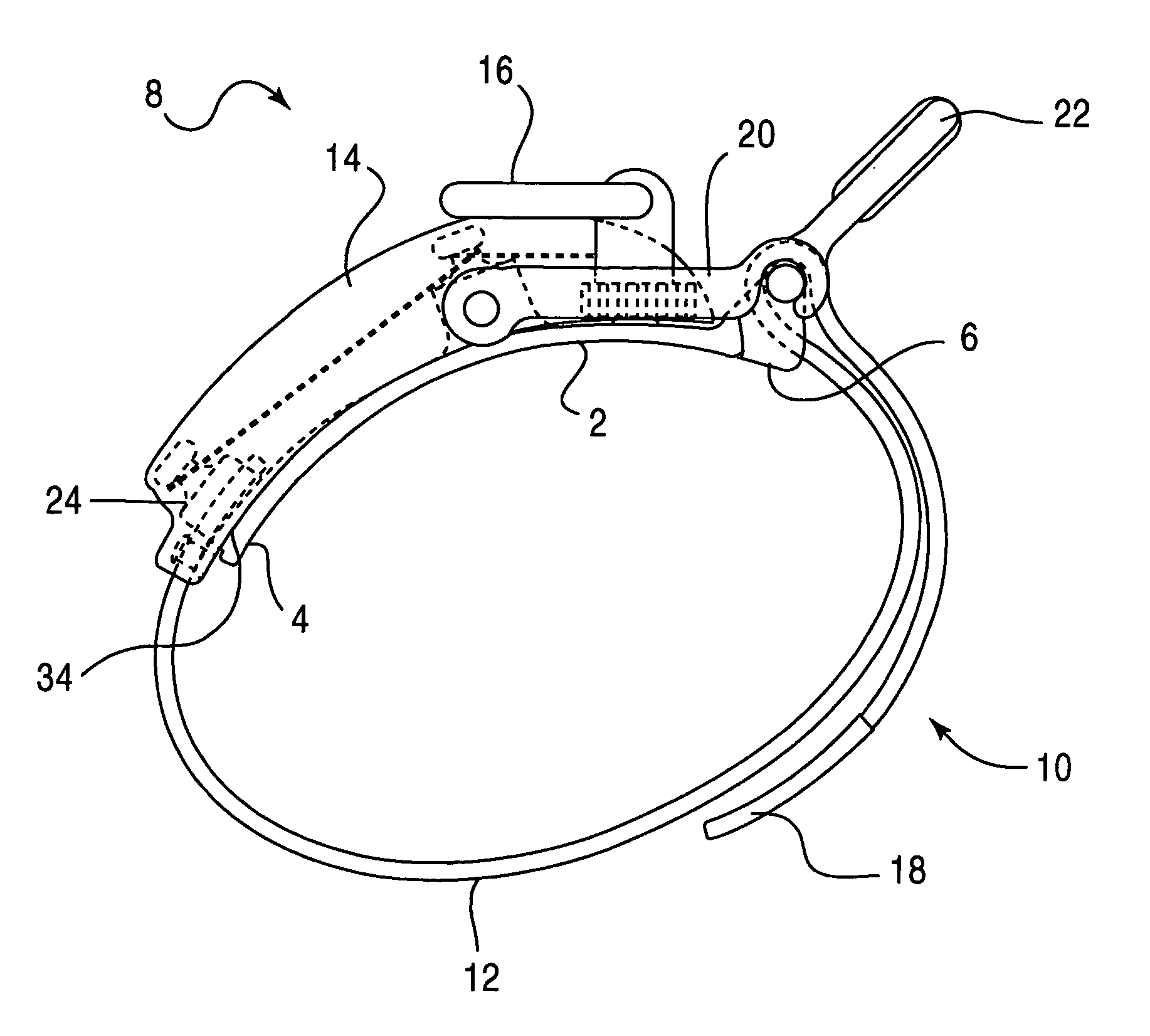
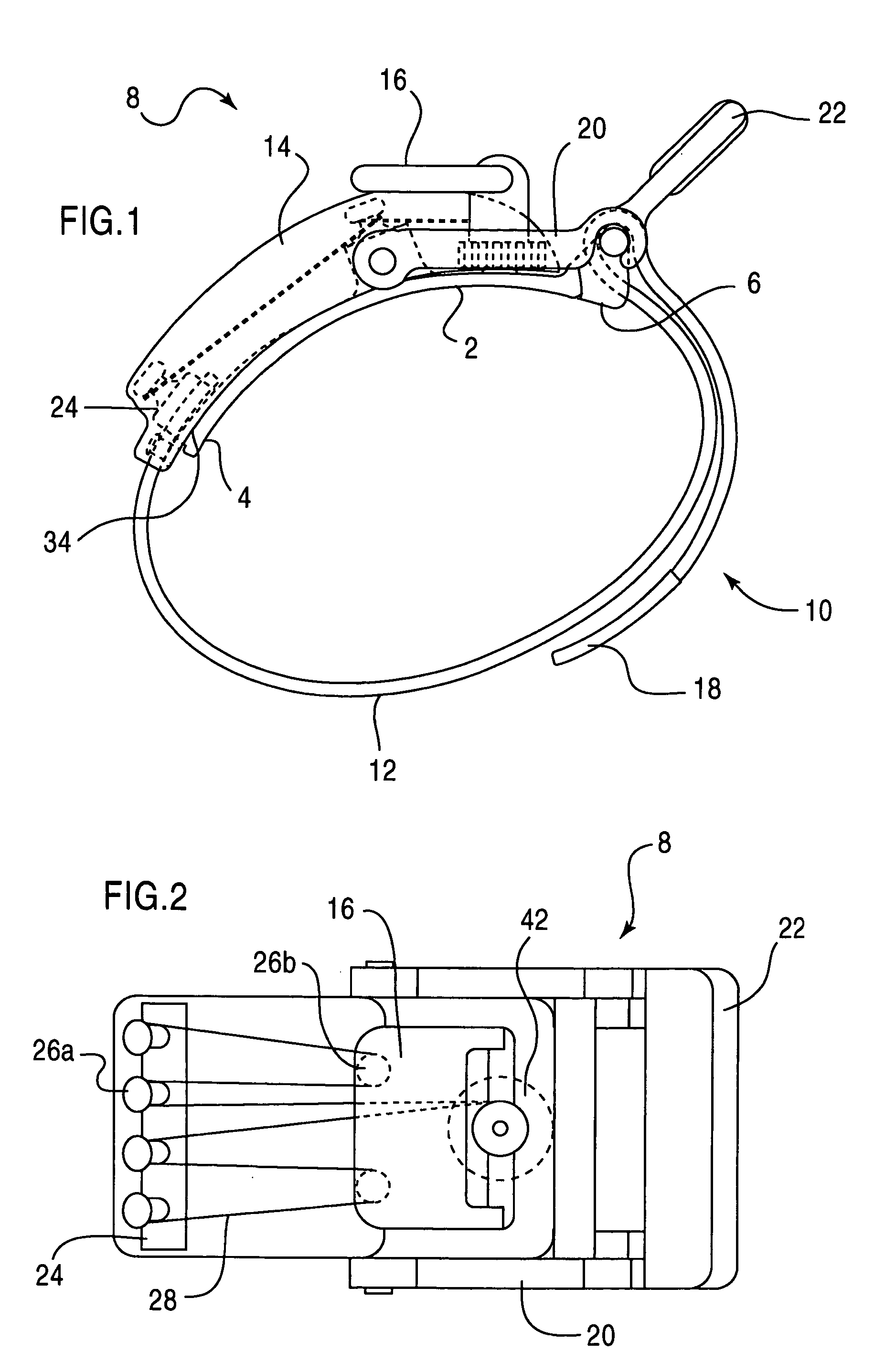
Mechanical advantage tourniquet
InactiveUS20050113866A1Quick and easy applicationEfficiently and effectively compressTourniquetsElectric power systemTourniquet time
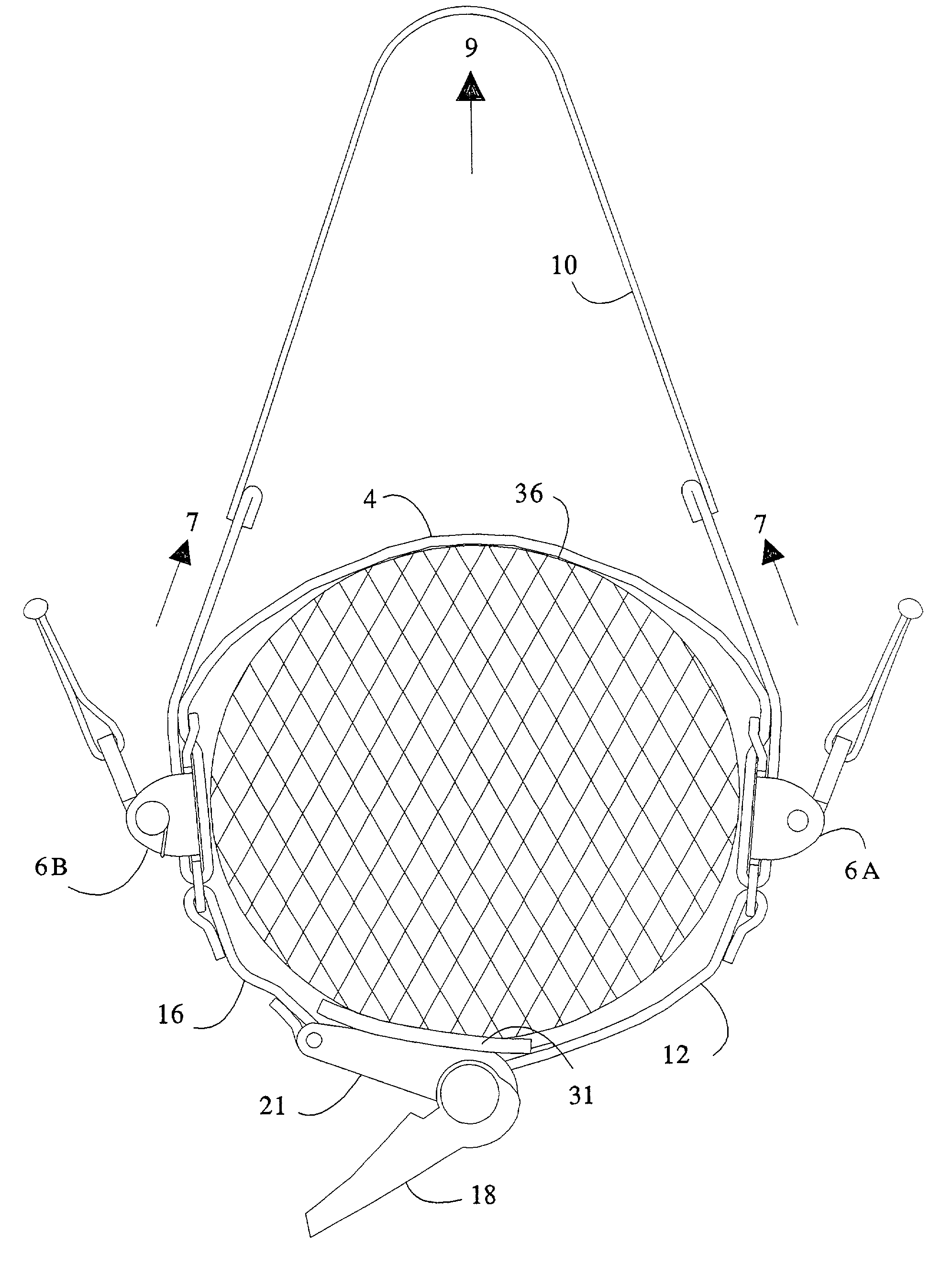
A pressure control apparatus for restricting a flow of blood through or from a body part includes at least one arcuate member for attaching to the body part. The at least one arcuate member has a first end and an opposite second end. The first end includes a hook for fastening to a buckle mounted at the opposite second end. A mechanical advantage power system includes a turnkey and is connected to the at least one arcuate member and serves to adjusting a pressure of the apparatus on the body part by turning the turnkey. An elongated strap is disposed on at least a circumferential portion of the arcuate member for circumferentially tightening the apparatus around the body part. A locking device closes the apparatus around the body part and is attached to the at least one arcuate member. A cover or shroud is disposed on an outer perimeter of the at least one arcuate member for enclosing a portion of the mechanical advantage power system.
Owner:PYNG MEDICAL CORP
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
InactiveUS20080132820A1Different compressibilityDifferent resilienceNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersTrauma surgeryTourniquet time
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:BUCKMAN ROBERT F +2
