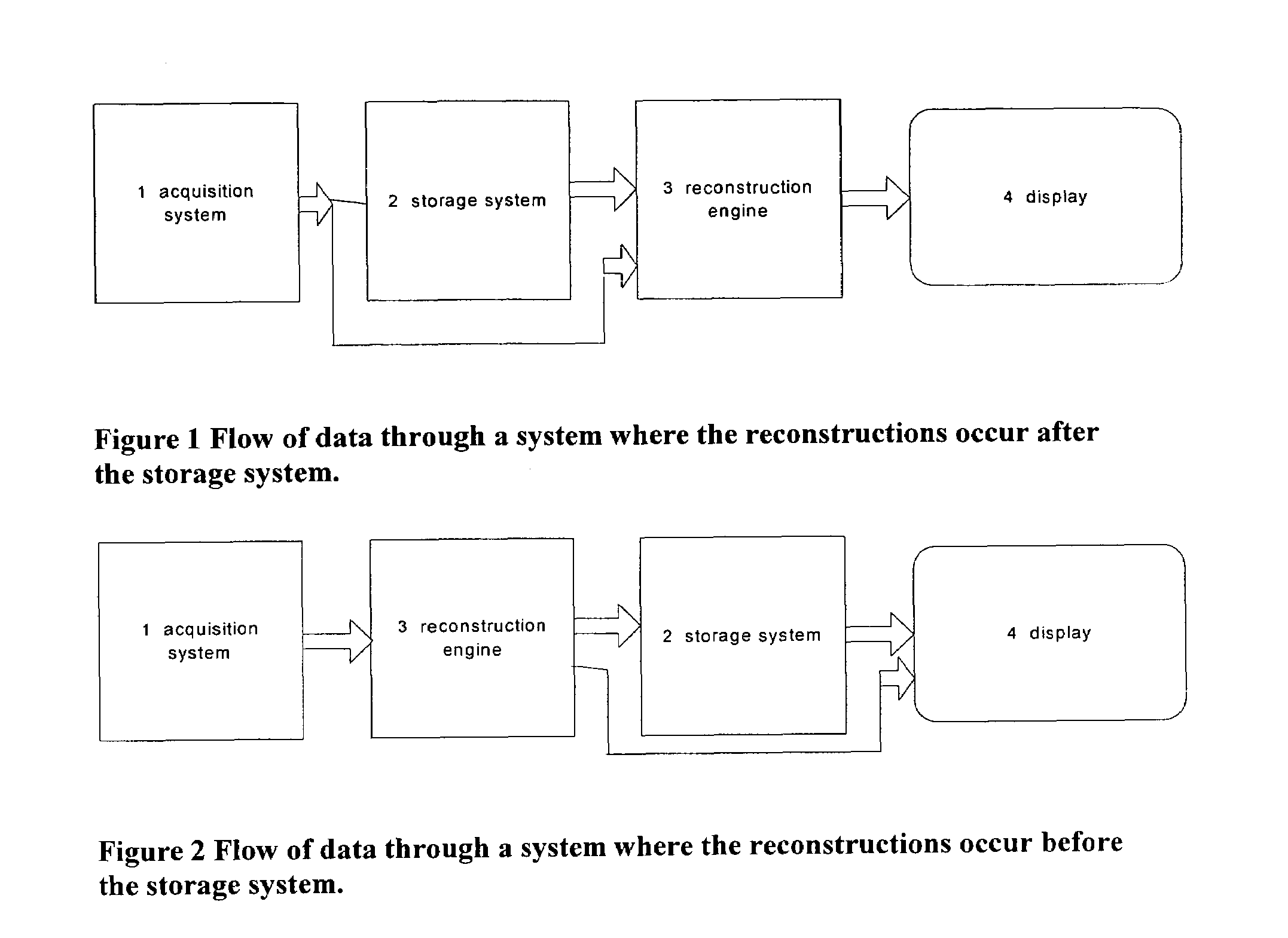
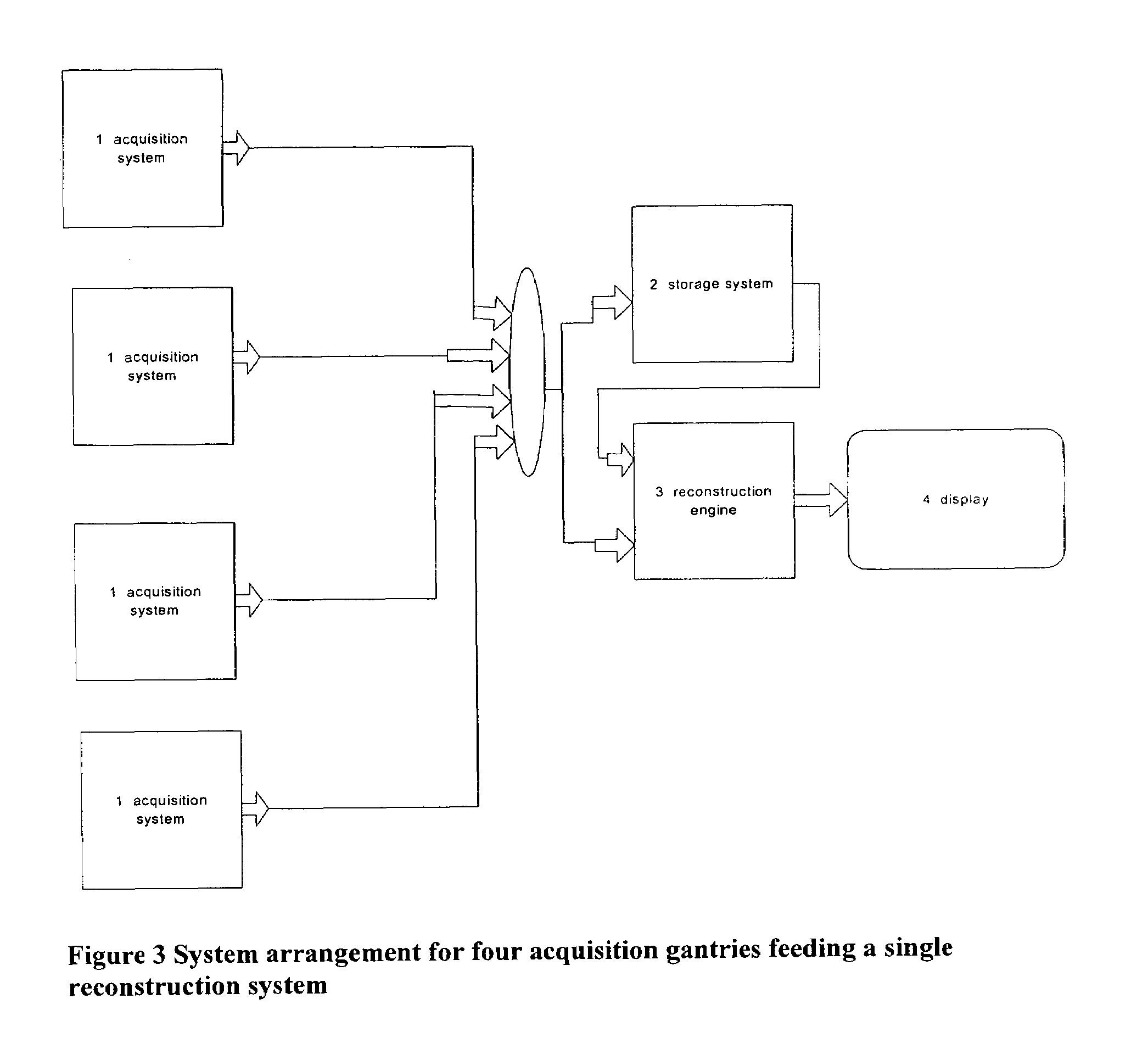
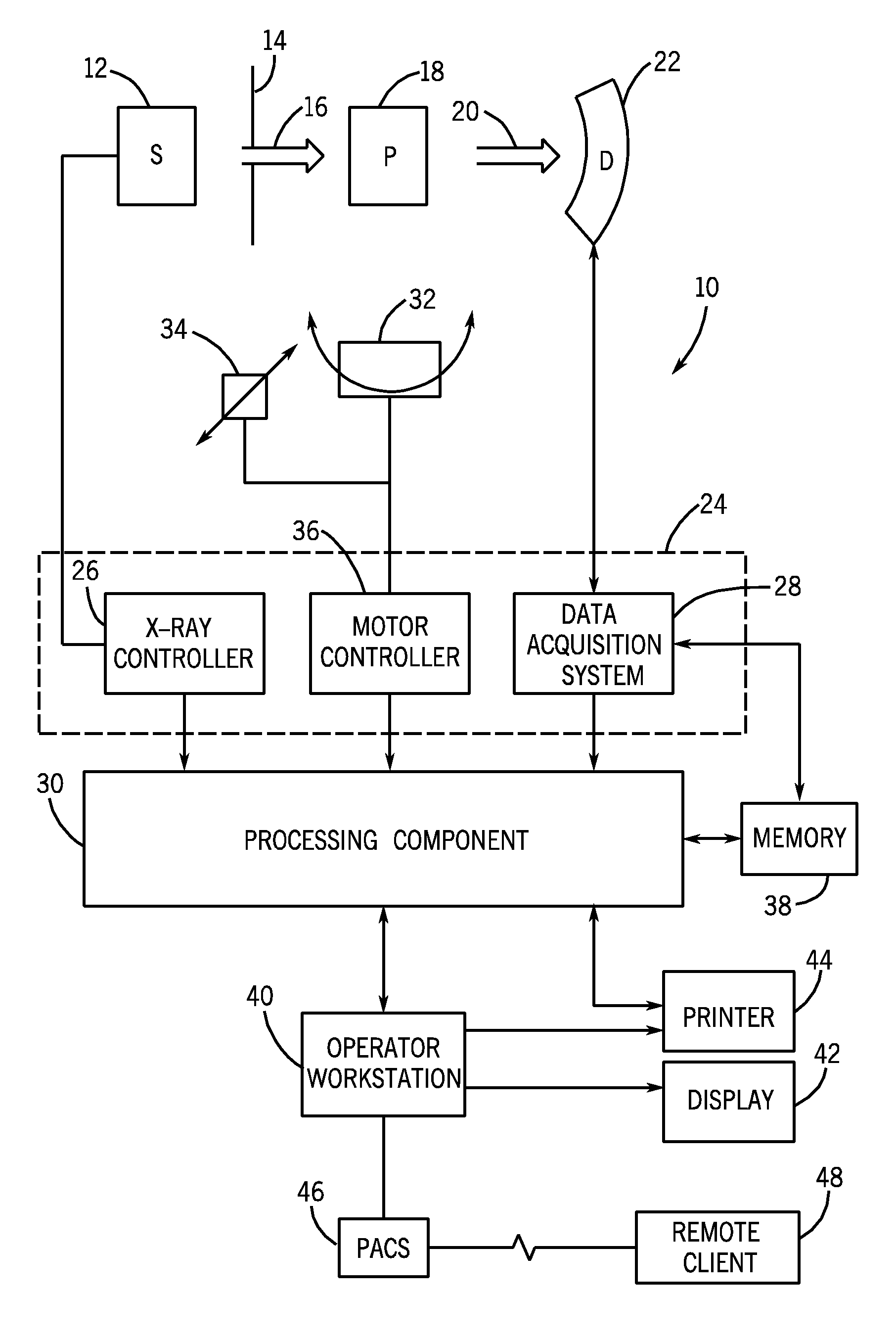
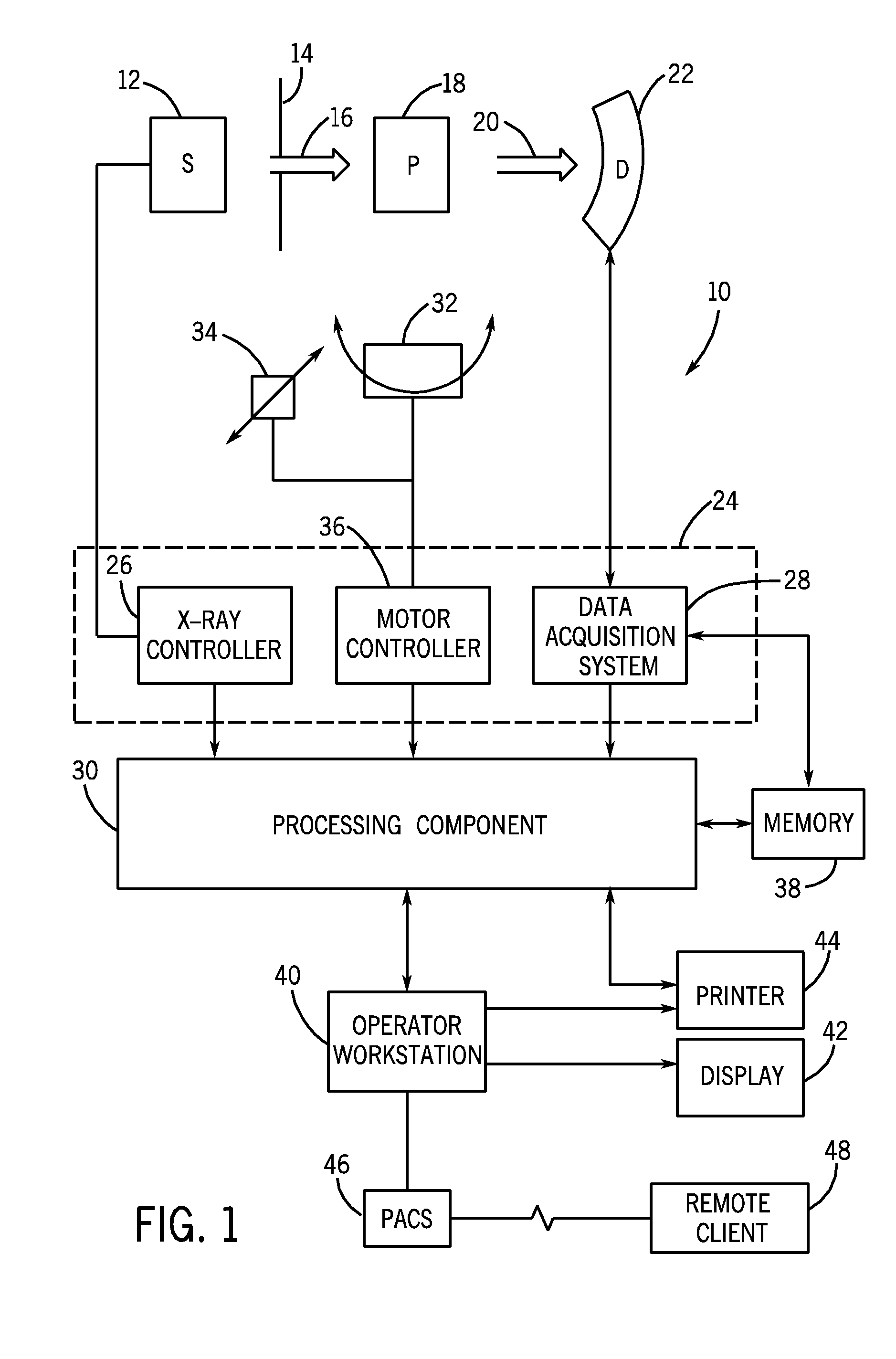
Patents
Literature
1013results about "Tomosynthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
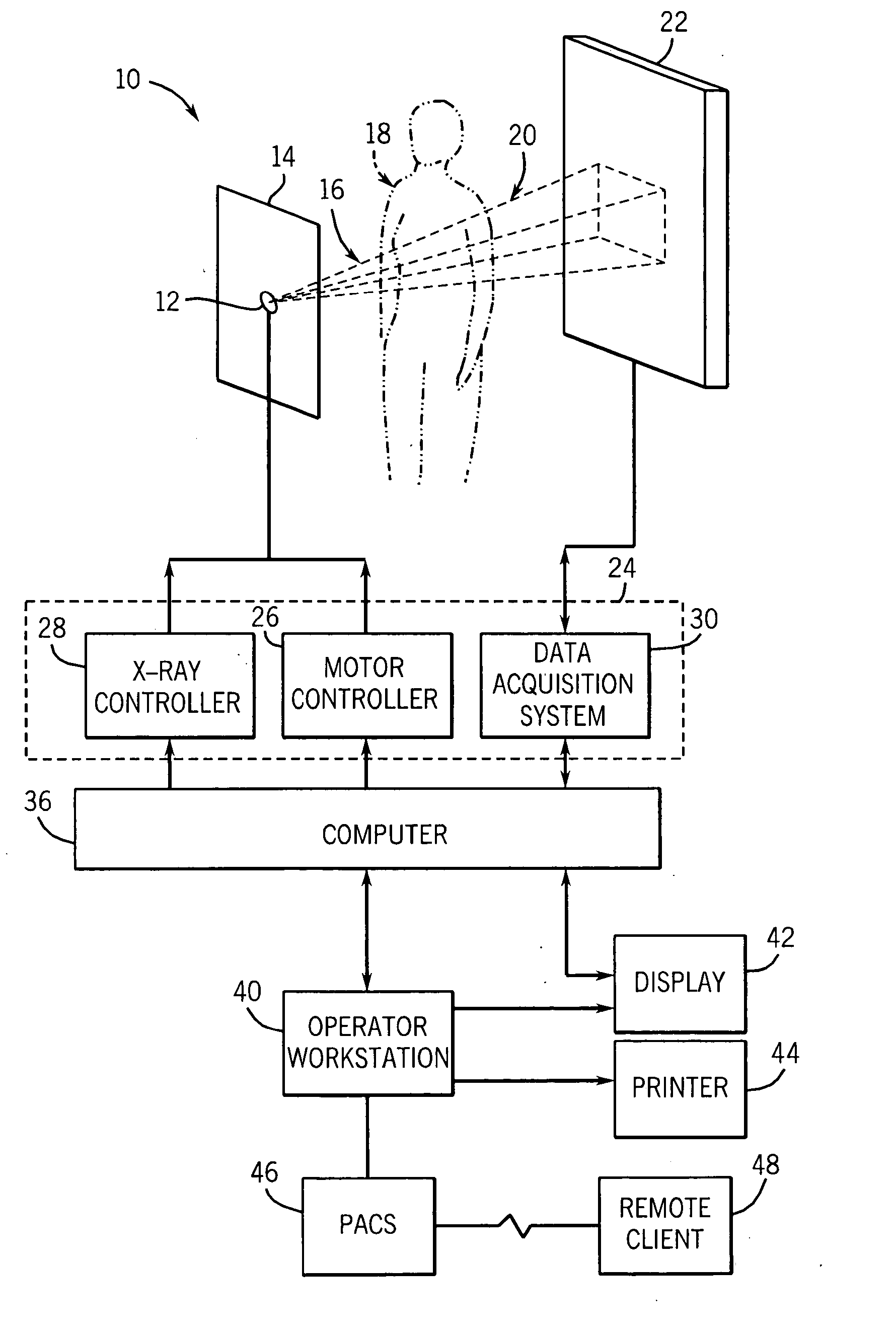
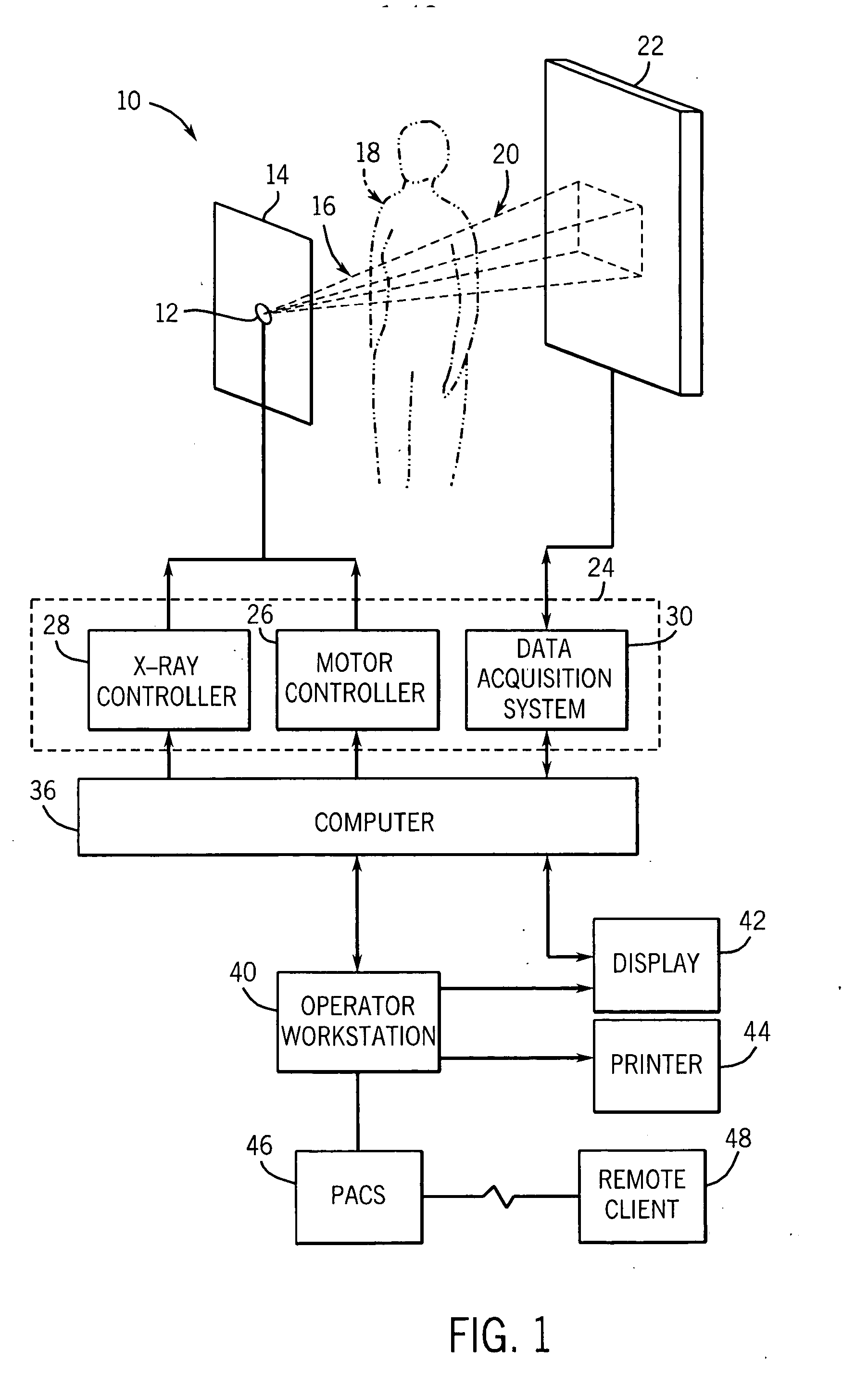
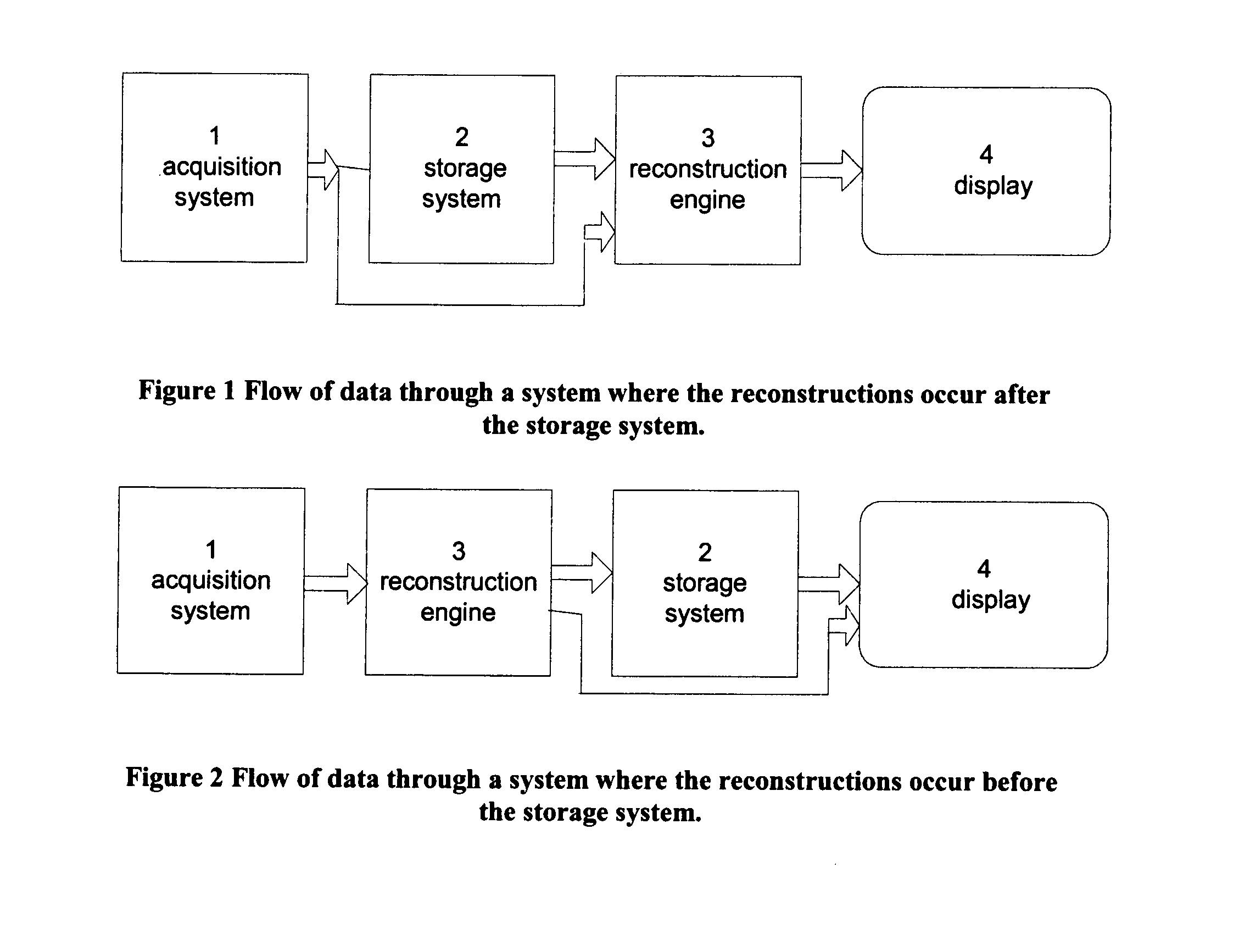
Method to detect a retained surgical object
An imaging method, executed at least in part by a computer, tracks the disposition of surgical supplies used in an operation and identifies a radiographic imaging technique for detecting a retained surgical foreign object according to the tracking. One or more radiographic images are acquired in the operating room. The acquired image content is analyzed to identify one or more candidate foreign objects. At least a portion of the acquired image content is displayed with the one or more candidate foreign objects in the acquired image content highlighted.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
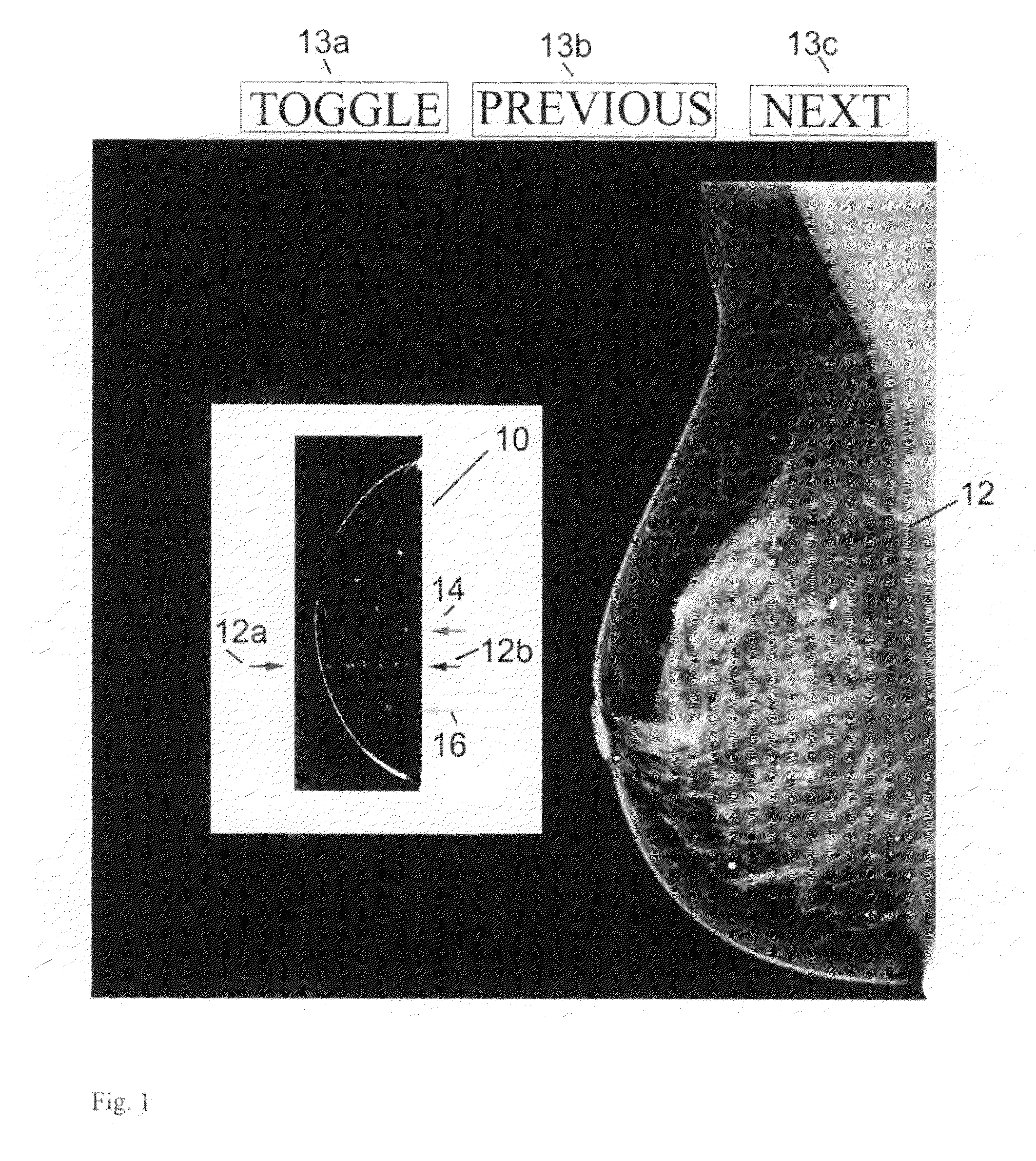
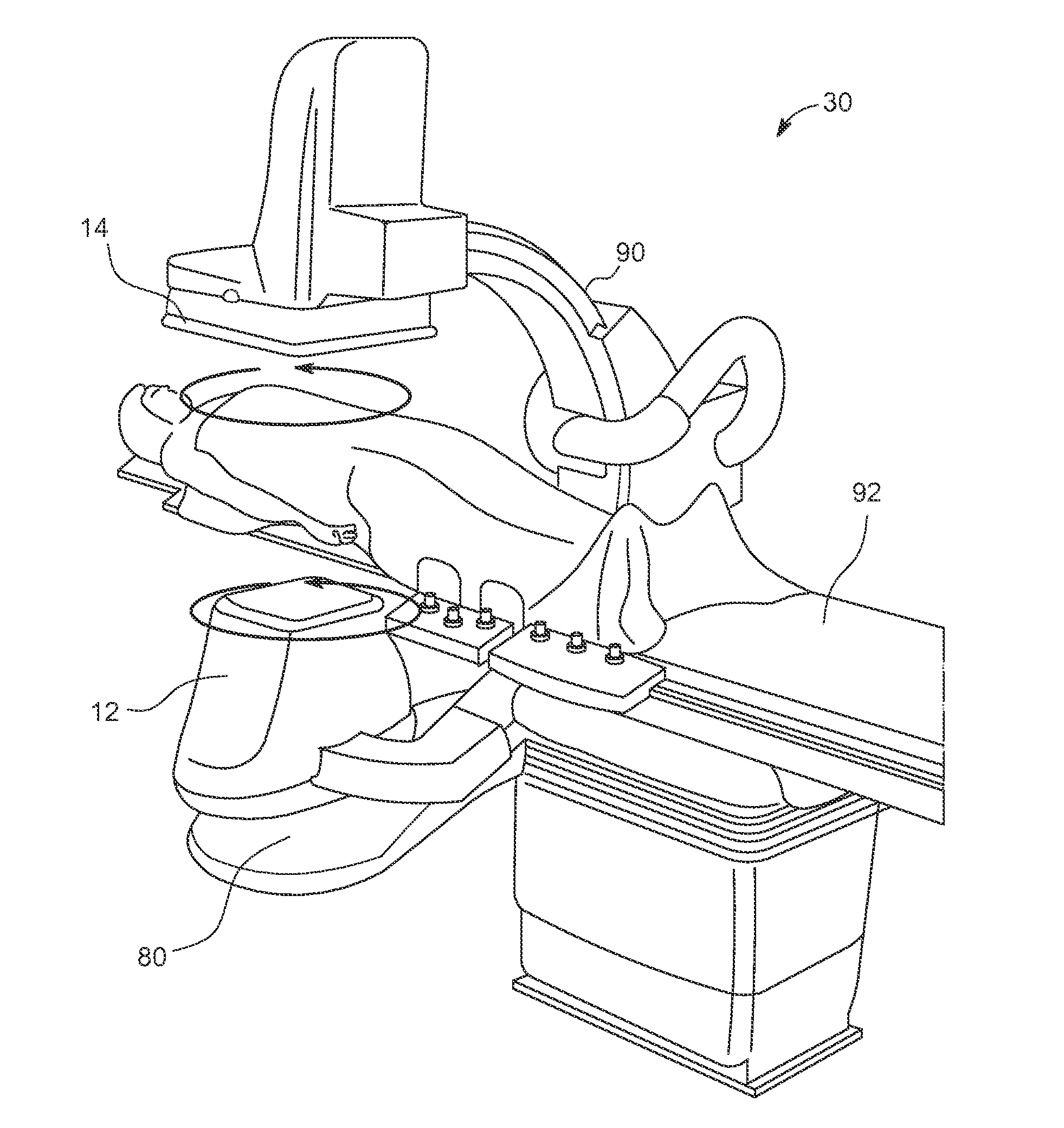
X-ray mammography/tomosynthesis of patient's breast
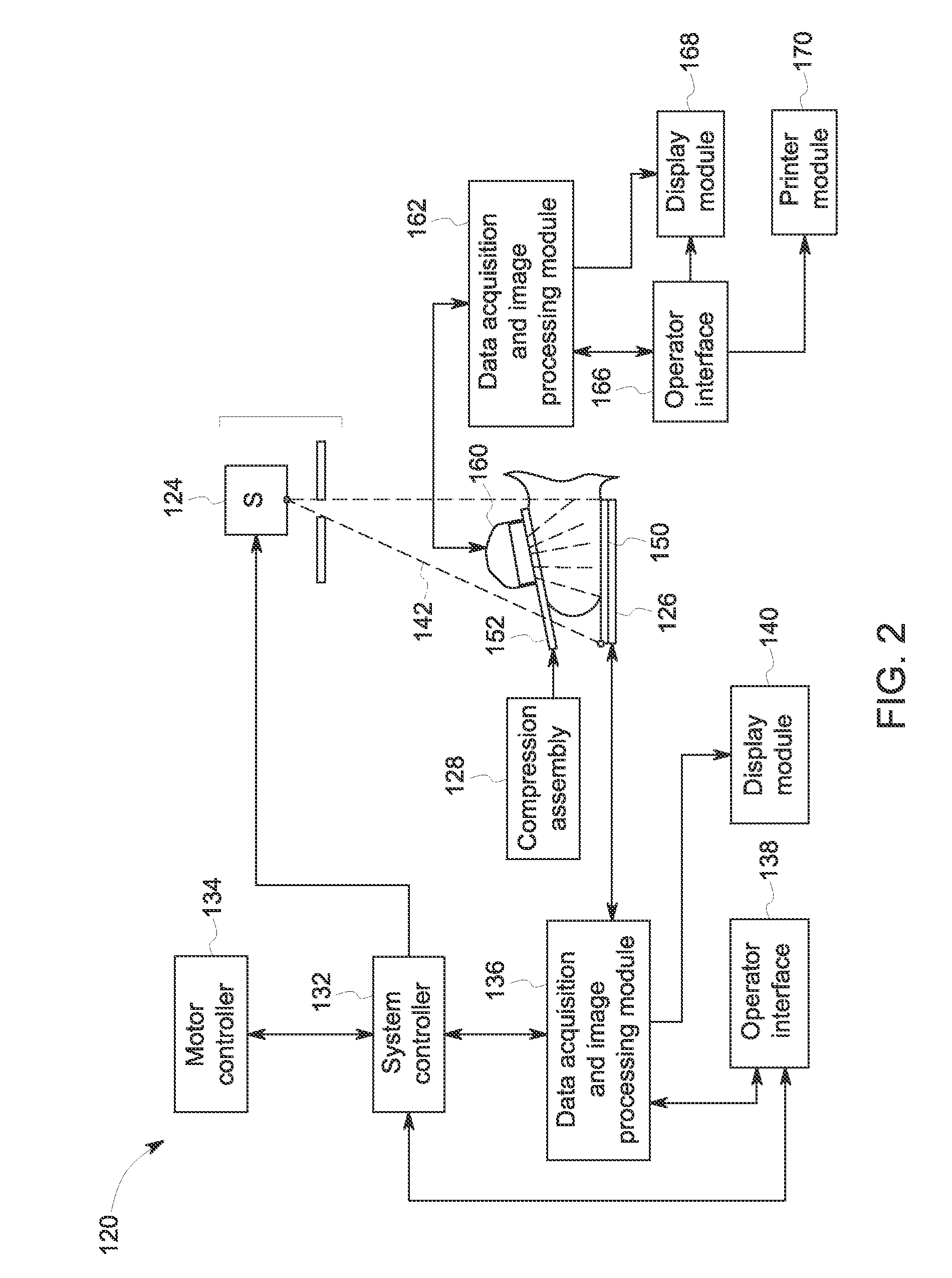
A breast x-ray system and method using tomosynthesis imaging in which the x-ray source generally moves away from the patient's head. The system may include an operation mode in which it additionally takes mammogram image data.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
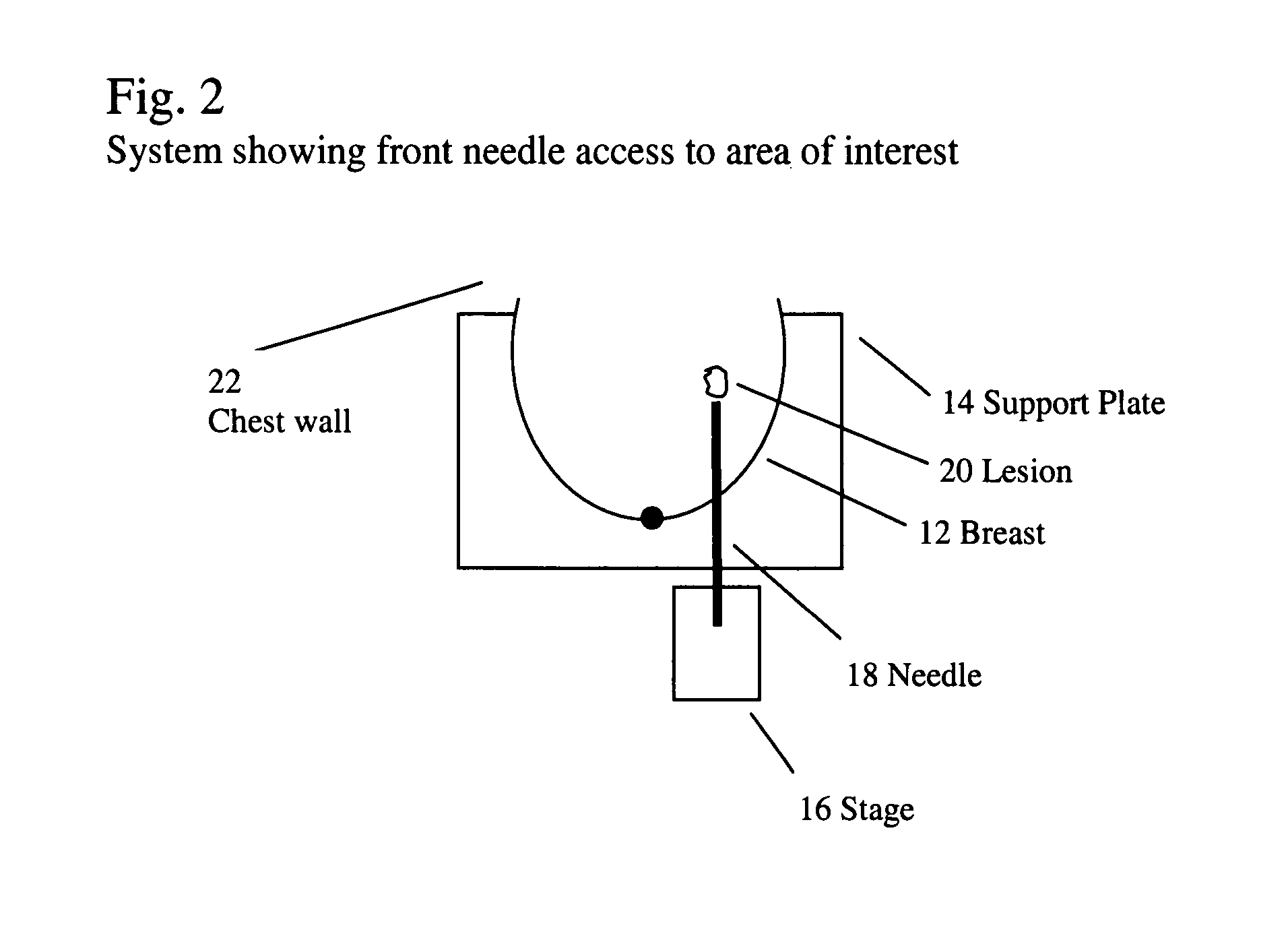
Breast biopsy and needle localization using tomosynthesis systems
ActiveUS20080045833A1High contrast visibilityImprove visibilityTomosynthesisVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTomosynthesisNeedle localization
