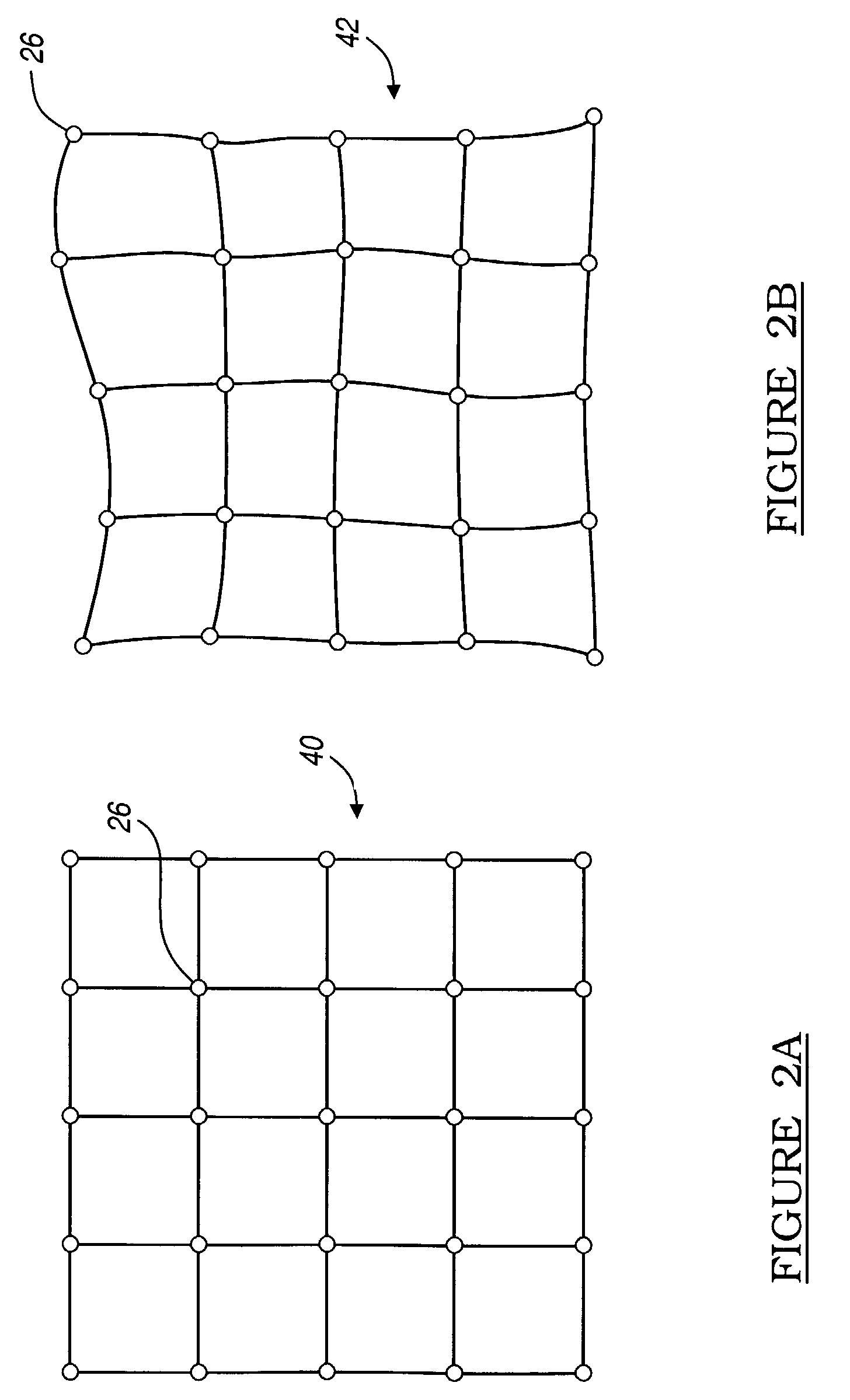
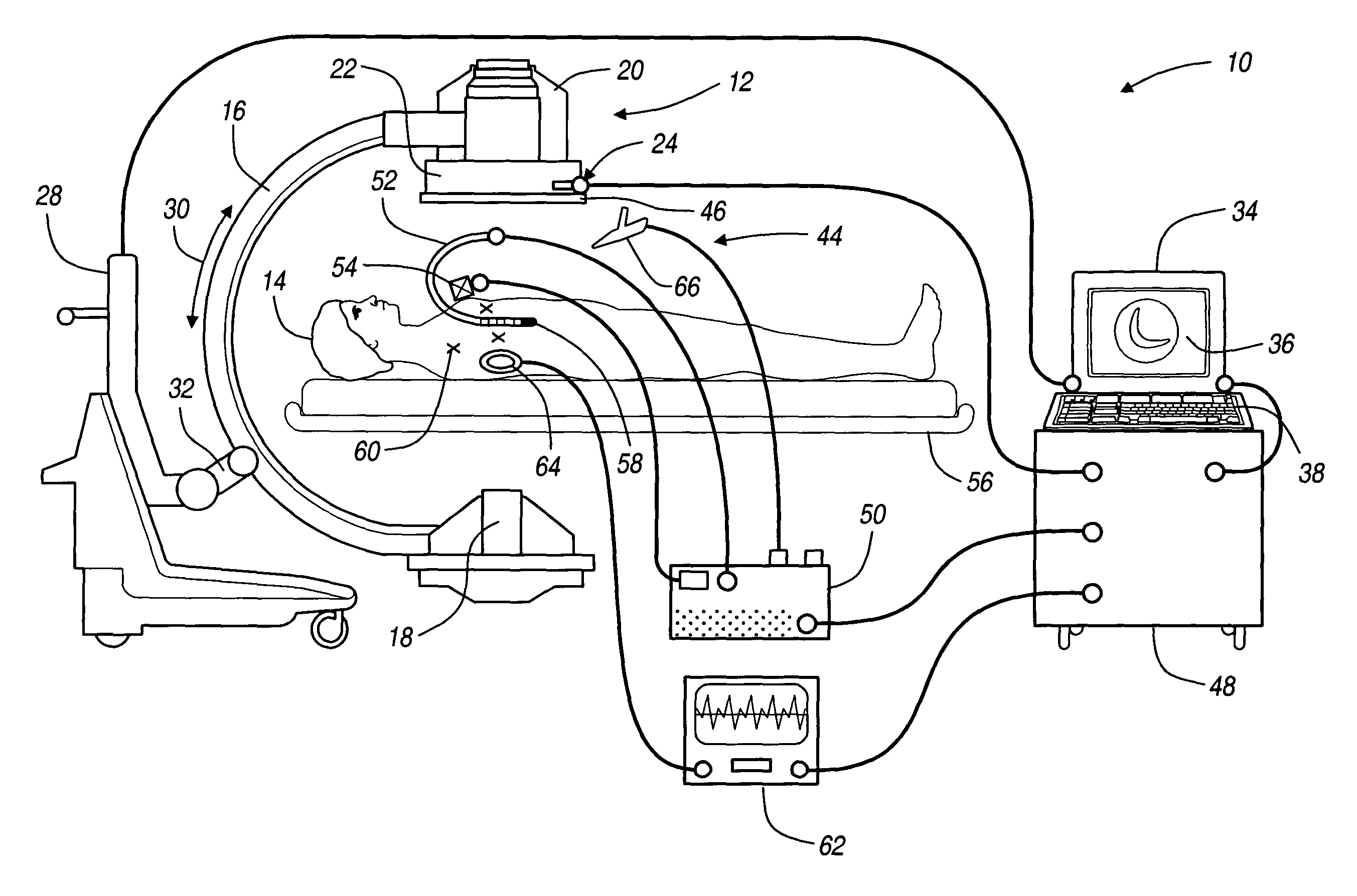
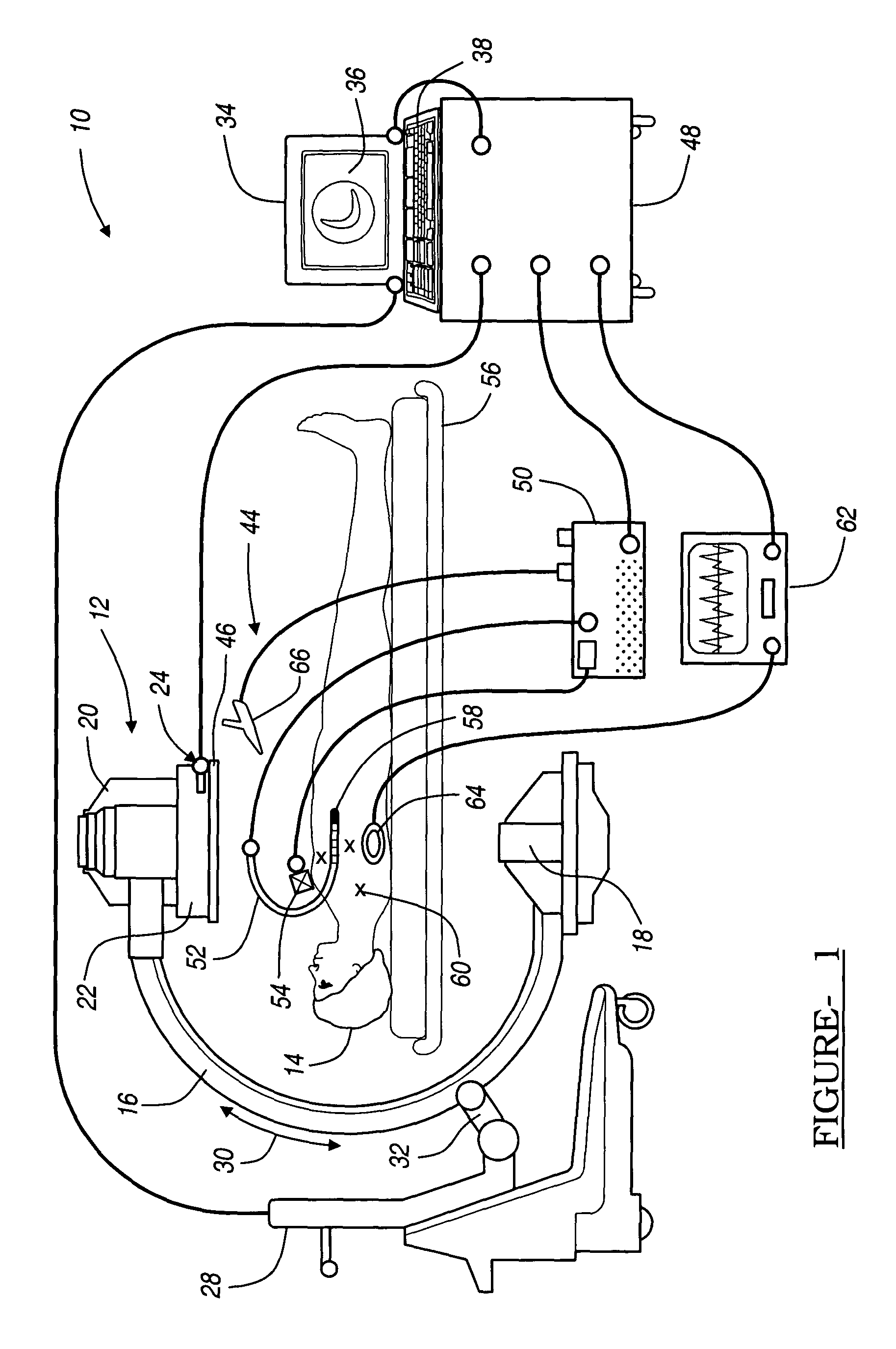
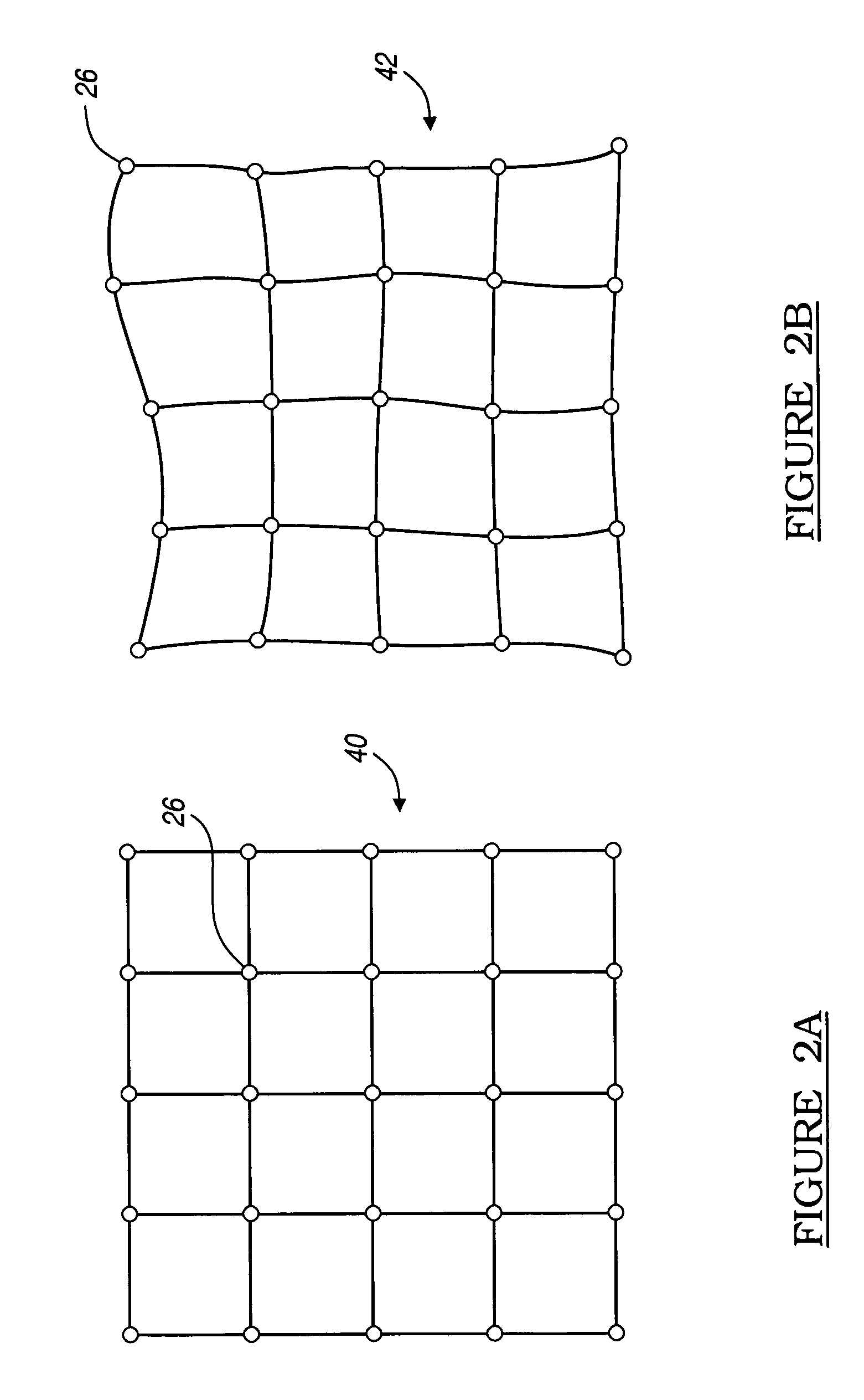
Patents
Literature
2415results about "Foreign body detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
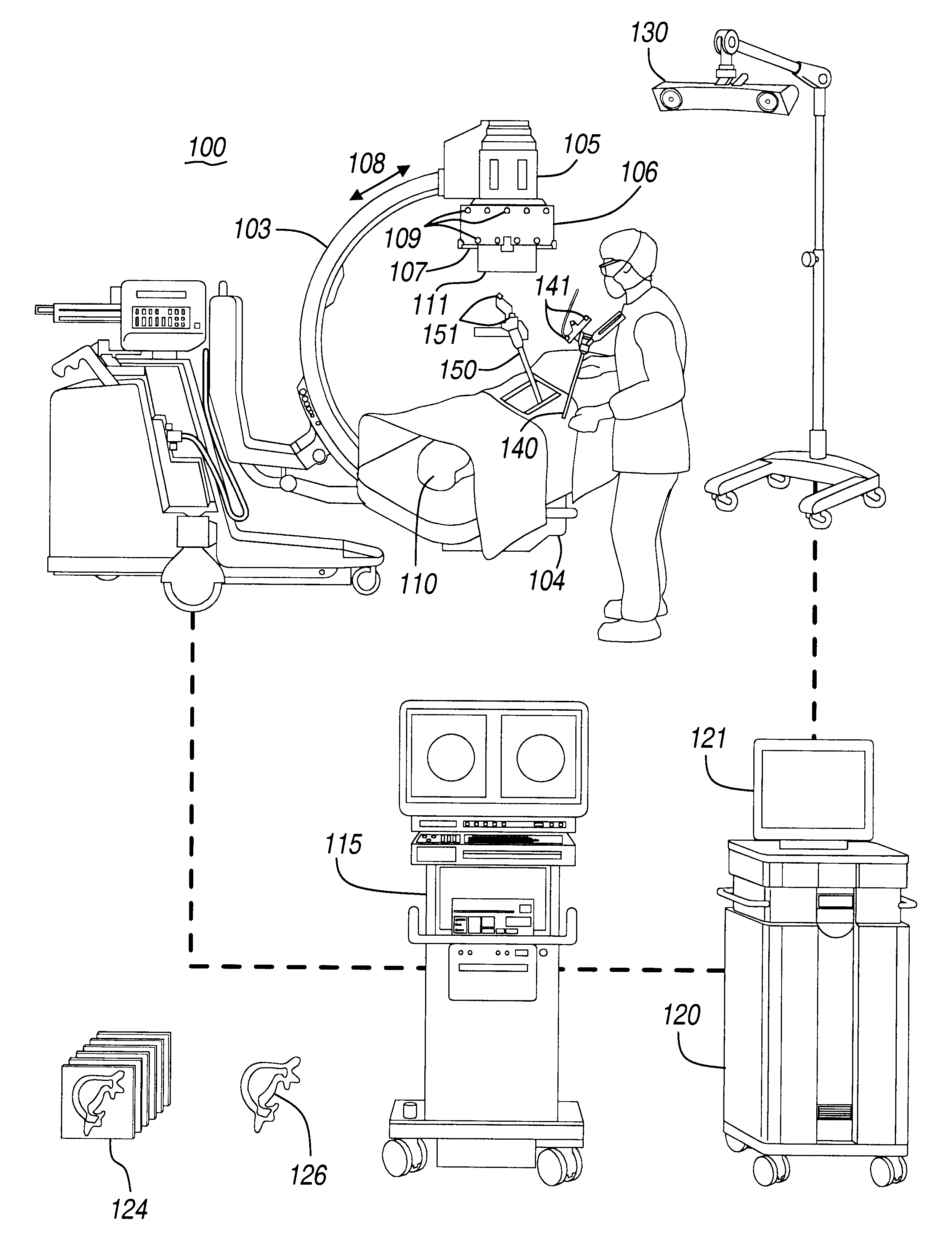
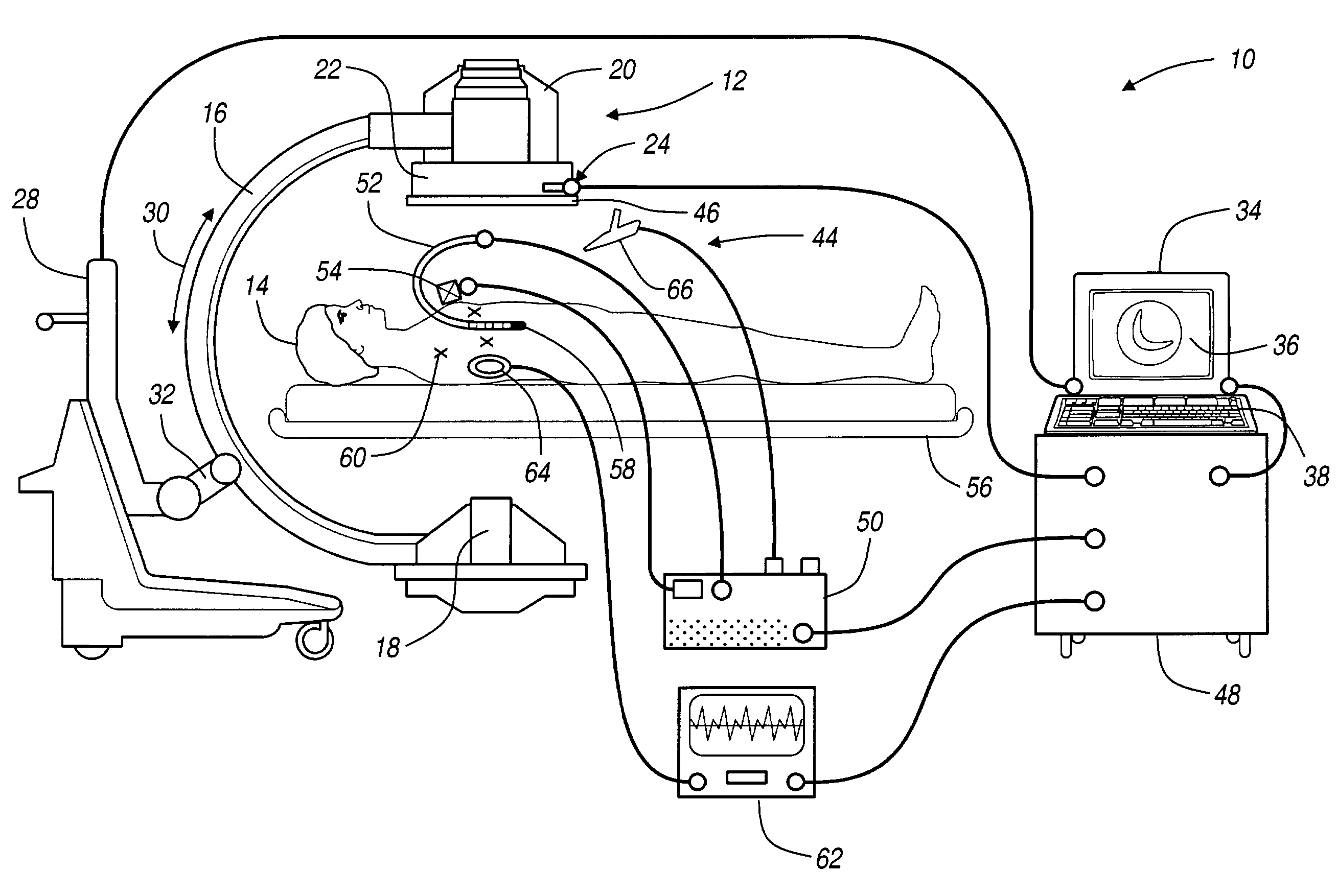
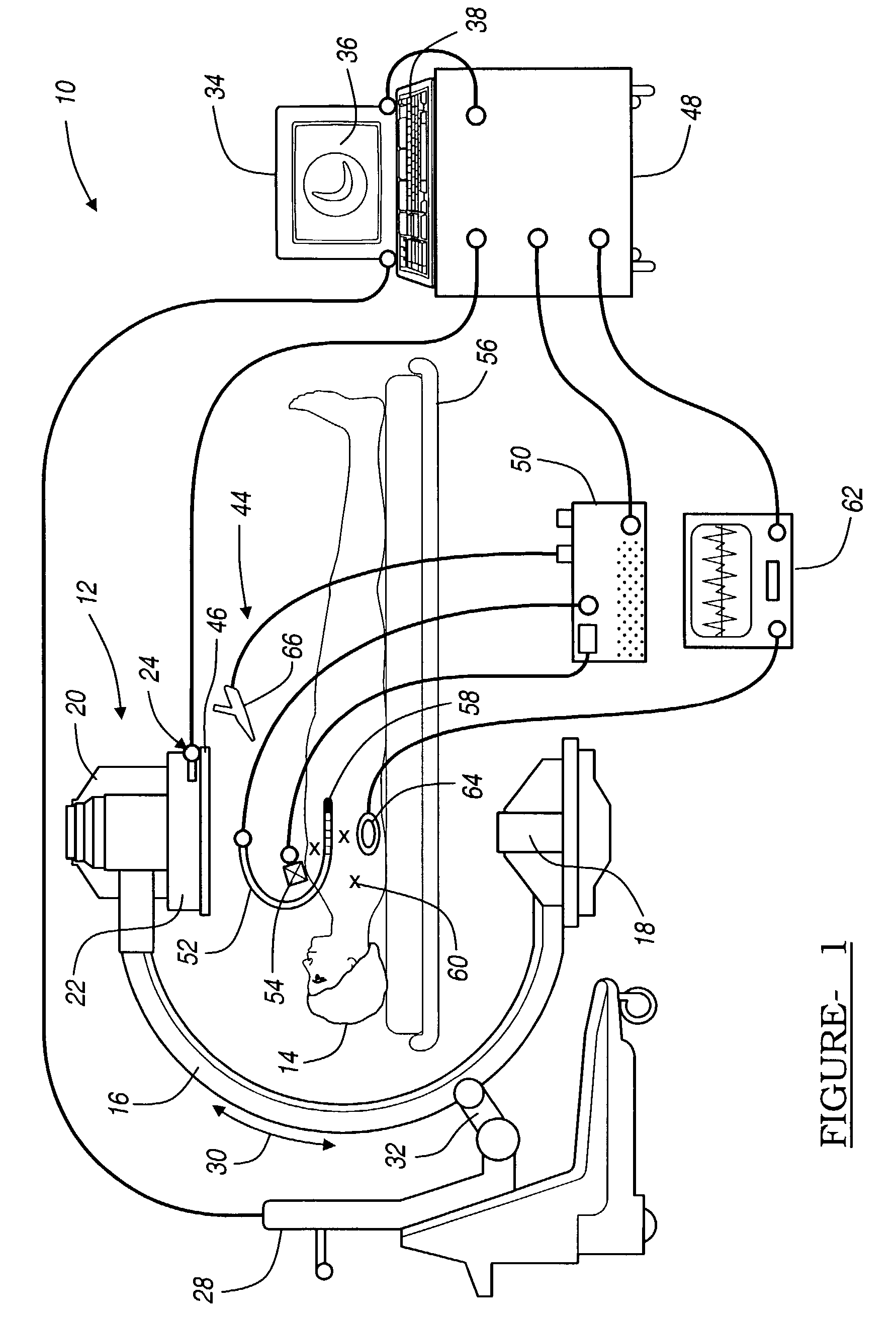
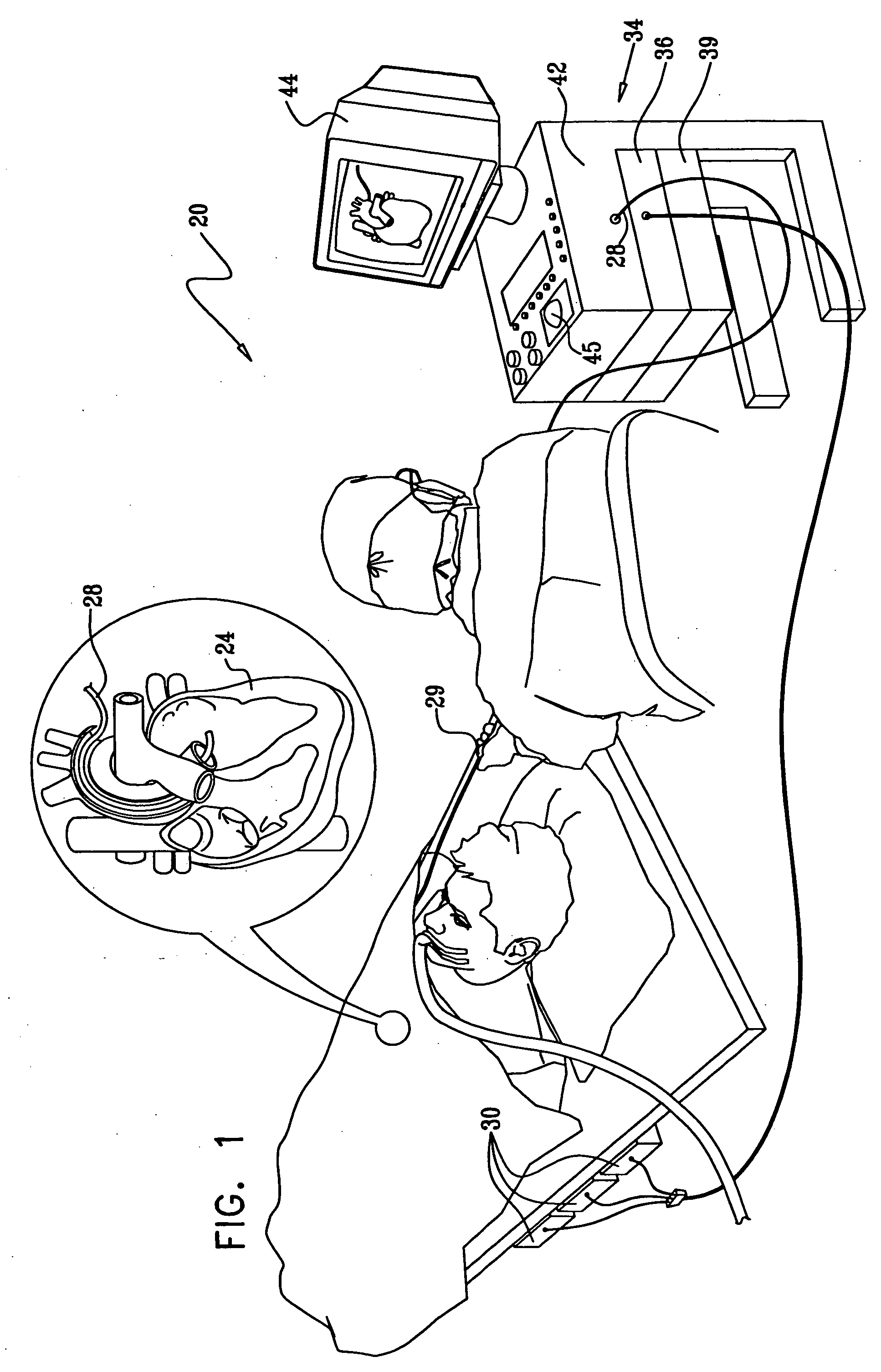
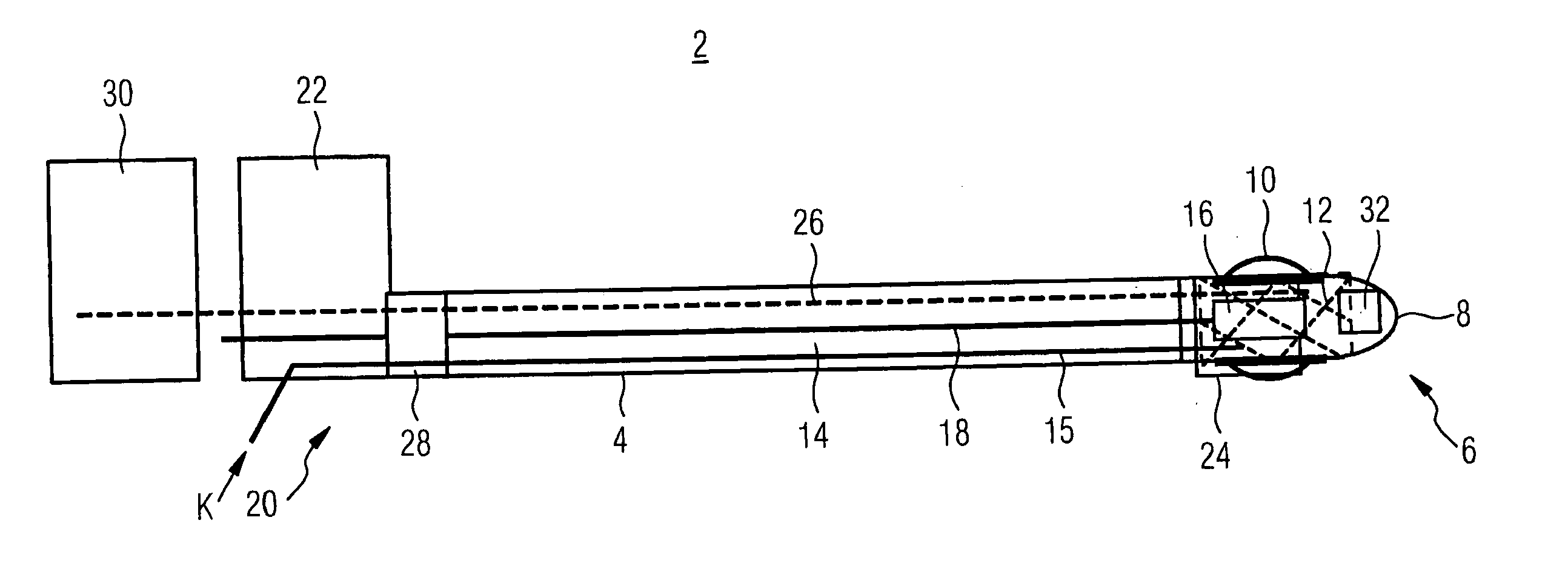
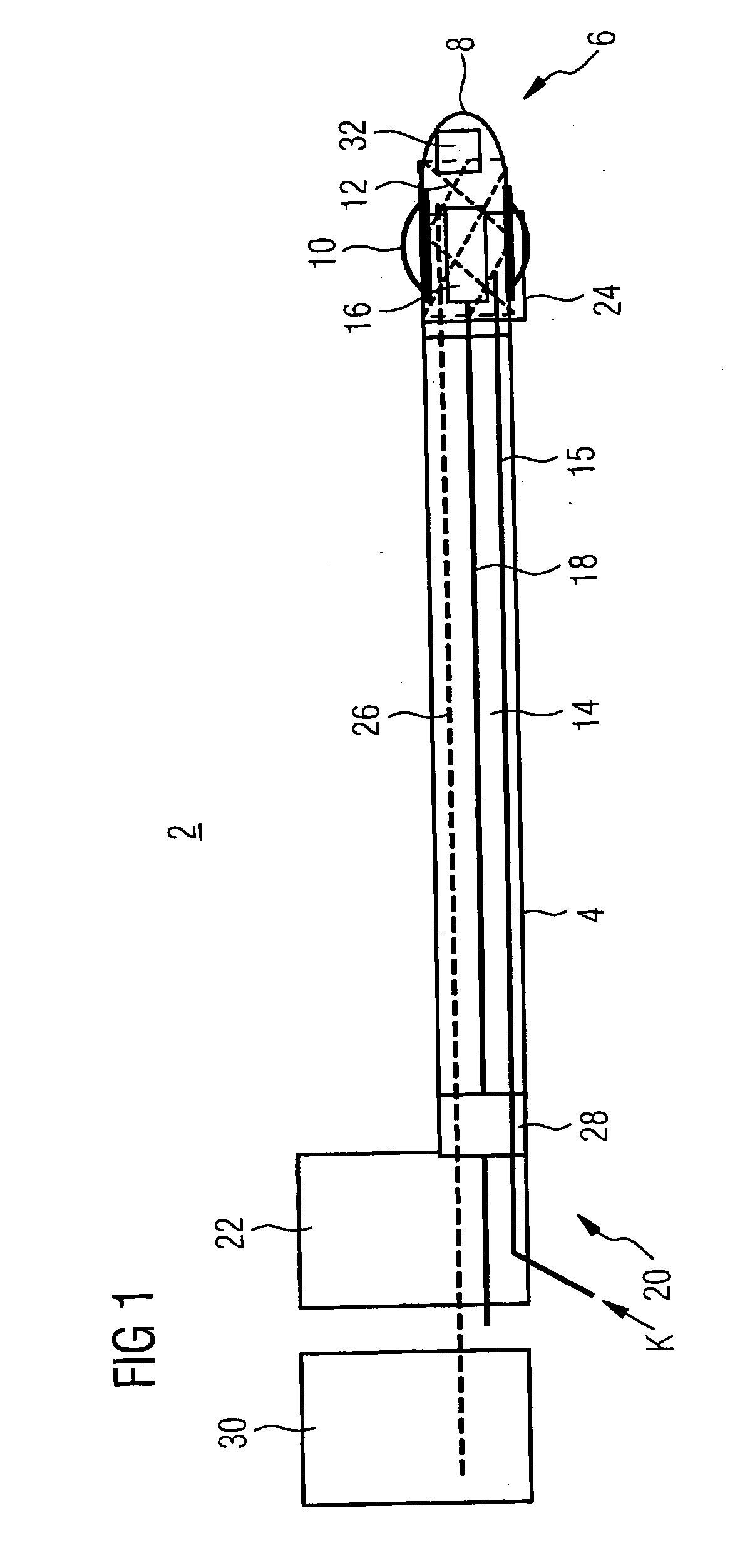
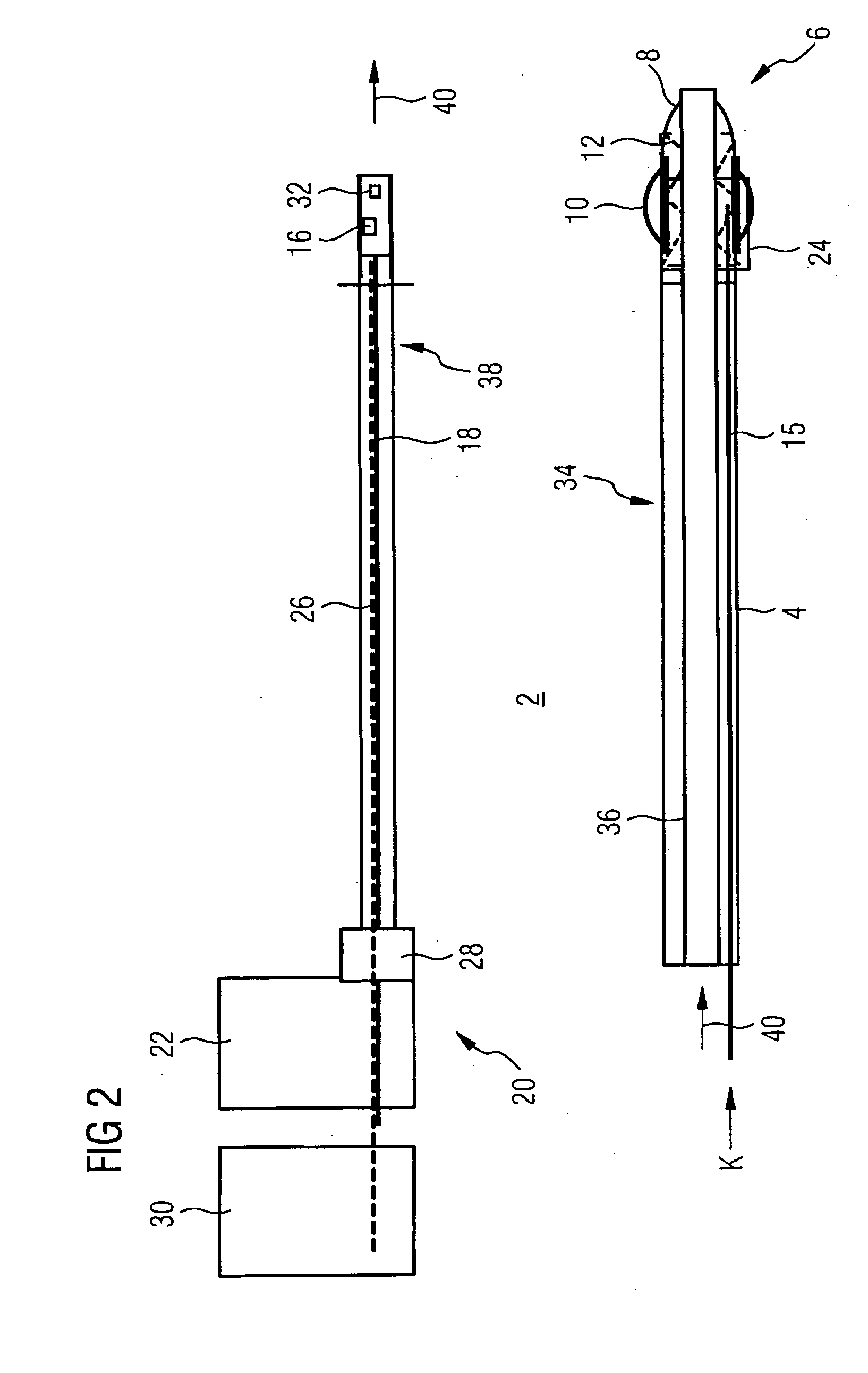
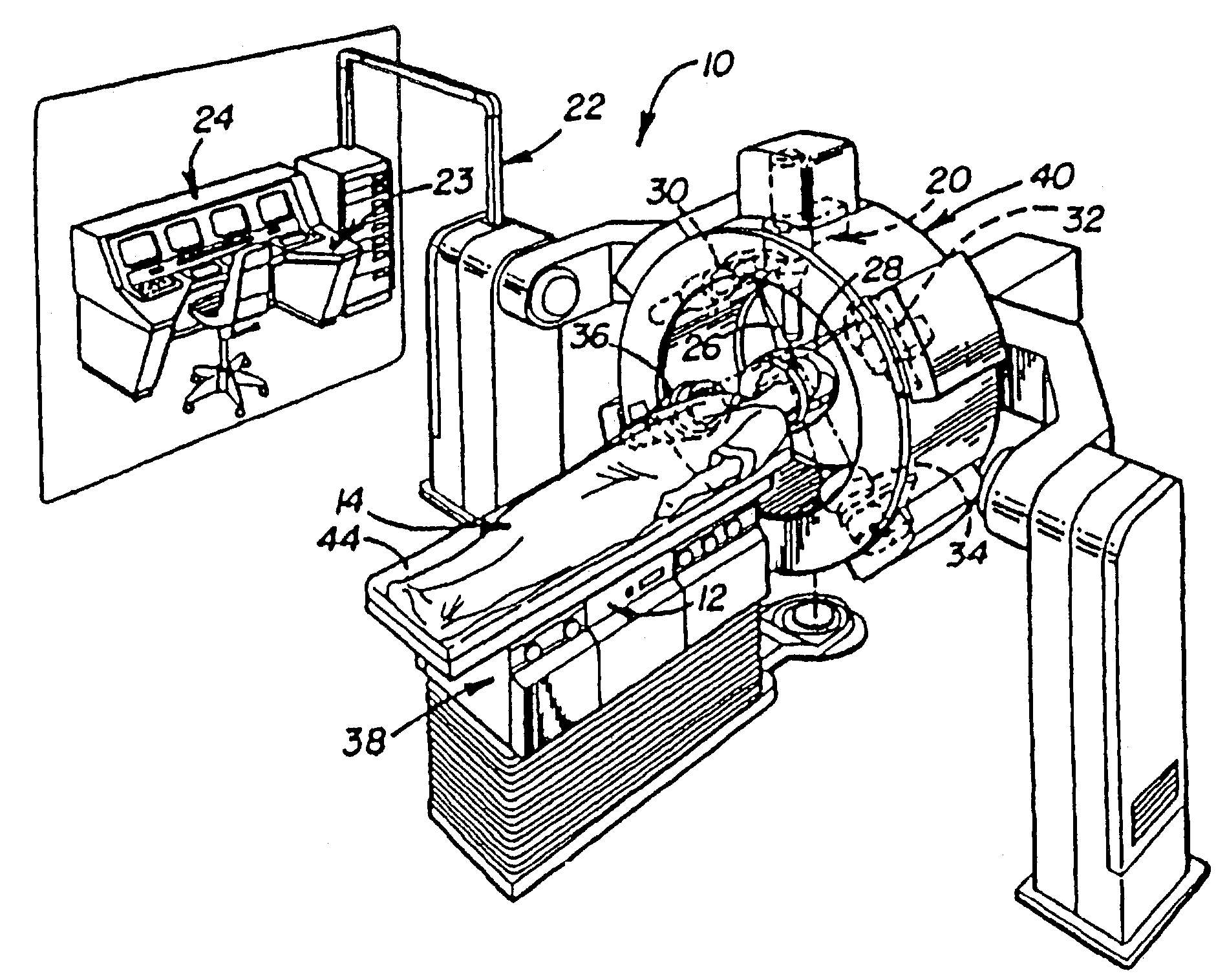
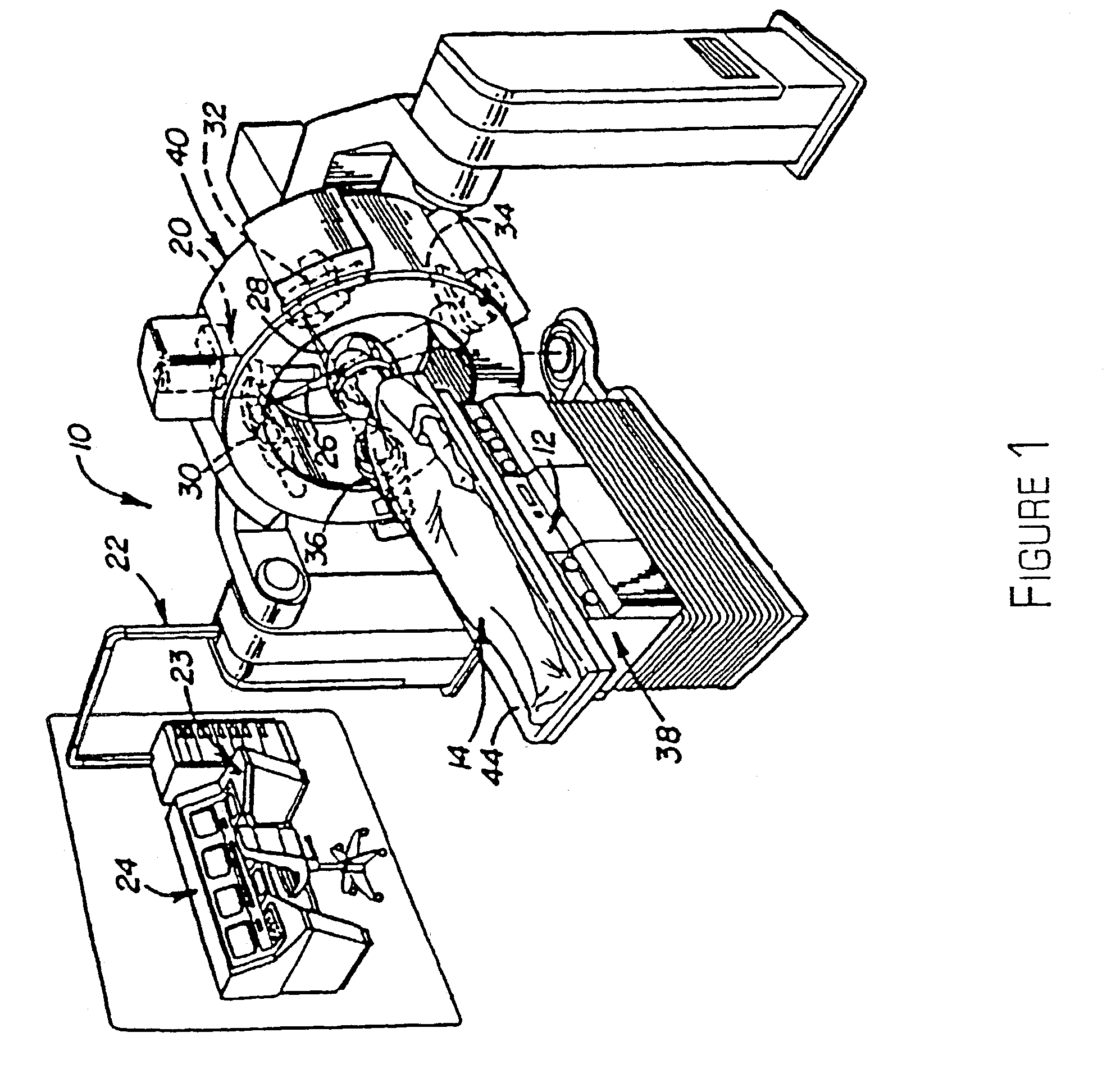
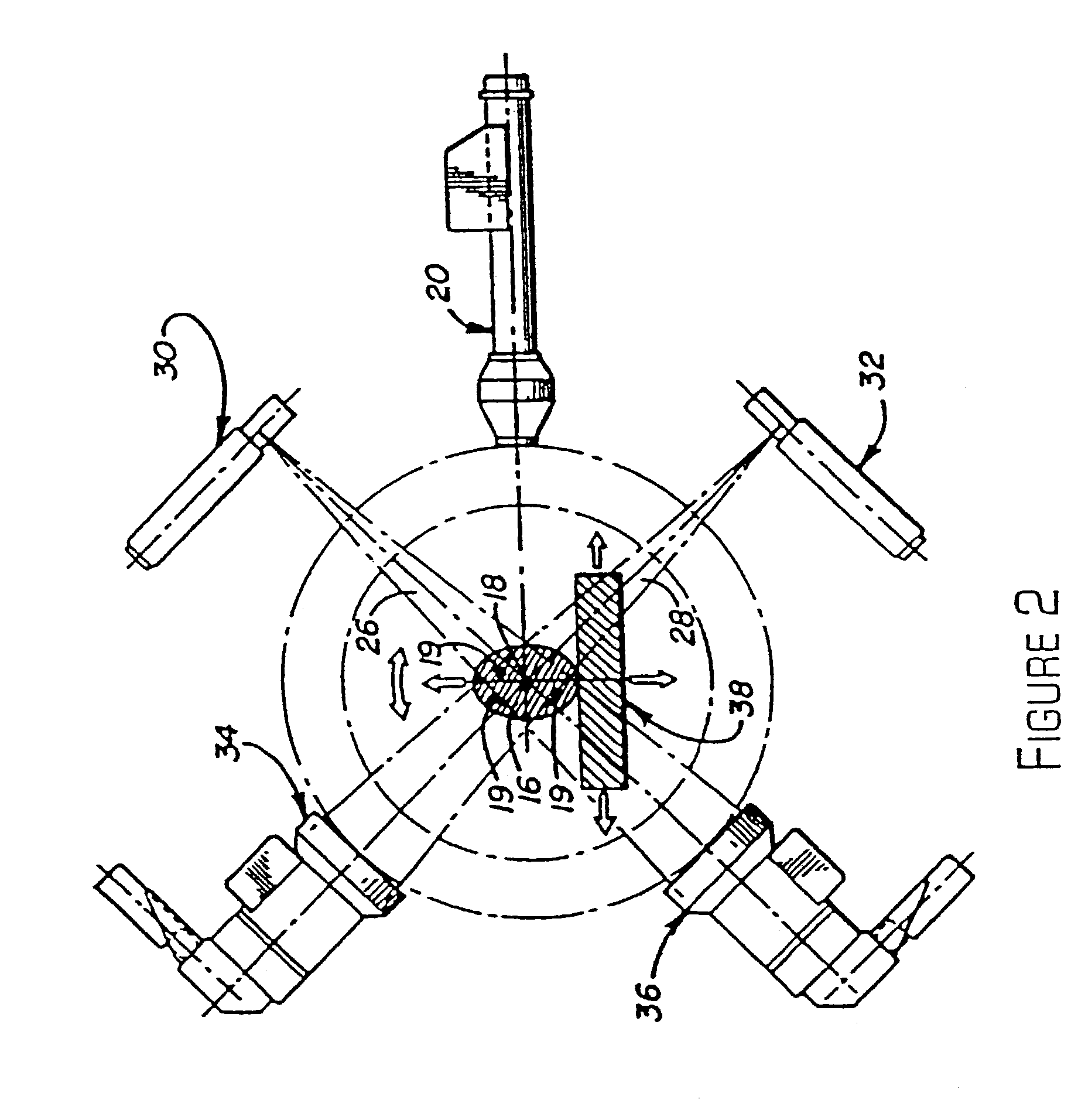
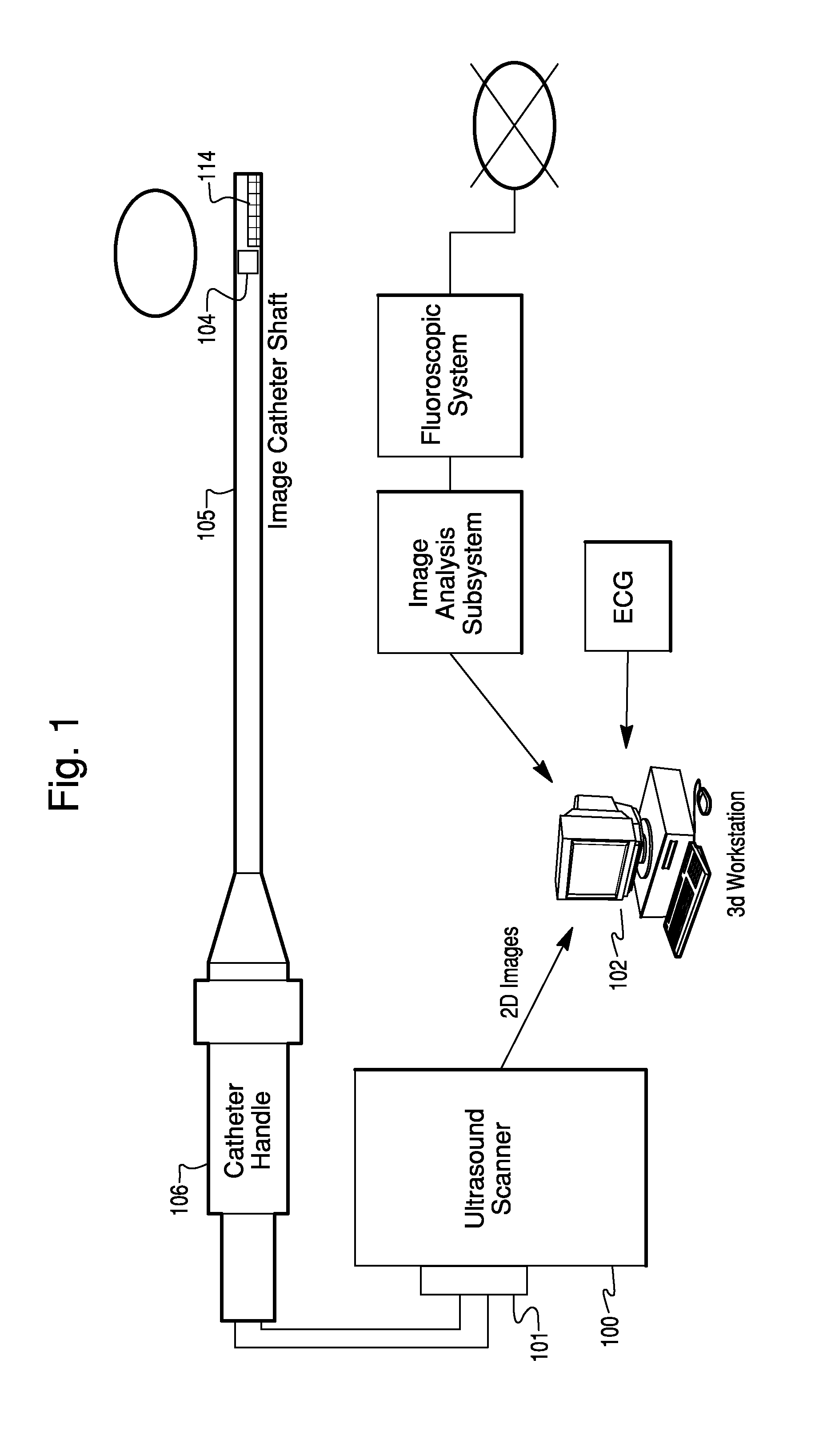
Navigational guidance via computer-assisted fluoroscopic imaging
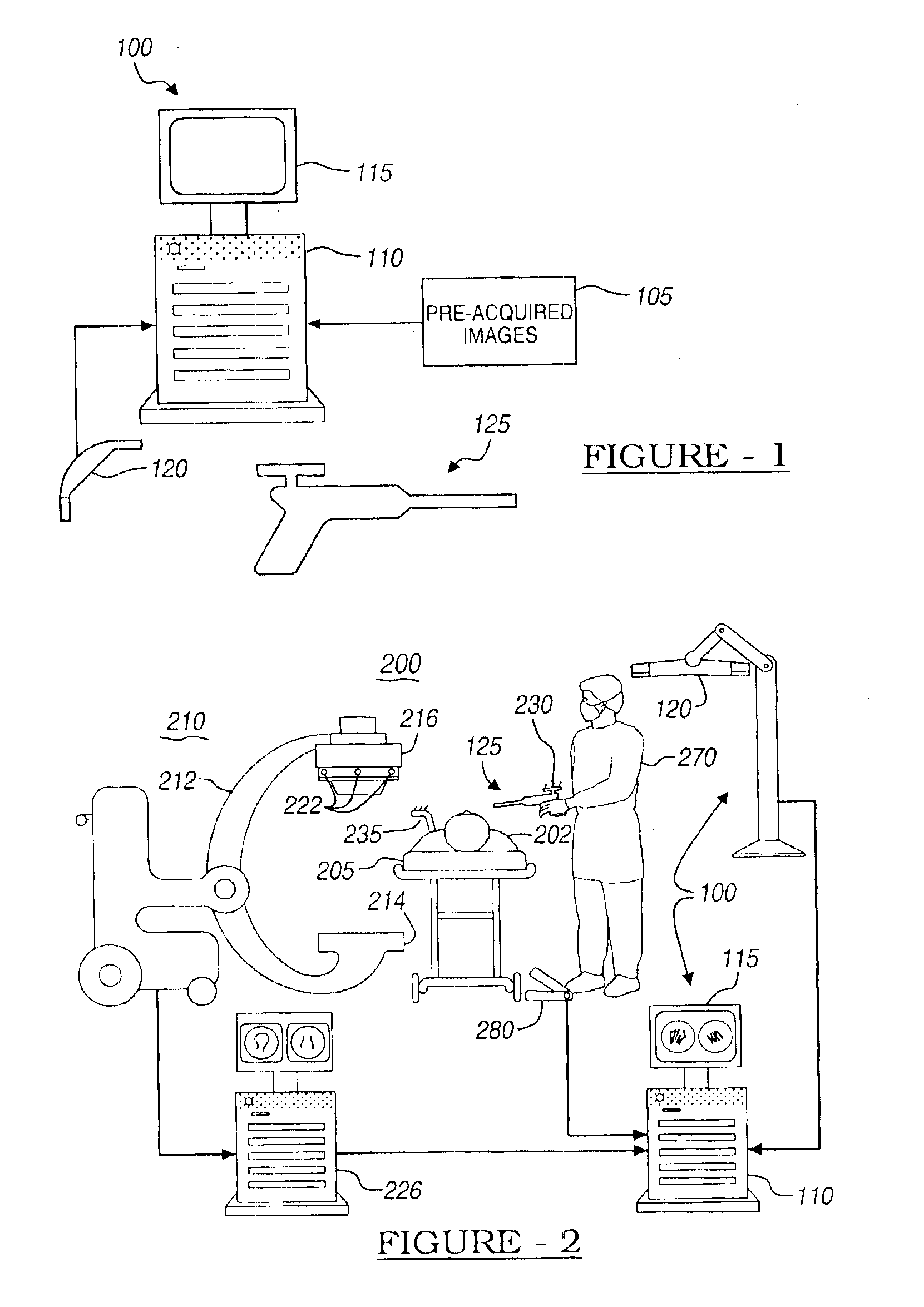
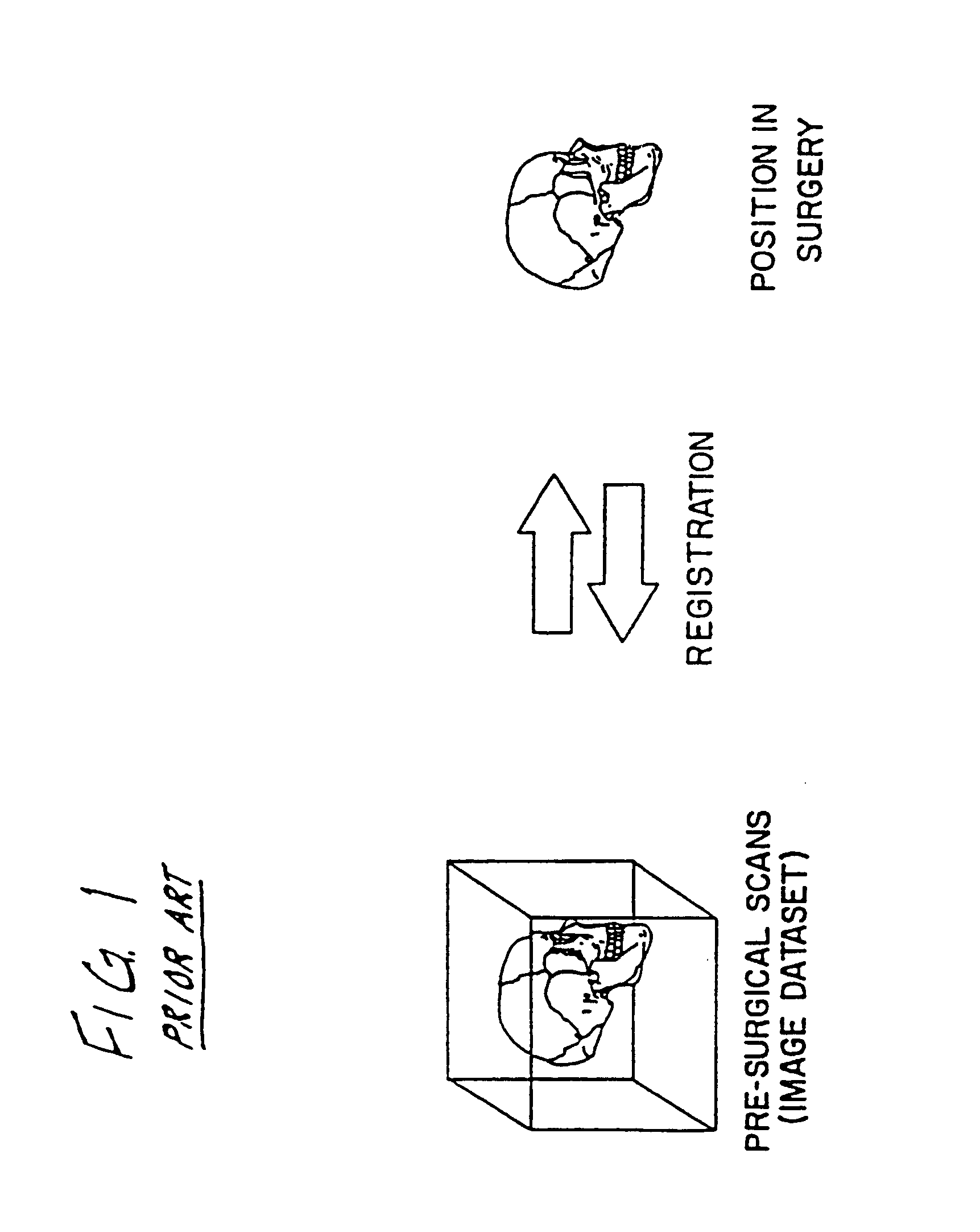
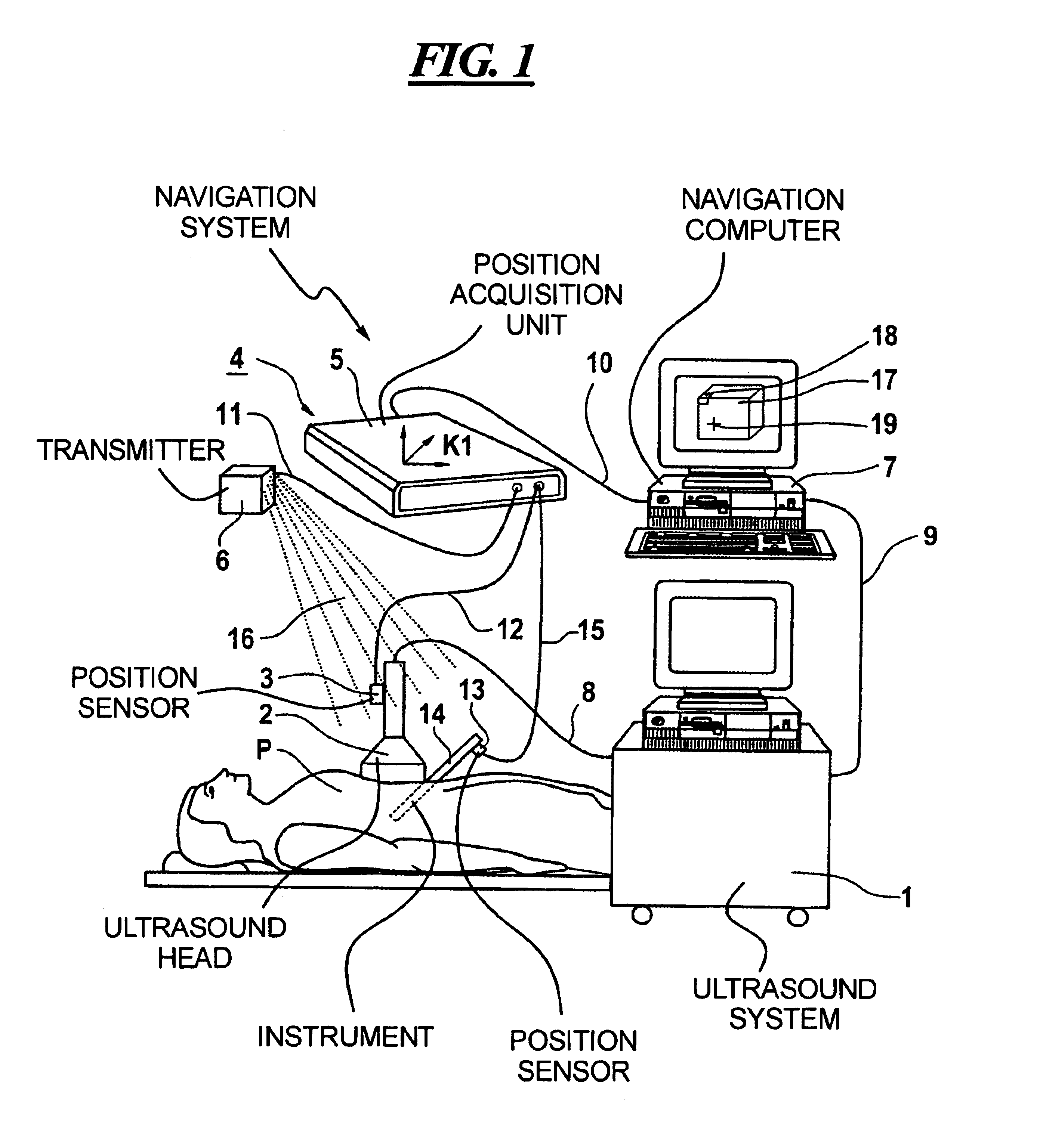
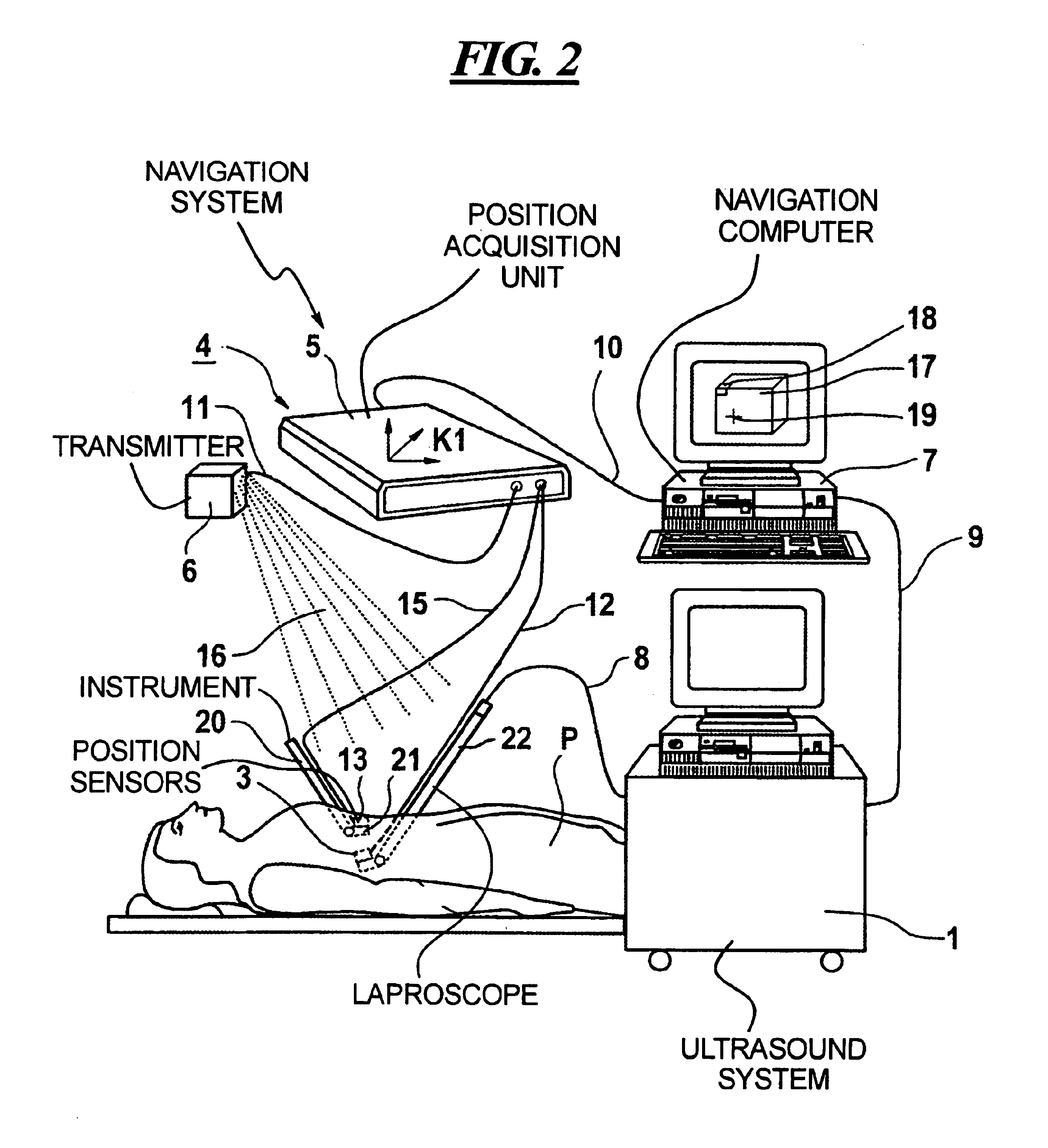
Digital x-ray images taken before a surgical procedure by a fluoroscopic C-arm imager are displayed by a computer and overlaid with graphical representations of instruments be used in the operating room. The graphical representations are updated in real-time to correspond to movement of the instruments in the operating room. A number of different techniques are described that aid the physician in planning and carrying out the surgical procedure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
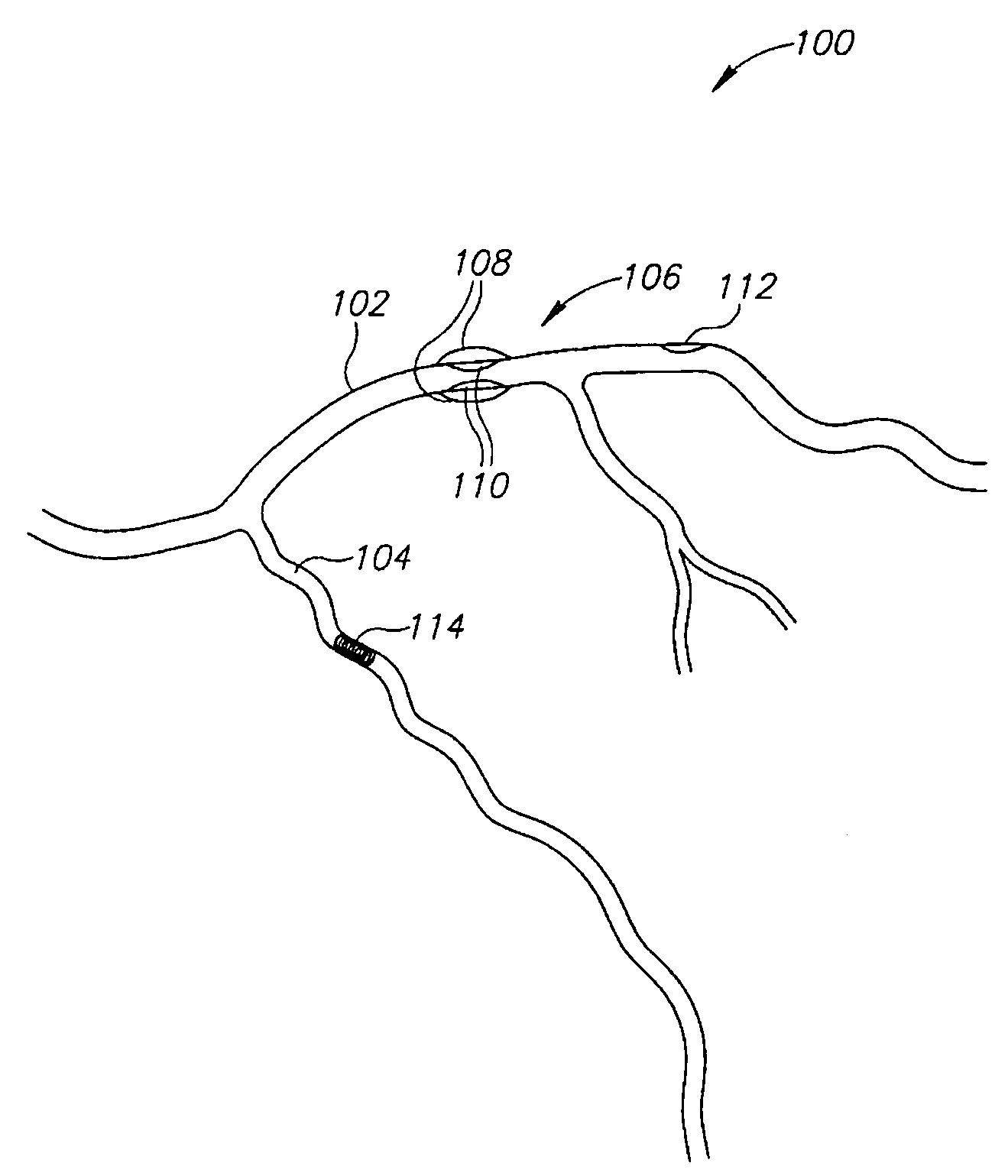
System and method for determining the location of a catheter during an intra-body medical procedure
A system and method of displaying at least one point-of-interest of a body during an intra-body medical procedure. The method is effected by (a) establishing a location of the body; (b) establishing a location of an imaging instrument being for imaging at least a portion of the body; (c) defining at least one projection plane being in relation to a projection plane of the imaging instrument; (d) acquiring at least one point-of-interest of the body; and (c) projection said at least one point-of-interest on said at least one projection plane; such that, in course of the procedure, the locations of the body and the imaging instrument are known, thereby the at least one point-of-interest is projectable on the at least one projection plane even in cases whereby a relative location of the body and the imaging instrument are changed.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Navigation system for cardiac therapies
InactiveUS7599730B2Accurate identificationReduce exposureSurgical needlesSurgical navigation systemsDisplay deviceNavigation system