Tourniquet
A self-regulating tourniquet has a pressure source, a pressure applicator apparatus associated with the pressure source and operative to apply pressure therefrom to a limb and a pressure regulator associated with the pressure source and the pressure applicator operative to restrict the pressure transferred from the pressure source to the limb to a designated maximum pressure applied to the limb. The pressure source and the pressure applicator may be separate modules that are adapted to be engaged by connecting means and establish gas passage from the pressure source to the pressure applicator.
Owner:AMISAR SHAI +1
Mechanical advantage tourniquet
InactiveUS7582102B2Quick and easy applicationEfficiently and effectively compressTourniquetsTourniquet timeMechanical advantage
Owner:PYNG MEDICAL CORP
Radial compression hemostasis band with doppler confirming vascular patency
A hemostatic compression system facilitates patent hemostasis of an arterial access site on the arm of a wearer. The system includes a radial compression band and a Doppler probe. The radial compression band includes an elongated arm band sized to receive the arm. The compression band also includes a pressure surface coupled to the arm band and facing radially inward for compressive engagement with the access site. The Doppler probe is coupled to the arm band adjacent the pressure surface and is configured to sense blood flow through the artery. Hemostatic compression applied by the radial compression band is variable in response to the sensed blood flow so as to ensure patency of the artery during hemostasis of the site.
