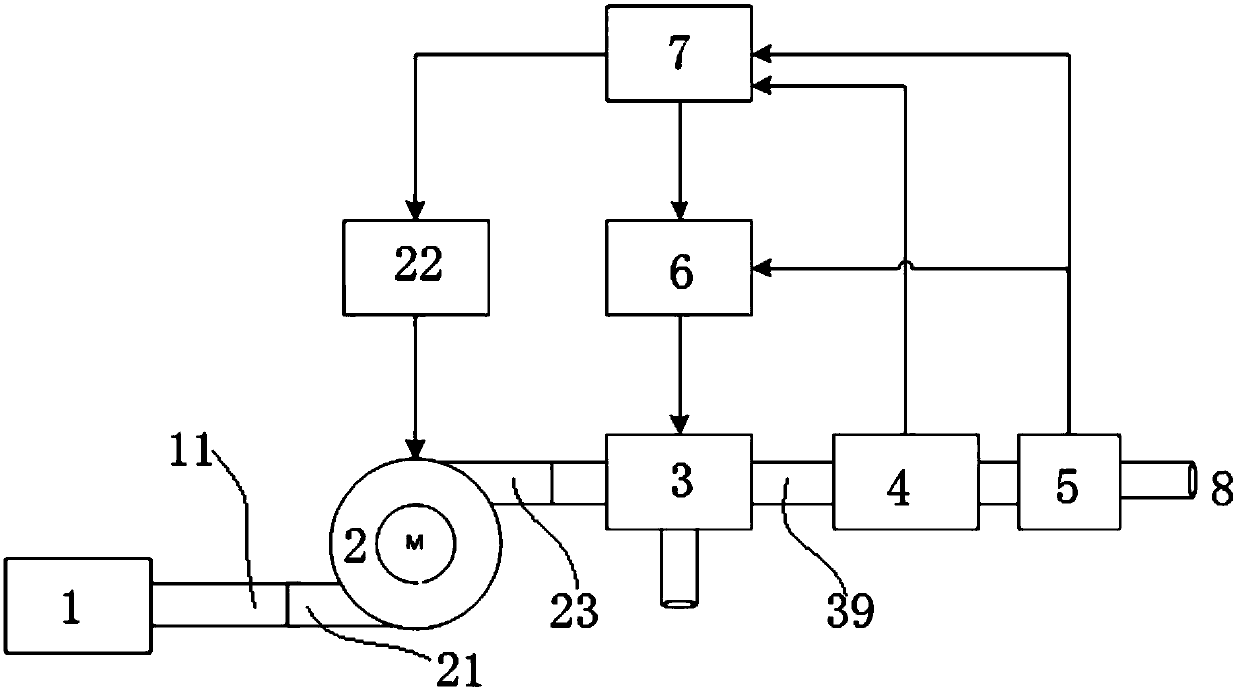
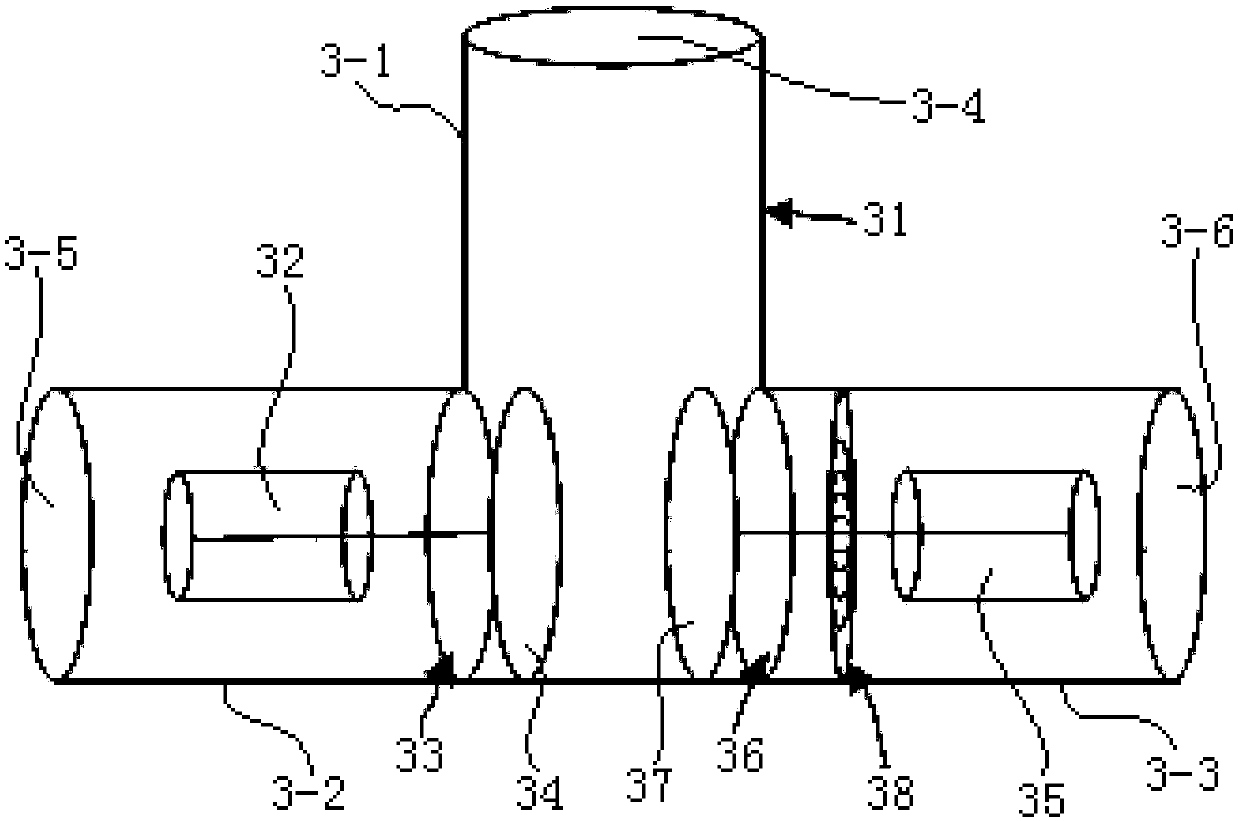
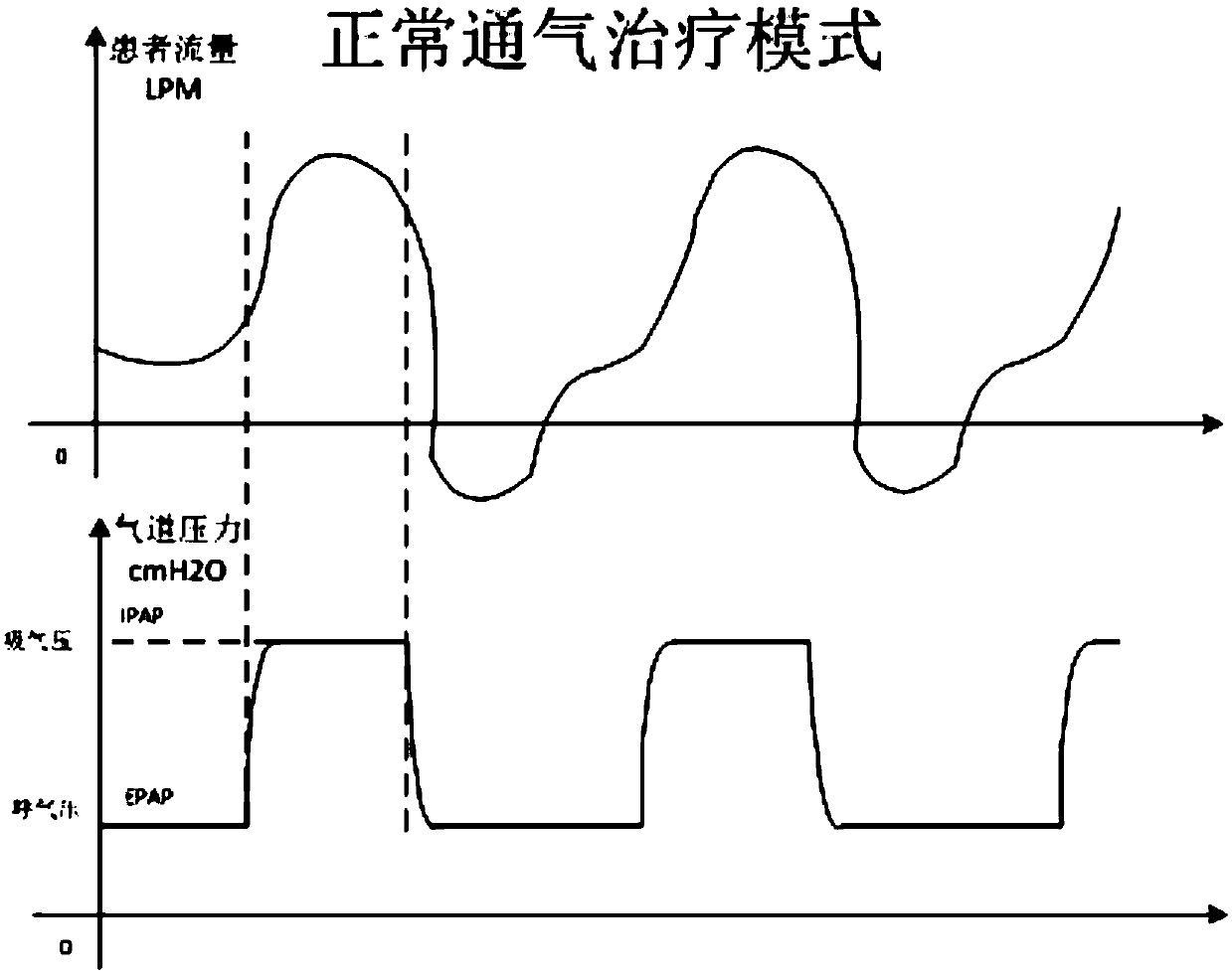
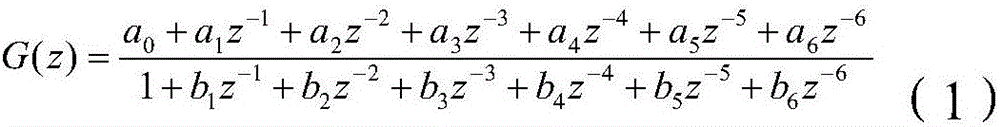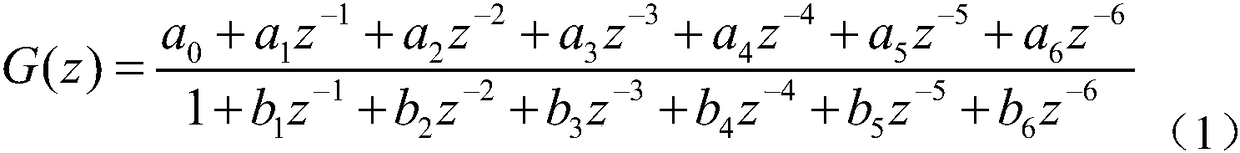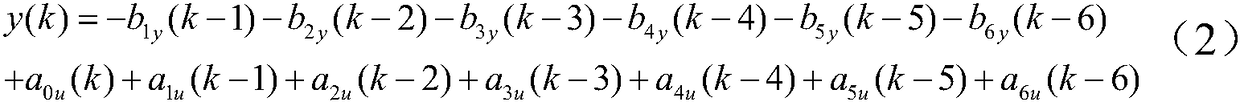Patents
Literature
114 results about "Respiratory muscle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
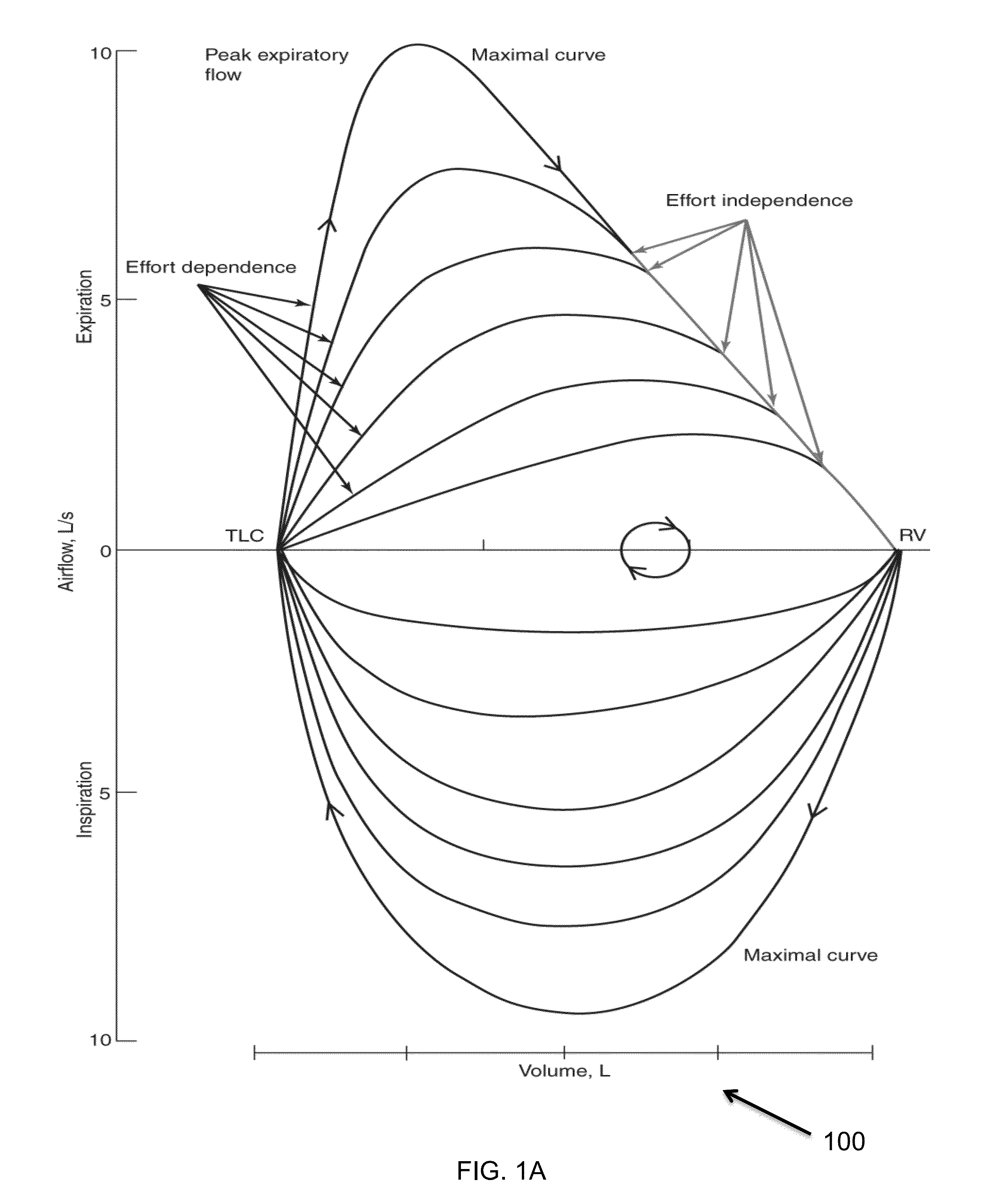
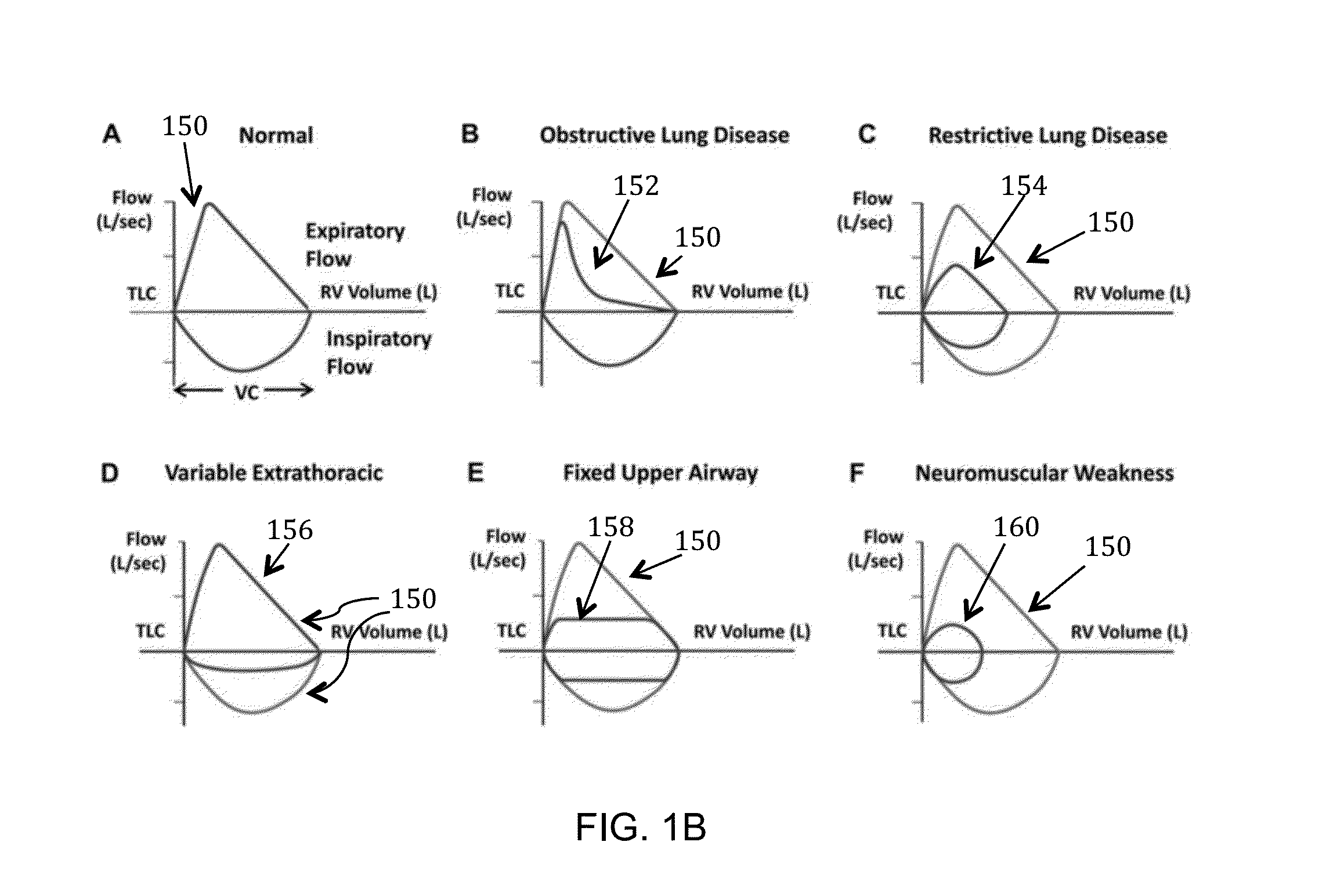
Respiratory muscles. the muscles that produce volume changes of the thorax during breathing. The inspiratory muscles include the hemidiaphragms, external intercostals, scaleni, sternomastoids, trapezius, pectoralis major, pectoralis minor, subclavius, latissimus dorsi, serratus anterior, and muscles that extend the back.
