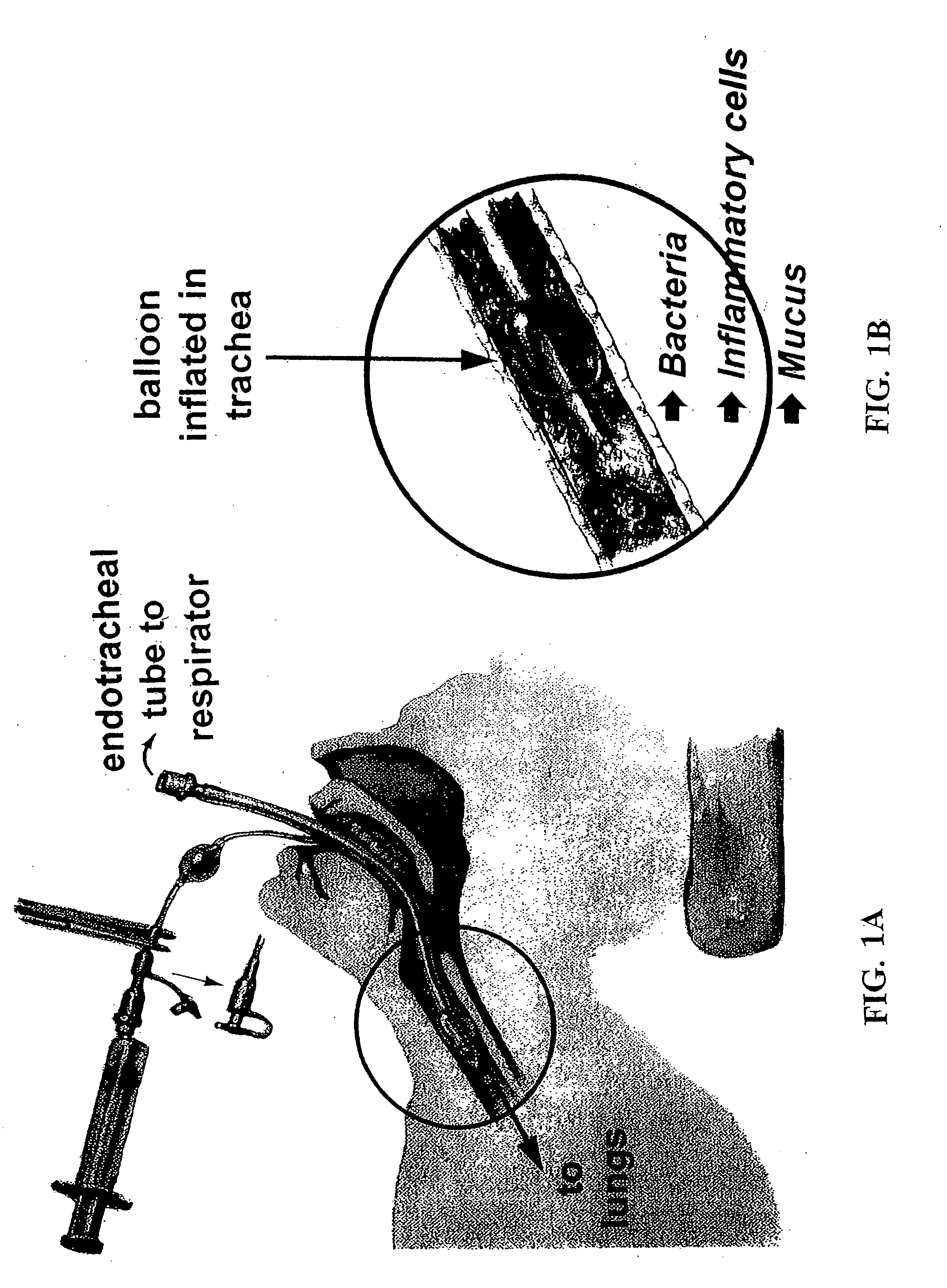
Patents
Literature
56 results about "Ventilator circuit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
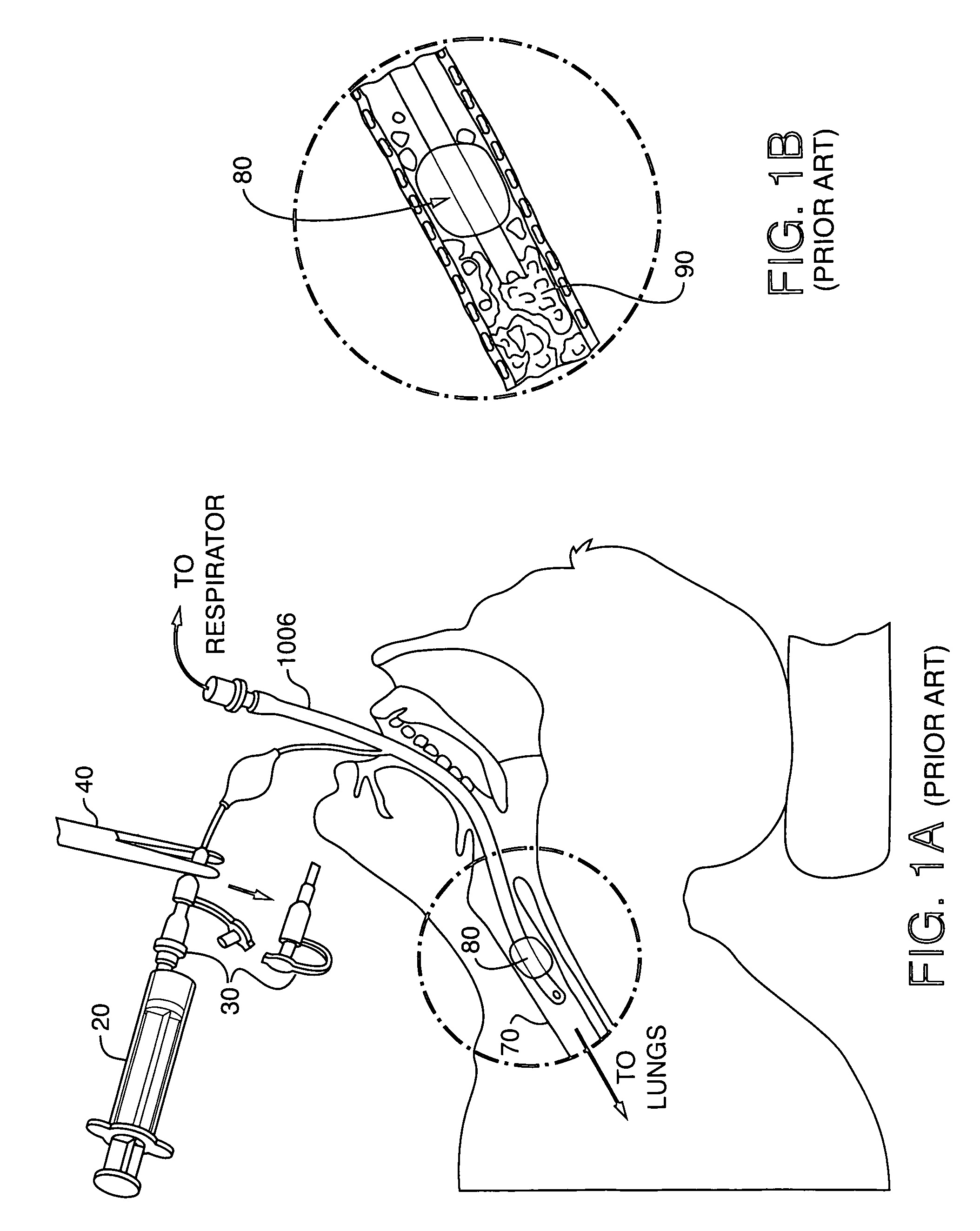
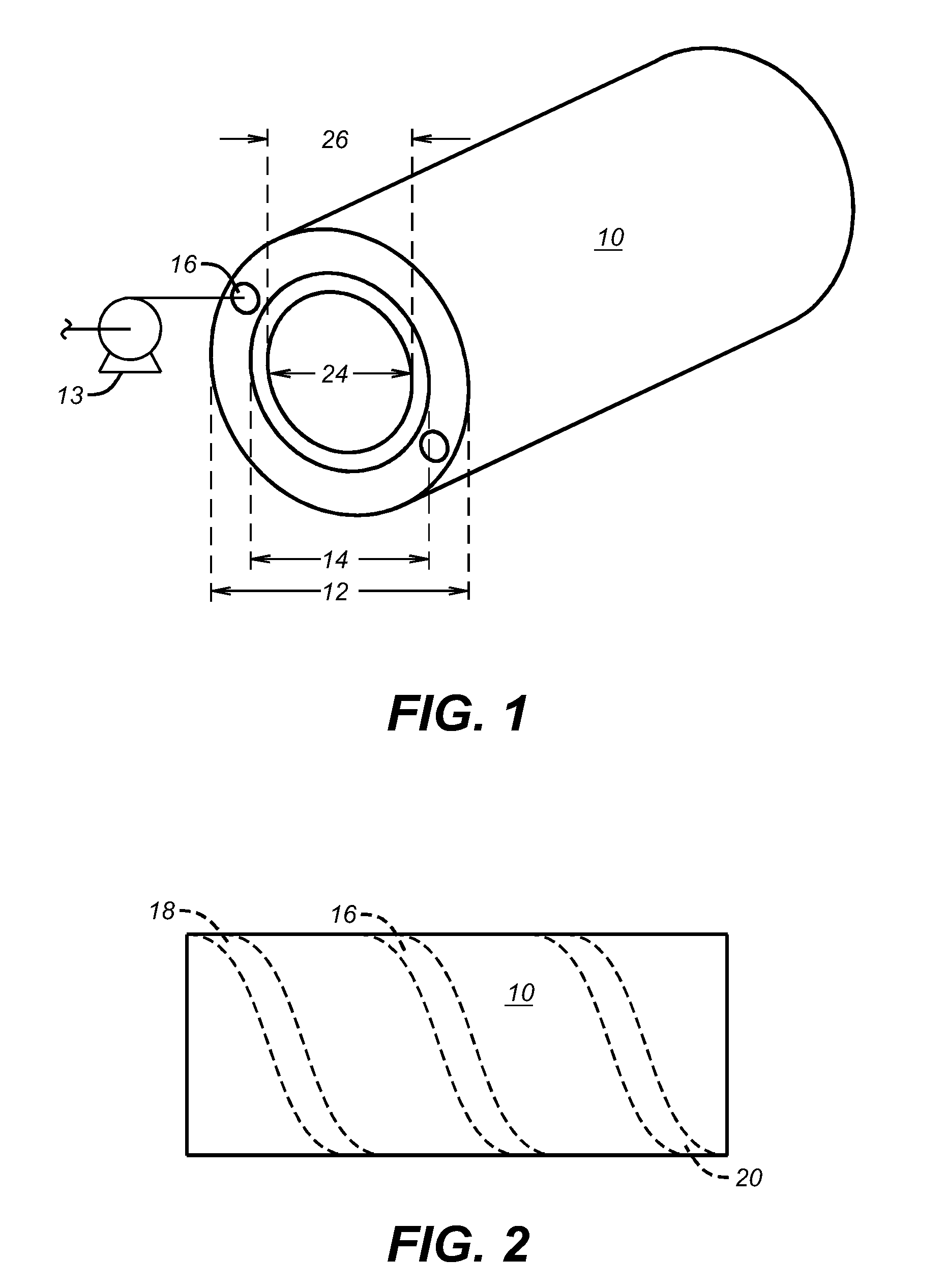
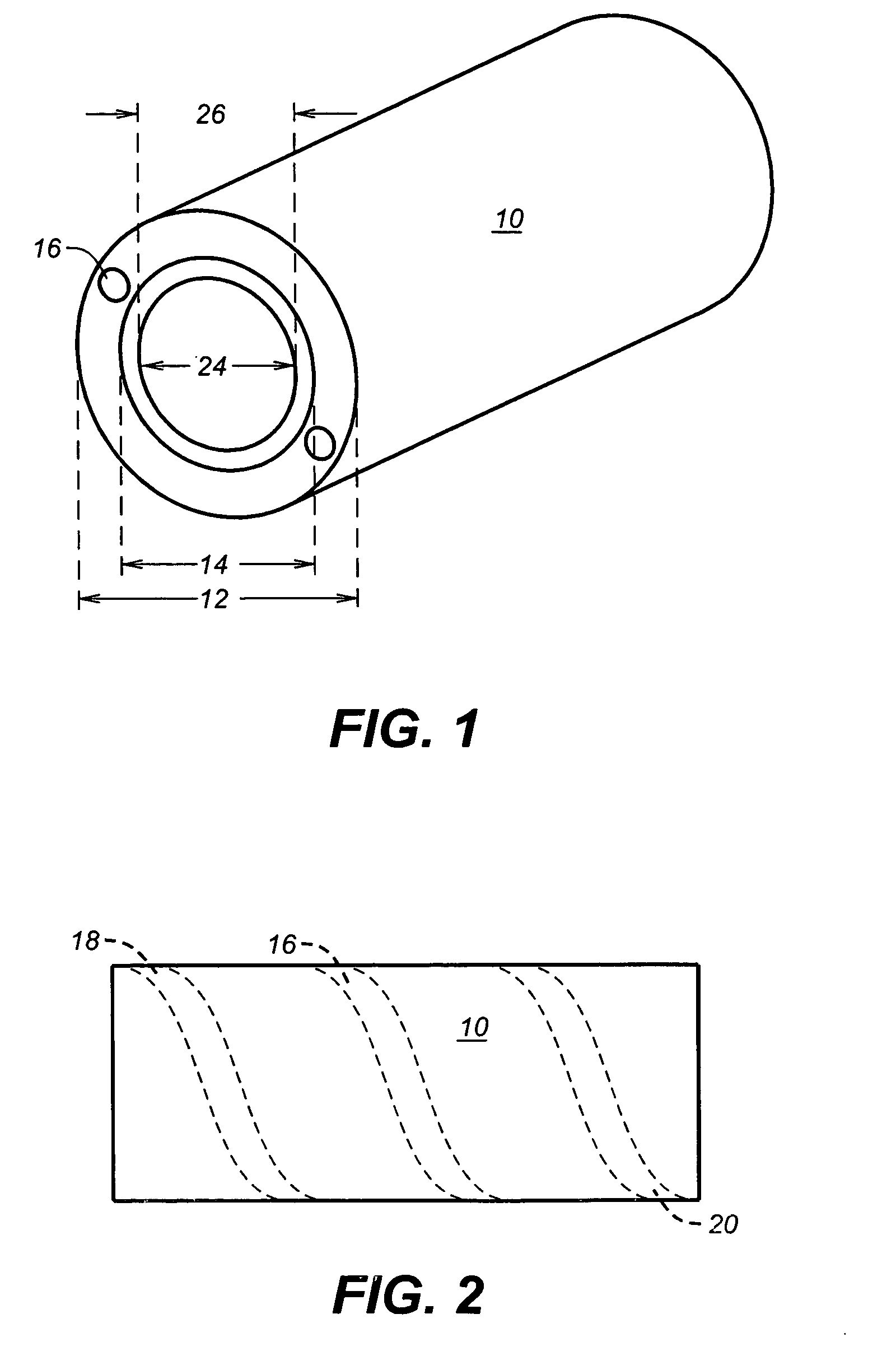
A breathing system or breathing circuit is a medical device used to deliver oxygen, remove carbon dioxide, and deliver inhalational anaesthetic agents to a patient. Originally developed for use in anaesthesiology, many variants of breathing system are in clinical use, but most comprise a source of fresh gas flow, a length of breathing tubing to direct the gas, an adjustable pressure limiting valve to control pressure within the system and direct waste away, and a reservoir bag to allow assisted ventilation.
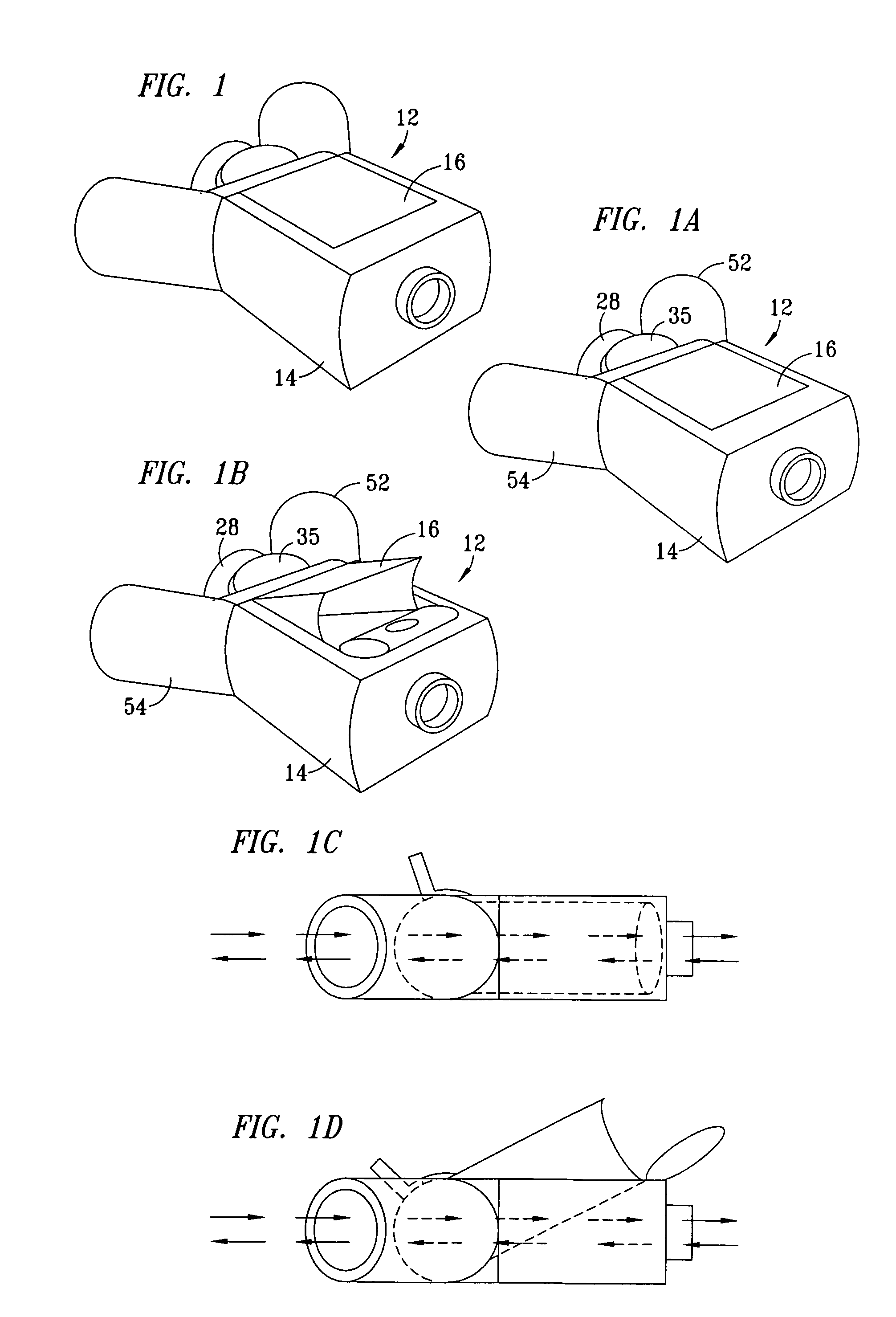
Methods and systems for operating an aerosol generator
InactiveUS20050217666A1Improve security levelImprove delivery efficiencyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseAmikacin
A method of treating a patient with a pulmonary disease, where the method includes delivering a dose of aerosolized medicament intermittently to a ventilator circuit coupled to the respiratory system of