Patents
Literature
234 results about "X ray dose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tomosynthesis X-ray mammogram system and method with automatic drive system
InactiveUS6882700B2Radiation diagnosis data transmissionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationTomosynthesisX-ray
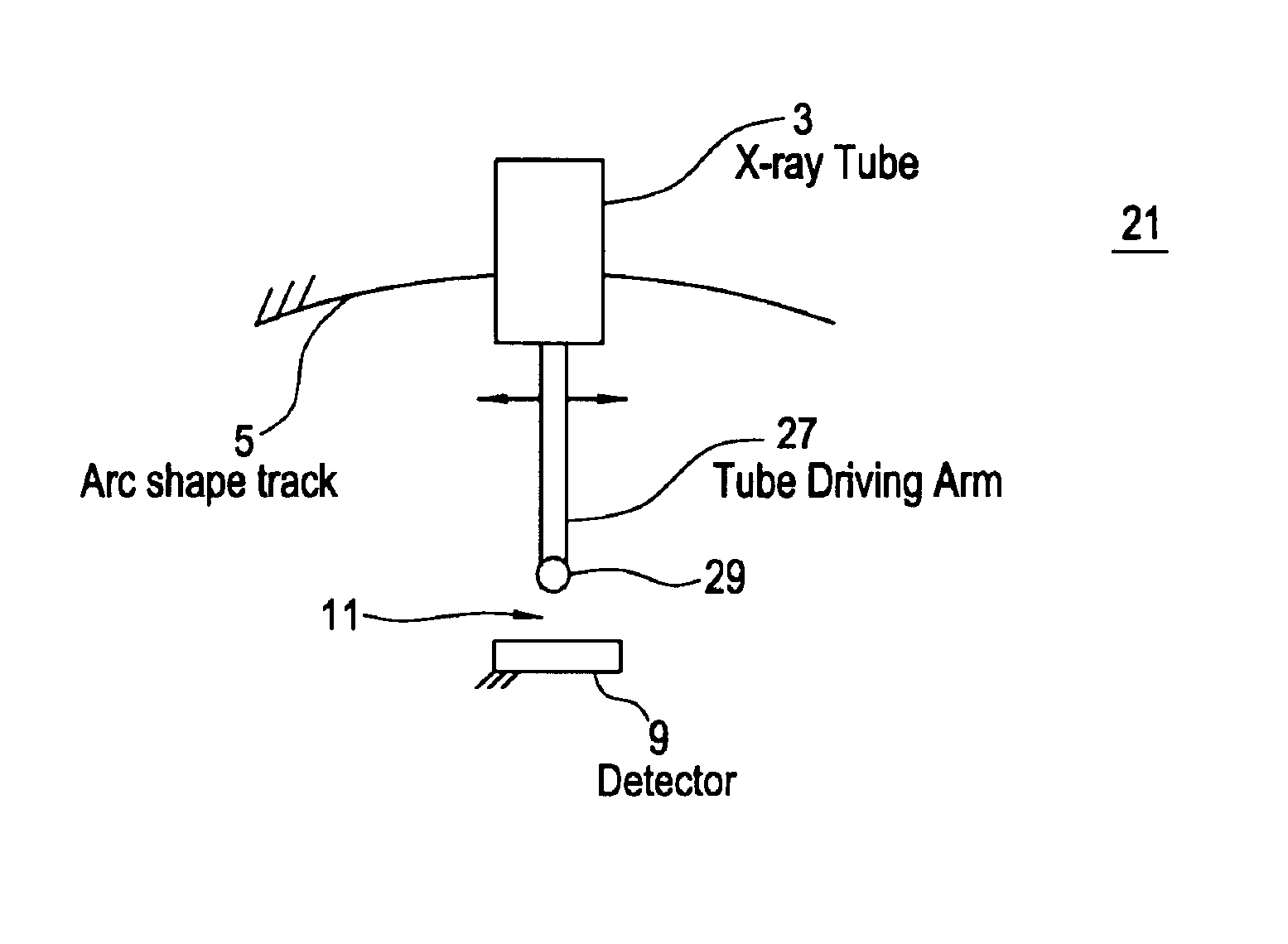
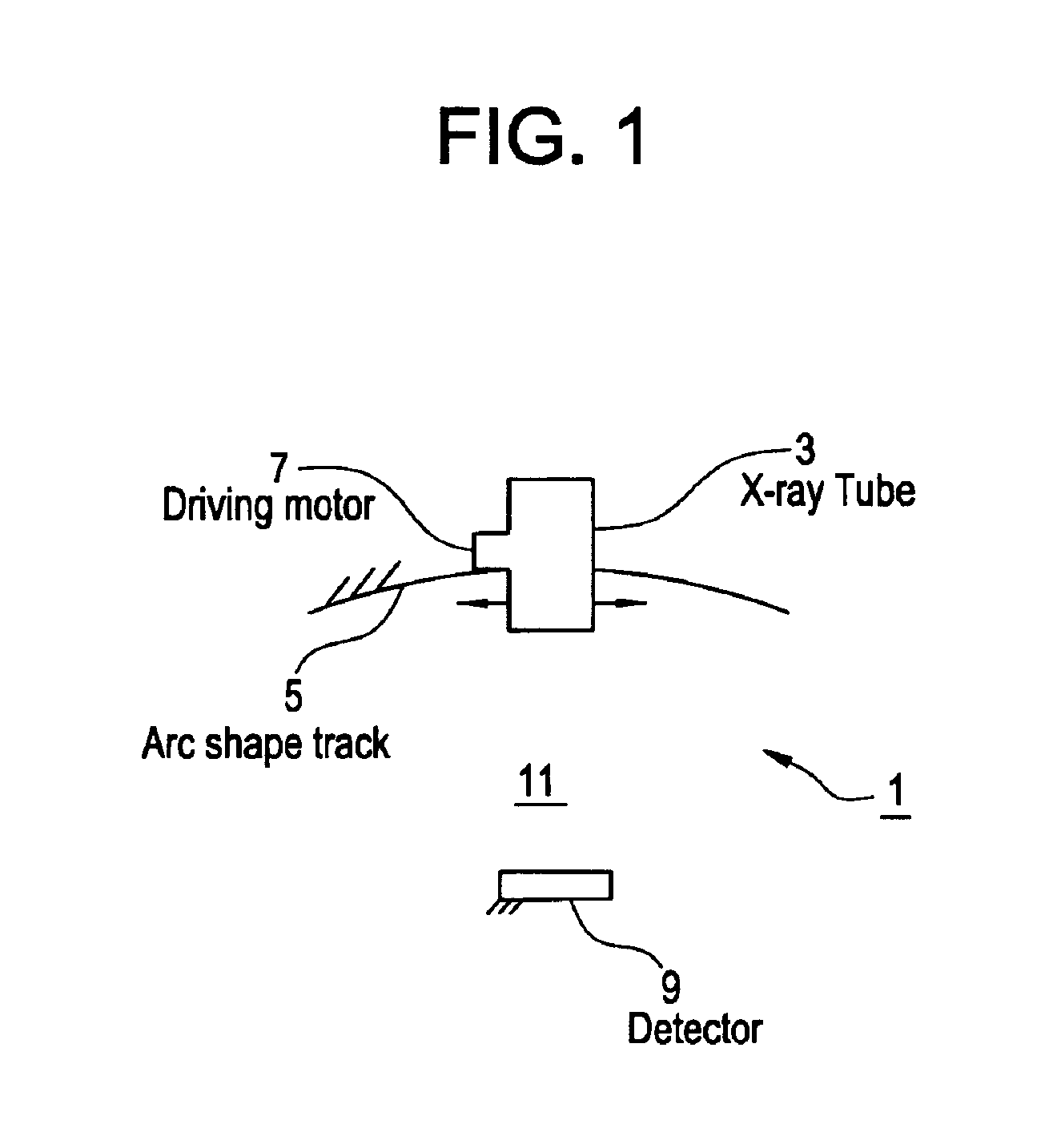
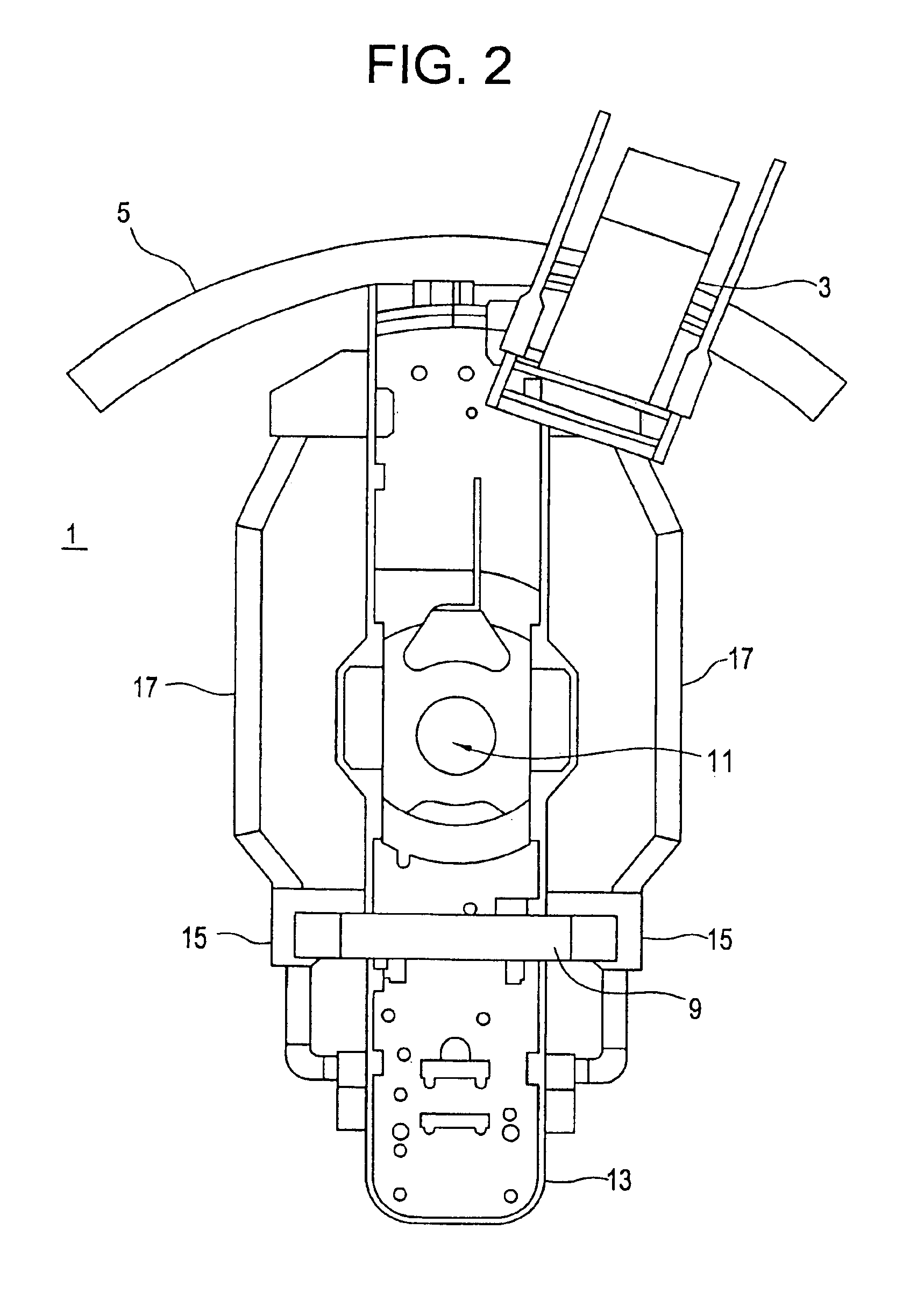
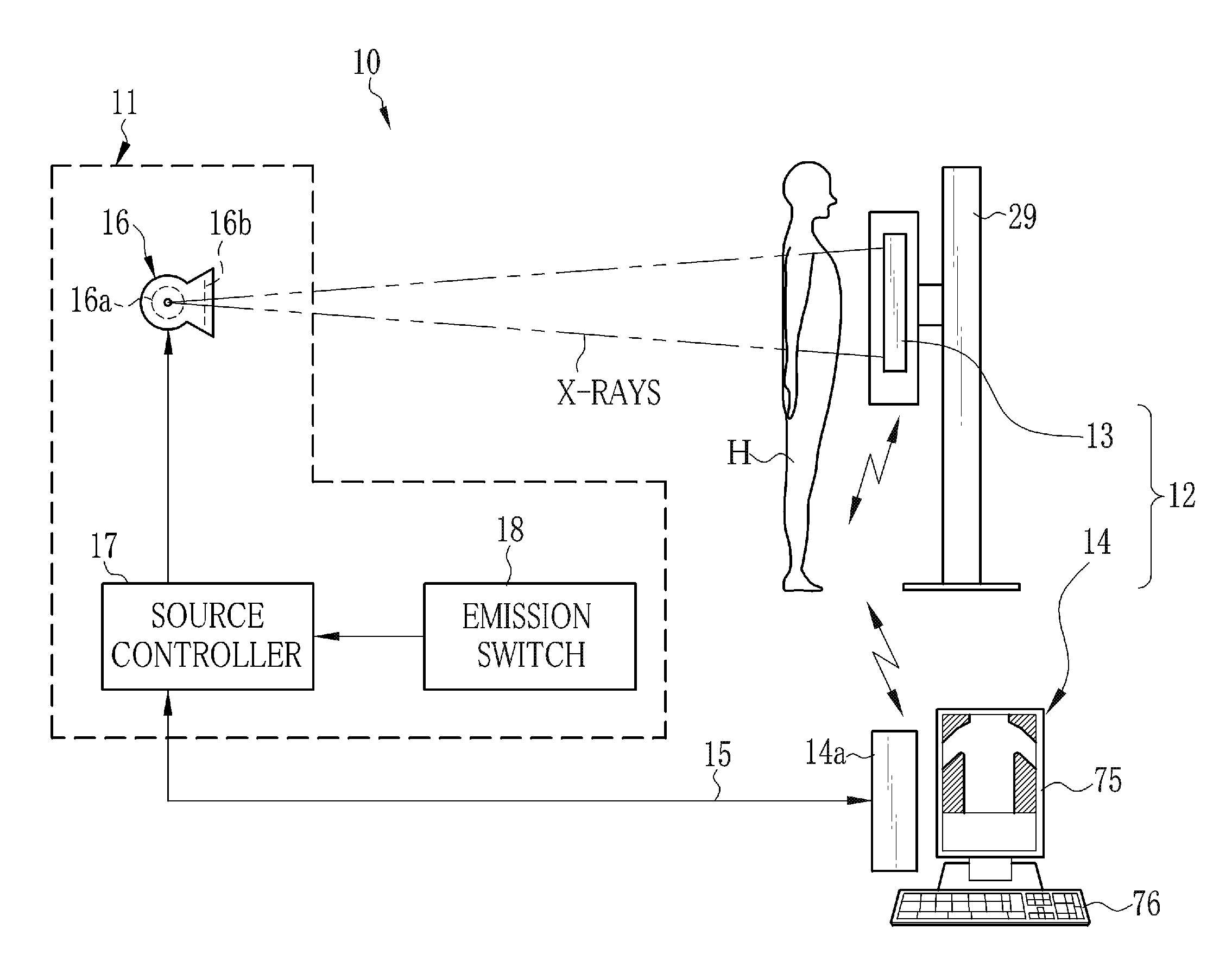
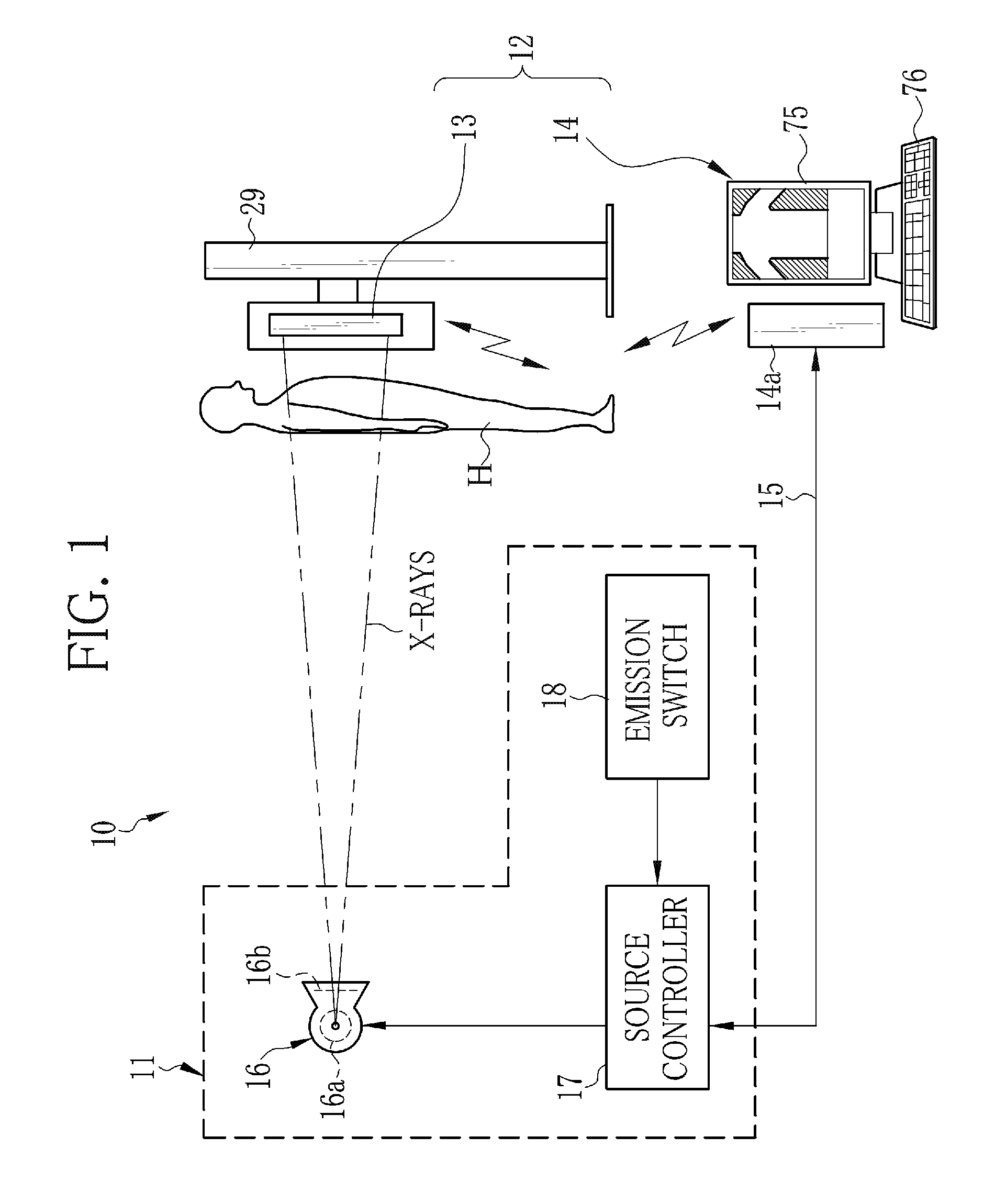
An imaging system includes an X-ray source adapted to move in an arc shaped path and a stationary electronic X-ray detector. The system also includes a track and a mechanical driving mechanism which is adapted to move the X-ray source in the arc shaped path. A tomosynthesis X-ray imaging method includes mechanically moving an X-ray source in a stepped motion on an arc shaped path around an object using a track and irradiating the object with an X-ray dose from the X-ray source located at a plurality of steps along the arc shaped path. The method also includes detecting the X-rays transmitted through the object with an electronic X-ray detector, and constructing a three dimensional image of the object from a signal output by the electronic X-ray detector.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method for obtaining a picture of the internal structure of an object using x-ray radiation and device for the implementation thereof
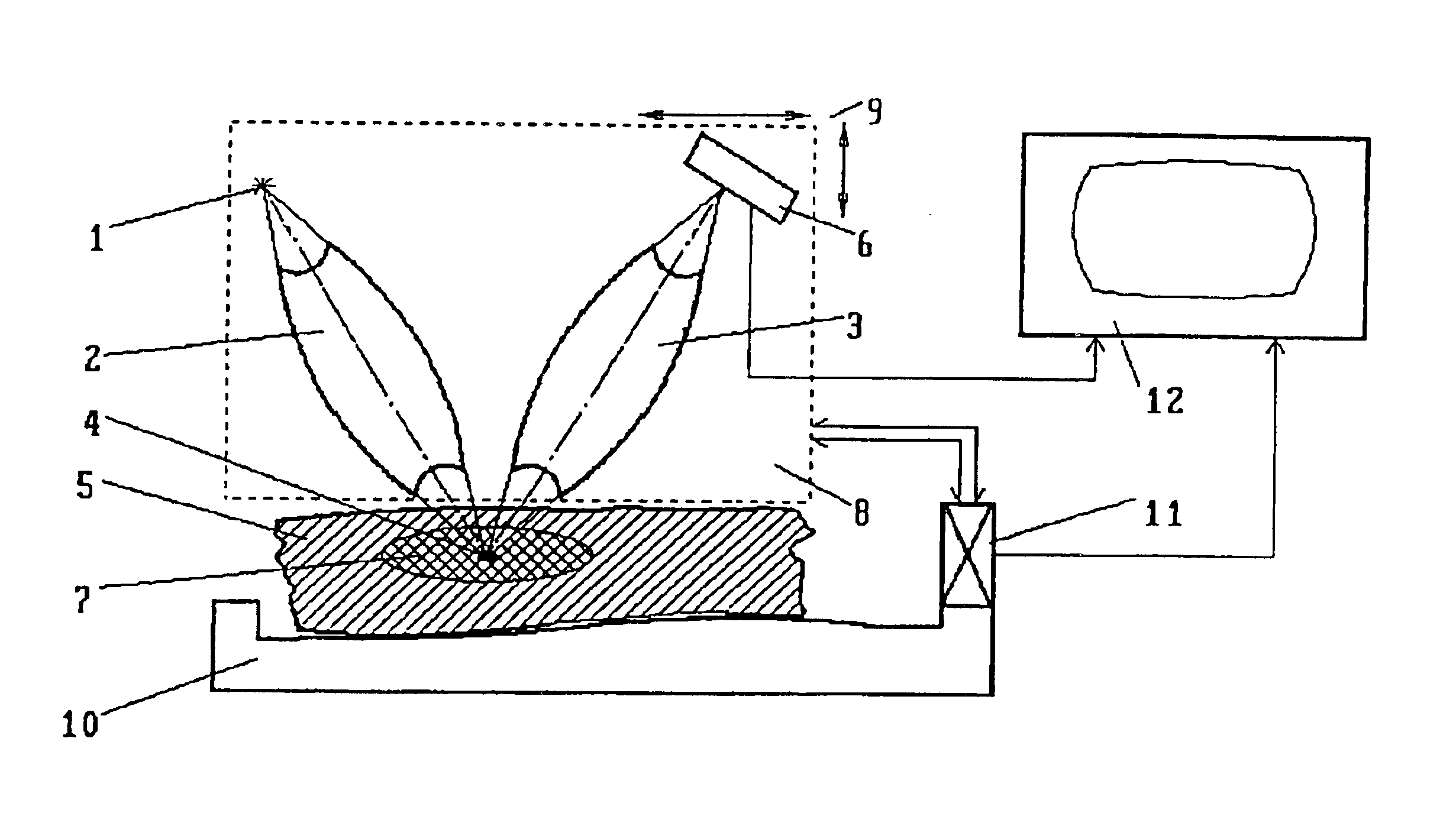
InactiveUS6754304B1Improve accuracyReduce usageX-ray spectral distribution measurementHandling using diffraction/refraction/reflectionX-rayX ray dose
Owner:KUMAKHOV MURADIN ABUBEKIROVICH
Method And System For Dynamic Low Dose X-ray Imaging
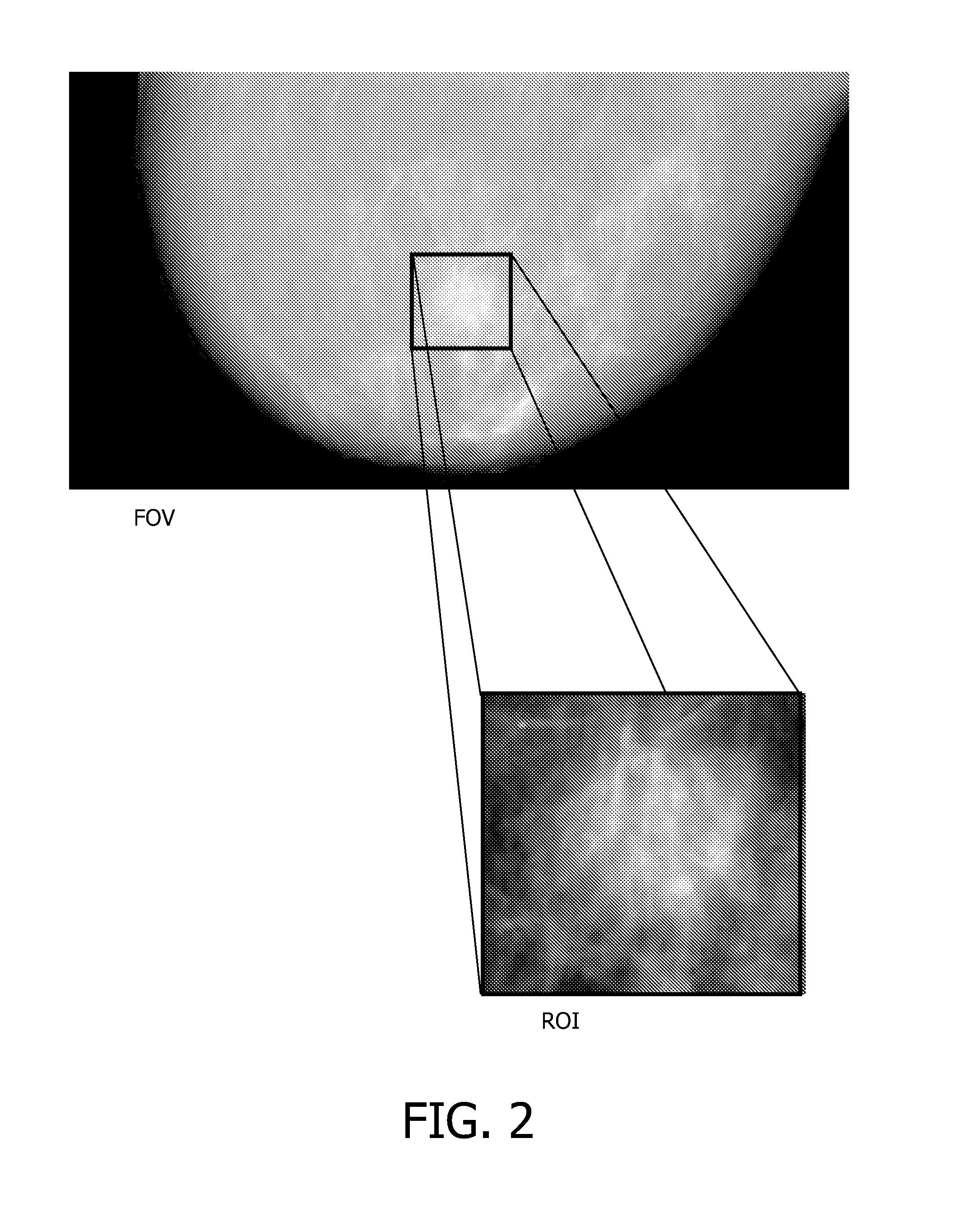
InactiveUS20080118023A1Reduce decreaseReduce detectionTomosynthesisHandling using diaphragms/collimetersX-rayX ray dose
A method and system for performing fluoroscopic imaging of a subject has high temporal and spatial resolution in a center portion of the captured dynamic images. The system provides for reduced X-ray dose to the patient associated with that part of the X-ray beam associated with a peripheral portion of the captured images although temporal, and in some embodiments spatial, resolution is reduced in the peripheral portion of the image. The system uses a rotating collimator to produce an X-ray beam having narrow wing portions associated with the peripheral portions of the image, and a broader central region associated with the high resolution center portion of the images.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
