Patents
Literature
635 results about "Breathing system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
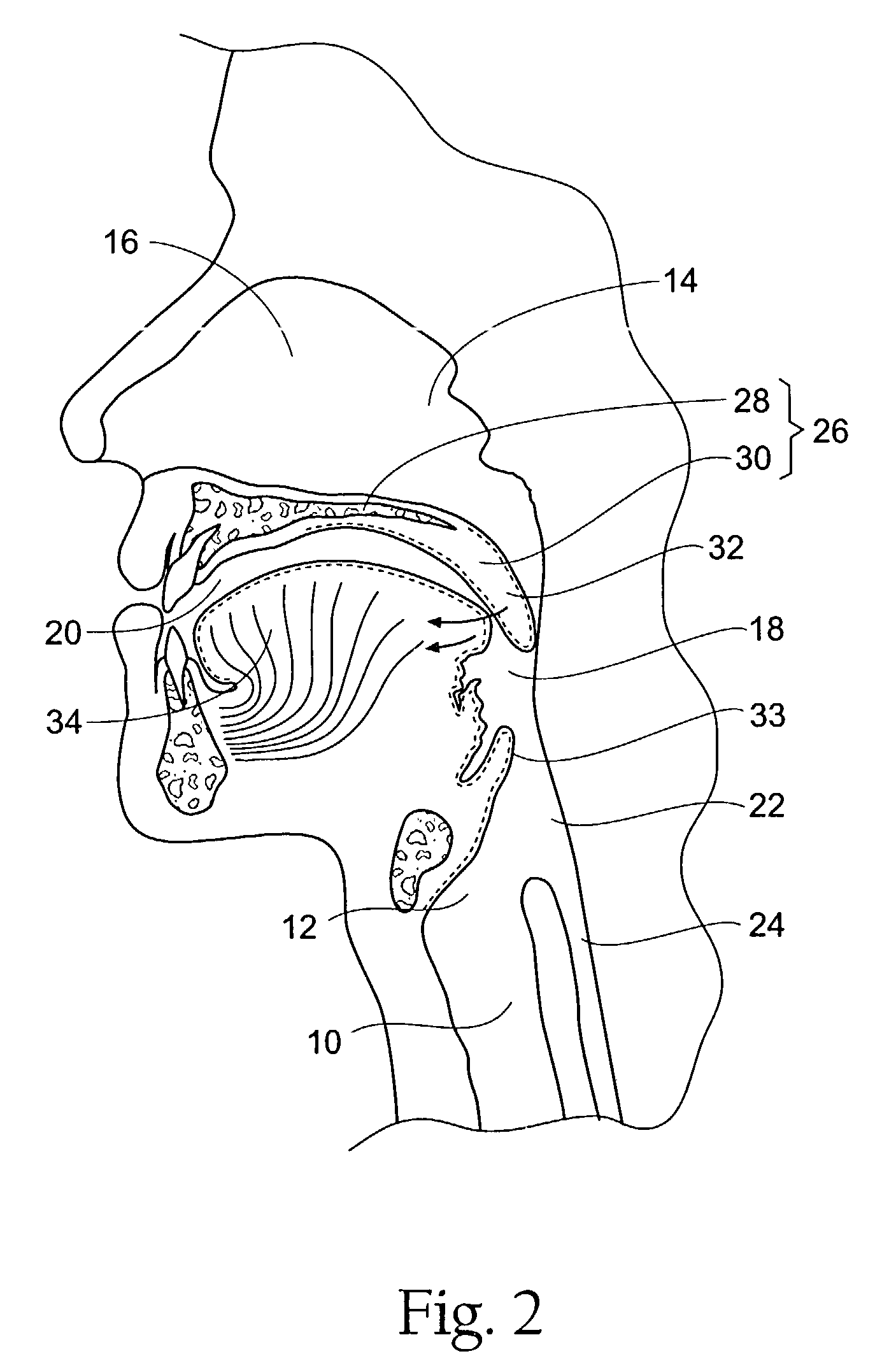
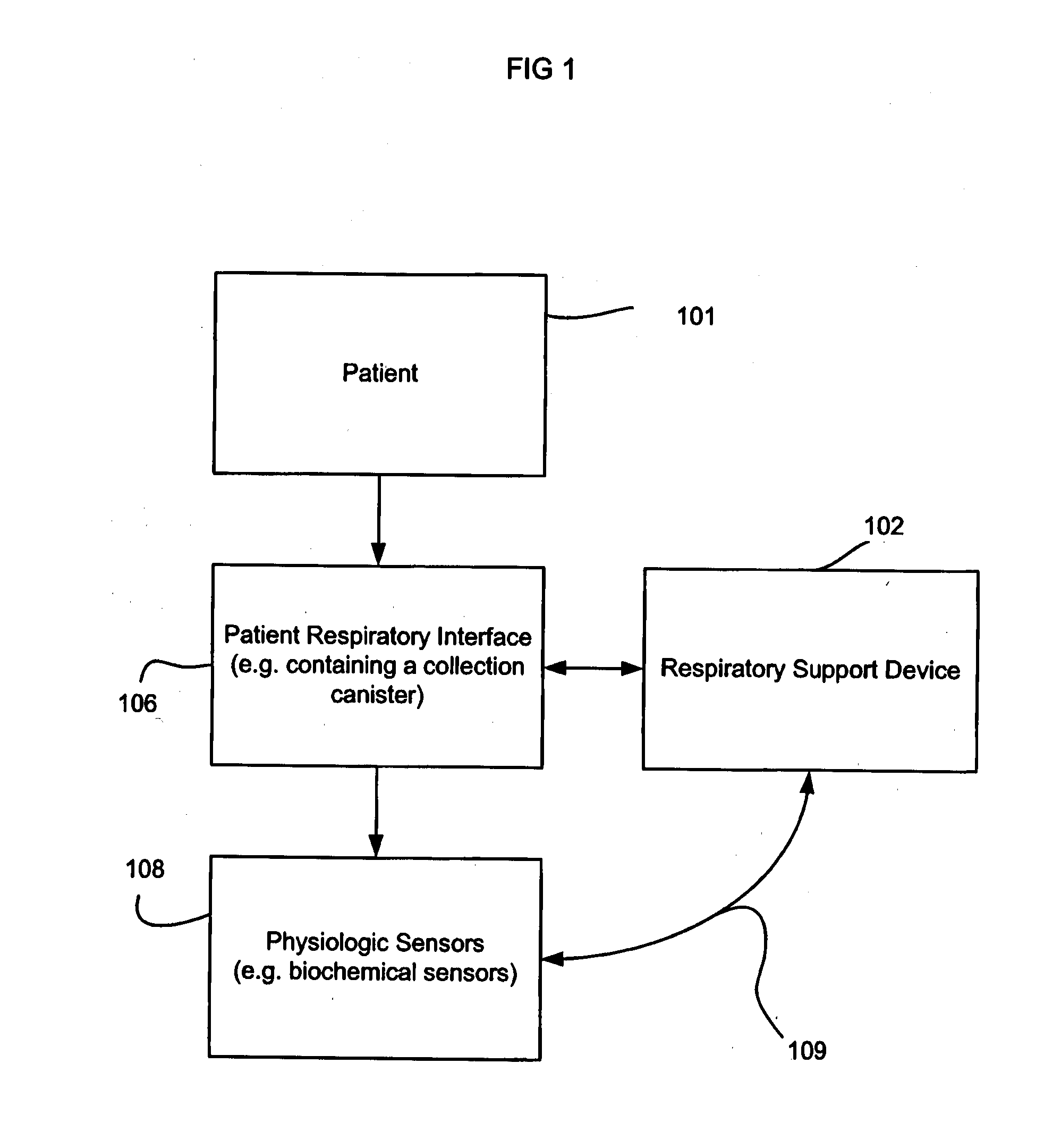
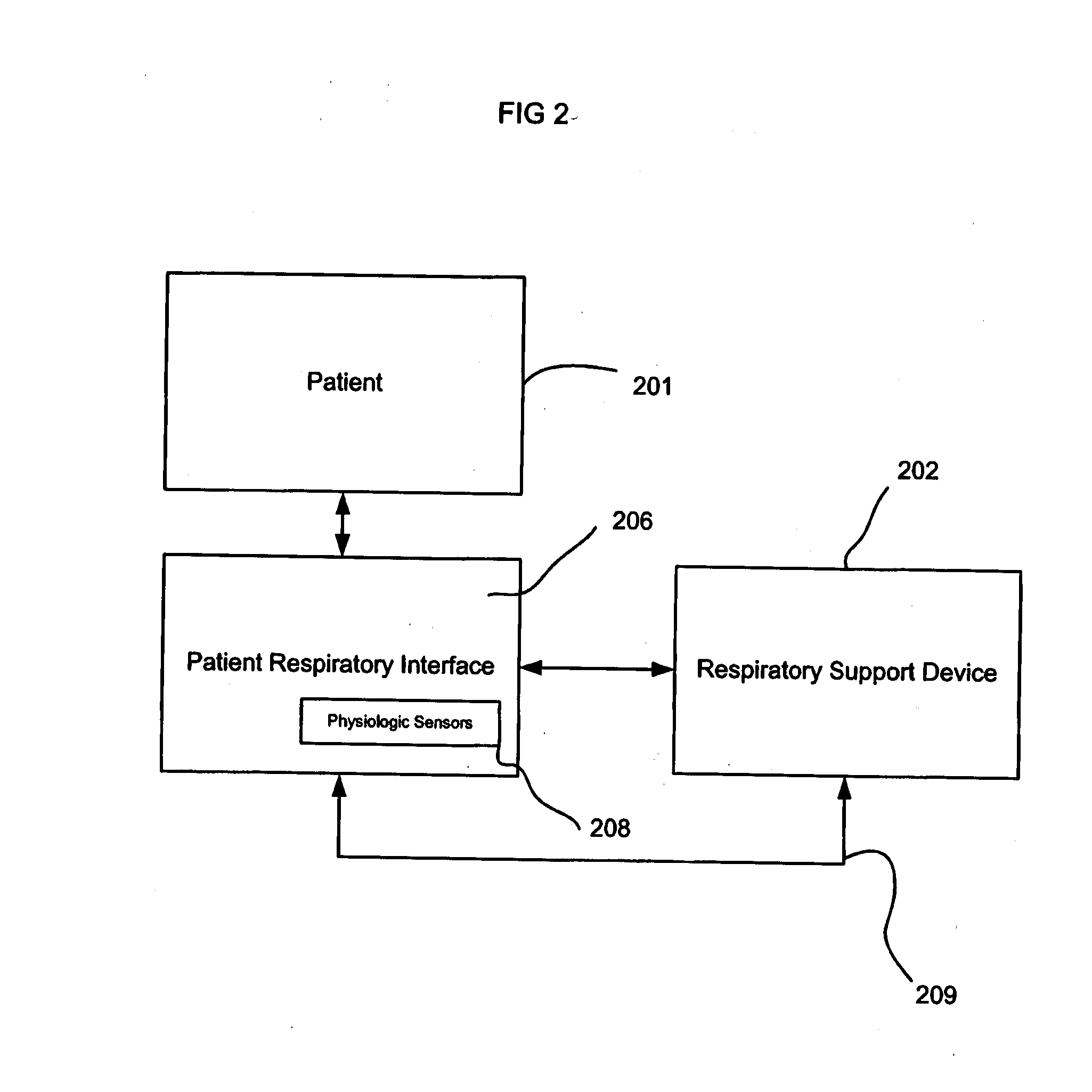
The human respiratory system is the system which controls breathing and enables us to breathe. Breathing includes inhaling and exhaling of the air in the body, absorption of the oxygen from air into our body for providing energy, and removal of carbon dioxide (by-product of the respiration) out of our body.
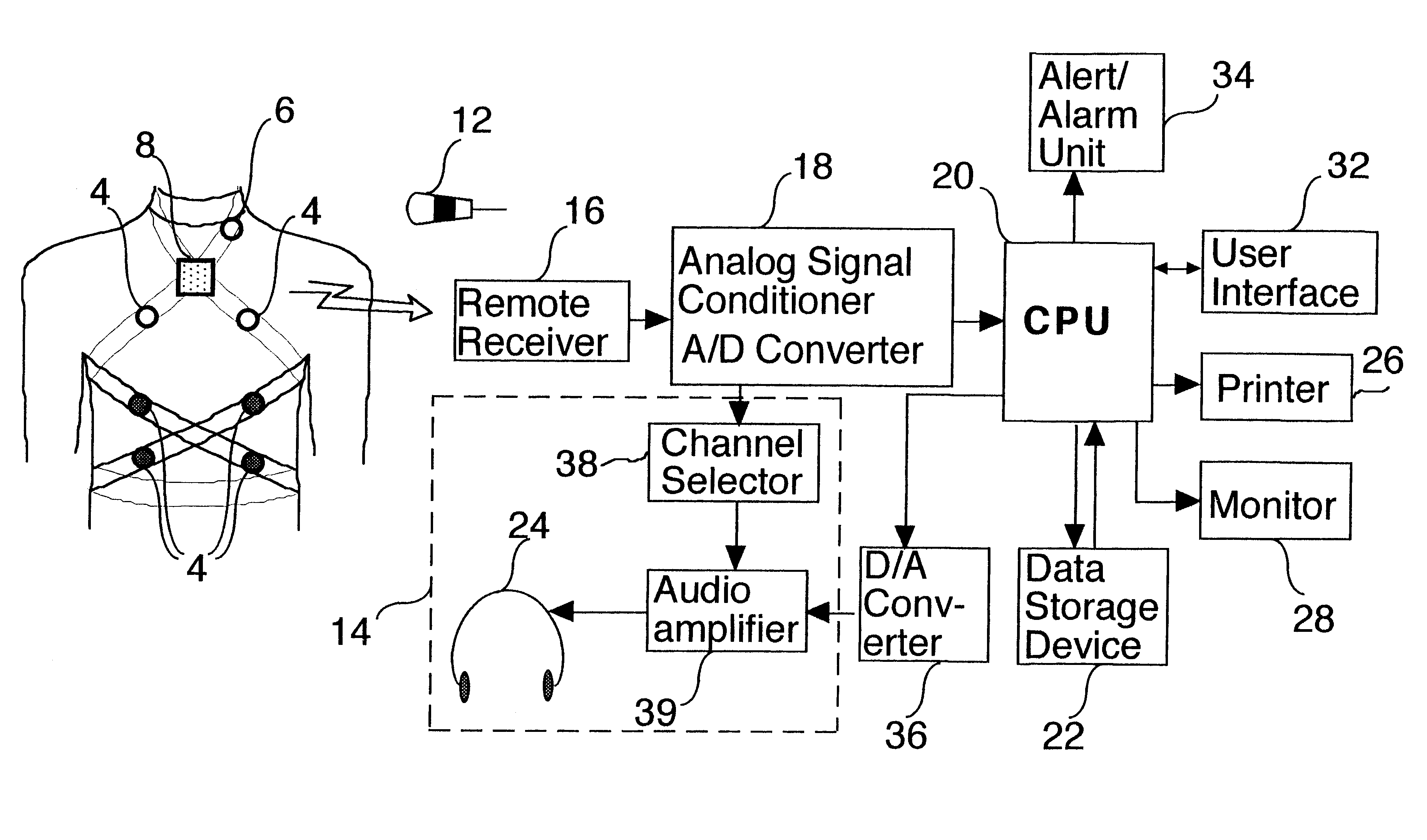
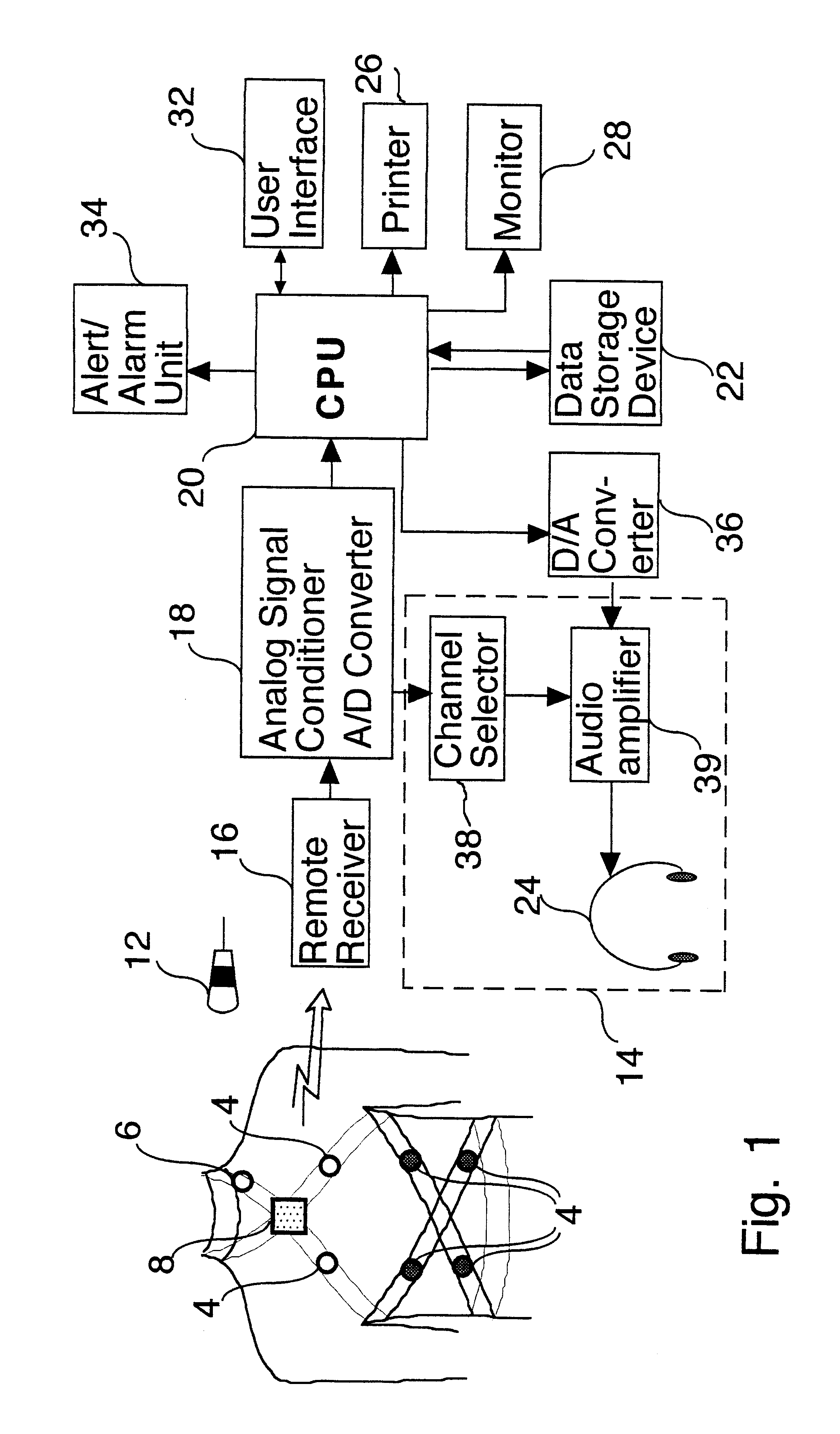
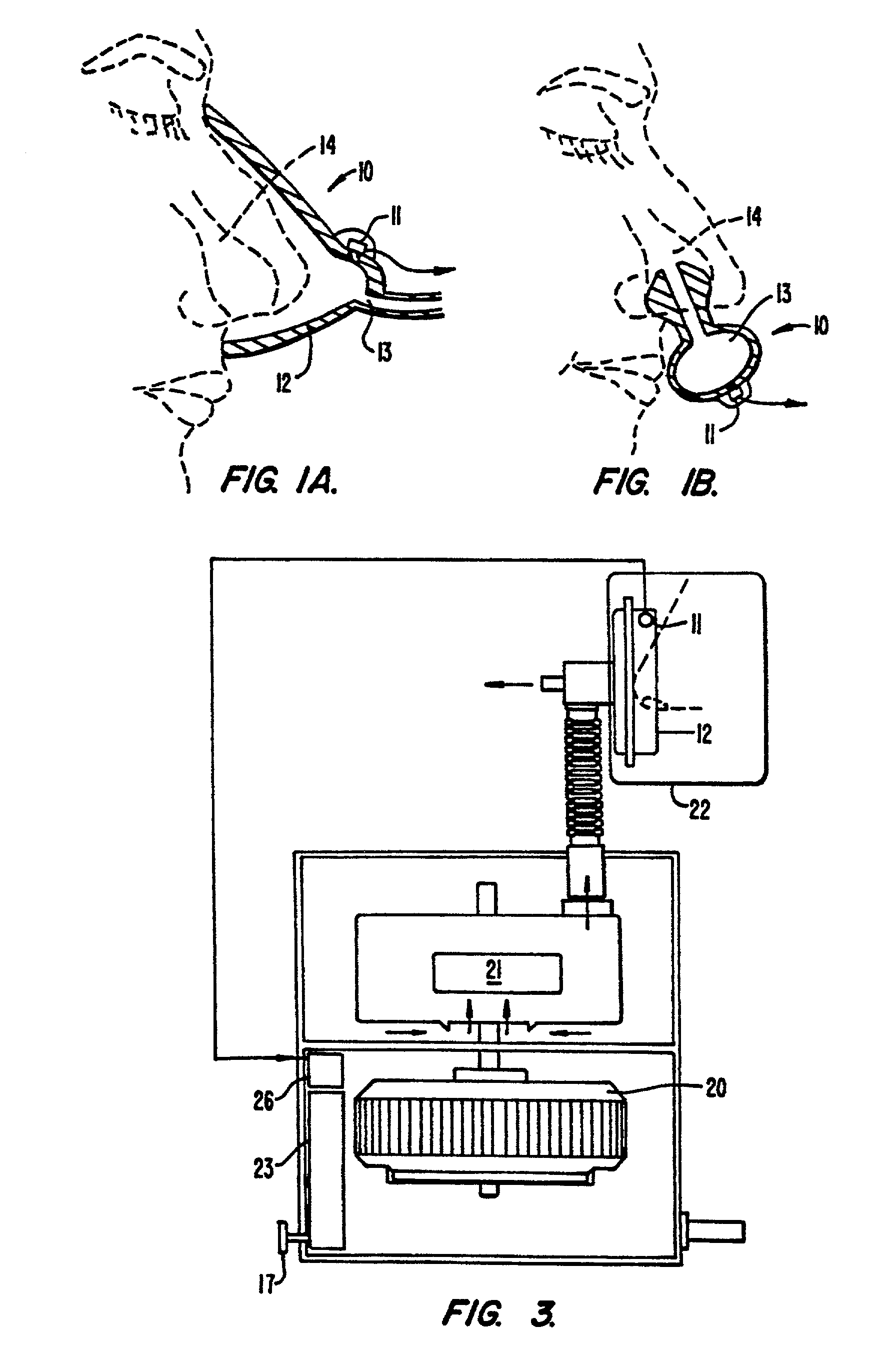
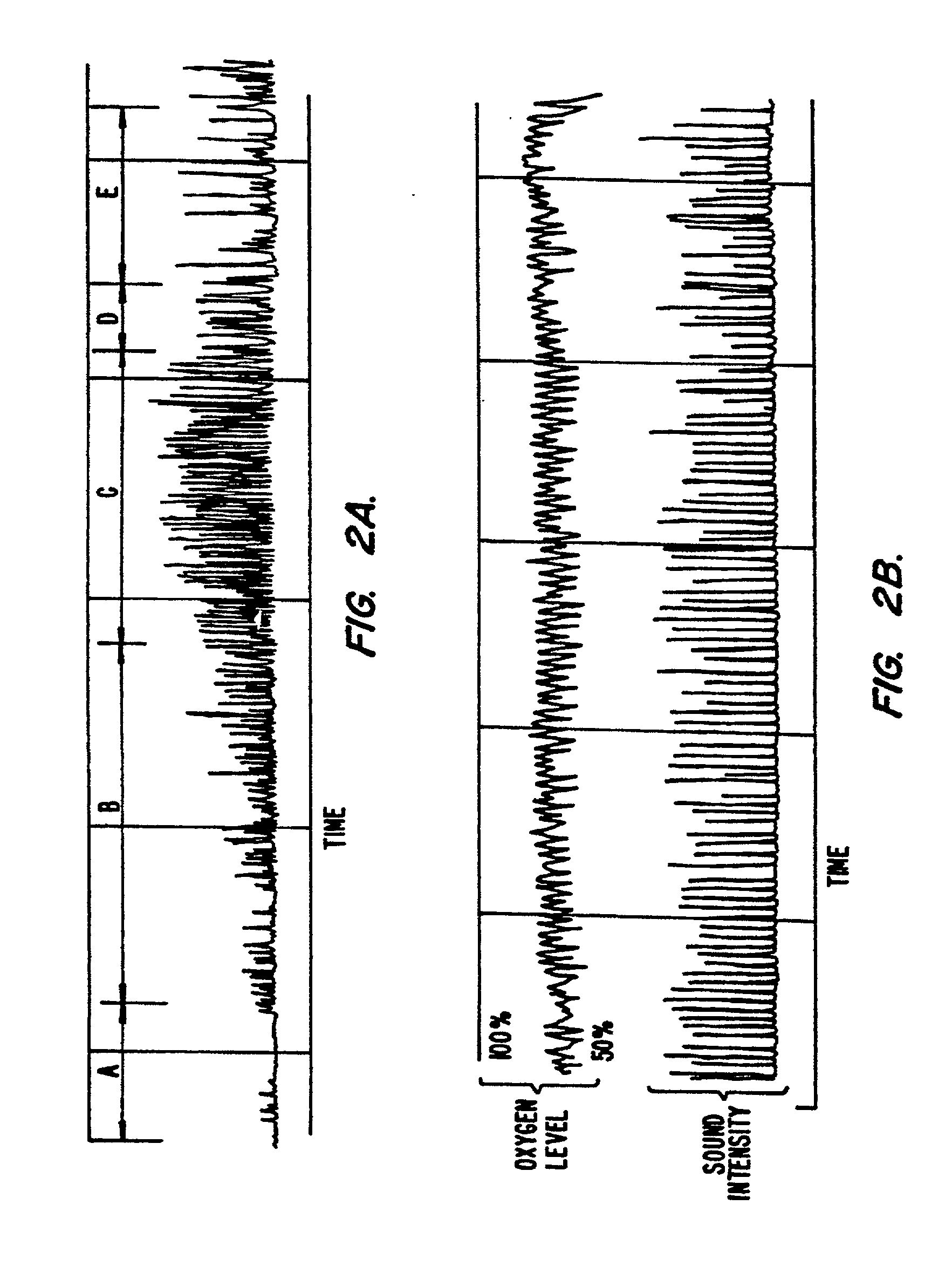
Phonopneumograph system
InactiveUS6261238B1Improve abilitiesReduce impactStethoscopeRespiratory organ evaluationMedicineRespiratory system
A method of analyzing breath sounds produced by a respiratory system, the method comprising: measuring breath sounds produced by the respiratory system; tentatively identifying a signal as being caused by a breath sound of a given type if it meets a first criteria characteristic of the breath sound of the given type; and confirming said identification if a tentatively identified signal meets a second criteria characteristic of the breath sound of the given type.