Owner:MEDICAL INGENUITIES
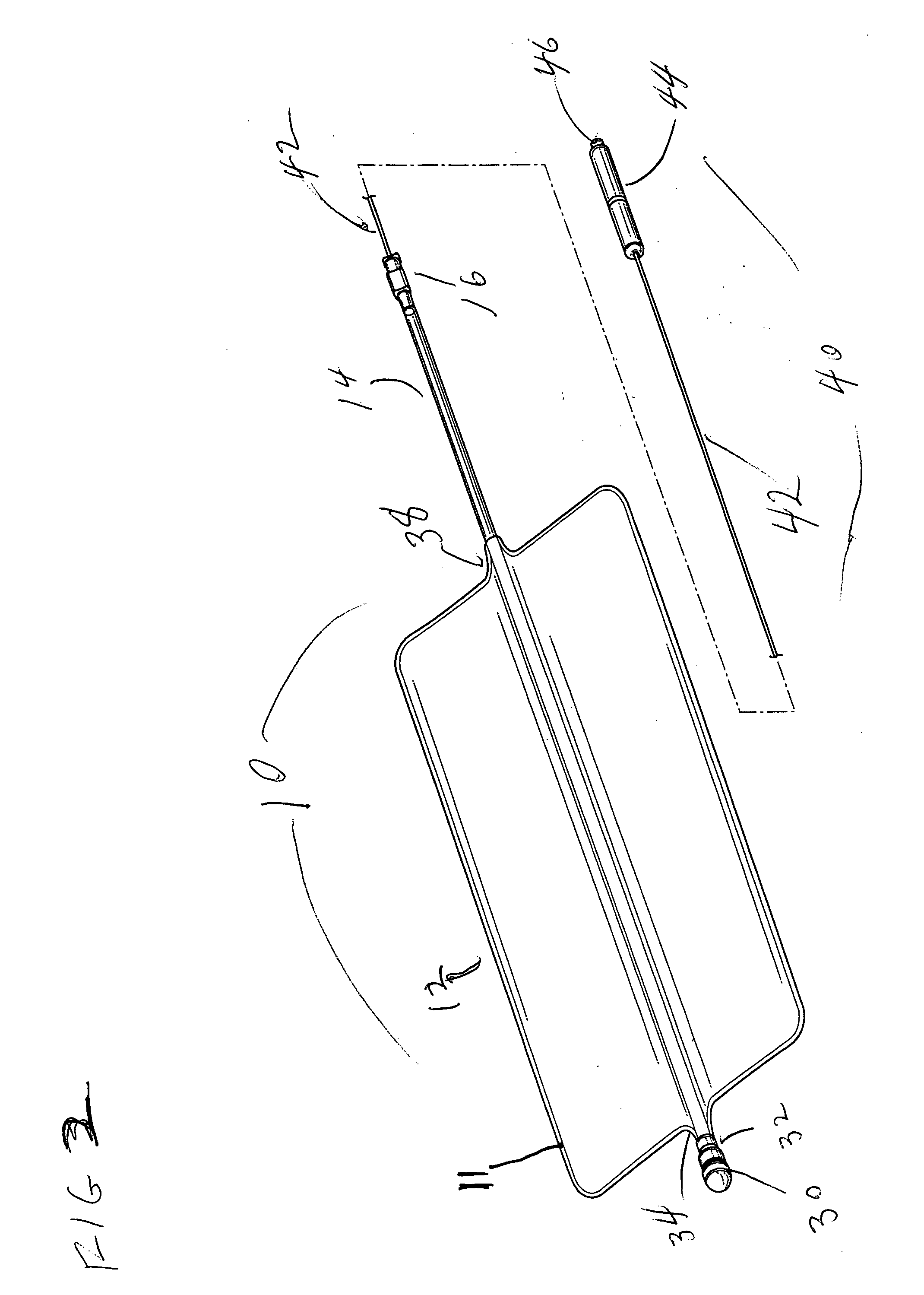
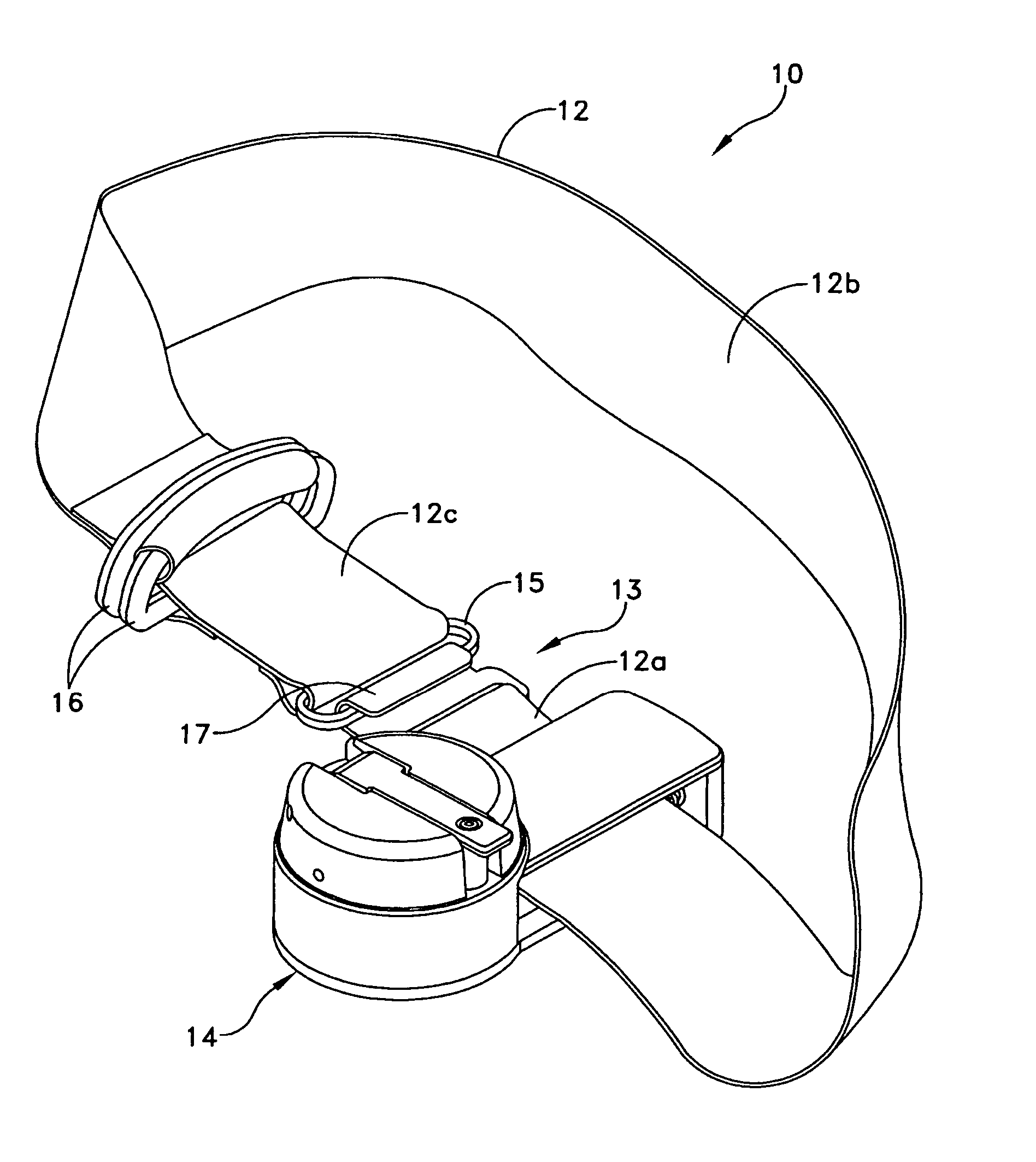
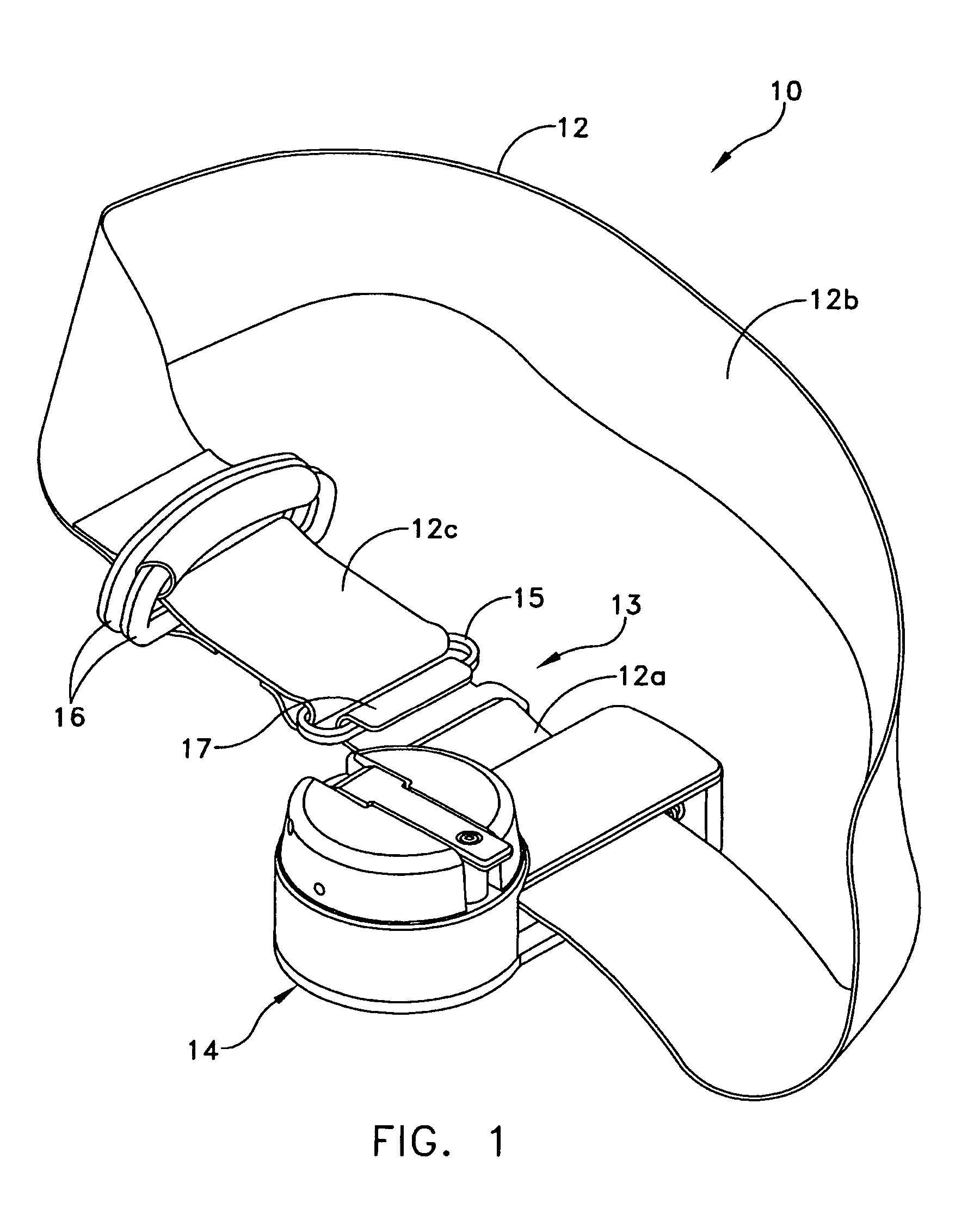
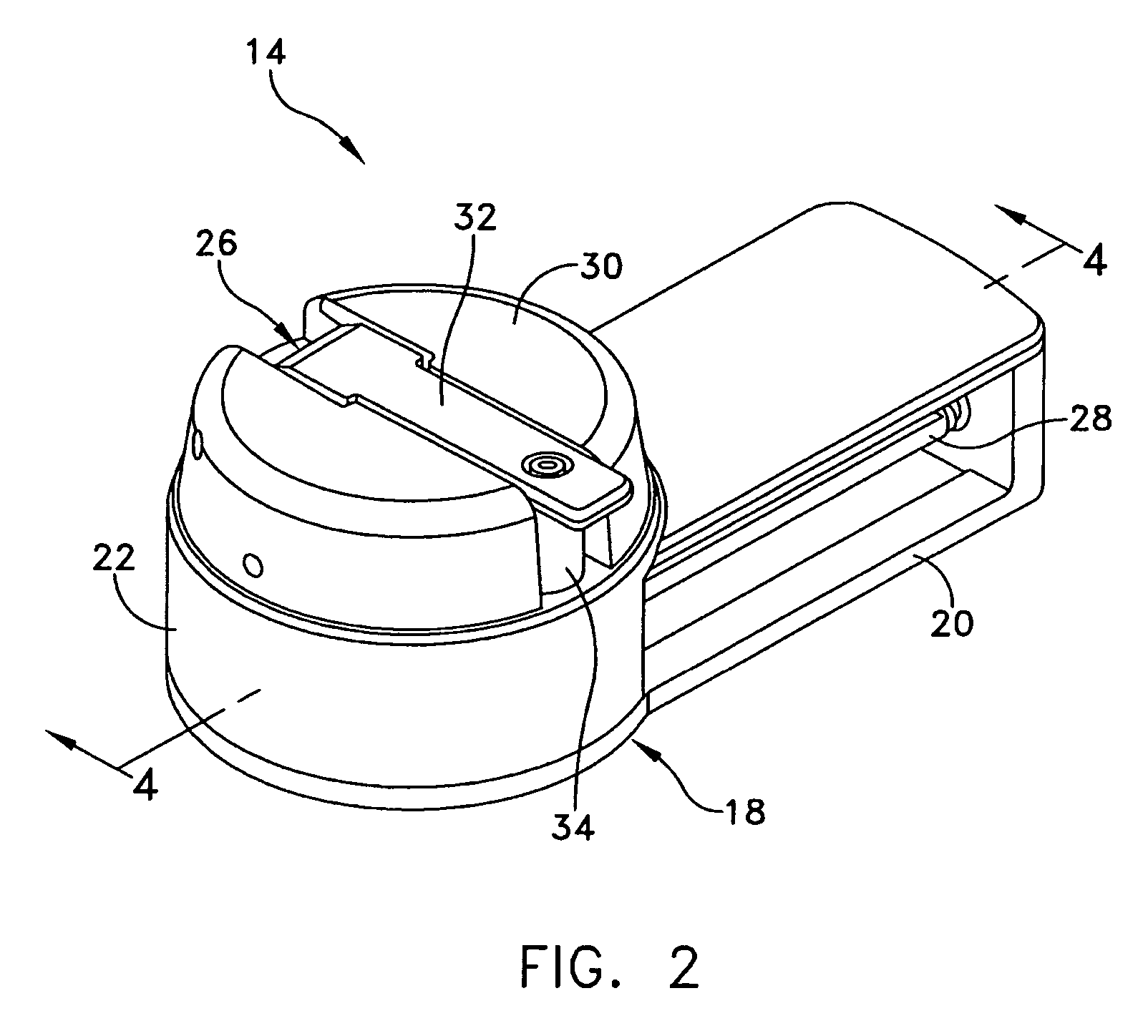
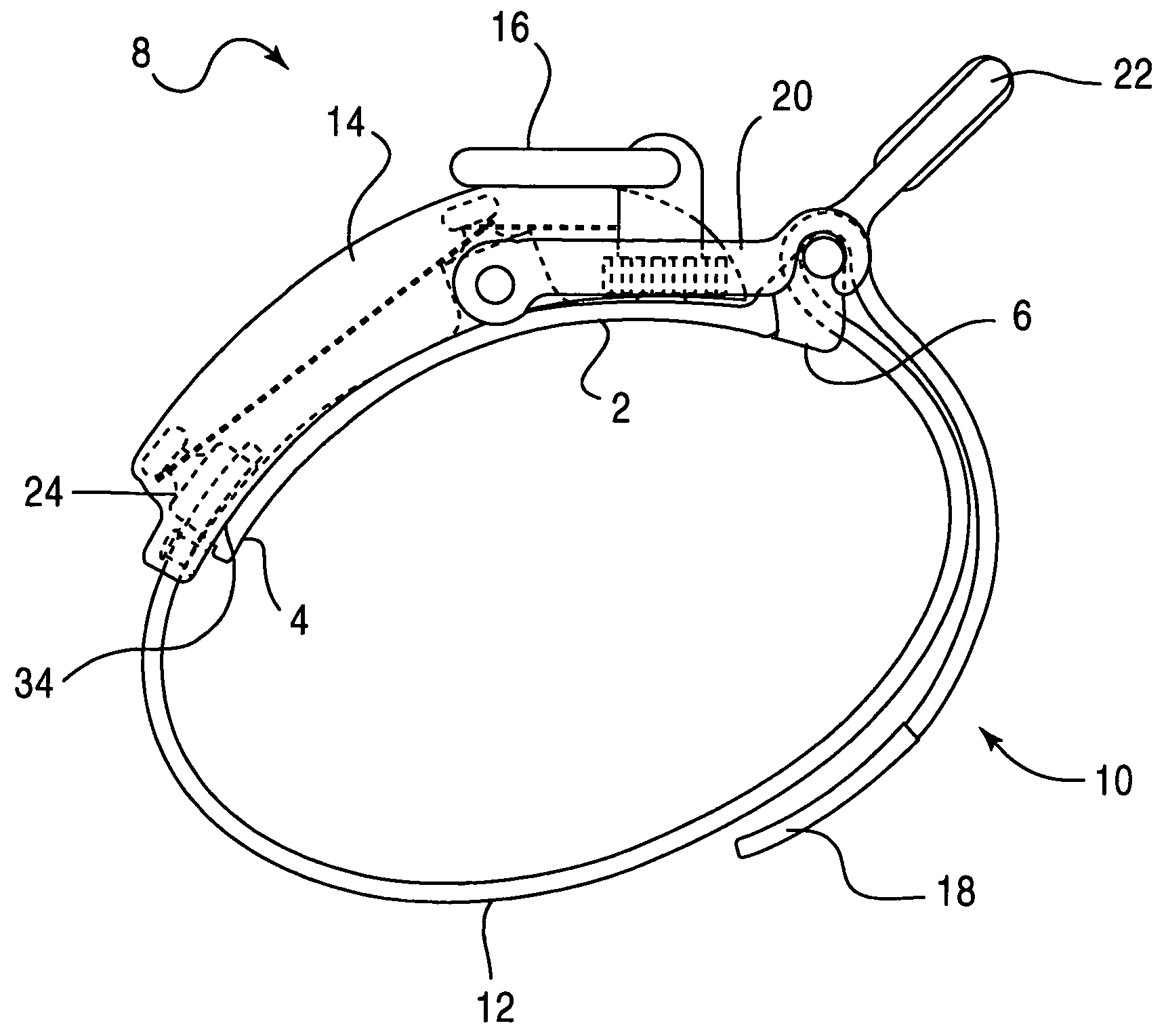
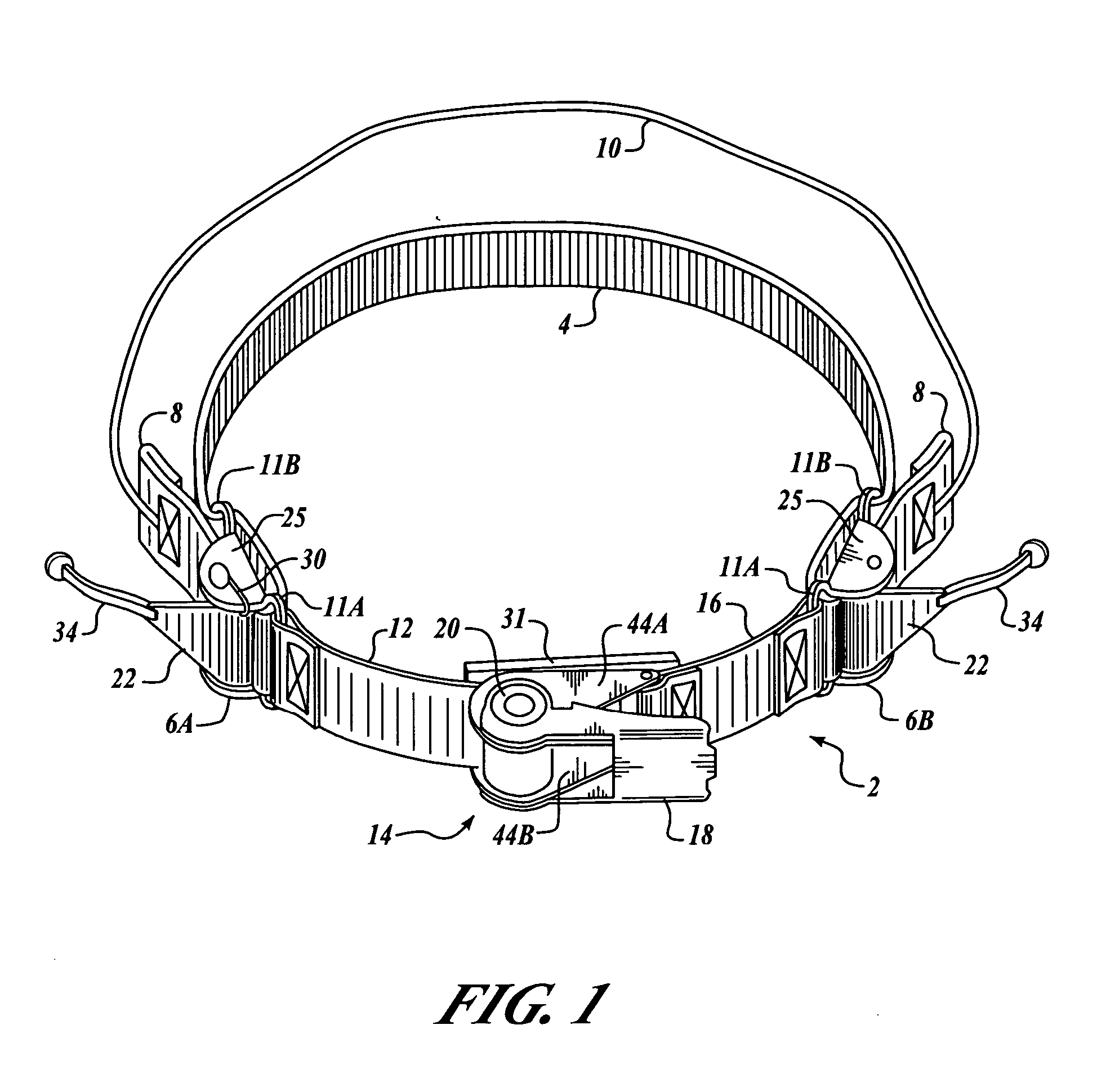
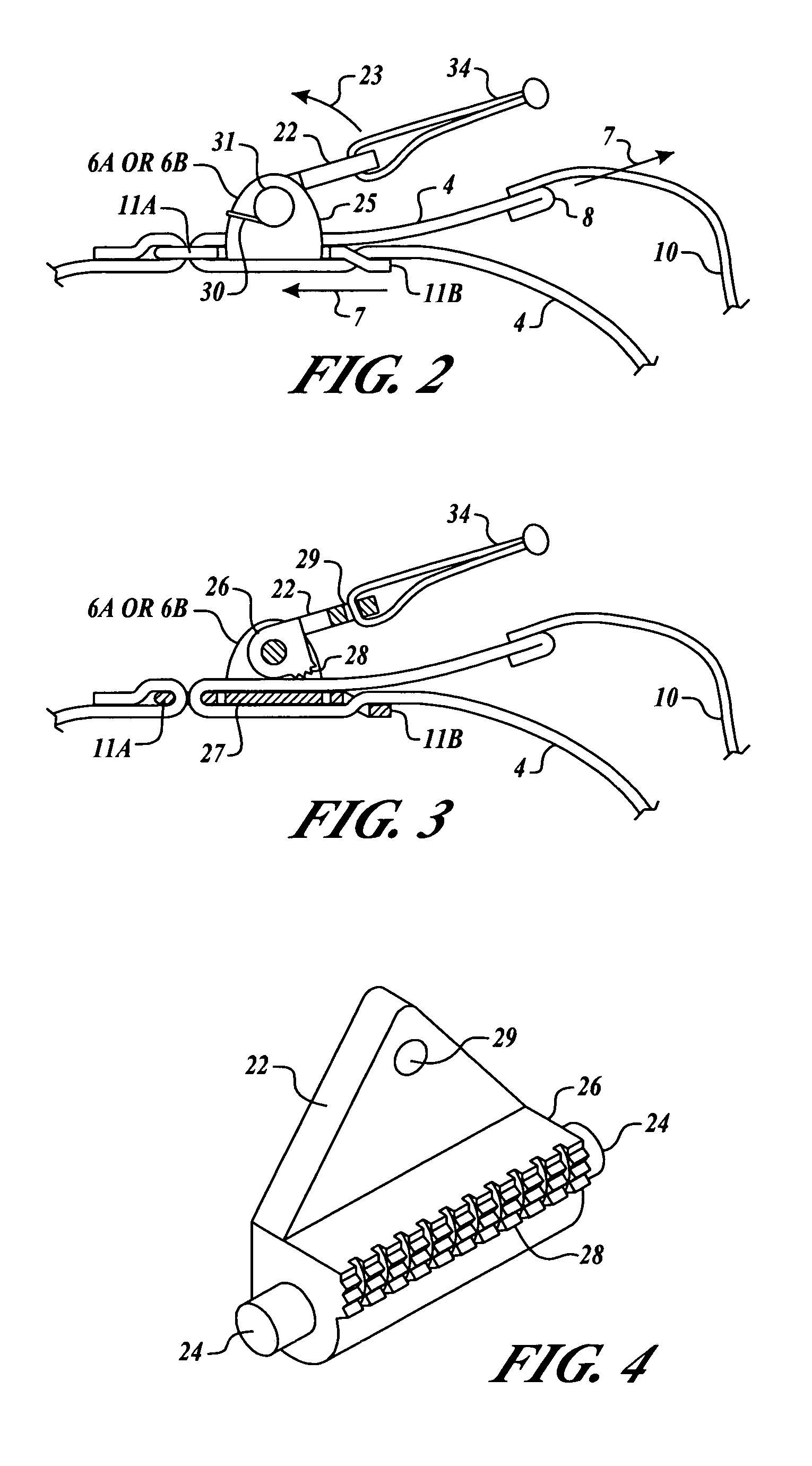
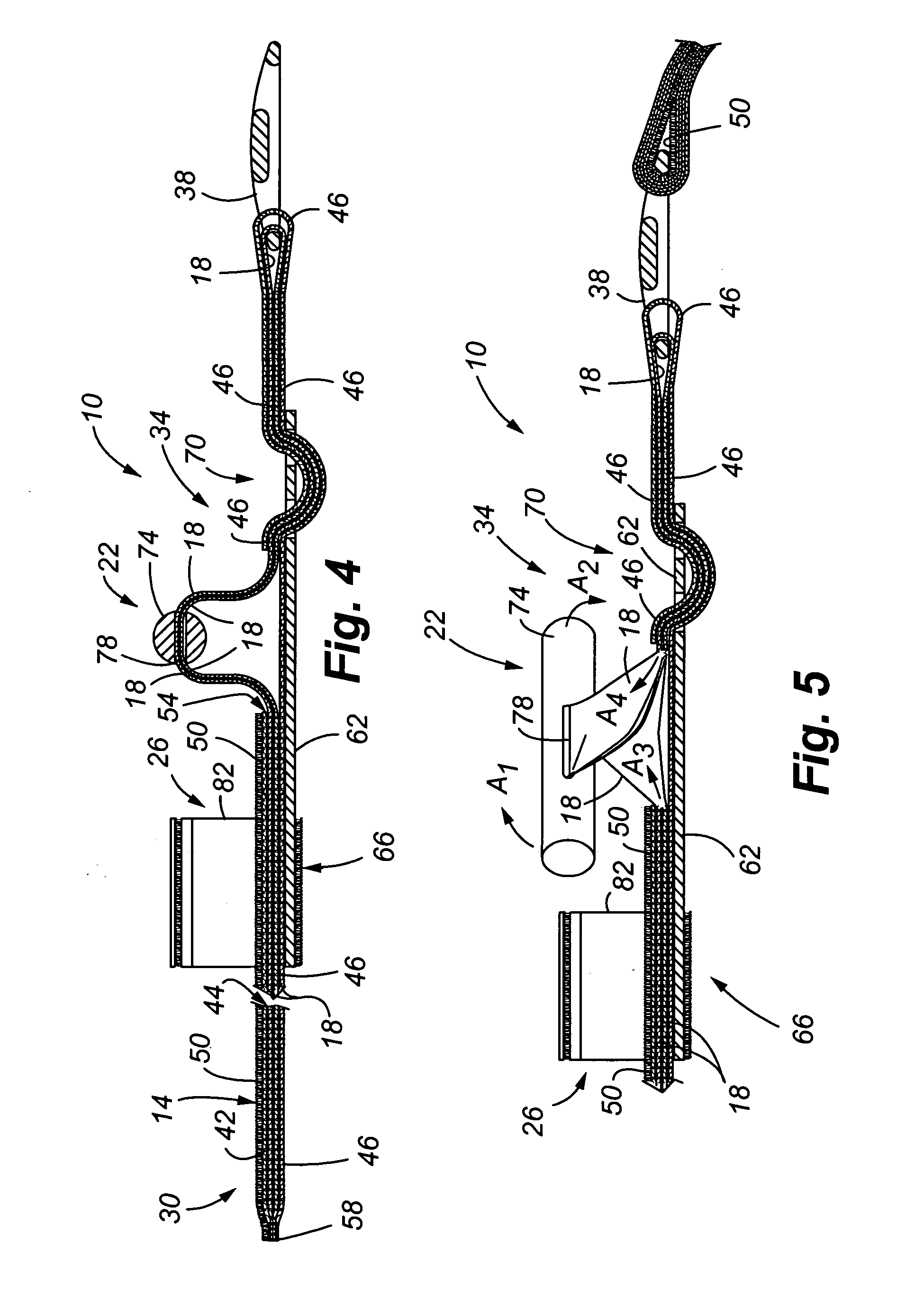
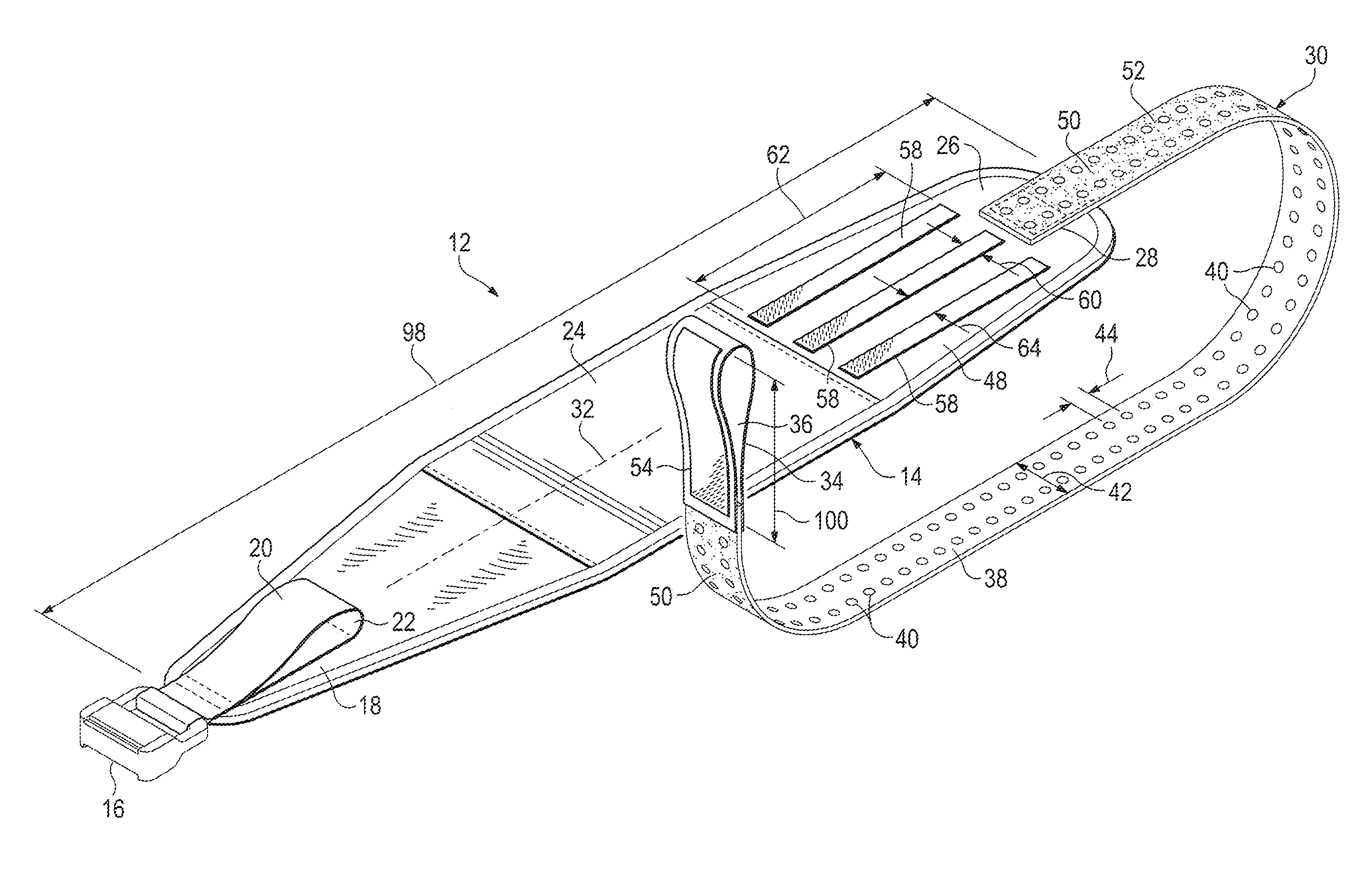
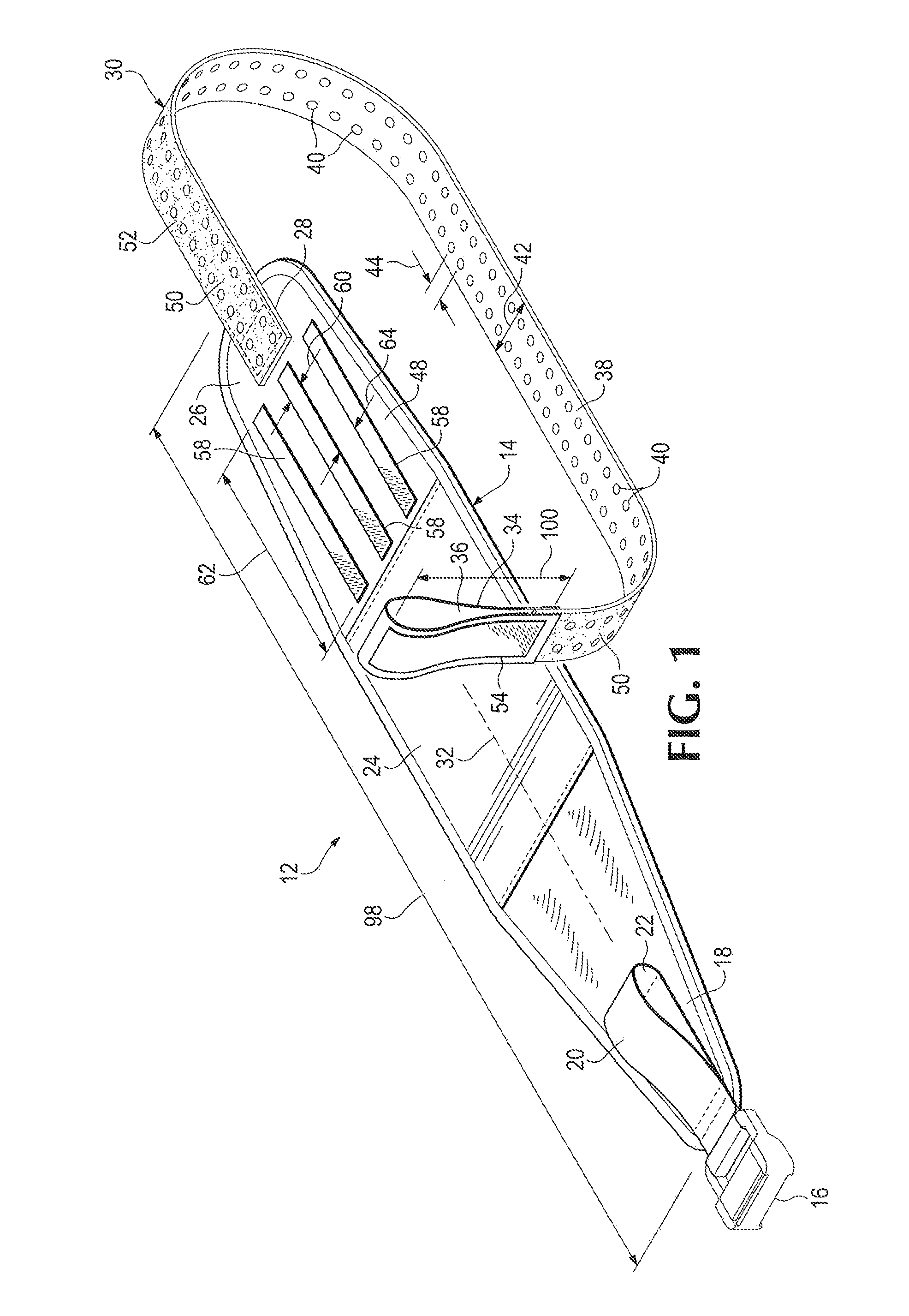
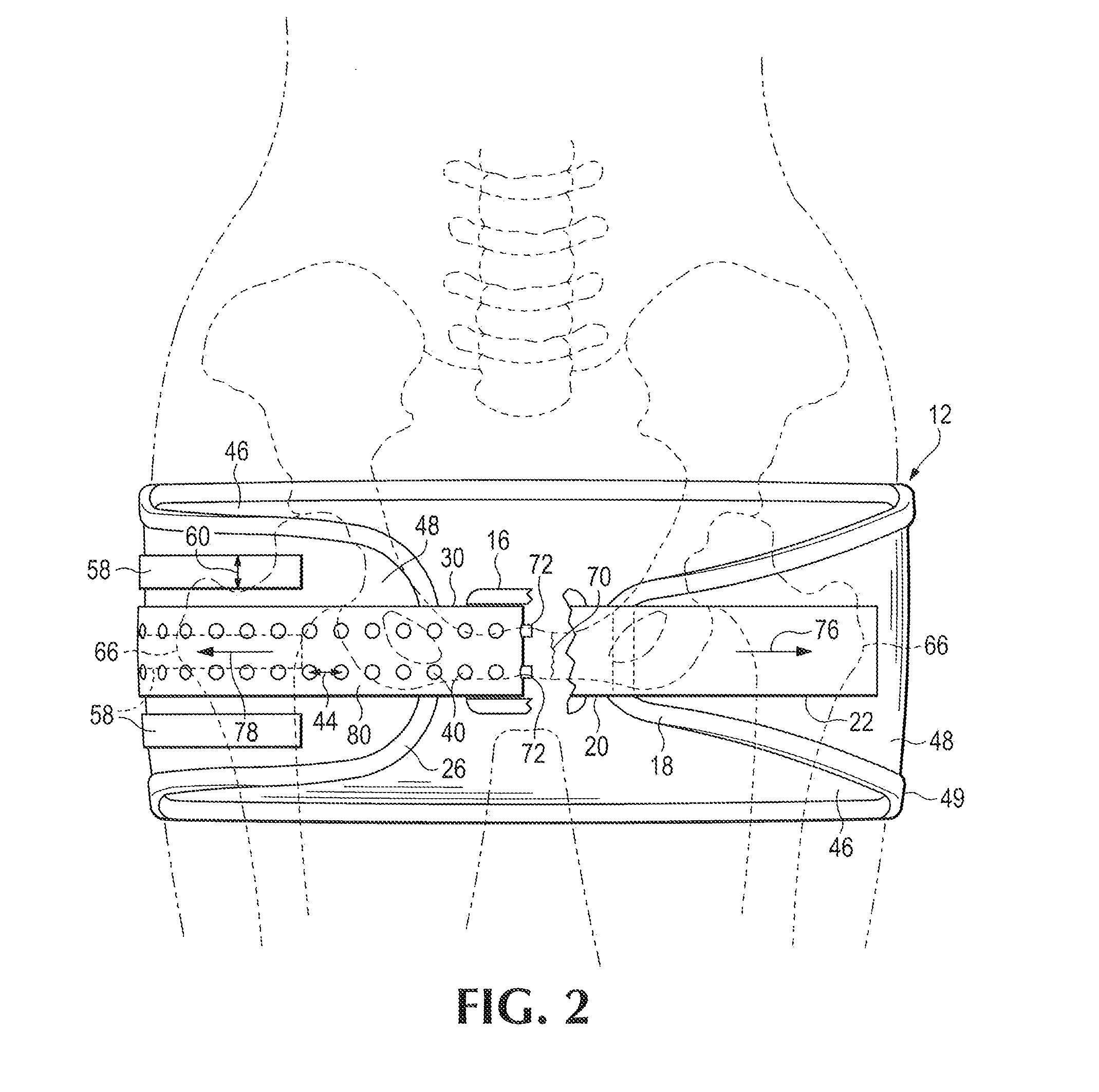
Tourniquet assembly
ActiveUS20100057120A1Shorten the lengthMinimize and reduce bunchingRestraining devicesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesTourniquet timeEngineering
A tourniquet assembly including an elongate main strap, attachment means for attaching the first end of the main strap to the second end of the main strap, a windlass strap including a first end secured to the front of the main strap near the attachment means and a second end secured to the main strap a predetermined distance away from the attachment means, an elongate windlass crank attachable to the windlass strap during use so that as the crank is rotated the windlass strap twists, effectively shortening the length of the windlass strap and tightening the main strap for use as a tourniquet during use. anchor means for anchoring the attachment means in a position for applying the tourniquet may be disposed on the back side of the main strap.
