Patents
Literature
241 results about "Projection View" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
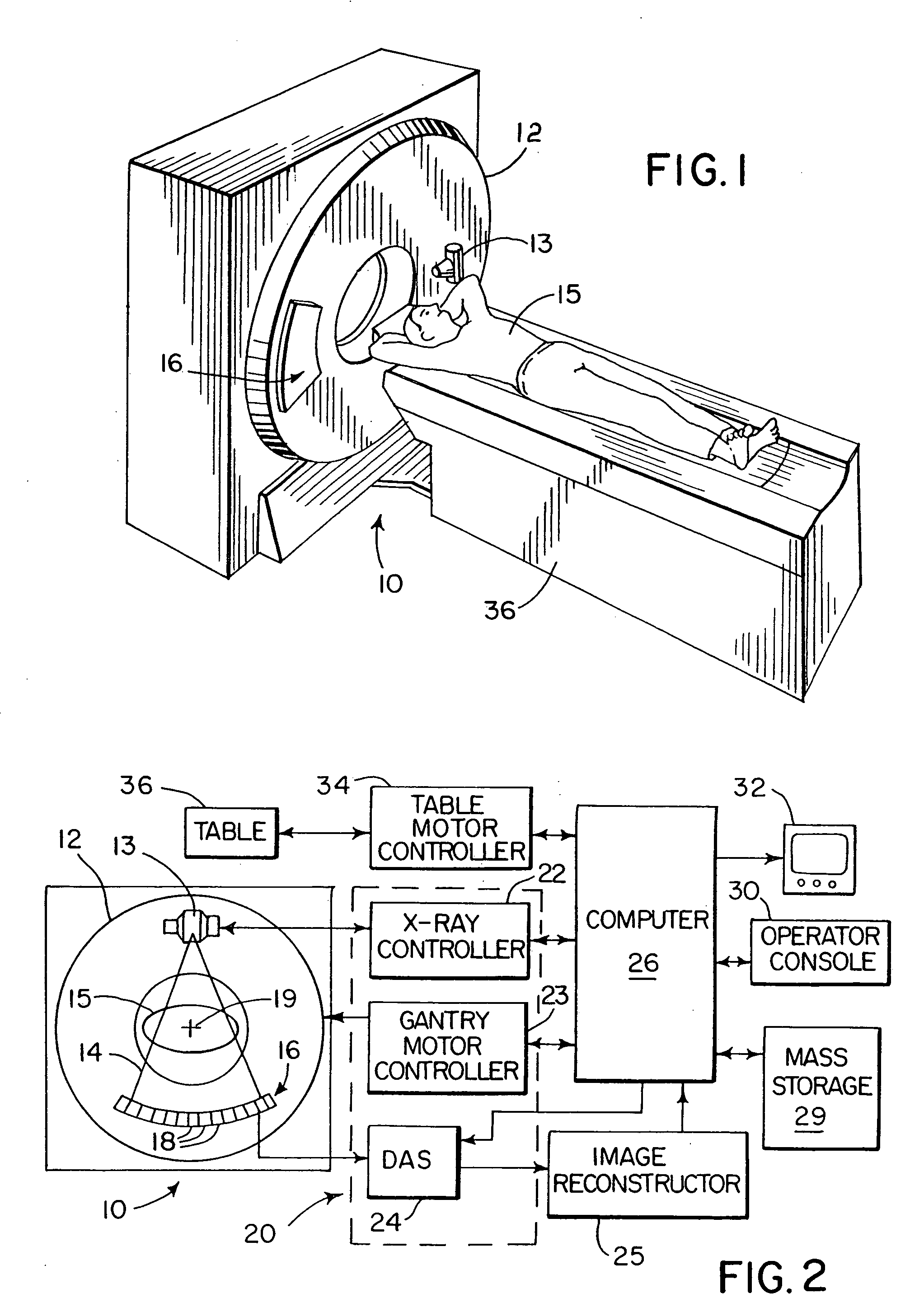
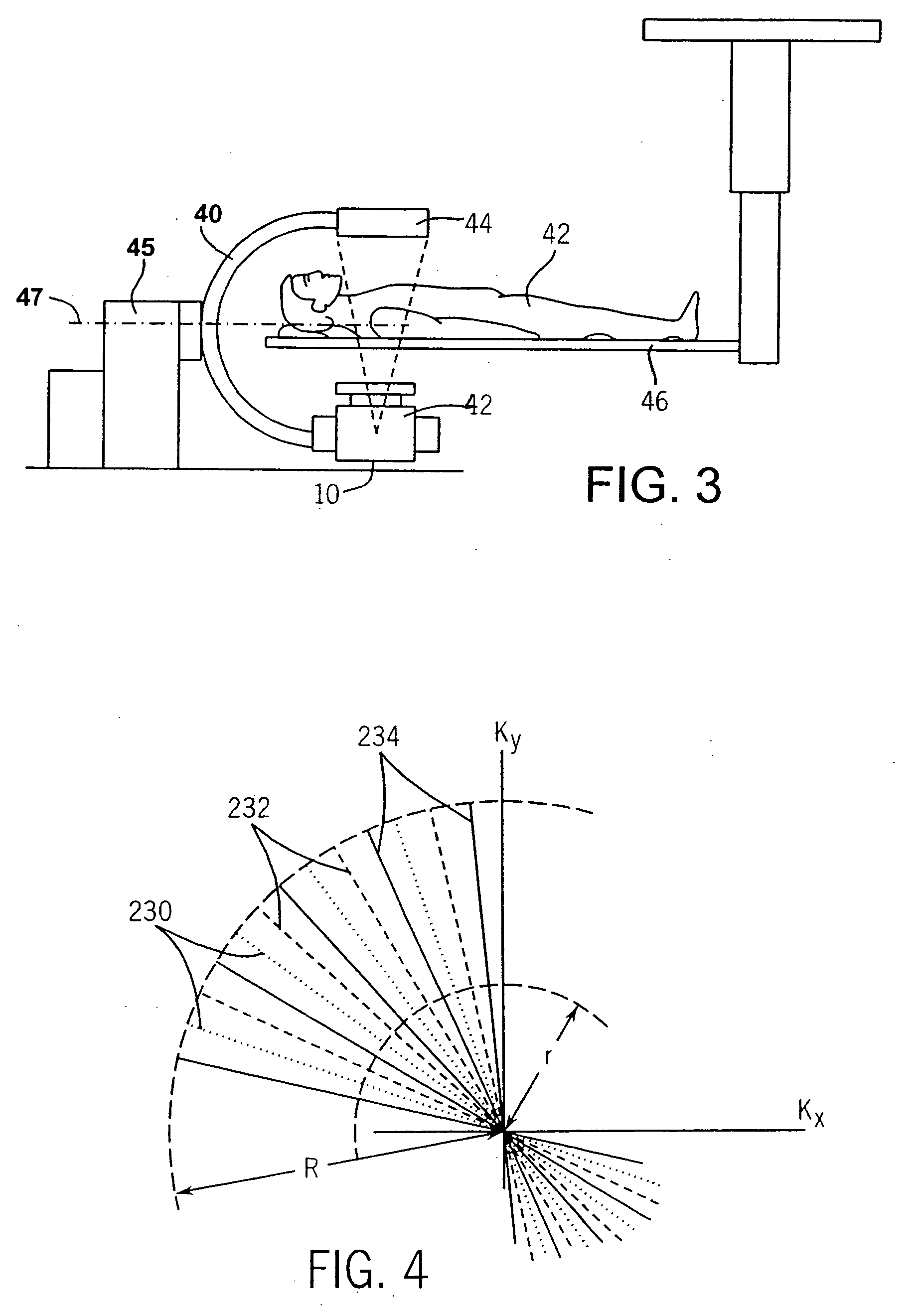
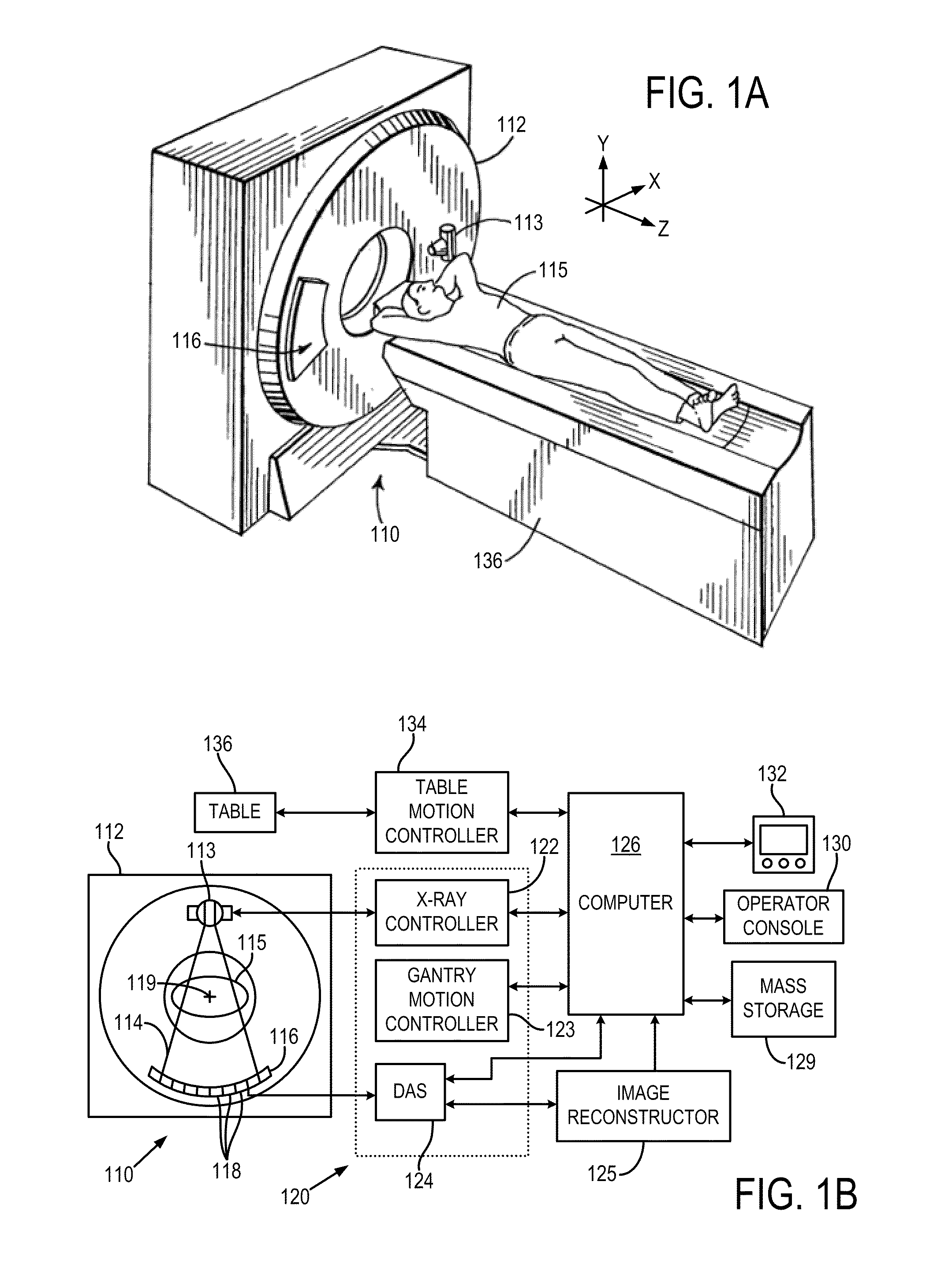
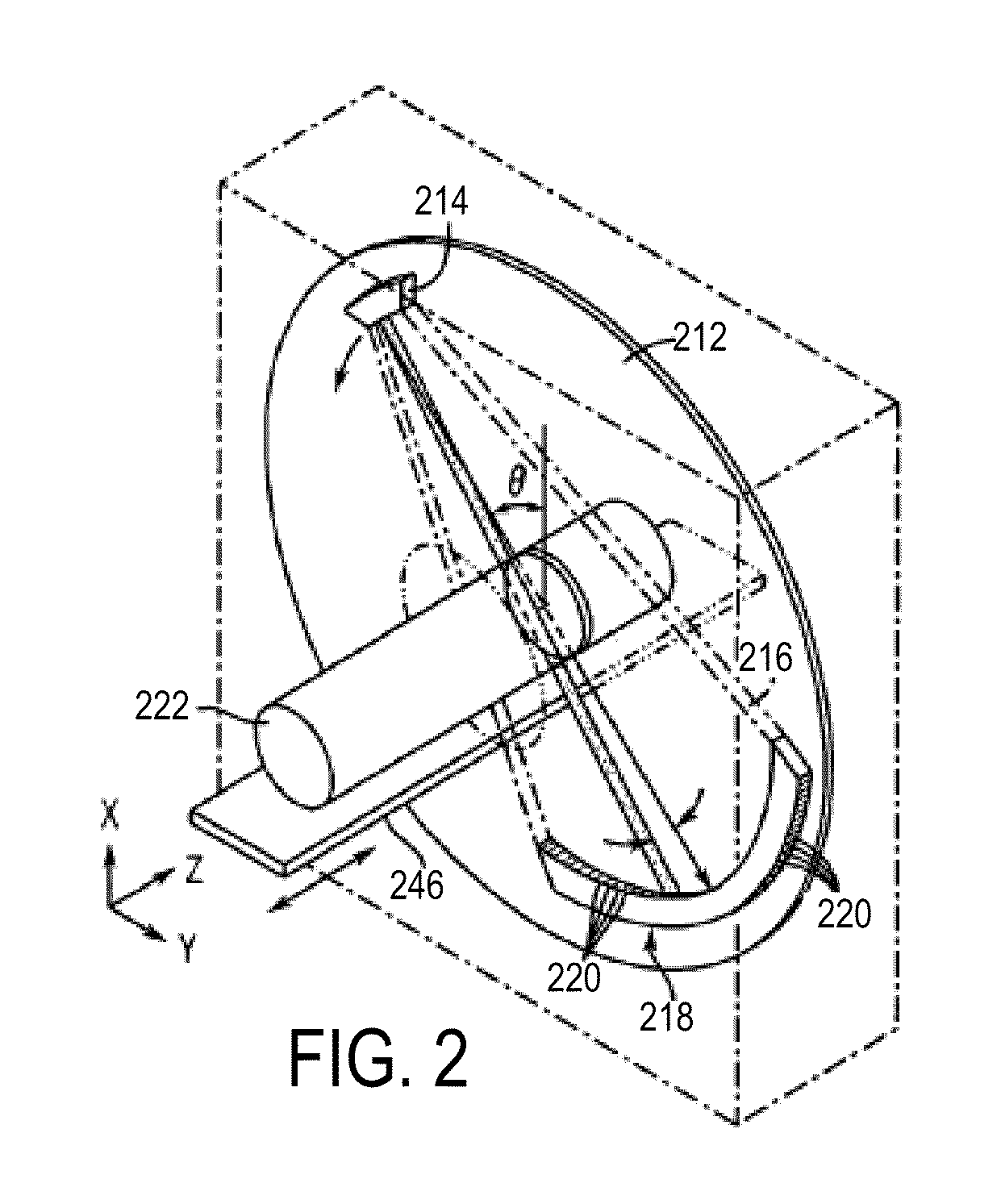
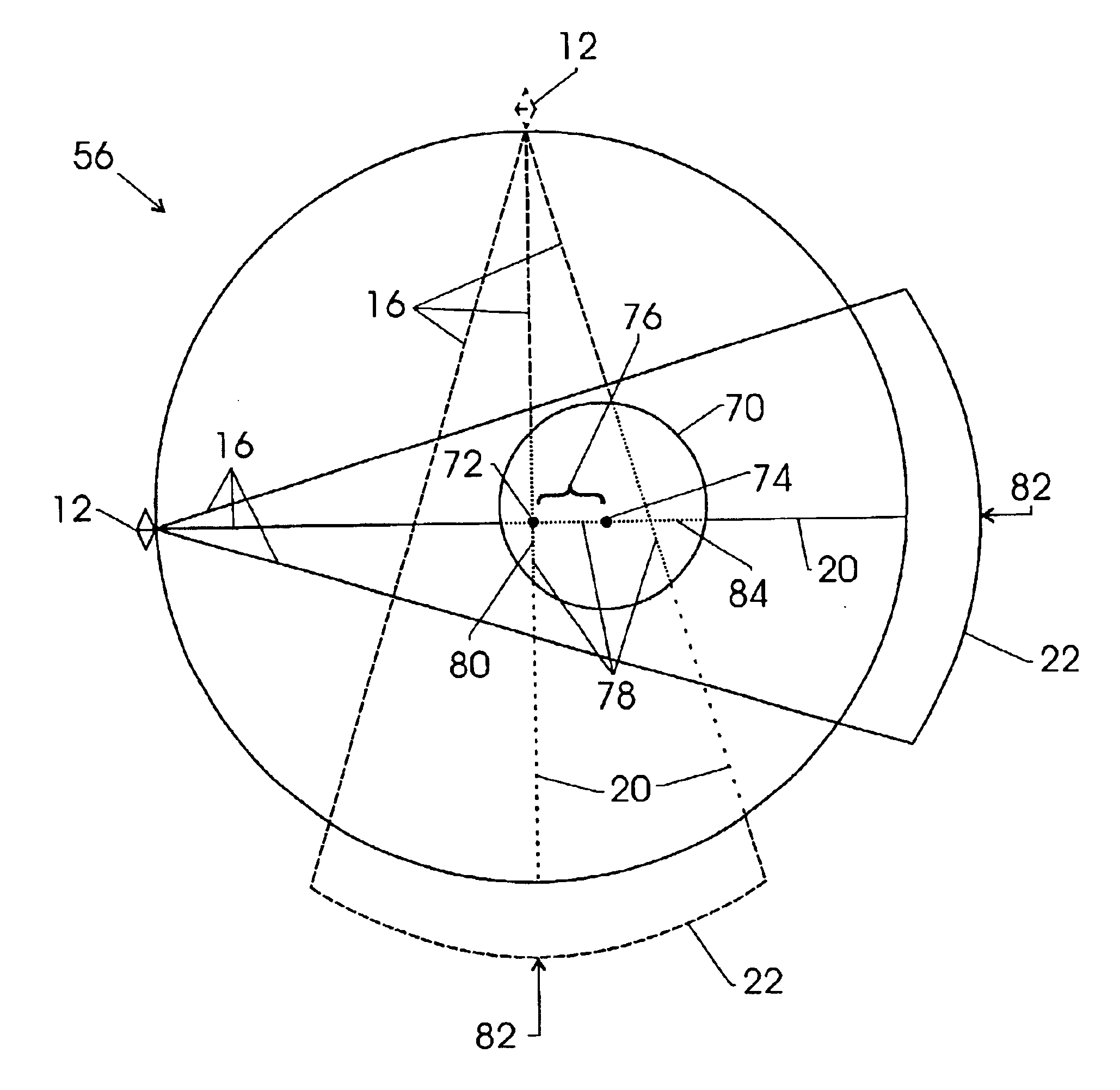
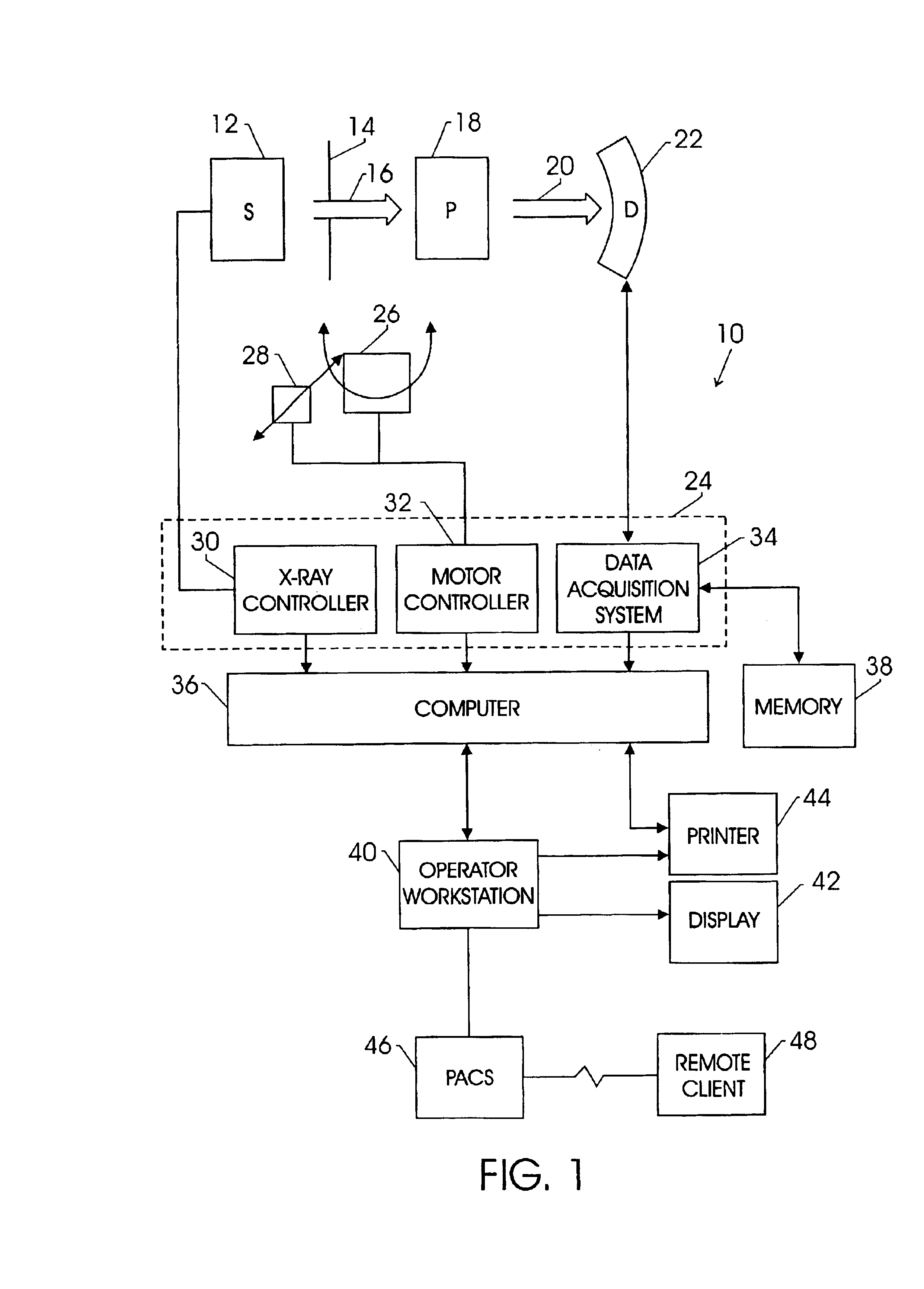
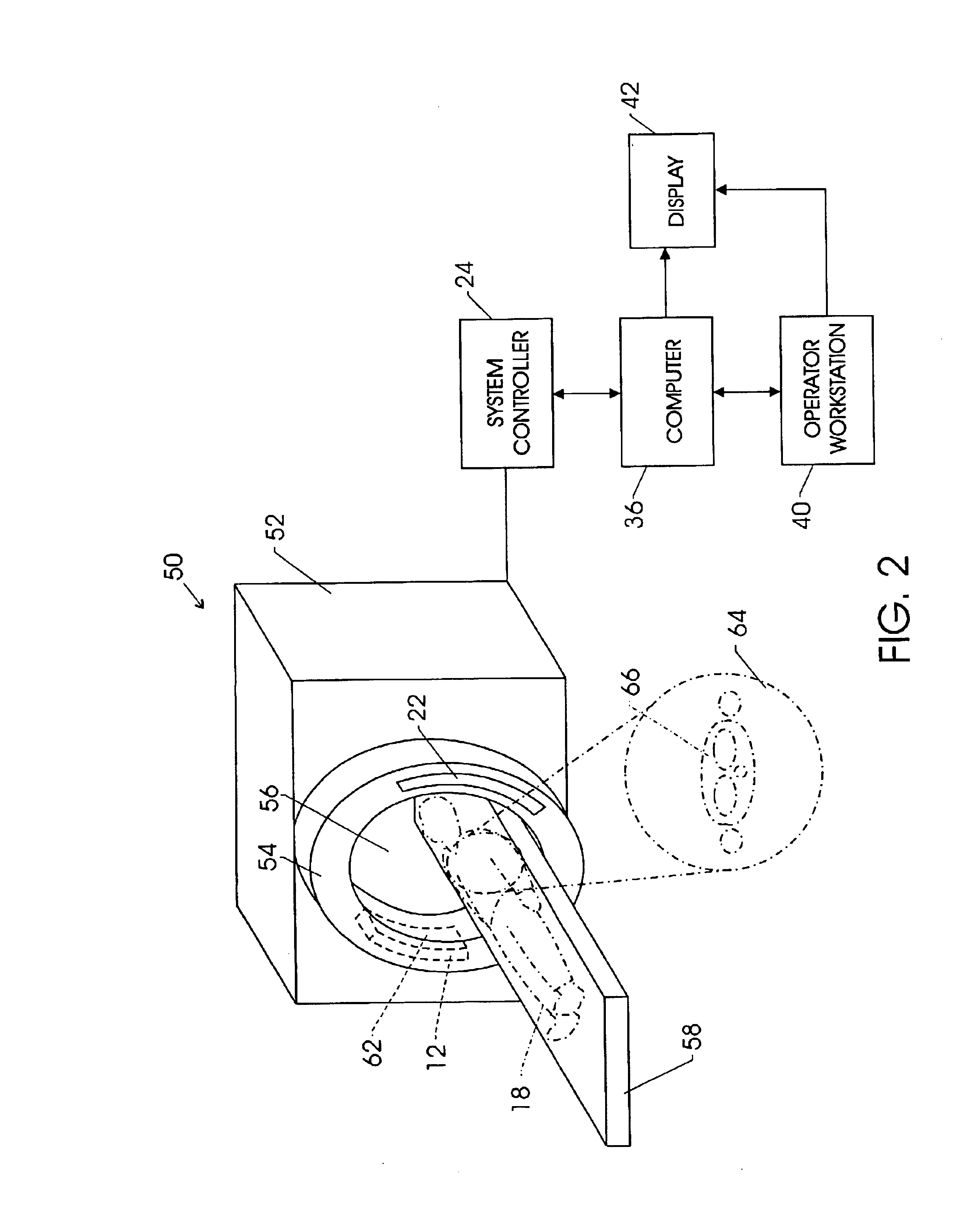
Detector data acquired in a specified direction from the subject. It represents a view from a certain direction.
Compact GPS tracker and customized mapping system
InactiveUS6198431B1Navigational calculation instrumentsPosition fixationDocking stationTopographic map
A light weight compact portable GPS receiver and transmitter for use on the person during outdoor activity, data logging receiver, data logging software supported by battery pack and modified active GPS patch antenna with chips, download connector, download docking station, charging units, mapping software to transfer the GPS data onto various maps including ortho-rectified, flat topographical maps, 3-D projection view topographical maps and street maps.
