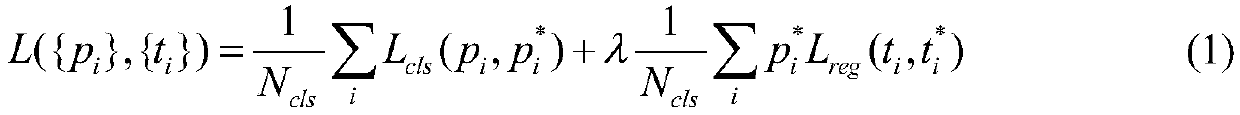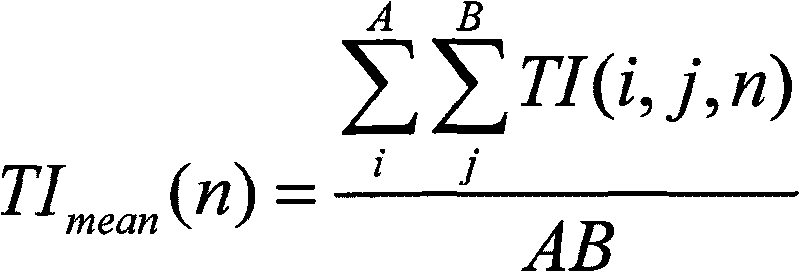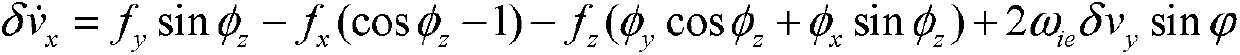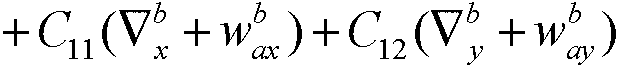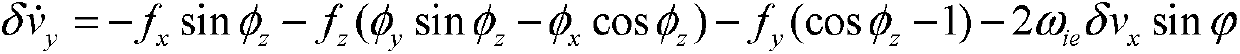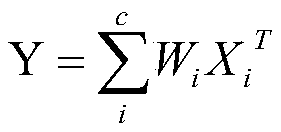Patents
Literature
135results about How to "No loss of precision" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
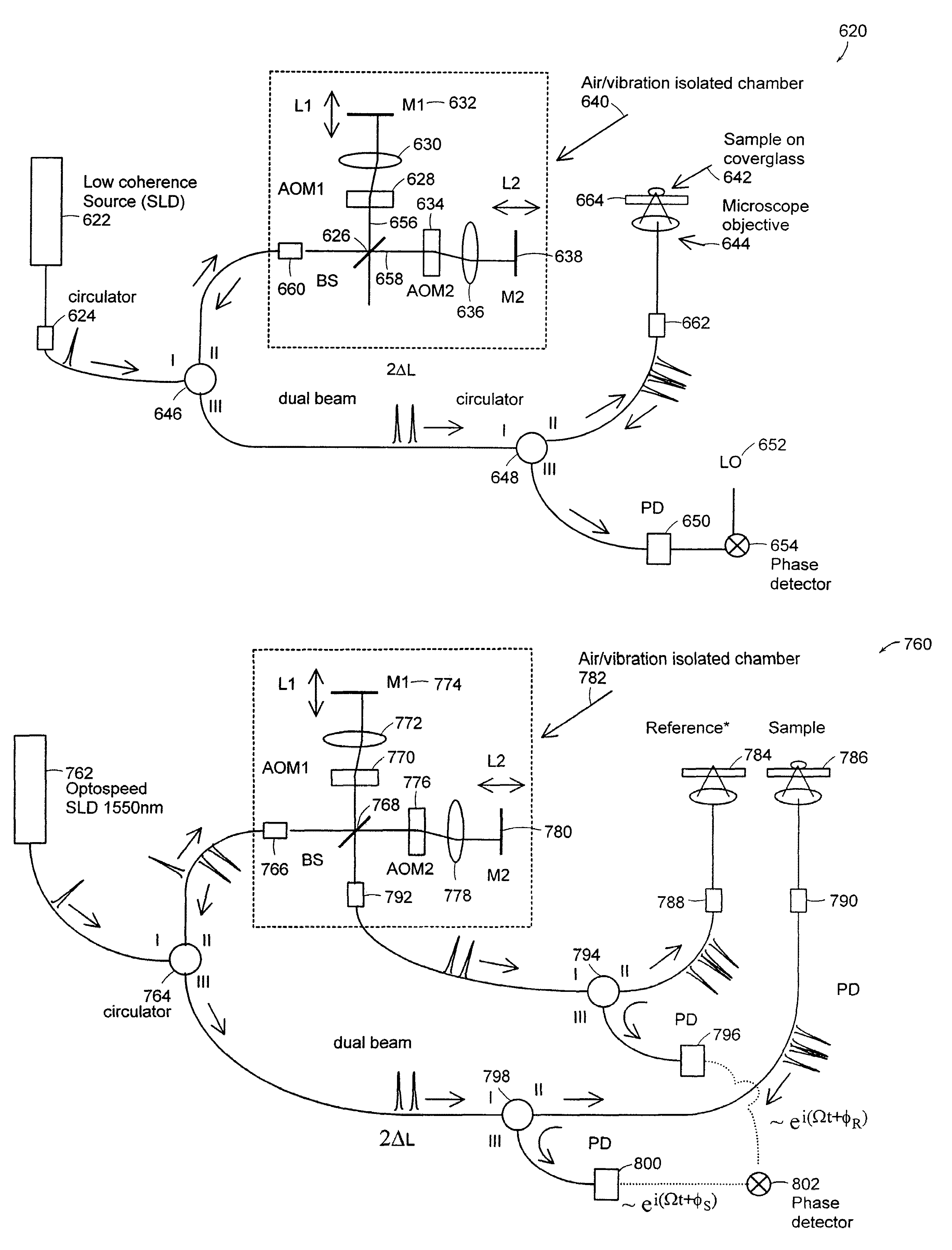
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050057756A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7365858B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Biosensor and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050150762A1No loss of precisionAid stabilityImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteElectrical connection
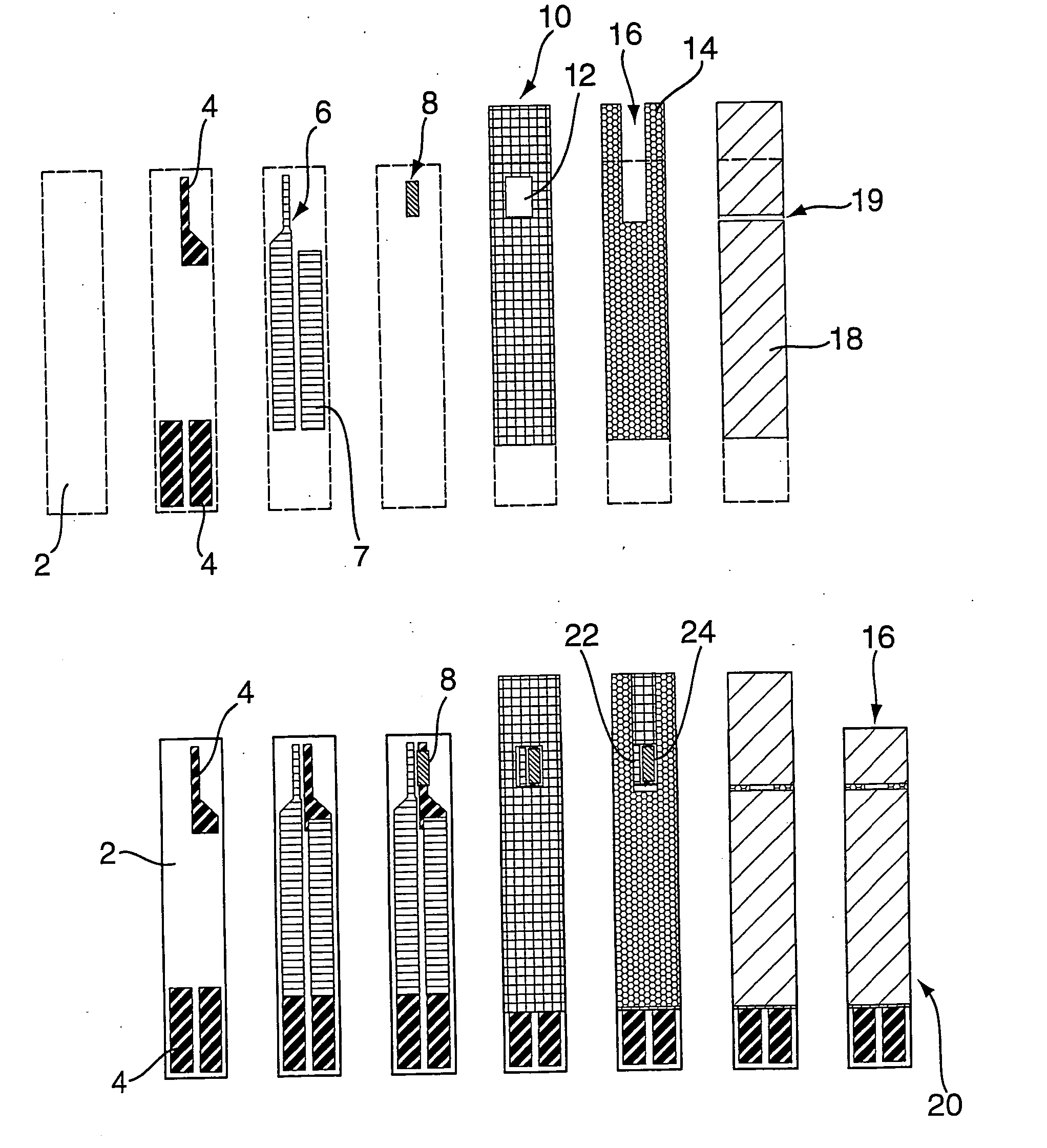
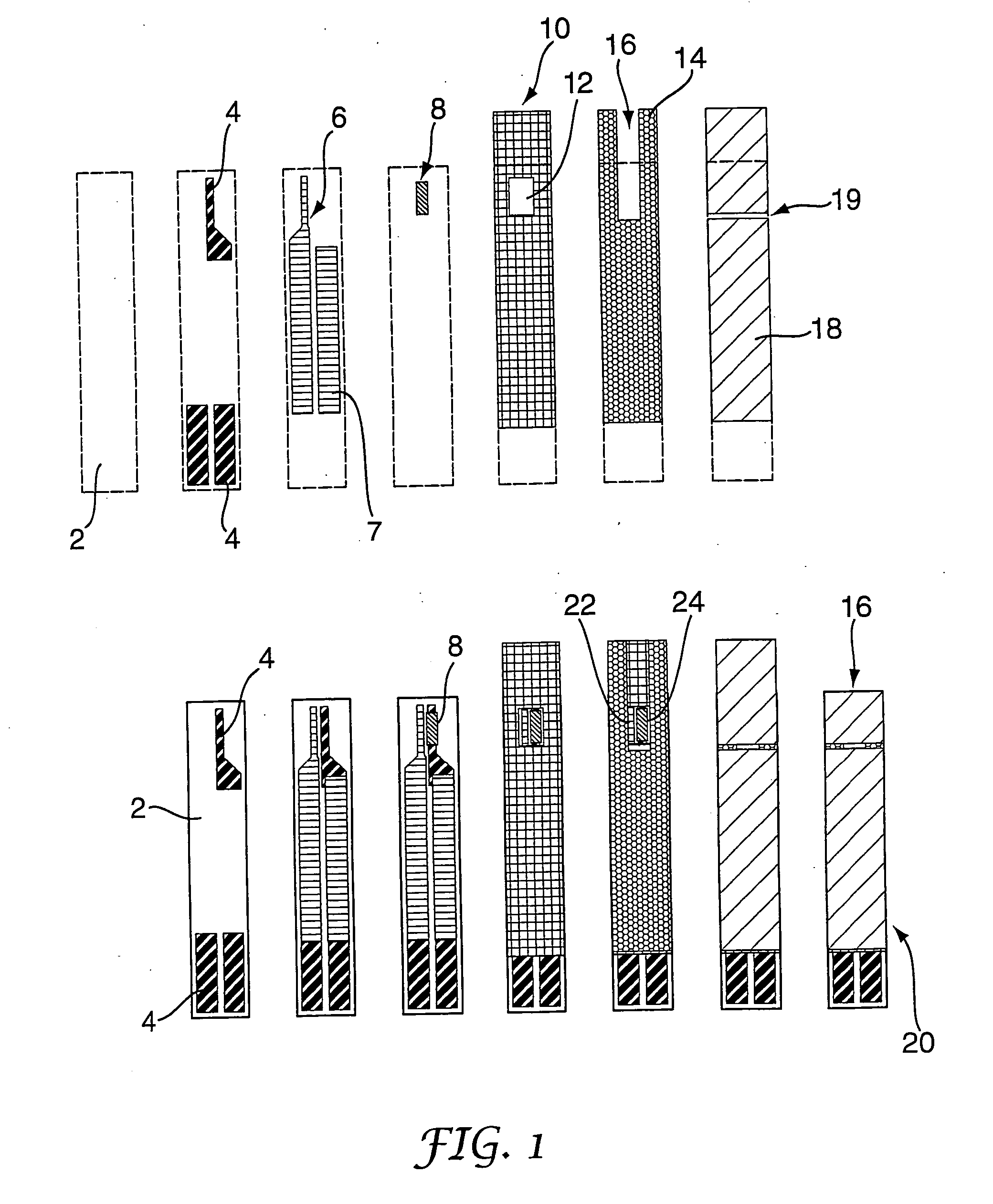
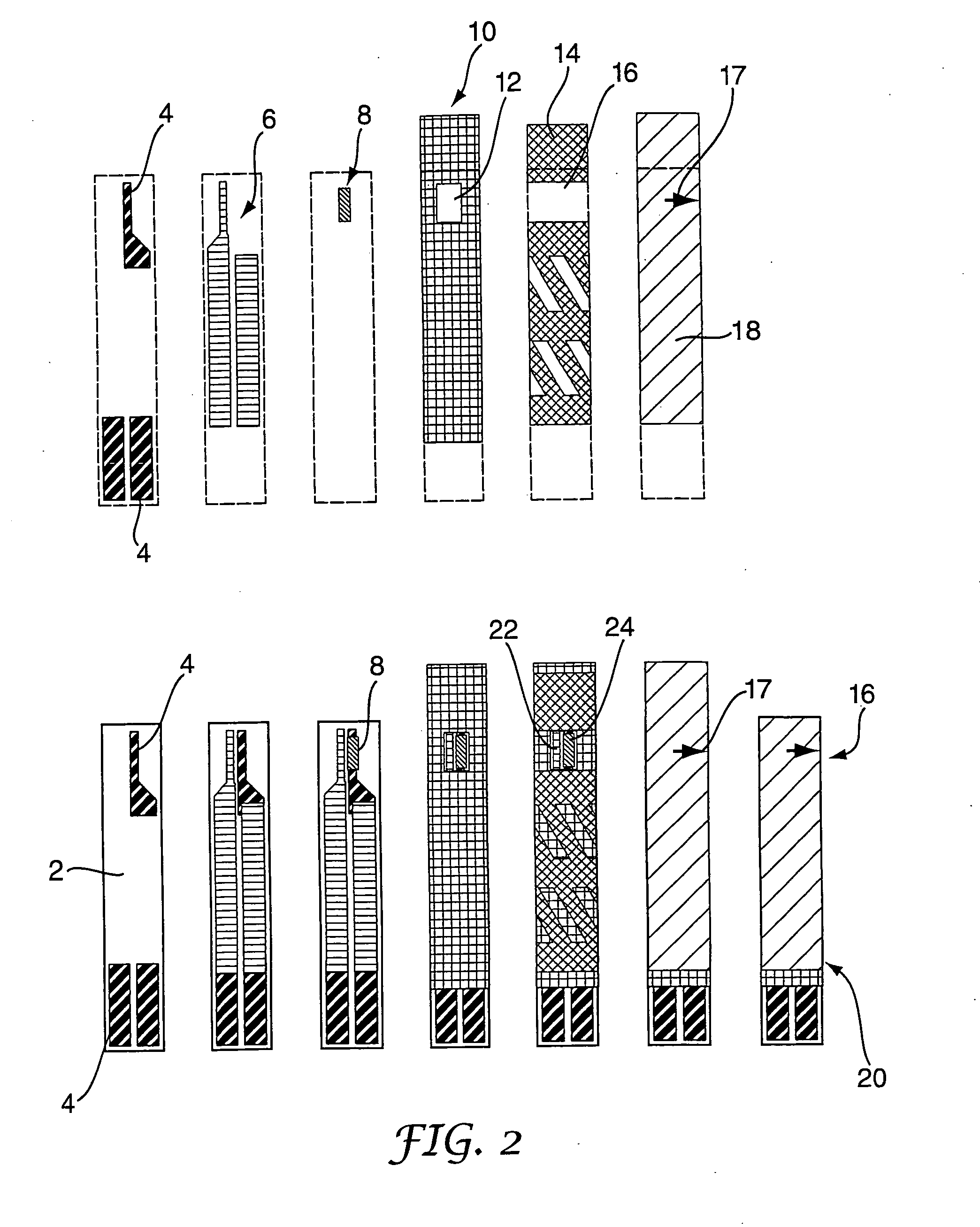
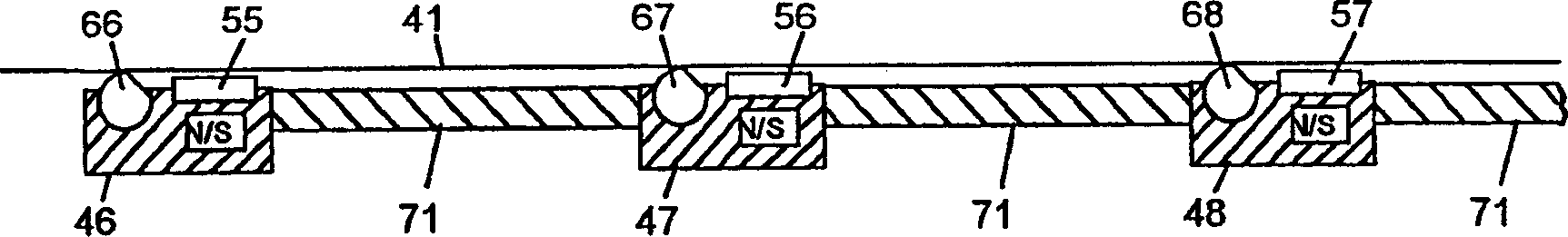
A biosensor (20) for indicating electrochemically the catalytic activity of an enzyme in the presence of a biological fluid containing an analyte acted upon by said enzyme comprises: [0001](a) a first substrate (2); [0002](b) a second substrate (18) overlying at least a part of the first substrate (2); [0003](c) a working electrode (24) on one of the substrates, the working electrode (24) including a catalytically-active quantity of said enzyme; [0004](d) a counter electrode (22) on one of the substrates; [0005](e) conductive tracks (4, 6) connected to said working (24) and counter (22) electrodes for making electrical connections with a test meter apparatus; [0006](f) a spacer layer (14) having a channel (16) therein and disposed between the first substrate (2) and the second substrate (18), the spacer layer channel (16) co-operating with adjacent surfaces to define a capillary flow path which extends from an edge of at least one of said substrates (2, 18) to said electrodes (22, 24); wherein the electrodes (22, 24) are arranged such that a fluid sample which flows along the capillary flow path from said edge will substantially completely cover the working electrode (24) before the fluid sample makes contact with any part of the counter electrode (22).