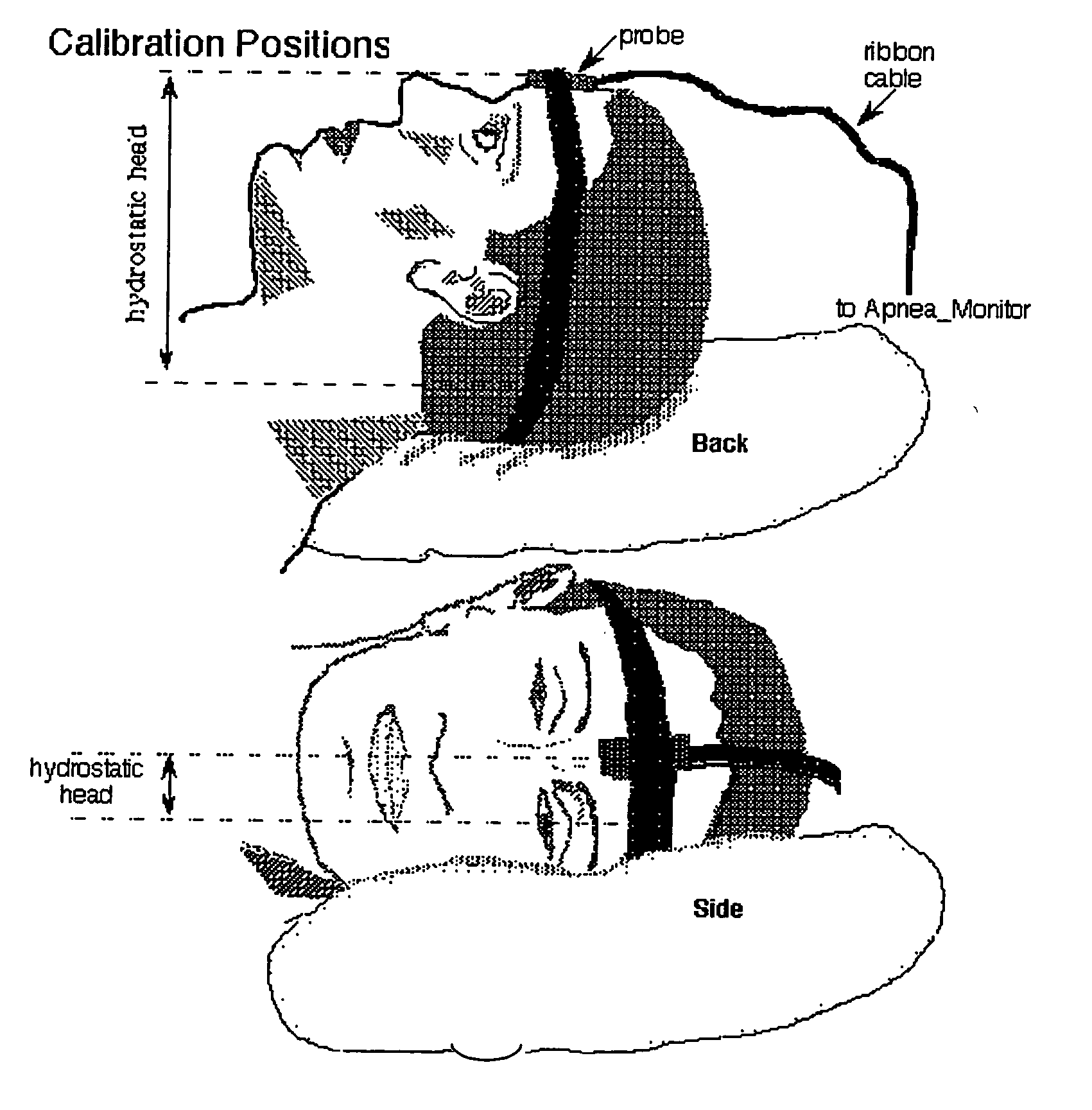
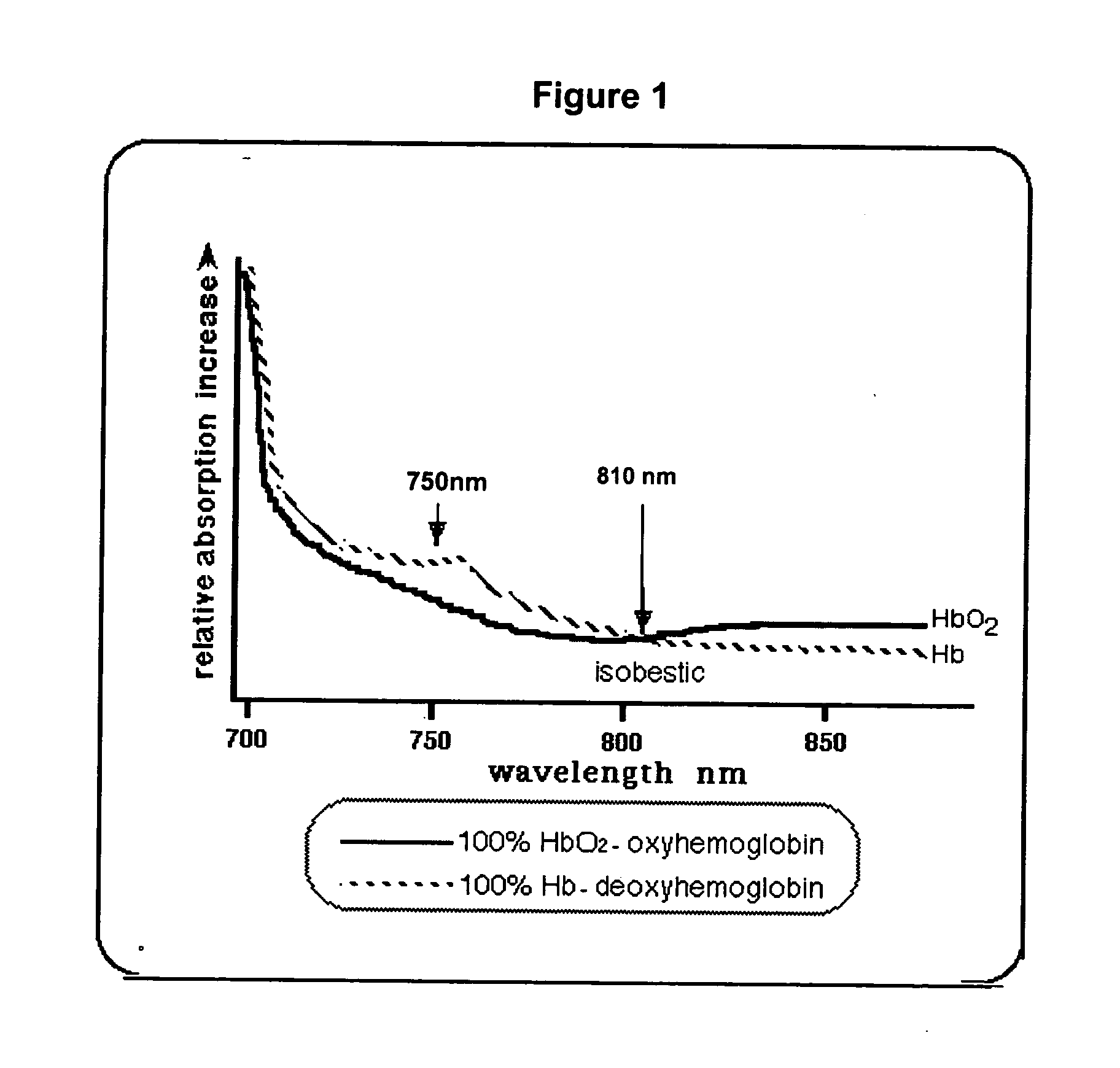
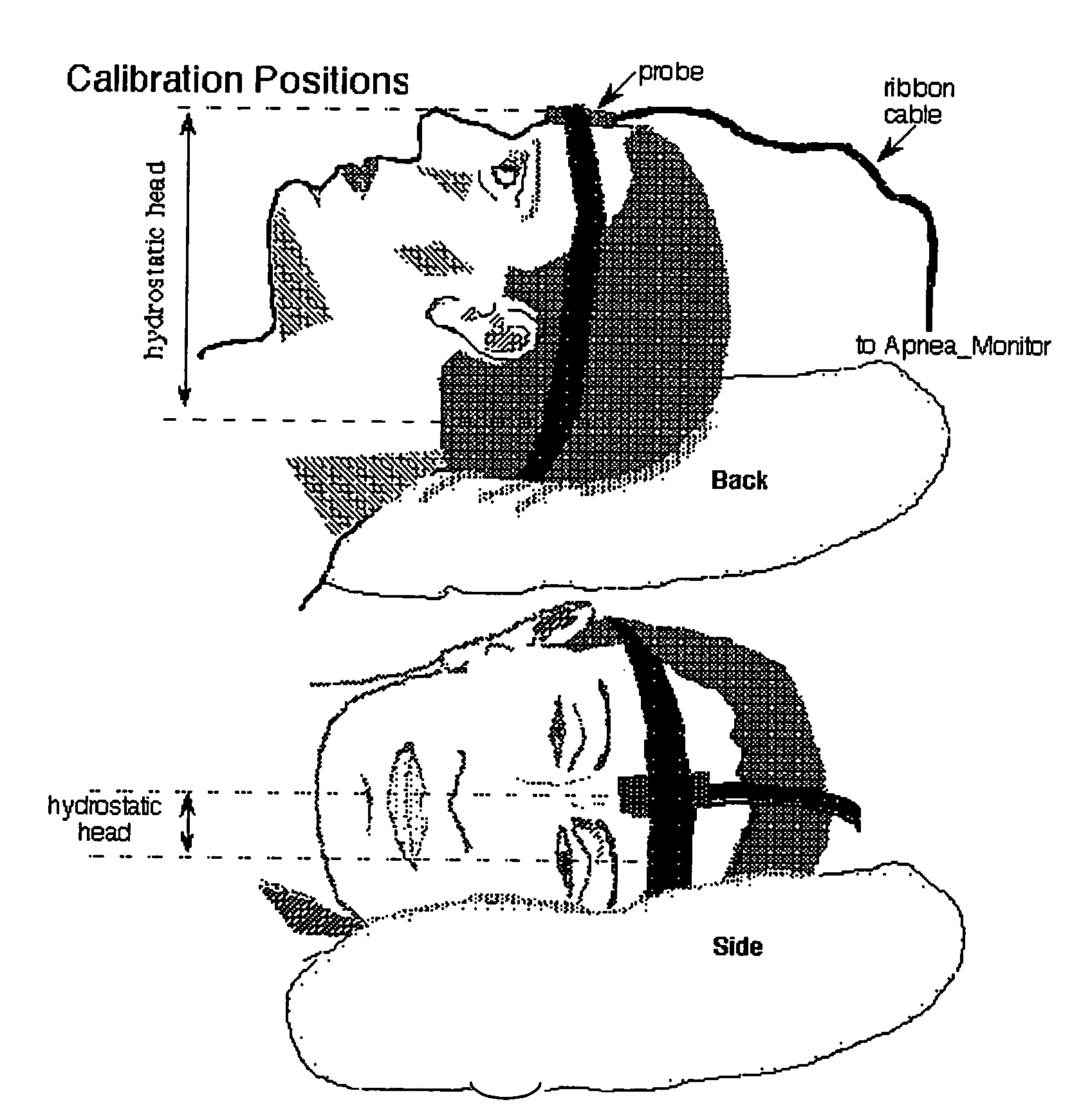
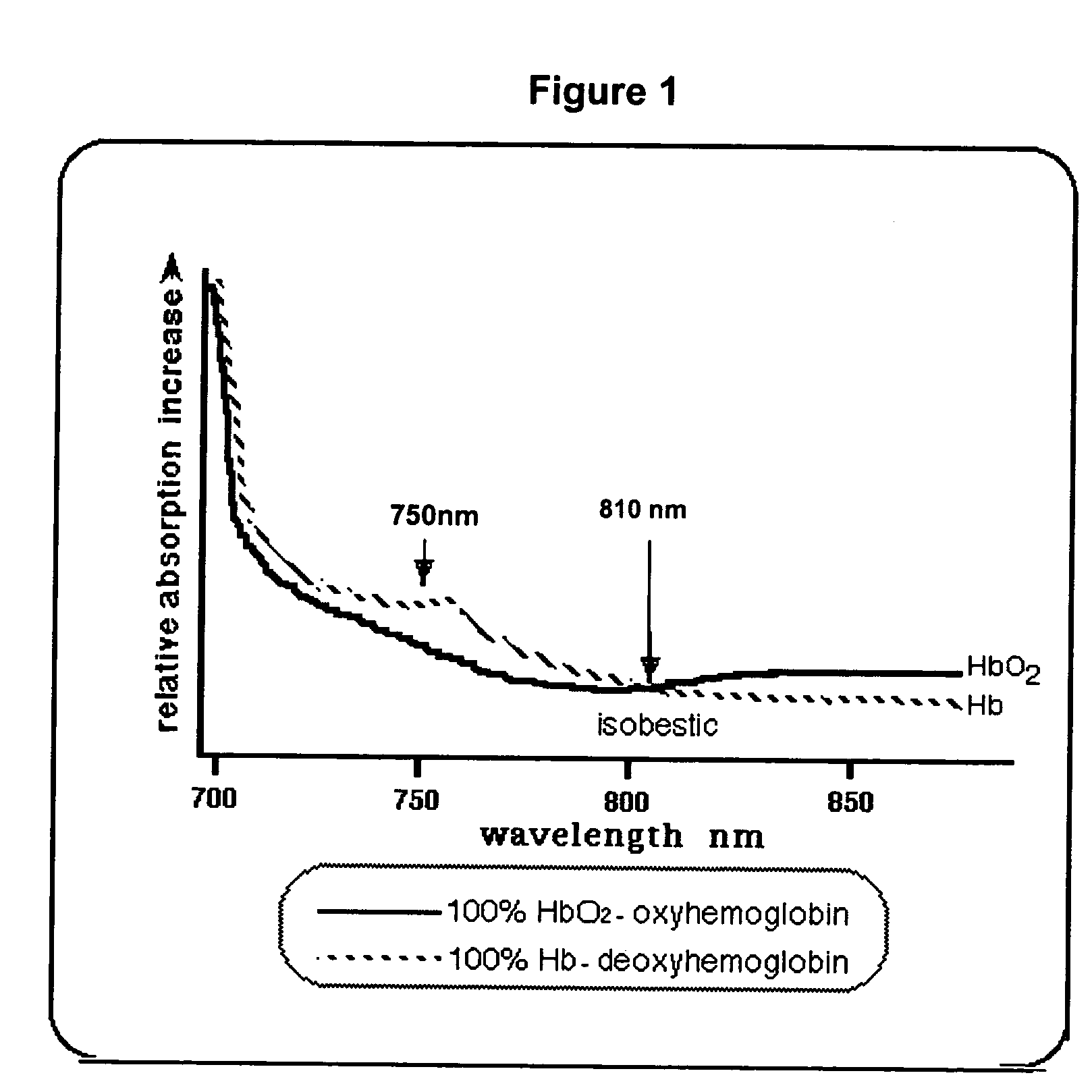
Methods and apparatus for patient monitoring
InactiveUS20050222502A1Reduce the impactReduce impactRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsRespiratory muscleHypopnea
A respiratory monitoring apparatus that detects changes in physiological parameters relevant to respiration, including blood oxygen and blood volume, using near infrared spectroscopy. Methods for diagnosing respiratory-related events including hypoxia index, hypopnea, arousal, tissue oxygen debt, and respiratory muscle events or distinguishing central from obstructive sleep apnea are also disclosed.
Owner:PORT A NIRS PTY LTD
Method and Device Using Myoelectrical Activity for Optimizing a Patient's Ventilatory Assist
ActiveUS20080121231A1Avoid fatigueRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory musclePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
The present invention relates to a method and device for determining a level of ventilatory assist to a ventilator-dependent patient, in which a critical threshold of a respiration-related feature is calculated. Fatigue of a respiratory muscle of the ventilator-dependent patient develops when the critical threshold is reached by the respiration-related feature. The level of ventilatory assist to the ventilator-dependent patient is controlled in relation to the critical threshold of the respiration-related feature so as to prevent fatigue of the patient's respiratory muscle.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
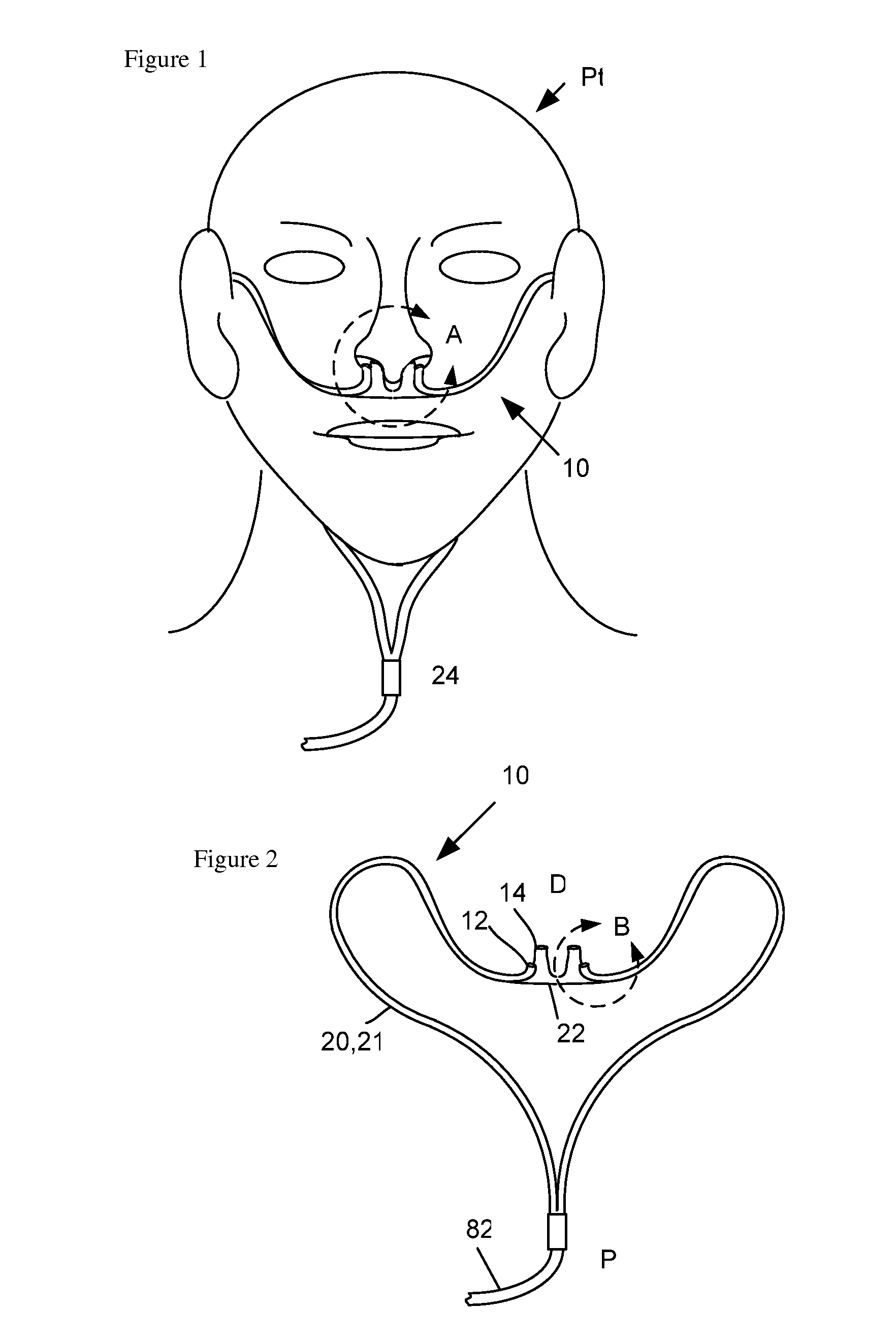
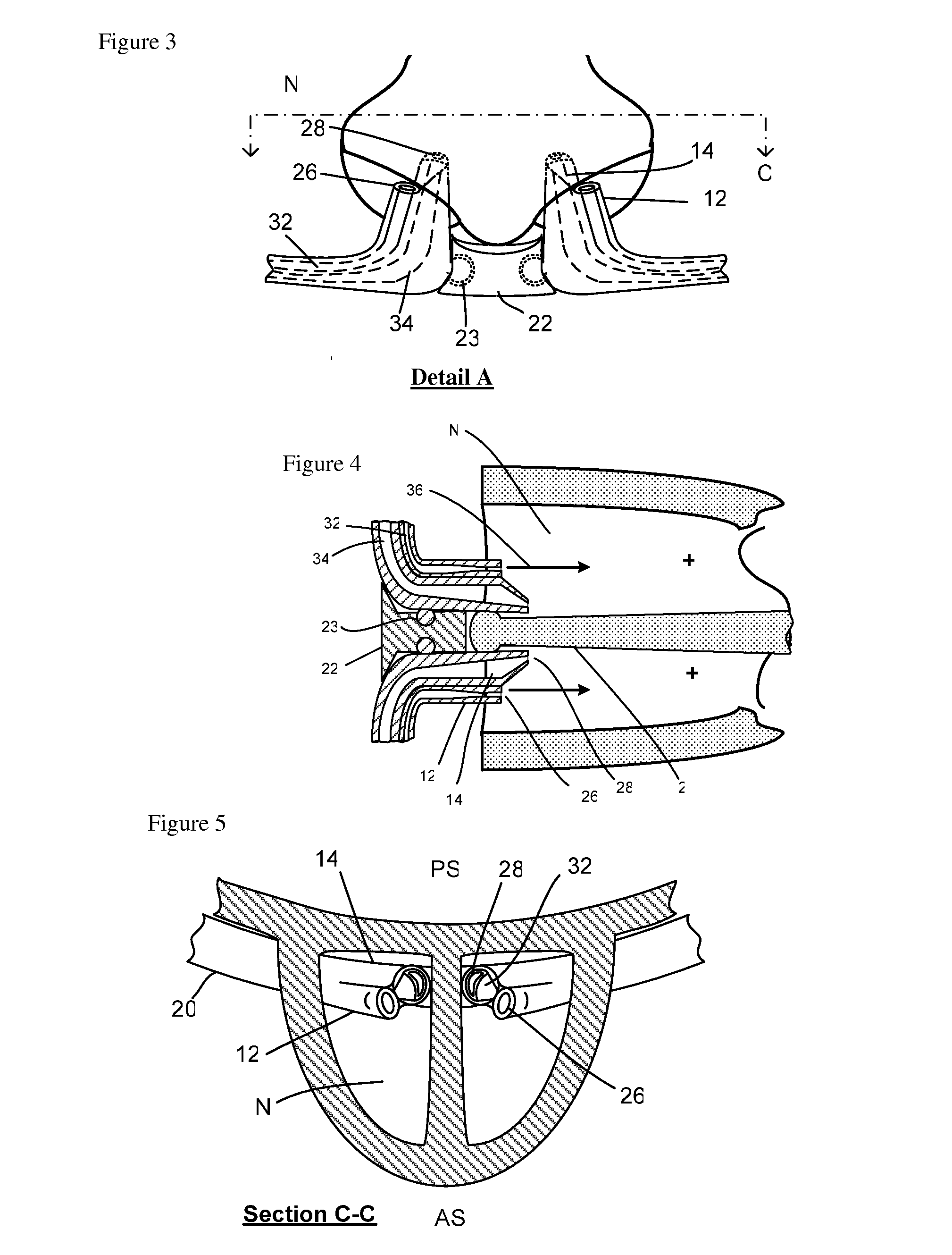
Methods and devices for intramuscular stimulation of upper airway and swallowing muscle groups
InactiveUS20070123950A1Avoid aspirationReduce disadvantagesElectrotherapyChiropractic devicesRespiratory muscleUpper esophageal sphincter
Devices and methods were discovered that successfully provided patient autonomous control of both hyolaryngeal elevation, anterior hyoid motion and opening of the upper esophageal sphincter for swallowing by intramuscular stimulation of two muscles. The technology allows patient self stimulation of swallowing and can return oral feeding to dysphagia patients. Indwelling electrode stimulation of only two muscles generated as much as 80 % of normal synergistic movement leading to swallowing. The devices and methods also are useful for control of other upper respiratory muscle groups involved in speech and voice. Calibration techniques may be used in combination for greater freedom in setting and using electrodes over extended implantation time periods. These methods and devices can control complex movements of body solids such as bone and cartilage and tissues by electro stimulation of a minimum set of muscles simultaneously.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method and device using myoelectrical activity for optimizing a patient's ventilatory assist
ActiveUS8256419B2Avoid fatigueRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory muscleIntensive care medicine
The present invention relates to a method and device for determining a level of ventilatory assist to a ventilator-dependent patient, in which a critical threshold of a respiration-related feature is calculated. Fatigue of a respiratory muscle of the ventilator-dependent patient develops when the critical threshold is reached by the respiration-related feature. The level of ventilatory assist to the ventilator-dependent patient is controlled in relation to the critical threshold of the respiration-related feature so as to prevent fatigue of the patient's respiratory muscle.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
Non-contact monitoring of spatio-temporal respiratory mechanics via depth sensing
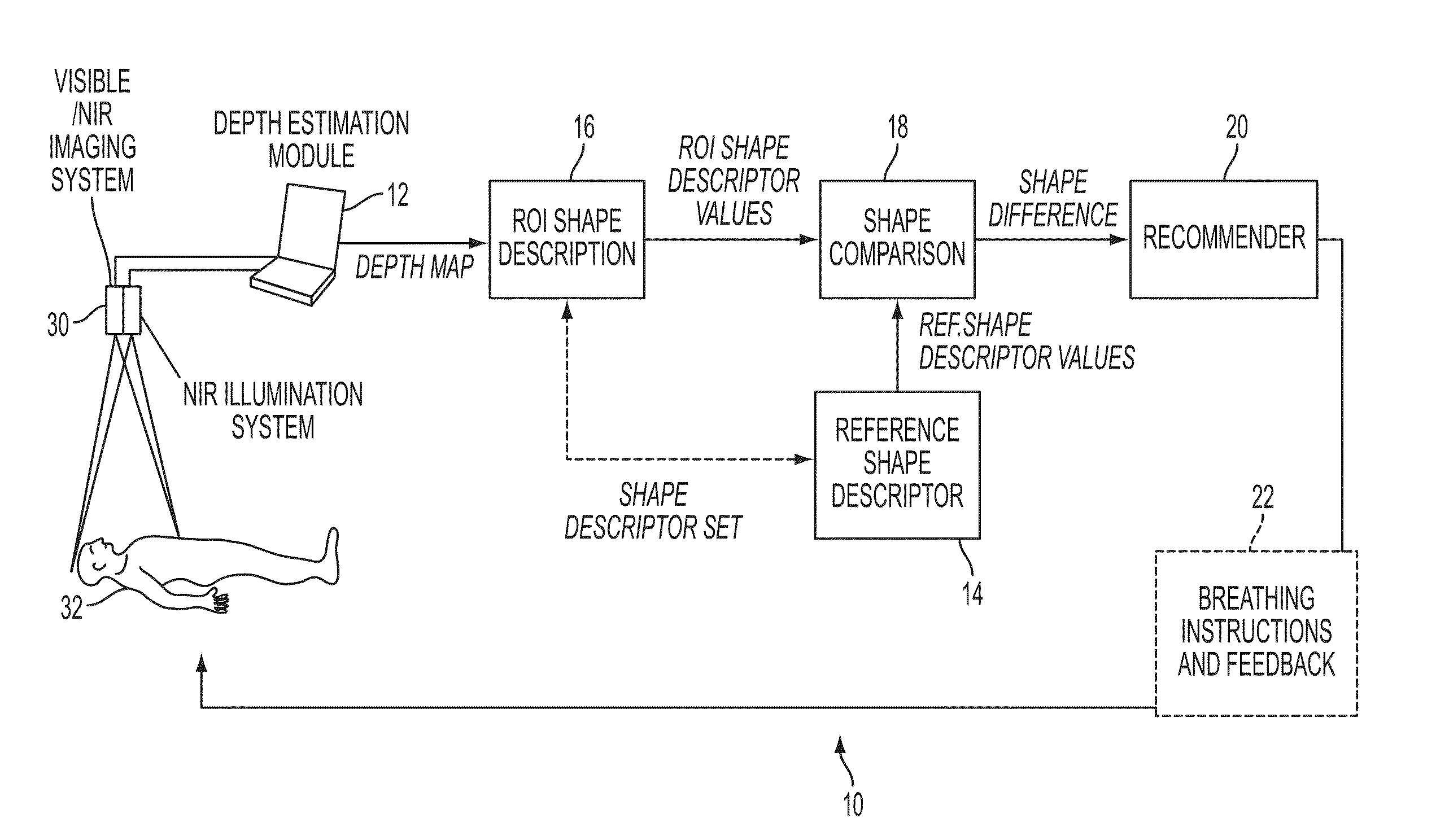
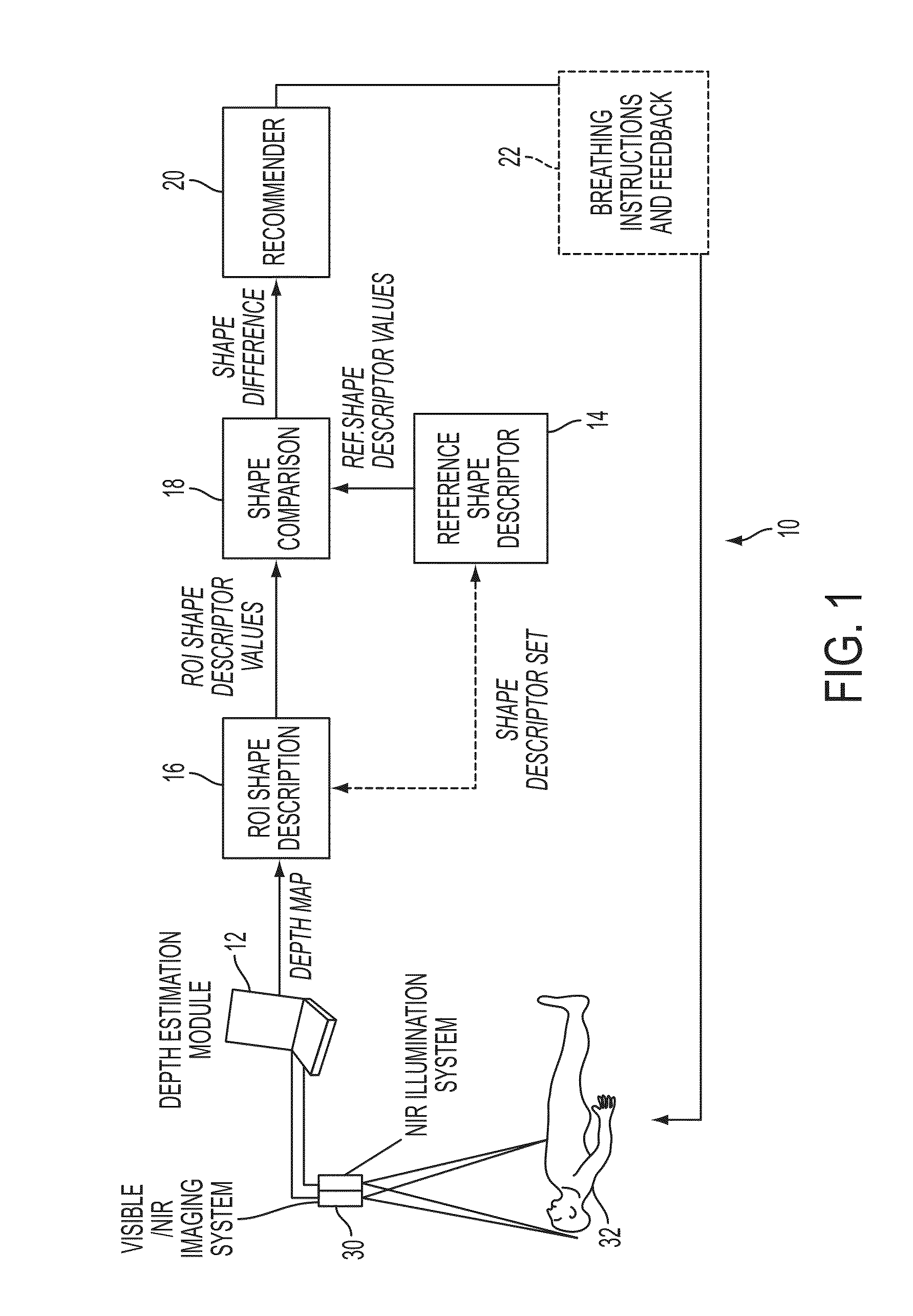
Systems and methods are proposed for non-contact monitoring of spatio-temporal mechanics comprising motion patterns of respiratory muscles, lungs and diaphragm. The depth capable sensors system is comprised of modules, including a depth estimation module, a reference shape generation module, a region of interest shape estimation module, and a shape comparison module. A recommender module is optionally included. The acquisition of spatio-temporal respiratory mechanic data comprising a time varying sequence of spatially dependent representations of the respiratory mechanics of the subject are processed for identifying differences between the subject's actual respiratory mechanics and desired mechanics that can improve the health of the subject, or identify particular maladies.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Nasal Ventilation Cannula System and Methods
A nasal cannula ventilation system is described for treating lung disease or for exercise conditioning, incorporating a Venturi system. The ventilation cannula comprises unique positioning features to positively locate a gas delivery nozzle in an optimal location to optimize Venturi performance, patient comfort and fitment to the patient. The cannula is low profile, making it as realistic to wear and use as a standard oxygen cannula, and is simple rending the cost reasonable. The ventilation cannula uses a simple low cost ventilator as a gas delivery control system which is compatible with existing gas sources. The system is used (1) during stationary use to unrest the respiratory muscles to increase tolerance to activity after a treatment session, or (2) to enable activity within a distance from a stationary gas source, (3) during ambulatory use using a portable gas source to enable mobility, and (4) for enhanced fitness conditioning.
