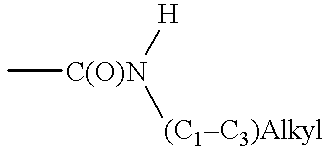Patents
Literature
32 results about "Neuronal Transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Any process in which a presynaptic cell transfers a signal to a postsynaptic cell, by either release of a neurotransmitter or by passage of an electrical current via specialized channels. This process is essential to all neuronal functions.
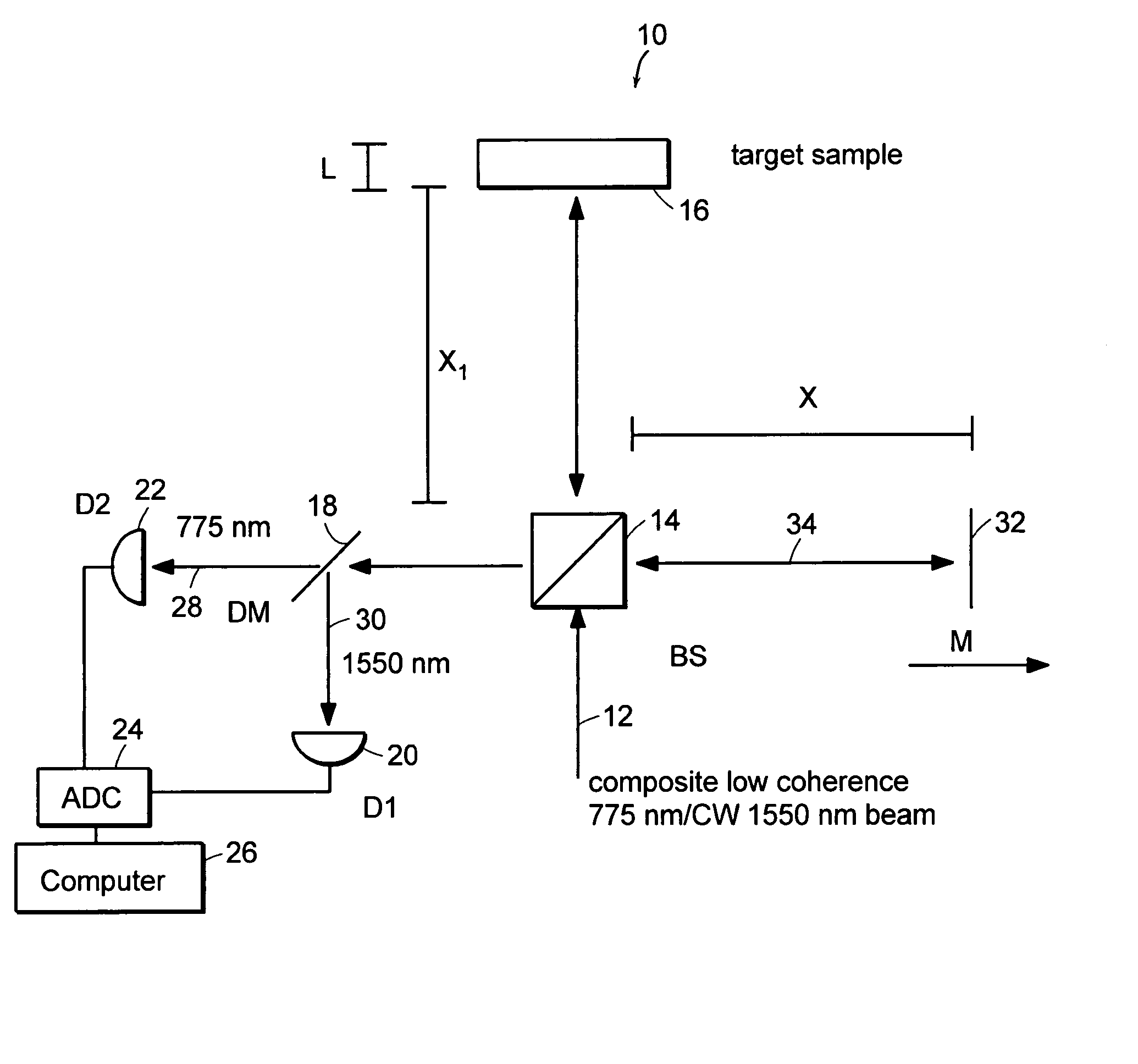
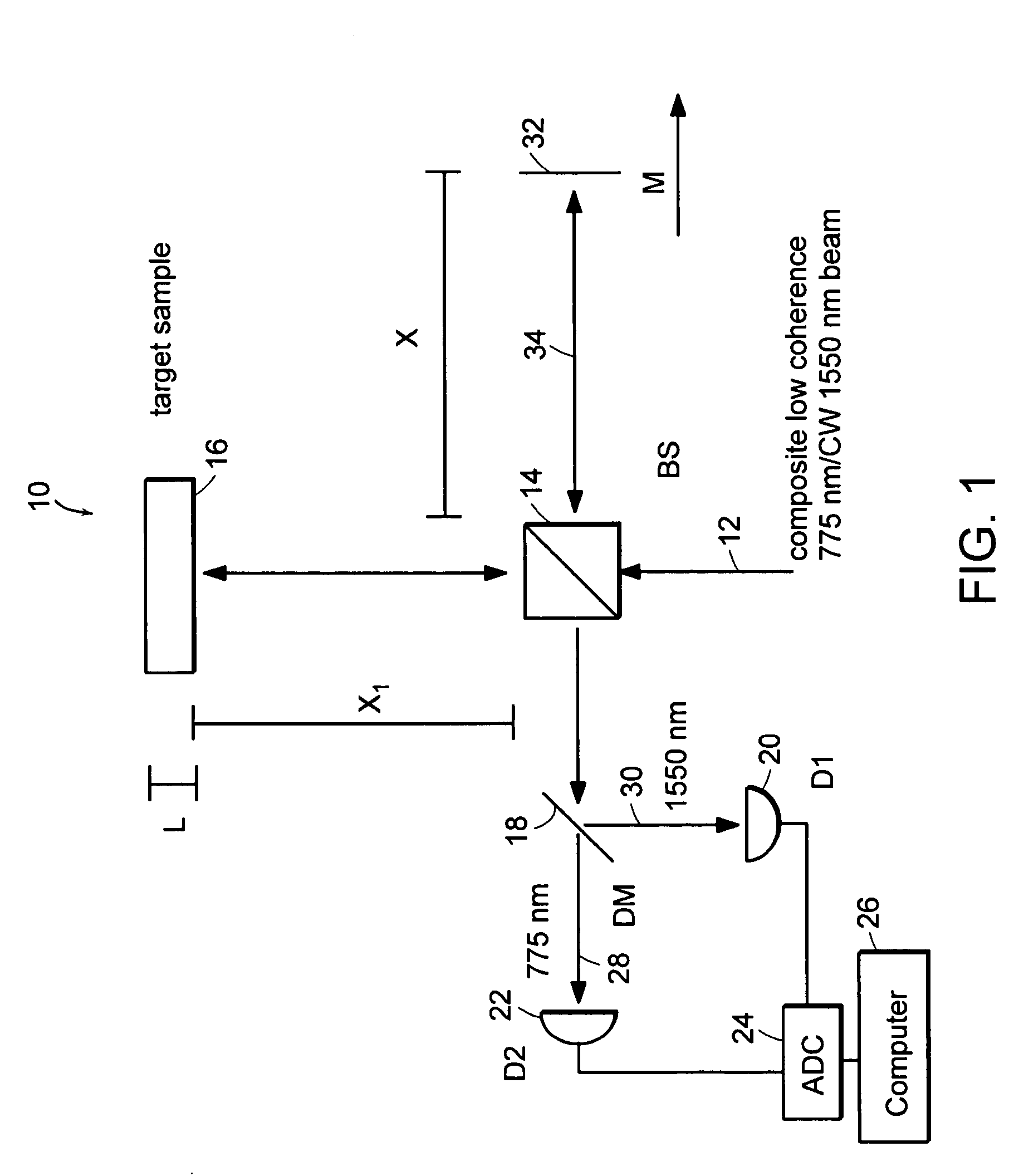
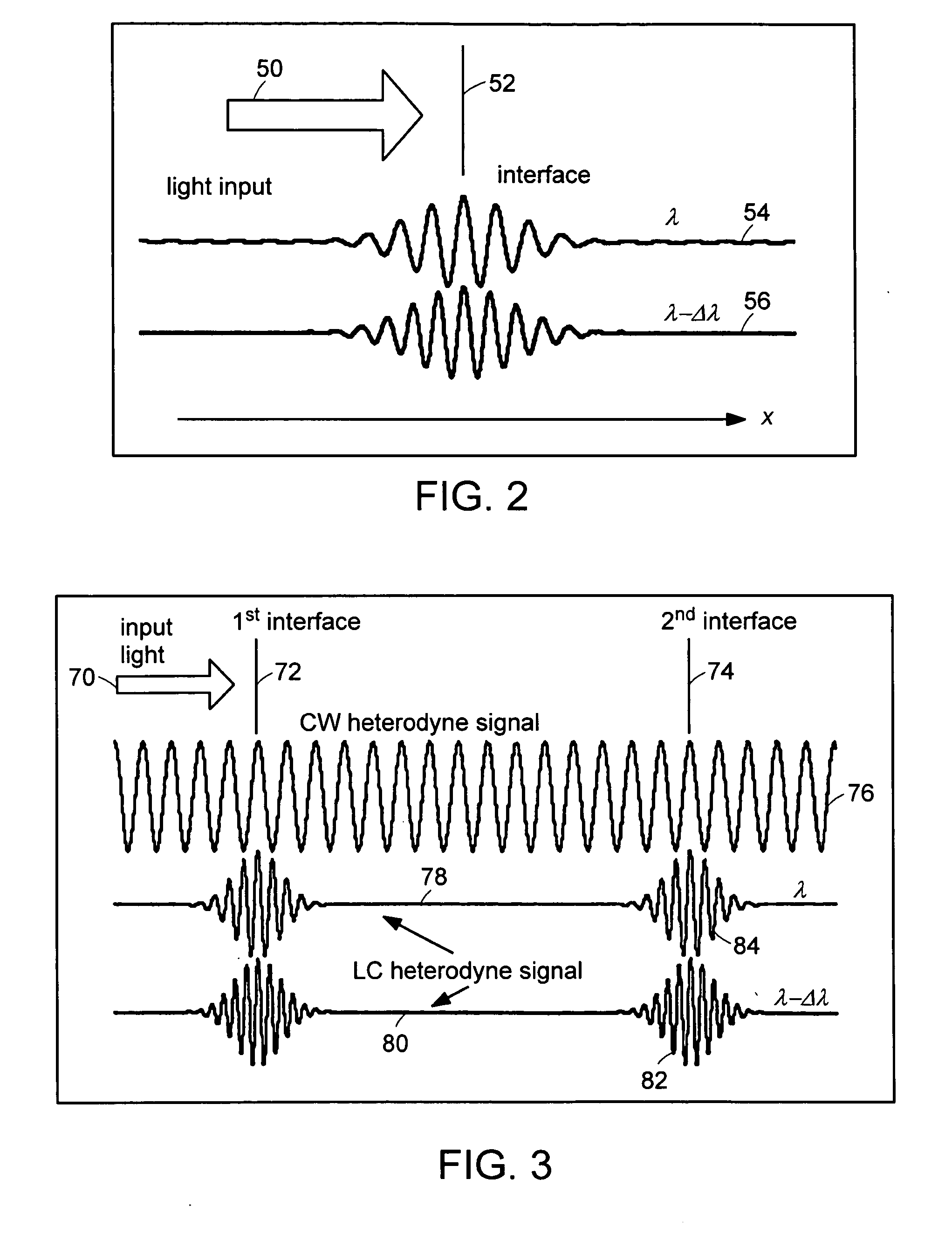
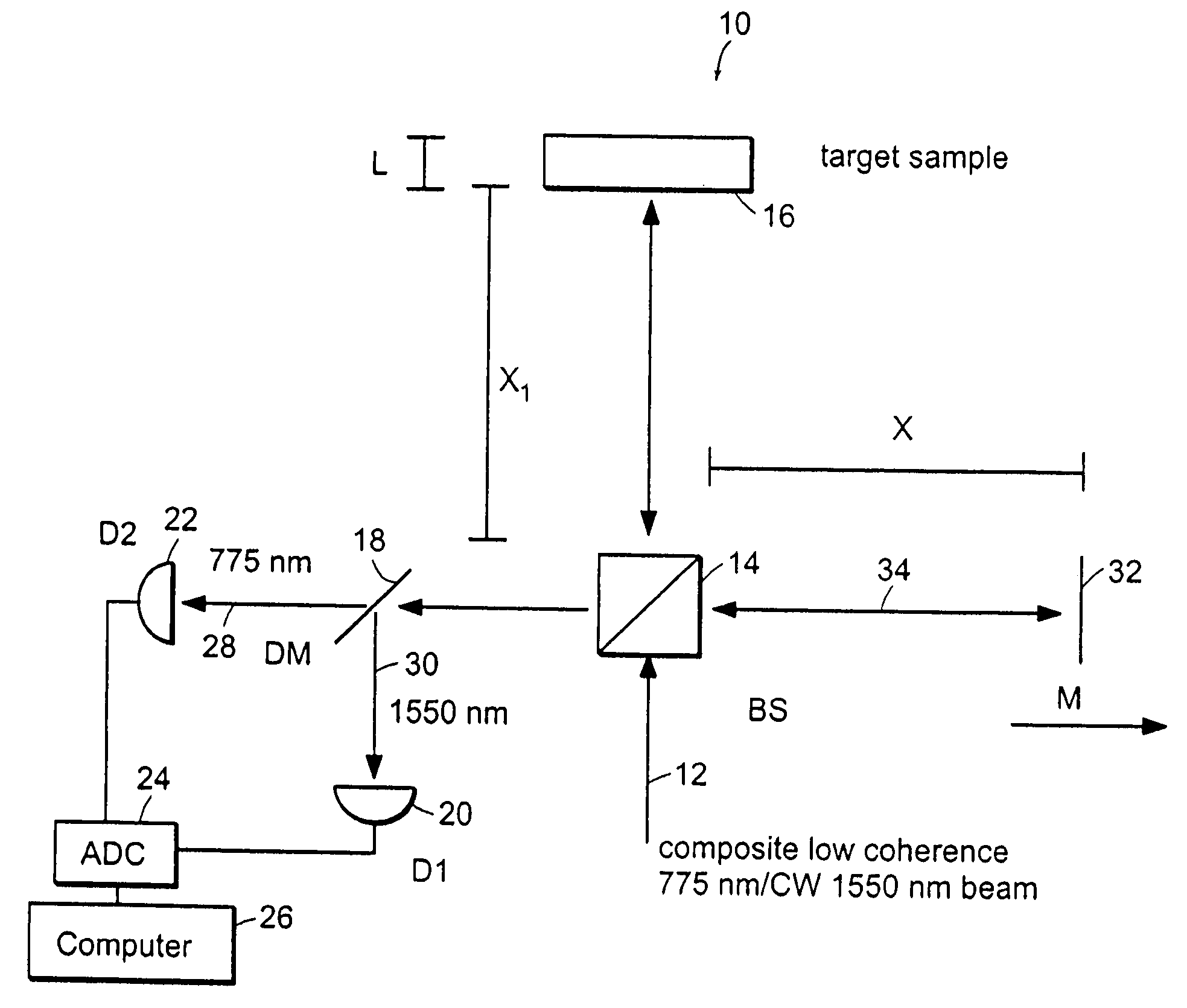
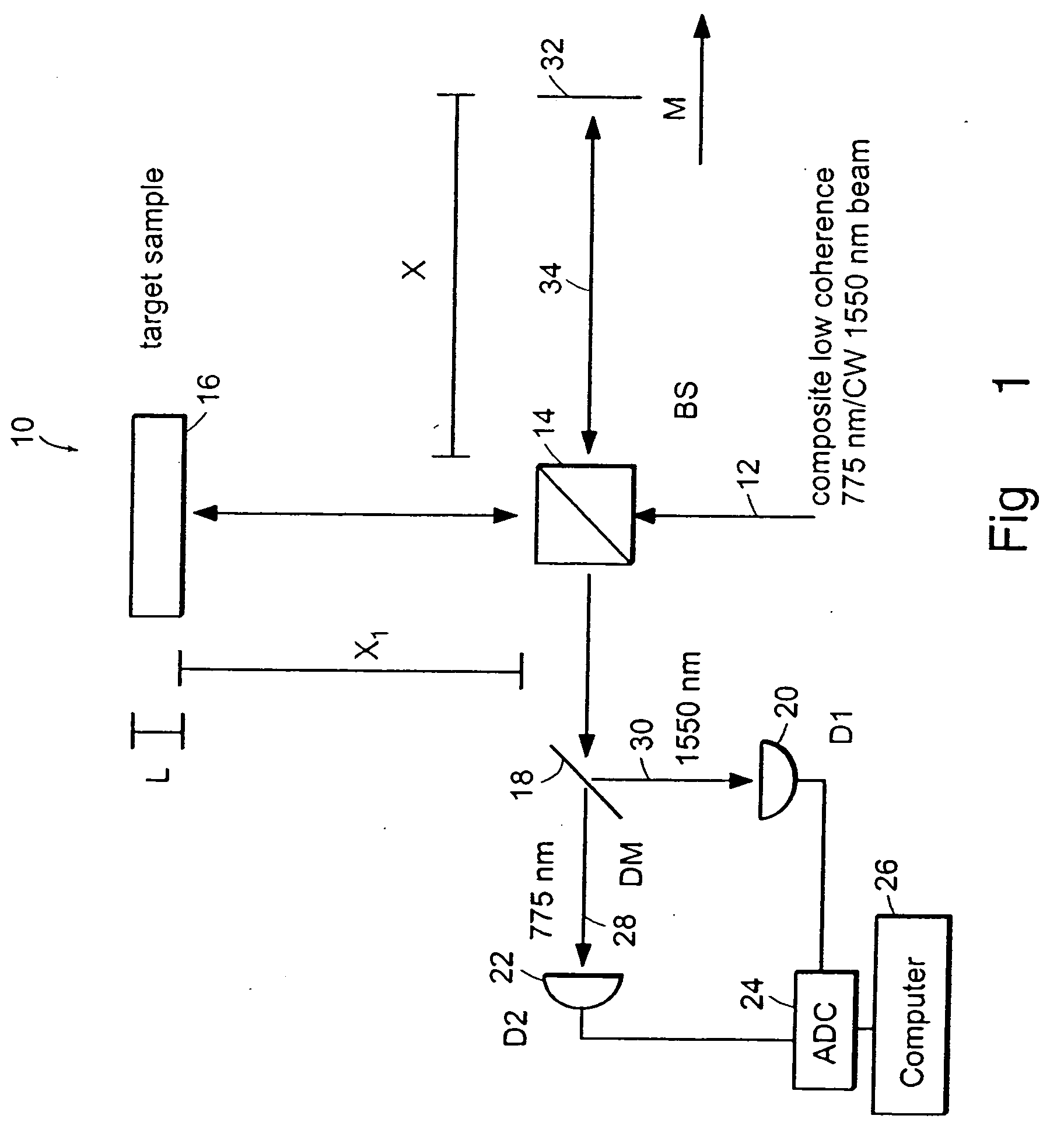
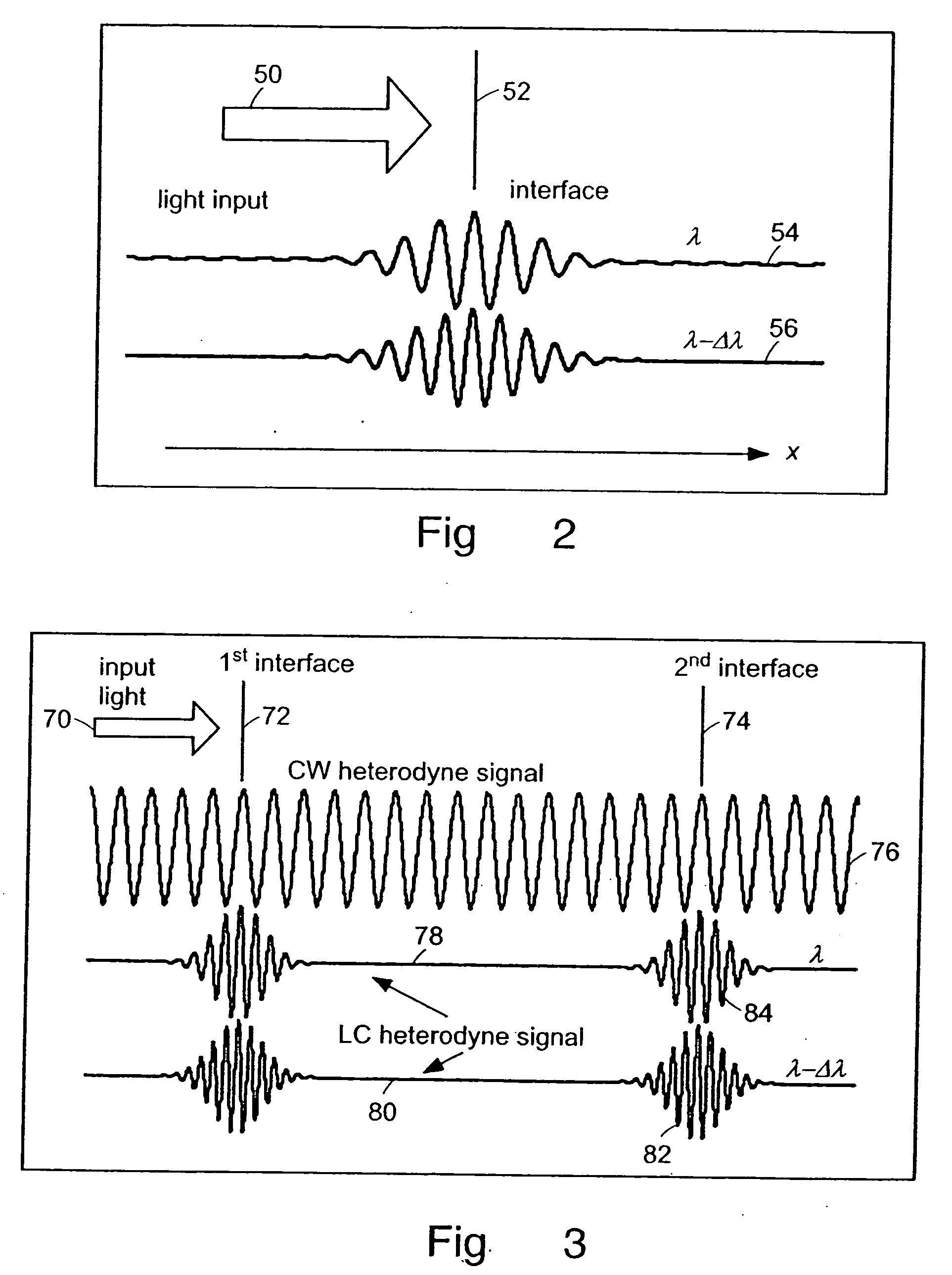
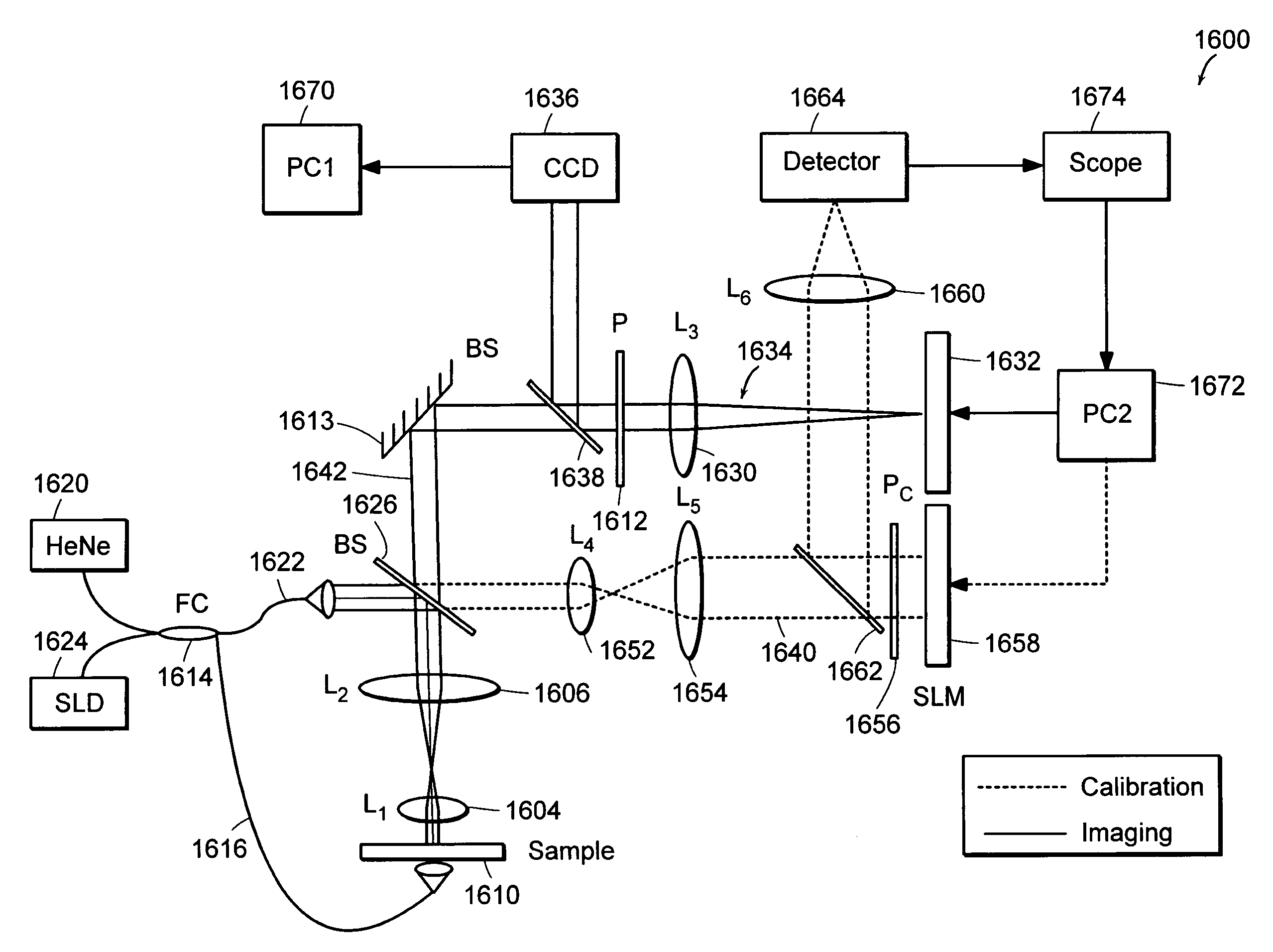
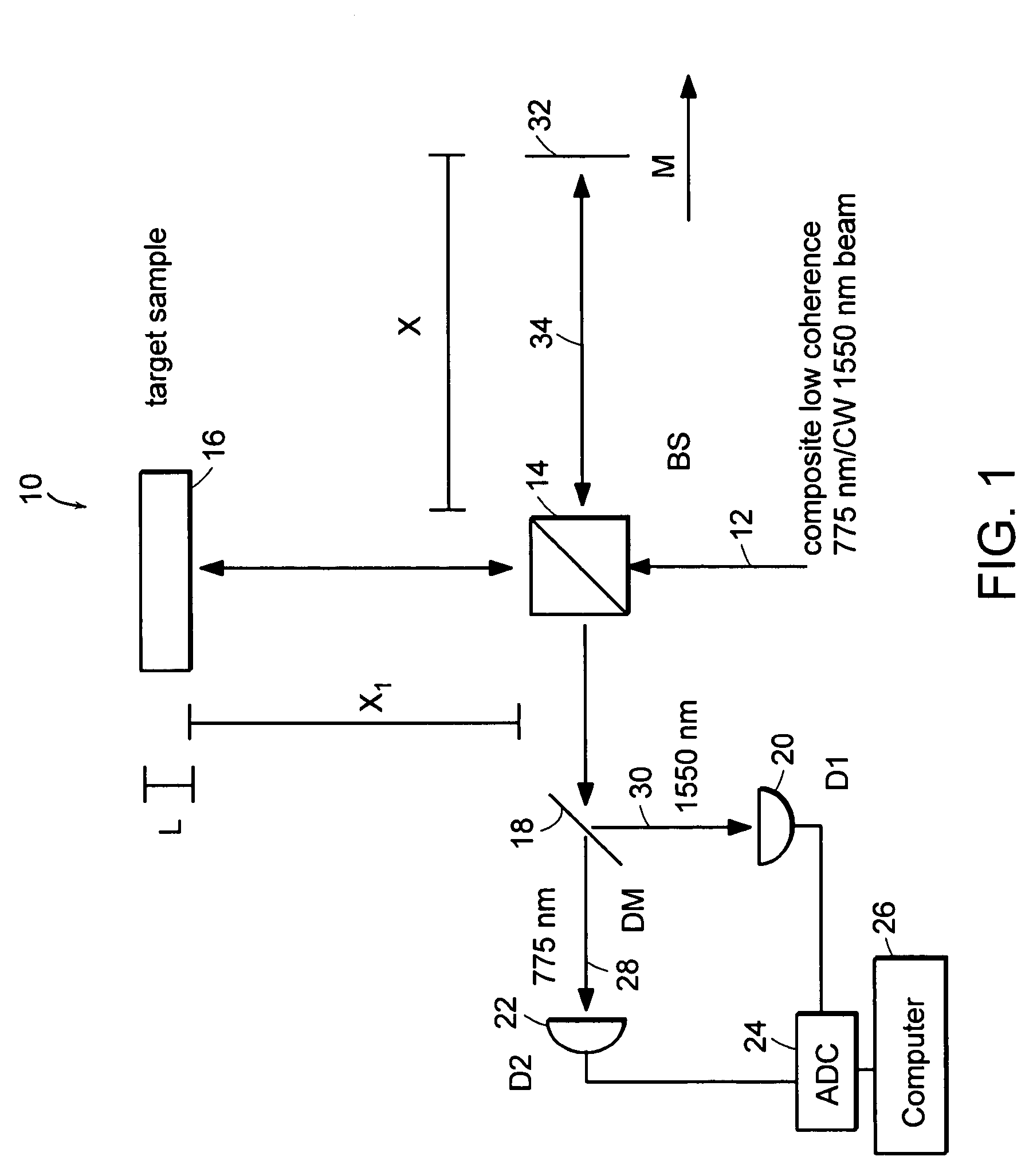
Systems and methods for phase measurements
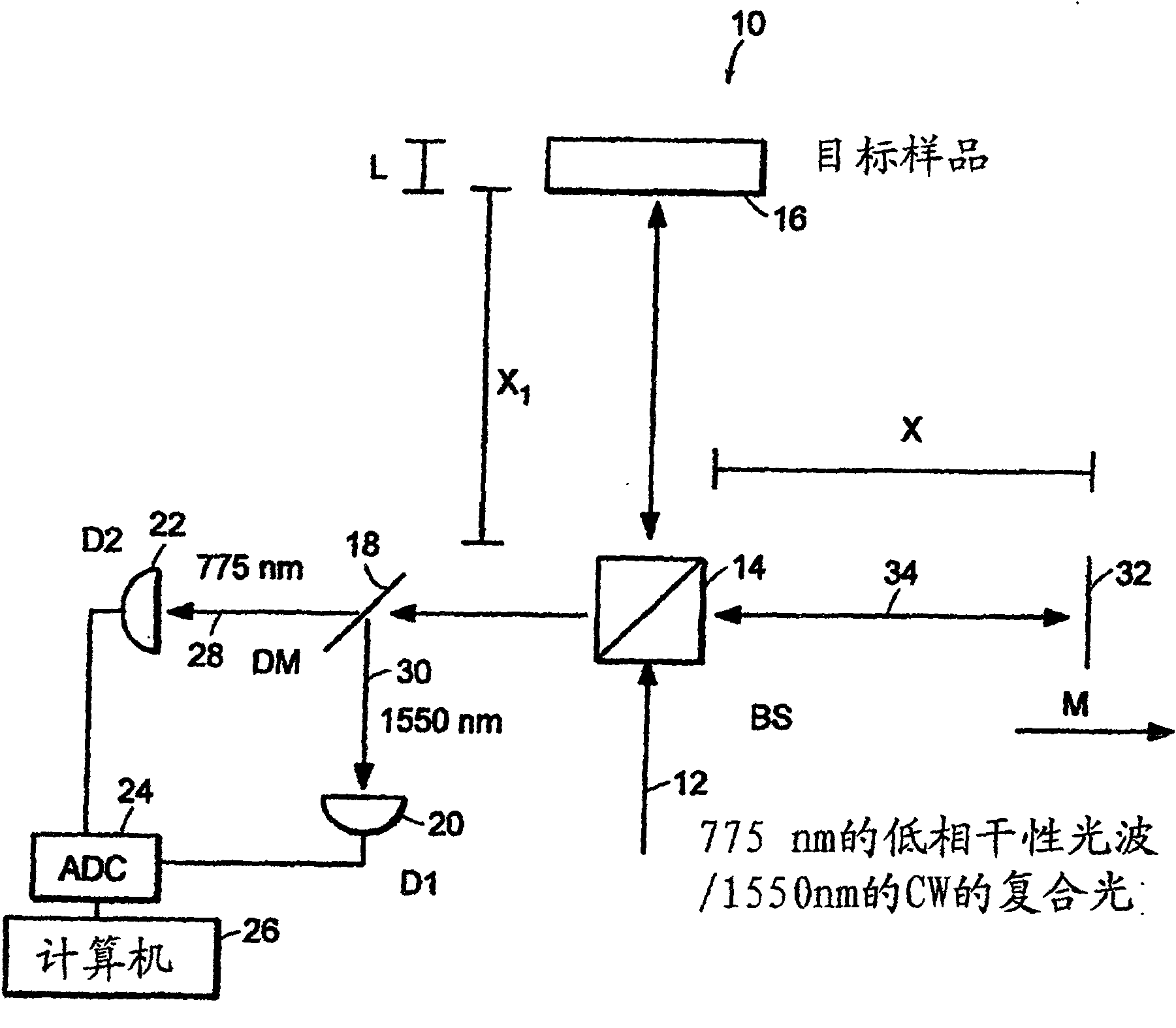
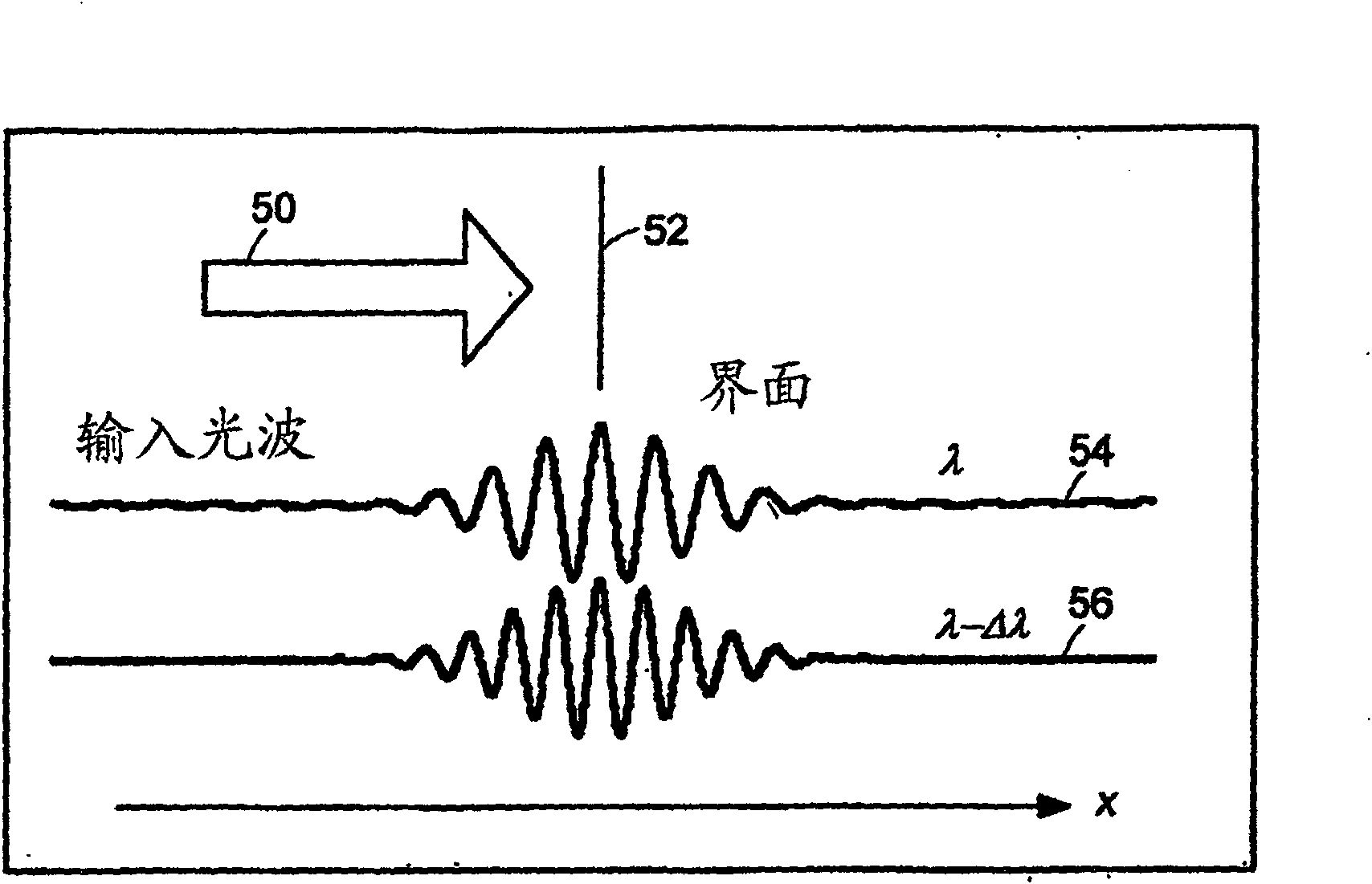
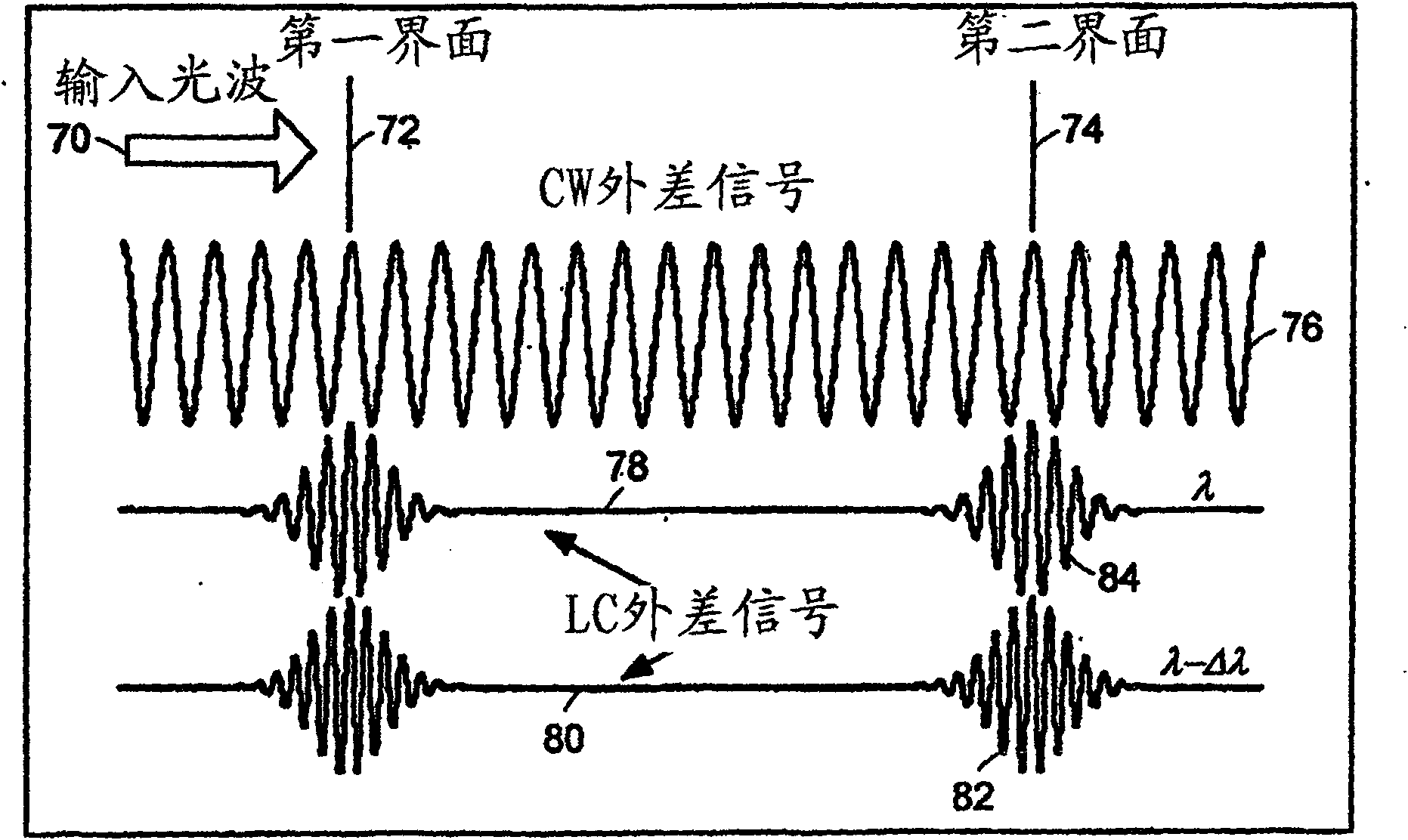
InactiveUS20050057756A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsCellular componentPhase noise
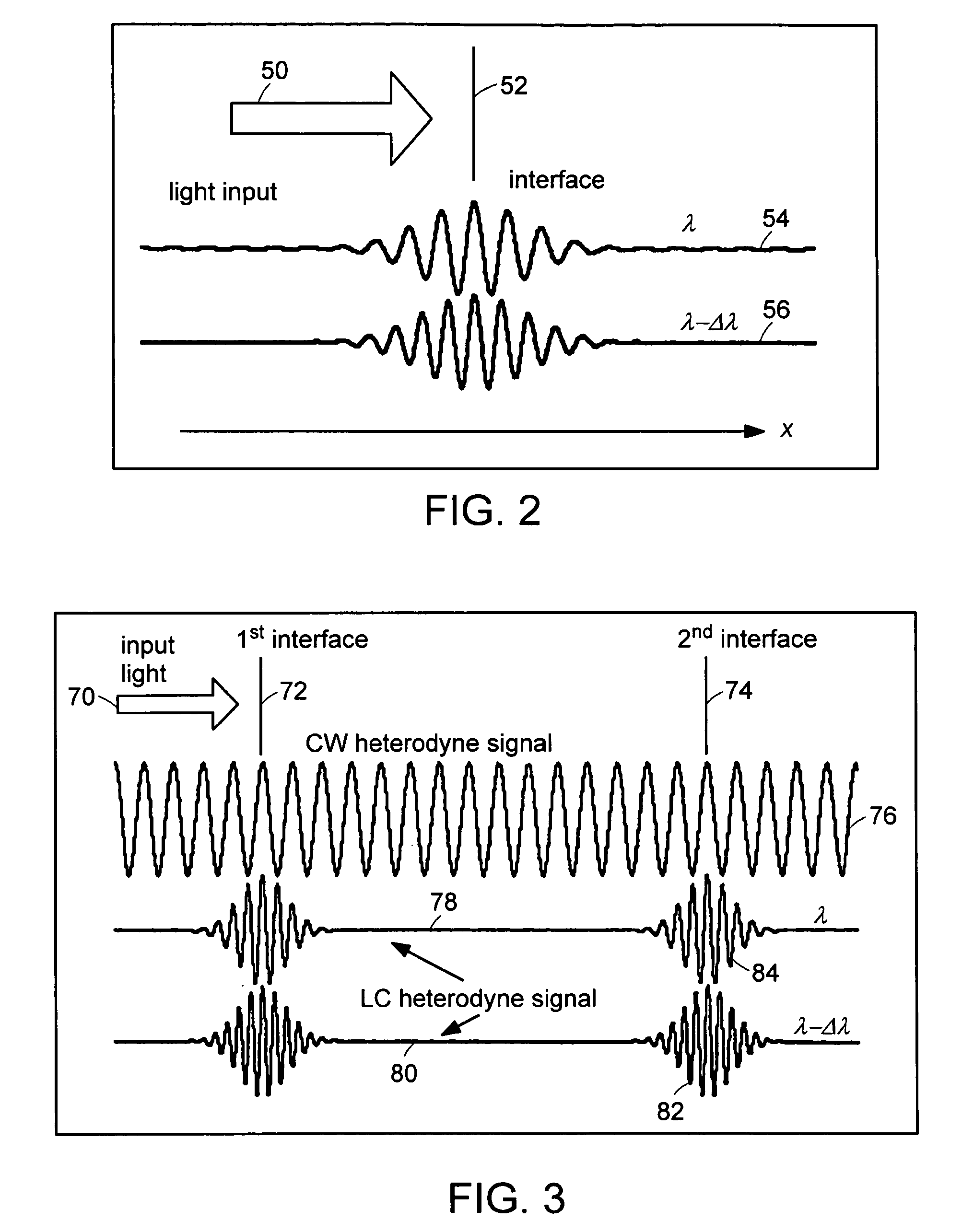
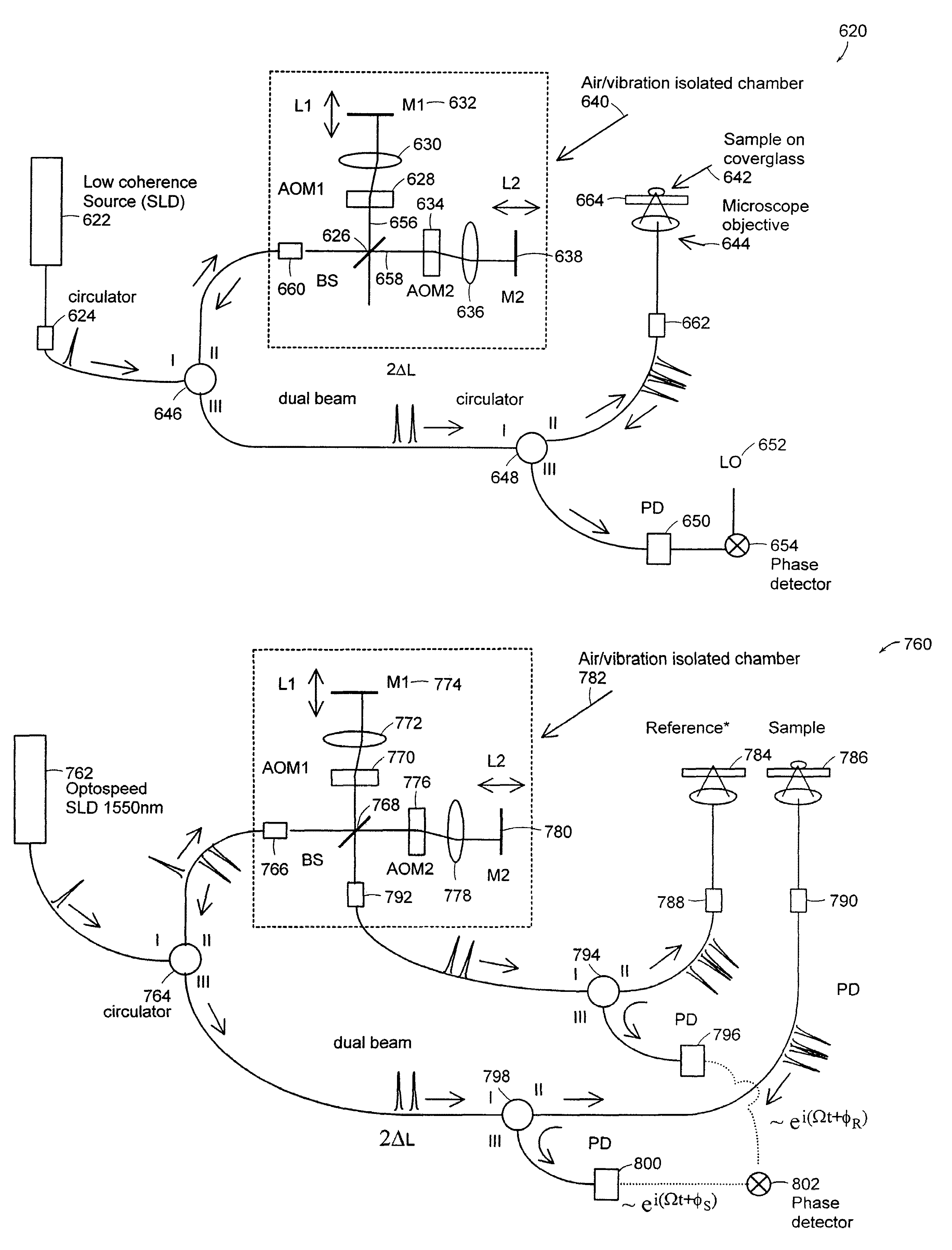
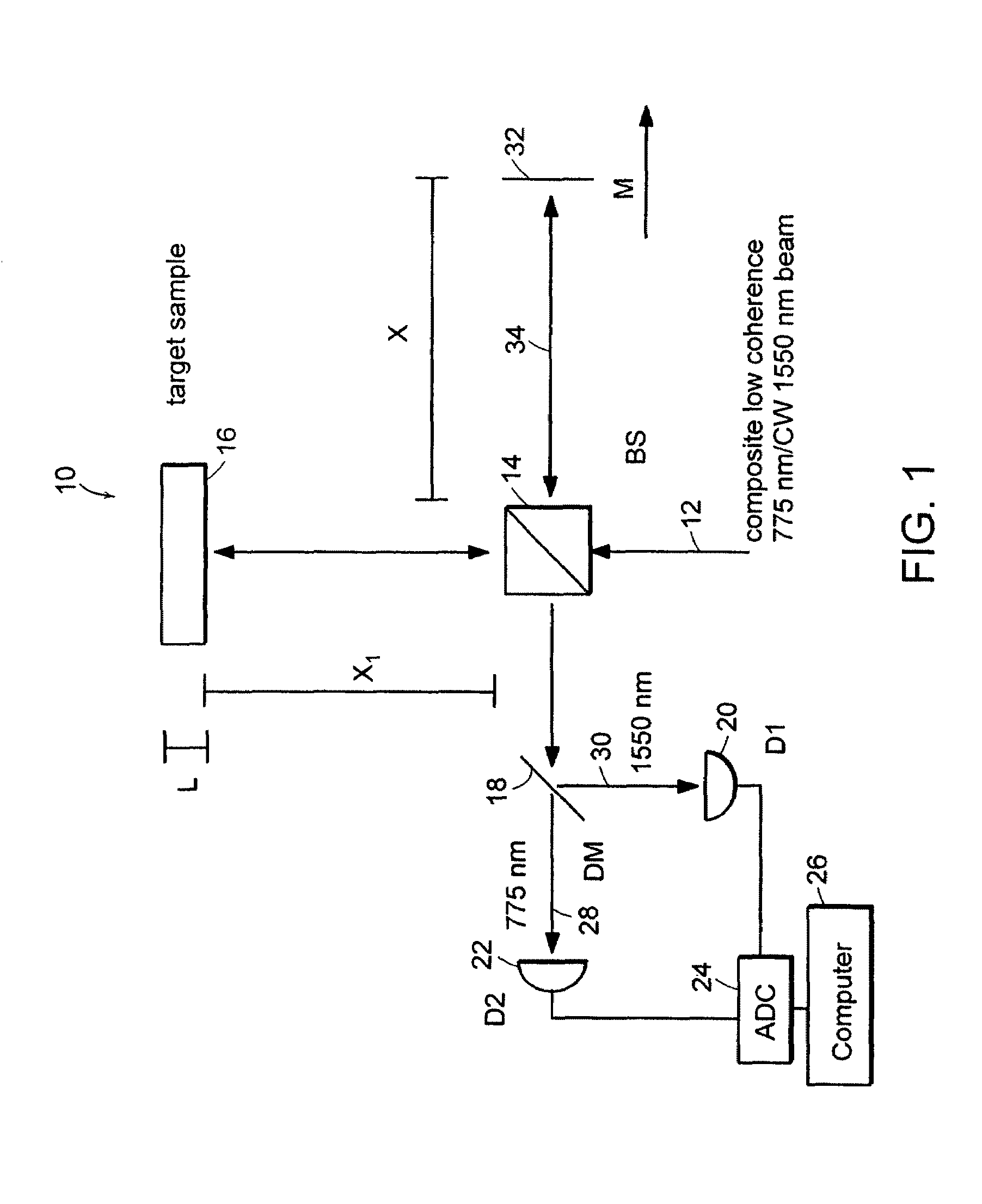
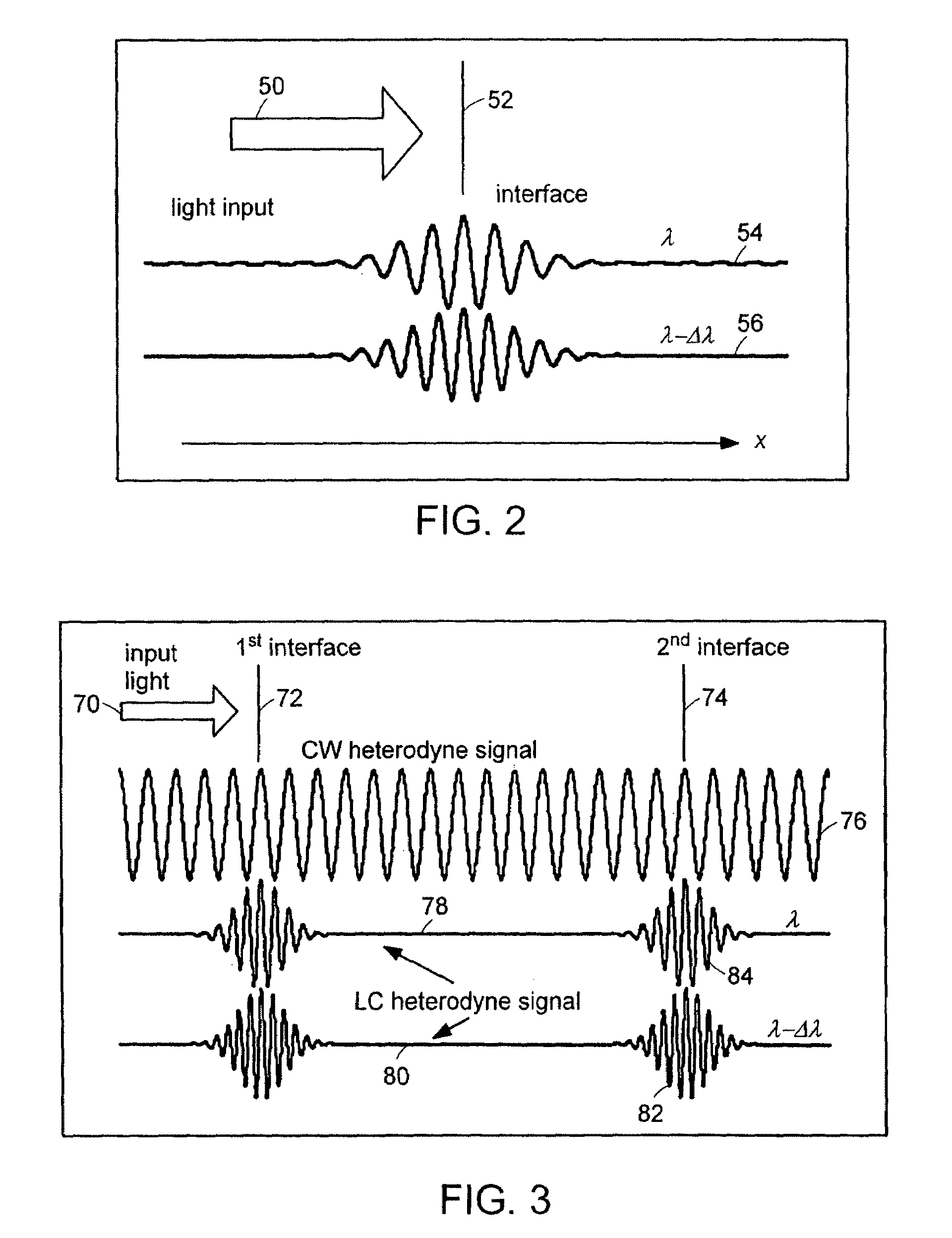
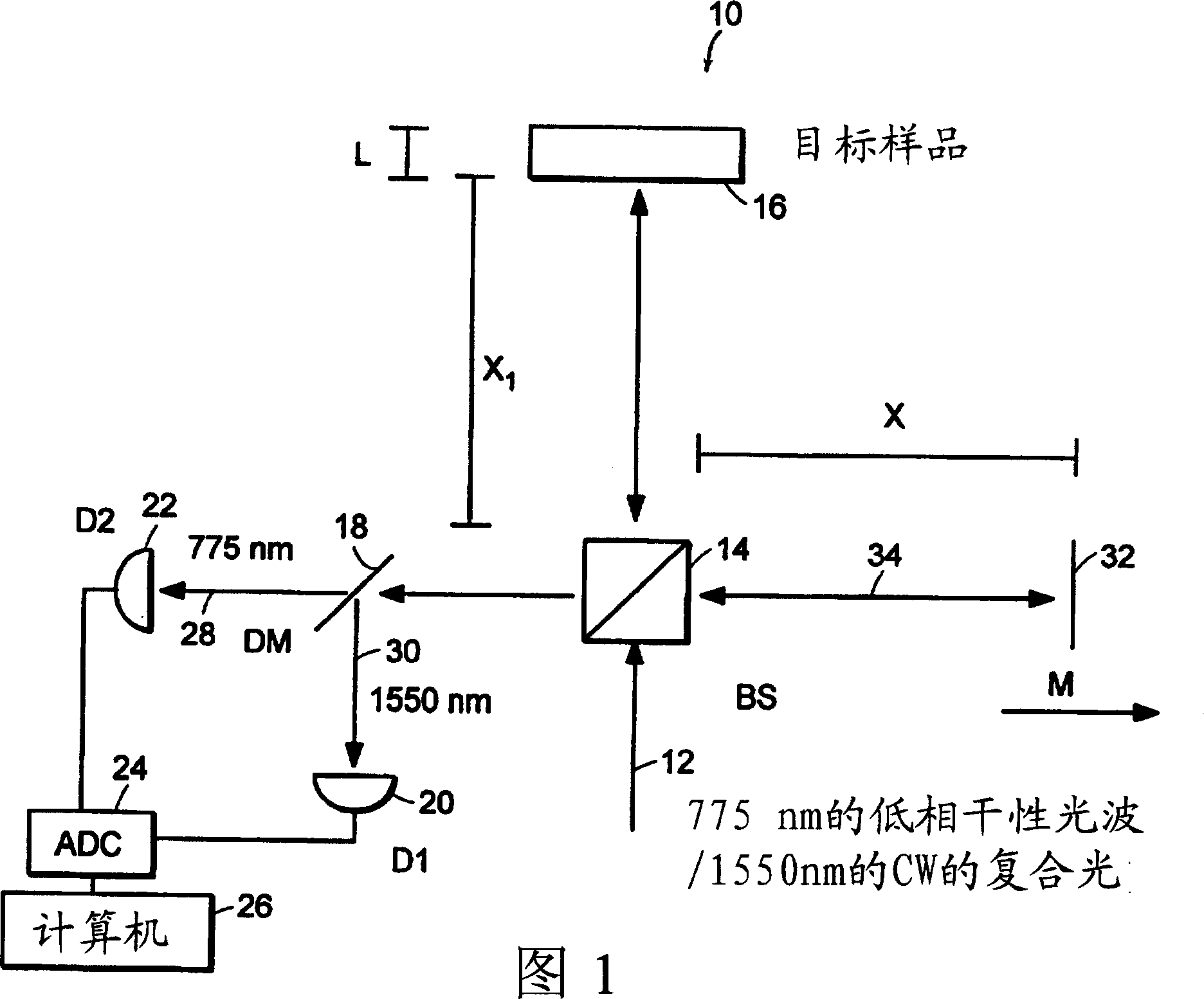
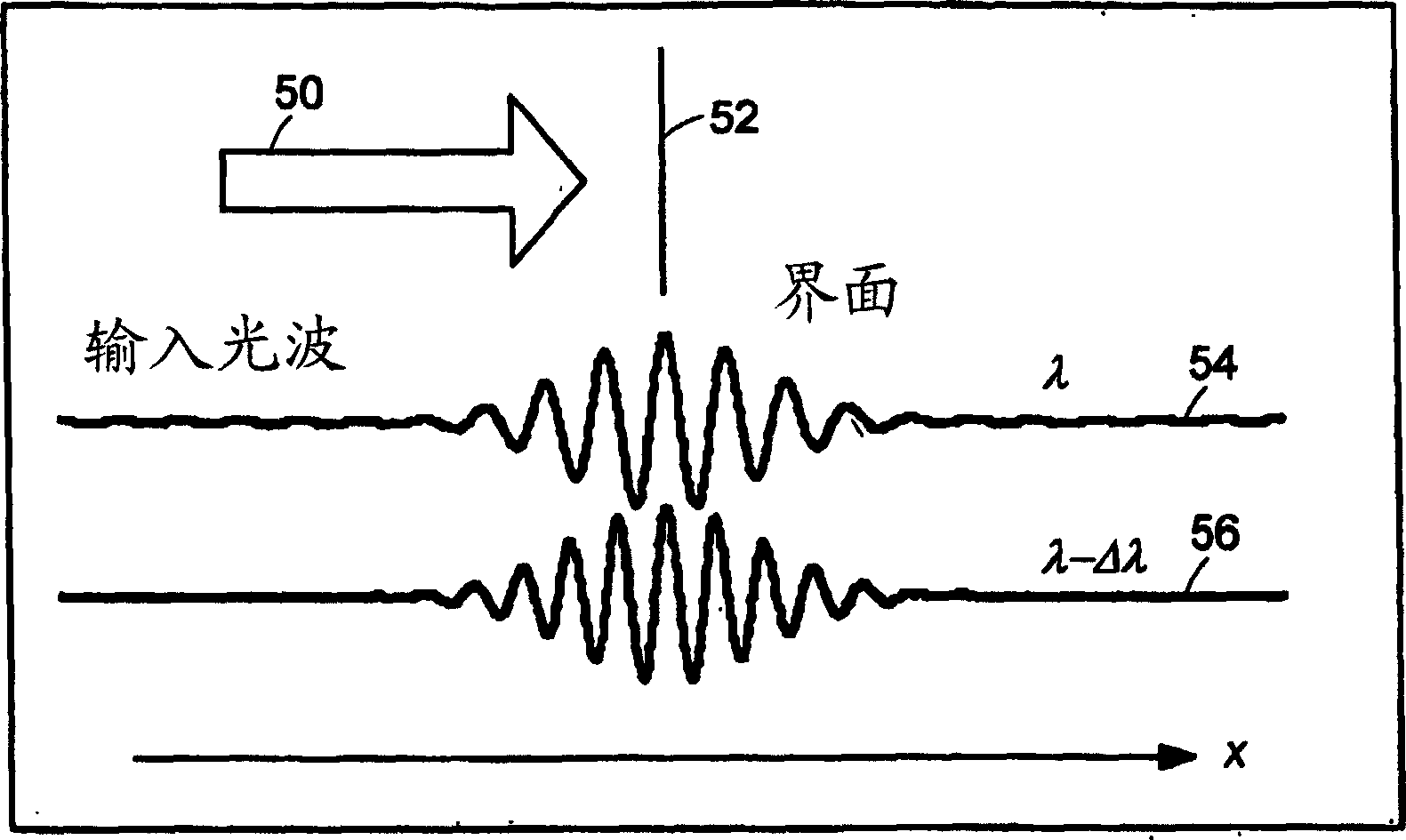
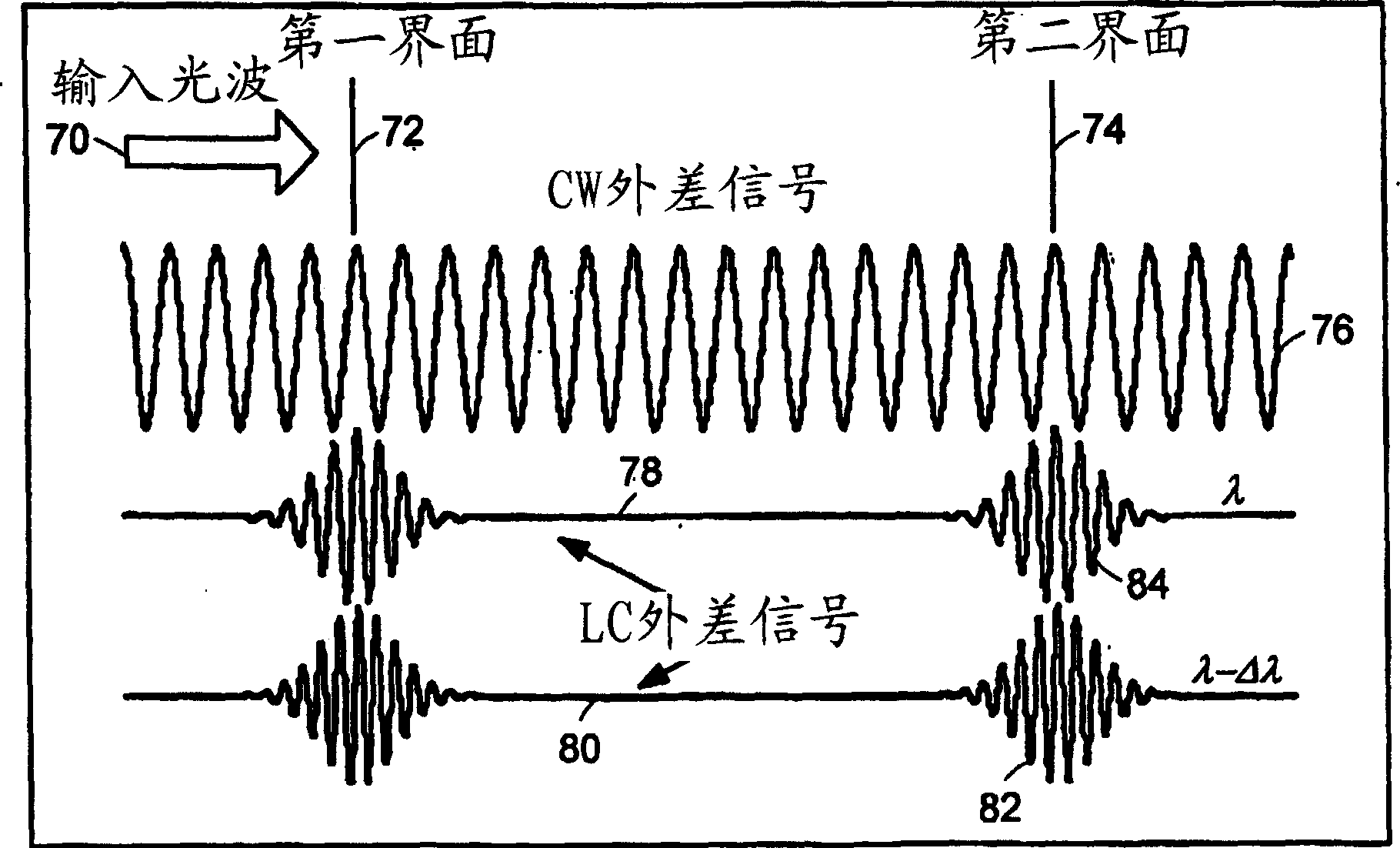
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7365858B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7557929B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
System and method for measuring phase
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
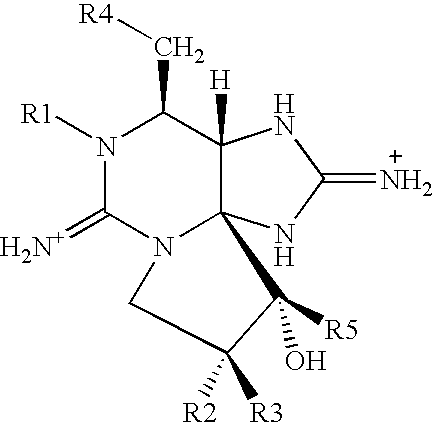
Phycotoxins and Uses Thereof
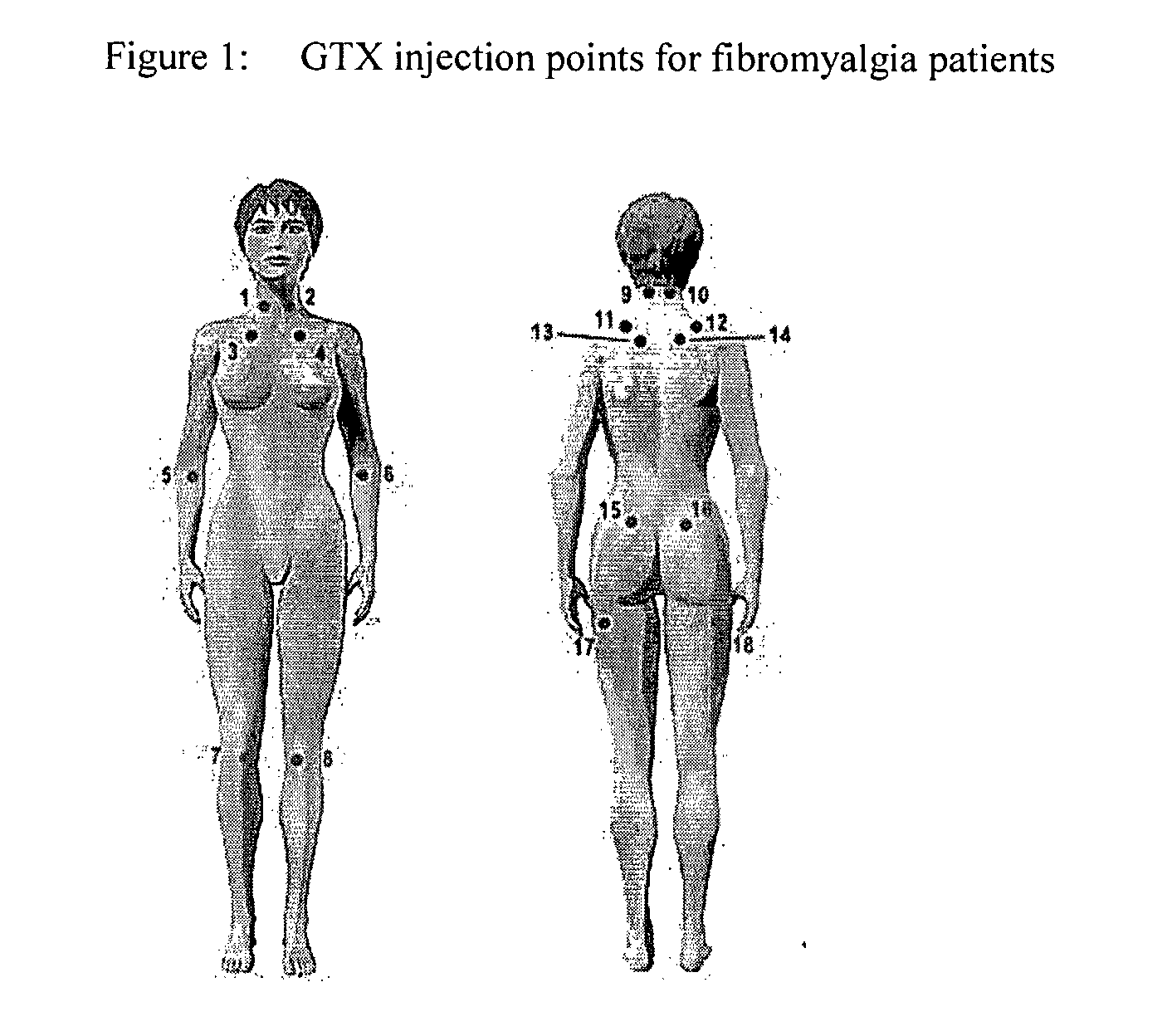
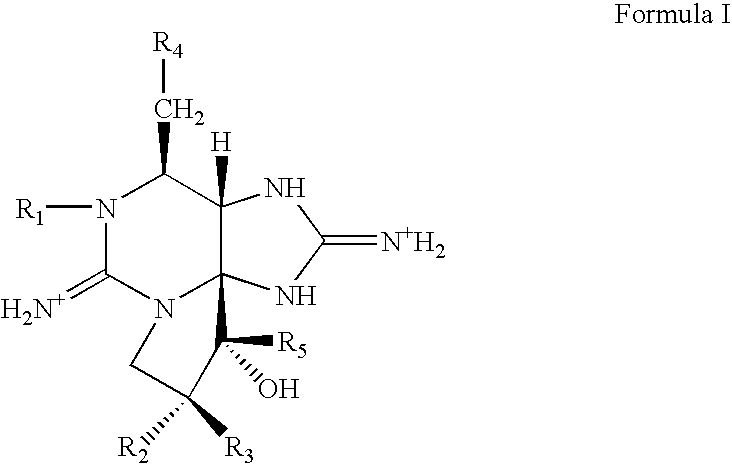
