Patents
Literature
63 results about "Trauma surgery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Trauma surgery is a surgical specialty that utilizes both operative and non-operative management to treat traumatic injuries, typically in an acute setting. Trauma surgeons generally complete residency training in General Surgery and often fellowship training in trauma or surgical critical care. The trauma surgeon is responsible for initially resuscitating and stabilizing and later evaluating and managing the patient. The attending trauma surgeon also leads the trauma team, which typically includes nurses and support staff as well as resident physicians in teaching hospitals.
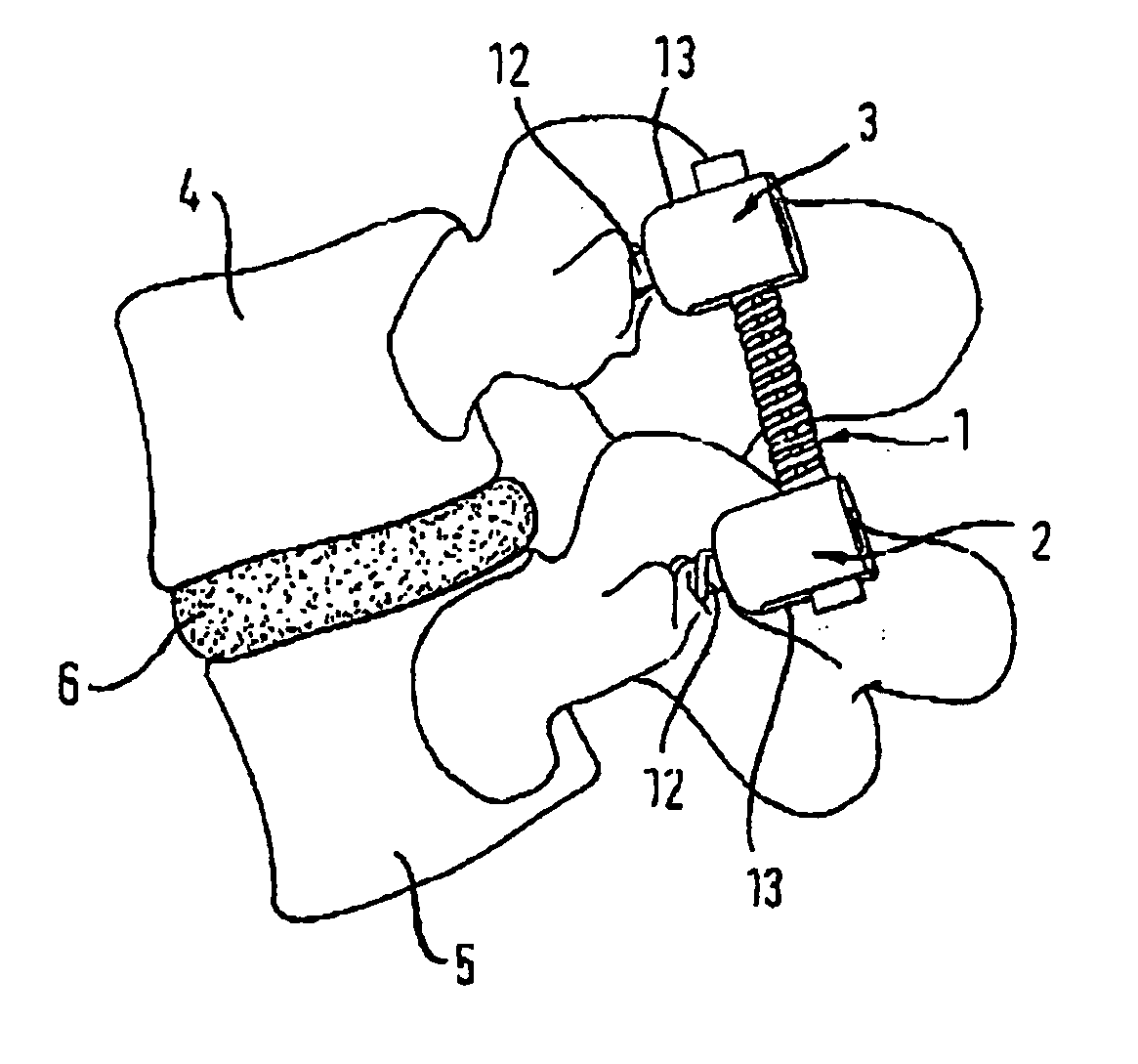
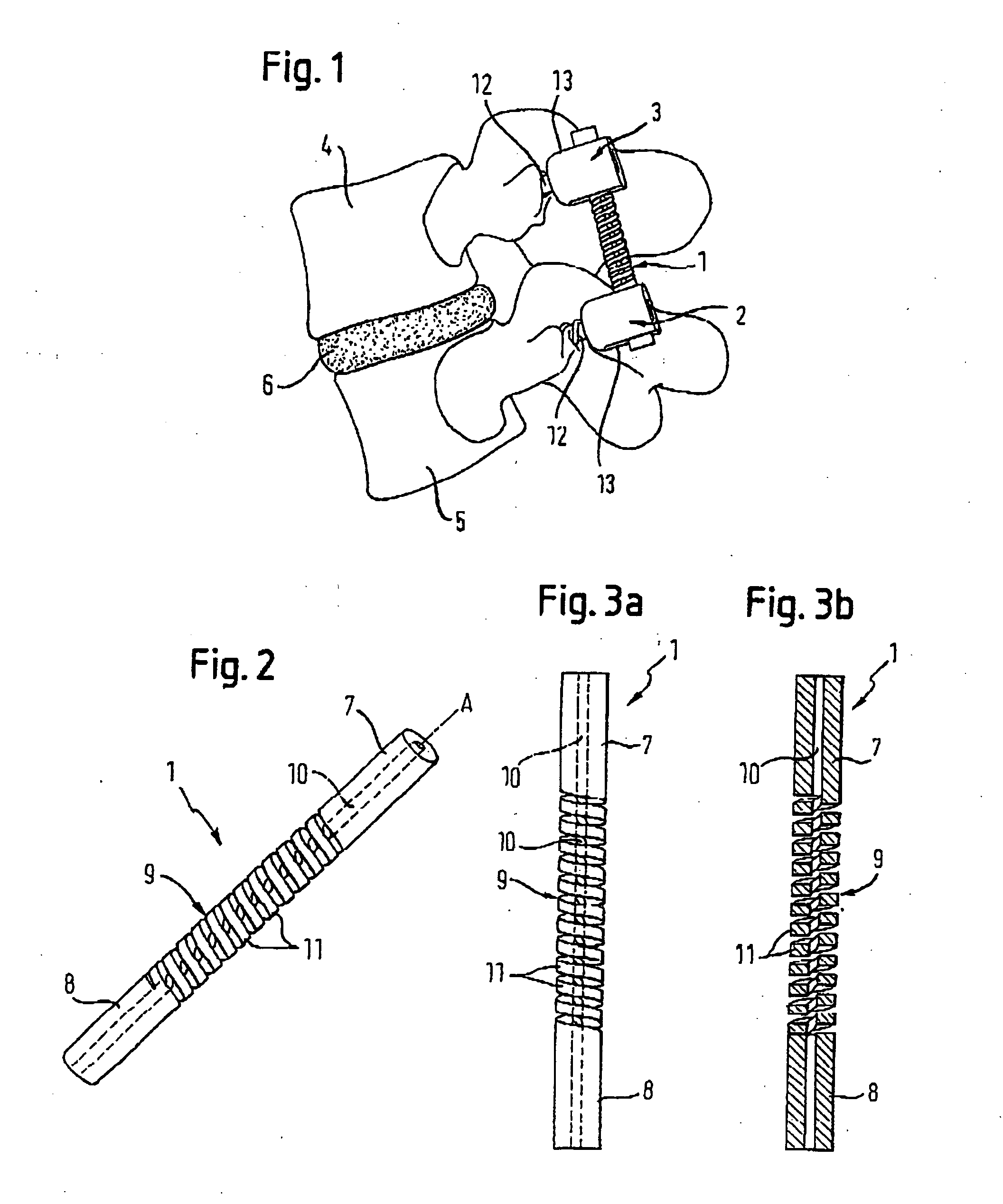
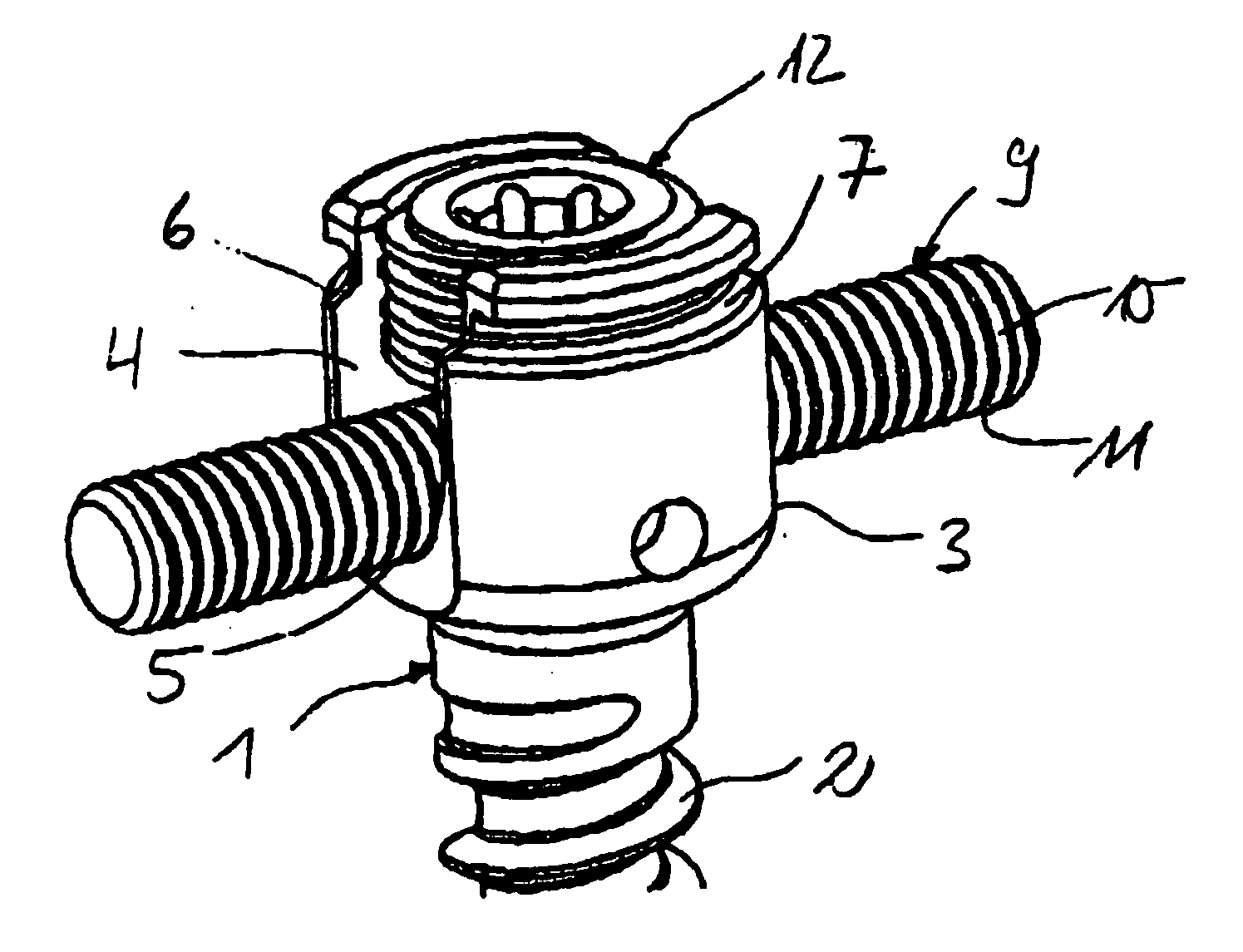
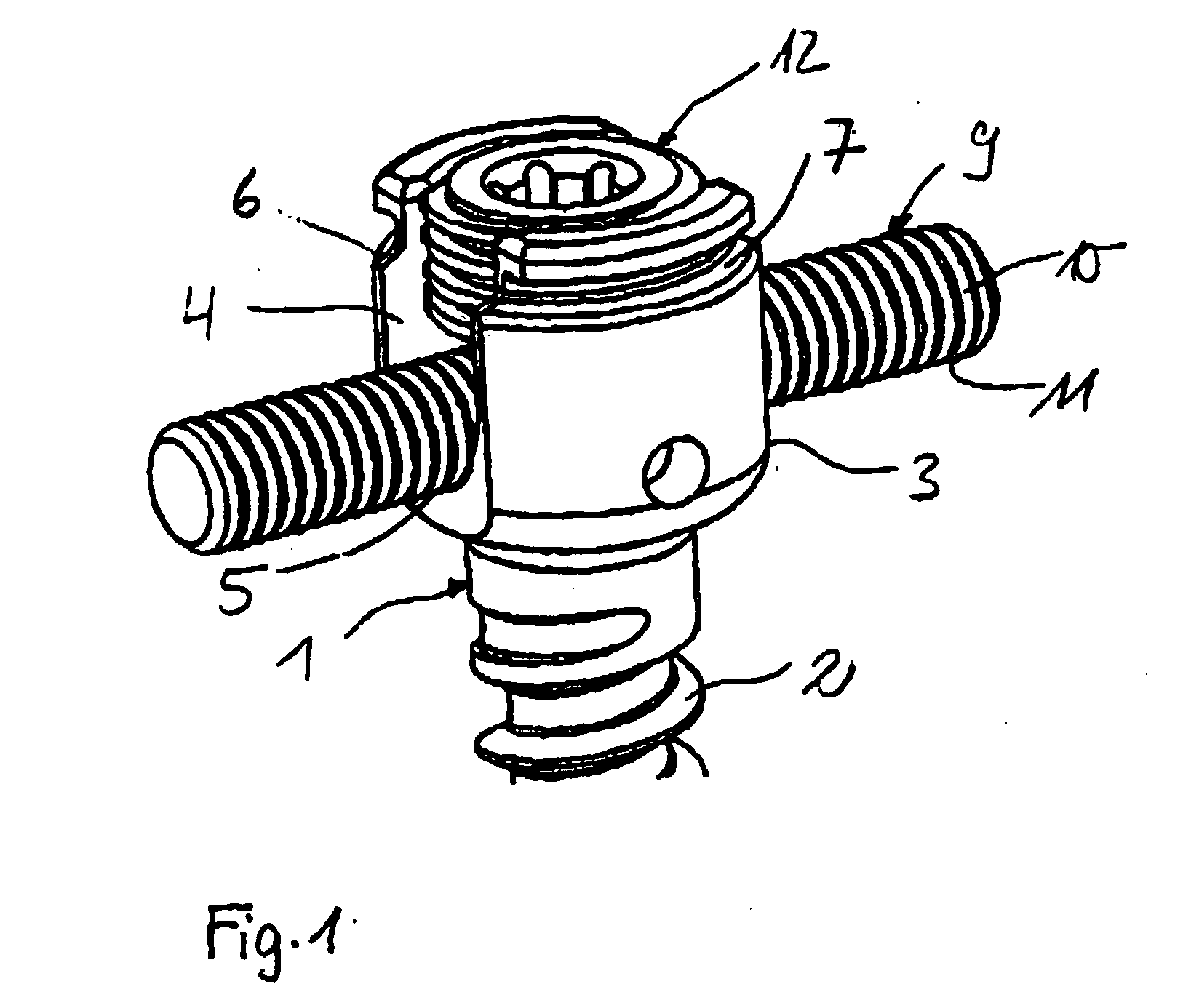
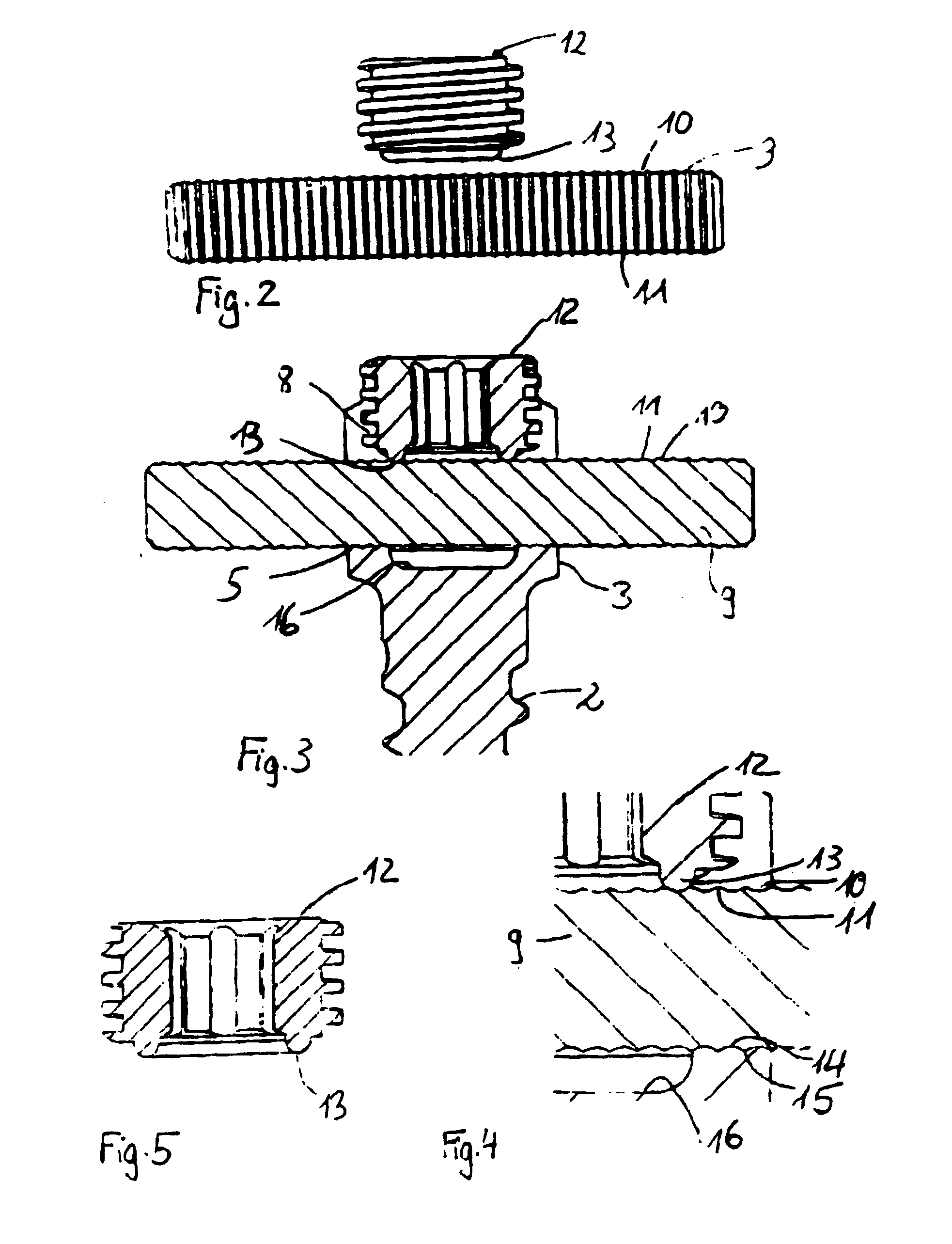
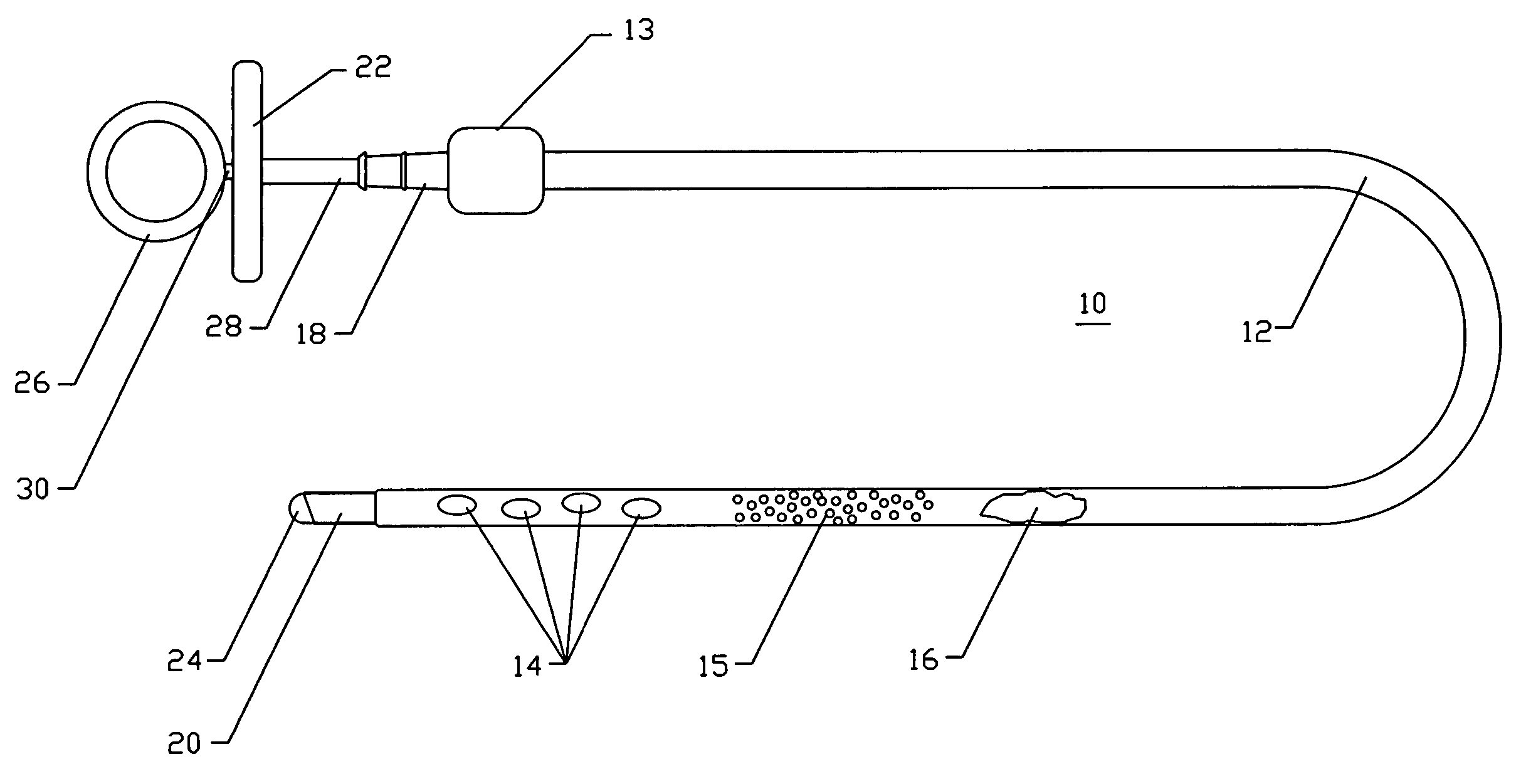
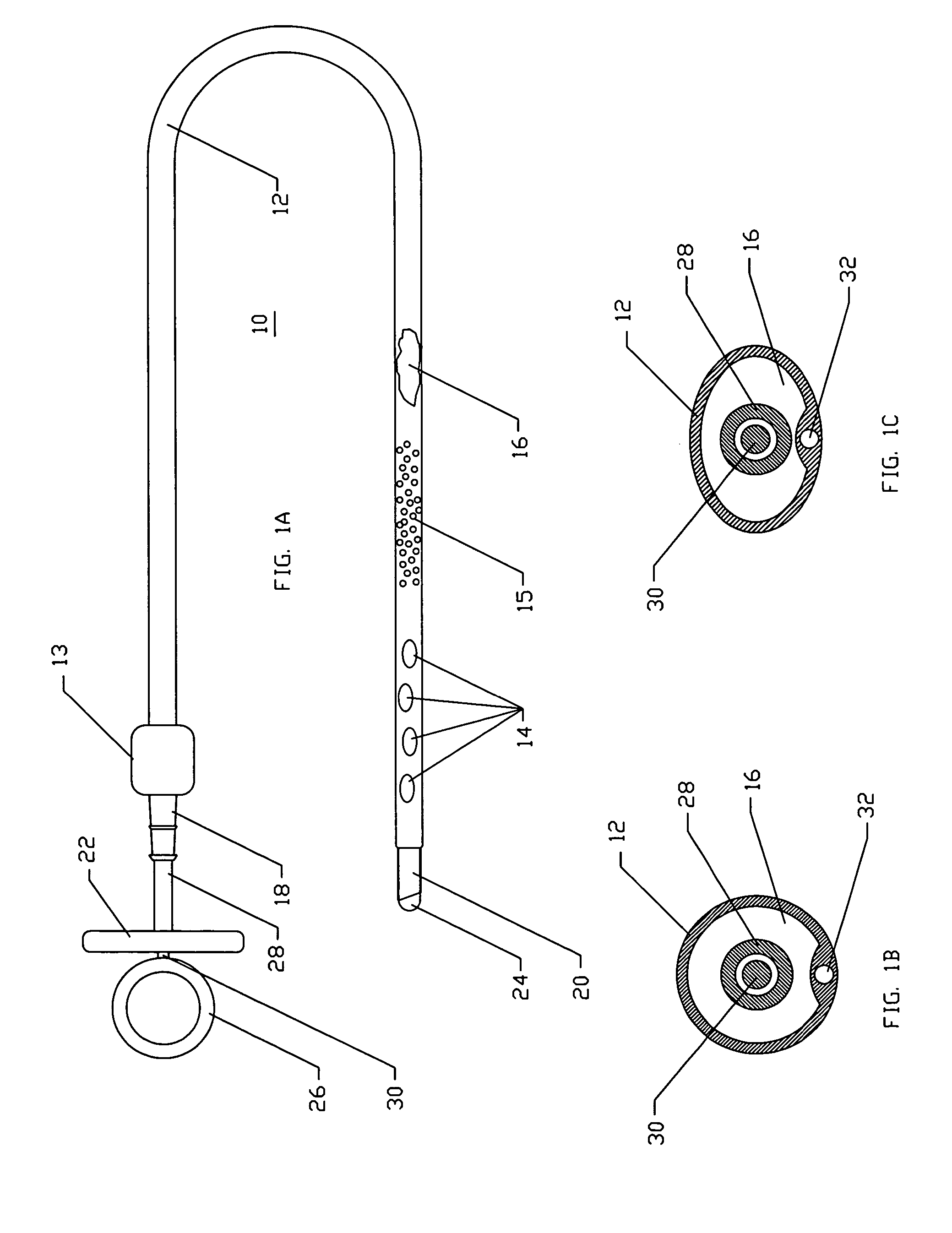
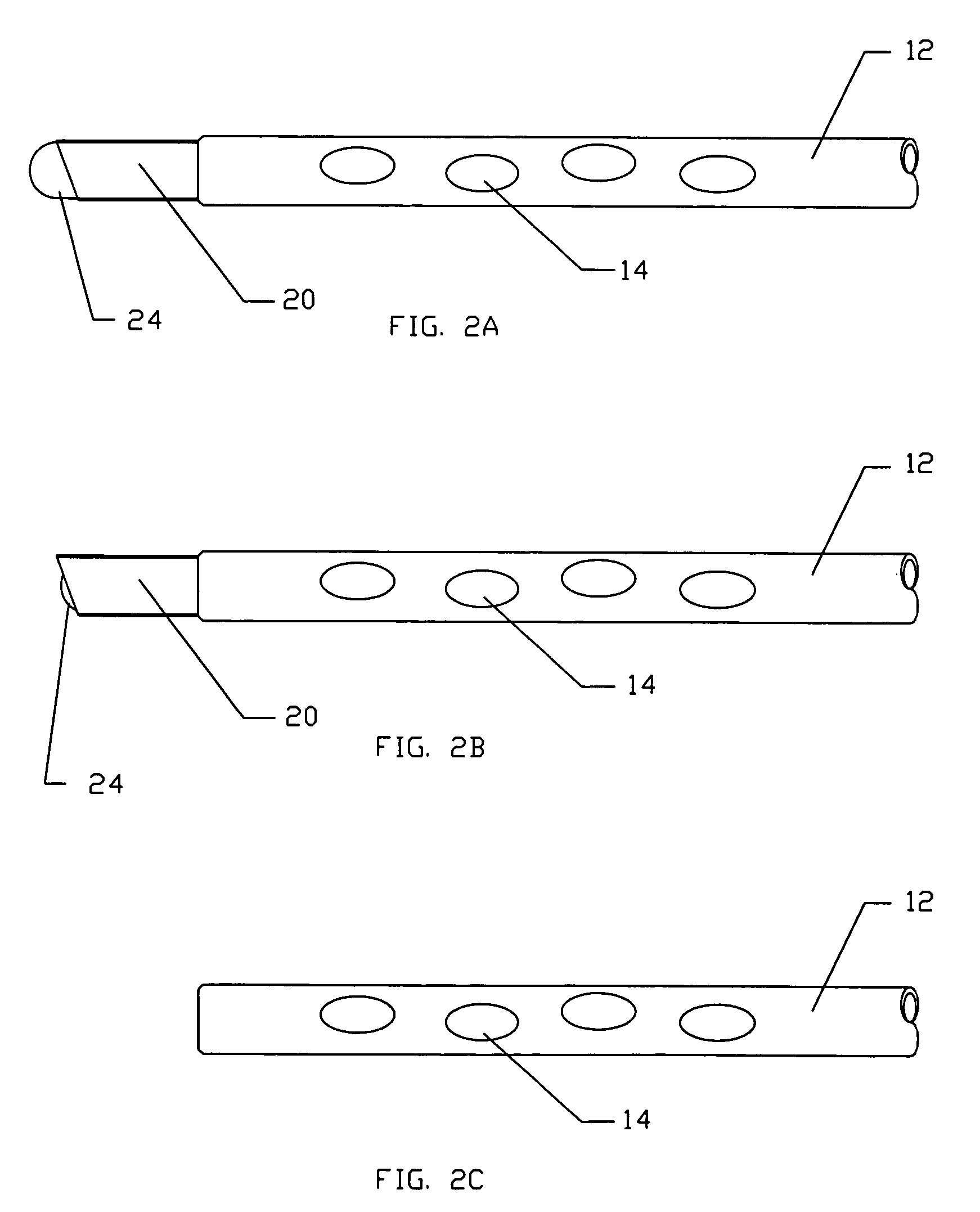
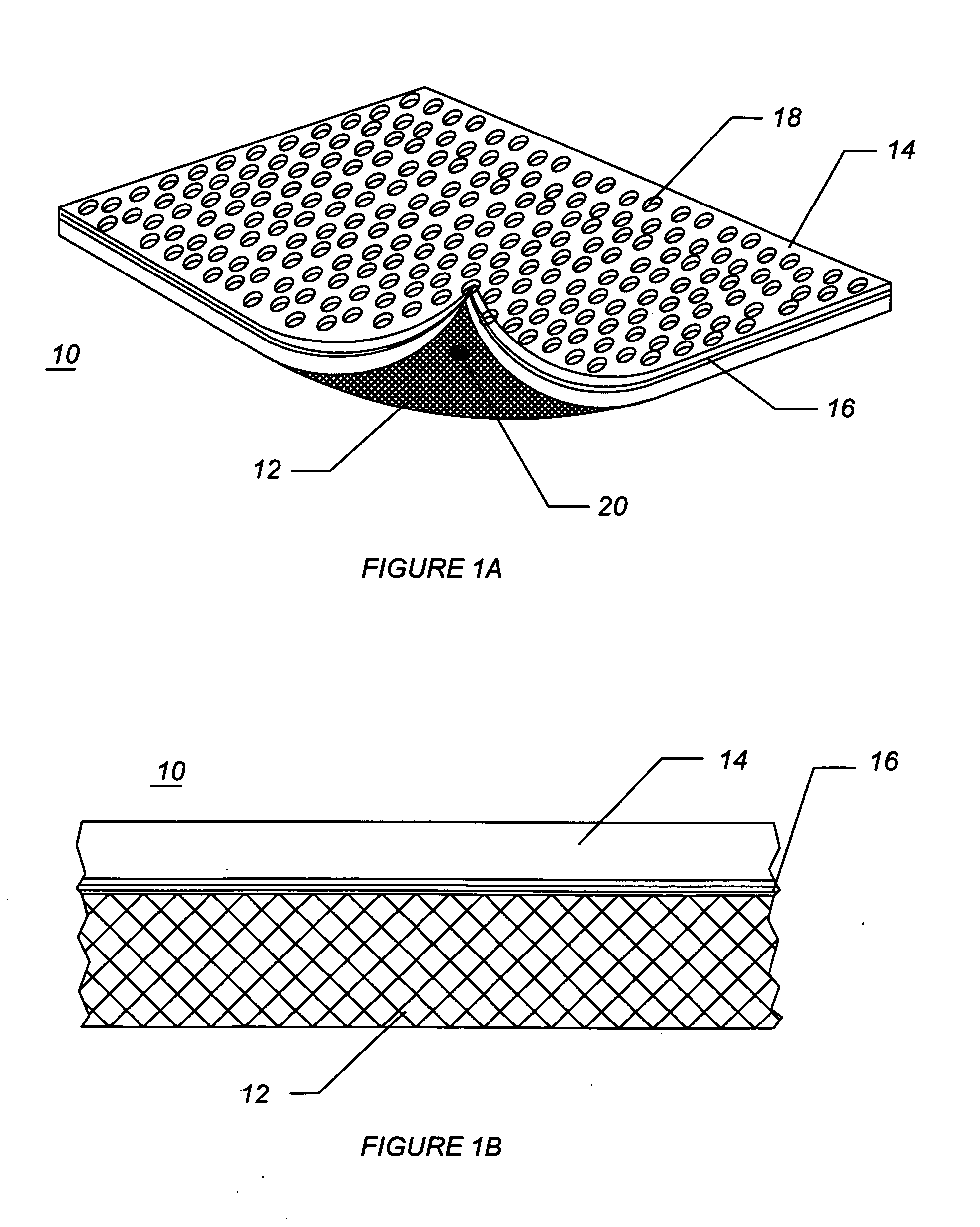
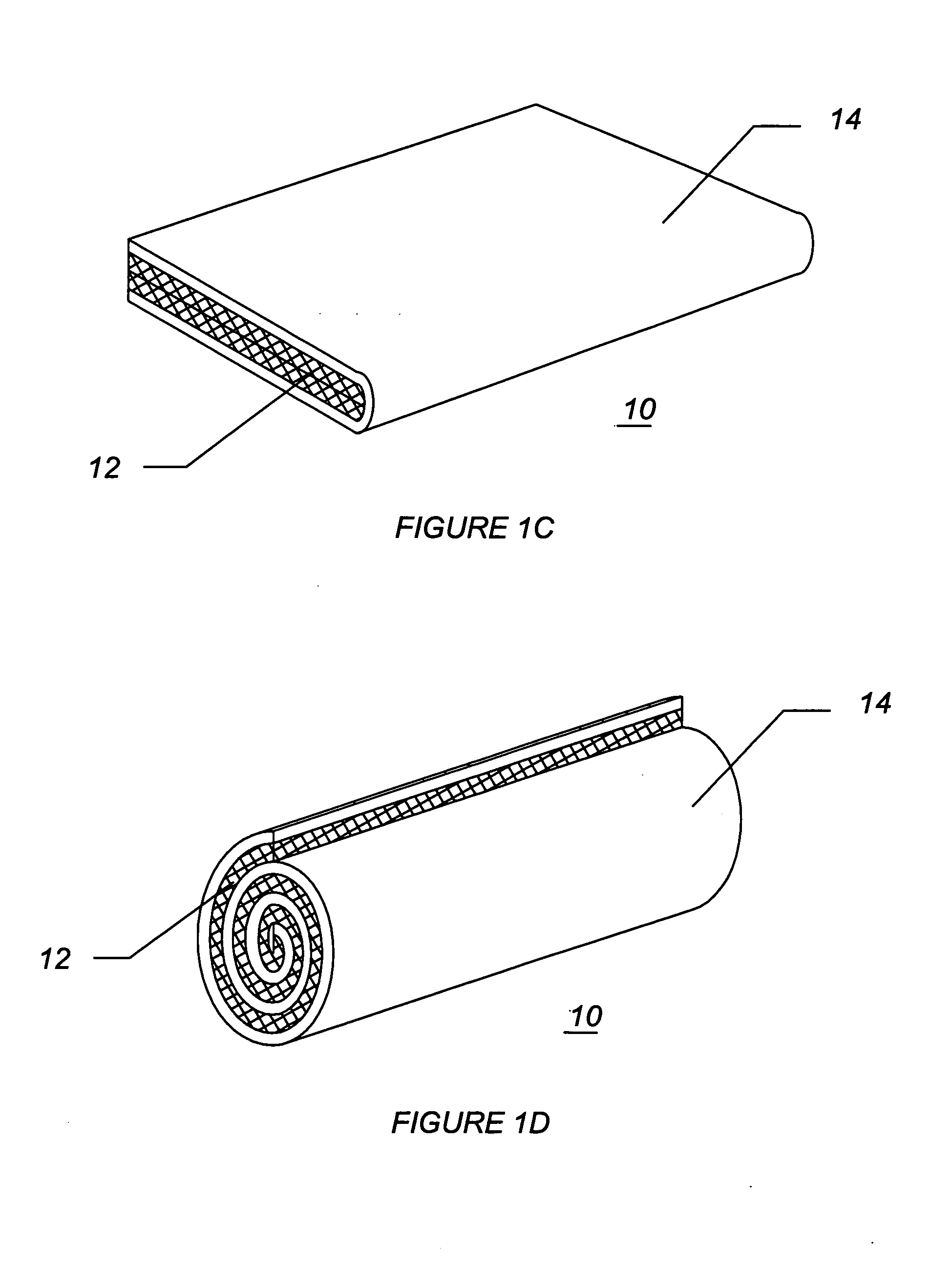
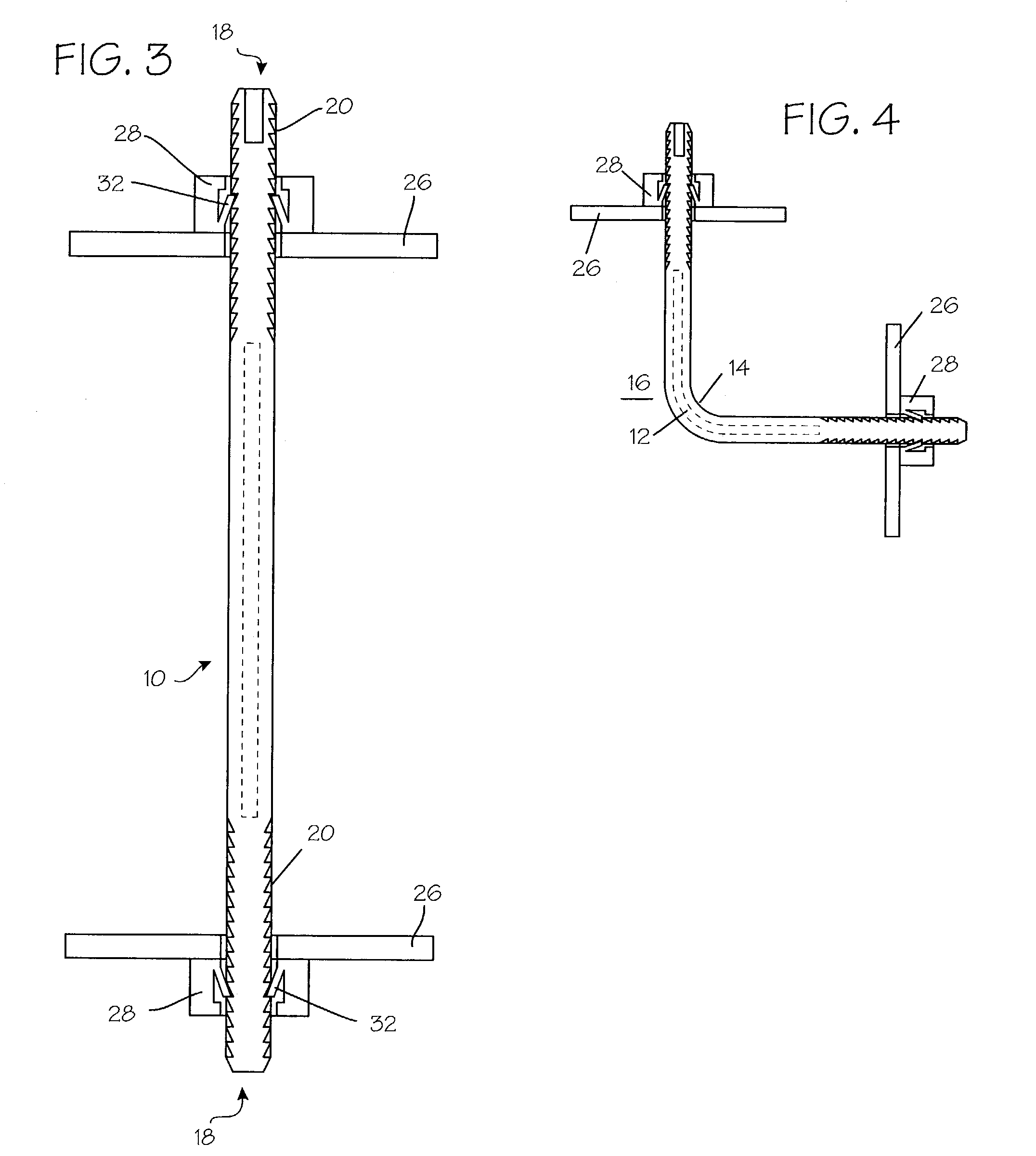
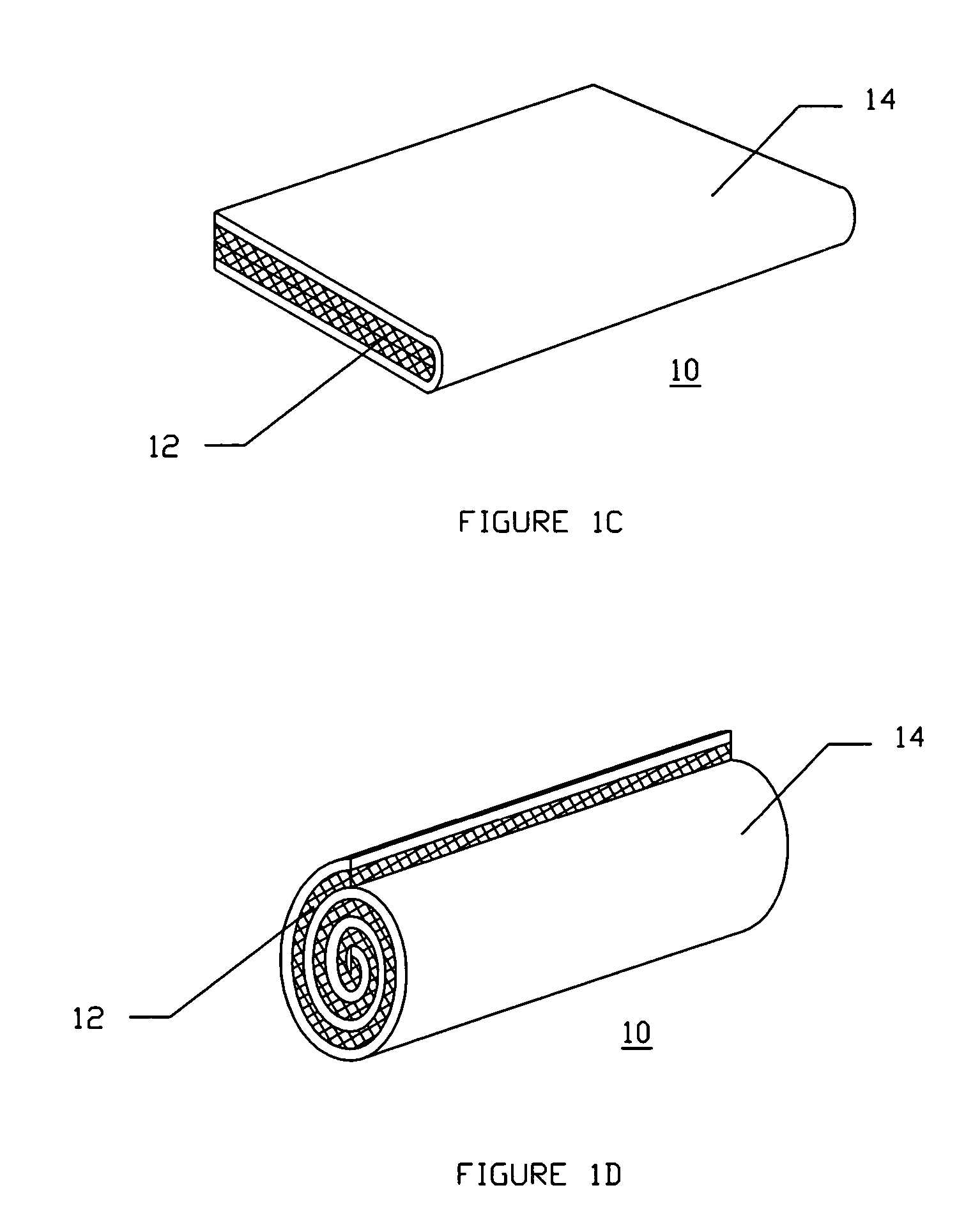
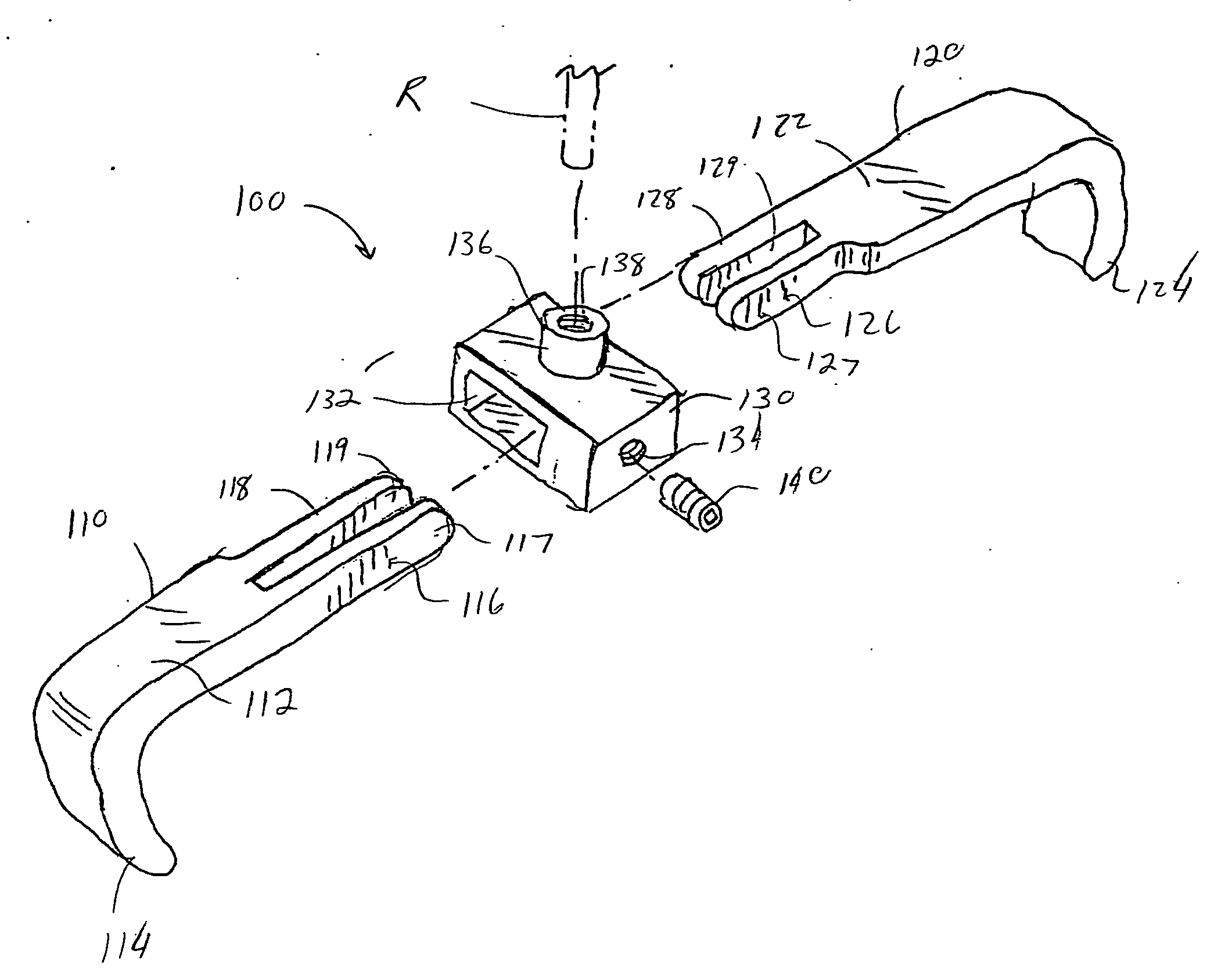
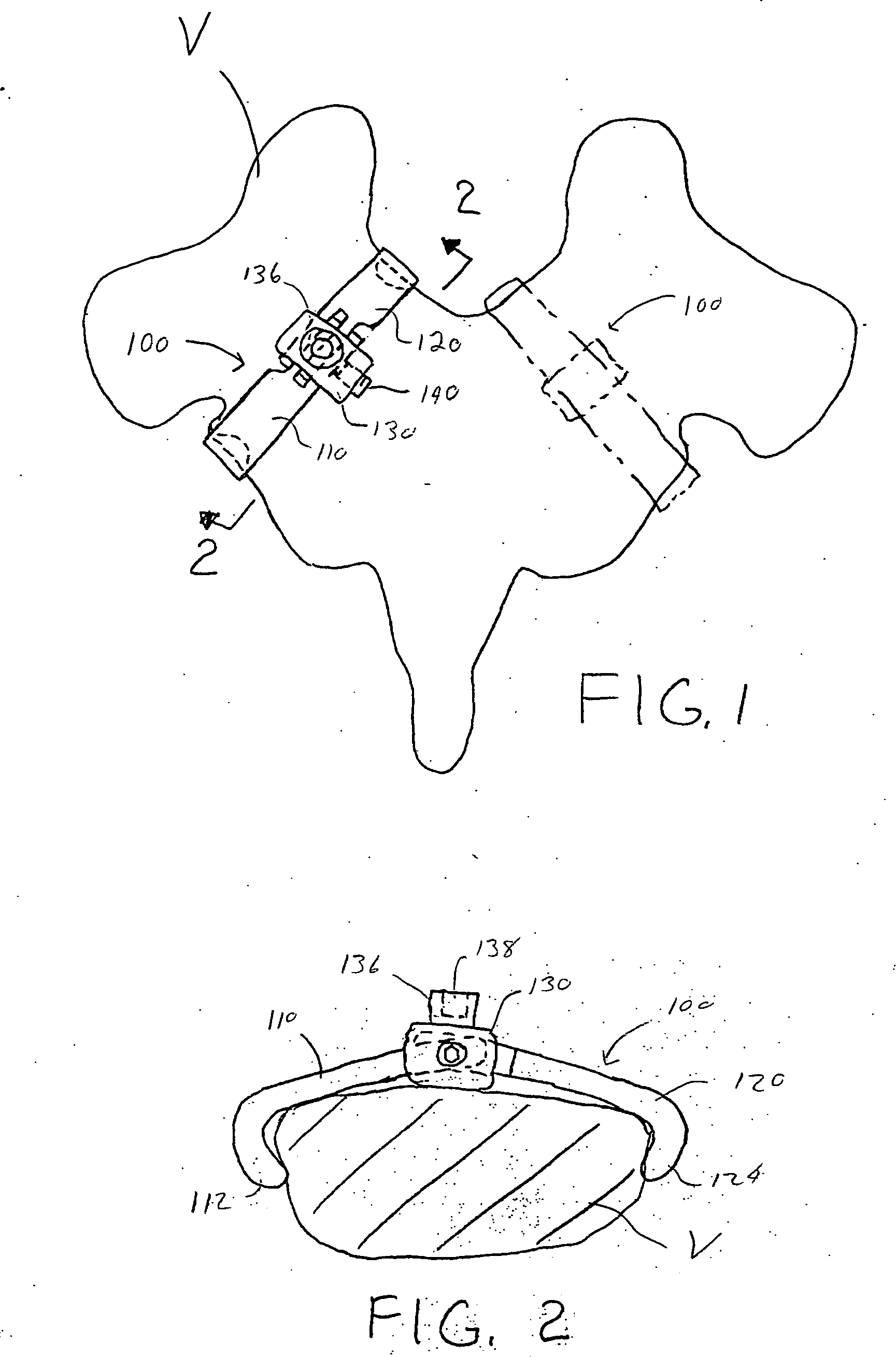
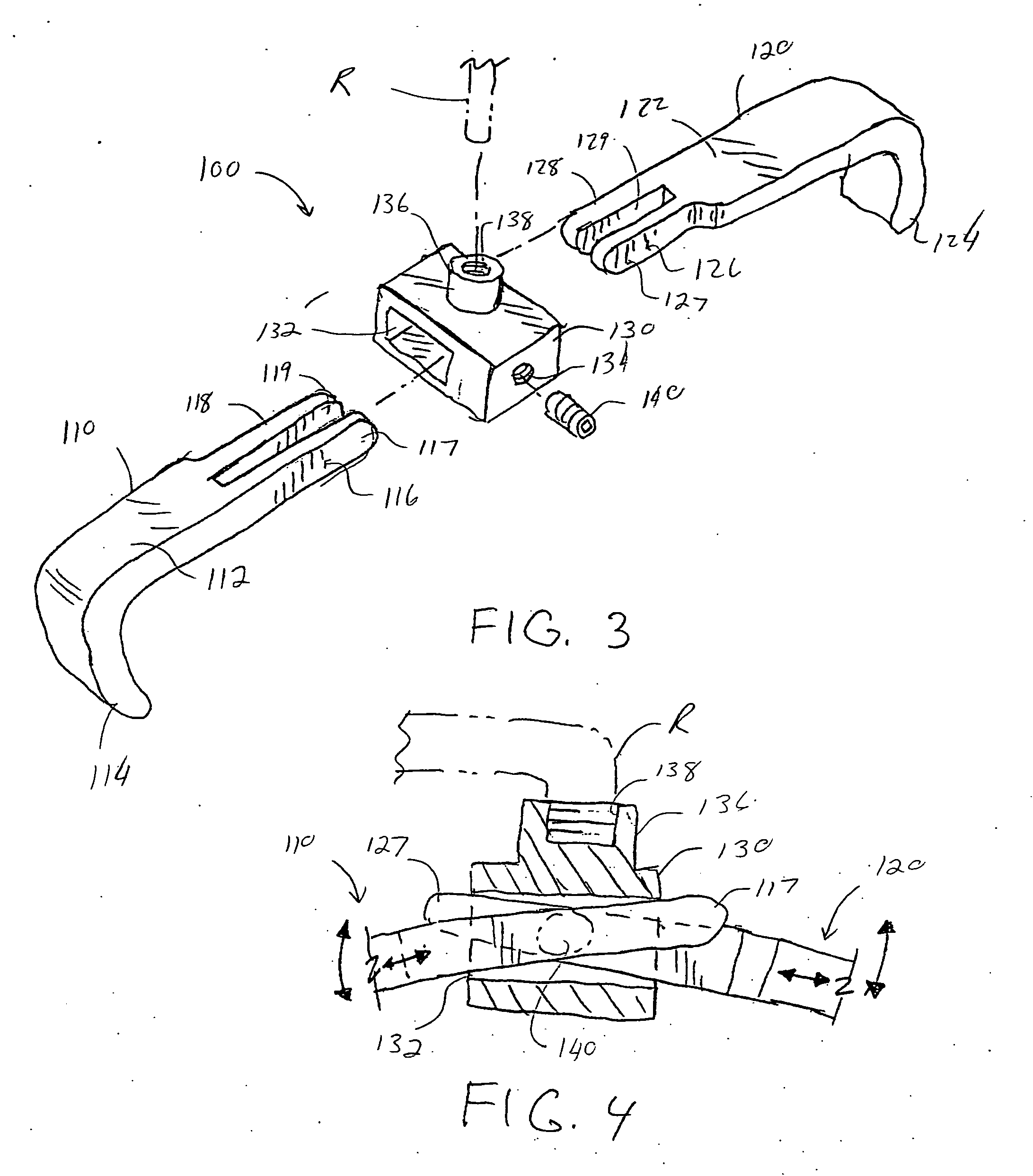
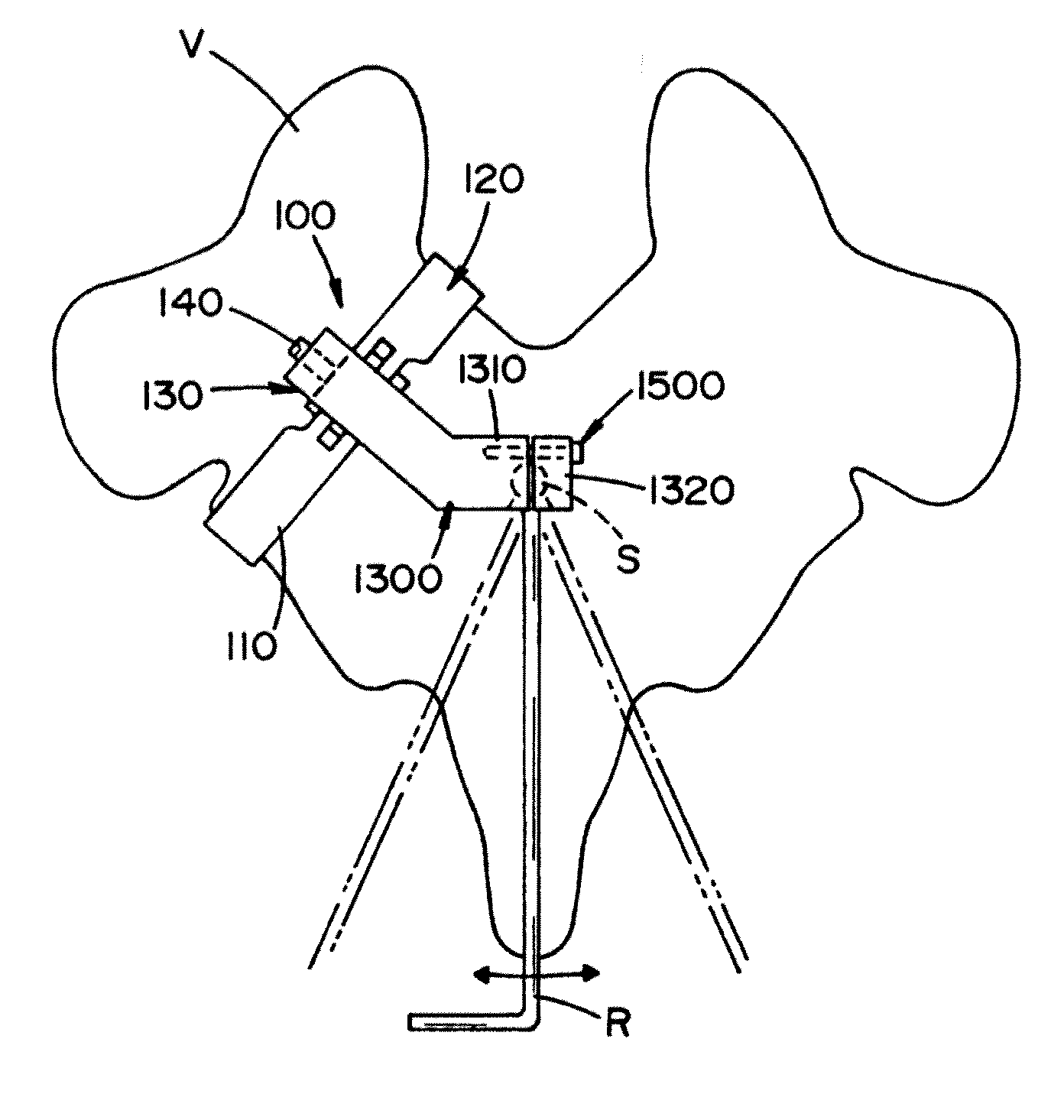
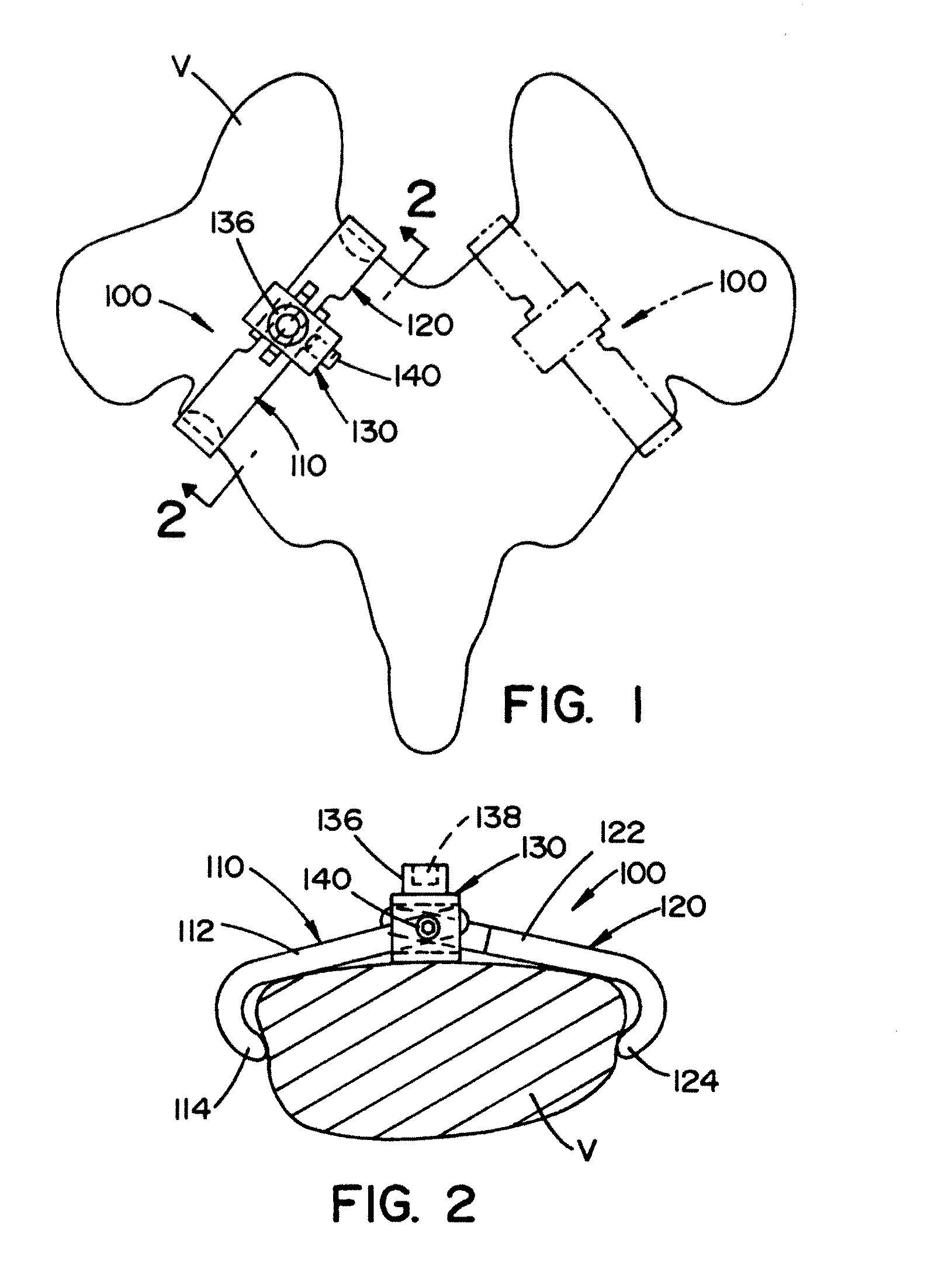
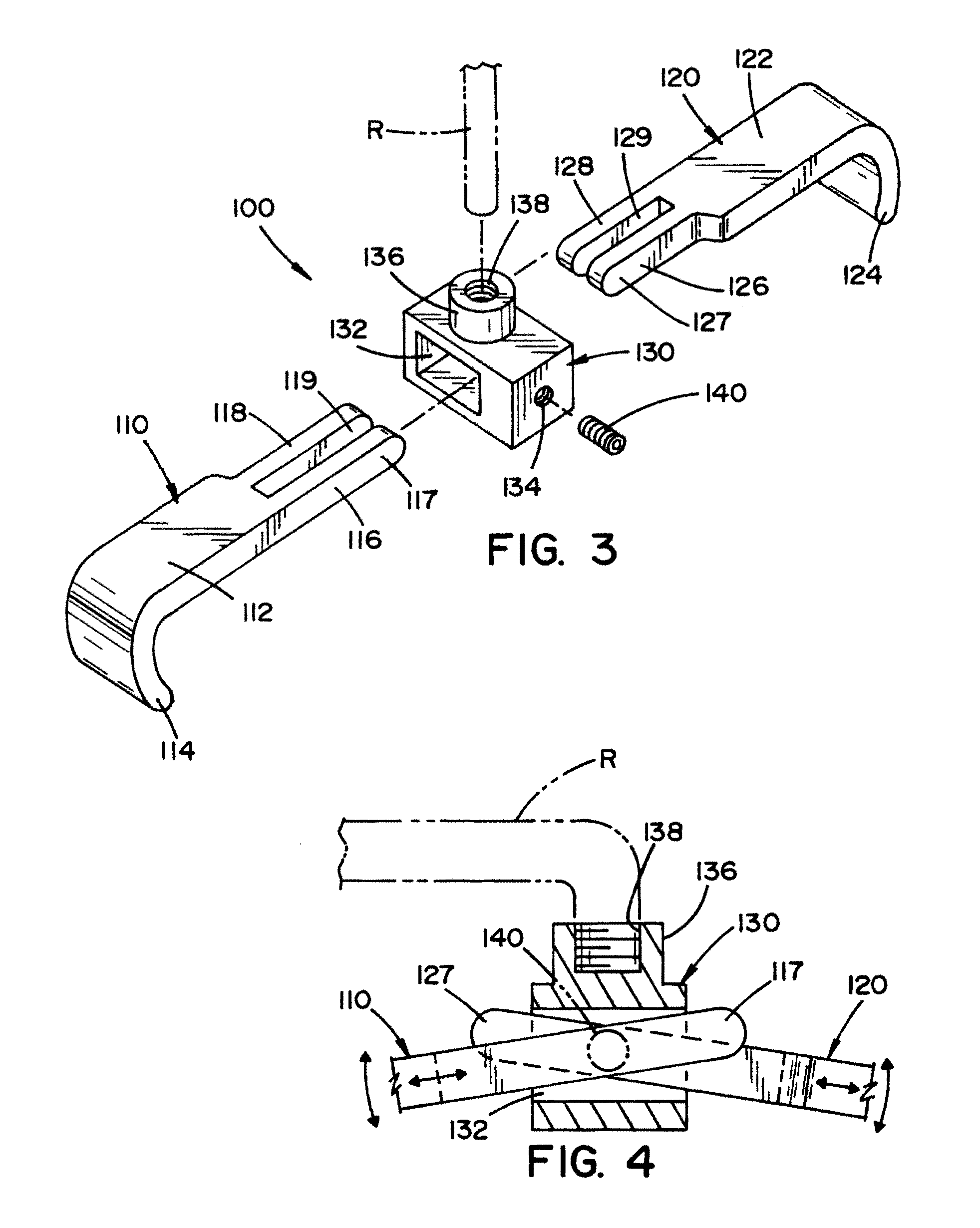
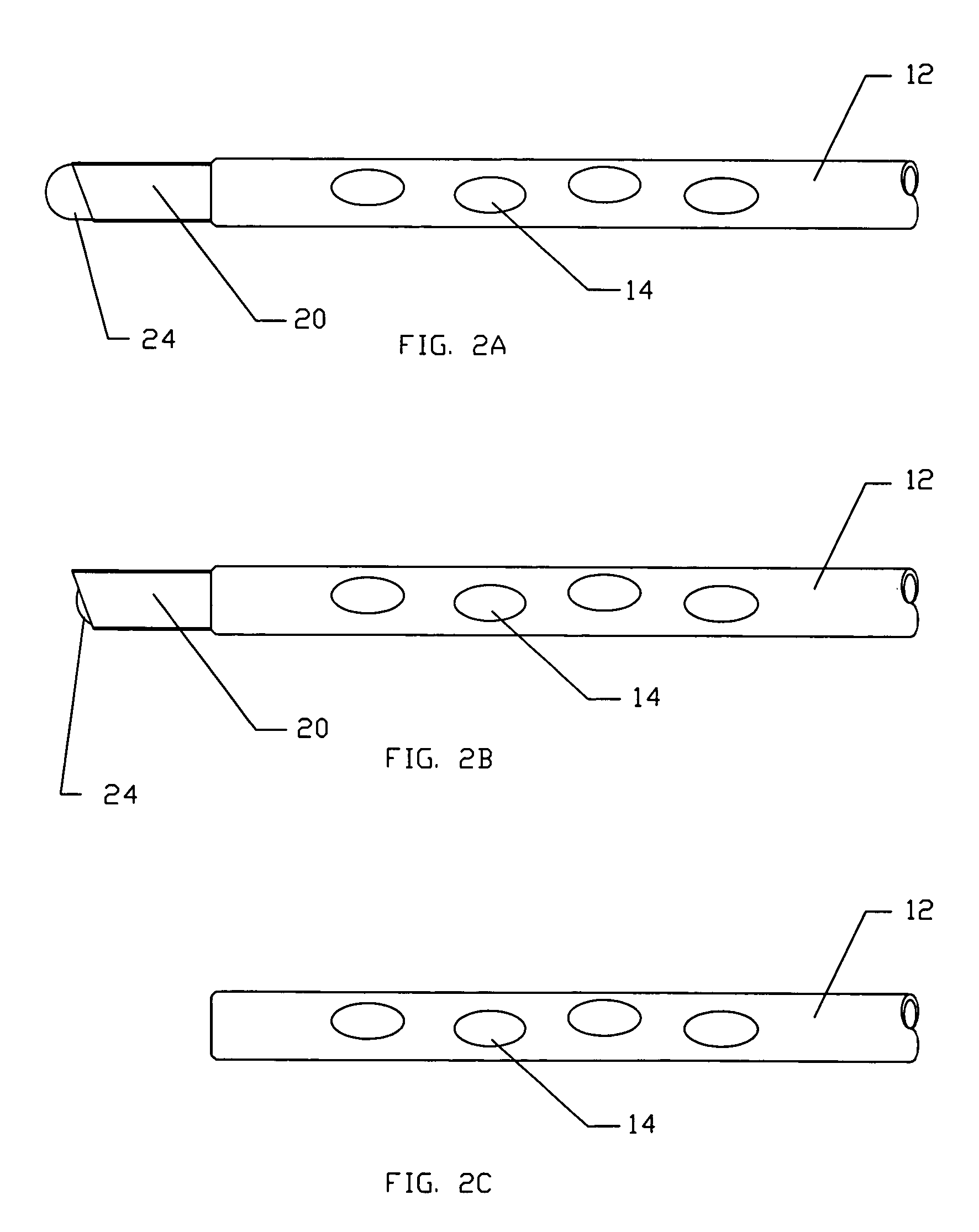
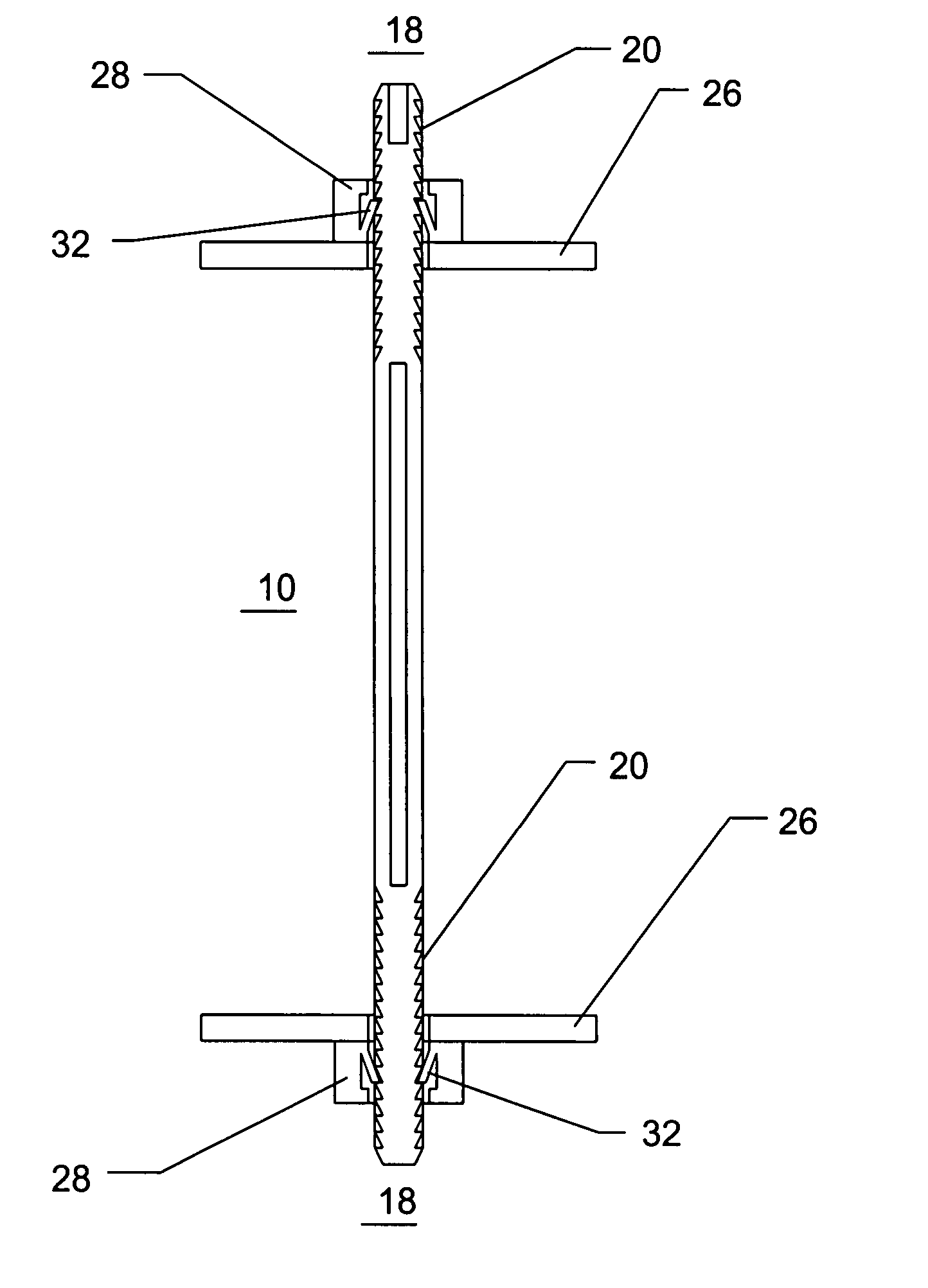
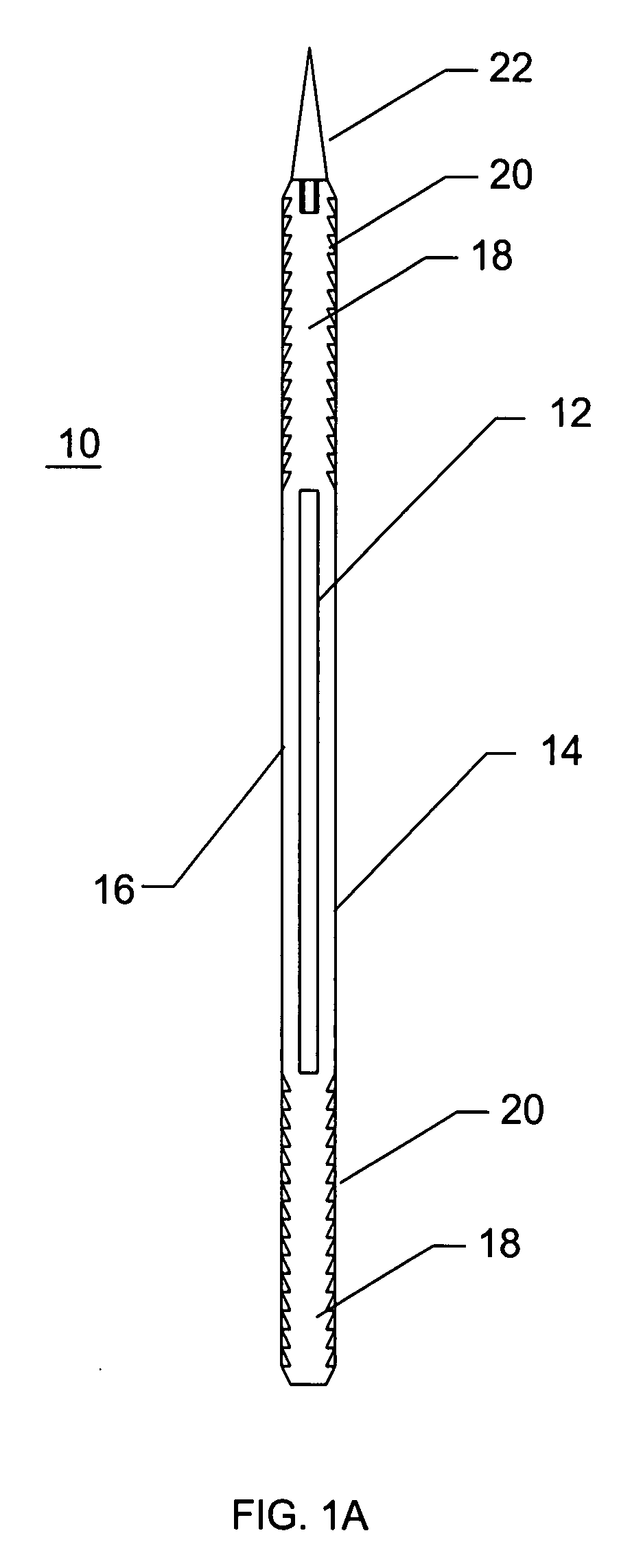
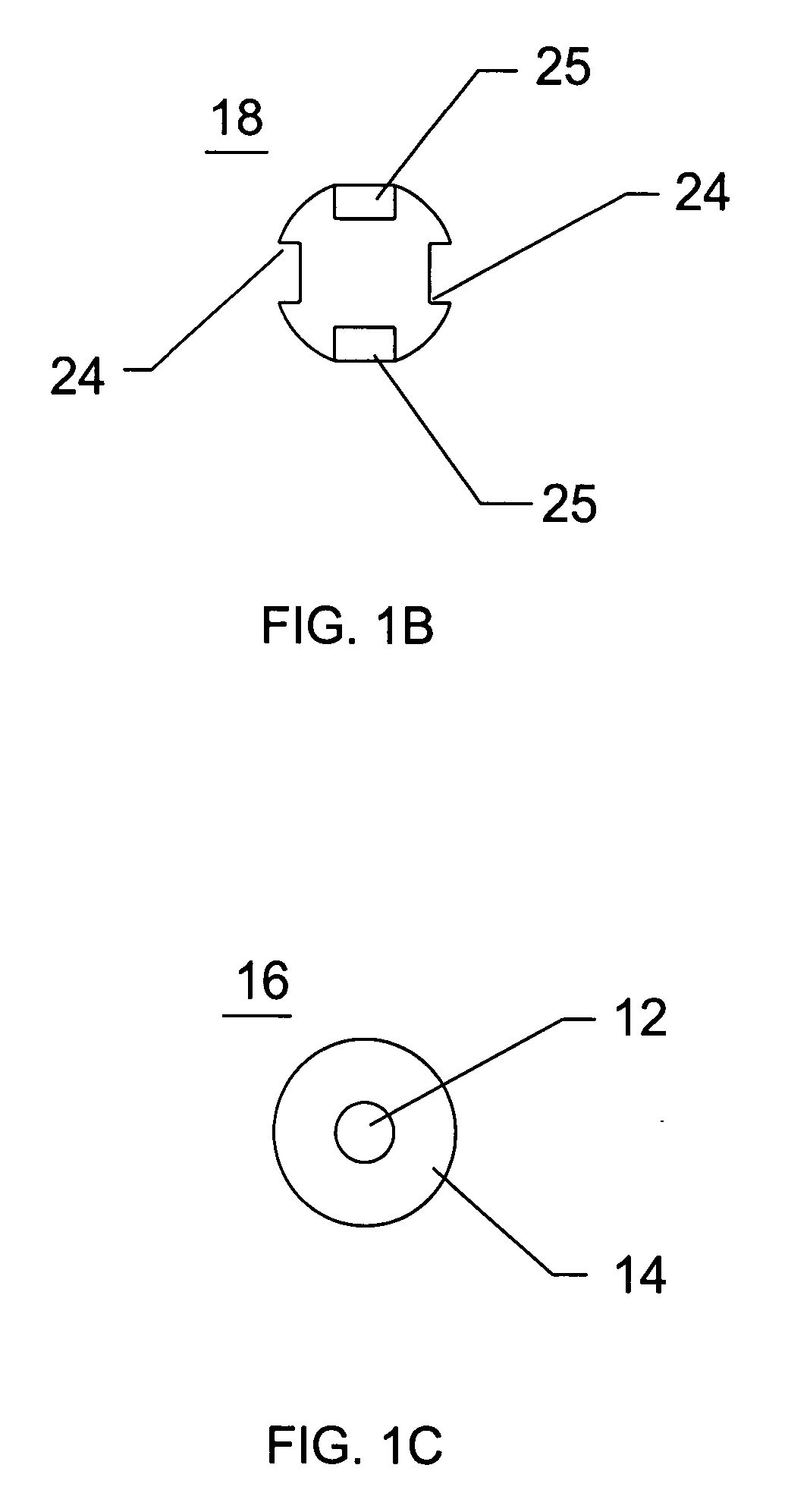
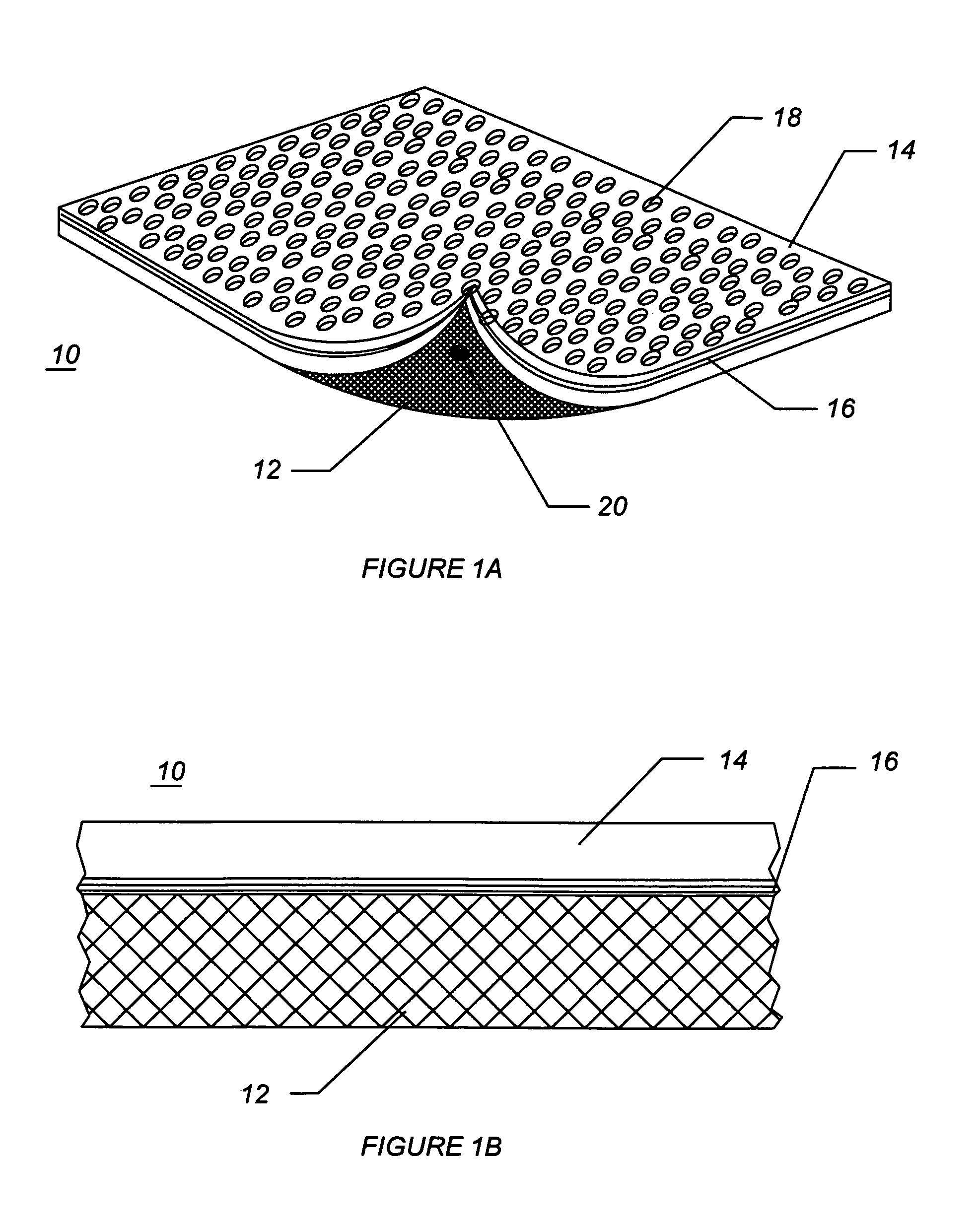
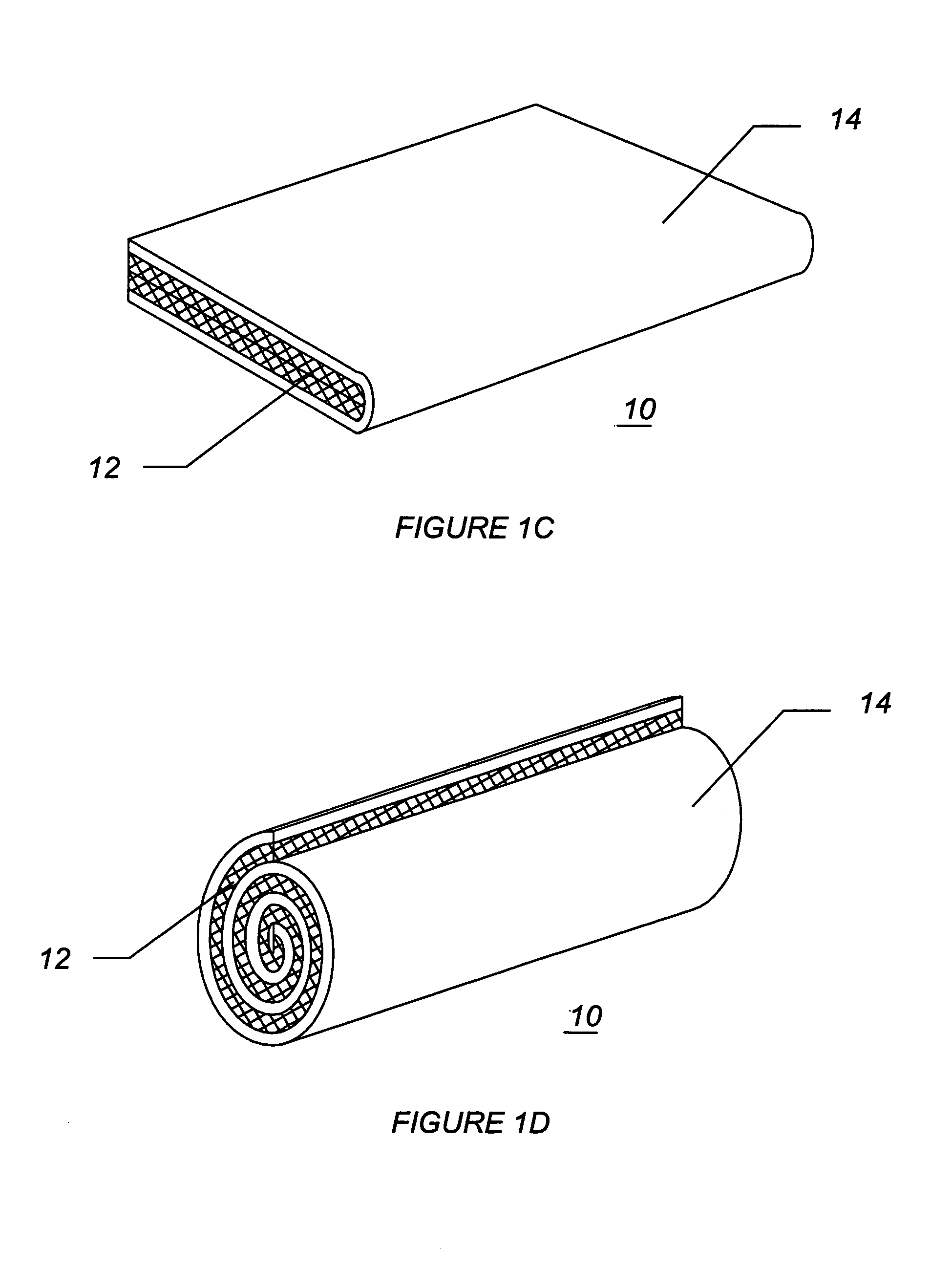
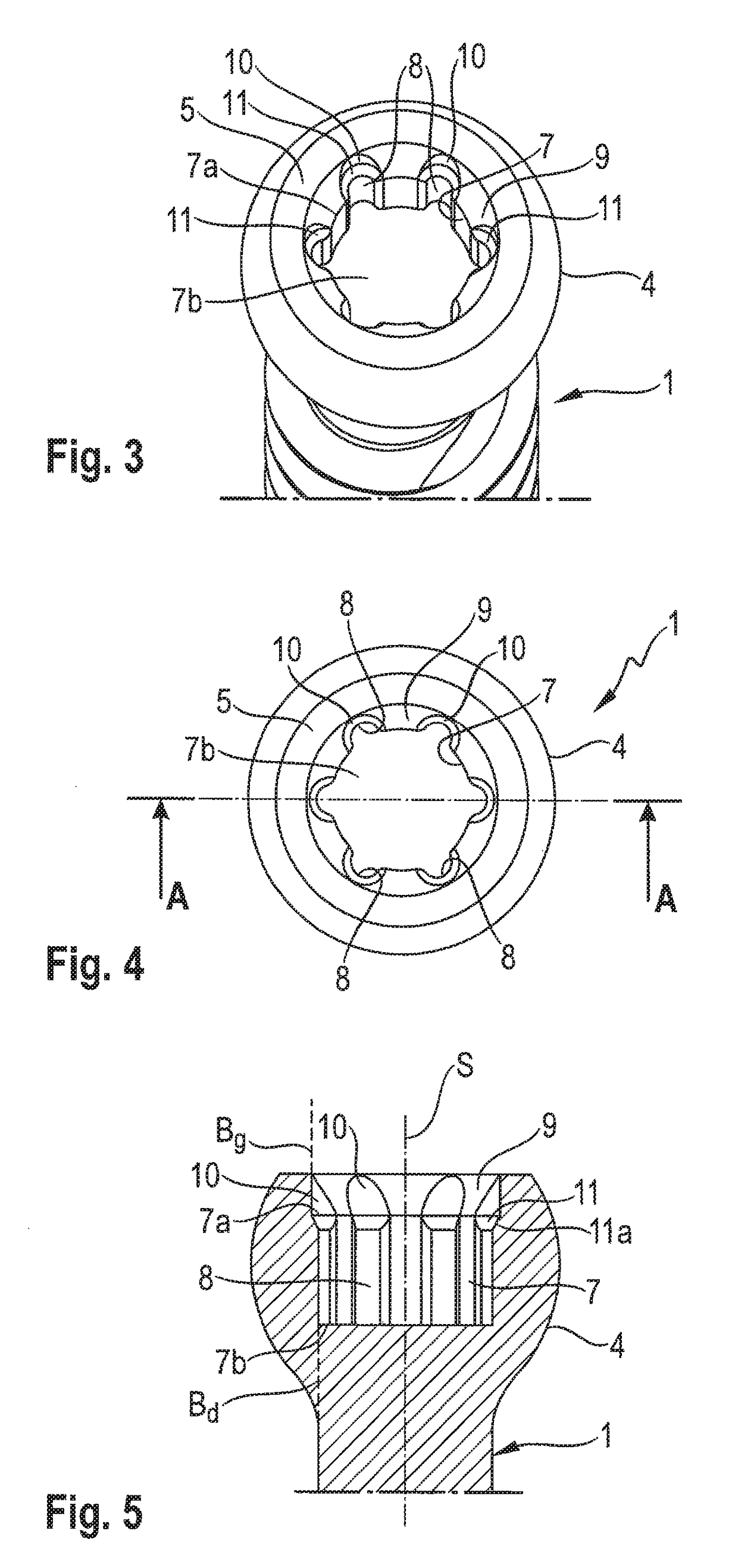
Rod-shaped implant element for application in spine surgery or trauma surgery, stabilization apparatus comprising said rod-shaped implant element, and production method for the rod-shaped implant element
ActiveUS20050085815A1Reliable fixed positioningEasily realizedSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisTrauma surgeryBone anchor
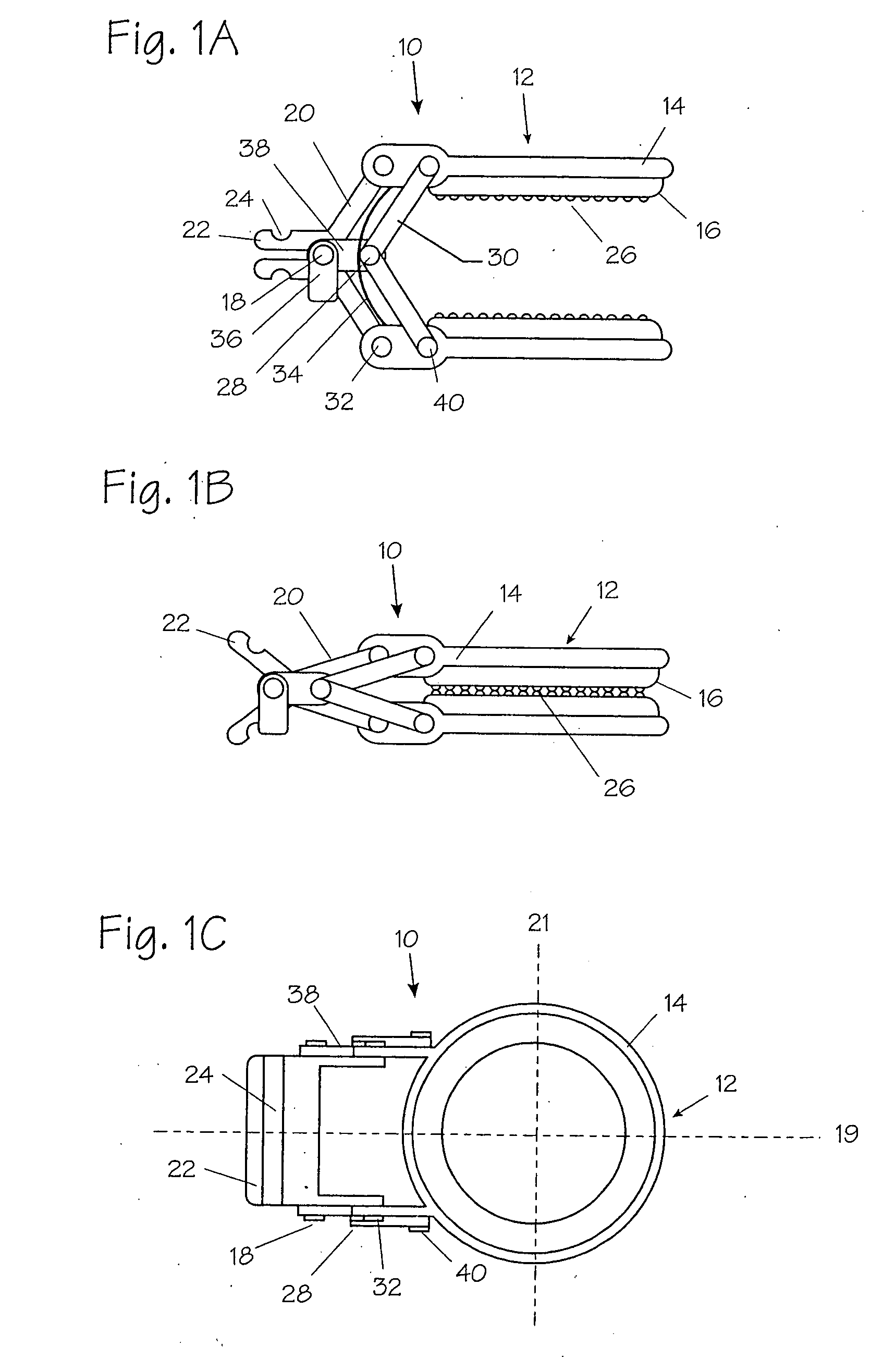
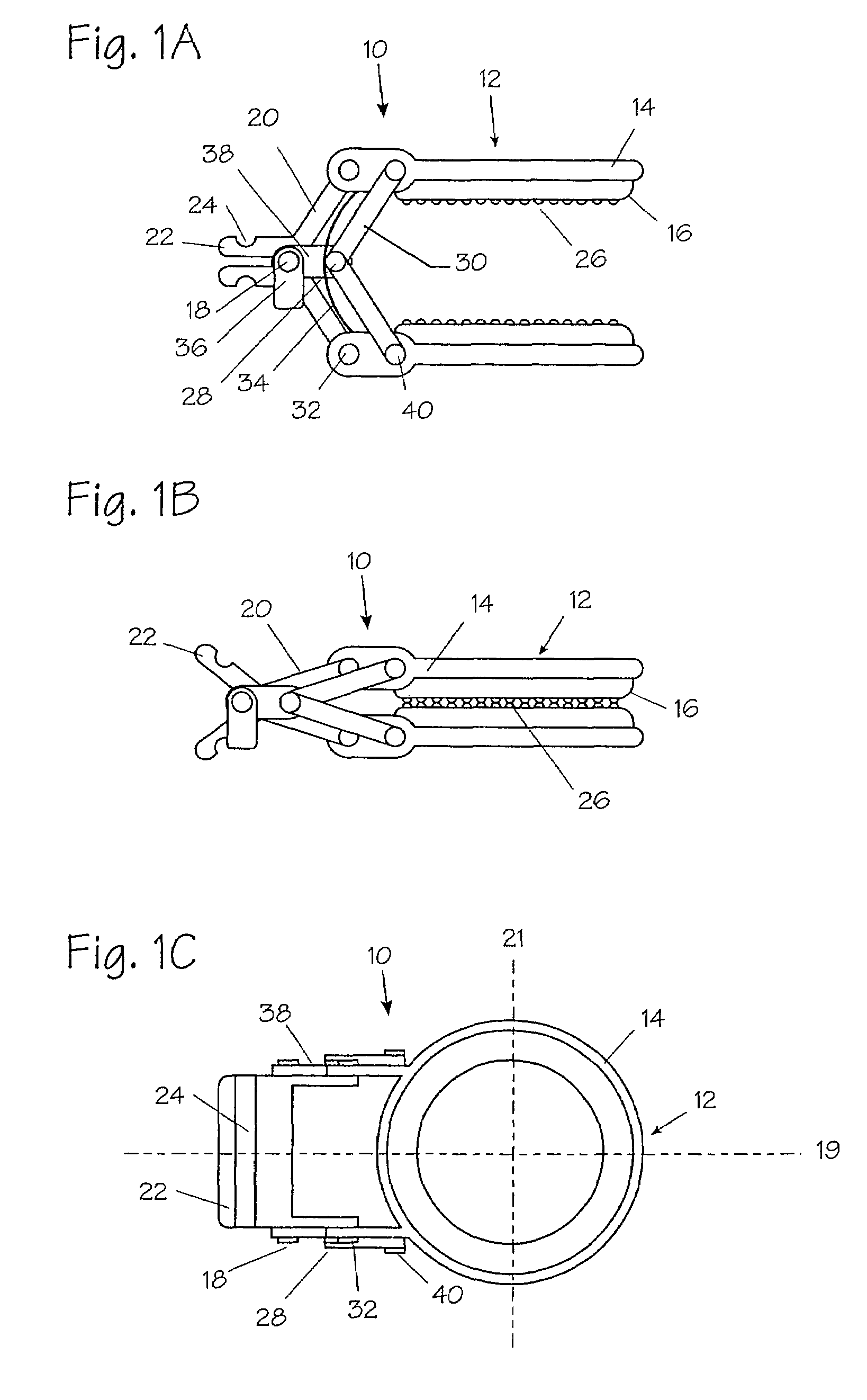
A rod-shaped implant element (1, 100, 101, 102, 300) is disclosed for the connection of bone anchoring elements, Each bone anchoring element has an anchoring section (12) to be anchored in the bone and a receiver member (13) to be connected to the rod-shaped implant element The rod-shaped implant element has at least one rigid section (7, 8) that is configured to be placed in the receiver member (13). It also has a flexible section (9, 90, 900, 902) that is adjacent to the rigid section. The flexible section and the rigid section are formed in one piece. Also disclosed is a stabilization apparatus using a rod-shaped implant element and at least two of the bone anchoring elements. The stabilization apparatus can limit the movement of two vertebrae or parts of a bone in relation to each other in a defined manner.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
Method and apparatus for vascular and visceral clipping