Owner:KIRKHAM JEFFREY B
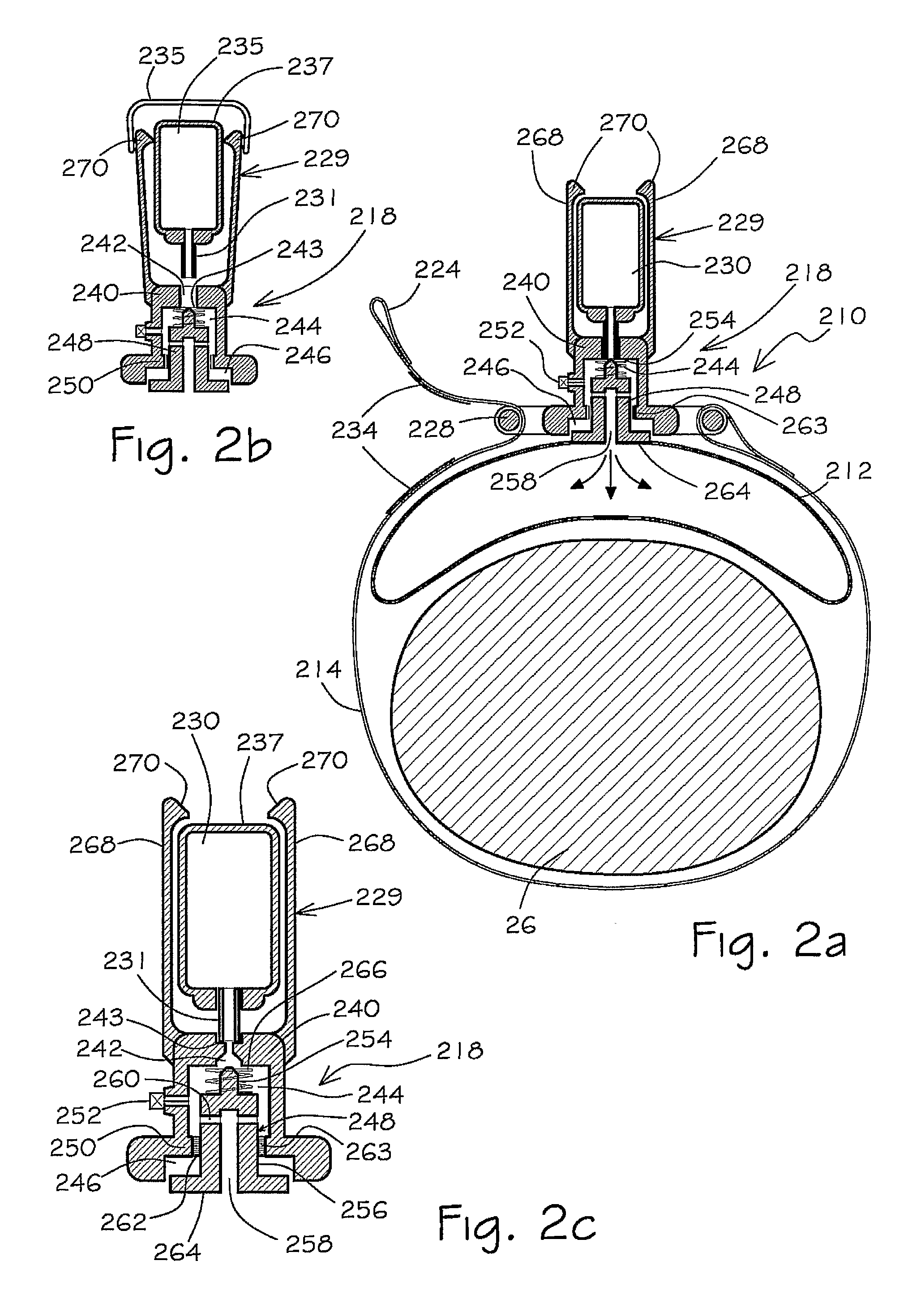
Low-cost disposable tourniquet cuff
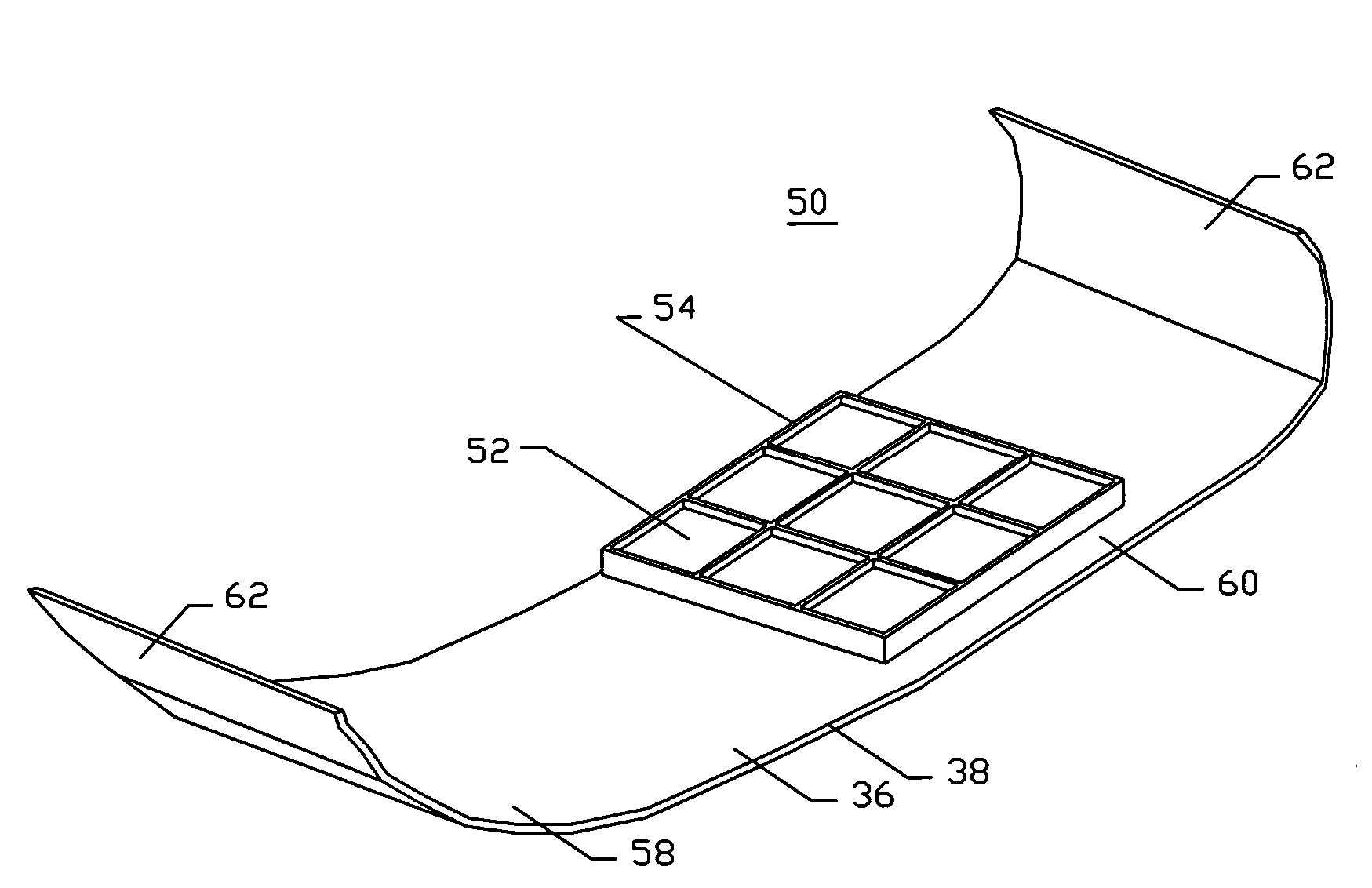
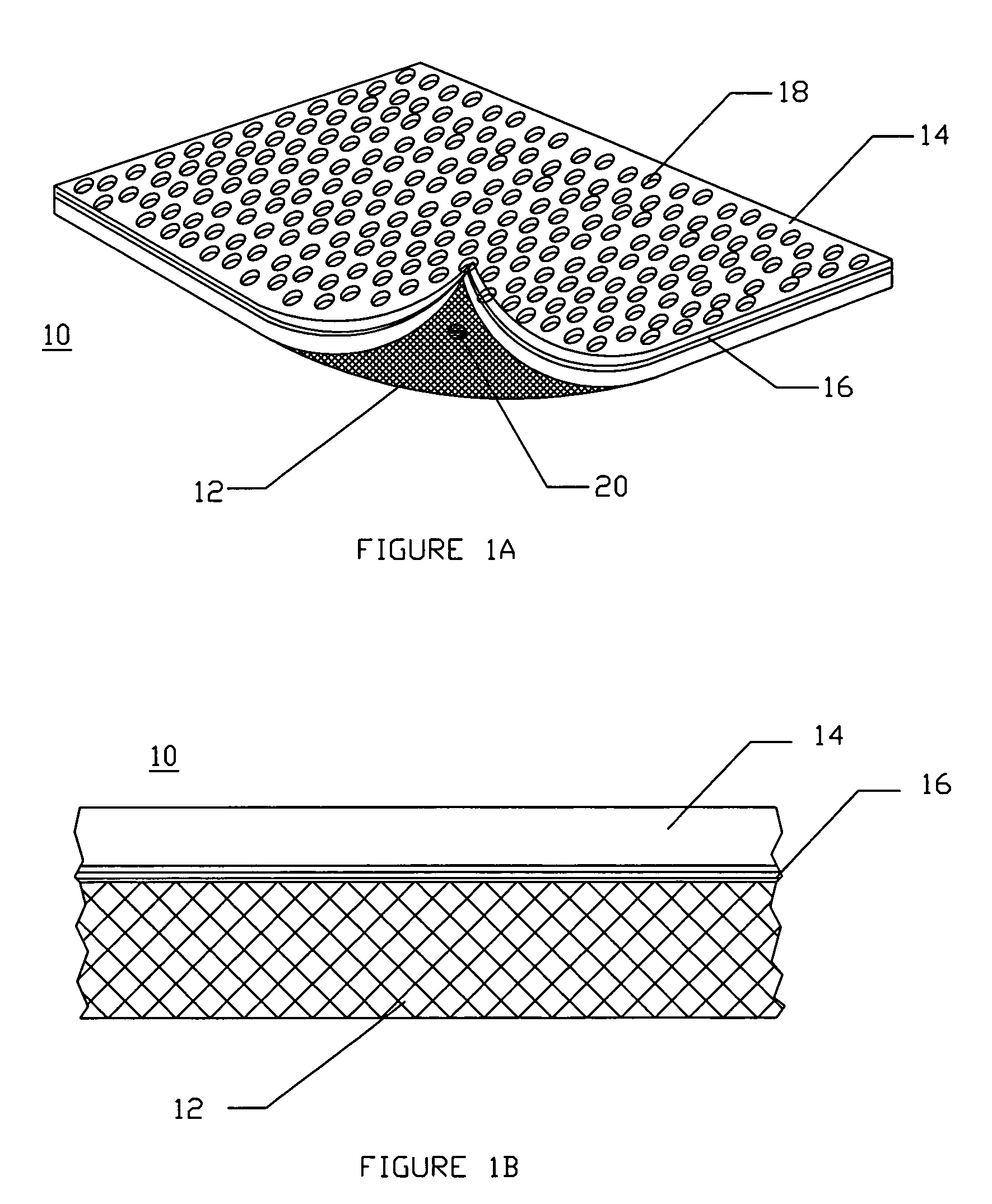
A low-cost disposable tourniquet cuff includes: a first sheet formed of flexible material that is impermeable to gas; a second sheet facing the first sheet and formed of flexible material impermeable to gas; a bladder seal joining the first sheet to the second sheet around a perimeter to form an inflatable bladder within the perimeter; port means communicating pneumatically with the bladder and releasably connectable to a tourniquet instrument; stiffener means contained within the inflatable bladder and formed of gas-impermeable material less flexible than the first sheet, wherein the stiffener means has a stiffener width dimension less than the bladder width dimension and is joined to the first sheet to form a non-inflatable portion of the first sheet; and securing means attached to the non-inflatable portion of the first sheet and adapted to allow a surgical user to releasably secure the cuff around the limb at the desired location so that the bladder overlaps upon itself.
Owner:MCEWEN JAMES A +3
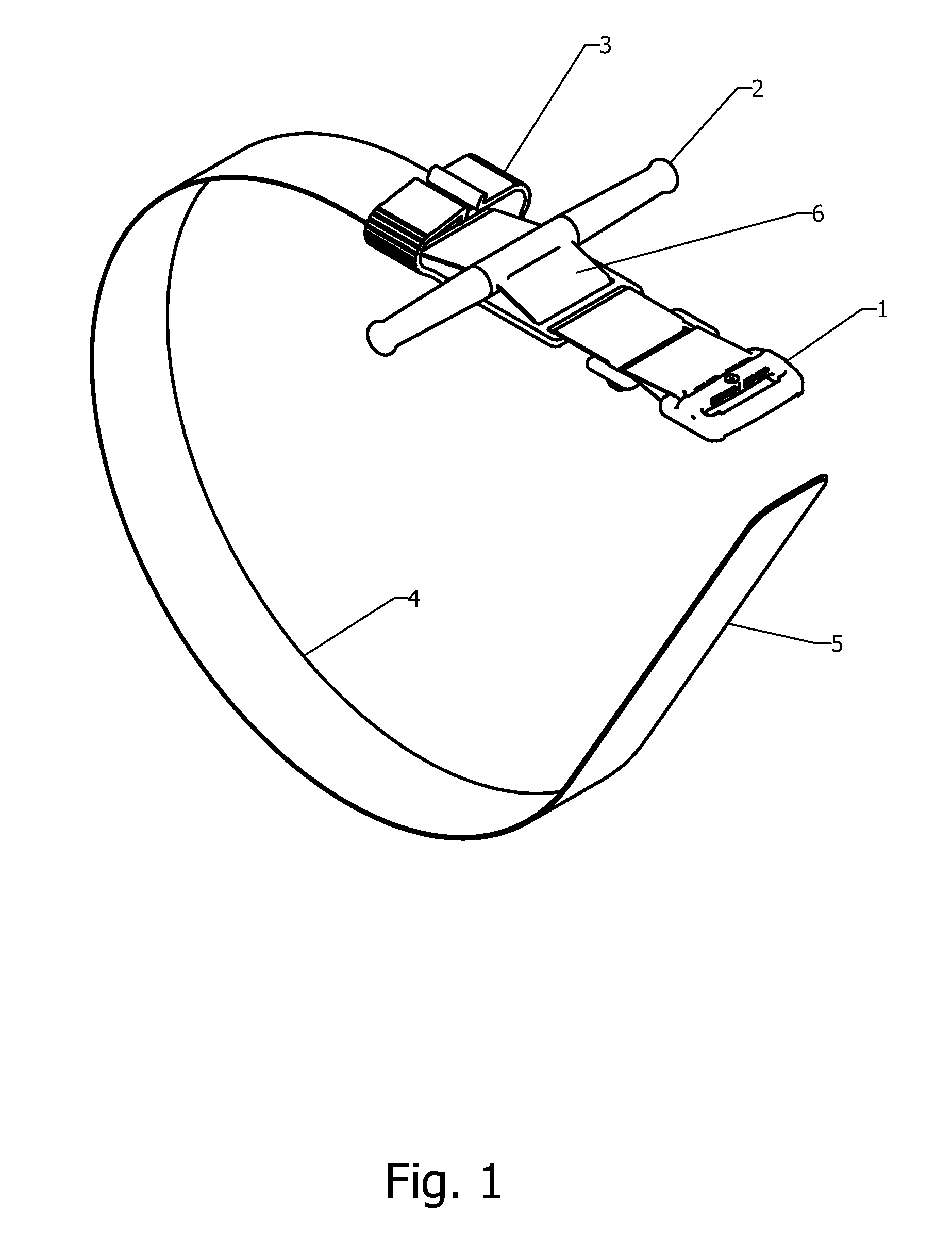
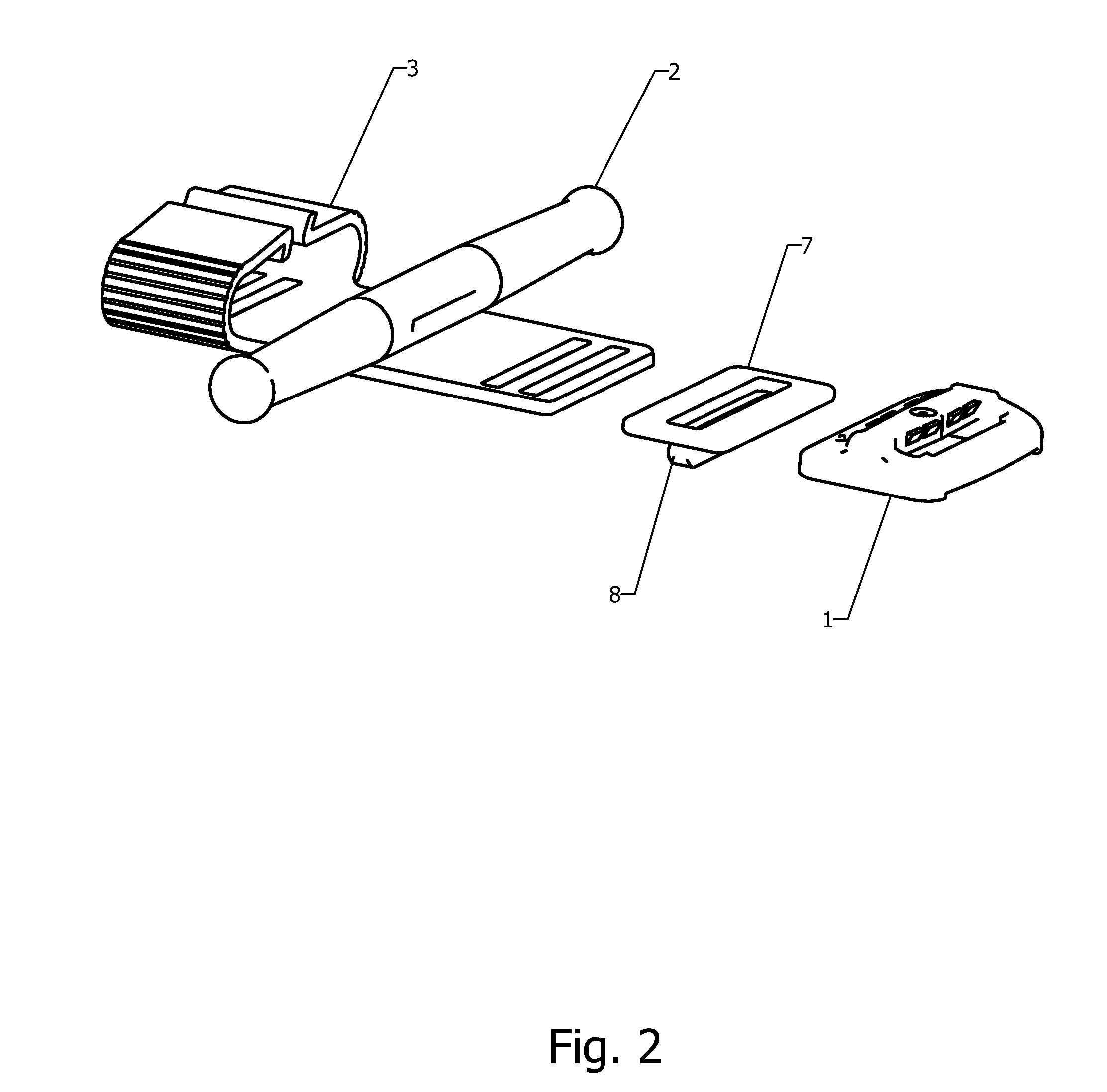
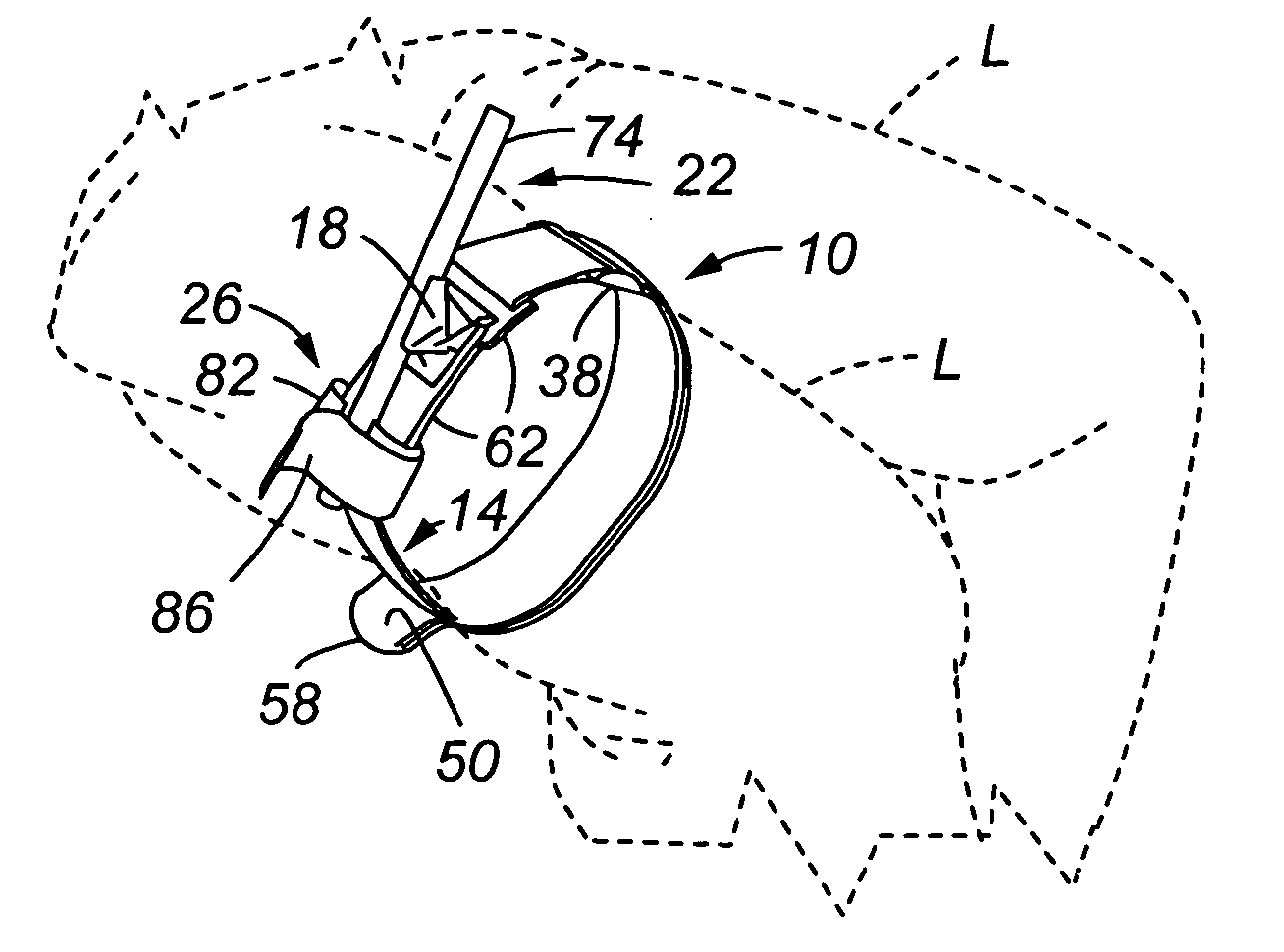
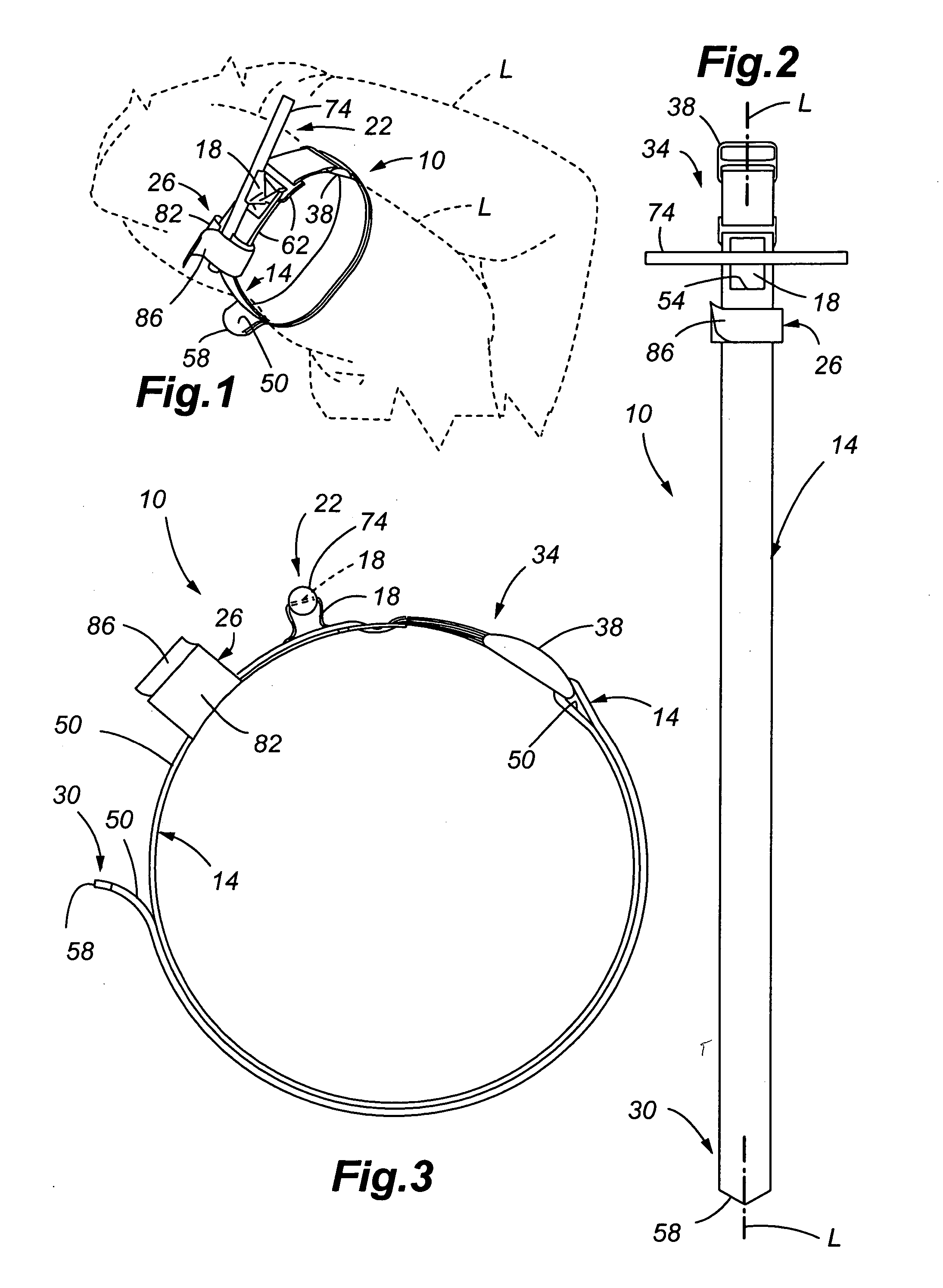
Self-Locking Tourniquet and Automated Timer
Tourniquet assemblies are provided including a pressure applicator adapted to be secured around a limb and a tensioning mechanism for applying a working tension to the pressure applicator. The tensioning mechanism may include a platform, a clip and a tensioning member. The tensioning mechanism may be configured to apply the working tension via rotation of the tensioning member, and the clip may be configured to receive, and at least temporarily inhibit rotation of, the tensioning member. A tension indicator may also be provided including a base configured to attach to a tourniquet strap, a platform configured to move relative to the base when subjected to a tourniquet working pressure, and one or more tactile or visual indicators configured to provide a variable tactile or visual indicator based on the tourniquet working pressure.