Owner:ISONEA ISRAEL
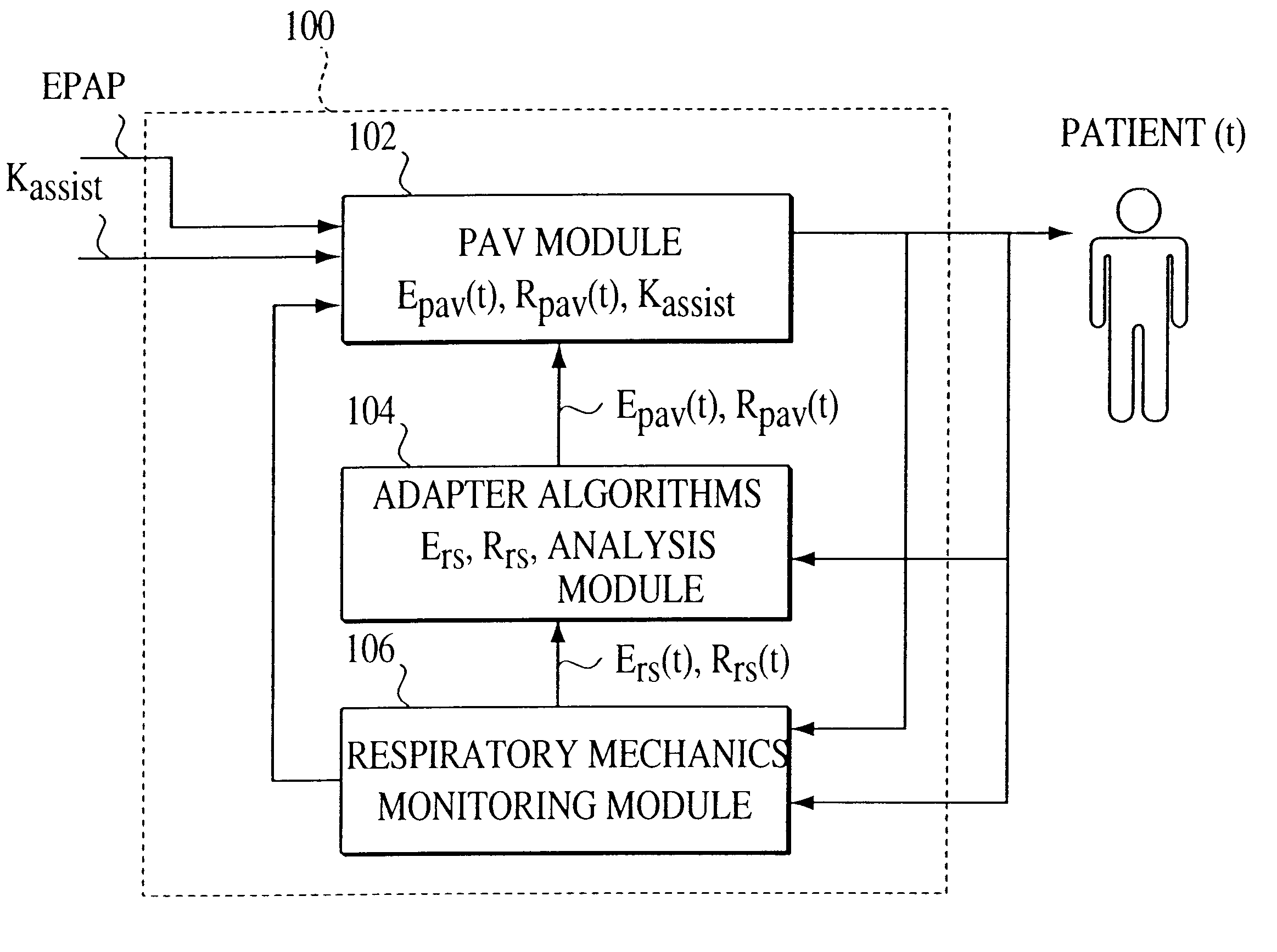
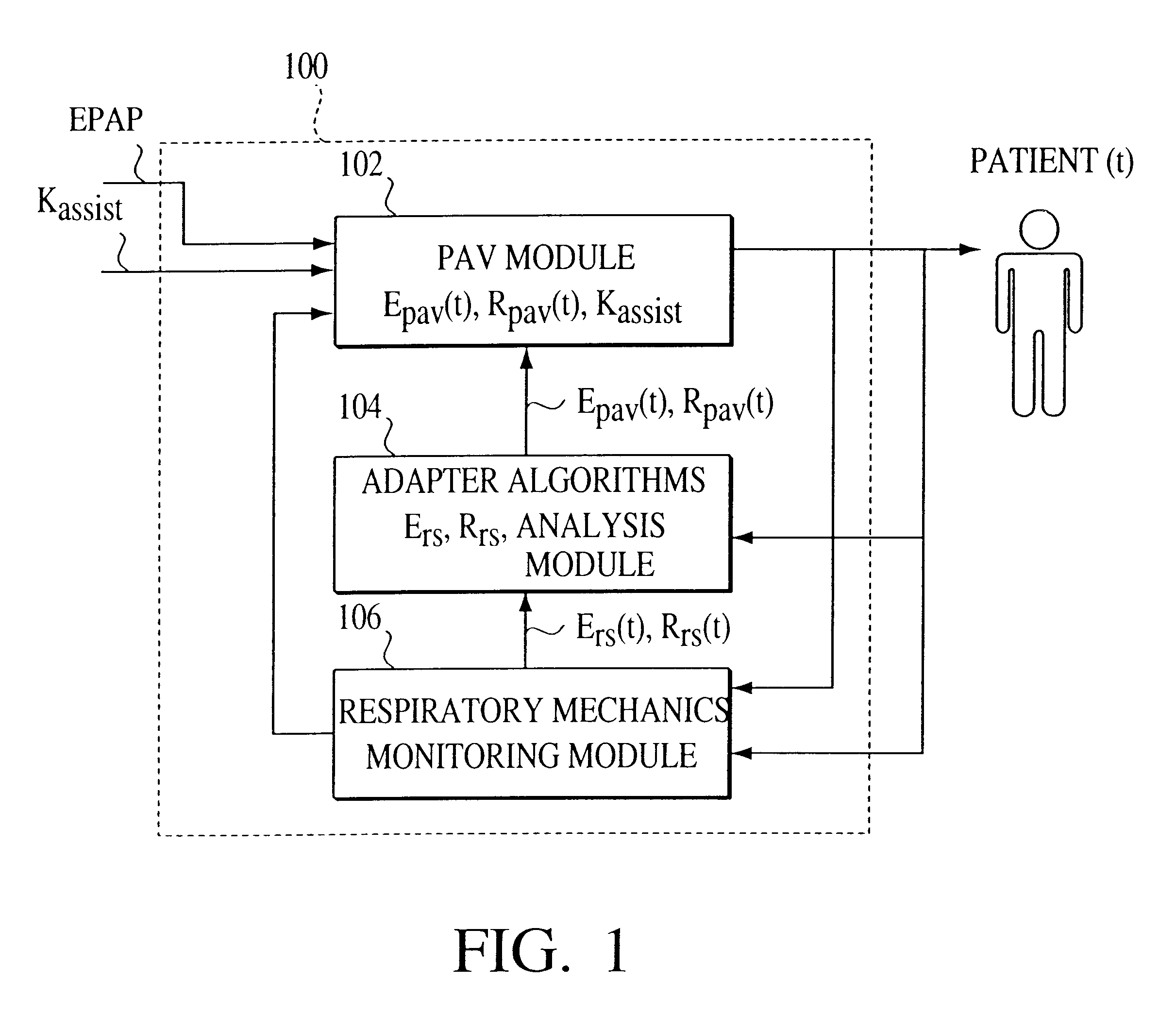
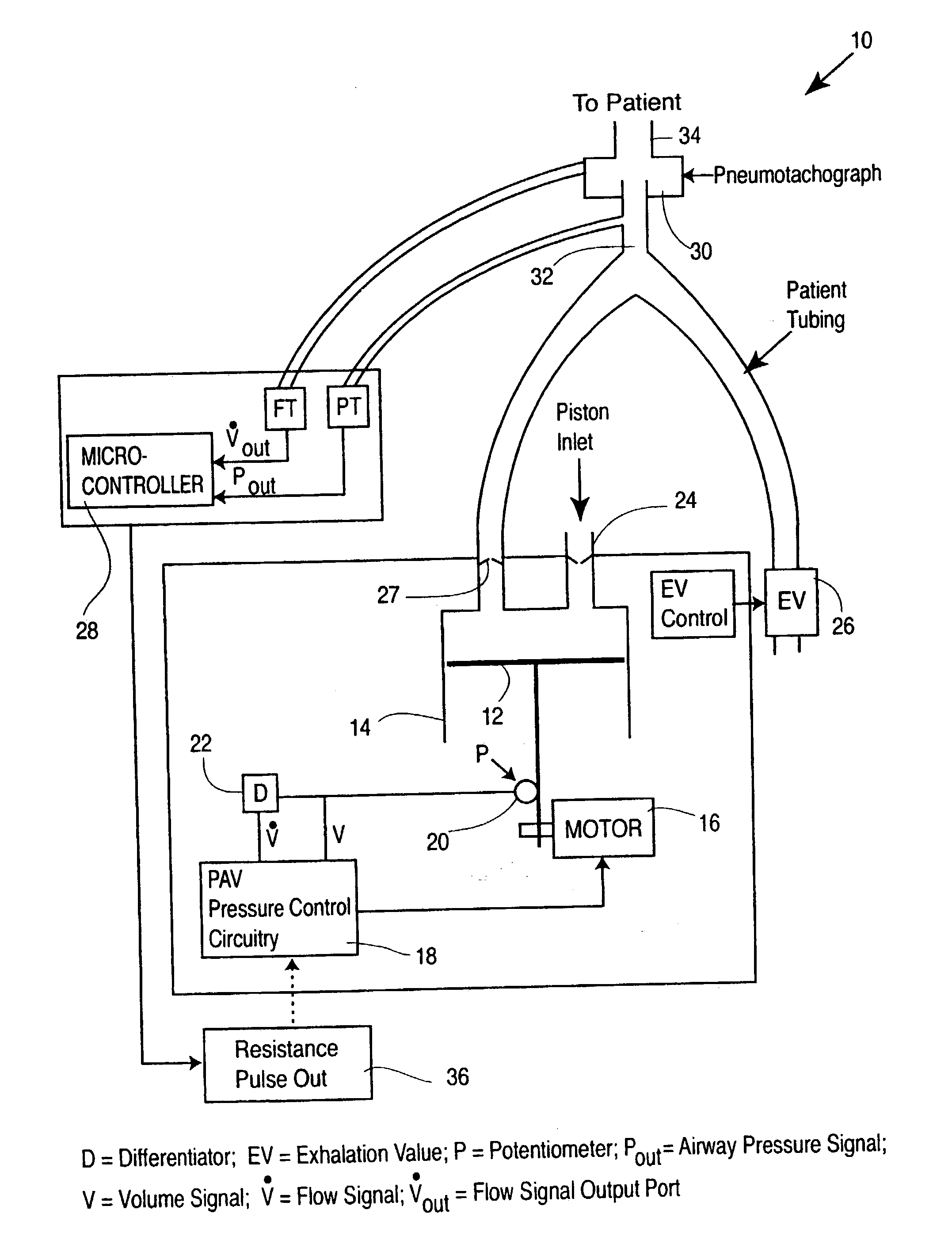
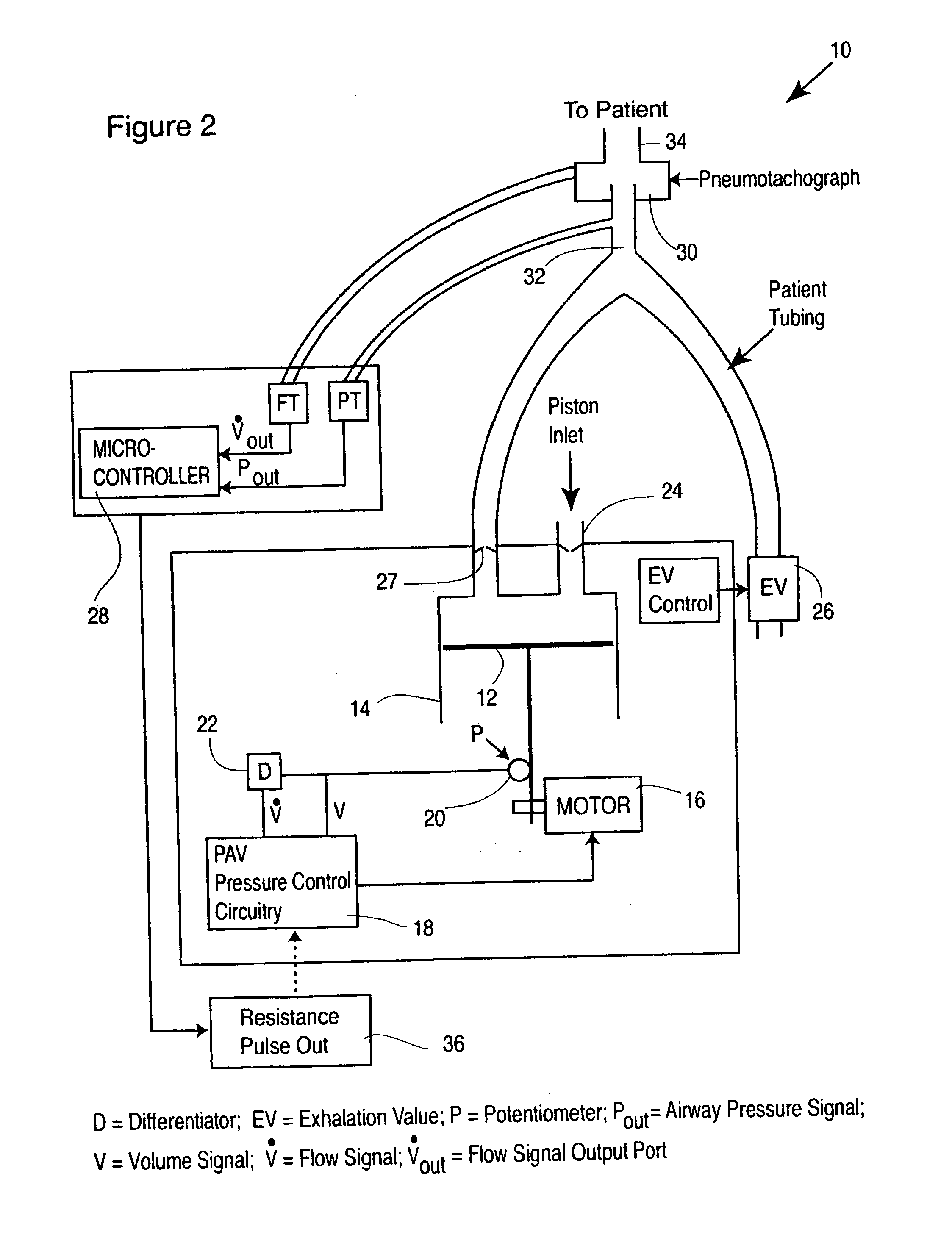
Apparatus and method for determining respiratory mechanics of a patient and for controlling a ventilator based thereon
InactiveUS6257234B1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesIntensive care medicineElastance
A ventilation system is controlled by detecting the resistance and elastance of the patient's respiratory system and adjusting the flow supplied by the ventilator accordingly. In one embodiment, the resistance is detected by controlling the ventilator to superimpose at least one forced single oscillation on the flow and observing the reaction of the respiratory system. In another embodiment, the elastance is detected by controlling the ventilator to supply a pressure which has the effect of temporarily occluding the respiratory system, waiting until the respiratory system has reached equilibrium, and observing the resulting state of the respiratory system. The detection techniques of these two embodiments can be used together.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Foam containing unique oil globules
InactiveUS20060233721A1Insufficient hydration of skinCosmetic preparationsAerosol deliveryActive agentNose
The present invention provides a foamable composition for administration to the skin, body surface, body cavity or mucosal surface, e.g., the mucosa of the nose, mouth, eye, ear, respiratory system, vagina or rectum. The foamable oil in water emulsion composition includes: an oil globule system, selected from the group consisting of oil bodies; and sub-micron oil globules, about 0.1% to about 5% by weight of an agent, selected from the group consisting of a surface-active agent, having an HLB value between 9 and 16; and a polymeric agent, and a liquefied or compressed gas propellant at a concentration of about 3% to about 25% by weight of the total composition, water and optional ingredients are added to complete the total mass to 100%. Upon release from an aerosol container, the foamable composition forms and expanded foam suitable for topical administration.
Owner:FOAMIX PHARMACEUTICALS LIMITED
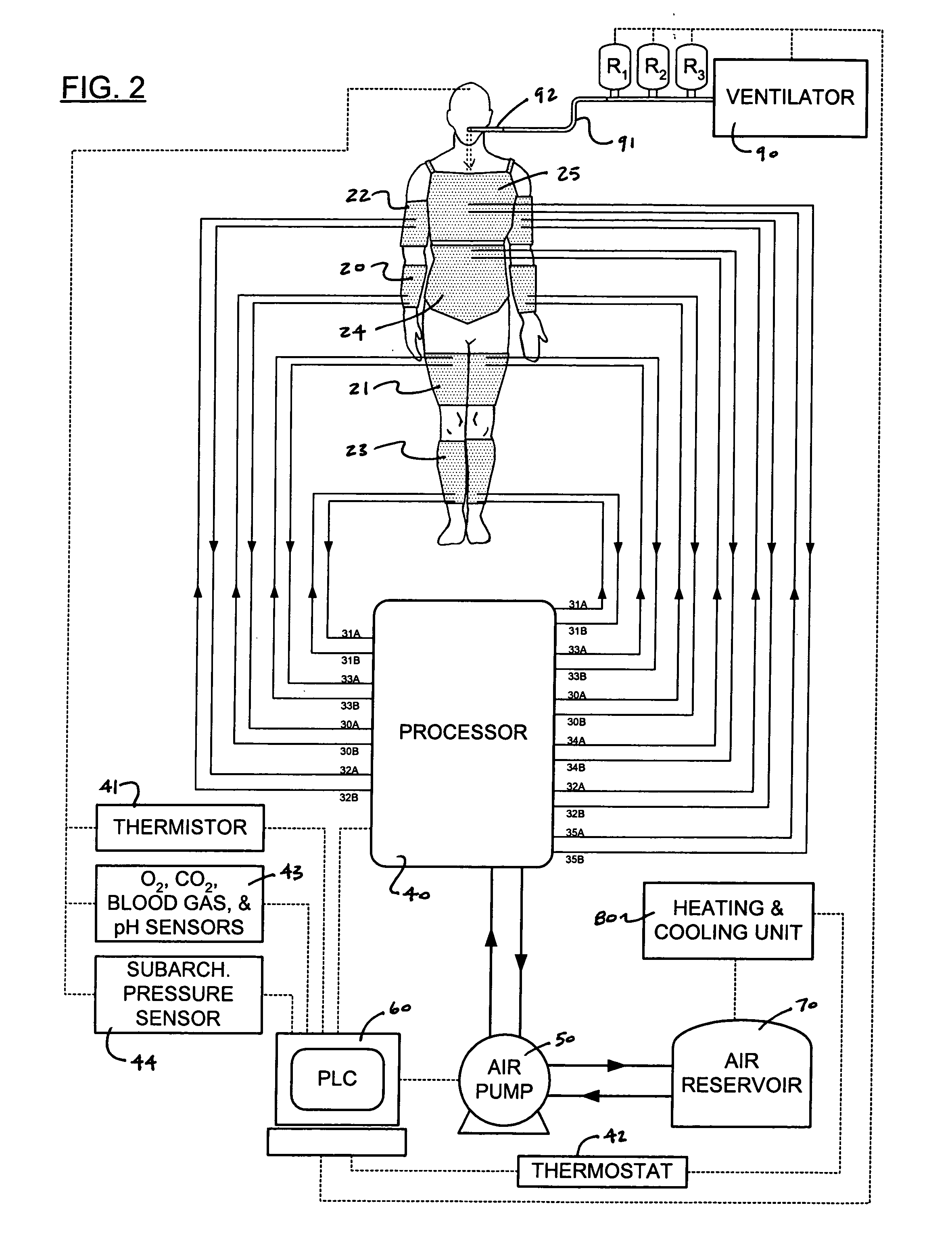
External pressure garment in combination with a complementary positive pressure ventilator for pulmocardiac assistance
InactiveUS20050126578A1Promote circulationFacilitate patient mobilityElectrotherapyPneumatic massageBreathing systemExpired air
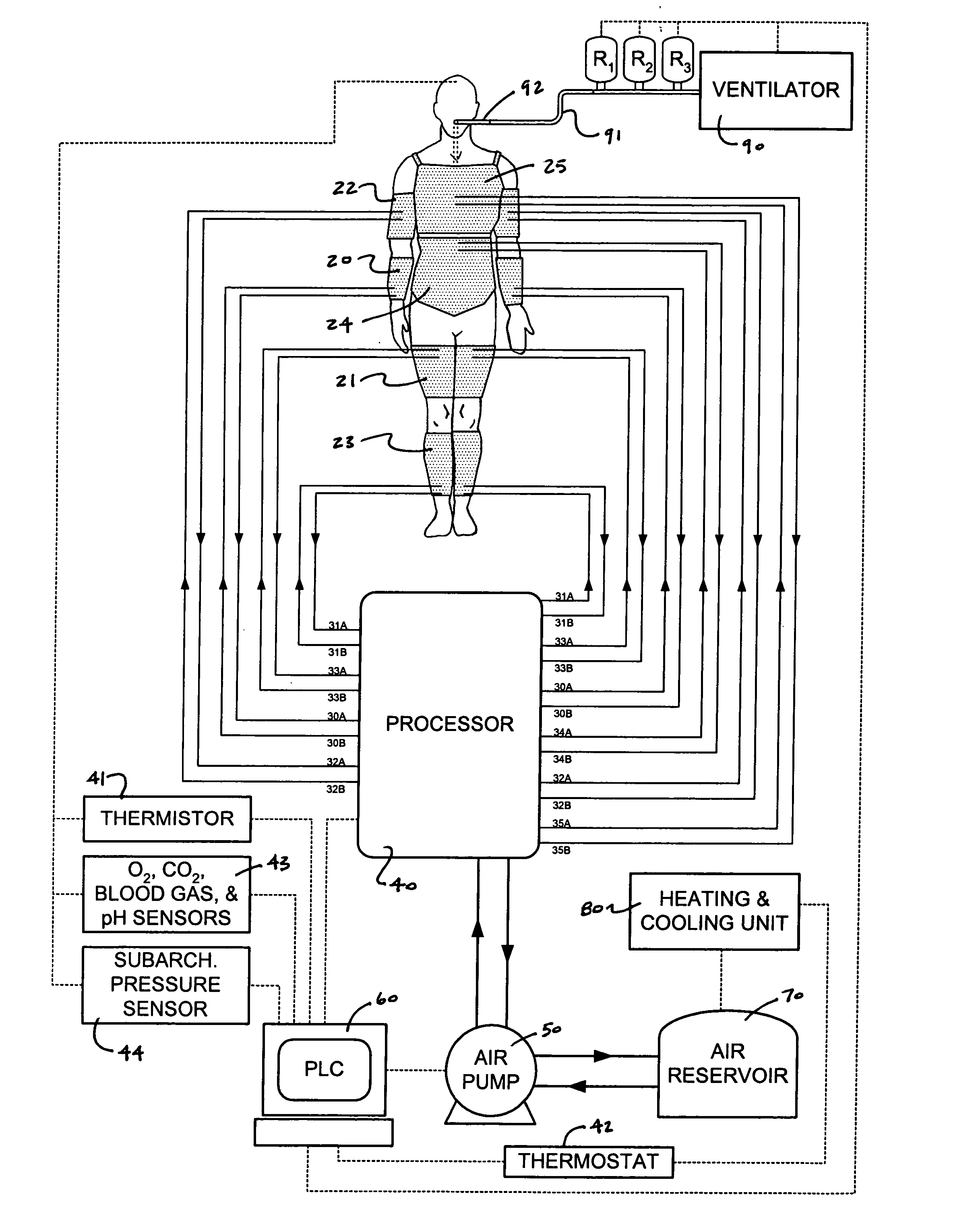
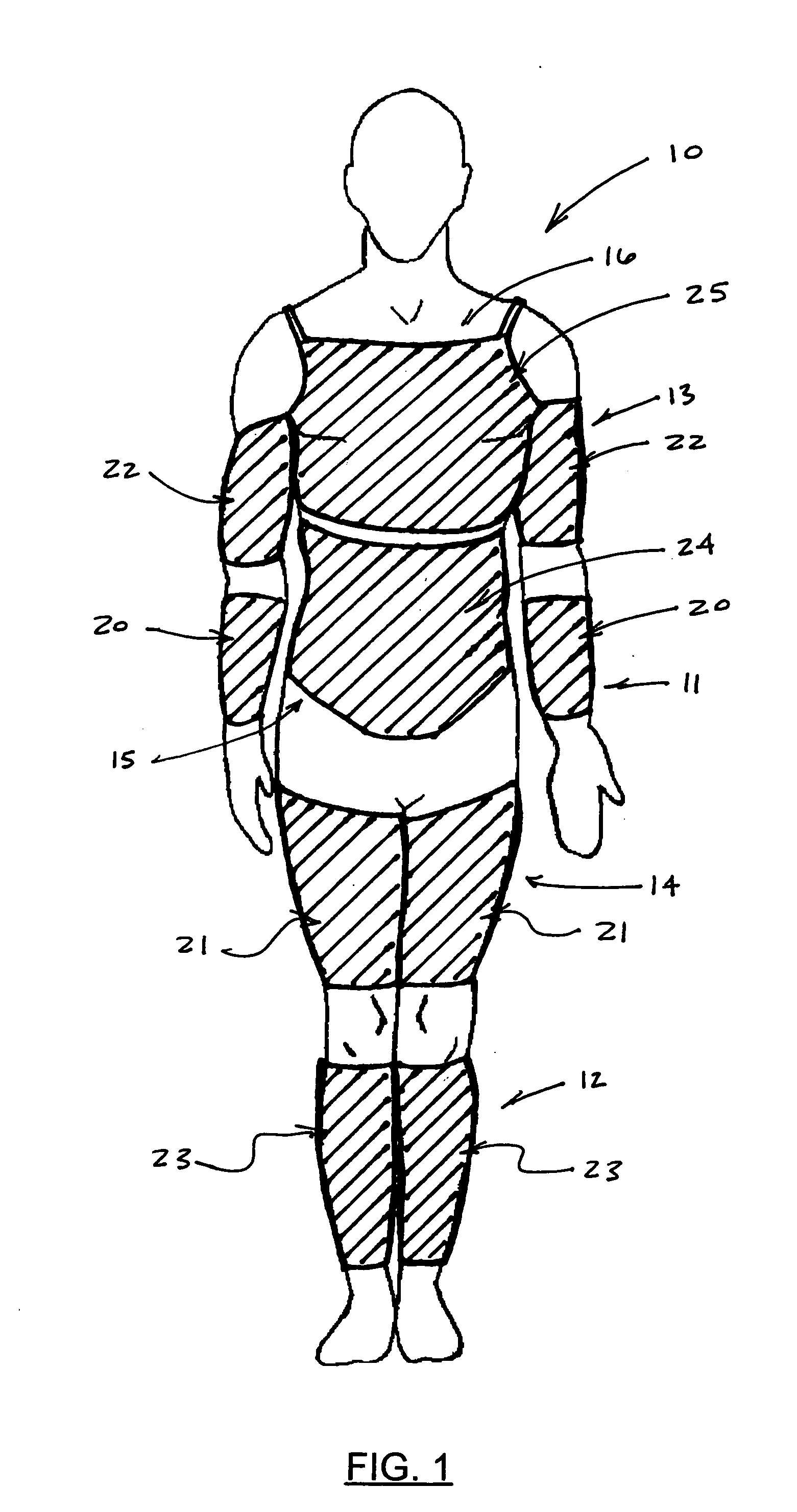
A pulmocardiac assistance apparatus is disclosed for use in the medical technology field to provide expiratory and inspiratory functionality to patients with respiratory disorders. The pulmocardiac assistance device of the present invention functions to collect body response feedback and manages this feedback to achieve an optimum response. The device includes an integrated set of pressure cuffs for pressuring different parts of the body in accordance with a predetermined sequence to induce the patient to breathe out or expire air from the lungs or to even produce an assisted cough, as well as to promote circulation of blood from the extremities of the body to the head. The pulmocardiac assistance device further includes a programmable logic controller which accepts inputs from sensors (e.g. patient temperature, blood gas concentrations, arterial pH level) and makes calculations to control both ventilator and pressure cuffs.