InactiveUS20050251183A1Convenient treatmentMinimizing chanceSnap fastenersClothes buttonsTrauma surgeryLarge intestine
Devices and methods for achieving hemostasis and leakage control in hollow body vessels such as the small and large intestines, arteries and veins as well as ducts leading to the gall bladder and other organs. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting, and most especially during damage control procedures. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdomen, extremities, neck or thoracic region. The devices utilize removable or permanently implanted, broad, soft, parallel jaw clips with minimal projections to maintain vessel contents without damage to the tissue comprising the vessel. These clips are applied using either standard instruments or custom devices that are subsequently removed leaving the clips implanted, on a temporary or permanent basis, to provide for hemostasis or leakage prevention, or both. These clips overcome the limitations of clips and sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The clips come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The clips may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for vascular and visceral clipping
InactiveUS7322995B2Convenient treatmentMinimizing chanceSnap fastenersClothes buttonsTrauma surgeryChest region
Devices and methods for achieving hemostasis and leakage control in hollow body vessels such as the small and large intestines, arteries and veins as well as ducts leading to the gall bladder and other organs. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting, and most especially during damage control procedures. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdomen, extremities, neck or thoracic region. The devices utilize removable or permanently implanted, broad, soft, parallel jaw clips with minimal projections to maintain vessel contents without damage to the tissue comprising the vessel. These clips are applied using either standard instruments or custom devices that are subsequently removed leaving the clips implanted, on a temporary or permanent basis, to provide for hemostasis or leakage prevention, or both. These clips overcome the limitations of clips and sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The clips come in a variety of shapes and sizes. The clips may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
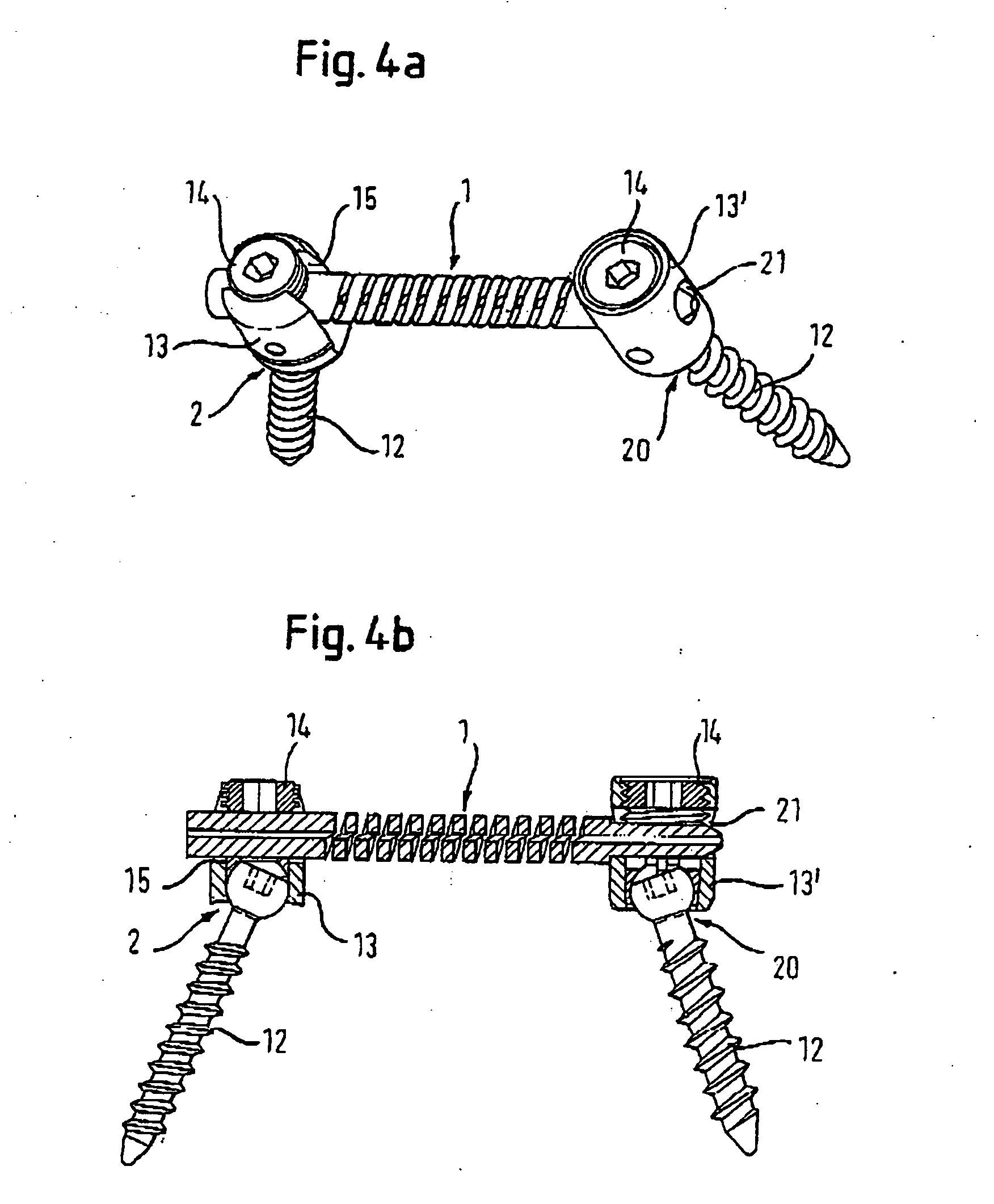
Bone anchoring assembly
InactiveUS20070233086A1Easy to fixHigh strengthInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTrauma surgeryEngineering
A bone anchoring assembly for use in spinal surgery or trauma surgery includes an anchoring element having a shaft and a receiving part having a substantially U-shaped cross-section with a base connected to said shaft and two free legs forming a channel for receiving a rod having an at least partially structured surface. The bone anchoring assembly further includes a locking member cooperating with the receiving part for locking said rod in the channel. At least on the locking member or in the receiving part an engagement portion for engaging said structured surface of the rod is provided. The locking member, the rod and the receiving part cooperate in such a manner that as soon as the engagement portion comes into engagement with the structured surface the rod is held in the receiving part in a form-locking manner preventing movement of the rod.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