Owner:HYPOGUARD (UK) LTD
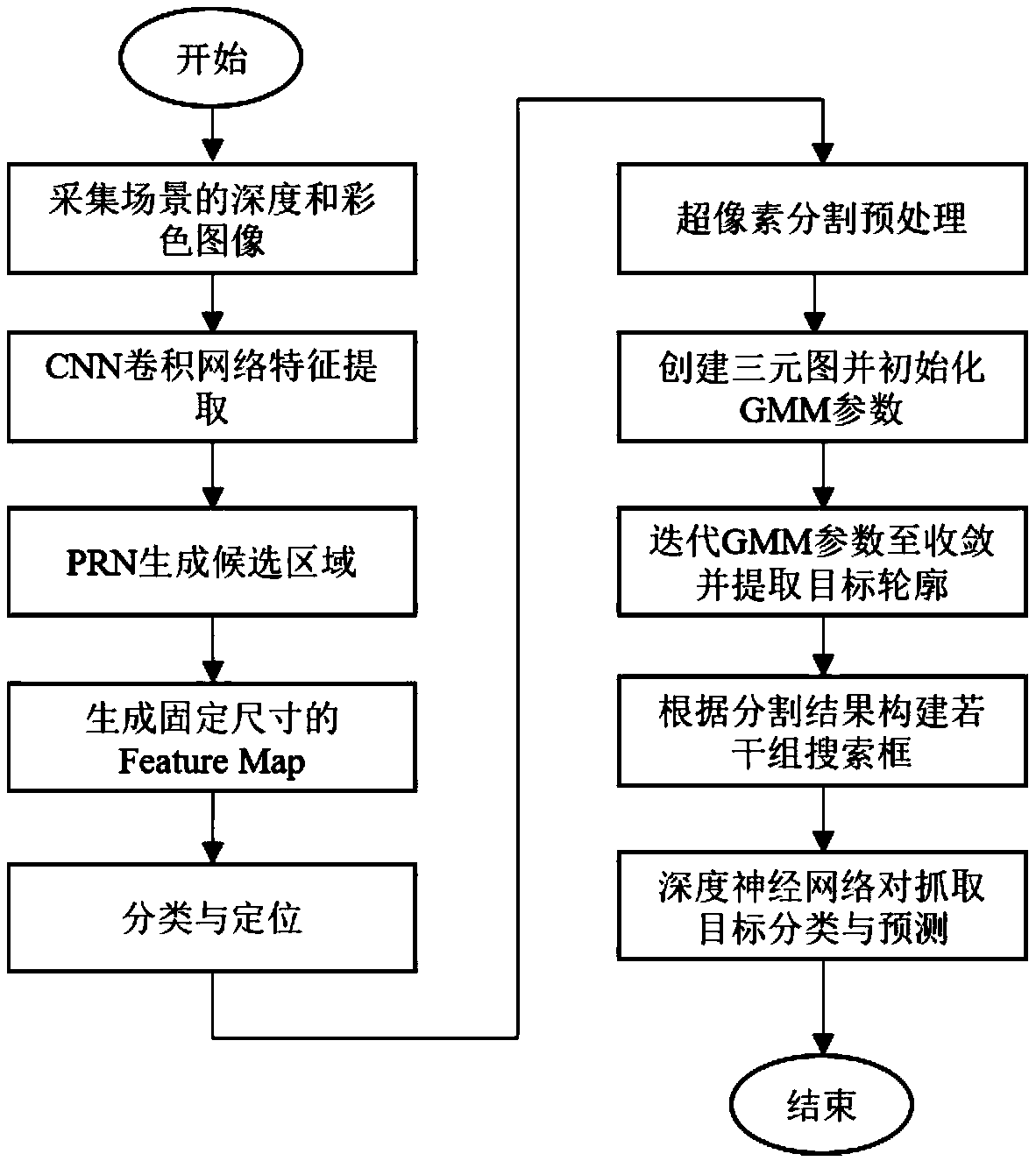
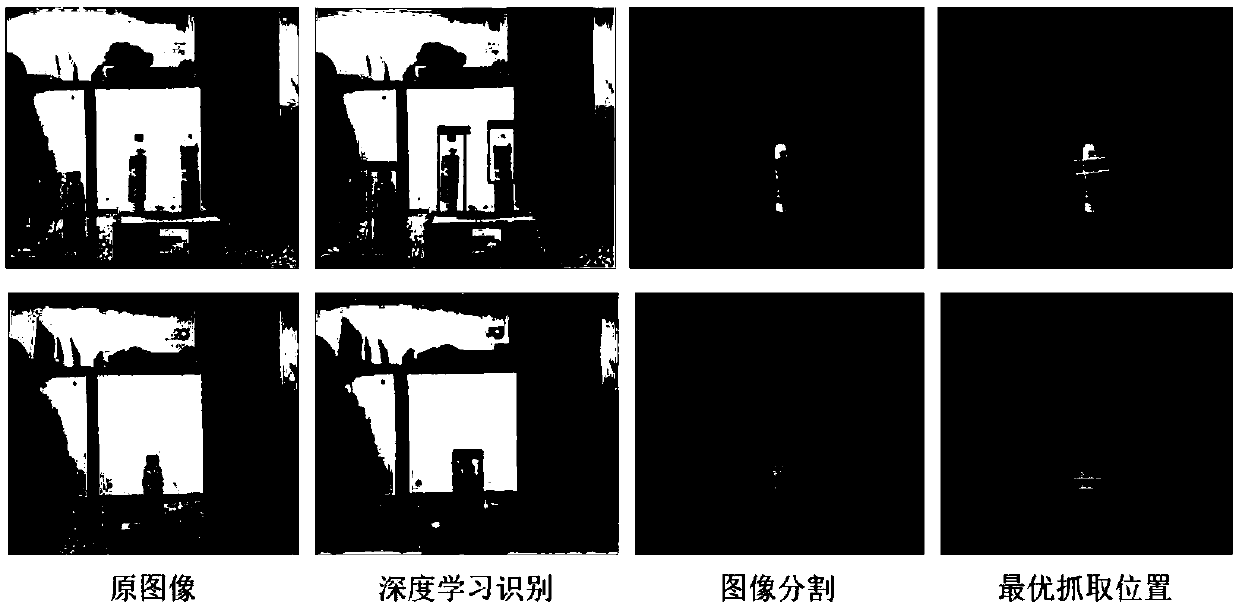
Target identification and capture positioning method based on deep learning
ActiveCN108648233AHigh similarityGuaranteed Segmentation AccuracyImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageLocation detection
The invention discloses a target identification and capture positioning method based on deep learning, and belongs to the field of machine vision. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, utilizing a Kinect camera to collect the depth and the color image of a scene; then, using a Faster R-CNN (Regions with Convolutional Neural Network features) deep learning algorithm to identify ascene target; according to an identified category, selecting a captured target area as the input of a GrabCut image segmentation algorithm; through image segmentation, obtaining the outline of the target so as to obtain the specific position of the target as the input of a cascade neural network for carrying out optimal capture position detection; and finally, obtaining the capture position and the capture gesture of a mechanical arm. Through the method, the instantaneity, the accuracy and the intelligence of target identification and positioning can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
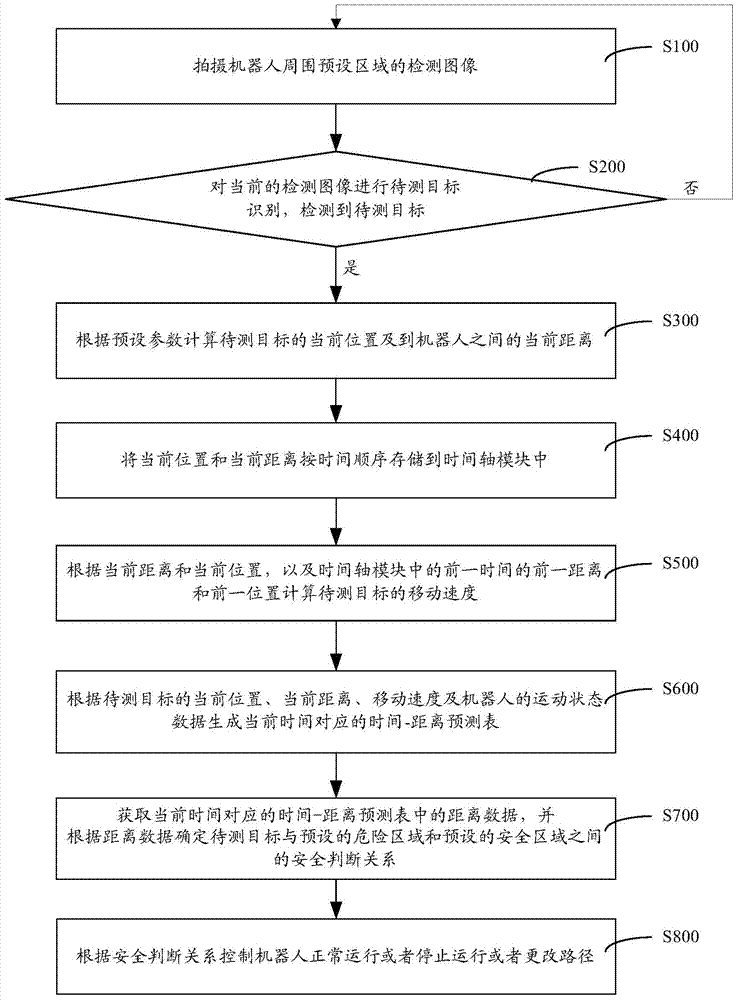
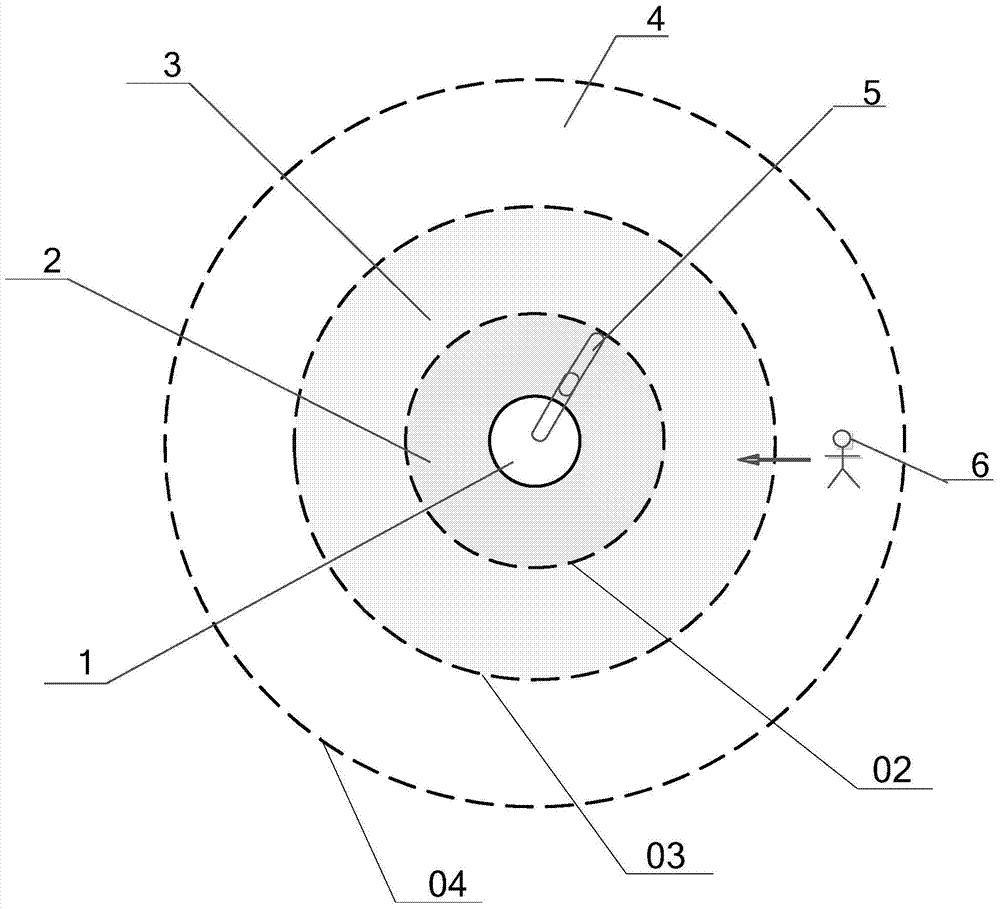
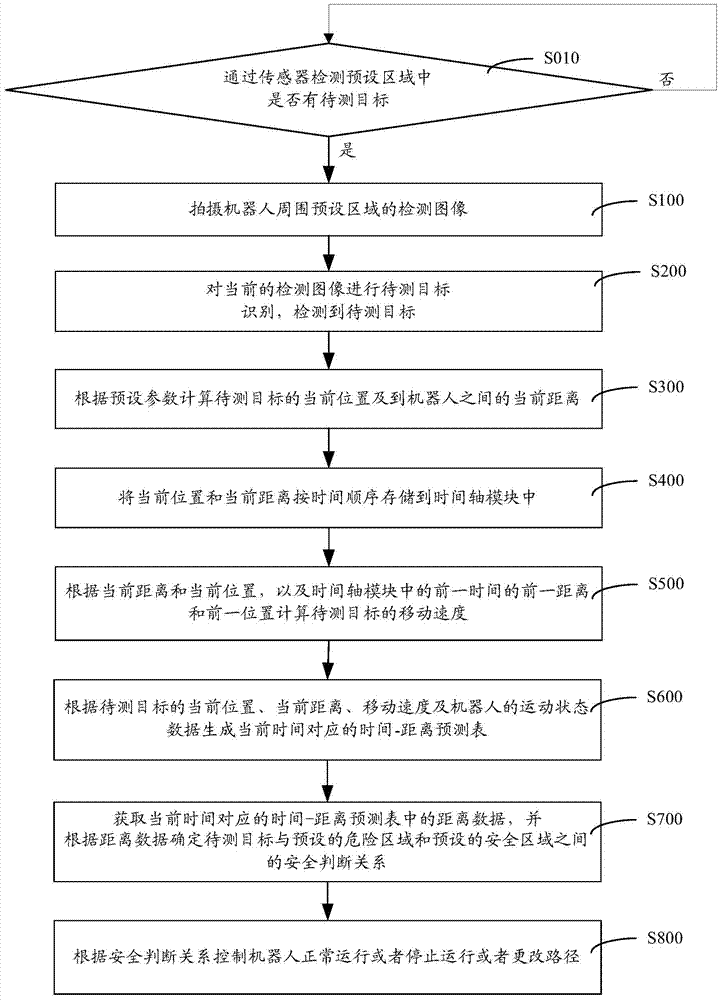
Industrial robot safety protection intelligent control method and system
The invention discloses an industrial robot safety protection intelligent control method and system. The method comprises the following steps that a detection image of a preset area around a robot is taken; to-be-detected target recognition is carried out on the current detection image; if a target to be detected is recognized in the current detection image, the current position and the current distance between the target to be detected and the robot are computed according to preset parameters; the current position and the current distance are stored in a time shaft module according to the time sequence; according to the current distance, the current position and the former distance and former position of the former time in the time shaft module, the moving speed of the target to be detected is computed; according to the current position, current distance and the moving speed of the target to be detected and the moving state data of the robot, the safe judgment relation between the target to be detected and the preset dangerous area as well as between the target to be detected and the preset safe area is determined; the robot is controlled to normally operate or stop operating or change a path according to the safe judgment relation. The safety of staff can be effectively ensured.
Owner:ZHUHAI GREE INTELLIGENT EQUIP TECH RES INST CO LTD +1
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS7557929B2No loss of precisionReduce coherenceOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Citrus recognition method based on improved YOLOv4
ActiveCN111709489AOvercoming memory consumptionOvercome timeCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesPattern recognitionData set