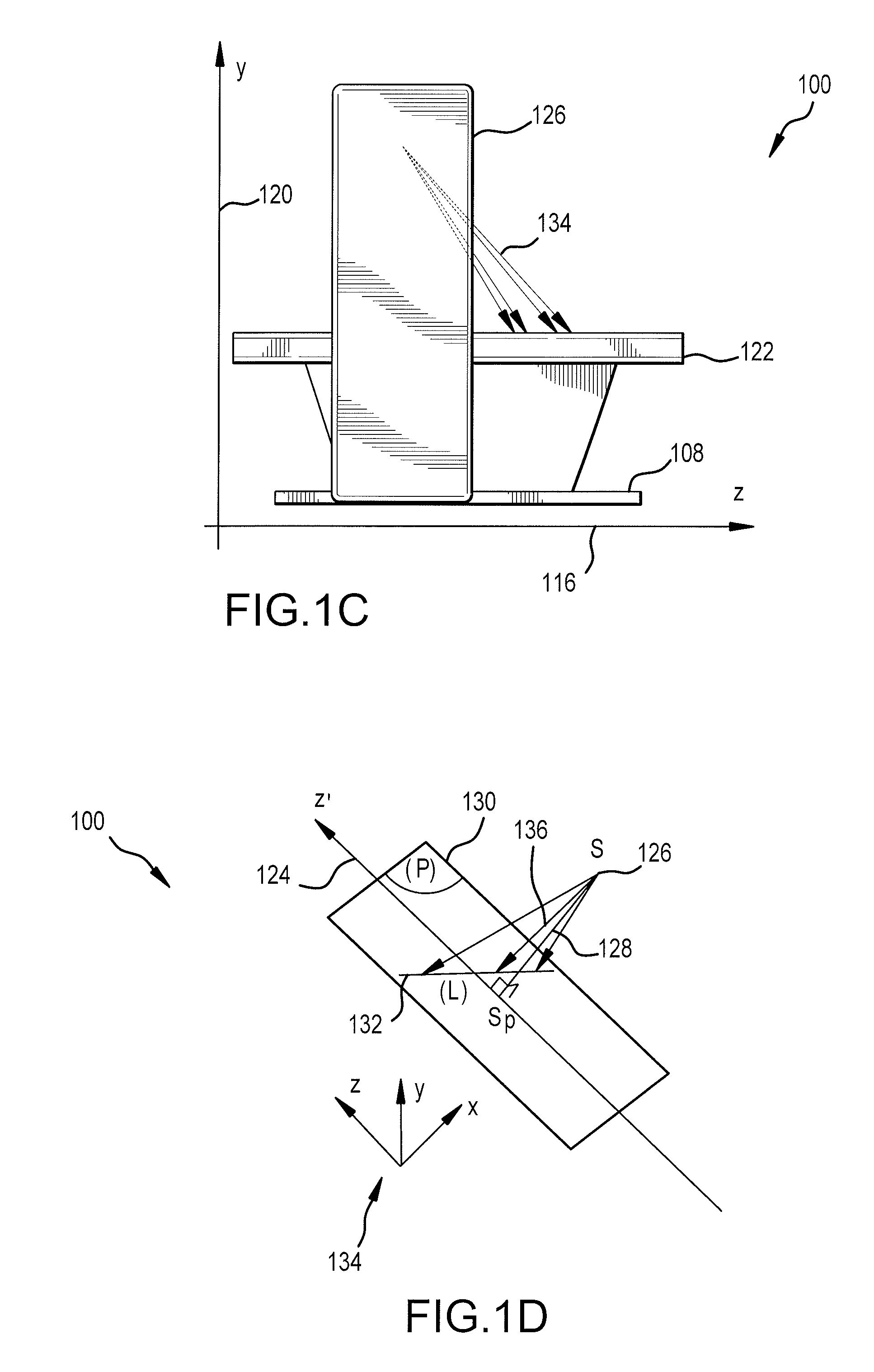
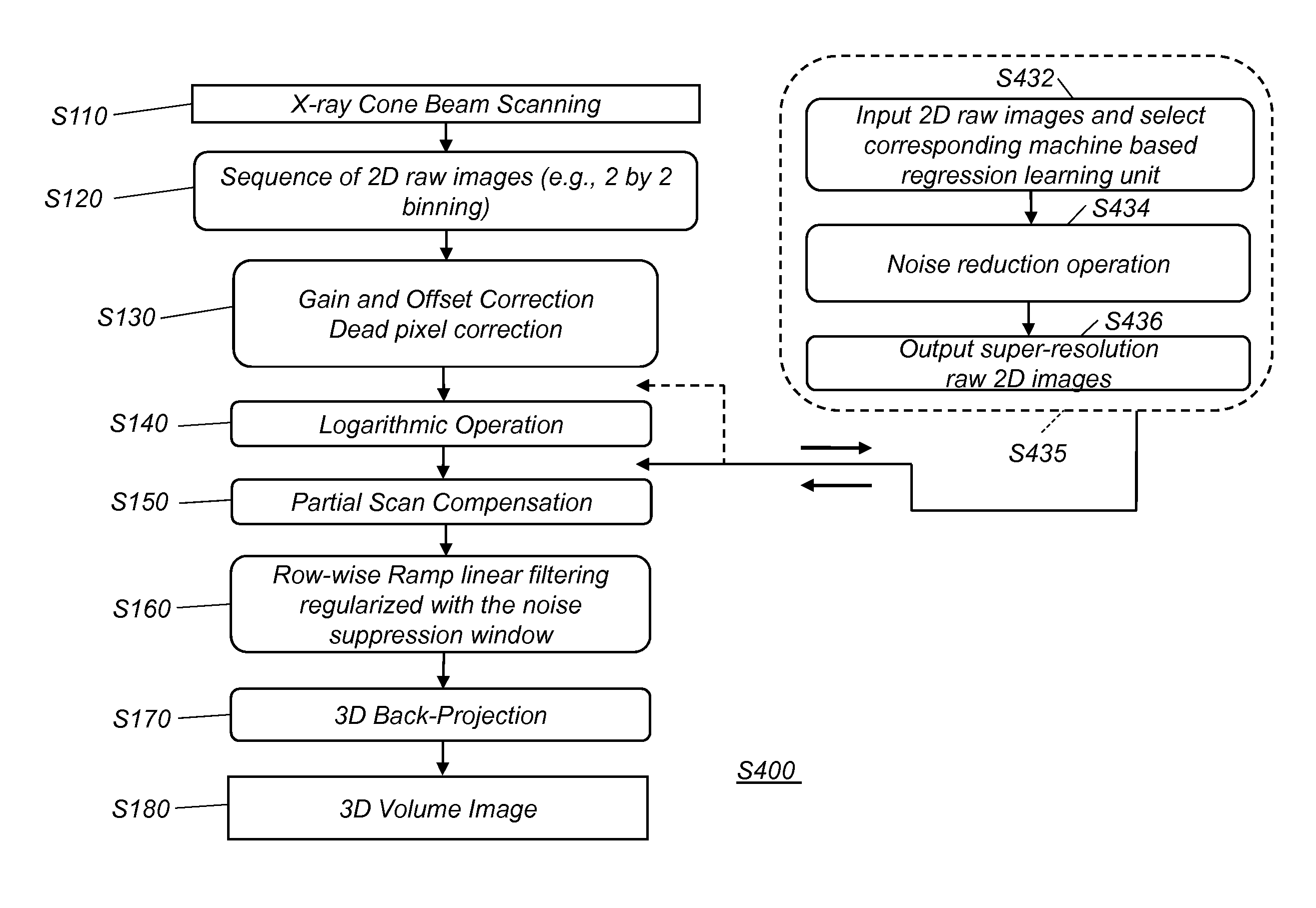
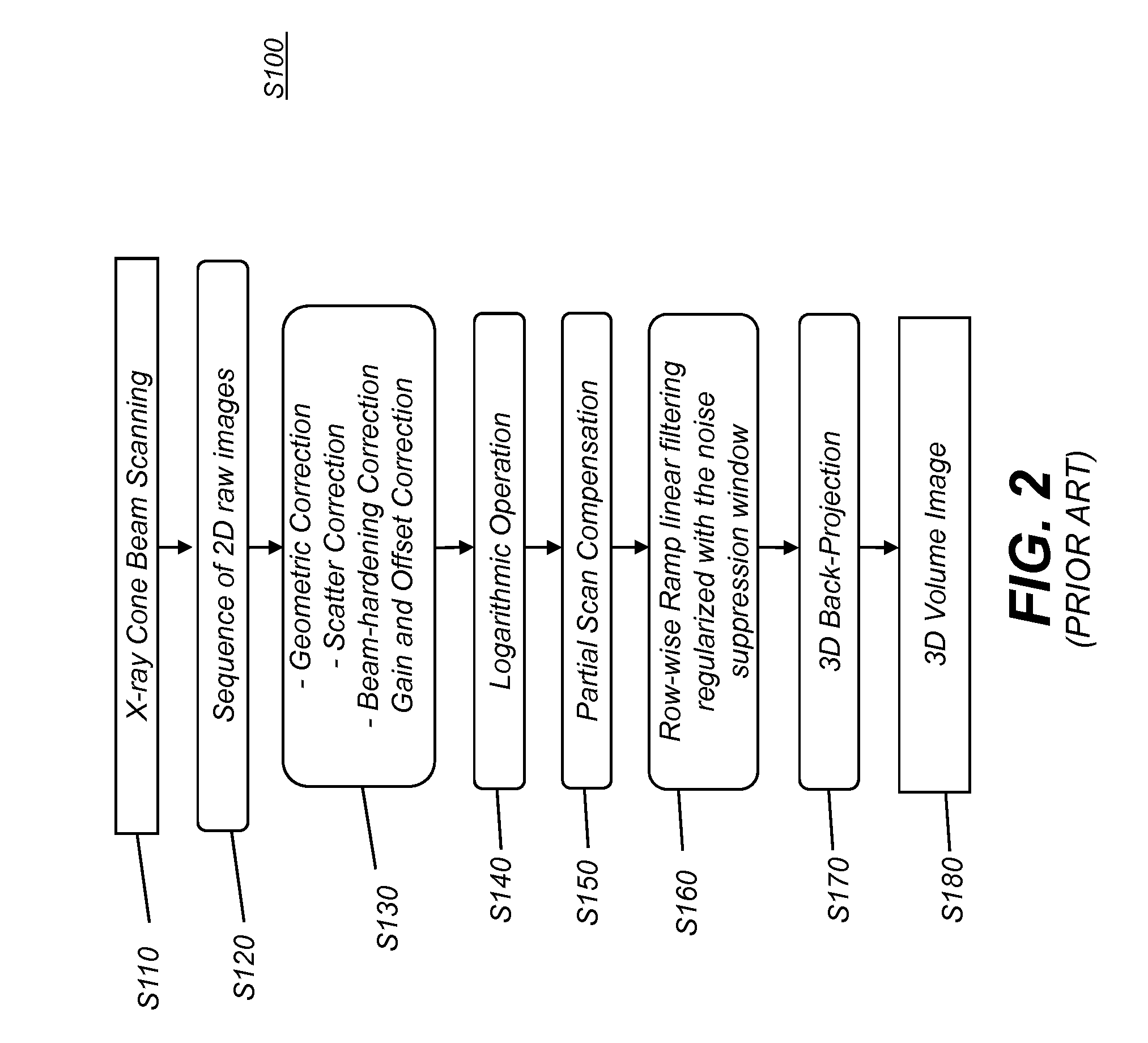
Noise suppression for low x-ray dose cone-beam image reconstruction
InactiveUS20130051516A1Reduce noiseMaintain image quality characteristicReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationProjection imageX ray dose
Embodiments of methods and / or apparatus for 3-D volume image reconstruction of a subject, executed at least in part on a computer for use with a digital radiographic apparatus can obtain image data for 2-D projection images over a range of scan angles. For each of the plurality of projection images, an enhanced projection image can be generated. In embodiments of imaging apparatus, CBCT systems, and methods for operating the same can, through a de-noising application based on a different corresponding object, maintain image reconstruction characteristics (e.g., for a prescribed CBCT examination) while reducing exposure dose, reducing noise or increase a SNR while an exposure setting is unchanged.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Radiographic imaging control apparatus and method
ActiveUS20050169425A1Improve image processing capabilitiesSimple processX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-rayX ray dose
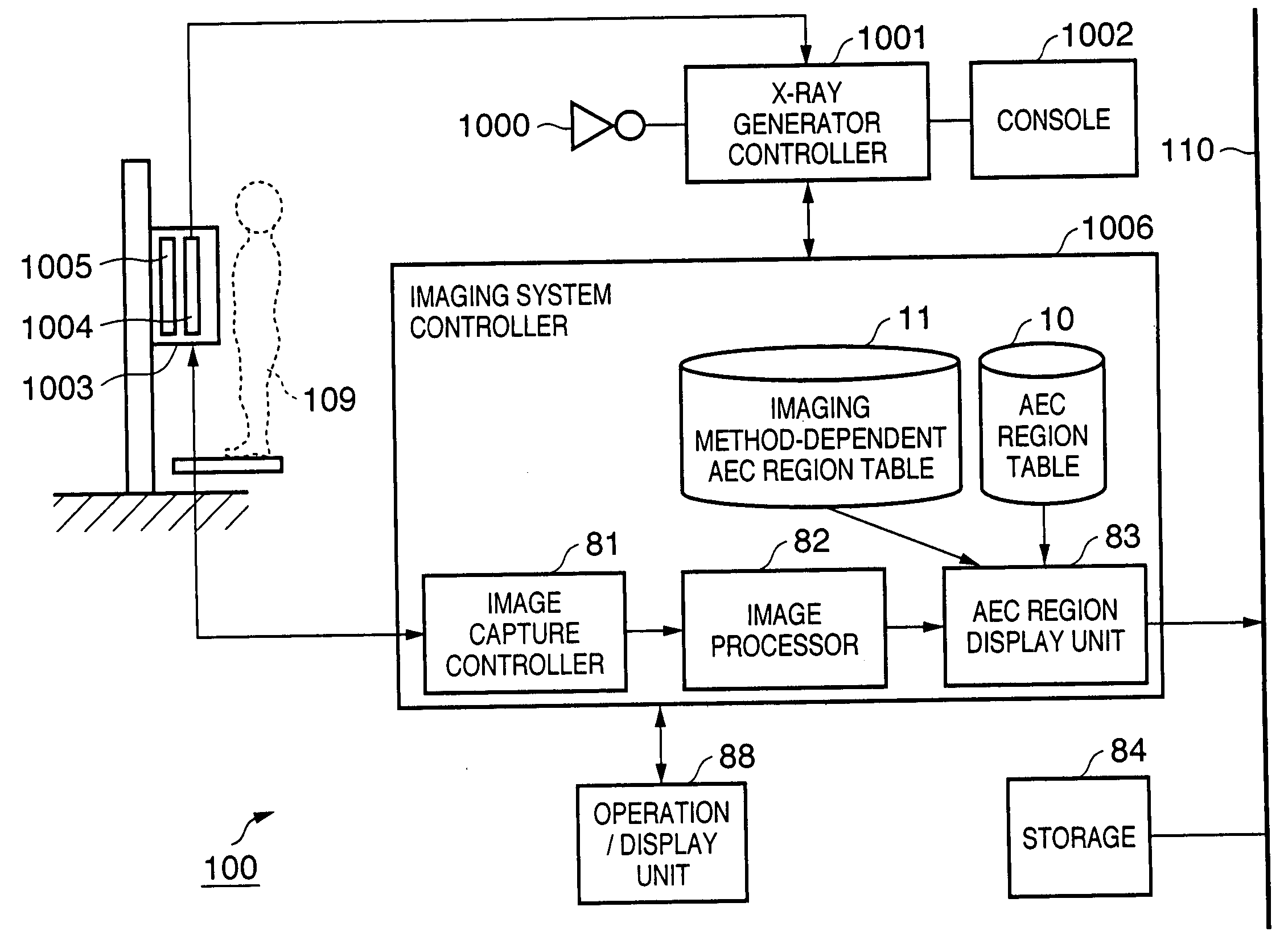
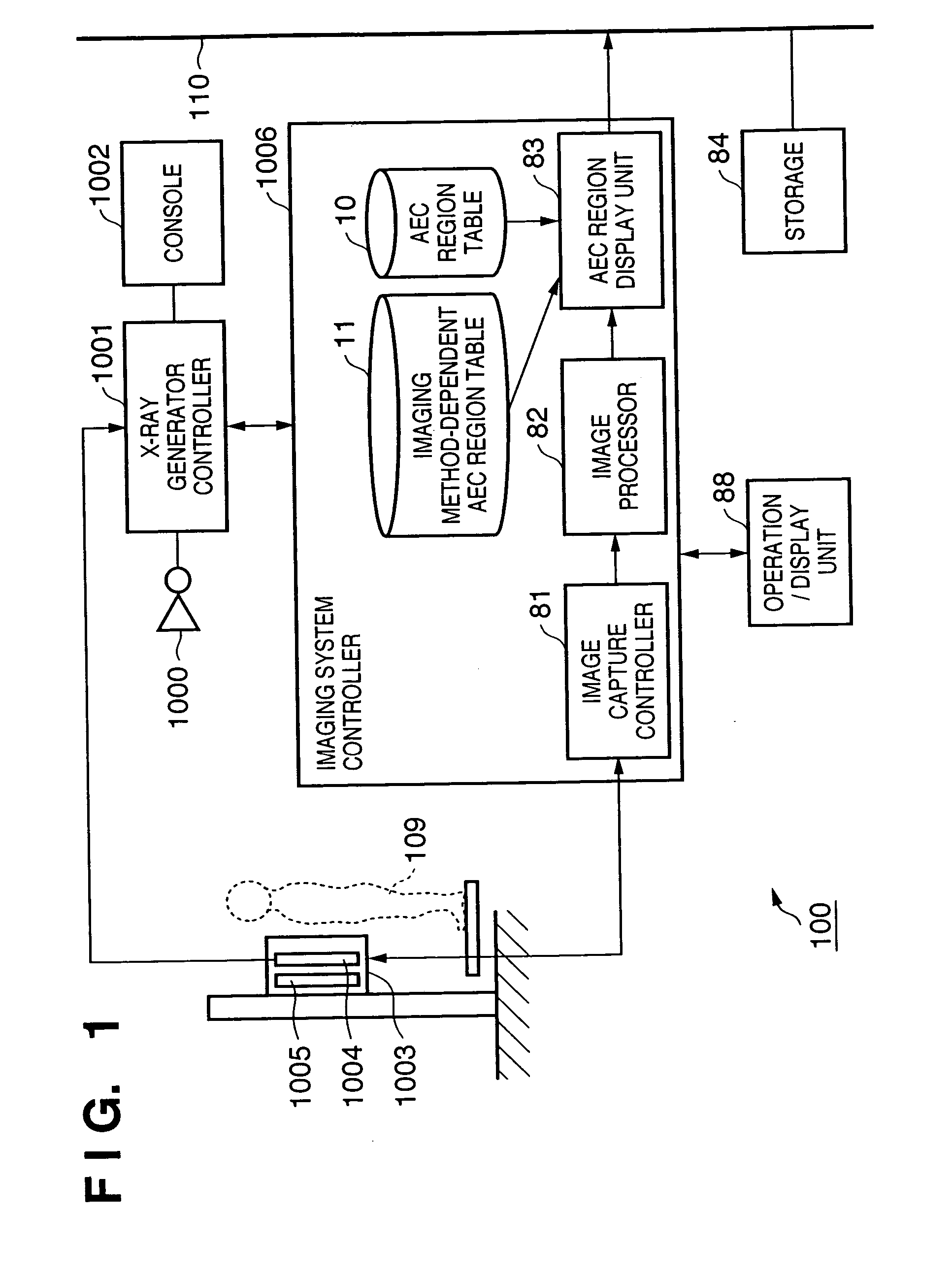
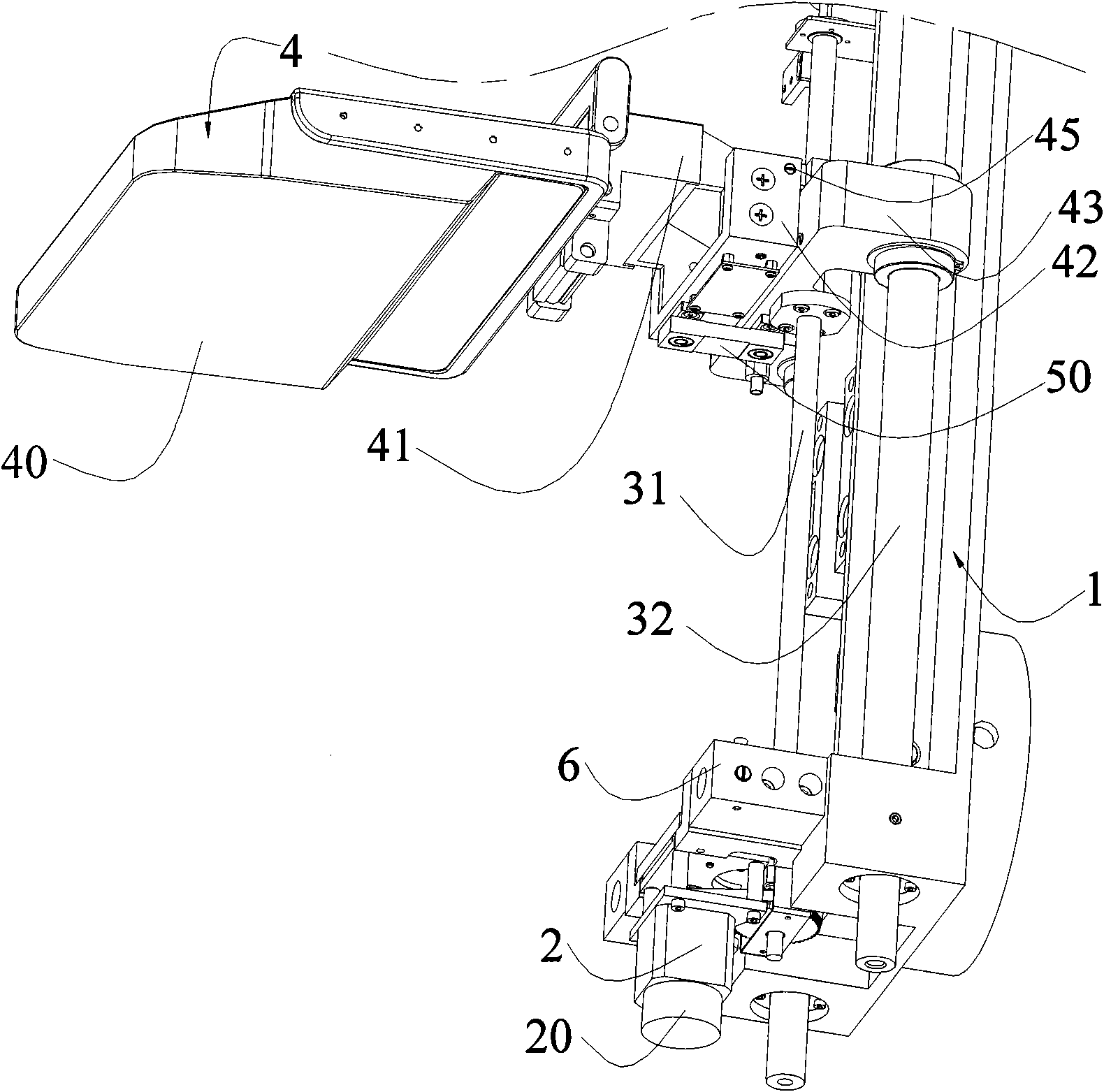
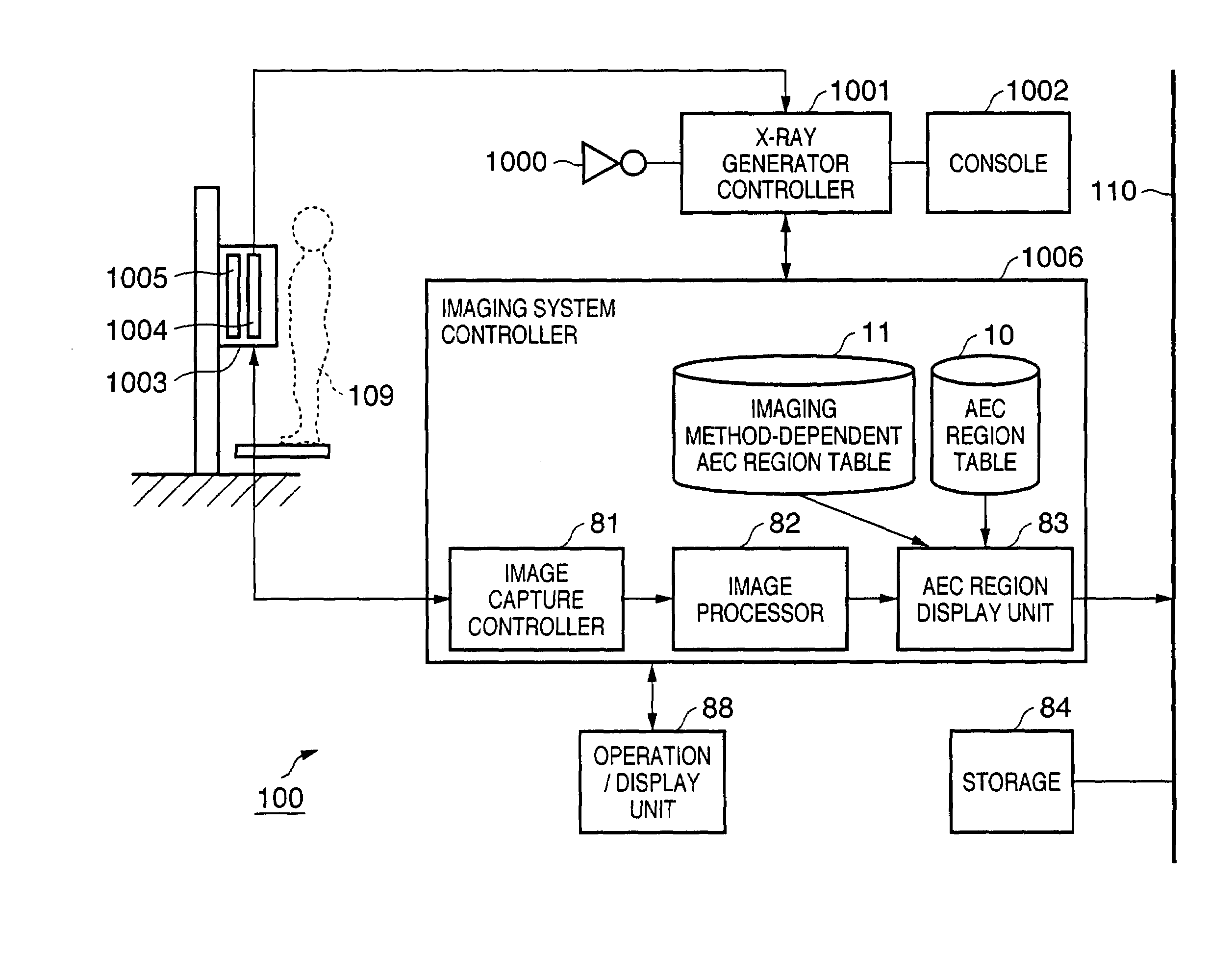
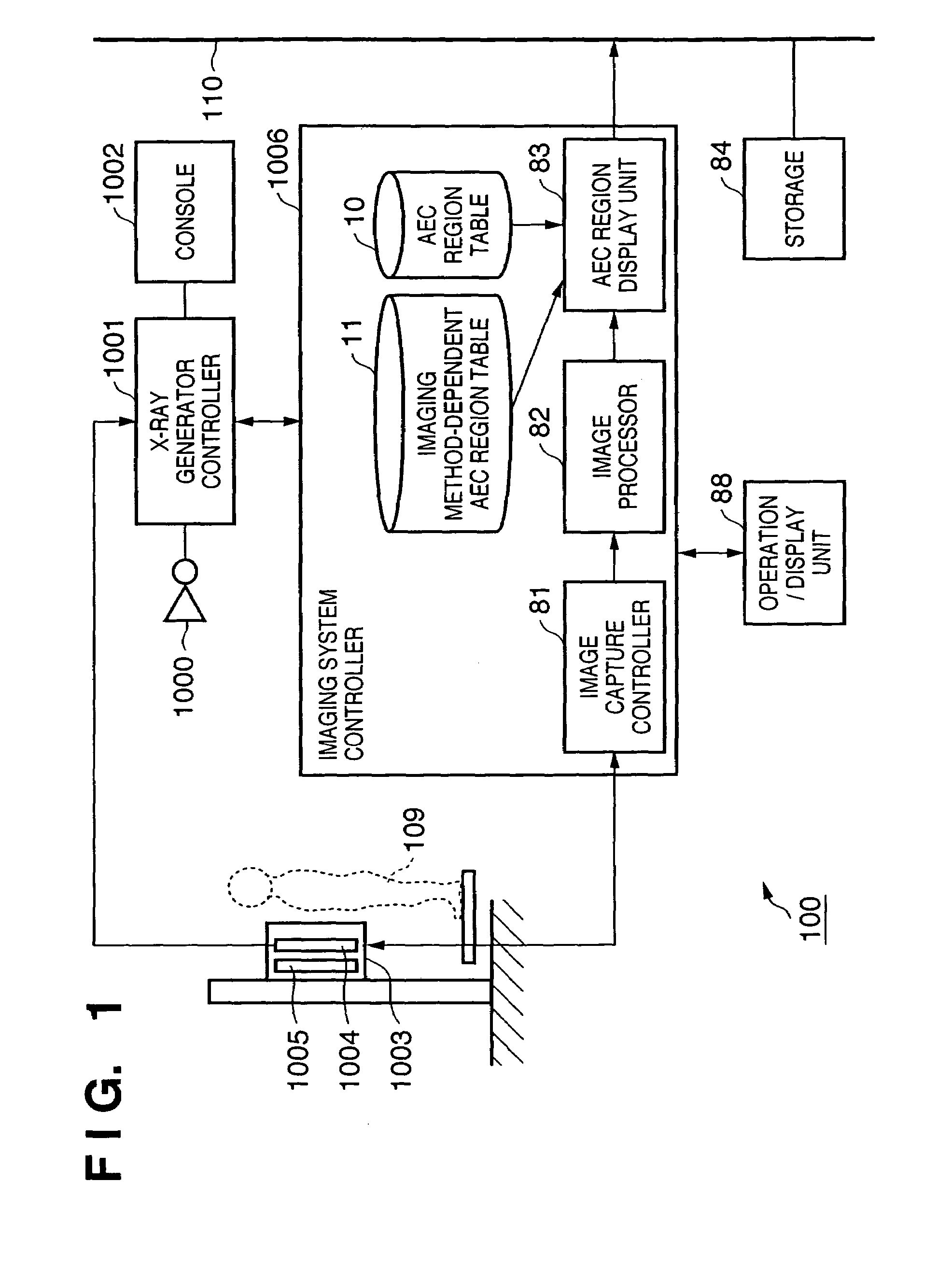
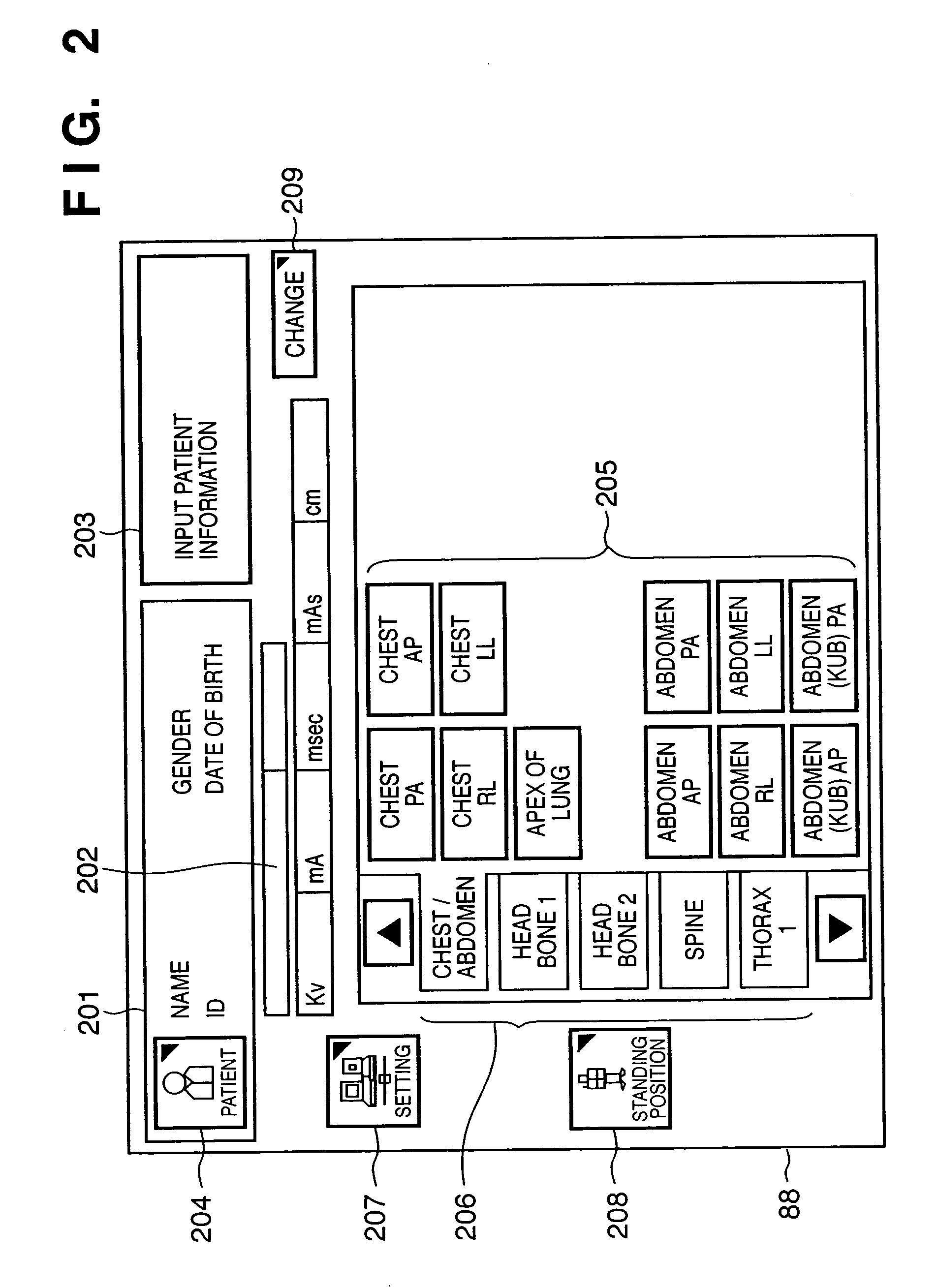
An X-ray imaging control apparatus acquires radiographic data obtained from an X-ray imaging apparatus which controls an X-ray dose upon X-ray imaging by detecting the X-ray dose in one or a plurality of detection regions, and displays a radiographic image on the basis of the acquired radiographic data. At this time, detection region information indicating the position and range of each detection region used in the X-ray imaging apparatus upon generating the radiographic data is acquired. Based on this detection region information, an image indicating each detection region is superimposed on the displayed radiographic image.
