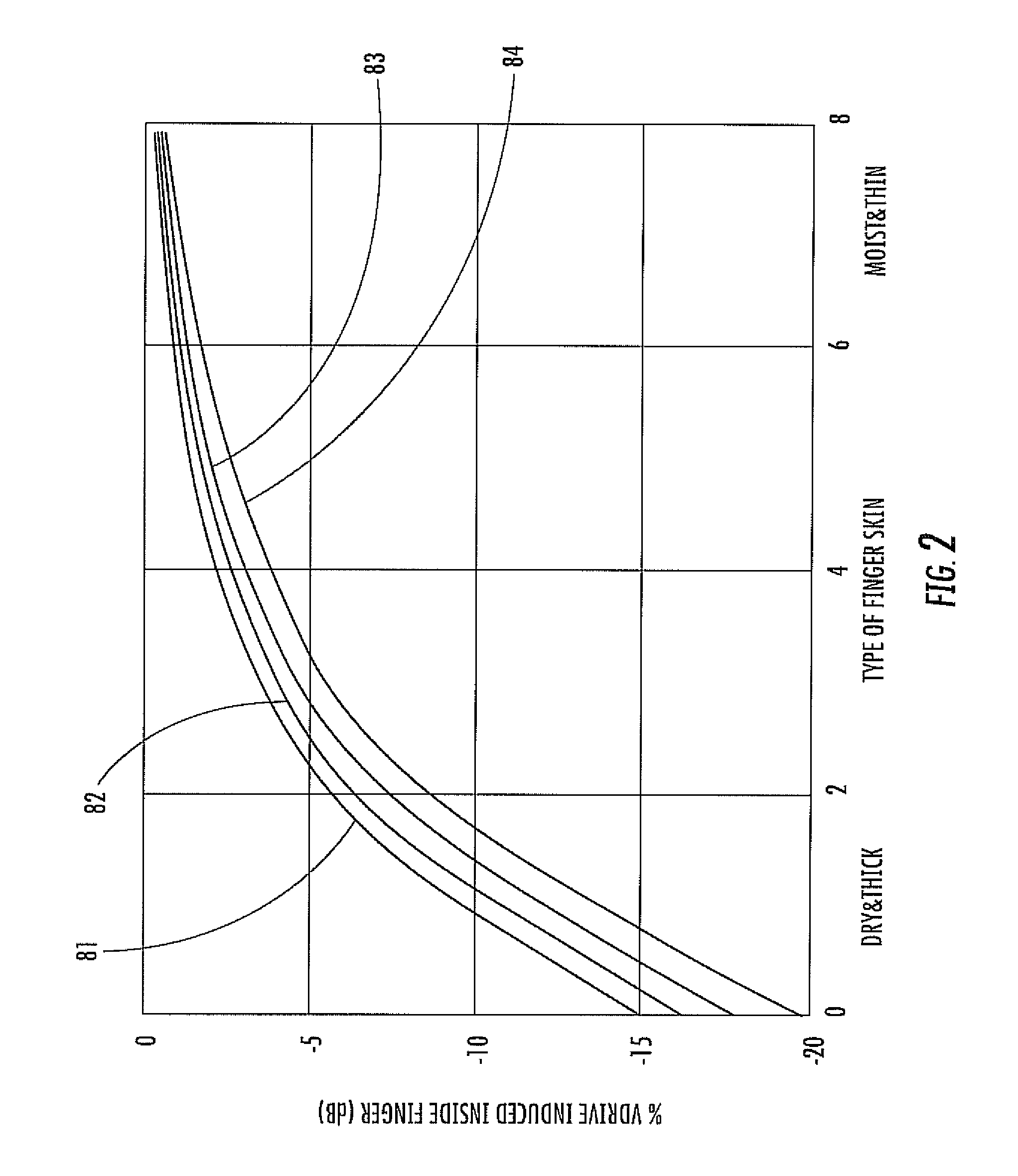
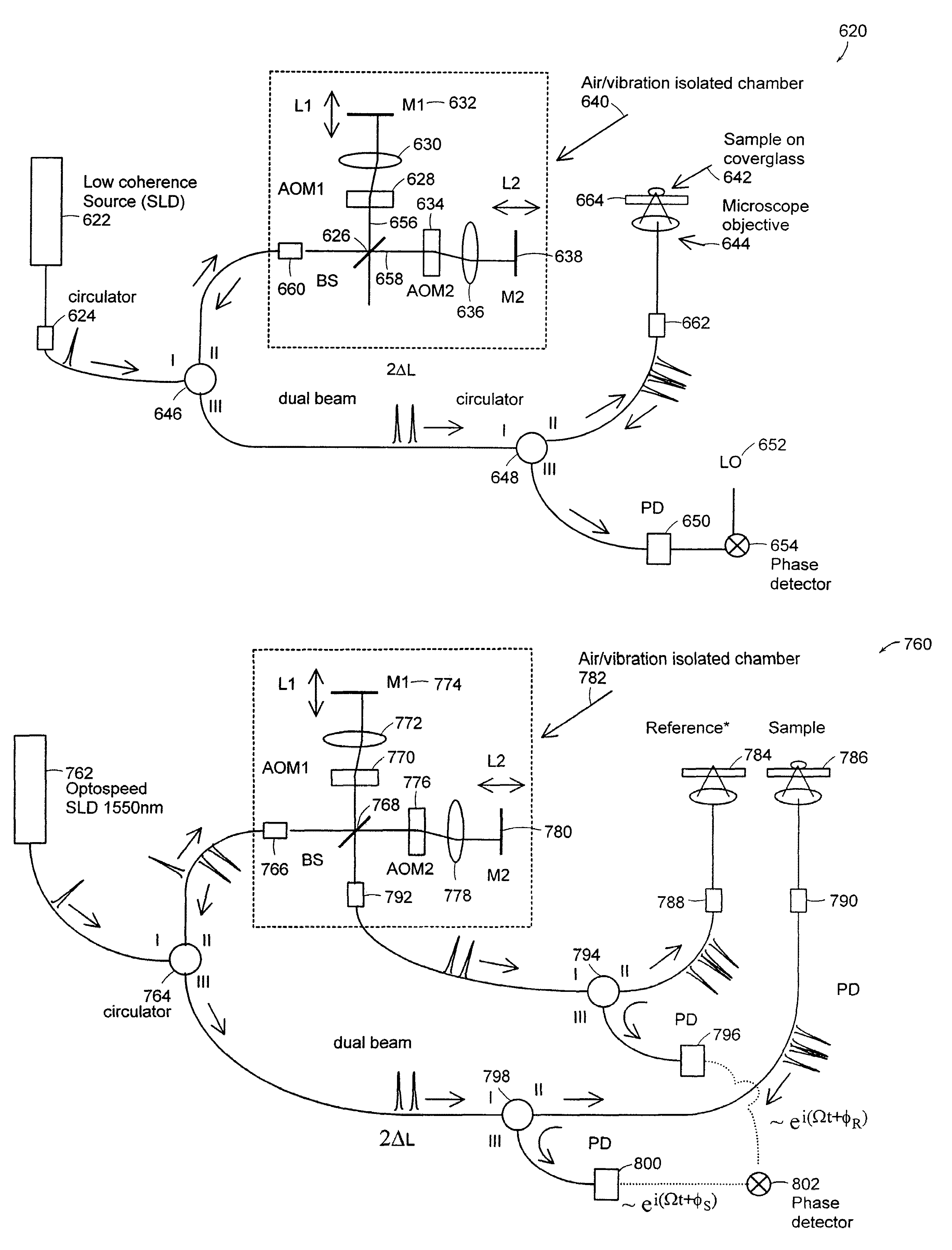
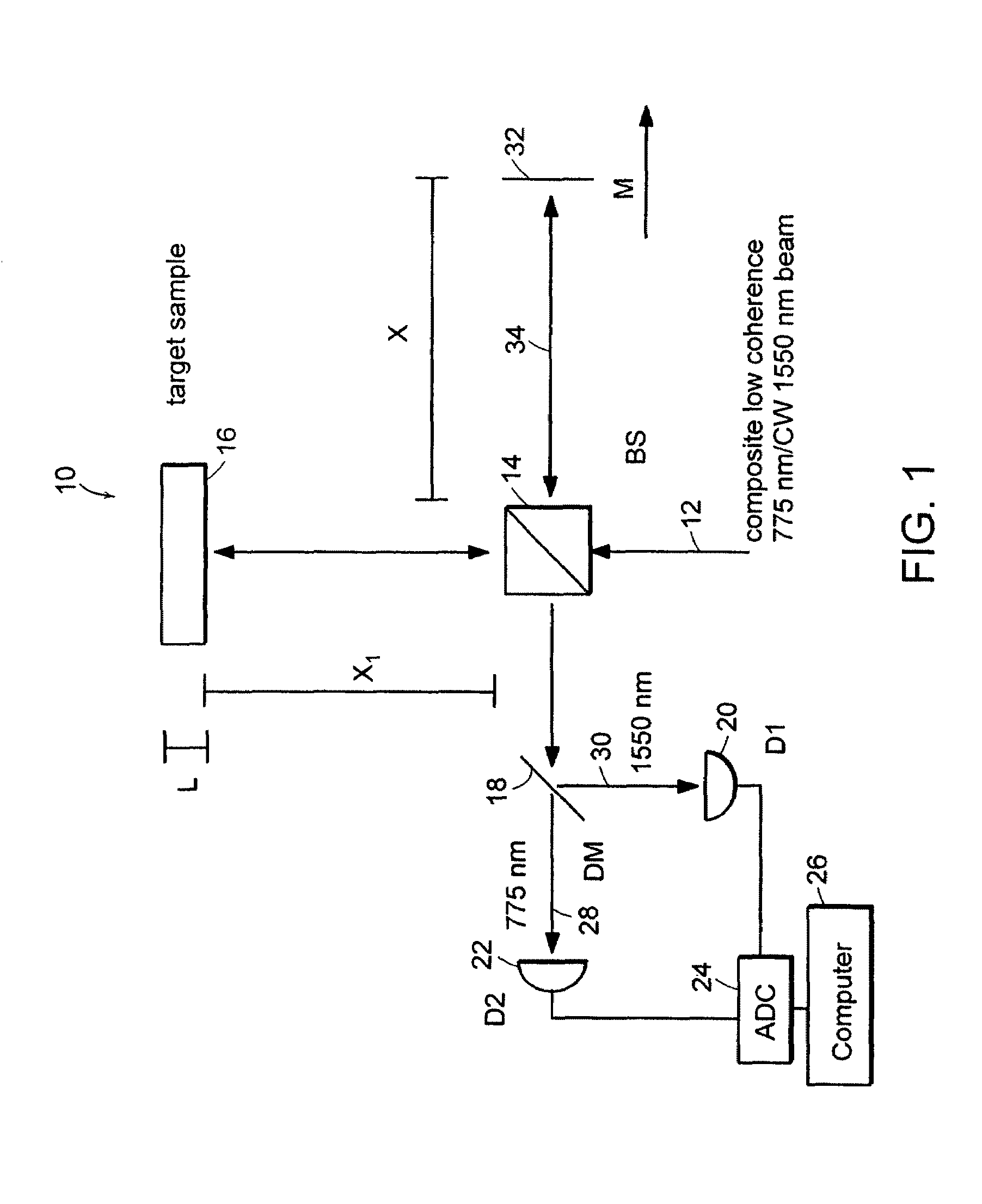
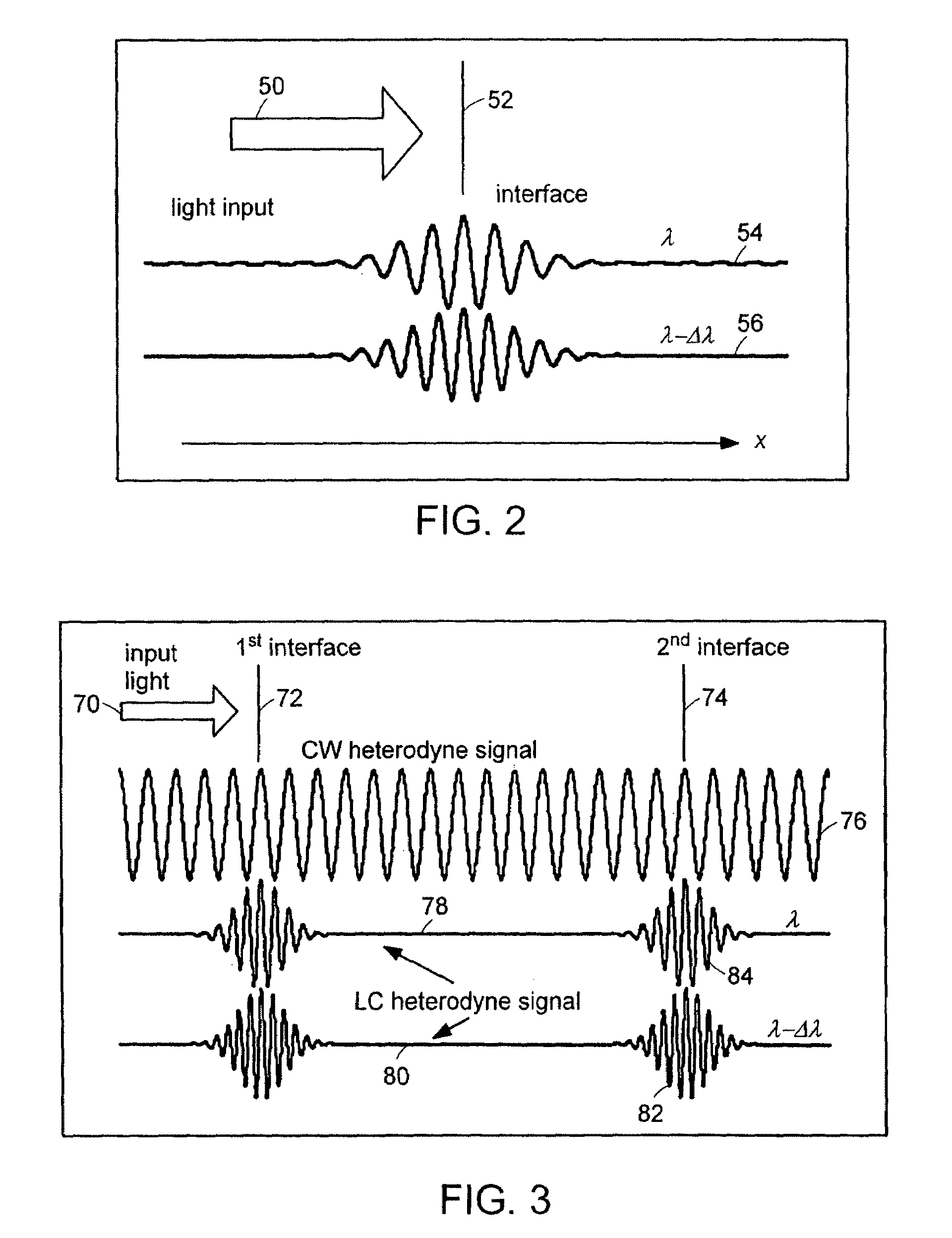
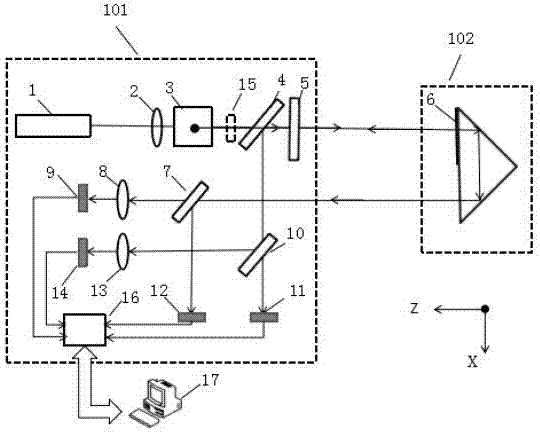
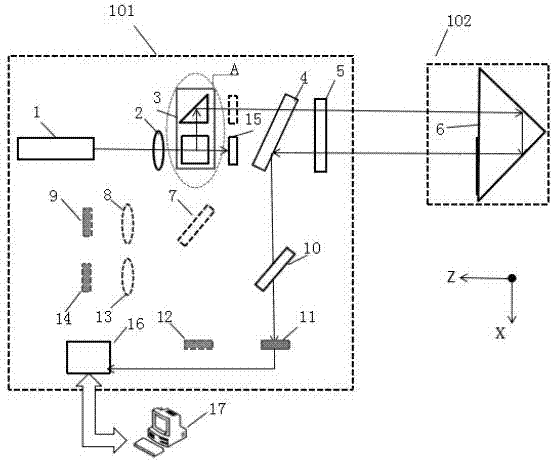
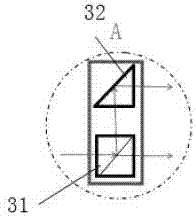
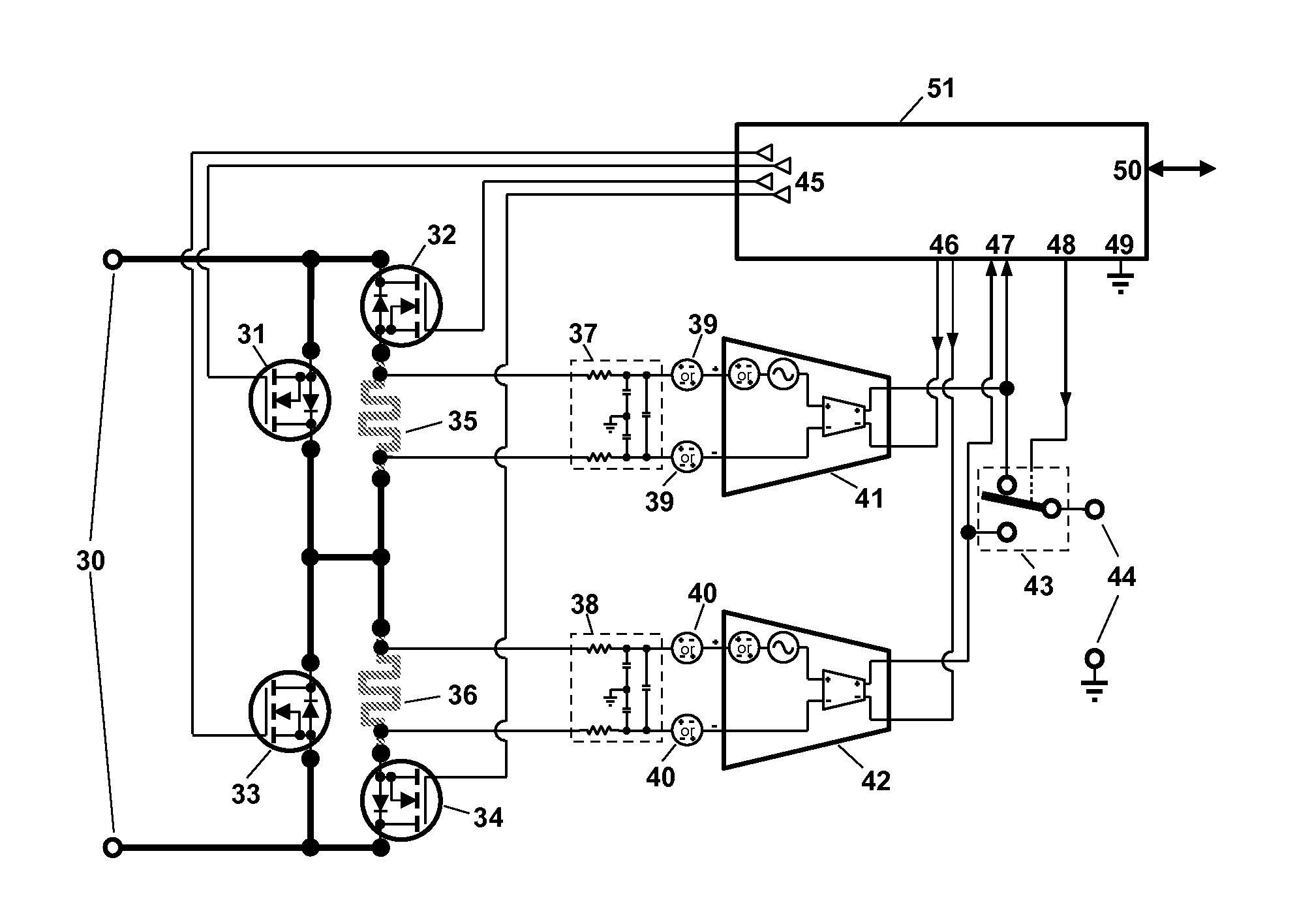
Patents
Literature
321 results about "Differential measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The differential method of measurement is of great importance in checking measuring devices, which is the comparison with a standard of the measure being checked (for example, standard cells connected in counterseries). The differential method is also used in testing materials and articles by means of comparison with a standard sample.
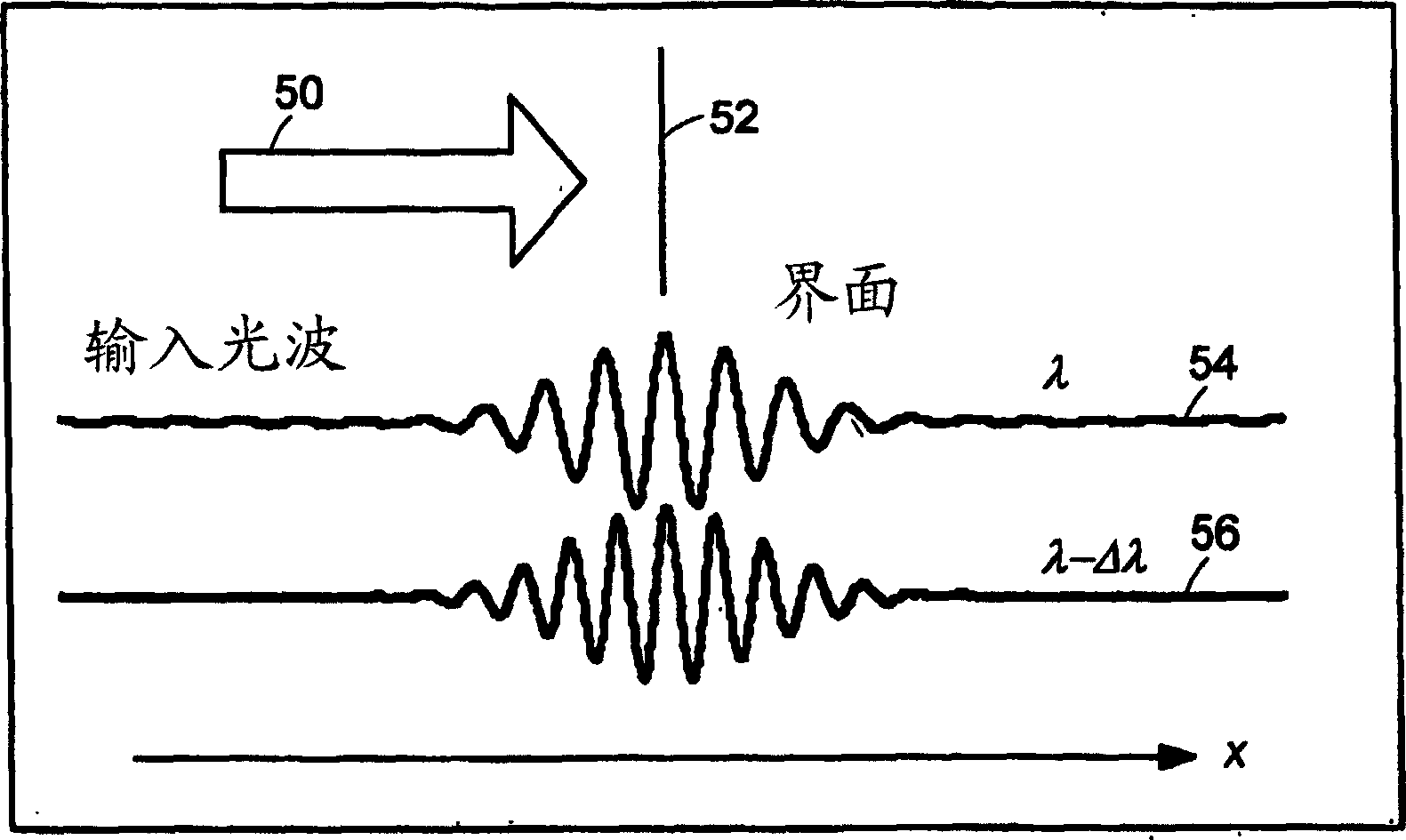
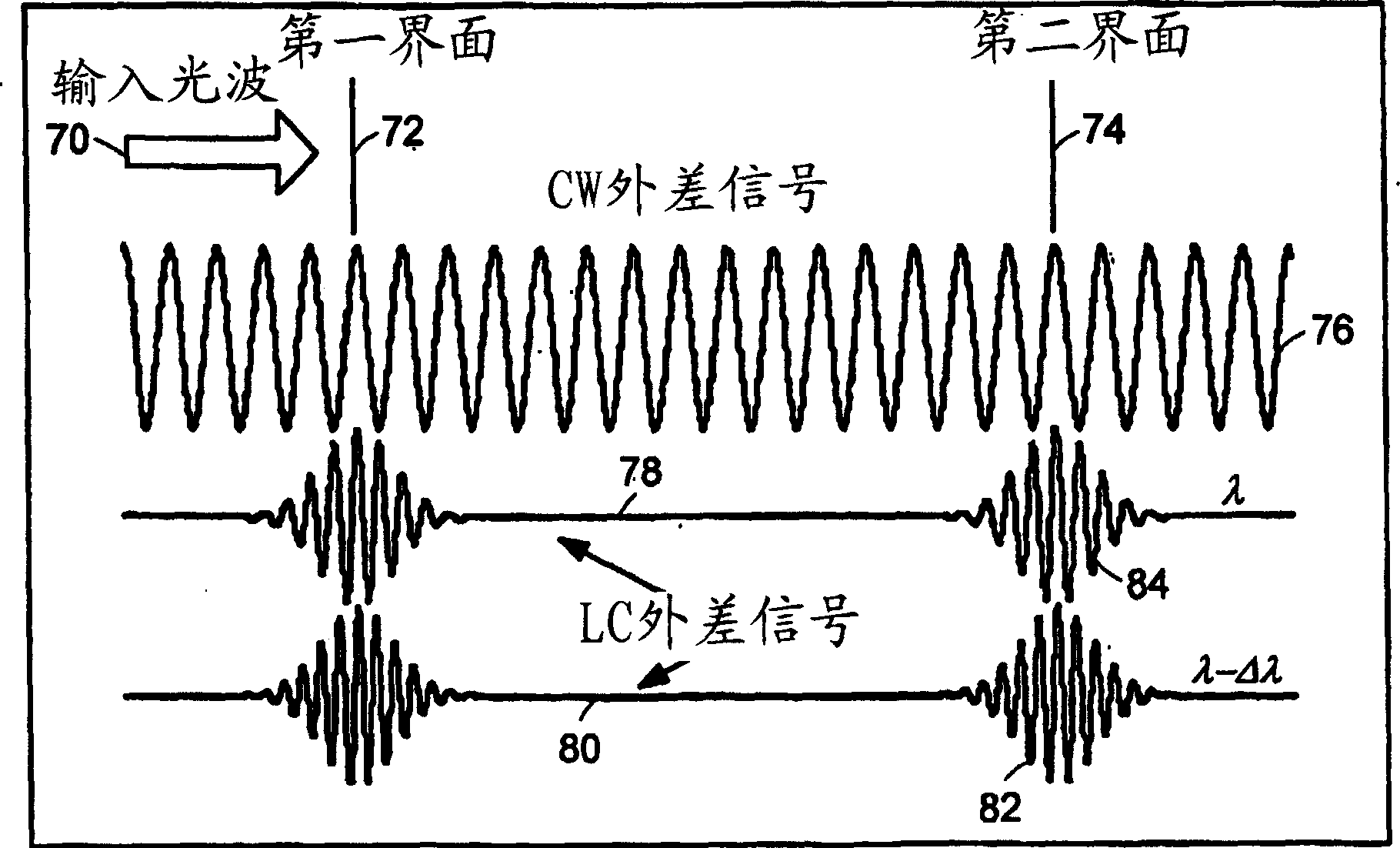
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050057756A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsCellular componentPhase noise
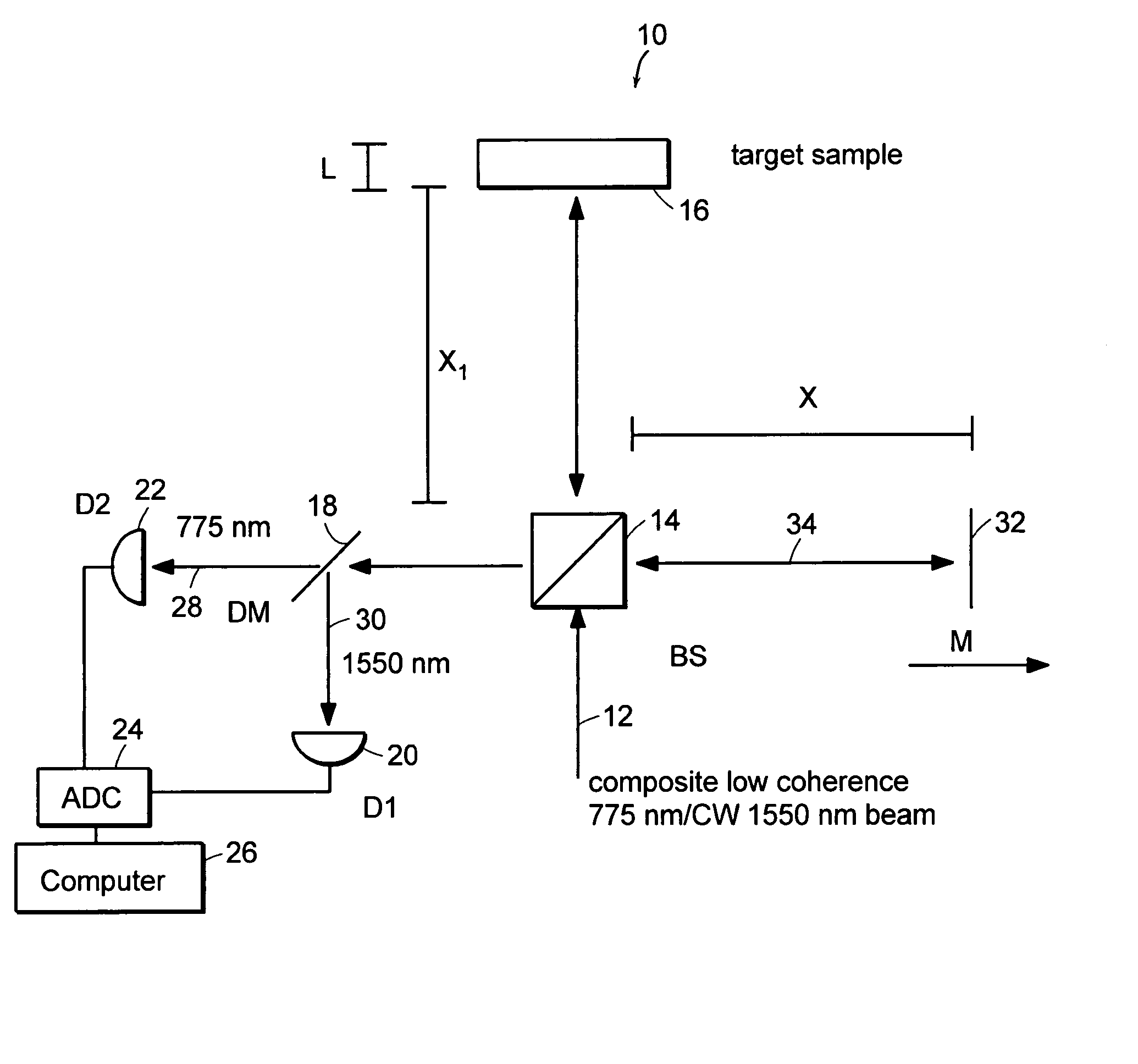
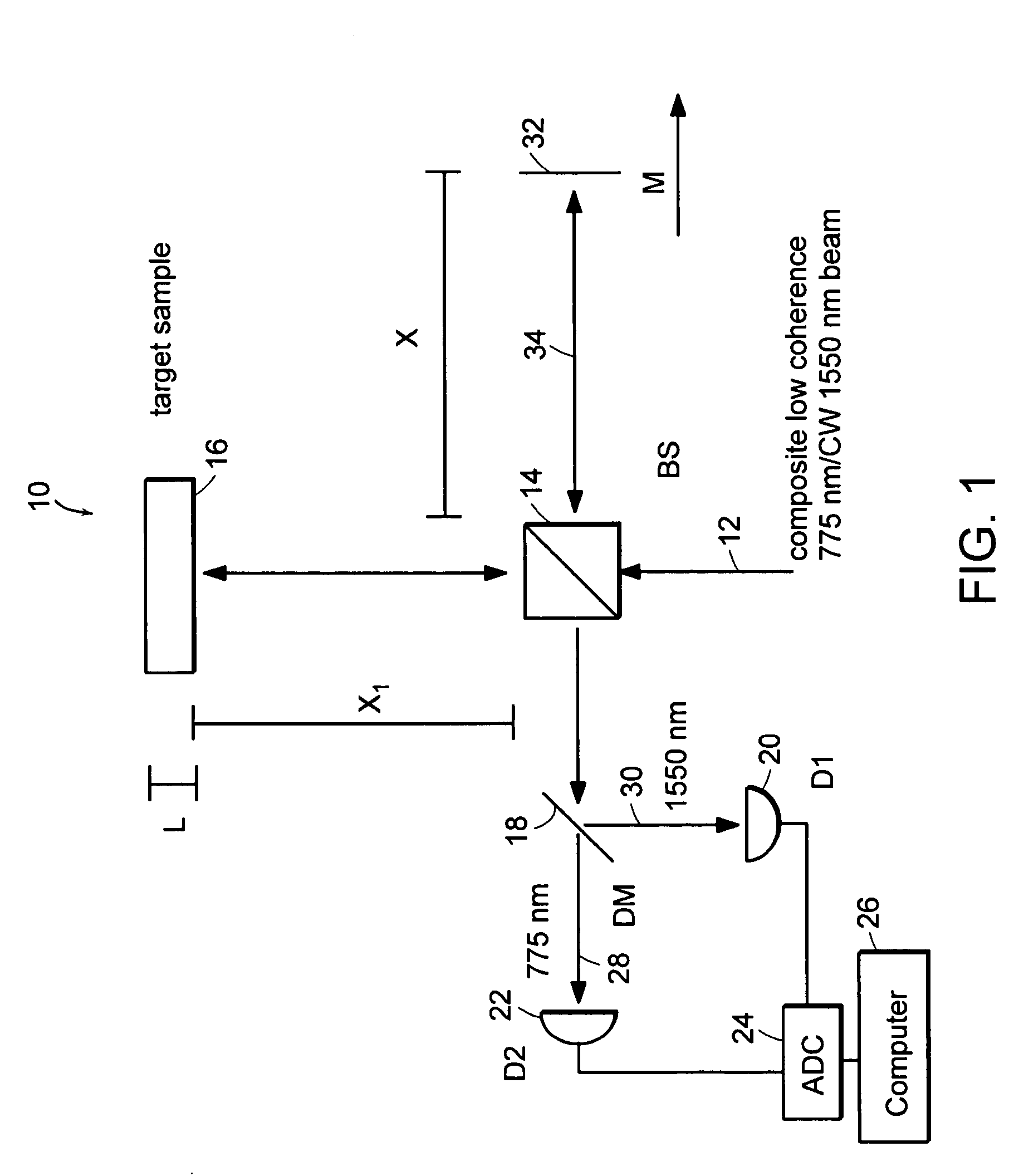
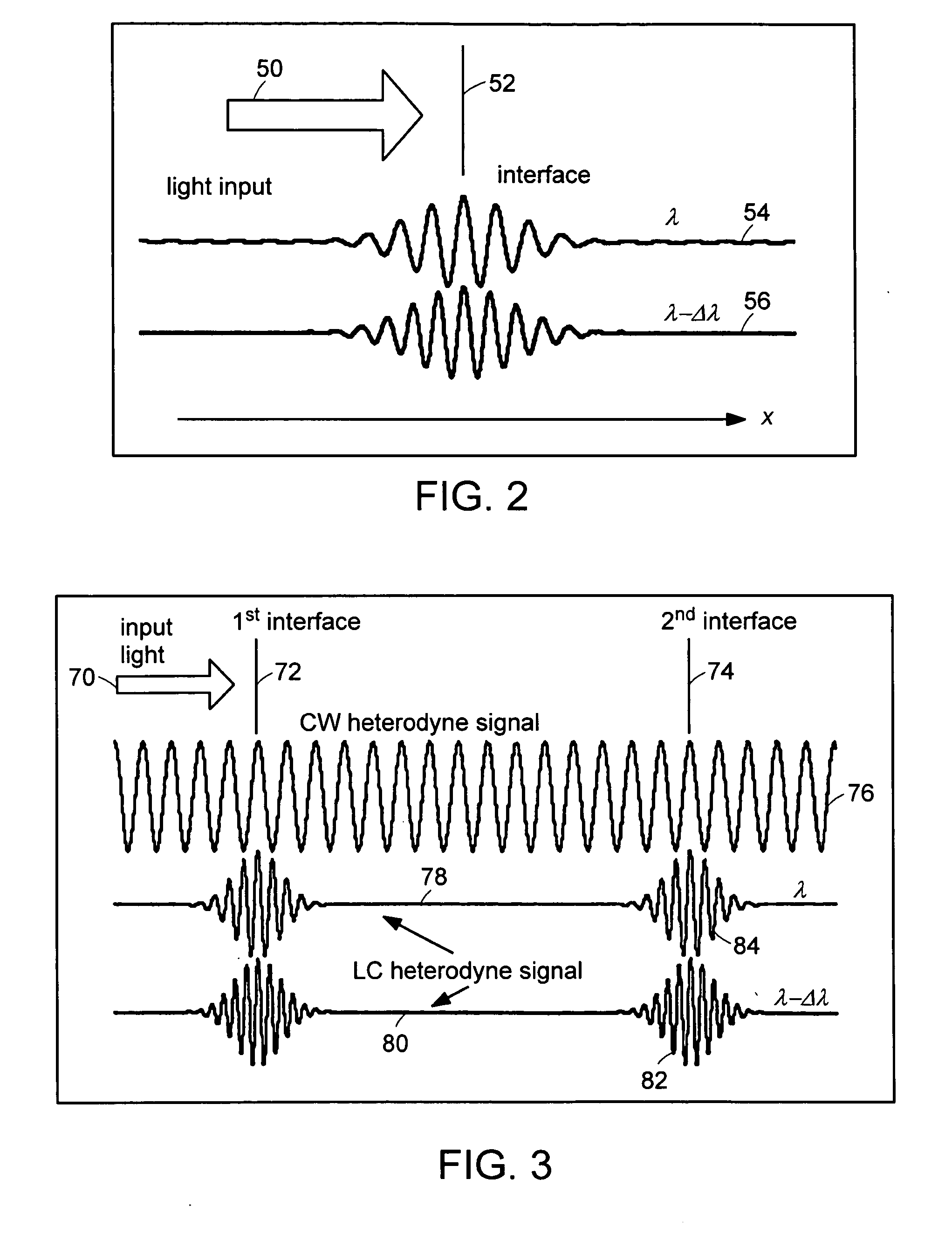
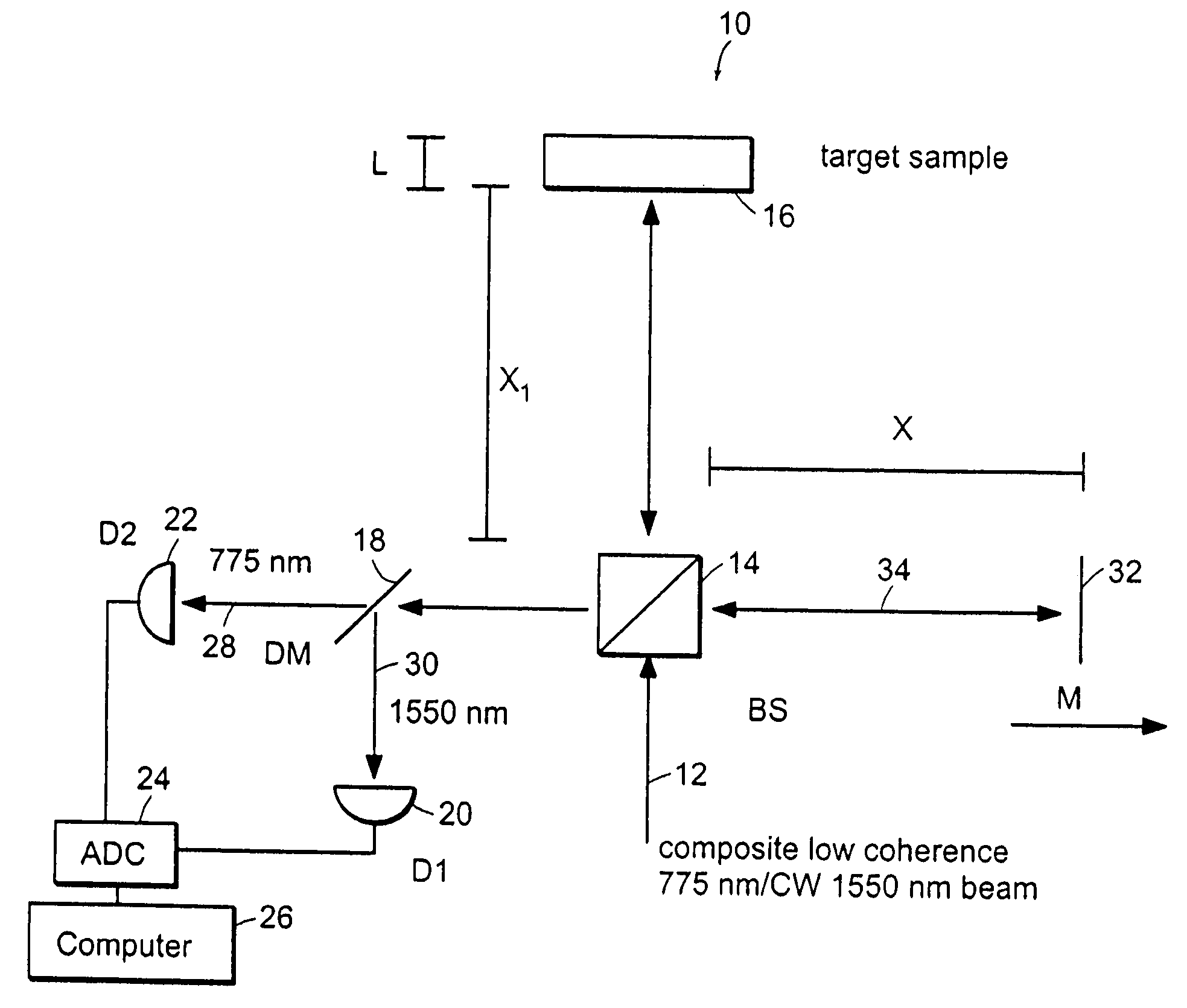
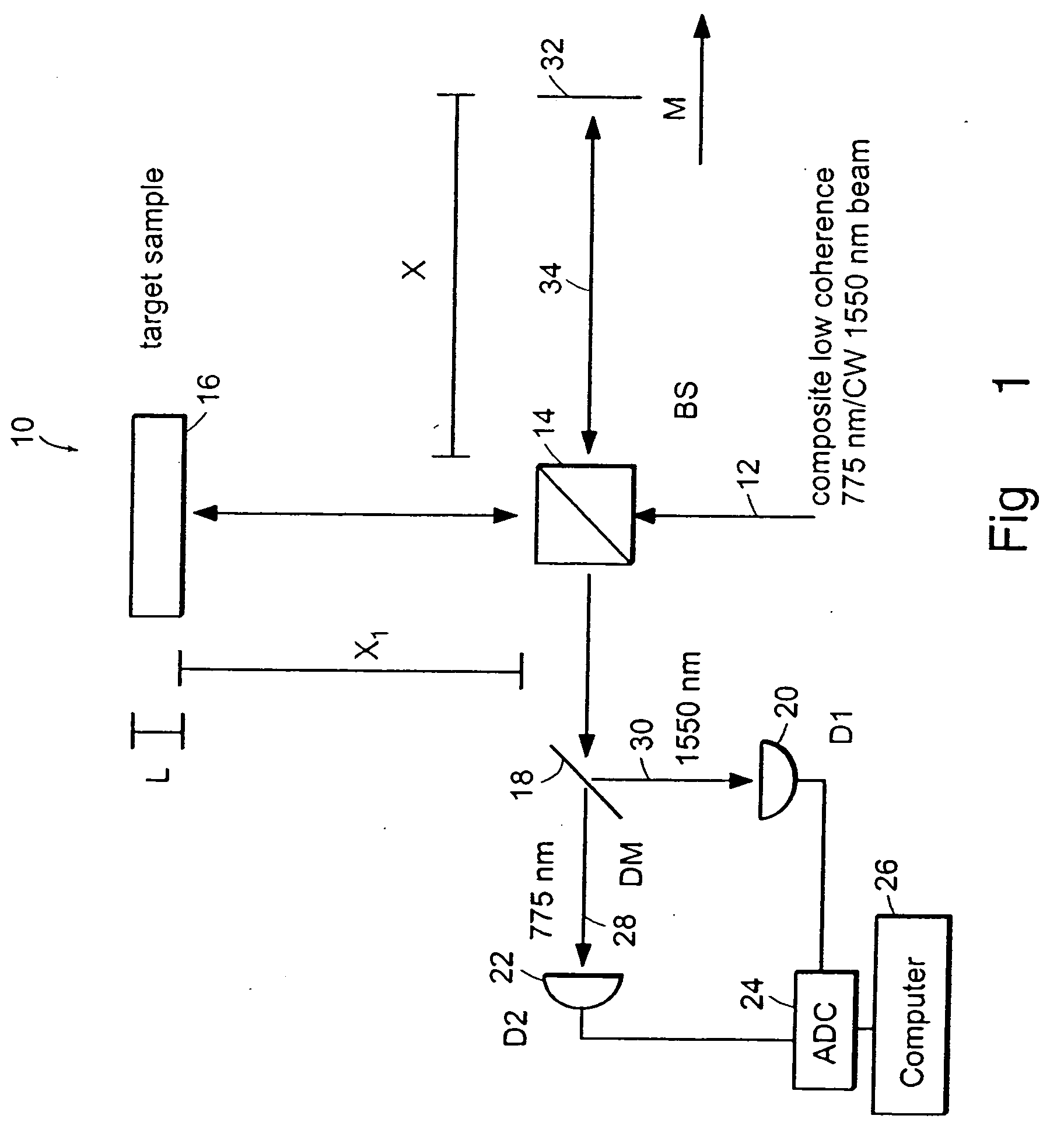
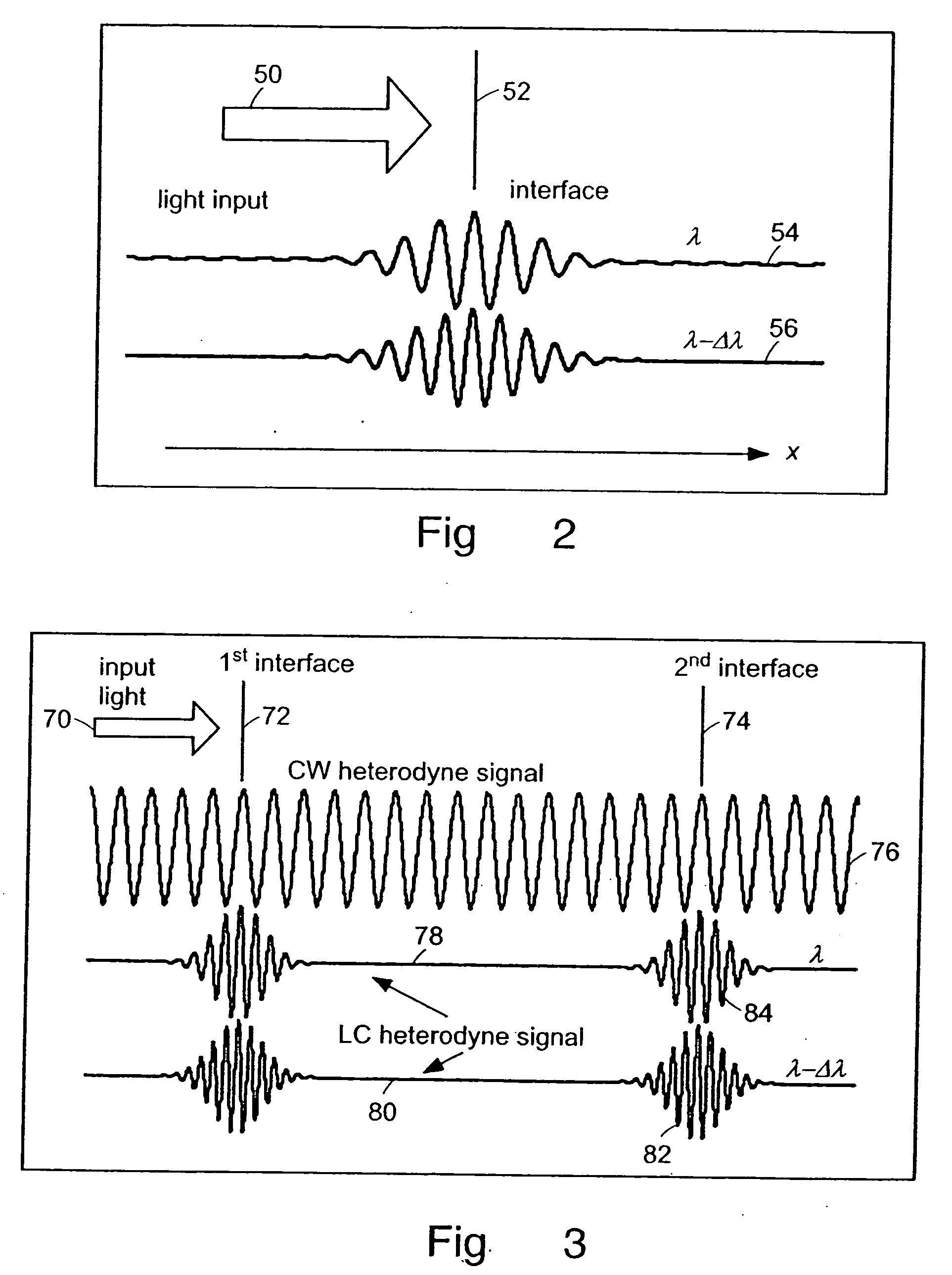
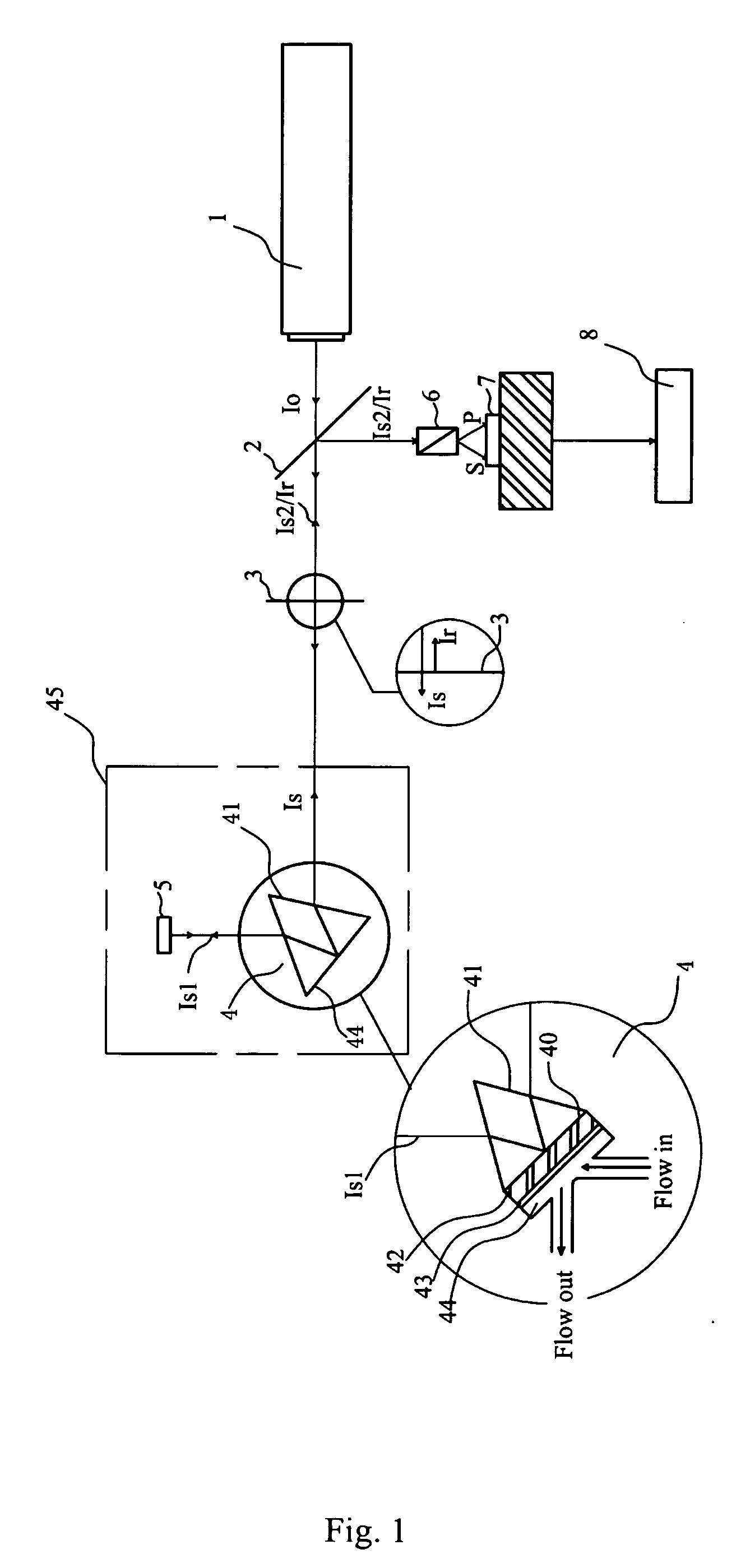
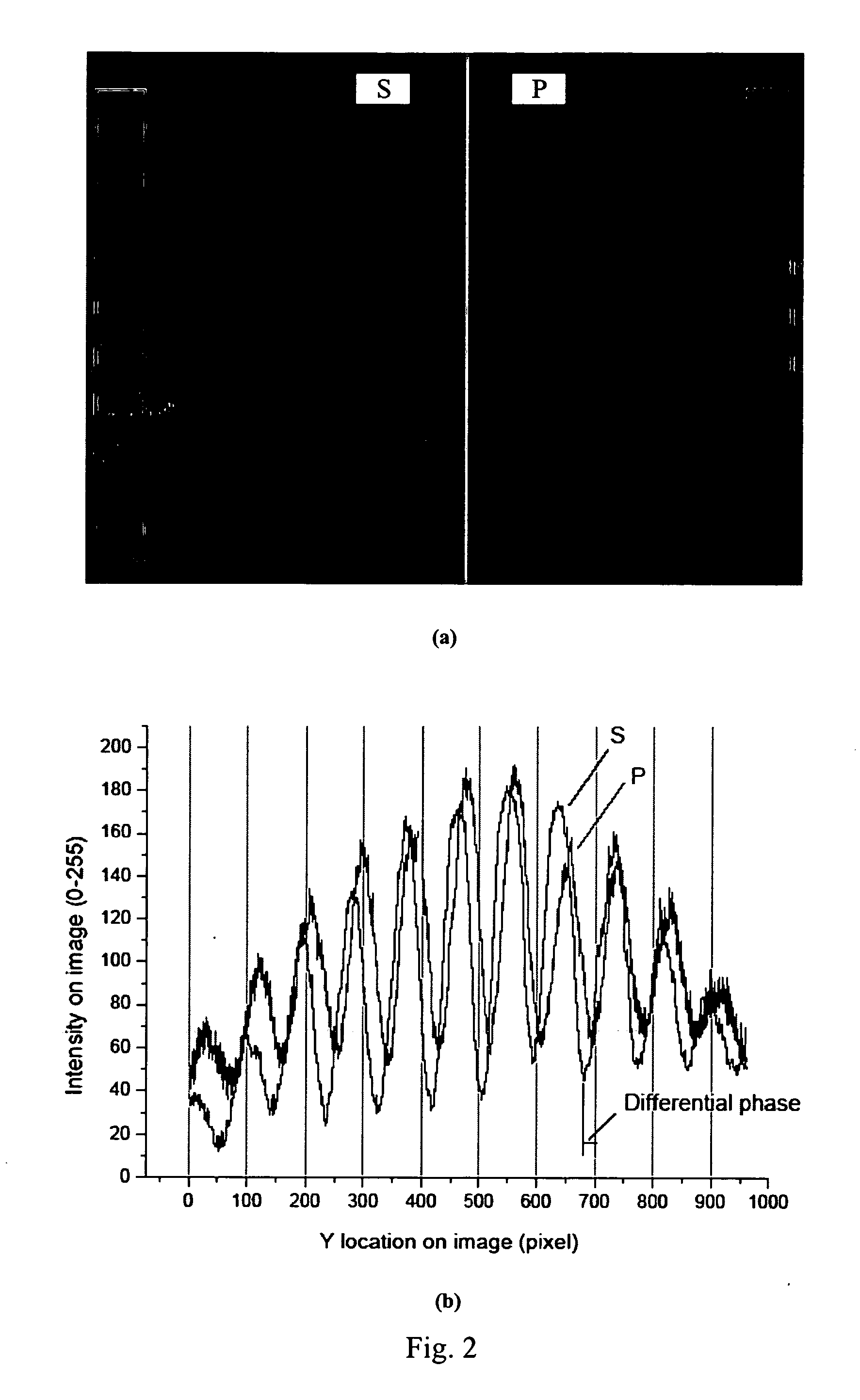
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
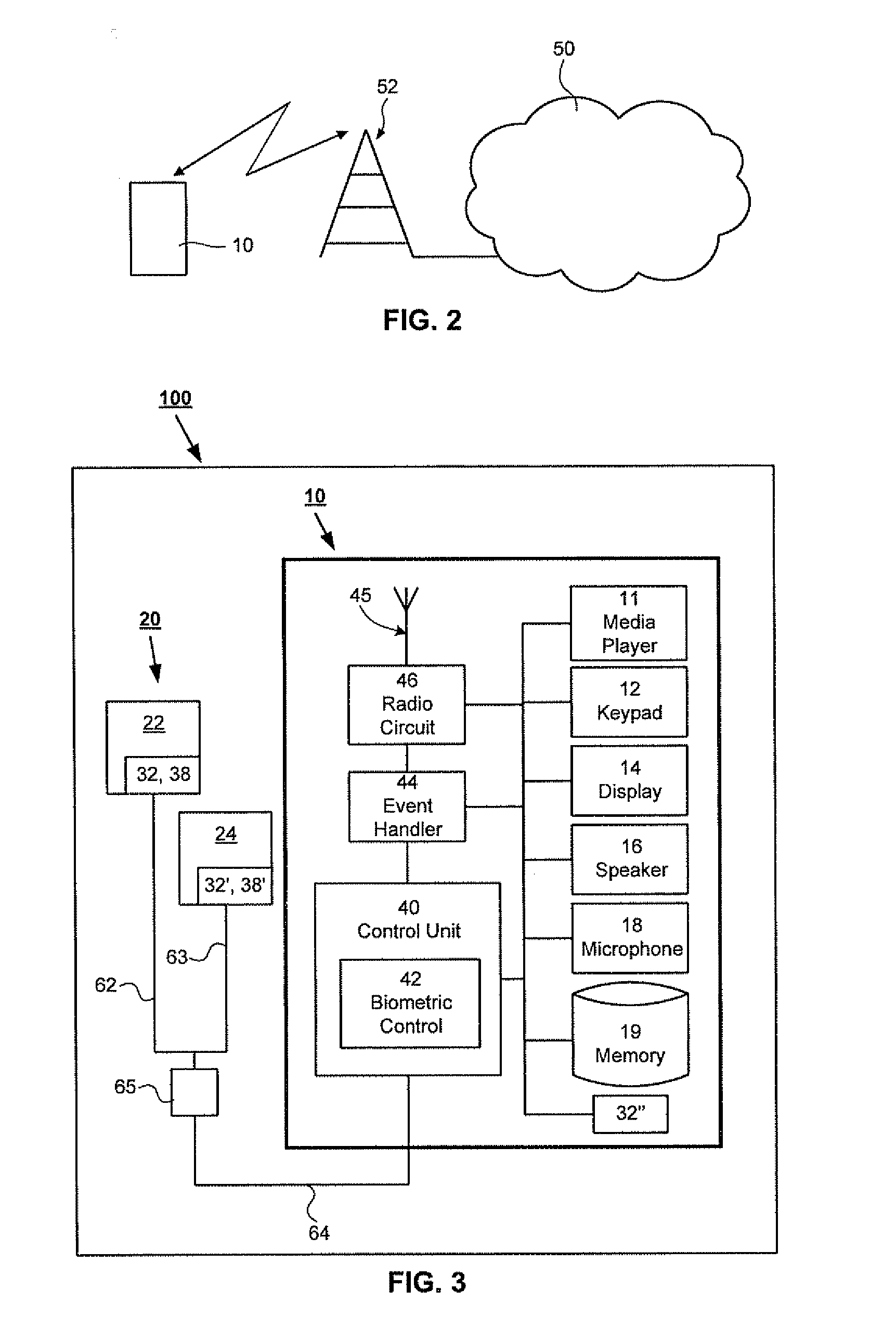
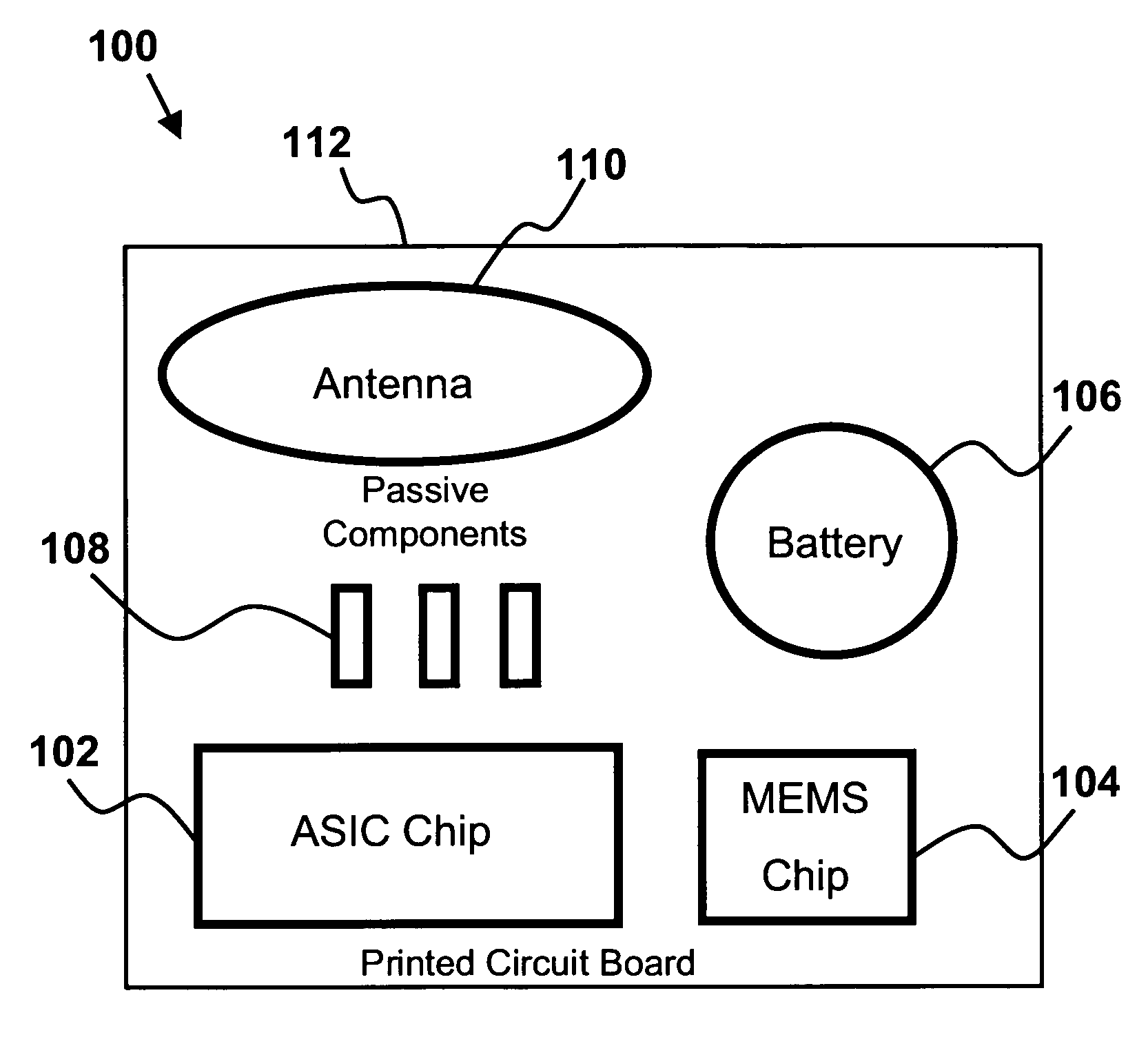
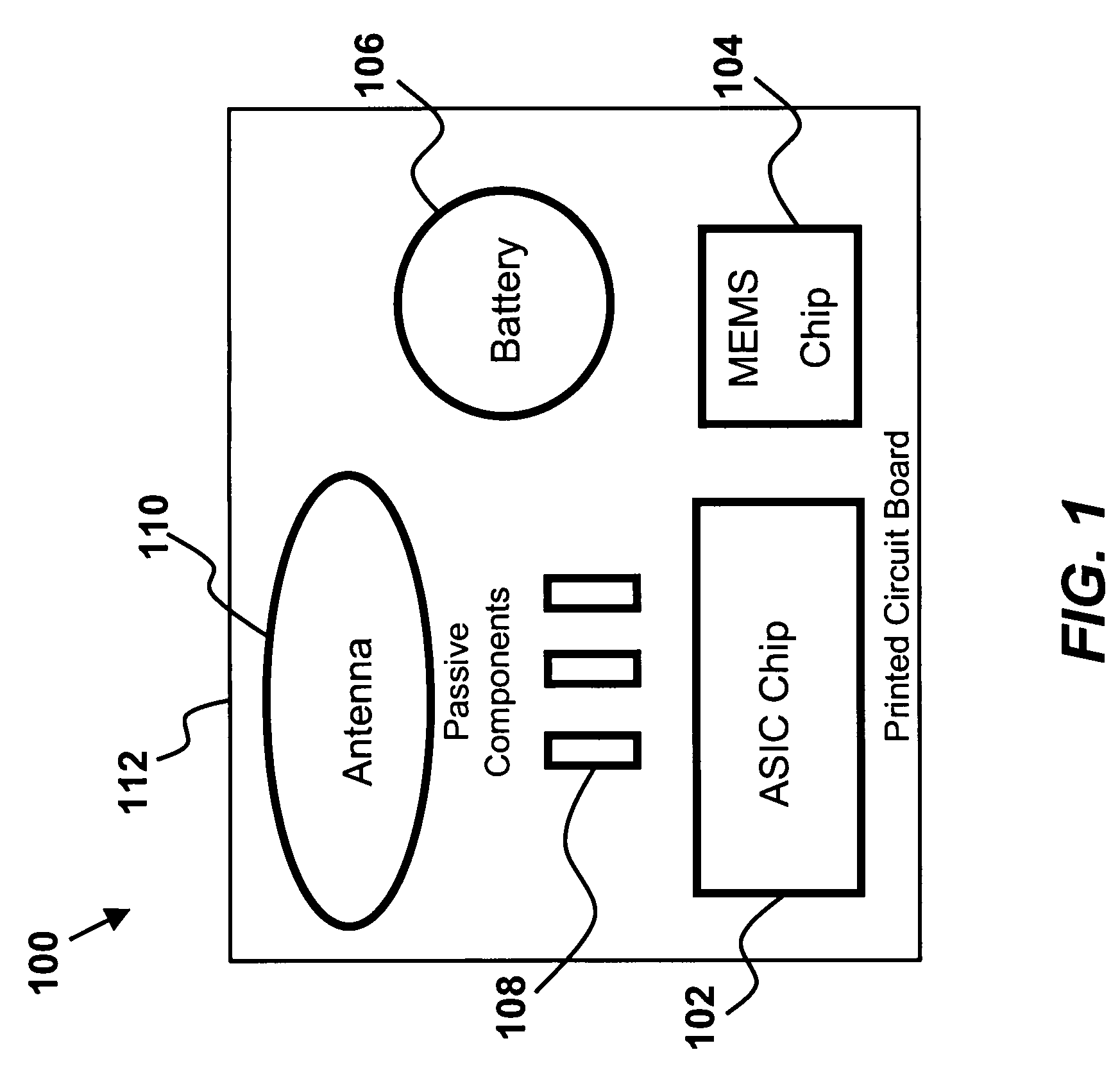
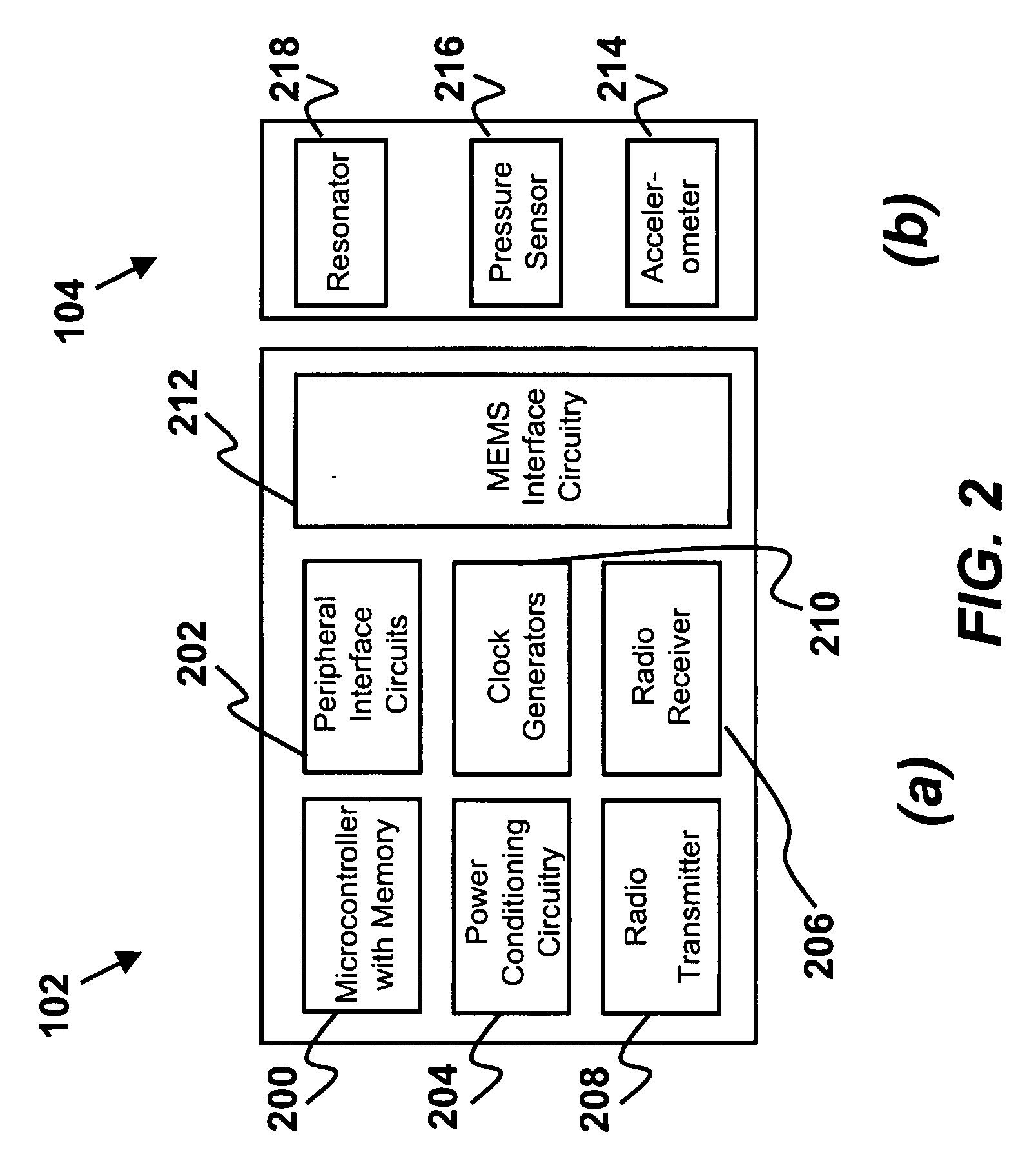
Portable device with biometric sensor arrangement
InactiveUS20080255430A1Improve measurement qualityElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyDifferential measurementEngineering
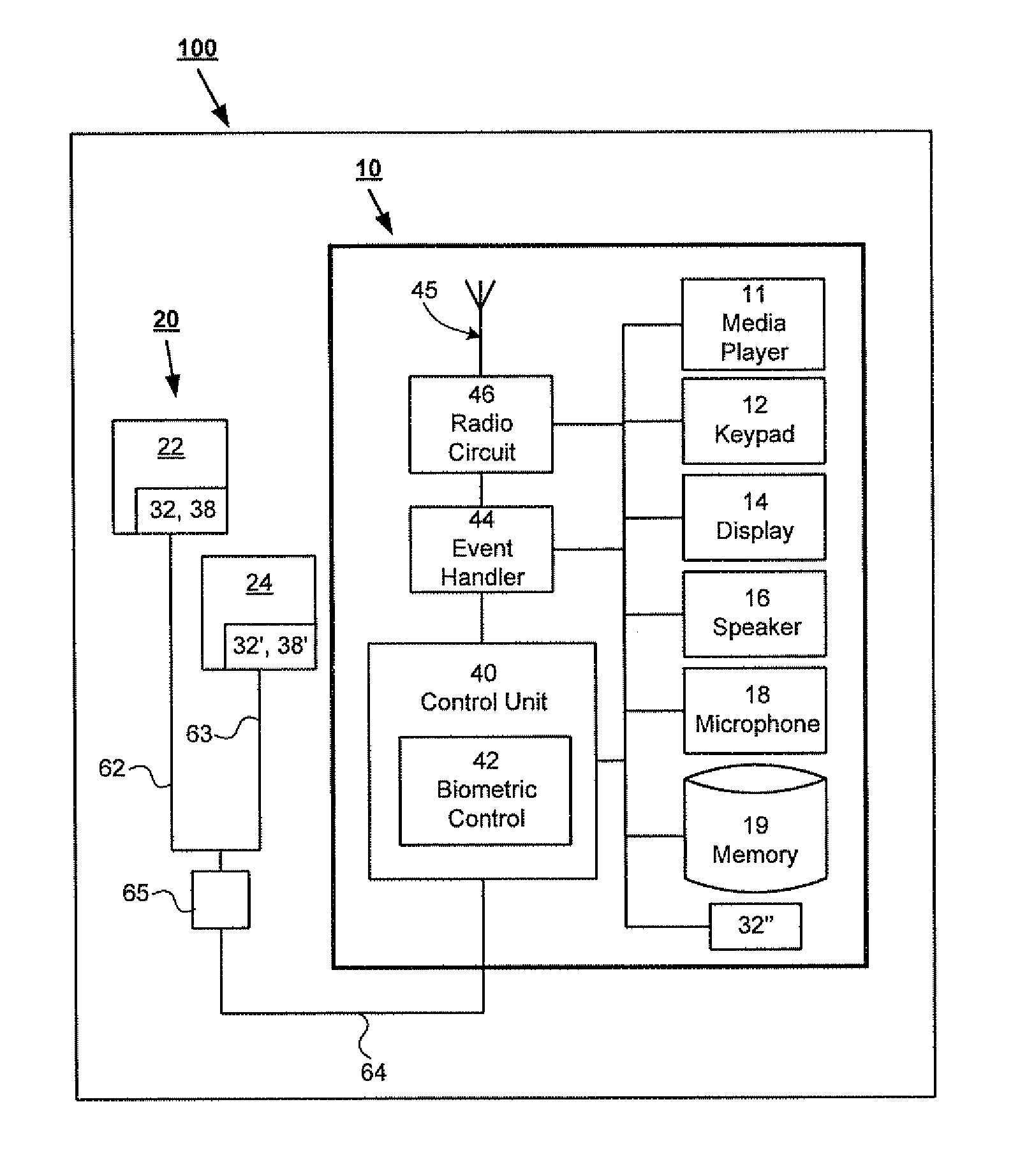
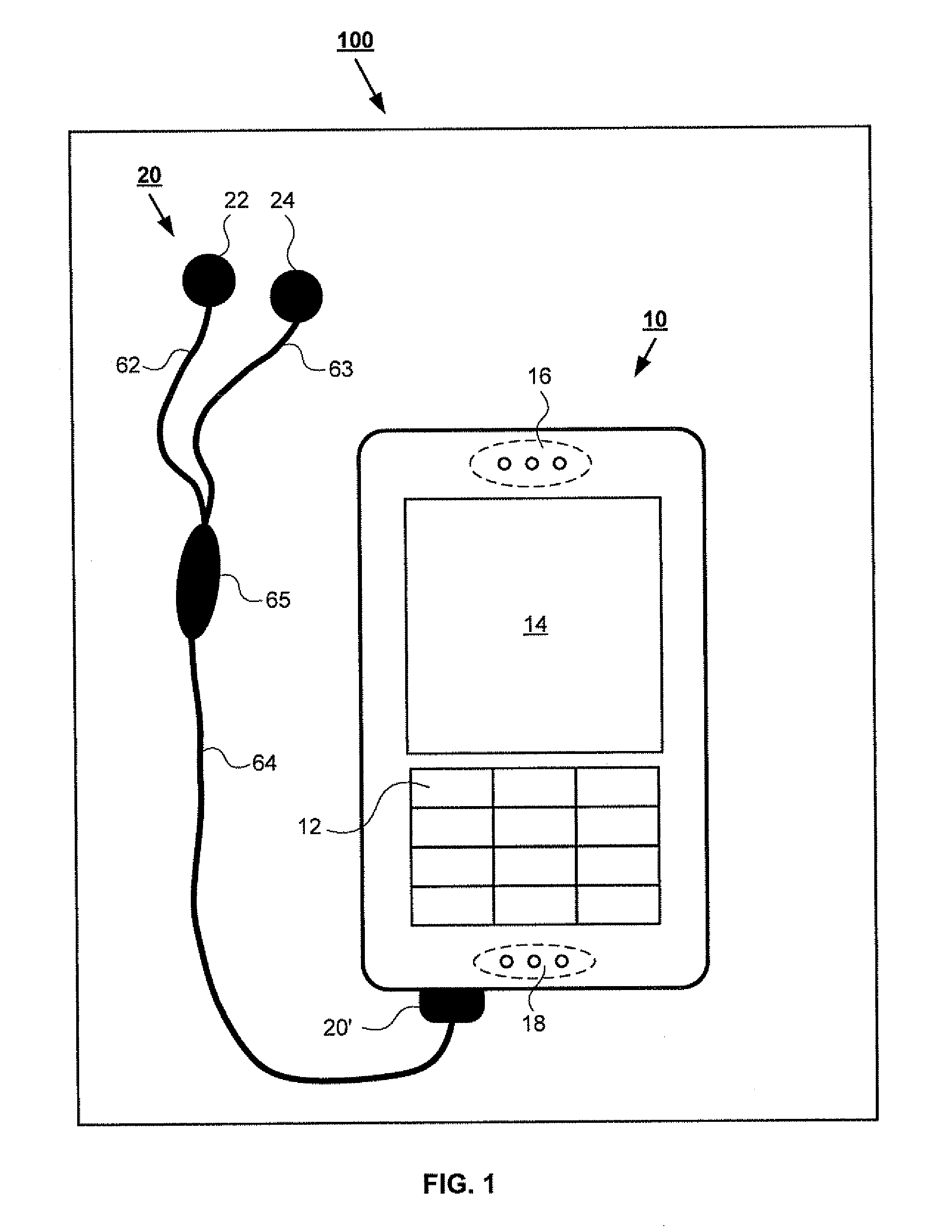
The present invention is directed to a biometric sensor system 100 for measuring one or more physical or behavioral characteristic of a user, which system comprises: an information presenting unit 20 provided with a first sound presenting unit 22 and a second sound presenting unit 24 for operatively presenting sounds to a user, a portable device 10 provided with a sound producing unit 11, 40, 44, 46 for producing sounds to said sound presenting units 22, 24, and a biometric control unit 42 for controlling said measurement. The information presenting unit 20 comprises at least a first biometric sensor unit 32 and a second biometric sensor unit 32′ arranged to operatively enable a differential measurement of one or more physical or behavioral characteristic of a user, and the biometric control unit 42 is arranged to operatively control the biometric sensor units 32, 32′ so as to provide a differential measurement.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7365858B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
