Patents
Literature
294 results about "Offset calibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zero offset calibration is the process in which the zero offset value is updated for the power meter. This is an important process as it ensures the power meter has an up to date value for 0 or no load on the power meter. Depending on the head unit used, this process may be referred to as calibration or zero reset.
Real-time radiation sensor calibration
InactiveUS20050029453A1Television system detailsRadiation pyrometryRadiation sensorOffset calibration
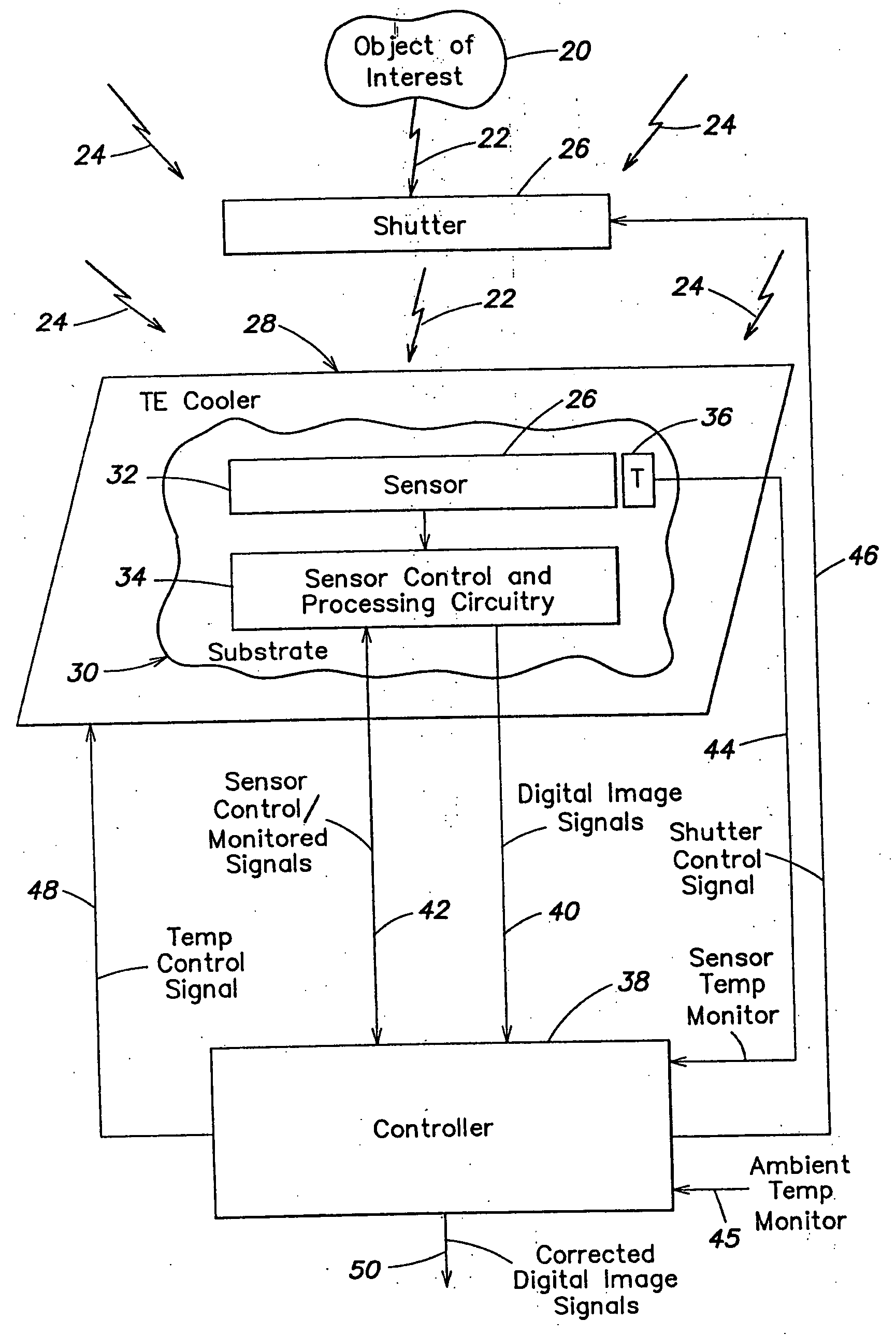
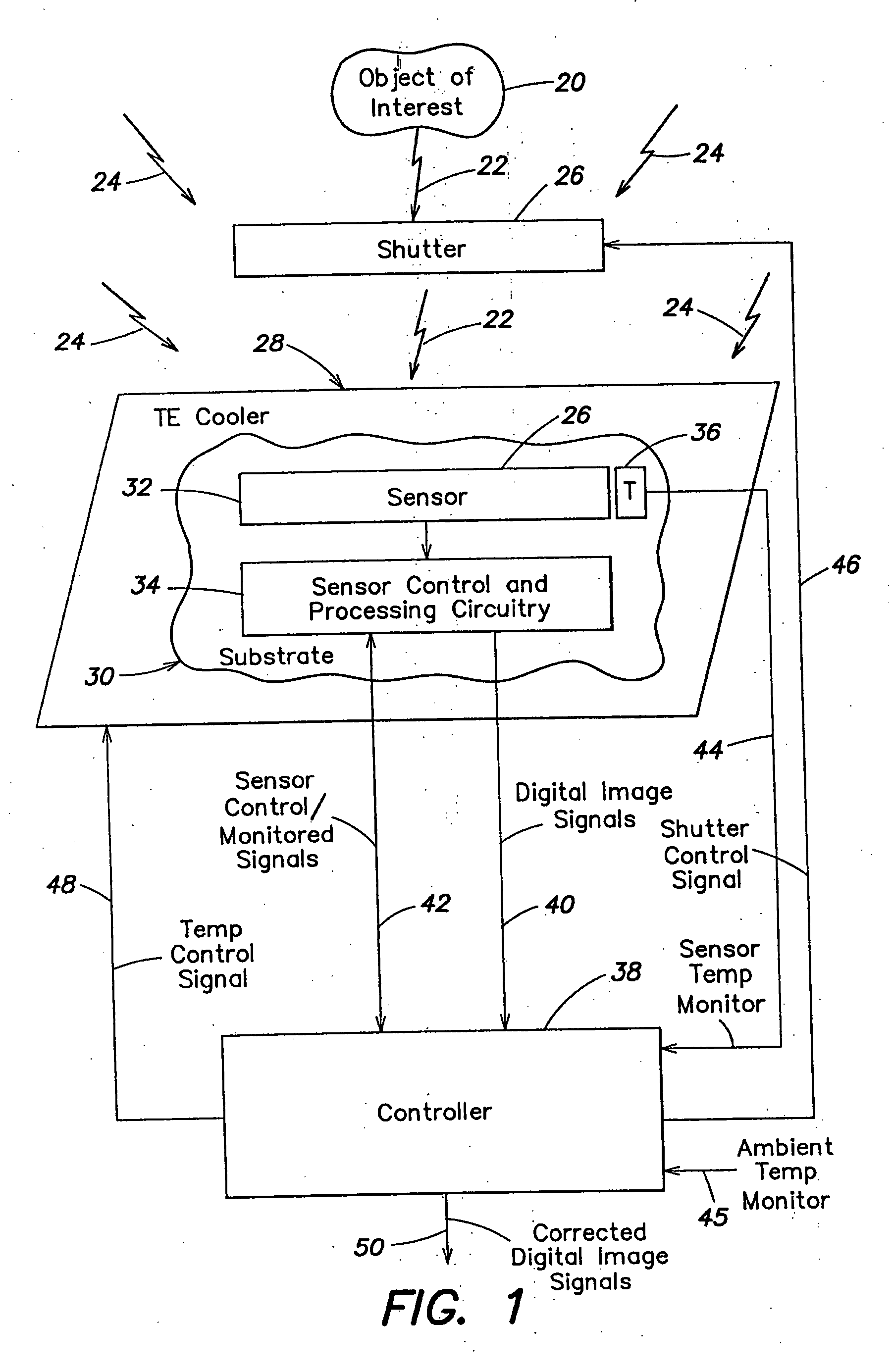
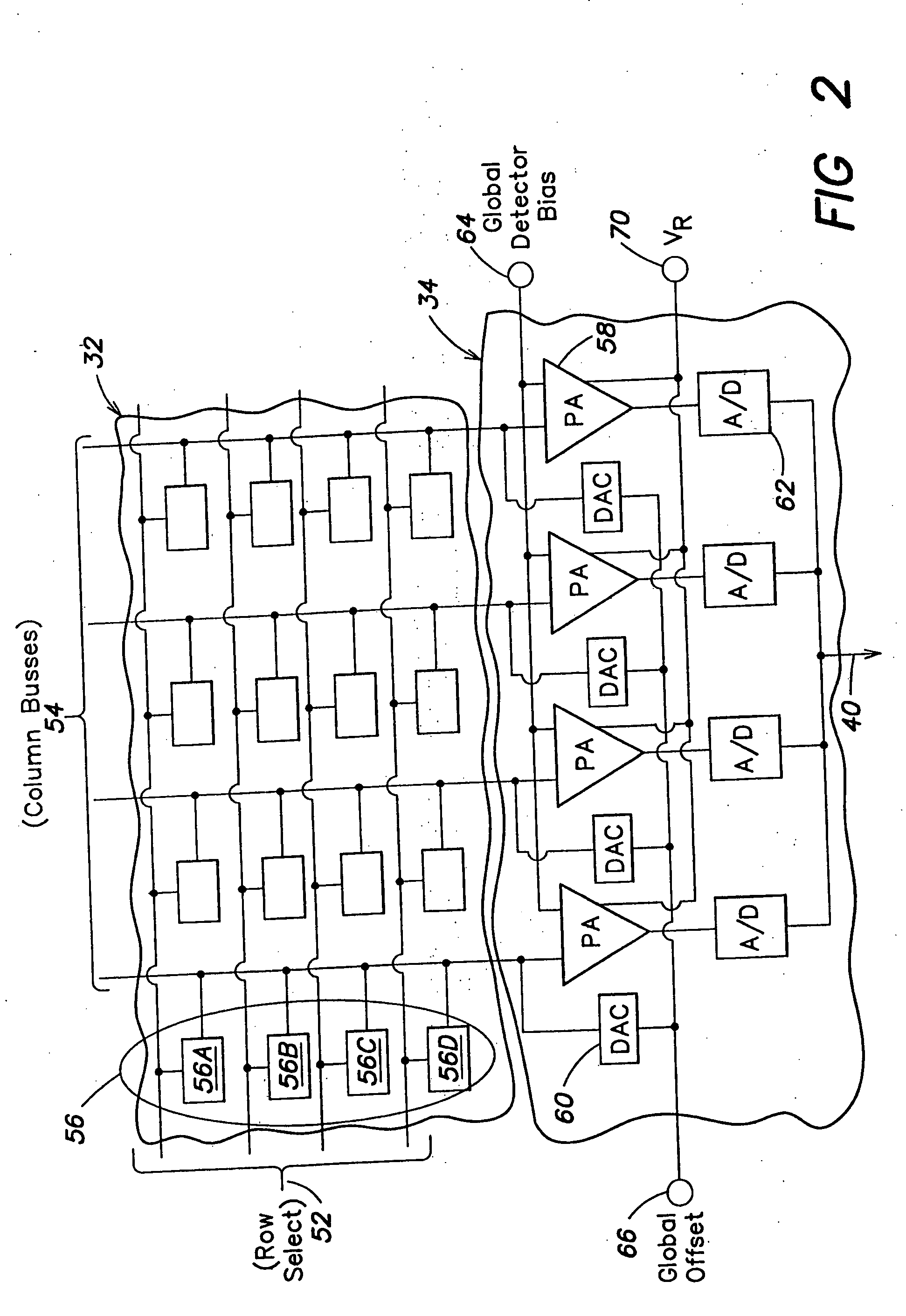
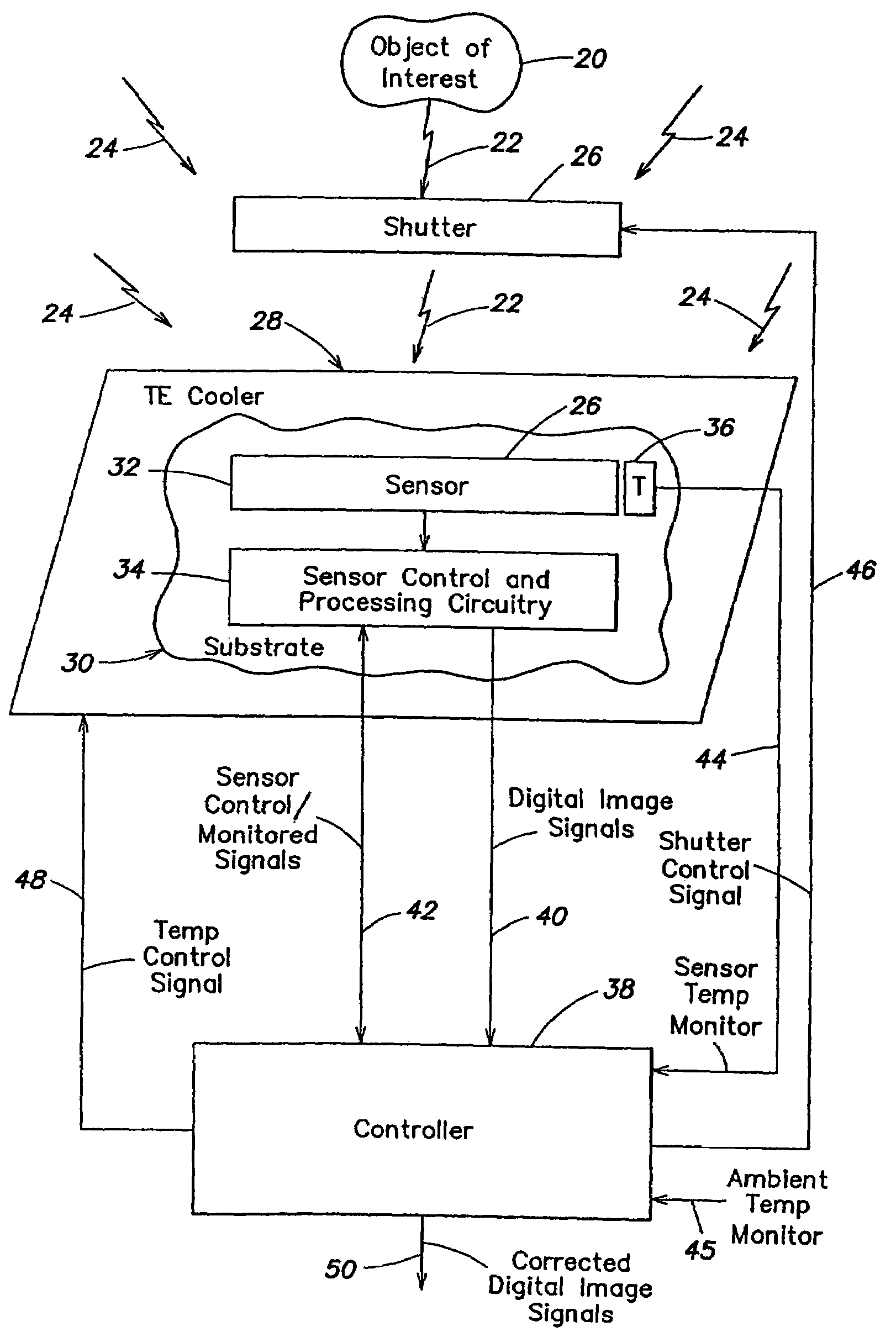
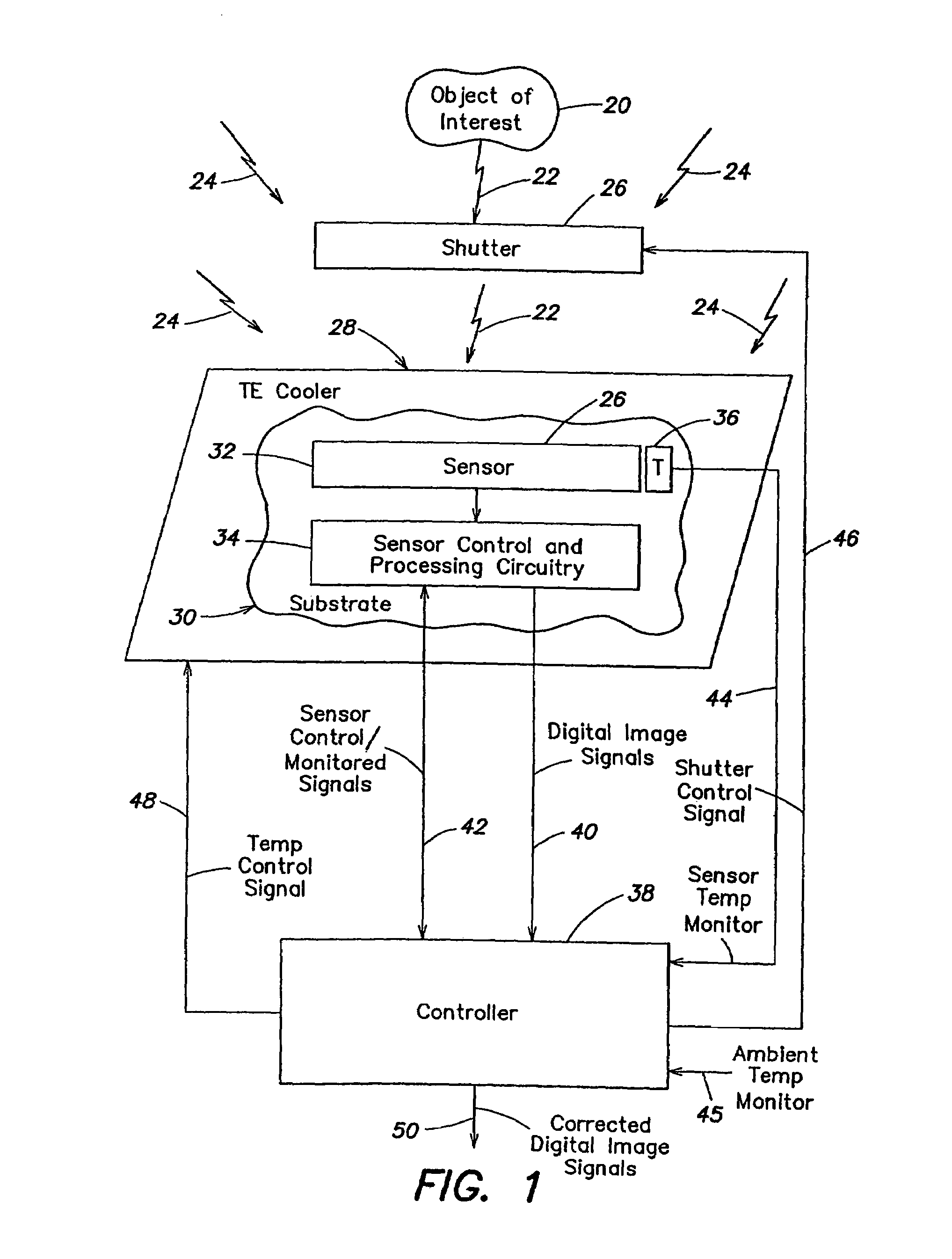
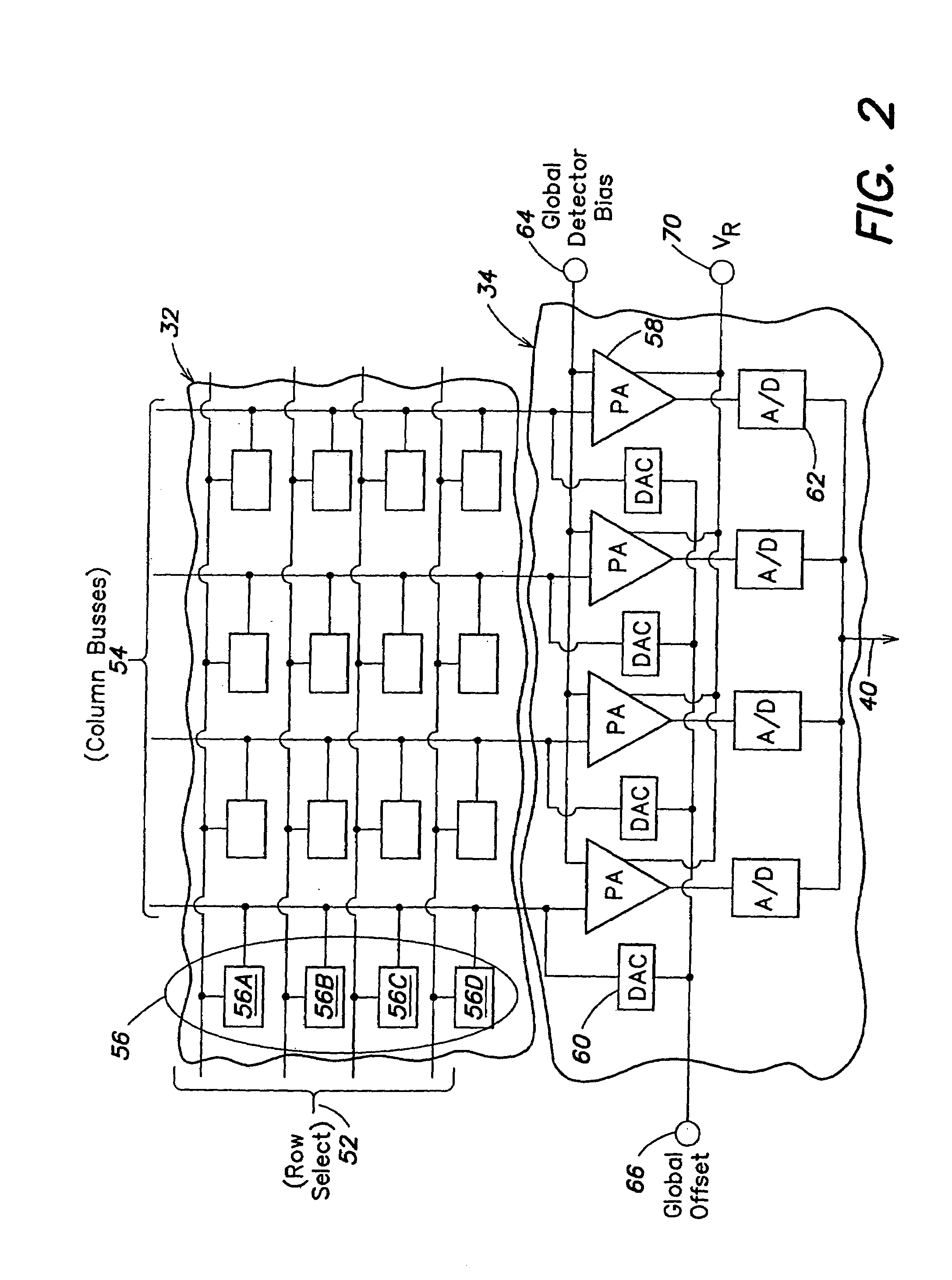
One embodiment of the invention is directed to methods and apparatus for determining a variation of a calibration parameter of a pixel of the thermal sensor during operation of the imaging apparatus, after an initial calibration procedure. Another embodiment of the invention is directed to methods and apparatus for calculating a gain calibration parameter using first and second ambient temperature values and respective first and second resistance values for a pixel of a sensor. A further embodiment of the invention is directed to calculating an offset calibration parameter for at least one pixel using a gain of the at least one pixel between first and second times and an ambient temperature at a third time, wherein the pixel is exposed to both scene and ambient radiation at the third time.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
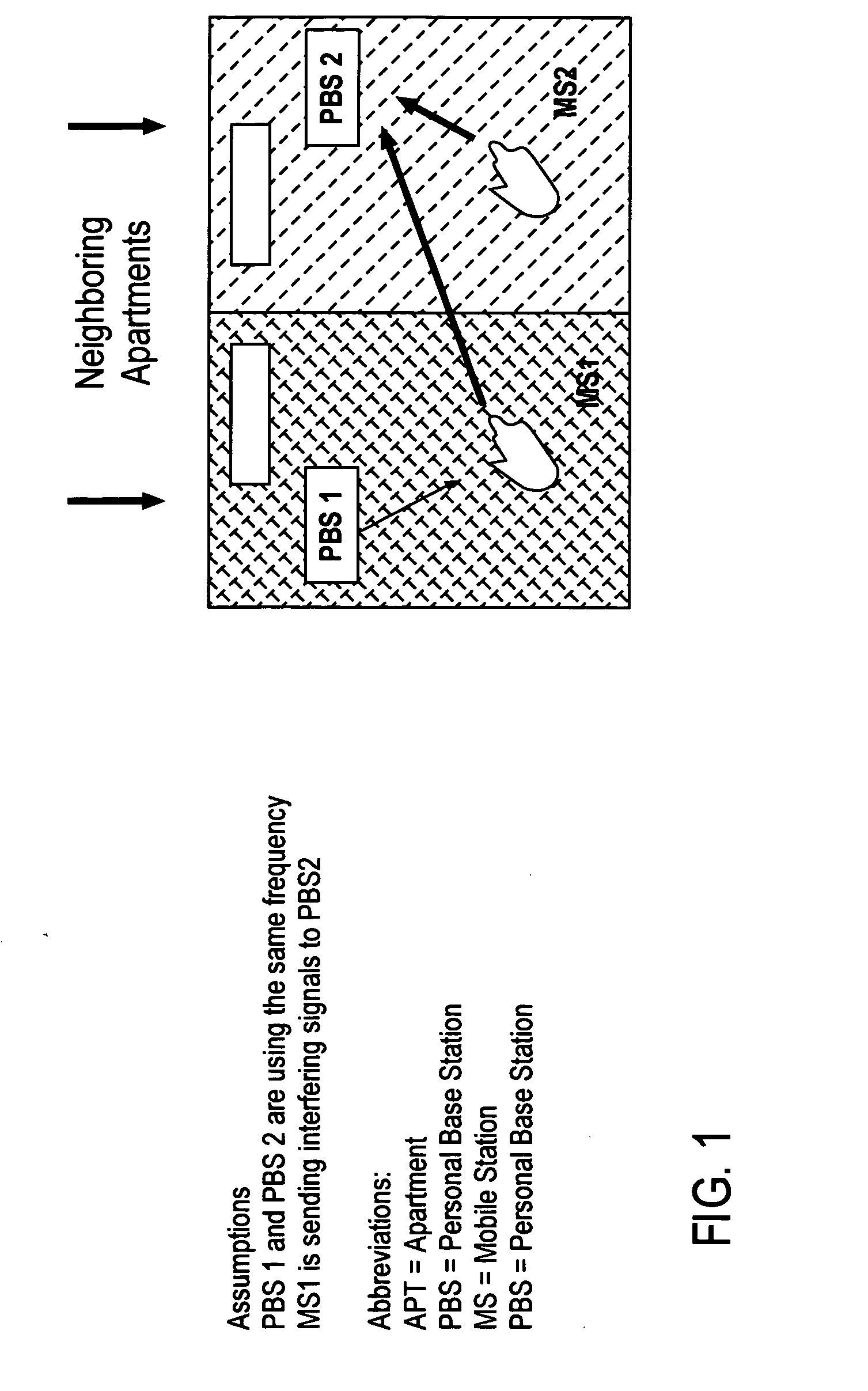
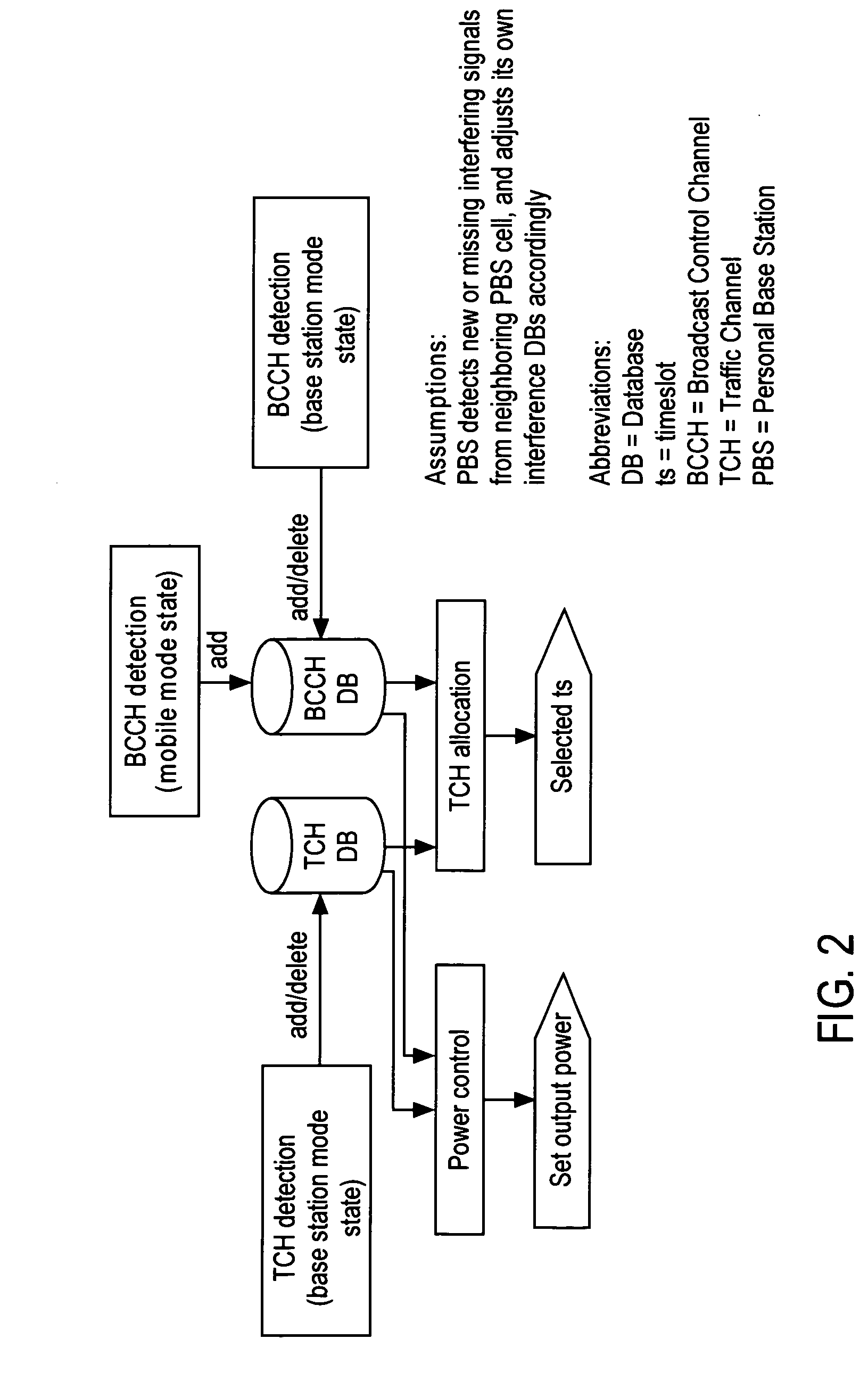
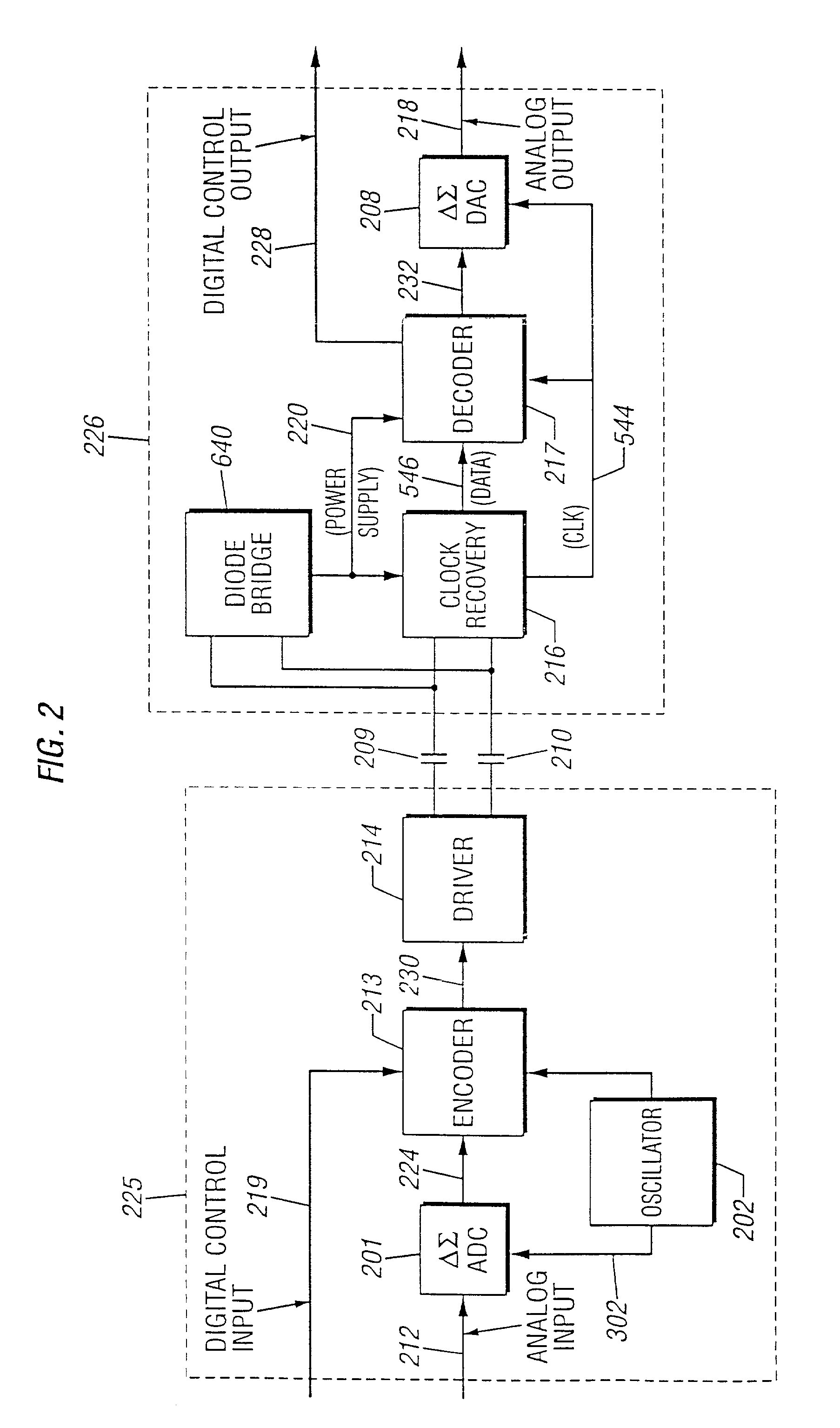
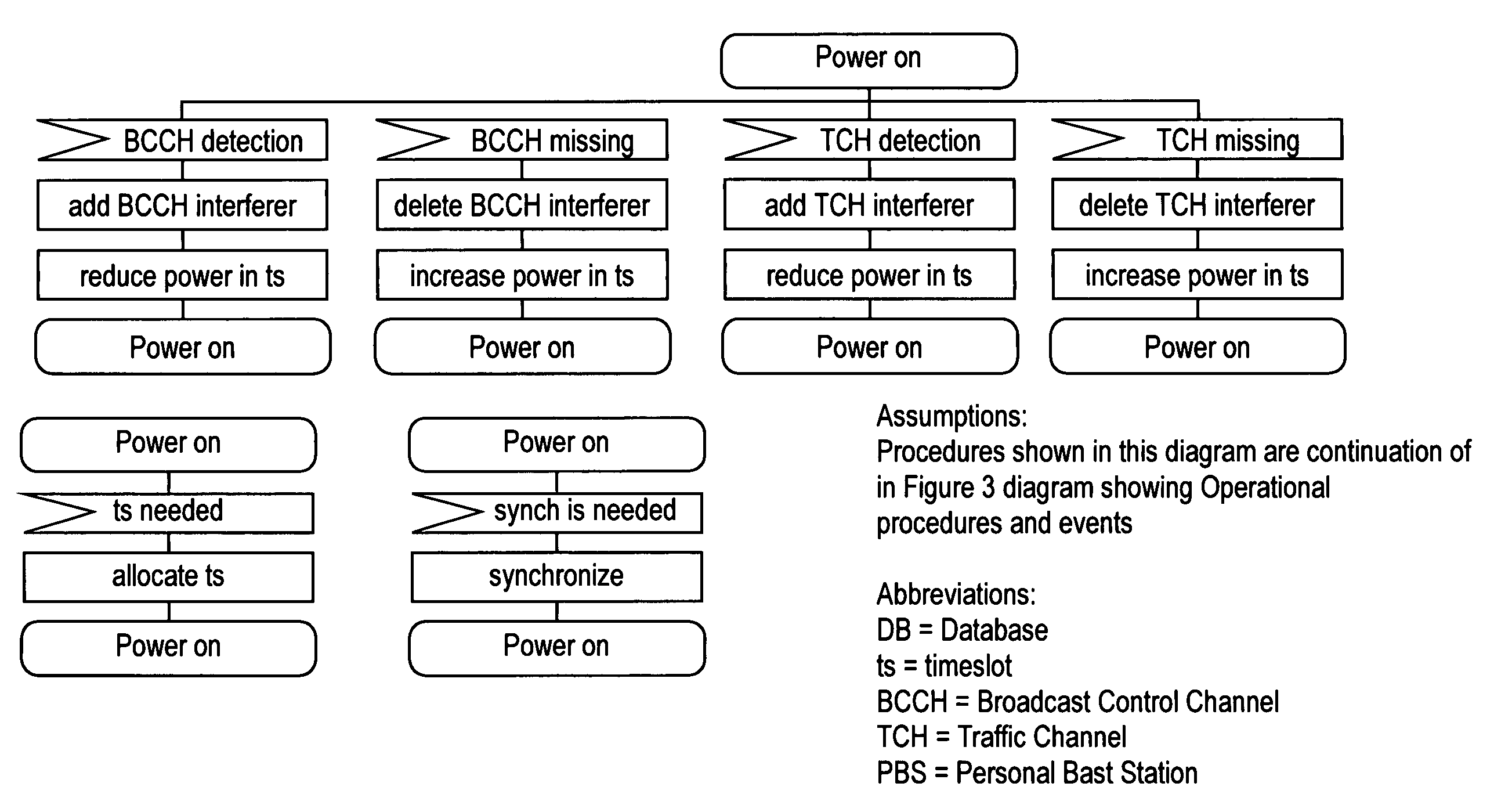
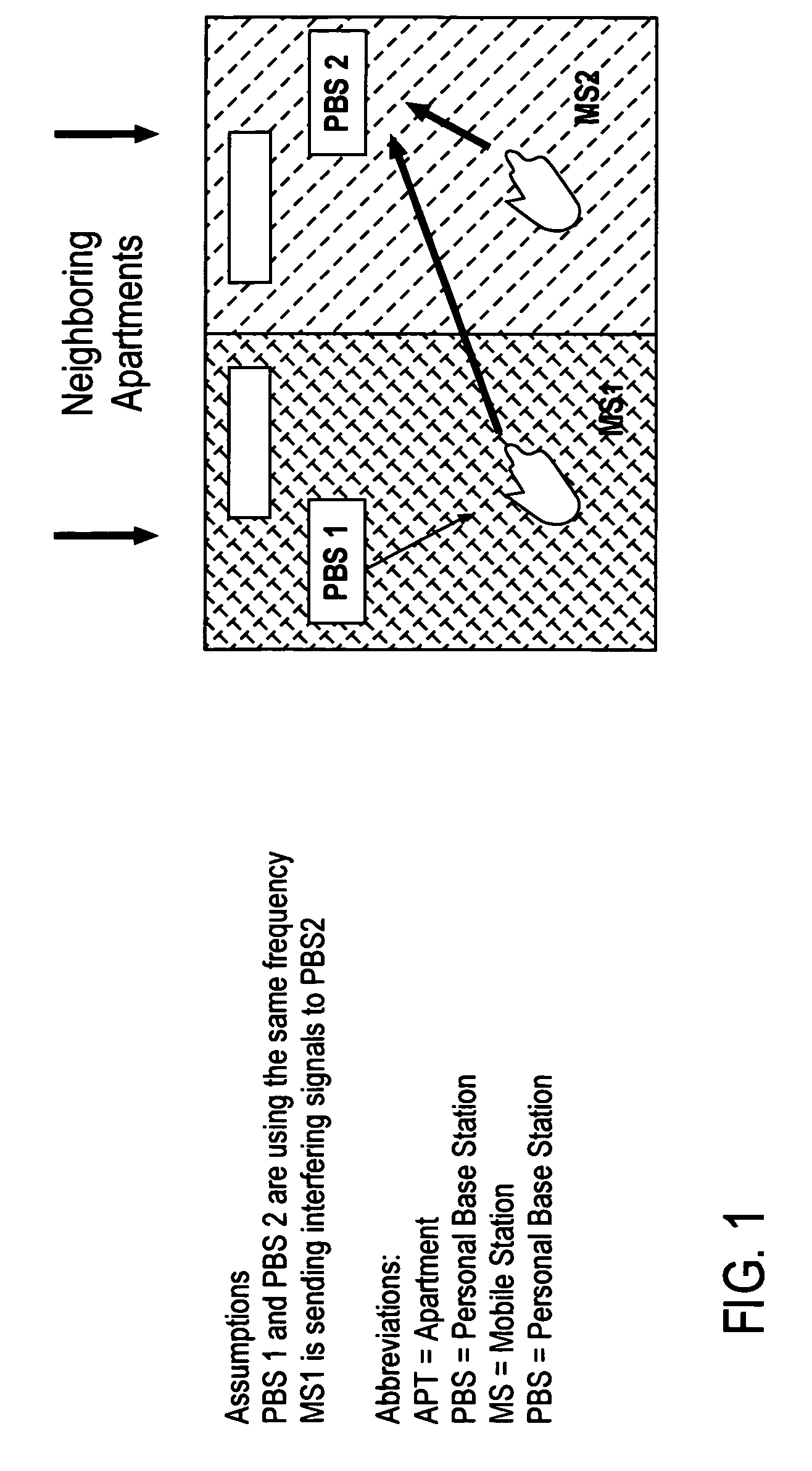
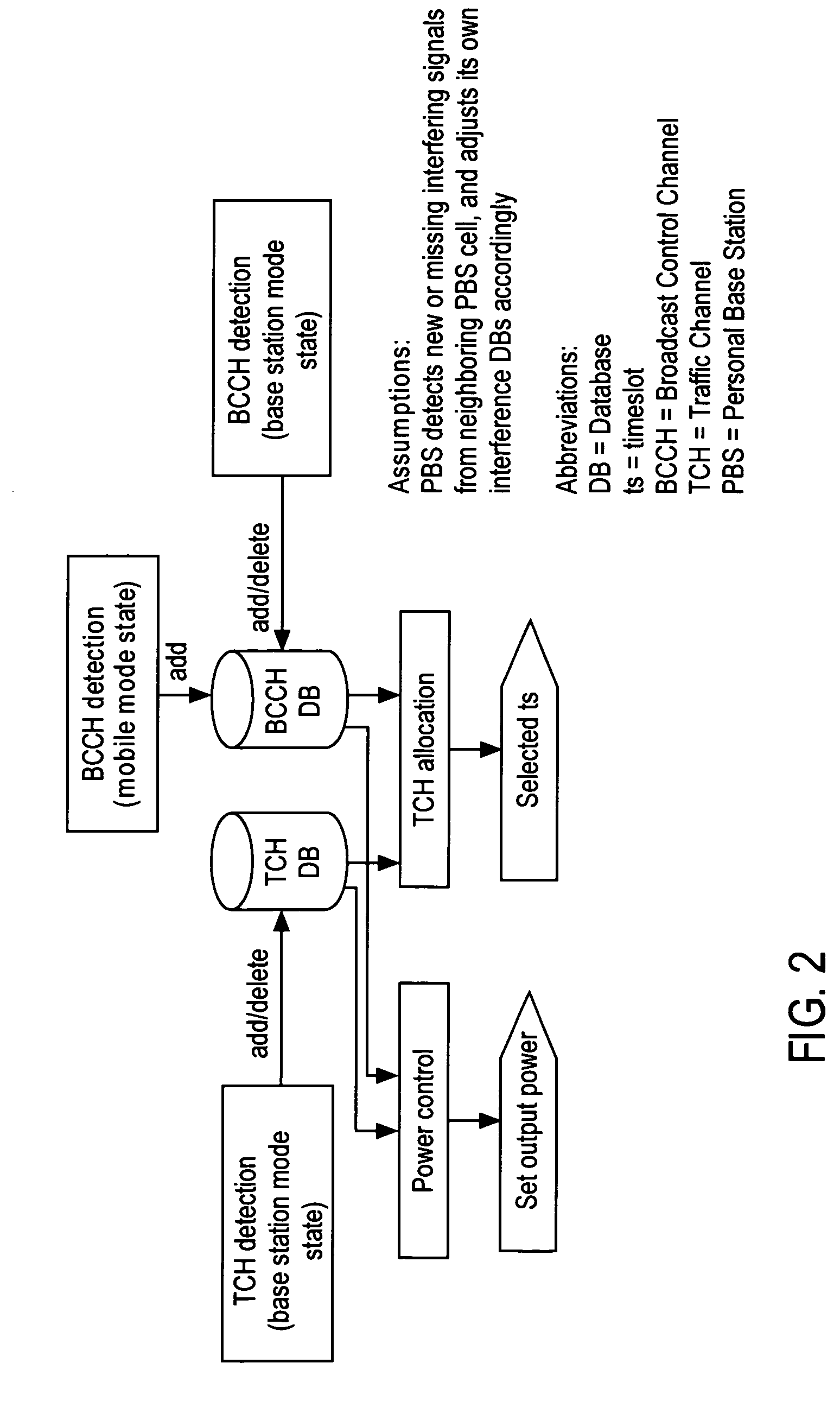
Base station interference control using timeslot resource management
InactiveUS20080130593A1Reduce in quantityReduced strengthEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexOffset calibrationResource management
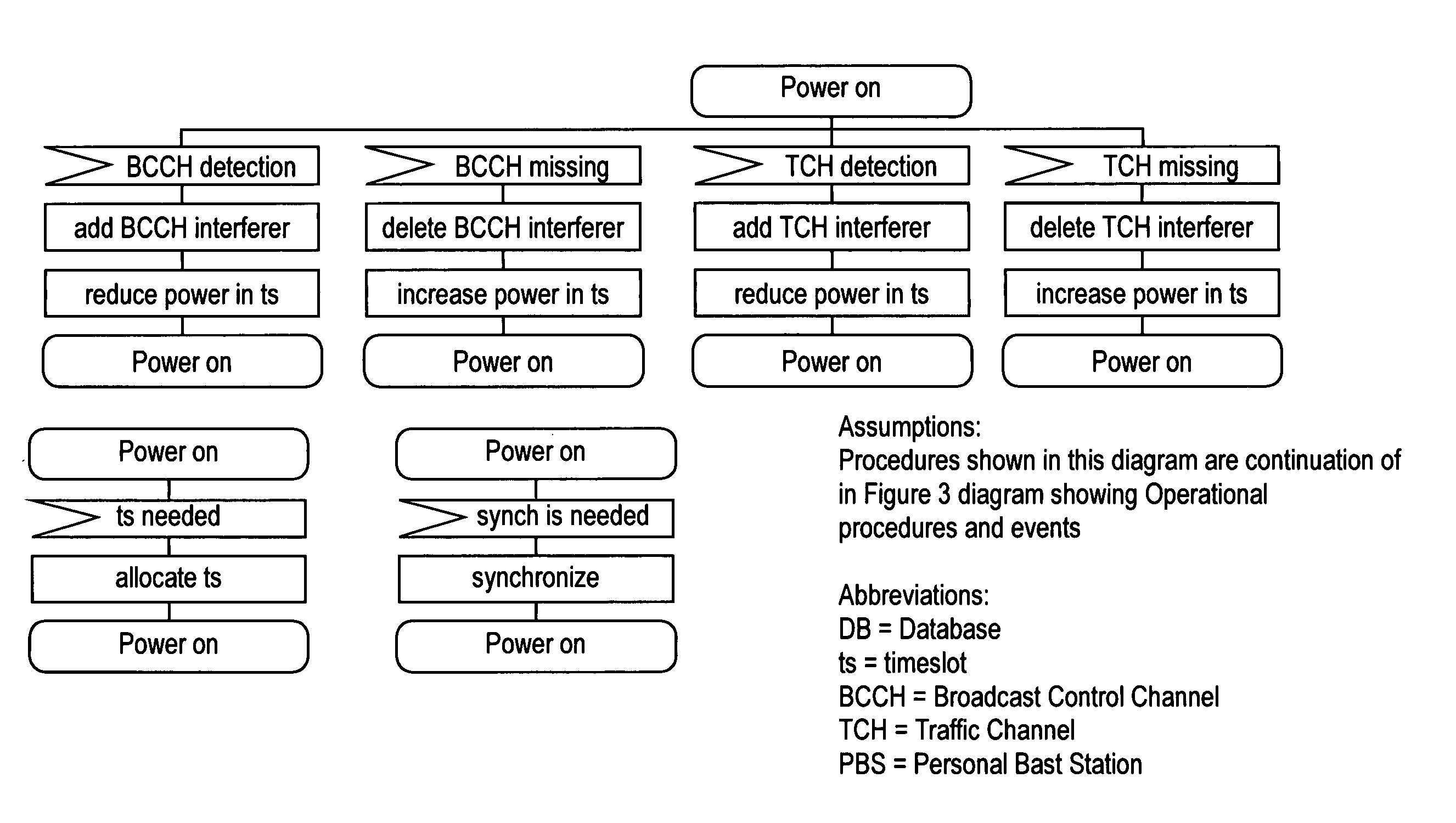
