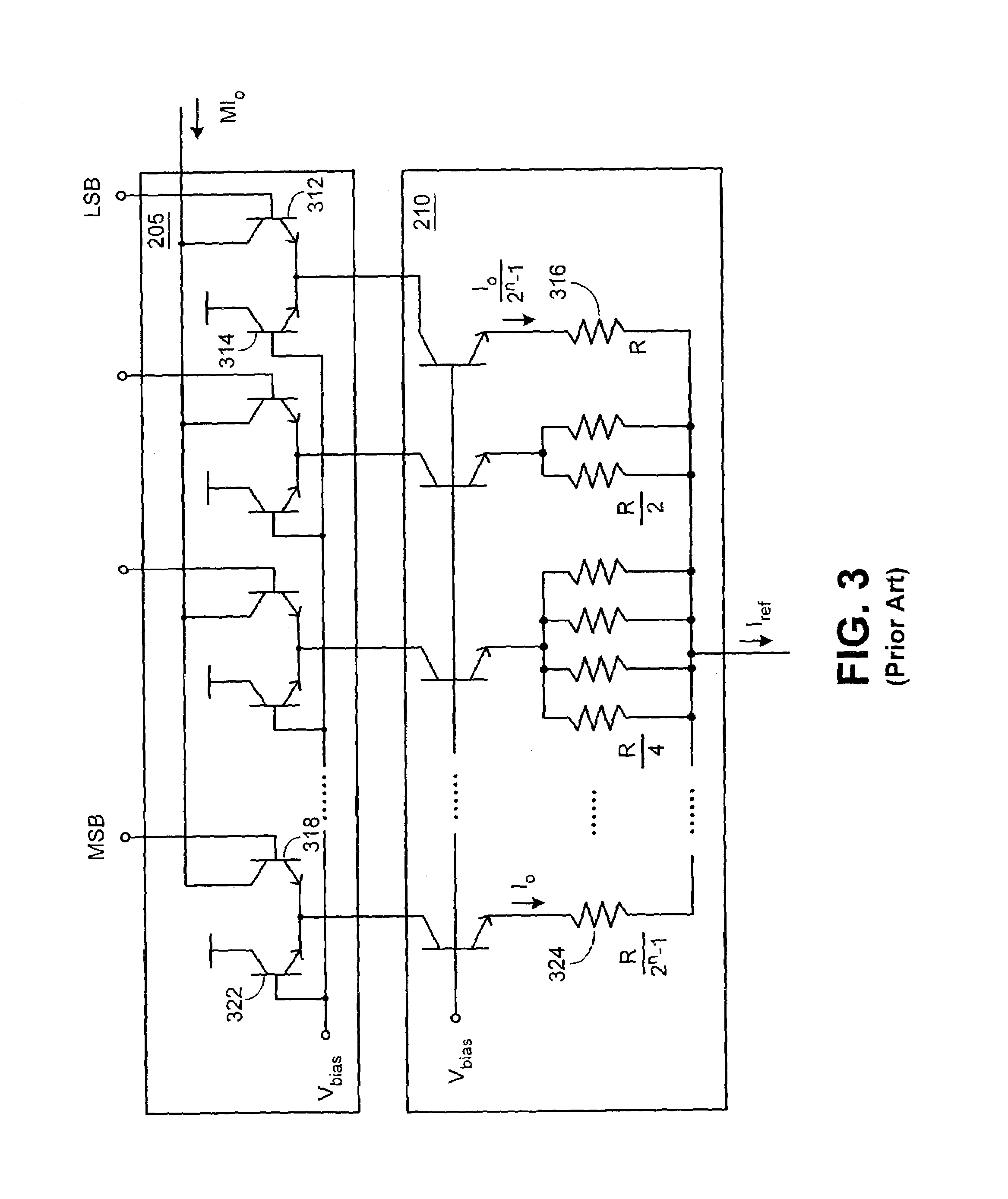
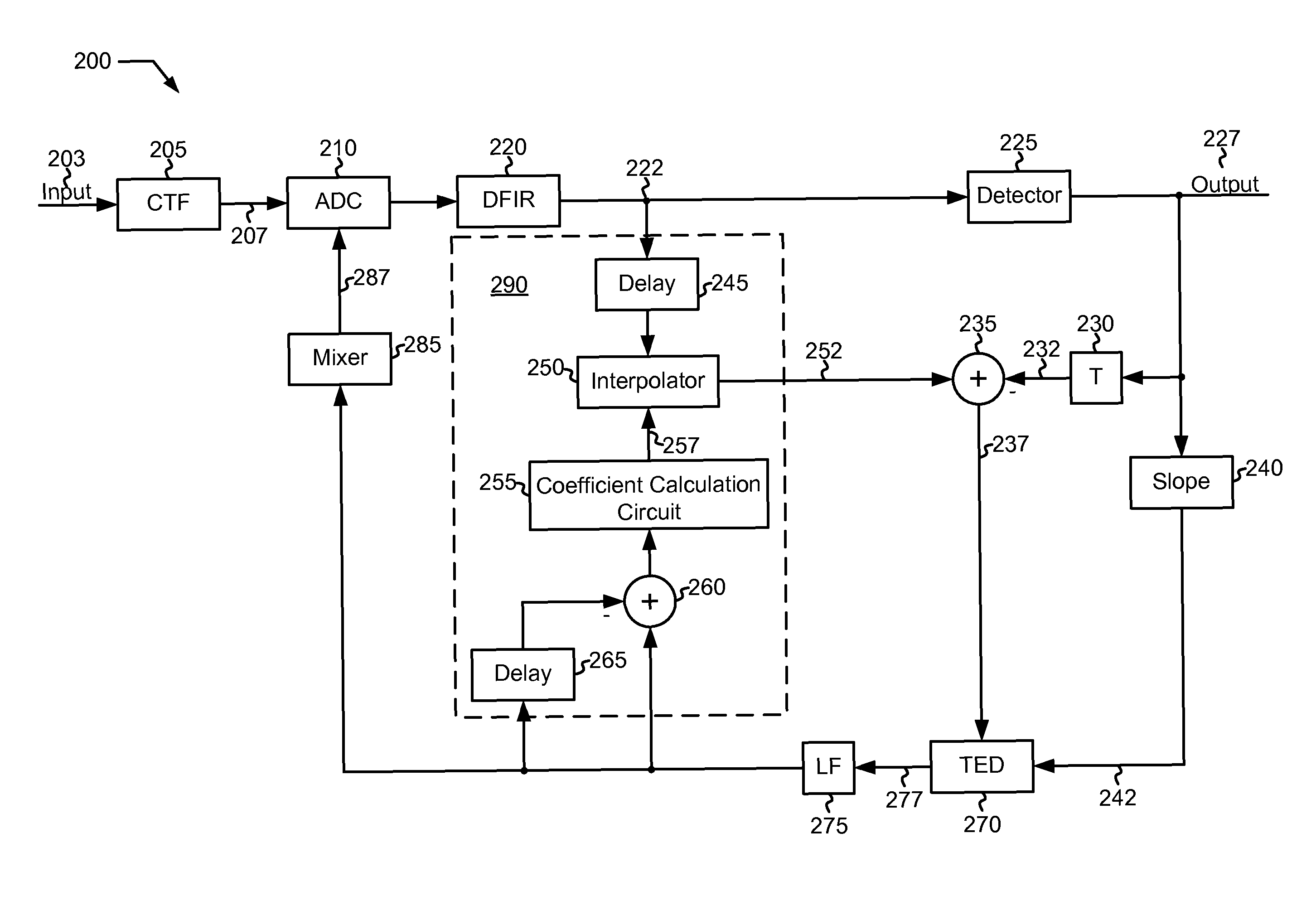
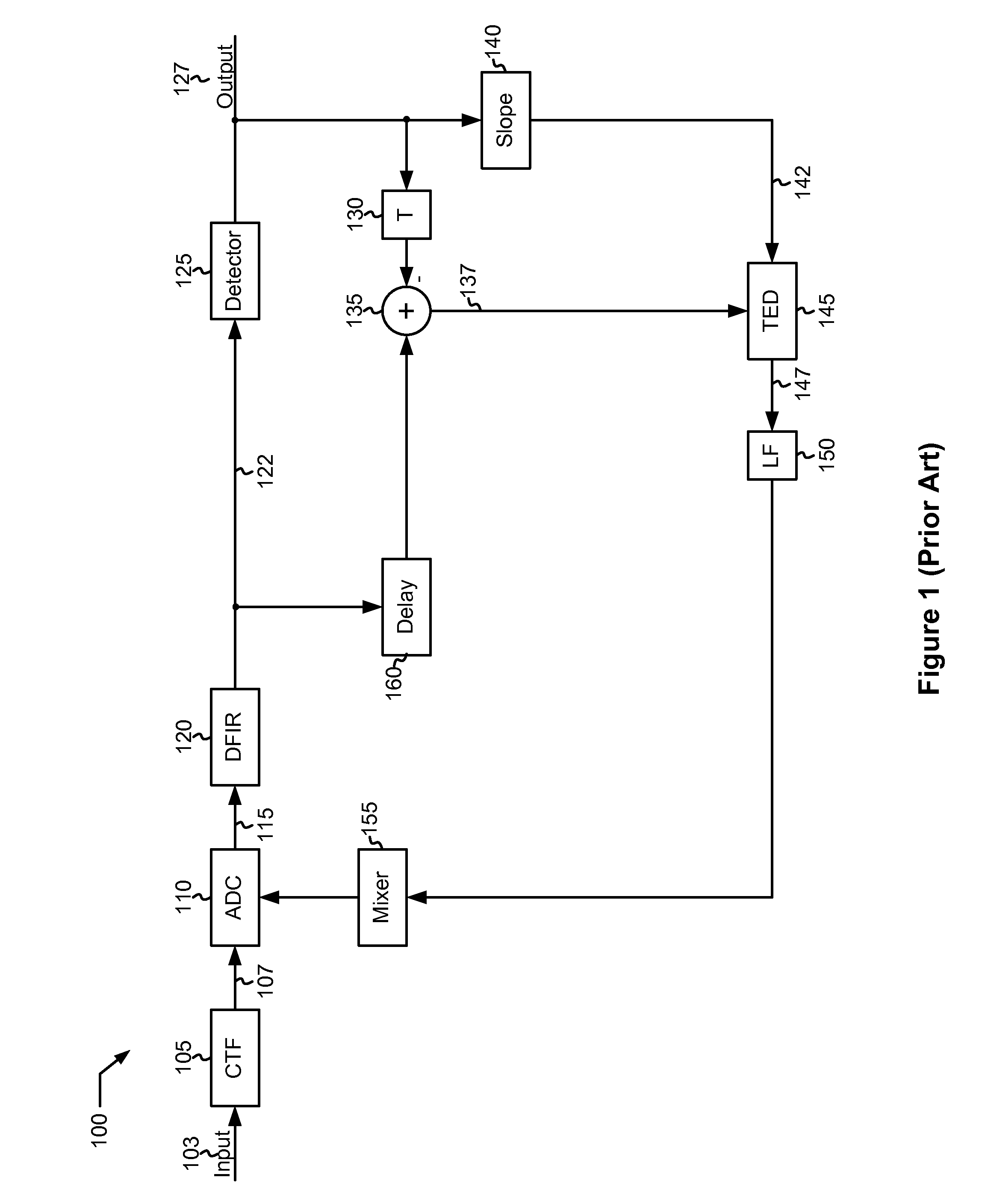
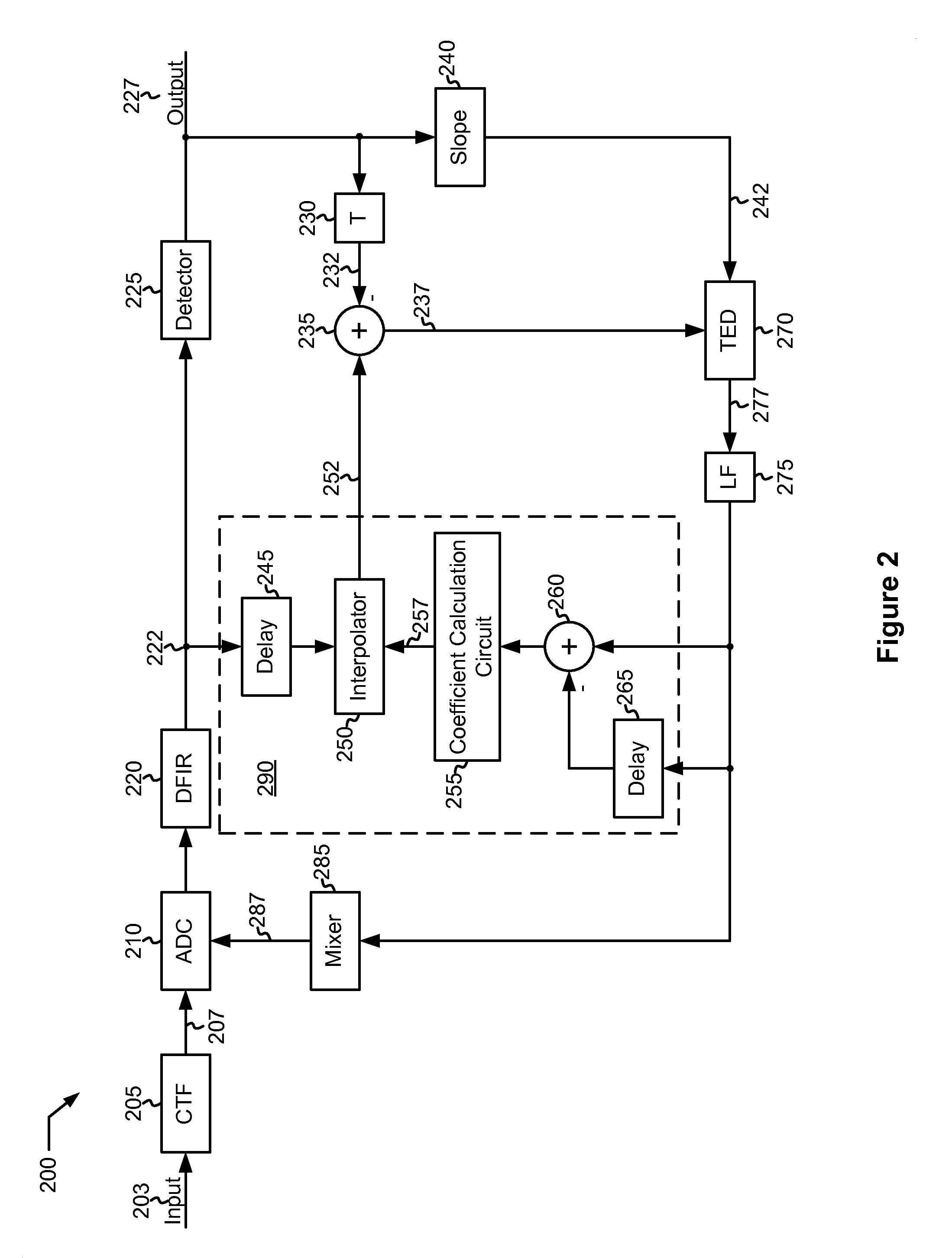
Patents
Literature
3235results about "Analogue/digital conversion calibration/testing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
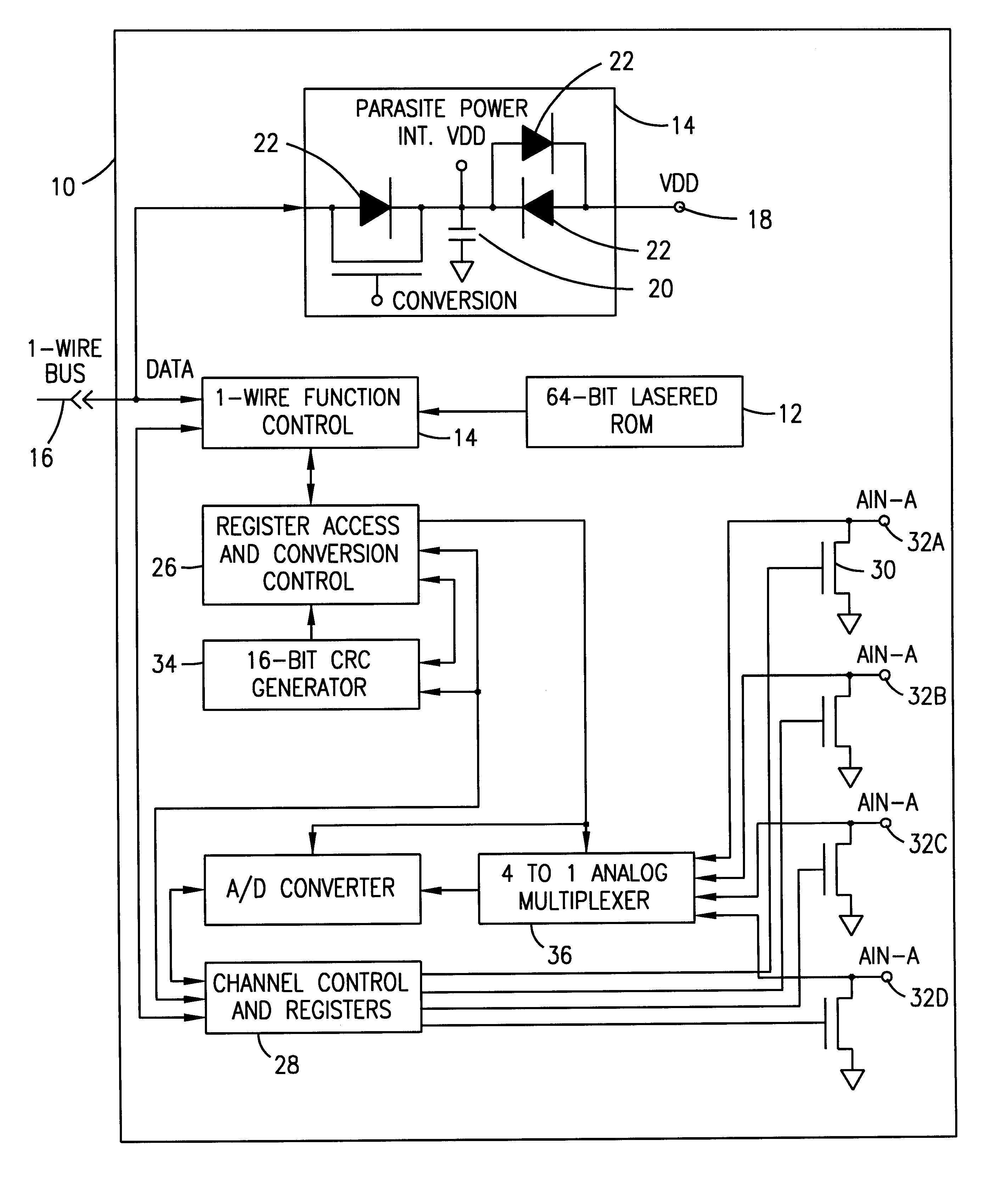
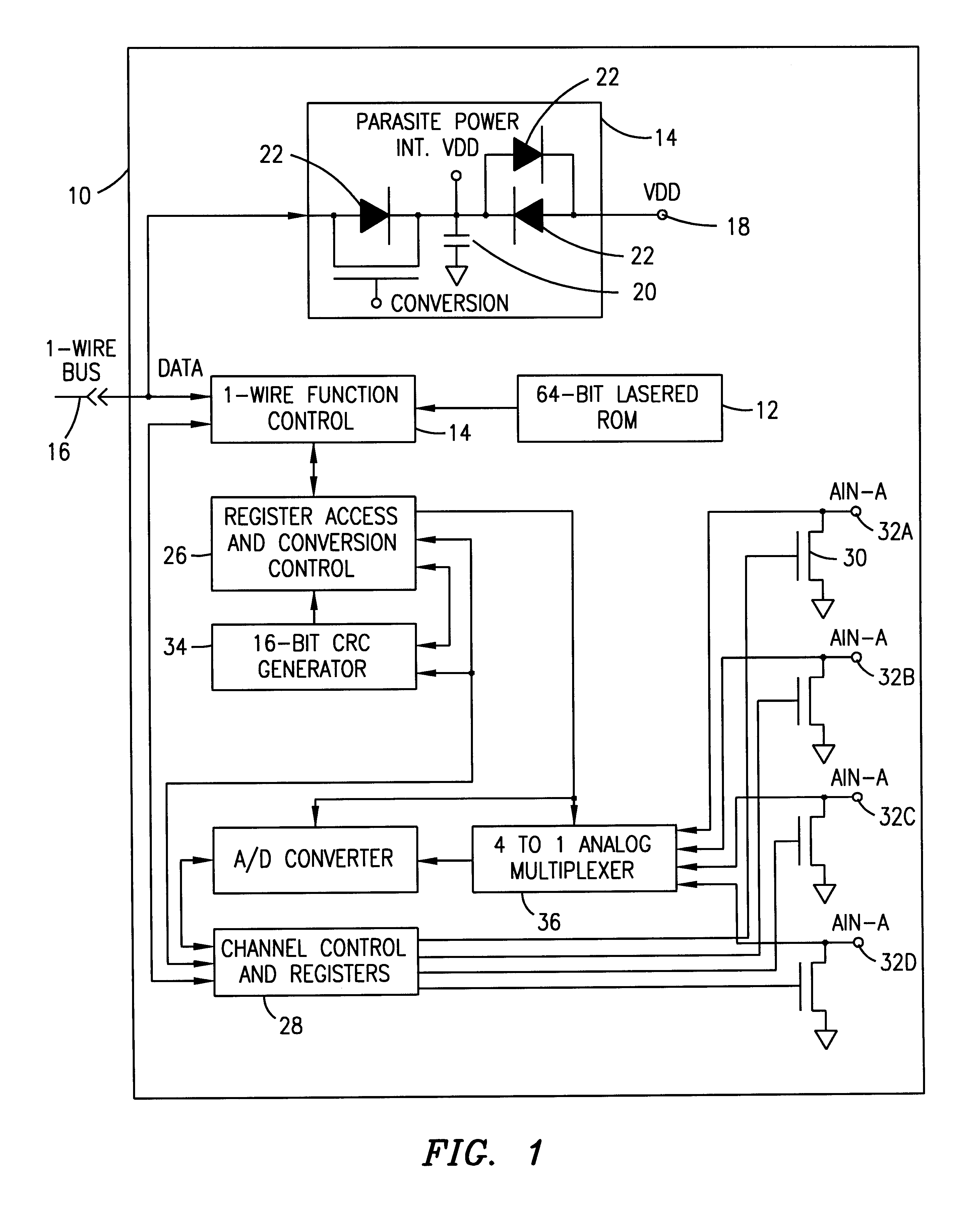
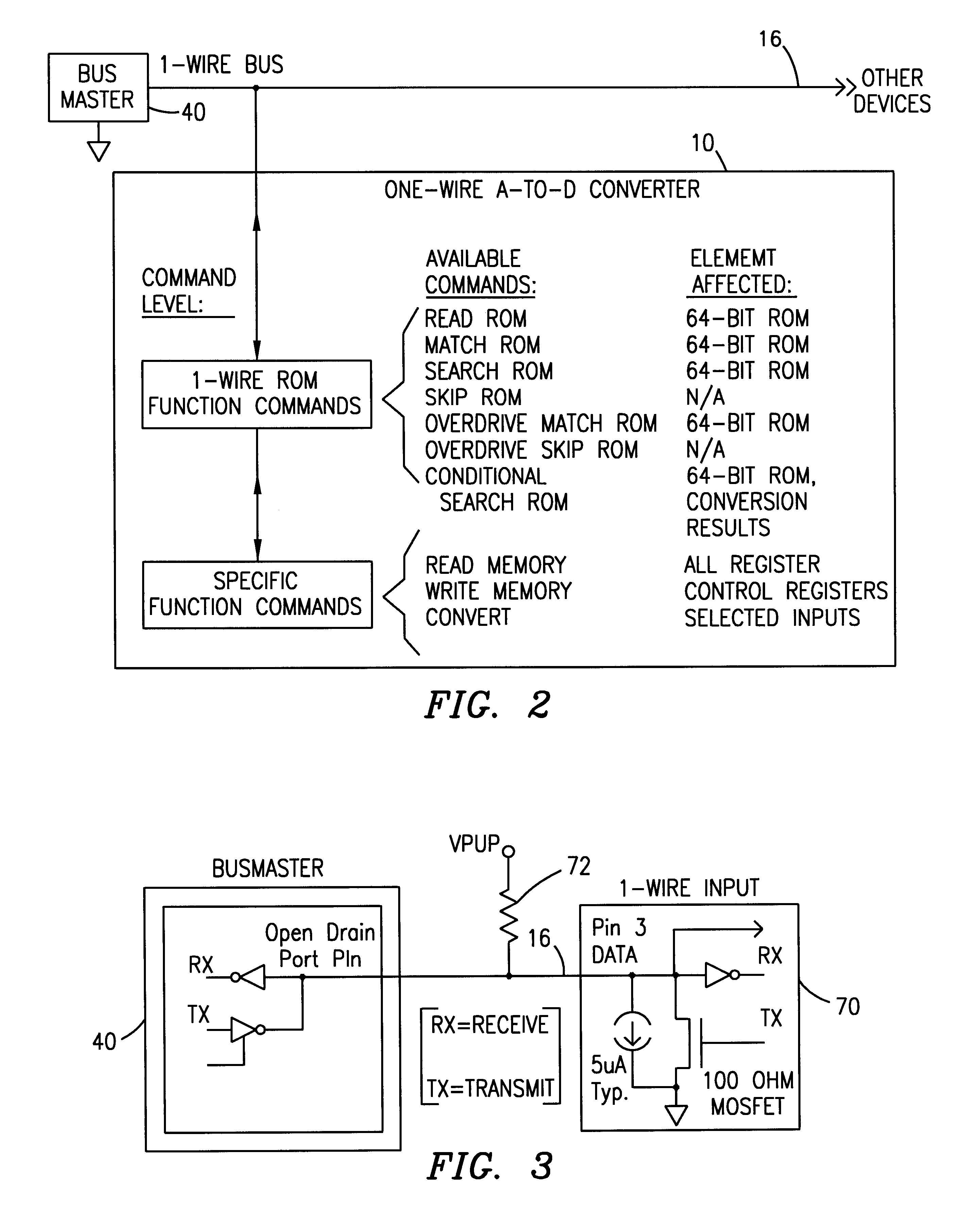
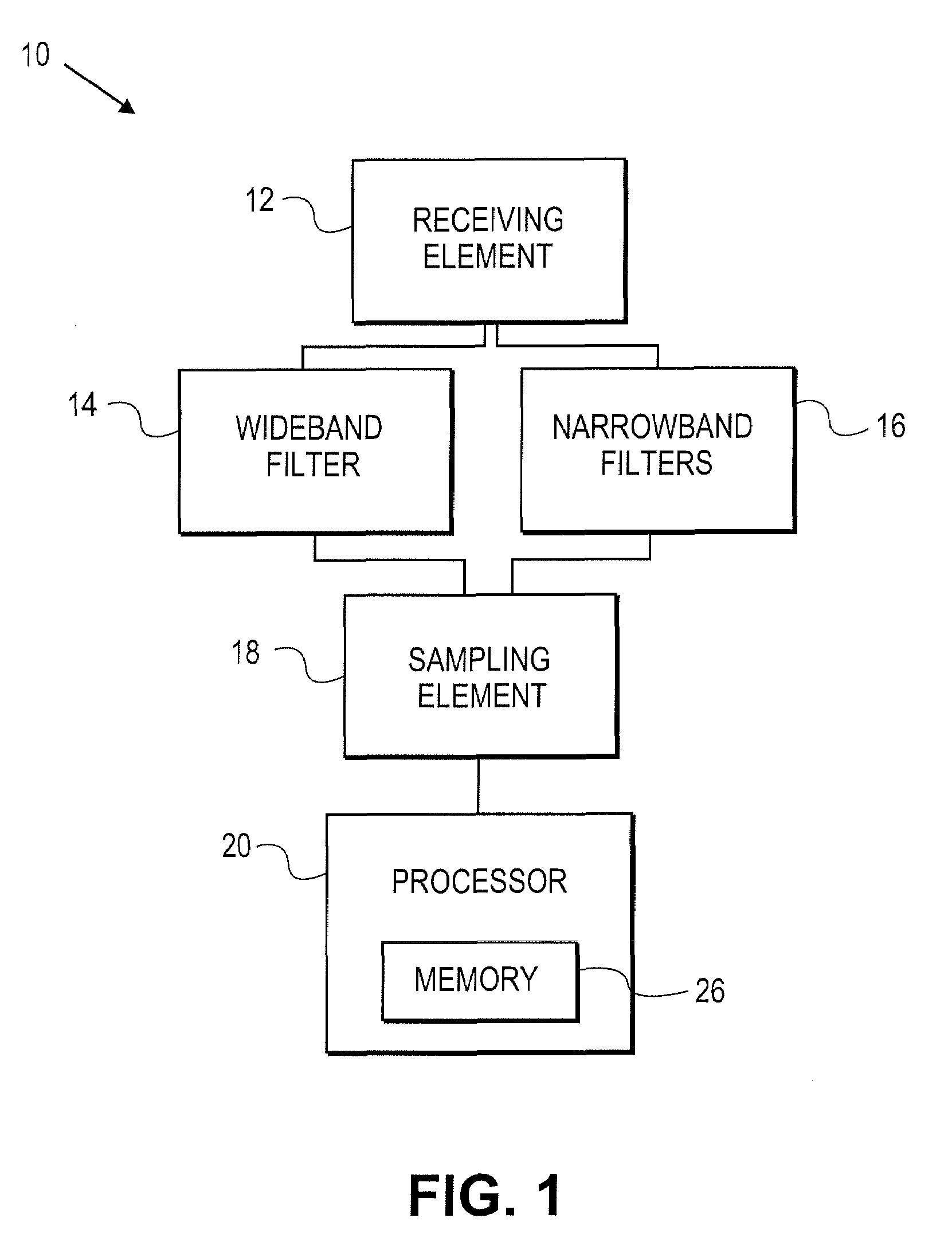
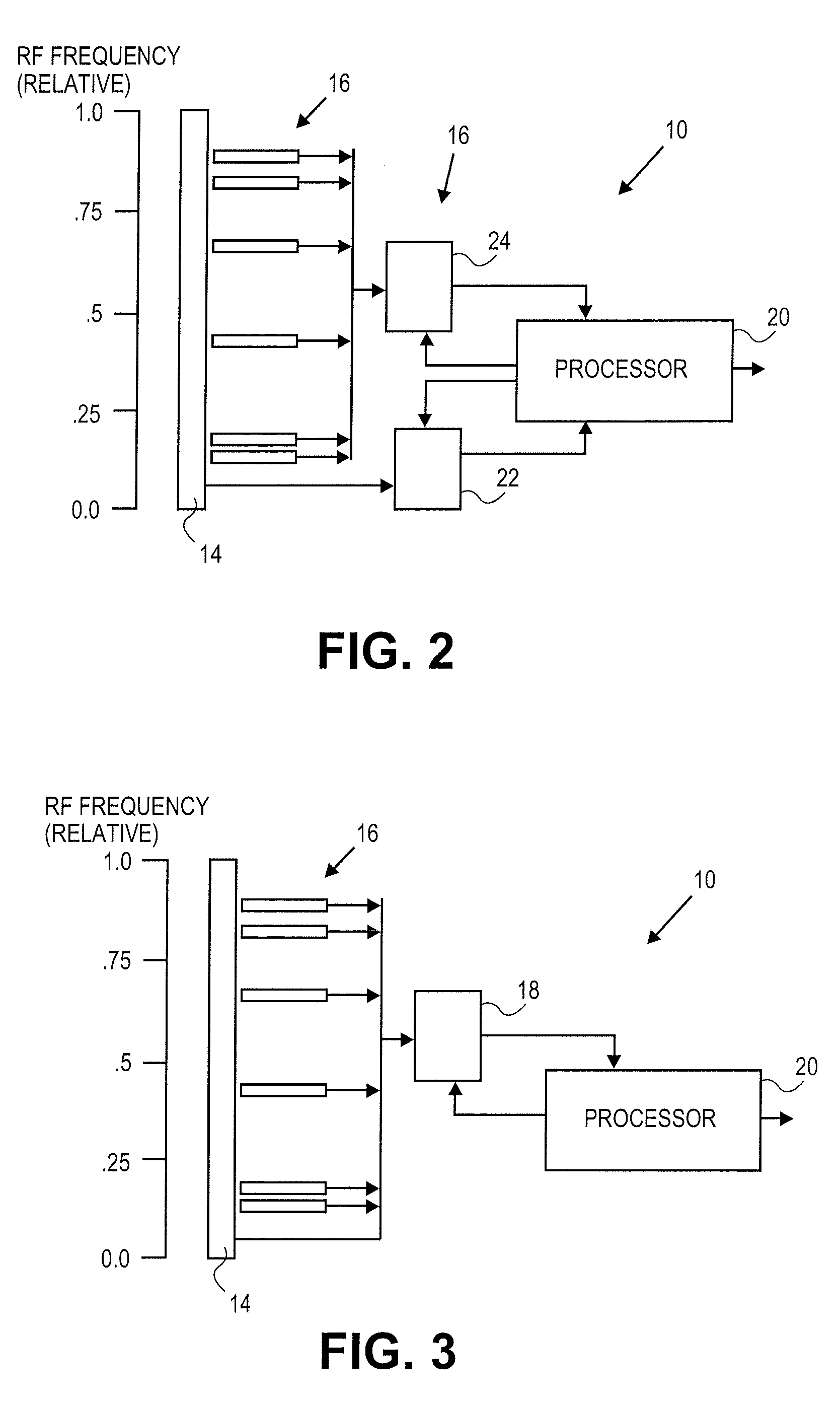
One-wire device with A-to-D converter
InactiveUS6239732B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersĆuk converterAnalog signal
A low power integrated circuit having analog to digital conversion circuitry capable of receiving a plurality of analog signals and converting them to a digital value. The digital value is then transmitted, upon request, over a single wire bus. The accuracy of the analog to digital conversion circuitry can be calibrated via trim codes stored in an onboard EPROM.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
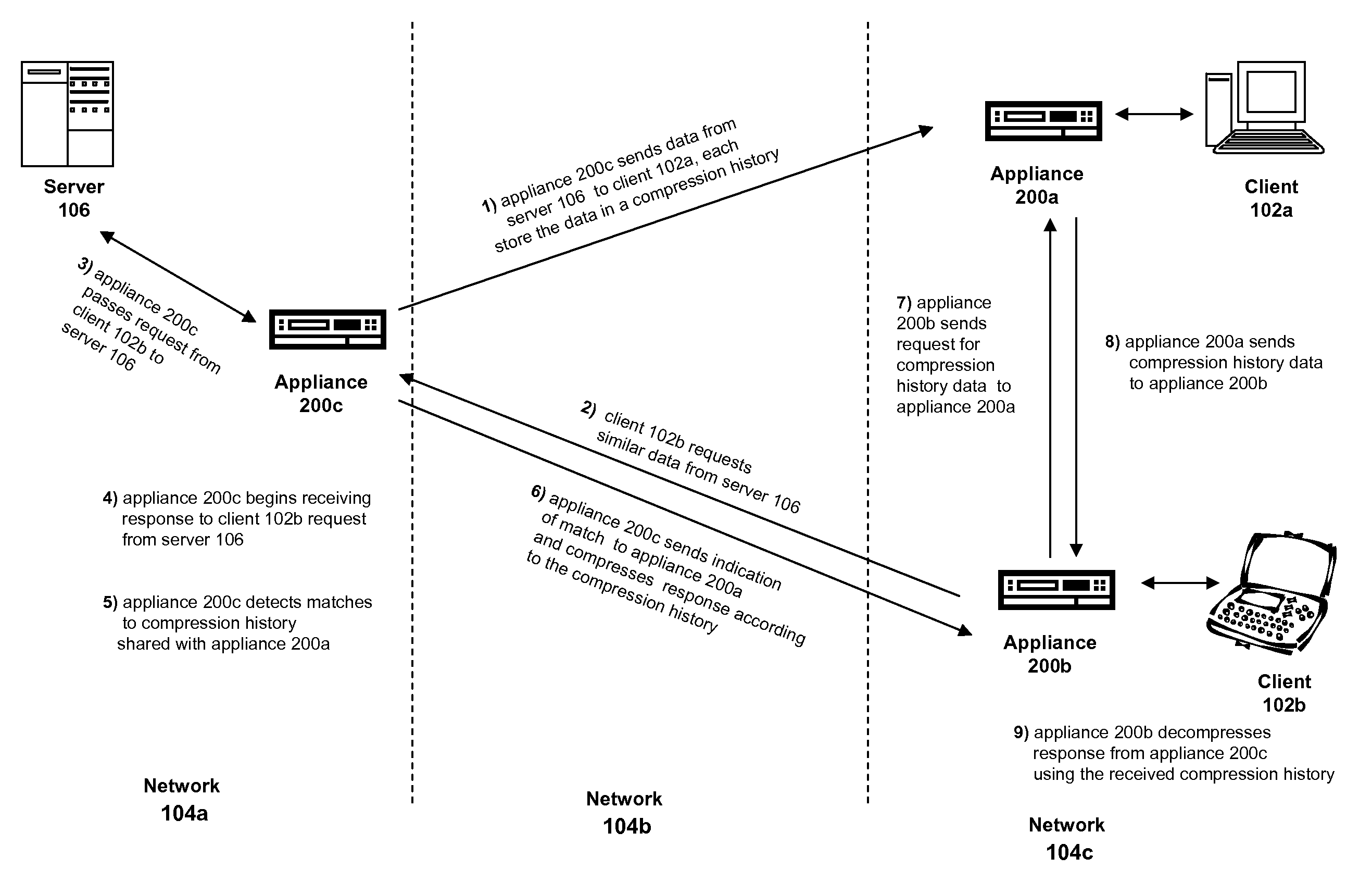
Systems and methods for sharing compression histories between multiple devices
ActiveUS7532134B2Improve compression efficiently and speedIncrease the lengthElectric signal transmission systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionApplication specificParsing
Systems and methods of storing previously transmitted data and using it to reduce bandwidth usage and accelerate future communications are described. By using algorithms to identify long compression history matches, a network device may improve compression efficiently and speed. A network device may also use application specific parsing to improve the length and number of compression history matches. Further, by sharing compression histories and compression history indexes across multiple devices, devices can utilize data previously transmitted to other devices to compress network traffic. Any combination of the systems and methods may be used to efficiently find long matches to stored data, synchronize the storage of previously sent data, and share previously sent data among one or more other devices.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
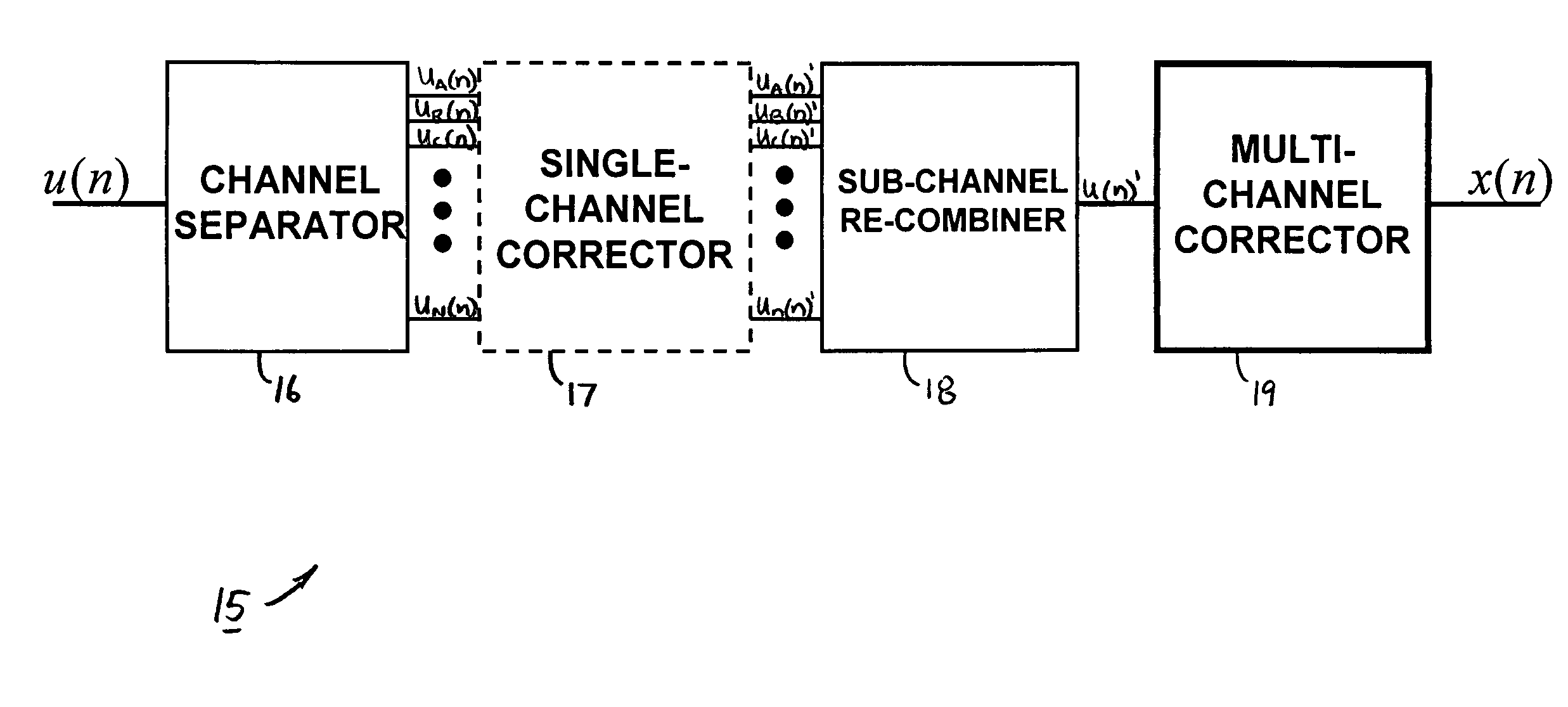
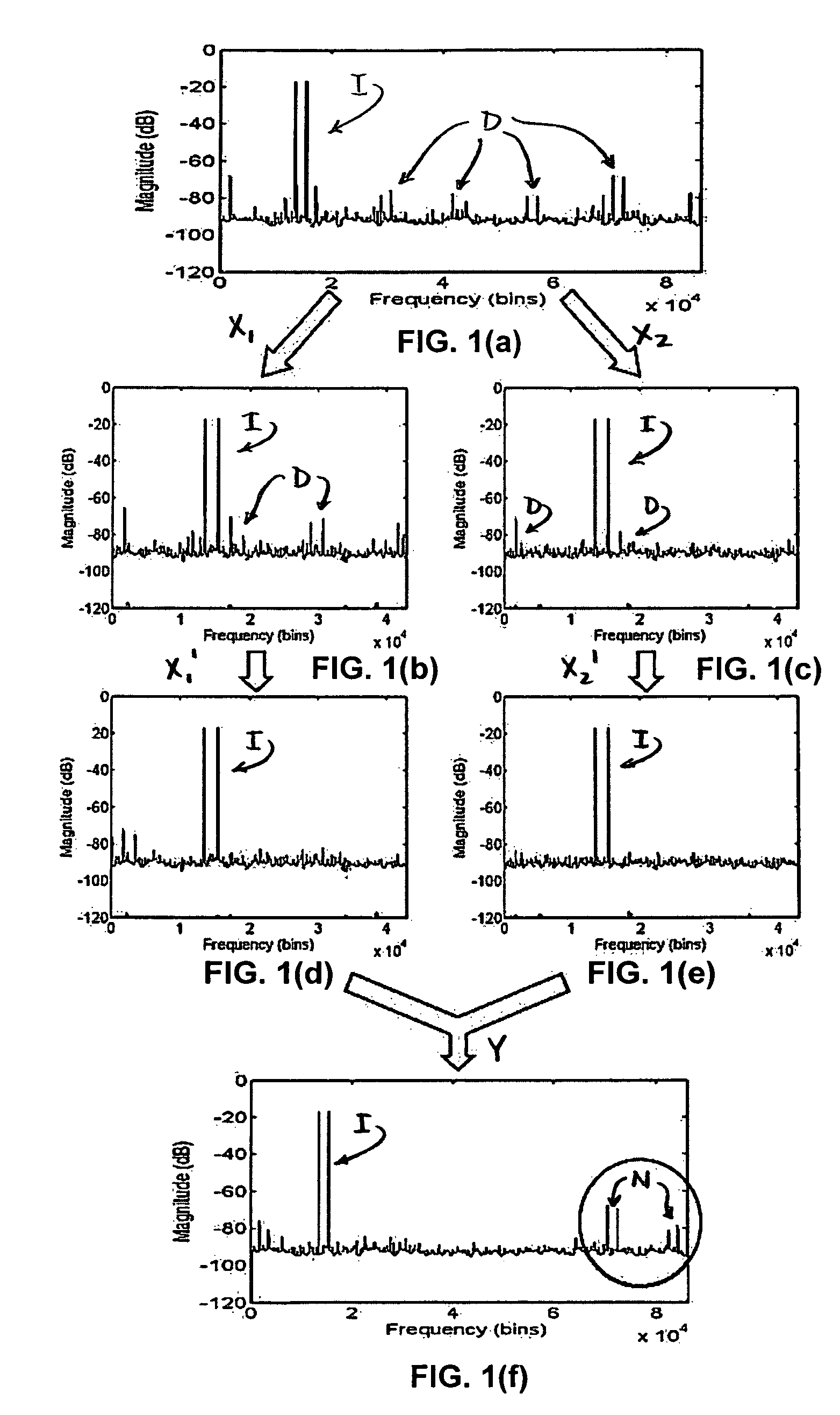
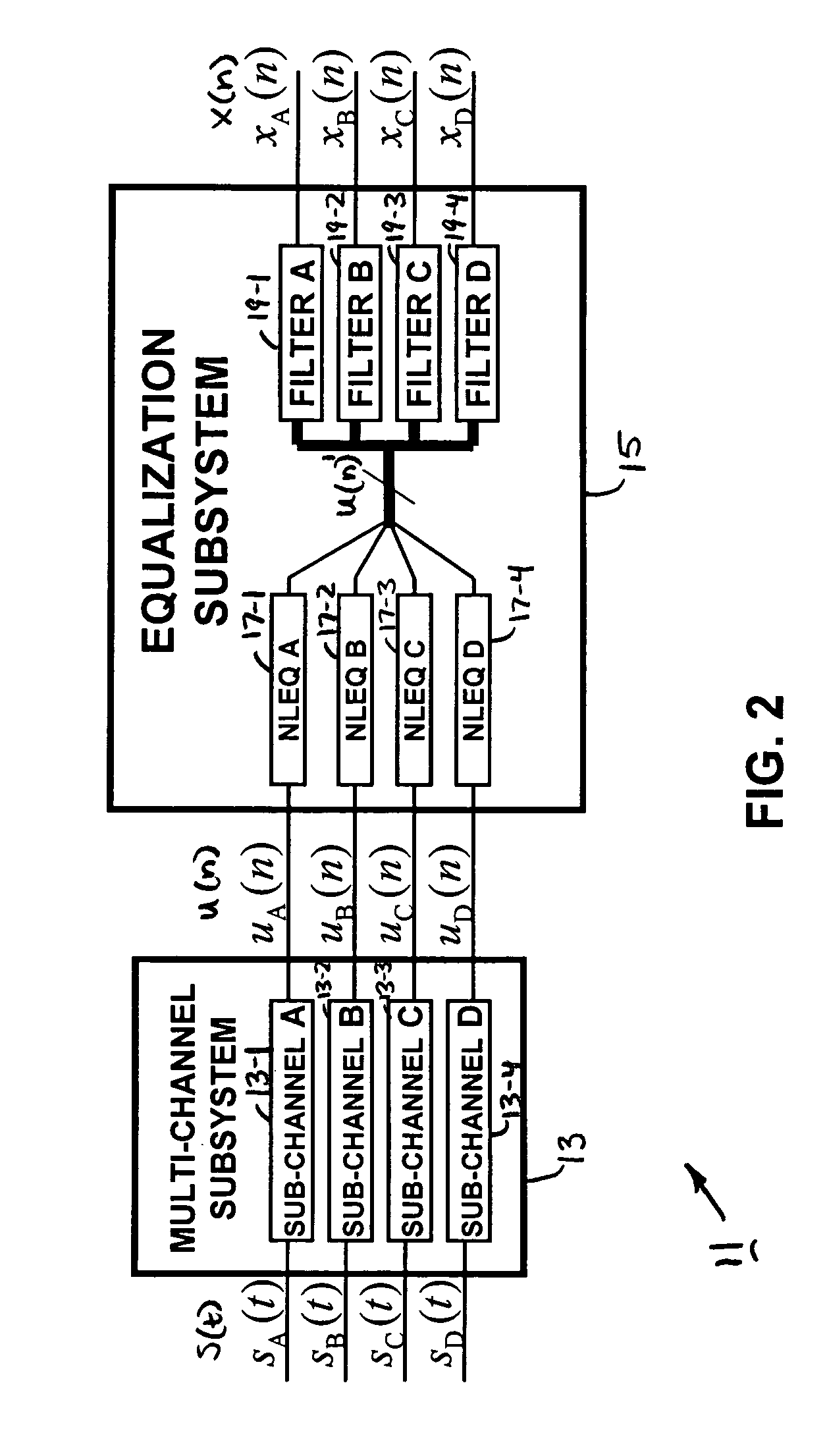
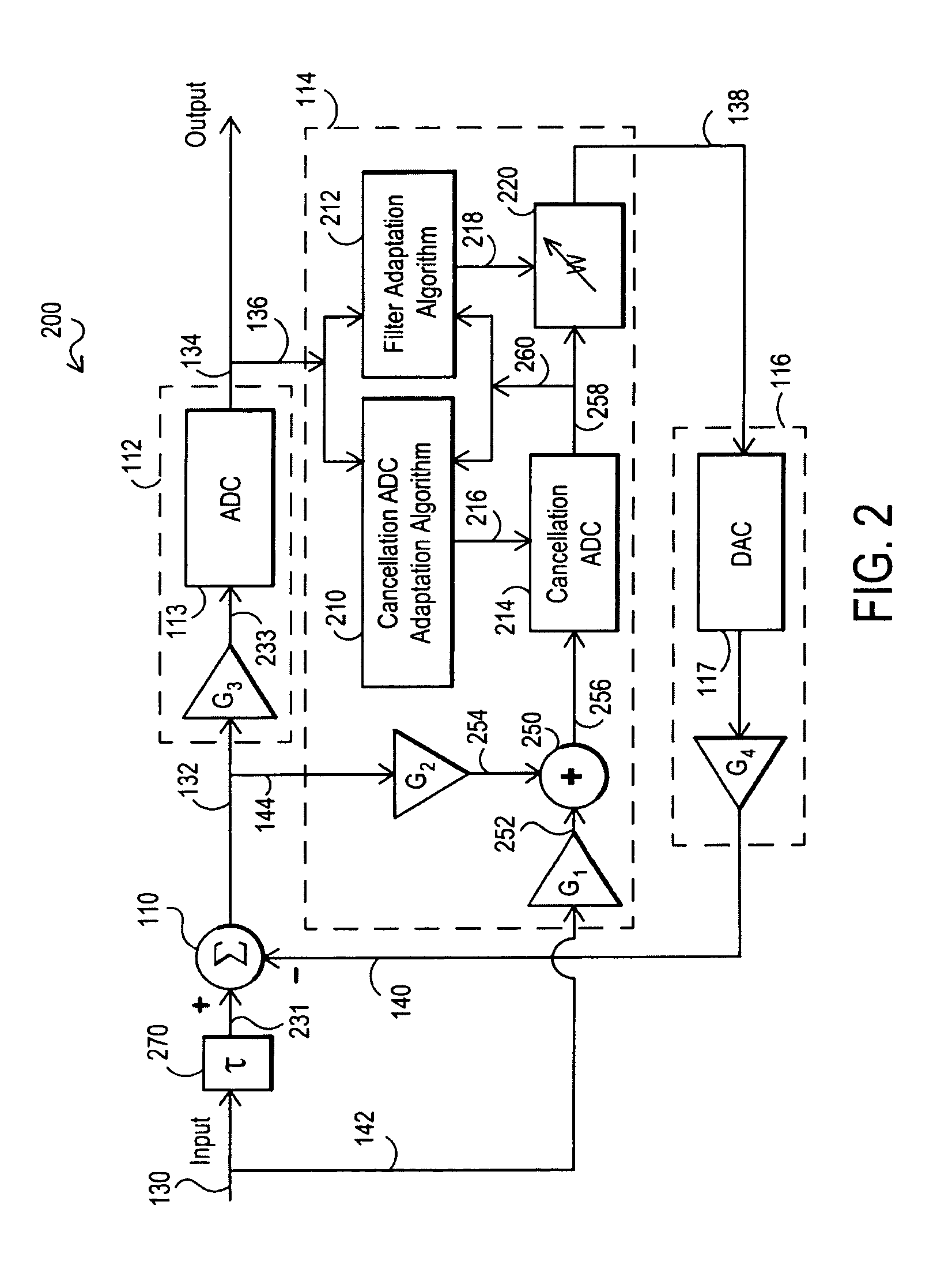