Methods, devices, apparatuses and systems are disclosed for performing mammography, such as utilizing tomosynthesis in combination with breast biopsy.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Tetrahedron beam computed tomography
ActiveUS7760849B2Reduce exposureReduce the ratioMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisSoft x ray
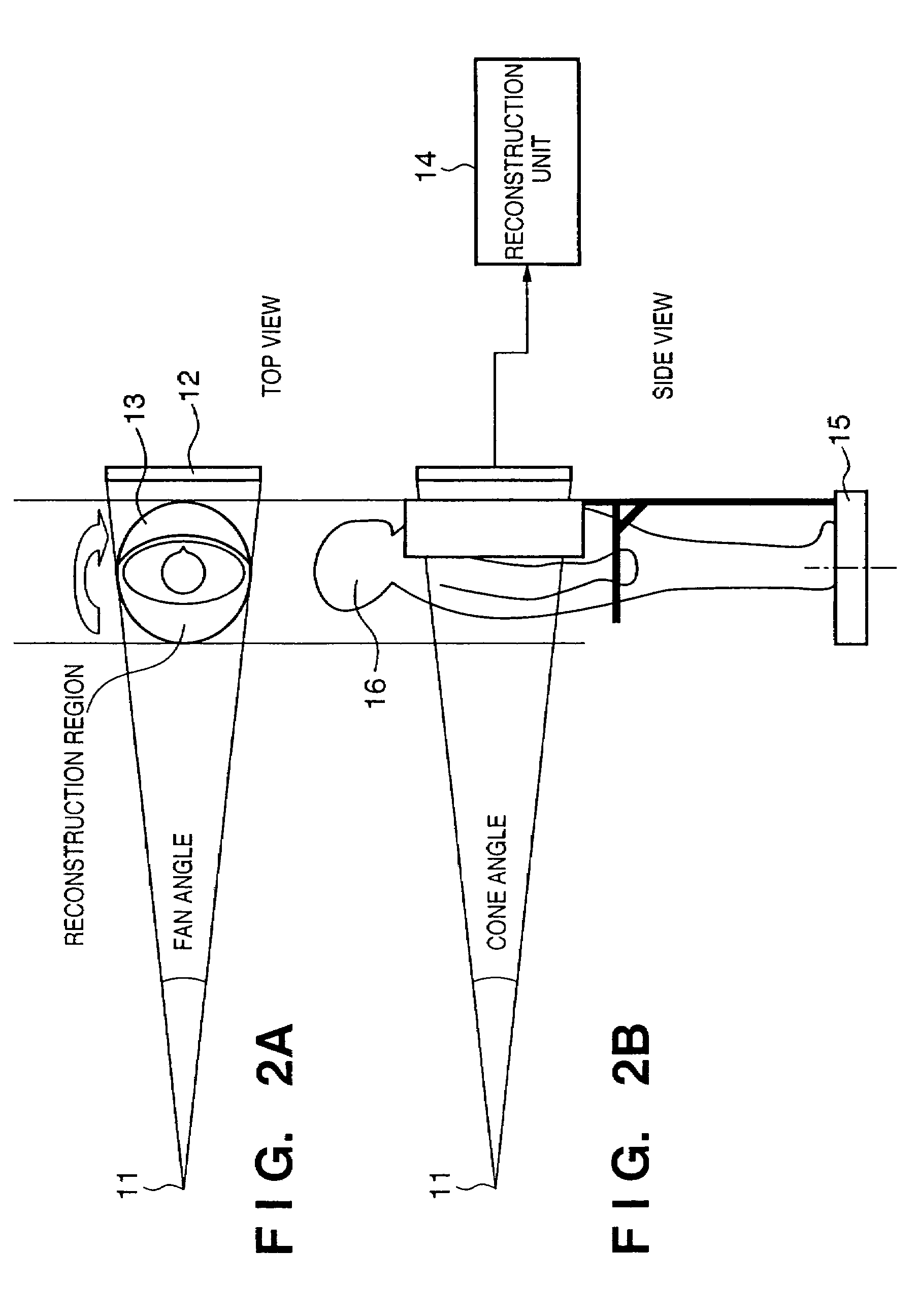
A method of imaging an object that includes directing a plurality of x-ray beams in a fan-shaped form towards an object, detecting x-rays that pass through the object due to the directing a plurality of x-ray beams and generating a plurality of imaging data regarding the object from the detected x-rays. The method further includes forming either a three-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography, digital tomosynthesis or Megavoltage image from the plurality of imaging data and displaying the image.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
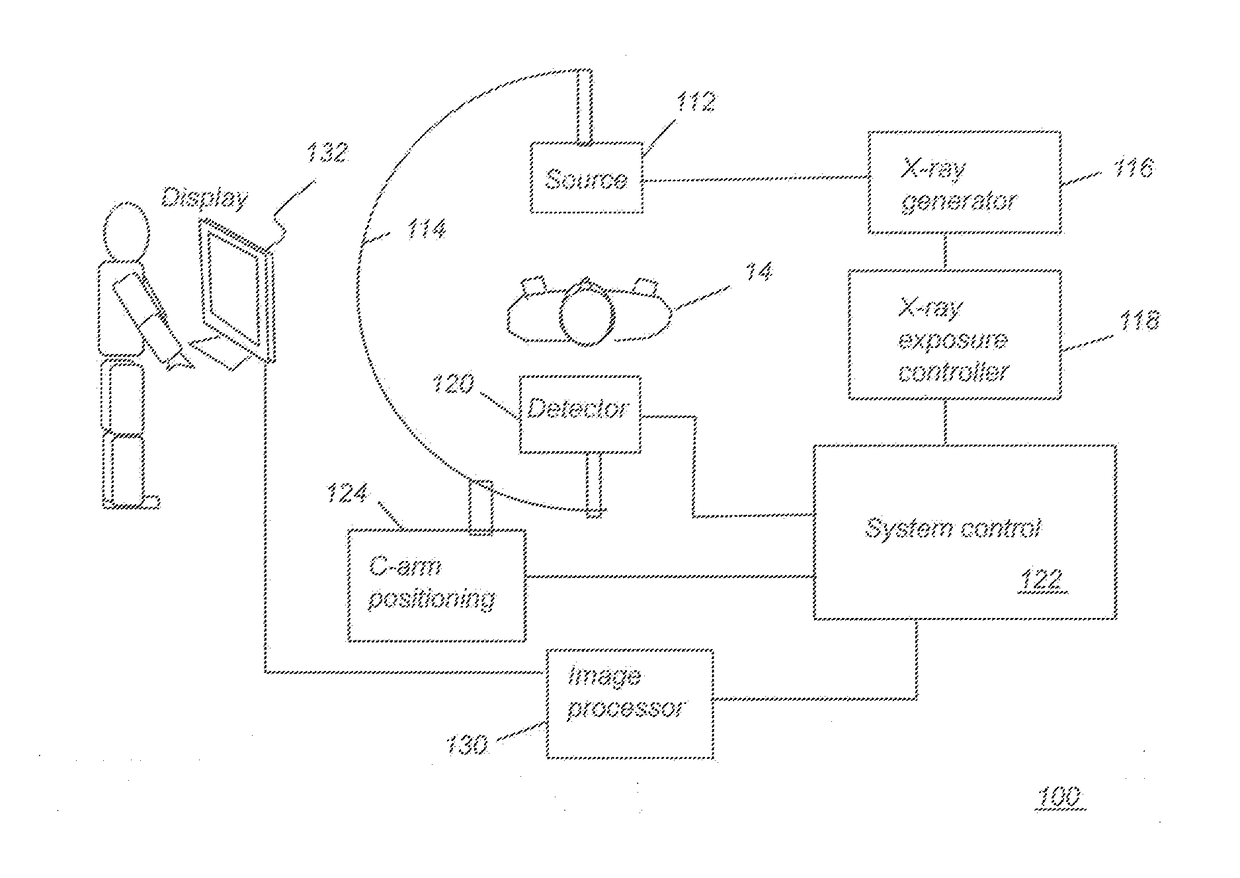
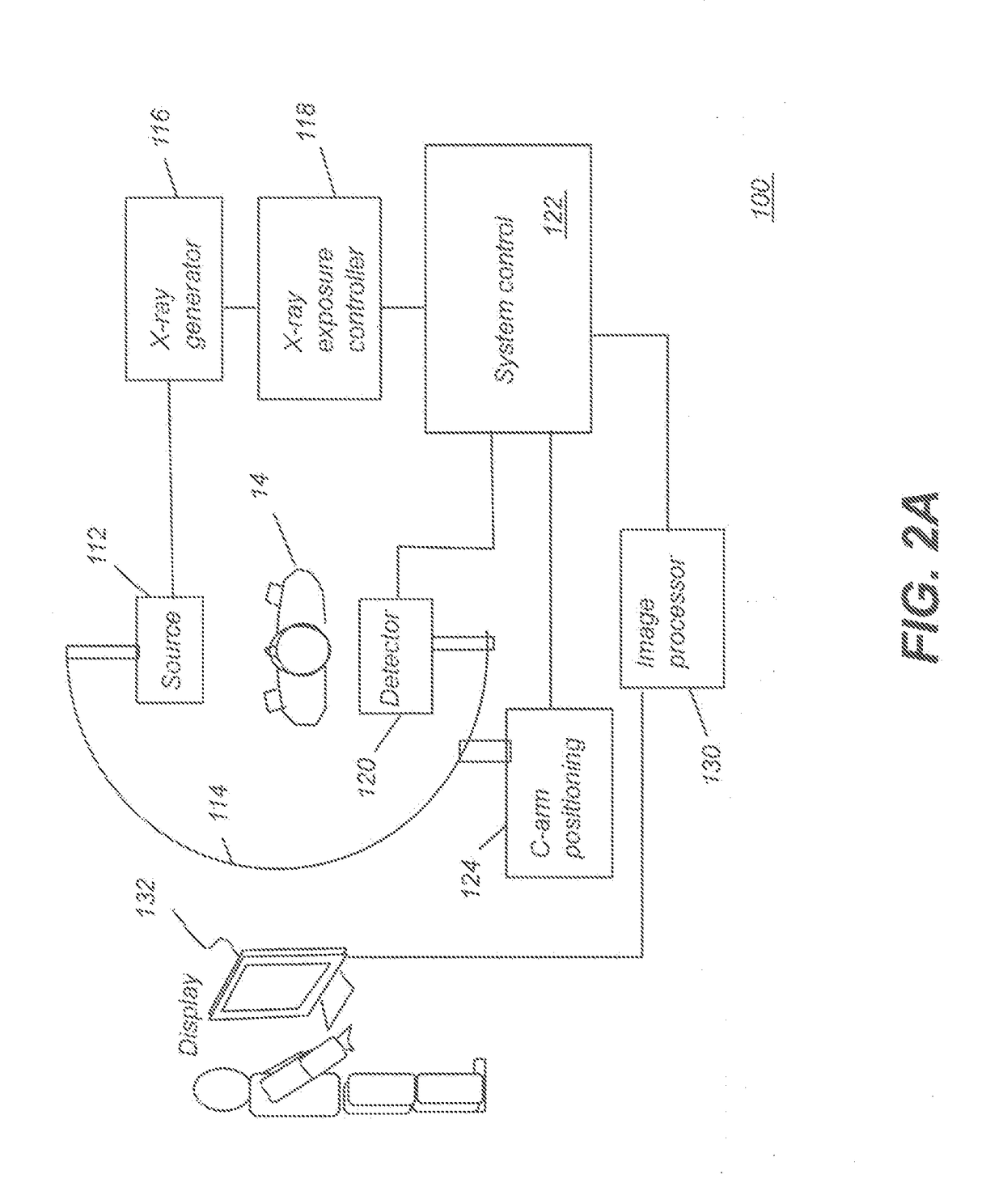
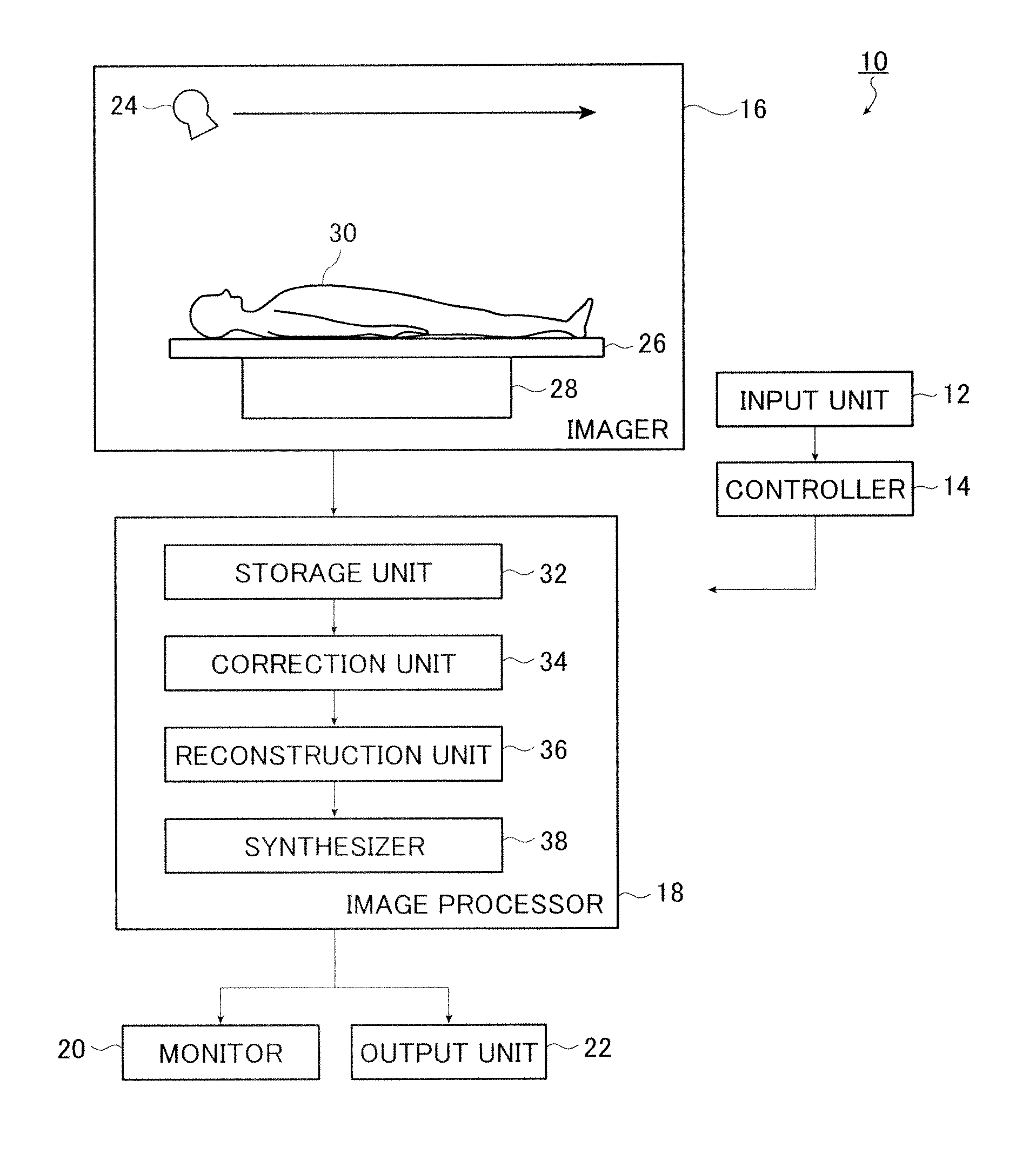
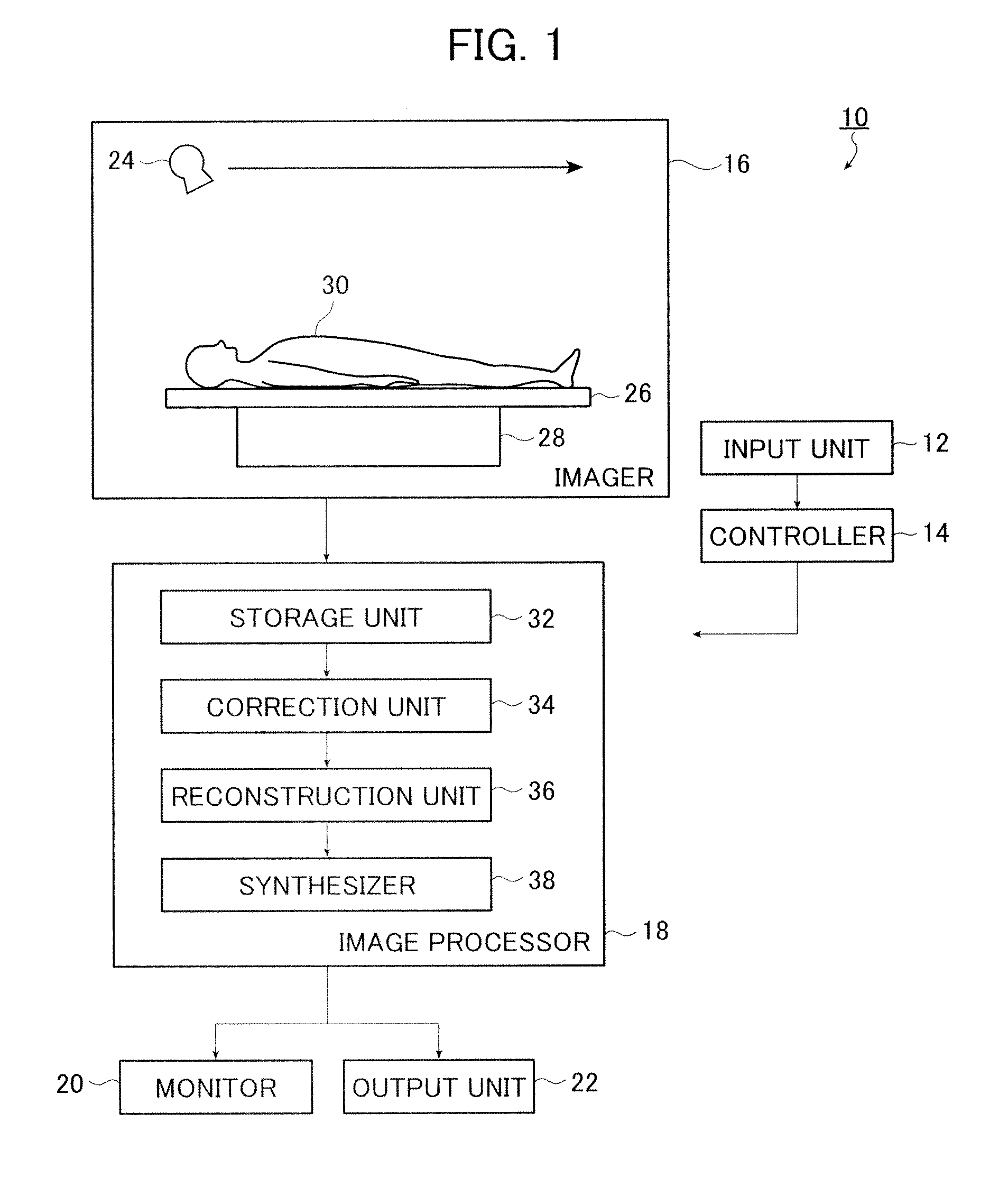
X-ray imaging apparatus and its control method
InactiveUS7315606B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingX-rayX ray image
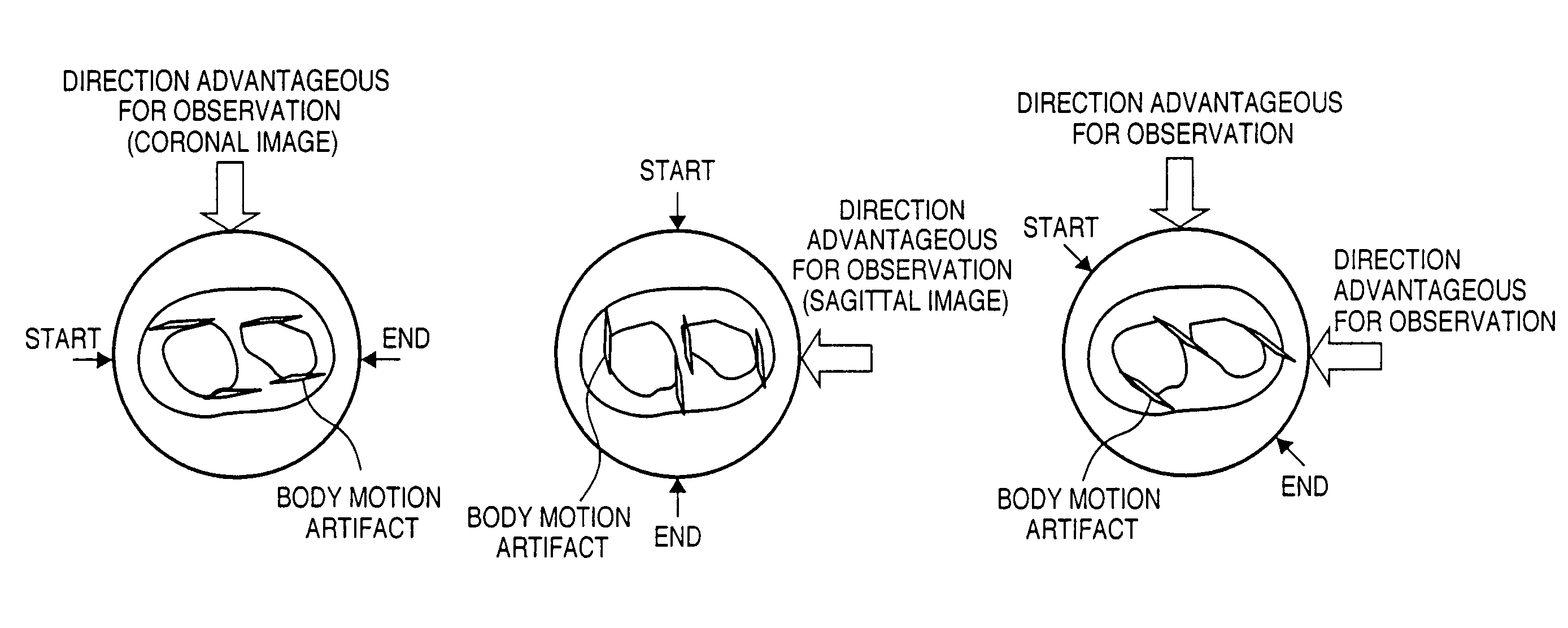
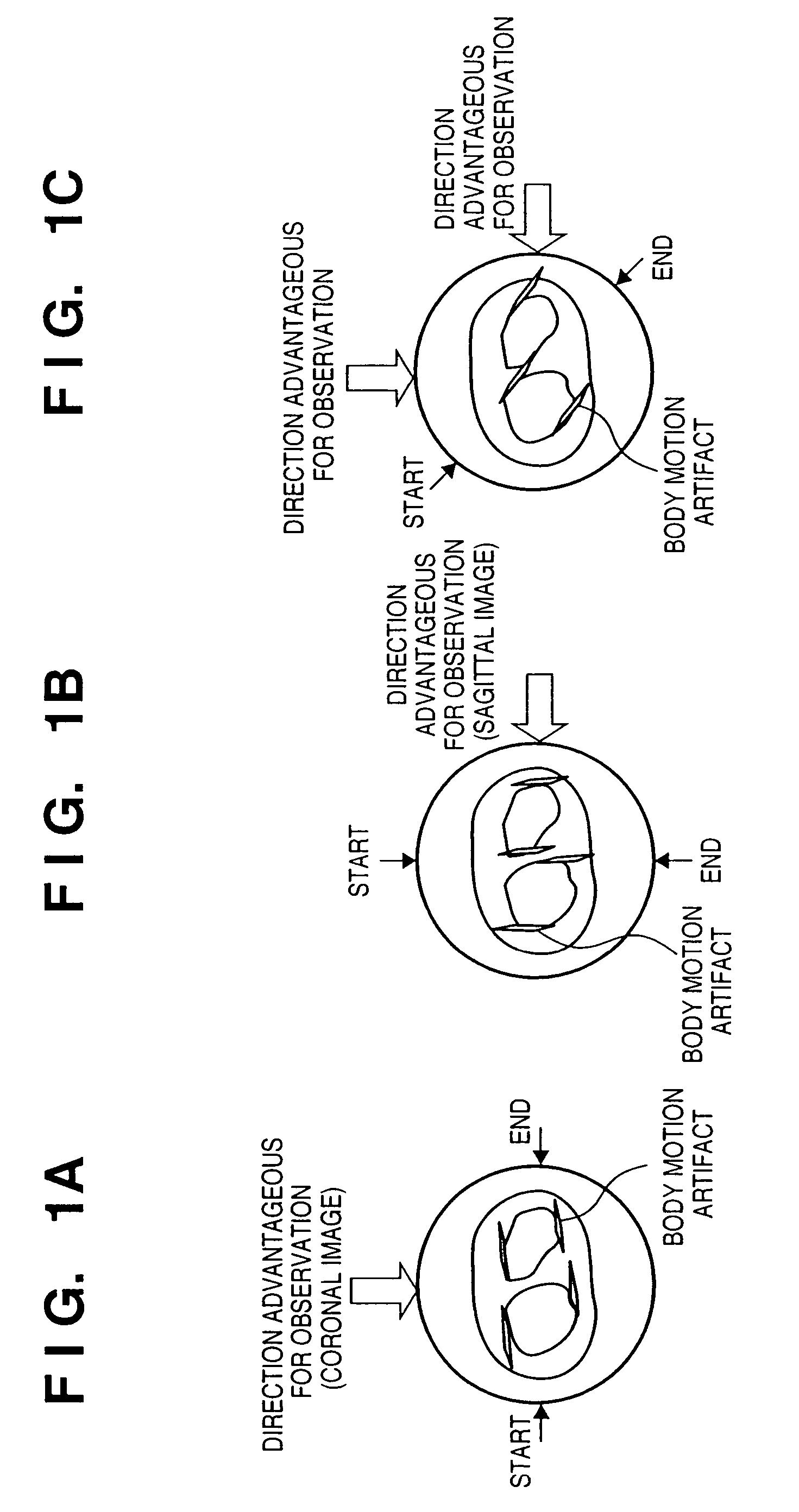
In an X-ray imaging apparatus, which has a radiation source for generating radiation, and a detector for detecting the amount of radiation of the radiation, a subject is relatively rotated with respect to radiation which is radiated from the radiation source in the direction of the detector, and radiation amount data for image reconstruction is acquired in a predetermined rotation section. At this time, a desired observation direction perpendicular to the rotation axis in association with the subject is designated, and the position of the predetermined rotation section is determined on the basis of the designated observation direction.