An image guided catheter navigation system for navigating a region of a patient includes an imaging device, a tracking device, a controller, and a display. The imaging device generates images of the region of the patient. The tracking device tracks the location of the catheter in the region of the patient. The controller superimposes an icon representing the catheter onto the images generated from the imaging device based upon the location of the catheter. The display displays the image of the region with the catheter superimposed onto the image at the current location of the catheter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION INC
Navigation system for cardiac therapies
ActiveUS7697972B2Accurate identificationReduce exposureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesRadiologyDisplay device
An image guided navigation system for navigating a region of a patient includes an imaging device, a tracking device, a controller, and a display. The imaging device generates images of the region of a patient. The tracking device tracks the location of the instrument in a region of the patient. The controller superimposes an icon representative of the instrument onto the images generated from the imaging device based upon the location of the instrument. The display displays the image with the superimposed instrument. The images and a registration process may be synchronized to a physiological event. The controller may also provide and automatically identify an optimized site to navigate the instrument to.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
Methods and devices for performing procedures within the ear, nose, throat and paranasal sinuses
Devices, systems and methods for performing image guided interventional and surgical procedures, including various procedures to treat sinusitis and other disorders of the paranasal sinuses, ears, nose or throat.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
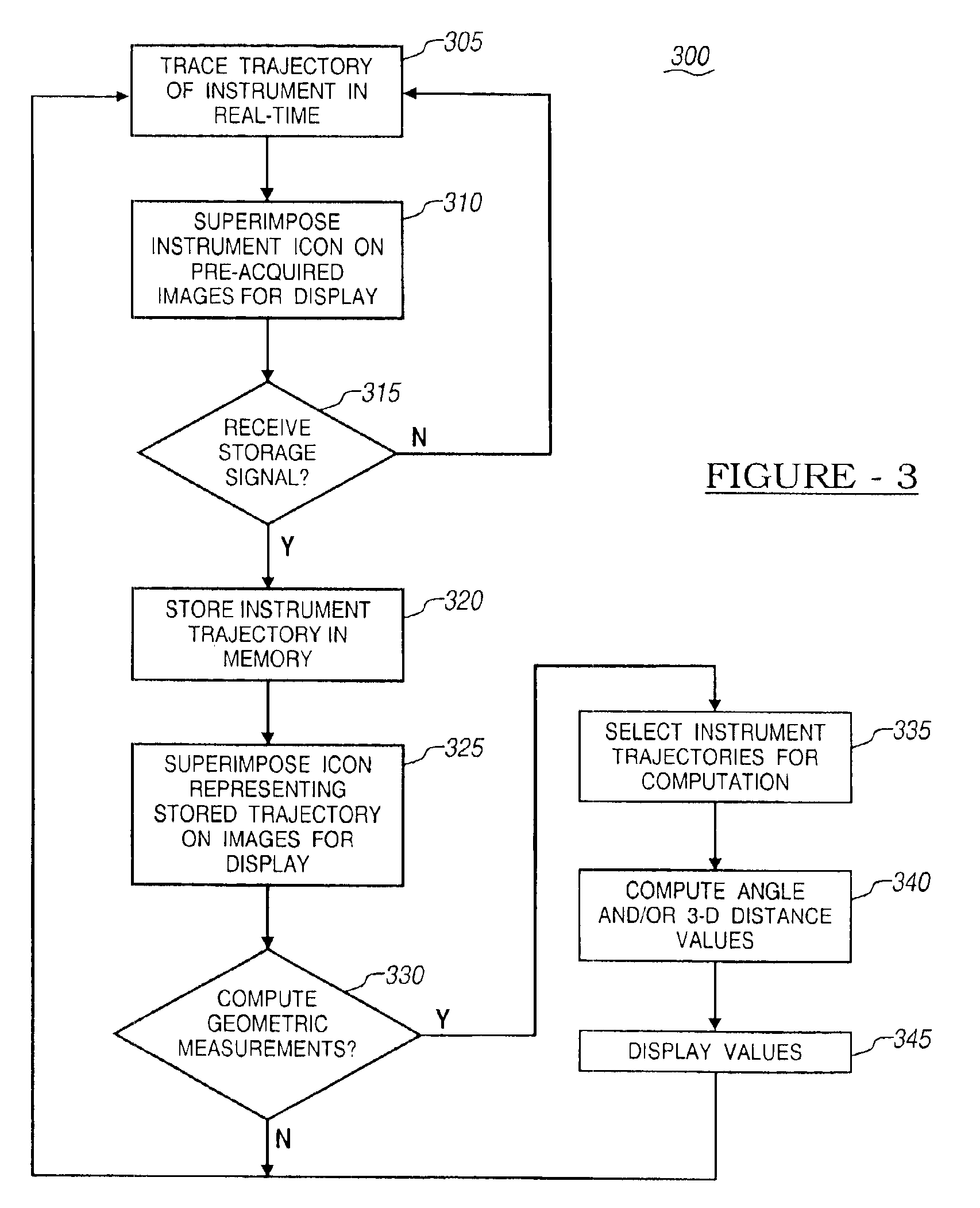
Trajectory storage apparatus and method for surgical navigation systems
InactiveUS6920347B2Saving additional trajectoryUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsNavigation systemTime trajectory
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for use within an image-guided surgical navigation system for the storage and measurement of trajectories for surgical instruments. An icon representing the real-time trajectory of a tracked instrument is overlaid on one or more pre-acquired images of the patient. At the surgeon's command, the navigation system can store multiple trajectories of the instrument and create a static icon representing each saved trajectory for display. The surgeon may also measure a planar angle between any two trajectories. The angle is computed in the plane of the image, and therefore will be computed separately for each image displayed. Furthermore, the surgeon has the option of computing and displaying the three-dimensional distance between two points defined by any two trajectories.
Owner:MEDTRONIC NAVIGATION
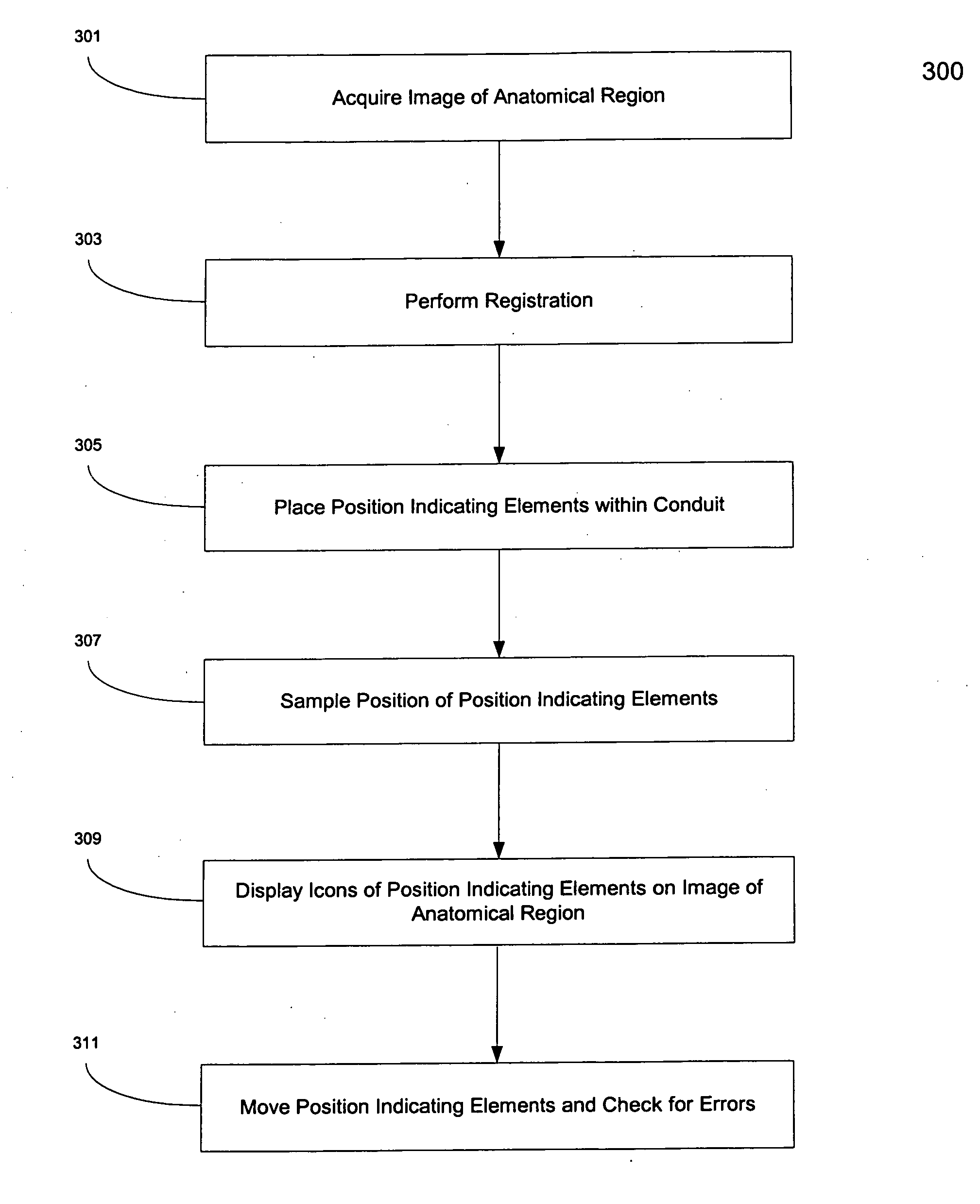