Owner:PSR GROUP
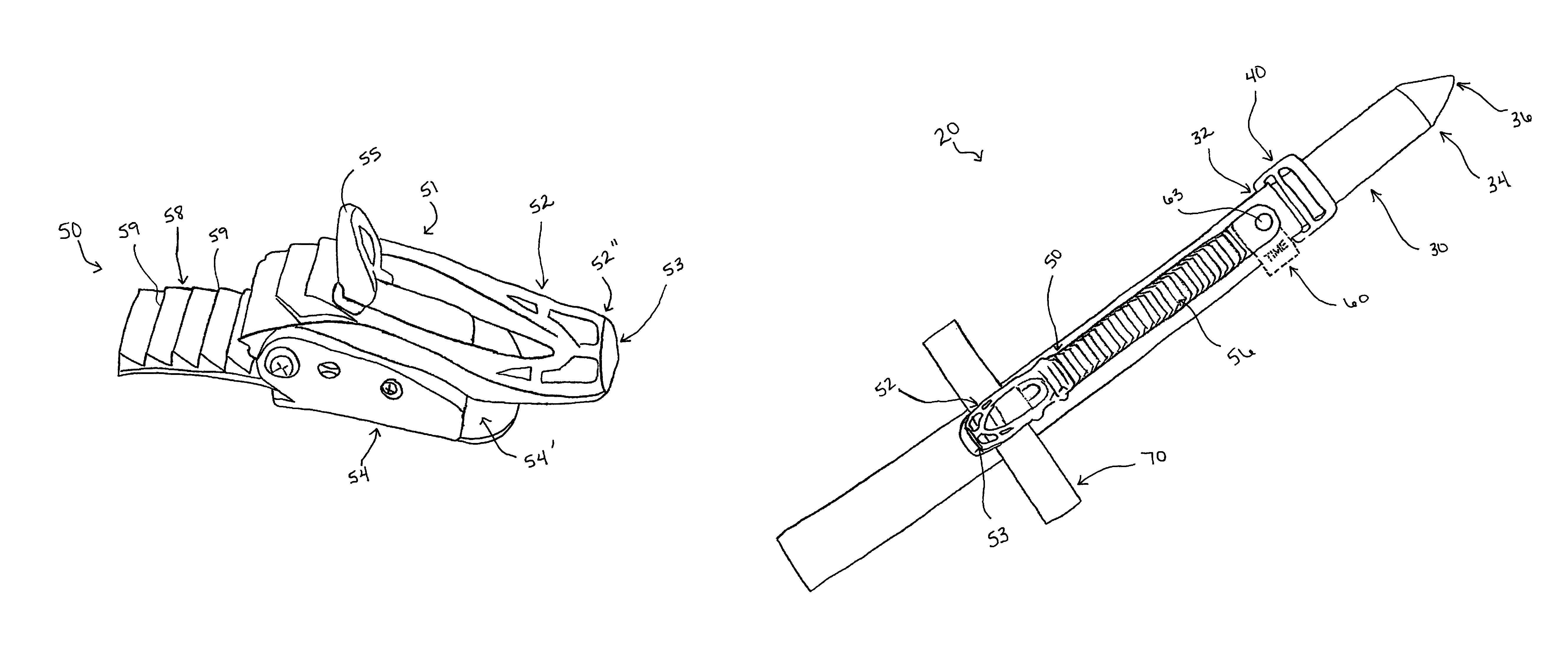
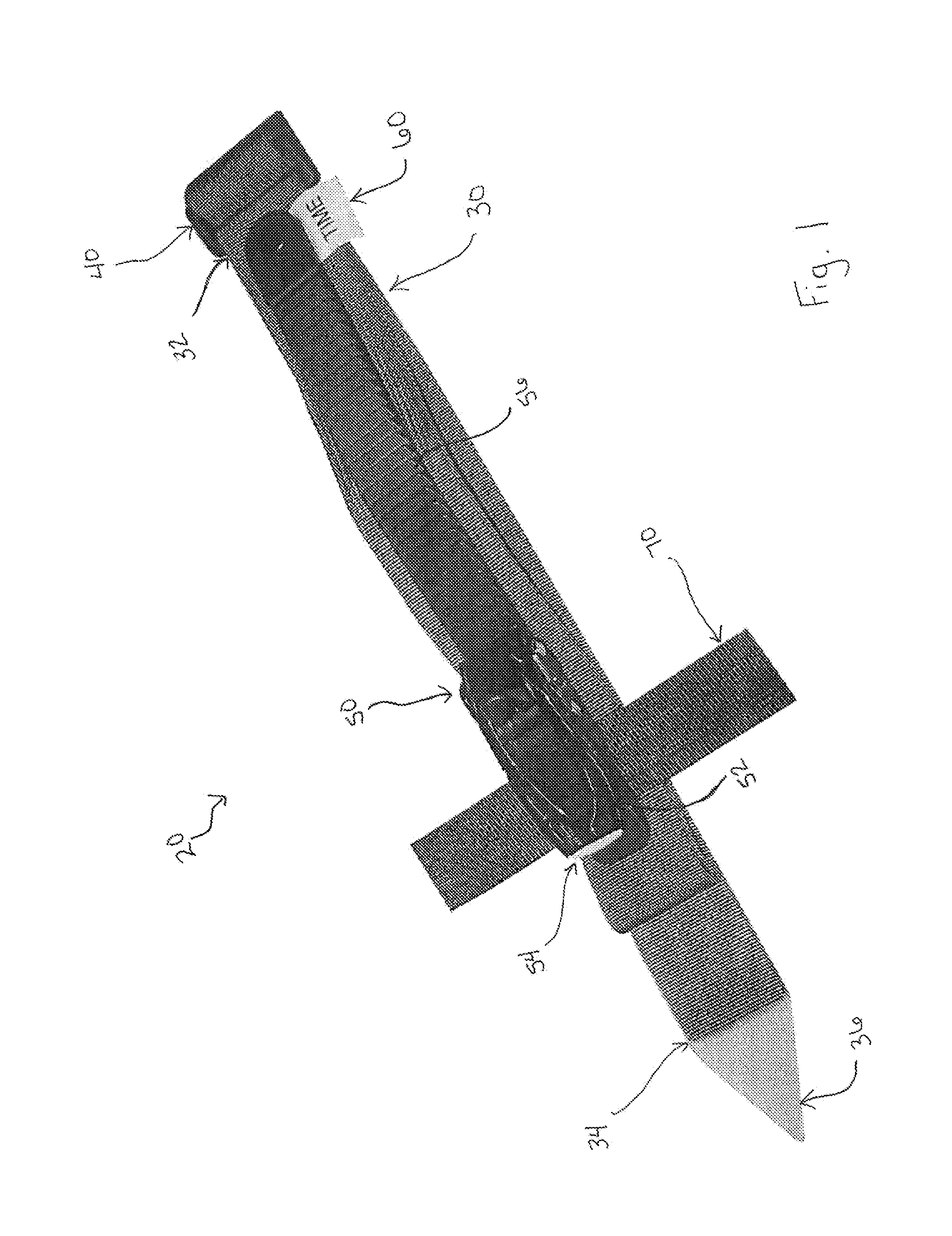
Rapid use field tourniquet
ActiveUS8652164B1Prevents and minimizesPrevents and minimizes frictionDiagnosticsTourniquetsFine motor skillTourniquet time
The tourniquet is a lightweight, compact, and highly efficient device that can be used to assist in the control of life threatening extremity hemorrhage. The tourniquet utilizes a ratchet mechanism to obtain a mechanical advantage when tightening the tourniquet. A ratchet assembly is located a distance away from a strap end of the tourniquet and overlays a contiguous portion of the strap, allowing the tourniquet to be tightened while minimizing pinch, and further includes an elongated ratchet lever for ease of use, requiring minimal, if any, fine motor skills. The design also includes an indicator region for assistance in use of the device and a sealed and tapered strap-end with indicator for efficient use.
Owner:ASTON KEVIN
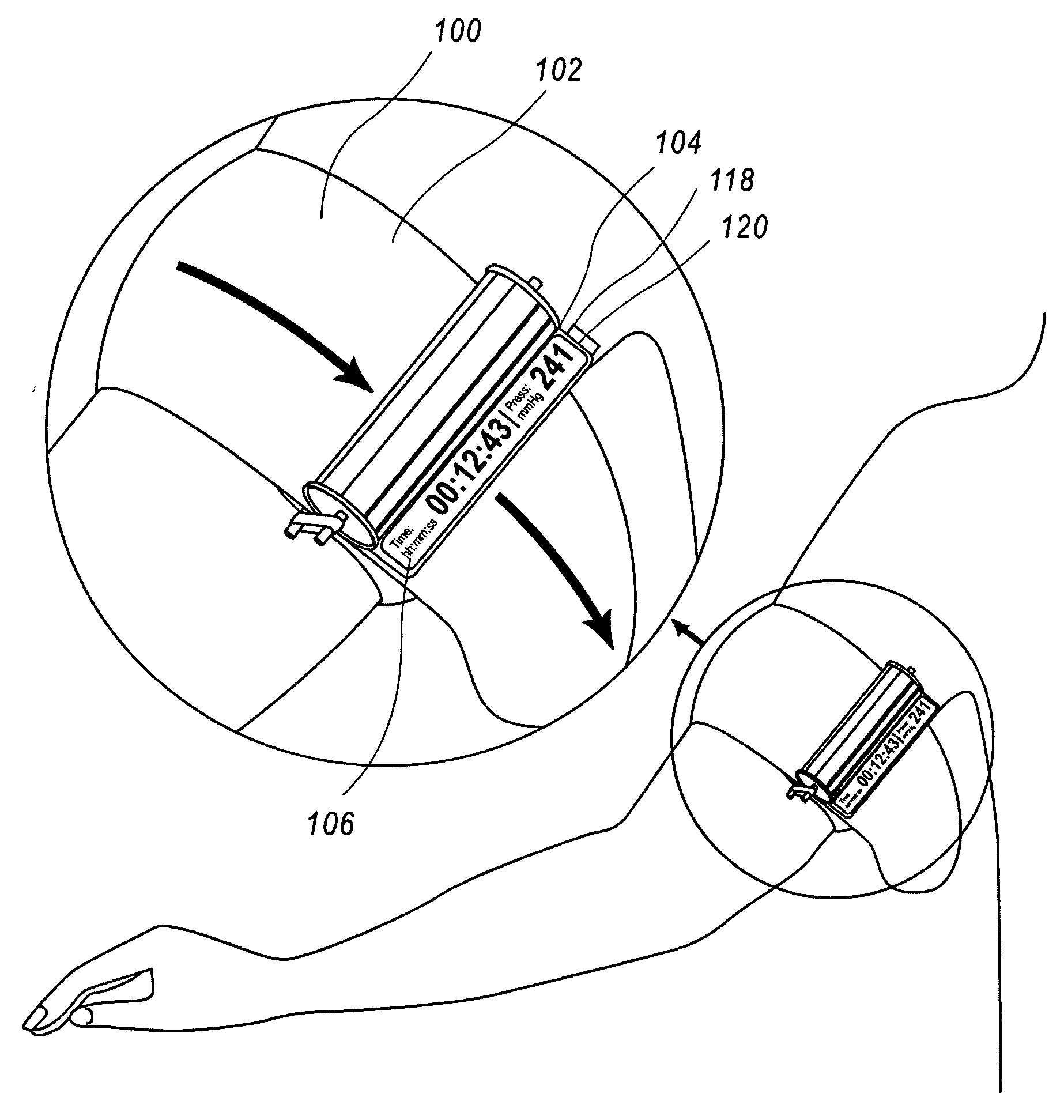
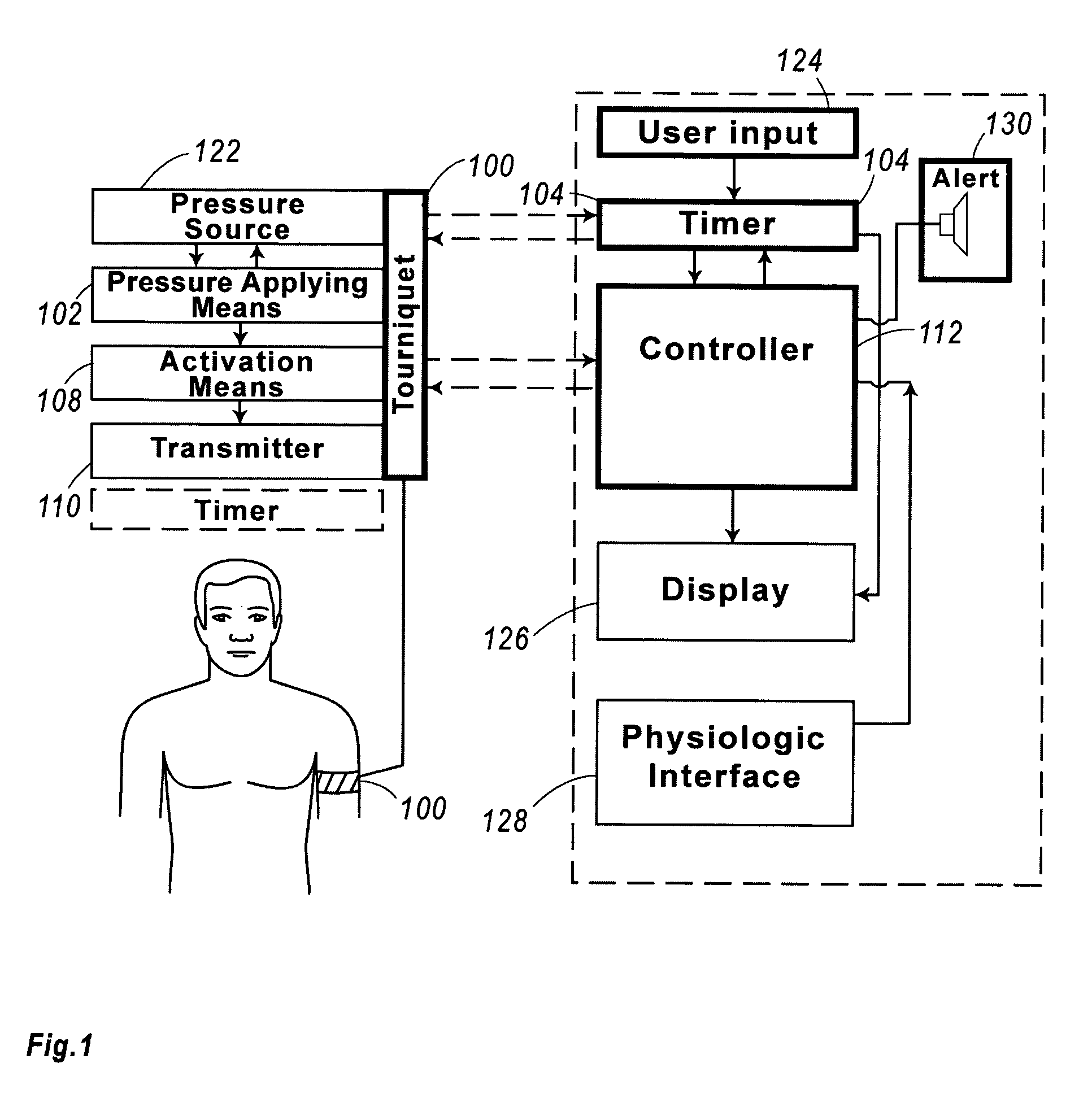
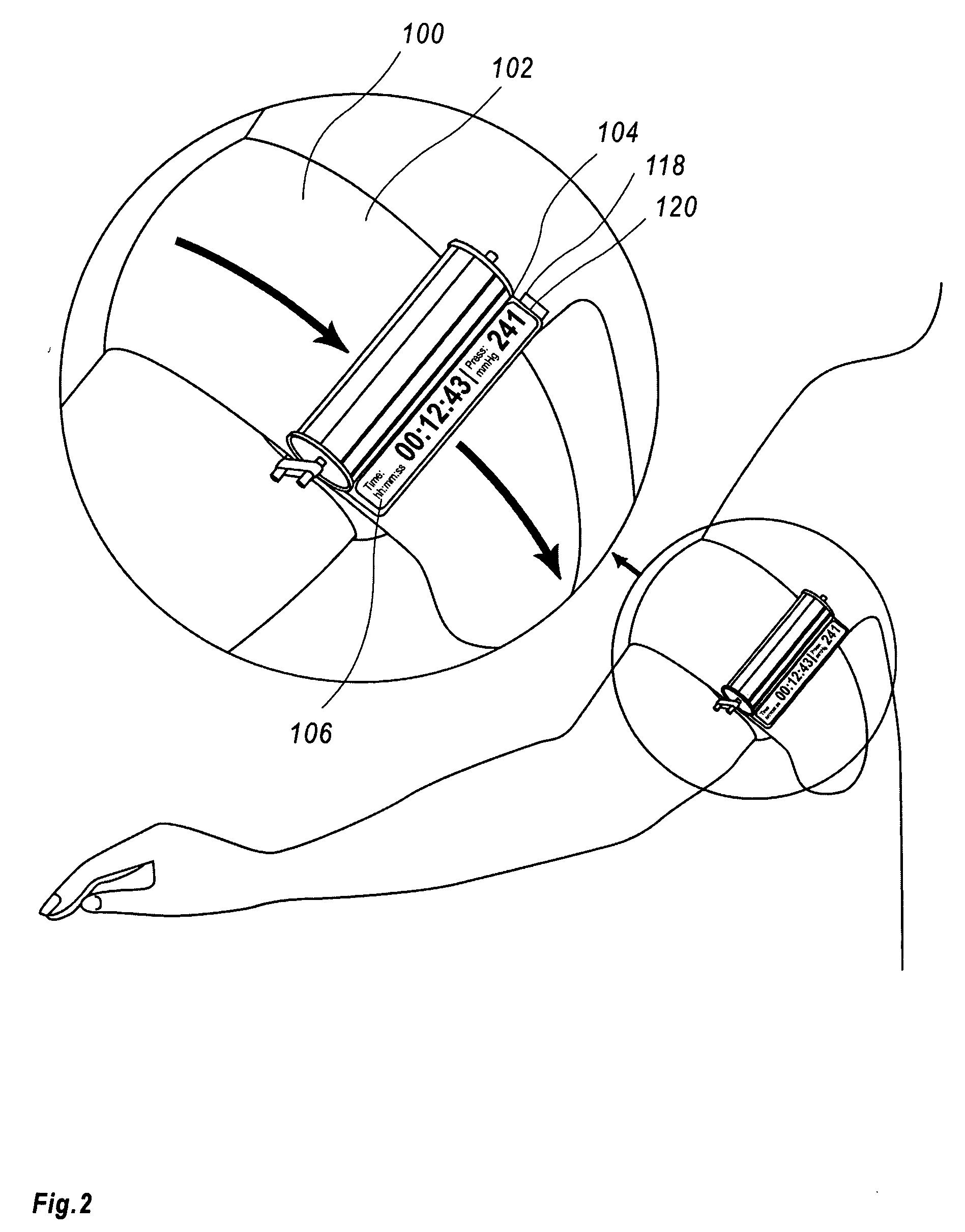
Tourniquet timer
ActiveUS20080177159A1Sufficient time to completeEnough timeCatheterTourniquetsSurgical operationTourniquet time
A timer for tourniquet, adapted for application in a surgery, emergency or military situations to stop arterial blood loss in an injured limb, which is optionally activated by use of the tourniquet and / or optionally provided in association with a monitor for a plurality of tourniquets.