Owner:CANON KK
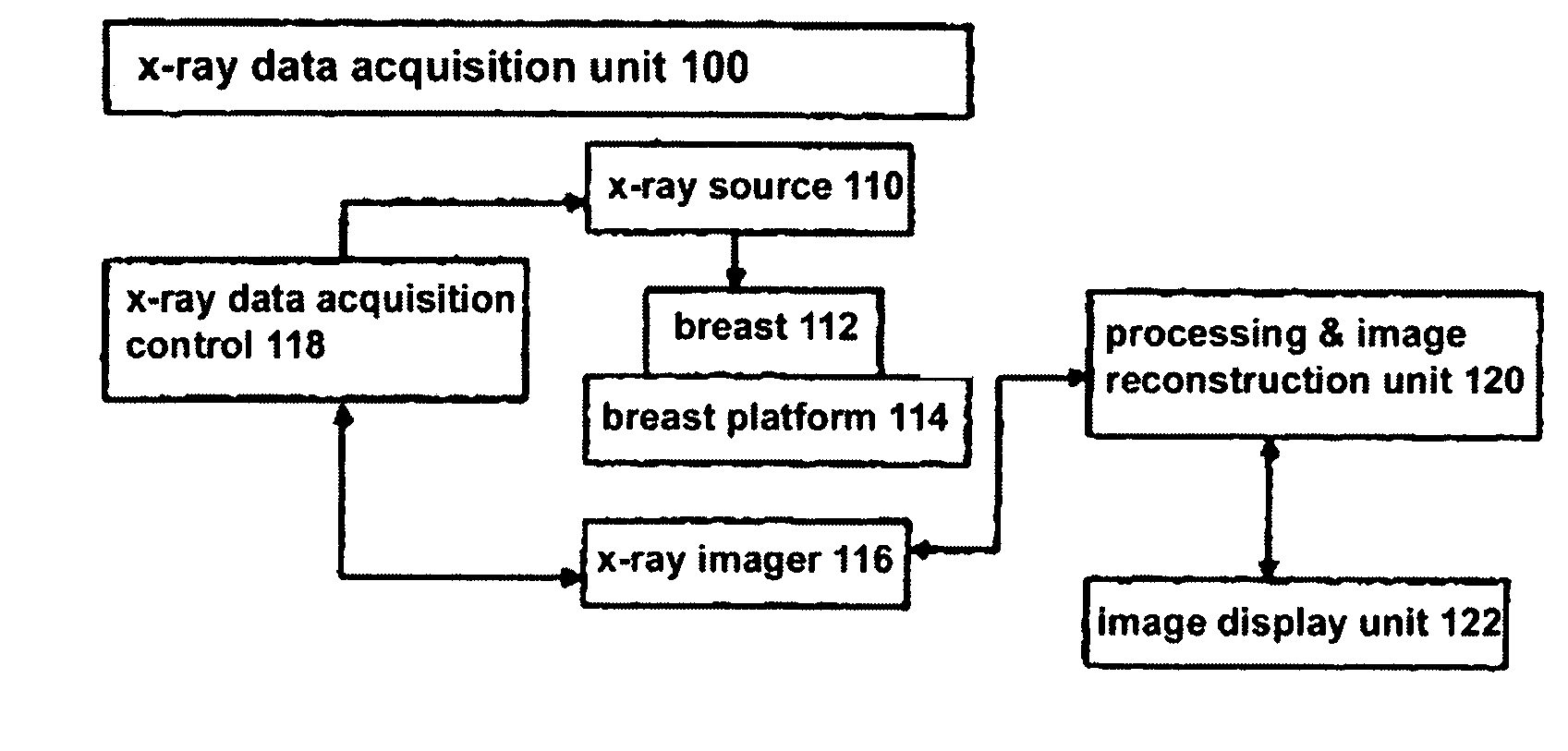
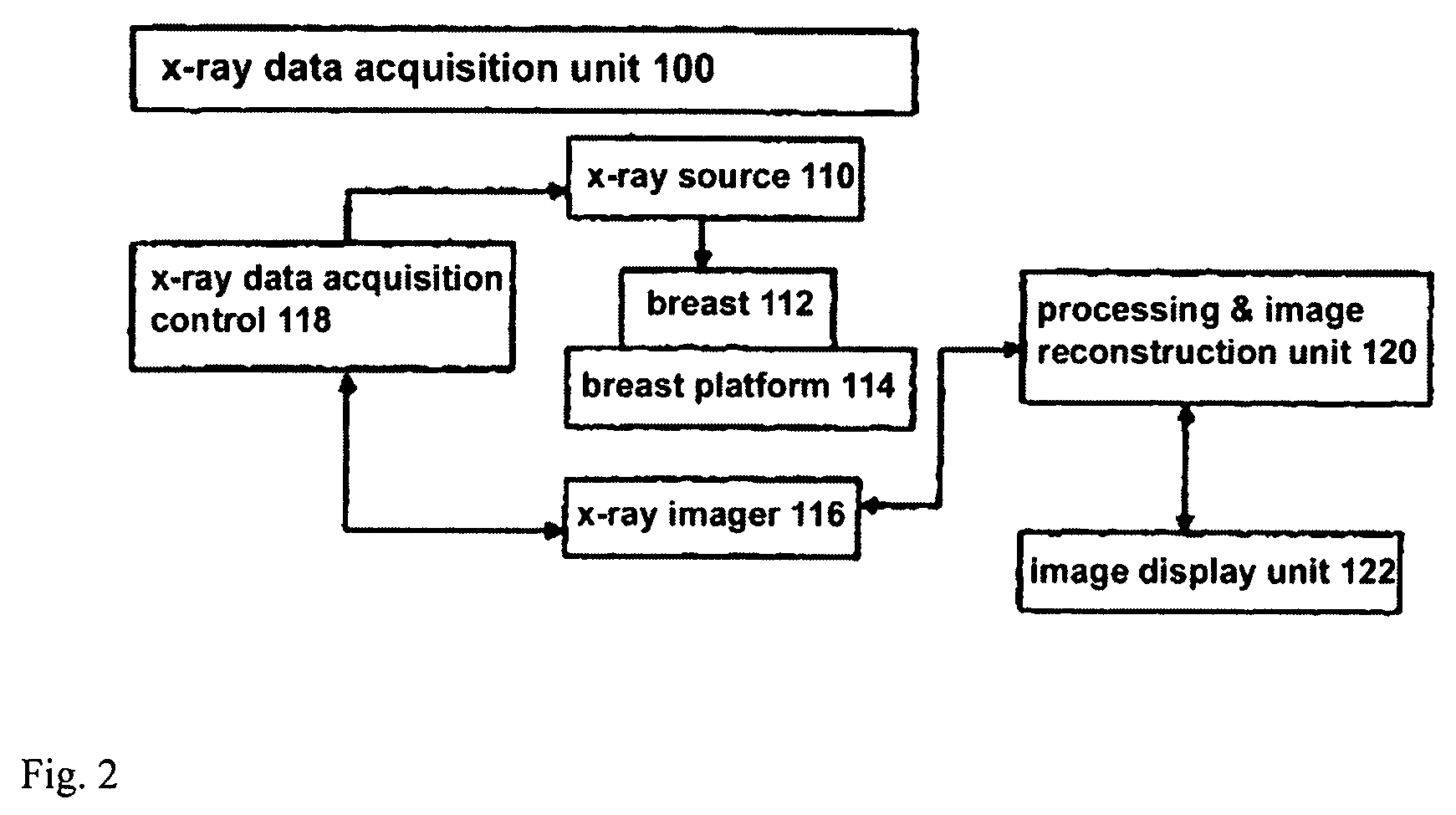
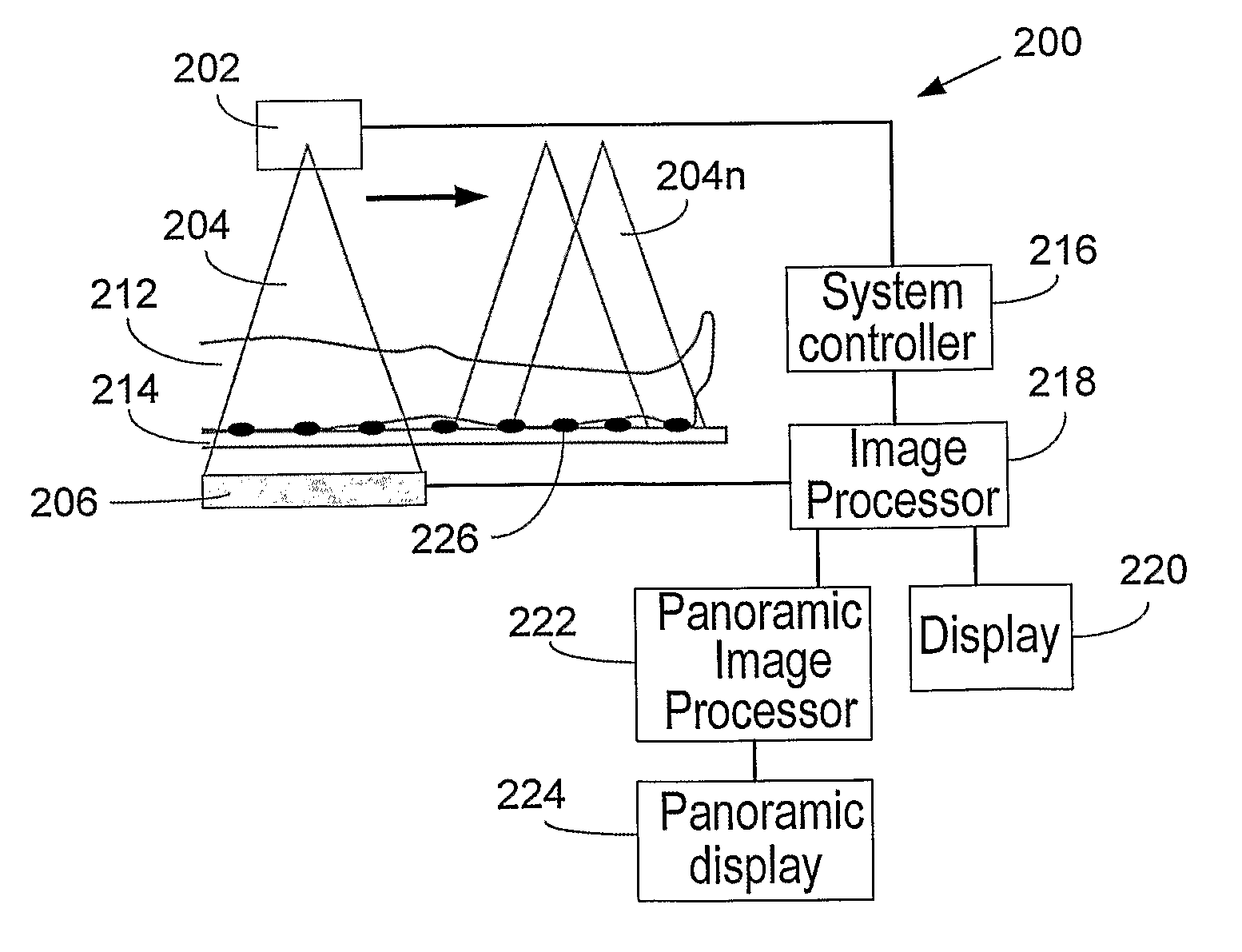
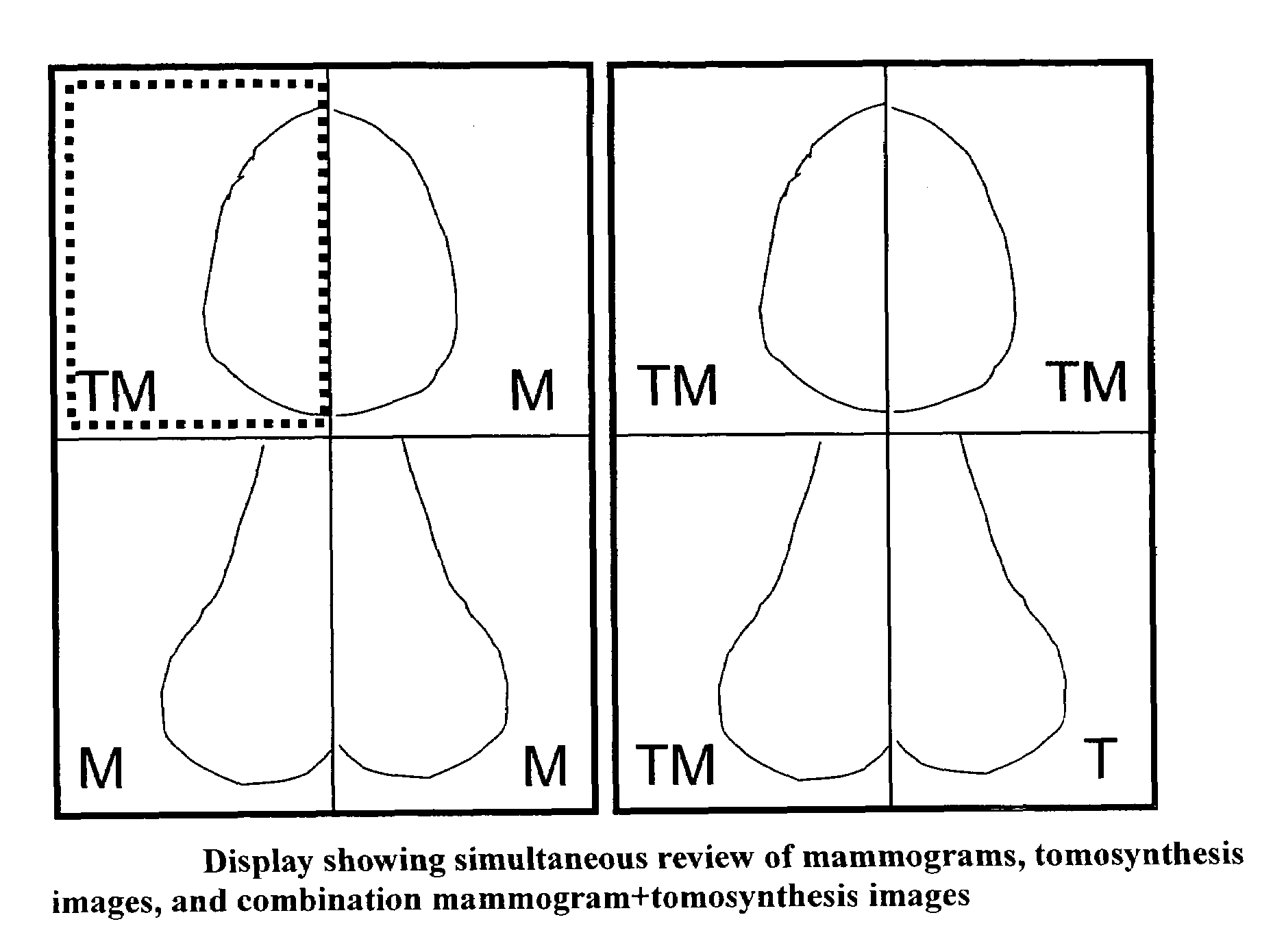
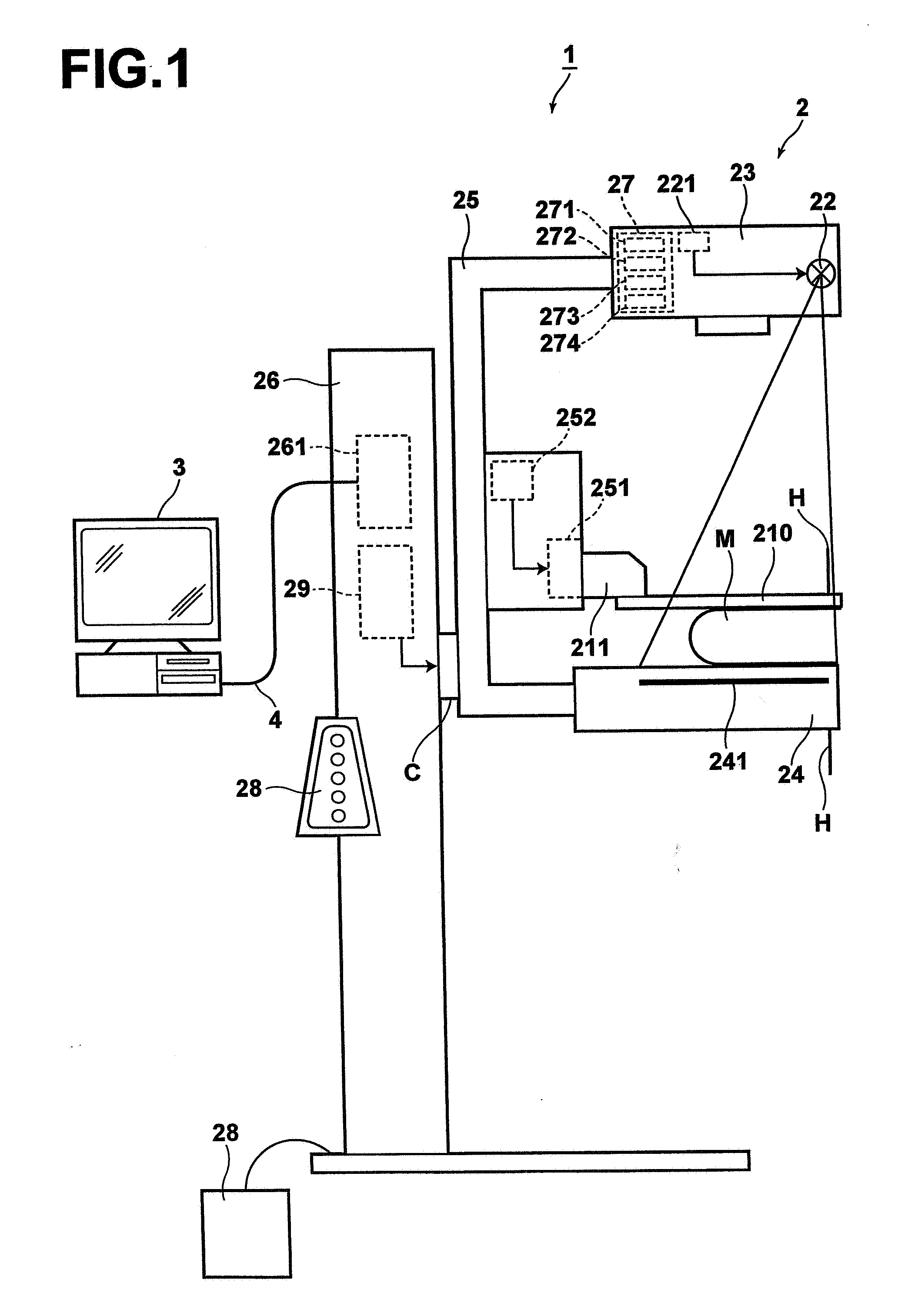
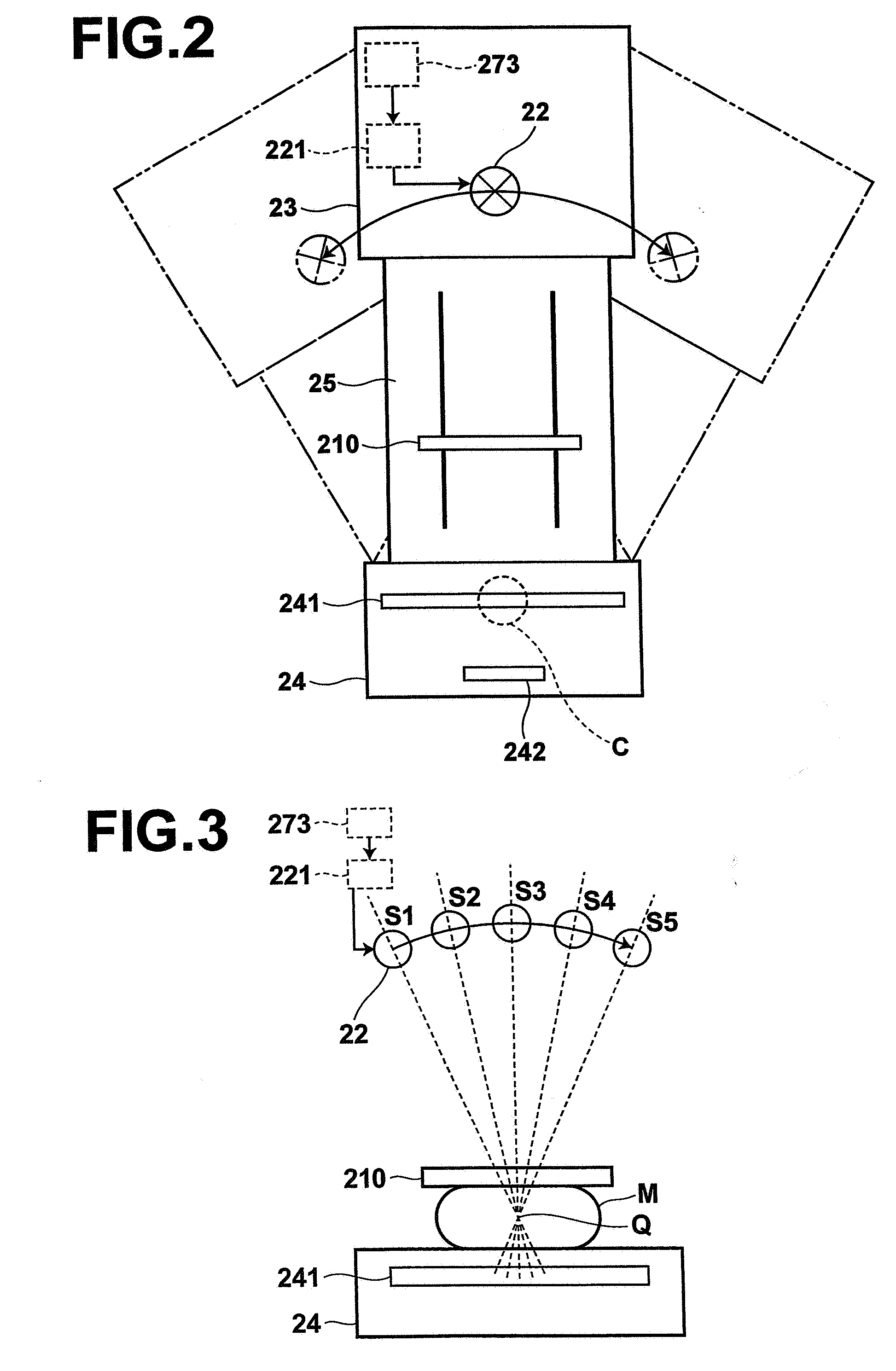
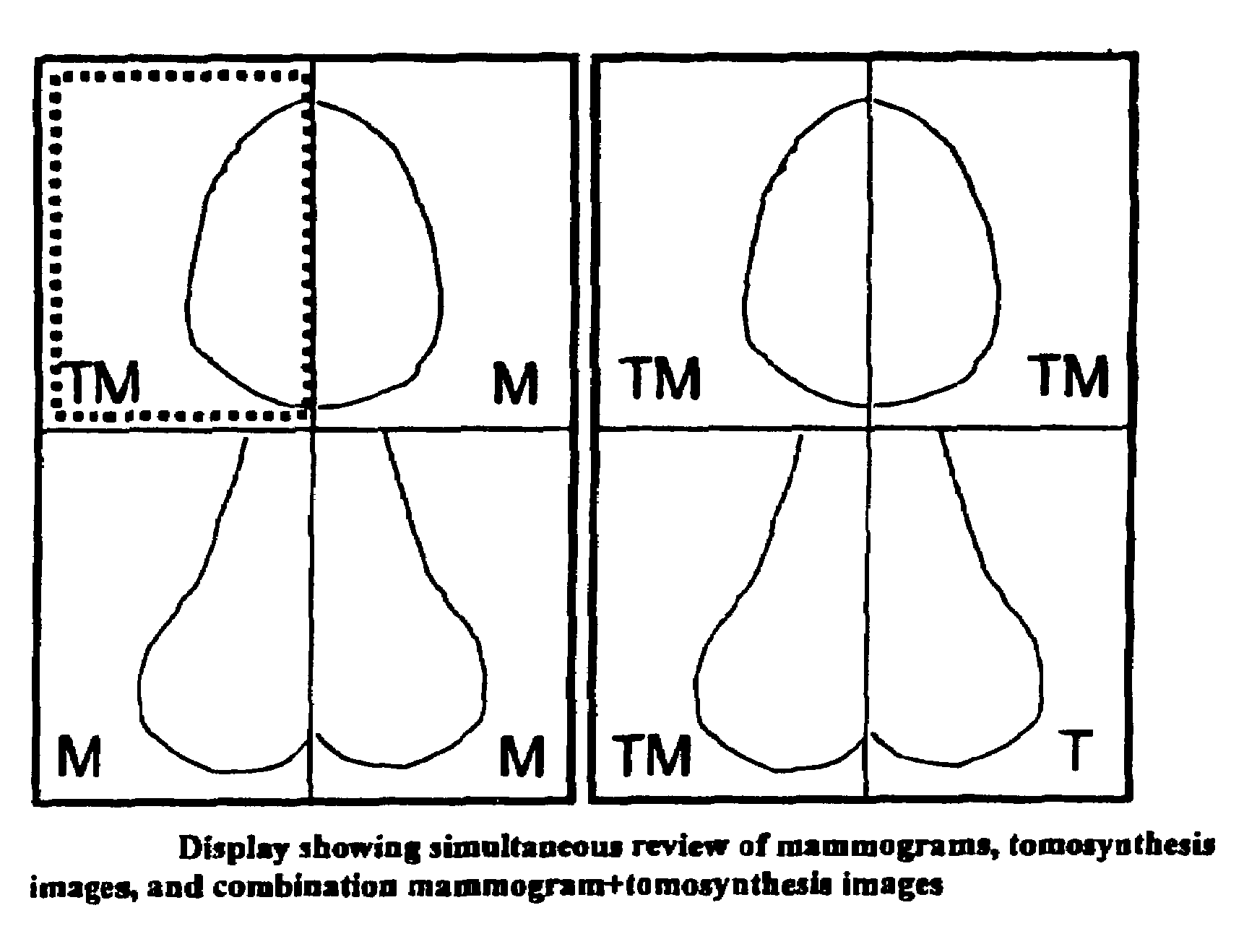
Image Handling and display in X-ray mammography and tomosynthesis
InactiveUS20080019581A1Easy to identifyImprove assessmentImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisProjection image
A method and system for acquiring, processing, storing, and displaying x-ray mammograms Mp tomosynthesis images Tr representative of breast slices, and x-ray tomosynthesis projection images Tp taken at different angles to a breast, where the Tr images are reconstructed from Tp images
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
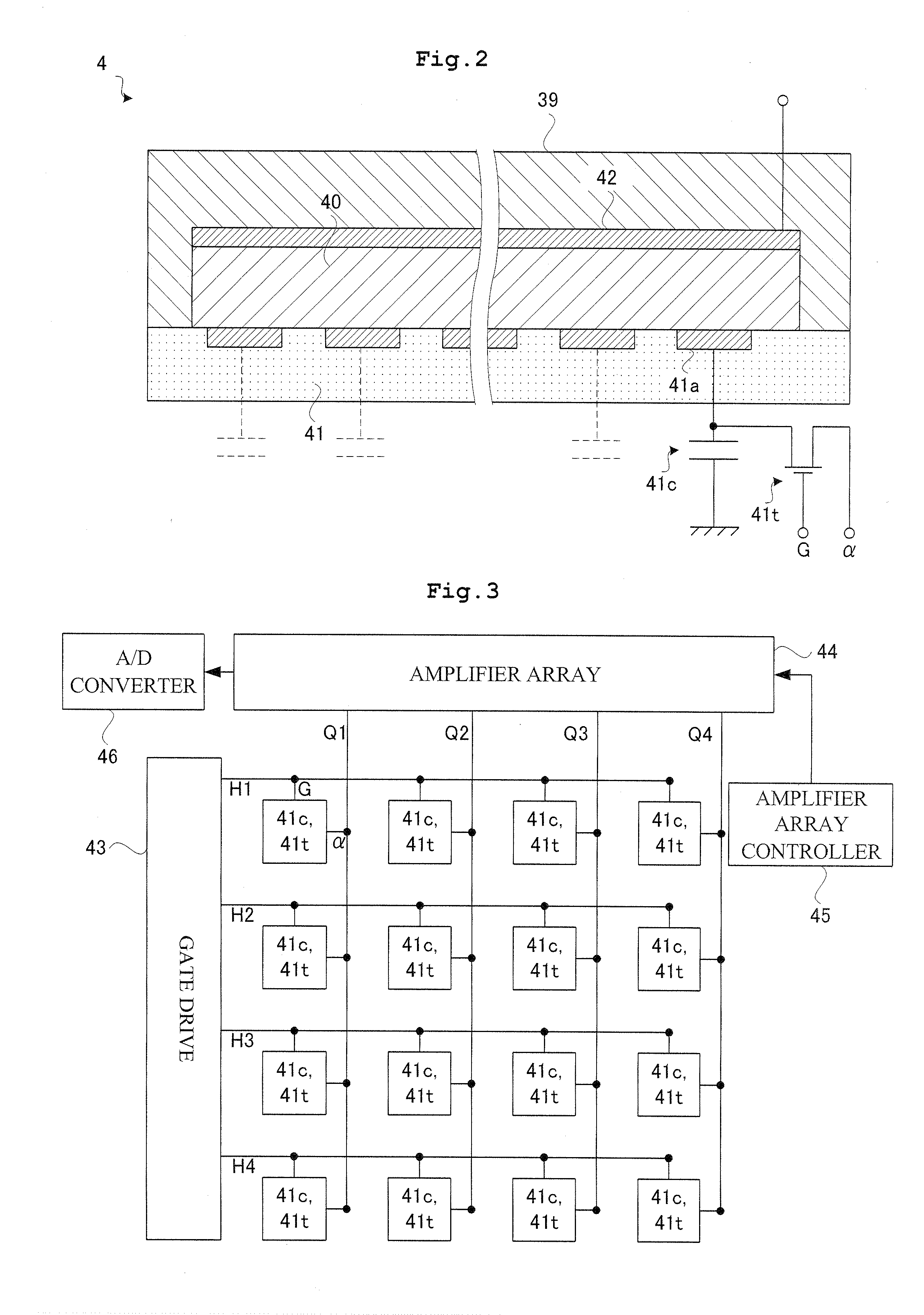
Radiographic apparatus
ActiveUS8798231B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingFluoroscopic imageFluorescence
One object of this invention is to provide radiography apparatus with suppressed exposure to a subject in tomography mode. An FPD provided in X-ray apparatus according to this invention converts X-rays into electric signals, and thereafter amplifies the signals to output them to an image generation section. According to this invention, an amplification factor is higher in a tomography mode than in a spot radiography mode. A tomographic image is obtained through superimposing two or more fluoroscopic image. In comparison of the fluoroscopic images, they differ from one another in appearance of the false image. Accordingly, superimposing the images may achieve cancel of the false images. In this way, the tomographic image finally obtained has no false image.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
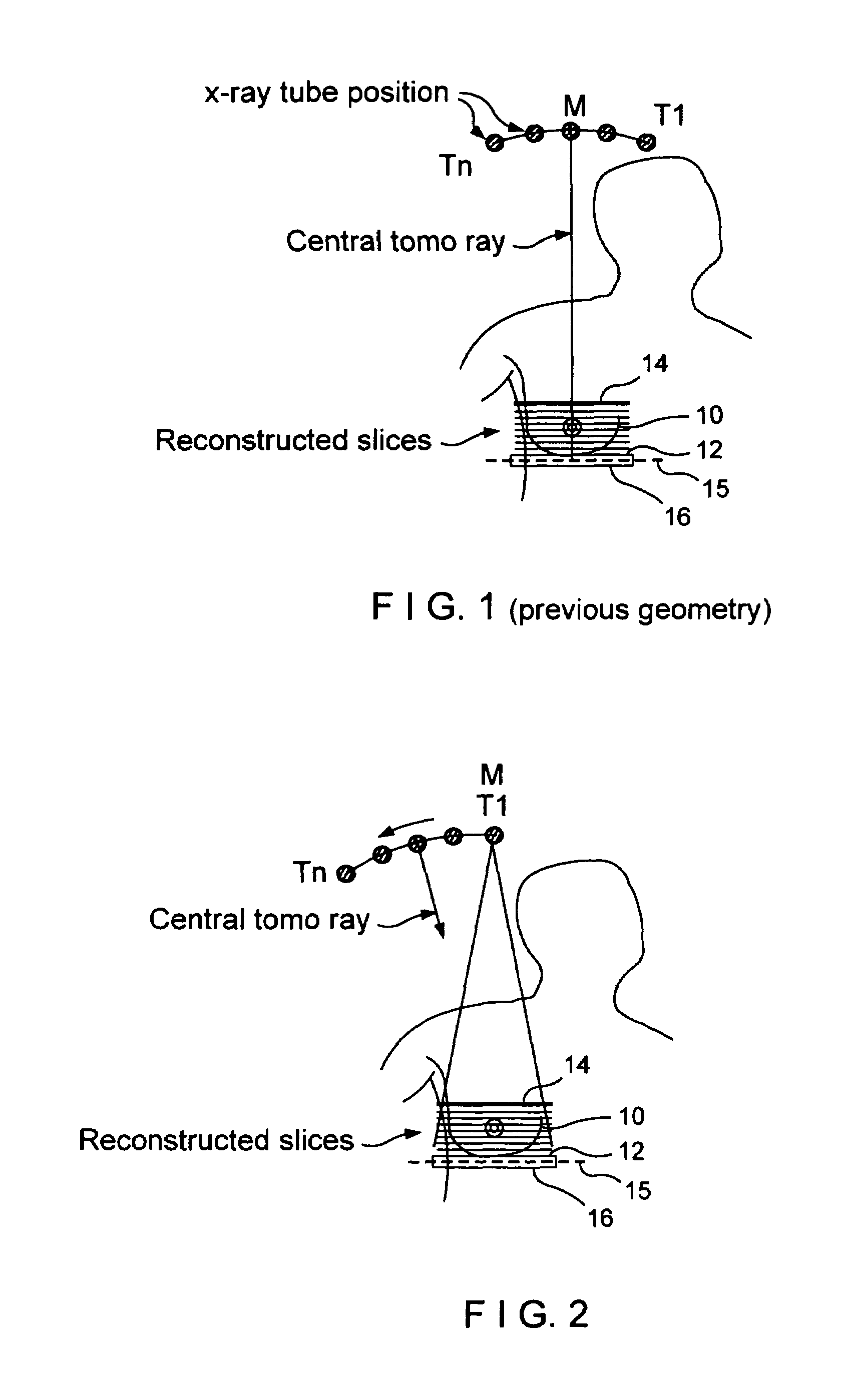
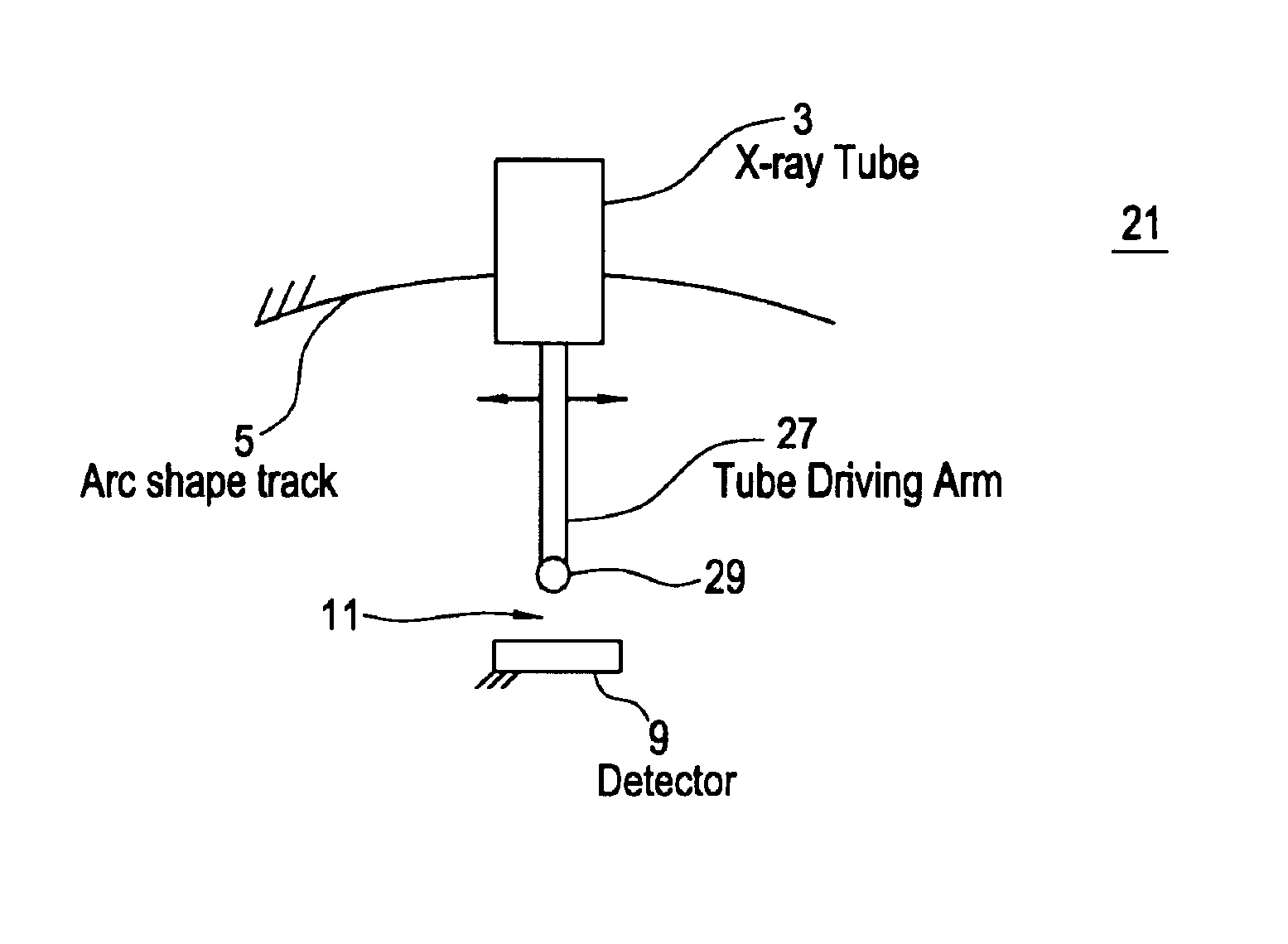
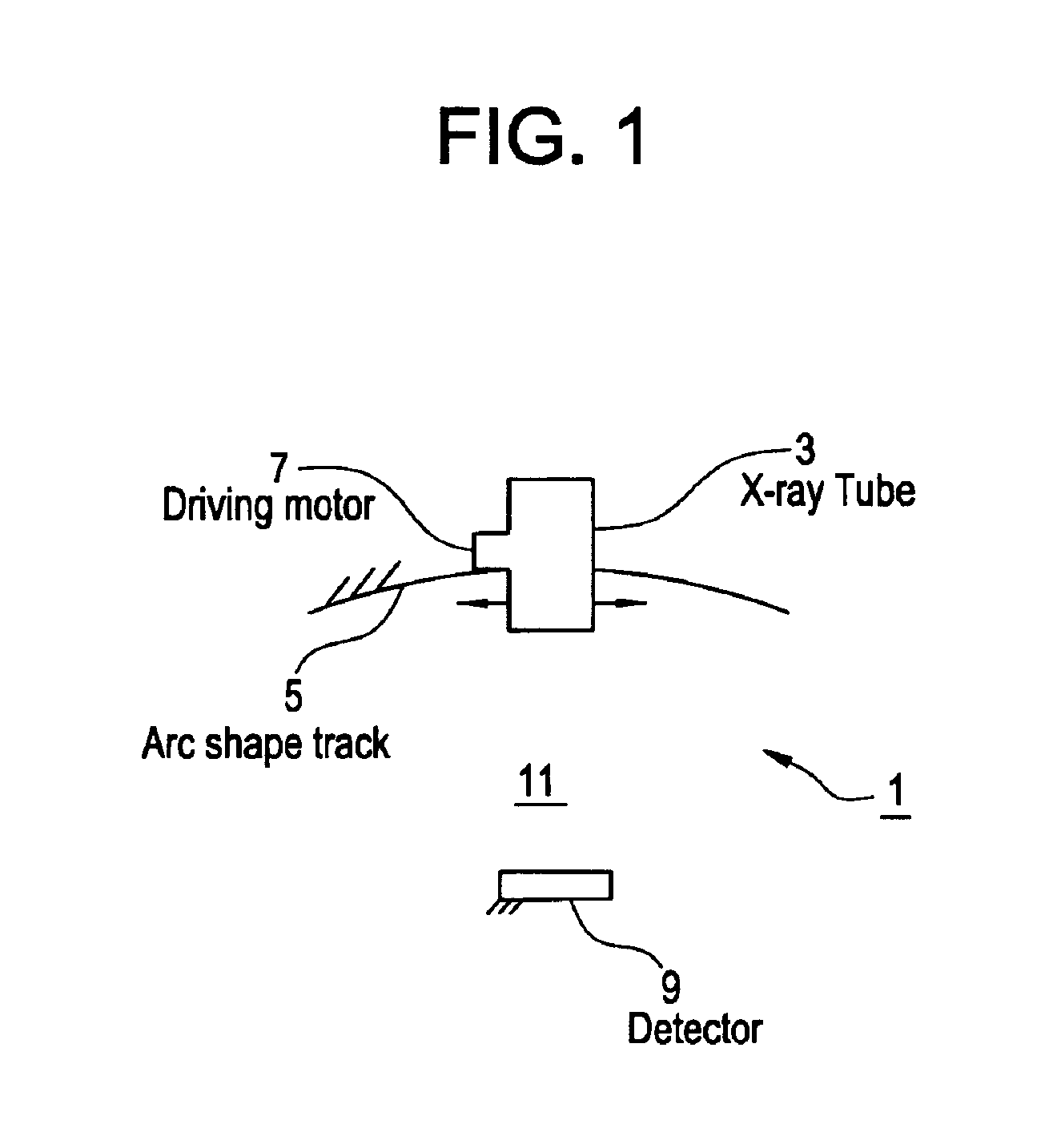
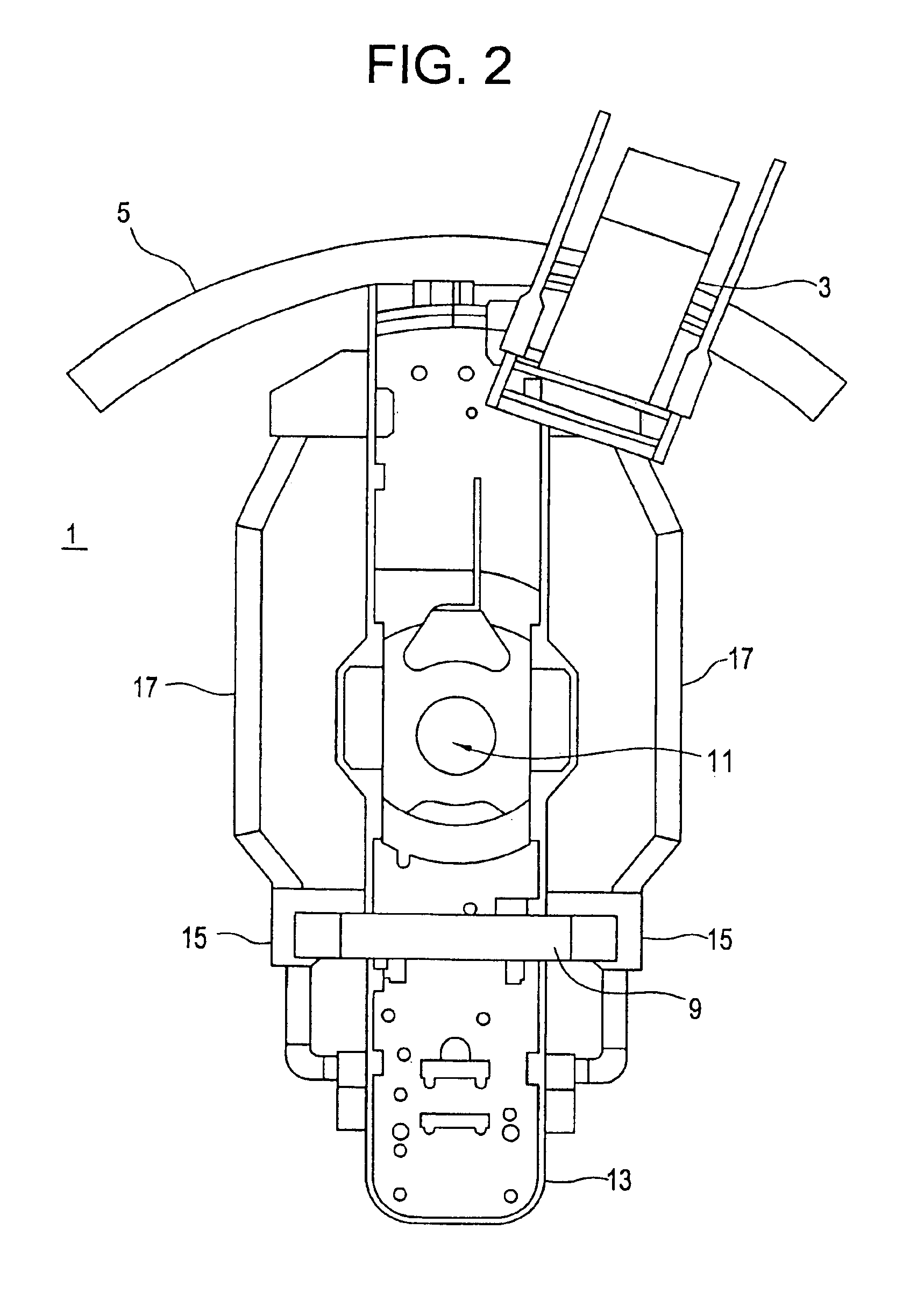
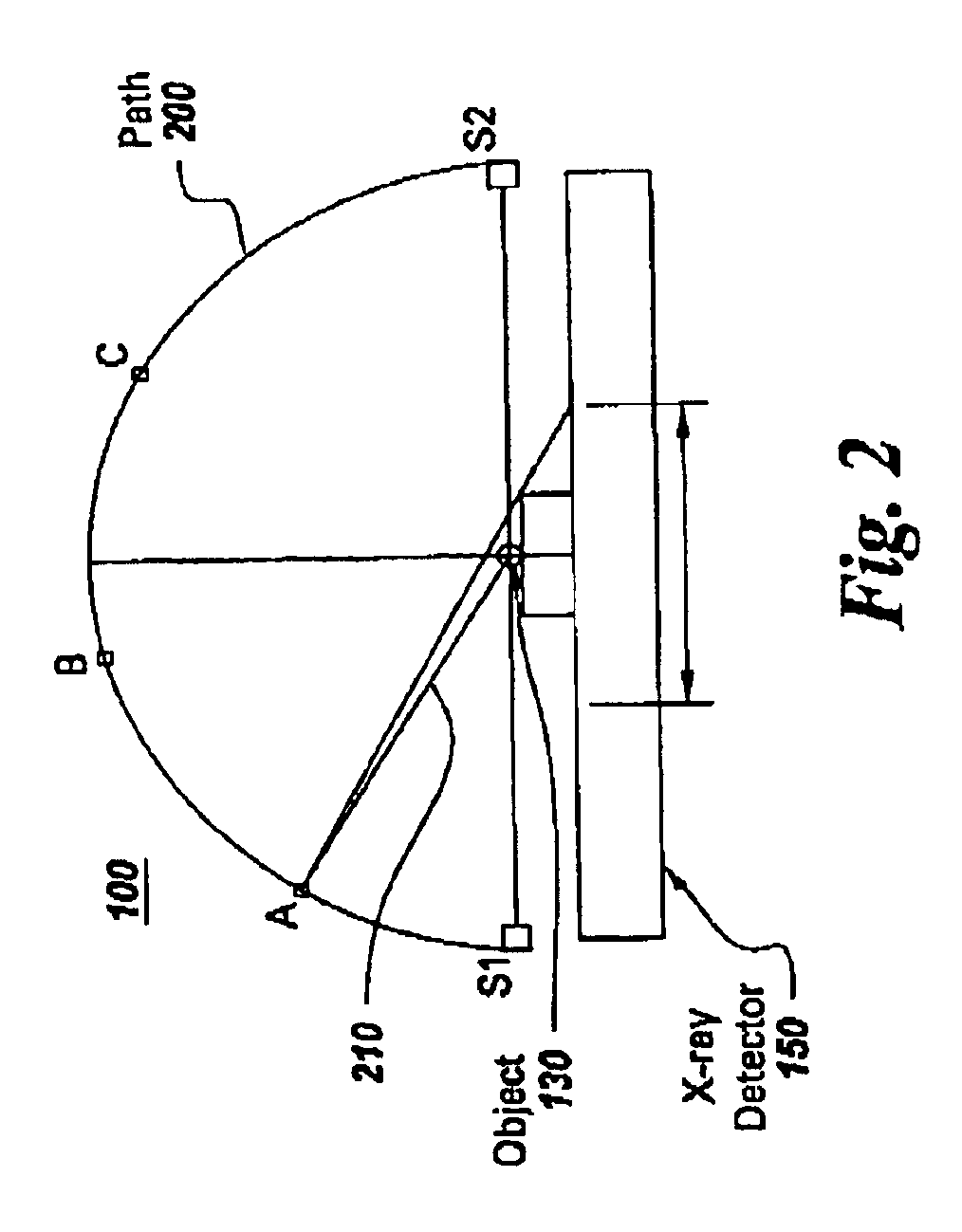
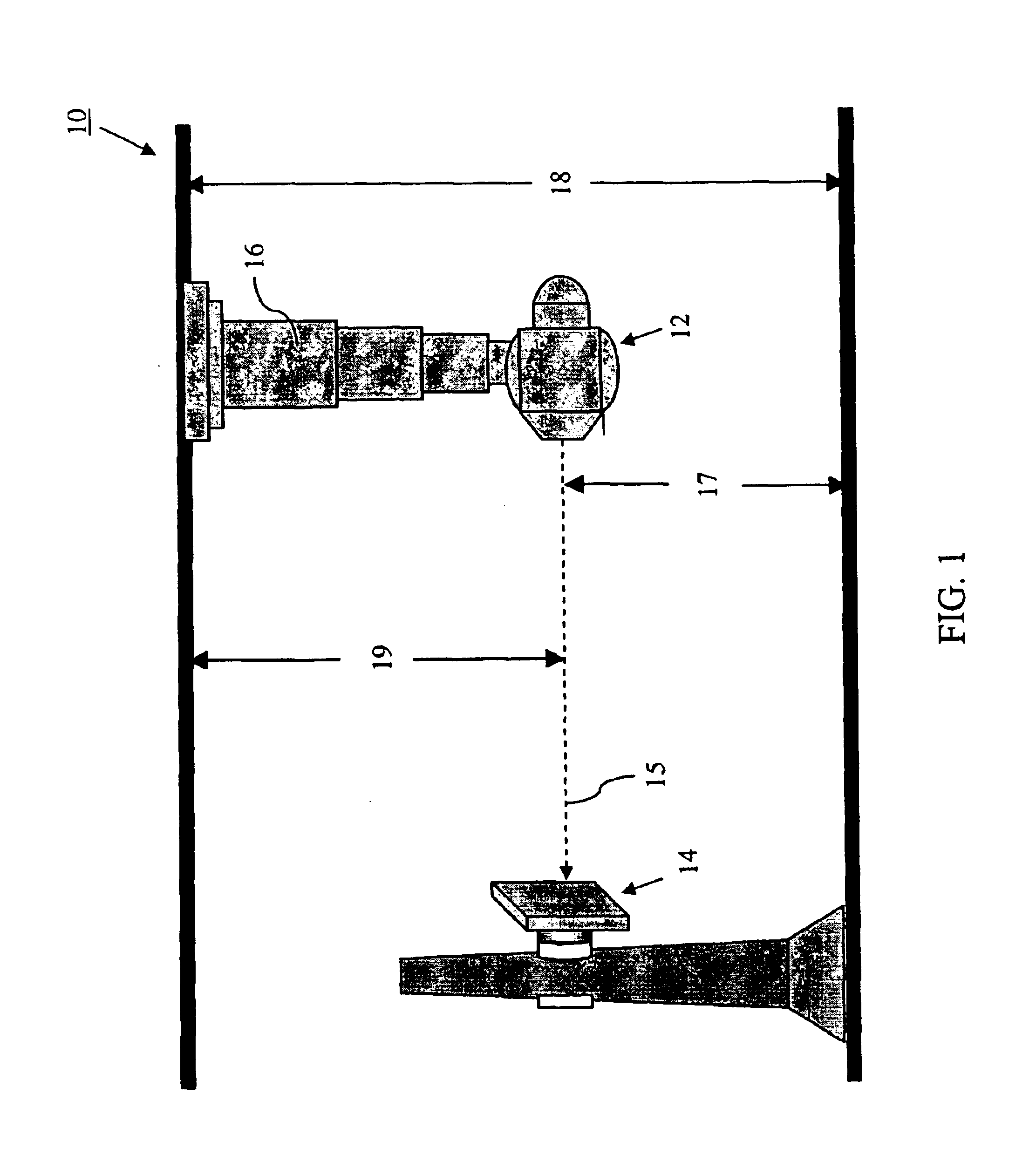
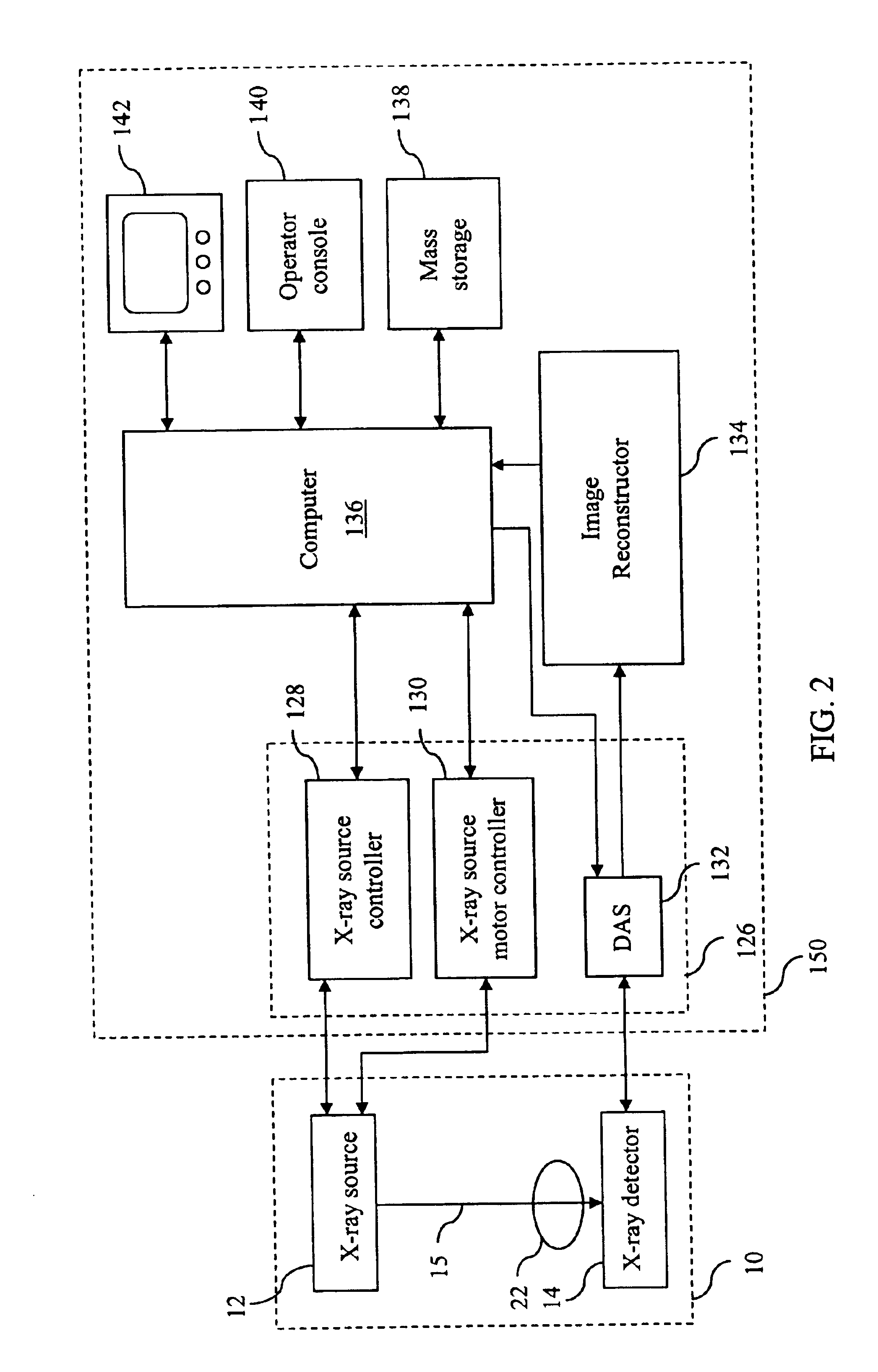
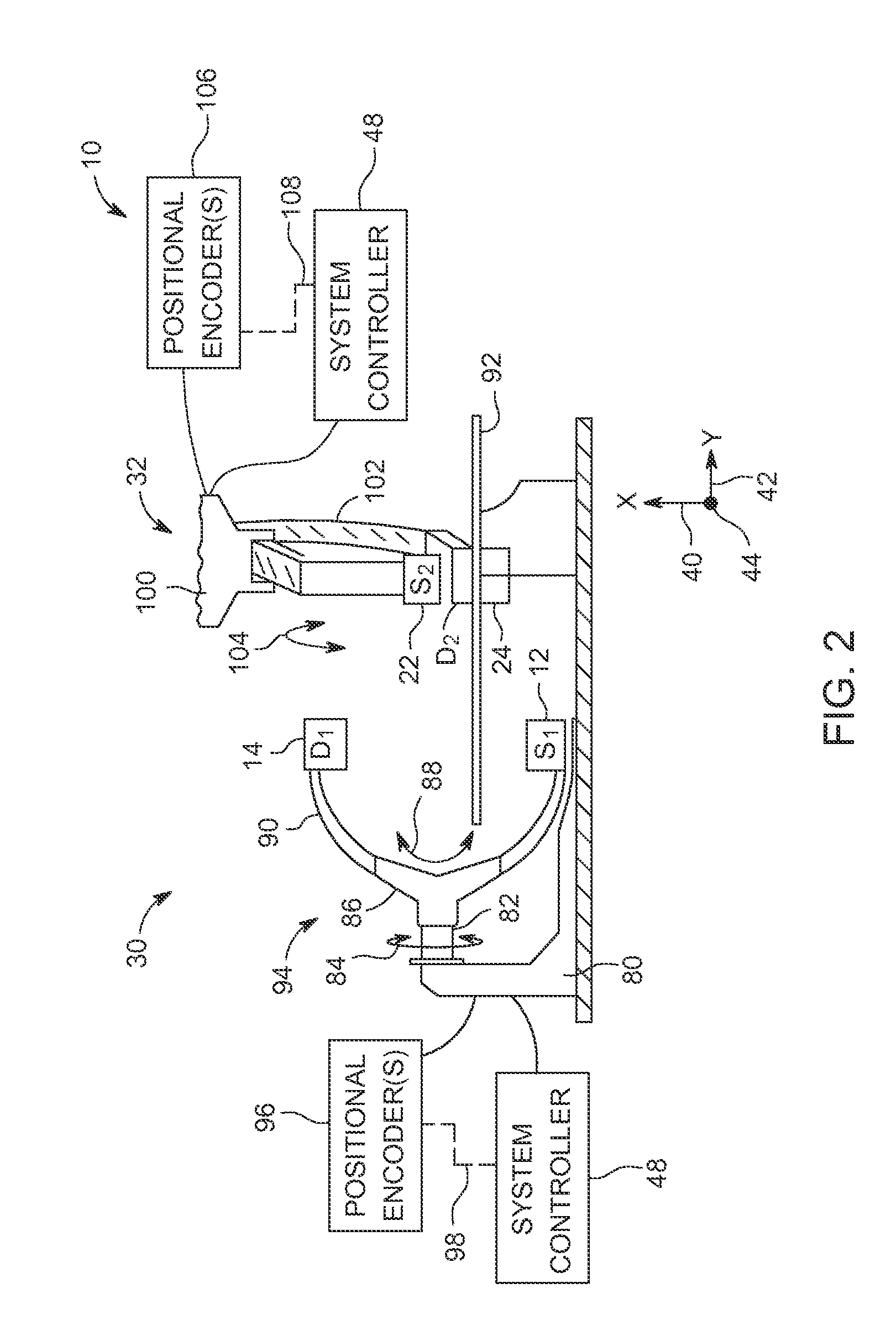
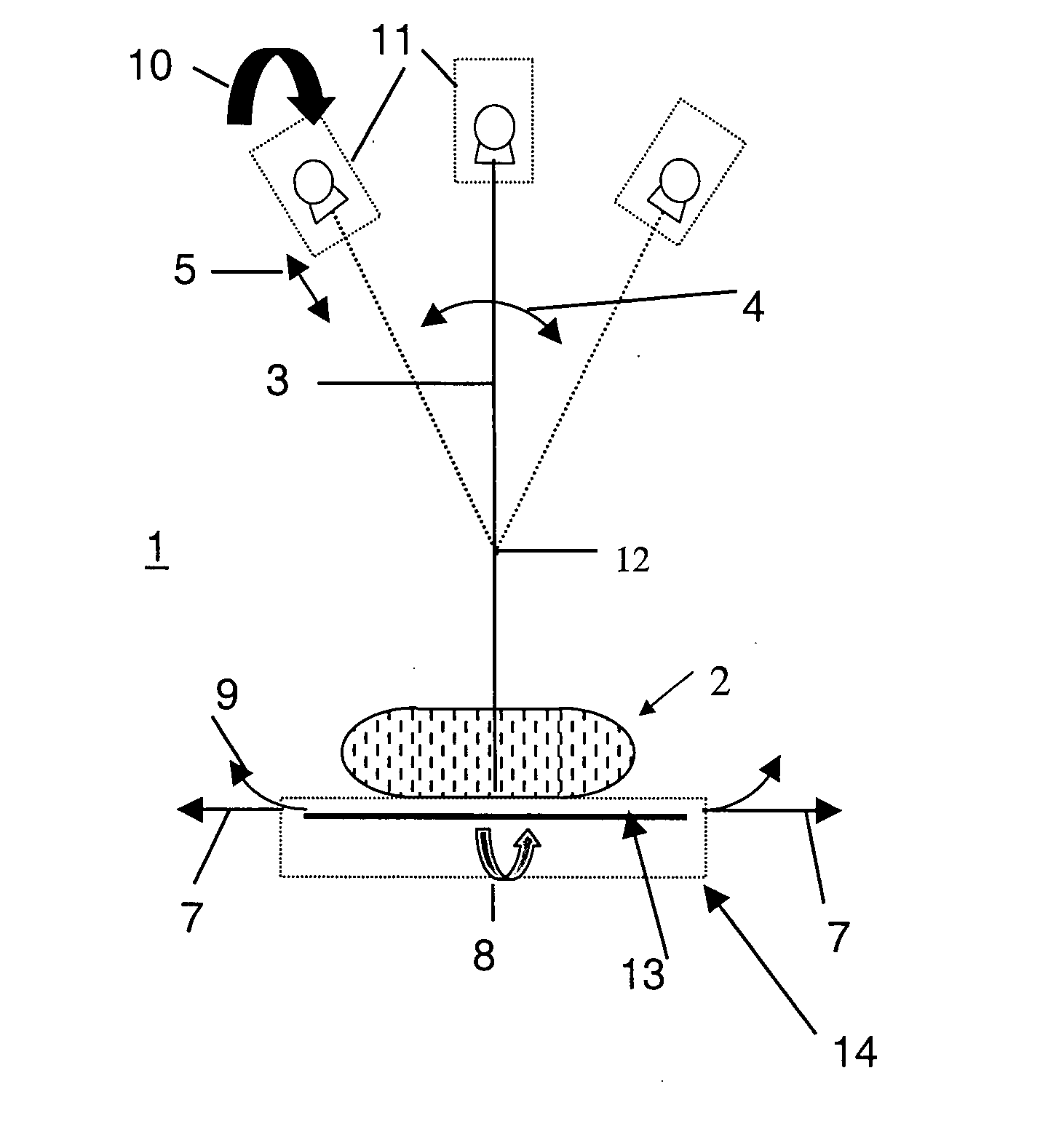
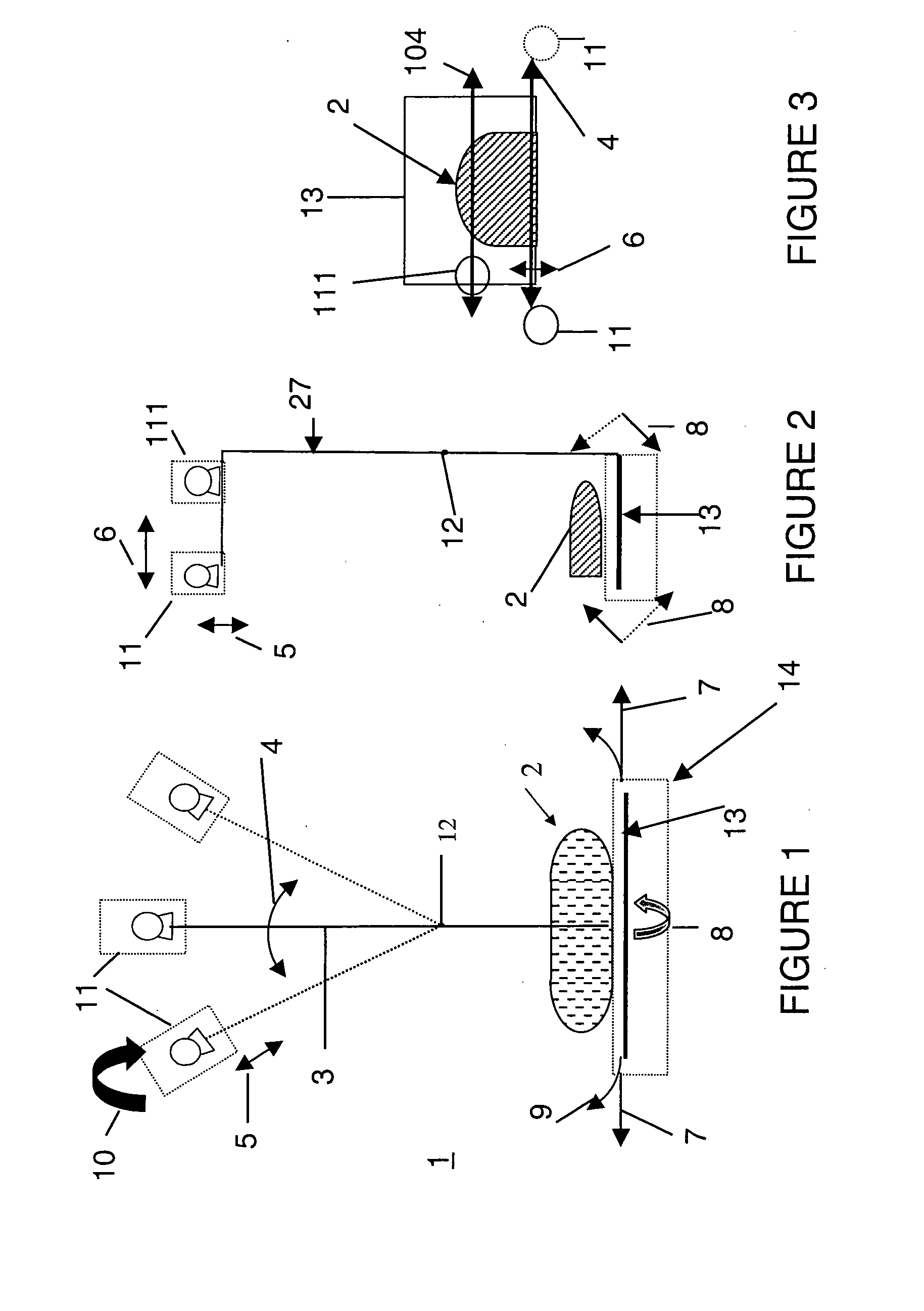
Tomosynthesis X-ray mammogram system and method with automatic drive system
InactiveUS6882700B2Radiation diagnosis data transmissionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesisX-ray
An imaging system includes an X-ray source adapted to move in an arc shaped path and a stationary electronic X-ray detector. The system also includes a track and a mechanical driving mechanism which is adapted to move the X-ray source in the arc shaped path. A tomosynthesis X-ray imaging method includes mechanically moving an X-ray source in a stepped motion on an arc shaped path around an object using a track and irradiating the object with an X-ray dose from the X-ray source located at a plurality of steps along the arc shaped path. The method also includes detecting the X-rays transmitted through the object with an electronic X-ray detector, and constructing a three dimensional image of the object from a signal output by the electronic X-ray detector.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
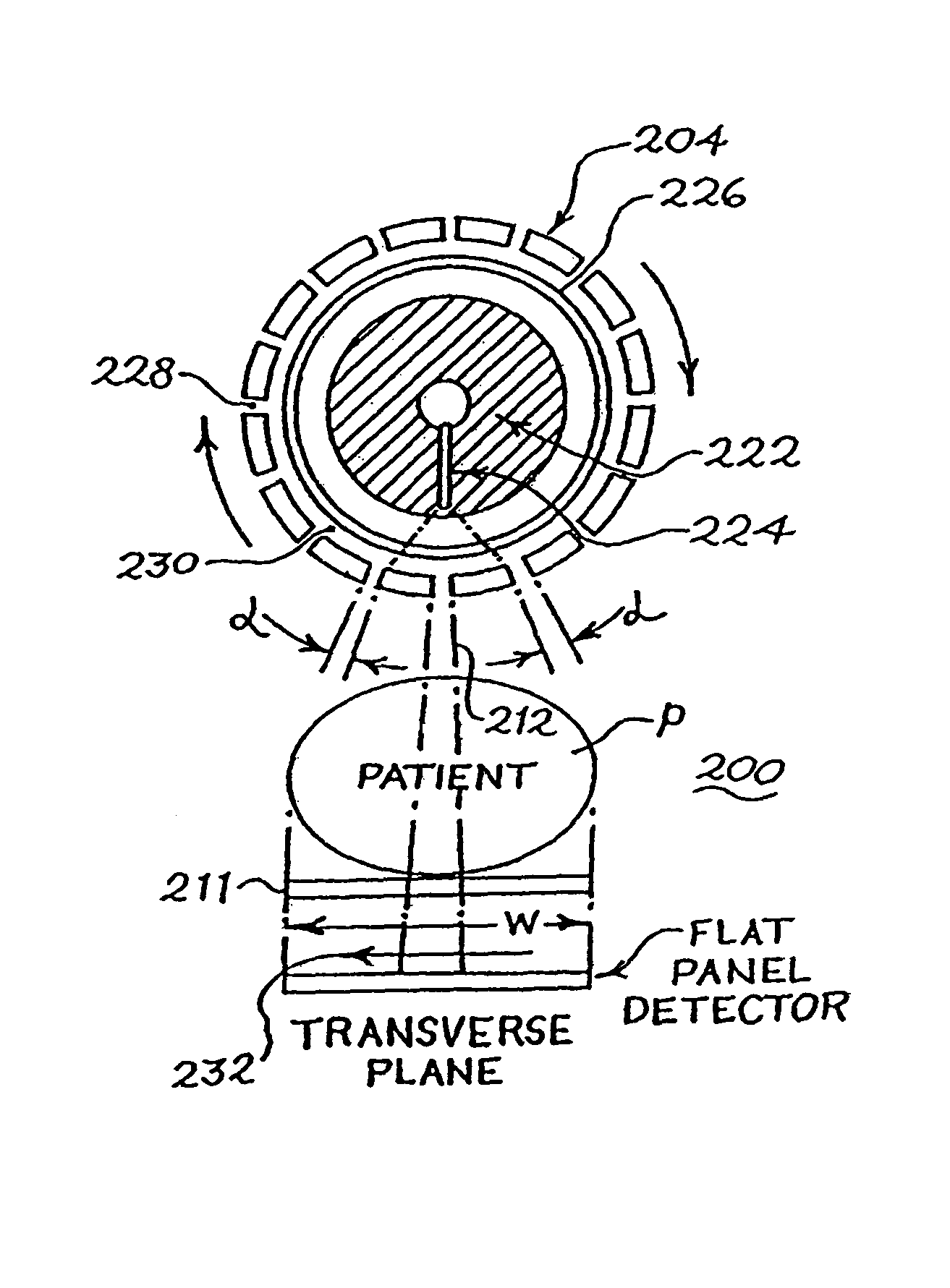
X-ray imaging system and x-ray imaging method
InactiveUS20120051498A1Reduce exposureReduced imaging timeReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayX ray image