Owner:GARRISON RICHARD +1
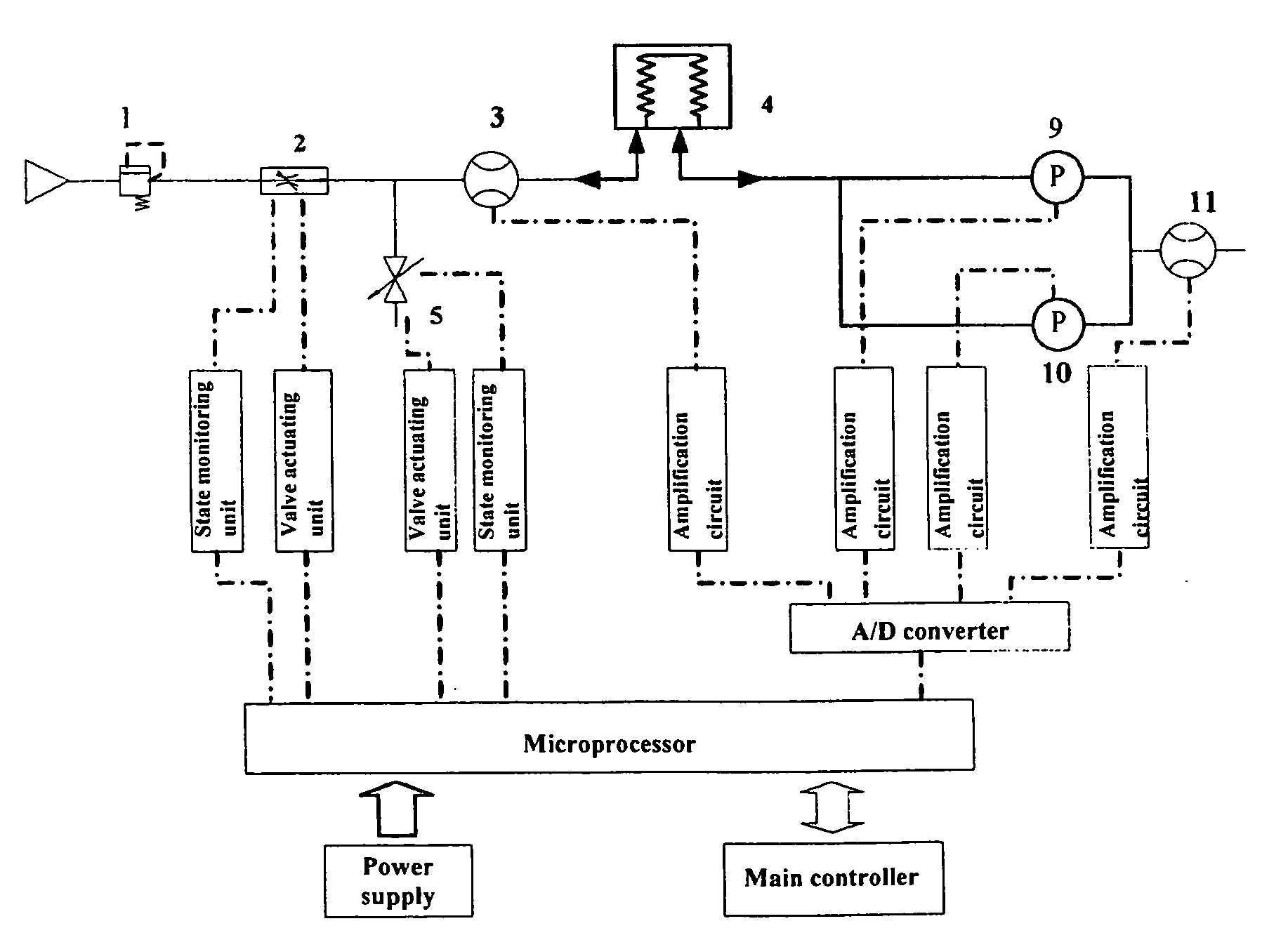
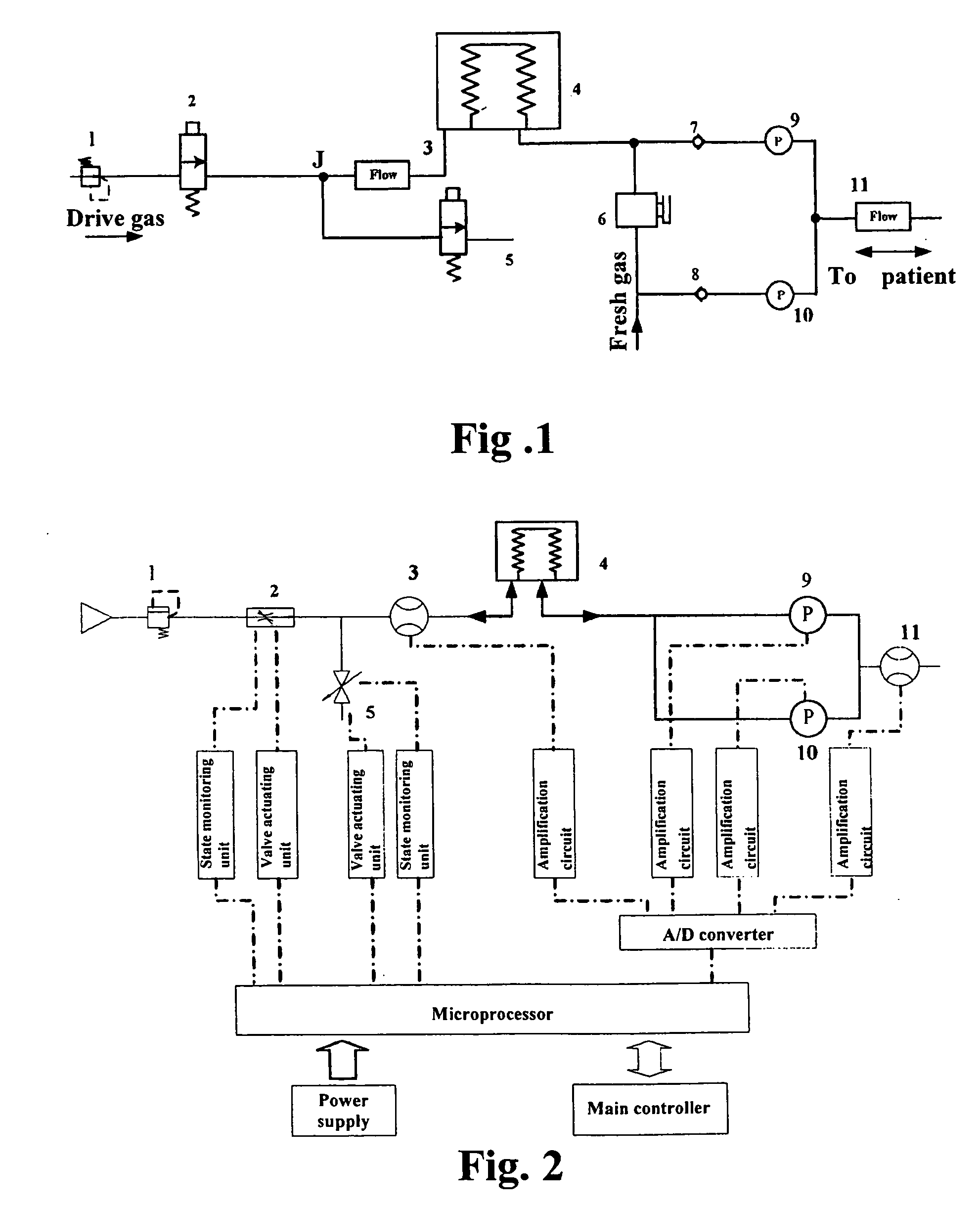
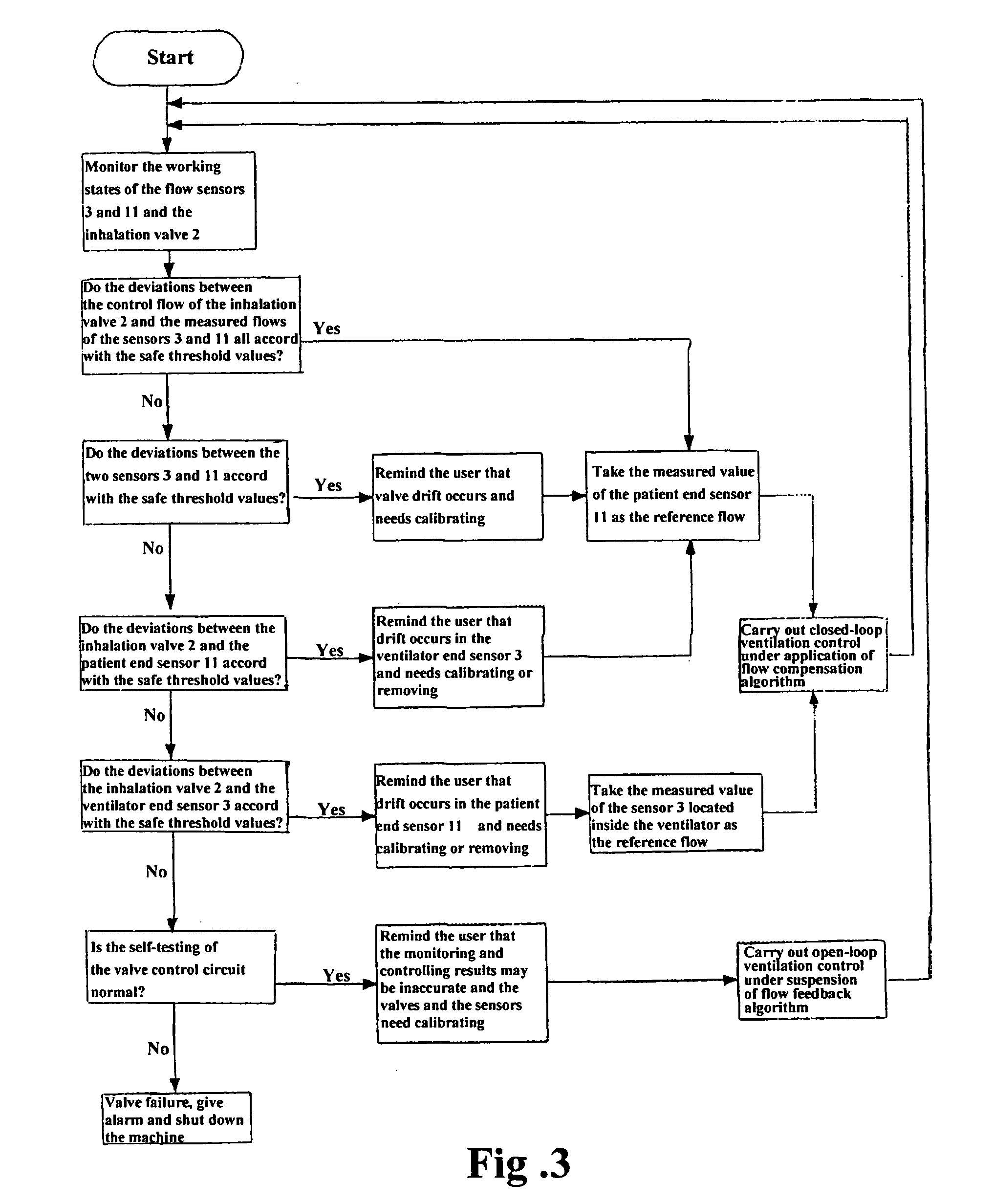
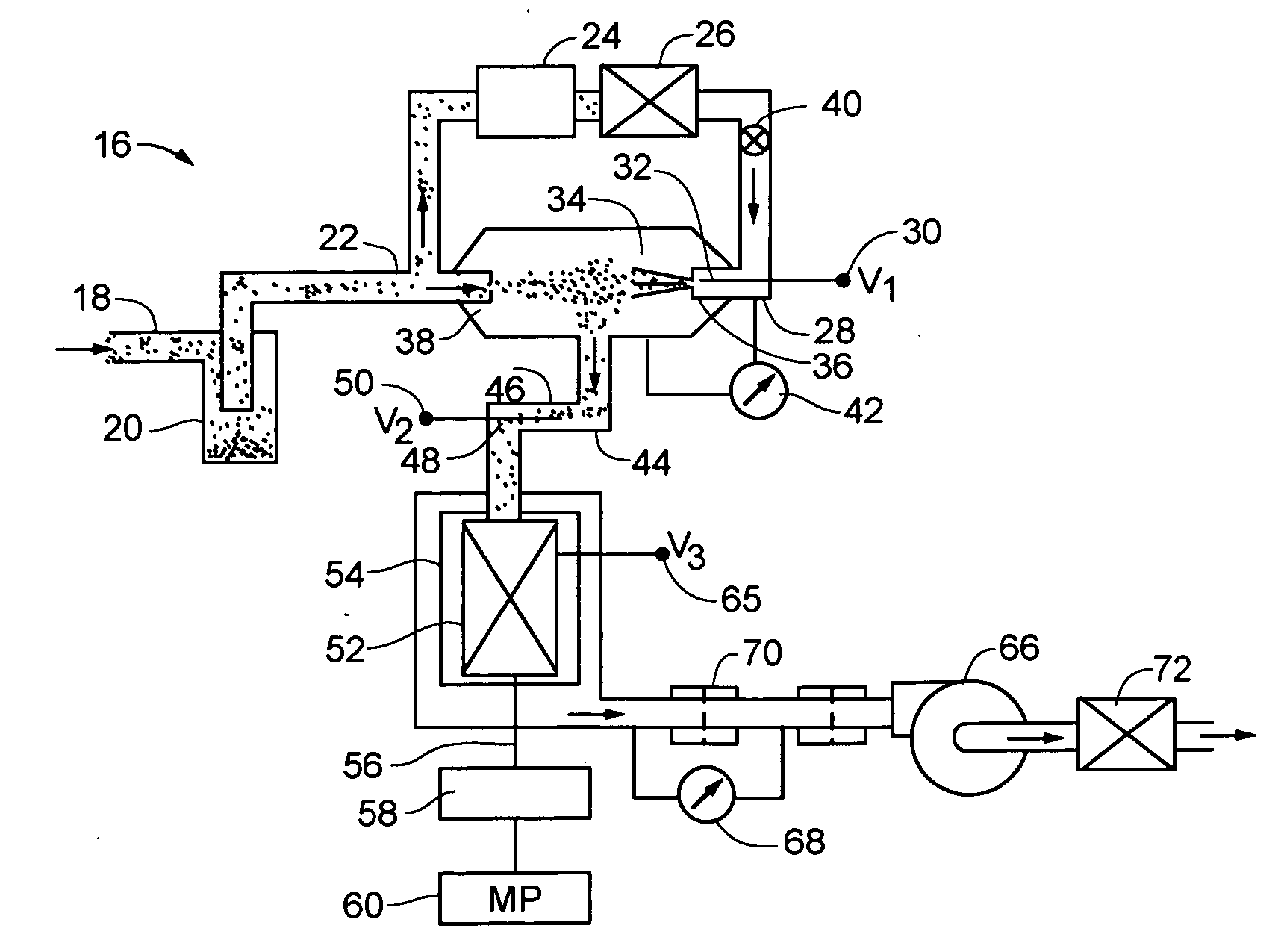
Method and an apparatus for monitoring and controlling flows
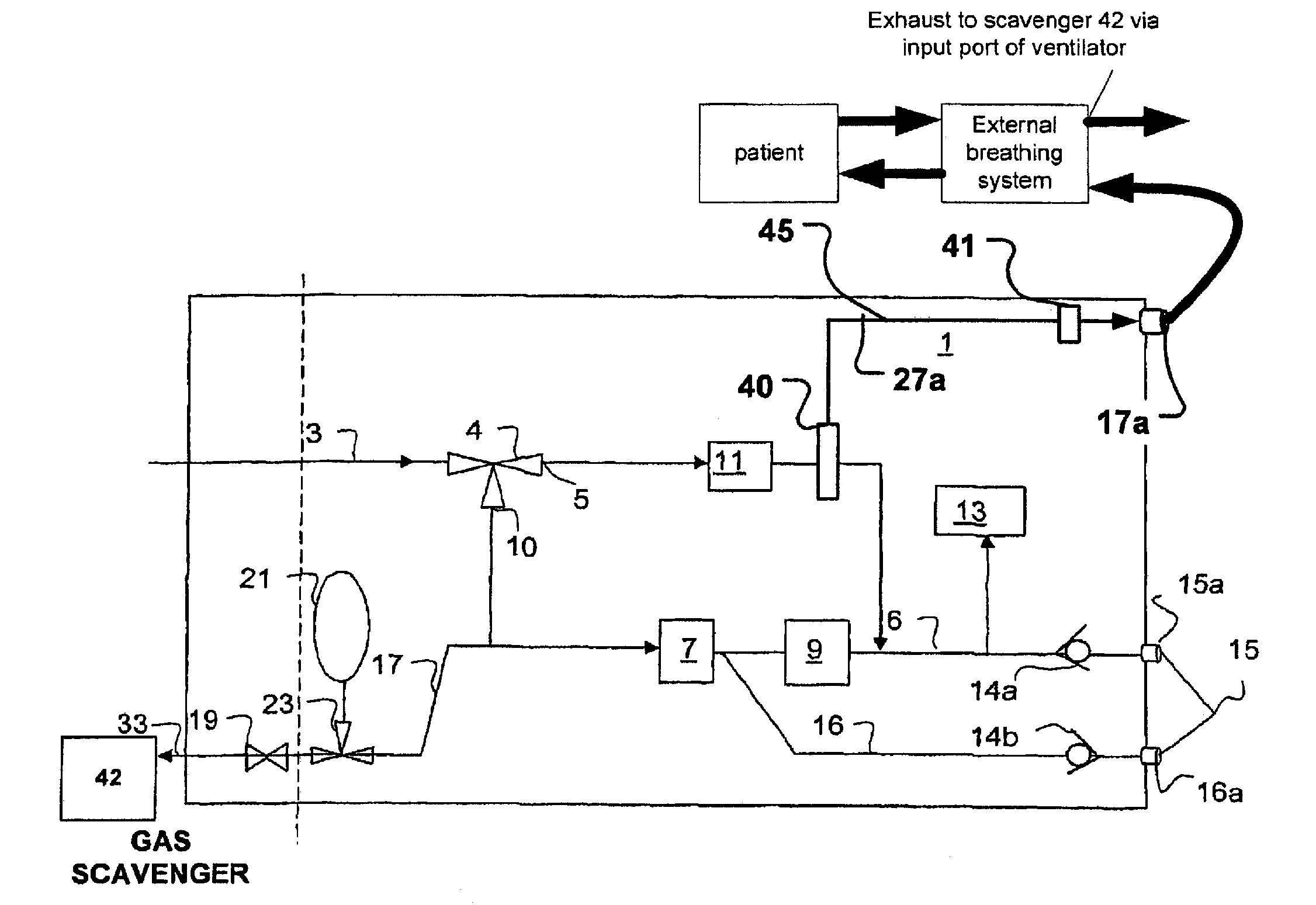
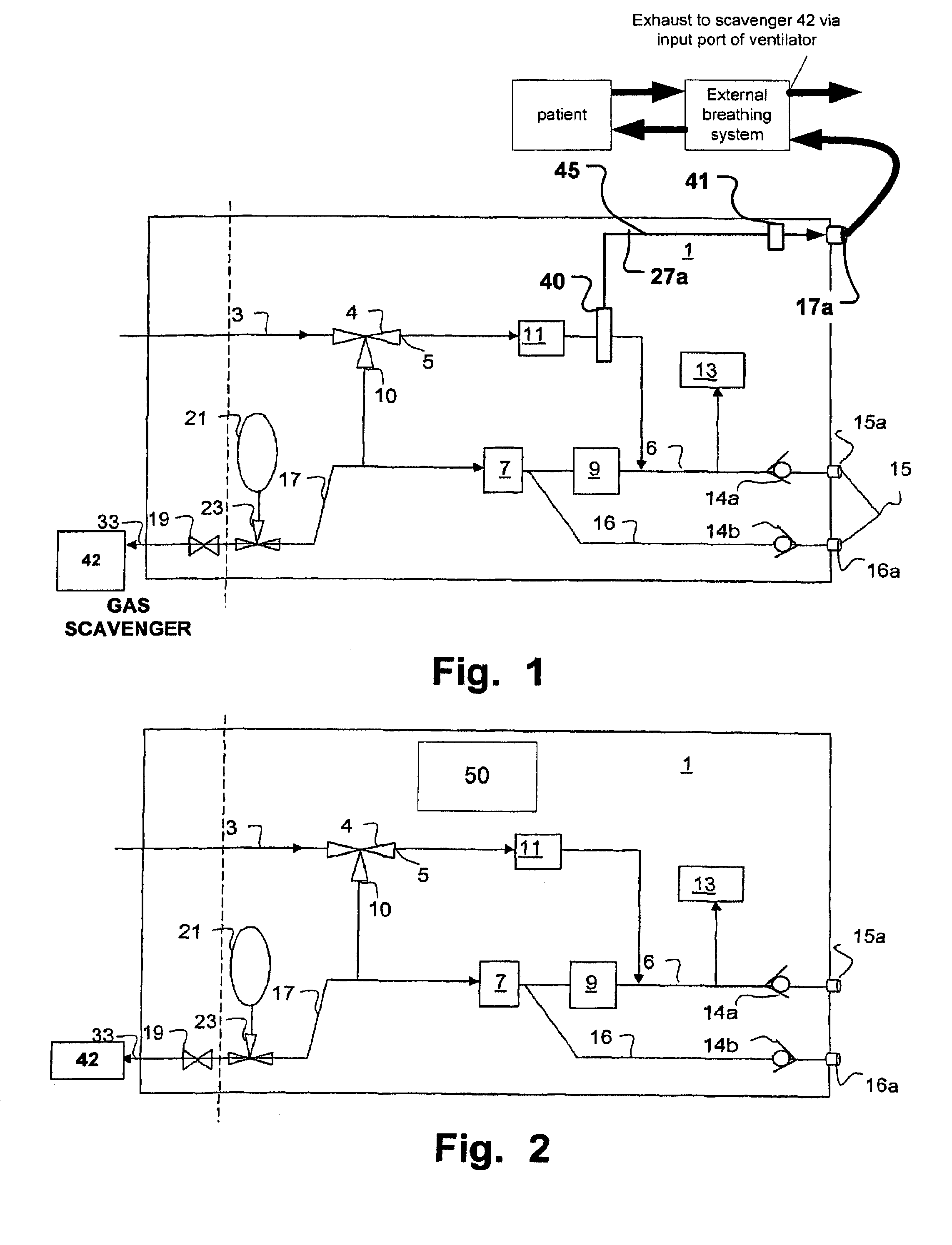
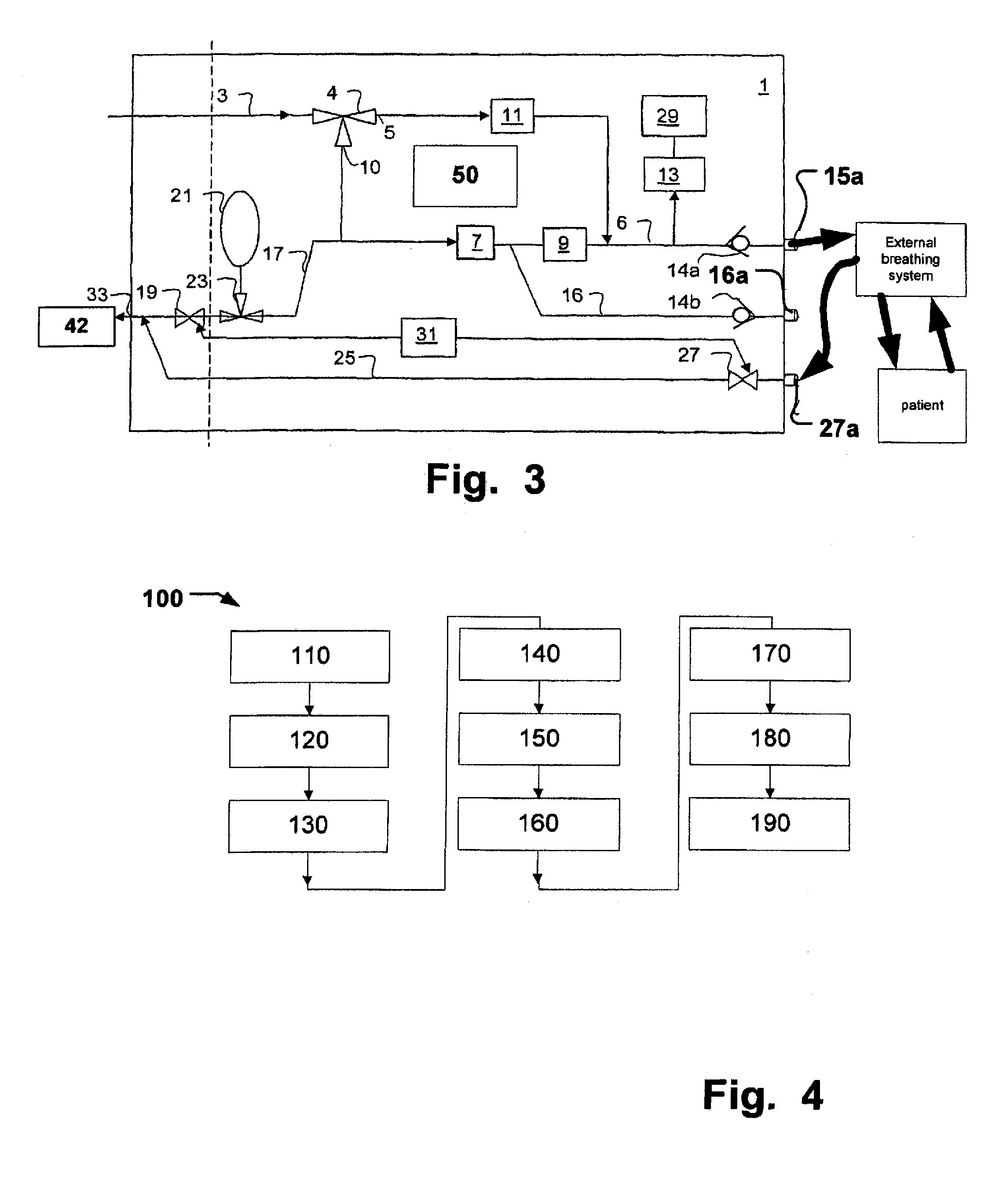
ActiveUS20070163579A1Accurate flow monitoringEasy to controlRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesExpired gasVALVE PORT
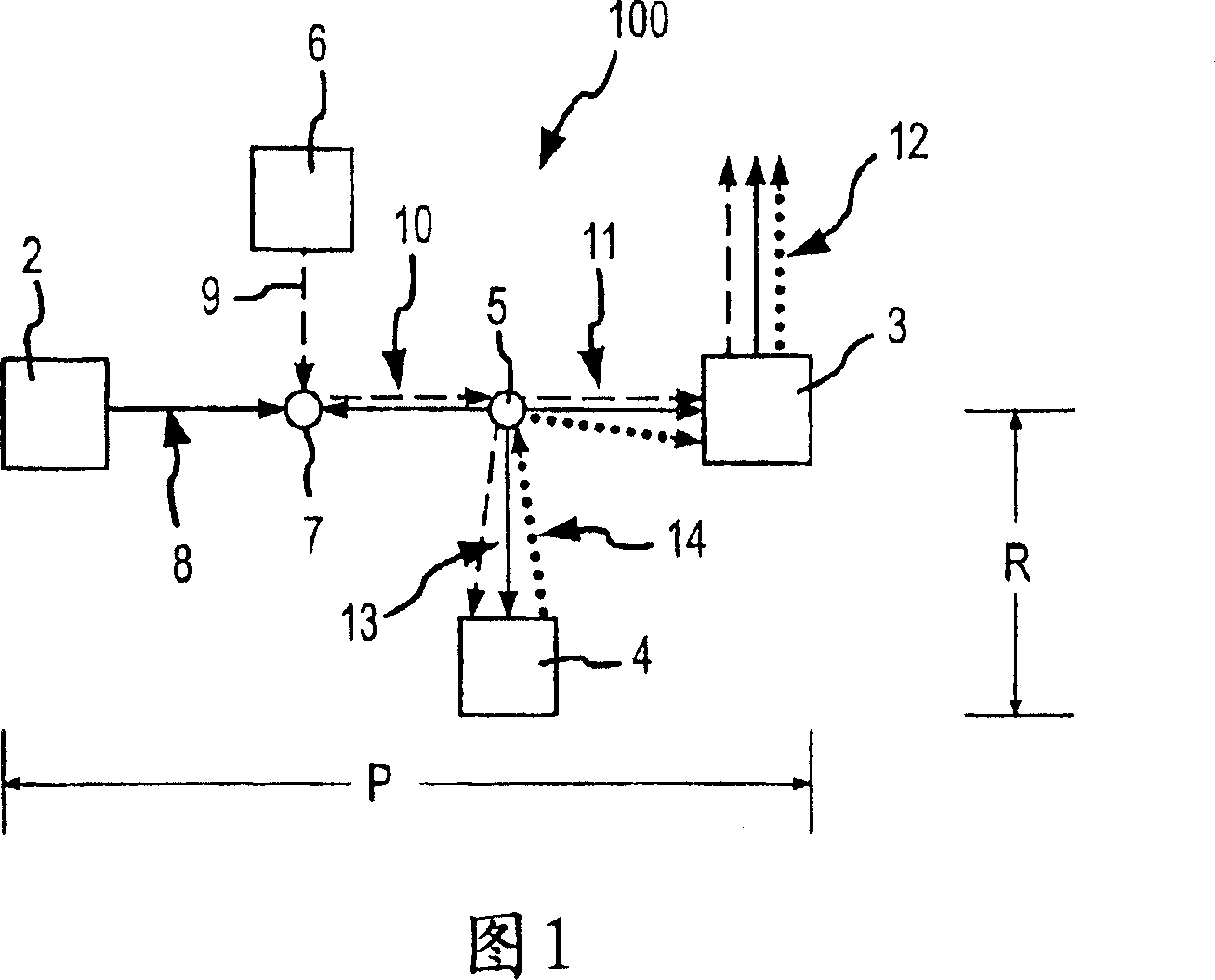
A method and an apparatus for monitoring and controlling flows in medical equipment including an anesthetic machine and a ventilator for influencing a patient's respiratory system are disclosed. The apparatus comprises a microprocessor and an airway system comprising drive gas conduits provided with an inhalation valve (2) and an exhalation valve (5) for gas discharging as well as a ventilator end flow sensor (3) for measuring the introduced or discharged drive gas flow through the valves. The airway system also comprises patient end breathing tubing in which a patient end flow sensor (11) for measuring the patient's inspired and expired gas flow is provided. By comparing the measured values of the two flow sensors against the characteristic curve of the inhalation valve (2), the microprocessor can judge the operation states and accuracy of the respective flow sensors and the inhalation valve (2).