The invention discloses a citrus recognition method based on improved YOLOv4. According to the method, a YOLOv4 network model structure is improved, an up-sampling module and a detection feature map sensitive to a small target are added, and citruses with relatively small individuals can be better identified; sparse training, channel pruning and layer pruning are carried out on a network model obtained through training, the defects of large memory consumption, long recognition time and the like caused by module addition are overcome, clustering is carried out by using a Canopy algorithm and ak-means + + algorithm, and a user can obtain an anchor frame parameter value more suitable for a data set of the user. When citrus recognition is carried out, an improved YOLOv4 network structure is adopted to train a citrus data set, and the obtained model can recognize a target with a small individual more accurately; before a network model is trained, through combination of layer pruning and channel pruning, the depth and the width of the model are compressed, and the training speed is improved on the premise that the precision is not lost; citrus on trees in different periods is recognized, the recognition precision is high, the speed is high, and the requirement for real-time recognition can be met.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
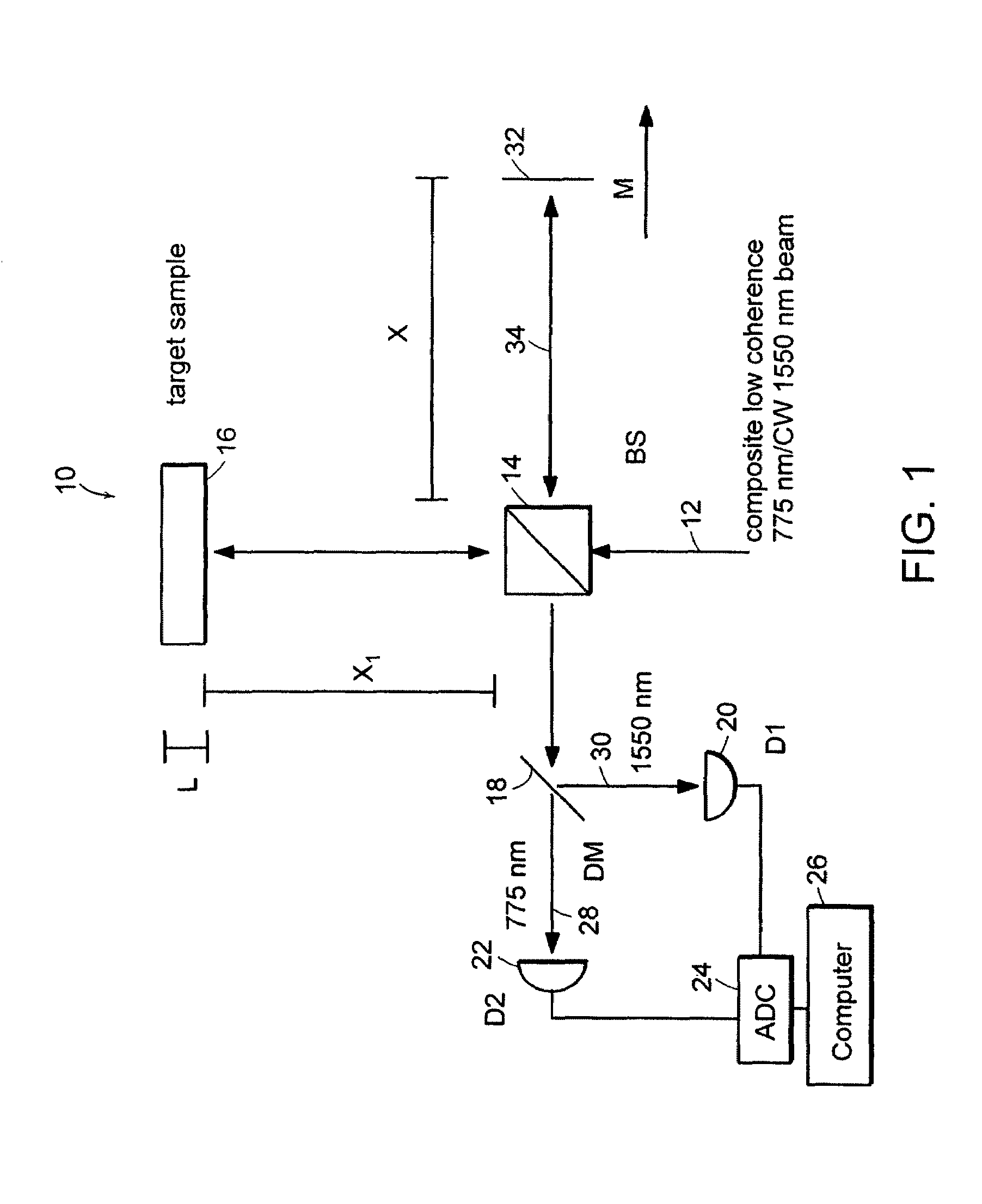
System and method for measuring optical distance
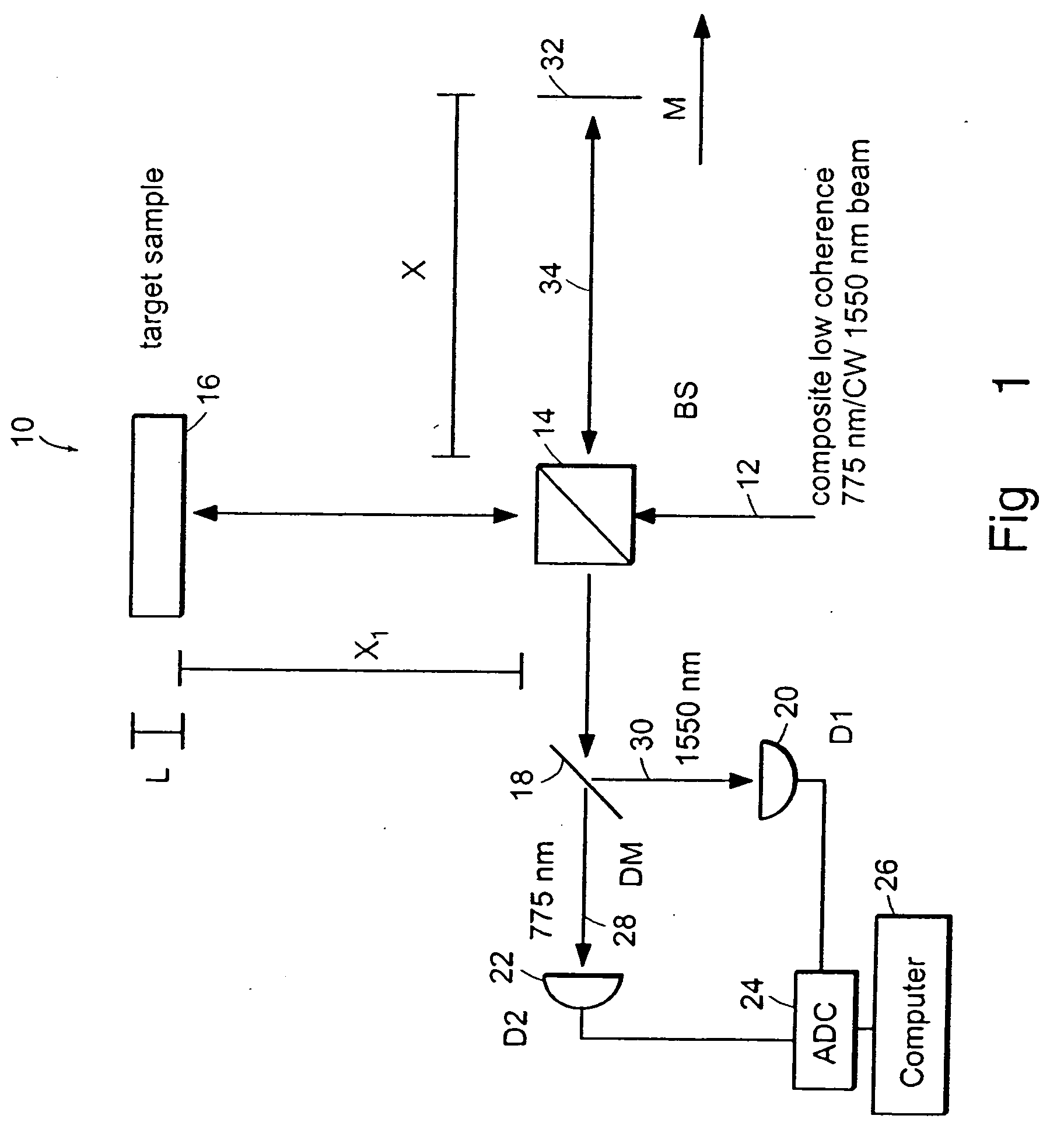
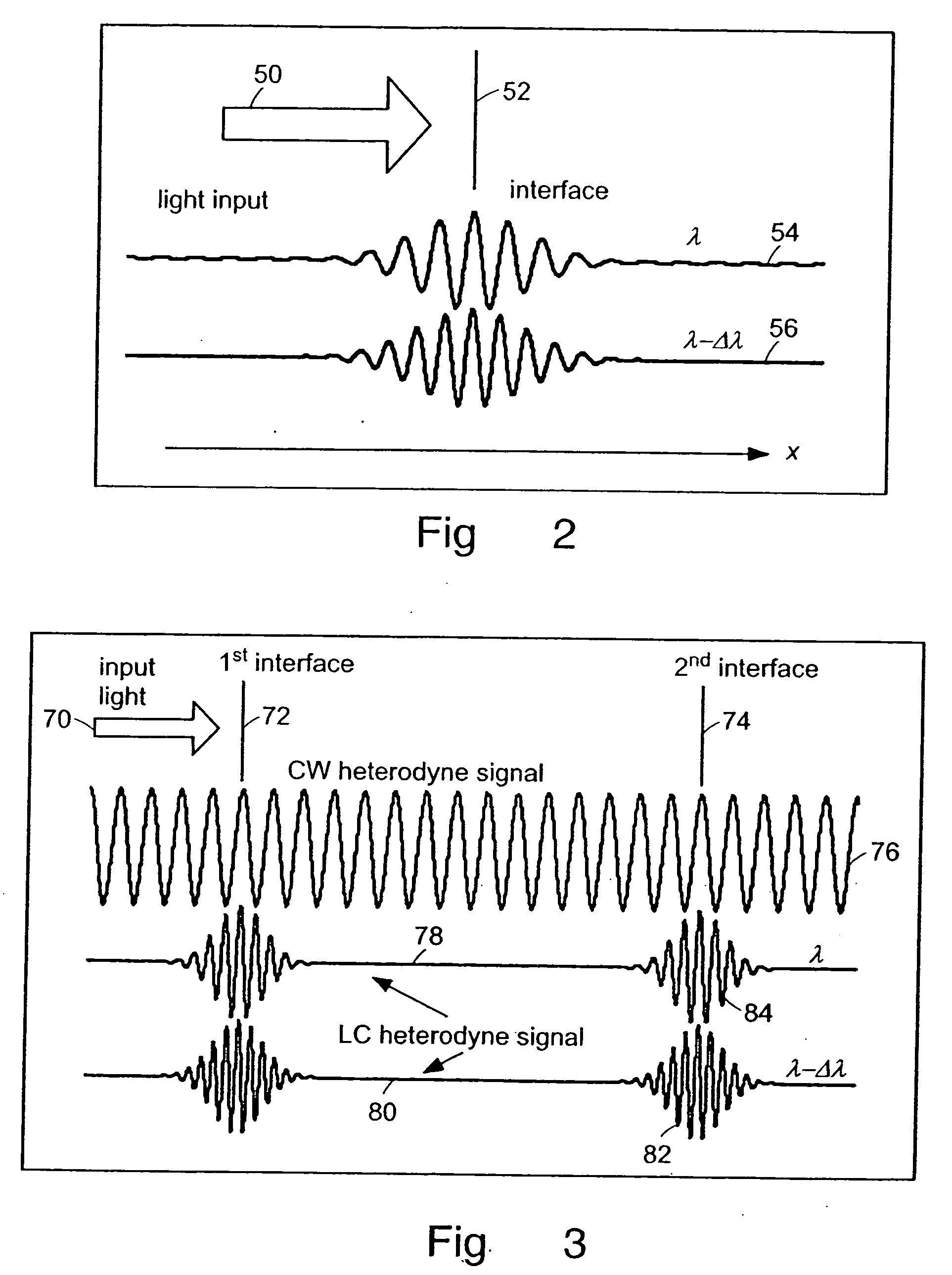
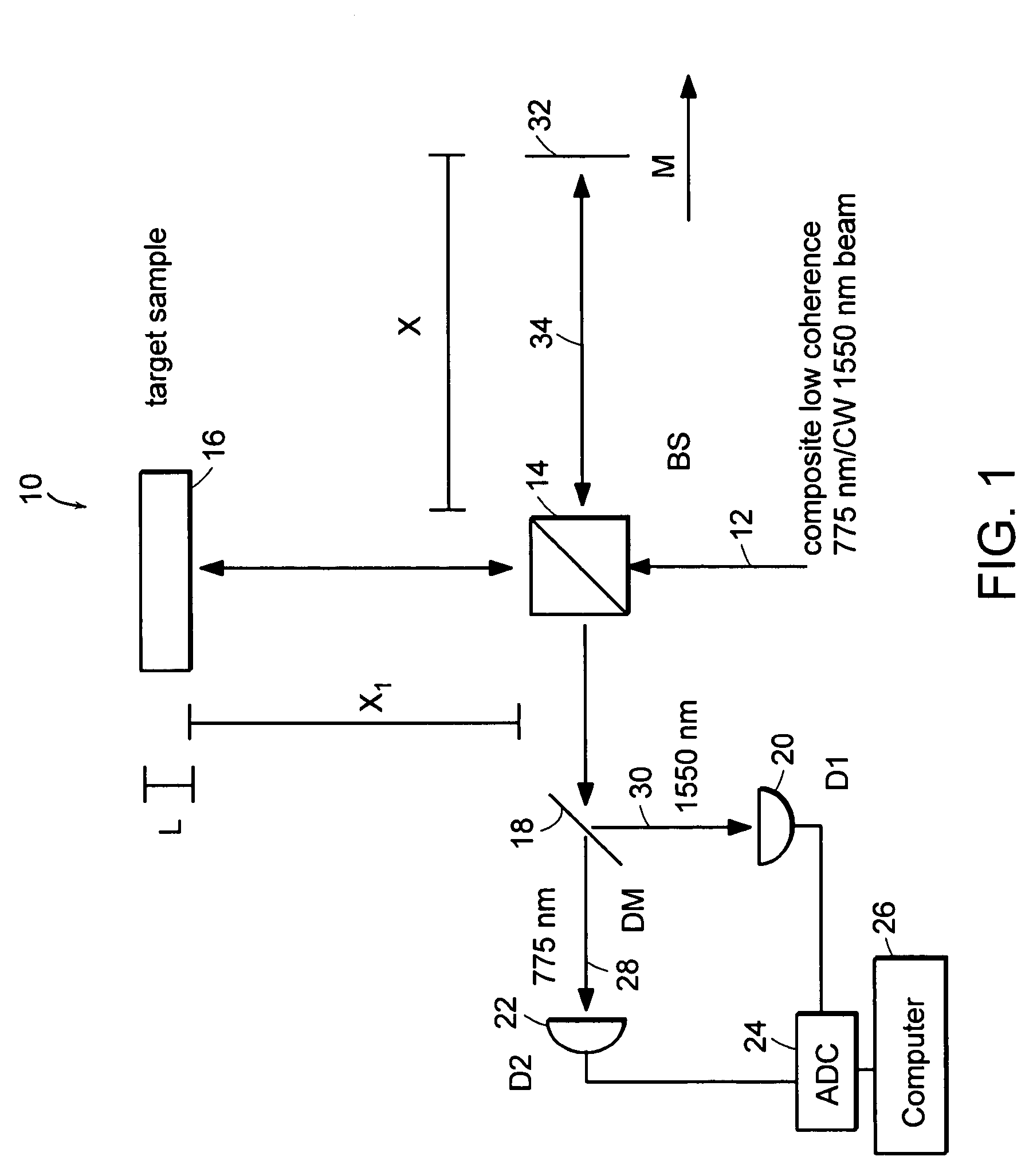
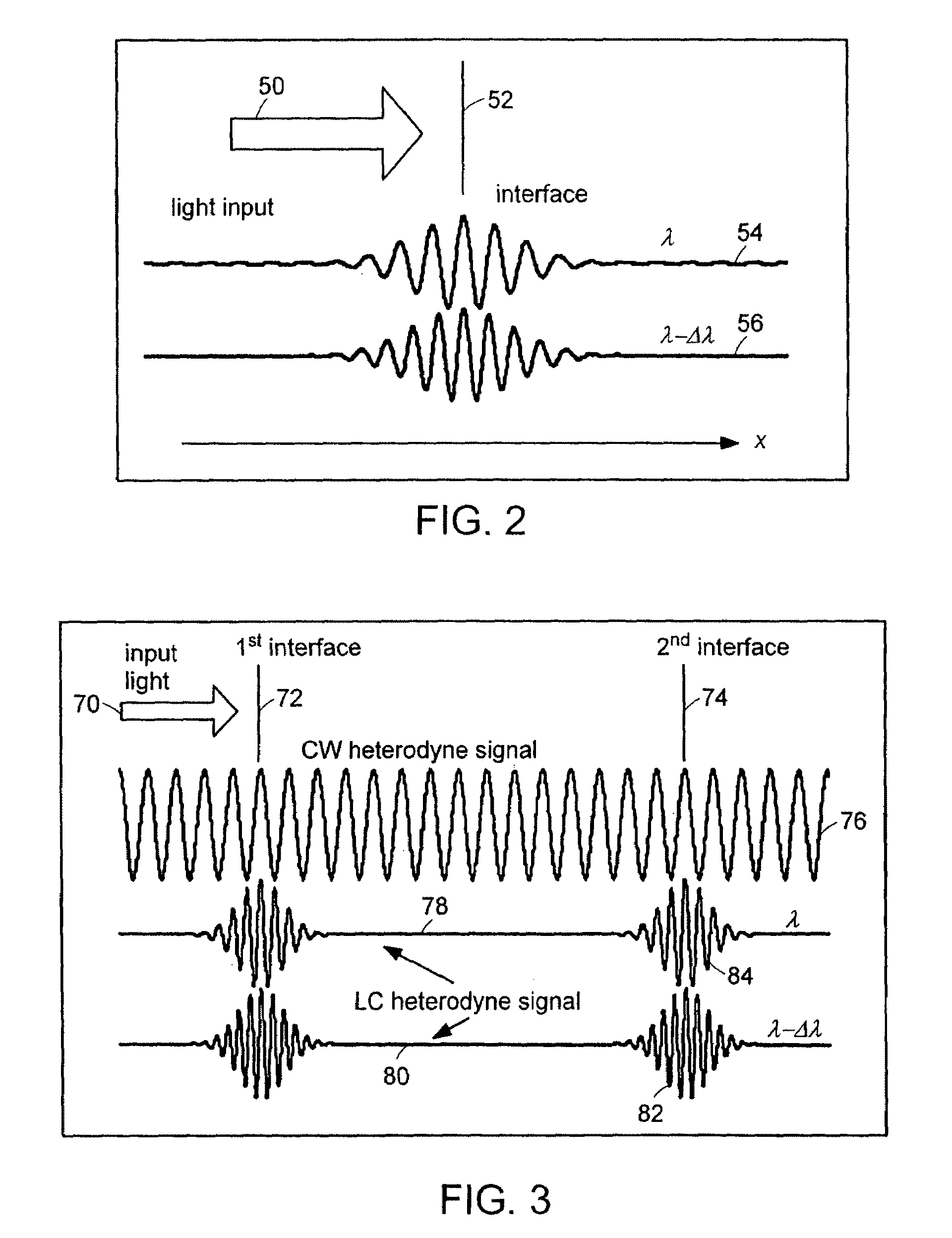
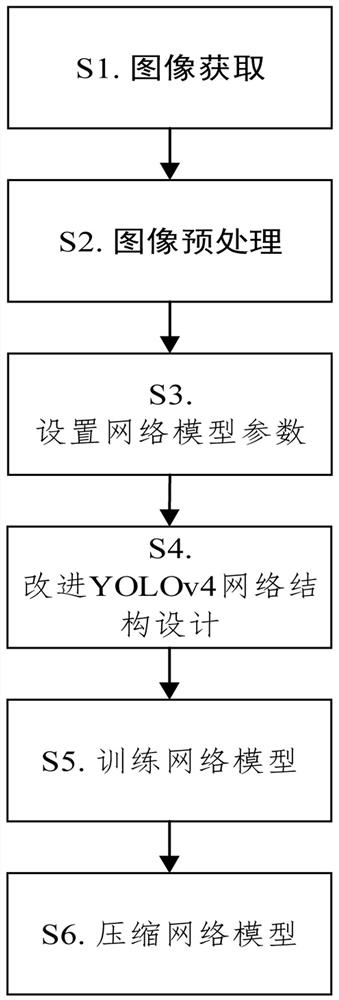
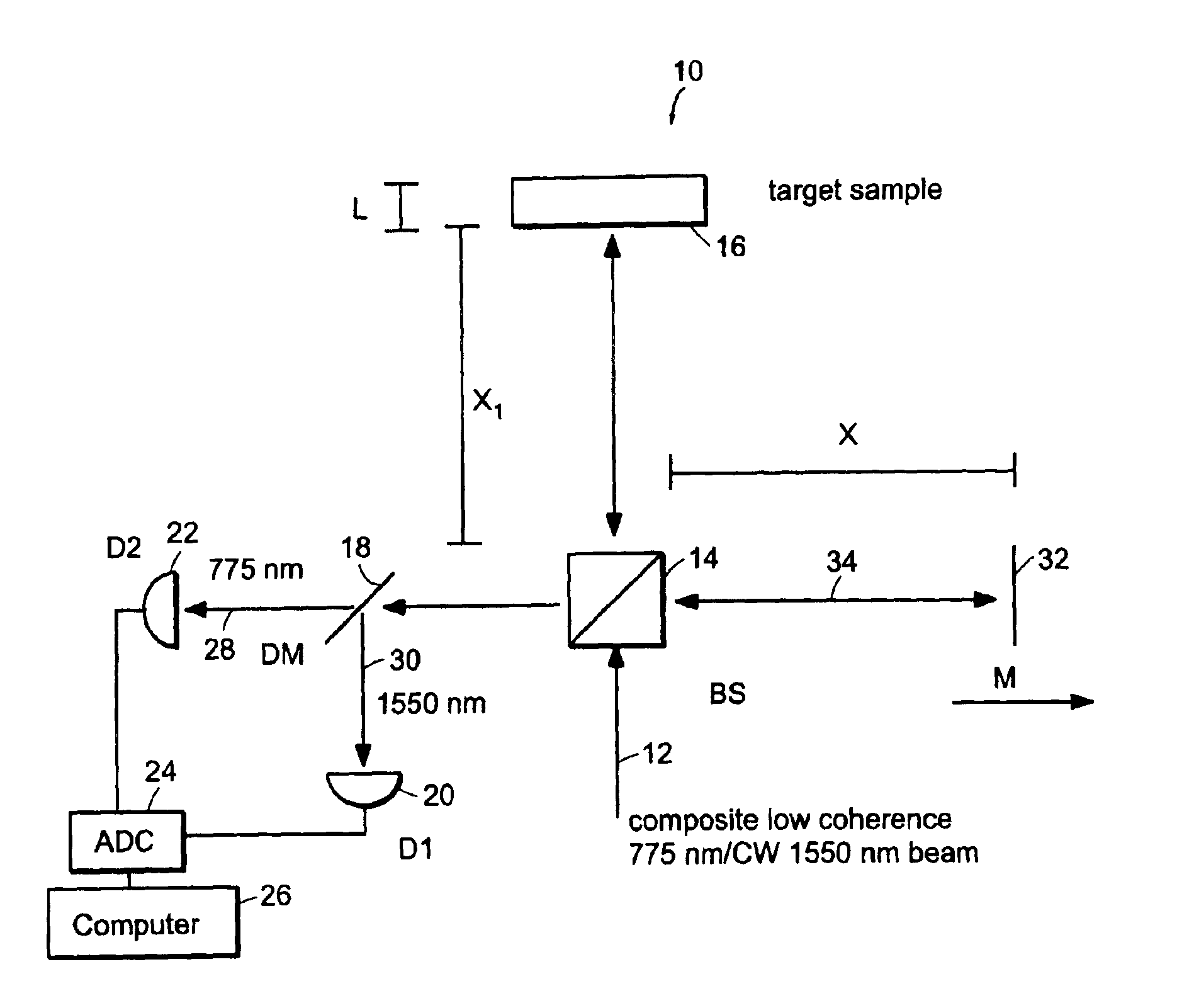
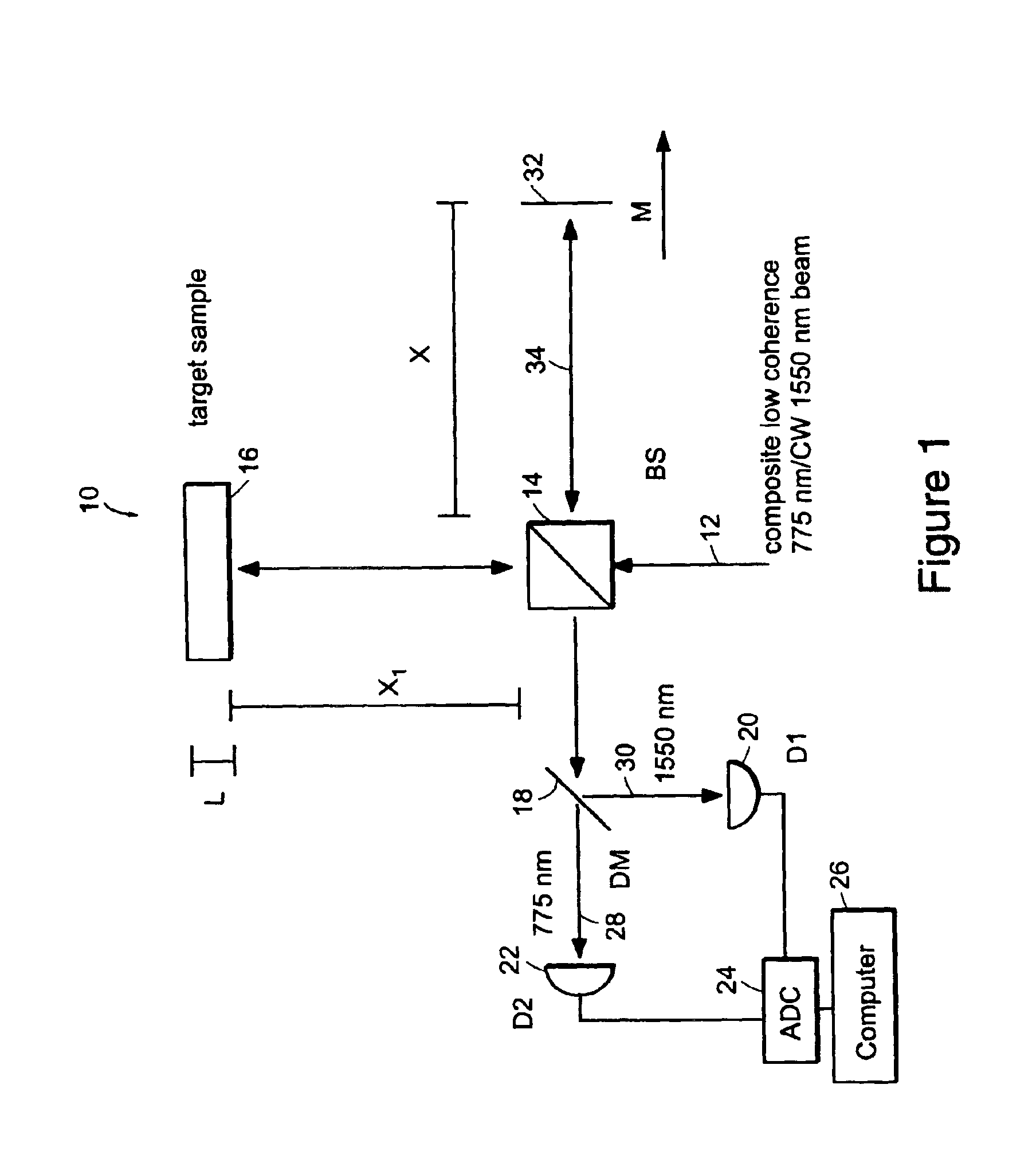
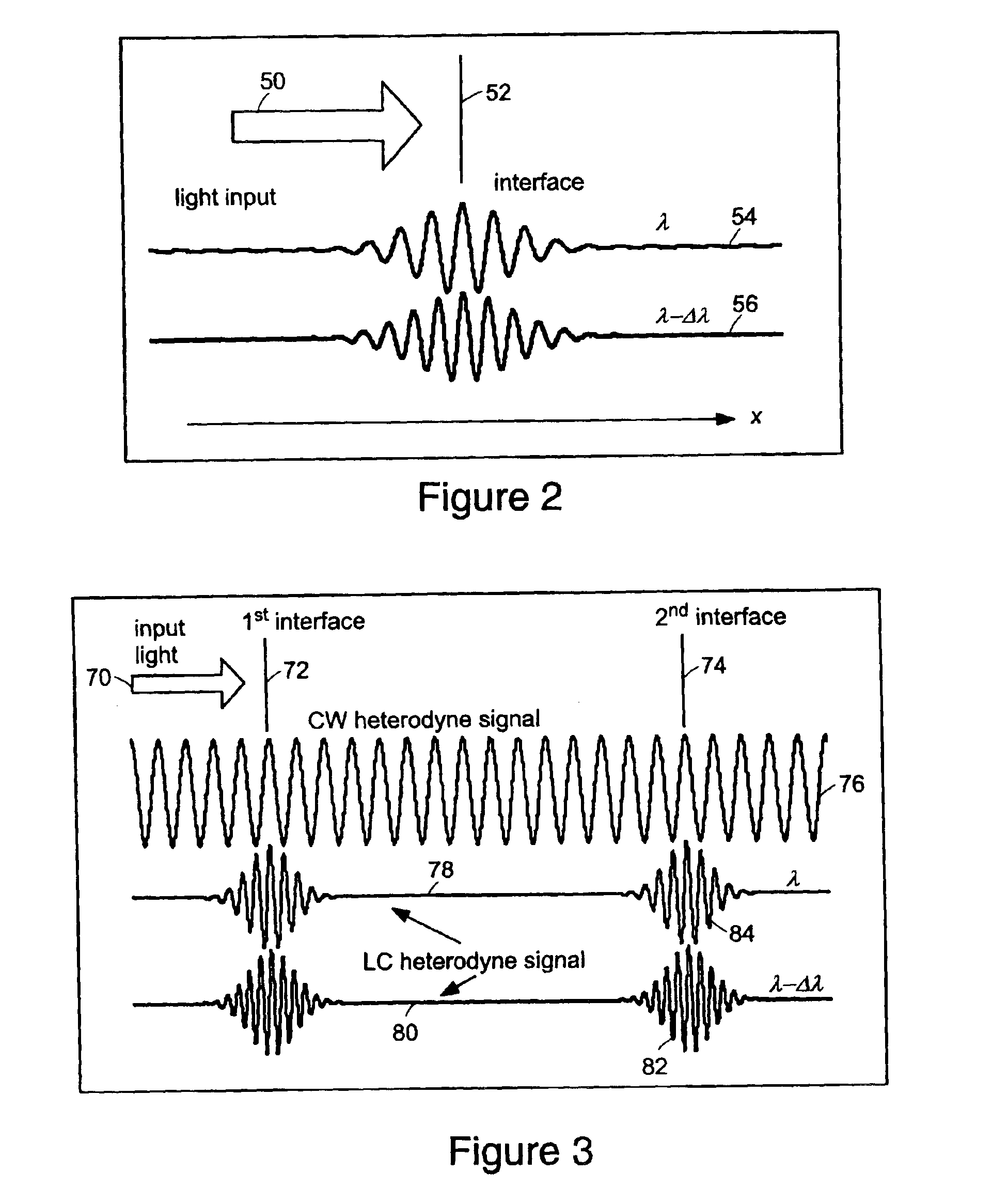
InactiveUS6934035B2Accurately measureAccurately determineOptical measurementsPhase-affecting property measurementsPhysicsMichelson interferometer
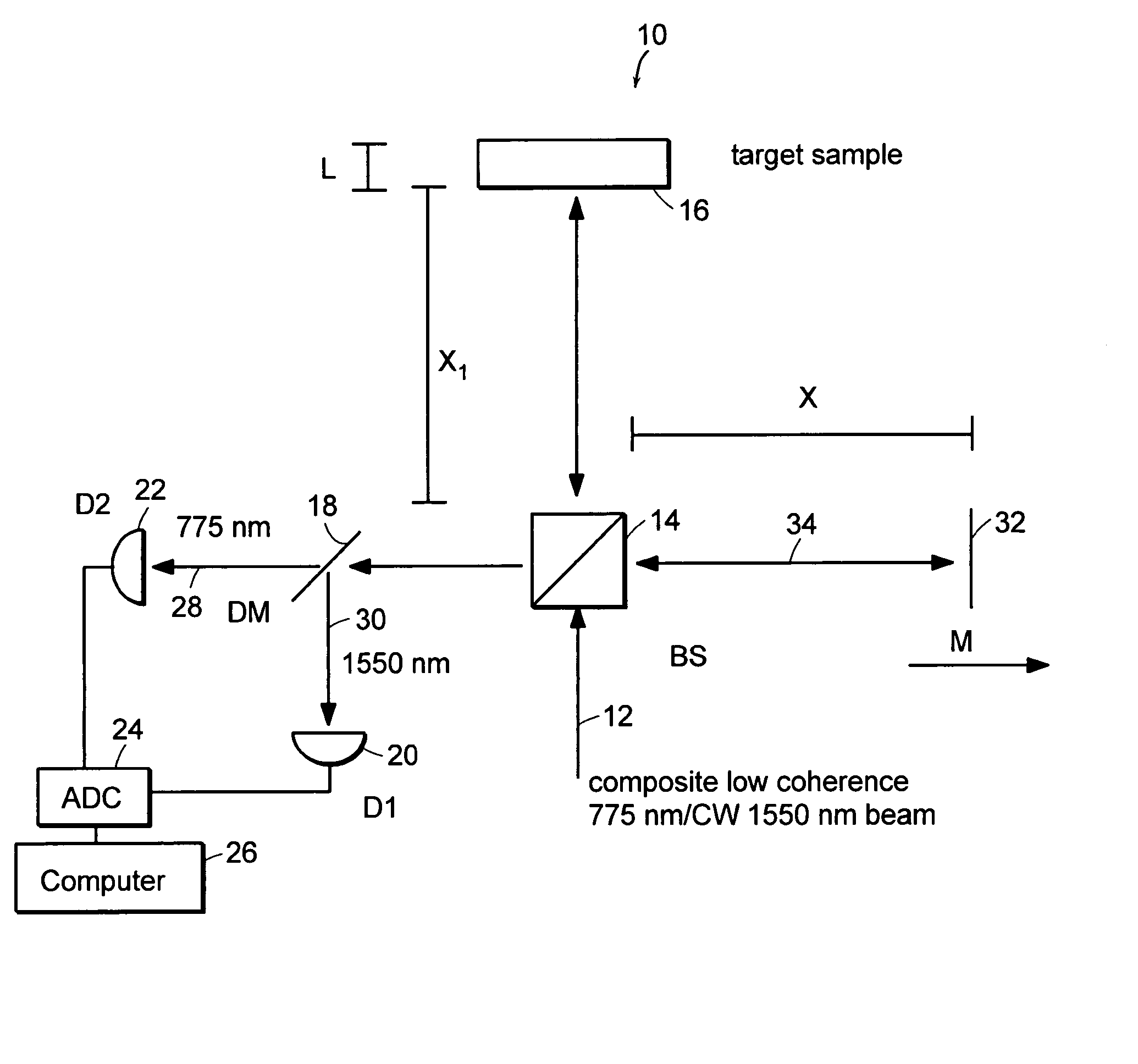
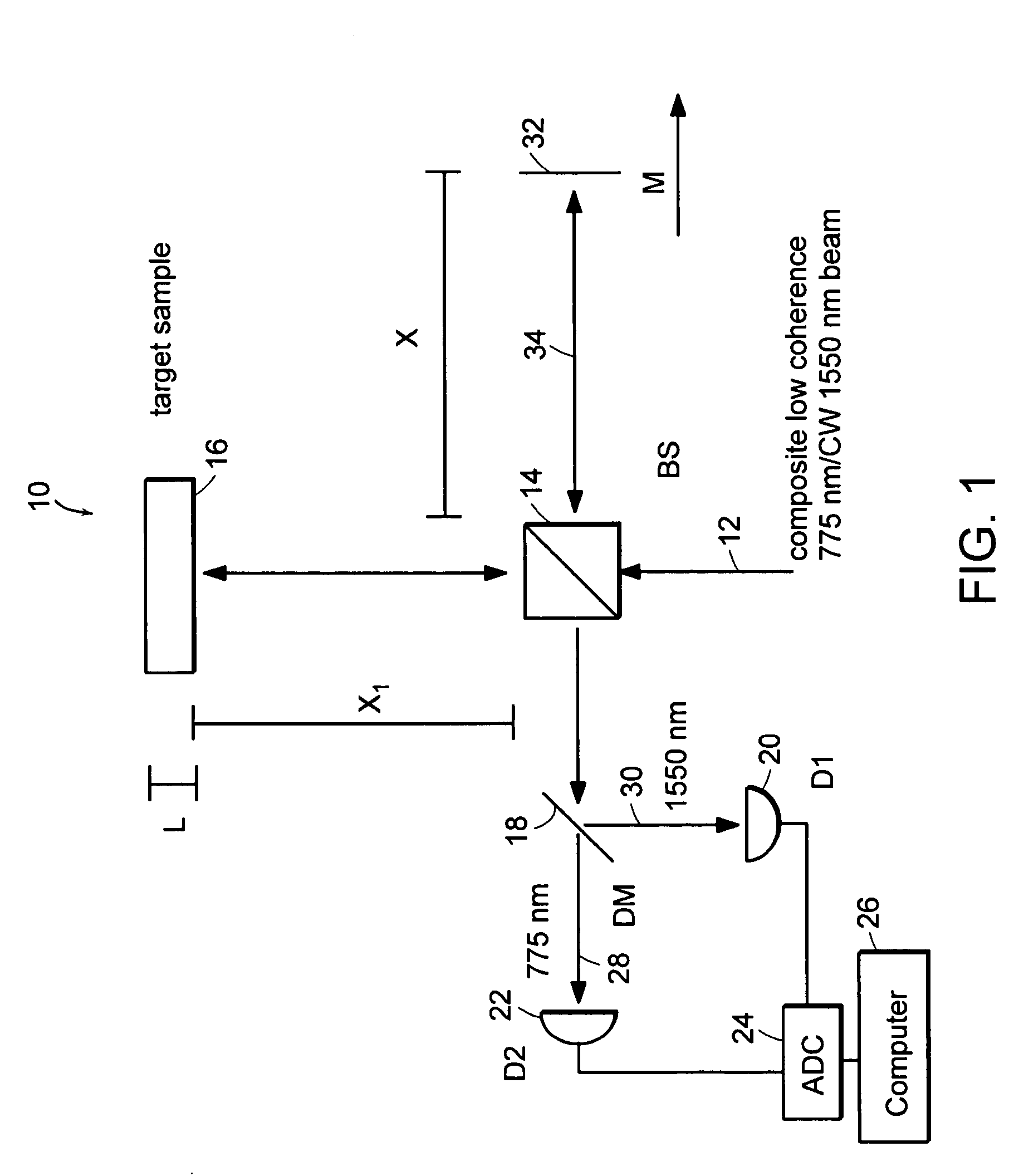
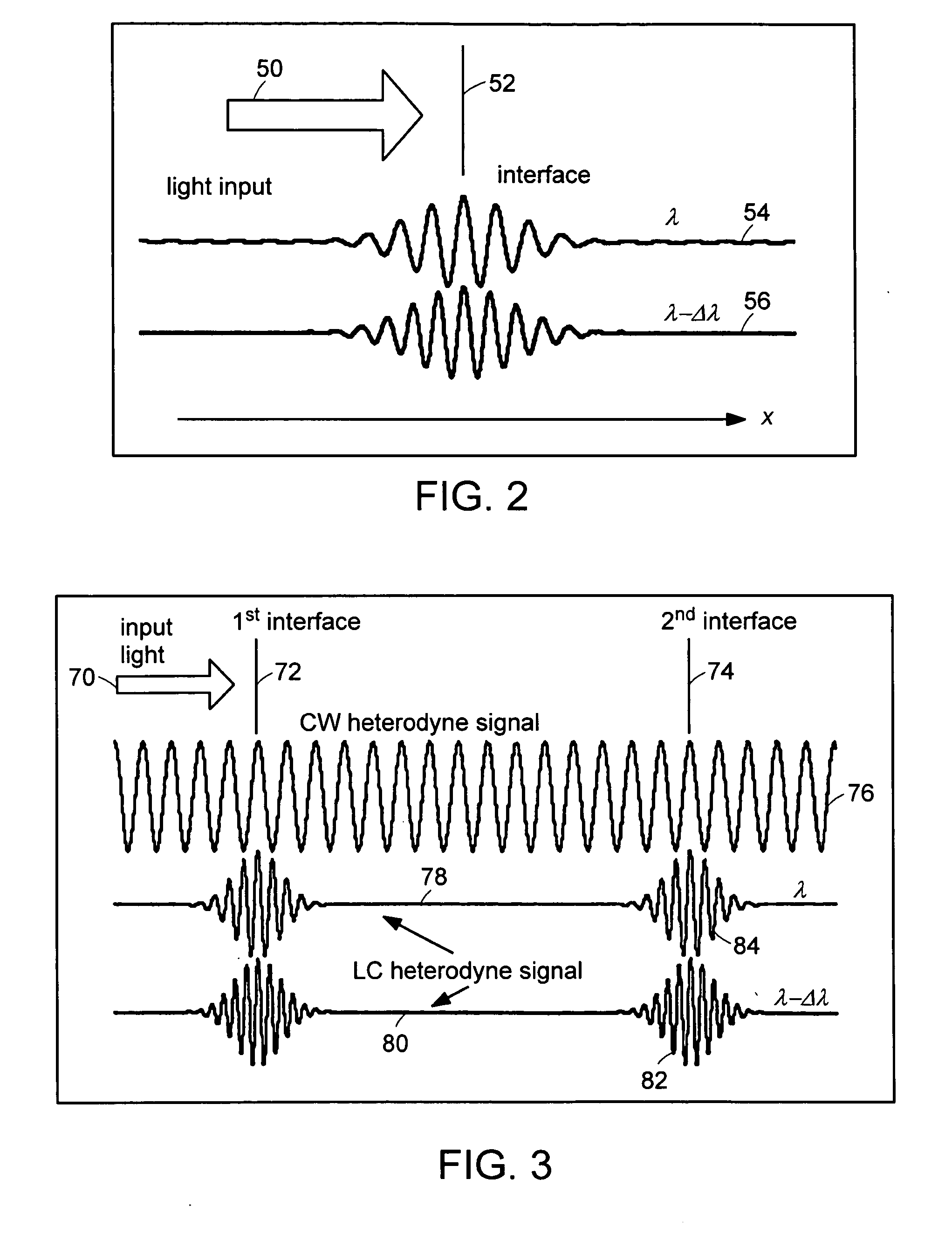
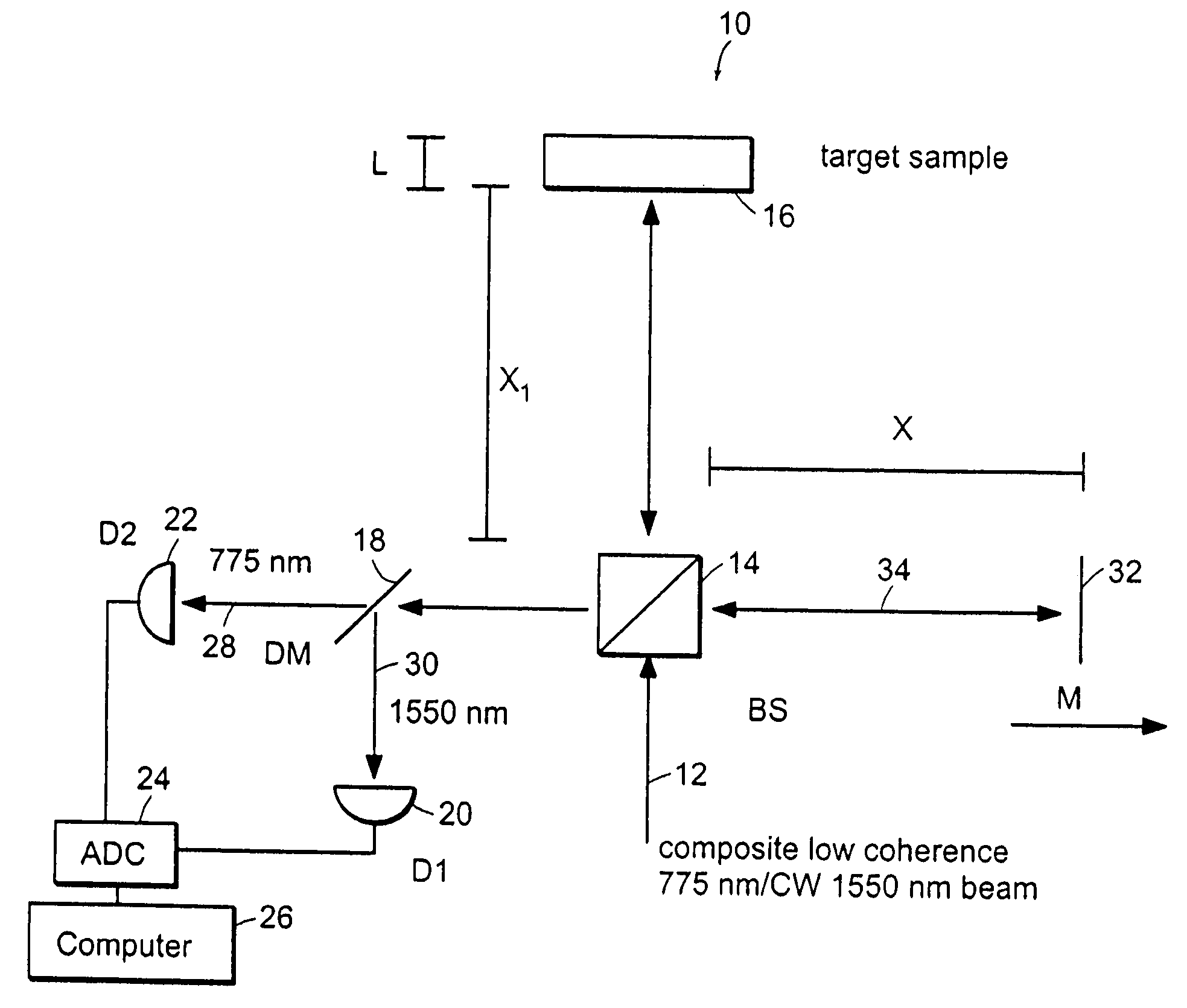
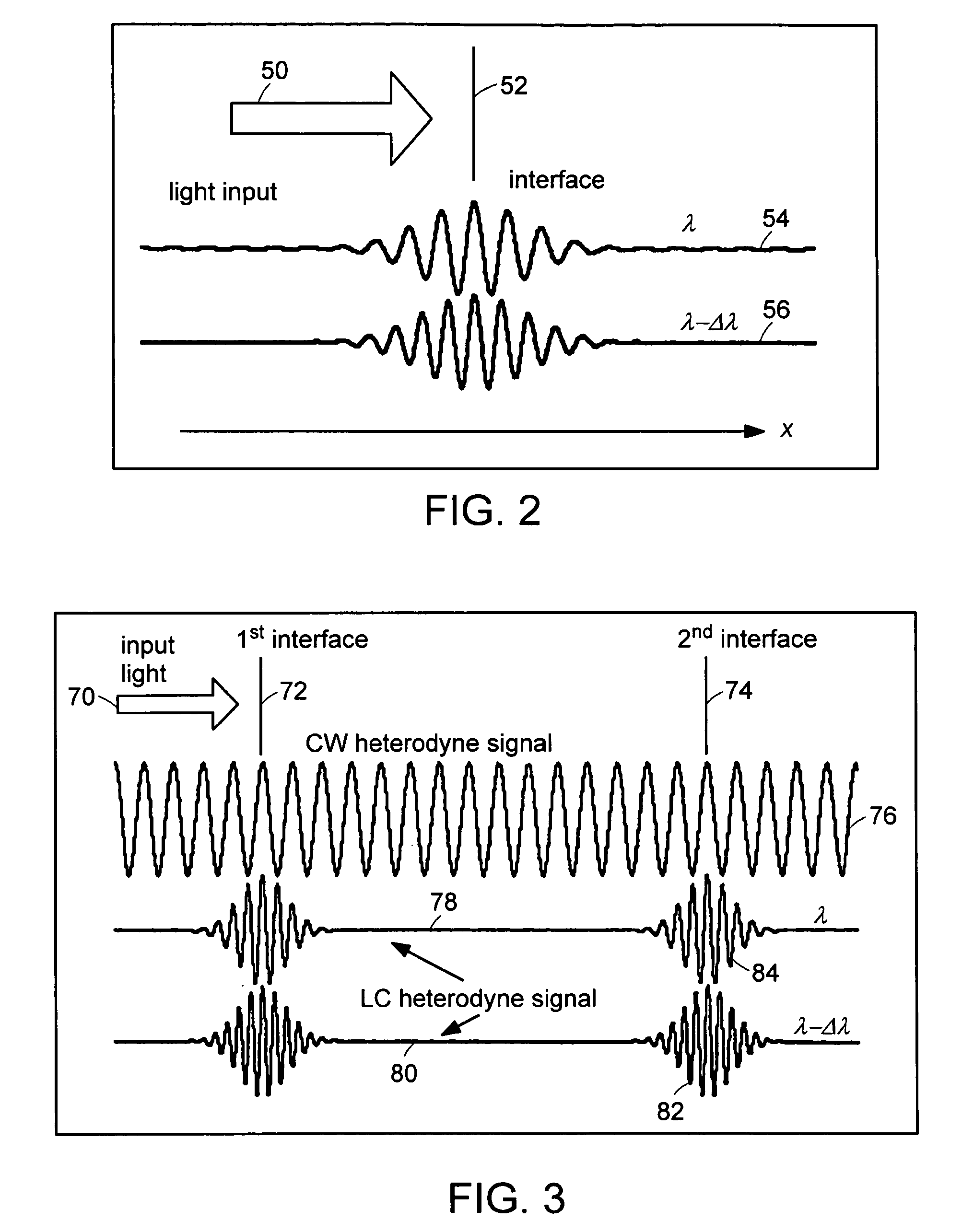
The methods of the present invention are directed at an accurate phase-based technique for measuring arbitrarily long optical distances with sub-nanometer precision. A preferred embodiment of the present invention method employs a interferometer, for example, a Michelson interferometer, with a pair of harmonically related light sources, one continuous wave (CW) and a second source having low coherence. By slightly adjusting the center wavelength of the low coherence source between scans of the target sample, the phase relationship between the heterodyne signals of the CW and low coherence light is used to measure the separation between reflecting interfaces with sub-nanometer precision. As the preferred embodiment of this method is completely free of 2π ambiguity, an issue that plagues most phase-based techniques, it can be used to measure arbitrarily long optical distances without loss of precision.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
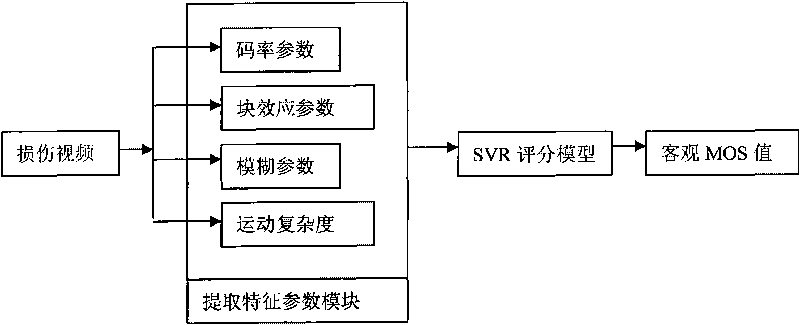
No-reference video quality evaluating method
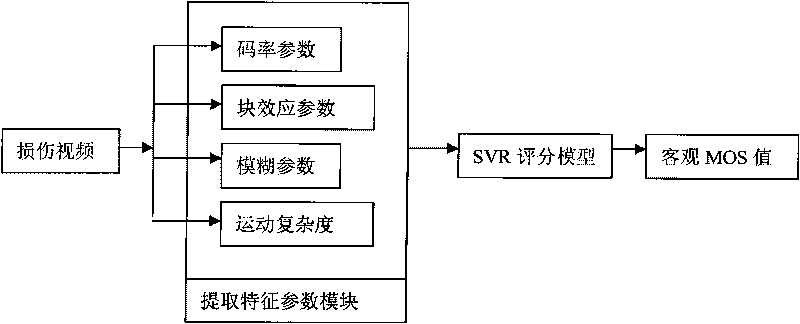
ActiveCN101742353ARealize the mappingNo loss of precisionTelevision systemsTime domainImage resolution
The invention provides a no-reference video quality evaluating method, and aims to solve the problems of low relevance between an objective MOS value and a subjective MOS value output by the conventional method, weak prediction accuracy and weak generalization ability thereof. The method comprises the following steps: extracting blocking effect parameters, blur parameters and code rate parameters of video received by a receiving end; setting motion complexity parameters for the video according to the decoded time domain of the video; outputting the objective MOS value by using an evaluation model which is acquired in advance based on support vector (SV) regression (SVR) according to the blocking effect parameters, the blur parameters, the code rate parameters and the motion complexity parameters; and acquiring higher relevance with the subjective MOS value. On characteristic parameter selection, TS stream parameters are integrated with main sense injury parameters; and the evaluation model determining method adopts a method of the support vector regression. The method is applicable to videos in different resolution ratios, in particular to videos with encoder injury.