An X-ray imaging system is for irradiating a subject with X ray from an X-ray source at a plurality of different angles to acquire X-ray images, and reconstructing an X-ray tomographic image from the X-ray images. The system comprising a region setting unit for setting a region of interest on a pre-shot image or a previously acquired X-ray tomographic image, an imaging control unit for continuously varying an aperture formed by collimator blades according to a position of the X-ray source to image the region of interest and acquiring projection data of the X-ray images in accordance with the position of the X-ray source, and an image reconstructing unit for reconstructing the X-ray tomographic image from the projection data of the X-ray images of the region of interest. The aperture formed by the collimator blades are varied so that all the X-ray images formed on the X-ray detector is rectangular regardless of the position of the X-ray source.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
X-ray mammography/tomosynthesis of patient's breast
A breast x-ray system and method using tomosynthesis imaging in which the x-ray source generally moves away from the patient's head. The system may include an operation mode in which it additionally takes mammogram image data.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
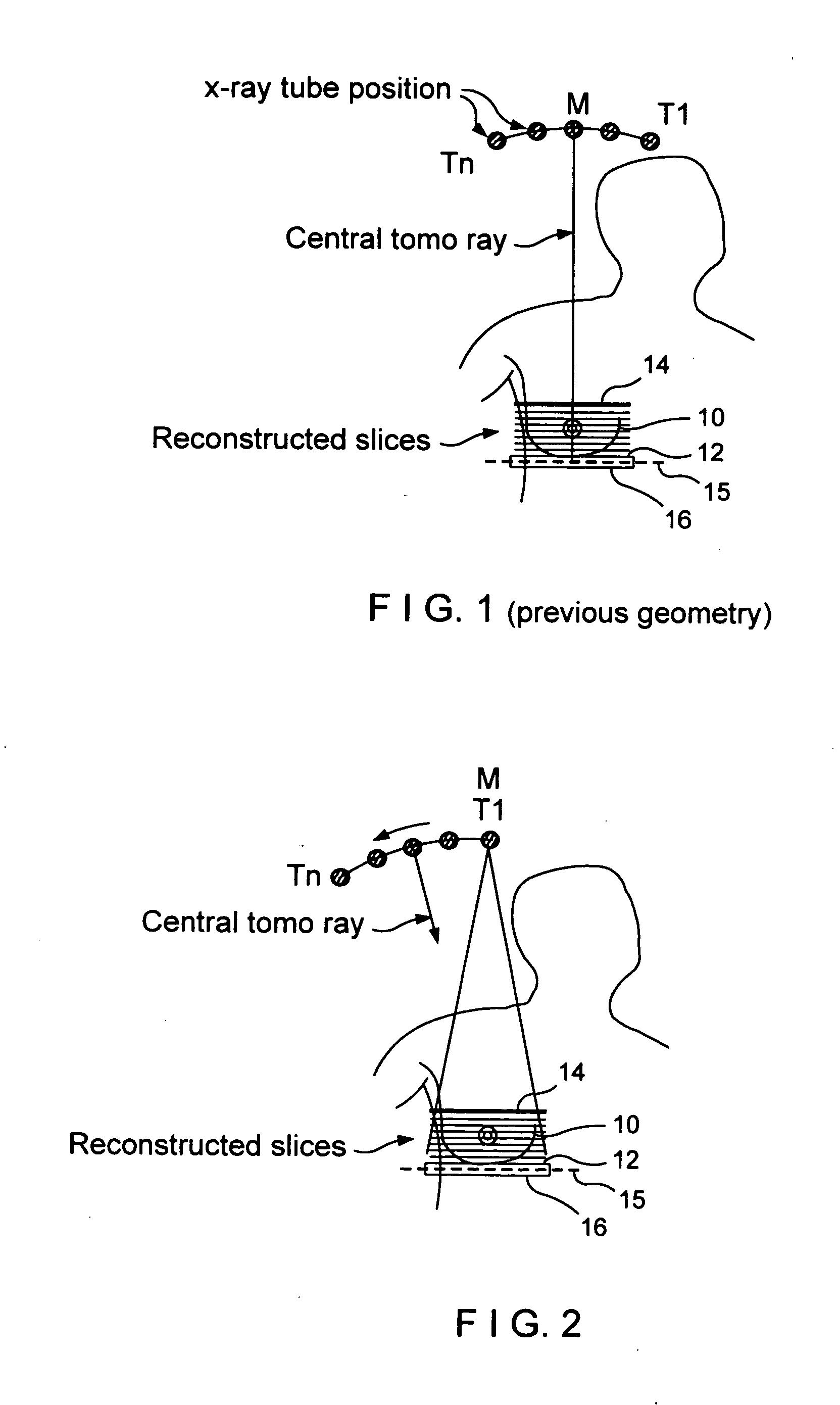
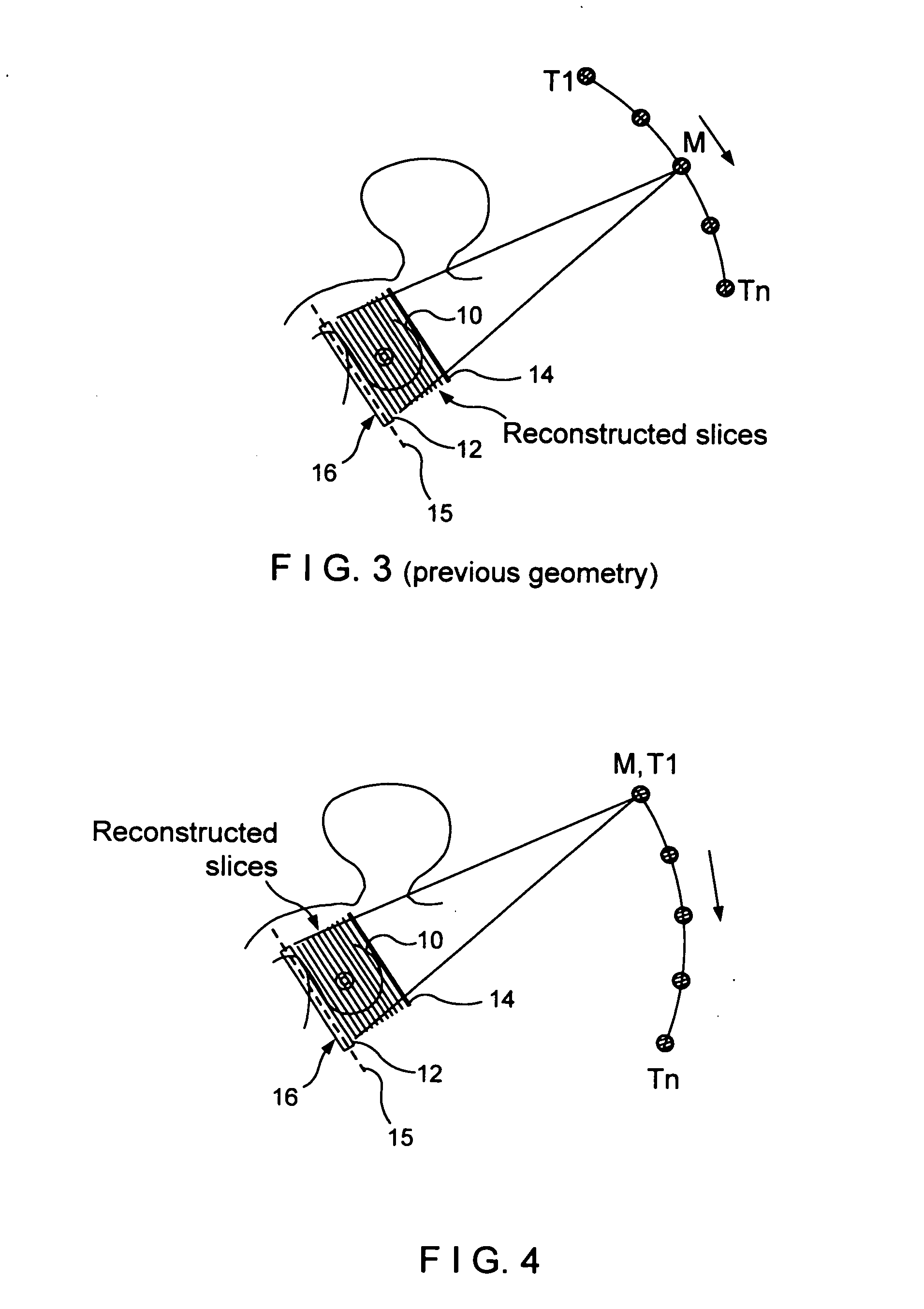
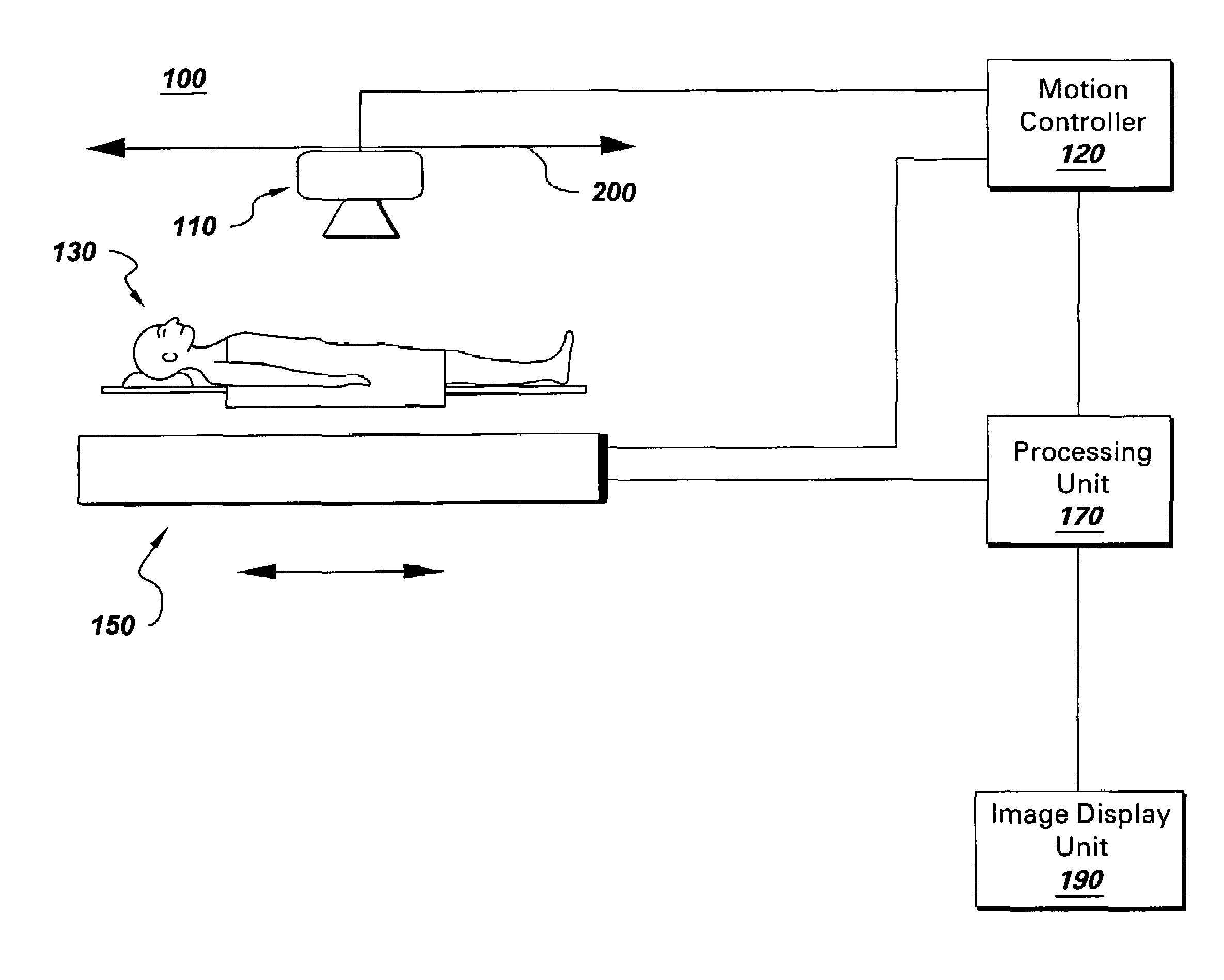
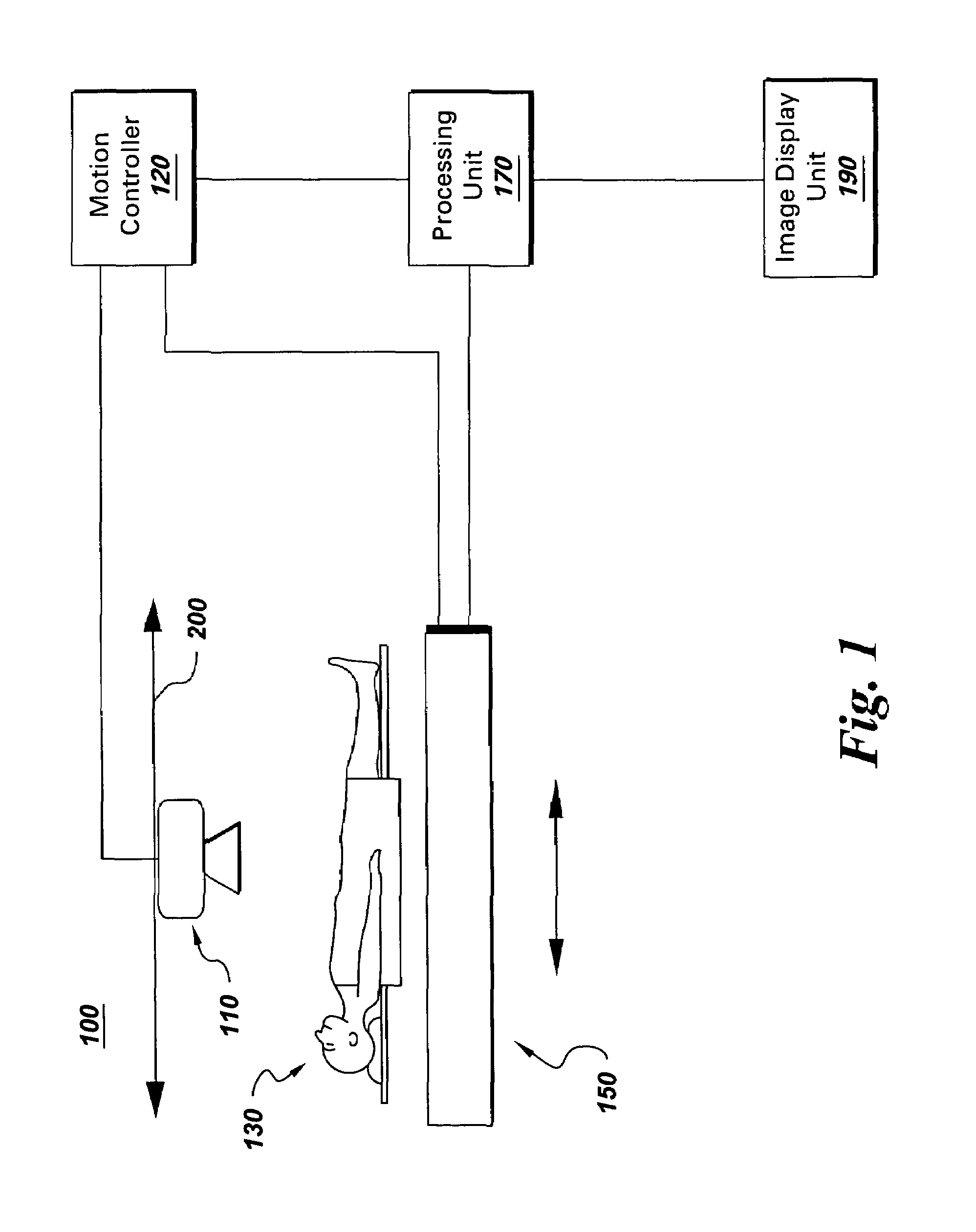
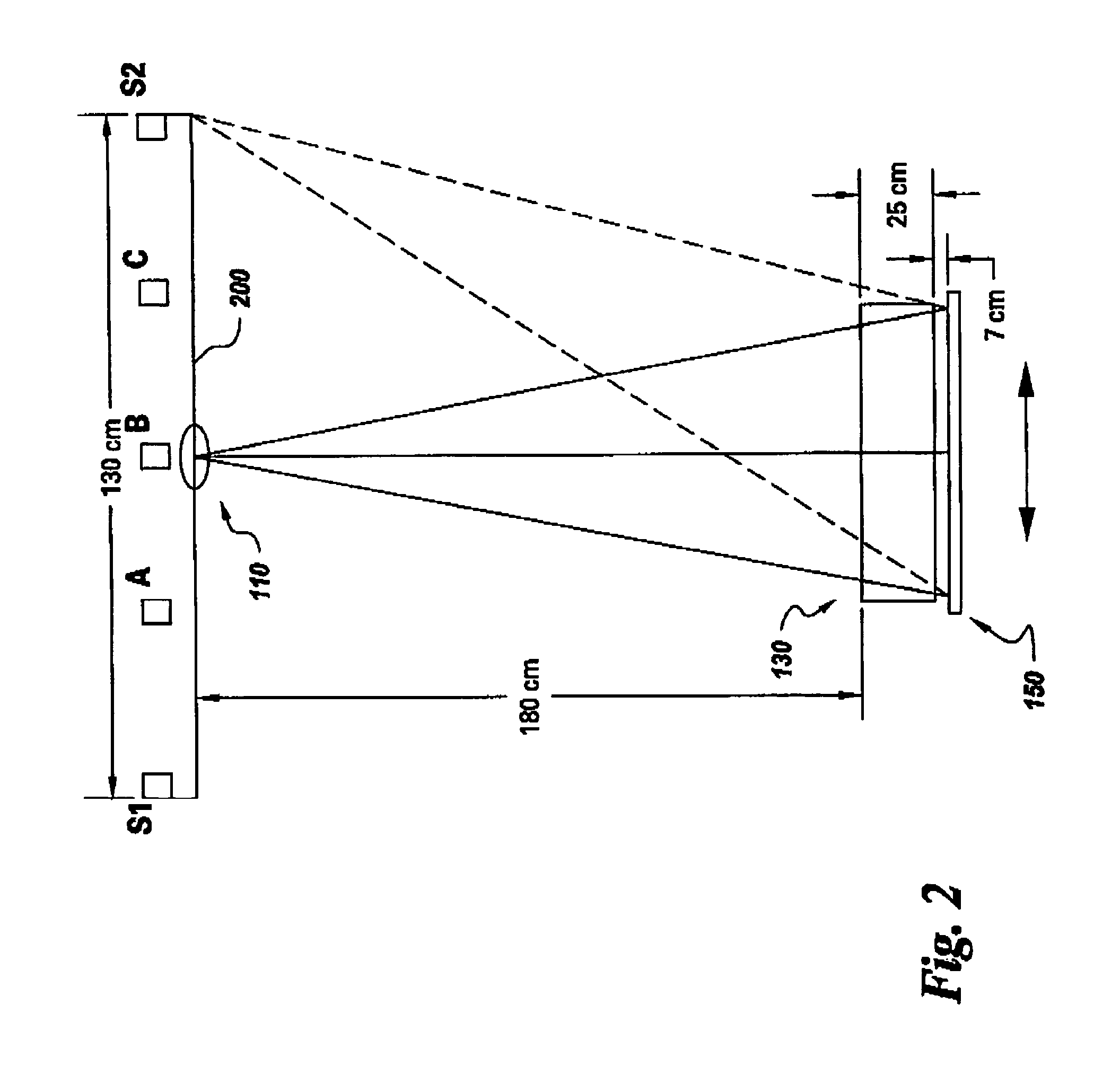
Continuous scan tomosynthesis system and method
InactiveUS6940943B2Vibration minimizationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisTomosynthesisContinuous scanning
An imaging system for performing tomosynthesis on a region of an object comprises an x-ray source, motion controller, an x-ray detector and a processing unit. The x-ray source is positioned at a predetermined distance from the object and continuously moves along a path relative to the object at a plurality of predetermined locations. The x-ray source transmits x-ray radiation through the region of the object. The motion controller is coupled to the x-ray source and continuously moves the x-ray source along the path relative to the object. The x-ray source minimizes vibration in the imaging system due to continuous movement. The x-ray detector is positioned at a predetermined distance from the x-ray source and detects the x-ray radiation transmitted through the region of the object, thus acquiring x-ray image data representative of the region of the object. The processing unit is coupled to the x-ray detector for processing the x-ray image data into at least one tomosynthesis image of the region of the object.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system for simultaneously viewing rendered volumes
InactiveUS20050135555A1Reduce artifactsReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationViewpointsComputer graphics (images)
A technique is provided for concurrently viewing volumes that may be rendered using visualization techniques incorporating one or more functions, such as depth-dependent weighting functions. In one aspect, the viewing technique may provide for the concurrent viewing of volumes, such as overlapping volumes, from different viewpoints. In accordance with this aspect, the relative position of display may convey the relative viewpoints. In addition, the viewing technique may provide for concurrently displaying volume renderings of a volume in which the volume renderings are generated using different functions, such as weighting and / or transfer functions. In this manner, the effect of the functions on visual properties of structures within the volume may be observed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
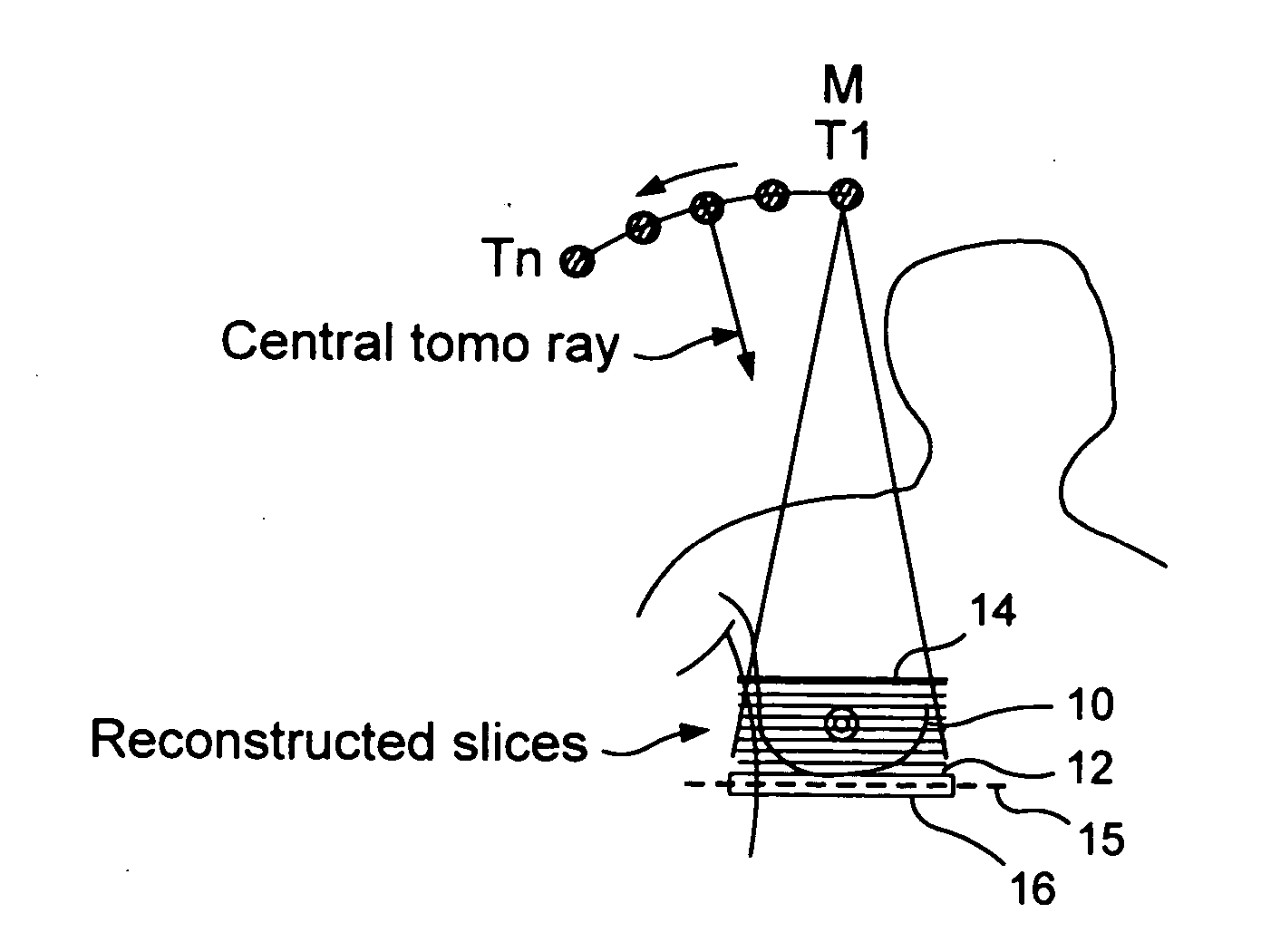
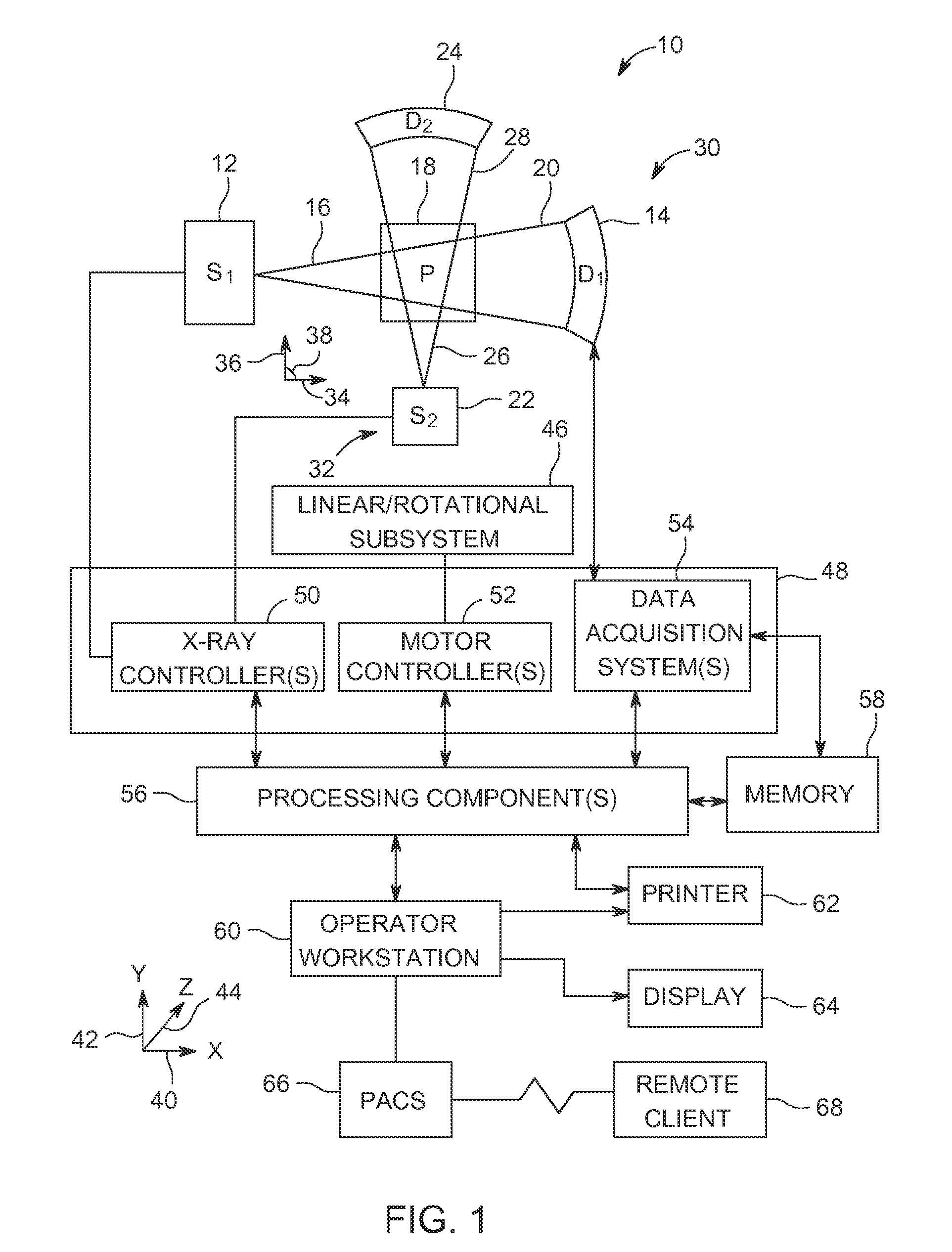
Full field digital tomosynthesis method and apparatus
ActiveUS7110490B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisObject based