Owner:MAPTEK LLC
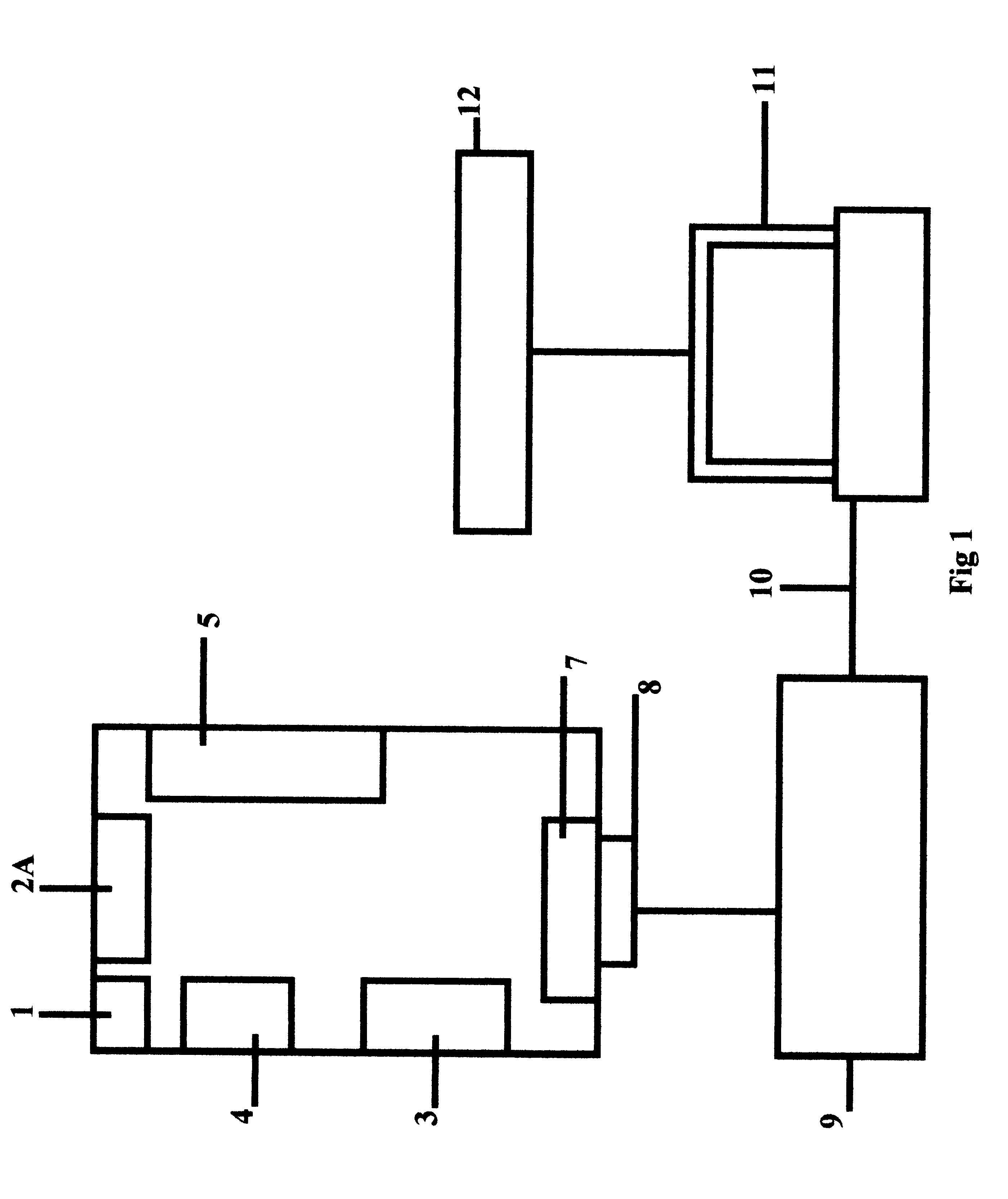
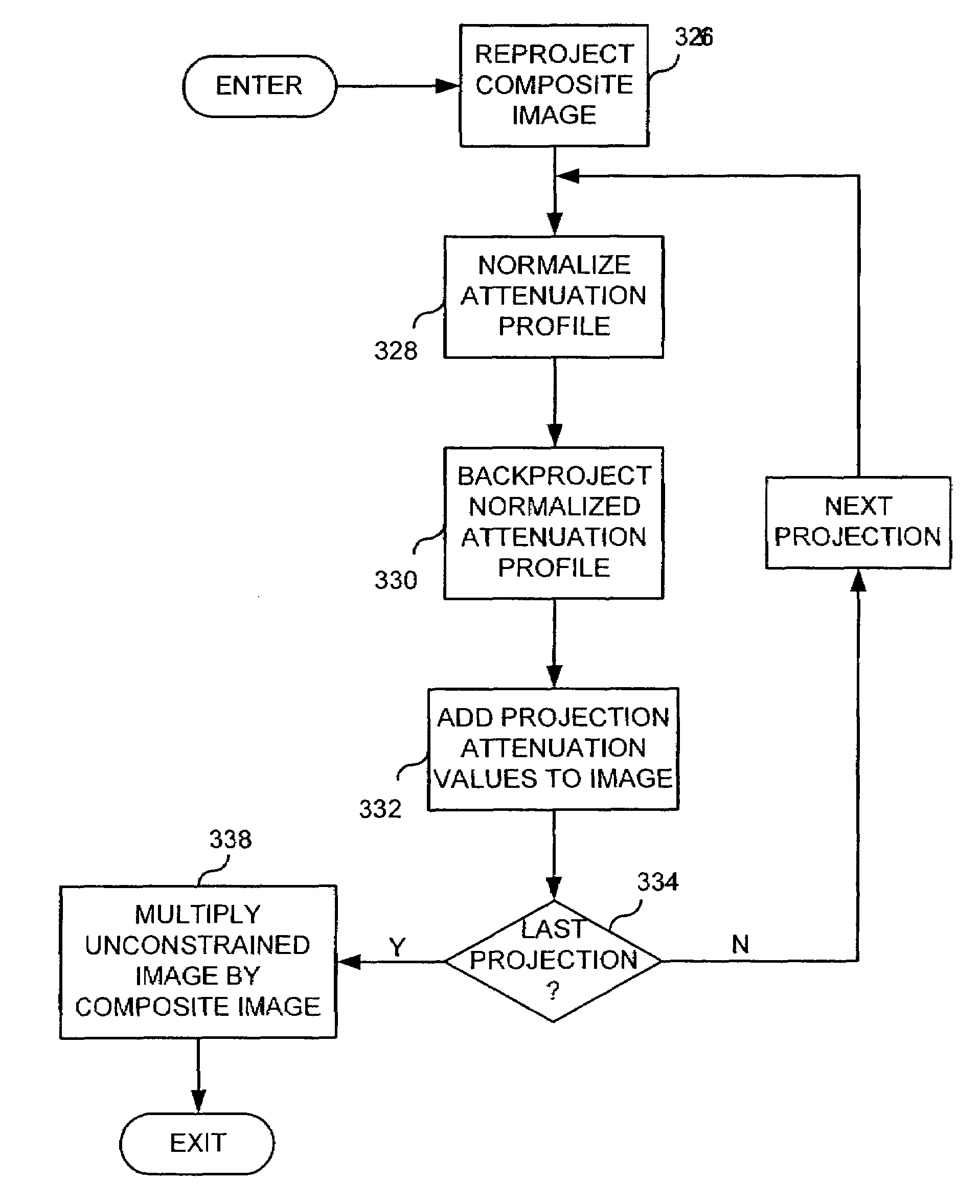
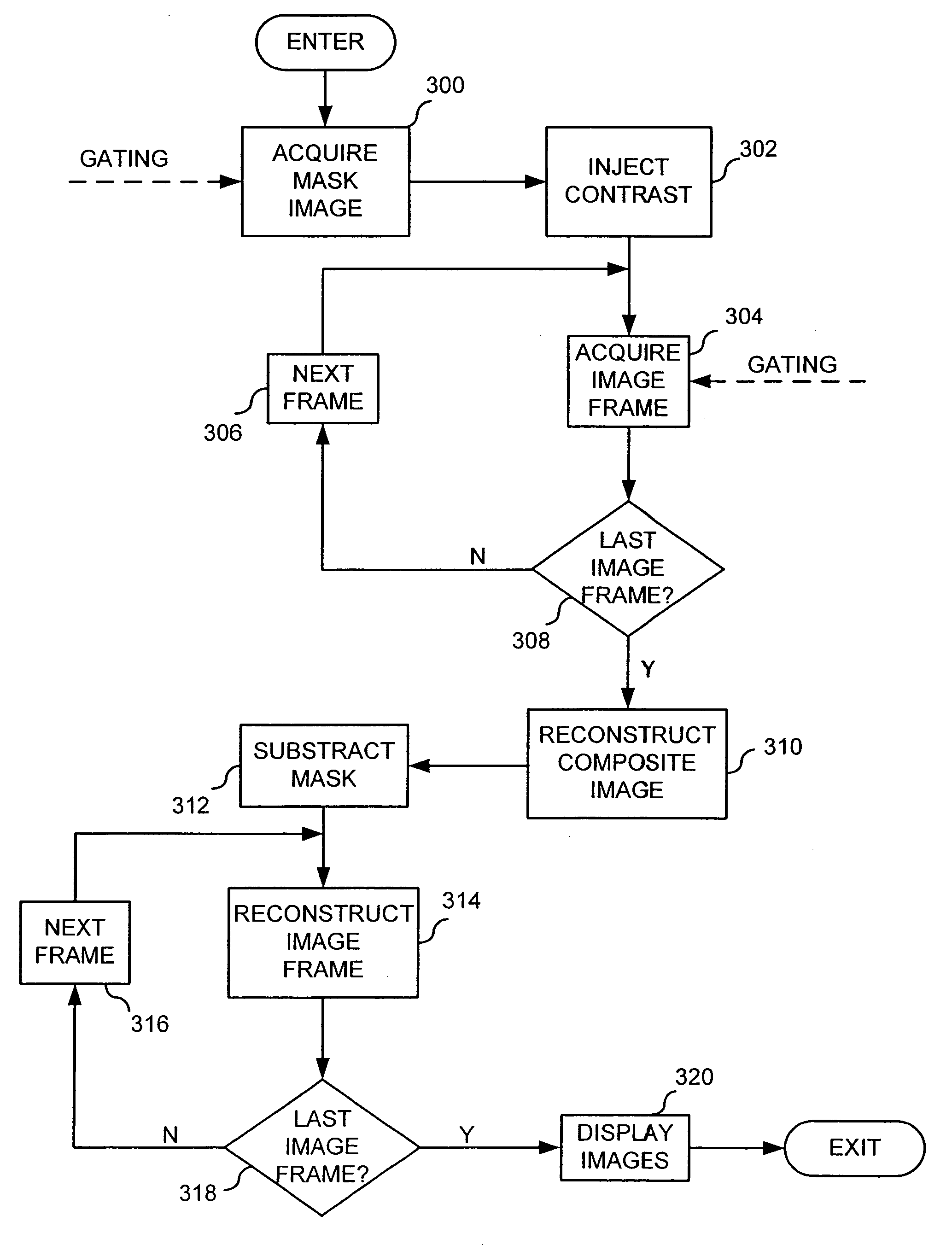
Backprojection reconstruction method for CT imaging
ActiveUS7545901B2Simple methodLower doseReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiologyBack projection
Two-dimensional or three-dimensional, time-resolved CT frame images are acquired during a dynamic study of a subject. A composite image is produced and this is used to reconstruct each CT frame image by weighting the backprojection of each projection view acquired for that image frame by the corresponding value in the composite image. This weighted backprojection enables artifact-free image frames to be produced with far fewer projection views of the subject. The composite image may be reconstructed from views acquired separately, or it may be produced by combining views acquired during the course of the dynamic study.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
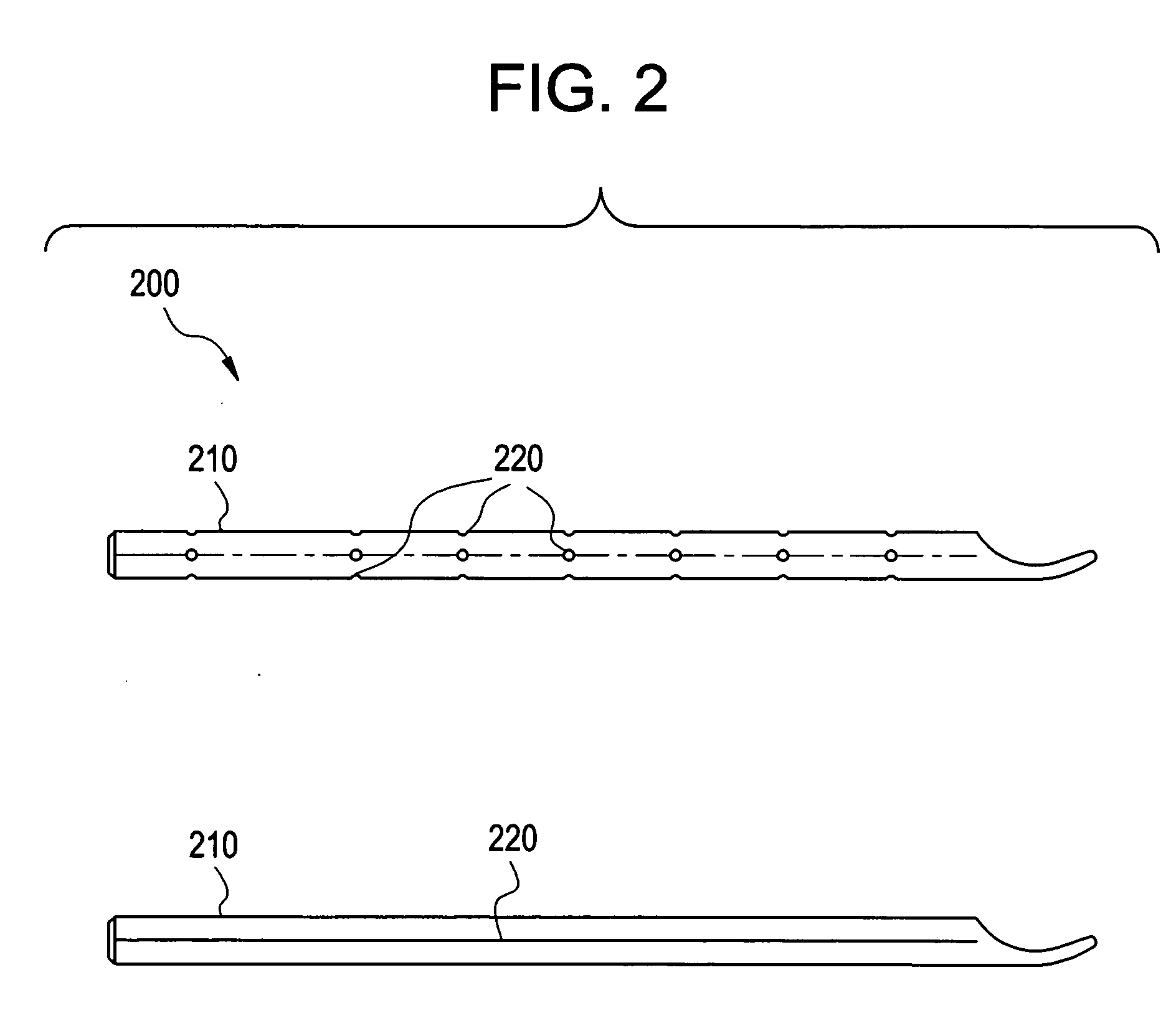
Method and system for geometric distortion free tracking of 3-dimensional objects from 2-dimensional measurements
InactiveUS20050228270A1Easy to trackSurgical navigation systemsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsData setImaging data
Certain embodiments of the present invention provide a method and system for improved tracking of an internal object, such as an implant or part of the anatomy, during an image-guided operation. In an embodiment, the method may include obtaining a plurality of fiducials for an internal object from a plurality of projection views, obtaining a plurality of measurements for the internal object using the plurality of fiducials, forming a three-dimensional model of the internal object using the plurality of measurements from a plurality of projection views for use in tracking the internal object, and performing an image-guided operation using an image data set and a three-dimensional representation of the internal object. The fiducials may be indentations, curves, grooves and / or identifying features in the internal object. In an embodiment, the representation of the internal object is compared to a computer-generated model of the internal object.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Backprojection reconstruction method for CT imaging
ActiveUS20070009080A1Improved image reconstructionImprove time resolutionReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiologyBack projection
Two-dimensional or three-dimensional, time-resolved CT frame images are acquired during a dynamic study of a subject. A composite image is produced and this is used to reconstruct each CT frame image by weighting the backprojection of each projection view acquired for that image frame by the corresponding value in the composite image. This weighted backprojection enables artifact-free image frames to be produced with far fewer projection views of the subject. The composite image may be reconstructed from views acquired separately, or it may be produced by combining views acquired during the course of the dynamic study.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
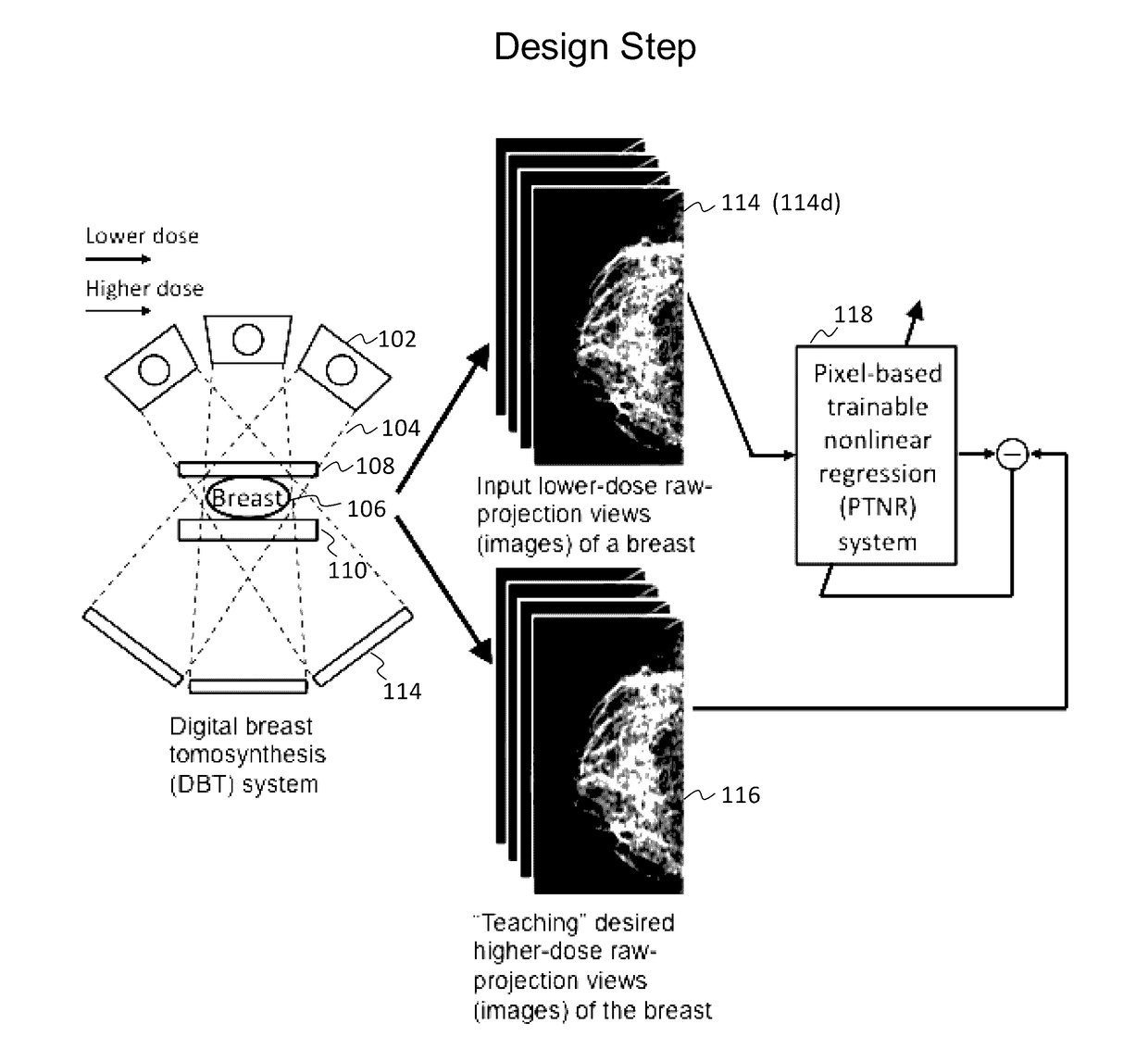
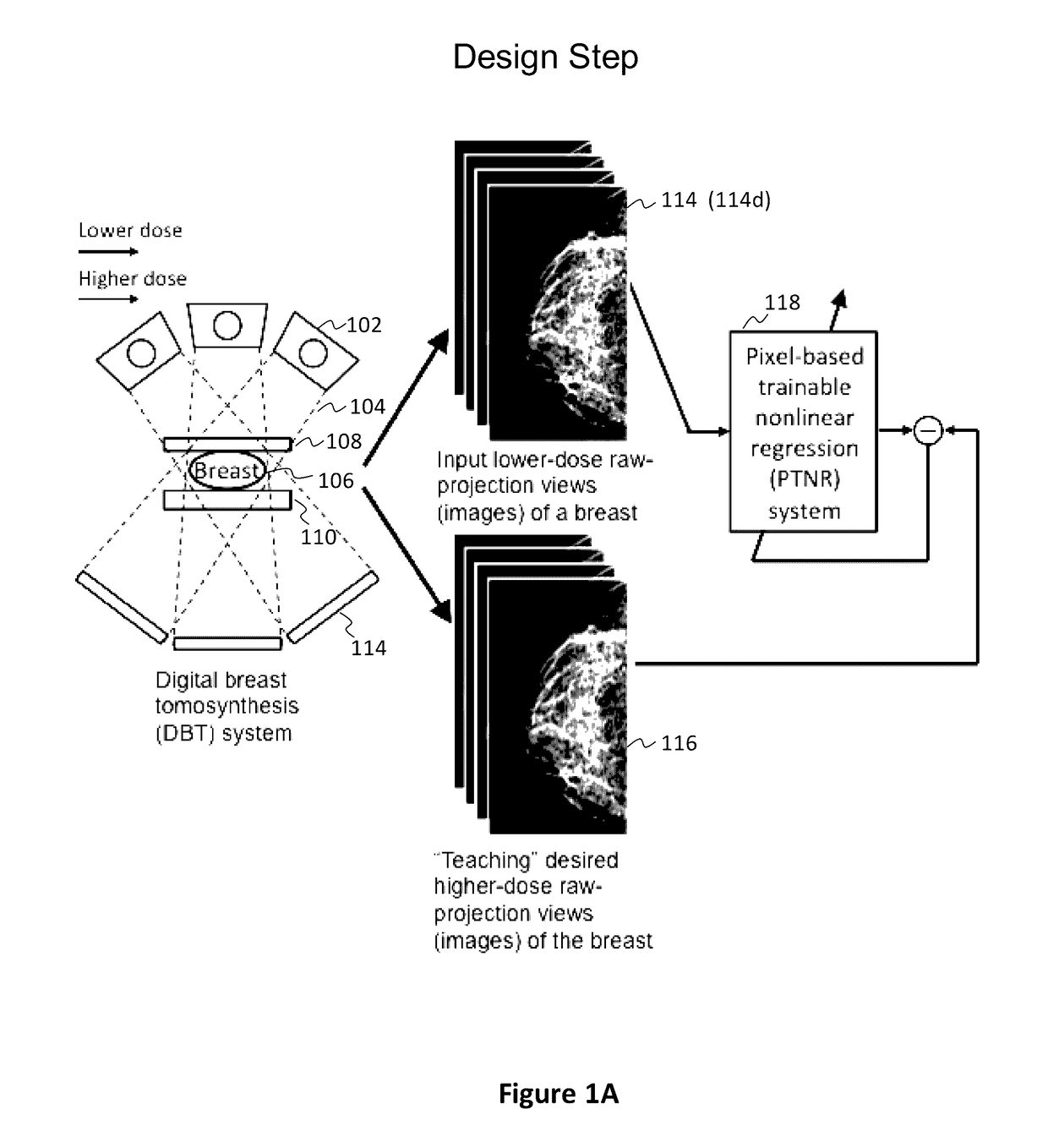
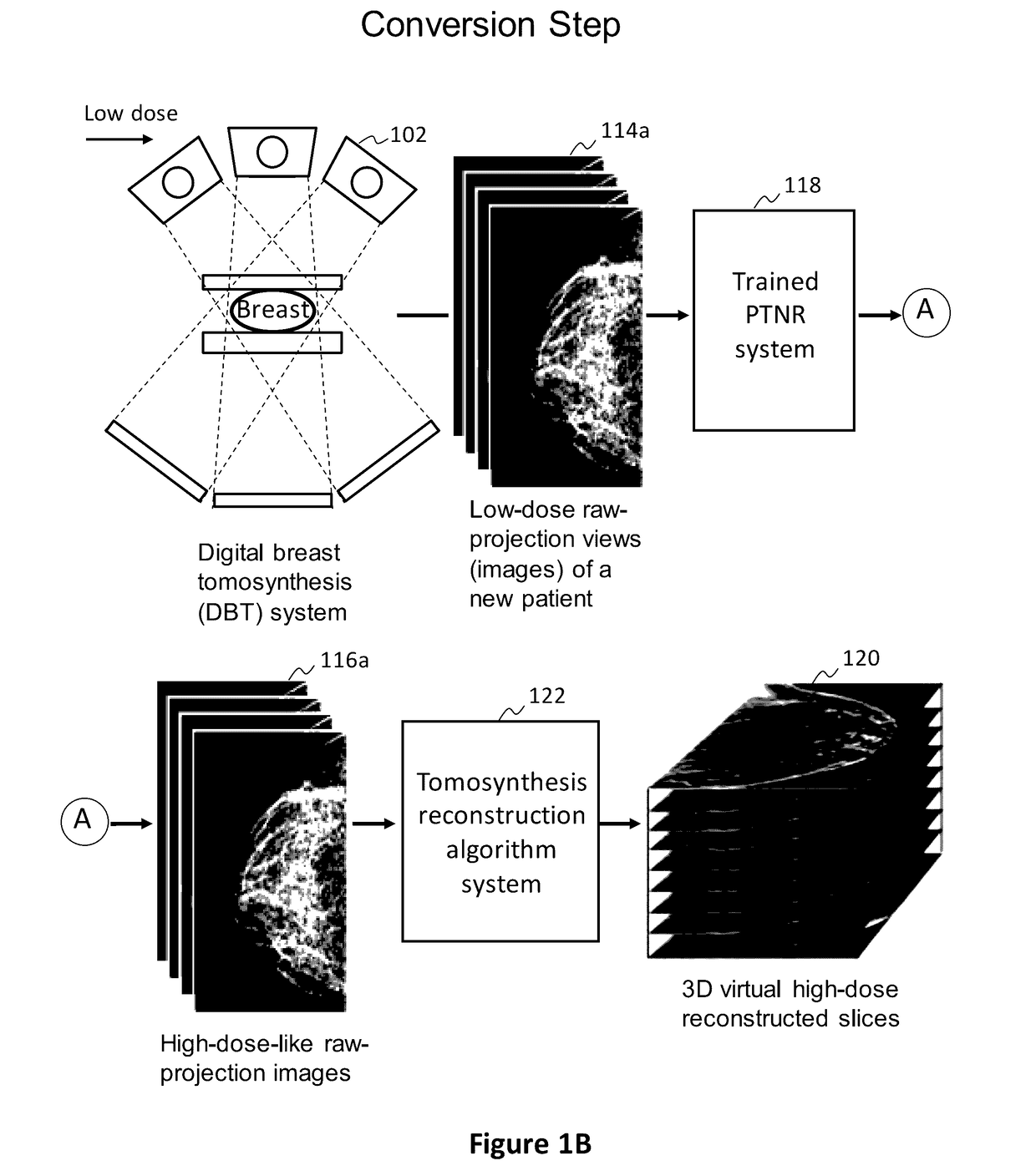
Converting low-dose to higher dose 3D tomosynthesis images through machine-learning processes
ActiveUS20170071562A1Quality improvementReduce noiseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomosynthesisImaging quality
A method and system for converting low-dose tomosynthesis projection images or reconstructed slices images with noise into higher quality, less noise, higher-dose-like tomosynthesis reconstructed slices, using of a trainable nonlinear regression (TNR) model with a patch-input-pixel-output scheme called a pixel-based TNR (PTNR). An image patch is extracted from an input raw projection views (images) of a breast acquired at a reduced x-ray radiation dose (lower-dose), and pixel values in the patch are entered into the PTNR as input. The output of the PTNR is a single pixel that corresponds to a center pixel of the input image patch. The PTNR is trained with matched pairs of raw projection views (images together with corresponding desired x-ray radiation dose raw projection views (images) (higher-dose). Through the training, the PTNR learns to convert low-dose raw projection images to high-dose-like raw projection images. Once trained, the trained PTNR does not require the higher-dose raw projection images anymore. When a new reduced x-ray radiation dose (low dose) raw projection images is entered, the trained PTNR outputs a pixel value similar to its desired pixel value, in other words, it outputs high-dose-like raw projection images where noise and artifacts due to low radiation dose are substantially reduced, i.e., a higher image quality. Then, from the “high-dose-like” projection views (images), “high-dose-like” 3D tomosynthesis slices are reconstructed by using a tomosynthesis reconstruction algorithm. With the “virtual high-dose” tomosynthesis reconstruction slices, the detectability of lesions and clinically important findings such as masses and microcalcifications can be improved.