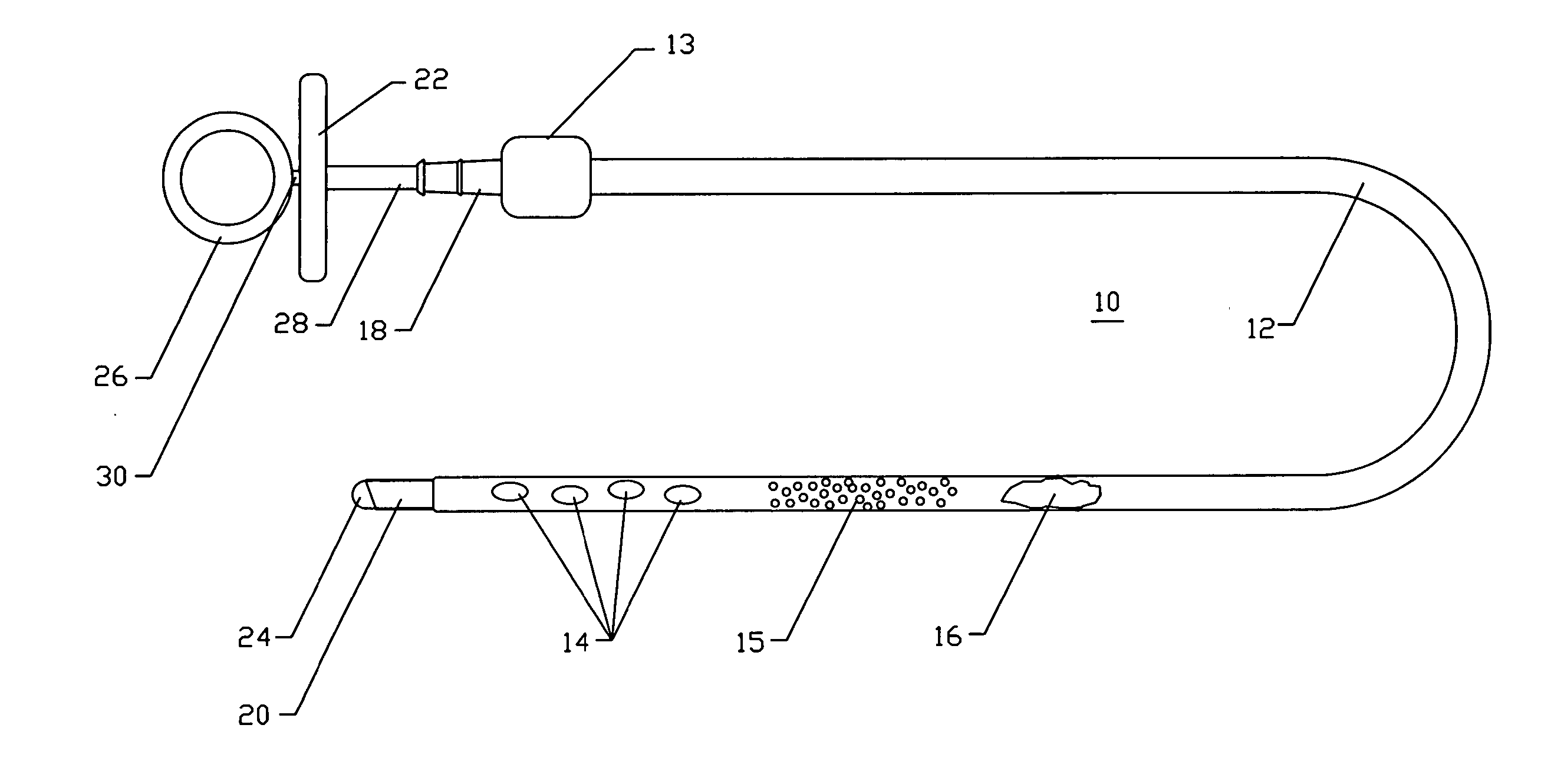
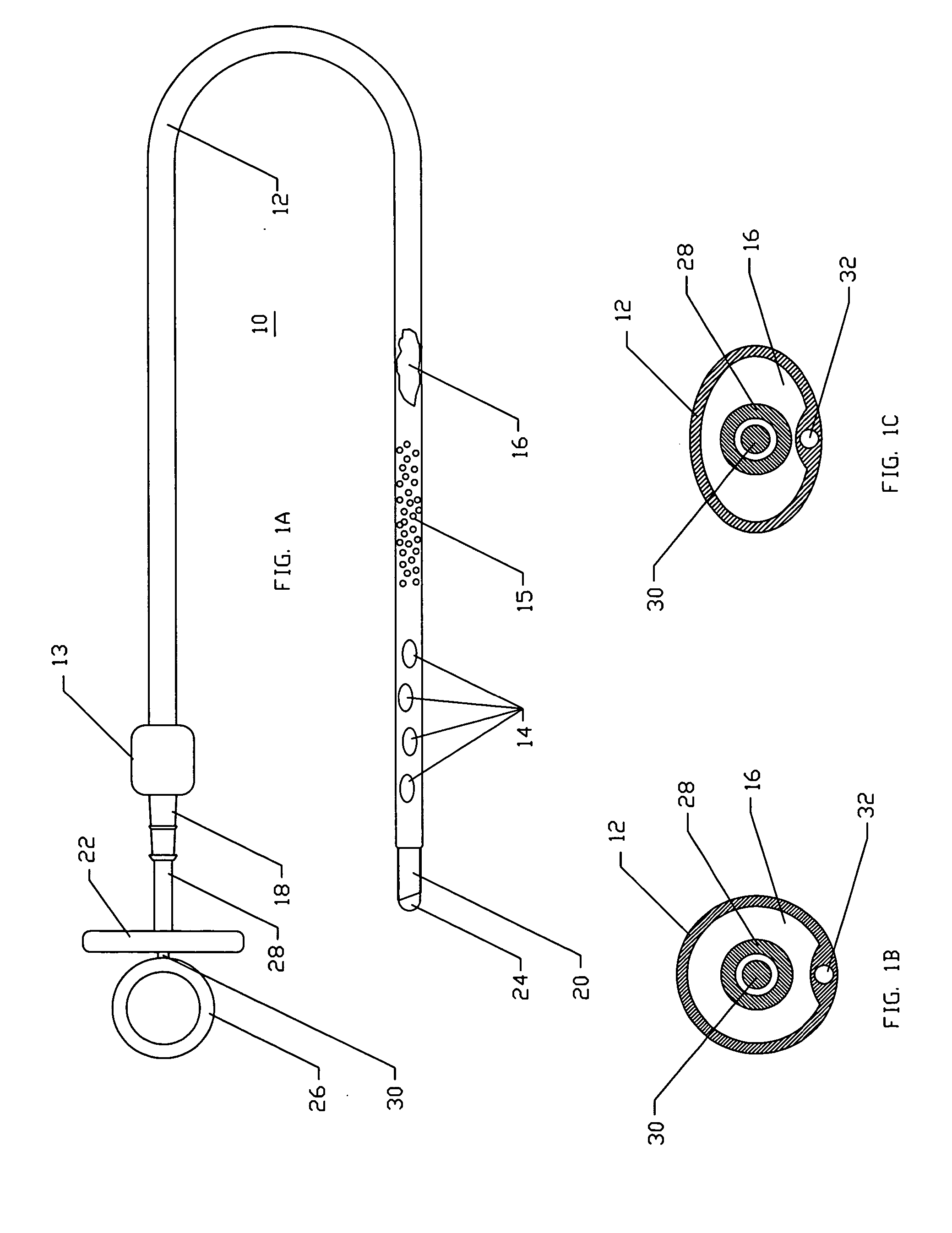
Method and apparatus for rapid deployment chest drainage
InactiveUS7135010B2Maintains sterility and cleanlinessSimple methodCannulasInfusion syringesInjury causeTrauma surgery
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving chest drainage in humans or other animals. Chest drainage is often required following traumatic injury or surgery. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting. The devices utilize a chest tube with a cutting distal end and a central blunt trocar. The blunt trocar or obturator shields the sharp cutting distal end of the chest tube until controllably retracted. Once the blunt trocar or obturator is retracted, the chest tube is advanced out through its sterile, protective package and into the patient. The blunt trocar is advanced back into its position to shield the sharp tip of the chest tube during patient insertion. The chest tube also includes a hold-down mechanism that is created by an adhesive seal to the patient's chest and ribbons or straps that are wrapped around the chest tube once it is correctly positioned. The straps include adhesive ends to grip the chest tube once the straps are in place.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
InactiveUS20080132820A1Different compressibilityDifferent resilienceNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersTrauma surgeryTourniquet time
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:BUCKMAN ROBERT F +2
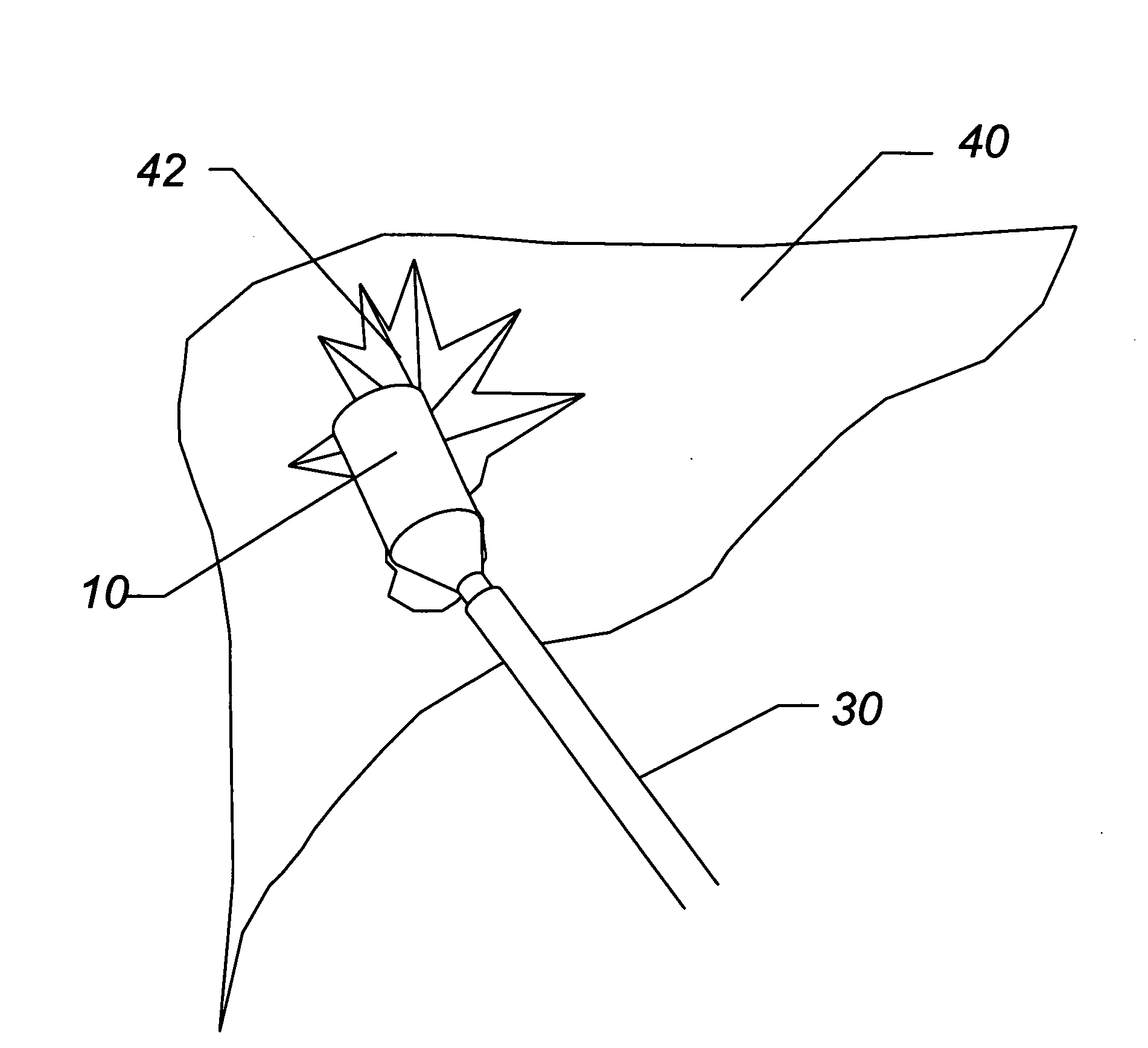
Method and apparatus for solid organ tissue approximation
InactiveUS7235090B2Improved haemostatic tissue appositionEasy and fast applicationIntravenous devicesSurgical veterinaryTrauma surgeryParenchyma
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in solid visceral wounds. Such devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdominal viscera. The devices utilize flexible, variable depth transfixing bolts that penetrate the viscera. These bolts are pulled tight to bring the tissue into apposition and hold said tissue in apposition while the wound heals. These bolts overcome the limitations of sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The bolts come in a variety of lengths and diameters. Since the bolts are flexible, the curvature may be adjusted by the surgeon. The devices are flexible, bendable, and conformable in their wet or dry state. They can be used either straight or through a broad range of curvatures to suit the needs of various pathologies. The bolts include pressure plates that are capable of exerting compressive pressure over broad areas of visceral wounds without causing tearing of the friable parenchyma. The bolts may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