Owner:CANON KK
Real-time feedback for preventing high dose c-arch geometry positions
ActiveUS20140307855A1Reduce total usageSmall impactLocal control/monitoringRadiation safety meansSoft x rayImaging quality
The present invention relates to an apparatus for aiding operation of an interventional x-ray imager during image acquisition, to a method of aiding operation of an x-ray imager, to an interventional x-ray imager, to a computer program element and to a computer readable medium. The X-ray imager is capable of varying X-ray dosages depending on differences in X-ray attenuation levels across an object of interest to be imaged and is capable of assuming any one of a plurality of imaging geometry positions when acquiring an image. An indication, visual, acoustic or haptic, to the operator of an X-ray imager is provided on the incurred change in X-ray dosage when changing from a current projection view to an updated projection view, provided that a given constant image quality is to be maintained throughout the different views.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
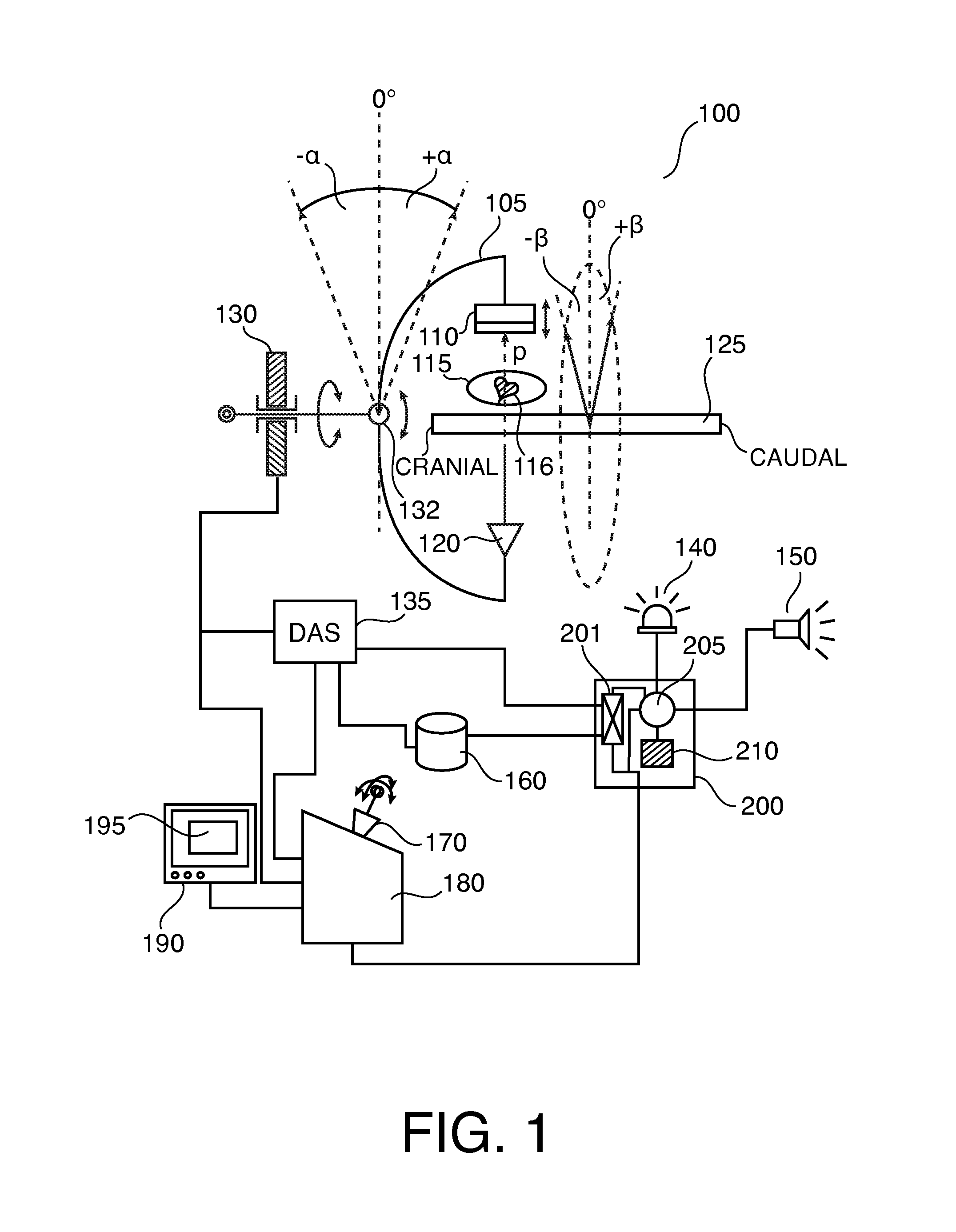
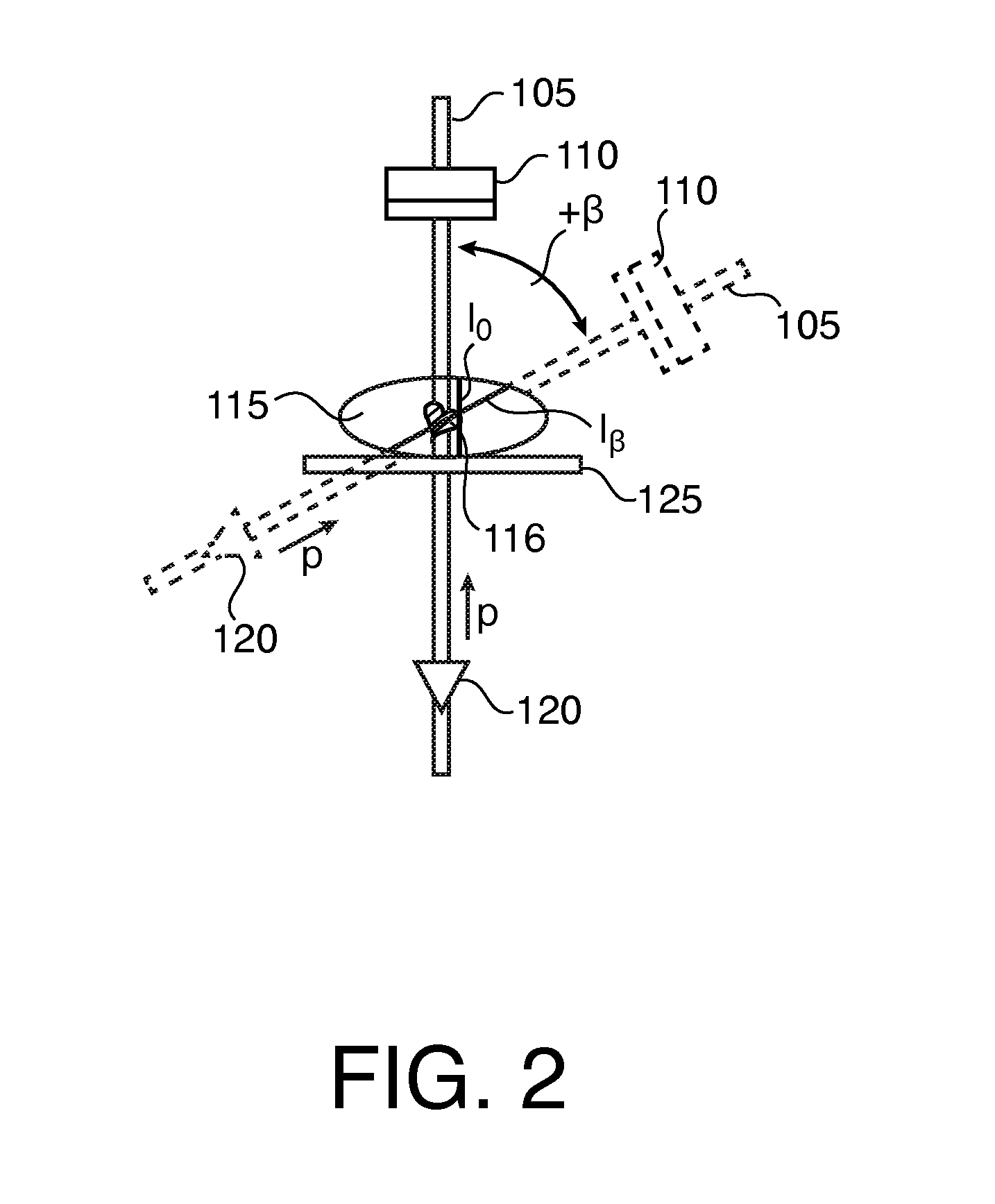
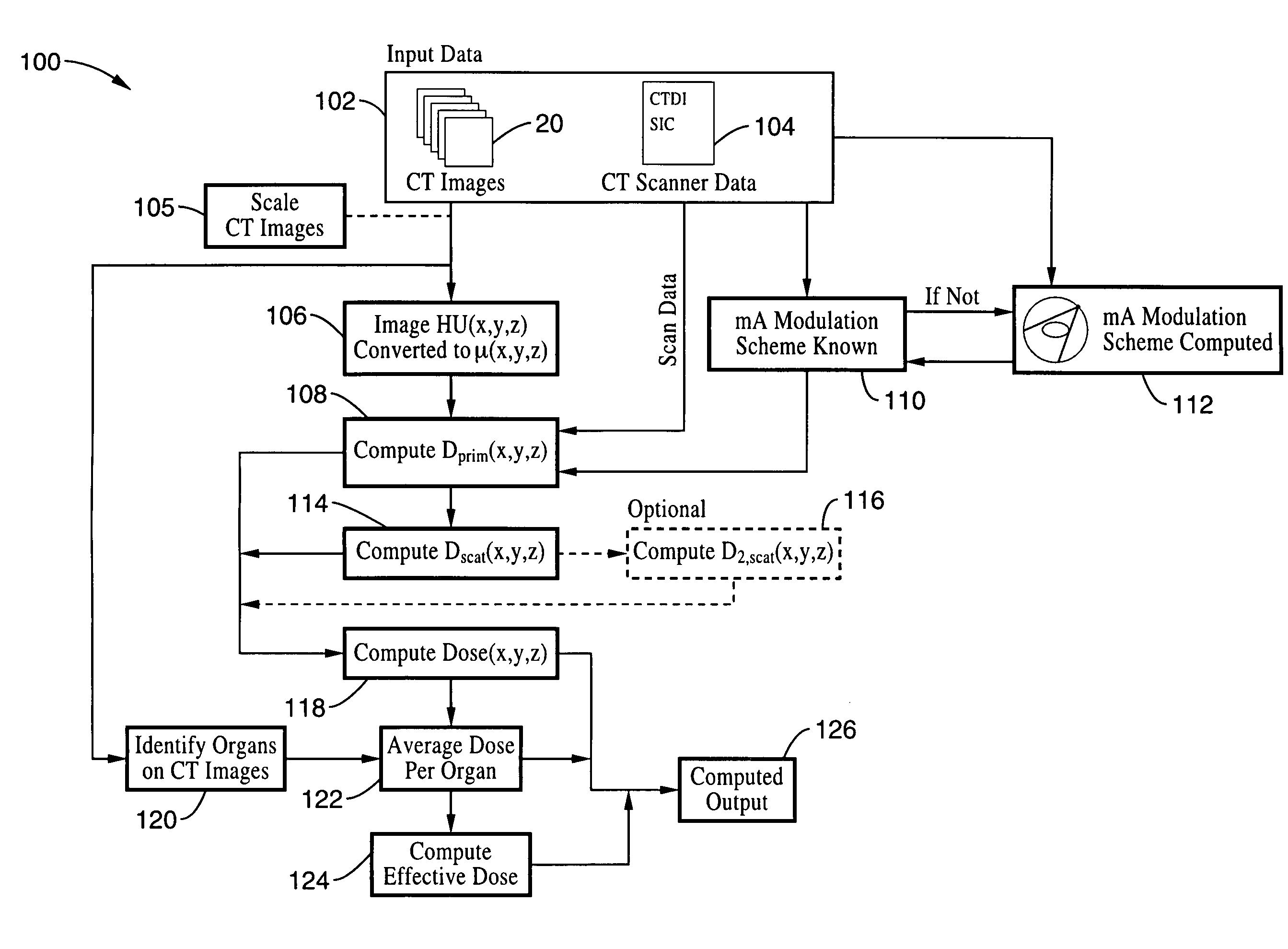
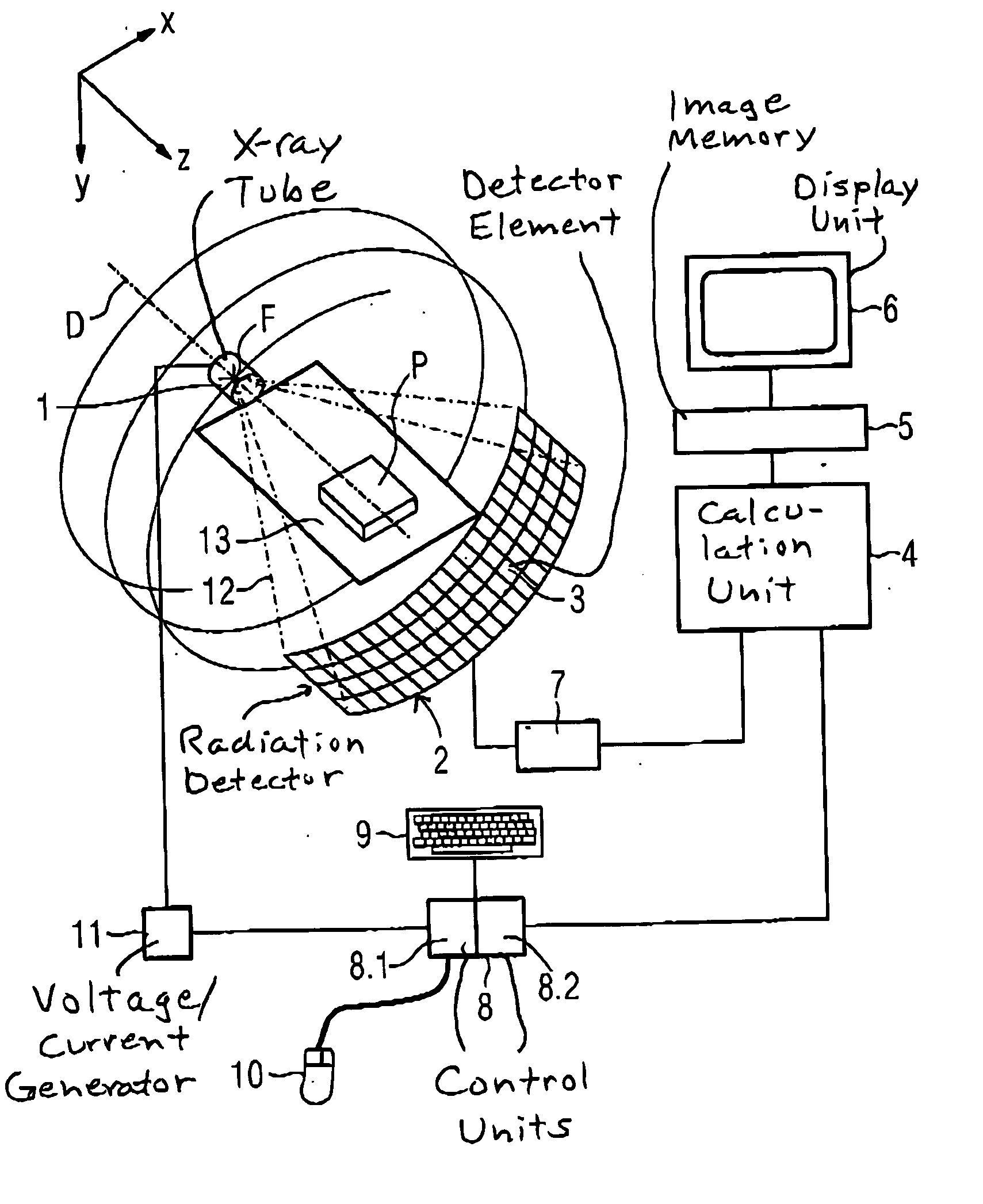
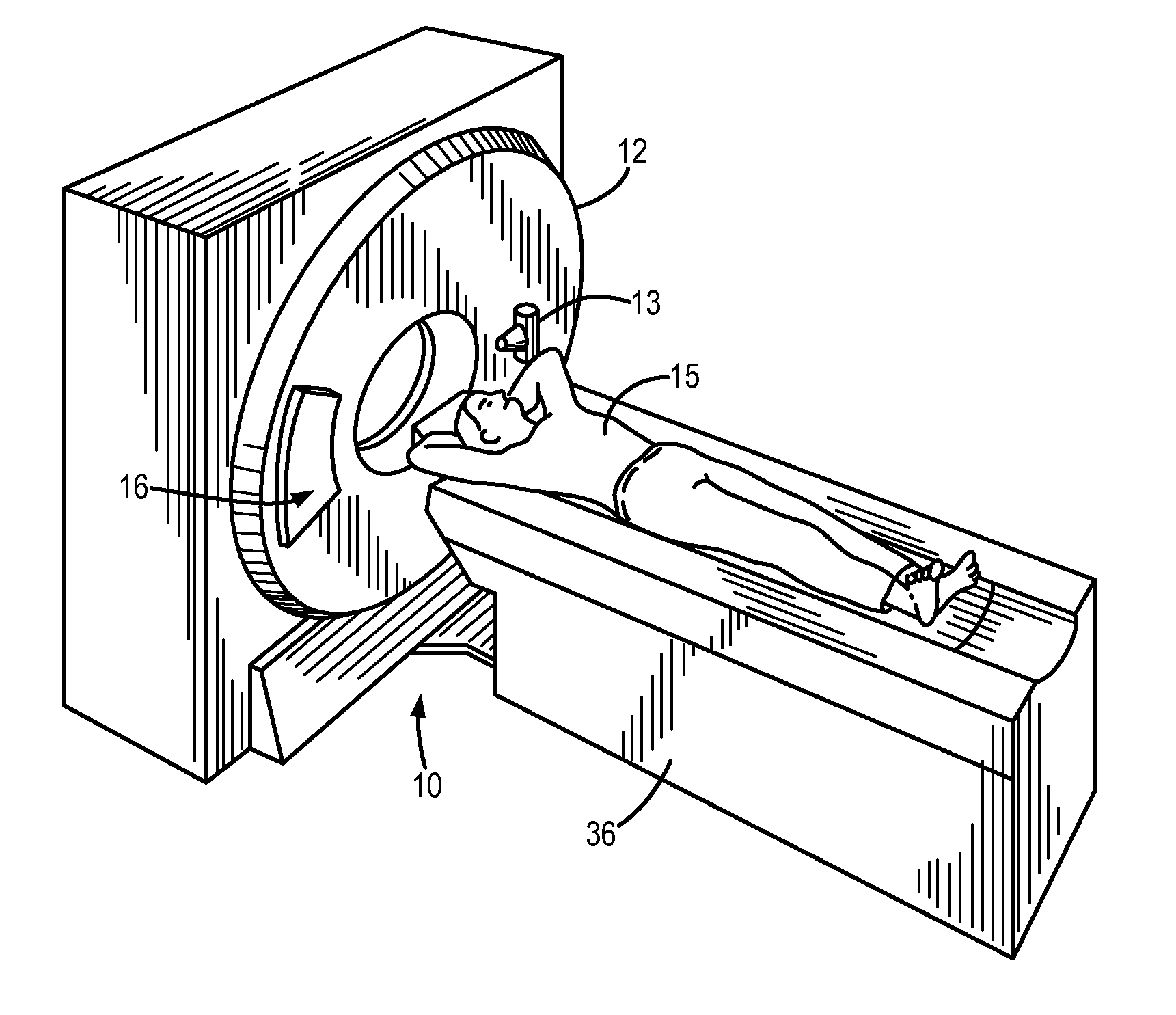
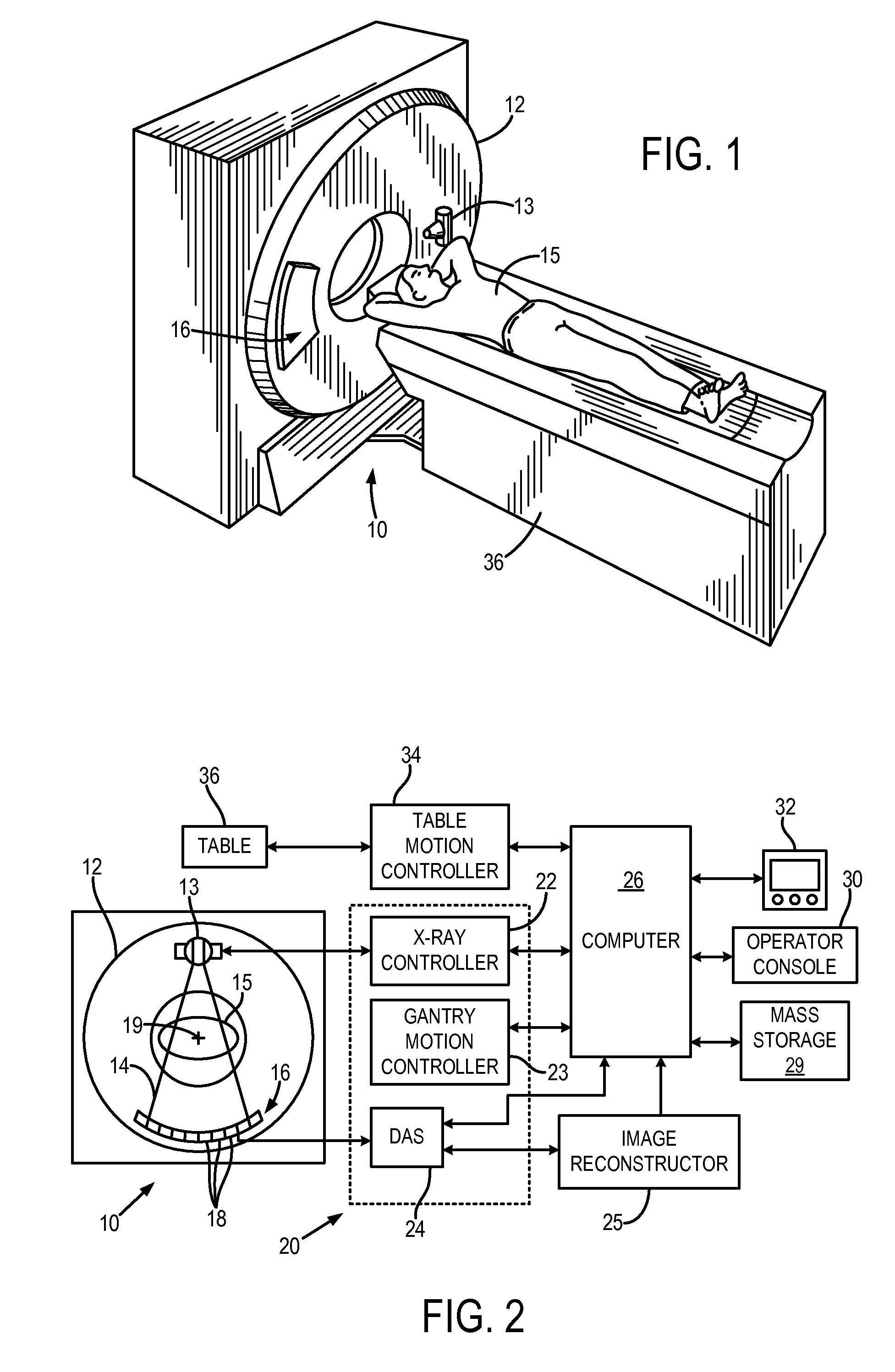
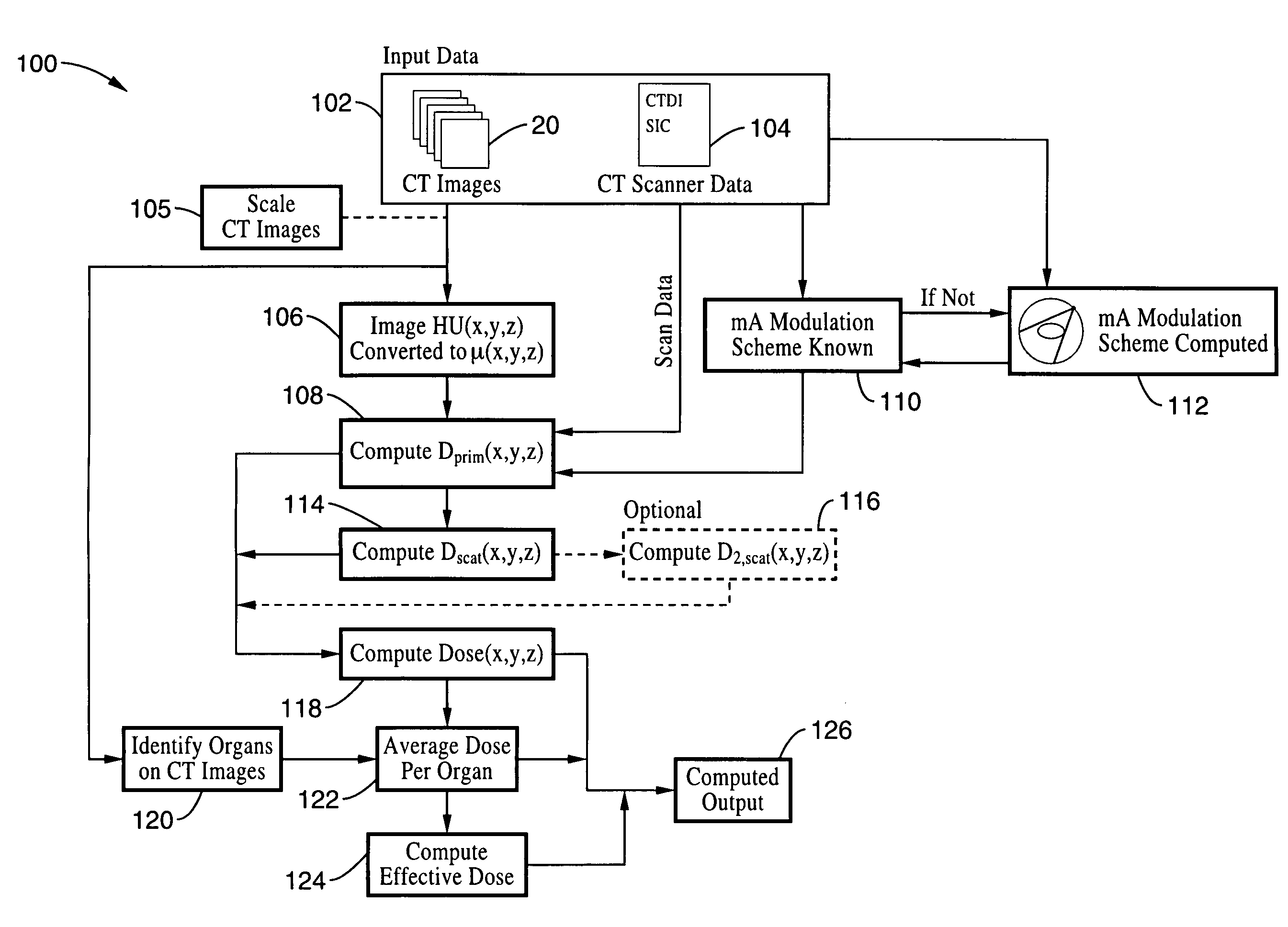
Method for computing patient radiation dose in computed tomography
ActiveUS20080292055A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputed tomographyX-ray
A system and method are disclosed for computing a radiation dose delivered to a patient during a computed tomography (CT) scan of the patient. The CT image dataset generated during the scan of the patient, and one or more parameters relating to a x-ray source are used to calculate the radiation dose delivered to the patient as a function of the CT image data set and the one or more parameters of the x-ray source. The radiation dose is generally found by calculating a primary x-ray dose distribution and scattered x-ray dose distribution from the CT image dataset and taking the sum of the primary x-ray dose distribution and scattered x-ray dose distribution.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
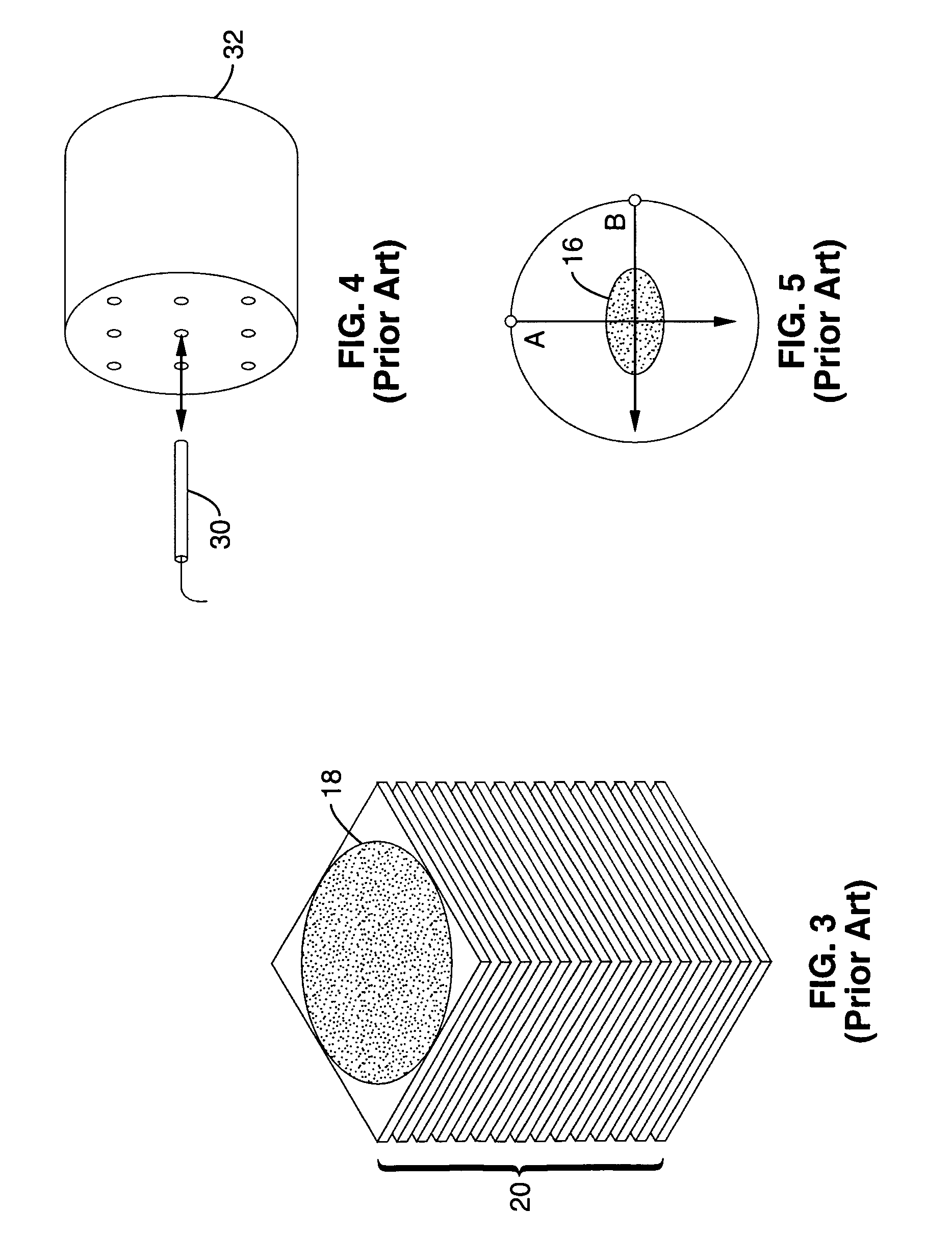
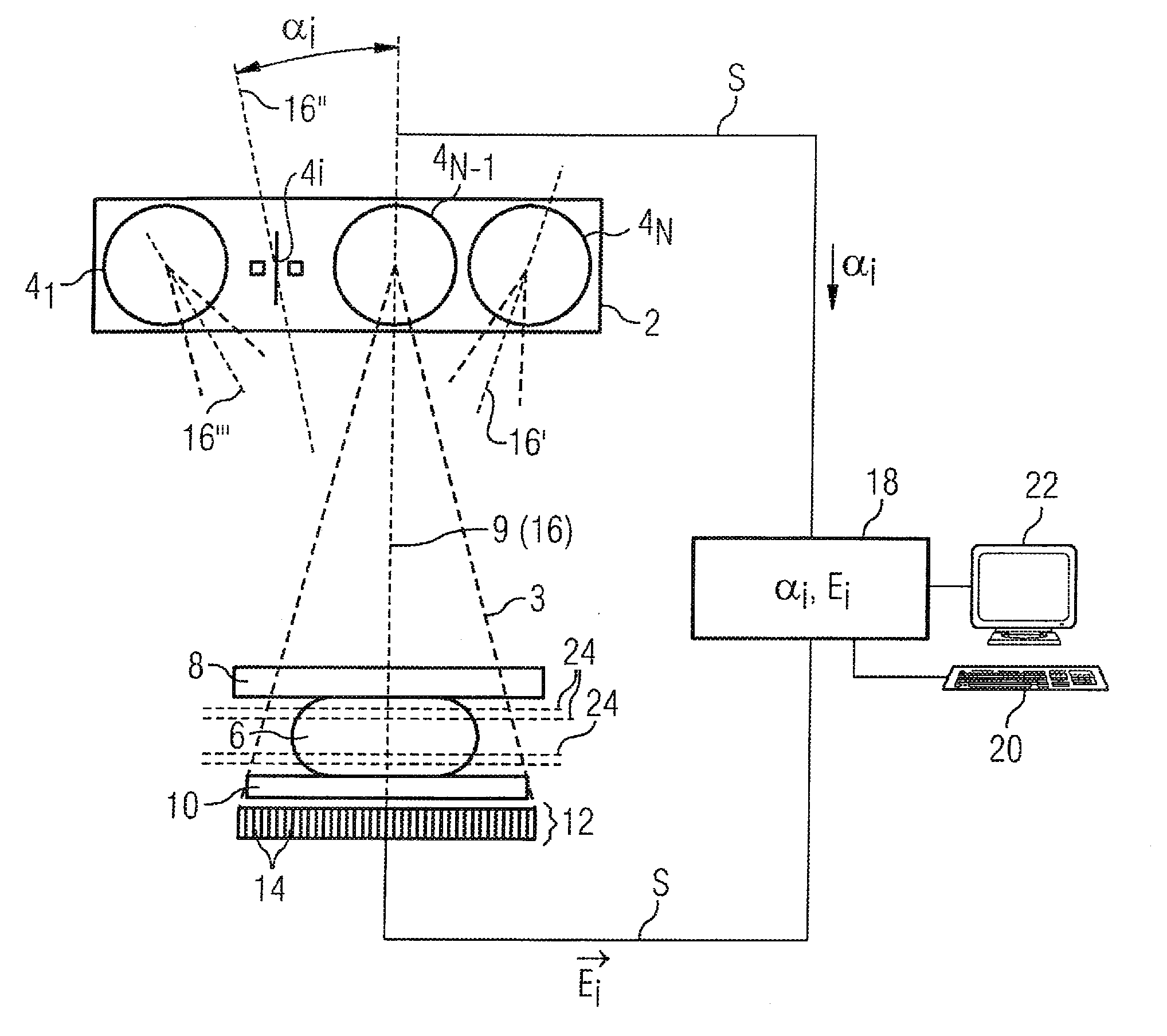
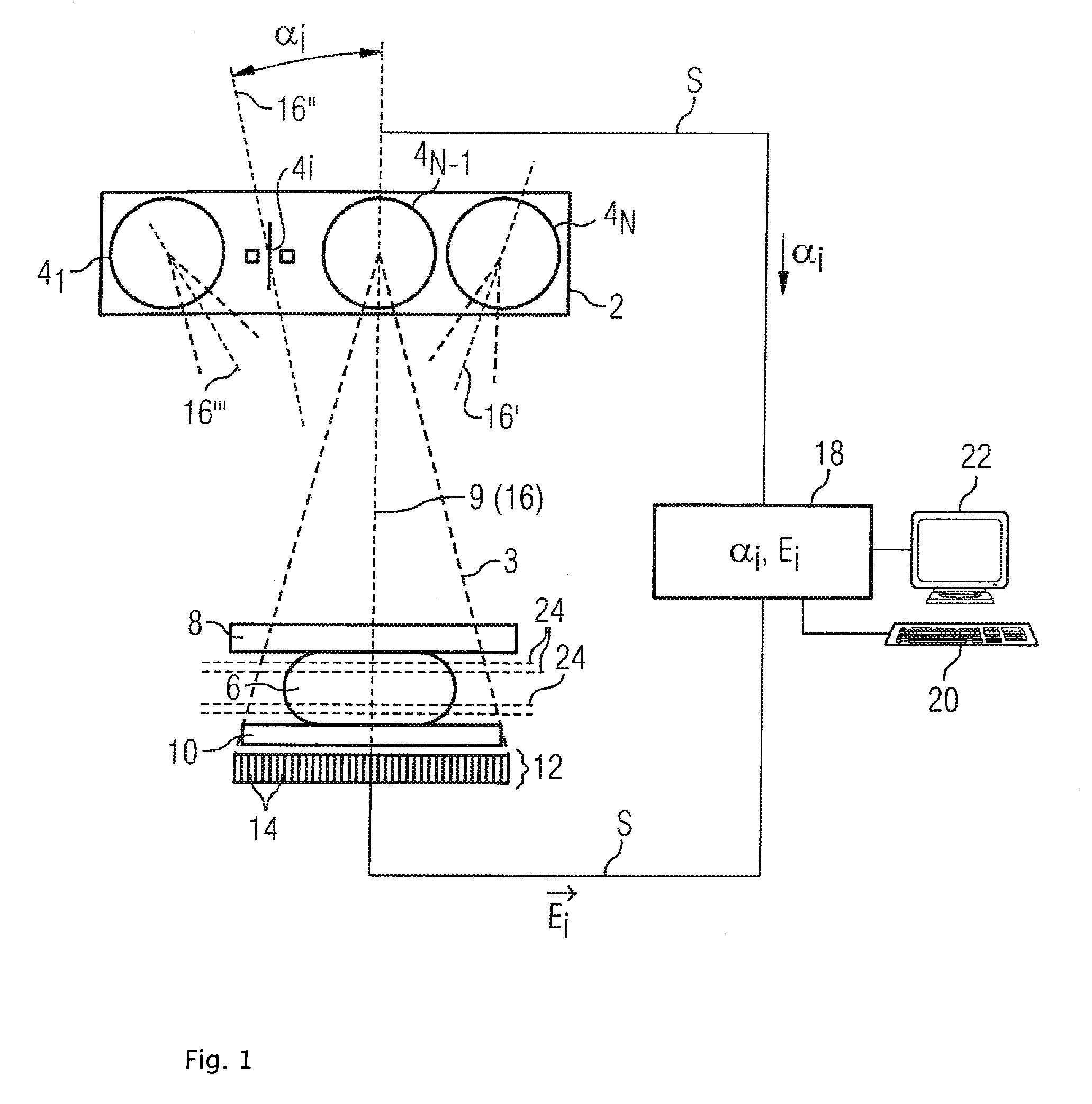
Method and device for producing a tomosynthetic 3D x-ray image
InactiveUS20100034450A1Increase doseLarge doseMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingProjection image3d image
In a method and device for producing a tomosynthetic 3D x-ray image, a number of 2D projection images of an examination subject are acquired using a fixed x-ray source. The x-ray source has multiple, individually controllable emitters that respectively emit a single x-ray dose from various different directions. The tomosynthetic 3D image is reconstructed from the individual 2D projection images, and at least one 2D projection image is composed of multiple individual images.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
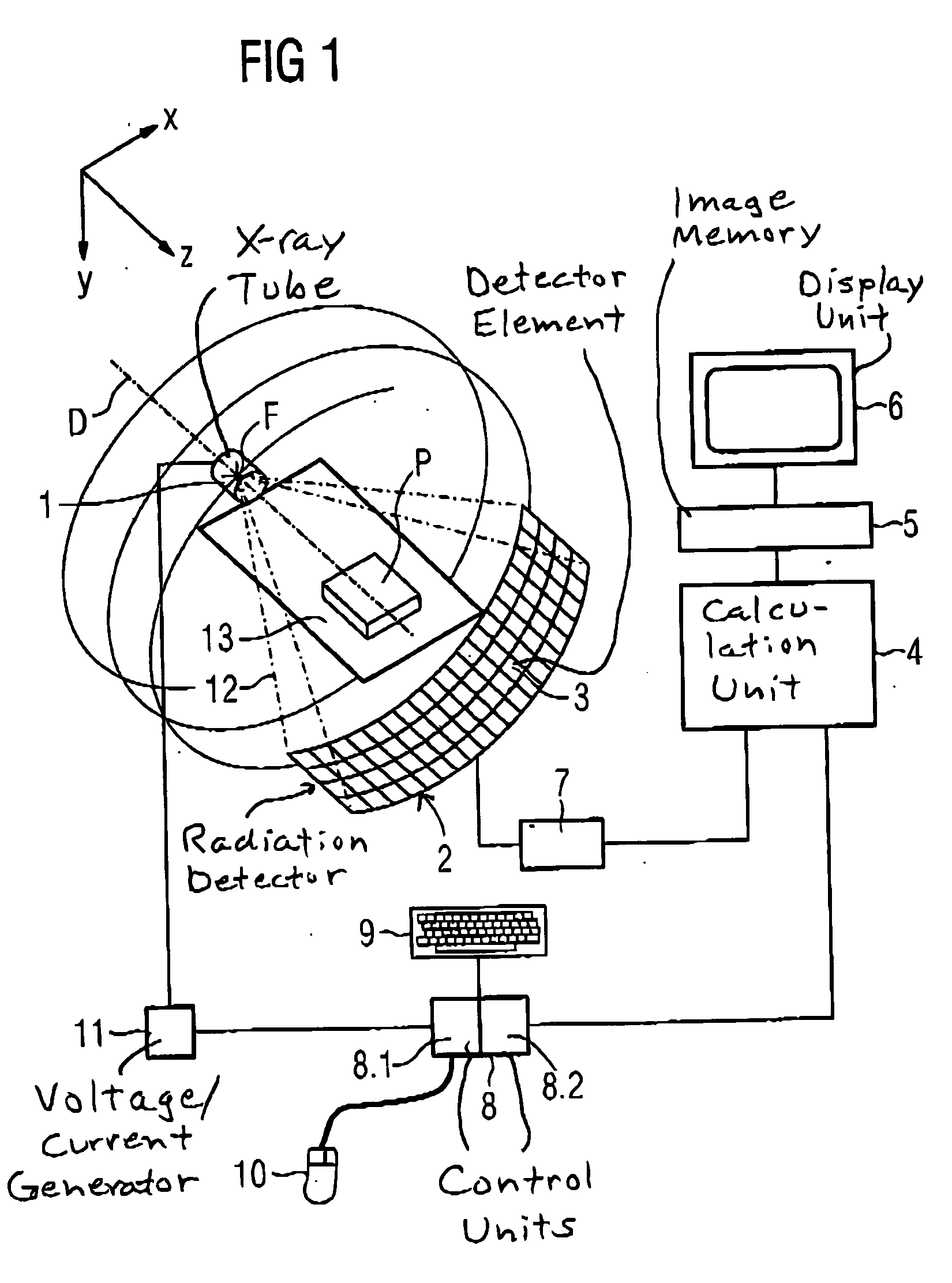
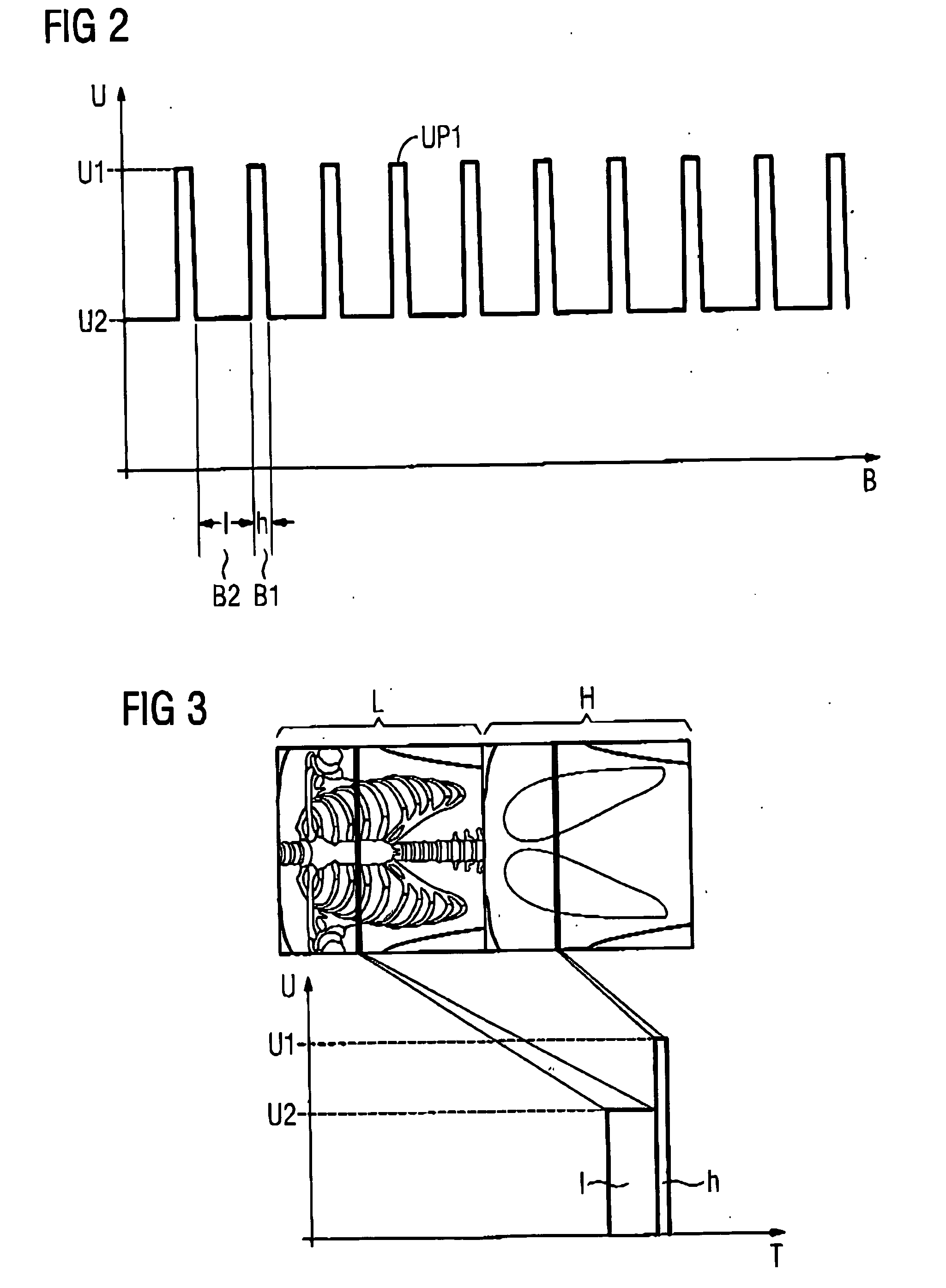
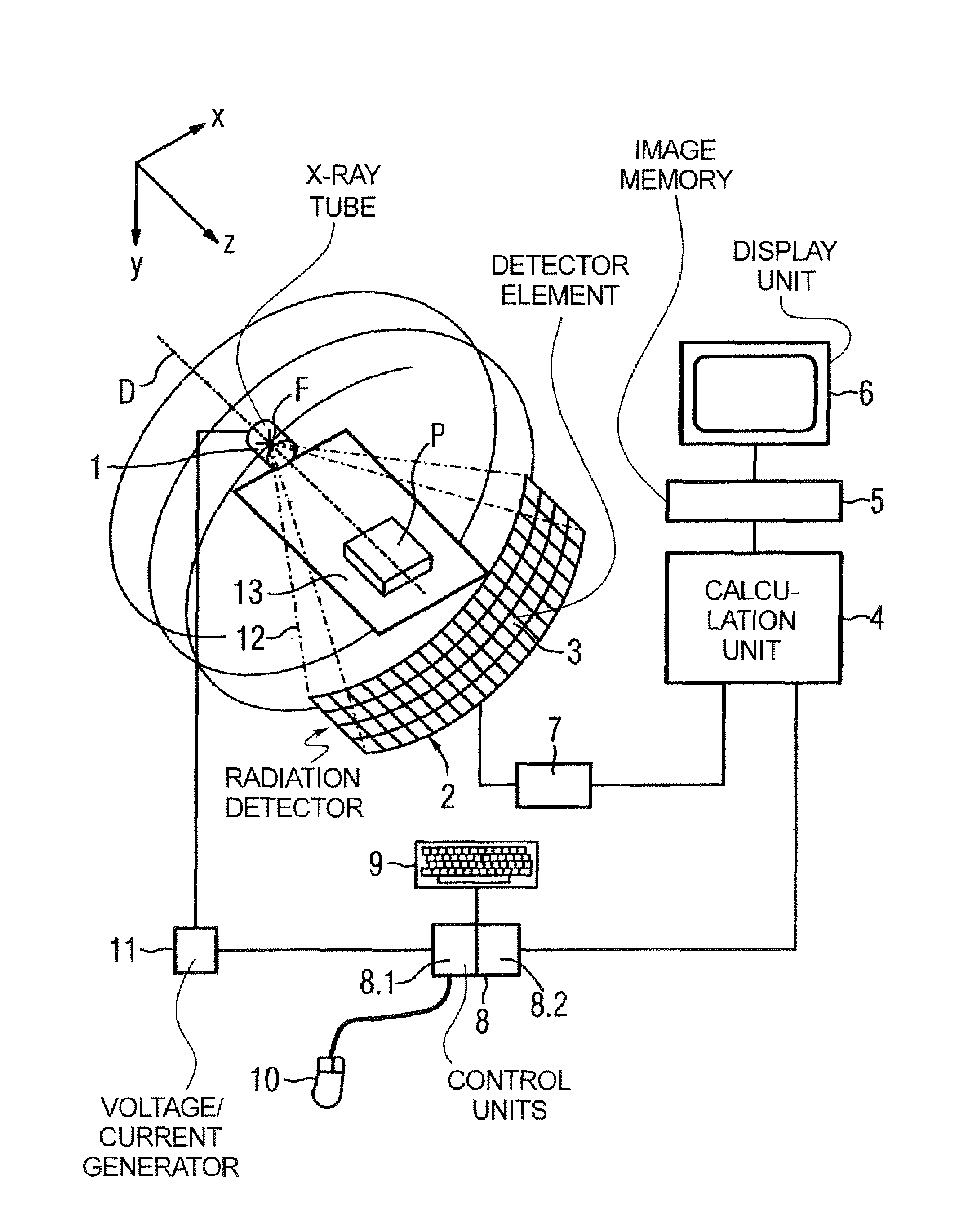
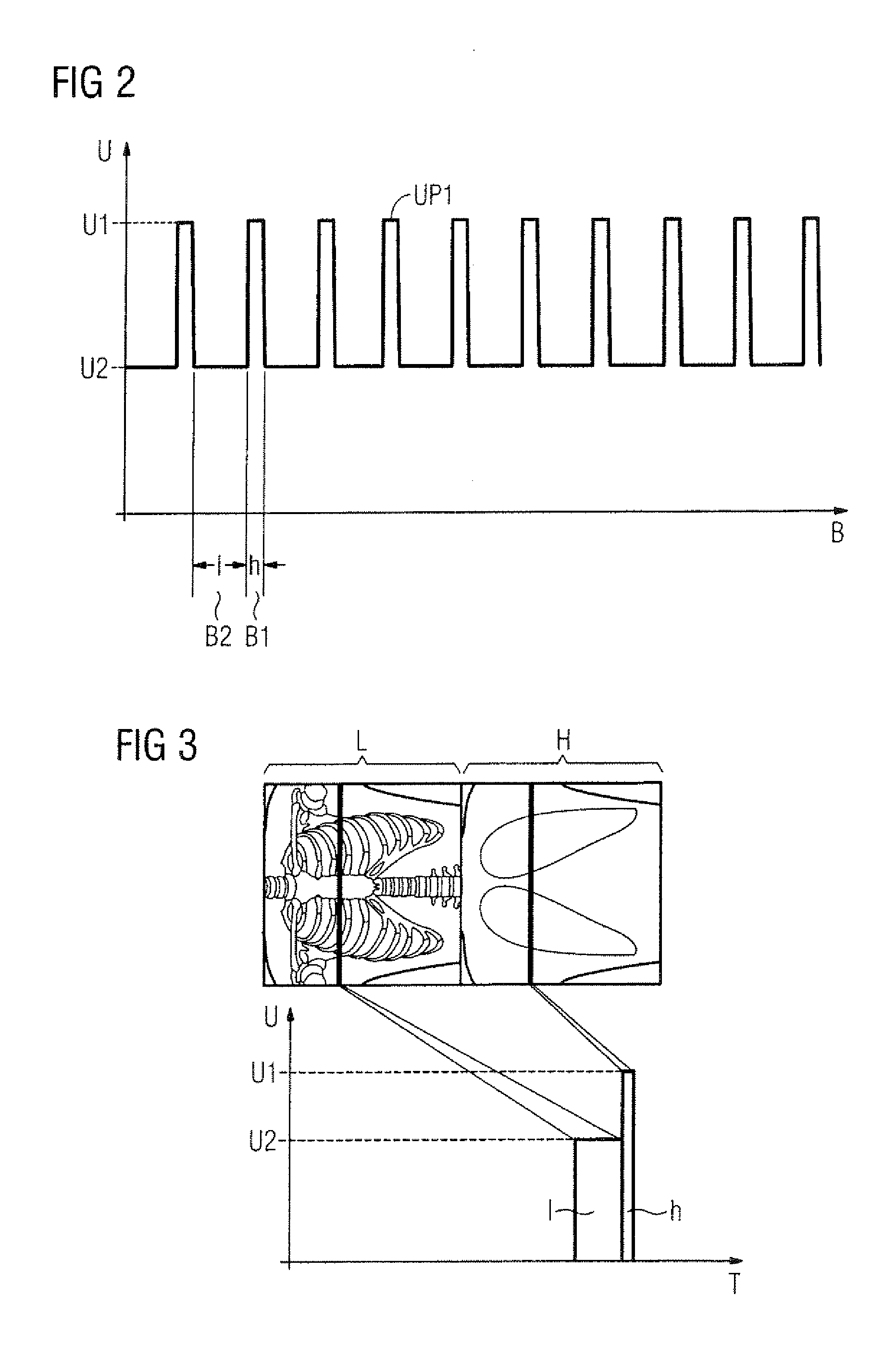