System and method of multi-channel signal calibration
InactiveUS7796068B2Electric signal transmission systemsPhysical parameters compensation/preventionSignal processingDistortion
A signal processing system for reducing calibration-related distortions in a complete-channel signal generated by a multi-channel subsystem, such as an interleaved ADC, includes a channel separator for separating the distorted digital signal into its various sub-channels and a single-channel corrector for independently processing each sub-channel to reduce distortion products present therein. The system additionally includes a subchannel re-combiner for combining the plurality of sub-channels processed by the single-channel corrector and a multi-channel corrector for calibrating each of plurality of sub-channels relative to one another to yield an equalized, complete-channel output signal. The multi-channel corrector includes a bank of optimized filters, each filter being assigned to a corresponding sub-channel of the complete-channel signal. In one embodiment, one of the plurality of sub-channels is selected as an ideal reference signal and the filters assigned to the remaining sub-channels are optimized to yield outputs which match the ideal reference signal.
Owner:RAZ GIL M
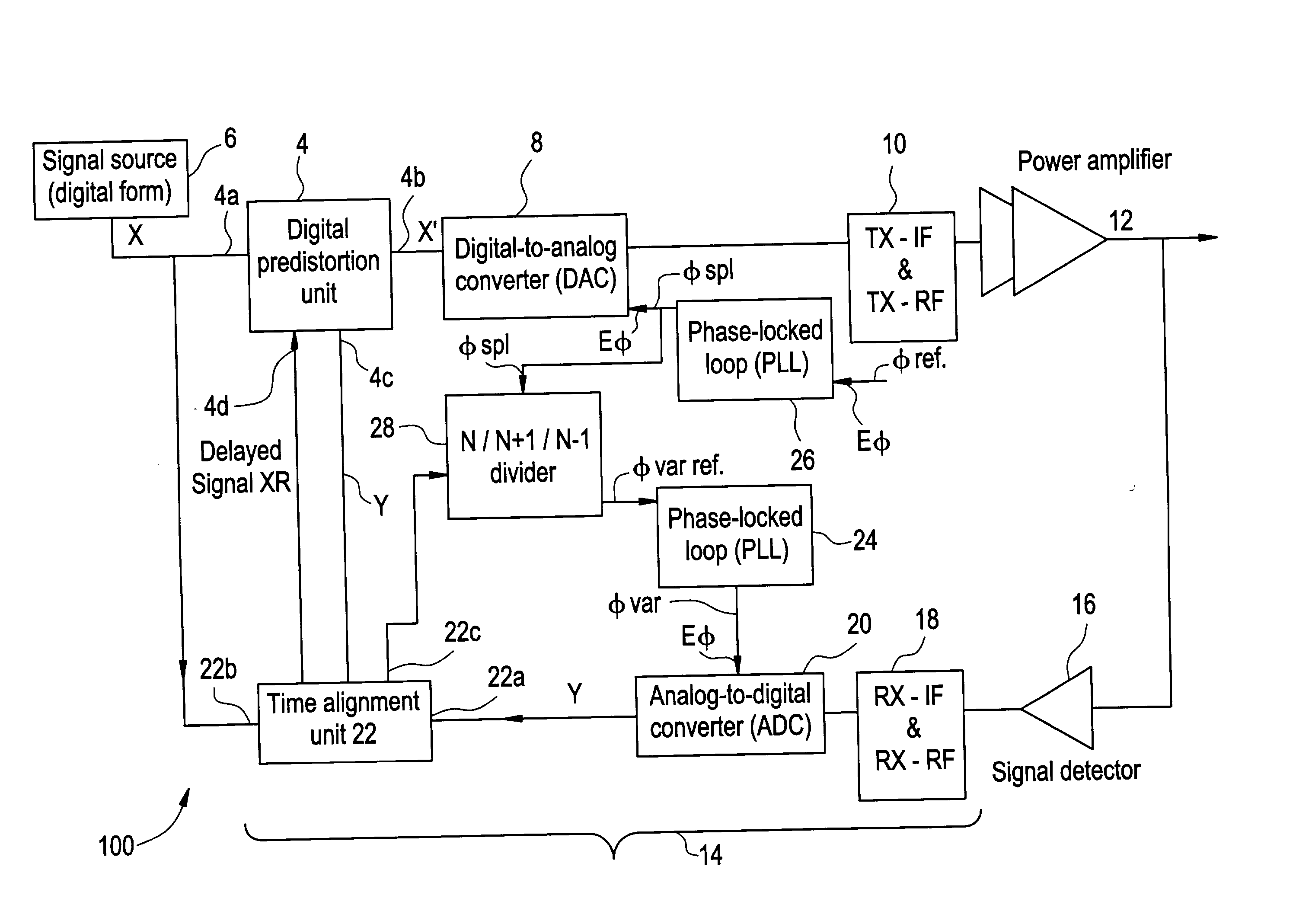
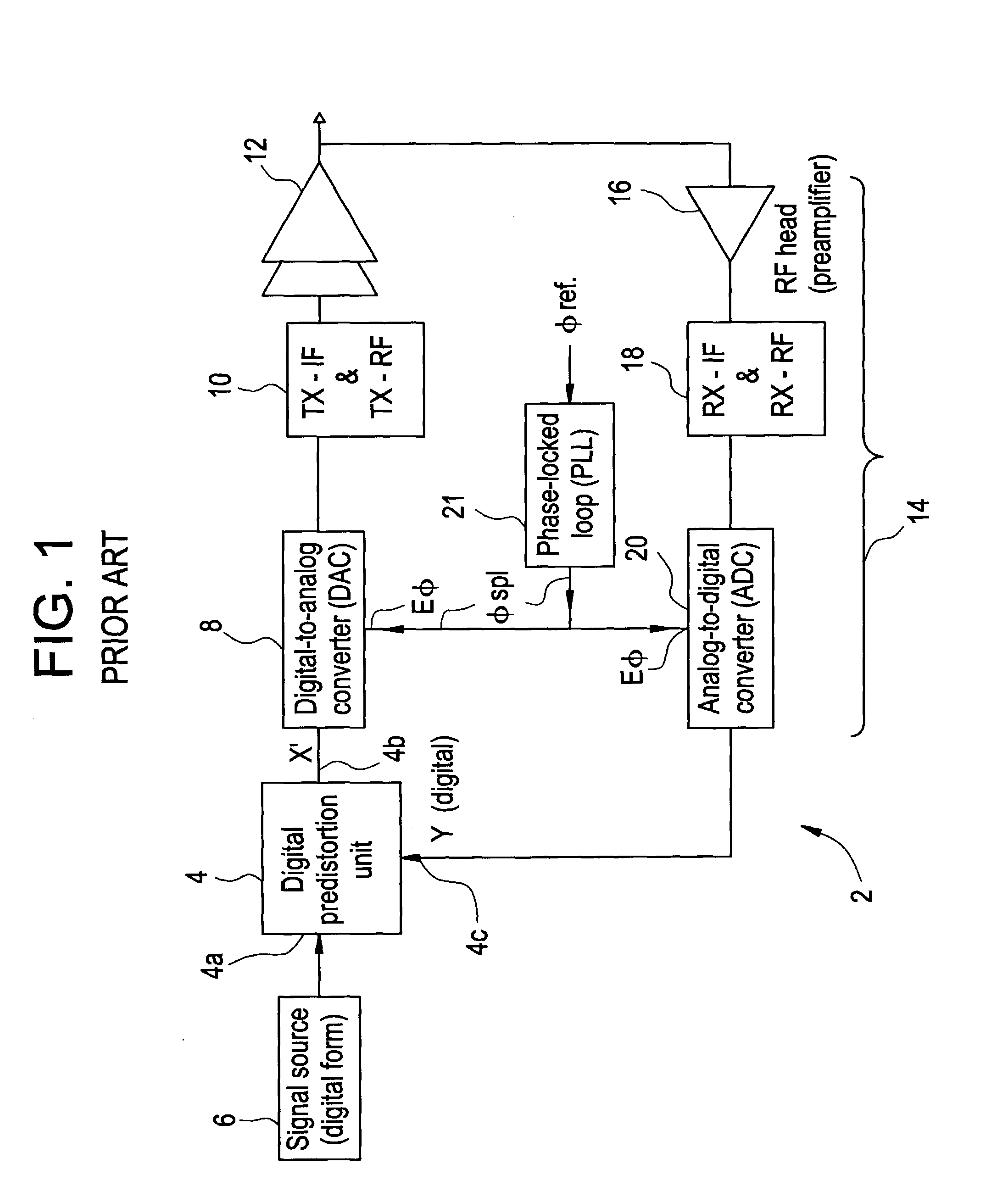
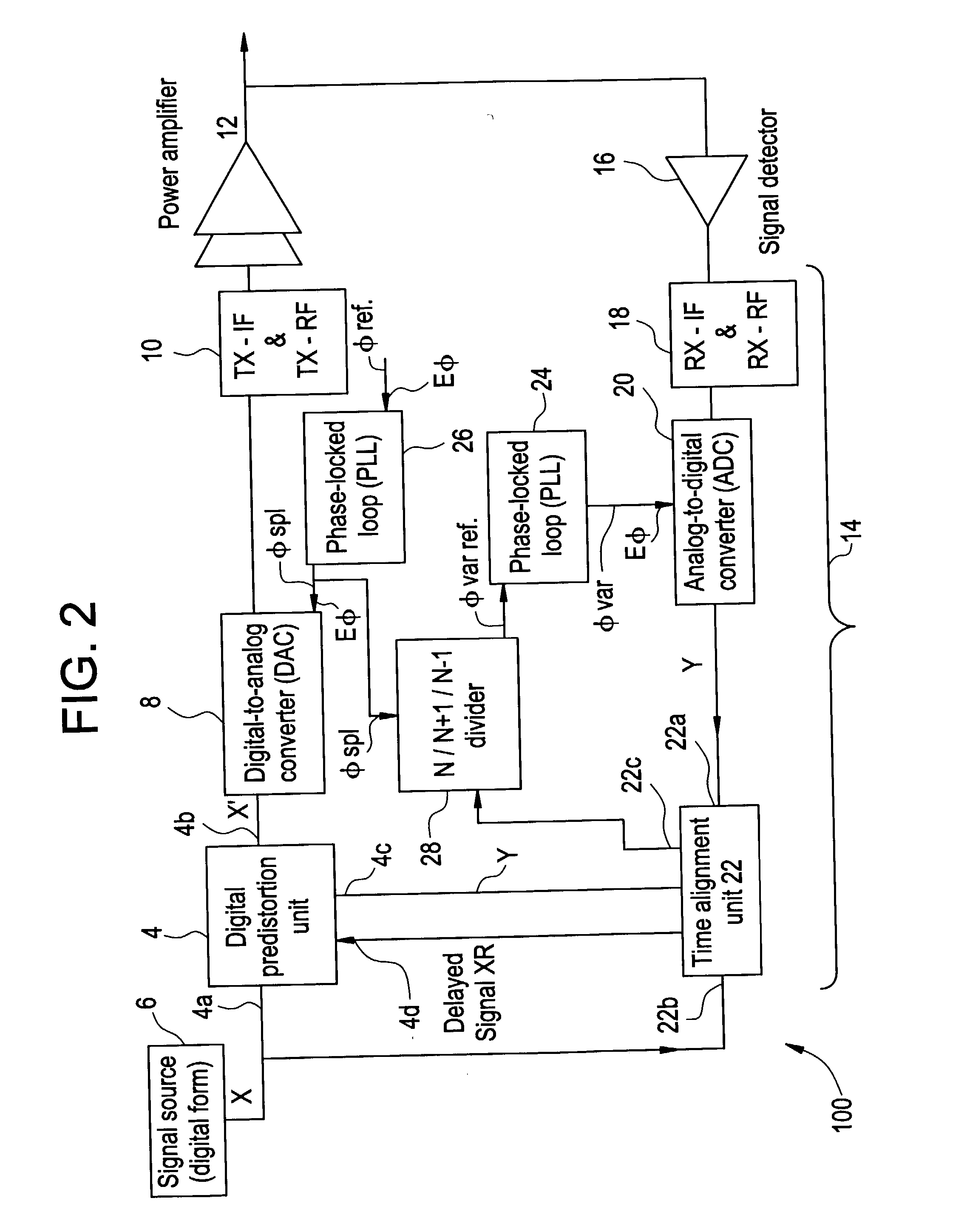
Method and apparatus for preparing signals to be compared to establish predistortion at the input of an amplifier
InactiveUS20030156658A1Improve electricity efficiencyImprove performance efficiencyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsAudio power amplifierUnit of time
The invention relates to a method of preparing signals (X and Y) to be compared to establish predistortion at the input of an amplifier (12), the signals comprising a signal (X) before amplification and a signal (Y) after amplification by said amplifier. Preparation includes time aligning (22) the signal before amplification (X) with the signal after amplification (Y) before using them to establish said predistortion. The invention preferably operates in two stages, namely a stage of coarse time alignment, in which the signal before amplification (X) is subjected to a time delay comprising an integer number of first time units, and a stage of fine time alignment, in which a delay or advance value of a fraction of the first time unit is determined.