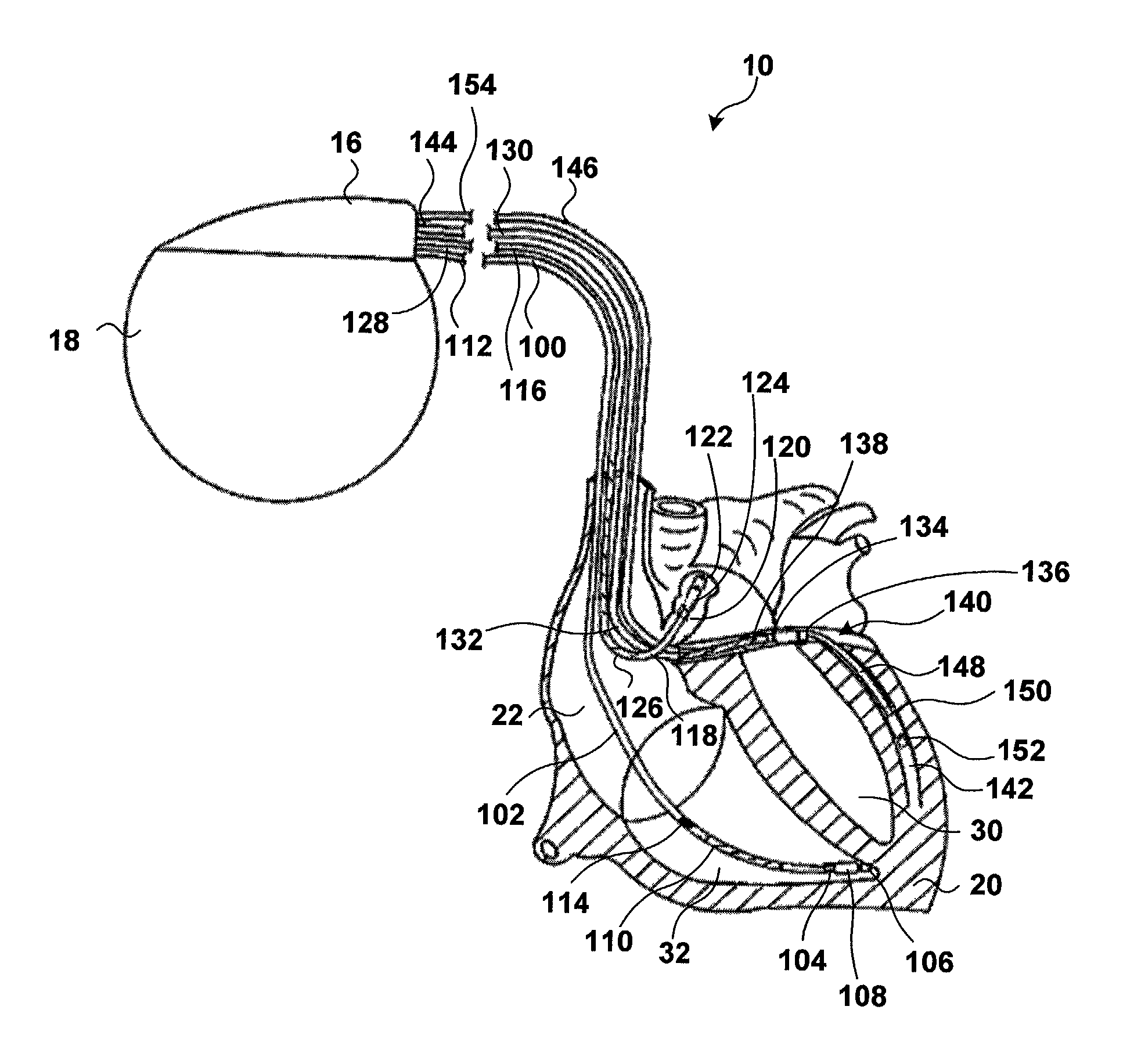
Cardiac output measurement using dual oxygen sensors in right and left ventricles
InactiveUS7164948B2Easy to deployAvoiding excessive formationTransvascular endocardial electrodesCatheterMeasurement deviceCardiac pacemaker electrode
A pacemaker provides multi-chamber pacing with a pacing interval that can be programmed and adapted in response to cardiac output measurements for a given patient. In a typical embodiment, the pacemaker may provide pacing stimuli to both ventricles of a heart. In addition, the invention may include a measurement device that incorporates first and second blood oxygen saturation sensors for deployment in the left and right ventricle. The oxygen saturation sensors provide a differential measurement that can be used to calculate cardiac output in accordance with the Fick method. The oxygen saturation sensors may be carried by a common trans-septal lead that positions one of the sensors proximate the right ventricle and the other sensor proximate the left ventricle. Alternatively, the oxygen saturation sensors may be deployed via separate leads. Whether single or dual leads are used to carry the oxygen saturation sensors, a respective lead may optionally carry electrodes for sensing, pacing, or both.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for determining and assessing a characteristic of a material
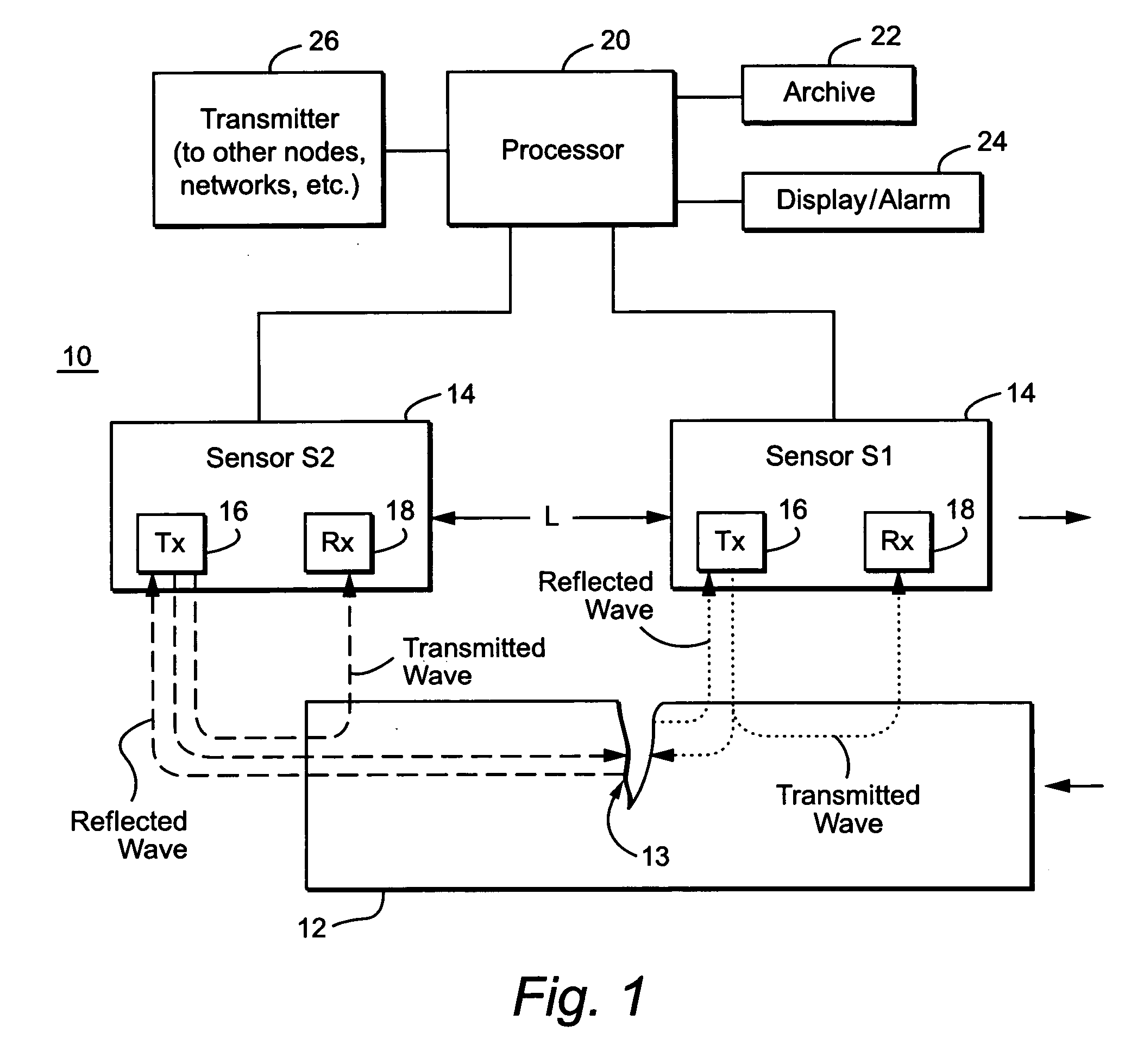
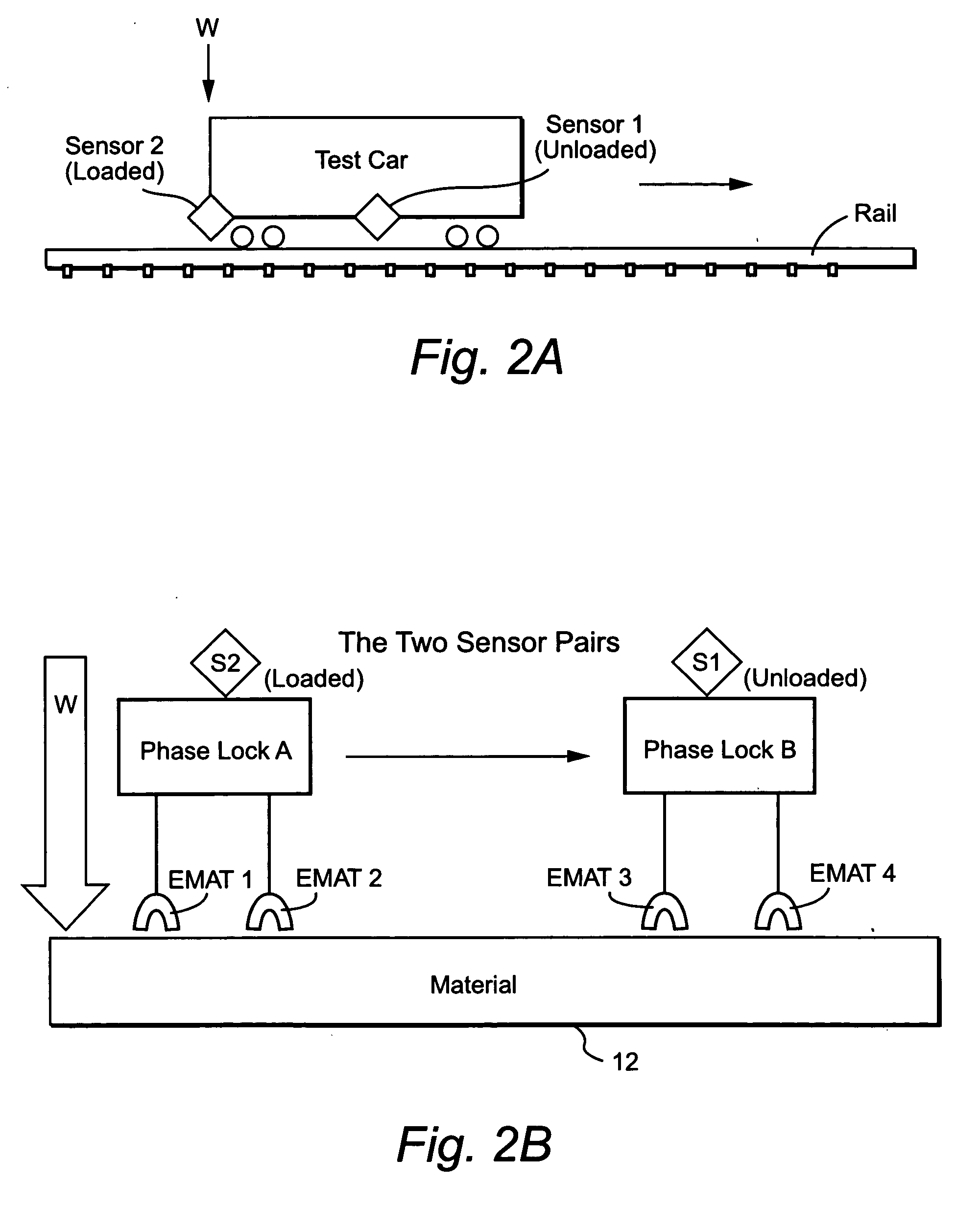
InactiveUS20050072236A1Low costImprove accuracyAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDifferential measurementCrazing
An acoustic energy-based, non-contact or contact testing approach provides low cost, highly accurate, and reliable information to (a) identify flaws and anomalies and (b) assess the integrity of a particular material. This approach is not hindered by surface conditions or impediments, and indeed, looks beneath the surface of the material by propagating an acoustic wave through the material using two differential transducers. A dynamic differential measurement is made of the material under a load condition and an unloaded condition that allows identification and assessment of various characteristics of the