A personal base station configured to connect to the Internet and establish a small area of wireless coverage including means for controlling interference with neighboring personal base stations using a timeslot management mechanism. Timeslot management mechanisms include timeslot interference detection, timeslot power reduction, timeslot allocation, timeslot offset calibration, and timeslot synchronization management that minimizes the number of frequencies required to control inter-cell interference between neighboring personal base stations.
Owner:INTEL CORP
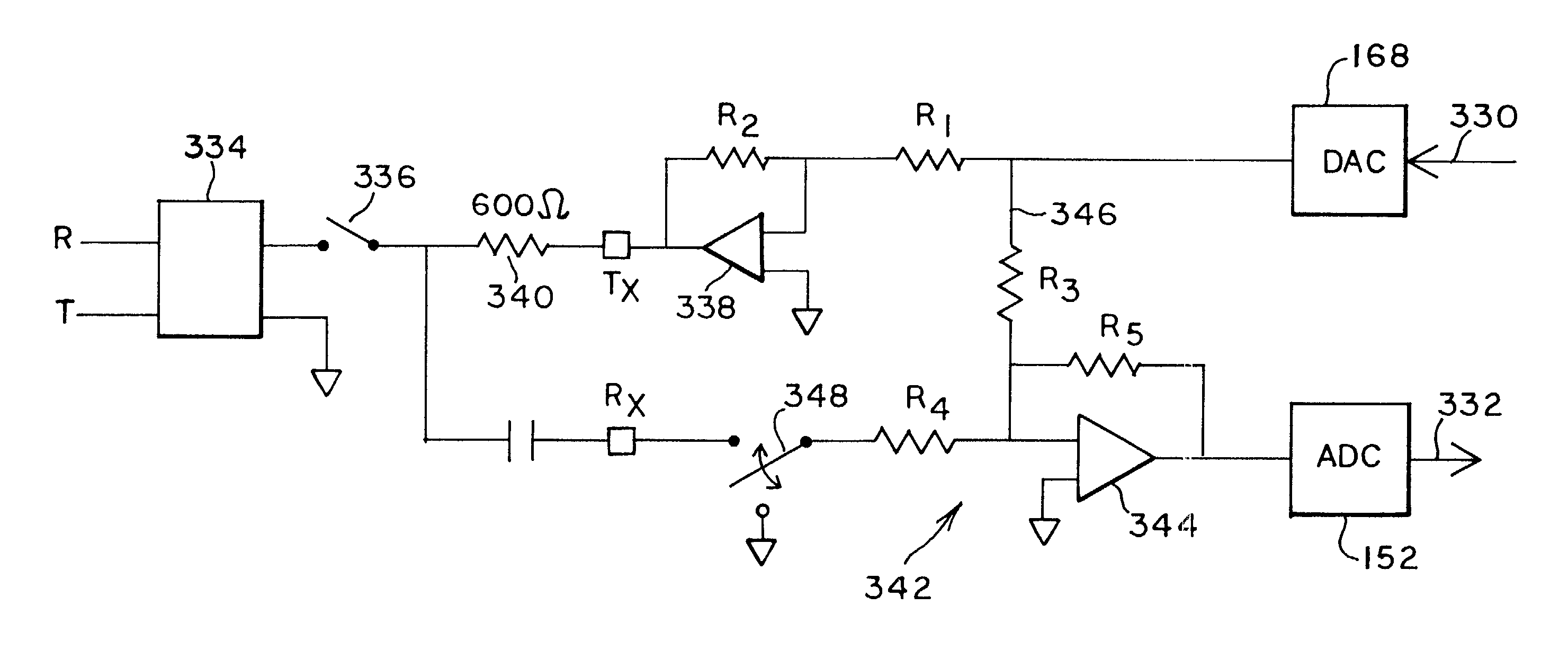
Digital isolation system with hybrid circuit in ADC calibration loop
InactiveUS7050509B2Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceModem device
An improved digital capacitive isolation barrier system is provided that is suitable for use in a telephone or modem where the locally powered circuits must be effectively isolated from the public telephone system, while permitting data transfer across the barrier. In particular, an automatic ADC offset calibration system is provided for determining the magnitude of the ADC offset signal required in the system during a calibration operation, and for providing the calibrated ADC offset signal during normal operation of the isolation barrier system. A modified hybrid circuit is provided for isolating the system input from the telephone line during calibration, and for completing the calibration loop. Fixed bias signals are also provided for the ADC and for a DAC in the system. In a preferred embodiment, the ADC is located on the isolated side of the isolation barrier, while the integrator and register that determine and hold the offset signal are located on the powered side of the isolation barrier.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Base station interference control using timeslot resource management
InactiveUS7555300B2Reduce in quantityReduced strengthEnergy efficient ICTTime-division multiplexThe InternetResource management
A personal base station configured to connect to the Internet and establish a small area of wireless coverage including means for controlling interference with neighboring personal base stations using a timeslot management mechanism. Timeslot management mechanisms include timeslot interference detection, timeslot power reduction, timeslot allocation, timeslot offset calibration, and timeslot synchronization management that minimizes the number of frequencies required to control inter-cell interference between neighboring personal base stations.
