Patents
Literature
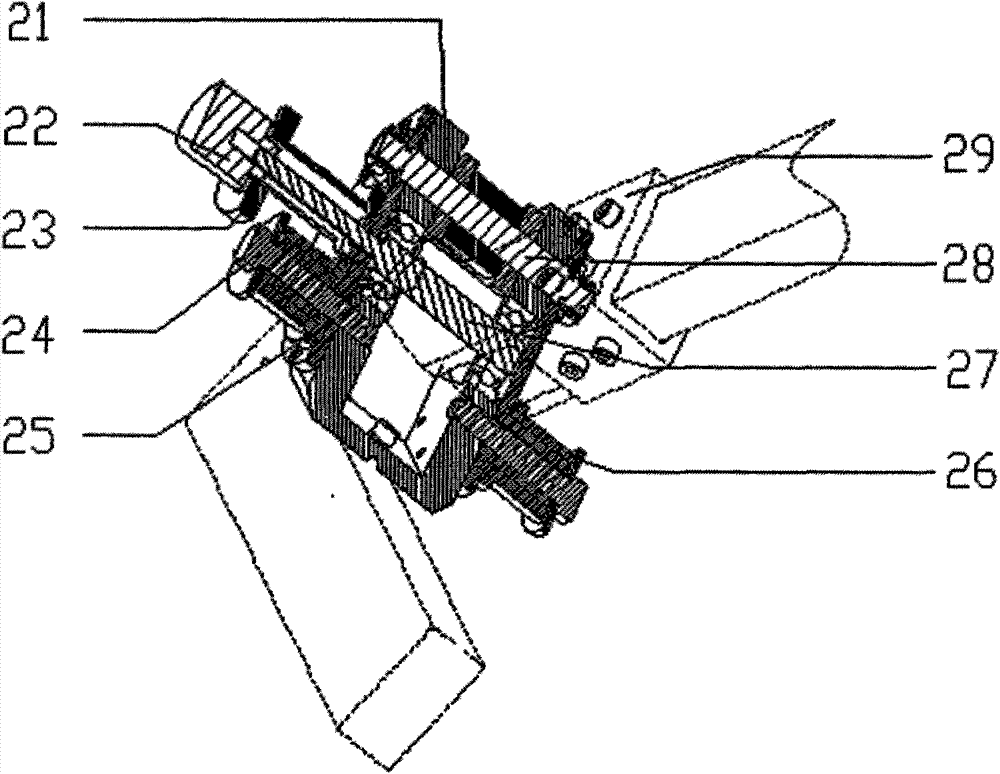
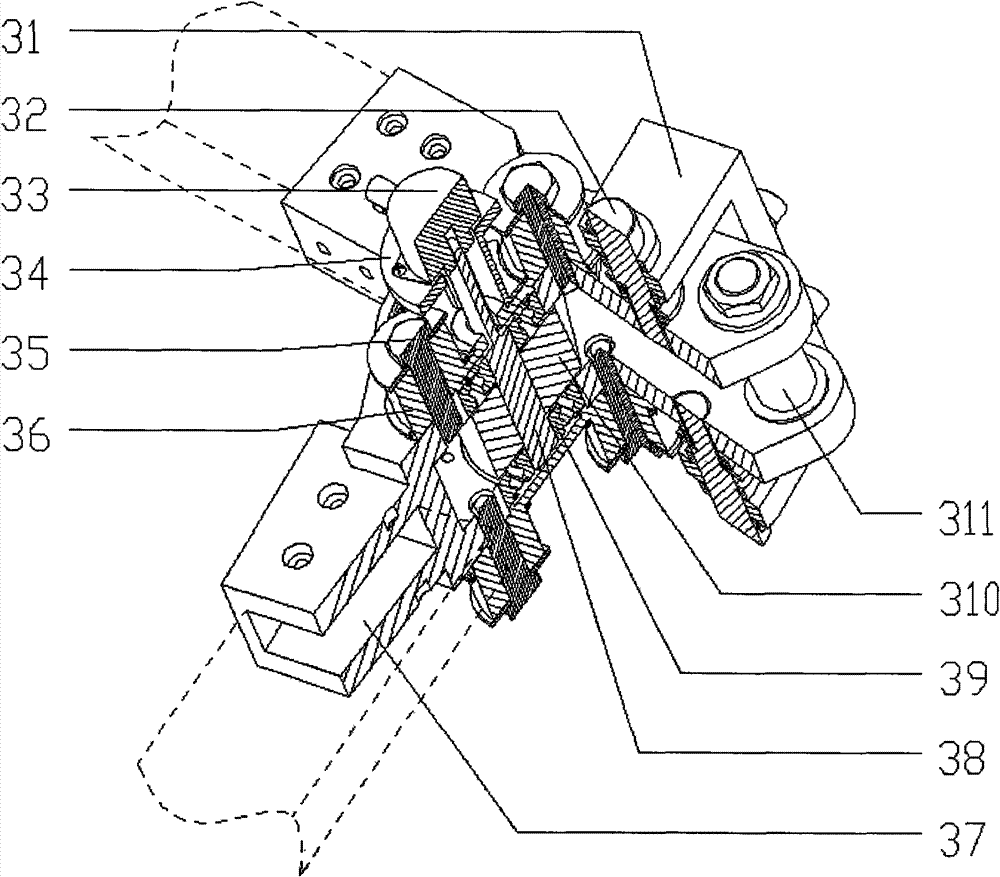
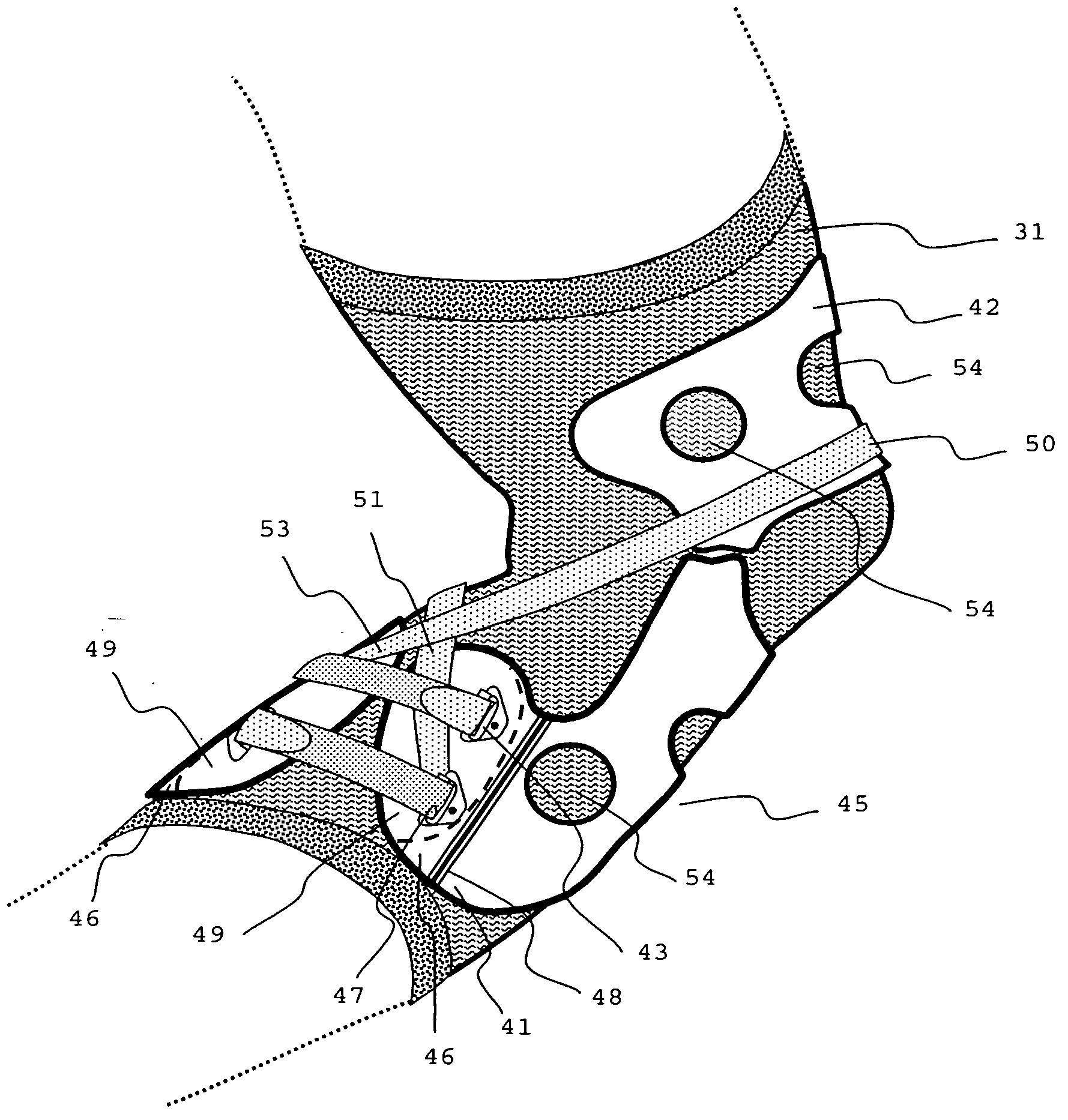
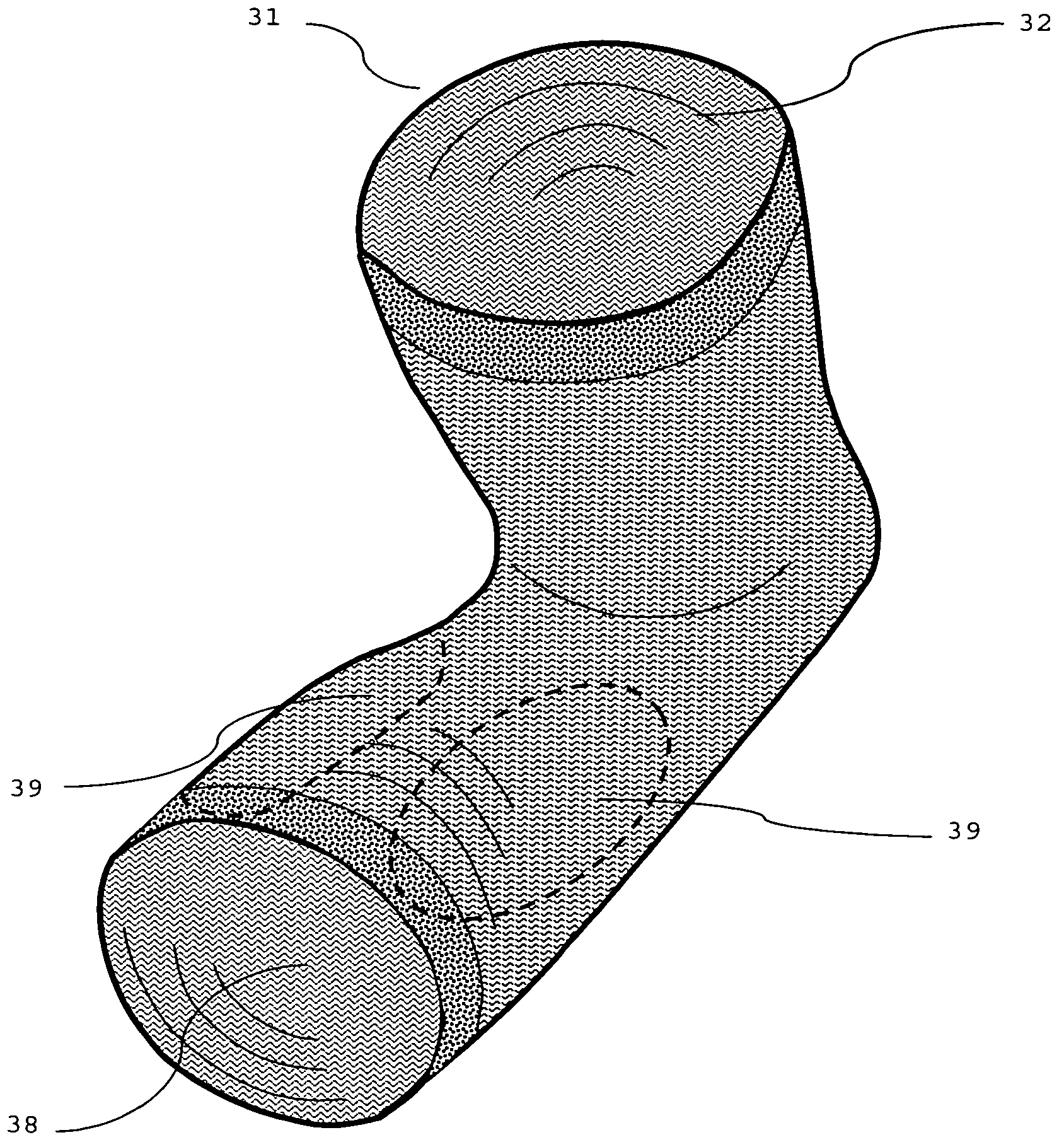
131 results about "Limb joint" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
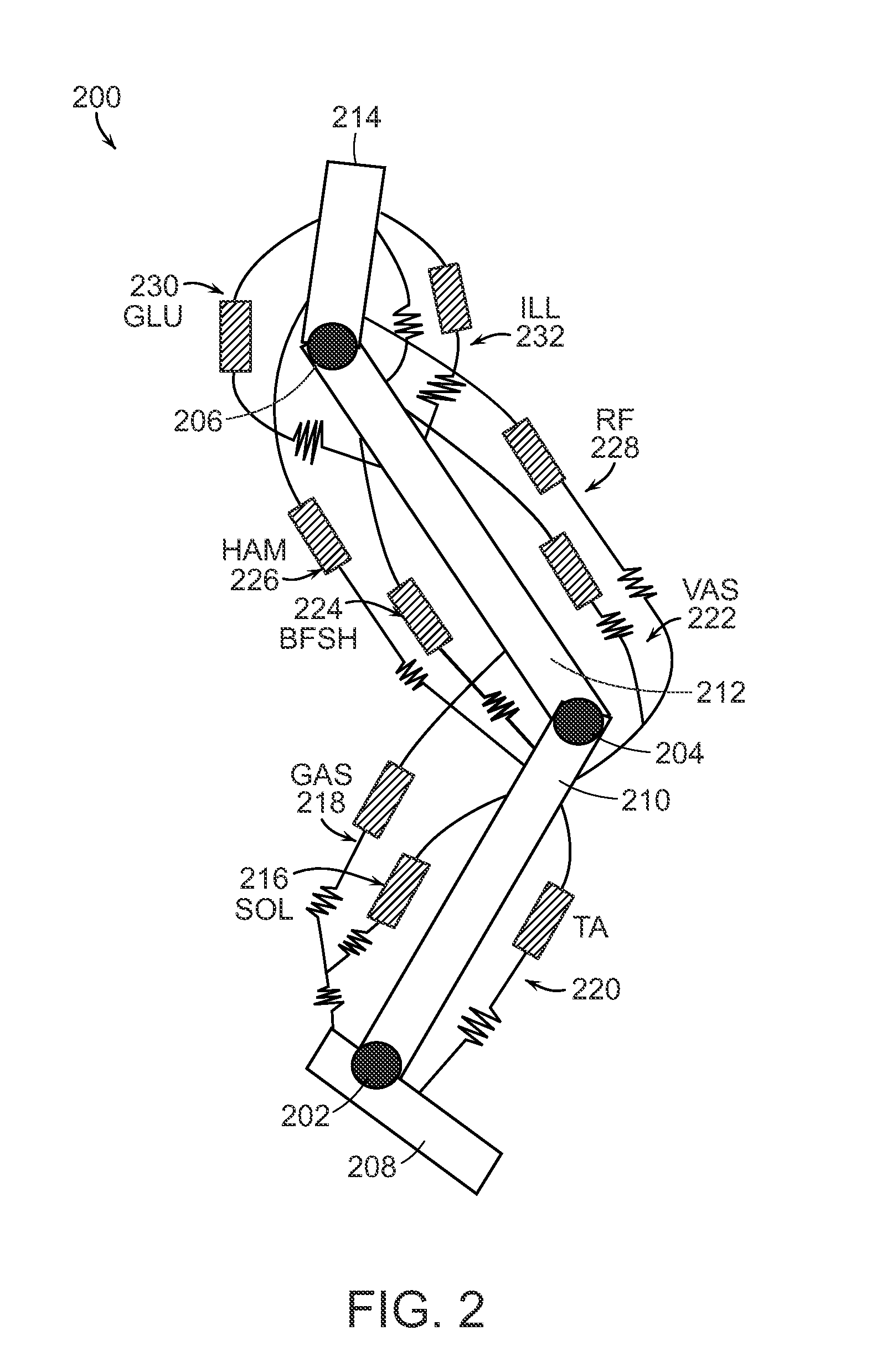
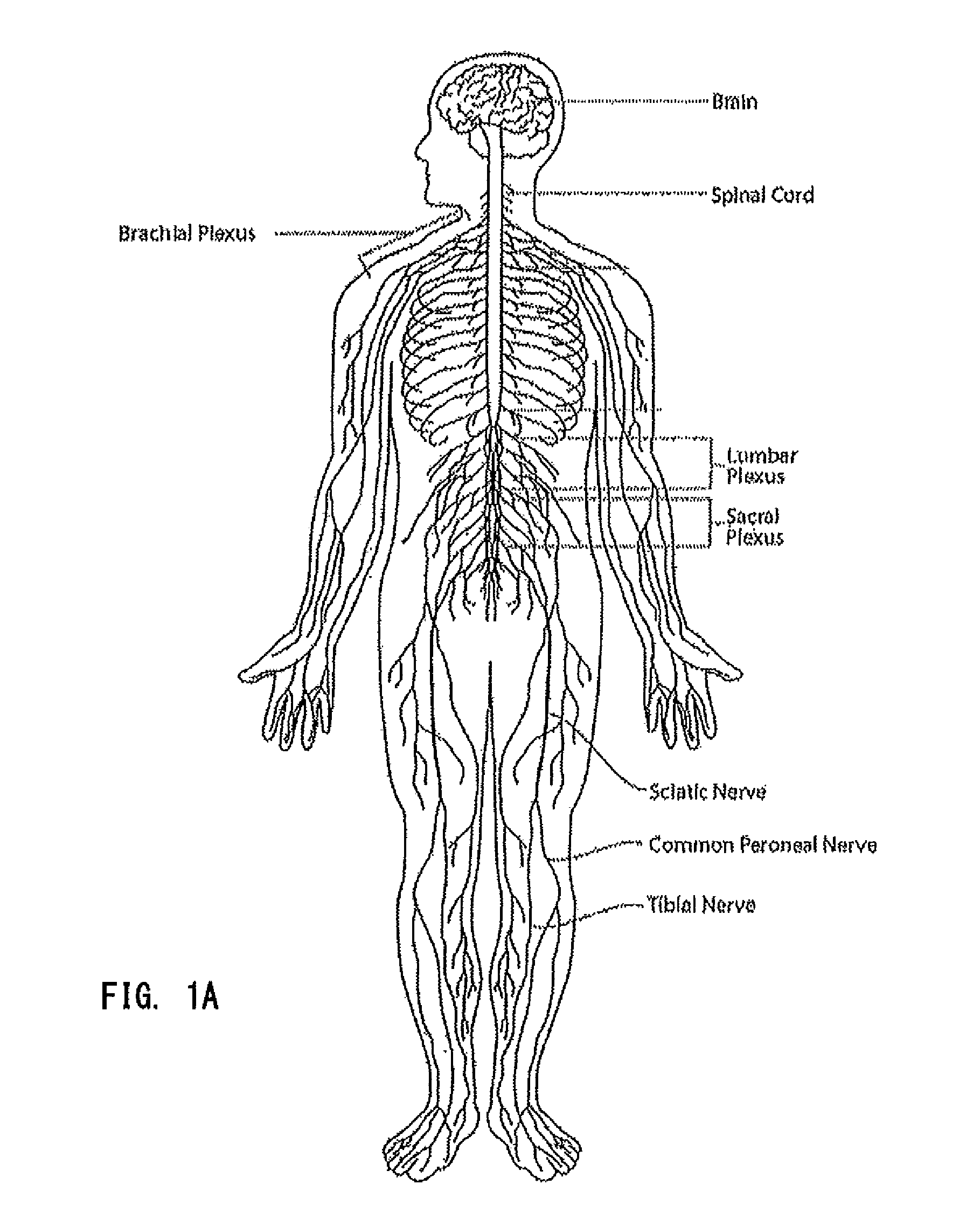
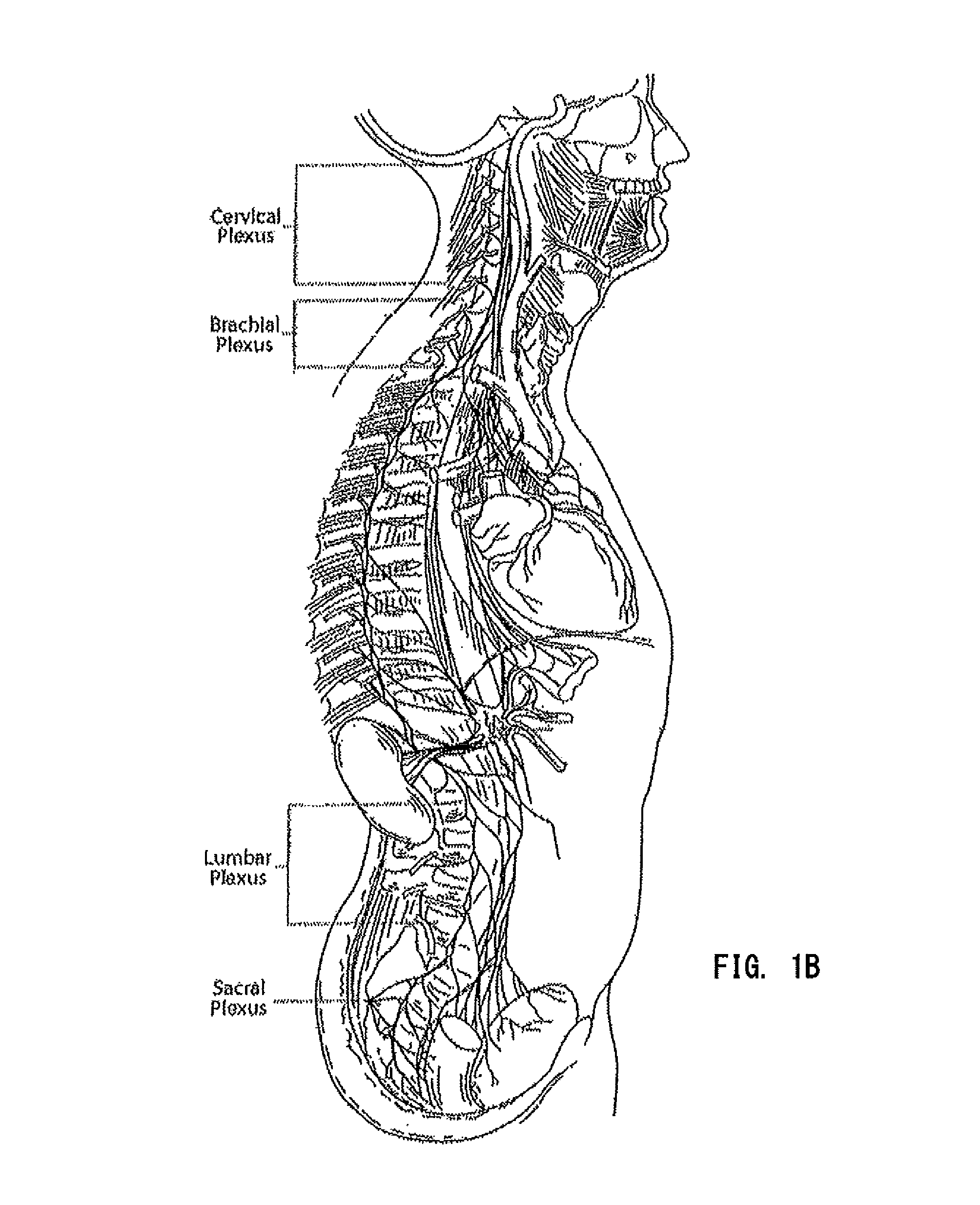
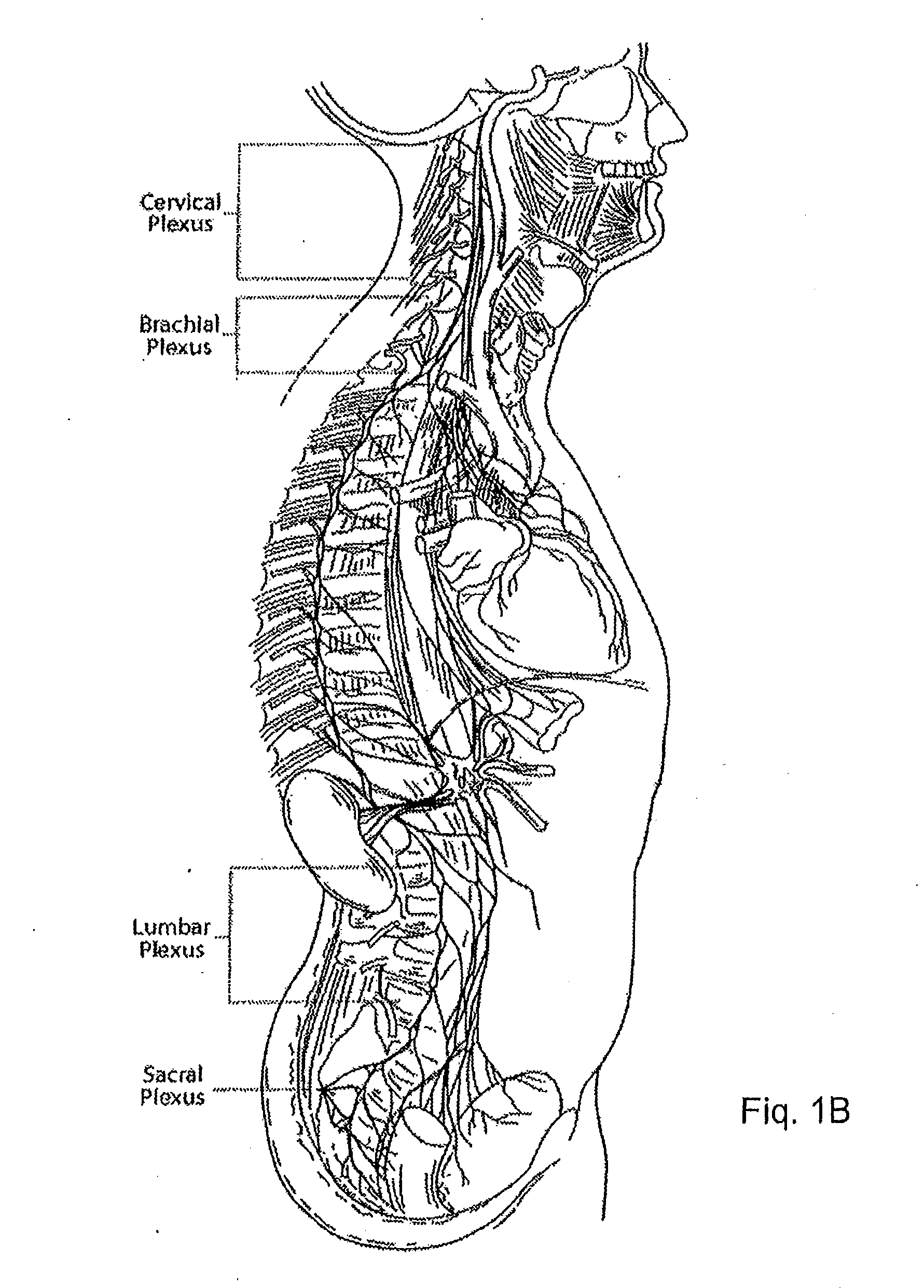
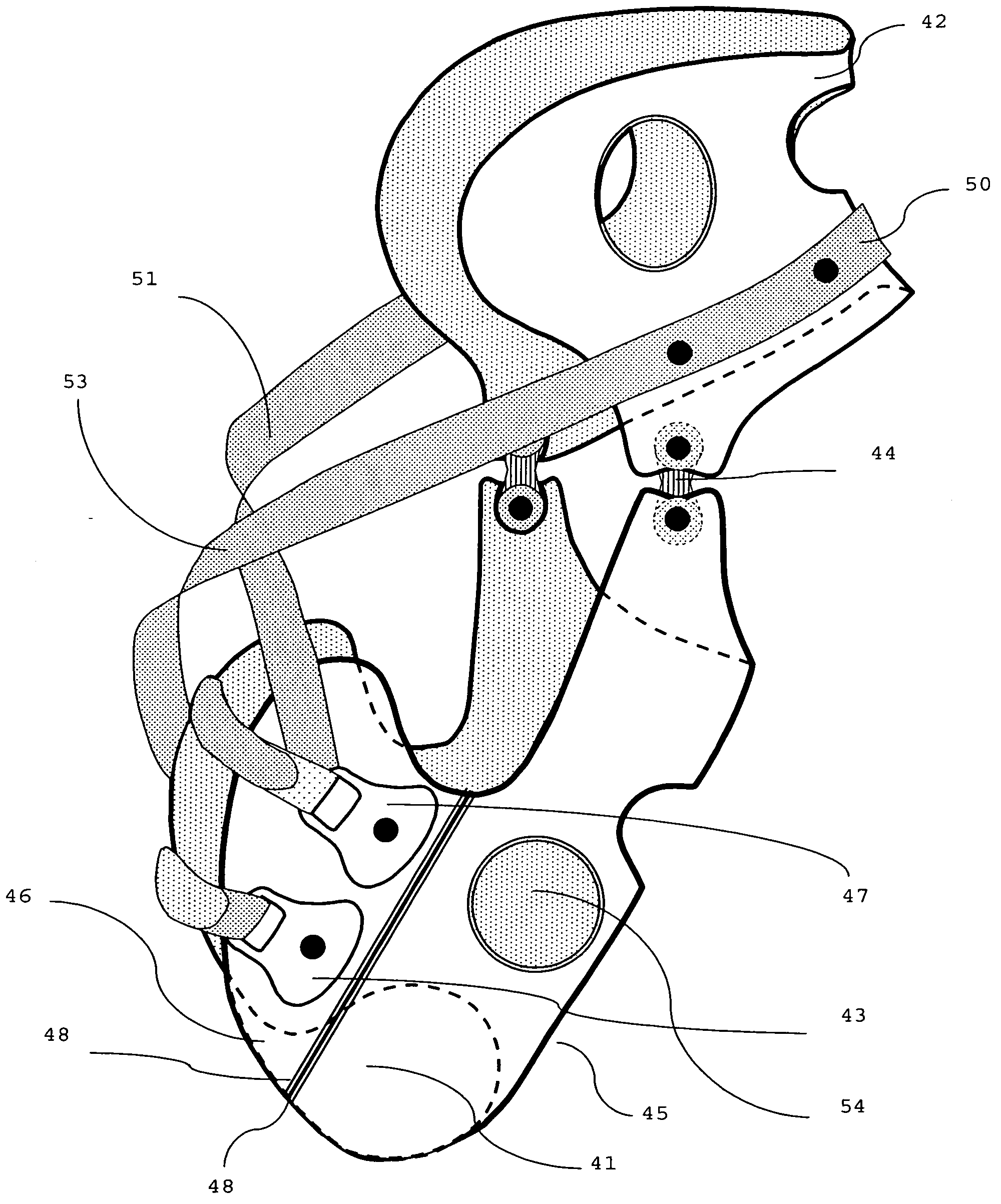
The joints in the lower limb include the sacroiliac joint, hip joint and knee joint, plus two important foot joints: the subtalar and the transverse tarsal joint, which permit inversion and eversion of the foot.