material. Multiple “windows” of information may be generated that permit (a) direct detection of flaws, defects, and anomalies using a scattering technique, (b) detection of crack closure and opening used to assess the stability of the material, (c) determination of strain on the material which relates to its performance, and (d) determination of defect dynamics linked to the defect size and stability.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
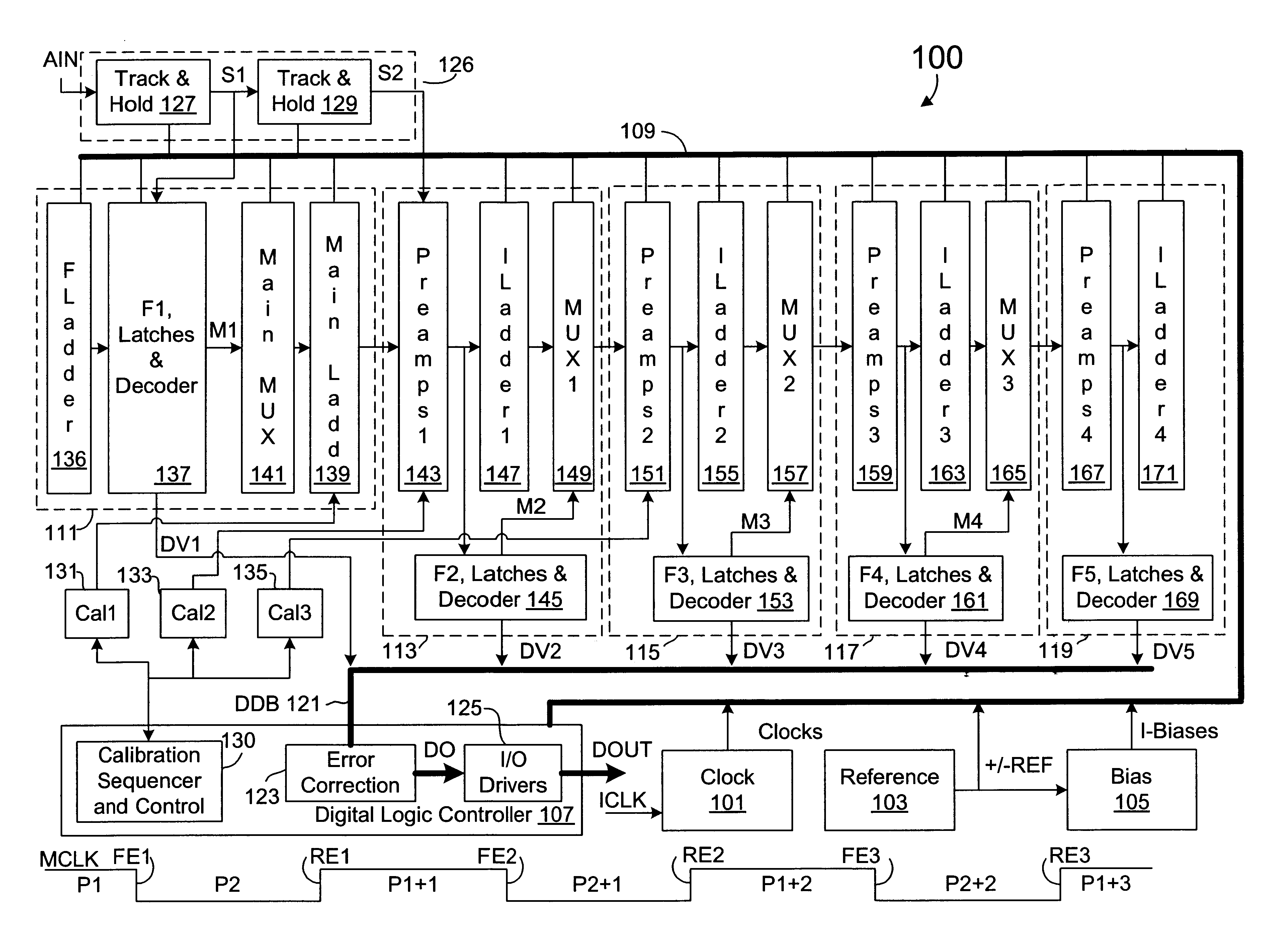
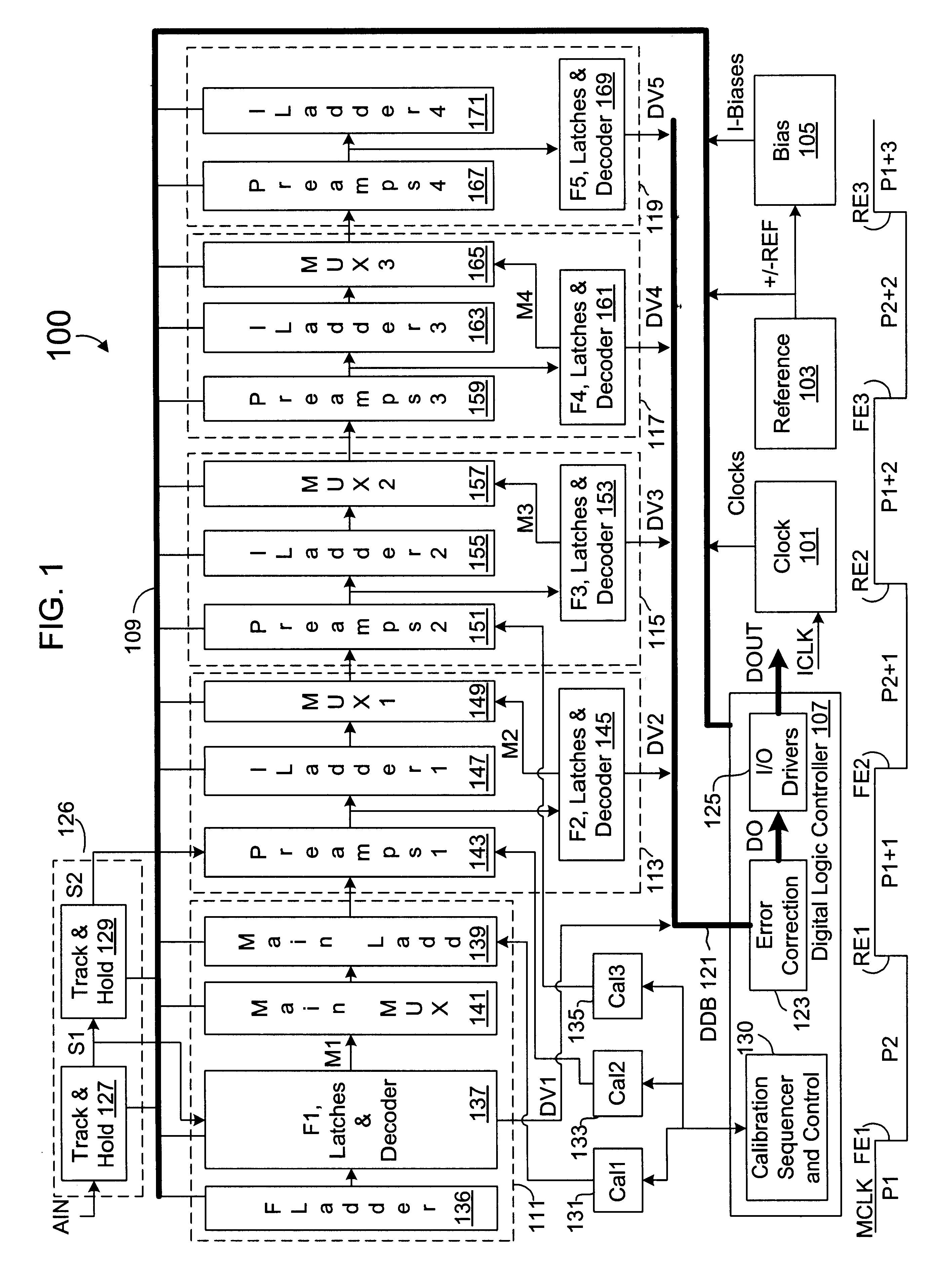
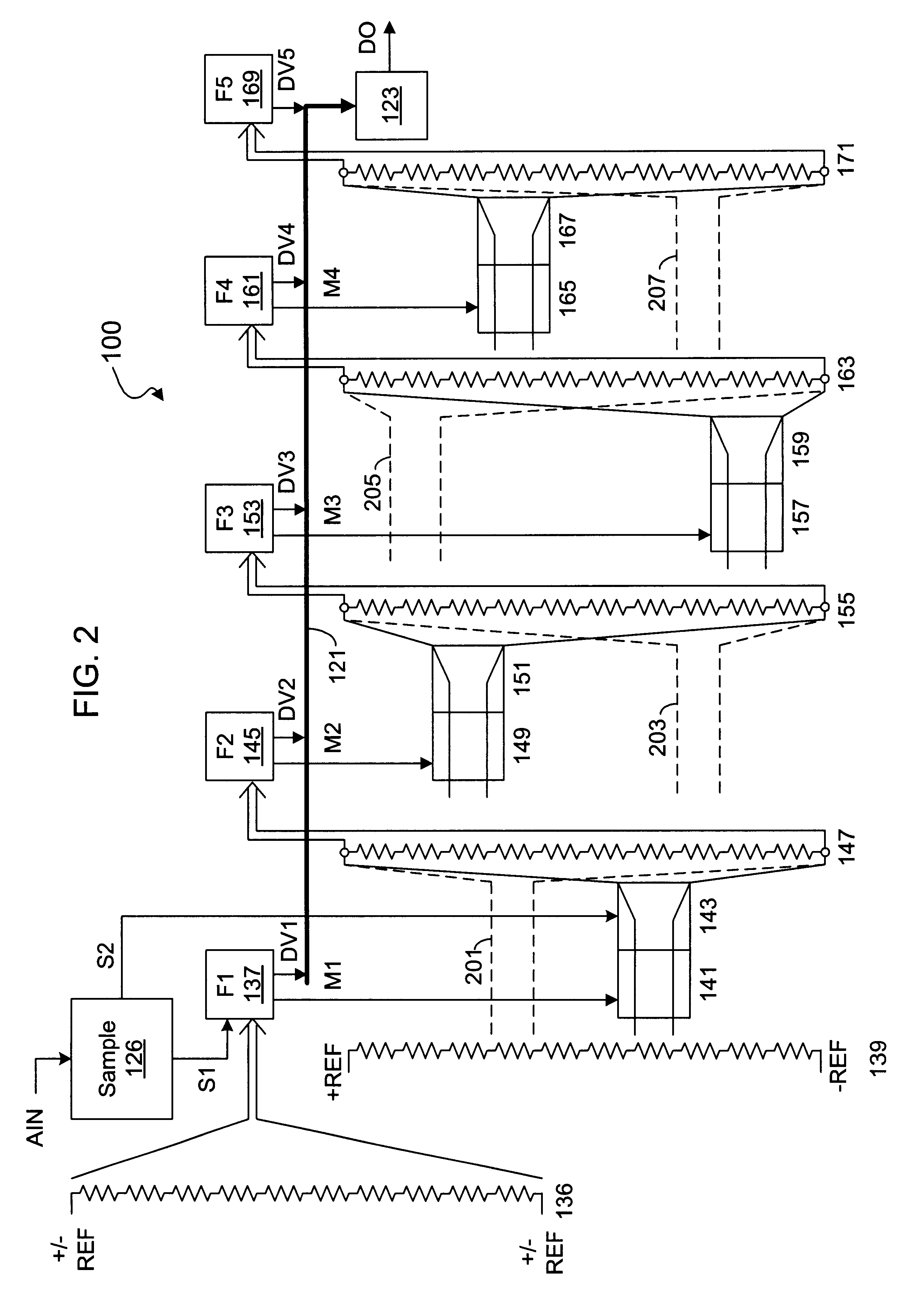
Calibration of resistor ladder using difference measurement and parallel resistive correction
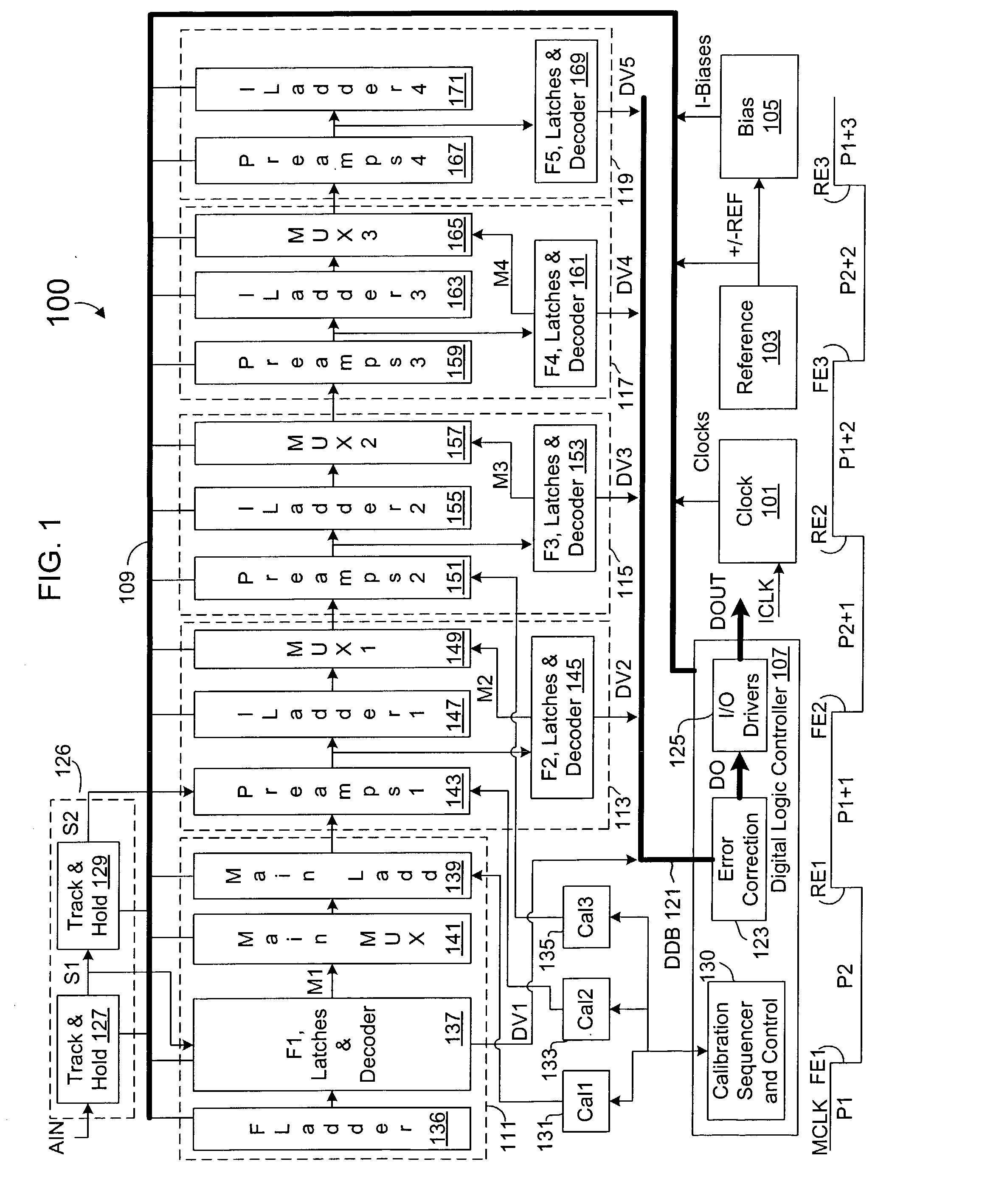
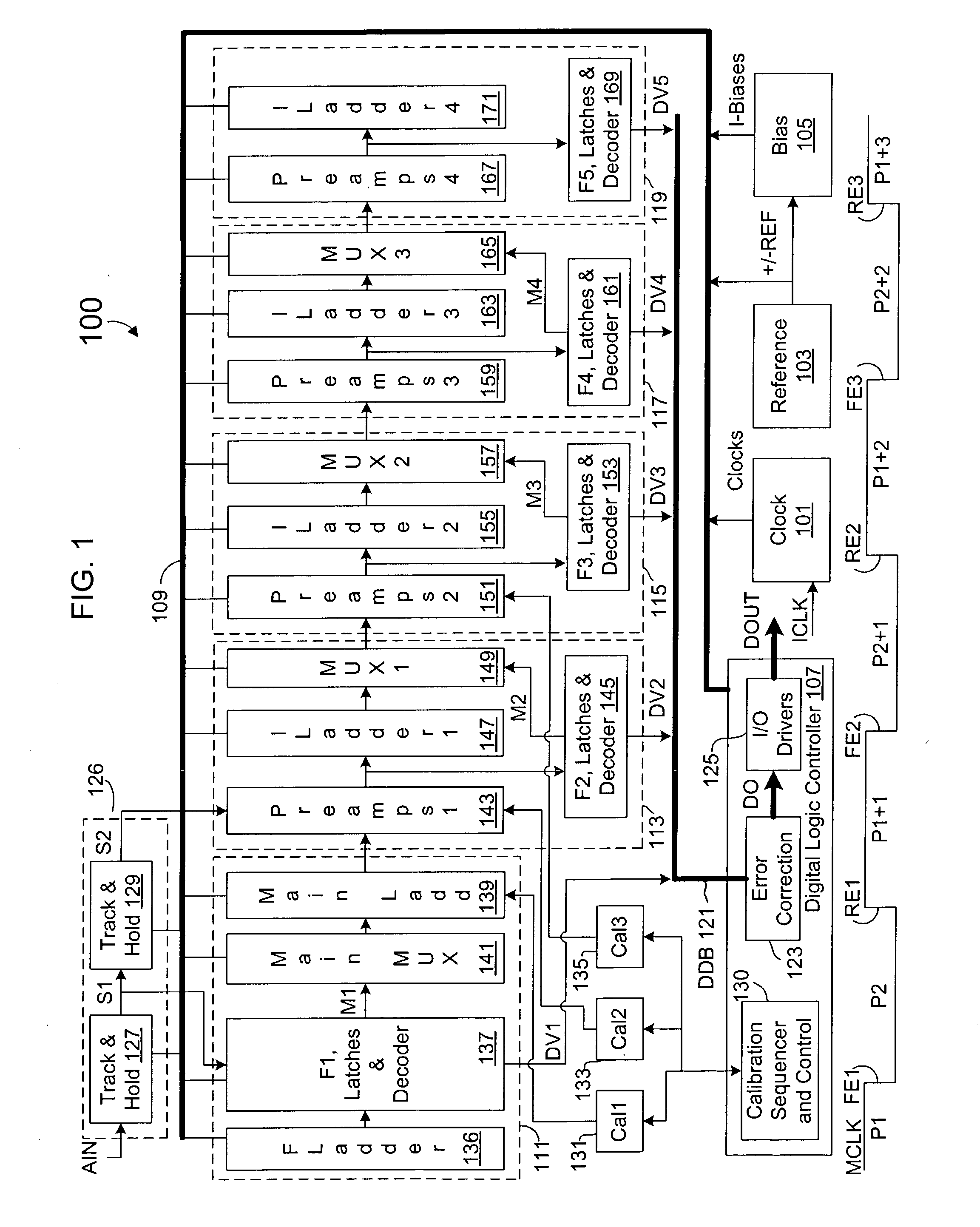
InactiveUS20030151532A1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDifferential measurementComplementary pair
A calibration system and method for a resistor ladder that employs relative measurement and adjustment between pairs of resistors. The system includes a resistor tree of complementary pairs of programmable resistors coupled to the resistor ladder, a measurement circuit that measures voltage differences between complementary pairs of programmable resistors, and control logic. The control logic controls the measurement circuit to measure a voltage difference between each complementary pair of programmable resistors and adjusts the relative resistance of each complementary pair of programmable resistors to equalize voltage. The measurement is facilitated by a sigma-delta ADC that converts a measured voltage difference into a bit stream. The programmable resistors are implemented with binary weighted resistors that are digitally adjusted one LSB at a time. Lower and upper adjustment thresholds may be employed to avoid unnecessary over-adjustments while maintaining a requisite level of accuracy.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
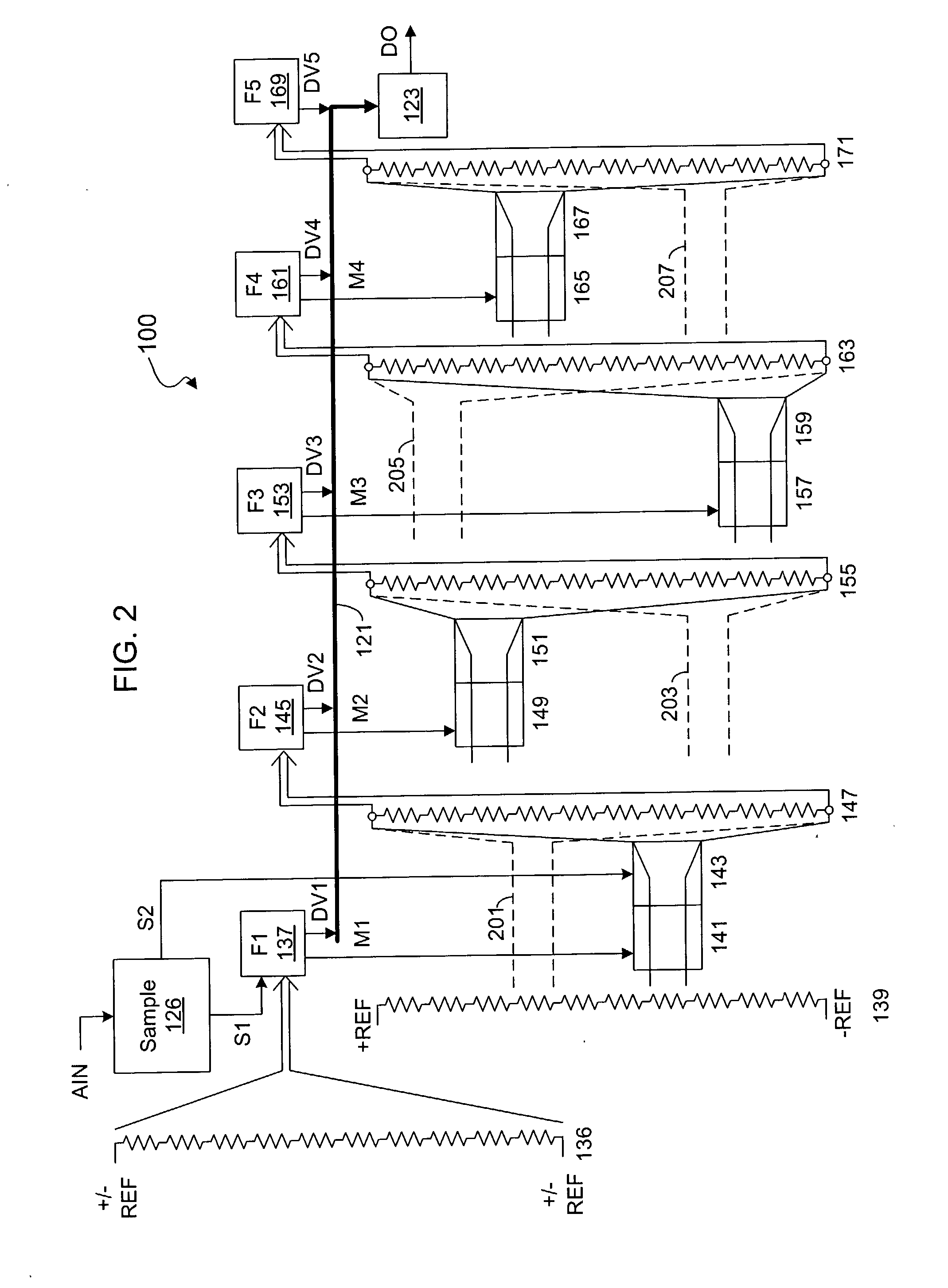
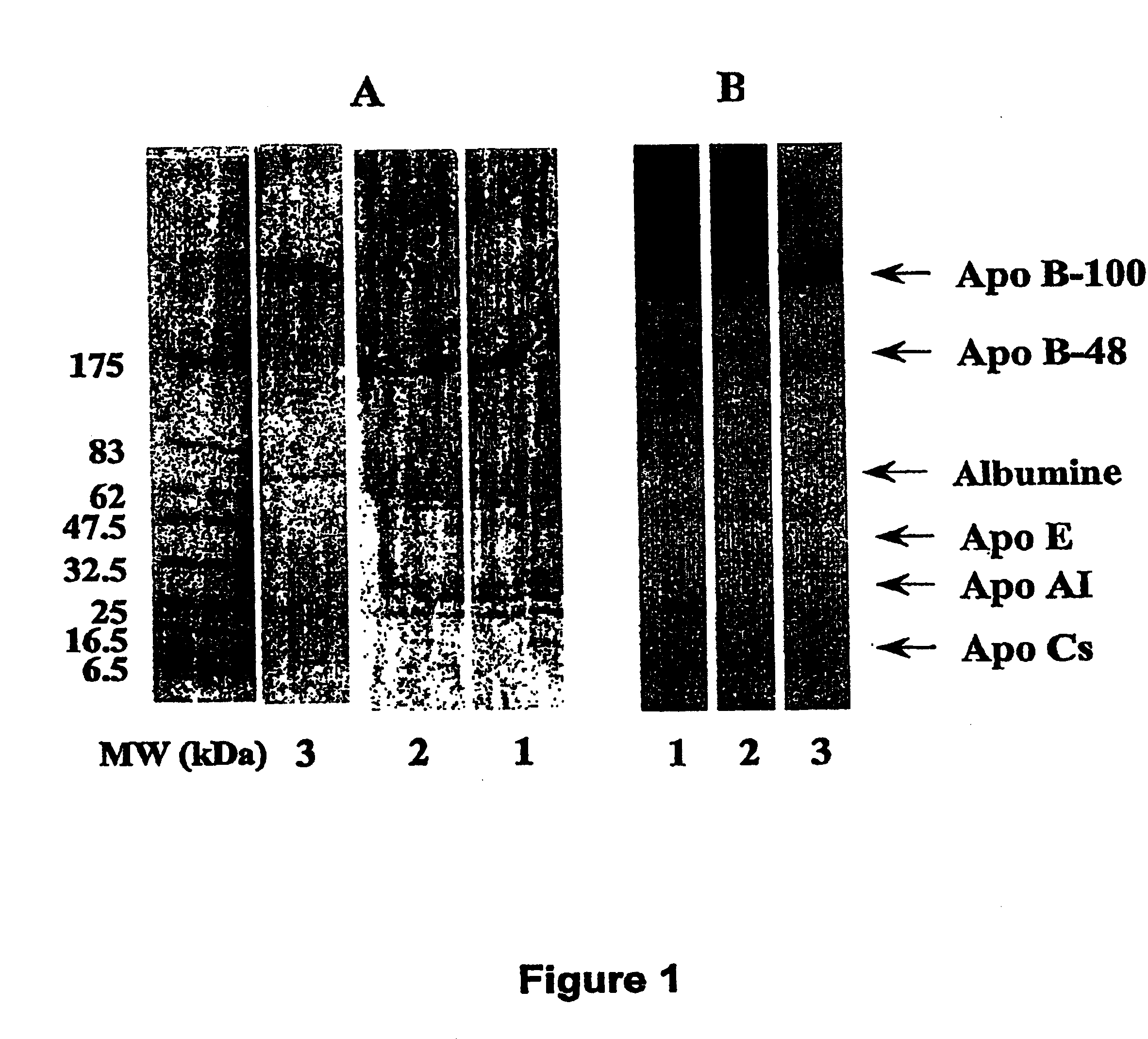
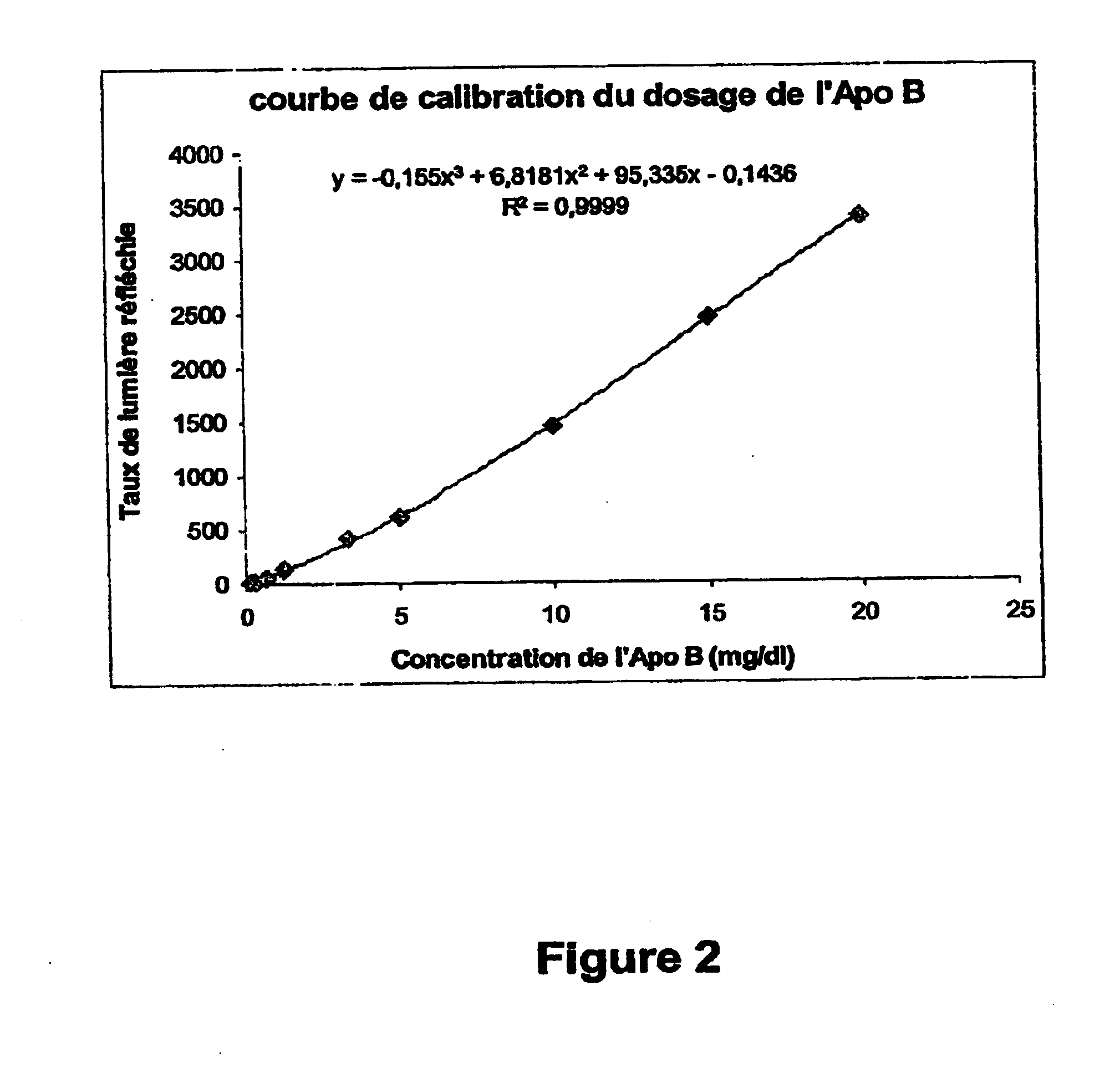
Compositions and methods for apo-b48 and apo-b100 assay
InactiveUS20050152900A1High affinityAbsenceApolipeptidesMetabolism disorderDifferential measurementApolipoprotein B48