Owner:THE RES INST OF TELECOMM TRANSMISSION MIIT +2
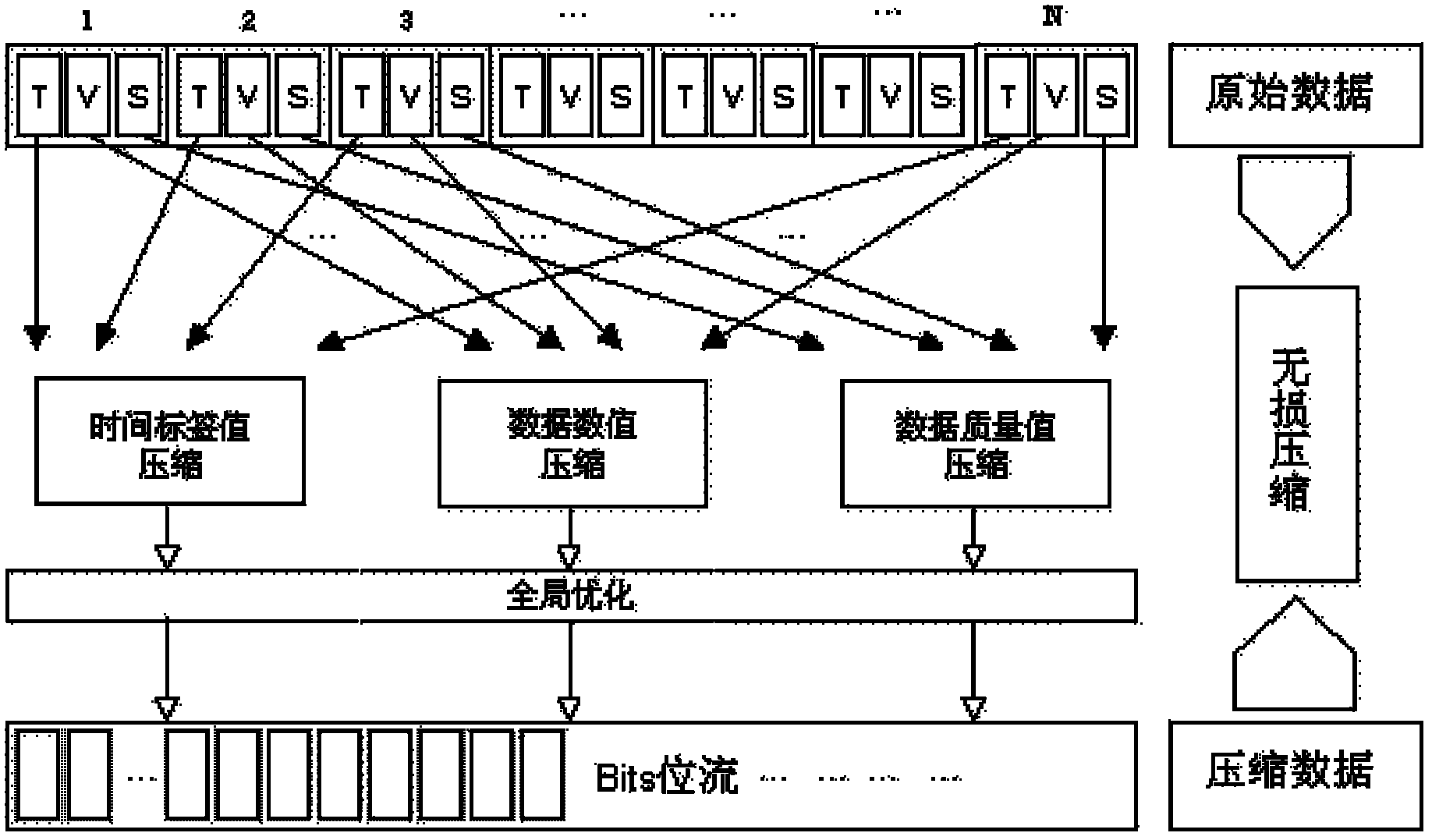
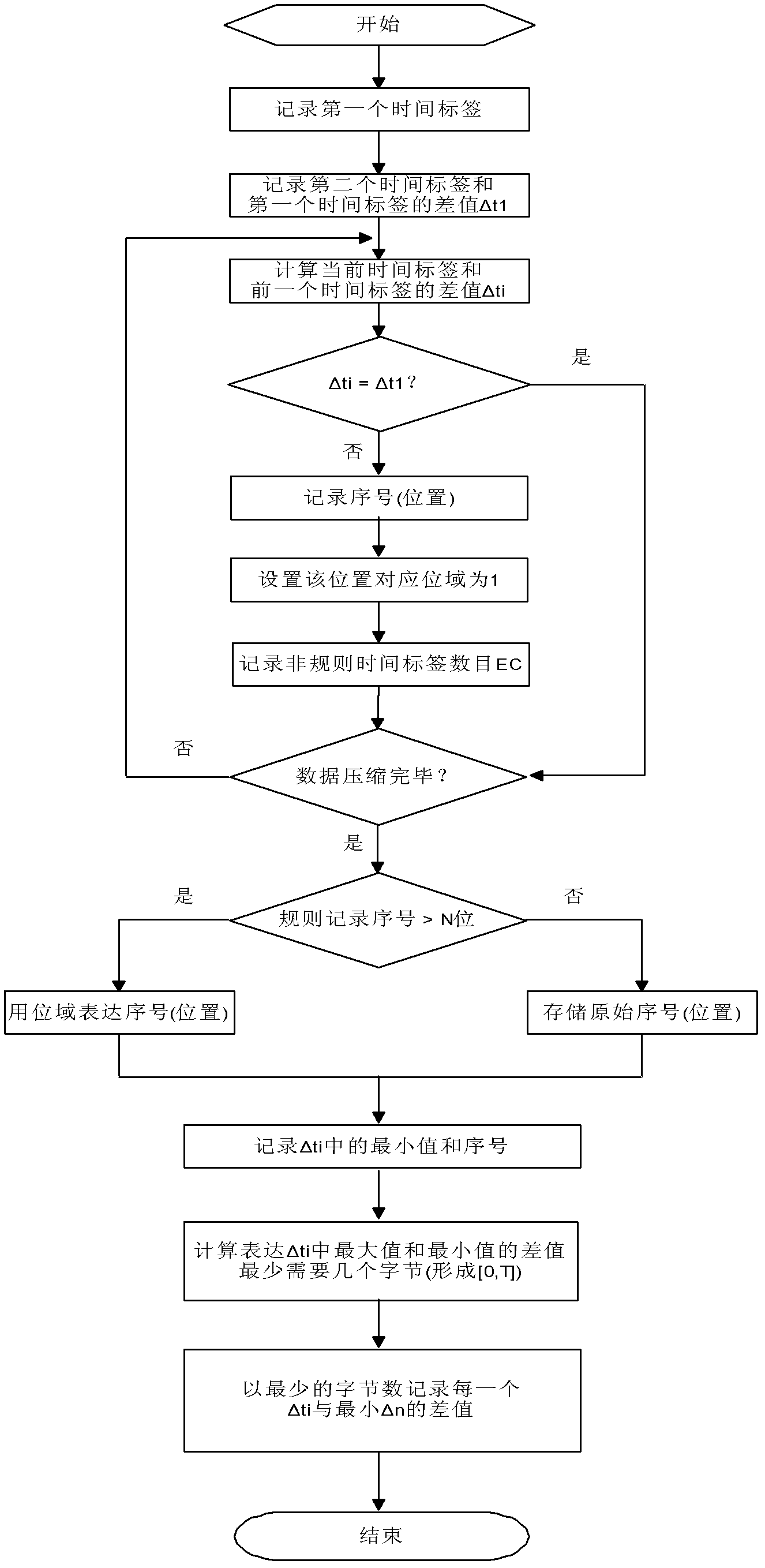
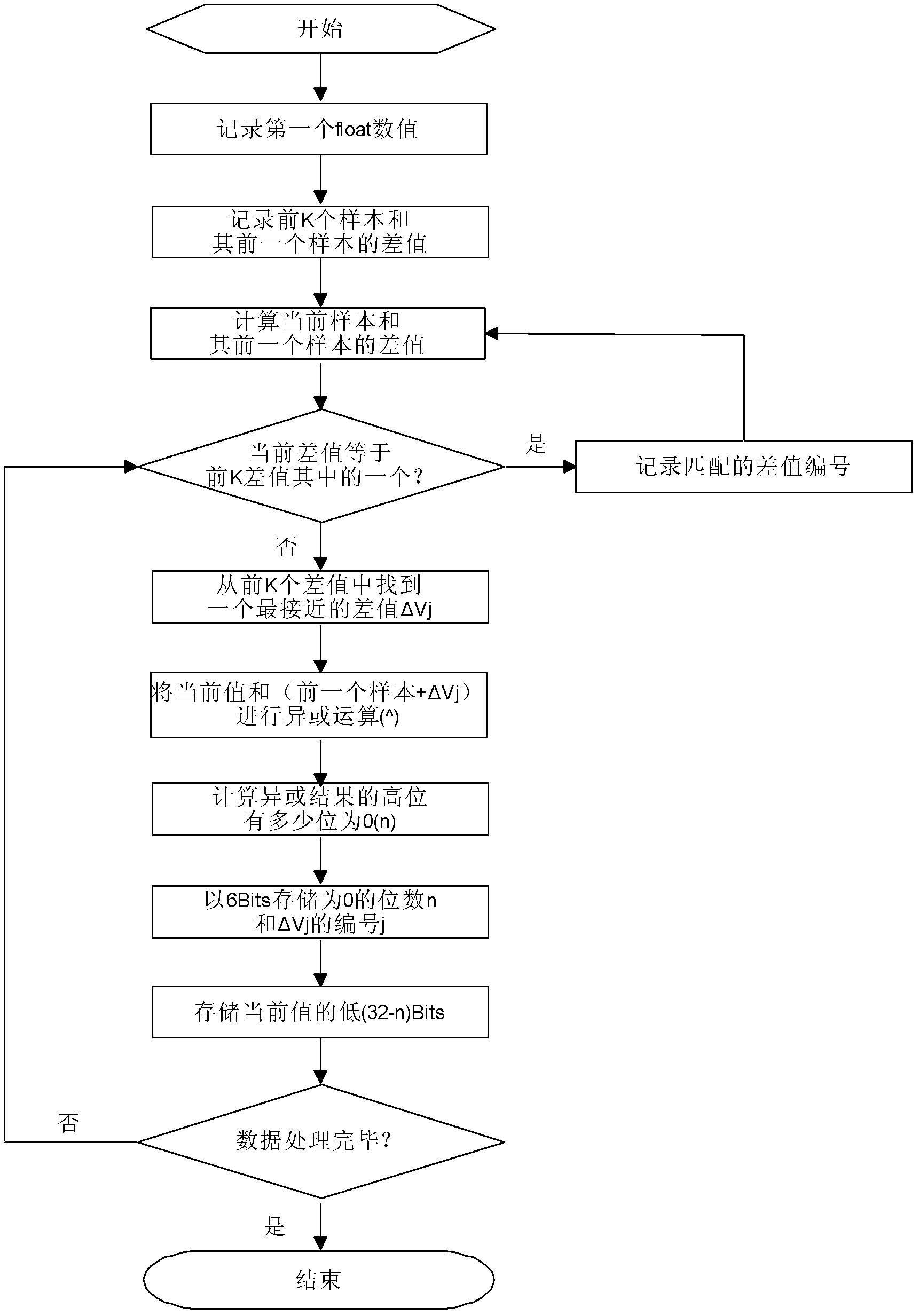
Real-time holographic lossless compression method for productive time sequence data
The invention discloses a real-time holographic lossless compression method for productive time sequence data, which comprises the steps of: respectively independently compressing three numerical ranges of each data in N productive time sequence data: a time label, a data value and data quality; respectively forming time label compression data, data value compression data and data quality compression data; and combining the three compression data into a complete compression data. In the method, productive time sequence data and files of each industry can be efficiently compressed in a lossless mode; and urgent demands of industries with enormous productive data, such as basic industry, electrics, telecommunication, chemical engineering, steel and the like for transmission, distribution, computing processing and storage of time sequence data can be satisfied.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
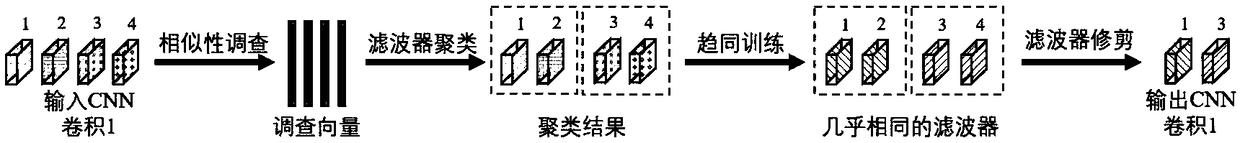
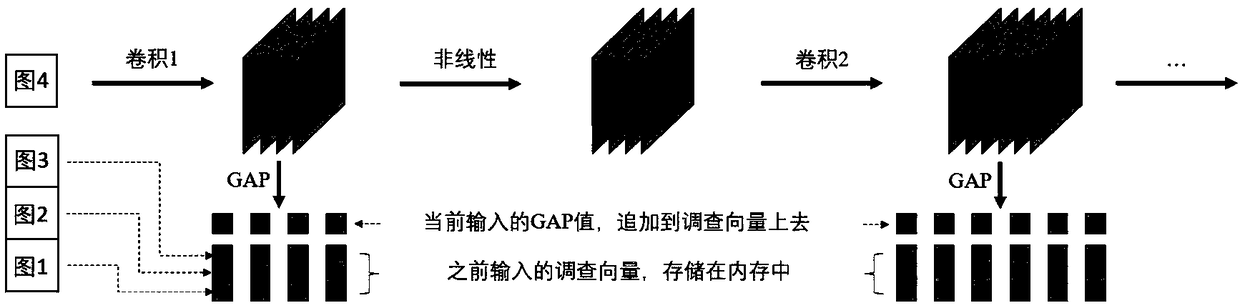
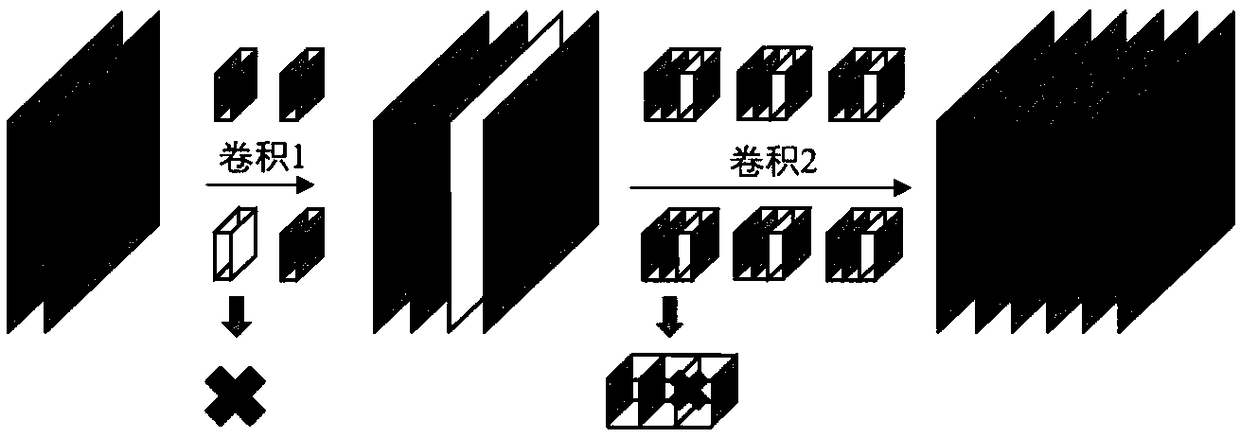
Convolutional neural network filter pruning technology based on similarity learning
ActiveCN108846445ANo loss of precisionPreserve precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesModel representationSimilarity learning
The invention provides a convolutional neural network filter pruning technology based on similarity learning. The method comprises the steps of obtaining the similarity between different filters through similarity survey; performing clustering on the filters according to the similarity; enabling the filters in the same cluster to become more and more similar through convergent training; and finally pruning the filters after the convergent training. The technology solves the problem that the model representation capability is reduced and needs to be re-trained in a convolutional neural networkfilter pruning process, so that the representation capability and precision of a network can be better retained; and in addition, the precision loss of the convolutional neural network is hardly caused, the precision of a model does not need to be restored through re-training, and the better balance of model precision and efficiency is achieved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Neural-network-model compression method, system and device and readable storage medium
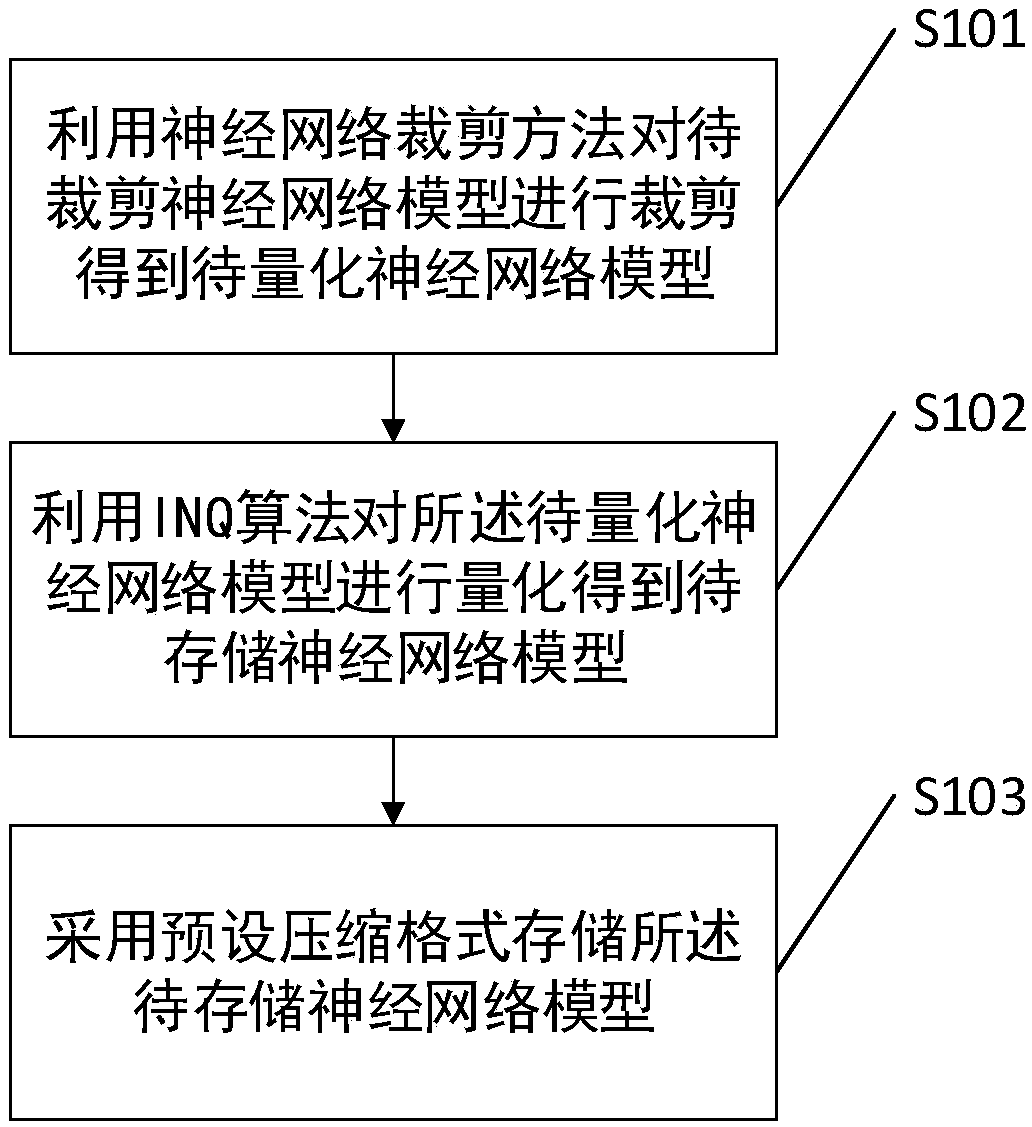
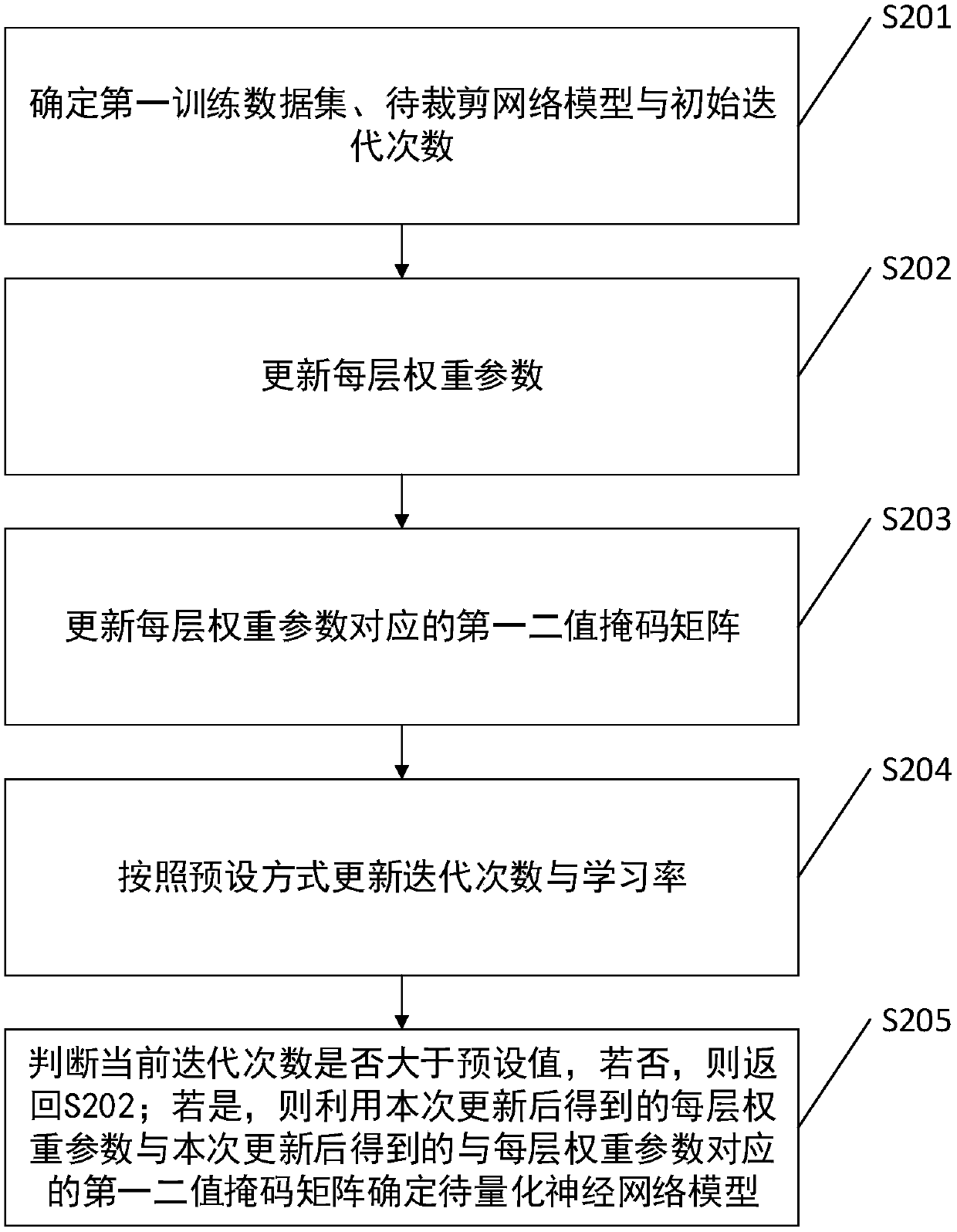
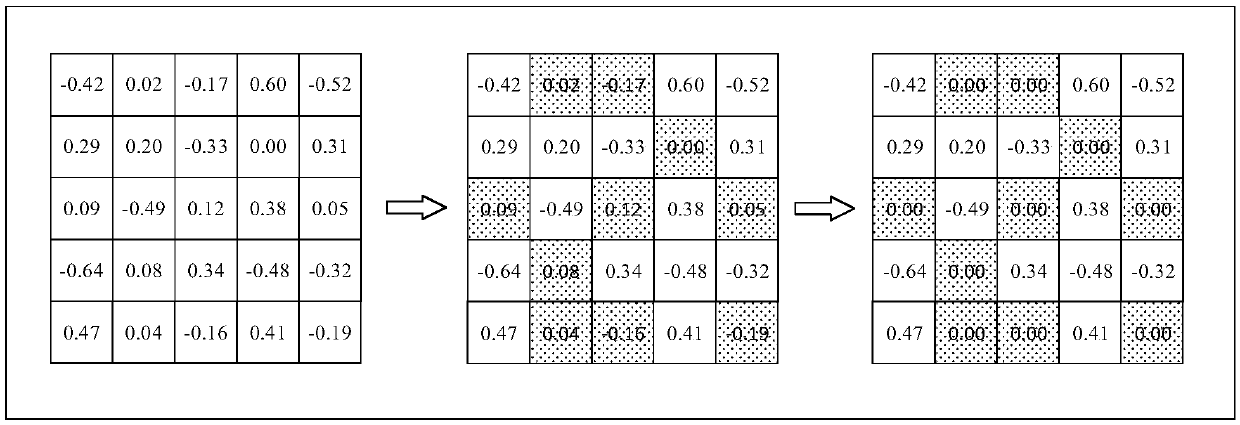
InactiveCN108229681ASmall sizeNo loss of precisionNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsAlgorithmQuantized neural networks