the patient. Also, a method of treating a patient with a pulmonary disease, where the method includes taking the patient off a ventilator, and administering to the patient, a nebulized aerosol comprising from about 100 μg to about 500 mg of a medicament. Additionally, an aerosolized medicament for the treatment of a pulmonary disease, where the medicament includes amikacin mixed with an aqueous solution having an adjusted pH from about 5.5 to about 6.3. The pH is adjusted by adding hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide to the aqueous solution.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Methods and systems for operating an aerosol generator
ActiveUS20070267010A1Improve security levelImprove delivery efficiencyRespiratorsBiocideDiseaseAmikacin
A method of treating a patient with a pulmonary disease, where the method includes delivering a dose of aerosolized medicament intermittently to a ventilator circuit coupled to the respiratory system of the patient. Also, a method of treating a patient with a pulmonary disease, where the method includes taking the patient off a ventilator, and administering to the patient, a nebulized aerosol comprising from about 100 μg to about 500 mg of a medicament. Also a method of treating a patient with a pulmonary disease, the method comprising administering an aerosolized first medicament comprising amikacin to the patient and administering, systemically a second medicament comprising an antibiotic to the patient that also treats the pulmonary disease, wherein a resulting amikacin concentration in the lung and / or pulmonary system is therapeutically-effective, and an amount of the systemically administered antibiotics is reduced.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
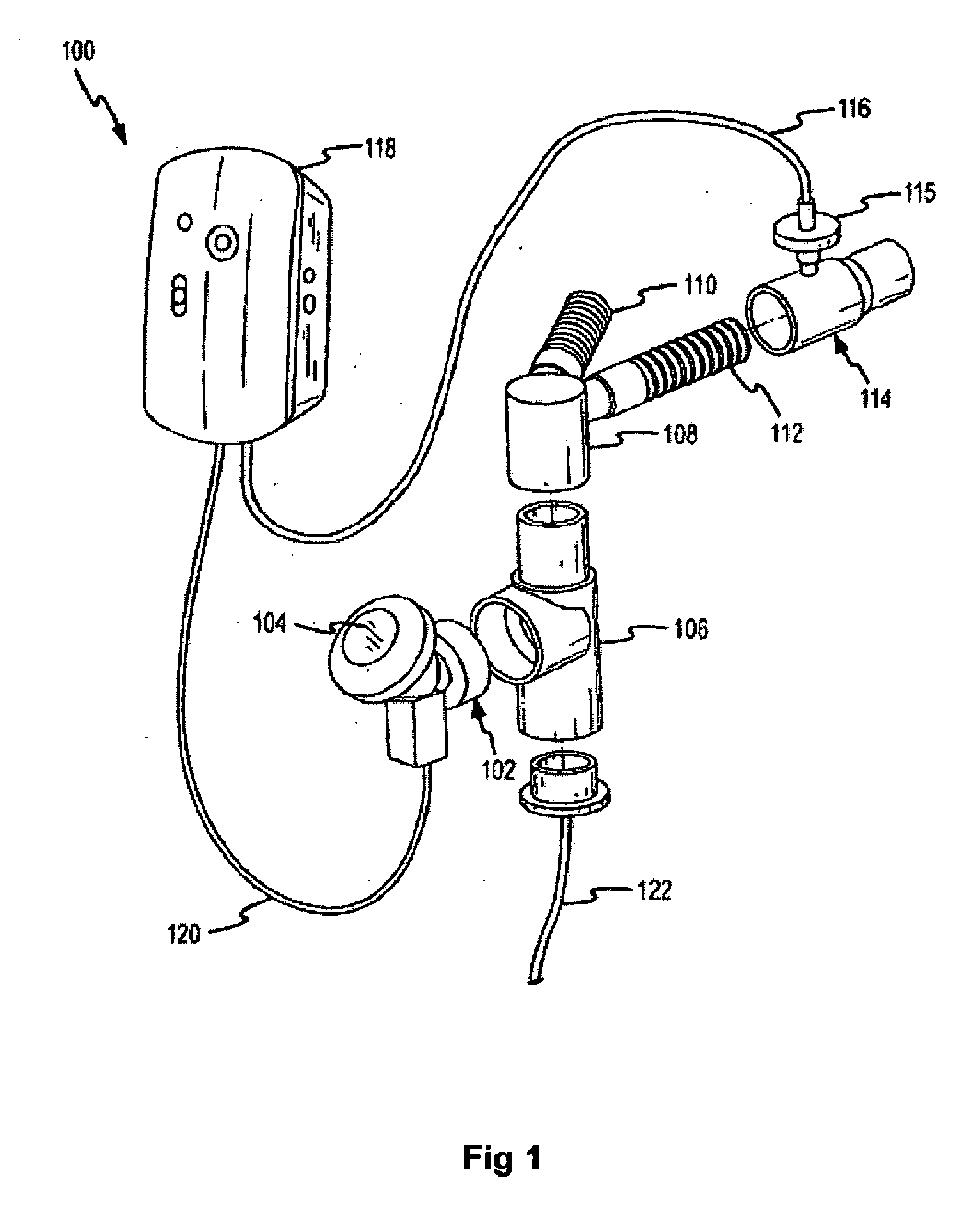
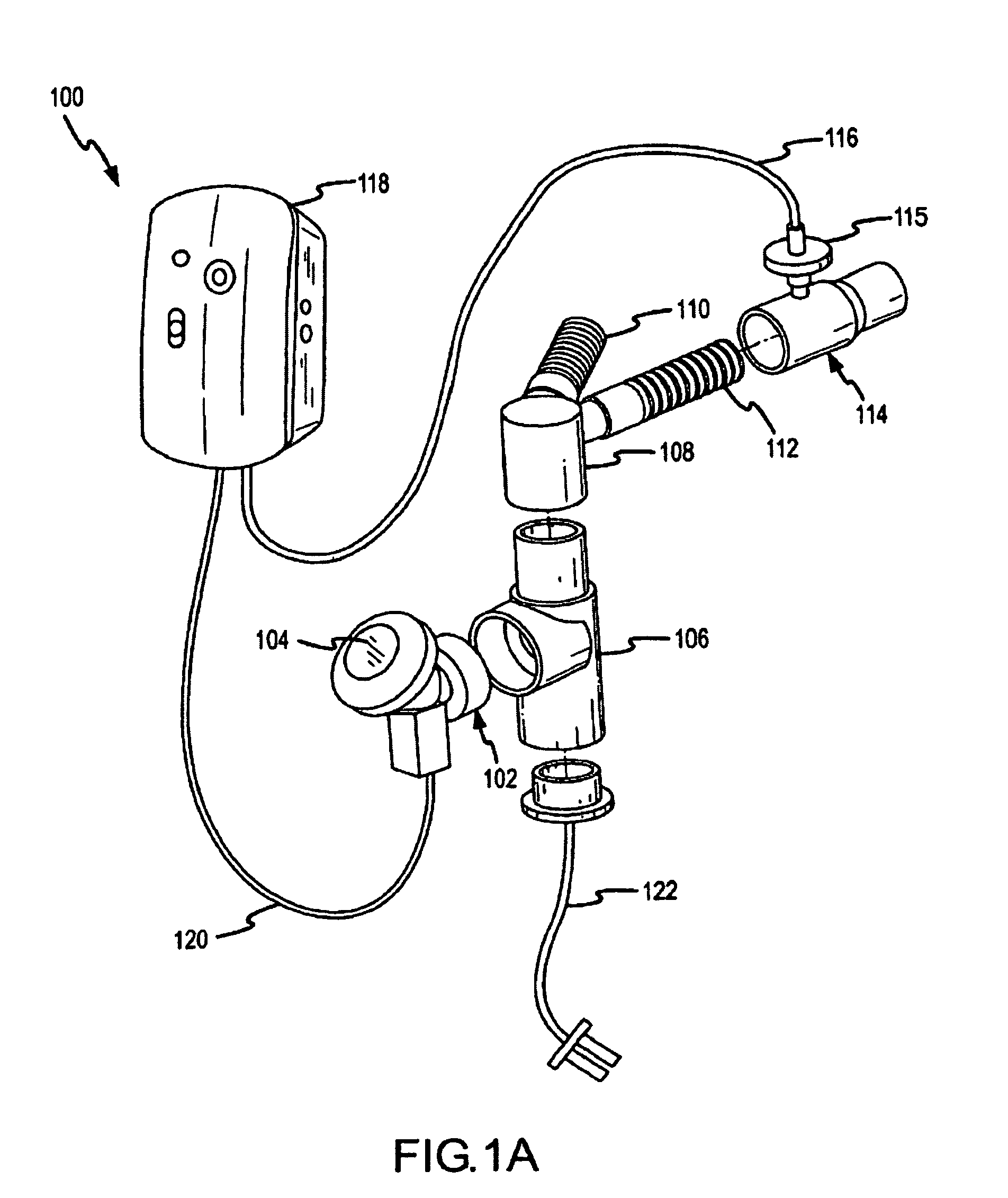
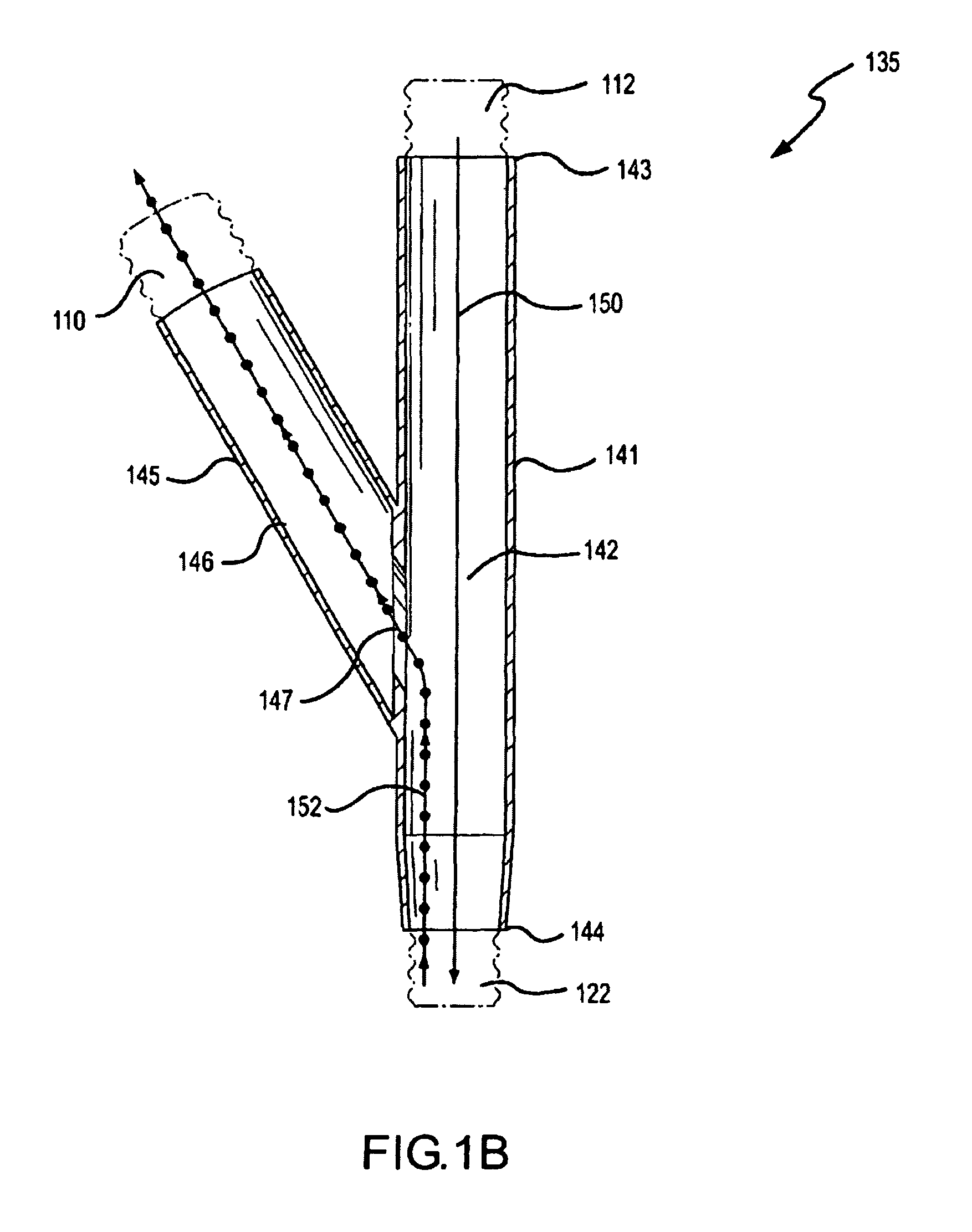
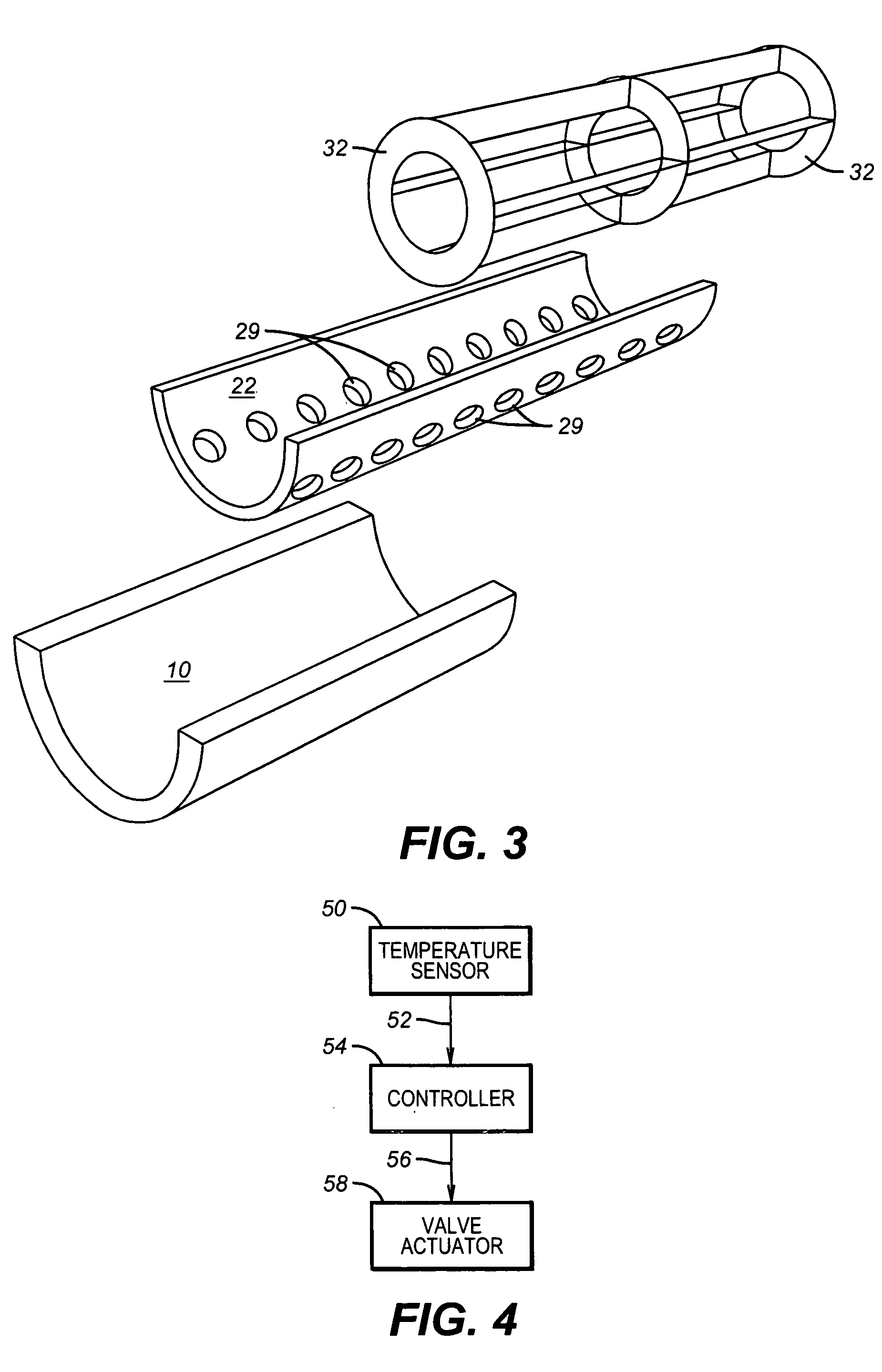
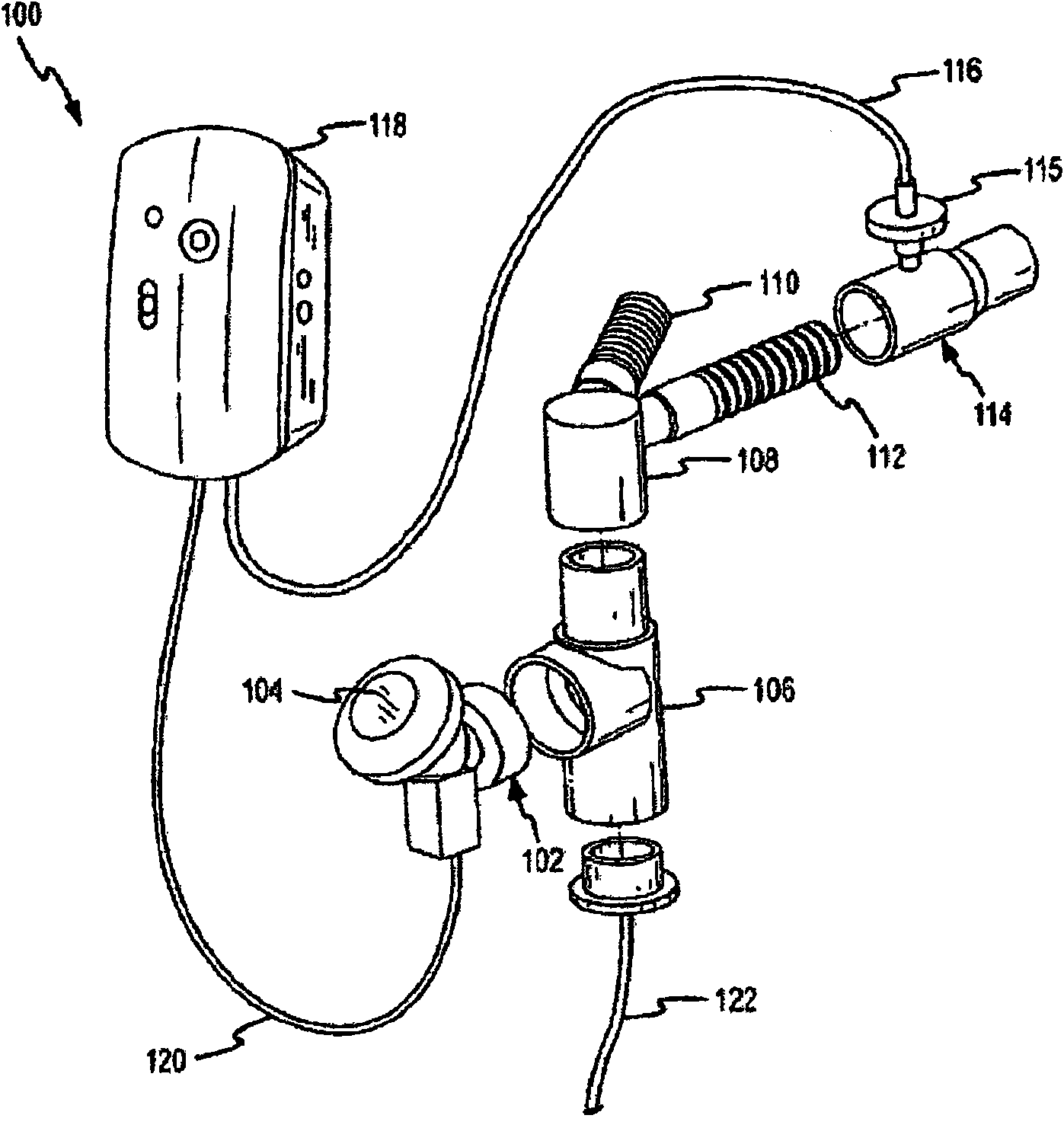
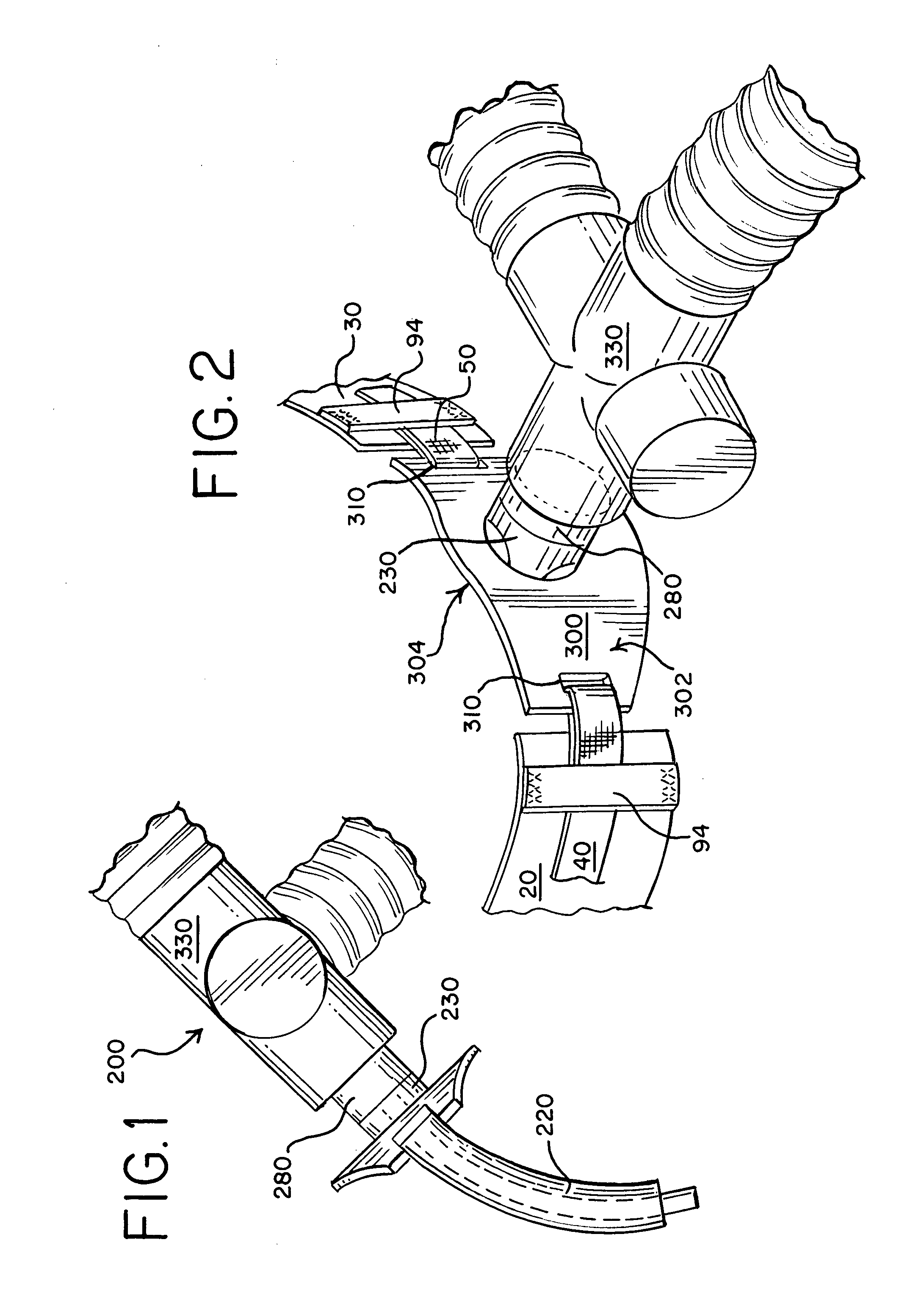
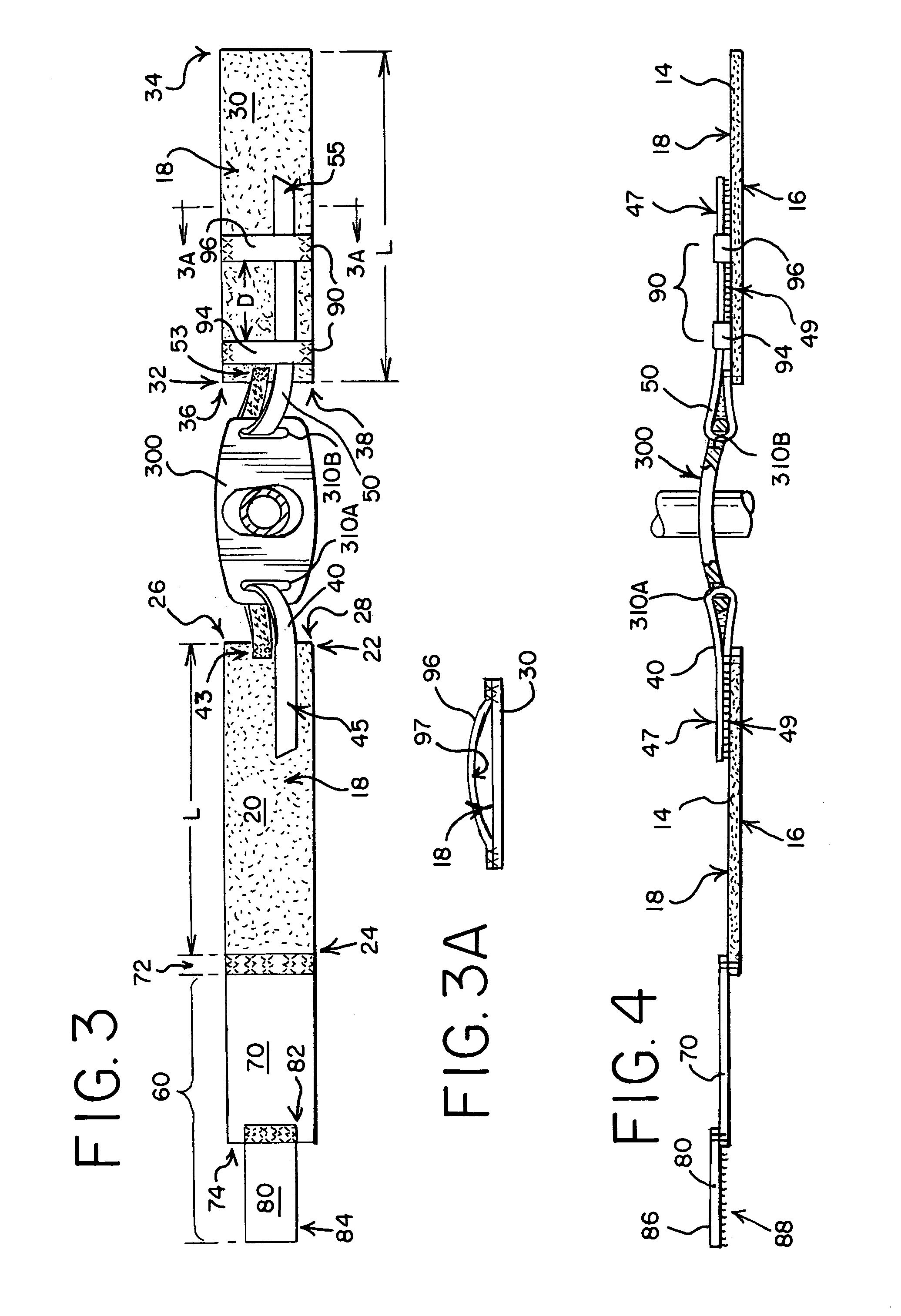
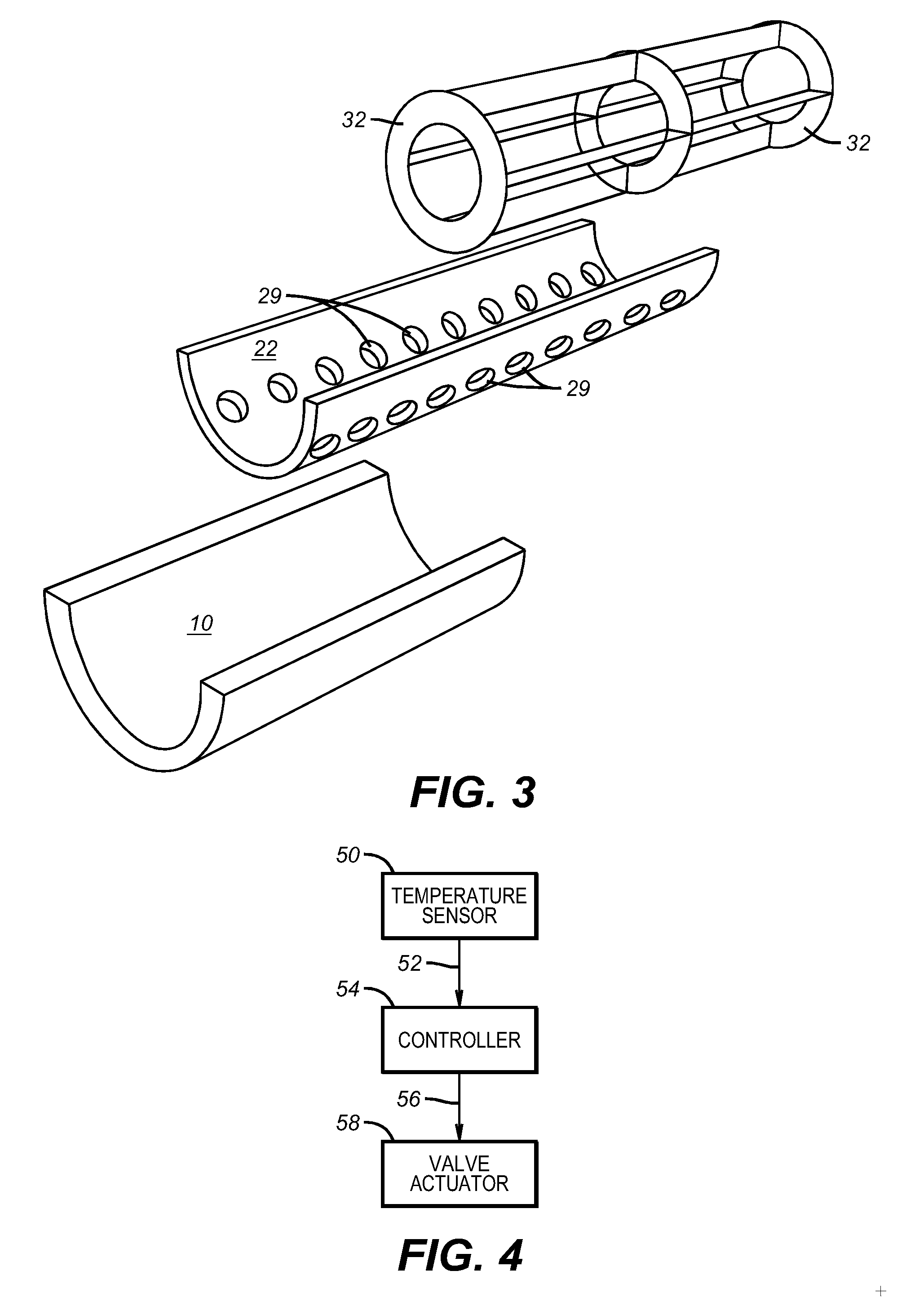
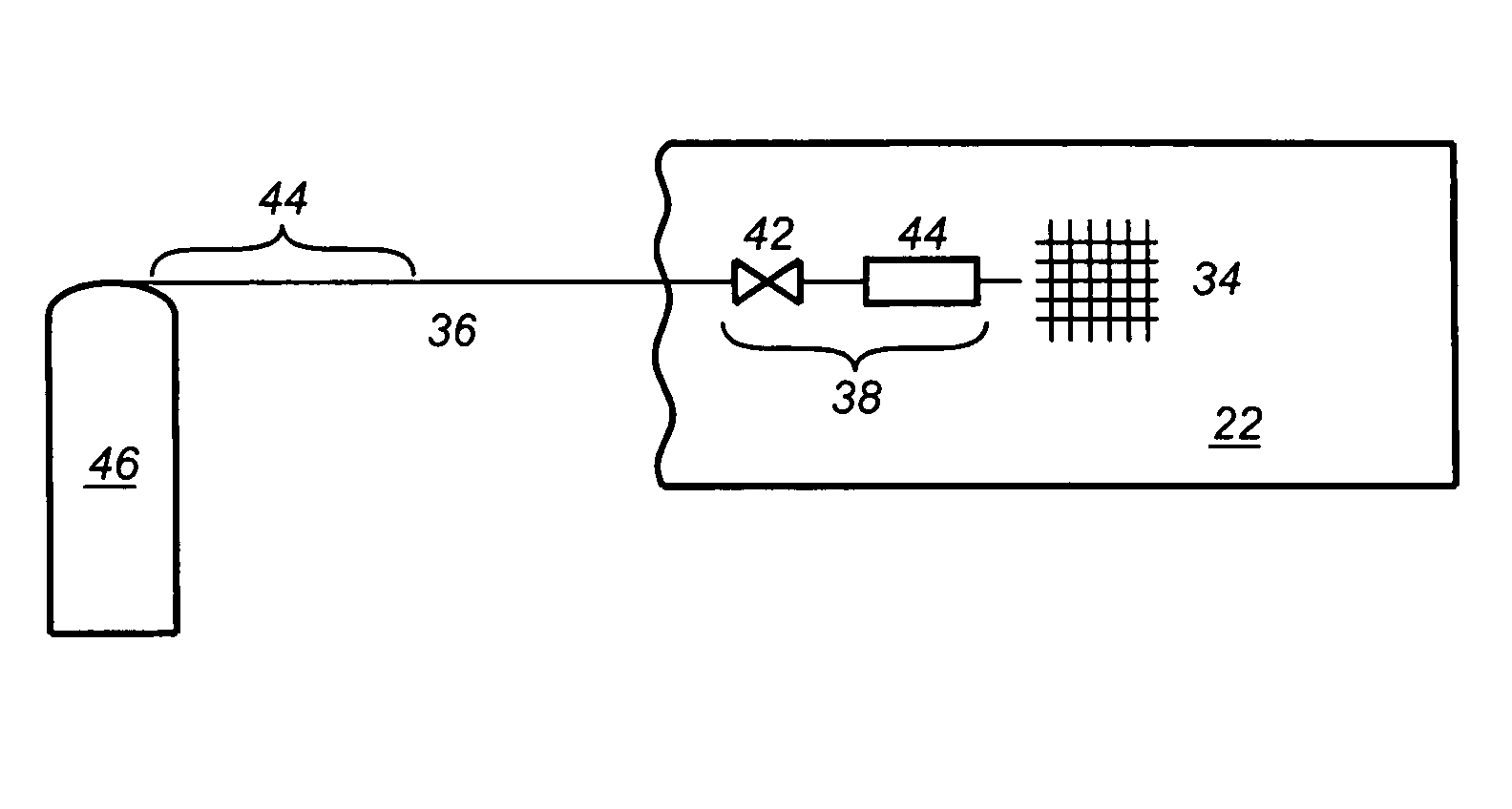
Humidification in breathing circuits
InactiveUS20090241948A1Accurate and repeatable changeEasy to controlRespiratorsSurgical needlesEngineeringVentilator circuit
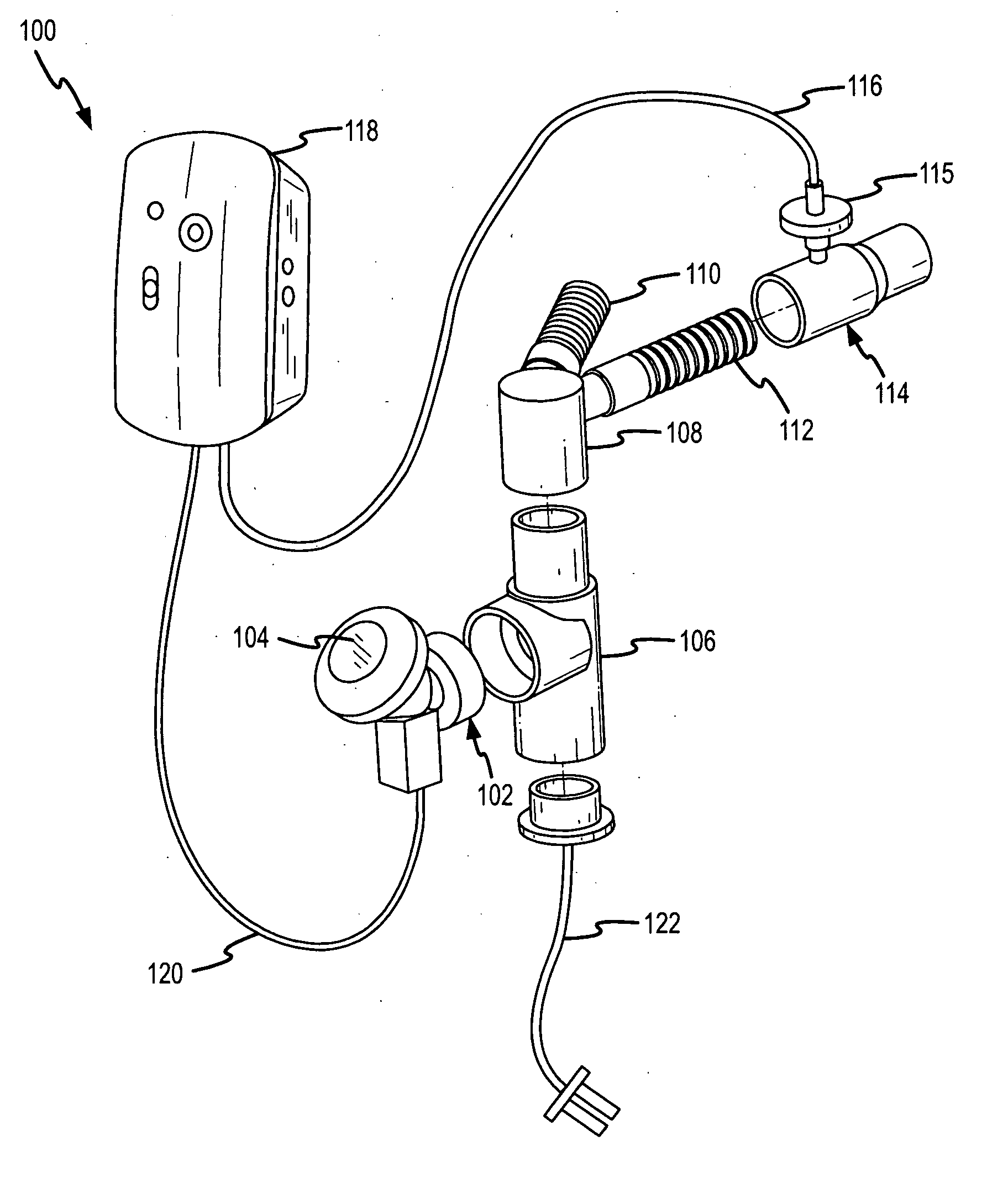
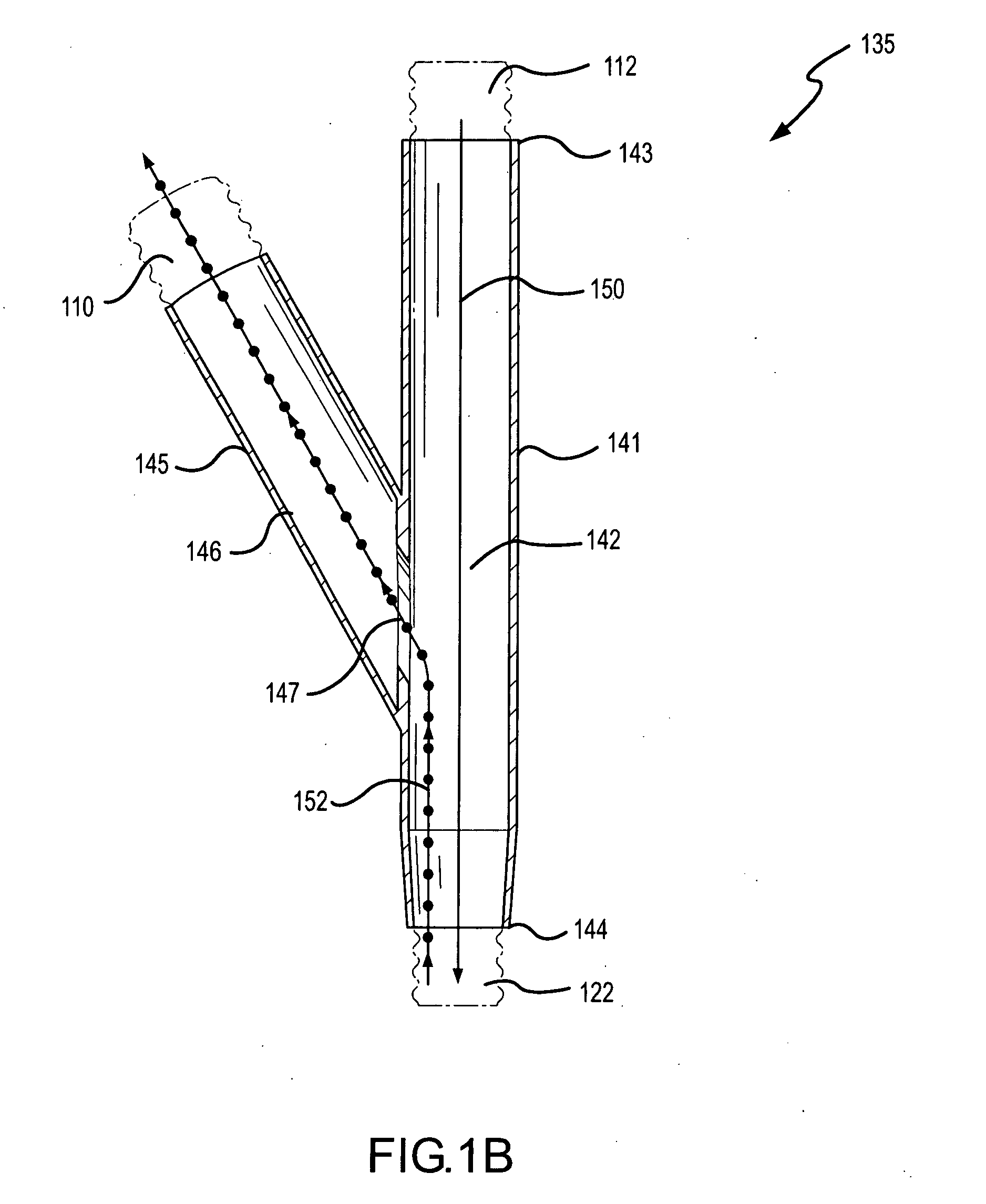
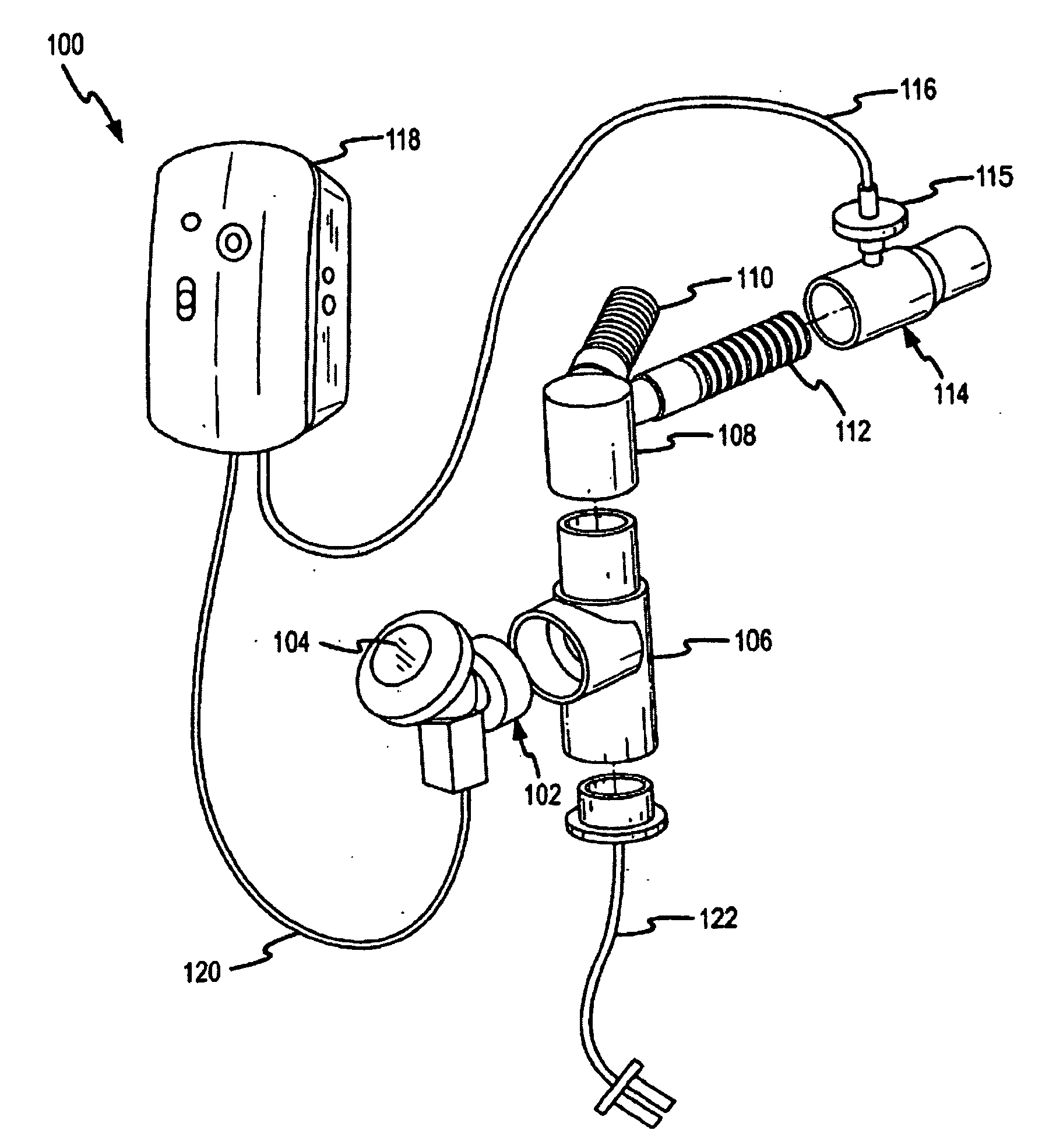
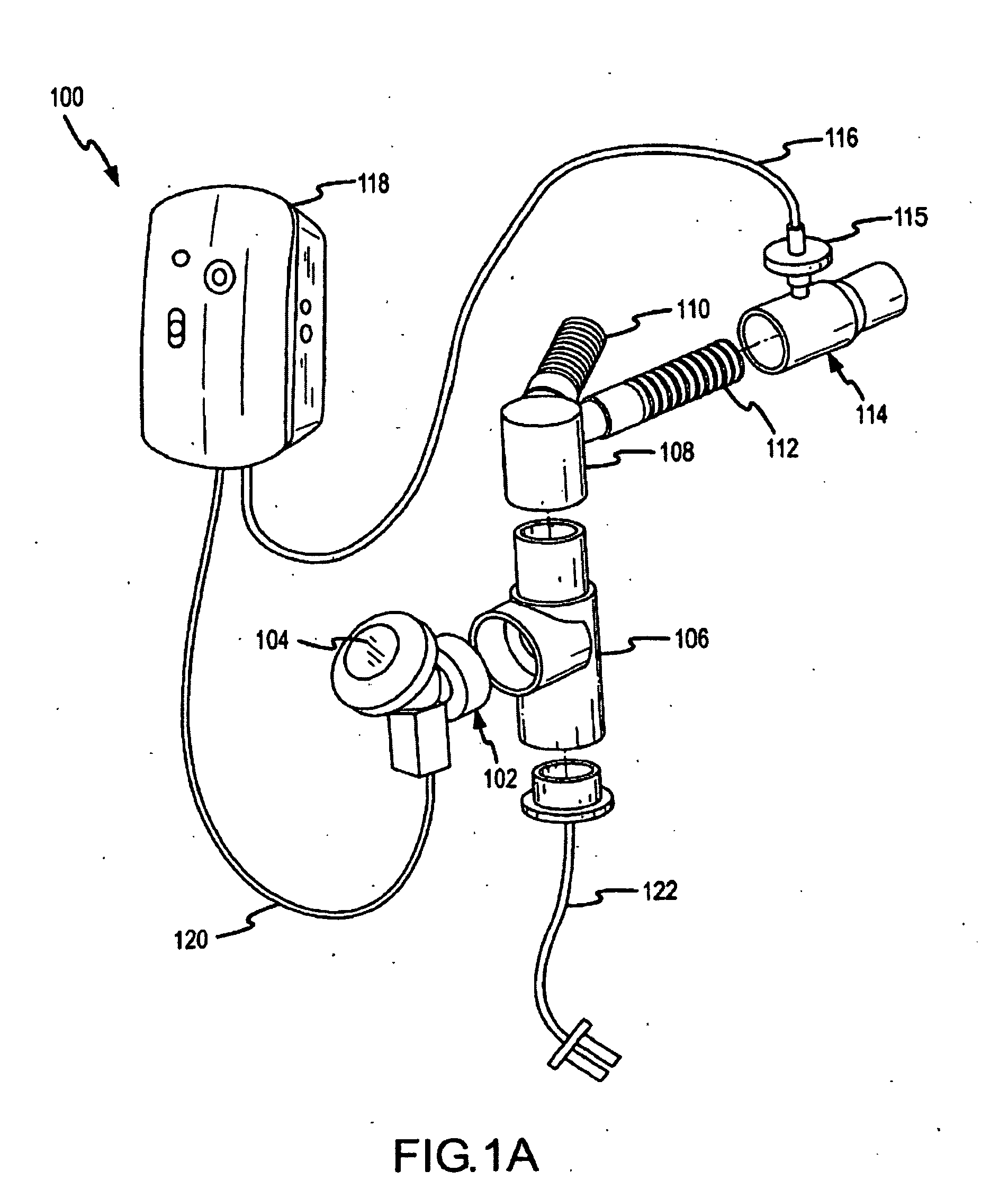