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising tricyclic 3,4-propinoperhydropurines and uses thereof for blocking neuronal transmission which are useful in treating anal fissure and other wounds and muscle disorders are provided. Also provided are methods of treating wounds and muscle disorders by administering the composition of the invention to a muscle or in the vicinity of a muscle either topically or by injection.
Owner:PHYTOTOX LTD
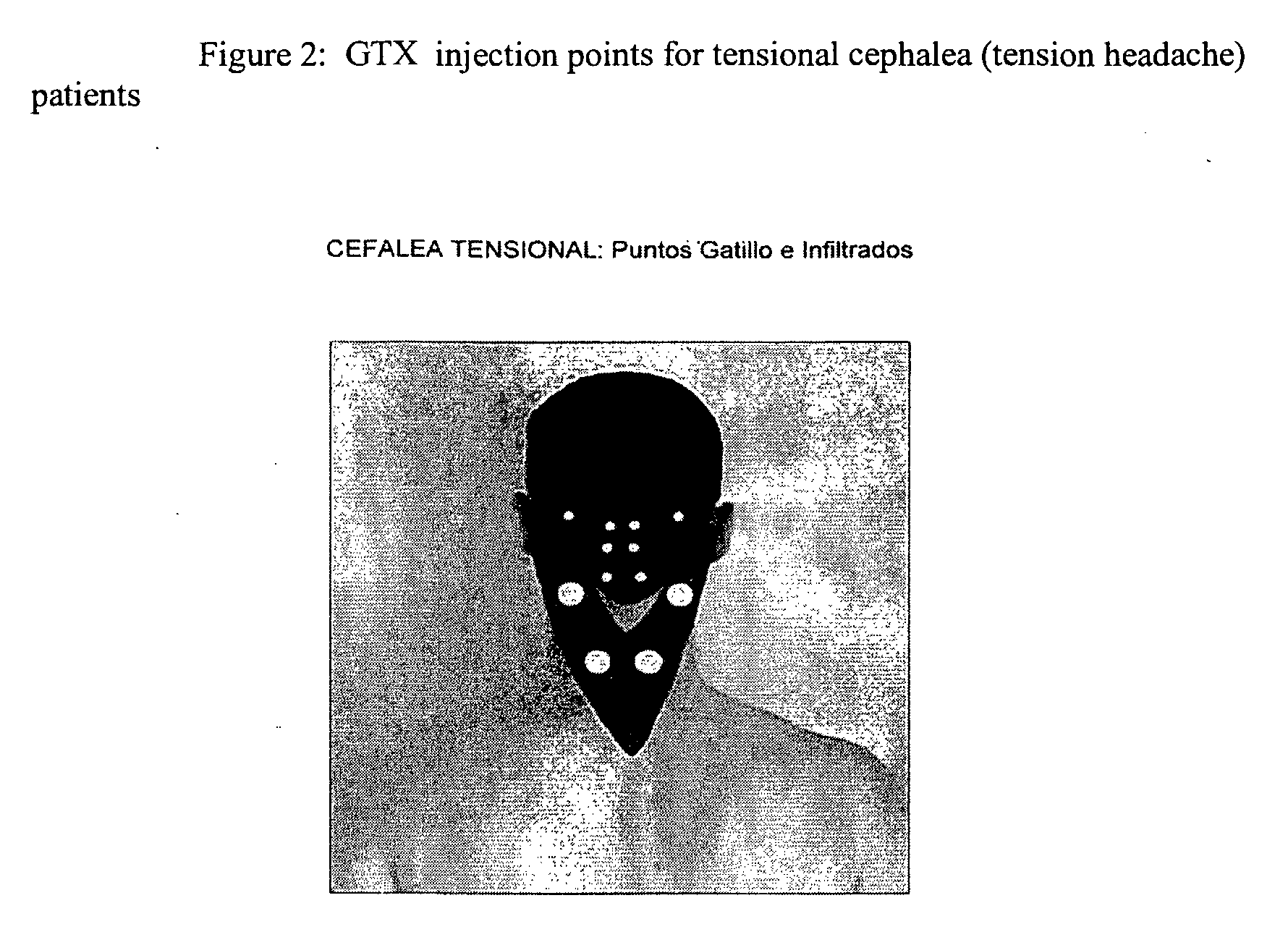
Method for treating tension-type headache with inhibitors of nitric oxide and nitric oxide synthase
InactiveUS6284794B1BiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTension-Type HeadachesNeuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase
Tension-type headache is treated by interacting with neuronal transmission in relation to pain in connection with headache in a way which prevents or decreases sensitization of second order nociceptive neurons. In particular, treatment is performed by administration of an effective amount of a substance which prevents or decreases central sensitization. Important examples of such substances are substances which interact with nitric oxide, such as nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitors, such as L-NMMA or L-NAME or L-NIO or L-NNA. According to a broader aspect of the invention tension-type headache is treated by administration of substances which are effective in preventing or decreasing pain in connection with tension-type headache, such as the substances mentioned above. Accordingly, the invention relates to treatment of tension-type headache by administration of substances which substantially inhibit the activity of nitric oxide synthase (NOS), such as NOS inhibitors, such as L-NMMA or L-NAME or L-NIO or L-NNA.