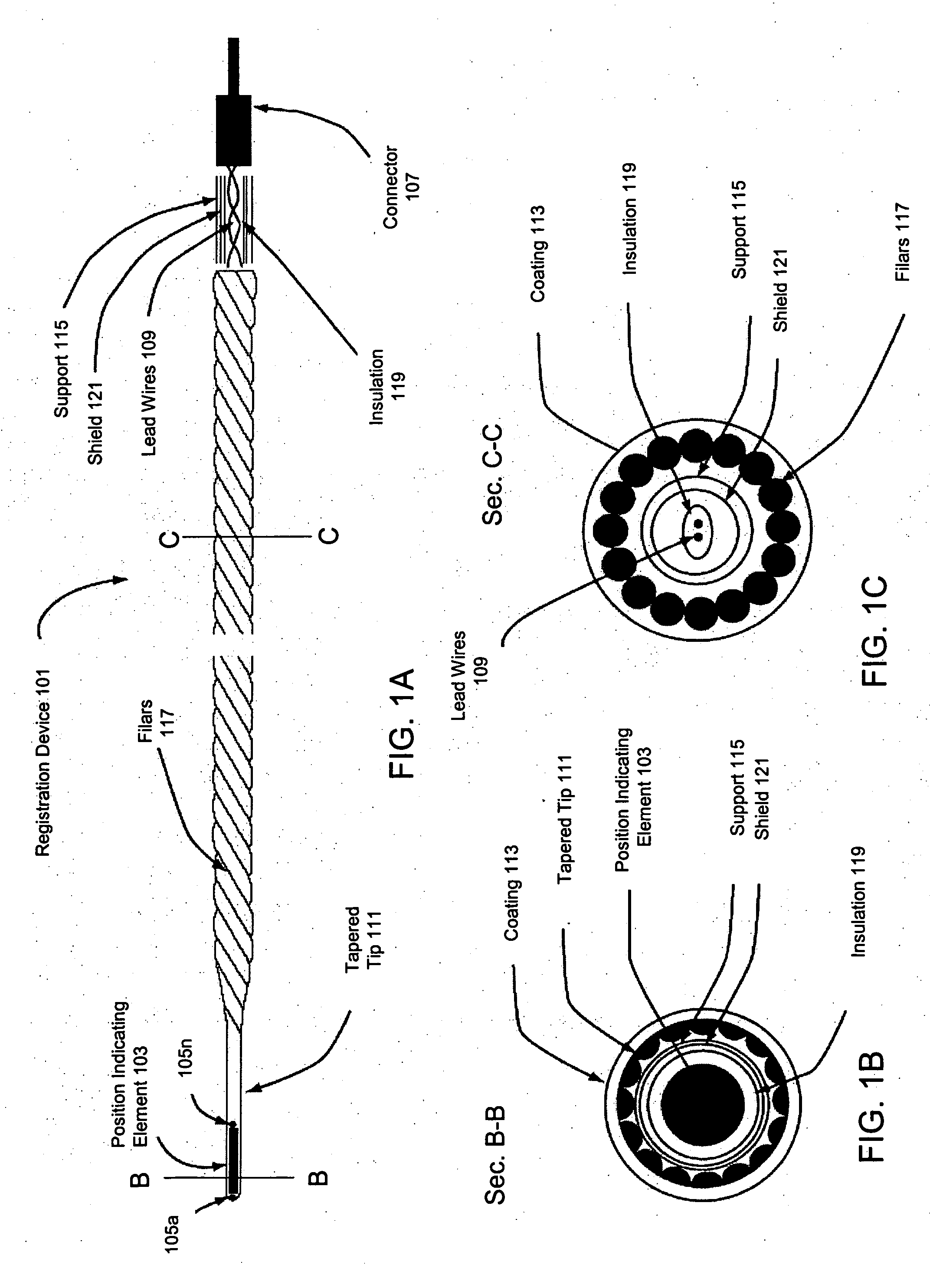
Method and apparatus for registration, verification, and referencing of internal organs
InactiveUS20050182319A1Sufficient informationPrevent material seeping into the deviceAudiometeringCatheterOrgan systemBiomedical engineering
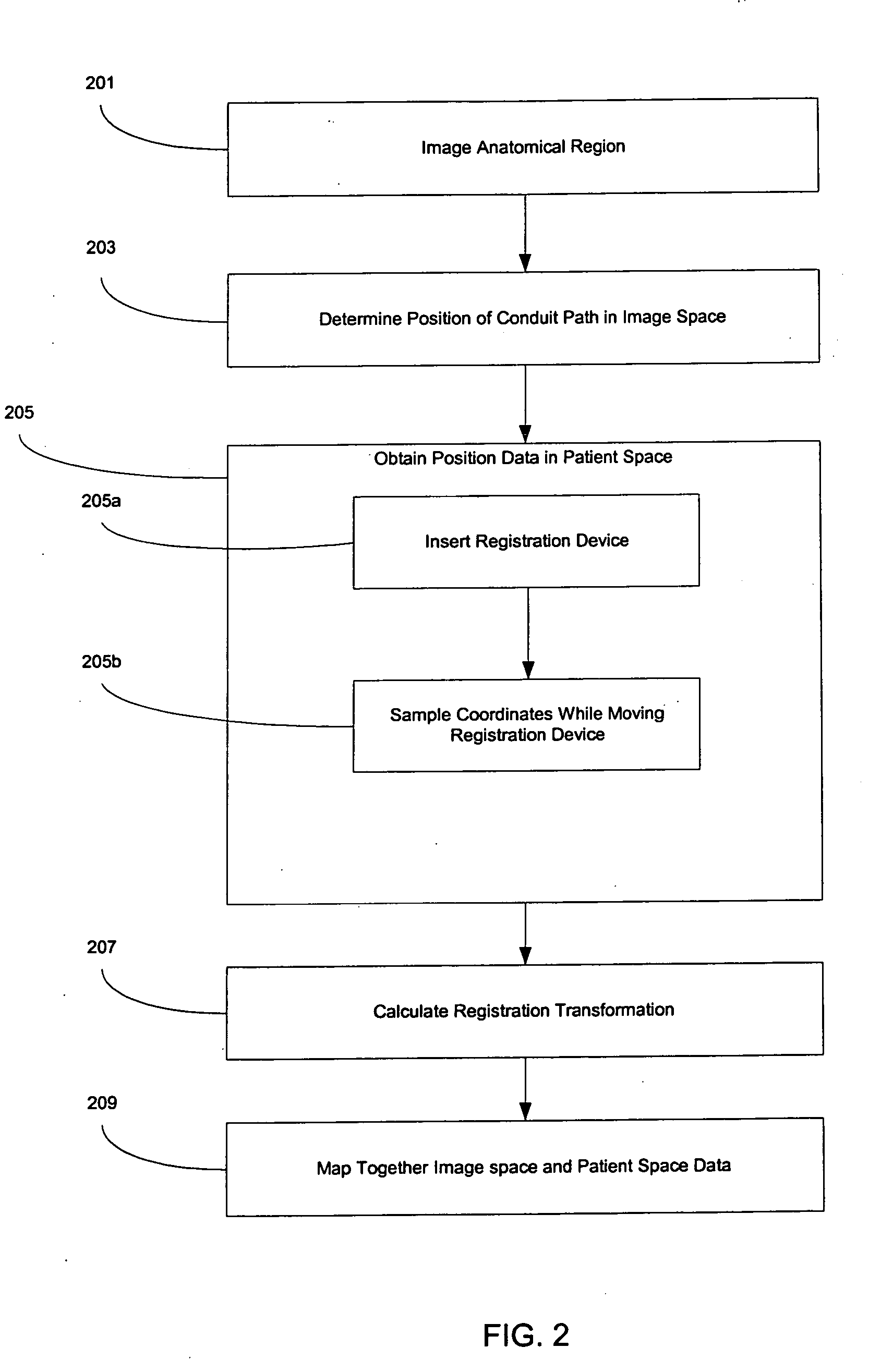
Systems and methods for registering, verifying, dynamically referencing, and navigating an anatomical region of interest of a patient are provided. In one embodiment, the anatomical region of interest is imaged using an imaging device such as, for example, an x-ray device. A tracked registration device may then be removably inserted in a conduit within the anatomical region and the position of the registration device may be sampled by a tracking device as the registration device is moved within the anatomical region through the catheter. The sampled position data is registered to the image data to register the path of the conduit to the anatomical region of interest. The same or a similar device may be used to dynamically reference the movements affecting the anatomical region and modify the registration in real time. The registration may also be verified.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
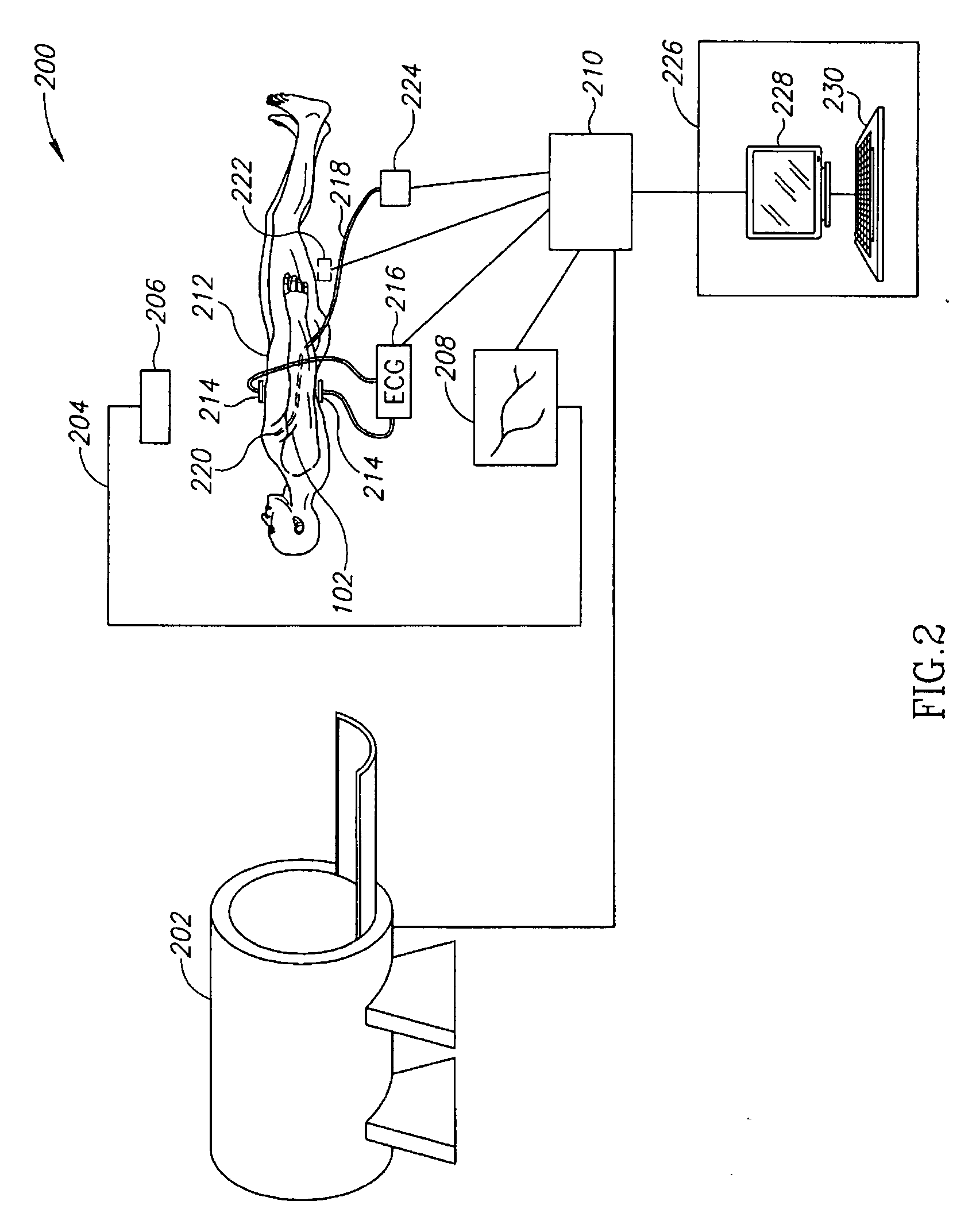
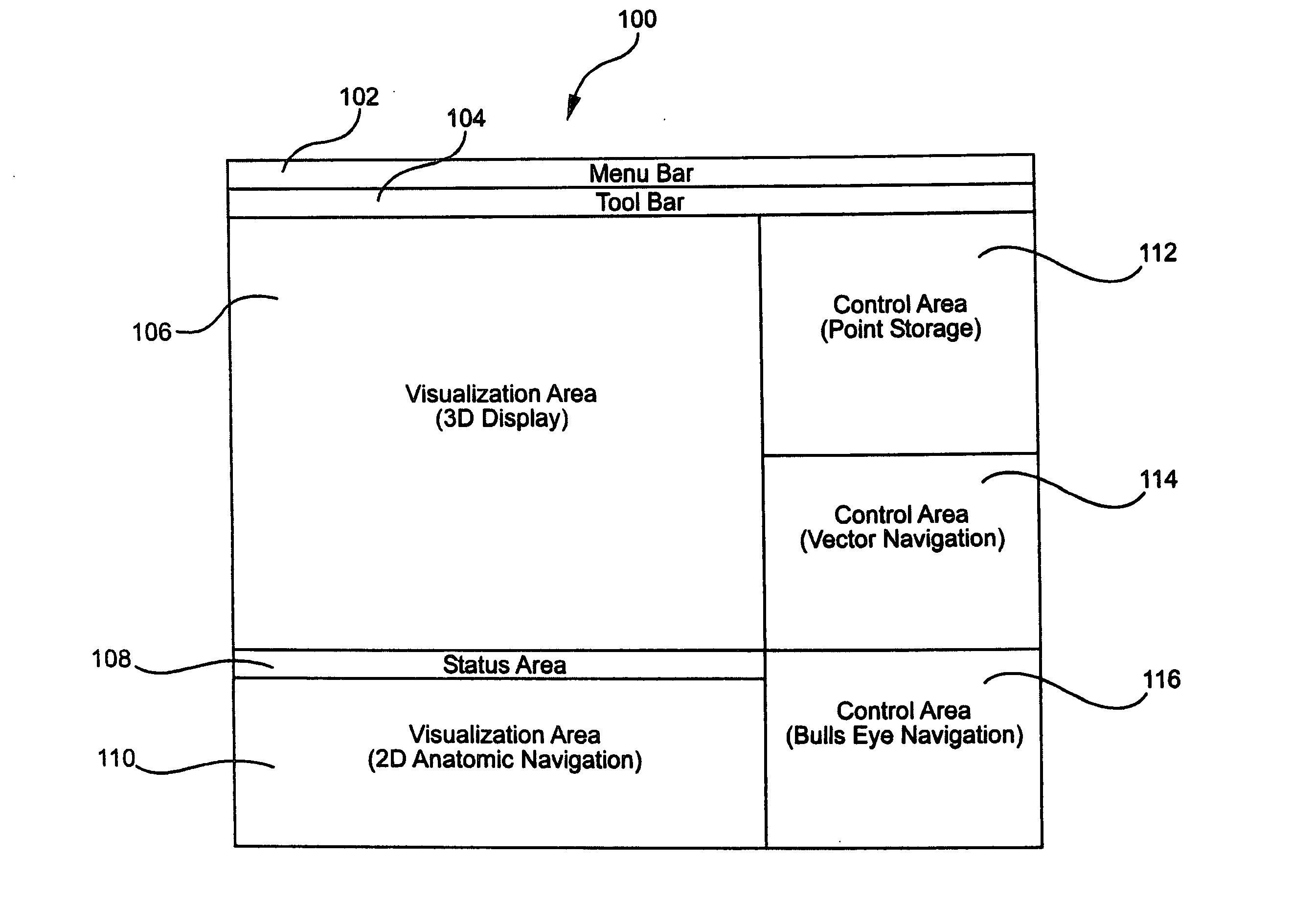
Multi-user touch-based control of a remote catheter guidance system (RCGS)
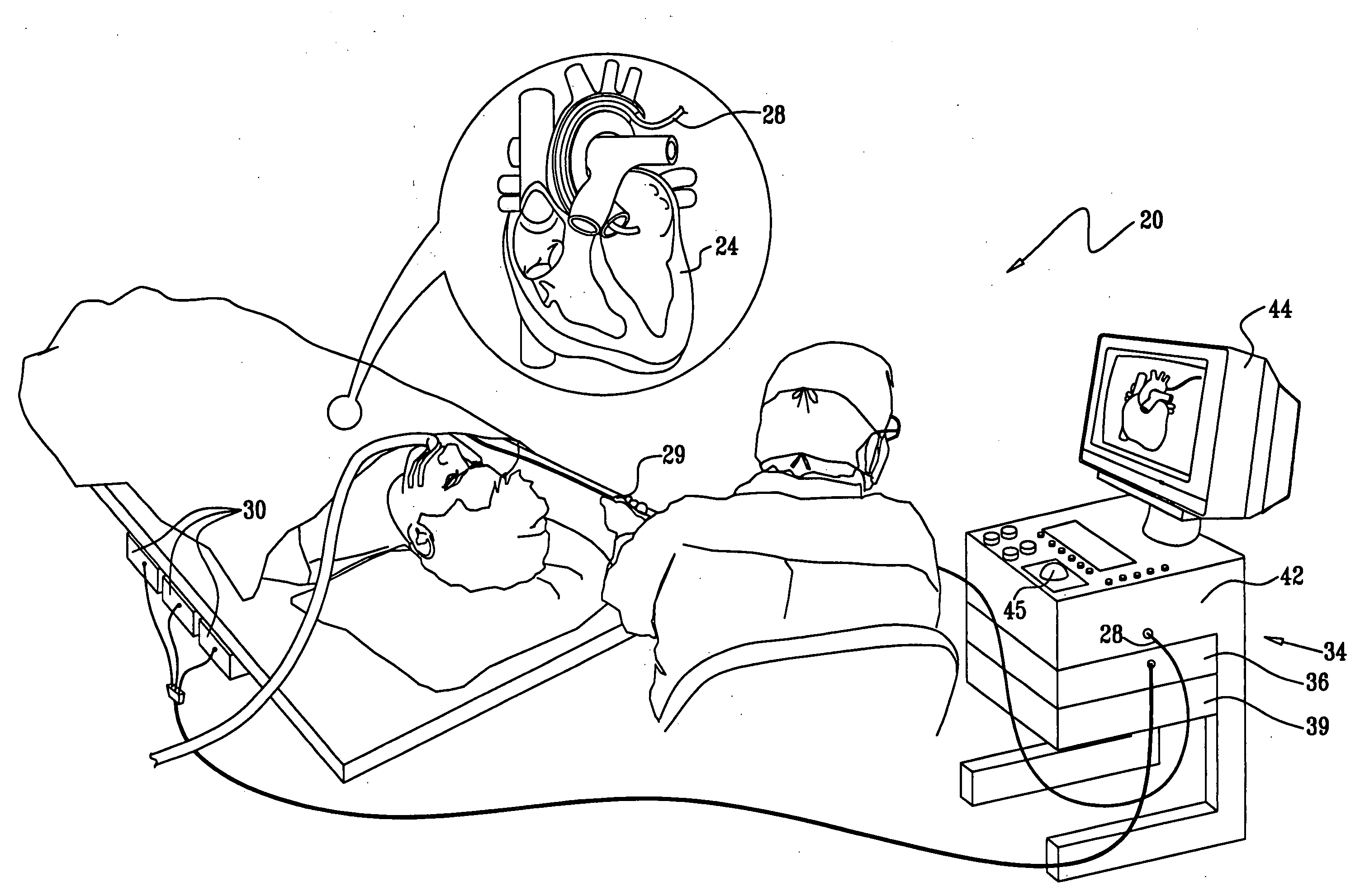
ActiveUS8920368B2Mechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesElectrocardiographyGuidance systemControl system
A control system for a medical remote catheter guidance system includes an ECU, a computer-readable memory coupled to the ECU, and user interface (UI) logic stored in the memory configured to be executed by the ECU. The user interface logic receives input from a touch screen display with respect to a view of an anatomical model, associates a user type with the input, and interprets the input according to the associated user type and input. The user interface logic may be further configured to receive simultaneous inputs from at least two different users and to associate different user types with each of said simultaneous inputs. The user interface logic may associate each input with a user type according to a location of the input on the touch screen display.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Implantable product with improved aqueous interface characteristics and method for making and using same
InactiveUS20050129735A1Rapidly and accurately visualizedEliminates air-interference issueUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsStentsLaparoscopyCardiac echo
An implantable medical device including a porous membrane that is treated with a hydrophilic substance to obtain rapid optimum visualization using technology for viewing inside of a mammalian body. These technologies include ultrasound echocardiography and video imaging such as that used during laparoscopic procedures.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