Owner:INTEL CORP
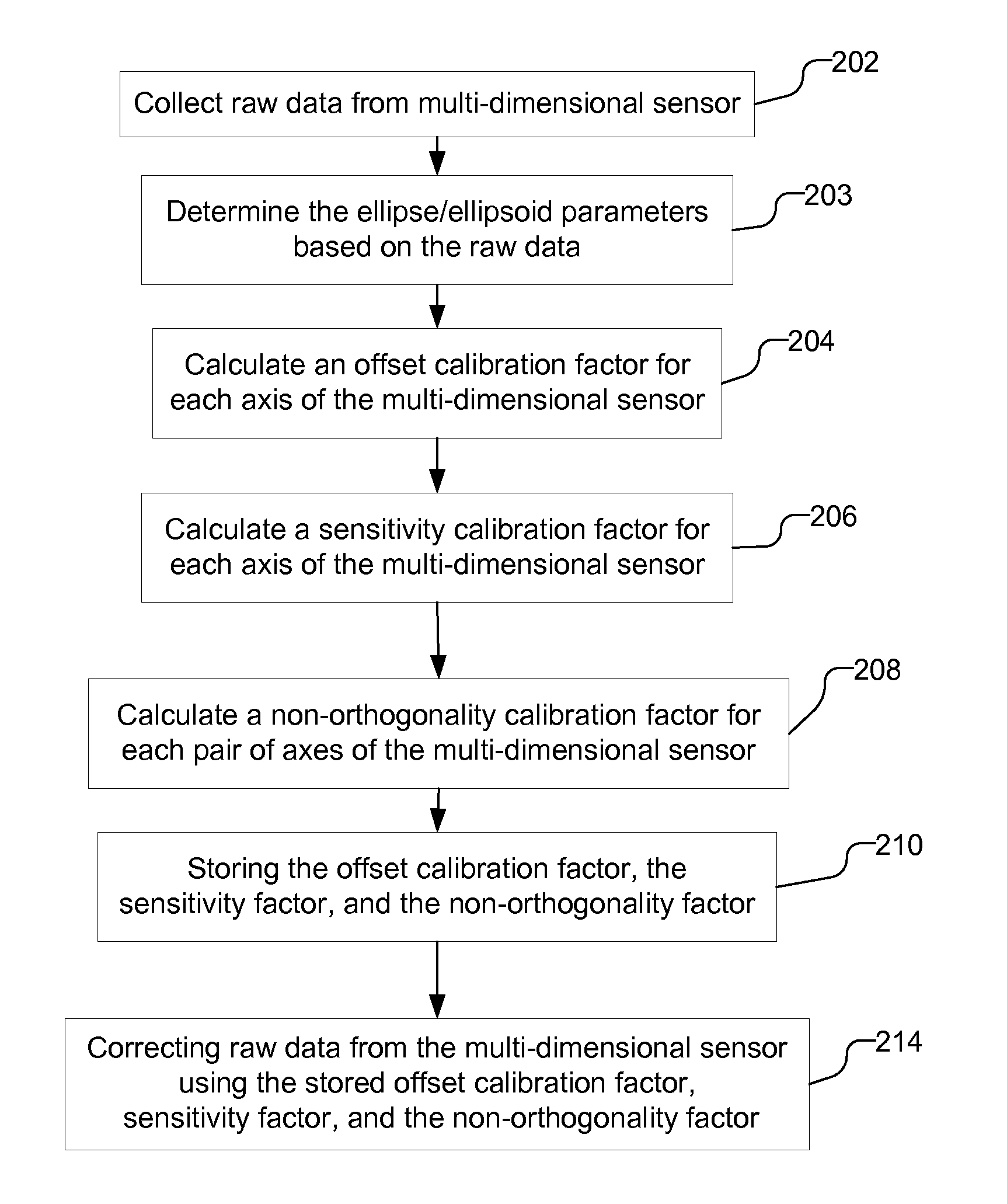
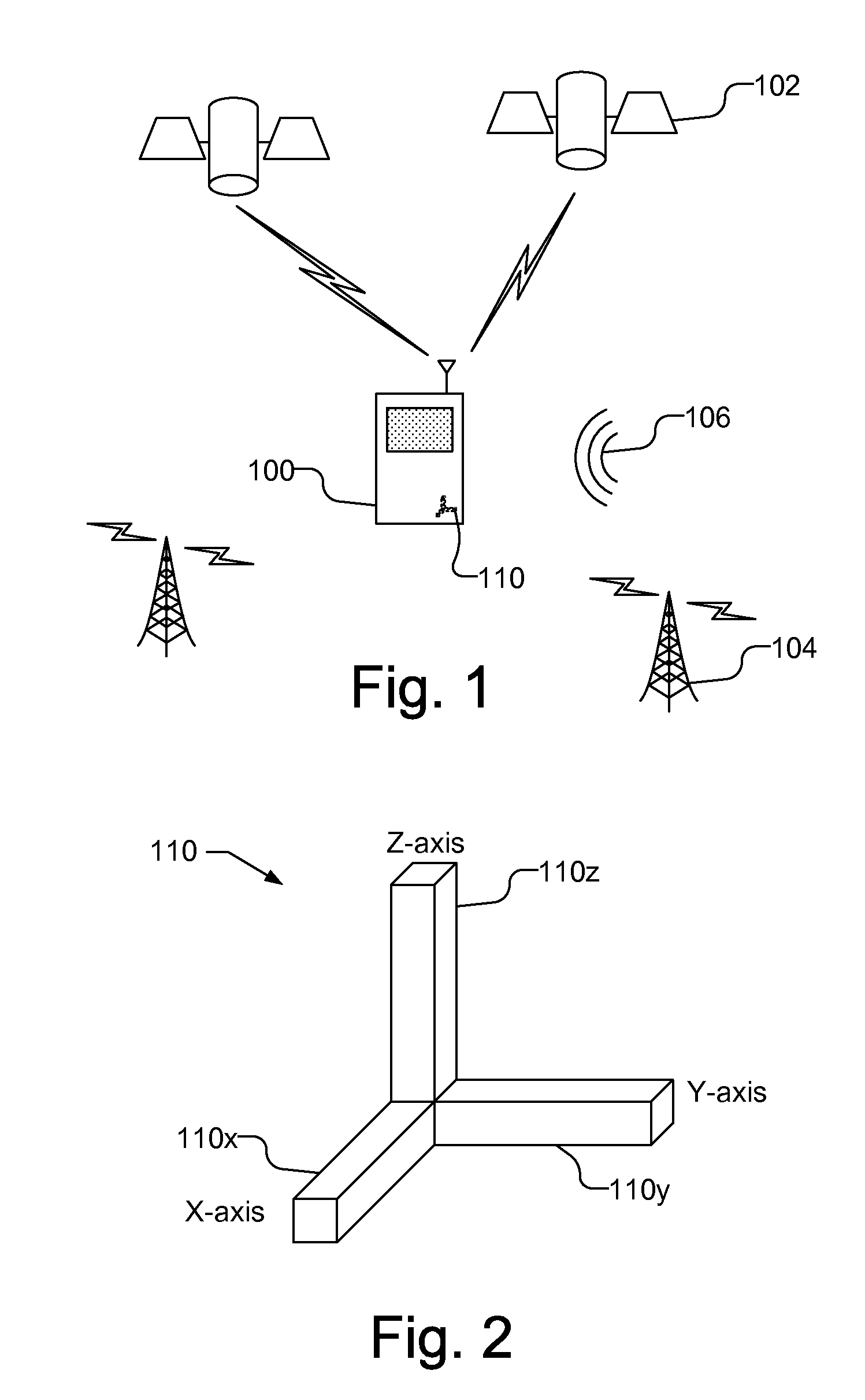
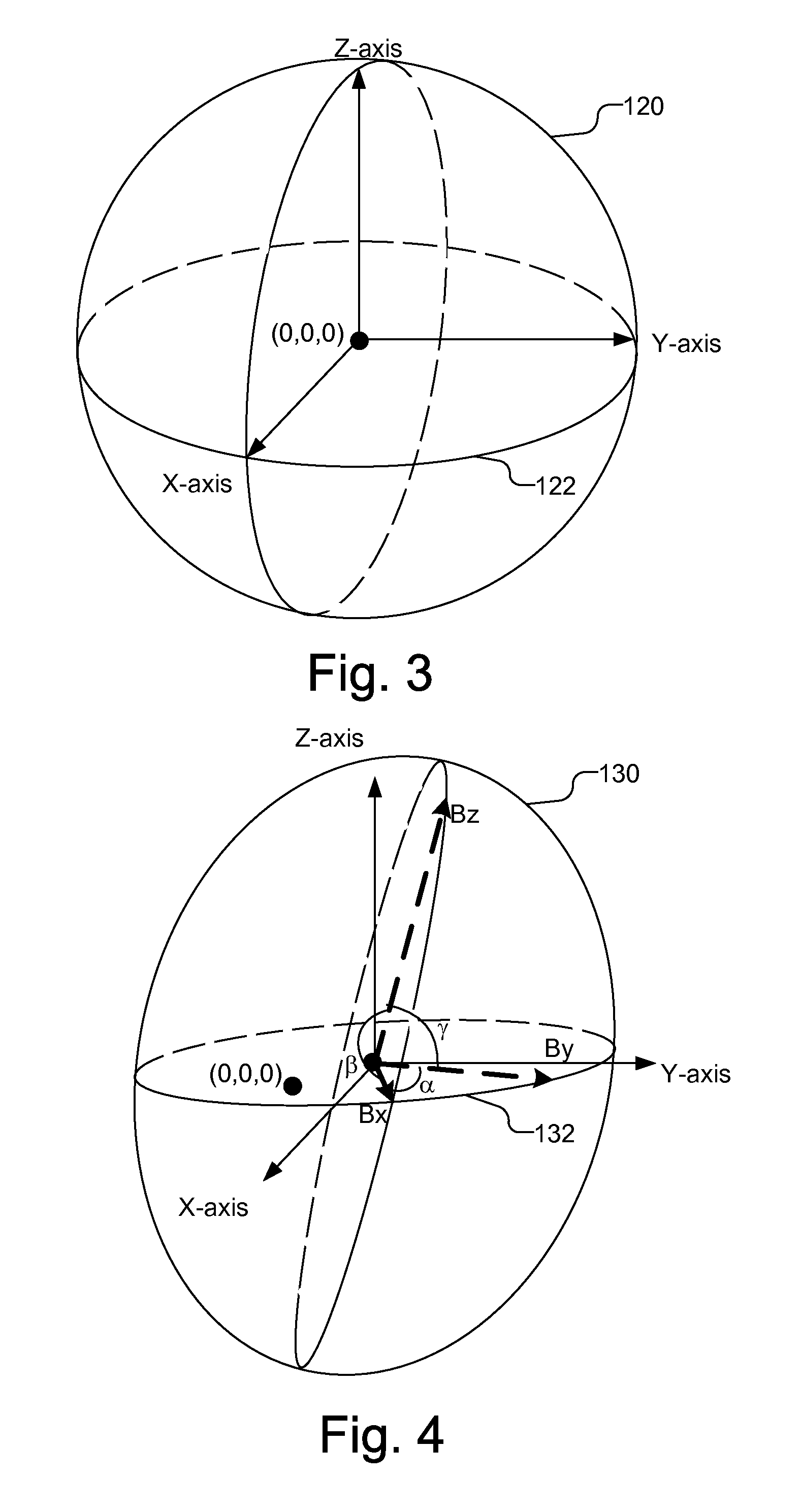
Calibrating multi-dimensional sensor for offset, sensitivity, and non-orthogonality
InactiveUS20110106477A1Testing/calibration apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAccelerometerEllipse
A multi-dimensional sensor, a magnetometer or accelerometer, is calibrated based on the raw data provided by the sensor. Raw data is collected and may be used to generate ellipse or ellipsoid parameters, for a two-dimensional or three-dimensional sensor, respectively. An offset calibration factor is calculated based on the raw data, e.g., the determined ellipse or ellipsoid parameters. A sensitivity calibration factor is then calculated based on the offset calibration factor and the raw data. A non-orthogonality calibration factor can then be calculated based on the calculated offset and sensitivity calibration factors. Using the offset, sensitivity and non-orthogonality calibration factors, the raw data can be corrected to produce calibrated data.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
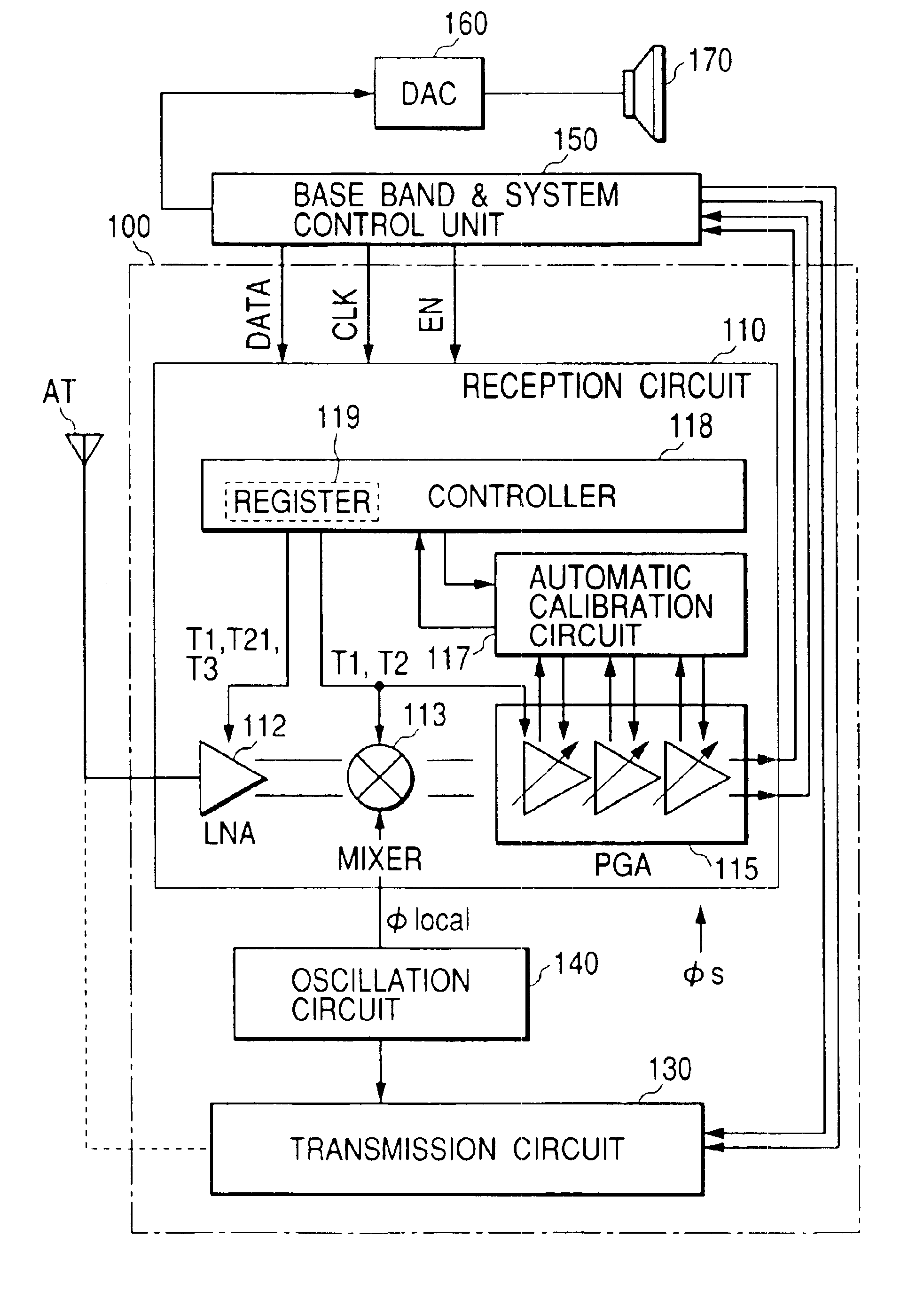
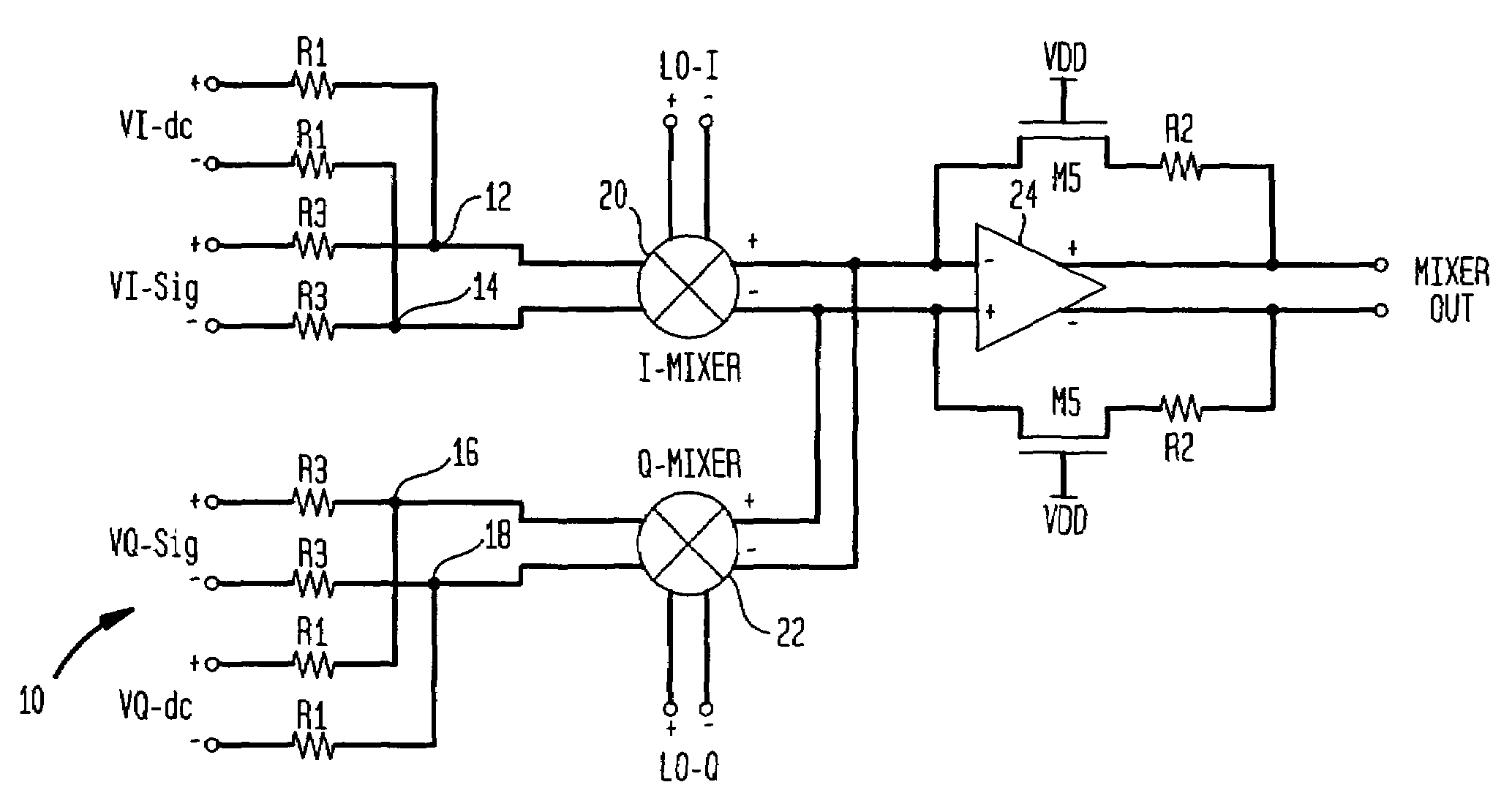
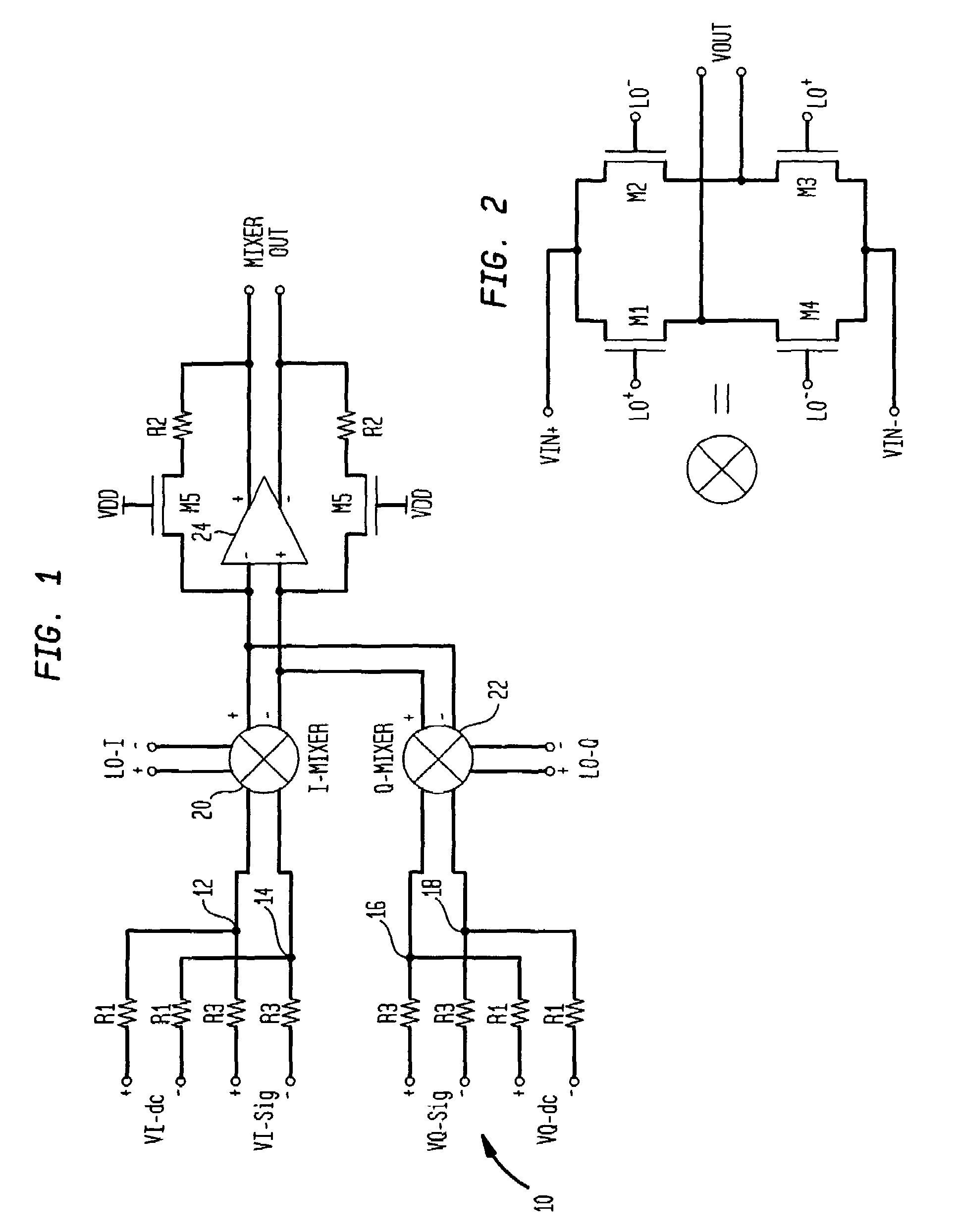
Signal processing semiconductor integrated circuit device and wireless communication system
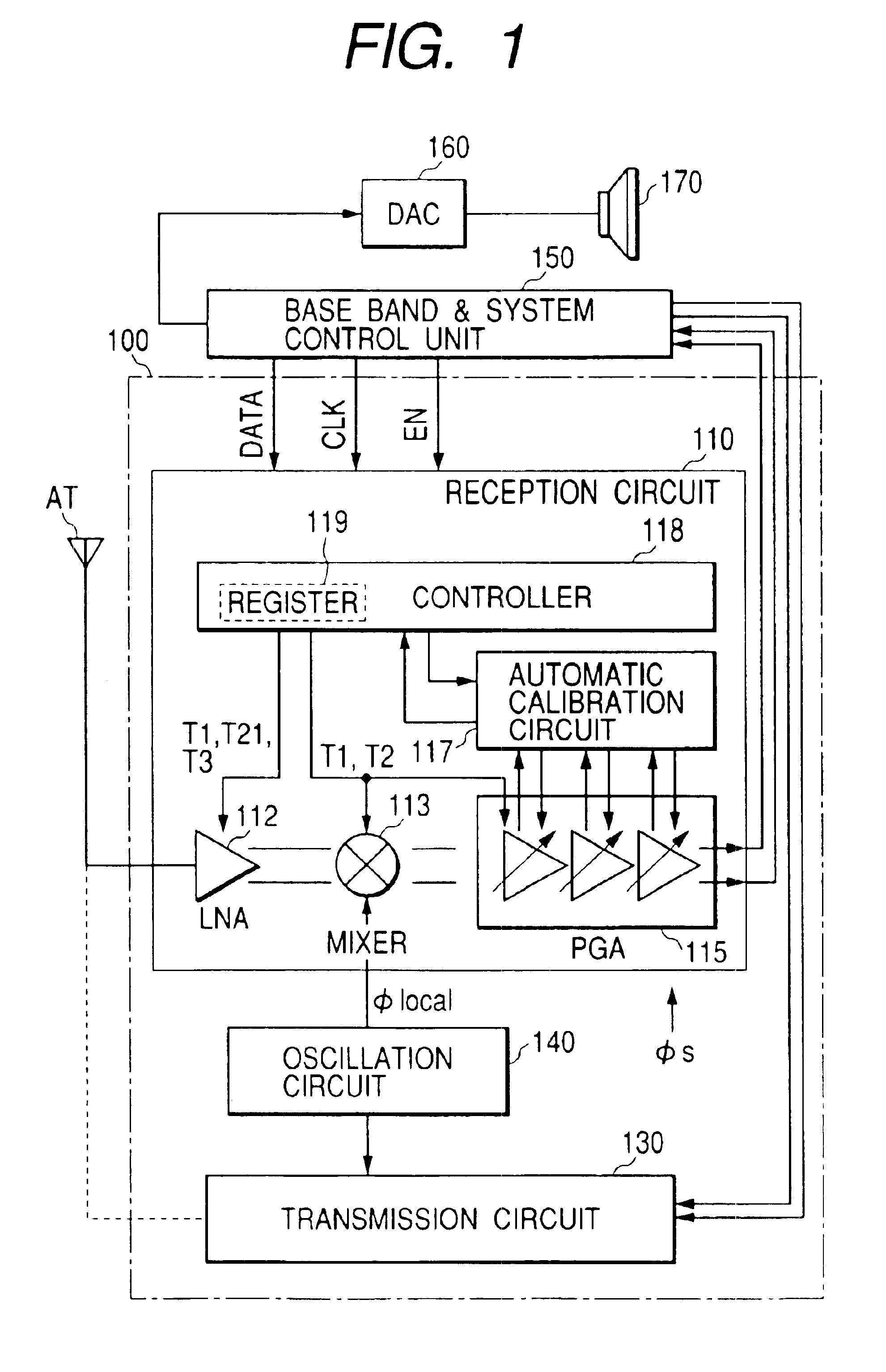
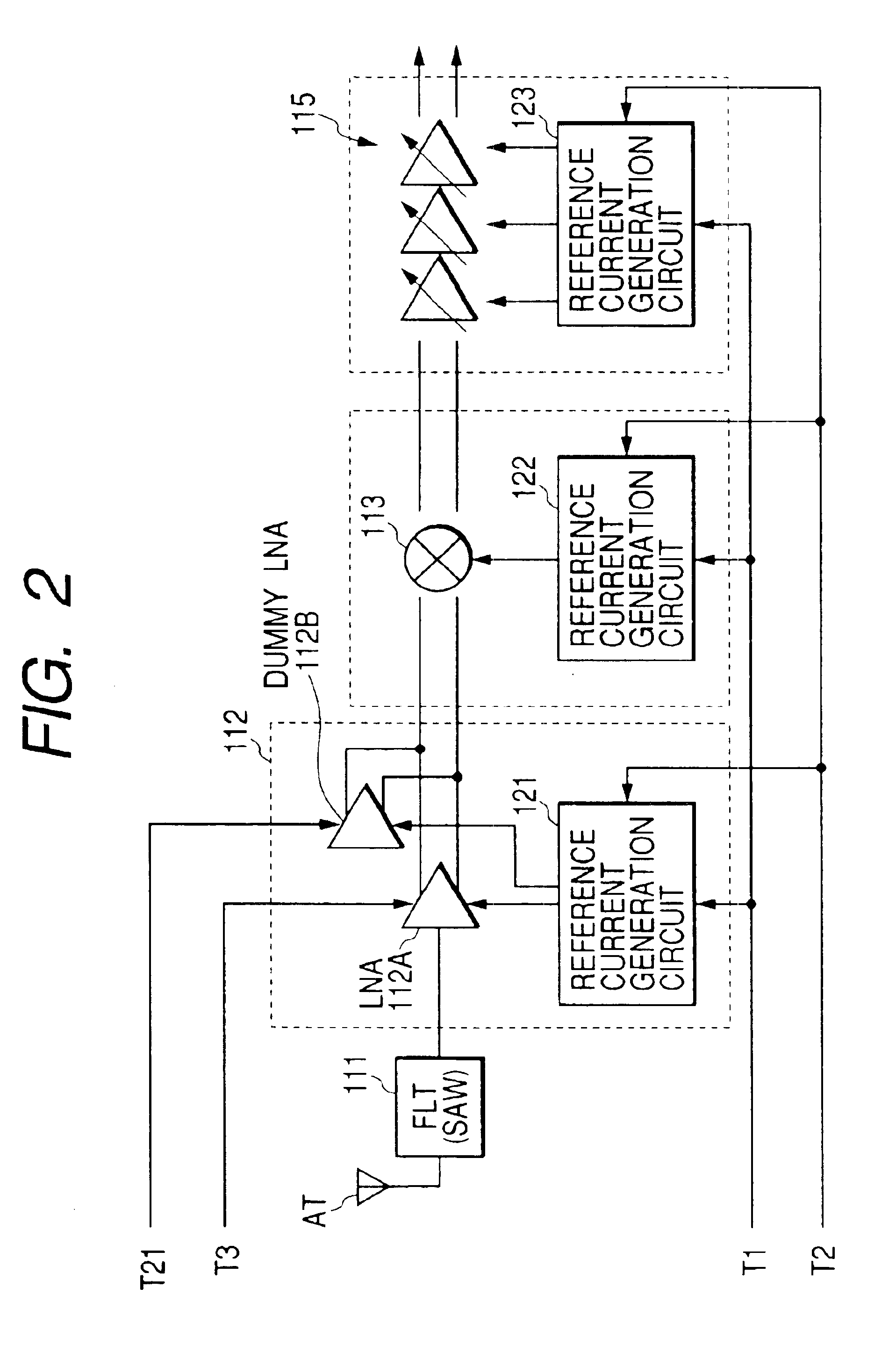
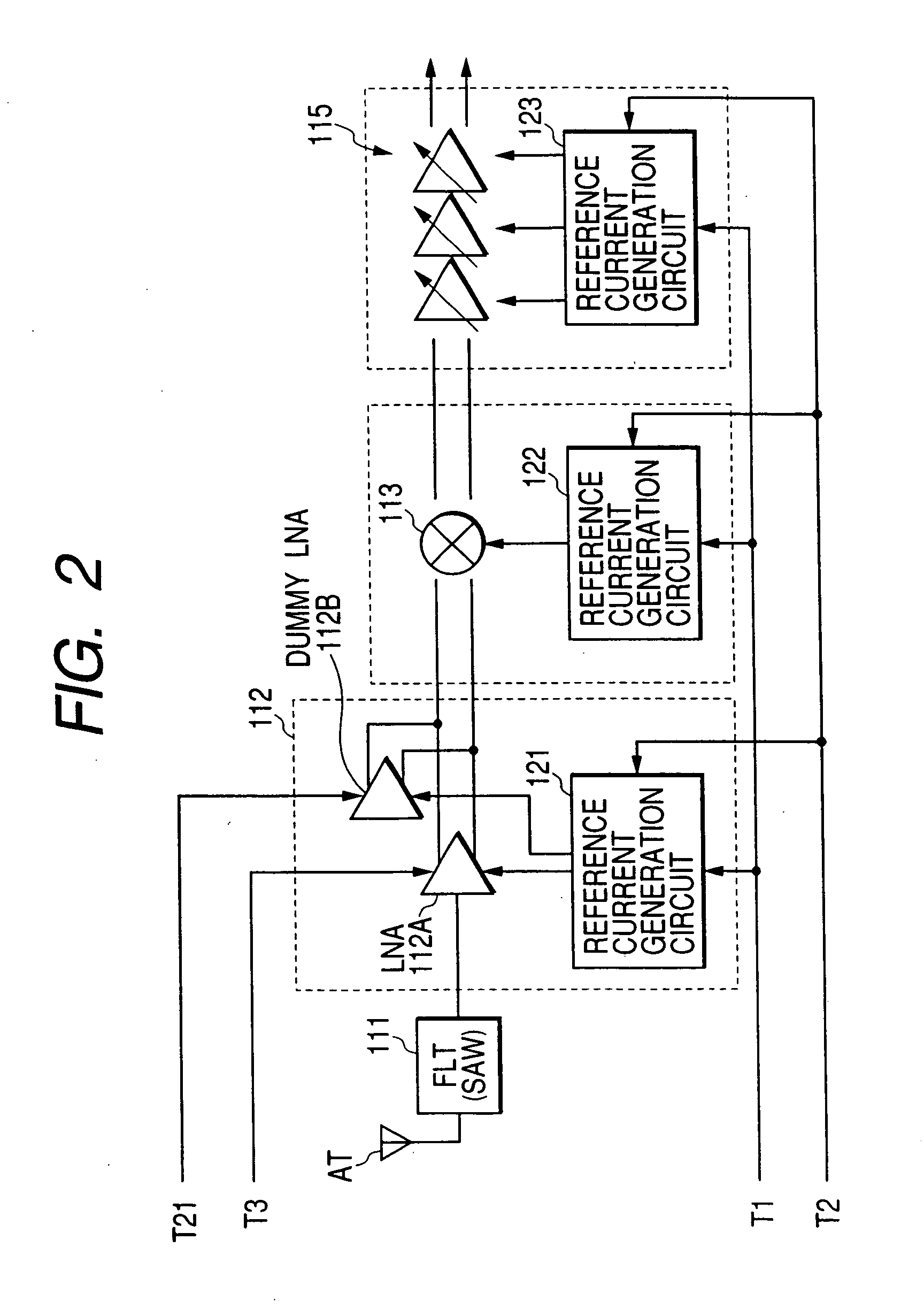
InactiveUS6909882B2Stabilized reception characteristicImprove receiver sensitivityResonant long antennasModulation transference balanced arrangementsCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
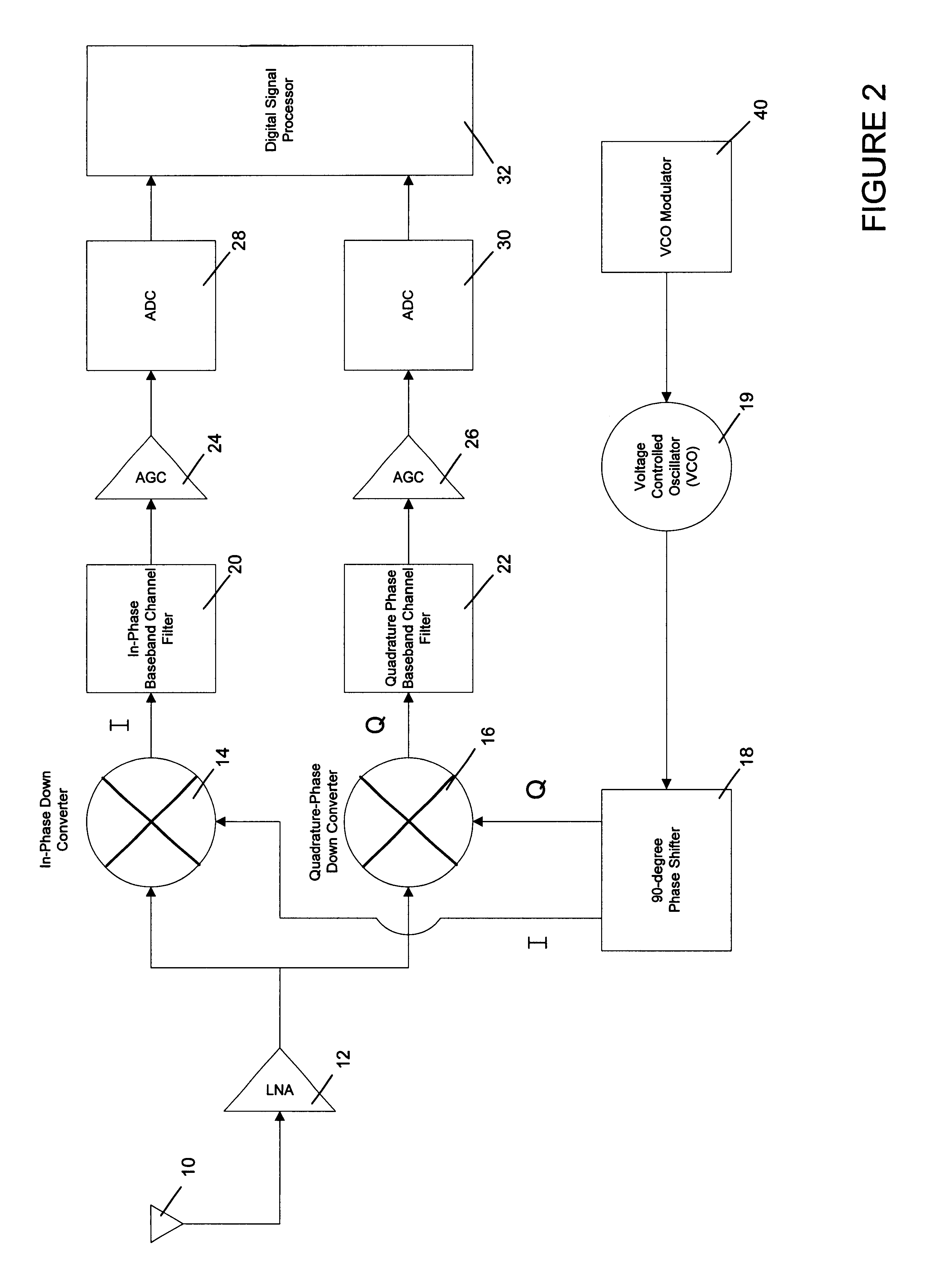
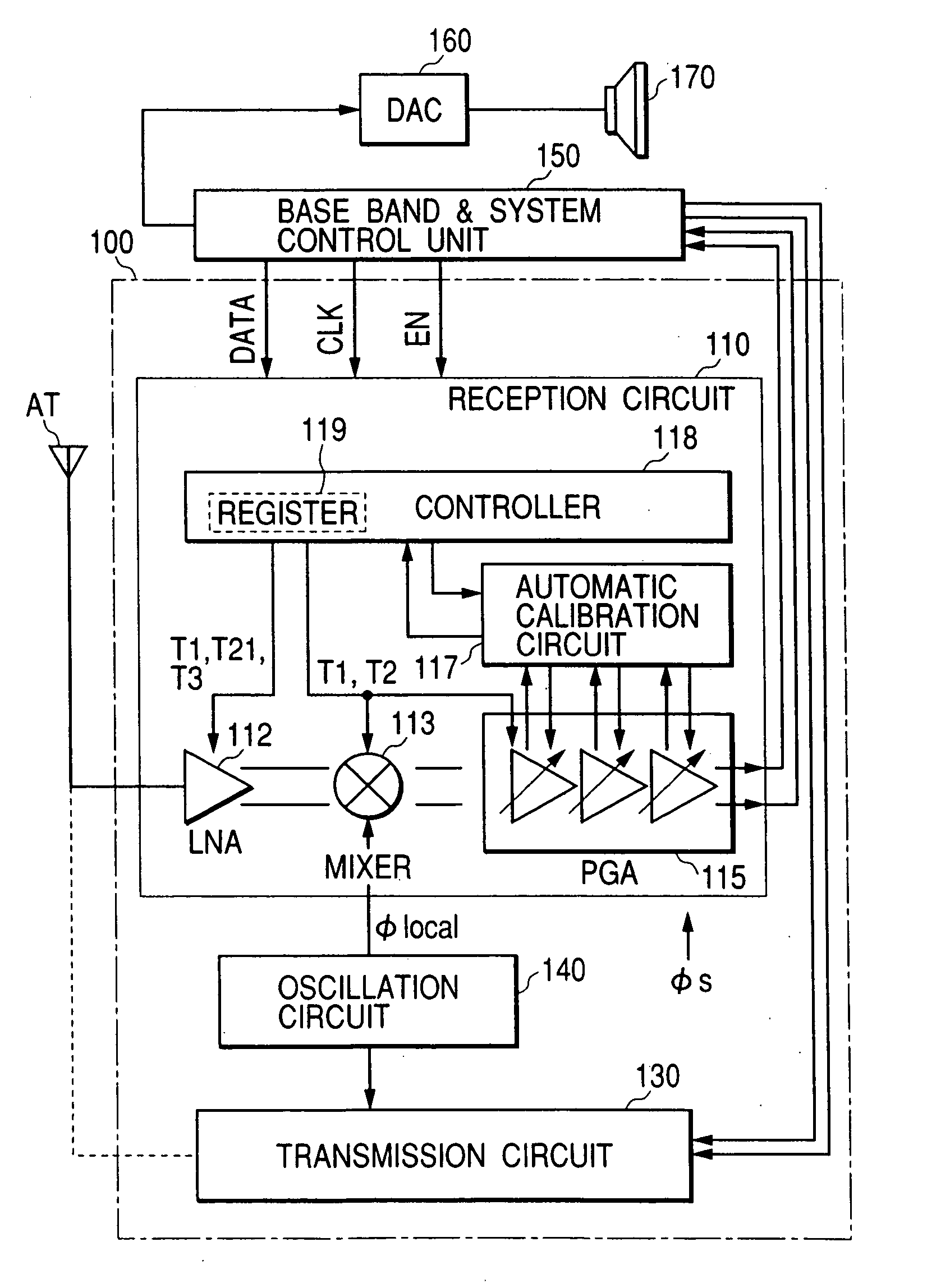
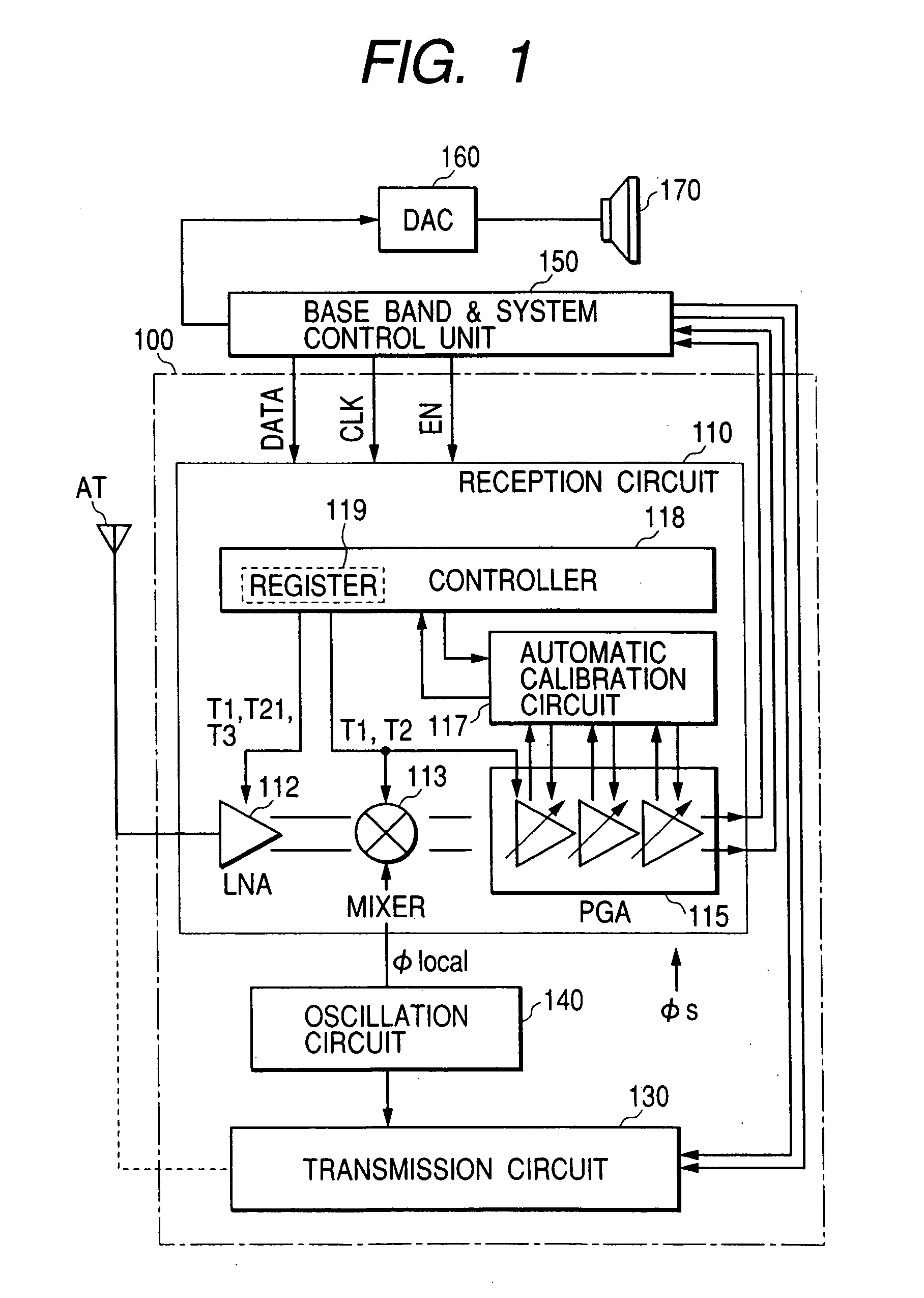
The invention provides a signal processing semiconductor integrated circuit of the direct conversion system, which includes a dummy amplifier having the same circuit configuration as a low noise amplifier being the first stage amplifier, in which the DC offset calibrations on the subsequent stage amplifiers are carried out during shifting into the reception mode in a state that the low noise amplifier is deactivated and the dummy amplifier is activated. Thereby, the invention achieves to suppress generation of the DC offsets resulting from the leakage noises of the local oscillator during shifting into the reception mode, and to enhance the reception sensitivity.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and apparatus for calibrating DC-offsets in a direct conversion receiver
InactiveUS6868128B1Reduce sizeSmall sizeDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCarrier regulationDirect-conversion receiverOffset calibration
A novel method and apparatus for calibrating DC offsets in a direct conversion receiver. The present DC offset calibration method and apparatus comprises a direct conversion receiver equipped with a frequency shifter means and a DC offset measurement and correction technique. In accordance with the present invention, DC offsets are calibrated in direct conversion receivers through an inventive method including two steps: a DC offset measurement step and a DC offset correction step. In the DC offset measurement step the frequency of a local oscillation signal (typically generated by a voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO)) is shifted by a selected frequency shift value during the inactive time intervals of the receiver. DC offsets are measured while the frequency of the down-conversion oscillation signal is shifted by the frequency shift value. Before the inactive time interval expires, the frequency of the down-conversion oscillator signal is shifted back to its original value. In the DC offset correction step of the present invention incoming signals are corrected using a correction means that removes the DC offset measured during the DC offset measurement step.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Real-time radiation sensor calibration
One embodiment of the invention is directed to methods and apparatus for determining a variation of a calibration parameter of a pixel of the thermal sensor during operation of the imaging apparatus, after an initial calibration procedure. Another embodiment of the invention is directed to methods and apparatus for calculating a gain calibration parameter using first and second ambient temperature values and respective first and second resistance values for a pixel of a sensor. A further embodiment of the invention is directed to calculating an offset calibration parameter for at least one pixel using a gain of the at least one pixel between first and second times and an ambient temperature at a third time, wherein the pixel is exposed to both scene and ambient radiation at the third time.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