The invention concerns compositions and methods for assay or detection of apolipoprotein-B48 in samples. In particular, it concerns a method for differential measurement of apolipoprotein-B48 (“Apo-B48”) and apolipoprotein-B100 (“Apo-B100”) in biological samples. The invention also concerns synthetic products of Apo-B100, the corresponding antibodies, kits containing same, and their uses for detecting, differentially quantifying and / or recording an amount of Apo-B48 and / or Apo-B100 in a sample, or for quantifying and / or recording atherogenic lipoparticles in a sample. The products, materials and kits hereinabove can also be used for differentially modulating the levels of Apo-B48 and / or Apo-B100 or their activity, in vitro or in vivo, and for regulating lipid metabolism in a subject.
Owner:GENFIT SA
Exhaust back pressure sensor using absolute micromachined pressure sense die
ActiveUS7073375B2Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusDifferential pressurePressure sense
Sensor systems and methods are disclosed, which generally incorporate isolation between the sensor's electronics and the sensed media. The sensor's electronic circuit can incorporate one or more application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) that processes and outputs the signal for both absolute and differential measurements. Such a sensor can be adapted for use in exhaust gas re-circulation (EGR) systems utilized with automotive gasoline engines. Such a sensor can also be utilized for measuring differential pressure across diesel particular filters and / or applications in which differential pressure is required for system control and / or monitoring purposes. The absolute pressure sensor disclosed herein can therefore sense the exhaust pressure on automotive engines and other mechanical and / or electromechanical devices and machines.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
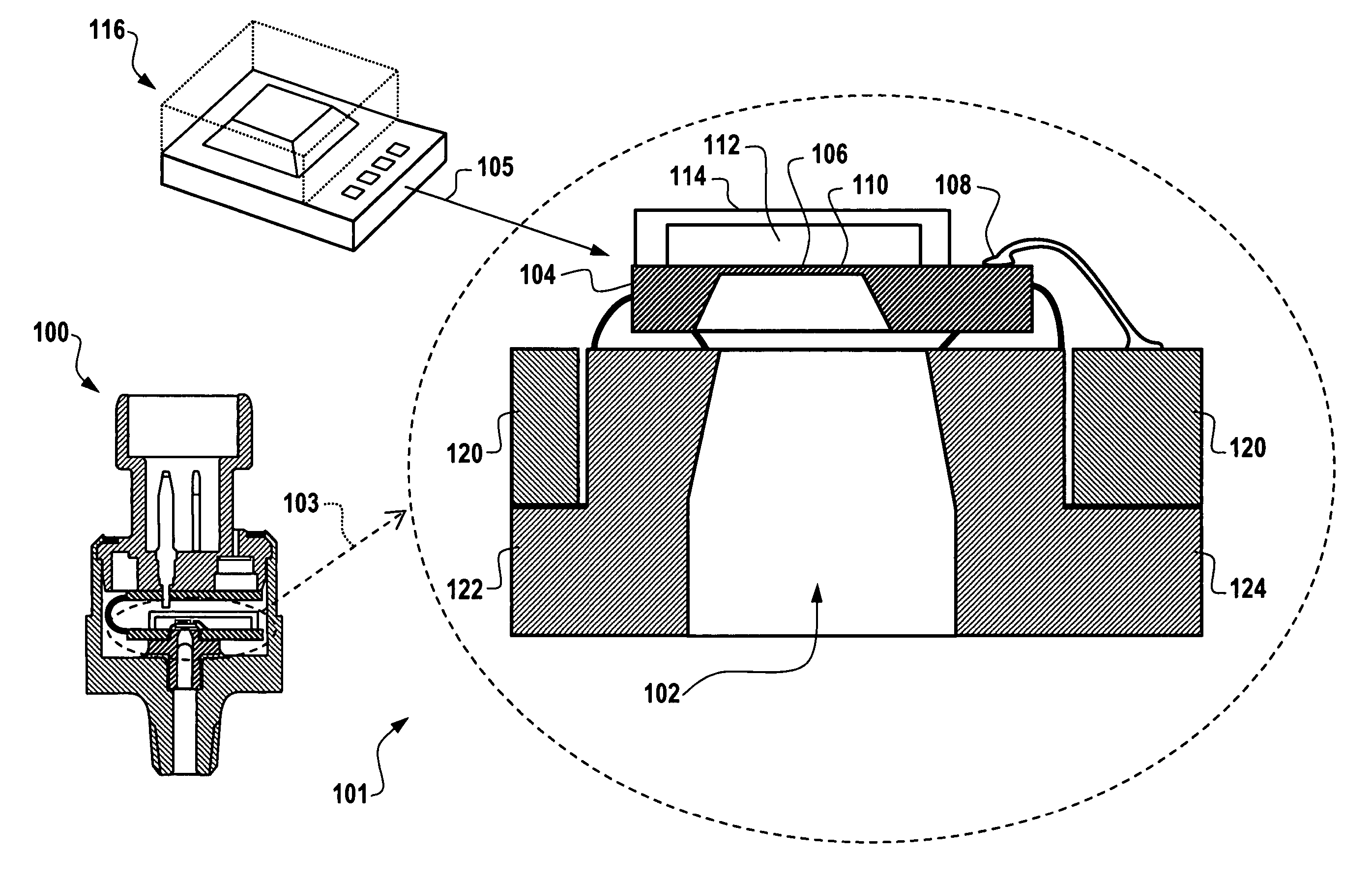
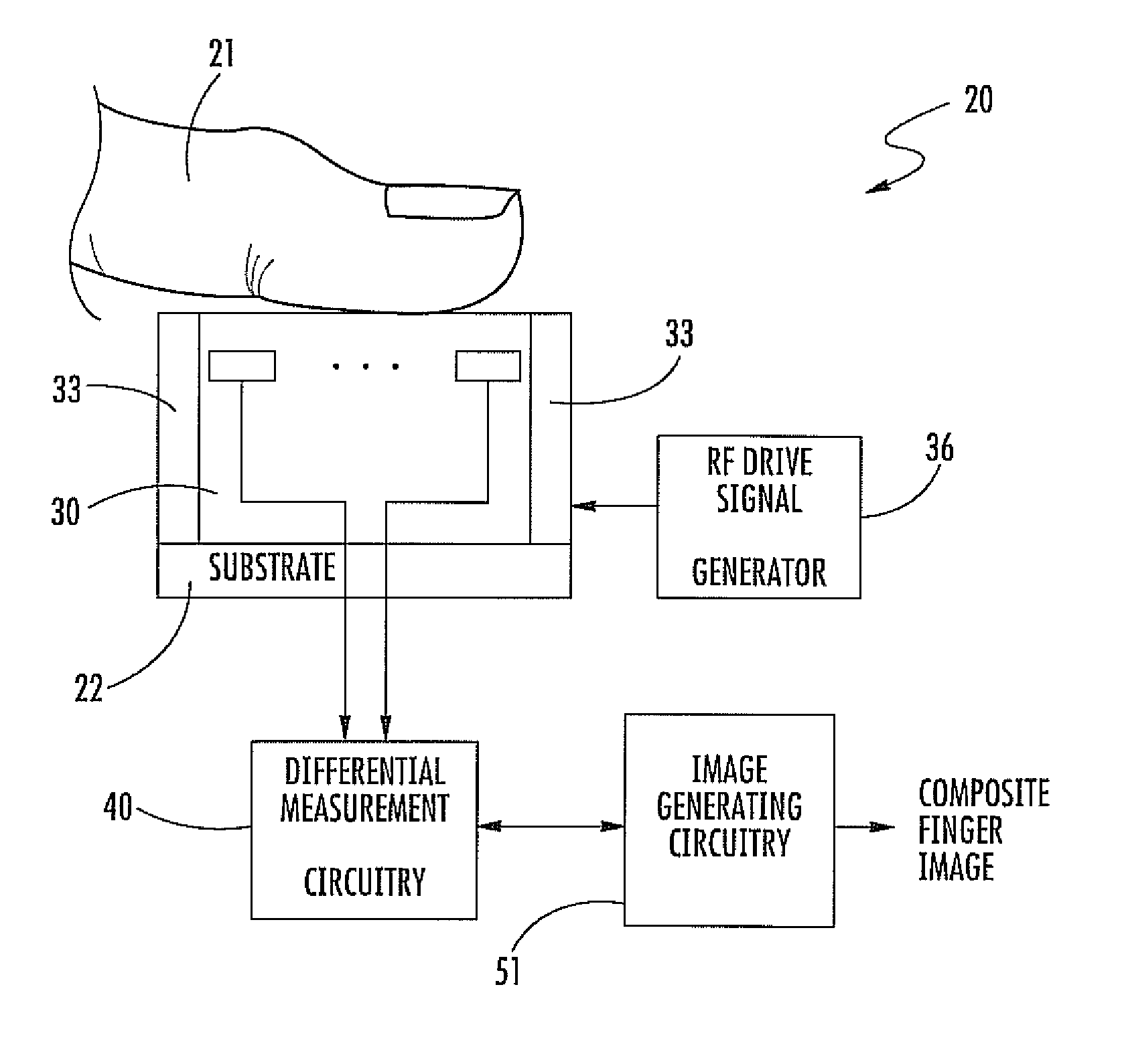
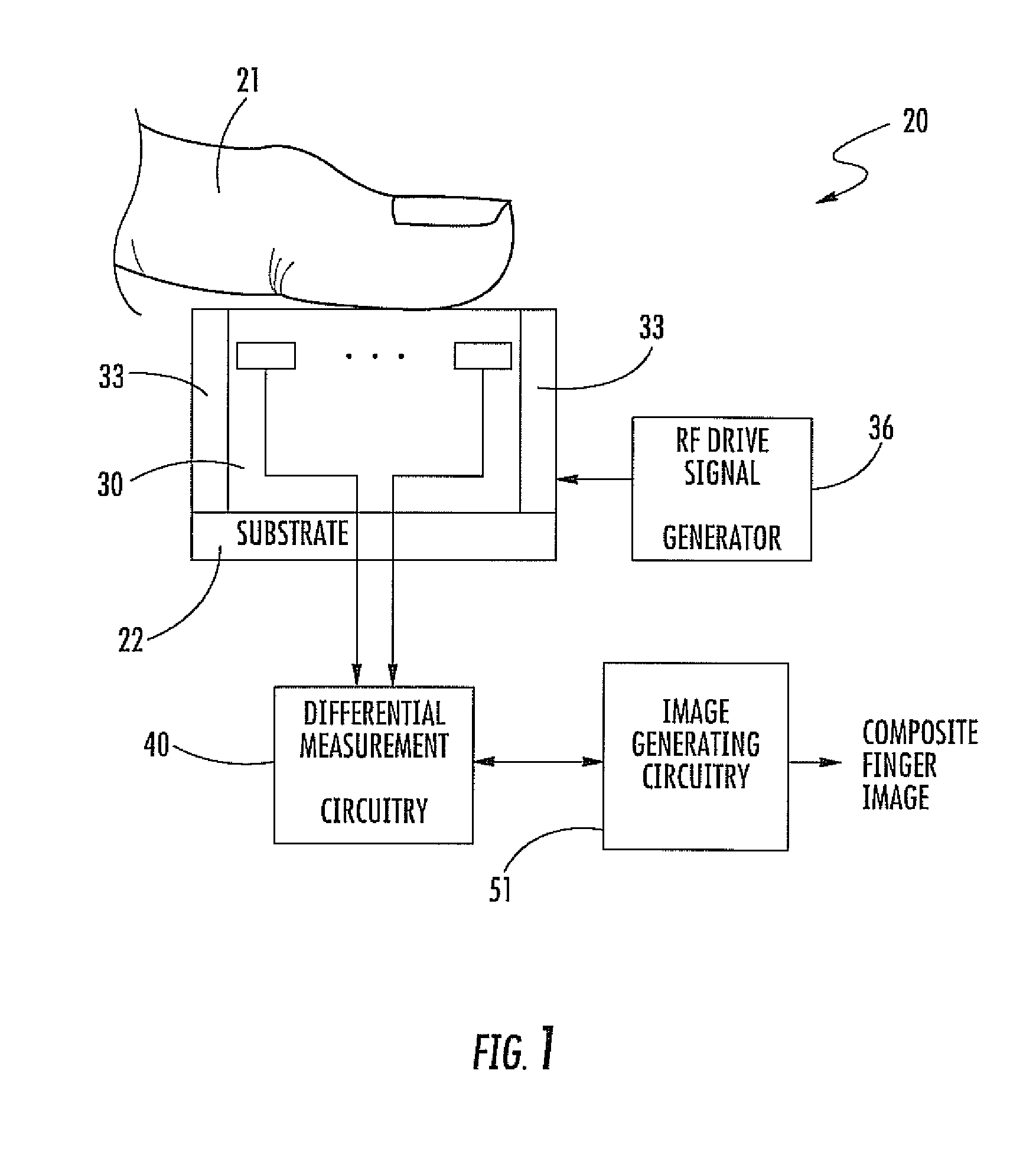
Finger sensing device including differential measurement circuitry and related methods
ActiveUS8888004B2Reduce noiseResistance/reactance/impedenceSensing record carriersDifferential measurementEngineering
A finger sensing device may include an array of finger sensing pixels to receive a user's finger adjacent thereto. Each finger sensing pixel may include a finger sensing electrode. The finger sensing device may include a finger drive electrode configured to couple a drive signal through the user's finger to the array of finger sensing pixels. The finger sensing device may also include differential pixel measurement circuitry coupled to the array of finger sensing pixels and configured to generate a plurality of interpixel difference measurements for adjacent pairs of the finger sensing pixels.