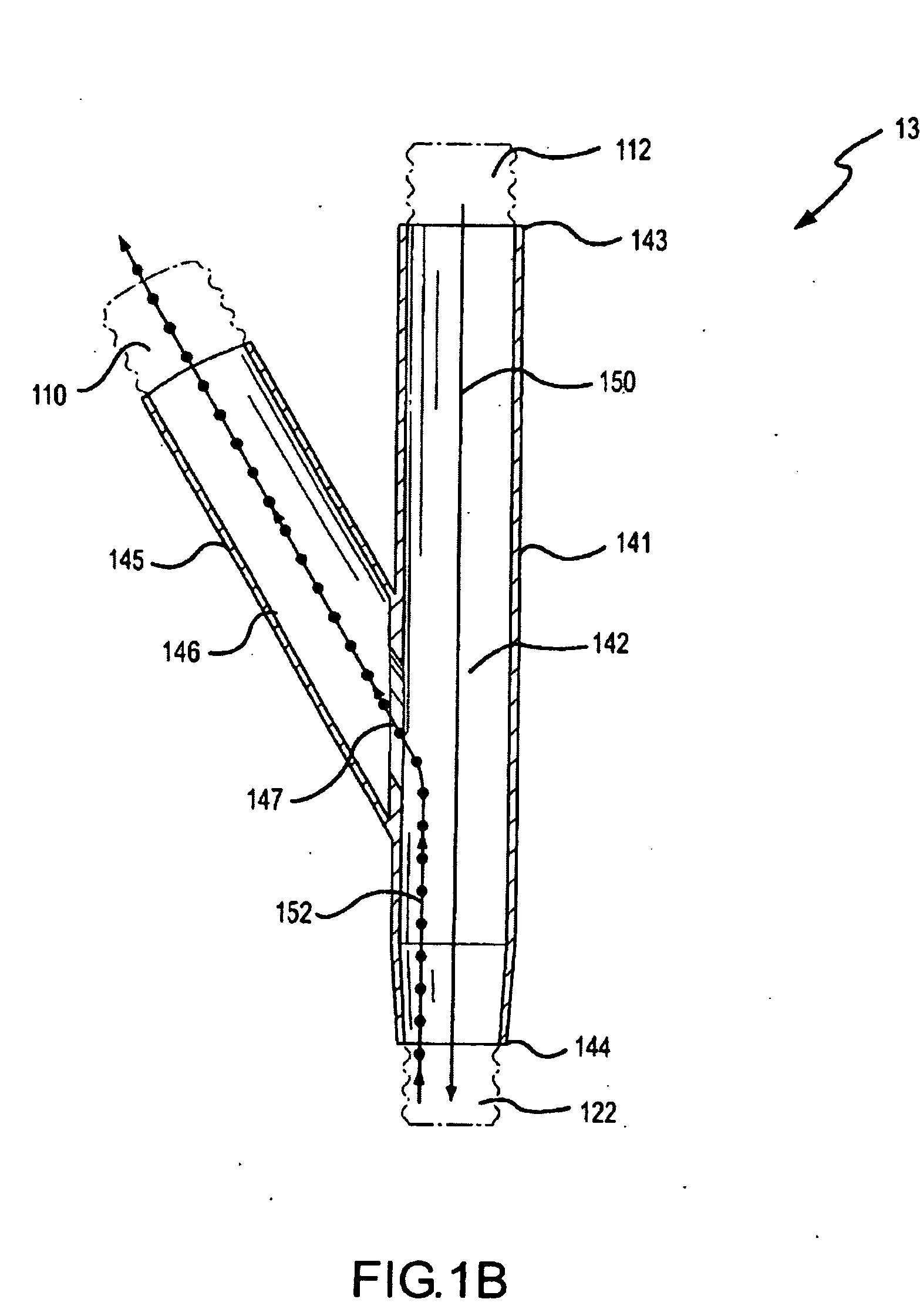
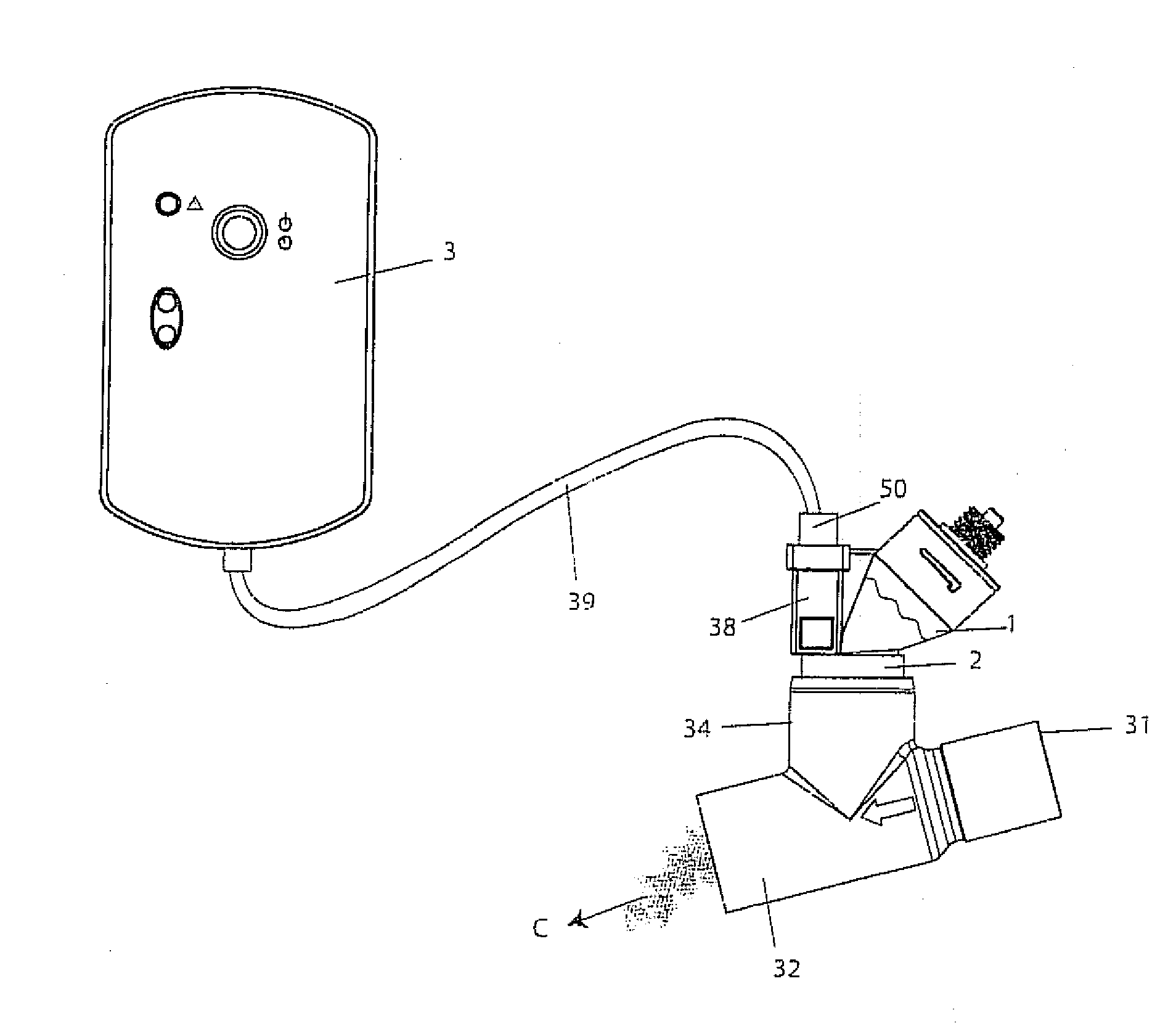
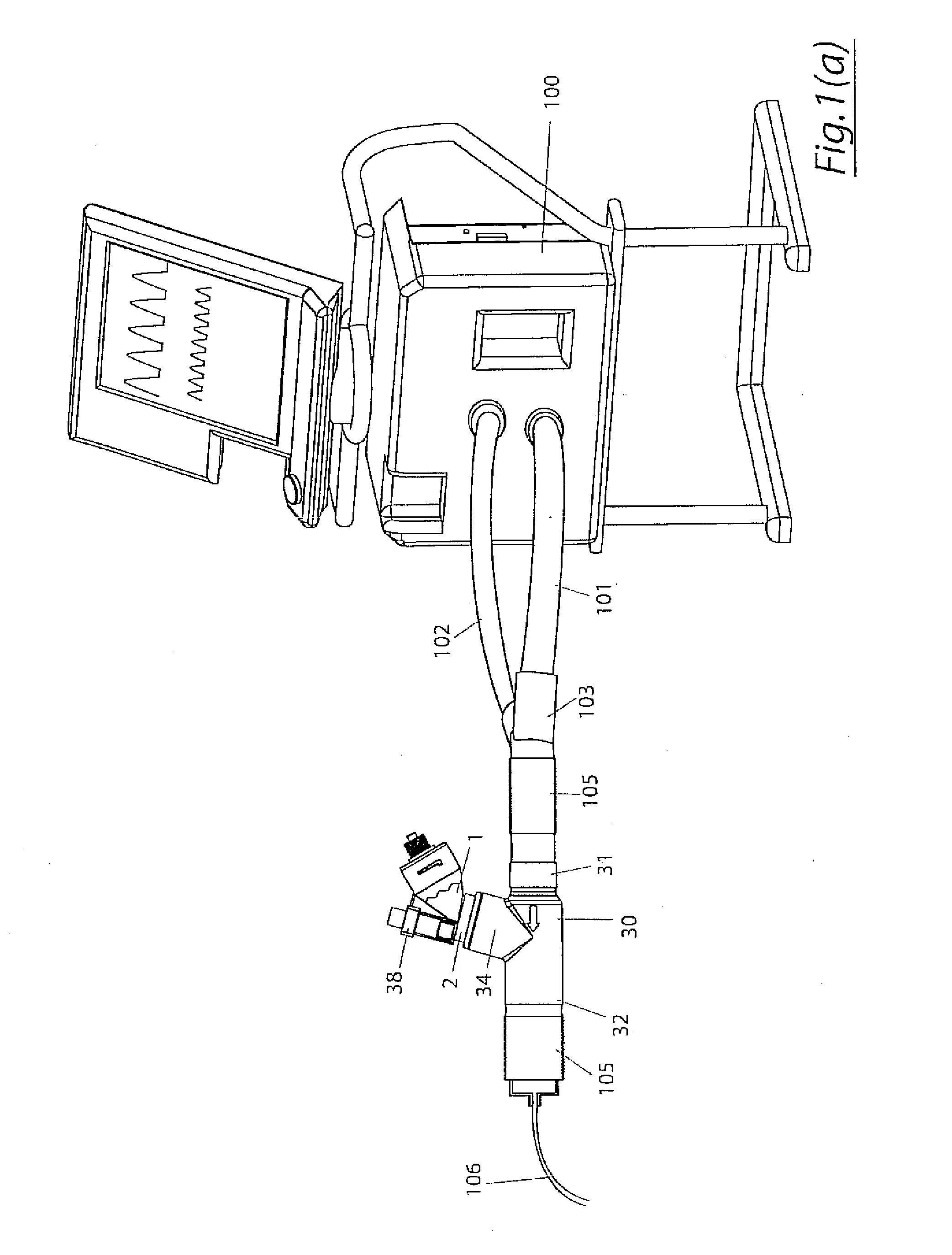
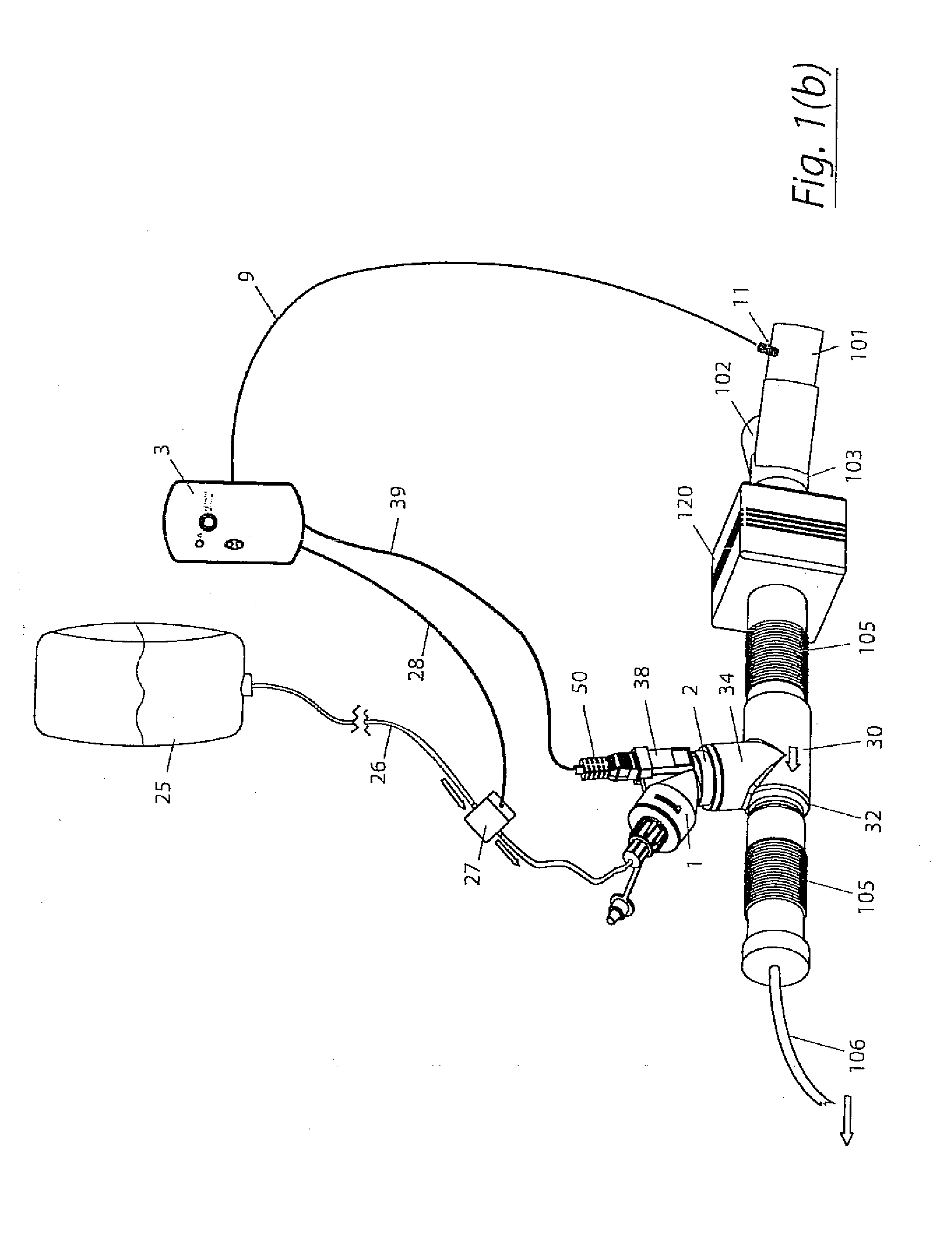
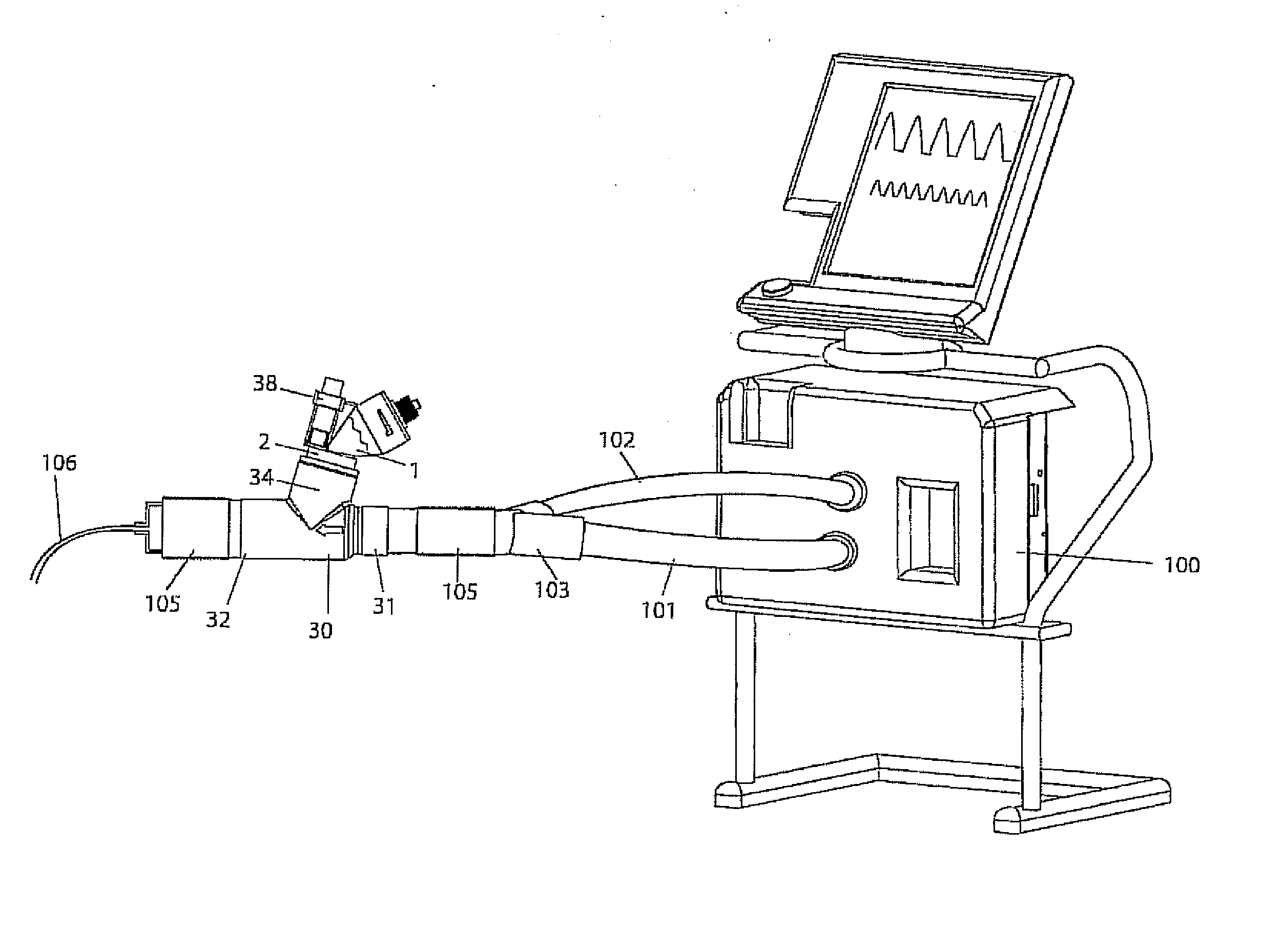
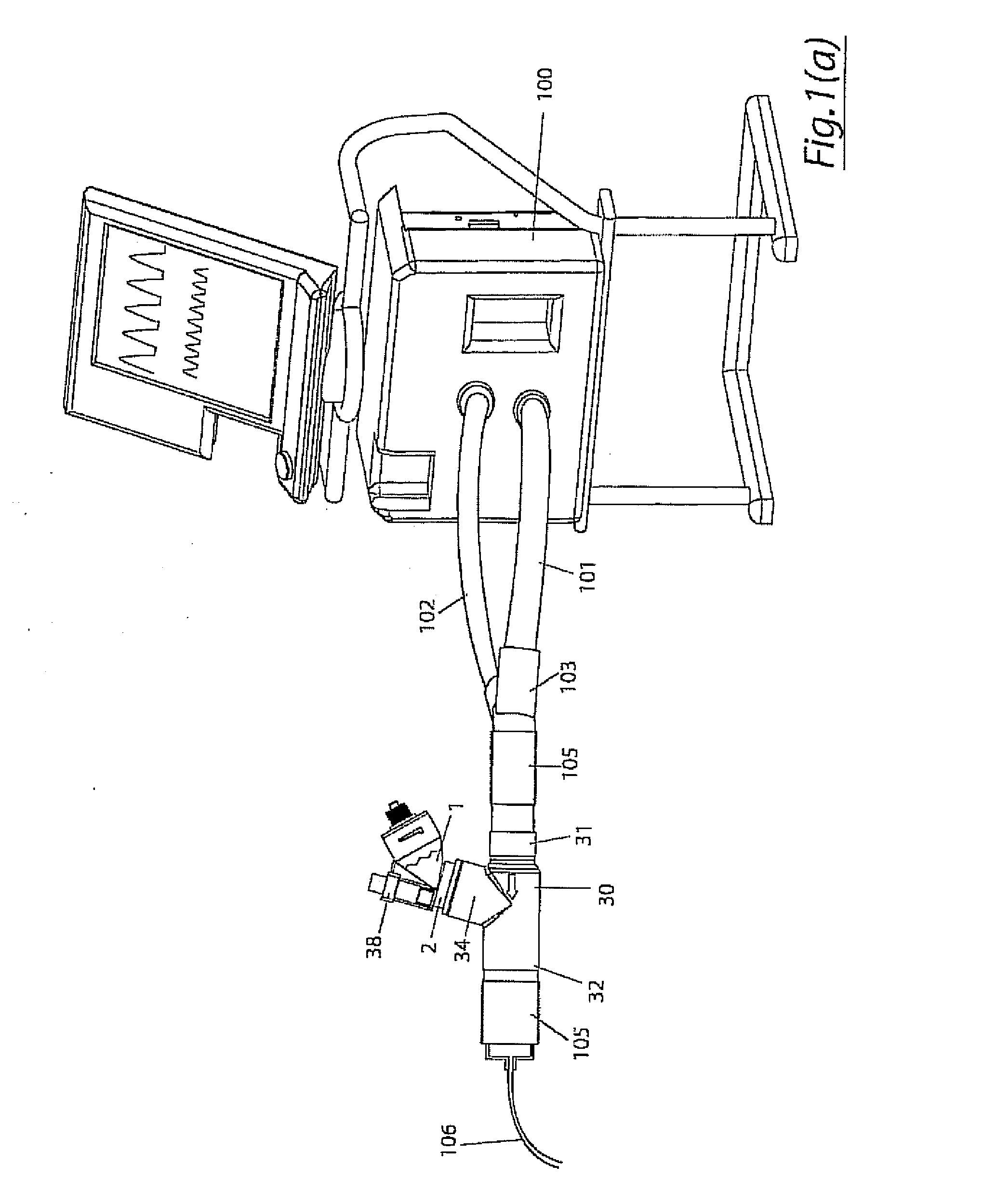
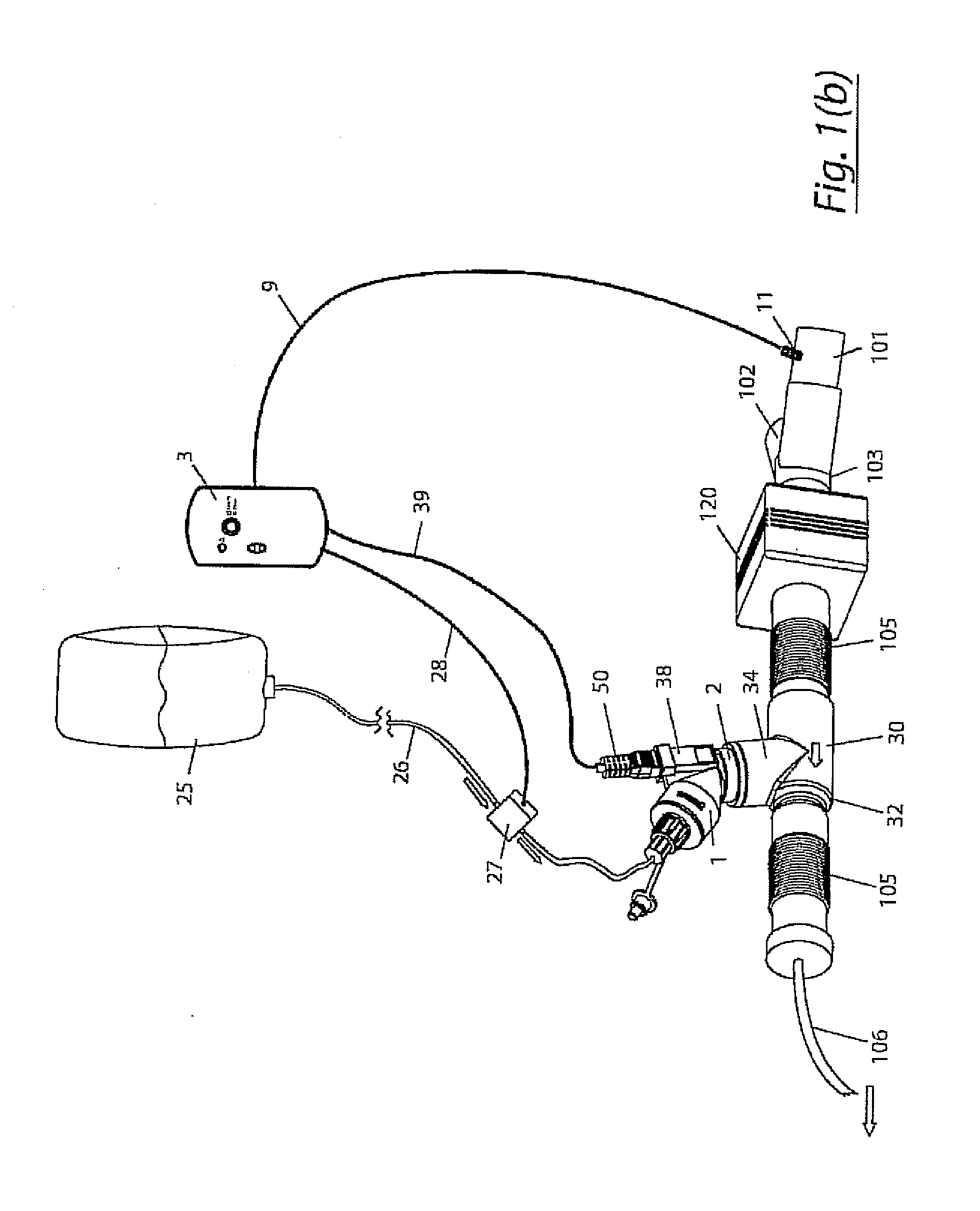
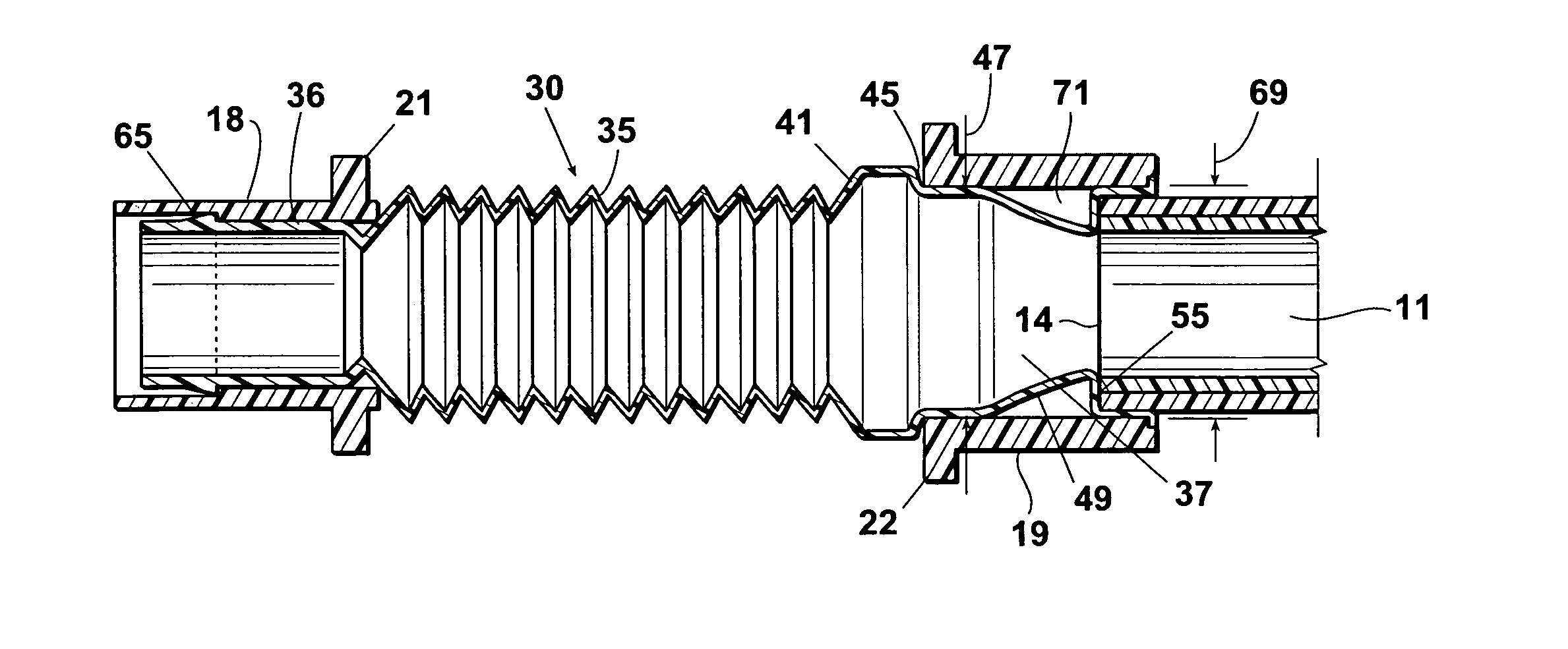
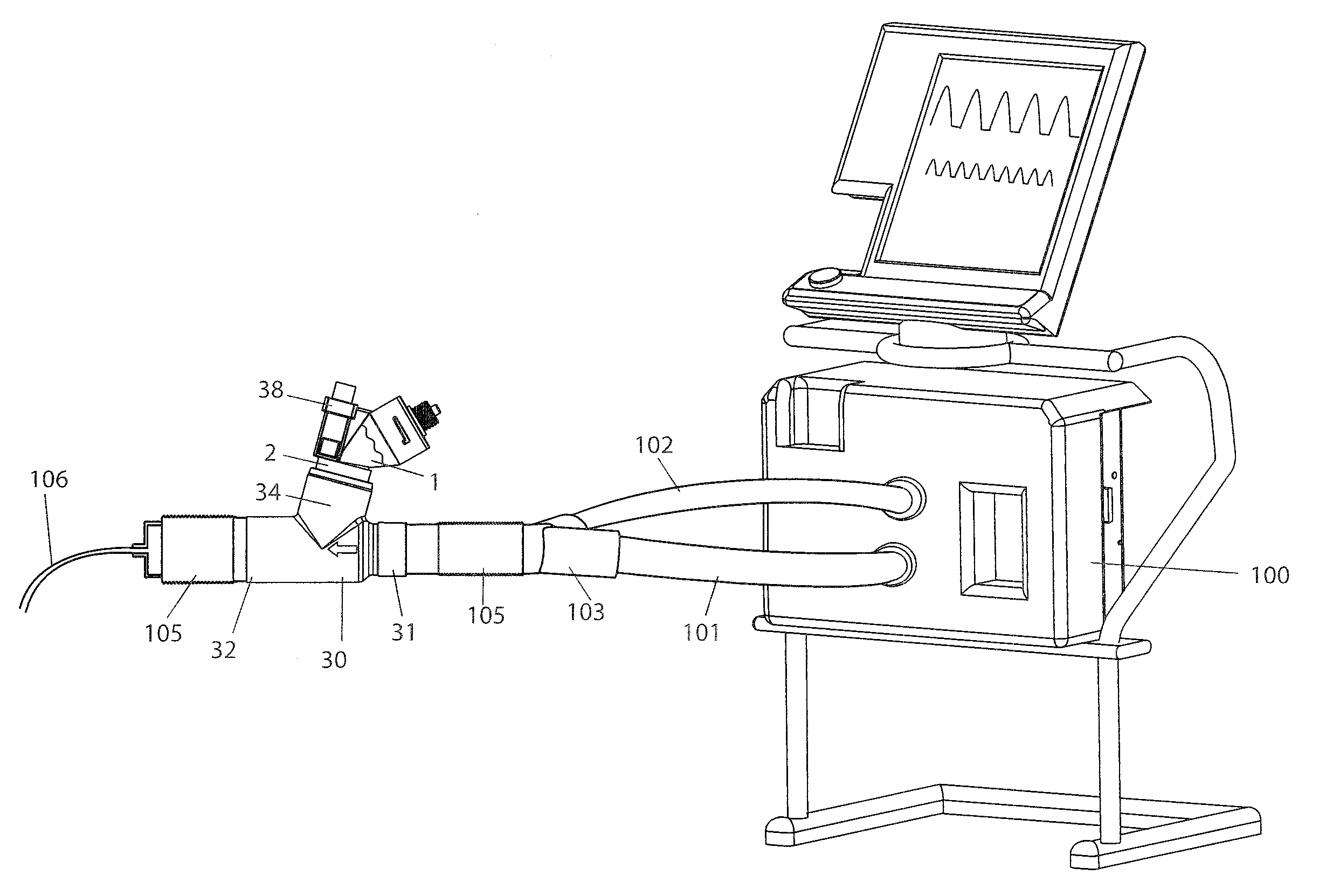
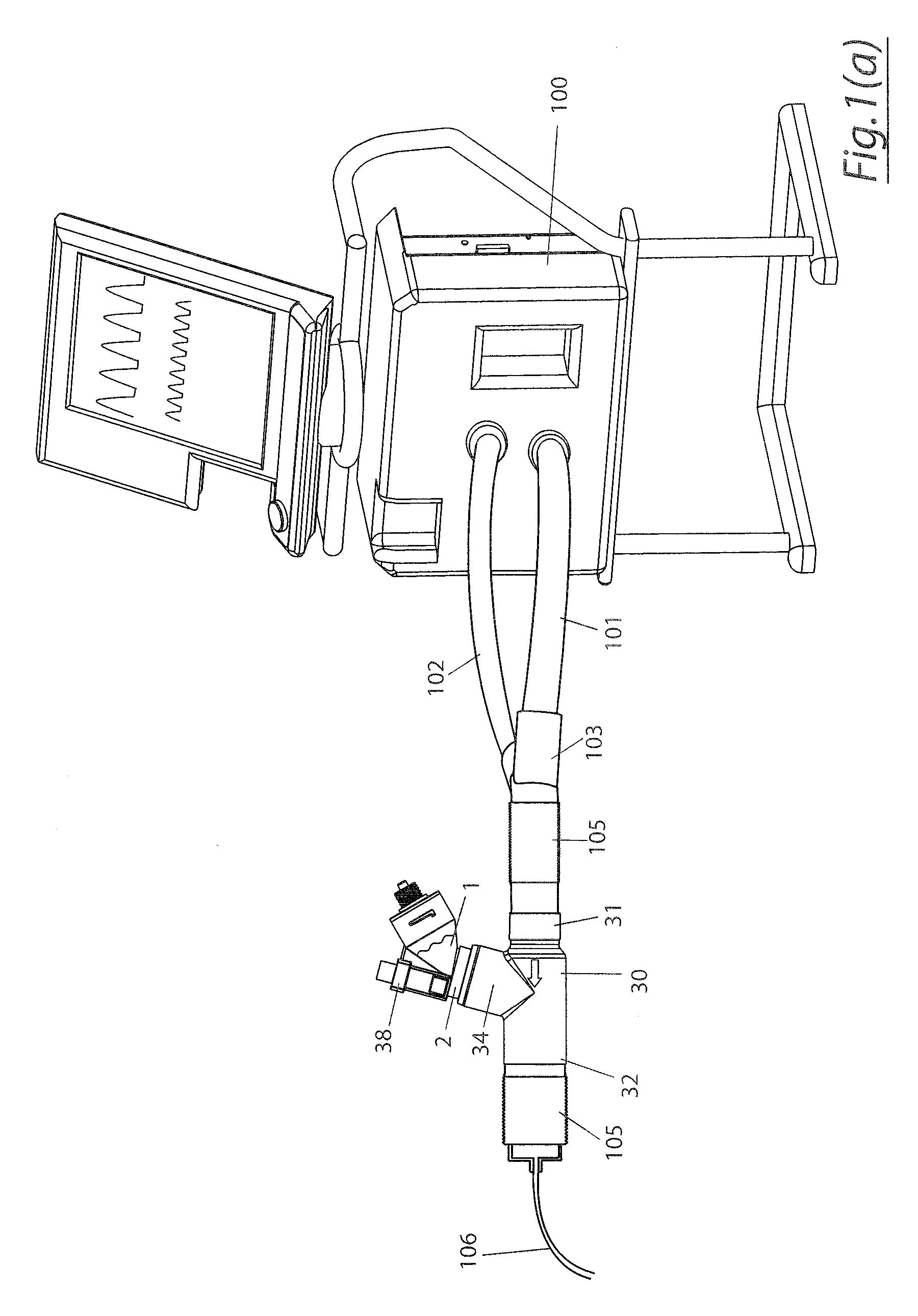
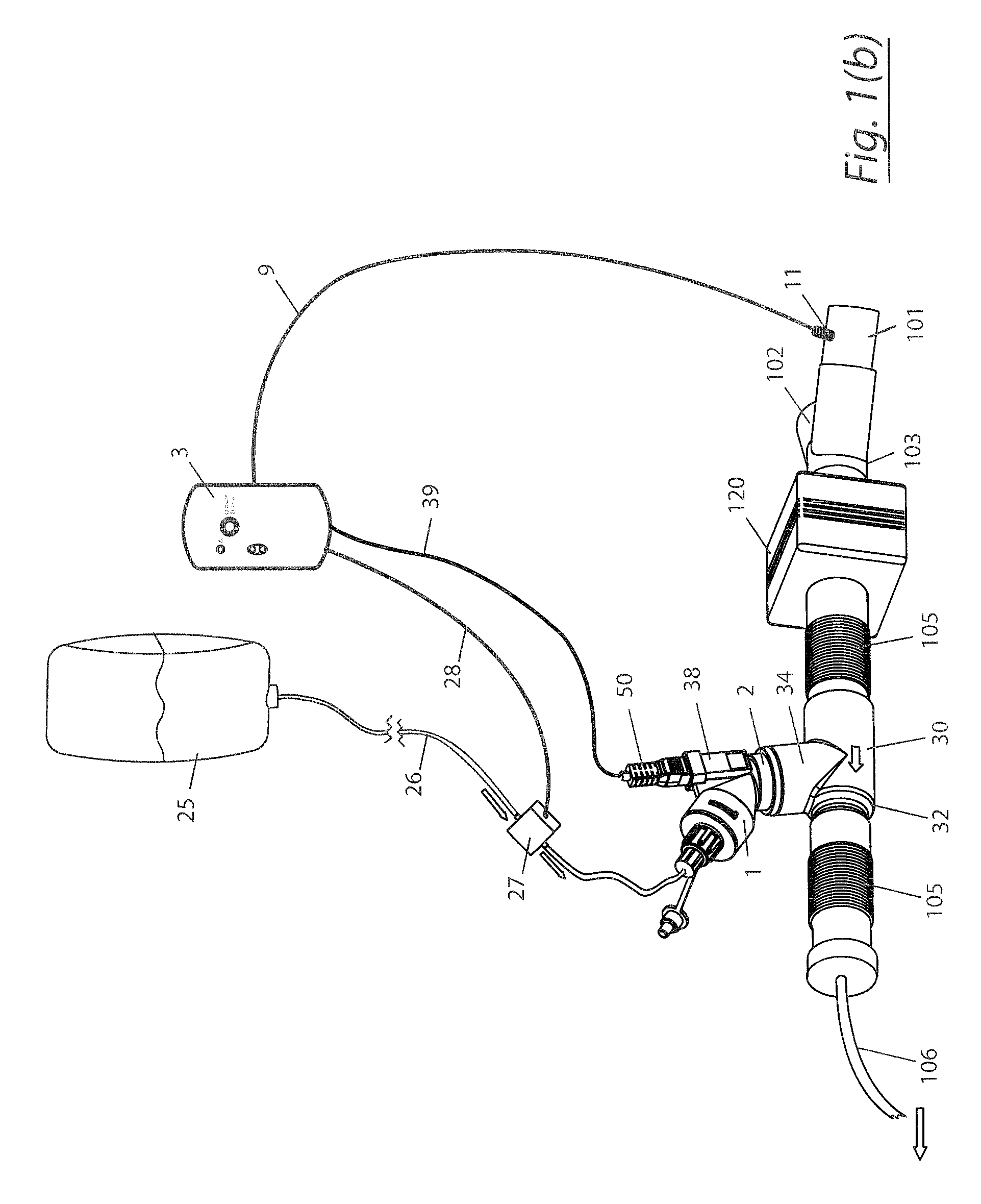
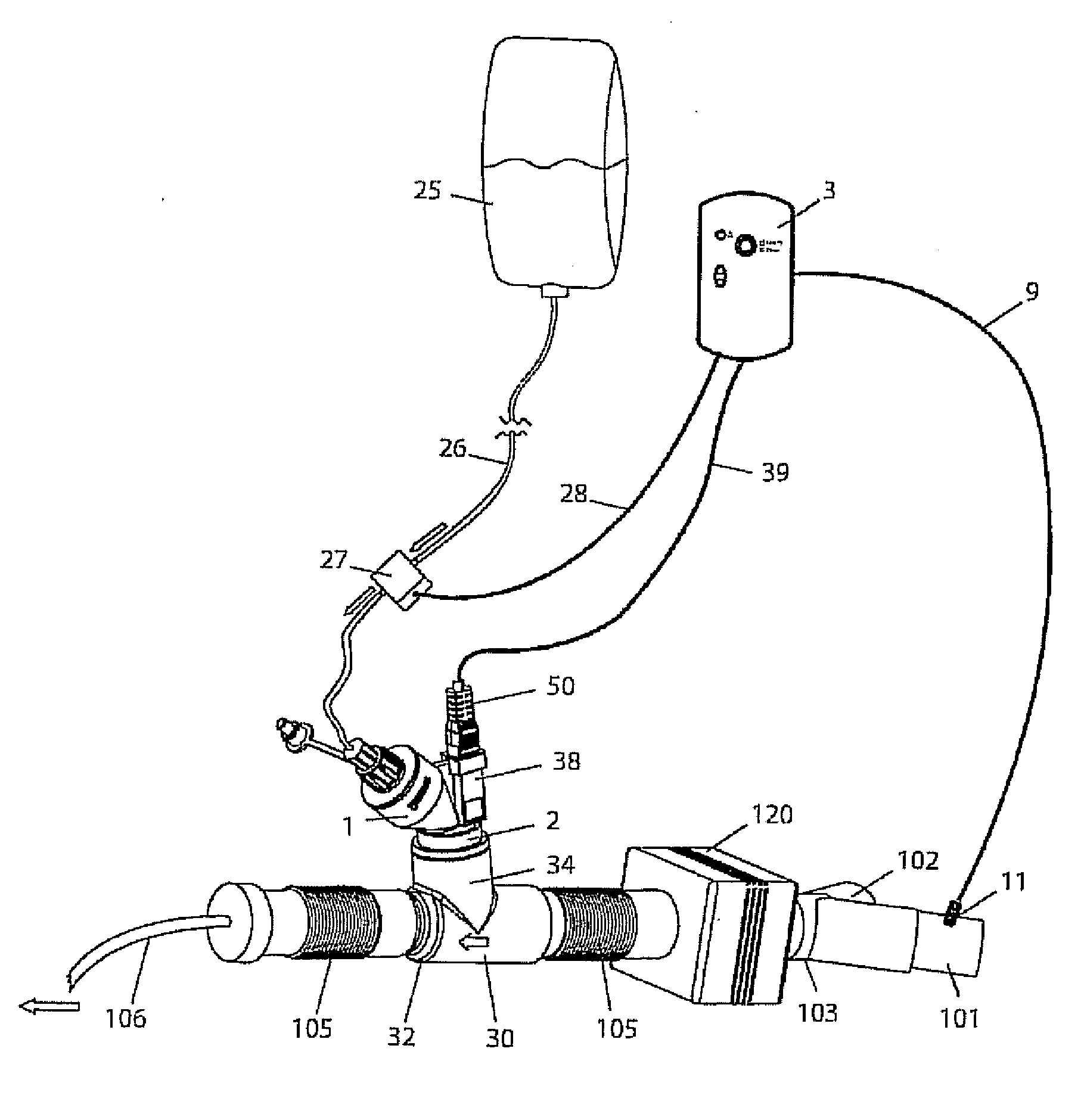
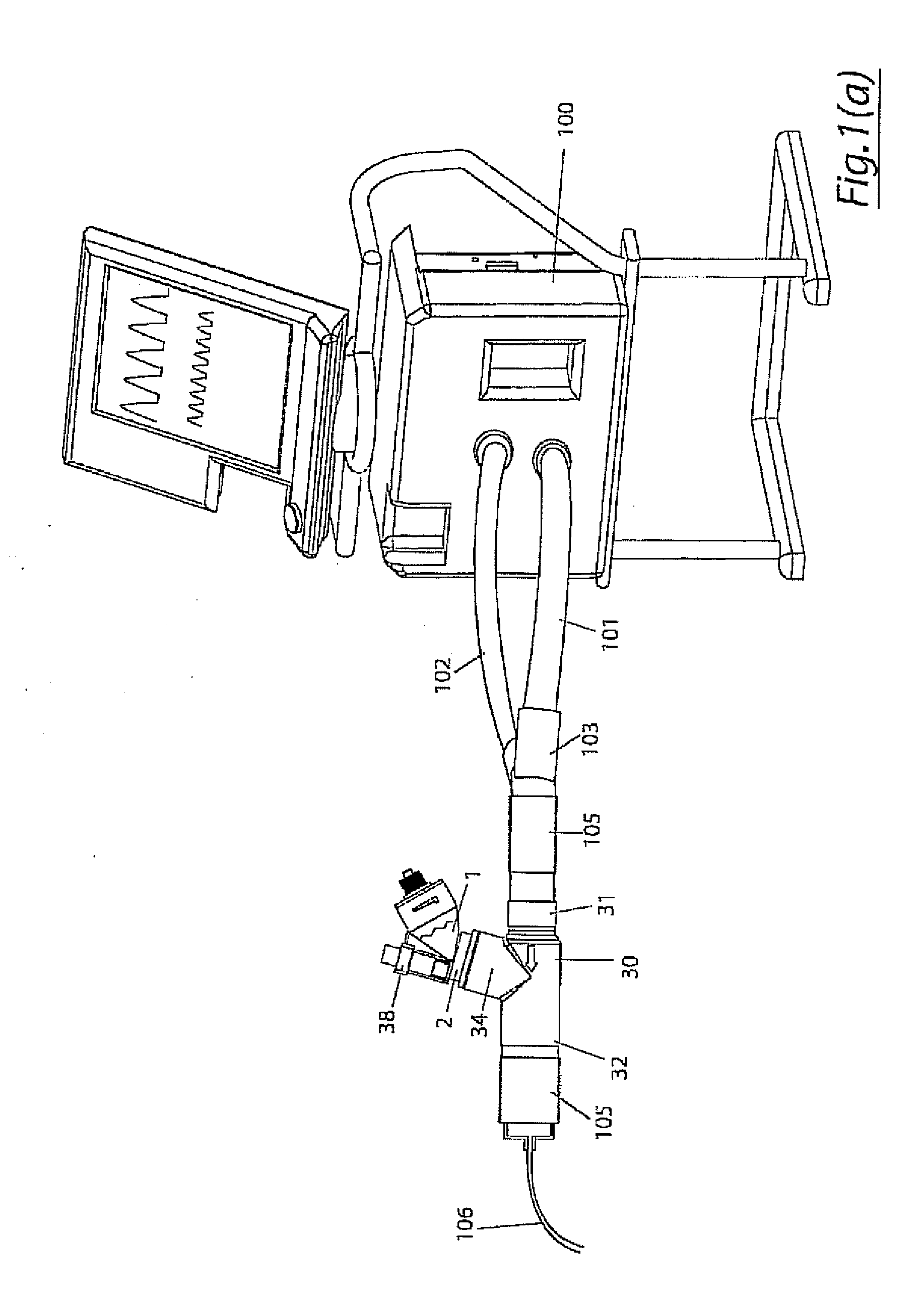
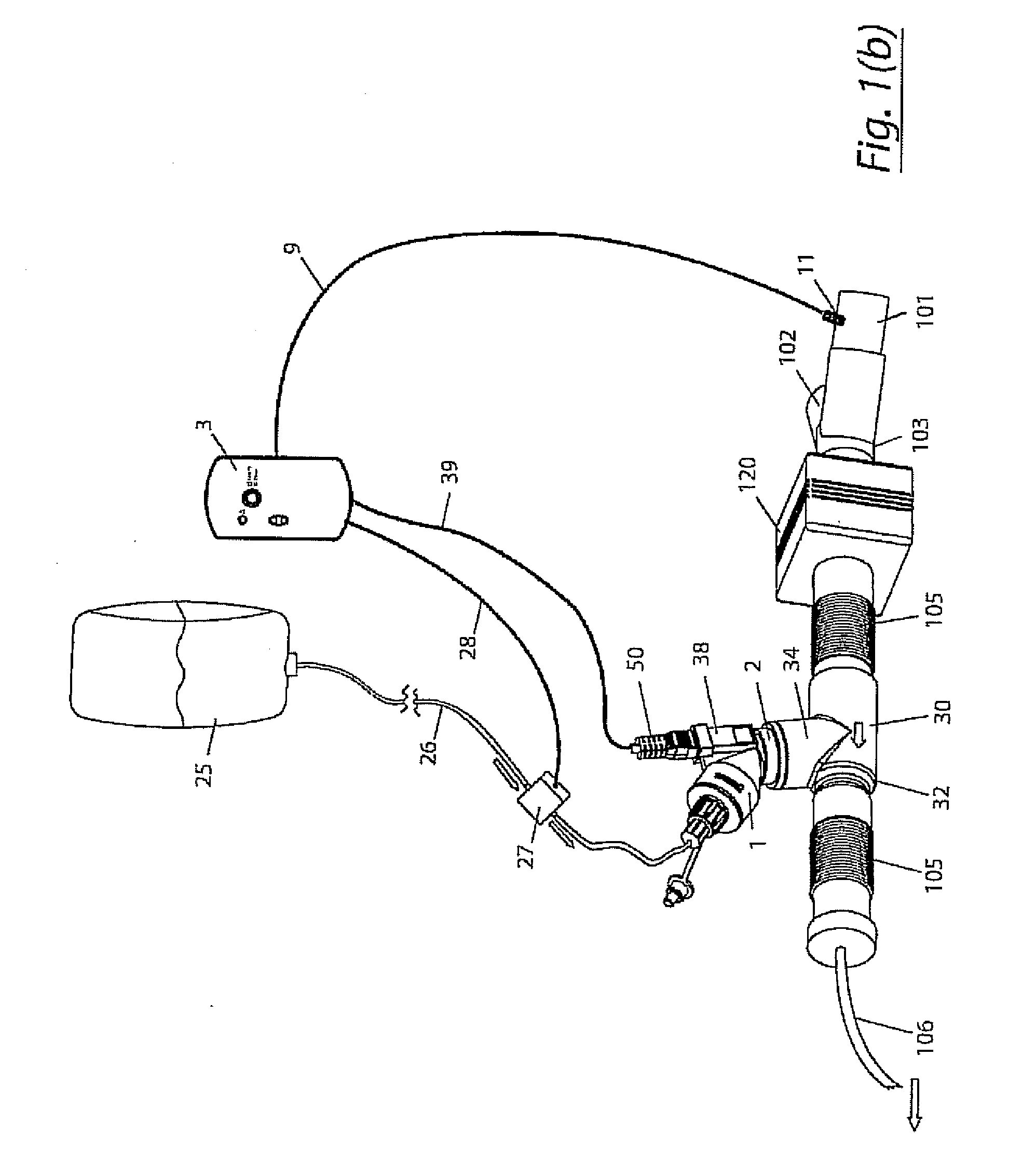
A method for humidifying gas in a ventilator circuit 100, 101, 102, 105, 106 comprises aerosolising a humidifying agent such as water or saline using an aerosol generator 2 and delivering the aerosolised humidifying agent to the inspiration line 101 of the ventilator circuit coupled to the respiratory system of a patient. The aerosol generator 2 comprises a vibratable member 40 having a plurality of apertures extending between a first surface and a second surface. A controller 3 controls the operation of aerosol generator 2, for example in response to the flow of air in the inspiration line 101 as detected by a sensor 11.