The invention discloses a neural-network-model compression method, system and device and a computer-readable storage medium. The method includes: utilizing a neural-network clipping method to clip a to-be-clipped neural network model to obtain a to-be-quantized neural network model; utilizing an INQ algorithm to quantize the to-be-quantized neural network model to obtain a to-be-stored neural network model; and using a compression format to store the to-be-stored neural network model. Therefore, according to the neural-network-model compression method provided by the embodiment of the invention, the neural network model is cropped, the INQ algorithm is used at the same time to quantify the same after cropping, thus a model size can be reduced in a case of effectively guaranteeing no loss of model precision after compression, thus the problem of excessive consumed resources can be solved, and calculation can be accelerated.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Three-dimensional point cloud matching method and system
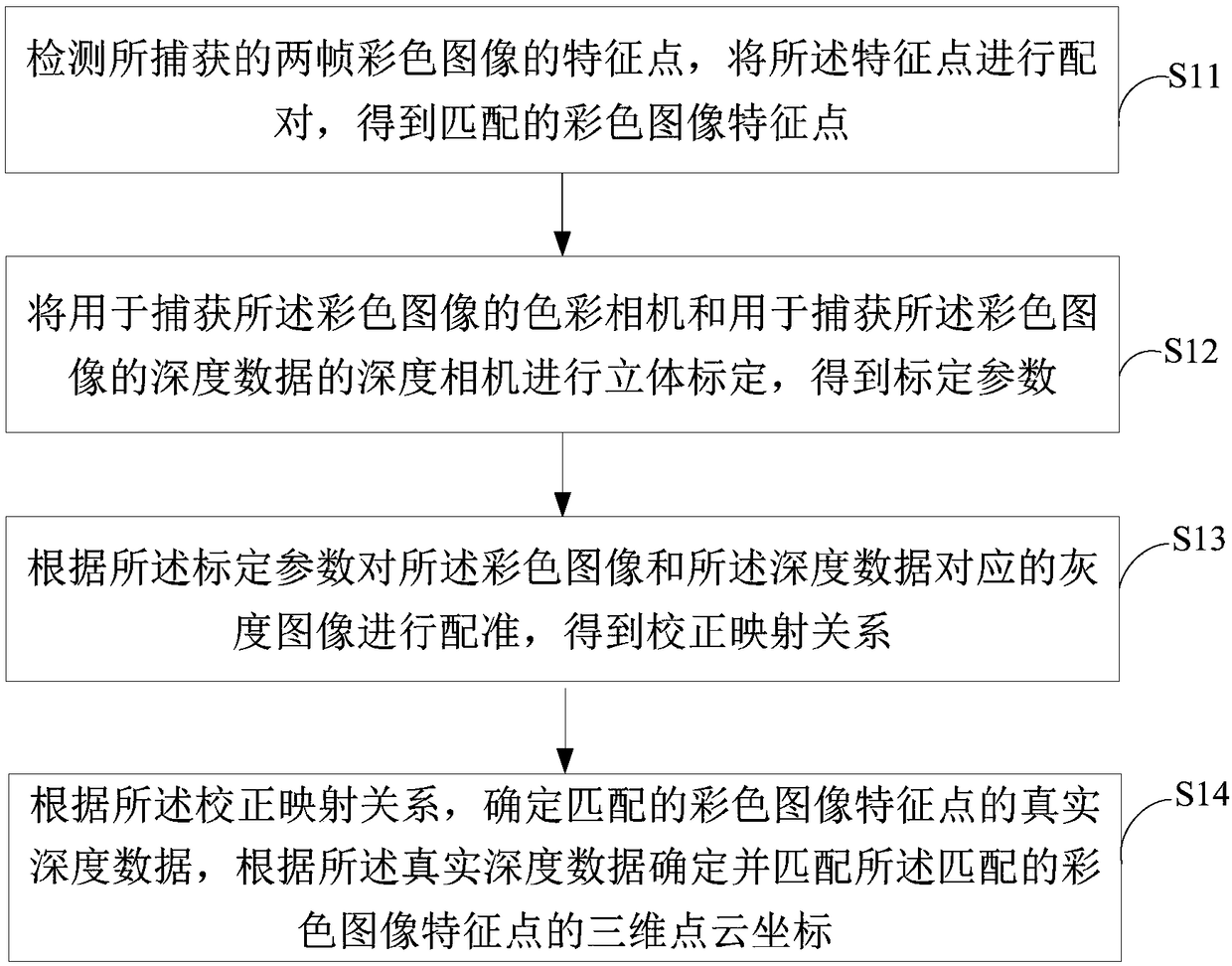
ActiveCN108510530AImprove exact matchImprove matching accuracyImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageImaging processing
The invention is applicable to the technical field of image processing, and provides a three-dimensional point cloud matching method and system. The three-dimensional point cloud matching method comprises the steps of detecting feature points of two color images, and pairing the feature pints; performing stereo calibration on a color camera and a depth camera to obtain calibration parameters; performing registration on the color images and grayscale images corresponding to depth data according to the calibration parameters to obtain a correction mapping relation; determining true depth data ofthe matched color image feature points according to the correction mapping relation, and then calculating and matching three-dimensional point cloud coordinates of the color image feature points. According to the method, a new mismatch filtering process is added when the feature points of the two color images are matched so as to improve the matching accuracy; a novel stereo calibration based scheme is designed when the true floating-point type depth data corresponding to the feature points is obtained, the mapping process is simplified, it is guaranteed that the precision is not reduced, andhigh-precision matching of the three-dimensional point cloud is realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN LAUNCH DIGITAL TECH
Convolution theorem based face verification accelerating method
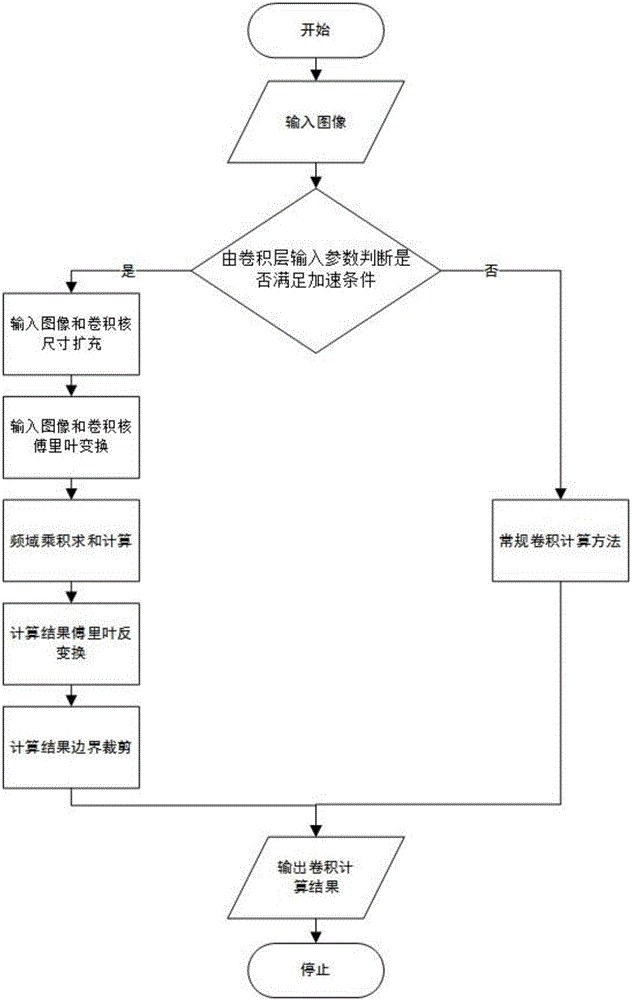
ActiveCN106709441ANo loss of precisionWill not affect accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionConvolution theoremFrequency domain
The invention relates to a convolution theorem based face verification accelerating method, and belongs to the field of face verification in computer vision. For a face verification system adopting a CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) technology, a convolution theorem method is adopted to replace the conventional convolution computation method to perform convolution computation on a convolution layer meeting an acceleration condition on the basis of using a GPU parallel computation platform. The convolution theorem shows that convolution in the space domain is equivalent to product in the frequency domain. Through transforming time-consuming convolution computation into product computation in the frequency domain, the computation amount can be significantly reduced, and the computation speed of a CNN is accelerated. In allusion to problems of great computational burden and slow operation speed of the face verification system, the method enables the operation speed of the face verification system to be obviously improved, and the processing capacity for mass data can be improved.