Owner:APPLE INC
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7557929B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Rolling angle measurement method and device based on grating
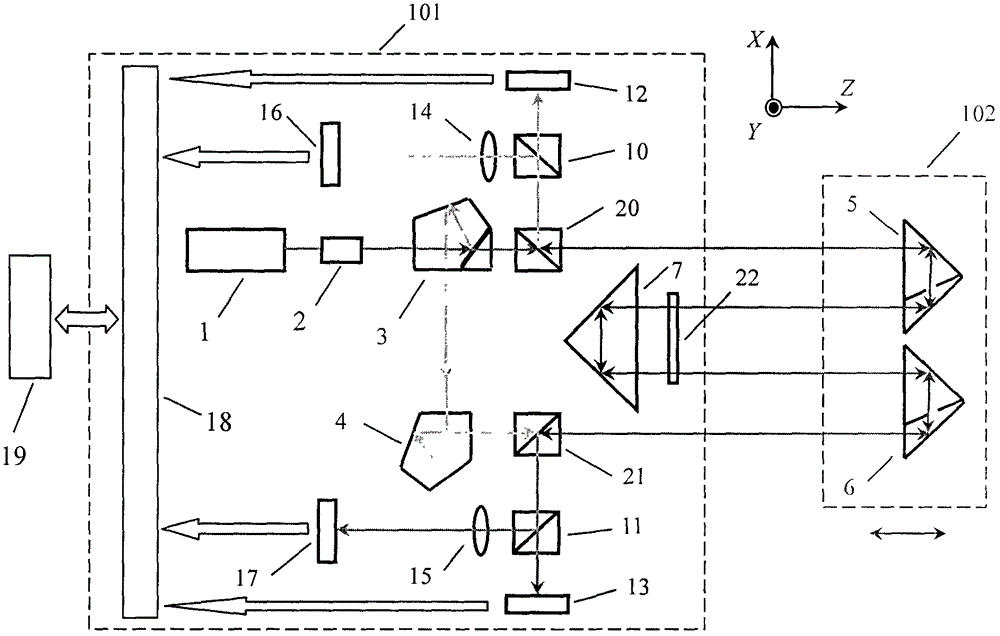
The invention discloses a roll angle measuring method based on a grating and a device thereof, which belongs to the technical field of photoelectric detection. A laser lases and emerges directly, or emerges after collimation through a collimating lens; the light is directly incident on a one-dimensional plane transmission grating, or reversely incident on the grating through a retrodirective reflector; plus-minus first stage diffracted light from the grating is focused to form two diffracted light points through a lens; a photodetector is used to detect the variations in positions of the two focused light points, thus figuring out a roll angle. The optical structure of the device is compact and simple, and brings convenience to practice; in addition, the accuracy, the stability and the economical efficiency are also high. The grating is used as a sensitive device; error separation is achieved, and the interference-free feature is improved by using the differential measurement of double diffracted beams; few optical devices are used; and the power of the light source is low; the cost is low; mobile parts do not require to be provided with cables; the angle measurement distinguishability is as high as 0.5 and even higher; different requirements of measurement accuracy can be met just by replacing the grating with gratings having different numbers of lines.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
System and method for measuring phase
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Full optical path drift compensation high-precision roll angle measuring method and device
The invention discloses a full optical path drift compensation high-precision roll angle measuring method and a device, and belongs to the technical field of photovoltaic testing. By using a pair of retro-reflector as sensitive device, the roll angle information is obtained through the parallel two-beam differential measurement, in which the parallel beam through a set of double pentagonal prism and a pentagonal prism splitting the collimated laser beam after splitting obtained by the dual beam parallelism prism precision guaranteed without adjustment, greatly enhance the feasibility and practicability of measurement methods; by using a rectangular prism as beam translation and reverse means that two beams measuring light path completely overlap, and the light path direction reciprocal use This feature, in twice while improving measurement resolution, combined with a total path of the light drift compensation method, can achieve all-optical laser beam path is completely drift compensation, to resolve the current measuring method using laser collimation of the laser beam cannot completely eliminate the drift angle the impact of the common problems that can achieve the roll angle measurement resolution of better than 0.1 'accuracy of better than 1'; compact optical structure of the present invention, the adjustment is simple, no more freedom crosstalk error, moving parts without cable, easy on-site measurement .
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Signal conditioning methods and circuits for a capacitive sensing integrated tire pressure sensor
ActiveUS20080022762A1Reduce errorsElectric signal transmission systemsTyre measurementsEngineeringVoltage reference
A tire pressure monitoring system is provided that includes a switched capacitor circuit having a clock with two non-overlapping clock phases that control a state of analog switches of the switched capacitor circuit. The system uses tire pressure sensor MEMS capacitors that are measured differentially. A capacitance-to-voltage converter is connected to the MEMS sense capacitor, and a sigma-delta converter having a comparator with a first digital output state and a second digital output state is used. The first output state is a sum of reference voltages and the second output state is a difference of the reference voltages. An average value of the capacitance-to-voltage converter output is driven to a zero value and a digital output is provided of the average output states that is equal to a difference between the MEMS capacitors divided by their sum multiplied by a ratio of the reference voltages.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
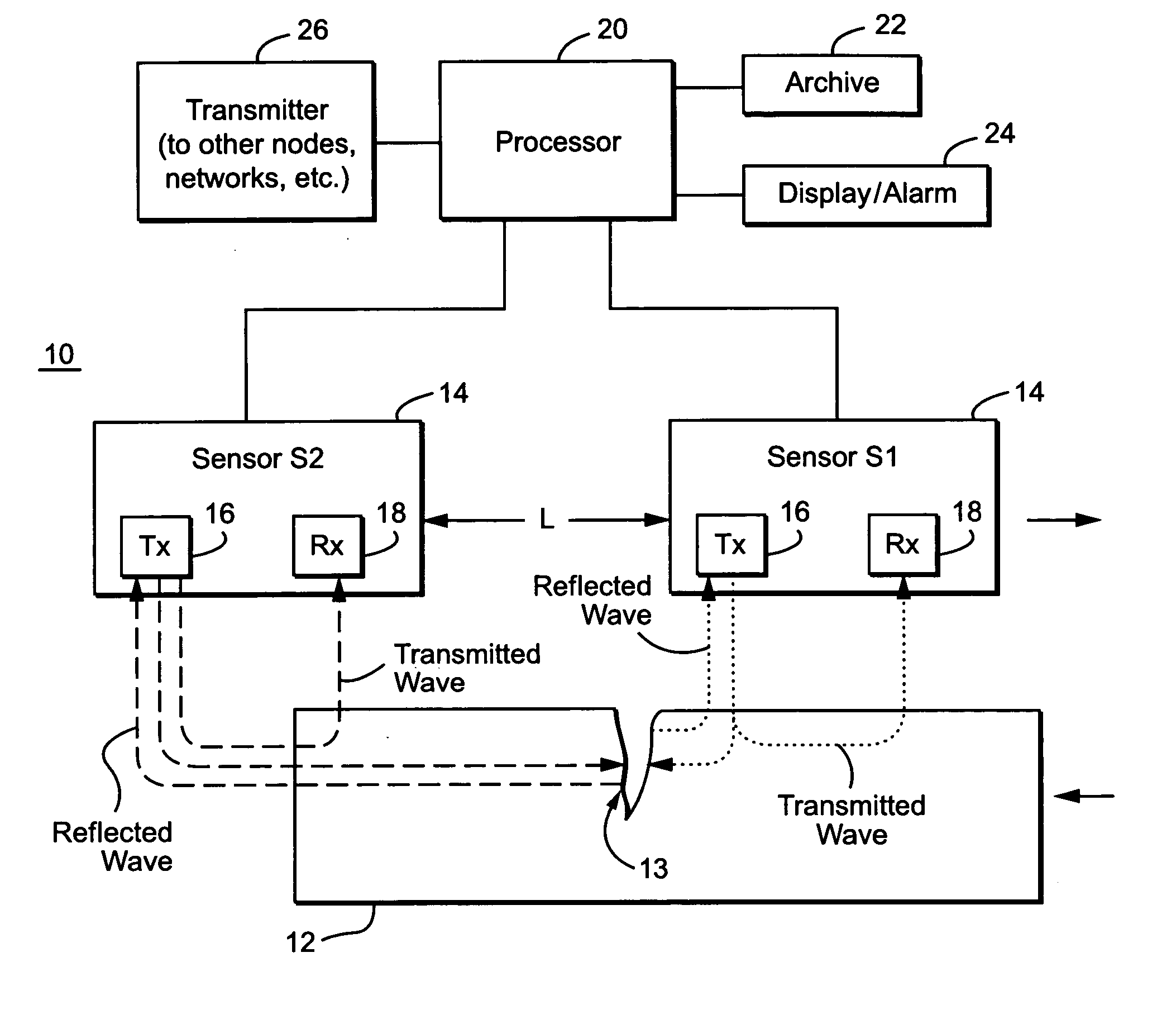
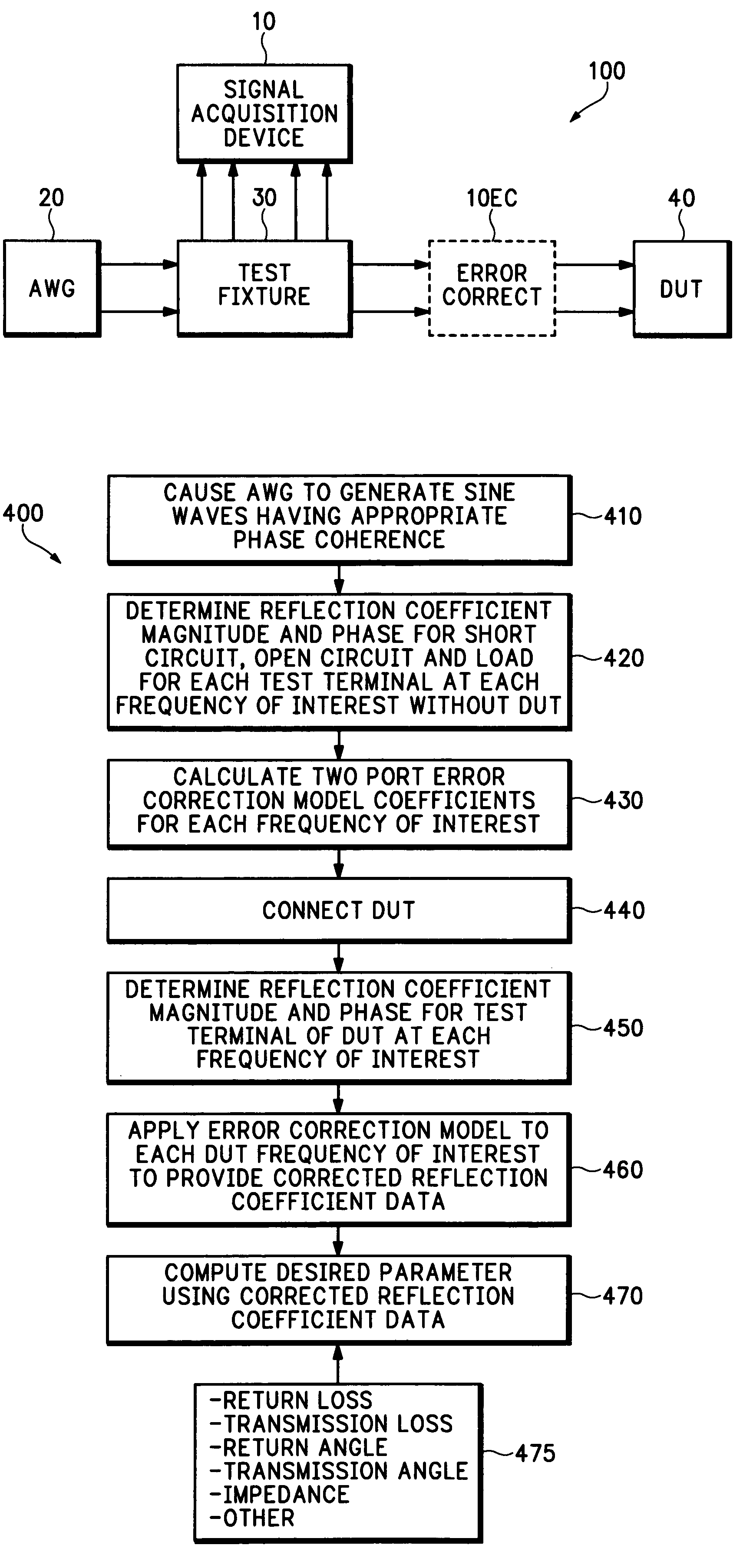
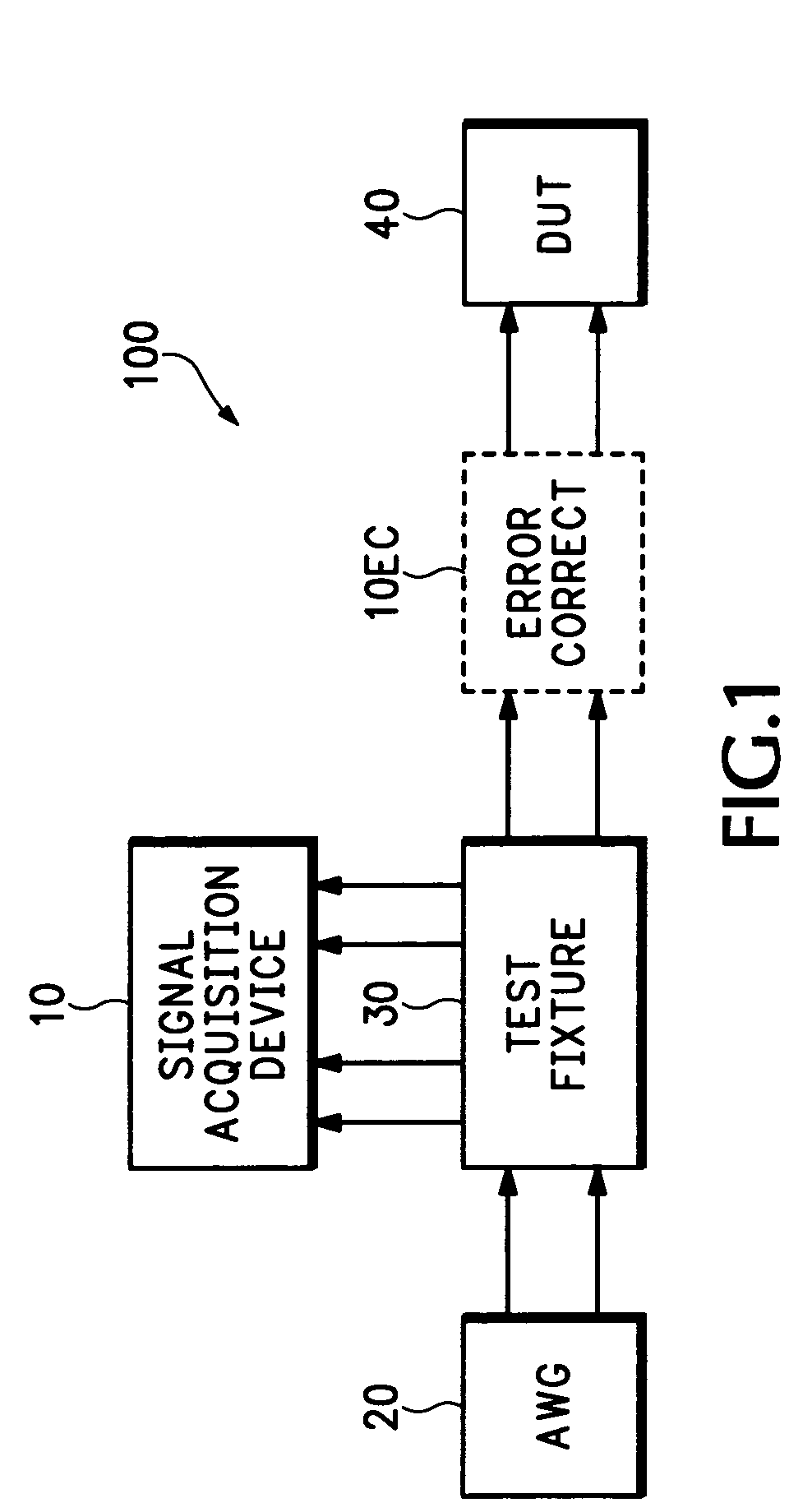
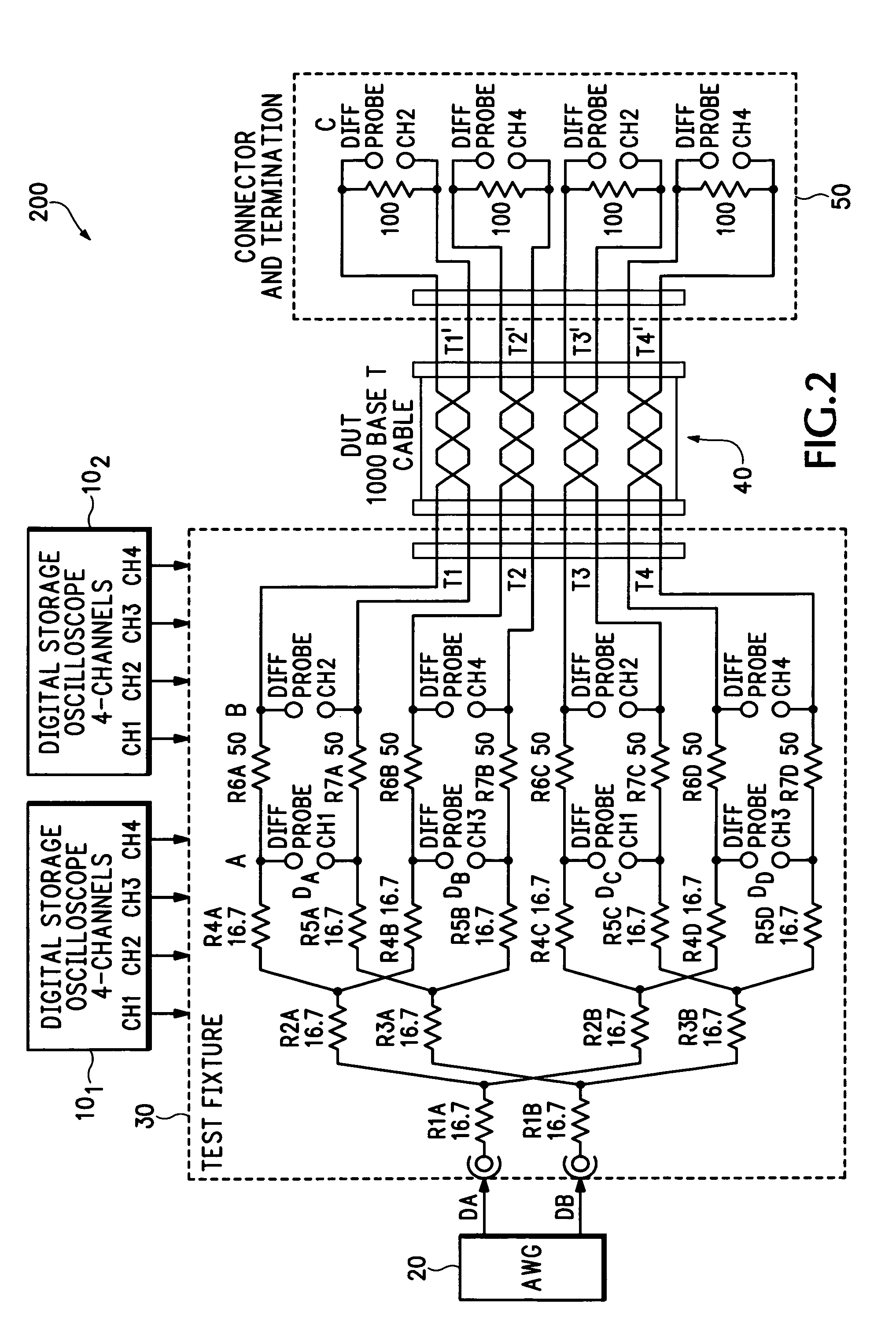
Oscilloscope based return loss analyzer
ActiveUS7271575B2Spectral/fourier analysisResistance/reactance/impedenceFrequency spectrumDifferential measurement
A system, apparatus and method for performing differential return loss measurements and other measurements as a function of frequency uses a digital storage oscilloscope (DSO) having spectral analysis functions. A waveform generator generates a differential test signal in the form of a series of pulses where each pulse includes spectral components associated with each of a plurality of frequencies of interest. A test fixture presents the differential test waveform to a load including at least one of a device under test (DUT), a short circuit, an open circuit and a balanced load. A signal acquisition device differentially measures the test waveform during each of the load conditions. The signal acquisition device computes an error correction parameter using measurements made during the short circuit, open circuit and balanced load conditions. The correction parameter tends to offset signal acquisition errors within measurements made during the DUT load condition.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Method for measuring static state weight difference in two sides of elvator balancing coefficient
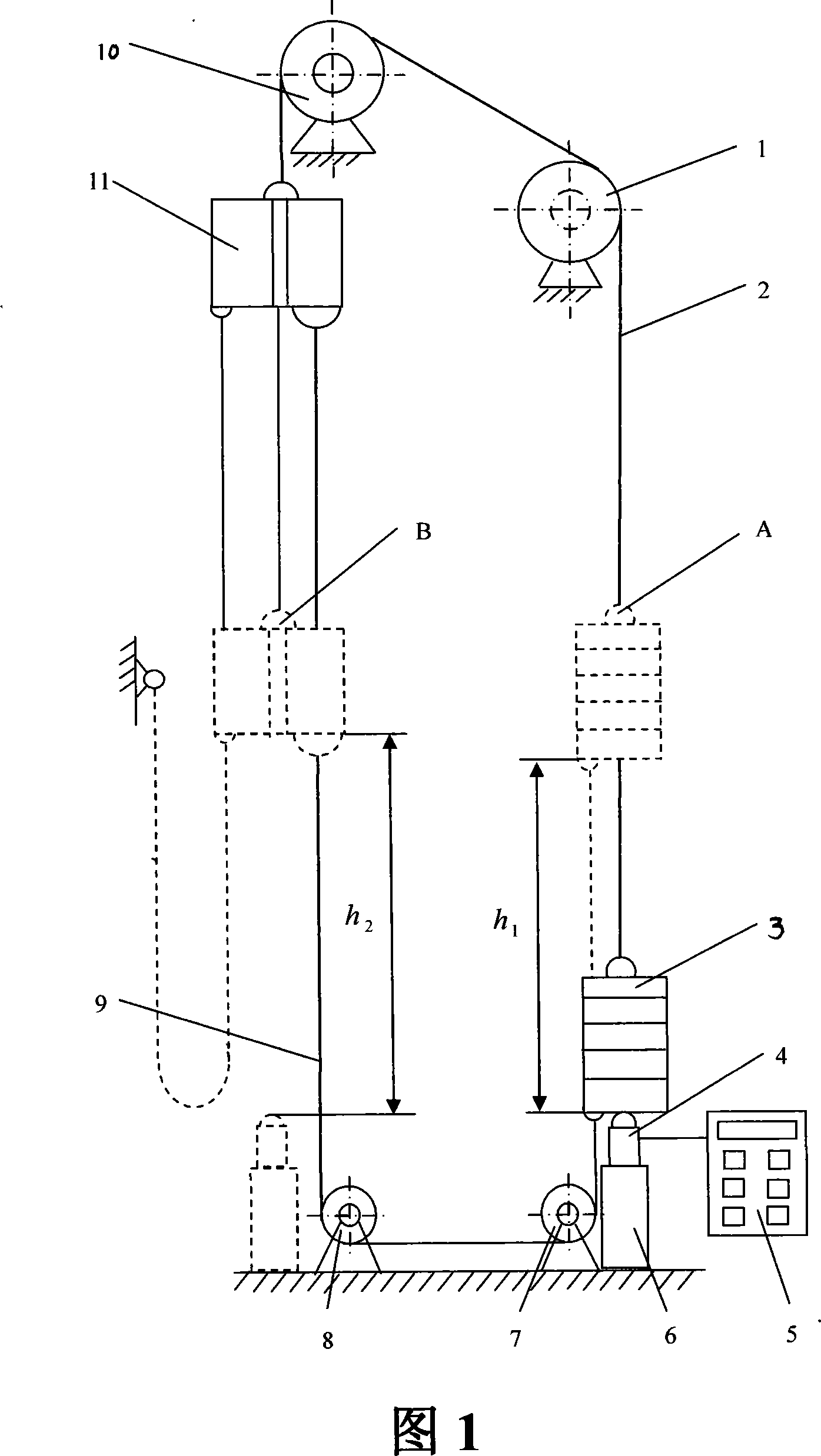
InactiveCN101082530AMeasure directlyAccurate measurementStatic/dynamic balance measurementElevatorsCarrying capacityFast measurement
The invention discloses a static two sides weight differential measurement method of lift coefficient of balance according to the lift balance coefficient formula (I)through measuring the weight differential Wg=(W-G) of the pair weight and the sedan wing and gives the lift rated load capacity Q then calculates the balance coefficient K. The method is that: at the condition of lift with no-load layouts the force transducer at the bottom of well corresponding with the pair weight and the pair weight falls down to the bottom of well and contacts with the force transducer then measures the weight differential Wg1 of the pair weight side and the sedan wing side; installs the poise with the carrying capacity QP in the sedan wing (QP is greater than the one-half of the lift rated carrying capacity) layouts the force transducer at the bottom of well corresponding with the sedan wing the sedan wing falls down to the bottom of well and contacts with the force transducer then measures the weight differential Wg2 of the sedan wing side and the pair weight side and calculates the balance coefficient K according to the formula(II)following the weight differentia Wg1, Wg2, the lift rated carrying capacity Q, and the bearing capacity QP. According to this method develop the lift balance coefficient test device which can measure the lift balance coefficient directly, accurately, and rapidly at the static case.