Owner:NEURAXON INC
Self routing unit circuit and control method thereof
ActiveCN102663497ASmall structureEasy to integrate at scalePhysical realisationNeural network systemSelf routing
The invention discloses a self routing unit circuit and a control method thereof. The circuit of the present invention is suitable for a large-scale interconnected neural network system. The synaptic connection of a front neuron and three or more back neurons employ the self routing circuit unit. Three or more branches in parallel connection are provided, and each parallel branch is formed by one or more bipolar resistive memristors. Each branch has a different structure, with differences of the number of the resistive memristors, the connection directions of polarities and parallel and series connection modes, the self routing unit circuit corresponding to specific voltage is formed. According to the circuit of the invention, the circuit can automatically choose to transmit a signal to the back neurons, the circuit is simple, a structure is small and large-scale integration is facilitated; the circuit is a non volatile circuit, and once set, the circuit is not needed to be reset again when a condition is unchanged.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
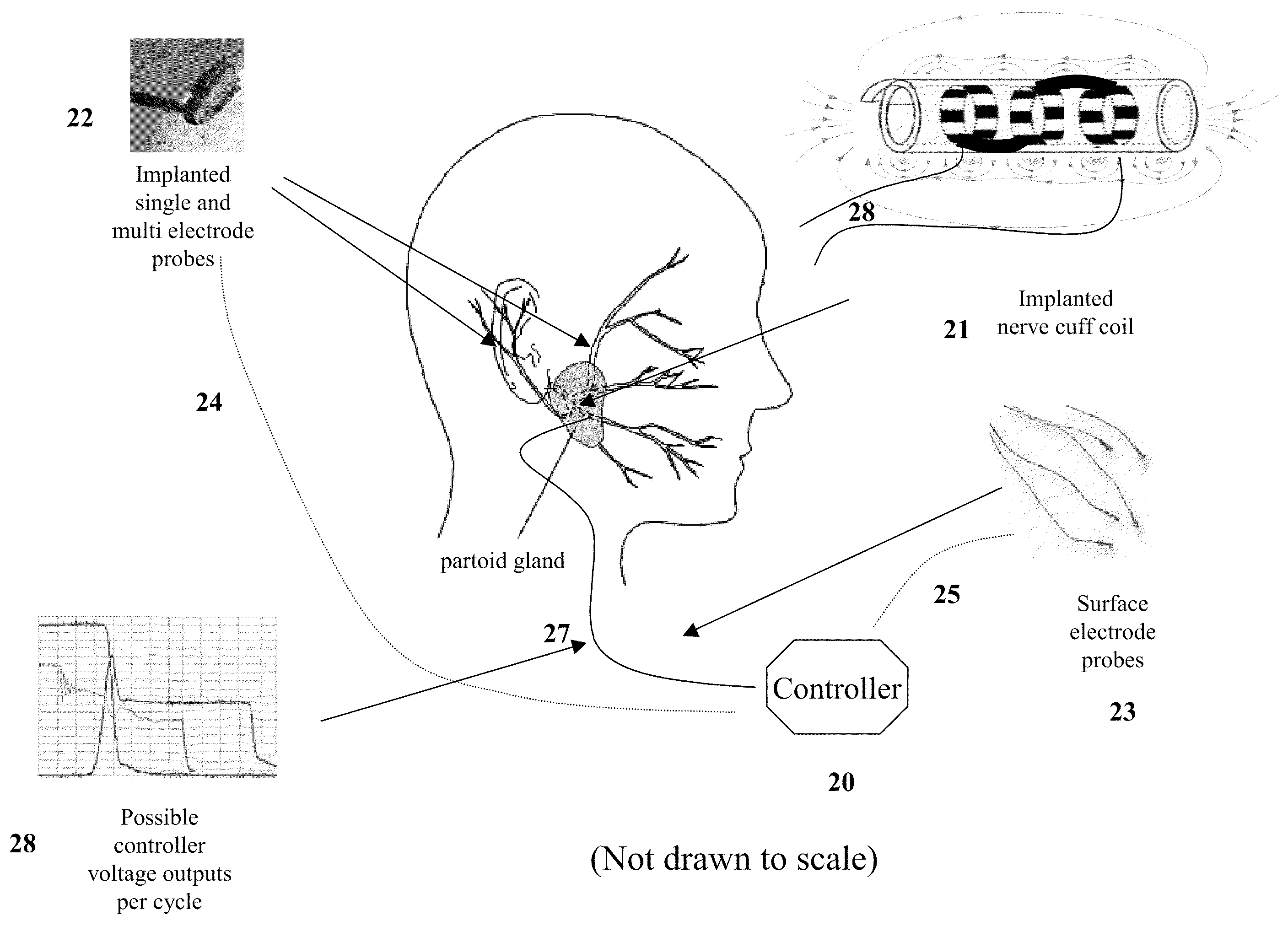
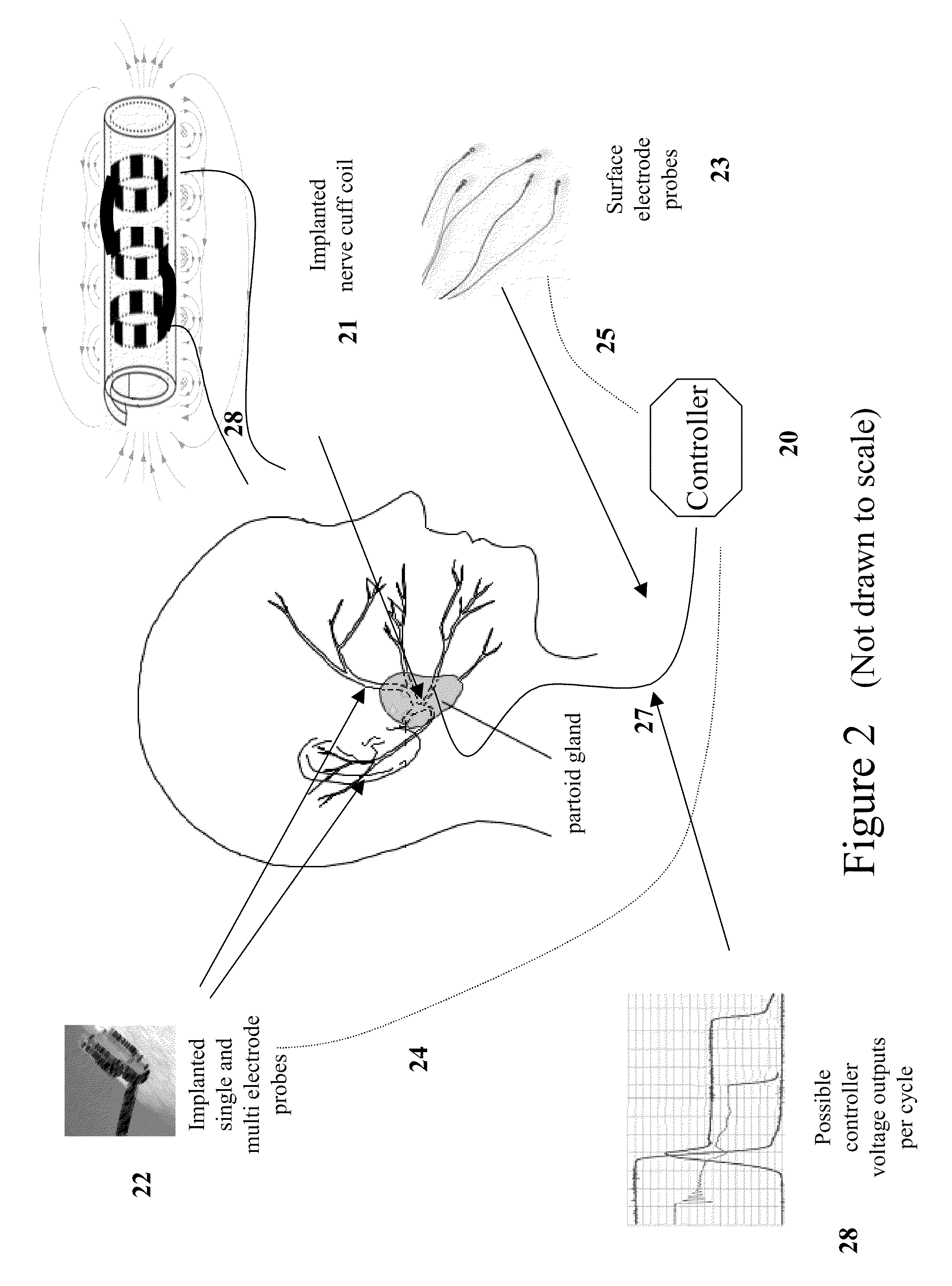
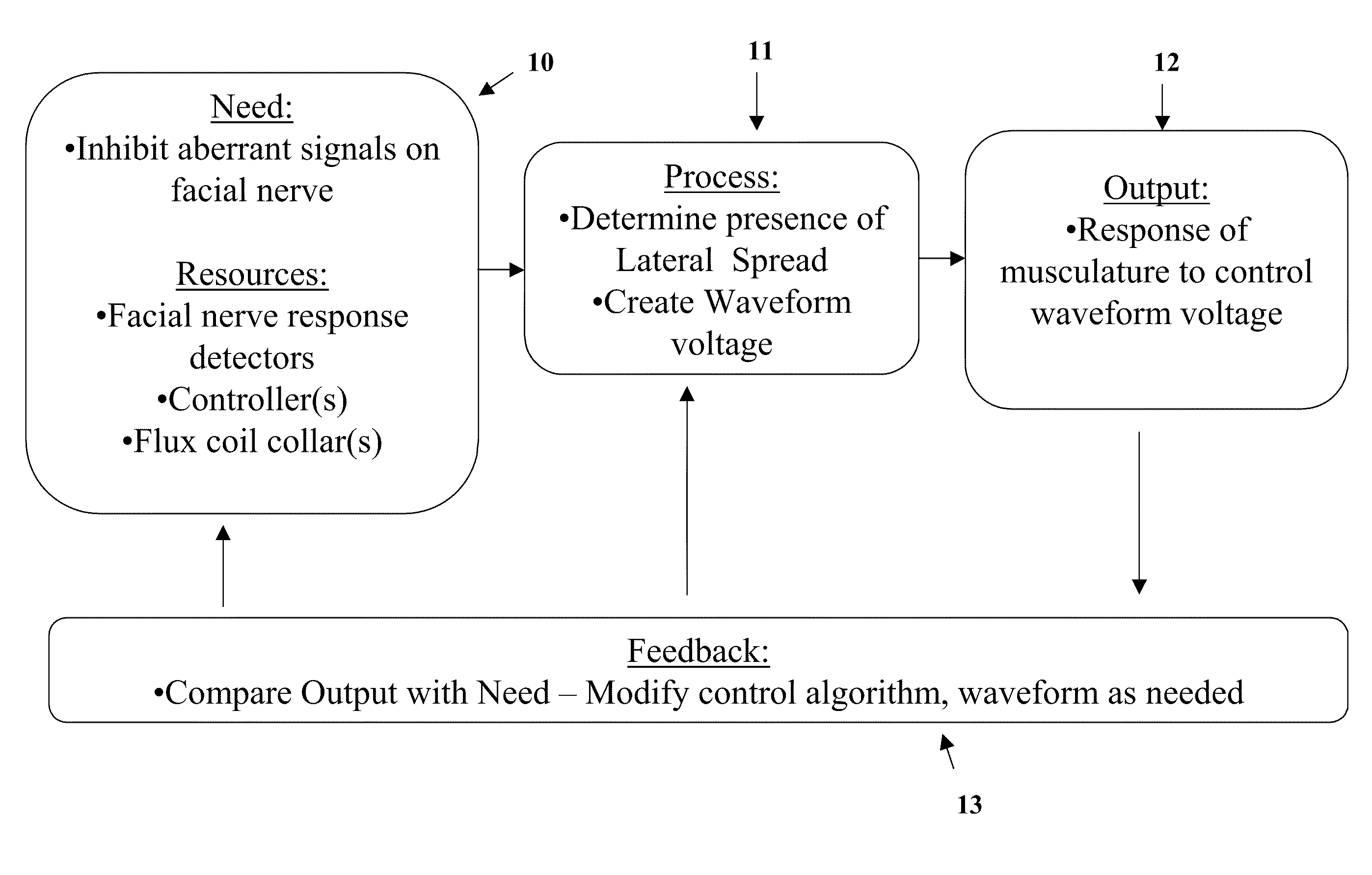
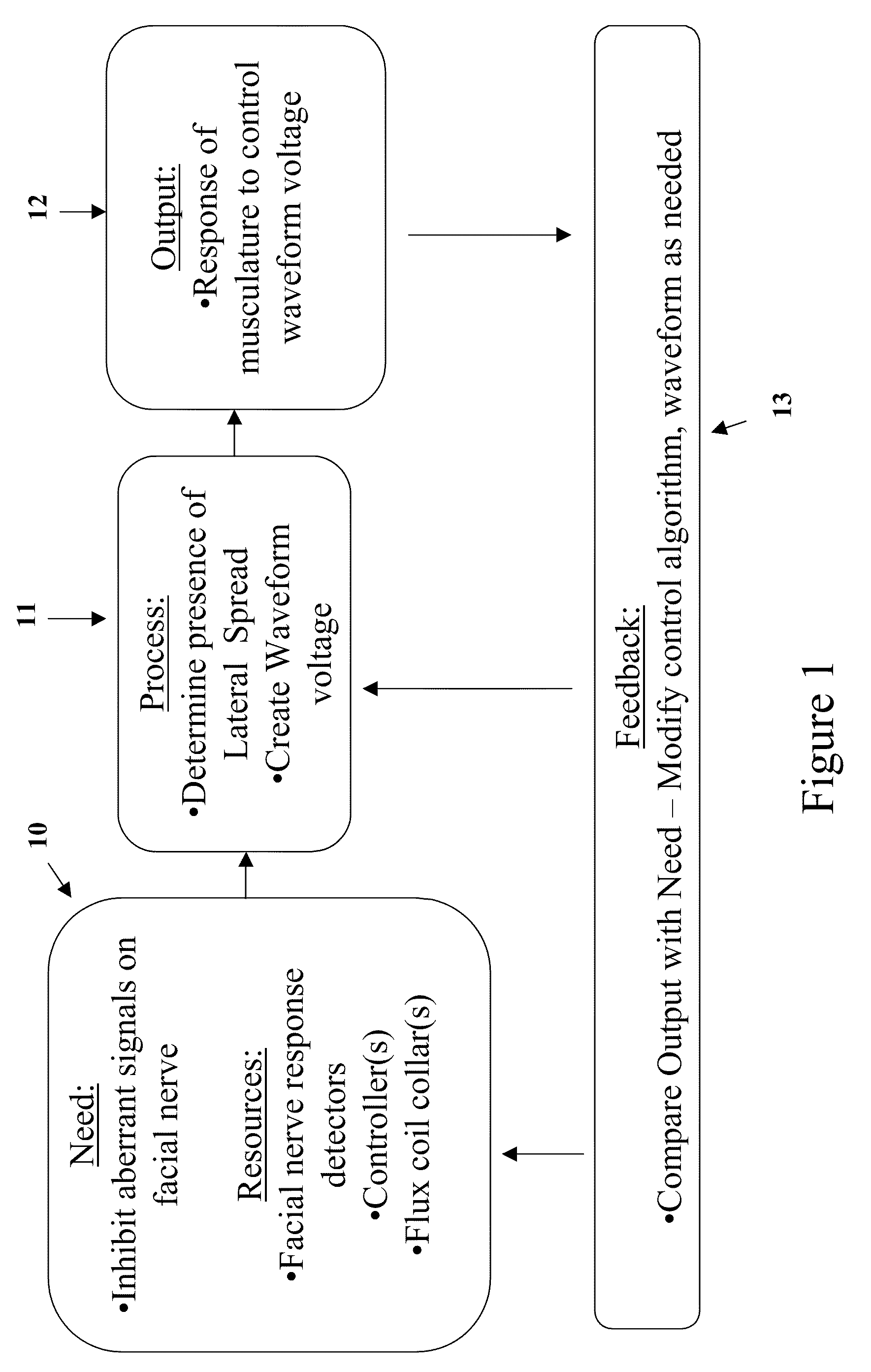
Induced Modulation of Neuronal Transmission
The invention is directed to a method of treating movement disorders by the modulation of neuronal transmission using time-variant non-conservative magnetic fields. The invention is also directed to a method for treating dystonias.