Owner:ALARA SYST
Real-time feedback for preventing high dose c-arch geometry positions
ActiveUS20140307855A1Reduce total usageSmall impactLocal control/monitoringRadiation safety meansSoft x rayImaging quality
The present invention relates to an apparatus for aiding operation of an interventional x-ray imager during image acquisition, to a method of aiding operation of an x-ray imager, to an interventional x-ray imager, to a computer program element and to a computer readable medium. The X-ray imager is capable of varying X-ray dosages depending on differences in X-ray attenuation levels across an object of interest to be imaged and is capable of assuming any one of a plurality of imaging geometry positions when acquiring an image. An indication, visual, acoustic or haptic, to the operator of an X-ray imager is provided on the incurred change in X-ray dosage when changing from a current projection view to an updated projection view, provided that a given constant image quality is to be maintained throughout the different views.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
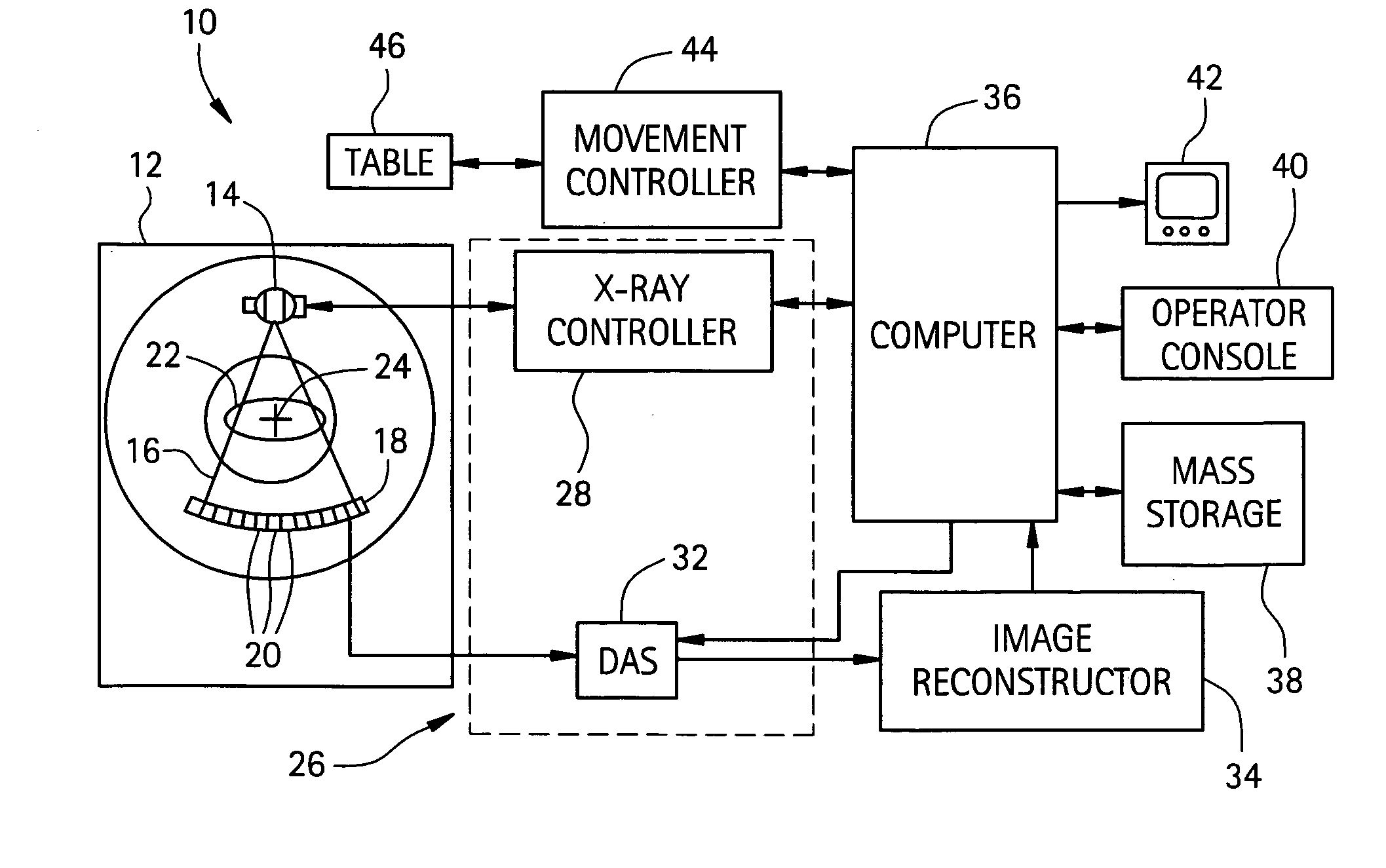
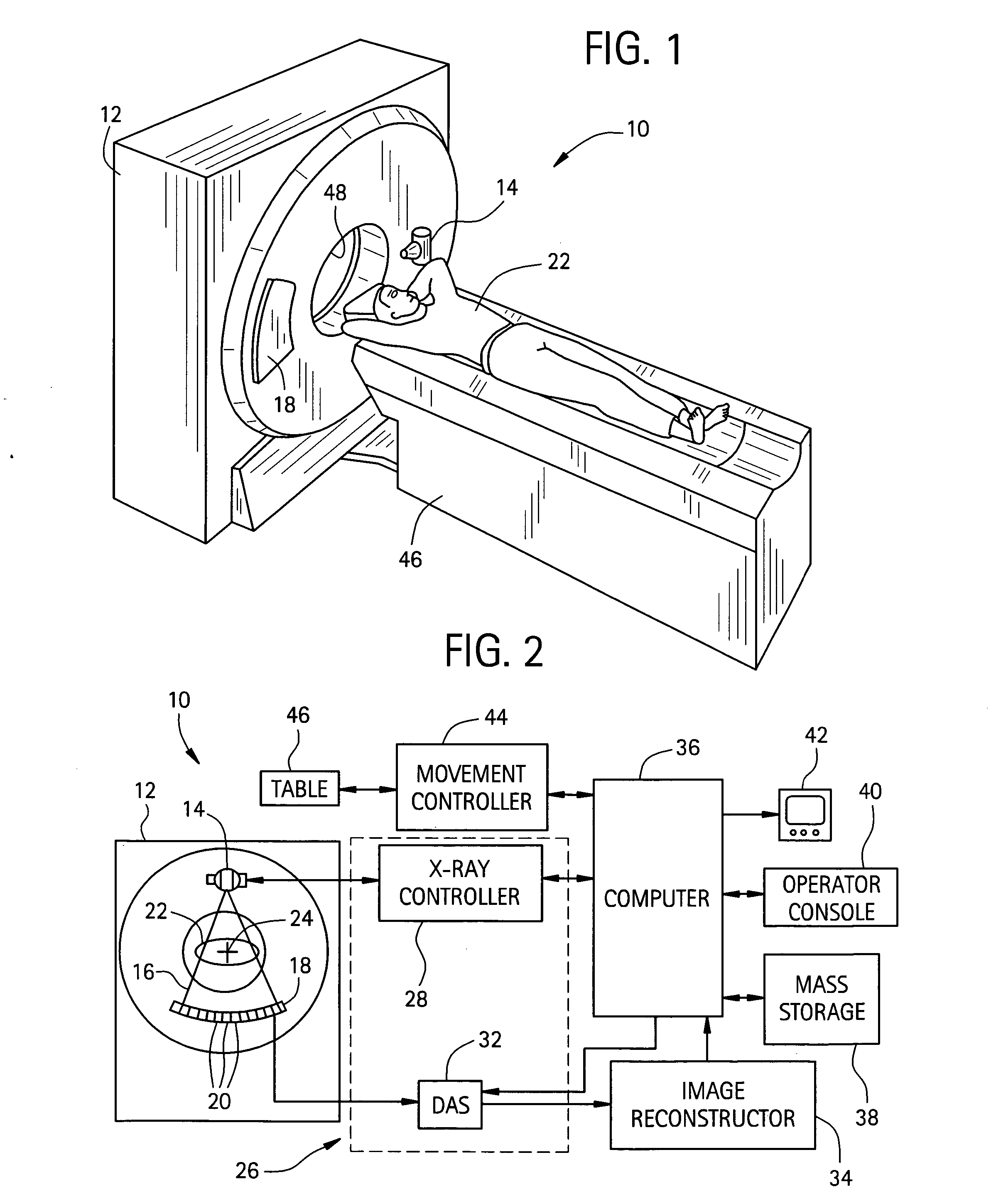
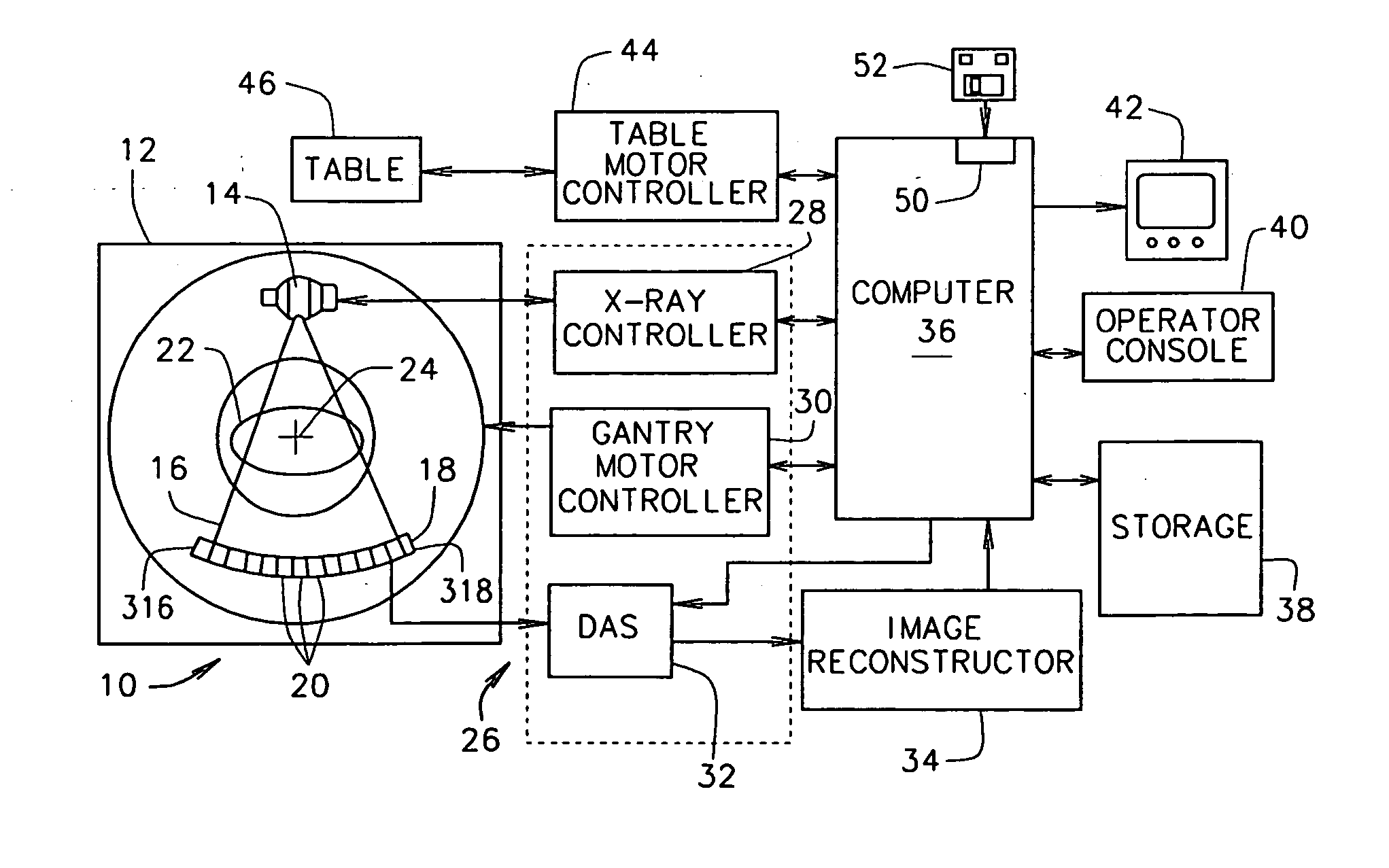
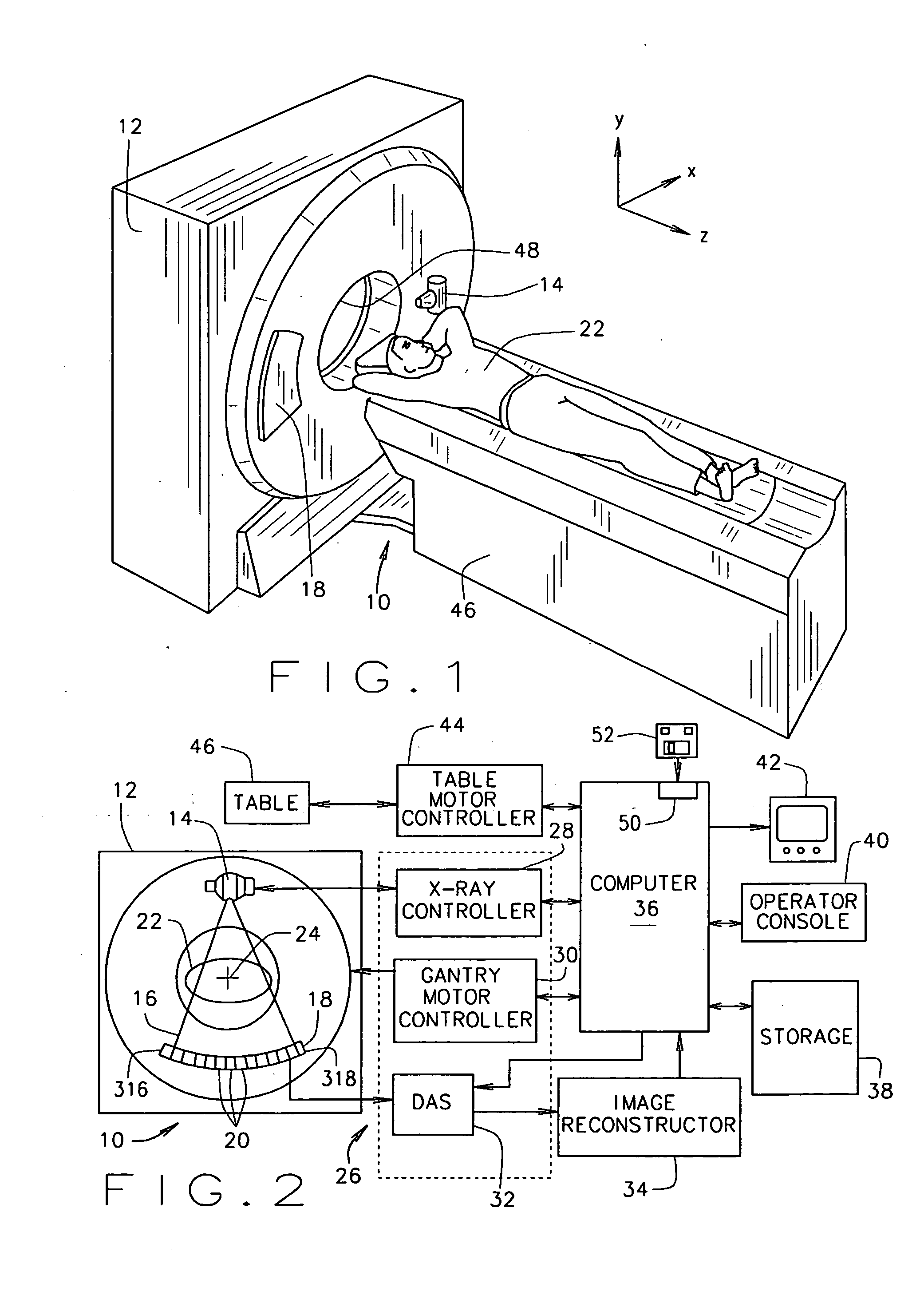
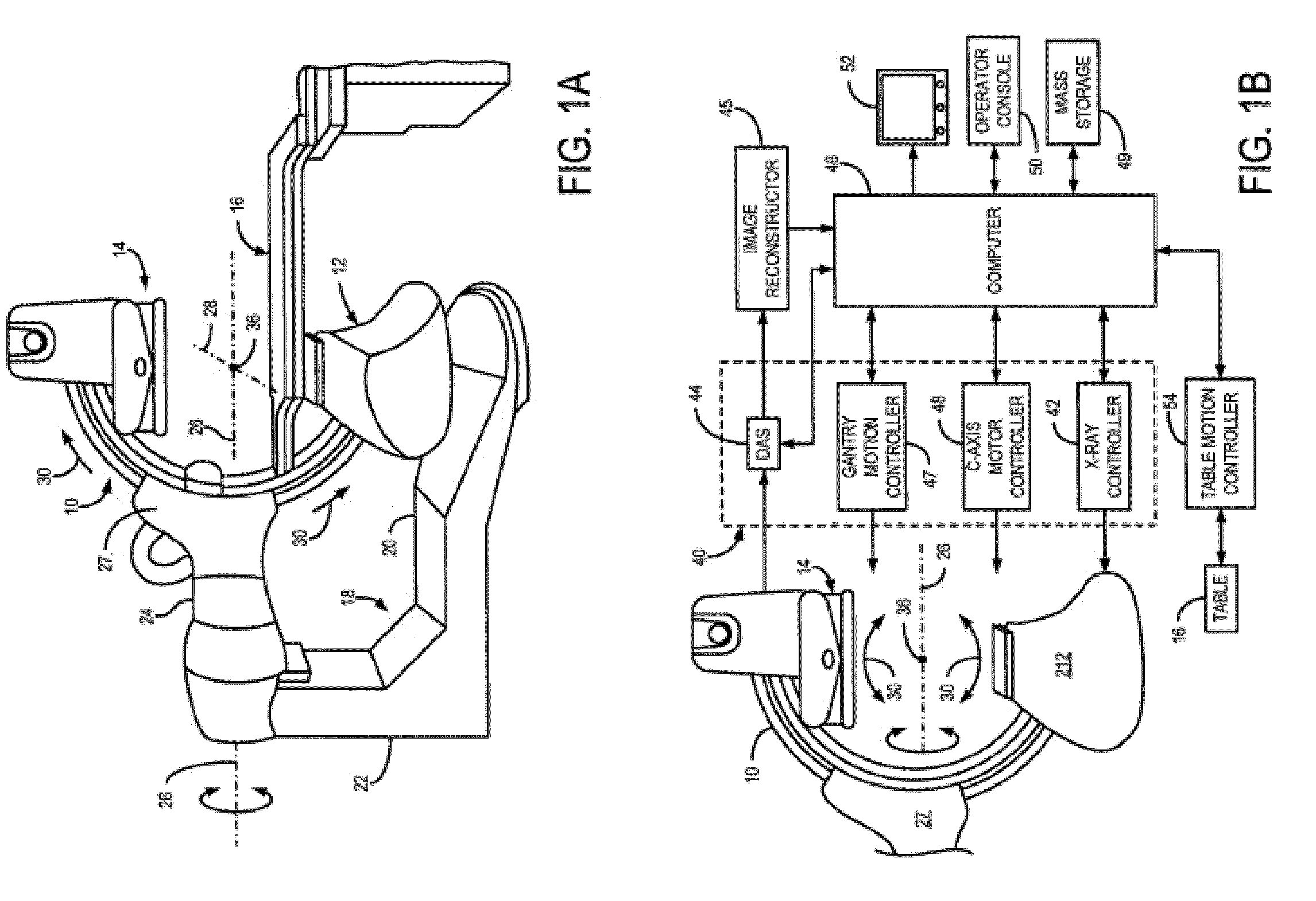
System and method for defective detector cell and DAS channel correction
ActiveUS20050063513A1Minimize the numberMinimize impactTelevision system detailsComputerised tomographsImaging processingData acquisition
A method and system for an improved data acquisition system with an image detector array and an image processing system which finds a malfunctioning cell, interpolates a signal for the malfunctioning cell using neighboring channels of the cell, and corrects the interpolation with an error rate found in performing interpolations on neighboring rows with cells which are not malfunctioning. The image processing system may include a DAS and a reconstruction system. The step of finding a malfunctioning cell may be accomplished through a variety of methods, such as measuring discrepancies between a cell's and its neighboring cell's average readings over time and exposing the cells to x-rays which should produce similar readings in all the cells and comparing the cells' signals, looking for discrepancies. The step of interpolating and the step of correcting may take into consideration cells within the same projection view as the malfunctioning cell.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
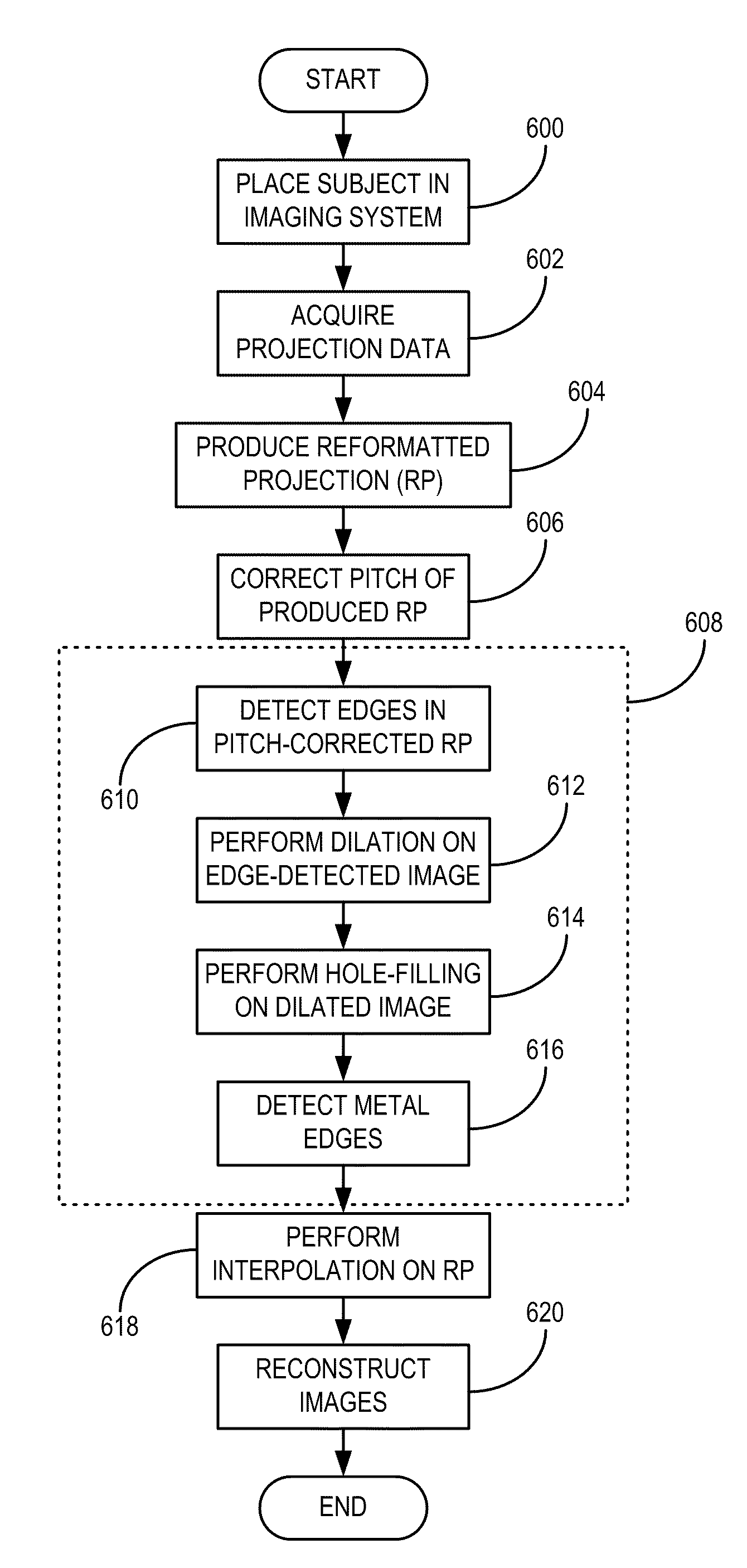
System and Method for Highly Attenuating Material Artifact Reduction in X-Ray Computed Tomography
The present invention is a method for reducing artifacts caused by highly attenuating materials in x-ray computed tomography (“CT”) images. The method includes combining projection views acquired at equivalent view angles to generate a projection plane data set, from which a reformatted projection is produced. The reformatted projection is then processed to detect and segment regions corresponding to objects composed of metals, metal alloys, or other highly attenuating materials. These segmented regions are then removed from the reformatted projection and the removed portions replaced by attenuation information interpolated from portions of the reformatted projection adjacent the removed portions. The interpolated reformatted projection is then mapped back to a projection plane data set, and an image of the subject is reconstructed from the projection views contained in that data set. The reconstructed image, therefore, is one in which artifacts caused by highly attenuating materials are substantially suppressed.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
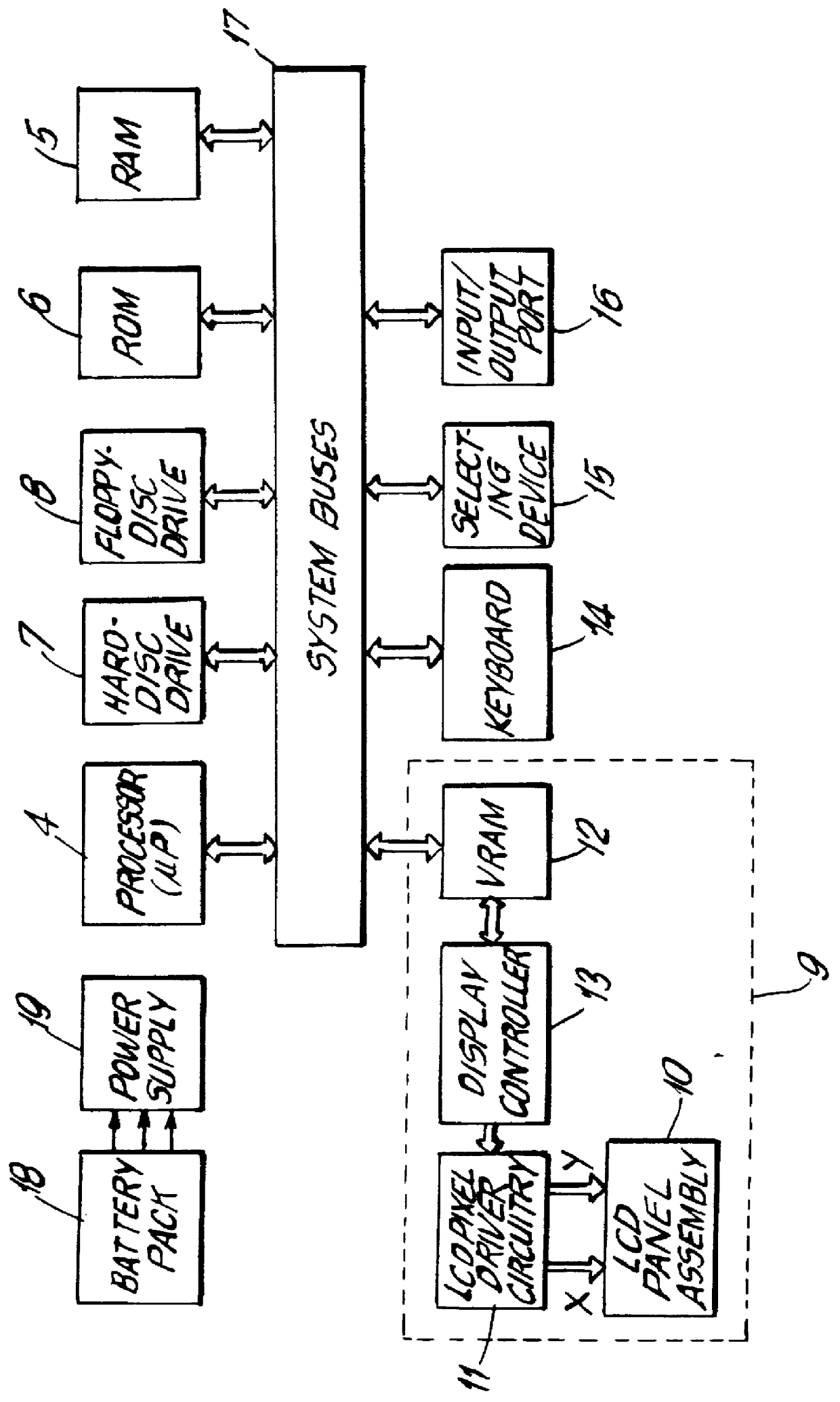
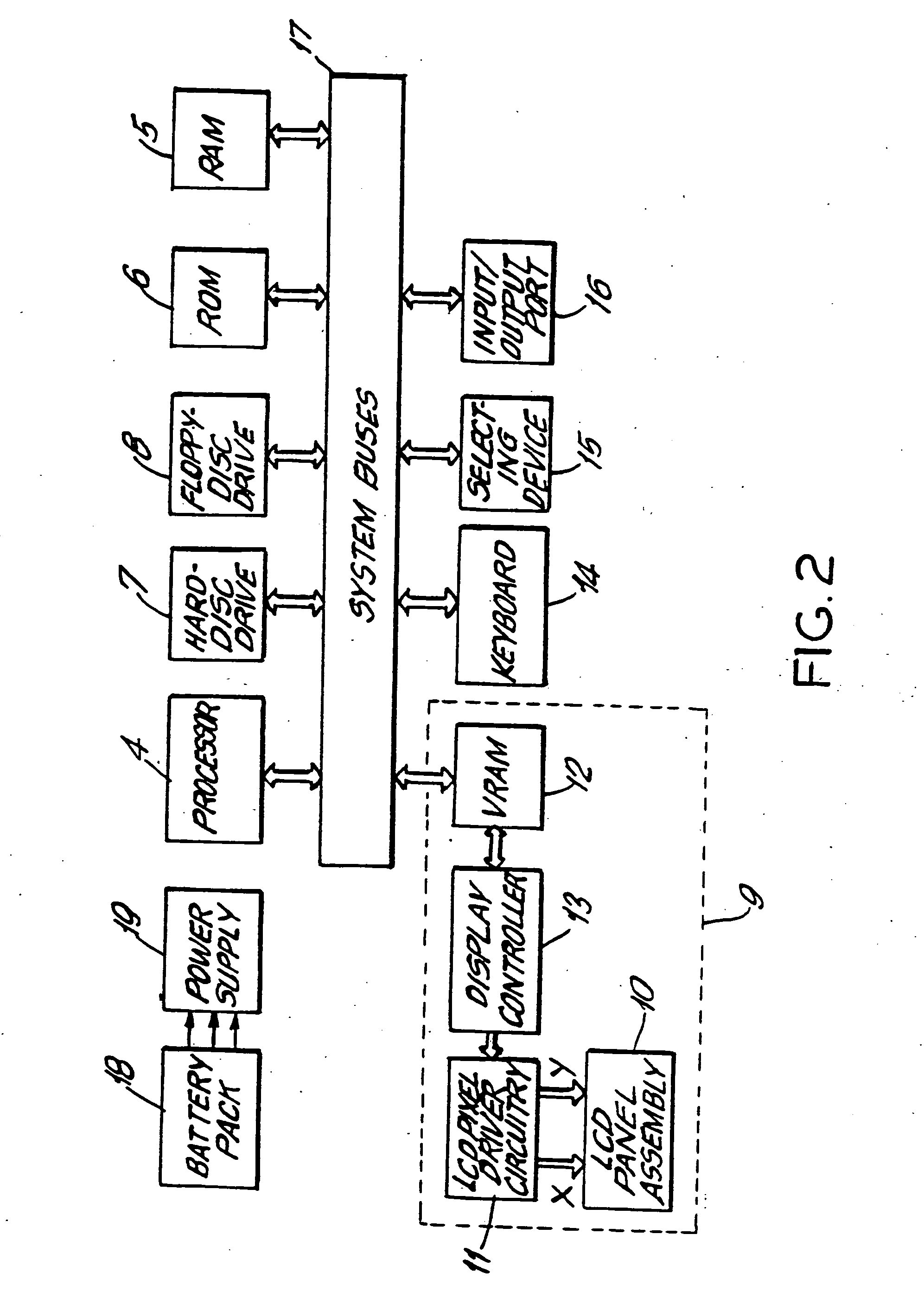
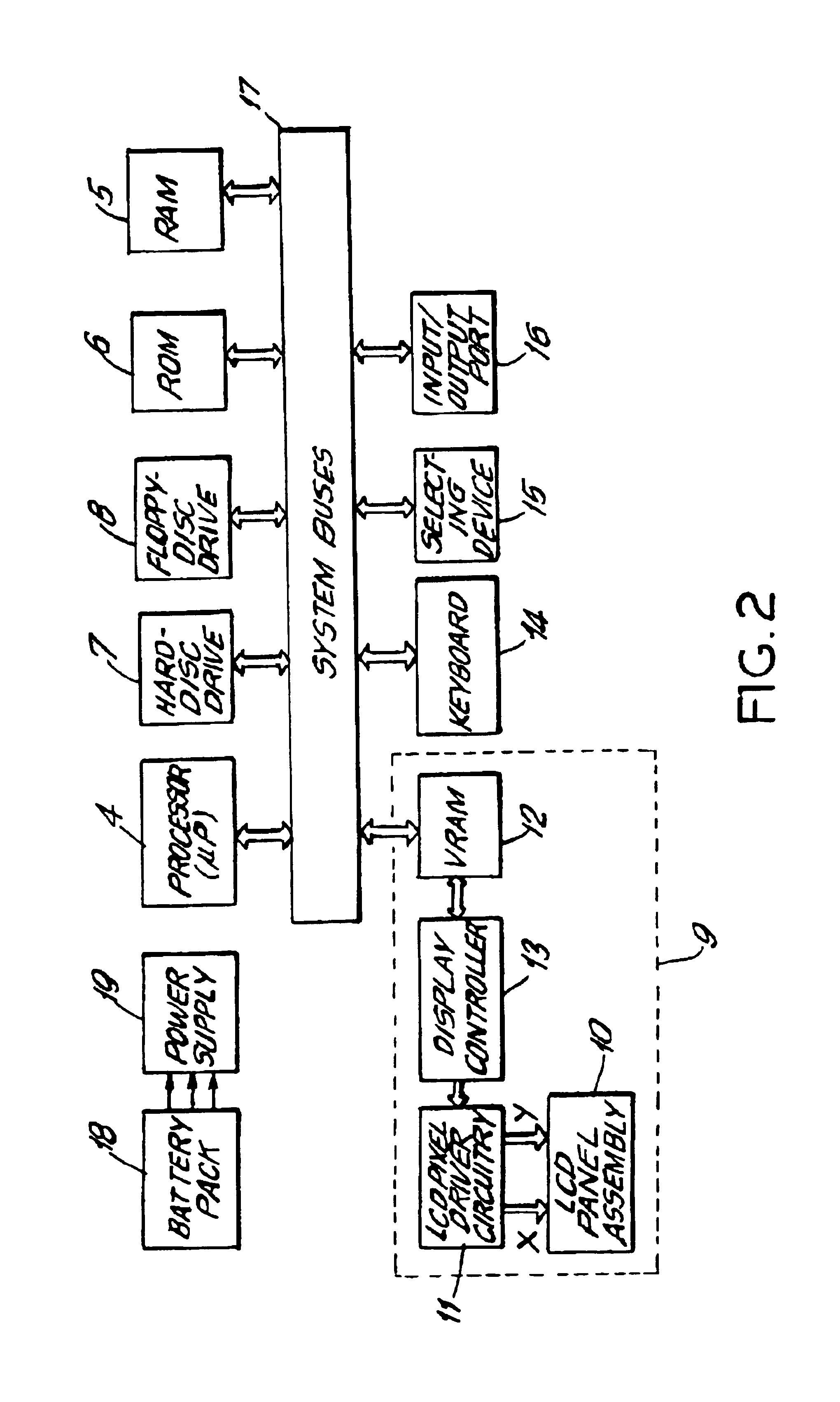
Electro-optical backlighting panel for use in computer-based display systems and portable light projection device for use therewith
InactiveUS6104447AInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsOperation modeTouchscreen
An electro-optical backlighting panel construction for use in portable computer-based systems having direct and projection viewing modes of operation. In the illustrative embodiments of the present invention, the electro-optical backlighting panel is integrated with a LCD display panel, a micropolarization panel, and a touch-screen writing panel to provide several different types of portable computer-based systems including, for example, a portable notebook computer, a computer-driven image display device, and a portable pen-computing device. In general, each of these computer-based systems are capable of selectively displaying color video images on an actively driven display surface, or projecting such video images onto a wall surface or projection screen. These computer-based systems can be easily reconfigured for projection viewing without any sort of physical modification to the LCD display panel assembly. If desired, these computer-based systems can be used to directly view "spatially-multiplexed" images of 3-D objects or imagery during the direct viewing mode, and when desired these spatially-multiplexed images can be projected onto a wall surface or projection screen during the projection viewing mode. When the spatially-multiplexed images are viewed through electrically-passive polarized glasses, the 3-D object is perceived with stereoscopic depth sensation in either mode of viewing.