Owner:SHENZHEN MINDRAY BIO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD
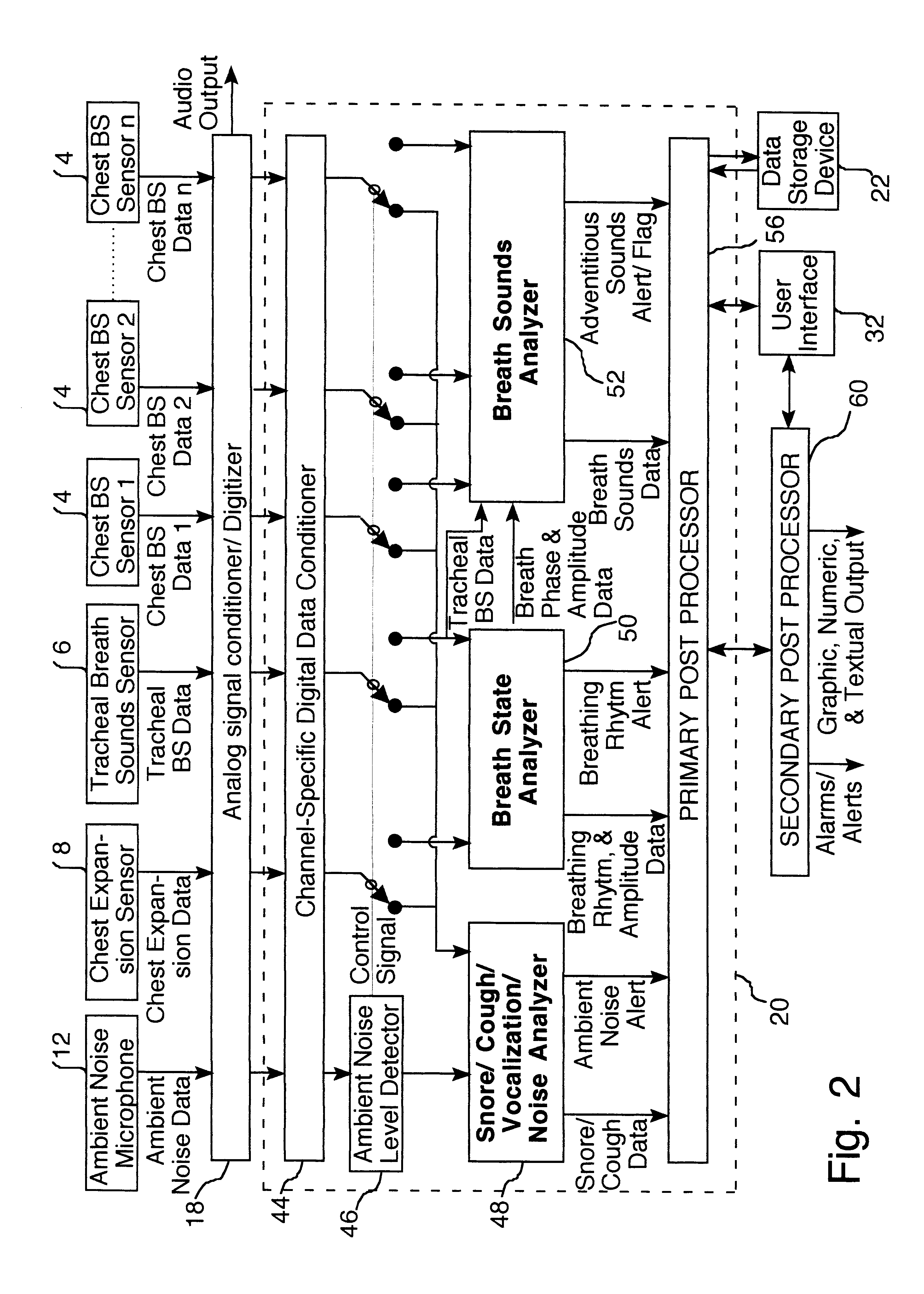
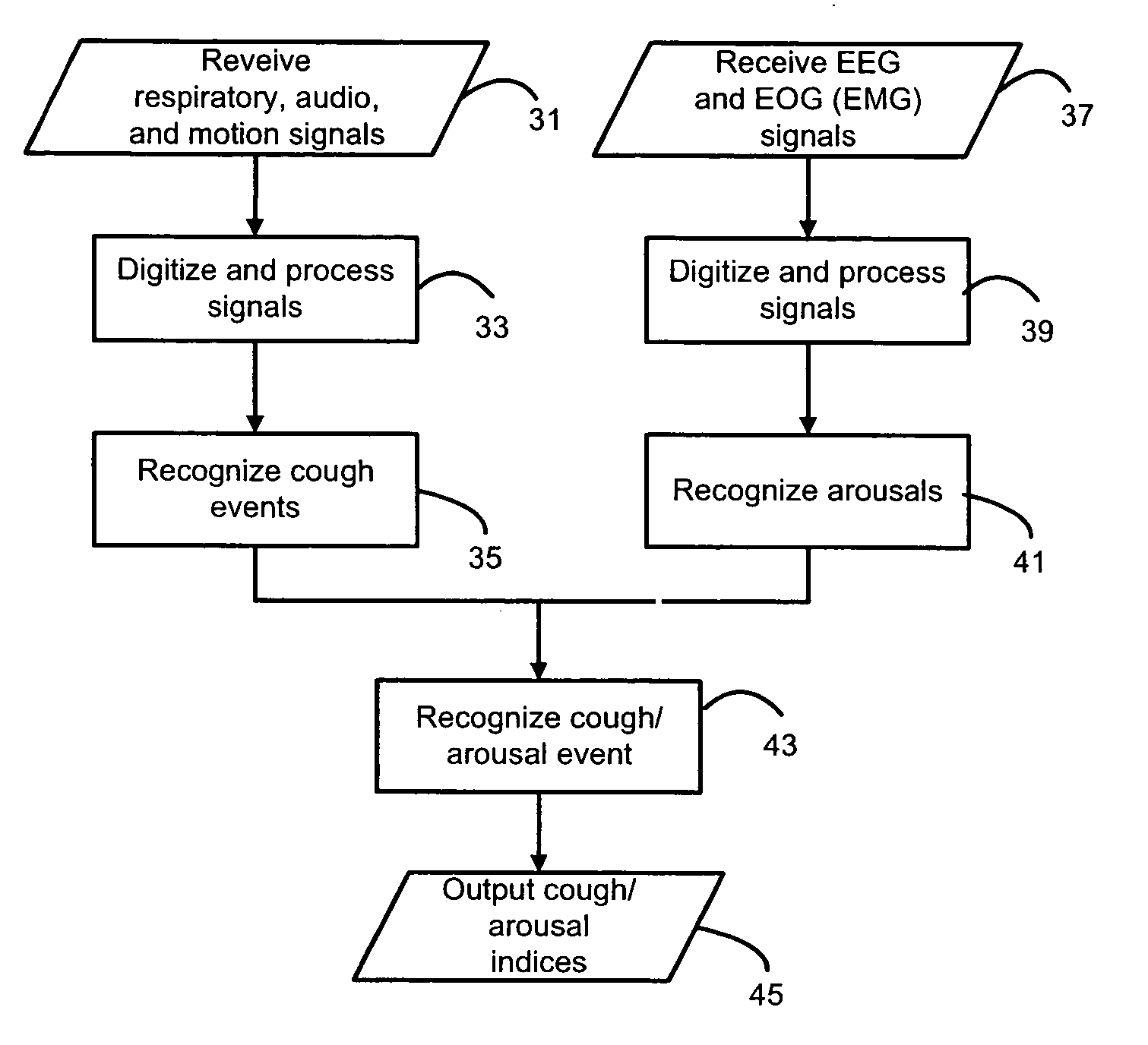
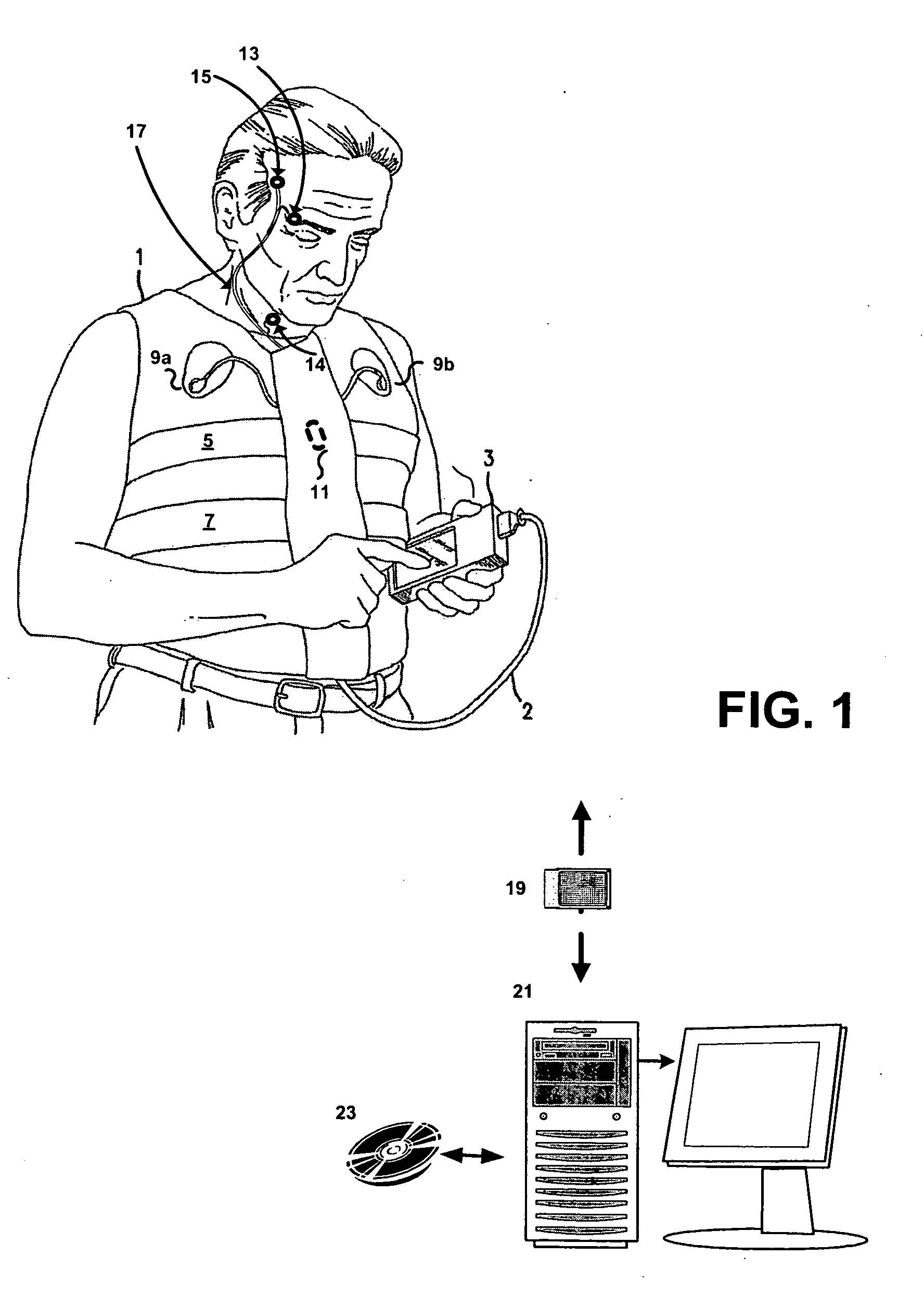
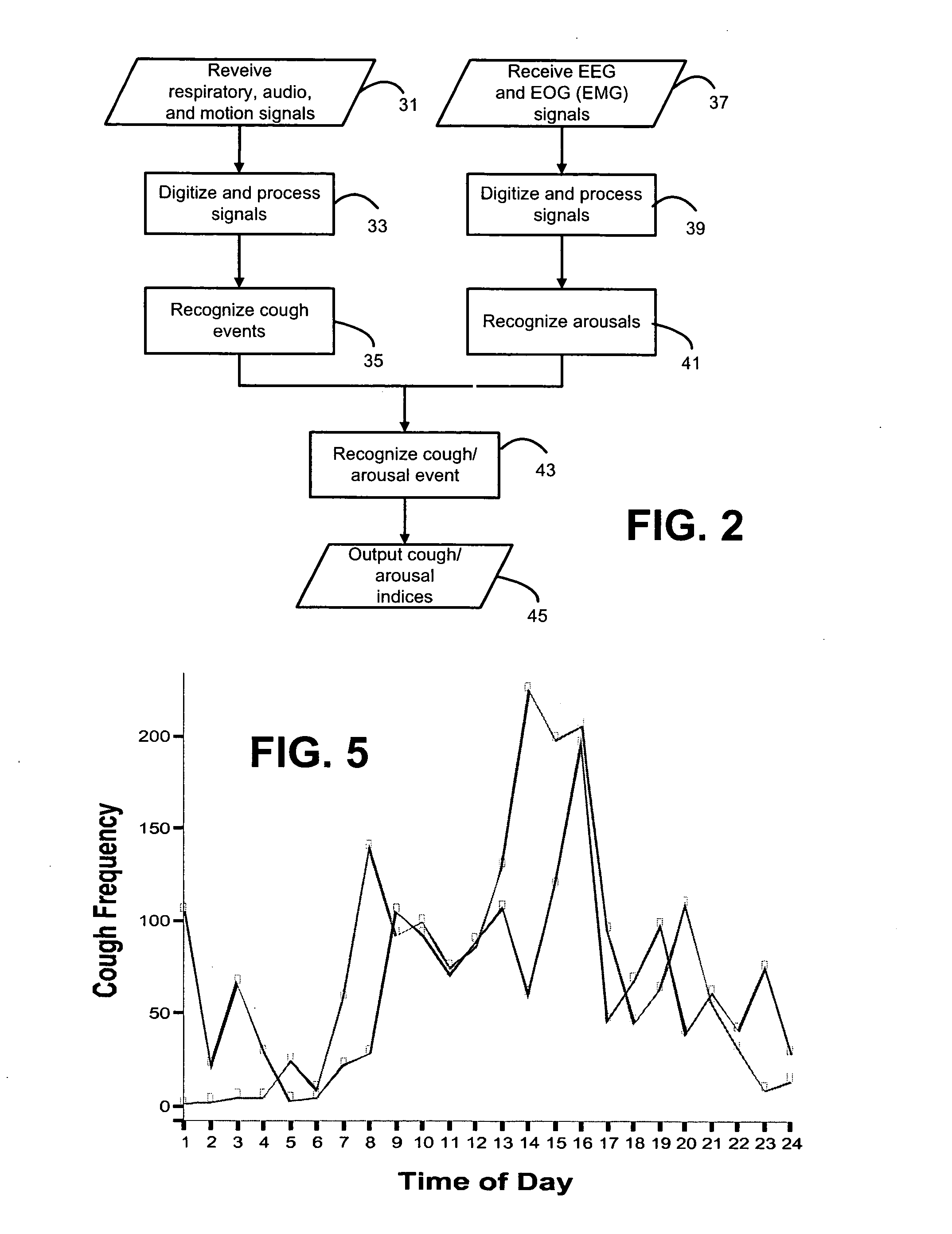
Systems and methods for monitoring cough
The present invention provides systems and methods for monitoring subjects, especially during sleep. Respiratory and sound data are recorded and coughs arousal are recognized as joint events in both of these signals having selected characteristics. Further, cough-arousal events during sleep are recognized when a likely cough occurs in association with a recognized EEG arousal. Cough arousal events are combined into a cough arousal index that reflects disease severity and sleep disruption due to cough. The methods of this invention are computer-implemented and can be provided as a program product including a computer readable medium. Measurements and indices provided by this invention can be used to monitor and to treat respiratory diseases.
Owner:ADIDAS
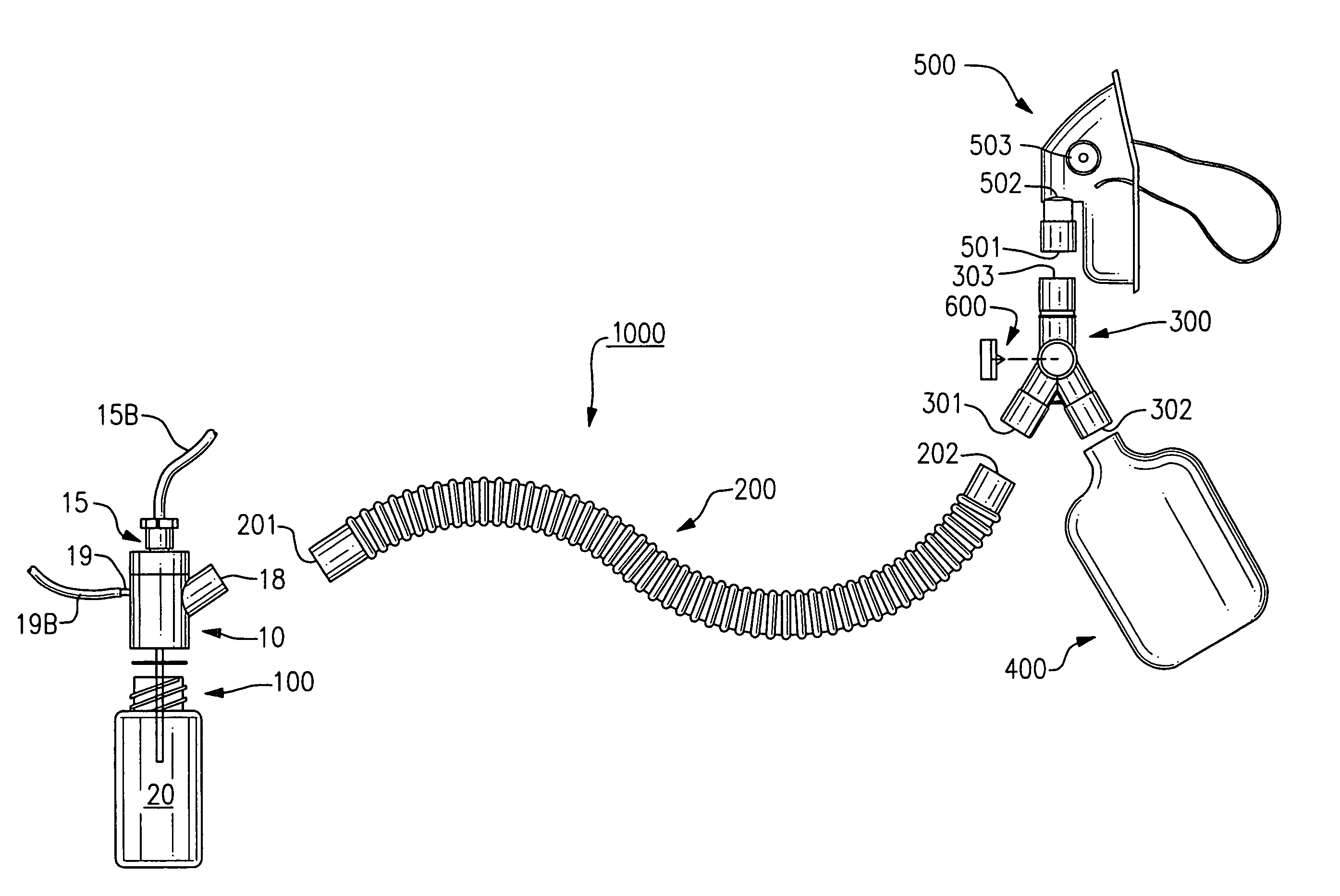
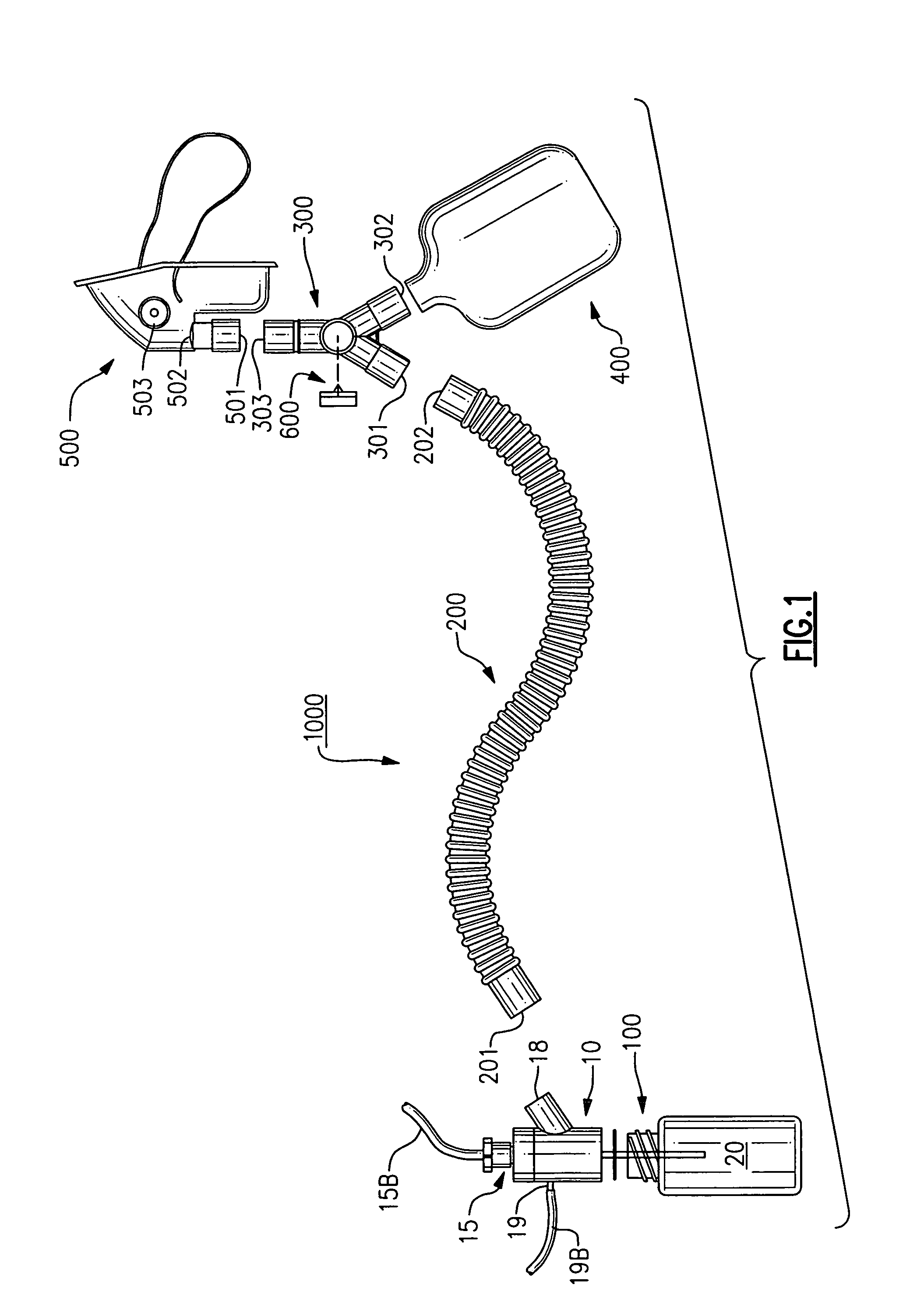
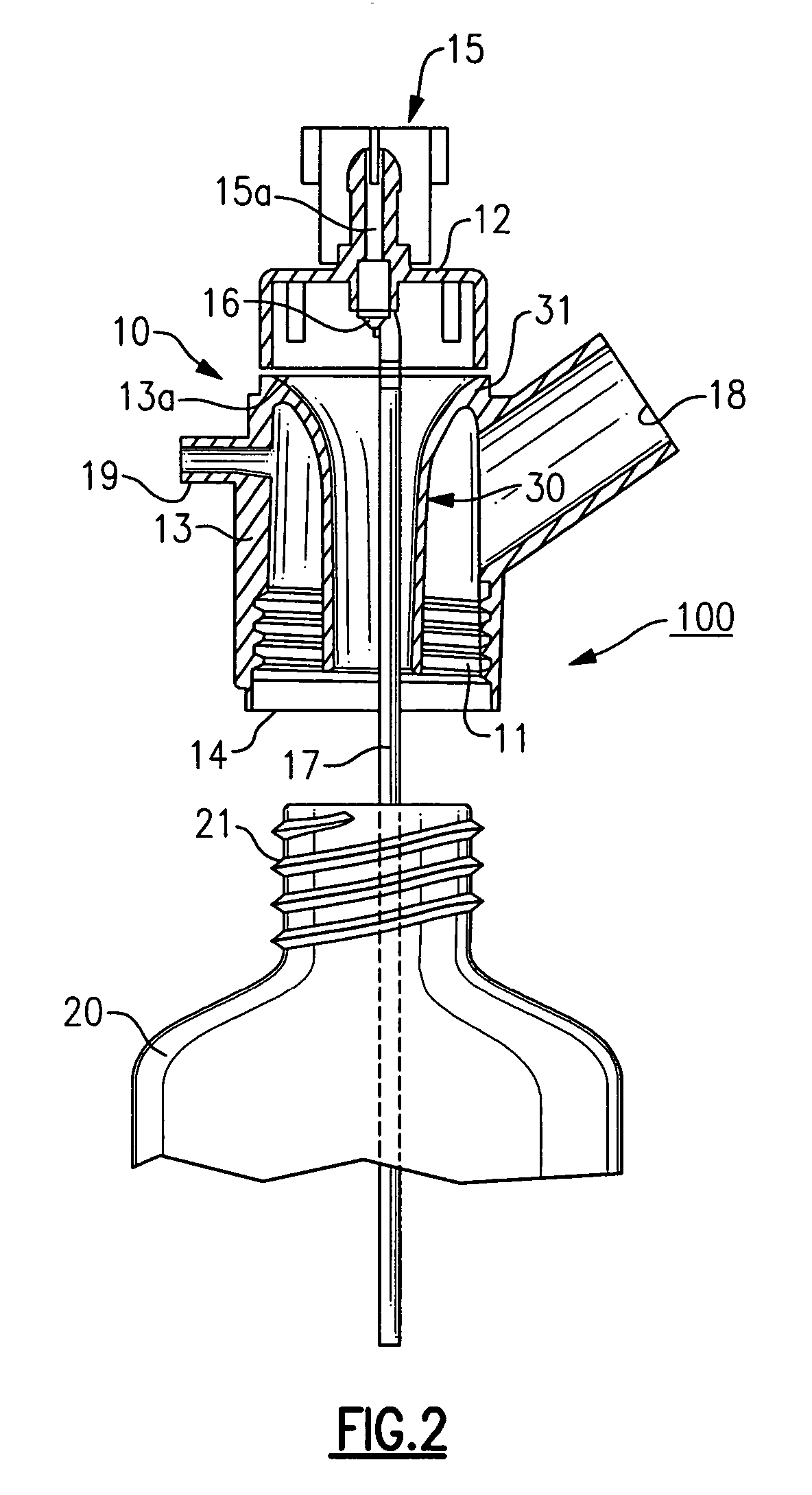
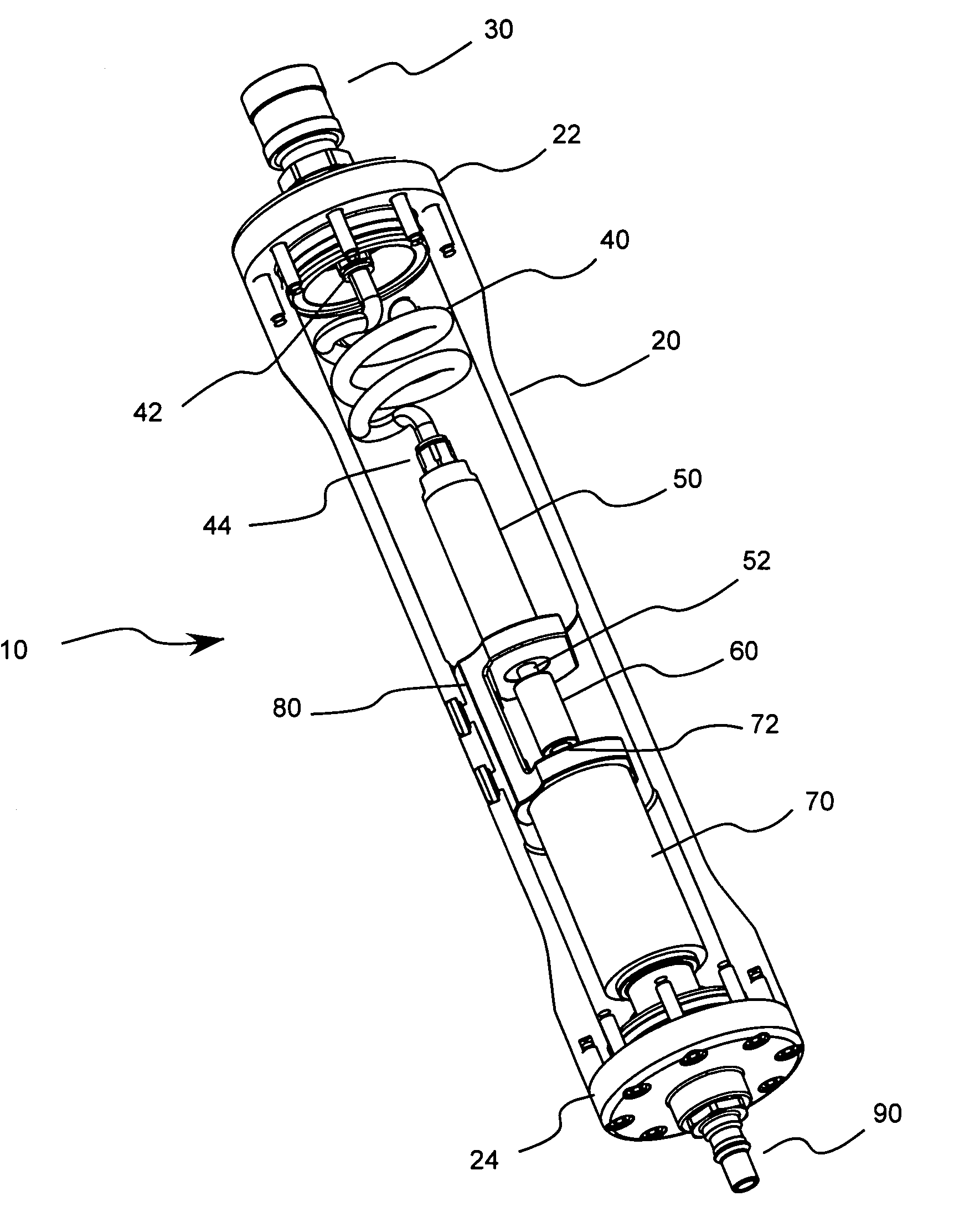
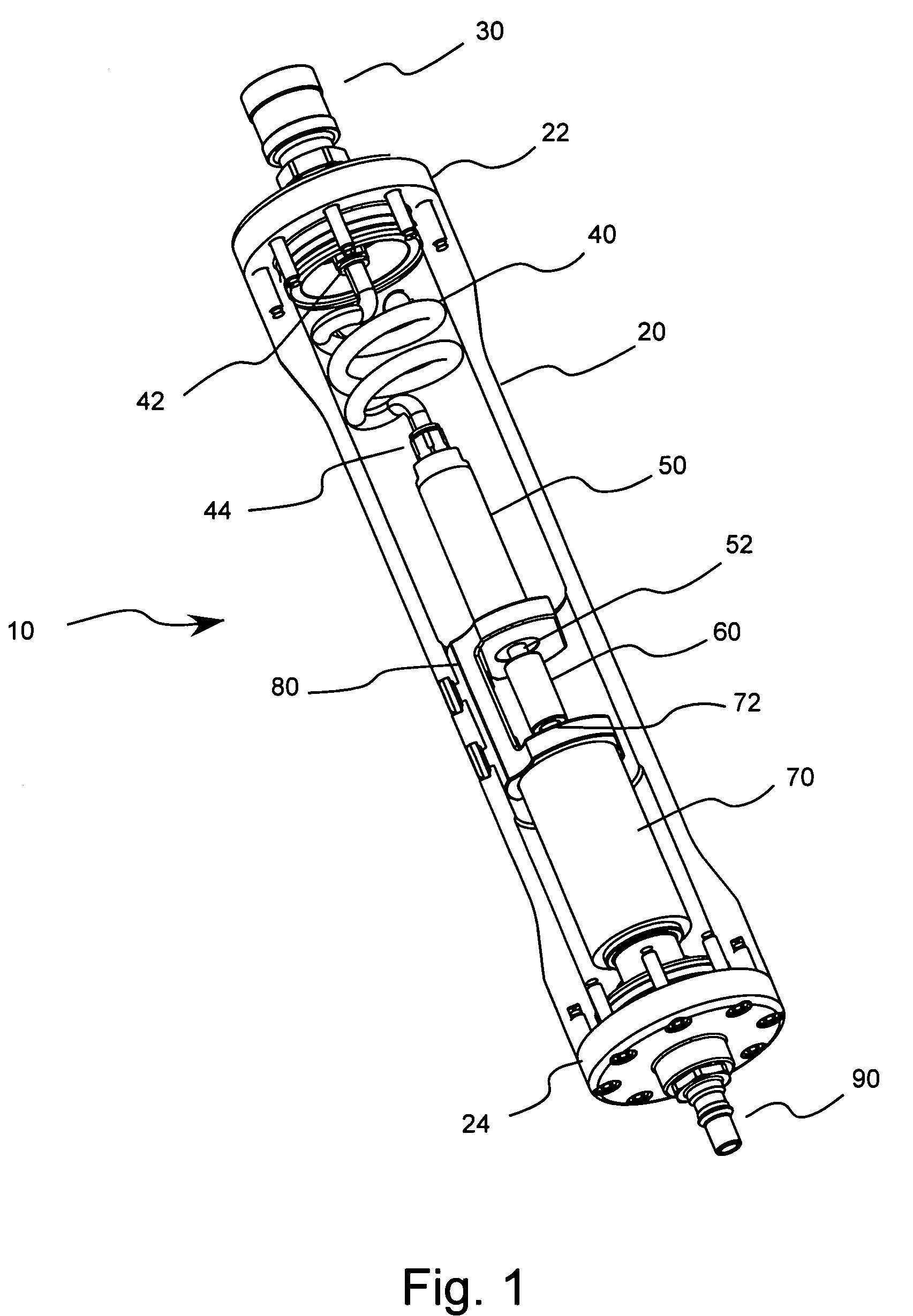
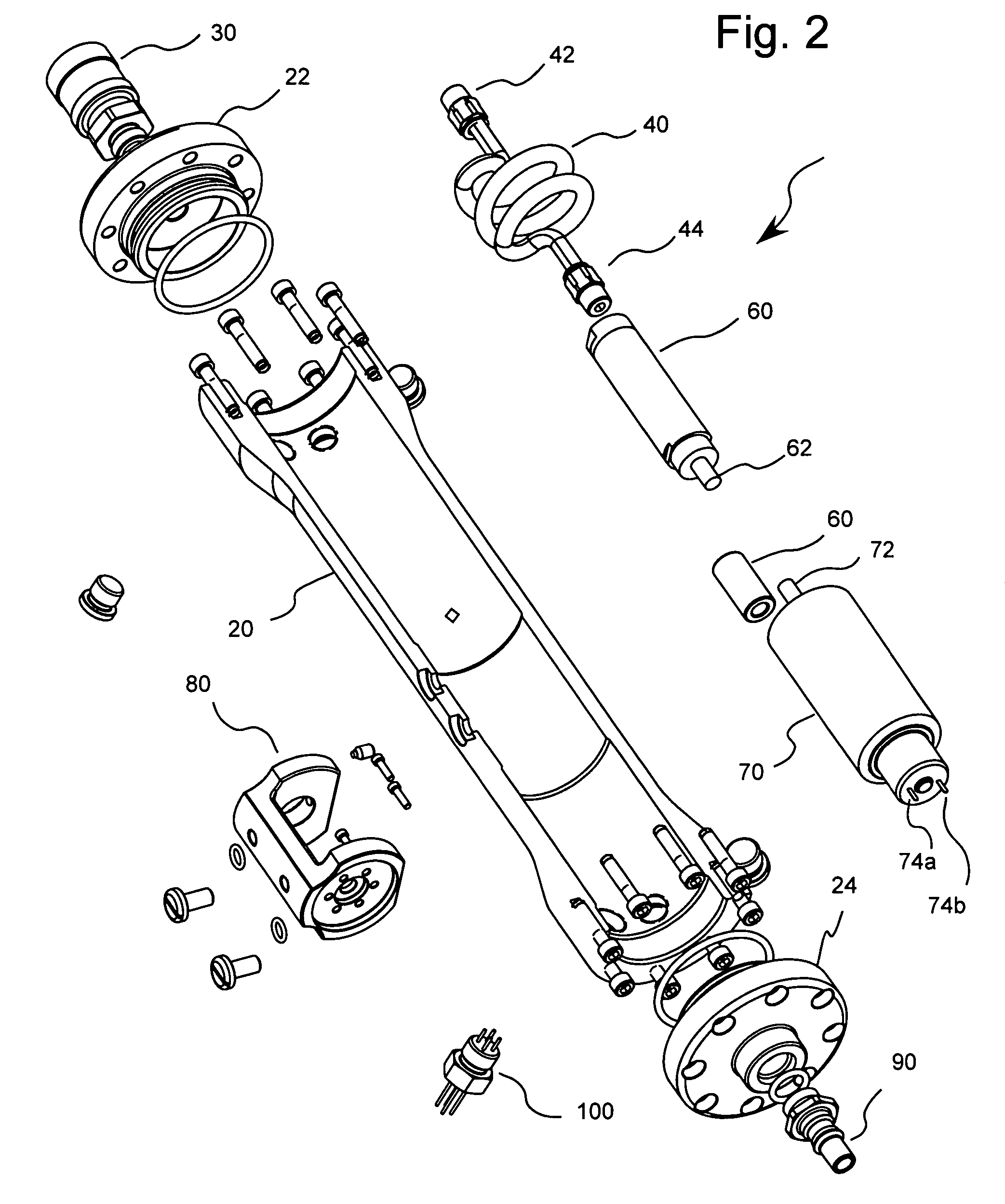
Nebulizer breathing system
An improved nebulizer breathing system wherein a supplemental gas may be introduced into the nebulizer head at a position after the liquefied medication has been fractured or nebulized, so that the introduction of the supplemental gas does not effect the rate at which the nebulized liquefied medication is applied to the user, and the mixture of gases to be administered to a patient is added to the breathing system at a position removed from the point at which the gas mixture is administered to the patient.