Owner:WONDKA ANTHONY DAVID
Methods and devices for intramuscular stimulation of upper airway and swallowing muscle groups
Devices and methods were discovered that successfully provided patient autonomous control of both hyolaryngeal elevation, anterior hyoid motion and opening of the upper esophageal sphincter for swallowing by intramuscular stimulation of two muscles. The technology allows patient self stimulation of swallowing and can return oral feeding to dysphagia patients. Indwelling electrode stimulation of only two muscles generated as much as 80 % of normal synergistic movement leading to swallowing. The devices and methods also are useful for control of other upper respiratory muscle groups involved in speech and voice. Calibration techniques may be used in combination for greater freedom in setting and using electrodes over extended implantation time periods. These methods and devices can control complex movements of body solids such as bone and cartilage and tissues by electro stimulation of a minimum set of muscles simultaneously.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
System and method for neuromorphic controlled adaptive pacing of respiratory muscles and nerves
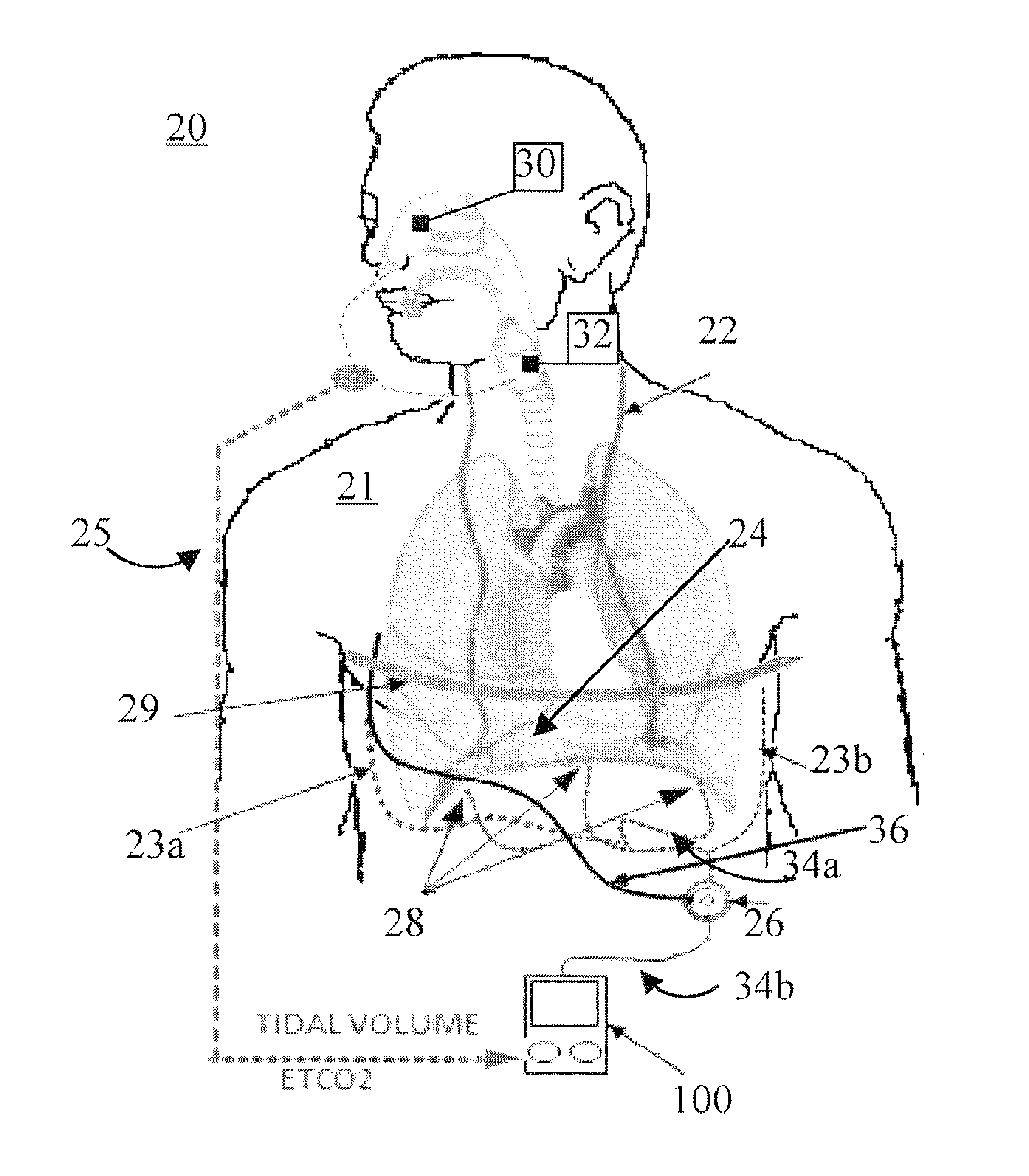
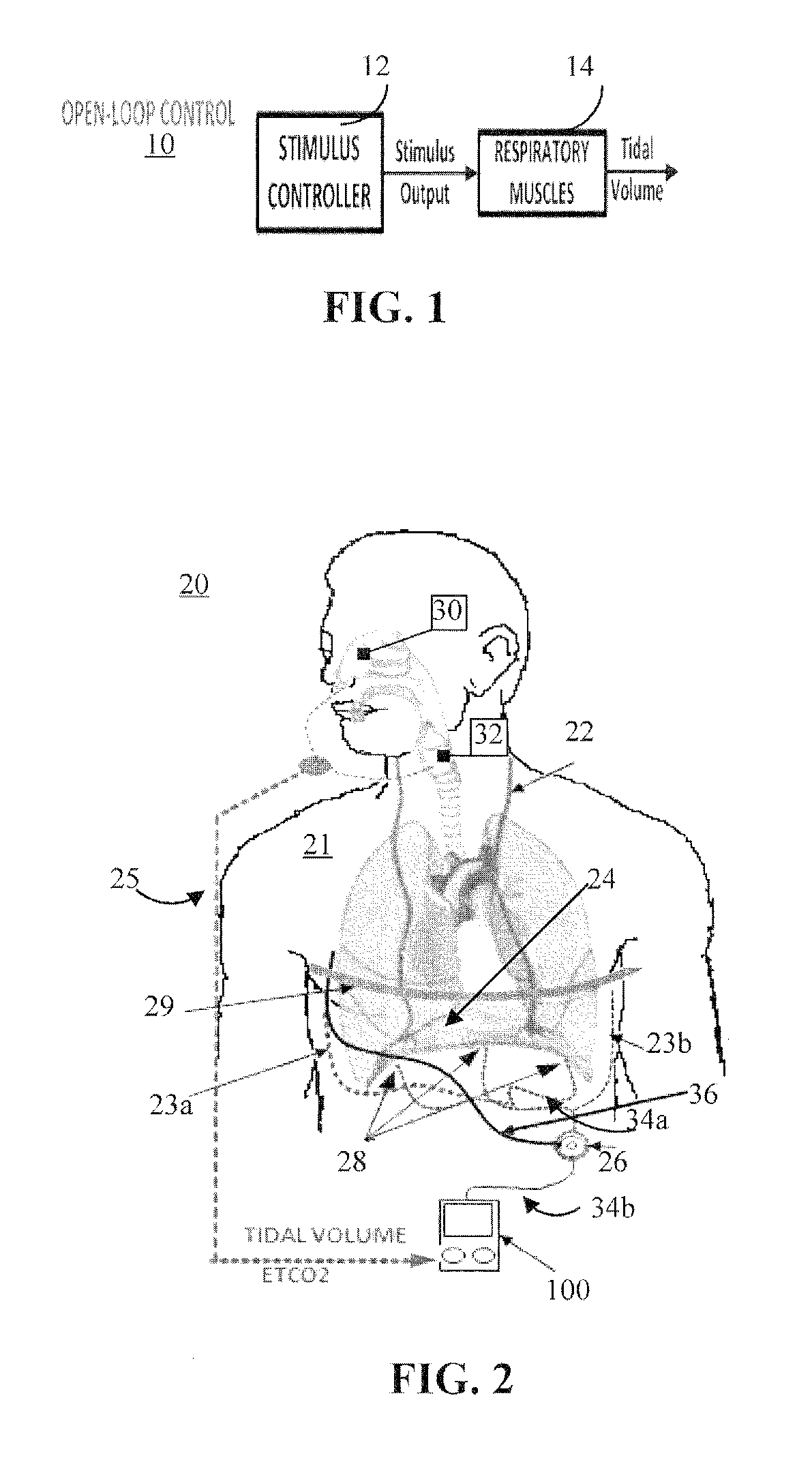
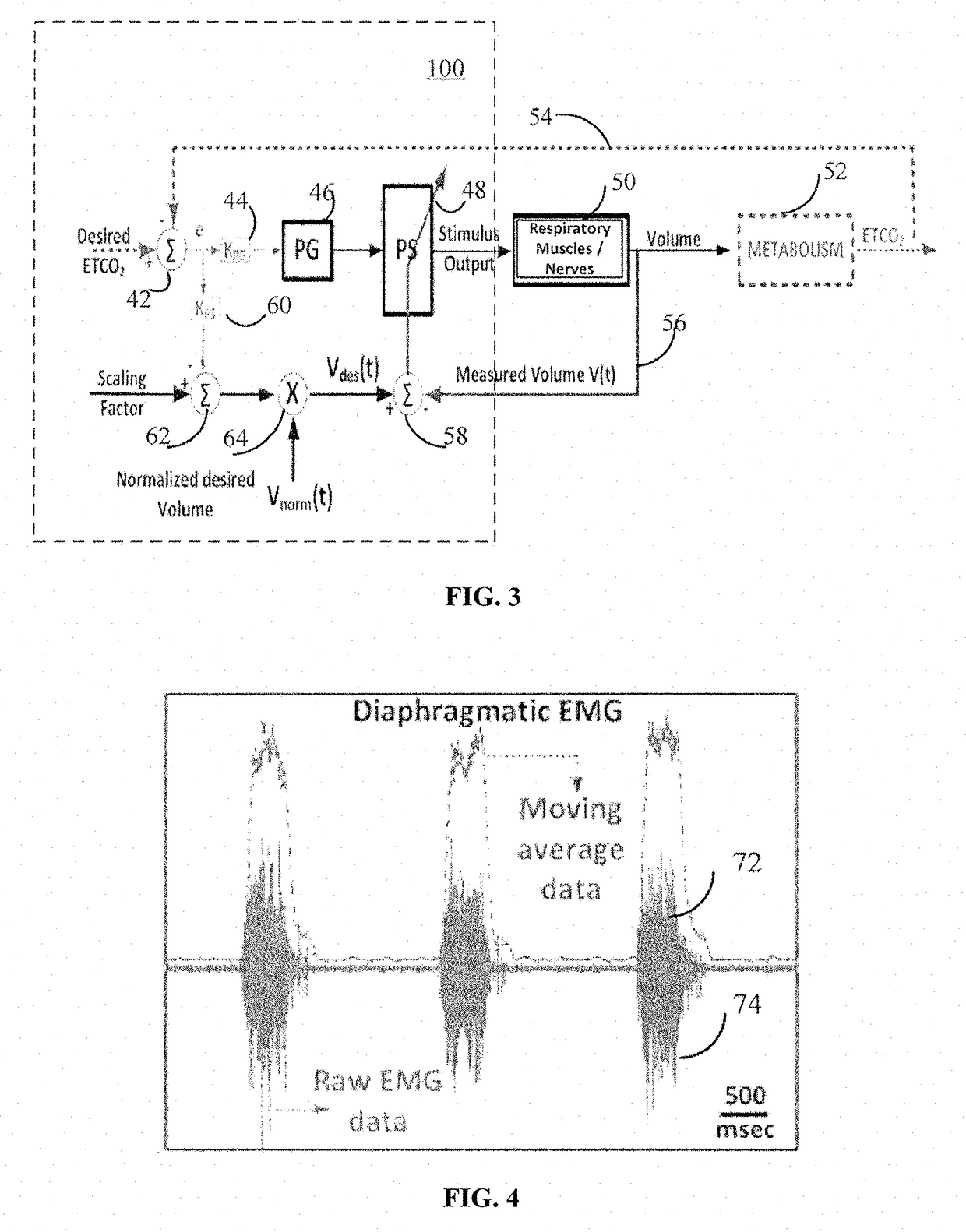
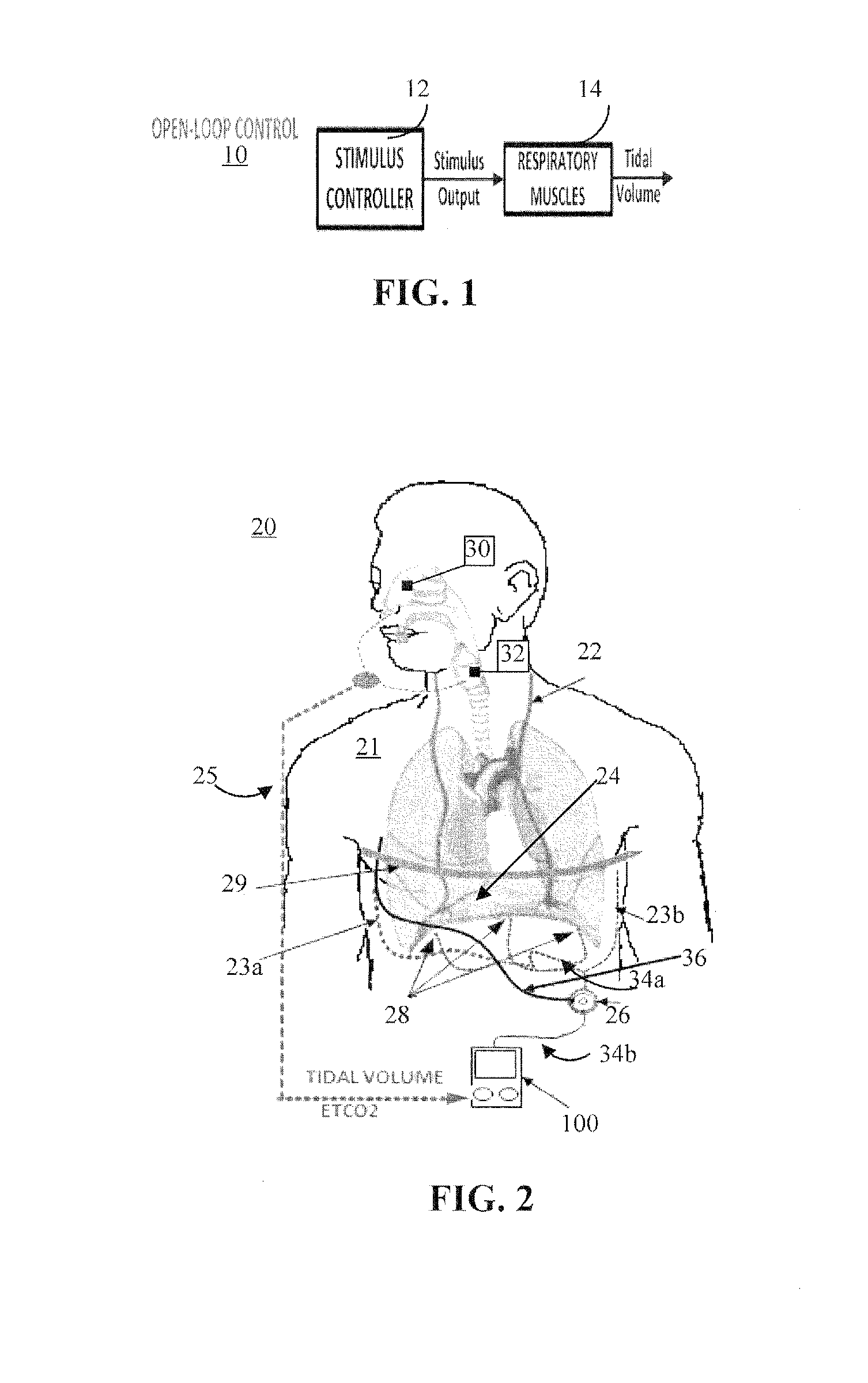
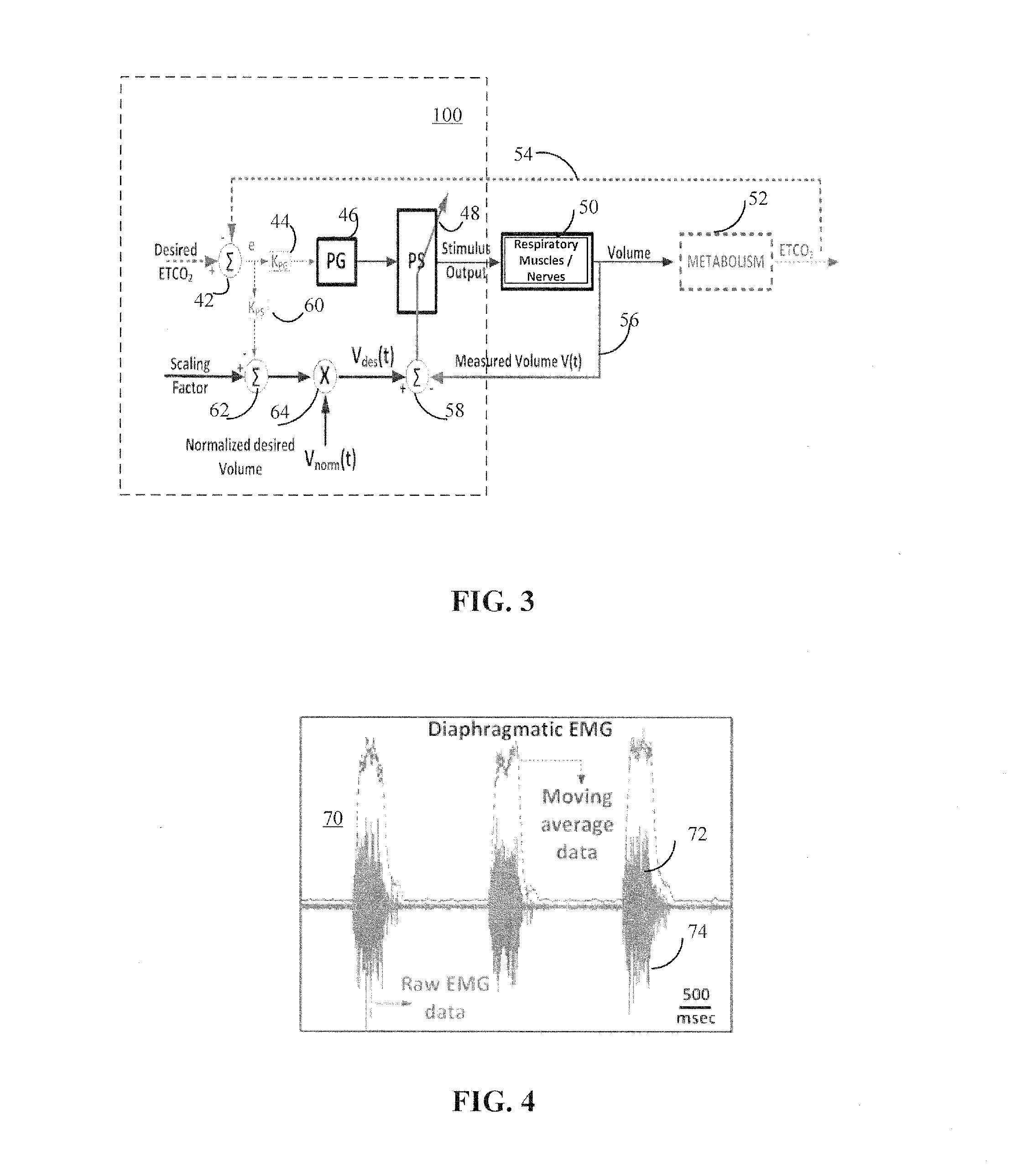
ActiveUS20180117334A1Reduce developmentExtending period of time offElectrotherapyArtificial respirationClosed loopElectrical stimulations
Adaptive systems and methods for automatically determining and continuously updating stimulation parameters for adjusting ventilation to accommodate a patient's specific physiology, metabolic needs, and muscle state are disclosed herein. Having a closed loop implementation, the system may comprise a controller including a neuromorphic controlled adaptive feed-forward Pattern Generator / Pattern Shaper (PG / PS) assembly, which controls respiratory muscle movement using electrical stimulation. This PG / PS assembly comprises a biomimetic design where the pattern generator includes a neural network mimicking the simplified connectivity pattern of respiratory related neurons in the brain stem to produce a rhythmic breathing pattern frequency and the pattern shaper includes a neural network mimicking the simplified connectivity pattern of neurons to produce a stimulus control signal. This biomimetic design for the controller automatically customizes and continually updates stimulation parameters to achieve a desired breathing pattern and, thereby, slow the development of muscle fatigue.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
System and method for neuromorphic controlled adaptive pacing of respiratory muscles and nerves
ActiveUS9872989B2Reduce developmentExtending period of time offElectrotherapyArtificial respirationClosed loopElectrical stimulations
Adaptive systems and methods for automatically determining and continuously updating stimulation parameters for adjusting ventilation to accommodate a patient's specific physiology, metabolic needs, and muscle state are disclosed herein. Having a closed loop implementation, the system may comprise a controller including a neuromorphic controlled adaptive feed-forward Pattern Generator / Pattern Shaper (PG / PS) assembly, which controls respiratory muscle movement using electrical stimulation. This PG / PS assembly comprises a biomimetic design where the pattern generator includes a neural network mimicking the simplified connectivity pattern of respiratory related neurons in the brain stem to produce a rhythmic breathing pattern frequency and the pattern shaper includes a neural network mimicking the simplified connectivity pattern of neurons to produce a stimulus control signal. This biomimetic design for the controller automatically customizes and continually updates stimulation parameters to achieve a desired breathing pattern and, thereby, slow the development of muscle fatigue.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Pulmonary rehabilitation training system based on respiratory-muscle electrical signal feedback
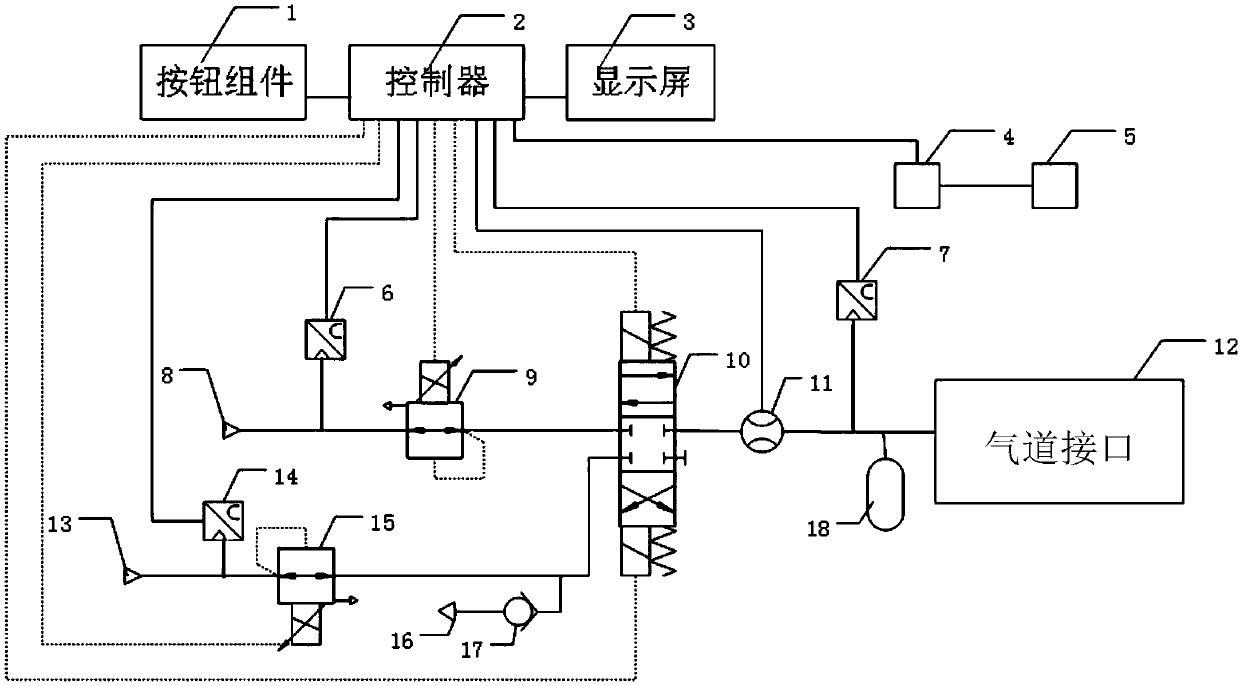
ActiveCN107802993AIntelligent pressure adjustmentIntelligently adjust flowRespiratorsMedical devicesRespiratory musclePositive pressure
The invention discloses a pulmonary rehabilitation training system based on respiratory-muscle electrical signal feedback. The pulmonary rehabilitation training system comprises a controller, a magnetic directional valve, a flow sensor and an electrode connected with the controller through an amplifying circuit, wherein the magnetic directional valve and the flow sensor are connected with the controller. One way of the magnetic directional valve is communicated to an airway interface through the flow sensor. The other two ways of the magnetic directional valve are communicated with a pressureproportion regulating valve A and a pressure proportion regulating valve B, and the magnetic directional valve is switched and selected in the two ways. The pressure proportion regulating valve A is connected with a medical positive pressure air source. The pressure proportion regulating valve B is connected with a medical negative pressure air source. The pulmonary rehabilitation training systemis mainly used for a patient difficult in mechanical ventilation weaning, senses the tolerance of the patient in the pulmonary rehabilitation training process, intelligently adjusts the pressure and flow of breathing airflow in the rehabilitation training process, improves interpersonal coordination degree, avoids man-machine counteraction and lung injuries and promotes recuperation of autonomousrespiration ability.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