Owner:REVEO
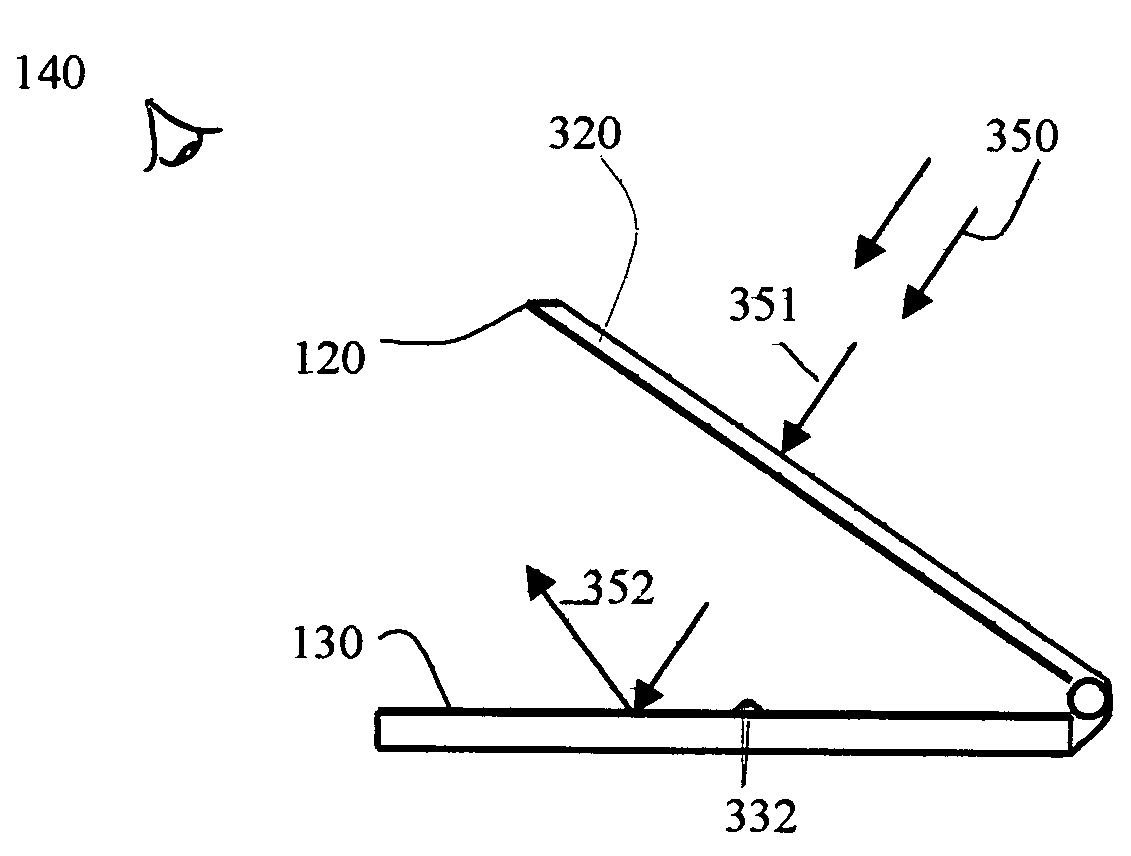
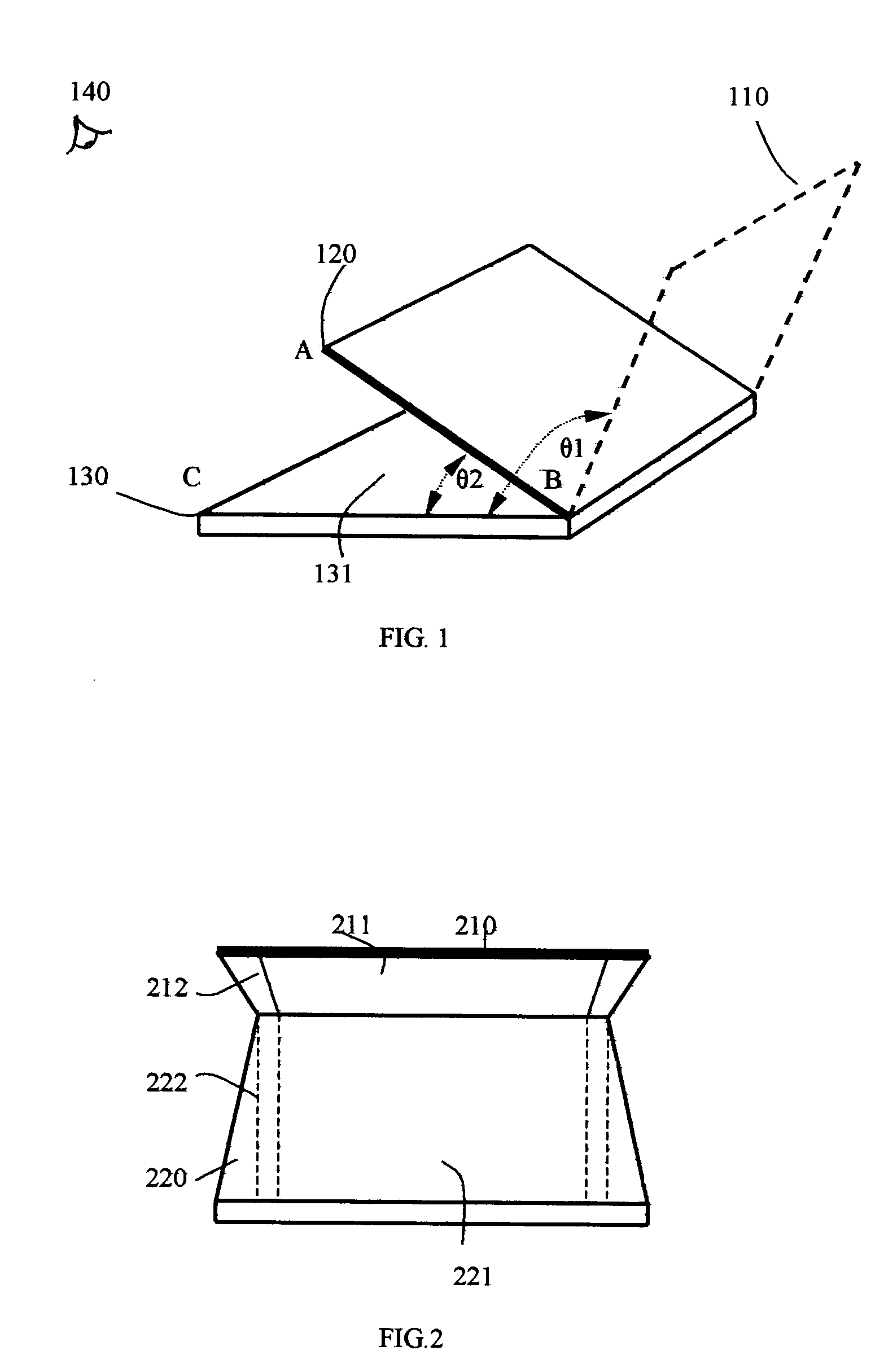
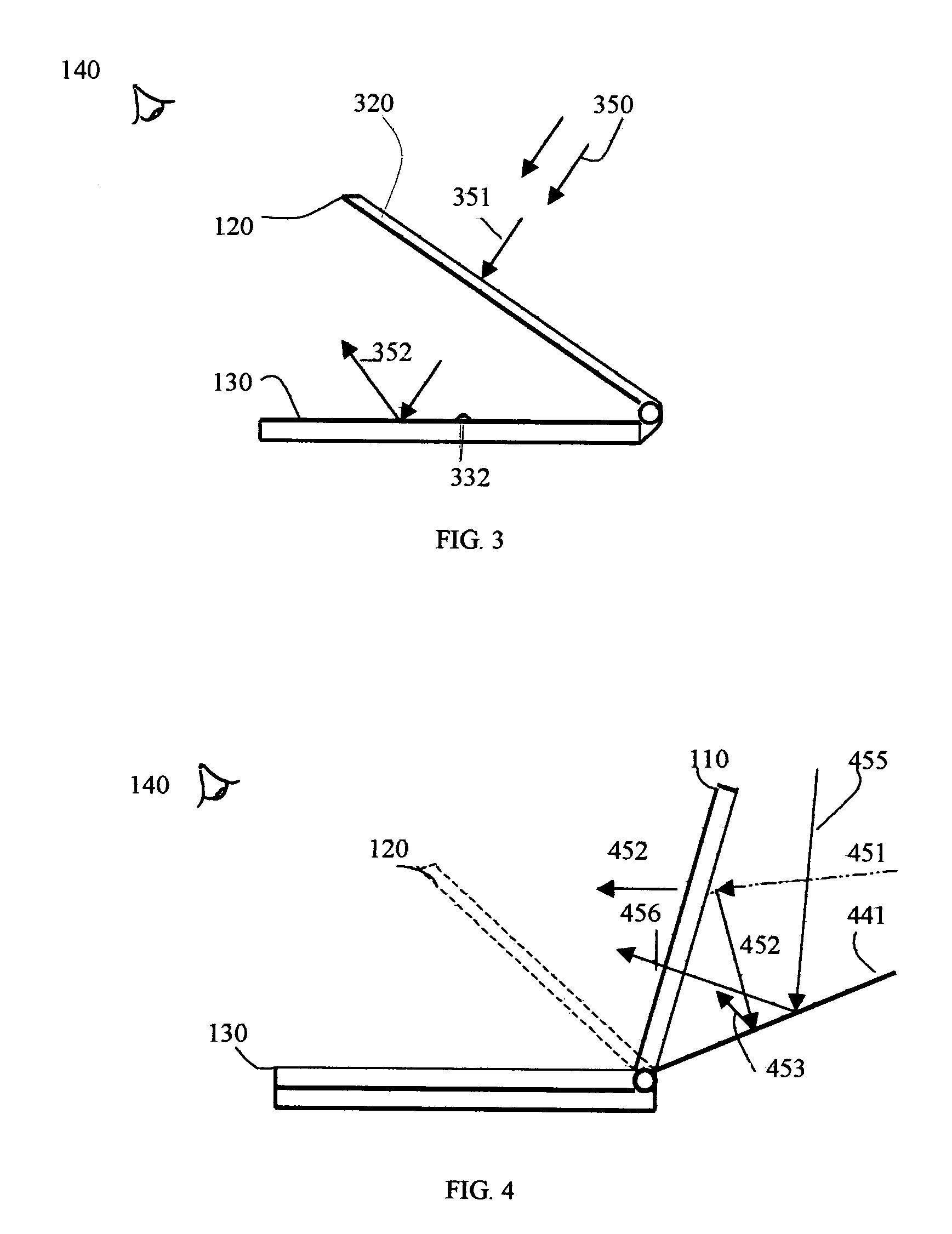
Sunlight readable direct-view and projection-view computing device
The present invention relates to a sunlight readable computing device, especially, to a full color direct-view and projection-view computing device. When the computing device works in the direct-view mode, the display panel tilt up to the conventional display position and it has a wide, open viewing angle; when the computing device works in the projection view mode, the display panel tilt down and forms a projection image via a mirror plate with a sufficient high contrast ratio and superior readability even directly under sunshine. The solar ambient light can be utilized as the lighting source in both direct-view and projection-view display modes, thus remarkably reduces the power consumption and substantially prolongs the operation time of the computing device.
Owner:MA YAO DONG
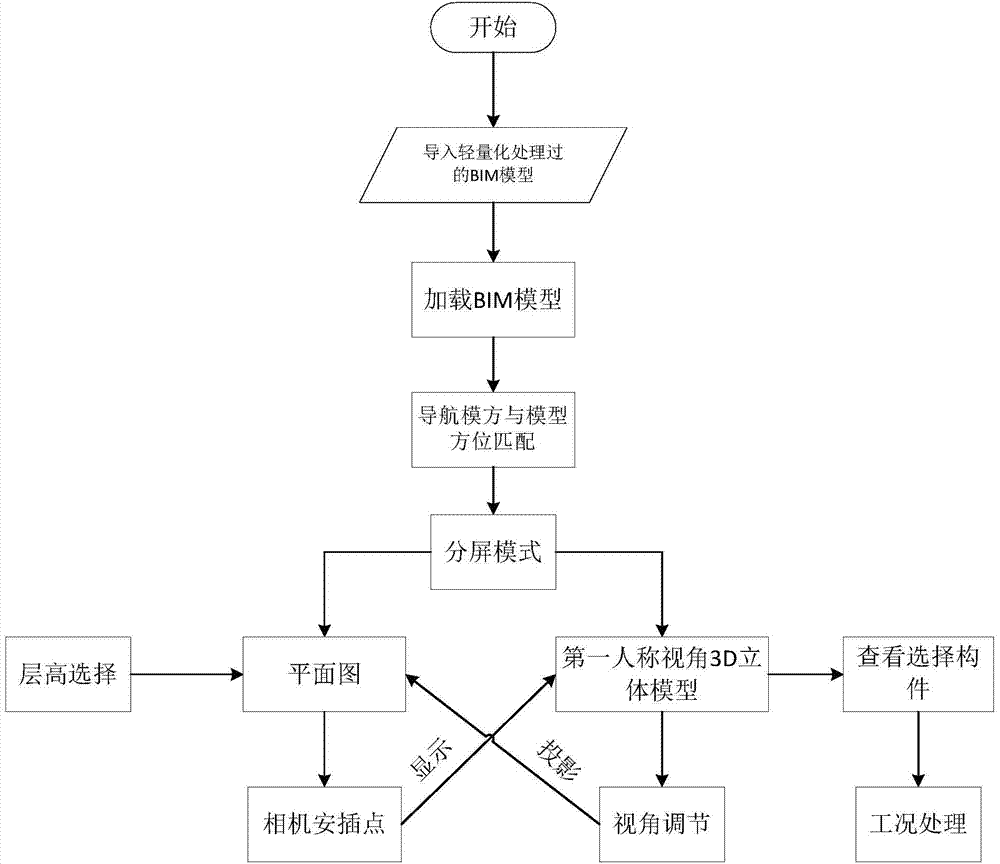
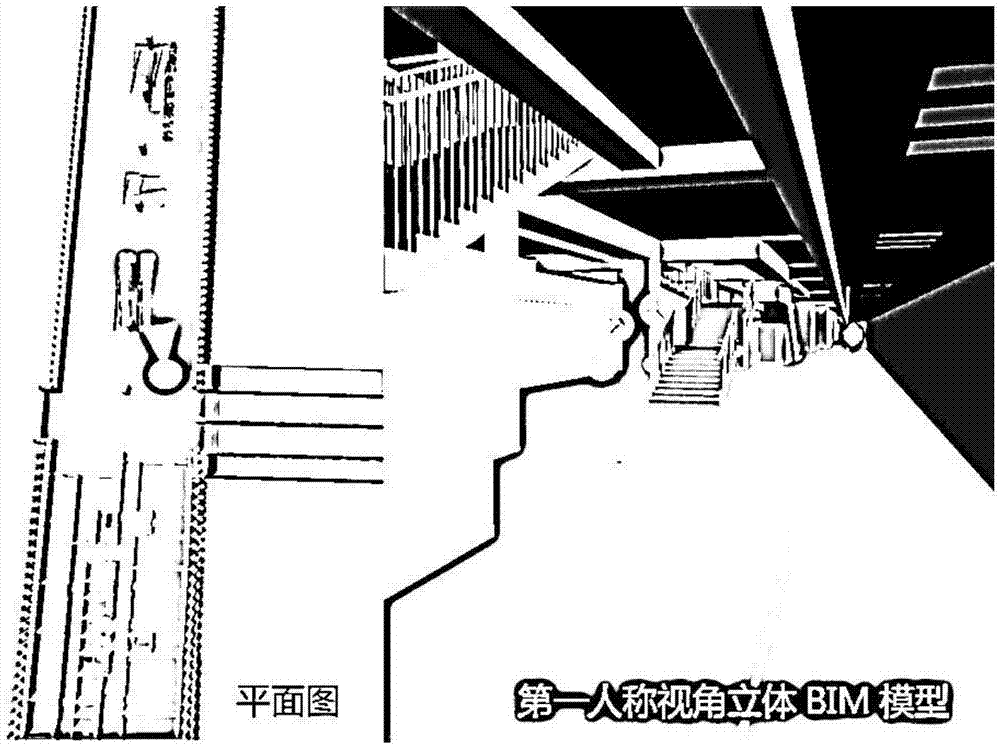
(Building Information Modeling) BIM based plan graph and first view-angle split-screen synchronous display method and system
ActiveCN104765905AEasy to viewEasy to operateSpecial data processing applicationsVirtual cameraConstruction management
The invention provides a BIM based plan graph and first view-angle split-screen synchronous display method and system. The method comprises loading and displaying a BIM stereo model; matching a navigation norm with a model bearing; generating a corresponding plane graph and placing a virtual camera; generating a corresponding first-person view-angle graph according to the camera position and view-angle information; displaying the view-angle bearing through the navigation norm visually, and providing a compass function; adjusting the view angle of the first-person view-angle graph according to user instructions, an adjusting the projection view angle direction of the virtual camera in the plane graph according to current view-angle data; and using the plane graph and the virtual camera projection as one portion and the first-person view-angle graph as the other portion to be displayed synchronously in a same screen. By means of the method and the system, a plane drawing and the first-person view-angle stereo graph are combined, the model bearing and the compass are combined, and accordingly, detail members can be observed and searched visually, the site actual engineering member and model member matching problem can be determined visually, construction management is facilitated, the requirement for the personnel technology is reduced, and even general workers can observe, record and search for the detail members according to images displayed on the same screen.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGZHU INFORMATION TECH
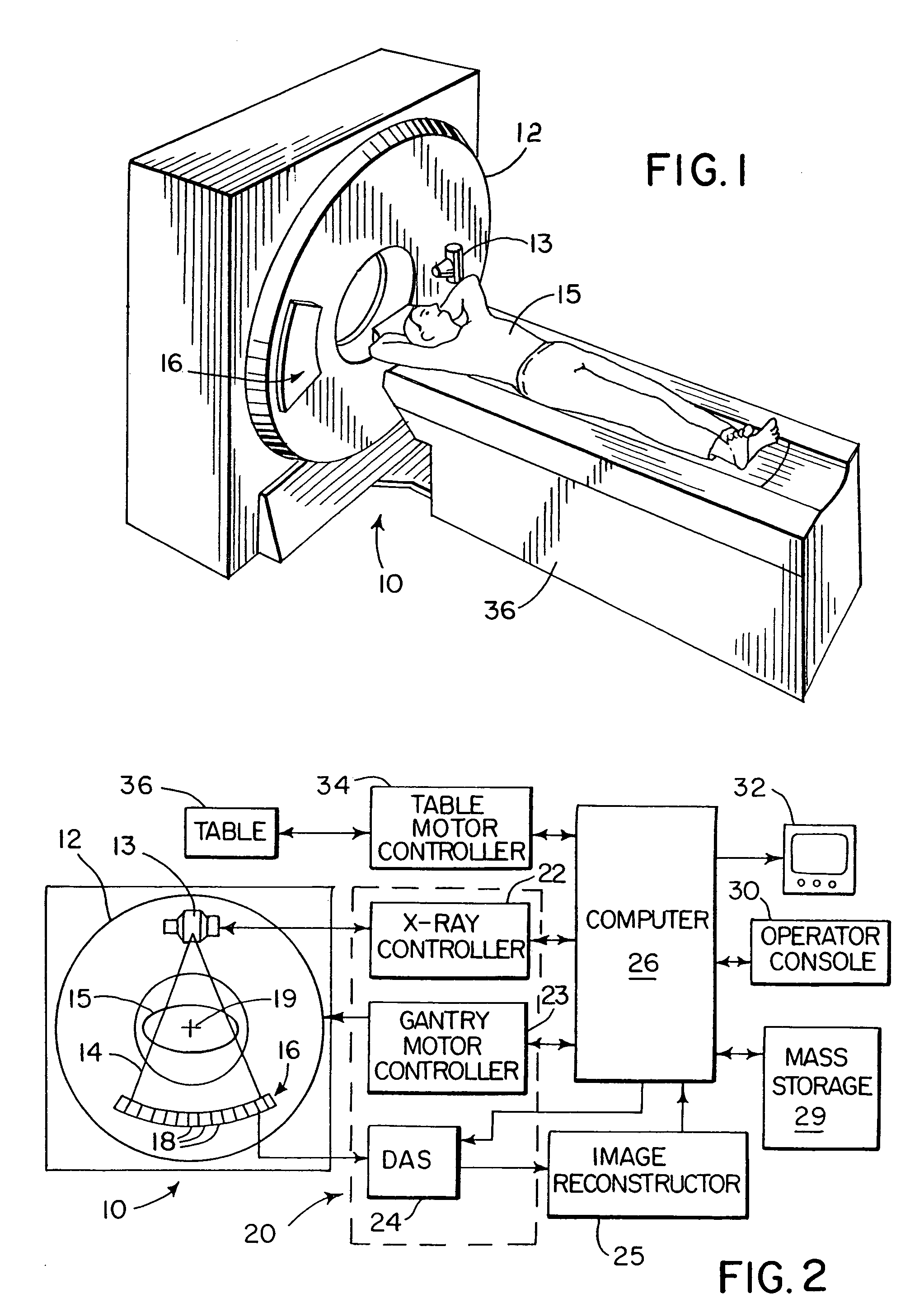
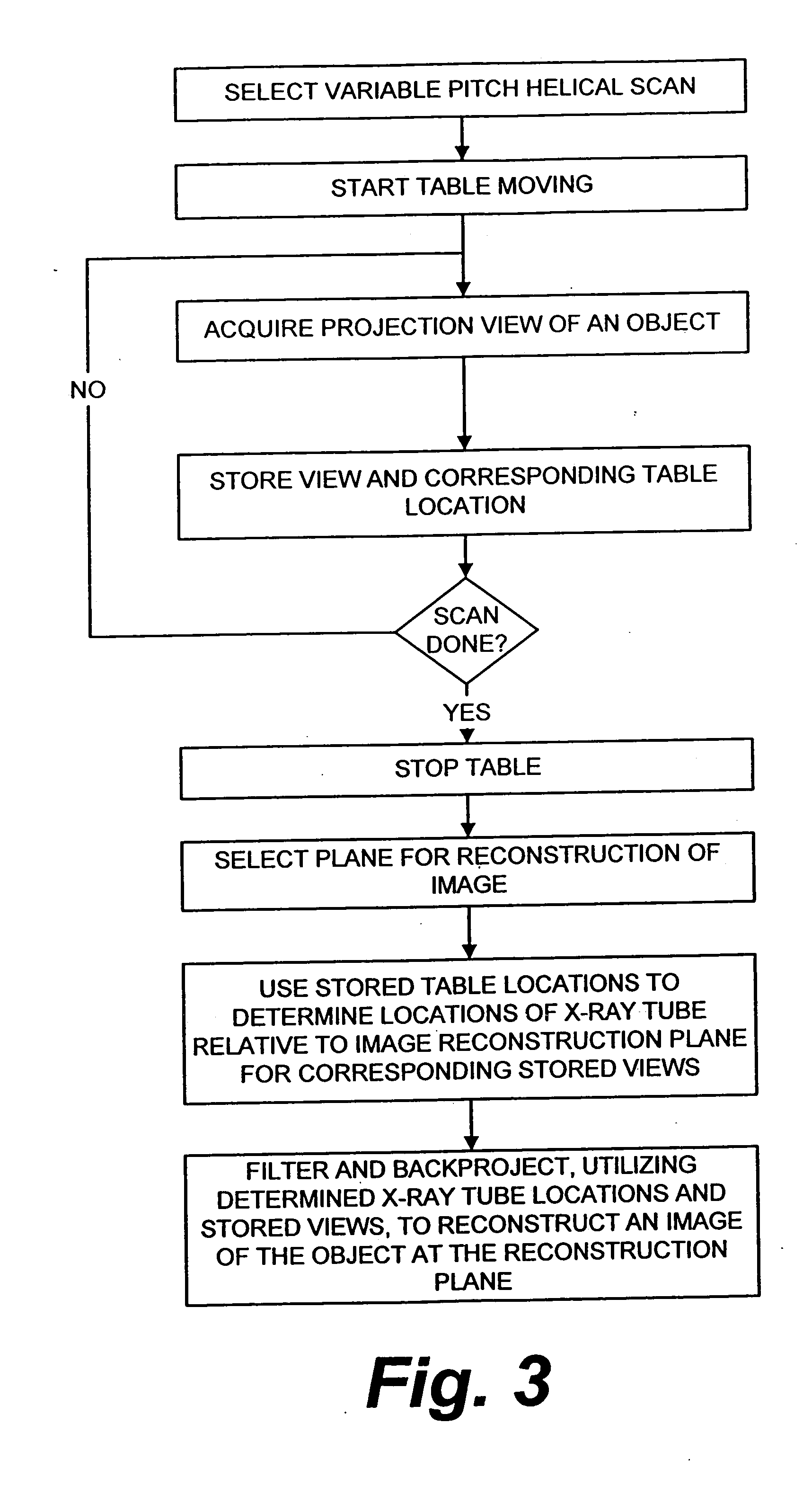
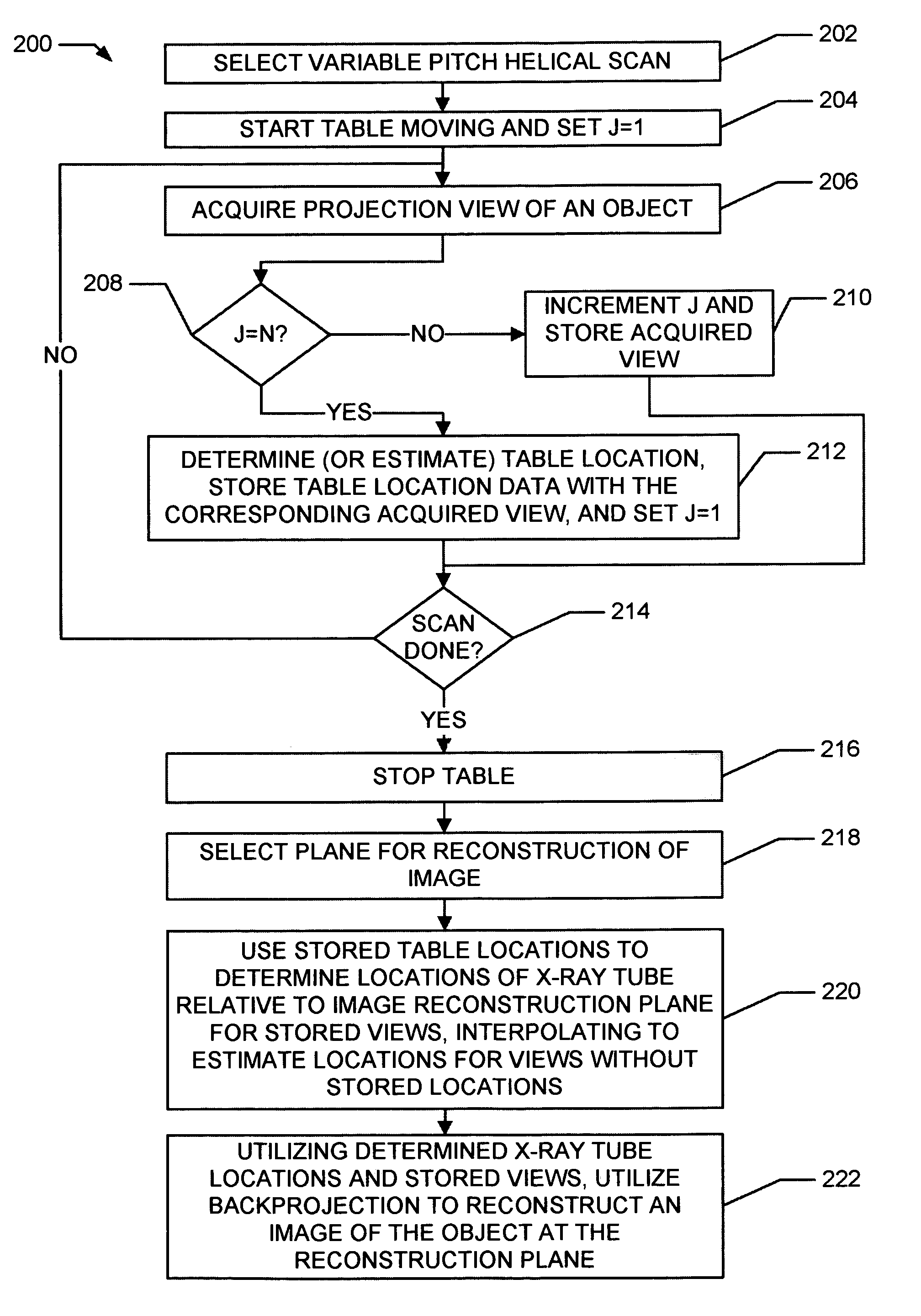
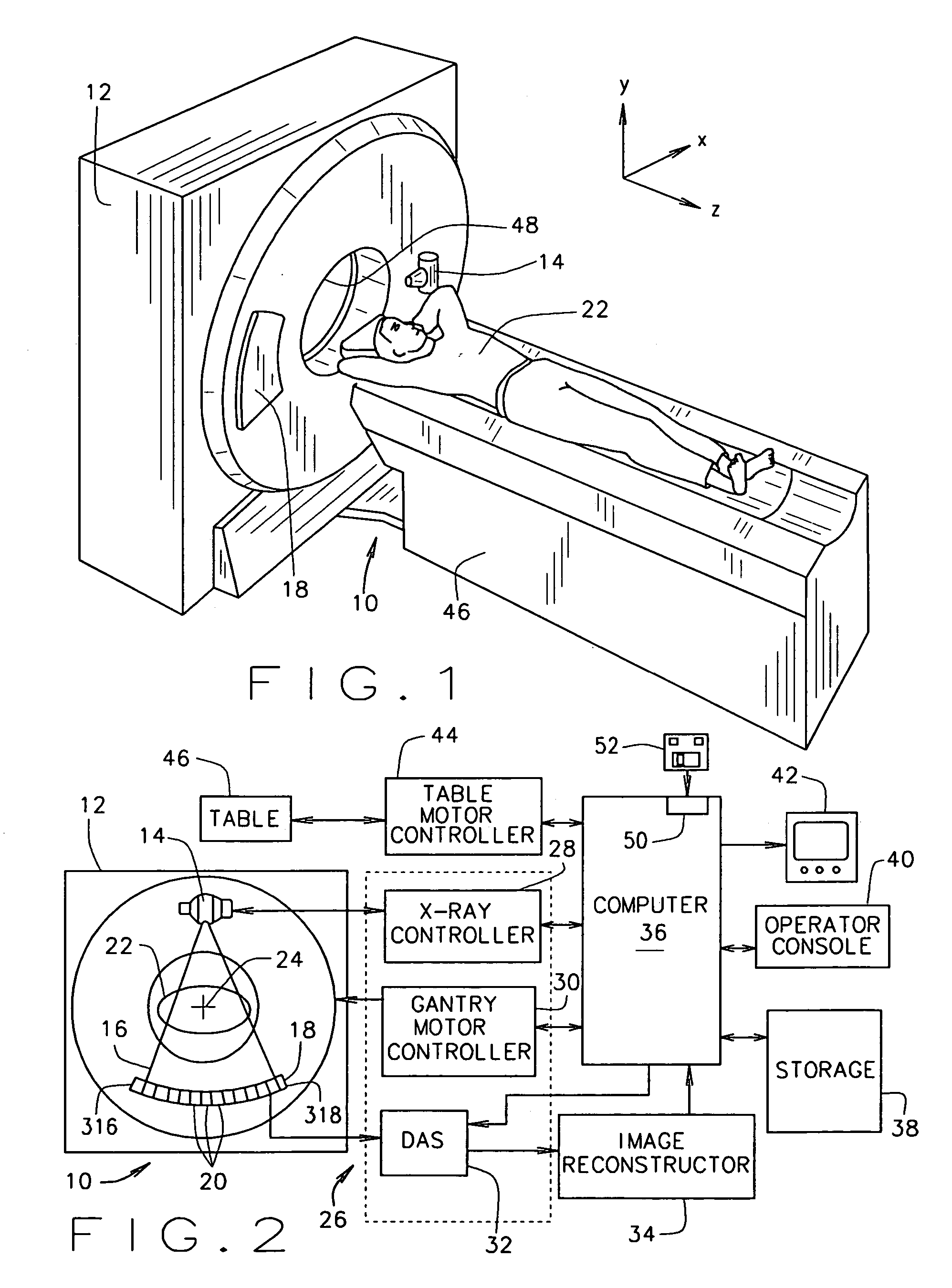
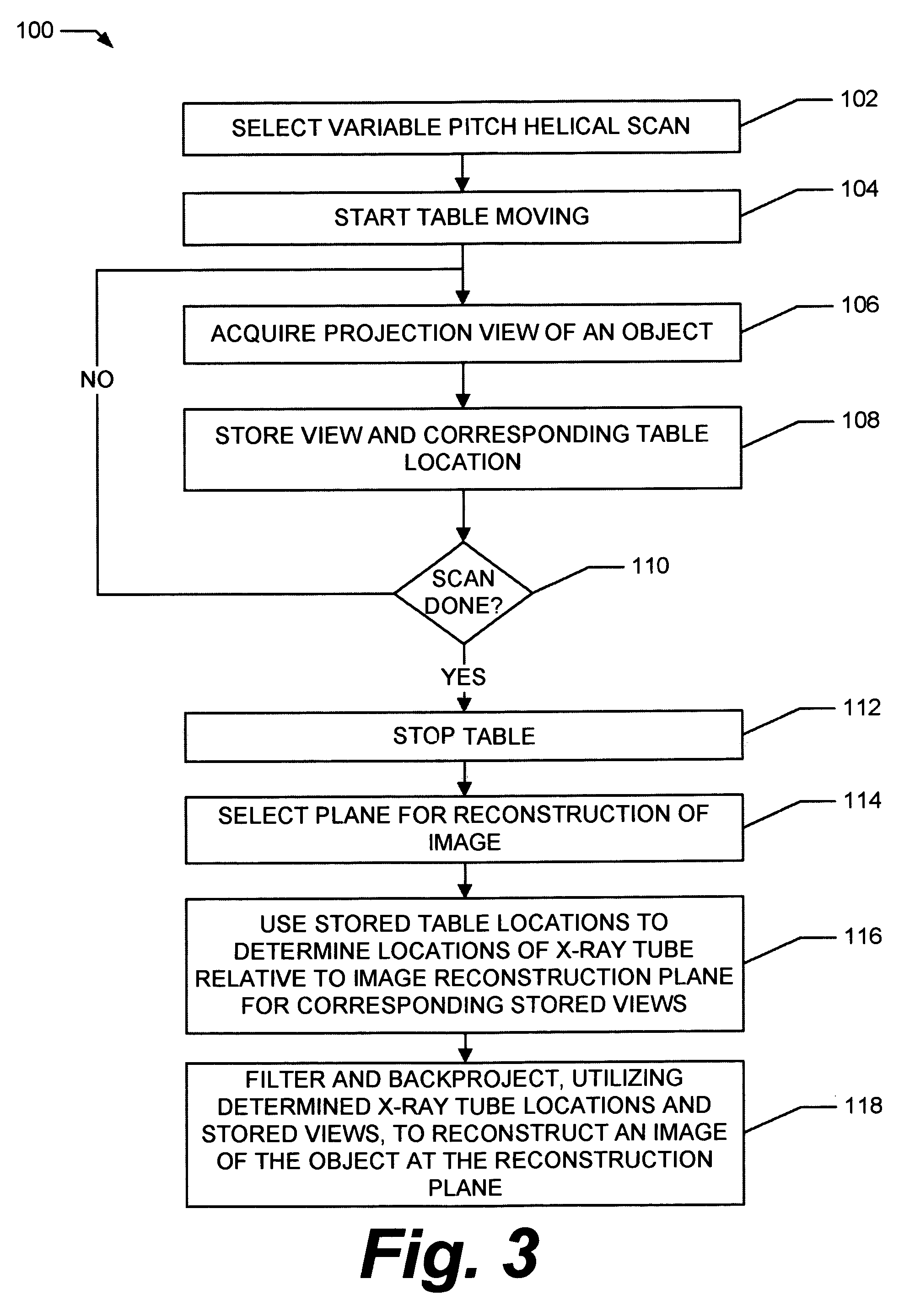
Methods and apparatus for dynamical helical scanned image production
Some configurations of the present invention thus provide a method for producing images of an object. The method includes dynamically helically scanning an object on a moving table utilizing a scanning imaging system. During the scan, projection views of the object are acquired and stored together with corresponding table locations. A plane for reconstruction of an image of the object is selected. The stored table locations are used to determine geometric variables applicable to the stored projection views; and the stored projection views are filtered and backprojected utilizing the geometrical variables to reconstruct an image of the object at the reconstruction plane.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
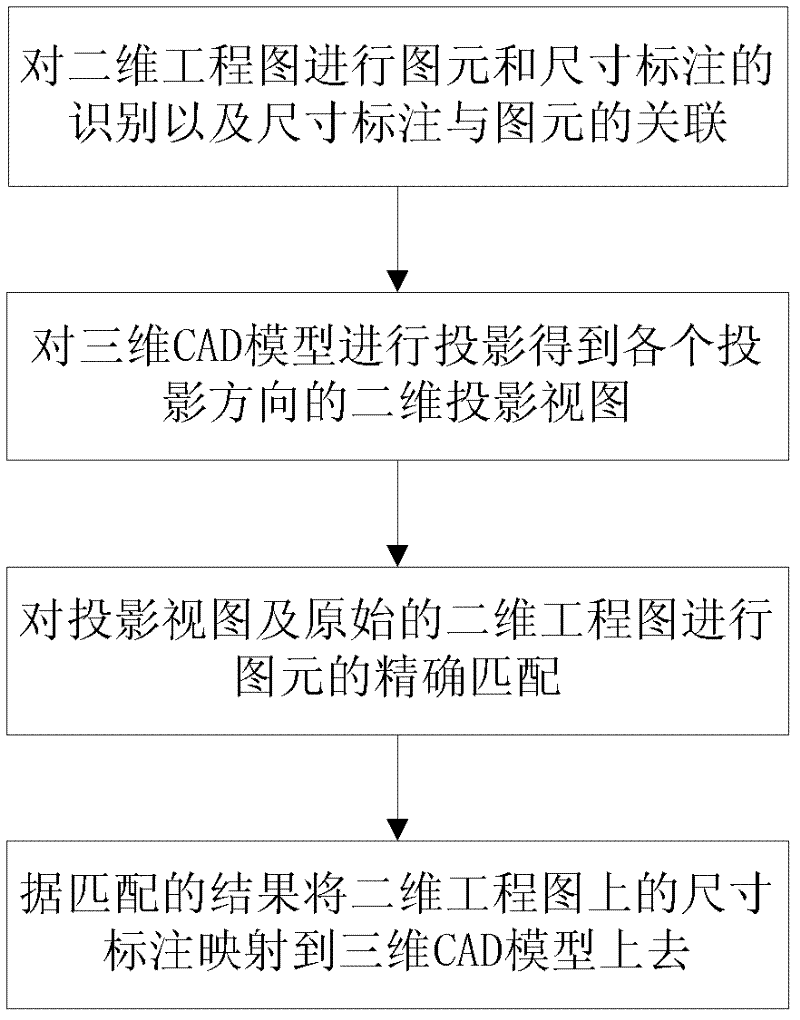
Method for translating dimensions on two-dimensional engineering drawing to three-dimensional CAD (computer aided design) model
InactiveCN102568038ACorrectly implement the mappingAchieve matchingImage data processingSpecial data processing applicationsComputer Aided DesignComputer science