Owner:PETTINELLI EUGENE EUSTIS
Use and application of a pharmaceutical composition containing a mixture of natural- origin heterocyclical guanidine, for cosmetology, wound healing, focal dystonia and muscular spasm- related clinical pathologies
Pharmaceutical compositions comprising tricyclic 3,4-propinoperhydropurines and uses thereof for blocking neuronal transmission are provided.
Owner:PHYTOTOX LTD
Artificial neural network with hardware training and hardware refresh
InactiveUS6513023B1Intuitive accuracyAdvantage of speed simplicityDigital computer detailsDigital dataNerve networkAudio power amplifier
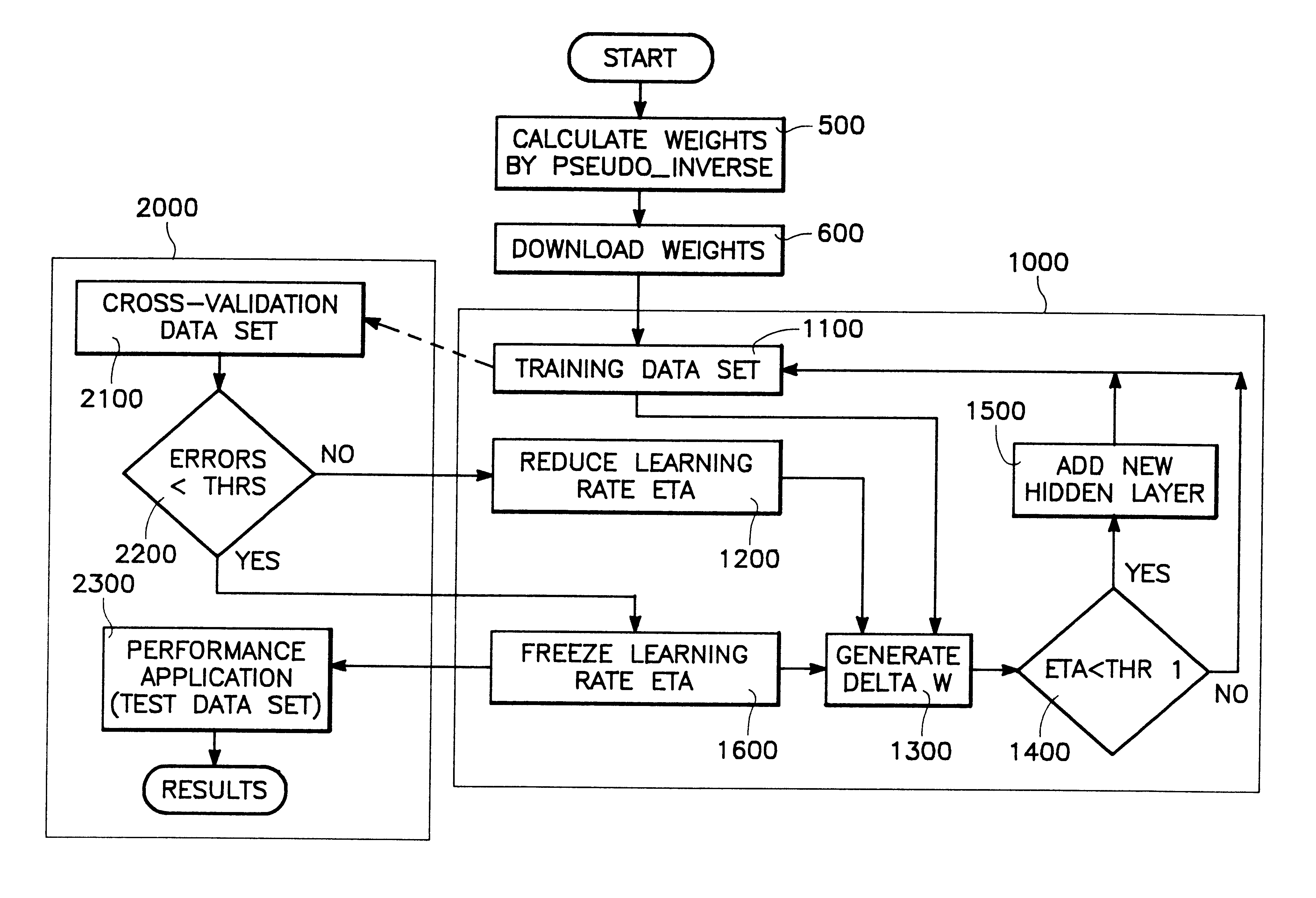
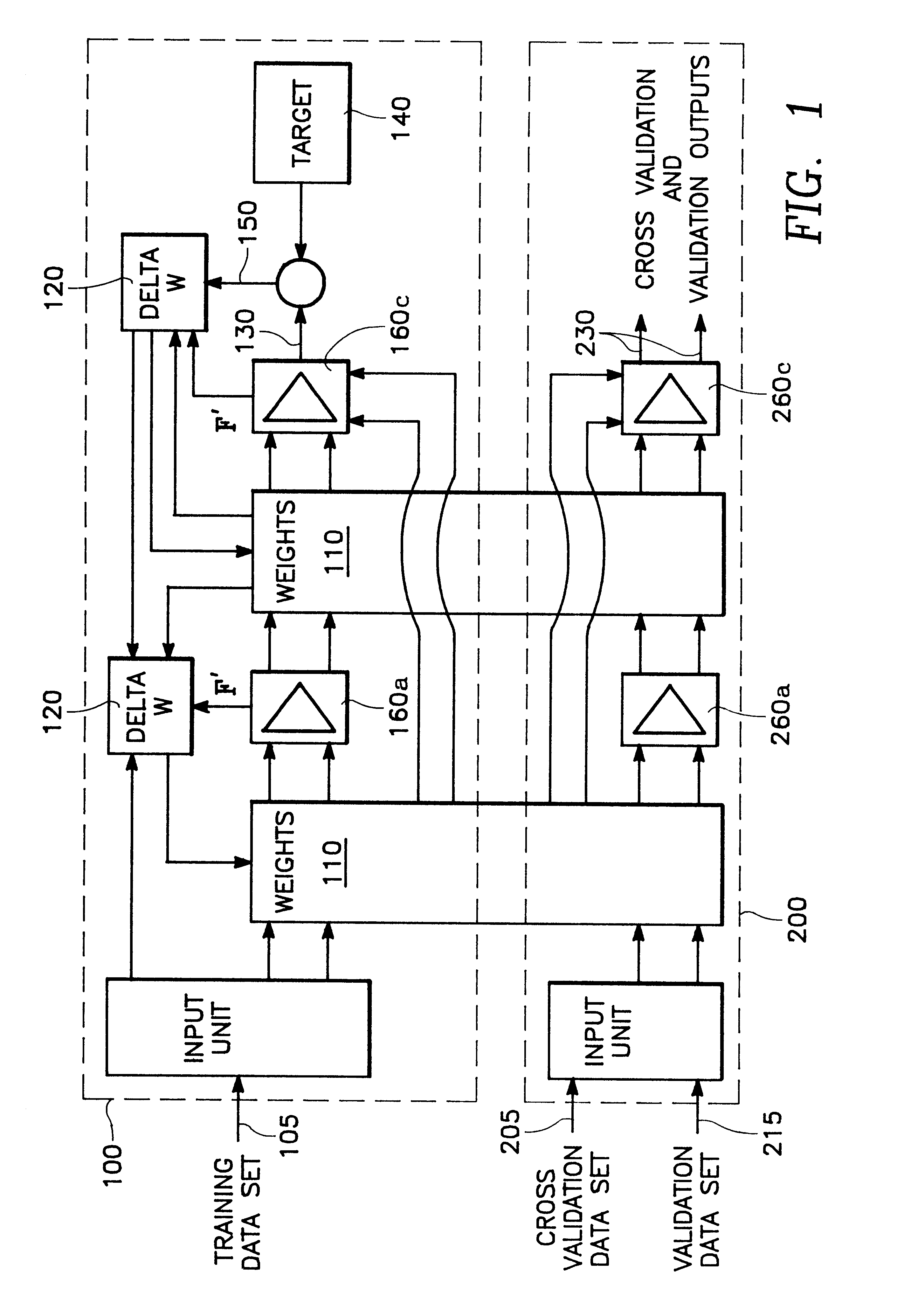
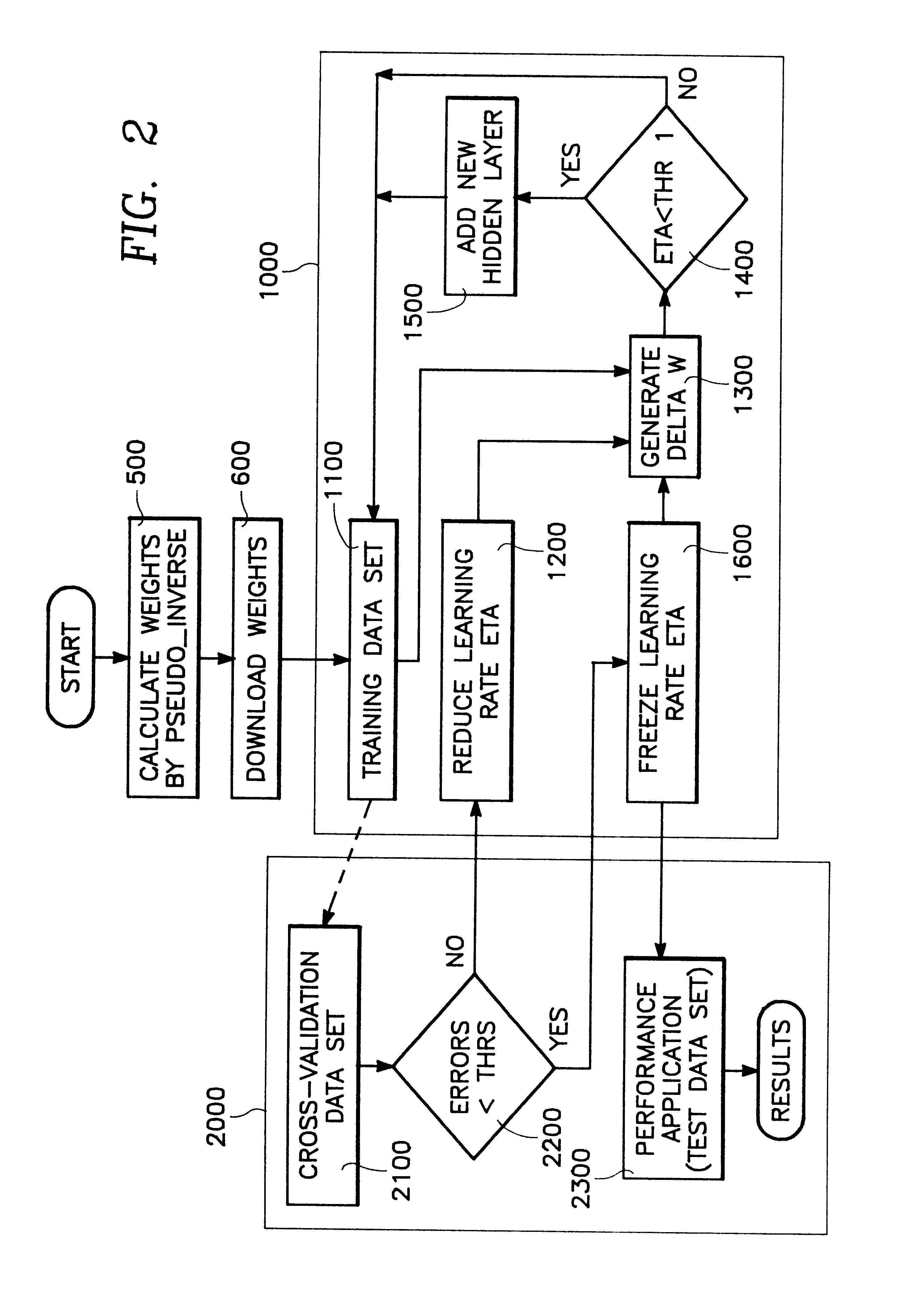
A neural network circuit is provided having a plurality of circuits capable of charge storage. Also provided is a plurality of circuits each coupled to at least one of the plurality of charge storage circuits and constructed to generate an output in accordance with a neuron transfer function. Each of a plurality of circuits is coupled to one of the plurality of neuron transfer function circuits and constructed to generate a derivative of the output. A weight update circuit updates the charge storage circuits based upon output from the plurality of transfer function circuits and output from the plurality of derivative circuits. In preferred embodiments, separate training and validation networks share the same set of charge storage circuits and may operate concurrently. The validation network has a separate transfer function circuits each being coupled to the charge storage circuits so as to replicate the training network's coupling of the plurality of charge storage to the plurality of transfer function circuits. The plurality of transfer function circuits may be constructed each having a transconductance amplifier providing differential currents combined to provide an output in accordance with a transfer function. The derivative circuits may have a circuit constructed to generate a biased differential currents combined so as to provide the derivative of the transfer function.
Owner:NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTATION U S GOVERNMENT AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE
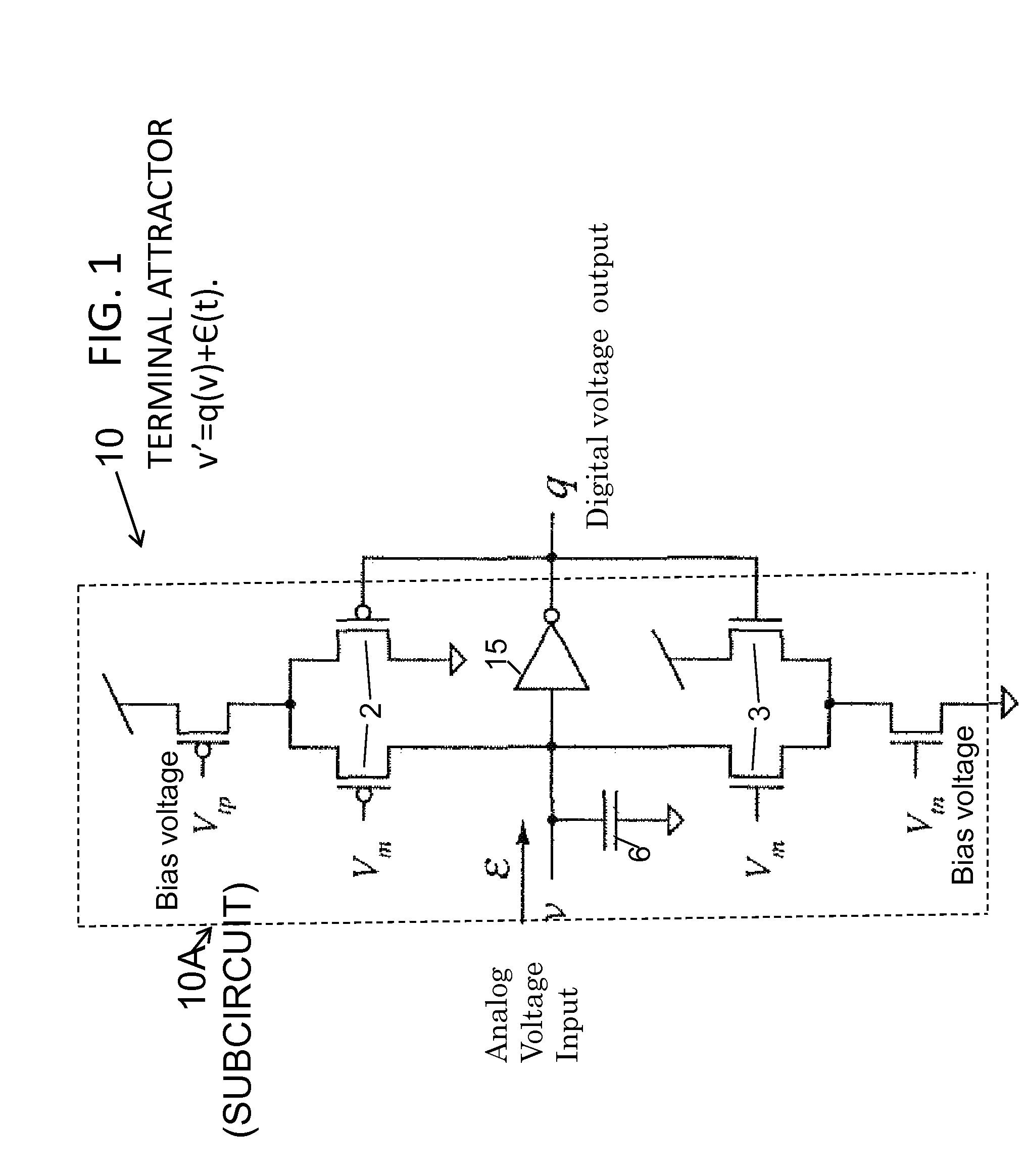
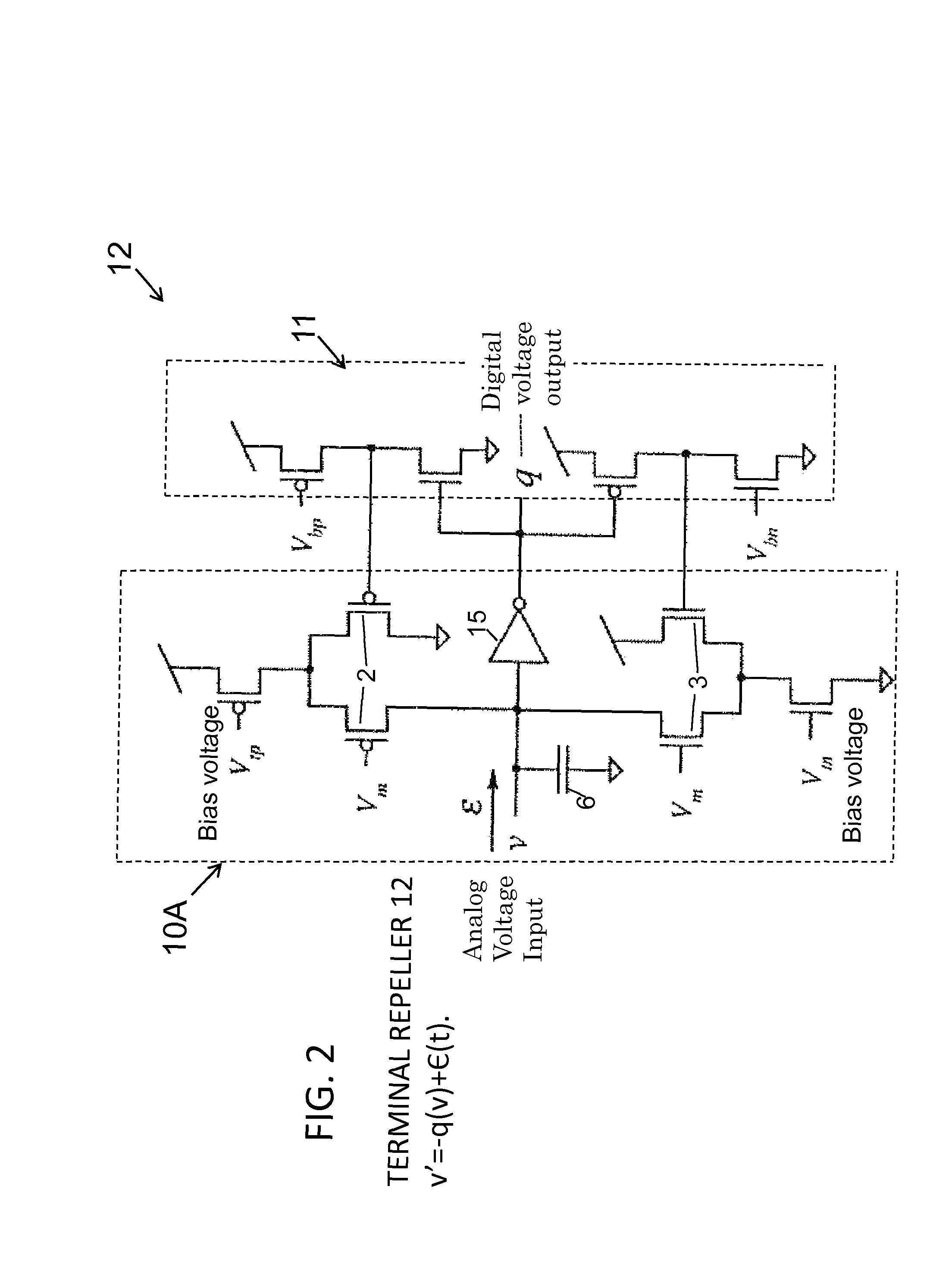
Apparatus and method for using analog circuits to embody non-lipschitz mathematics and properties using attractor and repulsion modes
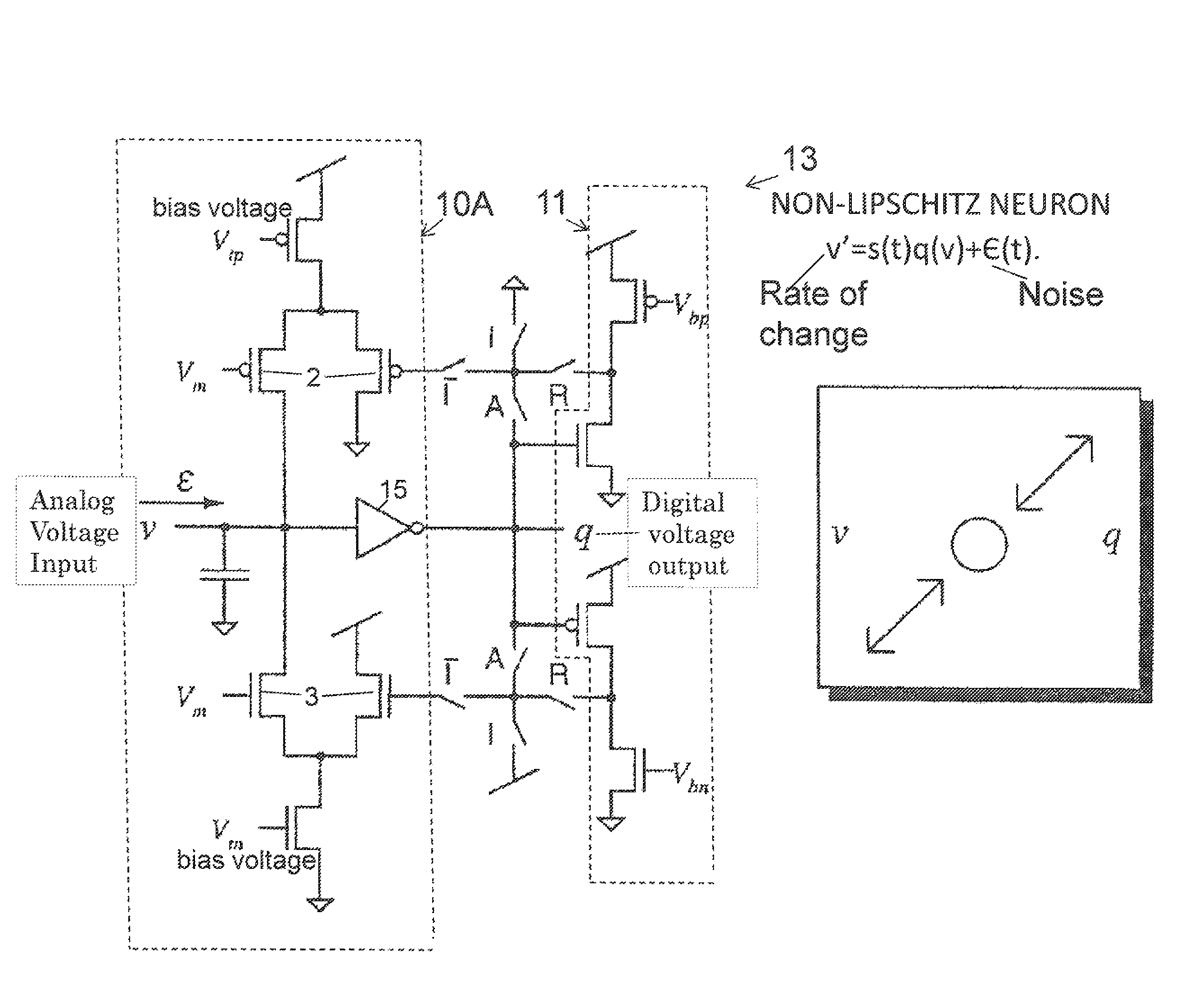
A network of coupled neurons for implementing Non-Lipschitz dynamics for modeling nonlinear processes or conditions comprising: a plurality of neurons, each being configurable in attractor and repulsion modes of operation, and programmable by an external signal; a plurality of synaptic connections for connecting at least a portion of the plurality of neurons for passage of data from one neuron to another; feedback circuitry for incrementing and decrementing an analog voltage output depending upon the output of the synaptic connection; whereby by the circuit solves Non-Lipschitz problems by programmably controlling the attractor and repulsion modes. A method of programming a network for solving Non-Lipschitz problems comprising providing a plurality of neurons, each programmable into a plurality of modes including repulsion and attraction modes; interconnecting the plurality of neurons using synaptic connections; providing feedback to at least one of the neurons; whereby by programming the neurons Non-Lipschitz terminal dynamics can be achieved.