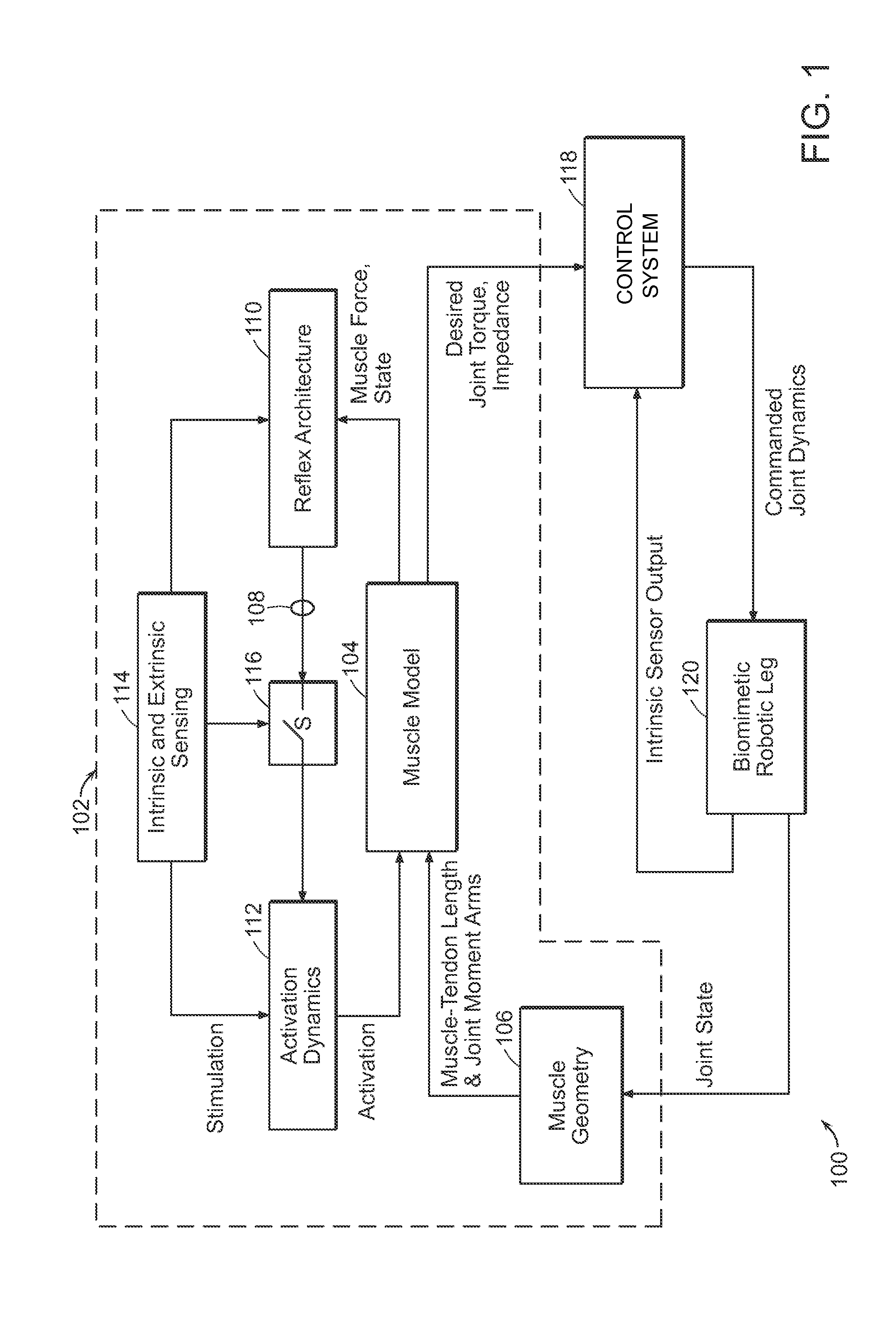
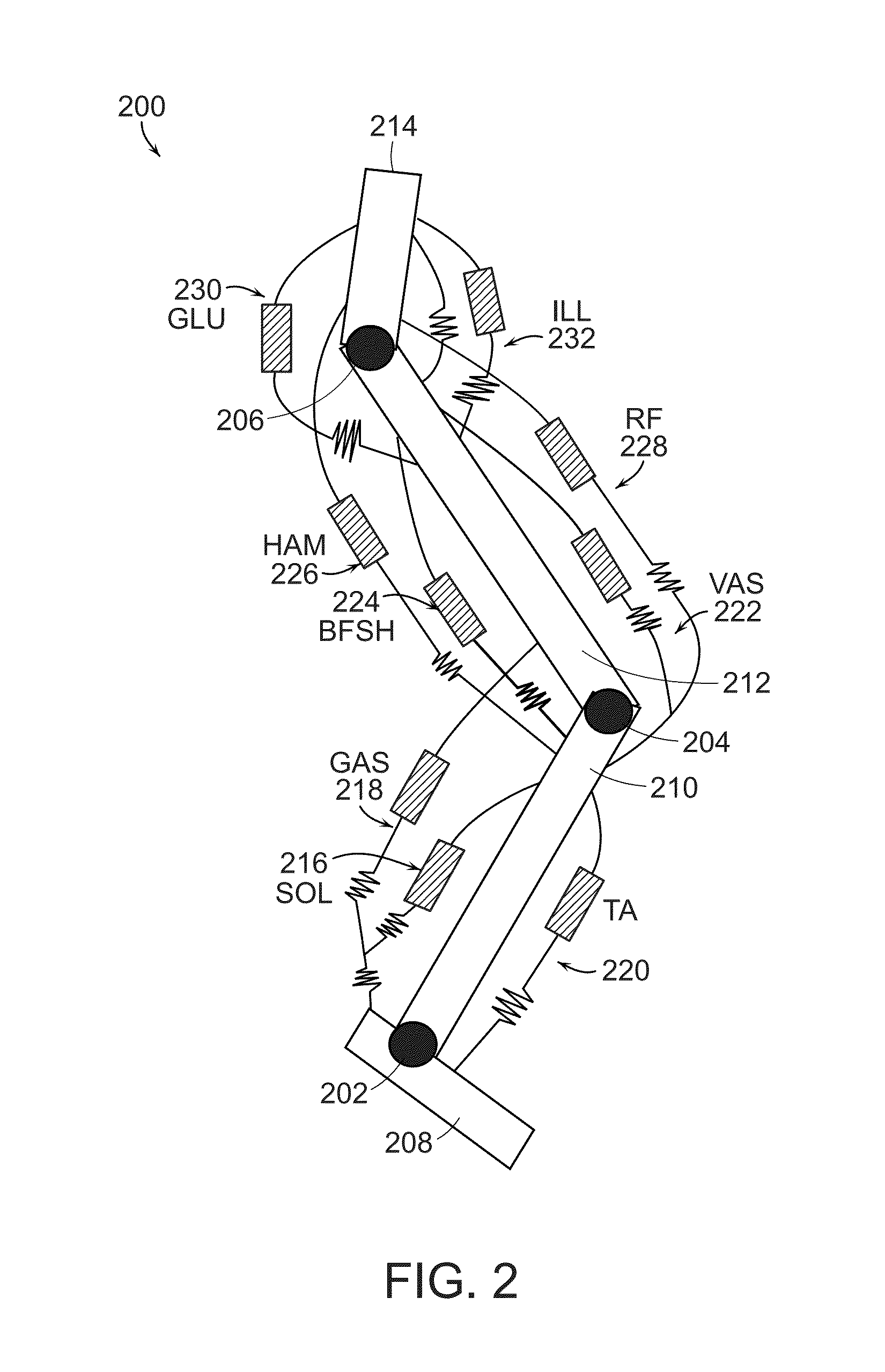
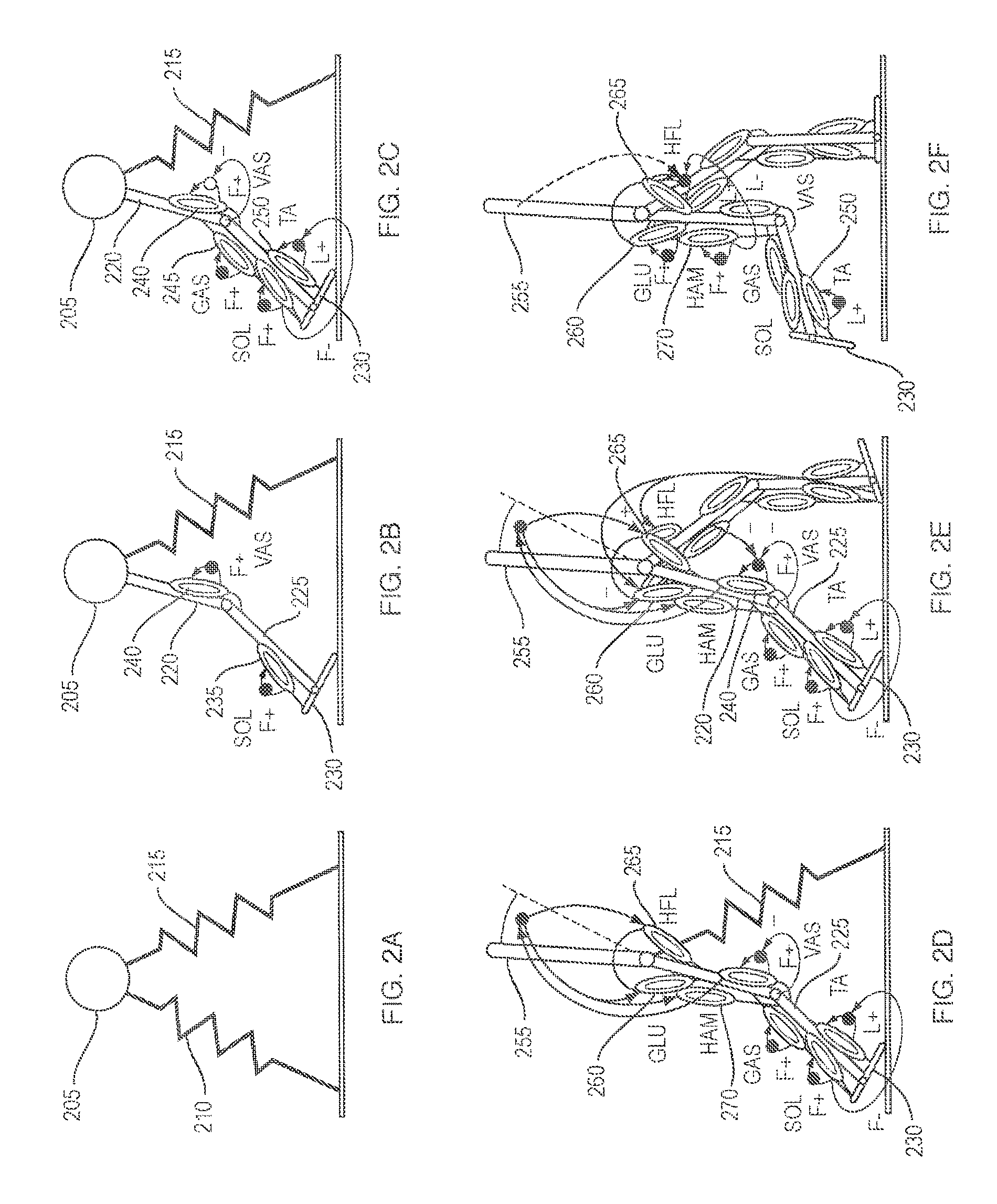
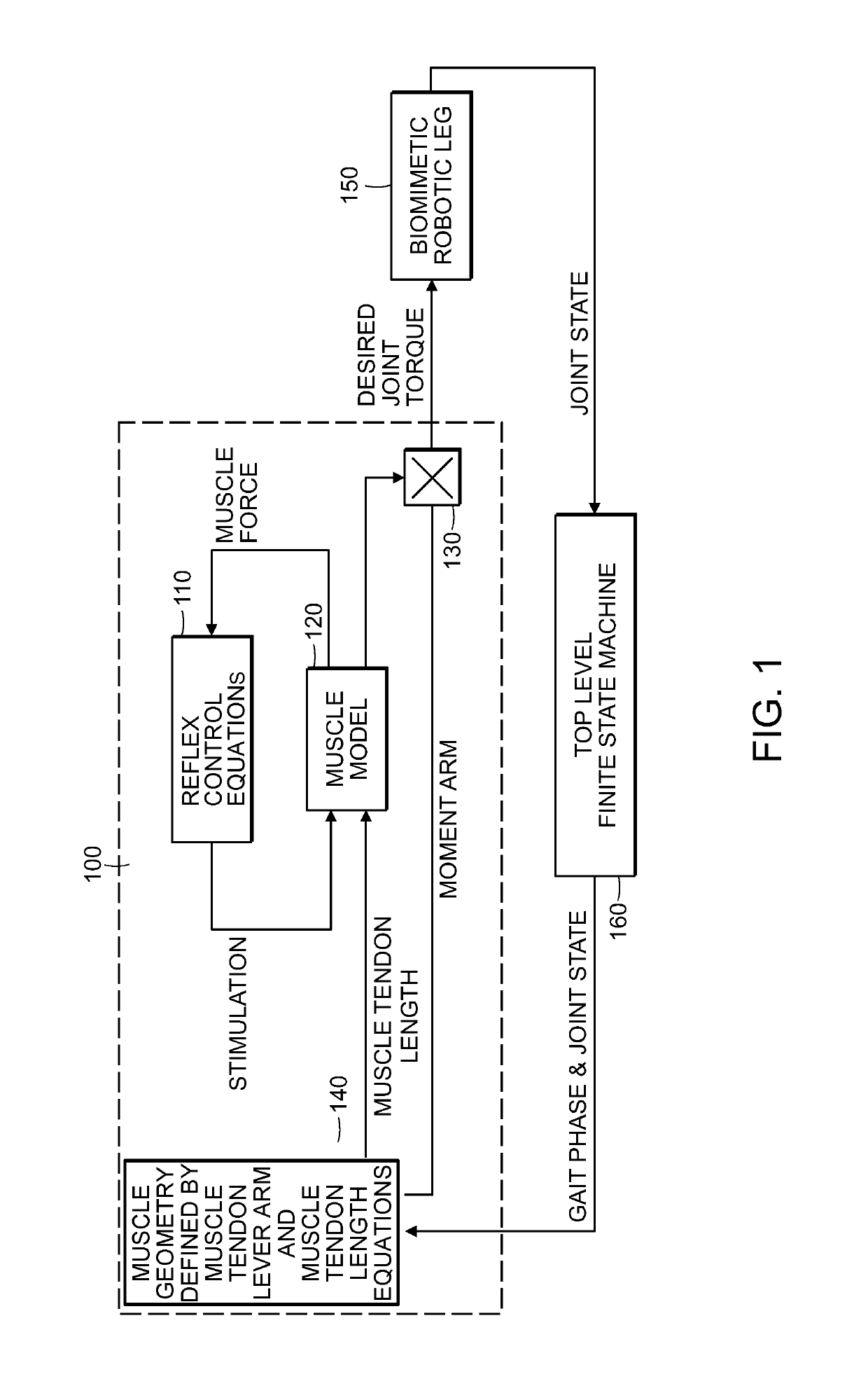
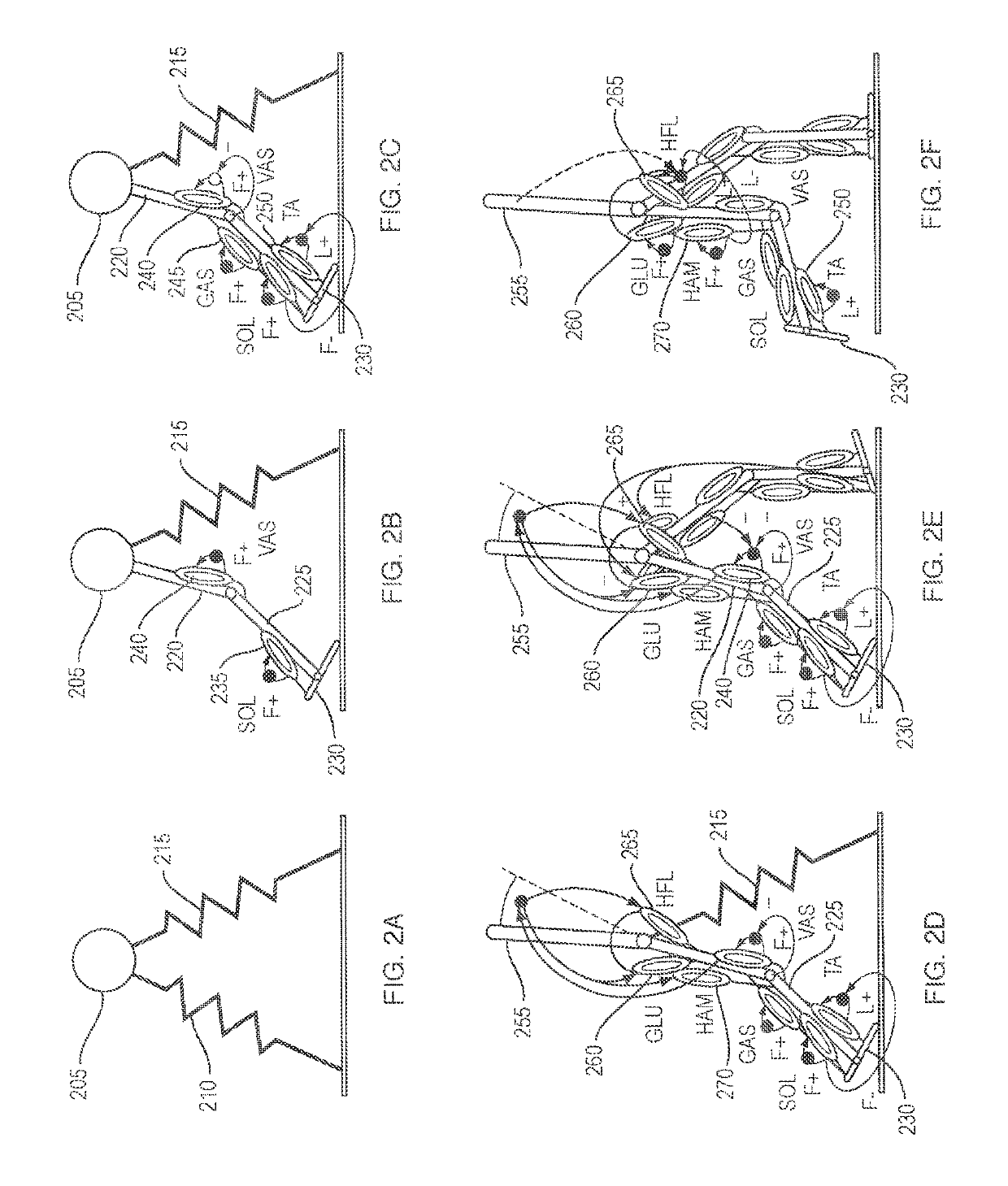
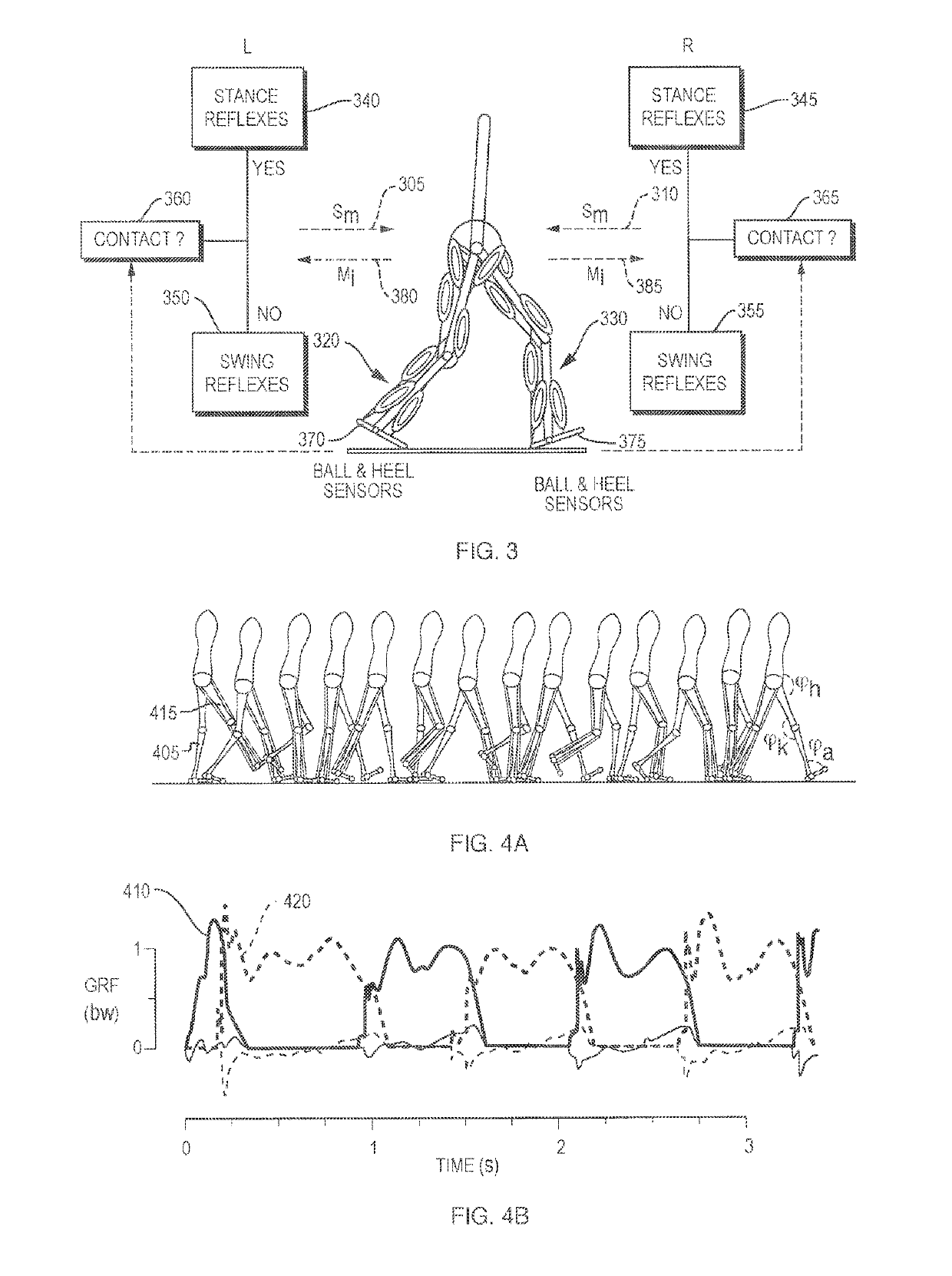
Neuromuscular Model-Based Sensing And Control Paradigm For A Robotic Leg
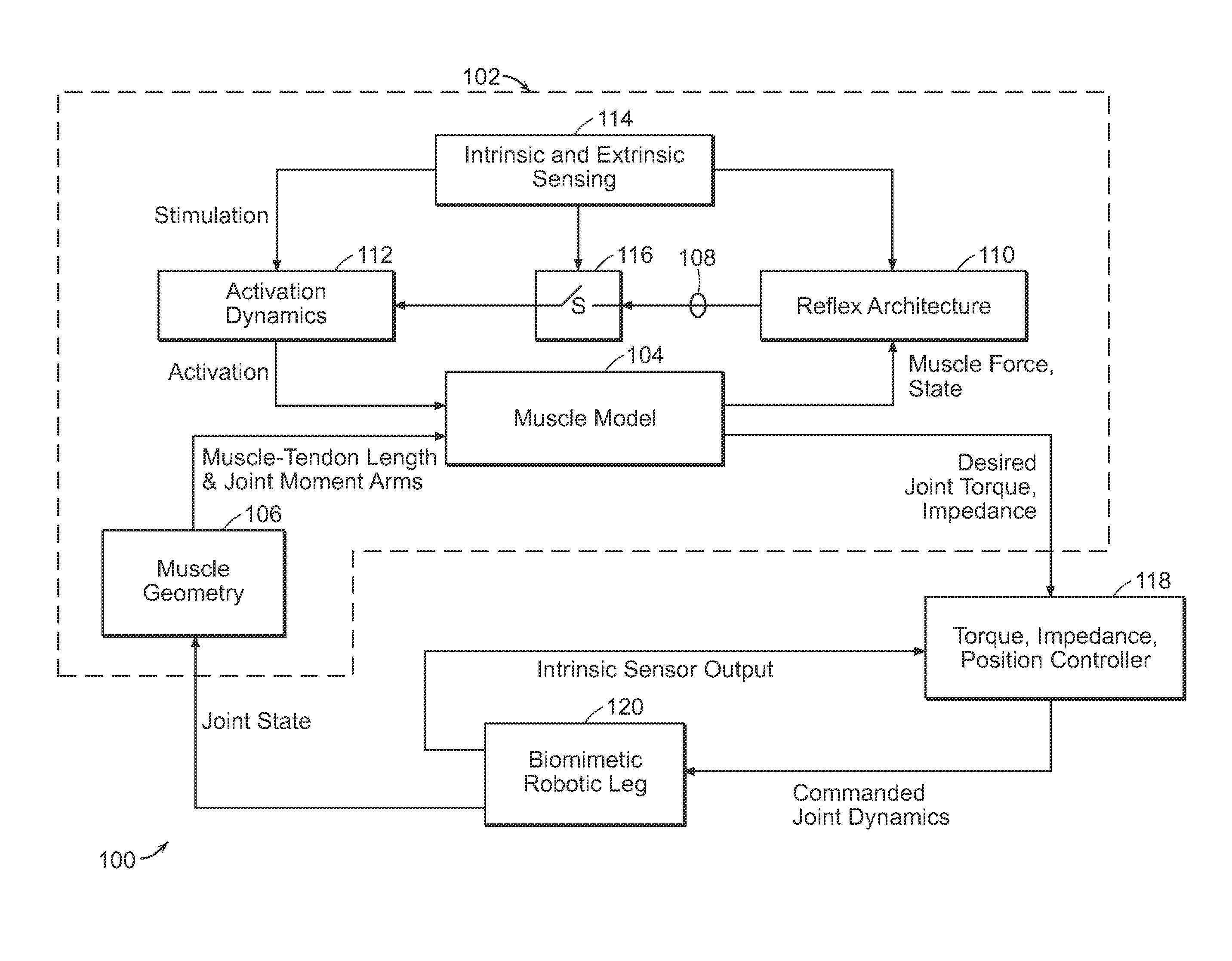
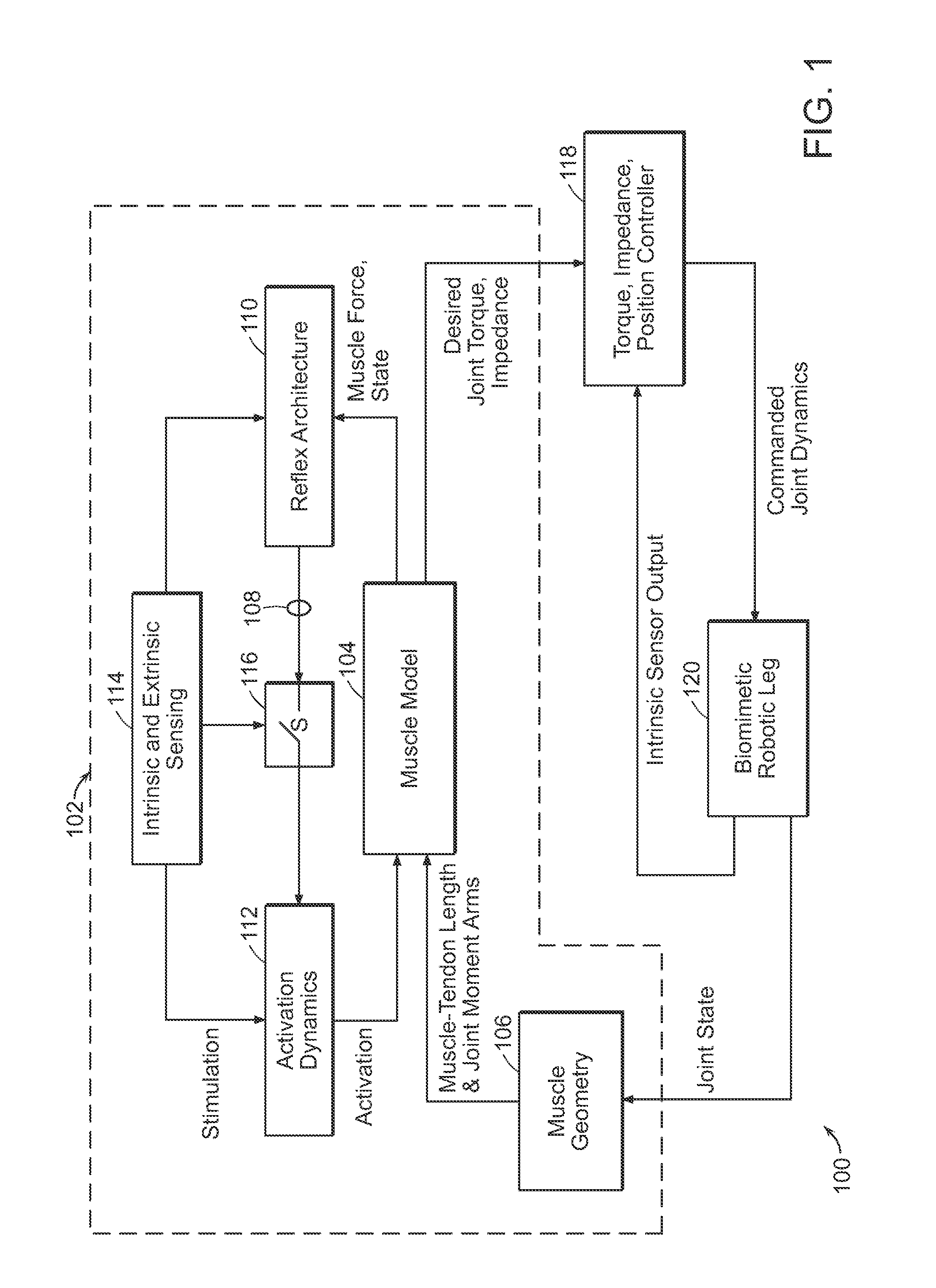
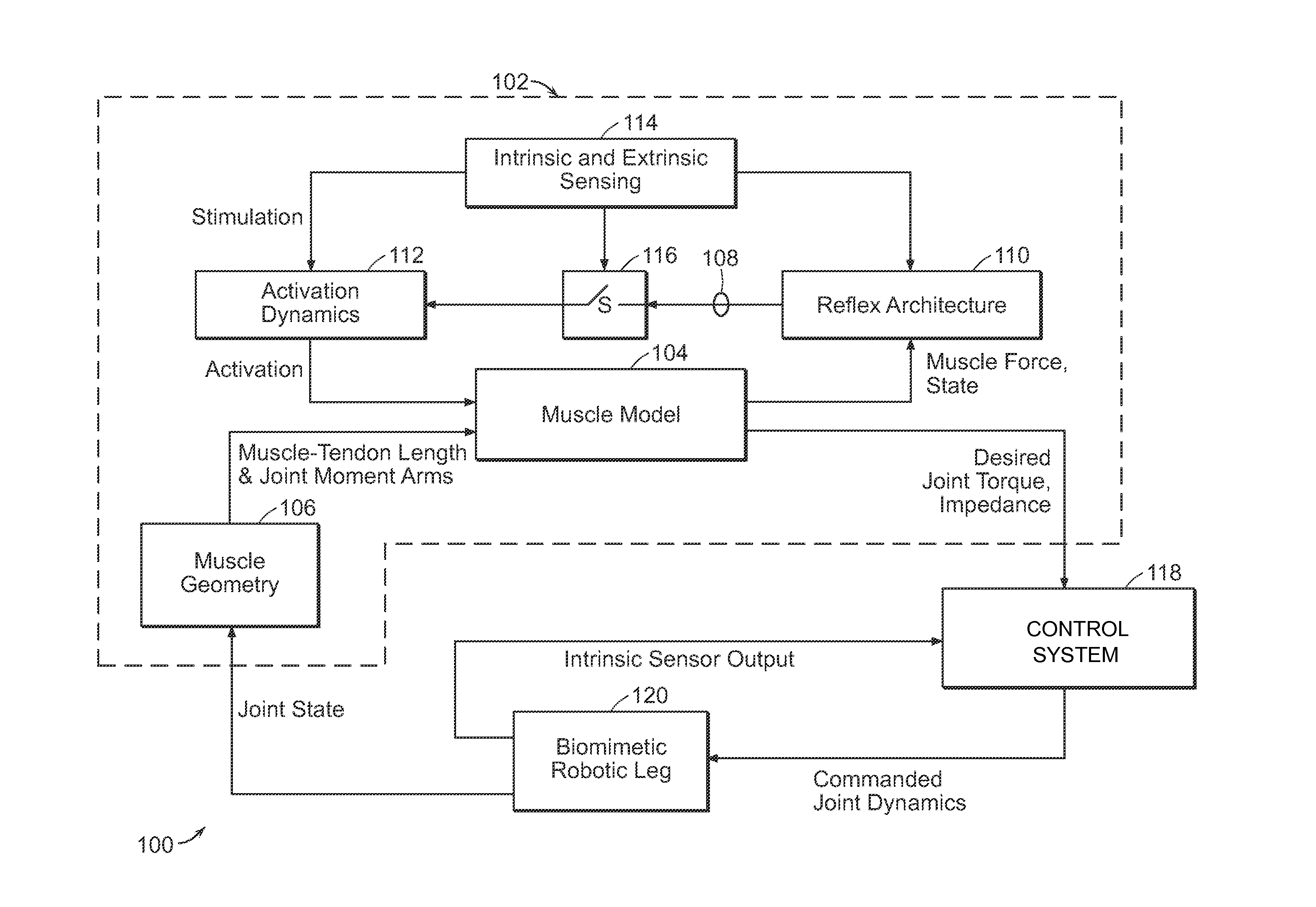
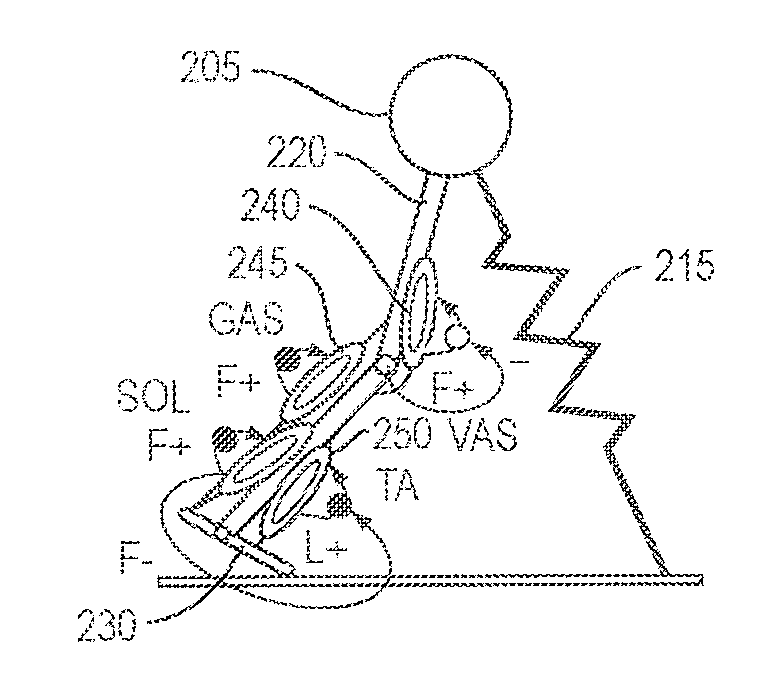
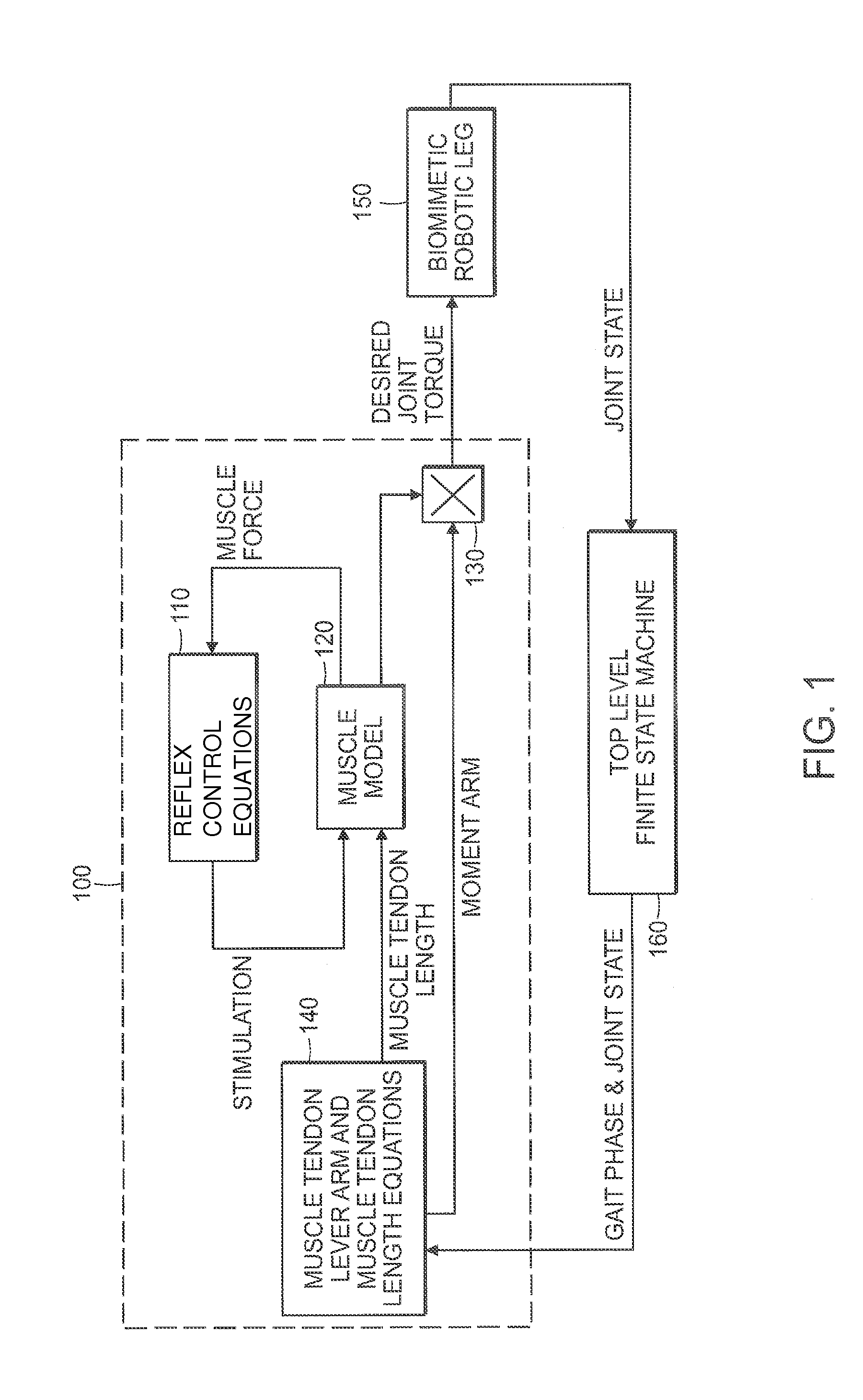
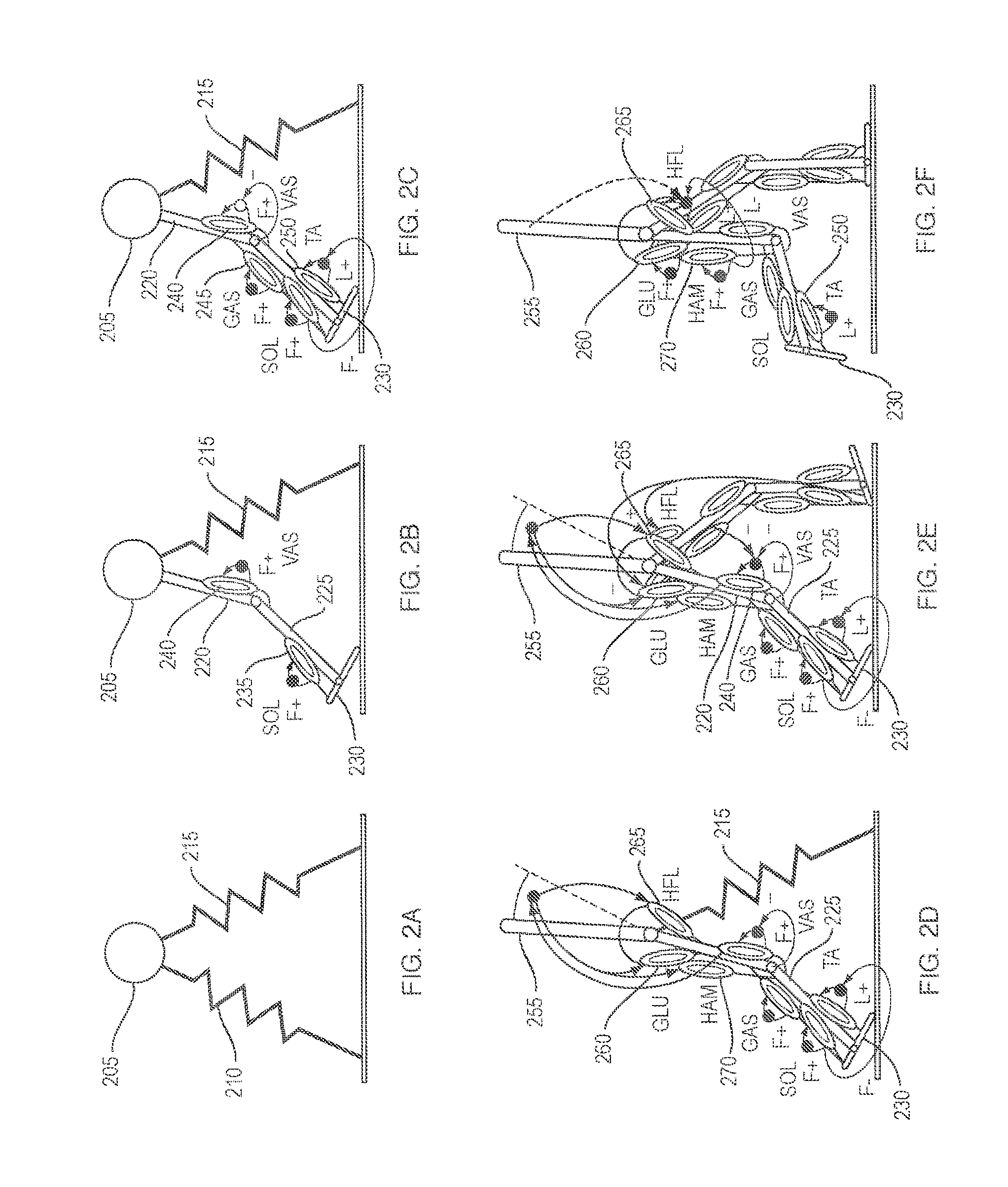
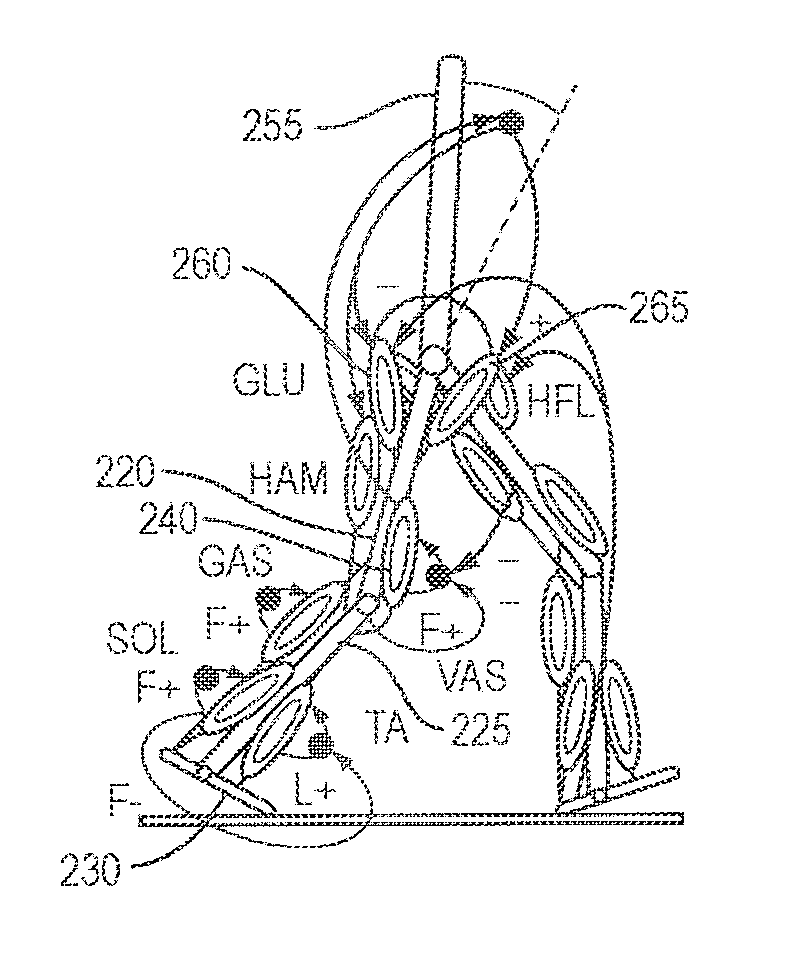
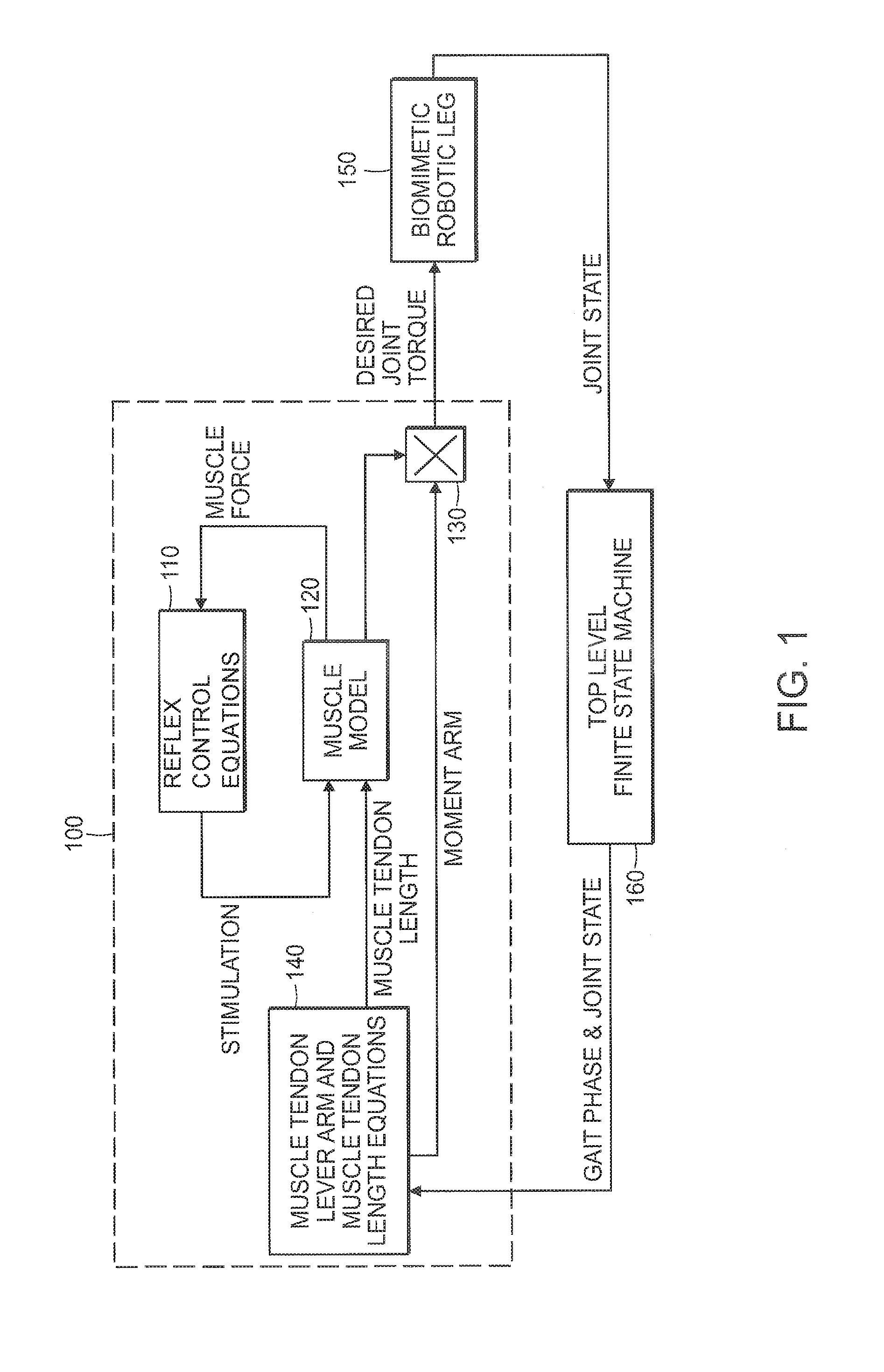
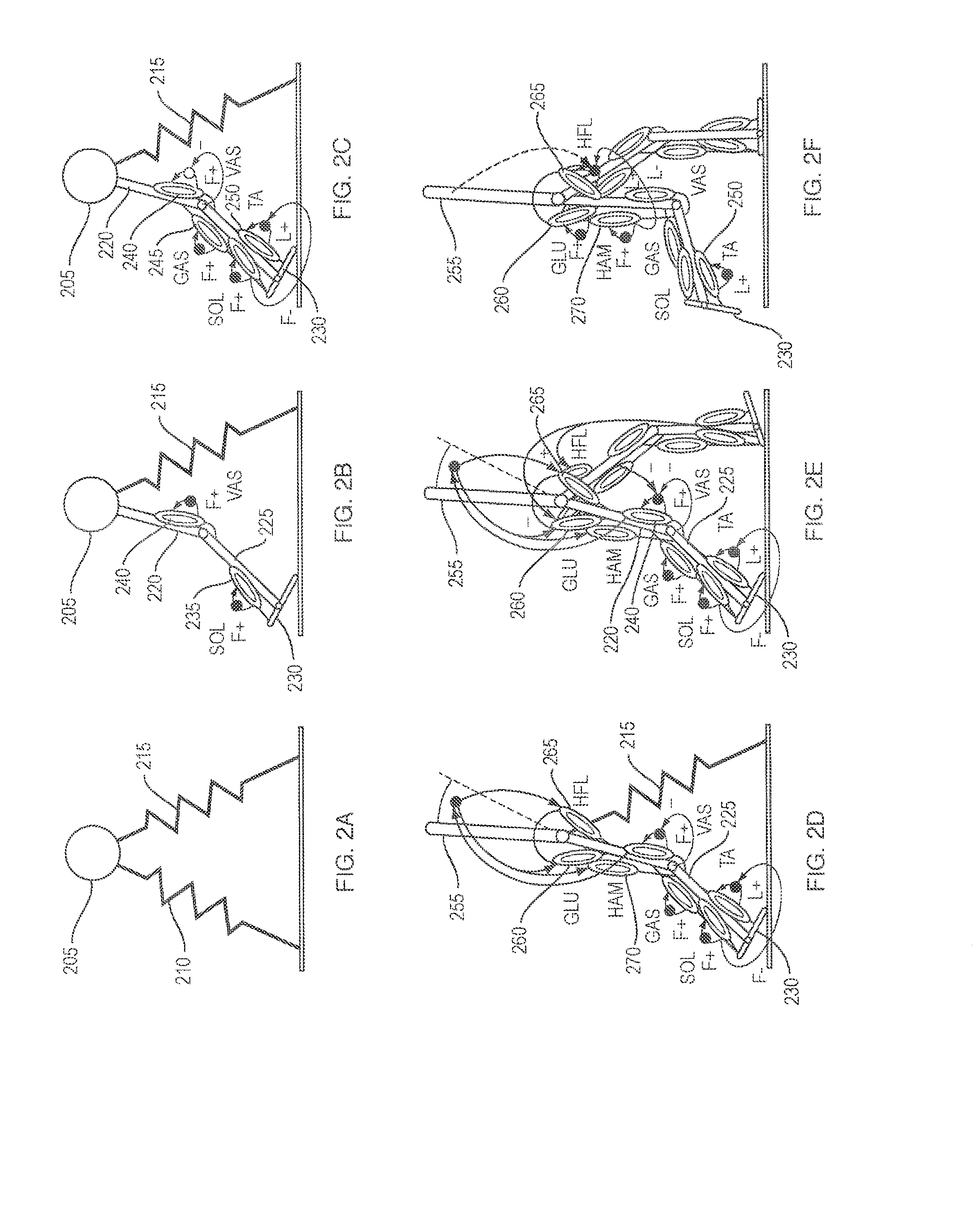
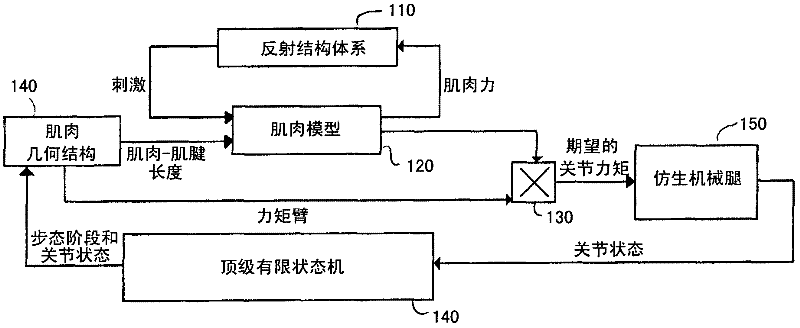
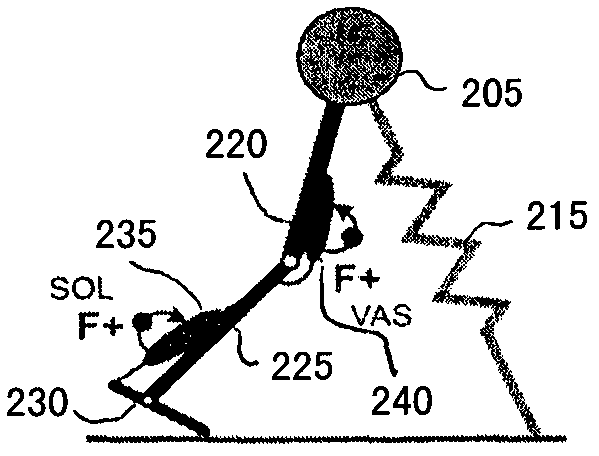
A neuromuscular model-based controller for a robotic limb having at least one joint includes a neuromuscular model having a muscle model, muscle geometry and reflex feedback loop to determine at least one torque or impedance command to be sent to the robotic limb. One or more parameters that determine relation between feedback data and activation of the muscle model are adjusted consequent to sensory data from at least one of an intrinsic sensor and an extrinsic sensor. A controller in communication with the neuromuscular model is configured to receive the at least one torque or impedance command and controls at least one of position, torque and impedance of the robotic limb joint.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Neuromuscular model-based sensing and control paradigm for a robotic leg
A neuromuscular model-based controller for a robotic limb having at least one joint includes a neuromuscular model having a muscle model, muscle geometry and reflex feedback loop to determine at least one torque or impedance command to be sent to the robotic limb. One or more parameters that determine relation between feedback data and activation of the muscle model are adjusted consequent to sensory data from at least one of an intrinsic sensor and an extrinsic sensor. A controller in communication with the neuromuscular model is configured to receive the at least one torque or impedance command and controls at least one of position, torque and impedance of the robotic limb joint.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