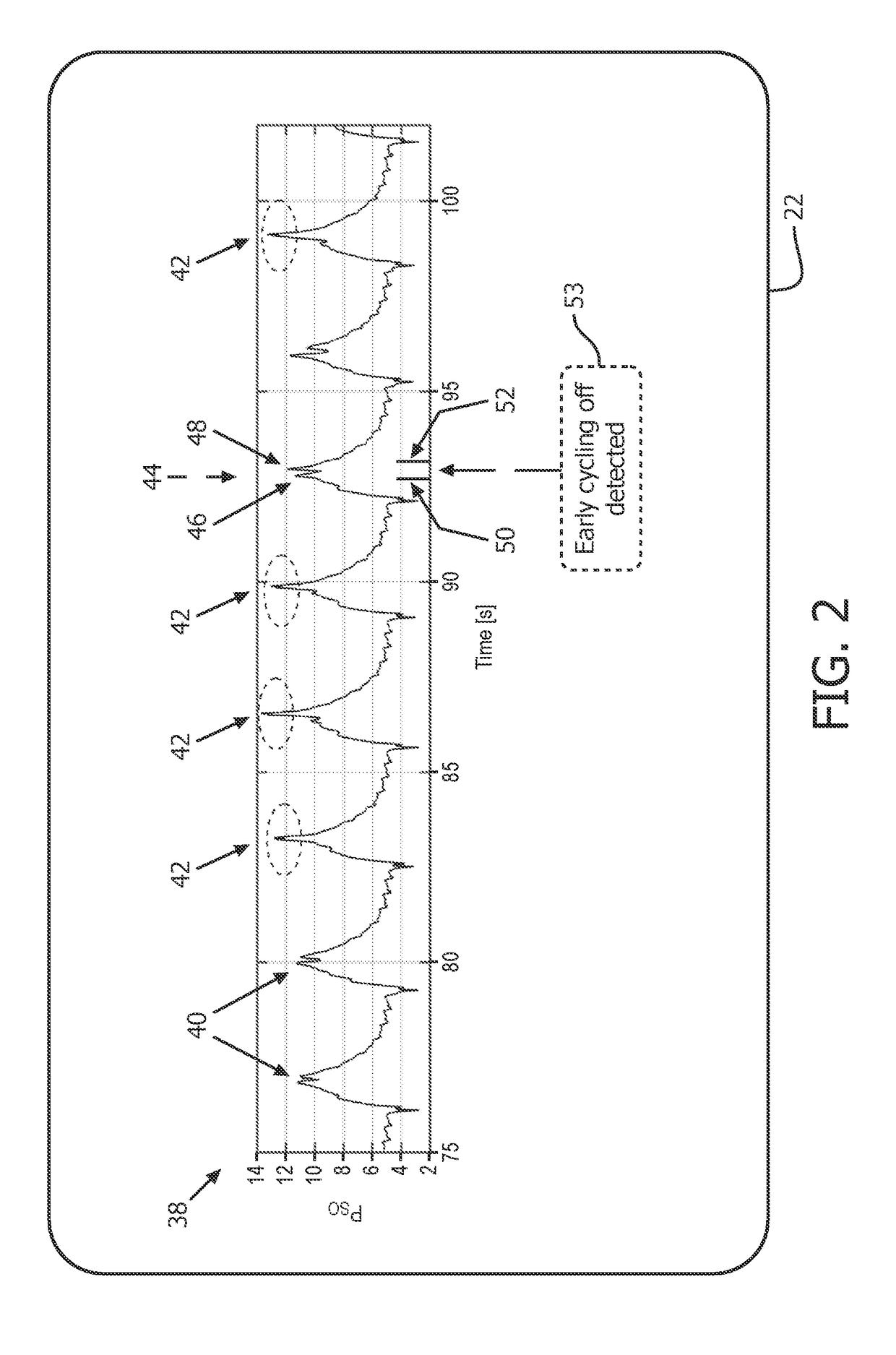
Methods and apparatus for patient monitoring
Owner:PORT A NIRS PTY LTD
System and method for neuromorphic controlled adaptive pacing of respiratory muscles and nerves
ActiveUS20160287877A1Reduce developmentExtending period of time offElectrotherapyArtificial respirationClosed loopElectrical stimulations
Adaptive systems and methods for automatically determining and continuously updating stimulation parameters for adjusting ventilation to accommodate a patient's specific physiology, metabolic needs, and muscle state are disclosed herein. Having a closed loop implementation, the system may comprise a controller including a neuromorphic controlled adaptive feed-forward Pattern Generator / Pattern Shaper (PG / PS) assembly, which controls respiratory muscle movement using electrical stimulation. This PG / PS assembly comprises a biomimetic design where the pattern generator includes a neural network mimicking the simplified connectivity pattern of respiratory related neurons in the brain stem to produce a rhythmic breathing pattern frequency and the pattern shaper includes a neural network mimicking the simplified connectivity pattern of neurons to produce a stimulus control signal. This biomimetic design for the controller automatically customizes and continually updates stimulation parameters to achieve a desired breathing pattern and, thereby, slow the development of muscle fatigue.
Owner:FLORIDA INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY
Ventilator device for treating obstructive sleep apnea and method for its control
InactiveCN101104092AAuto-continuationAutomatic intermittent measurementRespiratorsRespiratory muscleTreatment sleep
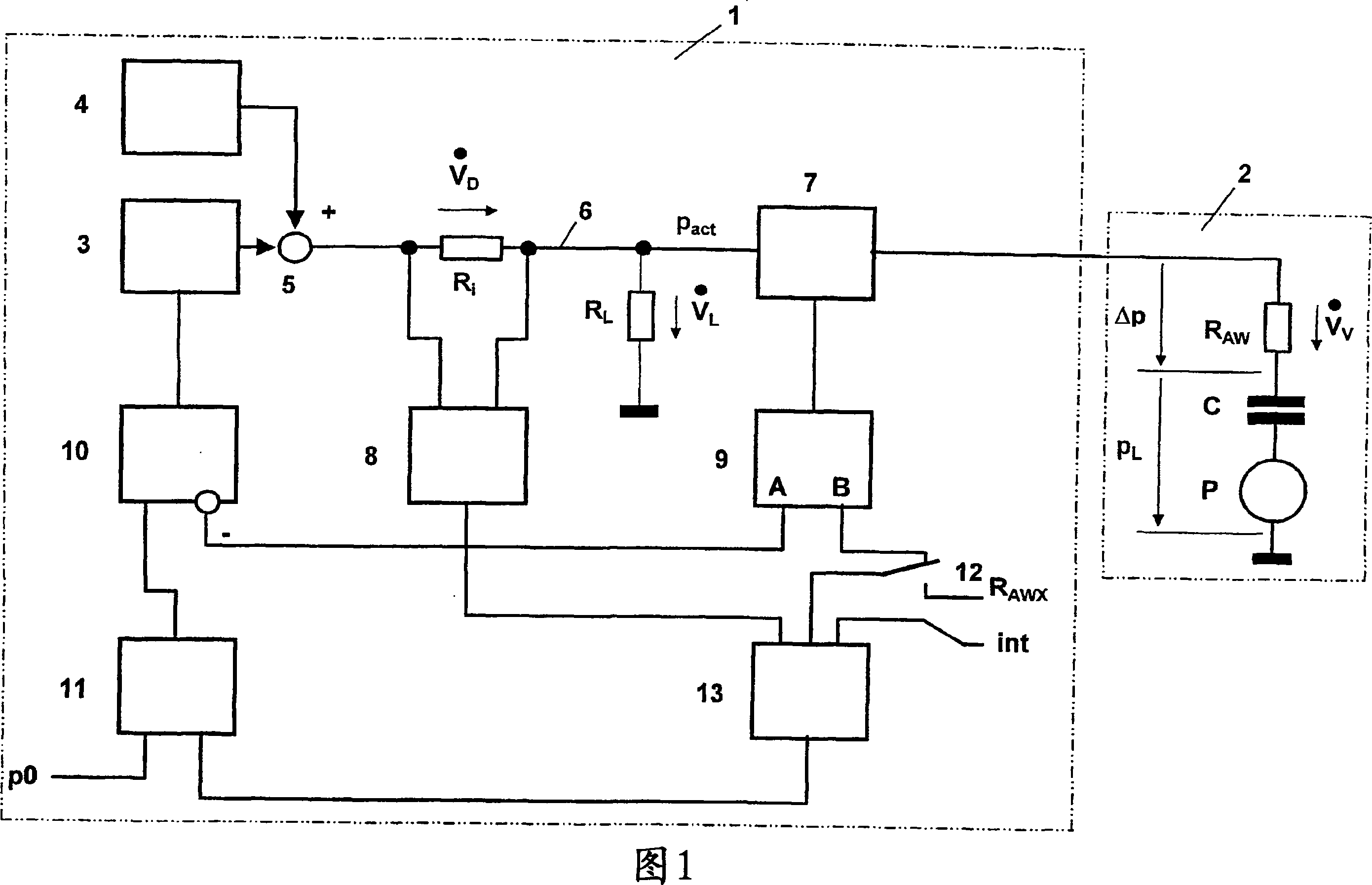
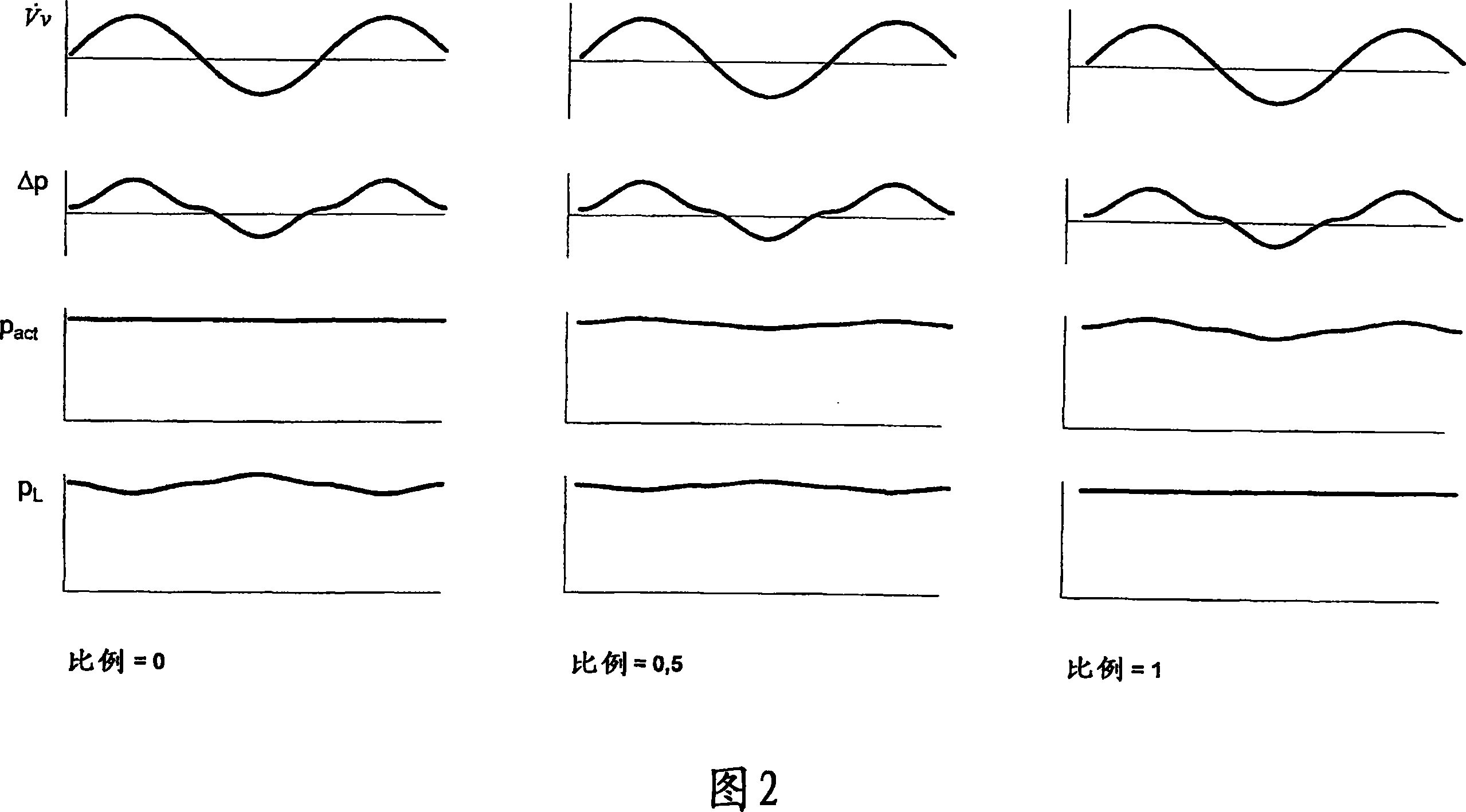
The present invention relates to a manpower respirator for treatment of obstructive sleep apnea, which comprises a pressure generator (3) for generating an artificial atmosphere with a therapy pressure (pact), a pressure regulating device (10) for controlling the pressure generator, and a respiration soft tube (6) as well as a respiratory mask (7) for supplying the artificial atmosphere to a patient (2). The manpower respirator is characterized in that it has a controller (13), which is used for continuously determining a loss pressure (Delta p) resulting over a respiratory tract resistance (RAW) of a respiratory tract of the patient, and for proportional adjustment of the therapy pressure progress in the process of the determined loss pressure. The manpower respirator reduces the burden of the patient breathing muscle distinctly and the result of delay treatment, and makes the treatment process be more comfortable.
Owner:HOFFRICHTER
Myoelectrically activated respiratory leak sealing
InactiveUS20050011519A1Adequate of gas flowReduce decreaseTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTraffic volumeLung
The method and system are for sealing / unsealing (regulating) airway leaks occuring between the ventilator circuit and respiratory airways during lung ventilatory support in response to myoelectrical activity of diaphgram. Myolectrical activity of a patient's respiratory-related muscle is sensed to detect respiratory effort, and to produce a myoelectrical signal representative of the sensed muscle myoelectrical activity. Respiratory flow and pressure can also be measured to produce respective respiratory pressure and respiratory flow signals. A logic trigger sealing / unsealing of airway leaks in relation to the myoelectrical signal, respiratory flow signal and / or respiratory pressure signal to assist respiration of the patient. The amplitude of the myoelectrical signal Is compare to a given threshold, and airway leaks are sealed when the amplitude of the myoelectrical signal is higher than this threshold. Increment of myoelectrical signal amplitude can be also detected to trigger the airway leak regulating device to seal the airway leaks, while decrement of the myoelectrical signal amplitude can be detected to unseal the airway leaks and thus permit air evacuation from the patient's lungs.
Owner:MONTREAL UNIV DE
Method and device for generating of a signal that reflects respiratory efforts in patients on ventilatory support
A method and device for generating a signal that mirrors changes in the level of effort exerted by respiratory muscles of patients on mechanical ventilatory support comprising: monitoring and storing airway pressure (Paw), rate of gas flow (F), and volume of gas flow (V), and generating a composite pressure signal using resistive pressure units (KF) determined from elapsed data and selected to minimize step changes in the calculated signal and elastic pressure units (Kv) determined from elapsed data by steps comprising: —scanning stored F or Paw during exhalation and identifying where their trajectory transiently reverses direction to detect transients; —selecting points within the exhalation that are at preselected distances away from the transients; —calculating the value of Kv required to force the values of the calculated signal at said selected points in elapsed breaths to be substantially equal when the selected value of KF is used as the flow coefficient.