Owner:SMITHS MEDICAL ASD INC
Patient breathing system
ActiveUS20090000621A1Good flexibilityEliminate disadvantagesRespiratorsBreathing filtersBreathing systemIntensive care medicine
A patient breathing system includes a ventilator that provides a driving gas flow to generate patient inspiration. The ventilator further includes a gas inlet for driving gas, the patient breathing system being connectable to a circle which includes an inspiratory hose and an expiratory hose connected to patient, through which circle expired gases can be circulated back to the patient. The circle further includes a fresh gas inlet, an arrangement for enabling the gas flow in a desired direction, a unit for removal of the exhaled carbon dioxide, and a ventilator port for the ventilator connection. The patient breathing system further includes an arrangement by which driving gas of the ventilator has been separated from the patient gases flowing in the circle.
Owner:SUNMED GRP HLDG LLC
Method of automatically controlling a respiration system and a corresponding respirator
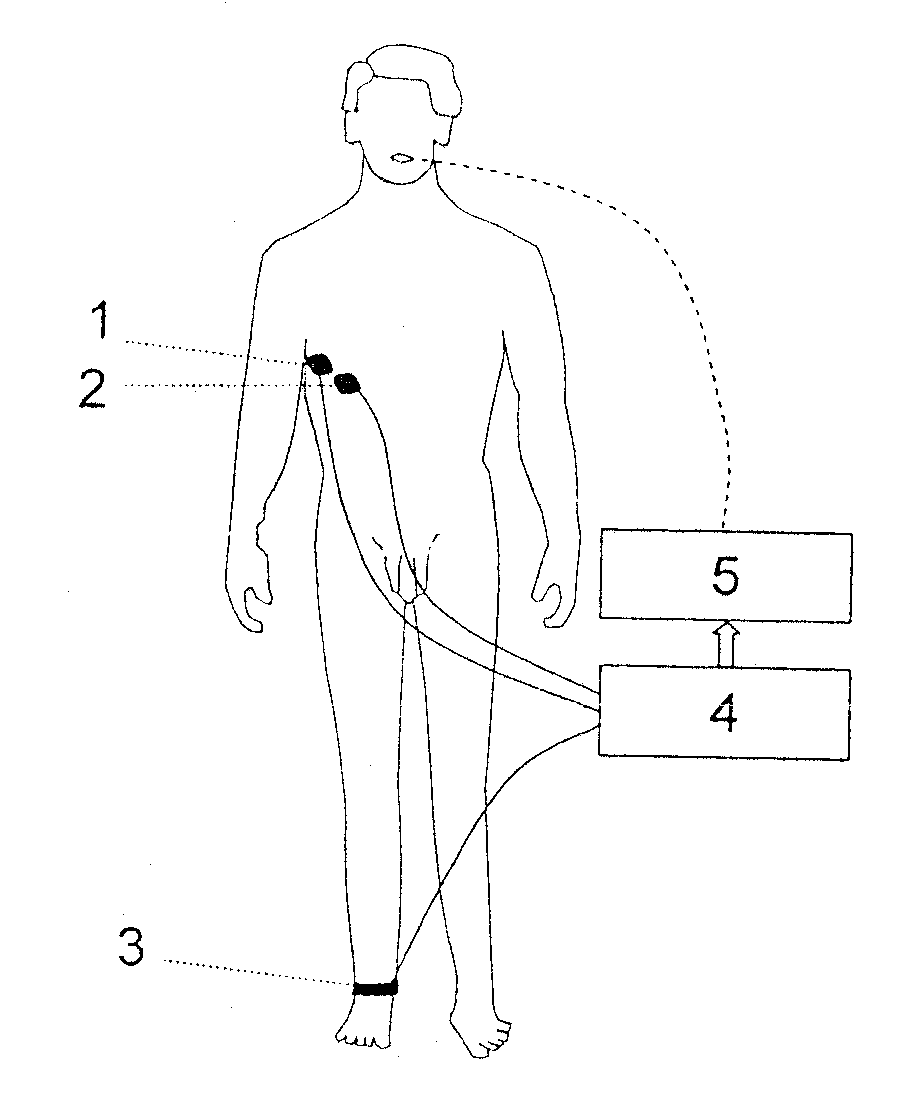
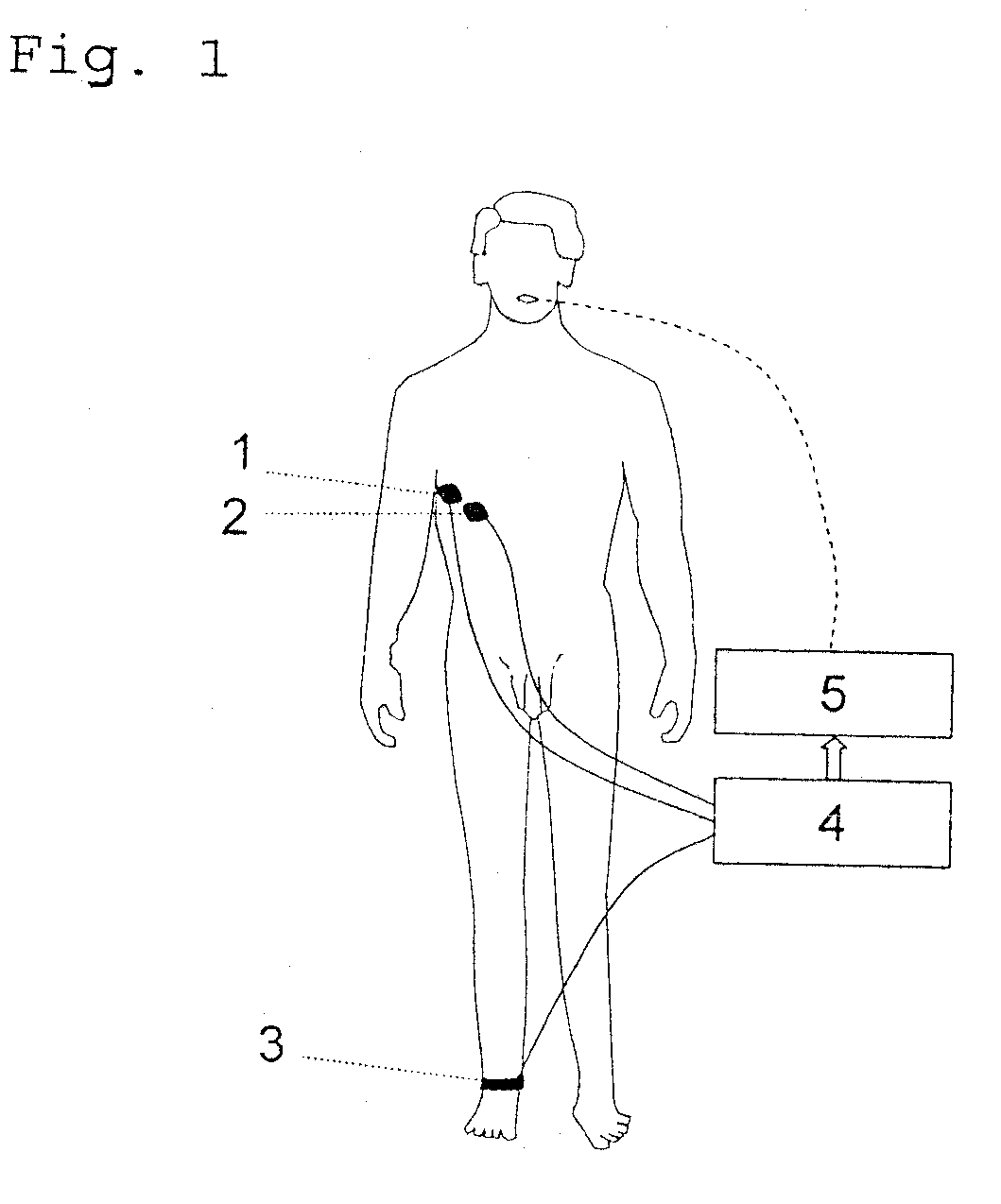
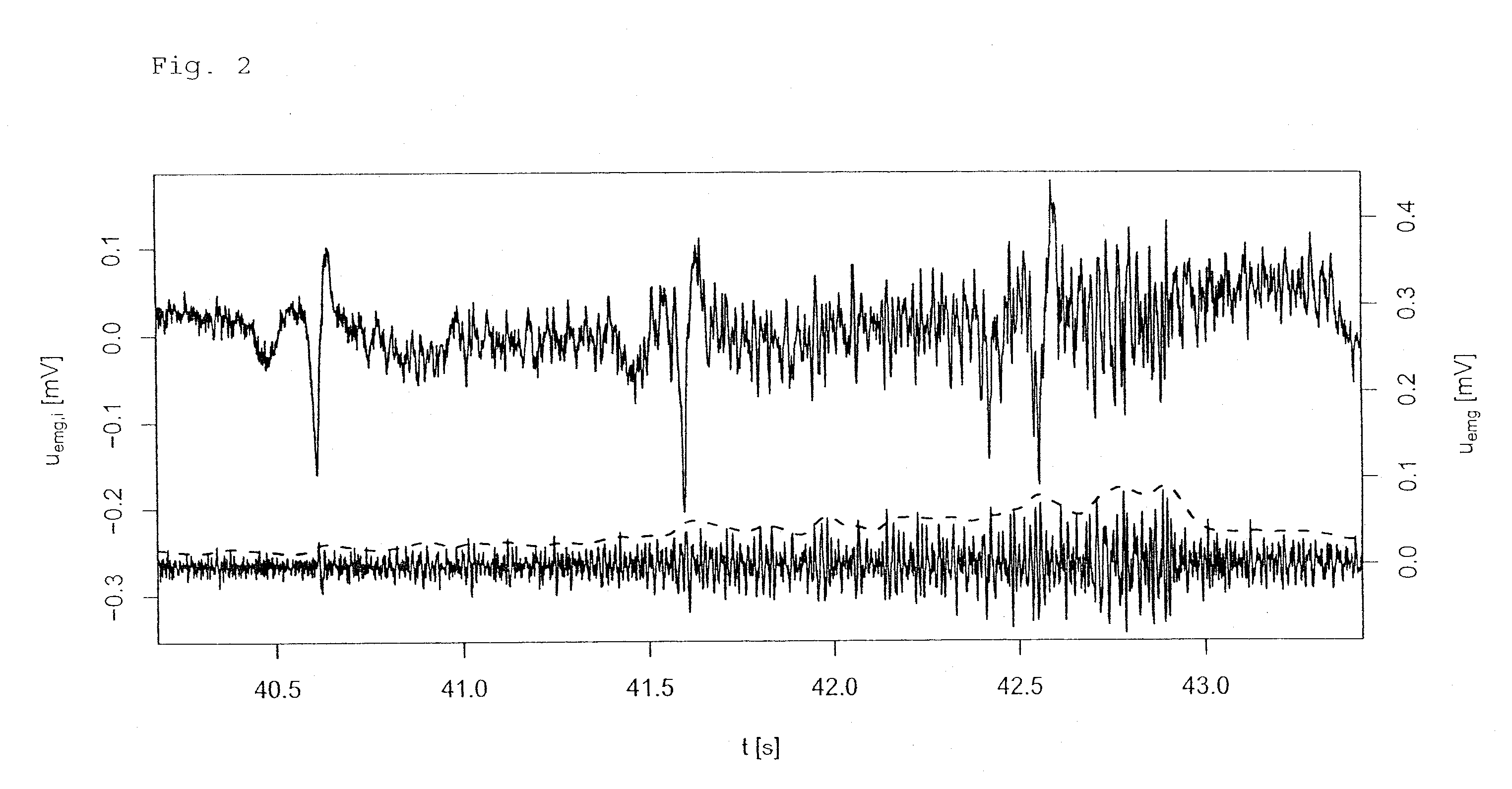
ActiveUS20090159082A1Convenient for patientAccurate operationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutomatic controlProportional Assist Ventilation
A method of automatically controlling a respiration system for proportional assist ventilation with a control device and with a ventilator. An electrical signal is recorded by electromyography with electrodes on the chest in order to obtain a signal uemg(t) representing the breathing activity. The respiratory muscle pressure pmus(t) is determined by calculating it in the control unit from measured values for the airway pressure and the volume flow Flow(t) as well as the patient's lung mechanical parameters. The breathing activity signal uemg(t) is transformed by means of a preset transformation rule into a pressure signal pemg(uemg)(t)) such that the mean deviation of the resulting transformed pressure signal pemg(t) from the respiratory muscle pressure pmus(t) is minimized. The respiratory effort pressure ppat(t) is determined as a weighted mean according to ppat(t)=a·pmus(t)+(1−a)·pemg(t), where a is a parameter selected under the boundary condition 0≦a≦1. The airway pressure paw(t) to be delivered is calculated as a function of preselected degrees of assist VA (Volume Assist) and FA (Flow Assist) by sliding adaptation aspaw(ti)=k0+∑j=1nkj·paw(ti-j)+∑j=0nhj·ppat(ti-j)wherein ti is a current point in time and ti−j, wherein j=1, . . . , n, are previous points in time of a periodical time-discrete sampling, and kj and hj, wherein j=1, . . . , n are parameters dependent on resistance (R), elastance (E), positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), intrinsic PEEP (iPEEP), Volume Assist (VA) and Flow Assist (FA) and the sampling time Δt, and the ventilator is set by the control unit so as to provide this airway pressure paw(ti)
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Method and apparatus for determining respiratory system resistance during assisted ventilation
InactiveUS20030159695A1Reduces computational requirement necessary to determine requiredSimple methodRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTraffic volumeAssisting ventilation
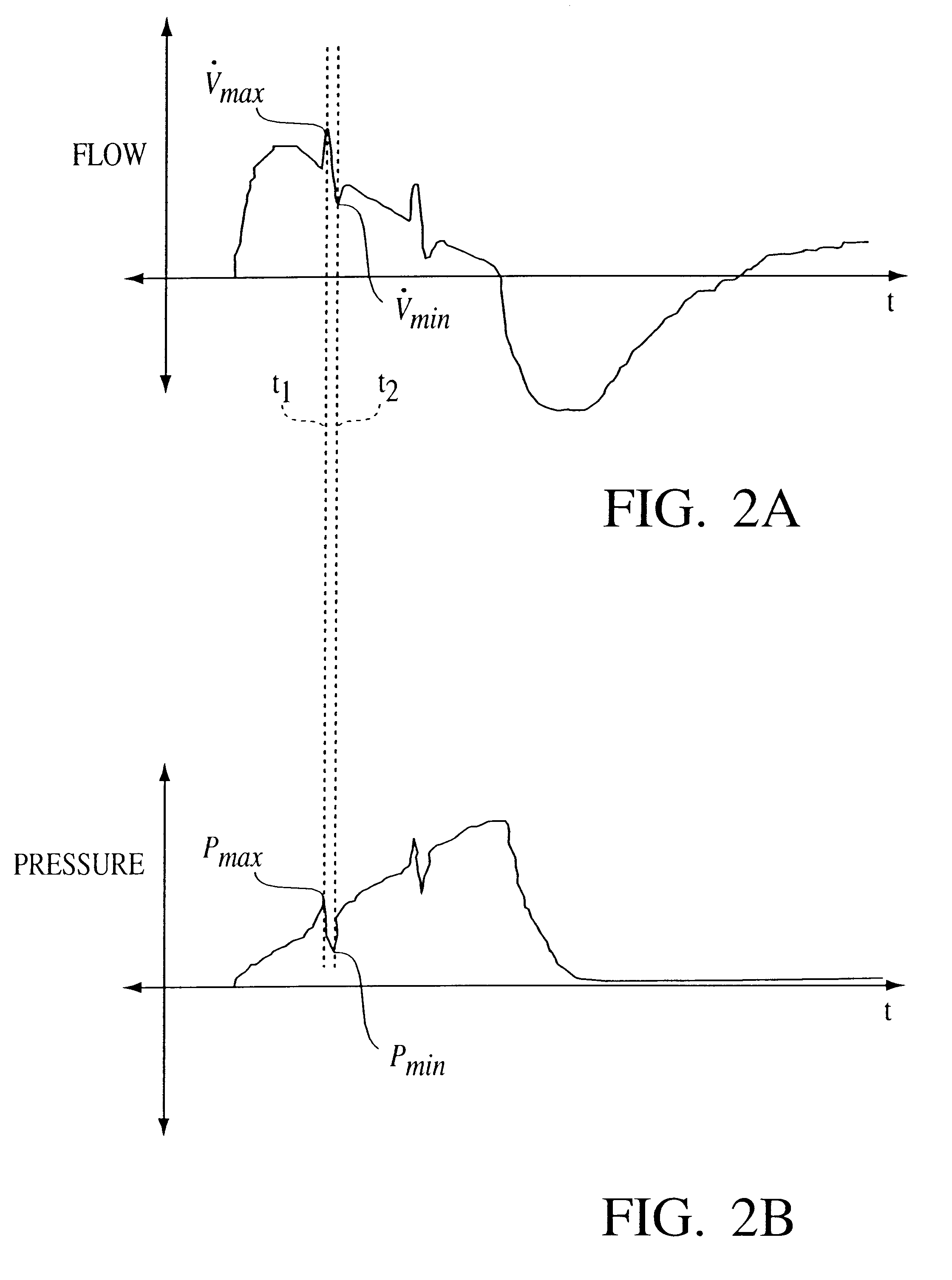
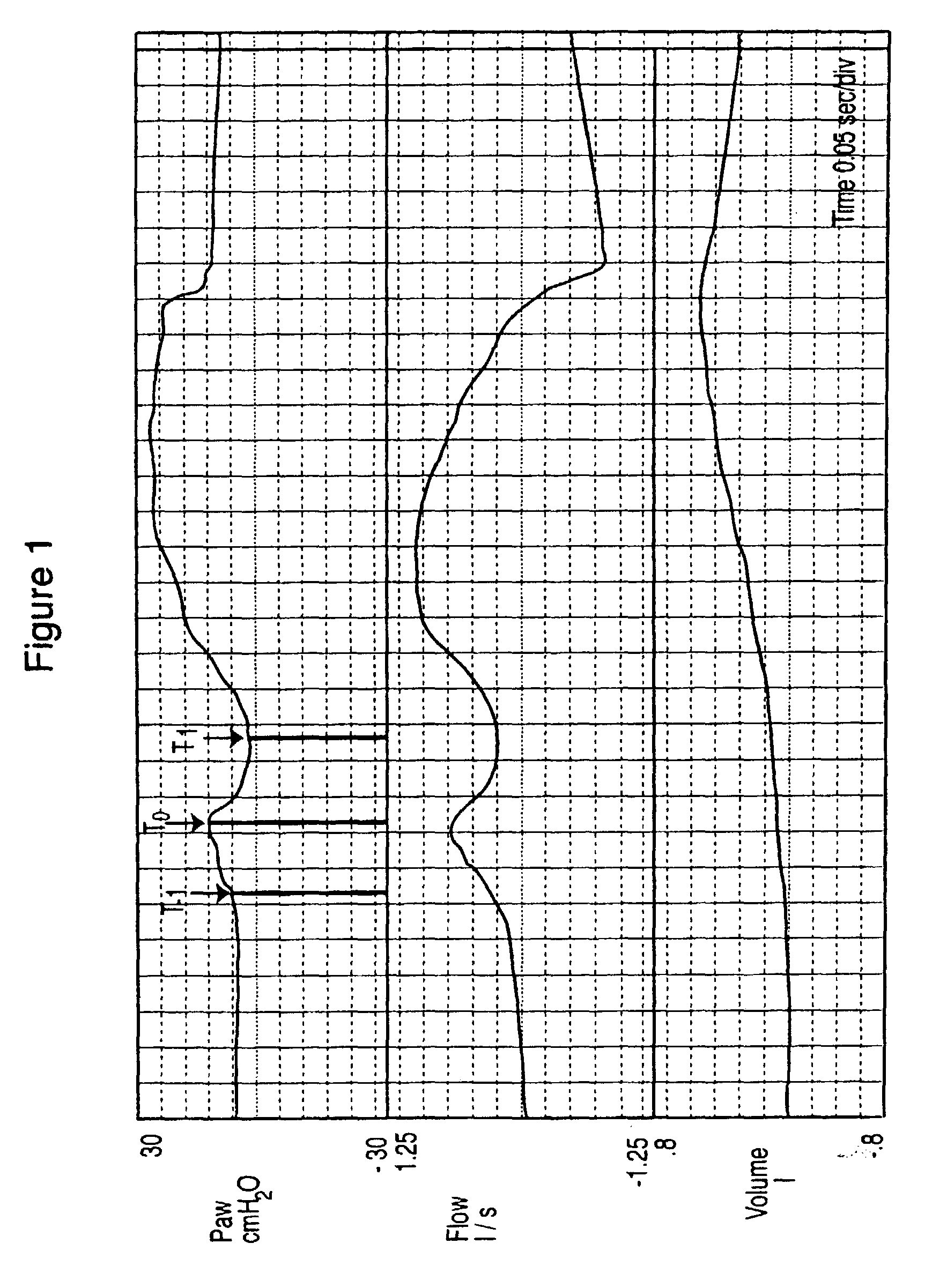
Method and apparatus are described for determining respiratory system resistance (R) in a patient receiving gas from a ventilator. A negative pulse in the pressure and / or flow output of the ventilator during selected inflation cycles is generated and Paw, V dot and V are measured at a point (T0) near the beginning of the pulse, at a point (T1) near the trough of the negative pulse and at a point (T-1) preceding T0. The value of R is calculated from the difference between Paw. V dot and V at TO and at TI and where the change in patient generated pressure (Pmus) in the interval TO-TI is estimated by extrapolation from the different between Paw, V dot and V and T0 and at T-I, in accordance with Equation 8.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
Systems and methods for moving and/or restraining tissue in the upper respiratory system
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Device for monitoring breathing during sleep and ramped control of CPAP treatment
InactiveUS20020007127A1Decrease air pressureImprove sound qualityElectrocardiographyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTraffic volumeEngineering
A CPAP apparatus including: a variable pressured air source and means to vary the air pressure delivered therefrom; a nose piece for sealed air communication with a patient's respiratory system; an air communication line from the air source to the nose piece; a sound transducer adapted to be in sound communication with the patient's respiratory system; and a feedback system controlling the output pressure of the air source in response to an output from the transducer so as to increase the output air pressure from said air source, in response to detection of sound indicative of snoring, in accordance with a predefined procedure. The sound transducer, in its most general form, comprises a pressure transducer which, in addition to detecting snoring sounds, can detect other respiratory parameters such as the rate of breathing, inhaled air flow volume, and inhaled air flow rate. Output air pressure from air source is increased in response to one or more of these parameters in accordance with a pre-defined procedure.