Owner:ARMY US SEC THE
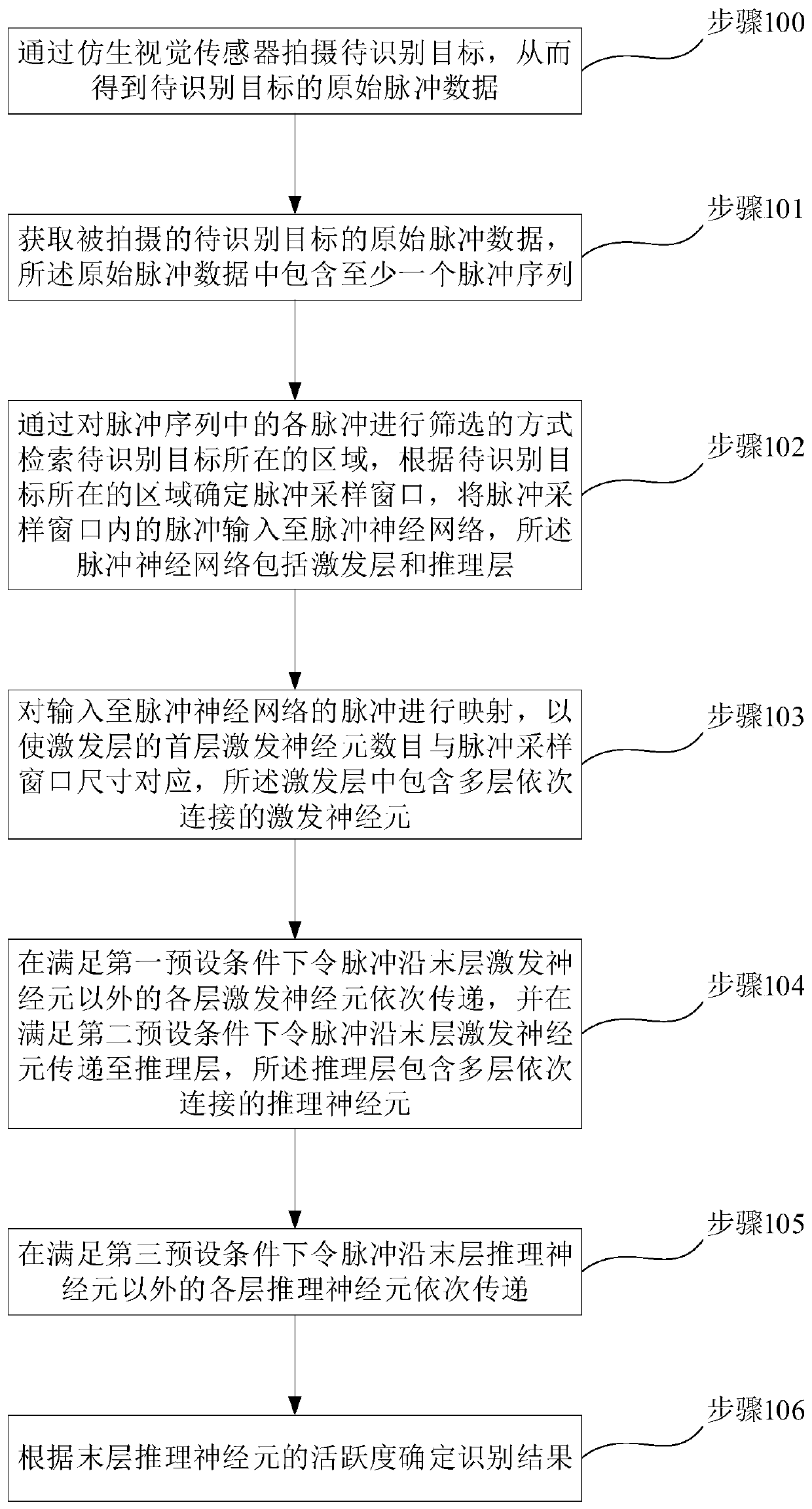
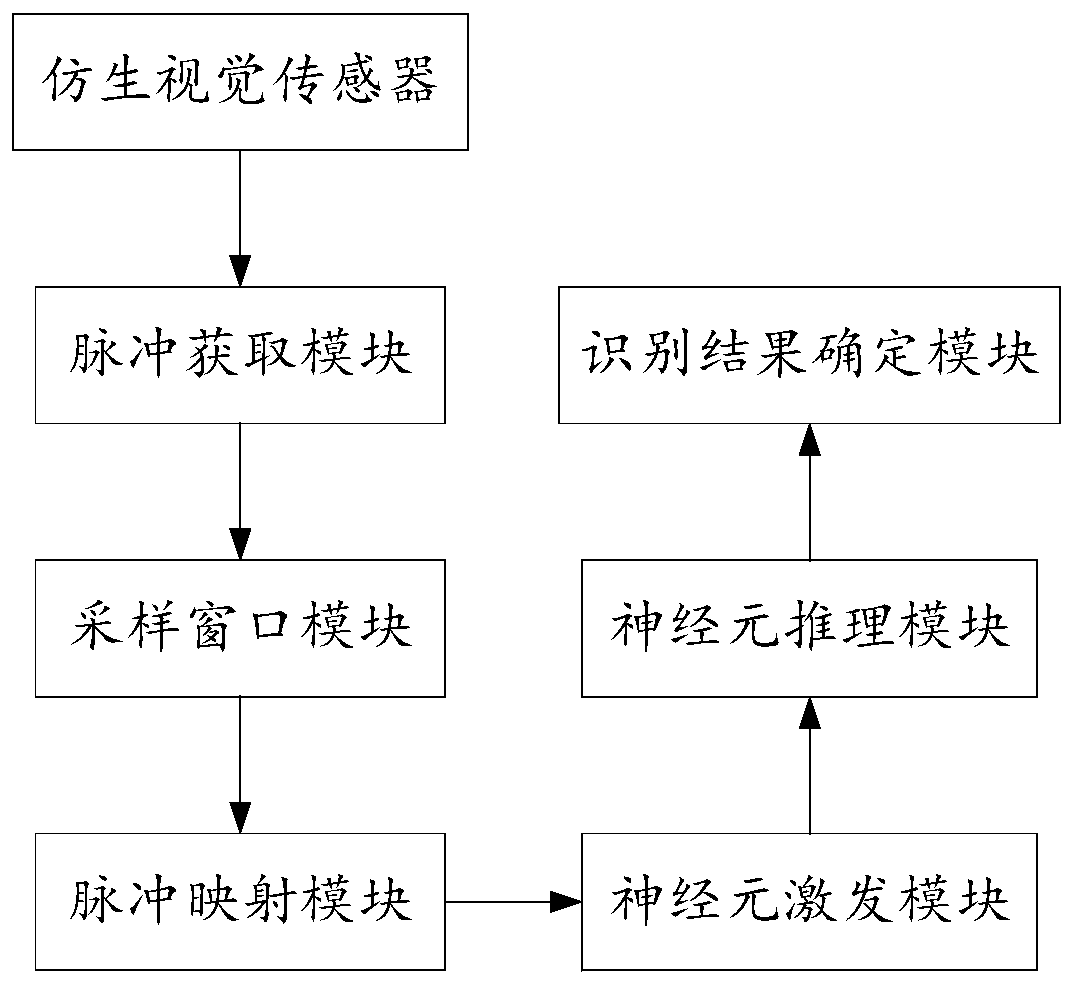
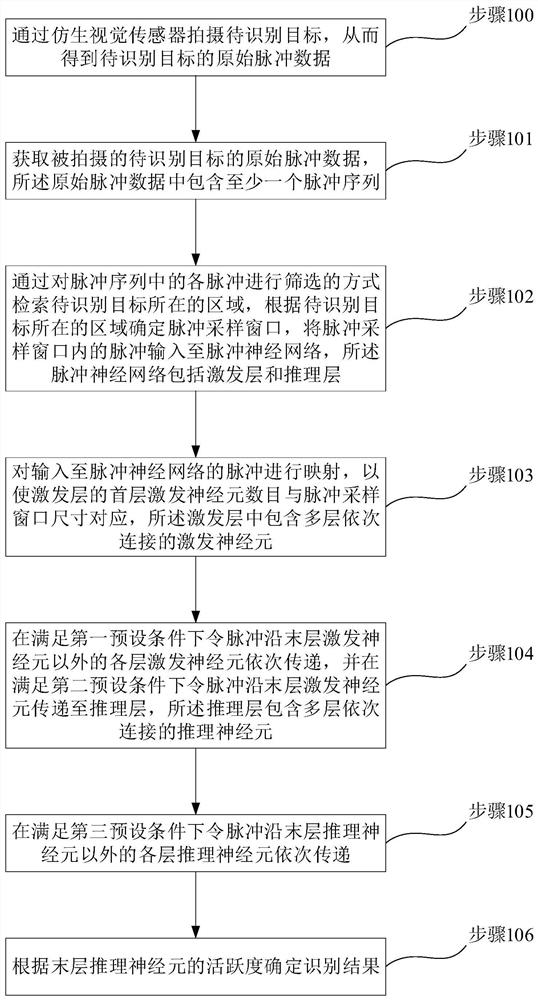
Target recognition method, device and system and computer readable storage medium
ActiveCN111275742ARealize speed measurementAccurate identificationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionGoal recognition
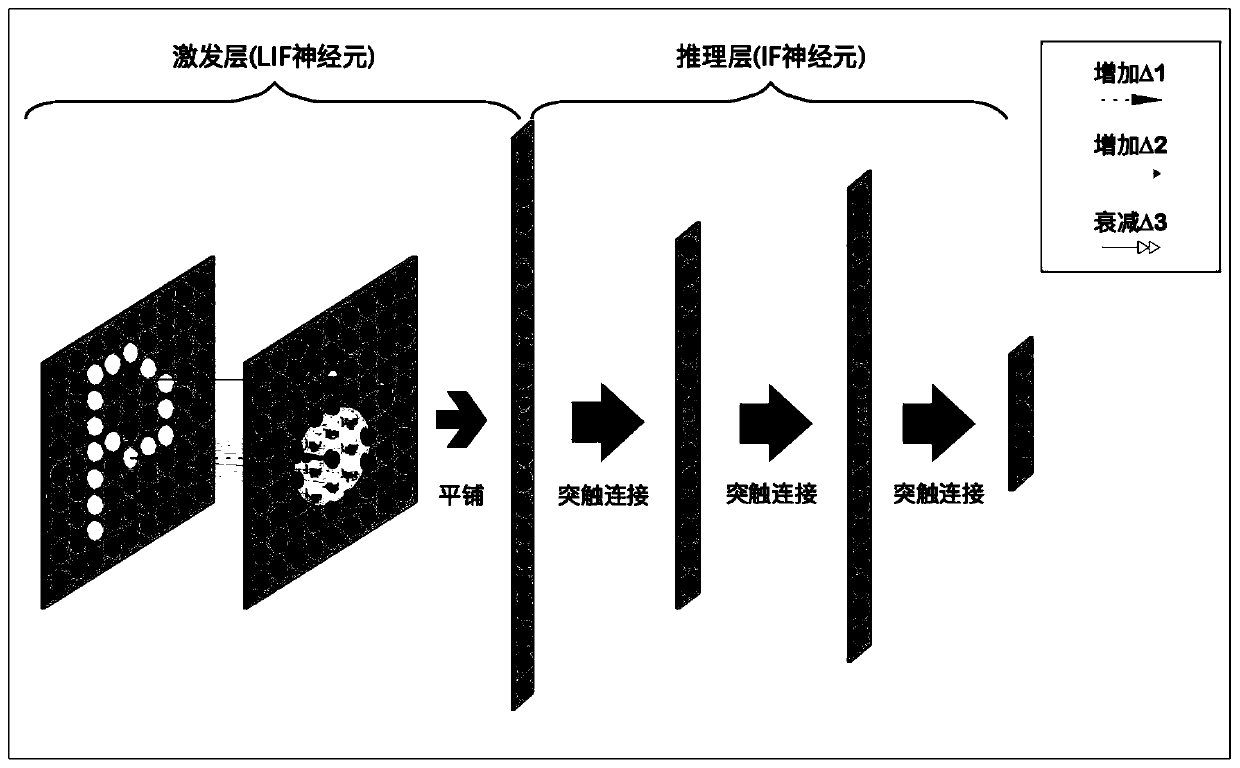
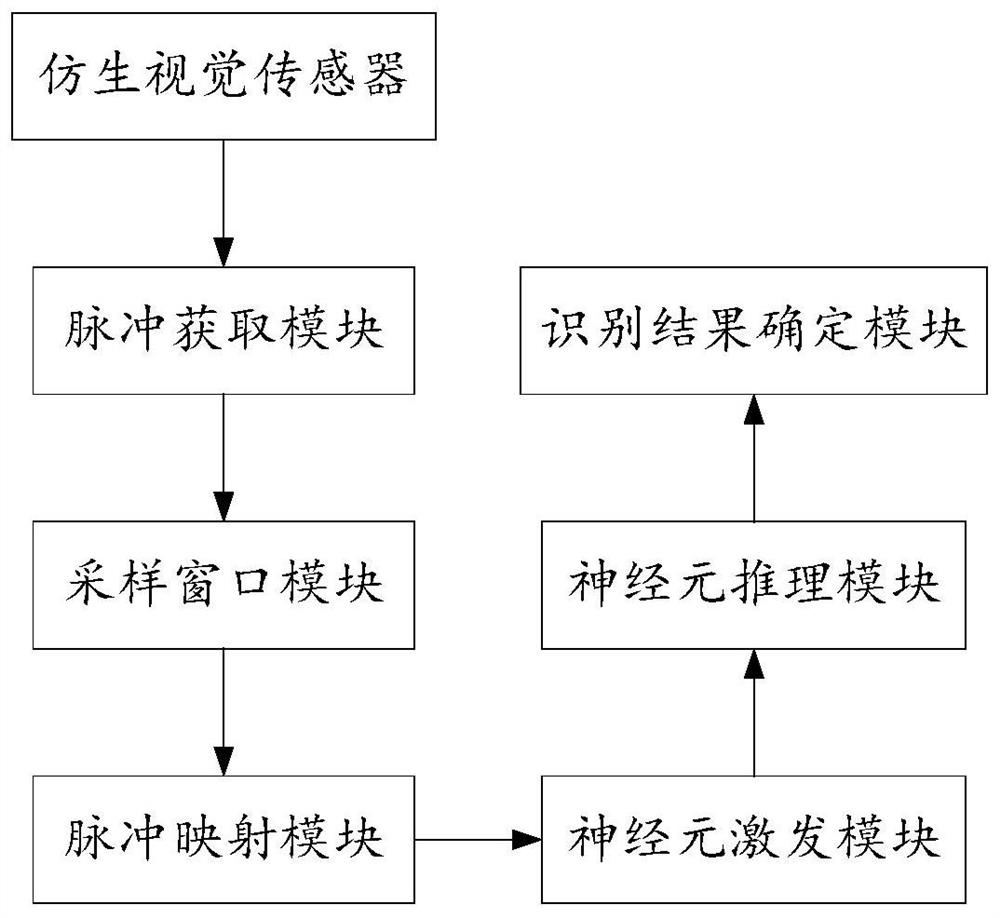
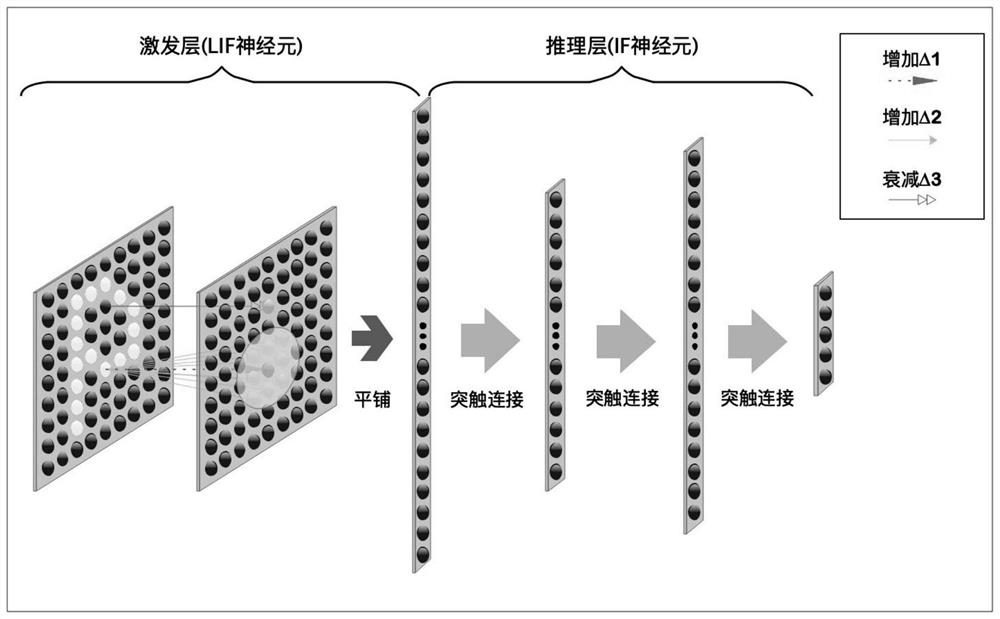
The invention discloses a target recognition method, device and system and a computer readable storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining raw pulse data, determining a pulse sampling window, and inputting pulses in the pulse sampling window into a pulse neural network, mapping the pulse input to the pulse neural network, sequentially transmitting the pulse along each layerof excitation neurons except the last layer of excitation neurons, transmitting the pulse to an inference layer along the last layer of excitation neurons, sequentially transmitting the pulse along each layer of inference neurons except the last layer of inference neurons, and determining an identification result; the device comprises a pulse acquisition module, a sampling window module, a pulsemapping module, a neuron excitation module, a neuron reasoning module and an identification result determination module. The system comprises the device. The method can achieve the accurate and quickrecognition of a to-be-recognized target, can be better suitable for a target with a higher movement speed, and can give consideration to the recognition accuracy and calculation amount.