Owner:深圳市小枫科技有限公司
Initial alignment method of large azimuth misalignment angle of strapdown inertial navigation system based on RBCKF (rao-black-wellised cubature kalman filter)
InactiveCN103344260AShorten the timeNo loss of filtering accuracyNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsState variableCubature kalman filter
The invention discloses an initial alignment method of a large azimuth misalignment angle of a strapdown inertial navigation system based on an RBCKF (rao-black-wellised cubature kalman filter), relates to the initial alignment method of the large azimuth misalignment angle of the strapdown inertial navigation system, and aims at solving the problems that the accuracy of the filtering method is low and easily diffused when the nonlinearity of the system is strong, and even EKF (exend kalman filter) filtering cannot be applied when the system is not continuous. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, building an error model for initial alignment of the large azimuth misalignment angle; 2, selecting an initial filtering value; 3, calculating a Cubature point set; 4, updating the time of a state variable and a measurement stable; and 5, updating a measurement equation. The initial alignment method is applied to the field of initial alignment of strapdown inertial navigation under the large azimuth misalignment angle.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
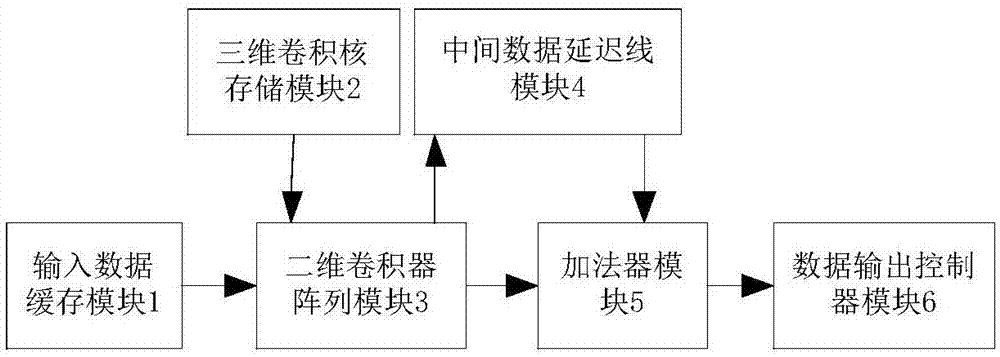
FPGA-based three-dimensional convolver
InactiveCN107403117AFast operationImprove input efficiencyComputing operations for integral formationComplex mathematical operationsComputer architectureParallel computing
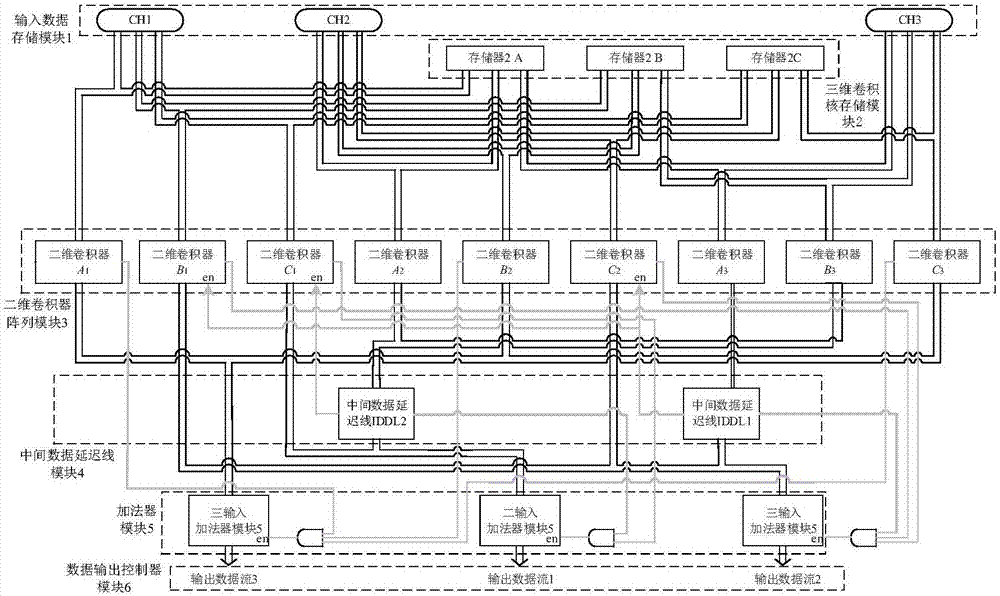
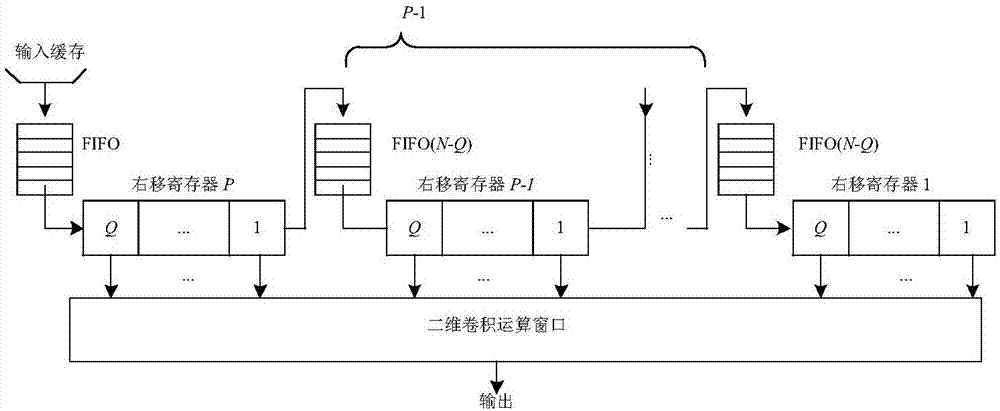
The invention discloses an FPGA-based three-dimensional convolver, and aims at solving the technical problem that input data is repeatedly loaded in the prior art. The FPGA-based three-dimensional convolver comprises six modules realized in an FPGA: an input data storage module, a three-dimensional convolution kernel storage module, a two-dimensional convolver array module, an intermediate data delay line module, a summer module and a data output controller module, wherein the input data storage module is used for carrying out input cache on a to-be-processed feature map; the three-dimensional convolution kernel storage module is used for storing a three-dimensional convolution kernel in the FPGA in a form of a plurality of two-dimensional convolution kernels; the two-dimensional convolver array module is used for convolving the to-be-processed feature map and the three-dimensional convolution kernel and then outputting the convolved to-be-processed feature map and three-dimensional convolution kernel; the intermediate data delay line module is used for adding convolution results of appointed two-dimensional convolver, delaying the adding result and then outputting the adding result; the summer module is used for adding output of the two-dimensional convolver array module and output of an intermediate data delay line and then carrying out output; and the data output controller module is used for controlling the sequence of a plurality of outputs of the summer module. The FPGA-based three-dimensional convolver is capable of remarkably enhancing the three-dimensional convolution operation speed and can be used for the aspect of target tracking or behavior detection.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Posture recognition system and method, and storage medium
ActiveCN108304819ALower requirementSmall amount of calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionUpper limbComputer science
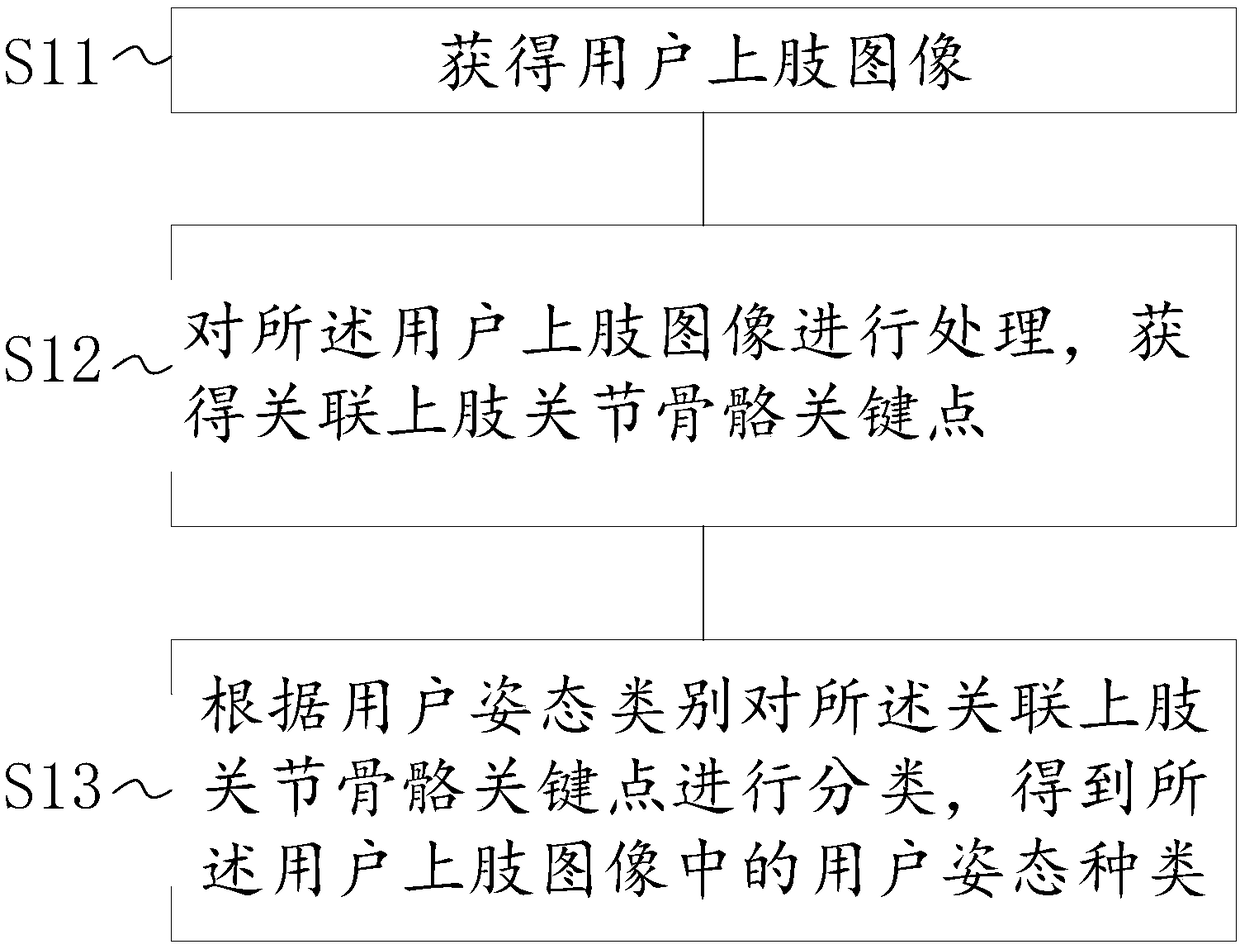
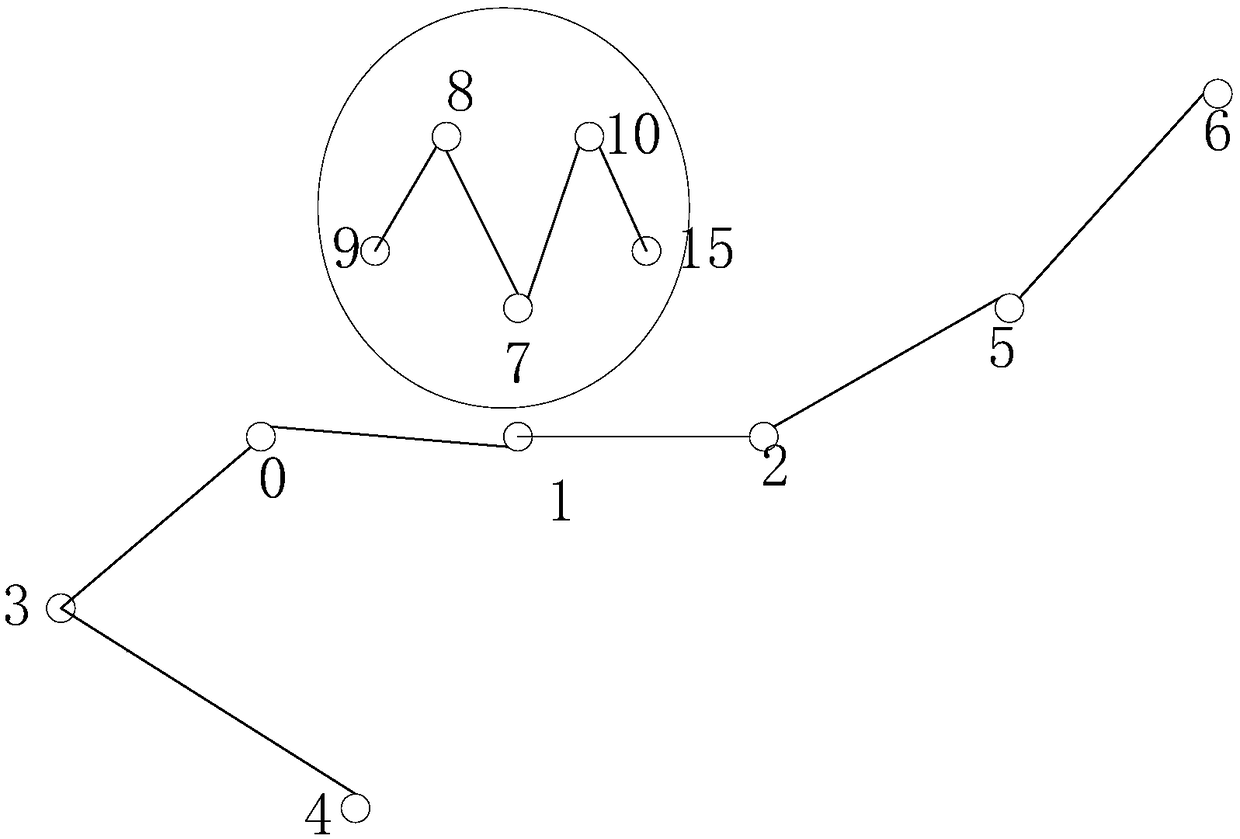
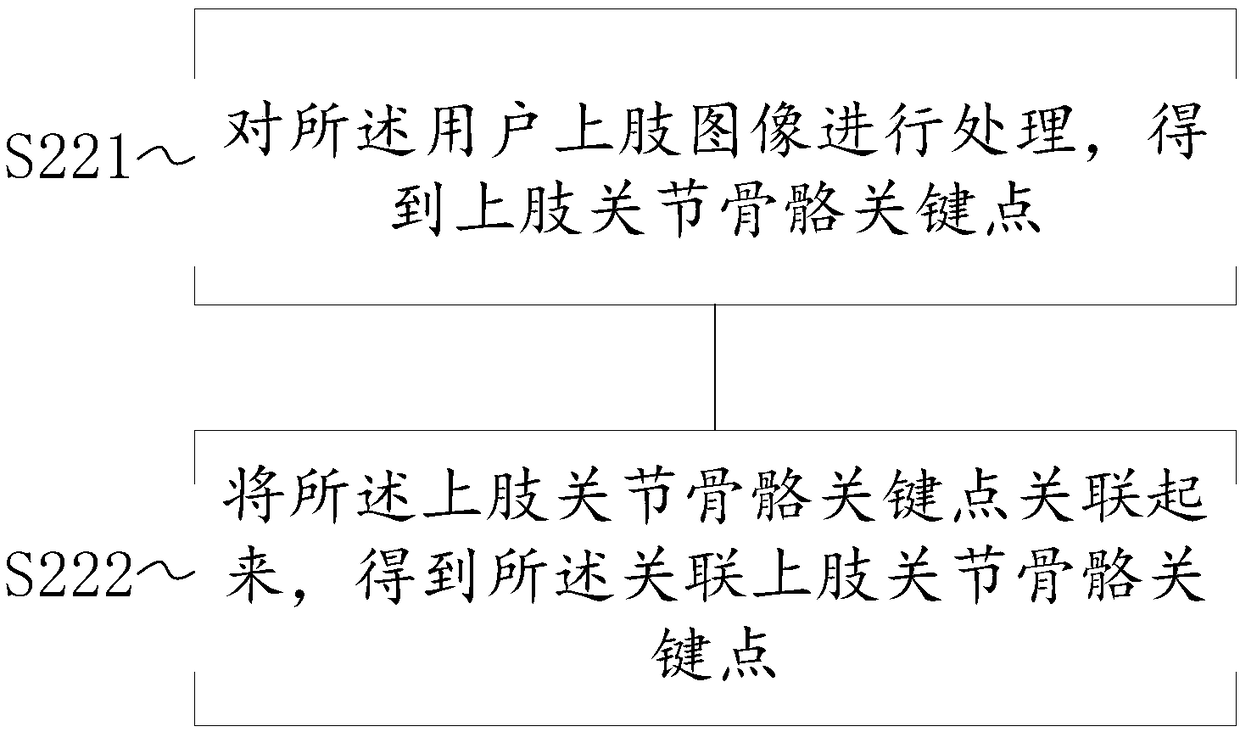
Embodiments of the invention provide a posture recognition system and method, and a storage medium. The method includes: obtaining an upper limb image of a user; processing the upper limb image of theuser, and obtaining associated upper limb joint bone key points; and classifying the associated upper limb joint bone key points according to the user posture categories, and obtaining the user posture category of the upper limb image of the user. By employing the system and method, and the storage medium, the accuracy of posture recognition of the upper limb image of the user can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING CENTURY TAL EDUCATION TECH CO LTD
Convolutional neural network model based data processing method and device
ActiveCN107395211AImplement compressed storageNo loss of precisionCode conversionNeural architecturesCircuit trainingConvolution
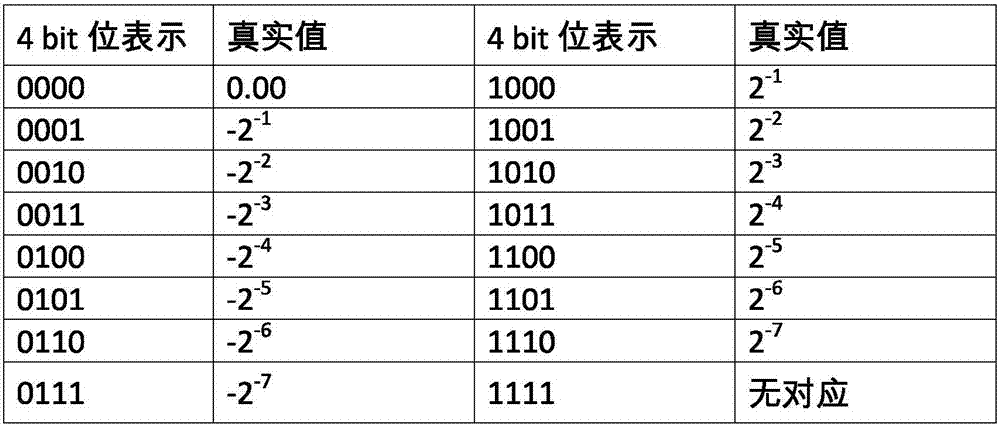
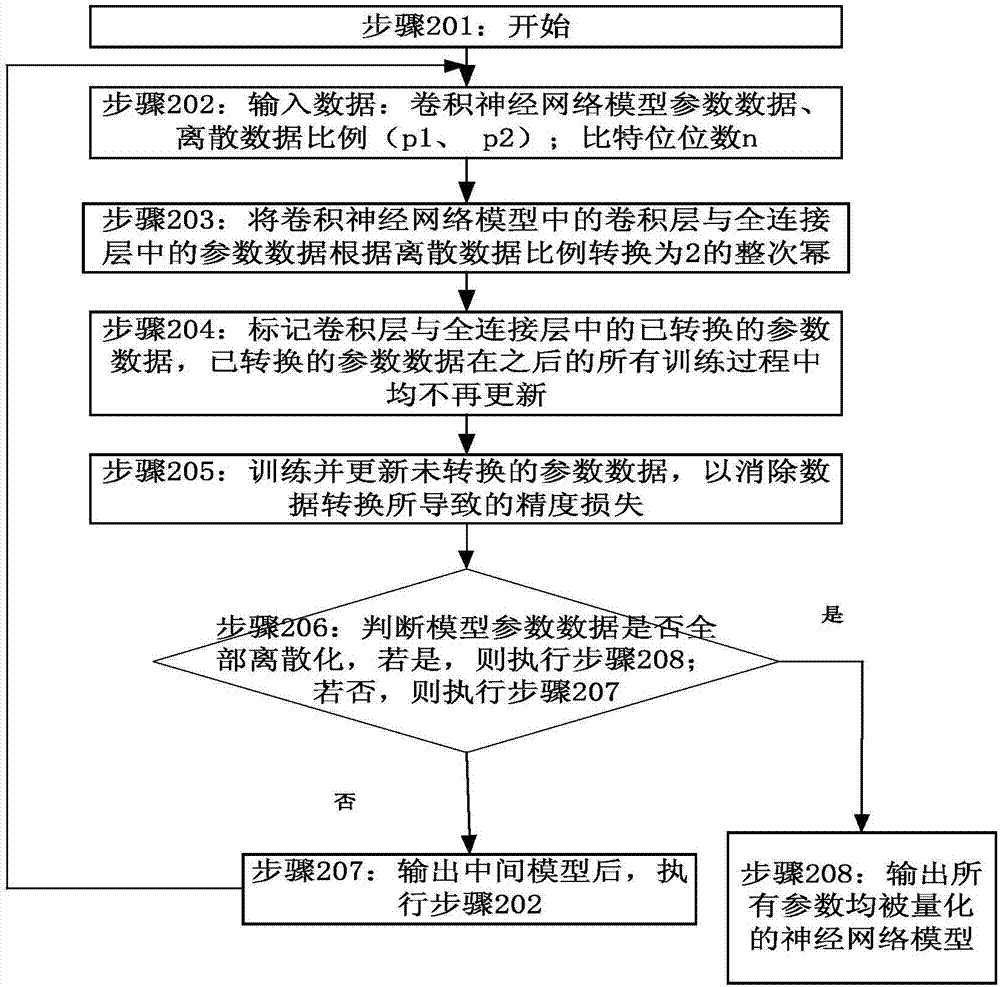
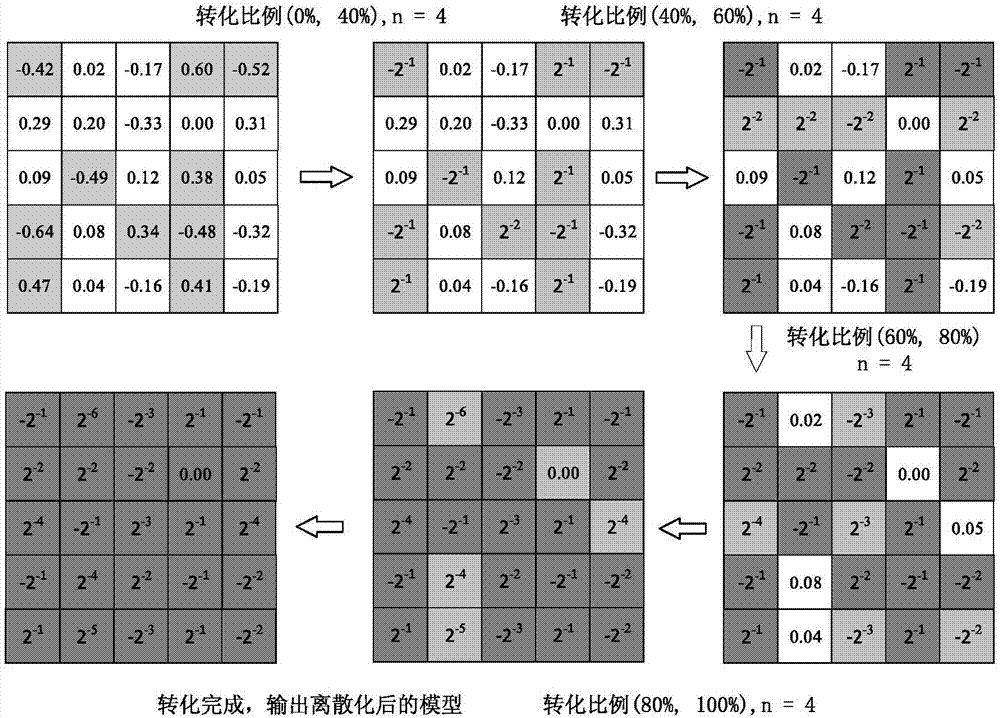
The invention provides a convolutional neural network model based data processing method and device. The method includes steps: cyclically training parameter data of a convolutional layer and / or a full connection layer in a convolutional neural network model to acquire discrete data in a preset format; storing the discrete data in the preset format by preset bits. According to the technical scheme, the parameter data are converted into the discrete data which are then stored by the preset bits, and consequently compression storage of the model is realized while accuracy loss of the model after conversion is avoided; due to adoption of the discrete data in the preset format, operation efficiency is greatly improved.