X-ray tomography apparatus and operating method for generating multiple energy images
ActiveUS20060109951A1Simple wayConstant currentMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHigh energyX-ray
In a tomography apparatus and a method for operating a tomography apparatus for generation of multiple energy images, in which high-energy projections and low-energy projections are acquired by alternating adjustment of a voltage and a further control variable (namely the current or the exposure time), given a set first voltage value and a set first control value of the further control variable, and given a set second voltage value and a set second control value of the further control variable, x-rays generated by an x-ray radiator exhibit essentially the same x-ray dose or photon flow.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and system for dynamic low dose X-ray imaging
A method and system for performing fluoroscopic imaging of a subject has high temporal and spatial resolution in a center portion of the captured dynamic images. The system provides for reduced X-ray dose to the patient associated with that part of the X-ray beam associated with a peripheral portion of the captured images although temporal, and in some embodiments spatial, resolution is reduced in the peripheral portion of the image. The system uses a rotating collimator to produce an X-ray beam having narrow wing portions associated with the peripheral portions of the image, and a broader central region associated with the high resolution center portion of the images.
Owner:FOREVISION IMAGING TECH LLC
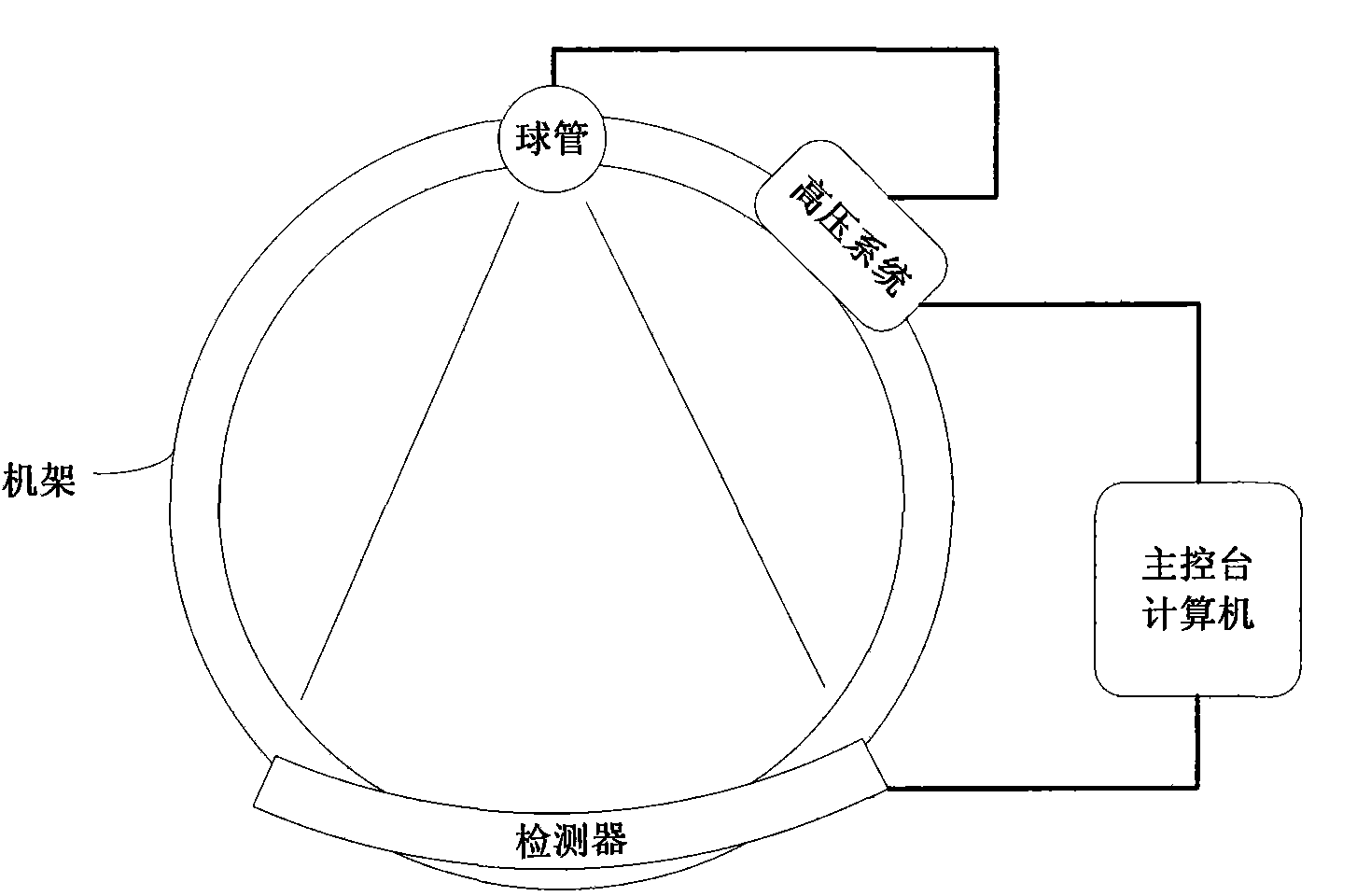
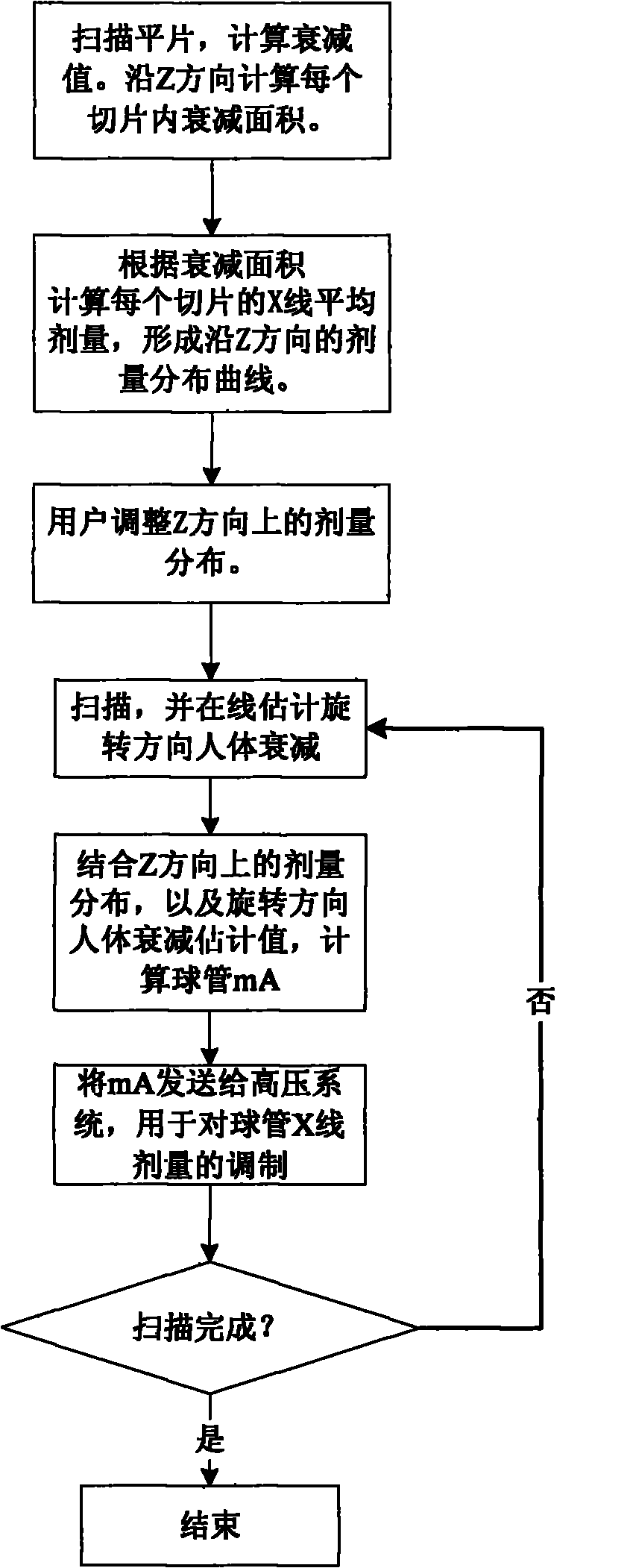
On-line dose modulation method of X-ray CT (Computed Tomography) machine
ActiveCN102100562AReduce overexposureReduce the problem of underexposureComputerised tomographsTomographyUltrasound attenuationComputed tomography
The invention relates to an on-line dose modulation method of an X-ray CT (Computed Tomography) machine, which comprises the following steps: scanning plain film data, extracting Z-direction attenuation information of a human body, and calculating the attenuation area of the human body in each cut film along the Z direction; according to the attenuation area, calculating the average X-ray dose in each cut film to form a dose distribution curve along the Z direction, and supplying to a user as an initial recommended value, so that the user can adjust the dose distribution in the Z direction as required; scanning a patient, and simultaneously carrying out on-line estimation on the attenuation value of the rotation direction of the patient to obtain an attenuation estimated value; combining the dose distribution in the Z direction with the attenuation estimated value of the human body in the rotation direction to calculate a bulb tube mA value; transmitting the mA value to a high-pressure system, and carrying out high-frequency dose adjustment; and finishing the on-line dose modulation process if the scanning is completed. The invention reduces the overexposure and underexposure possibly caused by assuming sine laws. Besides, the invention does not assume that what passes through the central passage is the maximum attenuation, so that the dose modulation is better matched with the shape of the actual object.