A tomosynthesis system for forming a three dimensional image of an object is provided. The system includes an X-ray source adapted to irradiate the object with a beam of X-rays from a plurality of positions in a sector, an X-ray detector positioned relative to the X-ray source to detect X-rays transmitted through the object and a processor which is adapted to generate a three dimensional image of the object based on X-rays detected by the detector. The detector is adapted to move relative to the object and / or the X-ray source is adapted to irradiate the object with the beam of X-rays such that the beam of X-rays follows in a non arc shaped path and / or a center of the beam of X-rays impinges substantially on the same location on the detector from different X-ray source positions in the sector.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
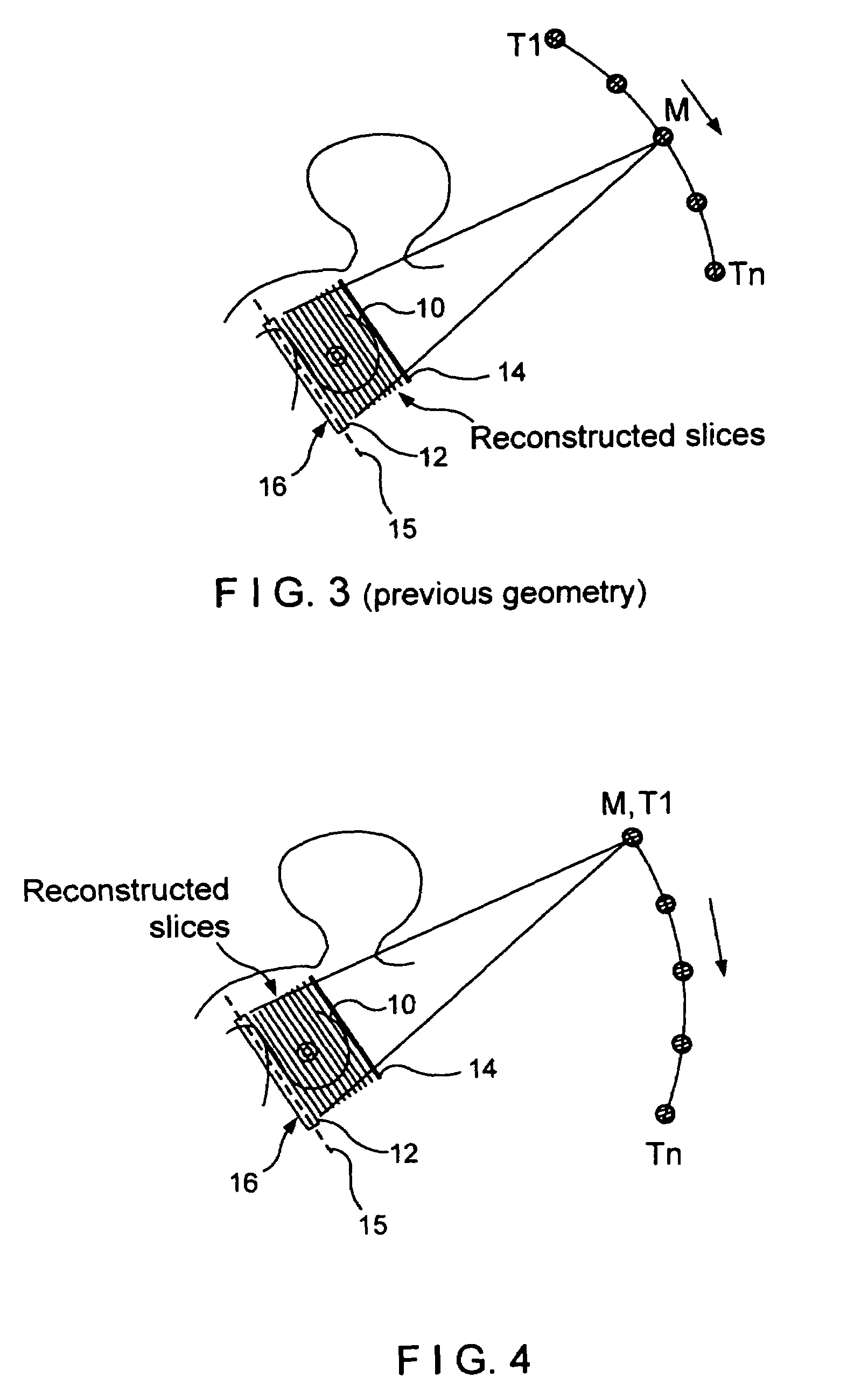
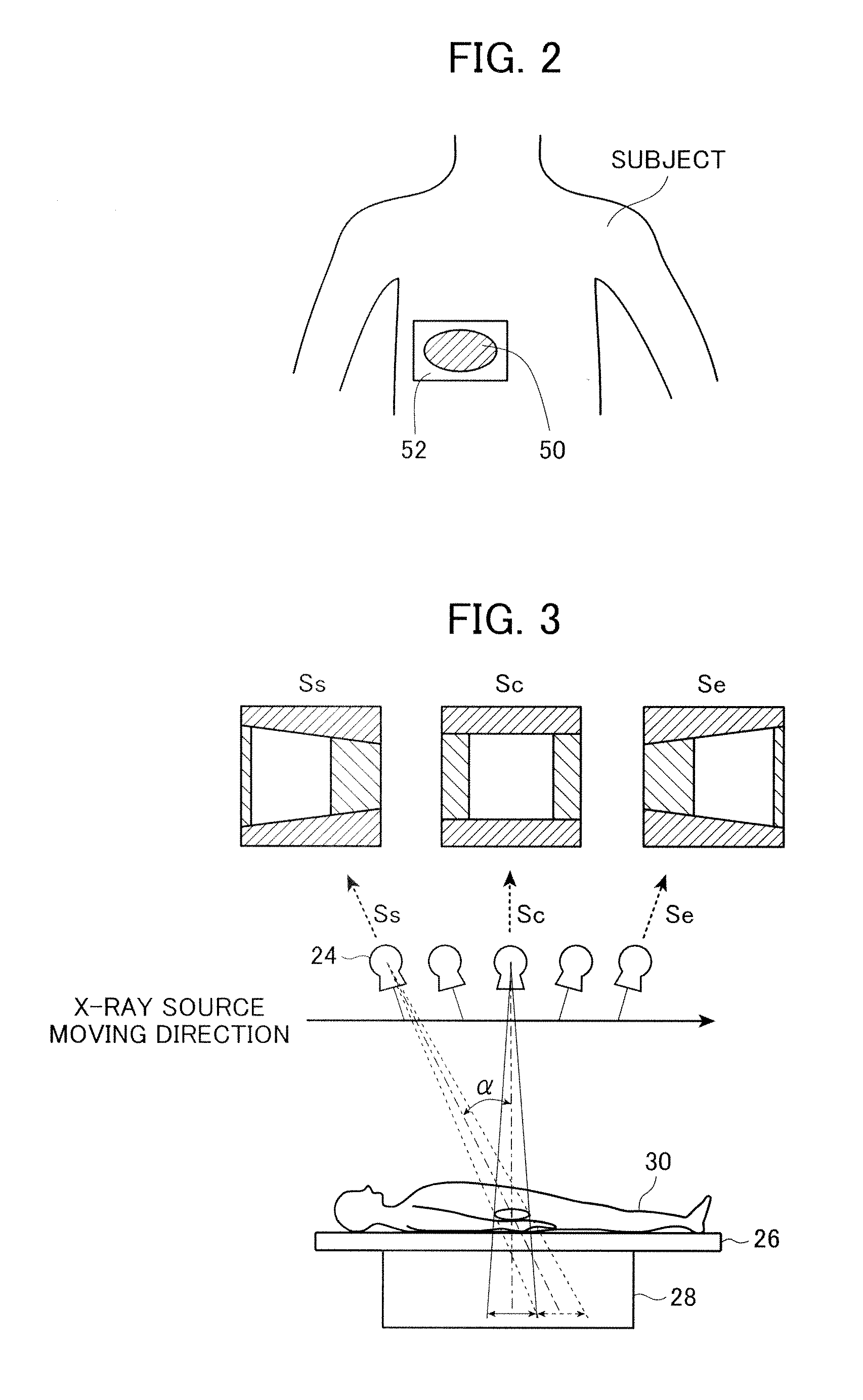
Radiographic tomosynthesis image acquisition utilizing asymmetric geometry
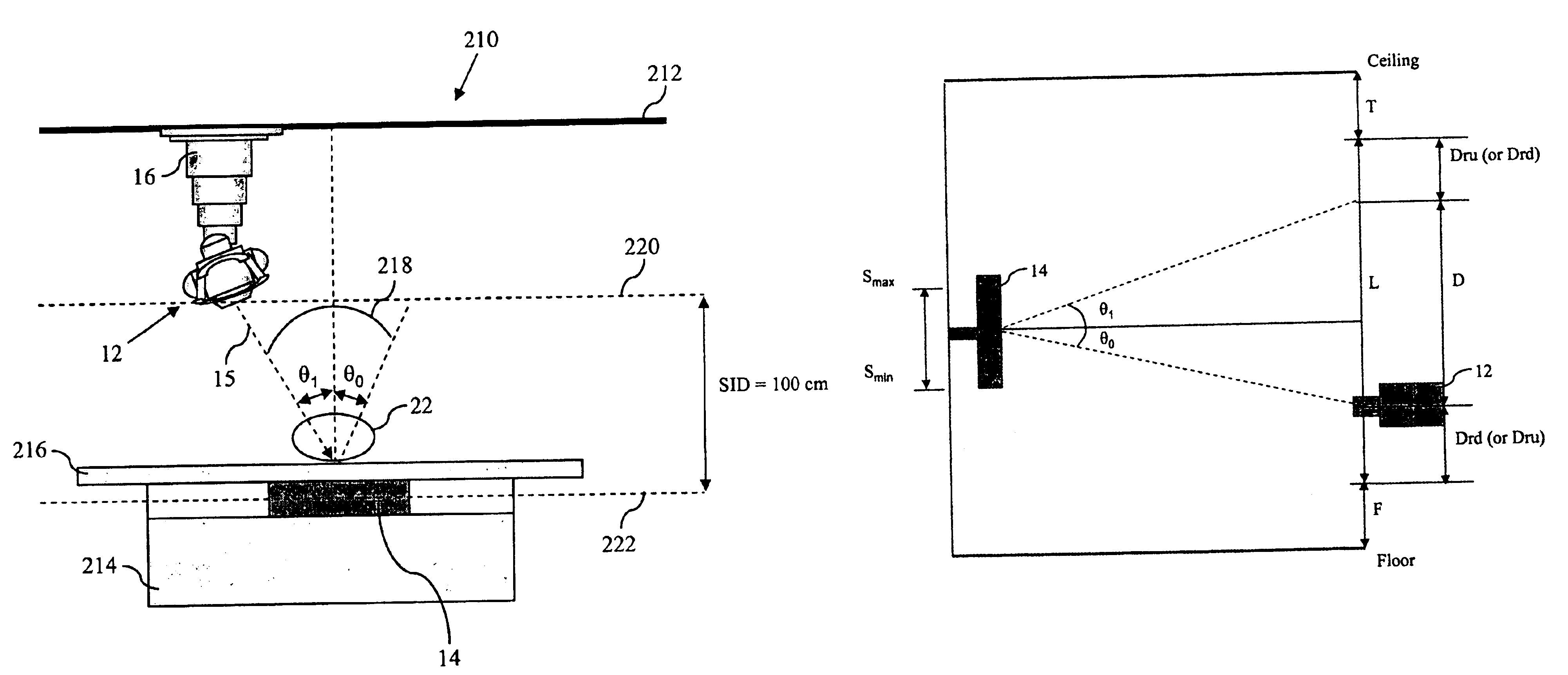
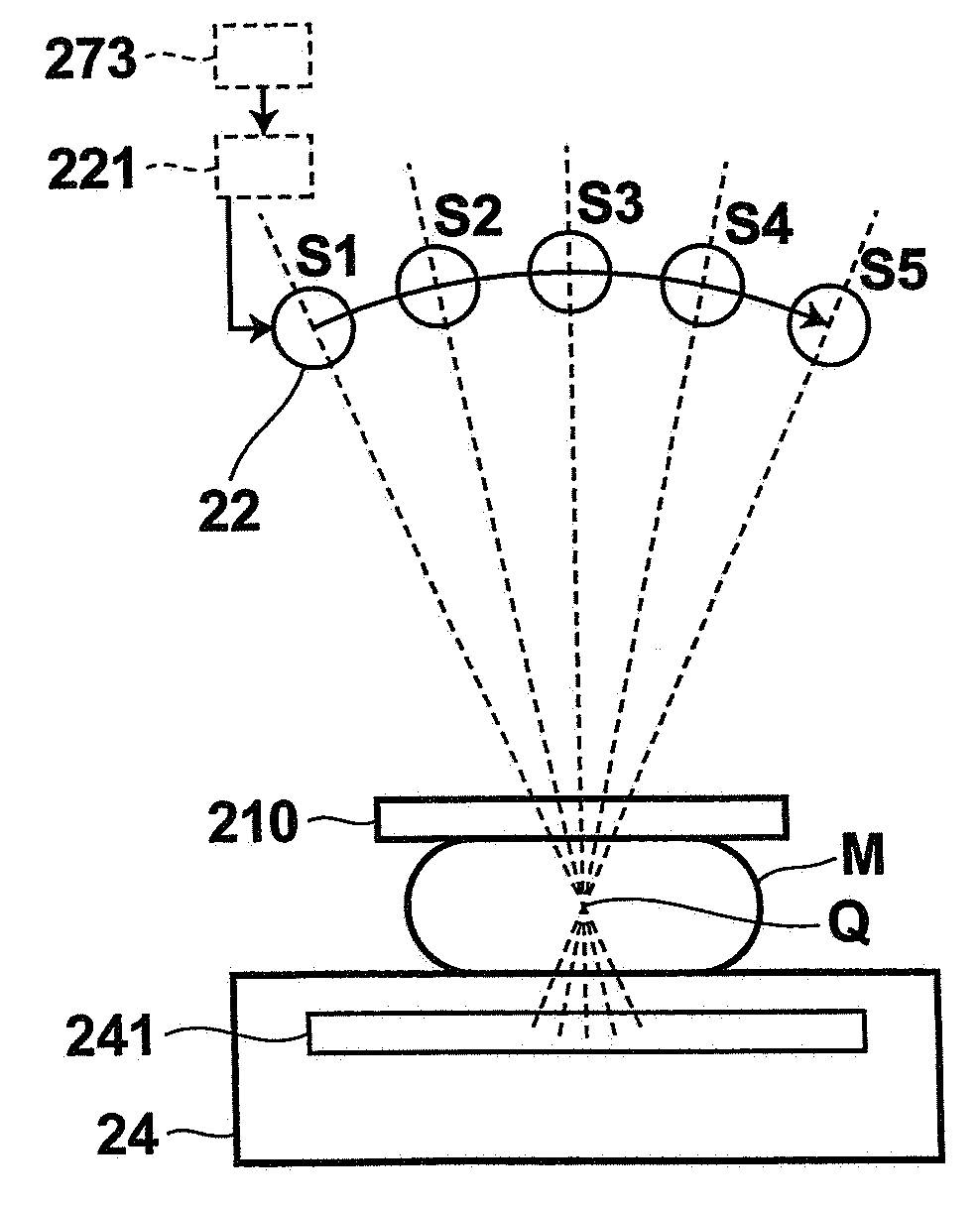
InactiveUS6885724B2High sensitivityImprove image qualityTomosynthesisX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentSoft x rayTomosynthesis
Systems and methods that utilize asymmetric geometry to acquire radiographic tomosynthesis images are described. Embodiments comprise tomosynthesis systems and methods for creating a reconstructed image of an object from a plurality of two-dimensional x-ray projection images. These systems comprise: an x-ray detector; and an x-ray source capable of emitting x-rays directed at the x-ray detector; wherein the tomosynthesis system utilizes asymmetric image acquisition geometry, where θ1≠θ0, during image acquisition, wherein θ1 is a sweep angle on one side of a center line of the x-ray detector, and θ0 is a sweep angle on an opposite side of the center line of the x-ray detector, and wherein the total sweep angle, θasym, is θasym=θ1+θ0. Reconstruction algorithms may be utilized to produce reconstructed images of the object from the plurality of two-dimensional x-ray projection images.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Breast tomosynthesis with display of highlighted suspected calcifications
Systems and methods that facilitate the presentation and assessment of selected features in projection and / or reconstructed breast images, such as calcifications that meet selected criteria of size, shape, presence in selected slice images, distribution of pixels that could be indicative of calcification relative to other pixels or of other image features of clinical interest.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
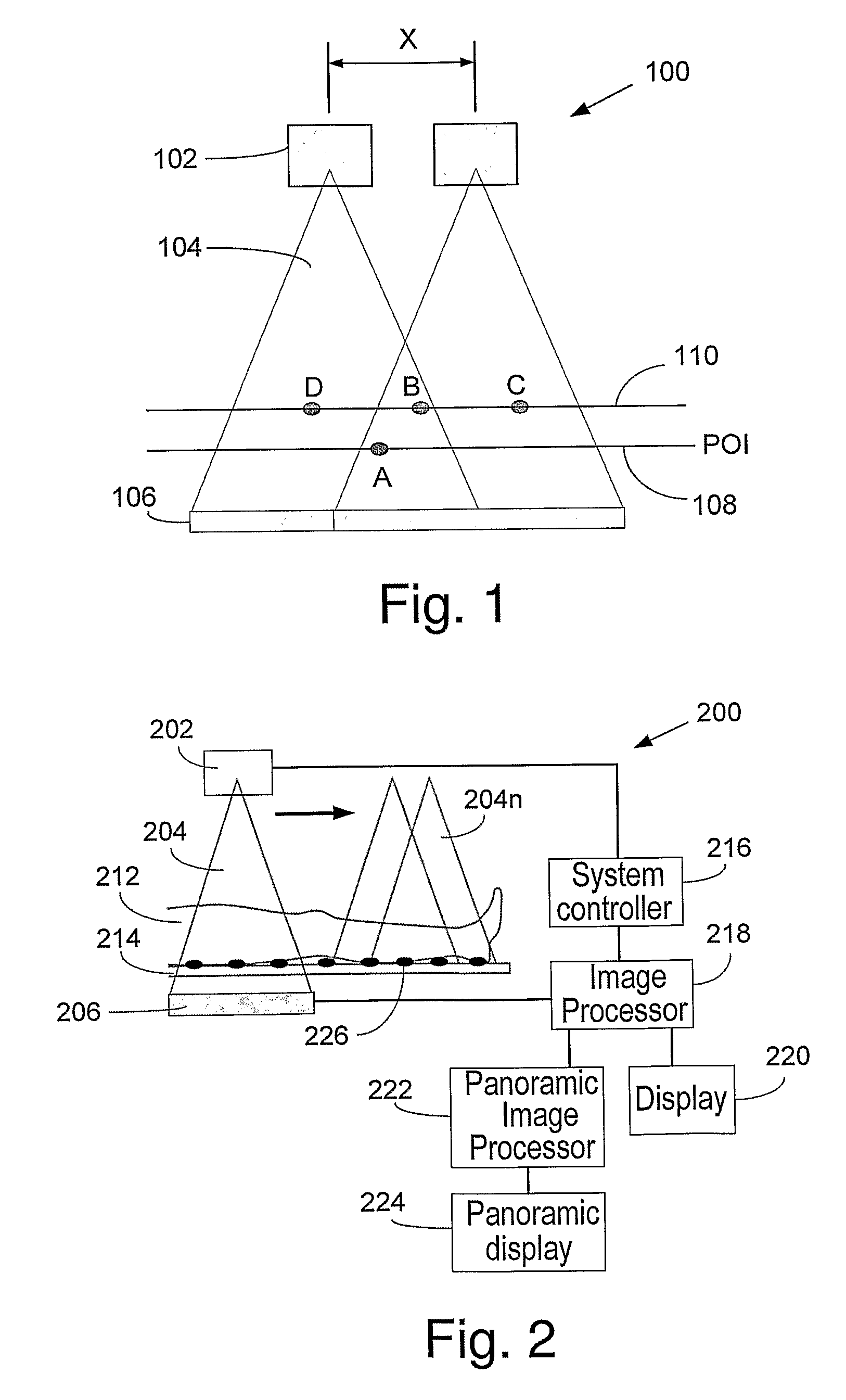
Method and system for stitching multiple images into a panoramic image
Disclosed is a method for generating a panoramic image of a region of interest (ROI) which is larger than a field of a view of a radiation based imaging device, comprising, positioning markers along the ROI, acquiring a set of images along the ROI, wherein the acquired images have at least partially overlapping portions, aligning at least two separate images by aligning a common marker found in both images and compensating for a difference between a distance from a radiation source to the marker element and the distance from the radiation source to a plane of interest.
Owner:ORTHOPEDIC NAVIGATION
Image handling and display in X-ray mammography and tomosynthesis
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Tissue classification in medical images
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method And System For Dynamic Low Dose X-ray Imaging
InactiveUS20080118023A1Reduce decreaseReduce detectionTomosynthesisHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayX ray dose
A method and system for performing fluoroscopic imaging of a subject has high temporal and spatial resolution in a center portion of the captured dynamic images. The system provides for reduced X-ray dose to the patient associated with that part of the X-ray beam associated with a peripheral portion of the captured images although temporal, and in some embodiments spatial, resolution is reduced in the peripheral portion of the image. The system uses a rotating collimator to produce an X-ray beam having narrow wing portions associated with the peripheral portions of the image, and a broader central region associated with the high resolution center portion of the images.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