Owner:YRT
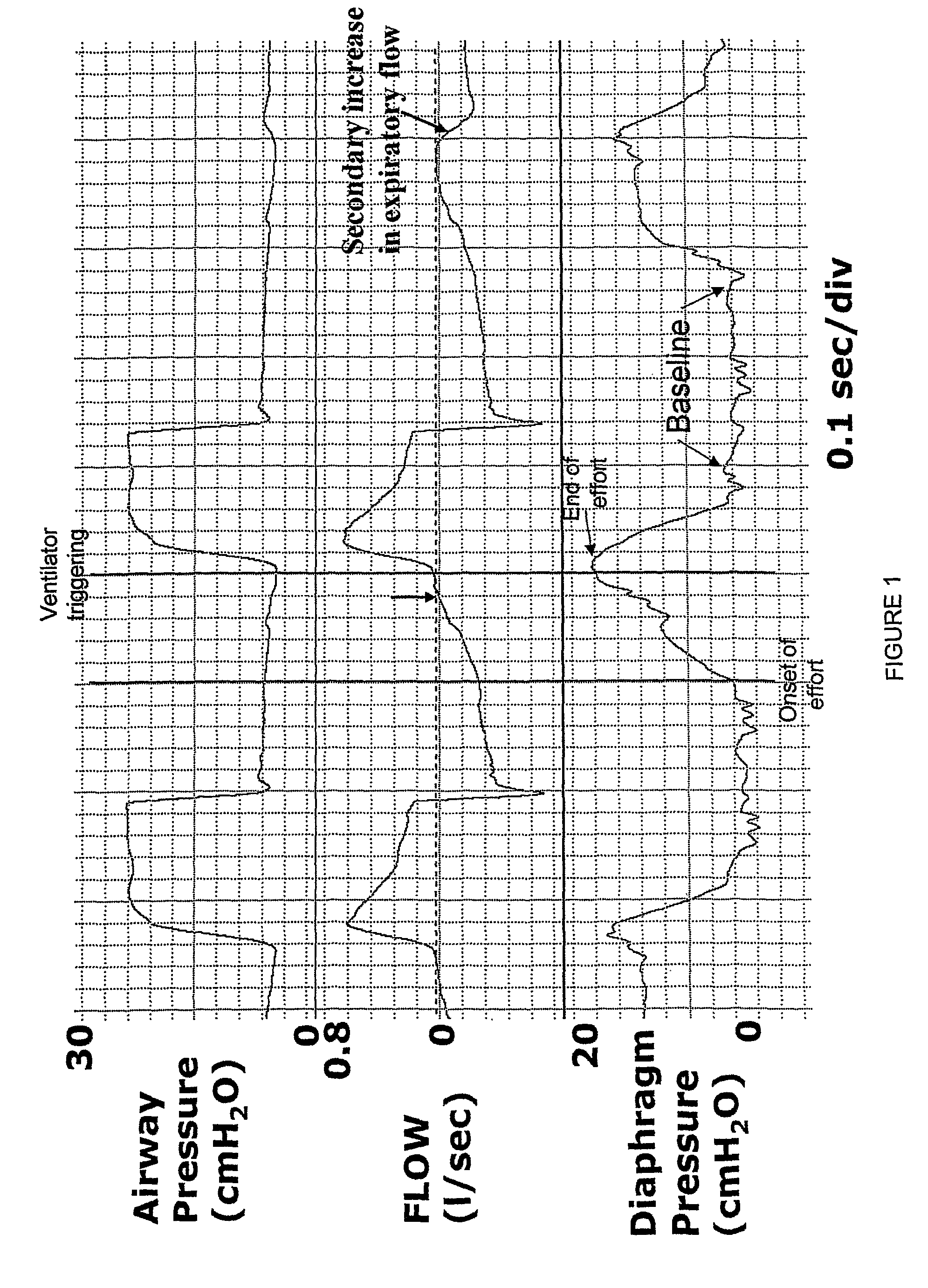
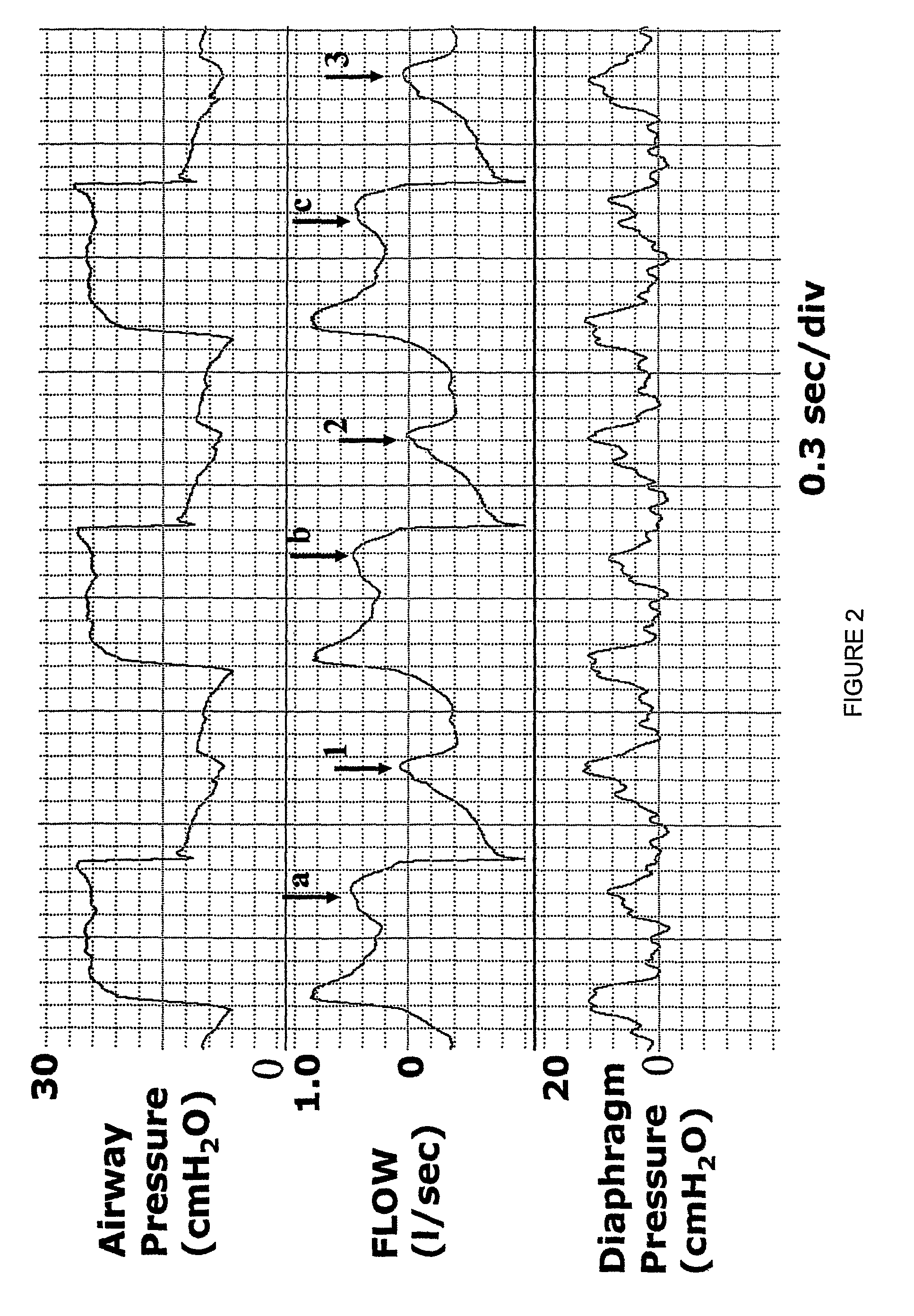
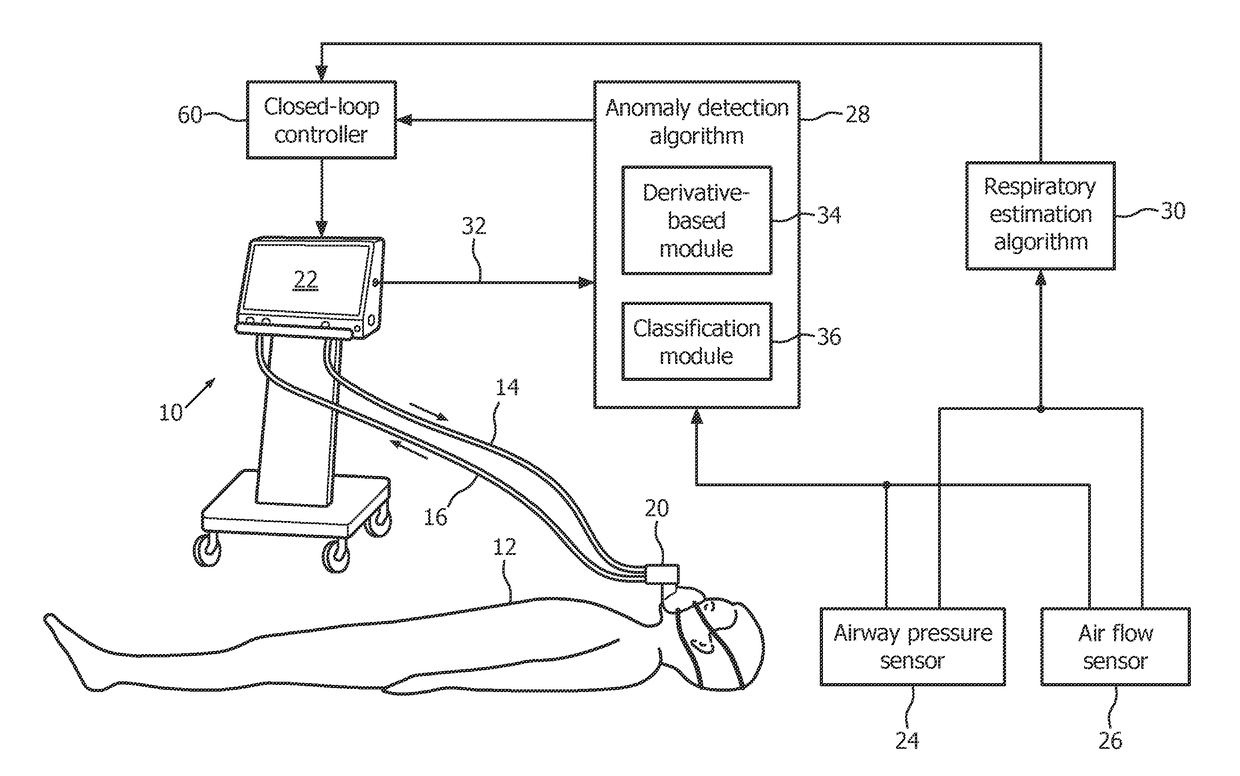
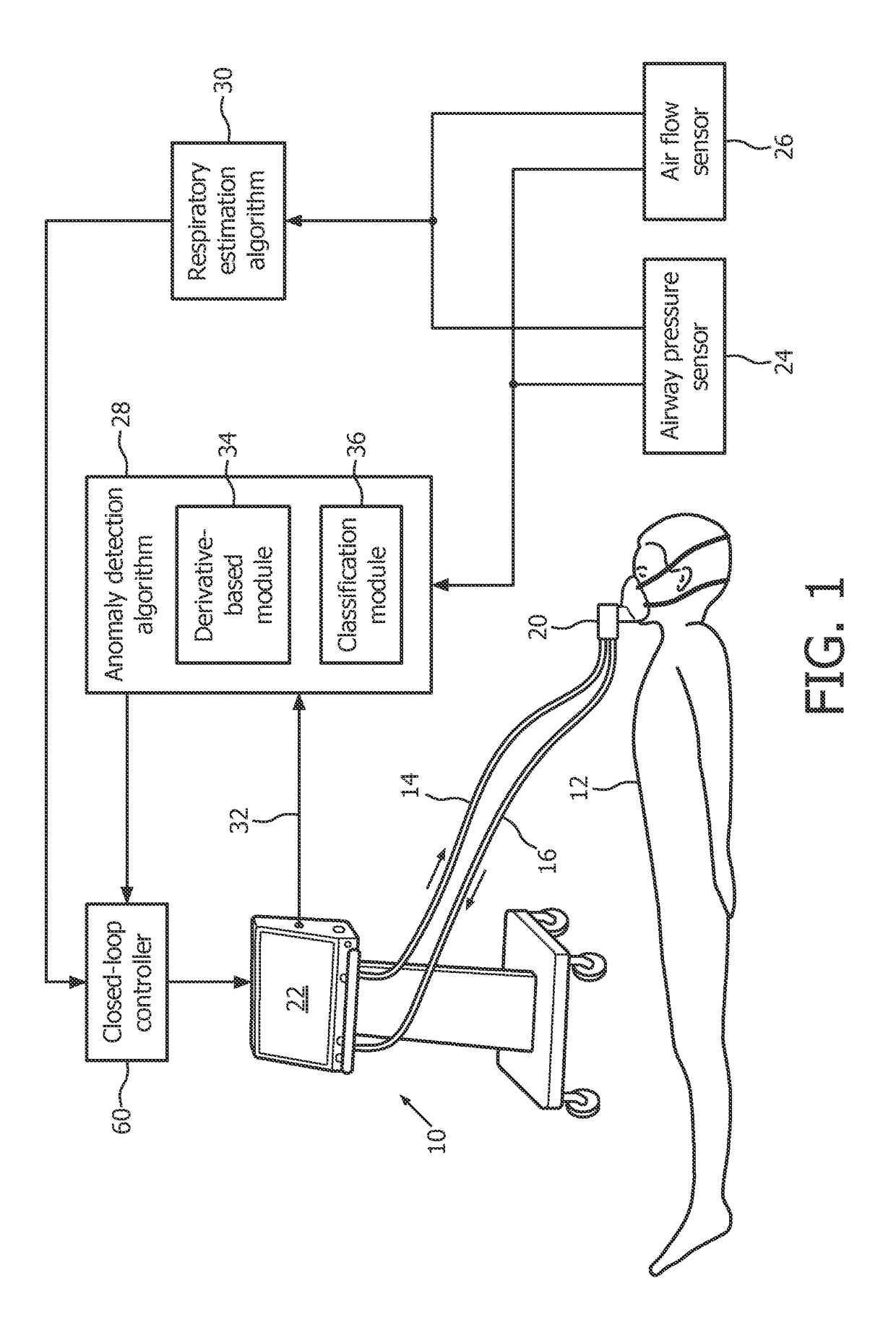
Anomaly detection device and method for respiratory mechanics parameter estimation
ActiveUS20180304034A1Easy to monitorAdjustment of settingRespiratorsElectrocardiographyRespiratory muscleAnomaly detection
A mechanical ventilation device (10) includes a mechanical ventilator. At least one airway sensor (24, 26) is configured to measure at least one of airway pressure and airway air flow as a function of time for a patient on the mechanical ventilator. At least one microprocessor (28, 30) is programmed to analyze at least one of airway pressure and airway air flow measured by the airway sensor to detect a spontaneous respiration anomaly in respiratory muscle pressure as a function of time generated by a patient on the mechanical ventilator. A display component (22) is configured to display an indication of a spontaneous respiration anomaly detected by the anomaly detection component.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Therapeutic agent for spinal cord injuries
InactiveUS6090823AHealing and ameliorating injuryInhibition transitionBiocideNervous disorderRespiratory muscleMedicine
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 00954 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 21, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 21, 1999 PCT Filed Mar. 24, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 35577 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 2, 1997(+)-N,N'-Propylene dinicotinamide or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof are outstanding drugs of high safety that can heal or ameliorate spinal cord injuries, prevent the transition from an incomplete cord injury to a complete injury, and minimize the consequences of spinal cord injuries including neurological disorders such as quadriplegia, paralysis of the respiratory muscle, damage to sensory functions and impairment of reflex functions, as well as impaired urinating or defecating functions.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Method of automatically controlling a respiration system and a corresponding respirator
ActiveUS8109269B2Convenient for patientAccurate operationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory muscleAutomatic control
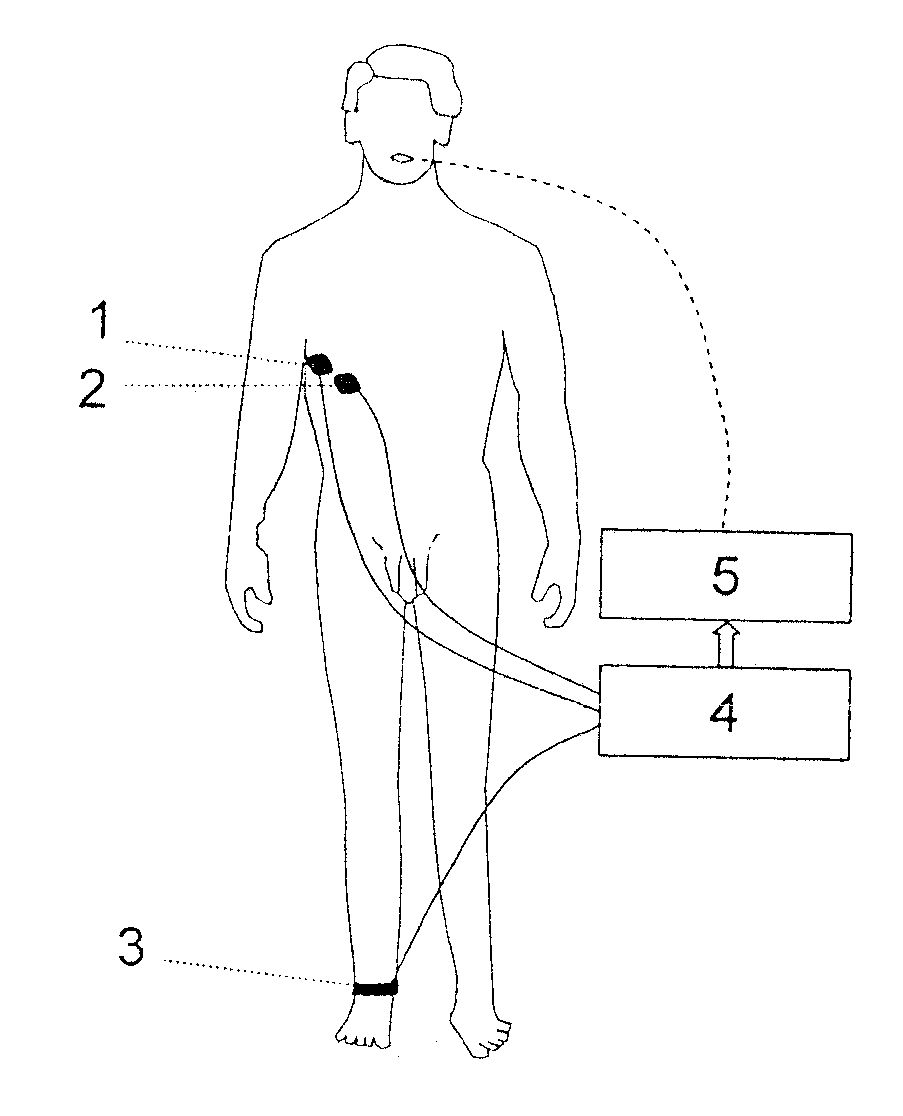
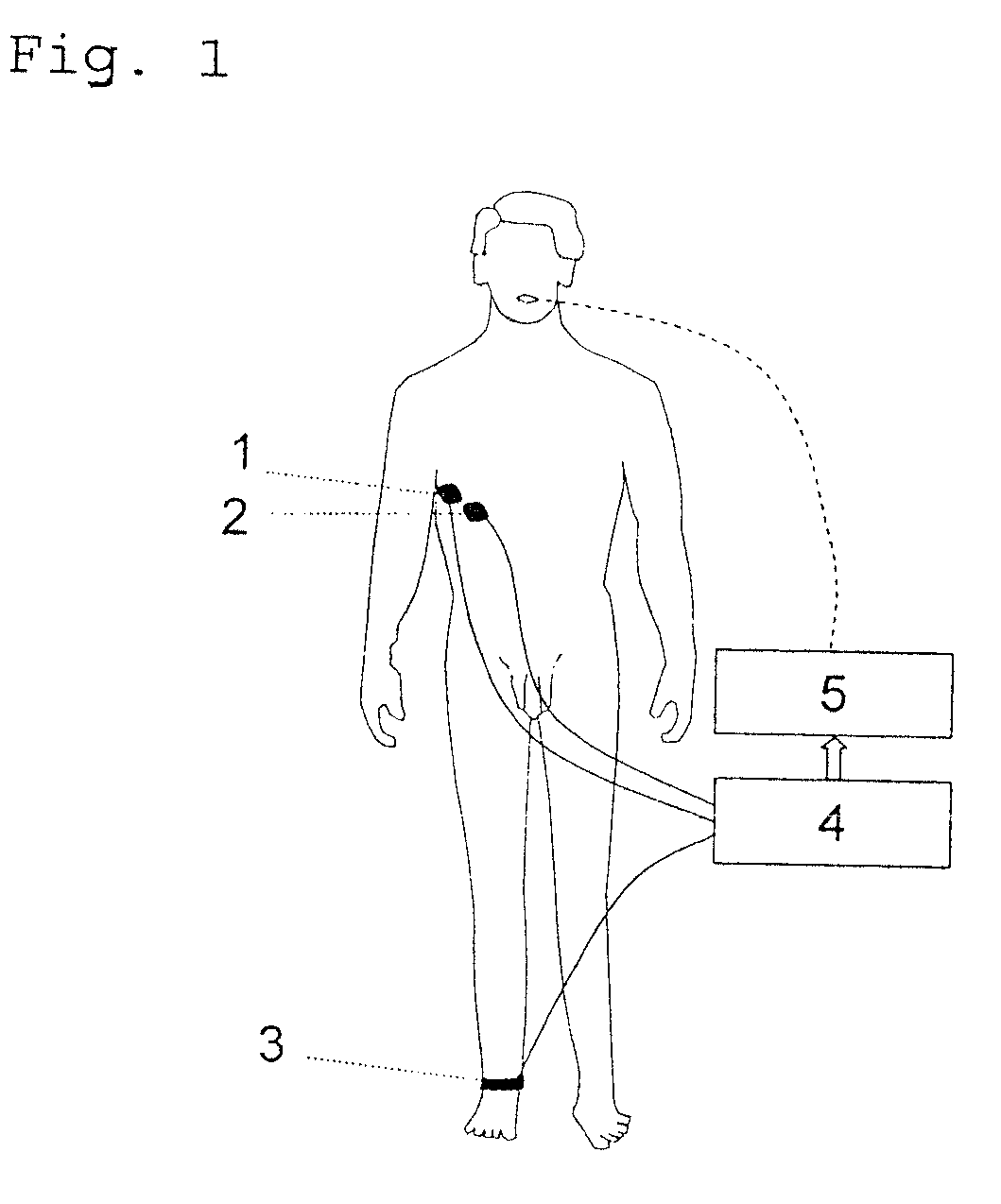
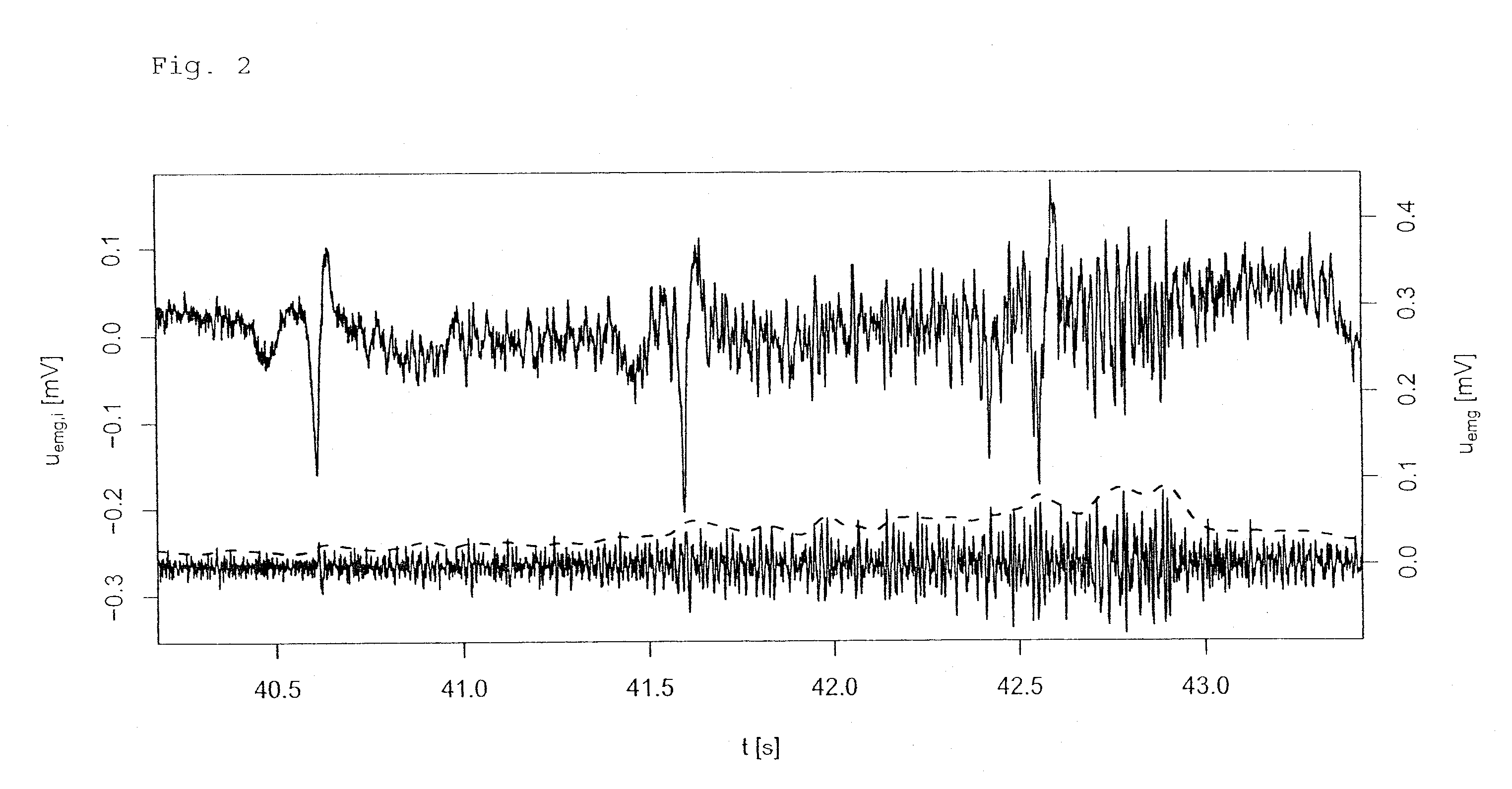
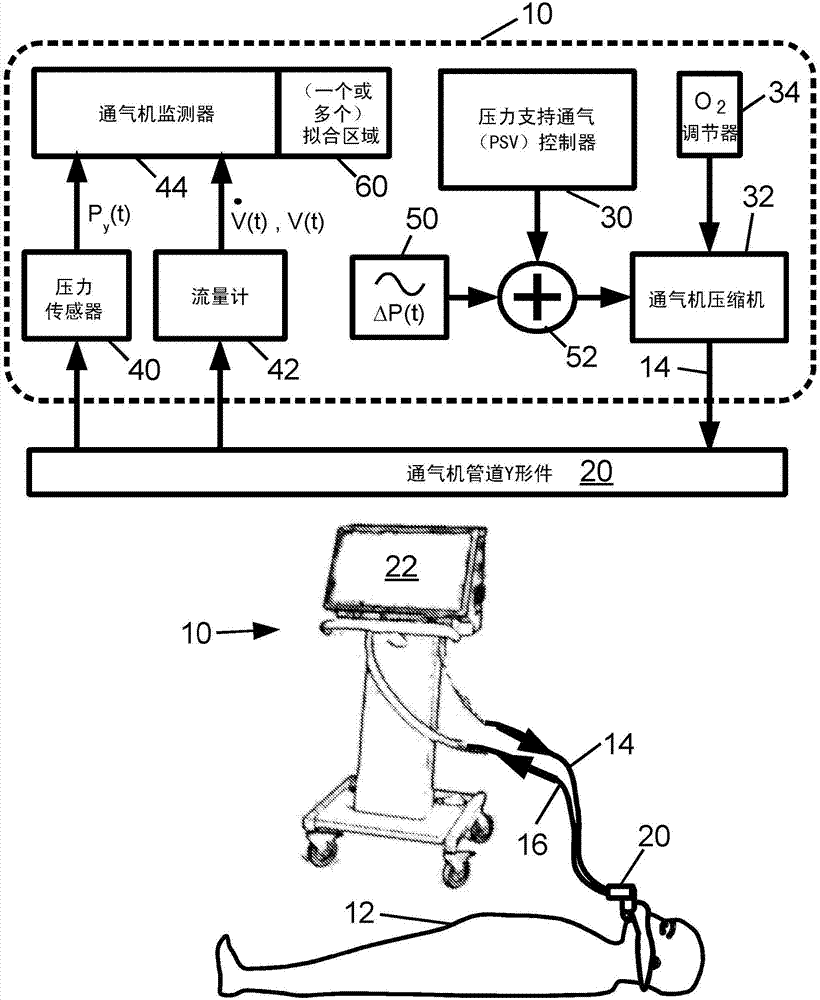
A method of automatically controlling a respiration system for proportional assist ventilation with a control device and with a ventilator. An electrical signal is recorded by electromyography with electrodes on the chest in order to obtain a signal uemg(t) representing the breathing activity. The respiratory muscle pressure pmus(t) is determined by calculating it in the control unit from measured values for the airway pressure and the volume flow Flow(t) as well as the patient's lung mechanical parameters. The breathing activity signal uemg(t) is transformed by means of a preset transformation rule into a pressure signal pemg(uemg)(t)) such that the mean deviation of the resulting transformed pressure signal pemg(t) from the respiratory muscle pressure pmus(t) is minimized. The respiratory effort pressure ppat(t) is determined as a weighted mean according to ppat(t)=a·pmus(t)+(1−a)·pemg(t), where a is a parameter selected under the boundary condition 0≦a≦1.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Breather valve, breath support device with respiratory muscle exercise mode and control method
InactiveCN109646783AFew partsRegulating pressureRespiratorsGymnastic exercisingRespiratory muscleInhalation
Owner:HUNAN MICOME ZHONGJIN MEDICAL SCI & TECH DEV CO LTD
Respiratory function training instrument
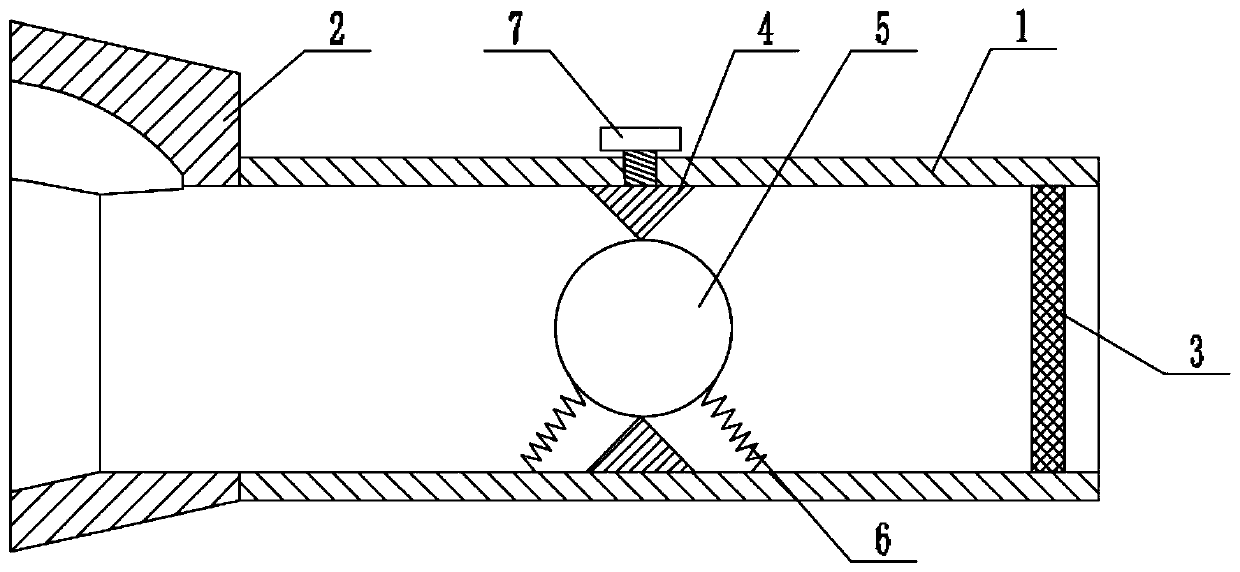
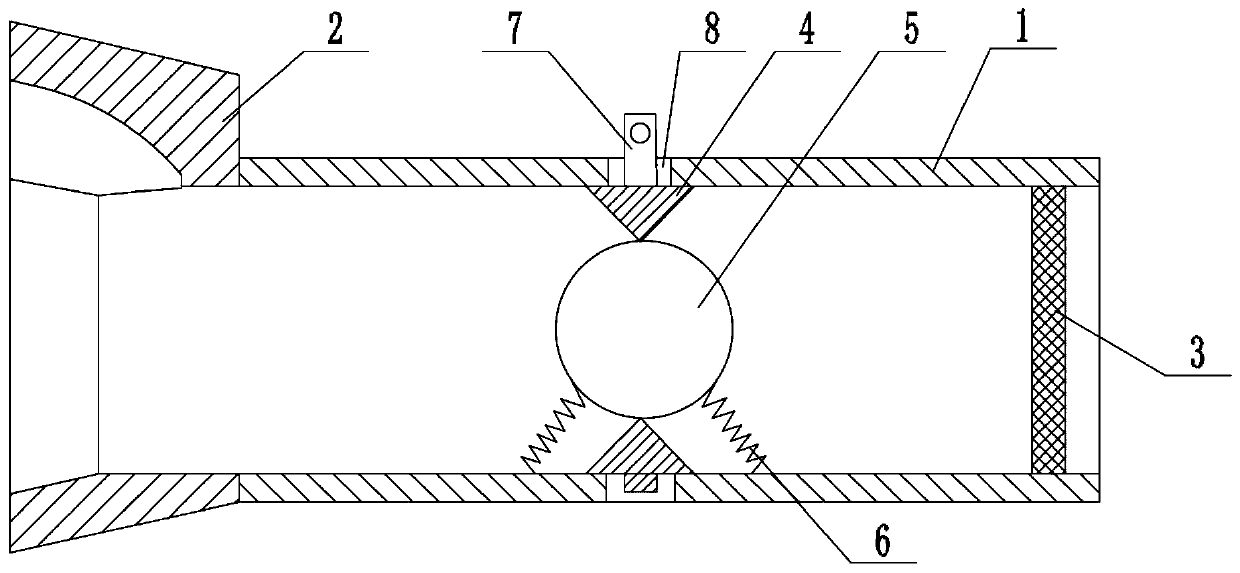
ActiveCN110237505AHigh strengthImprove toleranceFrictional force resistorsRespiratory muscleInterference fit
The invention relates to the field of medical apparatus and instruments, and provides a respiratory function training instrument. The respiratory function training instrument comprises a respiratory tube and a respirator mounted at one end of the respiratory tube, wherein the respiratory tube is internally provided with a resistance component which includes a resistance ring, a resistance ball and at least two elastic bodies; the outer circumference of the resistance ring is connected to the inner wall of the respiratory tube, and the inner circumference of the resistance ring is in interference fit with the resistance ball; and the elastic bodies are separately disposed on both sides of the resistance ring, one ends of the elastic bodies are connected to the inner wall of the respiratory tube, and the other ends of the elastic bodies are connected to the resistance ball. The respiratory function training instrument is provided with the resistance component to enable a patient to train the contraction and relaxation of respiratory muscles such as a diaphragm muscle in the inspiration process and the expiration process, thereby improving the strength and tolerance of the respiratory muscles to improve the training effect; and meanwhile, the respiratory function training instrument is simple in structure and convenient to carry.