System and method of recording and displaying in context of an image a location of at least one point-of-interest in a body during an intra-body medical procedure
The present invention provides a method of recording and displaying in context of an image a location of at least one point-of-interest in a body during an intra-body medical procedure. The method is effected by (a) establishing a location of the body; (b) inserting at least one catheter into a portion of the body, the at least one catheter including a first location implement; (c) using an imaging instrument for imaging the portion of the body; (d) establishing a location of the imaging instrument; (e) advancing the at least one catheter to at least one point-of-interest in the portion of the body and via a locating implement recording a location of the at least one point-of-interest; and (f) displaying and highlighting the at least one point-of-interest in context of an image of the portion of the body, the image being generated by the imaging instrument; such that, in course of the procedure, the locations of the body, the at least one catheter and the imaging instrument are known, thereby the at least one point-of-interest is projectable and displayable in context of the image even in cases whereby a relative location of the body and the imaging instrument are changed.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
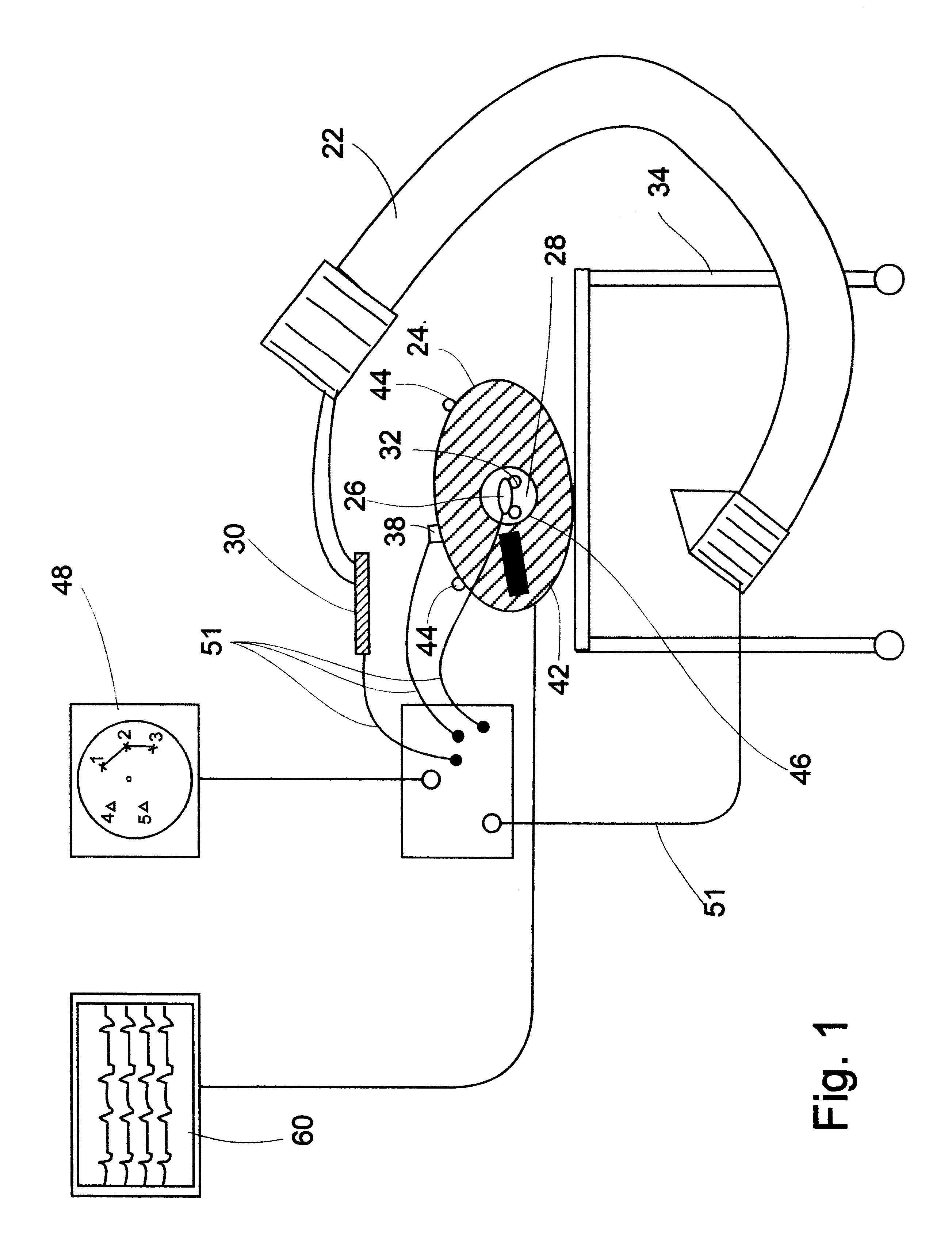
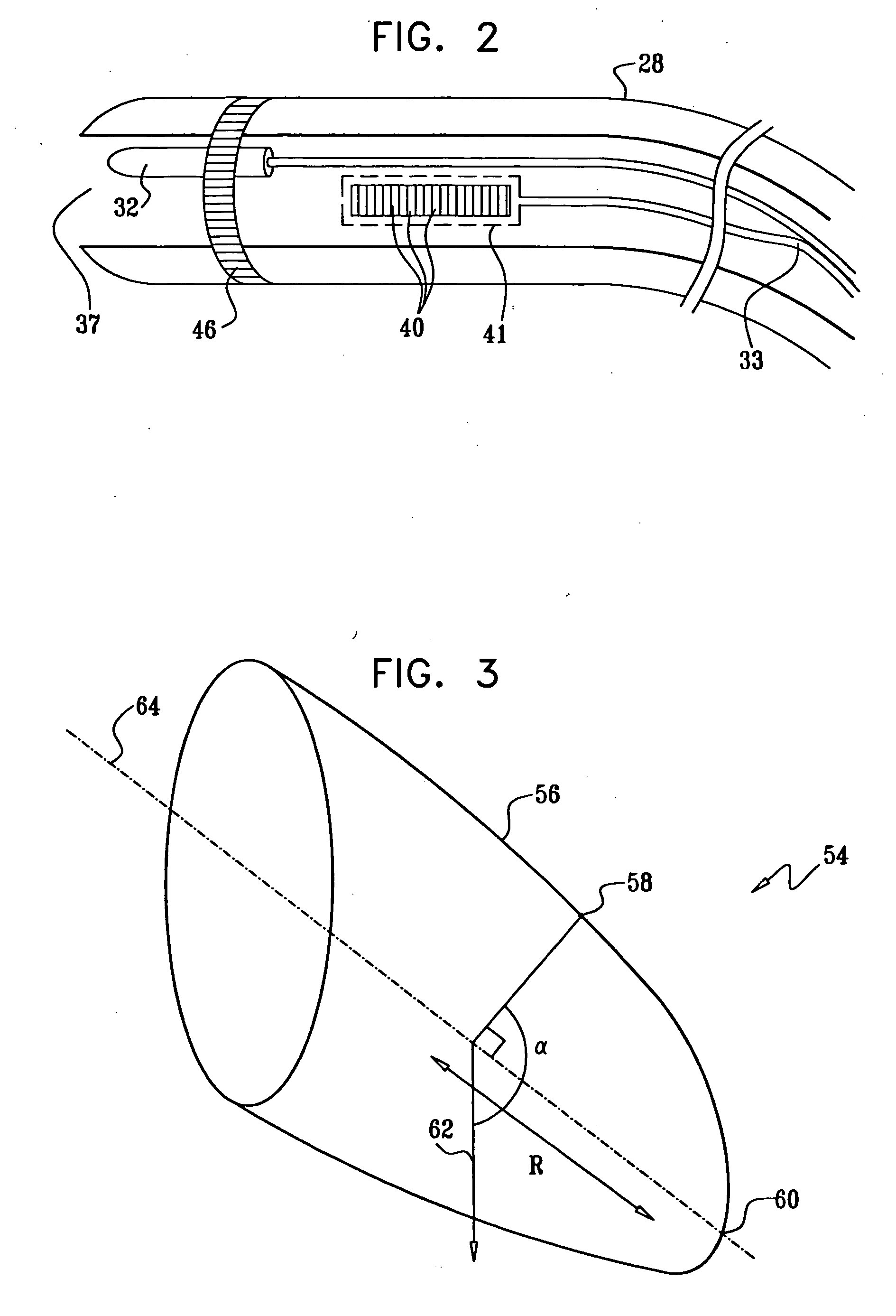
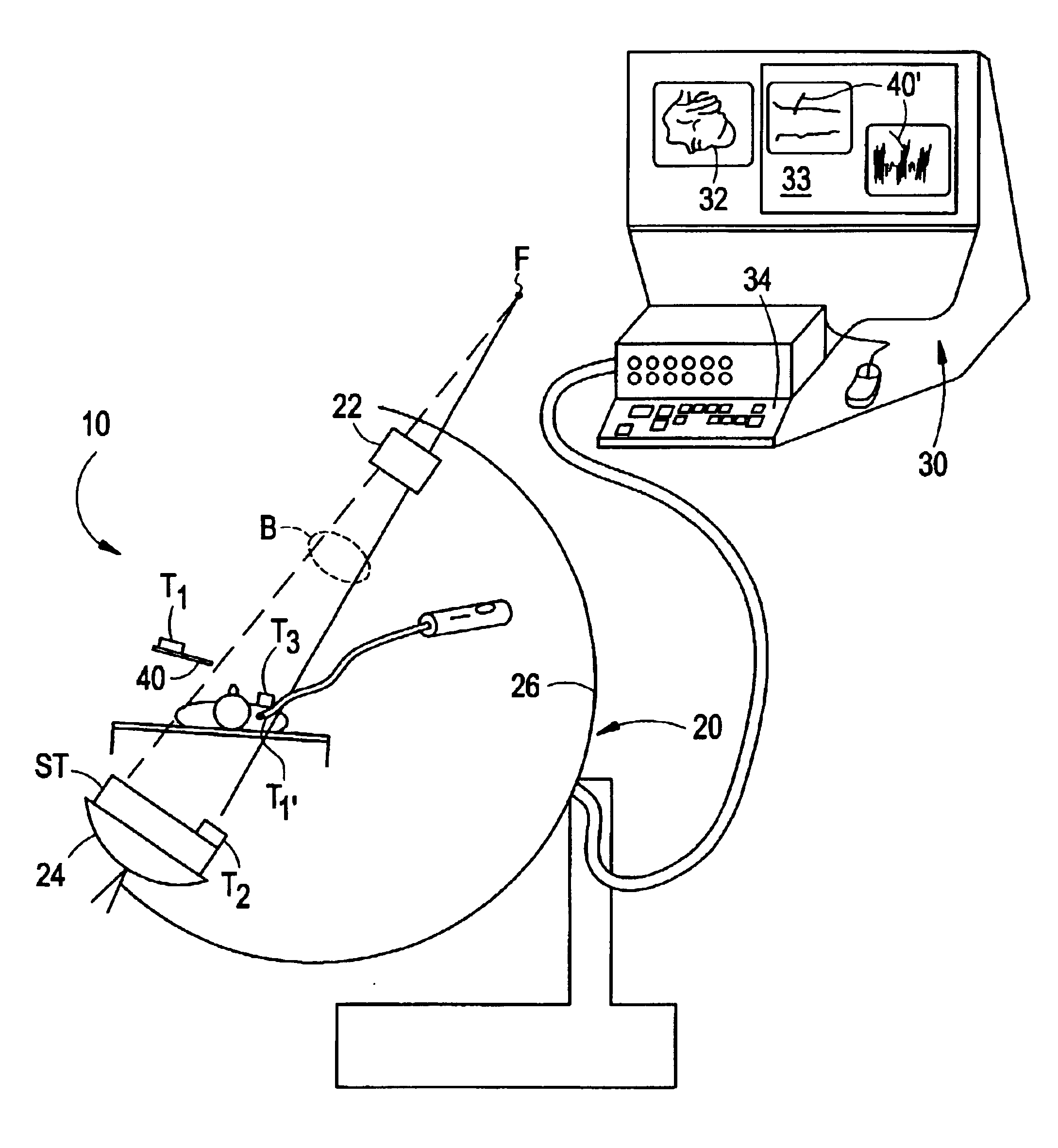
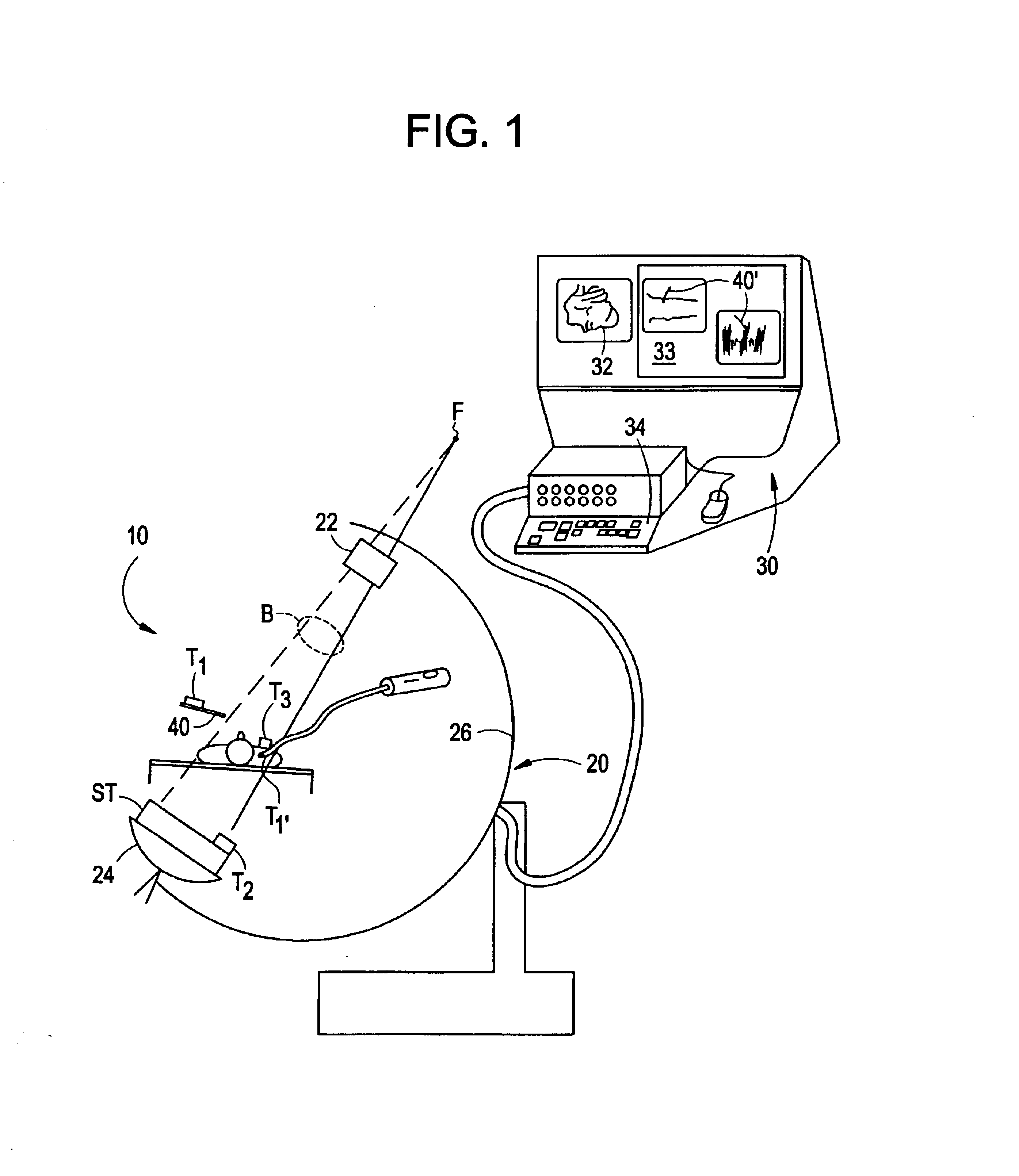
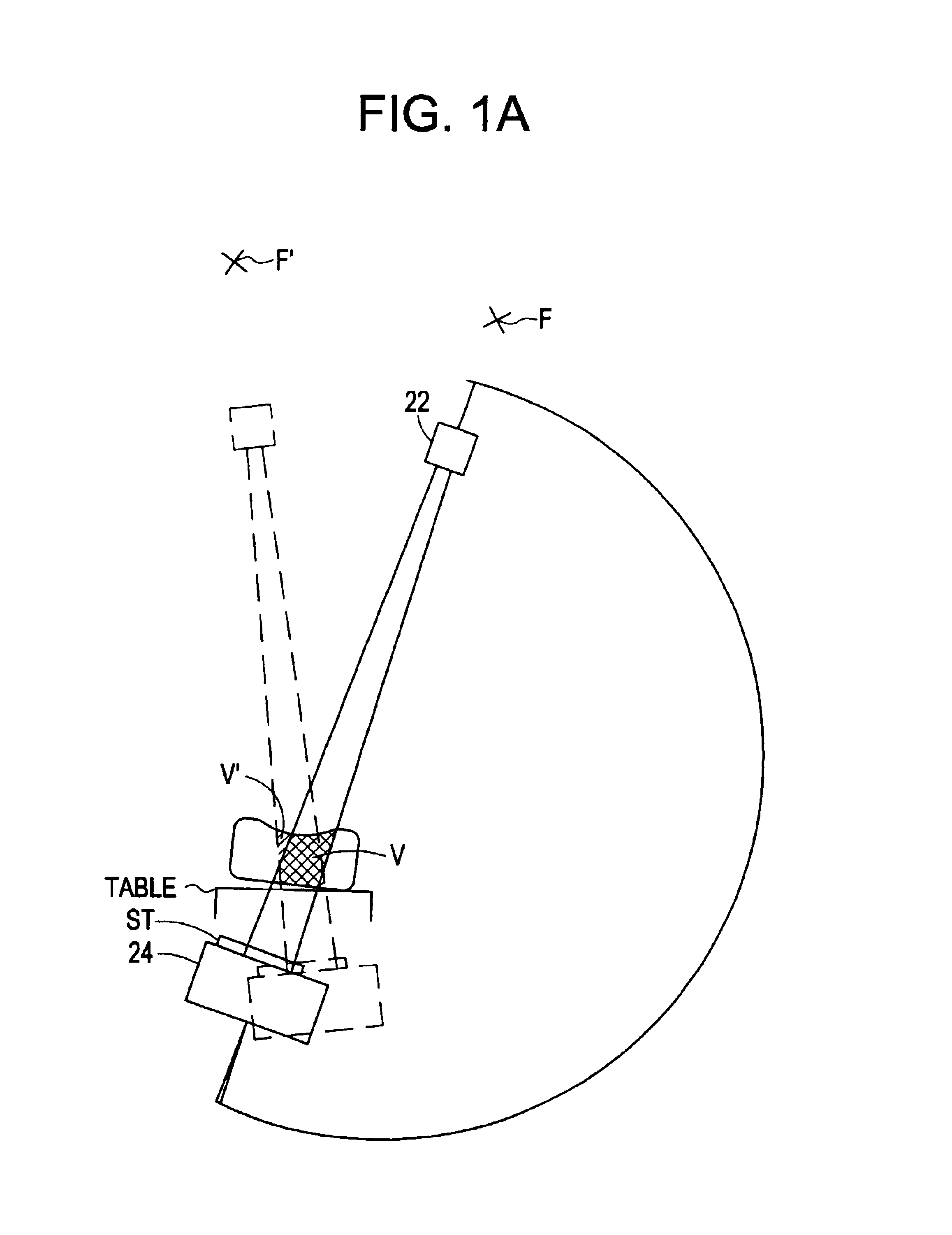
Fluoroscopic tracking and visualization system
InactiveUS6856827B2Quickly and accurately determineImprove accuracyX-ray spectral distribution measurementX-ray/infra-red processesDisplay deviceComputer vision
A system for surgical imaging and display of tissue structures of a patient, including a display and an image processor for displaying such images in coordination with a tool image to facilitate manipulation of the tool during the surgical procedure. The system is configured for use with a fluoroscope such that at least one image in the display is derived from the fluoroscope at the time of surgery. A fixture is affixed to an imaging side of the fluoroscope for providing patterns of an of array markers that are imaged in each fluoroscope image. A tracking assembly having a plurality of tracking elements is operative to determine positions of said fixture and the patient. One of the tracking elements is secured against motion with respect to the fixture so that determining a position of the tracking element determines a position of all the markers in a single measurement.