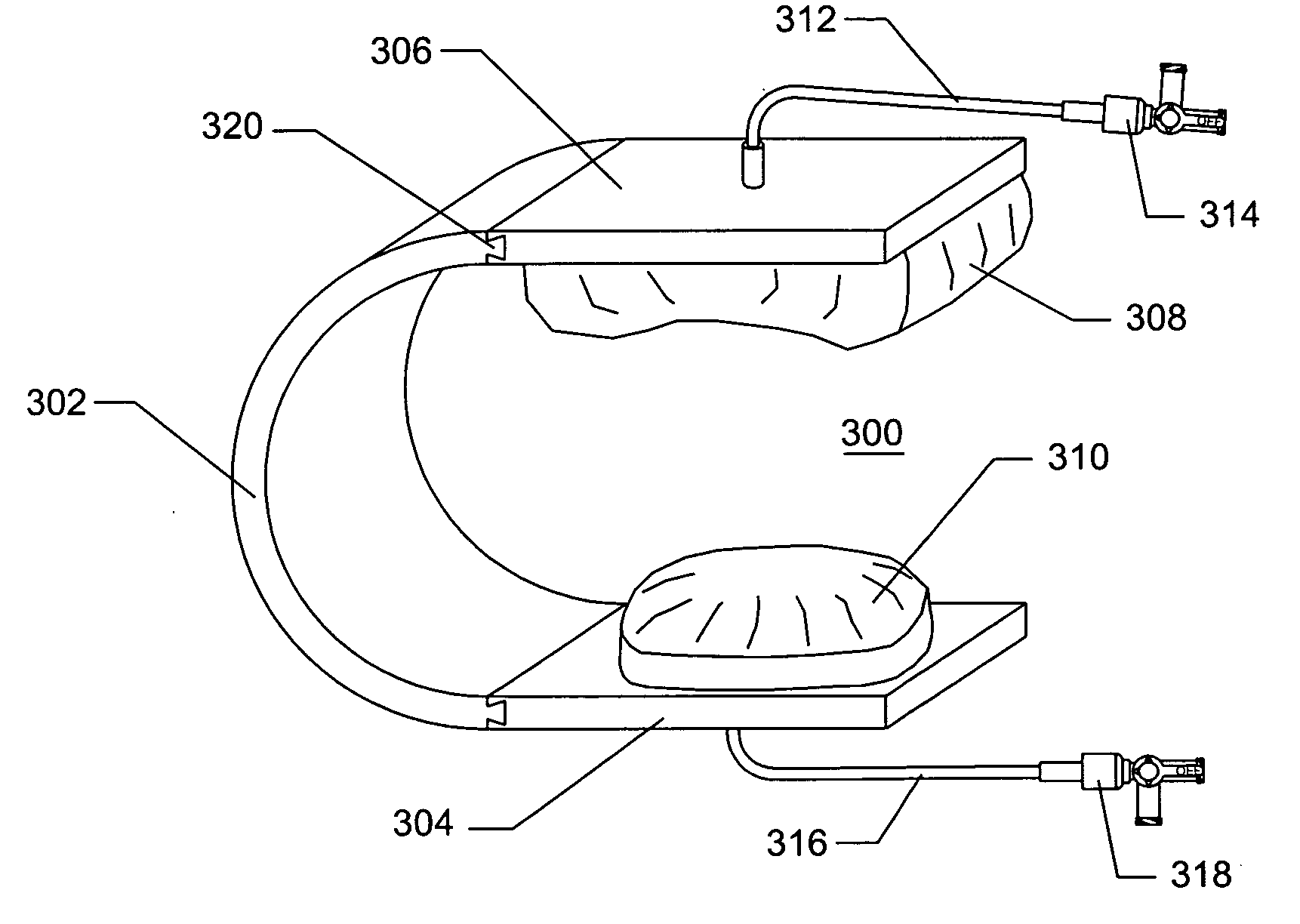
Surgical packing devices
InactiveUS20110028934A1Avoid lossImproved haemostatic packing devicesPlastersTourniquetsTrauma surgeryInjury mouth
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the body in regions such as the shoulder, pelvis, neck, or groin, where standard bandages are difficult to apply and where large blood vessels exist which can hemorrhage severely. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize packing pillows that are held in place by rigid structures that can cause the packing pillows to be brought into the wounds and be held in place while the packing pillows are inflated to fill the wounds, prevent bleeding, and tamponade hemorrhaging large blood vessels exposed therein.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
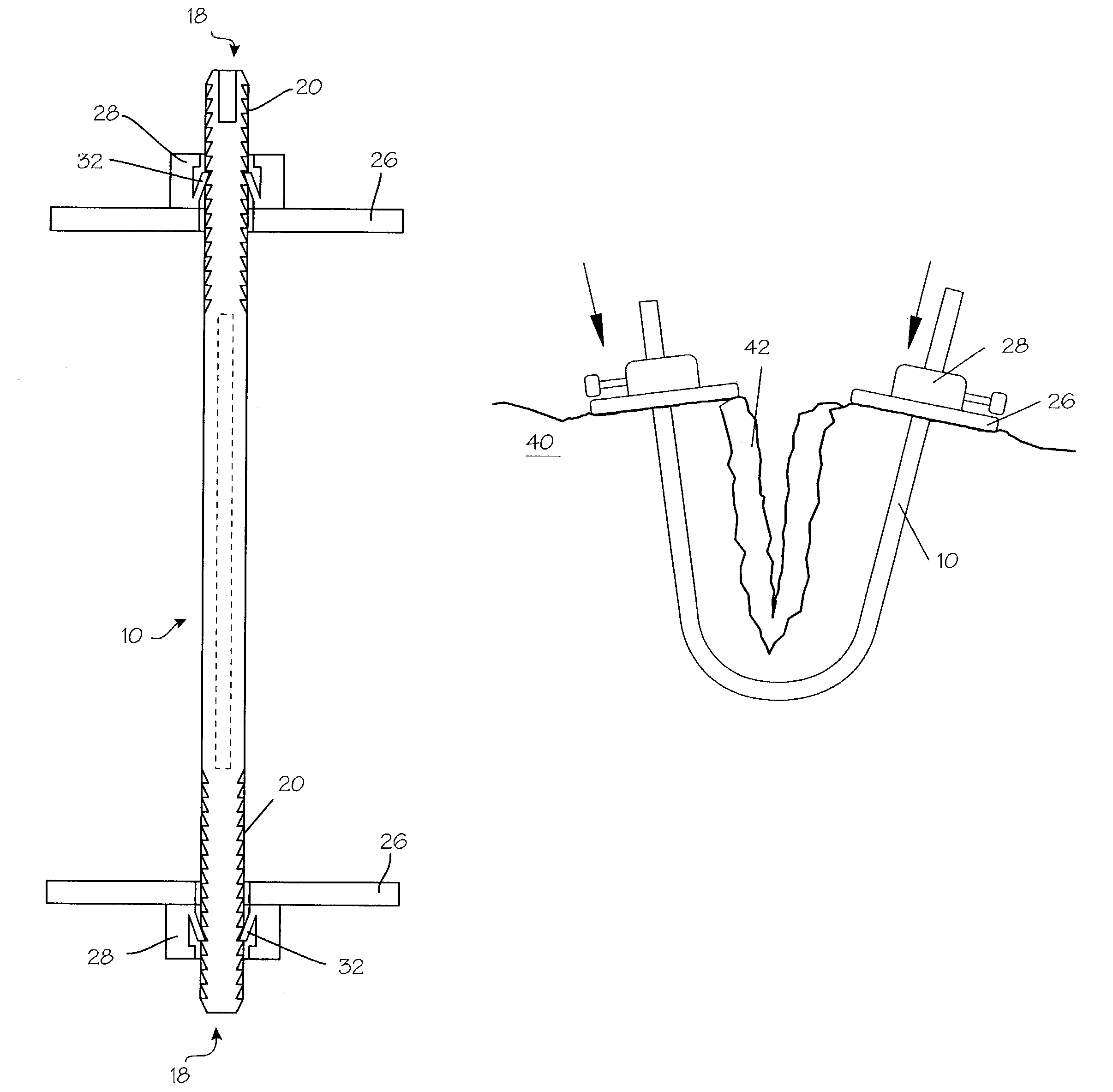
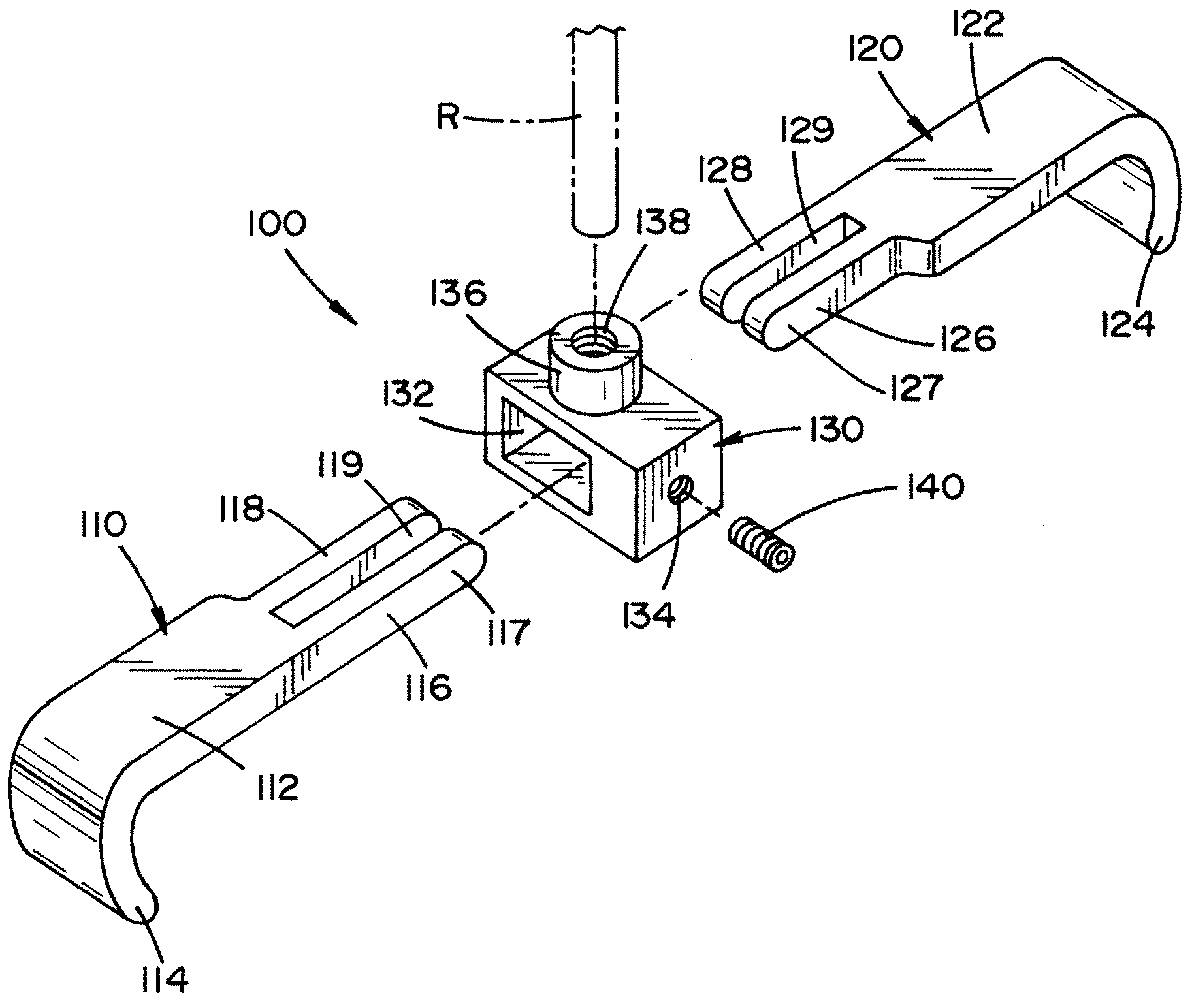
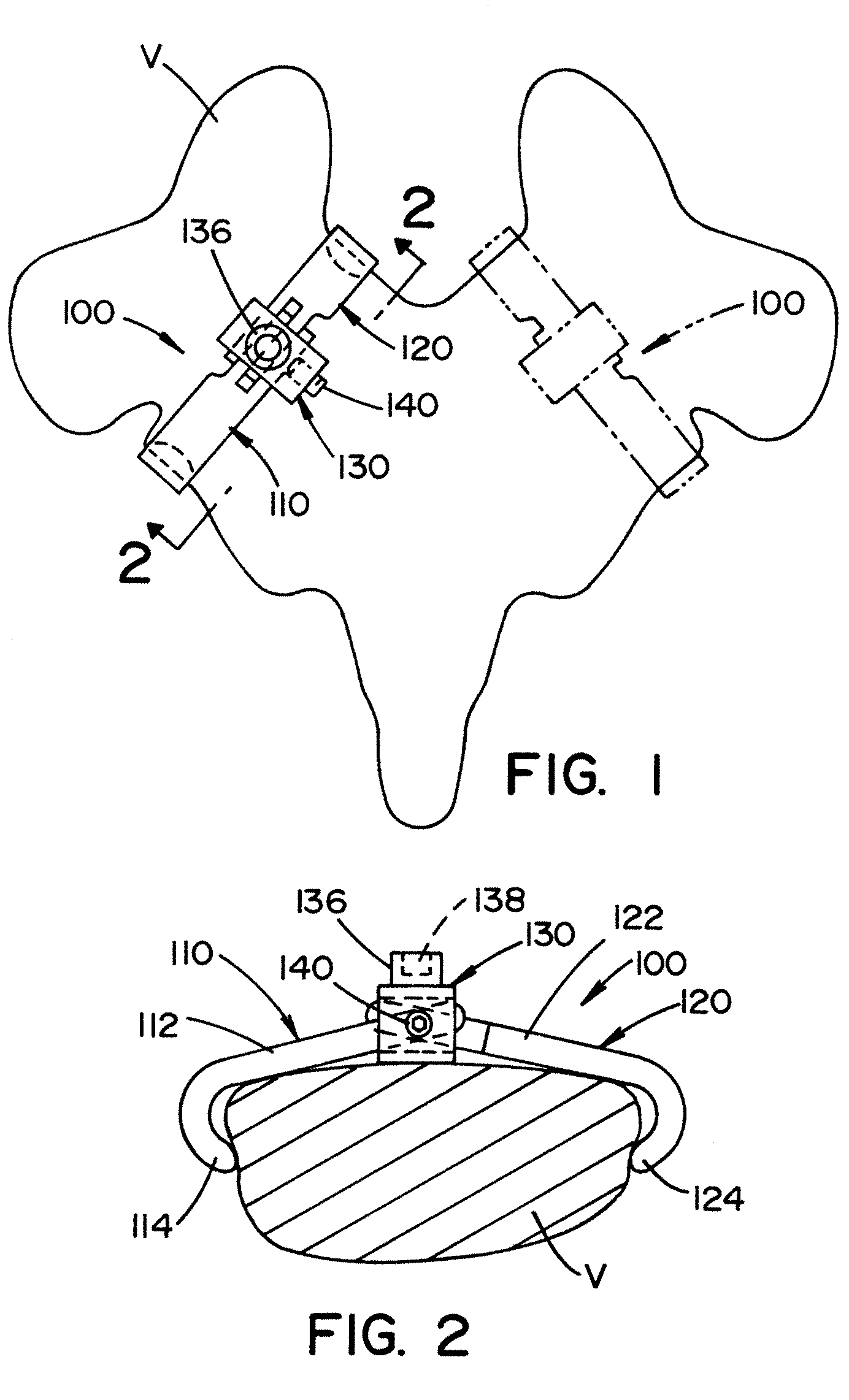
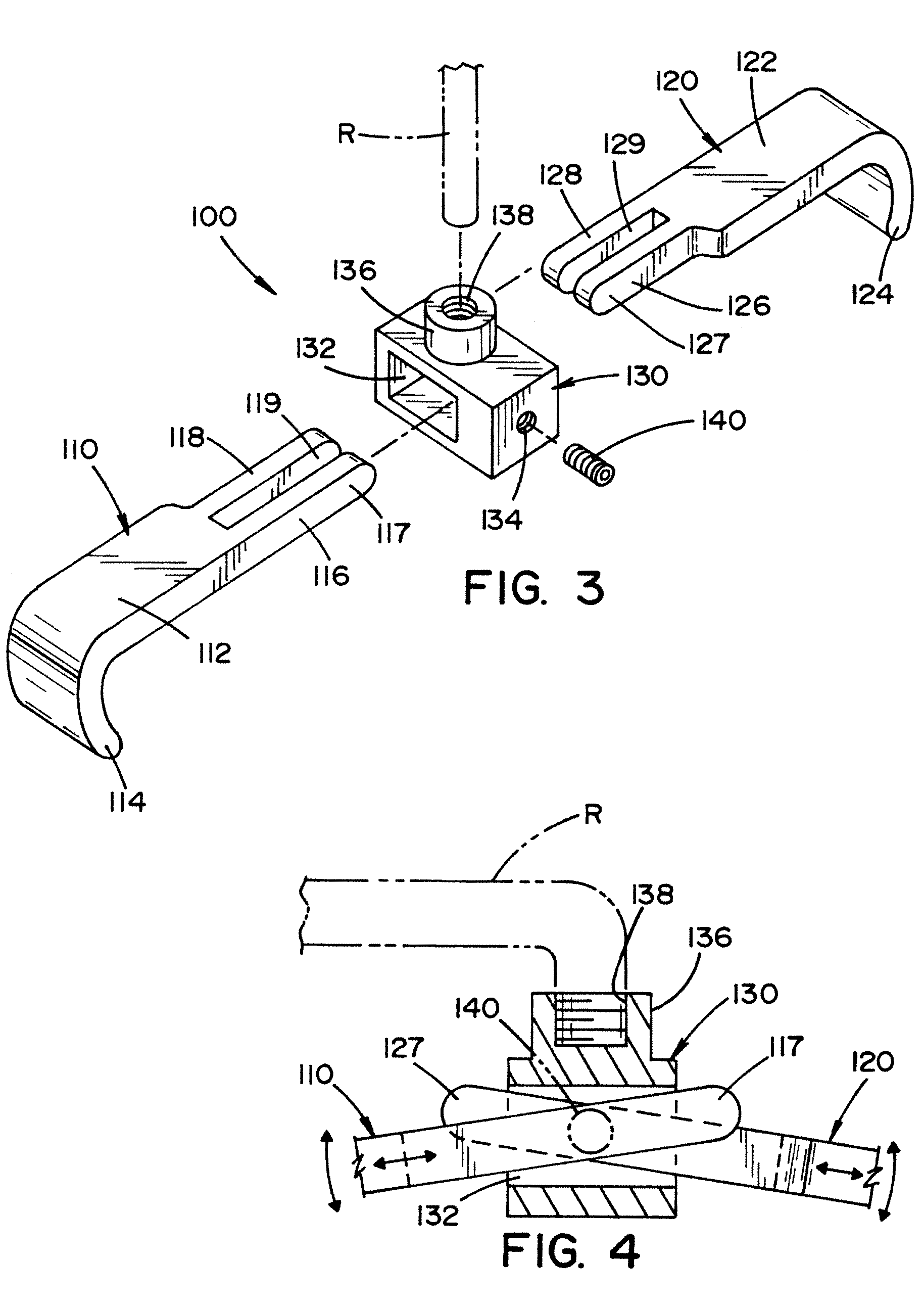
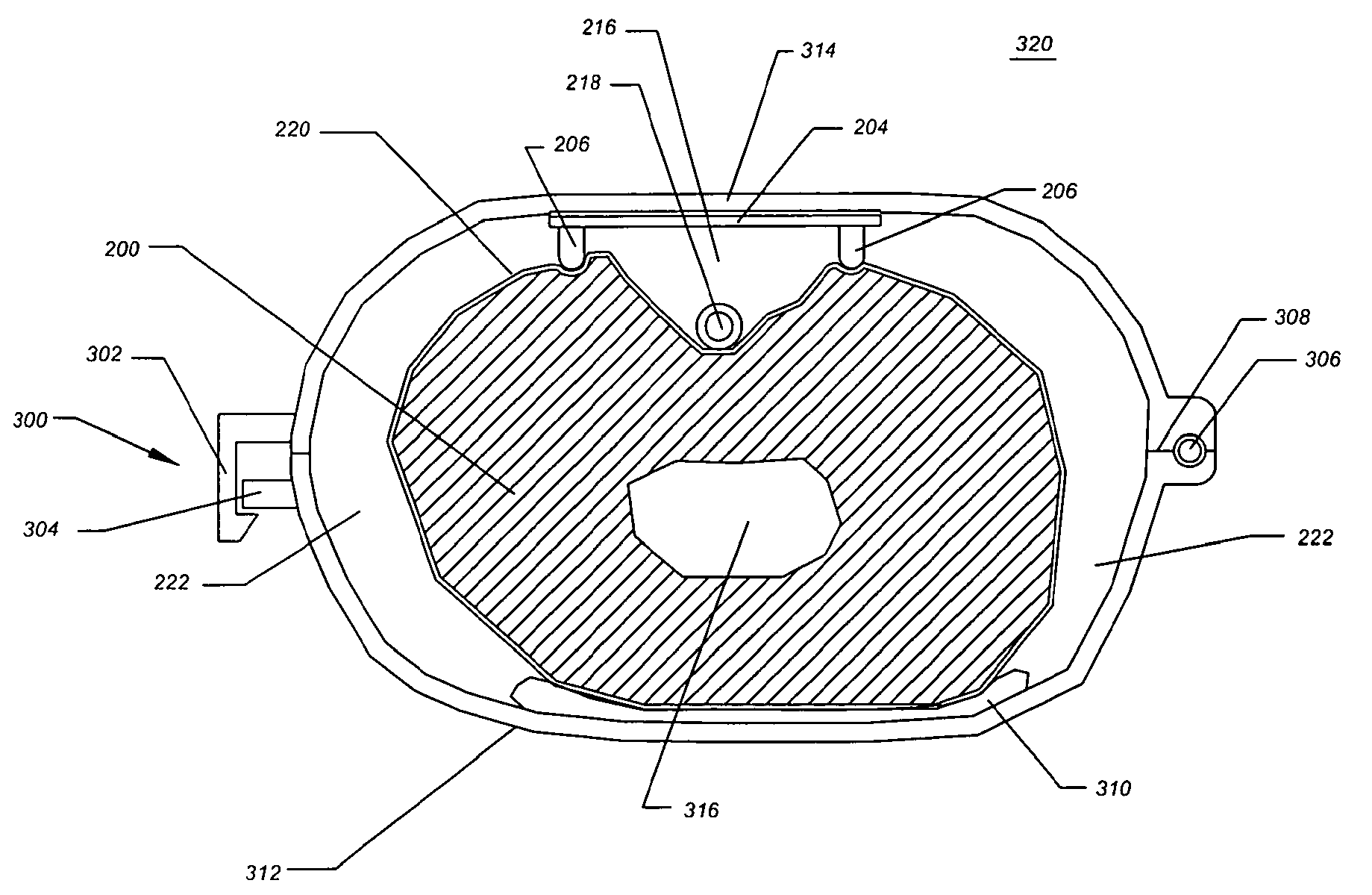
Trauma joint, external fixator and associated method
InactiveUS20070123856A1Shorten the timeSaving of surgeon ' timeInvalid friendly devicesFractureTrauma surgeryExternal fixator
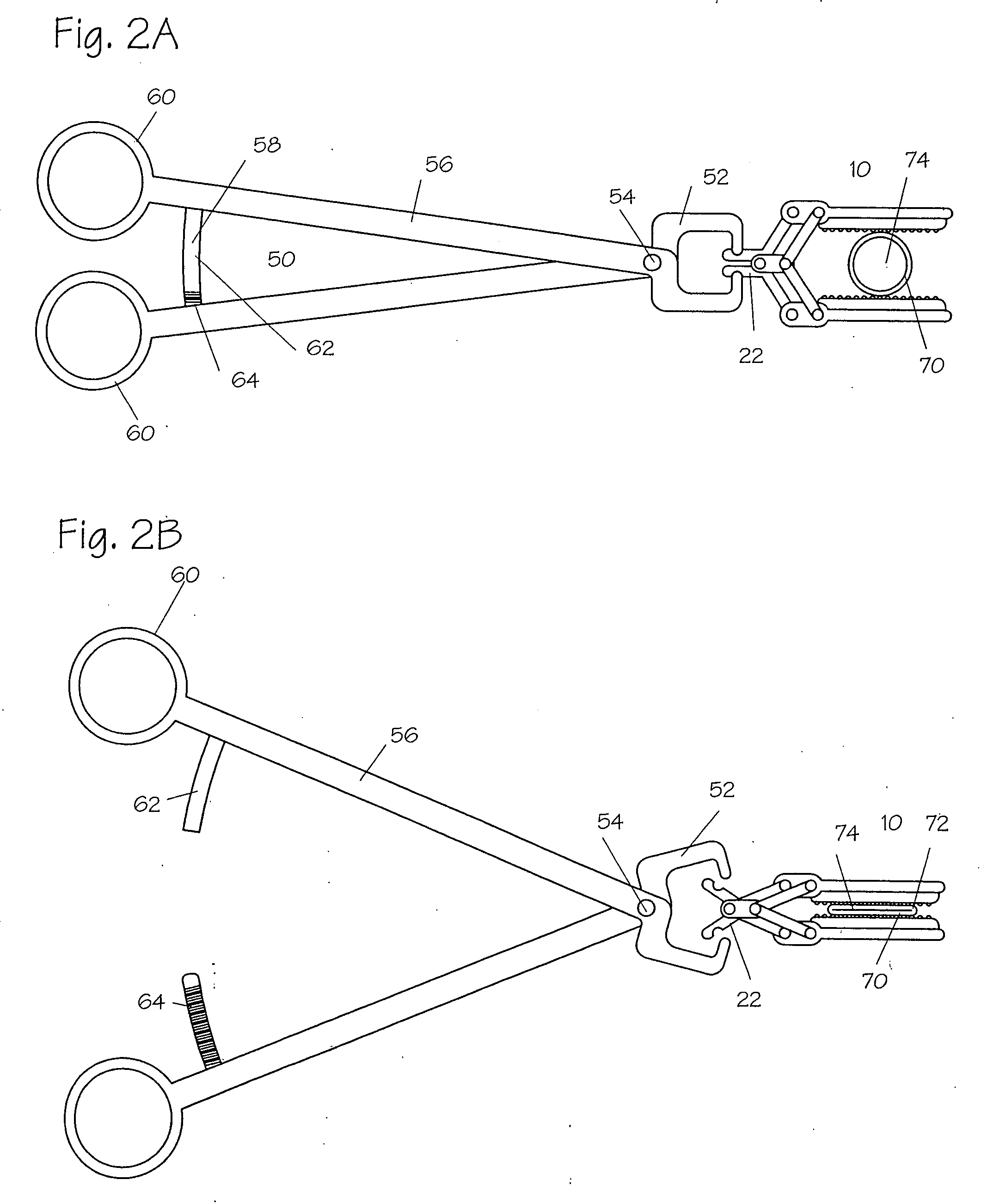
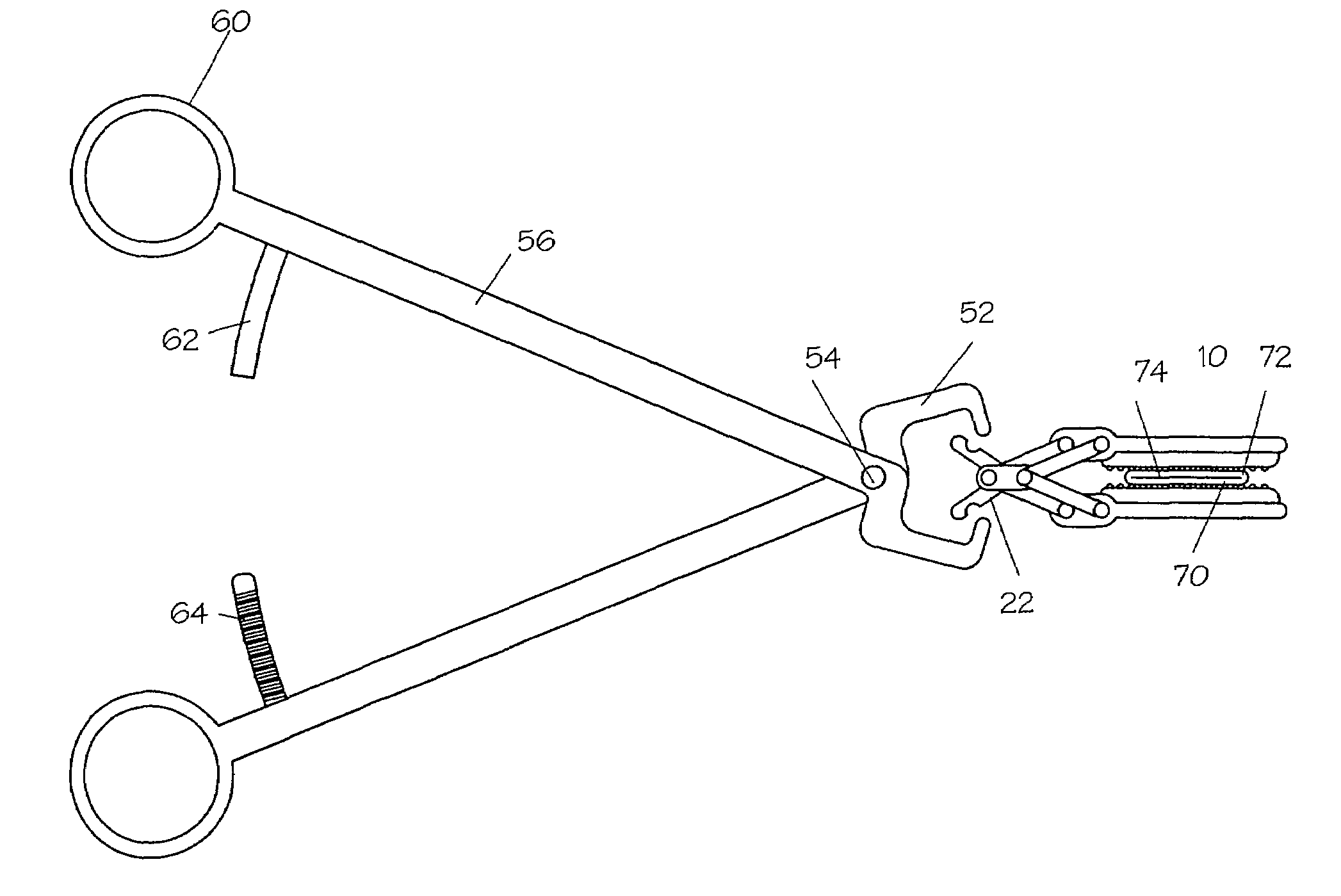
A device for use in an external fixator for use in trauma surgery for rigidly connecting a first object to a second object is provided. The device includes a body and a first articulating member for connecting the device to the first object. The first articulating member is lockable and un-lockable to the body to selectively provide articulation with and rigid connection to the body. The device further includes a second articulating member for connecting the device to the second object. The second articulating member is lockable and un-lockable to the body to selectively provide articulation with and rigid connection to the body. The body, the first articulating second and the second articulating member are adapted for simultaneous locking and unlocking to each other.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
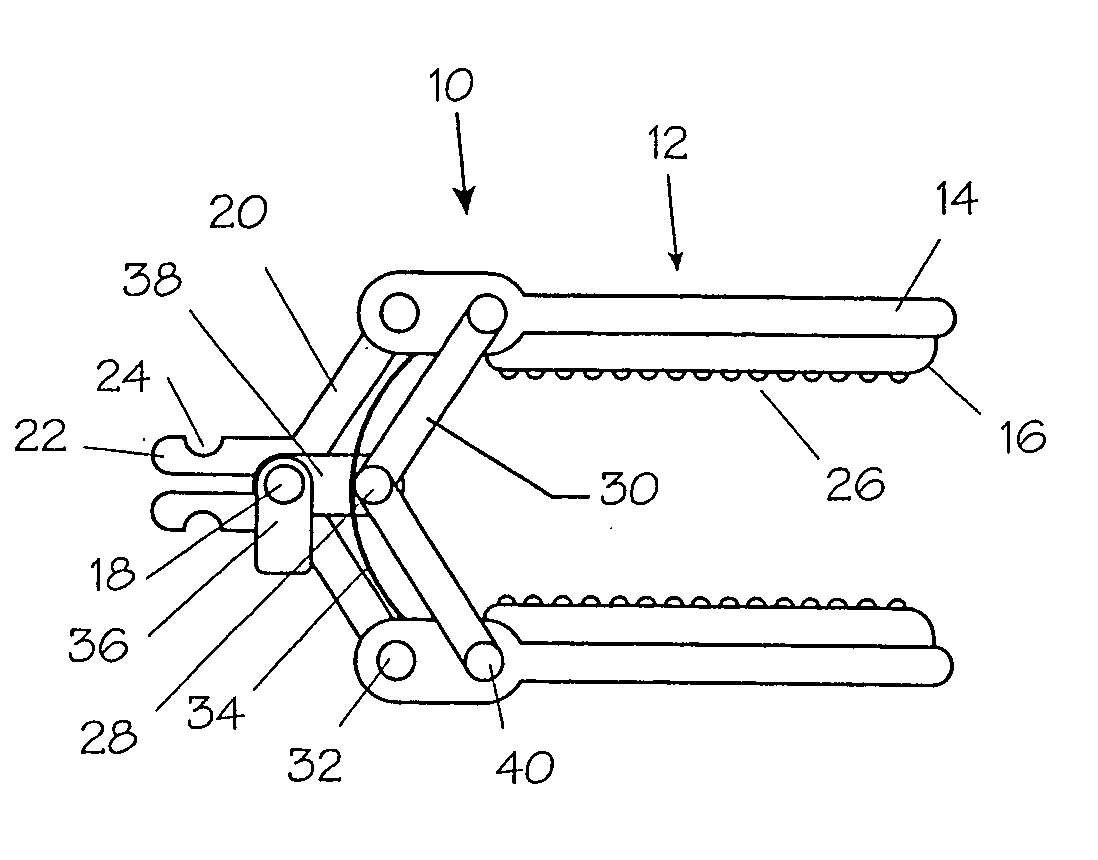
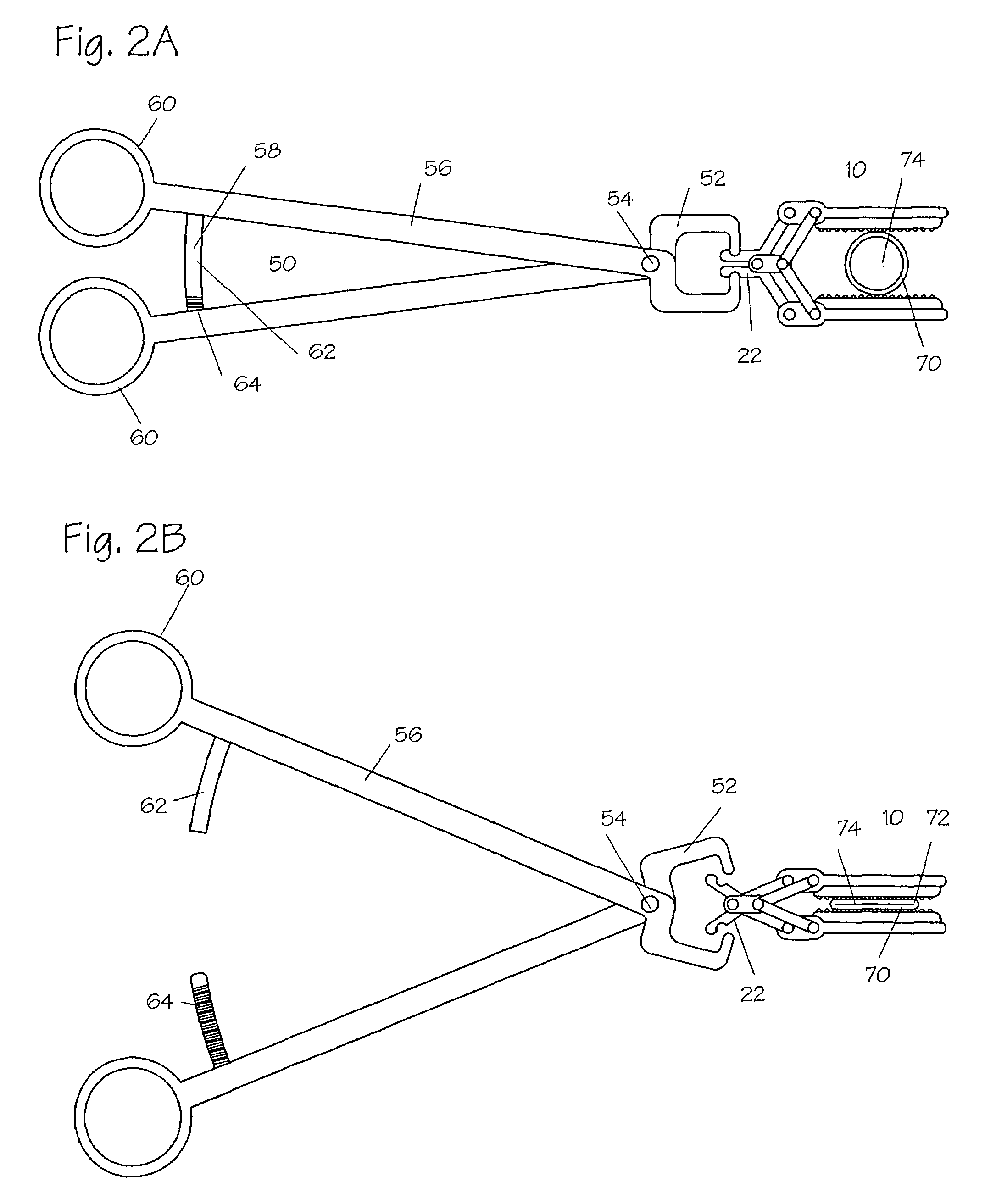
Vertebral pars interarticularis clamp a new spine fixation device, instrumentation, and methodology
InactiveUS7883532B2Improve the inconvenienceExtension of timeSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisTrauma surgerySpinal column
An improve spinal surgical implant used primarily in the posterior aspect of the spinal column for spinal reconstruction; revision surgery; deformity correction; and / or tumor surgery and / or trauma surgery of the cervical, thoracic and / or and lumbo-sacral spine.
Owner:SPINECO
Vertebral pars interarticularis clamp a new spine fixation device, instrumentation, and methodology
InactiveUS20060241591A1Improve the inconvenienceExtension of timeSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisTrauma surgerySpinal column
An improve spinal surgical implant used primarily in the posterior aspect of the spinal column for spinal reconstruction; revision surgery; deformity correction; and / or tumor surgery and / or trauma surgery of the cervical, thoracic and / or and lumbo-sacral spine.