Owner:CLANCY DERMOT JOSEPH +4
Treatment of pulmonary disorders with aerosolized medicaments such as vancomycin
InactiveUS20100282247A1Reduce in quantityReduce the amount requiredAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseGlycopeptide
A method of administering an aerosolized anti-infective, such as a glycopeptide, to the respiratory system of a patient. A ratio of an amount of the glycopeptide, such as vancomycin, delivered to the pulmonary system of the patient in a 24 hour period to a minimum inhibitory amount for the target organ for the same period is about 2 or more. A system to introduce aerosolized medicament to a patient may include a humidifier coupled to an inspiratory limb of a ventilator circuit wye, where the humidifier supplies heated and humidified air to the patient, and an endotracheal tube having a proximal end coupled to a distal end of the ventilator circuit wye. The system may also include a nebulizer coupled to the endotracheal tube, where the nebulizer generates the aerosolized medicament.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
HME shuttle system
InactiveUS7634998B1Improves physiological gas flow characteristicComponent can be removedRespiratorsBreathing masksNebulizerInhalation
An HME Filter is provided having with an integral housing having minimal components which eliminating components at the circuit “Y” connector. A closed circuit gas flow is maintained whether an internal filter material is or is not engaged, and with or without a nebulizer aerosolizing medications. The HME SHUTTLE continues to maintain the same closed circuit gas flow during the HME filter materials insertion into the HME SHUTTLE, throughout the course of the HME filter's use in the closed gas flow circuit and during the HME filter materials removal from the HME SHUTTLE. The placement for optimal patient care is to be located between the connection of inhalation and exhalation sides of mechanical ventilator circuit and endotracheal tube of an intubated patient. The HME SHUTTLE also accommodates the docking port for the use of an external nebulizer.
Owner:FENLEY ROBERT C
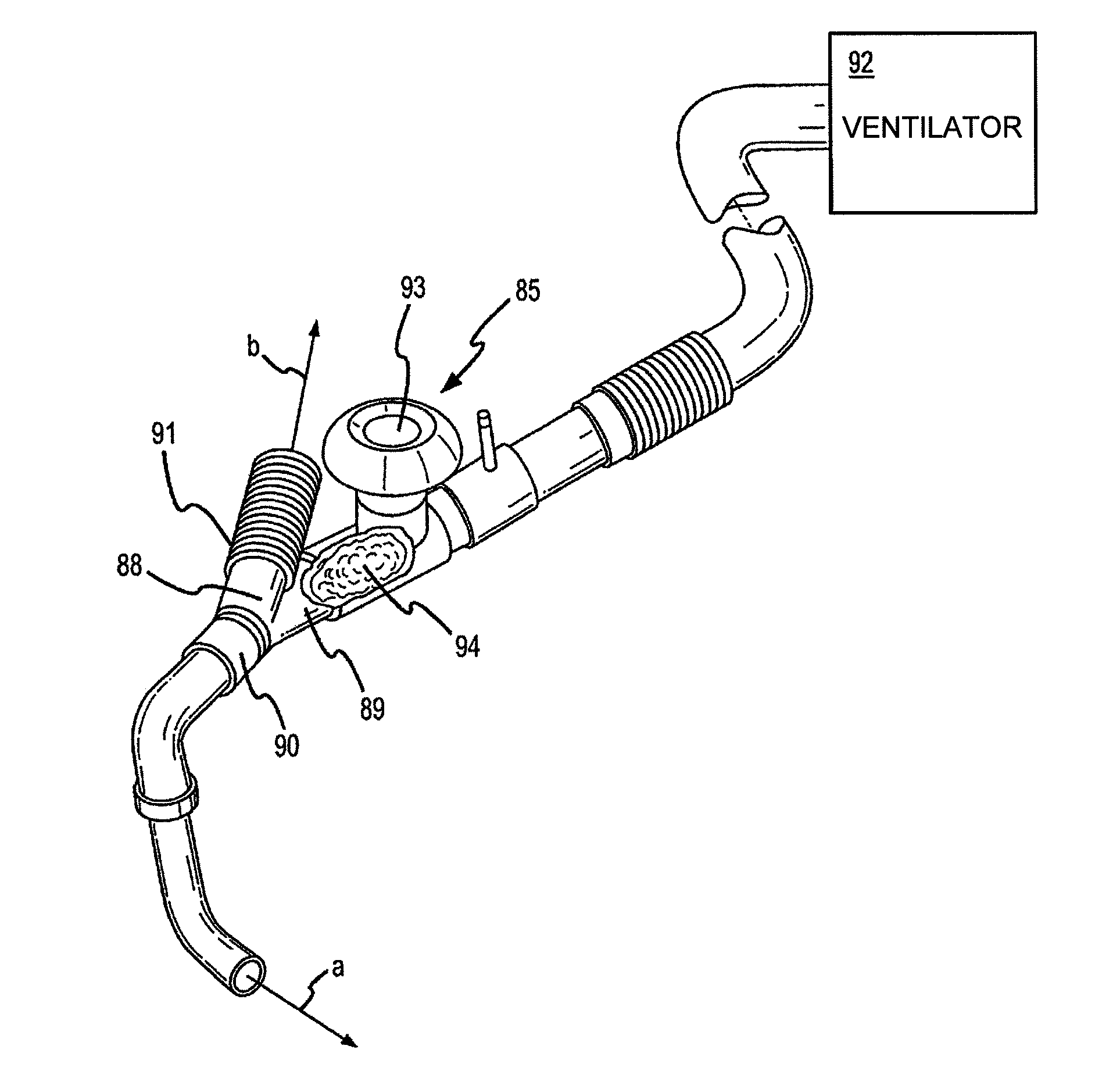
Methods, devices and formulations for targeted endobronchial therapy
ActiveUS20050235987A1Mortality rate is decreasedReduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsTracheal tubesTracheobronchitisRegimen
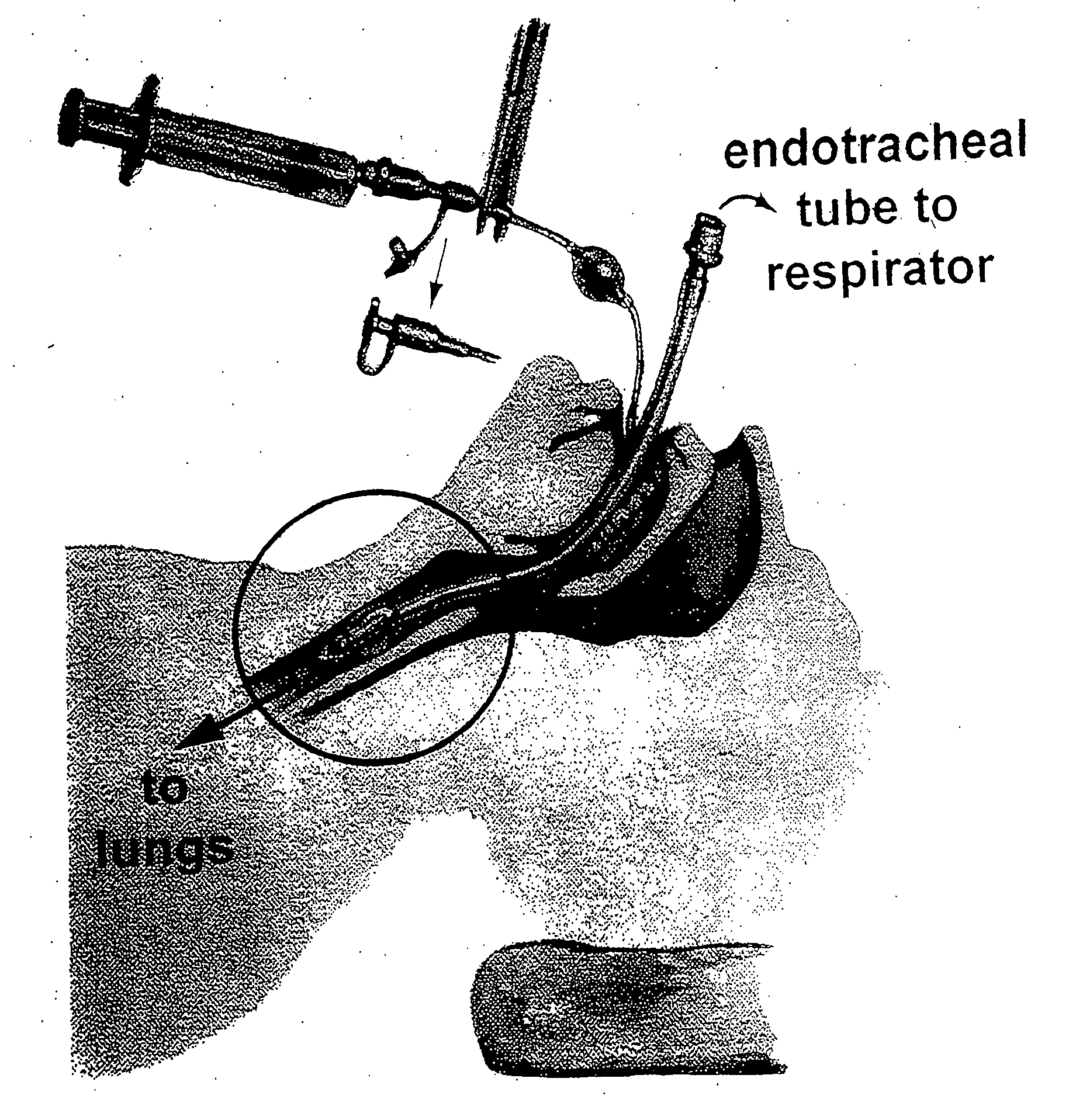
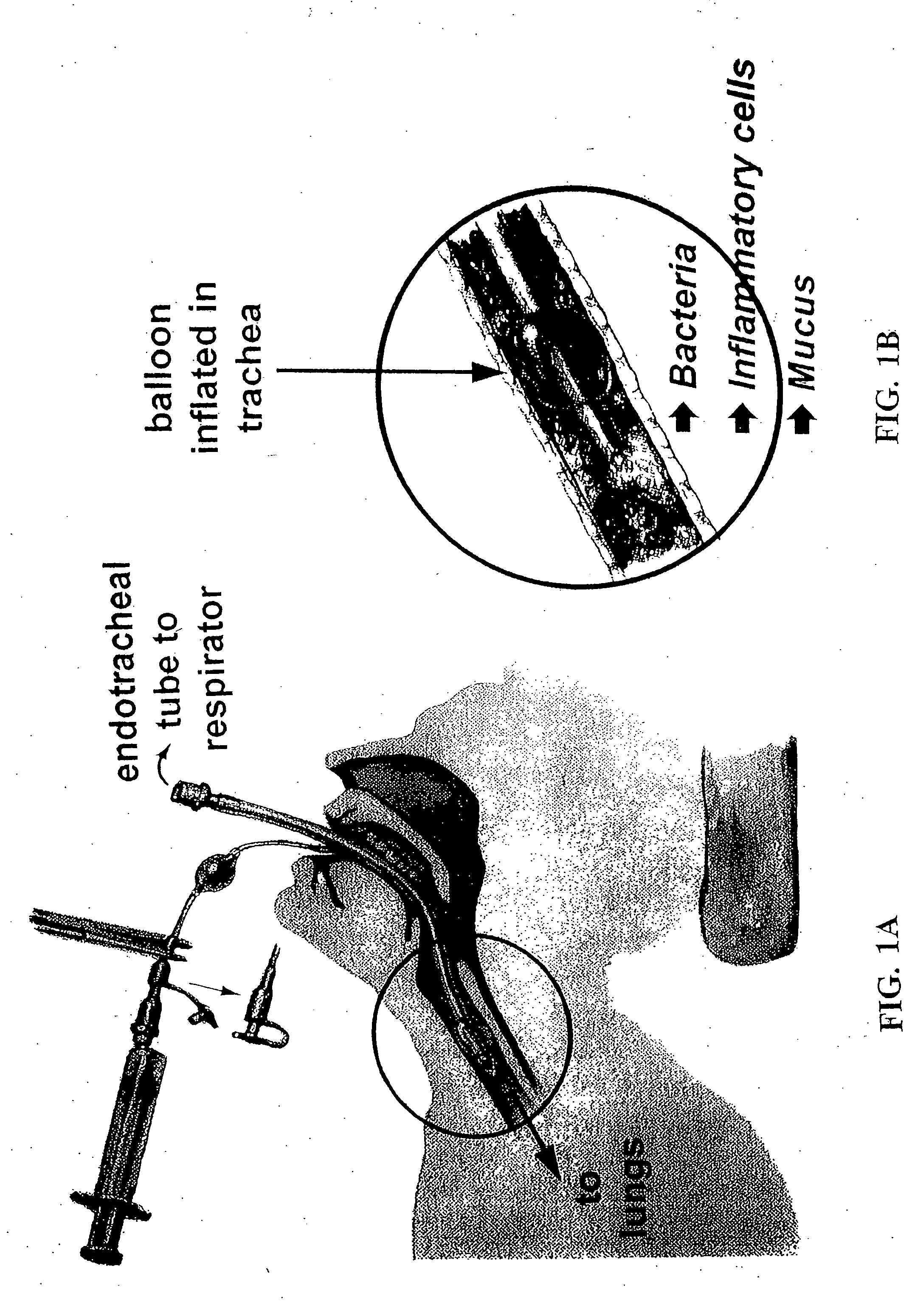
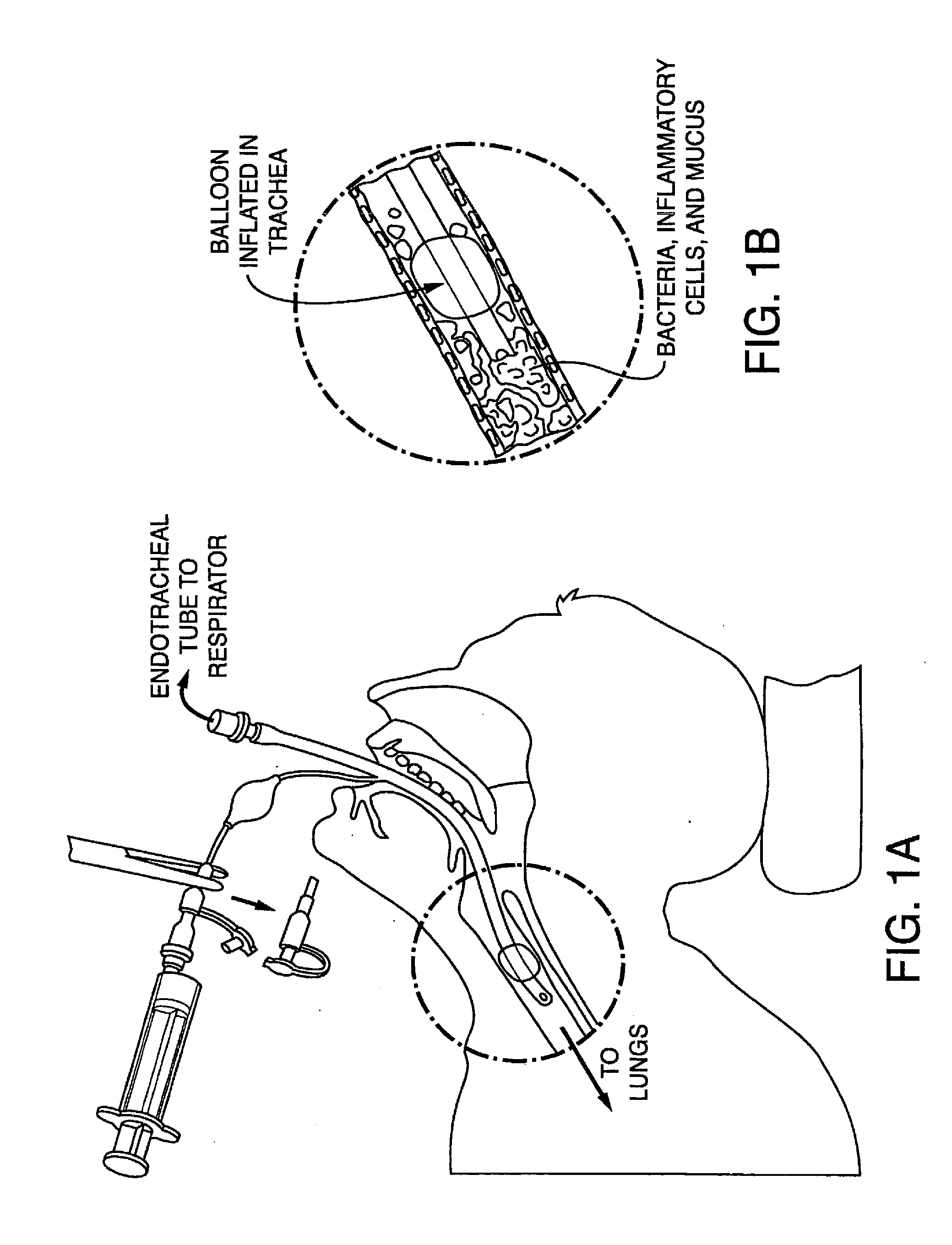
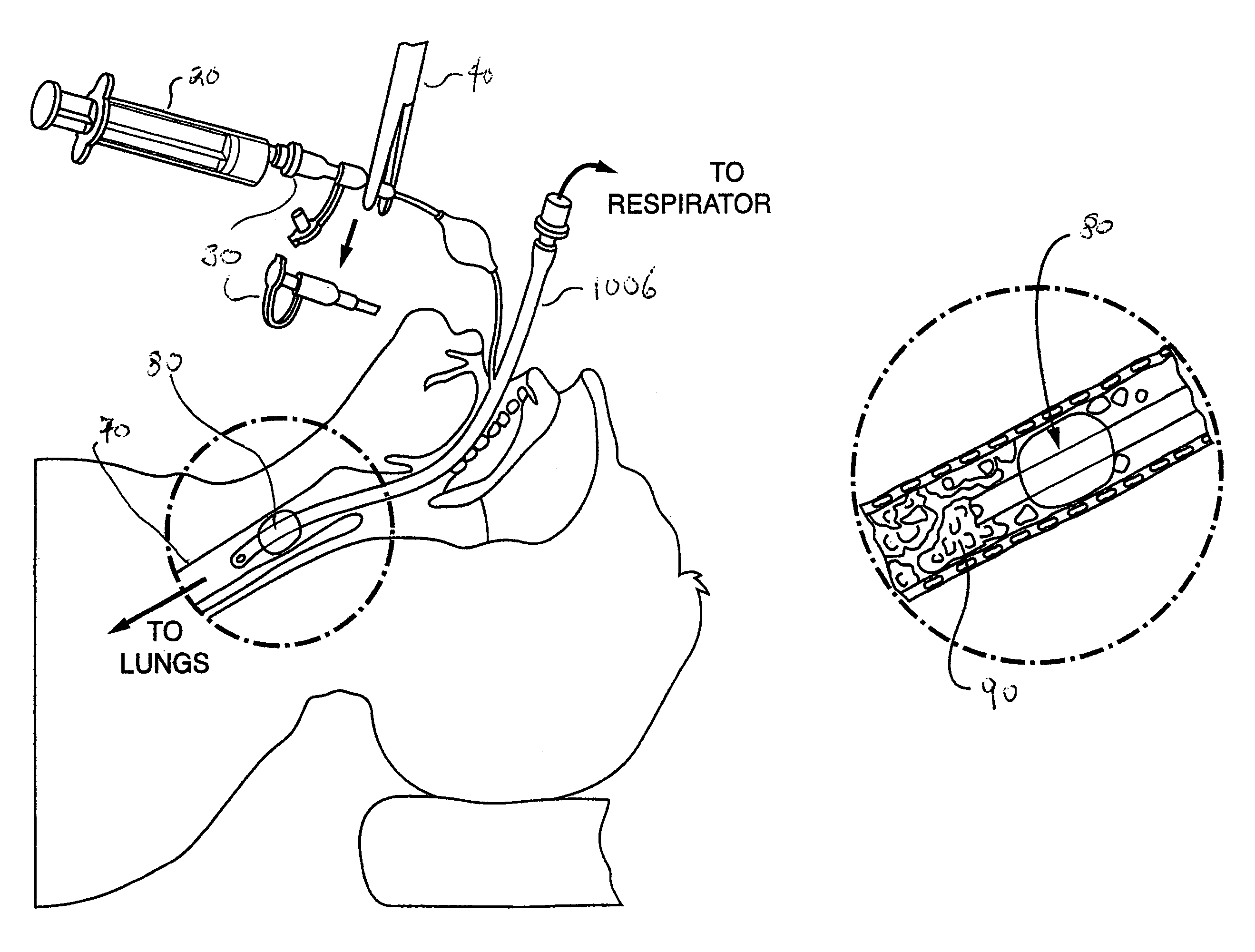
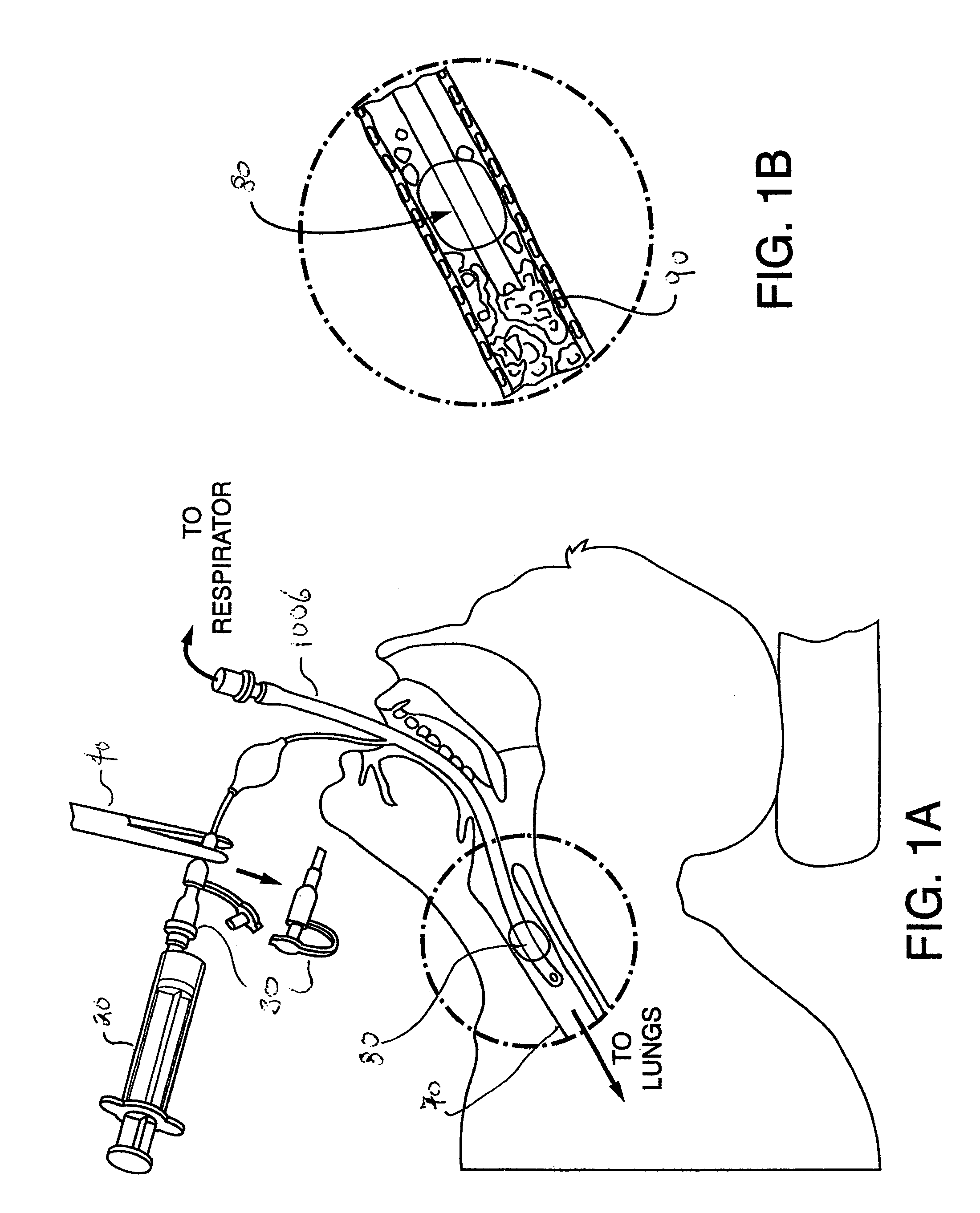
The present invention provides an improved means of treating tracheobronchitis, bronchiectasis and pneumonia in the nosocomial patient, preferably with aerosolized anti gram-positive and anti-gram negative antibiotics administered in combination or in seriatim in reliably sufficient amounts for therapeutic effect. In one aspect, the invention assures this result when aerosol is delivered into the ventilator circuit. In one embodiment the result is achieved mechanically. In another embodiment, the result is achieved by aerosol formulation. In another aspect, the invention assures the result when aerosol is delivered directly to the airways distal of the ventilator circuit. The treatment means eliminates the dosage variability that ventilator systems engender when aerosols are introduced via the ventilator circuit. The treatment means also concentrates the therapeutic agent specifically at affected sites in the lung such that therapeutic levels of administrated drug are achieved without significant systemic exposure of the patient to the drug. The invention further provides a dose control device to govern this specialized regimen.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Methods, devices and formulations for targeted endobronchial therapy
ActiveUS20050211245A1Mortality rate is decreasedReduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsTracheal tubesTracheobronchitisRegimen