Owner:山东鸿创科技有限公司
Remote rehabilitation training guidance system for chronic respiratory failure patient
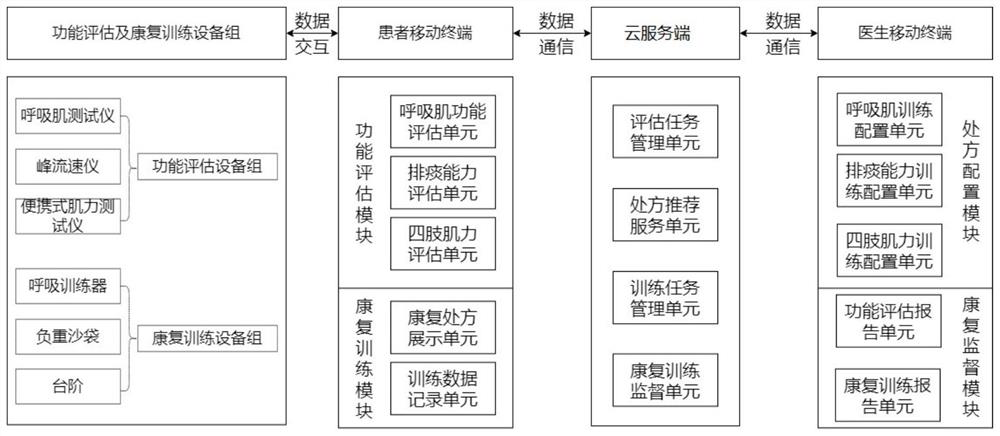
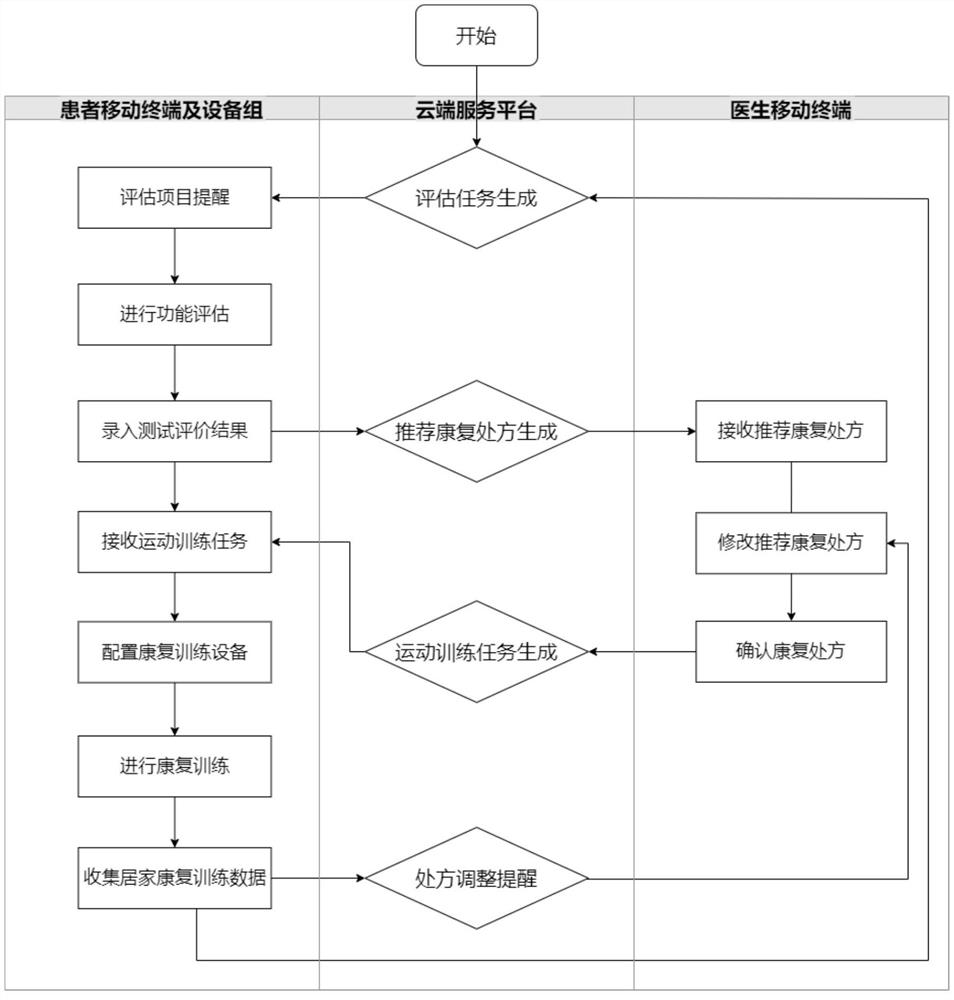
PendingCN114203274ARefined Training Classification SystemRealize individual customizationPhysical therapies and activitiesRespiratory organ evaluationChronic respiratory failureEmergency medicine
The invention discloses a remote rehabilitation training guidance system for chronic respiratory failure patients. The remote rehabilitation training guidance system comprises a function evaluation and rehabilitation training equipment group, a patient mobile terminal, a cloud server and a doctor mobile terminal, the system is characterized in that the function evaluation and rehabilitation training equipment group interacts with the patient mobile terminal, and the patient mobile terminal and the doctor mobile terminal communicate with the cloud server. According to the system, after obtained respiratory muscle test evaluation results, limb muscle force test evaluation results and sputum excretion ability test evaluation results of a patient are graded, recommended rehabilitation prescriptions corresponding to the grades are generated, and numeralization description is conducted on exercise intensity; the personalized customization of the recommended rehabilitation prescription can be realized, and the exercise amount of the patient in the home rehabilitation training can be accurately controlled, so that the patient is within the beneficial range of the exercise amount.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Portable respiratory function detection device with learning function
ActiveCN106901742AEasy to carryIncrease sound loudnessDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsDiseaseRespiratory flow
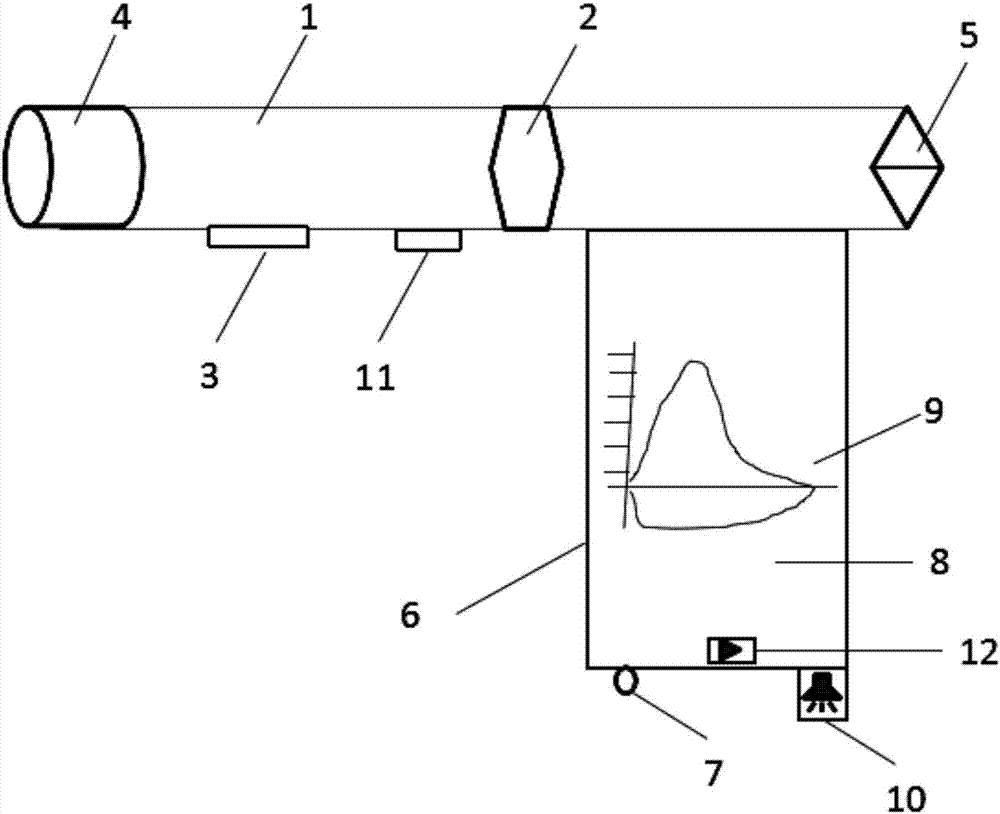
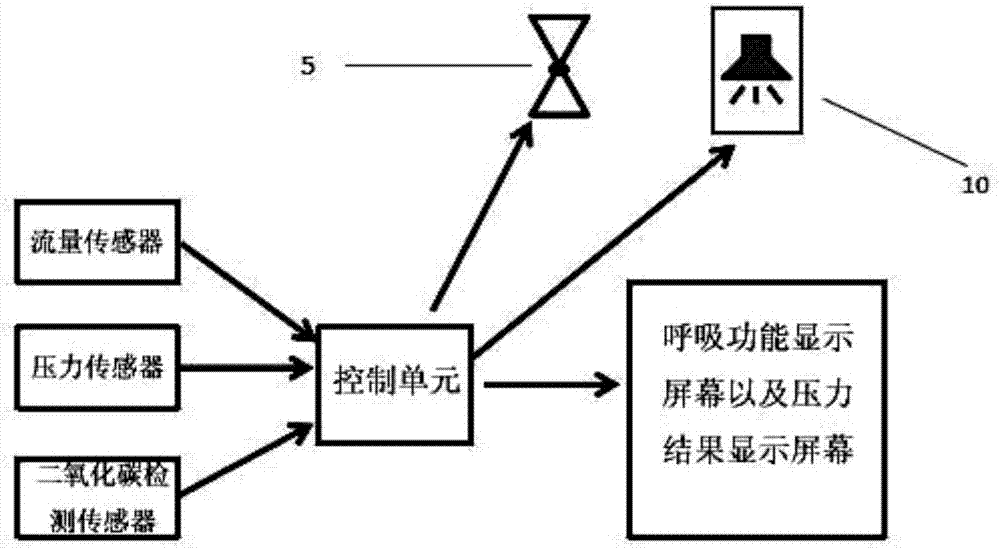
The invention discloses a portable respiratory function detection device with a learning function. The portable respiratory function detection device comprises a rigid breathing tube and a handle, wherein one end of the rigid breathing tube is connected with an interface unit and a valve is arranged at the other end; the handle is fixedly connected with a valve end of the rigid breathing tube; a control unit is arranged in the handle; a display screen for displaying a respiratory function and a pressure result connected with the control unit and a loudspeaker are embedded into a shell of the handle separately; a flow sensor electrically connected with the control unit, a pressure sensor and a carbon dioxide detector are arranged in the rigid breathing tube separately; and the control unit controls the opening and closing of the valve. The loudspeaker is controlled through respiratory flow, the larger the airflow is, the higher the sound is, and a subject quickly grasps main points of respiratory function detection with the help of auditory feedback, so that the lung function can be detected and whether the lung function damage is caused by an abnormal respiratory muscle function or an abnormal lung or a thorax disease can be identified when the lung function declines.
Owner:广州锐士伯医疗科技有限公司
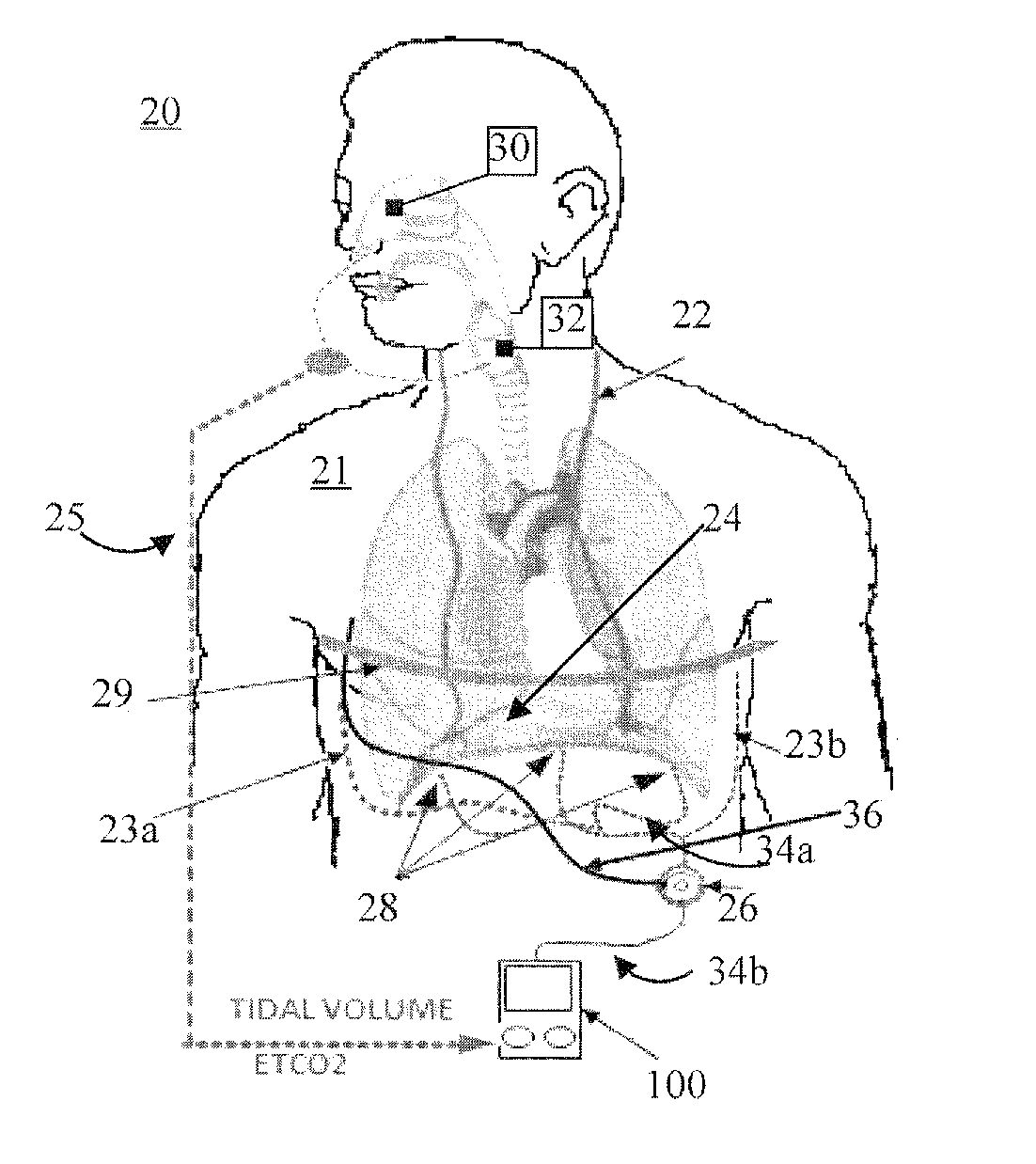
System and method for respiratory system assessment
InactiveUS20160100808A1Inertial sensorsRespiratory organ evaluationRespiratory muscleIntensive care medicine
A system and method comprise sampling a rate of airflow in a patients lungs during inspiration and / or expiration of the patient and outputting a corresponding airflow signal. Respiratory muscles signals of the patient are simultaneously sampled with the sampling of the airflow and outputted as a corresponding activity signal. The airflow signal and the activity signal are simultaneously displayed wherein a comparison of at least the airflow signal and the activity signal indicates physical properties of a respiratory system of the patient.