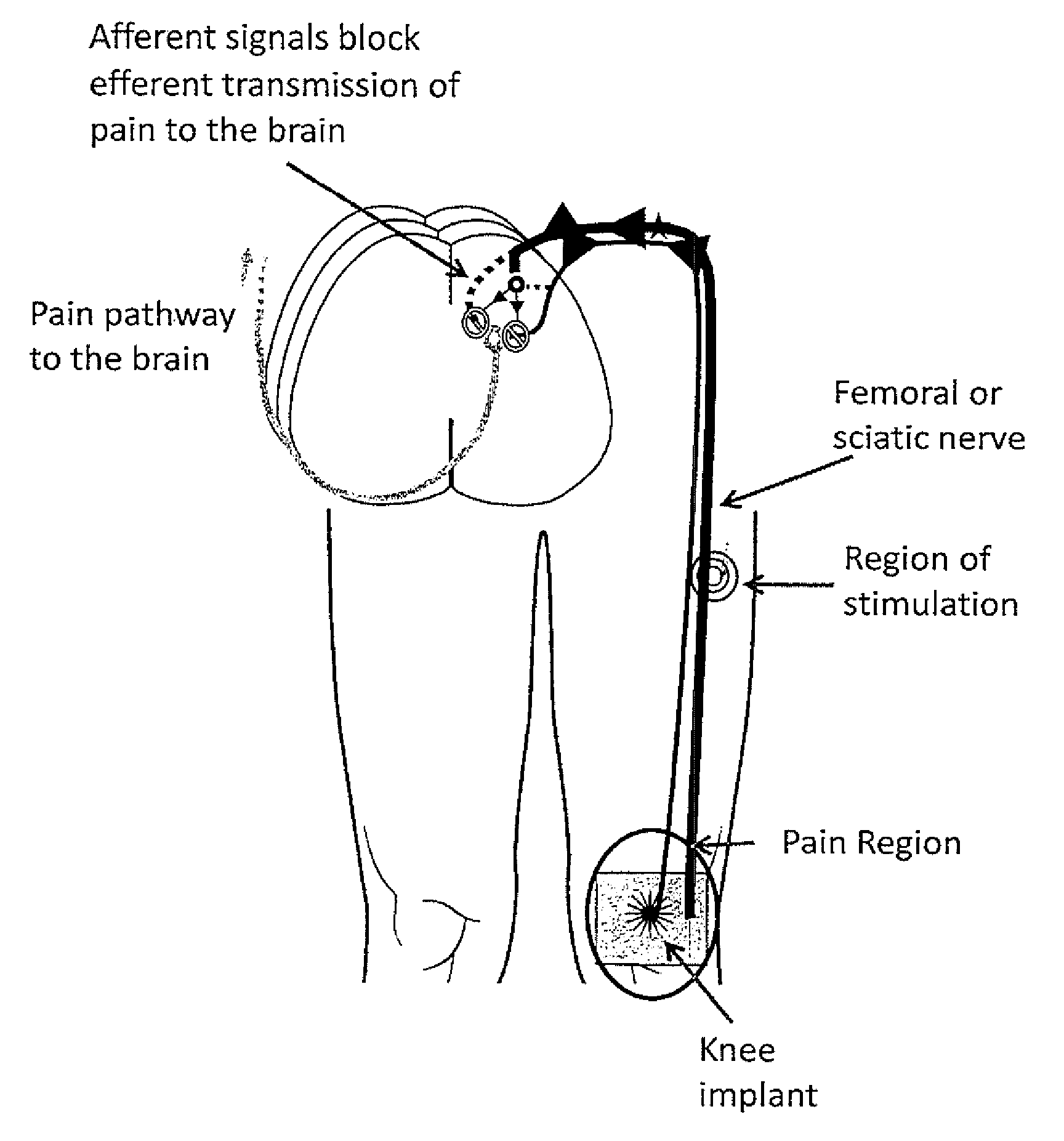
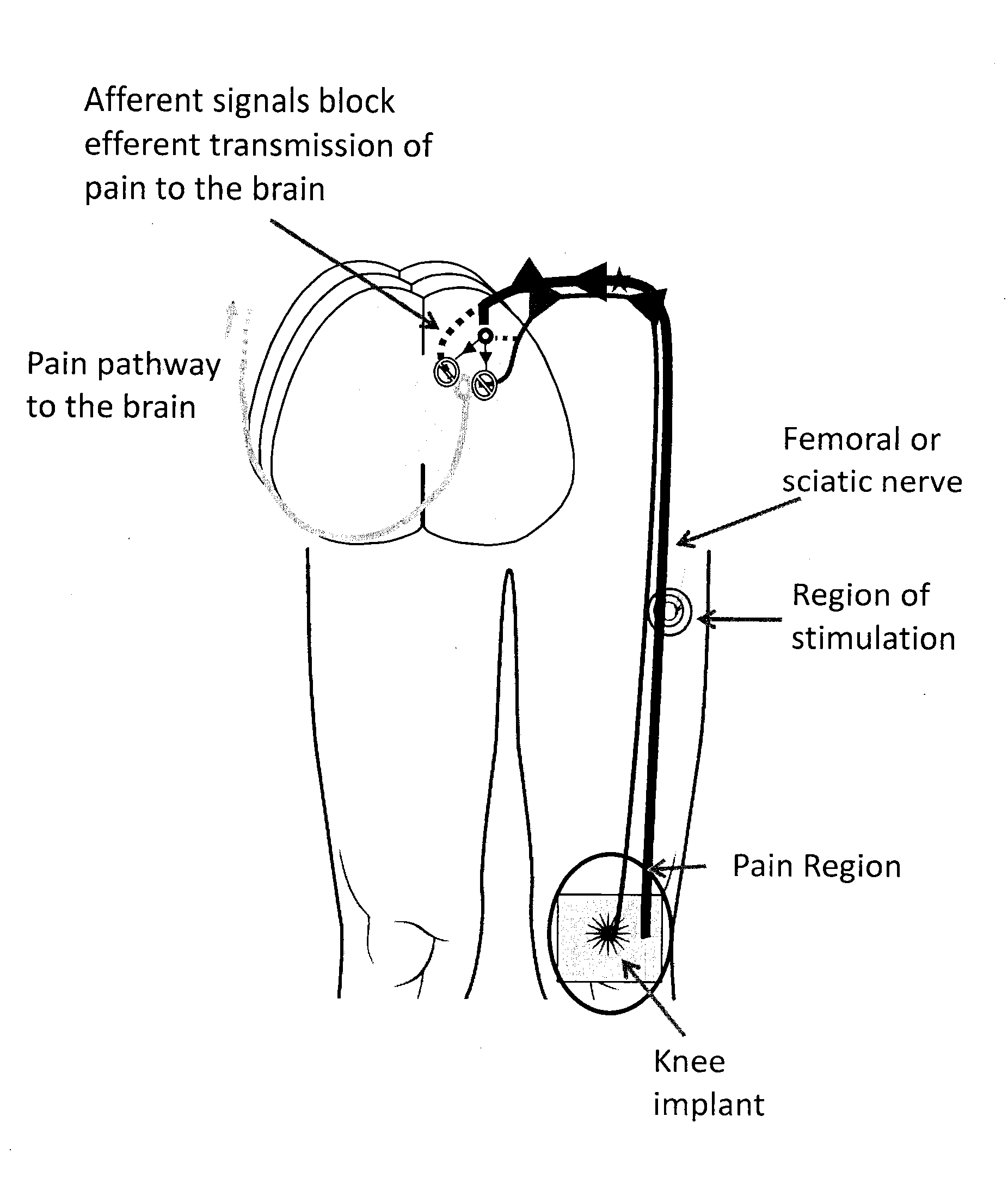
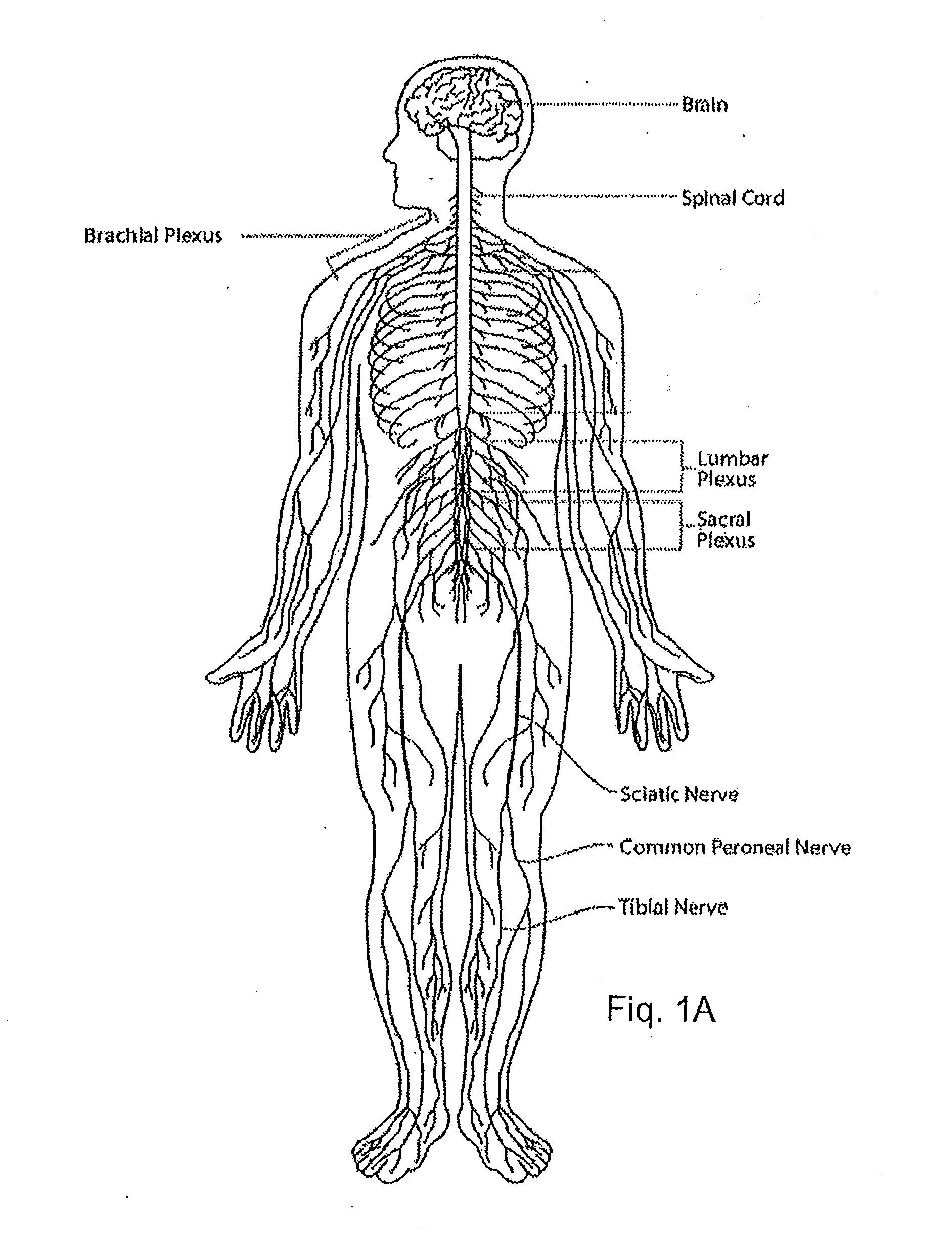
System and method for treatment of pain related to limb joint replacement surgery
It has been discovered that pain felt in a given region of the body can be treated by stimulating a peripheral nerve at a therapeutically effective distance from the region where pain is felt to generate a comfortable sensation (i.e., paresthesia) overlapping the regions of pain. A method has been developed to reduce pain in a painful region following limb joint replacement by stimulating a peripheral nerve innervating the painful region with an electrode inserted into tissue and spaced from the peripheral nerve. This method may be used to help alleviate postoperative pain in patients following total knee arthroplasty surgery or other limb joint replacement surgeries.
Owner:SPR THERAPEUTICS
Adjustable tension joint brace apparatus
InactiveUS6117097AEasy to adjustReduce tensionFeet bandagesNon-surgical orthopedic devicesLimb jointUpper limb
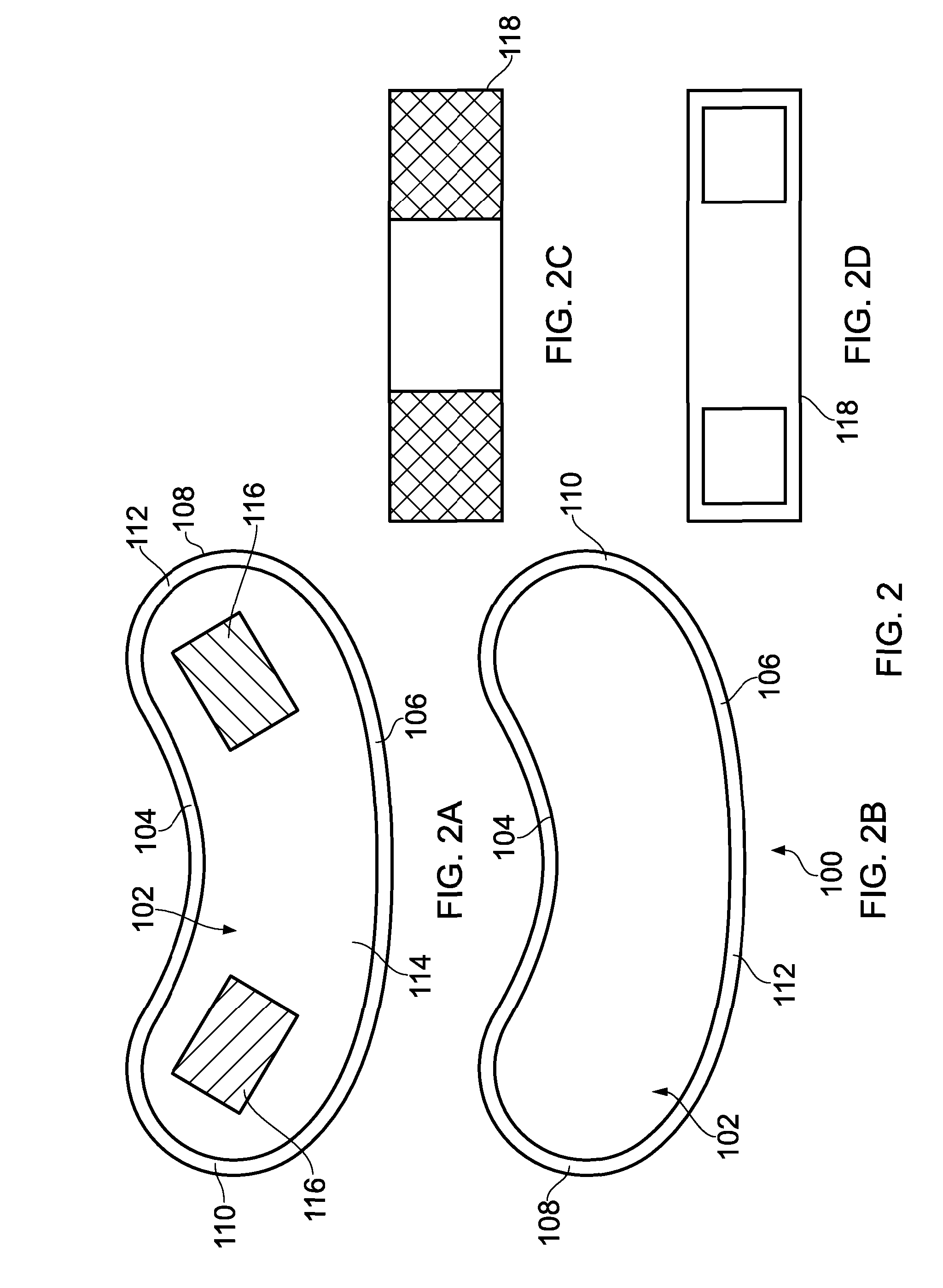
A brace apparatus for applying tension to the fore portion and the upper portion of a human limb about a limb joint in a direction of limb closure about the joint for joint therapy includes a limb fore portion engaging structure; a limb upper portion engaging structure; an elastic strip interconnecting the limb fore portion and the limb upper portion for creating a range of tension levels between the limb fore portion and the limb upper portion over which the limb fore portion and the limb upper portion move relative to each other; and a mechanism for adjusting the range of tension in the elastic strip. The limb fore portion engaging structure and the limb upper portion engaging structure preferably include a flexible tubular member sized to fit about the human limb at the joint, the tubular member having a longitudinal slit for opening the member