The present invention provides an improved means of treating tracheobronchitis, bronchiectasis and pneumonia in the nosocomial patient, preferably with aerosolized anti gram-positive and anti-gram negative antibiotics administered in combination or in seriatim in reliably sufficient amounts for therapeutic effect. In one aspect, the invention assures this result when aerosol is delivered into the ventilator circuit. In one embodiment the result is achieved mechanically. In another embodiment, the result is achieved by aerosol formulation. In another aspect, the invention assures the result when aerosol is delivered directly to the airways distal of the ventilator circuit. The treatment means eliminates the dosage variability that ventilator systems engender when aerosols are introduced via the ventilator circuit. The treatment means also concentrates the therapeutic agent specifically at affected sites in the lung such that therapeutic levels of administrated drug are achieved without significant systemic exposure of the patient to the drug. The invention further provides a dose control device to govern this specialized regimen.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Methods, devices and formulations for targeted endobronchial therapy
ActiveUS20050211253A1Mortality rate is decreasedReduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsTracheal tubesTracheobronchitisTreatment effect
The present invention provides an improved means of treating tracheobronchitis, bronchiectasis and pneumonia in the nosocomial patient, preferably with aerosolized anti gram-positive and anti-gram negative antibiotics administered in combination or in seriatim in reliably sufficient amounts for therapeutic effect. In one aspect, the invention assures this result when aerosol is delivered into the ventilator circuit. In one embodiment the result is achieved mechanically. In another embodiment, the result is achieved by aerosol formulation. In another aspect, the invention assures the result when aerosol is delivered directly to the airnvays distal of the ventilator circuit. The treatment means eliminates the dosage variability that ventilator systems engender when aerosols are introduced via the ventilator circuit. The treatment means also concentrates the therapeutic agent specifically at affected sites in the lung such that therapeutic levels of administrated drug are achieved without significant systemic exposure of the patient to the drug. The invention further provides a dose control device to govern this specialized regimen.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Valves, devices, and methods for endobronchial therapy
InactiveUS20070083677A1Mortality rate is decreasedReduce morbidityRespiratorsCheck valvesVentilator circuitVALVE PORT
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
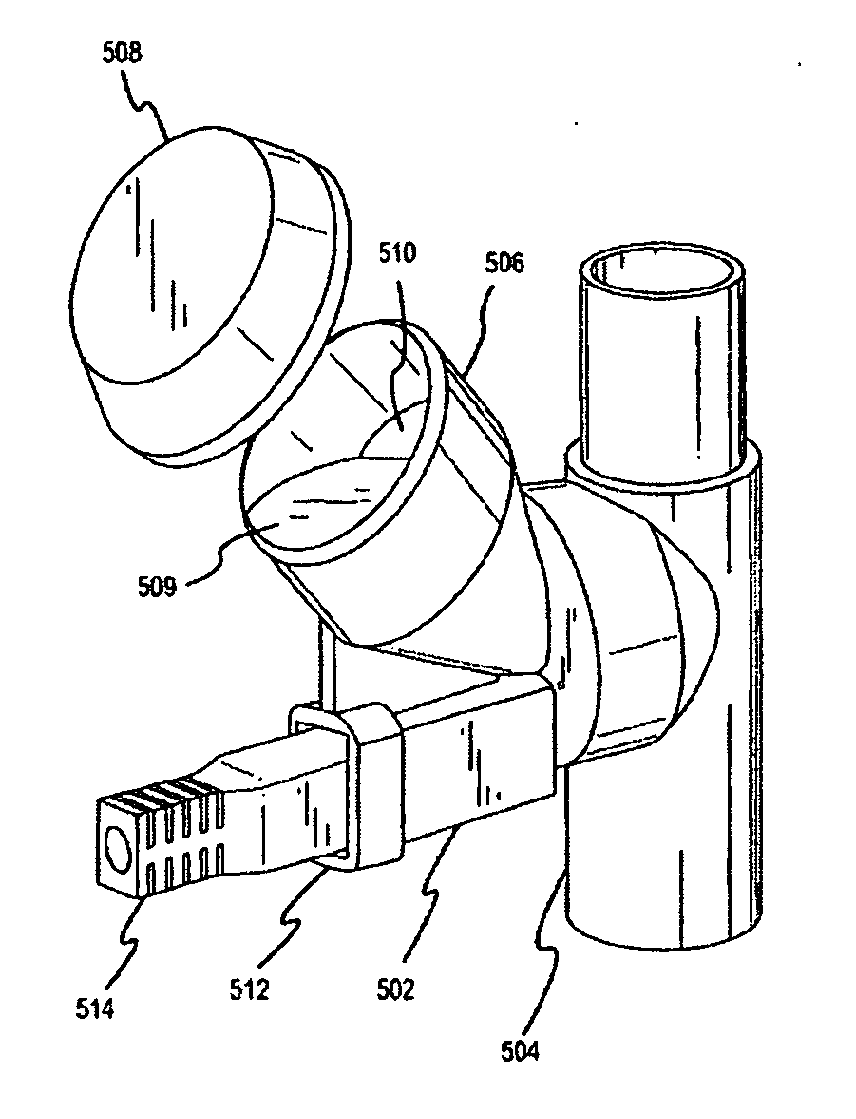
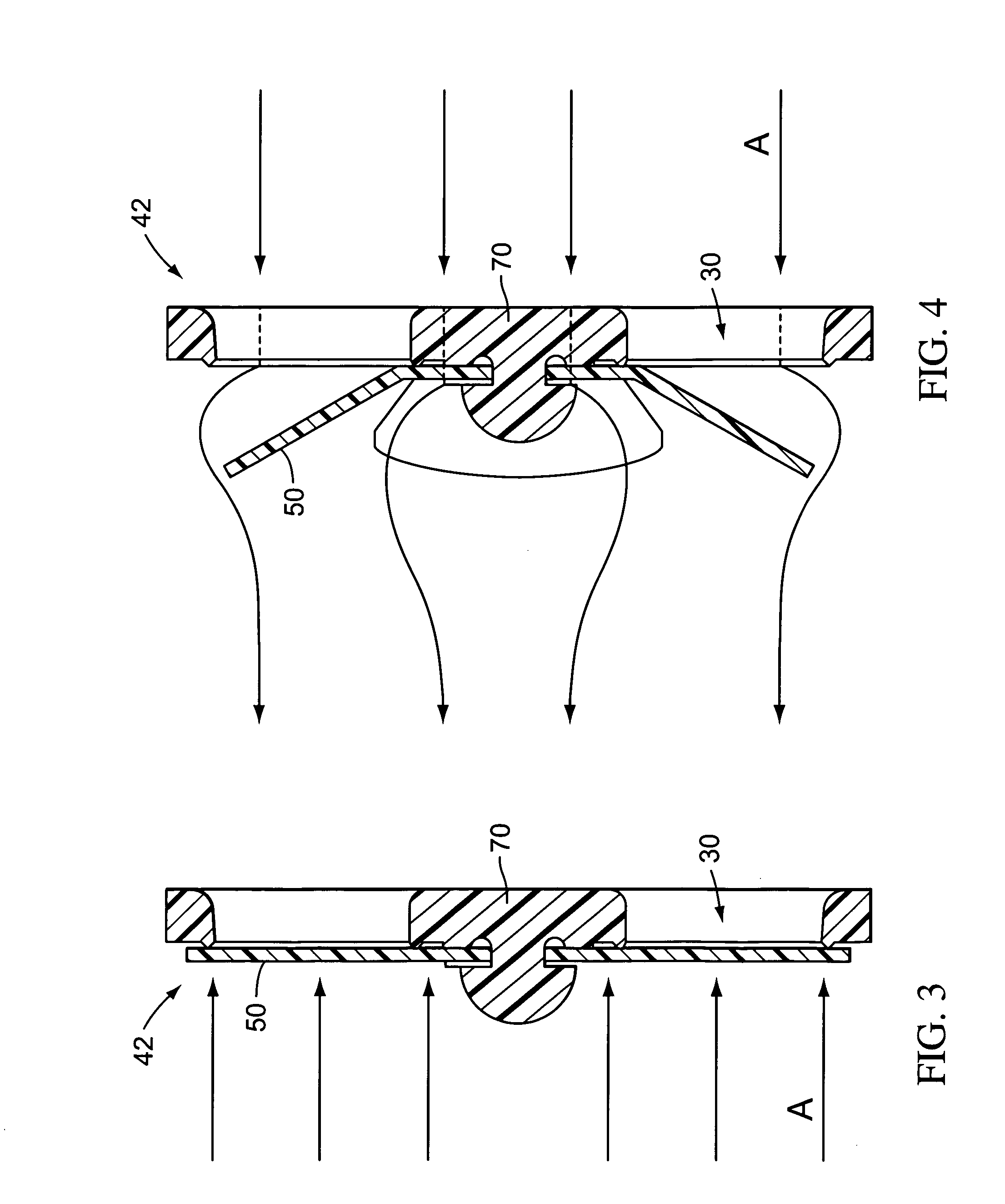
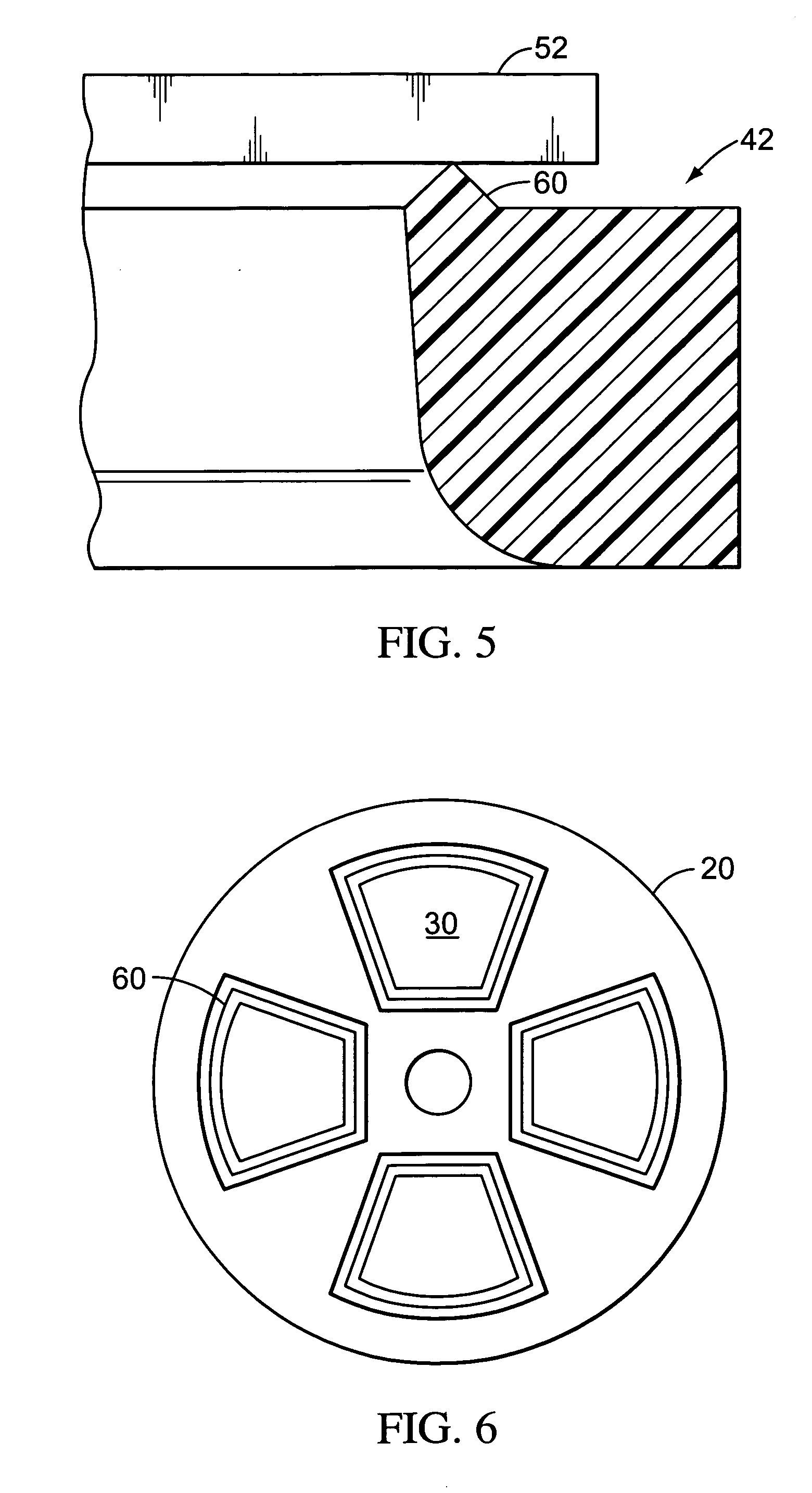
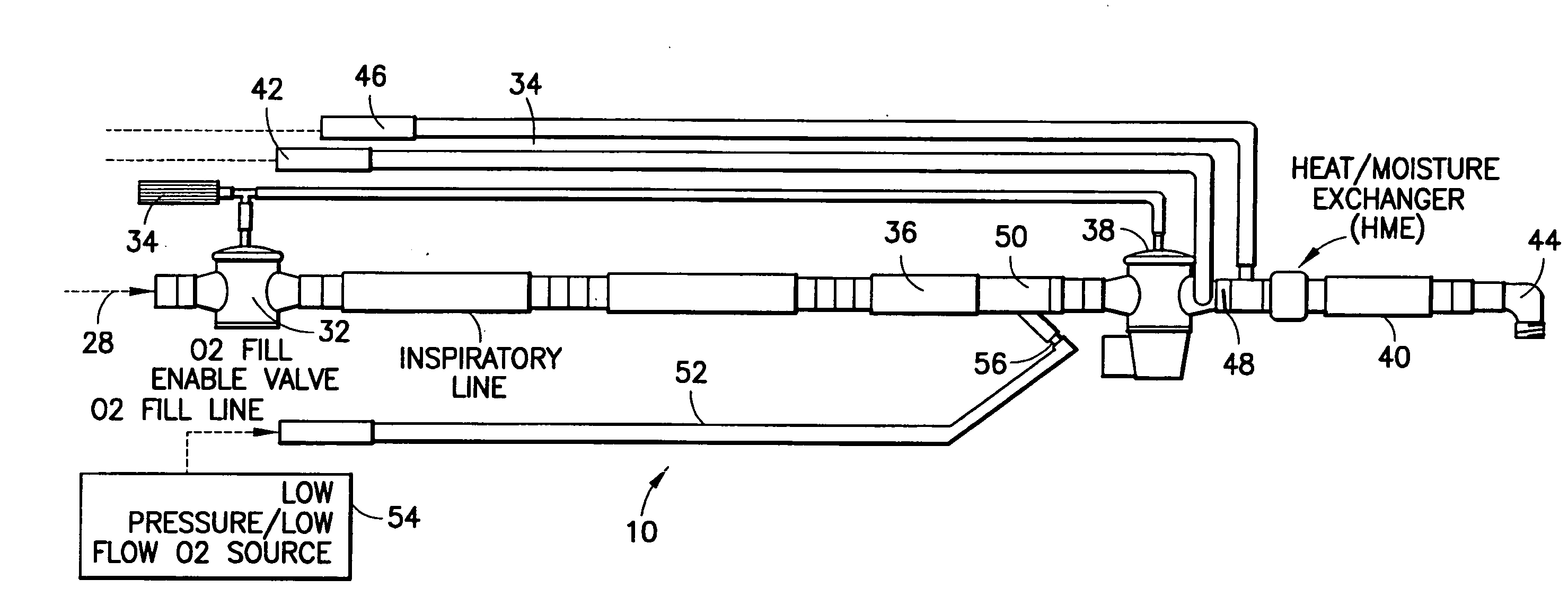
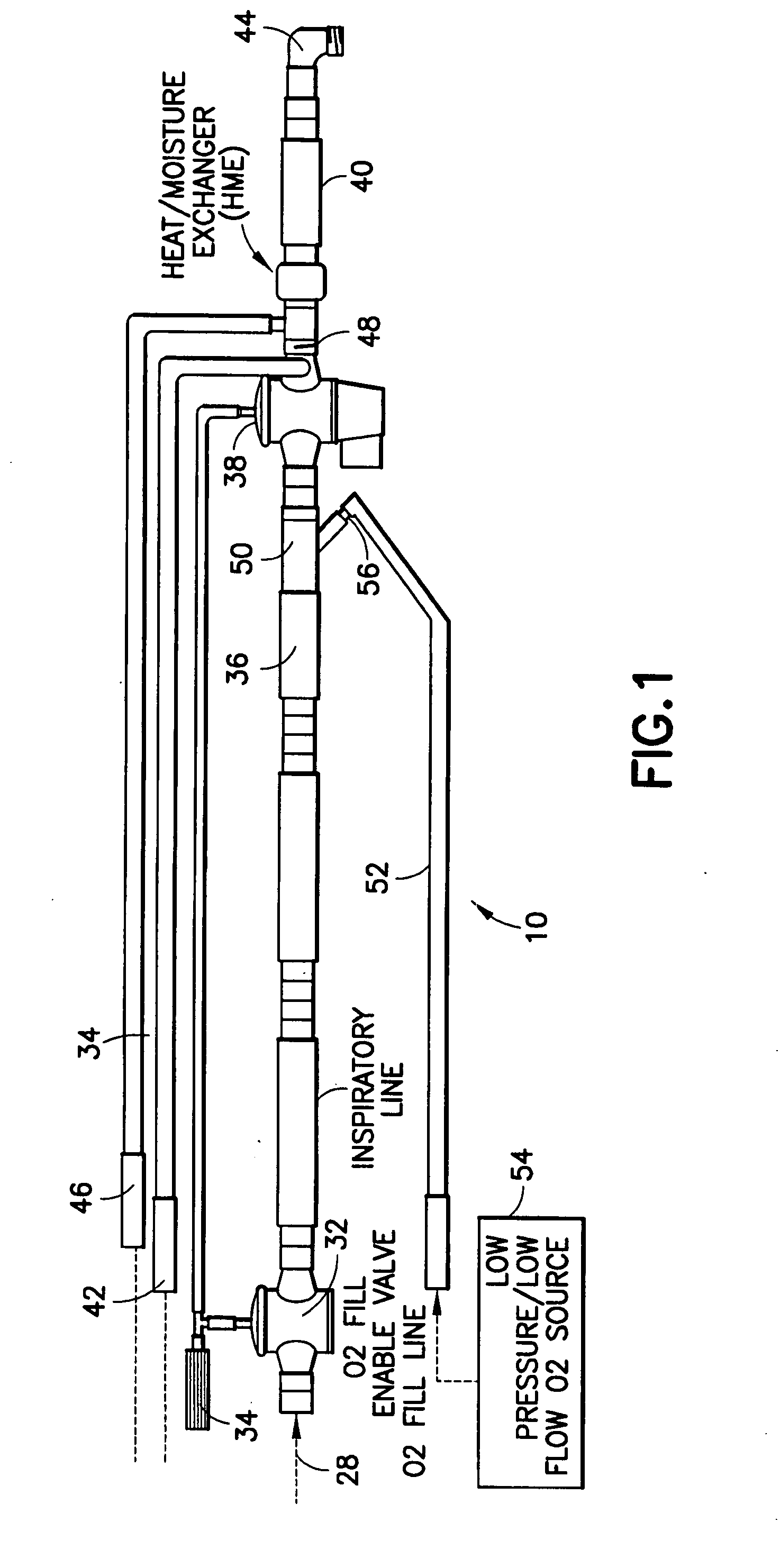
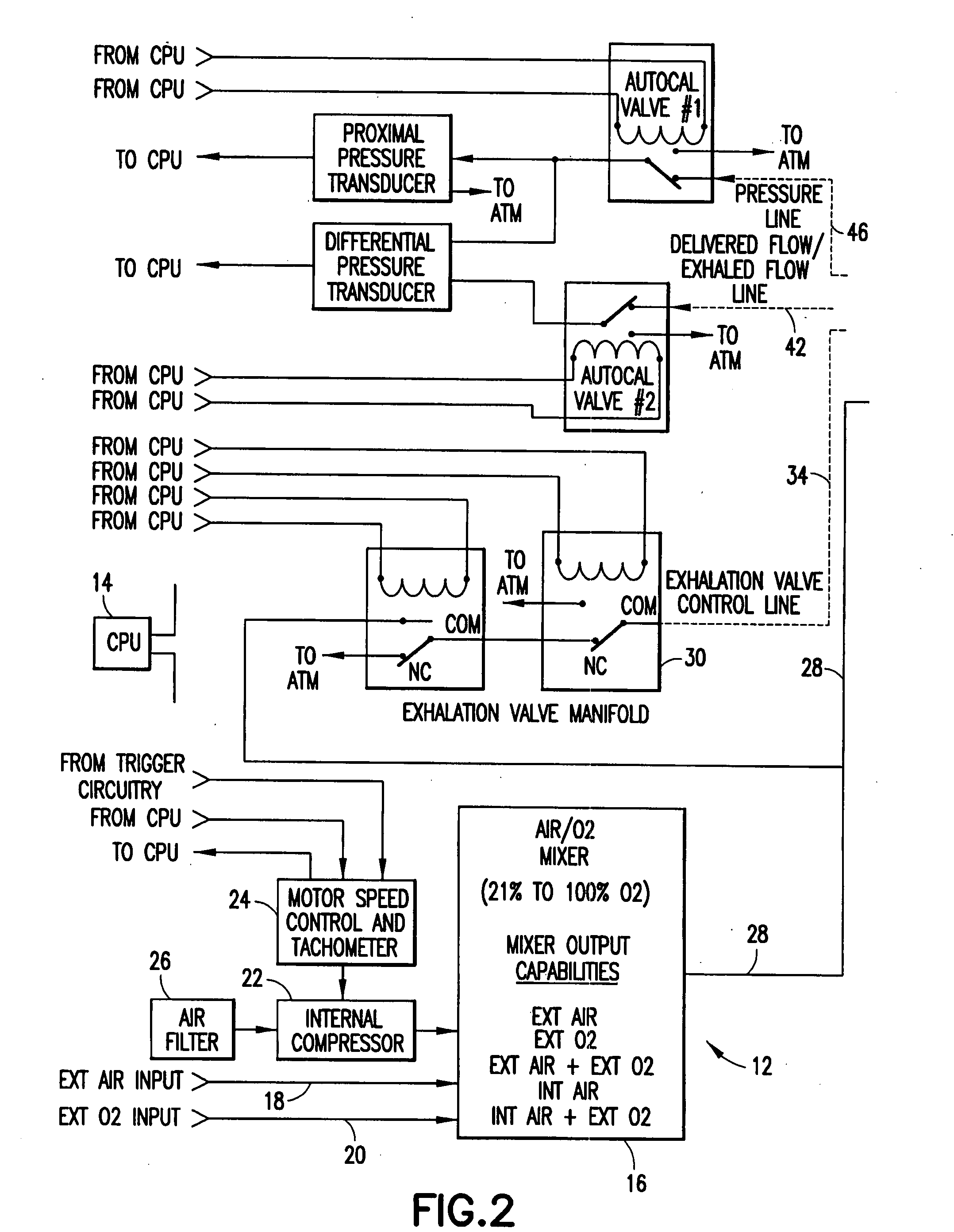
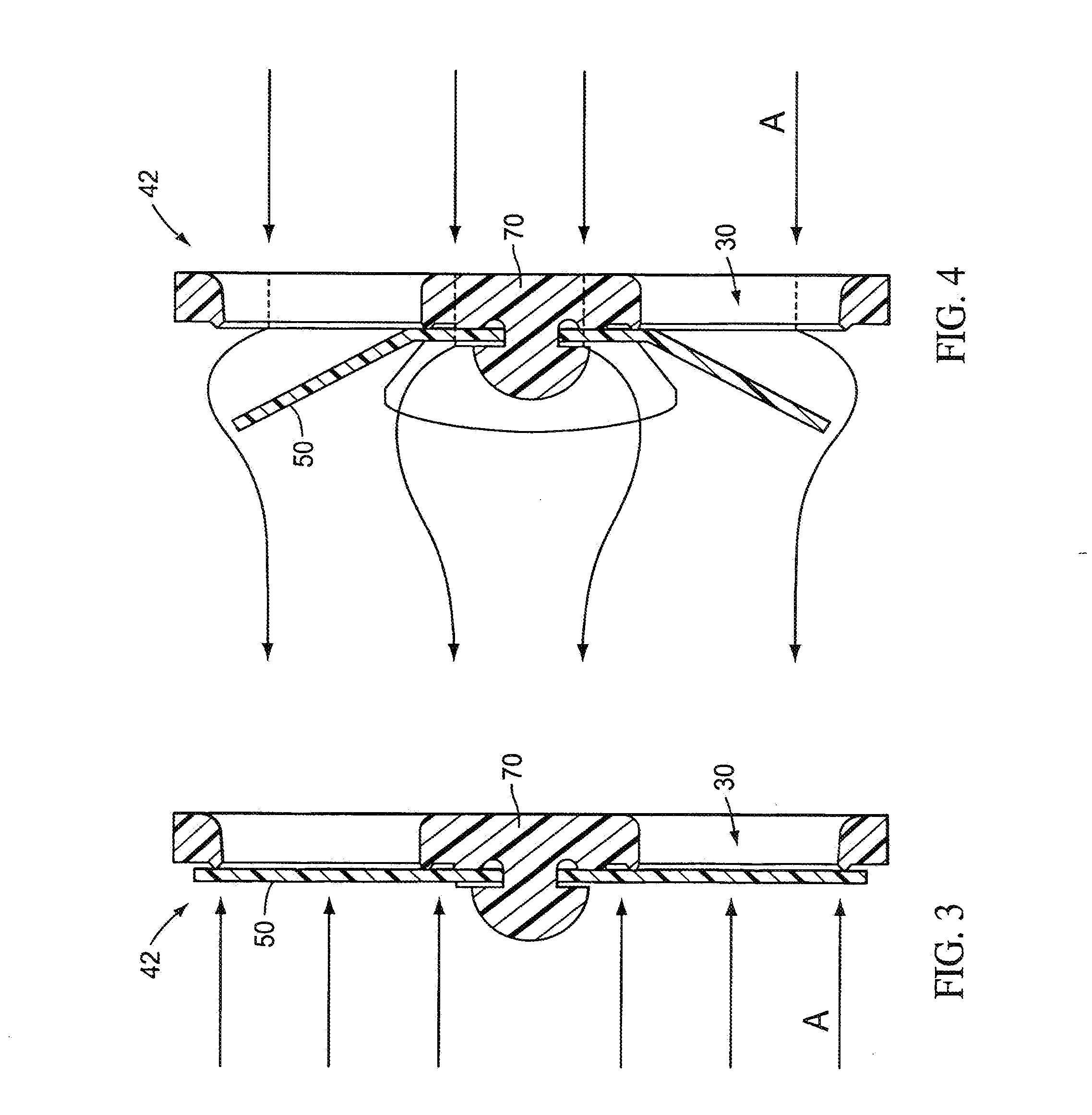
Ventilator circuit for oxygen generating system
ActiveUS20070272243A1Avoid flowOxygen richRespiratorsMedical devicesPercent oxyhemoglobinOxygen content
A ventilator circuit is provided for use with a ventilator and a low pressure low flow oxygen source to provide a hyper-oxygenated mixture of air and oxygen at the onset of inspiration. The ventilator circuit achieves this result by using its inspiratory limb to store oxygen between breaths. As a result, the oxygen content of dead space gas is increased before delivery to the distal alveoli of the patient. Accordingly, the ventilator circuit achieves an efficient use of available oxygen and requires less oxygen to a desired oxyhemoglobin percentage at the patient.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Myoelectrically activated respiratory leak sealing
InactiveUS7963283B2Reduce decreaseAdequate flowTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory flowRespiratory pressure
Owner:MONTREAL UNIV DE
Aerosolisation system
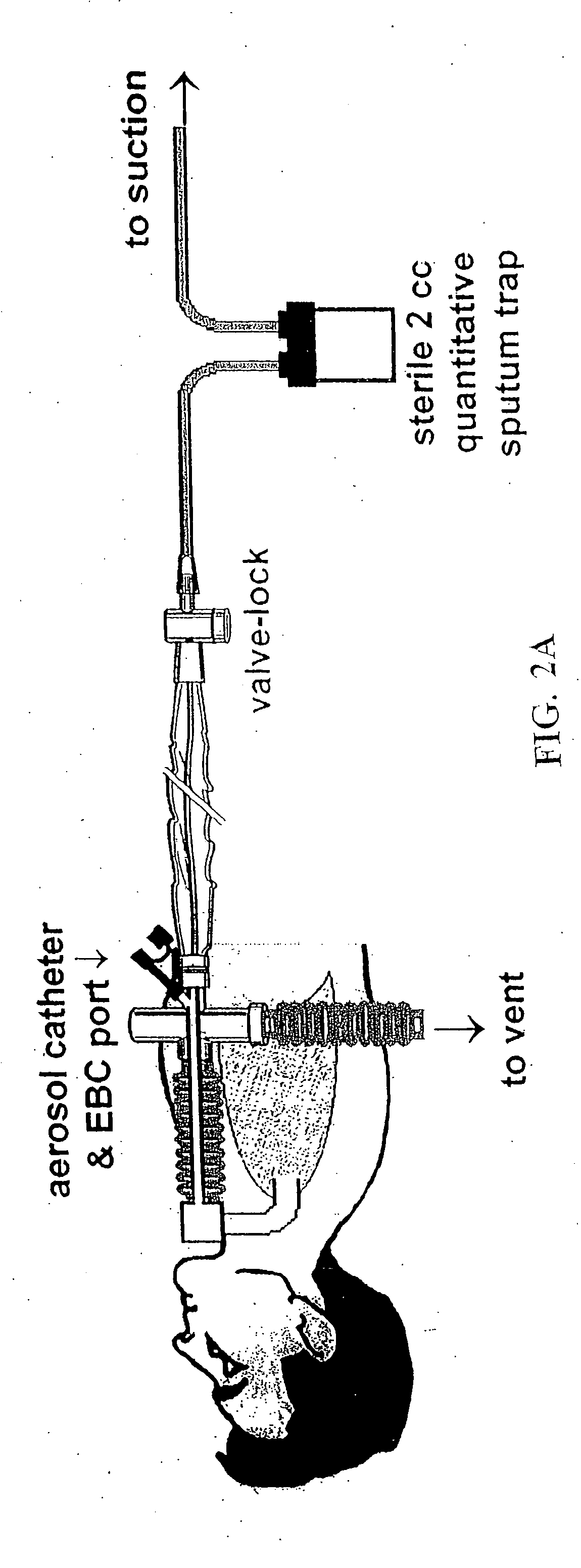
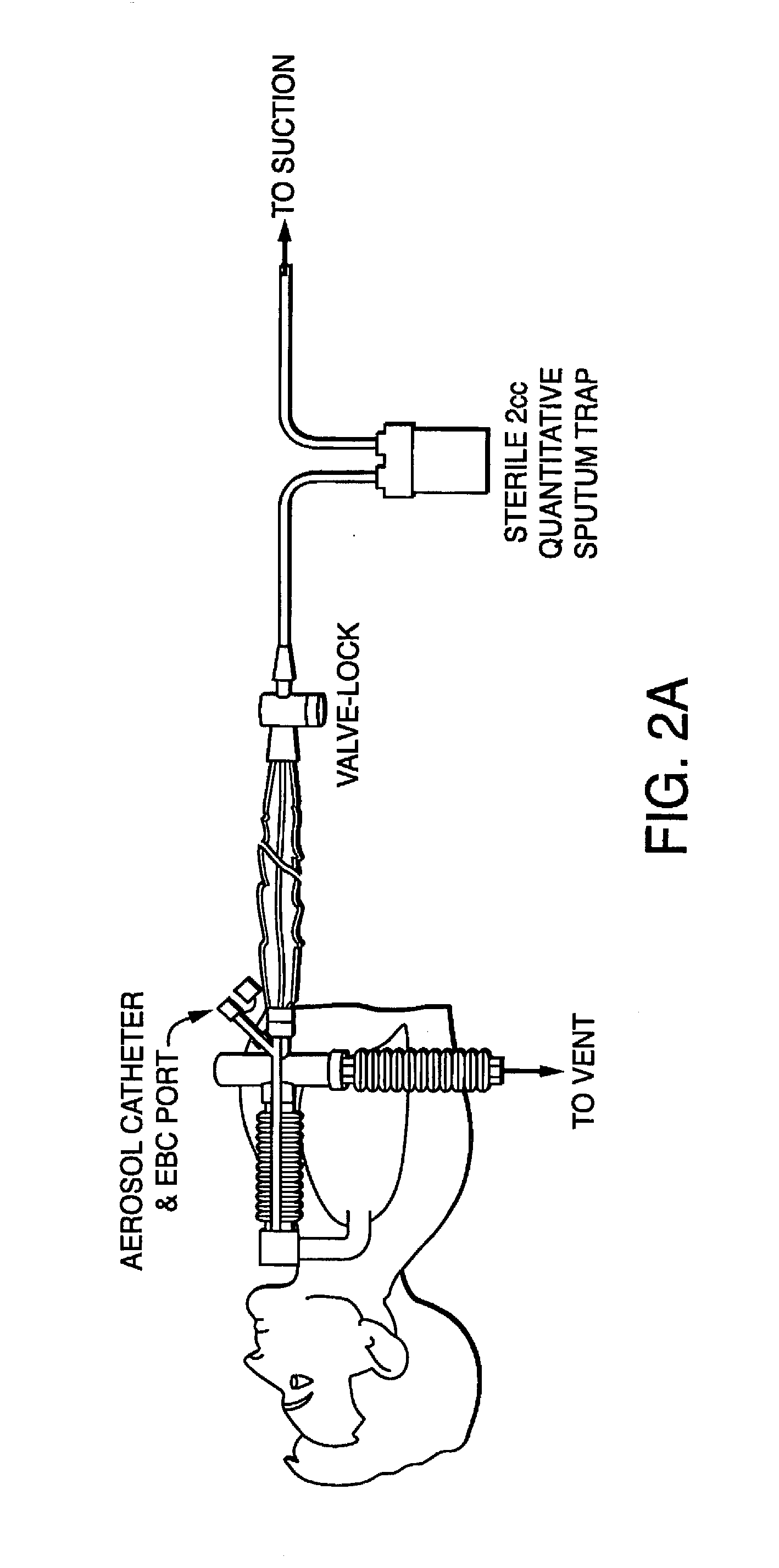
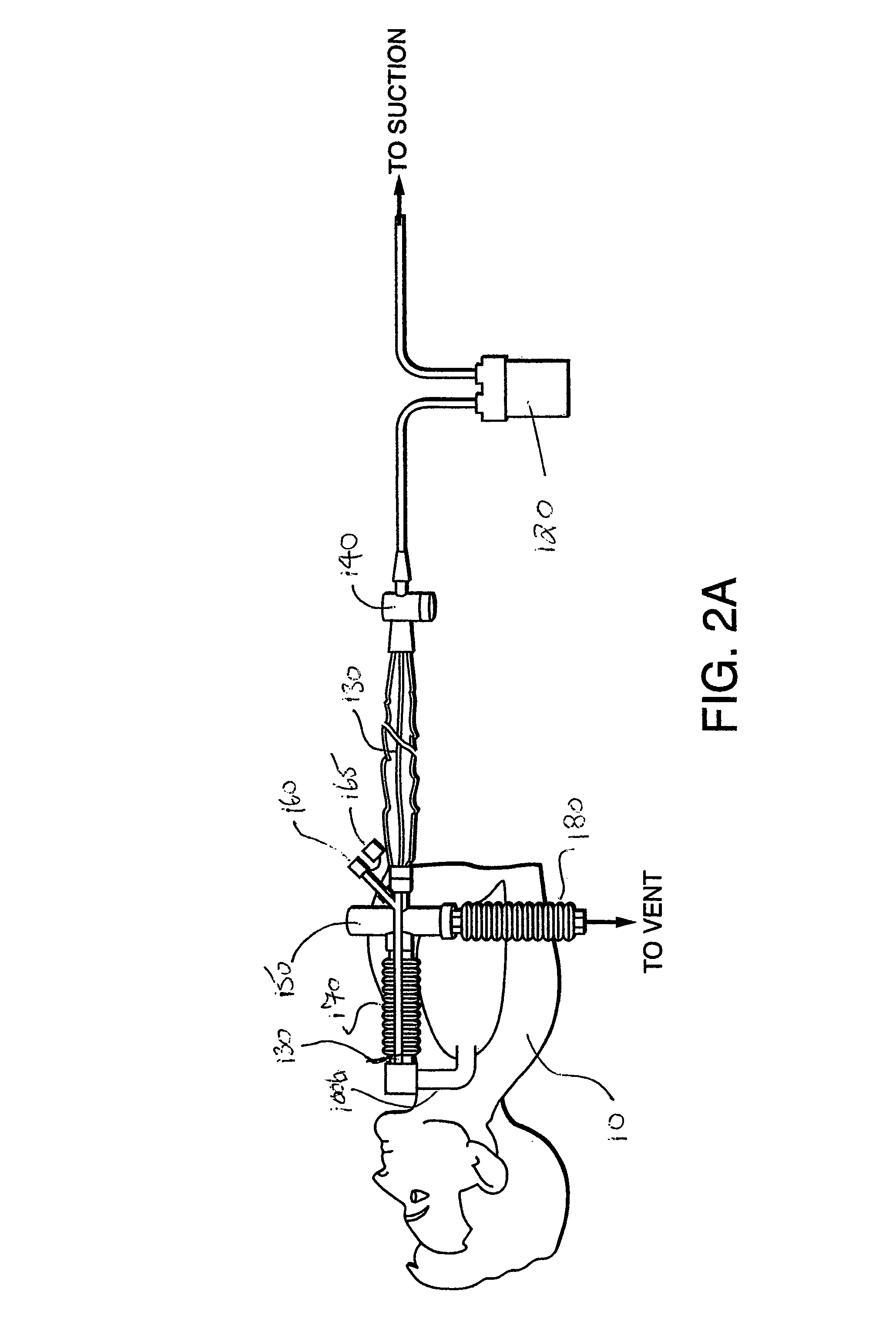
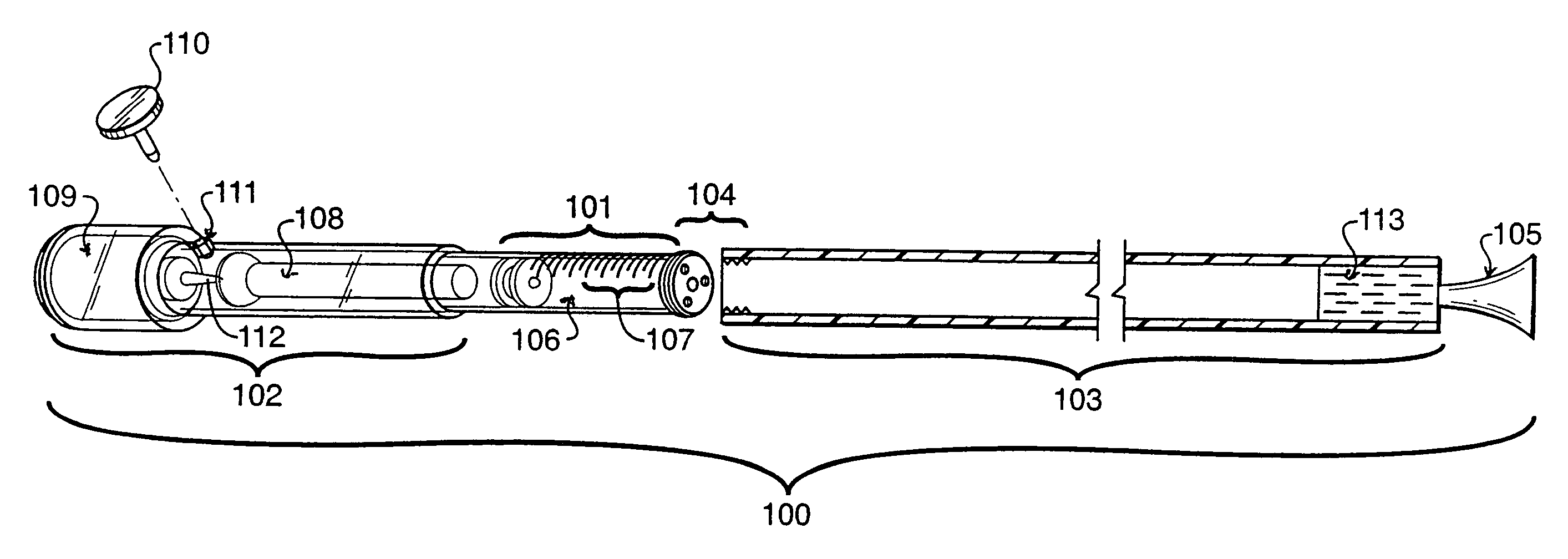
The invention provides a combination of a micro pump 27 or a micro valve with a vibrating mesh nebuliser 2. This is powered by a controller 3. The controller 3 may have modifications to provide the electrical drive mechanism for the pump 27 in addition to fulfilling the aerosol / nebuliser drive requirements. In one case the system is used for humidifying gas in a ventilator circuit. A humidifying agent (sterile water or sterile saline) is aerosolised and then delivered to a ventilator circuit 100 coupled to the respiratory system of a patient.
Owner:STAMFORD DEVICES LTD
Catheter guiding flexible connector