The invention discloses a method for translating dimensions on a two-dimensional engineering drawing to a three-dimensional CAD (computer aided design) model. The method is used for solving a technical problem that a three-dimensional CAD model dimension marking method in prior art is low in efficiency. The technical scheme of the method is as follows: projecting the three-dimensional CAD model to obtain a projection view of the three-dimensional CAD model; then respectively extracting pixel information of the projection view and the two-dimensional engineering drawing, and respectively representing the projection view and the two-dimensional engineering drawing in a spatial relation drawing structure with a pixel as an apex; and finally carrying out accurate pixel matching on two spatial relation drawings. A test result shows that the method can realize accurate pixel matching and can correctly realize dimension tolerance mapping from the two-dimensional engineering drawing to the three-dimensional model. By using the method, a high-efficiency and intelligent method is provided for a condition that the three-dimensional CAD model and the two-dimensional engineering drawing which are separate in prior arts are translated into a single model with three-dimensional dimension marks.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
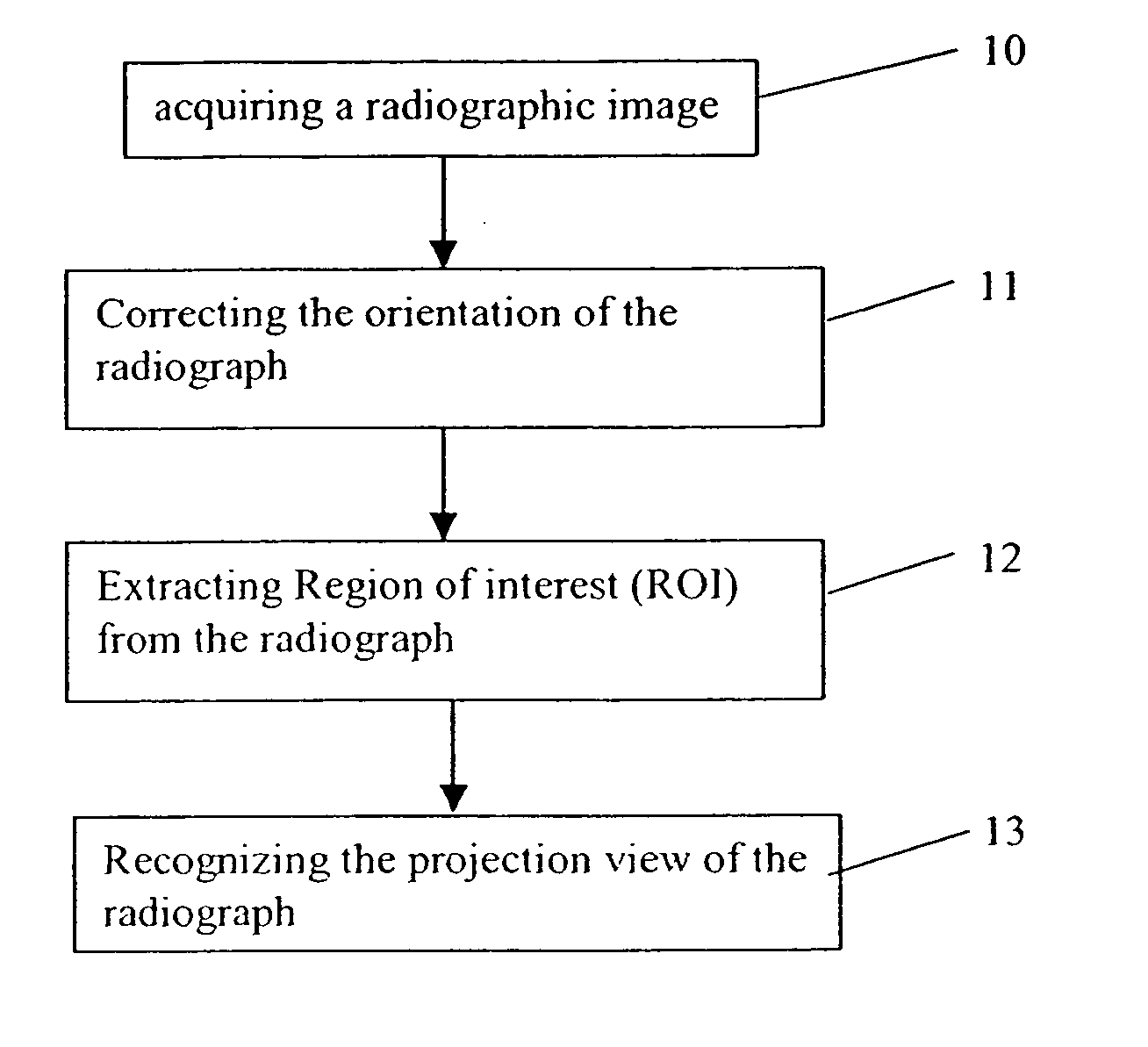
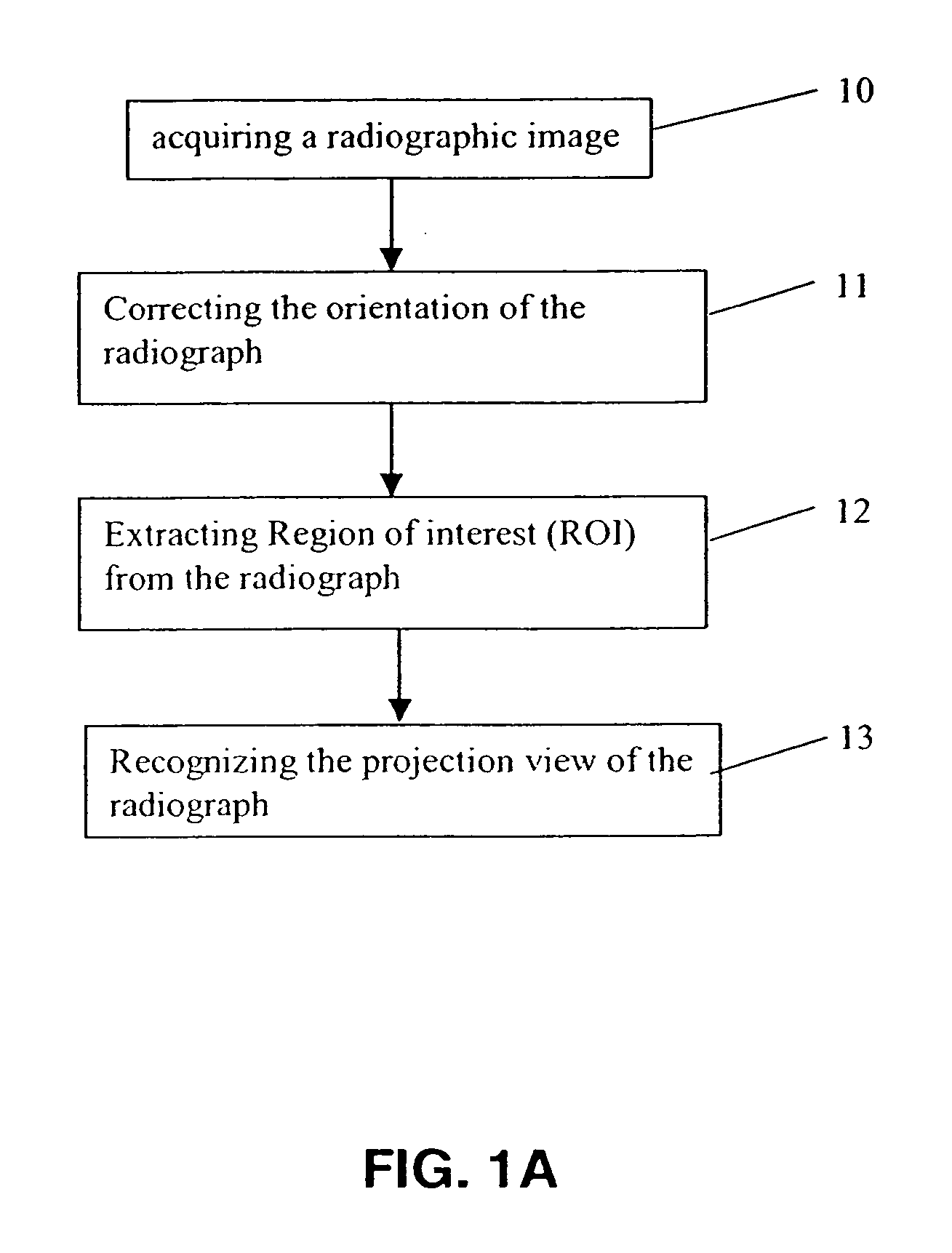
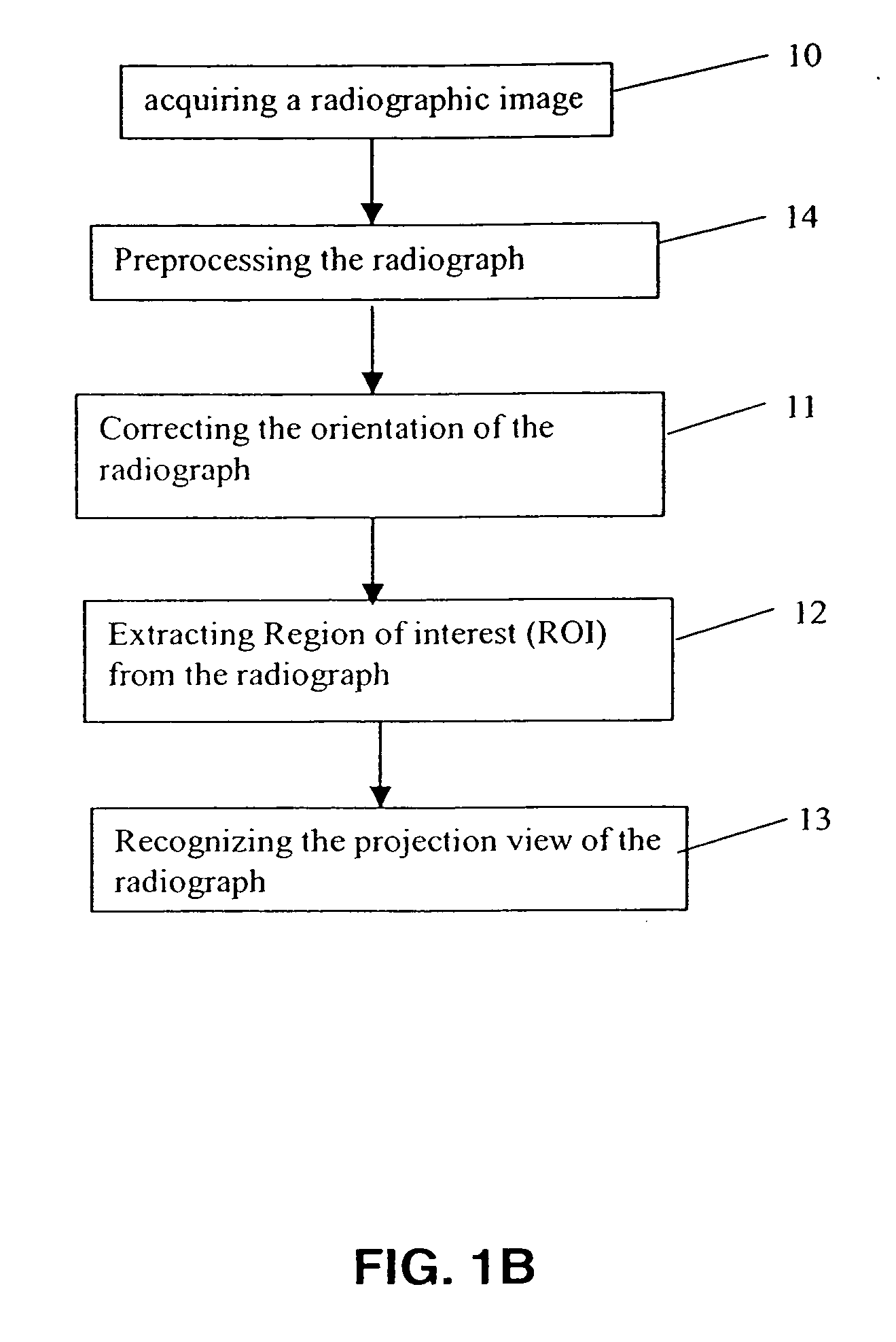
Method for recognizing projection views of radiographs
ActiveUS20060110021A1Improve robustnessEasy to identifyImage enhancementImage analysisComputer scienceProjection View
A method for recognizing the projection view of radiographs comprising the steps of correcting the orientation of the input radiograph, locating a region of interesting in the radiograph, recognizing the projection view of the radiograph.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Method and system for reconstructing cone-beam projection data with reduced artifacts
ActiveUS20090207964A1Need be addressReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationData setProjection View
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
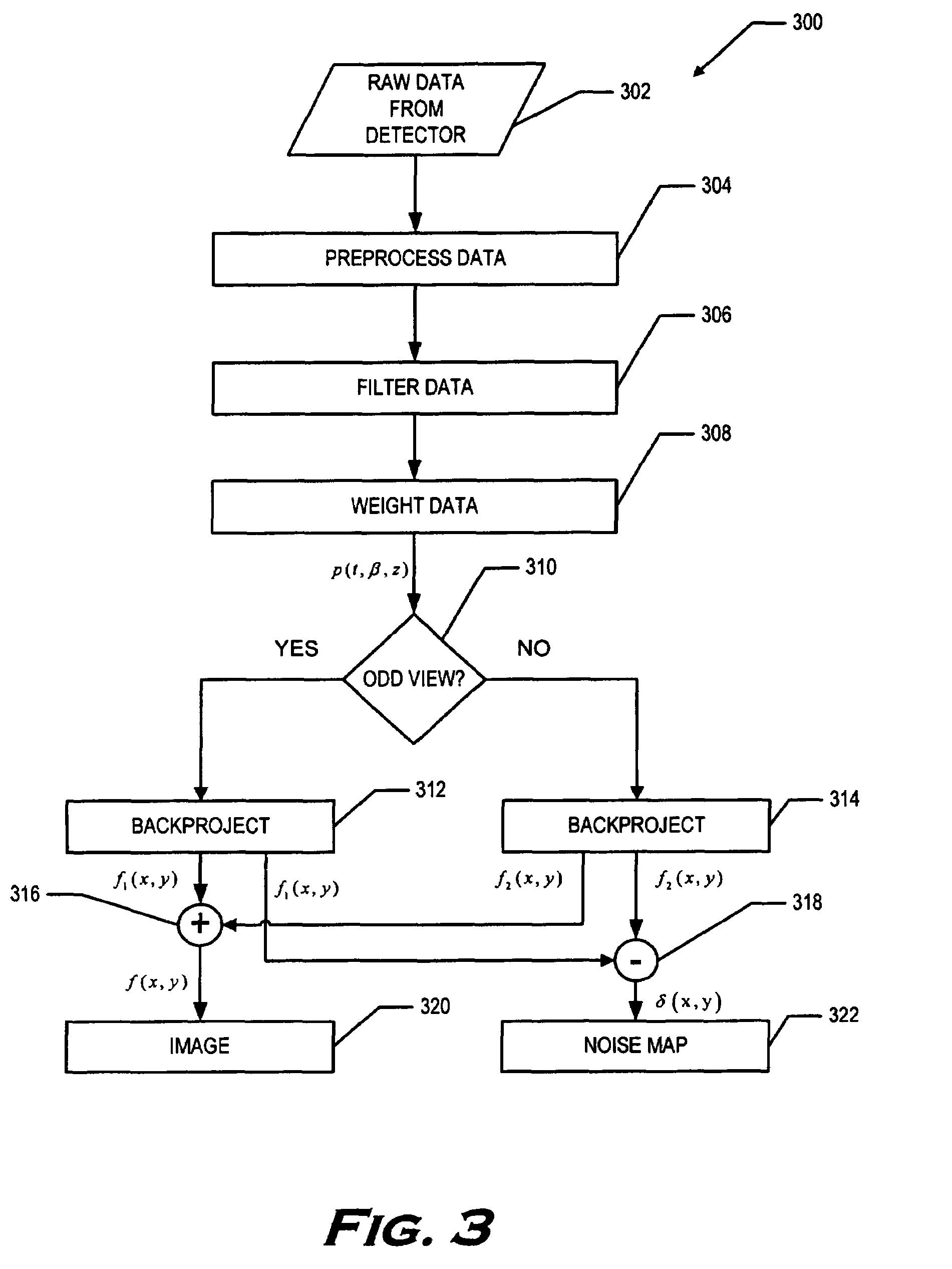
Methods and apparatus for noise estimation for multi-resolution anisotropic diffusion filtering
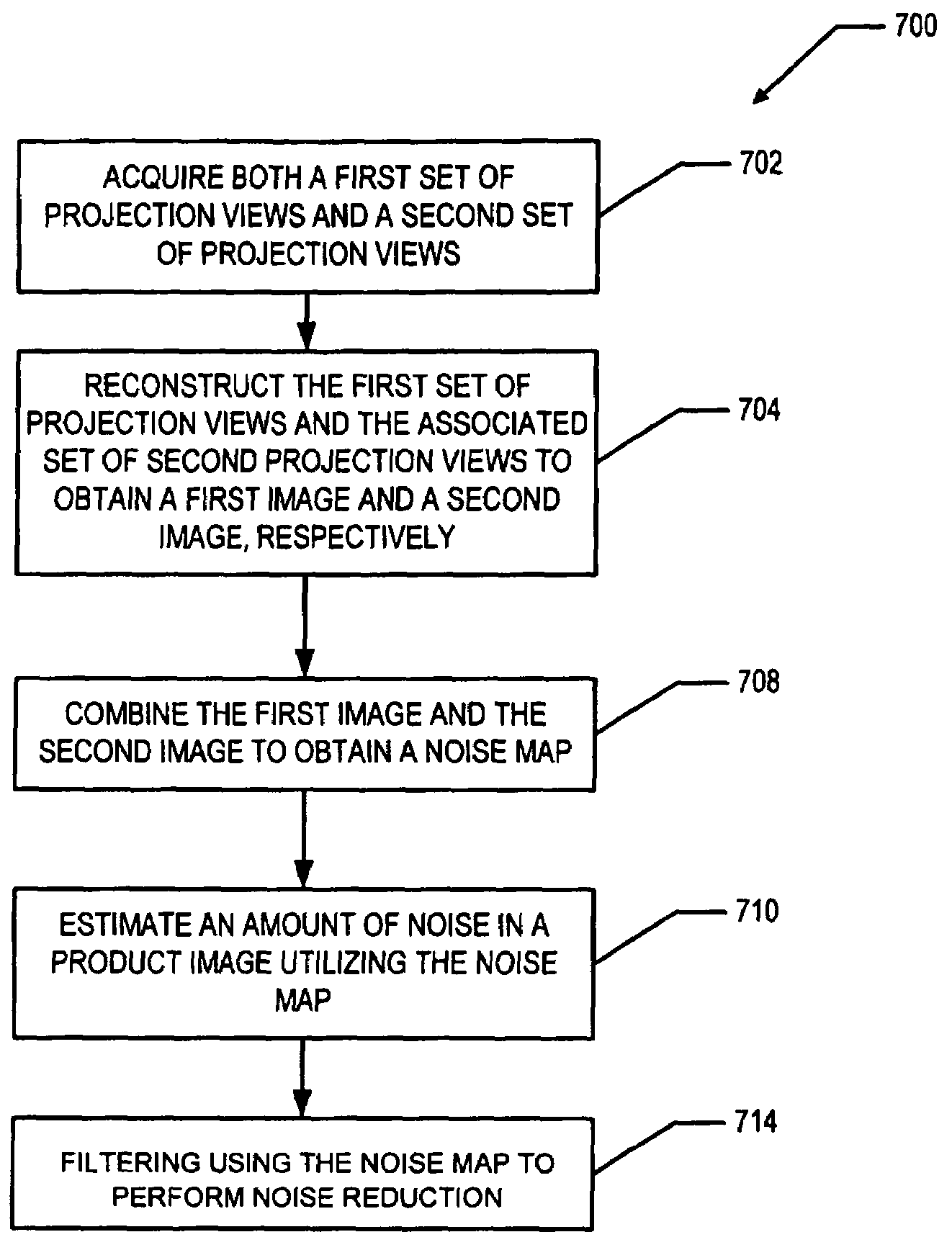
A method for reducing noise in a computed tomographic (CT) image includes acquiring both a first set of projection views and a second set of projection views, wherein for each projection view in the first set of projection views there is an associated projection view in the second set of projection views representing the same object scanned at substantially the same time from substantially the same position. The method further includes reconstructing the first set of projection views and the associated second set of projection views to obtain a first image and a second image, respectively. Next, the first image and the second image are combined to obtain a noise map and an amount of noise in a product image is estimated utilizing the noise map. The method also includes filtering using the noise map to perform noise reduction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Backlighting construction for use in computer-based display systems having direct and projection viewing modes of operation
InactiveUS7110052B1Minimal light scatteringEasy to reconfigureInput/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsOverhead projectorLight guide
A reconfigurable backlighting construction for use in portable computer-based systems having direct and projection viewing modes of operation is provided. These computer-based systems are capable of selectively displaying color video images on an actively driven display surface, or projecting such video images onto a wall surface or projection screen without the need for a bulky overhead projector, required by all prior art systems. These computer-based systems can be easily reconfigured for projection viewing without physical removal of the light guiding panel and its light diffusing structures. A portable light projection accessory device is also provided for use with the portable computer-based systems of the present invention. The portable light projection device has first and second housing portions that are interconnected by a foldable structure that permits the first and second housing portions to be selectively reconfigured for simple trouble-free use during the projection viewing mode of operation, and for compact storage during the direct viewing mode of operation.