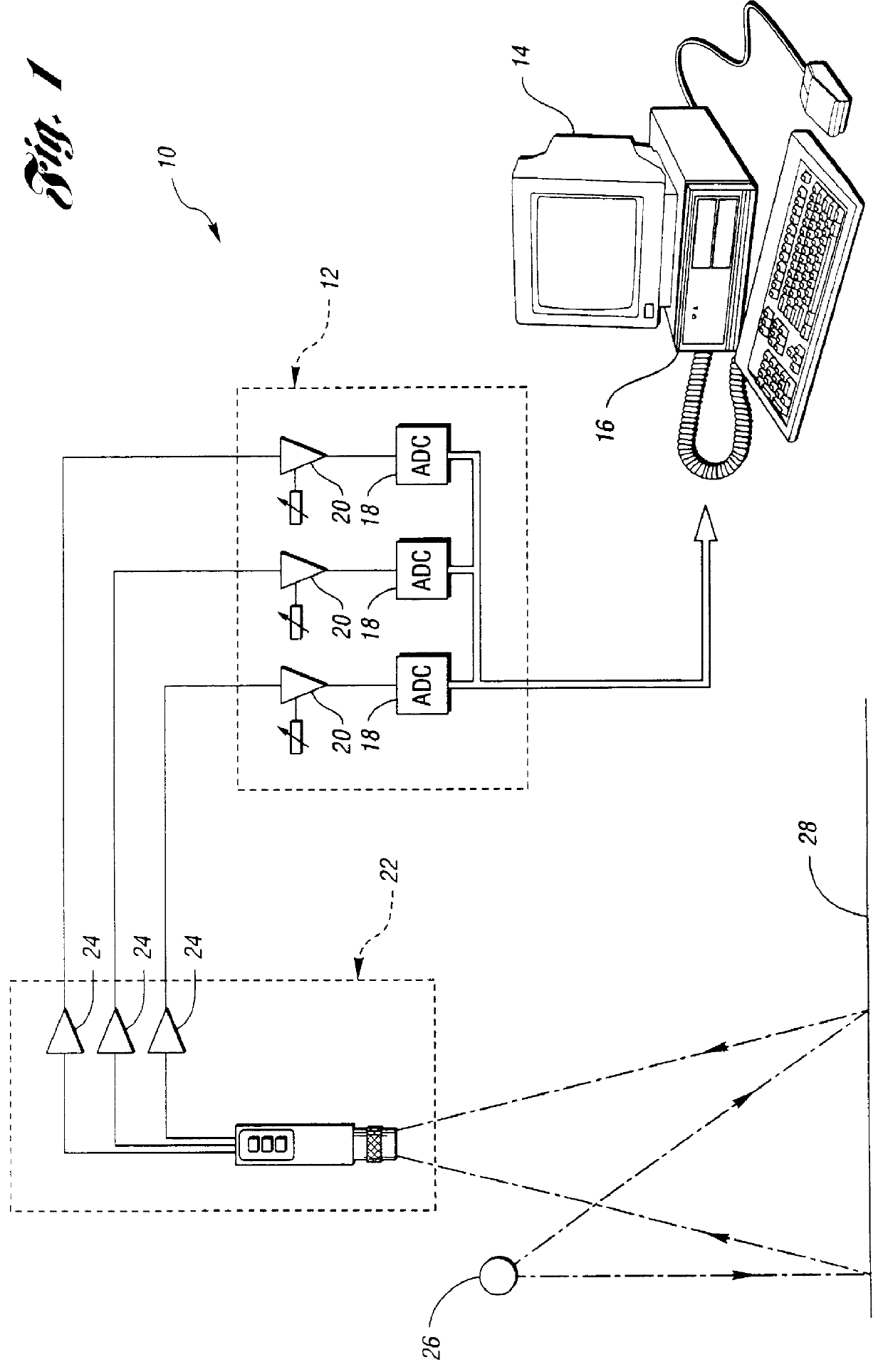
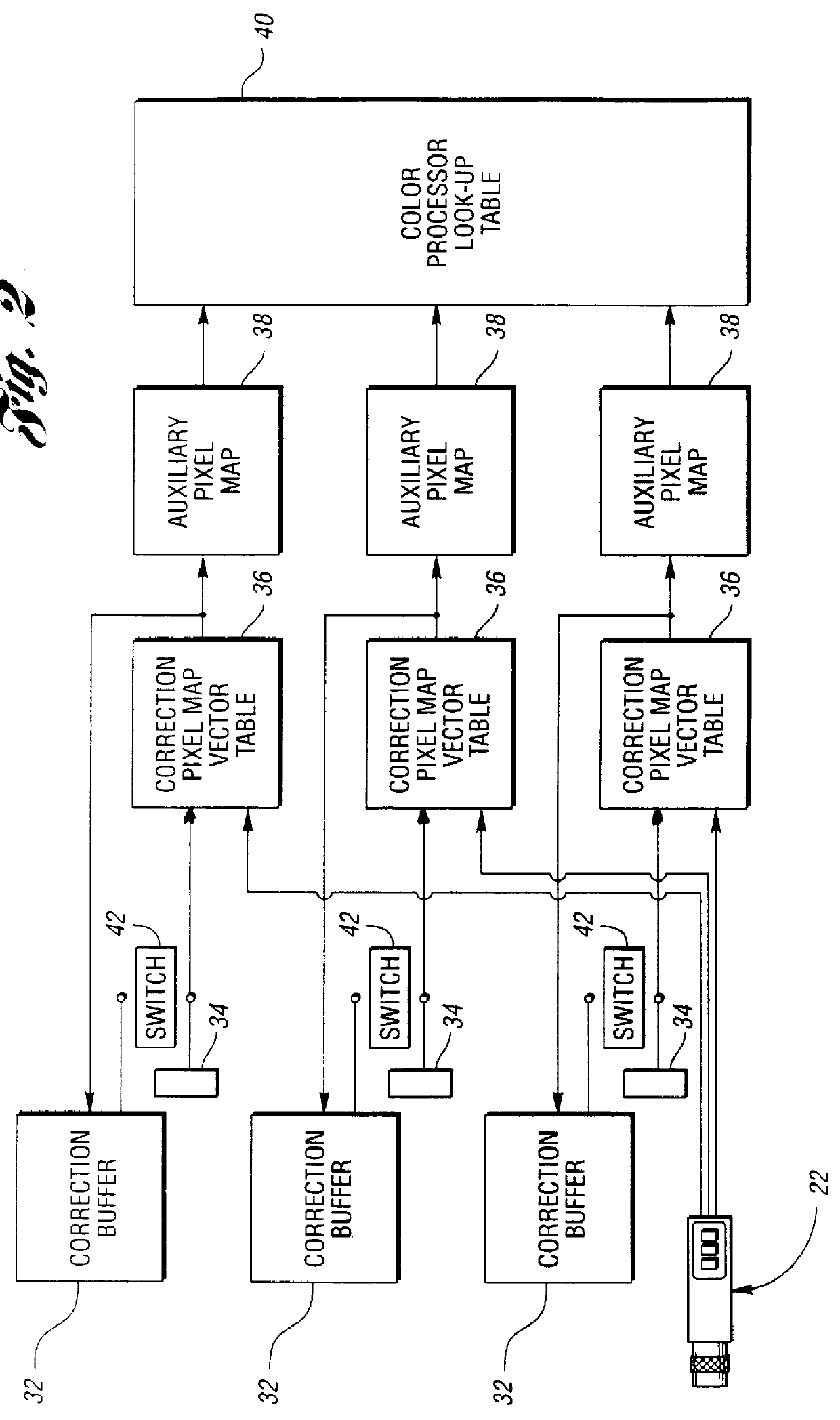
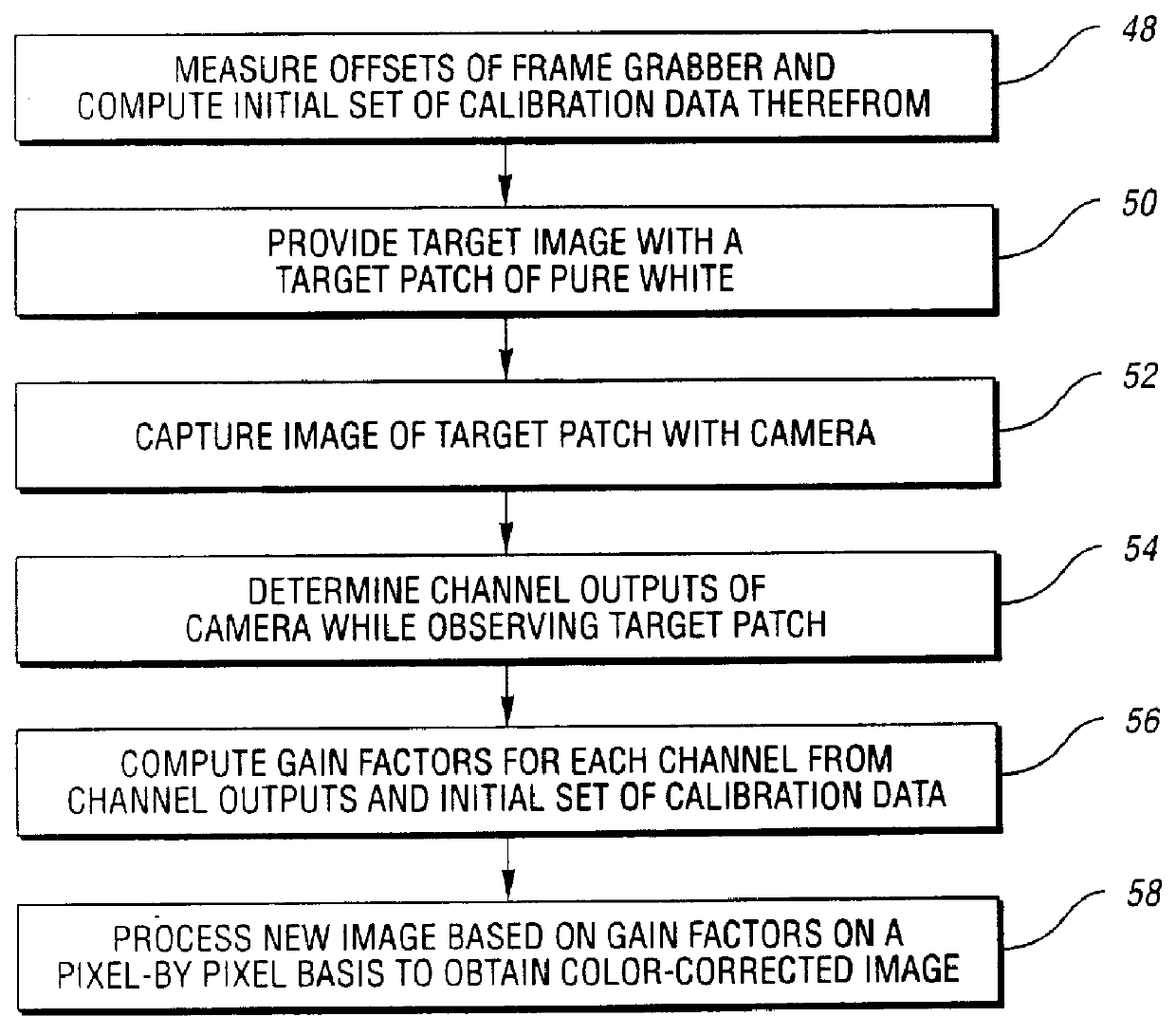
Method and system for automatically calibrating a color-based machine vision system
InactiveUS6016161AUneven illumination levelEffective imagingColor signal processing circuitsPicture signal generatorsImaging conditionColor correction
A calibration algorithm is provided for calibrating a machine vision system including a color camera, a framegrabber and an illumination source wherein subsequently acquired images are processed on a pixel-by-pixel basis. After framegrabber offsets are measured to obtain initial or offset calibration data, the camera is pointed at a target monotone patch of known reflectance such as pure white and the camera outputs for red, green and blue are determined while observing the monotone patch to obtain spatial calibration data. The gain for each of the output channels of the color camera is automatically determined from the initial calibration data. Applying the three gain factors to a subsequent image on the pixel-by-pixel basis allows one to end up with a color-corrected image without incurring any time performance penalty. At any time during an inspection process, a small area of white reflectance can be observed. The resulting dynamic white calibration data is used to correct for any medium to long term temporal variation in imaging conditions.
Owner:INTEGRAL VISION +1
DC offset calibration of ADC with alternate comparators
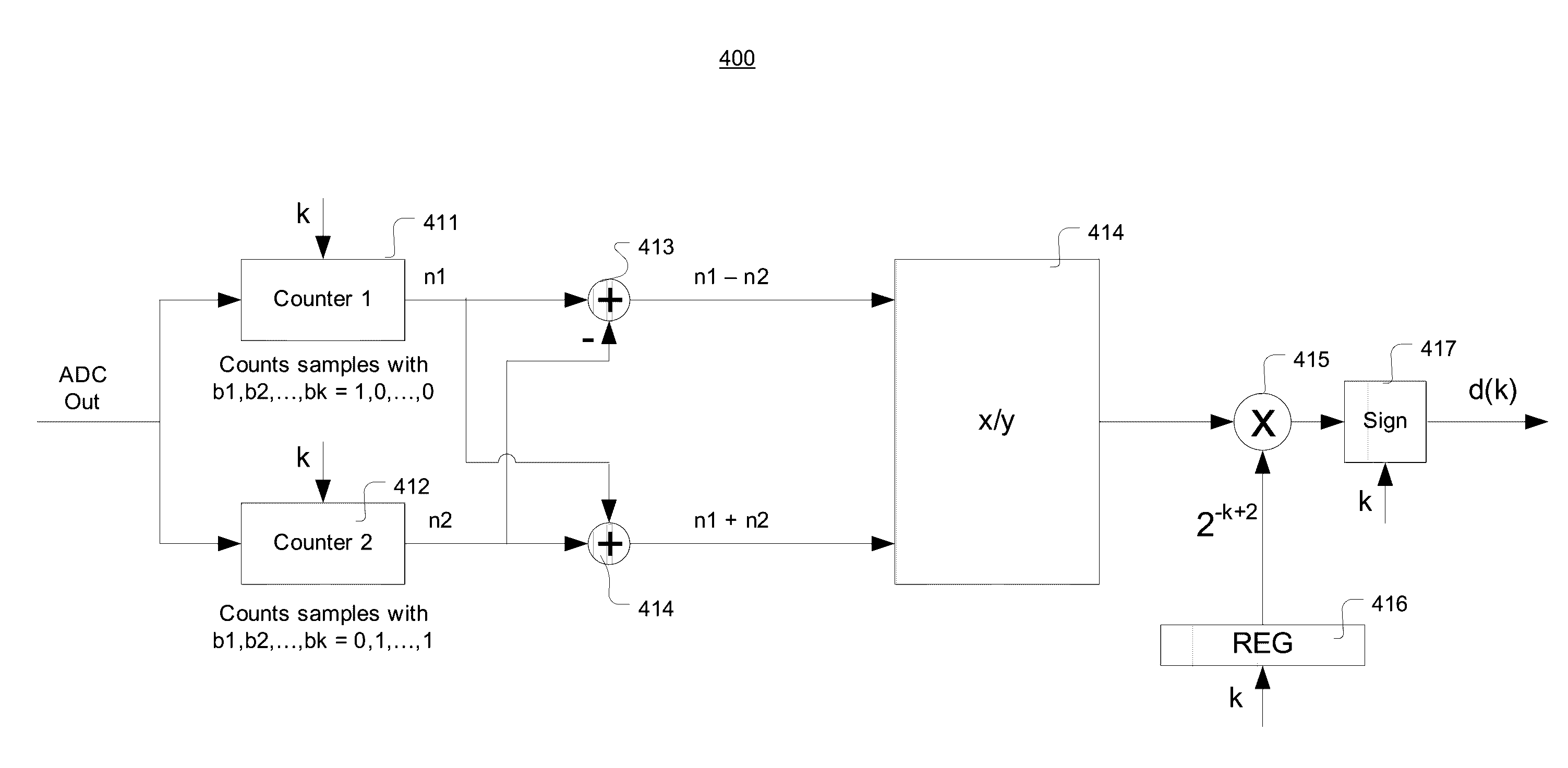
ActiveUS9496884B1Improve time efficiencyImprove power efficiencyElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersEngineeringVoltage range
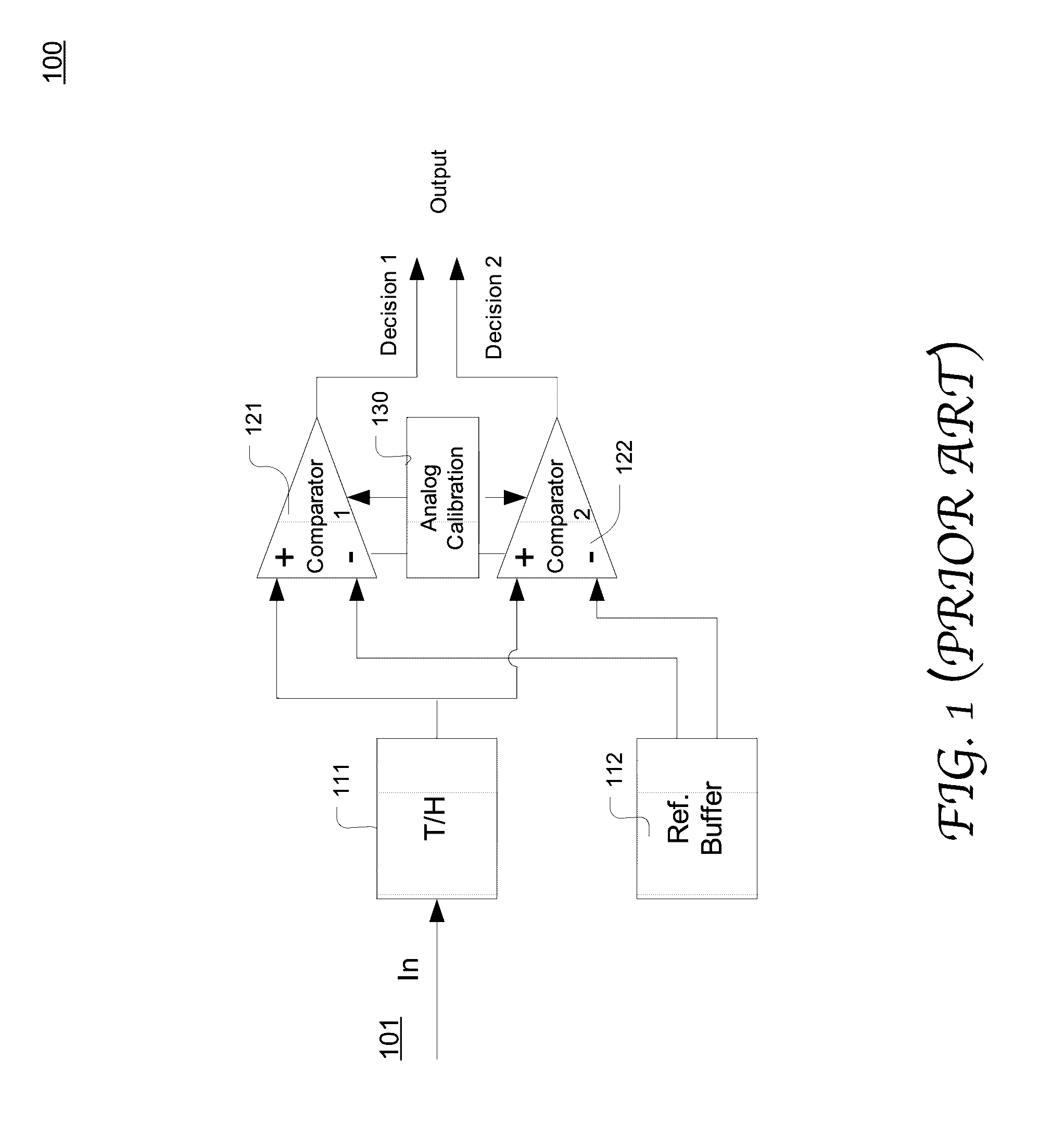
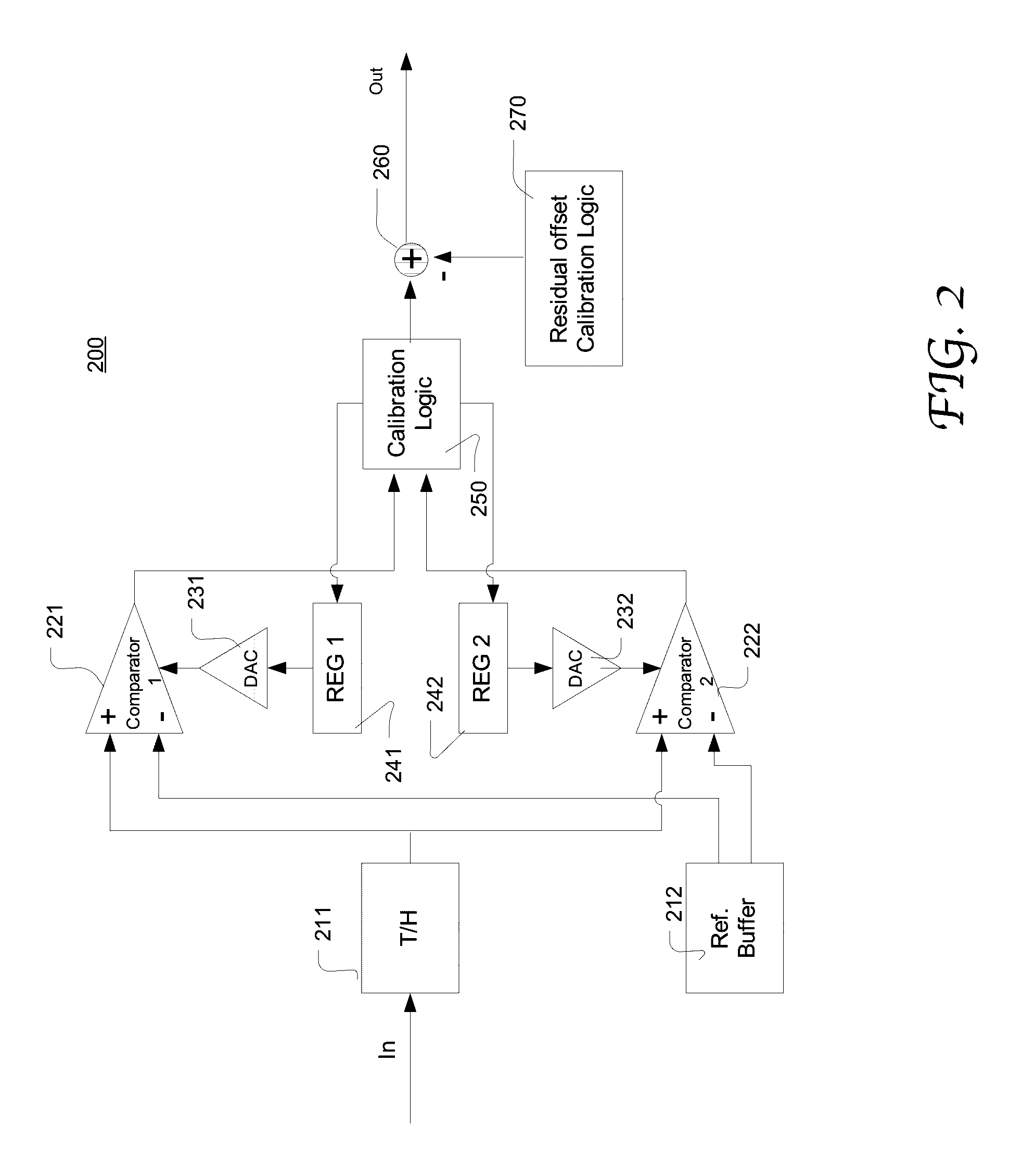
System and method of calibrating the DC offsets of alternate comparators in an ADC in the background based on the digital outputs of the ADC. In parallel with A / D conversion of a plurality of samples, the calibration logic uses two counters to count the occurrences of the ADC outputs that represent samples falling in a first analog range and a second analog range, respectively. The two ranges are symmetric about the MSB reference voltage and in combination cover the nominal voltage range of the bit. The DC offset is derived based on a ratio of the difference between the two counts and a sum of the two counts. The calibration logic may alternately calibrate the comparators. Each comparator may be calibrated successively based on various bits associated therewith.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
Multi-temperature programming for accelerometer
ActiveUS20070204672A1Improves manufacturing test throughputImprove overall manufacturing test throughputAcceleration measurementThermometer testing/calibrationTemperature coefficientOffset calibration
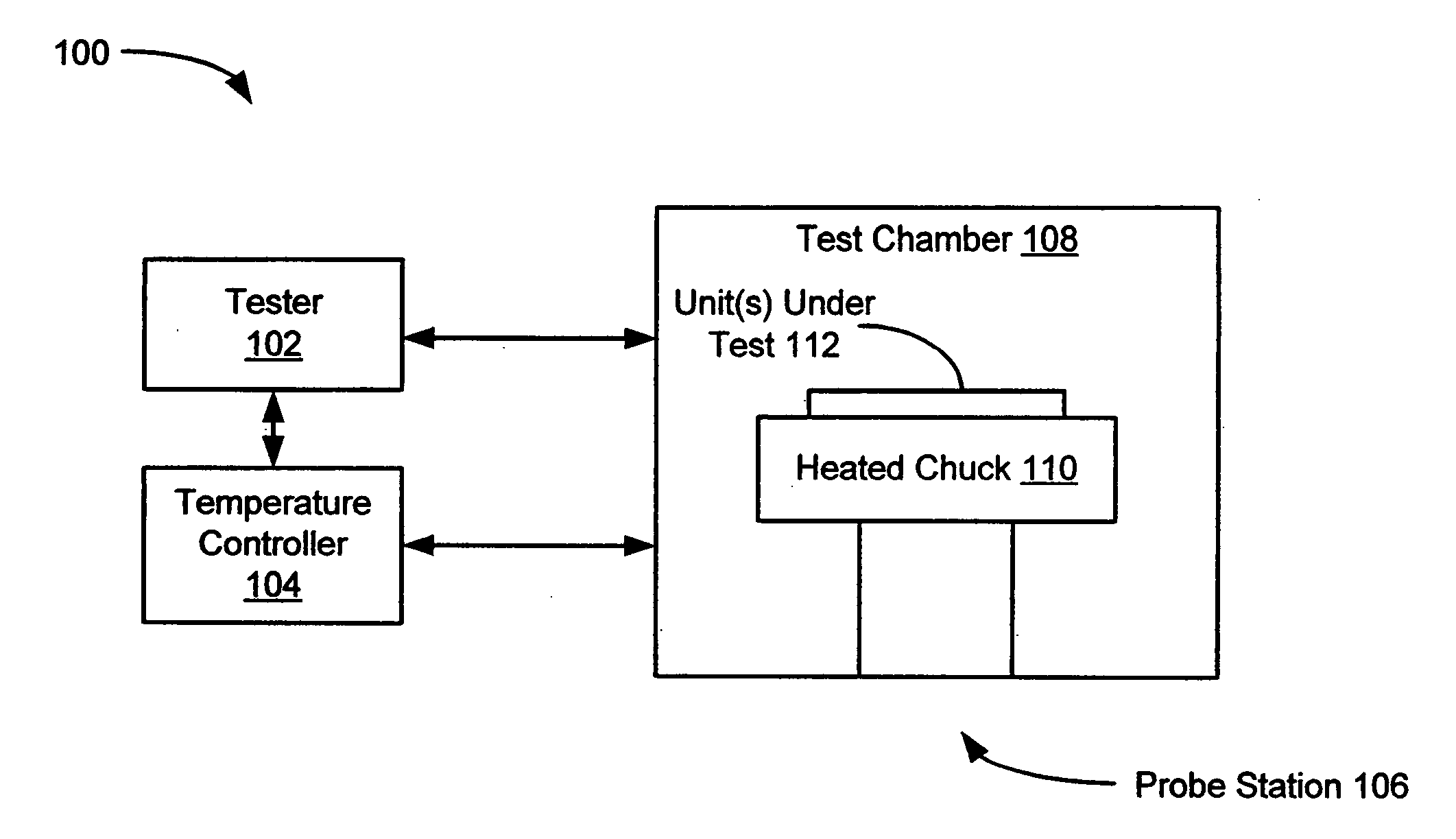
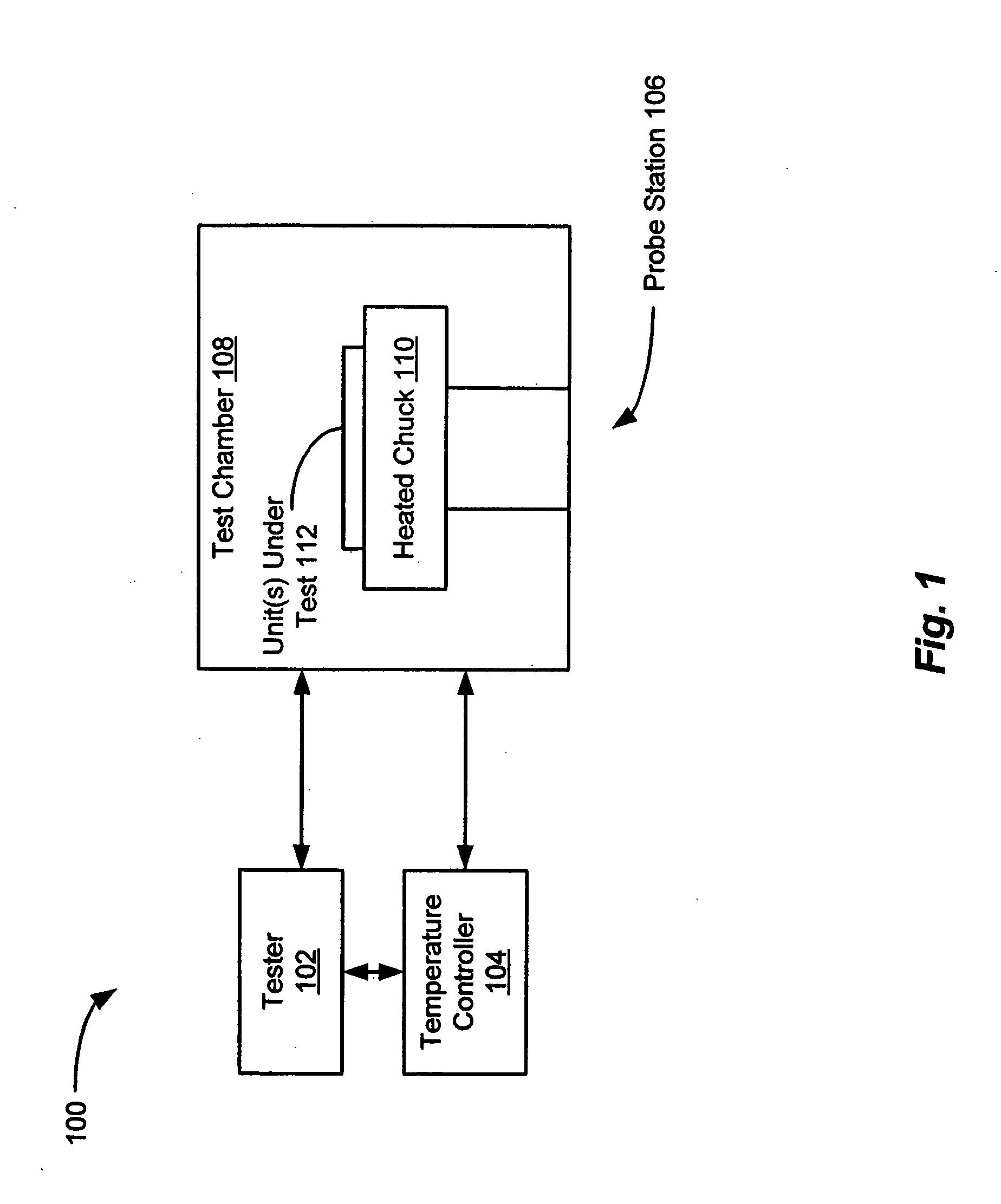
A system and method for testing and calibrating integrated sensor devices that improves the manufacturing test throughput of the devices. The system includes a tester, a temperature controller, and at least one probe station including a thermal chuck. The chuck can be heated to specified temperatures to achieve variable heating of a wafer, PCB, or pallet disposed thereon. The temperature controller adjusts the temperature of the chuck to a first specified level. The tester performs at least one first measurement of the output offset of each integrated sensor embodied as a die on the wafer, or as a device on the PCB or pallet. Next, the temperature controller adjusts the temperature of the chuck to a second specified level, and the tester performs at least one second measurement of the output offset of each integrated sensor at the second temperature level. The offset temperature coefficient (OTC) of each sensor is calculated based upon the output offset measurements performed at the first and second temperature levels, and optimal settings for calibrating the respective sensors are determined based upon the calculated OTC values. After the temperature of the chuck is brought back down to the first specified level, the tester programs the output offset calibration settings into each sensor.