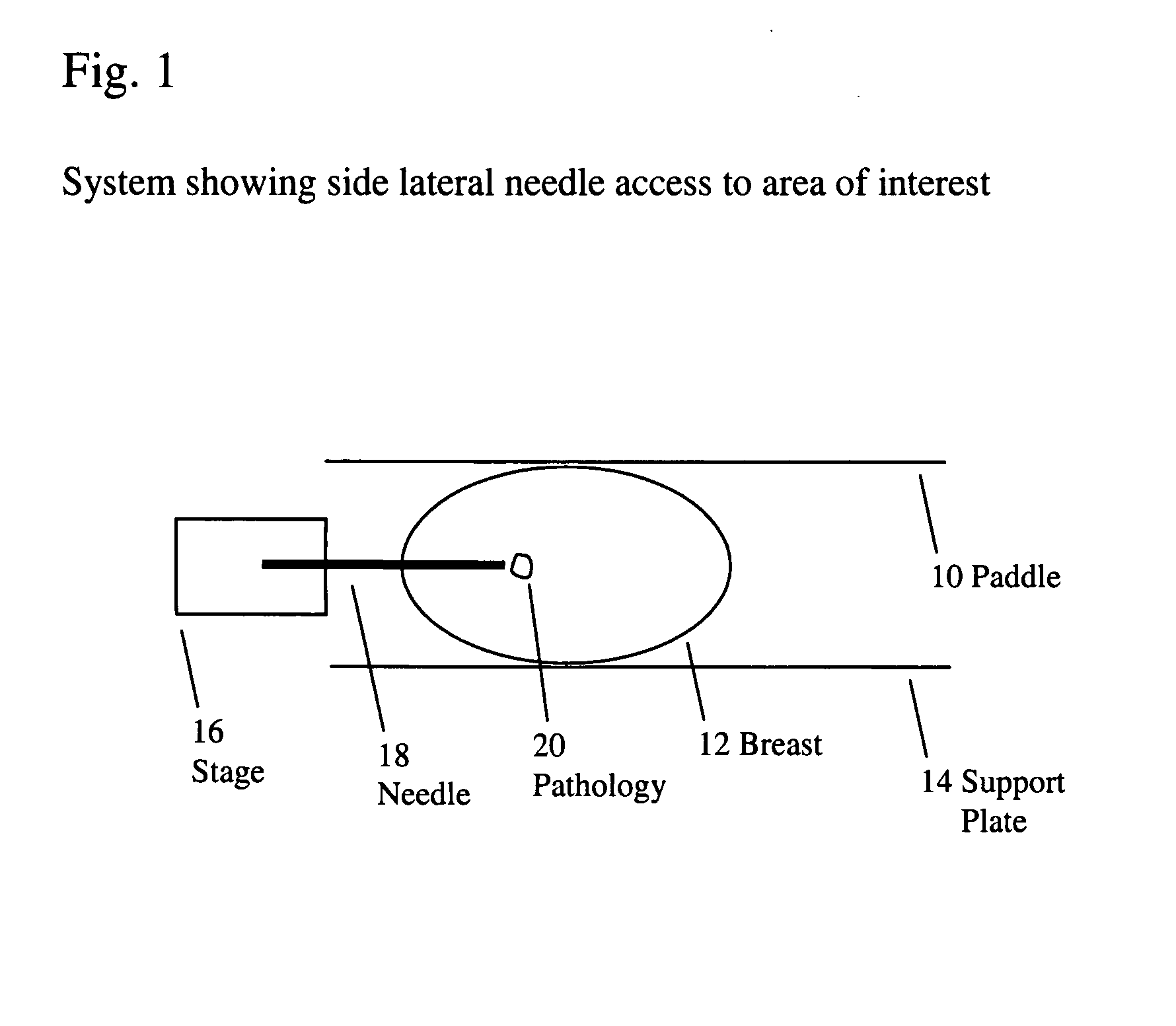
Tomographic imaging for interventional tool guidance
The present disclosure relates to the identification and tracking of a navigational instrument (e.g., a needle) in three-dimensions, with substantially real-time image updates of the instrument and updates of the tissue at an equal or lower rate. In certain embodiments, the images are acquired using a C-arm tomosynthesis system configured to move the X-ray source and detector in respective planes above and below the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
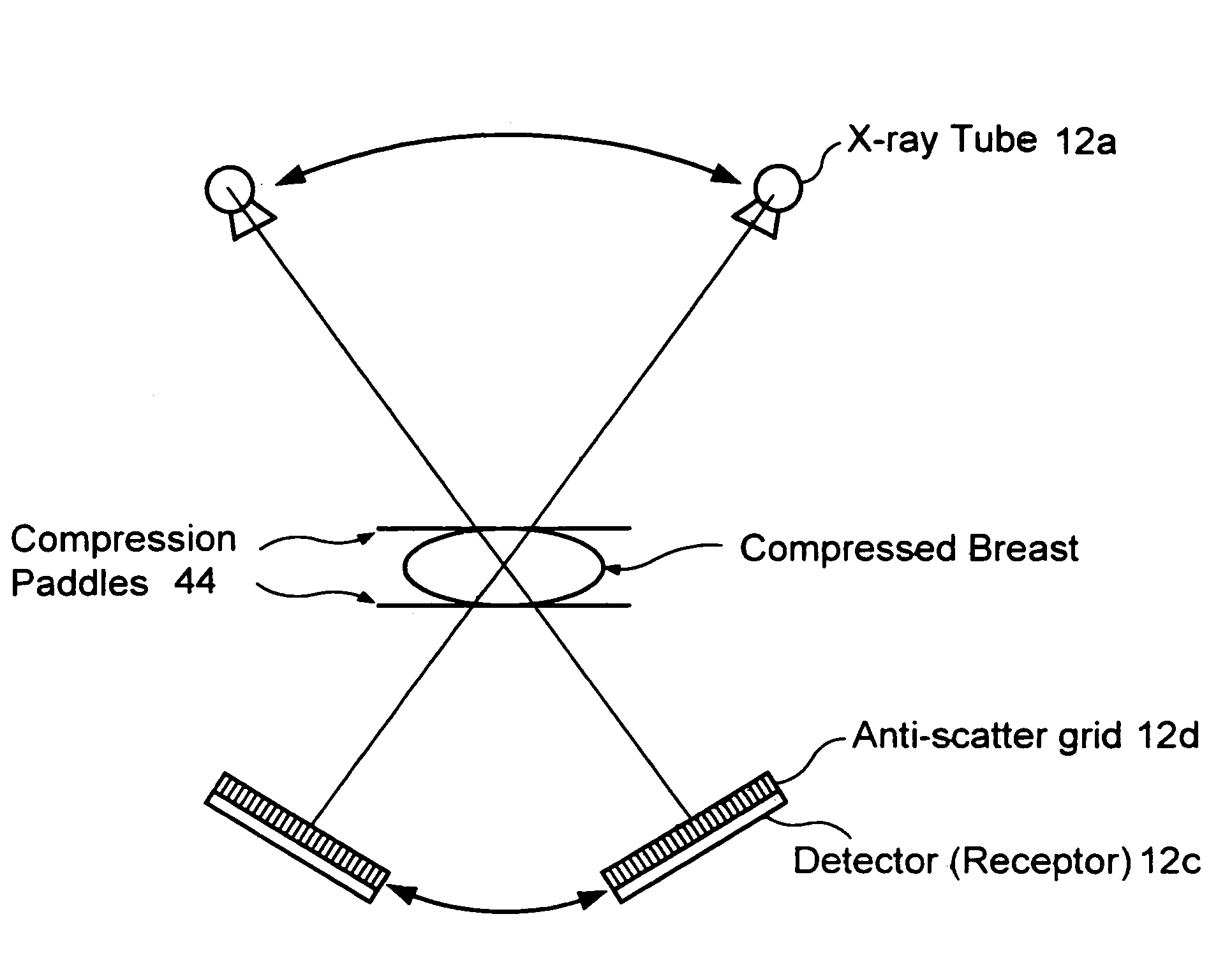
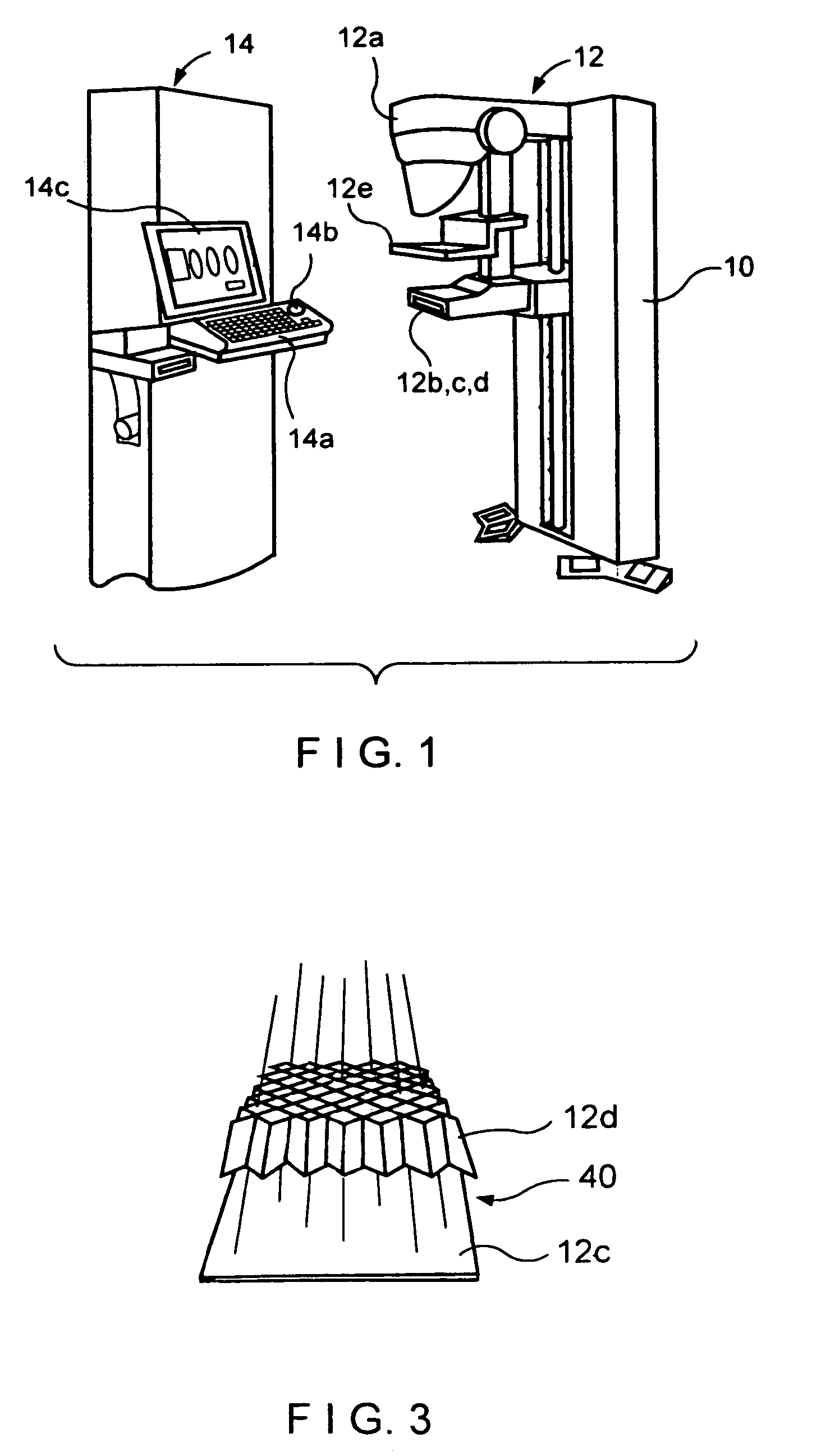
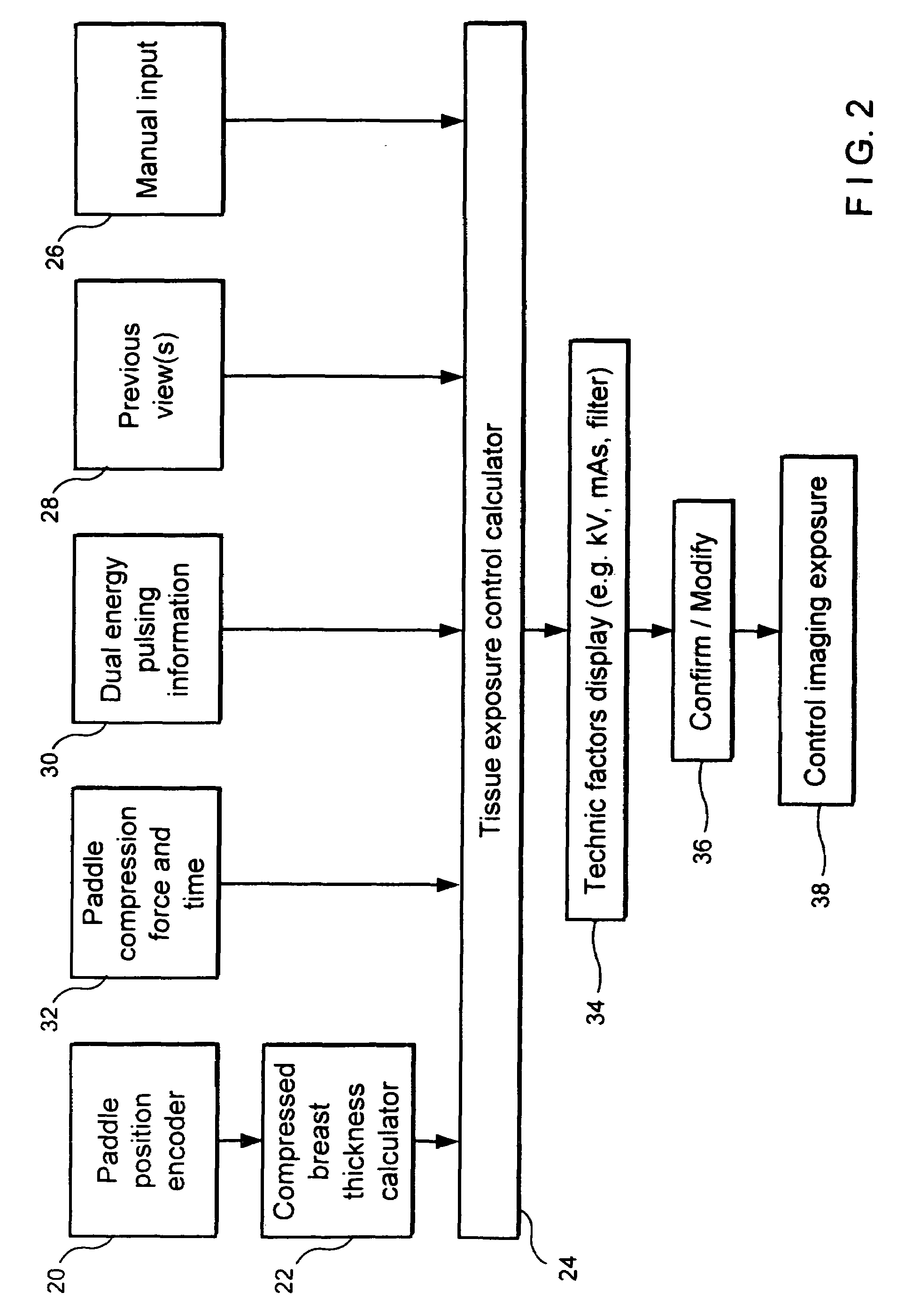
Full field mammography with tissue exposure control, tomosynthesis, and dynamic field of view processing
InactiveUS7430272B2Effective and advantageous exposure controlImprove tomosynthesisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisDynamic field
A mammography system using a tissue exposure control relying on estimates of the thickness of the compressed and immobilized breast and of breast density to automatically derive one or more technic factors. The system further uses a tomosynthesis arrangement that maintains the focus of an anti-scatter grid on the x-ray source and also maintains the field of view of the x-ray receptor. Finally, the system finds an outline that forms a reduced field of view that still encompasses the breast in the image, and uses for further processing, transmission or archival storage the data within said reduced field of view.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Tomographic mammography method
InactiveUS20060291618A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisX-ray
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Continuous scan RAD tomosynthesis system and method
InactiveUS6970531B2Vibration minimizationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayTomosynthesis
An imaging system for performing tomosynthesis on a region of an object comprises an x-ray source, motion controller, an x-ray detector and a processing unit. The x-ray source is positioned at a predetermined distance from the object and continuously moves along a linear path relative to the object. The x-ray source transmits x-ray radiation through the region of the object at a plurality of predetermined locations. The motion controller is coupled to the x-ray source and continuously moves the x-ray source along the path relative to the object. The x-ray source minimizes vibration in the imaging system due to continuous movement. The x-ray detector is positioned at a predetermined distance from the x-ray source and detects the x-ray radiation transmitted through the region of the object, thus acquiring x-ray image data representative of the region of the object. The processing unit is coupled to the x-ray detector for processing the x-ray image data into at least one tomosynthesis image of the region of the object.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
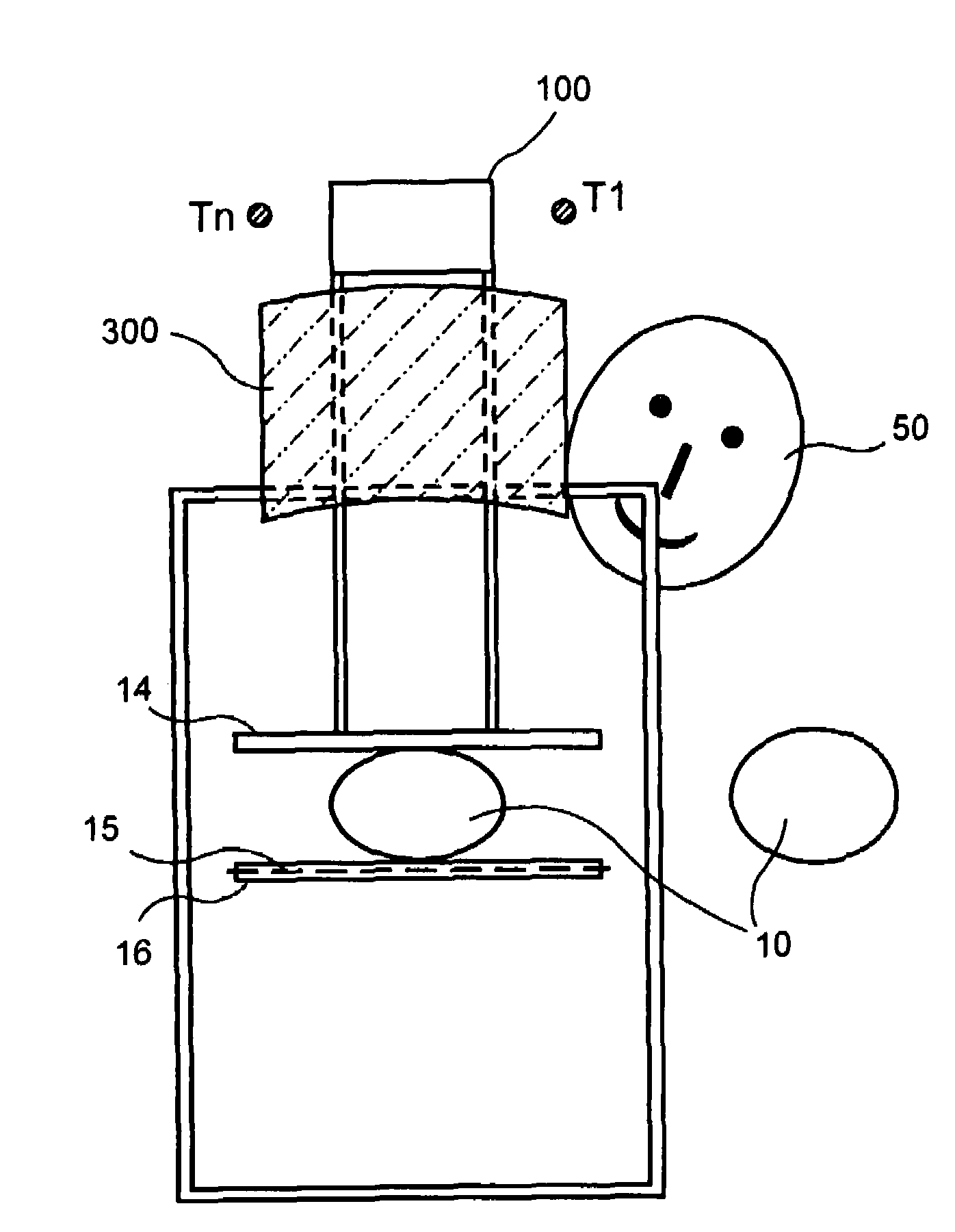
System and method for dual energy and/or contrast enhanced breast imaging for screening, diagnosis and biopsy
ActiveUS20120238870A1Facilitate x-ray screeningEasy diagnosisTomosynthesisVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsVascularityTomosynthesis
Systems and methods for x-ray imaging a patient's breast in combinations of dual-energy, single-energy, mammography and tomosynthesis modes that facilitate screening for and diagnosis of breast abnormalities, particularly breast abnormalities characterized by abnormal vascularity.