Owner:REVEO
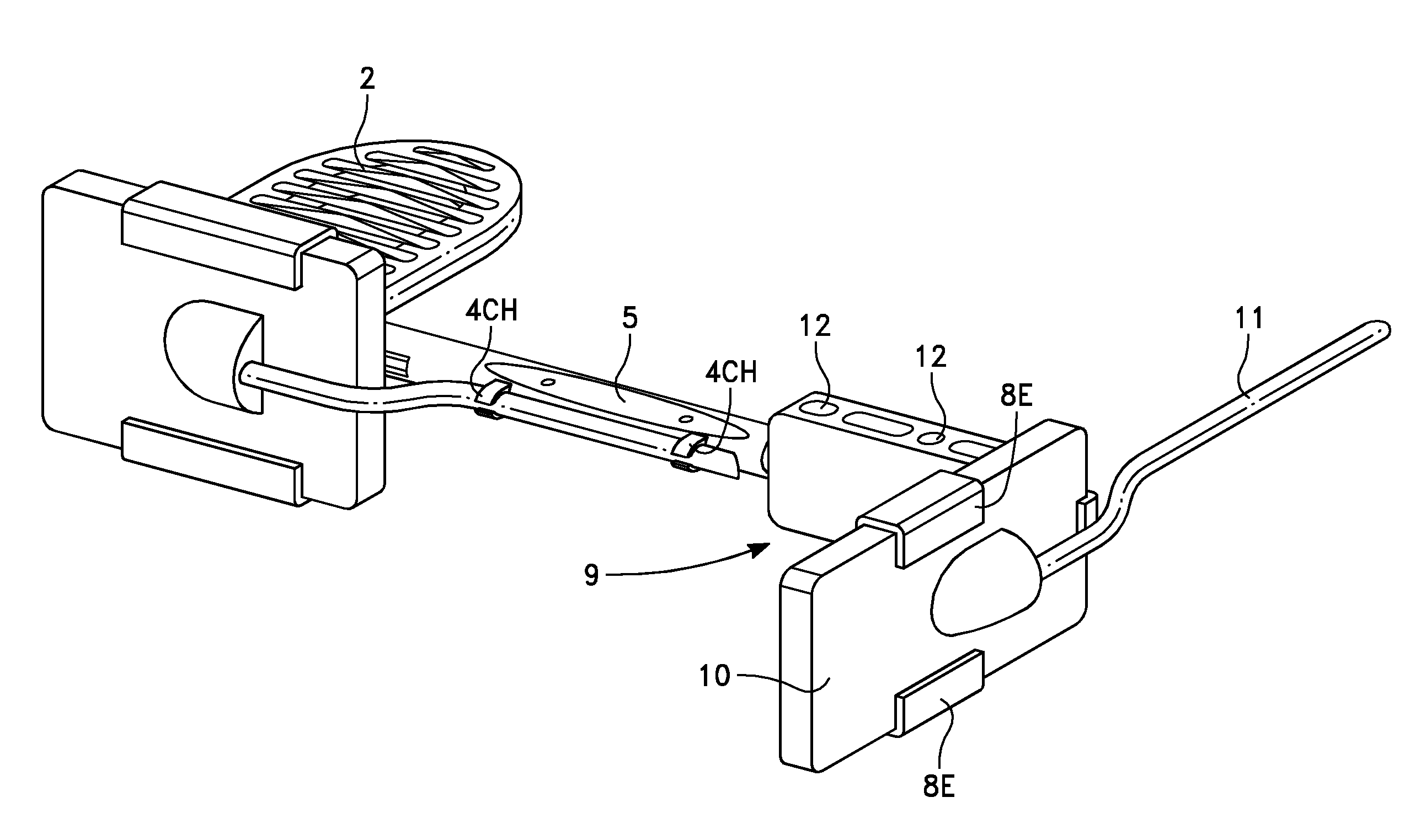
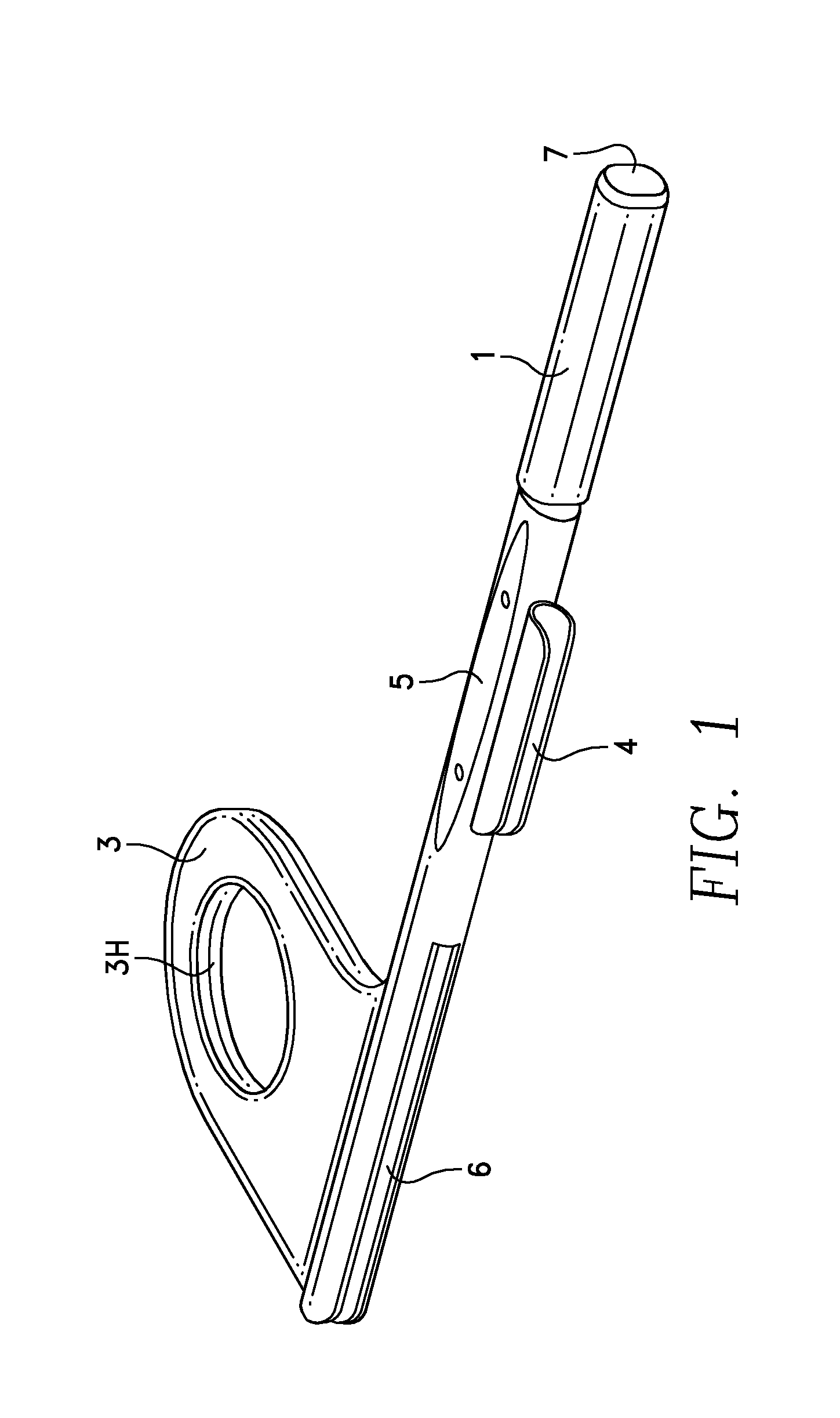
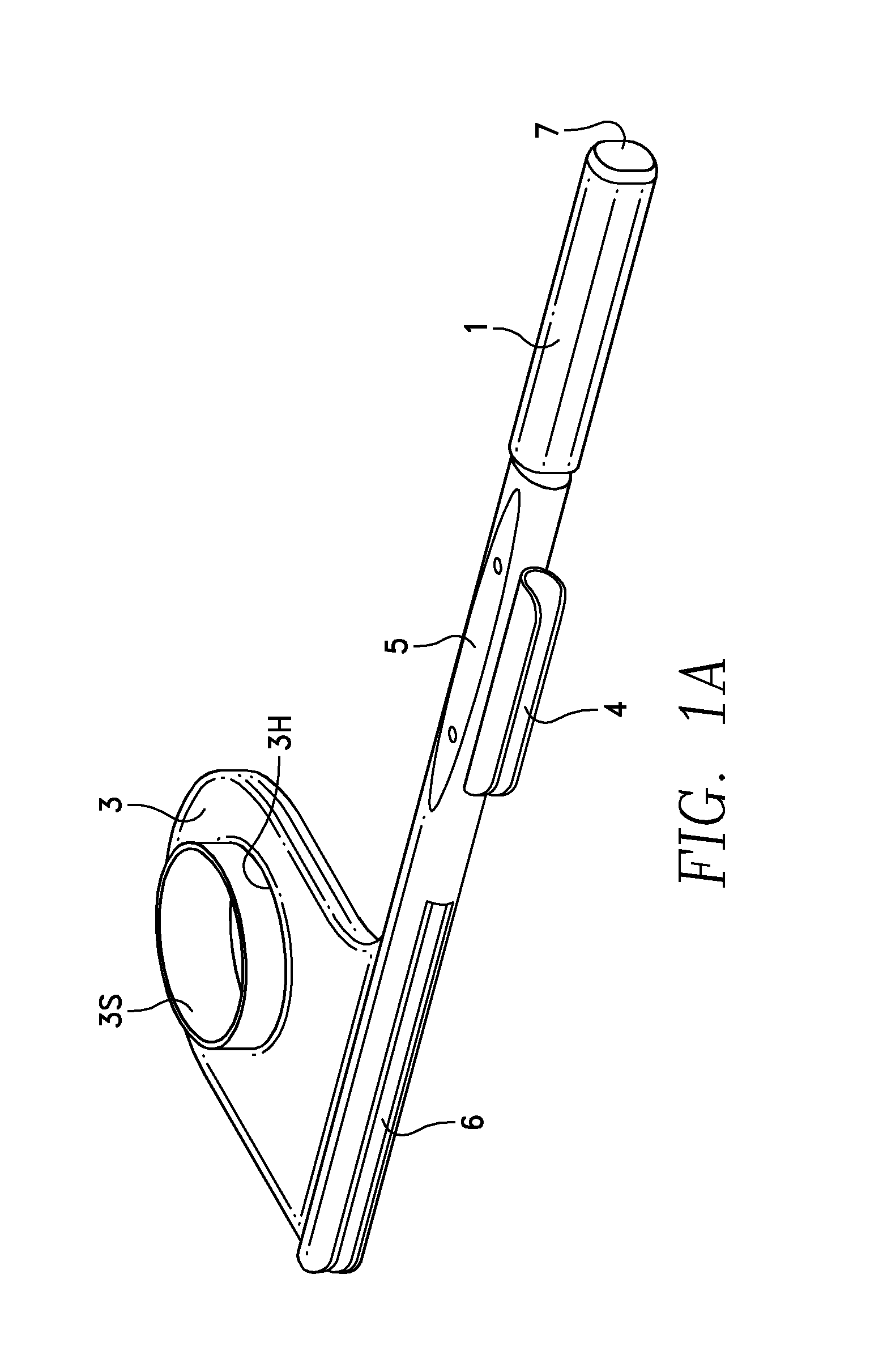
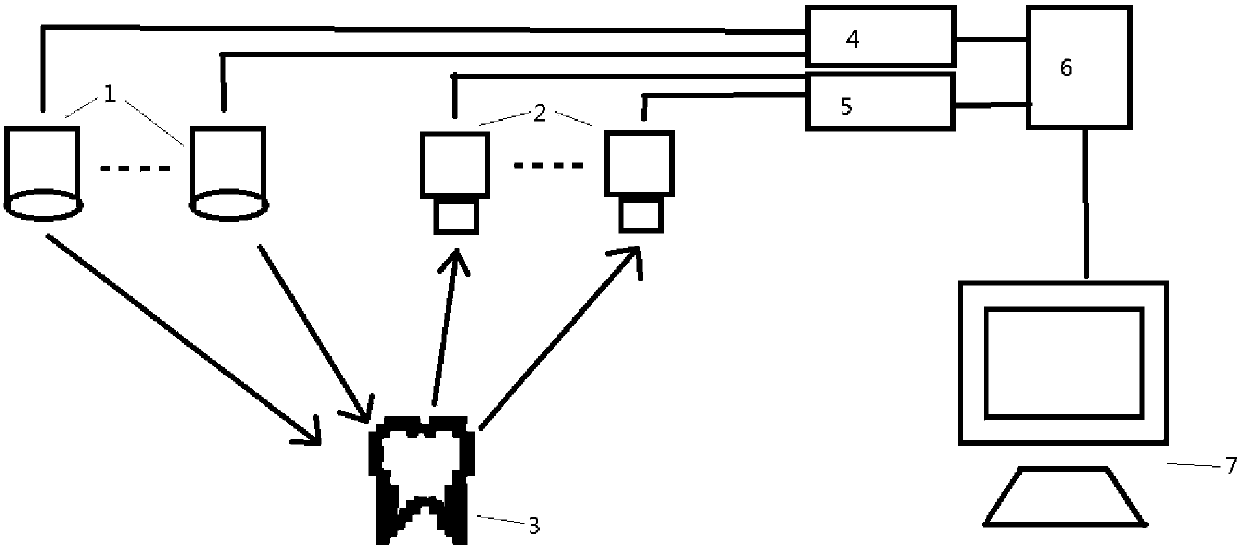
Universal intraoral digital sensor holder for existing digital sensor systems in dentistry
ActiveUS9216003B1Easy to disassembleReduce pressureDentistryRadiation diagnostics for dentistryMultiple sensorEngineering
A universal dental digital sensor holder has a bite block connected to a rod that has a connector which is used to flexibly attach a sensor holder so as to allow rotational movement of the sensor relative to the bite block and multiple sensor holders are removably connected to the connector so that they can be used to obtain different radiographic projection views due to their differing configurations for holding the intraoral sensor in the patient's mouth. The bite block can have an opening formed in it fitted with a sleeve to allow access to a tooth located beneath the opening in the patient's mouth. A cable protector can be formed in the rod adjacent an anterior bite surface so that an intraoral sensor cable can be held adjacent the rod and at least partially protected from one or more teeth biting the anterior bite surface.
Owner:CYBER MEDICAL IMAGING
Methods and apparatus for dynamical helical scanned image production
The present invention provides a method for producing images of an object. The method includes dynamically helically scanning an object on a moving table utilizing a scanning imaging system. During the scan, projection views of the object are acquired and stored together with corresponding table locations. A plane for reconstruction of an image of the object is selected. The stored table locations are used to determine geometric variables applicable to the stored projection views; and the stored projection views are filtered and backprojected utilizing the geometrical variables to reconstruct an image of the object at the reconstruction plane.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Backlighting construction for use in computer-based display systems having direct and projection viewing modes of operation
InactiveUS20050007514A1Minimal light scatteringEasy to reconfigureTelevision system detailsProjectorsOverhead projectorOperation mode
A reconfigurable backlighting construction for use in portable computer-based systems having direct and projection viewing modes of operation. In the illustrative embodiments of the present invention, the backlighting construction is integrated with a LCD display panel, a micropolarization panel, and a touch-screen writing panel to provide several different types of portable computer-based systems including, for example, a portable notebook computer, a computer-driven image display device, and a portable pen-computing device. In general, each of these computer-based systems are capable of selectively displaying color video images on an actively driven display surface, or projecting such video images onto a wall surface or projection screen without the need for a bulky overhead projector, required by all prior art systems. These computer-based systems can be easily reconfigured for projection viewing without physical removal of the light guiding panel and its light diffusing structures. If desired, these computer-based systems can be used to directly view “spatially-multiplexed” images of 3-D objects or imagery during the direct viewing mode, and when desired these spatially-multiplexed images can be projected onto a wall surface or projection screen during the projection viewing mode. When the spatially-multiplexed images are viewed through electrically-passive polarized glasses, the 3-D object is perceived with stereoscopic depth sensation in either mode of viewing. A portable light projection accessory device is provided for use with the portable computer-based systems of the present invention. In the illustrative embodiments, the portable light projection device has first and second housing portions that are interconnected by a foldable structure that permits the first and second housing portions to be selectively reconfigured for simple trouble-free use during the projection viewing mode of operation, and for compact storage during the direct viewing mode of operation.
Owner:FARIS SADEG M +1
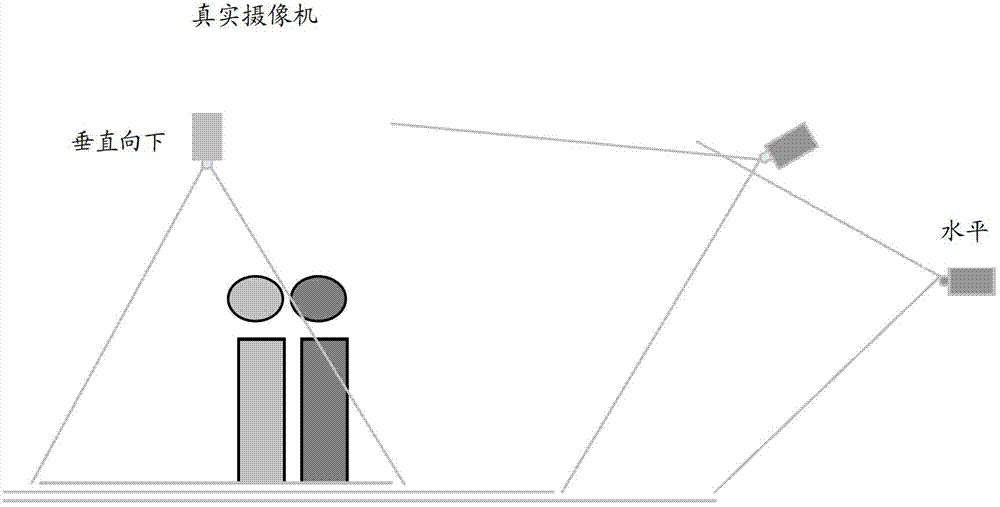
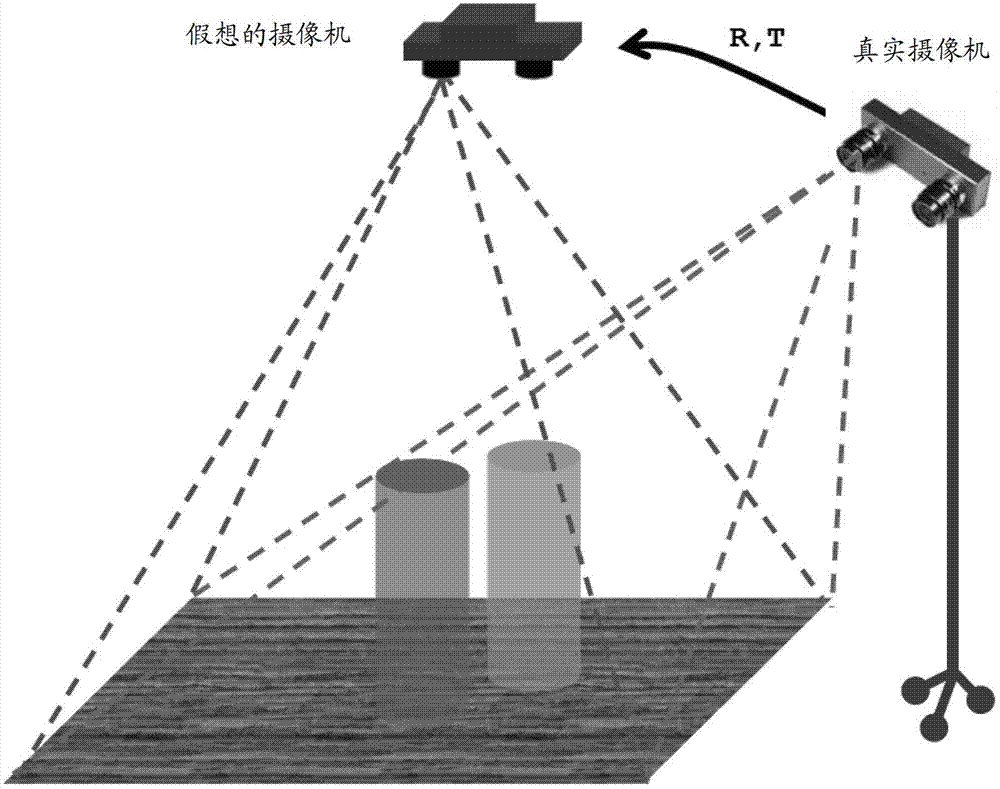
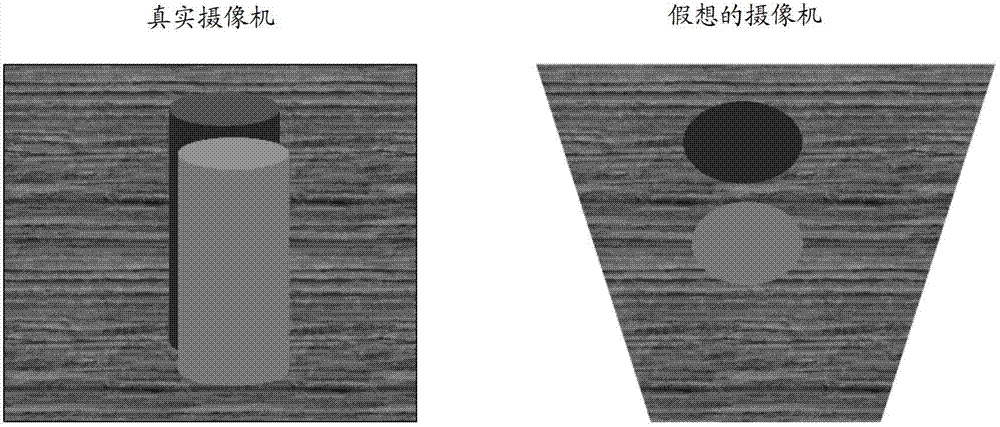
Object detecting method and device based on stereoscopic camera
InactiveCN103593641AAccurate detectionDetect accurate and as manyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionObject basedComputer science
The invention discloses an object detecting method and device based on a stereoscopic camera. The method includes the following steps: carrying out coordinate conversion on a stereoscopic image which is obtained during the stereoscopic camera shooting an object, obtaining a stereoscopic image which is equivalent to an image of an object which is shot by an imaginary camera in a preset direction and obtaining a planar projection view of the stereoscopic image which undergoes the coordinate conversion, in a preset projection direction; with respect to the projection view, carrying out object detection based on detection parameters; calculating areas in which object shield is detected; with respect to positions in areas in which the object shield is detected, adjusting the detection parameters; and with respect to the positions in the areas in which the object shield is detected, detecting the object based on the adjusted detection parameters. The object detection method and device effectively avoids effects of the shield on object detection and tracking so that the object can be detected more accurately through making use of already available image data as far as possible.