for placement of the member about the limb; and a tubular member fastener at the longitudinal slit releasibly fastening the slit against opening and thereby securing the member about the limb. The elastic strip is preferably connected to the member adjacent to the fore limb portion and to the member adjacent to the upper limb portion. The mechanism for adjusting the range of tension optionally includes a button secured to the strip and a longitudinal series of button holes in the member for receiving the button, so that the range of tension in the elastic member is selected by selecting a button hole for receiving the button.
Owner:RUIZ ANDRES F
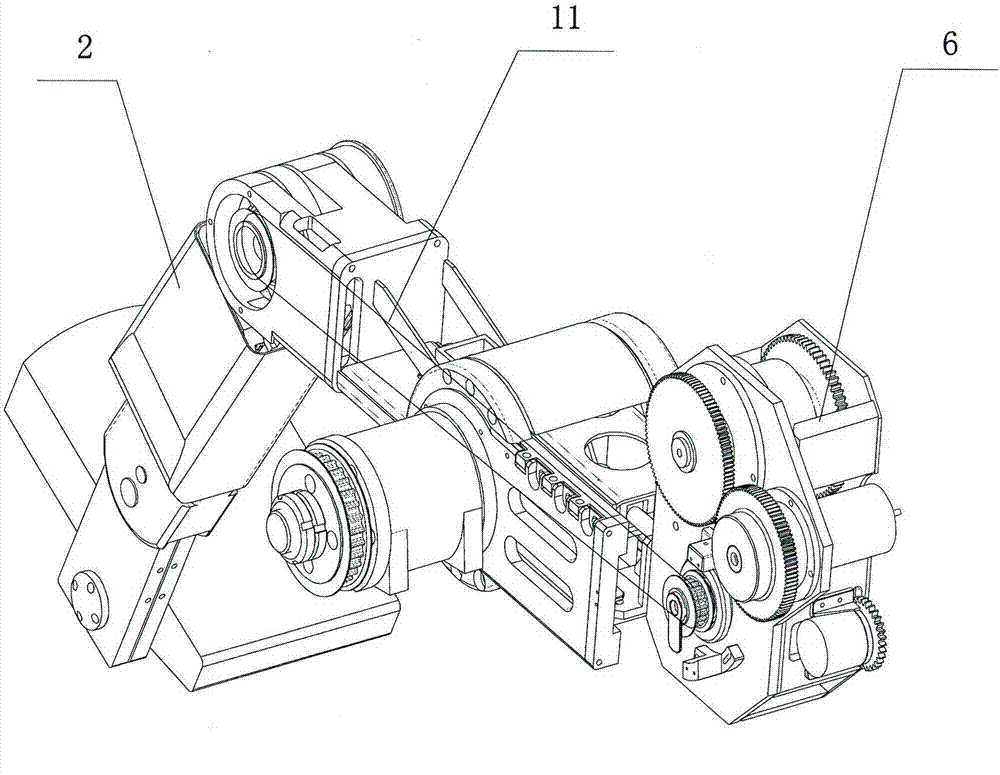
Rehabilitation training robot for lower limb joint
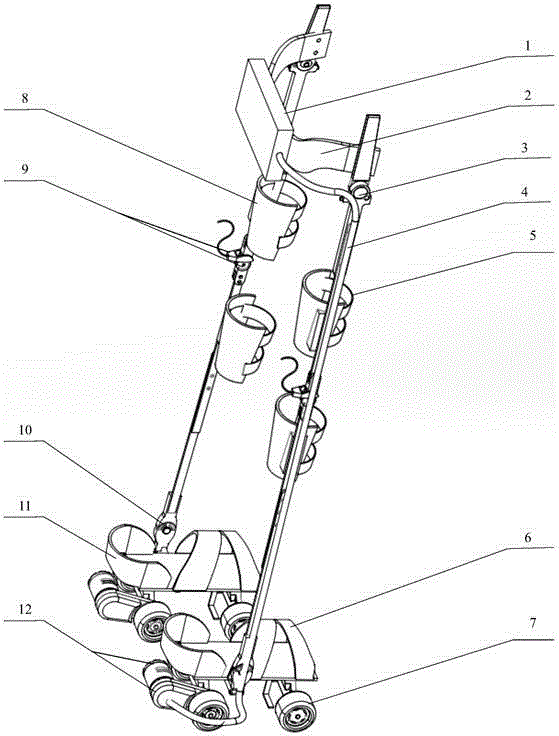
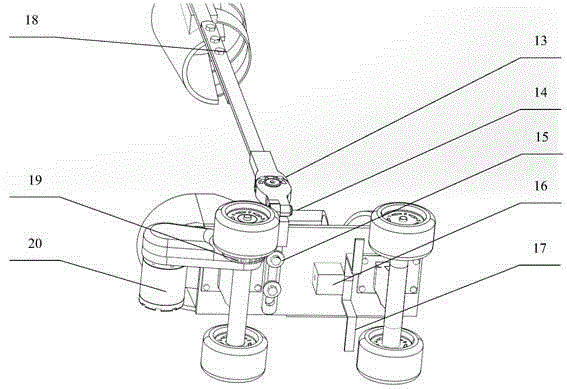
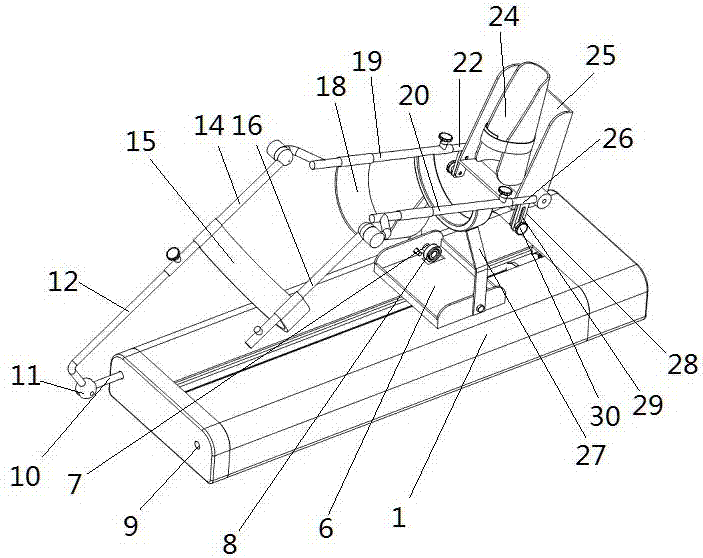
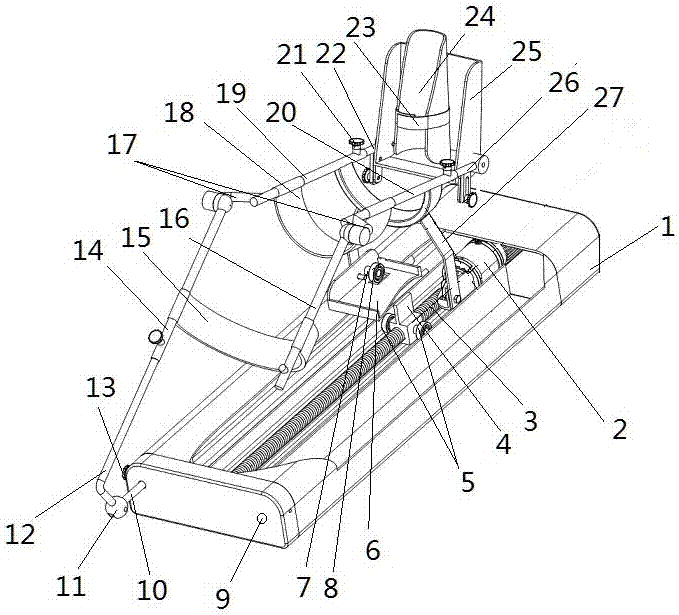
The invention discloses a rehabilitation training robot for lower limbs, and aims to provide a rehabilitation training robot which is simple in structure, easy to process and compact in structure of each joint driving device. The key point of the technical scheme comprises a driving device for ankle joints, a driving device for knee joints and a driving device for hip joints; and a shank part and a thigh part are telescopic to adapt patients with different heights. The driving device for the knee joints is placed at the rear end behind a thigh rotating joint and is used as a counter weight for balancing the weight of a movement part of the robot; and the driving device for the hip joints is placed on a base and does not participate in the movement of the robot, so that the weight of the movement part of the robot is greatly reduced. The driving of the joints is realized by a motor through a reducer; and a moment (force) sensor is arranged, and an absolute position encoder and an electromagnetic brake are arranged on the knee joints and the hip joints. The rehabilitation training robot is mainly used for performing passive training, active training or assisted training on the patients with lower limb disability.