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Tomographic image obtainment apparatus and method
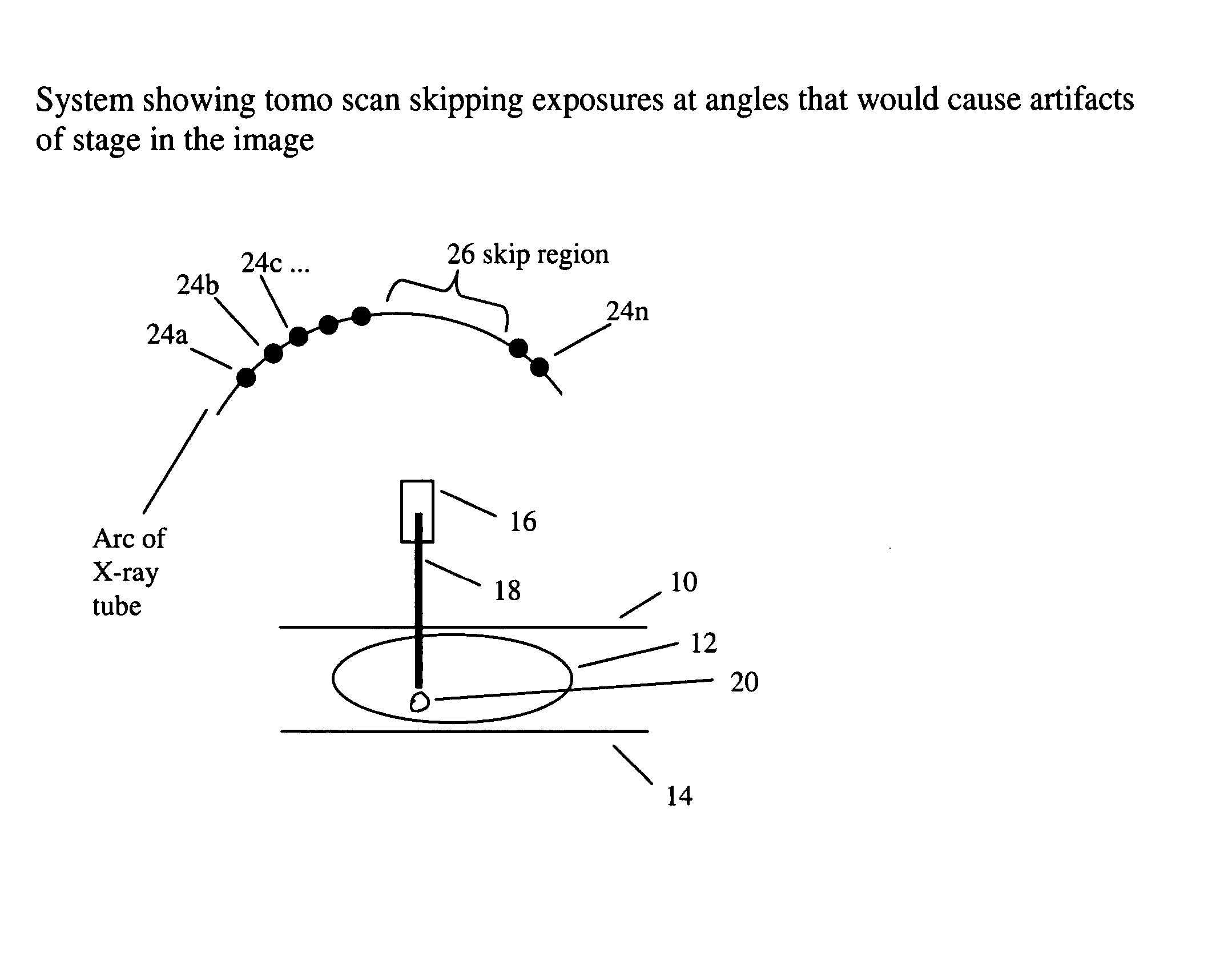
ActiveUS20080101537A1Reduce intervalAccurate acquisitionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAnatomical structuresTomographic image
When radiographic images are obtained by radiography using a tomographic image obtainment apparatus, the degree of overlap of anatomical structures of a subject is obtained. Further, a condition of exposure, such as angles θ of radiography, is changed based on the degree of overlap. The angles θ of radiography are angles at which a radiation irradiation unit performs radiography at a plurality of positions to obtain a plurality of radiographic images. The tomographic image obtainment apparatus produces a tomographic image by reconstructing the tomographic image from a plurality of radiographic images obtained by irradiating the subject with radiation from various directions.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Image handling and display in x-ray mammography and tomosynthesis
InactiveUS7616801B2Easy to displayEnhance the imageImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisProjection image
Owner:HOLOGIC INC
Optical recovery of radiographic geometry
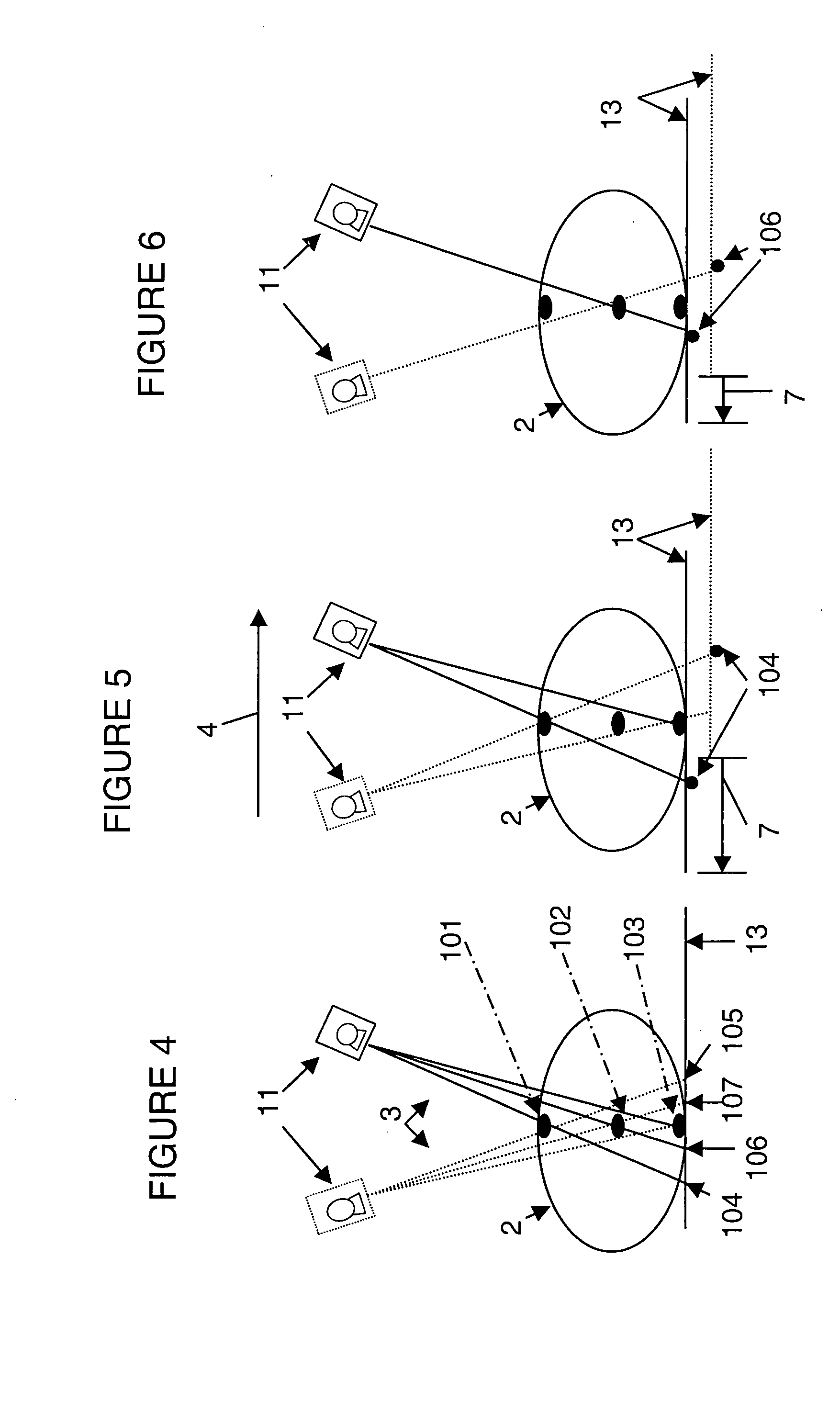
InactiveUS6978040B2Easy procedureImage analysisMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGeometric relationsGeometry processing
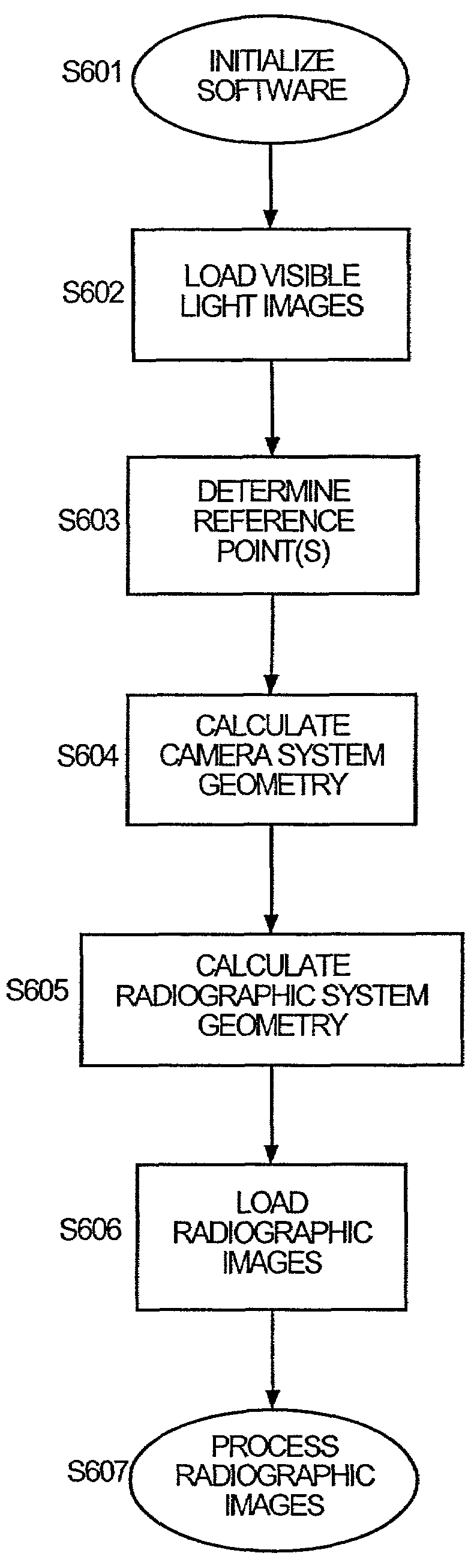
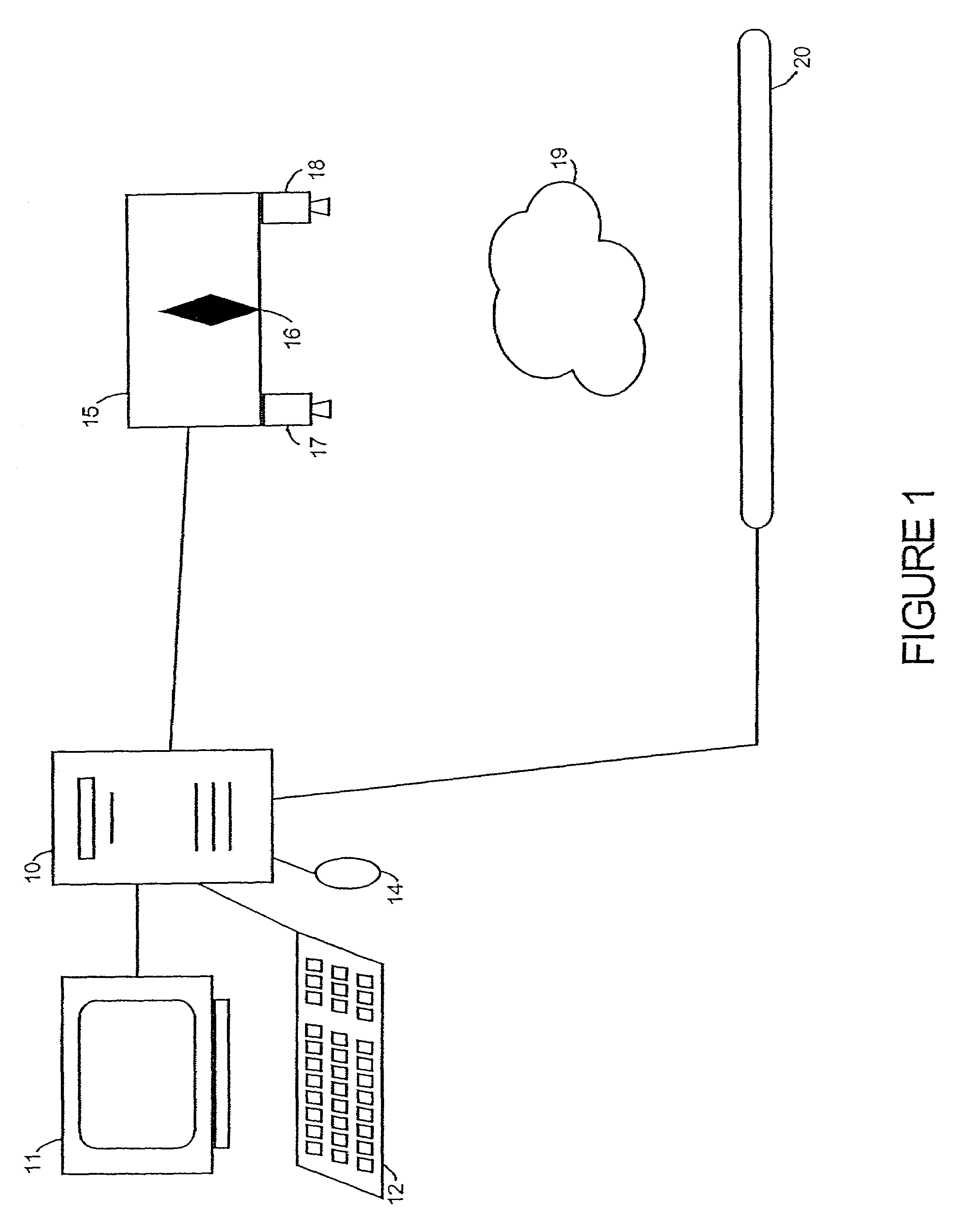
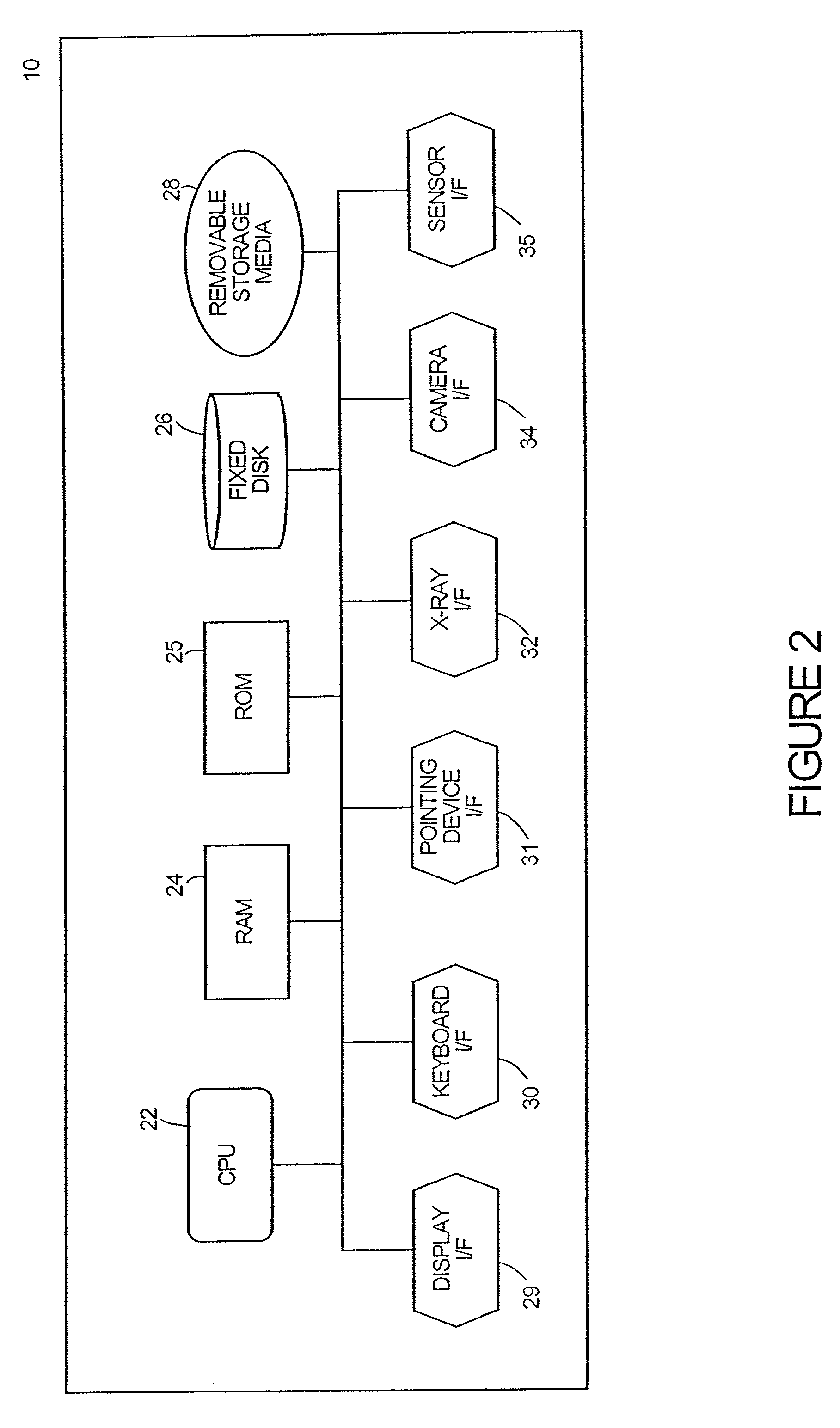
Processing of up to a plurality of radiographic images of a subject, includes the capture of at least two visible light images of the subject, two or more of the visible light images in correspondence to at least one radiographic image. The visible light images are captured by one or more visible light cameras, each visible light camera in a known geometric relation to the radiographic source. Radiographic geometry of each radiographic image is calculated relative to the radiographic source and the subject through stereoscopic analysis of the visible light images and through reference to the known geometric relation between the one or more visible light cameras and the radiographic source. Three-dimensional radiographic information on the subject is generated and manipulated by processing the up to a plurality of radiographic images based on the recovered radiographic geometry.