Owner:RICOH KK
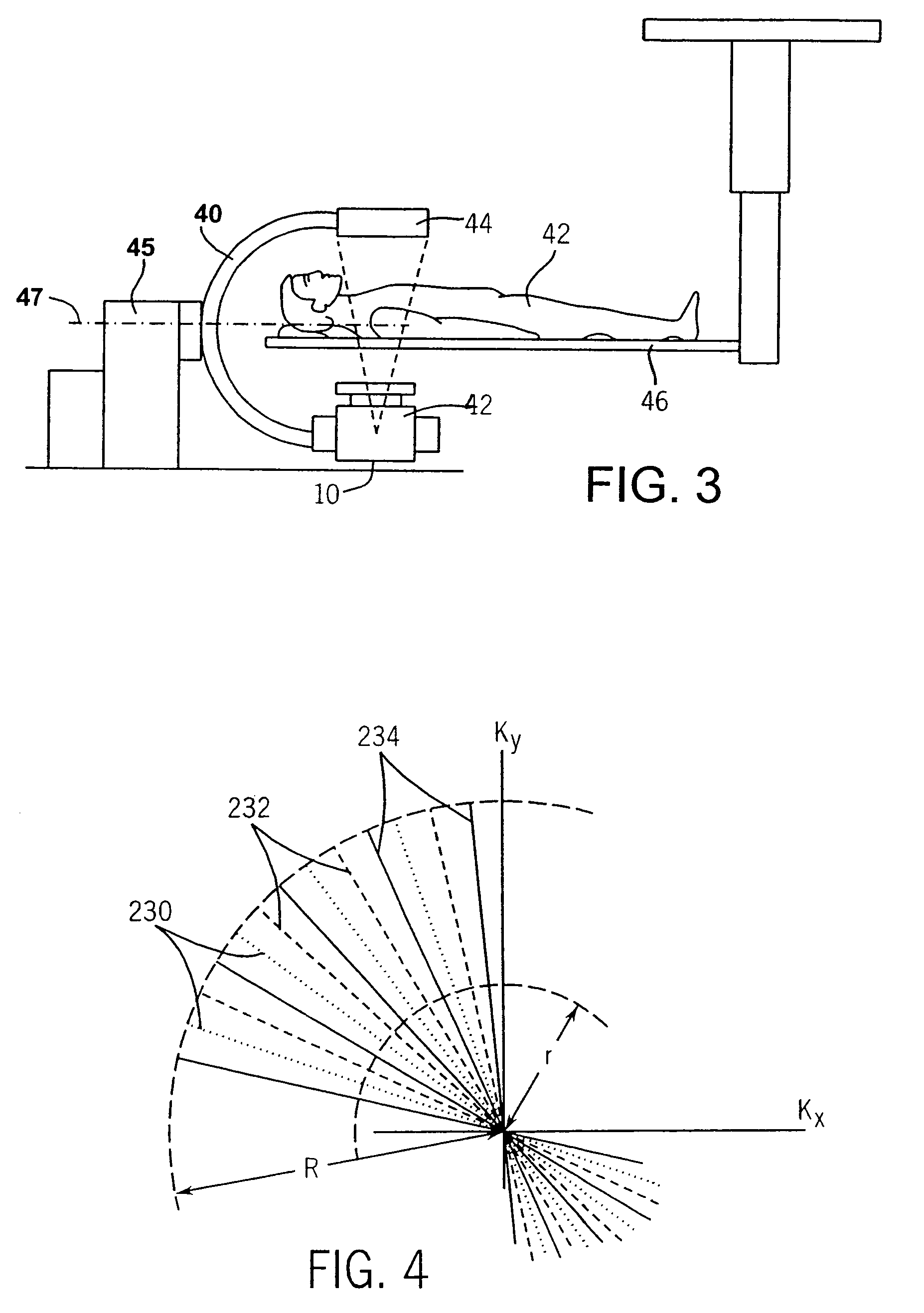
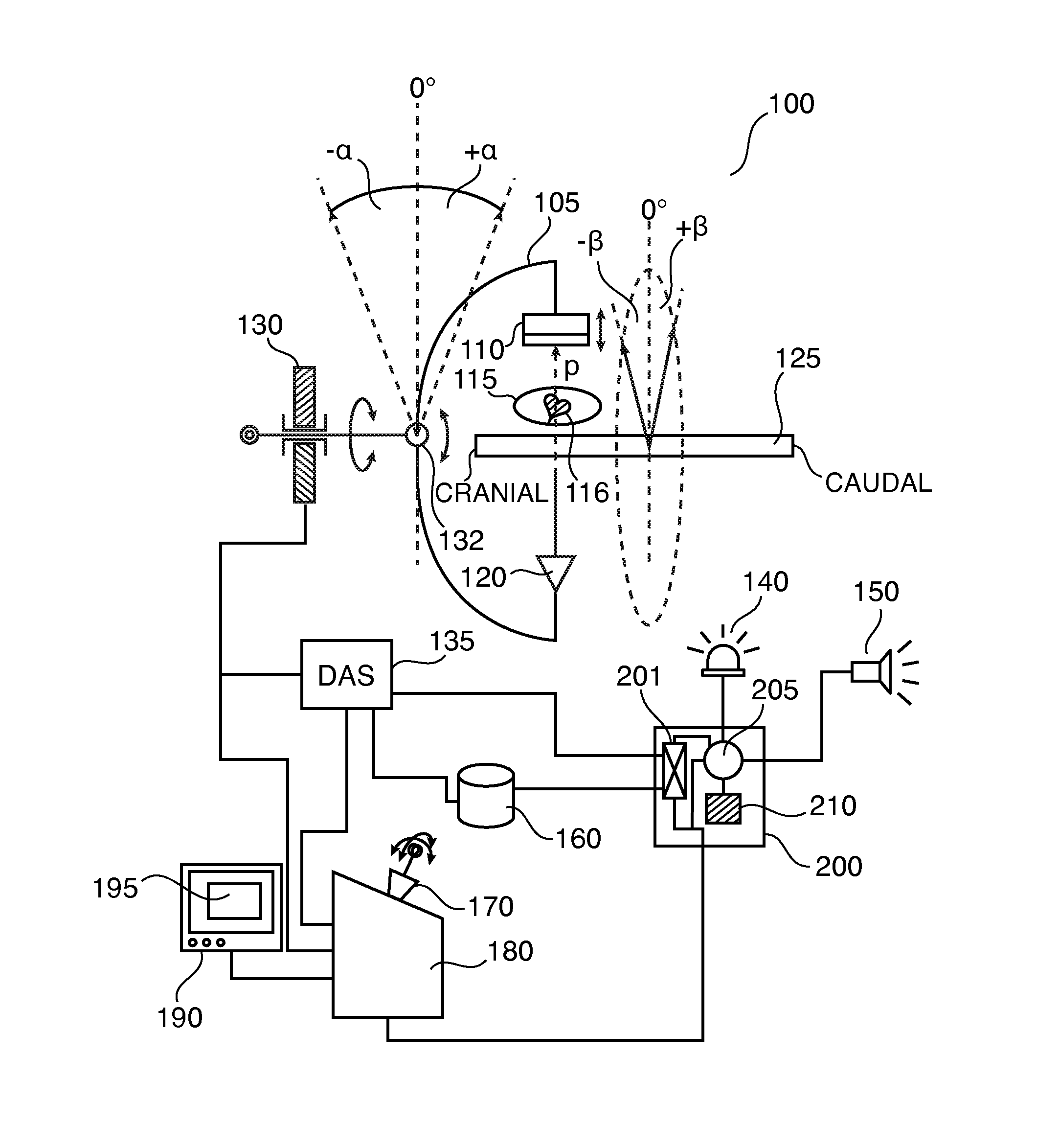
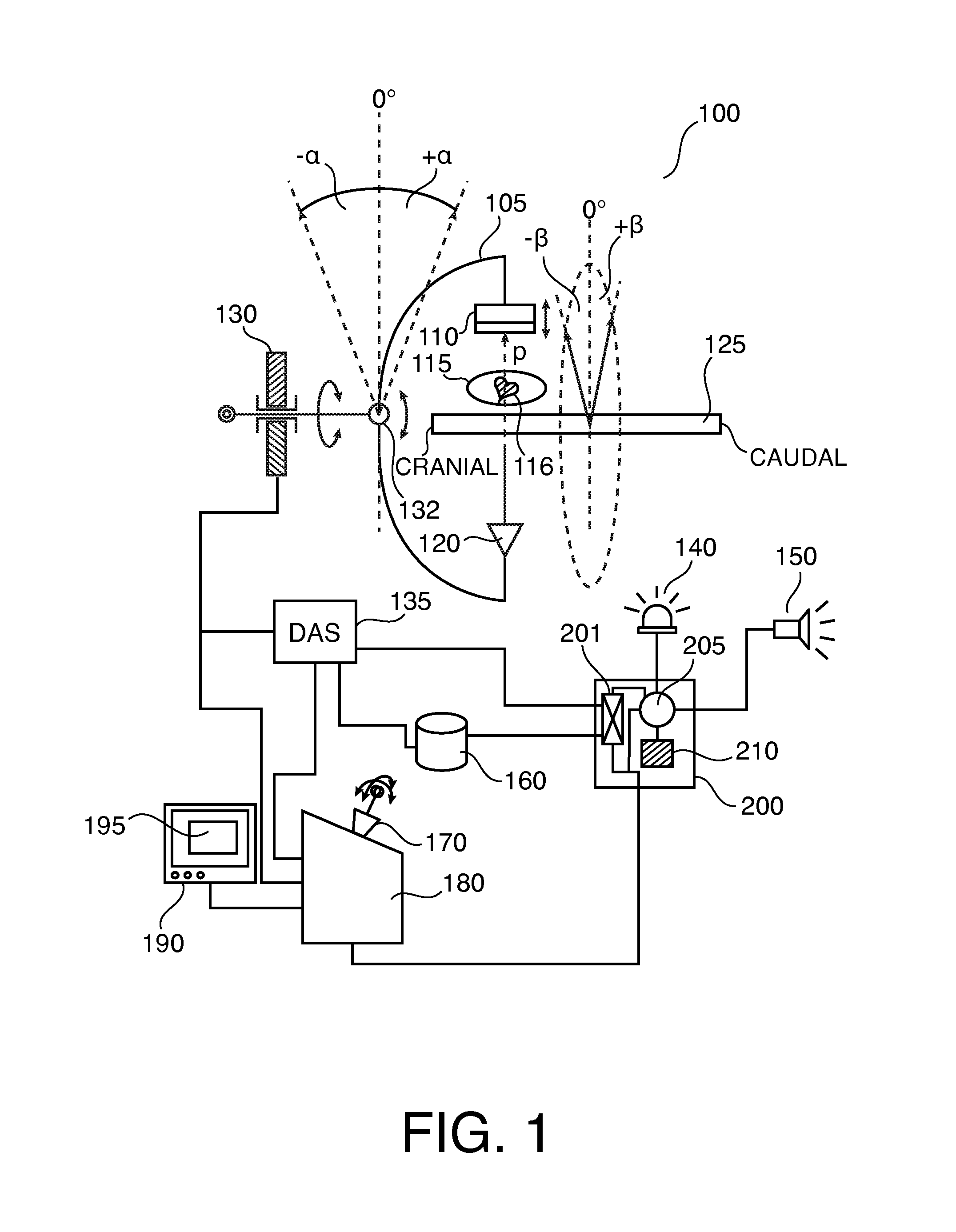
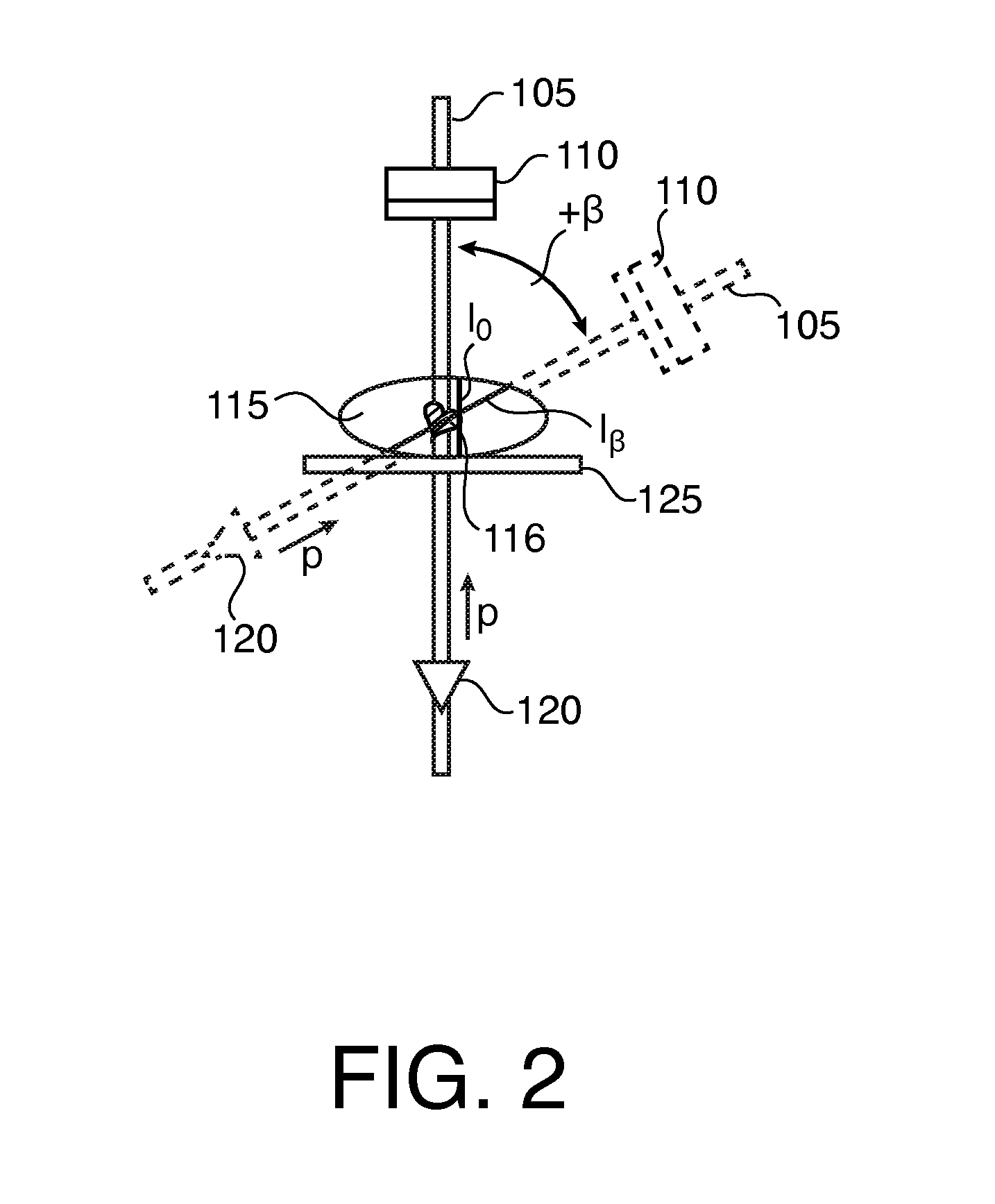
Dynamic Tomography Angle Selection
ActiveUS20140307934A1Accurate tomographic imagingAccurate imagingReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionTomographyTest object
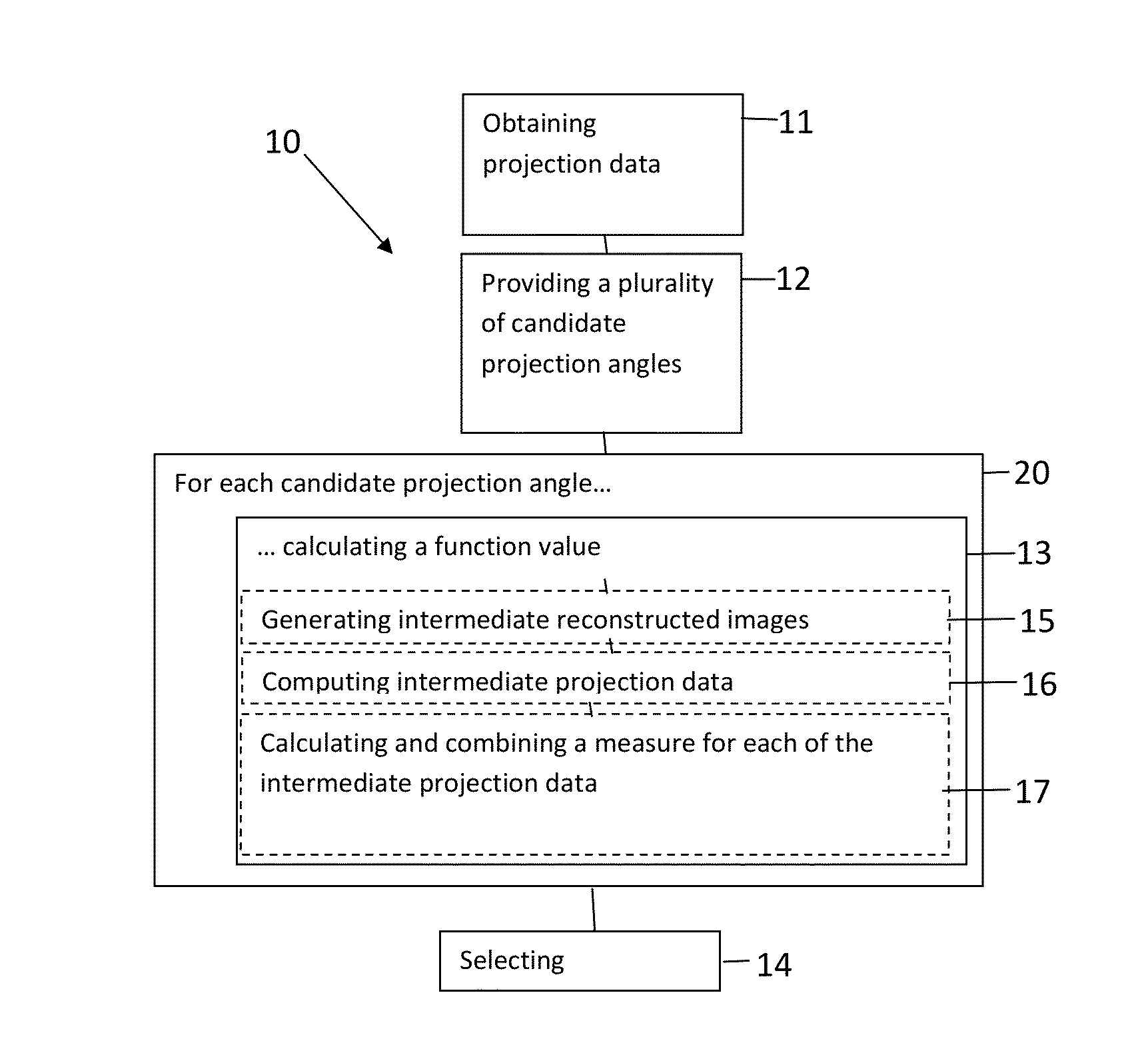
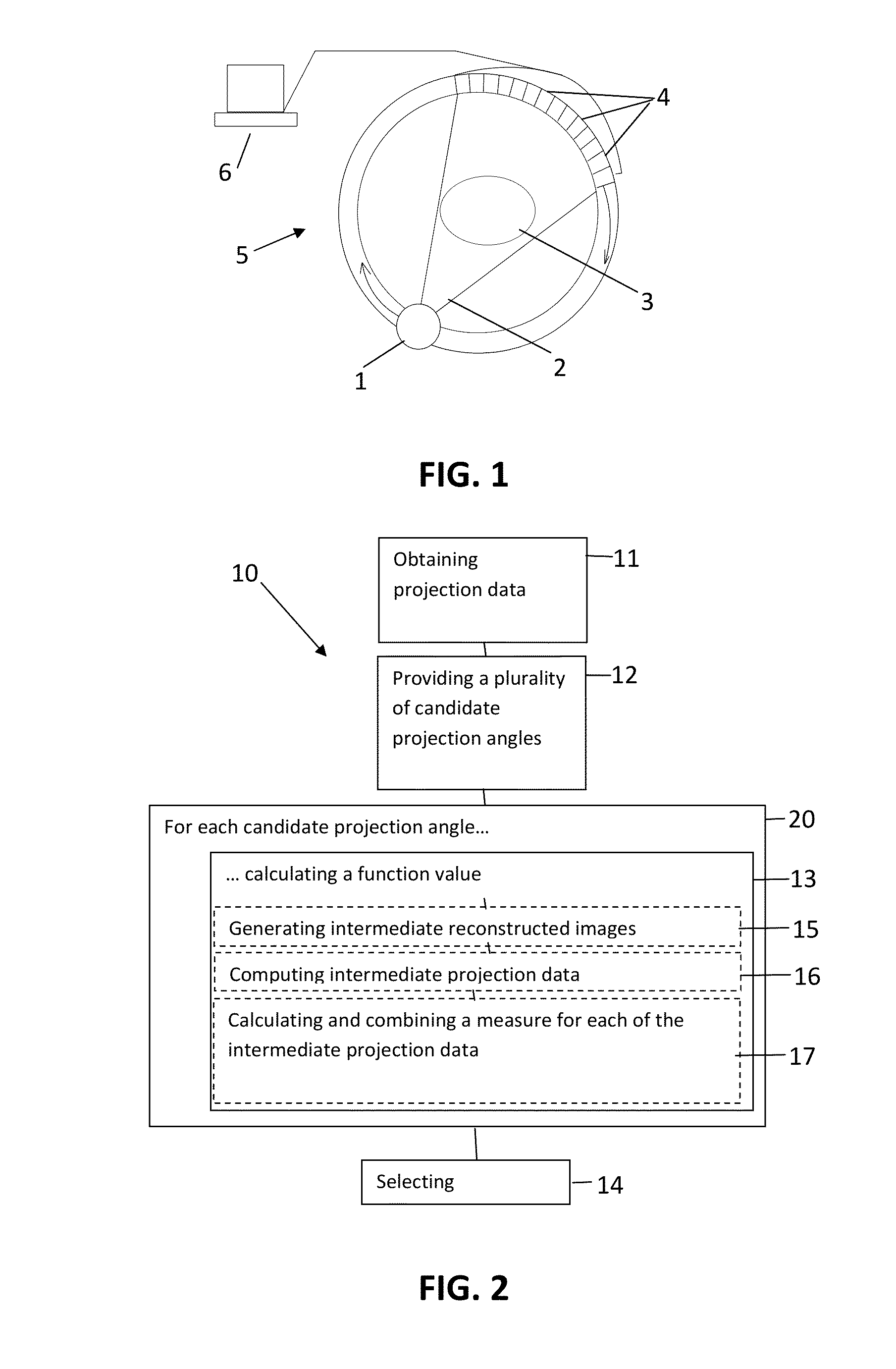
A method for determining a projection angle for use in tomographic imaging comprises obtaining projection data including at least one projection view from at least one projection angle. The at least one projection view is generated by scanning a test object with a tomographic imaging device. Each projection view comprises at least one observation value obtained at least one detection location, providing a plurality of candidate projection angles, for each candidate projection angle, calculating a function value indicative of an amount of information that may be gained by adding to the projection data a further projection view generated by scanning of the test object with the tomographic imaging device from the candidate projection angle, and selecting a candidate projection angle from the plurality of candidate projection angles taking into account the function values. A corresponding system and computer program product also is provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ANTWERP +1
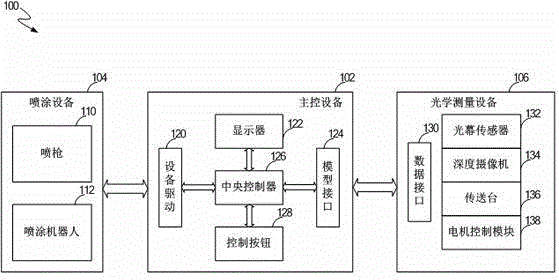
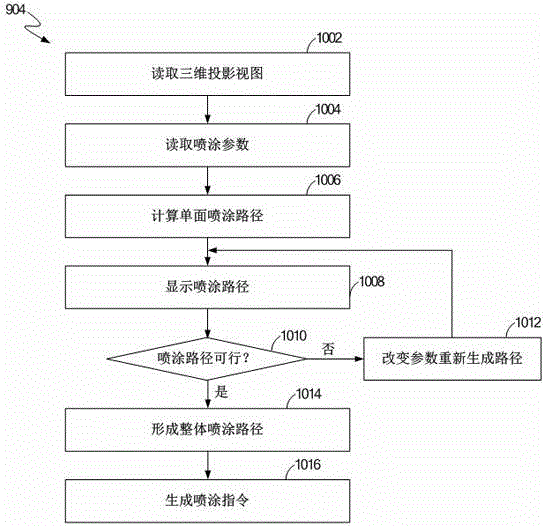
Method for controlling paths of spray robot
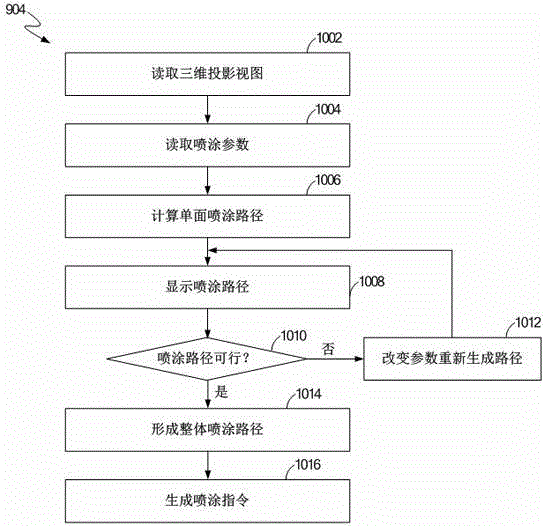
ActiveCN104525422ASimple and fast operationImprove spraying accuracySpraying apparatusDisplay deviceComputer science
The invention discloses a method for controlling paths of a spray robot. The method includes the following steps that three-dimensional projection views of a sprayed workpiece are read; spray parameters of the spray robot are read; according to the three-dimensional projection views and the spray parameters, the spray path on each single face of the sprayed workpiece is calculated; the spray path on each single face is displayed on a displayer; user commands are read; according to the user commands, the spray parameters are modified; according to the modified spray parameters, the spray path on each single face of the sprayed workpiece is calculated; according to the spray path on each single face, a whole spray path is generated; spray commands are generated, so that the spray robot is controlled to spray the sprayed workpiece.
Owner:成都思达特电器有限公司
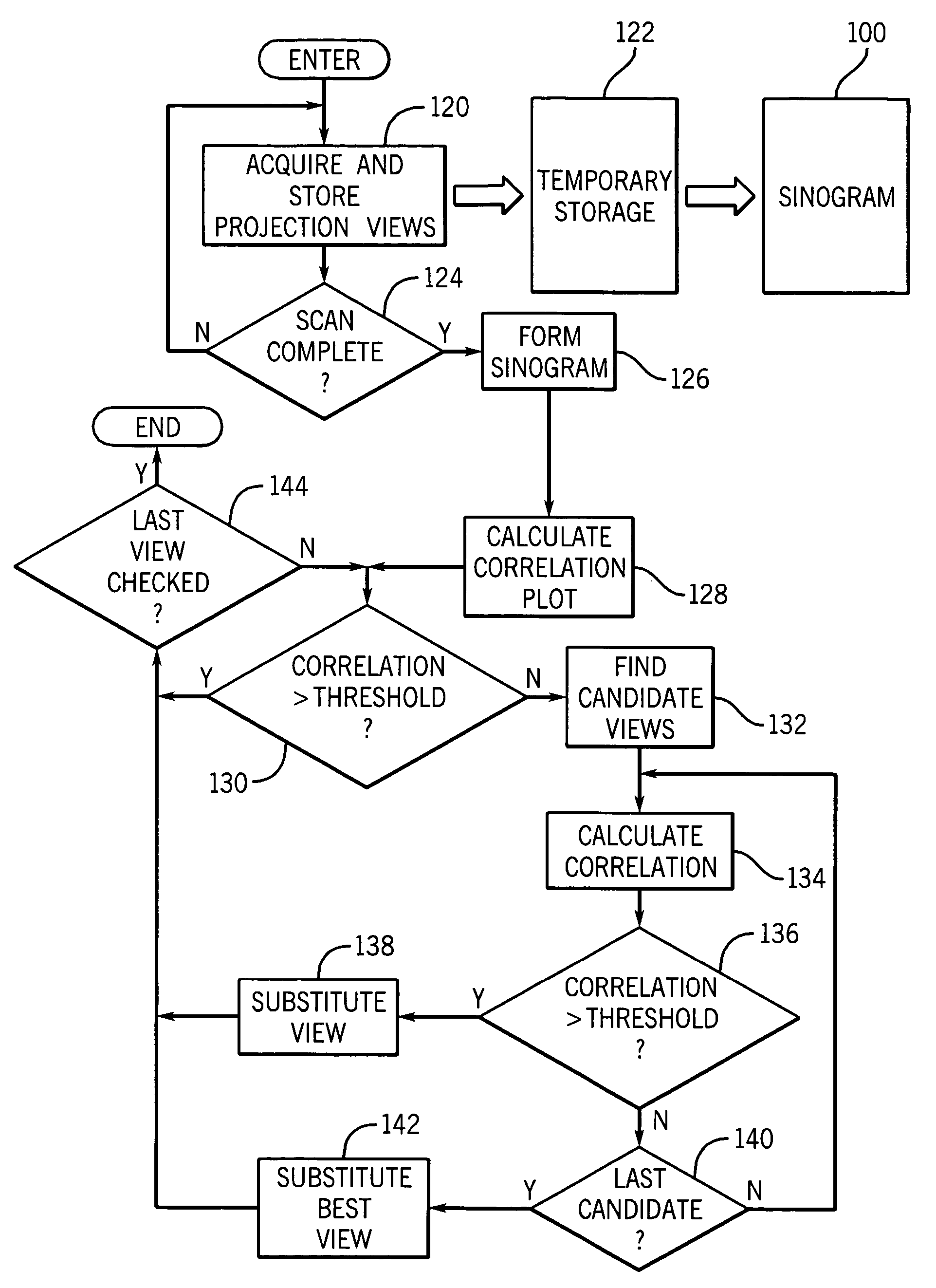
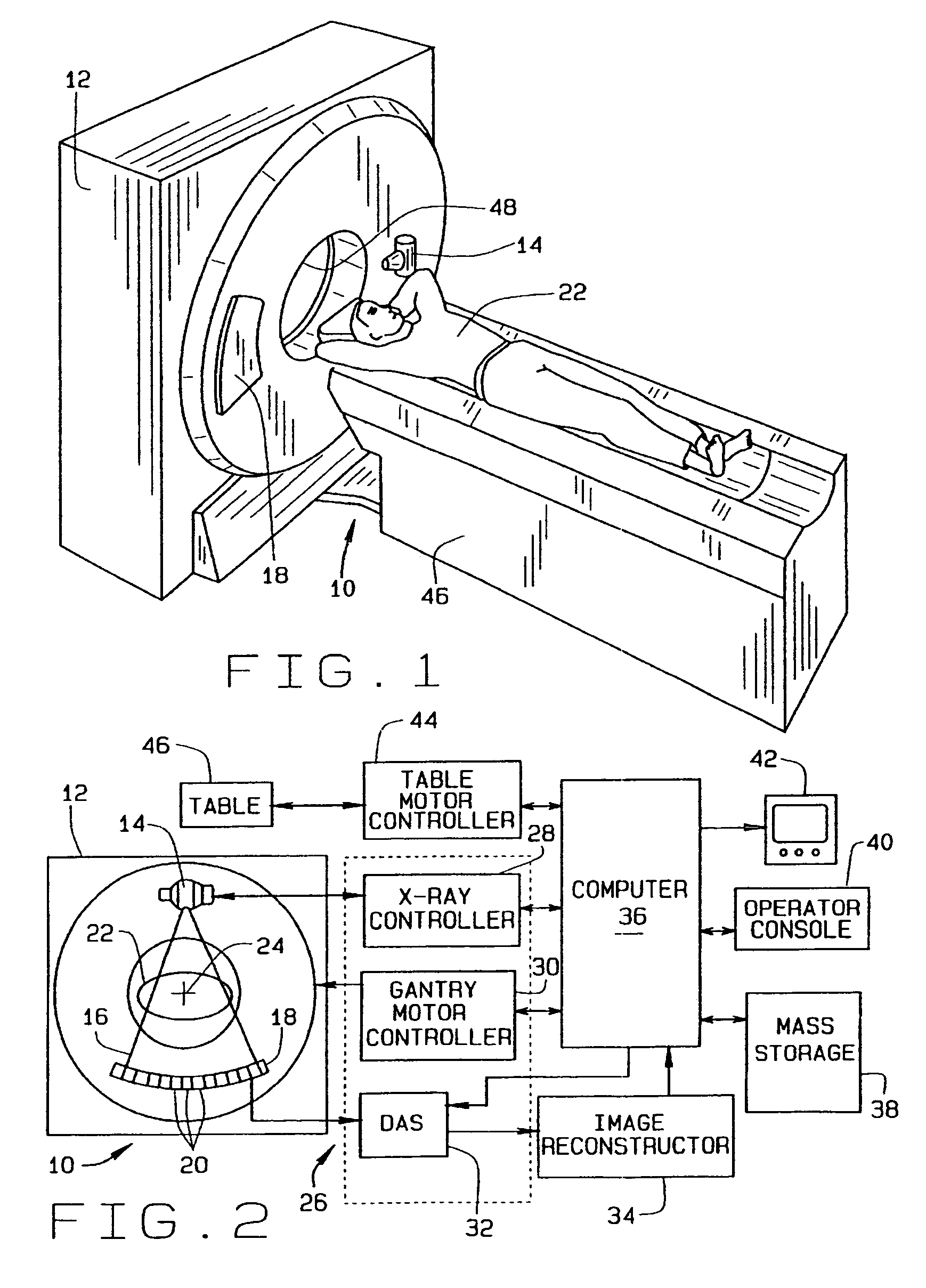
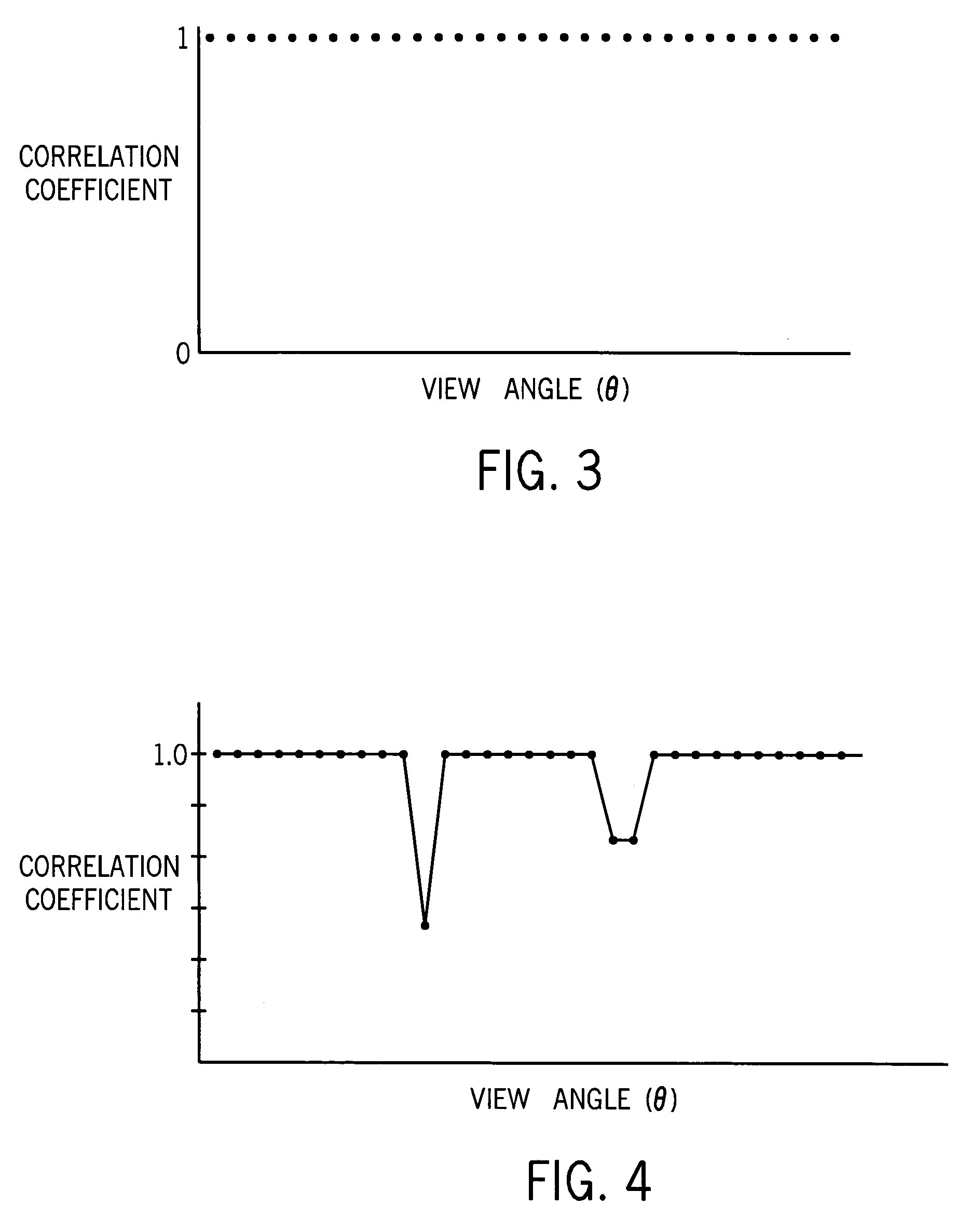
Projection gating of x-ray CT scan
InactiveUS7154987B2Reconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputed tomographyX-ray
An x-ray CT system performs a scan by acquiring projection views from which an image is reconstructed. In a prospective embodiment, the correlation of adjacent views is calculated as the scan is performed and is used to detect subject motion as the scan is being performed. In a retrospective embodiment, the correlation of adjacent views is calculated and is used to detect subject motion after the scan is completed. In the first embodiment substitute projection views are acquired by continuing the scan and in the second embodiment redundant projection views acquired during the scan are substituted until the best possible image is produced.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method and apparatus for calibrating detector spectral response
InactiveUS6848827B2Increase coverageQuick calibrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSpectral responseOffset calibration
The present technique provides for the spectral calibration of the detector elements of a CT detector using one or more offset calibration phantoms. The offset phantoms provide greater coverage of the detector elements as well as spectral response data associated with penetration lengths ranging in length from a minimum chord of the phantom to the diameter of the phantom. The spectral response as a function of penetration length can be obtained for each detector element by comparing the fitting of each projection view to the corresponding measured projection view over all view angles. The fitting information may then be employed to derive the coefficients of the spectral response curve for each detector element, which may in turn be employed to provide rapid correction of the spectral response for each element.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
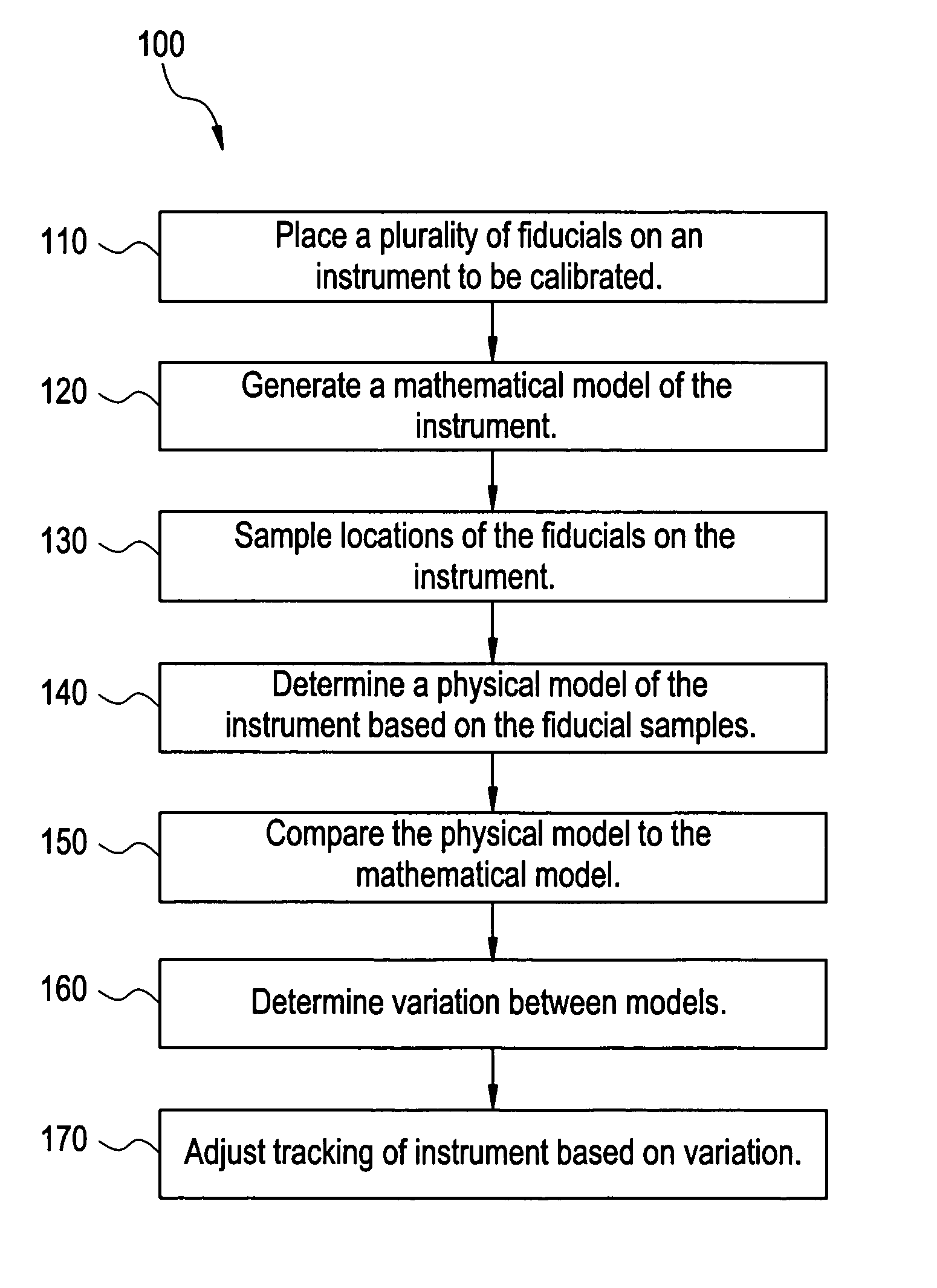
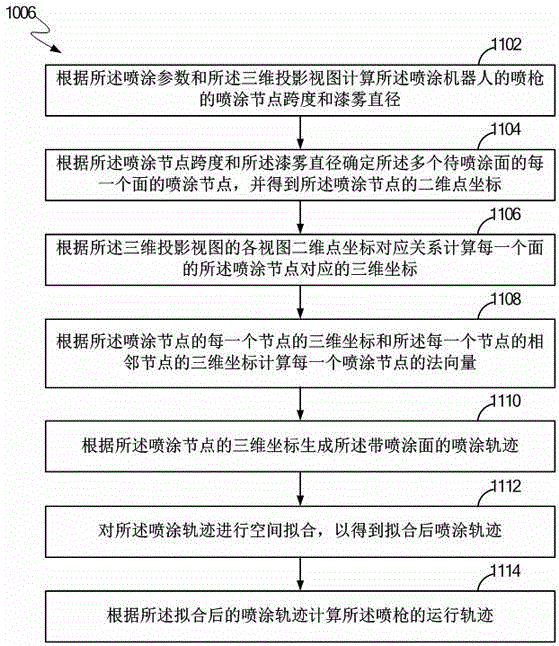
Method for controlling spraying gun of spraying robot
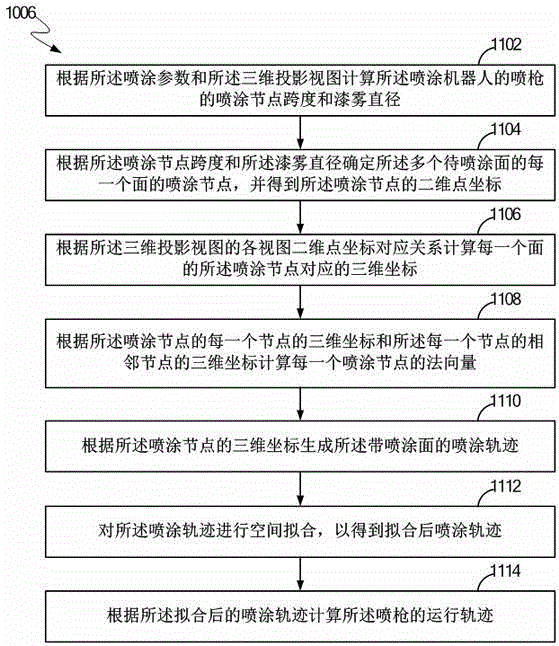
ActiveCN104549850ASimple and fast operationImprove spraying accuracySpraying apparatus3D modellingNODALComputer science
The invention discloses a method for controlling a spraying gun of a spraying robot. The method comprises the steps of determining a plurality of surfaces of a workpiece, to be spayed according to a three-dimensional projection view; determining a spraying joint of each of the plurality of surfaces to be sprayed according to the spraying parameters and the three-dimensional projection view, and obtaining a two-dimensional point coordinate of the spraying joint; calculating a three-dimensional coordinate corresponding to the spraying joint of each surface according to the correspondence relation of the two-dimensional point coordinate of each view of the three-dimensional projection view; calculating a normal vector of each spraying joint according to the three-dimensional coordinate of each of the spraying joints and the three-dimensional coordinate of the joint adjacent to each joint; generating a spraying track of the spraying surface according to the three-dimensional coordinates of the spraying joints; performing spatial fit for the spraying track to obtain the fitted spraying track; calculating the spraying track and the normal vector of the spraying gun by the formula in the specification according to the fit track and the normal vector of the spraying joints.