Owner:RESMED LTD
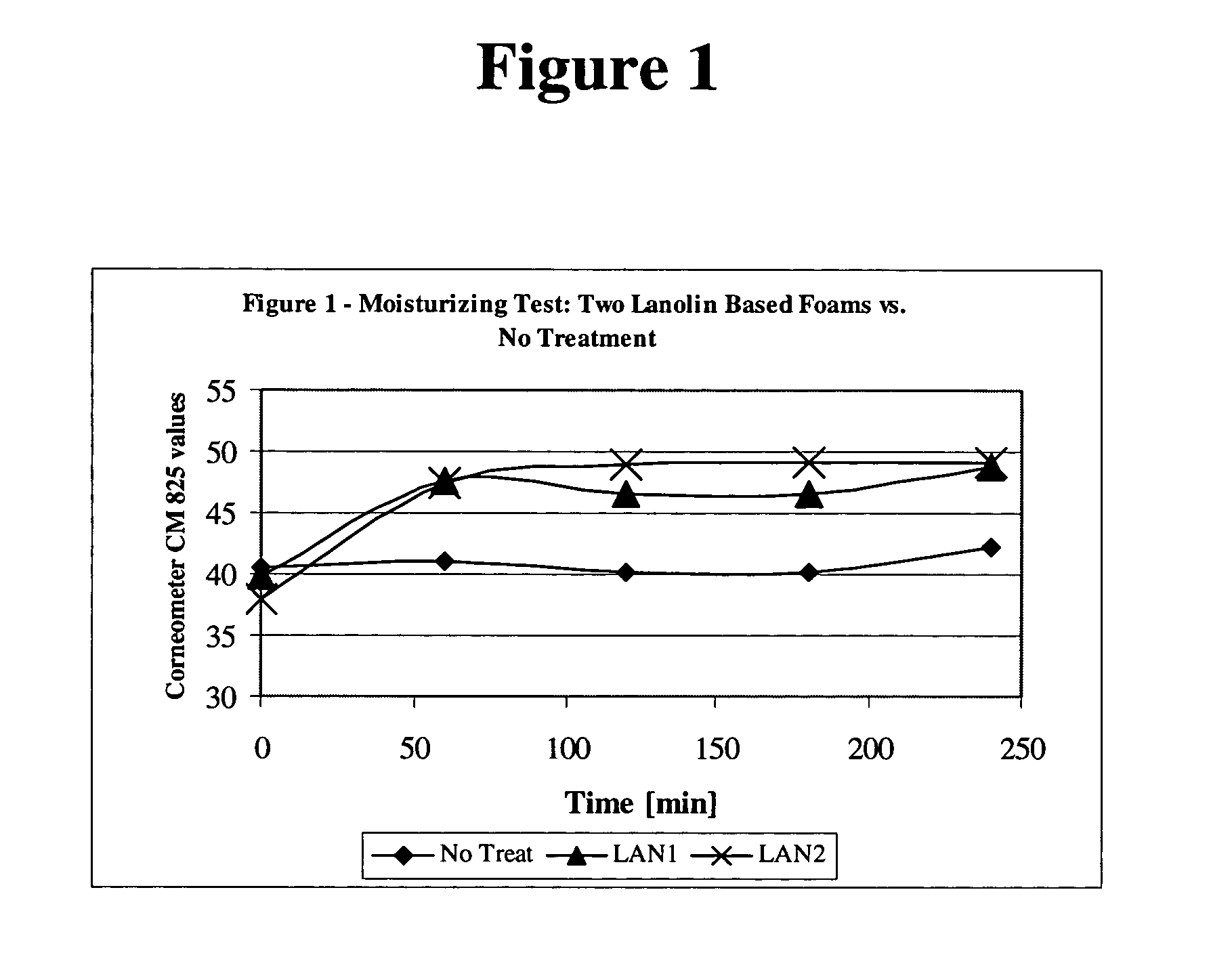
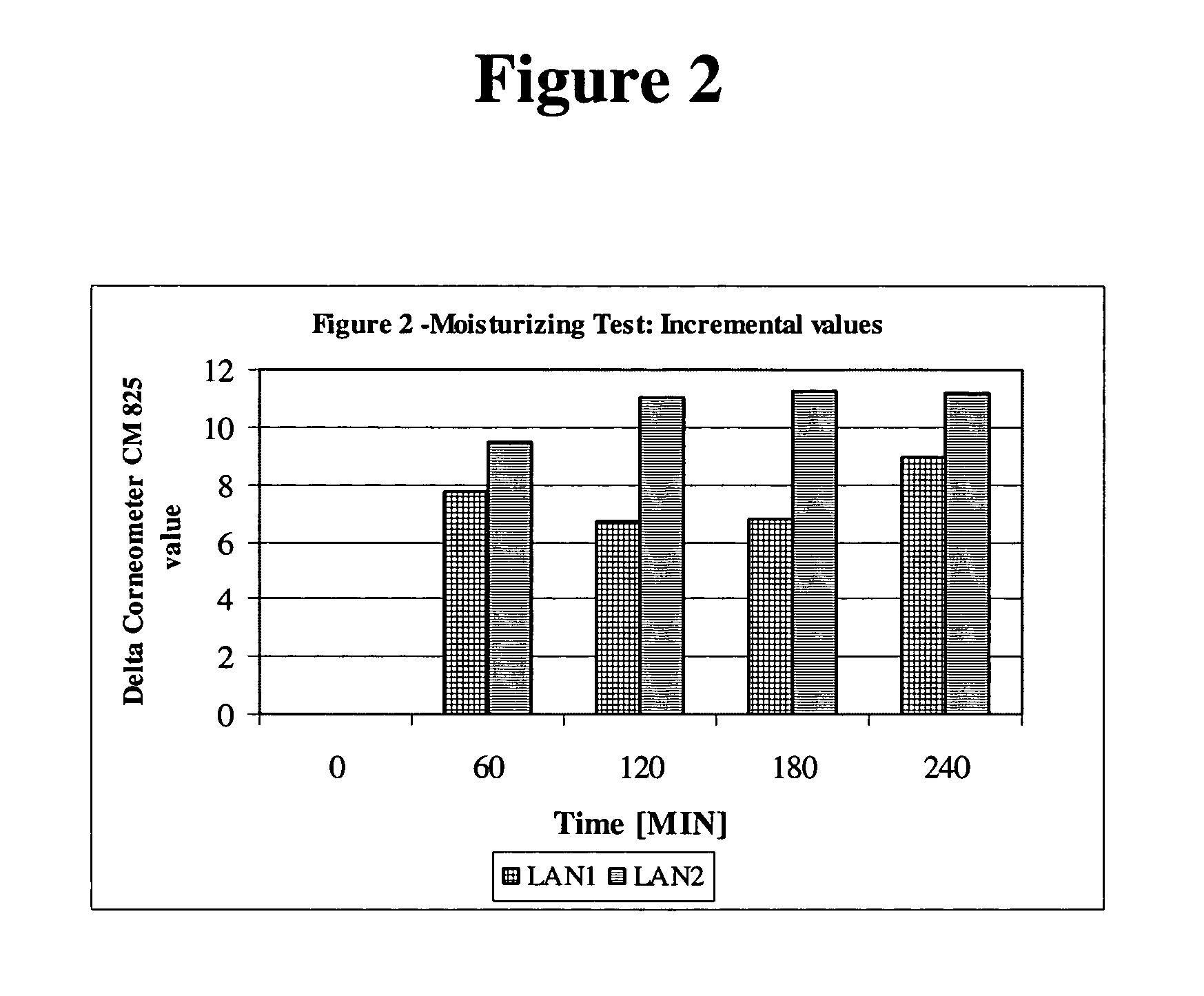
Moisturizing foam containing lanolin
Owner:VYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
Device and method for assessing asthma and other diseases
InactiveUS7347825B2Rapid pro-inflammatory necrosisHigh viscosityWithdrawing sample devicesSynthetic resin layered productsAcetic acidDisease
Device and method for non-invasively monitoring asthma and other respiratory diseases, as well as non-respiratory diseases. The method includes collecting condensate from a subject's breath, testing the condensate to determine its acetic acid / acetate level or concentration, and evaluating these properties to determine the presence, absence or status of a respiratory or non-respiratory disease in the subject. The method may also include, prior to the testing step, standardizing the volatile substances that may be present within the condensate in a degassing or gas standardizing step. The device includes a mouthpiece apparatus configured to receive breath from a subject, a condensation apparatus to condense the subject's breath and produce a condensate, and a collection apparatus having a collection chamber containing means for testing the condensate to determine the acetic acid and / or acetate concentration. The device may also include a system for removing or standardizing the volatile substances that may be present with the condensate. The device and method may be utilized without condensing a subject's breath and collecting the same.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
System and method of monitoring respiratory airflow and oxygen concentration
InactiveUS20090107501A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksData controlEngineering
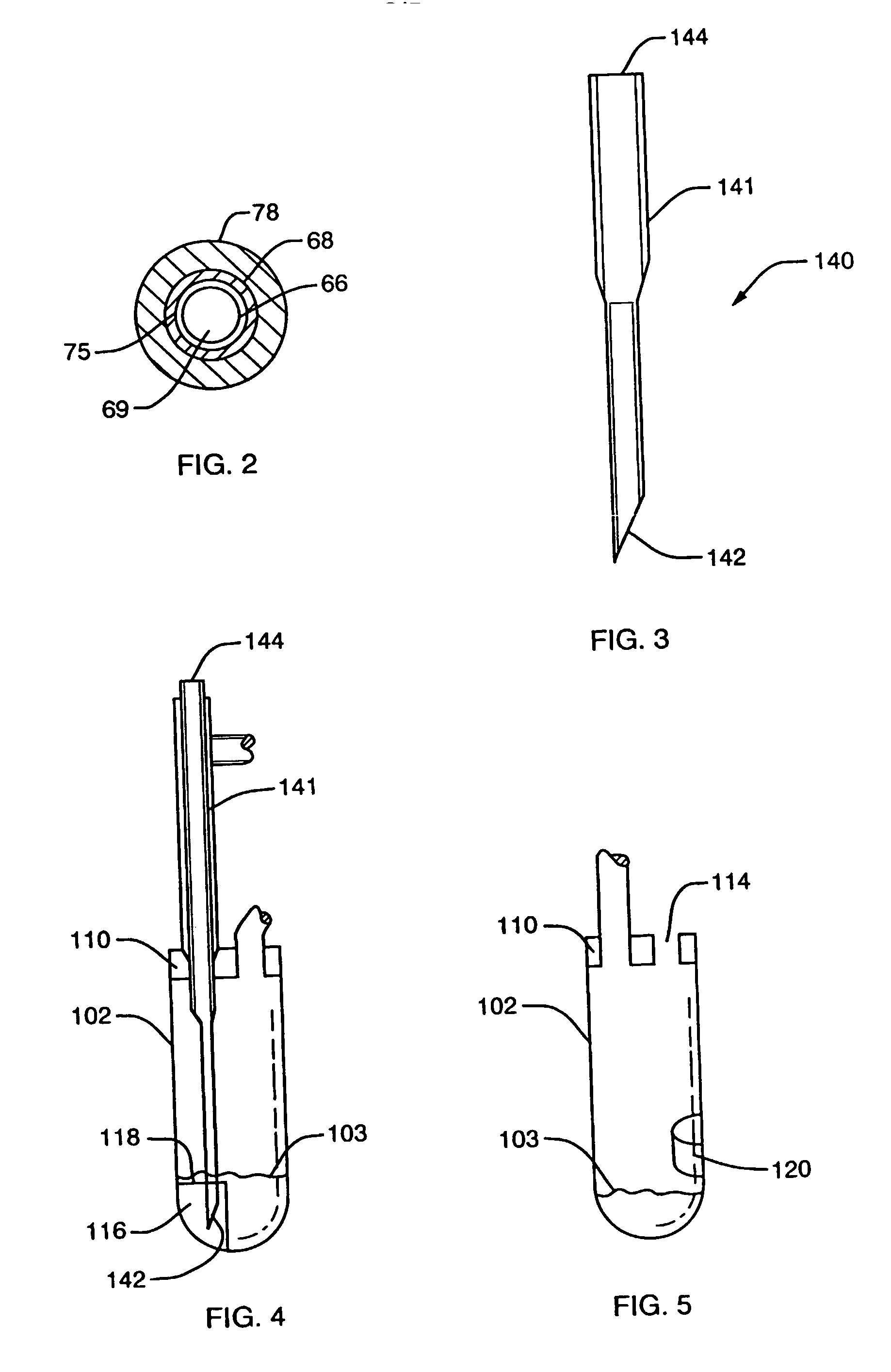
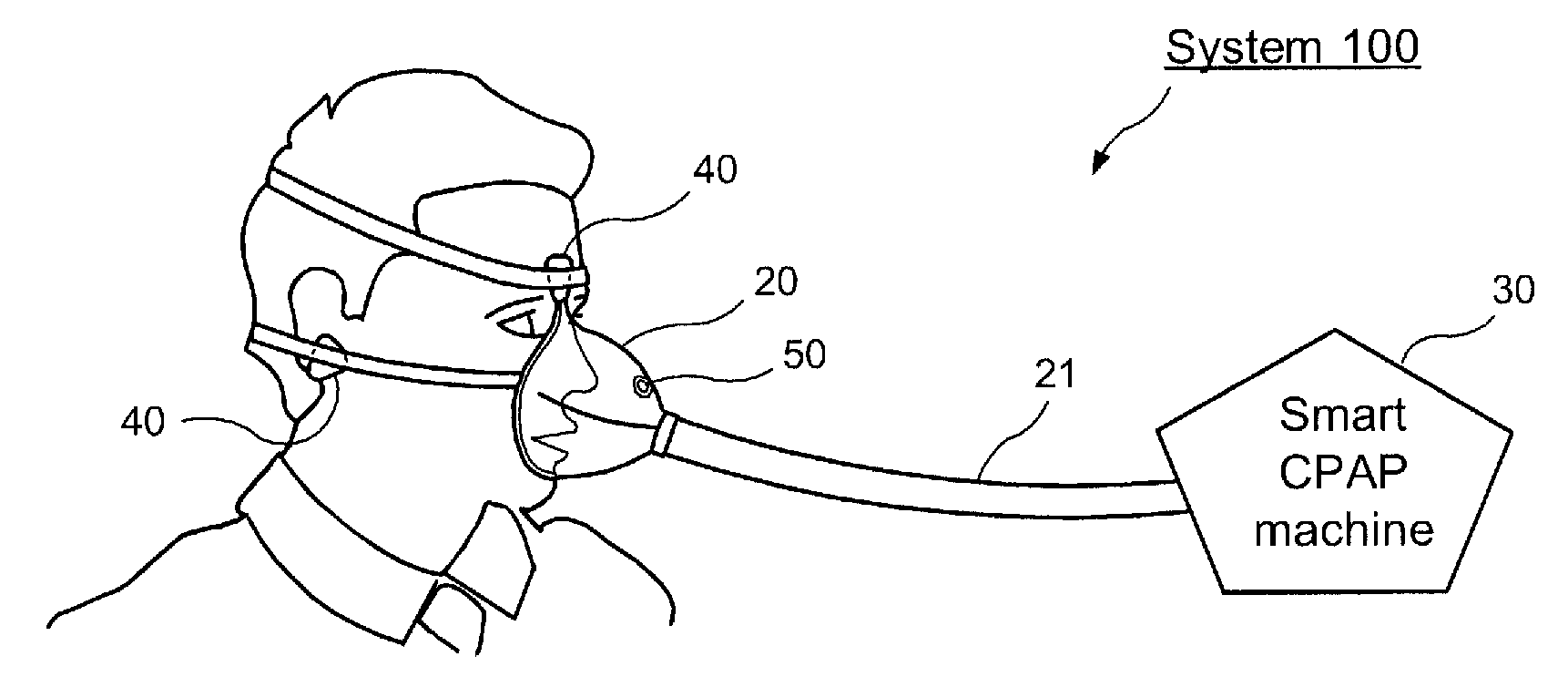
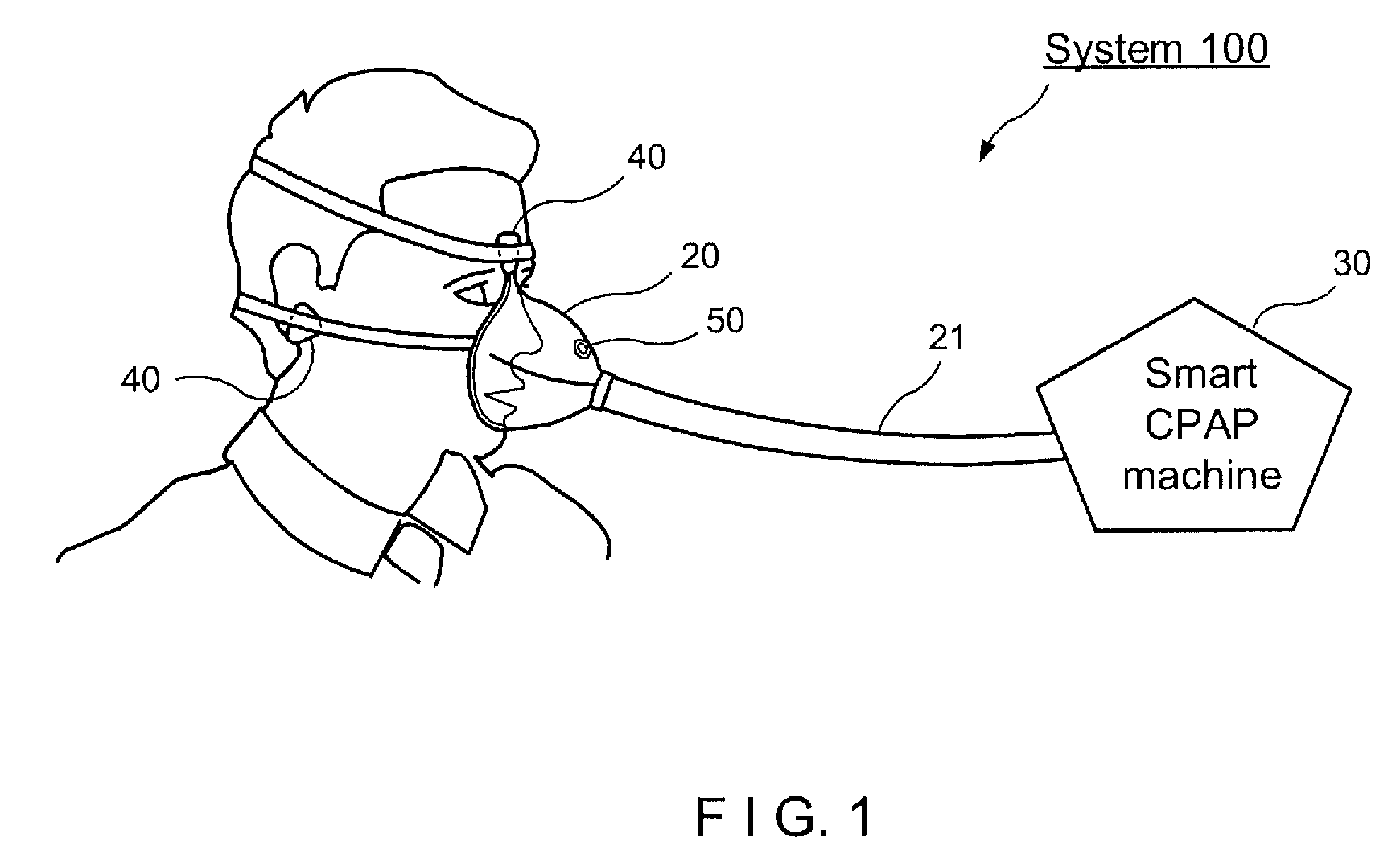
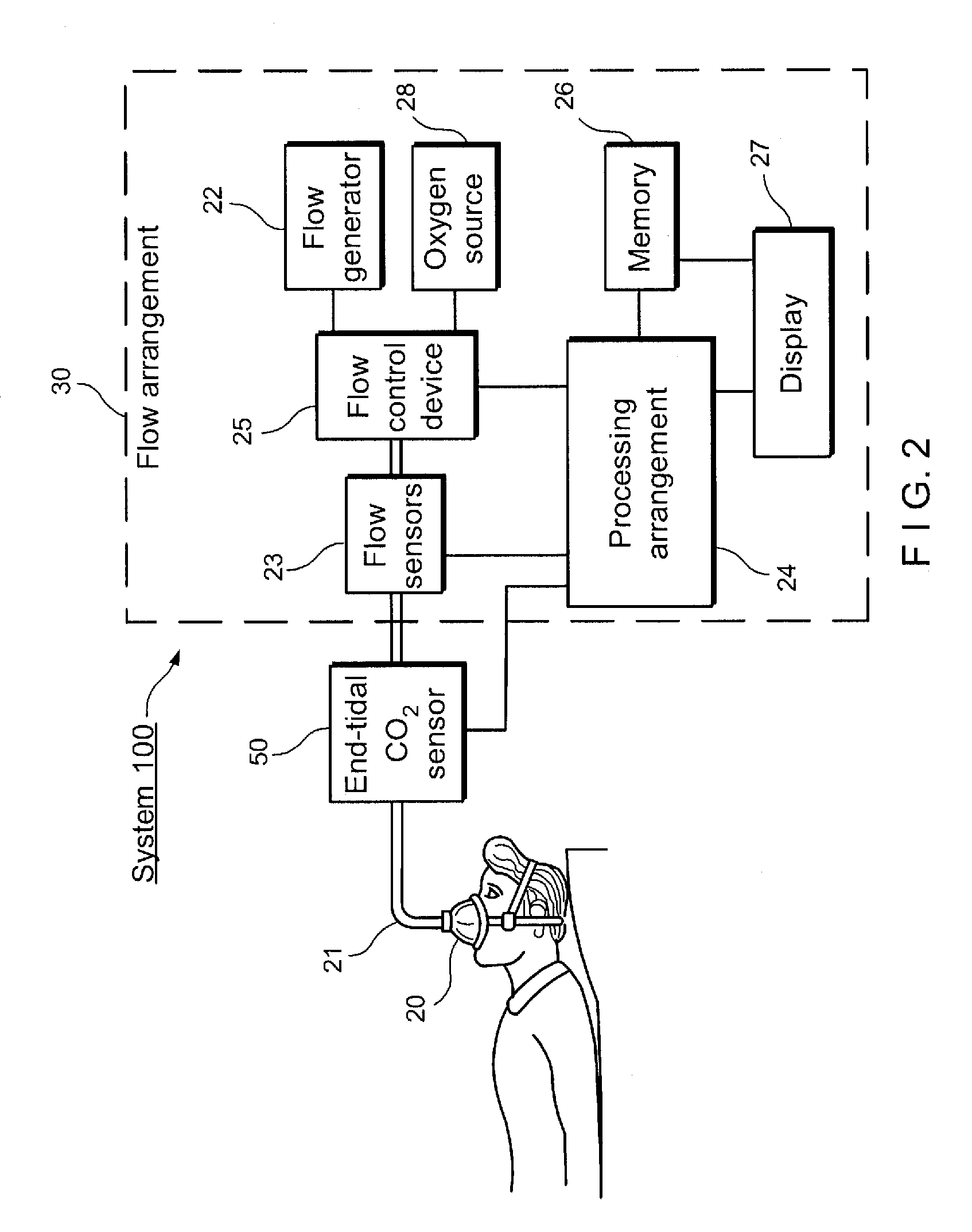
Described is system and method of monitoring respiratory airflow and oxygen concentration. The system may include a first sensor producing data corresponding to an airflow in a respiratory system of a body; a second sensor producing data corresponding to an oxygen concentration in the body; a generator supplying a pressurized airflow; an oxygen source supplying oxygen; a conduit through which the pressurized airflow and oxygen are delivered to the respiratory system; and a processing arrangement for processing the data from the first and second sensors and for controlling the generator and the oxygen source based on the processed data.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Devices, systems and methods for generating electricity from gases stored in containers under pressure
A breathing system includes a container to store a gas under pressure, wherein the gas includes air or oxygen. The container includes an outlet through which the gas exits the container. The breathing system further includes a generator system including a generator in operative connection with the container outlet such that energy is supplied to the generator by the pressurized gas. The generator converts the energy supplied by the pressurized gas to electrical energy. The system further includes a fluid path in connection with the generator through which pressurized gas passes after providing energy to the generator and a respiration facepiece in fluid connection with the fluid path.
Owner:MINE SAFETY APPLIANCES CO +1
Instruments for measuring nanoparticle exposure
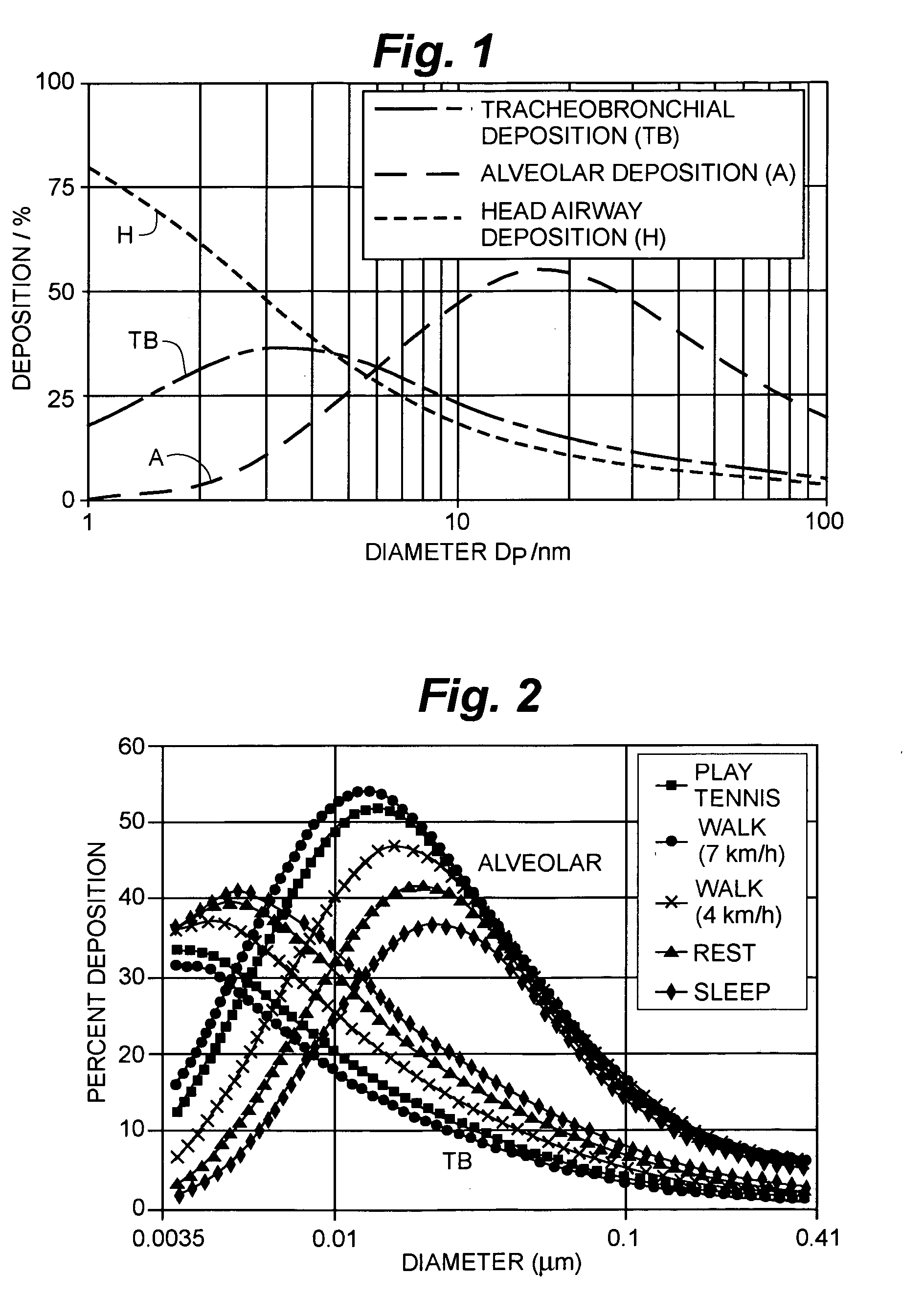
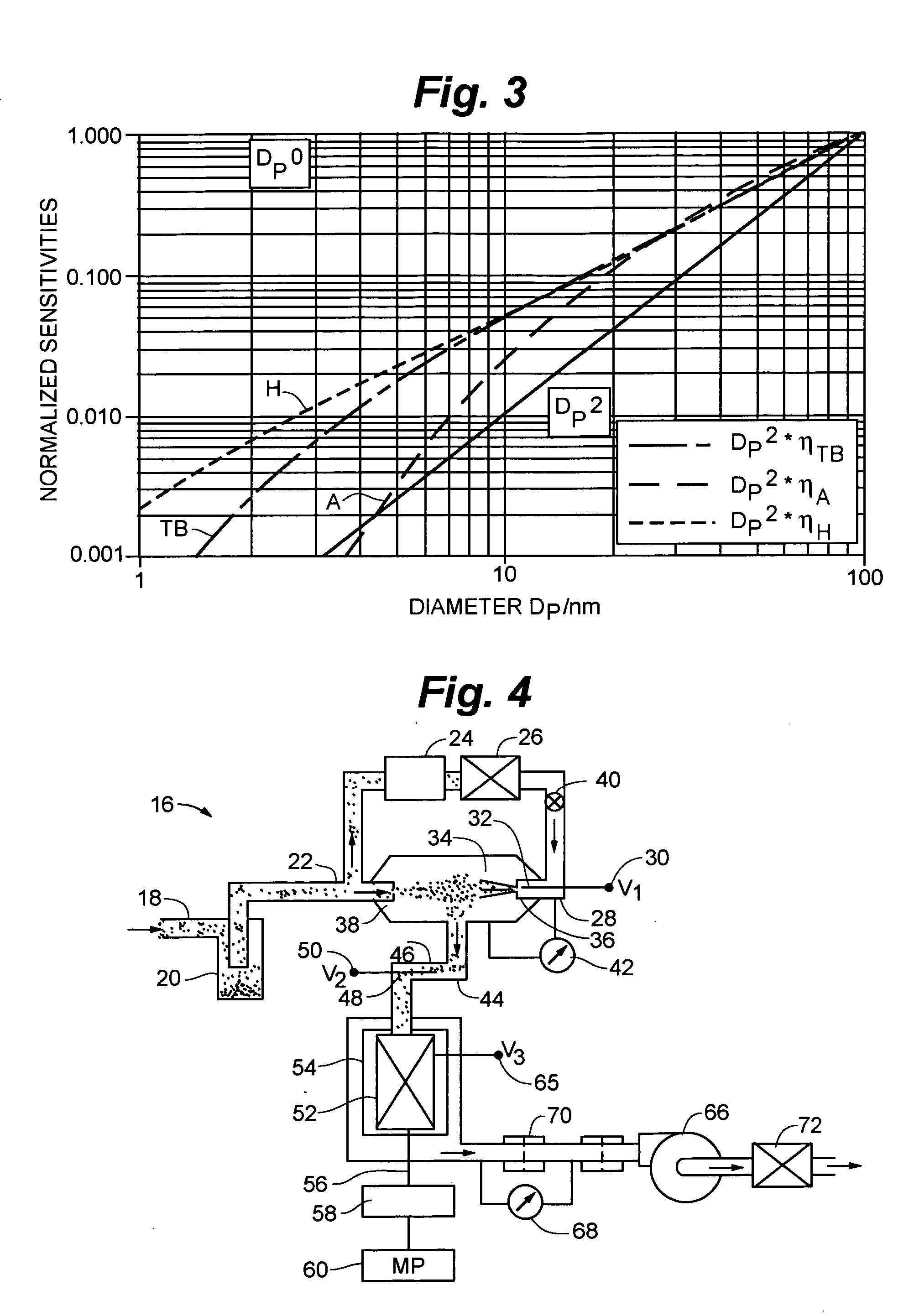
ActiveUS20060284077A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle separator tubesElectrical mobilityElectrically conductive
An instrument for non-invasively measuring nanoparticle exposure includes a corona discharge element generating ions to effect unipolar diffusion charging of an aerosol, followed by an ion trap for removing excess ions and a portion of the charged particles with electrical mobilities above a threshold. Downstream, an electrically conductive HEPA filter or other collecting element accumulates the charged particles and provides the resultant current to an electrometer amplifier. The instrument is tunable to alter the electrometer amplifier output toward closer correspondence with a selected function describing particle behavior, e.g. nanoparticle deposition in a selected region of the respiratory system. Tuning entails adjusting voltages applied to one or more of the ion trap, the corona discharge element and the collecting element. Alternatively, tuning involves adjusting the aerosol flow rate, either directly or in comparison to the flow rate of a gas conducting the ions toward merger with the aerosol.
Owner:TSI INC
Energy Trigger
A method and apparatus for facilitating breathing using a mechanical breathing gas ventilator is presented. The patient effort is deduced from a measured flow signal and analyzed with respect to the energy in the breathing system comprising the mechanical ventilator and the patient. When a predetermined energy threshold has been reached the ventilator responds to the breathing pattern change.