Owner:EVOLIUM
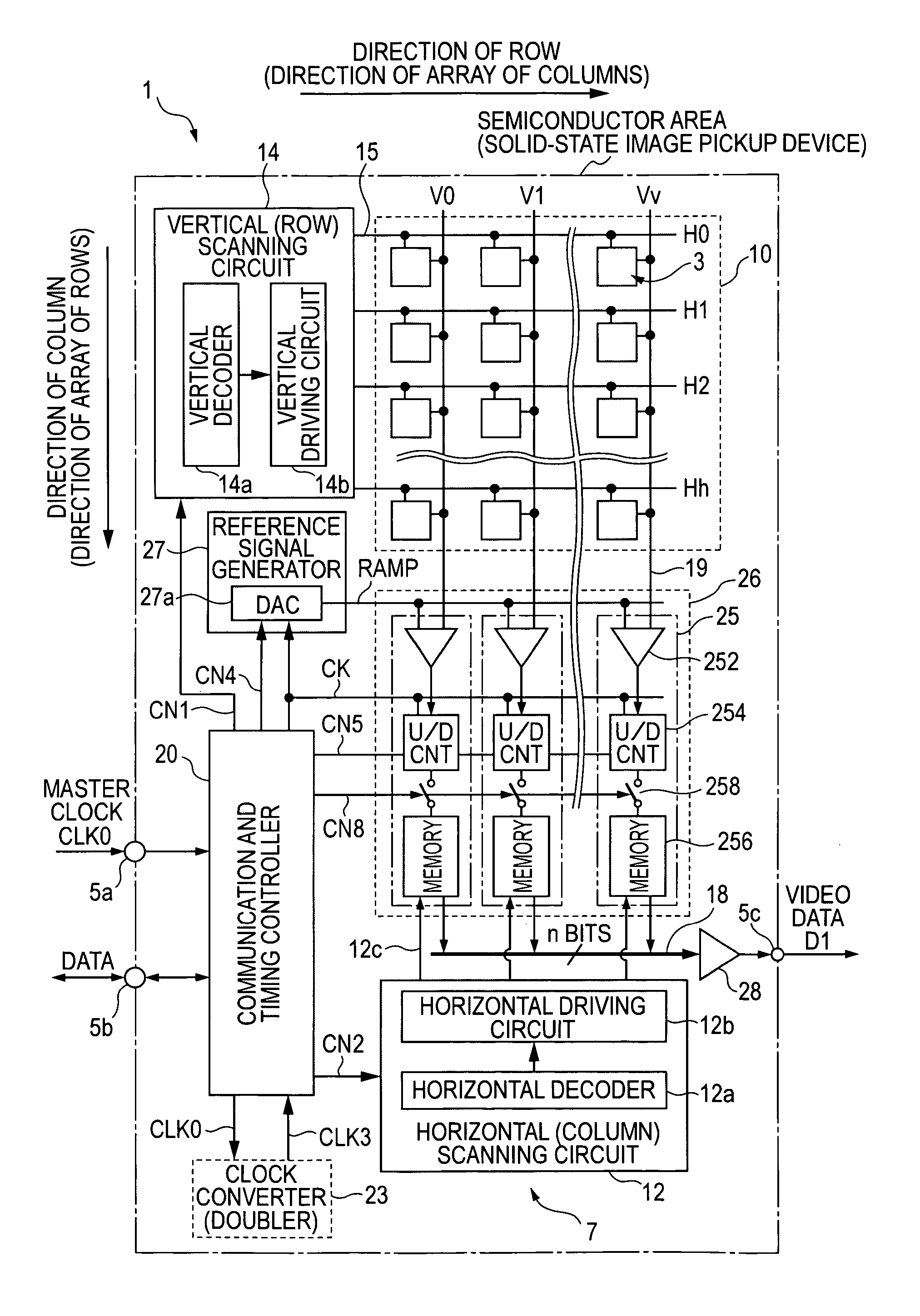
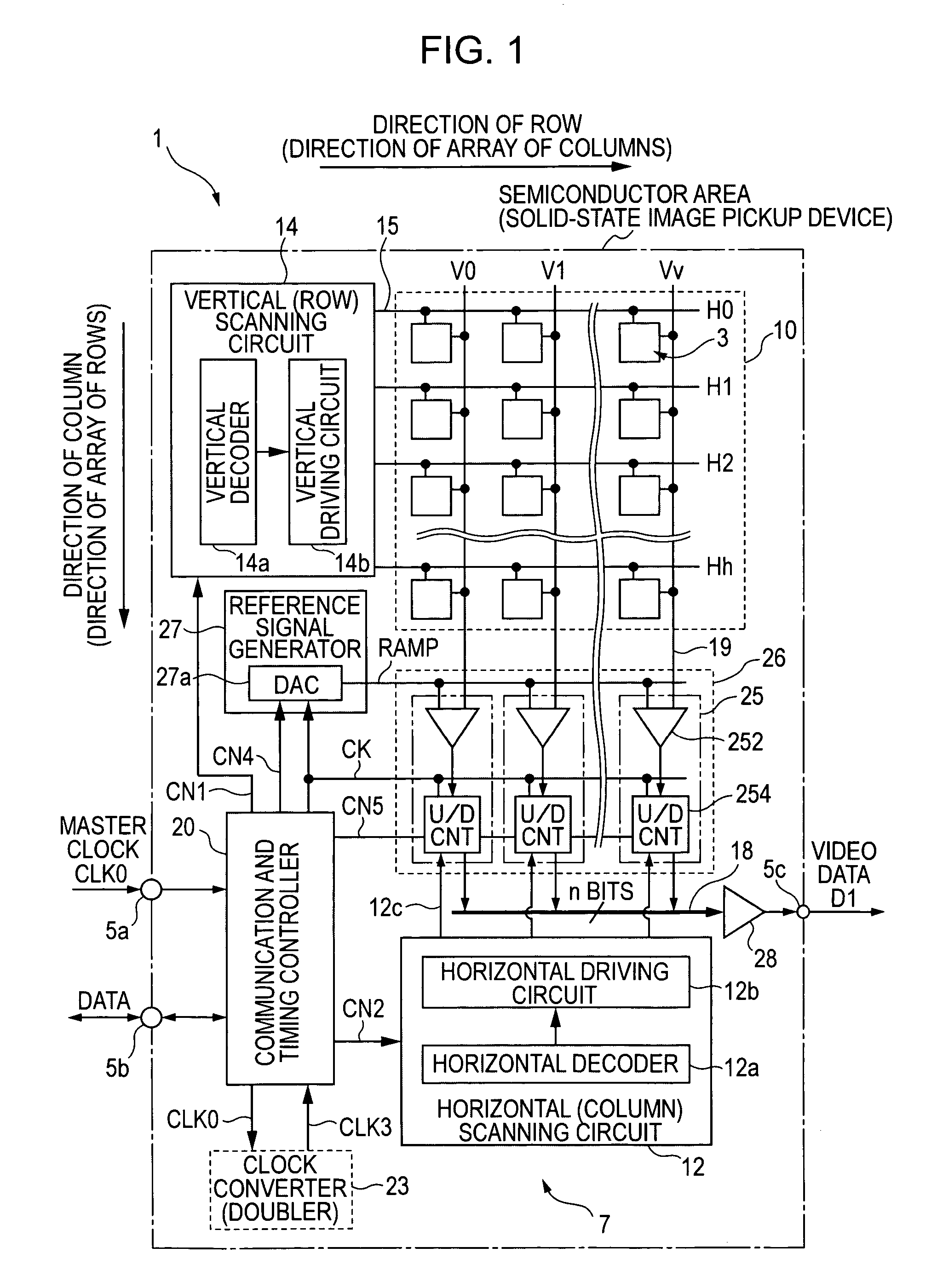
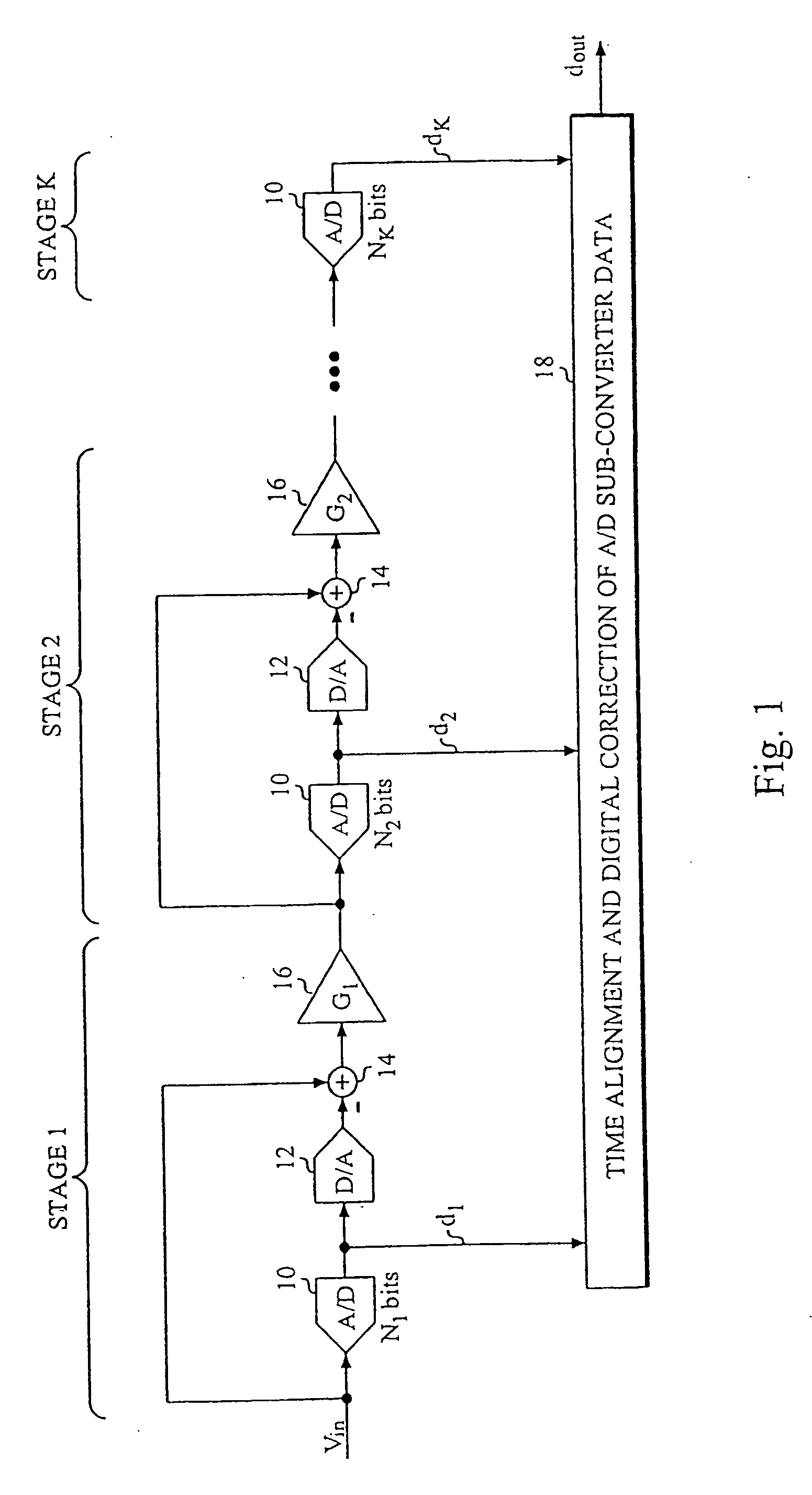
Method and apparatus for AD conversion, semiconductor device for detecting distribution of physical quantity, and electronic apparatus
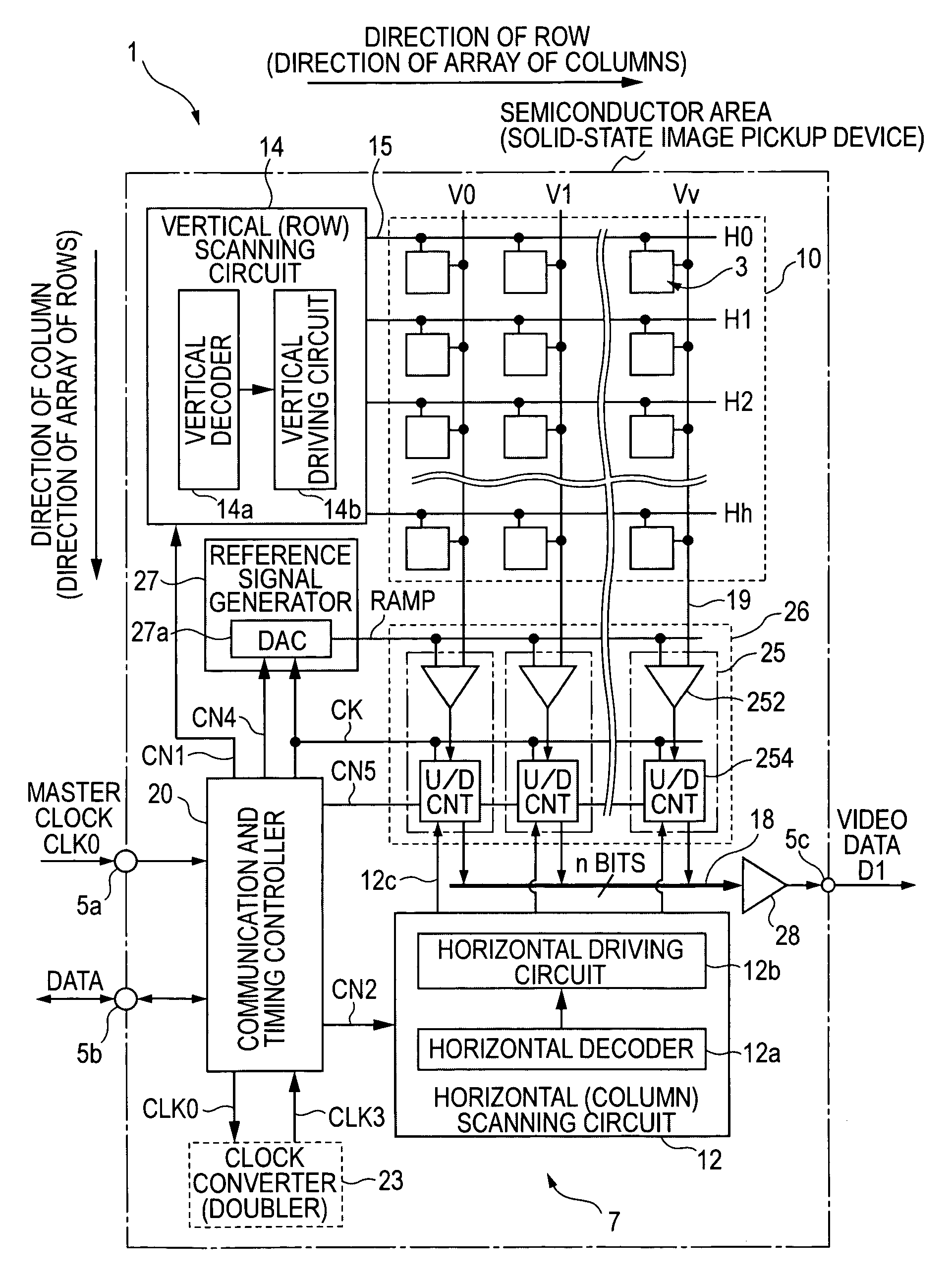
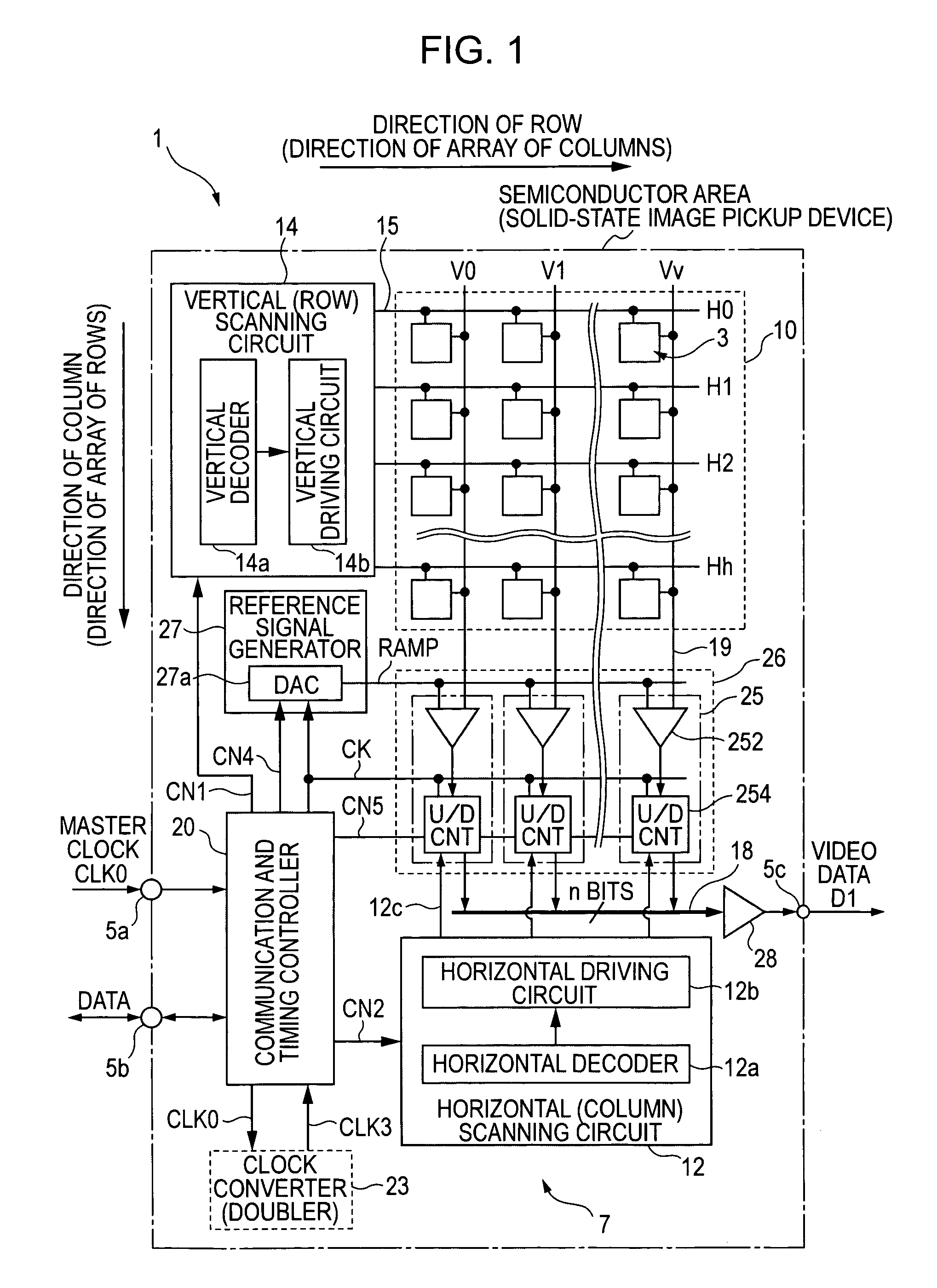
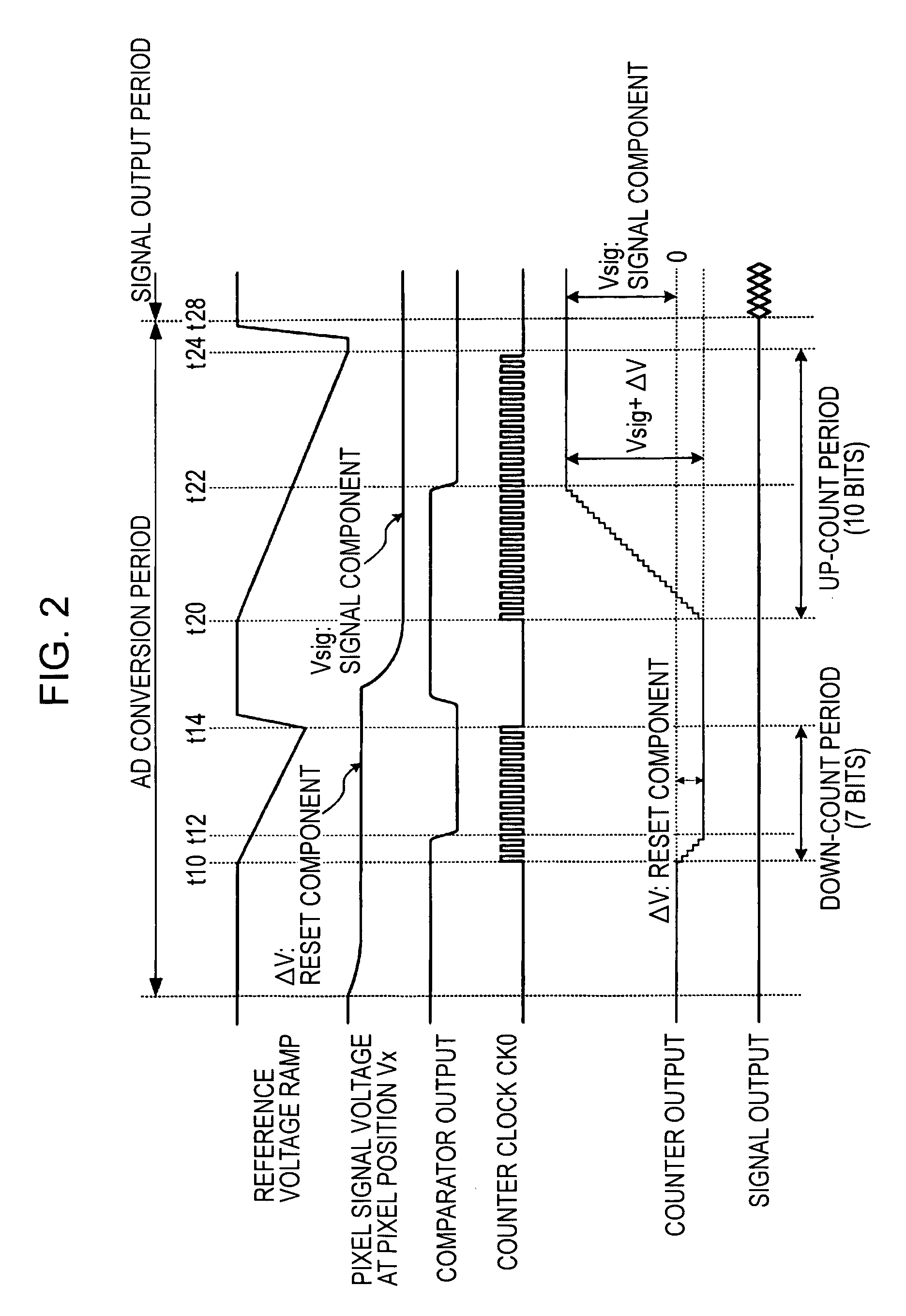
ActiveUS7129883B2Small amountA large amountTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsDevice materialControl signal
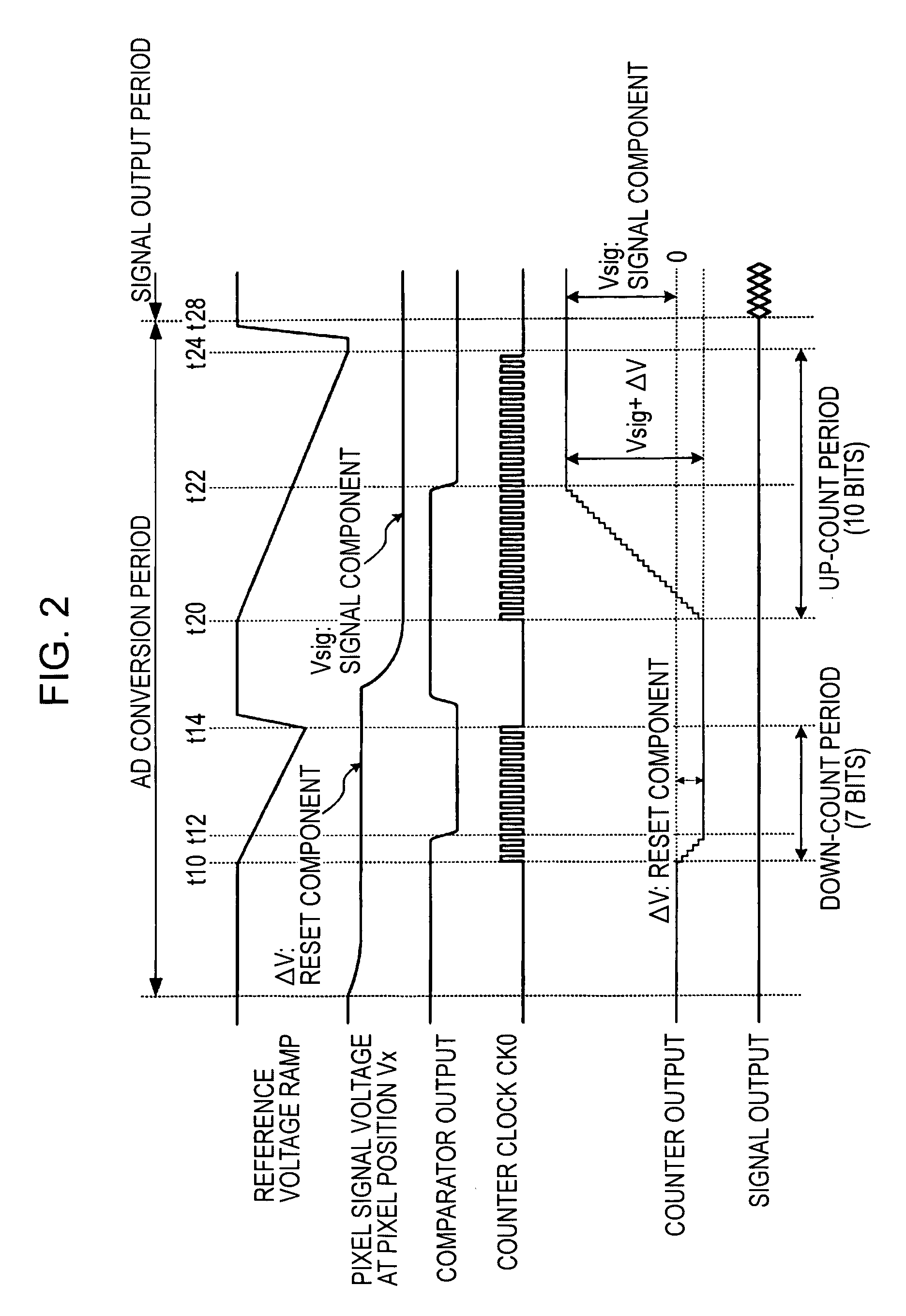
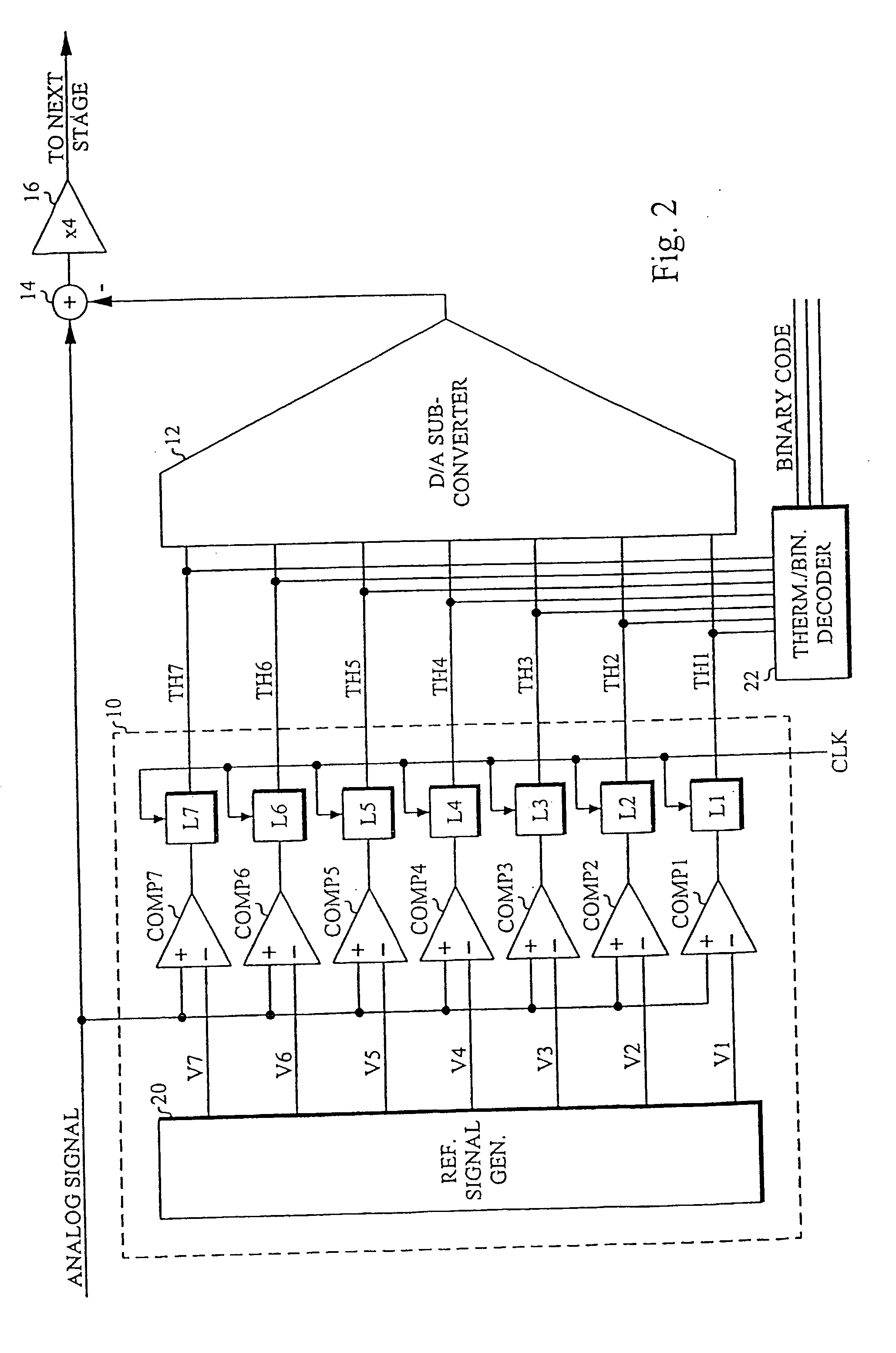
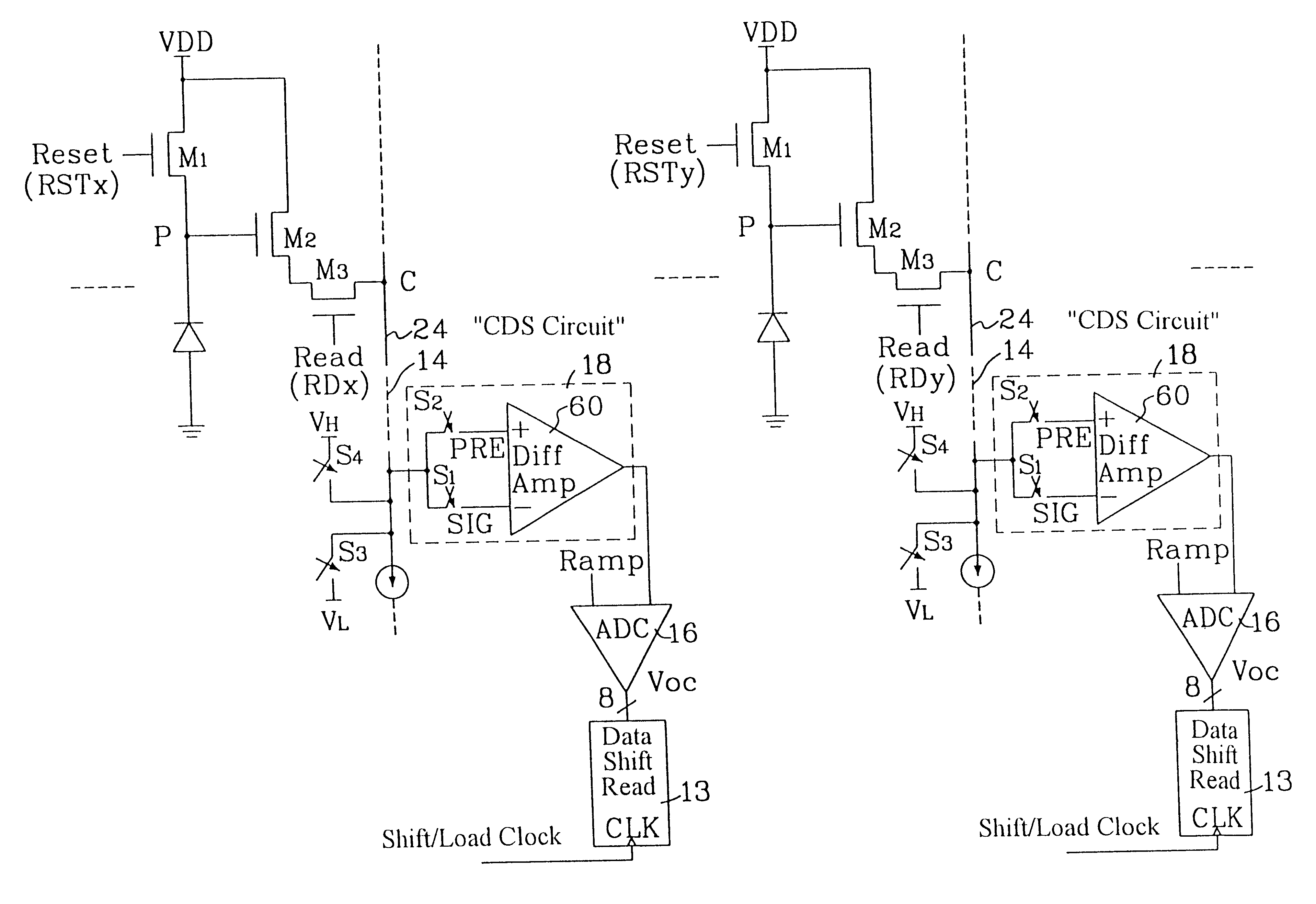
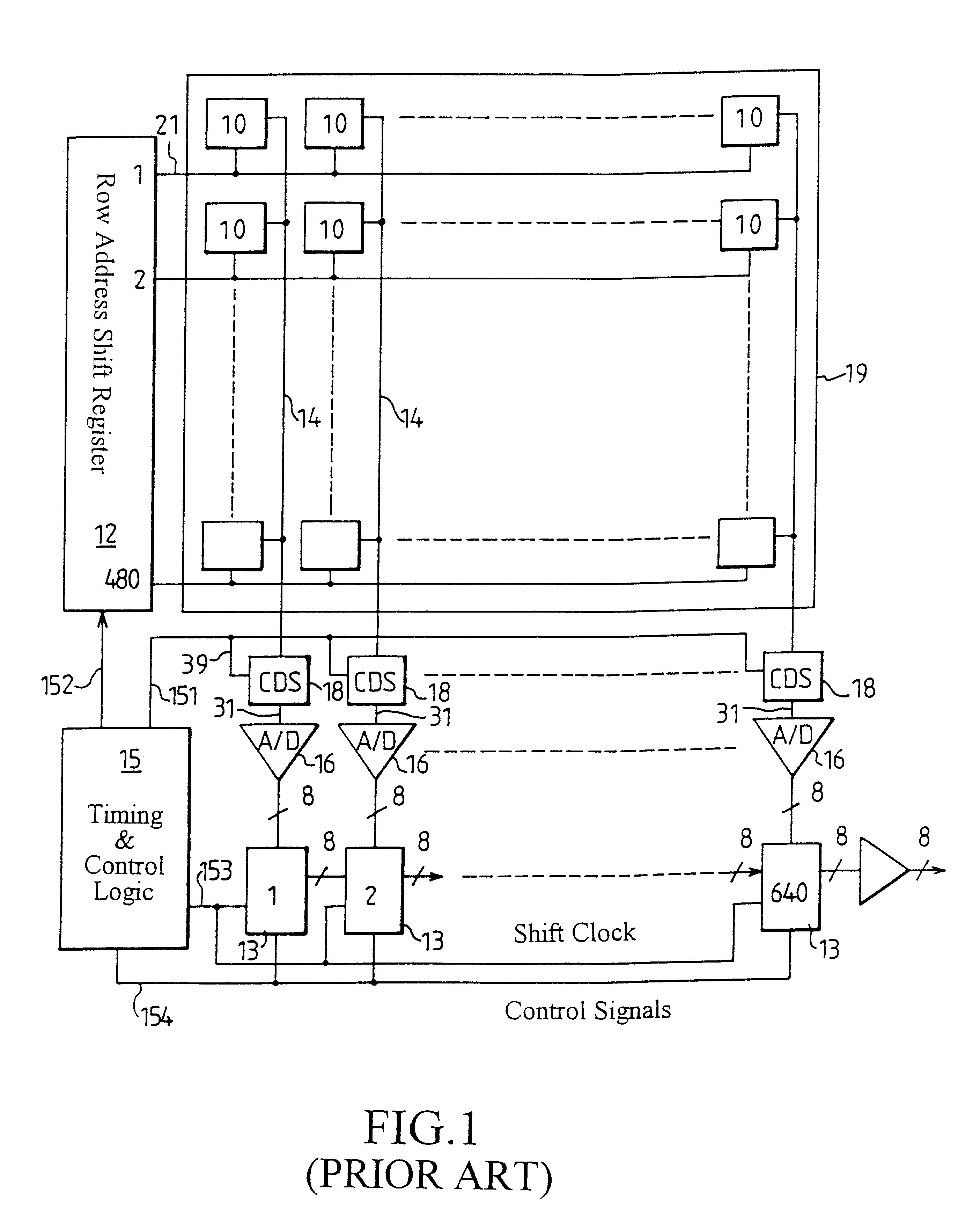
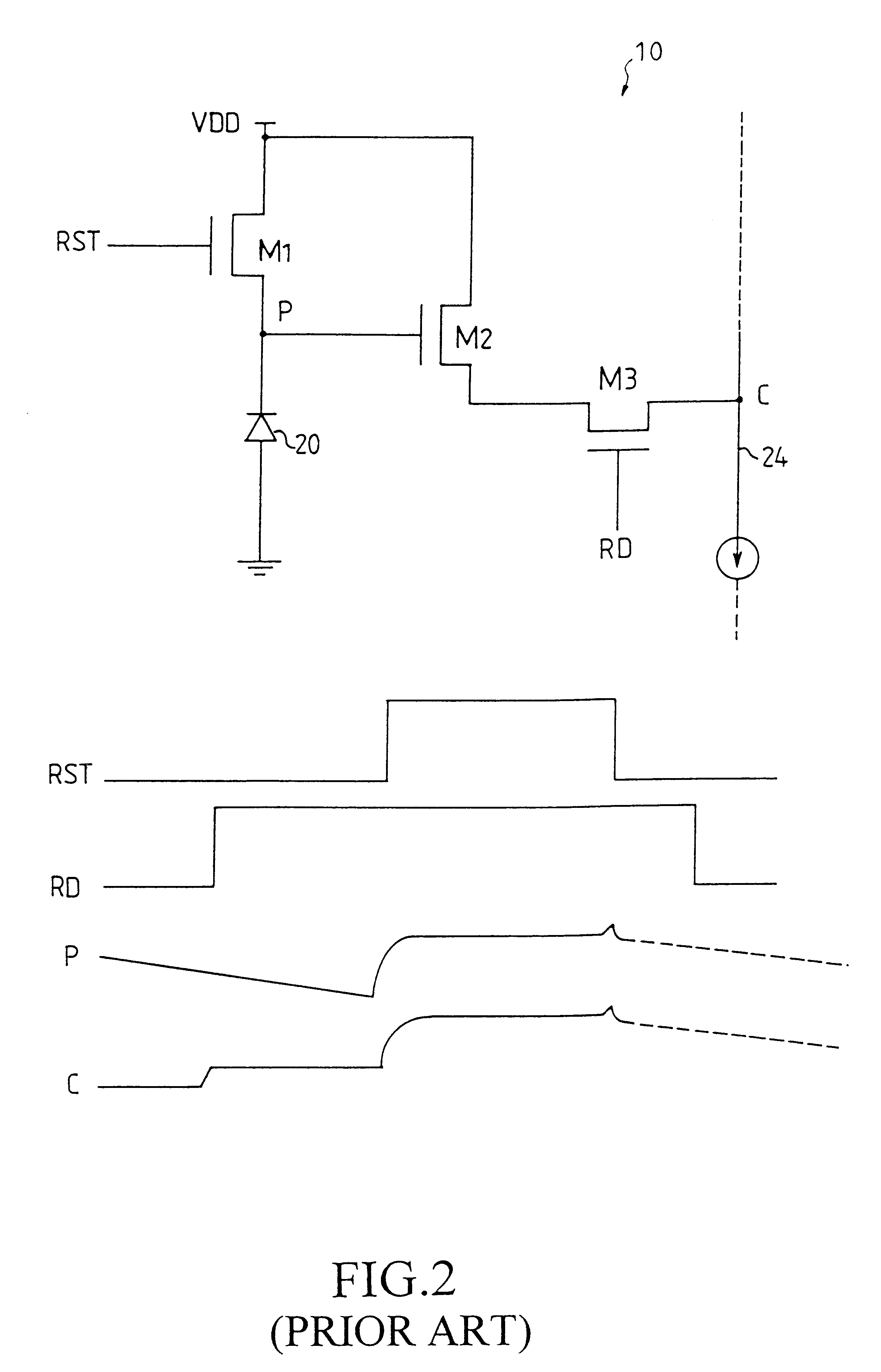
A column analog-to-digital converter having a voltage comparator and a counter is arranged for each a vertical signal line. The voltage comparator compares a pixel signal inputted via the vertical signal line at each row control signal line with a reference voltage, thereby generating a pulse signal having a length in time axis corresponding to the magnitude of a reset component and a signal component. The counter counts a clock to measure the width of the pulse signal until the end of the comparison operation of the comparator, and stores a count at the end of the comparison. A communication and timing controller controls the voltage comparator and the counter so that, in a first process, the voltage comparator performs a comparison operation on a reset component with the counter performing a down-counting operation, and so that, in a second process, the voltage controller performs the comparison operation on a signal component with the counter performing an up-counting operation.