Owner:CANON KK
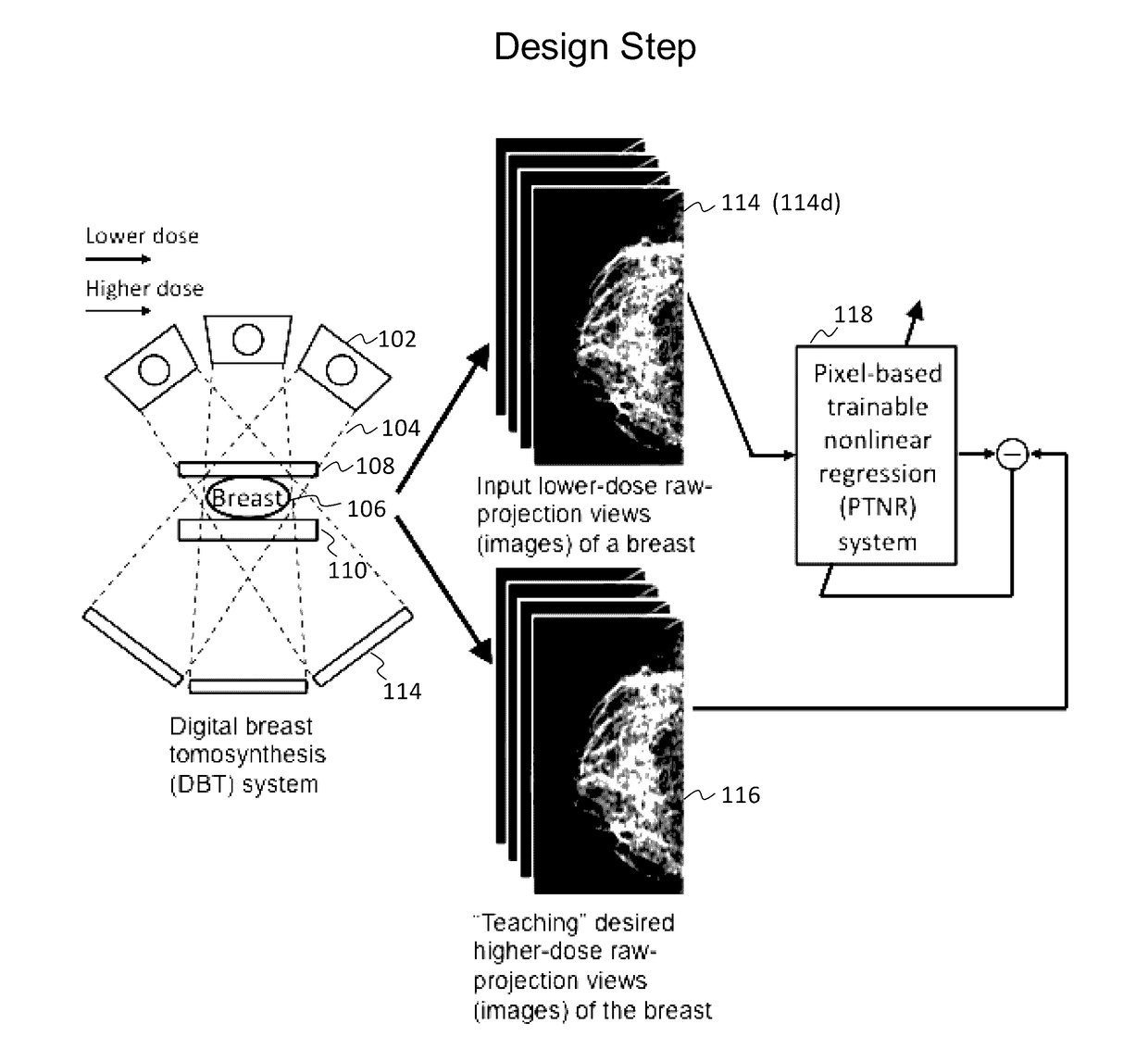
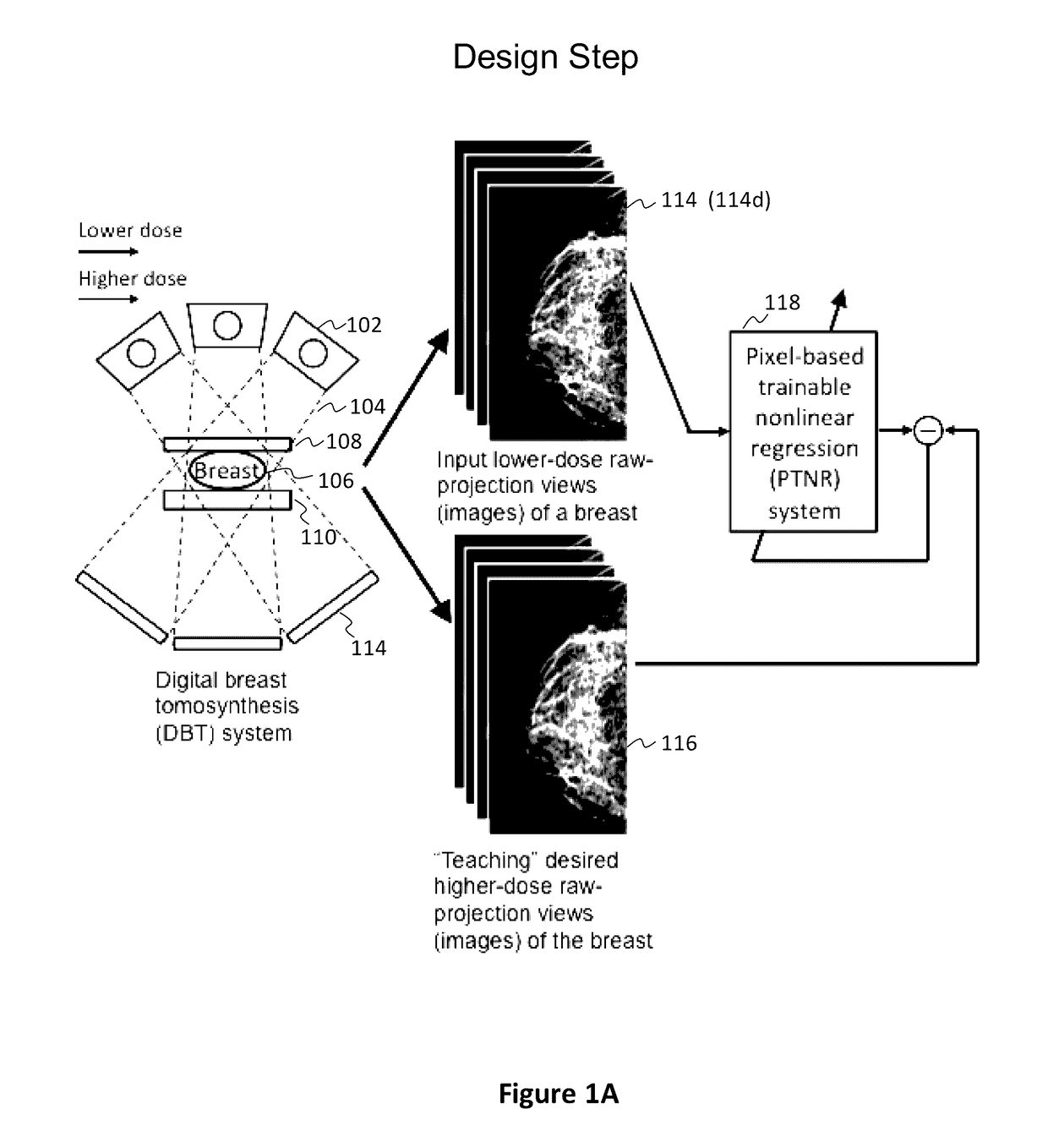
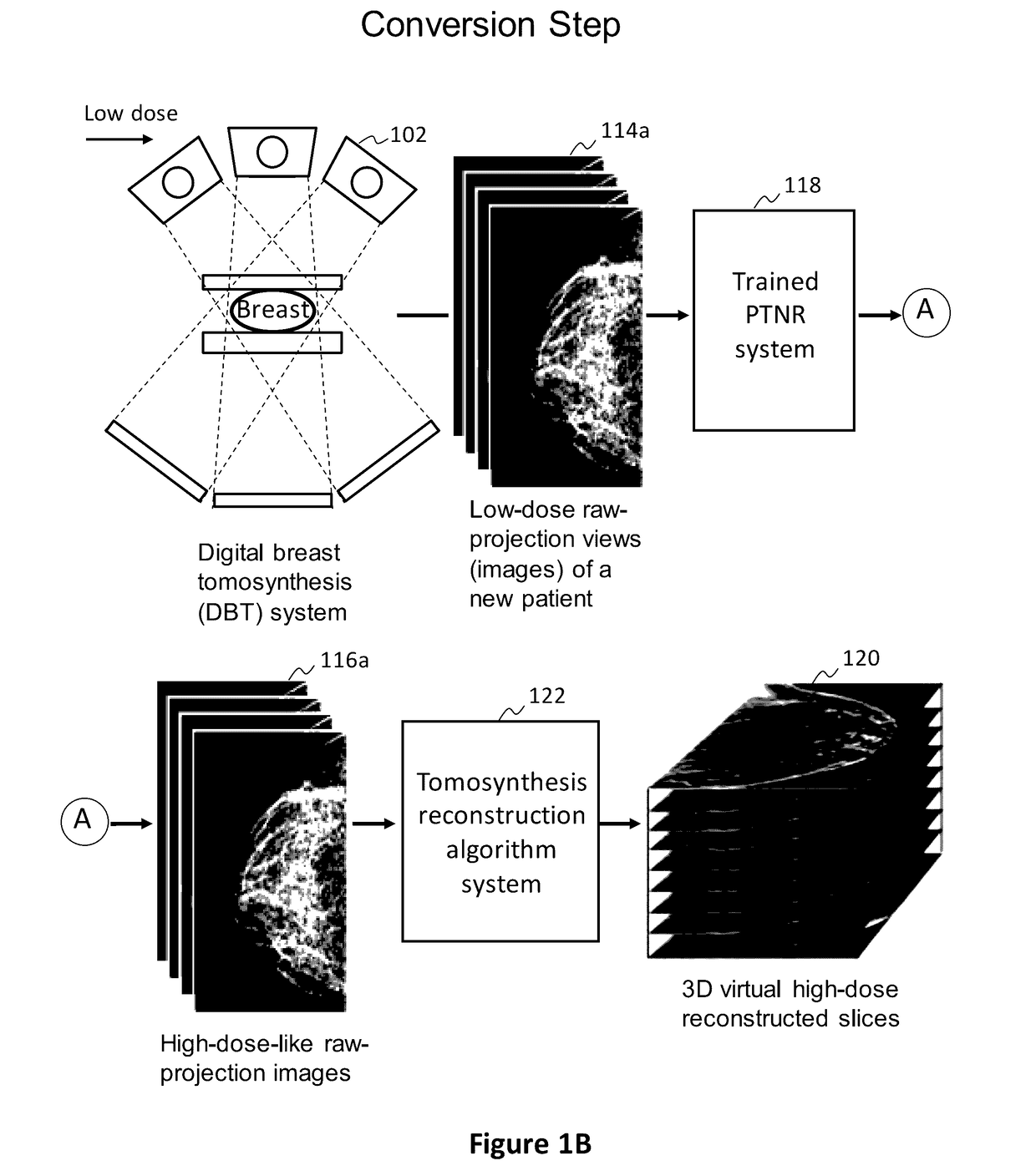
Converting low-dose to higher dose 3D tomosynthesis images through machine-learning processes
ActiveUS20170071562A1Quality improvementReduce noiseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisImaging quality
A method and system for converting low-dose tomosynthesis projection images or reconstructed slices images with noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like tomosynthesis reconstructed slices, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme called a pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input raw projection views (images) of a breast acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of raw projection views (images together with corresponding desired x-ray radiation dose raw projection views (images) (higher-dose). Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose raw projection images to high-dose-like raw projection images. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose raw projection images anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) raw projection images is entered, the trained PTNR outputs a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it outputs high-dose-like raw projection images where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. Then, from the “high-dose-like” projection views (images), “high-dose-like” 3D tomosynthesis slices are reconstructed by using a tomosynthesis reconstruction algorithm. With the “virtual high-dose” tomosynthesis reconstruction slices, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
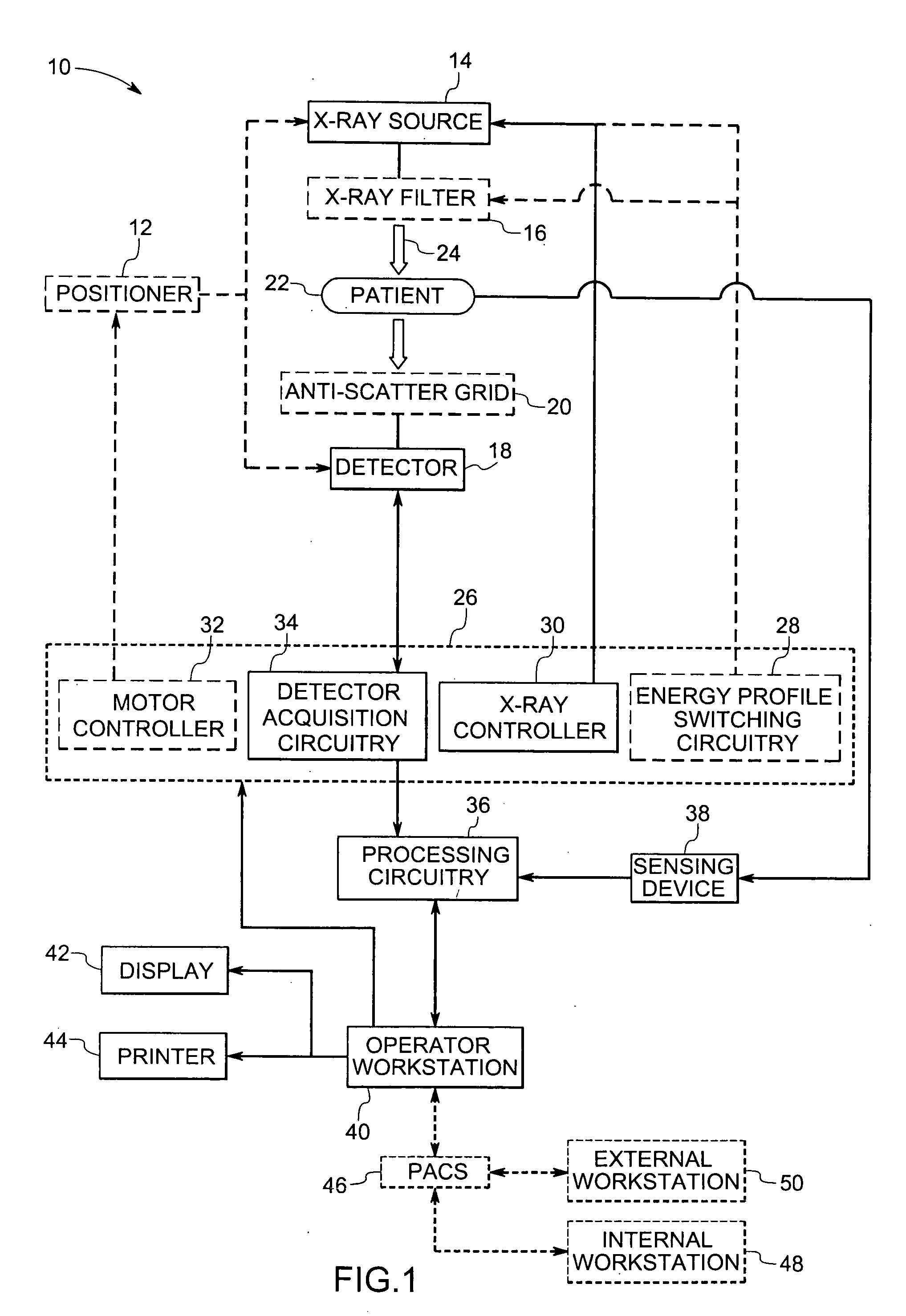
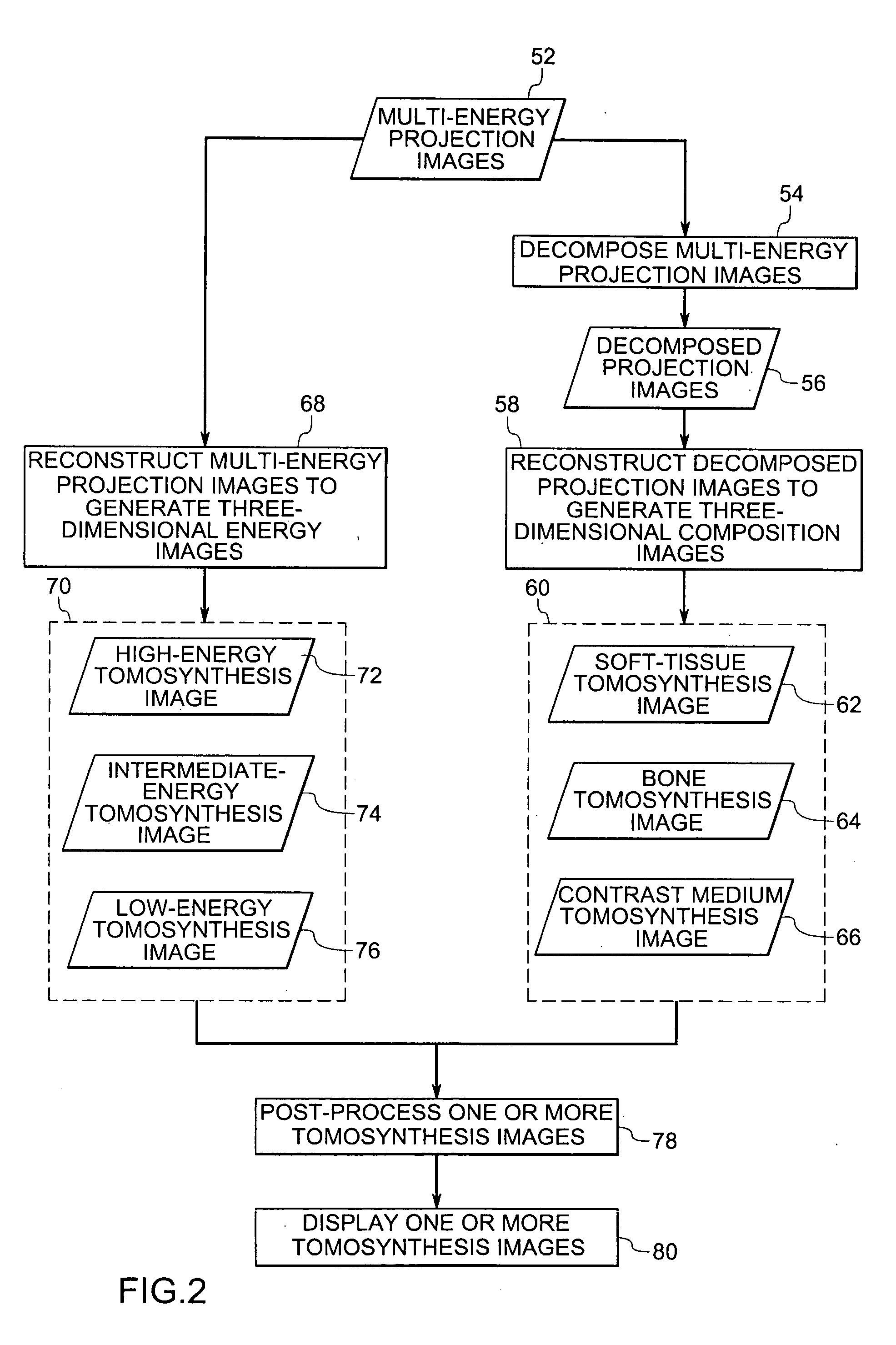
Method and system for multi-energy tomosynthesis
Briefly in accordance with one embodiment, the present technique provides a multi-energy tomosynthesis imaging system. The system includes an X-ray source configured to emit X-rays from multiple locations within a limited angular range relative to an imaging volume. The imaging system also includes a digital detector with an array of detector elements to generate images in response to the emitted X-rays. The imaging system further includes a detector acquisition circuitry to acquire the images from the digital detector. The imaging system may also include a processing circuitry configured to decompose plurality of images based on energy characteristics and to reconstruct the plurality of images to generate a three-dimensional multi-energy tomosynthesis image.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
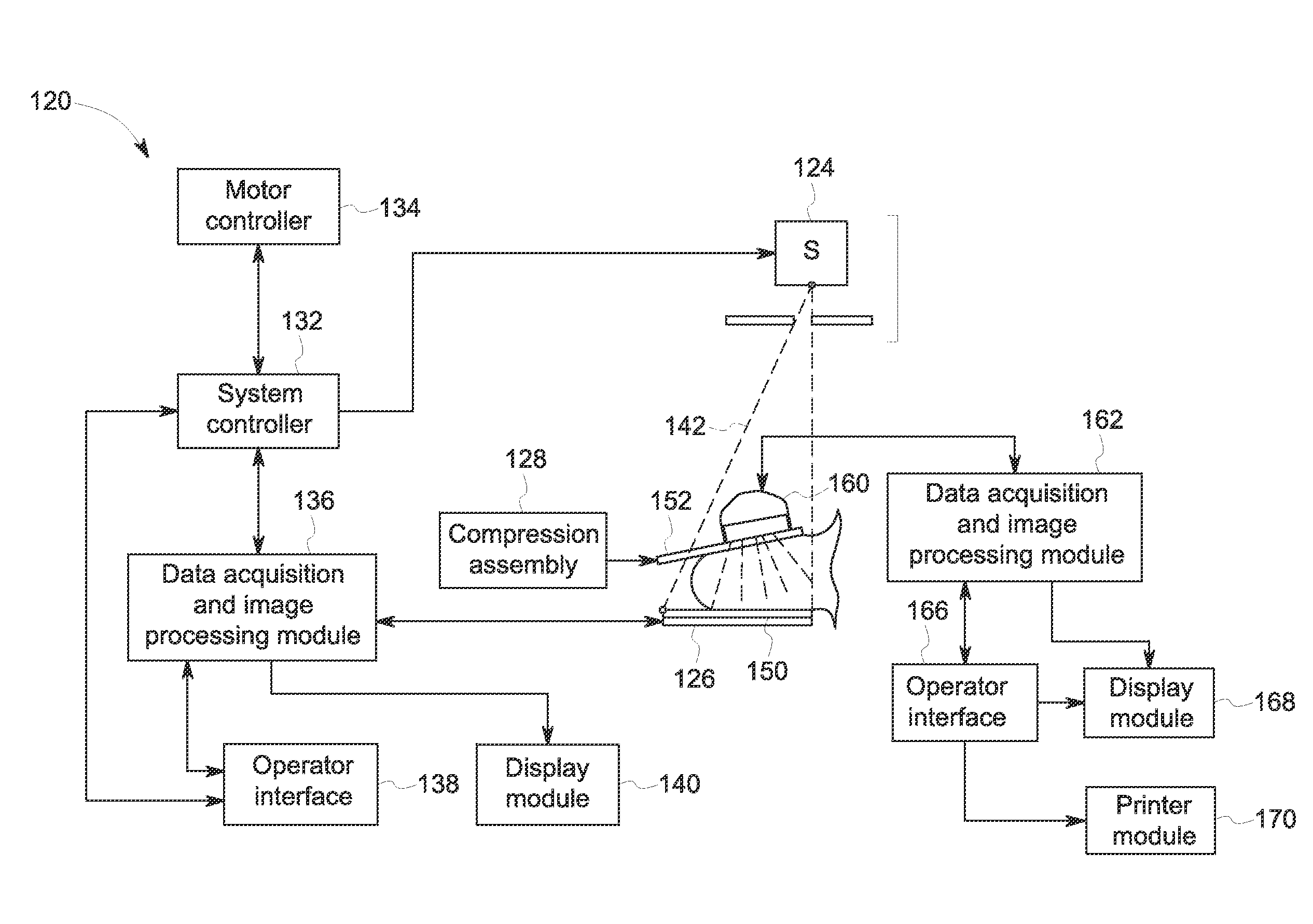
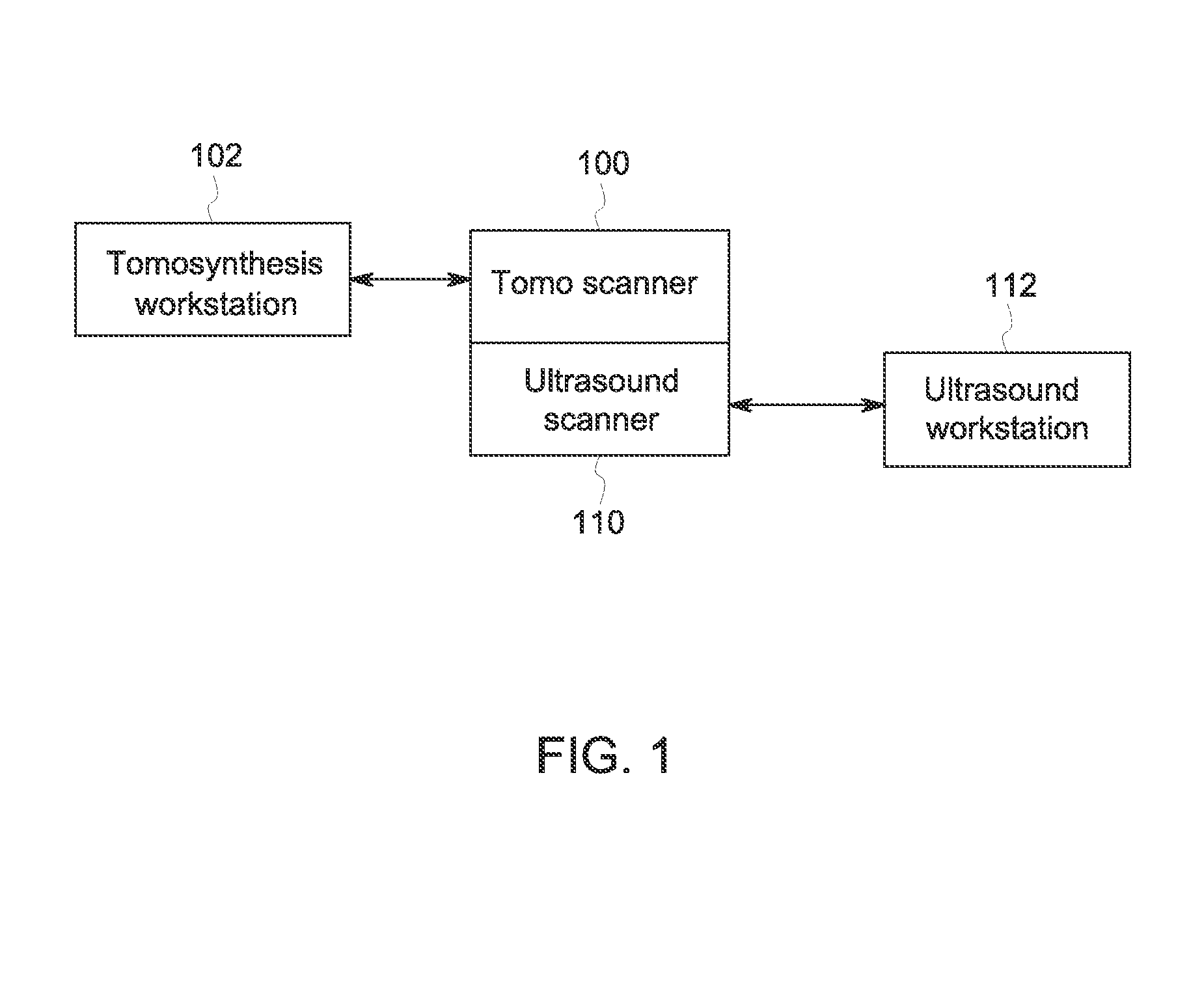
Breast imaging method and system
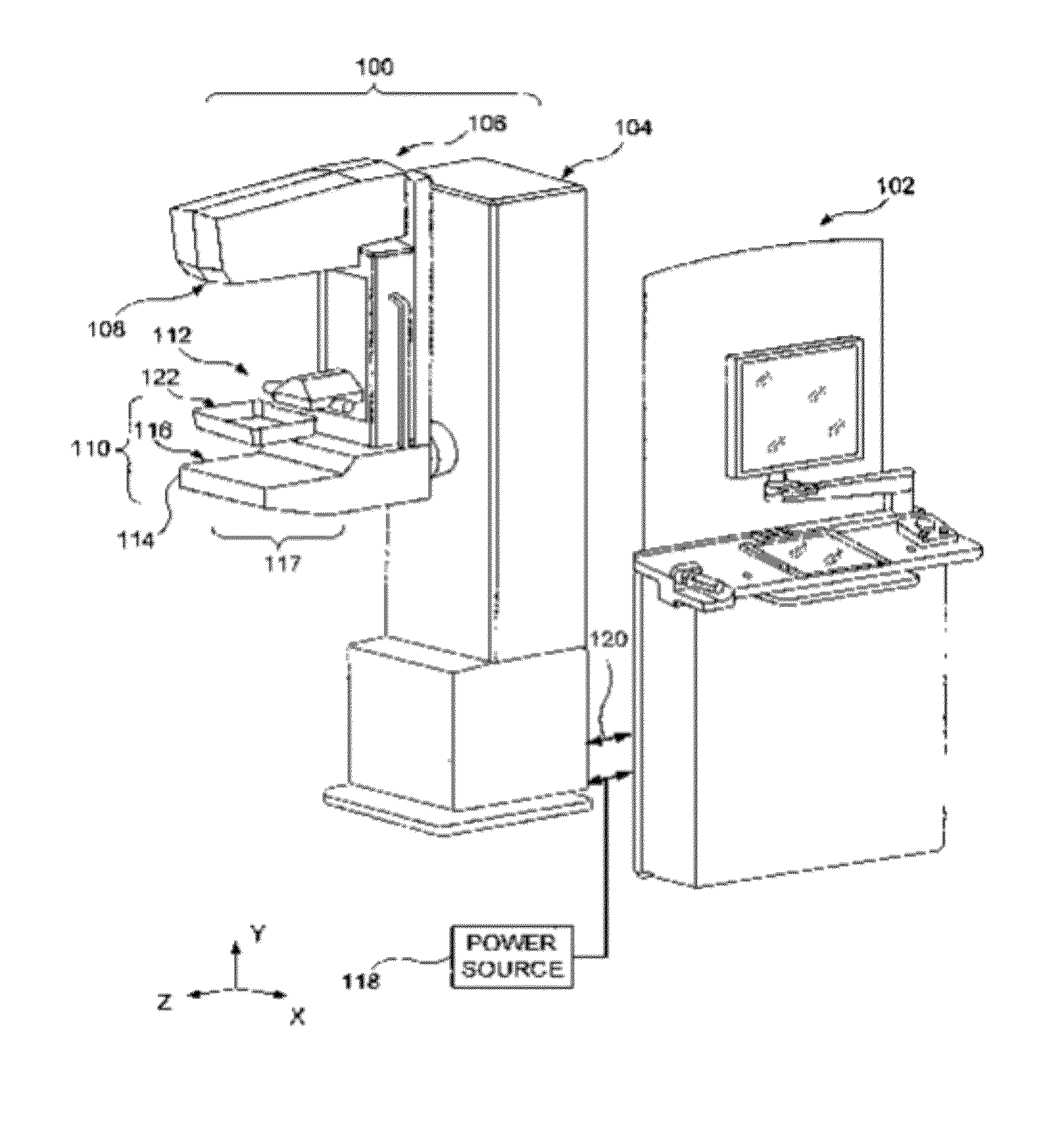
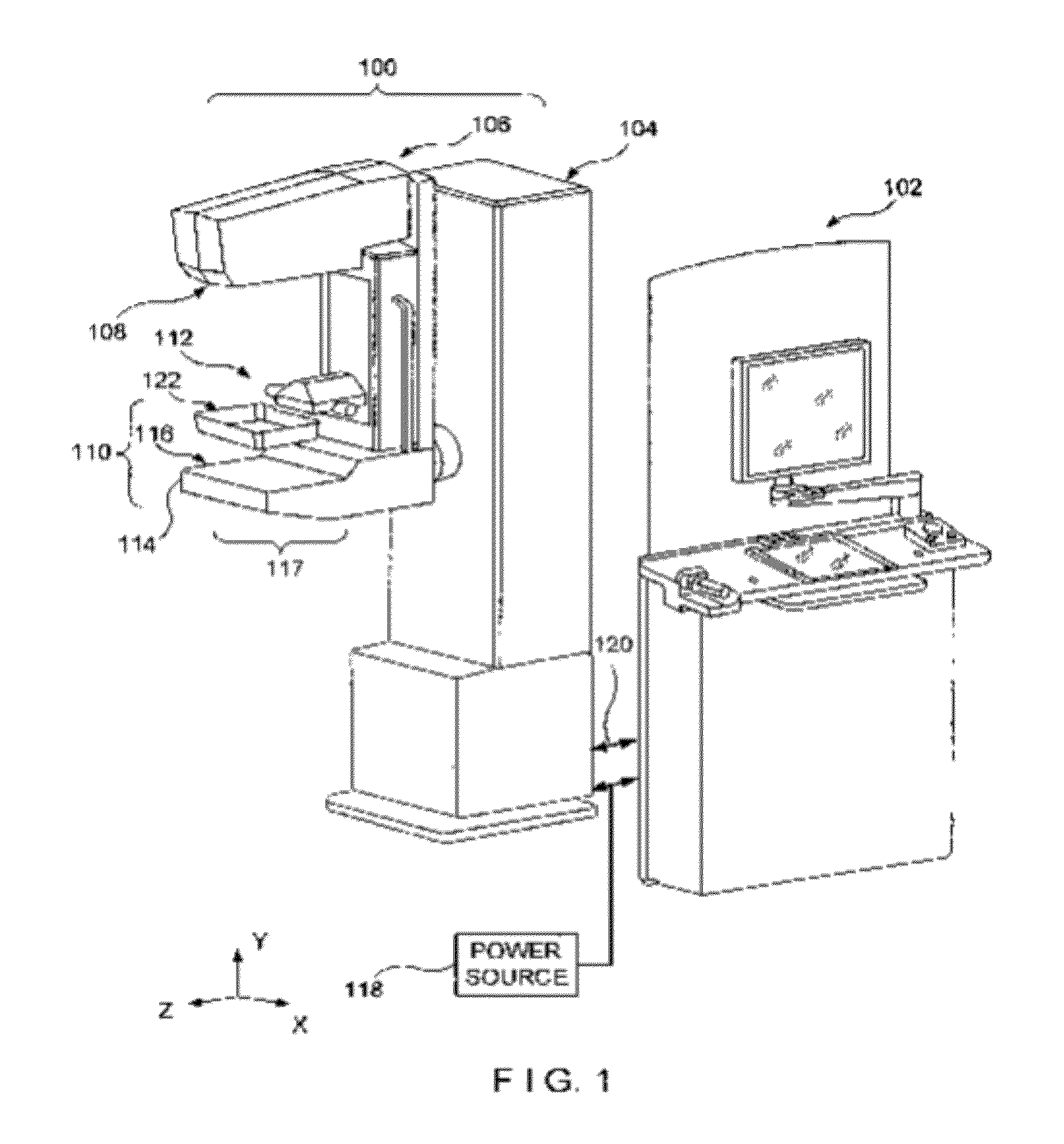
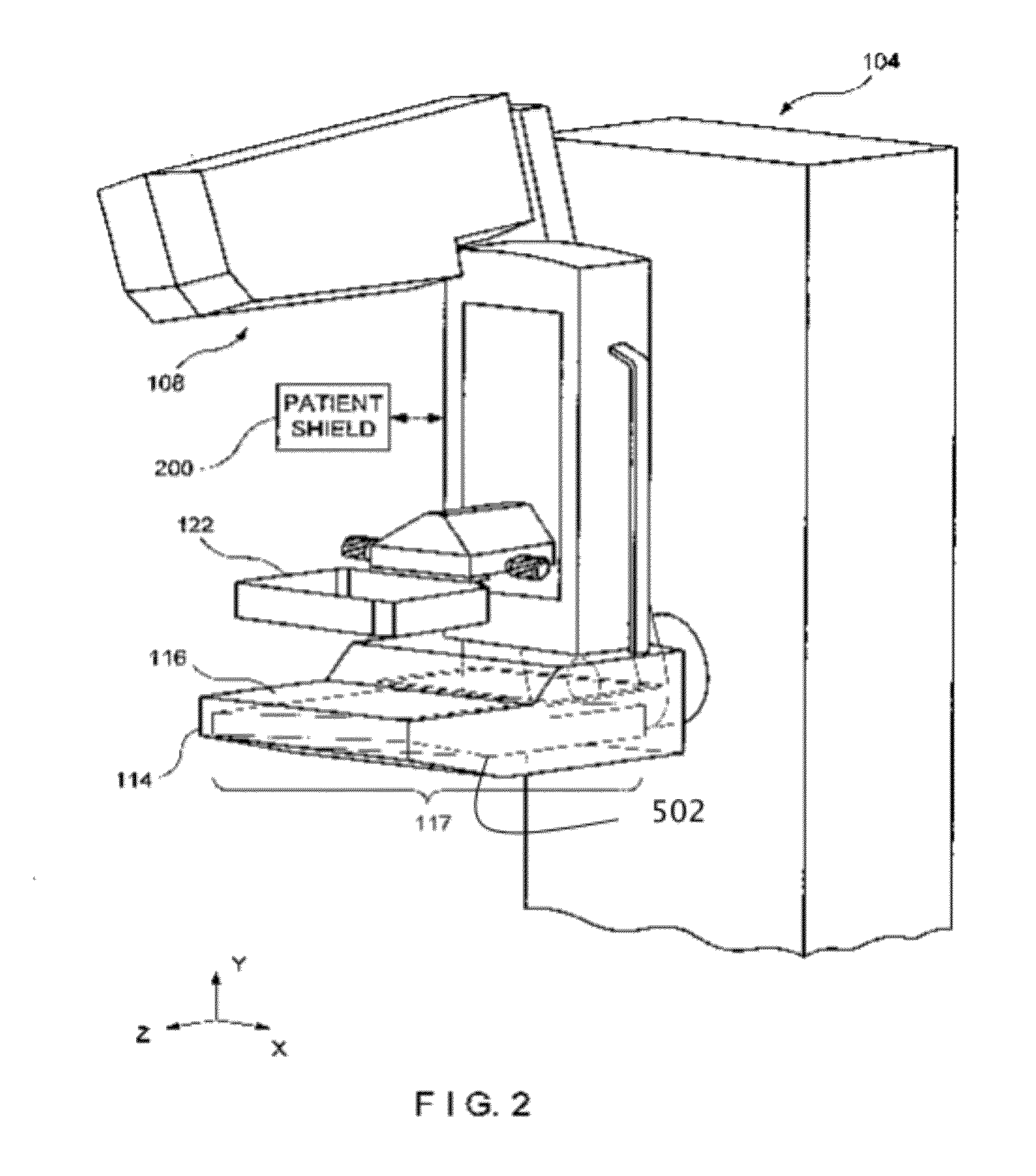
ActiveUS20160166234A1Reduce compressionOrgan movement/changes detectionTomosynthesisTomosynthesisUltrasound imaging
An ultrasound scan probe and support mechanism are provided for use in a multi-modality mammography imaging system, such as a combined tomosynthesis and ultrasound imaging system. In one embodiment, the ultrasound components may be positioned and configured so as not to interfere with the tomosynthesis imaging operation, such as to remain out of the X-ray beam path. Further, the ultrasound probe and associated components may be configured to as to move and scan the breast tissue under compression, such as under the compression provided by one or more paddles used in the tomosynthesis imaging operation.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com