Owner:SPINECO
Vertebral pars interarticularis clamp a new spine fixation device, instrumentation, and methodology
InactiveUS20110178552A1Improve the inconvenienceExtension of timeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnTrauma surgery
An improved spinal surgical implant used primarily in the posterior aspect of the spinal column for spinal reconstruction; revision surgery; deformity correction; and / or tumor surgery and / or trauma surgery of the cervical, thoracic and / or lumbo-sacral spine.
Owner:SPINECO
Method and apparatus for rapid deployment chest drainage
InactiveUS20050234390A1Risk minimizationMaintains sterility and cleanlinessCannulasInfusion syringesTrauma surgeryProtection sex
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving chest drainage in humans or other animals. Chest drainage is often required following traumatic injury or surgery. The devices and methods disclosed herein are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting. The devices utilize a chest tube with a cutting distal end and a central blunt trocar. The blunt trocar or obturator shields the sharp cutting distal end of the chest tube until controllably retracted. Once the blunt trocar or obturator is retracted, the chest tube is advanced out through its sterile, protective package and into the patient. The blunt trocar is advanced back into its position to shield the sharp tip of the chest tube during patient insertion. The chest tube also includes a hold-down mechanism that is created by an adhesive seal to the patient's chest and ribbons or straps that are wrapped around the chest tube once it is correctly positioned. The straps include adhesive ends to grip the chest tube once the straps are in place.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
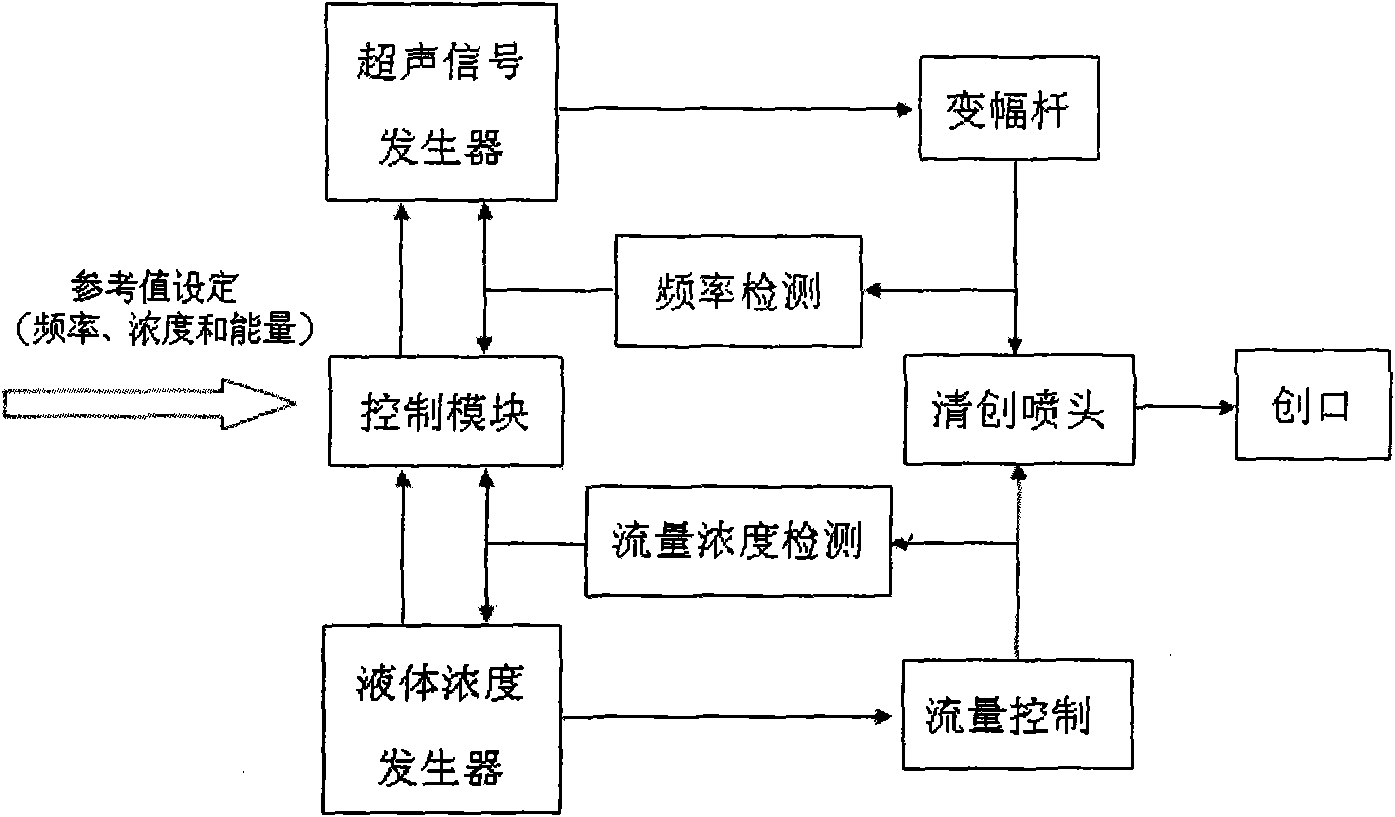
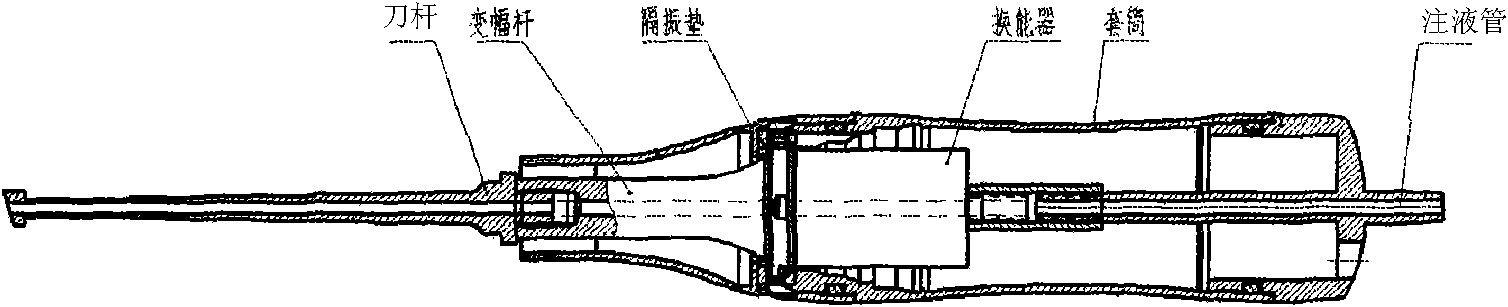
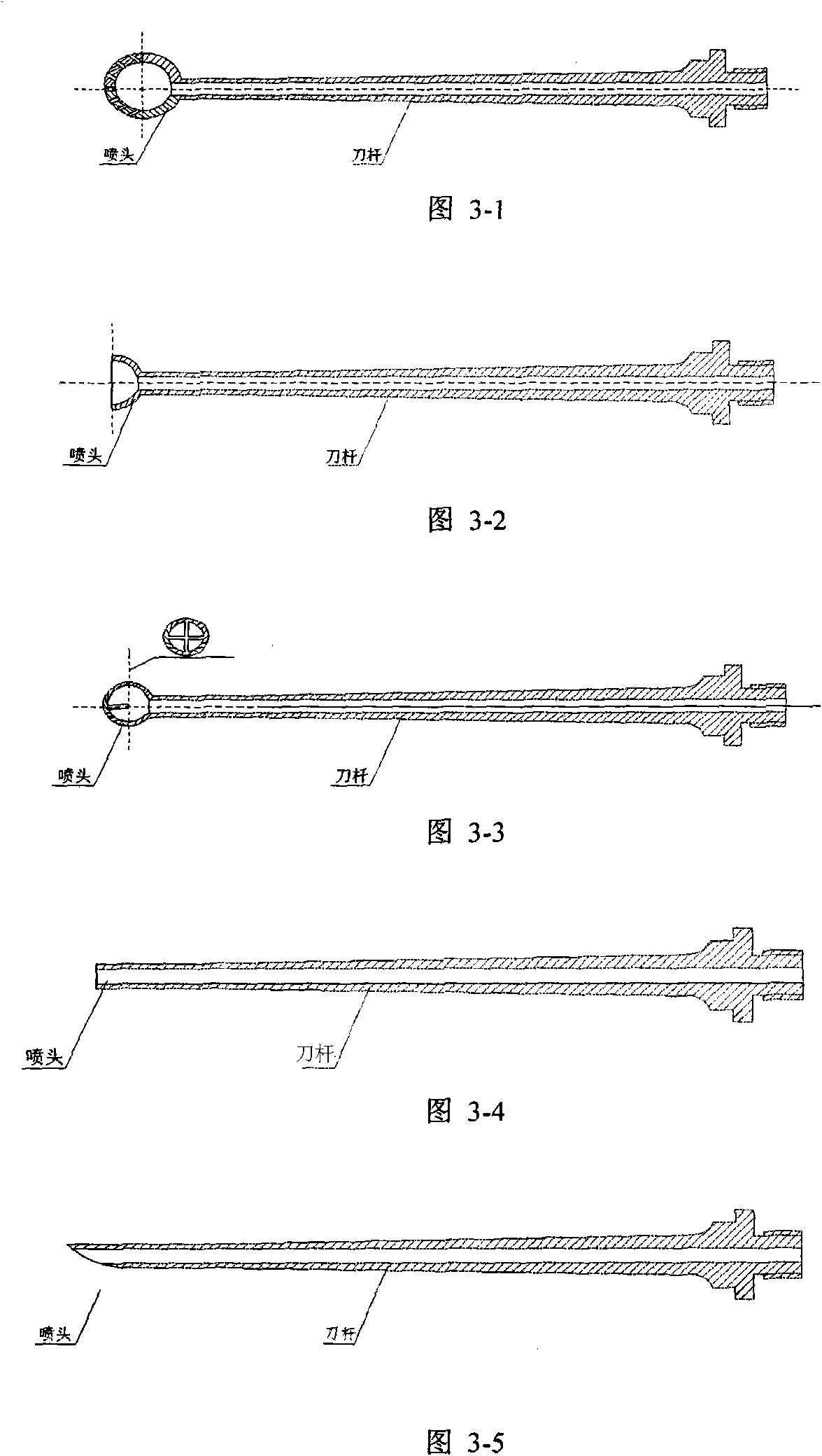
Ultrasonic debridement surgical system
InactiveCN101632849AControl concentrationControl flowMedical applicatorsFluid jet surgical cuttersTrauma surgeryTransformer
The invention relates to an ultrasonic debridement surgical system which comprises a main machine, a debridement handle and a backpedaling brake. The surgical system is characterized in that the main machine comprises an ultrasonic signal control system and a fluid concentration / rate control system, wherein the ultrasonic signal control system comprises an ultrasonic signal generator and a frequency measuring and controlling device; the fluid concentration / rate control system comprises a fluid concentration generator and a rate / concentration measuring and controlling device; and the debridement handle comprises a transducer, an amplitude transformer and an ultrasonic debridement tool bar. By controlling the concentration and the rate of flushing fluid and the size of ultrasonic energy, the system can effectively perform debridement according to patient's condition, and is convenient for different trauma operations.