Owner:成都思达特电器有限公司
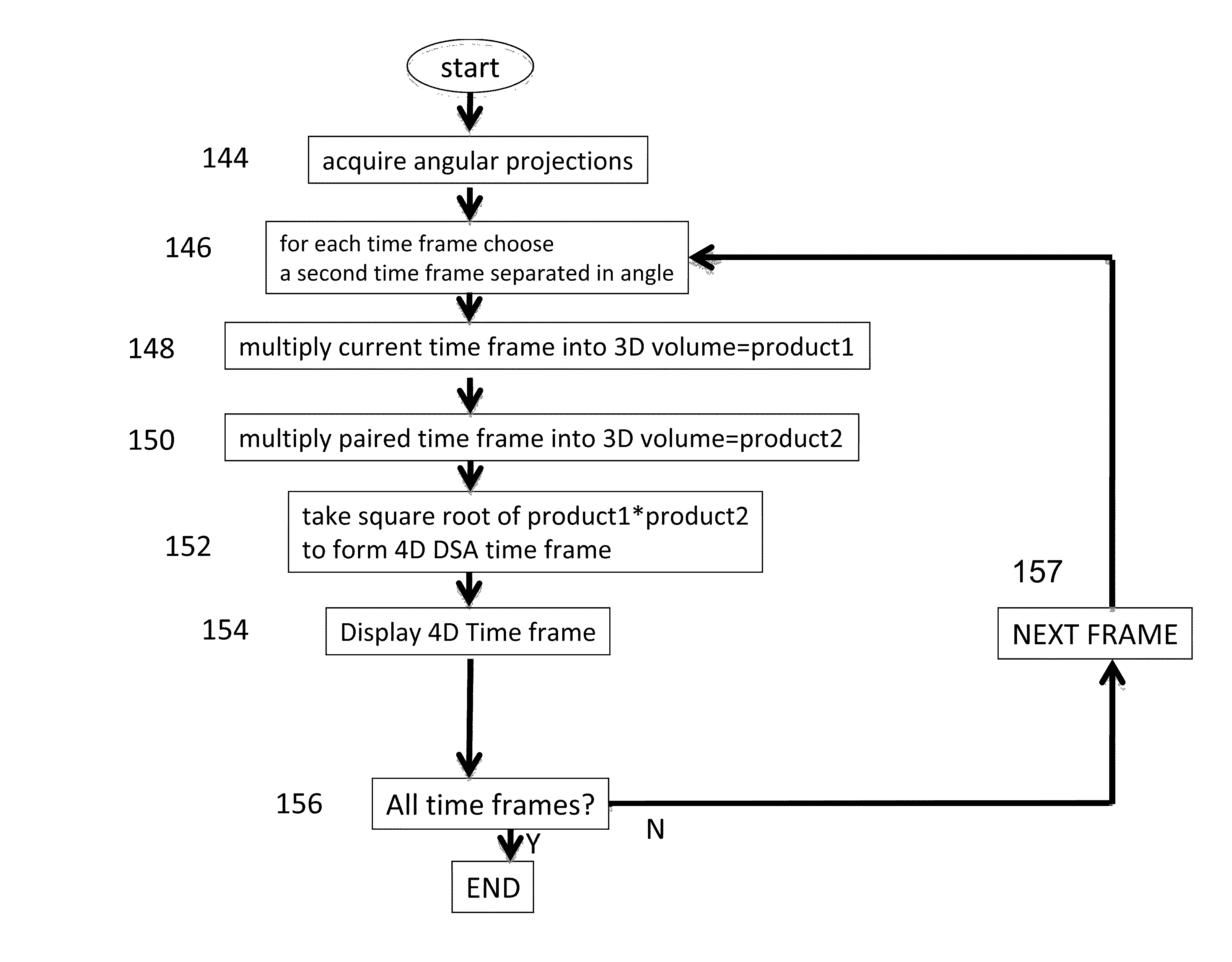
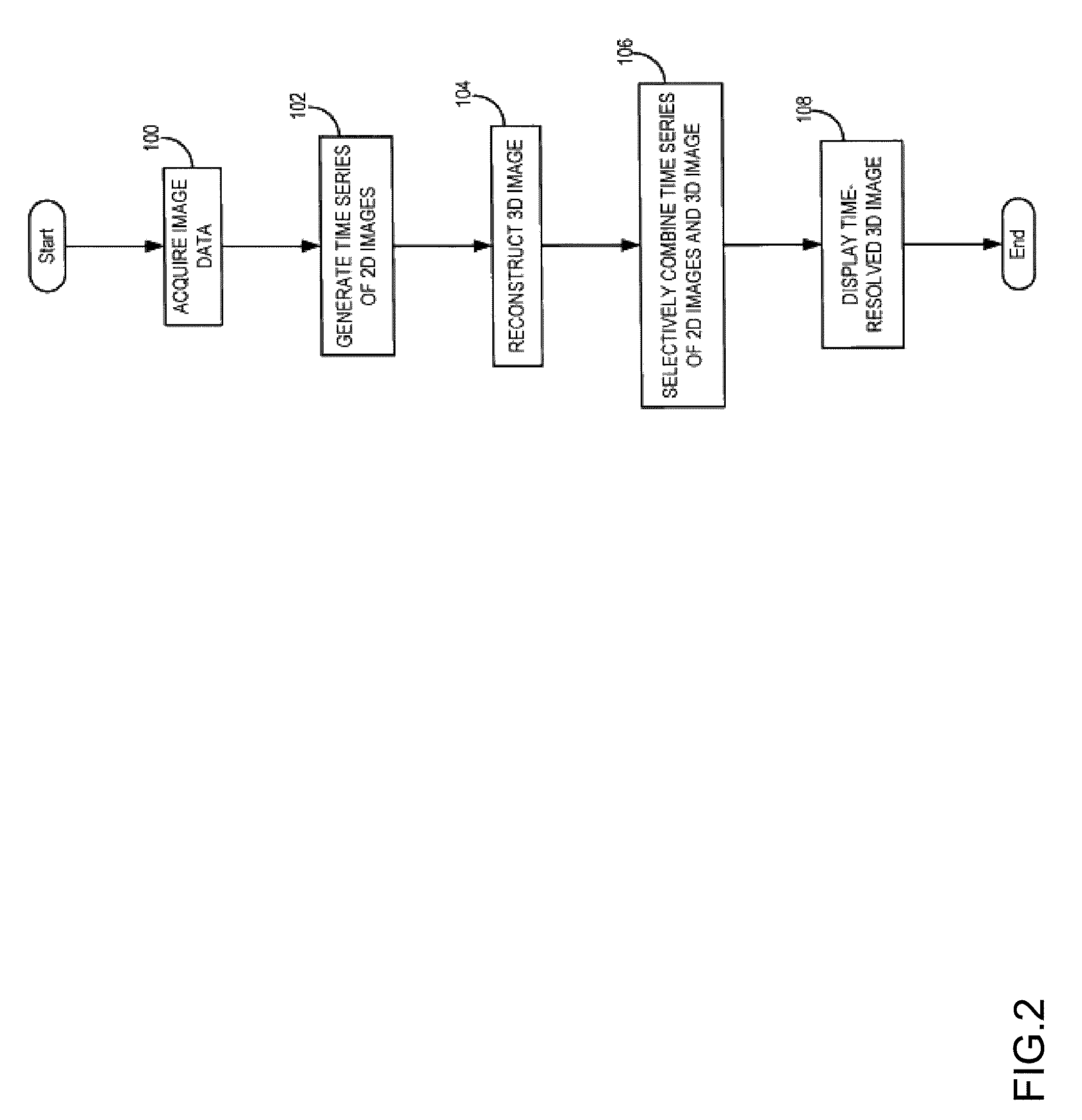
System and method for four dimensional angiography and fluoroscopy
ActiveUS8654119B2Eliminate the effects ofImprove approximationReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMultiple injectionTemporal resolution
A method for generating time-resolved 3D medical images of a subject by imparting temporal information from a time-series of 2D medical images into 3D images of the subject. Generally speaking, this is achieved by acquiring image data using a medical imaging system, generating a time-series of 2D images of a ROI from at least a portion of the acquired image data, reconstructing a 3D image substantially without temporal resolution from the acquired image data, and selectively combining the time series of 2D images with the 3D image. Selective combination typically involves registering frames of the time-series of 2D images with the 3D image, projecting pixel values from the 2D image frames “into” the 3D image, and weighting the 3D image with the projected pixel values for each frame of the time-series of 2D images. This method is particularly useful for generating 4D-DSA images (that is, time-resolved 3D-DSA images) from a time-series of 2D-DSA images acquired via single plane or biplane x-ray acquisitions with 3D images acquired via a rotational DSA acquisition. 4D-DSA images can be generated either by using multiple injections or by using a single injection by combining a time-series of 2D-DSA images generated from individual projections from a rotational x-ray acquisition with a 3D image reconstructed from substantially all of the projection views acquired during the rotational x-ray acquisition. These DSA images may have a spatial resolution on the order of 5123 pixels and a temporal resolution of about 30 frames per second, which represents an increase over traditional 3D-DSA frame rates by a factor of between 150 and 600.
Owner:CMS MEDICAL +1
Electro-optical backlighting panel for use in computer-based display systems and portable light projection device for use therewith
InactiveUS6917391B1Improve performanceAvoid disadvantagesTelevision system detailsProjectorsProjection screenDisplay device
An electro-optical backlighting panel construction for use in portable computer-based systems having direct and projection viewing modes of operation. In the illustrative embodiments of the present invention, the electro-optical backlighting panel is integrated with a LCD display panel, a micropolarization panel, and a touch-screen writing panel to provide several different types of portable computer-based systems including, for example, a portable notebook computer, a computer-driven image display device, and a portable pen-computing device. In general, each of these computer-based systems are capable of selectively displaying color video images on an actively driven display surface, or projecting such video images onto a wall surface or projection screen. These computer-based systems can be easily reconfigured for projection viewing without any sort of physical modification to the LCD display panel assembly.
Owner:REVEO
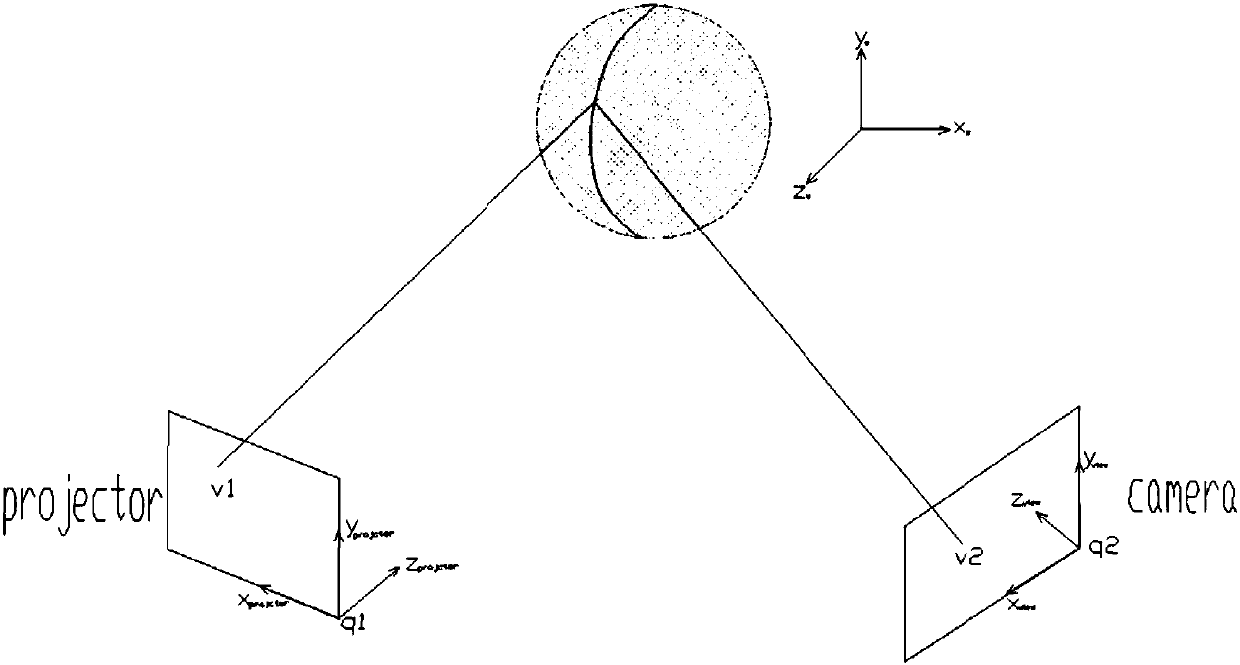
Area array structure optical system-based three-dimensional reconstruction method and system
ActiveCN108242064AImprove 3D reconstruction accuracyImprove efficiencyImage analysisCamera imagePoint cloud
The invention discloses an area array structure optical system-based three-dimensional reconstruction method and system. The method comprises the following steps that: the projection plane coordinatesof a projector in a projection coordinate system are obtained according to the physical coordinates of the projector and the calibration parameters of the projector; the first camera plane coordinates of a camera in a camera imaging coordinate system are obtained according to the physical coordinates of the camera and the calibration parameters of the camera, and the first camera plane coordinates are converted to the projection coordinate system, so that the second camera plane coordinates of the camera in the projection coordinate system can be obtained; the forward projection view and reverse projection view of an acquired image are obtained, and a target area is encoded according to the difference image of the forward projection view and the reverse projection view; the point cloud image of the target area is obtained according to the projection plane coordinates and the second camera plane coordinates, and a depth image is generated according to the point cloud image; and three-dimensional reconstruction is performed on a target object according to the point cloud image and the depth image. The method of the embodiments of the invention has the advantages of high precision and high efficiency of three-dimensional reconstruction.
Owner:HEFEI MEIYA OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
3D Autostereoscopic Display System With Multiple Sets Of Stereoscopic Views
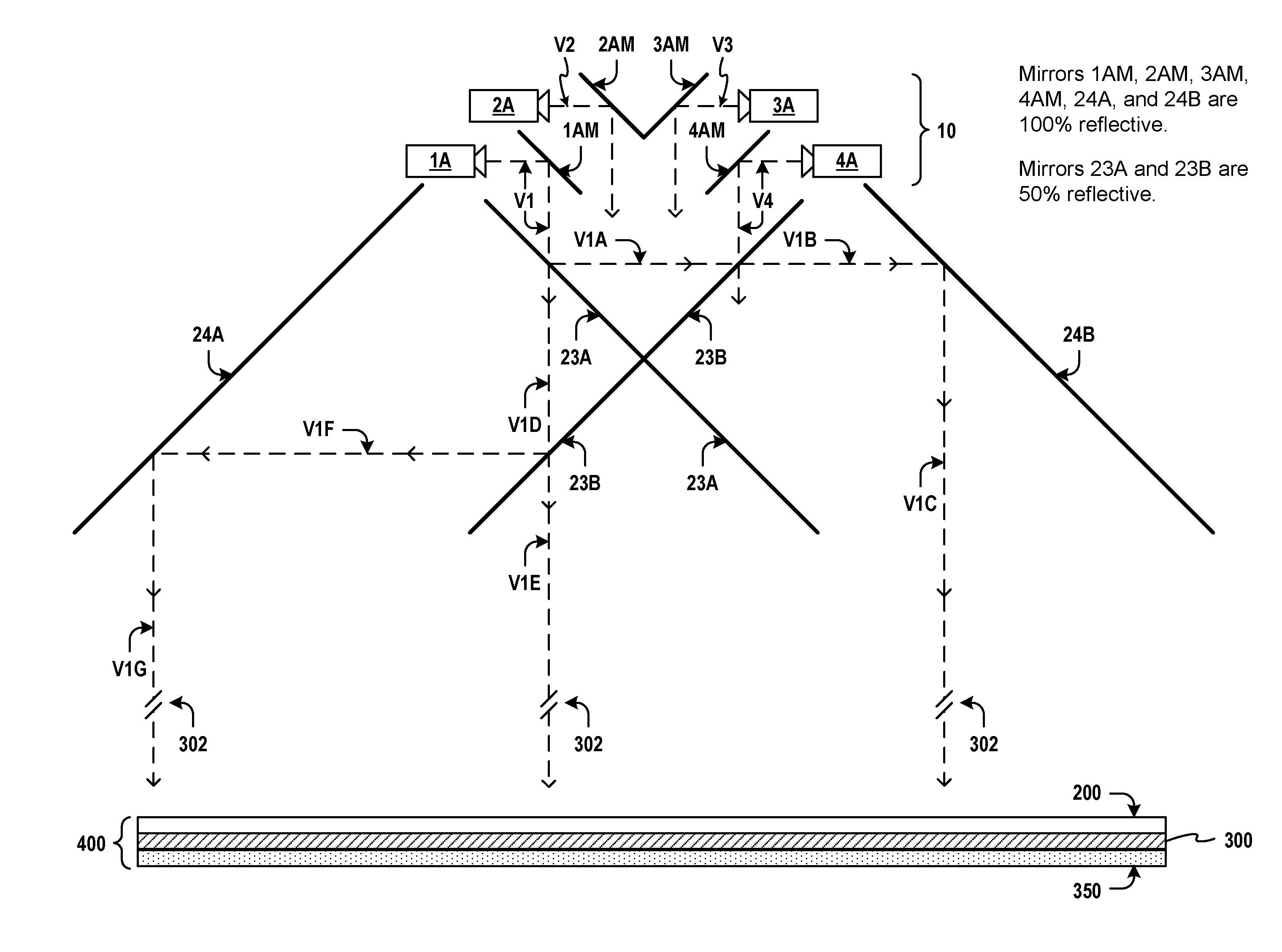
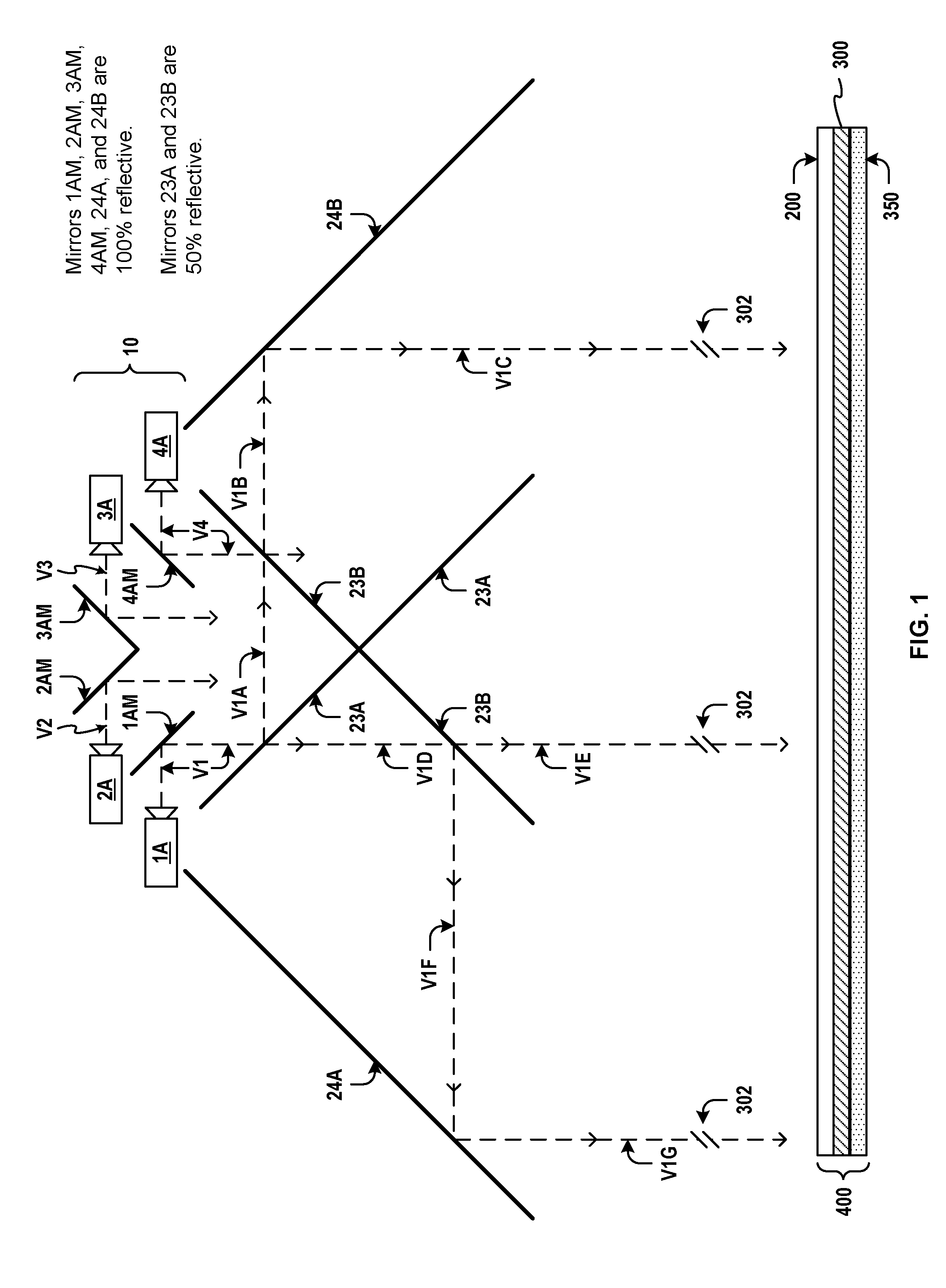
Multiple sets of view channels originate from multiple projected views modulated through an optic assembly comprising a Fresnel lens, a vertical dispersion lenticular lens, and a diffuser. Compact projection enclosures are formed using image-repeating mirrors to create a three-dimensional autostereoscopic viewing experience in free space without the use of special eyeglasses and without the use of view screens. Multiple sets of images are repeated within a viewing zone that may extend well beyond the confines of the enclosure and may be projected through and beyond a glass window. An observer walking past the window will see one view channel per eye, due in part to the repeated images, and due in part to the vertical dispersion of each projected view. Separate images for each view channel may be created by using two or more cameras spaced apart at a distance interval to match the average horizontal distance between the eyes of a human observer. Multiple views or multiple sets of view channels may be generated and projected.
Owner:NELSON BRADLEY +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com