Owner:NEUSOFT MEDICAL SYST CO LTD
Radiation imaging apparatus and control method thereof, and radiation imaging system
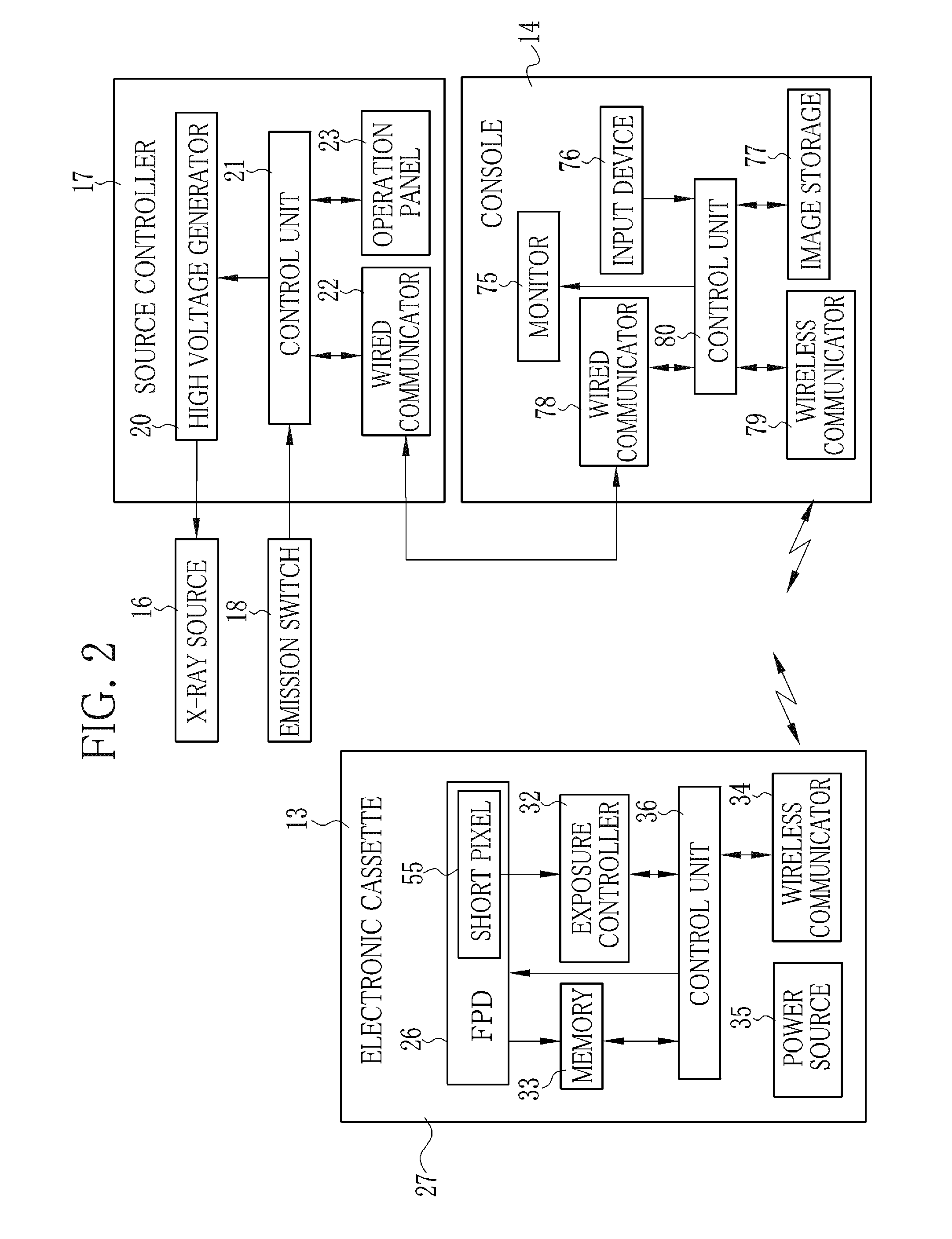
ActiveUS20130202086A1Improve image qualitySimple structureRadiation diagnostic image/data processingDosimetersRadiation imagingExposure control
An FPD detects an X-ray image of an object. The FPD includes a plurality of pixels arranged in its image capturing field. Each pixel receives X-rays emitted from an X-ray source, and outputs a pixel value in accordance with an X-ray dose applied thereto. A pixel determiner determines a minimum-value pixel out of the pixels based on the pixel values of the pixels. The minimum-value pixel is a pixel whose pixel value is the lowest. The pixel determiner sets the minimum-value pixel as an exposure control pixel. A comparator compares a first integrated value, which is an integrated value of the pixel values of the minimum-value pixel, with a predetermined first threshold value. The comparator performs X-ray emission control such that, when the first integrated value has reached the first threshold value, the X-ray source stops emitting the X-rays.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Method And Apparatus For Radiographic Imaging
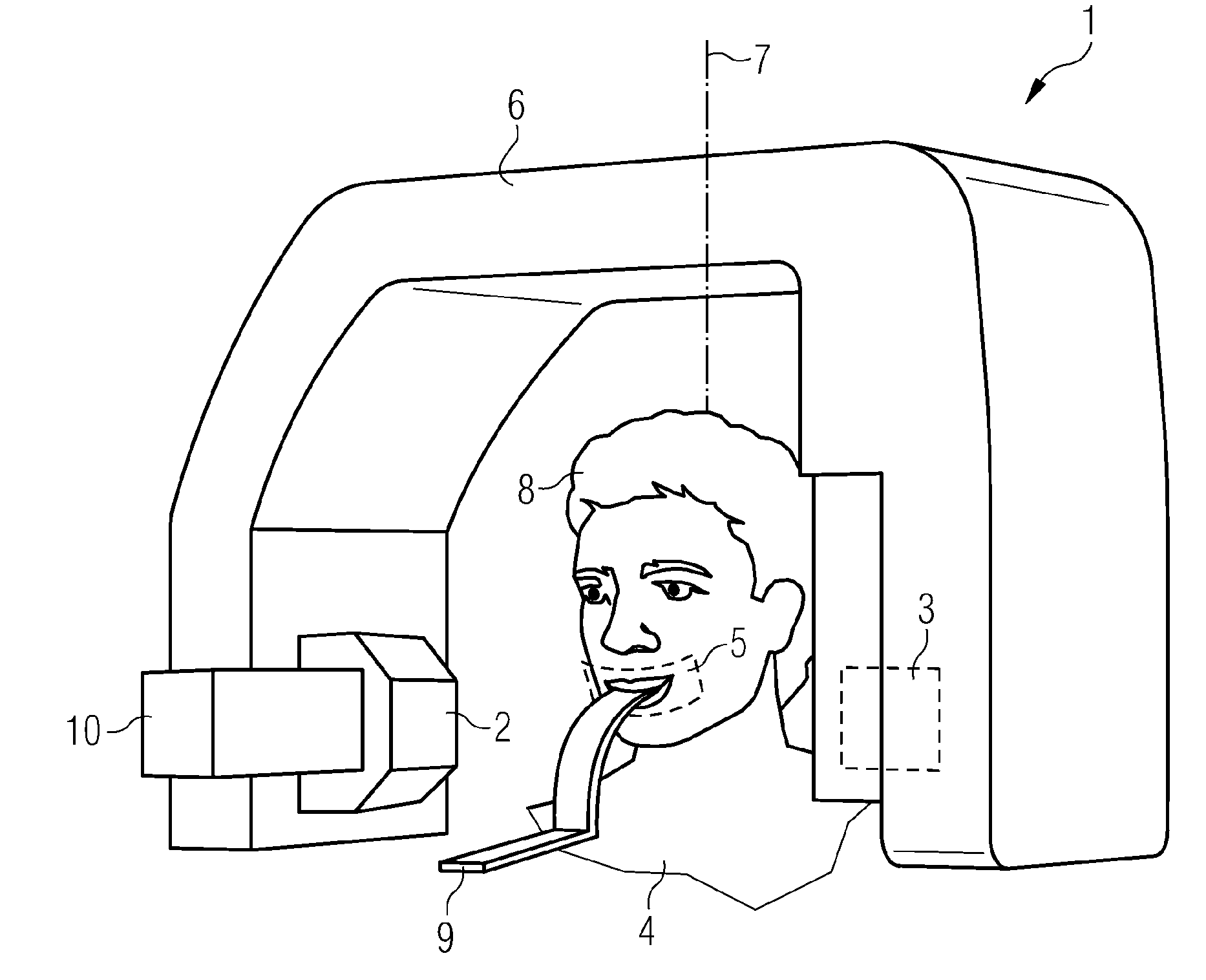
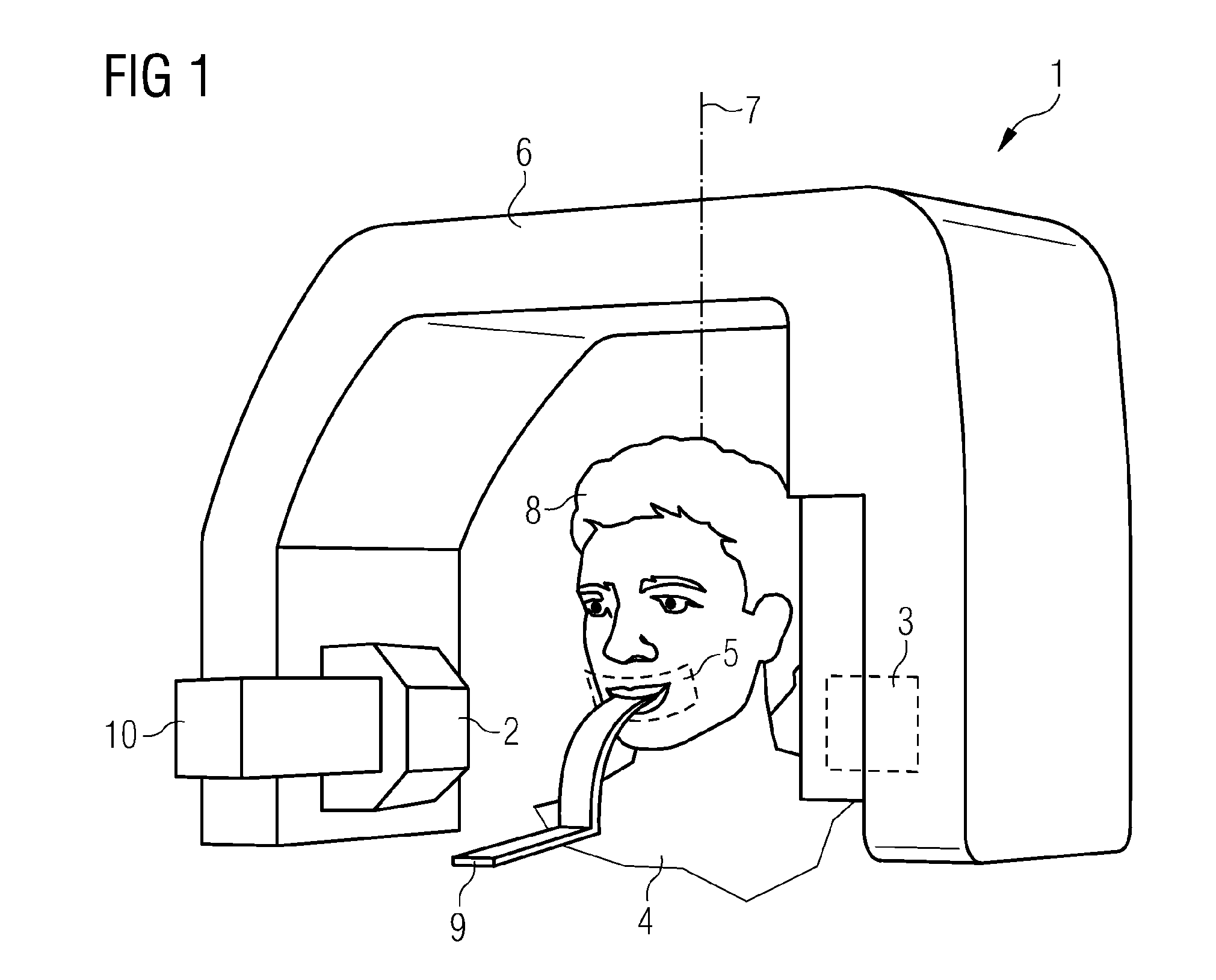
ActiveUS20090310741A1Precise positioningErrors caused by the inclination of the incisors can be avoidedPatient positioning for diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionReduced doseX-ray
A radiographic X-ray apparatus is equipped with multiple devices for the acquisition of anatomical data, in particular cameras. These devices are used to facilitate and automate the imaging process, providing: before exposure the automated identification of the specific anatomical features of the patient and the optimized presetting of the exposure technique factors and projection geometry, tailored on the actual anatomy of the patient; during exposure the optimized X-ray dose modulation, either automatically or selected by the operator, in order to correctly expose the various regions of interest, and accordingly impart reduced dose to other body parts, according to the actual anatomy of the patient and imaging requirements; after exposure the possibility to complement the radiographic image with additional information about the internal and external anatomy, providing valuable tools for the medical analysis and diagnosis.
Owner:CEFLA SOC COOP
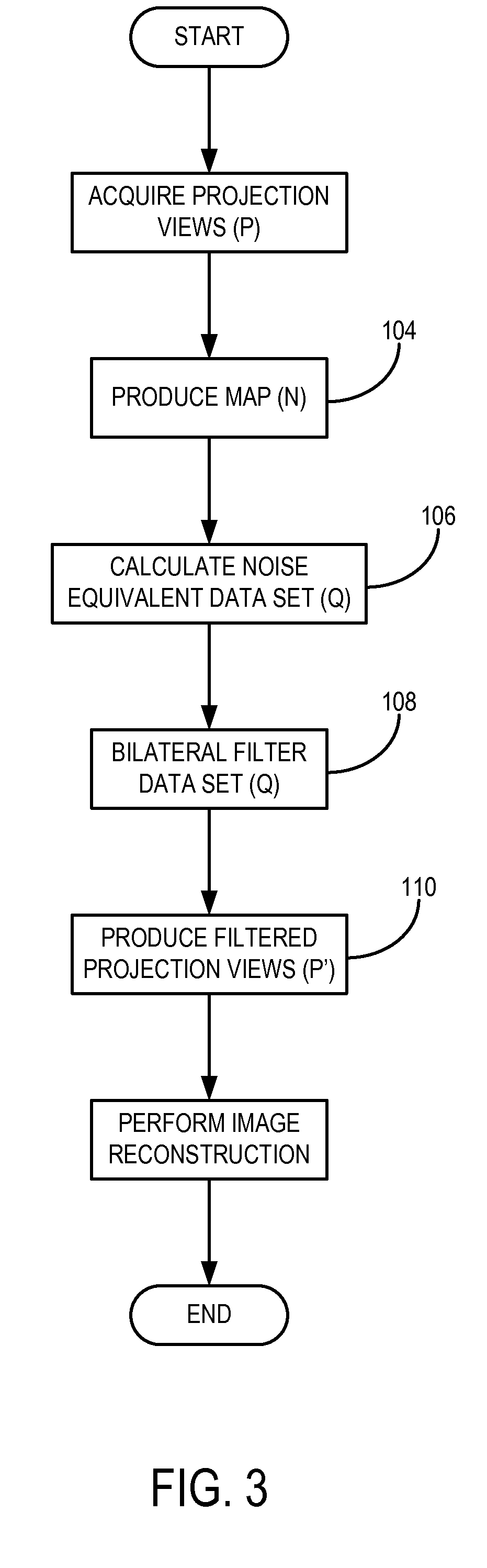
Projection-Space Denoising with Bilateral Filtering in Computed Tomography
ActiveUS20110286651A1EffectiveImprove filtering effectImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionComputed tomographyData set
Projection data acquired with an x-ray CT system is filtered using a bilateral filter to reduce image noise and enable the acquisition at lower x-ray dose without the loss of image diagnostic quality. The bilateral filtering is performed before image reconstruction by producing a noise equivalent data set from the acquired projection data and then converting the bilateral filtered values back to a projection data set suitable for image reconstruction.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Light element measurement
InactiveUS7006596B1Improve efficiencyFaster and accurate measurementX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayX ray dose
A spectrometer for detecting and quantifying elements in a sample. An exciter ionizes atoms in the sample, and the atoms thereby produce characteristic x-rays. A detector receives the x-rays and produces signals based on the x-rays. A filter system selectively blocks the x-rays from attaining the detector. The selective blocking of the x-rays is accomplished based on an energy of the x-rays. An analyzer receives the signals from the detector and detects and quantifies the elements in the sample based at least in part on the signals. In this manner, detector receives the light element x-rays, and the medium and heavy element x-rays are filtered out to avoid overwhelming the detector. This invention combines the large solid angle, high efficiency, and ability to measure the continuous background spectrum of the energy dispersive x-ray detector with the selectivity of the wavelength dispersive x-ray detector. It thus enables faster and more accurate measurement of light elements in thin films. This invention enhances the light element performance of a system by enabling higher throughput, lower e-beam and x-ray dose to the sample, and improved accuracy from the capability to measure the background radiation.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Method for the reconstruction of a body map
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Breast X-ray machine and method for realizing fully automatic exposure
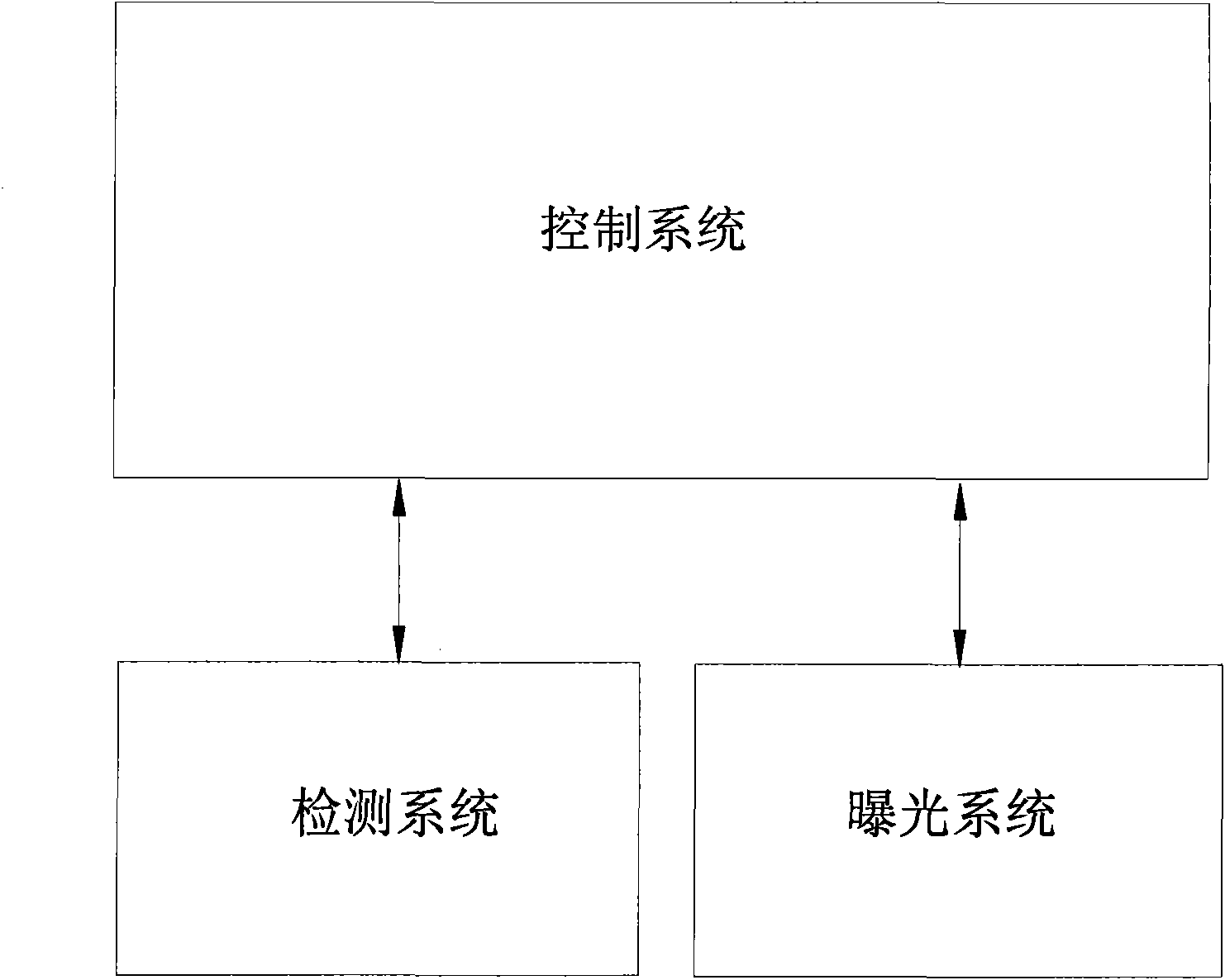