Owner:ANBARANI KEIVAN
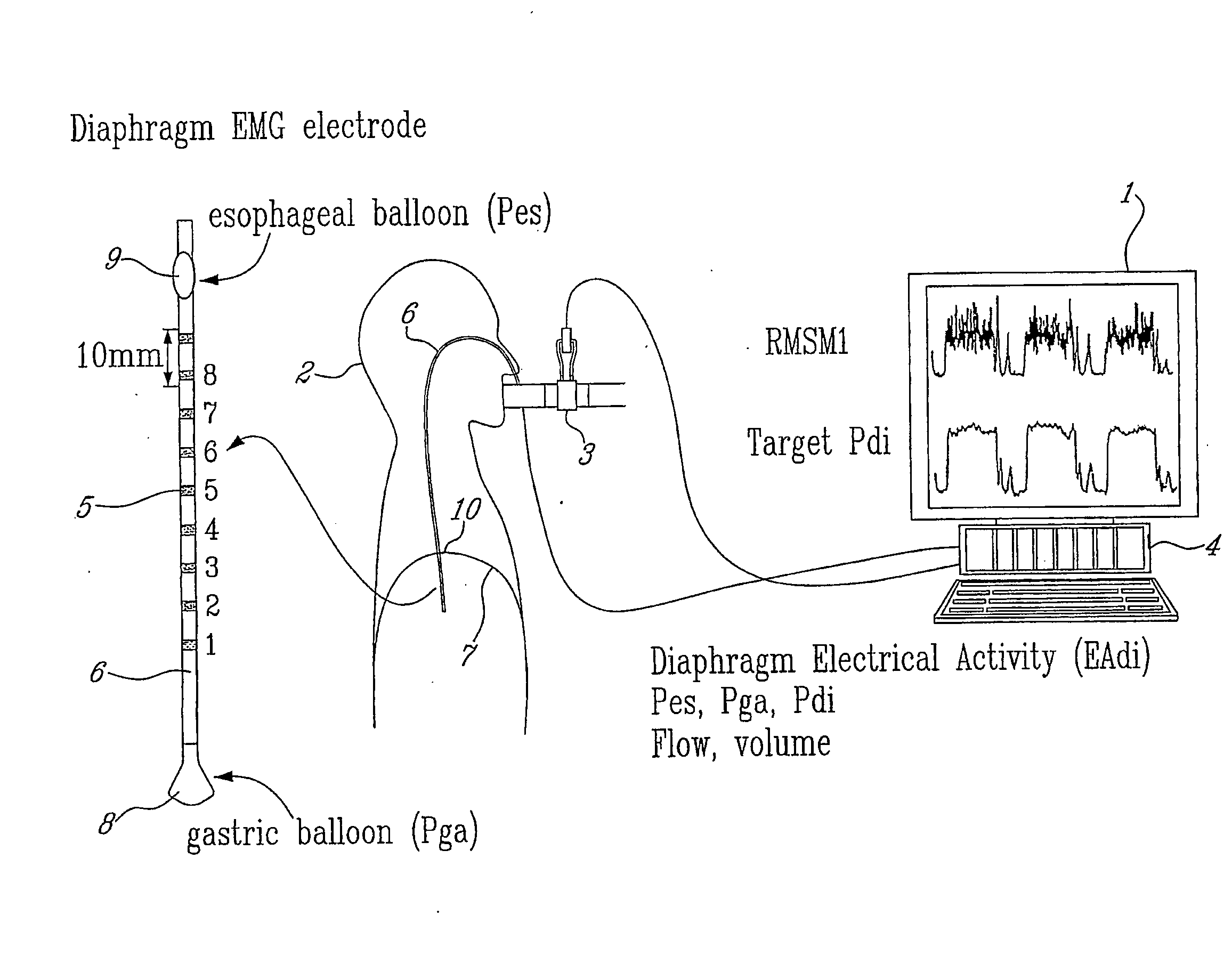
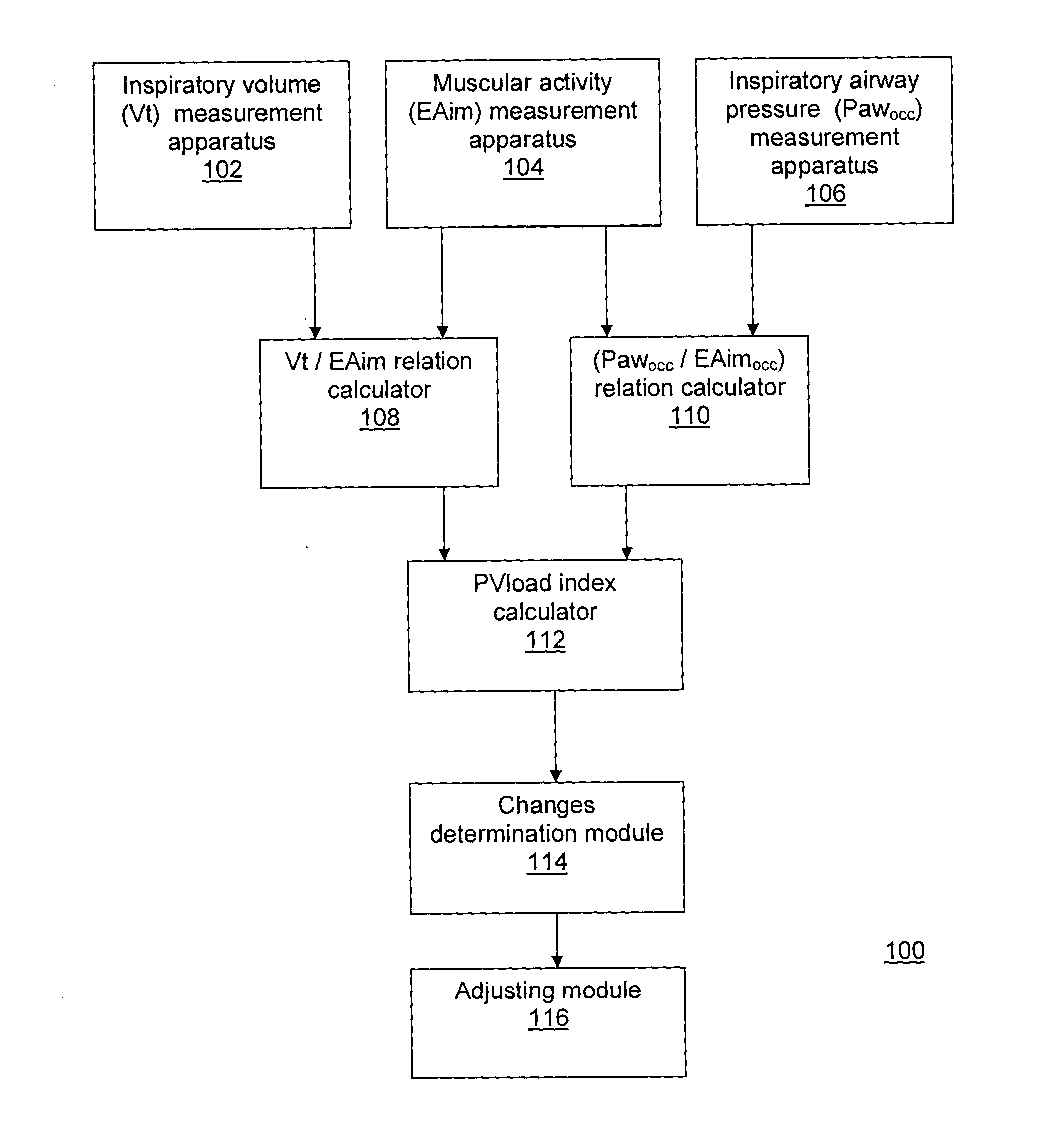
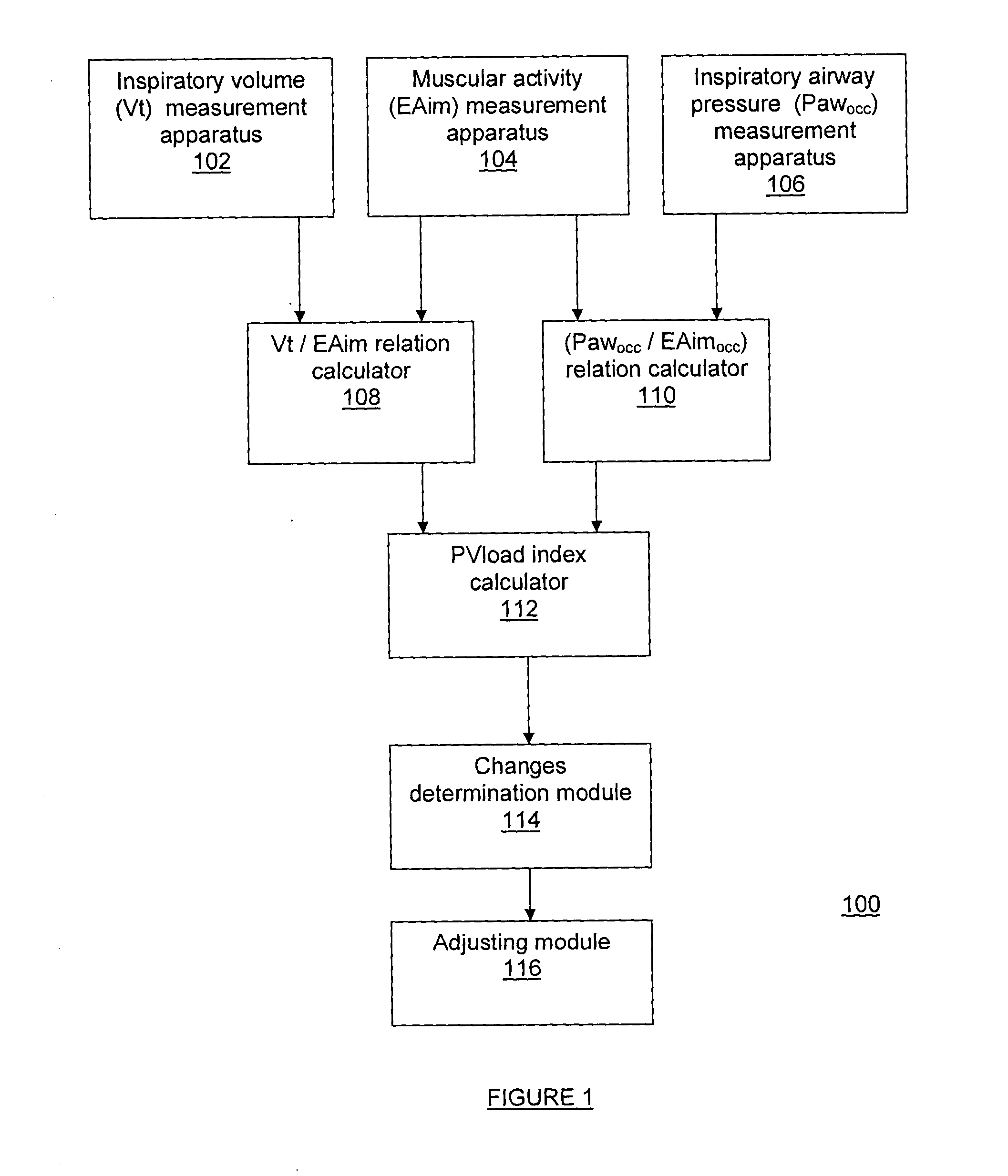
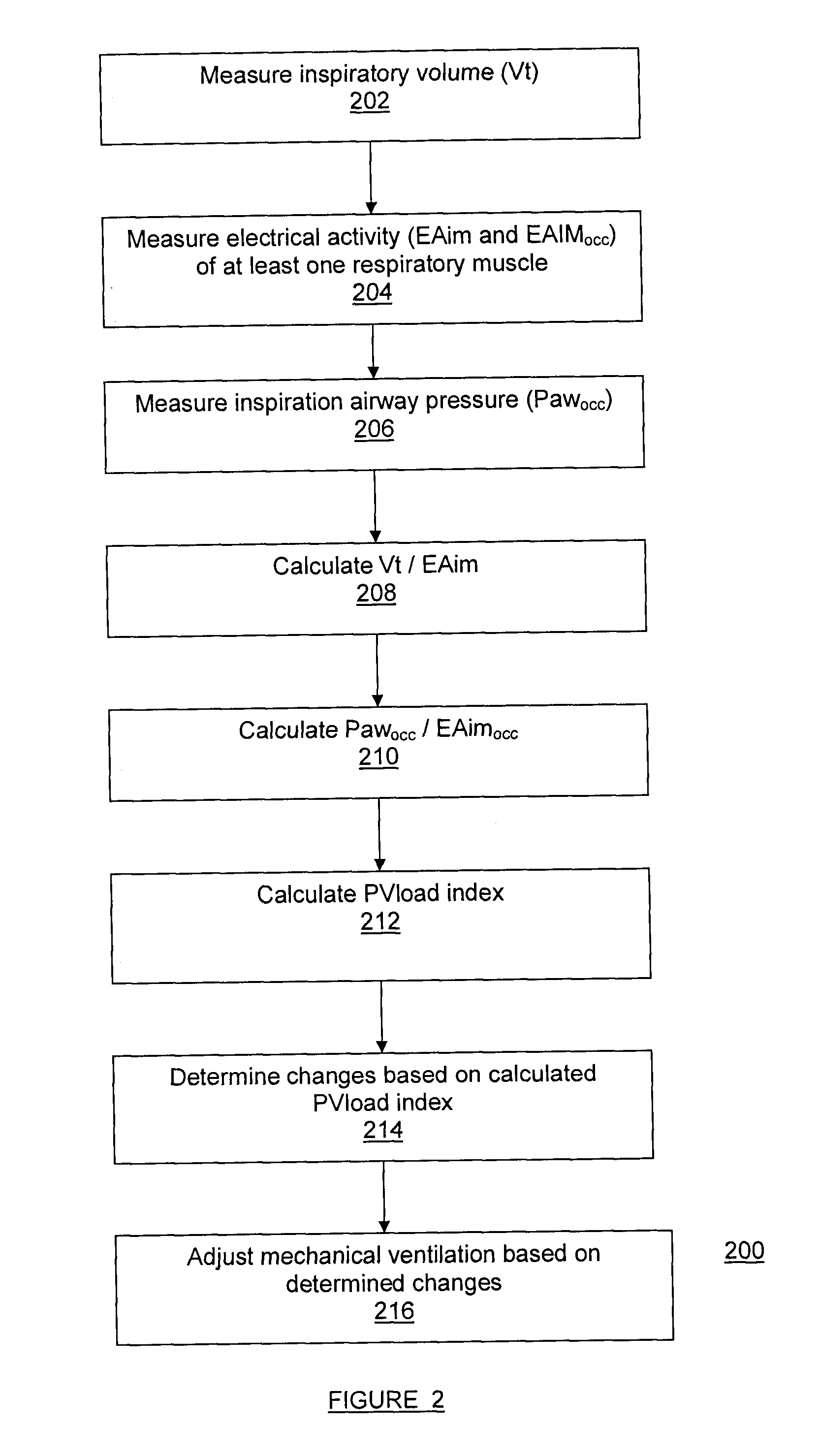
Method and system for measuring changes in inspiratory load
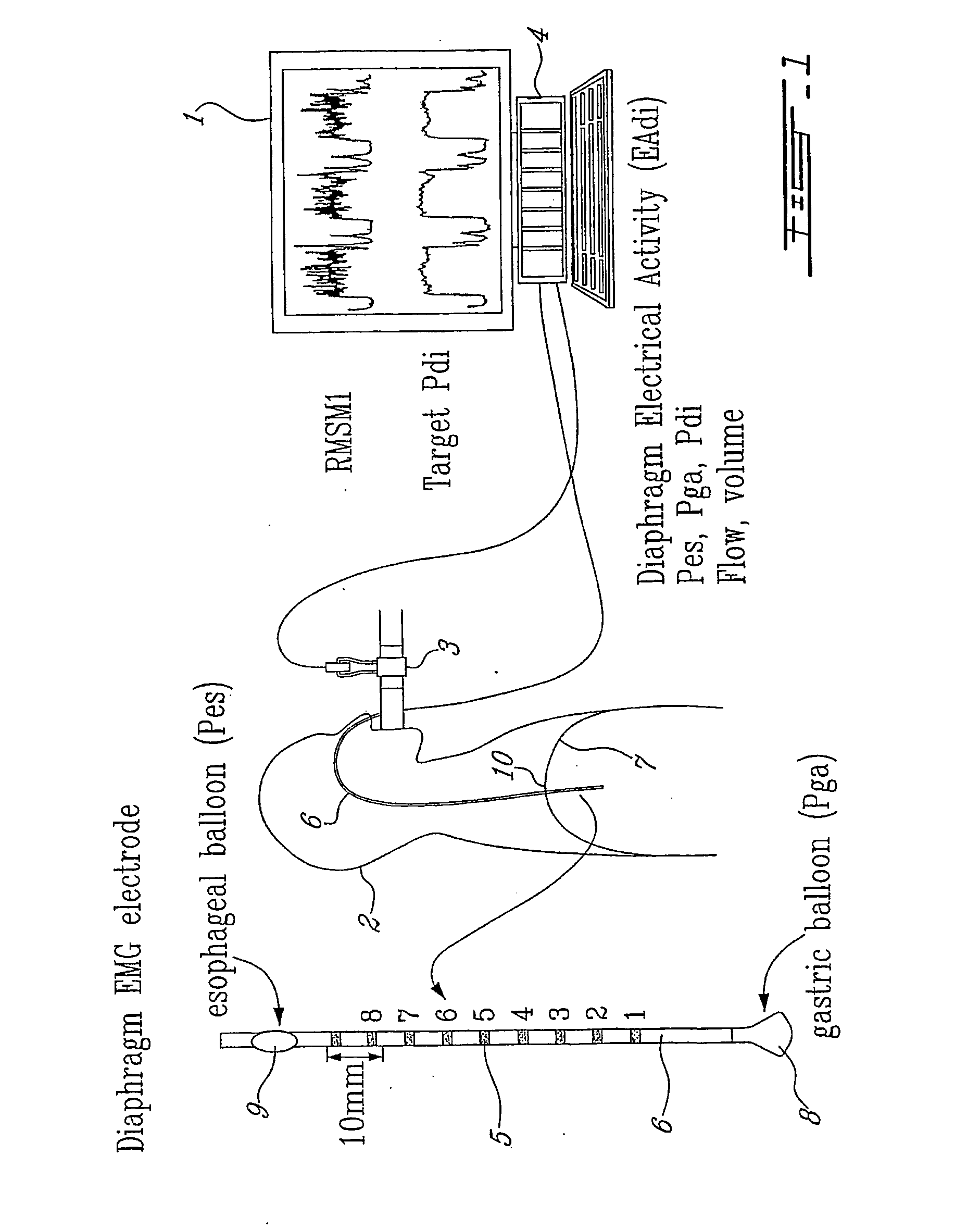
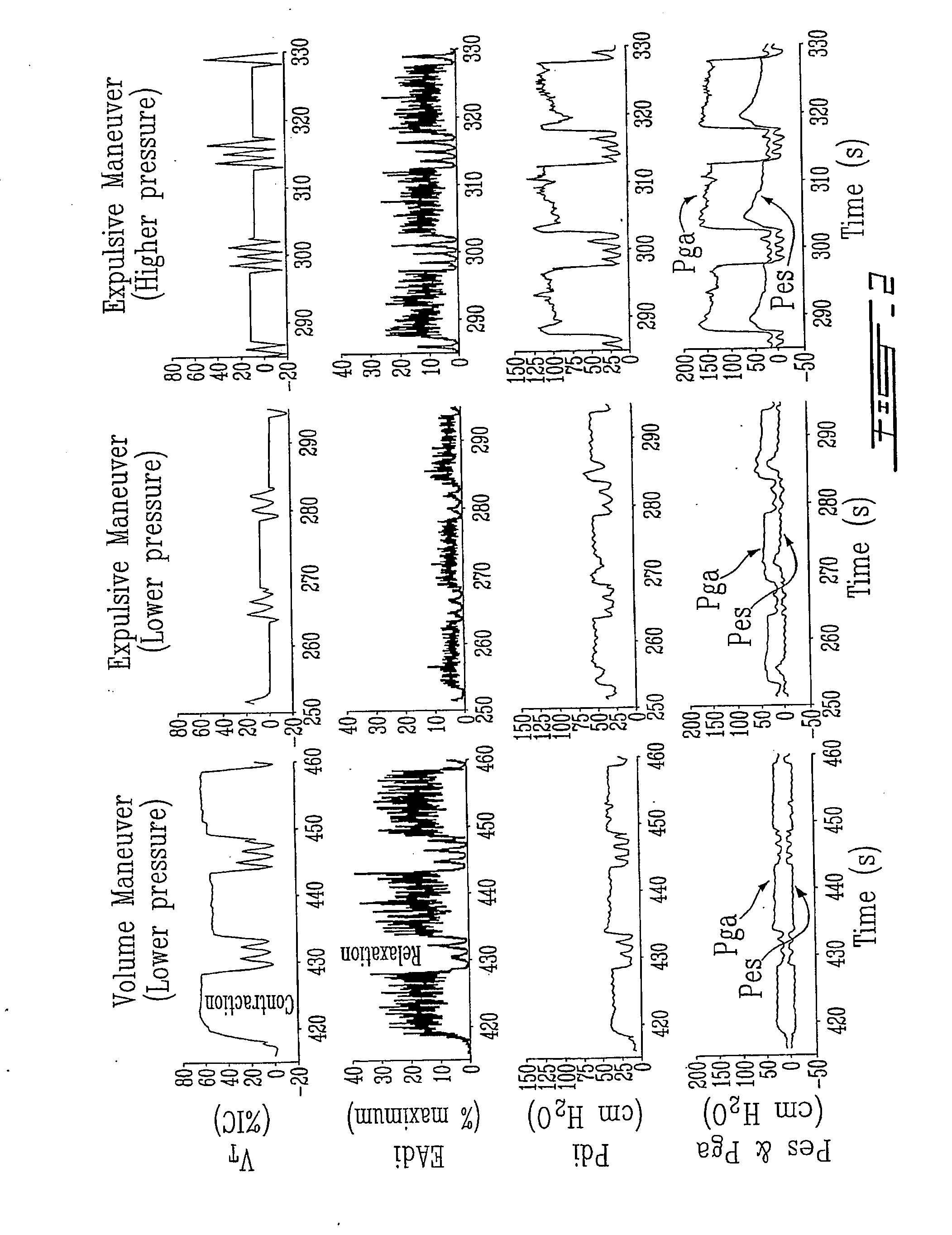
A method and system for measuring changes in inspiratory load of a patient's respiratory system during mechanical ventilation. The method and system calculate a first relation between a measured inspiratory airway pressure and a measured electrical activity of respiratory muscle, and a second relation between a measured inspiratory volume and the measured electrical activity. A load index is calculated from the first and second relations. Changes in inspiratory load are determined based on the load index.
Owner:ST MICHAELS HOSPITAL
Method and device for treating central sleep apnea
The invention discloses a method and device for treating central sleep apnea. The method includes the following steps that 1, surface electromyogram signals of respiratory muscles are collected; 2, filtering is carried out; 3, enveloping calculation of the surface electromyogram signals is carried out; 4, respiratory electromyogram sign signals are generated; 5, the oxyhemoglobin saturation of a patient is detected, wherein an oxyhemoglobin saturation probe clamped to a finger can be used; 6, if no respiratory electromyogram sign signal is collected in continuous 10 seconds and the decrease rate of oxyhemoglobin saturation exceeds 3%, external pacing is carried out on respiratory muscles. The method is applied to the device. The method and the device are precise, effective and good in use effect.