Owner:OHK MEDICAL DEVICES
Hemorrhage control simulator
ActiveUS20120045742A1Improve effectivenessRetention of trainingEducational modelsTouch PerceptionTourniquet time
A simulator trains for hemorrhage control using hemostatic agents, tourniquets, and / or other hemorrhage control techniques in a simulator that works with a wide variety of existing human surrogates. The simulator merges a live video feed of the surrogate and trainee's hands (or objects interacting with the surrogate) with a computer-generated visual representation of the wound and hemorrhaging blood to provide an immersive display experience to the trainee without requiring different surrogates for different simulated wounds. The trainee may wear pulse-generating glove(s) that simulate the patient's pulse where the trainee's finger tip contacts the surrogate. A sensorized substrate (e.g., load sensors, haptic output generators) may automatically be moved between the trainee and the surrogate to sense interaction with the surrogate and provide haptic feedback. The substrate may replace the surrogate altogether. The simulator may alternatively simulate events and objects other than wounds and humans.
Owner:SIMQUEST
Tourniquet device for single-handed operation
InactiveUS20050049630A1The process is convenient and fastQuickly and easily applyTourniquetsTourniquet timeEngineering
A first belt extends between and through two opposing slip buckles that allow the belt to be pulled freely through them but only in respective directions which shorten the belt segment between the buckles. Each slip buckle includes a release which when operated allows the belt to slip freely through said each buckle in either direction. A second belt is affixed at one end to one of the slip buckles, the other end being connected to a mechanism by which a user can spool the second belt to selectively shorten its free length. The spooling mechanism is coupled to the other slip buckle, preferably by means of a fixed length belt, to complete a tourniquet loop. Preferably the spooling mechanism includes a ratchet mechanism operated by a lever in a pumping manner. Preferably the loop can be opened and closed.
Owner:TACMED
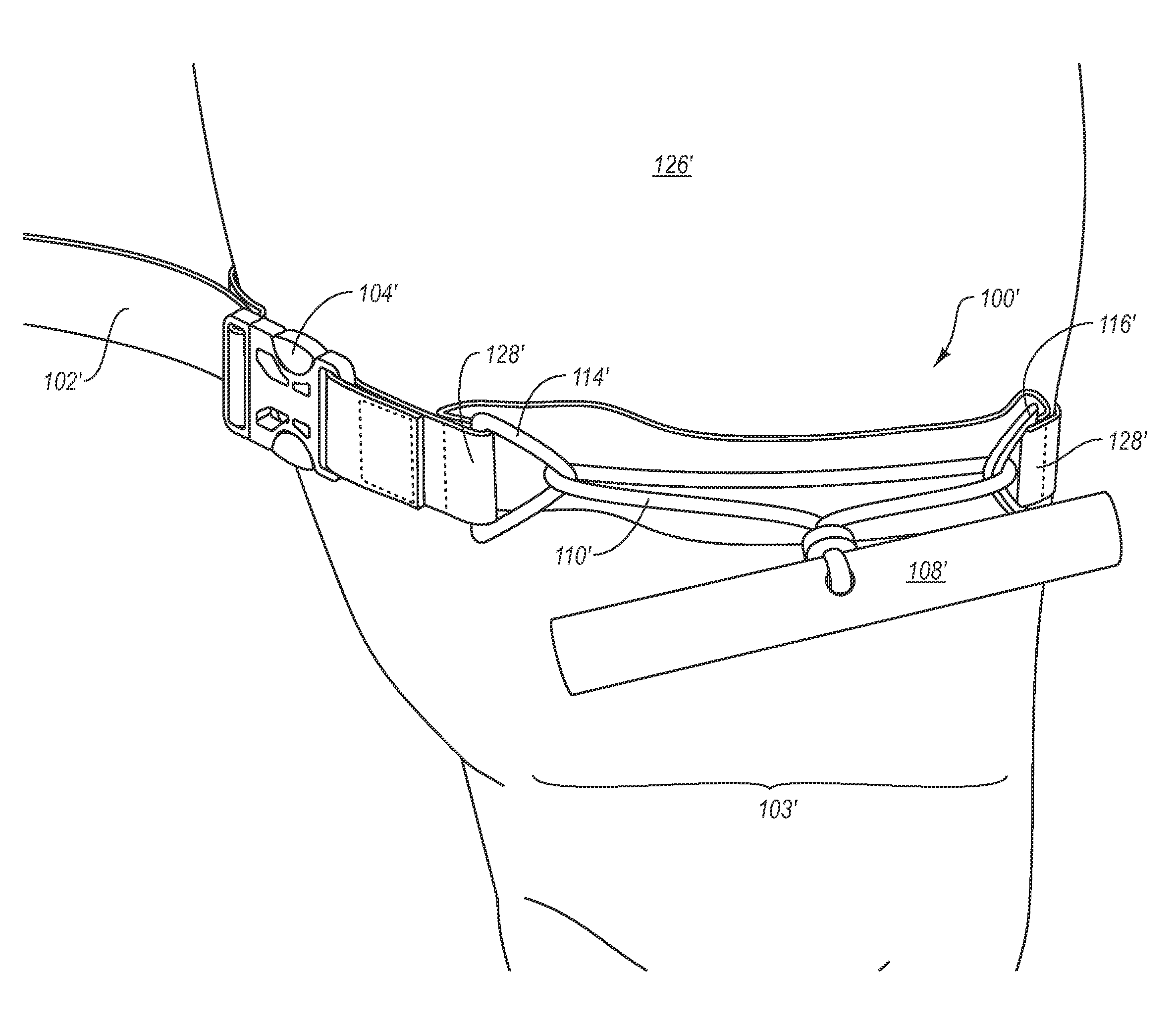
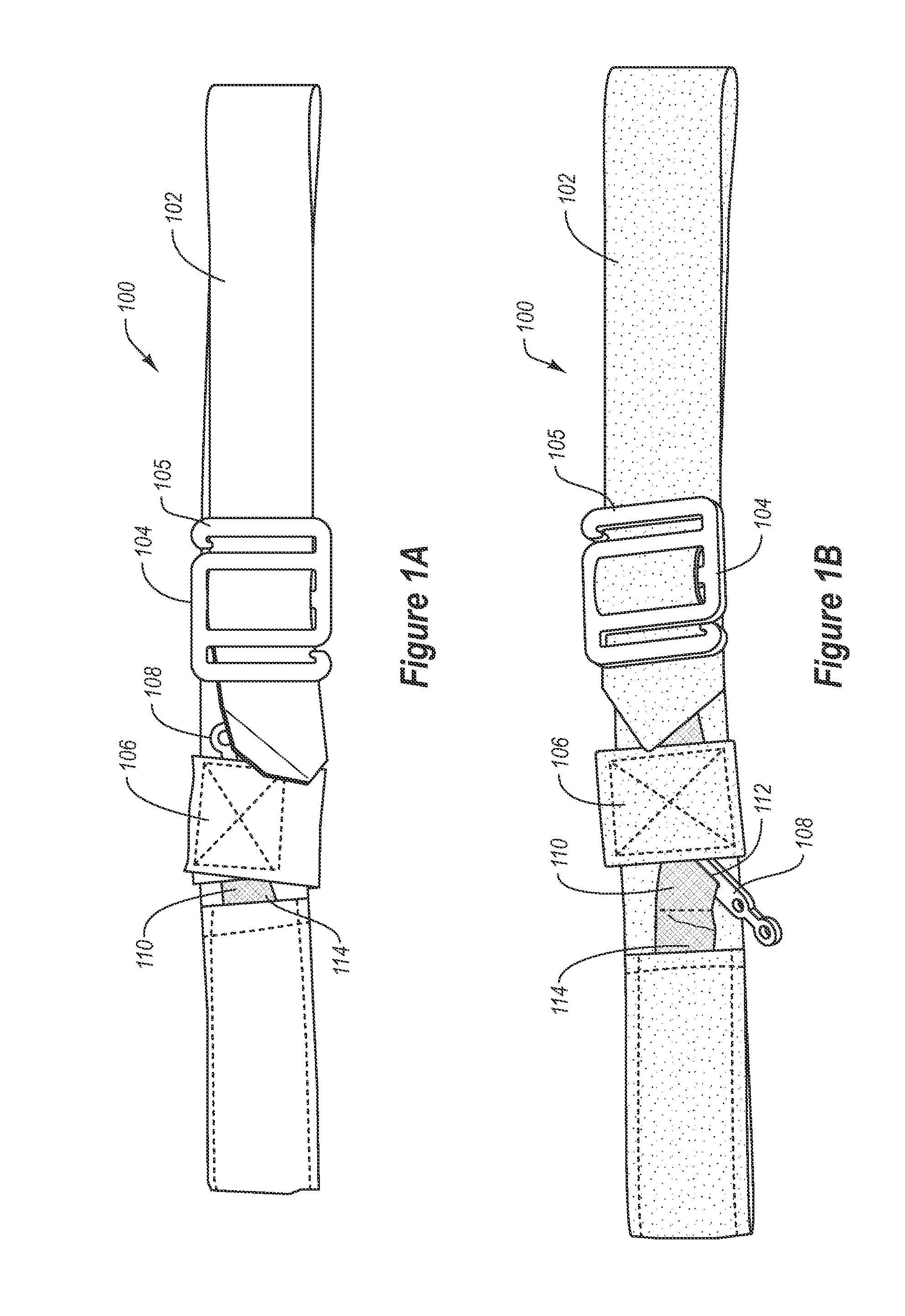
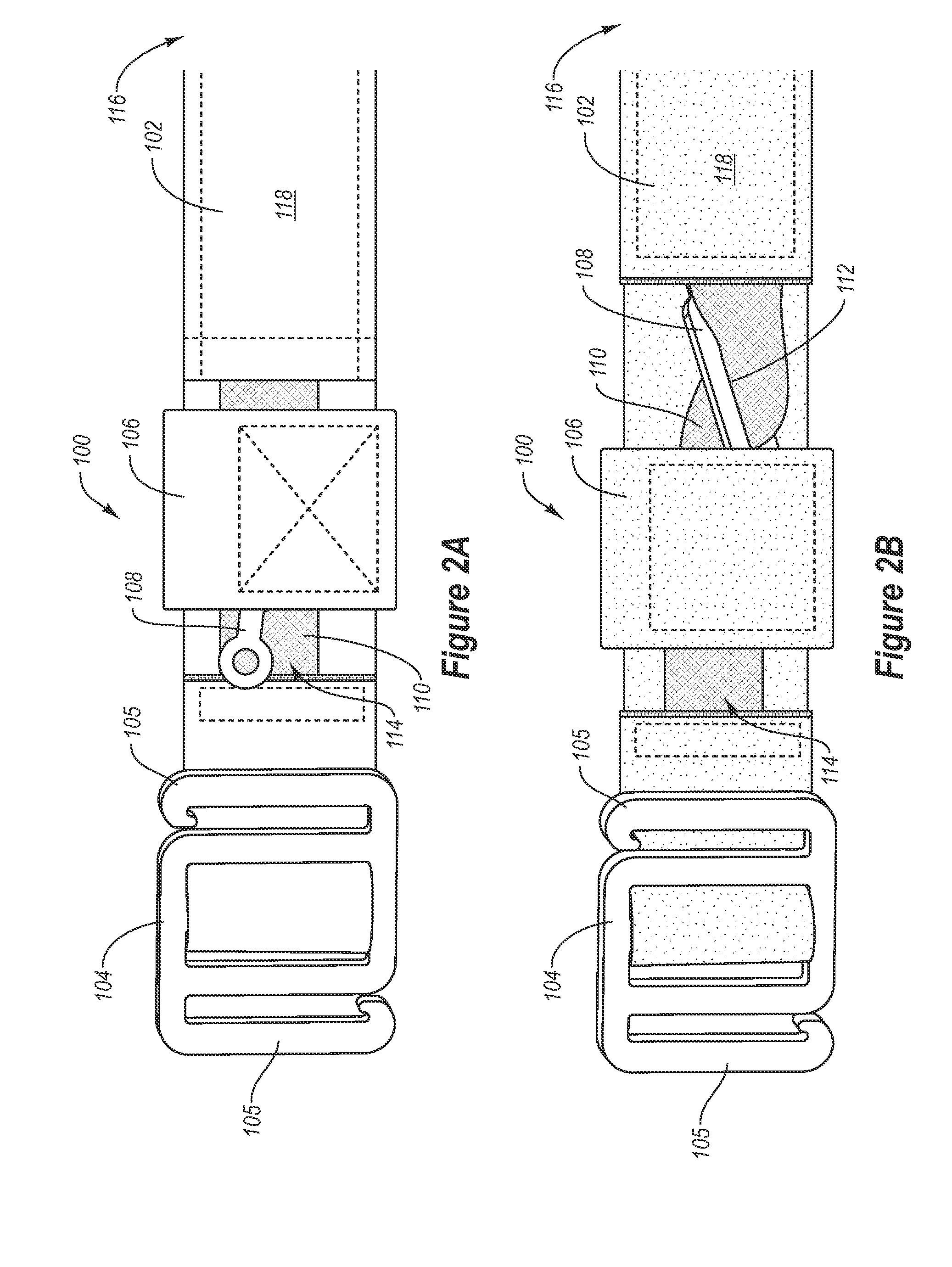
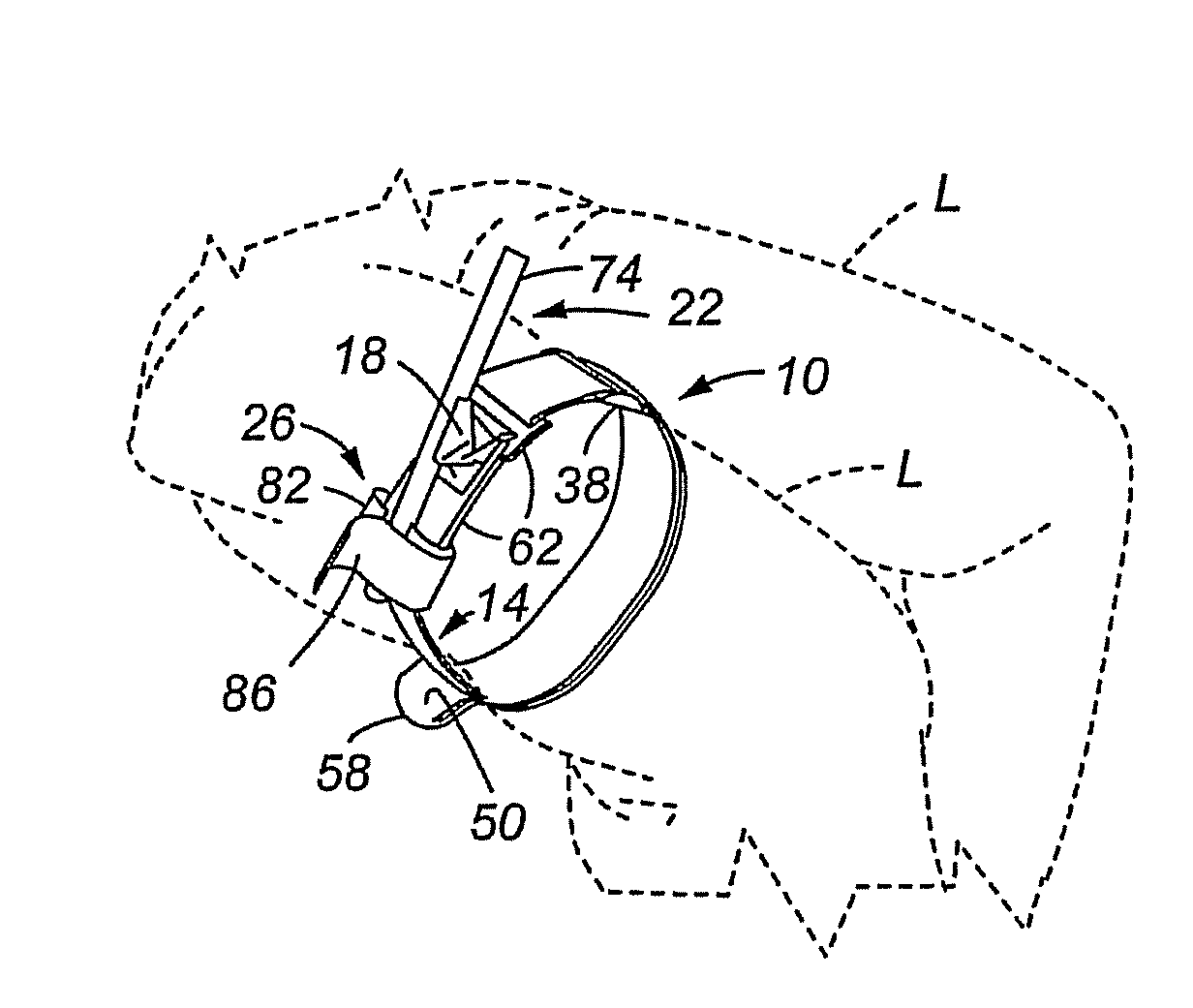
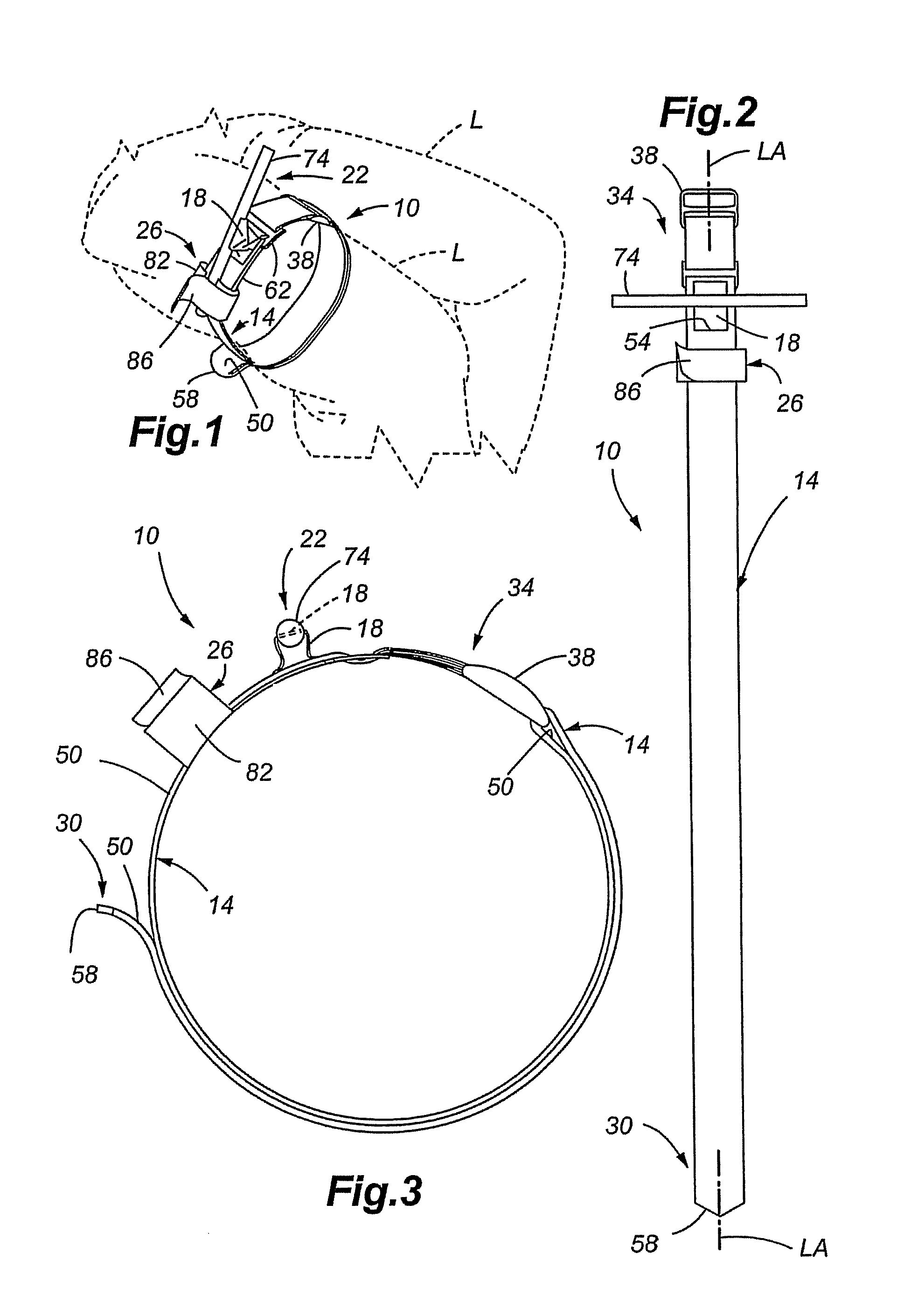
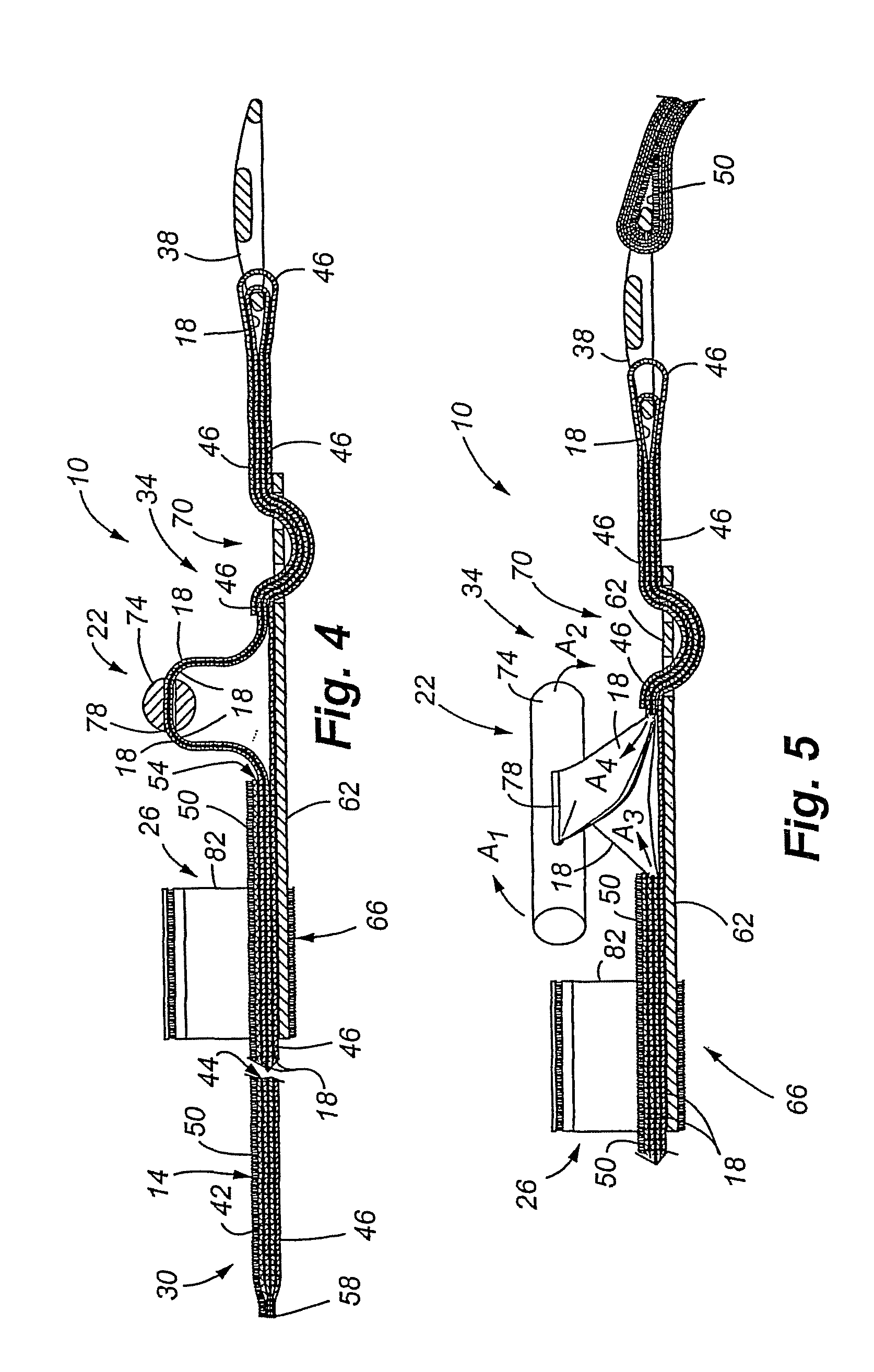
Tourniquet and method of use
A tourniquet for restricting a flow of blood in a body part is presented. In accordance with embodiments of the present invention, the tourniquet comprises a first elongated member, and a second elongated member in slidable engagement with the first elongated member. In addition, the tourniquet includes a tensioning mechanism connected to the second elongated member, wherein a compressive force is applied to the body part upon applying a tensile force to the second elongated member using the tensioning mechanism. The tourniquet is suited for emergency use, and may be applied by using only one hand. Thus, the tourniquet may be applied, manipulated and tightened by the wearer, even if the wearer is limited to the use of a single hand.
Owner:PHIL DURANGO
Device and method for control of hemorrhage
ActiveUS20130110019A1Reduce fracturesStabilizing pelvisRestraining devicesTourniquetsTourniquet timePelvic sling