Owner:BREAS MEDICAL
Devices, a computer program product and a method for data extraction
ActiveUS20120283581A1Improve certaintyImprove robustnessElectrocardiographyMedical devicesReflexBreathing system
A monitoring device receives a measurement signal obtained by a pressure sensor in an extracorporeal fluid system, such as an extracorporeal blood circuit for a dialysis machine which is in contact with a vascular system of a subject via a fluid connection. The monitoring device processes the measurement signal to identify pressure data that represents pulses originating from a first physiological phenomenon in the subject, excluding the heart of the subject. The first physiological phenomenon may be any of reflexes, voluntary muscle contractions, non-voluntary muscle contractions, a breathing system of the subject, an autonomous system of the subject for blood pressure regulation, or an autonomous system of the subject for body temperature regulation. The monitoring device may detect, present, track or predict a disordered condition of the subject using the pressure data, or monitor the integrity of the fluid connection based on the pressure data.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
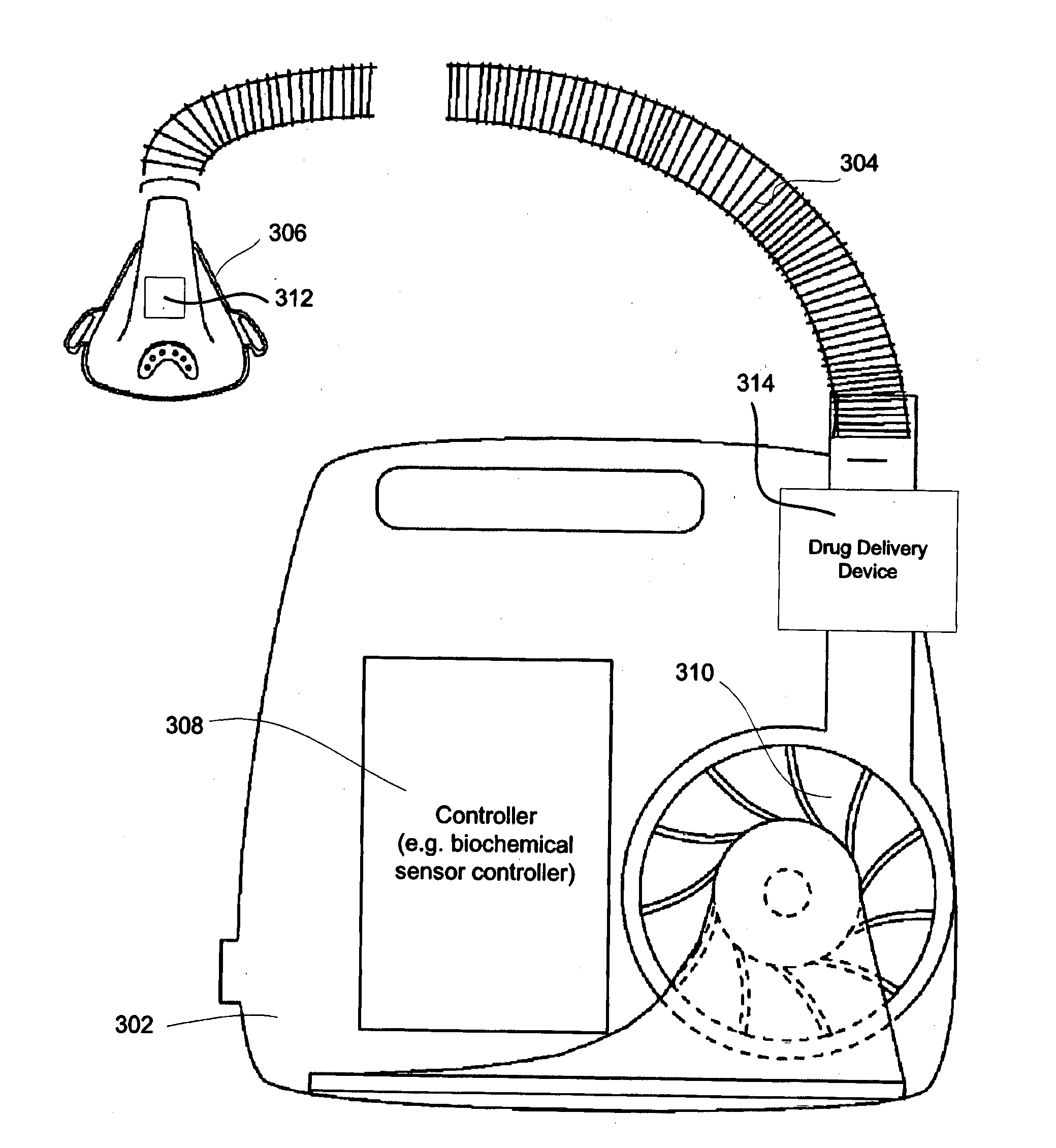
Respiratory treatment system including physiological sensors
An apparatus assesses a condition of a patient. The apparatus may contain a patient interface for communicating a treatment generated by a respiratory treatment apparatus to the respiratory system of a patient. The apparatus may also include a sensing module containing one or more electrochemical sensors to sense chemicals in exhaled breath in real time, or over an extended period of time. The apparatus may also include one or more collectors to accumulate a breath condensate over an extended period of time. The sample collectors may contain an absorbent material, and may also be adapted for replacement within a sensing module. The absorbent material may also include a preservative for preserving a chemical component of the breath, such as an analyte of the exhaled breath. The technology may provide treatment recommendations based on the detected condition of the breath condensate or the chemical components thereof.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Insufflation system, attachment and method
An insufflation system that includes a first tube that inserts into a patient's airway for providing a primary flow of breathing gas to such a patient. At least one insufflation catheter is provided in or within the first tube for delivering a flow of insufflation gas to the patient. In one embodiment, the flow of insufflation gas is delivered in a first direction generally toward the patient's lungs and in a second direction generally opposite the first direction so that the flow in the second direction creates a negative stagnation pressure that substantially cancels out the positive stagnation pressure generated by flow in the first direction. In second embodiment, an exhaust vent is provided in the first tube for exhausting a flow of gas from the first tube at a rate that is equivalent to the rate at which the flow of insufflation gas is being delivered to the patient's airway, thereby preventing over-inflation of the patient's respiratory system. A third embodiment of the present invention involves a combination of the two embodiments discussed above.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Aerosol delivery apparatus, method and preparation for pressure-assisted breathing systems
An improved pressure-assisted breathing system for delivering aerosolized medication. In addition, the present invention also provides methods and formulations for the treatment of respiratory diseases.
Owner:AEROGEN
Medical micropore atomization medicine absorber
InactiveCN101648041AImprove securitySave energyMedical atomisersInhalatorsBreathing systemBlood circulation
The invention relates to a medicine absorber, in particular to a medical micropore atomization medicine absorber. The medical micropore medicine absorber comprises a main body, the main body is provided with a medicine water box and a circuit device, the medicine water box is internally provided with a micropore piezoelectric ceramic atomization slice, the micropore piezoelectric ceramic atomization slice is connected with atomization control board in the circuit device, and the micropore piezoelectric ceramic atomization slice generates high frequency oscillation action under the control of the atomization control board, so that medicine water connected with the micropore piezoelectric ceramic atomization slice is absorbed by patients after the medicine water is vibrated out from the micropore on the micropore piezoelectric ceramic atomization slice to form fog. The invention can atomize the medicine water into fog with particle diameter in certain range and cause the fog to be absorbed by capillary of the breathing system via choke, trachea, bronchus and lung and then enter the blood circulatory system. The invention is mainly used for critical patients, comatose people and infant as well as patients unwilling to accept and unable to continuously accept drug administration in oral intake, injection and drop ways.
Owner:王成
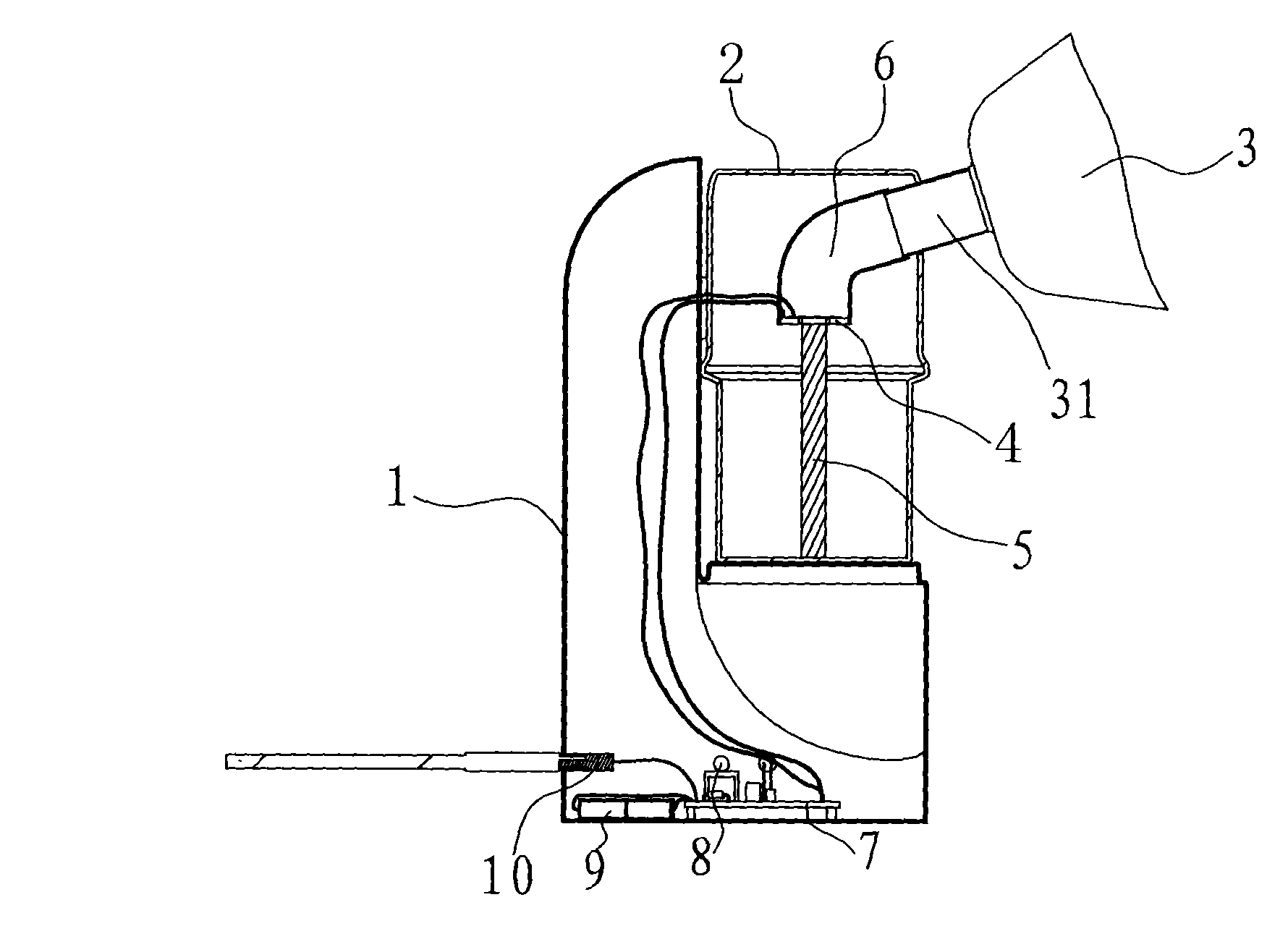
Anesthetic breathing apparatus and internal control method for said apparatus
InactiveUS20090293872A1Simple processFew partsRespiratorsInhalatorsBreathing systemIntensive care medicine
An anesthetic breathing apparatus has a breathing circuit having an inspiratory gas output port and an expiratory gas input port, and a control unit that sets the anesthetic breathing apparatus selectively in a first mode of operation to provide inspiratory gas, fresh gas and / or breathing gas recirculated in said breathing circuit, via said inspiratory gas output port, enable recirculation into said breathing circuit and / or evacuation via the expiratory input port for manual or mechanical ventilation by said anesthetic breathing apparatus. The control unit is also able to set the anesthetic breathing apparatus selectively in a second mode of operation to provide a flow of fresh gas via a fresh gas output port to an external breathing system connected thereto, disable recirculation and / or evacuation via the expiratory input port. An exhaust of the breathing circuit is connected to a gas input port of the anesthetic breathing apparatus for gas scavenging via said anesthetic breathing apparatus.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
Method for determining treatments using patient-specific lung models and computer methods