Owner:石成江 +1
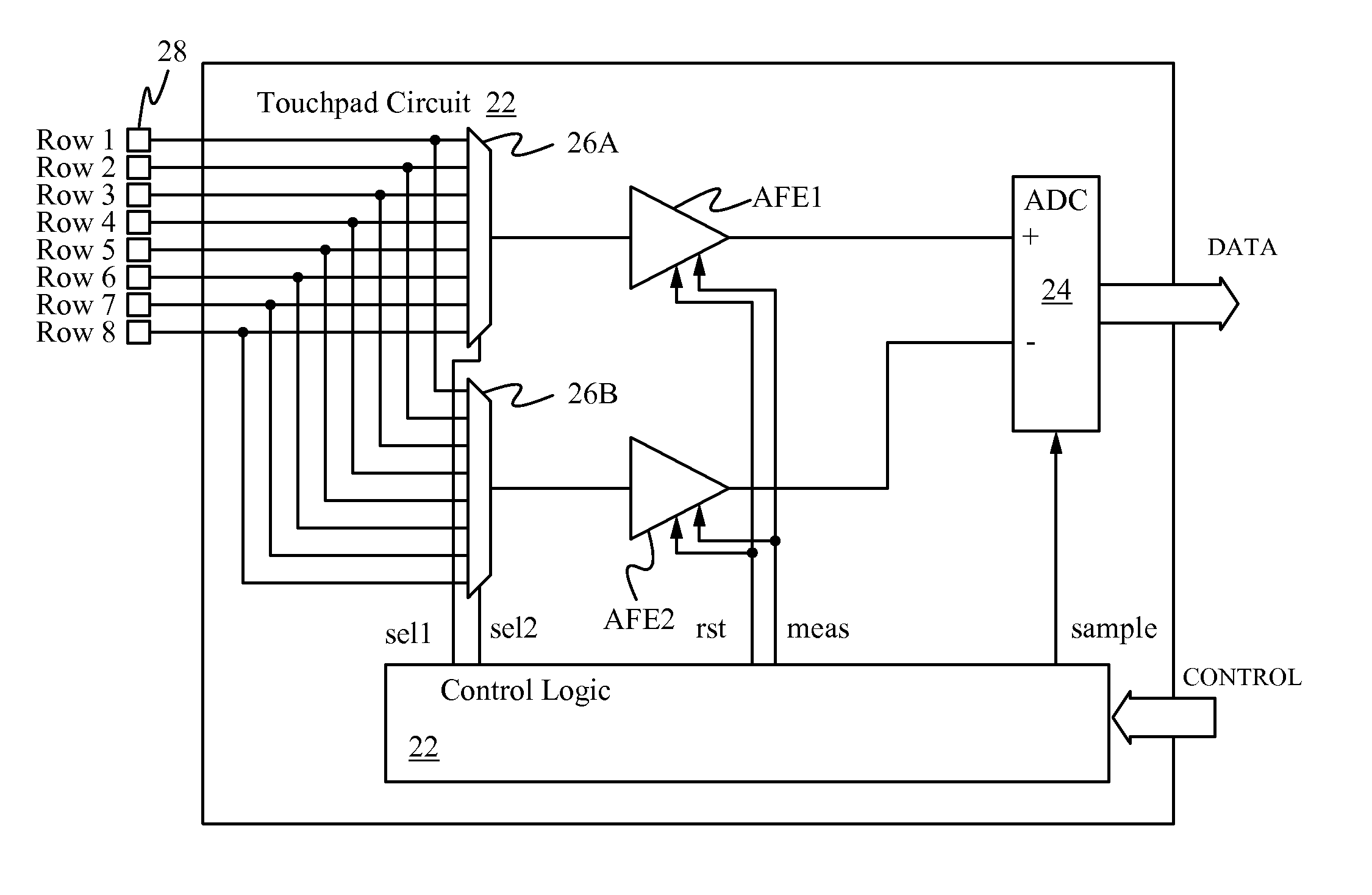
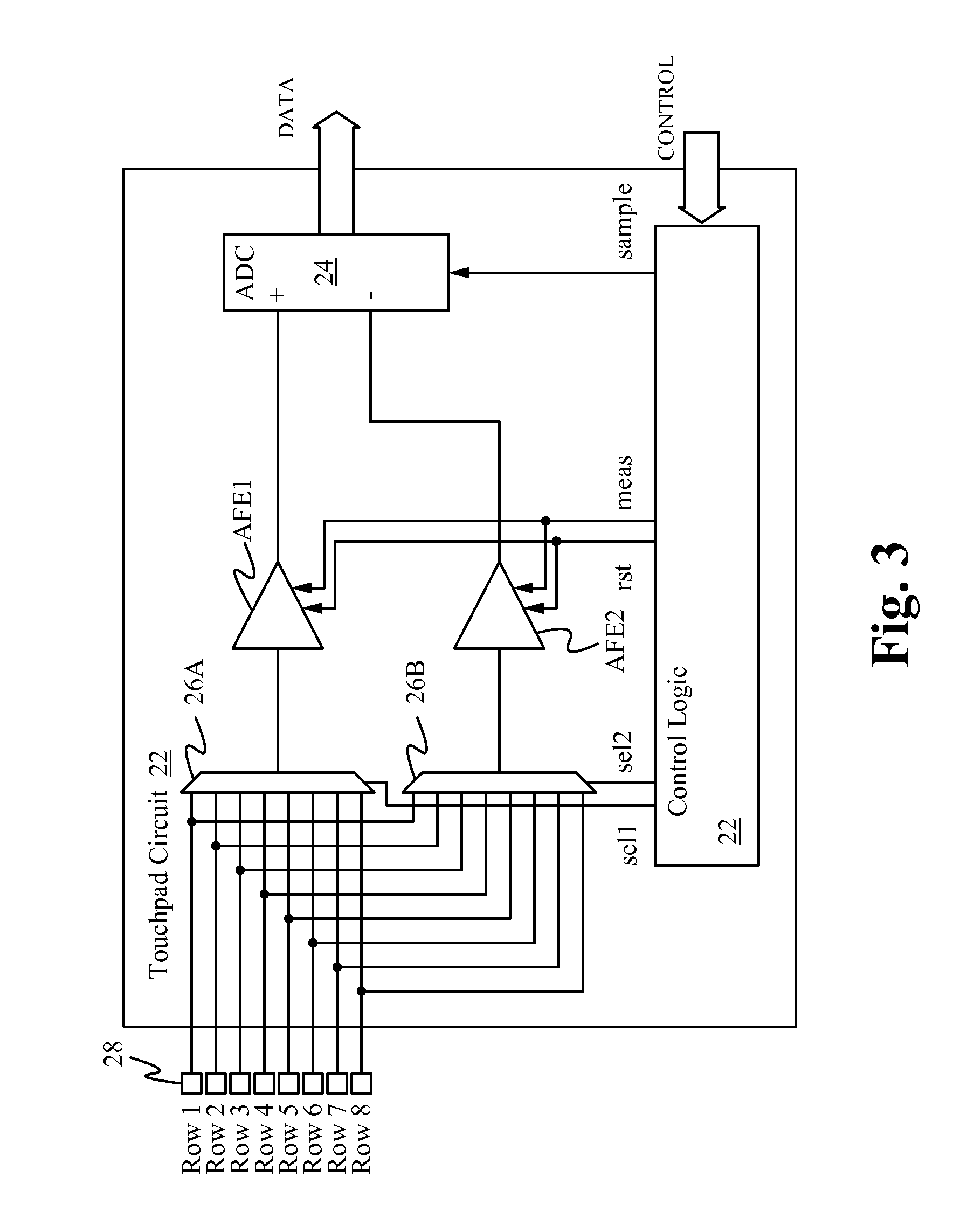
Noise cancellation technique for capacitive touchscreen controller using differential sensing
A differential sensing scheme provides a means for detecting one or more touch events on a touch sensitive device in the presence of incident noise. Instead of sensing one touch sensitive channel, such as a row, column, or single touch sensor, multiple touch sensitive channels are sampled at a time. By sampling two nearby channels simultaneously and doing the measurement differentially, noise common to both channels is cancelled. The differential sensing scheme is implemented using simple switch-capacitor AFE circuitry. The originally sensed data on each individual channel is recovered free of common-mode noise. The recovered sensed data is used to determine the presence of one or more touch events and if present the location of each touch event on the touch sensitive device.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Combined open and closed loop power control with differential measurement
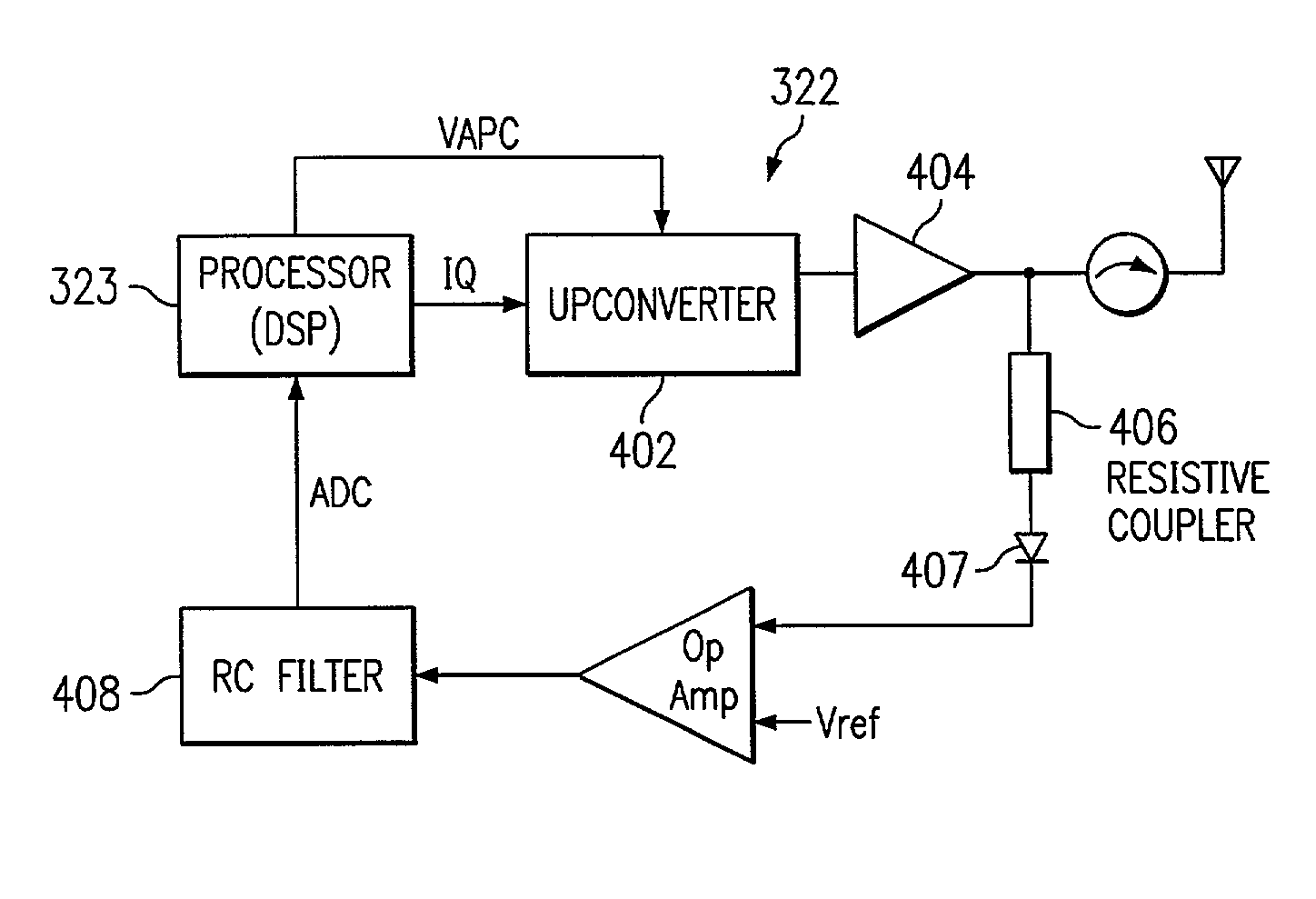
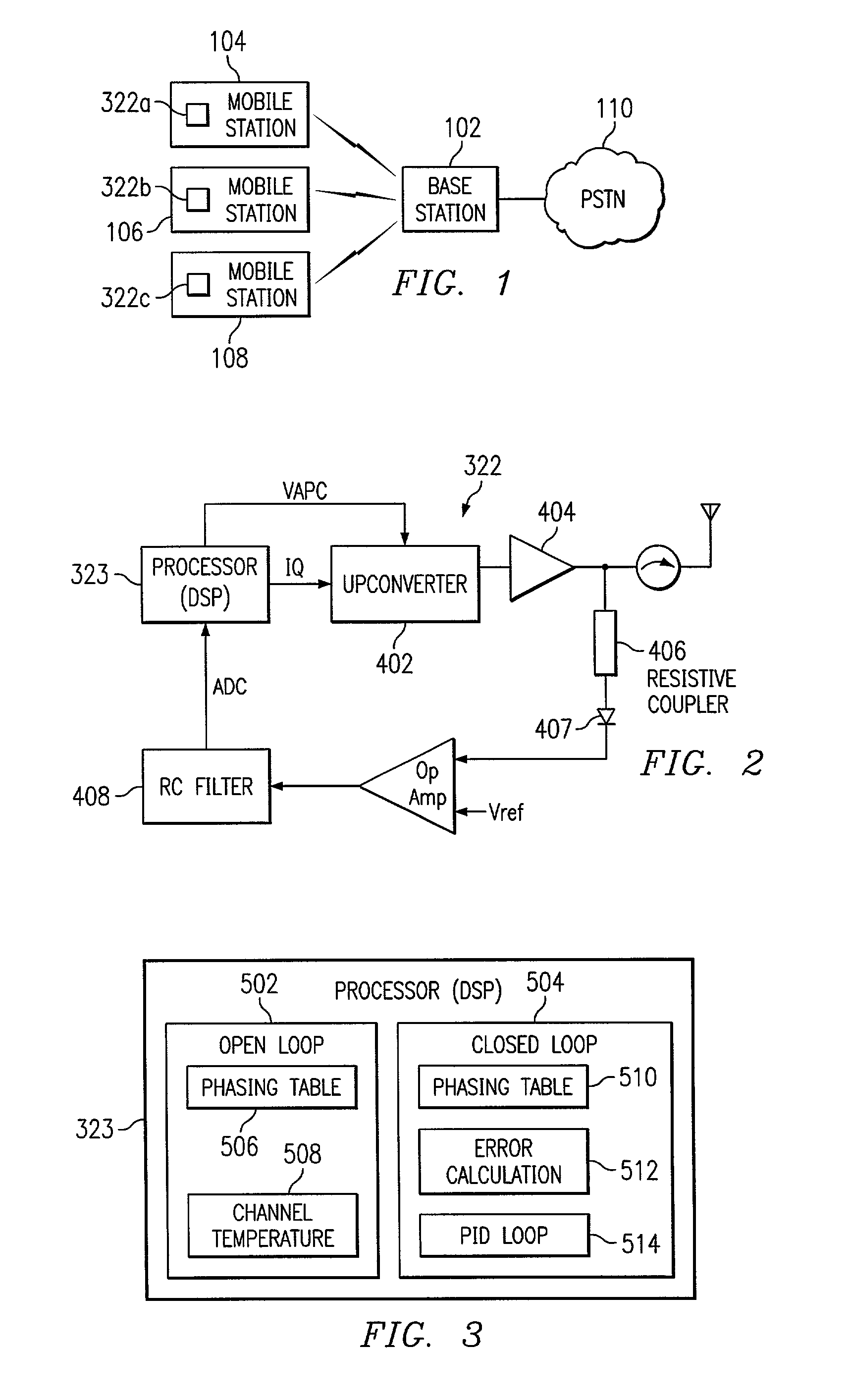
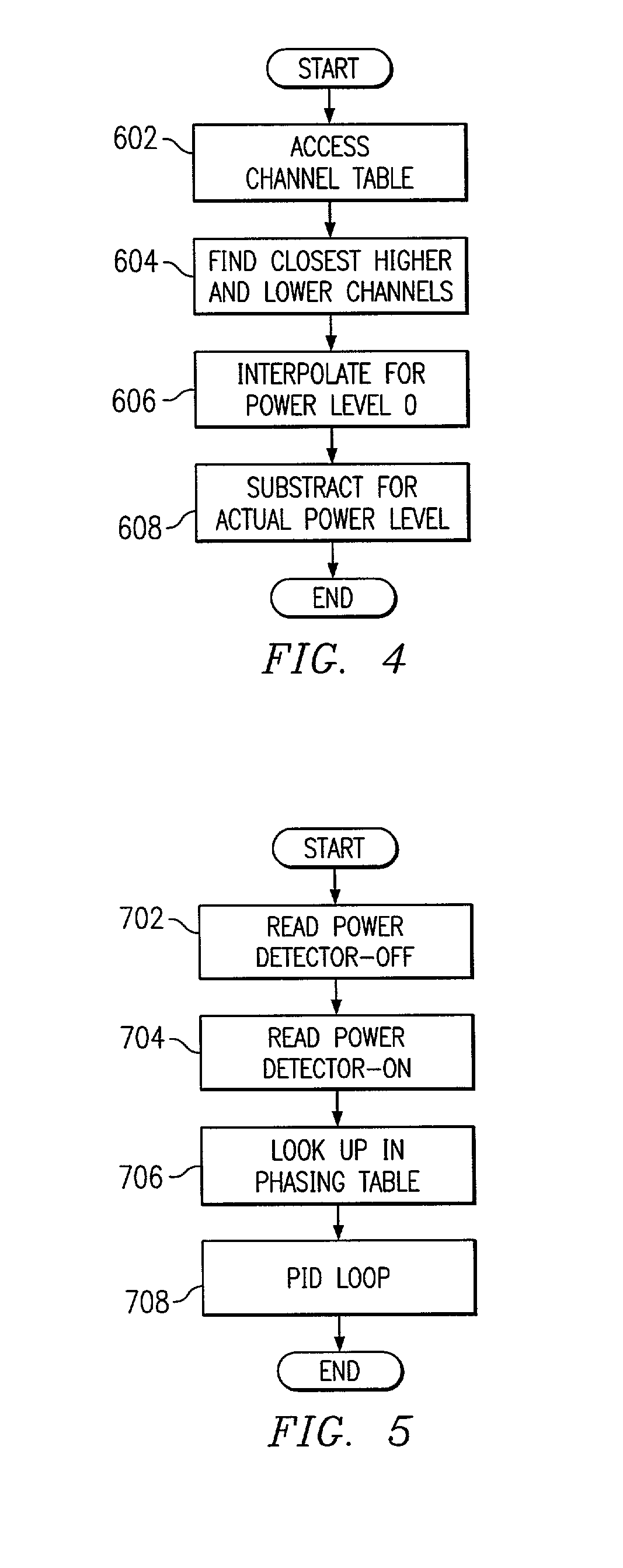
A power control system and method for a wireless telephone employs an open loop technique for relatively low power levels and a closed loop technique at higher power levels. In the open loop technique, a wireless telephone (104, 106, 108) stores a phasing table of automatic power control (APC) values for the power levels (which are used to control upconverter gain levels measured at different channels. In operation, a power controller (322) reads the power level and reads the APC value in the table. Another table stores the APC value for one power level as the channel and temperature are varied. This value is interpolated, as needed, during operation. The APC value for the open loop approach is determined by reading the input channel; finding the closest higher and closest lower channels in the temperature-channel table; interpolating between APC values for the temperature column of the closest lower temperature, to get the actual value. The difference between this value and the APC value for the actual power level in the phasing table is then obtained.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Calibration of resistor ladder using difference measurement and parallel resistive correction
InactiveUS6628216B2Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDifferential measurementComplementary pair
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Differential wideband vibration sensor
InactiveUS6220096B1Eliminates costly precision tuningIncrease capacitanceVibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesEngineeringField-effect transistor
This invention relates to an apparatus for making highly sensitive differential measurements of acceleration. The vibration sensor includes the use of moveable gate field effect transistors to sense the motion of a cantilever beam relative to the motion sensed by a reference structure, it also includes an actuator element formed by a pair of electrodes actuating electrostatically on the beam. A feedback control loop is also included for force balance operation resulting in a very wide dynamic range for the sensor.
Owner:INTERSCI
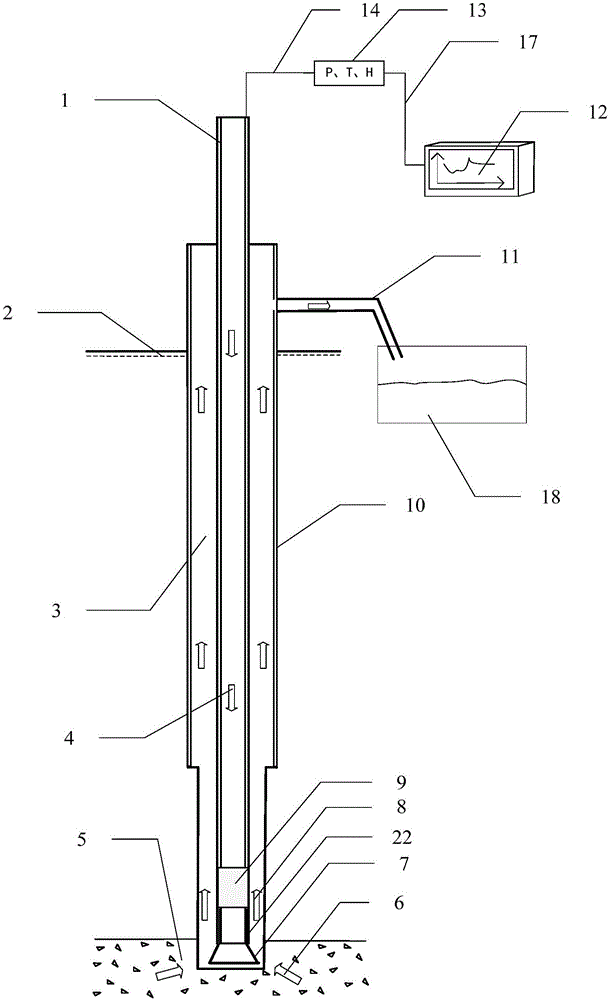
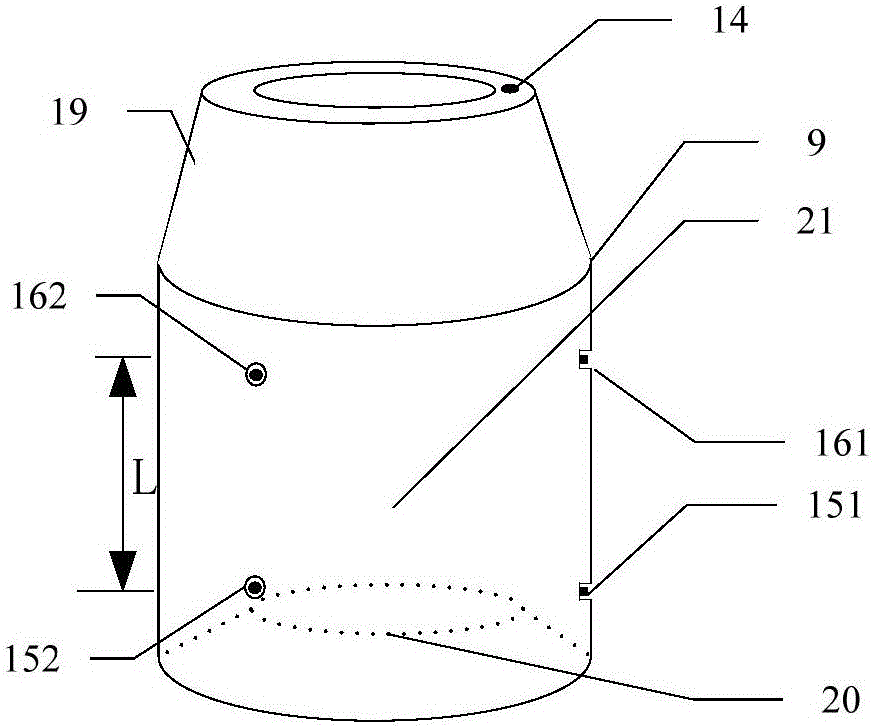
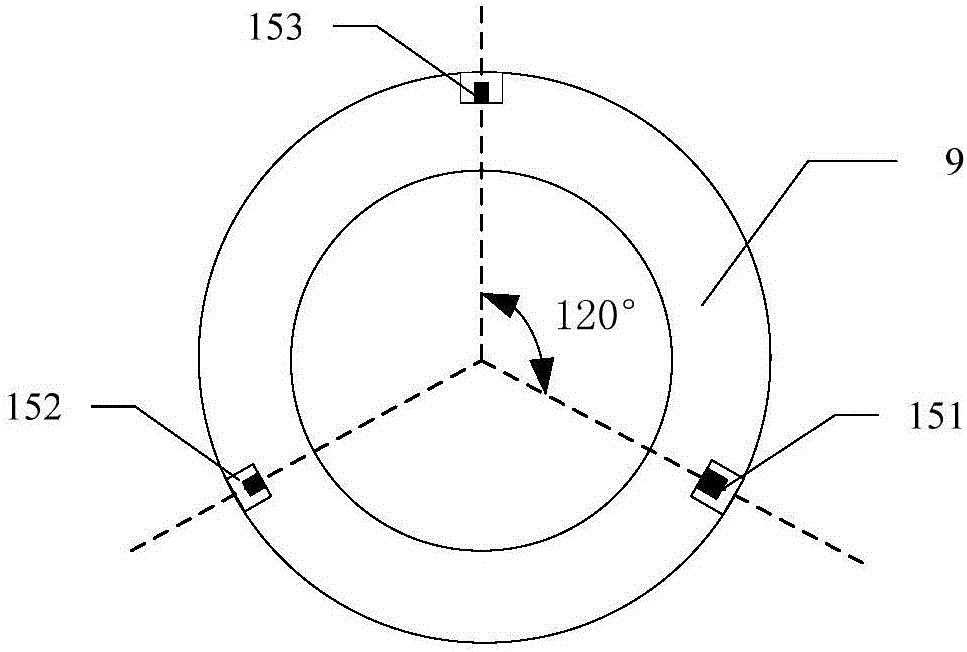
Gas migration monitoring device and monitoring method based on annulus pressure differential measurement while drilling
ActiveCN106194162AImprove monitoring accuracyHigh degree of automationSurveyConstructionsData connectionComputer terminal
The invention belongs to the technical field of petroleum engineering, and particularly relates to a gas migration monitoring device based on annulus pressure differential measurement while drilling in the drilling process. The gas migration monitoring device based on annulus pressure differential measurement while drilling comprises a nipple for gas migration monitoring while drilling, a central processing unit and a computer terminal; the two ends of the nipple for gas migration monitoring while drilling are connected with a drill collar and a drill pipe, and the two ends of the central processing unit are connected with a gas migration monitoring device body and the computer terminal; the computer terminal sends a measuring signal to the central processing unit through a data connection bus, the measuring signal is transmitted to the nipple for gas migration monitoring while drilling through an armored cable, a sensor group immediately conducts measurement work, the pressure P, the temperature T and the depth H of a corresponding position are obtained, the actual drilling fluid density is obtained through calculation, and if a difference between the actual drilling fluid density and theoretical density is larger than a gas migration discriminant value, well control prevention measures are started. The gas migration monitoring device is high in monitoring accuracy and extremely high in real-time performance, matching with the drill pipe is simple and convenient, the professional requirement on operation is low, the stability is good, and the automation degree is high.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Exhaust back pressure sensor using absolute micromachined pressure sense die
ActiveUS20060000265A1Internal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusDifferential pressurePressure sense
Sensor systems and methods are disclosed, which generally incorporate isolation between the sensor's electronics and the sensed media. The sensor's electronic circuit can incorporate one or more application specific integrated circuit (ASIC) that processes and outputs the signal for both absolute and differential measurements. Such a sensor can be adapted for use in exhaust gas re-circulation (EGR) systems utilized with automotive gasoline engines. Such a sensor can also be utilized for measuring differential pressure across diesel particular filters and / or applications in which differential pressure is required for system control and / or monitoring purposes. The absolute pressure sensor disclosed herein can therefore sense the exhaust pressure on automotive engines and other mechanical and / or electromechanical devices and machines.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
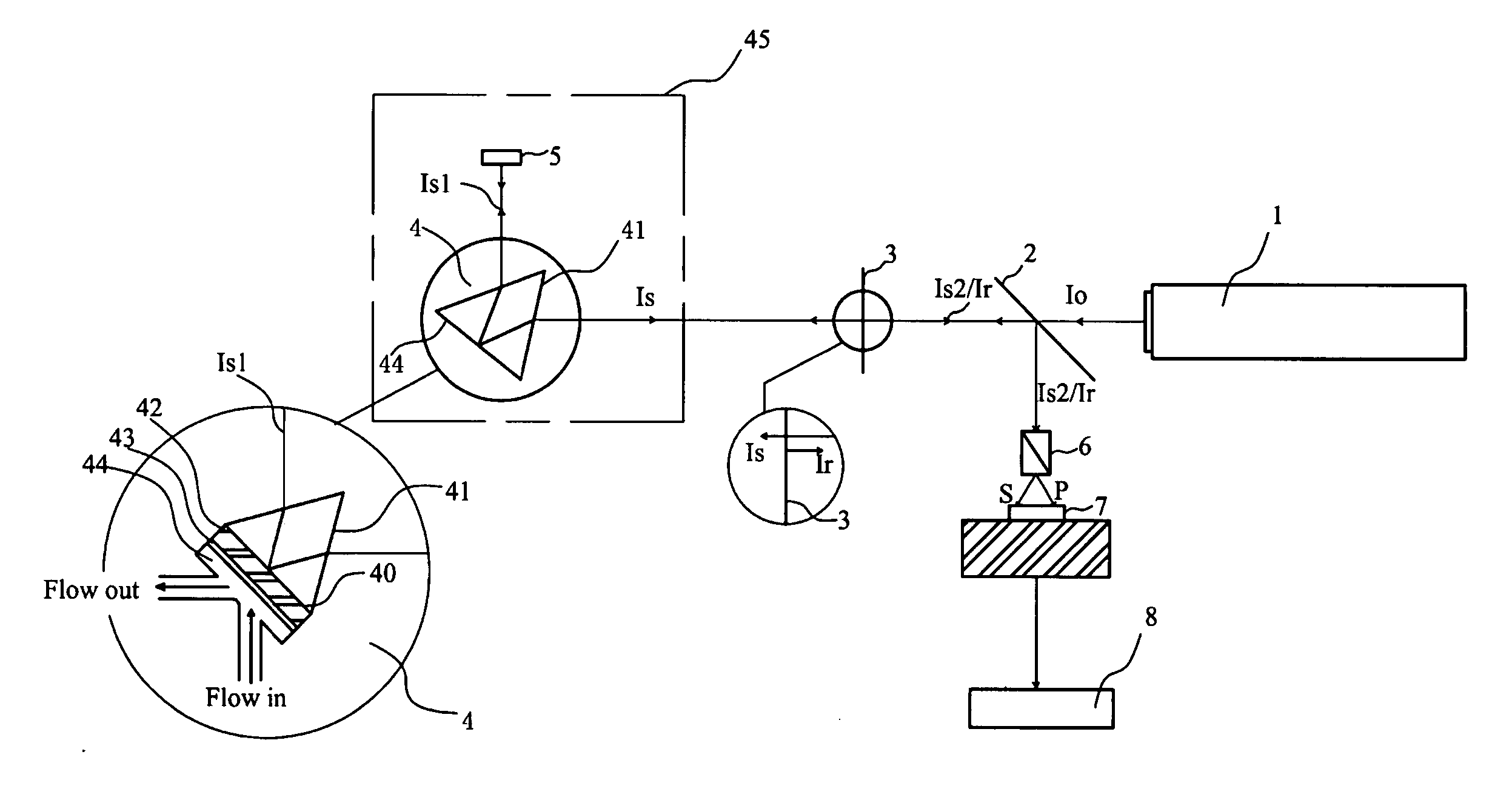
Optical sensing devices with SPR sensors based on differential phase interrogation and measuring method using the same
ActiveUS20070008546A1Enhance phase shiftPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansBeam splitterDifferential measurement
Disclosed is an optical sensing device, which comprises a light source emitting a light; a beam splitter; an SPR sensor unit comprising a sensing surface; and a detecting mechanism; and a converting unit converting the first beam and the second beam from the optical device into a two-dimensional interference fringe pattern. From the above-mentioned configuration, an extra phase shift of a detection beam in SPR phase measurement is obtained. The differential measurement approach has shown to achieve a sensitivity figure significantly better than the best result that can be obtained from the prior art in the field of the measurement based on an SPR sensor.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
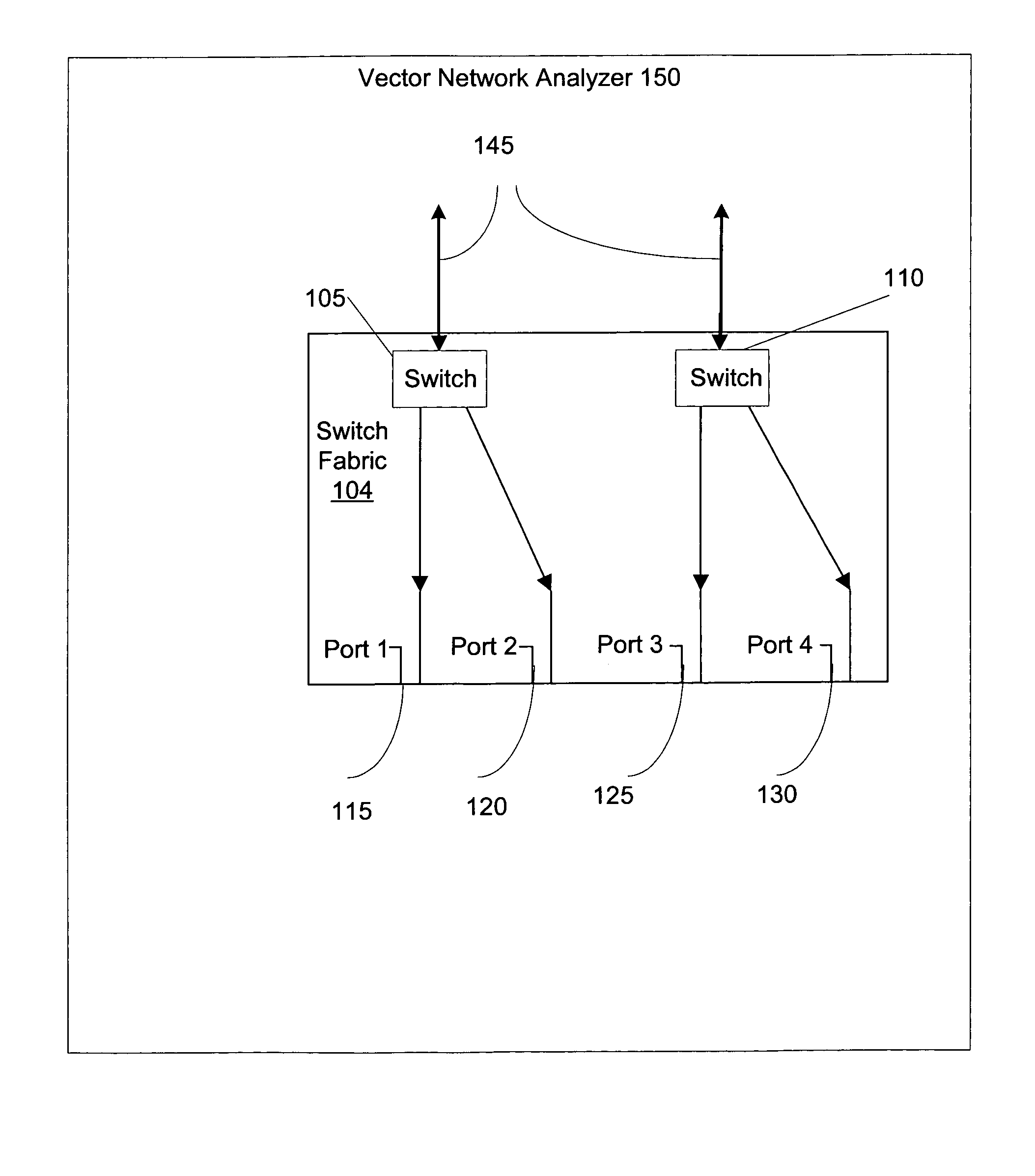
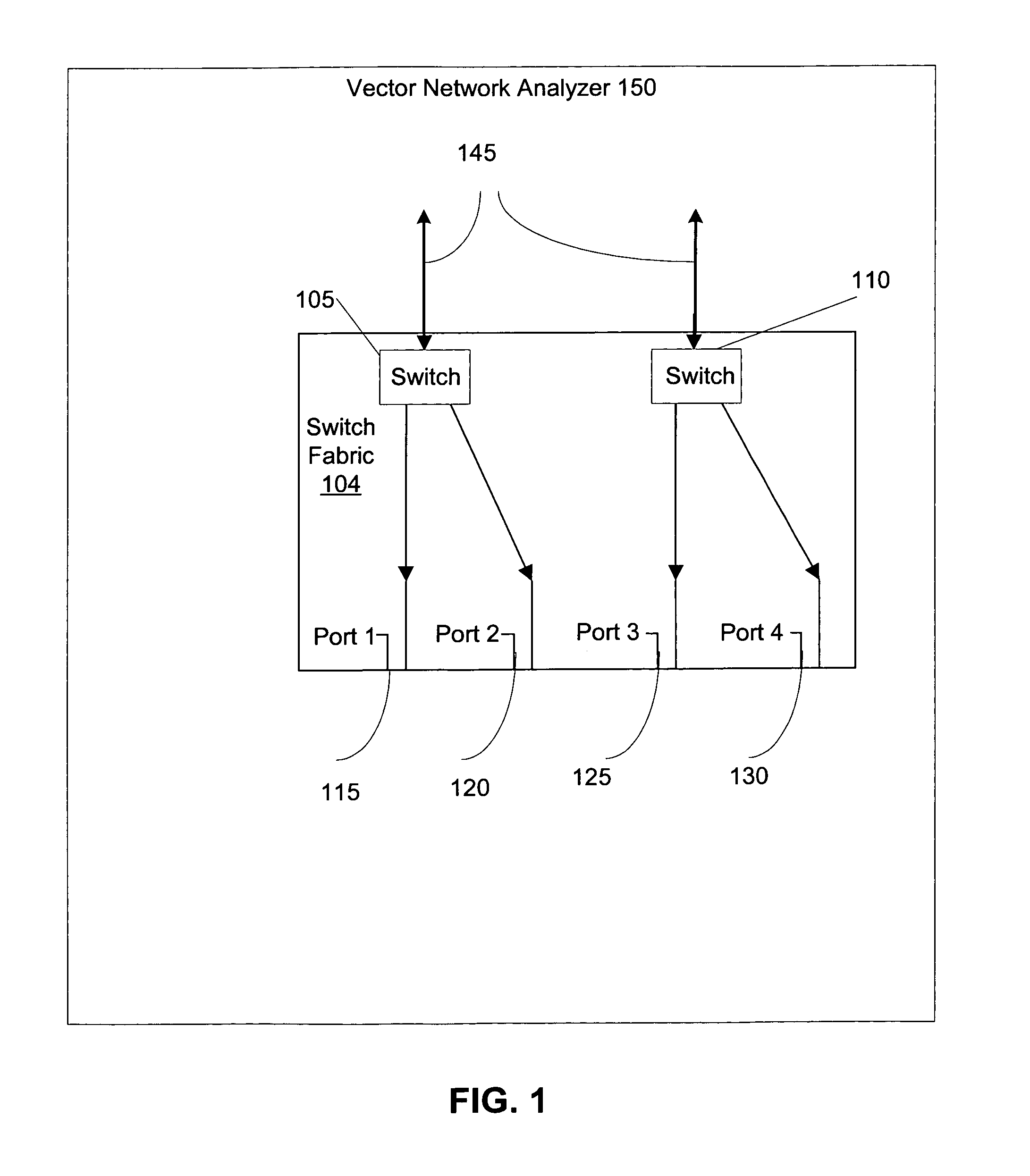
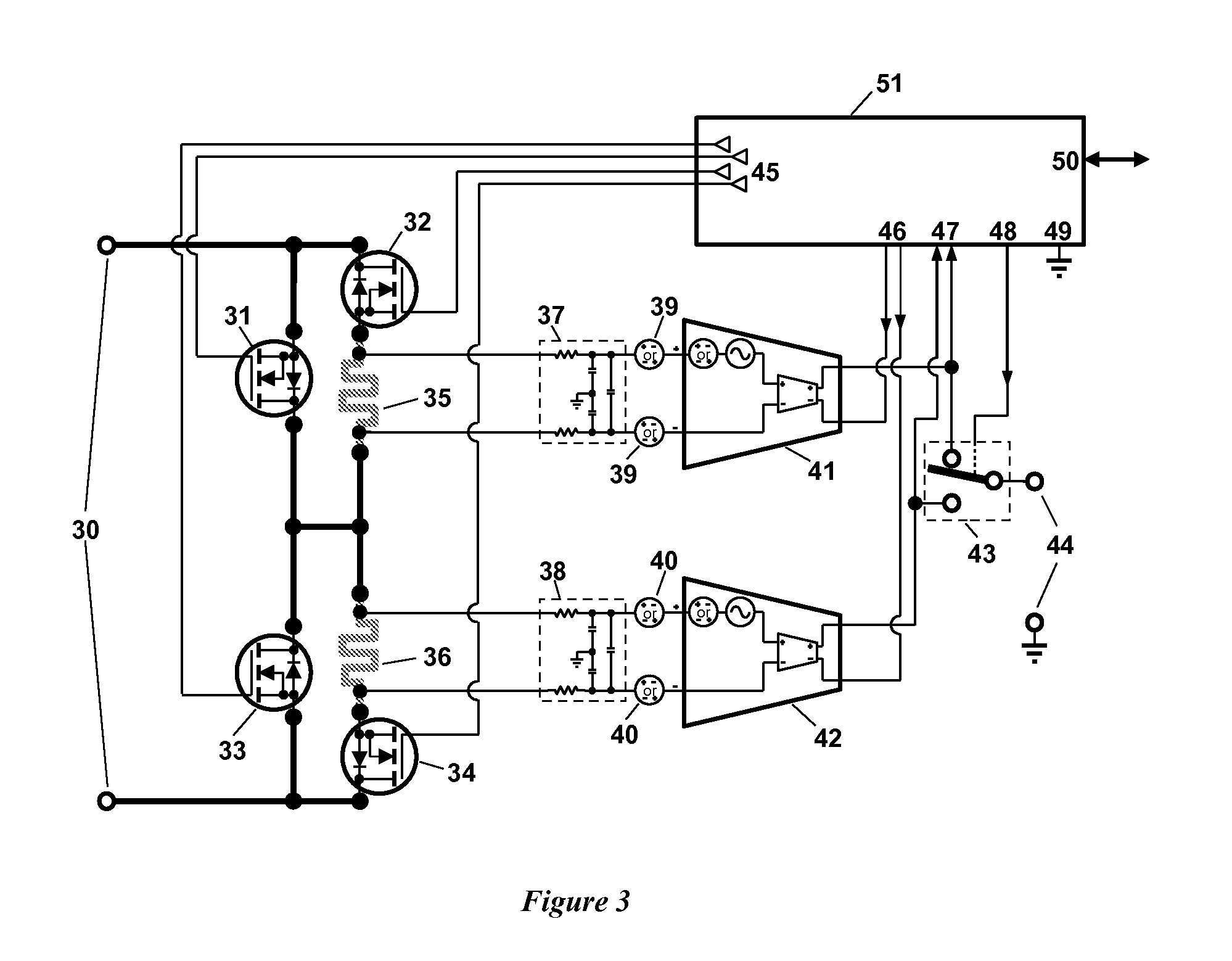
Calibration techniques for simplified high-frequency multiport differential measurements
Embodiments of the present invention are directed towards systems, methods, and computer readable media for performing multiport vector network analysis. Embodiments of the present invention relate to a multiport network analysis that is derived from a family of two port calibration techniques including Thru / Reflect / Line (TRL), Thru / Reflect / Match (TRM), Line / Reflect / Line (LRL), Line / Reflect / Match (LRM) and several others. An improved calibration method enables the use of a simplified switch matrix to perform accurate vector network analysis in communications and networking systems. After determining some characteristics through conventional methods, a two tier load match correction is performed on the results. The improved correction mechanism enables the system to perform comparably to systems with more complicated switch matrices.