A junctional and truncal tourniquet and a hip-girdling pelvic sling device for maintaining a desired amount of tension surrounding a person's hips and pelvis to securely support and stabilize a pelvis that has been fractured and for securing a pressure applying device to a person with a preferred amount of tension so that blood vessel-occluding pressure can be applied. Areas of mating types of fastener material such as mating hook-bearing fastener material and loop pile fastener material are arranged on the device to enable a strap to be secured at various effective lengths to provide a wide range of adjustability. The device may include inflatable bladders, and may be wrapped around a patient's torso to occlude blood vessels proximal to an injury on a limb. A bladder may be expandable in distinct tiers and may carry a separate and removable pressure-concentrating fitting. An auxiliary strap may be included and may be used to keep the junctional and truncal tourniquet in place on a patient's torso.
Owner:THE SEABERG
Elastic Tourniquet Capable of Infinitely Adjustable Compression
ActiveUS20120310273A1Easy constructionReduce manufacturing costTourniquetsElastic compressionTourniquet time
A tourniquet band is made of an elastic material and has a plush surace on one side and a series of hook fastener material patches on the reverse side. The woven structure includes a series of parallel elastic threads covered by a dense yet loosely coiled bundle of non-elastic threads. The non-elastic threads are oriented to form the plush surface while allowing the elastic core thread to elongate for applying pressure to a body part by elastic compression when the tourniquet is wrapped around the body part and secured by joining the hook material with the plush surface.
Owner:THORPE PATRICIA E
Tourniquet device for single-handed operation
A first belt extends between and through two opposing slip buckles which allow the belt to be pulled freely through them but only in respective directions which shorten the belt segment between the buckles. Each slip buckle includes a release which when operated allows the belt to slip freely through said each buckle in either direction. A second belt is affixed at one end to one of the slip buckles, the other end being connected to a mechanism by which a user can spool the second belt to selectively shorten its free length. The spooling mechanism is coupled to the other slip buckle, preferably by means of a fixed length belt, to complete a tourniquet loop. Preferably the spooling mechanism includes a rachet mechanism operated by a lever in a pumping manner. Preferably the loop can be opened and closed.
Owner:AMBACH ROBERT
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Tourniquet system
A tourniquet system having a strap, a clamp for selectively engaging the strap in which once the clamp engages the strap, the clamp permits the strap to pass substantially freely in a direction away from the clamp and substantially prevents the strap from passing in a direction towards the clamp and securing structure attached to the strap for securing the strap.
Owner:BROOKS SHAN L
Neural tourniquet
ActiveUS8729129B2BiocideNervous disorderCholinesterase inhibitionCholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway
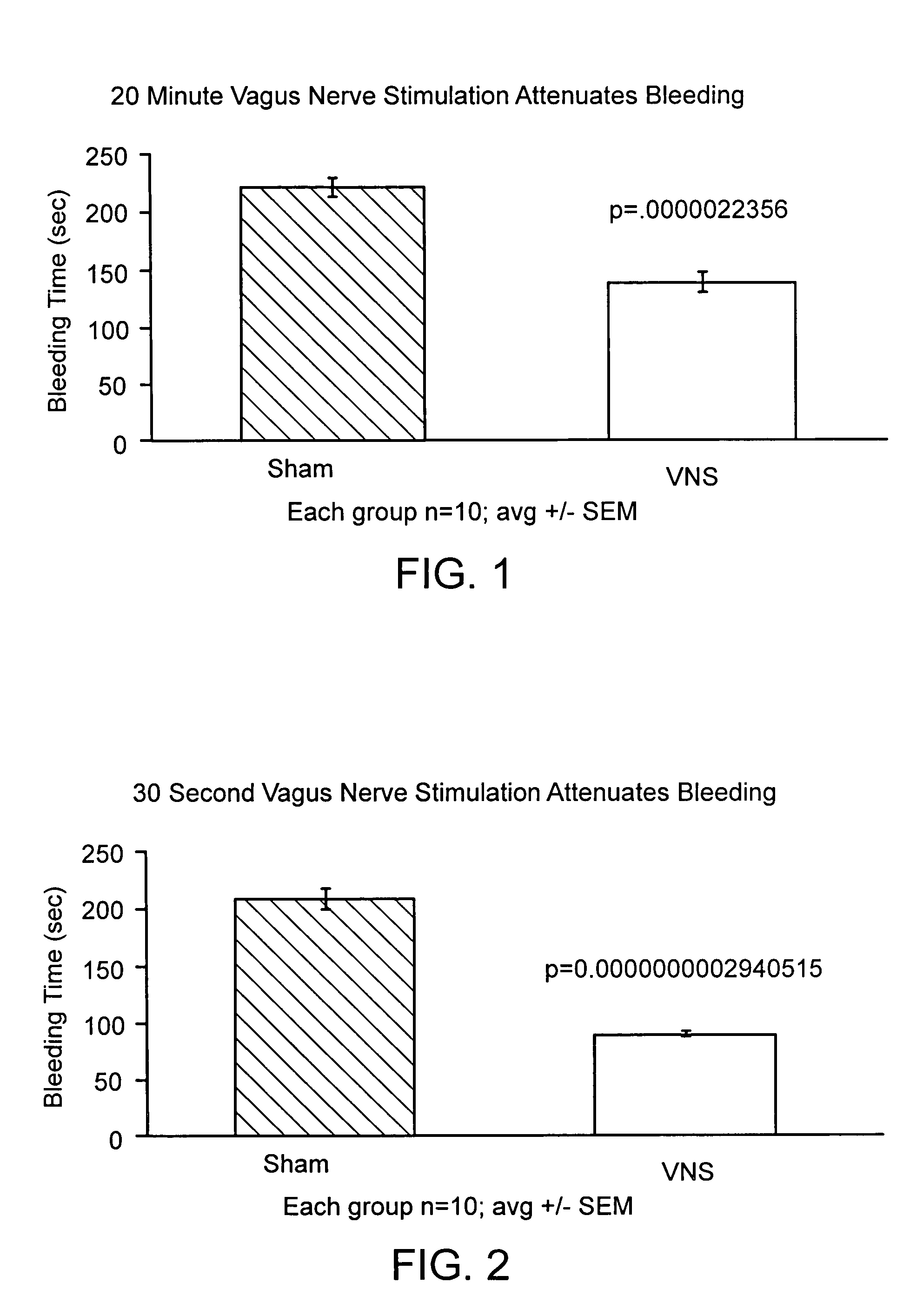
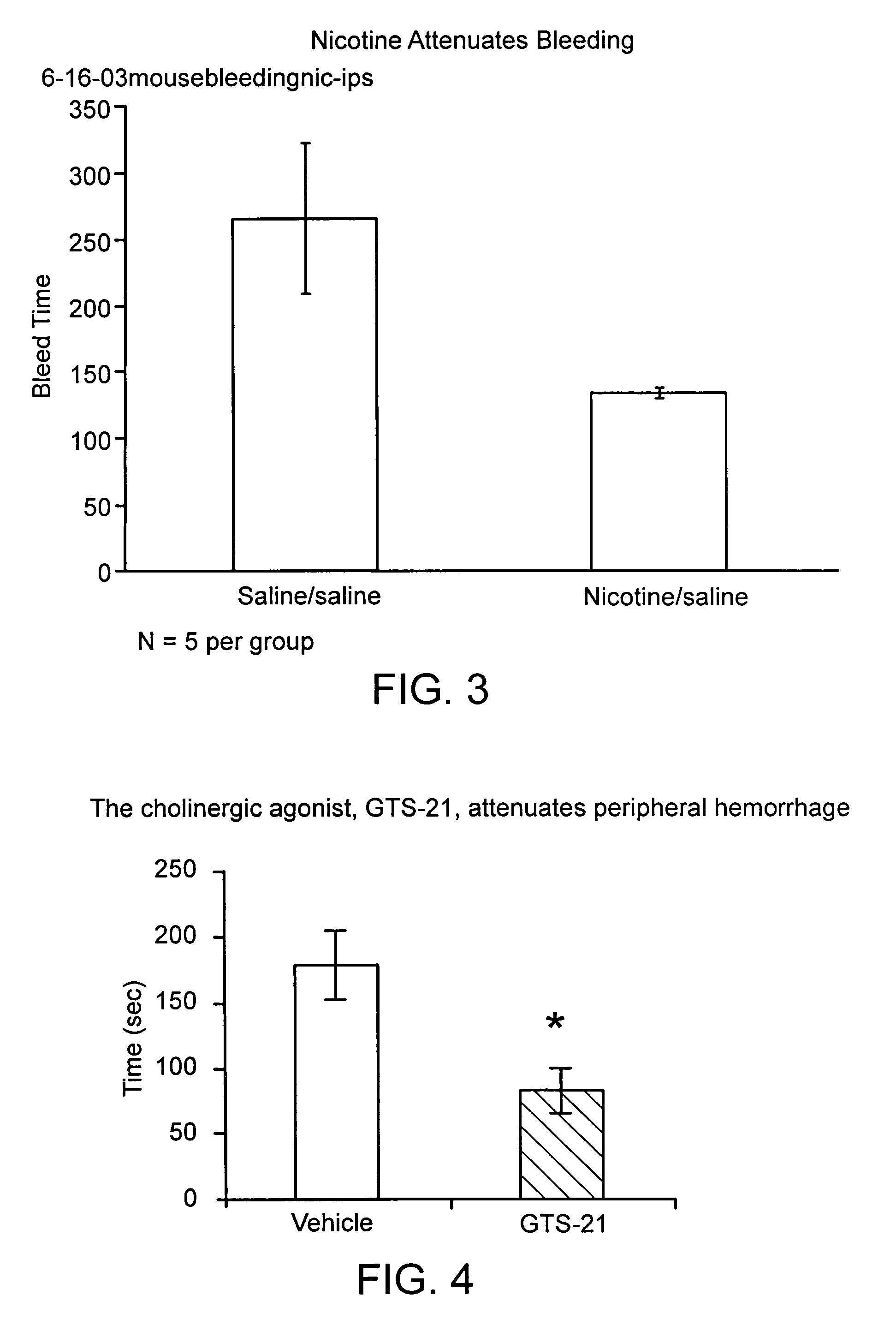
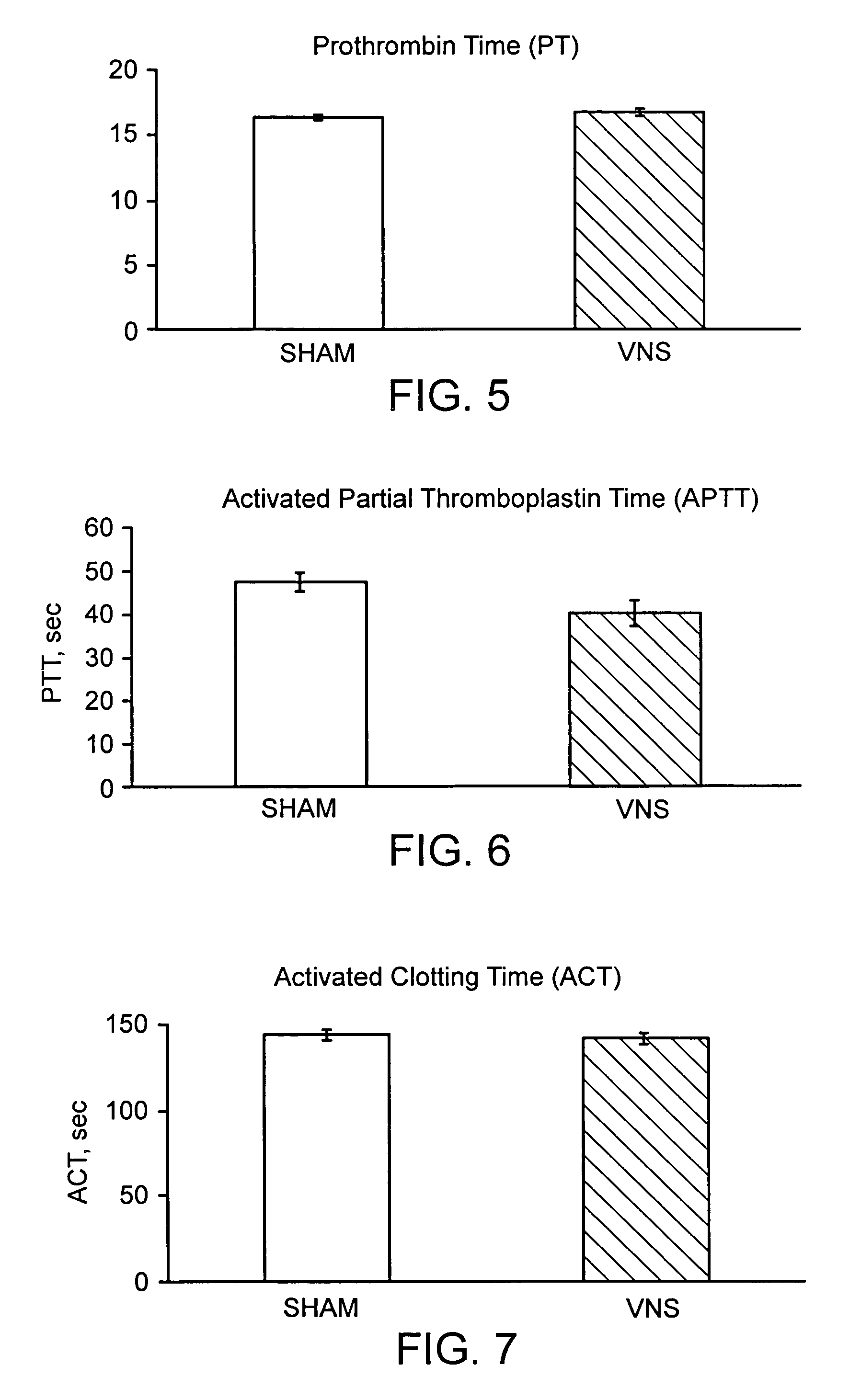
Disclosed is a method of reducing bleed time in a subject by activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in said subject. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway can be activated by direct or indirect stimulation of the vagus nerve. The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway can also be activated by administering an effective amount of cholinergic agonist or acetylcholinesterase inhibitor to the subject.