Owner:张毓笠 +2
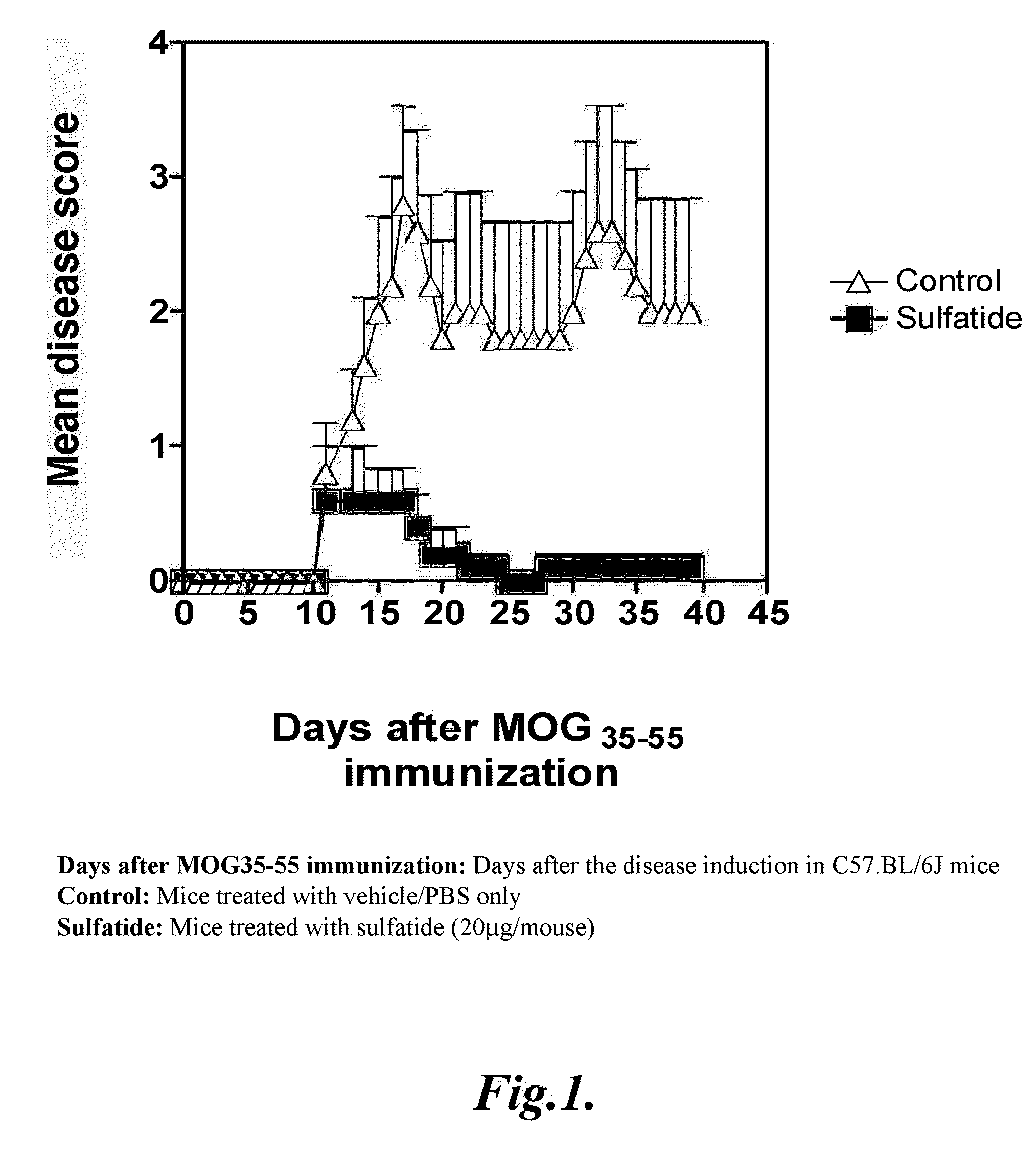
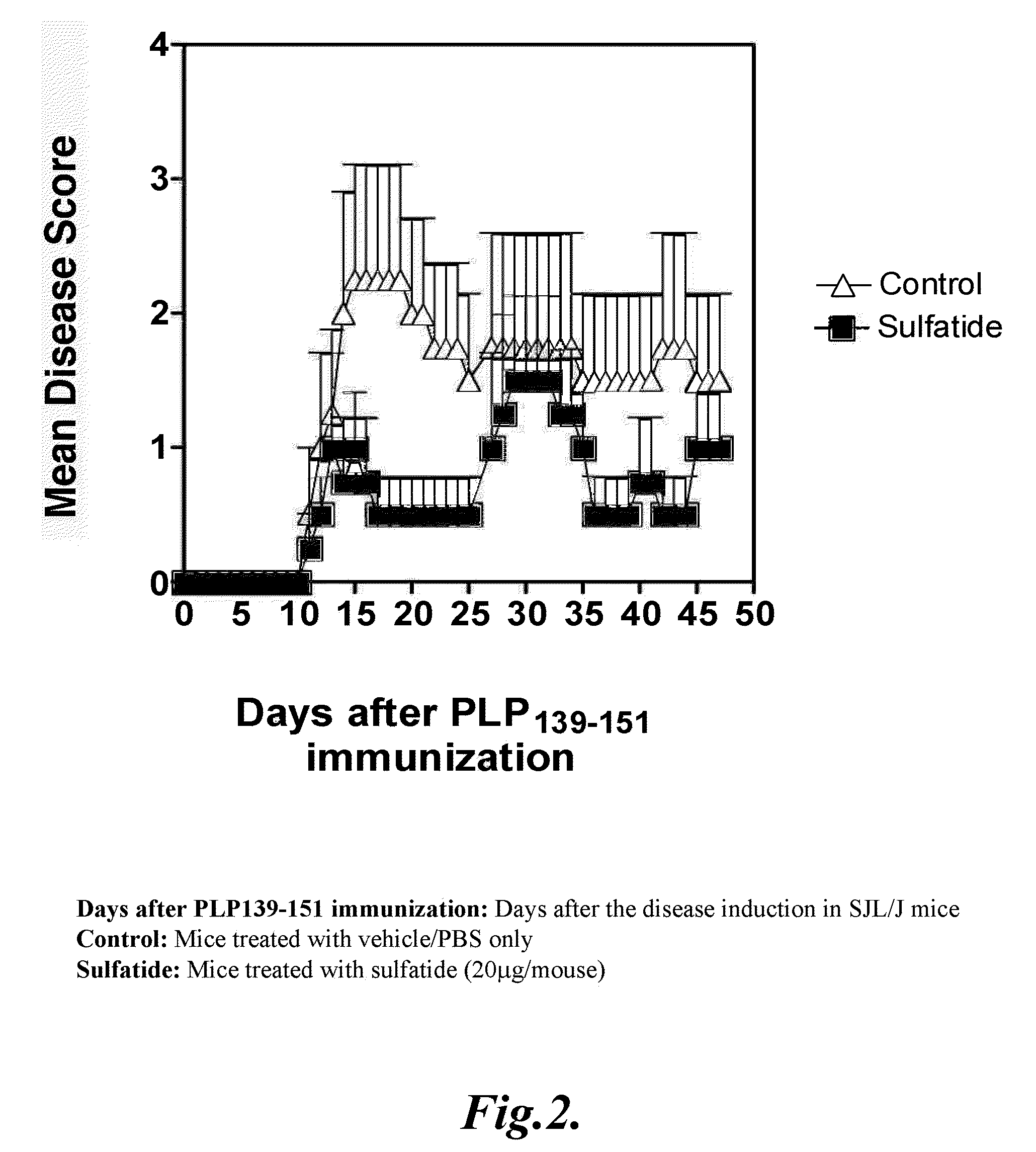
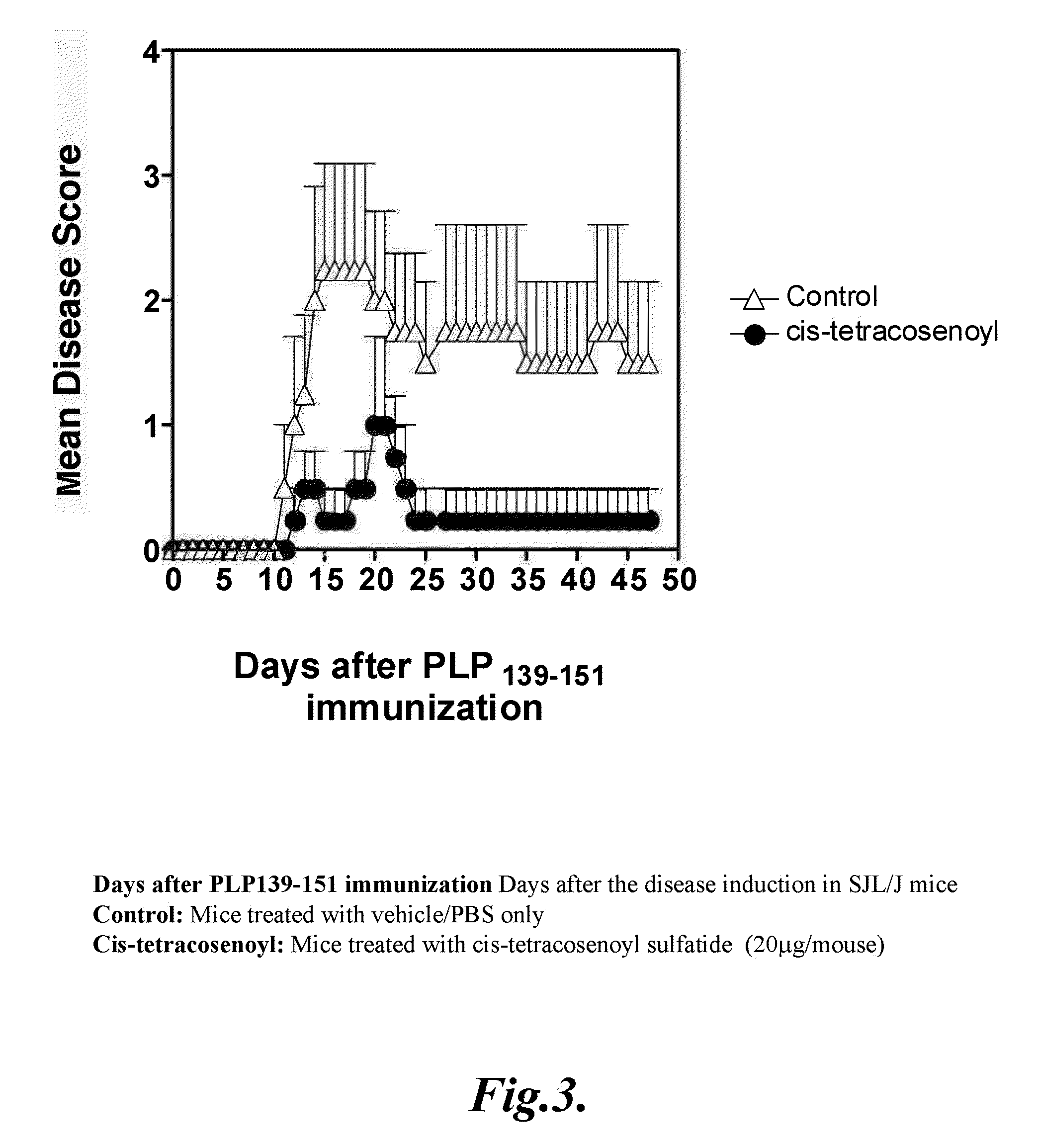
Prevention of hepatic ischemic reperfusion injury by administration of sulfatides
Hepatic ischemic reperfusion injury is a major complication of liver transplantation, resectional hepatic surgeries, trauma surgery and shock. Disclosed herein are methods for the prevention and treatment of ischemia and reperfusion injury with the administration of sulfatides. Also disclosed herein are methods of preventing and treating hepatic reperfusion injury by administering an amount of a sulfatide to the body of a patient effective to reduce or prevent the symptoms of the injury.
Owner:CHATURVEDI VIPIN KUMAR
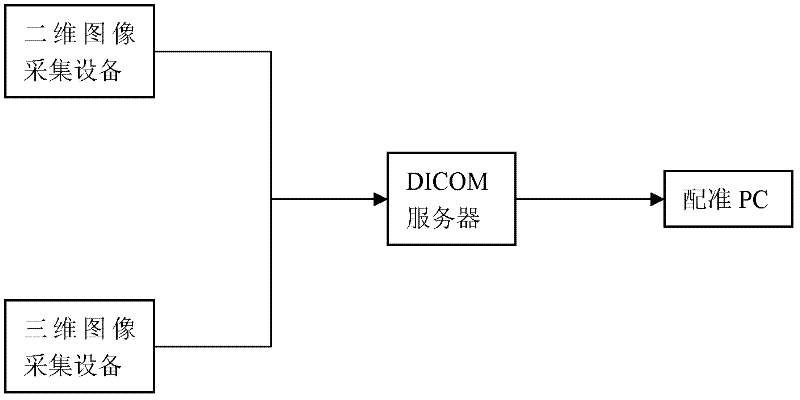
Fourier-Mellin domain based two-dimensional/three-dimensional image registration method
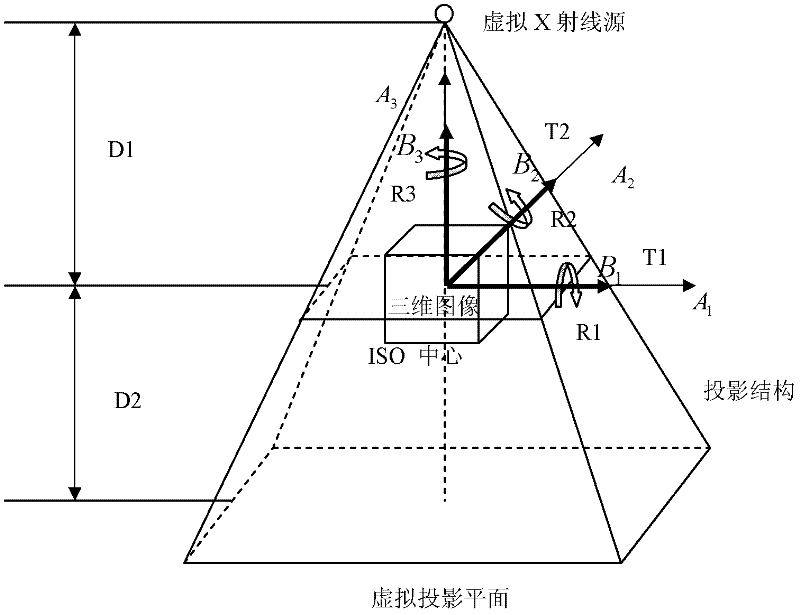
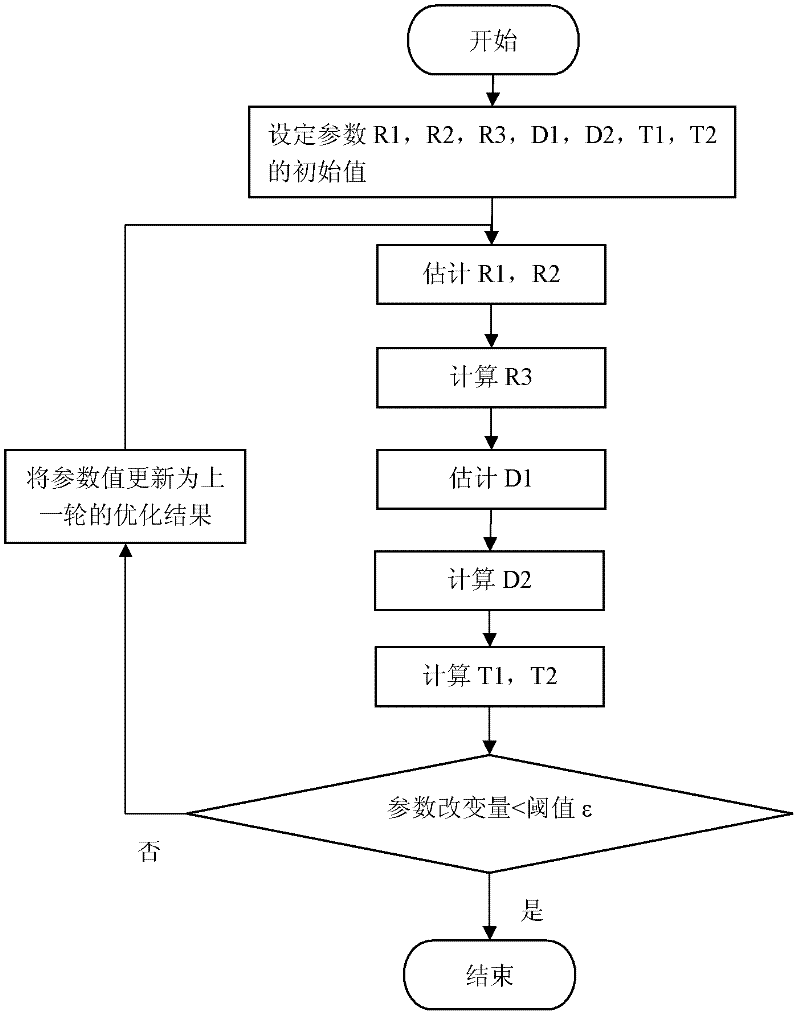
The invention discloses a Fourier-Mellin domain based two-dimensional / three-dimensional image registration method, which belongs to the field of medical image registration. The method can be applied to bone trauma surgery navigation systems, and used for associating a preoperative planning with intraoperative three-dimensional images so as to achieve the purpose of guiding an operation. The method is implemented through the following steps: by using the scale of images in a Fourier-Mellin domain, rotating and translating the coupling degree among invariably-separated to-be-optimized parameters; according to an estimated out-of-plane rotation parameter, calculating an in-plane rotation parameter; estimating the distance between an X ray and a three-dimensional image; estimating the distance between the three-dimensional image and a receiver; and calculating an in-plane translational sequence so as to carry out registration. The two-dimensional / three-dimensional image method disclosed by the invention lays a foundation for the reconstruction of preoperative data in intraoperative three-dimensional images.
Owner:北京格镭信息科技有限公司
Method and apparatus for solid organ tissue approximation
InactiveUS20070255315A1Easy to optimizeEasy and fast applicationForeign body detectionSurgical veterinaryTrauma surgeryParenchyma
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in solid visceral wounds. Such devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery or military setting. In such cases, the patient may have received trauma to the abdominal viscera. The devices utilize flexible, variable depth transfixing bolts that penetrate the viscera. These bolts are pulled tight to bring the tissue into apposition and hold said tissue in apposition while the wound heals. These bolts, or soft tissue rivets, overcome the limitations of sutures that are currently used for the same purposes. The bolts come in a variety of lengths and diameters. Since the bolts are flexible, the curvature can be adjusted by the surgeon. The devices are flexible, bendable, and conformable in their wet or dry state. They can be used either straight or configured in a broad range of curvatures to suit the needs of various pathologies. The bolts include pressure plates that are capable of exerting compressive pressure over broad areas of visceral wounds without causing tearing of the friable parenchyma. The bolts may be placed and removed by open surgery or laparoscopic access. The bolts can be placed into tissue where both sides of the bolt are exposed, or the bolts can be placed blindly into tissue where the bolt does not protrude out of the tissue at its distal end.
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
Surgical packing devices
InactiveUS8357831B2Avoid lossImproved haemostatic packing devicesPlastersTourniquetsTrauma surgeryInjury mouth
Owner:DAMAGE CONTROL SURGICAL TECH
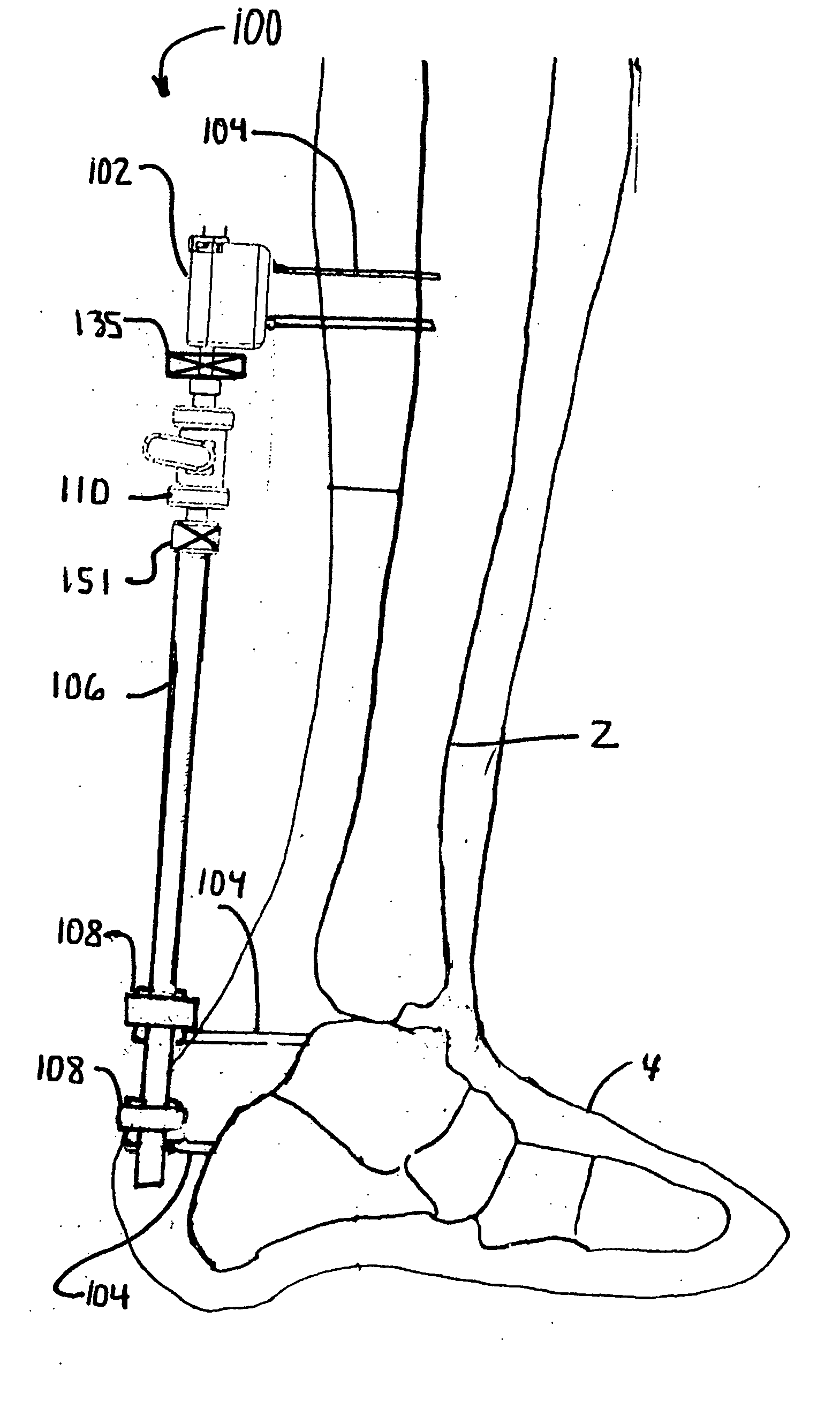
Boot for limb and ankle trauma surgery using modular distractor
A boot assembly apparatus, system and method for elevating the patient's limb when using a manual distractor unit is mounted upon a support frame attached to an operating table side rail. A foot strap is attached to the boot assembly apparatus and to the patient's ankle with a patient's knee support pad, extending from the distractor unit, is positioned under the patient's knee to provide traction to the patient's ankle, which is secured to the support frame. The boot assembly apparatus may be formed with a plurality of attachment points for the foot strap so as to provide improved access to the ankle area with advantages of allowing additional types of procedures a surgeon could perform on the patient and / or the ability of the surgeon to access the ankle area and lower leg.
Owner:INNOVATIVE MEDICAL PRODS
Method and apparatus for hemostasis
InactiveUS7943810B2FlexibilityDifferent compressibilityNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersTrauma surgeryTourniquet time
Devices and methods are disclosed for achieving hemostasis in patients who have received skin-penetrating wounds to the periphery, including the head, arms, and legs. Such haemostatic packing devices and methods are especially useful in the emergency, trauma surgery, or military setting. The devices utilize fluid impermeable barriers surrounded by exterior dams and pressure to achieve tamponade and hemostasis, primarily by exertion of force to hold the dams against the skin surrounding a wound. The devices are capable of serving as carriers for thrombogenic, antimicrobial or antipathogenic agents. The devices do not require the use of adhesives to work as they are attached to the patient using mechanical locking devices. Peripheral haemostatic packing devices include optional adhesive hemostatic barriers to attach at least a portion of the device to the skin or to assist with initial coupling of a hold-down strap to another strap using a more secure mechanical lock. The peripheral hemostatic packing system does not completely surround the extremity having the wound and therefore do not cause a tourniquet effect. The peripheral hemostatic packing system preferably is held against the skin surrounding a wound by a force that is generally unidirectional and substantially perpendicular to the plane in which the skin of the wound resides.