Owner:MEMSIC
Infrared two-point non-uniform calibrating method based on frame black body field diaphragm
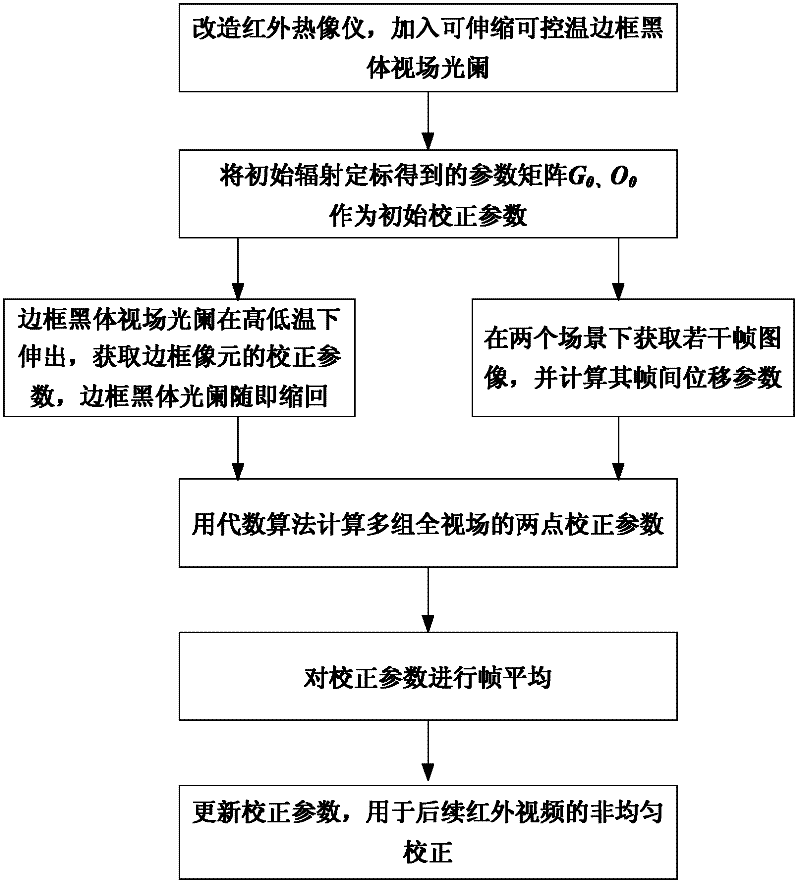
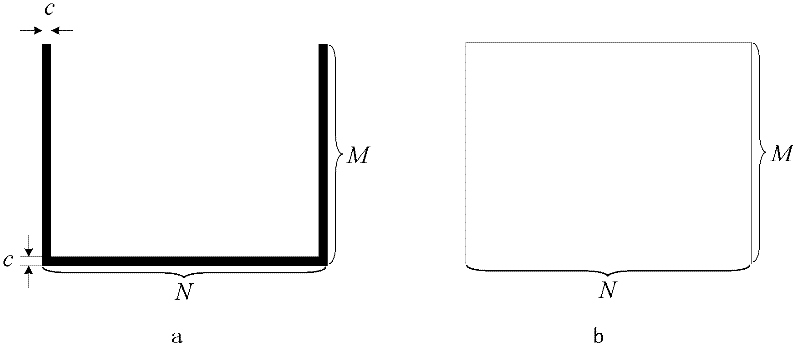
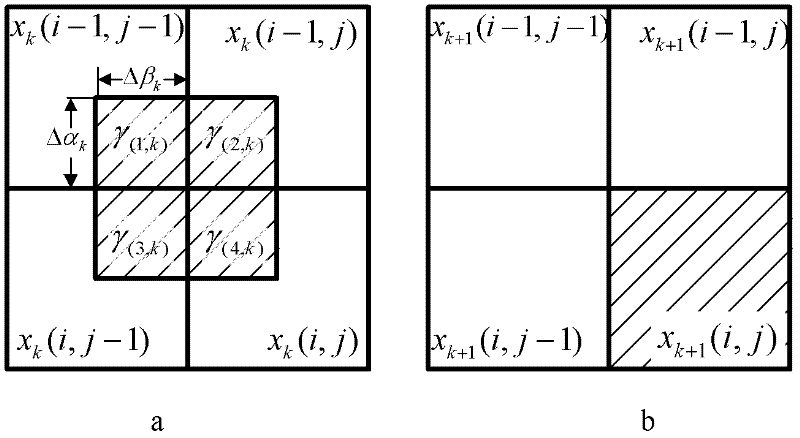
The invention relates to an infrared two-point non-uniform calibrating method based on a frame black body field diaphragm, belonging to the field of infrared thermal imaging. The method comprises the following steps of: arranging an automatically-telescopic frame black body field diaphragm on a diaphragm of an infrared thermal imager and performing two-point calibration under a frame to obtain a gain calibration factor and an offset calibration factor of a detection unit under the coverage of a frame black body; acquiring f frames of initially-calibrated images respectively on two scenes to obtain f-1 groups of inter-frame displacement parameters on every scene; and acquiring calibration parameters of f-1 groups of images with inter-frame displacement on an internal detection unit by adopting an algebraic method, and averaging the frames to obtain finial calibration matrixes G and 0 for calibrating the entire field of a subsequent infrared video. The method has the advantages of rapidness, self-adaption and system miniaturization, and can be applied to the fields of designing, production and manufacturing of refrigerating and non-refrigerating infrared focal plane detector thermalimaging systems, satellite infrared thermal imaging systems, infrared alarm systems, scientific researches and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
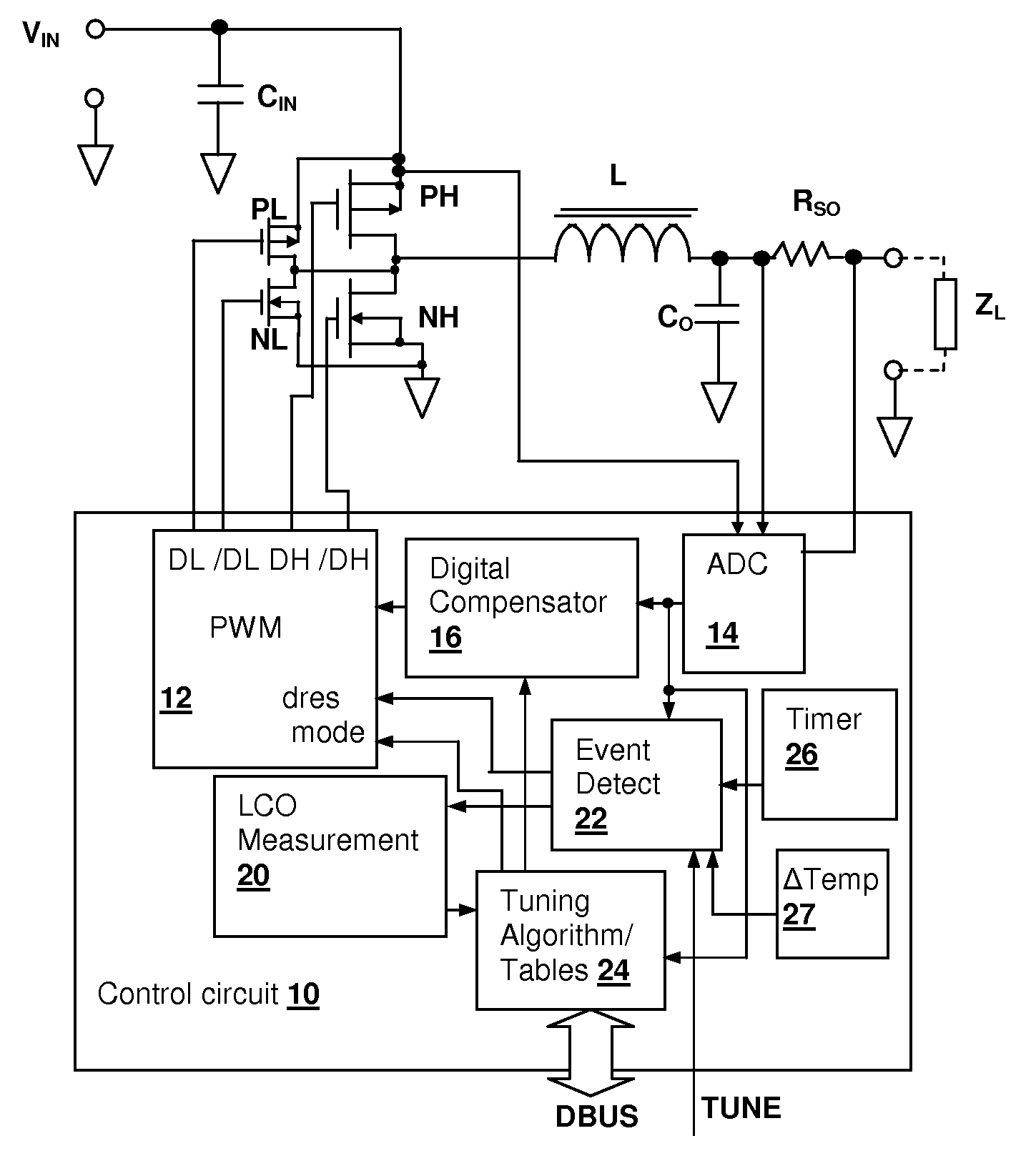
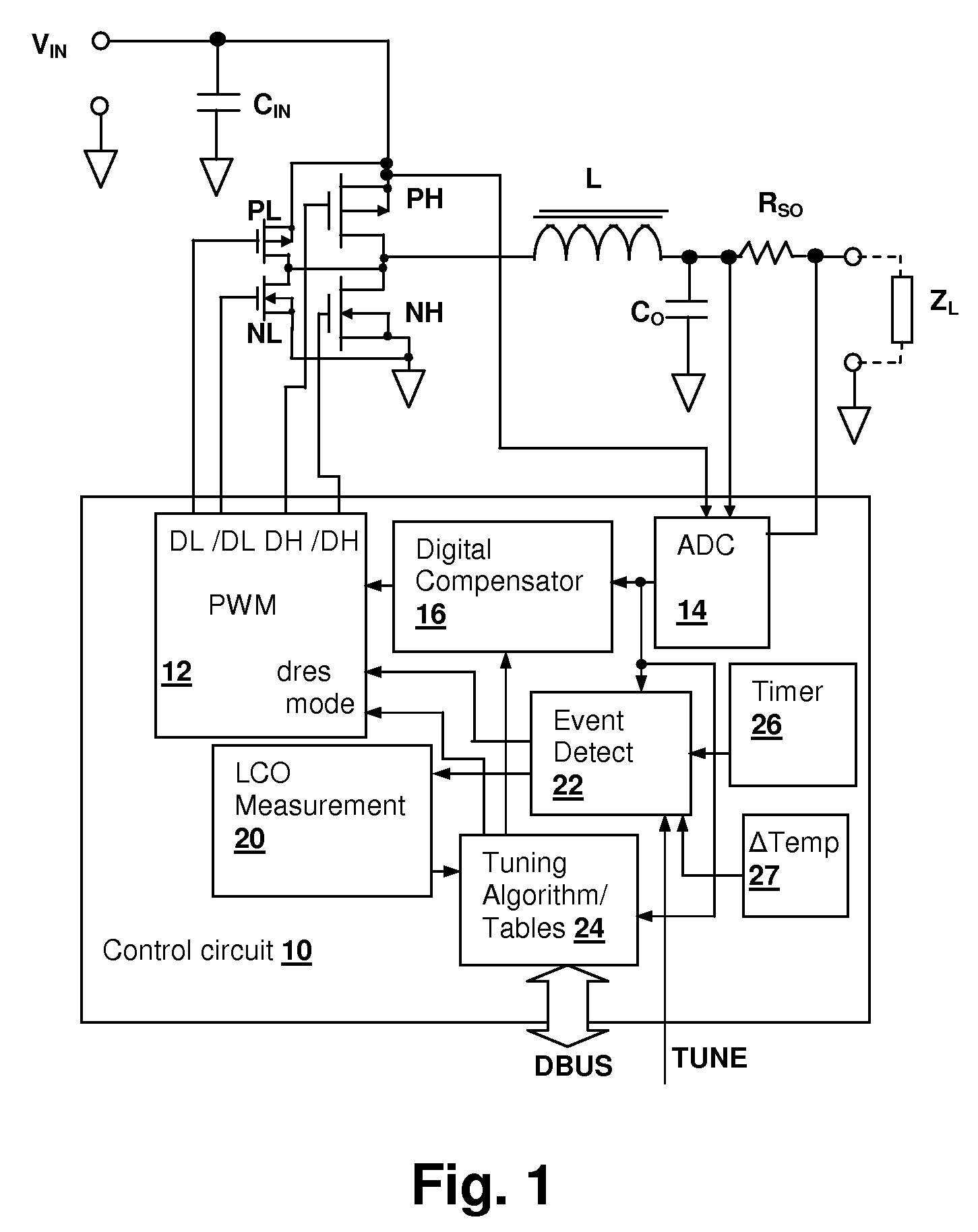
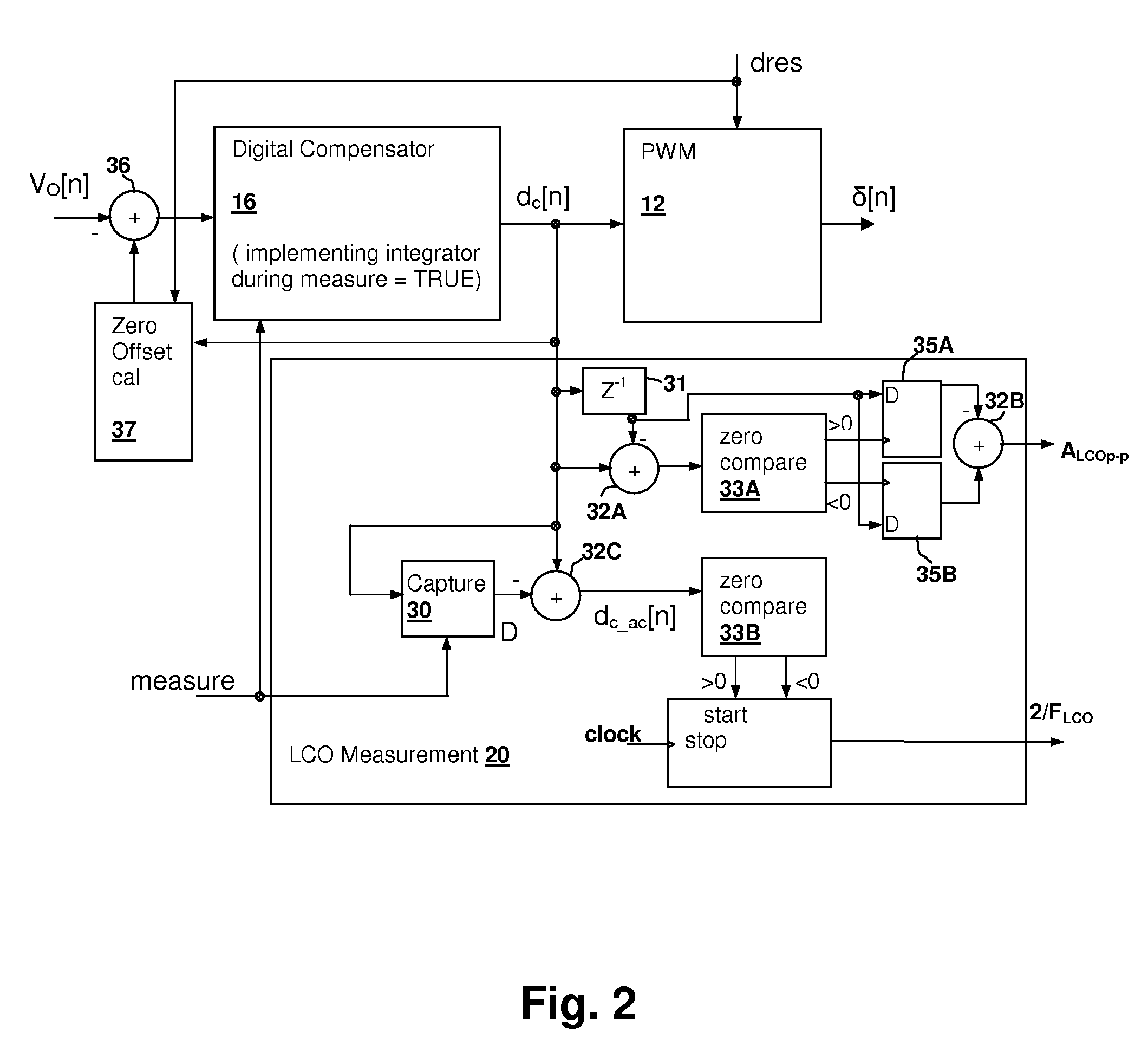
Limit-cycle oscillation (LCO) based switch-mode power supply (SMPS) response evaluation
ActiveUS7586767B1Reduce resolutionMechanical power/torque controlAc-dc conversion without reversalCharacteristic responseImage resolution
A limit-cycle oscillation (LCO) based switch-mode power supply (SMPS) response evaluation provides an effective mechanism for determining the characteristic response of an SMPS during normal operation of the SMPS. LCOs are induced in the SMPS loop by introducing a non-linearity in the loop, for example, decreasing the resolution of a pulse-width modulator that controls the SMPS switching circuit. The frequency and amplitude of the LCOs are determined and used to evaluate the characteristic response of the SMPS. In order to produce symmetric LCOs, which are more easily modeled, a zero-offset calibration circuit adjusts values provided to the pulse-width modulator, so that each value introduced during calibration is at the midpoint of a resolution cell. The frequency can be measured by counting between zero-crossings of the LCOs and the amplitude measured by capturing the LCO values immediately prior to each zero-crossing of a first difference of the LCO samples.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
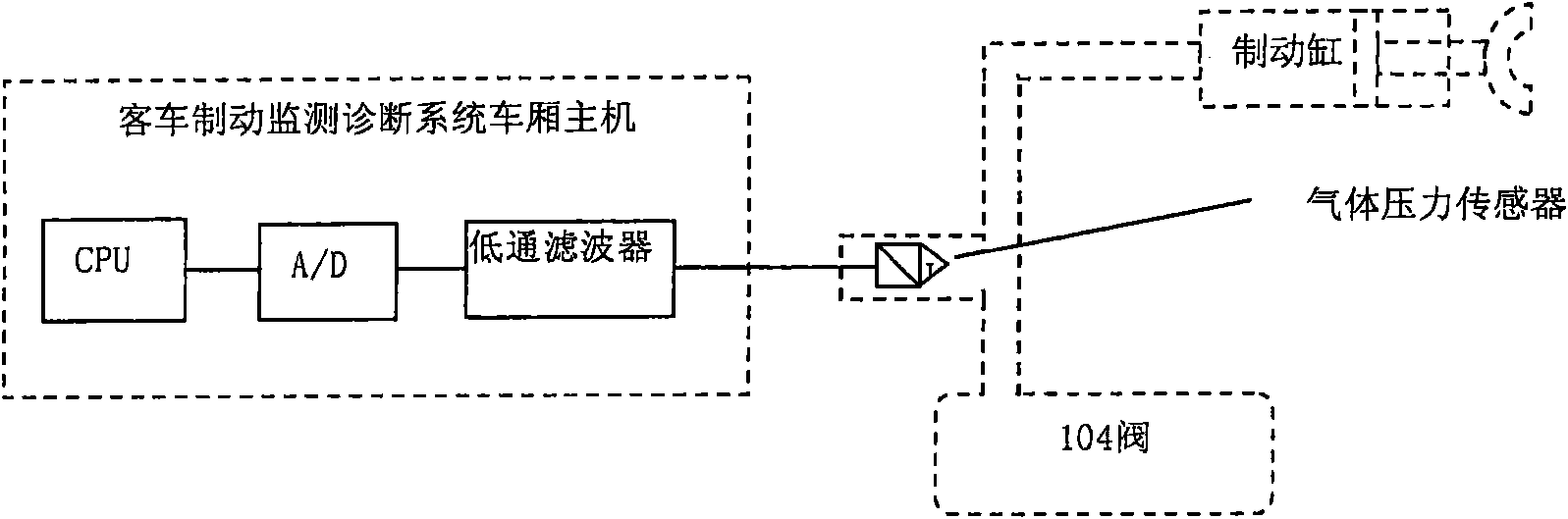
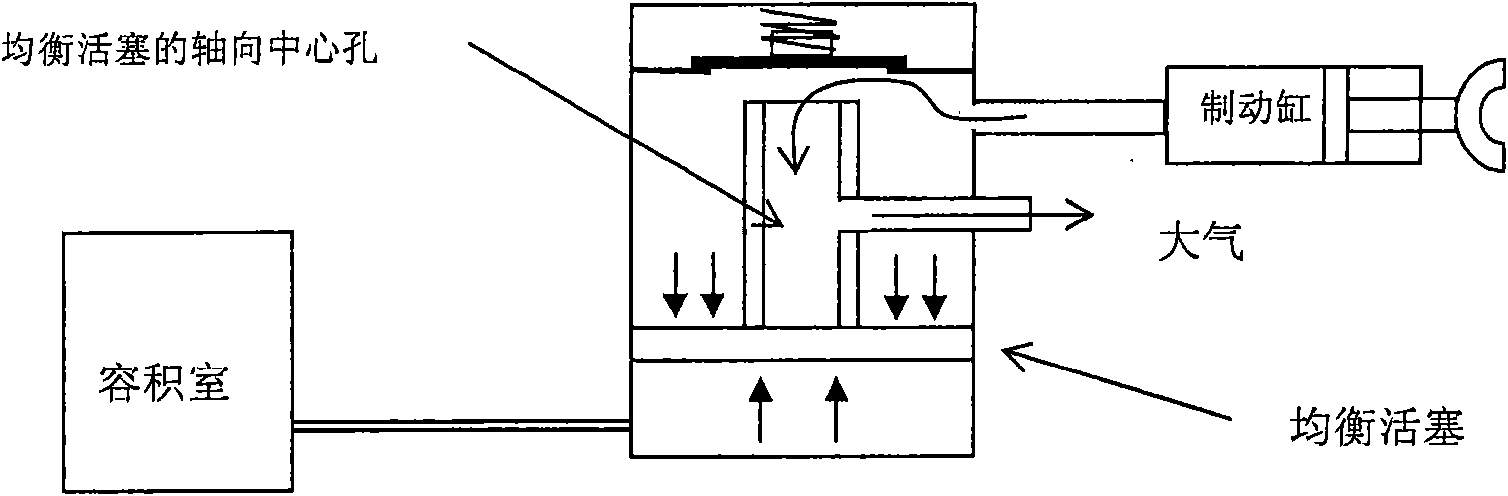
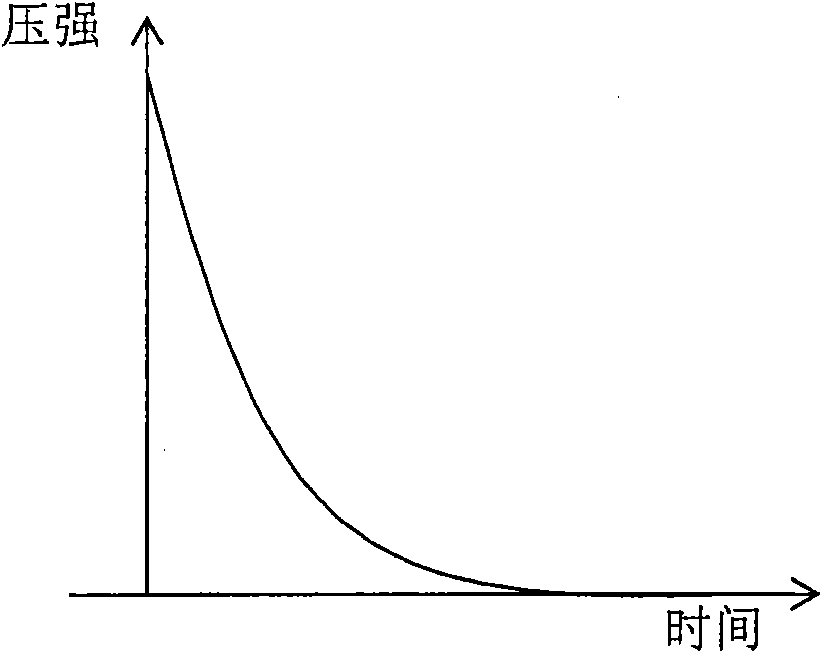
Method and device for zero point calibration of gas pressure sensor
InactiveCN101655406AEasy to operateReduce workloadFluid pressure measurementOffset calibrationWorkload
The invention provides a method and a dehvice for the zero point calibration of a gas pressure sensor, which comprises the steps that: when a brake cylinder is released, the pressure value of the brake cylinder is obtained; the releasing process is judged to be normal or abnormal according to the time the pressure value is obtained and according to the pressure value; when the releasing process isnormal, the pressure value of the brake value is judged to whether reach zero or not; when the pressure value of the brake reaches zero, the pressure value obtained currently is compared with a pre-stored composite error nominal value; when the pressure value obtained currently is smaller than or equal to the composite error nominal value, the pressure value obtained currently is regarded as a zero point correct value; and the zero point of the gas pressure sensor is calibrated according to the zero point correct value. The method and the device can solve the problem of zero point drift and have simple operation and lowered workload and calibration cost.