Owner:INSPUR SUZHOU INTELLIGENT TECH CO LTD
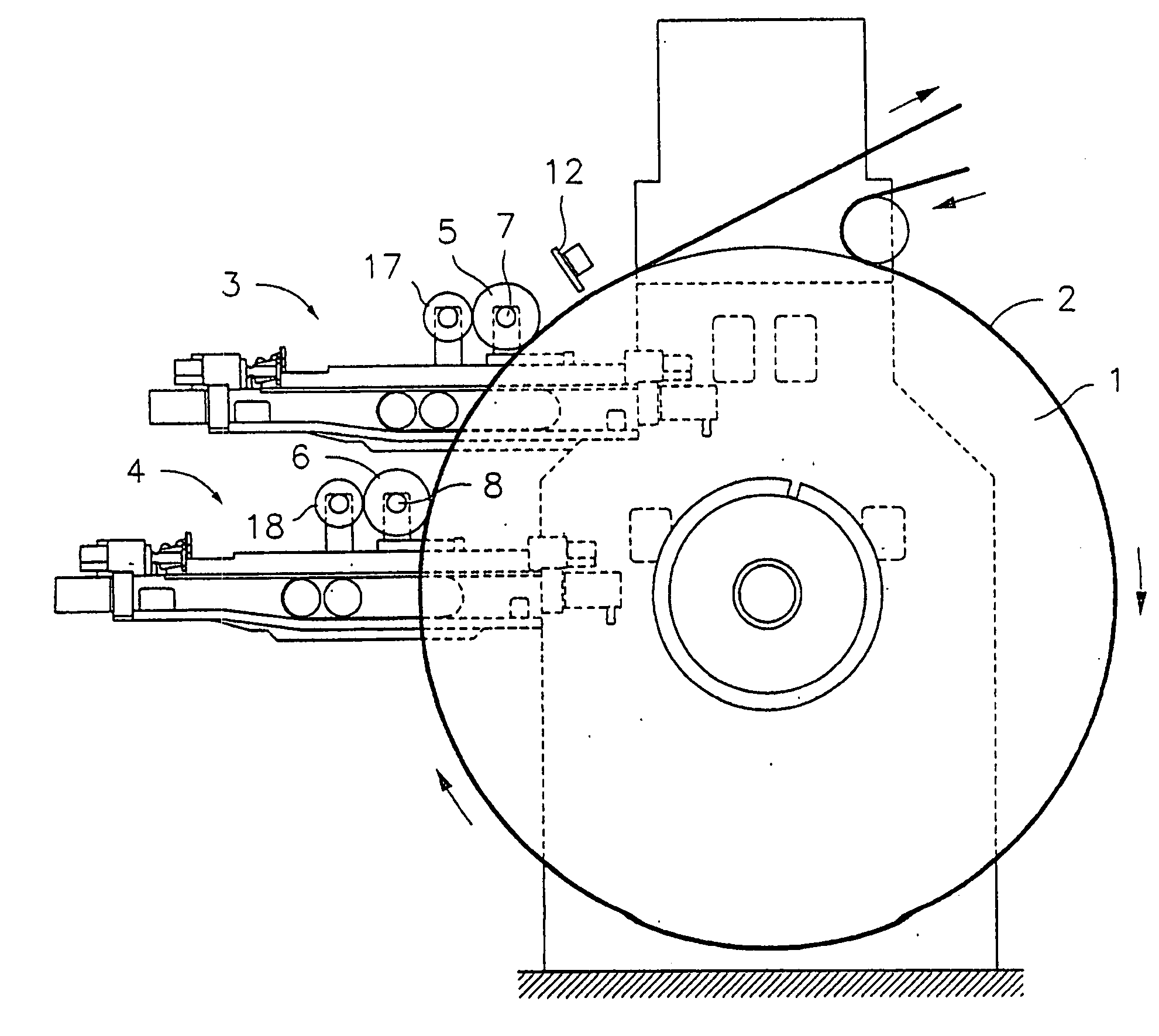
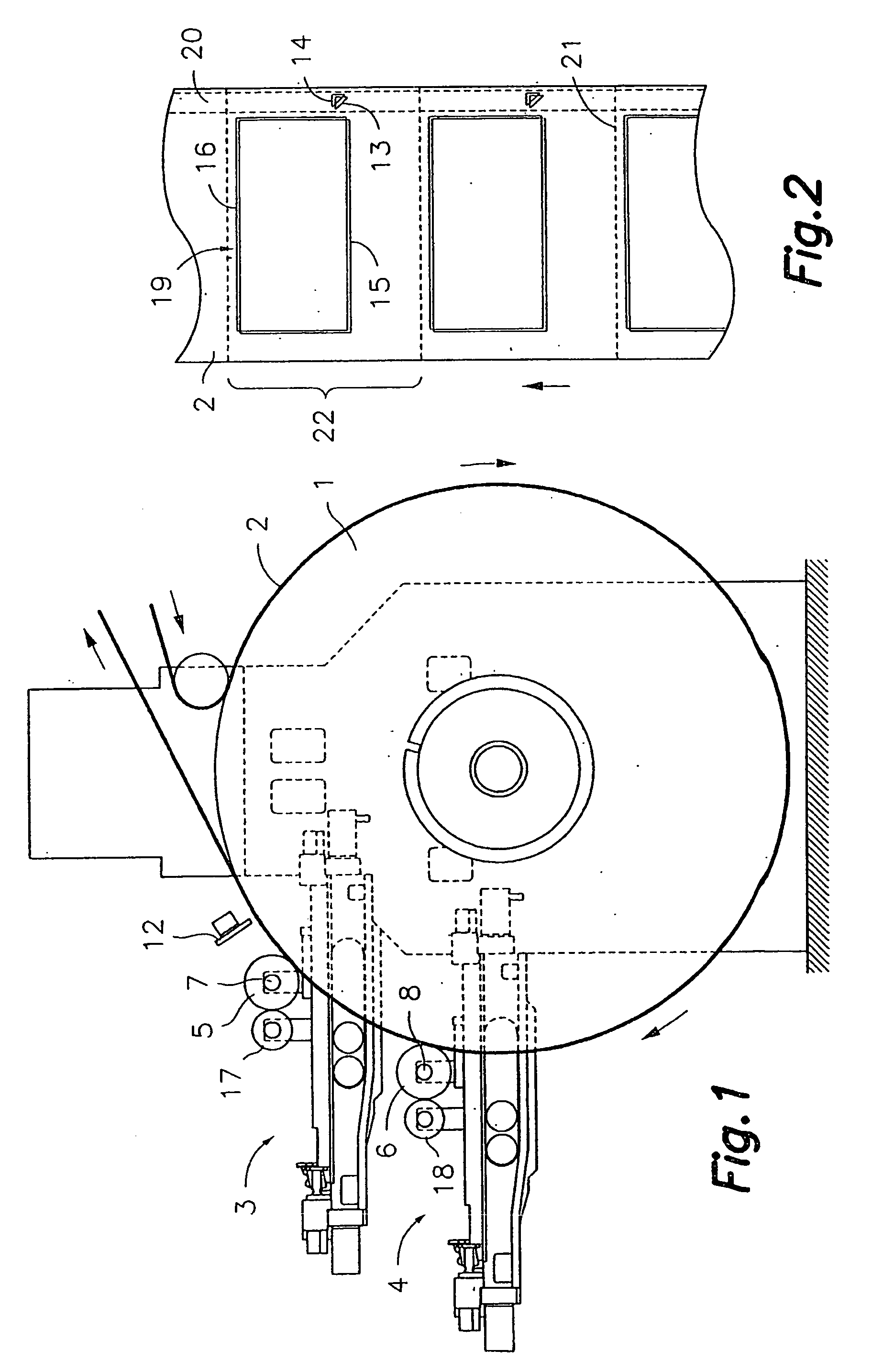
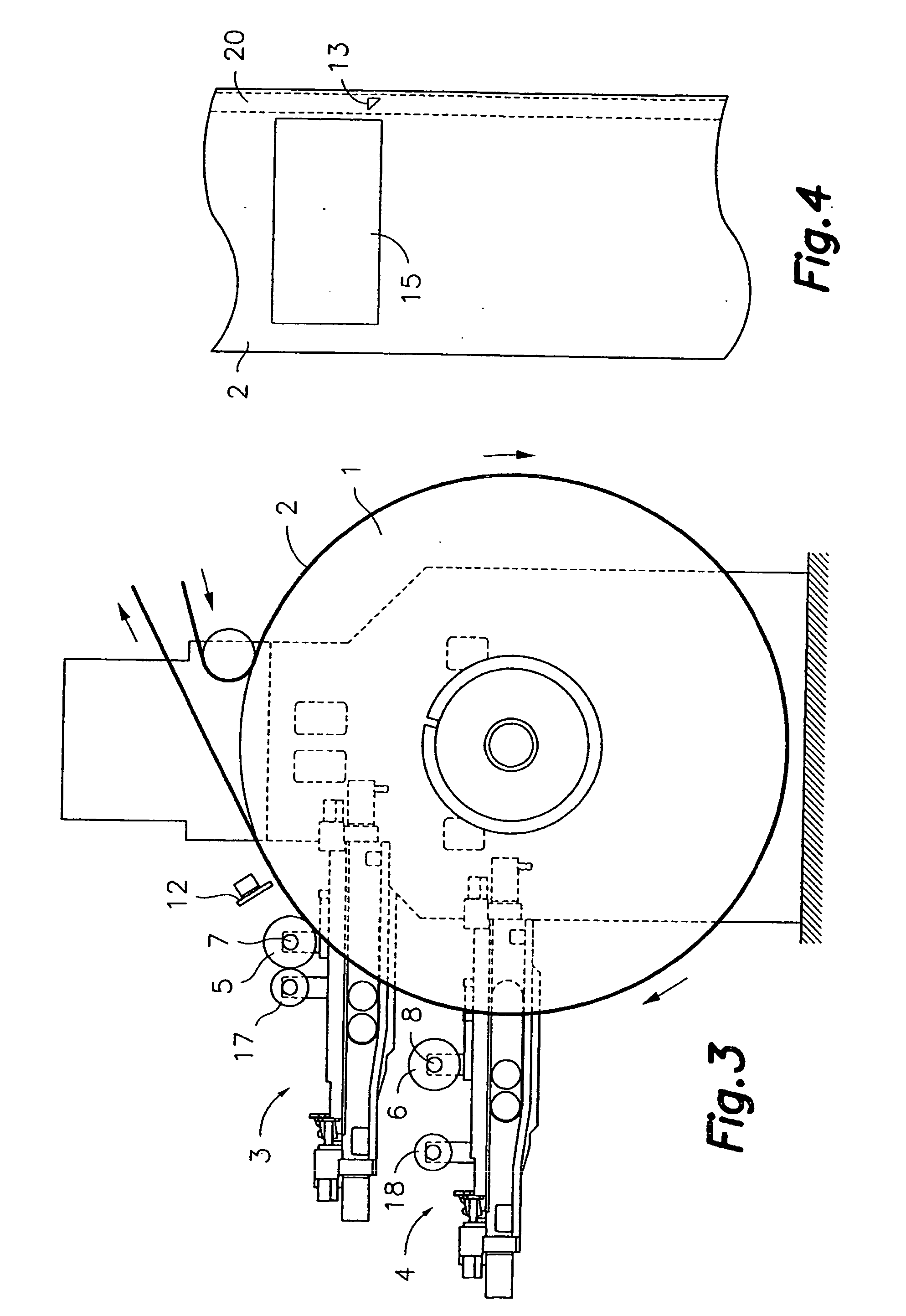
Method of registering different colours in flexography, and flexographic printer comprising a device for implementing said method
InactiveUS20060219109A1Less timeNo loss of precisionRotary pressesOther printing apparatusPrinting pressElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of registering various colours in flexography, and a flexographic printer comprising a device for implementing the method are provided. The printer comprises at least one supporting drum with at least first and second printing rollers and an optical sensor, downstream from the rollers. The method comprises consecutively printing first and second marks with the first and second rollers, using the sensor to generate first and second position signals that are representative of the positions of the first and second marks within a printing length and to generate adjustment signals by comparison of the second position signal with the first position signal, taken as reference, or the first and second position signals with a pre-established position signal. The positions of rollers are adjusted based on the adjustment signals.
Owner:COMEXI GRP IND
Prediction control method and system for magnetic levitation system
ActiveCN109991850ANo loss of precisionFeasibleAdaptive controlGaussian radial basis functionNon linear dynamic
The invention discloses a prediction control method and system for a magnetic levitation system. By historical data of the magnetic levitation ball system and through adopting a system identificationmethod, an autoregressive model which takes a Gaussian radial basis function network as a coefficient and has an exogenous variable is established to describe nonlinear dynamic characteristics betweenan input voltage of an electromagnetic winding and a position of a steel ball. An ARX model coefficient is fit by an RBF neural network, so that an RBF-ARX model can well depict the nonlinear dynamiccharacteristics of the magnetic levitation ball system. Then, on the basis of a principle of a predictive functional control algorithm, a structure of a control input is determined so as to completerolling optimization and error correction. The predictive functional control algorithm has higher tracking capacity and higher robustness than PID control, and has a smaller online calculation amountand a higher control speed than conventional model prediction control; and when a system set value is a step signal, the control method can implement unbiased tracking.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
High-speed AC five-axis linkage double swing head
PendingCN108188455AAvoid errorsImprove machining accuracyMilling machinesLarge fixed membersAviationEngineering
The invention discloses a high-speed AC five-axis linkage double swing head, and relates to the technical field of milling machine accessories. The high-speed AC five-axis linkage double swing head comprises a C-axis motor, an A-axis motor and an electric main shaft, wherein a C-axis speed reducer is arranged at one end of an output shaft of the C-axis motor, a C-axis connecting disc is arranged on one surface of the C-axis speed reducer, a main body is arranged on one surface of an output port of the C-axis speed reducer, and a main body left side protection cover is arranged on one side faceof the main body. According to the high-speed AC five-axis linkage double swing head, A-axis speed reducer fixing nuts are loosened, four left-hand nuts are used for adjusting the A axis, and therefore the A axis is parallel to the Z axis of a machine tool; the A-axis fixing nuts are strengthened, errors generated in the installation and production process are avoided, the working efficiency andthe production machining accuracy are improved, the production cost is reduced, the manual input is reduced, the production cycle is shortened, and the high-speed AC five-axis linkage double swing head can be widely applied to numerically-controlled machine tools in multiple fields such as molds, aviation, spaceflight, high-speed trains, war industry, scientific research, teaching, medical treatment and shipping.
Owner:浙江晨好智能科技有限公司
Image security retrieval method based on secret sharing in cloud environment
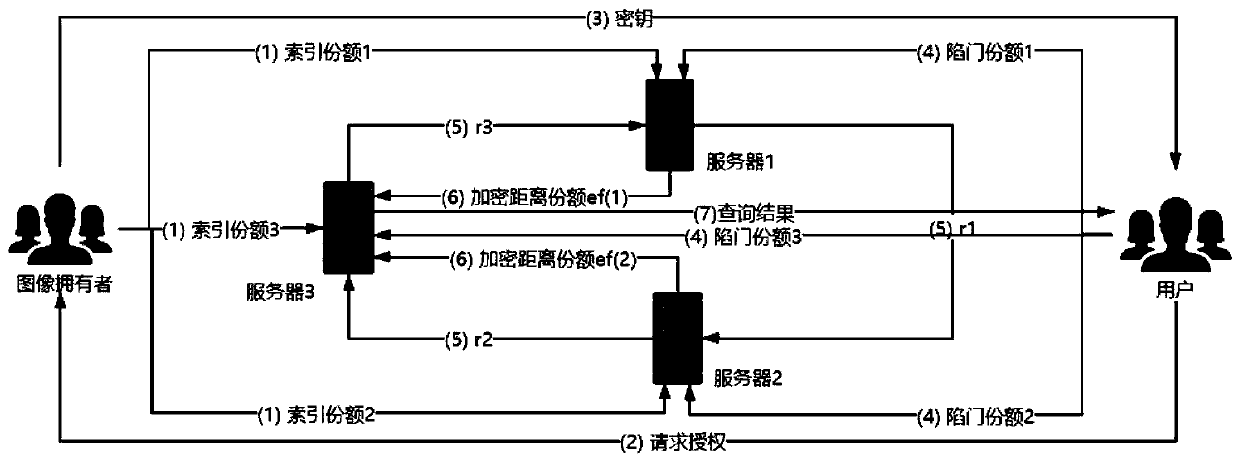
ActiveCN111541679AProtection securityIncrease the difficultyKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesCiphertextEngineering
The invention aims to provide an image security retrieval scheme based on secret sharing in a cloud environment, which realizes security retrieval of a cloud image by constructing an index share and atrap door share. A data owner generates a ciphertext image and an index share and uploads the ciphertext image and the index share to a cloud, during query, a user generates a trap door share and sends the trap door share to the cloud, and the cloud can calculate a distance share and return the ciphertext image closest to the query image, so that the security problem caused by using a unified keyfor encryption in an existing scheme can be solved. In order to prevent an attacker from analyzing image similarity information according to an original Euclidean distance to speculate an image, a random number and a secure multi-party calculation method are used to encrypt a distance share. The security of the scheme depends on a secret sharing technology, the common precision loss problem in image security retrieval is solved, and the retrieval precision is almost consistent with that of plaintext domain image retrieval.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for cutting sheet-metal plates into sheet-method strips and a cutting device for carrying out the same
InactiveCN1341046ANo loss of precisionSave spaceRegistering devicesMetal-working feeding devicesMetal stripsEngineering
The invention relates to a cutting device for cutting stacked sheet-metal plates into sheet-metal strips using a cutting unit (12). Holding and positioning means (25 to 29 and 13 to 16) are arranged above said stack. This makes a space-saving arrangement possible while maintaining a high degree of cutting precision. The cut sheet-metal strips are fed to another cutting unit by collectively feeding all strips up to a separating point. This simplifies the feeding device and the adaptation thereof to different sheet-metal thickness.
Owner:ELPATRONIC AG
Method and apparatus for previewing panoramic contents
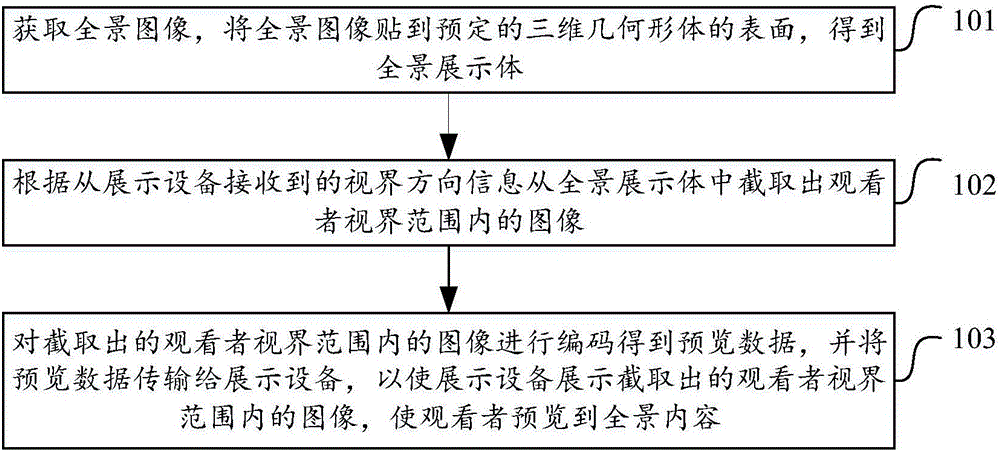
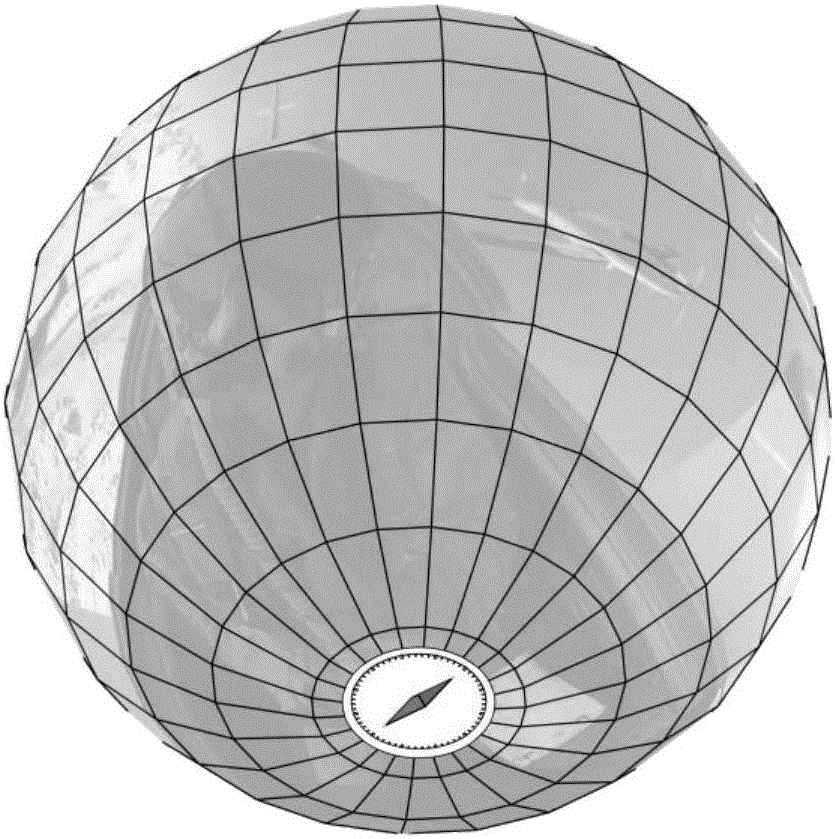
InactiveCN106453913ANo loss of precisionRising consumptionSubstation equipmentHigh level techniquesVisual field lossDisplay device
The invention discloses a method and apparatus for previewing panoramic contents. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a panoramic image, and adhering the panoramic image on the surface of a predetermined three-dimensional geometric body to obtain a panoramic display body; intercepting an image within a viewer visual field range from the panoramic display body according to visual field direction information received from a display device; and encoding the intercepted image within the viewer visual field range to obtain preview data, and transmitting the preview data to the display device, so that the preview data displays the intercepted image within the viewer visual field range, and thus a viewer previews the panoramic contents. By adoption of the method and apparatus disclosed by the invention, zooming of the panoramic image is not required, the original precision of the sensor input image is not lost, the display effect is clearer, moreover, the increase of excessive DDR bandwidth consumption and power consumption caused by image zooming is avoided, meanwhile only the image within the visual field is focused, thereby better meeting the mode of the human body to observe the outside, and the transmission of redundant data is reduced, so the network bandwidth is effectively used.