Owner:THE FEINSTEIN INST FOR MEDICAL RES
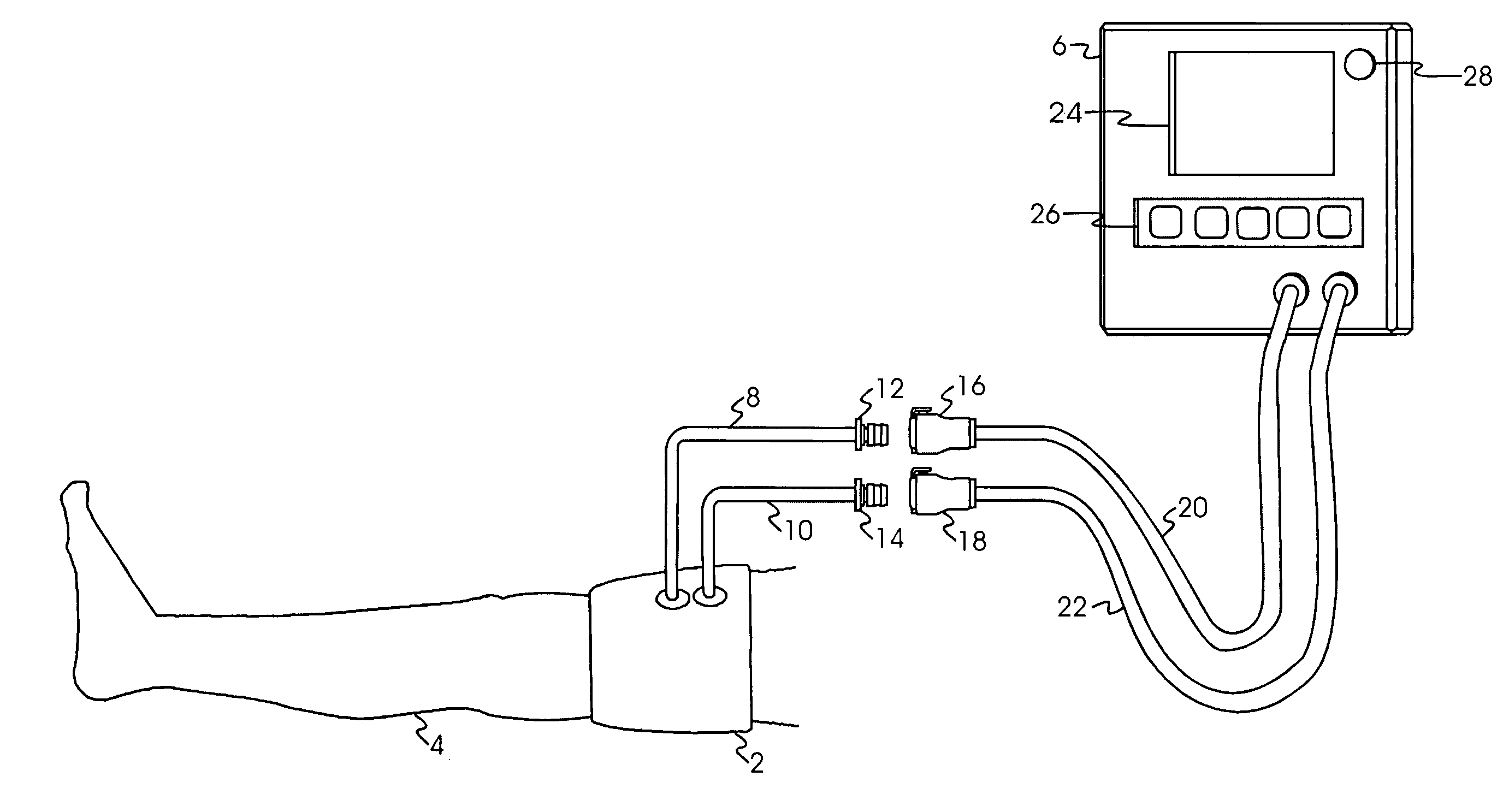
Occlusion detector for dual-port surgical tourniquet systems
A occlusion detector for a dual-port surgical tourniquet system comprises: a tourniquet cuff for encircling a patient's limb and including an inflatable portion that communicates pneumatically with a first cuff port and that communicates pneumatically with a second cuff port independently of the first cuff port; a tourniquet instrument that is releasably connectable to the first and second cuff ports to establish first and second pneumatic passageways between the tourniquet cuff and the tourniquet instrument, wherein the tourniquet instrument includes pressure sensing means communicating with the first pneumatic passageway for producing an indication of the pressure in the cuff over a time period suitably long for the performance of a surgical procedure, pressure regulation means communicating with the second pneumatic passageway for regulating the pressure in the cuff near a reference pressure level, and an occlusion detector for introducing a pneumatic pressure pulse into the first pneumatic passageway during an occlusion detection time period, for monitoring the pressure in the second pneumatic passageway during the occlusion detection time period, and for producing an occlusion alarm if a fluctuation of pressure in the second pneumatic passageway is not detected within the occlusion detection time period.
Owner:WESTERN CLINICAL ENG
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Tourniquet and method of use
A tourniquet for restricting a flow of blood in a body part is presented. In accordance with embodiments of the present invention, the tourniquet comprises a first elongated member, and a second elongated member in slidable engagement with the first elongated member. In addition, the tourniquet includes a tensioning mechanism connected to the second elongated member, wherein a compressive force is applied to the body part upon applying a tensile force to the second elongated member using the tensioning mechanism. The tourniquet is suited for emergency use, and may be applied by using only one hand. Thus, the tourniquet may be applied, manipulated and tightened by the wearer, even if the wearer is limited to the use of a single hand.
Owner:PHIL DURANGO
Tourniquet and method of use
A tourniquet for restricting a flow of blood in a body part comprises a first elongated member, and a second elongated member in slidable engagement with the first elongated member. In addition, the tourniquet includes a tensioning mechanism connected to the second elongated member, wherein a compressive force is applied to the body part upon applying a tensile force to the second elongated member using the tensioning mechanism. At least one embodiment of the present invention comprises a buckle having one or more of a raised intermediate bar and one or more teeth for contacting a portion of the first elongated member. The tourniquet is suited for emergency use, and may be applied by using only one hand. Thus, the tourniquet may be applied, manipulated and tightened by the wearer, even if the wearer is limited to the use of a single hand.
Owner:PHIL DURANGO
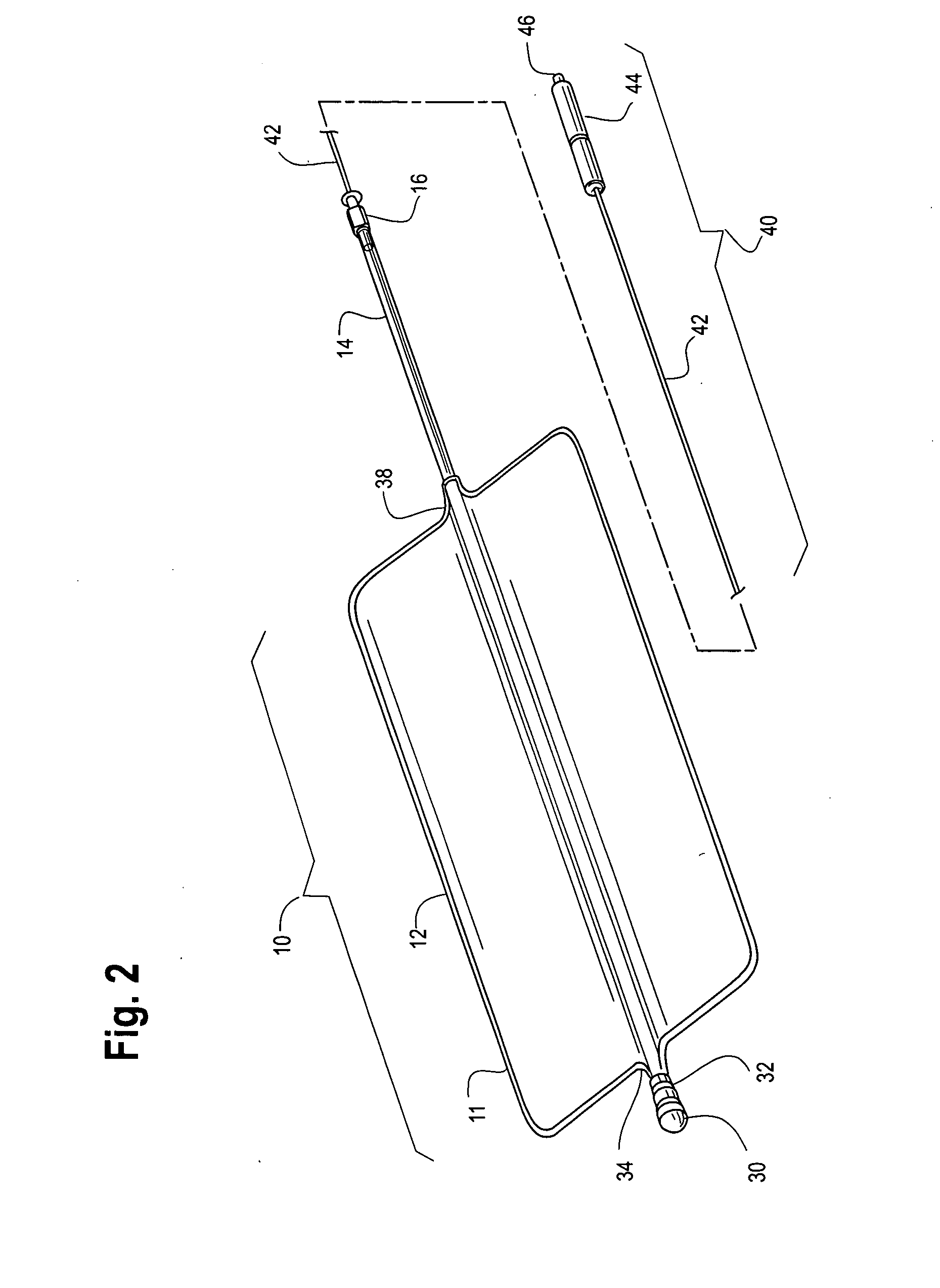
Enhanced system and method for wound track navigation and hemorrhage control
An internal compression tourniquet catheter system and method for wound track navigation for controlling hemorrhage from wounds. The preferred embodiments include an inflatable member constructed of thin, flexible, biocompatible, and puncture resistant material such that when deflated it lies flat and can be wrapped around the catheter shaft, which passes within and has a lumen to inflate it, to minimize overall diameter when deflated for insertion into the tissue track created by the wounding agent. The inflatable member is of large potential volume enabling full inflation with near zero internal pressure when unconstrained externally. When positioned within a wound track and inflated, the gas or liquid injected into the balloon lumen creates pressure because its expansion is constrained by the tissues of the wound, and that pressure is transmitted directly to the surrounding tissue of the wound track. The pressure exerted on the tissue can be precisely measured and controlled, automatically if appropriate, such that sufficient pressure is applied to tamponade bleeding, but not damage tissue. Since the balloon is of large potential volume, it can easily expand to fill and compress small, large, and irregular wound tracks and can successfully tamponade wounds that smaller, elastic balloon catheters would be unable to tamponade. The catheter system includes means to assist insertion into the wound track, including a rounded or bulbous exploring tip and an internal stylet. In it non-inflatable embodiments, the my devices are introduced into the wound track and deliver hemorrhage controlling agents or materials which are designed to promote clotting of the wound or to occupy space to assist in tamponade of the bleeding.
Owner:CARDIOCOMMAND
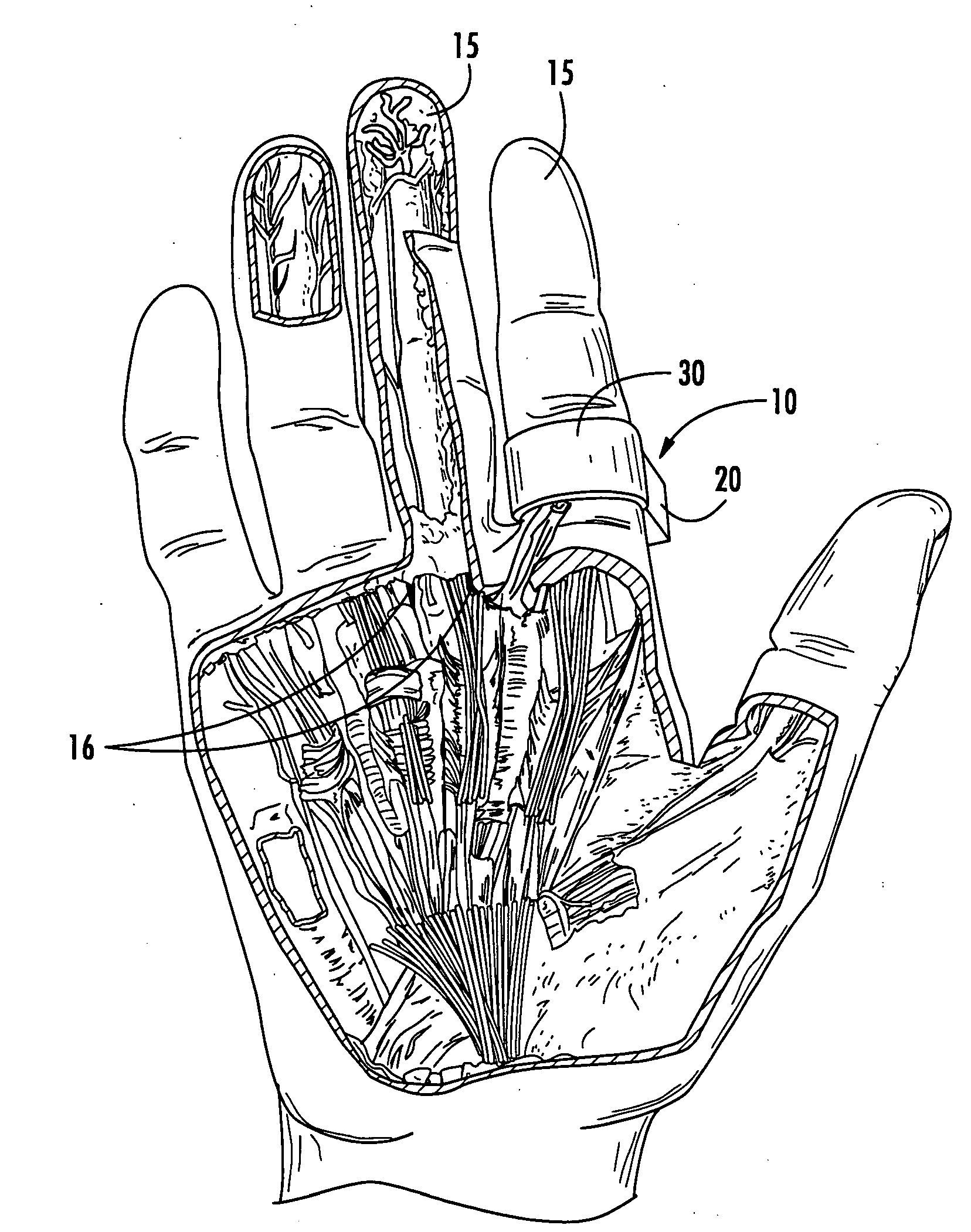
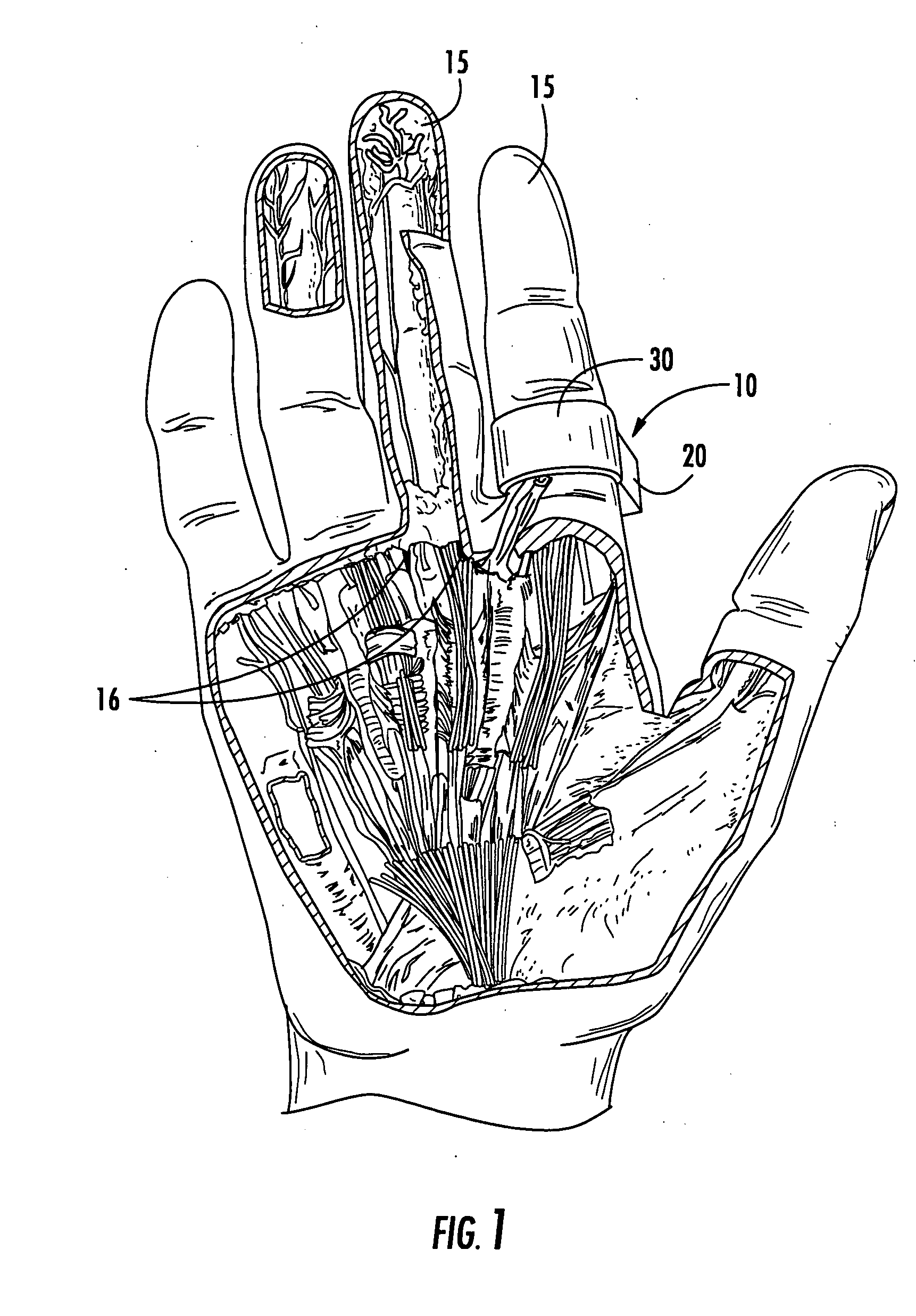
Disposable digital tourniquets and related methods of providing occlusion pressures to a single digit during surgical procedures
A single-use disposable digital tourniquet includes a generally rigid support body comprising first and second spaced apart cuff channels sized and configured to receive a cuff therethrough.
Owner:PIPER MEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com