A flexible connector couples the inlet end of a tracheotomy tube inner cannula to an outlet port of an in-line catheter. The catheter exit end of the connector is adapted to be serially coupled in pneumatic communication with the inlet end of the tracheotomy tube inner cannula and also to guide the downstream tip of the catheter into the inlet end of the inner cannula in response to pushing of the catheter upstream of the catheter outlet port. Thus, the in-line catheter can be inserted into the tracheotomy tube inner cannula with little likelihood of having to compress or “flip” the connector or disconnect the connector from the tracheotomy tube and the patient from the ventilator circuit.
Owner:LAZARUS MEDICAL
Valves, devices, and methods for endobronchial therapy
InactiveUS20150114504A1Mortality rate is decreasedReduce morbidityRespiratorsCheck valvesEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods and systems for operating an aerosol generator
ActiveUS8336545B2Improve security levelImprove delivery efficiencyRespiratorsBiocideAmikacinWhole body
A method of treating a patient with a pulmonary disease, where the method includes delivering a dose of aerosolized medicament intermittently to a ventilator circuit coupled to the respiratory system of the patient. Also, a method of treating a patient with a pulmonary disease, where the method includes taking the patient off a ventilator, and administering to the patient, a nebulized aerosol comprising from about 100 μg to about 500 mg of a medicament. Also a method of treating a patient with a pulmonary disease, the method comprising administering an aerosolized first medicament comprising amikacin to the patient and administering, systemically a second medicament comprising an antibiotic to the patient that also treats the pulmonary disease, wherein a resulting amikacin concentration in the lung and / or pulmonary system is therapeutically-effective, and an amount of the systemically administered antibiotics is reduced.
Owner:NEKTAR THERAPEUTICS INC
Humidification in Breathing Circuits
A method for humidifying gas in a ventilator circuit 100, 101, 102, 105, 106 comprises aerosolising a humidifying agent such as water or saline using an aerosol generator 2 and delivering the aerosolised humidifying agent to the inspiration line 101 of the ventilator circuit coupled to the respiratory system of a patient. The aerosol generator 2 comprises a vibratable member 40 having a plurality of apertures extending between a first surface and a second surface. A controller 3 controls the operation of aerosol generator 2, for example in response to the flow of air in the inspiration line 101 as detected by a sensor 11.
Owner:STAMFORD DEVICES LTD
Methods, Devices and Formulations for Targeted Endobronchial Therapy
InactiveUS20140014103A1Mortality rate is decreasedReduce morbidityTracheal tubesMedical devicesTracheobronchitisTreatment effect
The present invention provides a method and novel devices for treating tracheobronchitis and pneumonia in the intubated patient, preferably with aerosolized anti gram-positive and anti-gram negative antibiotics administered in combination or in seriatim in reliably sufficient amounts for therapeutic effect. In one embodiment the result is achieved mechanically. In another embodiment, the result is achieved by aerosol formulation. In a preferred embodiment, the invention assures the result when aerosol is delivered directly to the airways distal of the ventilator circuit. The devices eliminate the dosage variability that ventilator systems engender when aerosols are introduced via the ventilator circuit. The treatment also concentrates the therapeutic agent specifically at affected sites in the lung such that therapeutic levels of administrated drug are achieved without significant systemic exposure of the patient to the drug. The invention further provides a dose control device to govern this specialized regimen.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Portable fluid warming system
The present invention relates to a portable apparatus for warming biocompatible fluids for use in the treatment of injured patients. The present invention may be used to warm intravenous fluids for trauma resuscitation or to warm air from a ventilator circuit. The portable nature of the present invention makes it highly suitable for field applications, such as a forward surgical hospital near a combat zone.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
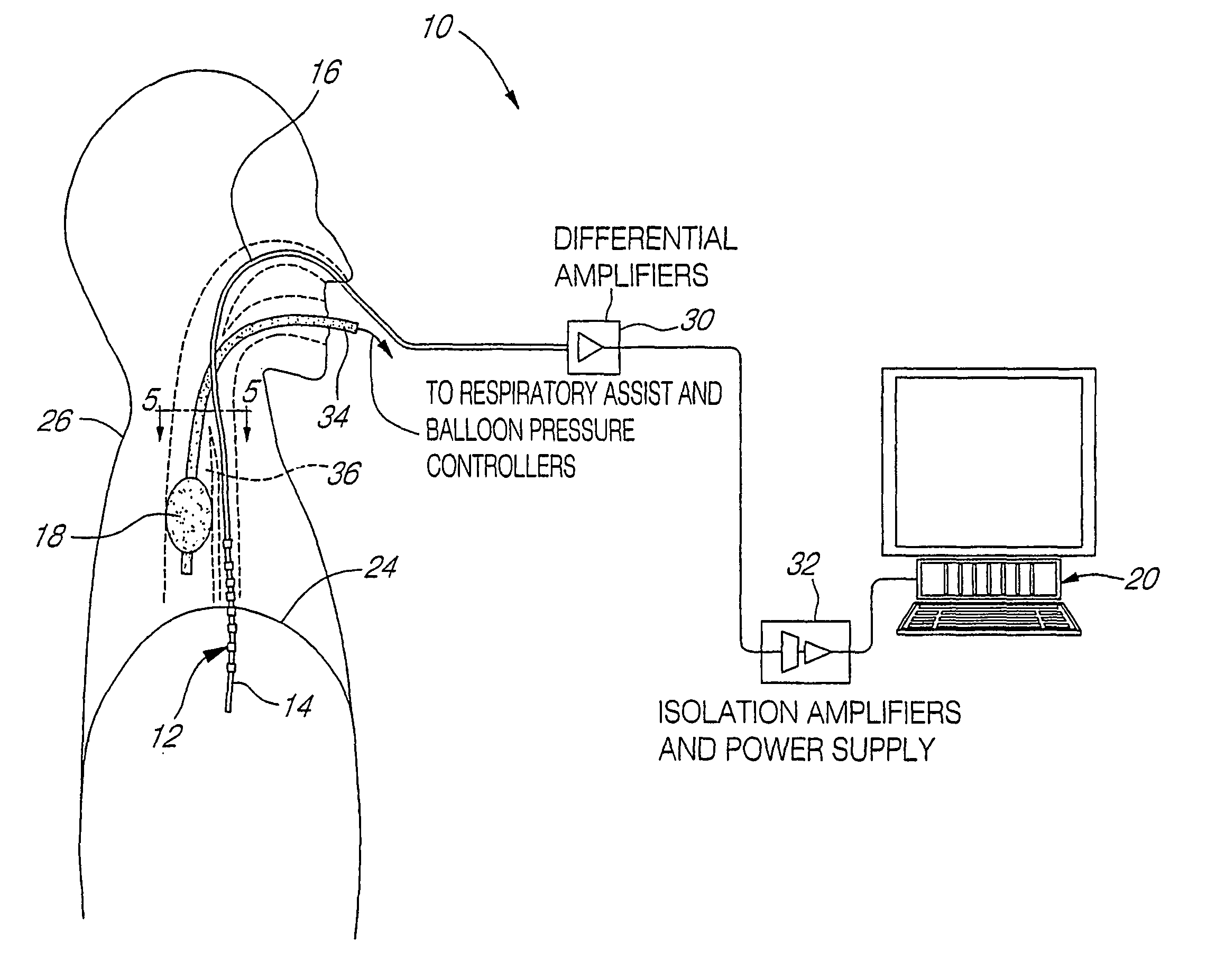
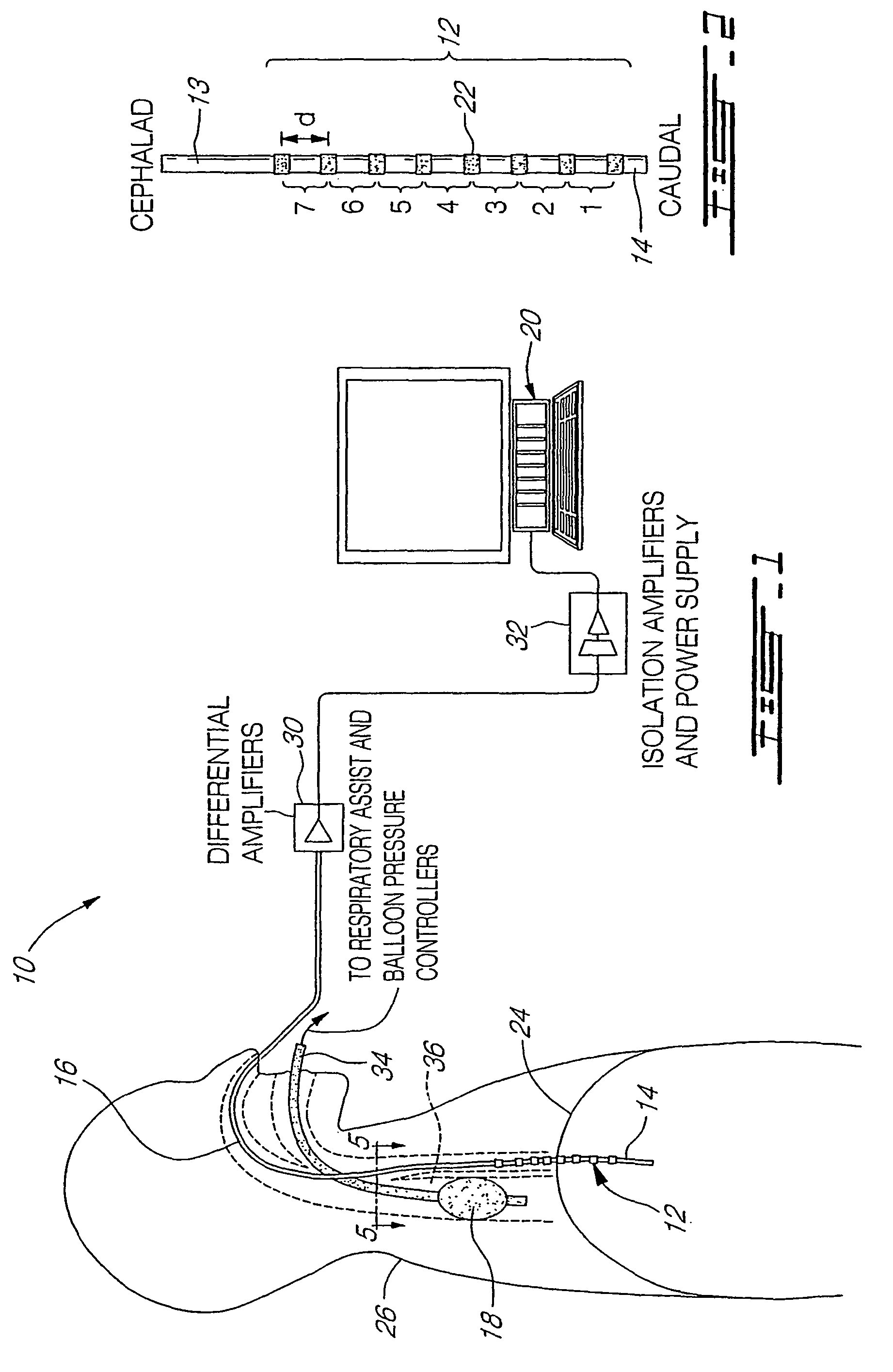
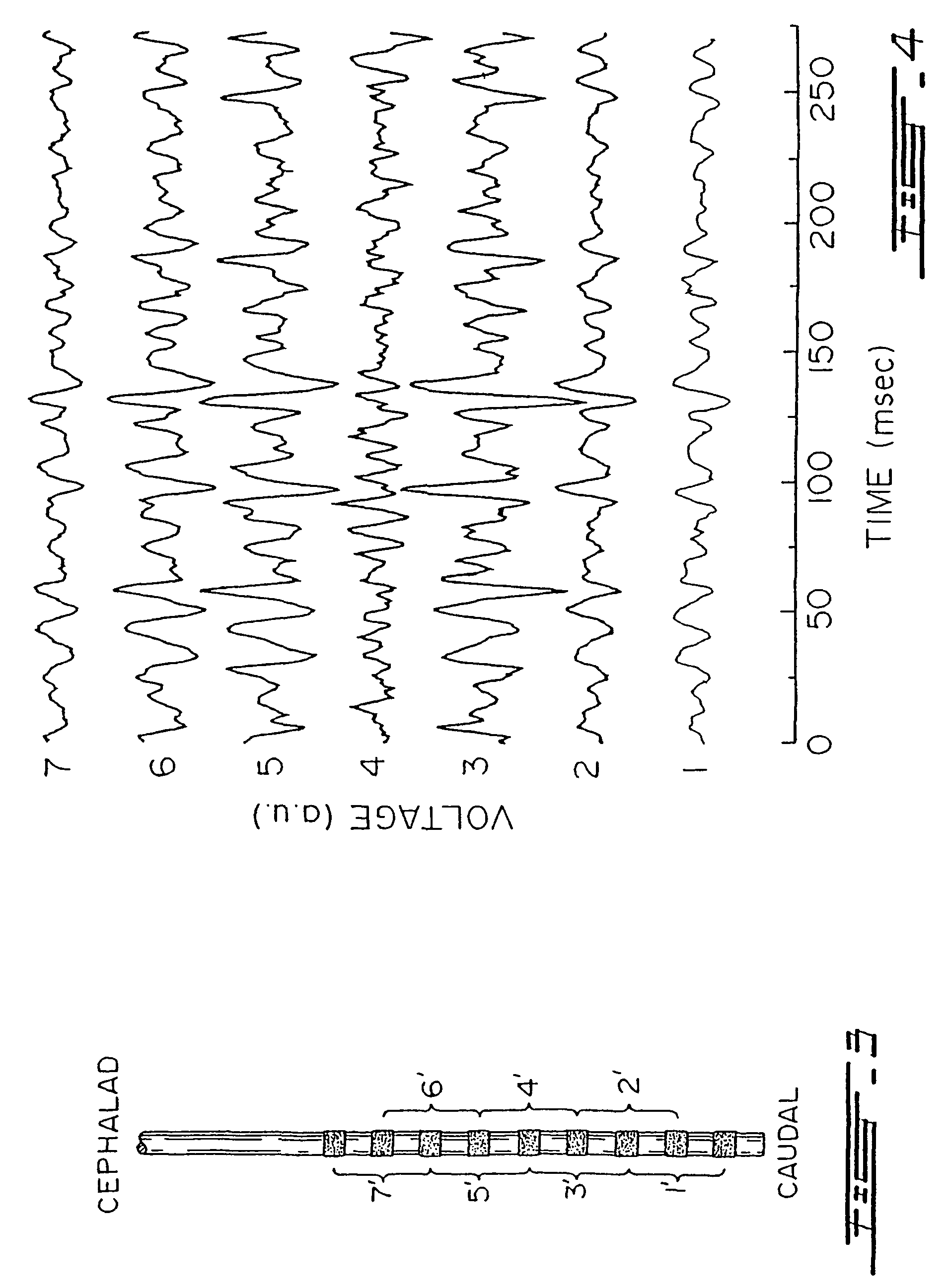
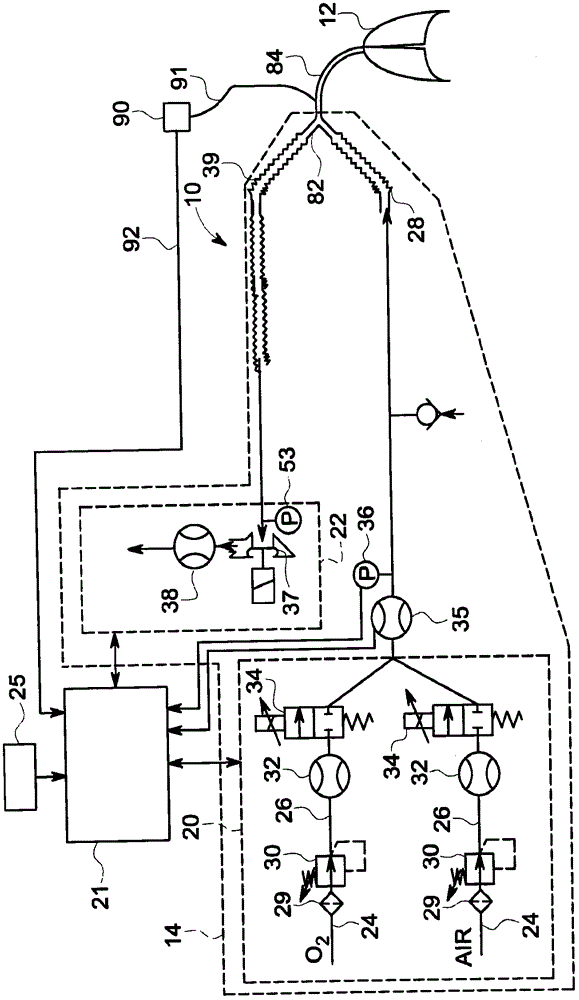
Method and arrangement for determining a ventilation need specific for a patient
InactiveUS20150114395A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBreathing gasEngineering
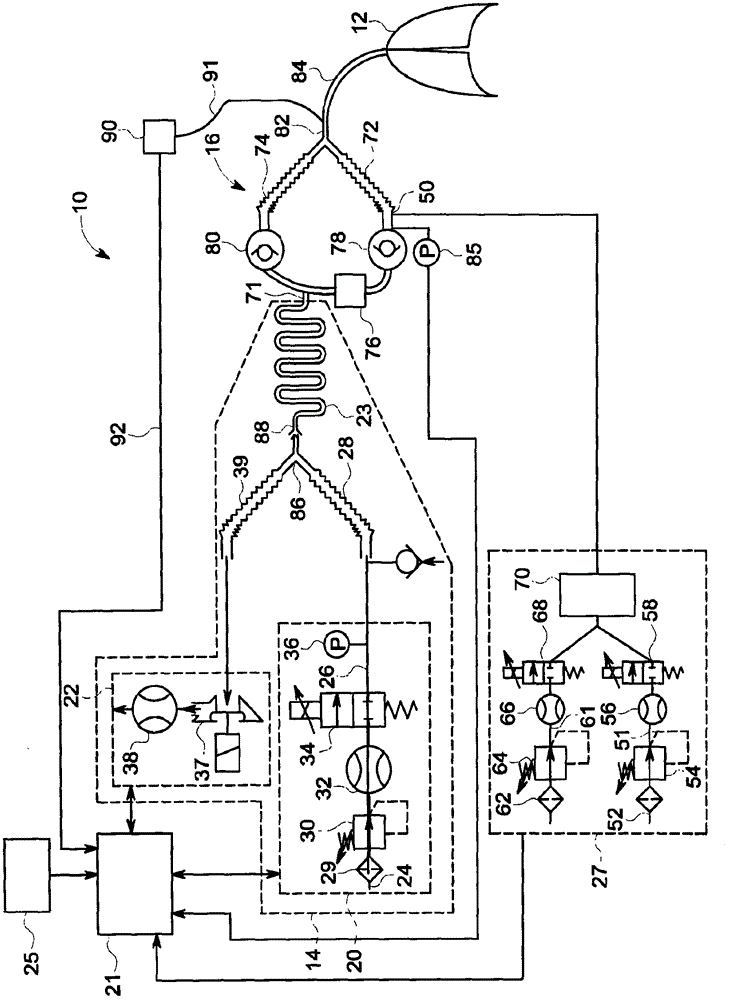