Owner:SONY CORP
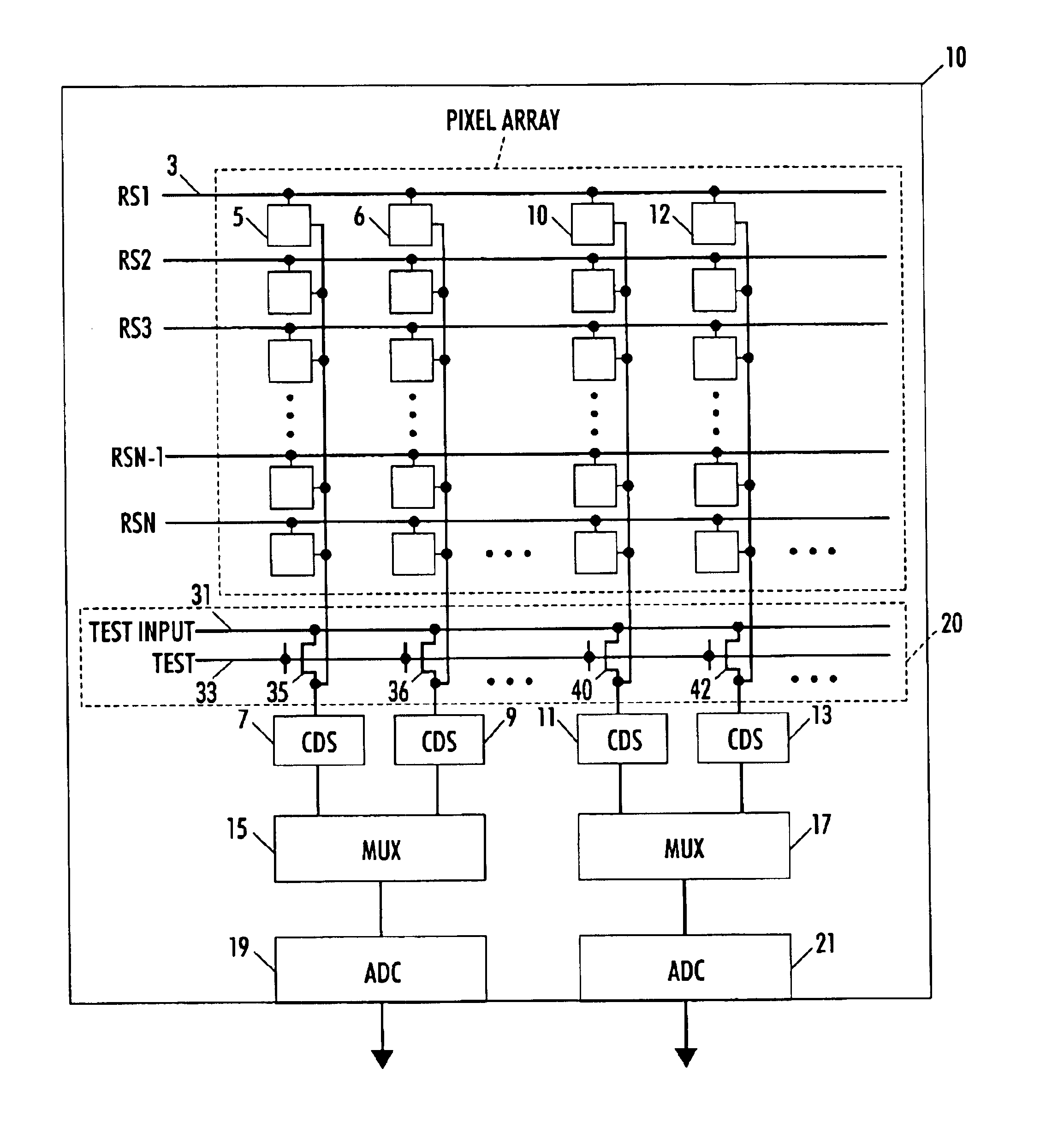
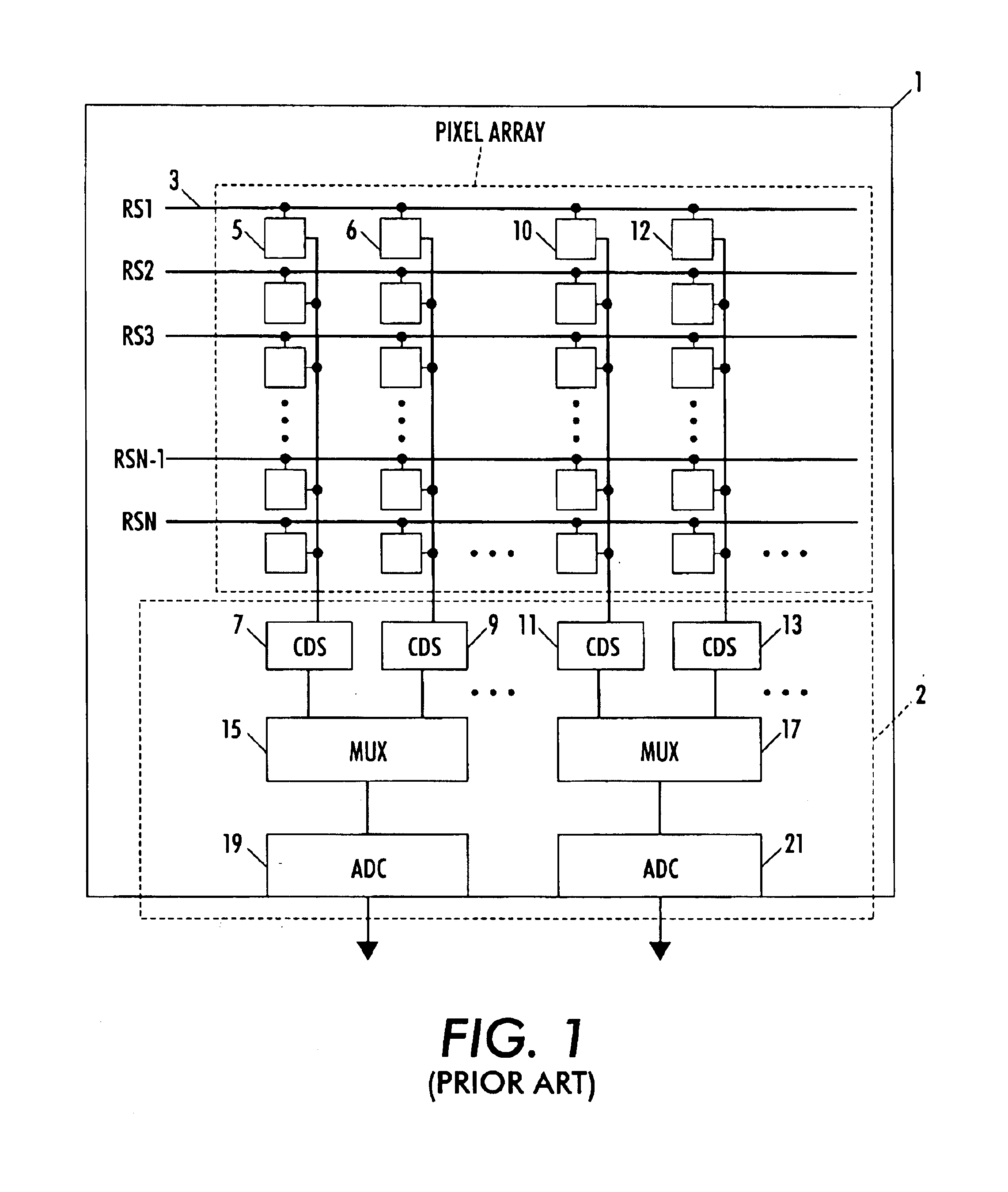
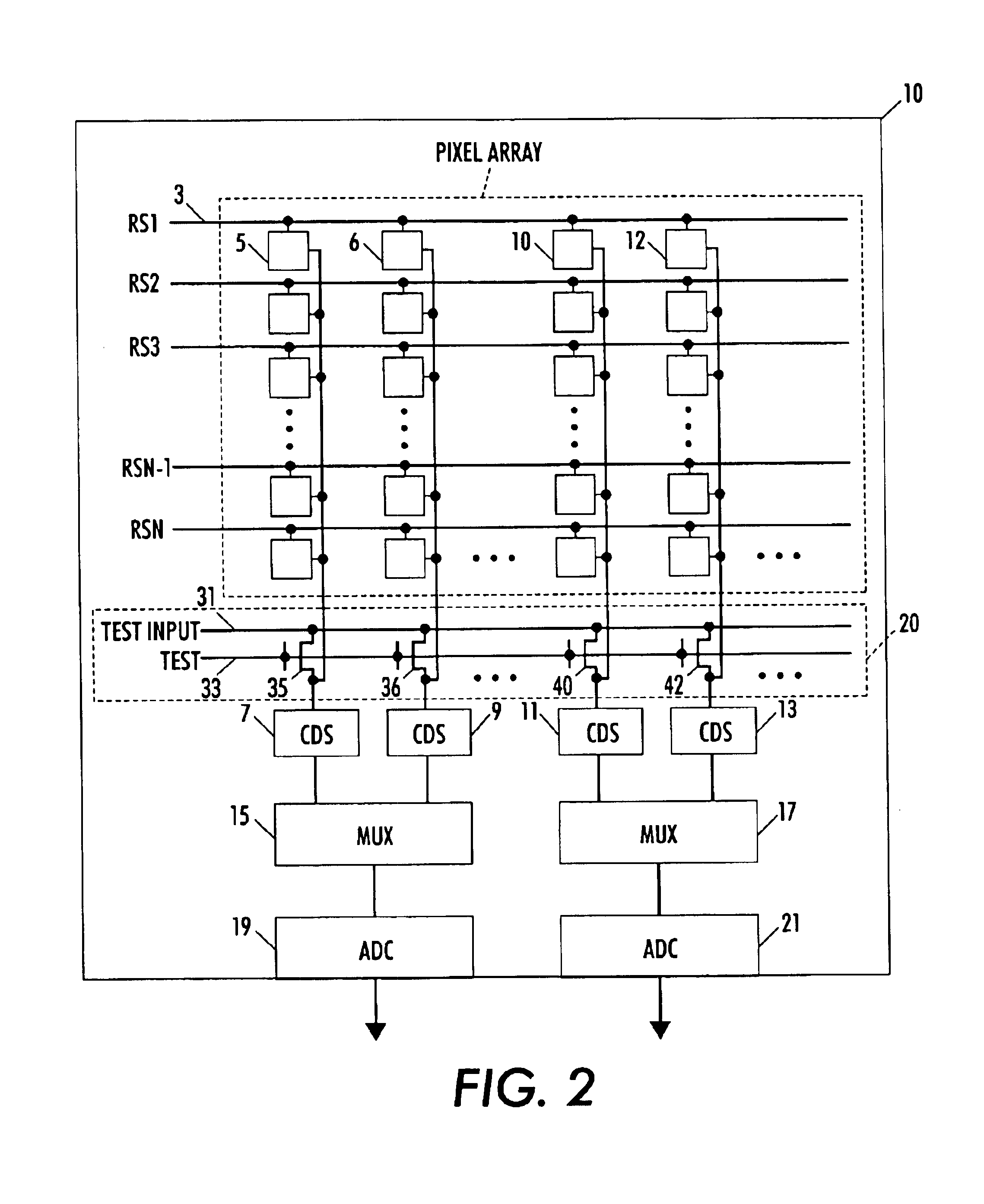
Circuit and method for cancellation of column pattern noise in CMOS imagers
ActiveUS6903670B1Corrects non-linearityCompensating for such errorTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsSignal processing circuitsAudio power amplifier
A circuit and method measure the output voltage of a CMOS pixel in a manner that substantially reduces all columnar pattern noise due to mismatches in the signal processing circuits including the correlated double sampling amplifiers and A / D converters. The circuit includes a test switch, operatively connected between a reference voltage source and a correlated double sampling amplifier, for applying a test voltage from the reference voltage source when the state of the test switch is ON to the correlated double sampling amplifier. The reference voltage source produces a voltage corresponding to a full-scale voltage level to enable the determination of a gain error in the correlated double sampling amplifier and / or A / D converter; a voltage corresponding to ground to enable the determination of an offset error in the correlated double sampling amplifier and / or A / D converter; and a plurality of analog voltages ranging from analog ground to a full-scale voltage level to enable the determination of non-linearity errors in the A / D converter.
Owner:SMAL CAMERA TECH
Method and apparatus for AD conversion, semiconductor device for detecting distribution of physical quantity, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20050206548A1Increase blockingEliminate needTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsControl signalDevice material
A column analog-to-digital converter having a voltage comparator and a counter is arranged for each a vertical signal line. The voltage comparator compares a pixel signal inputted via the vertical signal line at each row control signal line with a reference voltage, thereby generating a pulse signal having a length in time axis corresponding to the magnitude of a reset component and a signal component. The counter counts a clock to measure the width of the pulse signal until the end of the comparison operation of the comparator, and stores a count at the end of the comparison. A communication and timing controller controls the voltage comparator and the counter so that, in a first process, the voltage comparator performs a comparison operation on a reset component with the counter performing a down-counting operation, and so that, in a second process, the voltage controller performs the comparison operation on a signal component with the counter performing an up-counting operation.
Owner:SONY CORP
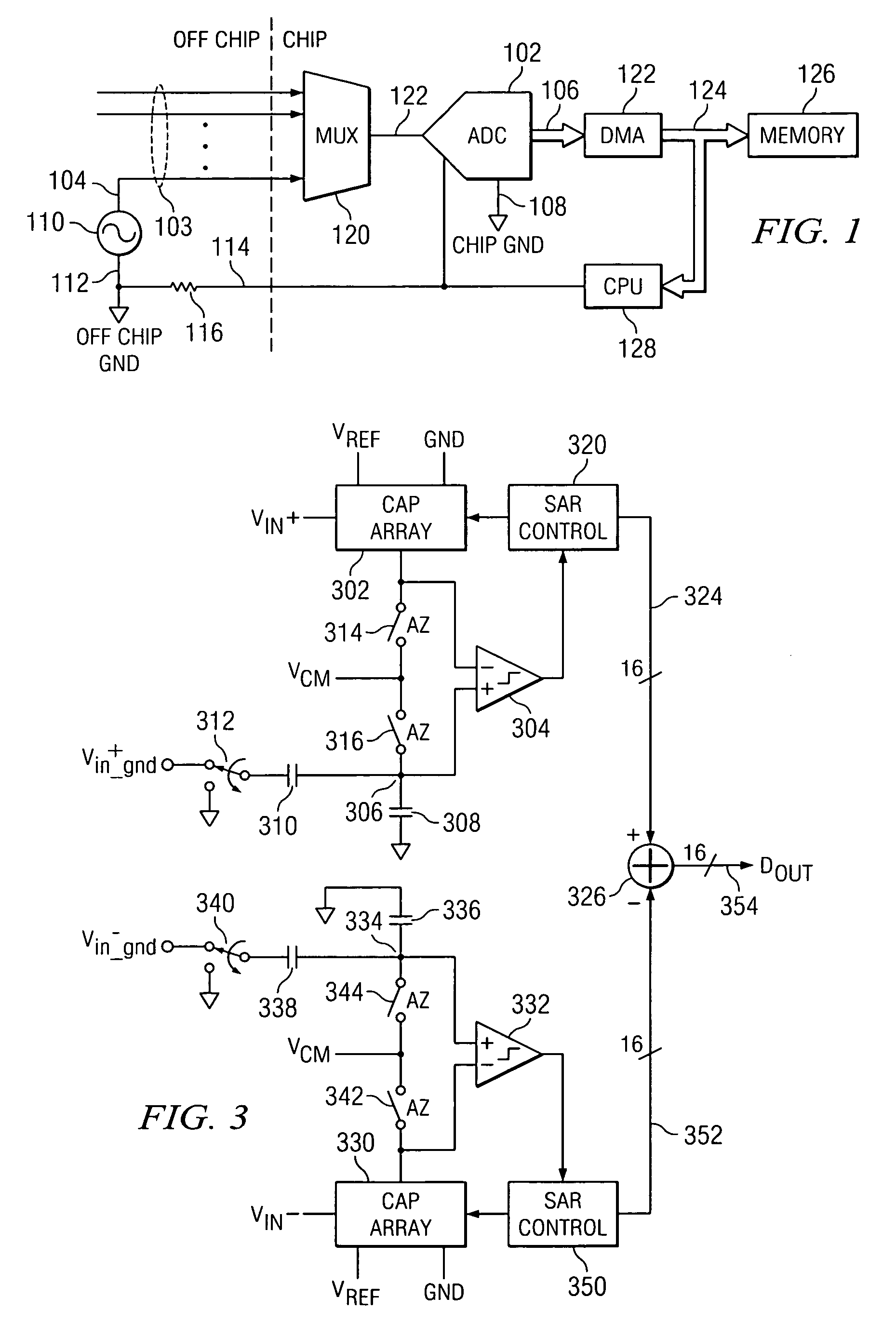
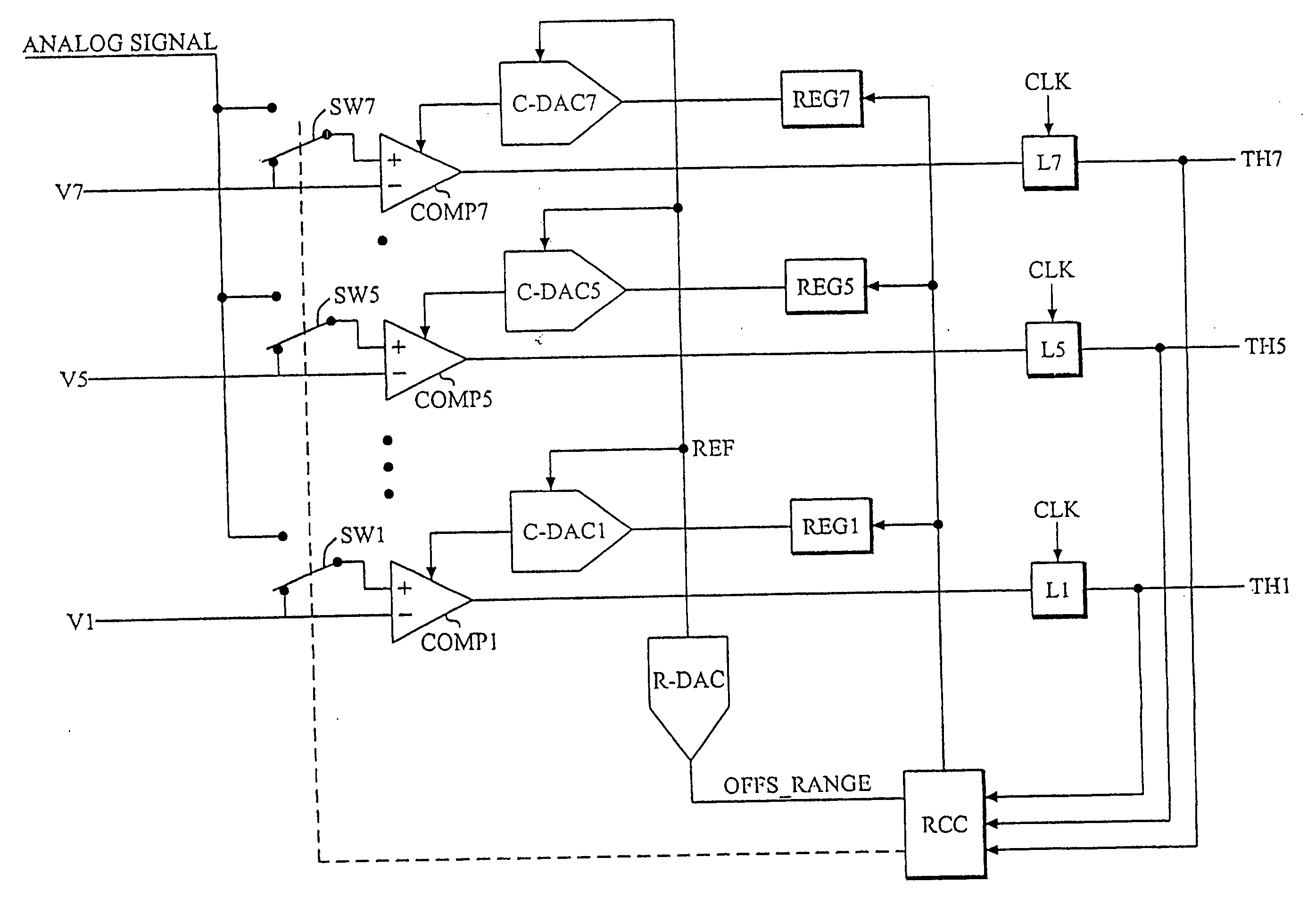
A/D converter calibration
InactiveUS6972701B2Increase profitImprove accuracyElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersA d converterComparator
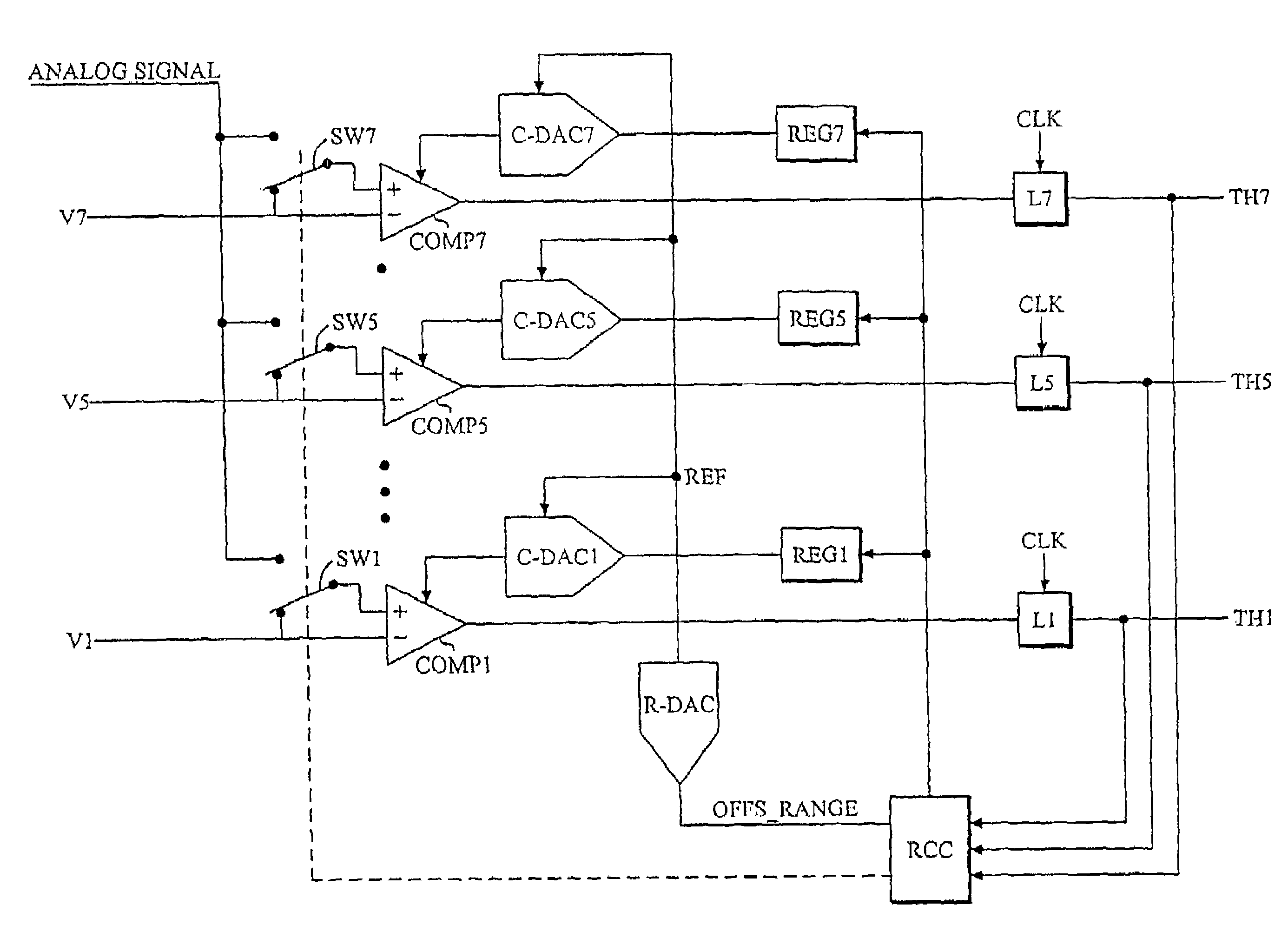
A D / A converter range calibration system in an A / D converter structure including a set of comparators with associated calibrating D / A converters includes means (RCC) for determining the offset error range for the entire set of comparators and means (R-DAC) for adjusting the dynamic range of each calibrating D / A converter to this offset error range.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
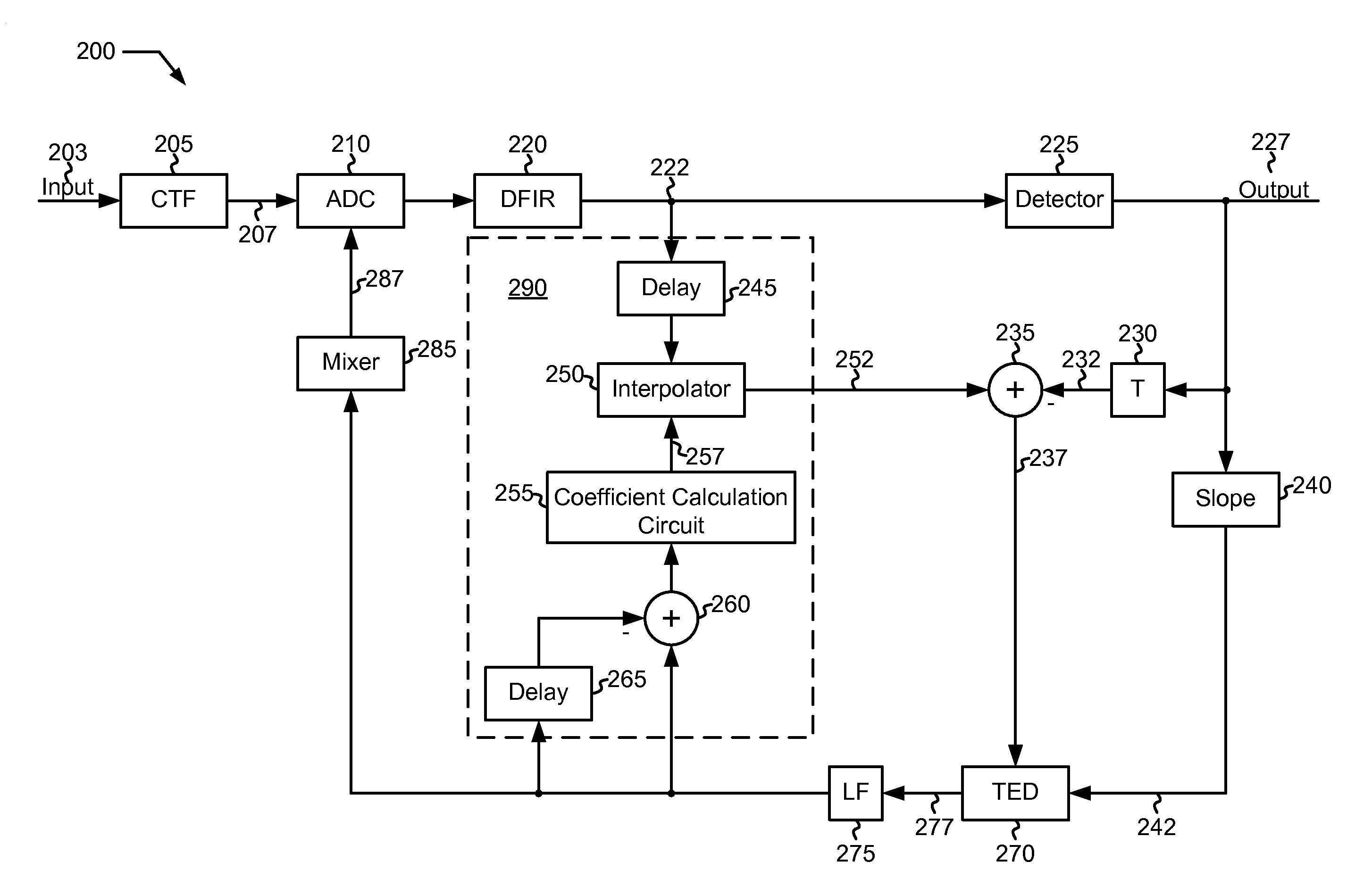
Systems and methods for mitigating latency in a data detector feedback loop
InactiveUS8018360B2Reduce latency impactLower latencyModification of read/write signalsElectric signal transmission systemsSampling instantData retrieval
Methods and systems for mitigating latency in a data detector feedback loop are included. For example, a method for reducing latency in an error corrected data retrieval system is included. The method includes performing an analog to digital conversion at a sampling instant to create a digital sample, and performing a data detection on the digital sample to create a detected output. The detected output is compared with the digital sample to determine a phase error. During an interim period, the digital sample is adjusted to reflect the phase error to create an adjusted digital sample. After the interim period, the sampling instant is adjusted to reflect the phase error.