Owner:ANRITSU CO
Quantum technology based alternating-current differential measurement system and method
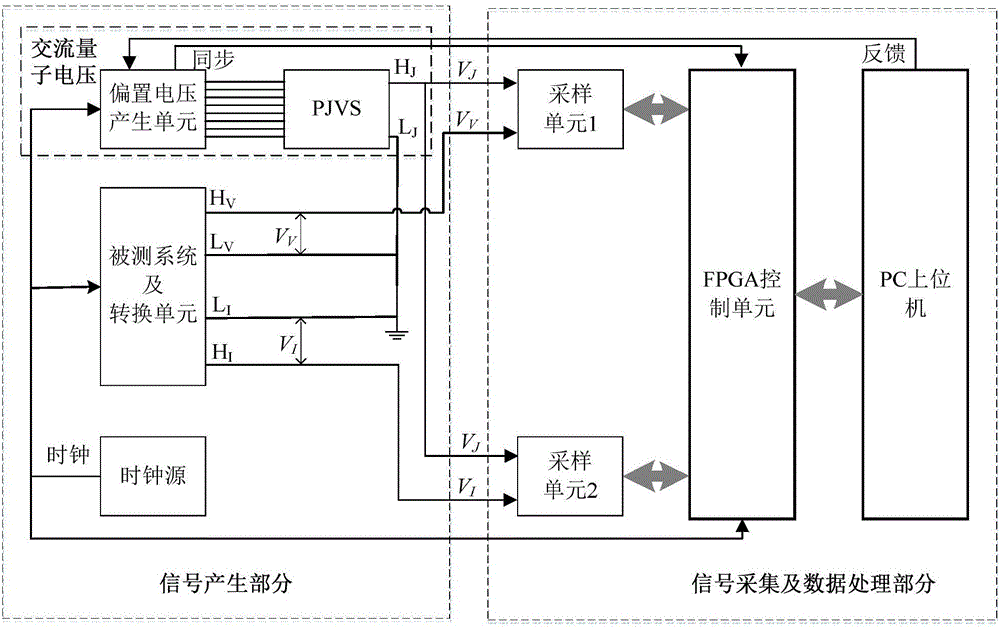
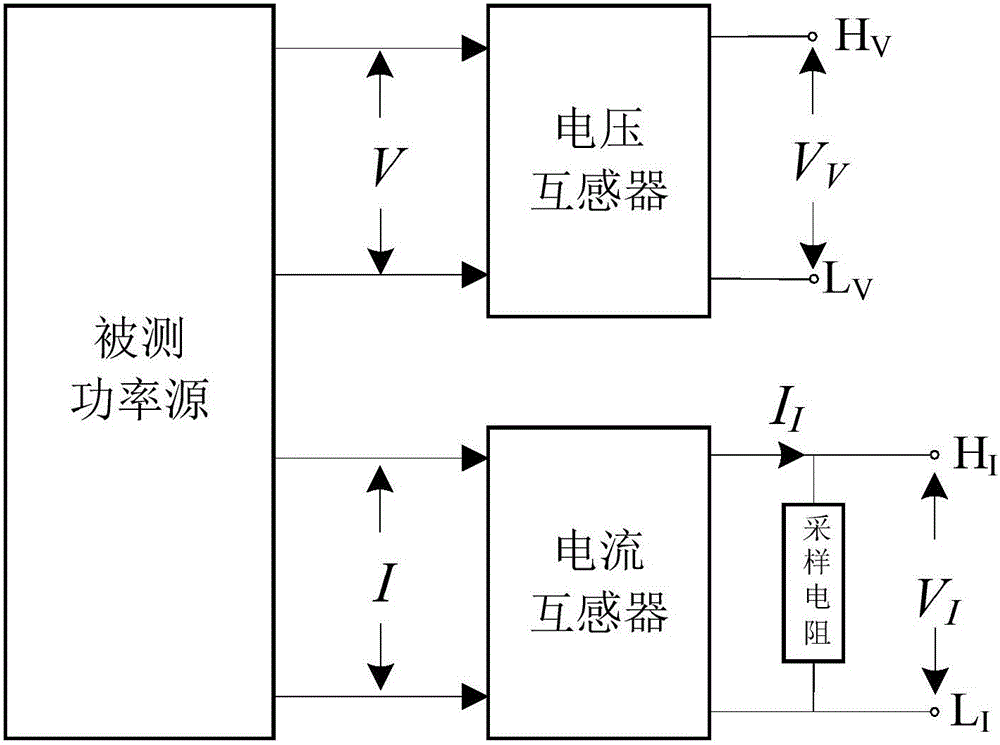
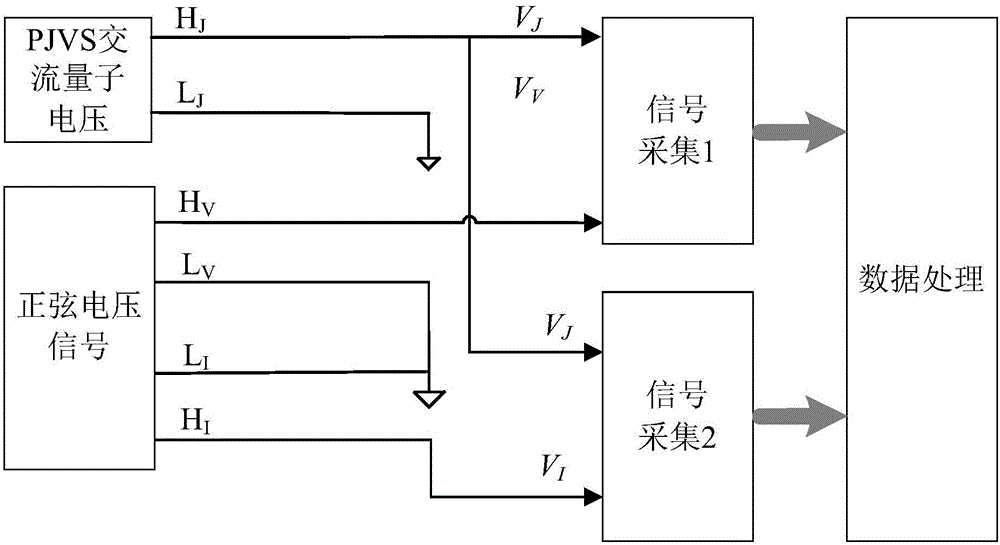
ActiveCN106771556AAccurate electric power valueHigh precisionElectric devicesPower measurement by digital techniqueQuantum technologyDifferential measurement
The invention provides a quantum technology based alternating-current differential measurement system and method and belongs to the field of metering. The system comprises a bias-voltage generation unit, a PJVS, a tested system and conversion unit, a clock source, a first sampling unit, a second sampling unit, an FPGA (field programmable gate array) control unit and a PC upper machine; the clock resource is connected with the bias-voltage generation unit, the tested system and conversion unit and the FPGA control unit respectively and provides time-base frequency for the bias-voltage generation unit, the tested system and conversion unit and the FPGA control unit; the bias-voltage generation unit generates bias current for the PJVS and drives the PJVS to output needed waveforms; the bias-voltage generation unit provides trigger signals for the FPGA control unit; the PJVS is connected with the first sampling unit and the second sampling unit respectively; the tested system and conversion unit is connected with the first and second sampling units respectively; the FPGA control unit is connected with the first and second sampling units and the PC upper machine respectively.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
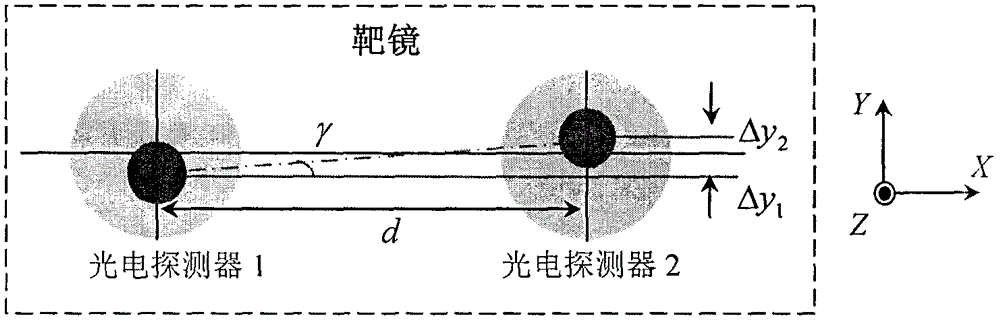
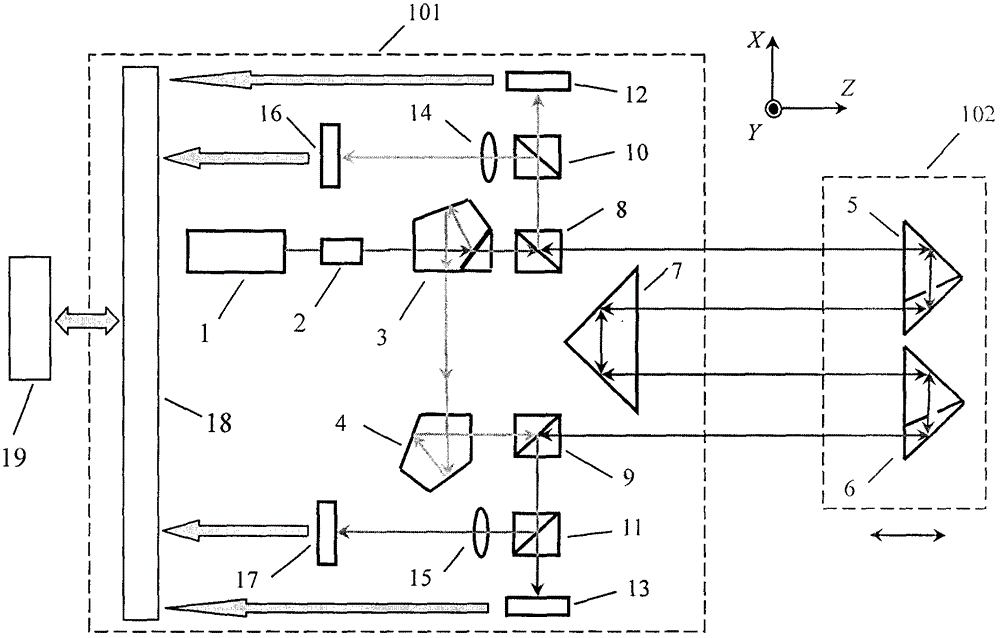
Method and device for simultaneously measuring five degrees-of-freedom errors based on light beam drift compensation
ActiveCN107228638AAchieving Photodrift CompensationAchieving Error SeparationUsing optical meansBeam splittingPrism
The invention provides a method and a device for simultaneously measuring five degrees-of-freedom errors based on light beam drift compensation. The method and the device are used for solving the problems of low measurement precision, small measurement range and poor anti-interference capability of the existing high-precision simultaneous measurement method for guide rail five degrees-of-freedom. A collimating lens, a prism assembly, a polarization beam splitting prism and a quarter-wave plate are arranged between a laser device and a right-angle prism plated with a beam splitting film, so as to realize processing of incident light and reflected light, information of the reflected light and transmitted light after beam splitting is received and measured by means of a four-quadrant detector and a position sensitive detector, and the measurement of pitch angle, deflection angle and rolling angle errors, horizontal straightness errors, vertical straightness errors and light drift compensation are realized. The method and the device utilize double beam differential measurement to realize error separation, enhance the anti-interference capability, employ few optical devices and are low in light source power and cost; the optical structure is simple, the operation is convenient, the moving parts are not required to be provided with cables, and the field measurement is facilitated; and the angle measurement resolution is high.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