Owner:SPIKE VISION (BEIJING) TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Neural network unit circuit based on memristor bridge synapses
ActiveCN110163364AReduce power consumptionReduce volumeNeural architecturesPhysical realisationFault toleranceNeuron
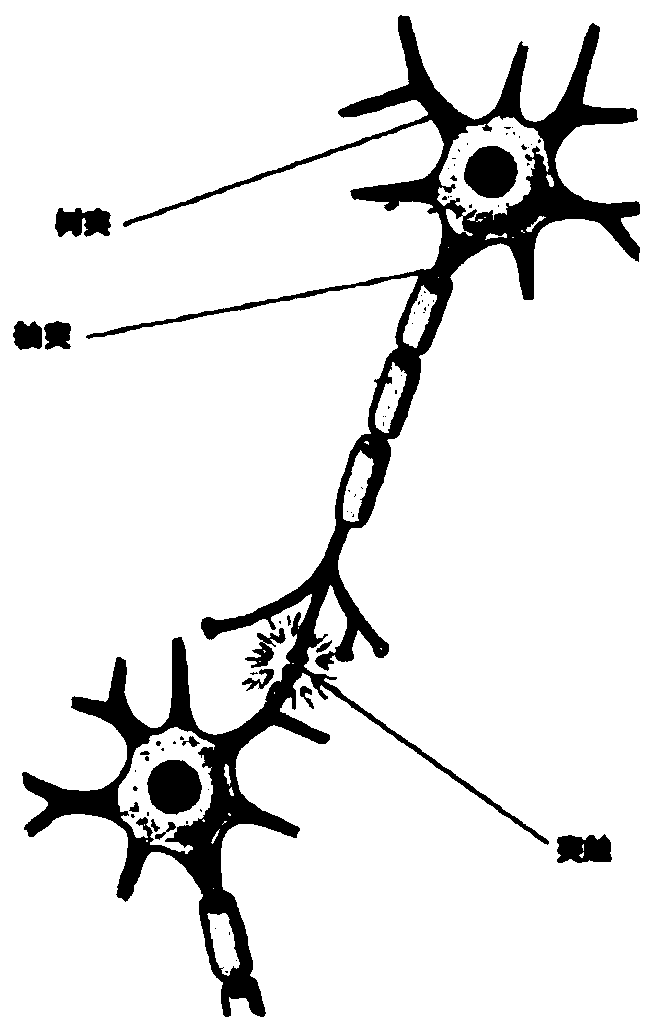
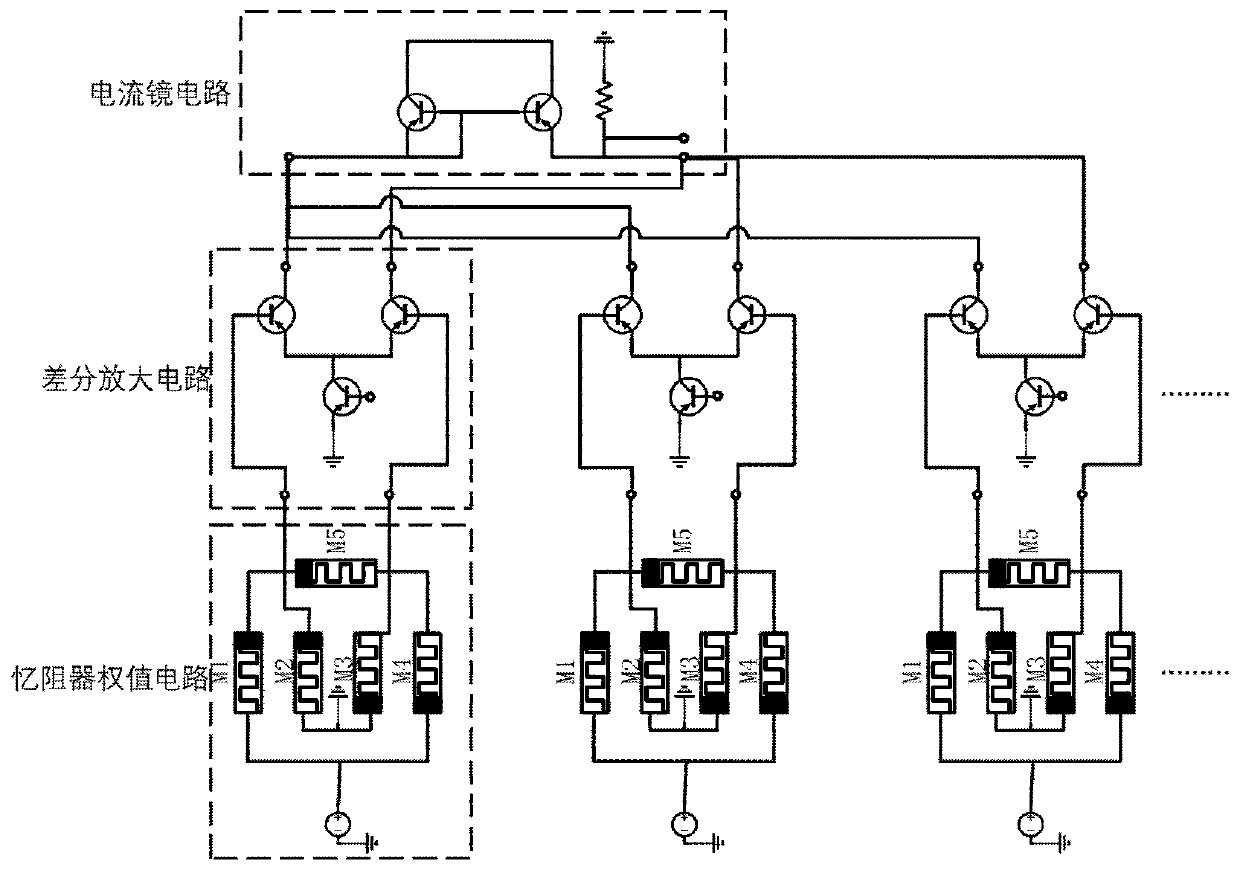
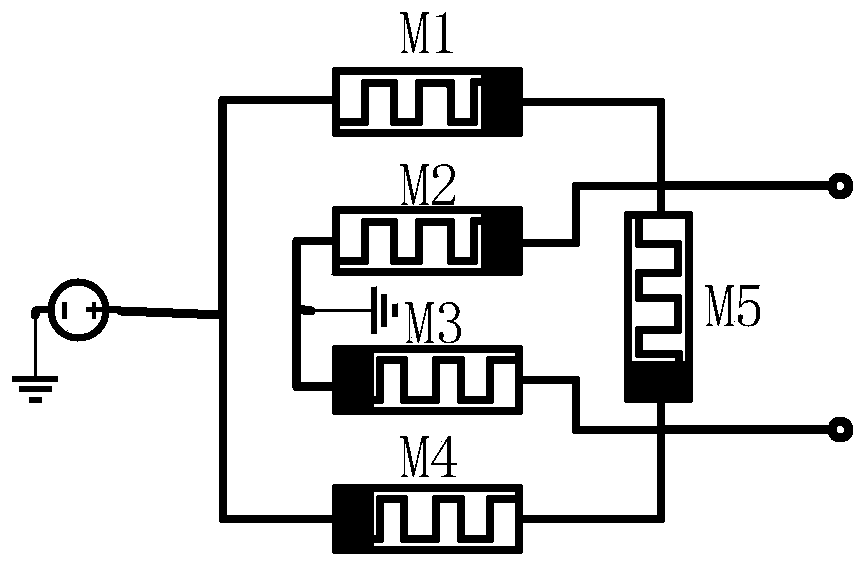
The invention discloses a neural network unit circuit based on a memristor bridge synapse, and the neural network unit circuit comprises a memristor weight circuit which is used for weighting a voltage signal transmitted by an upper-level neuron and transmitting the voltage signal downwards; a differential amplification circuit which is used for converting the voltage signal transmitted by the synapse into a current signal; and a current mirror circuit which is used for adding and summarizing the current signals transmitted by the synapses and transmitting the current signals to the next stageof neurons. The invention aims to solve the problems that a transistor-based hardware neural network is high in power consumption and large in size, and a neural network circuit based on a memristorarray is low in fault tolerance is solved. The memristor bridge composed of five memristors is used for simulating synapses in neurons, the differential amplification circuit is used for simulating axons of the neurons, the current mirror circuit is used for simulating dendrites of the neurons, the three parts play a role in signal weighting, voltage-current conversion, current accumulation and cascade voltage output respectively, and a neural network unit circuit is completely achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
System and method for measuring phase
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light.These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imagingorigins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in theirnative state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference withinthe cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
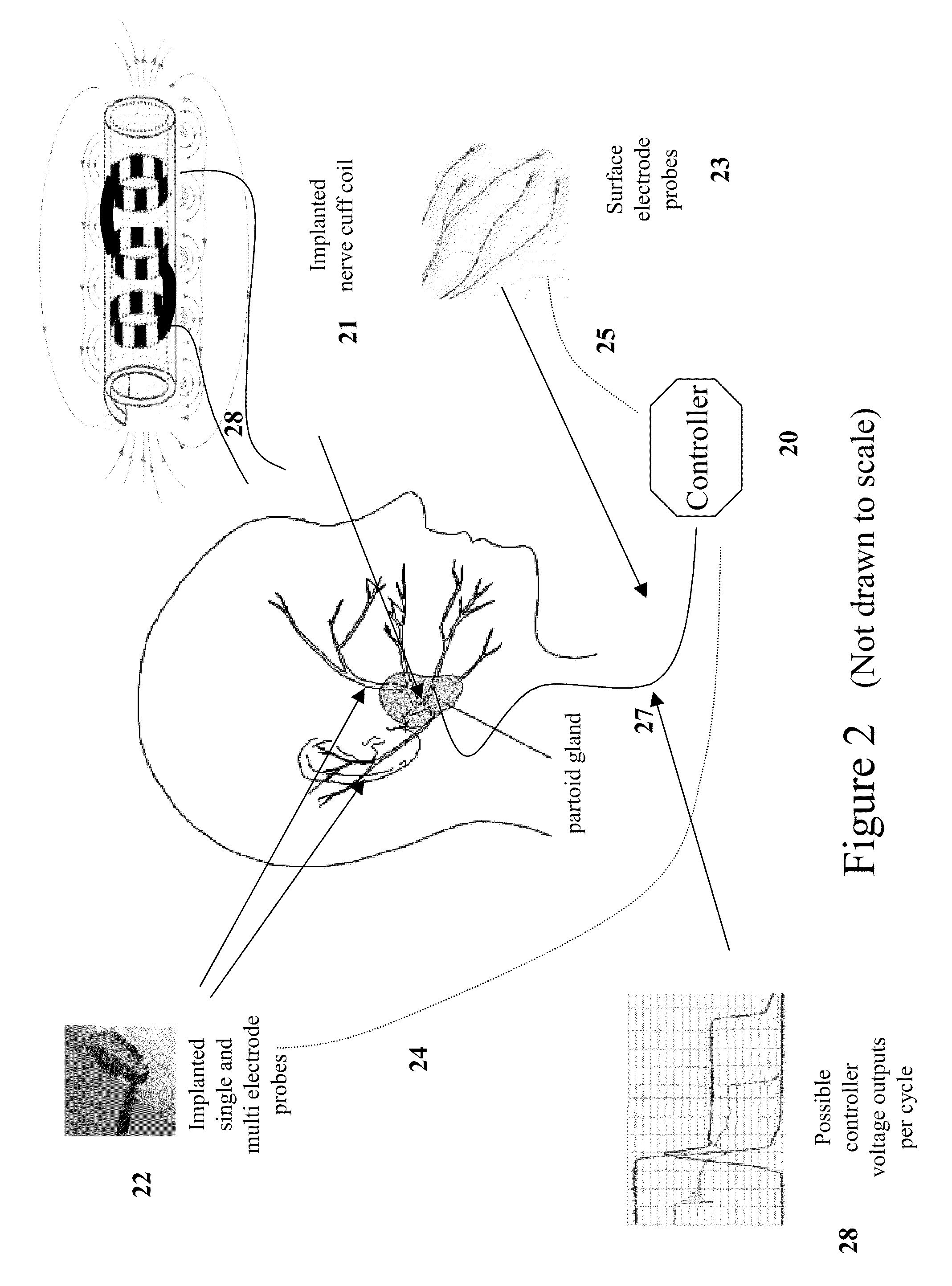
Device for neuronal therapies
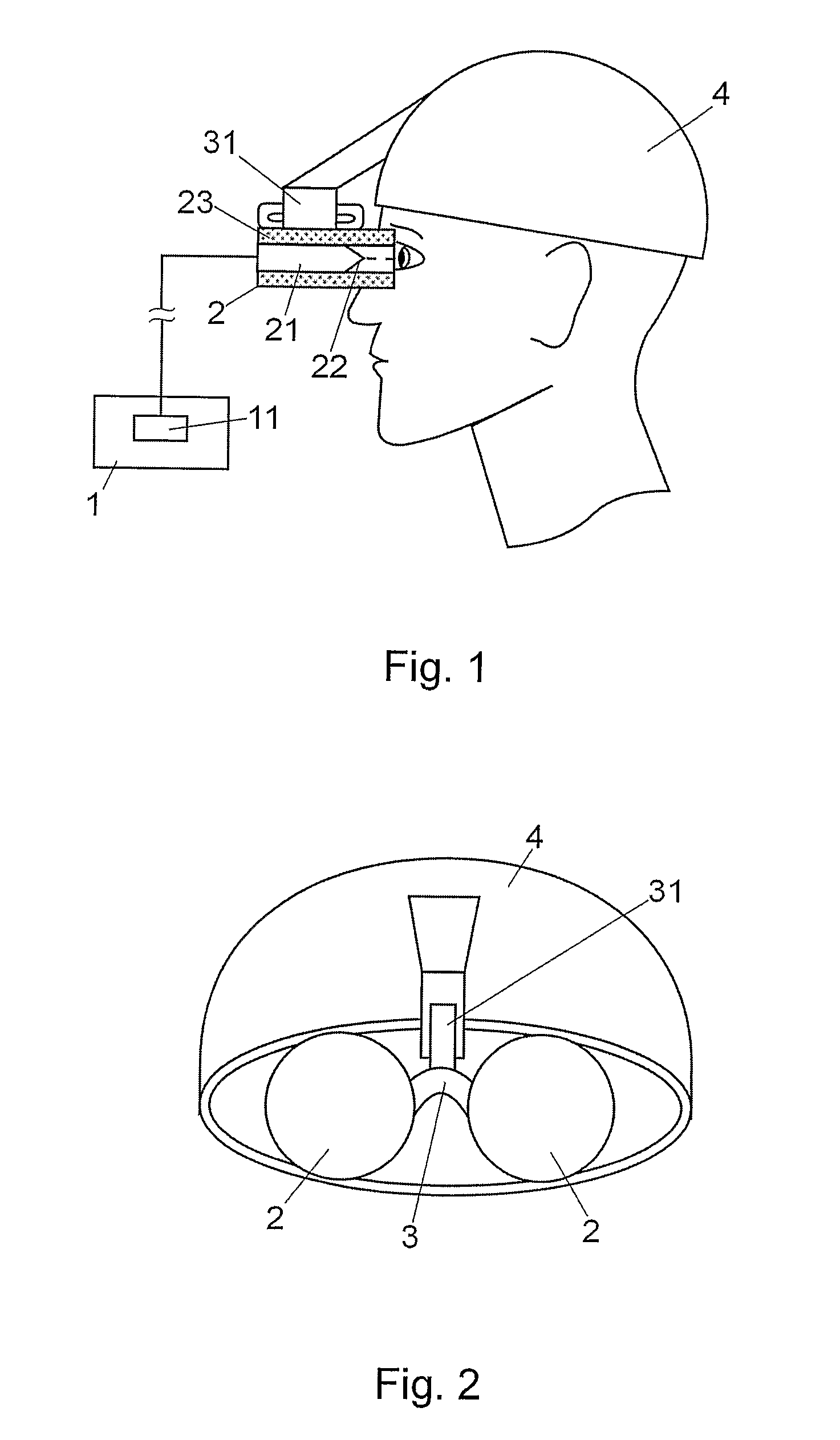
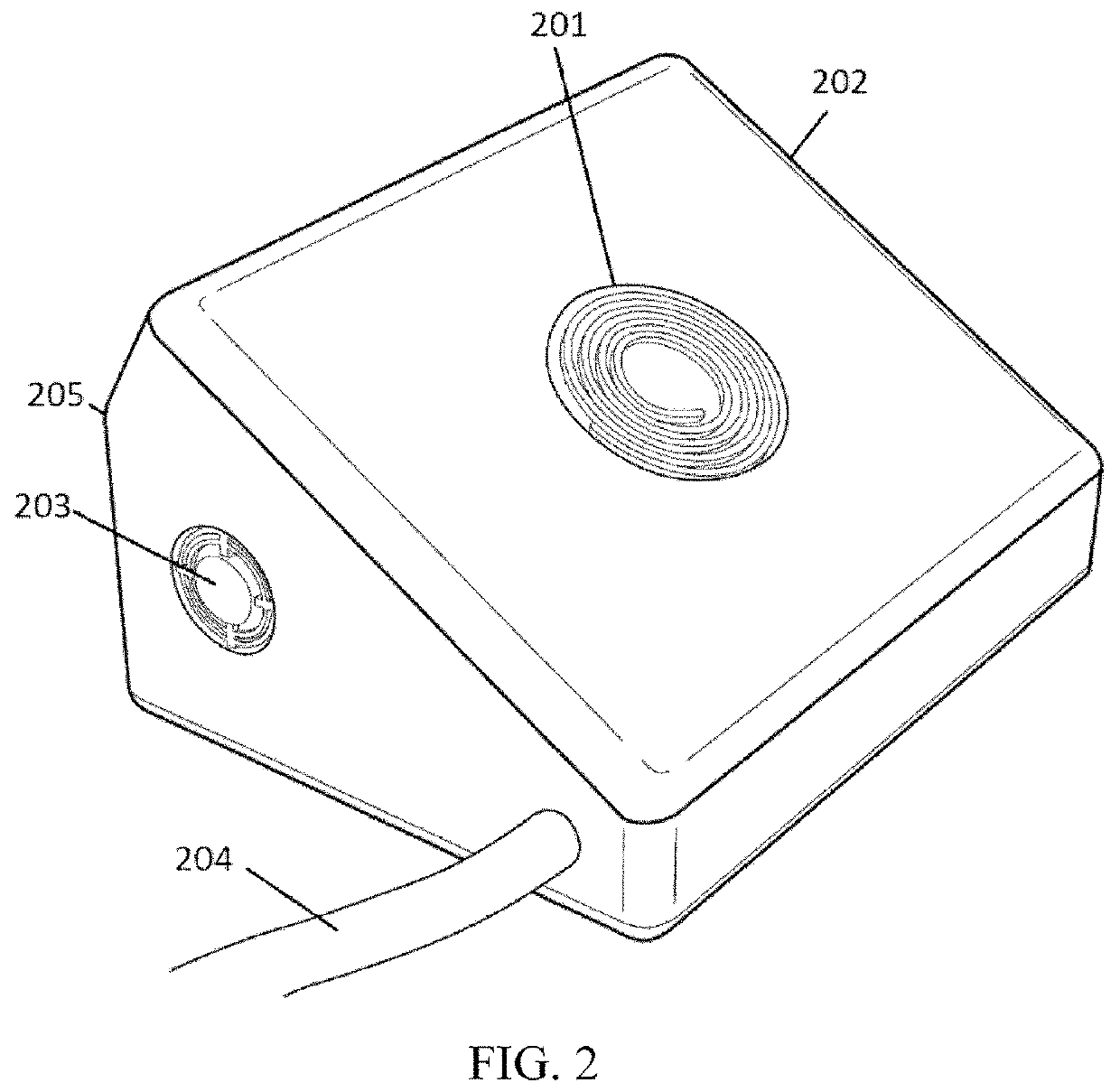
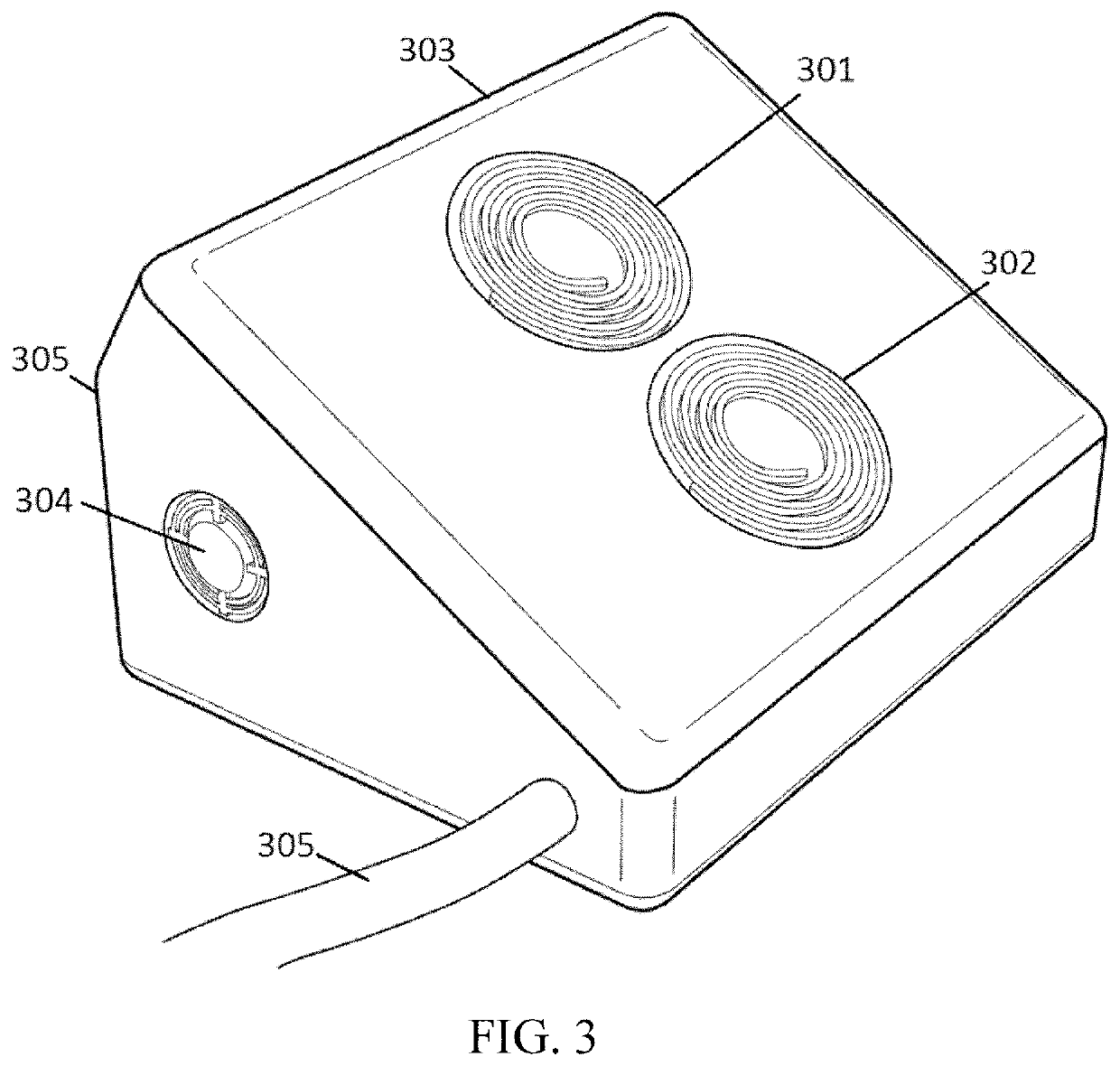
InactiveUS20100211121A1Easy plantarEasy heel contactElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringNervous systemPower flow
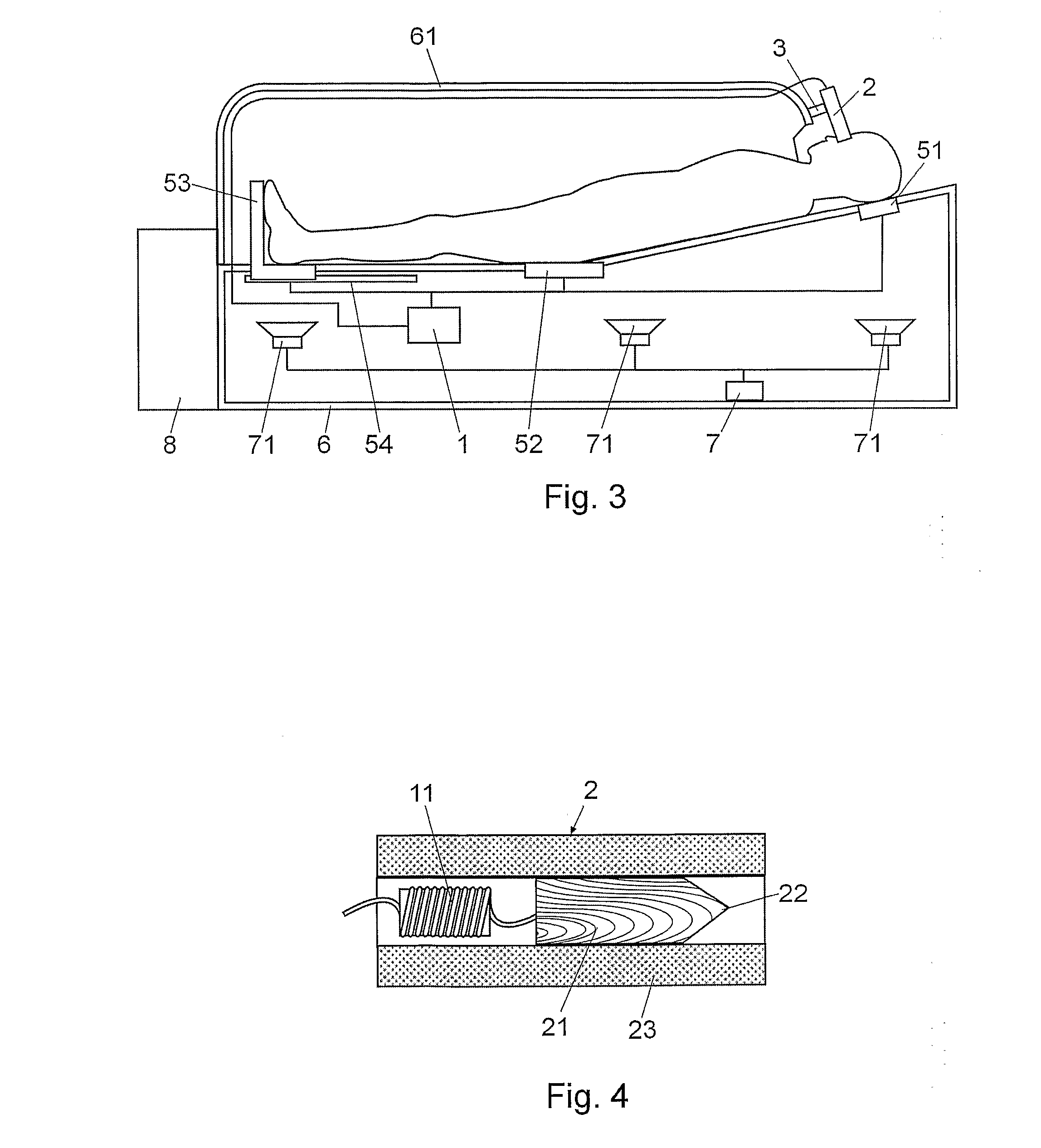
A device for neuronal therapies comprising a high frequency and / or very high frequency generator (1) functioning by means of coils (11), and associated with two main electrodes (2), which are respectively configured by a core (21) of insulating material with the front end (22) in point form and surrounded by a flexible insulating tubular body (23) extended on the point end (22) of the electrode for separate and safe positioning thereof with respect to the eyes of the patient on which said electrodes (2) are placed in a use operation, in order to cause stimulation of the nervous system and improvement of neuronal transmission by means of the circulation of high frequency currents. Both electrodes (2) are associated with at least one element for support (3) and positioning over the eyes of the patient, based on an element for fastening (4) to the head or a cabin (6).
Owner:NOVASONIX TECH SL
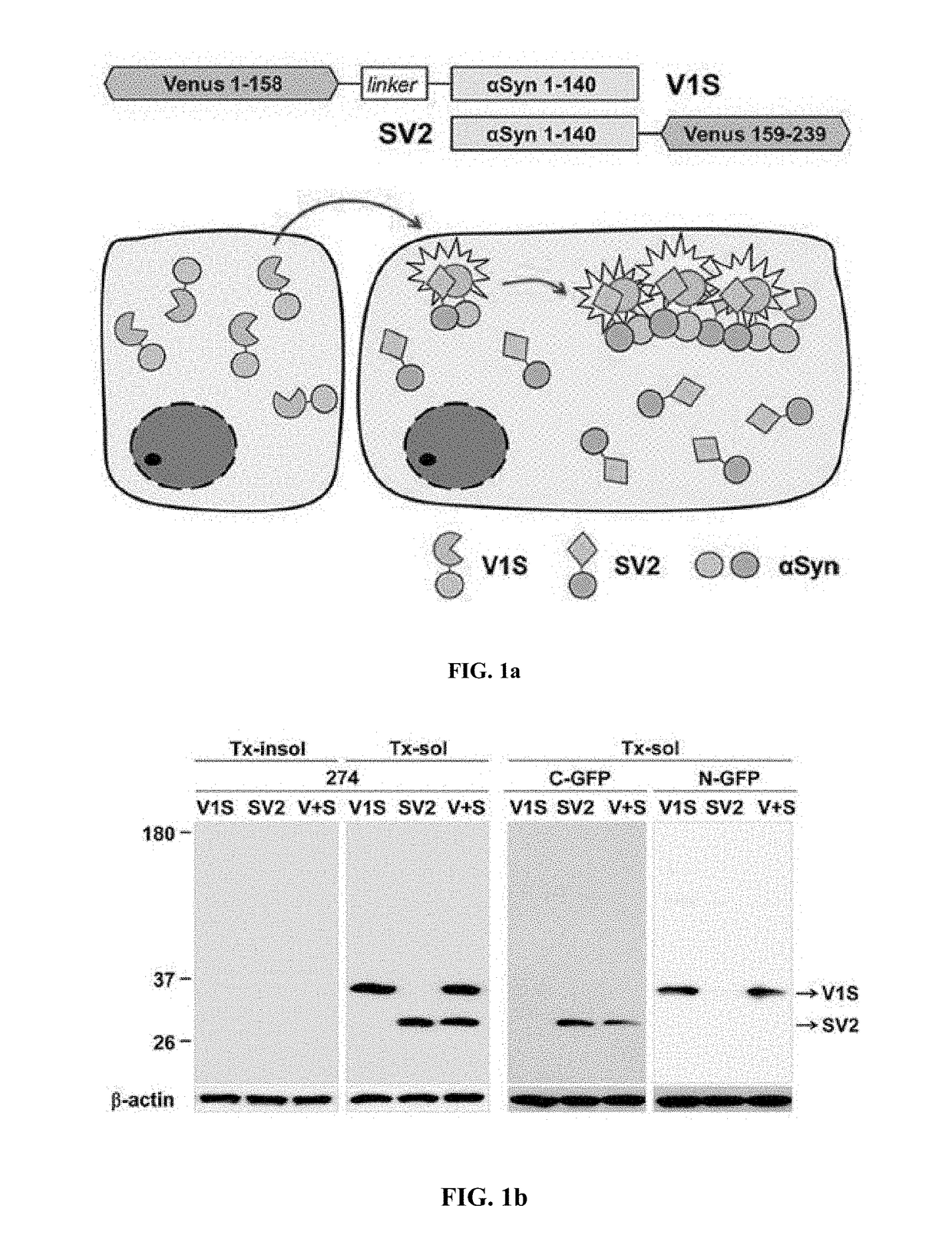
