Model-based neuromechanical controller for a robotic leg
A controller and mechanical technology, applied in the direction of manipulators, program-controlled manipulators, artificial legs, etc., can solve the problems such as the adaptation of controllers that do not allow environmental interference
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
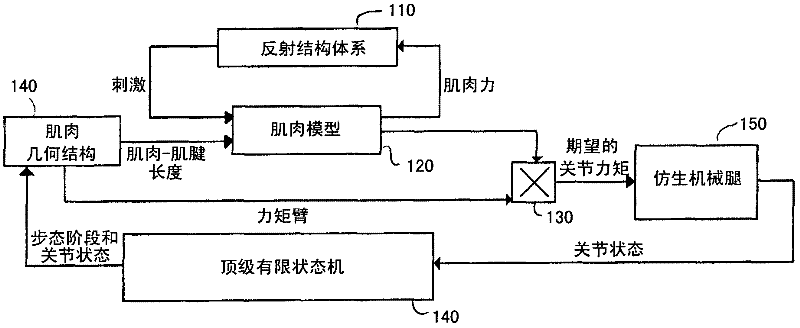
[0048] A control architecture proposes to manipulate the biomimetic moments of the ankle, knee, and hip joints of a powered leg prosthesis, orthosis, or exoskeleton during walking. In this implementation, the powered device includes moment-controllable artificial ankle and knee joints. Appropriate torques are provided to the user as determined by feedback information provided by sensors positioned at each joint of the robotic leg assembly. These sensors include, but are not limited to, angular joint displacement and velocity Hall effect sensors using digital encoders or similar, torque sensors at the knee and ankle joints, and at least one inertial measurement device located between the knee and ankle joints (IMU).
[0049] Sensory information from the joint state (position and velocity) of the robotic legs (hip, knee, and ankle) is used as input to a neuromuscular model of human locomotion. The model uses joint state sensor information from the robotic leg to determine the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com