Owner:STRYKER EURO HLDG I LLC +1
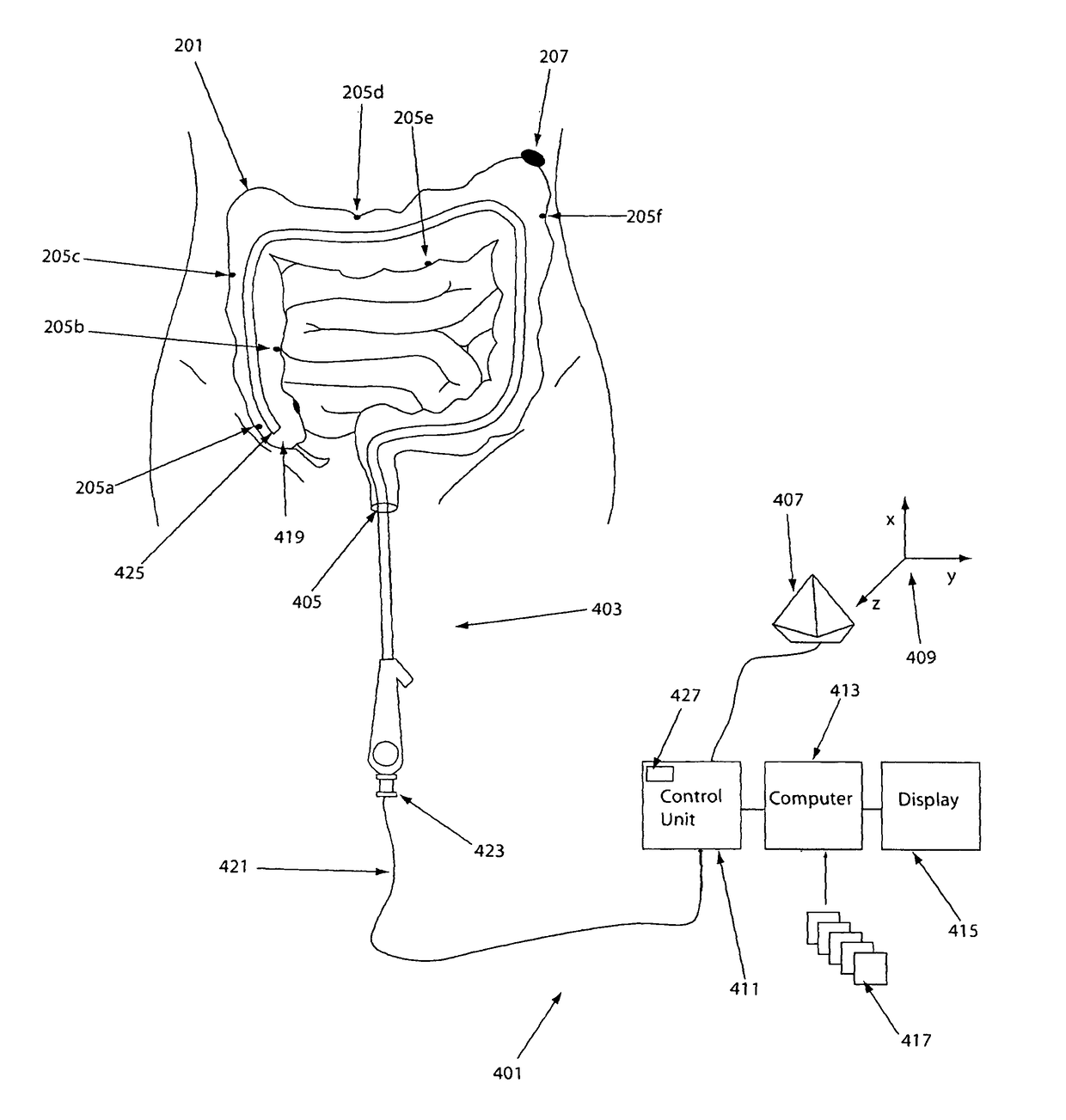
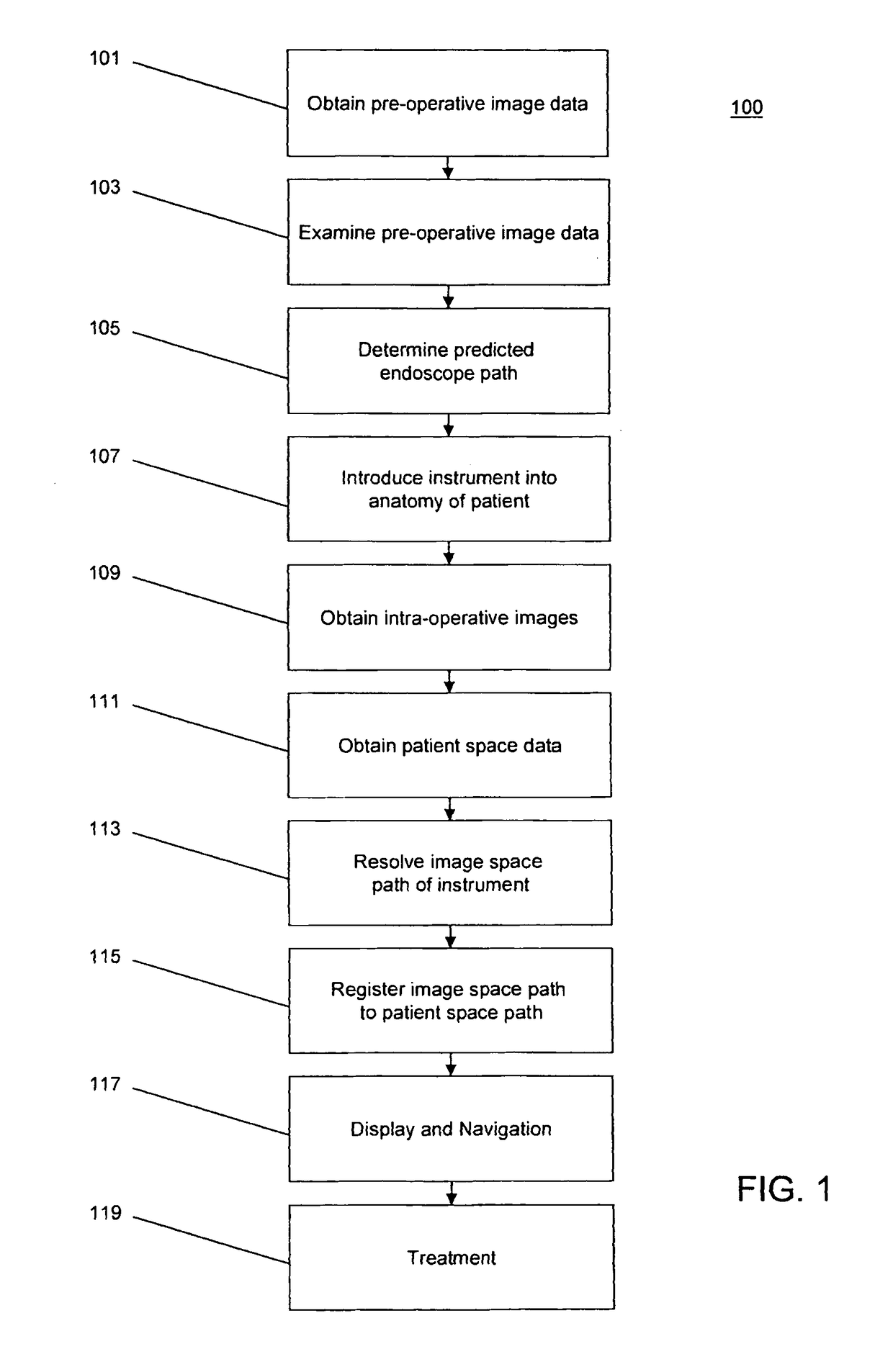
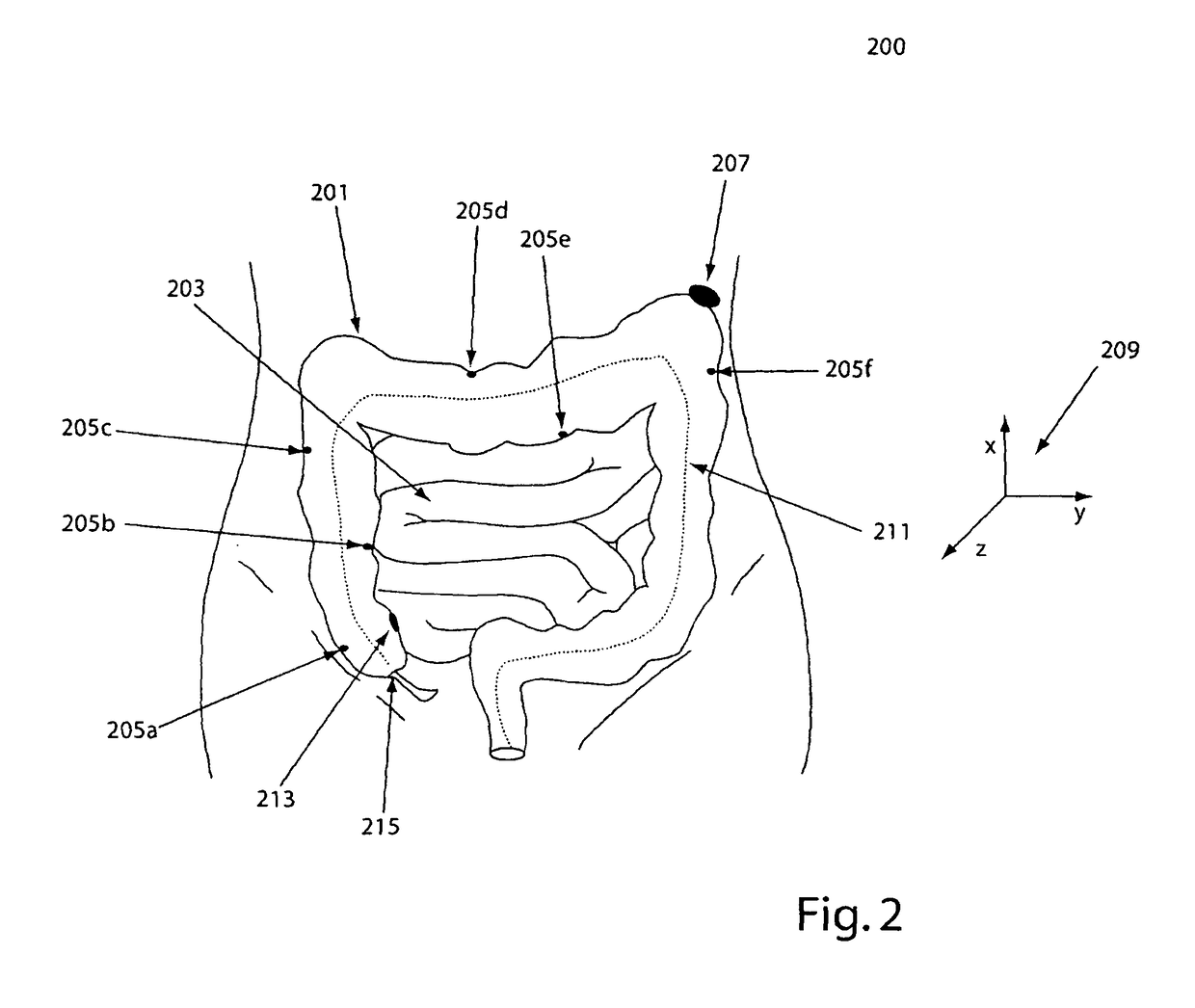
System, method and devices for navigated flexible endoscopy
The invention provides a method and system for performing an image-guided endoscopic medical procedure. The invention may include registering image-space coordinates of a path of a medical instrument within the anatomy of a patient to patient-space coordinates of the path of the medical instrument within the anatomy of the patient. In some embodiments, the image space coordinates of the path of the medical instrument may be predicted coordinates such as, for example, a calculated centerline through a conduit-like organ, or a calculated “most likely path” of the medical instrument within the anatomy of the patient. In other embodiments, the path of the medical instrument may be an actual path determined using intra-operative images of the patient's anatomy with the medical instrument inserted therein. The registered instrument may then be navigated to one or more items of interest for performance of the endoscopic medical procedure.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
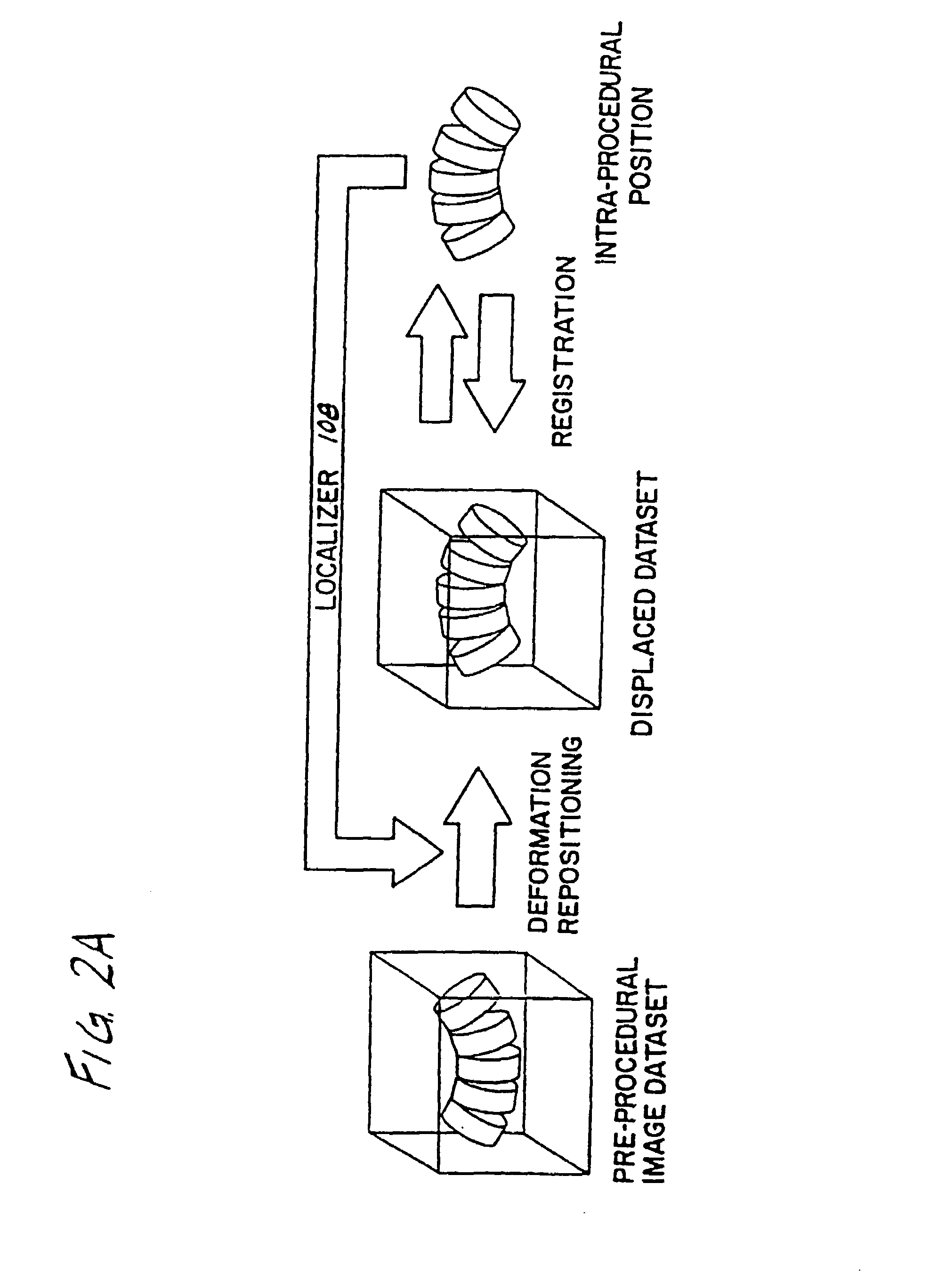
Surgical navigation systems including reference and localization frames
A system for use during a medical or surgical procedure on a body. The system generates an image representing the position of one or more body elements during the procedure using scans generated by a scanner prior or during the procedure. The image data set has reference points for each of the body elements, the reference points of a particular body element having a fixed spatial relation to the particular body element. The system includes an apparatus for identifying, during the procedure, the relative position of each of the reference points of each of the body elements to be displayed. The system also includes a processor for modifying the image data set according to the identified relative position of each of the reference points during the procedure, as identified by the identifying apparatus, said processor generating a displaced image data set representing the position of the body elements during the procedure. The system also includes a display utilizing the displaced image data set generated by the processor, illustrating the relative position of the body elements during the procedure. Methods relating to the system are also disclosed. Also disclosed are devices for use with a surgical navigation system having a sensor array which is in communication with the device to identify its position. The device may be a reference frame for attachment of a body part of the patient, such as a cranial reference arc frame for attachment to the head or a spine reference arc frame for attachment to the spine. The device may also be a localization frame for positioning an instrument relative to a body part, such as a localization biopsy guide frame for positioning a biopsy needle, a localization drill guide assembly for positioning a drill bit, a localization drill yoke assembly for positioning a drill, or a ventriculostomy probe for positioning a catheter.
Owner:SURGICAL NAVIGATION TECH +1
Segmentation and registration of multimodal images using physiological data
InactiveUS20070049817A1Improve accuracyMore rapidImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionData system
Systems and methods are provided for registering maps with images, involving segmentation of three-dimensional images and registration of images with an electro-anatomical map using physiological or functional information in the maps and the images, rather than using only location information. A typical application of the invention involves registration of an electro-anatomical map of the heart with a preacquired or real-time three-dimensional image. Features such as scar tissue in the heart, which typically exhibits lower voltage than healthy tissue in the electro-anatomical map, can be localized and accurately delineated on the three-dimensional image and map.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
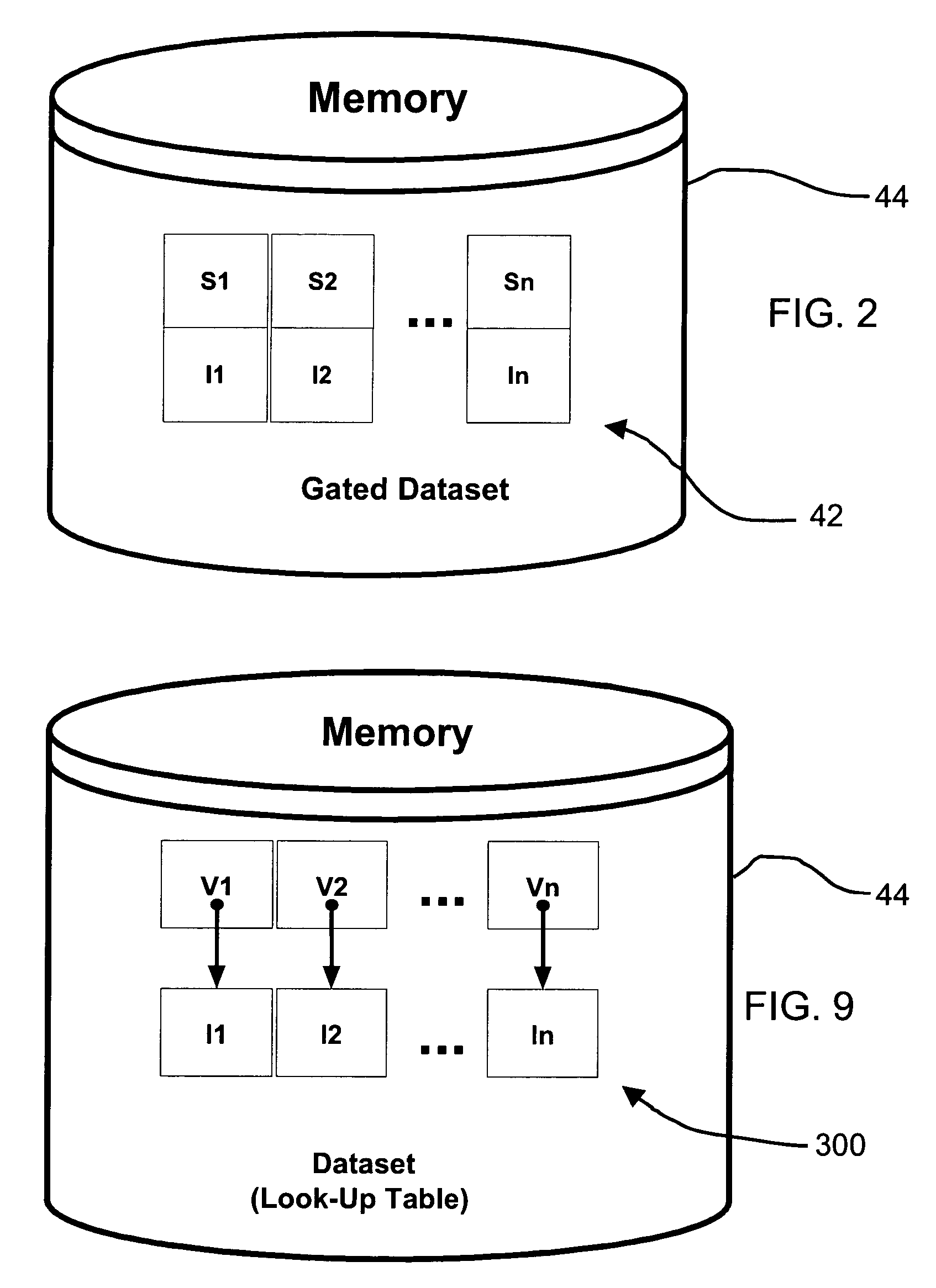
Methods, apparatuses, and systems useful in conducting image guided interventions
Methods, apparatuses, and systems relating to image guided interventions on dynamic tissue. One embodiment is a method that includes creating a dataset that includes images, one of the images depicting a non-tissue internal reference marker, being linked to non-tissue internal reference marker positional information, and being at least 2-dimensional. Another embodiment is a method that includes receiving a position of an instrument reference marker coupled to an instrument; transforming the position into image space using a position of a non-tissue internal reference marker implanted in a patient; and superimposing a representation of the instrument on an image in which the non-tissue internal reference marker appears. Computer readable media that include machine readable instructions for carrying out the steps of the disclosed methods. Apparatuses, such as integrated circuits, configured to carry out the steps of the disclosed methods. Systems that include devices configured to carry out steps of the disclosed methods.
Owner:VERAN MEDICAL TECH
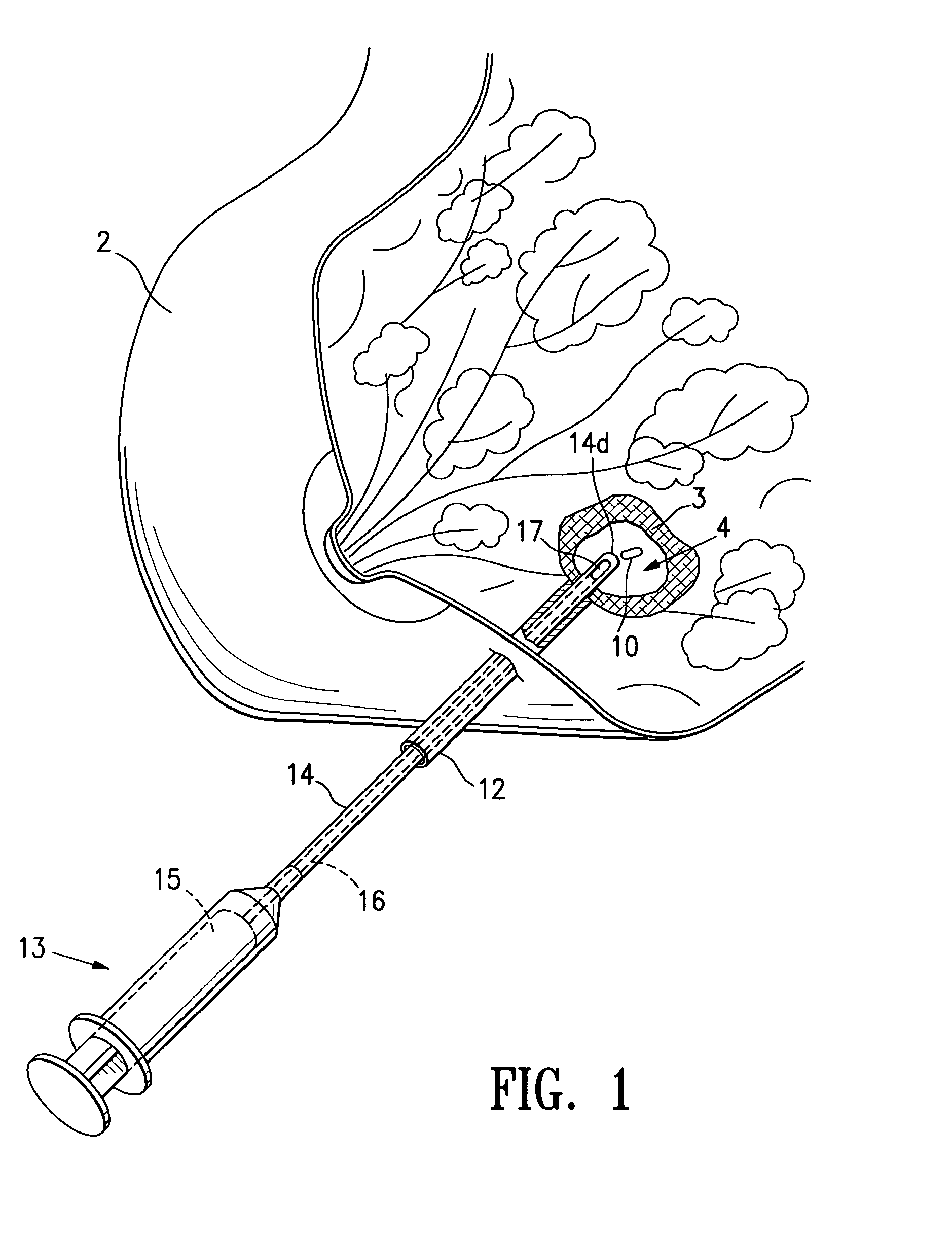
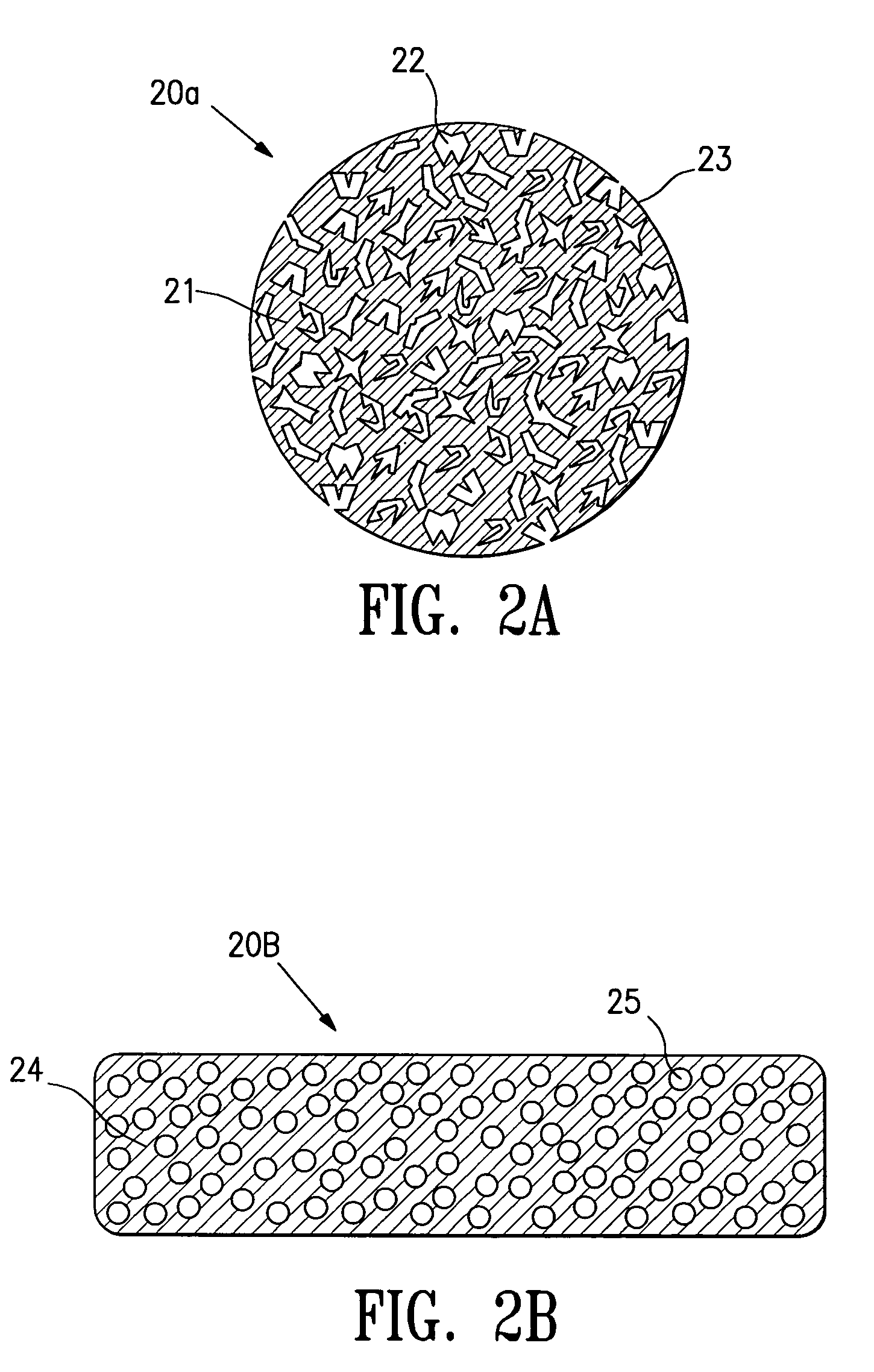
Tissue site markers for in vivo imaging
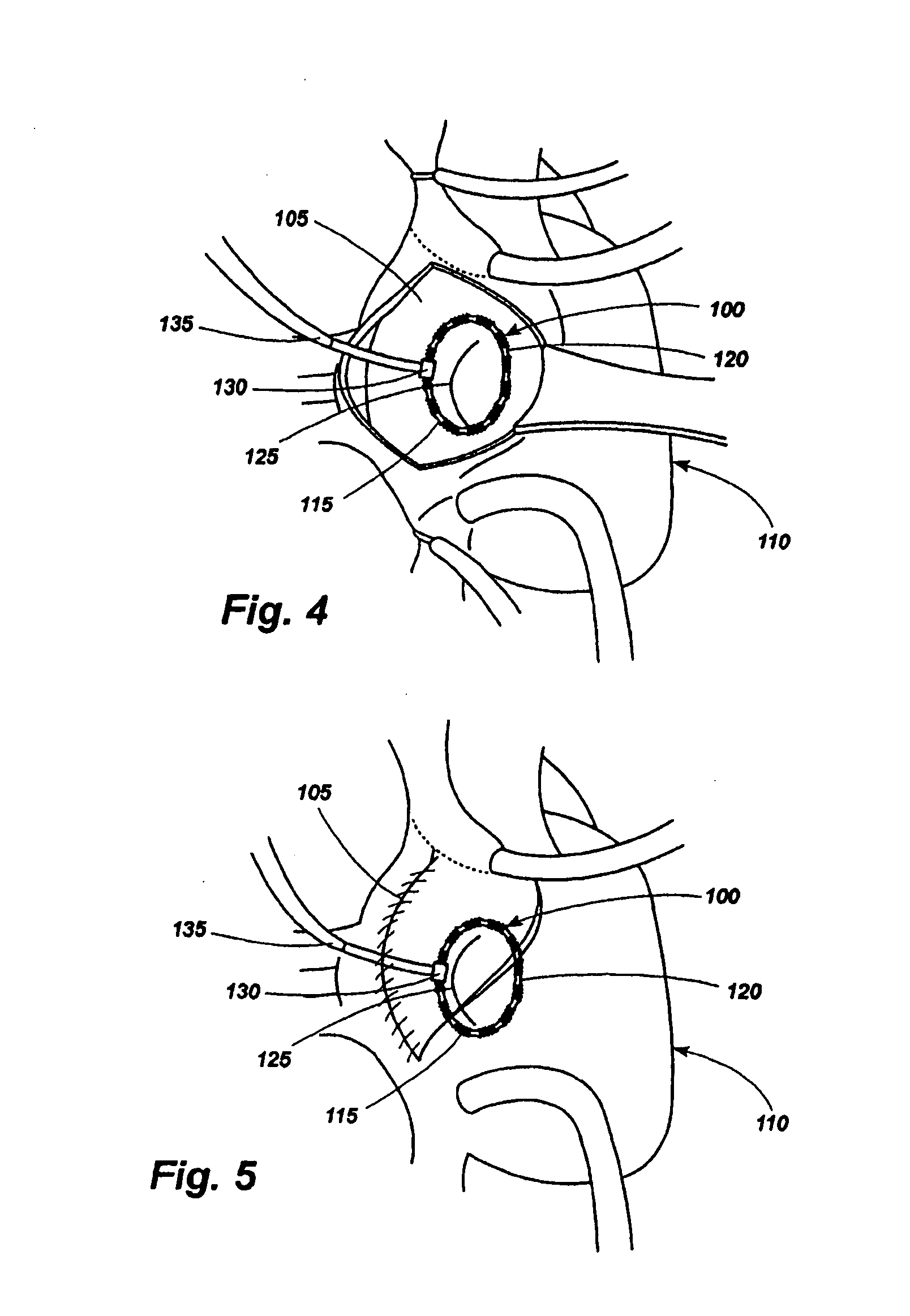
InactiveUS6993375B2Enhance acoustical reflective signature and signalEasy to detectLuminescence/biological staining preparationSurgical needlesContrast levelIn vivo
Owner:SENORX
Vascular image processing
InactiveUS20060036167A1The effect is accurateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterImaging processingData set
A method of estimating a position of a foreign object in the body, comprising: (a) providing a 3D data set of at least one blood vessel; (b) acquiring at least one 2D projection image of the vessel including the object; (c) registering the 2D projection image of the vessel to the 3D data set; and (d) using the registration to estimate a 3D position of said object restricted to be in a blood vessel, according to said 3D data set.