Owner:LOCOMOTIVE & CAR RES INST OF CHINA ACAD OF RAILWAY SCI
Sensor offset calibration using map information
ActiveUS20160061627A1Well formedInstruments for road network navigationRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesControl systemEngineering
Systems, processes, and techniques for calibrating an onboard sensor of a vehicle are presented here. The vehicle has a control system that is capable of performing at least some of the tasks related to the calibration procedure. An exemplary methodology collects vehicle status data and obtains navigation map data during operation of the vehicle. A current calibration factor is calculated for the onboard sensor, based on the collected vehicle status data and the obtained navigation map data. More specifically, the vehicle status and navigation map data can be used to determine when the current conditions are suitable for performing calibration. When the current conditions are satisfactory, the calibration factor is calculated. Thereafter, the onboard sensor can be calibrated in response to the current calibration factor.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and system of x-ray data calibration
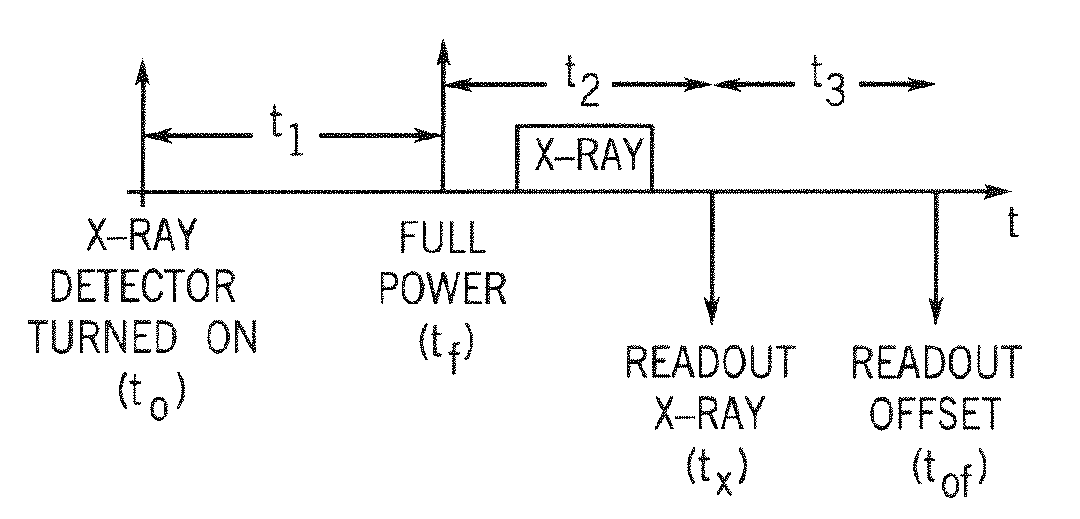
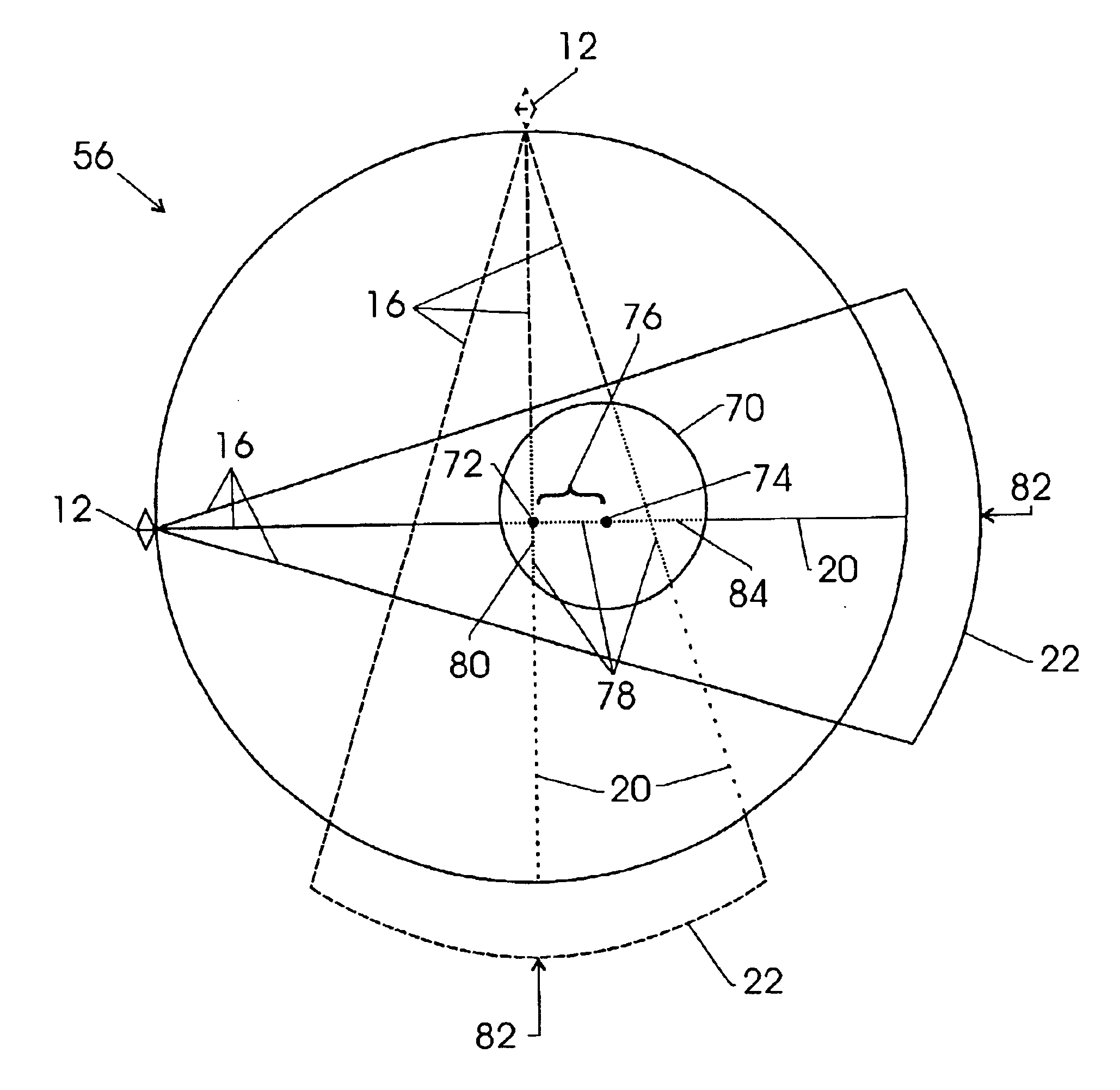
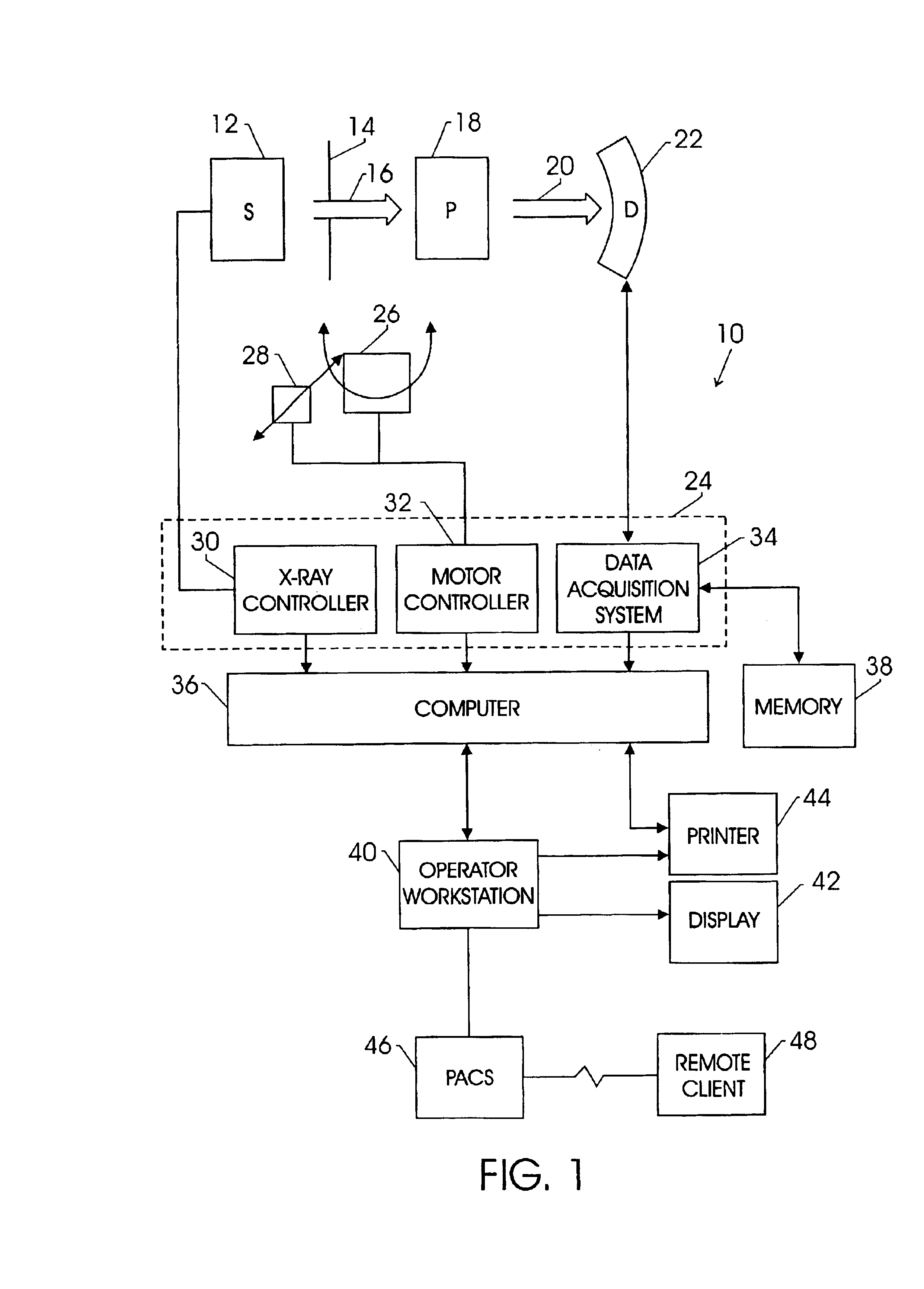
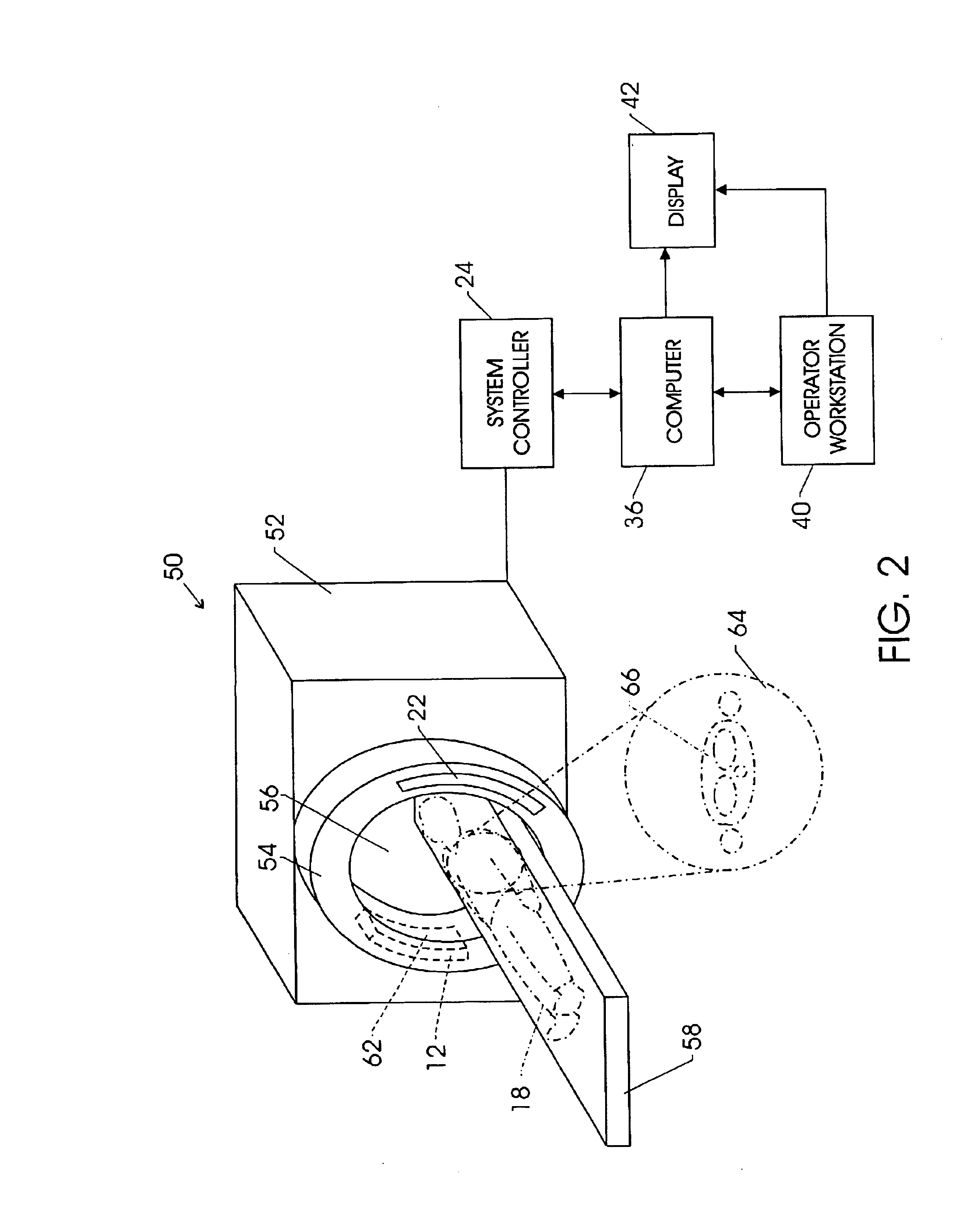
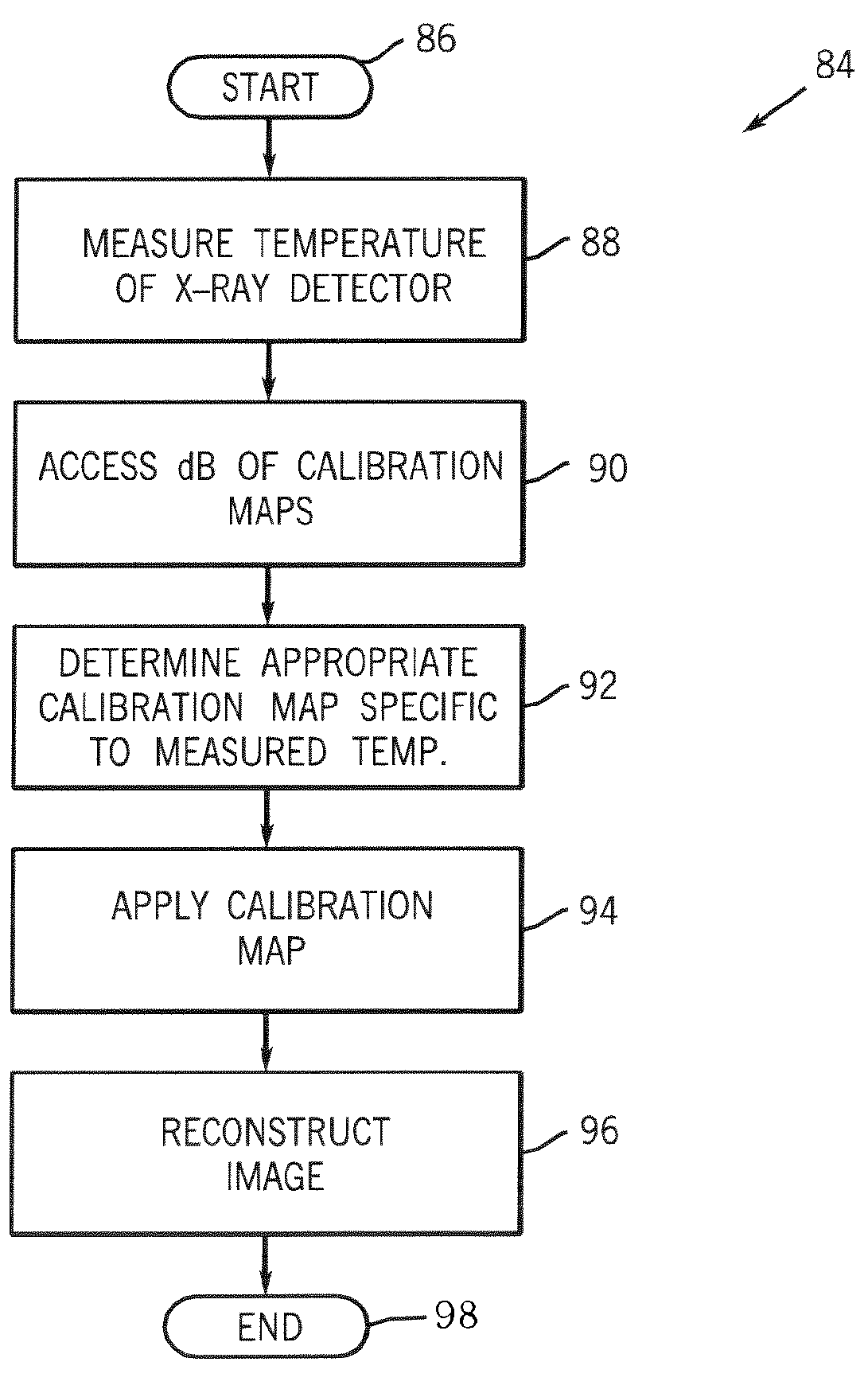
ActiveUS7381964B1Reduce the impactReduce artifactsTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesConversion factorData acquisition
A process of data calibration and correction is disclosed that utilizes feedback from a temperature sensor of an x-ray detector to isolate or otherwise select an appropriate calibration or correction map that is specific to the temperature of the x-ray detector during data acquisition. The method is also designed to take into account changes in power transients of an x-ray detector between the acquisition of imaging data and the acquisition of offset data. The method is particularly applicable in optimally selecting and applying gain correction, conversion factor, bad pixel, and offset calibrations.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
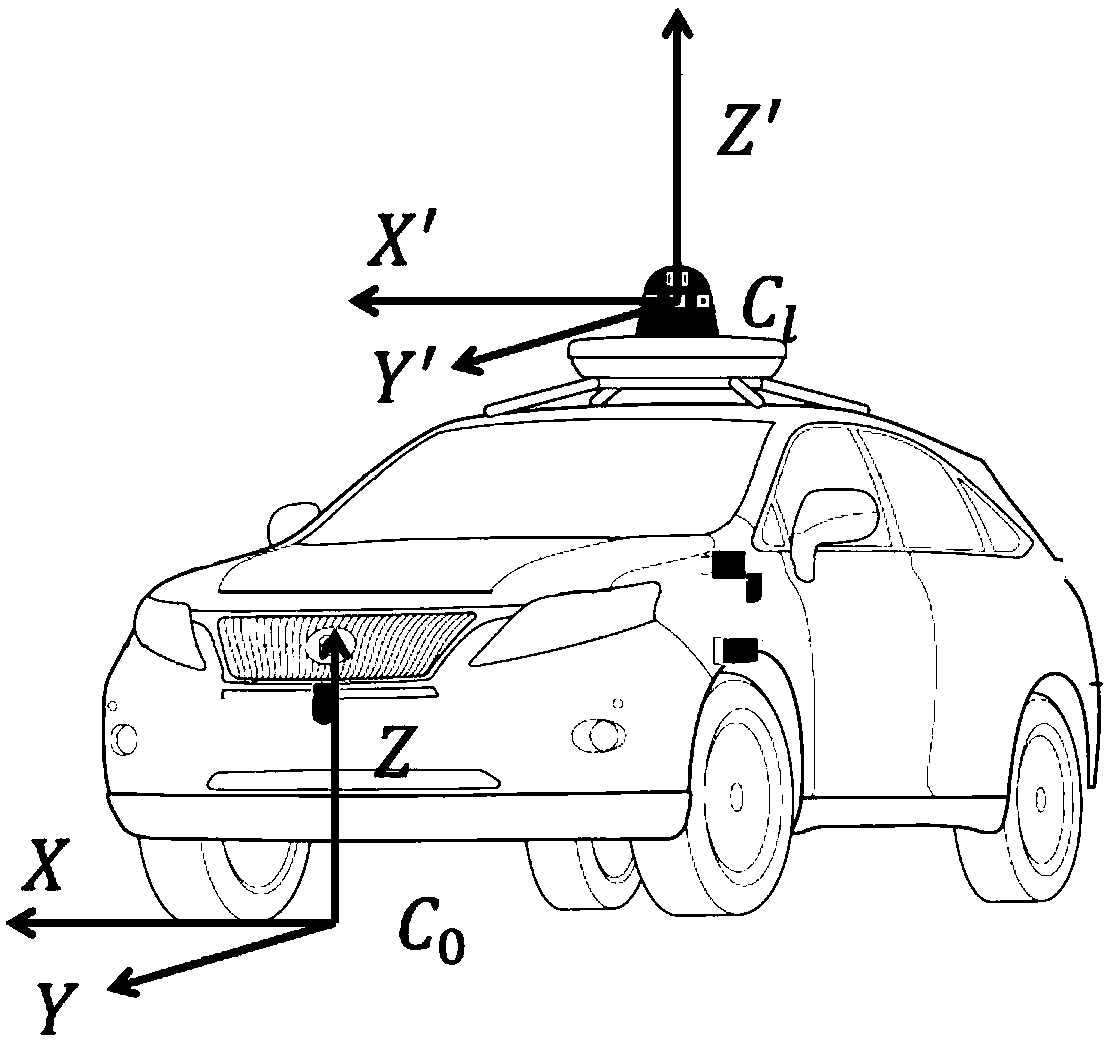
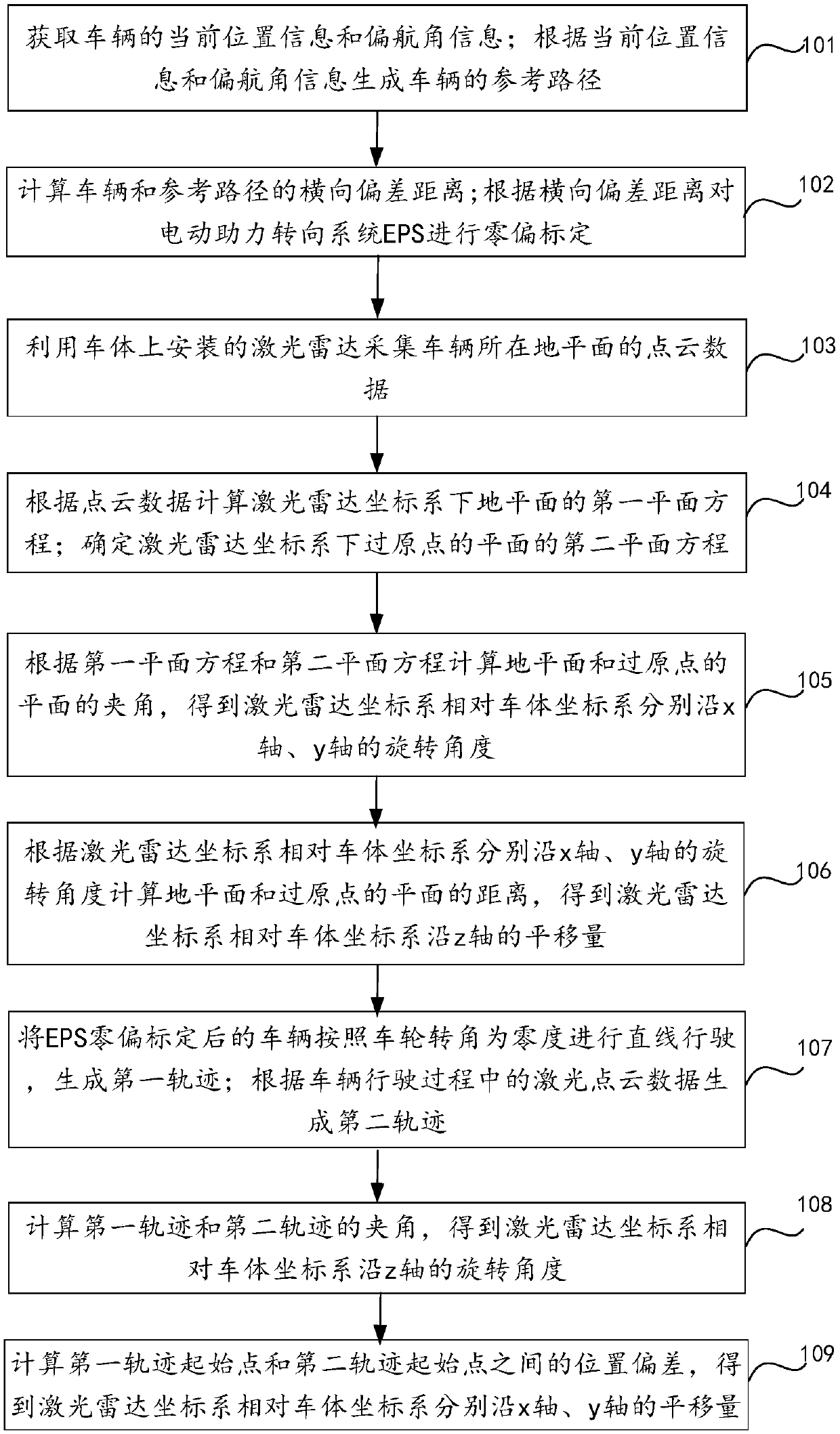
Combined calibration method for EPS zero offset and multi-line laser radar
ActiveCN109541571ASimplify the calibration processImprove calibration accuracyWave based measurement systemsElectric power steeringPoint cloud
The invention relates to a combined calibration method for an EPS (Electric Power Steering) zero offset and a multi-line laser radar. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining current position information, yaw angle information, and a reference path of a vehicle; calculating a lateral offset distance of the vehicle and the reference path; performing zero-offset calibration on the EPS; calculating an included angle and a distance between the ground plane and a plane crossing an origin to obtain an rotation angle of a laser radar coordinate system relative to a vehicle body coordinatesystem along the x axis and the y axis, and a shift amount along the z axis; performing linear driving on the vehicle after EPS zero offset calibration taking the wheel angle as zero degree to generate a first trajectory; generating a second trajectory according to laser point cloud data in the vehicle driving process; calculating the included angle of the first trajectory and the second trajectory to obtain the rotation angle of the laser radar coordinate system relative to the vehicle body coordinate system along the z-axis; and calculating a position deviation between a starting point of the first trajectory and the starting point of the second trajectory to obtain the shift amount of the laser radar coordinate system relative to the vehicle body coordinate system along the x-axis and the y-axis respectively.