Owner:LSI CORP +1
Method and apparatus for compressed sensing
InactiveUS7289049B1Electric signal transmission systemsCurrent/voltage measurementComputer scienceCompressed sensing
Embodiments of the present invention provide a method and apparatus for compressed sensing. The method generally comprises forming a first compressed sensing matrix utilizing a first set of time indices corresponding to a first sampling rate, forming a second compressed sensing matrix utilizing a plurality of frequencies and a second set of time indices corresponding to a second sampling rate, forming a combined compressed sensing matrix from the first compressed sensing matrix and the second compressed sensing matrix, and reconstructing at least a portion of the input signal utilizing the combined compressed sensing matrix. The first and second sampling rates are each less than the Nyquist sampling rate for the input signal.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
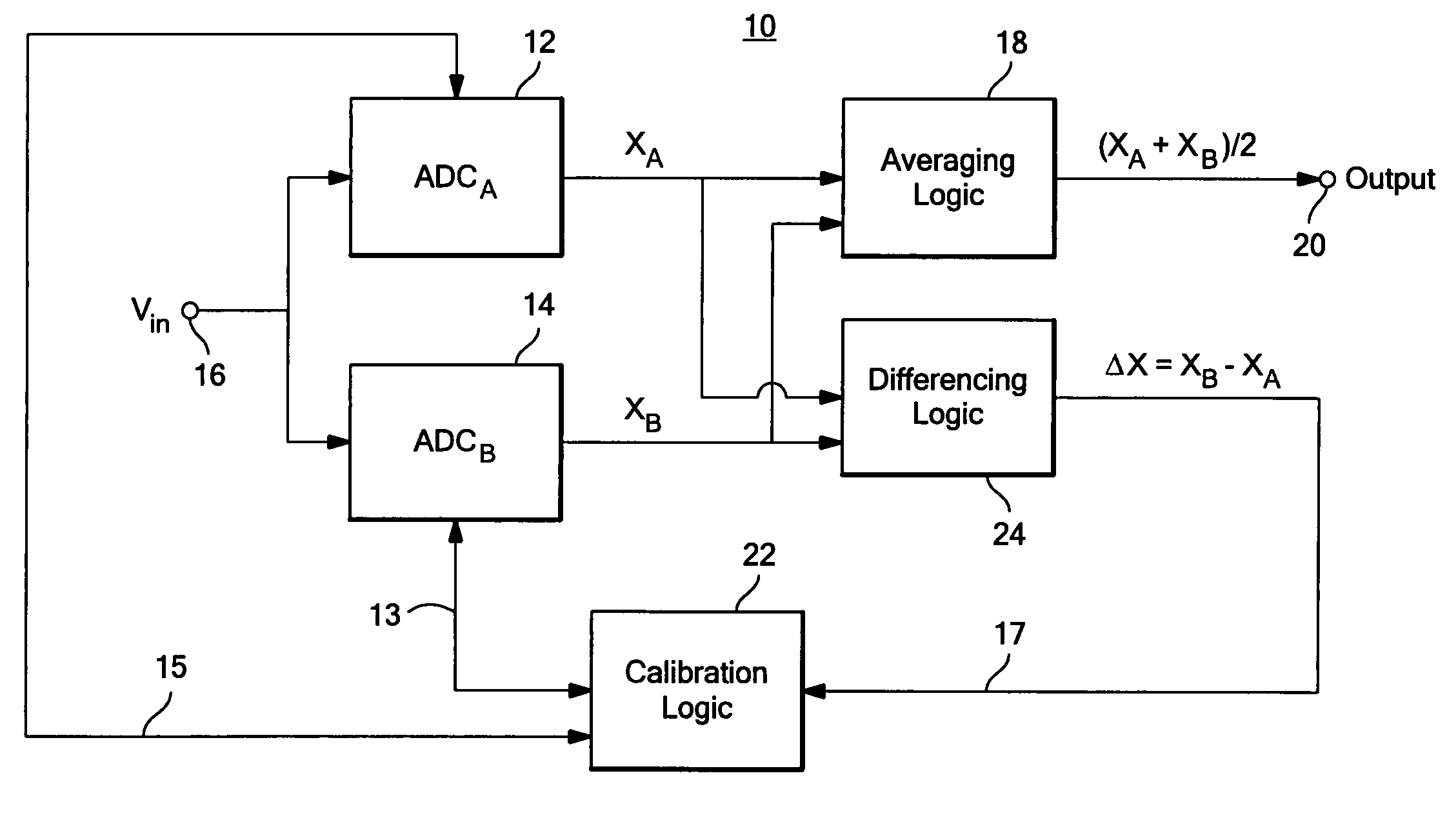
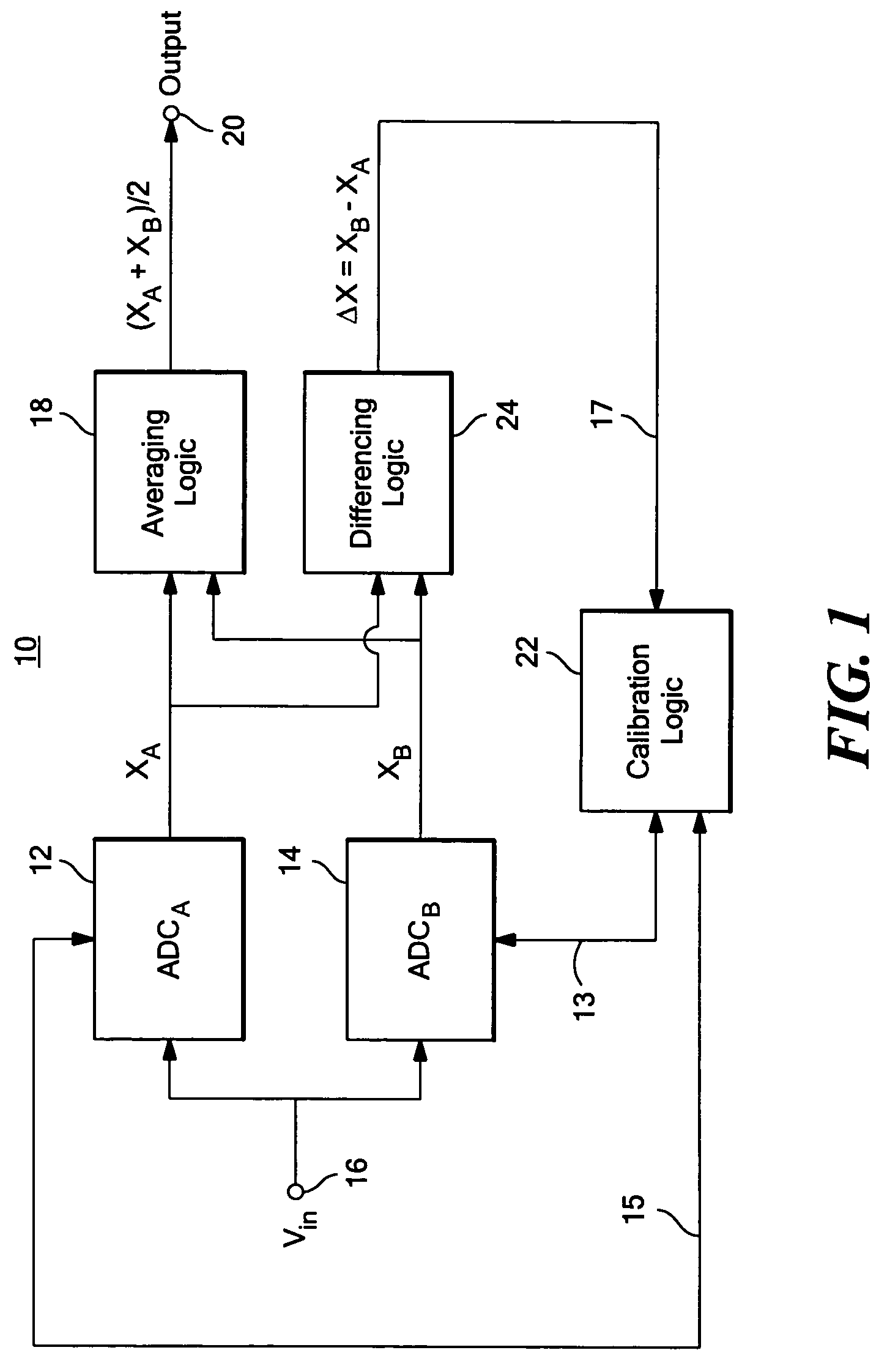
Calibratable analog-to-digital converter system
ActiveUS7312734B2Control areaLimited powerElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAnalog signalEngineering
A calibratable analog-to-digital converter system with a split analog-to-digital converter architecture including N Analog-to-Digital Converters (ADCs) each configured to convert the same analog input signal into a digital signal. Calibration logic is responsive to the digital signals output by the N ADCs and is configured to calibrate each of the ADCs based on the digital signals output by each ADC.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Method and circuit for dynamic calibration of flash analog to digital converters
InactiveUS6603416B2Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersEngineeringAnalog-to-digital converter
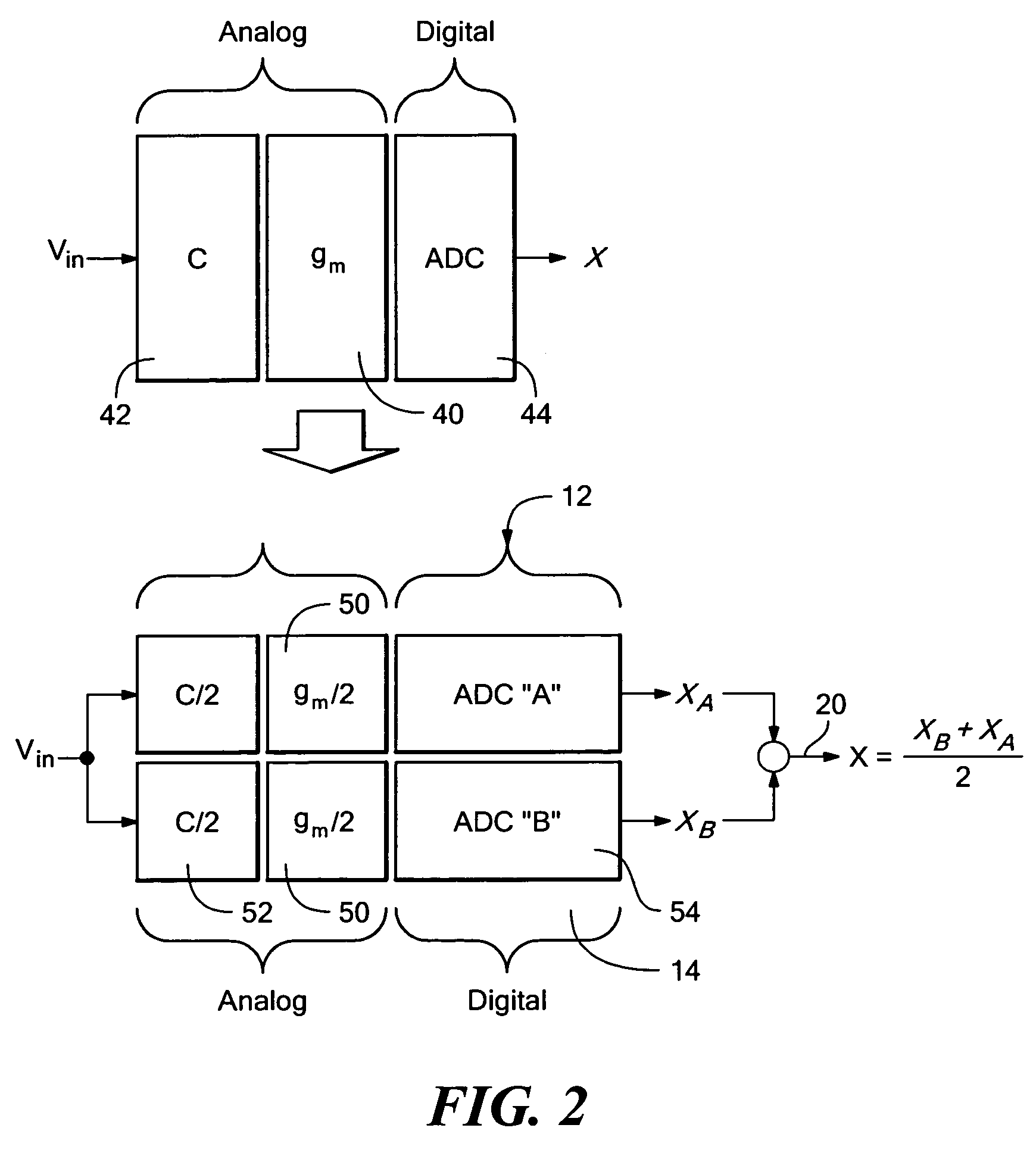
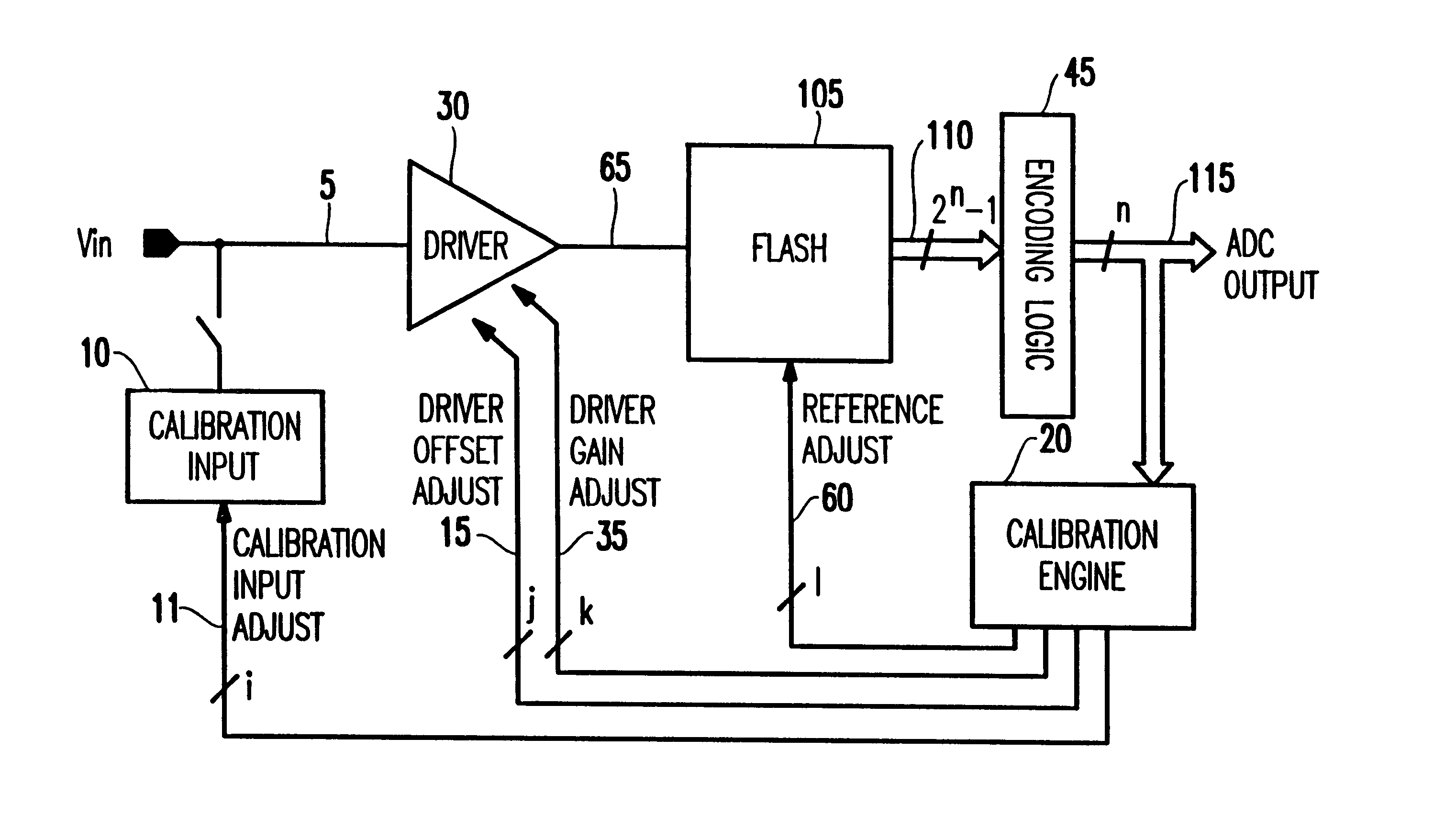
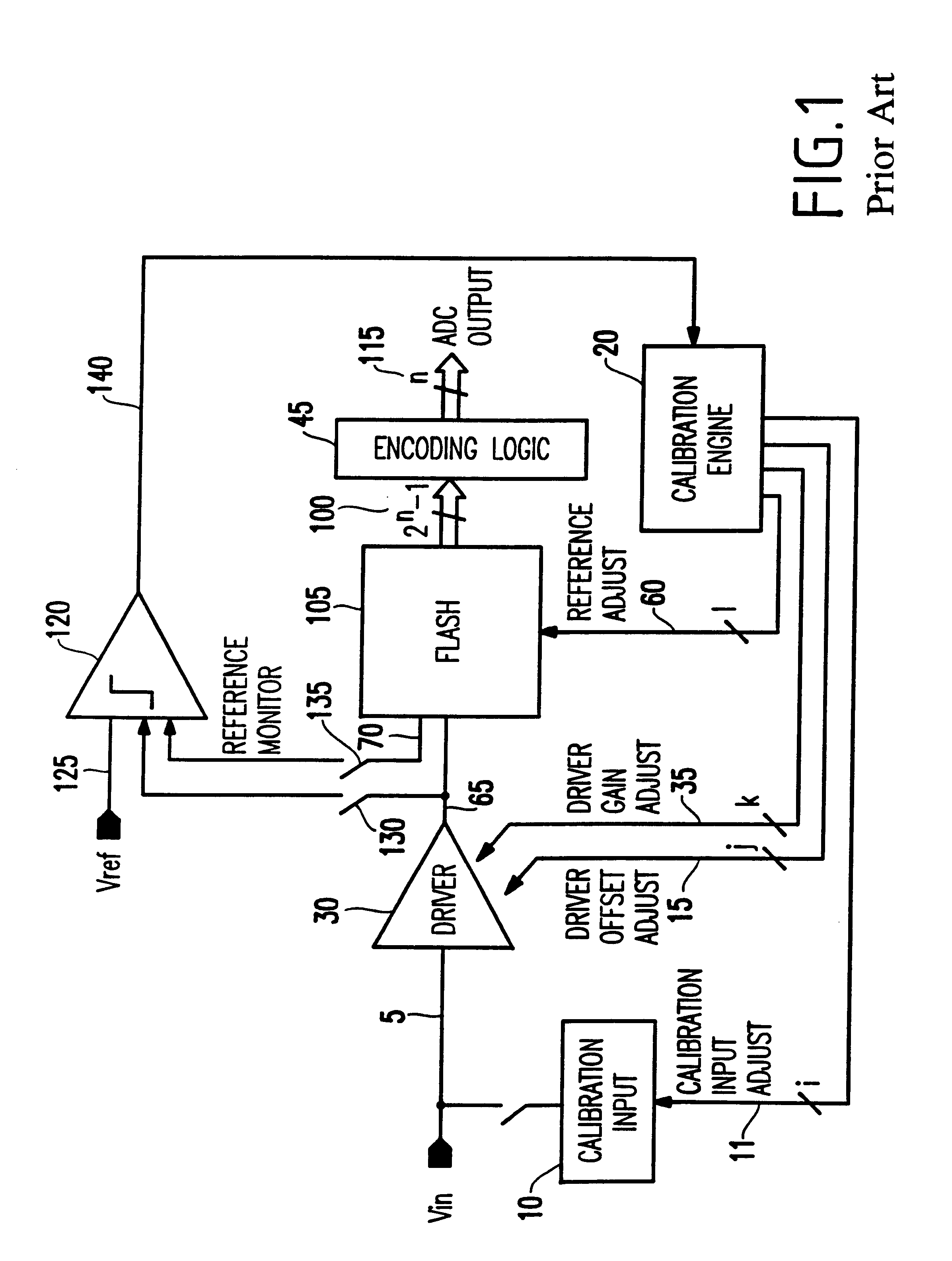
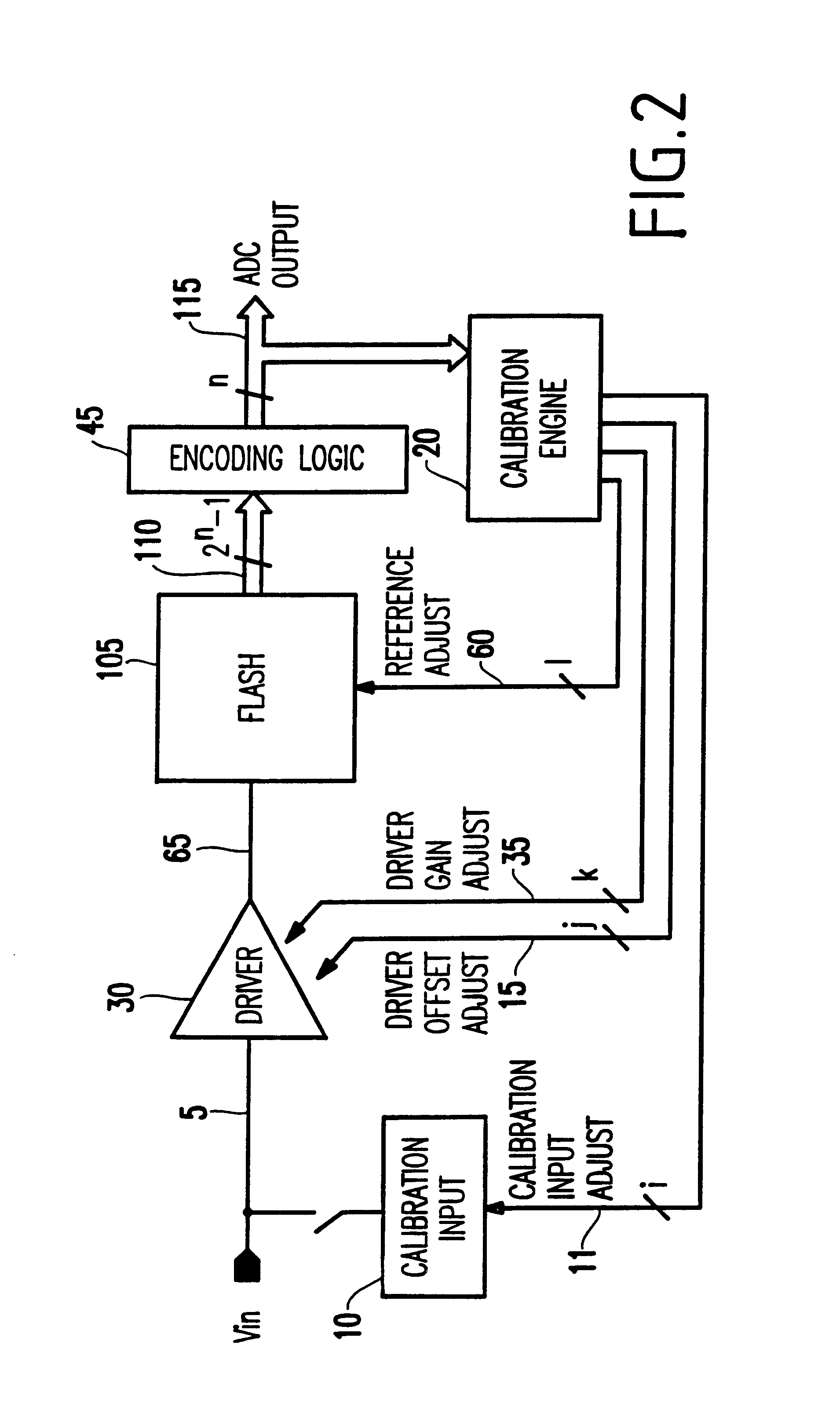
A method and structure for calibrating an analog to digital converter comprises an input signal; a driver receiving the input signal, wherein the driver outputs a driver output signal; a flash circuit receiving the driver output signal, wherein the flash circuit outputs a comparison result equaling 2n-1 digital outputs; an encoding logic unit encoding the comparison result into n digital bits as an output signal; a calibration engine outputting a calibration input adjust signal, a reference adjust signal, a driver gain adjust signal, a driver offset adjust signal; and a calibration input circuit receiving the calibration input adjust signal, wherein the driver receives the driver gain adjust signal and the driver offset adjust signal, wherein the flash circuit receives the reference adjust signal, wherein the calibration engine receives n digital bits, and controls an operation of the driver or flash circuit based on the output signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
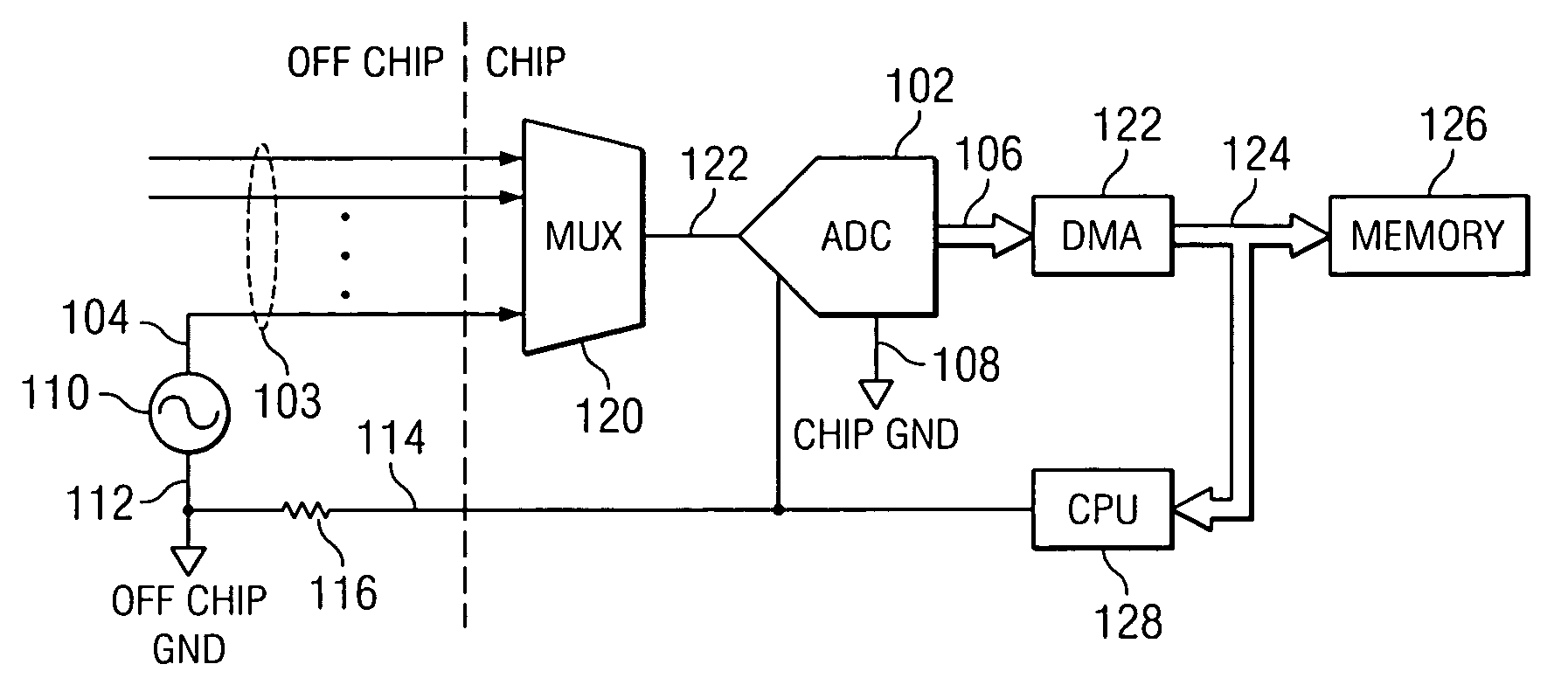
DMA controller that restricts ADC from memory without interrupting generation of digital words when CPU accesses memory
InactiveUS7188199B2Electric signal transmission systemsResistors with plural resistive elementsControl dataMixed-signal integrated circuit
DMA controller for mixed signal device. A mixed signal integrated circuit with memory control is disclosed. A data conversion circuit is provided that is operable to receive an analog input signal and convert discrete samples thereof at a predetermined sampling rate to a digital representations thereof as a plurality of digital words. A memory stores the digital words generated by the data conversion circuit. A processor is included on the integrated circuit and operable to access the memory to output select ones of the digital words for processing thereof in accordance with a predetermined processing algorithm. A memory access controller controls access to the memory by the data conversion circuit and the processor. The memory access controller is operable to restrict access to the memory by the data conversion circuit without interrupting the generation of digital words therefrom when the processor is accessing the memory, and allowing access to the memory by the data conversion circuitry when the processor is not accessing the memory, such that the data conversion circuit can transfer currently generated digital words and previously generated and non stored digital words for storage in said memory upon gaining access thereto.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
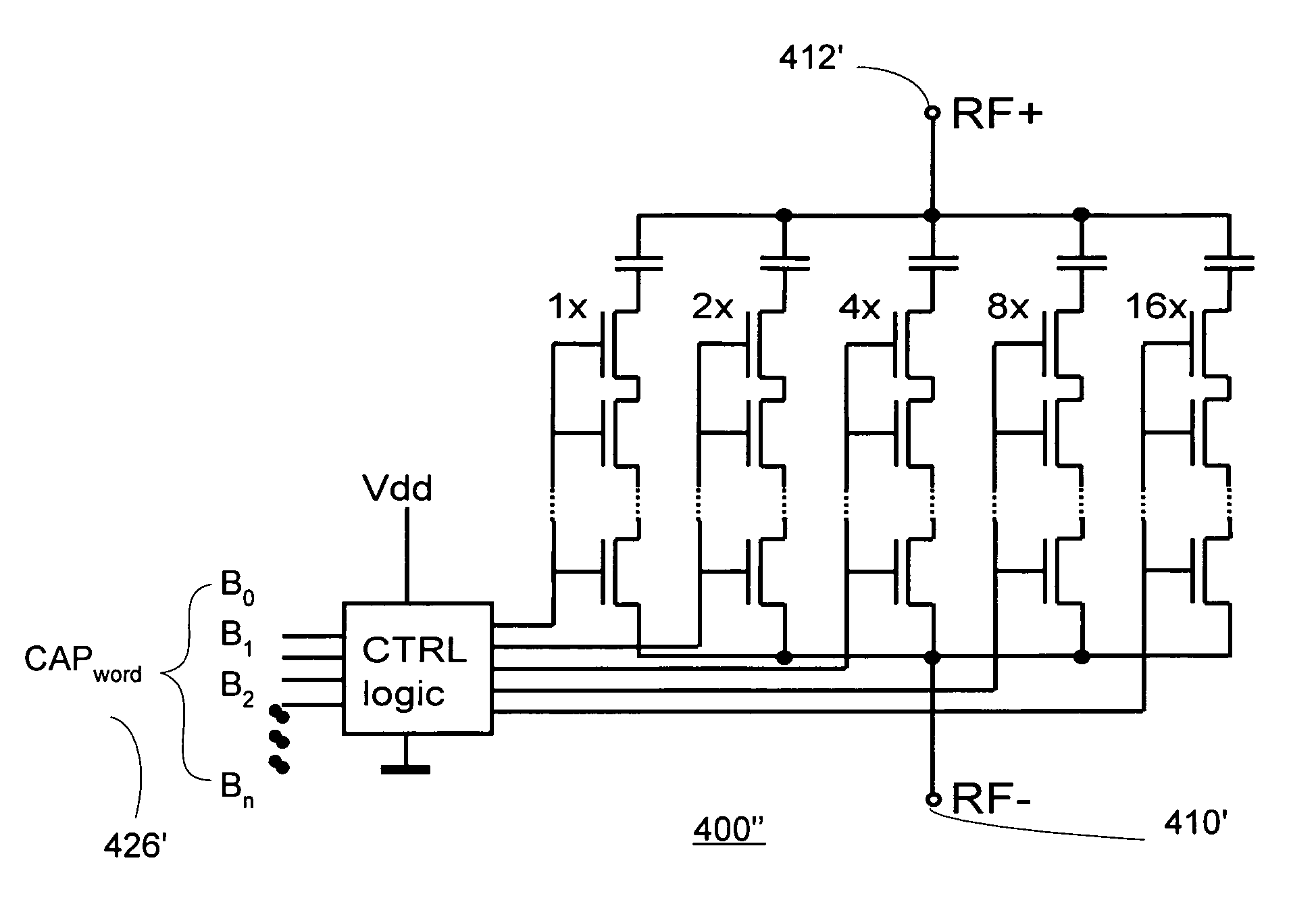
Method and apparatus for use in digitally tuning a capacitor in an integrated circuit device
ActiveUS9024700B2Easy to controlHigh Power Handling CapabilityMultiple-port networksImpedence matching networksCapacitanceLeast significant bit
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Floating-gate reference circuit
InactiveUS7034603B2Electric signal transmission systemsElectric analogue storesReference currentComparators circuits
Systems and methods are discussed for using a floating-gate MOSFET as a programmable reference circuit. One example of the programmable reference circuit is a programmable voltage reference source, while a second example of a programmable reference circuit is a programmable reference current source. The programmable voltage reference source and / or the reference current source may be incorporated into several types of circuits, such as comparator circuits, current-mirror circuits, and converter circuits. Comparator circuits and current-mirror circuits are often incorporated into circuits such as converter circuits. Converter circuits include analog-to-digital converters and digital-to-analog converters.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
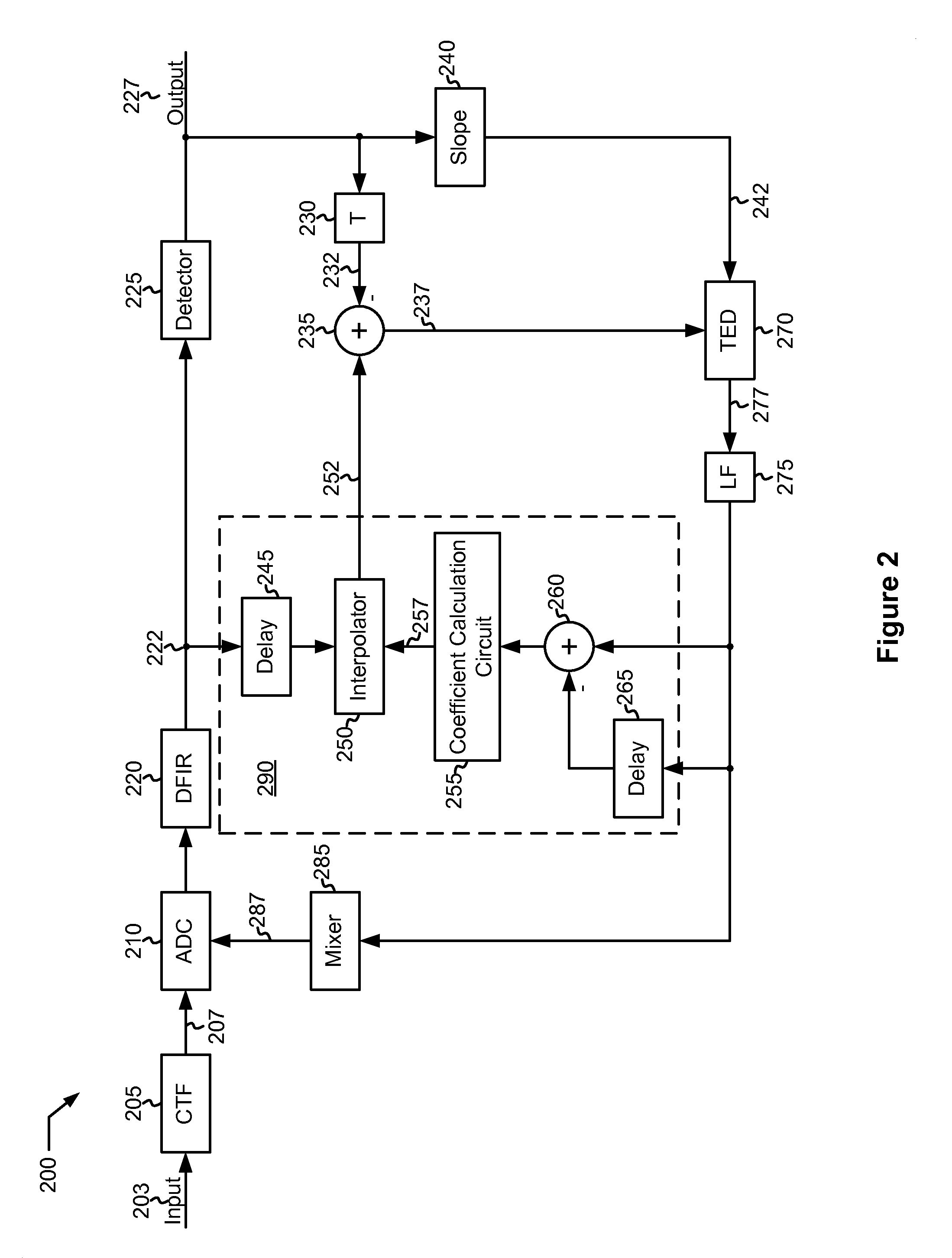
Systems and Methods for Mitigating Latency in a Data Detector Feedback Loop
ActiveUS20100164764A1Reduce latency impactLower latencyModification of read/write signalsElectric signal transmission systemsSampling instantData retrieval
Various embodiments of the present invention provide systems and methods for mitigating latency in a data detector feedback loop. For example, a method for reducing latency in an error corrected data retrieval system is disclosed. The method includes performing an analog to digital conversion at a sampling instant to create a digital sample, and performing a data detection on the digital sample to create a detected output. The detected output is compared with the digital sample to determine a phase error. During an interim period, the digital sample is adjusted to reflect the phase error to create an adjusted digital sample. After the interim period, the sampling instant is adjusted to reflect the phase error.