High-accuracy low-power current sensor with large dynamic range
ActiveUS20120086430A1Resistance/reactance/impedenceElectrical measurement instrument detailsShunt DeviceDifferential measurement
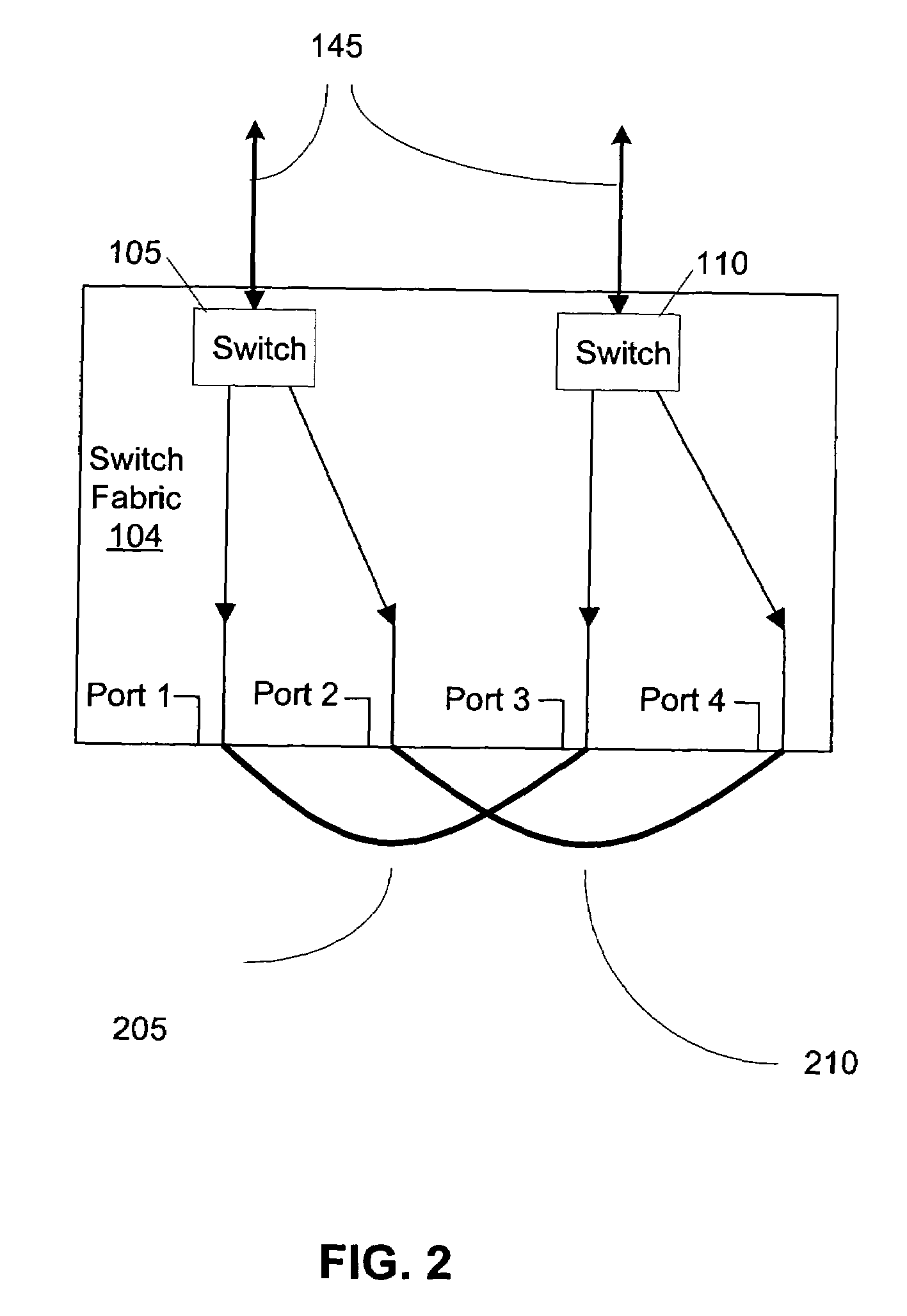
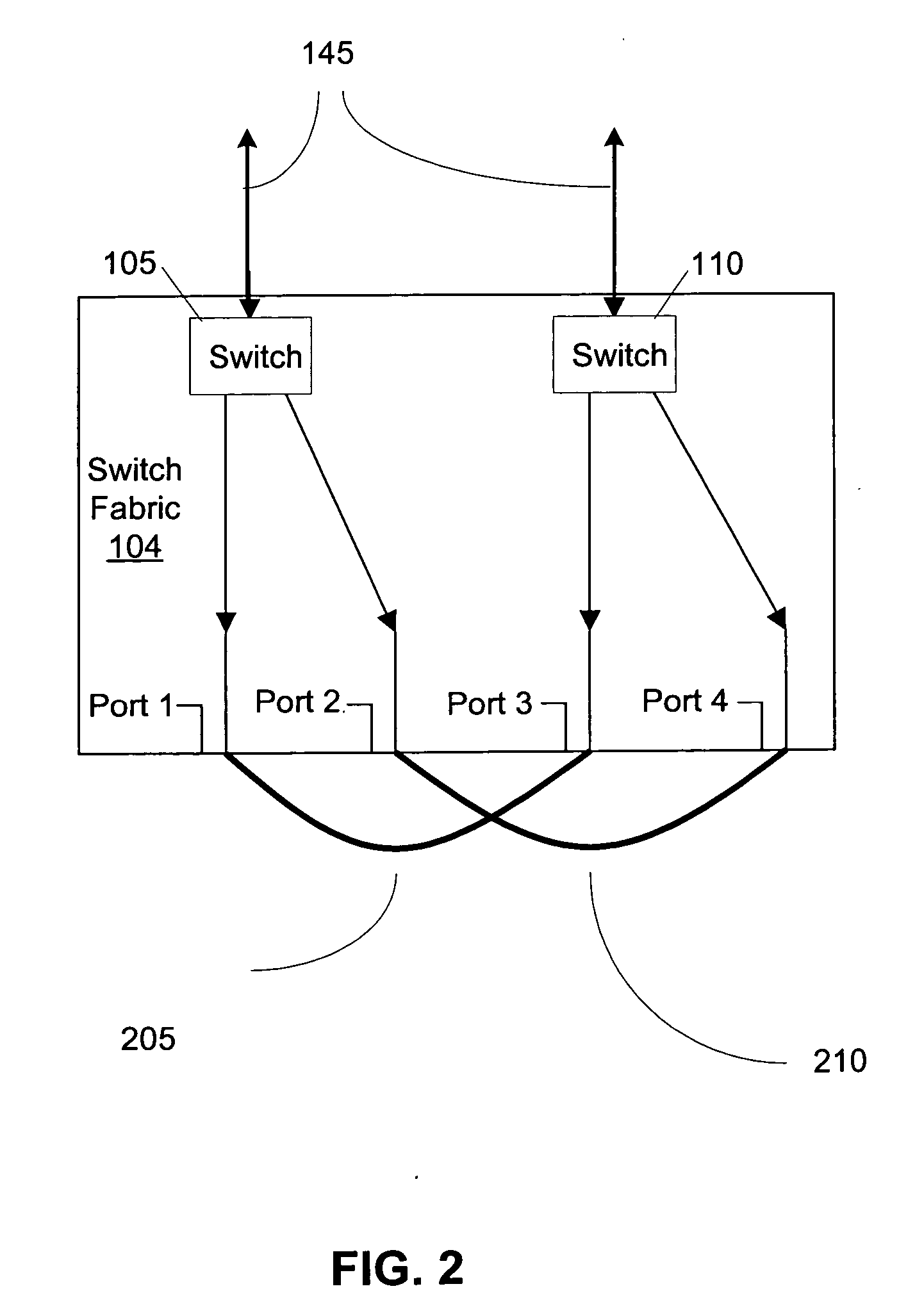
A current sensing approach makes use of two shunts in series, embedded in a switching fabric, each shunt the object of a differential measurement of voltage drop across the shunt. Methodical make-before-break cycling of the switches in the switching fabric permit real-time or very near-real-time measurement of nearly all of the errors such as offset errors present in each differential-measurement path. Additional differential measurement paths can be connected with the shunts, with RFI filtering at shorter time constants to serve electronic fuse needs.
Owner:SENSATA TECHNOLOGIES INC
Calibration techniques for simplified high-frequency multiport differential measurements
Embodiments of the present invention are directed towards systems, methods, and computer readable media for performing multiport vector network analysis. Embodiments of the present invention relate to a multiport network analysis that is derived from a family of two port calibration techniques including Thru / Reflect / Line(TRL), Thru / Reflect / Match(TRM), Line / Reflect / Line (LRL), Line / Reflect / Match (LRM) and several others. An improved calibration method enables the use of a simplified switch matrix to perform accurate vector network analysis in communications and networking systems. After determining some characteristics through conventional methods, a two tier load match correction is performed on the results. The improved correction mechanism enables the system to perform comparably to systems with more complicated switch matrices.
Owner:ANRITSU CORP
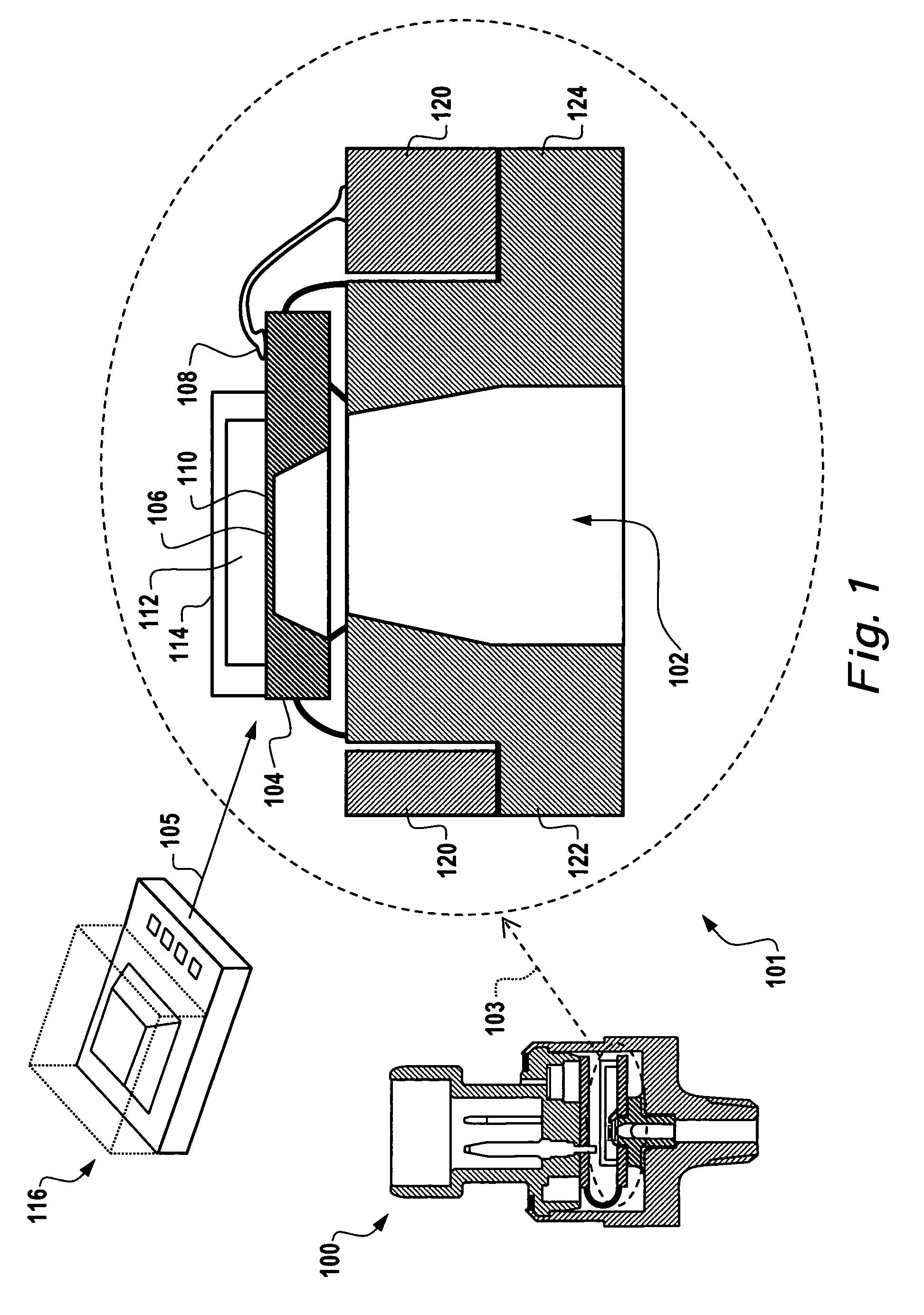
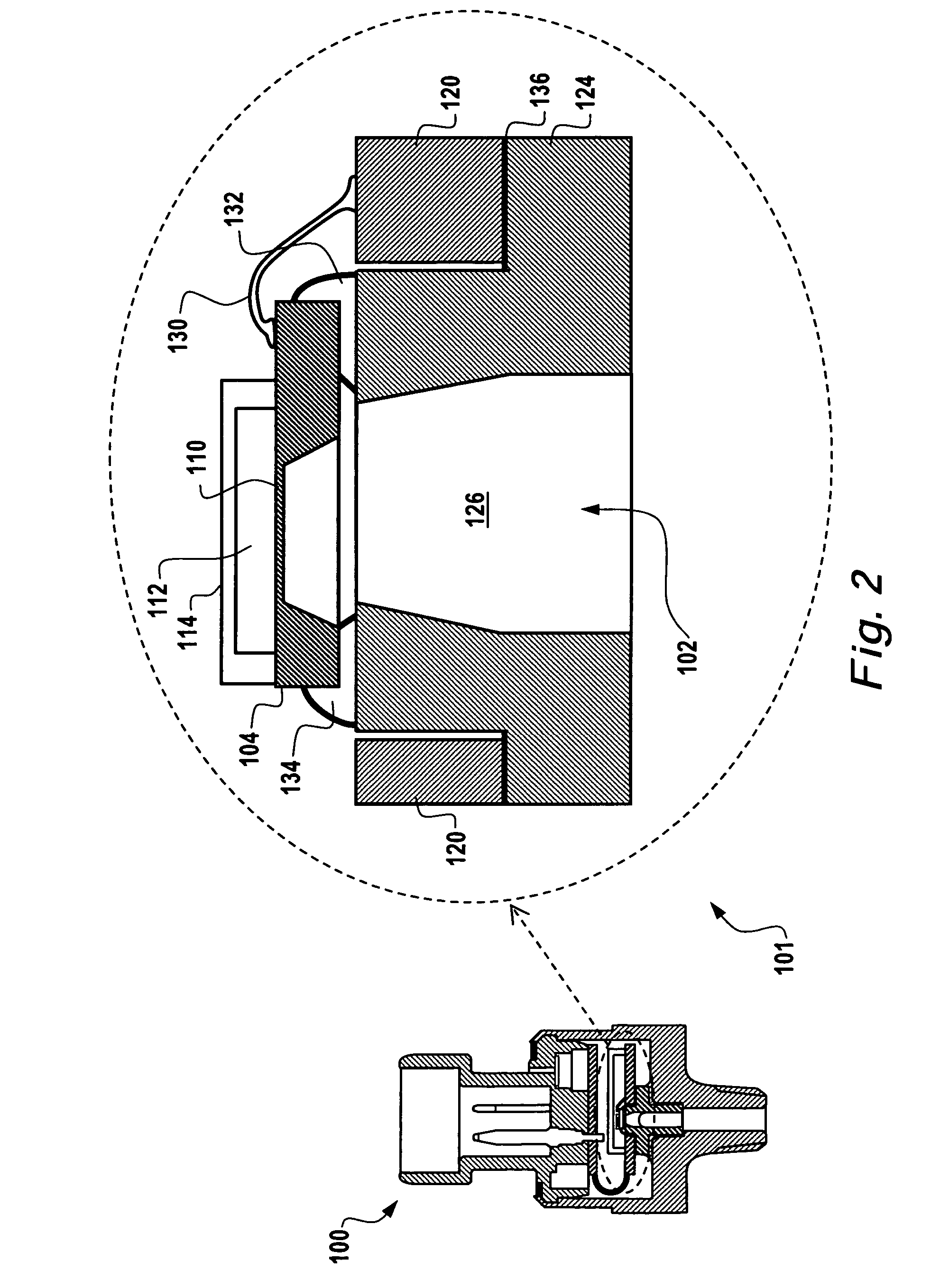
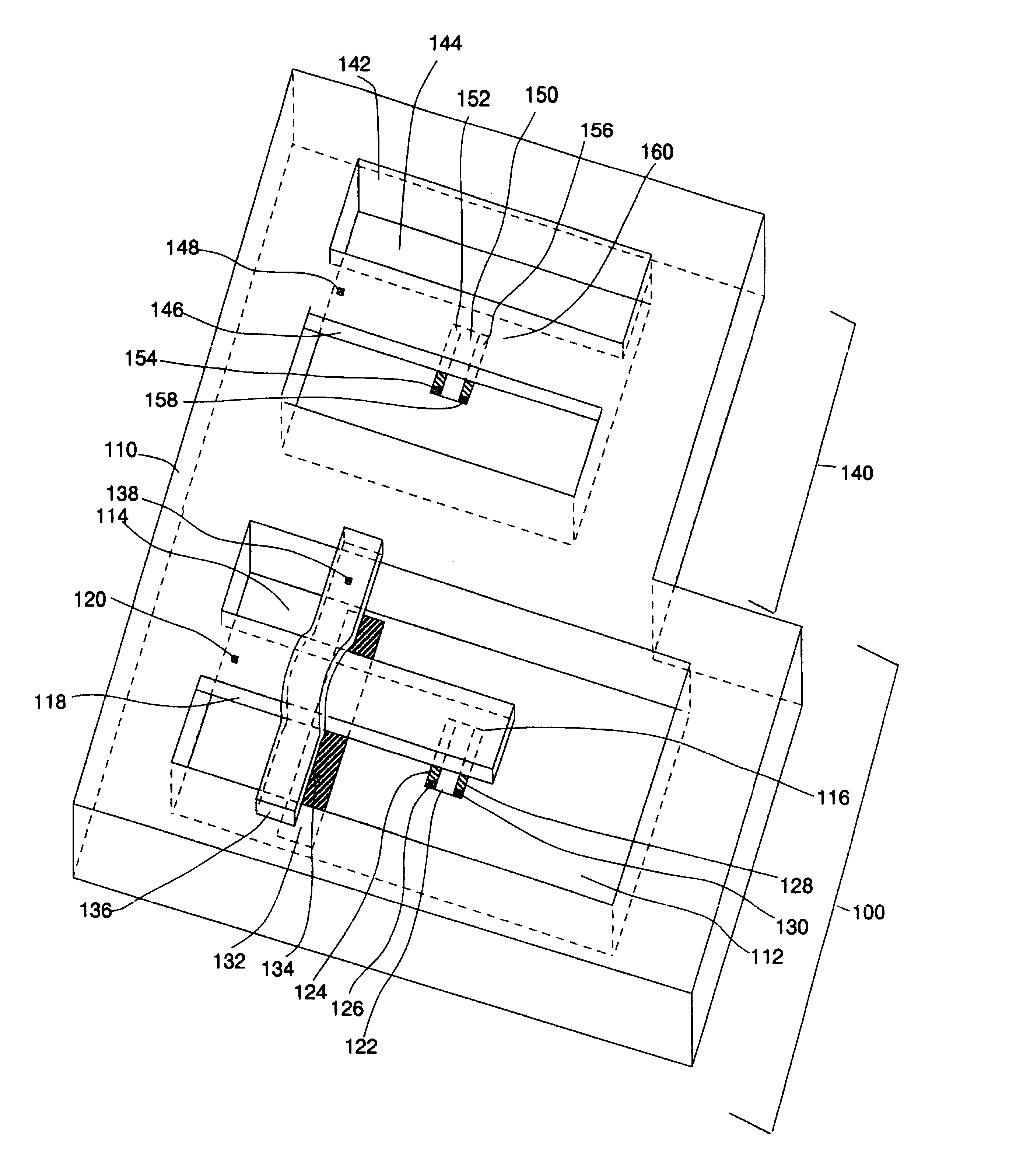
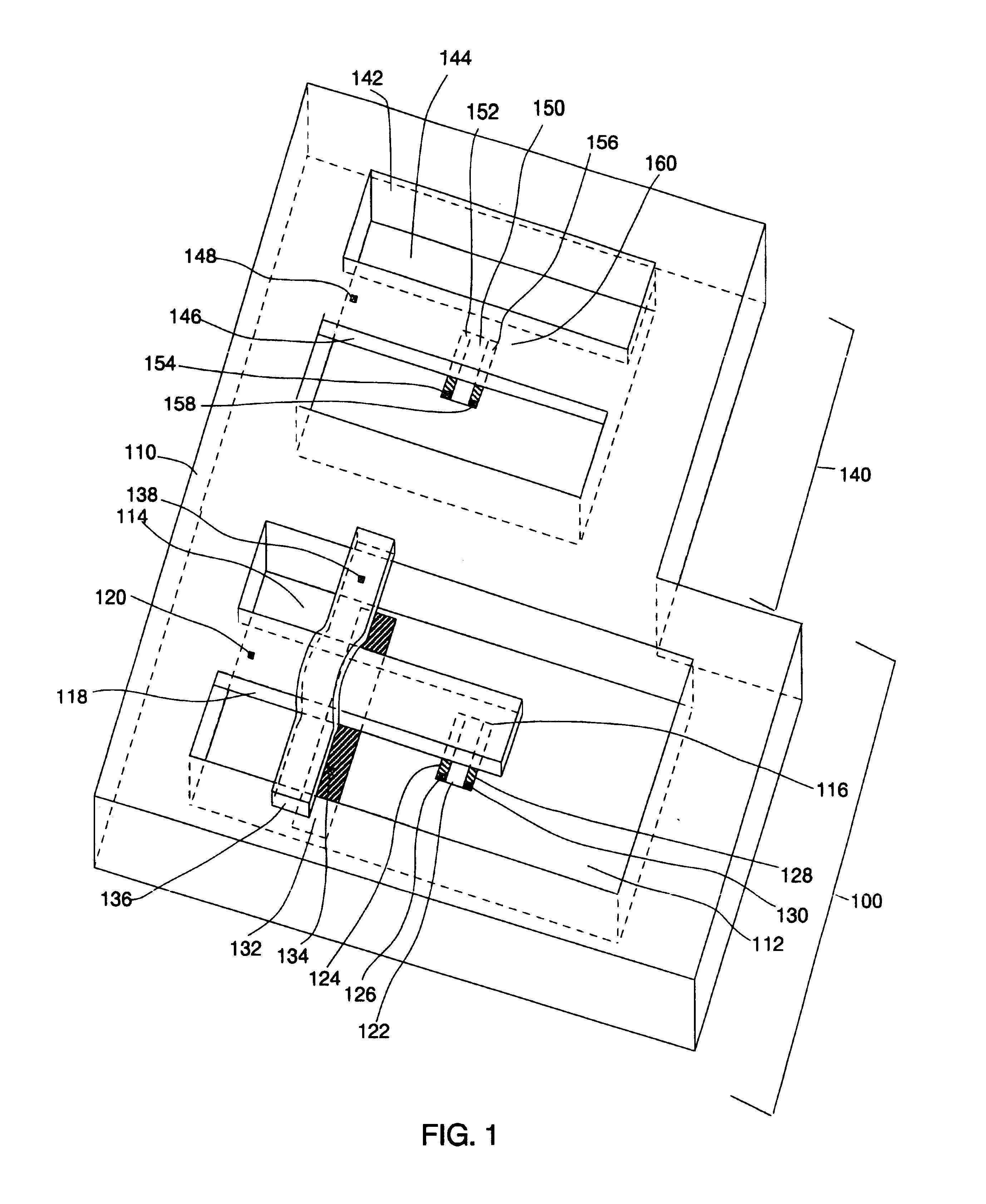
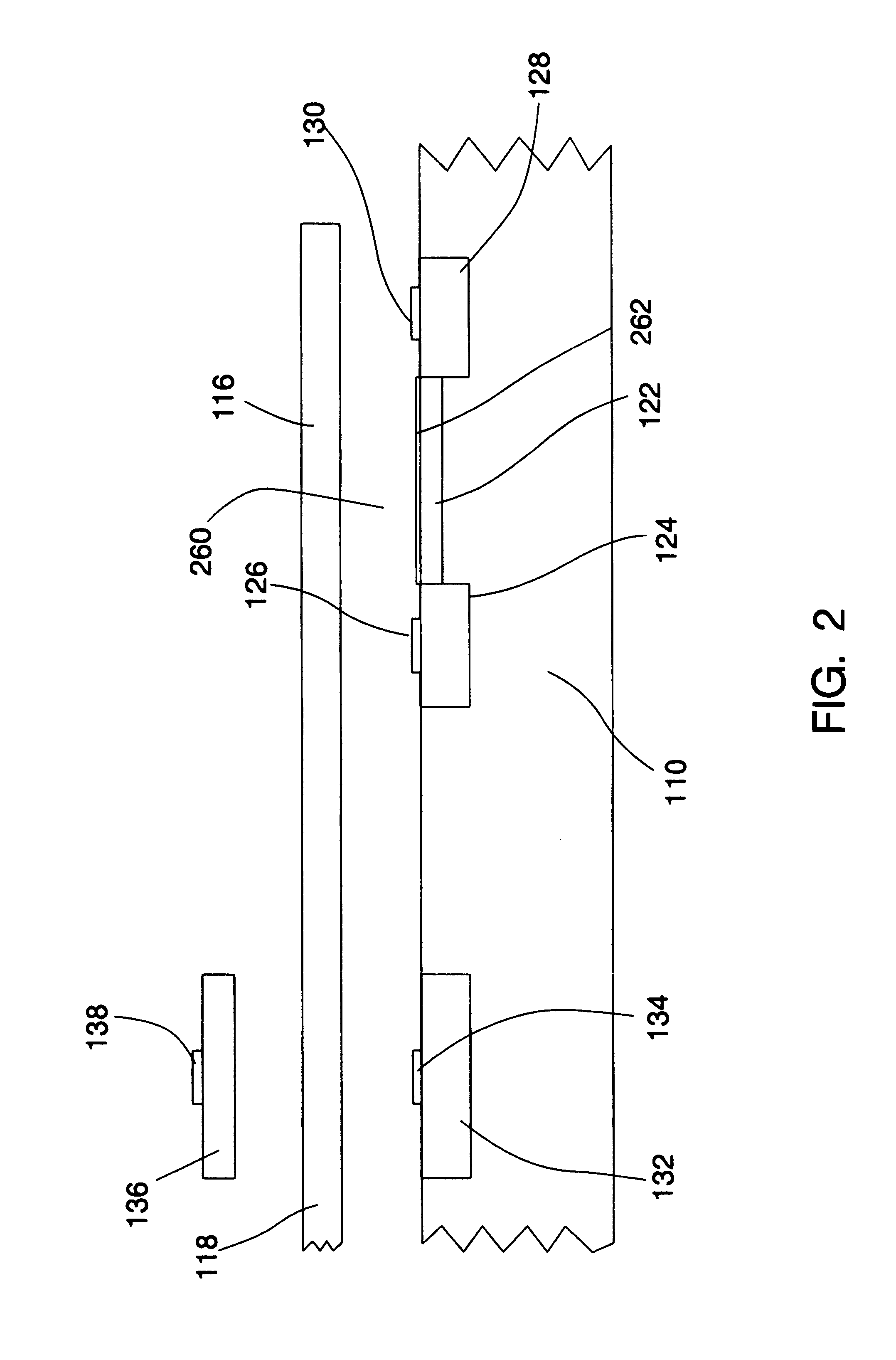
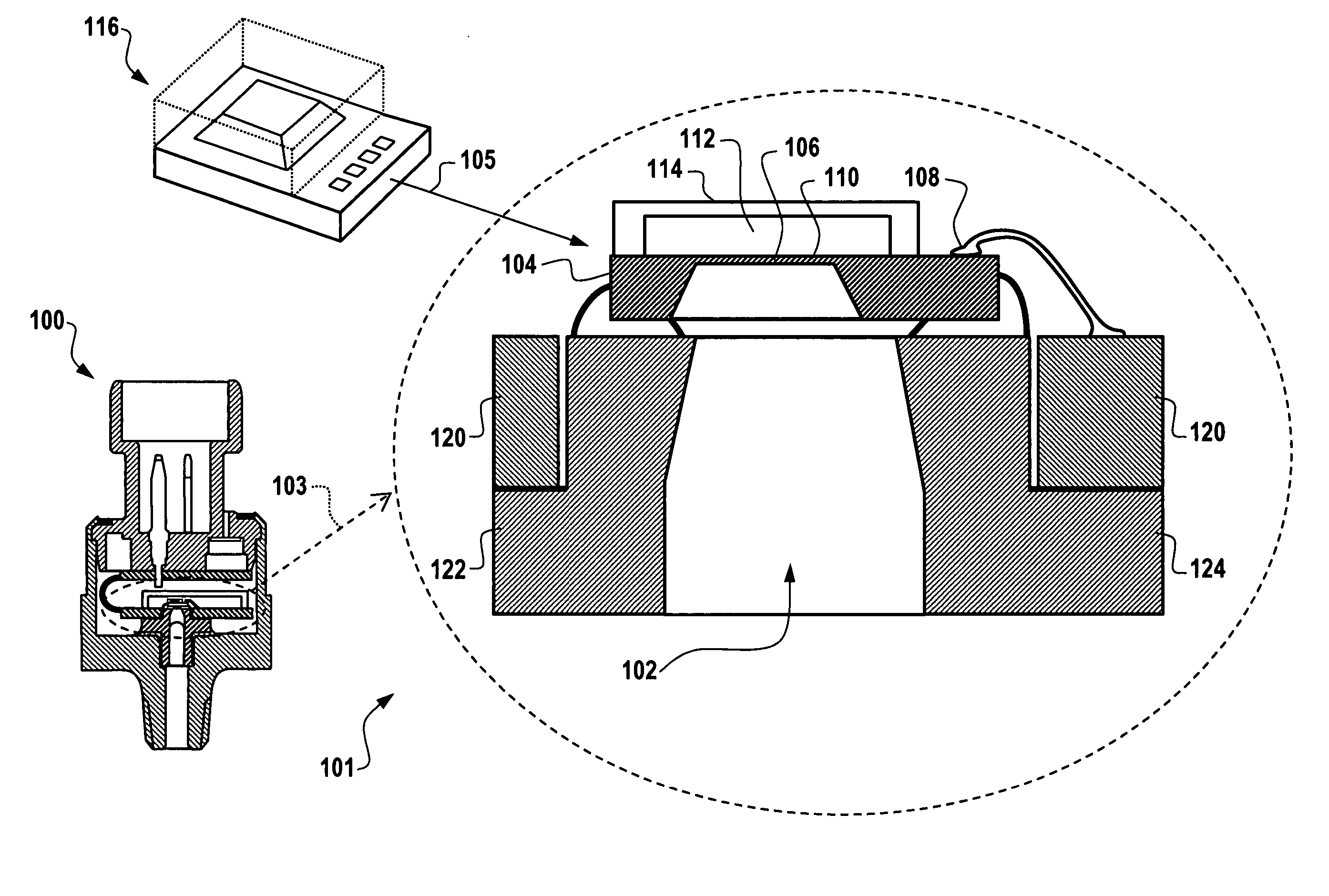
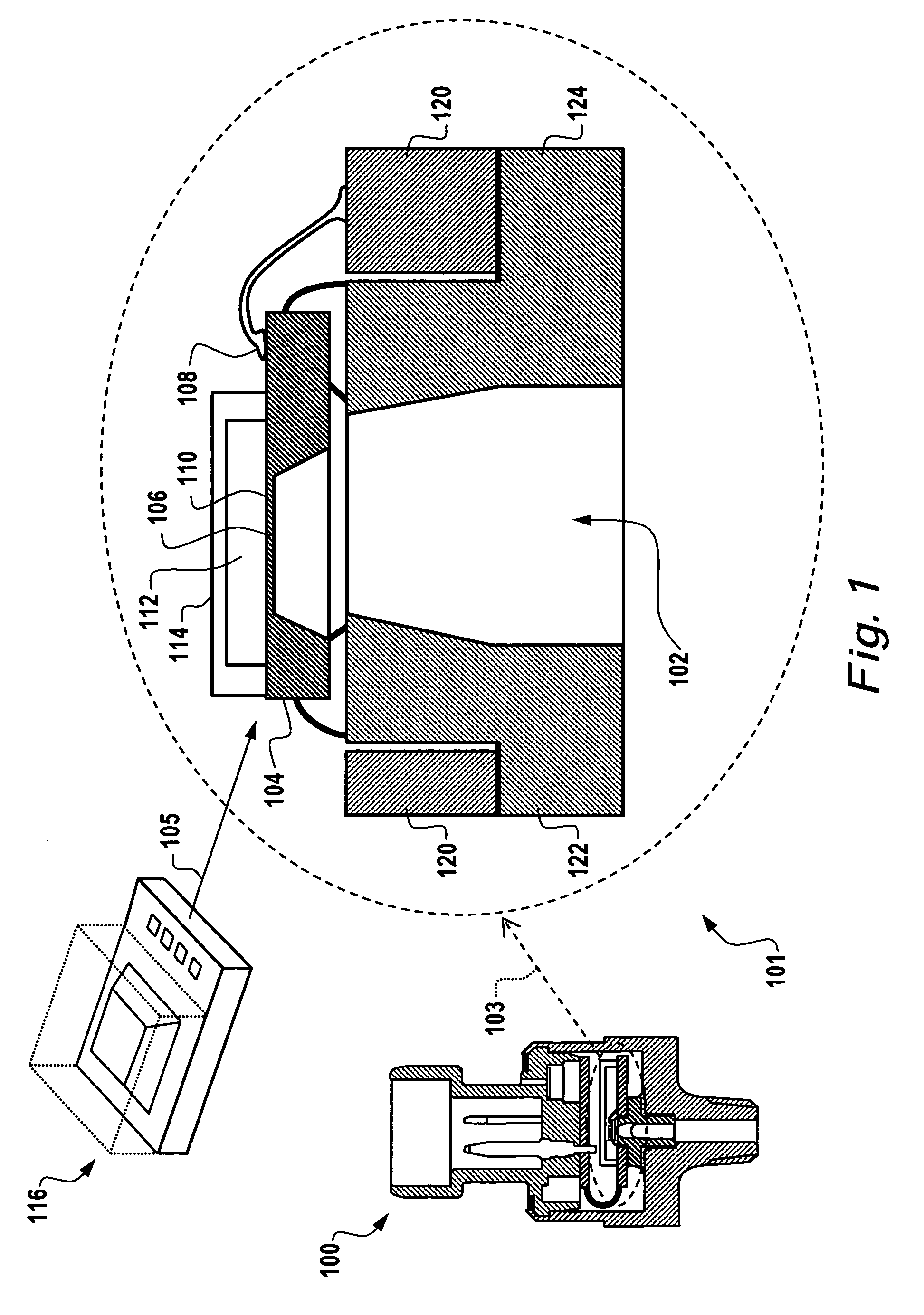
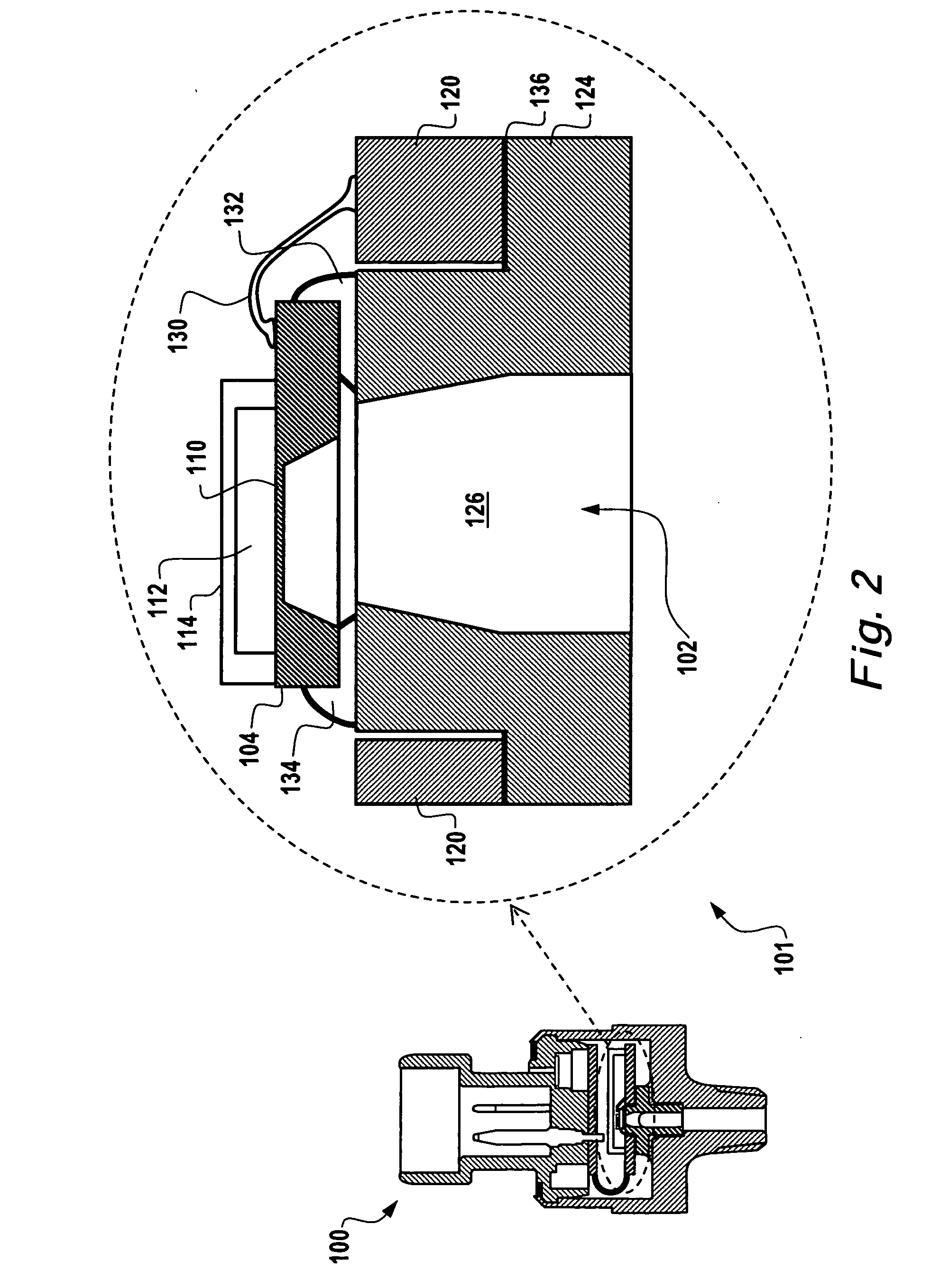
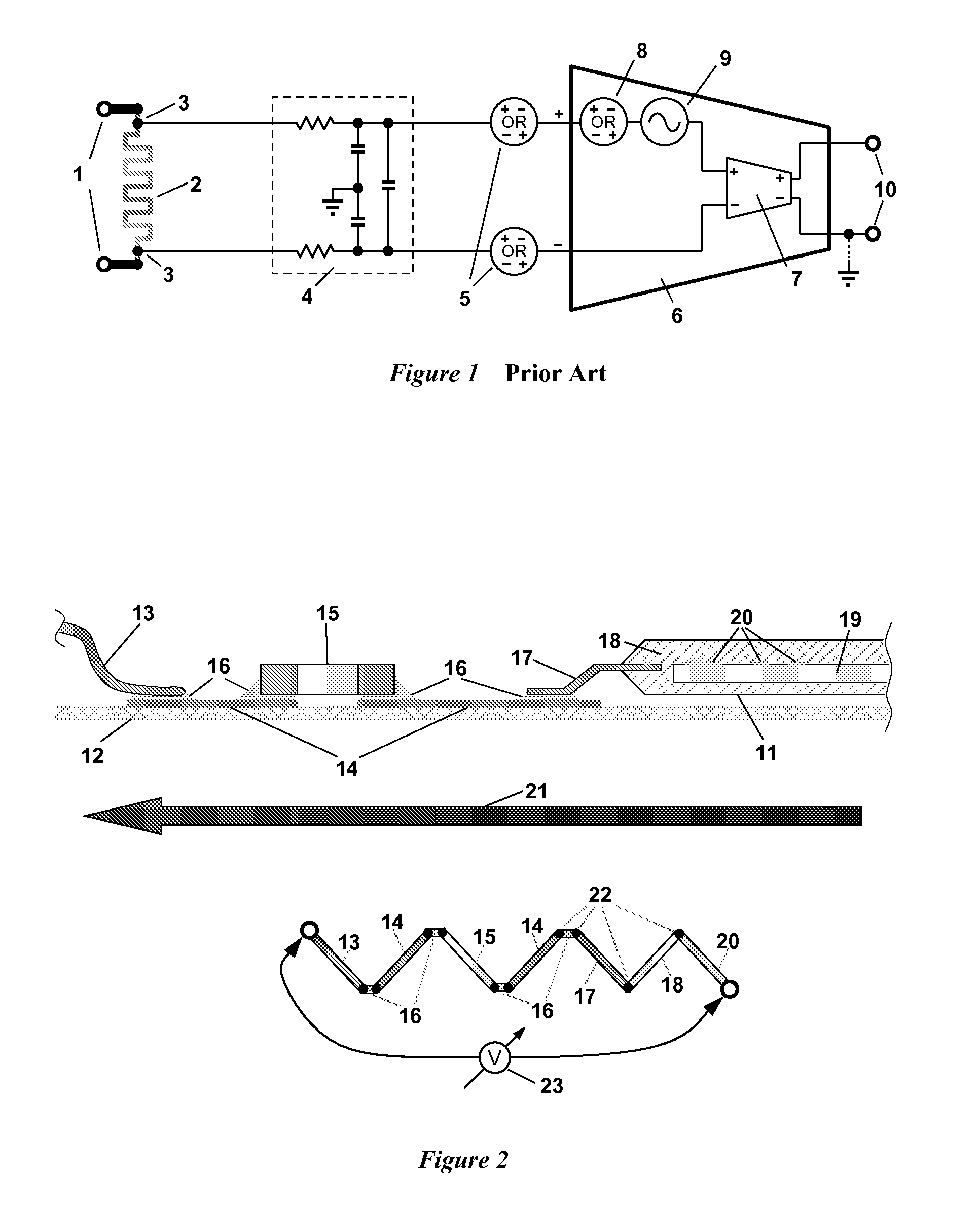
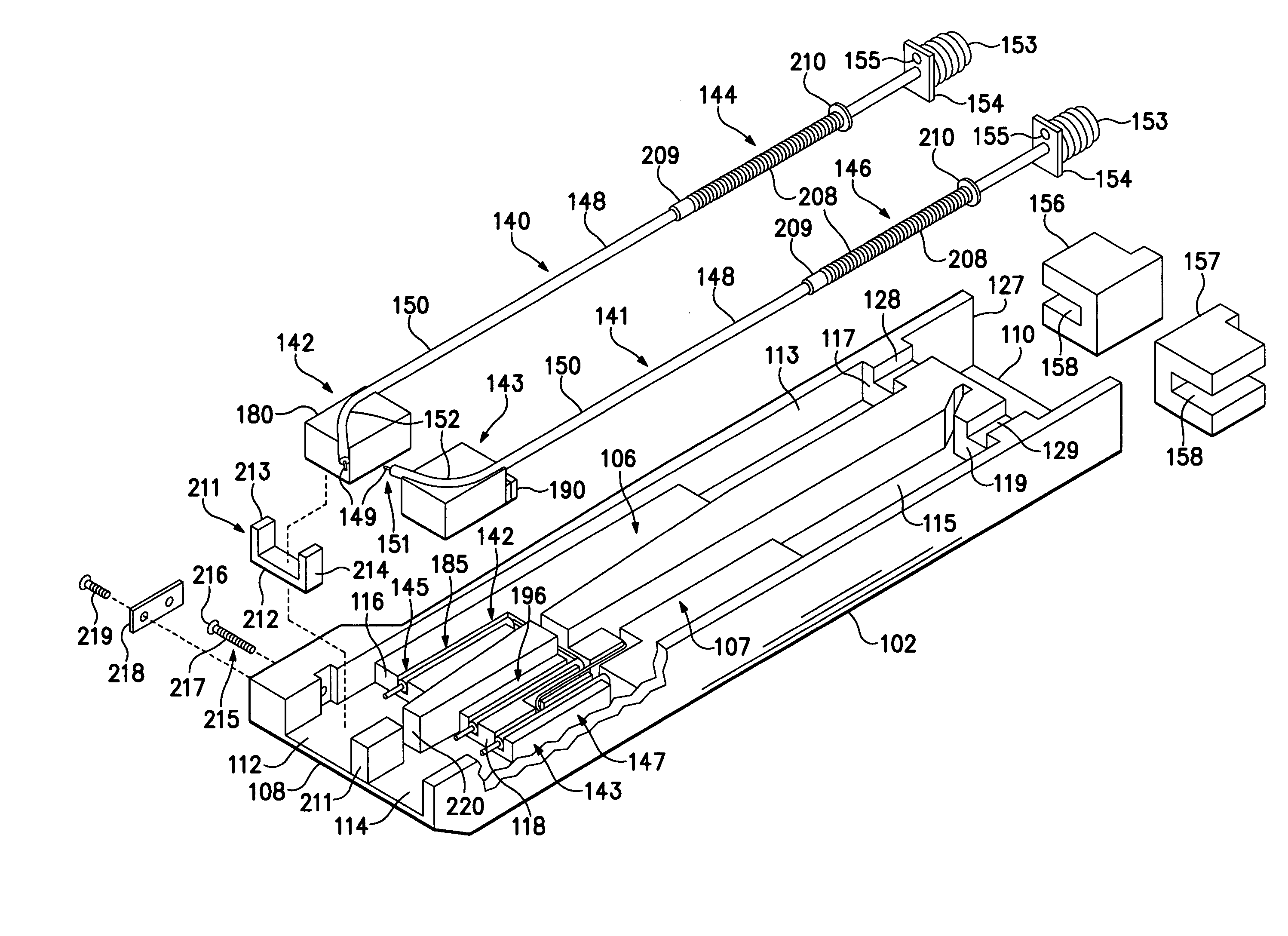
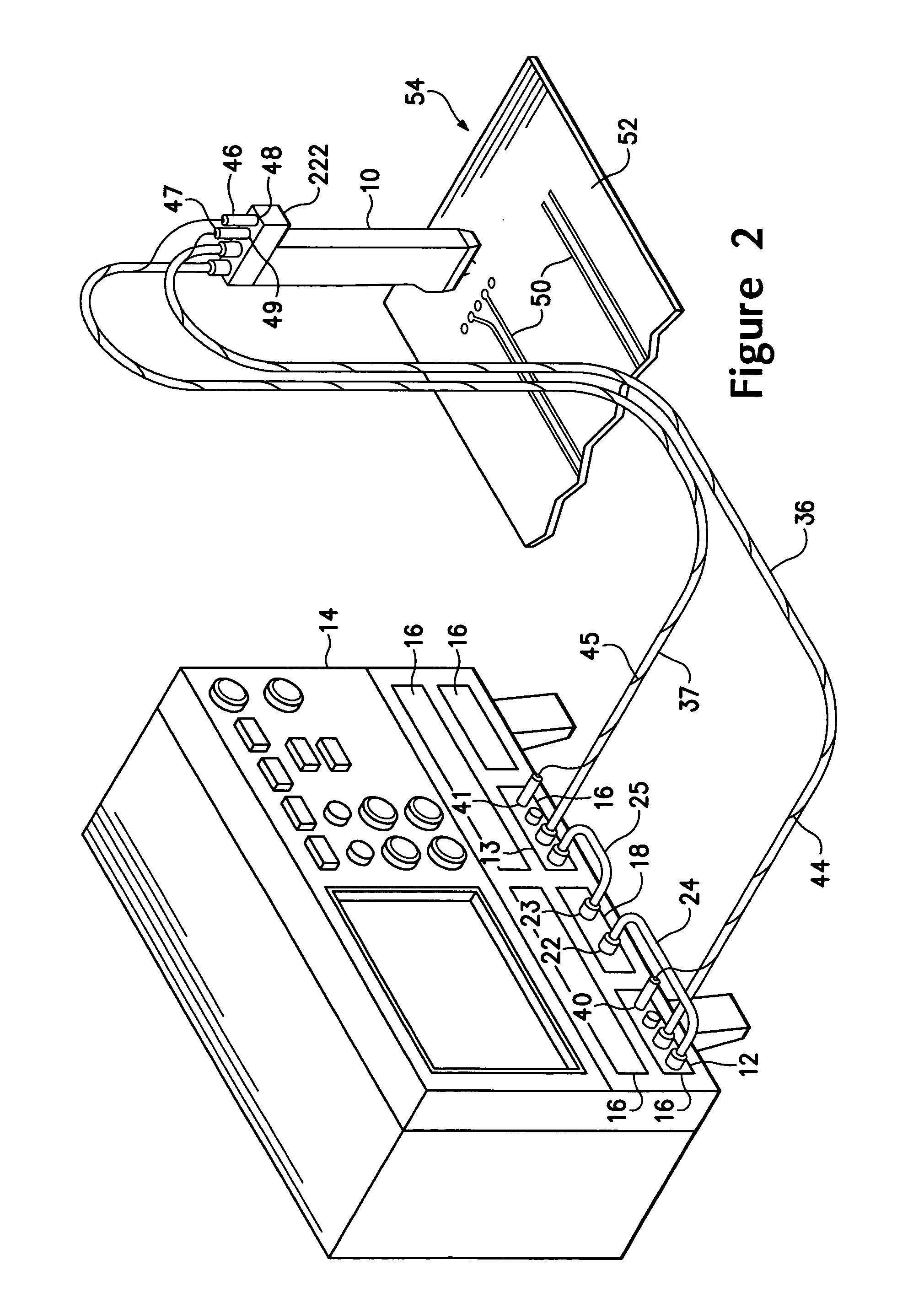
Differential measurement probe having retractable double cushioned variable spacing probing tips with EOS/ESD protection capabilities
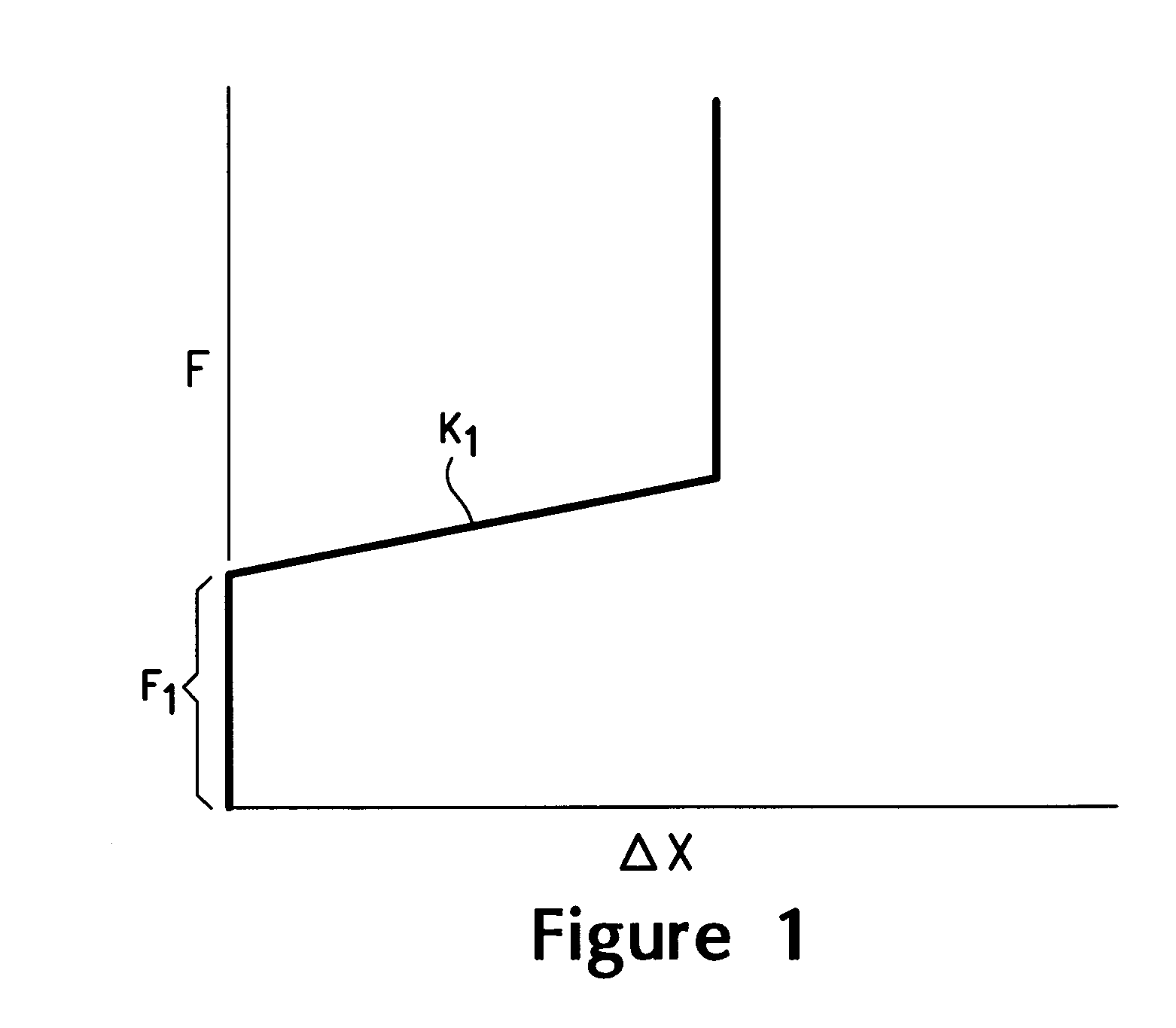
ActiveUS7167011B2Overload protection arrangementsElectrical testingDifferential measurementEngineering
A differential measurement probe has spring loaded, double cushioned probe assemblies and a pressure sensors disposed in a housing. The pressure sensors forms an electrical switch having an electrical AND function for passing an activation signal to a EOS / ESD protection control module in response to axial movement of the housing relative to the probe assemblies. First compressive elements produces first pre-loaded compressive forces and increasing compressive forces on the probe assemblies and second compressive elements produces second pre-loaded compressive forces and increasing compressive forces on the probe assemblies subsequent to the first increasing compressive forces on the probe assemblies. An adjustment member allows variable spacing of the differential probing tips.
Owner:TEKTRONIX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com