Owner:SHINA SYST
User interface for remote control of medical devices
InactiveUS20060025679A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSurgical manipulatorsRemote controlDisplay device
An interface for remotely controlling a medical device in a patient's body provides a two dimensional display of a three dimensional rendering of the operating region, and allows the user to select the orientation or location of the distal end of the medical device on the display and then operate a navigation system to cause the distal end of the medical device to approximately assume the selected orientation or location.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
Methods and devices for automated biopsy and collection of soft tissue
InactiveUS7226424B2Improved and more operationEasy and inexpensive to fabricateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesSingle-Use DeviceMultiple use
Instruments for performing percutaneous biopsy procedures are disclosed, which have advantageous features for improving functionality and performance over prior art devices. These instruments comprise two types, single-use devices, and multiple-use devices having active tissue capture capability. Improved features include the ability to retrieve and evaluate multiple tissue samples during a single insertion procedure, without physical handling of the samples, as well as constructional features, such as a molded tissue cassette housing, variant vacuum port embodiments suited for different tissue environments, and a method for backflushing the instrument to remove biological debris, among others.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
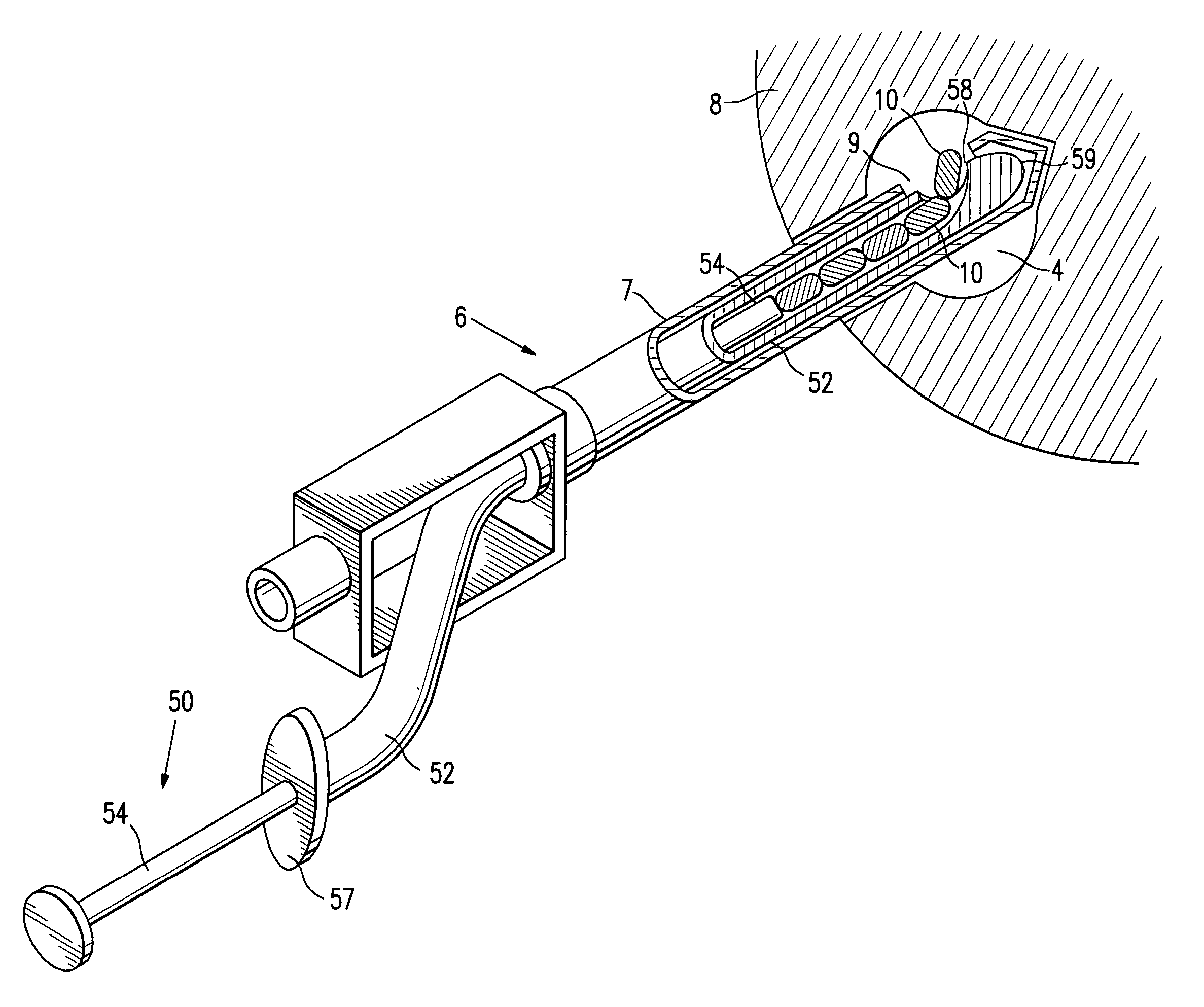
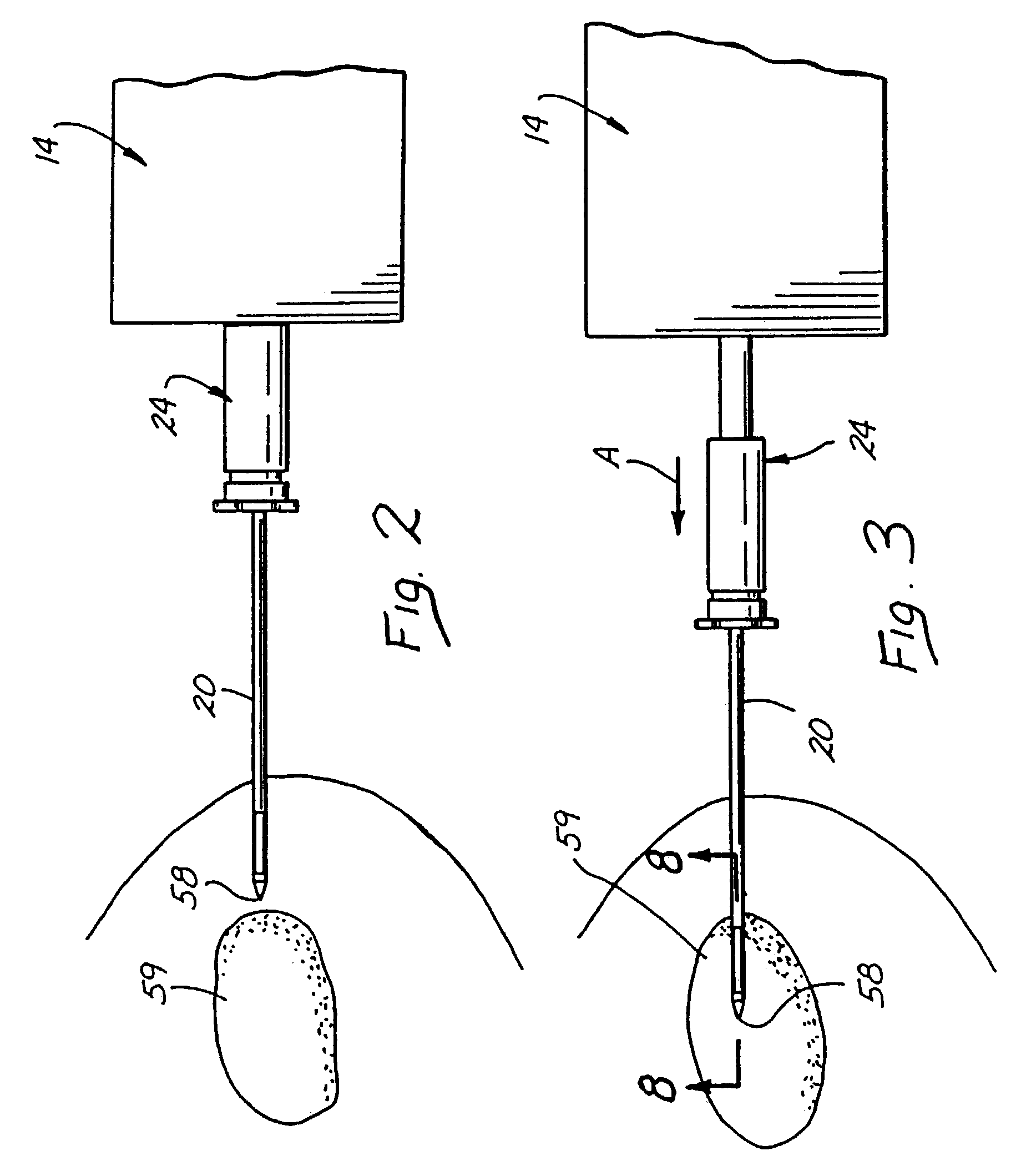
Cryocatheter for introduction into a body vessel together with medical investigation and treatment equipment
ActiveUS20070093710A1Load minimizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGuide needlesTherapeutic DevicesBlood vessel
A cryocatheter for introduction into a body vessel or into an organ, with a catheter inner surrounded by a catheter sheath, and with a catheter tip arranged at its distal end, with a feed line for an expansion or cooling agent arranged in the catheter sheath or the catheter inner, and with a balloon, arranged close to the catheter tip, which can be expanded and contracted again by means of the expansion and cooling agent, is to be constructed in such a way that by simple manipulation it can be positioned at a precise target position in the body vessel and, in addition, it minimizes the burden on the patient from invasive interventions. For this purpose, in accordance with the invention an image capture device, with at least one imaging sensor for mapping the region of the vessel around the balloon, is positioned in the region of the catheter tip.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
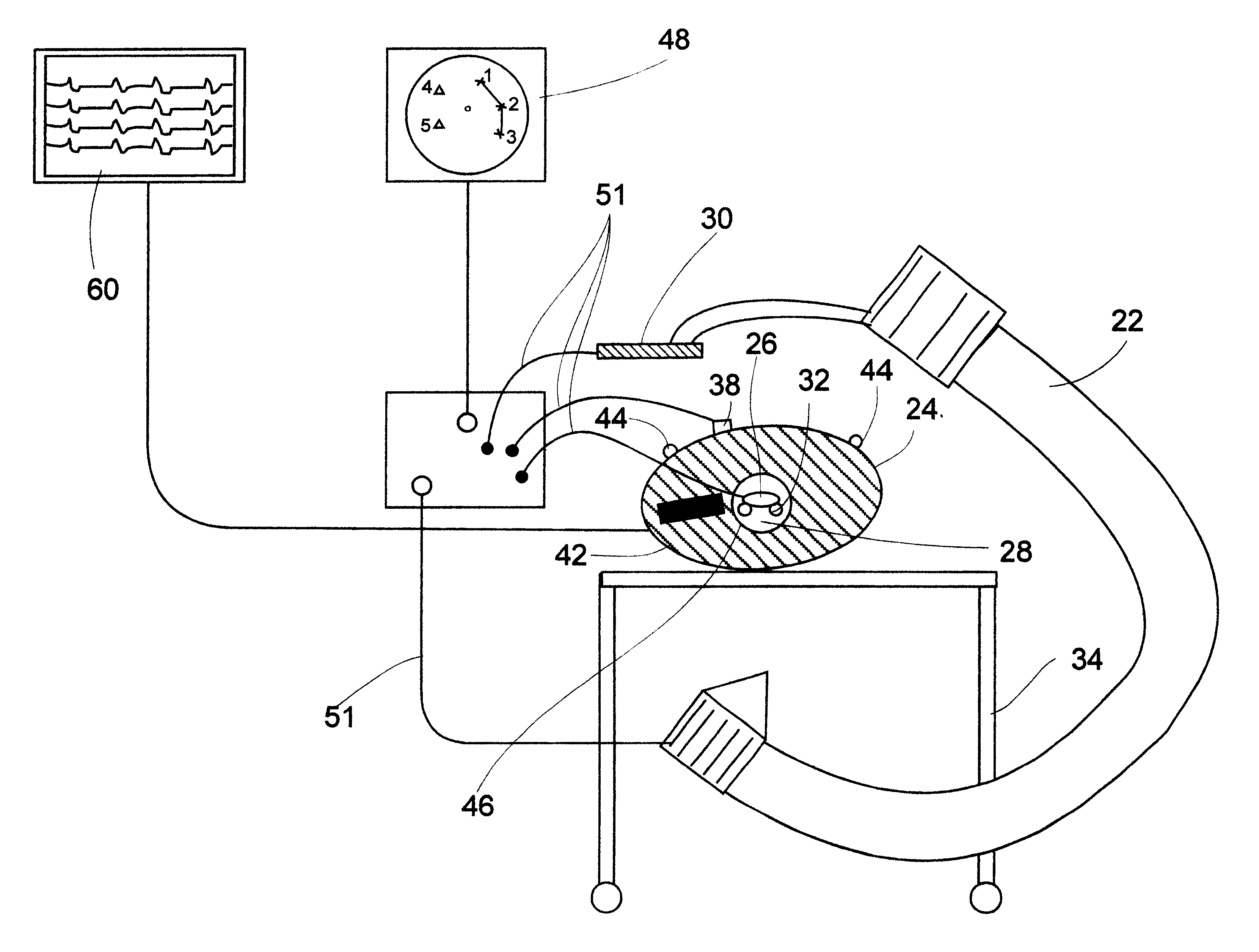
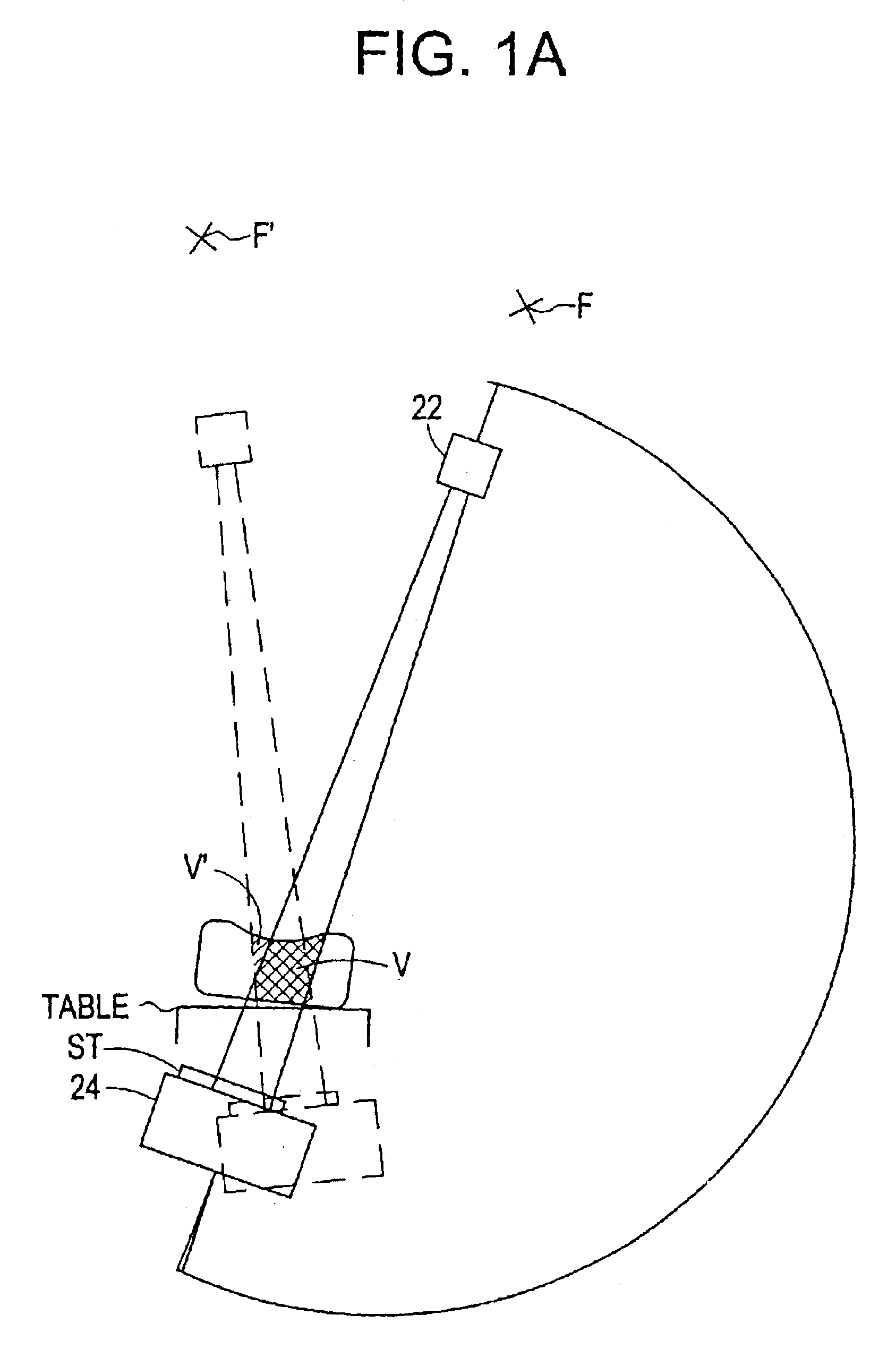
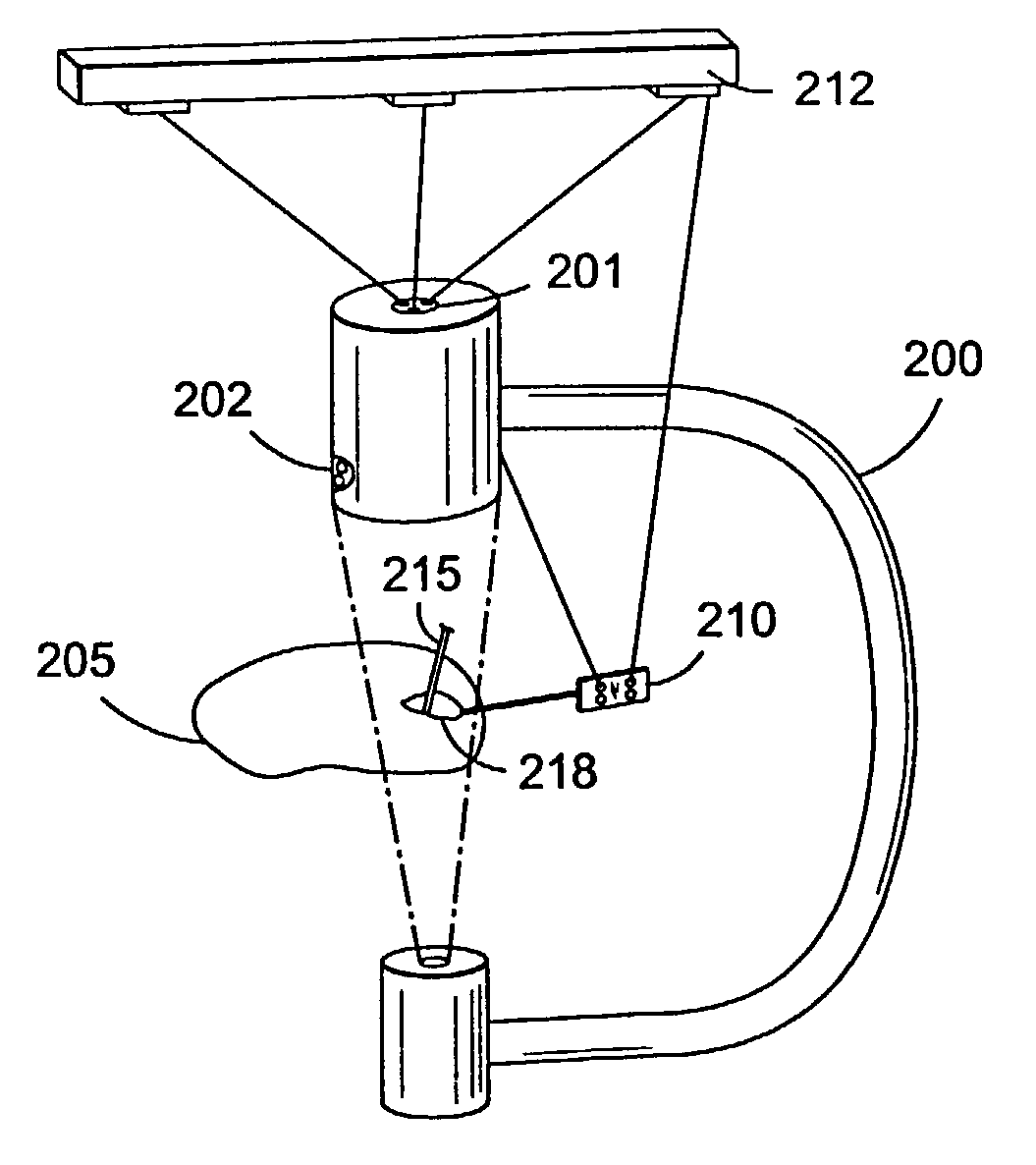
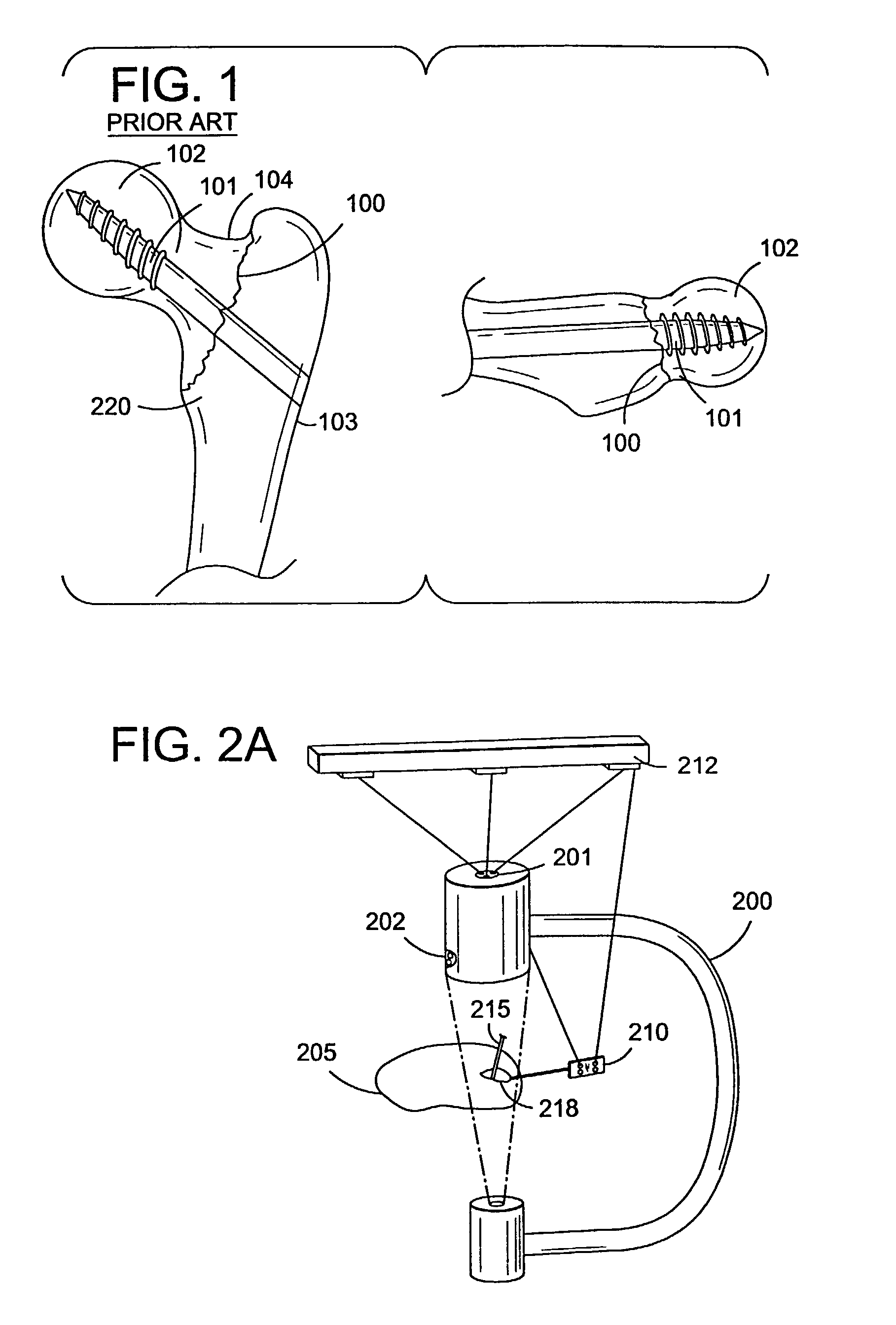
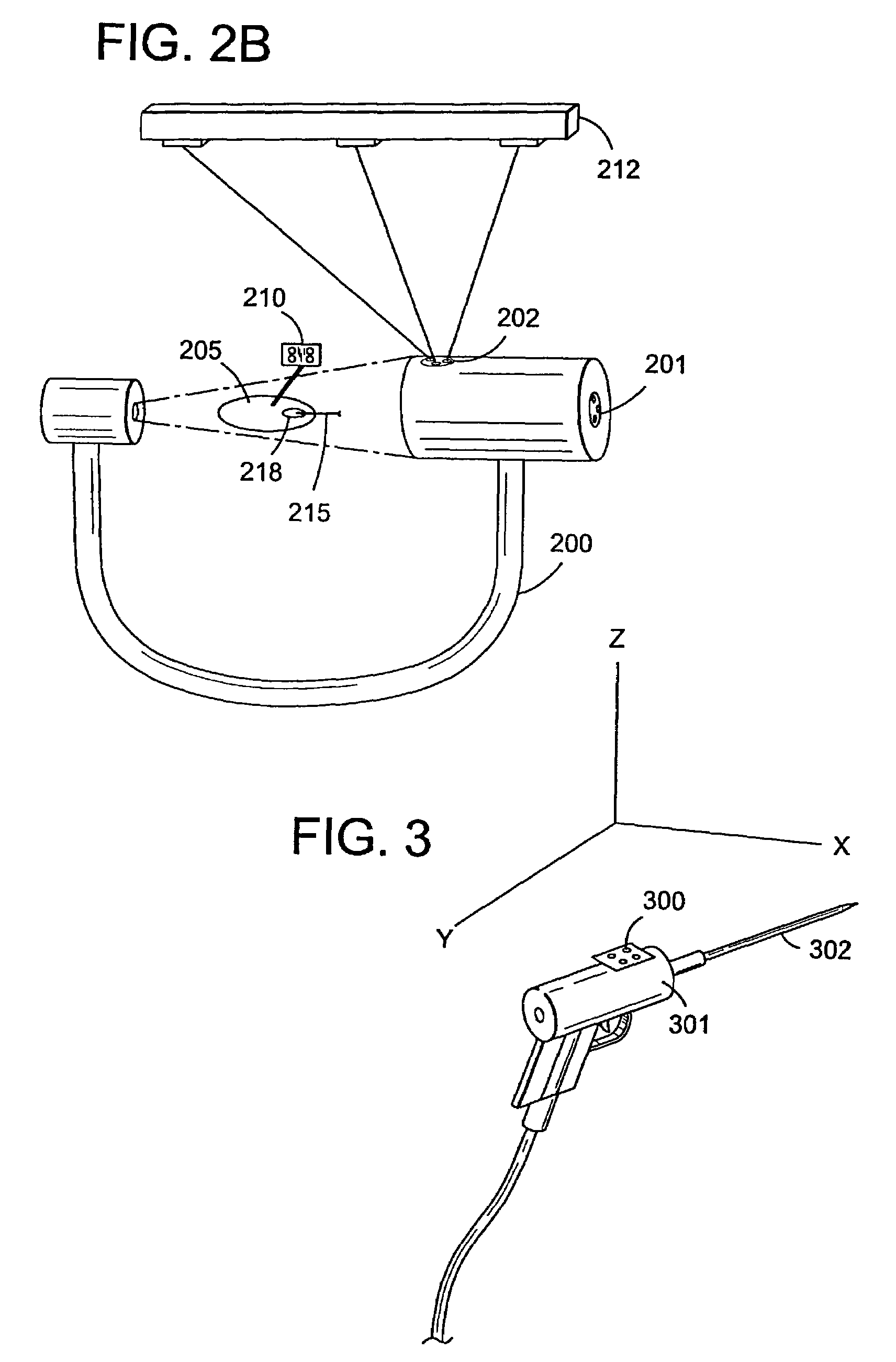
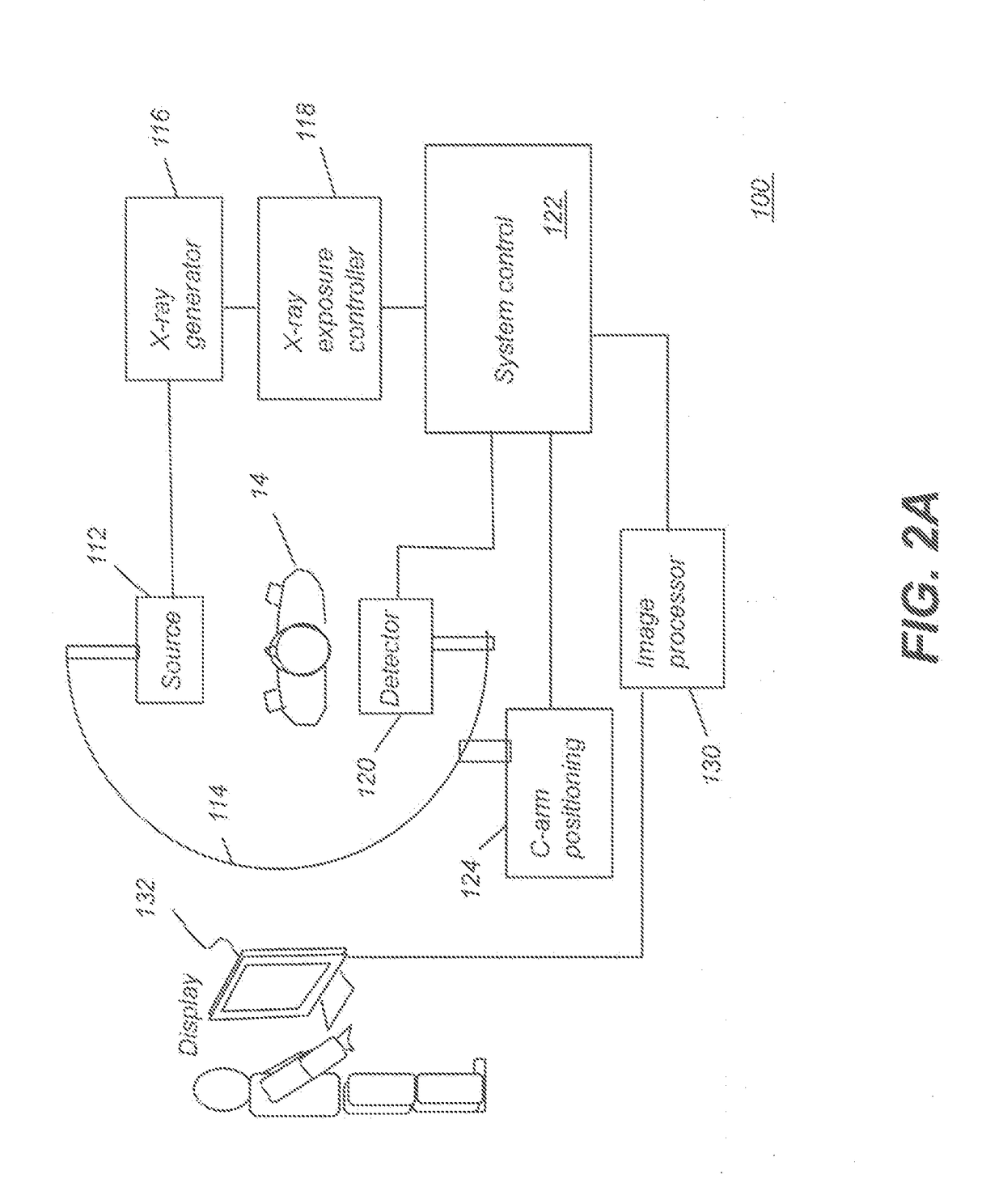
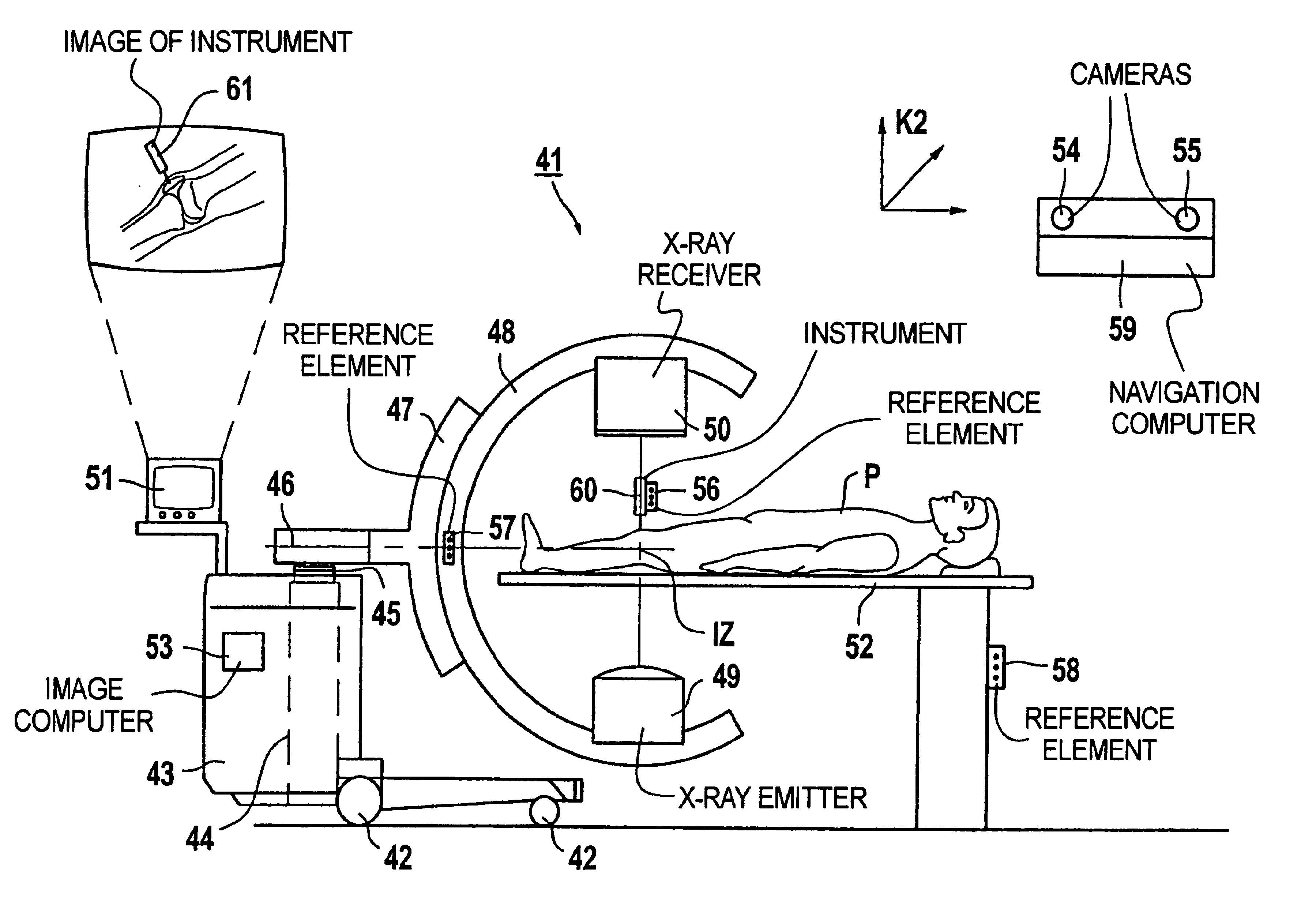
Fluoroscopic image guided orthopaedic surgery system with intraoperative registration
InactiveUS7130676B2Safely determineCheck the accuracy of the procedureSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringFluoroscopic imagingFluoroscopic image
A fluoroscopic image guided surgery system, comprising a C-arm fluoroscope for obtaining fluoroscopic images of an object bone, the C-arm fluoroscope including at least one set of emitters; a reference bar capable of attaching to an object bone, the reference bar including emitters; a surgical instrument for performing an operation, the instrument including emitters; a digitizer system in communication with the at least one set of emitters of the C-arm fluoroscope, the emitters of the reference bar, and the emitters of the surgical instrument so that the digitizer system can determine a position of each of the C-arm fluoroscope, the reference bar, and the surgical instrument; and a single fiducial marker for attachment to an object bone, the single fiducial marker being visible in the fluoroscopic images for determining a position of an object bone relative to the digitizer system.