Owner:浙江佑仁智能机器人有限公司
System and method for treatment of pain related to limb joint replacement surgery
It has been discovered that pain felt in a given region of the body can be treated by stimulating a peripheral nerve at a therapeutically effective distance from the region where pain is felt to generate a comfortable sensation (i.e., paresthesia) overlapping the regions of pain. A method has been developed to reduce pain in a painful region following limb joint replacement by stimulating a peripheral nerve innervating the painful region with an electrode inserted into tissue and spaced from the peripheral nerve. This method may be used to help alleviate postoperative pain in patients following total knee arthroplasty surgery or other limb joint replacement surgeries.
Owner:SPR THERAPEUTICS
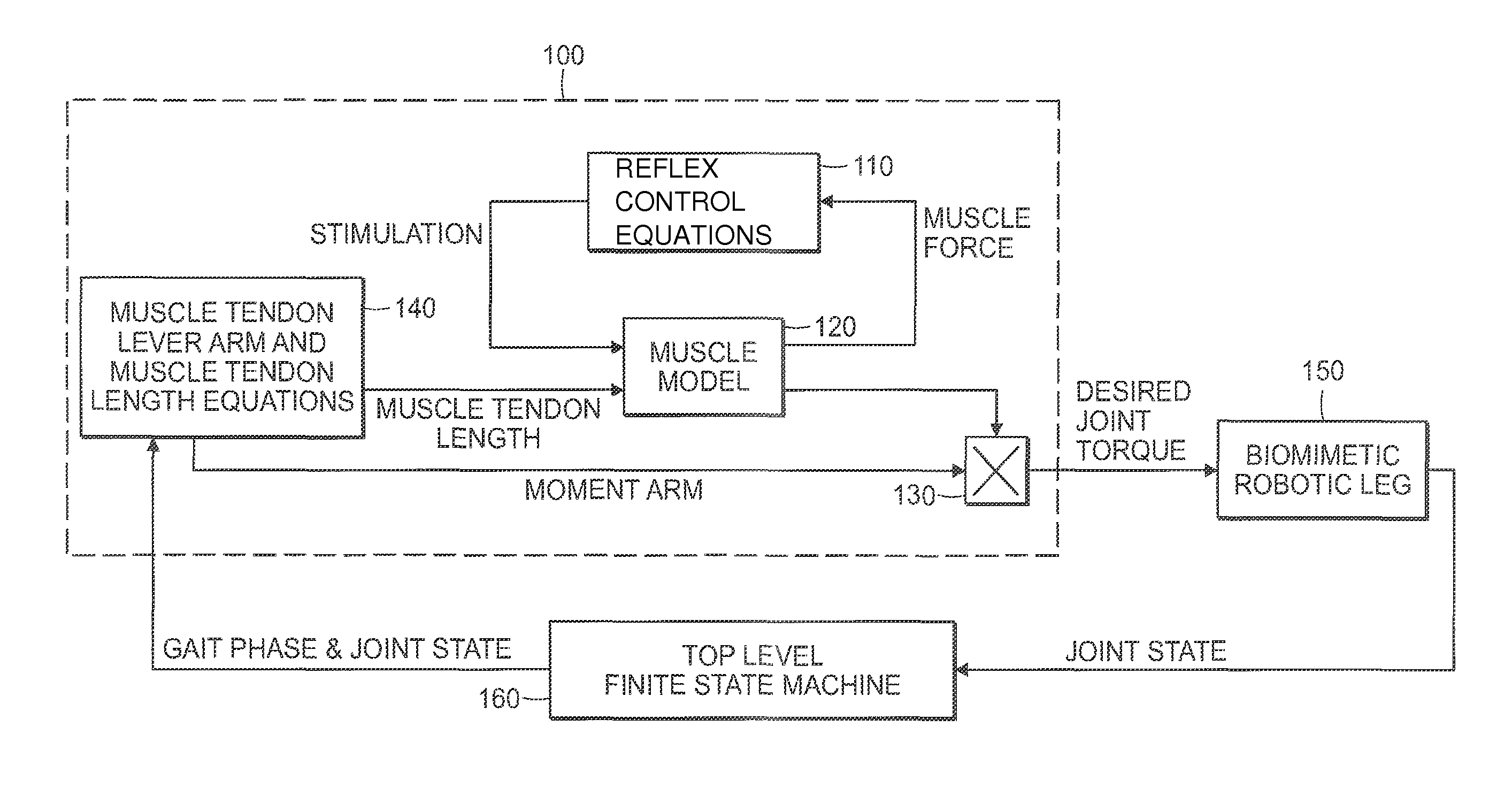
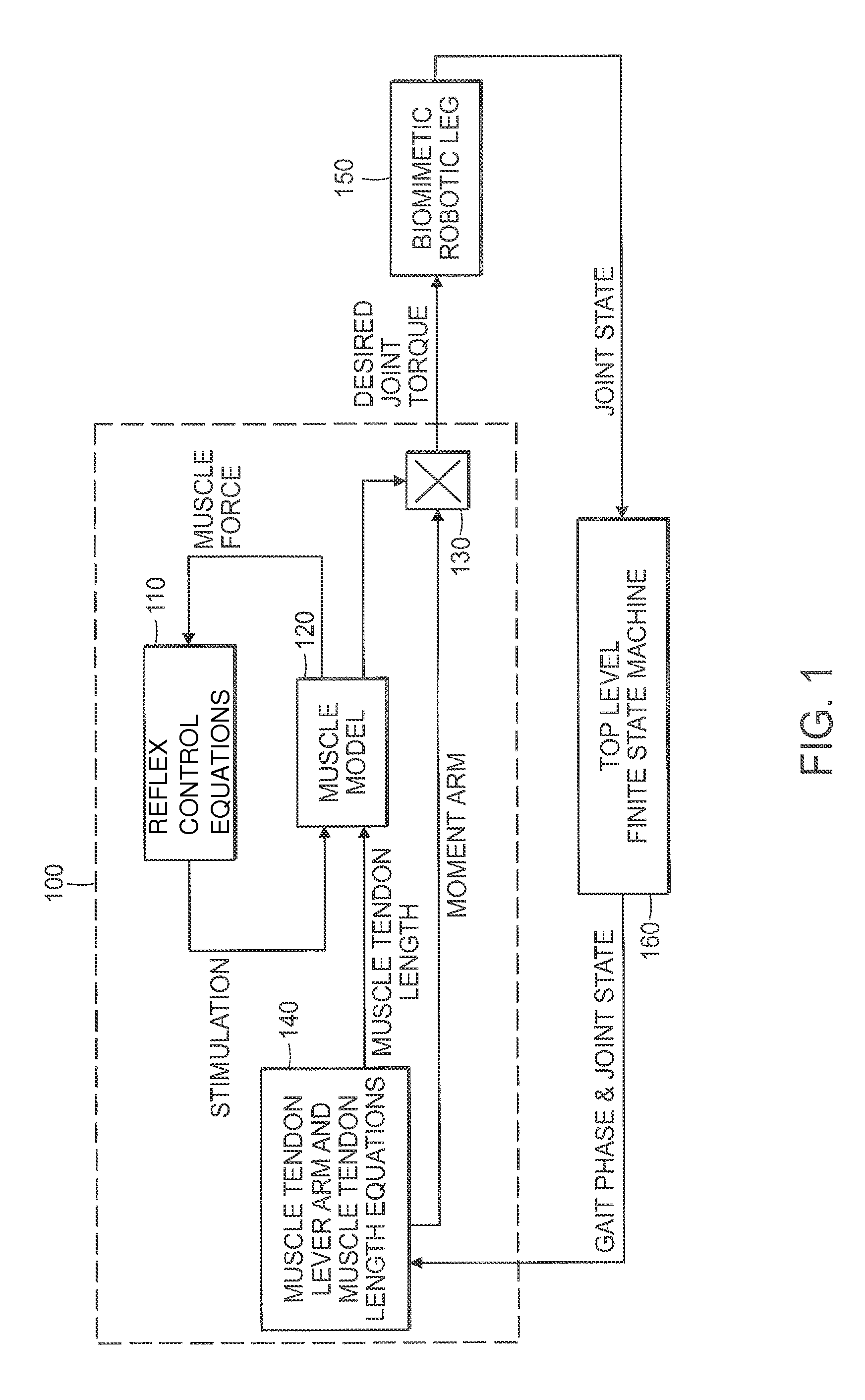
Model-Based Neuromechanical Controller For A Robotic Leg
A model-based neuromechanical controller for a robotic limb having at least one joint includes a finite state machine configured to receive feedback data relating to the state of the robotic limb and to determine the state of the robotic limb, a muscle model processor configured to receive state information from the finite state machine and, using muscle geometry and reflex architecture information and a neuromuscular model, to determine at least one desired joint torque or stiffness command to be sent to the robotic limb, and a joint command processor configured to command the biomimetic torques and stiffnesses determined by the muscle model processor at the robotic limb joint. The feedback data is preferably provided by at least one sensor mounted at each joint of the robotic limb. In a preferred embodiment, the robotic limb is a leg and the finite state machine is synchronized to the leg gait cycle.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Model-based neuromechanical controller for a robotic leg
A model-based neuromechanical controller for a robotic limb having at least one joint includes a finite state machine configured to receive feedback data relating to the state of the robotic limb and to determine the state of the robotic limb, a muscle model processor configured to receive state information from the finite state machine and, using muscle geometry and reflex architecture information and a neuromuscular model, to determine at least one desired joint torque or stiffness command to be sent to the robotic limb, and a joint command processor configured to command the biomimetic torques and stiffnesses determined by the muscle model processor at the robotic limb joint. The feedback data is preferably provided by at least one sensor mounted at each joint of the robotic limb. In a preferred embodiment, the robotic limb is a leg and the finite state machine is synchronized to the leg gait cycle.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
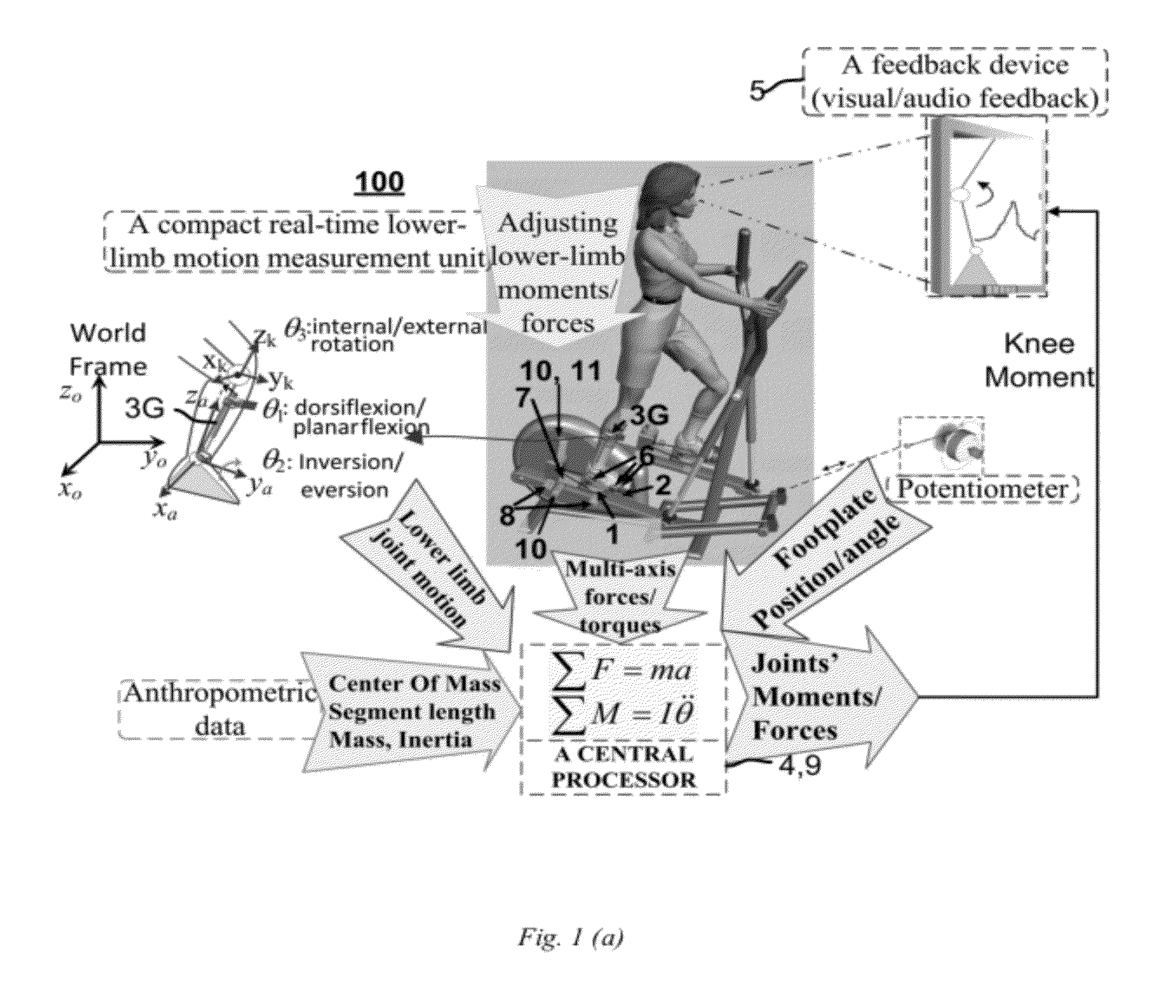
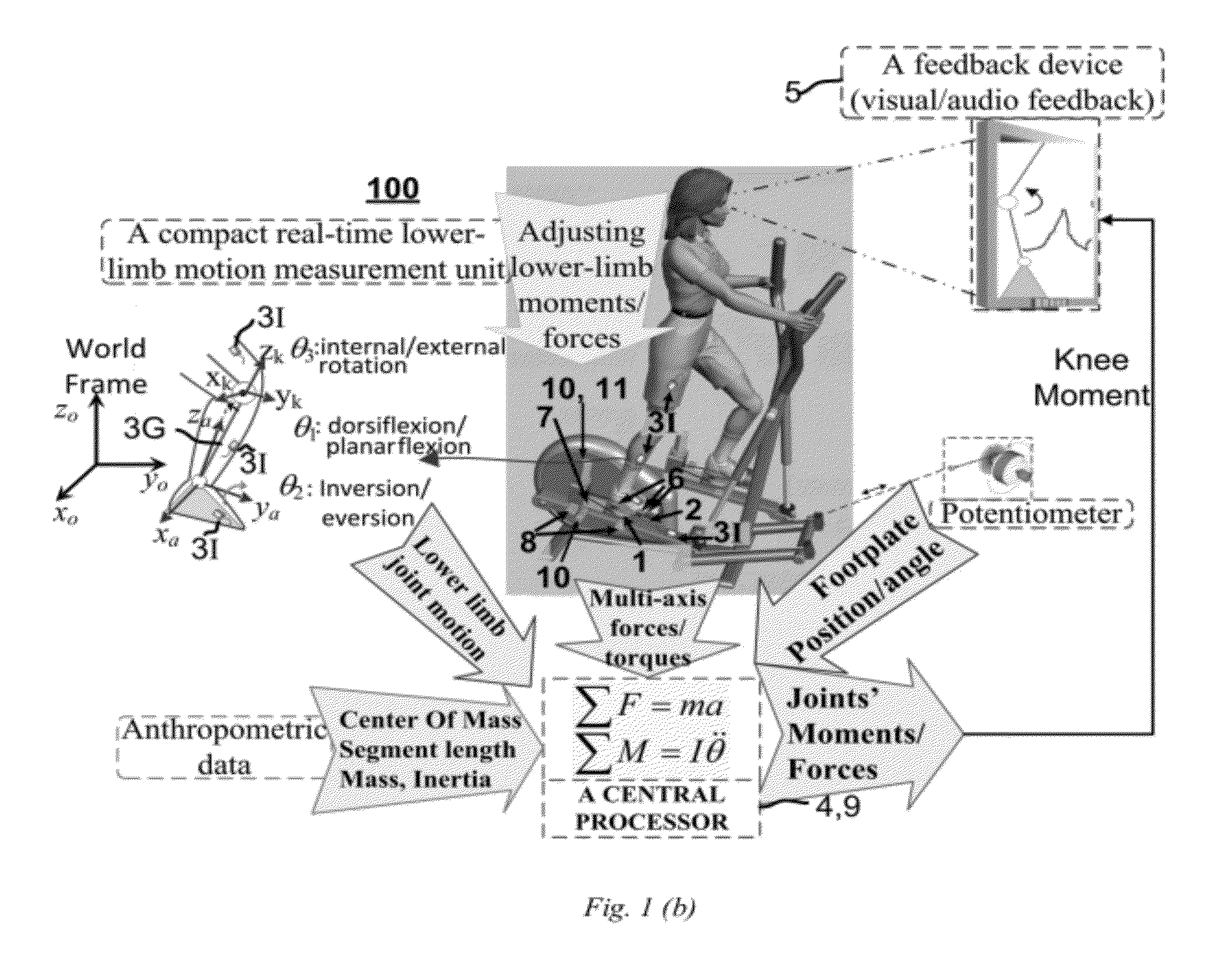
Apparatus and Method of Controlling Lower-Limb Joint Moments through Real-Time Feedback Training
InactiveUS20120277063A1Gymnastic exercisingDiagnostic recording/measuringClinical settingsEngineering
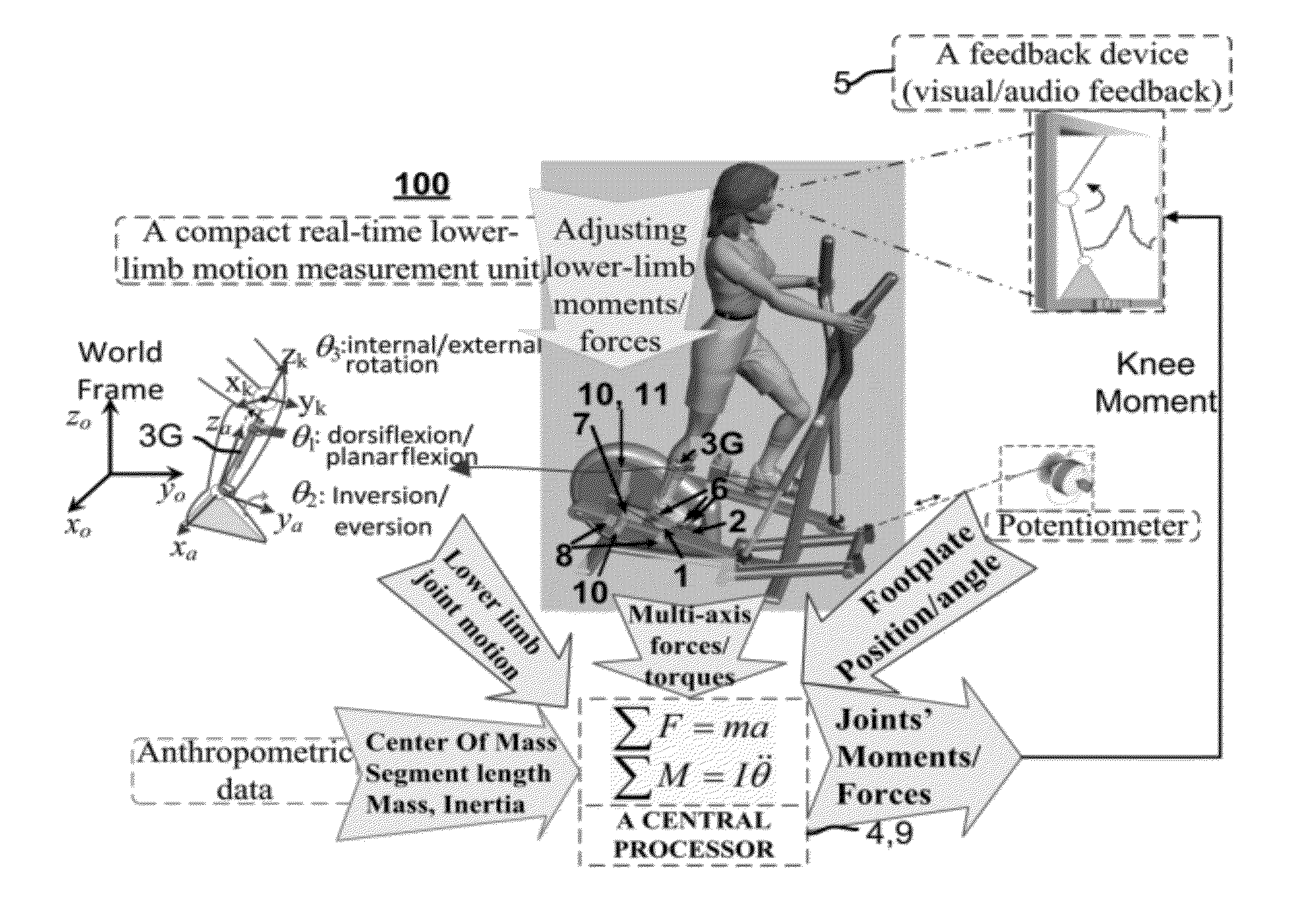
A real-time estimation of 3D moments of lower-limb joints using a robotic multi-axis training system with a 6-axis force / torque (F / T) sensors and a 6-DOF goniometer is described. A joint moment such as the knee abduction moment (KAM) can be determined in real-time without using sophisticated optoelectronic motion tracking system. The system also does not require computation of the COP location. The knee adduction moment or any other lower-limb 3D joint moments can be determined conveniently during stepping movement on the training system for real-time biofeedback training on controlling the targeted joint moment(s). The 6-DOF goniometer is convenient to use with other analog signals including the 6-axis F / T and locomotion variables. As an example application, combined with the frontal plane movement on the robotic multi-axis elliptical trainer, it provides a useful tool suitable for clinical setting to help patients with knee OA to reduce potentially damaging peak knee adduction moment through real-time feedback training.
Owner:REHABTEK
Method for controlling a robotic limb joint
A model-based neuromechanical controller for a robotic limb having at least one joint includes a finite state machine configured to receive feedback data relating to the state of the robotic limb and to determine the state of the robotic limb, a muscle model processor configured to receive state information from the finite state machine and, using muscle geometry and reflex architecture information and a neuromuscular model, to determine at least one desired joint torque or stiffness command to be sent to the robotic limb, and a joint command processor configured to command the biomimetic torques and stiffnesses determined by the muscle model processor at the robotic limb joint. The feedback data is preferably provided by at least one sensor mounted at each joint of the robotic limb. In a preferred embodiment, the robotic limb is a leg and the finite state machine is synchronized to the leg gait cycle.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Model-based neuromechanical controller for a robotic leg
A model-based neuromechanical controller for a robotic limb having at least one joint includes a finite state machine configured to receive feedback data relating to the state of the robotic limb and to determine the state of the robotic limb, a muscle model processor configured to receive state information from the finite state machine and, using muscle geometry and reflex architecture information and a neuromuscular model, to determine at least one desired joint torque or stiffness command to be sent to the robotic limb, and a joint command processor configured to command the biomimetric torques and stiffnesses determined by the muscle model processor at the robotic limb joint. The feedback data is preferably provided by at least one sensor mounted at each joint of the robotic limb. In a preferred embodiment, the robotic limb is a leg and the finite state machine is synchronized to the leg gait cycle.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Foot wheel driving paraplegia walking aided external skeleton
InactiveCN104856842AReduce energy consumptionIncrease walking enduranceWalking aidsProsthesisForce linesLimb joint
A foot wheel driving paraplegia walking aided external skeleton comprises a lower limb brace, a foot driving module and a power supply and a control circuit. The lower limb brace is used for supporting and fixing the lower limbs of a user, the foot driving module comprises wheels which are driven by power to make the user move forwards, and the power supply and the control circuit comprise a power supply module, a driving device and a signal receiving and sending device. By means of the foot wheel driving paraplegia walking aided external skeleton, the force lines of the limb joints do not need to be considered, a complex electromagnetic control scheme is not adopted to coordinate the movement of the joints, walking can be achieved only by controlling a foot motor, the equipment complexity can be reduced, the external skeleton is lighter and more convenient in structure, and the cost of the paraplegia walking aided external skeleton is lower.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Lower limb joint training device
PendingCN107198640ASimple structureLow costChiropractic devicesThighPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The invention discloses a lower limb joint training device which comprises a base and a linear movement mechanism. The linear movement mechanism is arranged on the lower portion of the lower limb joint training device, a fixing plate is connected onto a linear movement portion of the linear movement mechanism, a shank support frame is arranged above the fixing plate and is connected onto a support, the support is rotationally connected onto the fixing plate, a left brace rod of a foot tying device is connected with the shank support frame, two sides of a foot tying device frame are rotationally connected onto two support rods of the foot tying device, the foot tying device is arranged on the foot tying device frame, thigh support rods are rotationally connected with the front ends of shank support rods, an L-shaped connecting rod is connected with the front end of one of the two thigh support rods, the other end of the L-shaped connecting rod is connected onto a universal joint, and an adjusting rod is connected with the other end of the universal joint and is connected with the lower portion of the lower limb joint training device. The lower limb joint training device has the advantages of simple structure and low cost.
Owner:ANYANG XIANGYU MEDICAL EQUIP
Rehabilitation device for lower limb joints
The invention relates to a rehabilitation device for lower limb joints. The problems that an existing joint recovering device is single in recovering effect, and the effect is poor are effectively solved; the device comprises a slab, through grooves are formed in the slab, and piston cylinders capable of moving up, down, leftward and rightward are arranged in the through grooves; the upper end ofeach piston cylinder is rotatably connected with one transverse rod, first supporting plates are hinged with the left sides of the transverse rods, and sliding plates are arranged on the first supporting plates; semicircular arc plates are rotatably connected with the upper end surfaces of the sliding plates, pedal plates capable of swinging leftward and rightward are hinged to the upper ends of the semicircular arc plates, and pressing springs capable of making the pedal plates inclined rightward are arranged on the left sides of the pedal plates; rolling wheels are installed at the left endsof the first supporting plates, first ropes are fixed to the rolling wheels, and the other ends of the first ropes are fixed to the upper ends of the pedal plates; second supporting plates are fixedto the right sides of the transverse rods, reeling wheels are arranged at the front and back ends of each transverse rod respectively, and second ropes are arranged on the semicircular arc plates andrespectively wound around two second reeling wheels respectively in an opposite winding mode.