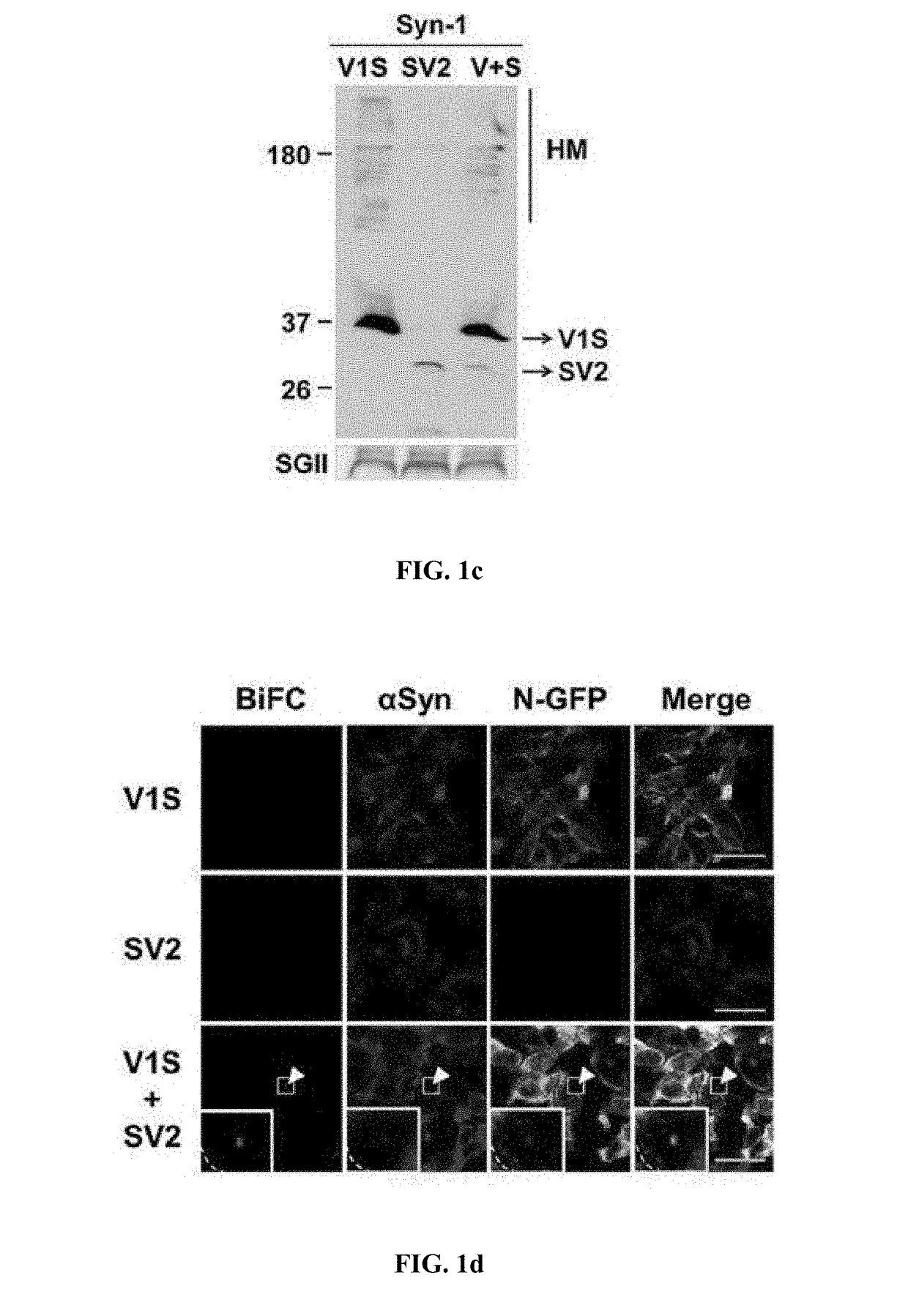
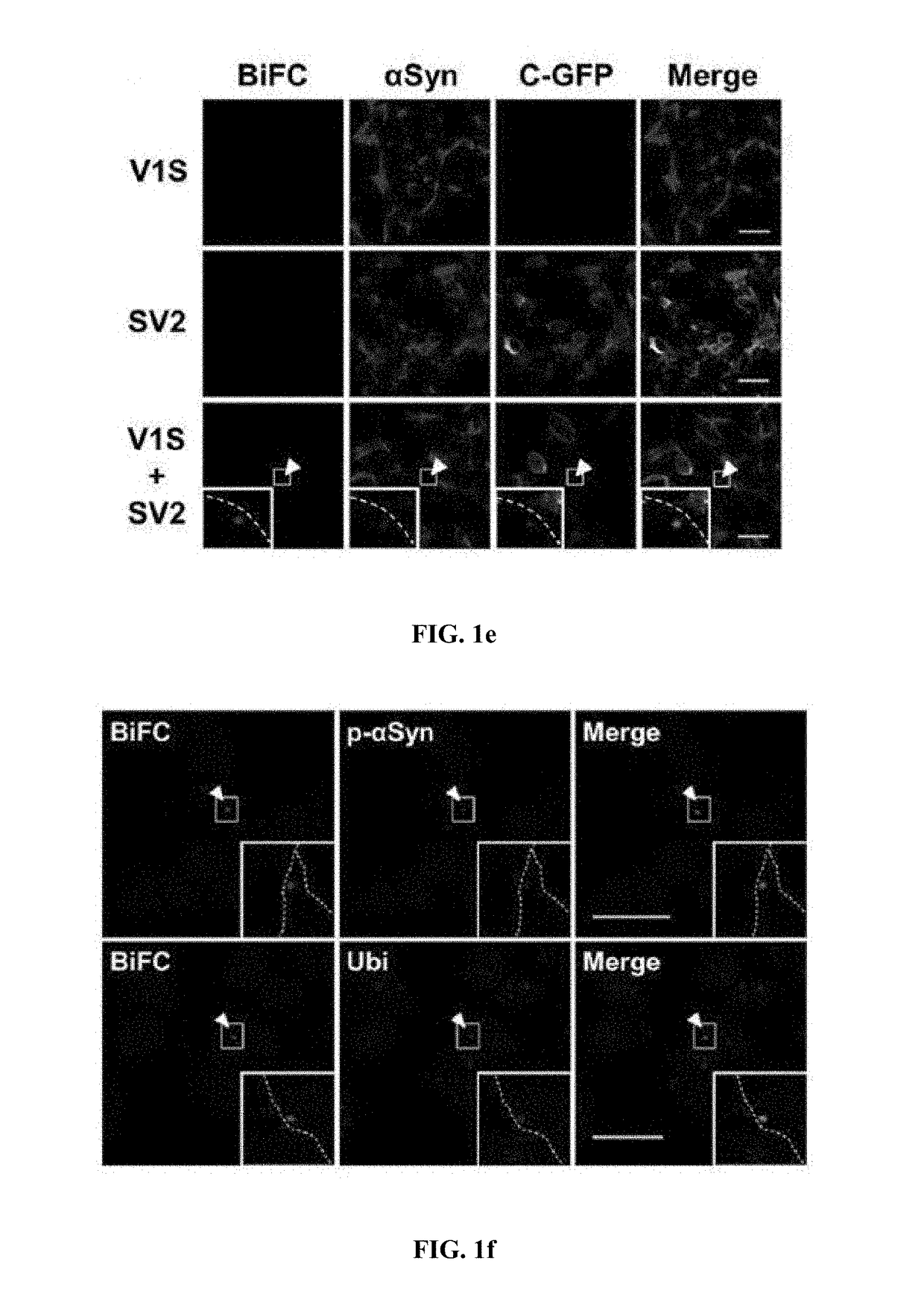
Method for measuring cell-to-cell transmission of alpha-synuclein aggregates using bimolecular fluorescence complementation system and method for screening a substance for preventing or treating neurodegenerative disease using the same
ActiveUS20160123961A1Restoring activity of proteinSlow spreadCompounds screening/testingCompound screeningProtein aggregationModel system
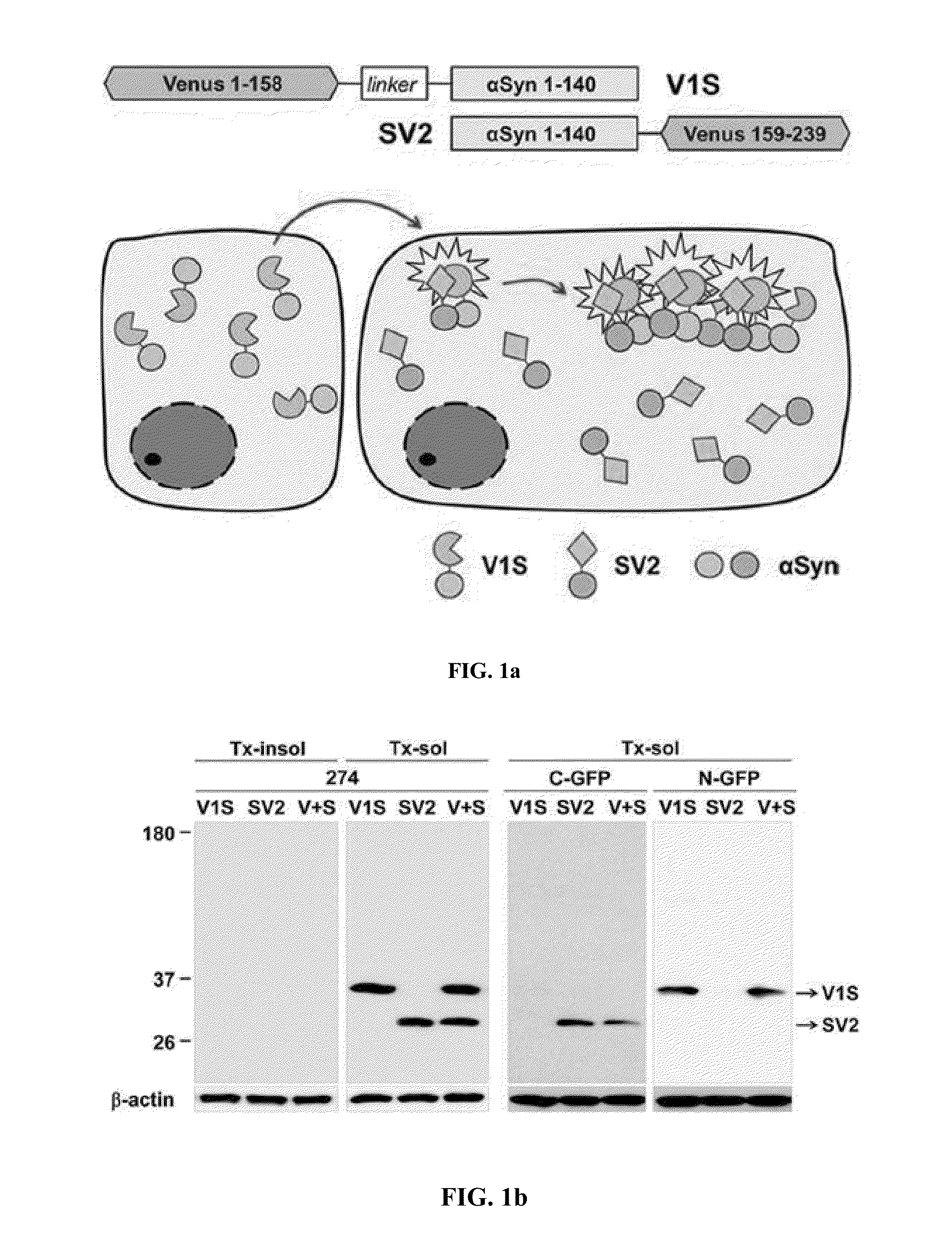
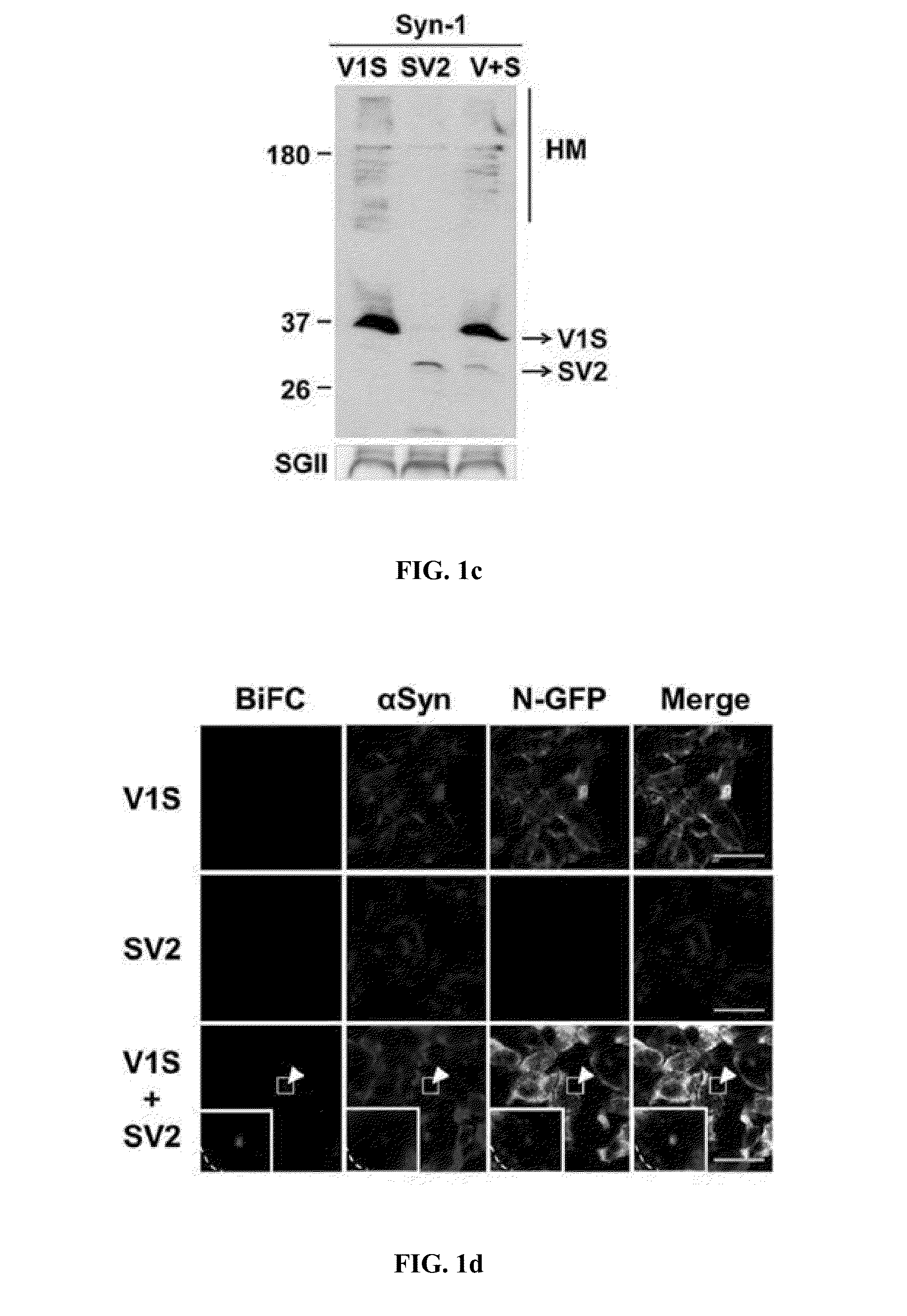
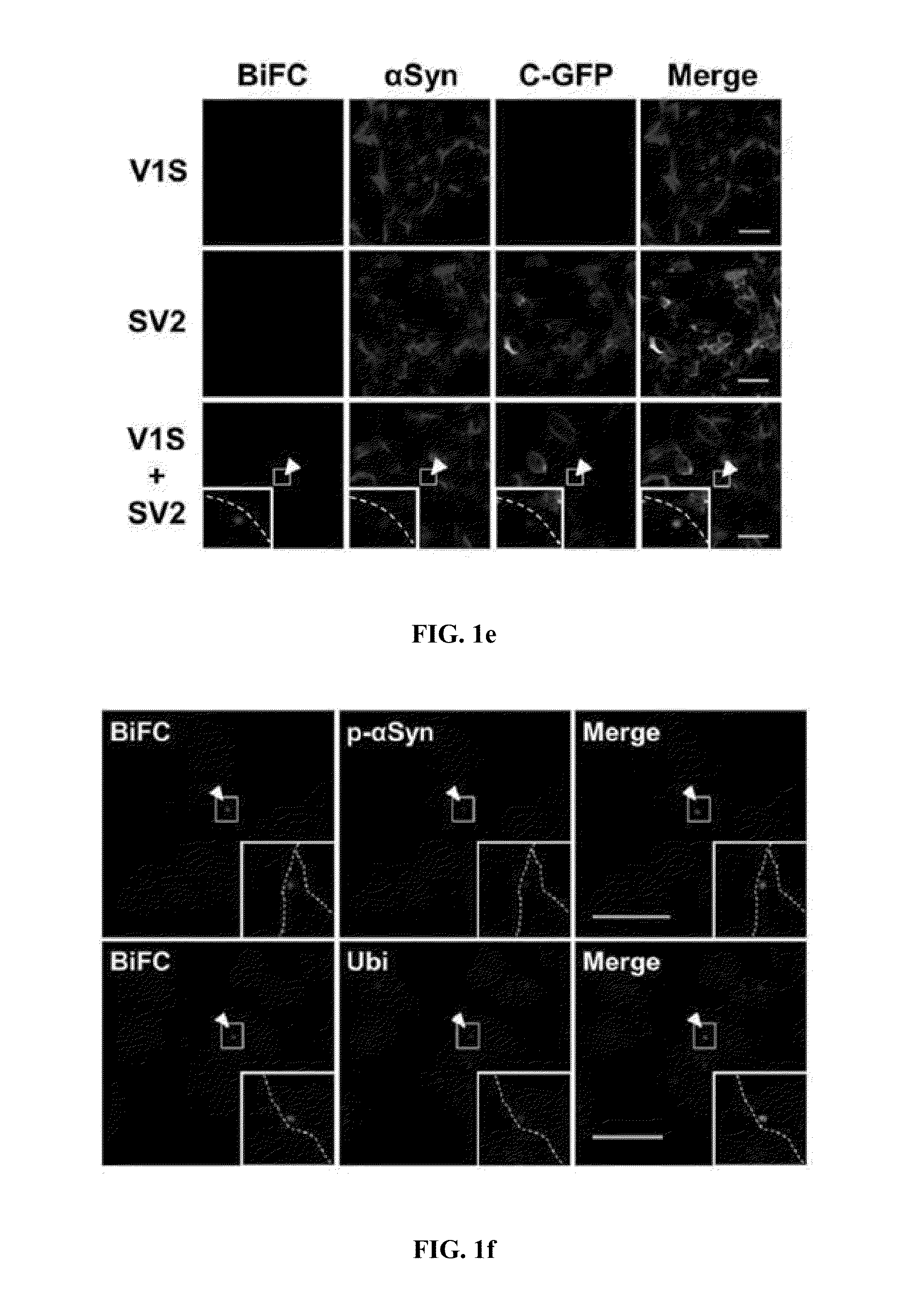
The present disclosure relates to dual-cell model and Caenorhabditis elegans model systems for measuring neuron-to-neuron transmission of protein aggregates, and more particularly to transgenic cell and animal model systems expressing fusion proteins of N-terminus or C-terminus of fluorescent proteins with α-synuclein proteins, methods for measuring continuous cell-to-cell transmission of α-synuclein aggregates using the same, and methods for screening substances for preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:NEURAMEDY CO LTD
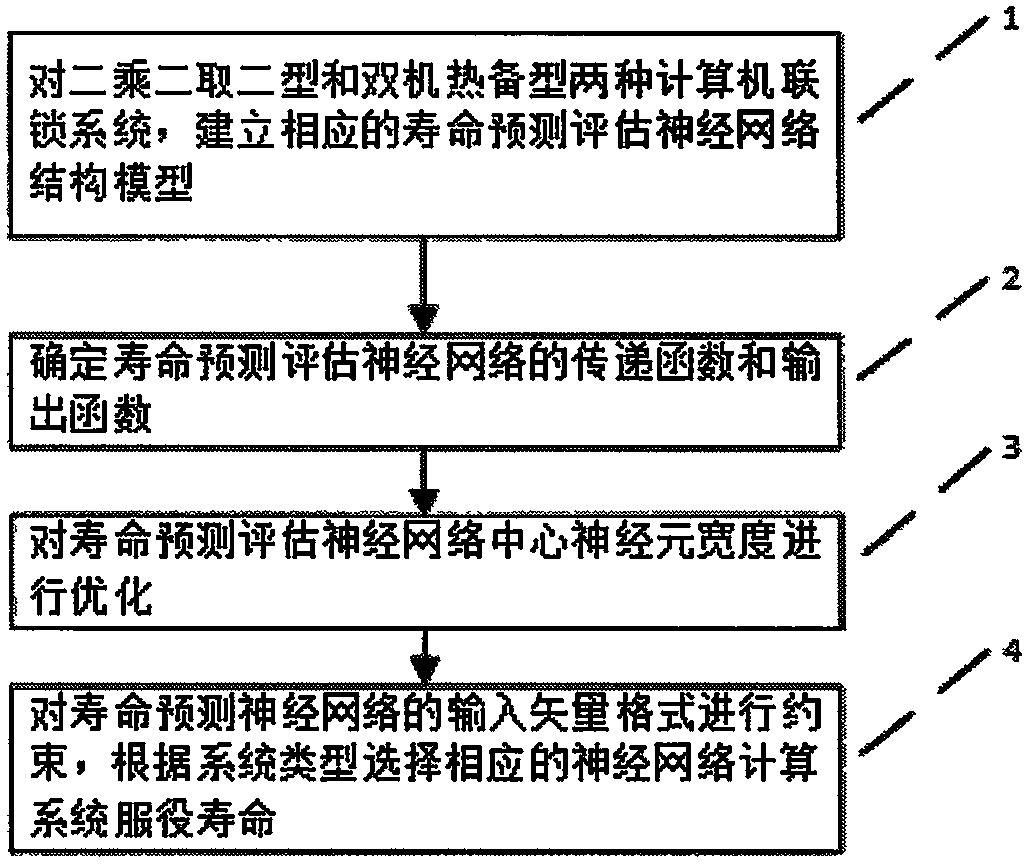
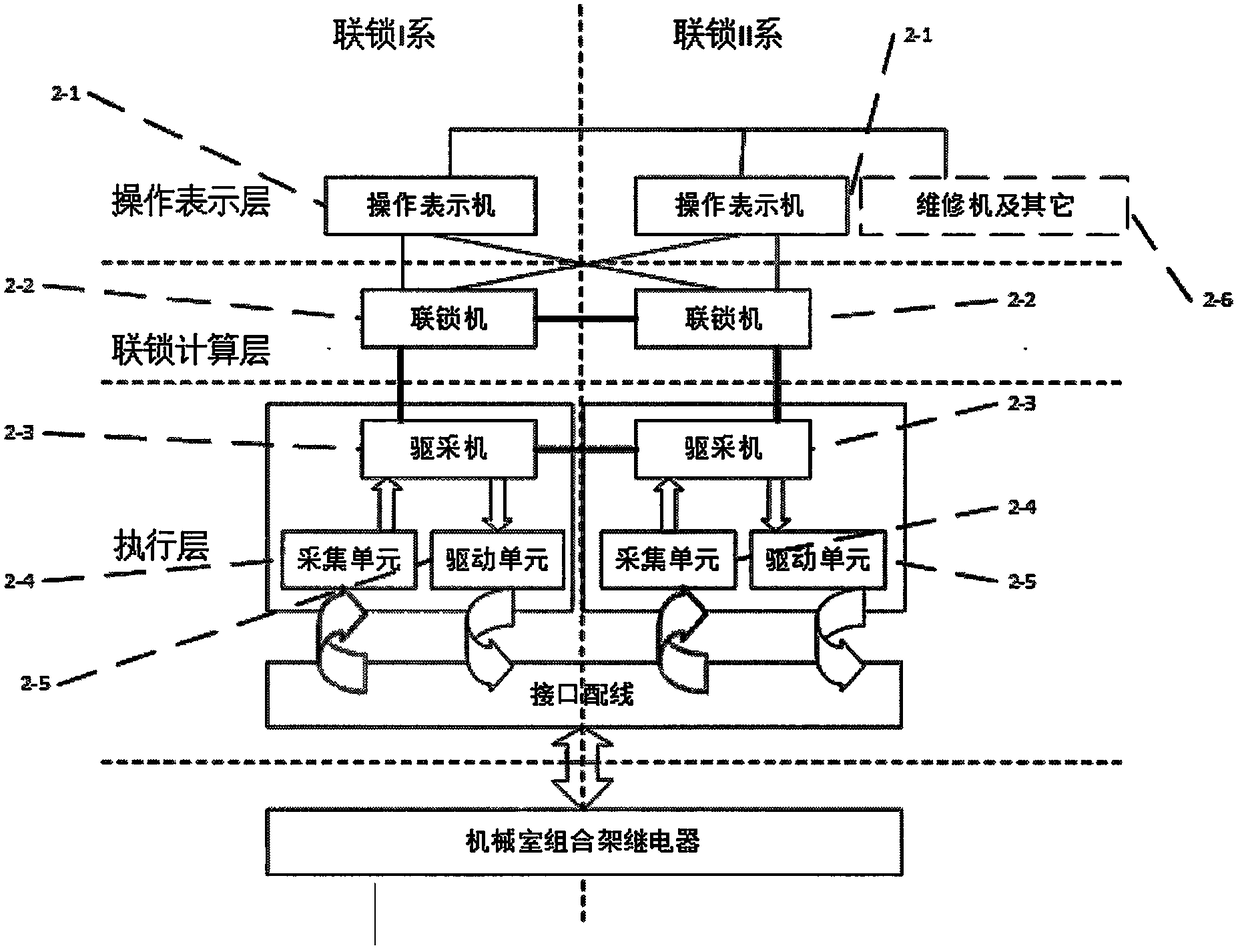
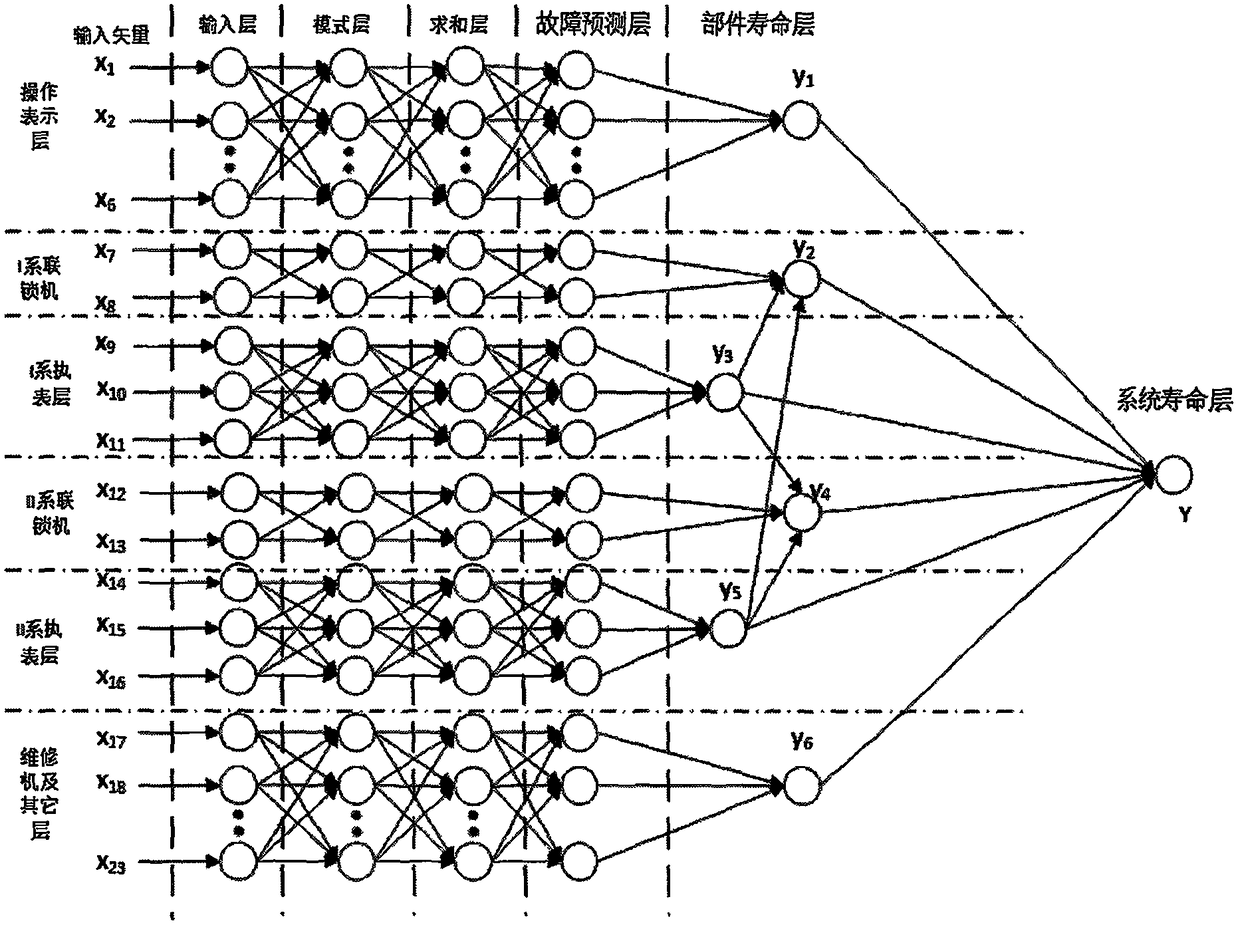
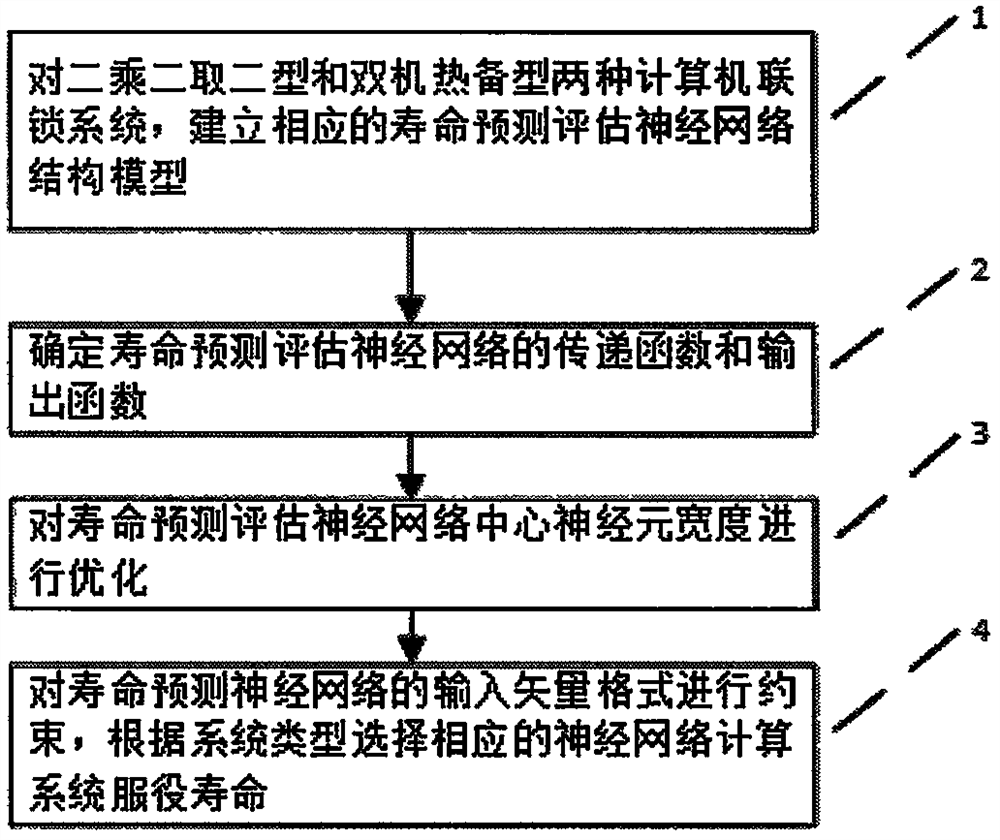
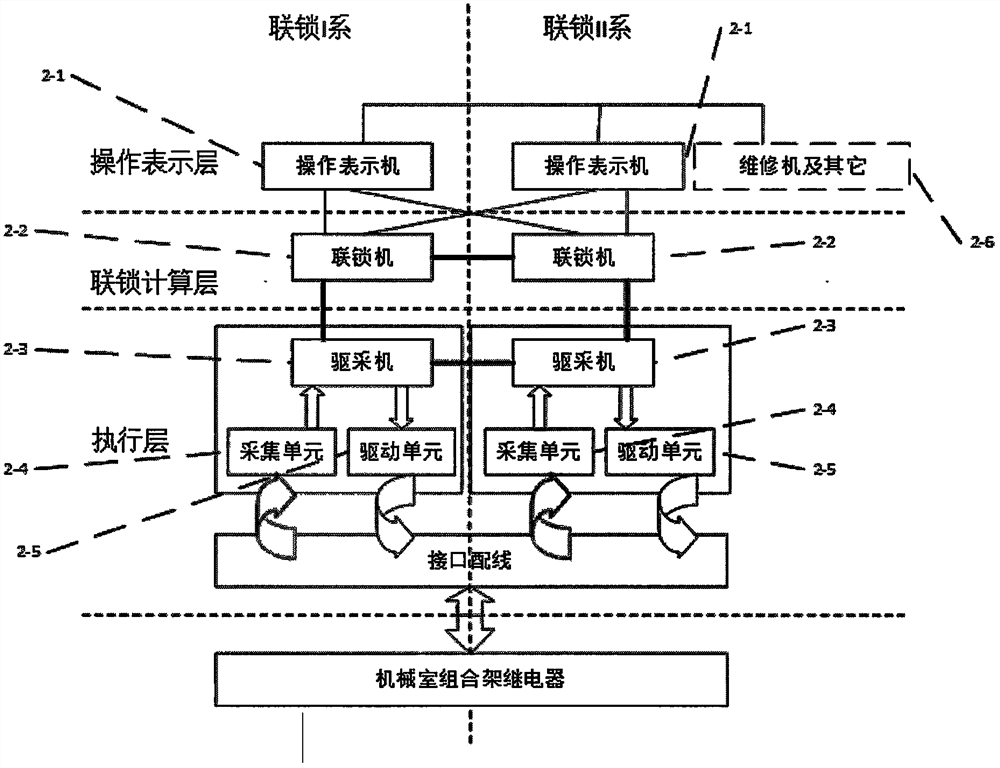
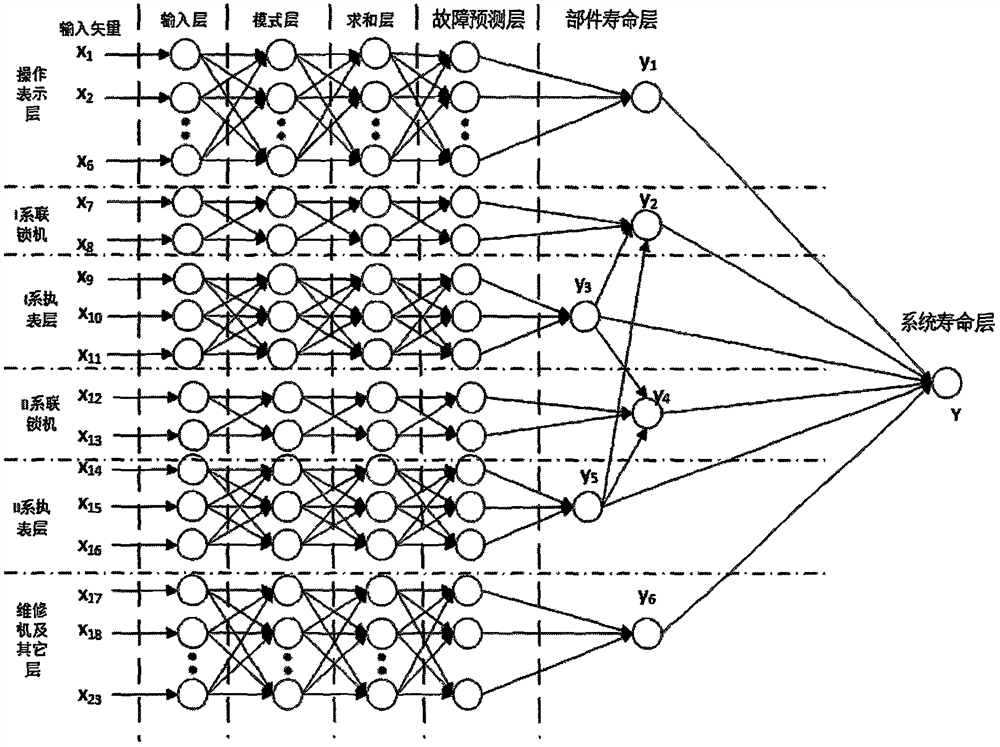
Method for predicting and evaluating service life of computer interlocking system
InactiveCN108107864AIn line with the actual situationImprove accuracyProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringEngineeringArtificial intelligence
The invention belongs to the technical field of rail traffic control operation and maintenance, and provides a method for predicting and evaluating the service life of a railway signal computer interlocking system based on a neural network. The method comprises the following steps: first, designing life prediction neural network structure models for double-machine hot standby and double 2-vote-2 computer interlocking systems respectively; then, improving the accuracy of prediction by controlling the neuron transfer function and output function of a life prediction neural network and optimizingthe center neuron width; and finally, constraining the format of the input vector of the life prediction neural network based on operation equipment fault data, and predicting and evaluating the service life of the interlocking systems. The results of example verification show that compared with other methods, the method of the invention is more in line with the actual operation of the interlocking systems, has high prediction accuracy and can effectively support the operation safety of the systems and improve the rate of return on investment of interlocking equipment.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAYS CORPORATION +1
High frequency magnetic foot stimulation
ActiveUS10716951B2Reduce transmissionComfortable seatElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
High frequency repetitive magnetic pulses may be used to treat pain in the foot of a person by relaxing the muscle and reducing communication of pain signals by neurons in the treatment region. A device is disclosed, which is floor mounted and incorporates a cooling mechanism and heat sink to allow high frequency magnetic stimulation to the person's foot.