Owner:SOFAMOR DANEK PROPERTIES
Method to detect a retained surgical object
An imaging method, executed at least in part by a computer, tracks the disposition of surgical supplies used in an operation and identifies a radiographic imaging technique for detecting a retained surgical foreign object according to the tracking. One or more radiographic images are acquired in the operating room. The acquired image content is analyzed to identify one or more candidate foreign objects. At least a portion of the acquired image content is displayed with the one or more candidate foreign objects in the acquired image content highlighted.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
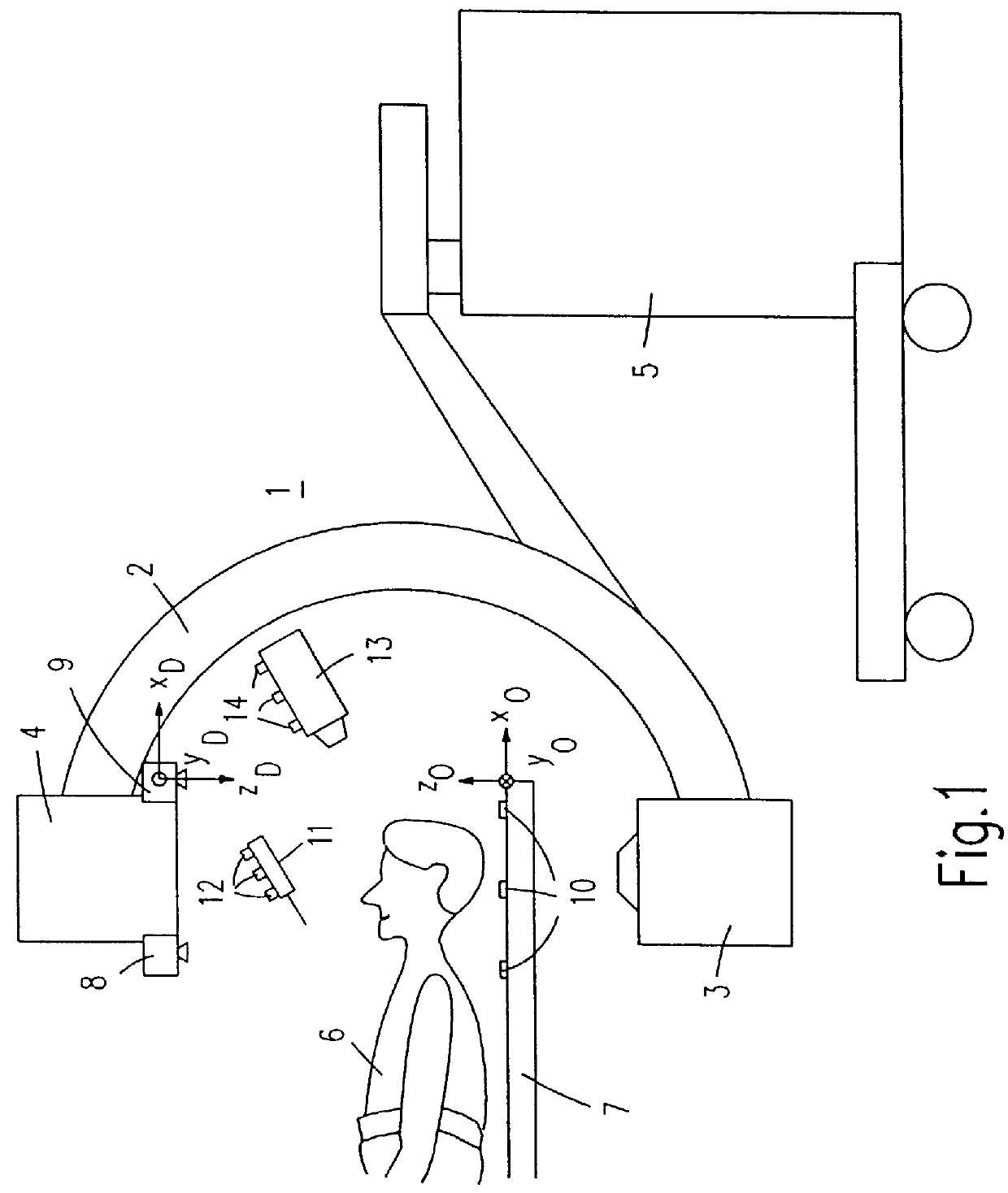
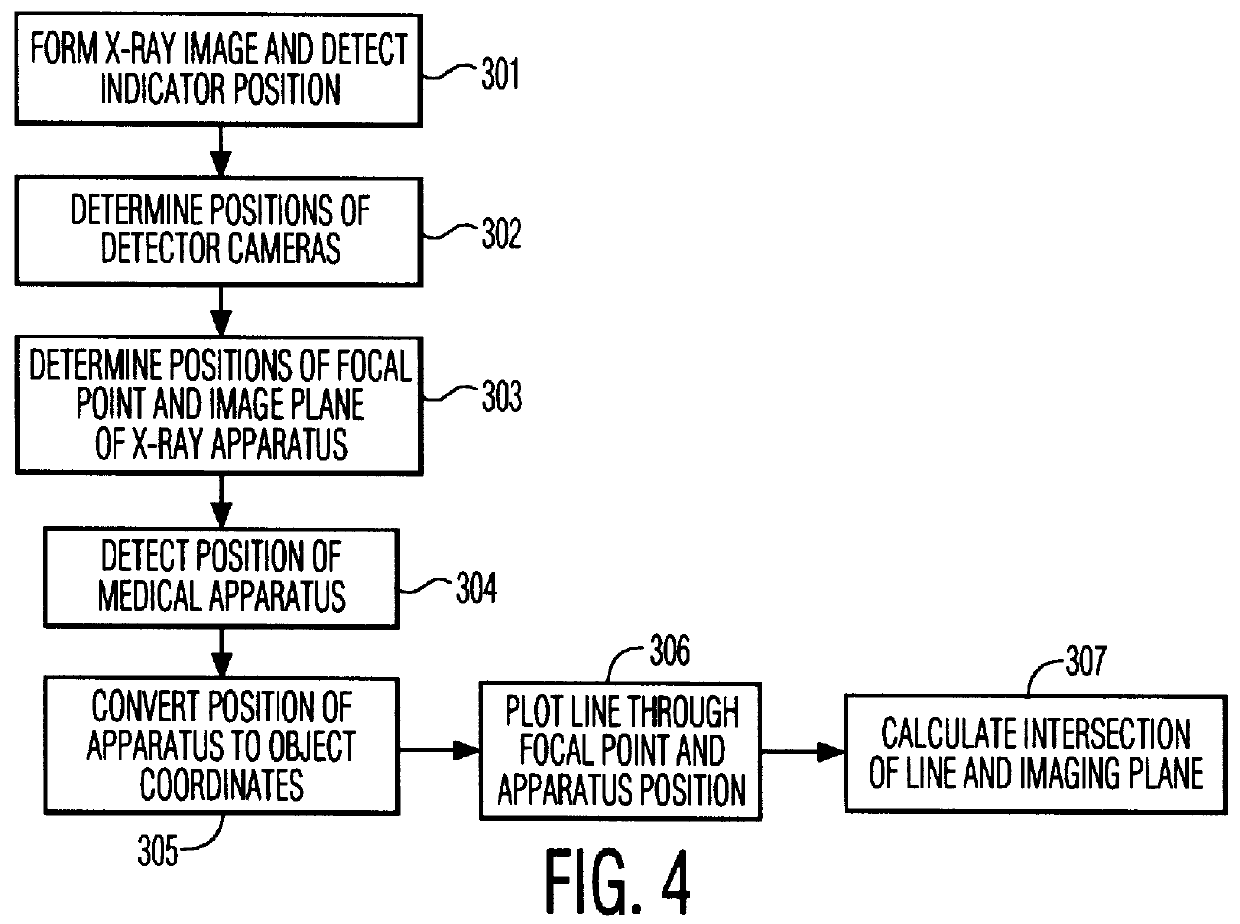
Method of and device for position detection in X-ray imaging
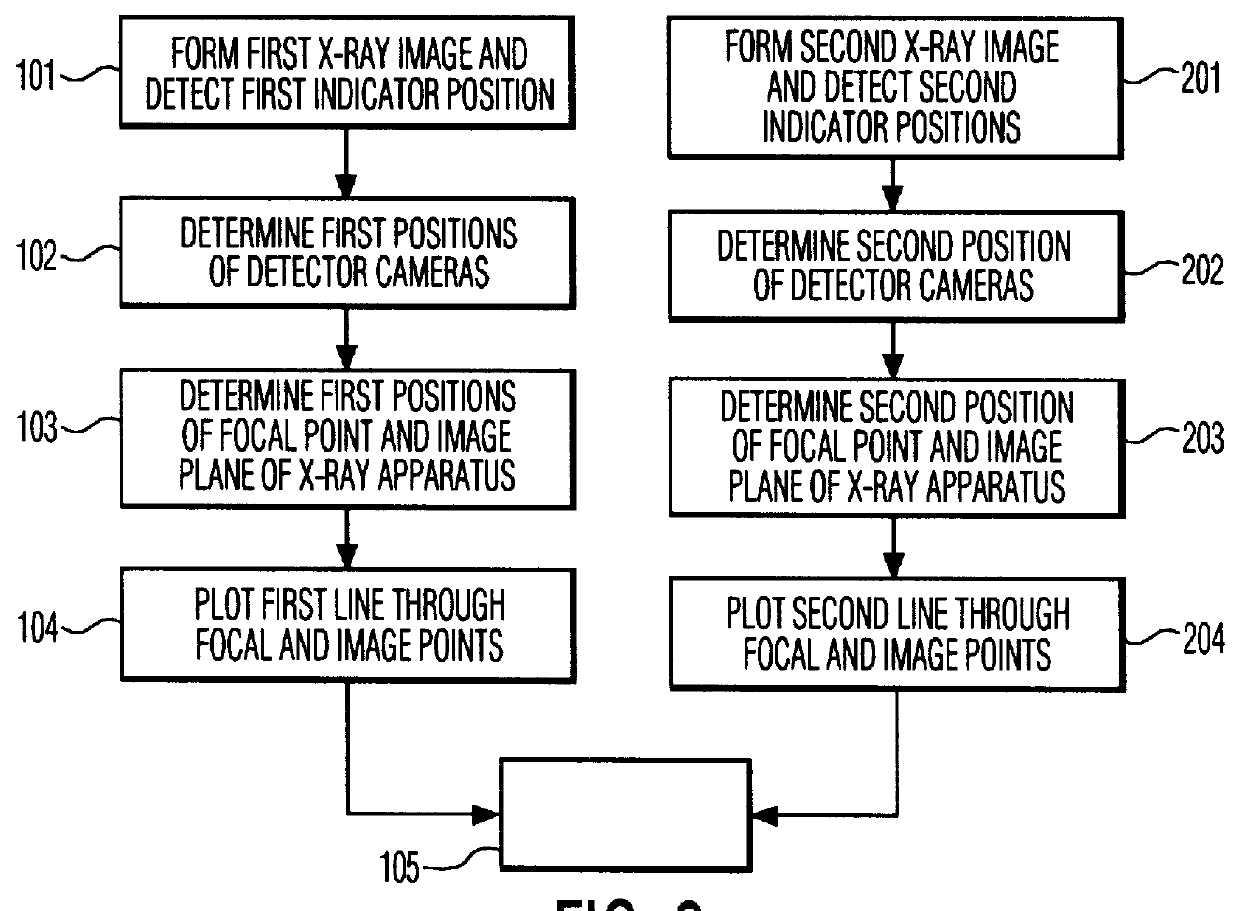
InactiveUS6050724AAccurately determineSimplified determinationSurgical navigation systemsForeign body detectionSoft x rayLocation detection
The invention relates to a method of position detection in X-ray imaging, and to a device for carrying out such a method by means of an X-ray apparatus, a detector device, including at least two detector elements, and an indicator device. The exact association of the X-ray image with the object imaged is very important notably for intraoperative imaging. Exact knowledge of the position and orientation of the components of the X-ray apparatus associated with the imaging system is required for this purpose. However, it is often problematic that the lines of sight of the position measuring system are obscured by attending staff or other apparatus. Therefore, in the device according to the invention the detector device is mounted on the X-ray apparatus and the indicator device is provided so as to be stationary on the object to be examined or stationary relative to the object to be examined. Also described is a method of position detection in X-ray imaging by means of such a device.
Owner:U S PHILIPS CORP
Method and apparatus for medical intervention procedure planning
InactiveUS7346381B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOperator interfaceData acquisition
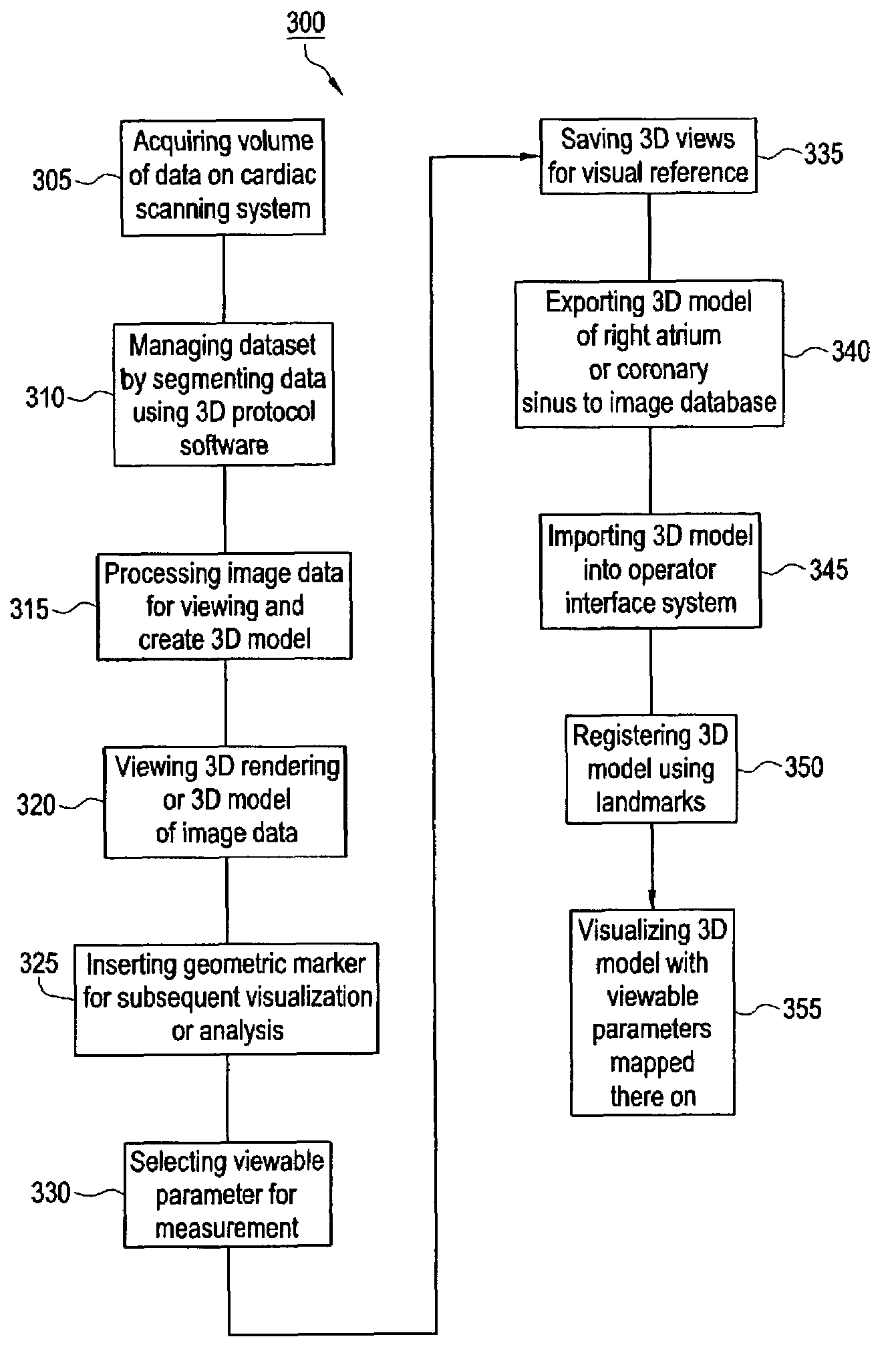
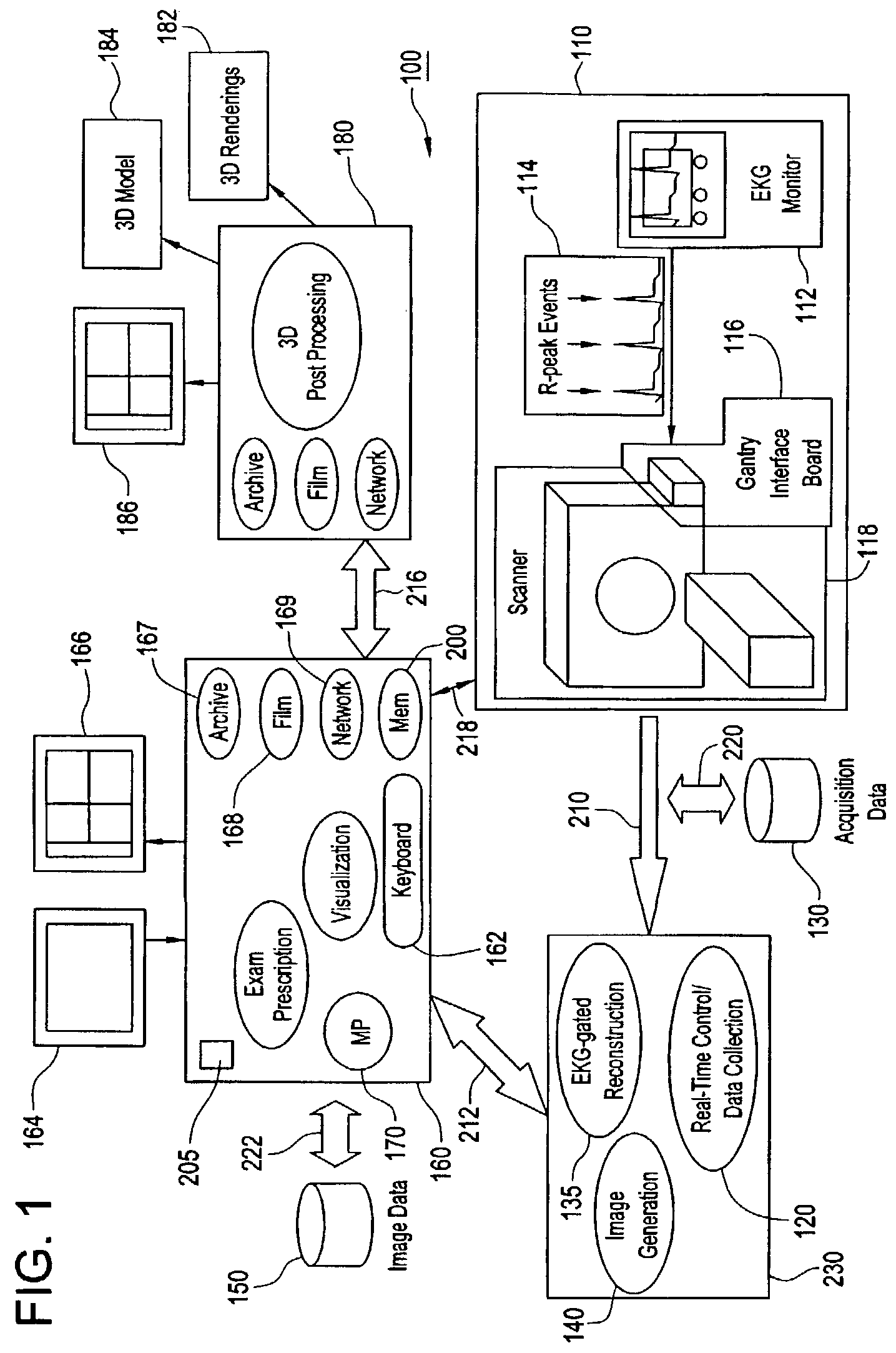
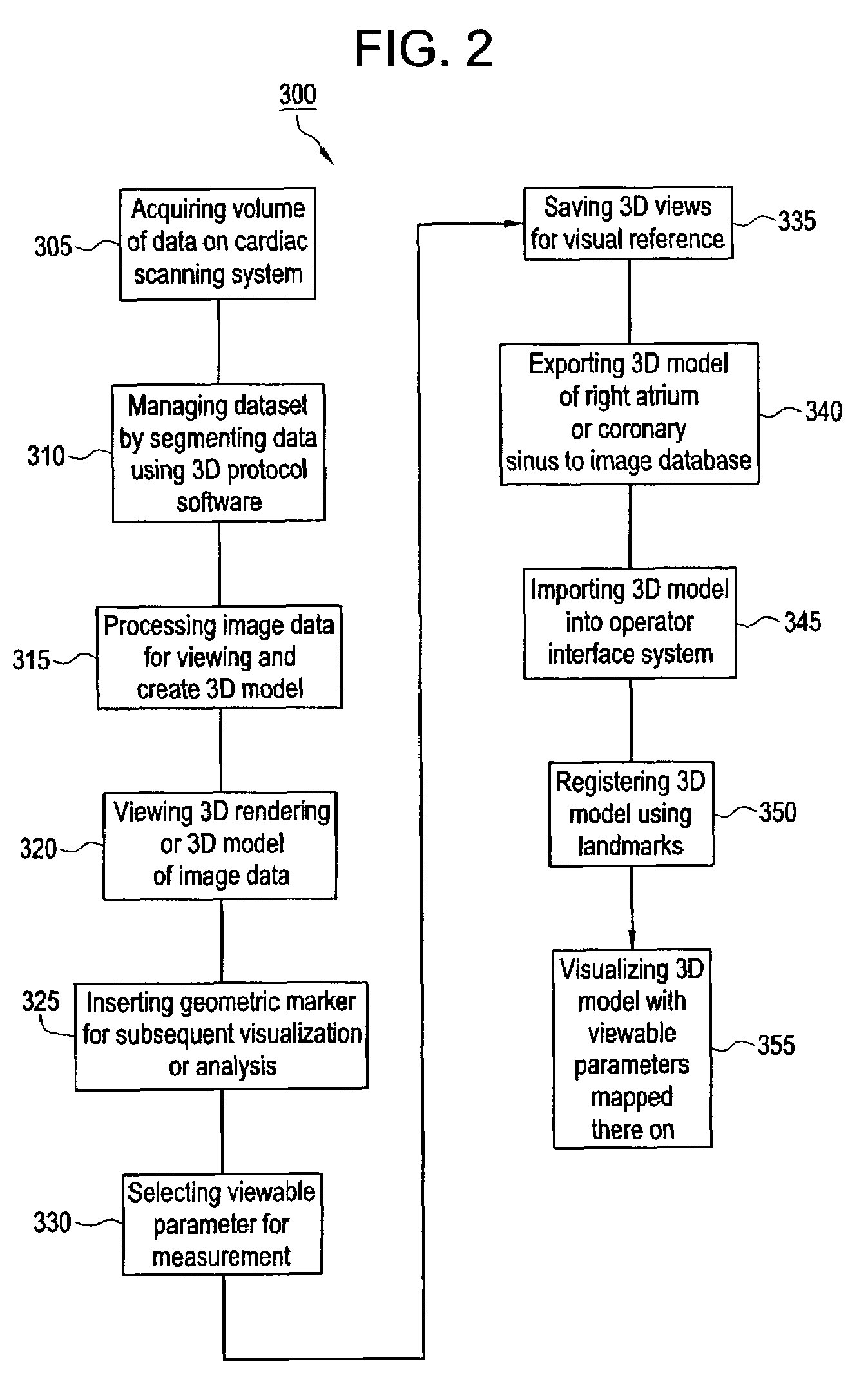
An imaging system for use in medical intervention procedure planning includes a medical scanner system for generating a volume of cardiac image data, a data acquisition system for acquiring the volume of cardiac image data, an image generation system for generating a viewable image from the volume of cardiac image data, a database for storing information from the data acquisition and image generation systems, an operator interface system for managing the medical scanner system, the data acquisition system, the image generation system, and the database, and a post-processing system for analyzing the volume of cardiac image data, displaying the viewable image and being responsive to the operator interface system. The operator interface system includes instructions for using the volume of cardiac image data and the viewable image for bi-ventricular pacing planning, atrial fibrillation procedure planning, or atrial flutter procedure planning.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
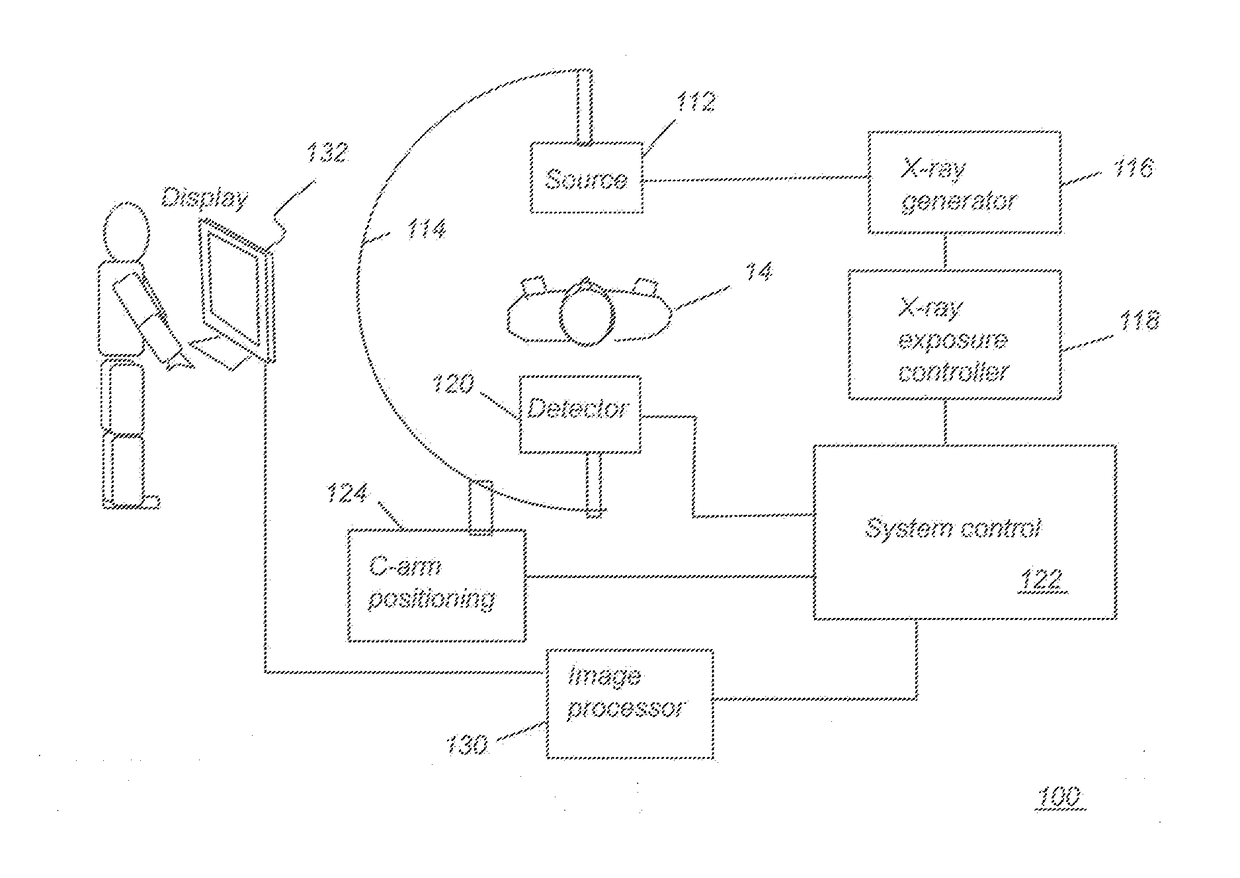
Apparatus and method for compensating for respiratory and patient motion during treatment
An apparatus and method for performing treatment on an internal target region while compensating for breathing and other motion of the patient is provided in which the apparatus comprises a first imaging device for periodically generating positional data about the internal target region and a second imaging device for continuously generating positional data about one or more external markers attached to the patient's body or any external sensor such as a device for measuring air flow. The apparatus further comprises a processor that receives the positional data about the internal target region and the external markers in order to generate a correspondence between the position of the internal target region and the external markers and a treatment device that directs the treatment towards the position of the target region of the patient based on the positional data of the external markers.