Owner:LSI CORPORATION +1
Calibration of resistor ladder using difference measurement and parallel resistive correction
InactiveUS20030151532A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDifferential measurementComplementary pair
A calibration system and method for a resistor ladder that employs relative measurement and adjustment between pairs of resistors. The system includes a resistor tree of complementary pairs of programmable resistors coupled to the resistor ladder, a measurement circuit that measures voltage differences between complementary pairs of programmable resistors, and control logic. The control logic controls the measurement circuit to measure a voltage difference between each complementary pair of programmable resistors and adjusts the relative resistance of each complementary pair of programmable resistors to equalize voltage. The measurement is facilitated by a sigma-delta ADC that converts a measured voltage difference into a bit stream. The programmable resistors are implemented with binary weighted resistors that are digitally adjusted one LSB at a time. Lower and upper adjustment thresholds may be employed to avoid unnecessary over-adjustments while maintaining a requisite level of accuracy.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
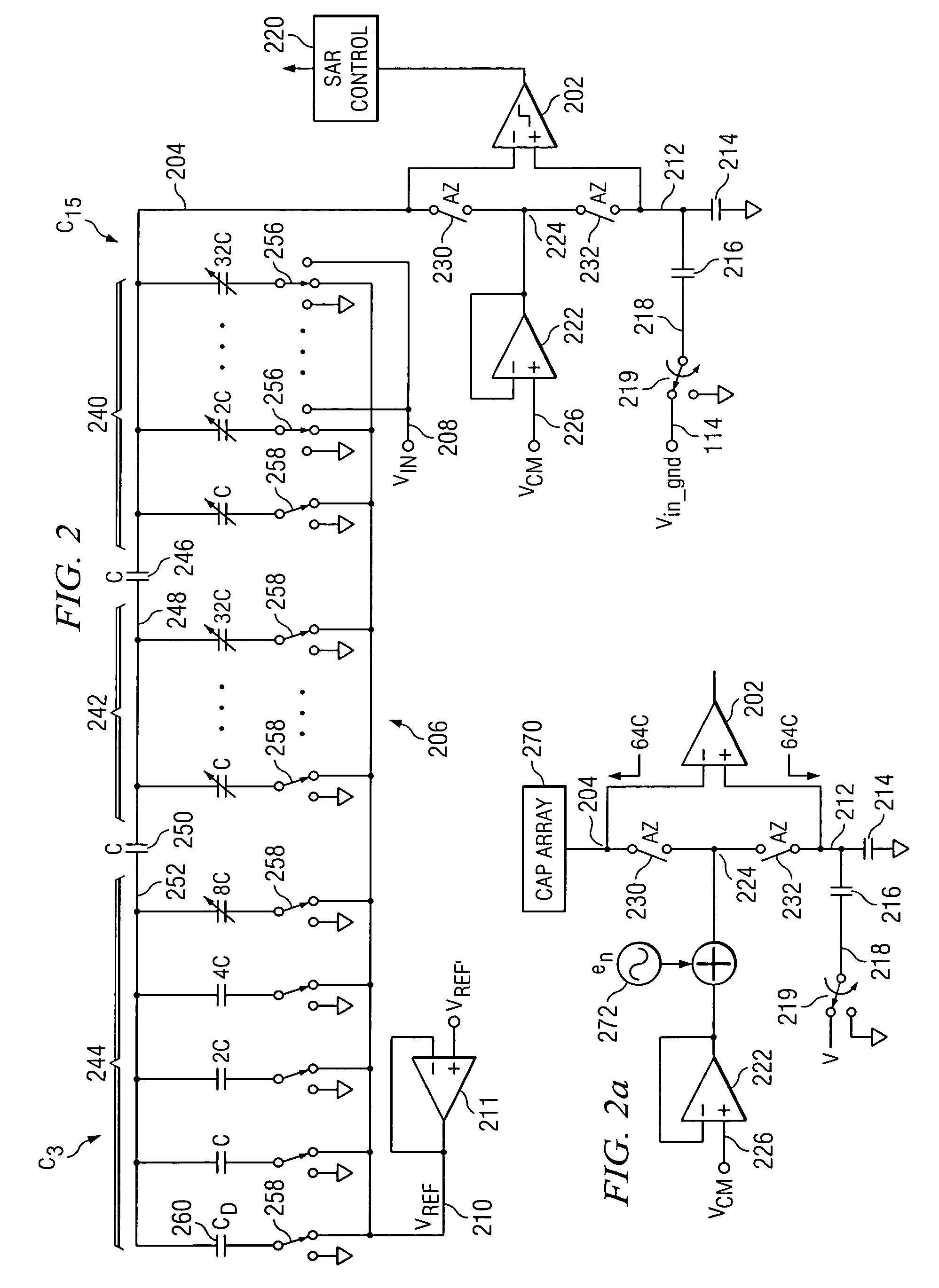
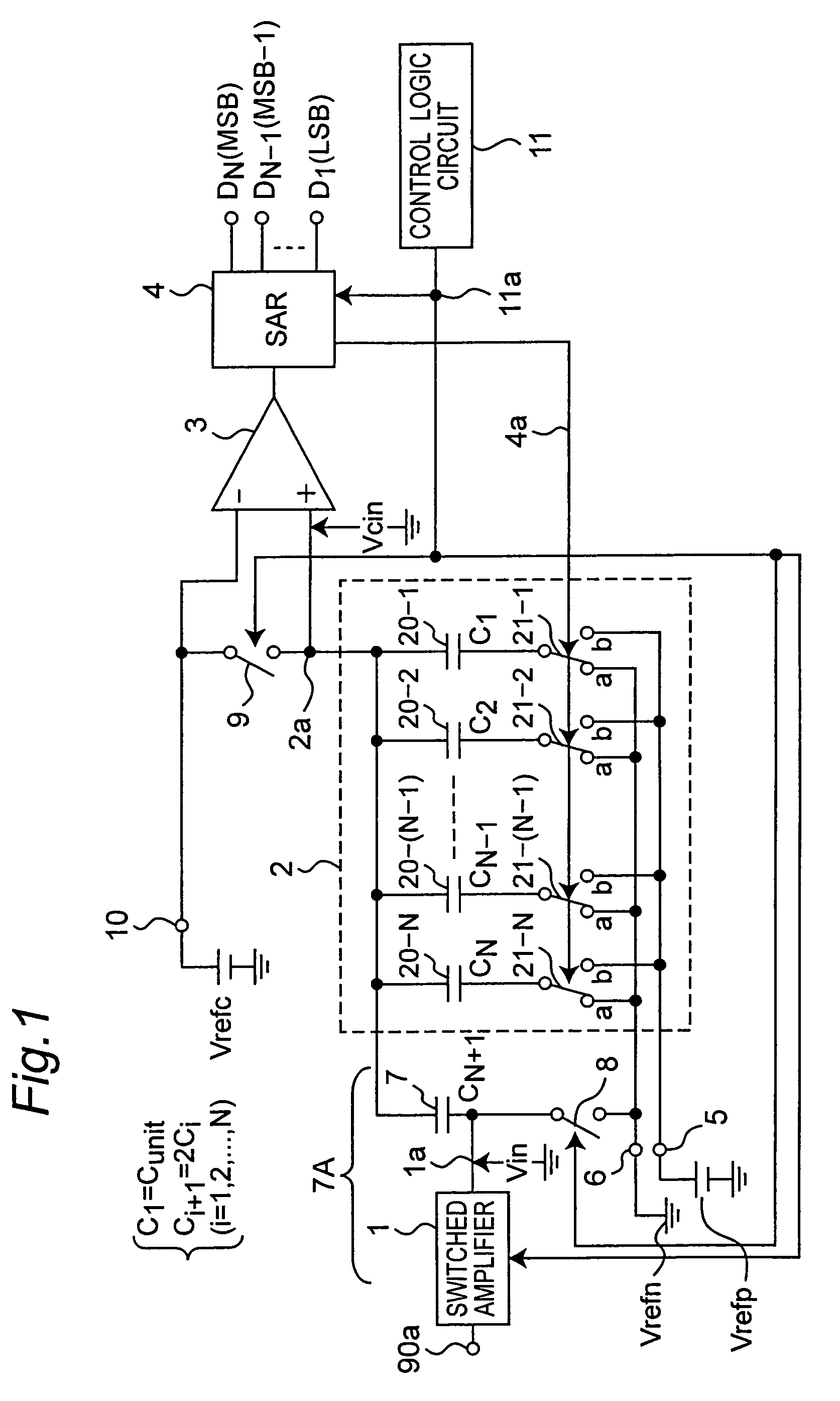
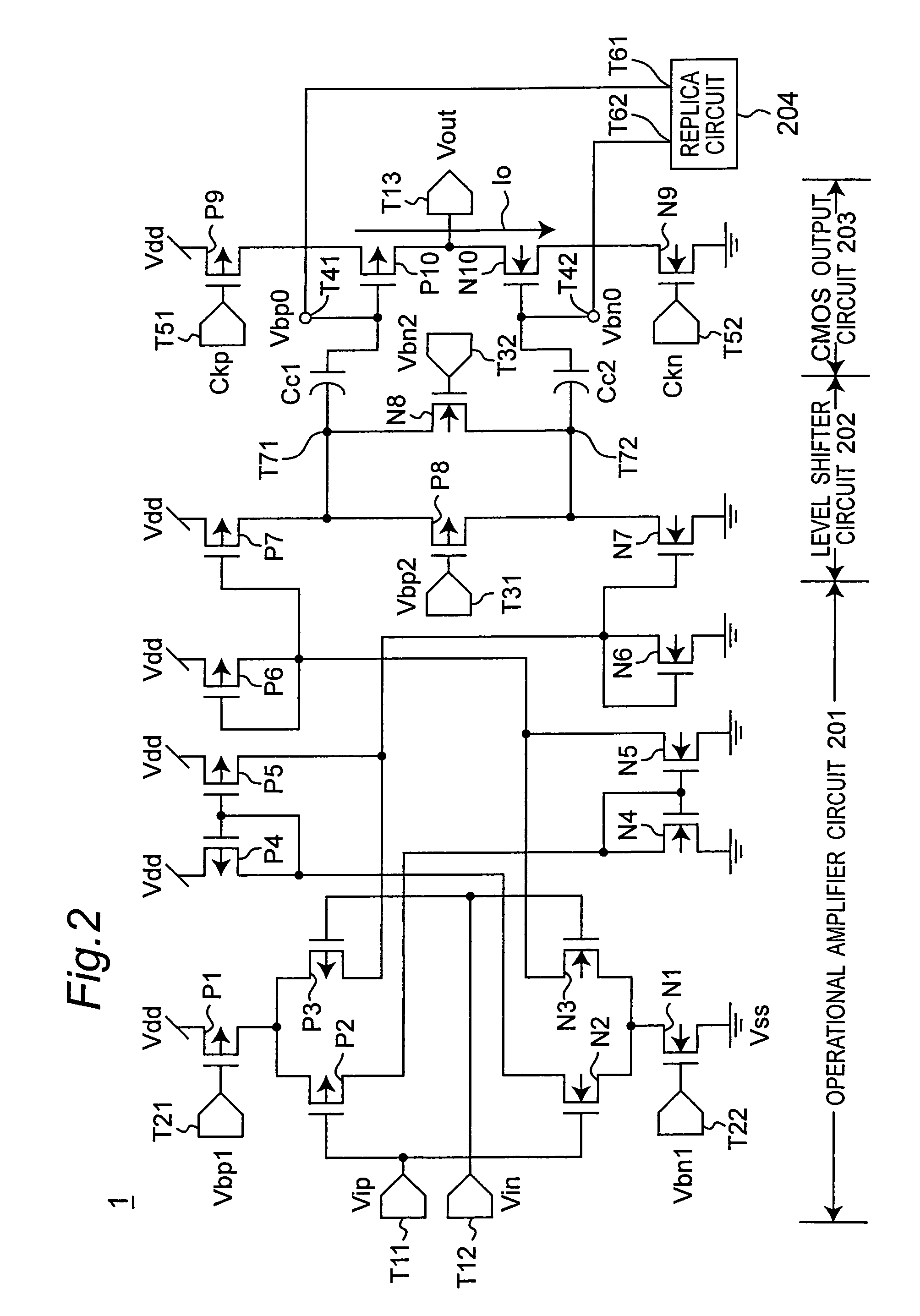
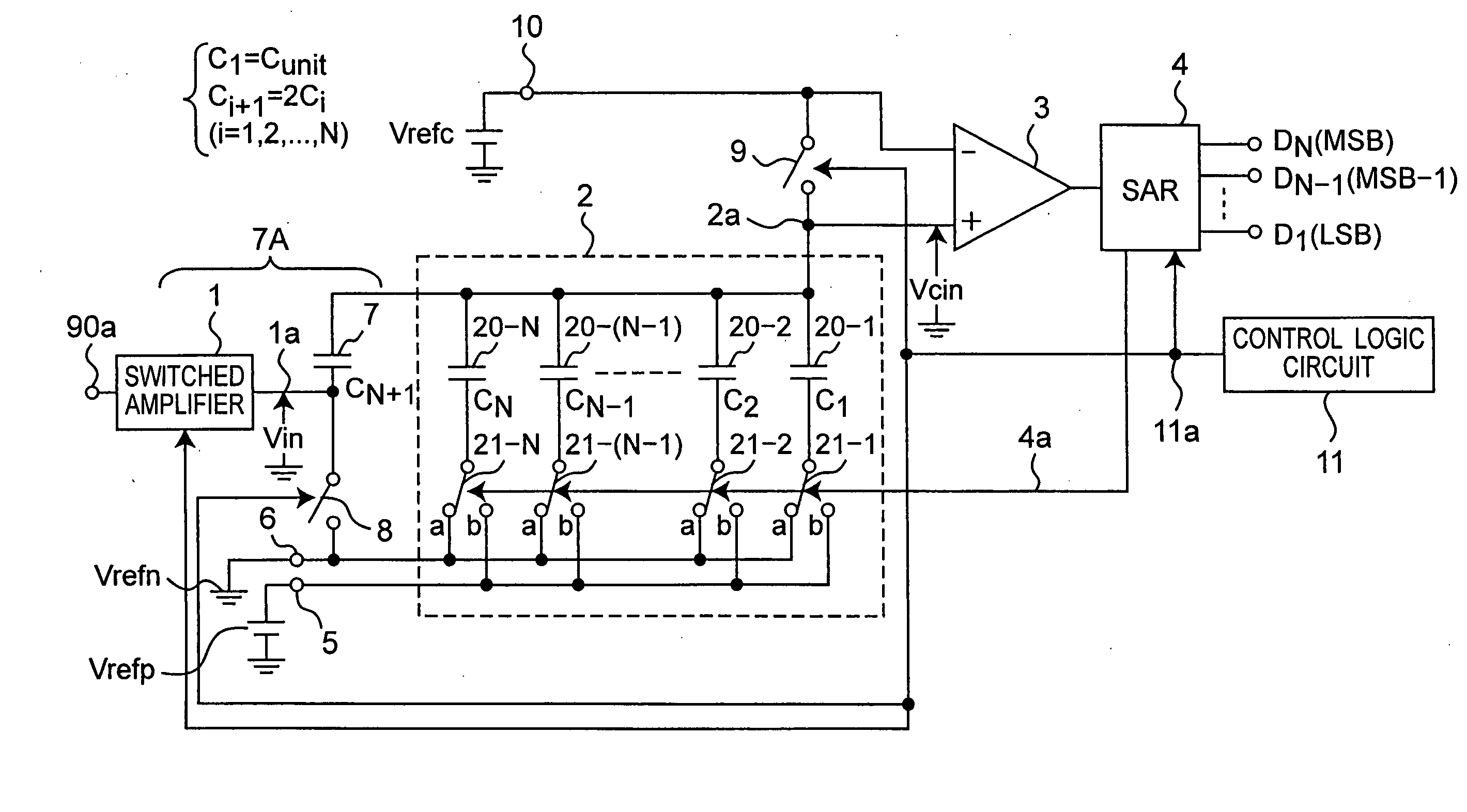
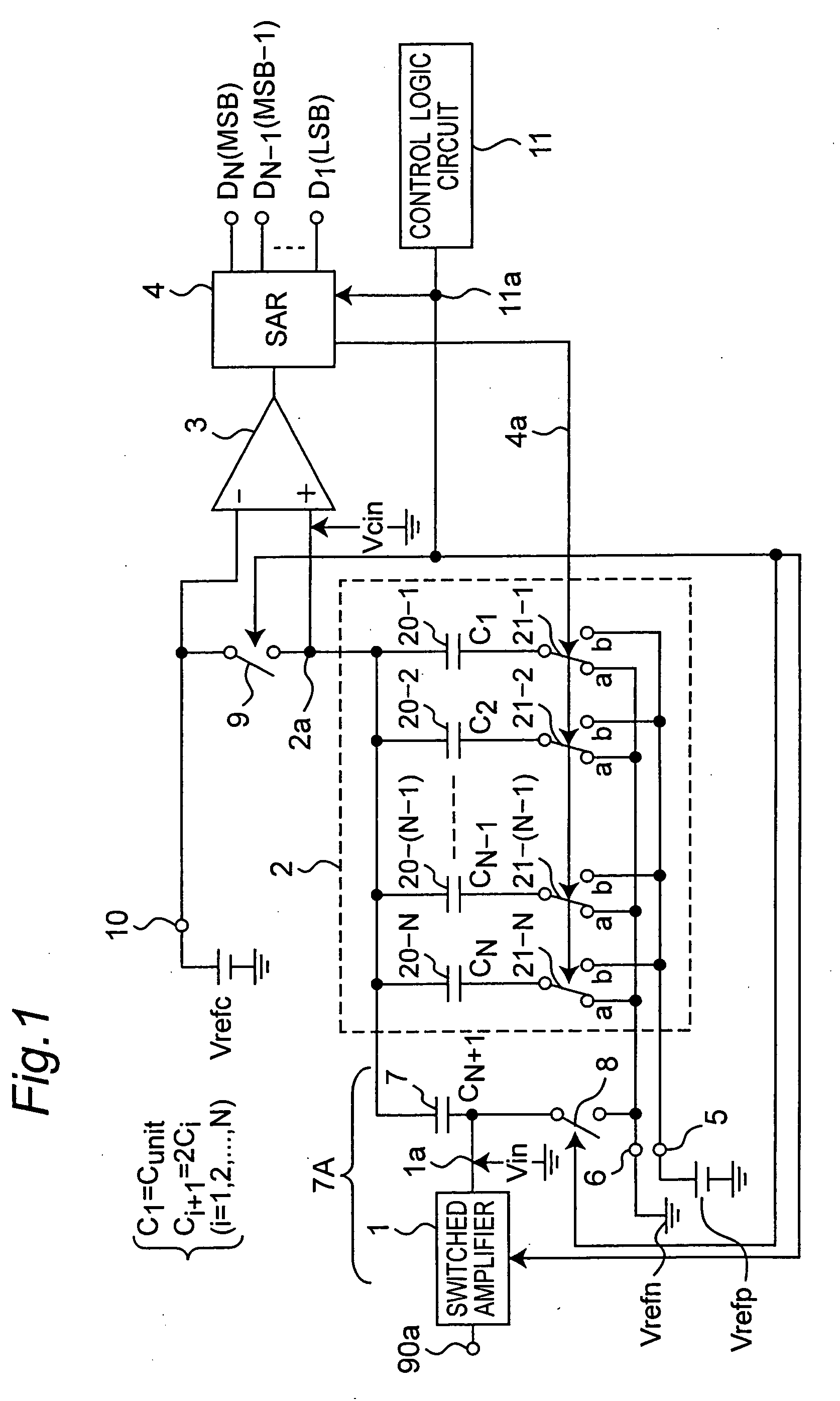
Analog to digital converter circuit of successive approximation type operating at low voltage
InactiveUS7015841B2Simple circuit configurationElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierLow voltage
In a sampling and holding, a control logic circuit connects another end of each capacitor of a DA converter to a ground potential, and outputs a sampled input analog signal from a switched amplifier to one end of a hold capacitor to hold. In a successive approximation, it controls a switched amplifier to set an output terminal thereof to a high-impedance state and the hold capacitor to connect the one end thereof to the ground potential. Then, it switches over connection of another end of each capacitor from the ground potential to a power supply voltage based on a digital value held by a successive approximation register to output an output voltage from another end of the hold capacitor to a comparator, and compares the output voltage from another end thereof with an intermediate reference voltage to obtain a digital value from the successive approximation register.
Owner:SEMICON TECH ACADEMIC RES CENT
A/D converter calibration
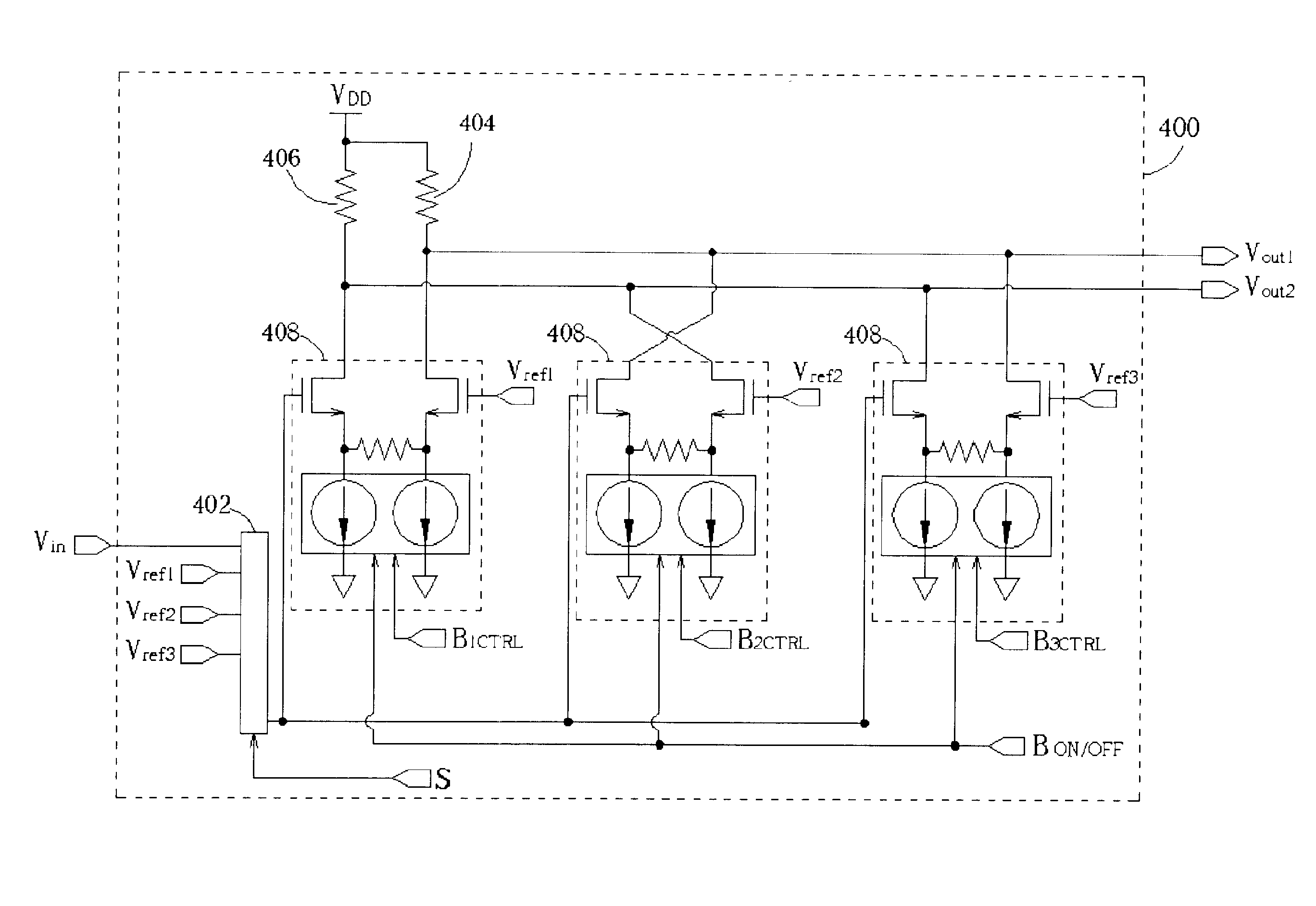
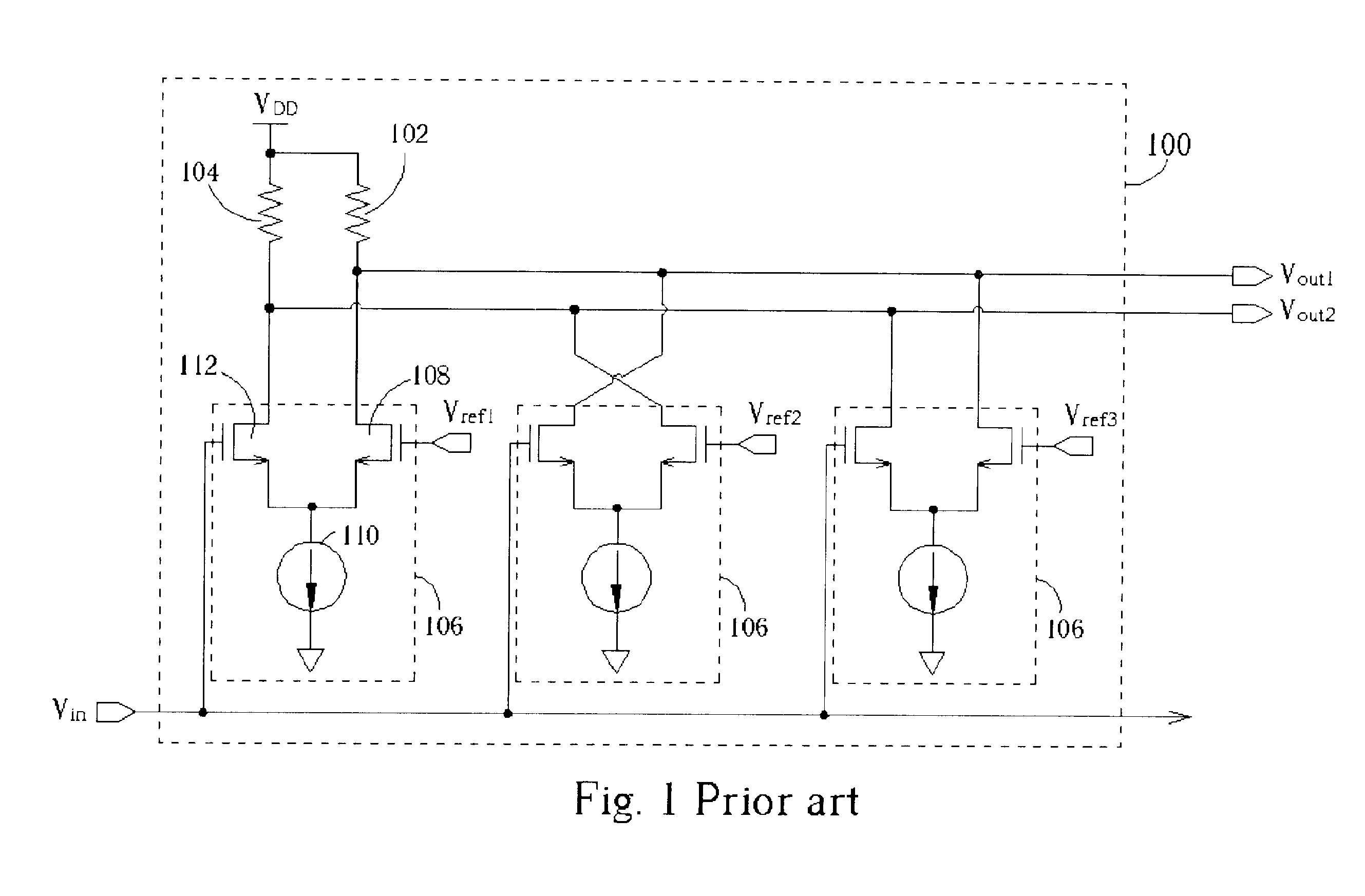
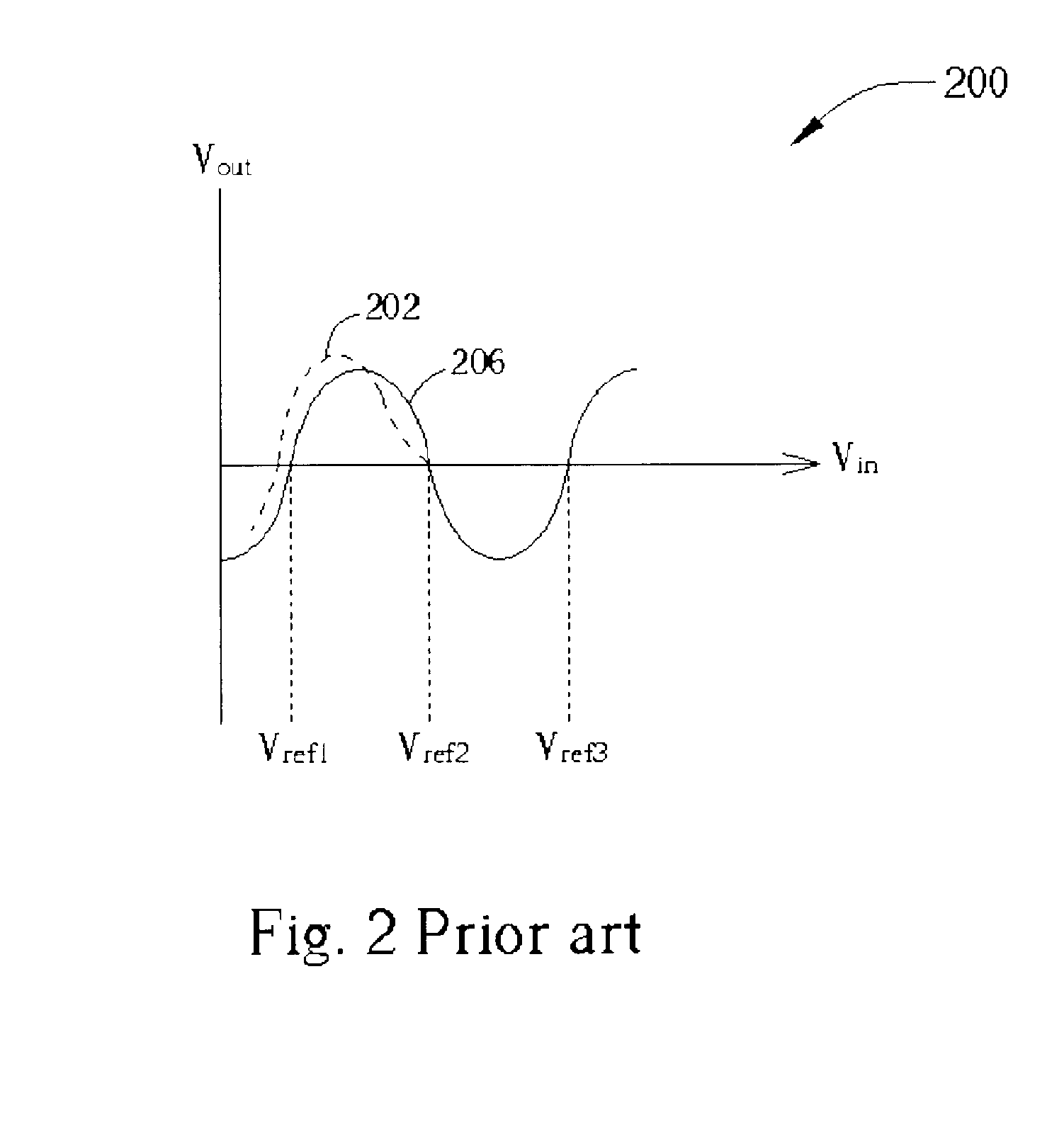
InactiveUS20050057379A1Increase profitIncrease overall A/D converter accuracyElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingEngineeringComparator
A D / A converter range calibration system in an A / D converter structure including a set of comparators with associated calibrating D / A converters includes means (RCC) for determining the offset error range for the entire set of comparators and means (R-DAC) for adjusting the dynamic range of each calibrating D / A converter to this offset error range.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Folding analog to digital converter capable of calibration and method thereof
ActiveUS6888482B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierControl signal
An ADC is disclosed comprising at least one folder receiving an input voltage, generating a first output voltage and a second output voltage, and including a plurality of amplifiers and calibration logic for generating bias control signals according to the first output voltage and the second output voltage. Each of the amplifier receives one of a plurality of reference voltages and comprises a bias circuit for providing a bias current to the amplifier based on at least one of a plurality of bias control signals. During calibration, the calibration logic provides the bias control signals to control the bias circuit of each amplifier in the folder such that the first output voltage is substantially the same as the second output voltage.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
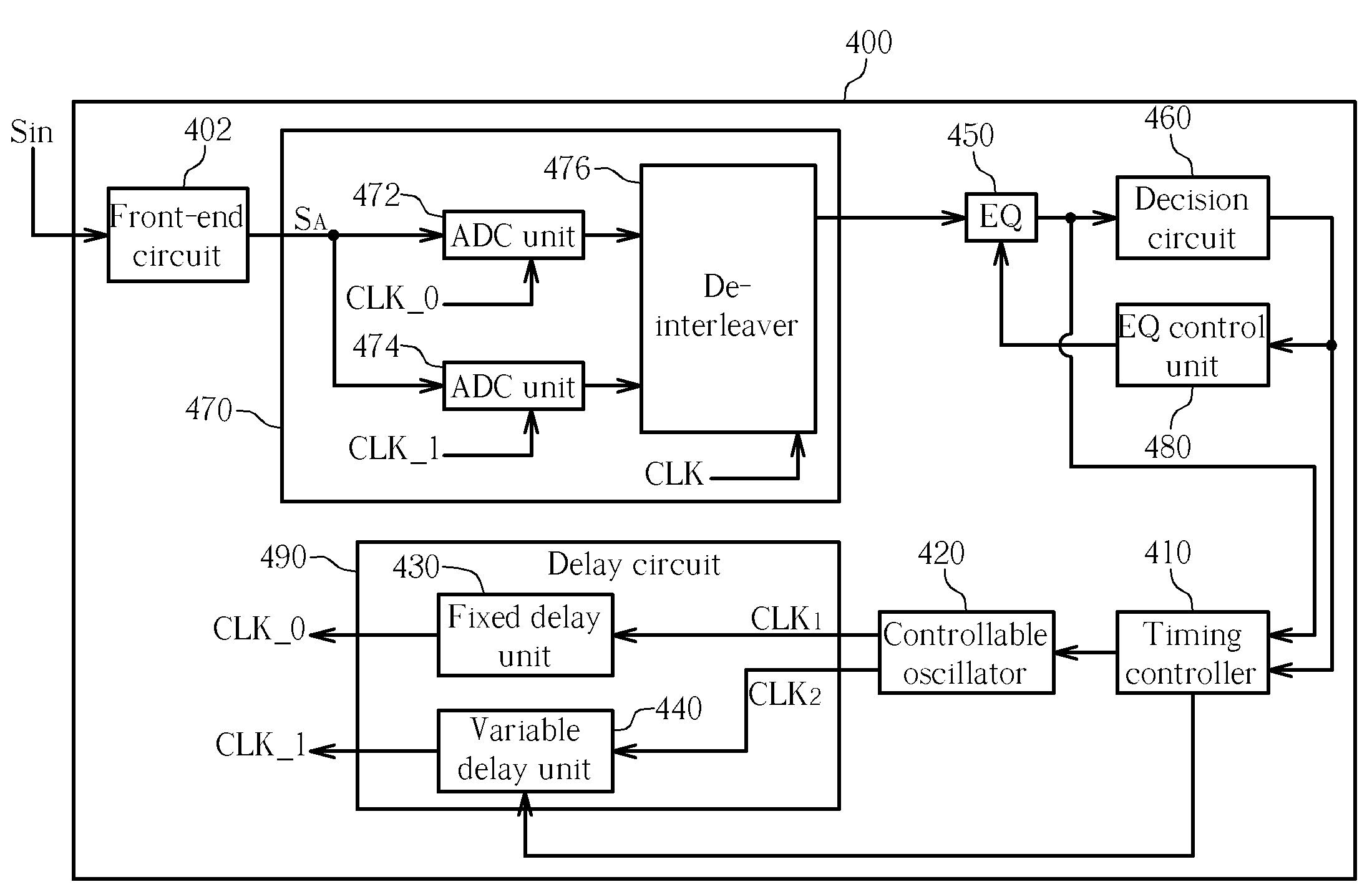
Receiver capable of correcting mismatch of time-interleaved parallel ADC and method thereof
ActiveUS7233270B2Electric signal transmission systemsPhysical parameters compensation/preventionTime interleavedAnalog-to-digital converter
A compensation method for a receiver is disclosed, the method includes: receiving and processing an incoming signal to generate an analog input signal; utilizing a time-interleaved parallel analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for converting the analog input signal to a digital input signal according to a plurality of clock signals of different phases; equalizing the digital input signal to generate a plurality of soft decision values; generating a plurality of hard decision values according to the soft decision values; calculating a plurality of error values according to the hard decision values and the soft decision values; and compensating the receiver according to at least part of the error values.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