The present invention concerns a method for determining optimised parameters for mechanical ventilation, MV, of a subject, comprising: a) obtaining data concerning a three-dimensional image of the subject's respiratory system; b) calculating a specific three-dimensional structural model of the subject's lung structure from the image data obtained in step a); c) calculating a specific three-dimensional structural model of the subject's airway structure from the image data obtained in step a); d) calculating a patient-specific three-dimensional structural model of the subject's lobar structure from the lung model obtained in step b); e) modeling by a computer, the air flow through the airway, using the models of the airway and lobar structure of the subject obtained in steps c) and d) at defined MV parameters; f) modeling by a computer, the structural behavior of the airway and the interaction with the flow, using the models of the airway and lobar structure of the subject obtained in steps b) and c) at defined MV parameters; g) determining the MV parameters which lead to a decrease in airway resistance and hence an increase in lobar mass flow for the same driving pressures according to the model of step d), thereby obtaining optimized MV parameters. It also relates to a method for assessing the efficacy of a treatment for a respiratory condition.
Owner:FLUIDDA RESPI
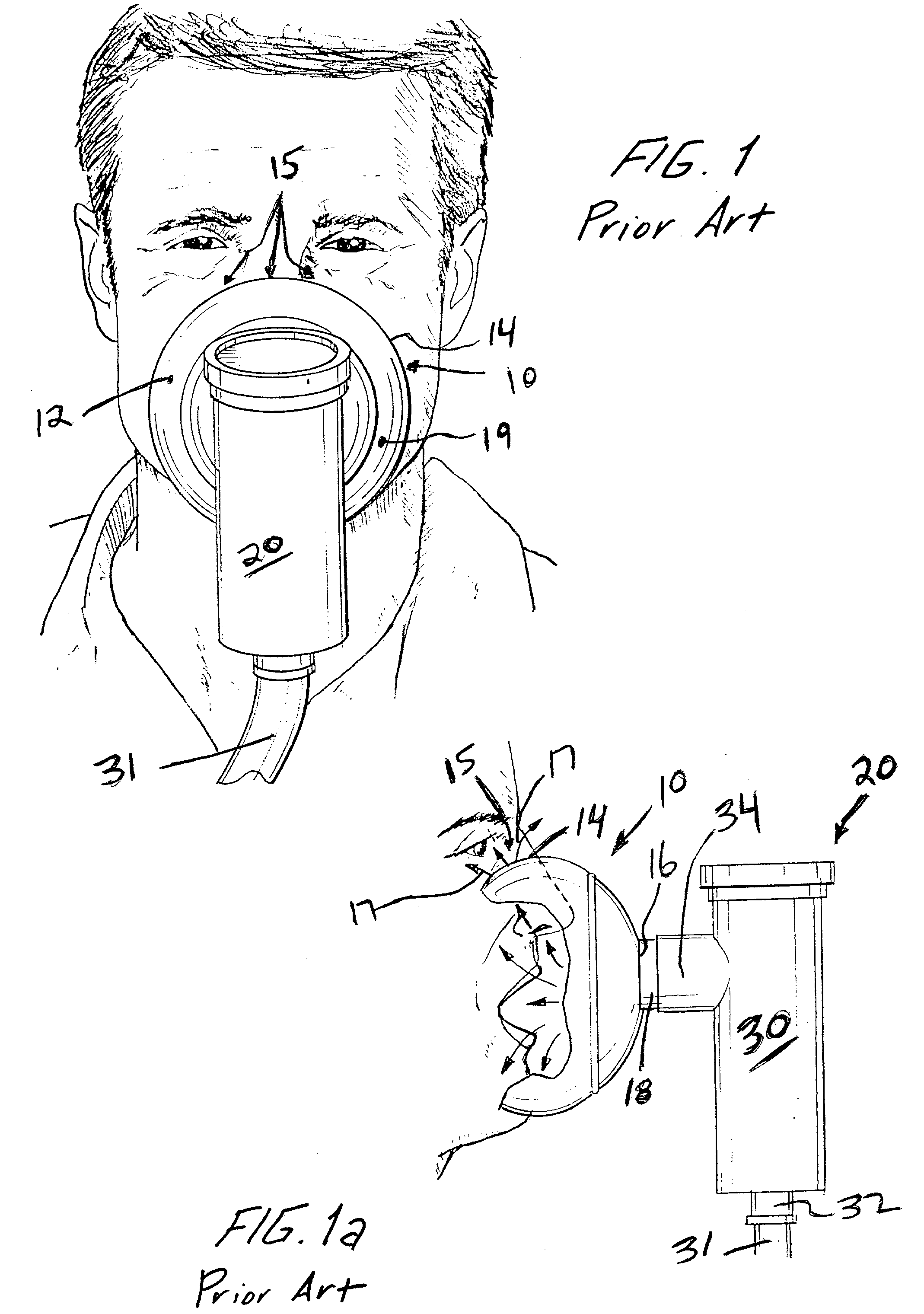
Face masks for use in pressurized drug delivery systems
Face masks for use in pressurized drug delivery applications, such as aerosol drug delivery systems, and a method of reducing aerosol deposition in the region of the eyes are presented. The face masks according to the various embodiments disclosed herein contain features that reduce the inertia of the aerosolized drug in perinasal areas. This results in a reduction in the amount of aerosolized drug that is deposited in the region of the eyes by inertial impaction, while at the same time, the features are constructed to maintain the flow of the aerosolized drug into the face mask so that the aerosolized drug is effectively delivered to the respiratory system of the patient.
Owner:SMALDONE GERALD C
System and Method for Assessing Real Time Pulmonary Mechanics
ActiveUS20120330177A1Accurate calculationAccurate informationRespiratorsRespiratory organ evaluationRestrictive lung diseaseTreatment effect
A system and method of calculating an accurate estimate of pulmonary mechanics of a patient, including but not limited to compliance, resistance, and plateau pressure without modification of ventilator flow pattern. The accurate estimation of pulmonary mechanics is derived from airway pressure and flow sensors attached to the patient using novel mathematical models. These estimated figures for pulmonary mechanics (respiratory system compliance and resistance) are important for monitoring patient treatment efficacy during mechanical ventilation and ensuring alveoli do not over distend to avoid baro- and / or volutrauma, especially in patients with restrictive lung diseases. The subject method of calculating these accurate estimated figures for pulmonary mechanics is based on linear or non-linear calculations using multiple parameters derived from the above-mentioned sensors.
Owner:CONVERGENT ENG +1
Systems and methods for monitoring and management of chronic disease
PendingUS20200297955A1Improve comfortIncrease costPhysical therapies and activitiesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesDiseaseEmergency medicine
Systems and methods assist with managing a chronic disease of a user such as a chronic respiratory or cardiac disease. The system may include a physiological monitor adapted to be carried by the user and operative to sense a physiological parameter of the user. The system may include a management device operatively coupled with the physiological monitor to receive the sensed physiological parameter of the user. The management device, such as with an included processor, may be configured to analyze the physiological and / or environmental parameters to detect a trigger pattern of the parameters, the trigger pattern indicative of a probable event of exacerbation of the chronic respiratory and / or cardiac condition. The management device may then generate automated responses based on the trigger pattern such as by providing instructions for activities and / or treatment for the chronic condition.
Owner:RESMED SENSOR TECH
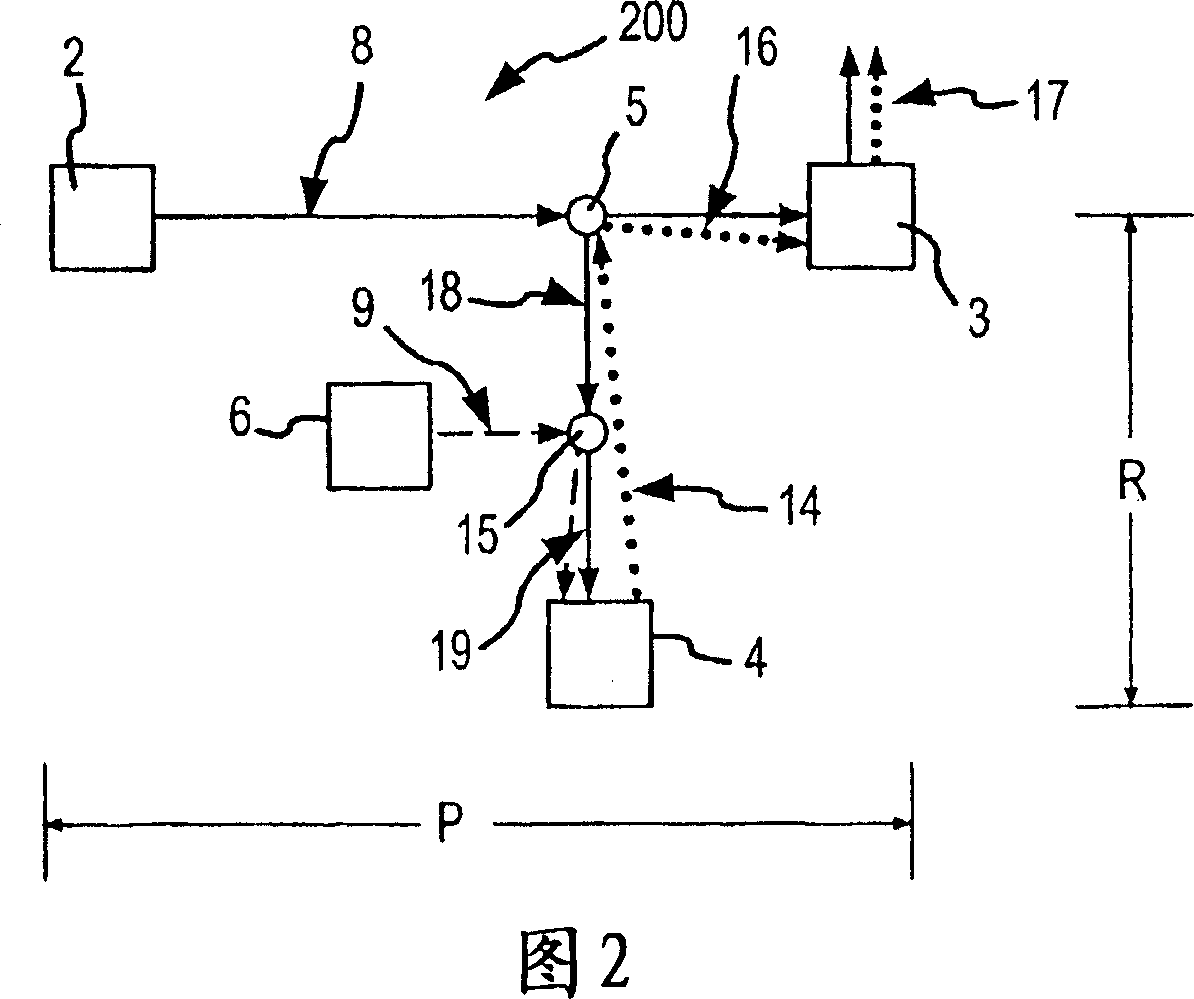
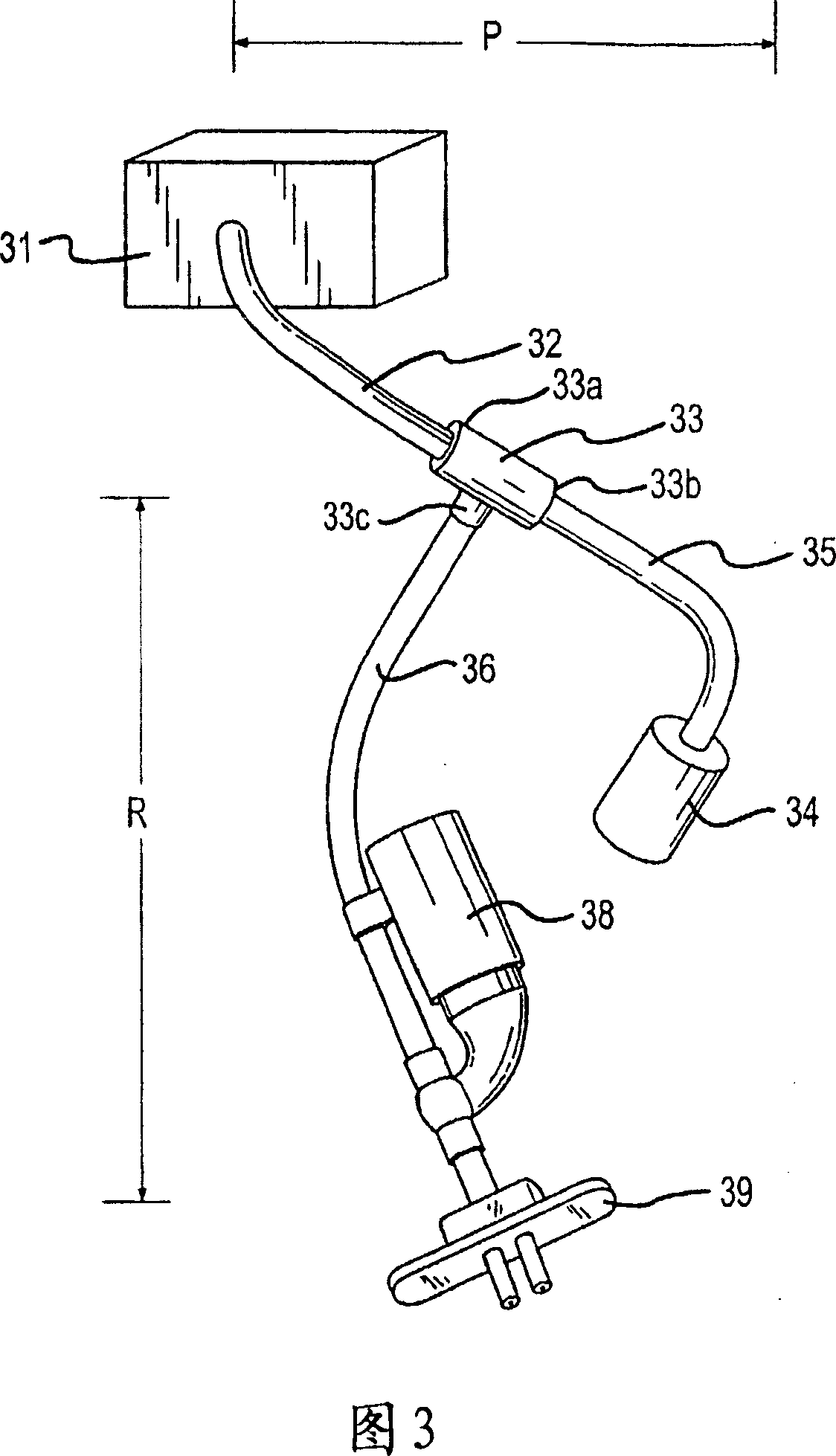
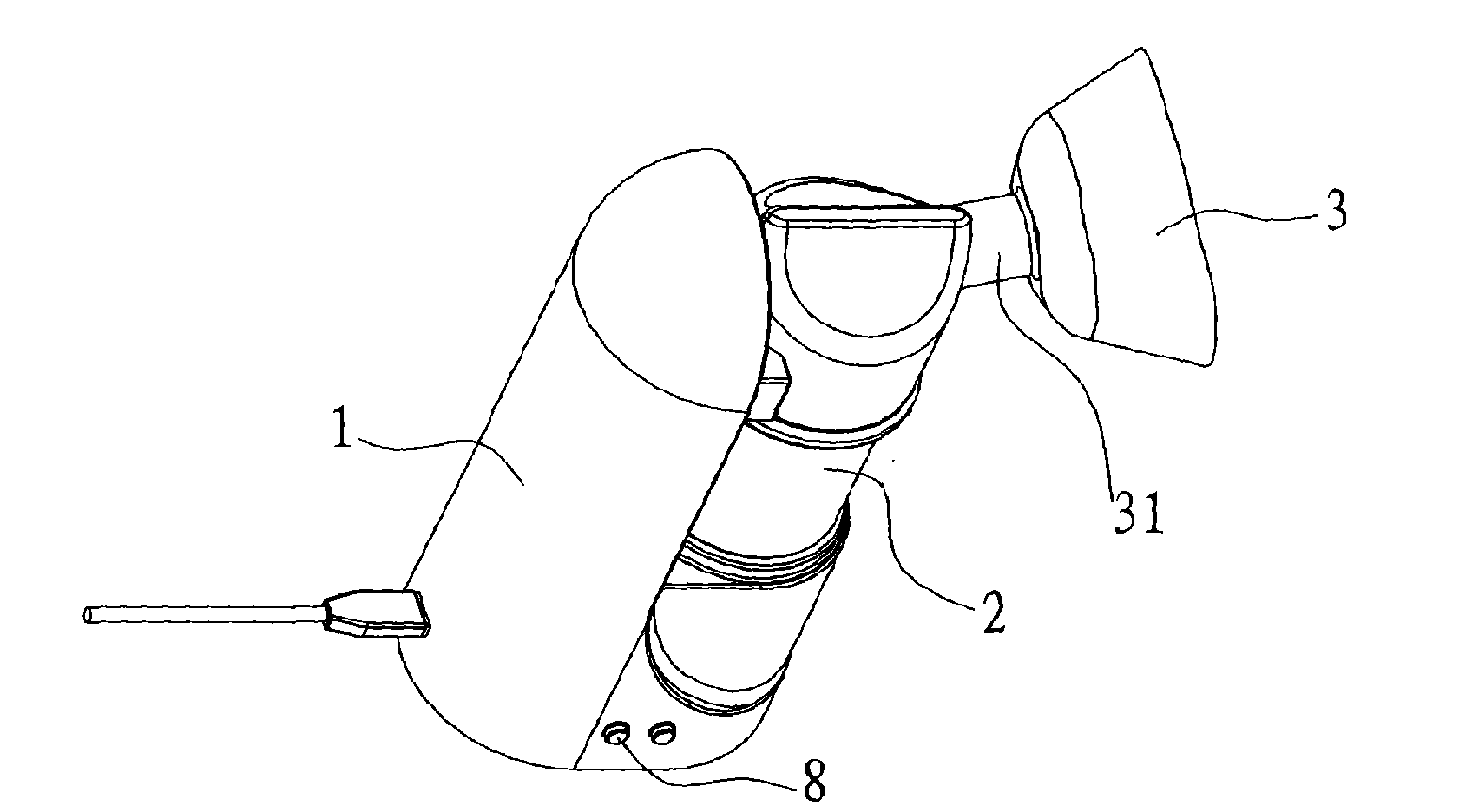
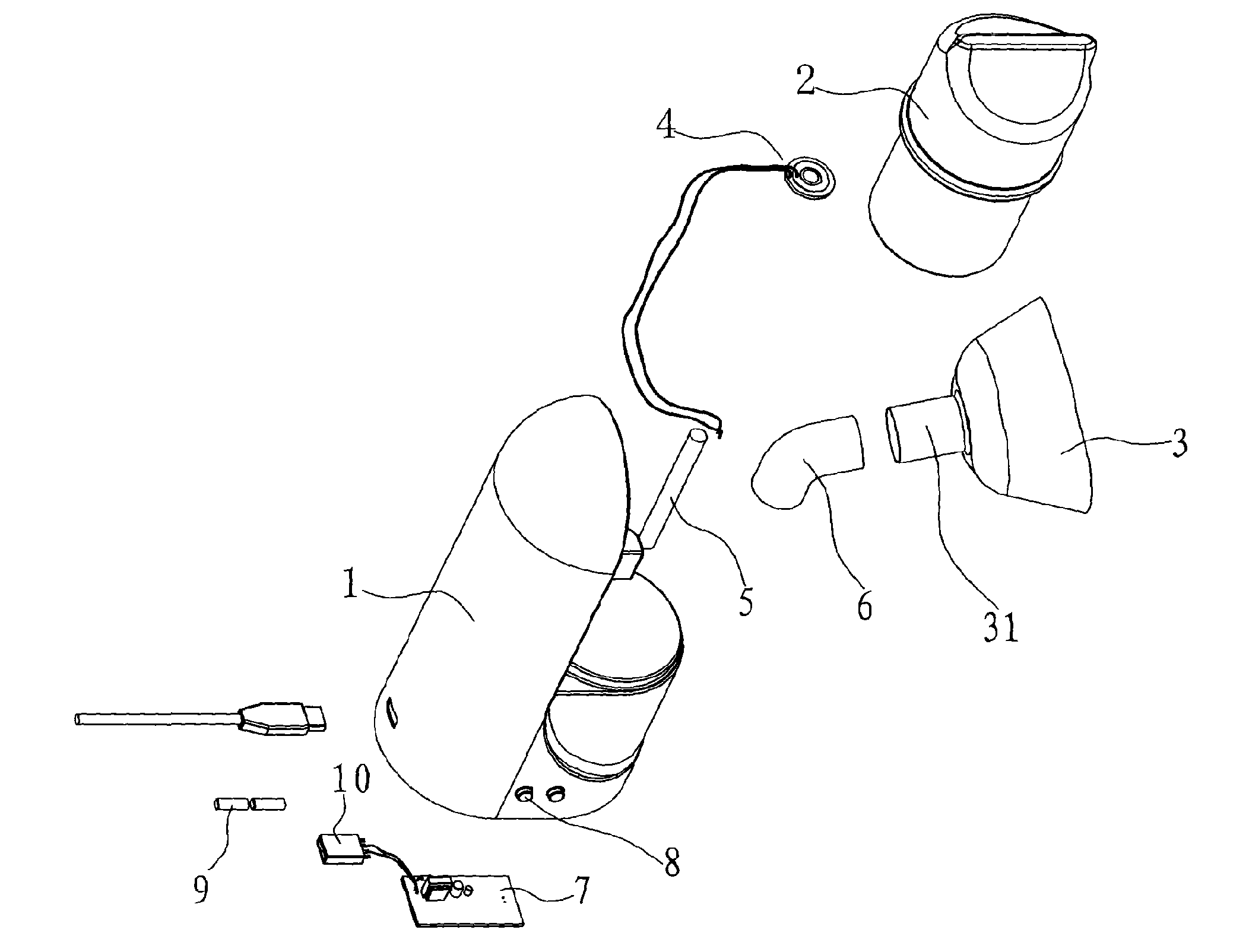
Respiration system
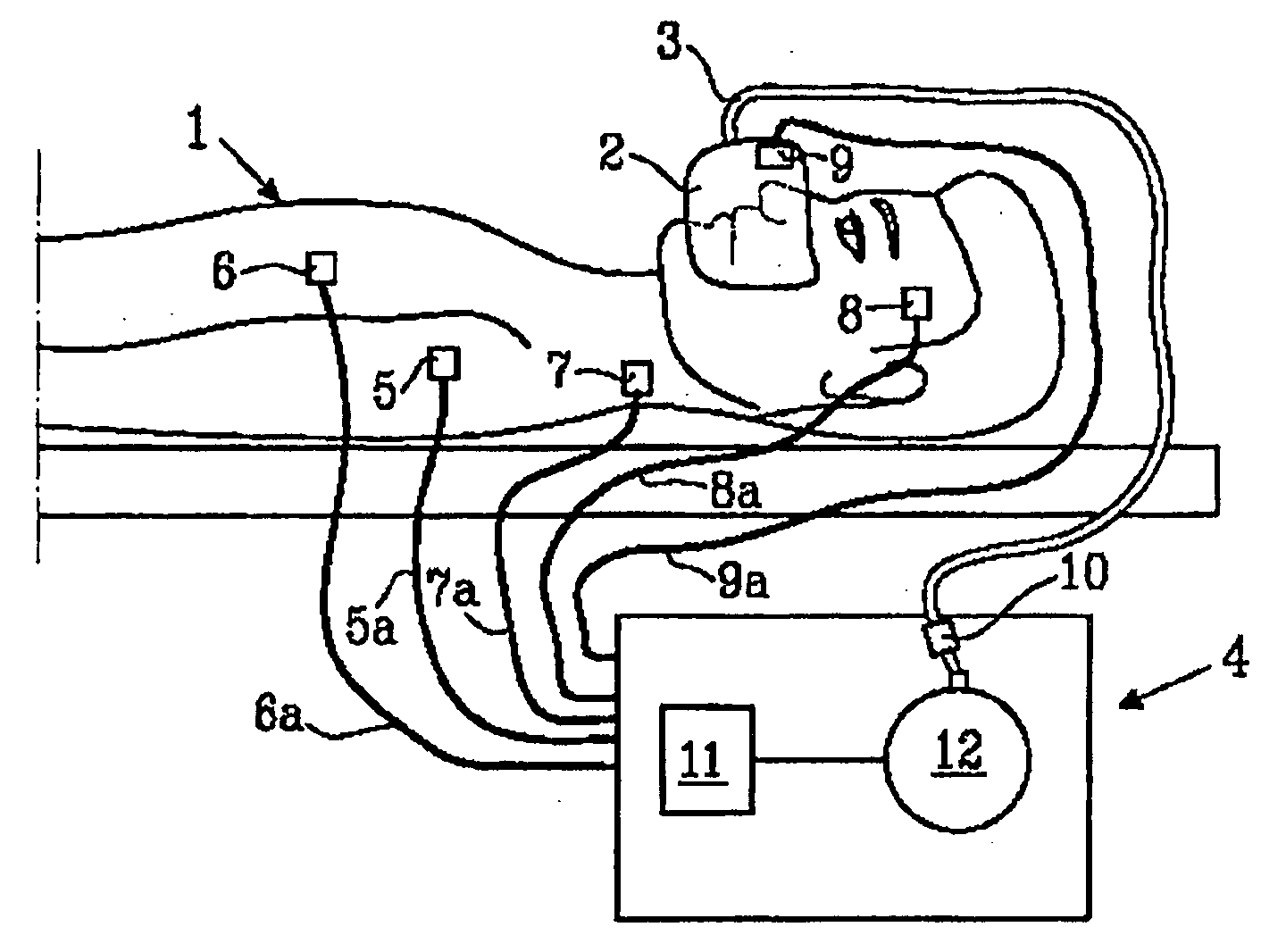
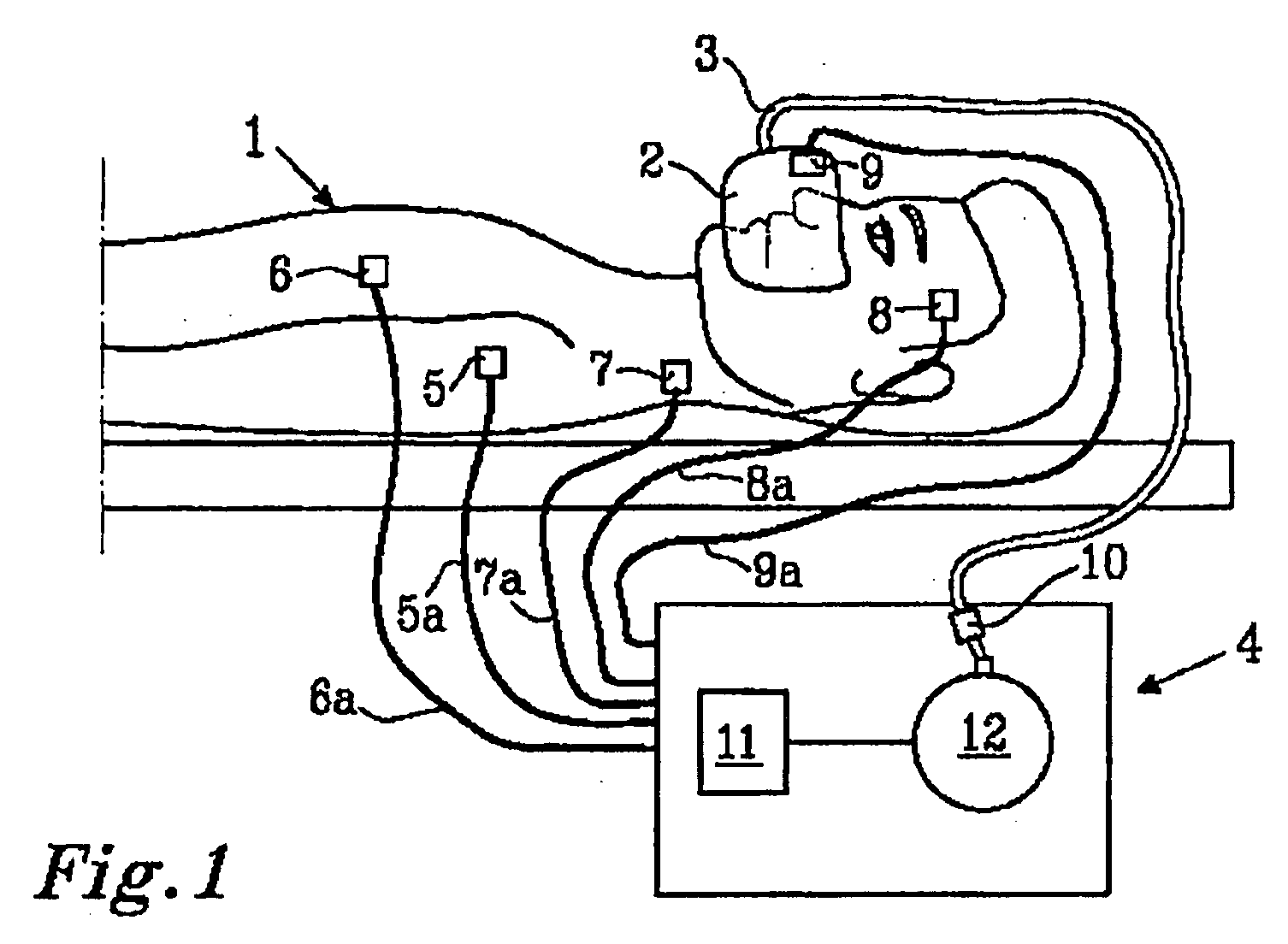
InactiveUS20090320850A1Simple and reliable to useReduce manufacturing costBreathing masksRespiratory masksEmergency medicineBreathing system
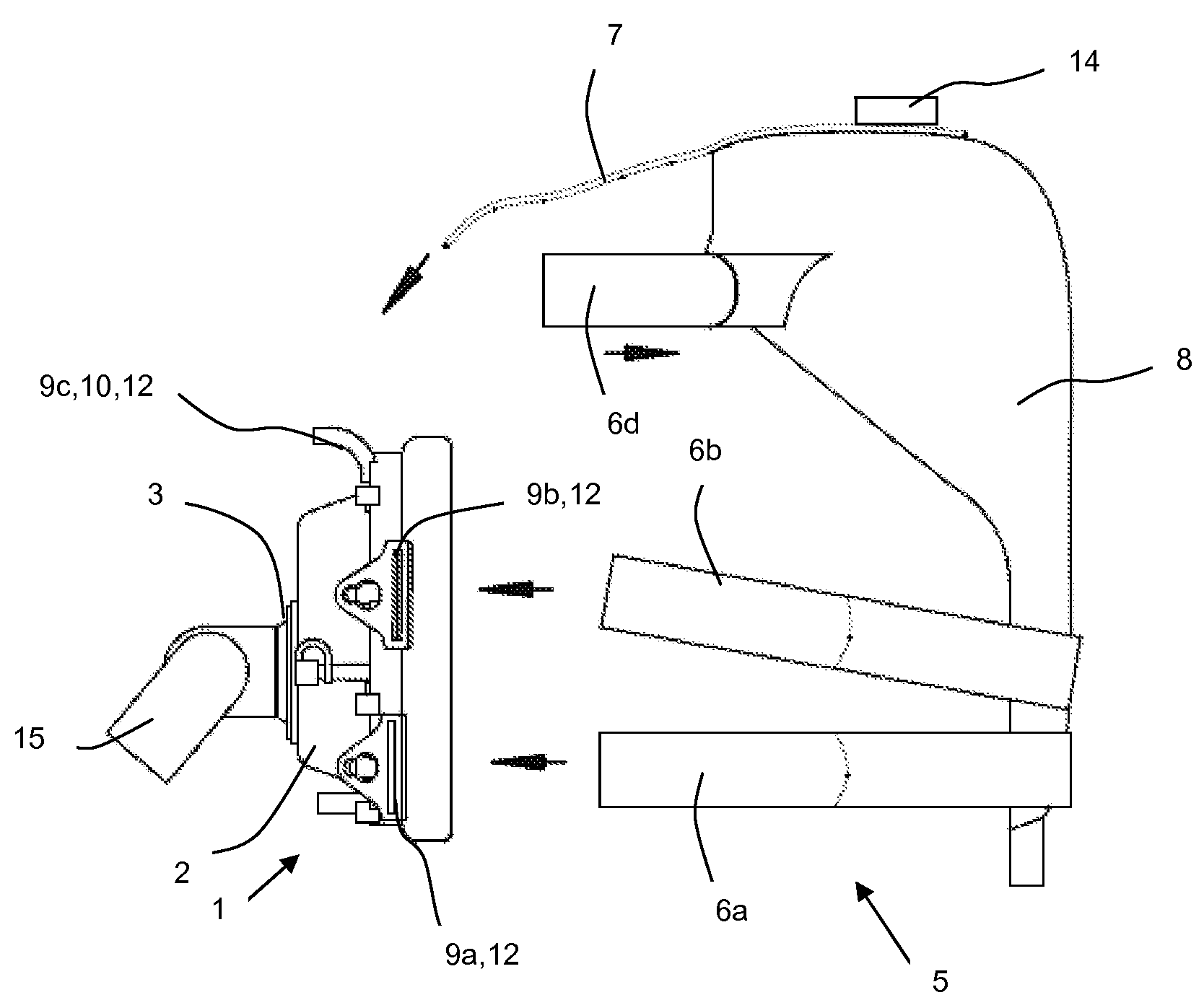
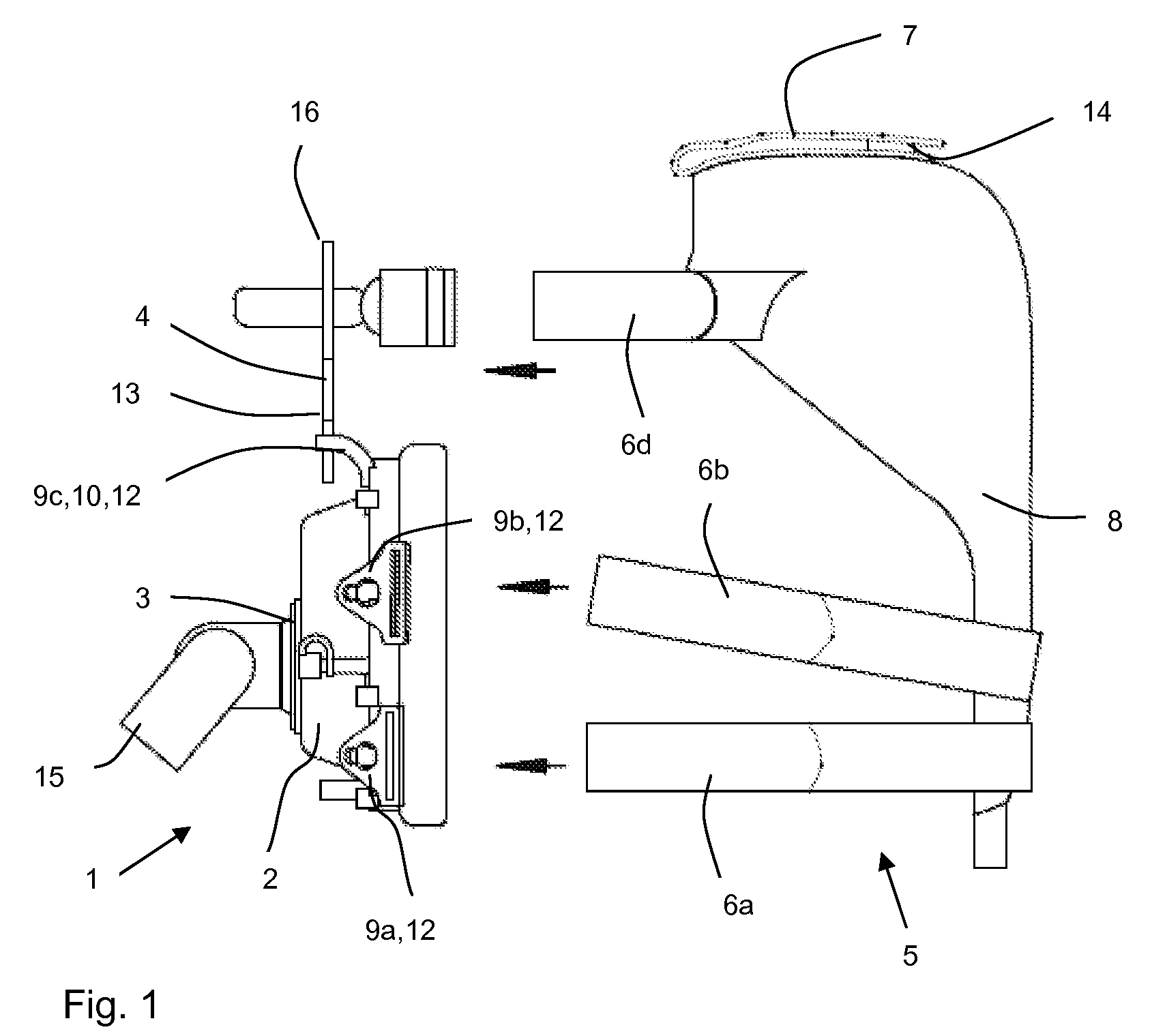
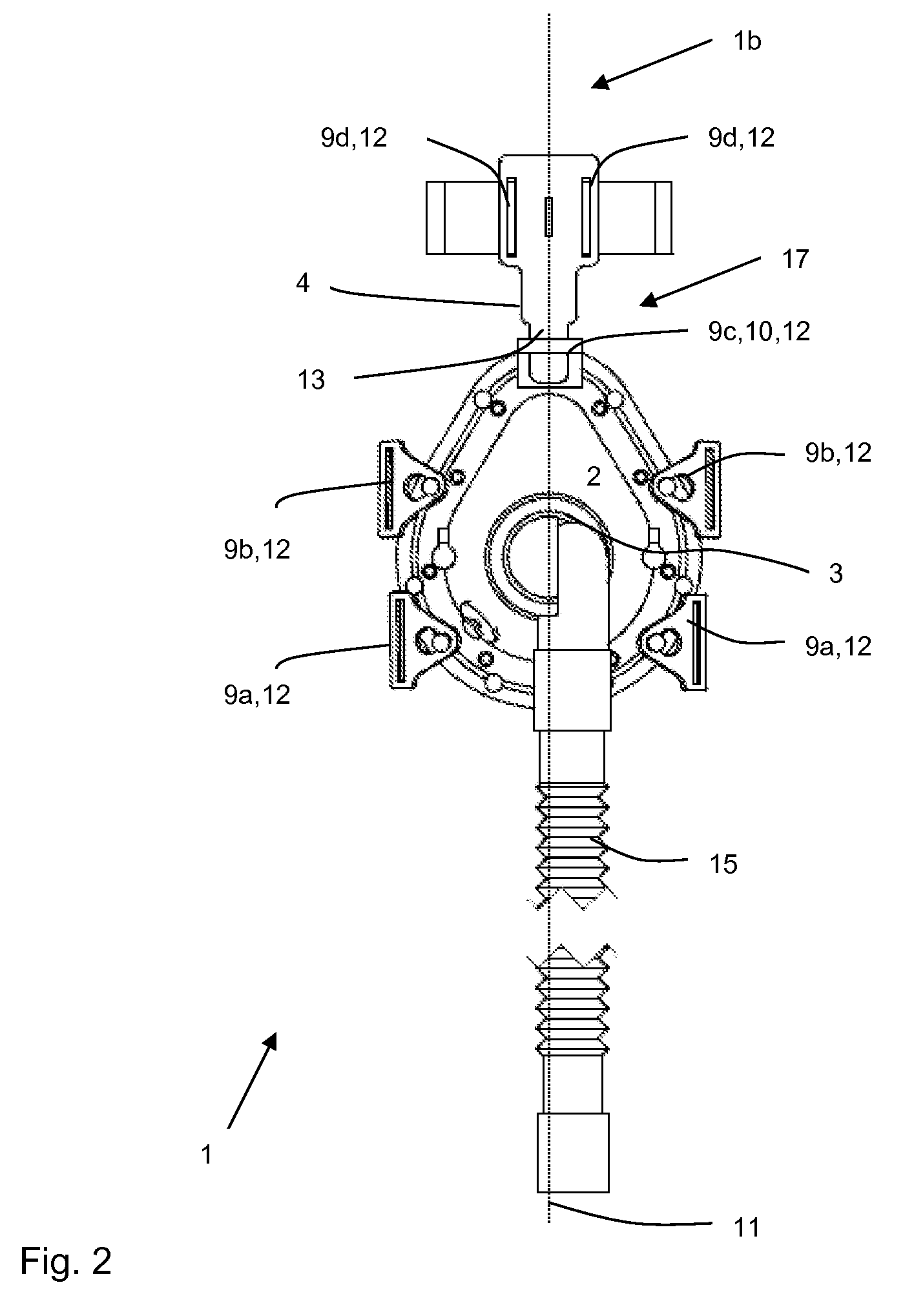
A respiration system (1) is provided with a breathing mask (2), a connection device (3) embodied on the breathing mask (2) for connecting the breathing mask (2) to a flexible air tube (15), a forehead support (4), and a band system (5) for attaching the breathing mask (2) to a head of a patient. An attaching device (9a, 9b, 9c, 9d) is arranged on the breathing mask (2) and on the forehead support (4) for the band system (5). The respiration system (1) is able to be adapted to the greatest variety of anatomies and requirements of a patient's head. Further, the respiration system (1) is simple and reliable to use and has low manufacturing costs. The forehead support (4) can be detachably connected to the breathing mask (2), so that the respiration system (1) can be used for respirating patients both with and without a forehead support (4).
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Device, system and method for detecting a cardiac and/or respiratory disease of a subject
ActiveUS20180125444A1Improve accuracyStrong specificityAuscultation instrumentsRespiratory organ evaluationDiseaseMedicine
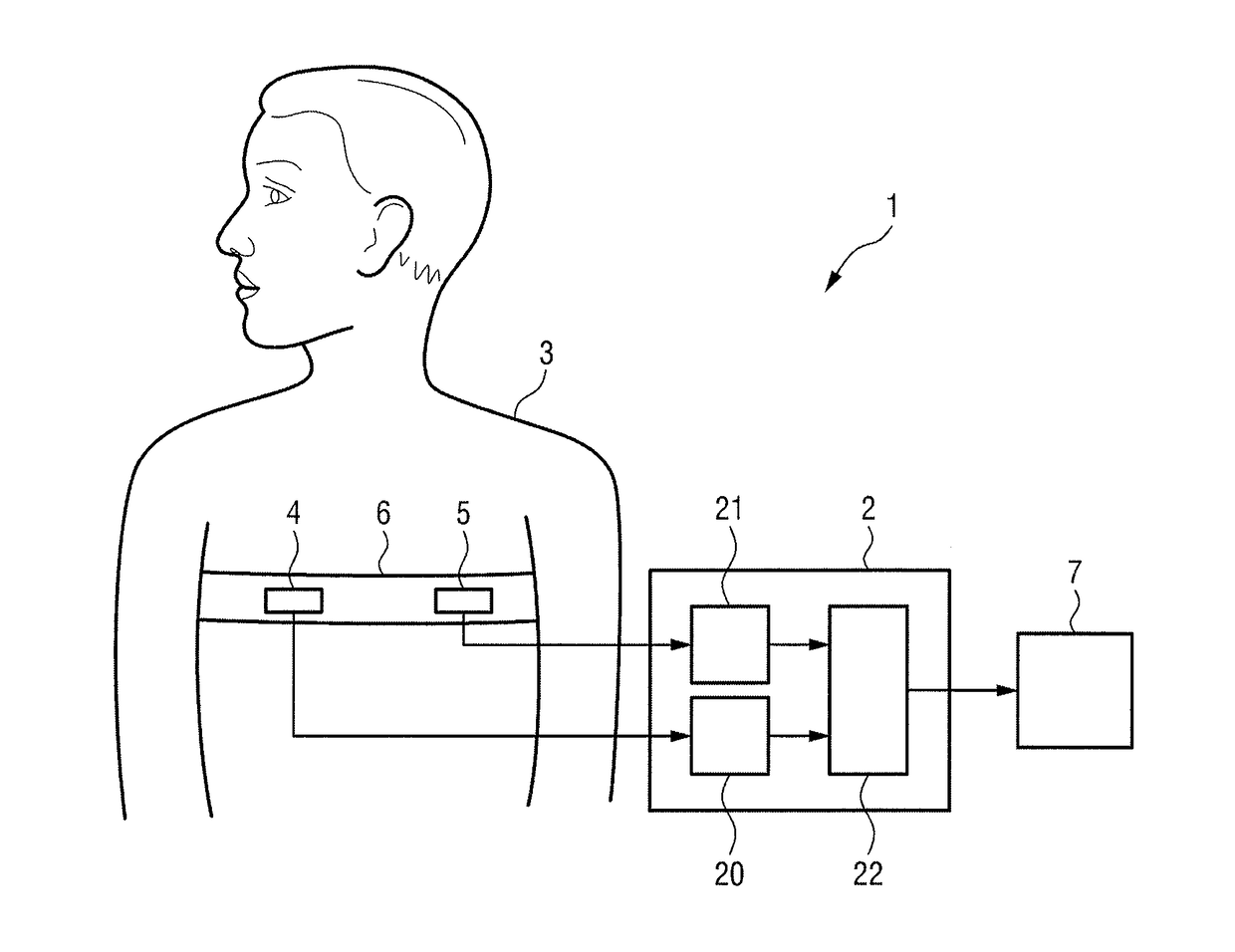
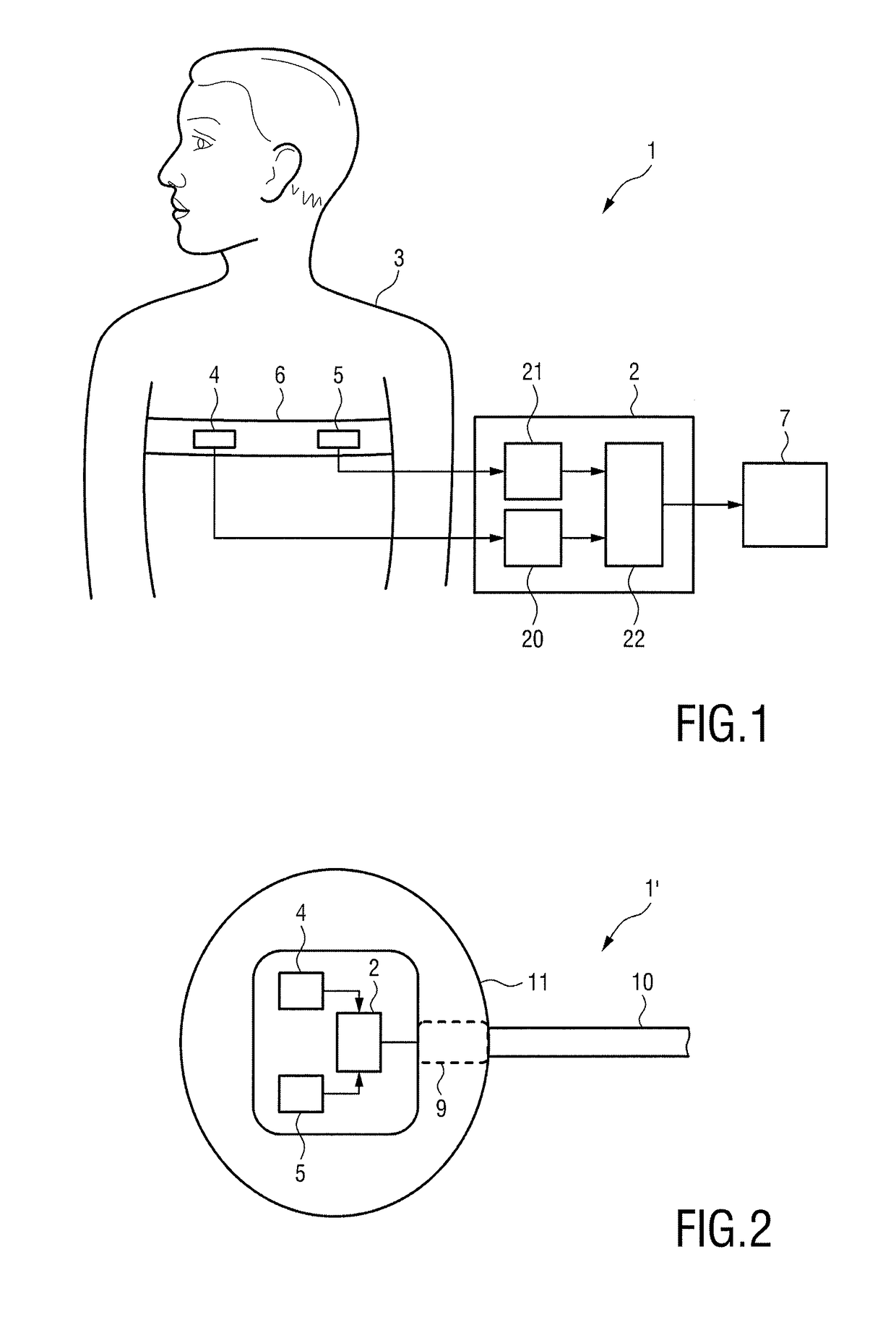
The present invention relates to device, system and method for detecting a cardiac and / or respiratory disease of a subject. The proposed device comprises a sound input (20) for obtaining a sound signal representing sounds generated by the subject's body; a motion input (21) for obtaining a motion signal representing motions generated by the subject's body; and a processor (22) for processing the obtained sound signal and motion signal. This processing includes identifying inhalation and / or exhalation periods of the subject based on the motion signal, detecting abnormal lung sounds during inhalation and / or exhalation periods based on the sound signal, determining abnormal lung sound characteristics of the detected abnormal lung sounds, determining breathing characteristics of the subject's breathing based on the sound signal, determining the phase of the abnormal lung sounds in the inhalation-exhalation cycle, and detecting a cardiac and / or respiratory disease of the subject based on the determined abnormal lung sound characteristics, the determined breathing characteristics and the determined phase of the abnormal lung sounds in the inhalation-exhalation cycle.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com