Owner:BUCKMAN ROBERT F +2
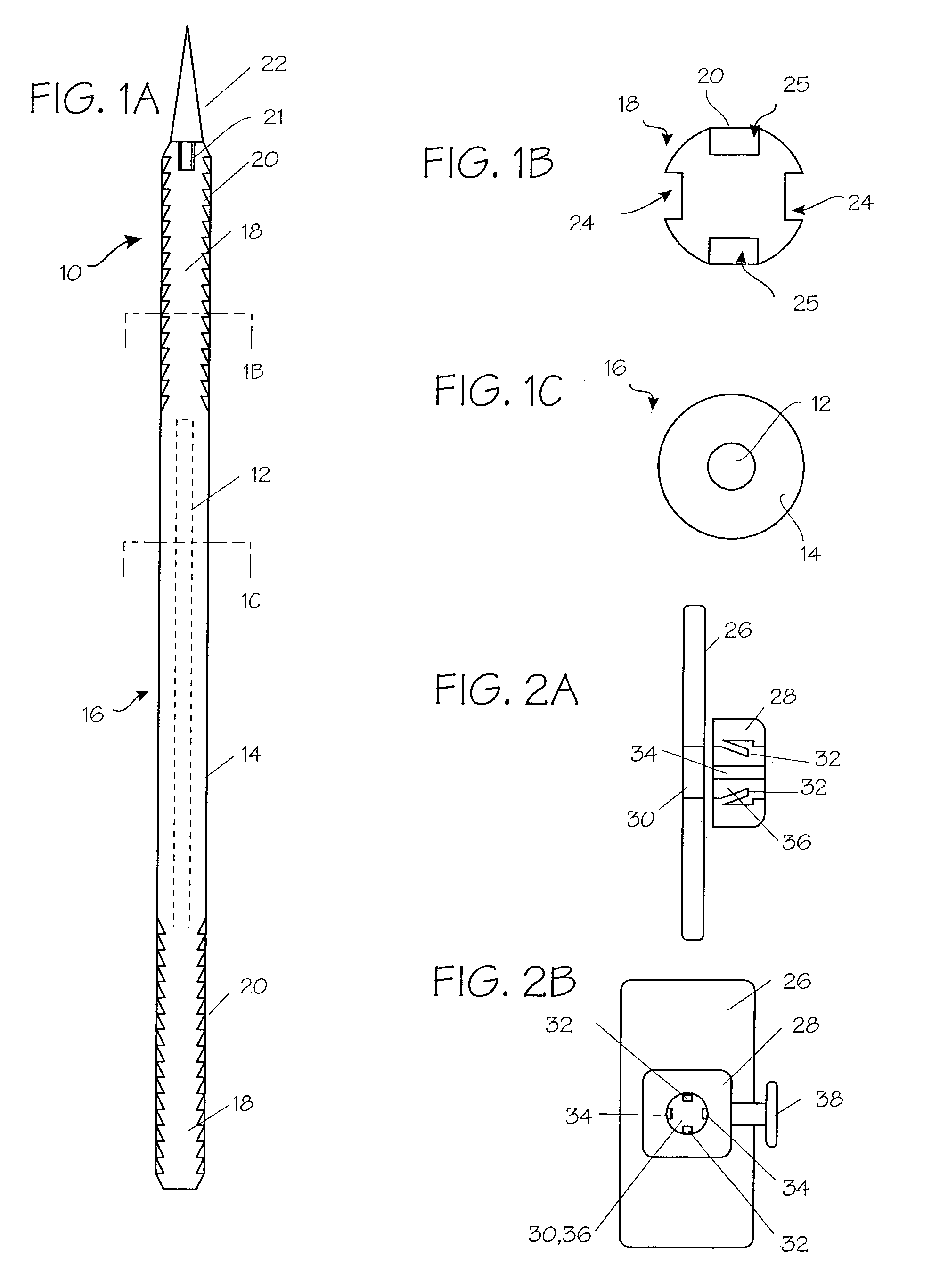
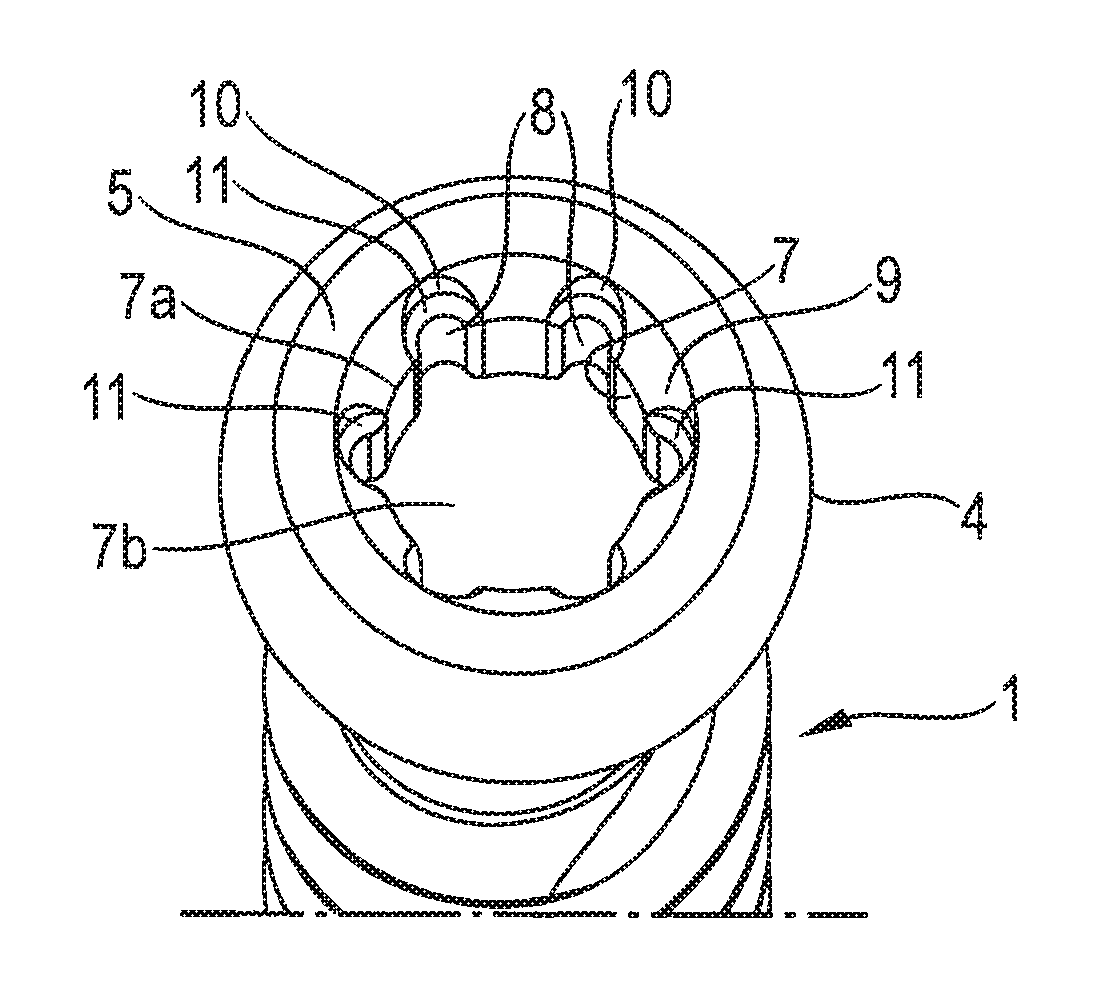
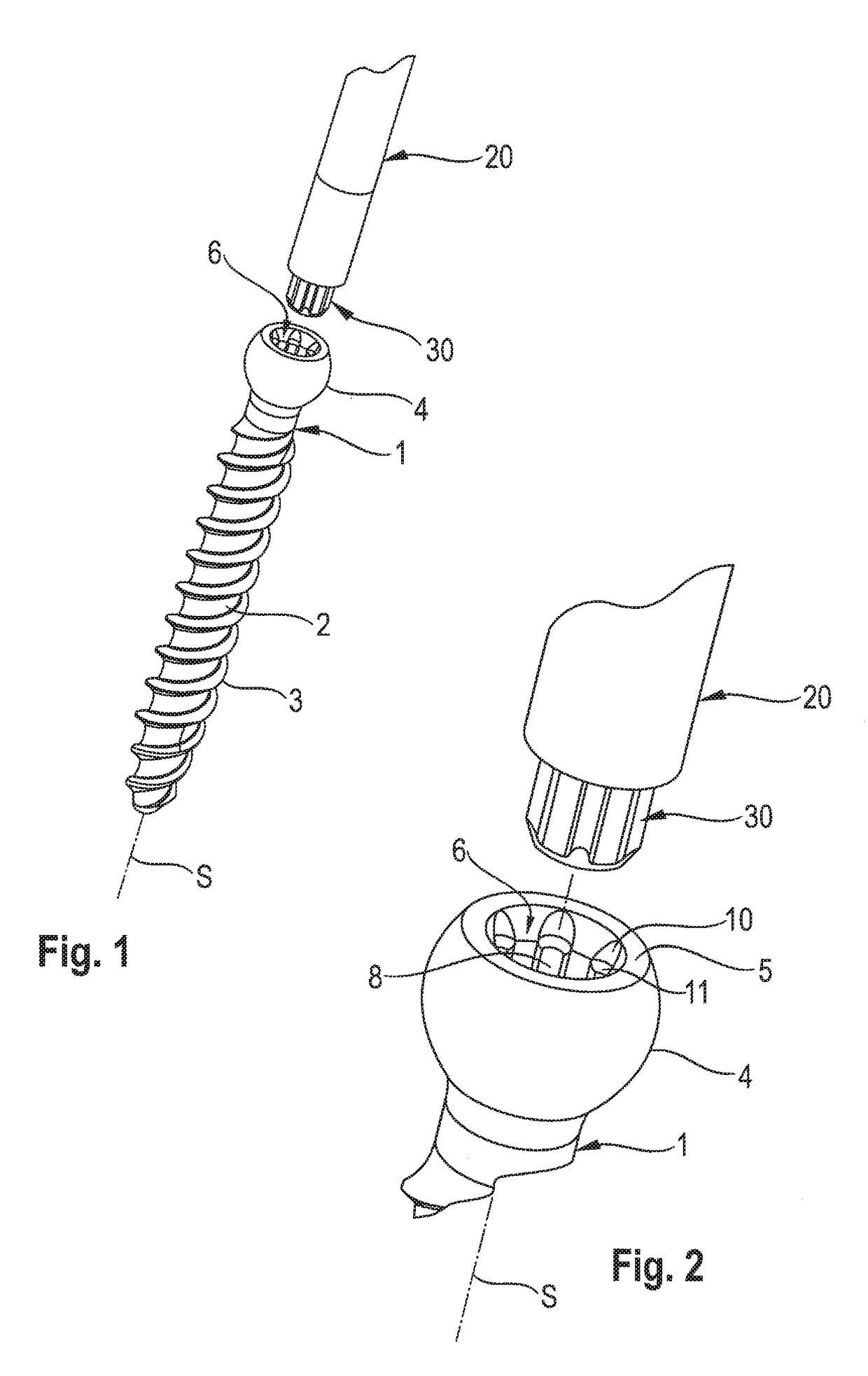
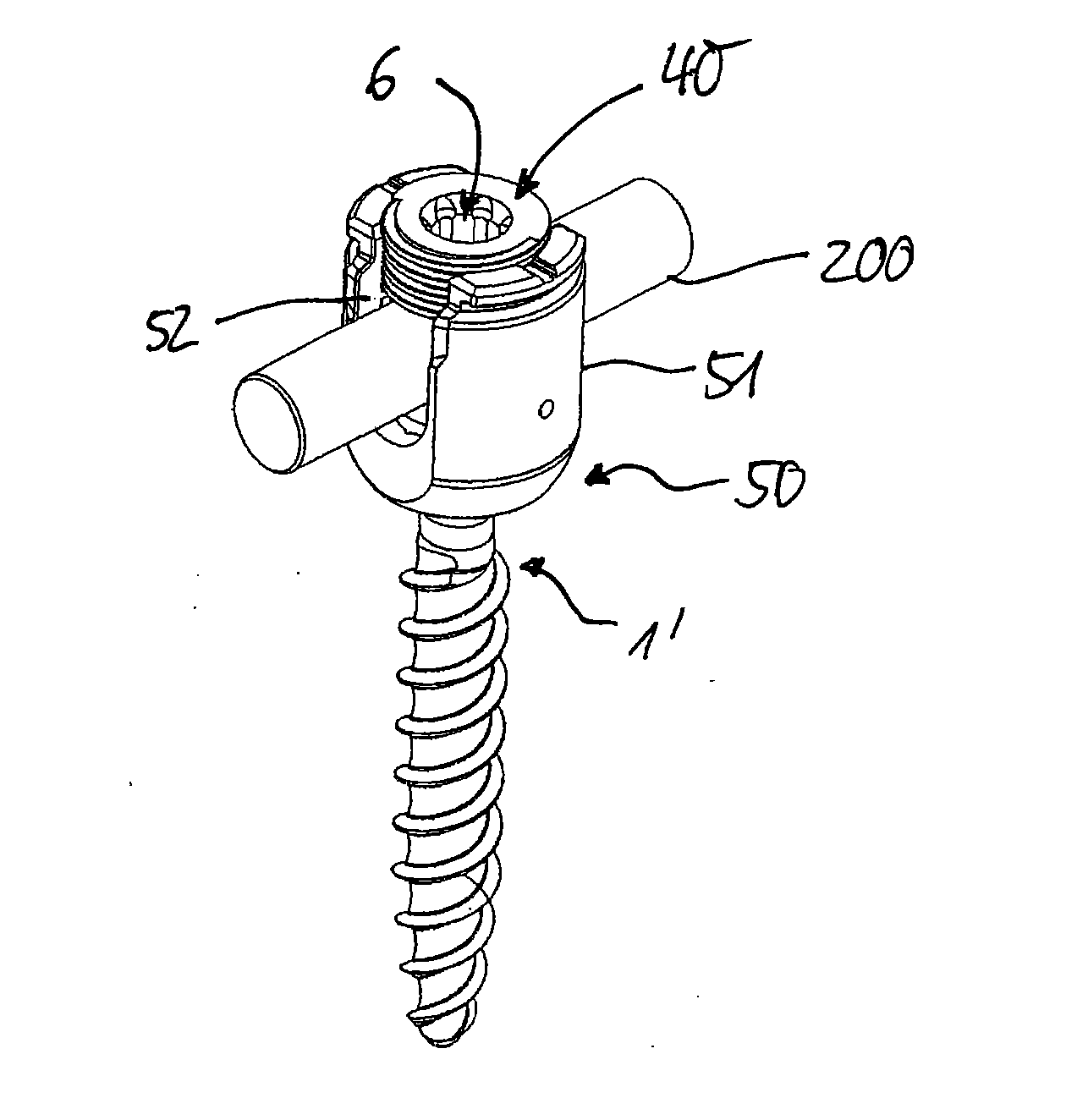
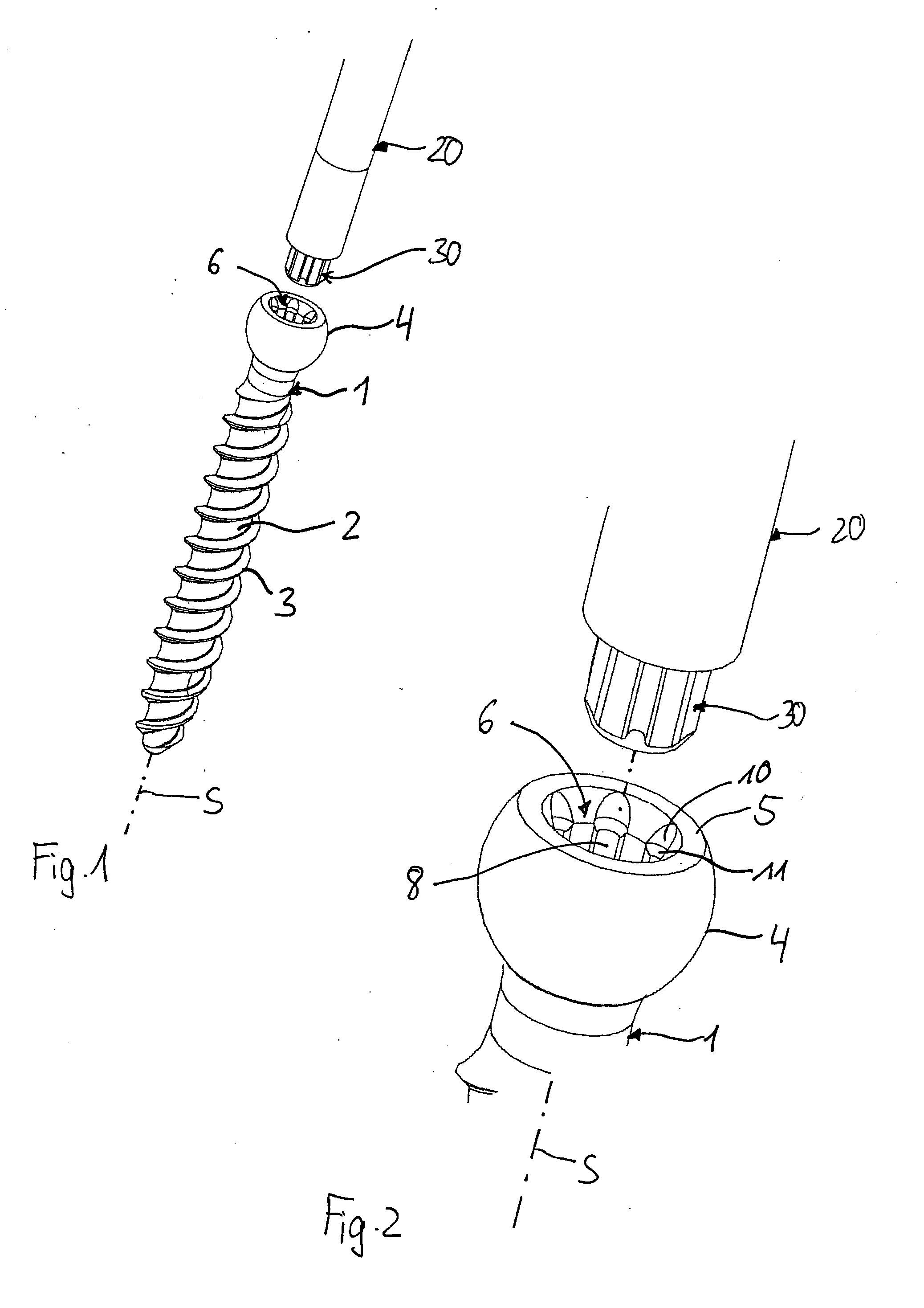
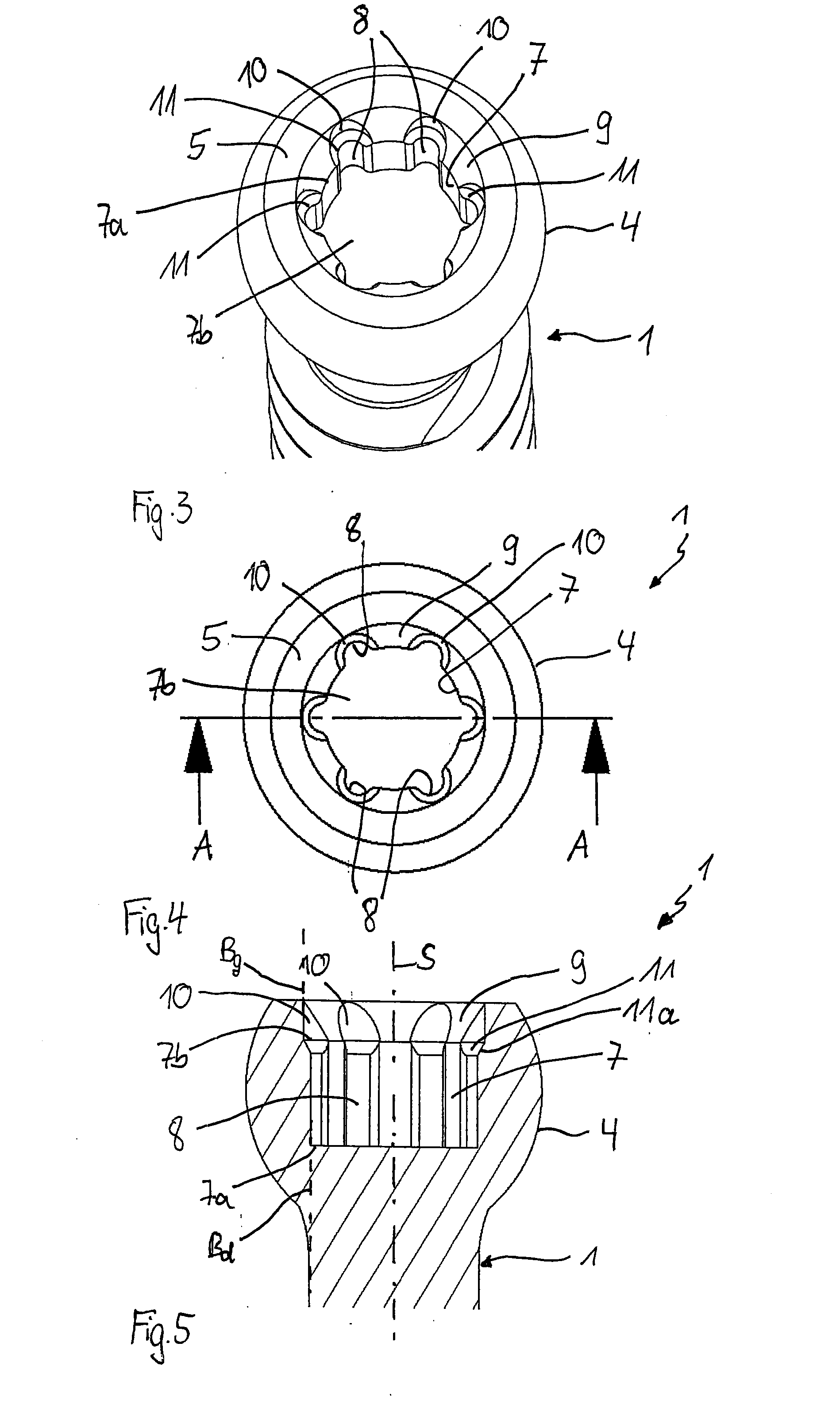
Screw element for use in spinal, orthopedic or trauma surgery and a system of such a screw element and a screw driver adapted thereto
ActiveUS9867639B2Precise positioningEasy to insertInternal osteosythesisFastenersTrauma surgeryEngineering
A screw element includes a screw axis, a shank for inserting in a bone, and a drive portion for engaging a screw driver. The drive portion includes a first wall defining a first recess and a second wall defining a second recess. Drive grooves are formed in the first wall and extend parallel to the screw axis. The second wall extends axially from a free end portion of the screw element to the first wall and has an inner diameter that continuously increases from the first wall towards the free end portion. A plurality of guide grooves are formed in the second wall at circumferential positions corresponding respectively to circumferential positions of the drive grooves. The guide grooves extend further radially from the screw axis than the drive grooves and guide the screw driver from the free end portion of the screw element to the drive grooves.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
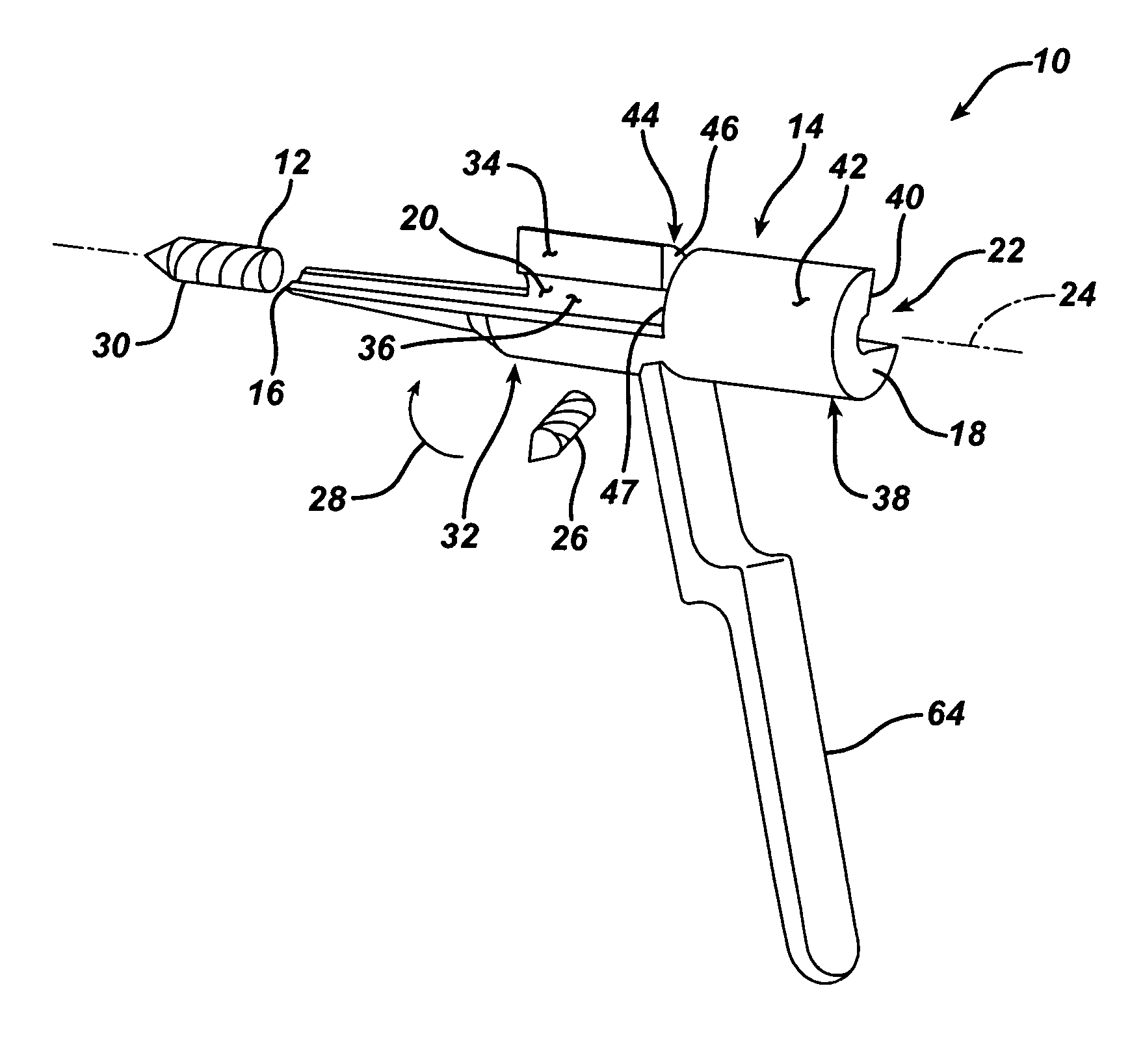
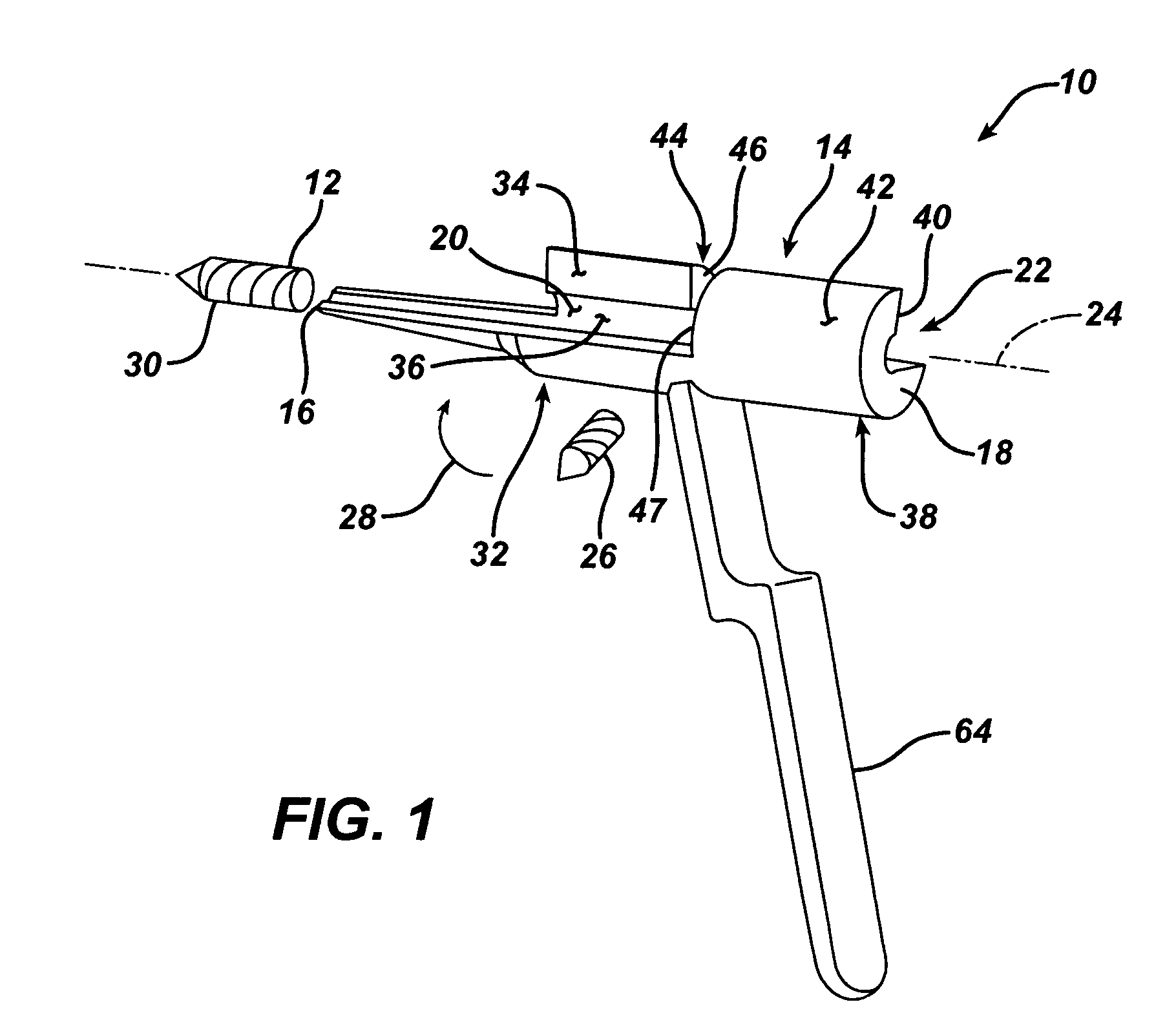
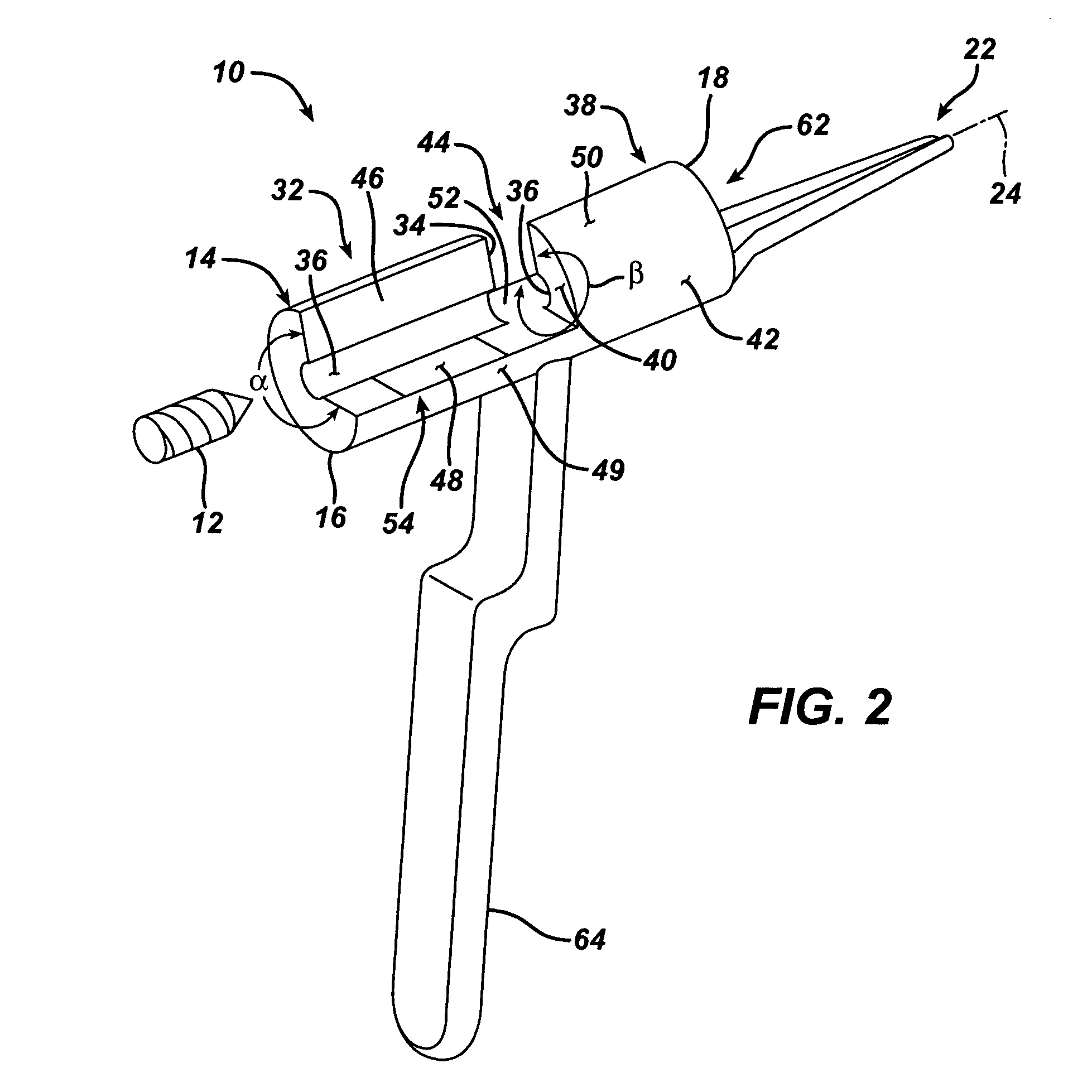
Trauma gage, kit and associated method
A depth gage for use with a drill in trauma surgery is provided. The gage cooperates with the drill for measuring the depth of the drill in a long bone when implanting an intramedullary nail in a patient. The depth gage including a body. The body defines first and second ends opposed to each other and an inner periphery defining a longitudinal aperture through the body for slidably receiving the drill. The longitudinal aperture defines a longitudinal axis of the longitudinal aperture. The body is adapted to permit the drill to be installed into the longitudinal aperture in a direction non-coincident with the longitudinal axis.