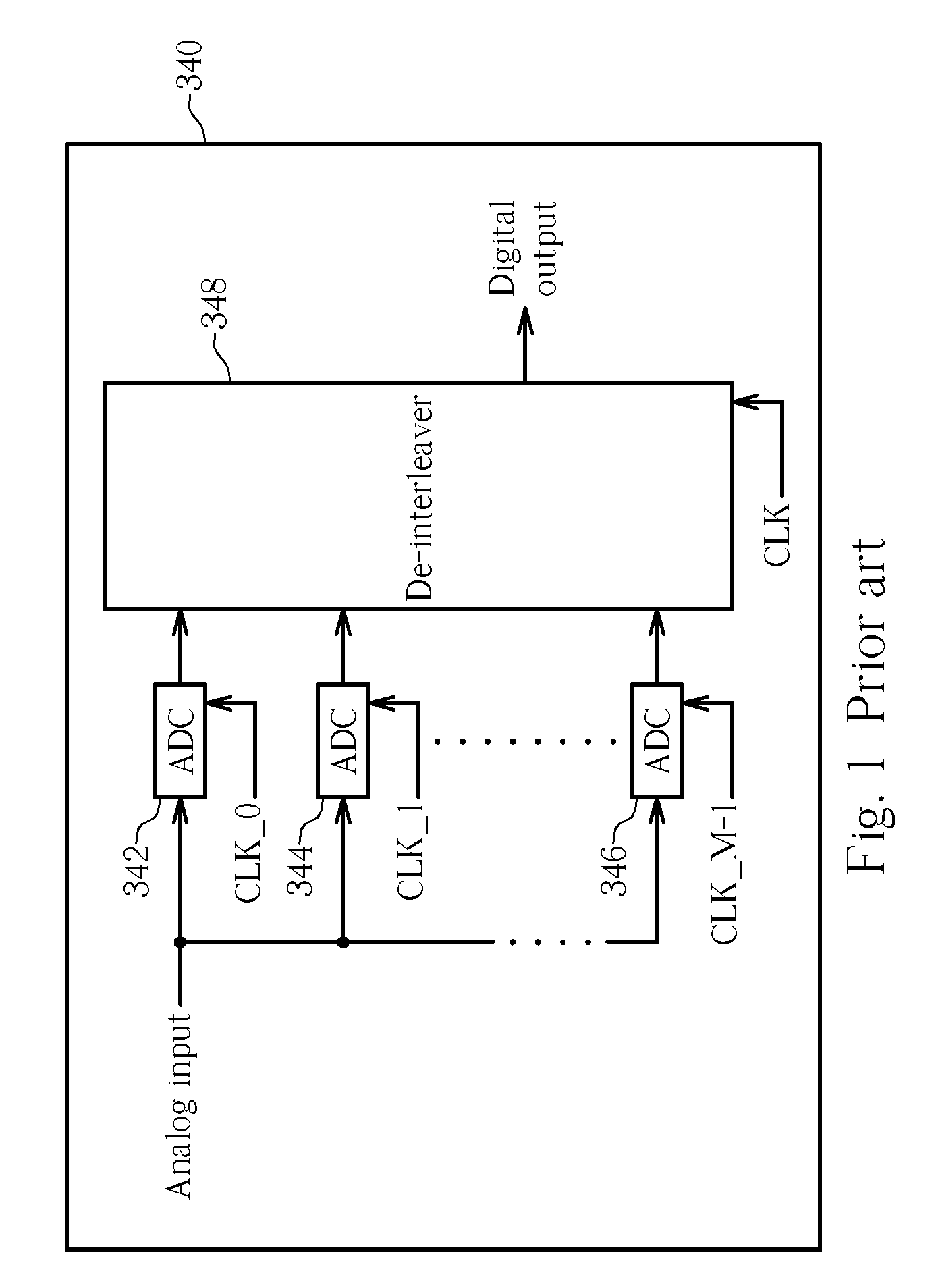
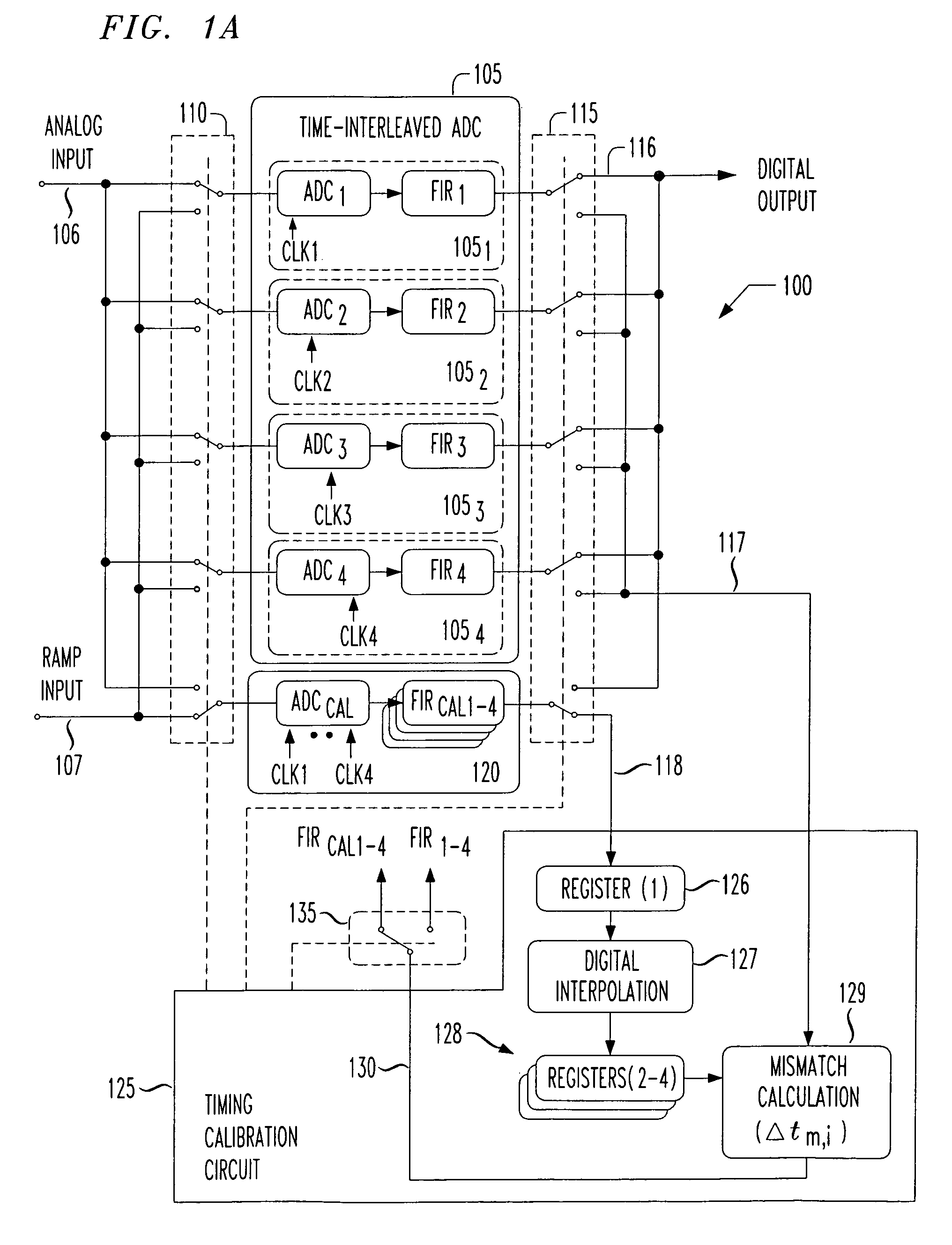
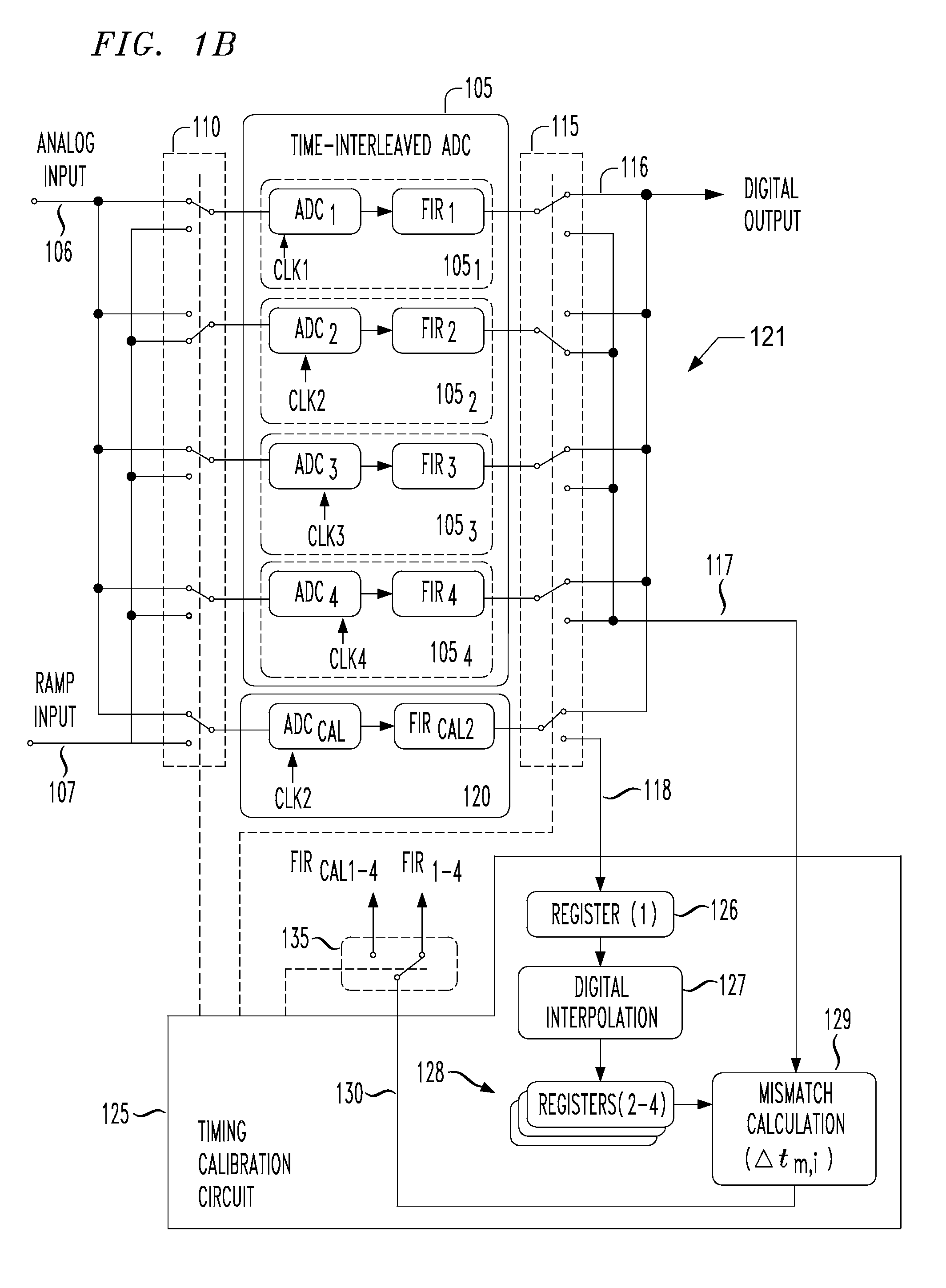
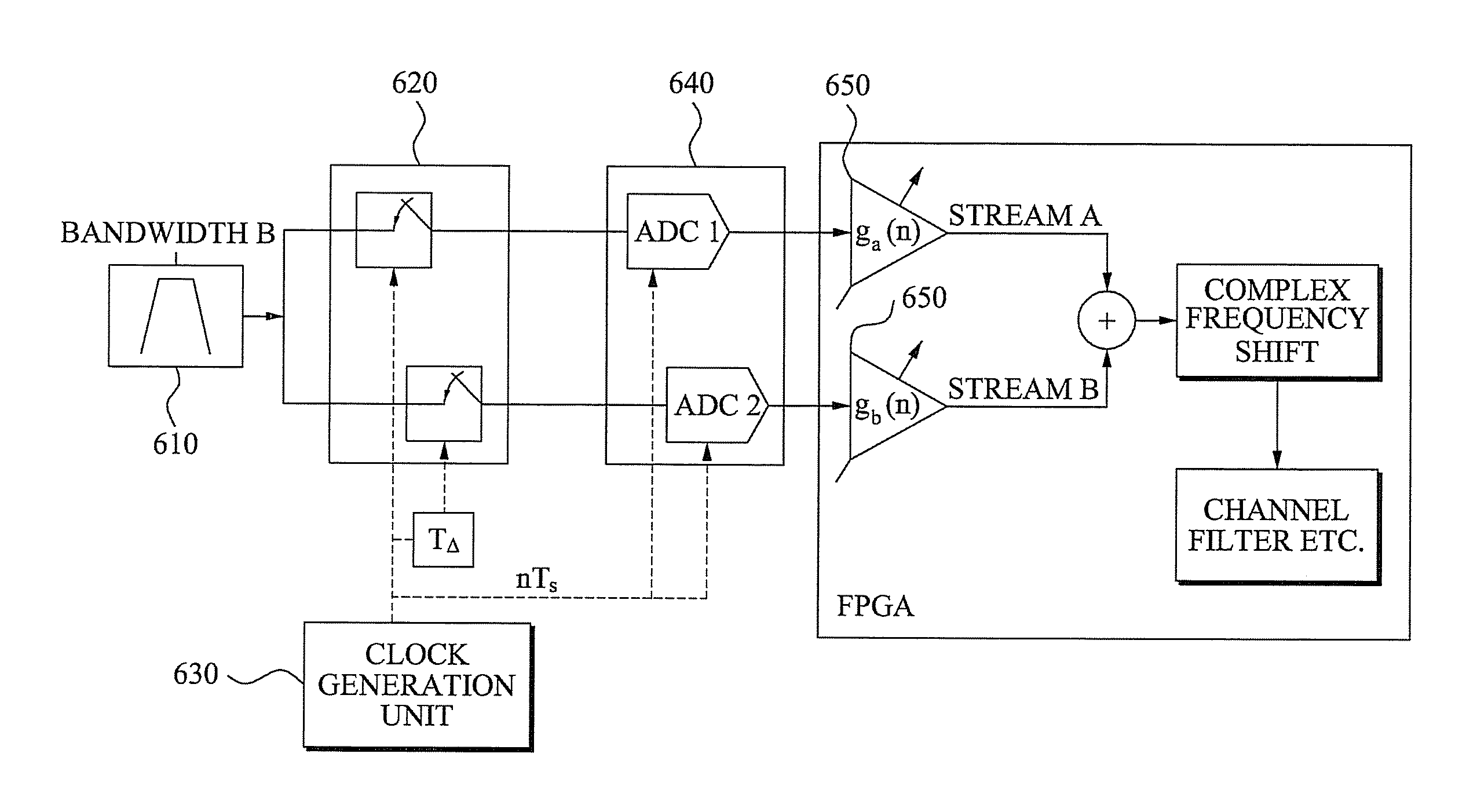
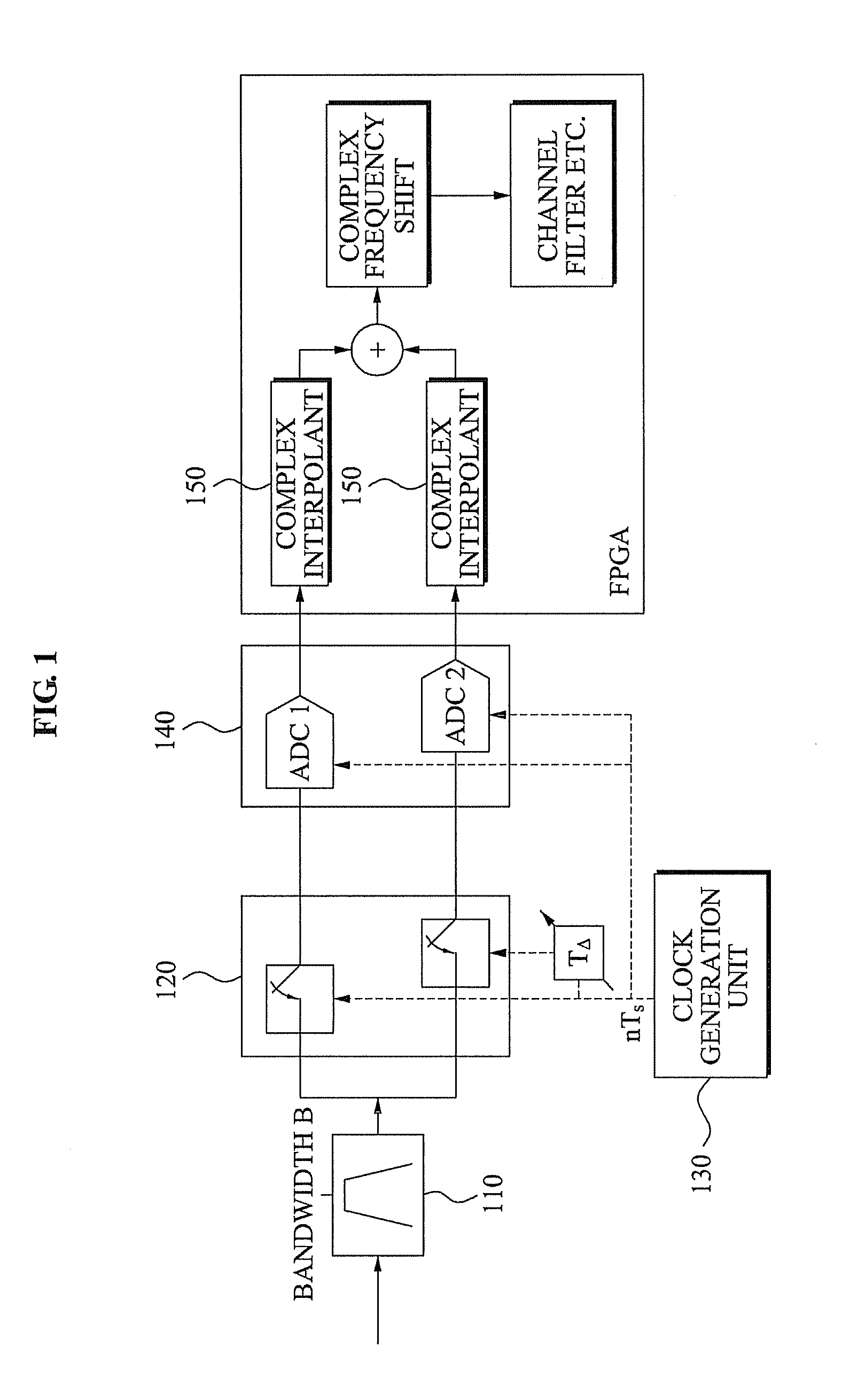
Digital background calibration for time-interlaced analog-to-digital converters
ActiveUS7227479B1Shorten the timeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersTime interleavedDigital converter
The present invention provides for background calibration of a time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter (TIADC). In one embodiment, a background calibrator includes a TIADC having a parallel array of time-interleaved main signal processors, each main signal processor including an ADC connected to a corresponding output FIR filter. The background calibrator also includes an auxiliary signal processor having an ADC connected to at least one corresponding output FIR filter. Additionally, the background calibrator further includes a timing calibration circuit, wherein the timing calibration circuit is configured to select one of the main signal processors, exchange the auxiliary signal processor with the selected main signal processor in the TIADC and connect the selected main signal processor to the timing calibration circuit. In an alternative embodiment, the timing calibration circuit is further configured to reduce a timing mismatch of the selected main signal processor.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Analog to digital converter circuit of successive approximation type operating at low voltage
InactiveUS20050200510A1Simple circuit configurationElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersCapacitanceLow voltage
In a sampling and holding, a control logic circuit connects another end of each capacitor of a DA converter to a ground potential, and outputs a sampled input analog signal from a switched amplifier to one end of a hold capacitor to hold. In a successive approximation, it controls a switched amplifier to set an output terminal thereof to a high-impedance state and the hold capacitor to connect the one end thereof to the ground potential. Then, it switches over connection of another end of each capacitor from the ground potential to a power supply voltage based on a digital value held by a successive approximation register to output an output voltage from another end of the hold capacitor to a comparator, and compares the output voltage from another end thereof with an intermediate reference voltage to obtain a digital value from the successive approximation register.
Owner:SEMICON TECH ACADEMIC RES CENT
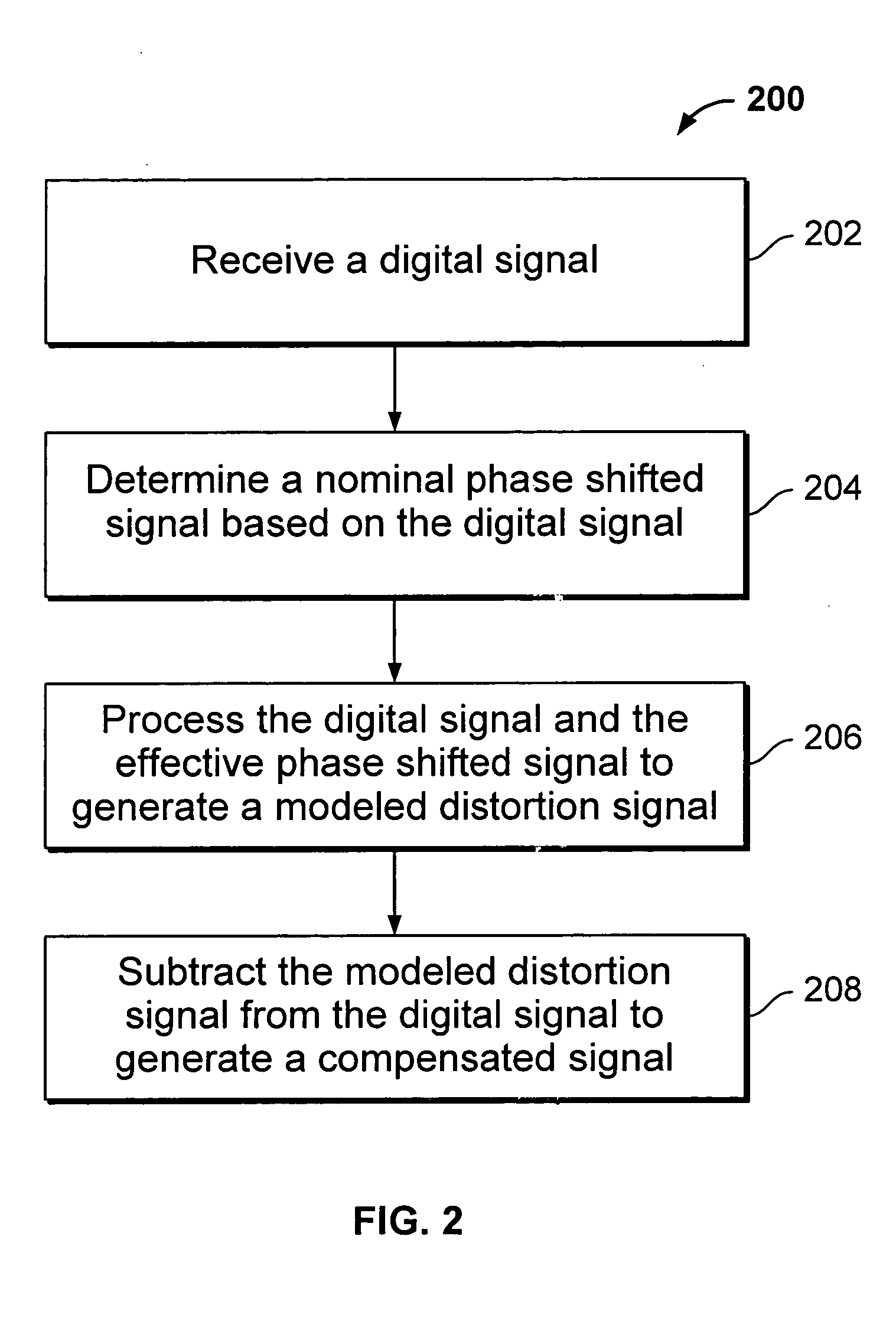
Digital linearizing system
InactiveUS20050219089A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionElectric signal transmission systemsNonlinear distortionPhase shifted
A method of compensating for nonlinear distortions in a digital signal comprises receiving the digital signal, generating a nominal phase shifted signal based on the digital signal, generating a modeled distortion signal based on the digital signal and the nominal phase shifted signal, subtracting the modeled distortion signal from the digital signal, and generating a compensated signal. A compensating system comprises an input interface configured to receive a digital signal having nonlinear distortion, and a distortion model coupled to the interface, configured to generate a nominal phase shifted signal based on the digital signal, generate a modeled distortion signal based on the digital signal and the nominal phase shifted signal, subtract the modeled distortion signal from the digital signal, and generate a compensated signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
All-analog calibration of sting-DAC linearity: application to high voltage processes
ActiveUS6897794B2Quantity minimizationLow costElectric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsVoltage referenceHigh pressure
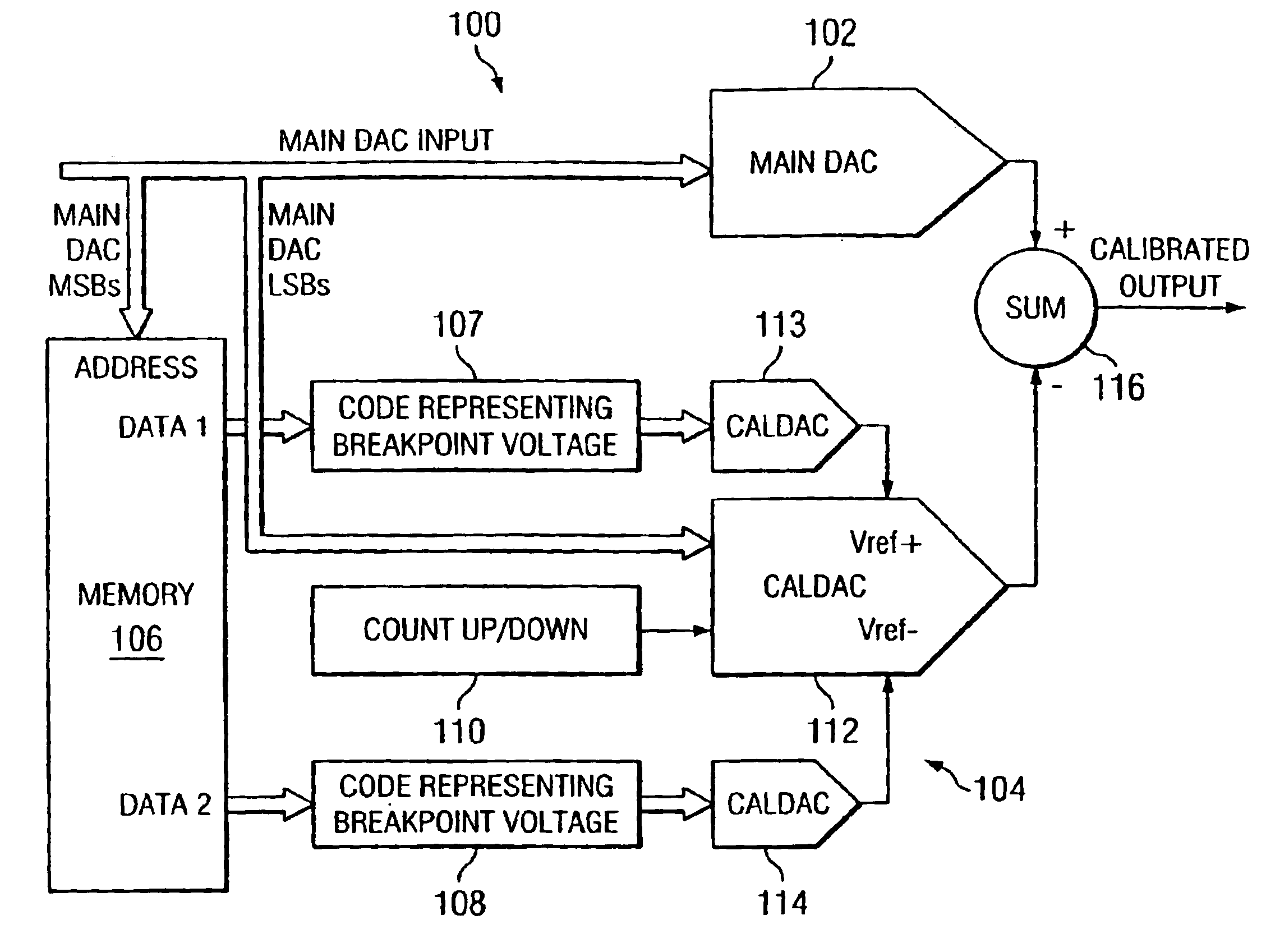
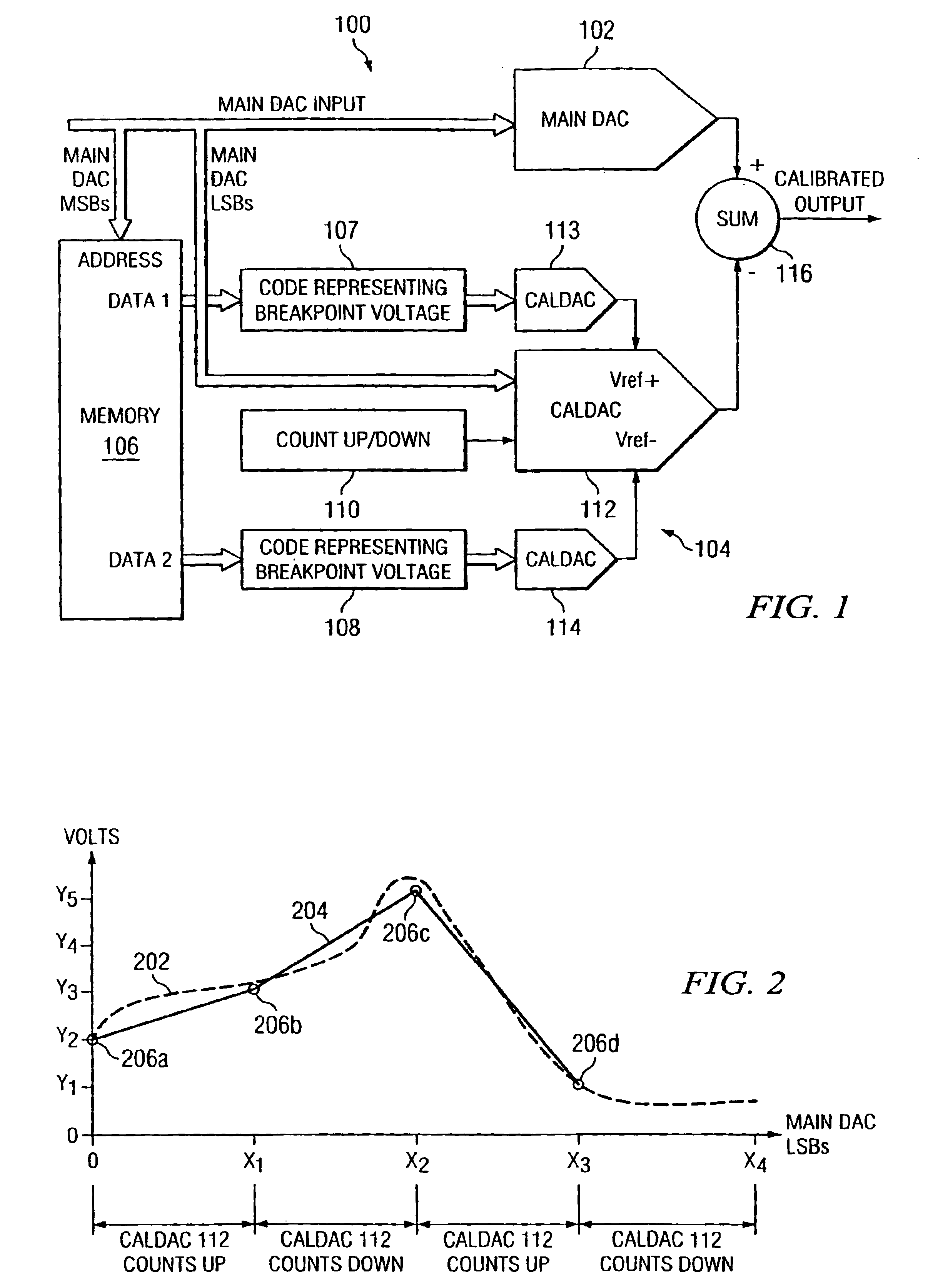
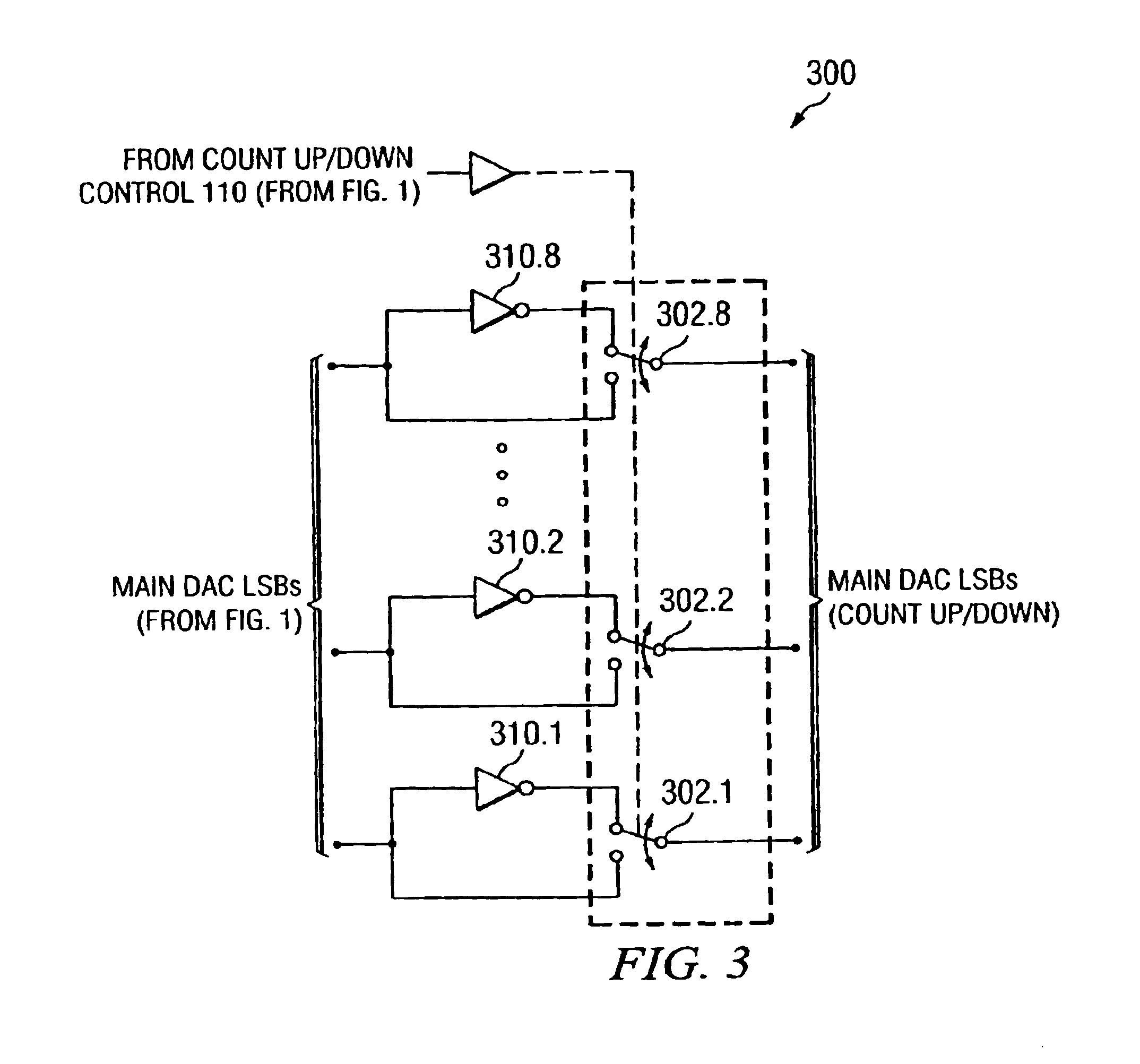
A system and method of calibrating a digital-to-analog converter (DAC) such as a resistor string DAC that reduces costs by making more efficient use of semiconductor die area. A digital-to-analog converter includes a main DAC to be calibrated, a memory, a plurality of calibration DACs, and an analog summing circuit. The main DAC receives digital input code values, and converts the respective input code values into an analog signal. A first calibration DAC receives a predetermined number of lower order bits of the respective input code values, and interpolates between a positive reference voltage and a negative reference voltage to generate linear waveforms for the PWL approximation. A second calibration DAC generates the positive reference voltage, and a third calibration DAC generates the negative reference voltage. The memory stores a plurality of PWL breakpoint code values representing respective integral non-linearity error values of the main DAC, and applies consecutive PWL breakpoint code values to the second and third calibration DACs, respectively, to generate the positive and negative reference voltages for the first calibration DAC.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