Owner:LEITON FUTURE RES INSTITUTION JIANGSU CO LTD
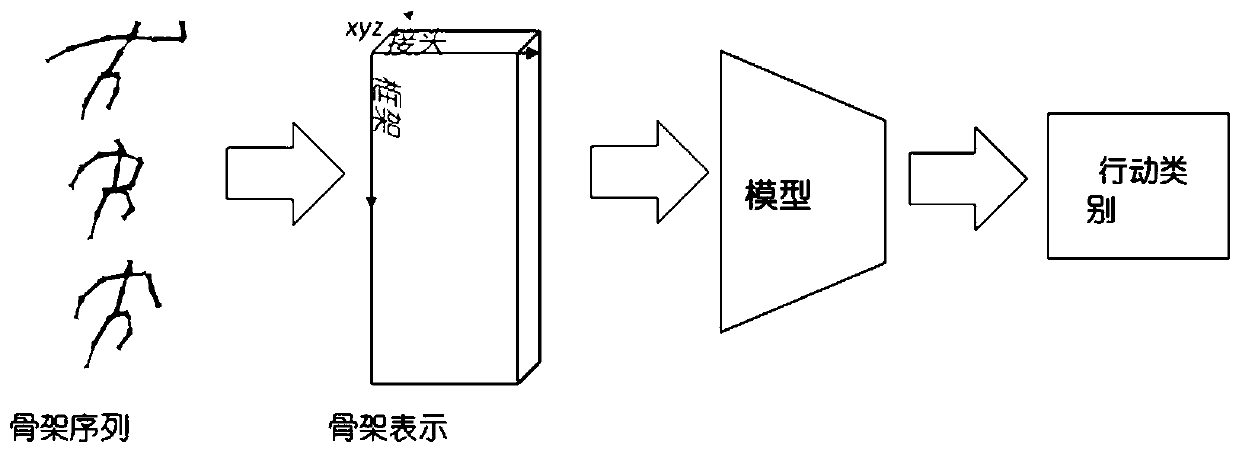
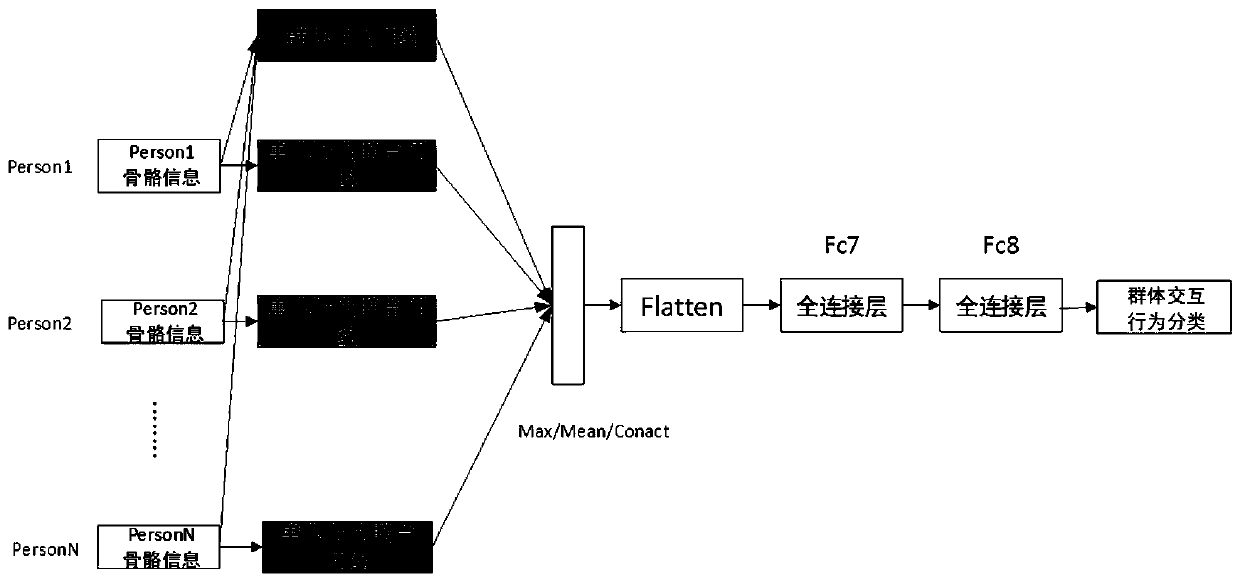
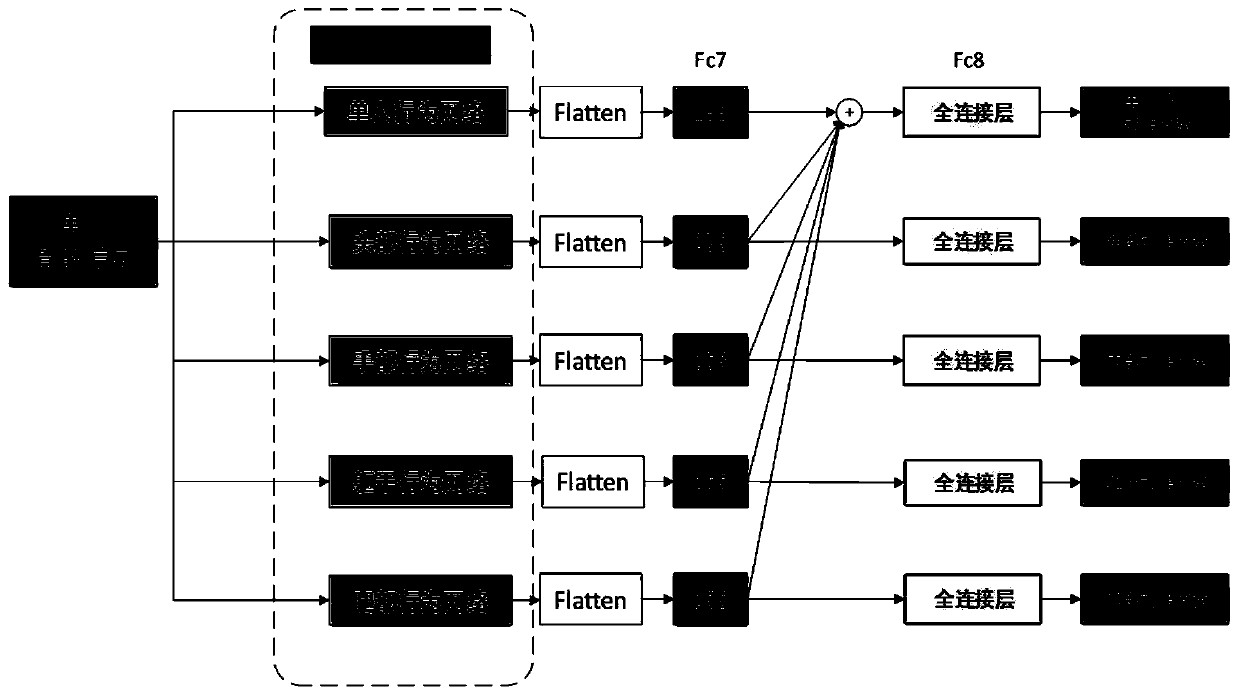
Video-based pedestrian and crowd behavior identification method
ActiveCN110472604AFeature learning is simple and effectiveEasy to learnCharacter and pattern recognitionCo-occurrencePedestrian behavior
The invention discloses a video-based pedestrian and crowd behavior identification method. The whole framework comprises a single-person limb part network, a single-person whole and limb joint networkand a multi-person network. The framework aims to jointly learn joint co-occurrence and time evolution in an end-to-end mode, and joint co-occurrence characteristics of skeleton sequence informationcan be learned simply and effectively by utilizing a CNN model by utilizing the global aggregation capability of the CNN. In the method, point-level features of each joint are learned independently, and then the features of each joint are regarded as channels of a convolution layer to learn hierarchical symbiotic features. Most importantly, in a designed single pedestrian behavior recognition joint network structure, multi-part limb network features are fused into single pedestrian motion features to enhance behavior recognition of a single pedestrian. Besides, in the designed crowd interaction behavior recognition network, the characteristics of the group behaviors are enhanced by utilizing the characteristics of the single person behaviors, and the group behaviors relate to activities such as embracing and handshaking of behaviors of multiple persons.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
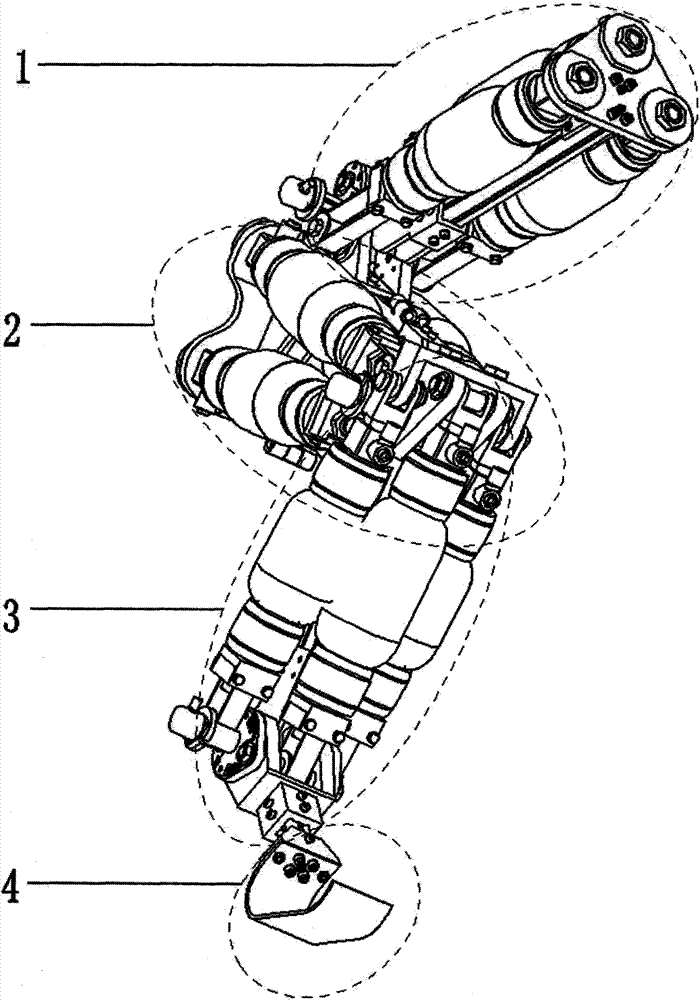
Pneumatic-muscles-based robot hind limb simulating cheetah
The invention provides a pneumatic-muscles-based robot hind limb simulating a cheetah. The structure of the robot hind limb comprises a hip unit 1, a thigh unit 2, a shin unit 3 and a foot unit 4, wherein the hip unit 1, the thigh unit and the shin unit respectively comprise a diaphysis and joint parts. The overall robot hind limb adopts a structural form that the diaphysis is placed inside and pneumatic muscles are placed outside to package the periphery of the diaphysis, the structural form is similar to the real body structure of an organism and approaches to a force-exerting form of the cheetah hind limb. The joint of the robot hind limb passes through a connector of upper and lower diaphyses by a connecting shaft and is supported by a rolling bearing; and one end of the connecting shaft extends out of the bearing to be connected with an angle sensor so as to obtain joint angle-rotating information and provide data for motion control. The joint ensures that linear force of the muscles is converted to rotating torque of the joint in a form of pulling (in opposite directions) of pneumatic muscles, and the rigidity is adjustable.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Orthosis for movement damping
ActiveCN103327938AAvoid harmControl passive movementNon-surgical orthopedic devicesStretch exerciseLimb joint
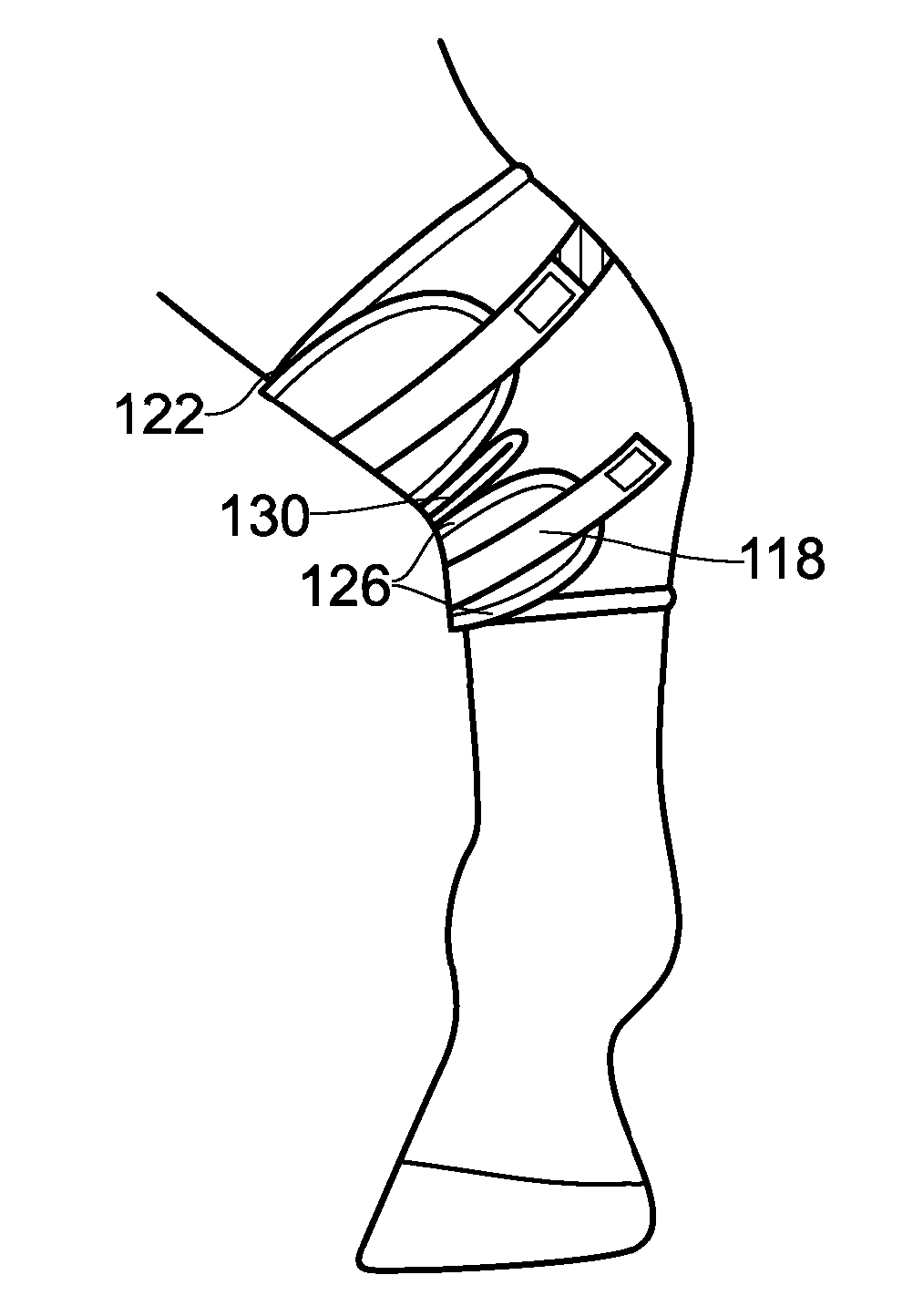
The invention relates to the technical field of orthoses and medical aids that are applied to the human or animal body in order to perform a supporting or movement-guiding function. The invention specifically makes available an orthosis for damping or limiting the flexion or extension movement of a limb joint, such as the elbow joint, knee joint, etc., and the prophylactic and therapeutic use of said orthosis.
Owner:BAUERFEIND GMBH & CO
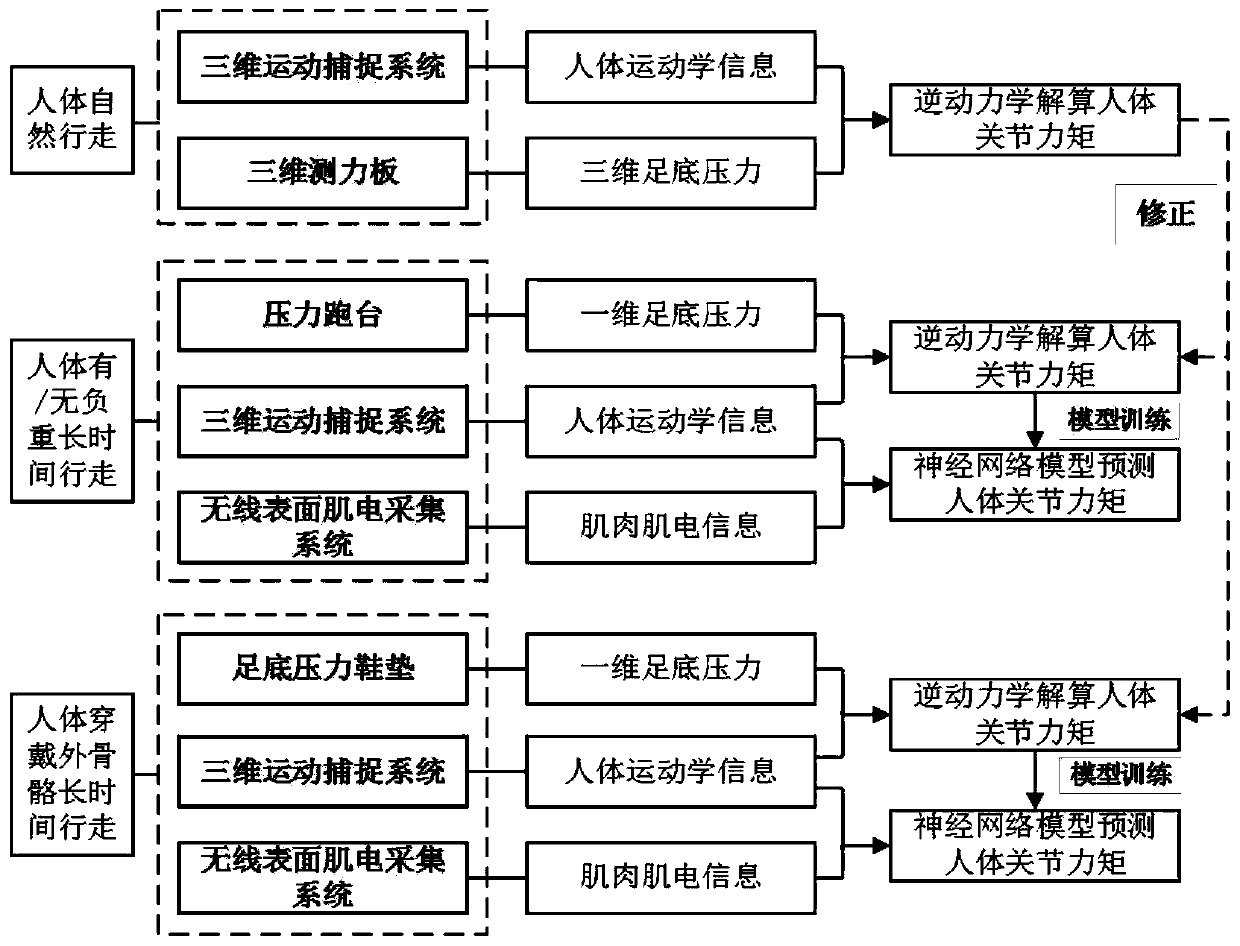
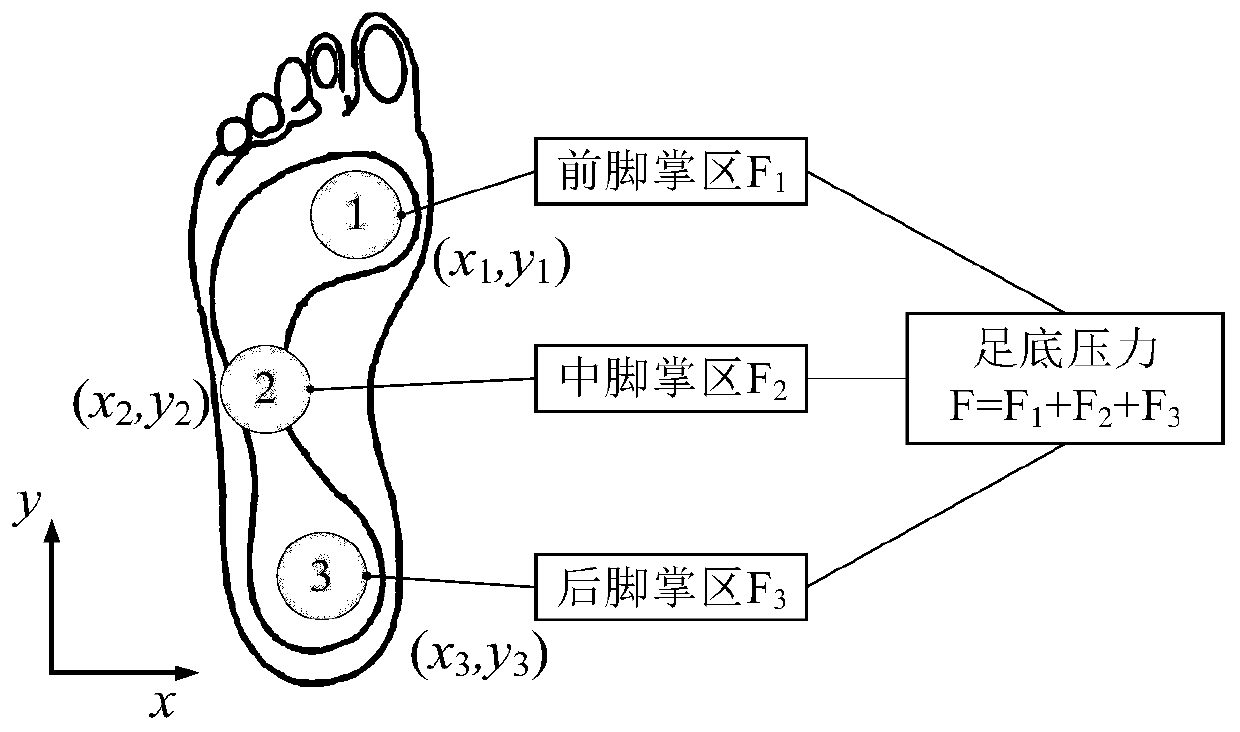
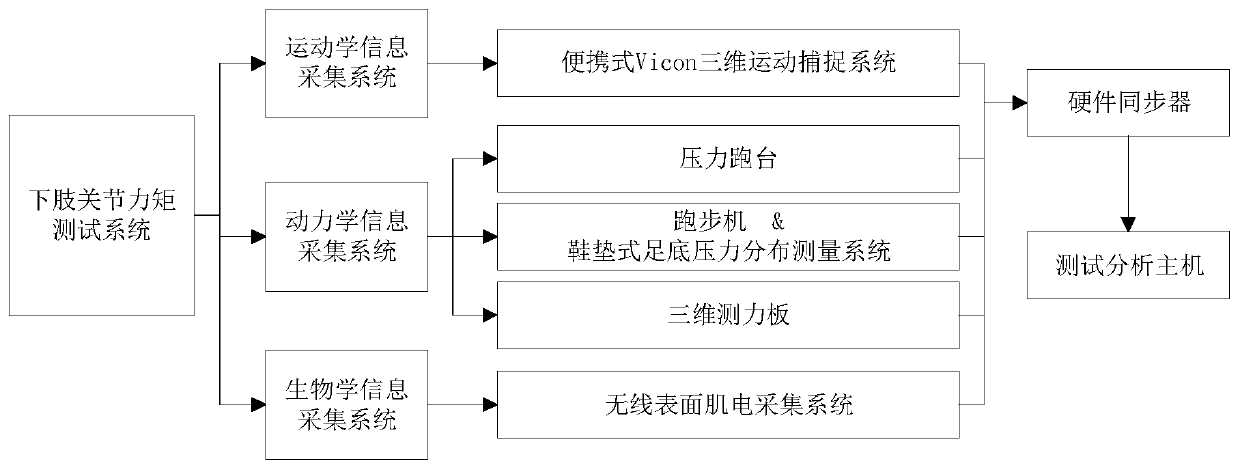
Method for detecting power assisting efficiency of load-bearing exoskeleton
ActiveCN110811553ASolve the mechanical propertiesReduce mistakesProgramme-controlled manipulatorJointsHuman bodyKnee Joint
The invention relates to a method for detecting the power assisting efficiency of a load-bearing exoskeleton. The method comprises the following steps of (1) when a person does not wear the exoskeleton and does not bear a heavy load, obtaining kinematic and dynamic information by using a three-dimensional motion acquisition system and a force measuring treadmill; and verifying a human body joint moment positive test model based on surface electromyogram signals by using the human body joint moment calculated by inverse dynamics as a reference; (2) when the person wears the exoskeleton and bearing a load G1, obtaining the relationship between the time and the moment of the hip joint, the knee joint and the ankle joint by a method based on the surface electromyogram signals; (3) when the person does not wear the exoskeleton and carries out a load bearing test of 0 to 40 kg, testing the relationship between the time and the moment of the hip joint, the knee joint and the ankle joint of the human body under different loads in the time period; and (4) obtaining the ratio of the effective load to the total load according to data, measured in experiments, between the load of the human body and the driving moment of the total joint of the human body when the exoskeleton is not worn under the condition of different loads. The invention provides a novel method for testing the lower limbjoint moment of the exoskeleton.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Hemiplegia balancing training instrument
InactiveCN103919662AAchieve self-protectionEasy to restore functionGymnastic exercisingChiropractic devicesTerra firmaAthletic training
The invention discloses a hemiplegia balancing training instrument which comprises a base, a main stand rod vertically arranged in the center of the front end of the base, a left electronic scale and a right electronic scale. The left electronic scale and the right electronic scale are symmetrically arranged on the base and used for supporting the corresponding lower limbs of a patient. A transverse holding rod with the height adjustable is horizontally arranged on the main stand rod, the main stand rod is arranged on a wall, the left electronic scale and the right electronic scale respectively comprise a display screen used for displaying stress data to remind the patient to keep lower limb stress balance, and the display screens are arranged on the left side and the right side of the main stand rod respectively corresponding to the electronic scales. According to the instrument, the limb joints and muscles of the hemiplegic patient can be exercised and trained, the function can be restored more easily, the patient can consciously control the body gravity center to carry out excursion, the stress of the lower limbs is coordinated to achieve balance, the abnormal gait of the patient can be prevented and treated, the instrument is suitable for training cerebral apoplexy patients, cerebral apoplexy patients and other hemiplegic patients before walking, and the solid foundation can be laid for the normal walking training of the hemiplegic patients.
Owner:宋涛
Method for using a model-based controller for a robotic leg
A model-based neuromechanical controller for a robotic limb having at least one joint includes a finite state machine configured to receive feedback data relating to the state of the robotic limb and to determine the state of the robotic limb, a muscle model processor configured to receive state information from the finite state machine and, using muscle geometry and reflex architecture information and a neuromuscular model, to determine at least one desired joint torque or stiffness command to be sent to the robotic limb, and a joint command processor configured to command the biomimetic torques and stiffnesses determined by the muscle model processor at the robotic limb joint. The feedback data is preferably provided by at least one sensor mounted at each joint of the robotic limb. In a preferred embodiment, the robotic limb is a leg and the finite state machine is synchronized to the leg gait cycle.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Lower limb rehabilitation training equipment and biped end executor thereof
PendingCN111449913AAchieving Synergistic Movement TrainingImprove walking abilityChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesHuman bodyBalance ability
The invention discloses lower limb rehabilitation training equipment and a biped end executor thereof. The biped end executor comprises two sets of execution devices which have the same structure andare arranged in parallel; each execution device comprises a linear motion mechanism used for achieving forward and backward motion of the corresponding foot, a lifting mechanism connected with the linear motion mechanism and used for achieving height lifting of the foot, and an ankle joint rotating mechanism connected with the lifting mechanism and used for achieving ankle joint rotation. The lower limb rehabilitation training equipment comprises a supporting frame, a weight reduction supporting mechanism used for carrying out weight reduction control on a human body during training, a biped end executor used for carrying out gait training, and a pelvis pose adjusting mechanism used for carrying out cooperative adjustment on a position and a pose of the pelvis of the human body during gaittraining of the lower limbs of the human body so as to achieve balance. The lower limb joint movement can be realized, and the pelvis cooperative movement can also be realized; and the walking capability and the balance capability of a patient can be effectively improved.
Owner:山东阁步乐仕智能科技有限公司
Artificial human joint
InactiveCN106205323ARealize a high degree of simulationMake sure the axis intersections are fixedEducational modelsHuman bodyLimb joint
The invention relates to an artificial human joint which comprises a first artificial bone connector and a second artificial bone connector. A joint ball seat is fixedly connected to the tail end of the first bone connector, a joint ball is fixedly connected to the tail end of the second bone connector, the joint ball seat is provided with a ball socket attaching to the surface of the joint ball, and the area of the surface covering the joint ball of the ball socket is smaller than one half of the total area of the surface of the joint ball. The joint ball seat and the joint ball are respectively made from a permeability magnetic material, and a magnetic attraction assembly is arranged in the joint ball seat. Under the magnetic attraction force of the magnetic attraction assembly, the joint ball seat and the joint ball are movably connected. The central axis of the joint ball seat coincides with the center of the joint ball. The central axis of the first artificial bone connector coincides with the central axis of the joint ball seat, and the central axis of the second artificial bone connector coincides with the central axis of the joint ball. The artificial human joint can achieve simulation of six main human limb joints through specific structures, meanwhile can ensure that crossing points of axes of bones connected on two sides of each joint are fixed, and high-degree simulation of the human limb joints is achieved.