The invention relates to a breast X-ray machine comprising a control system, an exposure system which is connected with the control system and controlled by the control system, and a detection system, wherein the detection system comprises a breast information collection device for collecting breast information and an X-ray information collection device for collecting X-ray information; and the control system controls the exposure system according to the breast information and the X-ray information. The control system can intelligently and dynamically adjust an exposure parameter according to the X-ray information collected by the X-ray information collection device and control the exposure system to carry out fully automatic exposure so as to realize an optimal exposure effect. In addition, a method for realizing the fully automatic exposure of the breast X-ray machine calculates the dosage of the X-ray required by realizing the optimal exposure effect according to the remain information of the X-ray so as to dynamically adjust the exposure parameter until the dosage of the X-ray reaches the required dosage, thereby realizing the optimal exposure effect.
Owner:SINO MEDICAL DEVICE TECH
Radiographic imaging control apparatus and method
ActiveUS7120229B2Improve image processing capabilitiesSimple processX-ray apparatusMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationSoft x rayX-ray
An X-ray imaging control apparatus acquires radiographic data obtained from an X-ray imaging apparatus which controls an X-ray dose upon X-ray imaging by detecting the X-ray dose in one or a plurality of detection regions, and displays a radiographic image on the basis of the acquired radiographic data. At this time, detection region information indicating the position and range of each detection region used in the X-ray imaging apparatus upon generating the radiographic data is acquired. Based on this detection region information, an image indicating each detection region is superimposed on the displayed radiographic image.
Owner:CANON KK
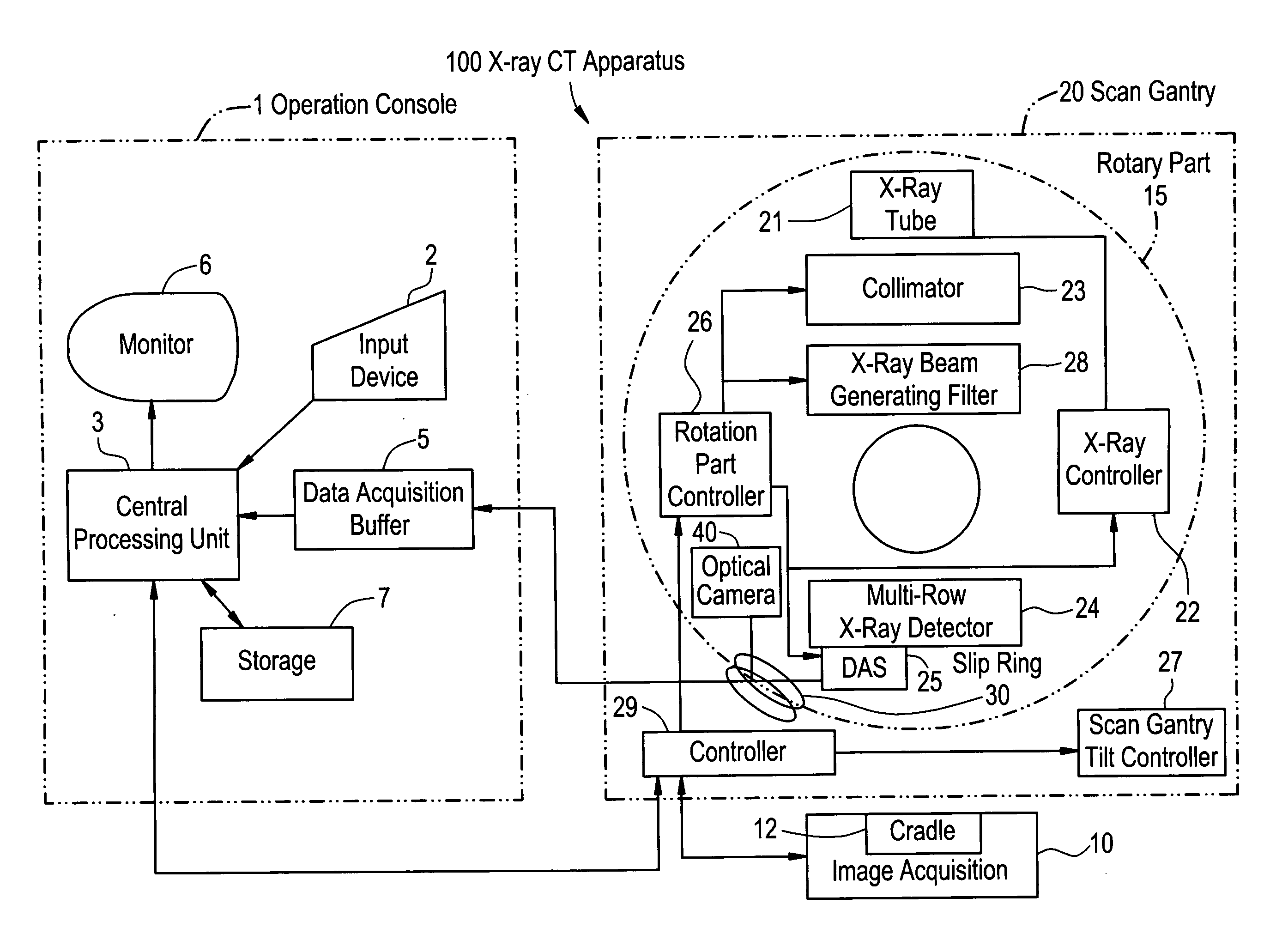
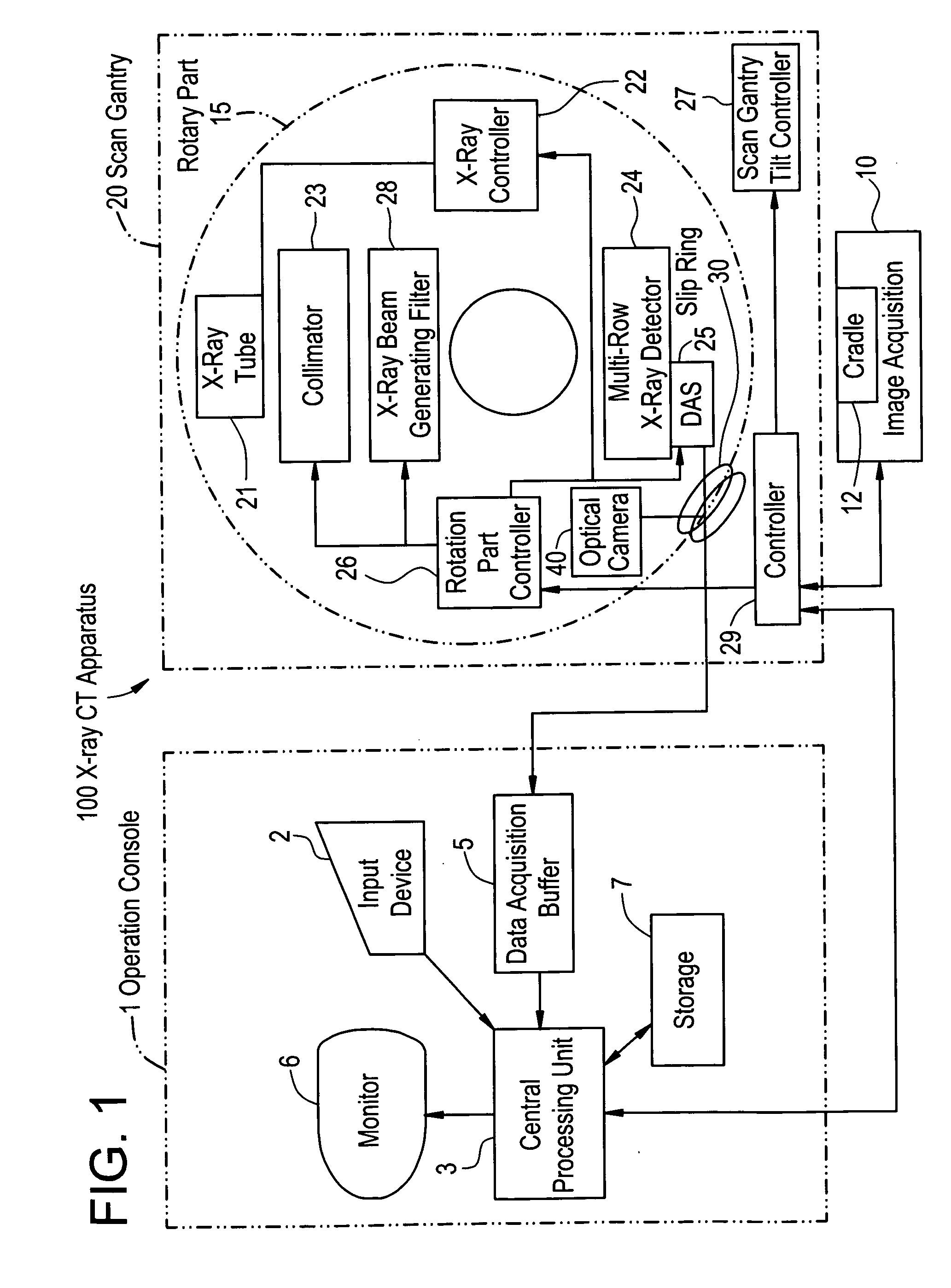
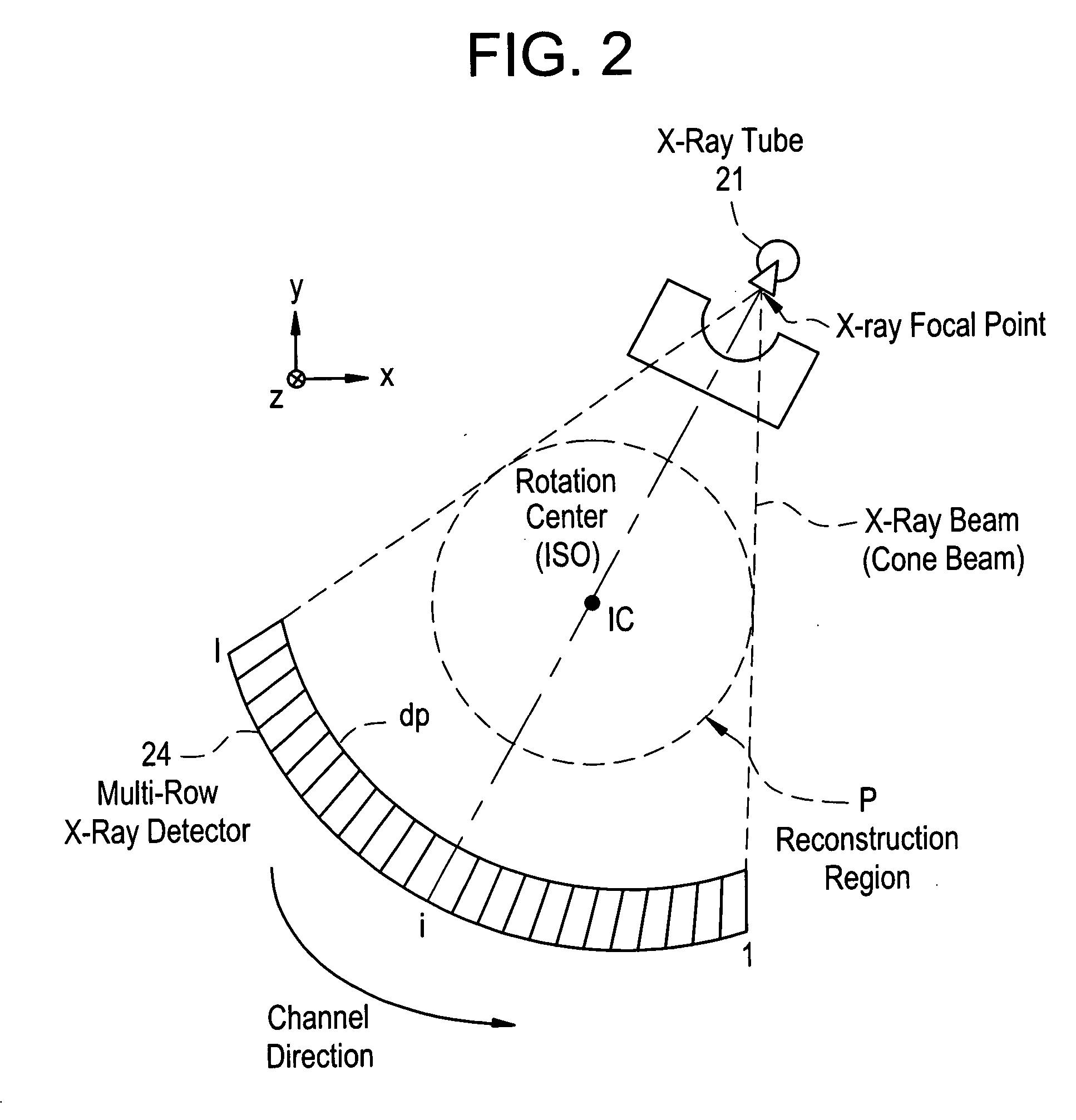
X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20070053480A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHelical scanX-ray
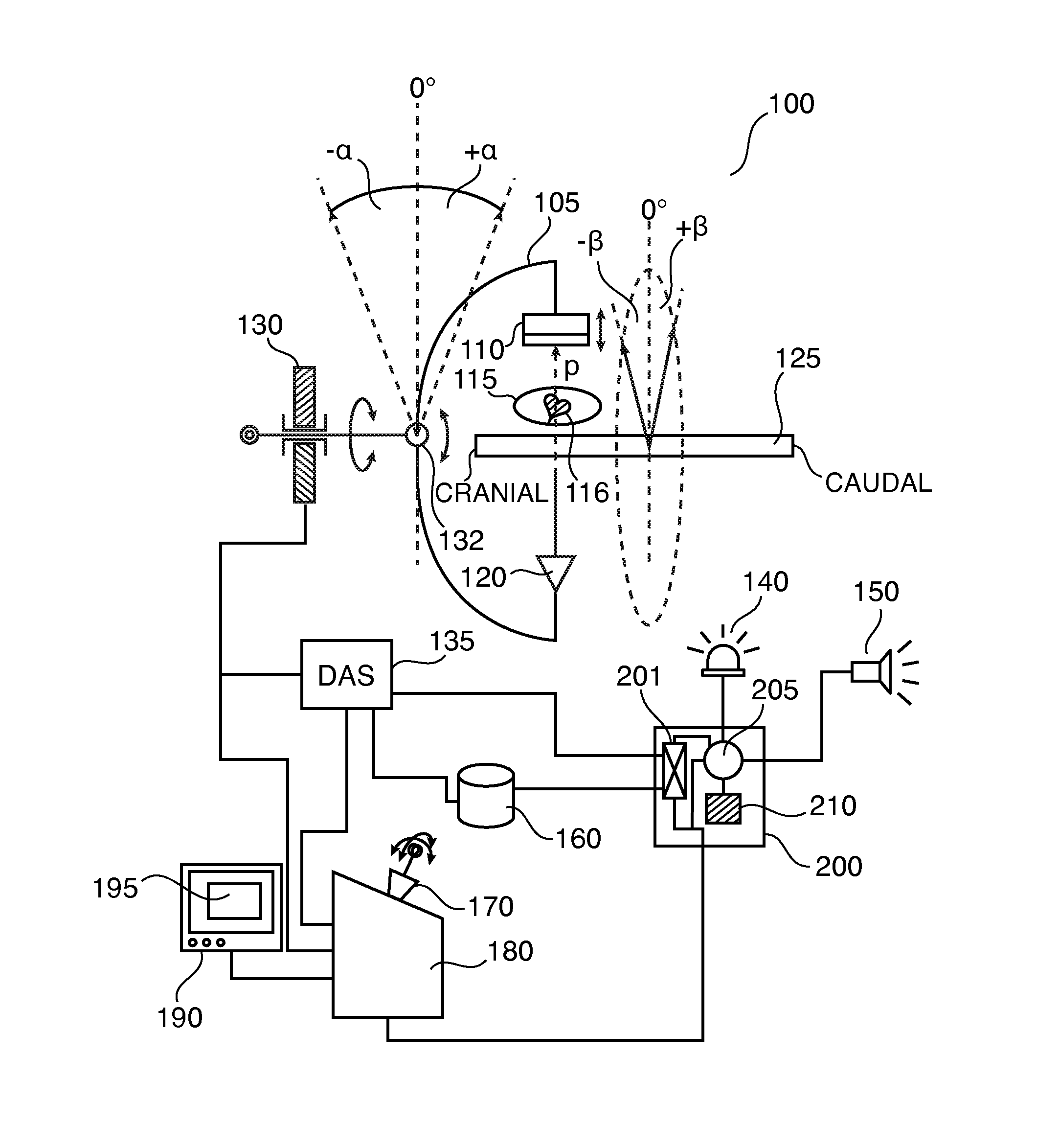
This invention provides an X-ray CT capable of presenting information of exposure to the operator by displaying X-ray dose information of each of regions of interest to be scanned by an X-ray CT apparatus, thereby encouraging reduction in exposure and optimization. X-ray dose information of each region to be scanned by a conventional scan (axial scan), a cine scan, a helical scan, or a variable-pitch helical scan of an X-ray CT apparatus is displayed so that the operator can recognize the X-ray dose information before acquisition of an image of a subject. The X-ray dose information can be predicated with higher precision and displayed by using a dose prediction value obtained by an interpolation value and an extrapolation value of the first or higher order on at least three or more kinds of phantom measurement values, not a simple prediction value such as a zero-th order interpolation value or a zero-th order extrapolation value obtained by using measurement values of two kinds of phantoms like in the present CTDI display.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
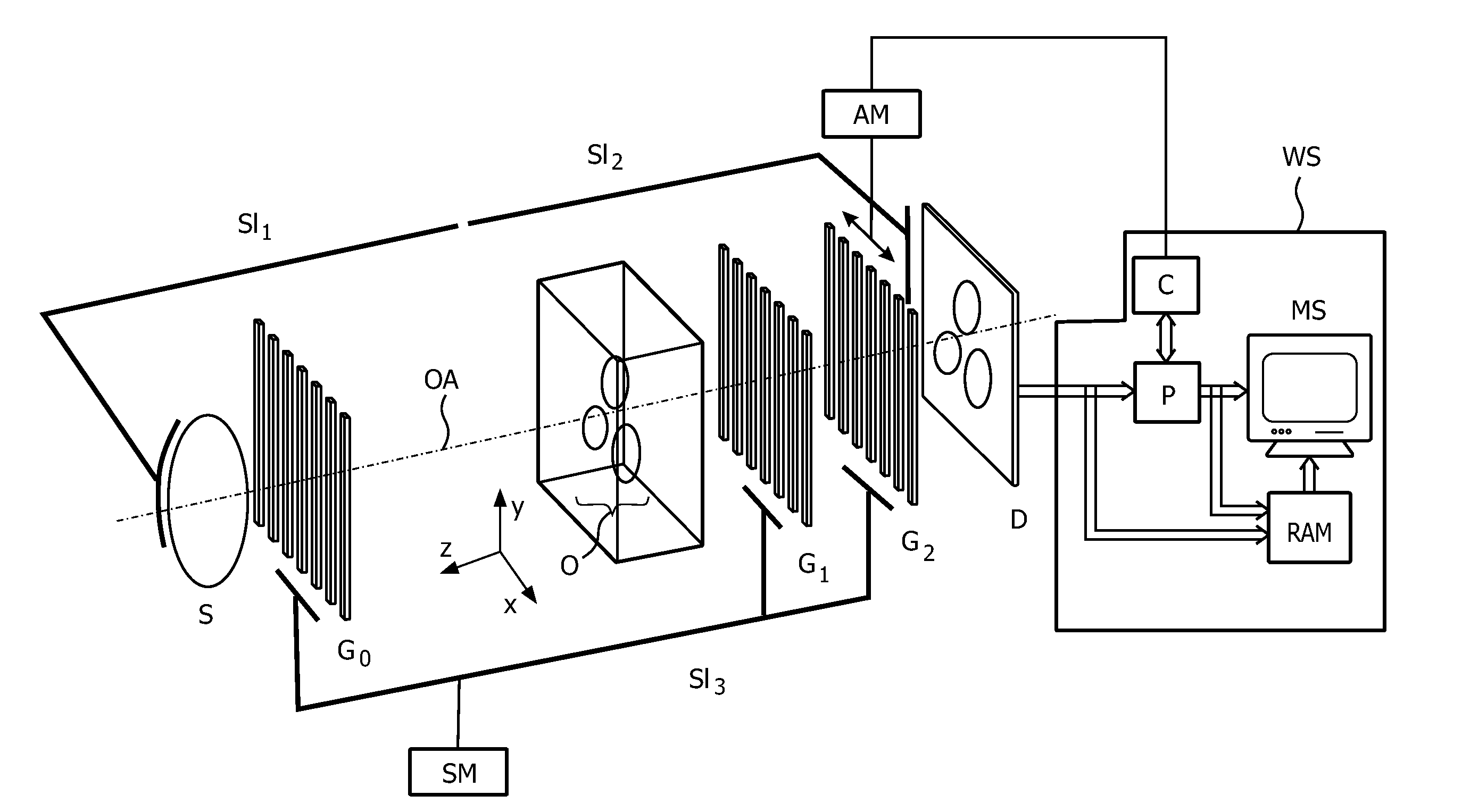
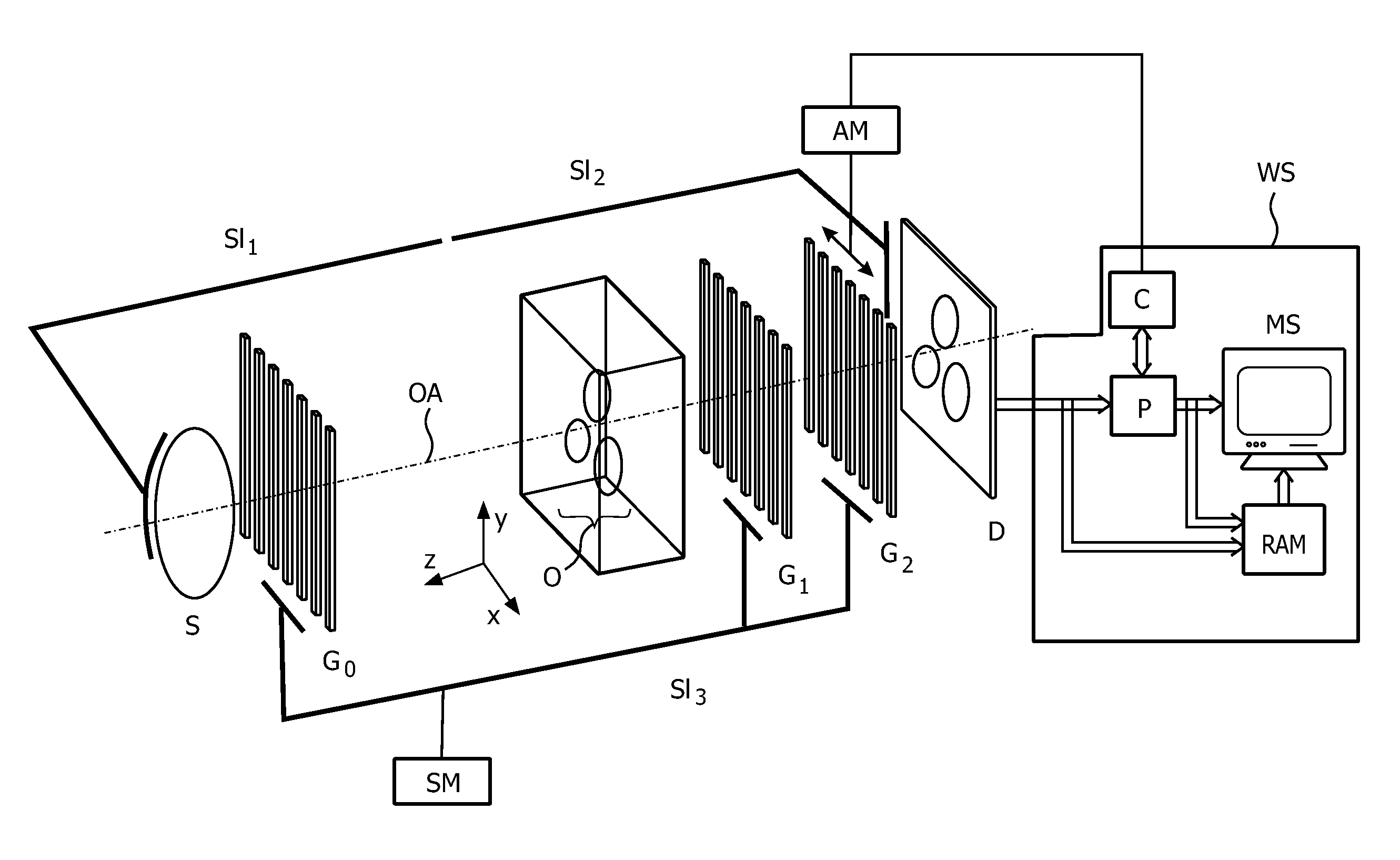
Phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS20120243658A1High contrast-to-noise ratioReduce exposureRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusLarge fovGrating
X-ray devices for Phase Contrast Imaging (PCI) are often built up with the help of gratings. For large field-of-views (FOV), production cost and complexity of these gratings could increase significantly as they need to have a focused geometry. Instead of a pure PCI with a large FOV, this invention suggests to combine a traditional absorption X-ray-imaging system with large-FOV with an insertable low-cost PCI system with small-FOV, The invention supports the user to direct the PCI system with reduced FOV to a region that he regards as most interesting for performing a PCI scan thus eliminating X-ray dose exposure for scanning regions not interesting for a radiologist. The PCI scan may be generated on the basis of local tomography.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
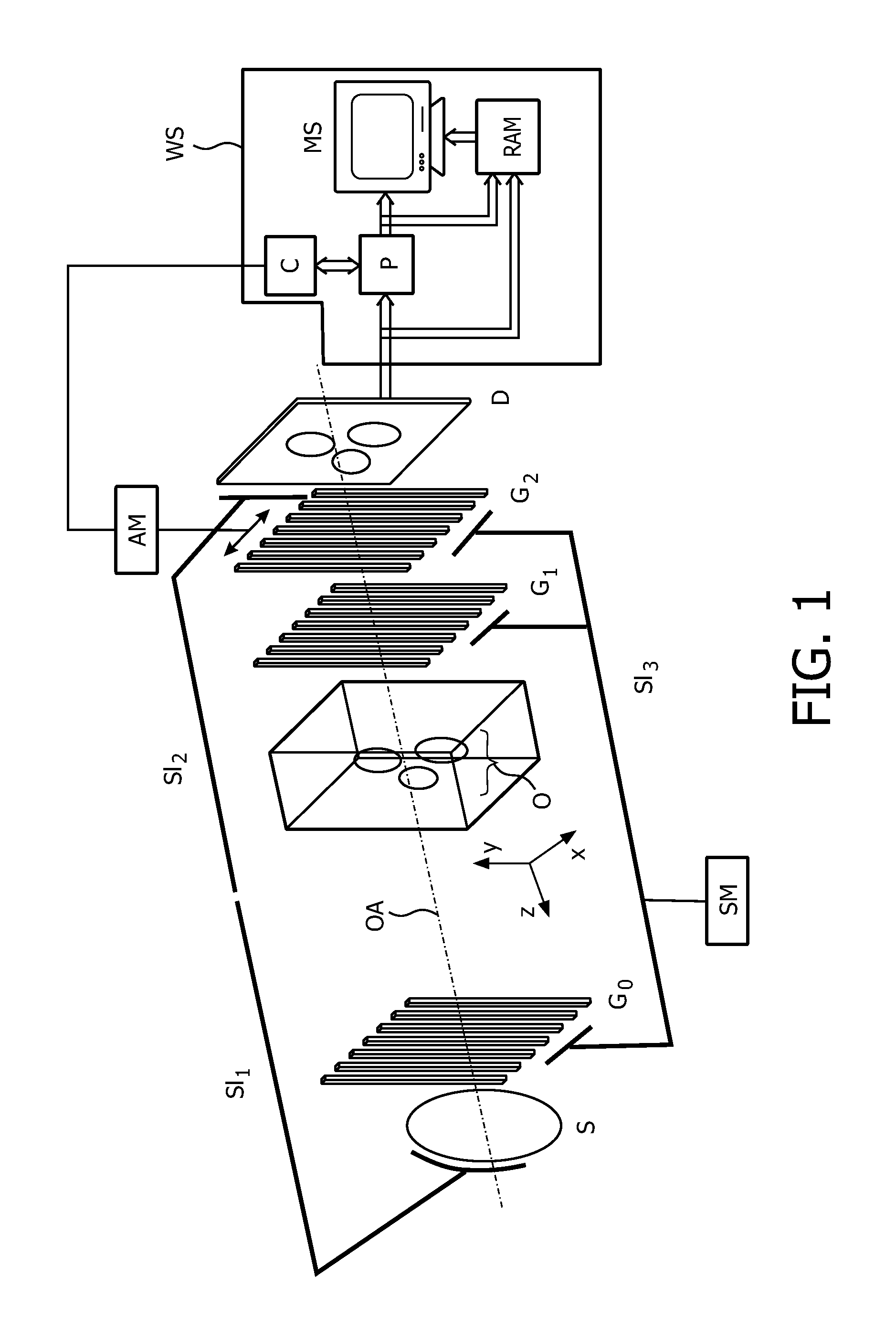
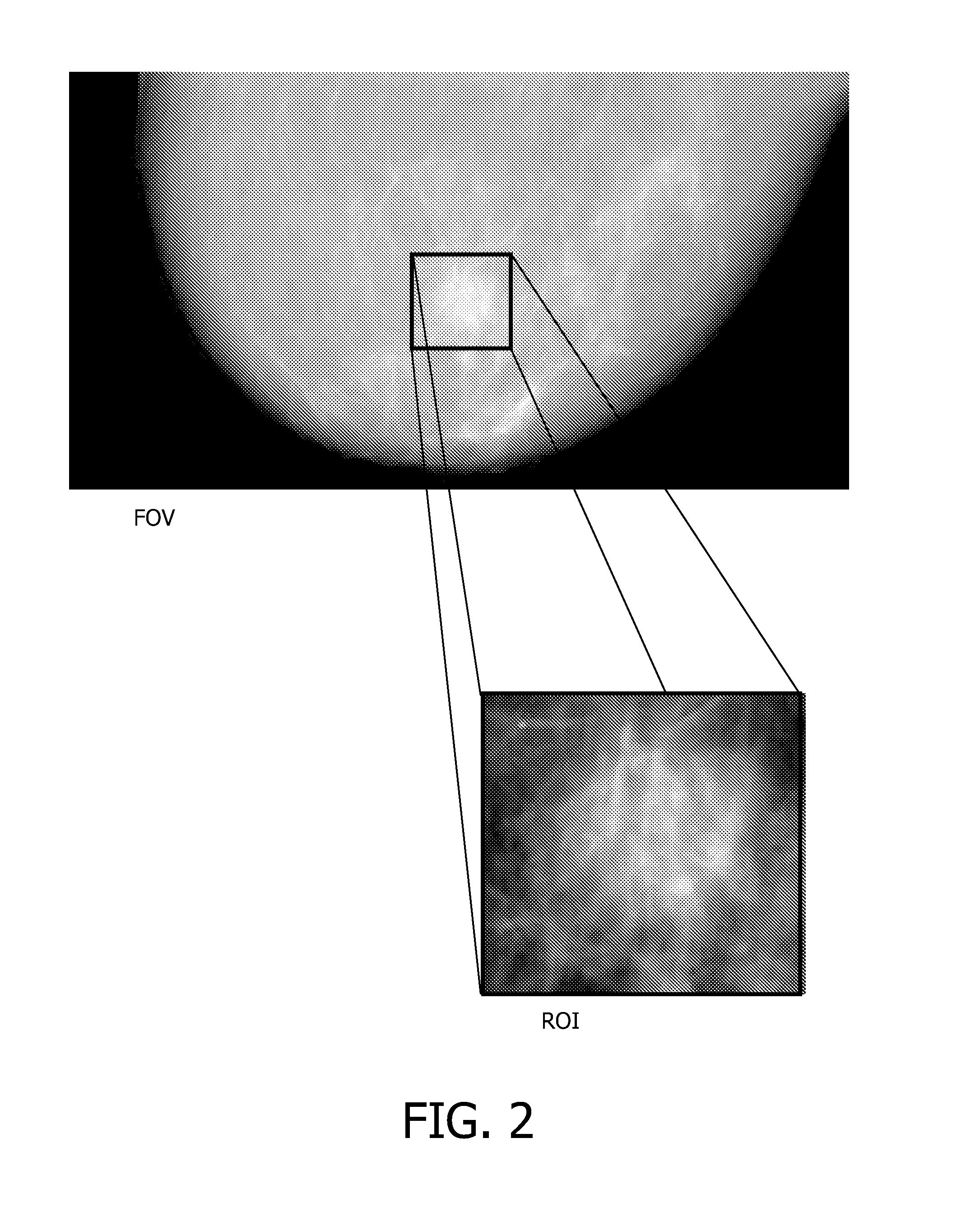
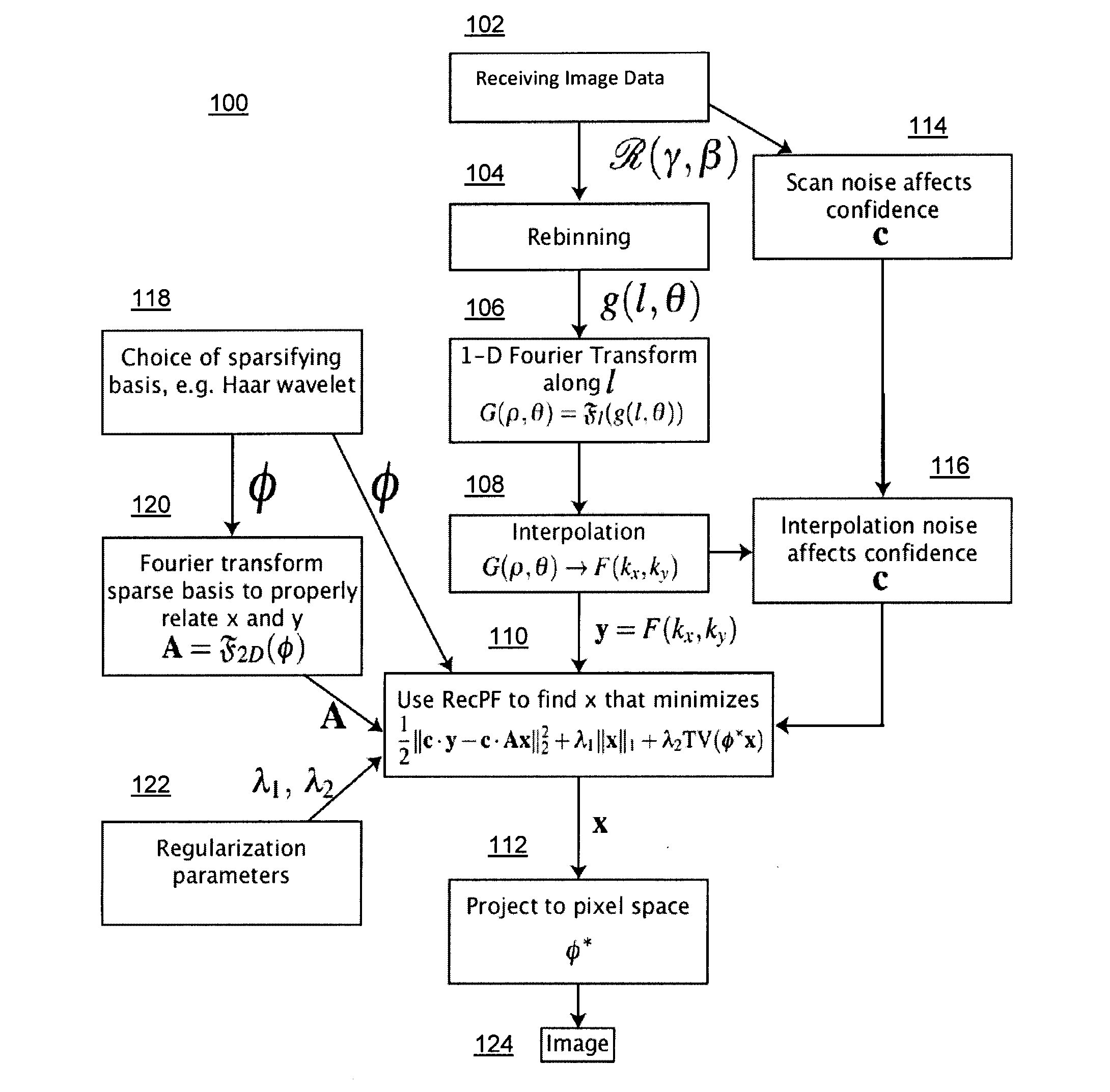
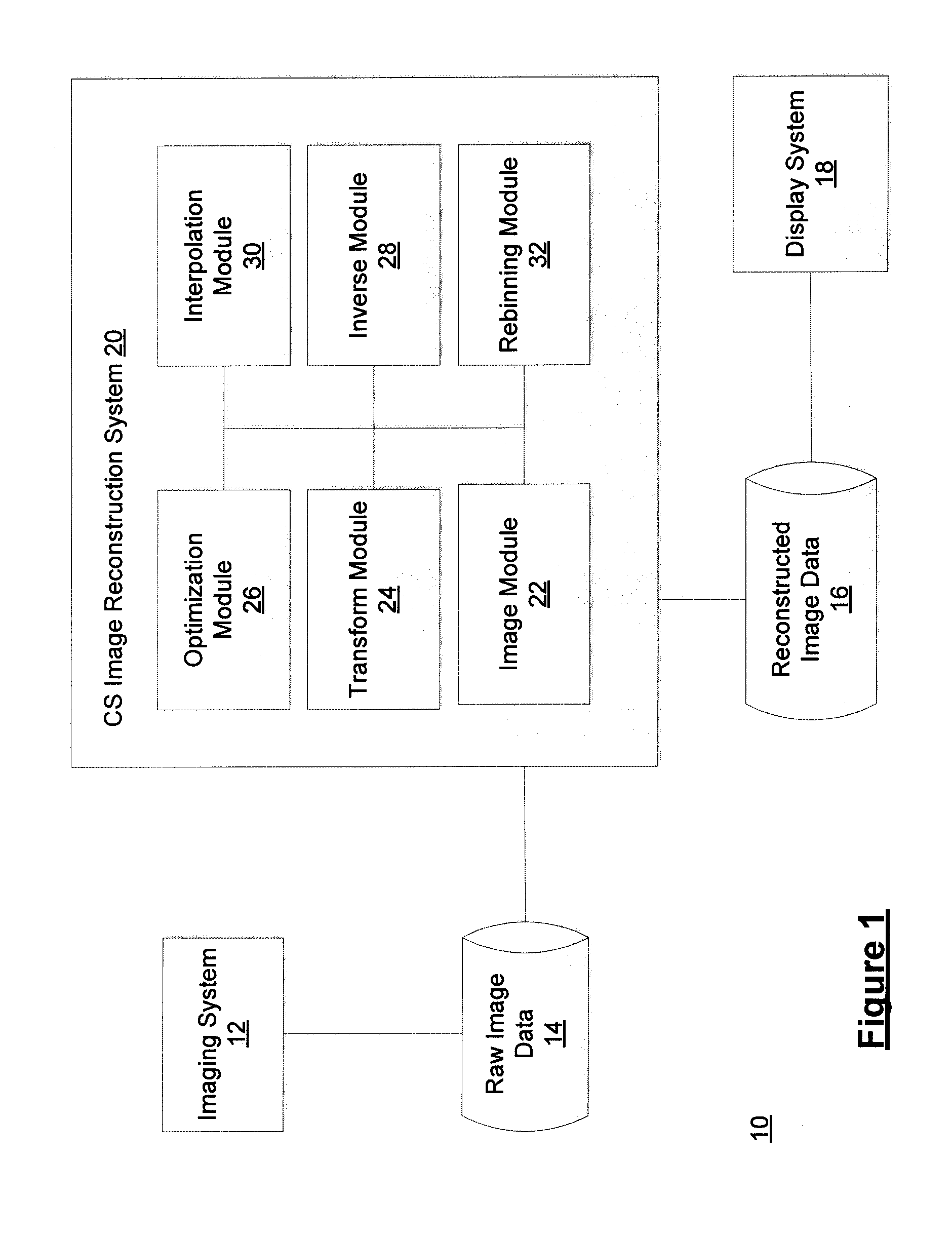
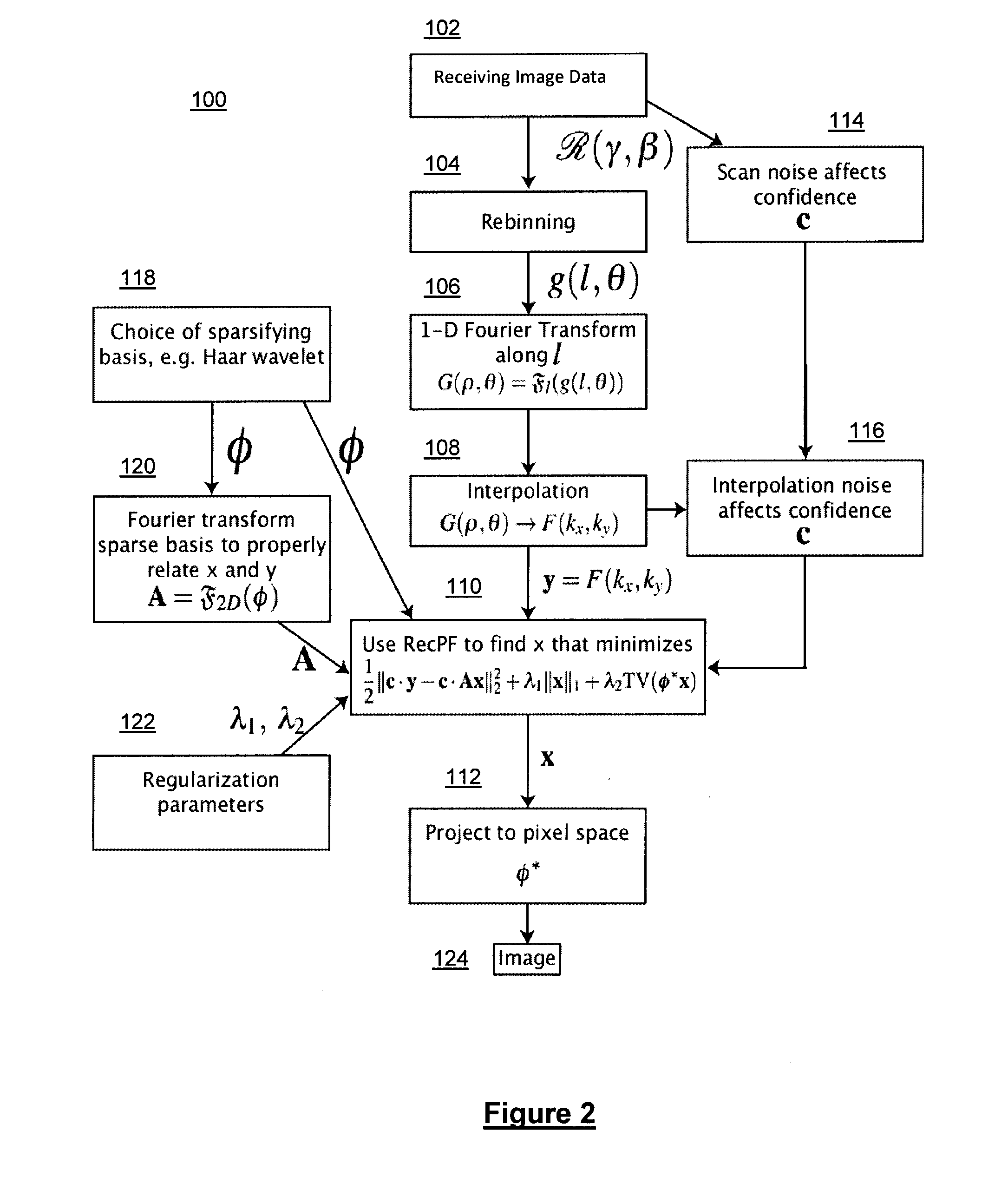
Method and system for compressed sensing image reconstruction
ActiveUS20150187052A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic Radiology ModalityComputation complexity
A Compressed Sensing (CS) based image reconstruction method and system is described herein which may be used to reduce the X-ray dose radiation in Computed Tomography (CT) or to decrease the scan duration in MR imaging (MRI). Methods and systems described herein may address problems that have hindered the clinical usage of CS, i.e. computation complexity and modeling problems. Using the described algorithm, high quality images may be recovered from undersampled data which may help to reduce the scan time and the exposed invasive radiations. Using the same set of data in conventional image reconstruction algorithms (e.g. Filtered Back Projection (FBP) in CT) may cause severe streak artifacts and may take significantly more time using Graphics Processing Units (GPU) and parallel clusters with the conventional CS-based methods. This method can be used other imaging modalities using Radon transform (such as C-Arm and electron tomography, for example).