Owner:DEPUY PROD INC
Mobile trauma surgery medical device for general surgery department
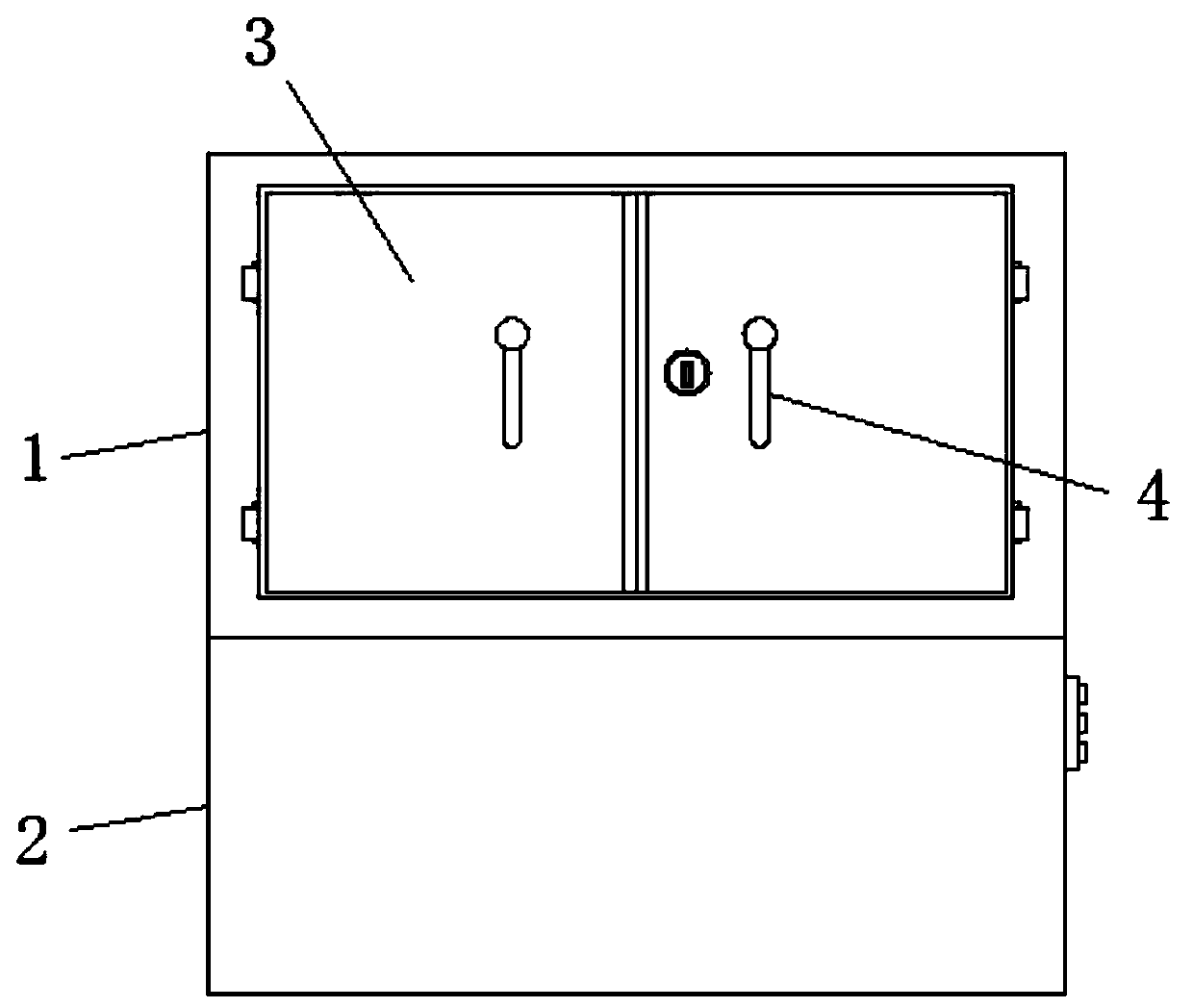
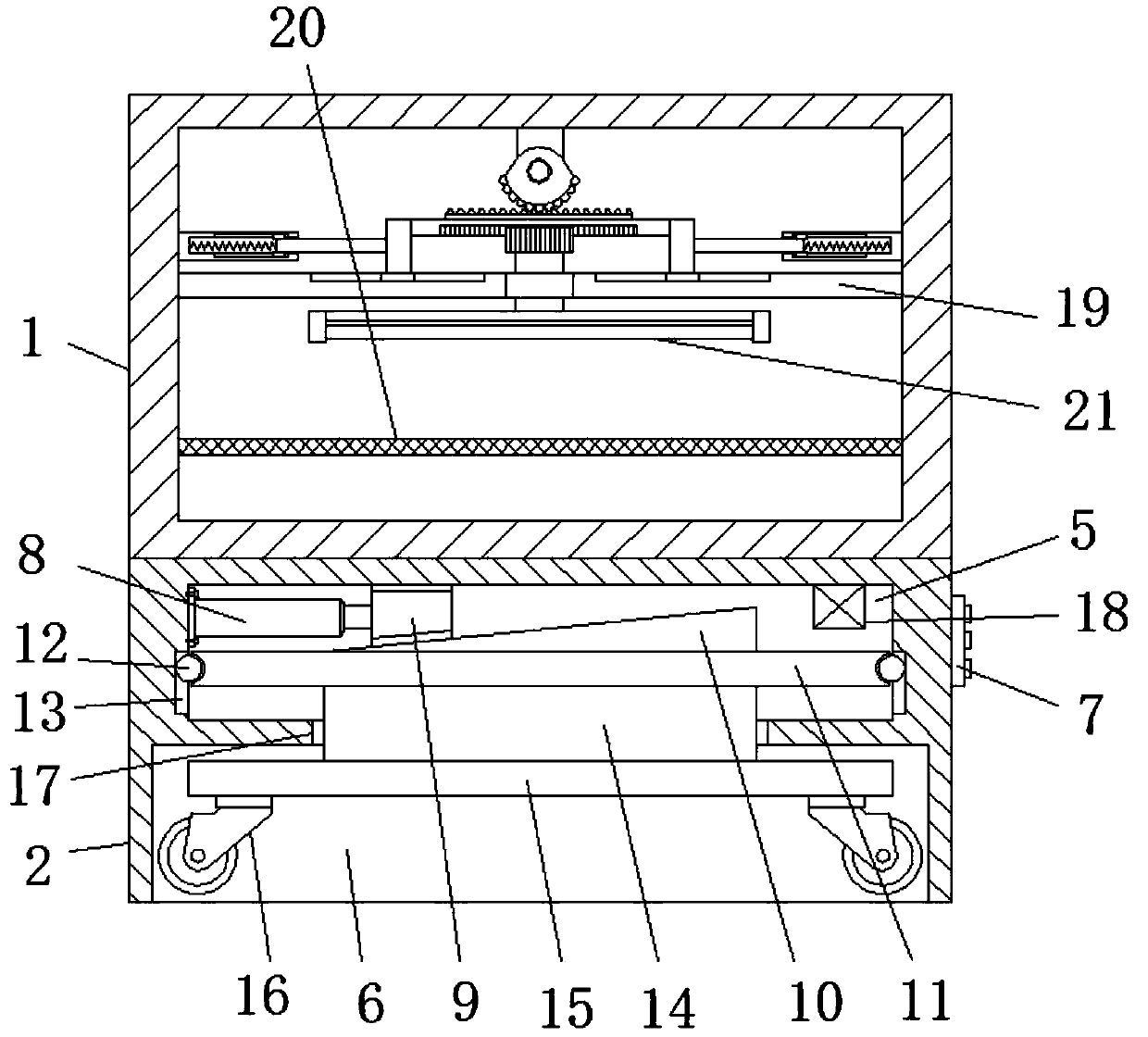
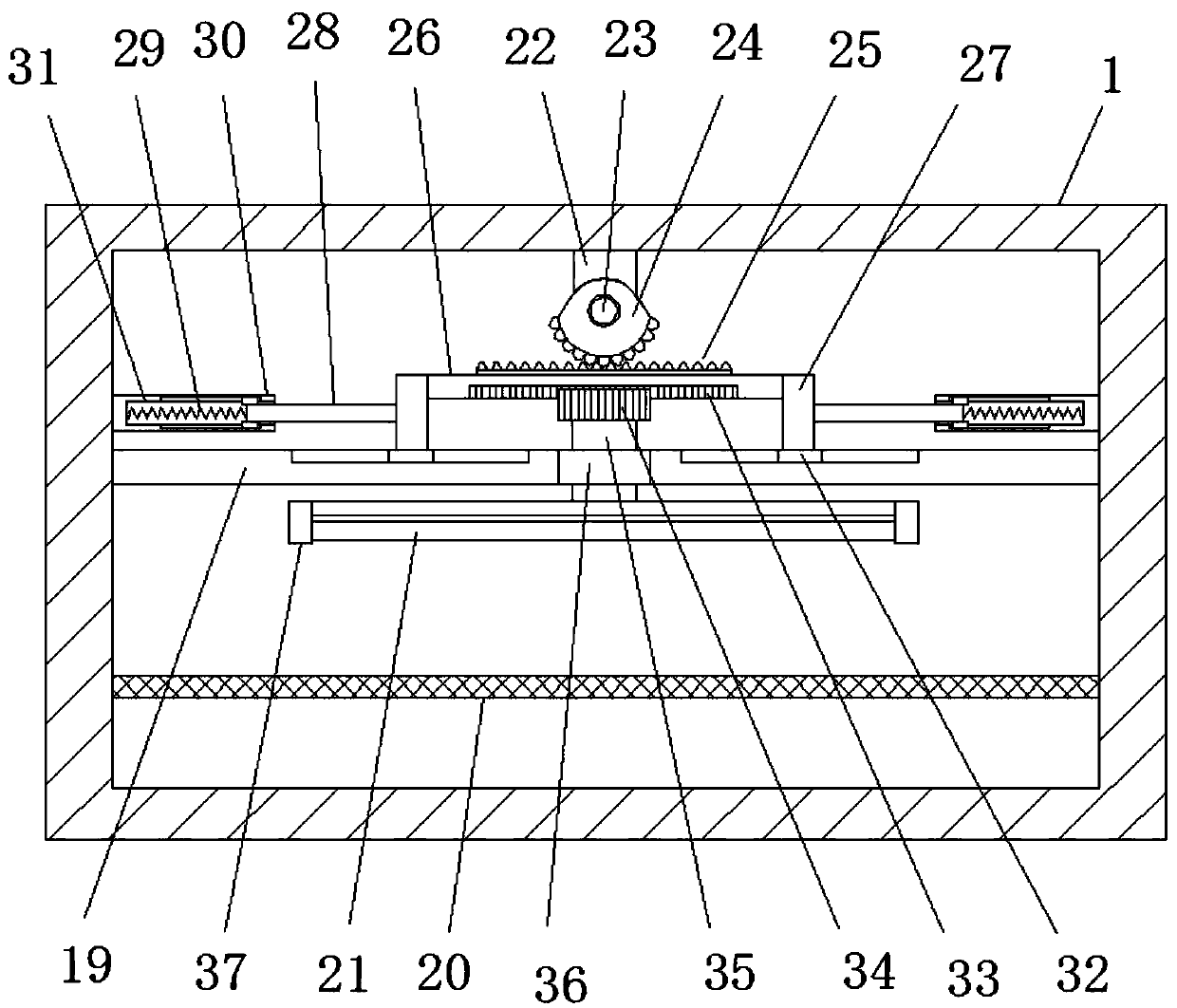
InactiveCN109966520AExpand the scope of work activitiesAvoid the limitations of working with smaller scopesLavatory sanitoryRadiationTrauma surgeryUv disinfection
The invention discloses a mobile trauma surgery medical device for a general surgery department. The mobile trauma surgery medical device comprises a disinfection chamber and doors rotationally hingedto the disinfection chamber, a moving base is fixedly arranged at the bottom of the disinfection chamber, the bottom of the moving base is provided with a groove, and the moving base is provided witha placement cavity above the groove. The mobile trauma surgery medical device for the general surgery department has advantages that a motion range of an ultraviolet disinfection lamp in operation can be expanded, limitation of a small operating range of a previous ultraviolet disinfection lamp is avoided, each surgical apparatus on a disinfection placement mesh plate can be disinfected, and utilization efficiency of the ultraviolet disinfection lamp can be improved; in addition, the whole device is convenient to move, and universal wheels can be collected in the groove of the moving base when the device is not used, so that the pressure of the universal wheels is relieved, and service lives of the universal wheels are prolonged.
Owner:刘凯
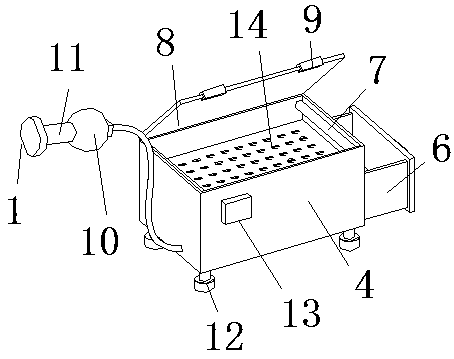
Medical device for clinical traumatic operation of general surgery department
InactiveCN110152093ASimple structureSimple and fast operationCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsTrauma surgeryCatheter
The invention discloses a medical device for a clinical traumatic operation of the general surgery department. The device comprises a treatment box body, wherein one inner side of the treatment box body is provided with a cleaning solution containing box, the lower end of one side of the cleaning solution containing box is connected with a water pumping bag through a conduit, and one end of the water pumping bag is connected with a connecting handle; one end of the connecting handle is provided with a cleaning head, one side of the cleaning head is attached with water absorbing cotton, a cleaning solution can be pumped to the cleaning head through the water pumping bag, and a wound of a patient can be cleaned and disinfected through the cleaning head to prevent the wound from being infected by bacteria. A supporting net frame can protect surgical instruments, the surgical instruments can be sterilized and disinfected by an ultraviolet sterilization lamp, and therefore convenience is provided for people. The medical device for the clinical traumatic operation of the general surgery department is simple in structure and convenient to operate, not only can the wounds of patients be cleaned to prevent the wounds of the patients from being infected, but also the surgical instruments can be sterilized and disinfected, and convenience is provided for people.
Owner:胡晓林
Screw element for use in spinal, orthopedic or trauma surgery and a system of such a screw element and a screw driver adapted thereto
ActiveUS20150289905A1Precise positioningEasy to operateInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsTrauma surgeryEngineering
A screw element for use in spinal, orthopedic or trauma surgery, the screw element including a screw axis (S) and a screw thread (3); a drive portion (6) for engagement with a screw driver (20), wherein the drive portion (6) comprises a first recess (7) with a wall and substantially longitudinally extending drive grooves (8) formed in the wall, a second recess (9) between a free end (5) of the screw element (1, 1′) and the first recess (7), wherein the second recess (9) has a wall and a gradually increasing inner diameter towards the free end (5); and wherein in the wall of the second recess (9) guide grooves (10) are formed at positions corresponding to the position of the drive grooves (8) that allow an engagement portion (30) of a screw driver to be guided to enter the drive grooves (8). Further, a system is provided that includes the screw element and a screw driver adapted thereto.
Owner:BIEDERMANN TECH GMBH & CO KG
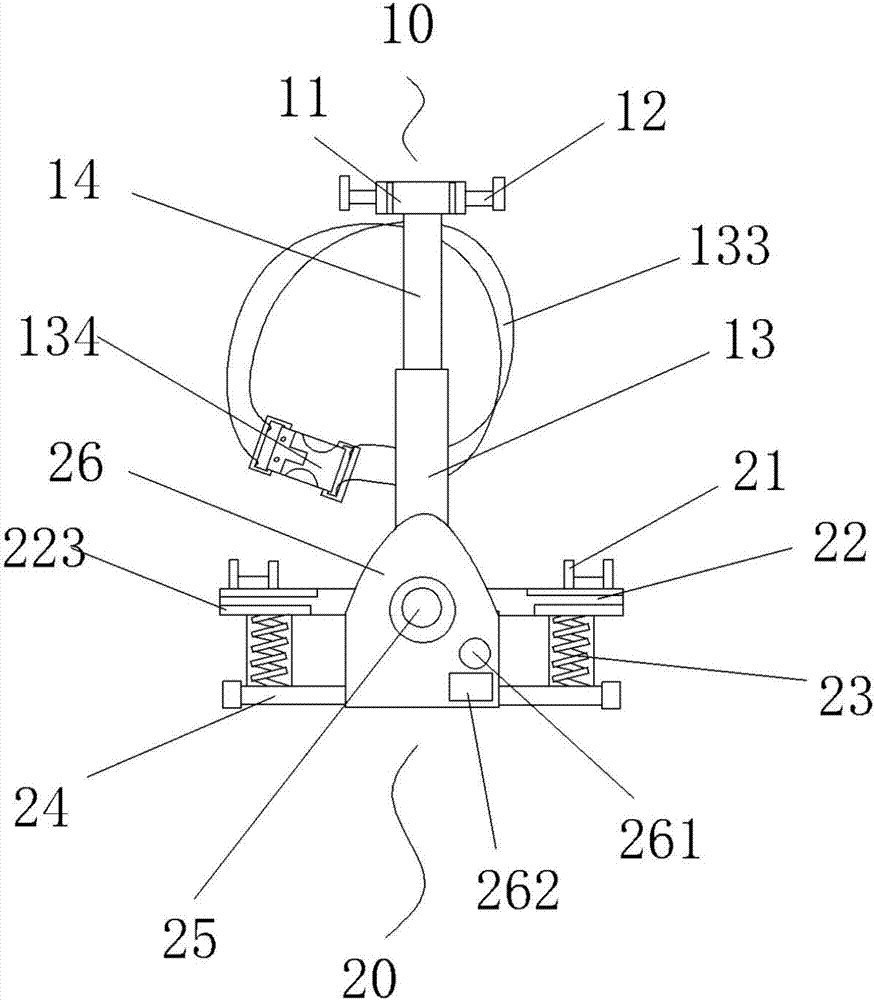
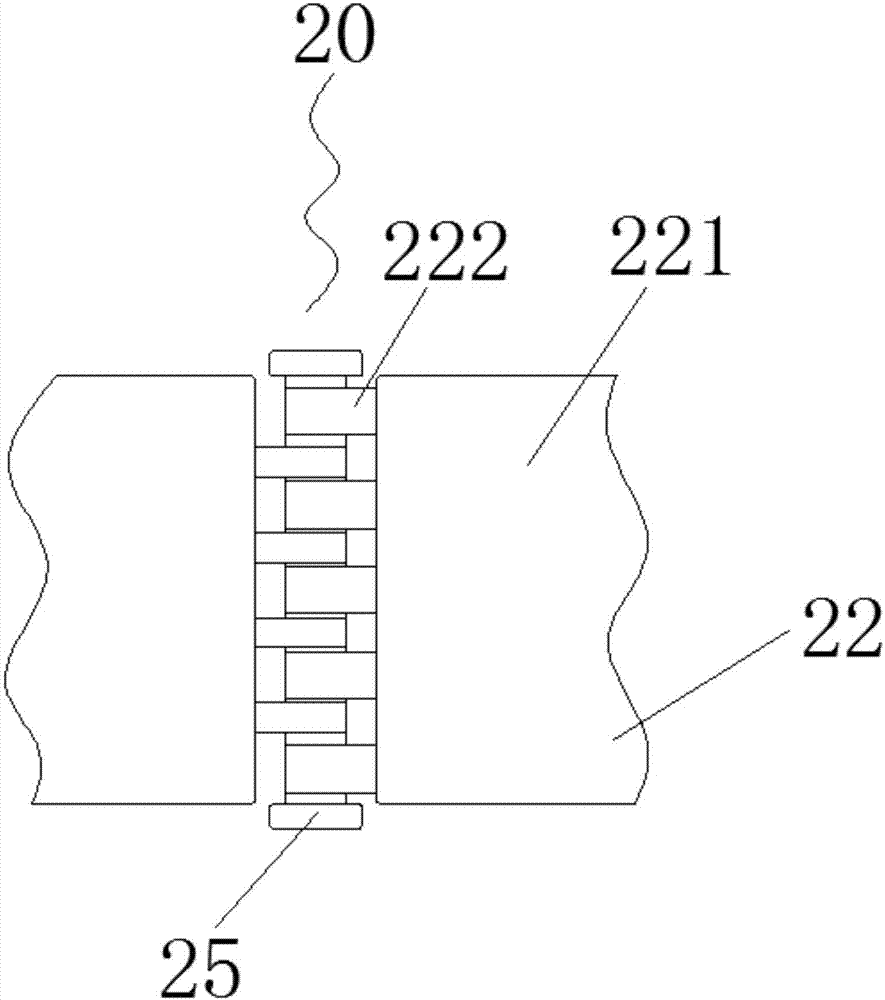
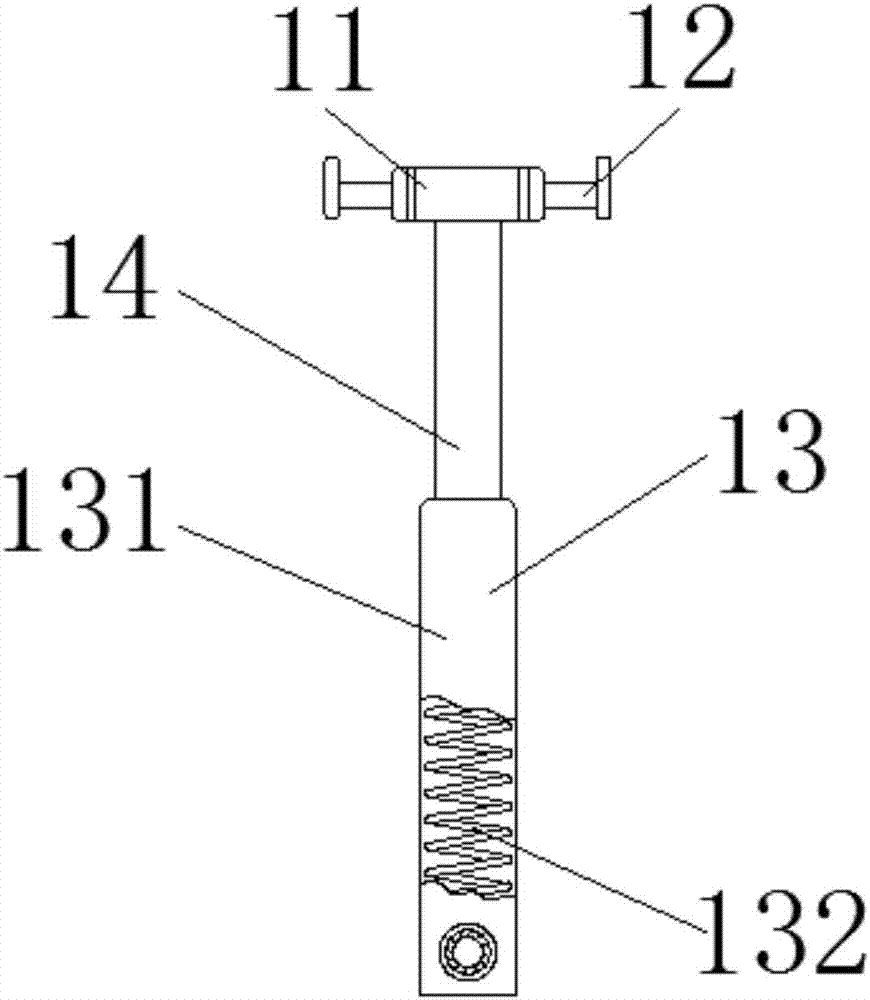
Low limb movement training device after brain trauma surgery
The invention discloses a low limb movement training device after brain trauma surgery. The low limb movement training device after the brain trauma surgery comprises a rotating assembly and a pedal assembly, the rotating assembly comprises a rotating shaft, rotating handles, a hollow pipe and a pressure shaft, and the rotating shaft is located at one end of the pressure shaft and fixedly connected with the pressure shaft; return springs are placed in spring boxes, when a patient puts the feet on pedals, due to the fact that sliding grooves are formed in the upper surfaces of the pedals, footclamping boards and the pedals are connected through the sliding grooves in a sliding mode, then the feet of the patient are fixed, later on, when the patient stands on the pedals, the return springsstretch out and draw back to provide upward supporting force for the patient and assist the patient in movement, convenience is brought to a user, an arranged pressure sensing alarm raises the alarm when the patient is in danger, and a medical worker is informed in time to rescue the patient, so that the safety of patient training is improved.
Owner:THE FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL OF NANTONG
Traditional Chinese medicine composition for preventing fracture postoperative lower limb deep venous thrombosis, and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111195292AStasis improvedRestore gasification functionDispersion deliveryBlood disorderDiseaseTrauma surgery
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine composition for preventing fracture postoperative lower limb deep venous thrombosis, and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of traditional Chinese medicines. In the traditional Chinese medicine science, the lower limb deep venous thrombosis is caused by trauma, surgery, pregnancy, malignant tumors, long-term bed lying of other diseases and the like, so that qi is injured after long-term sitting and long-term lying; qi deficiency is more serious after trauma and fracture operations; And Qi is a blood commander, unsmoothblood circulation is caused by Qi injury, and slow blood circulation is caused by unsmooth Qi, so that the blood circulation is blocked in the pulse. According to the etiology and pathogenesis of thedisease, astragalus membranaceus, angelica sinensis, cassia twigs, ligusticum wallichII, peach kernels, safflower carthamus, earthworms, leeches, pseudo-ginseng and other medicines are selected, so the composition can achieve qi tonifying and blood activating, remarkably reduces the incidence rate of postoperative deep venous thrombosis of lower limbs after clinical use, and is worthy of clinicalpromotion.
Owner:XIAN HONGHUI HOSPITAL
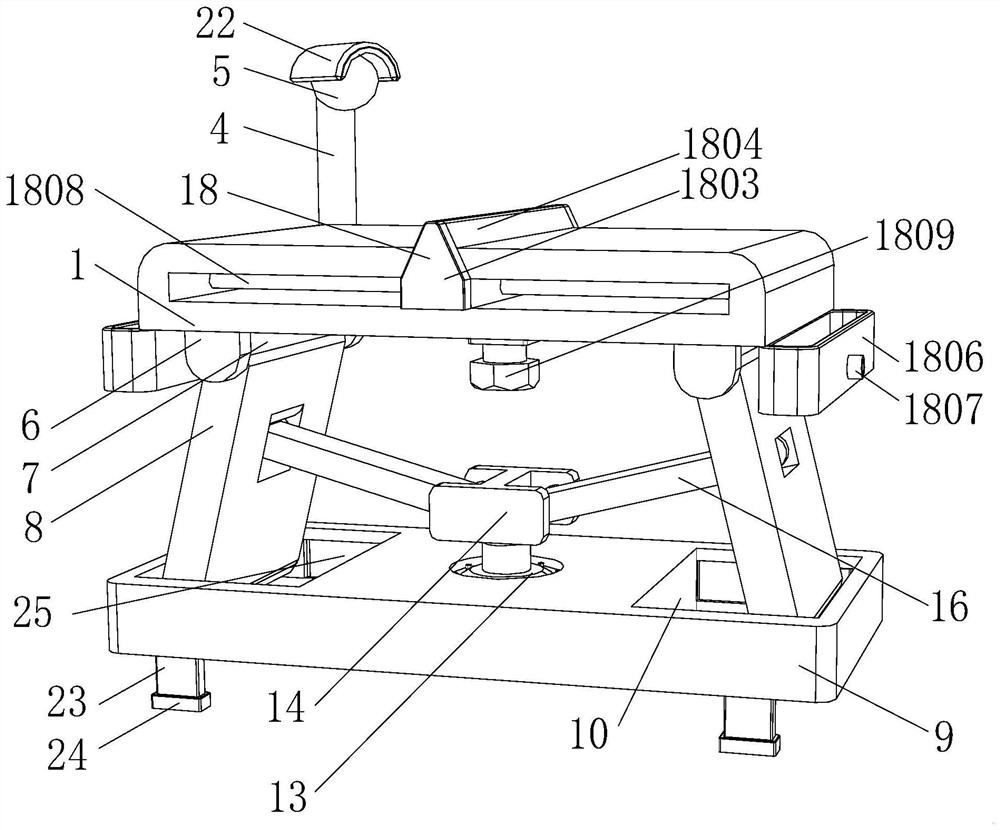
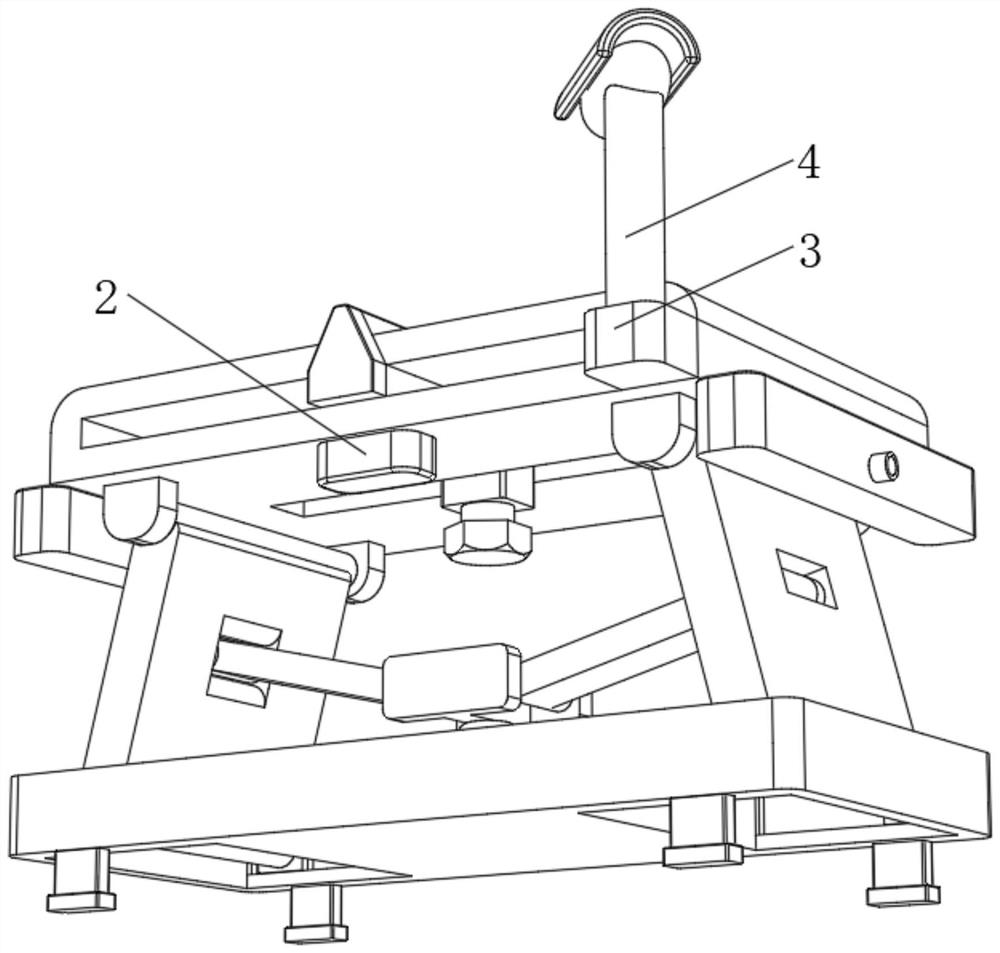
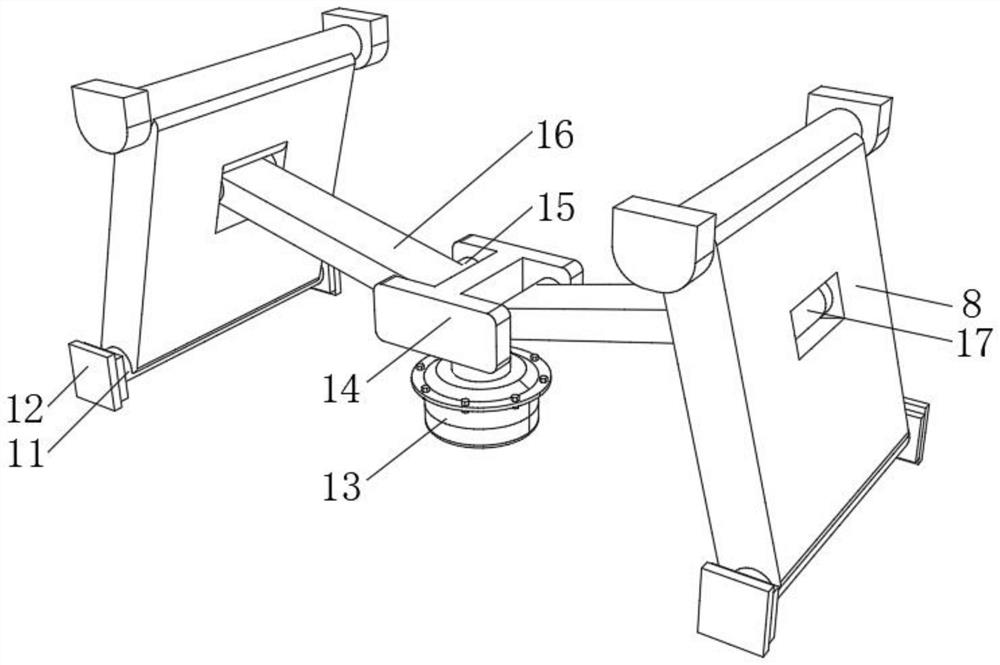
Intelligent control medical device for trauma surgery in general surgery department
The invention relates to the technical field of medical treatment, and discloses an intelligent control medical device for trauma surgery in the general surgery department. The intelligent control medical device comprises a working plate; auxiliary plates are fixedly connected to the four corners of the lower surface of the working plate; a bottom plate is arranged below the working plate; a hydraulic cylinder is fixedly connected to the bottom side wall of an inner cavity of the bottom plate; the hydraulic cylinder is arranged in a storage groove; a control block is fixedly connected to the output end of the hydraulic cylinder; both the interior of the left end and the interior of the right end of the control block are each rotatably connected with a control shaft; connecting plates are fixedly connected to the outer side walls of the control shafts; auxiliary holes are formed in the middle portions of supporting plates; connecting shafts are rotatably connected to the middle portionsof the supporting plates; and the outer side surfaces of the connecting plates are fixedly connected with the outer side walls of the connecting shafts. According to the intelligent control medical device for the trauma surgery in the general surgery department in the invention, due to cooperation of the hydraulic cylinder, the control block, the control shafts, the connecting shafts, the connecting plates, the auxiliary plates, an auxiliary shaft, a supporting shaft, a first sliding block and a first sliding groove, the height of the device can be adjusted.
Owner:广州极诣科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com