Owner:ACCURAY
Medical workstation, imaging system, and method for mixing two images
InactiveUS6895268B1Well mixedEffective supportGeometric image transformationSurgeryWorkstationComputer science
In a system, method and workstation, images of a first subject are acquired with an image signal acquisition unit, the position of the image signal acquisition unit is determined, the position of a second subject is determined and the position of the second subject relative to the image signal acquisition unit is also determined and an image of the second subject is mixed into an image of the first subject acquired with the image signal acquisition unit.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
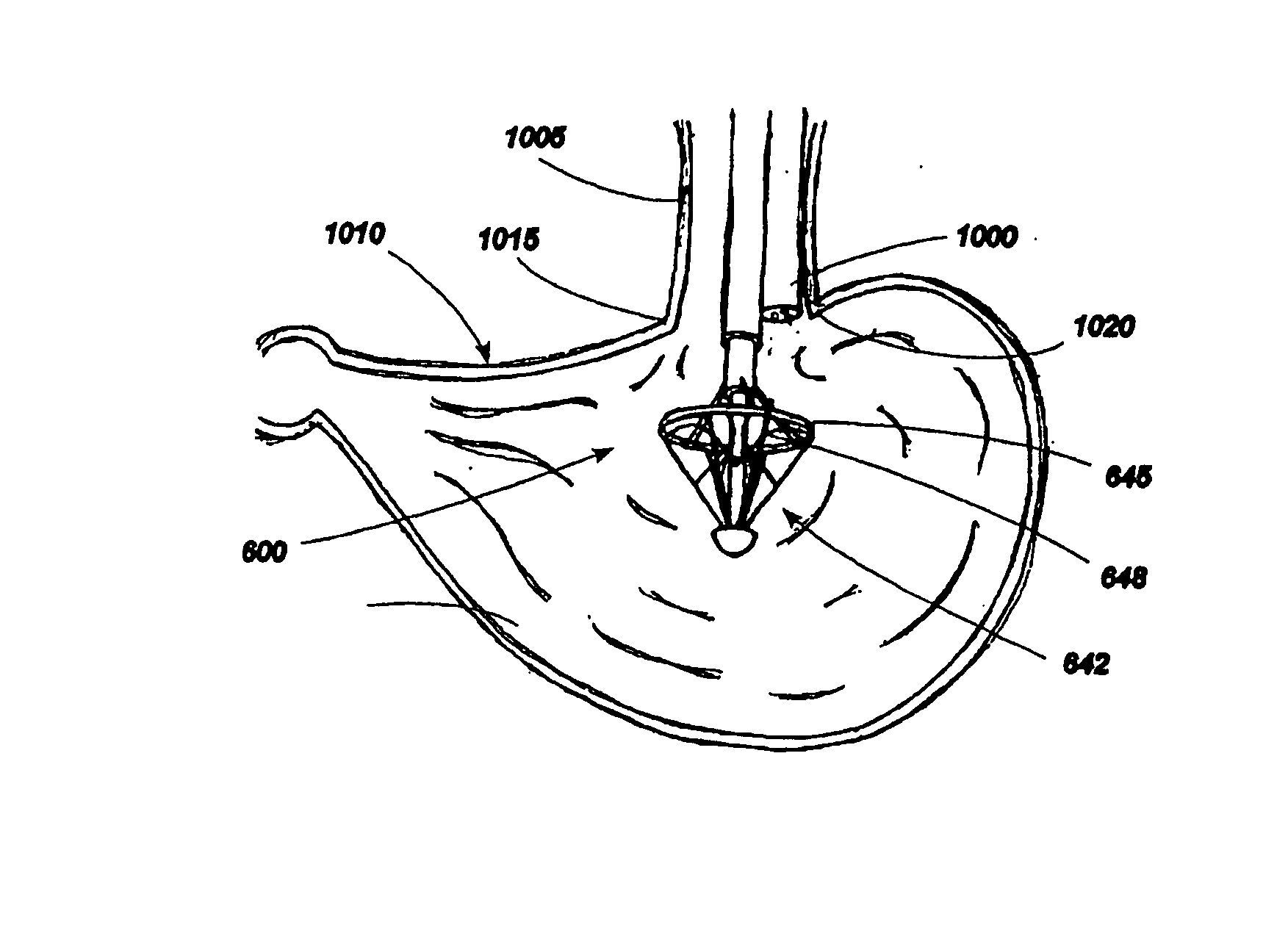
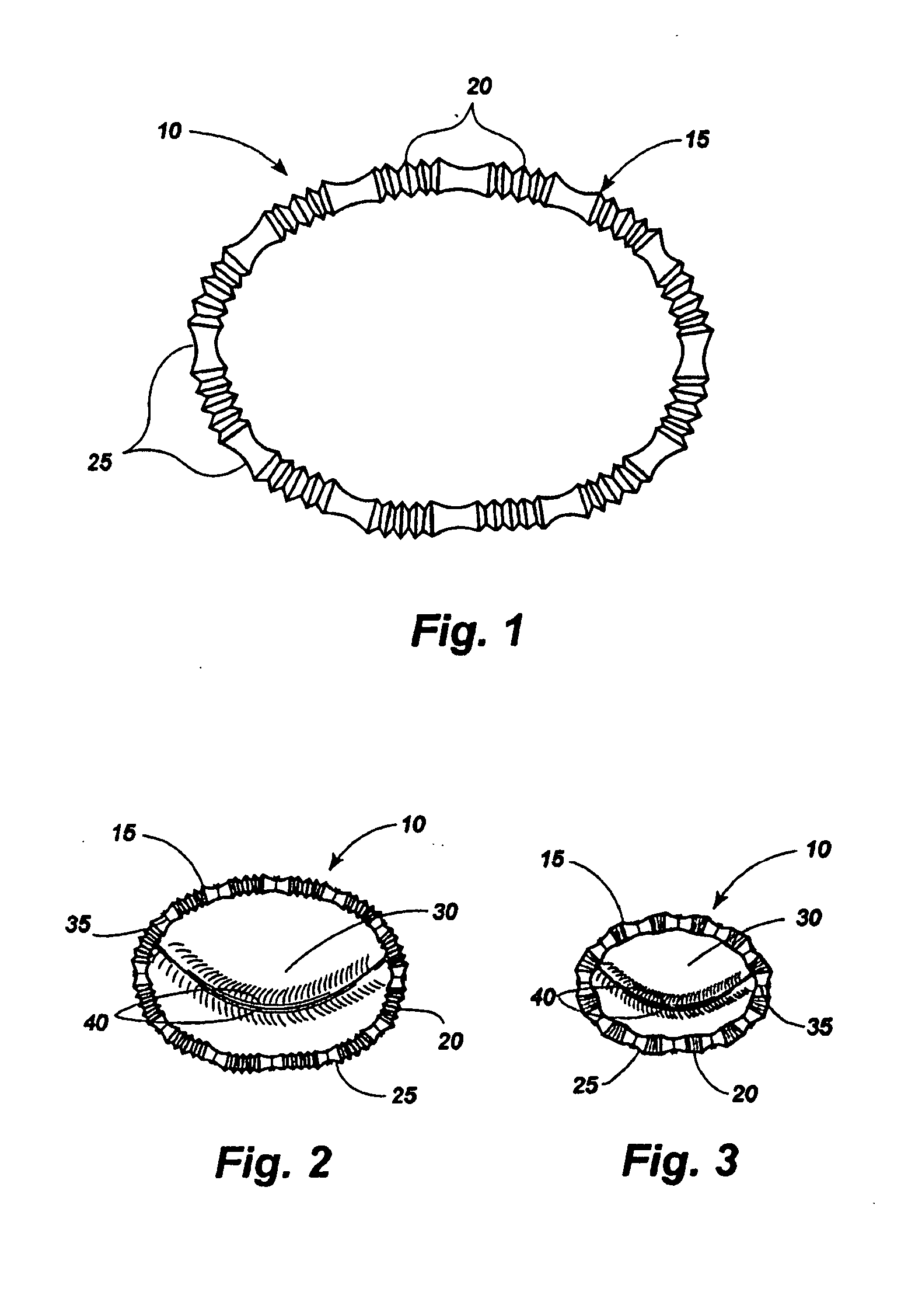
Implantable devices for controlling the size and shape of an anatomical structure or lumen
ActiveUS20080027483A1Suture equipmentsAnti-incontinence devicesAnatomical structuresMinimally invasive procedures
An implantable device system for controlling the dimensions of internal anatomic passages corrects physiologic dysfunctions resulting from a structural lumen which is either too large or too small. Implantable devices are disclosed which employ various mechanisms for adjusting and maintaining the size of an orifice to which they are attached. Systems permit the implants to be implanted using minimally invasive procedures and permit final adjustments to the dimensions of the implants after the resumption of normal flow of anatomic fluids in situ.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
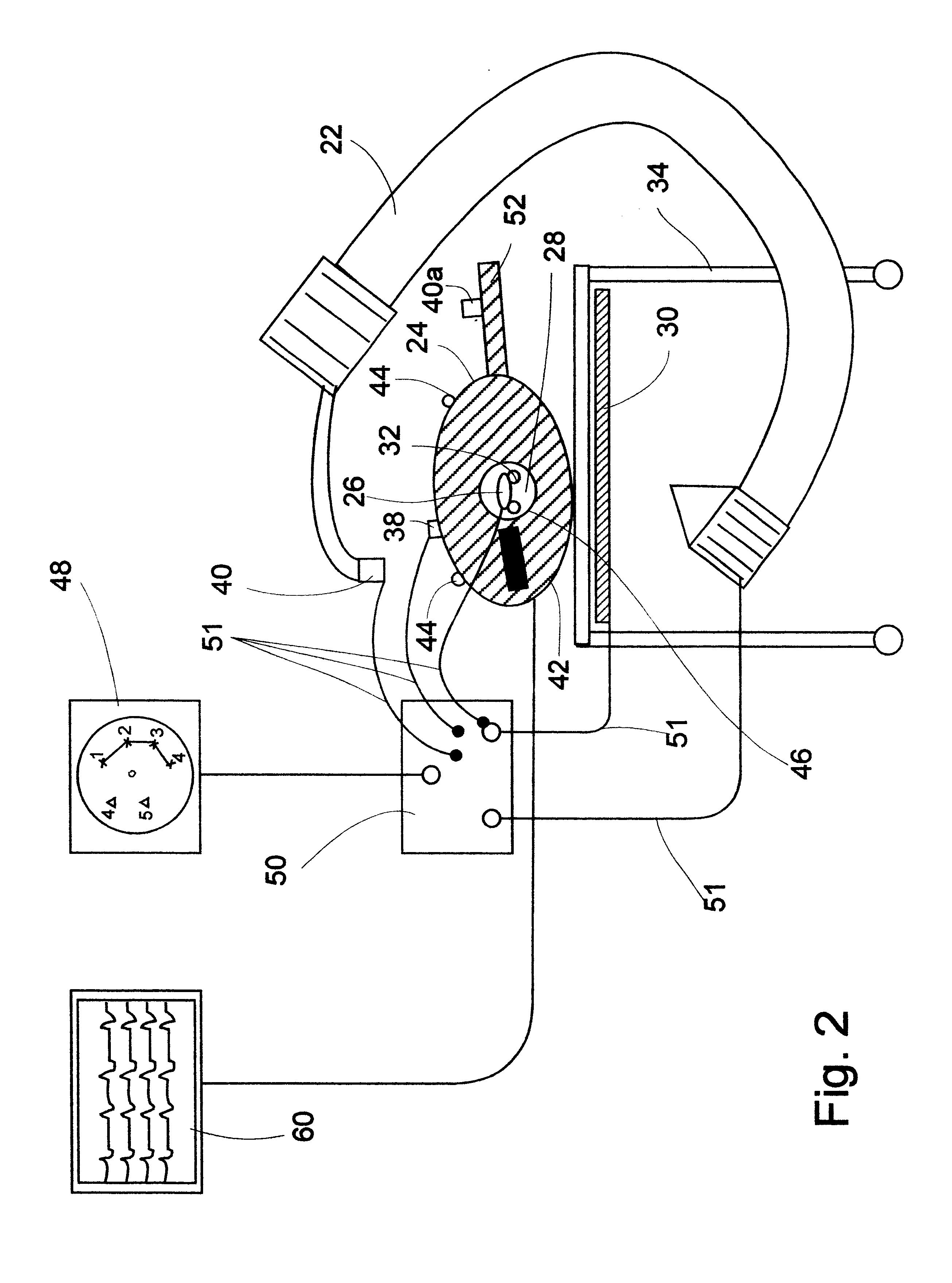
Fluoroscopic tracking and visualization system
InactiveUS6856826B2Quickly and accurately determineHigh position tracking accuracyX-ray spectral distribution measurementX-ray/infra-red processesPostural orientationComputer science
A method for surgical imaging and display including (i.) positioning a defined set of markers disposed in a pattern so as to be imaged in each pose or view of an imaging assembly, the set of markers being fixed in pre-determined positions in a rigid carrier, (ii.) securing a first tracking element against motion with respect to the rigid carrier so that determining a position of the first tracking element in a single measurement determines positions of all the markers of the set, and (iii.) identifying images of at least a subset of the markers in a first view.
Owner:STRYKER EURO HLDG I LLC +1
User interface for remote control of medical devices
InactiveUS20060041181A1Organ movement/changes detectionSurgical navigation systemsRemote controlDisplay device
An interface for remotely controlling a medical device in a patient's body provides a two dimensional display of a three dimensional rendering of the operating region, and allows the user to select the orientation or location of the distal end of the medical device on the display and then operate a navigation system to cause the distal end of the medical device to approximately assume the selected orientation or location.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
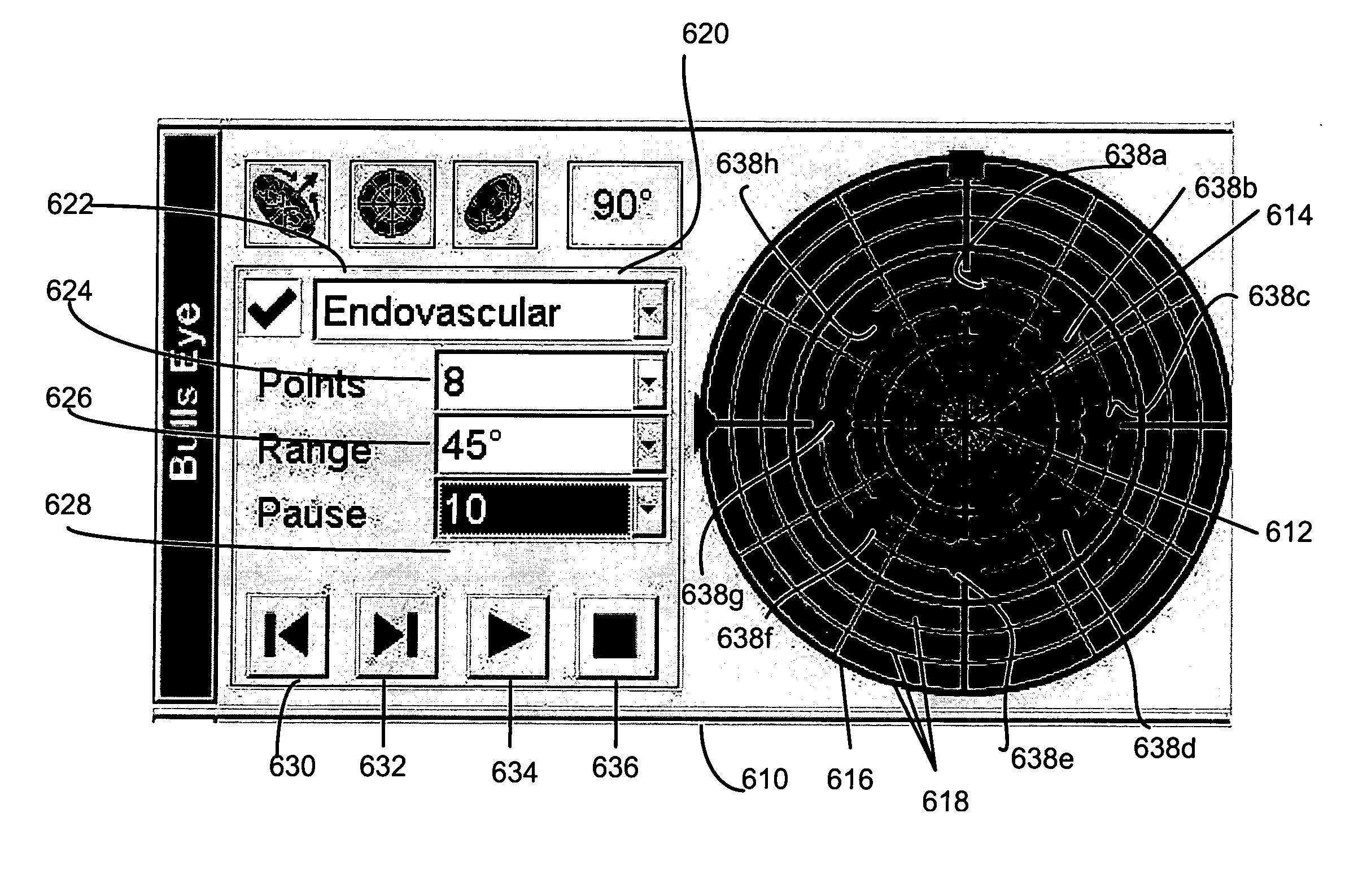
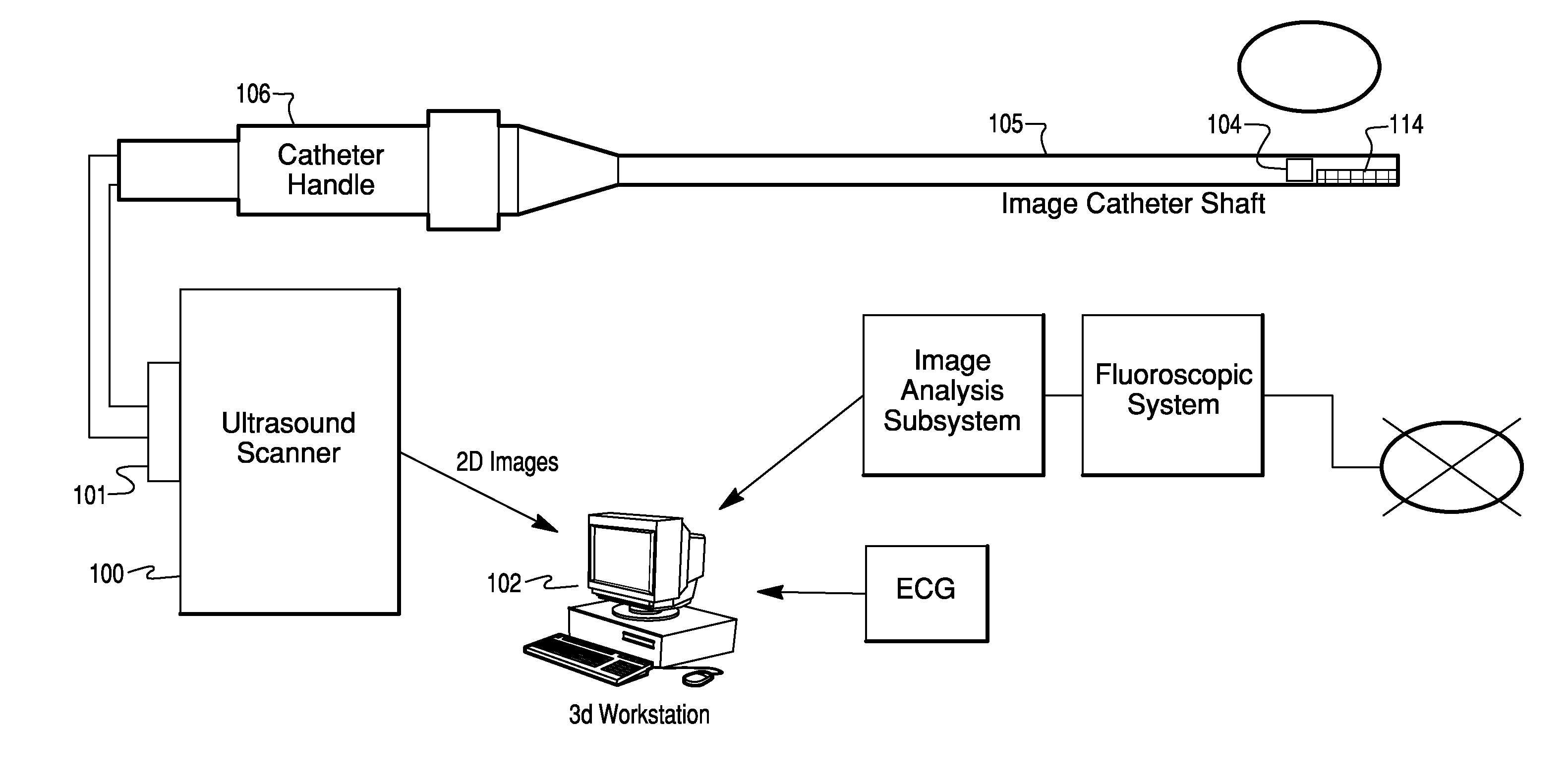
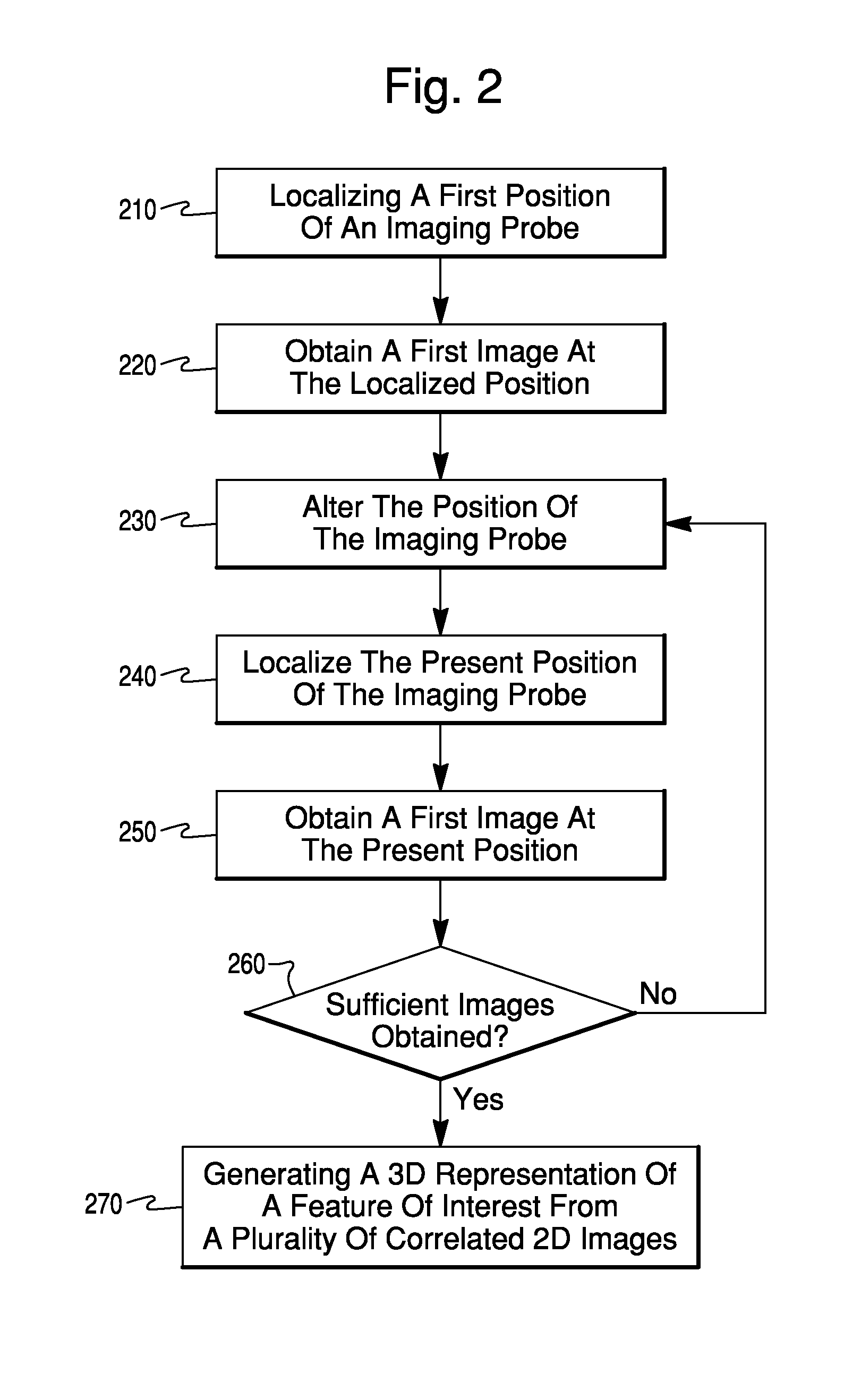
Catheter Position Tracking Methods Using Fluoroscopy and Rotational Sensors
Methods for determine the position and rotational orientation of the transducer array of an ultrasound imaging catheter within a patient include imaging the distal end of the catheter using fluoroscopy and determining the angular orientation based upon the shape and dimensions of the image of the transducer array and wire connecting harness. Additional rotational and translational information may be obtained from sensors located at the proximal end of the catheter. By combining position information obtained using fluoroscopy with information from relative rotation / translation sensors, the imaging transducer position and orientation can be determined more accurately. The resulting accurate imaging transducer position information enables combining multiple images from different positions or orientations to generate multi-dimensional images. Catheters including rotation and translation motion sensors at the proximal end, and radio-opaque materials near the distal end can be provided to enhance the methods.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com