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
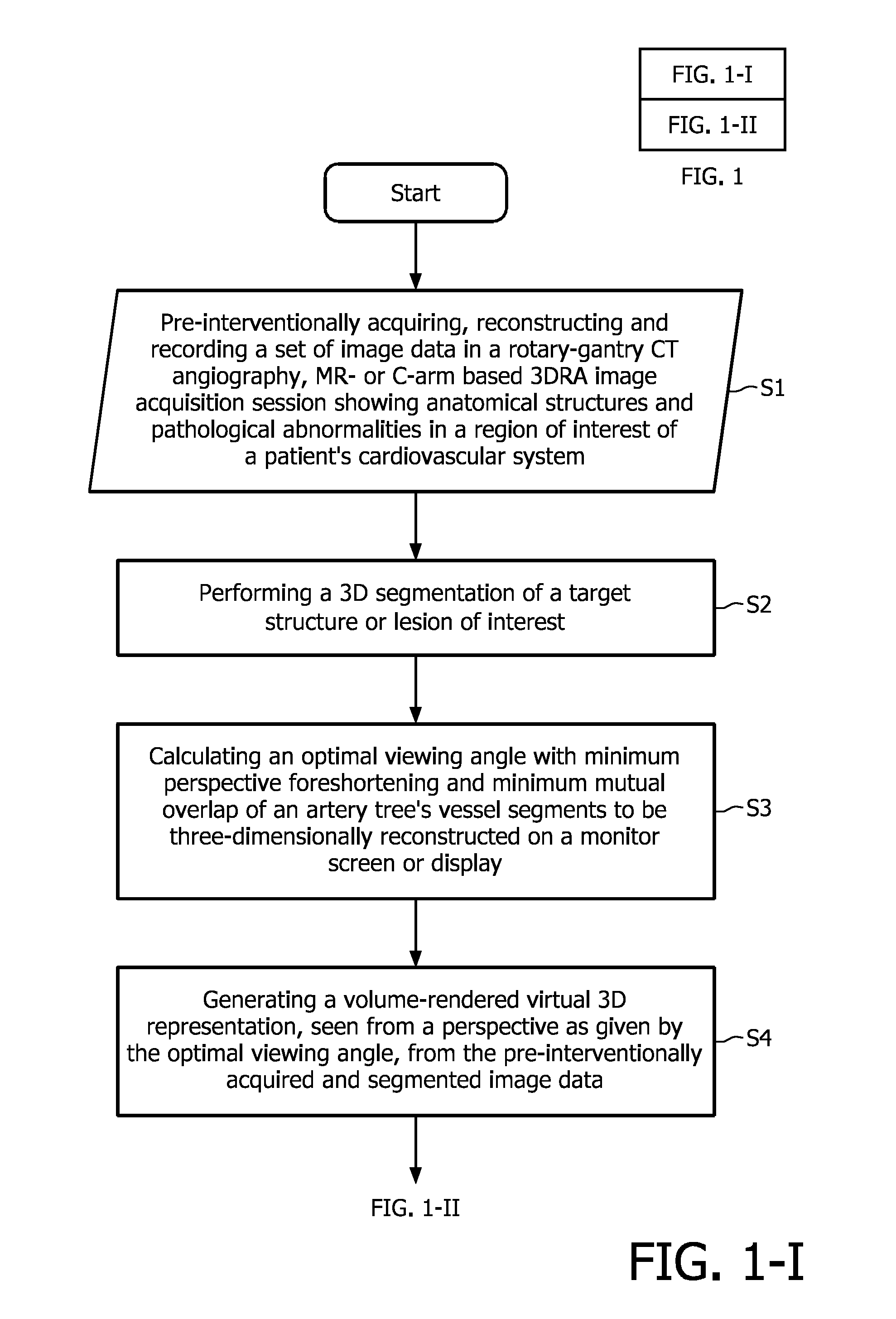
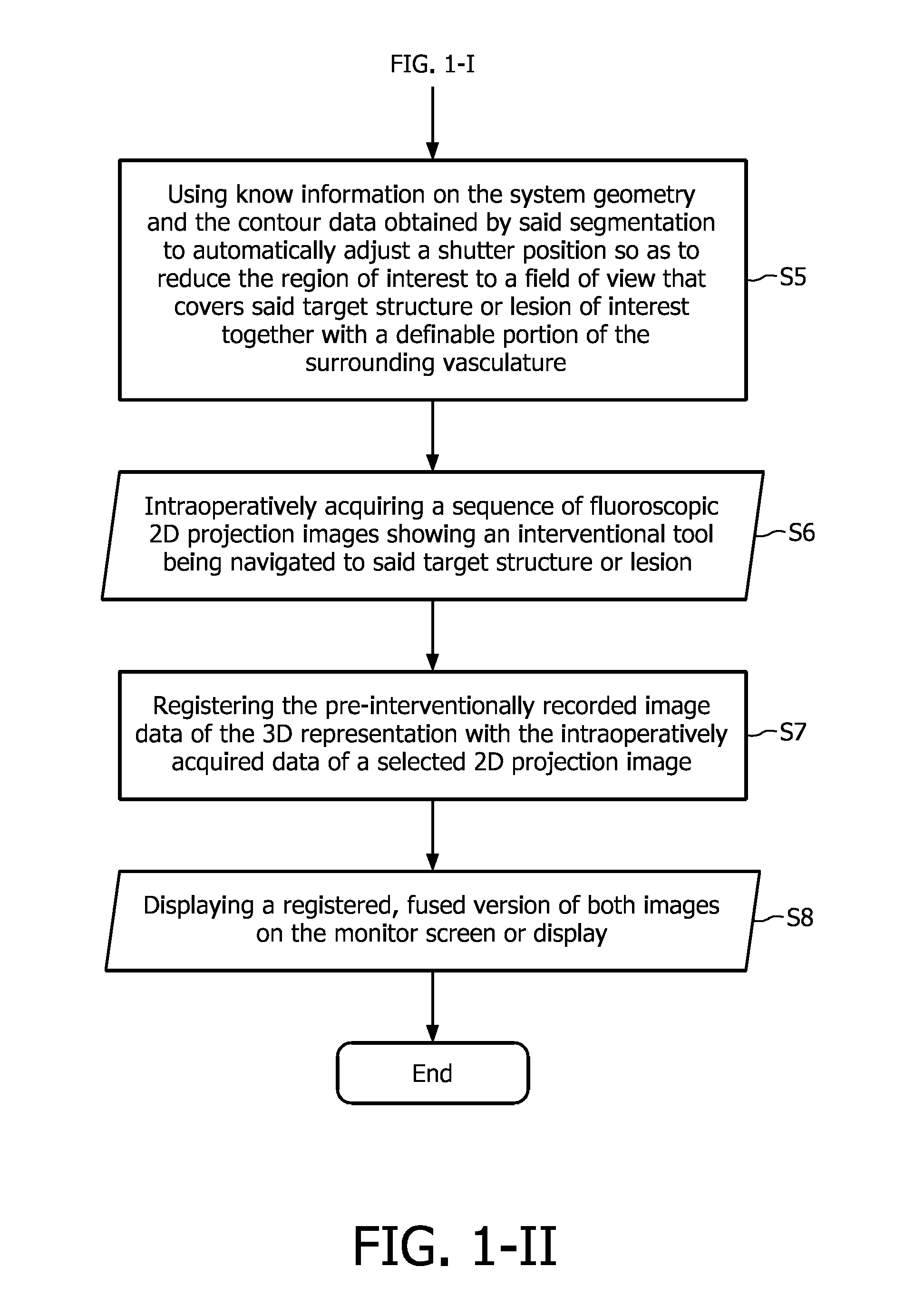
Angiographic image acquisition system and method with automatic shutter adaptation for yielding a reduced field of view covering a segmented target structure or lesion for decreasing X-radiation dose in minimally invasive X-ray-guided interventions
ActiveUS9280837B2Reduce radiation doseImprove directionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomography3d rotational angiography3d segmentation
The present invention refers to an angiographic image acquisition system and method which can beneficially be used in the scope of minimally invasive image-guided interventions. In particular, the present invention relates to a system and method for graphically visualizing a pre-interventionally virtual 3D representation of a patient's coronary artery tree's vessel segments in a region of interest of a patient's cardiovascular system to be three-dimensionally reconstructed. Optionally, this 3D representation can then be fused with an intraoperatively acquired fluoroscopic 2D live image of an interventional tool. According to the present invention, said method comprises the steps of subjecting the image data set of the 3D representation associated with the precalculated optimal viewing angle to a 3D segmentation algorithm (S4) in order to find the contours of a target structure or lesion to be examined and interventionally treated within a region of interest and automatically adjusting (S5) a collimator wedge position and / or aperture of a shutter mechanism used for collimating an X-ray beam emitted by an X-ray source of a C-arm-based 3D rotational angiography device or rotational gantry-based CT imaging system to which the patient is exposed during an image-guided radiographic examination procedure based on data obtained as a result of said segmentation which indicate the contour and size of said target structure or lesion. The aim is to reduce the region of interest to a field of view that covers said target structure or lesion together with a user-definable portion of the surrounding vasculature.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
X-ray tomography apparatus and operating method for generating multiple energy images
ActiveUS7209537B2Constant currentEasy to operateMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingHigh energyX-ray
In a tomography apparatus and a method for operating a tomography apparatus for generation of multiple energy images, in which high-energy projections and low-energy projections are acquired by alternating adjustment of a voltage and a further control variable (namely the current or the exposure time), given a set first voltage value and a set first control value of the further control variable, and given a set second voltage value and a set second control value of the further control variable, x-rays generated by an x-ray radiator exhibit essentially the same x-ray dose or photon flow.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Phase contrast imaging
ActiveUS9084528B2Reducing X-ray dose exposureReduce intensityRadiation/particle handlingX-ray apparatusLarge fovGrating
X-ray devices for Phase Contrast Imaging (PCI) are often built up with the help of gratings. For large field-of-views (FOV), production cost and complexity of these gratings could increase significantly as they need to have a focused geometry. Instead of a pure PCI with a large FOV, this invention suggests to combine a traditional absorption X-ray-imaging system with large-FOV with an insertable low-cost PCI system with small-FOV, The invention supports the user to direct the PCI system with reduced FOV to a region that he regards as most interesting for performing a PCI scan thus eliminating X-ray dose exposure for scanning regions not interesting for a radiologist. The PCI scan may be generated on the basis of local tomography.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and x-ray apparatus for determining the x-ray dose in an x-ray examination
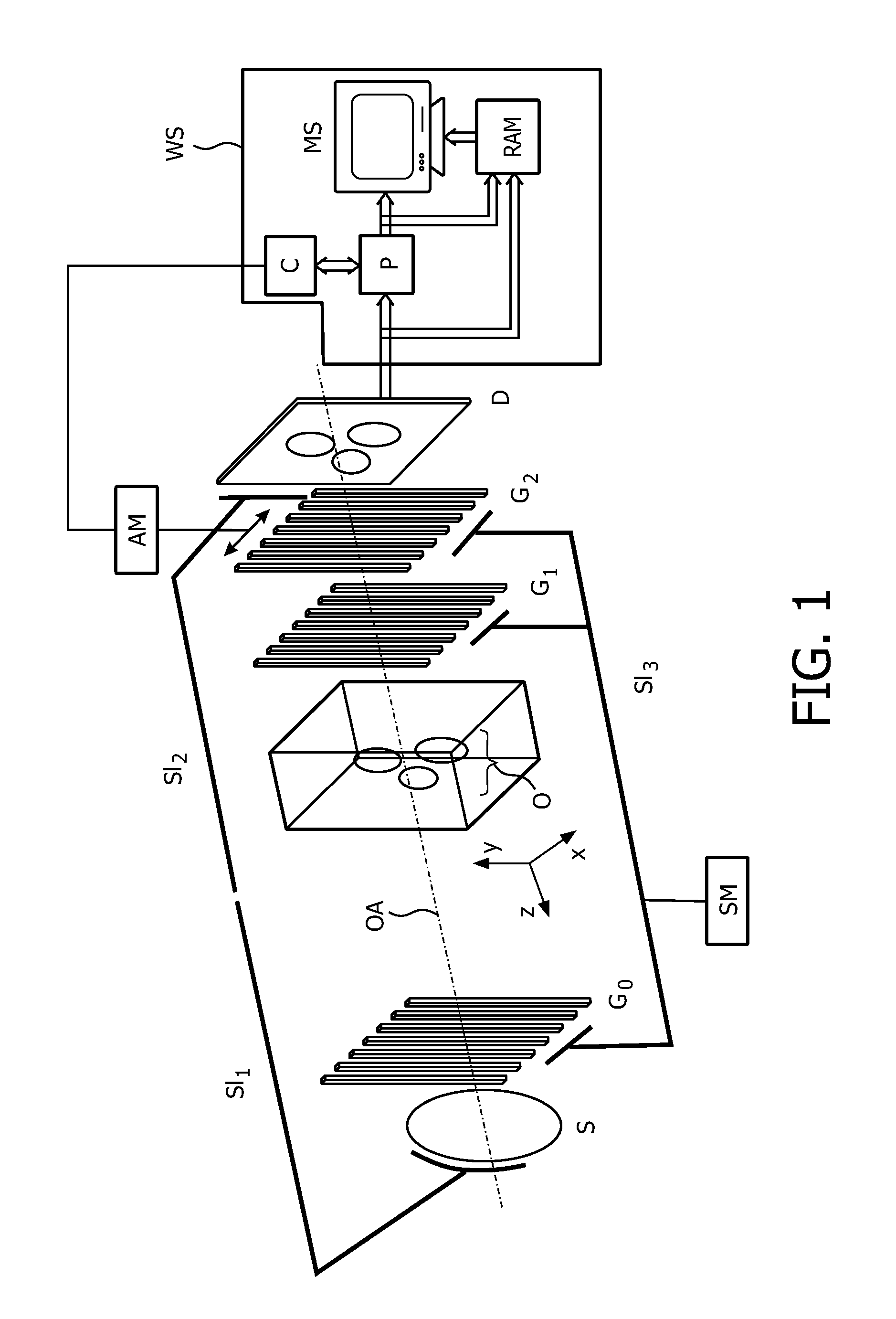
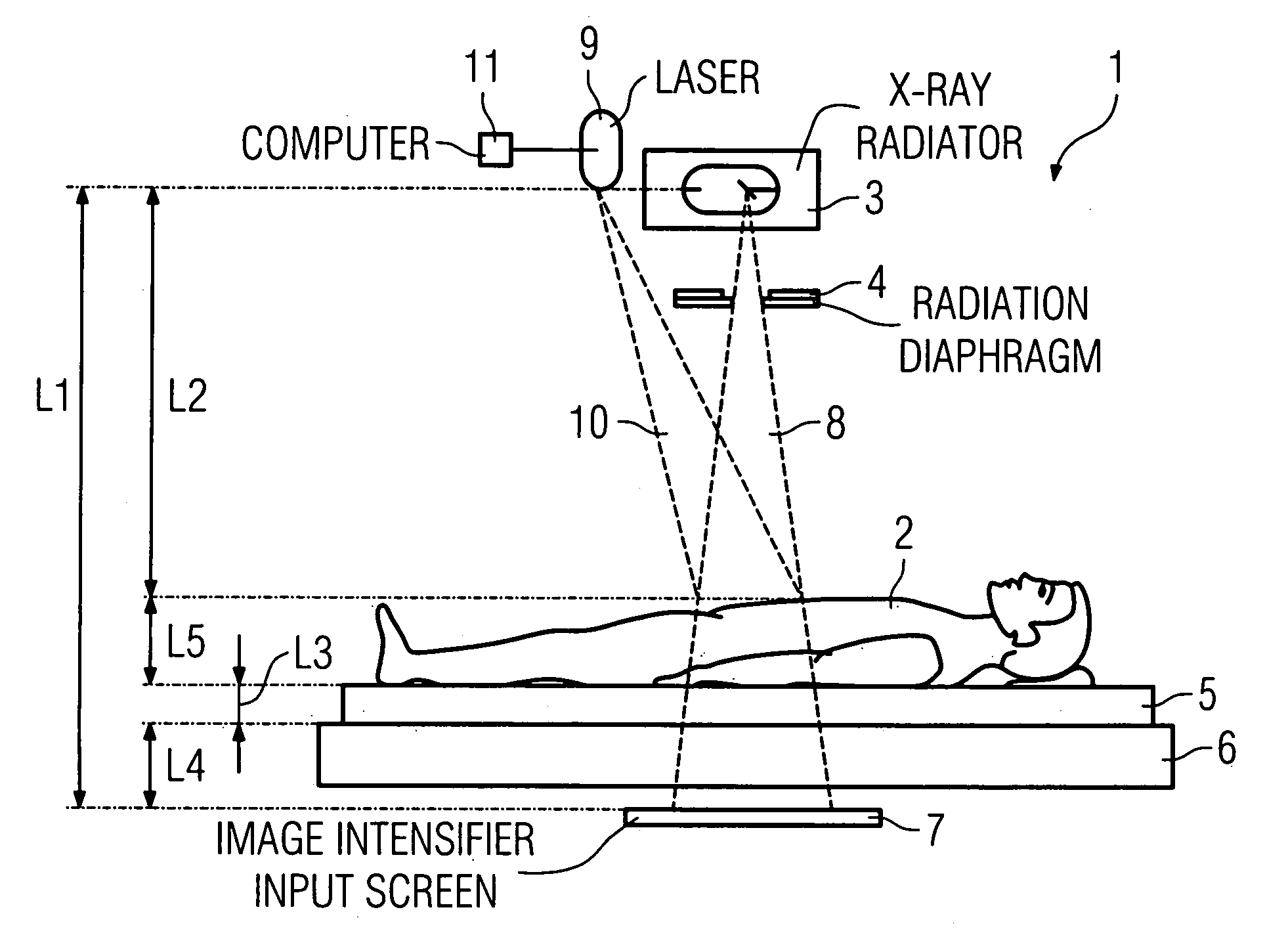
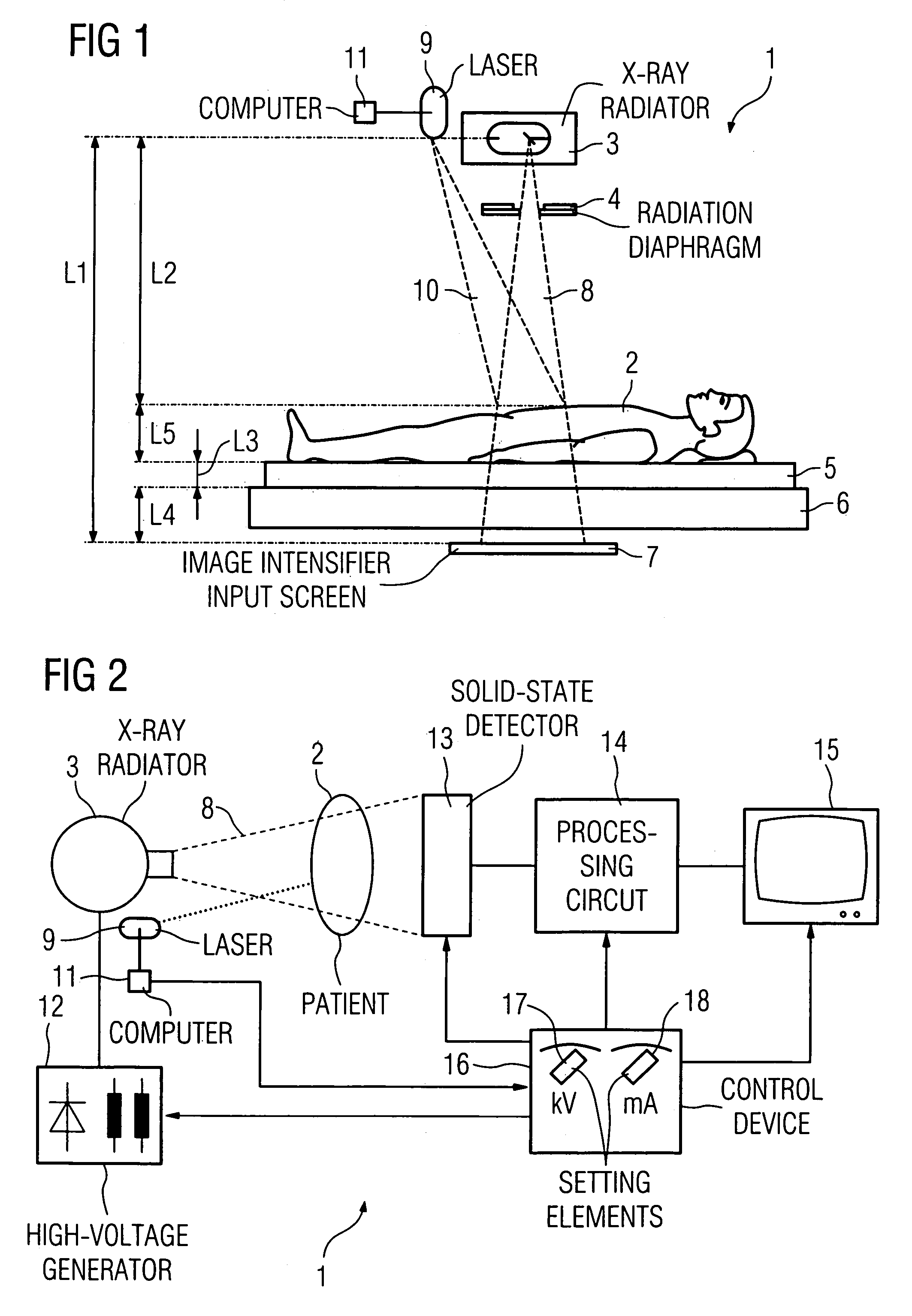
ActiveUS7054412B2Accurate measurementAvoid artifactsX-ray apparatusInstrumentsLaser rangingSoft x ray
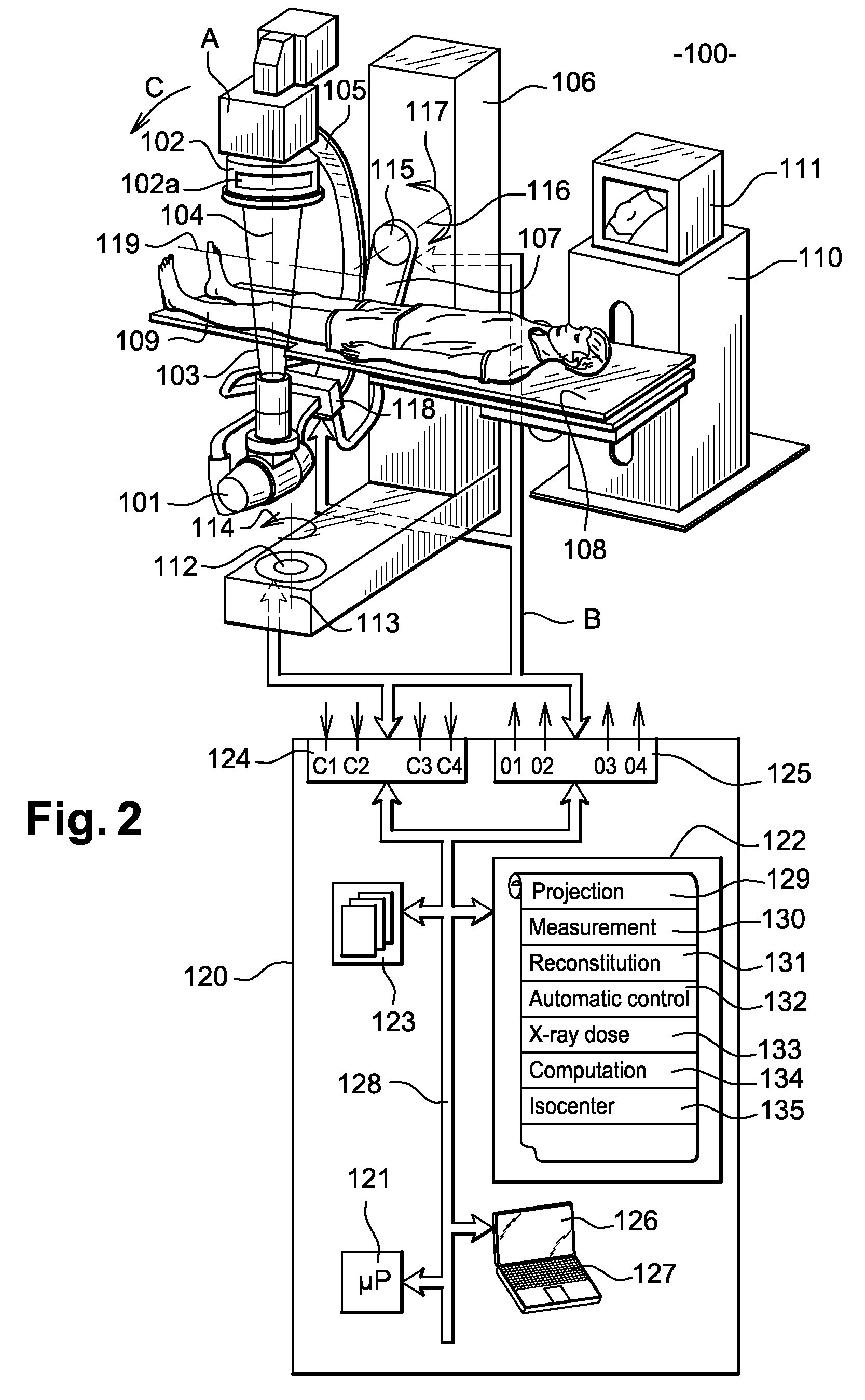
In an x-ray apparatus and method to determine the radiation dose in x-ray examinations, the x-ray apparatus has an x-ray radiator, an automatic exposure timer, and a laser range finder to detect the focus-patient separation between the x-ray radiator and a patient, and a computer device determines the necessary radiation dose using the thickness of the body part of the patient to be examined. The thickness is calculated from the acquired focus-patient distance and geometric data of the x-ray apparatus.
Owner:ADVANCED POWER CONVERSION +1
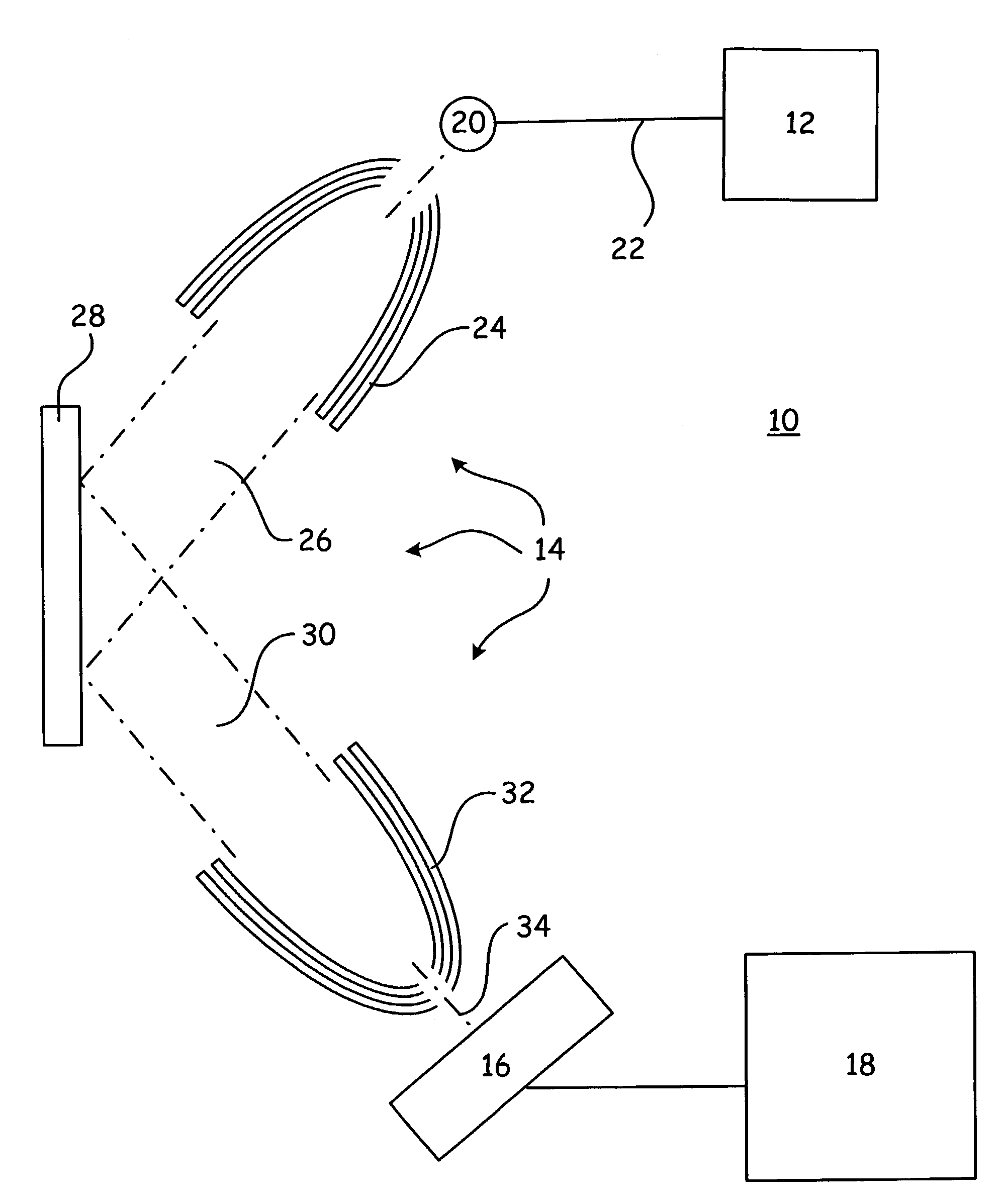
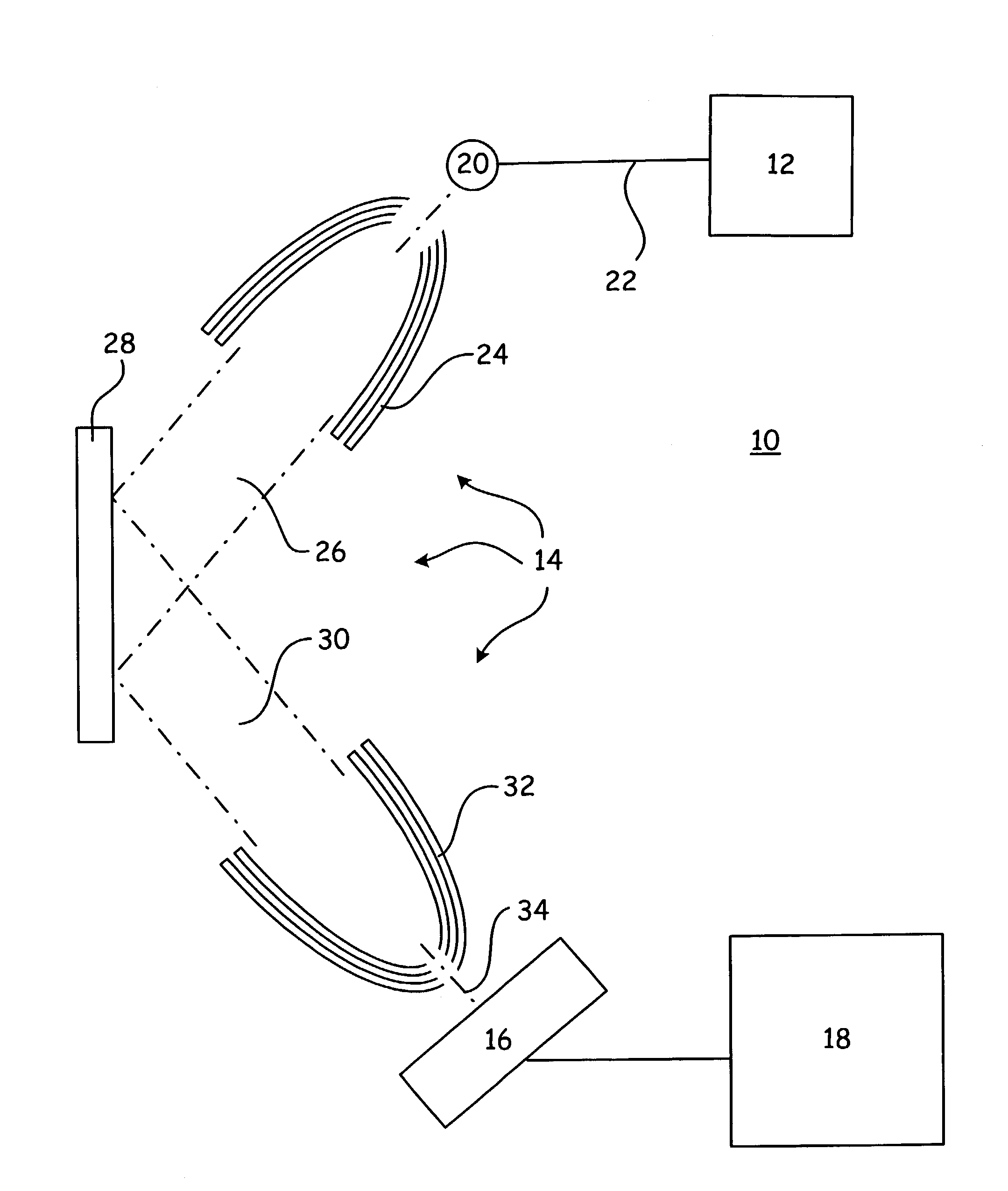
Method for the reconstruction of a body map
InactiveUS20080031413A1Inhibit injectionCharacter and pattern recognitionX-ray apparatusAutomatic controlX-ray
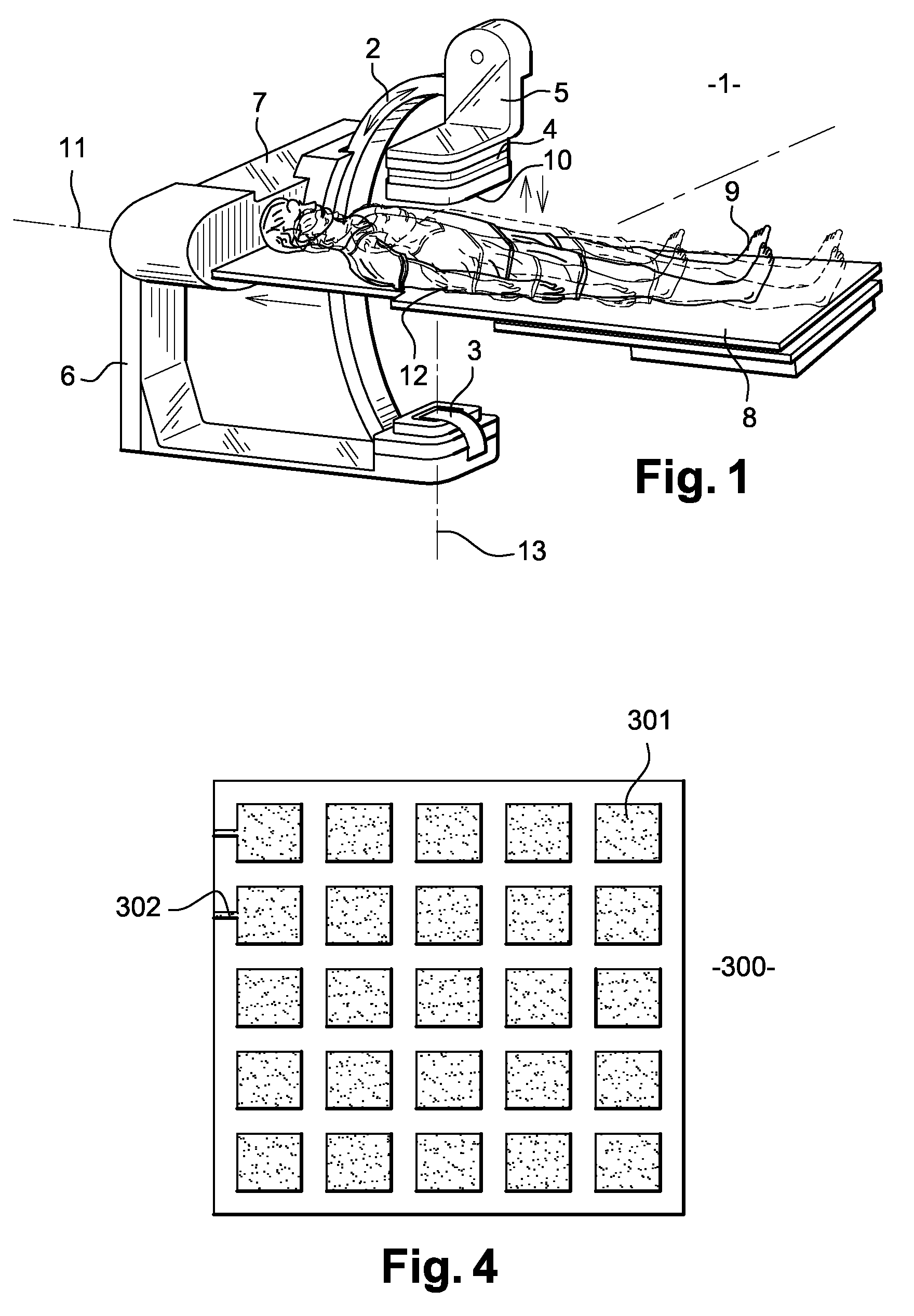
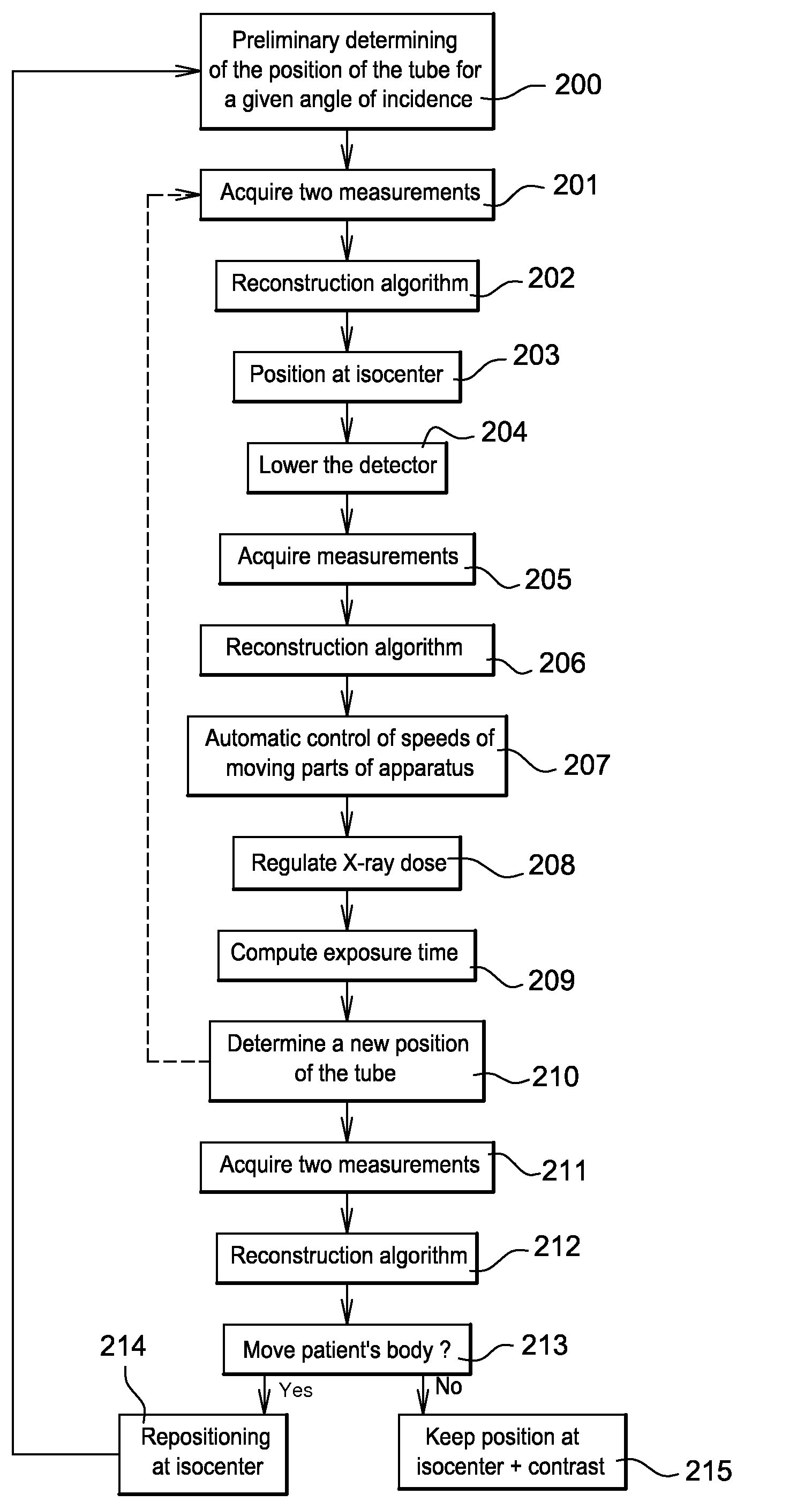
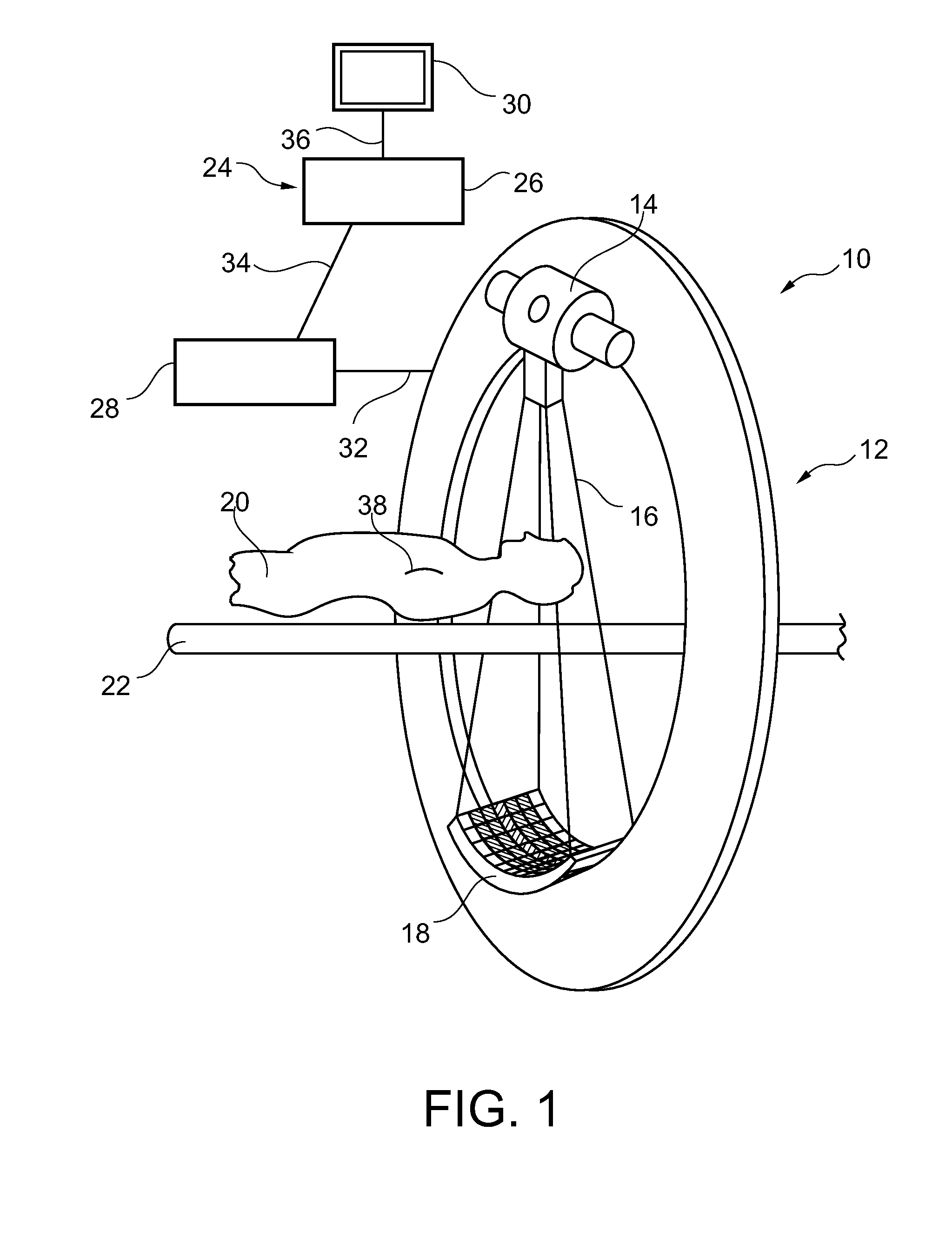