Owner:BEIJING ZHIXINGZHE TECH CO LTD
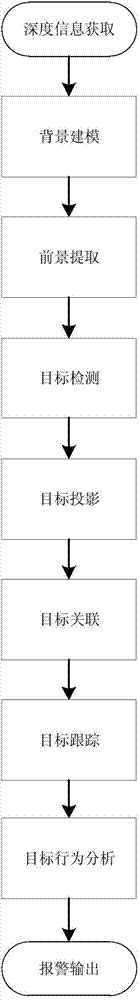
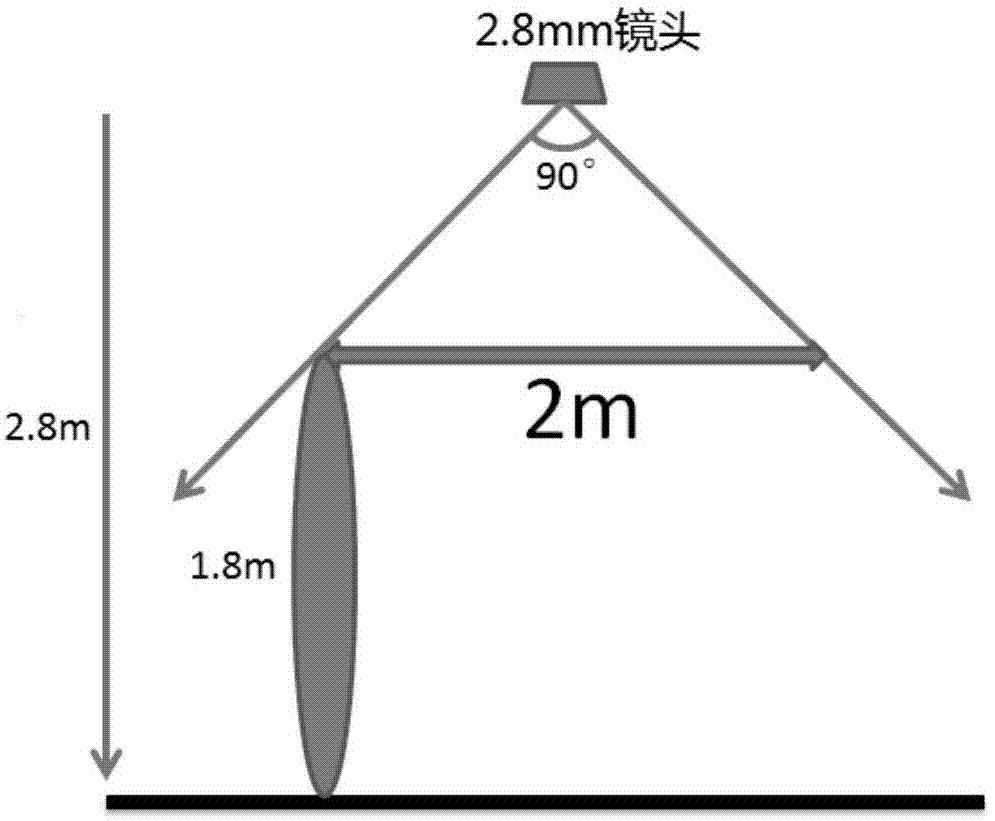
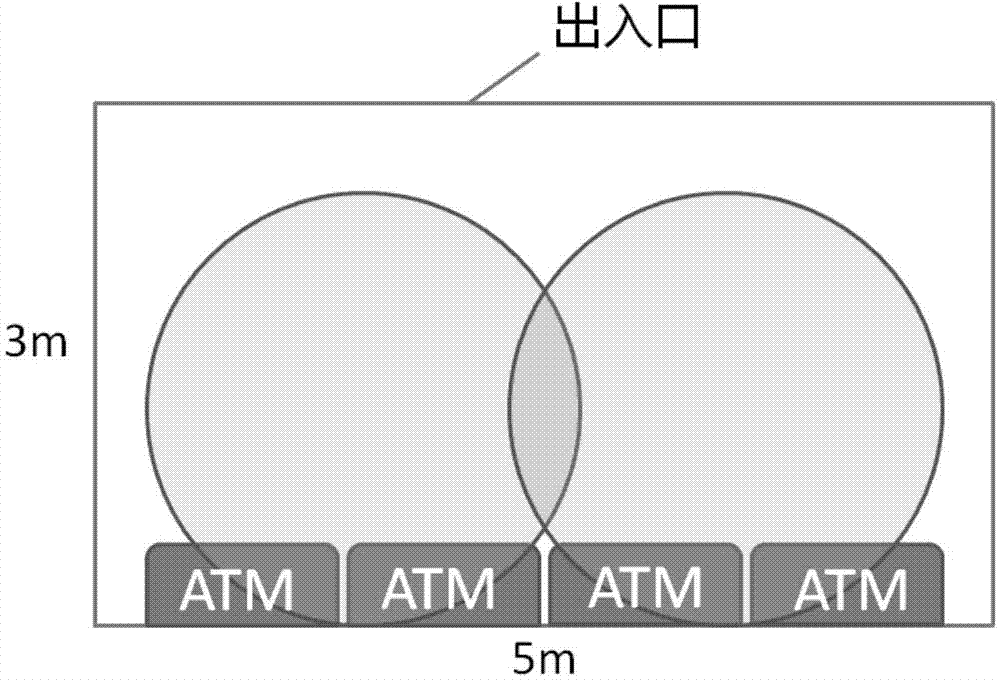
ATM self-service business hall behavior analysis method based on depth information
InactiveCN104268851AFull Coverage GuaranteedImprove stabilityImage enhancementImage analysisHuman bodyMulti camera
The invention relates to an ATM self-service business hall behavior analysis method based on depth information. Behavior analysis based on common two-dimensional cameras is adopted in the prior art, and the situation that targets cannot be accurately positioned exists. According to the ATM self-service business hall behavior analysis method, firstly, binocular cameras are adopted for serving as acquisition equipment for the depth information, background modeling is carried out on depth maps, a Gaussian mixture model of each pixel is learned and updated, and background distribution is determined; secondly, the probability value of each pixel in each new depth map is worked out, and clustering segmentation is carried out on a front depth map according to the DENCLUE algorithm; finally, pixels in each human body region in each camera are projected onto the ground, association of projected targets is carried out by using multi-camera offset calibration, and therefore target detection under the multiple cameras is achieved under a global coordinate system. The depth information is used and background modeling of RGB information is combined, so that the stability of target detection is greatly improved, and a good basis is provided for following behavior analysis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ICARE VISION TECH
DC offset calibration for a radio transceiver mixer
InactiveUS7039382B2Reducing DC offsetReducing DC offsetsModulation transference balanced arrangementsTransmission noise suppressionResistive couplingTransceiver
A mixer for a radio transceiver includes a commutating mixer switch having a first differential input port coupled to a DC offset cancellation path. The first differential input port of the mixer switch includes a first terminal coupled to a first end of a first resistor and a second terminal coupled to a first end of a second resistor. Second ends of the first and second resistors are configured to receive a differential input signal. The DC offset cancellation path may provide a resistively coupled DC calibration signal for reducing the magnitude of DC offsets that may be present at the input of the mixer switch. The concept can be used for either image or non-image reject mixers.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
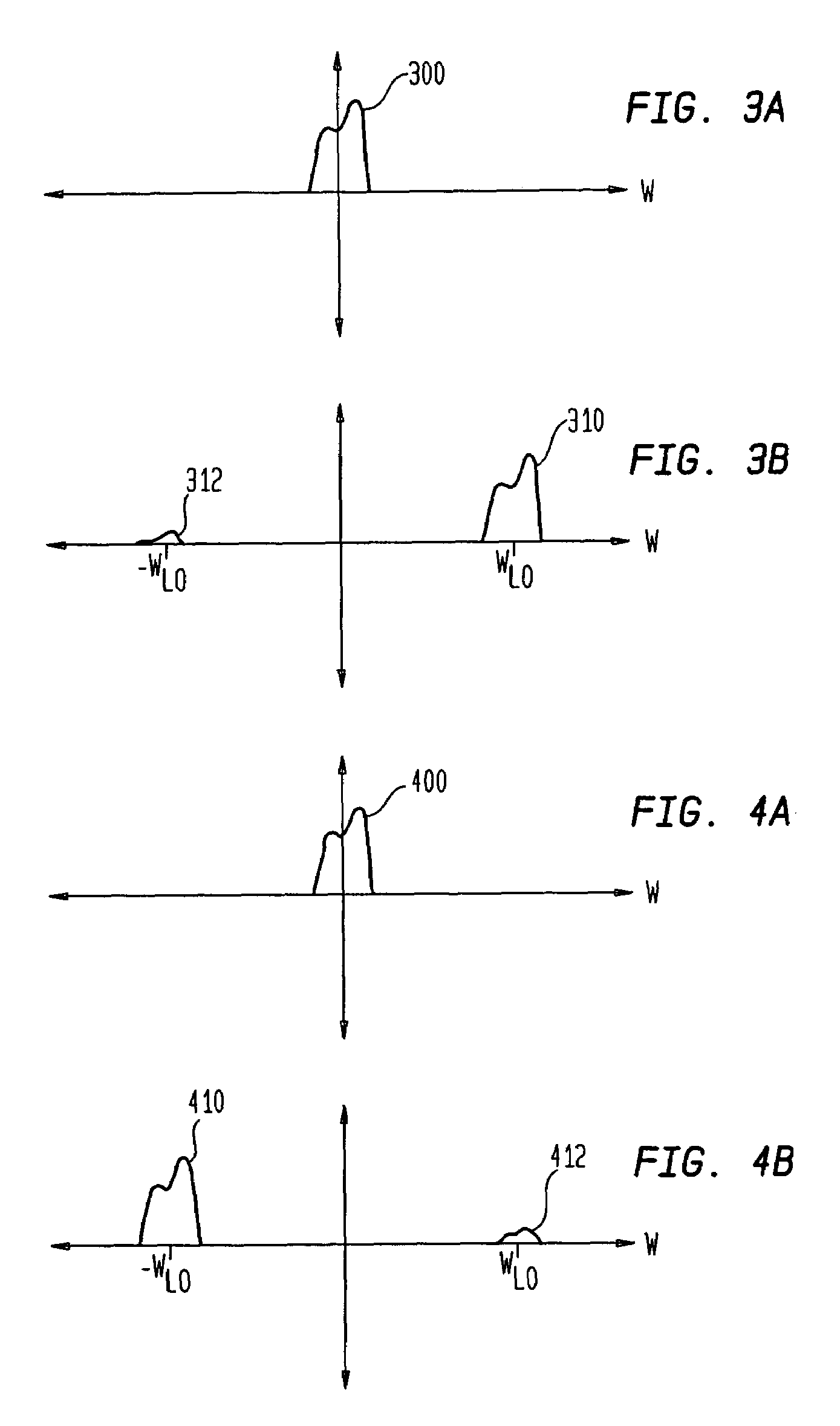
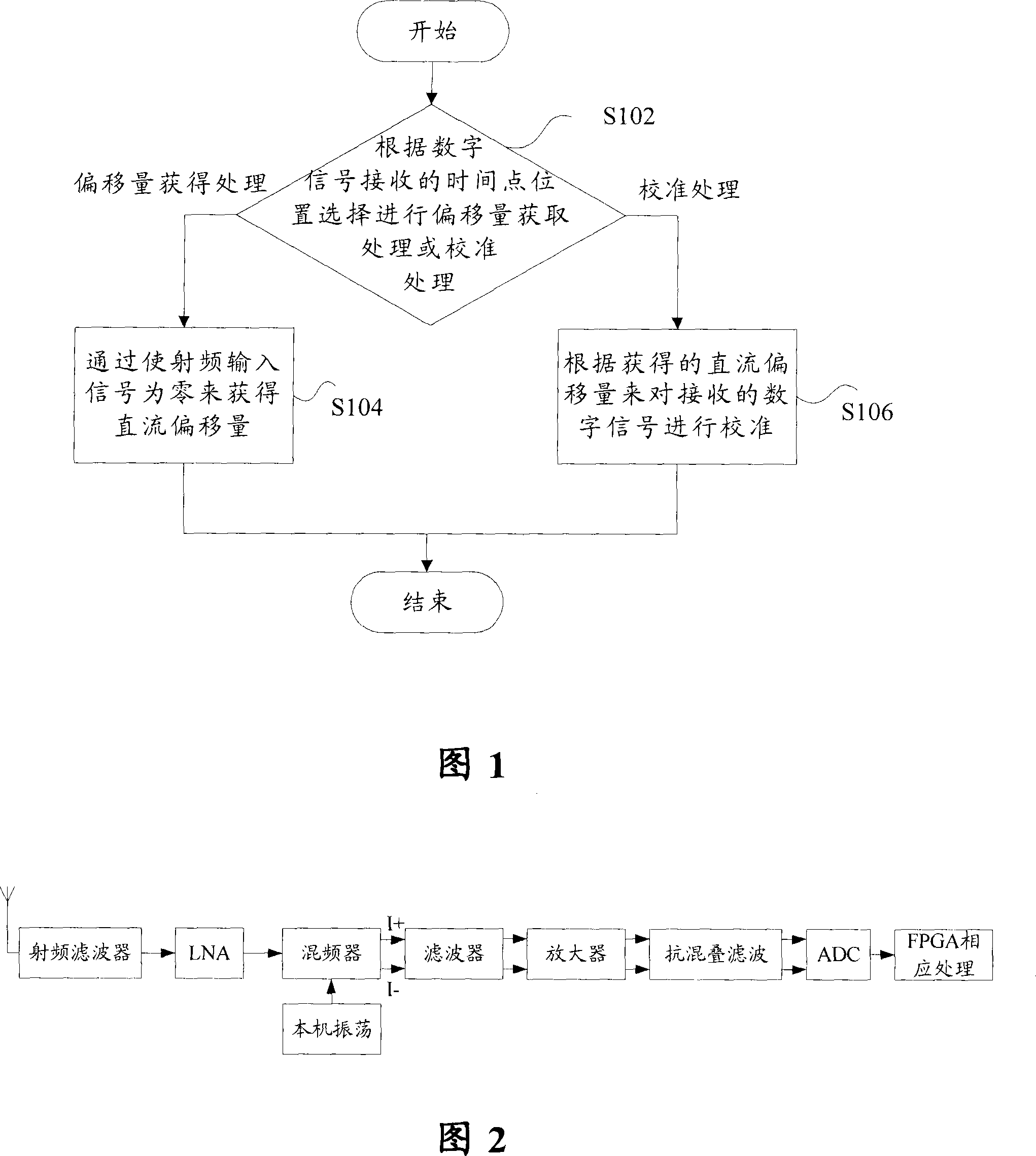
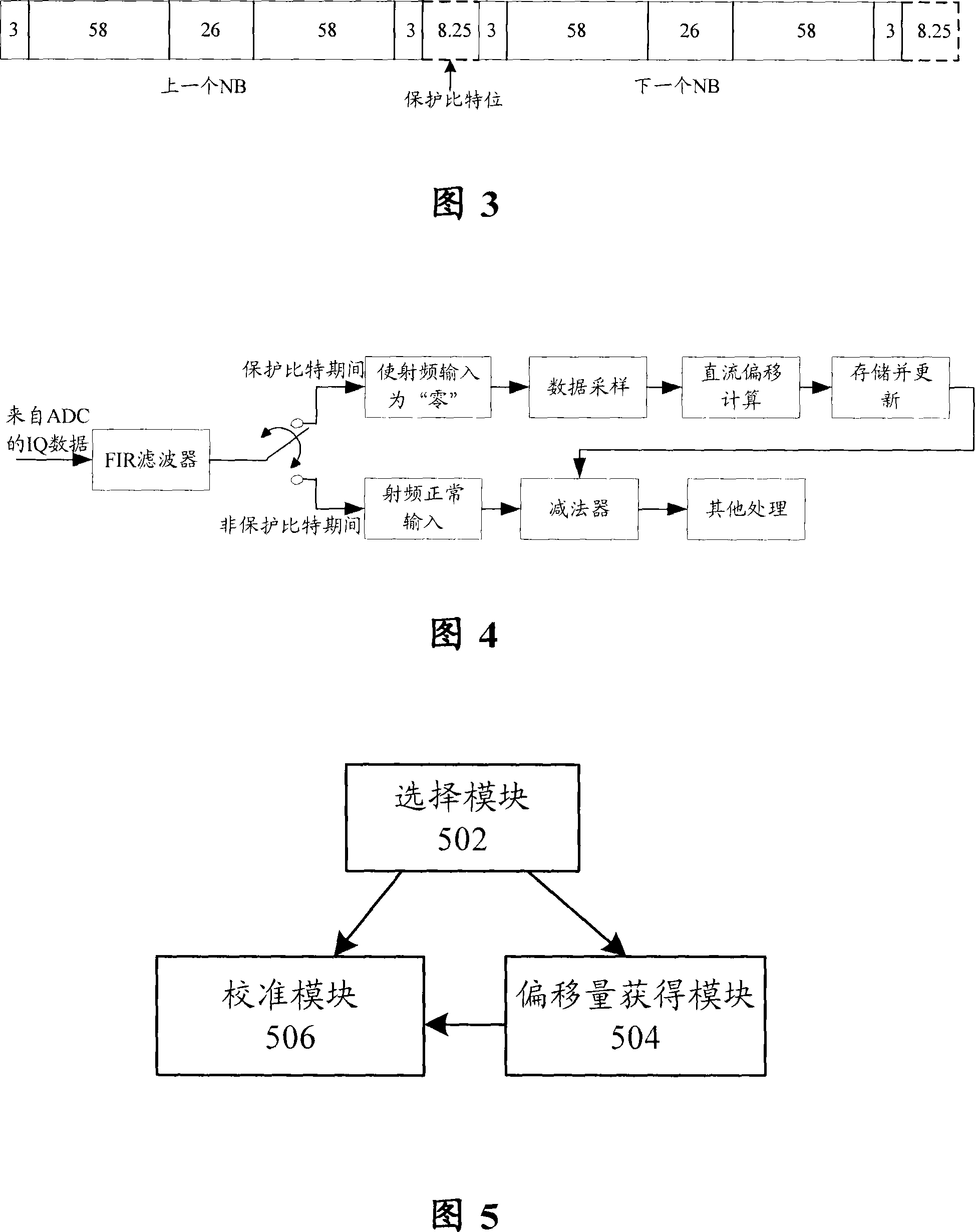
DC offset calibration method and apparatus
The invention discloses a DC offset calibration method, comprising the following steps: selecting to acquire the offset value or take calibration according to the time point position of receiving the digital signal; the offset is processed - DC offset is obtained by returning the RF input signal to zero; calibration processing - calibrating the digital signal received according to the DC offset. Also, the invention discloses a DC offset calibration device. The invention has the advantages that with the method and the device, the DC offset variation caused by temperature variation, circuit parameter variation or other reasons can be traced and calibrated without adding any additional complicated analog circuit or affecting the normal operation of a base station, and also the invention is simple to be implemented.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
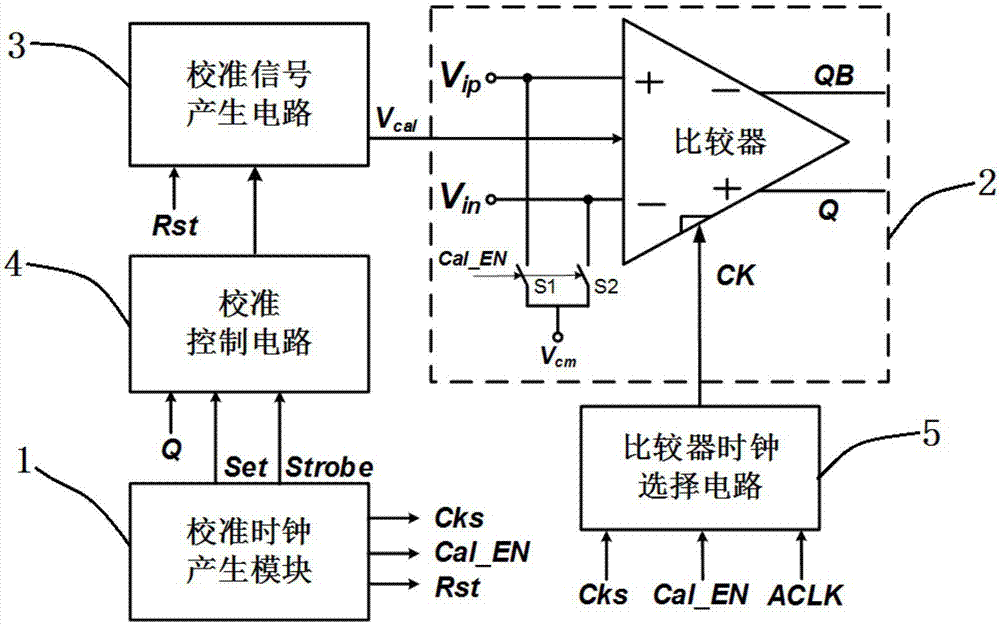
Offset calibration circuit for comparer in asynchronous successive approximation register analog-to-digital converter
ActiveCN107241098AHigh precisionInhibition effectAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingControl signalComputer module
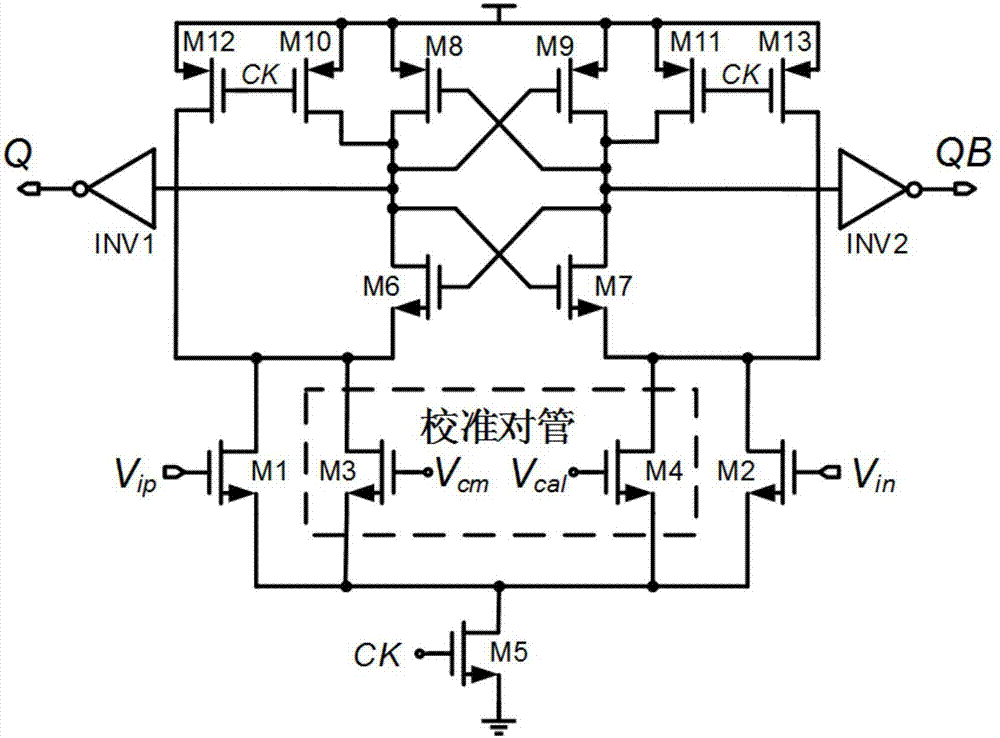
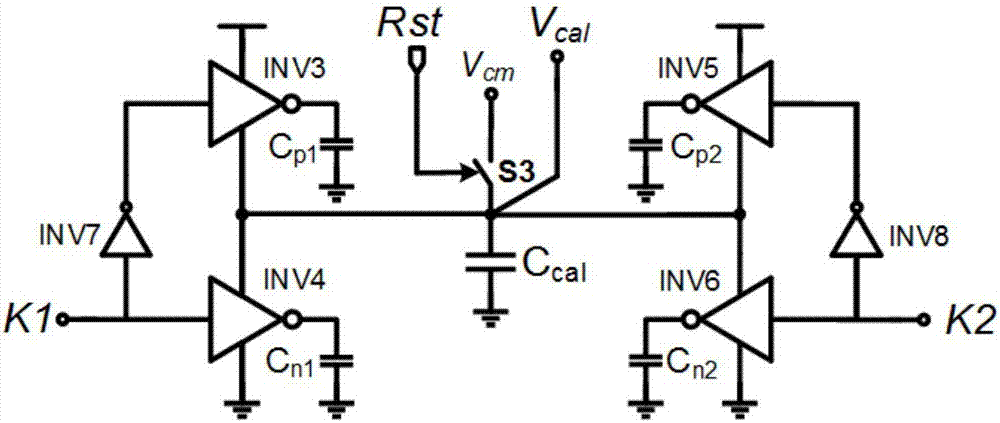
The invention discloses an offset calibration circuit for a comparer in an asynchronous successive approximation register analog-to-digital converter. The offset calibration circuit comprises a calibration clock generation module, a basic dynamic comparer with calibration pair transistors, a calibration signal generation circuit, a calibration control circuit and a comparer clock selection circuit. The calibration clock generation module is used for generating a global clock control signal for controlling offset calibration of the dynamic comparer. The basic dynamic comparer with calibration pair transistors comprises a basic single-level dynamic comparer, the calibration pair transistors connected with input pair transistors in parallel, a first switch S1 and second switch S2. The calibration signal generation circuit is used for generating a gate control voltage Vcal for one MOS transistor in the calibration pair transistors. The calibration control circuit is used for generating a control signal for the calibration signal generation circuit. The comparer clock selection circuit is used for generating a comparison and reset clock CK of the dynamic comparer. The offset calibration circuit is applied to offset calibration of the comparer of the asynchronous SAR ADC in a SoC system and is convenient and efficient.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Background comparator offset calibration technique for flash analog-to-digital converters
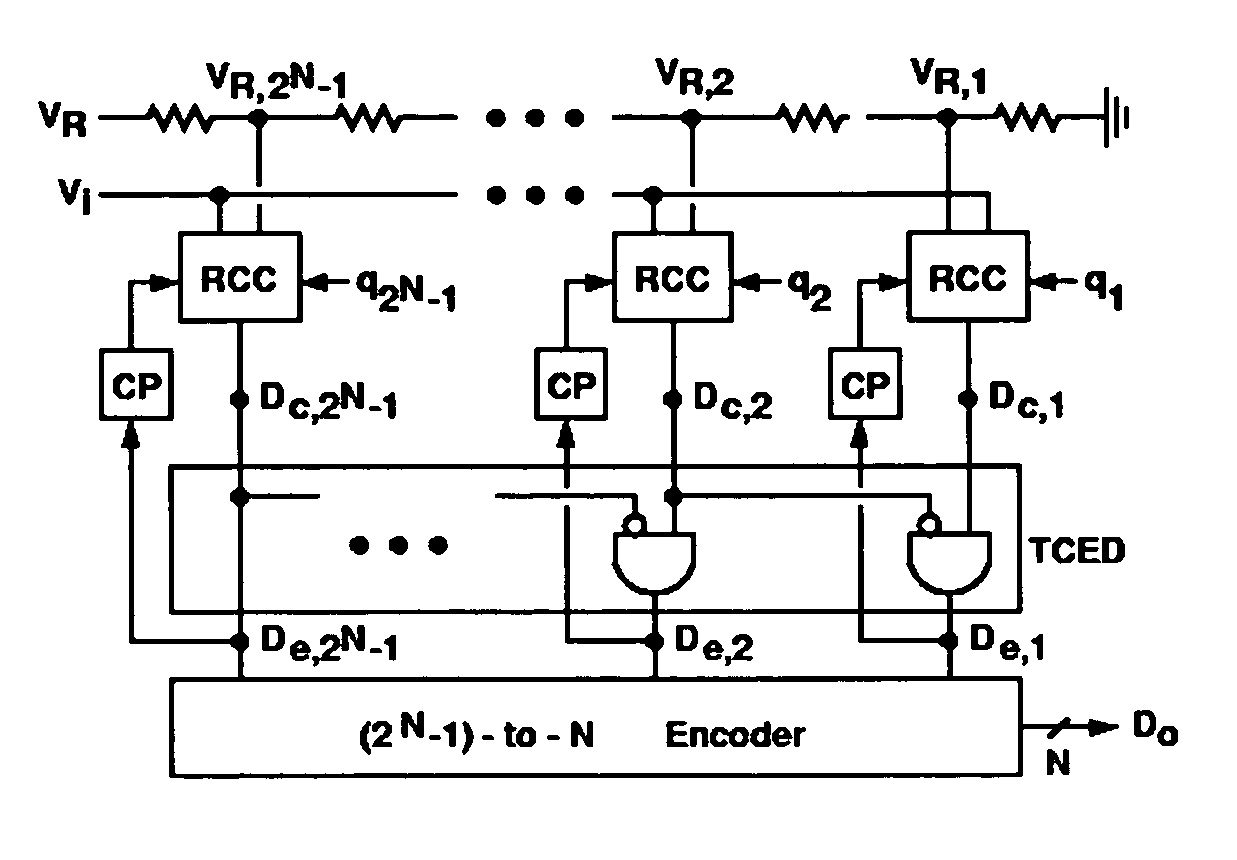
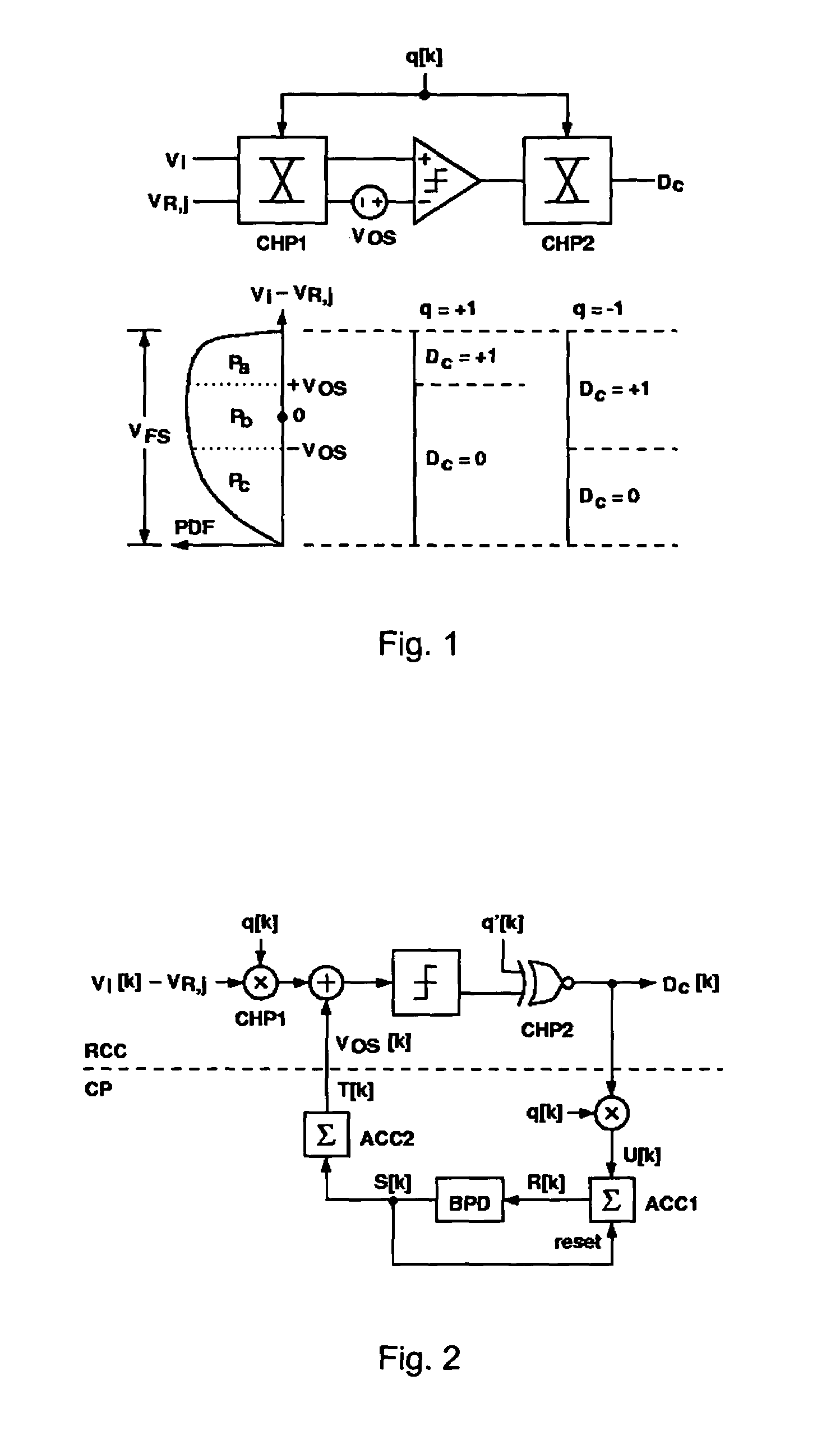
InactiveUS7064693B1Suppress fluctuation noiseReduce the impactElectric signal transmission systemsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesDigital down converterEngineering
A background-calibrated comparator and a background-calibrated flash analog-to-digital converter are disclosed for using in mixed-signal integrated circuit design in particular on the high-speed analog-to-digital converter circuit. Without affecting the operation of the comparator, the disclosure is directed at reducing the unpredictable input offset voltage originated from the variation of process parameters and environmental factors. The background-calibrated comparator includes a random chopping comparator, a calibration processor, and a random sequence generator. The background-calibrated flash analog-to-digital converter (ADC) includes a background-calibrated comparator array together with a reference voltage generator, a thermometer code edge detector, and a set of digital encoders.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Analog front end circuit and method of compensating for DC offset in the analog front end circuit
InactiveUS20050017883A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierLow-pass filter
DC offset is compensated for in an analog front end (AFE) circuit having an amplifier and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC). First data processed by the ADC are low pass filtered and estimated DC offset data of the ADC are obtained in ADC DC offset calibration mode. Second data processed by the ADC and the amplifier are low pass filtered, and a first DC offset of the ADC are substantially removed from the filtered second data by subtracting the estimated DC offset data from the filtered second data, thereby obtaining second compensated DC offset data of the amplifier in an amplifier DC offset calibration mode. The second compensated DC offset data is iteratively improved and first compensated DC offset data of the amplifier are obtained. The first compensated DC offset data are transformed into an analog signal, and the analog signal is subtracted from an input signal of the amplifier during operation mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High-speed low-kickback-noise dynamic comparer and circuit
InactiveCN107888171AReduce reset timeShorten the working cycleMultiple input and output pulse circuitsUltrasound attenuationDynamic noise