Owner:WAVE NEUROSCI INC
Induced modulation of neuronal transmission
Owner:PETTINELLI EUGENE EUSTIS
Method for measuring cell-to-cell transmission of α-synuclein aggregates using bimolecular fluorescence complementation system and method for screening a substance for preventing or treating neurodegenerative disease using the same
ActiveUS9757402B2Reduce formationShorten the progressCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseModel system
The present disclosure relates to dual-cell model and Caenorhabditis elegans model systems for measuring neuron-to-neuron transmission of protein aggregates, and more particularly to transgenic cell and animal model systems expressing fusion proteins of N-terminus or C-terminus of fluorescent proteins with α-synuclein proteins, methods for measuring continuous cell-to-cell transmission of α-synuclein aggregates using the same, and methods for screening substances for preventing or treating neurodegenerative diseases.
Owner:NEURAMEDY CO LTD
Self routing unit circuit and control method thereof
ActiveCN102663497BSmall structureEasy to integrate at scalePhysical realisationNeural network systemSelf routing
The invention discloses a self routing unit circuit and a control method thereof. The circuit of the present invention is suitable for a large-scale interconnected neural network system. The synaptic connection of a front neuron and three or more back neurons employ the self routing circuit unit. Three or more branches in parallel connection are provided, and each parallel branch is formed by one or more bipolar resistive memristors. Each branch has a different structure, with differences of the number of the resistive memristors, the connection directions of polarities and parallel and series connection modes, the self routing unit circuit corresponding to specific voltage is formed. According to the circuit of the invention, the circuit can automatically choose to transmit a signal to the back neurons, the circuit is simple, a structure is small and large-scale integration is facilitated; the circuit is a non volatile circuit, and once set, the circuit is not needed to be reset again when a condition is unchanged.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
A two-dimensional material heterojunction memristor and its preparation method
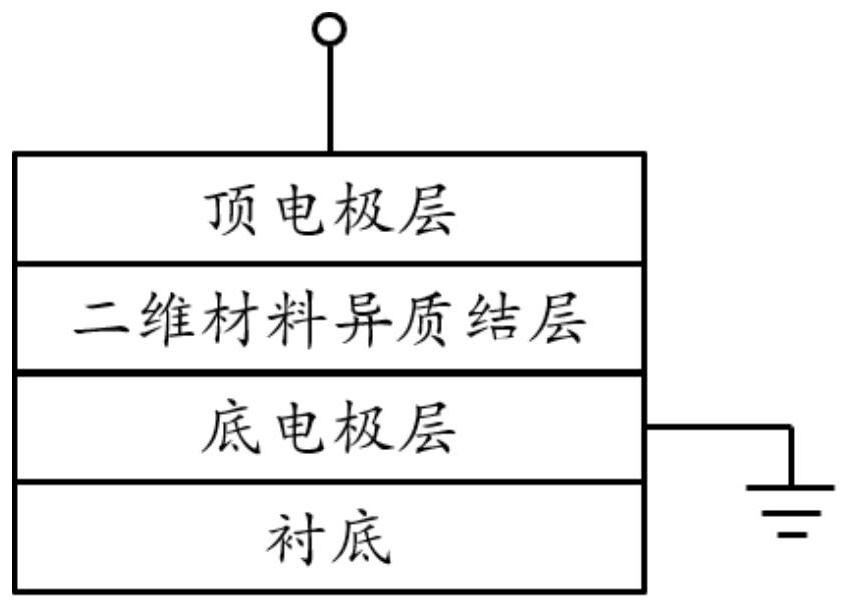
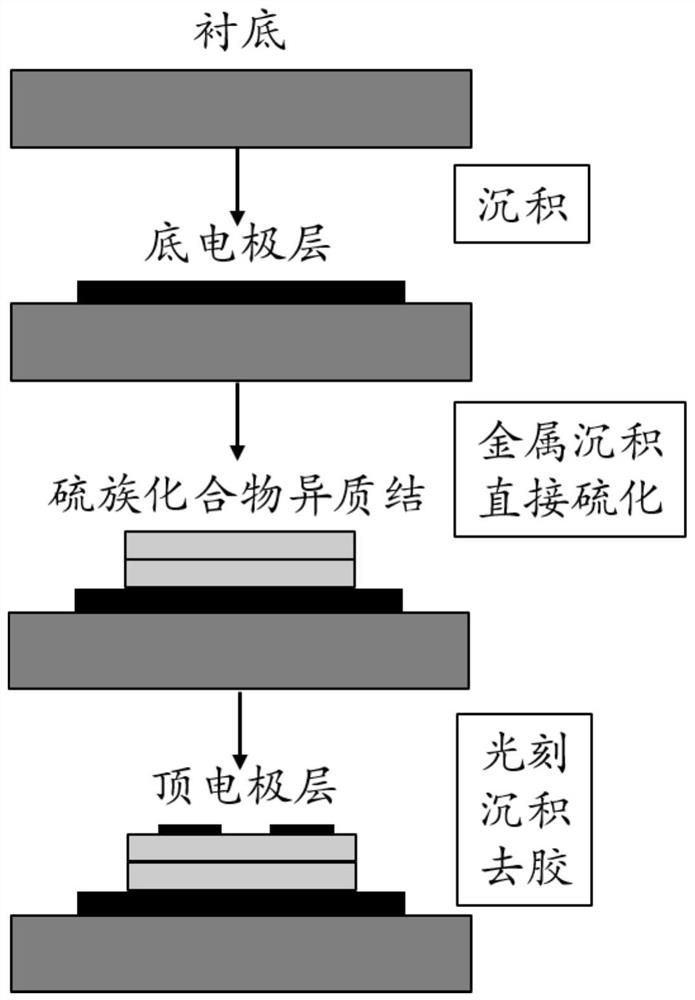
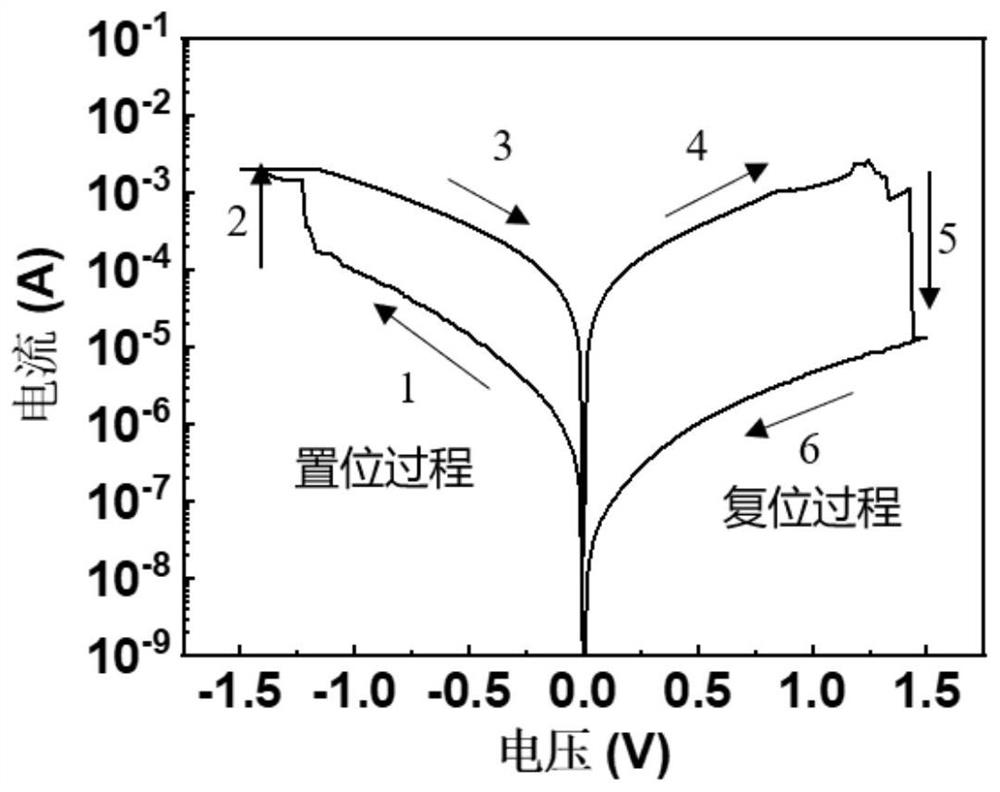
ActiveCN110518117BImprove growth efficiencyAvoid time costNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of microelectronic technology, and discloses a two-dimensional material heterojunction memristor and a preparation method thereof. The memristor includes a substrate, a bottom electrode layer, and a two-dimensional material heterojunction layer from bottom to top And the top electrode layer, wherein, the two-dimensional material heterojunction layer is used as the intermediate dielectric layer, which is a two-layer laminated structure composed of two different metal sulfur compounds, and each layer in the laminated structure corresponds to one of the metal sulfur compounds. The present invention improves the key functional layer materials used in the device and the overall structure design of the device. Compared with the prior art, a new type of memristor is constructed entirely based on two-dimensional materials, which subverts the traditional MIM structure and has a lower The working voltage, fatigue resistance and cycle stability characteristics of the memristor; moreover, the memristor shows a high degree of similarity to the synapse transmission information in the simulated neuron transmission information, and has great application in the development of brain-like structures in the future prospect.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High Frequency Magnetic Foot Stimulation
ActiveUS20200384281A1Reduce transmissionComfortable seatElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsPhysical medicine and rehabilitationEngineering
Owner:WAVE NEUROSCI INC
A Method for Prediction and Evaluation of Service Life of Computer Interlocking System
InactiveCN108107864BIn line with the actual situationImprove accuracyProgramme controlElectric testing/monitoringCentral neuronEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of rail traffic control operation and maintenance, and provides a method for predicting and evaluating the service life of a railway signal computer interlocking system based on a neural network. The present invention: first of all, aiming at the computer interlocking systems of the dual-computer hot standby type and the two-by-two-out type, respectively design a life prediction neural network structure model; secondly, by controlling the neuron transfer function and output of the life prediction neural network function, and the optimization of the width of the central neuron to improve the prediction accuracy; finally, based on the operating equipment failure data, the input vector format constraints of the life prediction neural network are performed to predict and evaluate the service life of the interlocking system. Through example verification, the results show that: compared with other methods, it is more in line with the actual operation of the interlocking system, with high prediction accuracy, which can effectively support the operation safety of the system and improve the return on investment of interlocking equipment.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAYS CORPORATION +1
Method for realizing excitation and inhibition functions of synapses
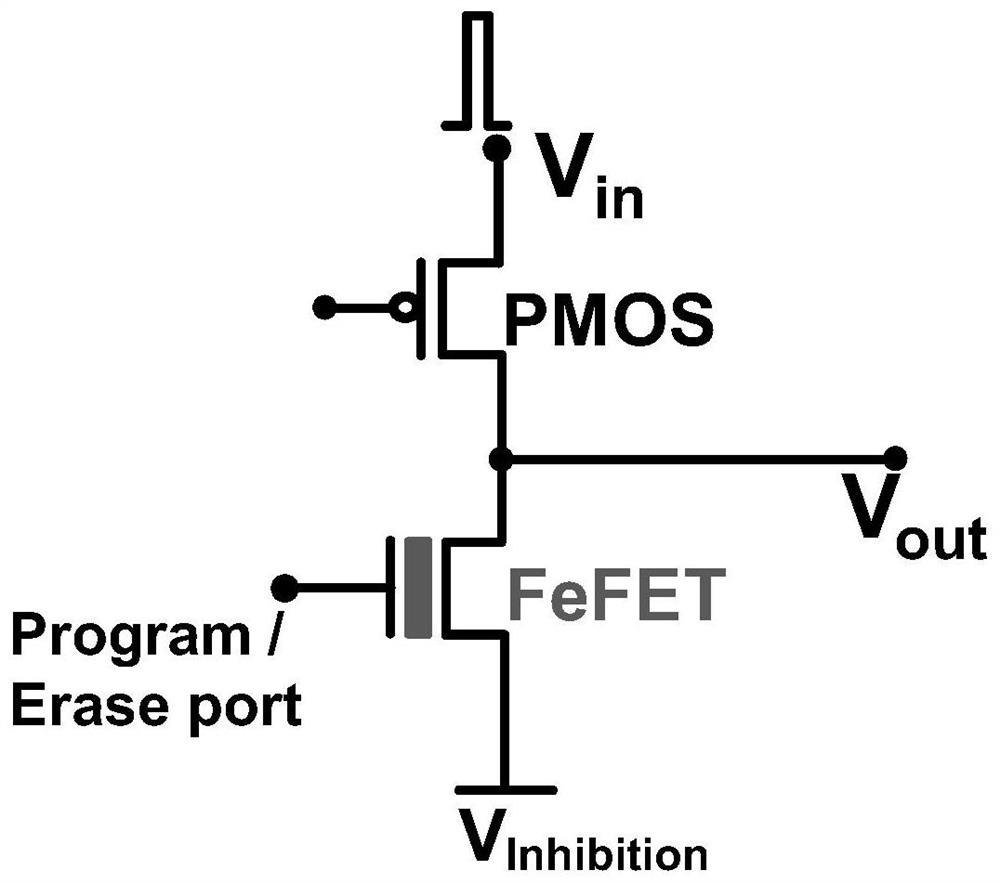
ActiveCN112381217AFunctionalWith non-volatile characteristicsPhysical realisationEnergy efficient computingMOSFETSynapse
The invention provides a method for realizing excitation and inhibition functions of synapses, and belongs to the technical field of synapse hardware in neuromorphic calculation. According to the method, a ferroelectric transistor FeFET and a PMOS are adopted to form a synapse circuit; the FeFET realizes the plasticity and memory characteristics of synapses, the gate end of the FeFET is used as aprogramming (or erasing) port, the source end of the FeFET is biased as suppression voltage, and the drain end of the FeFET is connected to the drain end of the PMOS and used as a synapse voltage output end; the source end of the PMOS is used as the pulse input end of a preceding-stage neuron, and the gate end of the PMOS is biased at a fixed power supply voltage; when the front-stage neuron transmits voltage output, the PMOS channel resistor and the FeFET channel resistor divide the voltage to generate synaptic excitation type or suppression type voltage output. Compared with a traditional MOSFET-based implementation mode, the method has the advantages that the hardware overhead can be remarkably reduced, the driving capacity is high, and large-scale high-interconnection neural network hardware implementation is facilitated.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Transdermal administration of phycotoxins
Pharmaceutical compositions for interfering with neuronal transmission comprising an effective amount of at least one tricyclic 3,4-propinoperhydropurine are disclosed. Preparations for facial rejuvenation are provided that comprise an effective amount of the composition of the invention and a facial cream. Methods of interfering with neuronal transmission comprising topical application of an effective amount of the pharmaceutical compositions of the invention are provided. In another aspect of the invention, effective amounts of the pharmaceutical compositions and a transdermal therapeutic system are provided for transdermal administration of at least one tricyclic 3,4-propinoperhydropurine. The pharmaceutical composition contains at least one at least one tricyclic 3,4-propinoperhydropurine, and may be formulated for transdermal drug delivery. The transdermal drug delivery system may be a laminated composite comprising a backing layer, a drug reservoir, and a means for affixing the composite to the skin.
Owner:ALGENIS SPA
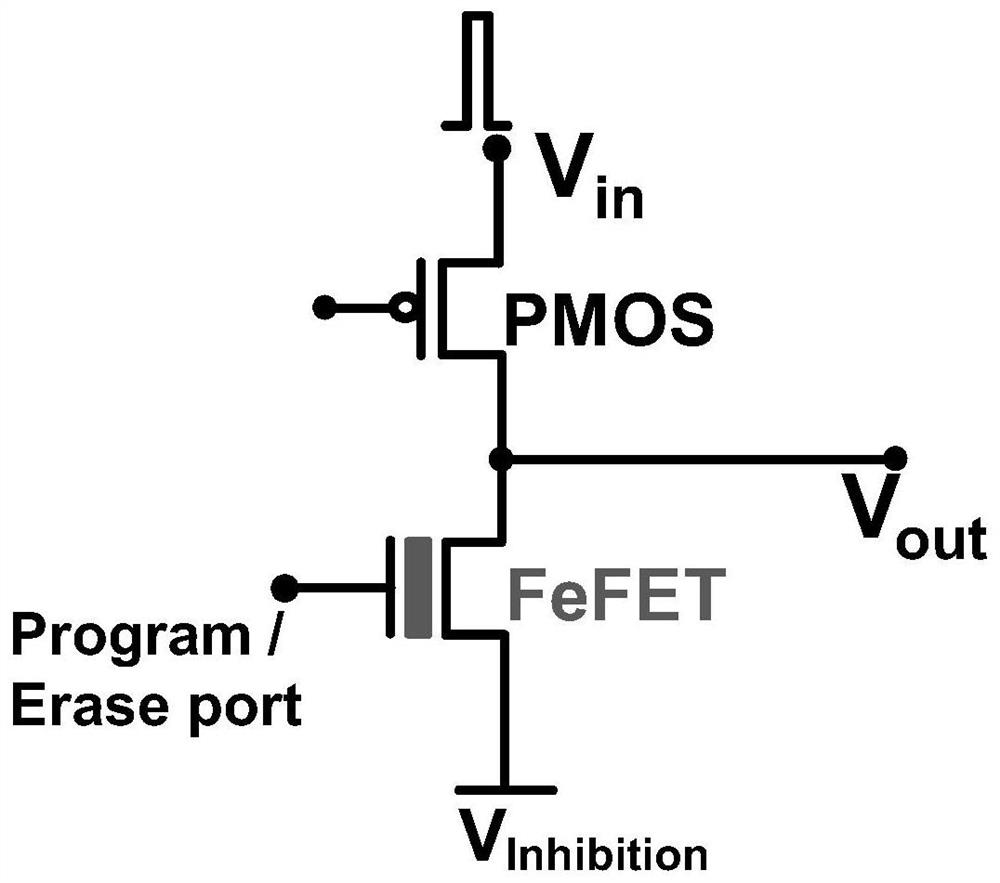
A method for realizing synapse with excitatory and inhibitory functions
ActiveCN112381217BFunctionalWith non-volatile characteristicsPhysical realisationEnergy efficient computingMOSFETSynapse
The invention proposes a method for realizing synapse with excitatory and inhibitory functions, which belongs to the technical field of synaptic hardware in neuromorphic computing. The method uses ferroelectric transistors FeFET and PMOS to form a synaptic circuit; FeFET realizes the plasticity and memory characteristics of synapse, the gate terminal of FeFET is used as a programming (or erasing) port, the source terminal is biased as a suppression voltage, and the drain terminal is connected to PMOS The drain terminal of the PMOS is used as the output terminal of the synaptic voltage; the source terminal of the PMOS is used as the pulse input terminal of the pre-neuron, and the gate terminal is biased at a fixed power supply voltage; The voltage produces either an excitatory or an inhibitory voltage output at the synapse. Compared with the traditional MOSFET-based implementation, the present invention can significantly reduce hardware overhead, has strong drive capability, and is beneficial to the hardware implementation of large-scale highly interconnected neural networks.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
A target recognition method, device, system and computer-readable storage medium
ActiveCN111275742BRealize speed measurementAccurate identificationImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSpiking neural network
Owner:SPIKE VISION (BEIJING) TECHNOLOGY CO LTD
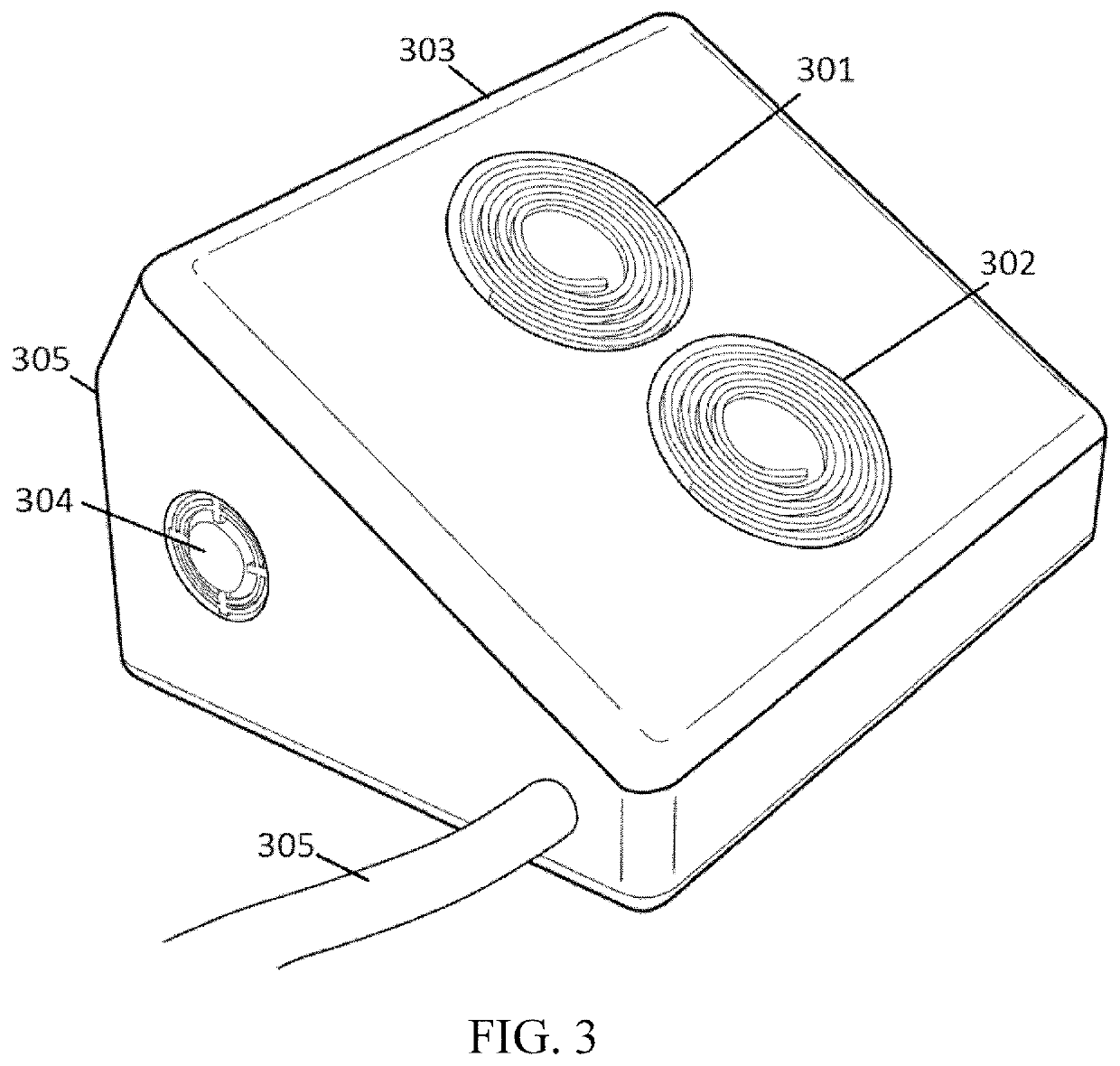
A multi-channel neuron signal acquisition control and transmission device
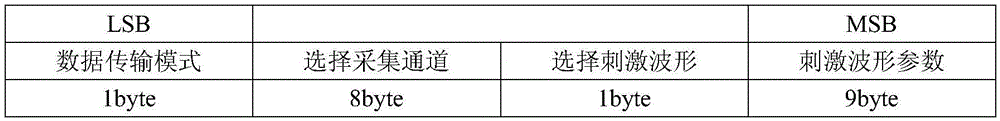
ActiveCN103584851BFlexible controlEasy to operateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsInformation analysisData acquisition
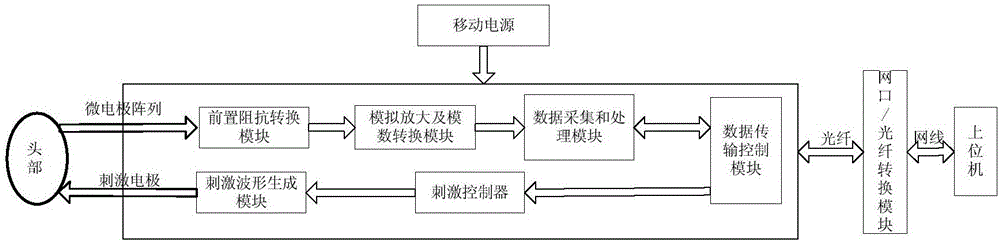
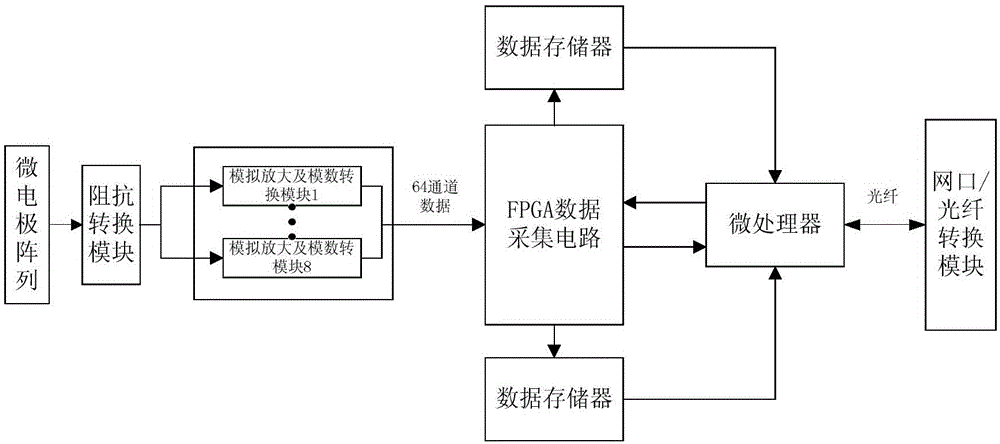
The invention discloses a multichannel neuron signal collection controlling and transmission device which comprises a preposed impedance conversion module, an analog amplification and analog-digital conversion plate, a data collection and processing module, a data transmission control module, a stimulation controller, a stimulation waveform generating module, a mobile power source, a network interface / optical fiber conversion module and an upper computer. Aiming at requirements of nerve electrophysiology on neutron information analysis, an FPGA (field programmable gate array)-based multichannel parallel collection device capable of performing synchronous stimulation is designed, the device is suitable for multichannel neutron signal extraction aiming at animals, and various programmable simulation waveforms are provided. The multichannel neuron signal collection controlling and transmission device is flexible to control and convenient to operate, parts of a control system can be simultaneously controlled to complete various nerve electrophysiological experiments to extract information that a user is interested in through an upper computer command packet, and the device is a novel reliable nerve electrophysiological experiment tool.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com