To perform a method for the reconstruction of a patient's body map, a detector has, in addition to the conventional sensors, an antenna placed in the direction of emission of the X-rays. At each position of the parts moving about the patient, electrodes of the antenna and the sensors simultaneously measure a distance between the patient's body and the detector. Means are used to carry out this reconstruction on the basis of the measured distances. The apparatus has means to achieve the following on the basis of this reconstruction: automatic control of the speeds of the moving parts of the apparatus, regulation of the X-ray dose and computation of the time of exposure to the X-rays.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-ray CT apparatus
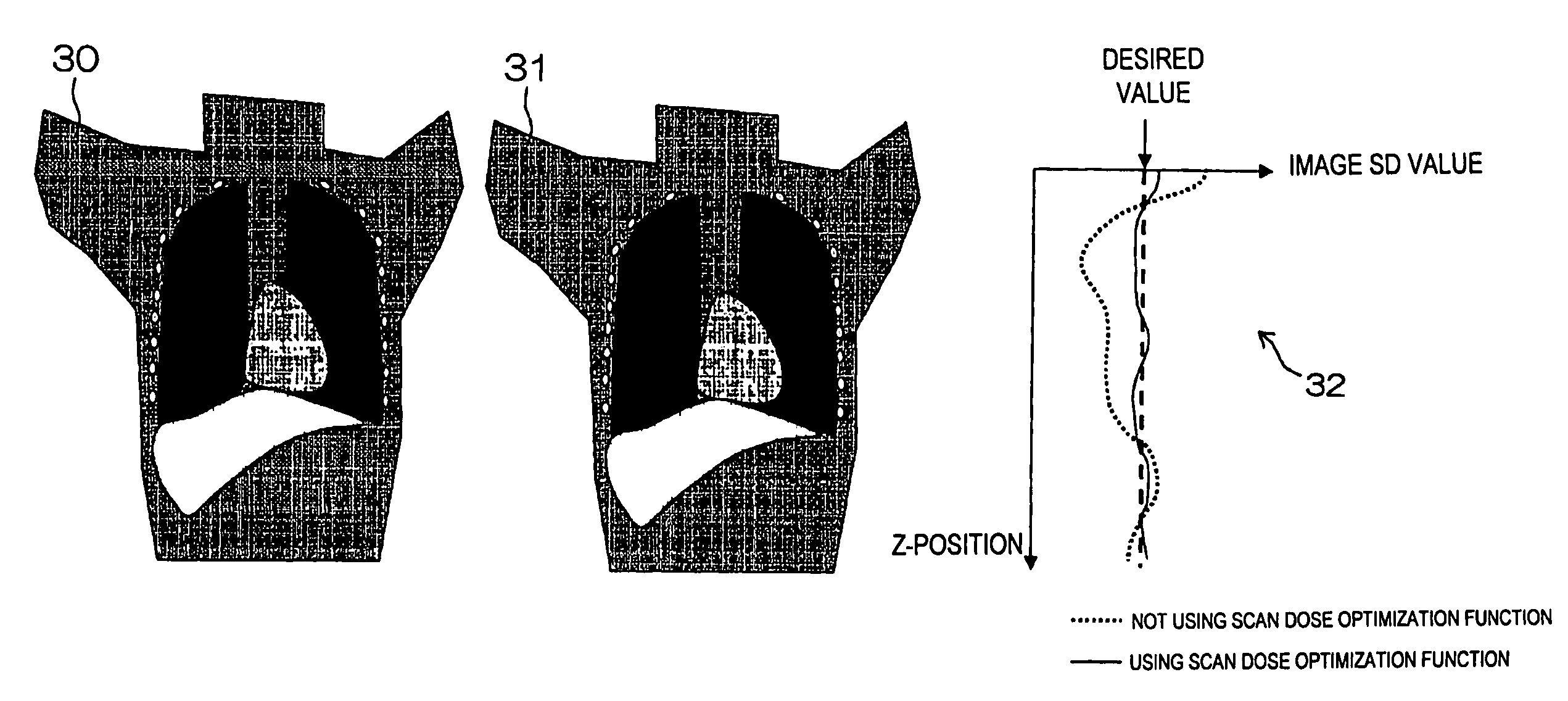
InactiveUS7602880B2Easily and concretely compareMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayImaging quality
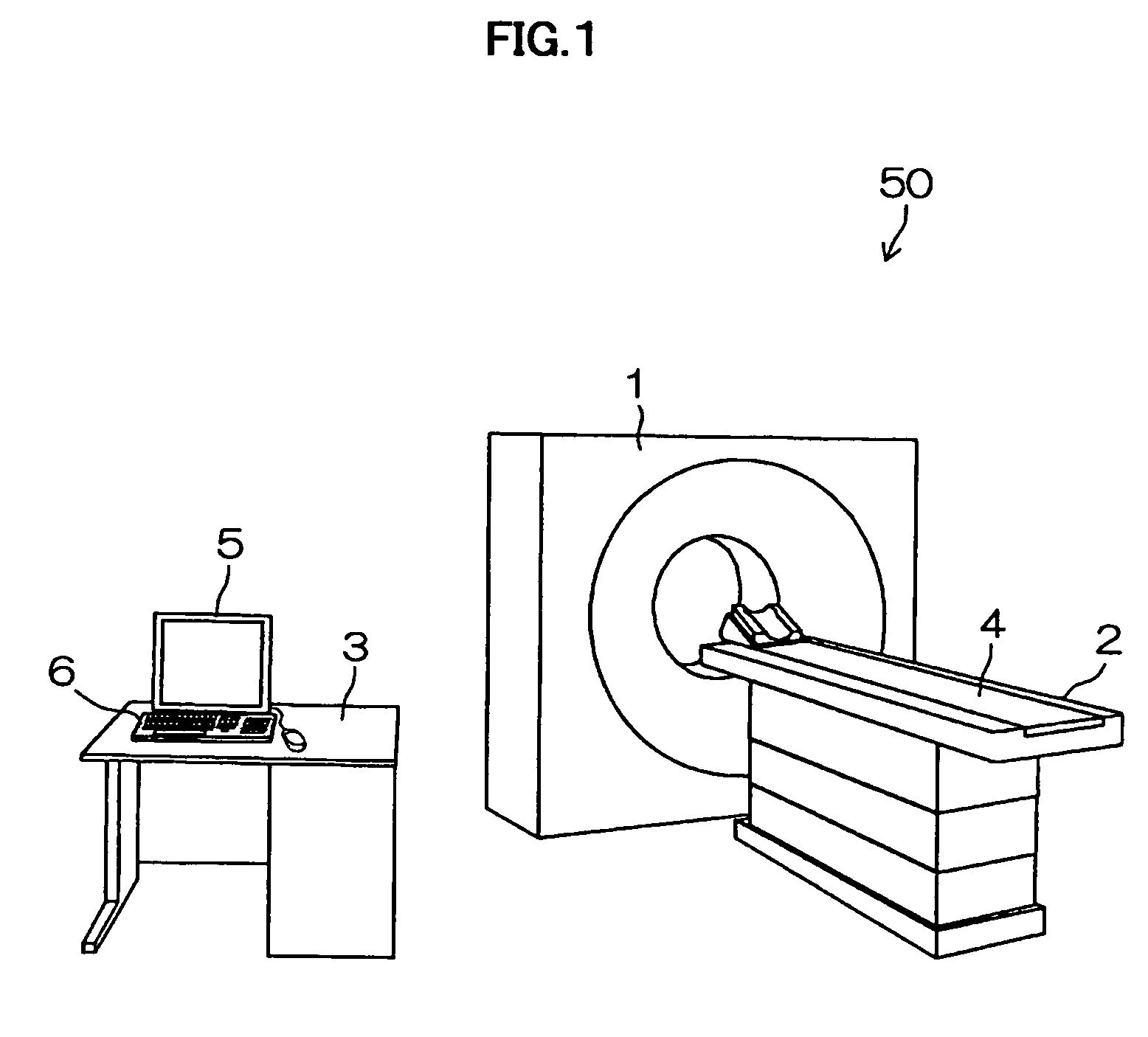
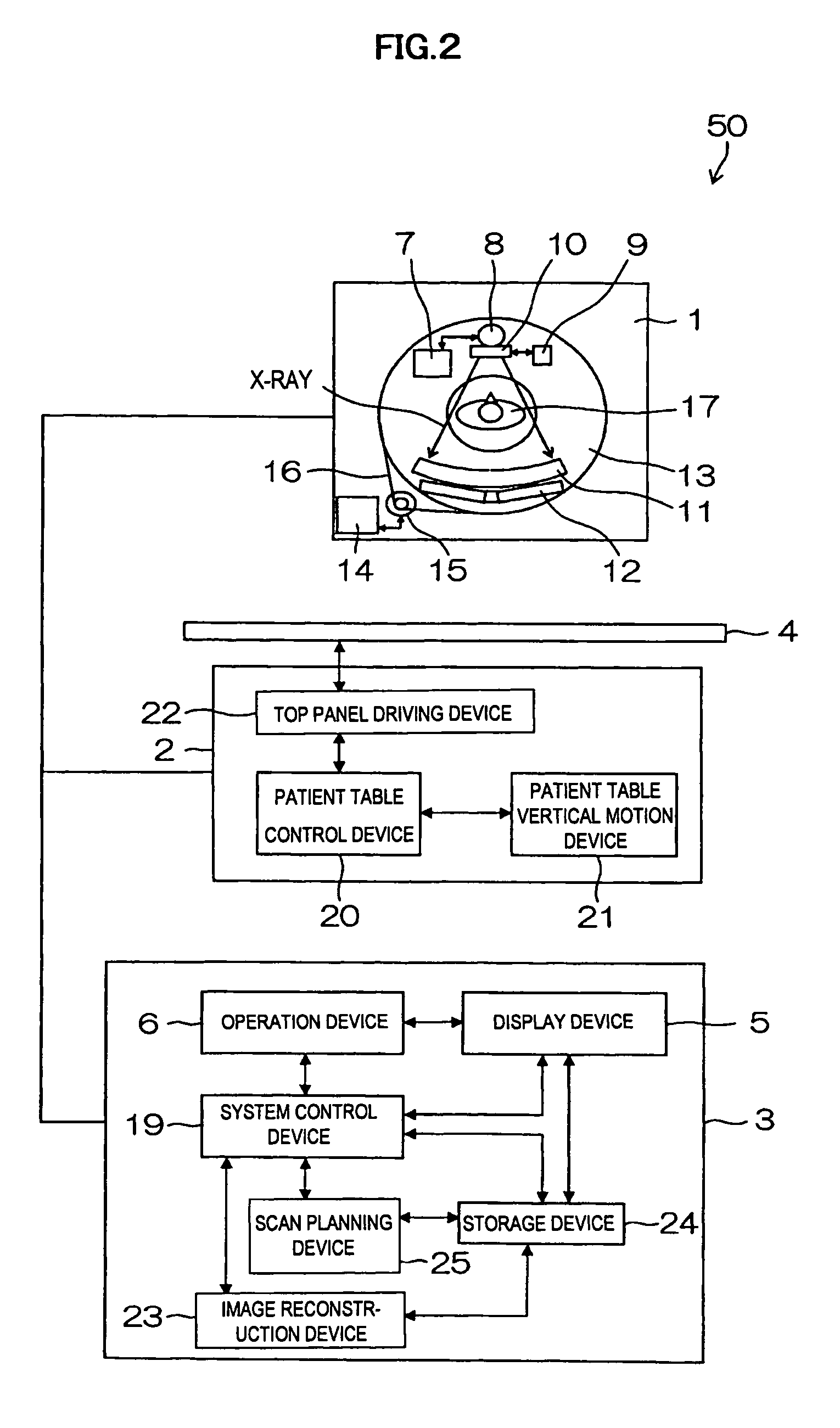
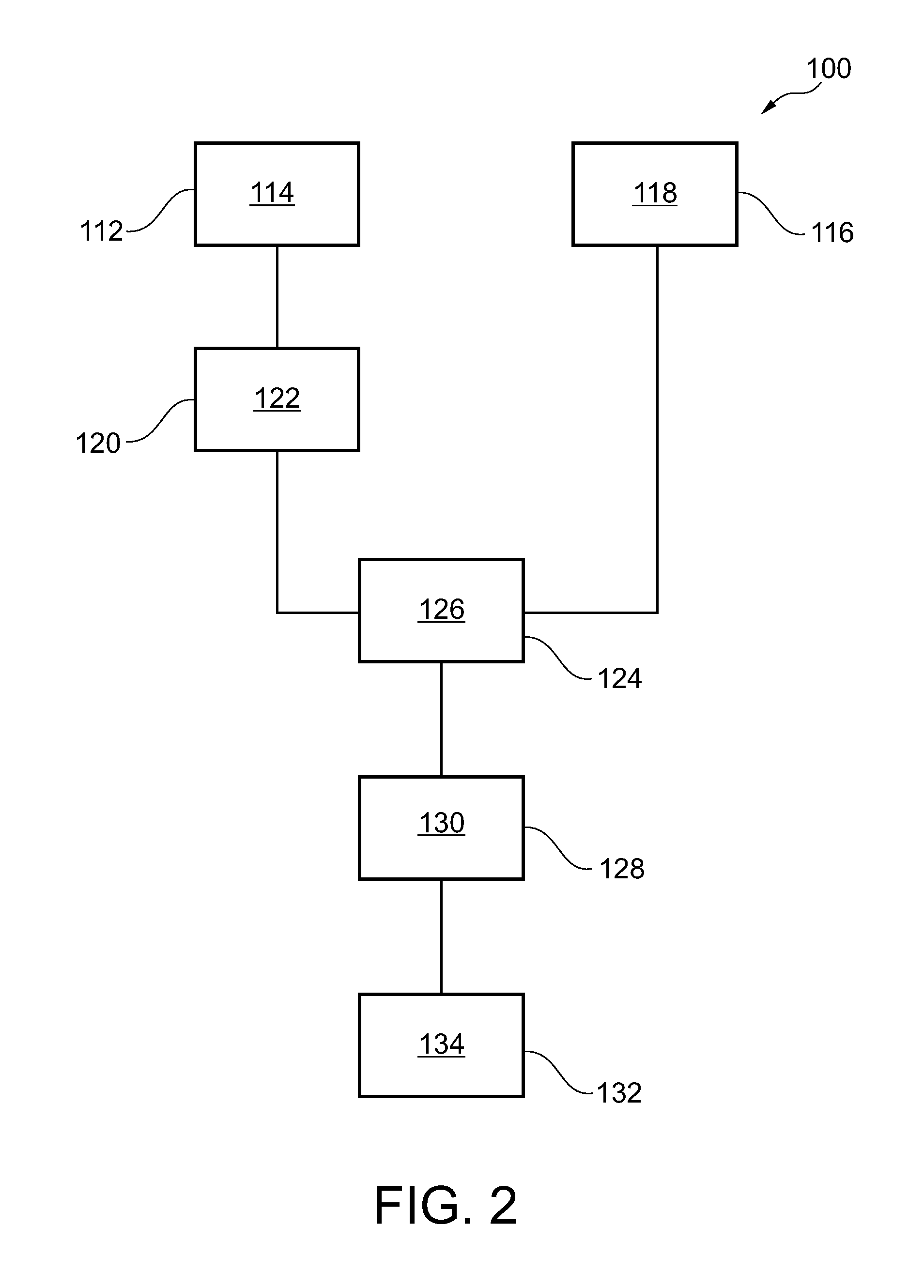
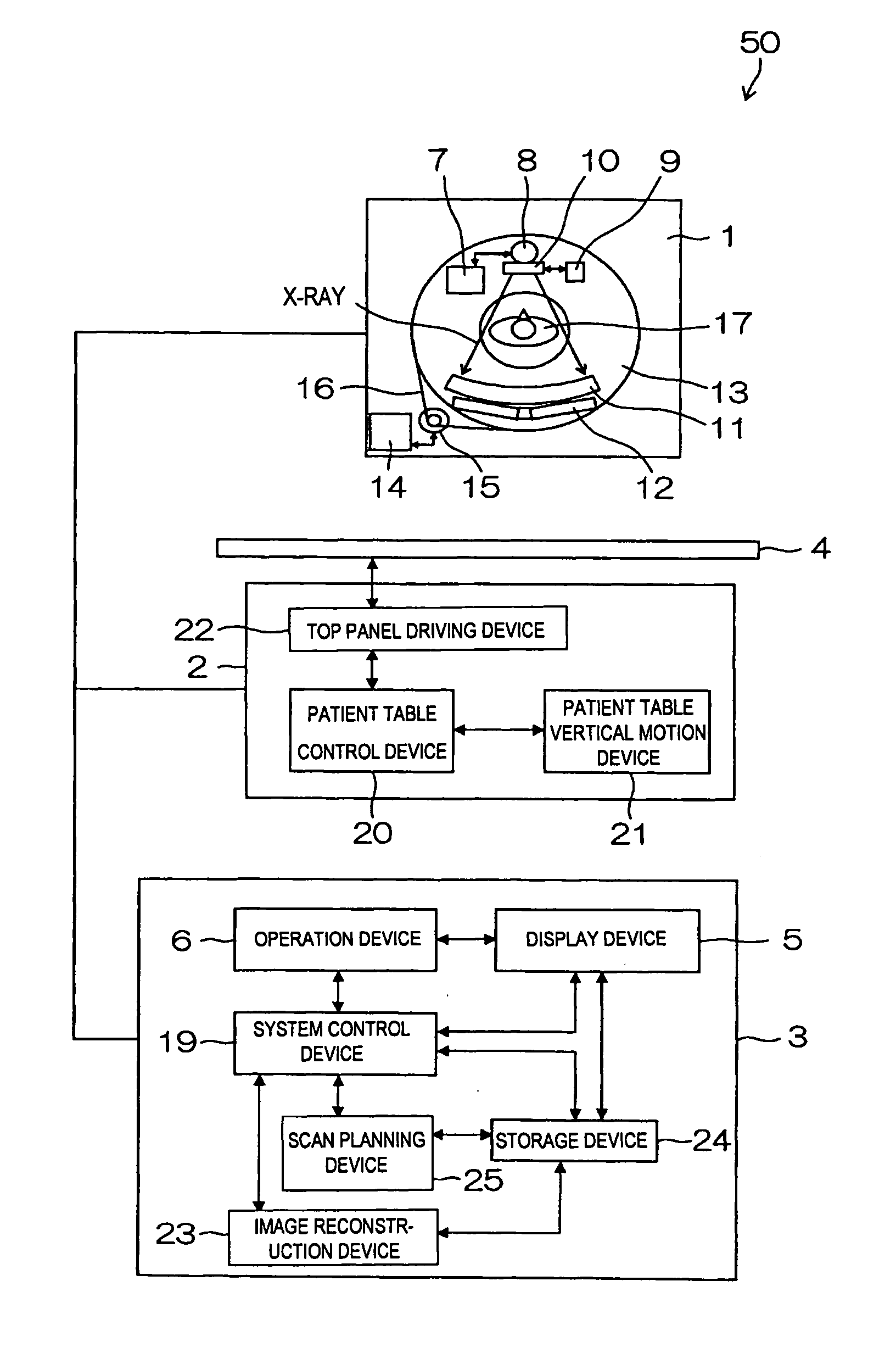
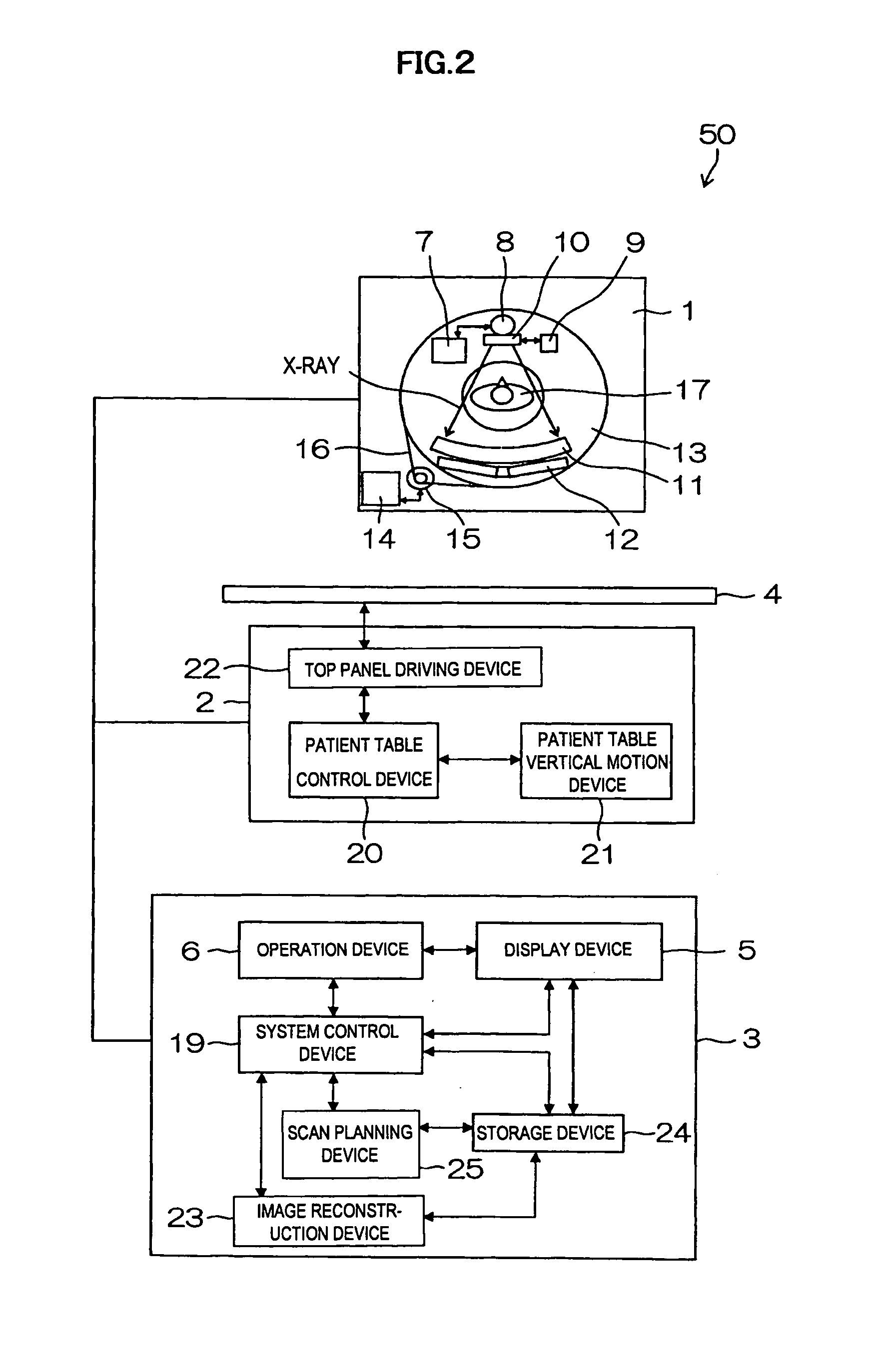
[Problems] To provide an X-ray CT apparatus capable of easily comparing image quality supposed to be obtained when not using a X-ray dose optimization function and image quality supposed to be obtained when using the X-ray dose optimization function at the stage of scan planning.[Means for Solving Problems] A 3-dimensional model of an object to be examined (17) is generated from scanogram projection data (S170). An image noise dispersion value corresponding to an imaging region of the object is predicted from the 3-dimensional model.The predicted image noise dispersion value is compared to a desired value of the image index value inputted by a user so as to calculate a modulation pattern of the irradiation X-ray amount (S200).By predicting the image quality supposed to be obtained when using and not using the X-ray dose optimization function, each of the predicted results is displayed so as to be compared on a display device (5) (S230).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
3d-originated cardiac roadmapping
InactiveUS20130116551A1Improve accuracyReduce the burden onSurgerySterographic imagingPattern recognitionX ray dose
The present invention relates to 3D-originated cardiac roadmapping. In order to improve the accuracy of the information provided to the user as navigation information, without any additional burden to the patient such as additional X-ray dose, a method is described comprising the steps of a) providing 3D+t image data of a vascular structure of an object; b) acquiring two-dimensional image data of the object, which object comprises the vascular structure, the 2D image data comprising at least one 2D image; c) projecting the vascular structure, thereby generating a plurality of mask images on the basis of a 3D+t image data; d) registering the at least one 2D image with one of the plurality of the mask images, wherein the registration comprises finding the maximum of a similarity factor between the mask images and the at least one 2D image; e) generating a combination of the at least one 2D image and a projection of the vascular structure on the basis of the 3D+t image data according to the registration; and f) displaying the combination as a guiding vessel tree projection. Thus improved cardiac roadmapping in form of a topographical roadmapping is provided since the roadmapping is based on three-dimensional data.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
X-ray CT apparatus
InactiveUS20090046833A1Easily and concretely compareMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingImaging qualityModulation pattern
[Problems] To provide an X-ray CT apparatus capable of easily comparing image quality supposed to be obtained when not using a X-ray dose optimization function and image quality supposed to be obtained when using the X-ray dose optimization function at the stage of scan planning.[Means for Solving Problems] A 3-dimensional model of an object to be examined (17) is generated from scanogram projection data (S170). An image noise dispersion value corresponding to an imaging region of the object is predicted from the 3-dimensional model.The predicted image noise dispersion value is compared to a desired value of the image index value inputted by a user so as to calculate a modulation pattern of the irradiation X-ray amount (S200).By predicting the image quality supposed to be obtained when using and not using the X-ray dose optimization function, each of the predicted results is displayed so as to be compared on a display device (5) (S230).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method for computing patient radiation dose in computed tomography
ActiveUS7627079B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x rayComputed tomography
A system and method are disclosed for computing a radiation dose delivered to a patient during a computed tomography (CT) scan of the patient. The CT image dataset generated during the scan of the patient, and one or more parameters relating to a x-ray source are used to calculate the radiation dose delivered to the patient as a function of the CT image data set and the one or more parameters of the x-ray source. The radiation dose is generally found by calculating a primary x-ray dose distribution and scattered x-ray dose distribution from the CT image dataset and taking the sum of the primary x-ray dose distribution and scattered x-ray dose distribution.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com