Owner:BEIJING MADV TECH CO LTD
Pruning method for embedded network model
InactiveCN109754080AReduce reconstruction errorImprove practicalityNeural architecturesNeural learning methodsNetwork modelComputer science
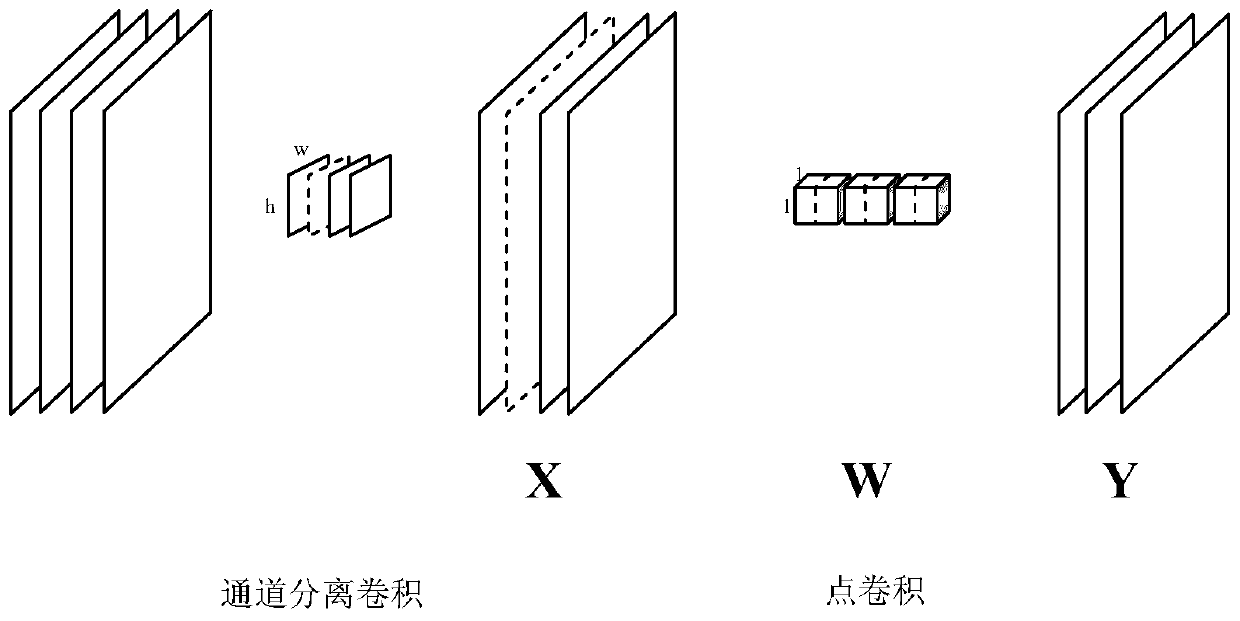
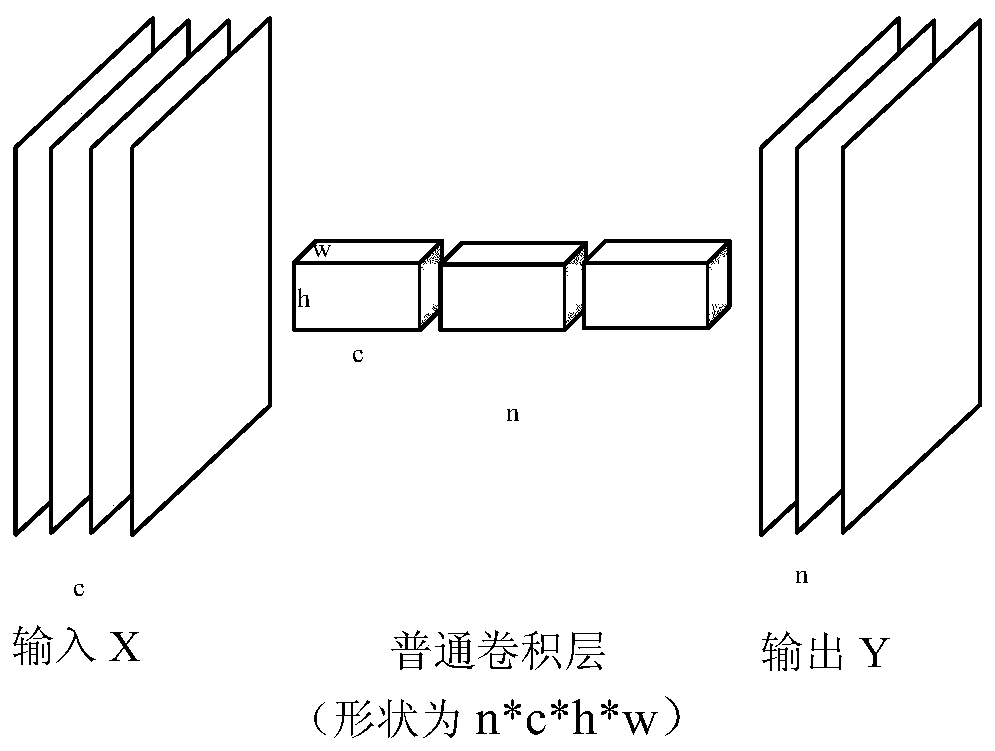
The invention discloses a pruning method for an embedded network model. The pruning method is used for solving the technical problem that an existing pruning method is poor in practicability. According to the technical scheme, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a mobienet SSD network model, and carrying out a forward operation to obtain data required by pruning calculation; Channels which are not important to a convolution layer calculation result are selected through lasso regression, and channels which have relatively low influence on a summation result in the channels are selected through a lasso algorithm; The Mobienet resolves an original layer of convolution into a channel separation convolution layer and a point convolution layer, and an input channel ofthe channel separation convolution layer is equal to an output channel of the channel separation convolution layer. According to the method, the reconstruction error is reduced to serve as the core,the lasso is used for picking out unimportant channels in all convolution layers, then channel trimming is conducted on all the convolution layers according to the special structure of the mobienet, compression acceleration of the mobienet SSD is completed, and the practicability is good.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Large-scale GNSS data processing method based on GPU
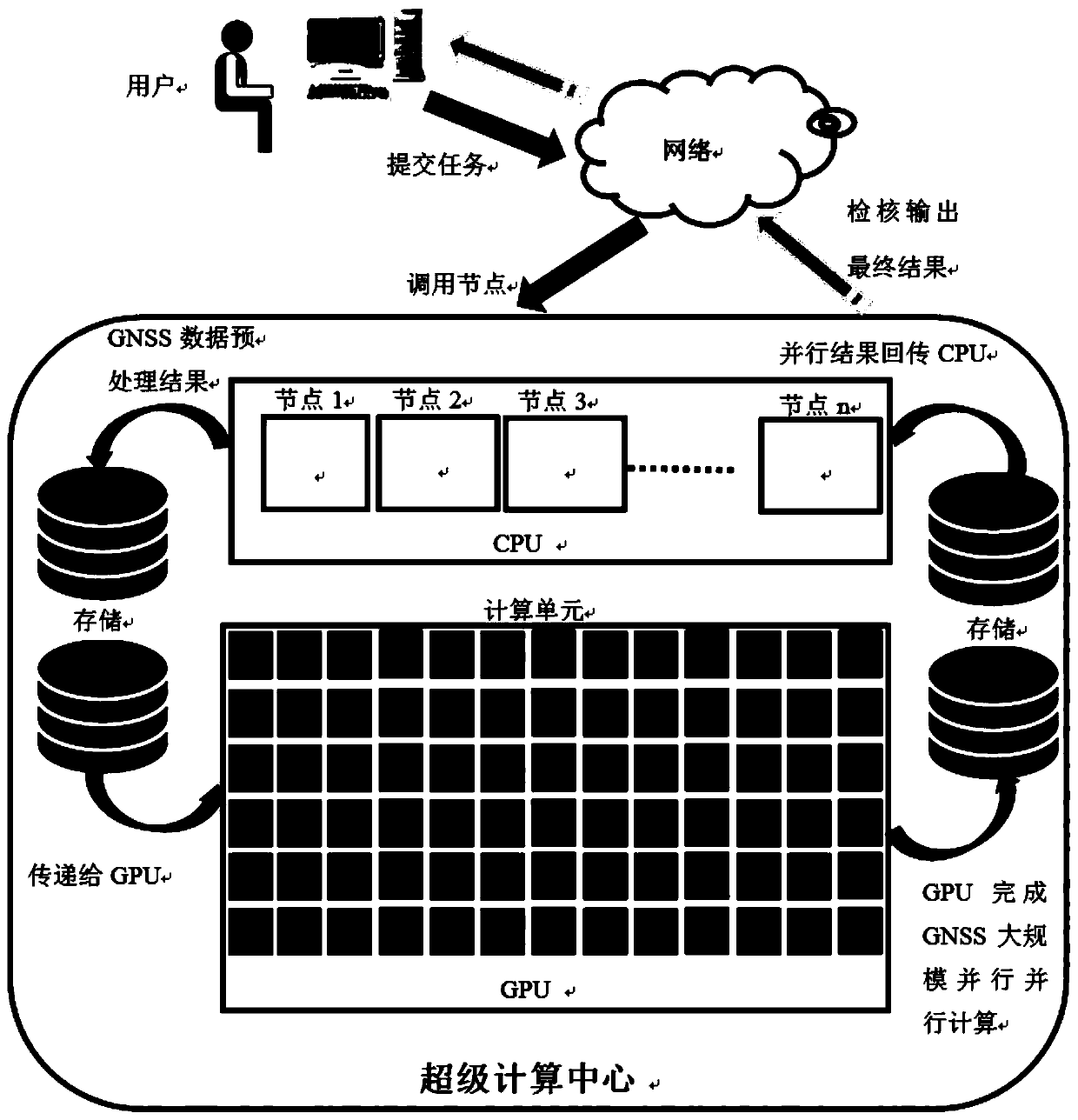
ActiveCN111208541AImprove solve timeNo loss of precisionSatellite radio beaconingComputational scienceEngineering
The invention provides a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit)-based large-scale GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) data processing method and solves a technical problem that whole network resolving consumes too long time in the GNSS large-scale data processing process in the prior art. The method comprises steps of reading and preprocessing data; constructing a normal equation; eliminating parameters; resolving the normal equation; and controlling data quality and outputting a result product. The method can be widely applied to the field of satellite navigation positioning.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
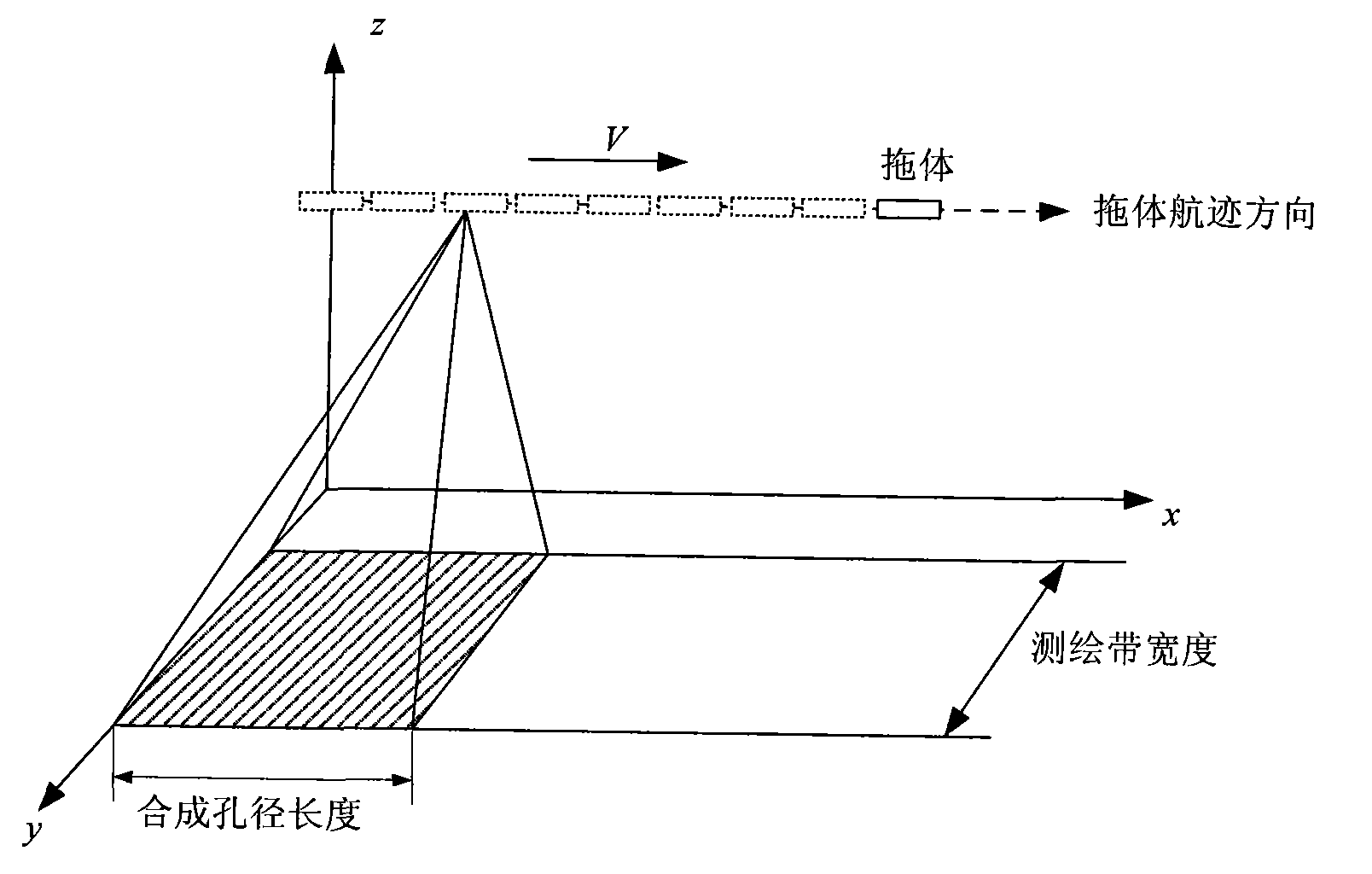
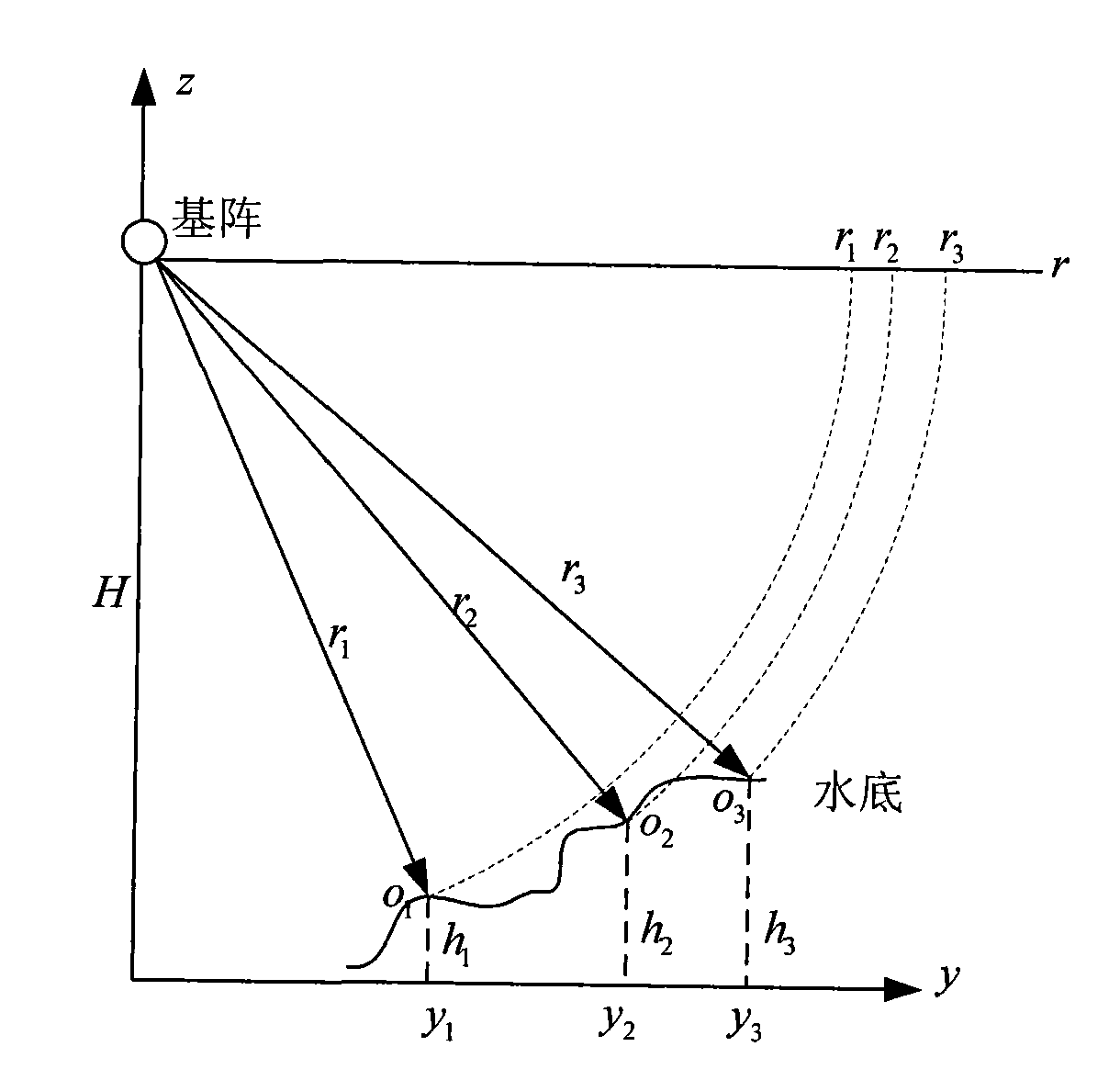
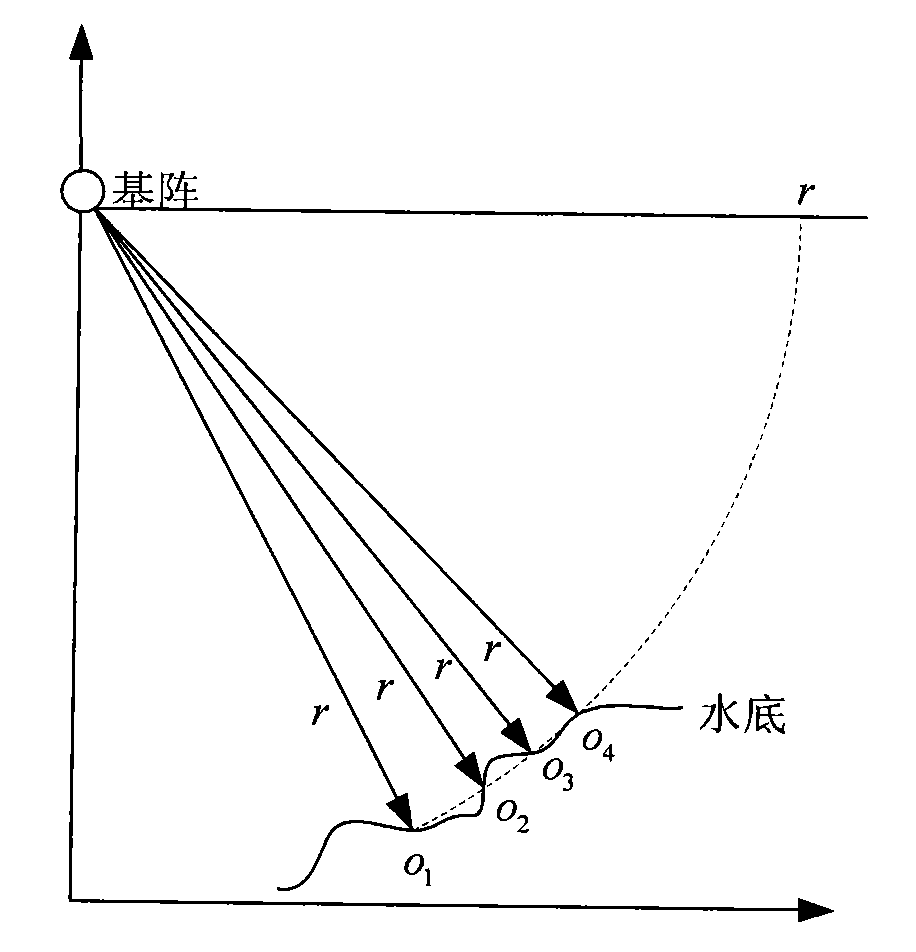
Rapid simulation method of synthetic aperture sonar signal
InactiveCN101598788AReduce target pointsReduce double countingAcoustic wave reradiationSynthetic aperture sonarDelayed time
The invention provides a rapid simulation method of a synthetic aperture sonar signal based on a time delay table, comprising the following steps: (1) setting each simulation parameter of a synthetic aperture sonar system; (2) constructing a height model of a target scene needed to be simulated; (3) projecting the height information of each target point in an oblique distance direction; (4) counting the number of target points in all directions and distances; (5) calculating the delayed time of each ping of the target point corresponding to one synthetic aperture length according to the distance and constructing the time delay table; (6) calculating the basic matrix positions of different pings according to the given speed, performing time delay superposition to a sending signal accordingto the value of the time delay table, and finally obtaining an original echoed signal of the synthetic aperture sonar. The method can improve the computational efficiency of synthetic aperture sonar simulation signals and effectively perform echoed signal simulation of synthetic aperture sonar under the condition with more target points, in particular under the condition with a large-scale landform scene.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
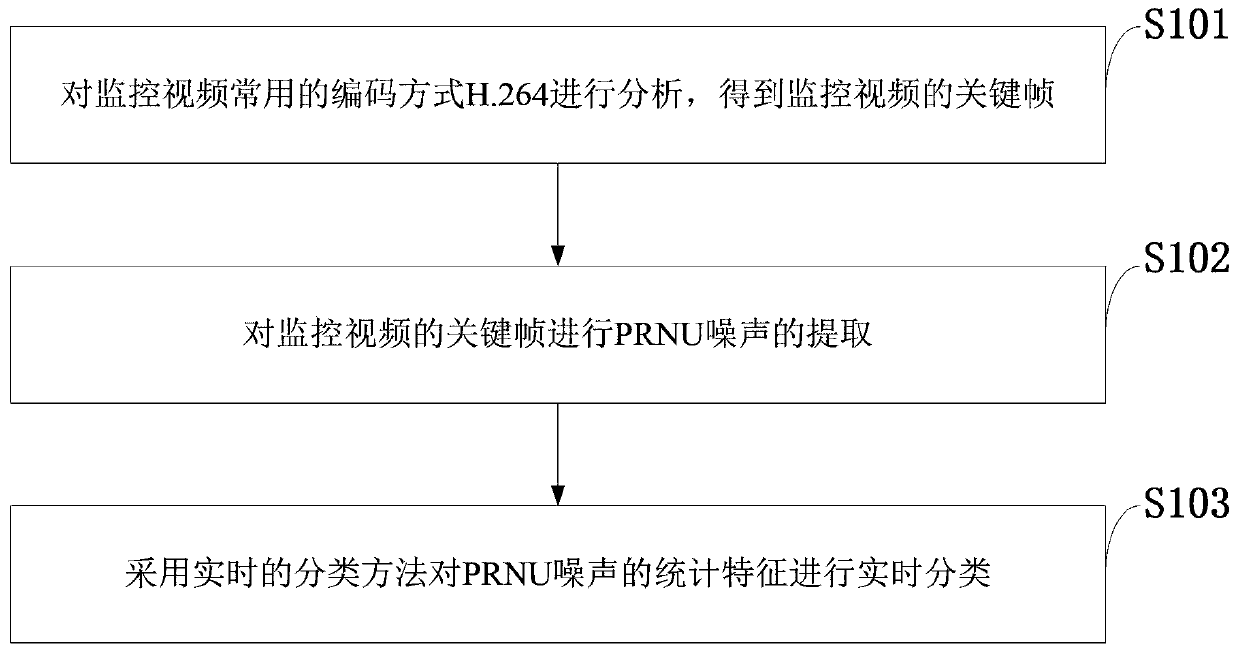
Monitoring system-oriented digital video real-time tracing method and urban video monitoring system
InactiveCN110121109AImprove accuracyReduce computational complexityCharacter and pattern recognitionClosed circuit television systemsDigital videoVideo monitoring
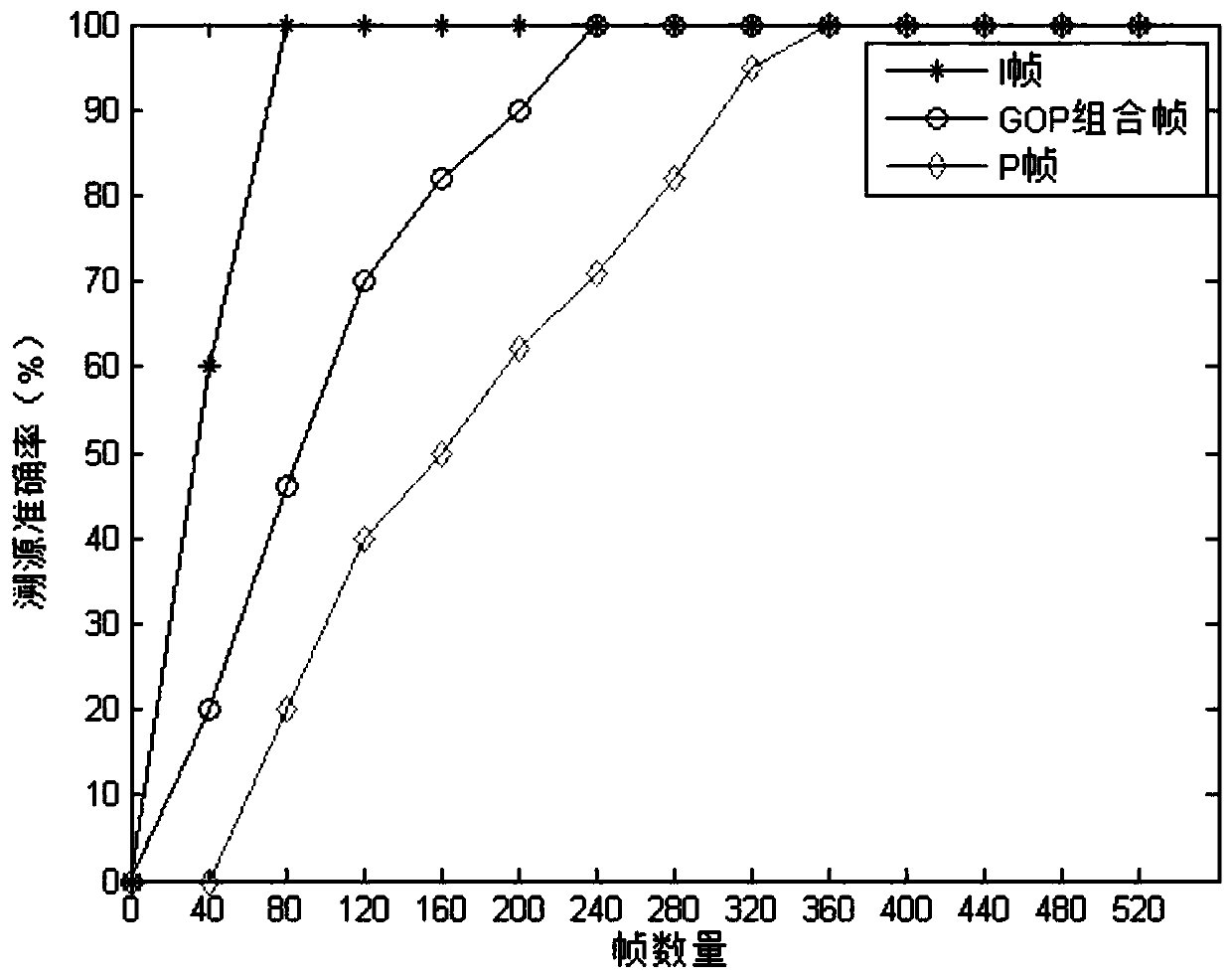
The invention belongs to the technical field of information security, and discloses a monitoring system-oriented digital video real-time tracing method and an urban video monitoring system. The methodincludes the following steps: analyzing a common coding mode H.264 of a monitoring video to obtain a key frame of the monitoring video; carrying out pRNU noise extraction on the key frame of the monitoring video; and carrying out real-time classification on the statistical characteristics of the PRNU noise by adopting a real-time classification method. According to the method, the accuracy of video source identification is improved, and meanwhile, the SFFS algorithm is used, so that the feature dimension can be reduced, the precision is not lost, and the calculation time and the system complexity can be reduced; the method is low in computational complexity and can be applied to videos of different sizes. In addition, the method is also robust for the found video processing and geometrictransformation, and the method is very steady for images subjected to basic image processing or geometric transformation. The method is very necessary in an actual application scene. Therefore, the technology can be used as an effective method for identifying the video source camera.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Power-maintained multi-circle absolute value encoder
InactiveCN102486383AHigh measurement accuracyReduce power consumptionConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyComputer scienceEncoder
The invention relates to a power-maintained multi-circle absolute value encoder. A power-maintained multi-circle absolute value encoder is always one of the most important technologies in industrial control and for the industrial control, encoder application has practical significance. However, it is critical to know how to accurately apply an encoder technology to reduce losses in the industrial control. According to the provided encoder, a low power consumption multi-circle absolute value technology is employed, so that it can be ensured that a vital role can be played in whole industrial control.
Owner:SHENYANG LIGONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com