The invention discloses a dynamic comparator with high speed and low kick noise, which belongs to the field of analog integrated circuits. Its structure includes: pre-amplification stage, current compensation branch for suppressing kickback noise, positive feedback regeneration stage composed of N-channel transistor and P-channel transistor cross-coupling unit, current between pre-amplification stage and positive feedback regeneration stage A control unit, a reset control unit, an offset calibration unit, and an inverter output driver stage. The two current compensation branches that suppress the kickback noise compensate the current attenuation of the main channel to ensure a constant working current of the input pair tube, thereby suppressing the influence of the kickback noise on the input signal, thereby increasing the size of the input pair tube and reducing offset voltage, increasing the response speed. Compared with the traditional comparator, the invention satisfies the requirement of high speed and low power consumption, and exhibits excellent kickback noise suppression ability.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF MICROELECTRONICS SHRIME PEKING UNIV
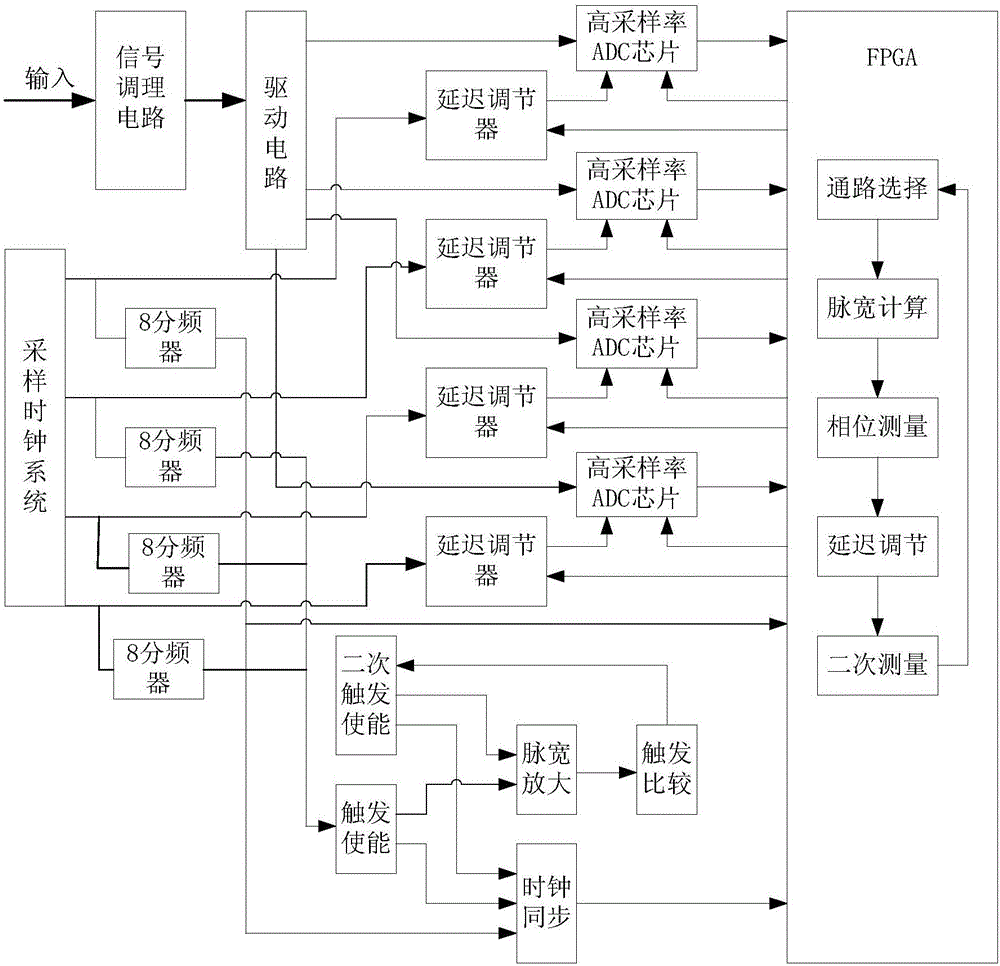
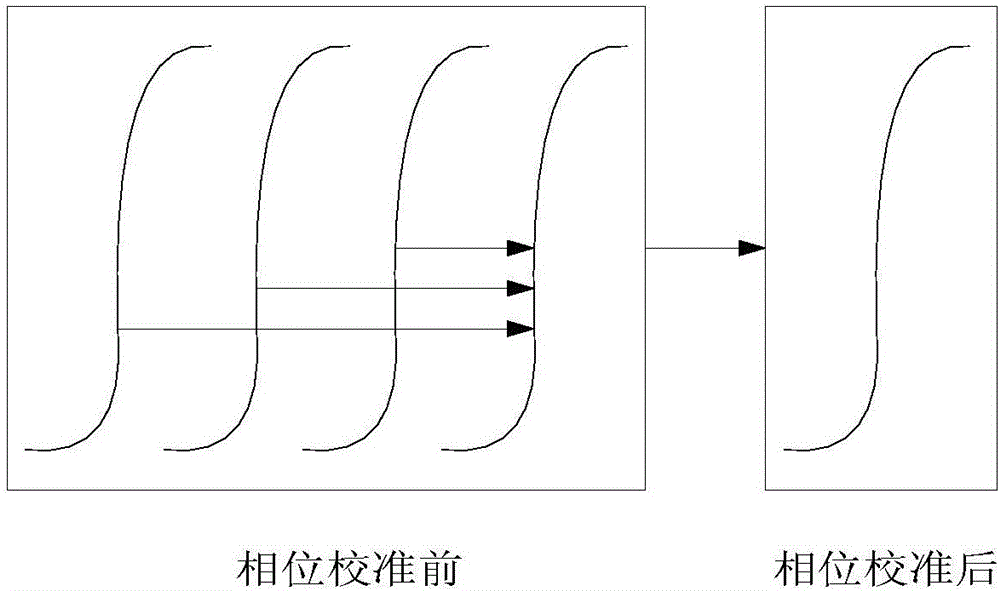
Multi-ADC high-speed crossing sampling calibration device and method
ActiveCN106603075AReduce uncertaintyImprove calibration efficiencyAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingWave shapePhase difference
The invention provides a multi-ADC high-speed crossing sampling calibration device and method, and the method comprises the steps: phase calibration, gain calibration and offset calibration. The phase calibration mainly solves a delay consistency problem of sampling clocks, the gain calibration mainly solves an amplitude consistency of four signals and the offset calibration mainly solves an offset consistency problem of four signals. Through the calibration of the phase, gain and offset of four-way ADCs with the 2.5 GSa / s sampling rate, the device and method enable the sampling rate of the four ADCs to reach 10 GSa / s during crossing sampling. Moreover, the waveform does not have distortion after data recombination, and the performance indexes meet the ideal requirements. A whole testing calibration control circuit is implemented through upper computer software and an FPGA. After calibration, the phase, gain and offset are guaranteed to be consistent, and a calibration result is complemented during collection display, thereby enabling the phase difference of four collection clocks to be 100ps, and enabling the gain and offset to be equal.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
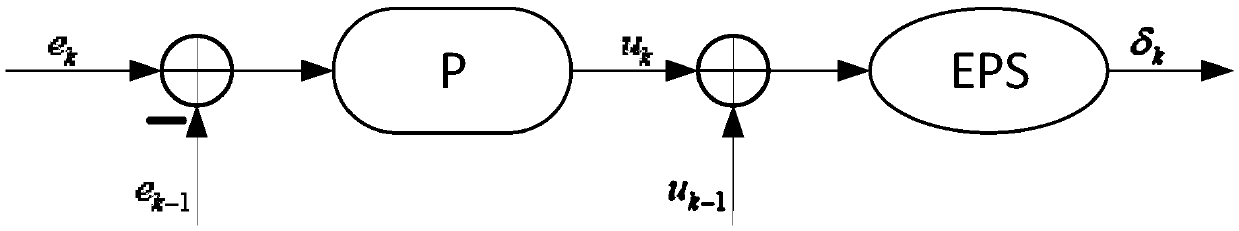
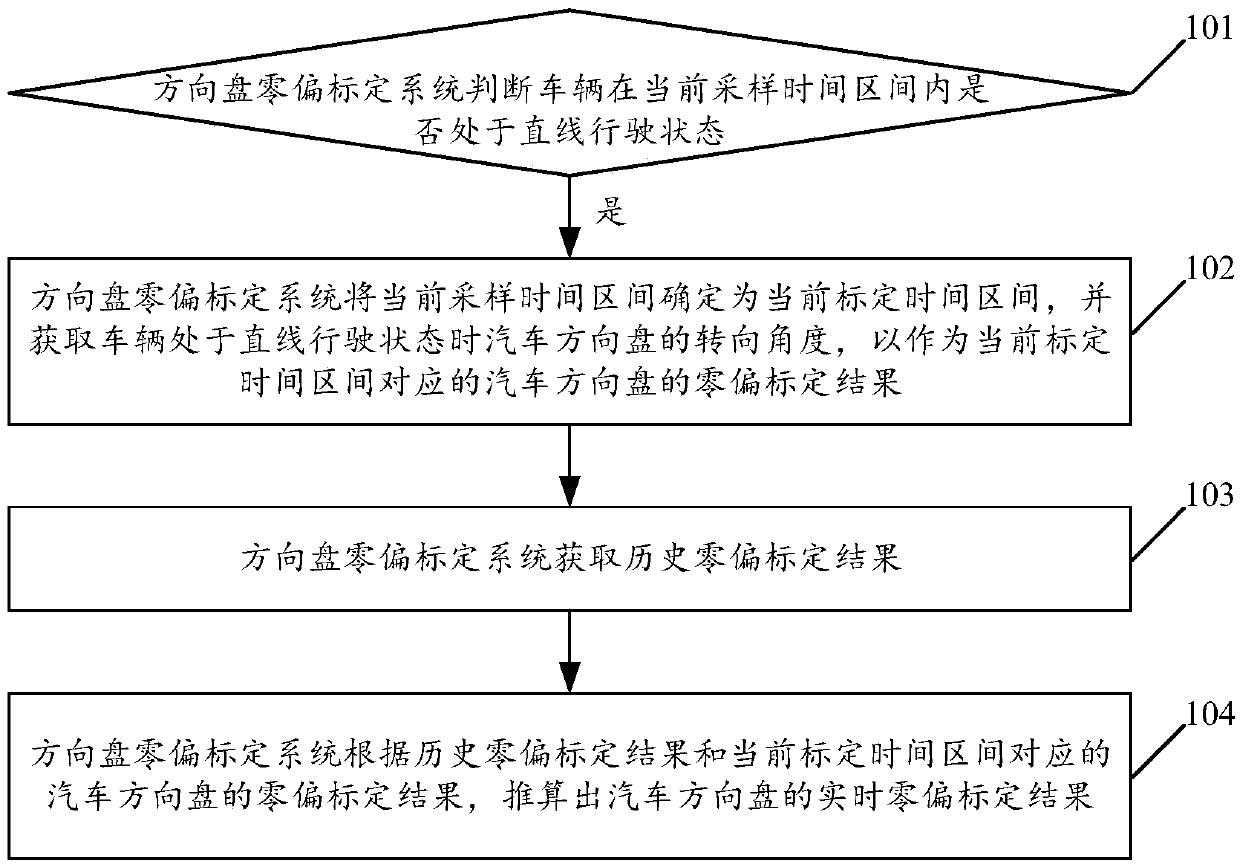
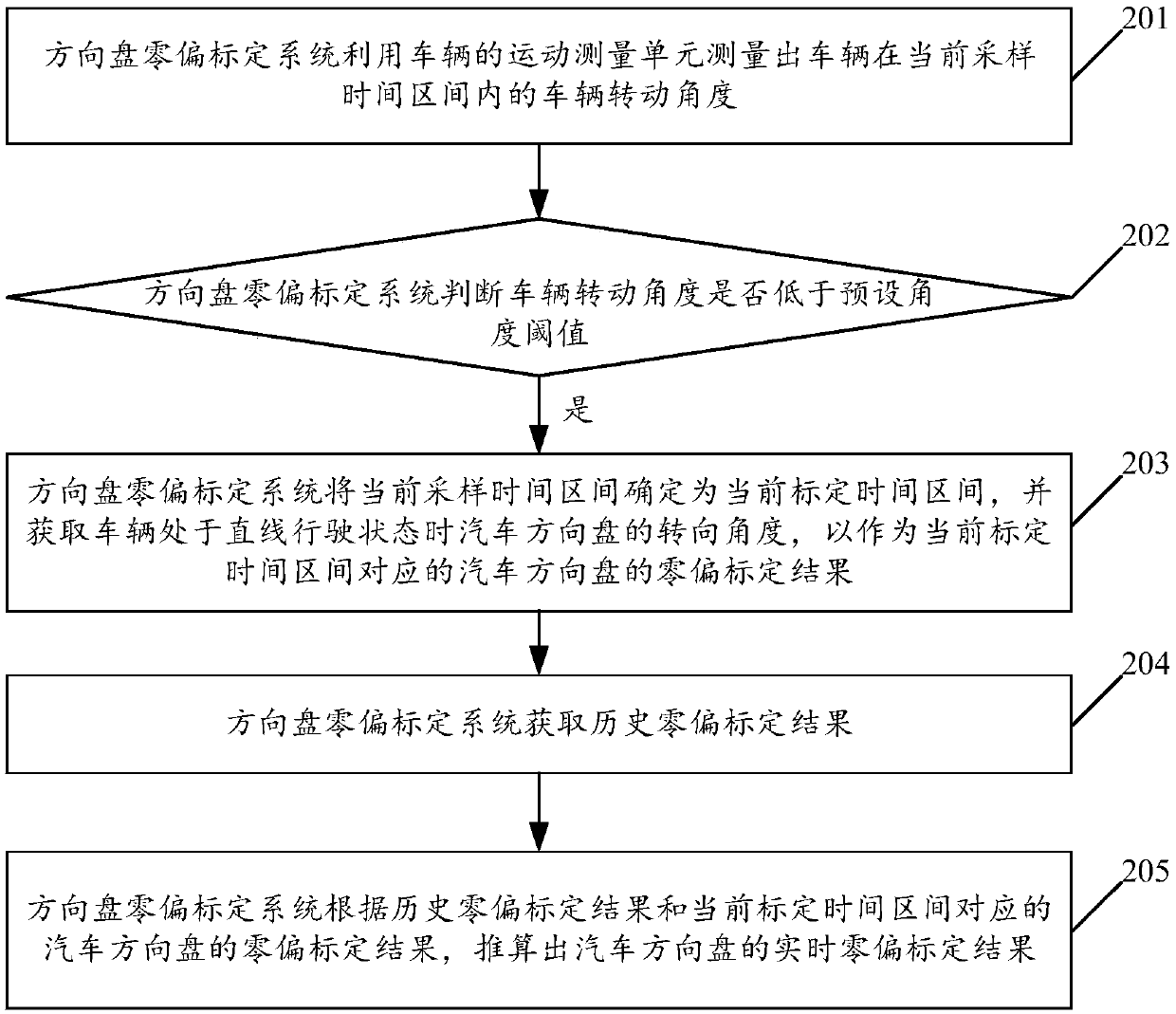
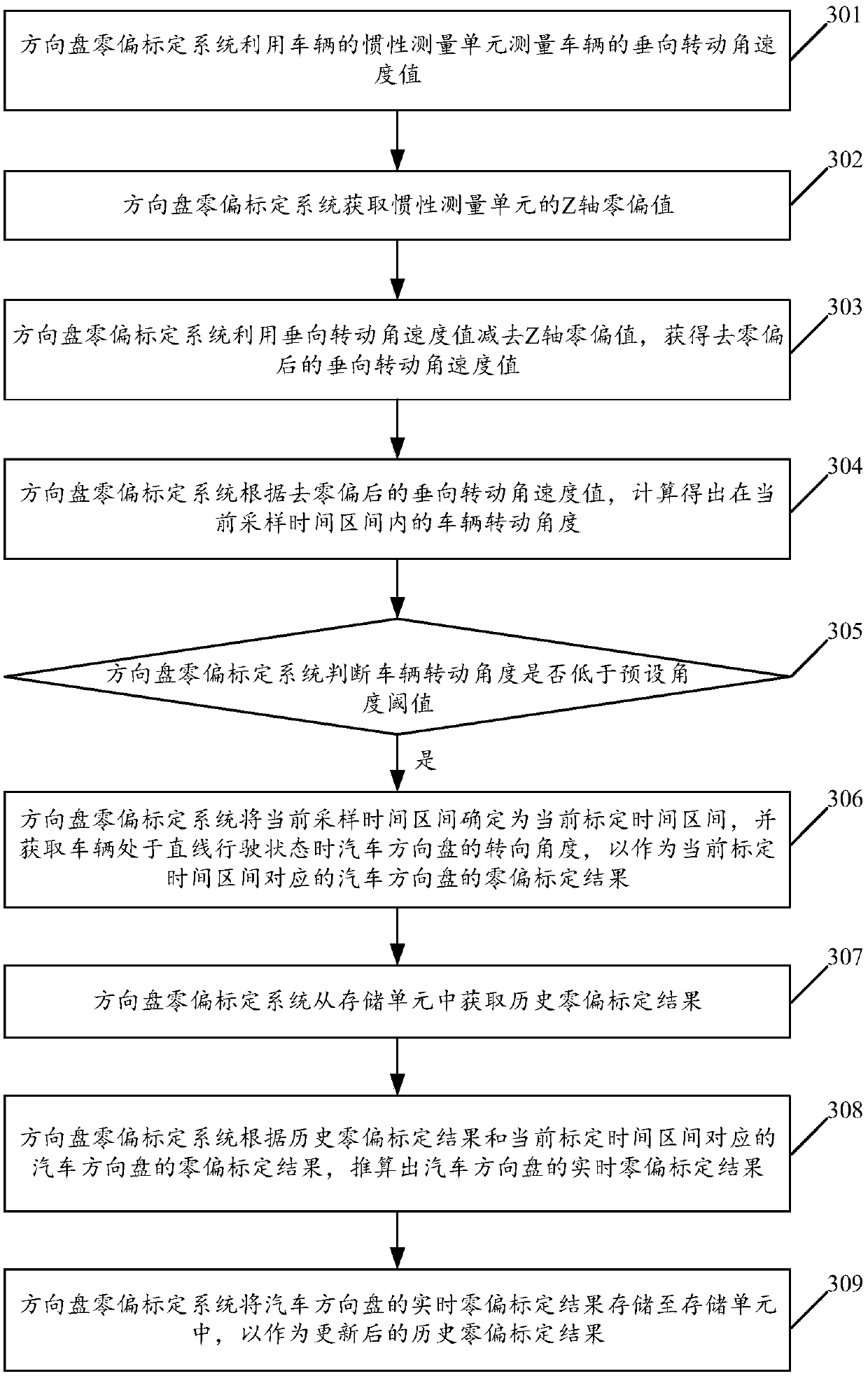
Vehicle, and method and system for automatically calibrating zero offset of steering wheel of vehicle
An embodiment of the invention relates to the technical field of automatic driving, and discloses a vehicle, and a method and a system for automatically calibrating zero offset of a steering wheel ofthe vehicle. The method includes judging whether the vehicle is in straight driving states in current sampling time intervals or not; determining that the current sampling time intervals are current calibration time intervals if the vehicle is in the straight driving states, and acquiring steering angles of the steering wheel of the vehicle when the vehicle is in the straight driving states; acquiring historical zero offset calibration results; calculating real-time zero offset calibration results of the steering wheel of the vehicle according to the historical zero offset calibration resultsand zero offset calibration results, which correspond to the current calibration time intervals, of the steering wheel of the vehicle. The steering angles are used as the zero offset calibration results, which correspond to the current calibration time intervals, of the steering wheel of the vehicle. The vehicle, the method and the system in the embodiment of the invention have the advantages thatthe zero offset of the steering wheel of the vehicle which is currently automatically driven can be automatically calibrated by the aid of the method and the system, and the zero offset measurement accuracy of the steering wheel of the vehicle can be improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU XIAOPENG MOTORS TECH CO LTD
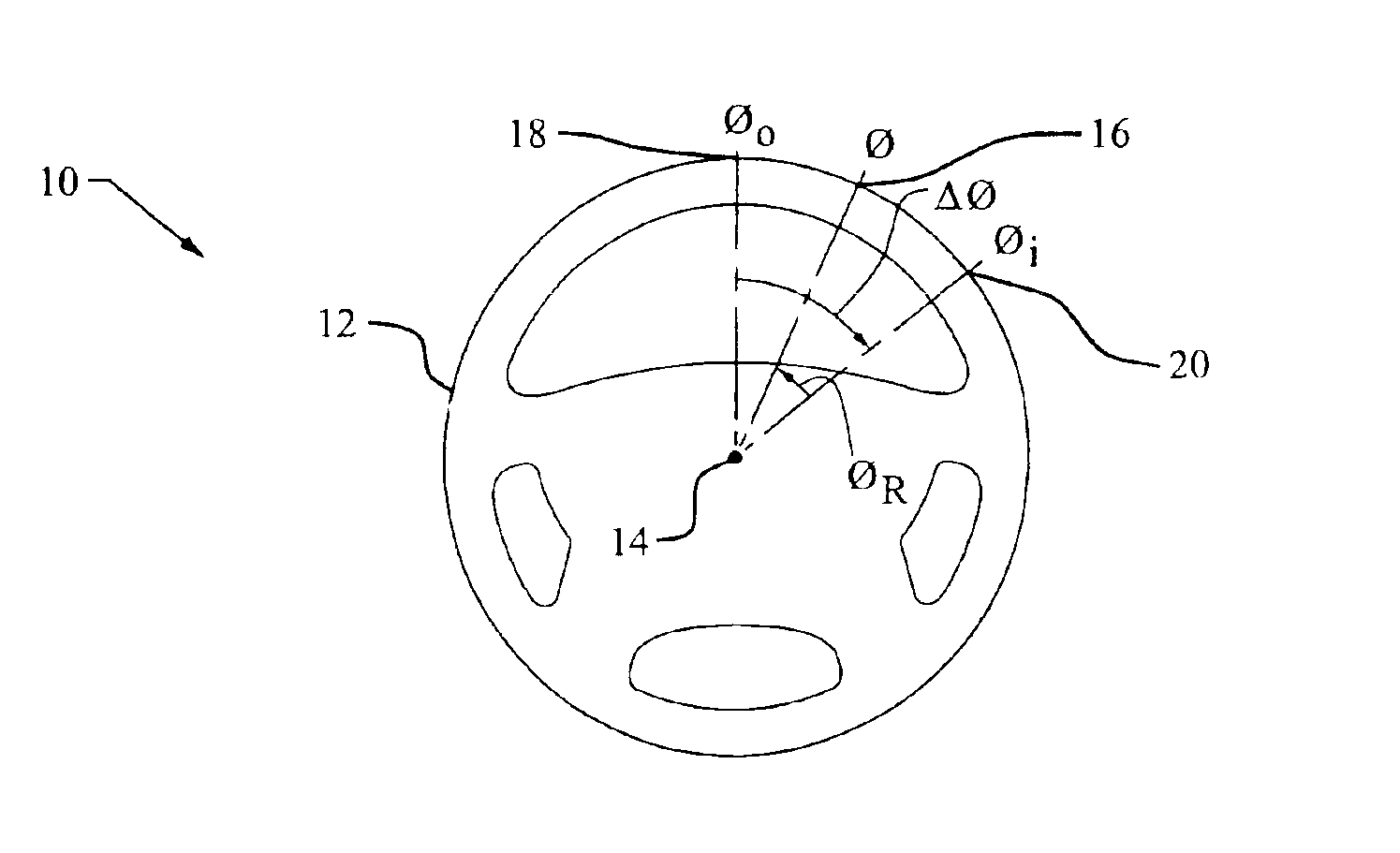
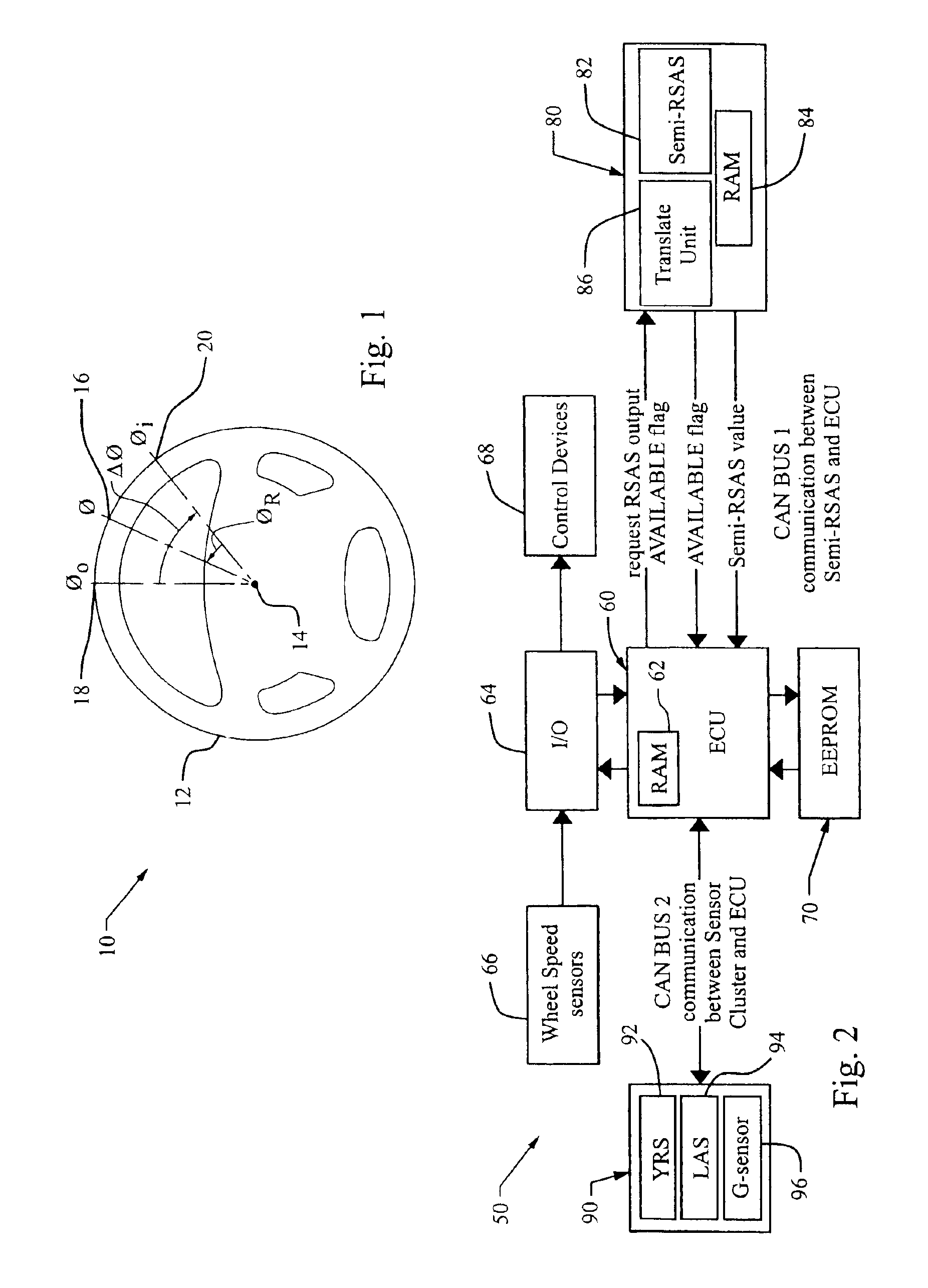
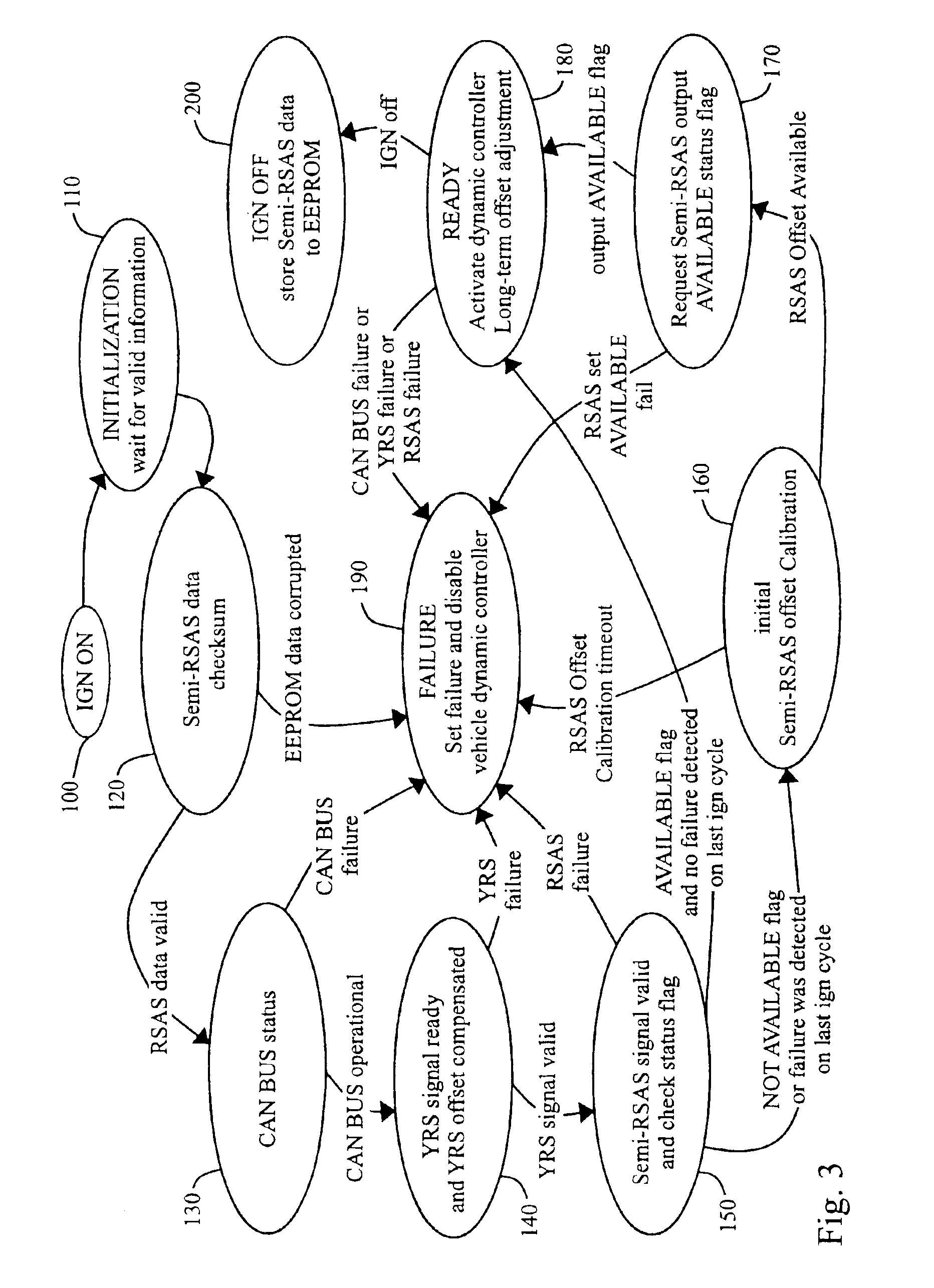
Offset calibration of a semi-relative steering wheel angle sensor
InactiveUS6895357B2Reduce system costReduce vehicle costTesting/calibration apparatusDigital data processing detailsVehicle dynamicsSteering wheel
A new method for determining an actual steering wheel angle is provided that does not require re-calculation of a steering center upon each ignition of the vehicle. Accordingly, the vehicle dynamic controller may be activated very quickly after ignition, while a less costly relative steering wheel angle sensor may be employed.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES INC
Method and apparatus for calibrating detector spectral response
InactiveUS6848827B2Increase coverageQuick calibrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSpectral responseOffset calibration
The present technique provides for the spectral calibration of the detector elements of a CT detector using one or more offset calibration phantoms. The offset phantoms provide greater coverage of the detector elements as well as spectral response data associated with penetration lengths ranging in length from a minimum chord of the phantom to the diameter of the phantom. The spectral response as a function of penetration length can be obtained for each detector element by comparing the fitting of each projection view to the corresponding measured projection view over all view angles. The fitting information may then be employed to derive the coefficients of the spectral response curve for each detector element, which may in turn be employed to provide rapid correction of the spectral response for each element.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system of x-ray data calibration
InactiveUS20080192899A1Reduce artifactsReduce the differenceTelevision system detailsInstrumentsConversion factorData acquisition
A process of data calibration and correction is disclosed that utilizes feedback from a temperature sensor of an x-ray detector to isolate or otherwise select an appropriate calibration or correction map that is specific to the temperature of the x-ray detector during data acquisition. The method is also designed to take into account changes in power transients of an x-ray detector between the acquisition of imaging data and the acquisition of offset data. The method is particularly applicable in optimally selecting and applying gain correction, conversion factor, bad pixel, and offset calibrations.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Signal processing semiconductor integrated circuit device and wireless communication system
InactiveUS20050186927A1Reduce receptionImprove receiver sensitivityModulation transference balanced arrangementsRadio transmissionCommunications systemAudio power amplifier
The invention provides a signal processing semiconductor integrated circuit of the direct conversion system, which includes a dummy amplifier having the same circuit configuration as a low noise amplifier being the first stage amplifier, in which the DC offset calibrations on the subsequent stage amplifiers are carried out during shifting into the reception mode in a state that the low noise amplifier is deactivated and the dummy amplifier is activated. Thereby, the invention achieves to suppress generation of the DC offsets resulting from the leakage noises of the local oscillator during shifting into the reception mode, and to enhance the reception sensitivity.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com