Owner:叶强 +2
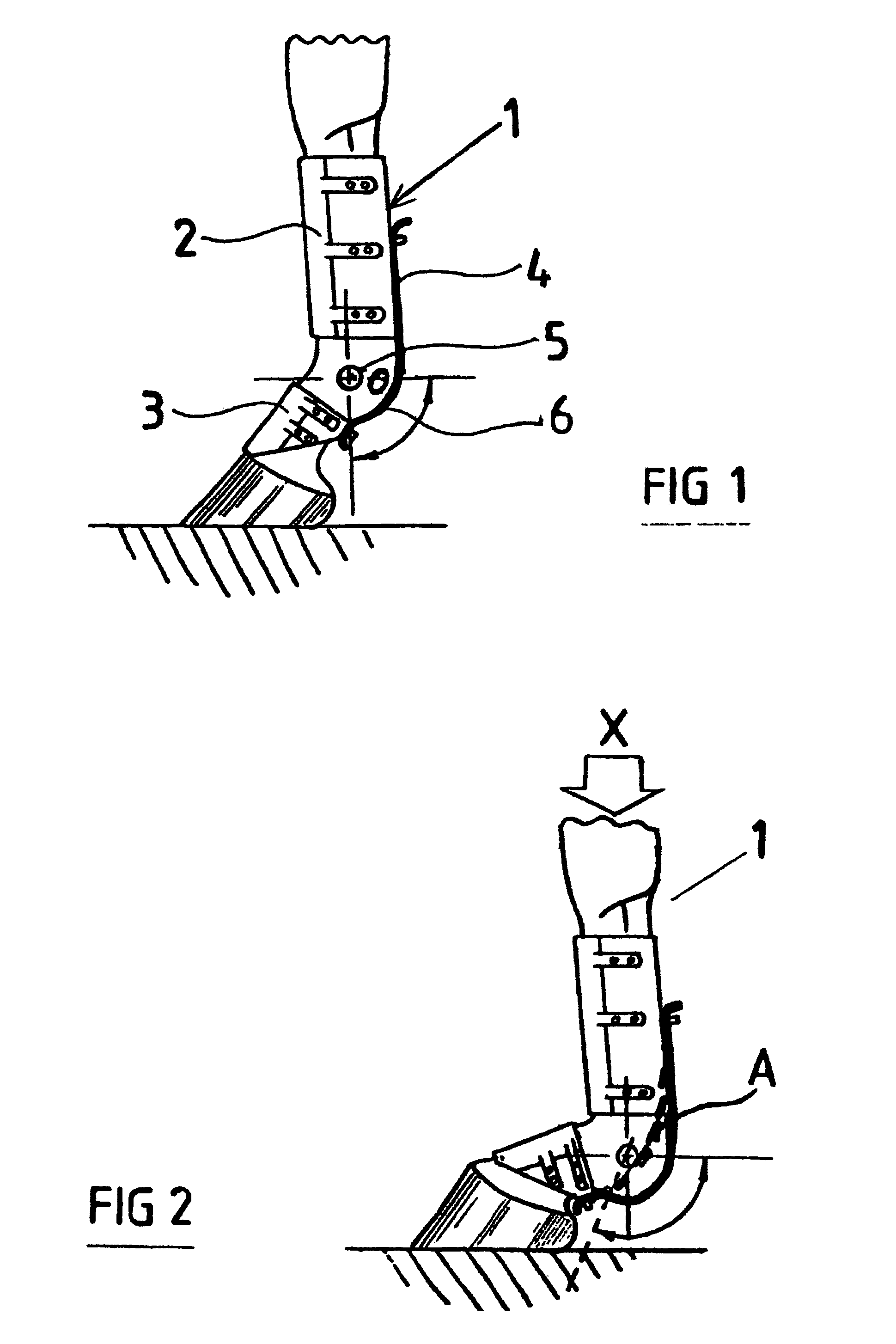
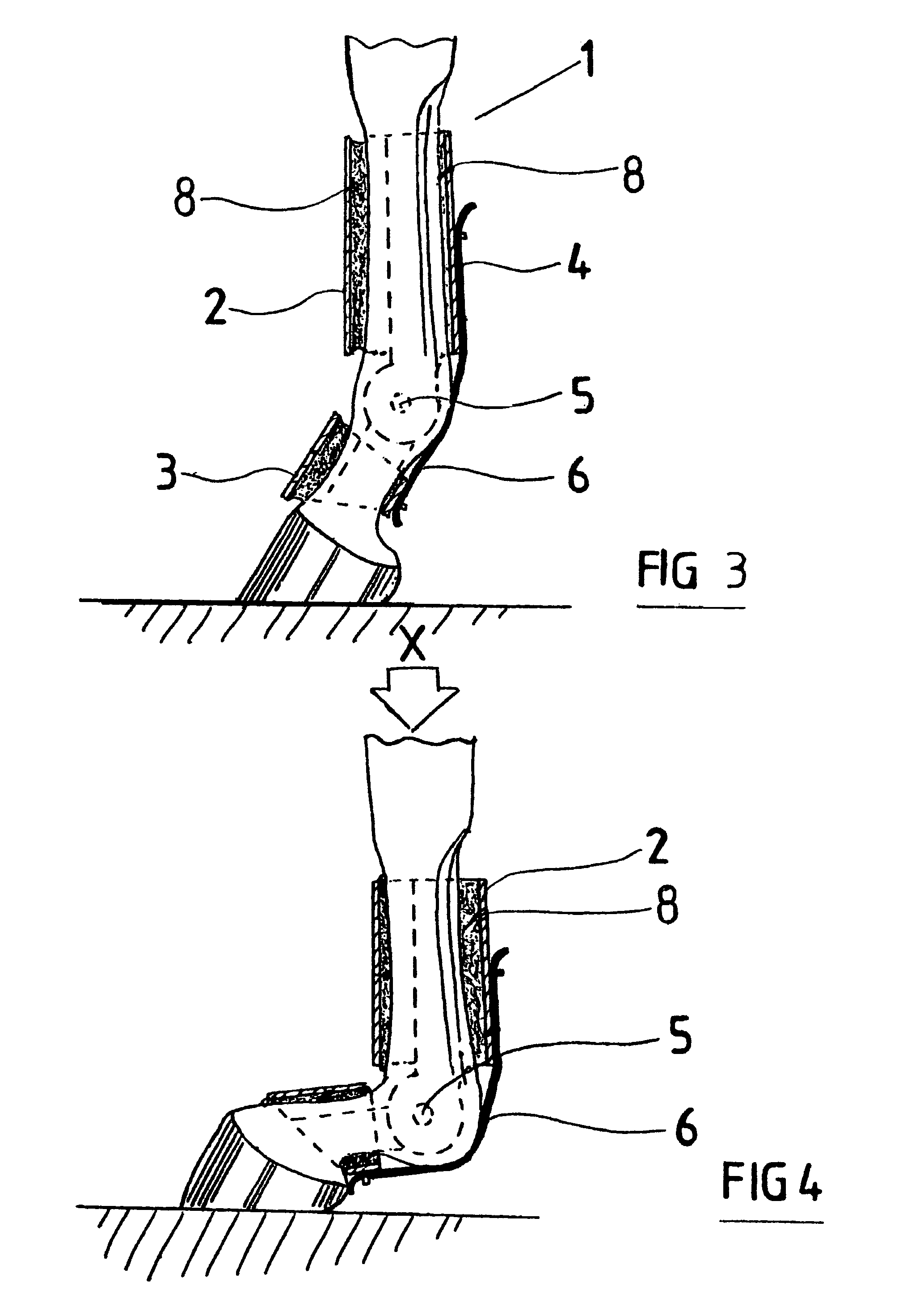
Tendon and ligament support for horse's fetlock joint
ActiveUS7559910B2Avoid injuryReduce harmDiagnosticsRestraining devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationLimb joint
A tendon and ligament support for a limb joint, such as an ankle joint, in particular a horse's fetlock joint. A first collar (1) is adapted to embrace the limb above the joint and a second collar (3) is adapted to embrace the limb below the joint. A connection provides articulation between and separation of the two collars, and is adapted to provide limited elongation of the ligaments and / or tendons under load, and includes a resistance-exerting pivot arrangement (11) resisting joint flexion or extension over a predetermined range of joint rotation, and an essentially inelastic part (12) for limiting joint extension across the posterior side of the joint connected to one or more points on each of the collars, and preferably adapted so as to mimic an artificial tendon or ligament arrangement.
Owner:DALY ANDREW SEAN GORDON
Chinese medicine used for treating shoulder neck pain and lumbocrural pain and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101530510AShort course of treatmentQuick resultsAntipyreticAnalgesicsDiseaseCervical spondylosis
The invention discloses a Chinese medicine (shoulder neck pain and lumbocrural pain eliminating liquid) used for treating shoulder neck pain and lumbocrural pain, and a preparation method thereof. The medicine consists of 9g of himalayan teasel root, 9g of dried tangerine peel, 9g of divaricate saposhnikovia root, 6g of eucommia bark, 6g of radix cyathulae, 9g of Chinese angelica, 6g of radix peucedani, 9g of Clematis chinensis, 6g of raidx astragali, 9g of radix paeoniae lactiflorae, 9g of rehmannia glutinosa, 9g of liquorice root, 9g of notopterygium incisum, 9g of szechuan lovage rhizome, 9g of straight ladybell root, 9g of cassia bark, 9g of medlar, 9g of medicinal indianmulberry root, 9g of Chinese taxillus twig, 500g of white sugar and 1000g of 55-degree liquor. The preparation method comprises the steps as follows: (1) the 19 medicines are put in a glass vessel; (2) 500g of white sugar and 1000g of 55-degree liquor are mixed in the medicine vessel which is placed for seven days after being sealed; and (3) medicinal liquor is taken out, and the cleaning solution is filtered out and put into bottles of 300ml; and a suction cup and an acupuncture pin are distributed simultaneously. The shoulder neck pain and lumbocrural pain eliminating liquid has the functions of activating meridians and stopping pain, dispelling wind and eliminating dampness, replenishing vital energy and nourishing blood, and strengthening muscle and bone, and is mainly used for treating sore swelling, numbness, pain and the like caused by scapulohumeral periarthritis, arthritis, lumbar muscle strain, lumbocrural pain, sciatica, cervical spondylosis, lumbar vertebra disease, hyperosteogeny of four limb joints, thus being a medicine with short treatment course, quick effect and high curative ratio.
Owner:王广同
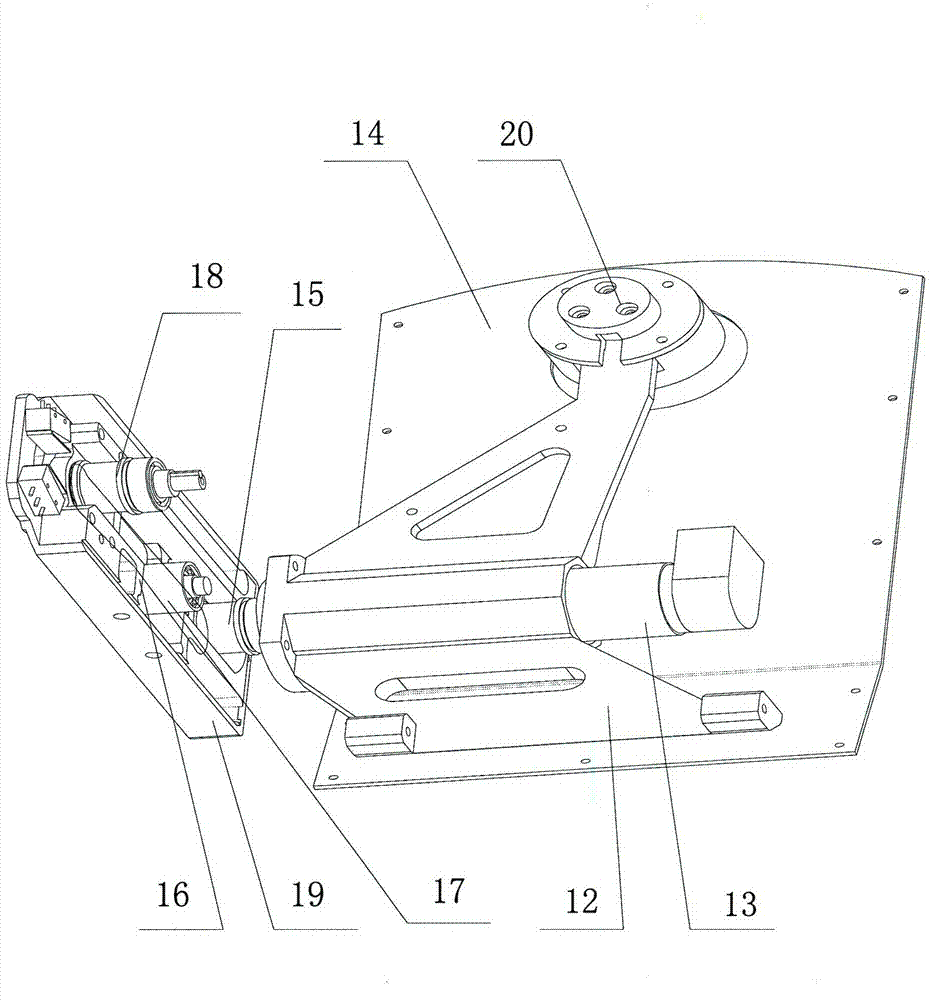
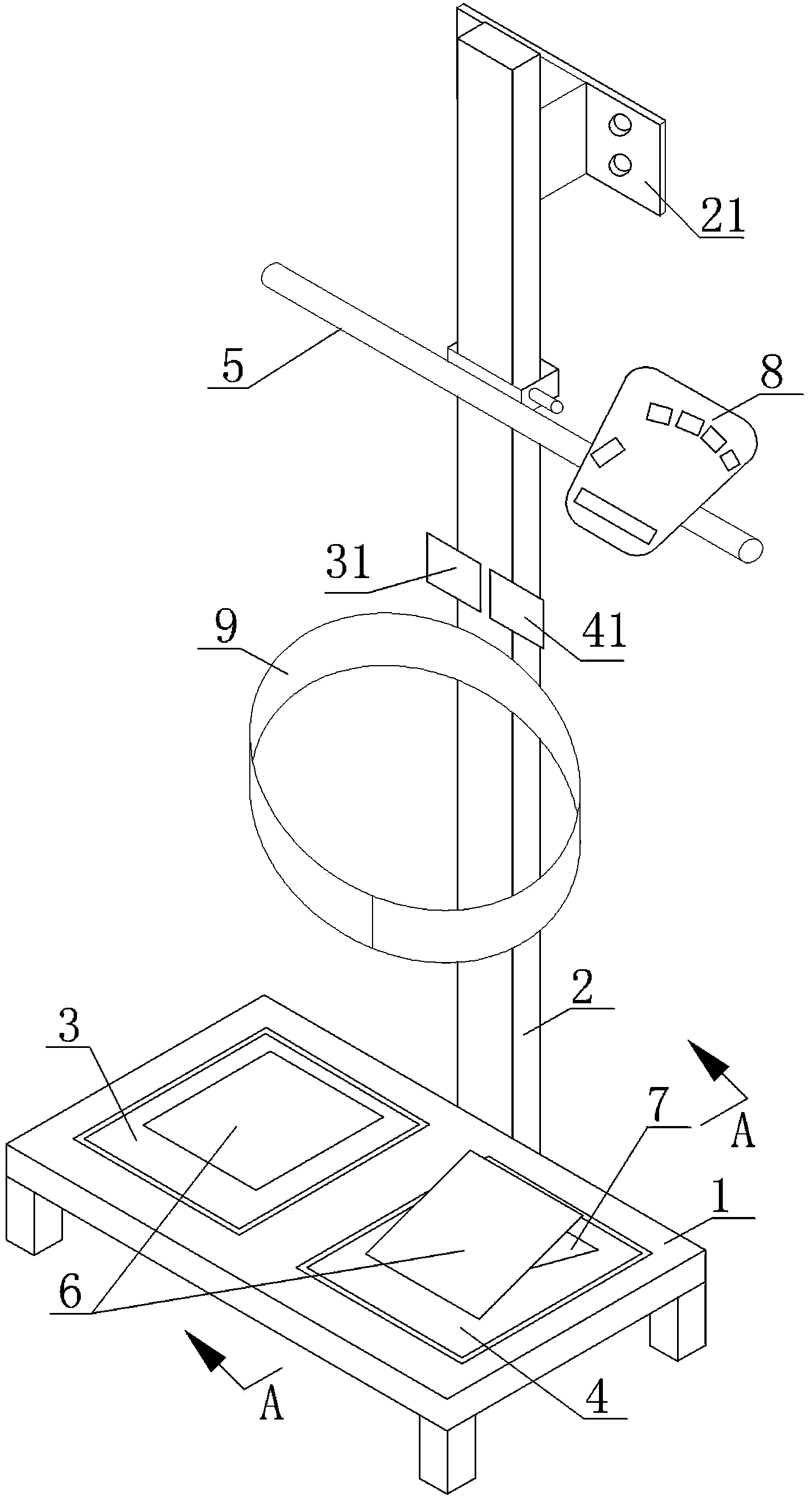
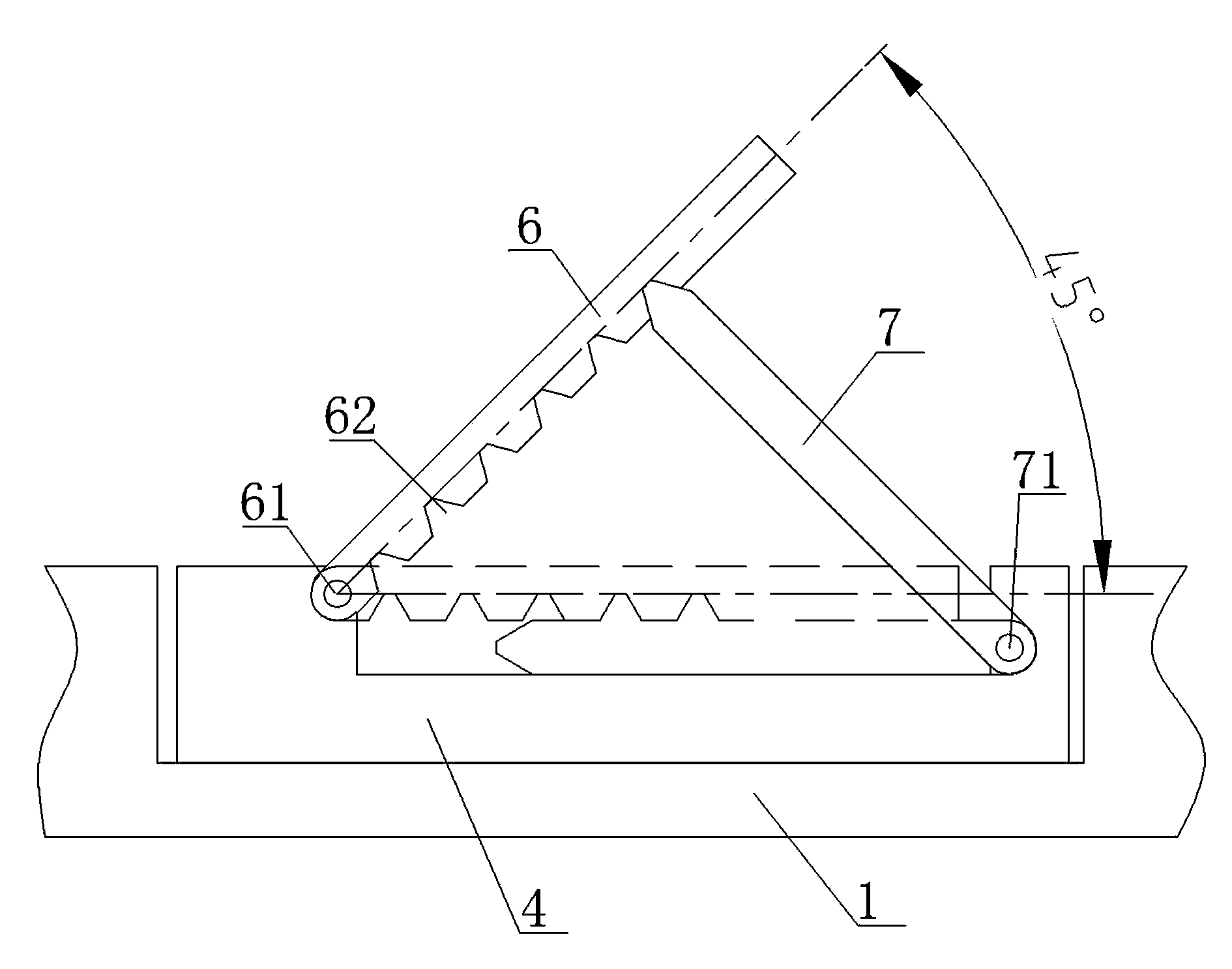
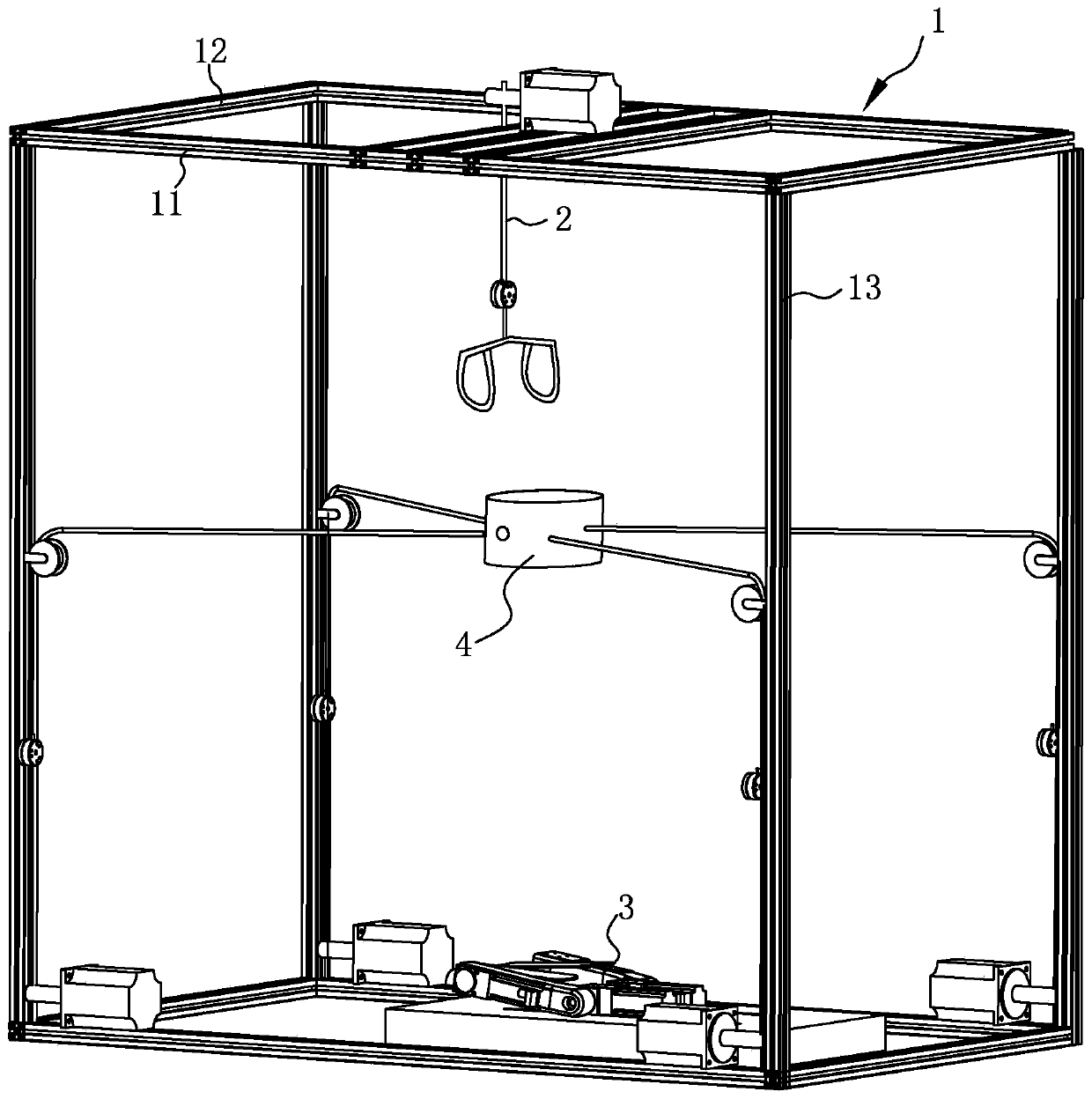
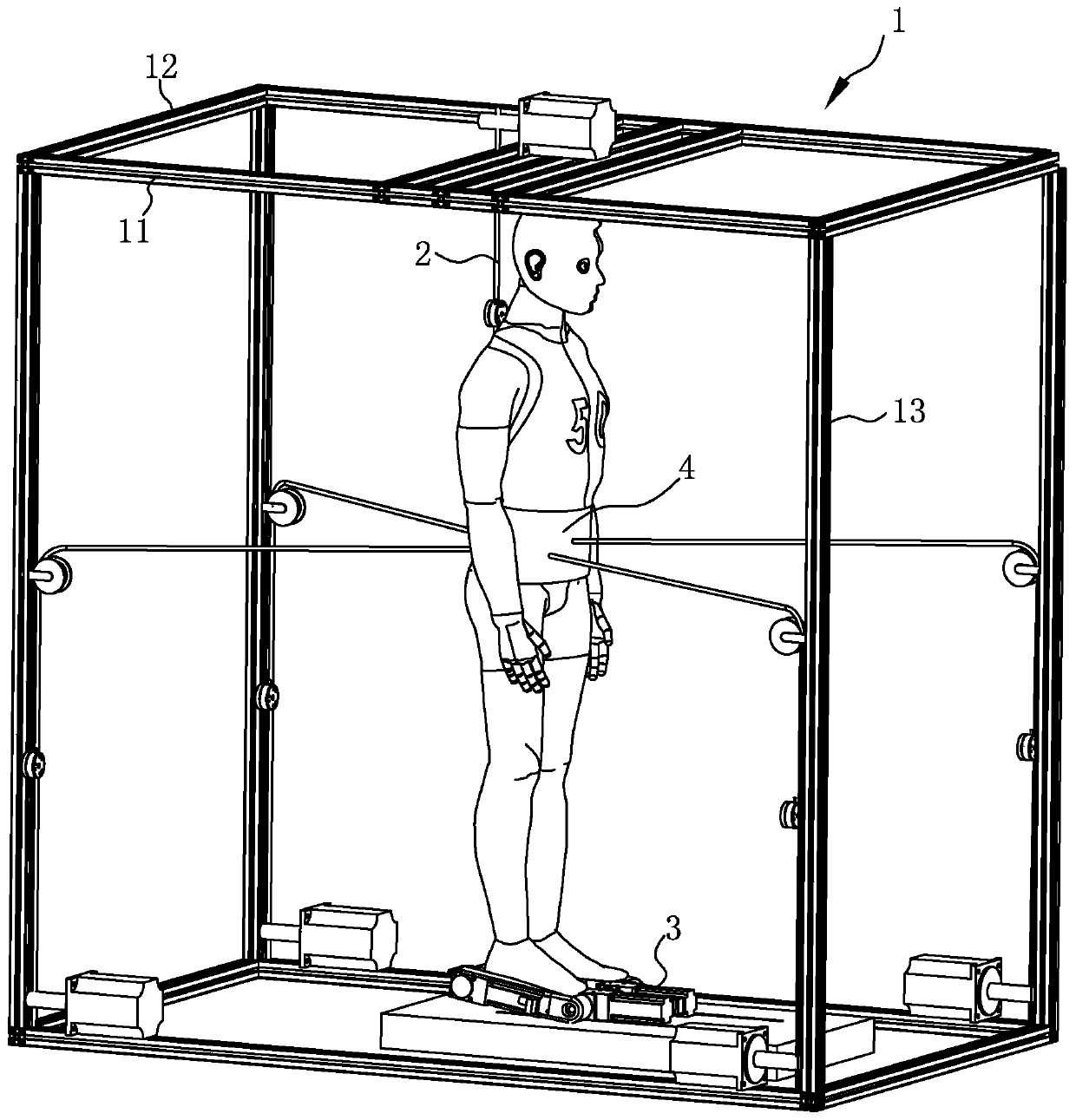
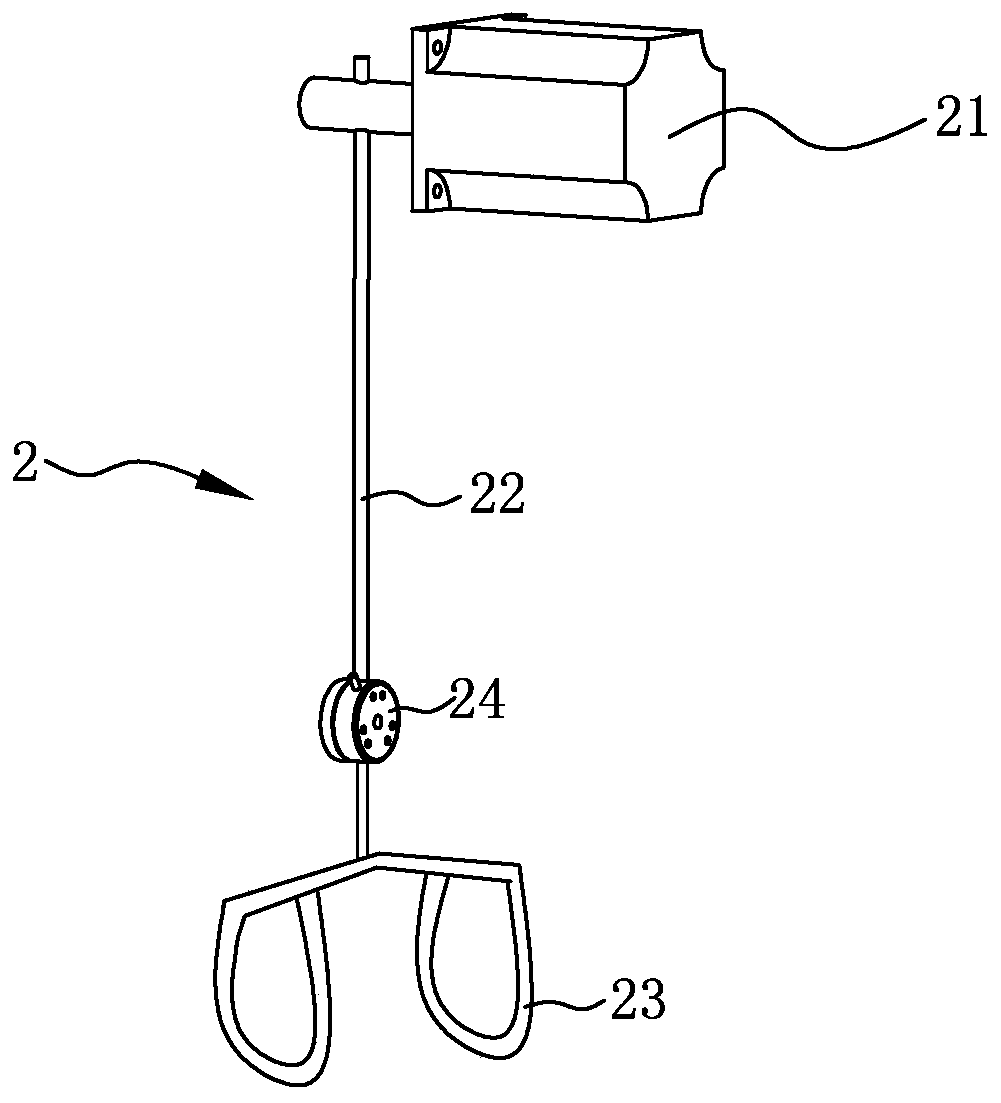
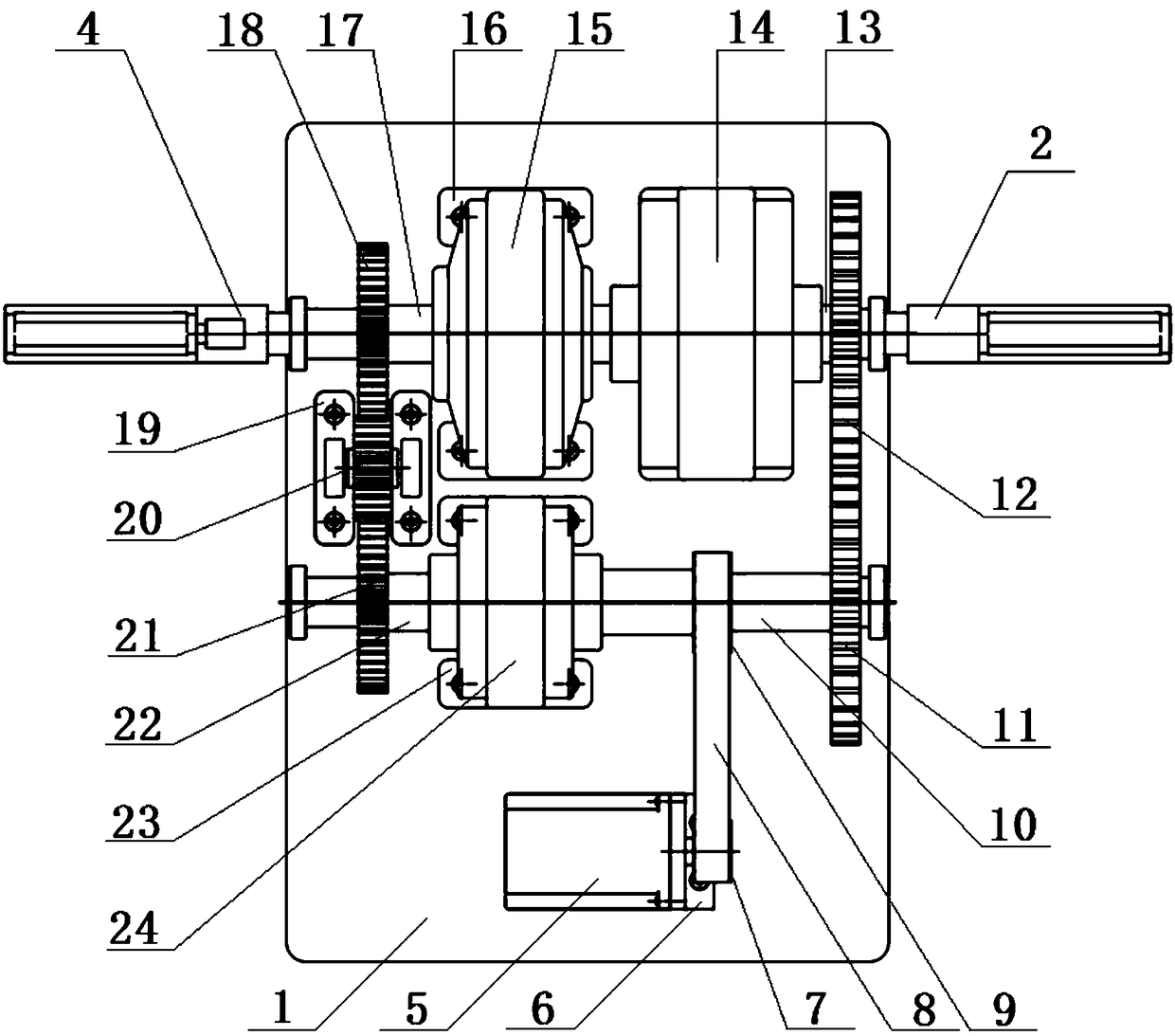
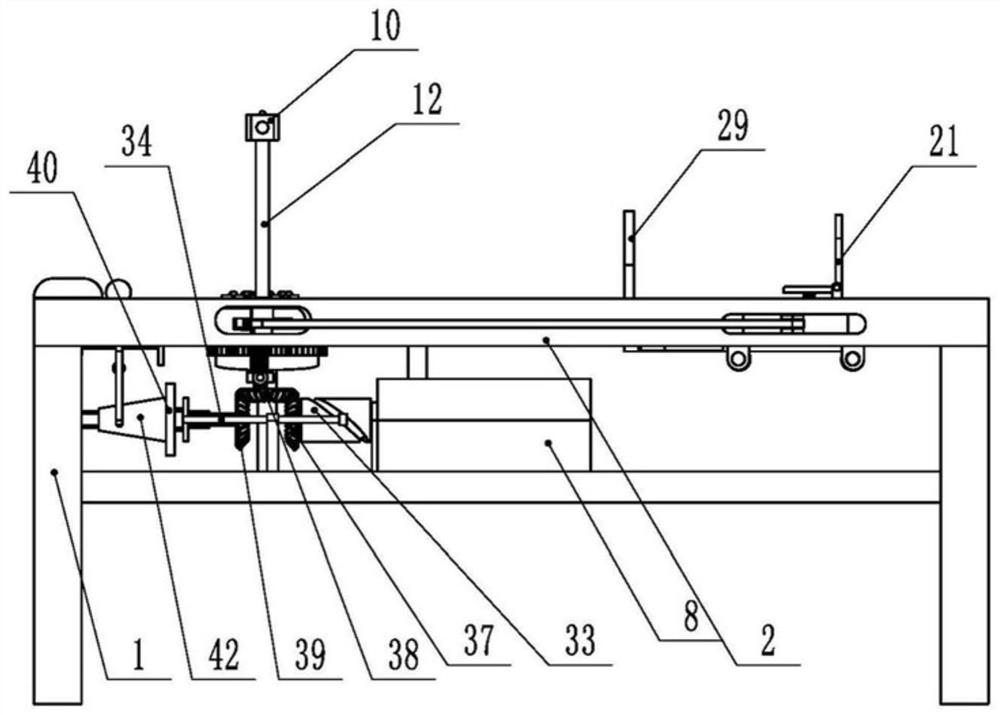
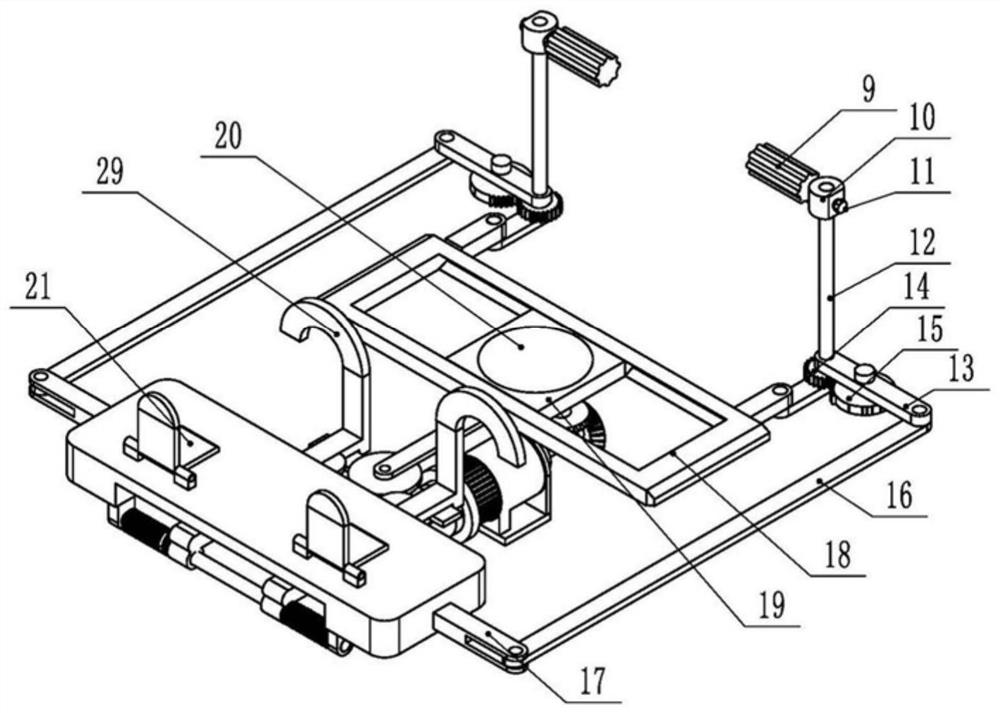
Limb joint rehabilitation training device
ActiveCN108273236AAdaptableChiropractic devicesMovement coordination devicesSeparated stateLimb joint
The invention relates to the technical field of rehabilitation training, and provides a limb joint rehabilitation training device. The limb joint rehabilitation training device aims at the solving thetechnical problem that existing limb joint rehabilitation training devices have a small application range. A power source is connected with a base, a first transmission mechanism is connected betweenthe power source and a first rotating shaft or between the power source and a second rotating shaft to convert power of the power source into the rotation of the first rotating shaft or the second rotating shaft, a first clutch is connected with the first rotating shaft and the second rotating shaft, and a second clutch is connected with the inner side end of a fourth rotating shaft and the innerside end of a third rotating shaft so that the first rotating shaft and the second rotating shaft can switch between a separated state and a jointed state and the third rotating shaft and the fourthrotating shaft can switch between a separated state and a jointed state; a second transmission mechanism transmits the rotation of the first rotating shaft to the fourth rotating shaft, a first limb operating piece is connected with the outer side end of the fourth rotating shaft, a third transmission mechanism transmits the rotation of the second rotating shaft to the fourth rotating shaft, and asecond limb operating piece is connected with the outer side end of the fourth rotating shaft.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
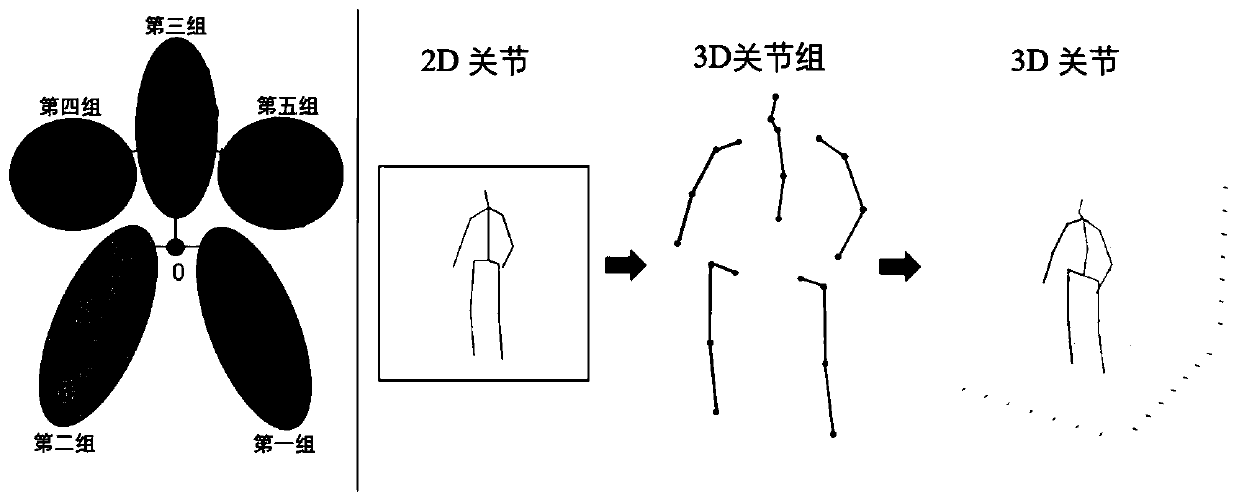
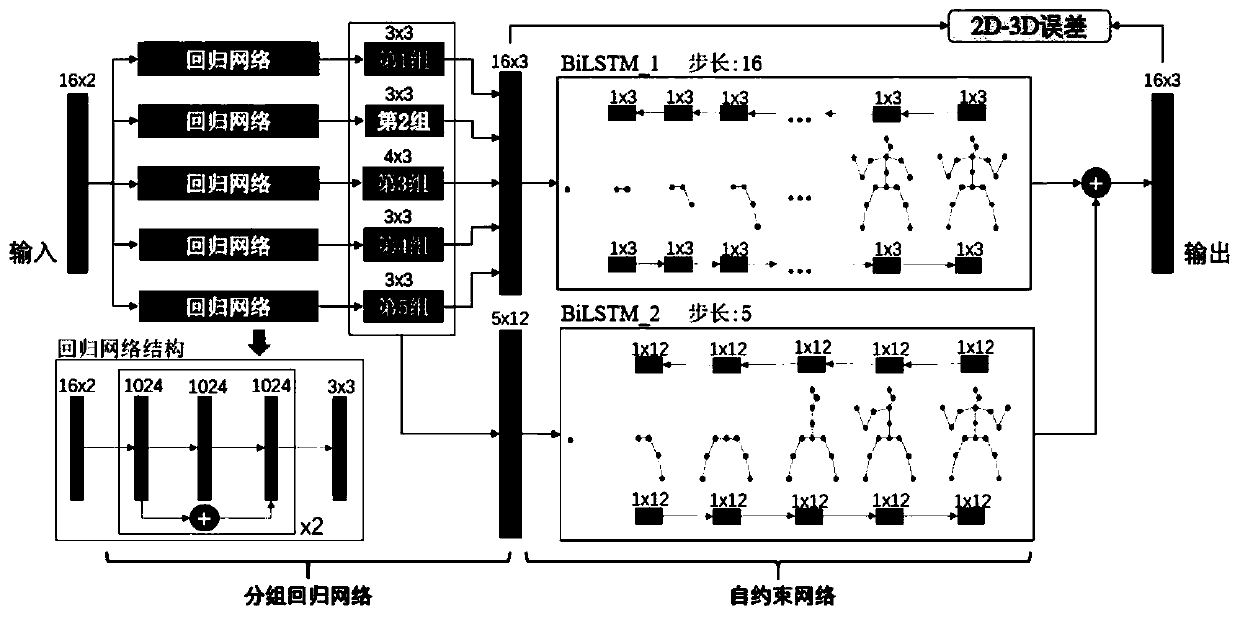
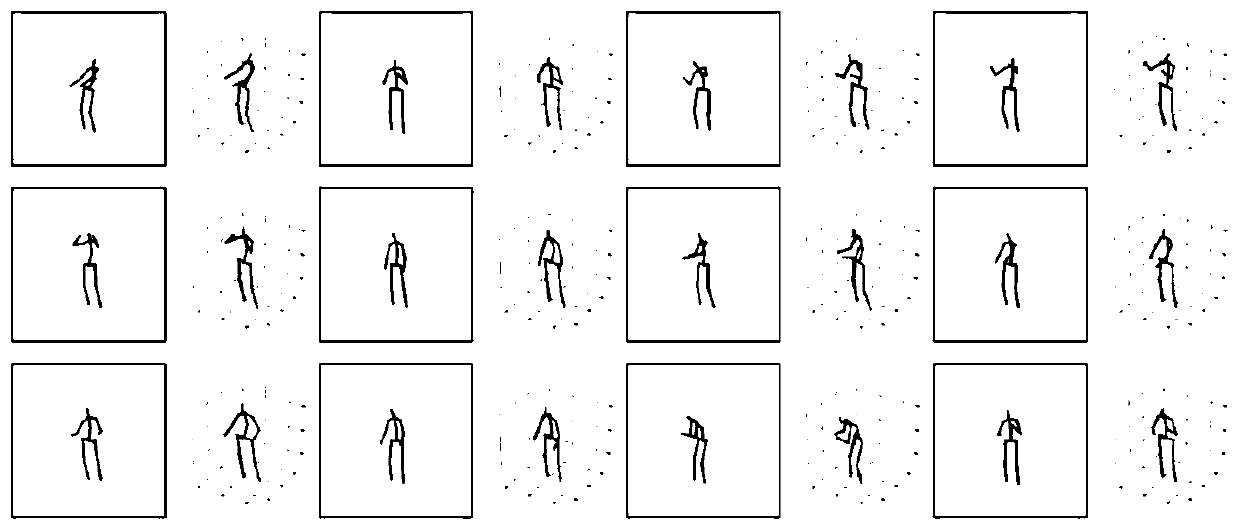
Human body three-dimensional joint point prediction method based on grouping regression model
ActiveCN110188700ADeepen influenceEase singleCharacter and pattern recognitionHuman bodyPredictive methods