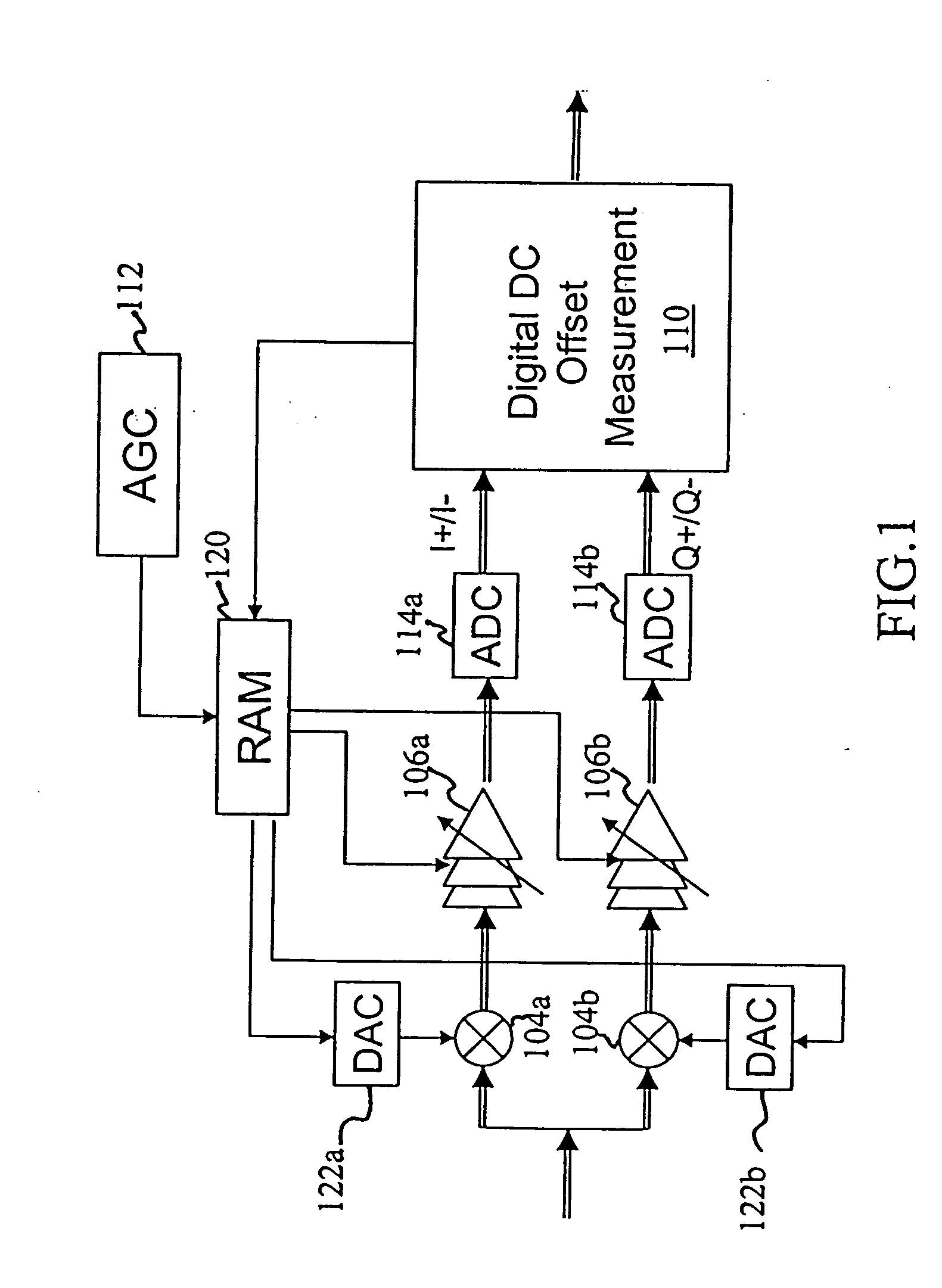
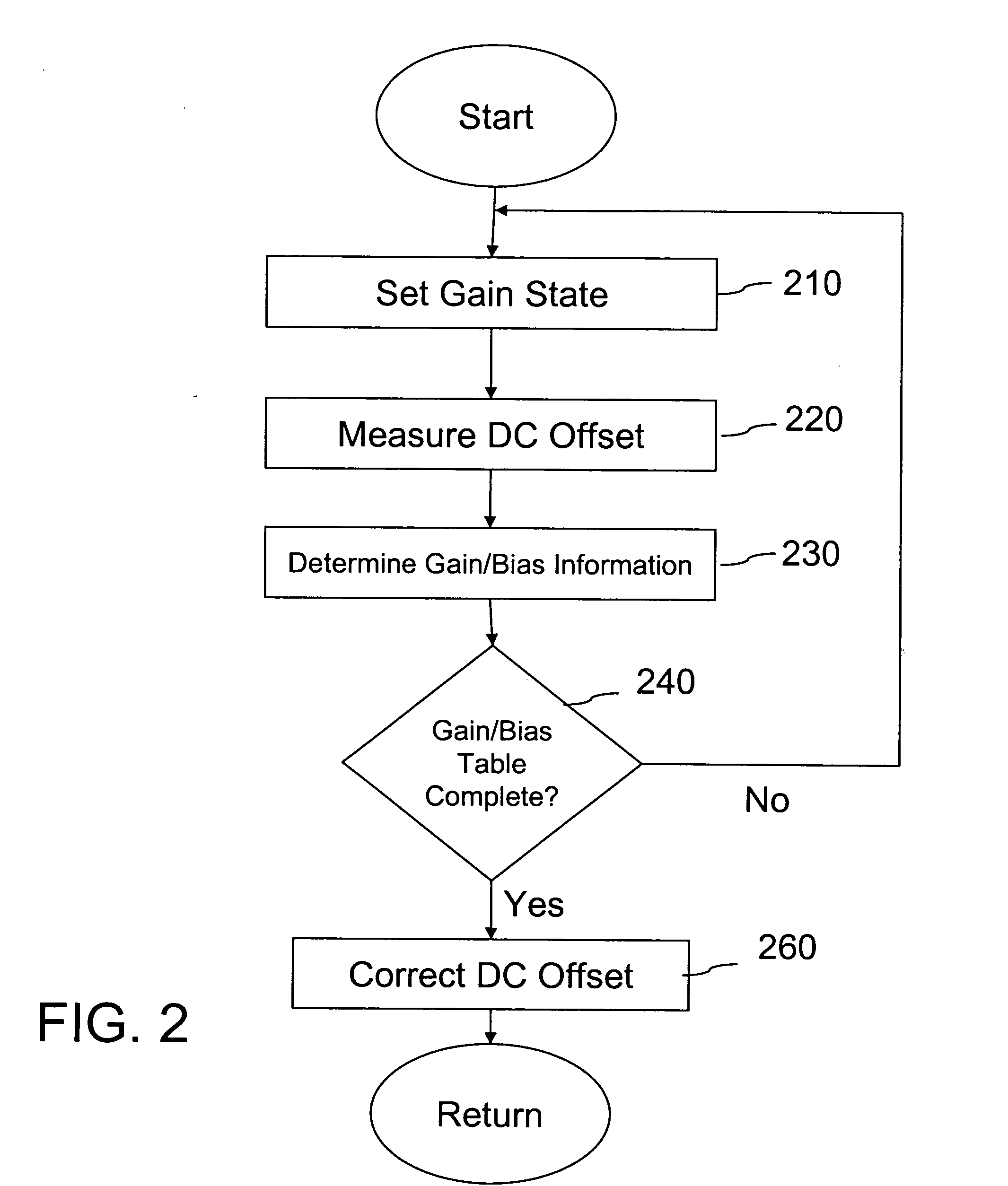
Hybrid DC offset cancellation scheme for wireless receiver
ActiveUS20050258989A1Remove offsetElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersNegative feedbackOffset cancellation
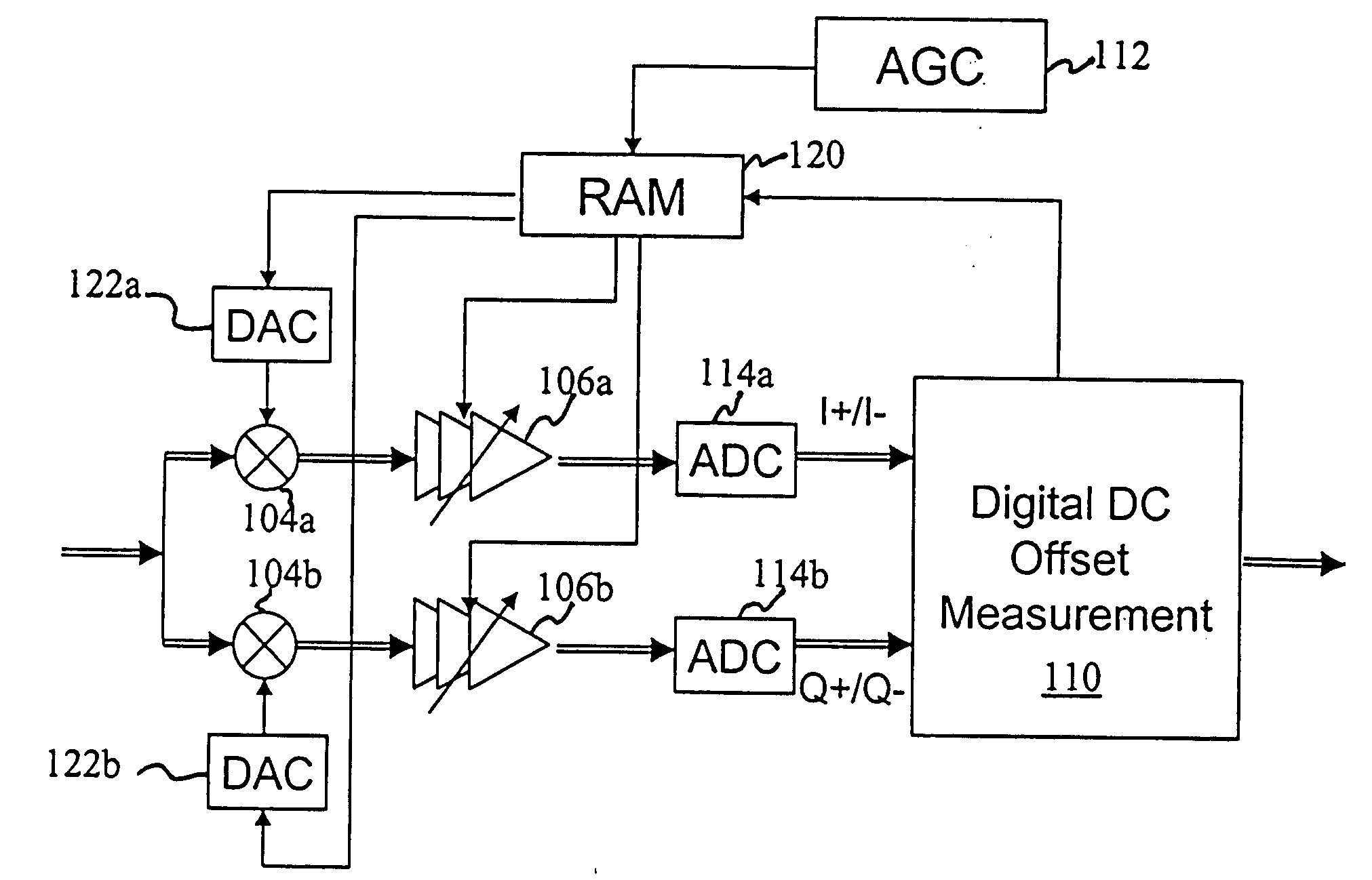
Systems and methods for canceling static and dynamic DC offsets by combining a digital DC offset correction scheme with an analog DC offset correction scheme. A feedback-based digital DC offset correction scheme provides different adjustment levels for a plurality of discrete gain states and the analog DC offset correction scheme operates in different cancellation modes dependent on a frame structure. A digital DC offset correction scheme collects DC offset control information and provides adjustment levels. In addition, a negative-feedback based switchable high pass filter has a plurality modes of operation, where one mode of operation includes an all-pass filter.
Owner:WIONICS RES +1
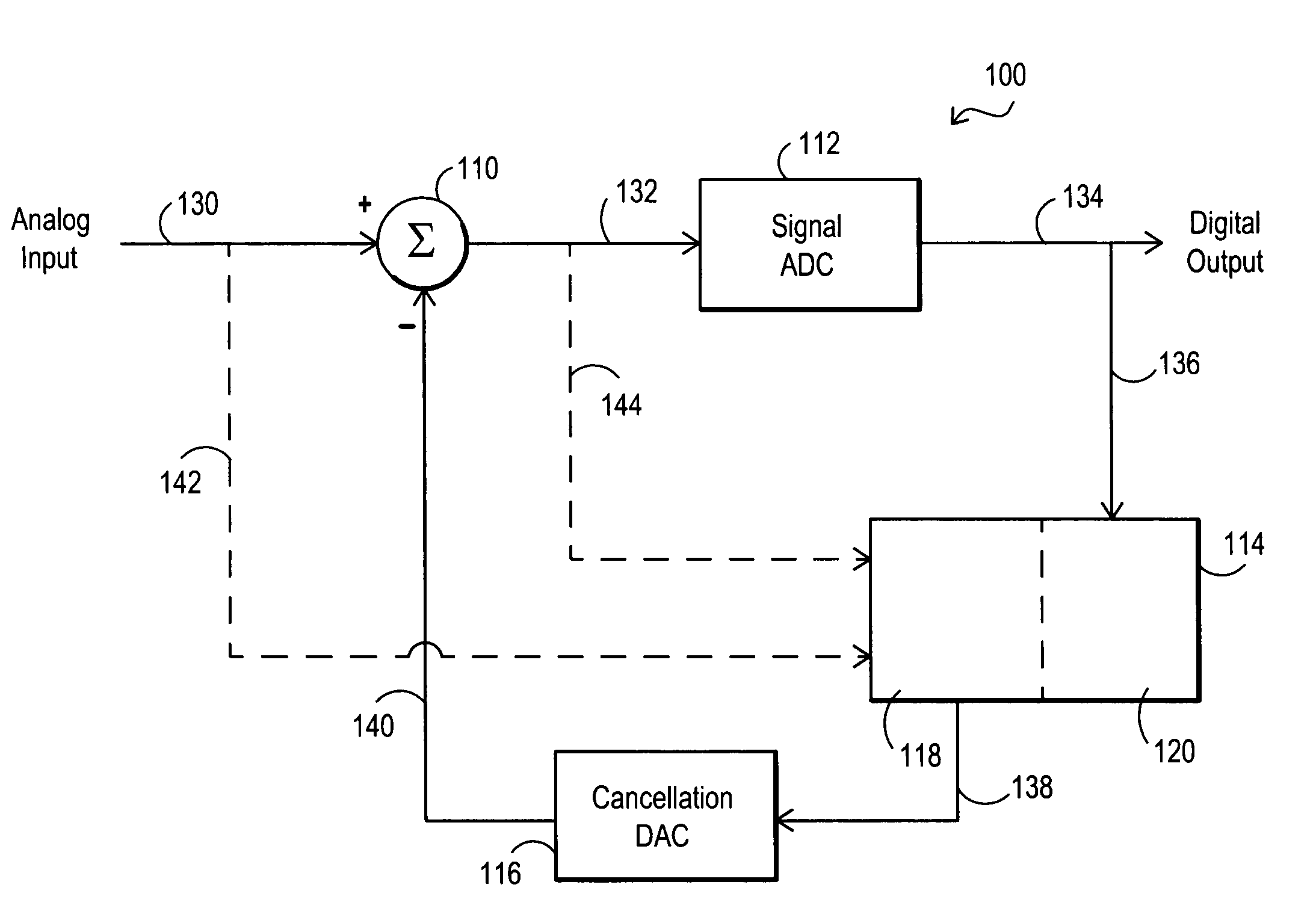
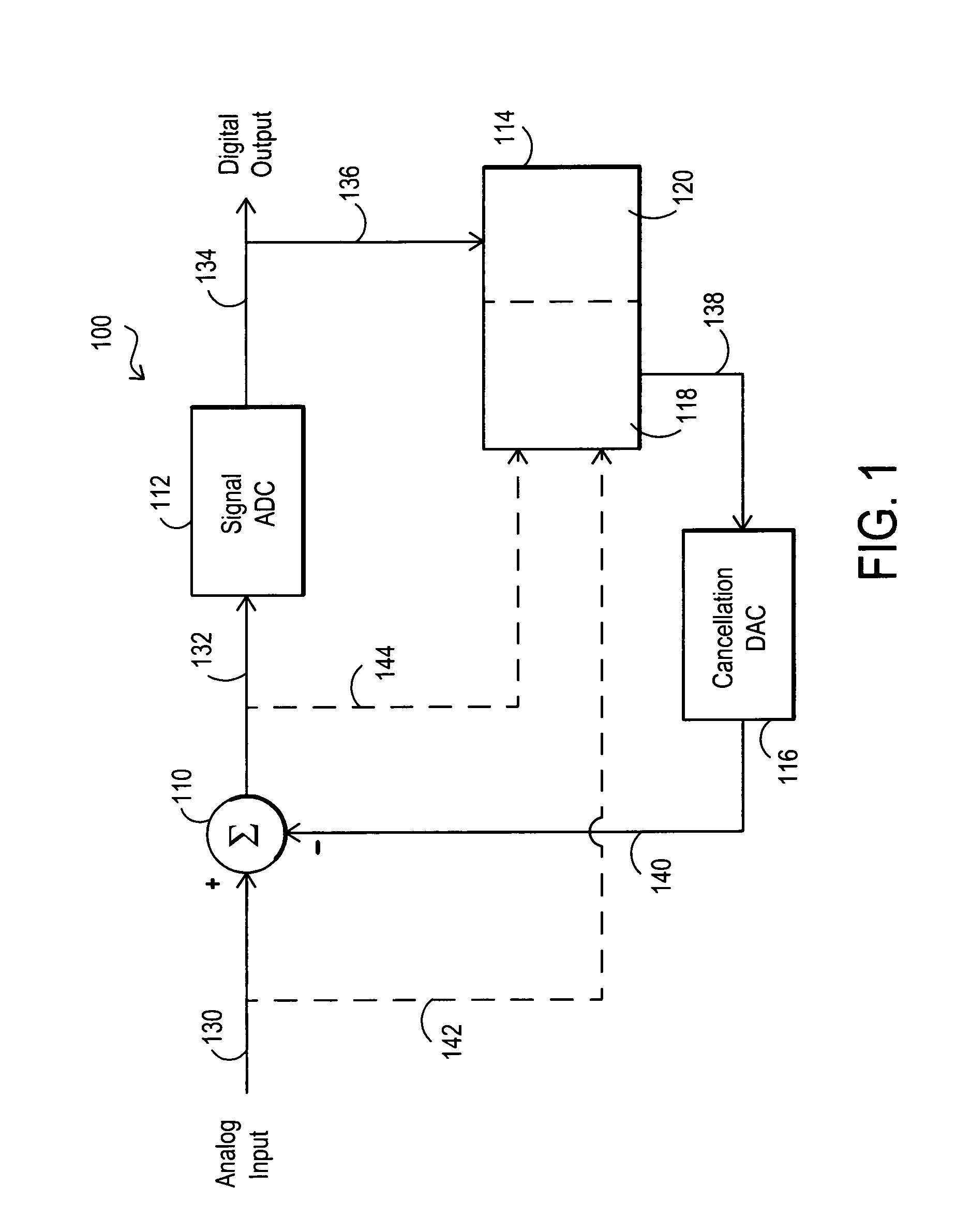
Systems and methods for multi-channel analog to digital conversion
InactiveUS6956517B1Increase effective dynamic rangeMore cost-effectiveElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersNegative feedbackEngineering
Systems and methods for analog to digital conversion that may be implemented using a digital to analog converter (DAC) to provide negative feedback to cancel signals at the input of an analog to digital converter (ADC), and that may be used to extend the effective dynamic range of an ADC. The systems and methods may be implemented in multi-channel environments.
Owner:L 3 INTEGRATED SYST +1
Digital direct conversion receiving apparatus and method
InactiveUS20100156690A1InhibitionElectric signal transmission systemsModulated-carrier systemsPhase conversionPhase difference
A digital direct conversion receiving apparatus, including: a phase conversion unit to down-convert a Radio Frequency (RF) signal into a plurality of sample signals, and generate a certain phase difference among the plurality of sample signals when the RF signal is down-converted; and a variable complex gain unit to remove an image component from the plurality of sample signals using the generated phase difference.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Autocalibration of the A/D converter within the CMOS type image sensor
A method for initializing a counter within a corresponding set of A / D converters of N sets of A / D converters of a single-chip CMOS-type image sensor in order to minimize none uniformity across the N sets of A / D converters is provided. The single chip CMOS type image sensor includes an image sense array having N columns of output lines for outputting N analog signals respectively; and a signal process device for generating N sets of digital signal each of which corresponds to one of N analog signals respectively. The signal process device has N input lines and N sets of A / D converter each of which including a counter for generating one of the N sets of digital signal respectively. The method comprises the steps of applying a predetermined reference voltage at each of N input lines of the signal process device such that a compensation value corresponding to each set of A / D converter is obtained. The method further preloads the counter of each corresponding set of A / D converter with the compensation value corresponding to each set of A / D converter.
Owner:ALCOR MICRO CORP
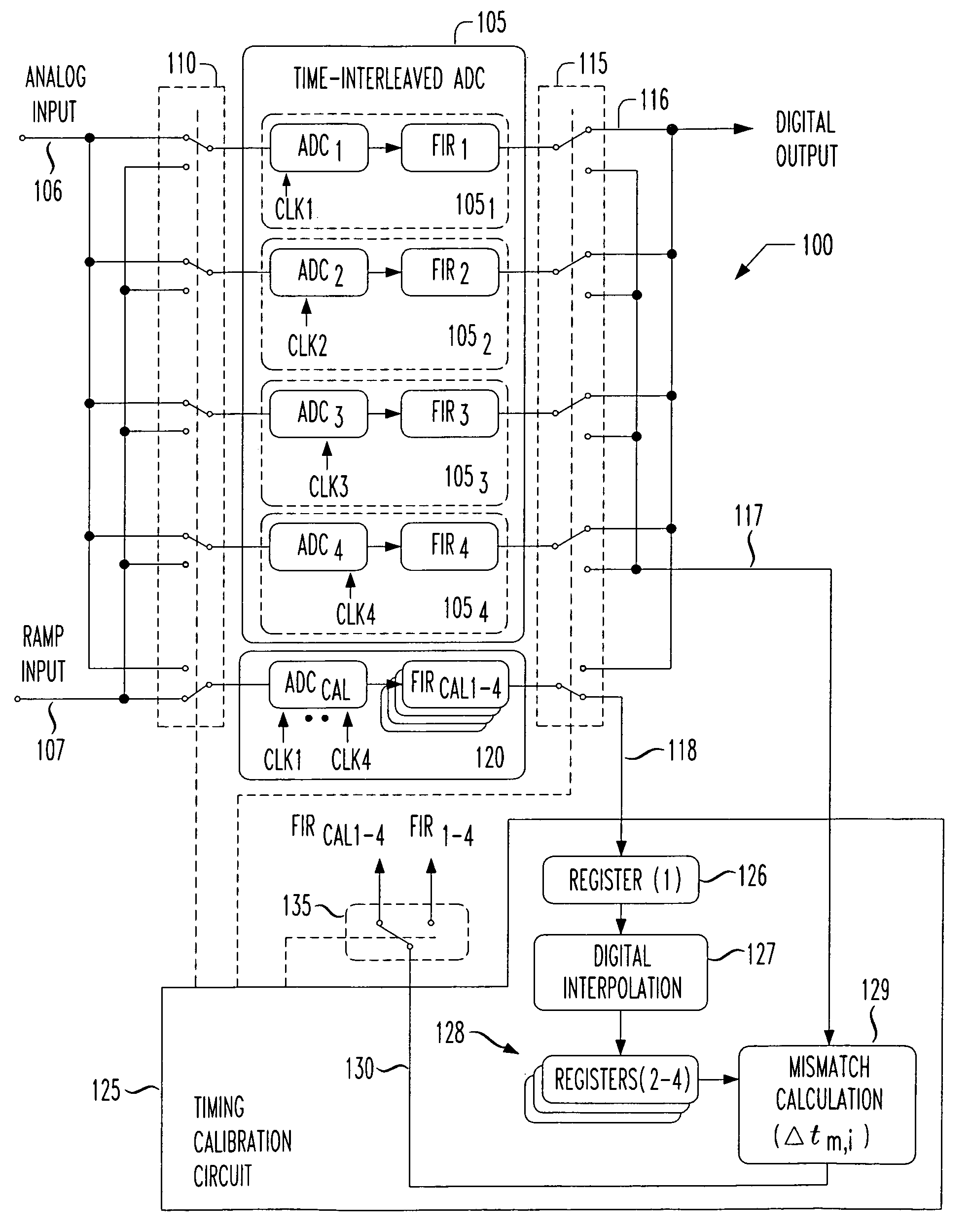
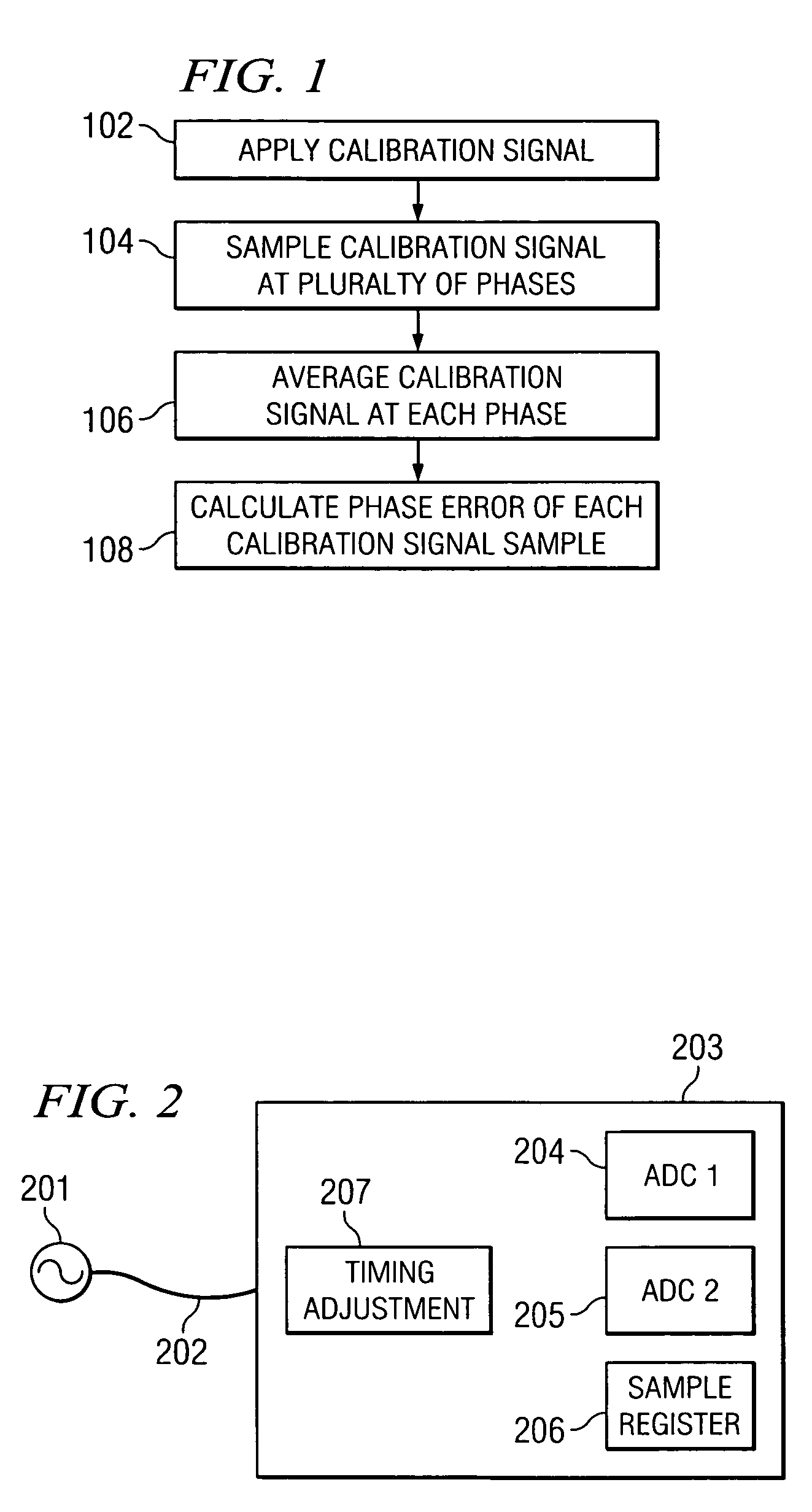
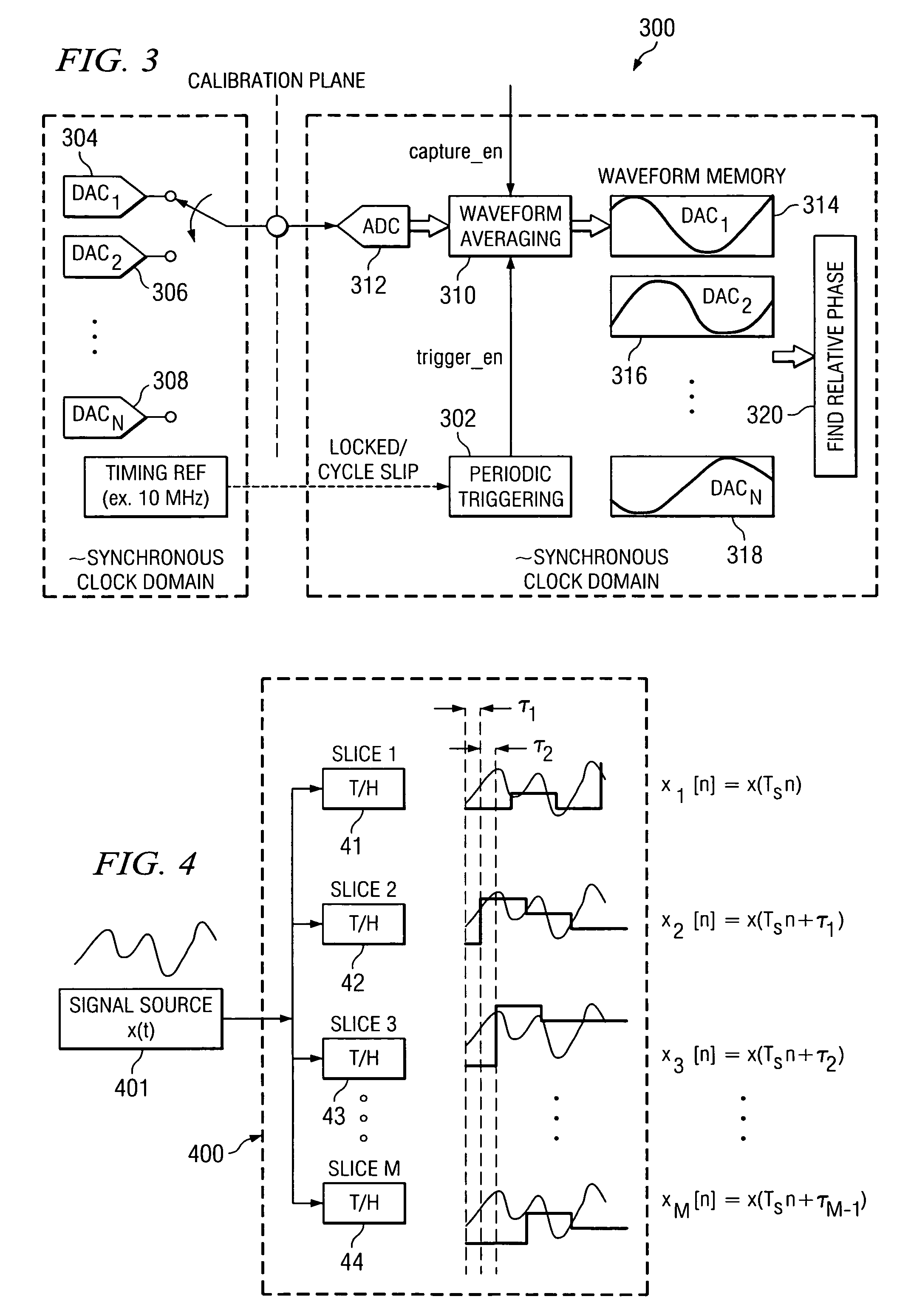
System and method for timing calibration of time-interleaved data converters
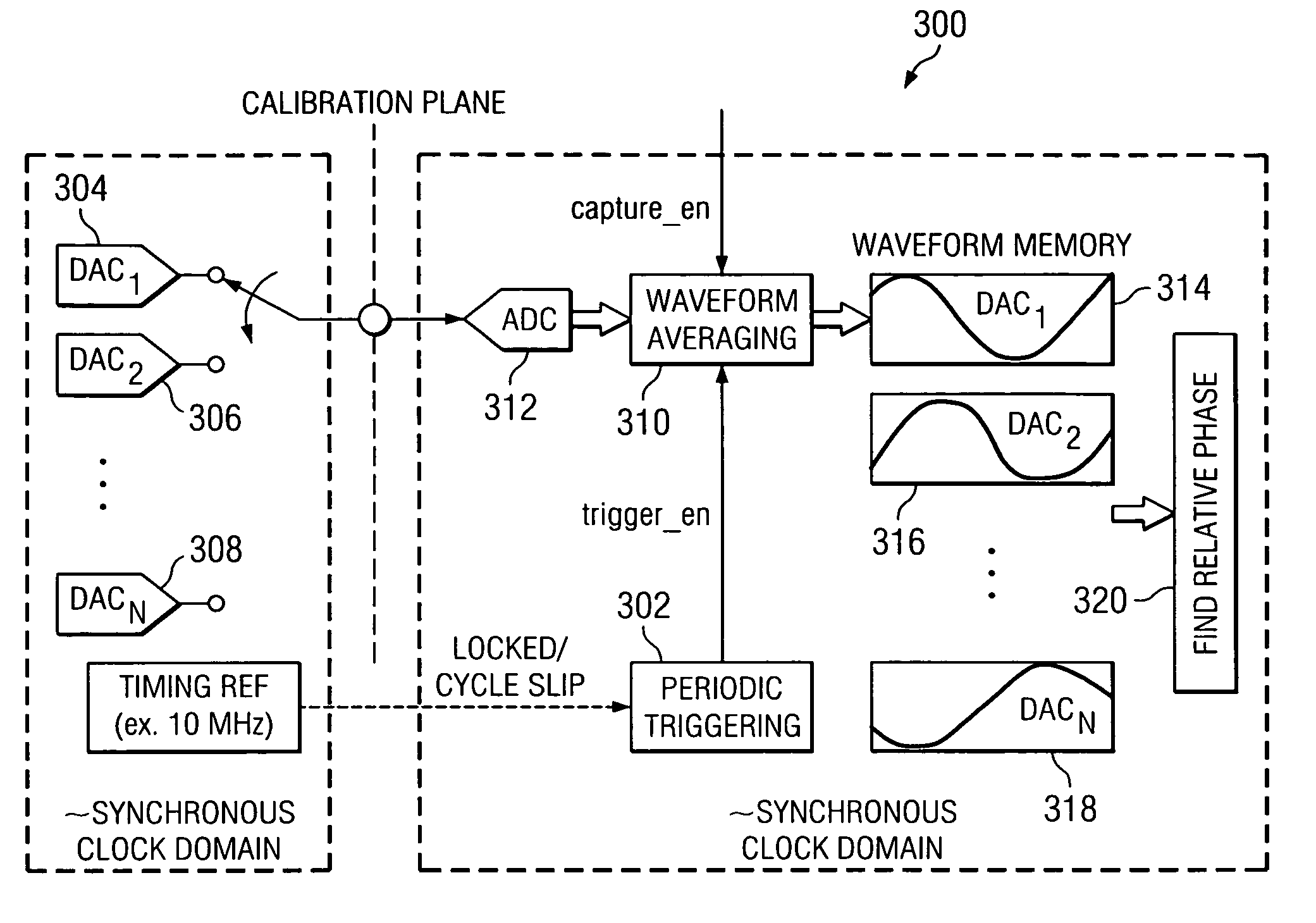
ActiveUS7148828B2Reduce supportShorten test timeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingFrequency spectrumTime interleaved
A method for calibrating time interleaved samplers comprising applying a calibration signal to a time-interleaved sampling device, wherein the signal is coherent with at least one sample clock on the device and is periodic and has a predetermined spectral content and frequency, sampling, by said time-interleaved sampling device, the calibration signal at a plurality of phases to form samples, averaging the formed samples, and calculating the phase error of each sample based on the average calibration signal sample.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH
Popular searches
Input/output processes for data processing Electric digital data processing Secret communication Transmitter/receiver shaping networks Synchronous/start-stop systems Bait Color television details Television system scanning details Single television signal transmission by single carrier Pulse automatic control
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com