Owner:广州雪利昂生物科技有限公司
Simultaneous estimation of respiratory parameters by regional fitting of respiratory parameters
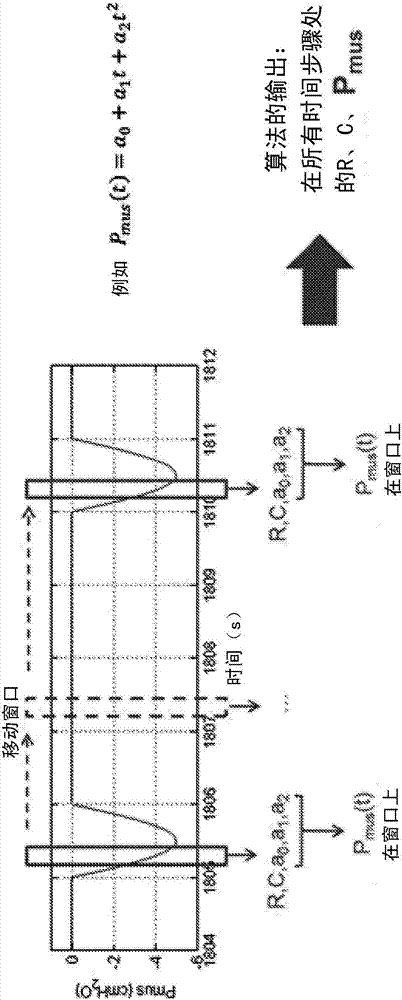
A medical ventilator (10) performs a method including: receiving measurements of pressure of air inspired by or expired from a ventilated patient (12) operatively connected with the medical ventilator;receiving measurements of air flow into or out of the ventilated patient operatively connected with the medical ventilator;dividing a breath time interval into a plurality of fitting regions (60); and simultaneously estimating respiratory system's resistance and compliance or elastance, and respiratory muscle pressure in each fitting region by fitting to a time series of pressure and air flow samples in that fitting region. In one approach, the fitting includes parameterizing the respiratory muscle pressure by a continuous differentiable function, such as a polynomial function, over the fitting region.In another approach, the fitting is to an equation of motion of the lungs in each fitting region, while monotonicity constraints and inequalities bounding at least the respiratory muscle pressure P mus (t) and respiratory system's resistence R and compliance C are applied to the respiratory muscle pressure in each region.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
A system and a corresponding method for estimating respiratory drive of mechanically ventilated patients
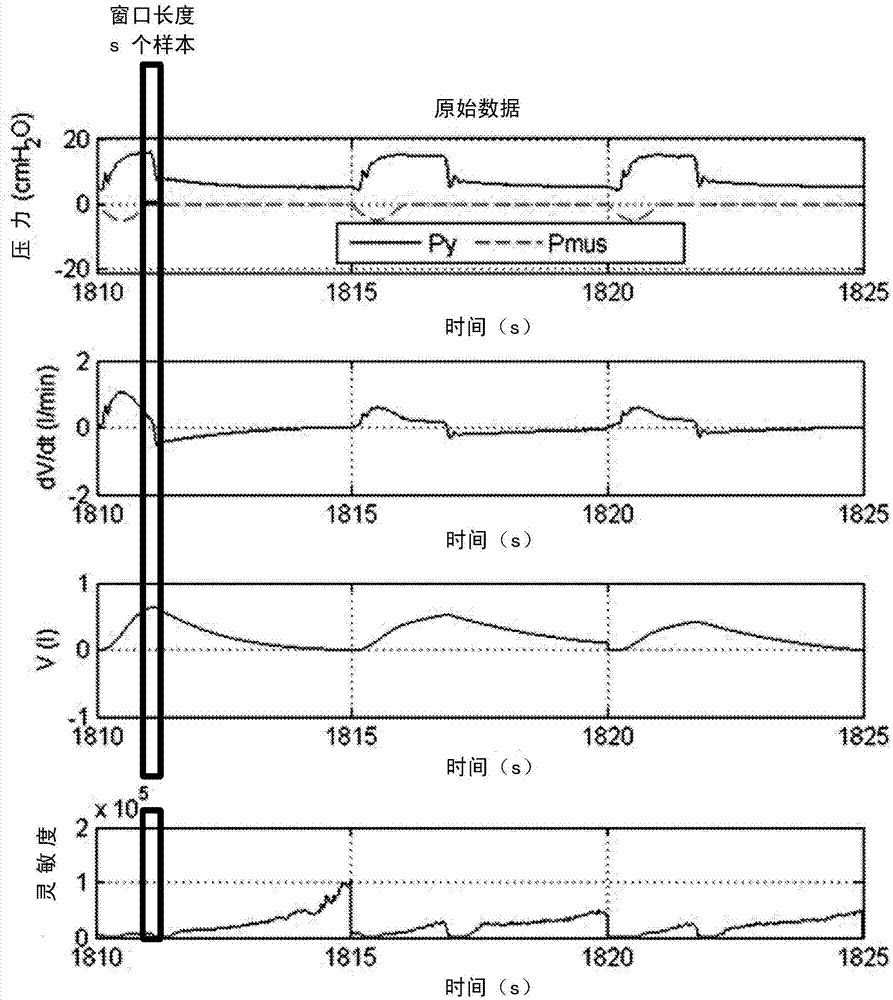
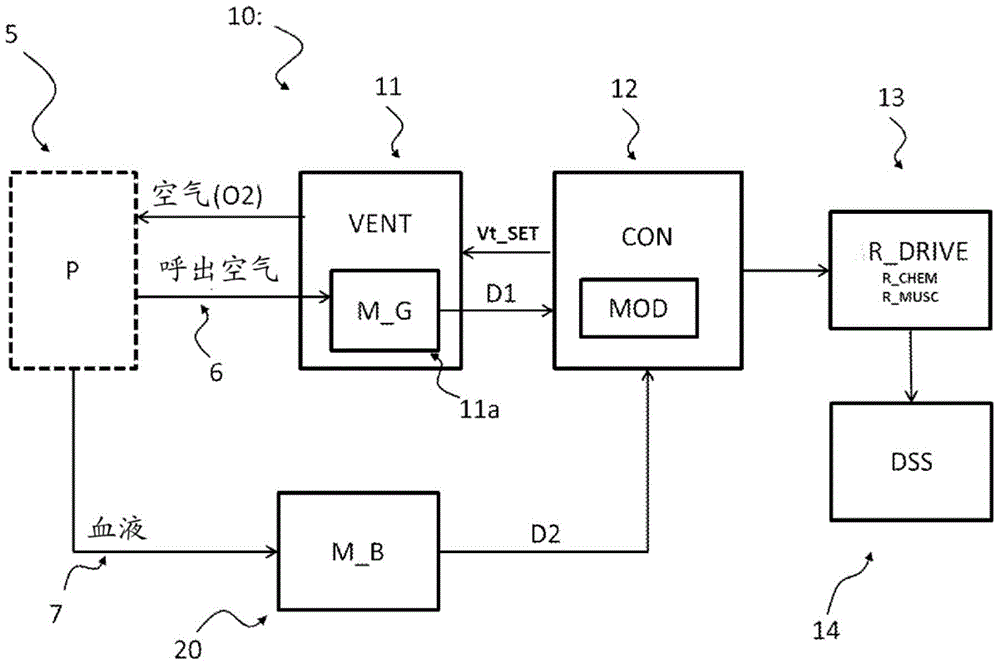
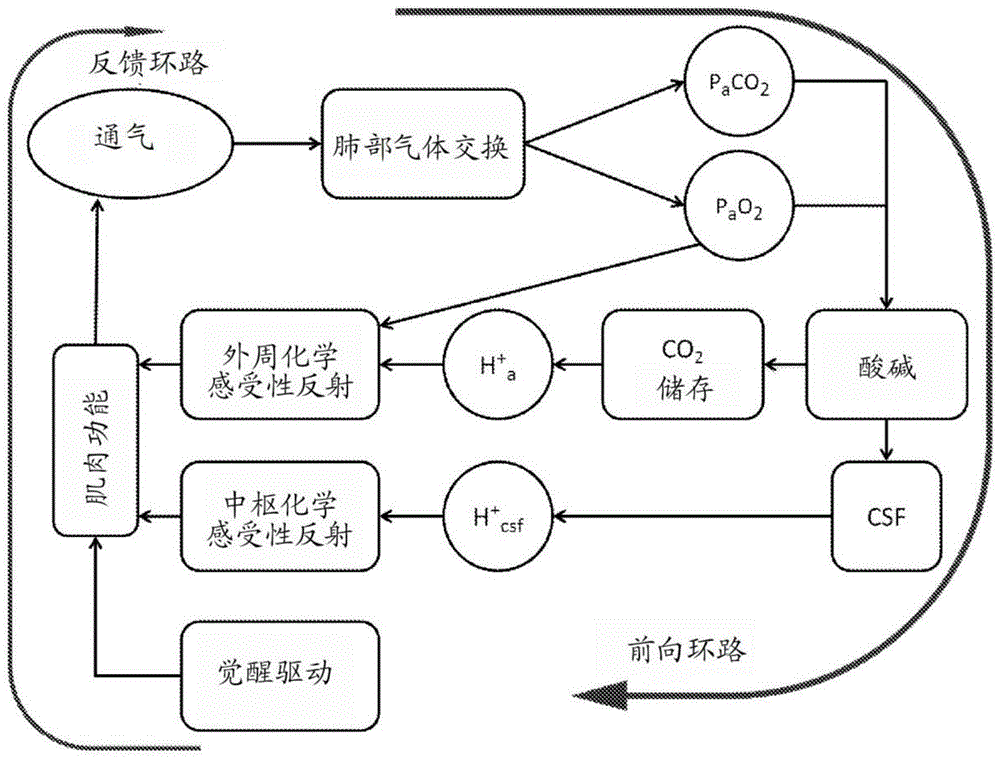
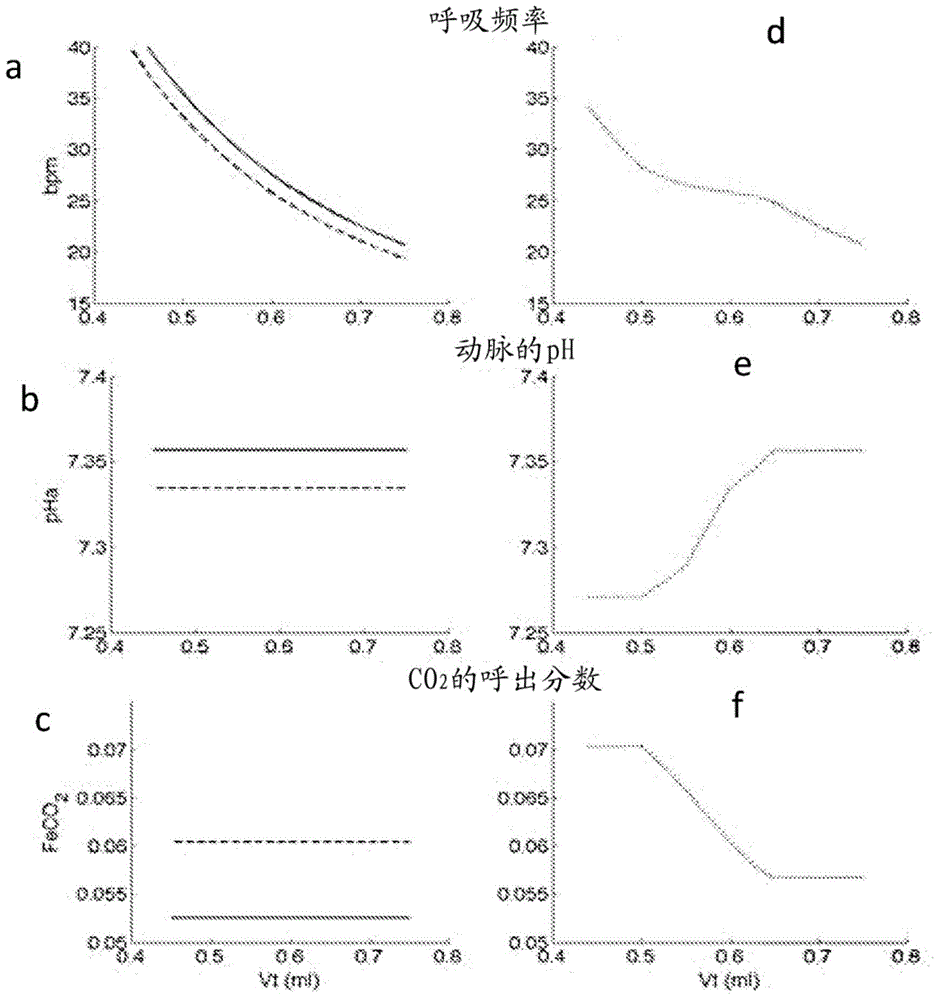
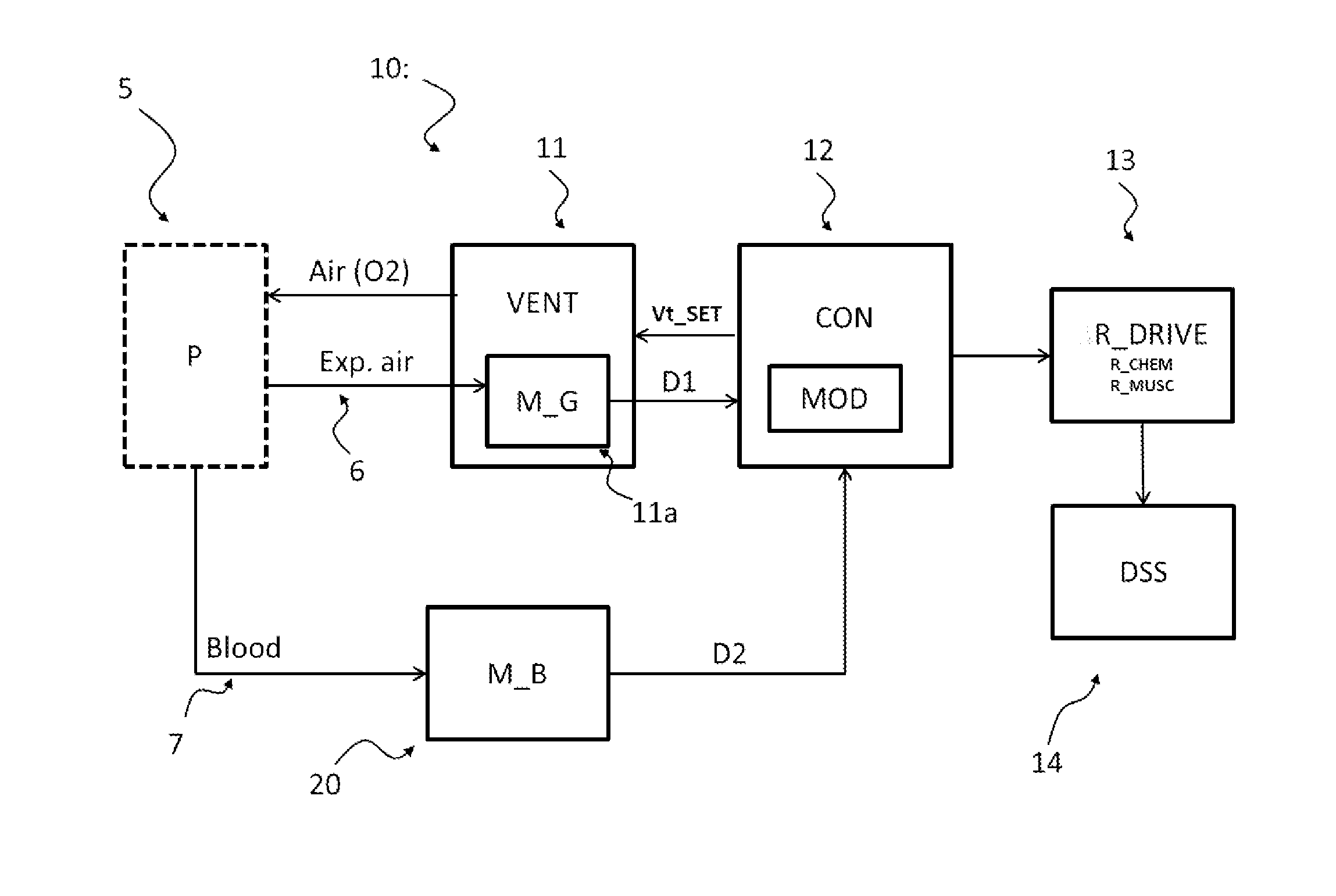
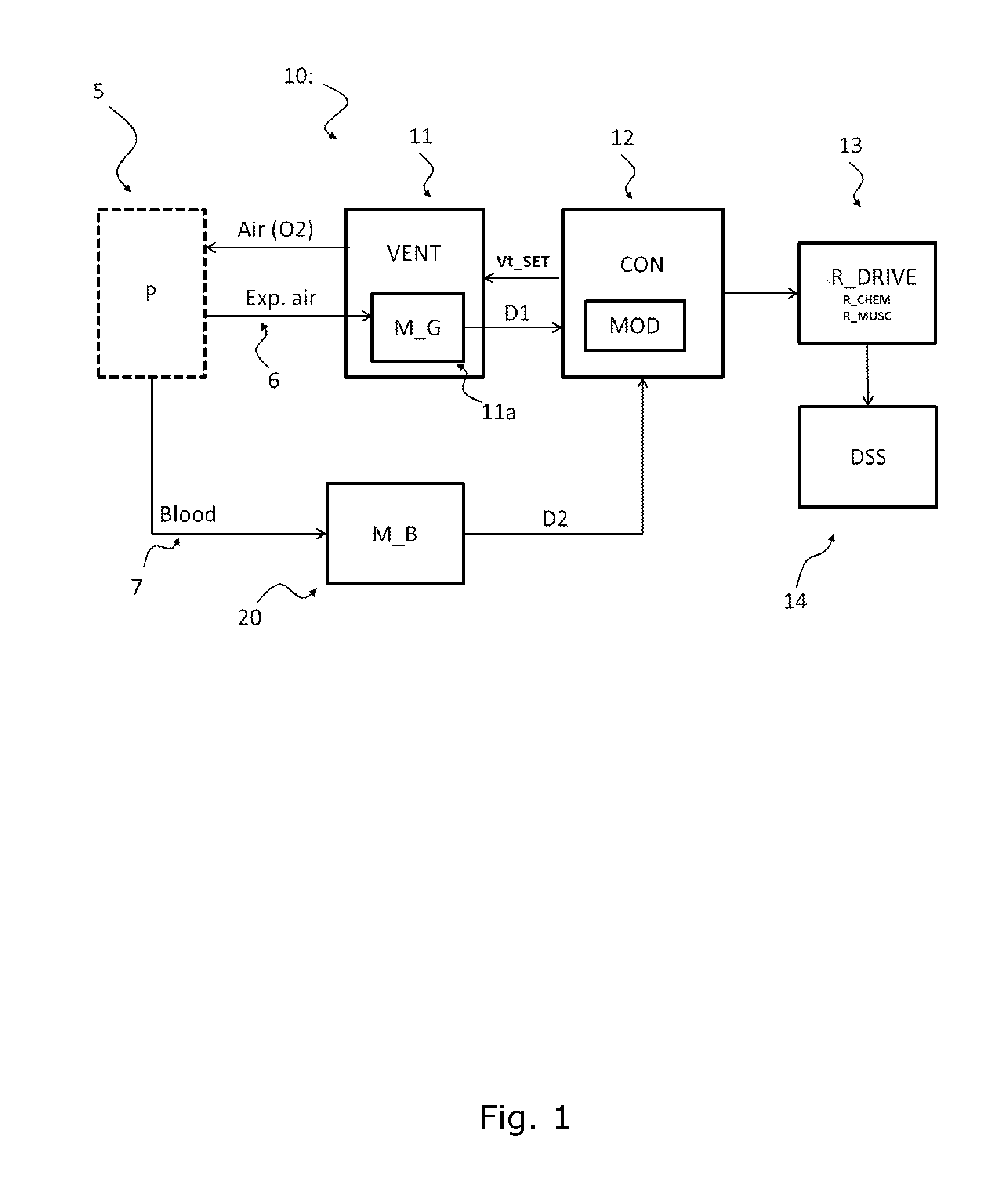
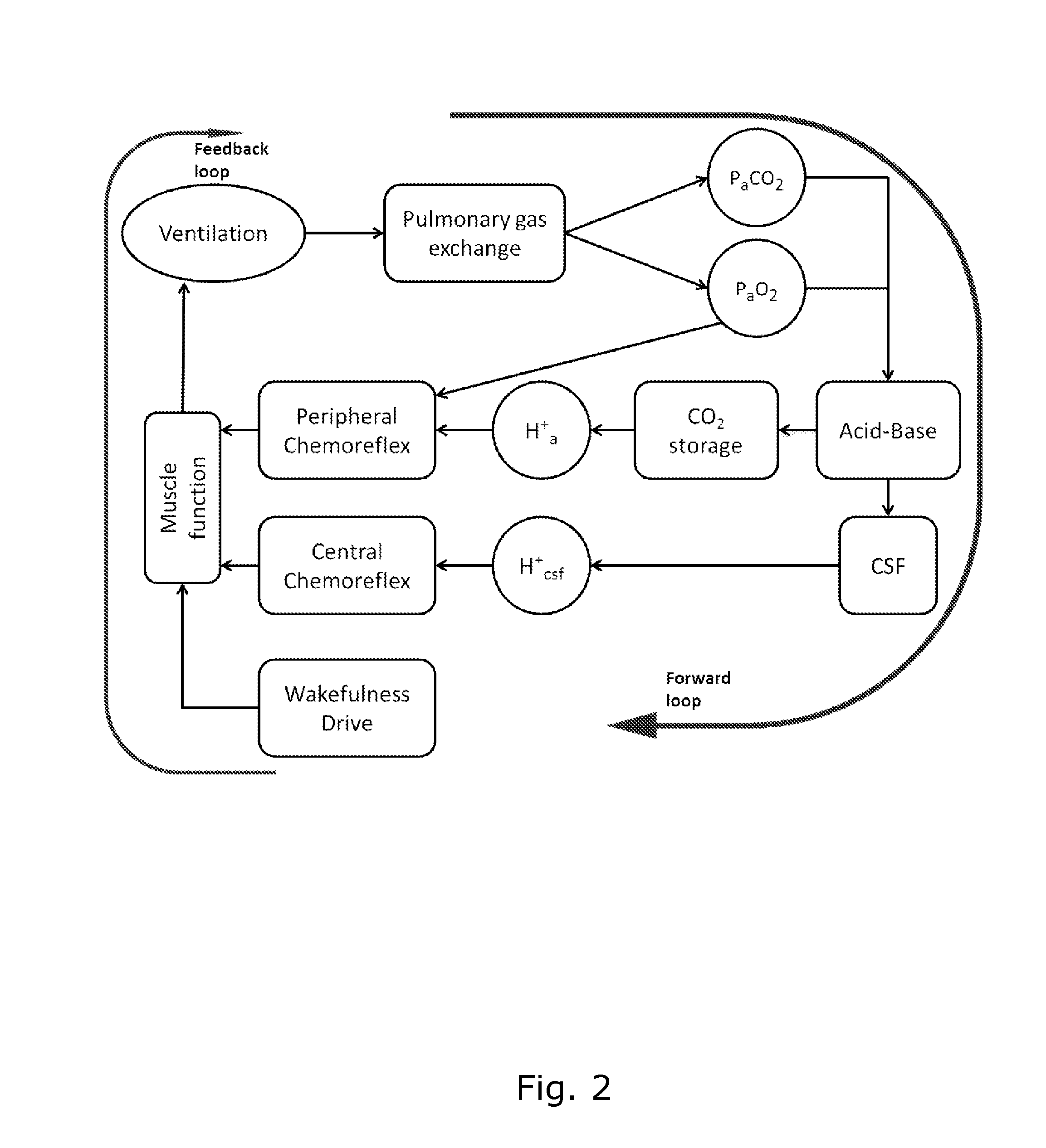
The present invention relates to a system (10) and a corresponding method for estimating the respiratory drive (R_DRIVE) of mechanically ventilated patients, and for preferably apportioning this respiratory drive into one, or more, components related to the chemical drive - i.e. the drive due to the chemoreceptor response- and / or the muscular drive - i.e. the contraction of respiratory muscles, for example the diaphragm. The principle of the invention is that respiratory drive can be obtained from measuring the patient's response to small changes in mechanical ventilation settings (Vt_SET), and that this can be apportioned into chemical and / or muscular effects depending upon the changes in respiratory frequency, and / or arterial or end tidal CO2 levels, and / or arterial blood p H.
Owner:COVIDIEN LP
Method and device for treating central sleep apnea
InactiveCN108175406AAchieve healingElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringRespiratory muscleMedicine
The invention discloses a method and device for treating central sleep apnea. The method comprises the following steps of 1) collecting surface electromyographic signals of respiratory muscles; 2) filtering by a filter; 3) performing envelope calculation on the surface electromyography signals; 4) generating electric mark signals of the respiratory muscles; 5), detecting blood oxygen saturation ofa patient by using a blood oxygen saturation probe clamped to a finger; 6), if the electric mark signals are not sampled in 10 seconds and the blood oxygen saturation drops by 3% or above, conductingexternal pacing on the respiratory muscles. The method is applied to the device. The method and device have the advantages of being accurate and effective, and the use effect is good.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
A system and a corresponding method for estimating respiratory drive of mechanically ventilated patients
ActiveUS20160121064A1Easy to understandEasy diagnosisRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory muscleRespiratory frequency
The present invention relates to a system (10) and a corresponding method for estimating the respiratory drive (R_DRIVE) of mechanically ventilated patients, and for preferably apportioning this respiratory drive into one, or more, components related to the chemical drive—i.e. the drive due to the chemoreceptor response—and / or the muscular drive—i.e. the contraction of respiratory muscles, for example the diaphragm. The principle of the invention is that respiratory drive can be obtained from measuring the patient's response to small changes in mechanical ventilation settings (Vt_SET), and that this can be apportioned into chemical and / or muscular effects depending upon the changes in respiratory frequency, and / or arterial or end tidal CO2 levels, and / or arterial blood p H.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
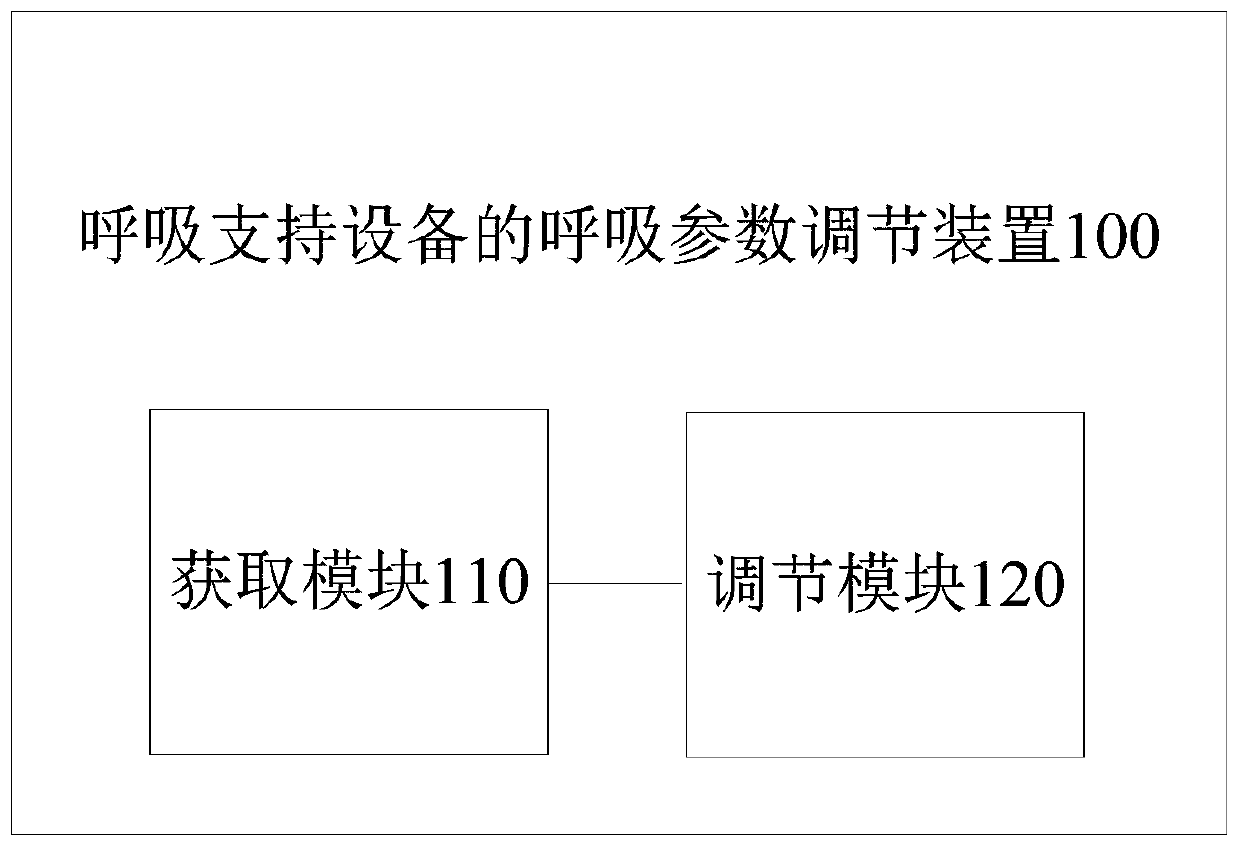
Respiratory parameter adjustment method and equipment for respiratory support device and respiratory support device
ActiveCN109718442AReduce dependenceReduce standby timeRespiratorsGymnastic exercisingRespiratory muscleRespiratory support
The present invention provides a respiratory parameter adjustment method and equipment for a respiratory support device and the respiratory support device. The method comprises the following steps: physical condition parameters of patients and current respiratory parameters of the respiratory support device are acquired, wherein the physical condition parameters at least comprise blood oxygen saturation and end-tidal carbon dioxide concentration value, and the respiratory parameters at least comprise ventilation control frequency and trigger sensitivity; and the respiratory parameters are adjusted according to the physical condition parameters to perform respiratory exercise on the patients. The respiratory parameters of the respiratory support device can be automatically adjusted to conduct the respiratory exercise on the patients, so that respiratory muscles are gradually restored, dependence on the respiratory support device is reduced, standby time is reduced and an offline successrate is improved.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com