The invention discloses a human body three-dimensional articulation point prediction method based on a grouping regression model. The method comprises the following steps: collecting human body 2d articulation point detection data; inputting the 2d joint point coordinates into a regression network with the same structure, obtaining 3d joint positions in different groups, and merging the obtained key three-dimensional positions into an integral joint vector; constructing a joint point self-constraint network and a joint group self-constraint network through BiLSTM, and accumulating 3d joint points output by the two self-constraint networks to obtain a fine-tuned 3d prediction joint; and calculating the Euclidean distance between the 3d predicted joint and the 3d joint through a loss function. According to the invention, a grouping regression structure is adopted in combination with the characteristic of human limb joint movement independence, four limbs and a trunk are divided into different joint groups, the 3d positions of joint points in each group are predicted respectively, and meanwhile, in order to make a prediction result closer to a real human body posture, a human body joint self-constraint network is designed by utilizing BiLSTM to adjust the prediction result, so that the accuracy is improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Laminated bandage comprising an activated carbon cloth
InactiveUS20140283851A1Reducing and preventing swellingReduction and prevention of swellingNon-adhesive dressingsVeterinary bandagesActivated carbonMedicine
The present invention relates to multi-layer products and methods utilising such products. Embodiments of the present invention have utility in the prevention and / or healing of wounds and skin disorders. More particularly, although not exclusively, the present invention relates to products and methods which have utility in the veterinary field. Embodiments of the present invention relate to products and methods which are for use in the prevention and / or healing of wounds and skin disorders in equines, namely, horses, ponies, donkeys and the like, particularly wounds and skin disorders which affect the limbs of such animals. Aspects of the present invention provide products and methods for supporting limb joints whilst allowing the joint to flex to enable movement.
Owner:EQUI MED
Limb bone joint rehabilitation training device
InactiveCN113274250AAchieving Synchronized WorkoutsRealize Circular Squeeze MassageChiropractic devicesRoller massageEngineeringUpper extremity joint
A limb bone joint rehabilitation training device comprises a power structure, the upper end of the power structure is connected with a limb training structure, and the limb training structure comprises an upper limb joint training assembly capable of conducting arc-shaped reciprocating rotation and reciprocating autorotation twisting on hand joints of a patient and a lower limb joint training assembly connected with the upper limb joint training assembly. The lower limb joint exercise assembly can perform up-down bending and stretching exercise and left-right opening and closing exercise on leg joints of the patient; the front end of the power structure is connected with a transmission structure, and the transmission structure is connected with a lumbar vertebra massage structure capable of conducting circumferential rotation and intermittent up-down protruding massage on the two side edges of the lumbar vertebra of a patient. The transmission structure is further connected with a cervical vertebra joint massage structure which can circularly extrude and massage different positions in front of and behind the cervical vertebra of the patient and automatically adjust the extrusion force, and the problems that a rehabilitation exercise device in the prior art is single in structure and cannot fully arouse the enthusiasm and autonomy of the patient in use are effectively solved.
Owner:LUOYANG CENT HOSPITAL
System and method for monitoring and correcting human body movement
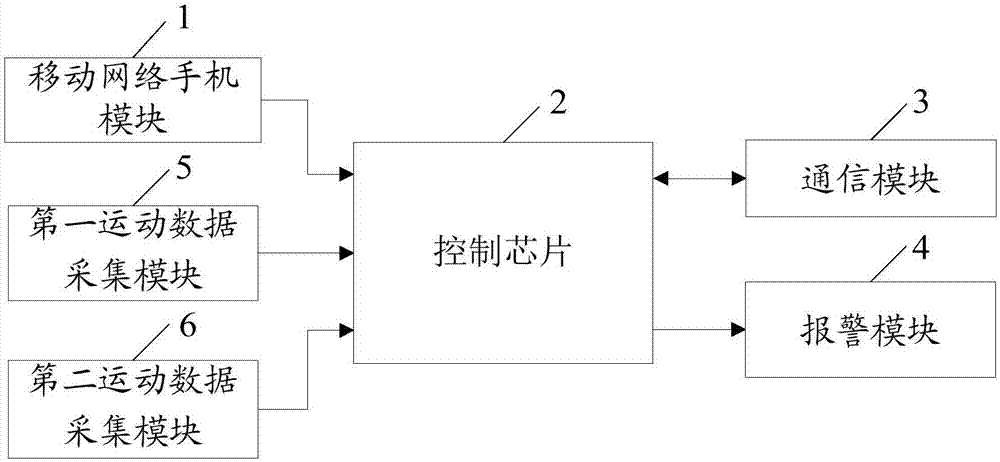
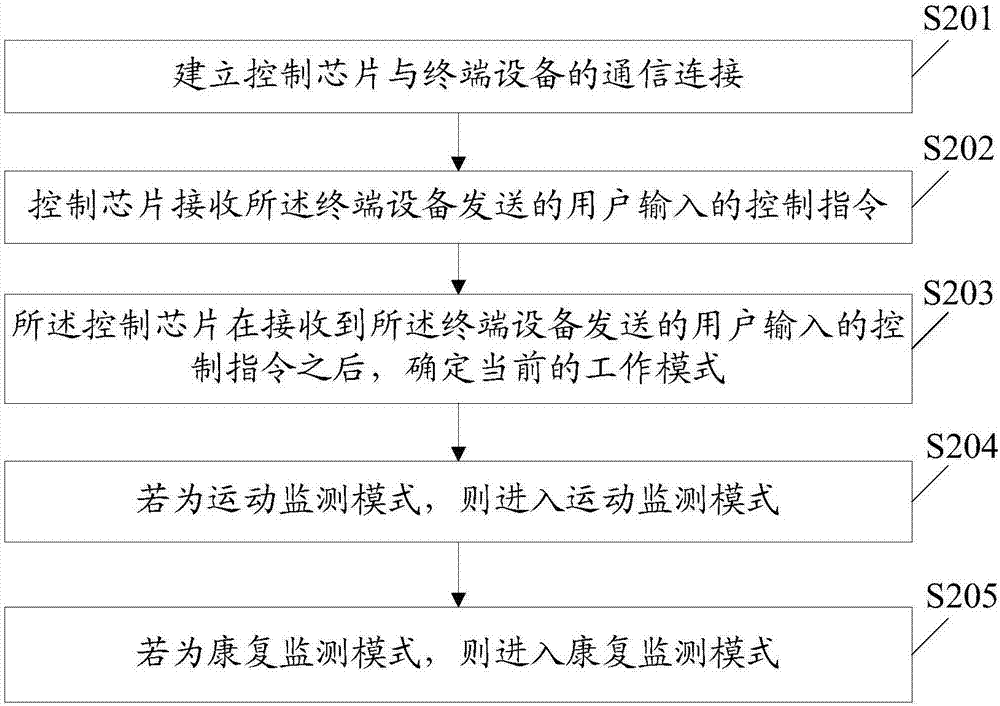
InactiveCN106902496ARealize monitoringRealize functionTransmission systemsGymnastic exercisingHuman bodyComputer module
The present invention provides a system and method for monitoring and correcting human motion. The system includes a network mobile phone module, a control chip, a communication module, an alarm module, a first motion data acquisition module arranged at the front end of the limb joints, and a first movement data acquisition module arranged at the rear end of the limb joints. The second exercise data acquisition module, the network mobile phone module, the communication module, the alarm module, the first exercise data acquisition module and the second exercise data acquisition module are respectively connected with the control chip. Dynamically collect the motion data values of the limb joints, compare the collected motion data values with the preset limb joint motion data thresholds in real time, if the collected limb joint motion data values exceed the preset limb joint values The range of motion data thresholds will be prompted through the vibration motor and buzzer to meet the needs of maintaining the correct posture, so as to realize functions such as monitoring and alarming of human body motion.
Owner:卢曼斯
Chinese medicine composition for treating cervical and lumbar disc disease
The invention involves a Chinese materia medica combination and its preparation technique, particularly involves a combination prescription and its preparation technique for treatment of dizziness hand numb and back and shoulder pain which is often seen in cervical syndrome; knee and loin aching and limp, lower extremity pain, heel pain often seen in lumbar spondylosis; limbs joint pain, intumesce, ankylosing spondylitis seen in rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis disease. They are made into necessary dosage form according to clinical needs.
Owner:BEIJING RUNDEKANG MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com