A method for determining a ventilation need specific for a patient is disclosed herein. The method includes providing a breath gas with a machine ventilator circuit from a starting pressure to lungs to start inspiration, and filling lungs to a predetermined breath gas pressure level. The method also includes determining in a control unit a filling volume of the breath gas needed to achieve the predetermined breath gas pressure level from the starting pressure, and determining in the control unit a lung elastic property based on a relationship between the determined filling volume of the breath gas and differences in the starting pressure and the predetermined breath gas pressure level. The method also includes determining in the control unit a respiration rate exploiting at least the lung elastic property. A corresponding arrangement is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Methods, devices and formulations for targeted endobronchial therapy
ActiveUS8245708B2Mortality rate is decreasedReduce morbidityTracheal tubesLiquid surface applicatorsTracheobronchitisRegimen
The present invention provides an improved method and novel devices for treating tracheobronchitis, bronchiectasis and pneumonia in the intubated patient, preferably with aerosolized anti gram-positive and anti-gram negative antibiotics administered in combination or in seriatim in reliably sufficient amounts for therapeutic effect. In one aspect, the invention assures this result when aerosol is delivered into the ventilator circuit. In one embodiment the result is achieved mechanically. In another embodiment, the result is achieved by aerosol formulation. In another aspect, the invention assures the result when aerosol is delivered directly to the airways distal of the ventilator circuit. The devices eliminate the dosage variability that ventilator systems engender when aerosols are introduced via the ventilator circuit. The treatment also concentrates the therapeutic agent specifically at affected sites in the lung such that therapeutic levels of administrated drug are achieved without significant systemic exposure of the patient to the drug. The invention further provides a dose control device to govern this specialized regimen.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
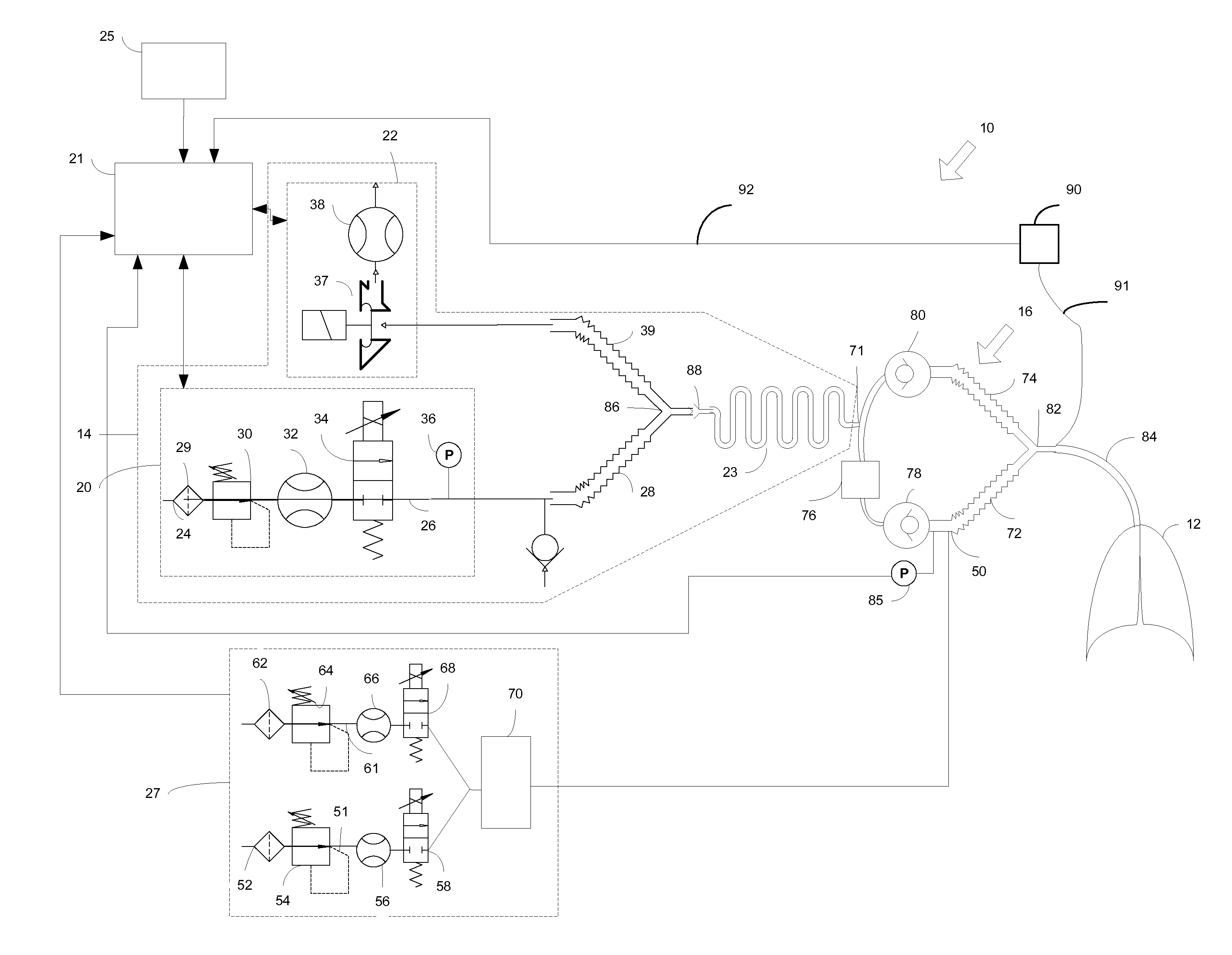
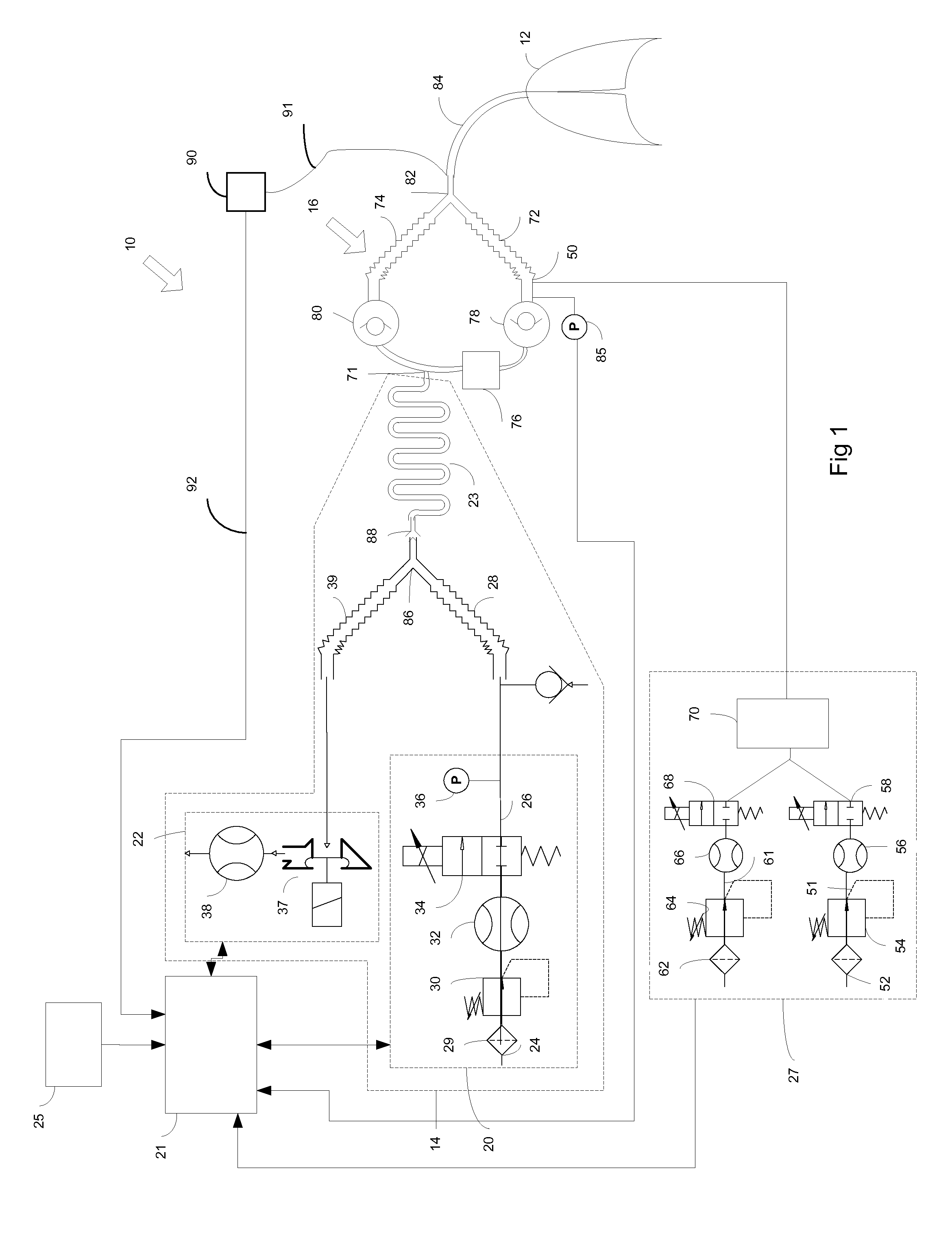
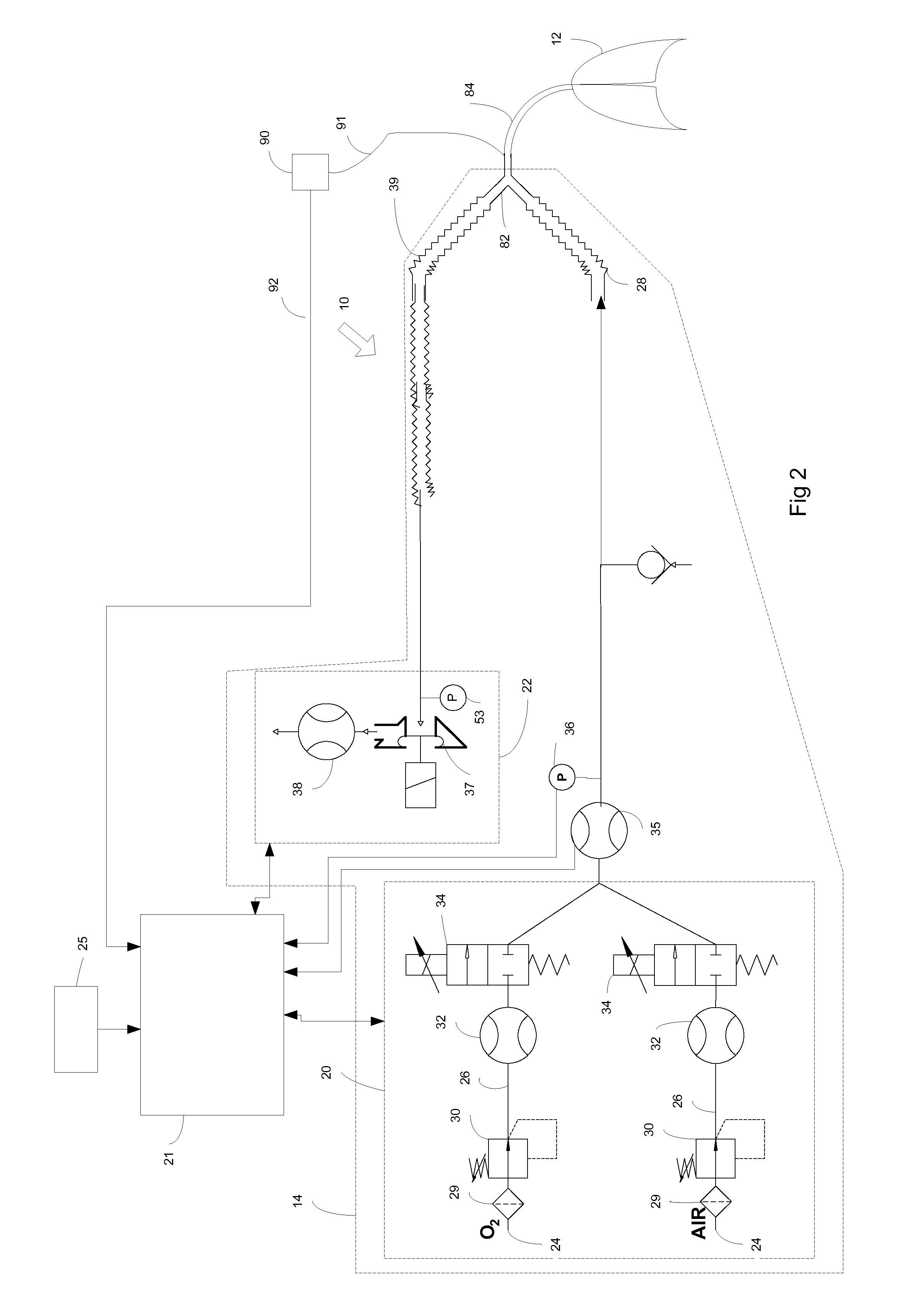
Method and arrangement for determining a vetilation need specific for a patient
A method (199) for determining a ventilation need specific for a patient is disclosed herein. The method includes providing (200) a breath gas with a machine ventilator circuit (14) from a starting pressure to lungs (12) of a patient to start inspiration, and filling said lungs to a predetermined breath gas pressure level. The method also includes determining (202) in a control unit (21) a filling volume of the breath gas needed to achieve the predetermined breath gas pressure level from the starting pressure, and determining (203) in the control unit a lung elastic property, such as compliance or elastance, based on a relationship between the determined filling volume of the breath gas and differences in the starting pressure and the predetermined breath gas pressure level. The method also includes determining (206) in the control unit a respiration rate exploiting at least the lung elastic property. A corresponding arrangement (10) is also provided.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Treatment of pulmonary disorders with aerosolized medicaments such as vancomycin
A method of administering an aerosolized anti-infective, such as a glycopeptide, to the respiratory system of a patient. A ratio of an amount of the glycopeptide, such as vancomycin, delivered to the pulmonary system of the patient in a 24 hour period to a minimum inhibitory amount for the target organ for the same period is about 2 or more. A system to introduce aerosolized medicament to a patient may include a humidifier coupled to an inspiratory limb of a ventilator circuit wye, where the humidifier supplies heated and humidified air to the patient, and an endotracheal tube having a proximal end coupled to a distal end of the ventilator circuit wye. The system may also include a nebulizer coupled to the endotracheal tube, where the nebulizer generates the aerosolized medicament.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Method for estimating leaks from ventilator circuits
InactiveUS20120078542A1RespiratorsMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateMedicineIntensive care medicine
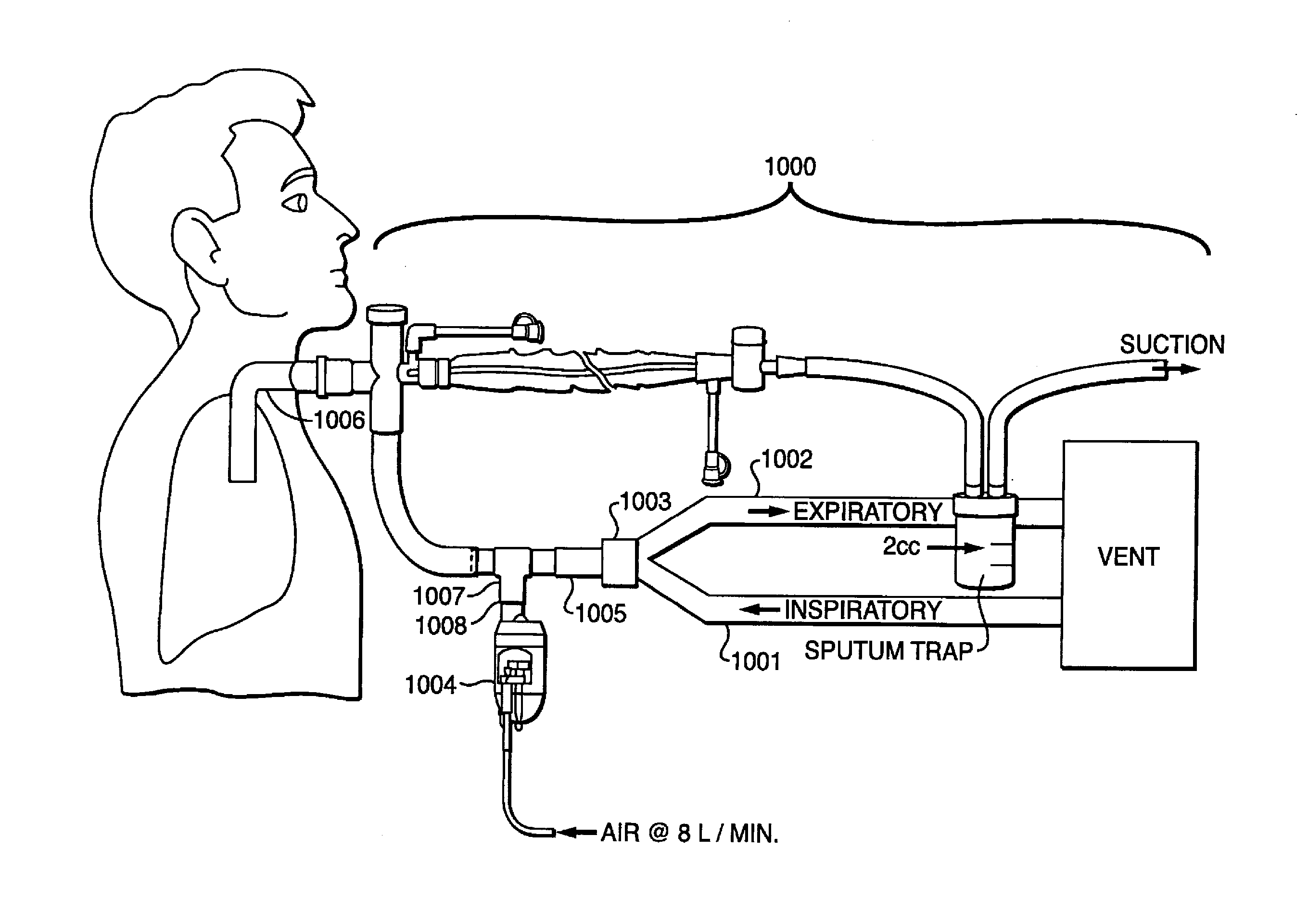
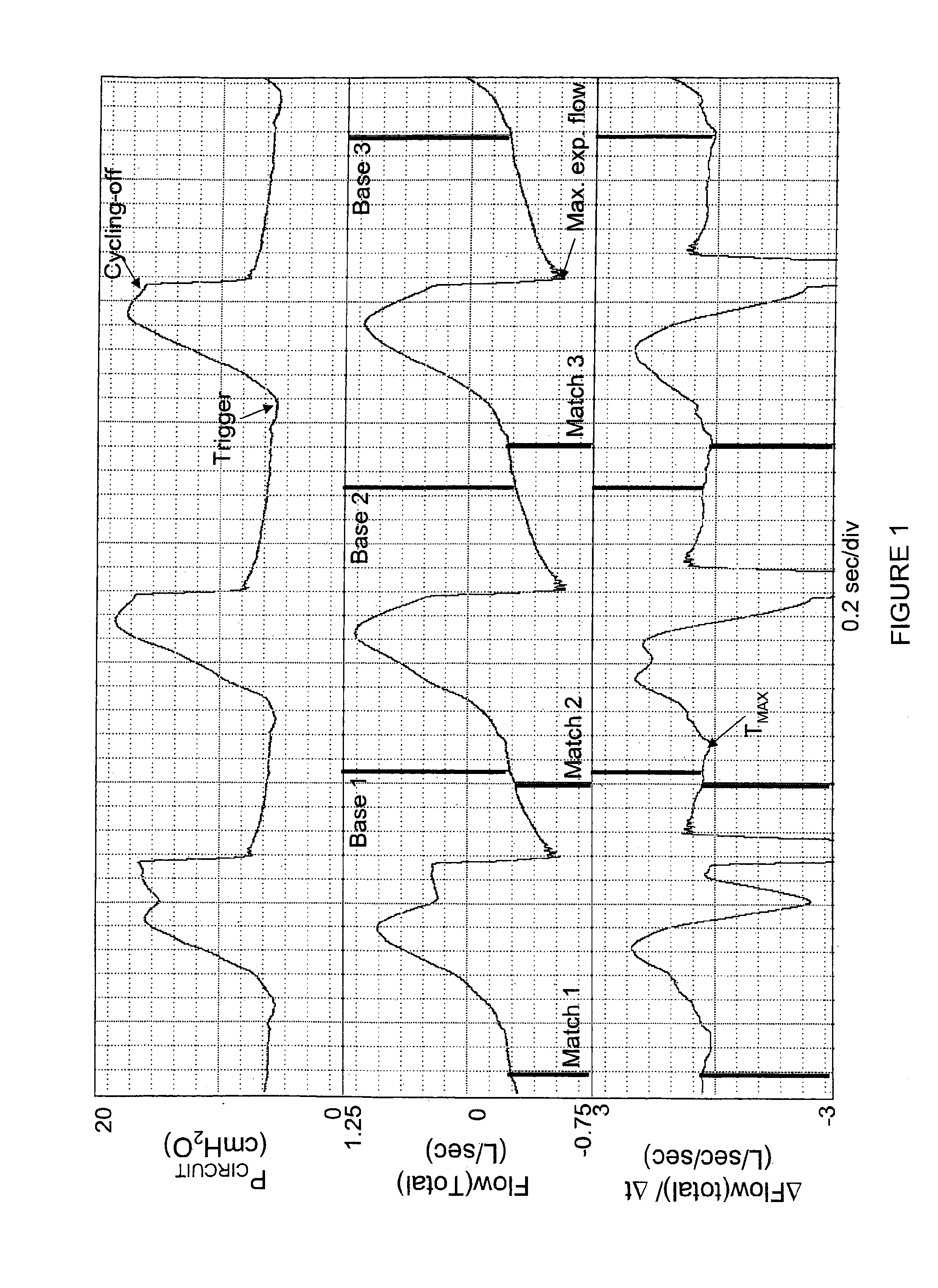
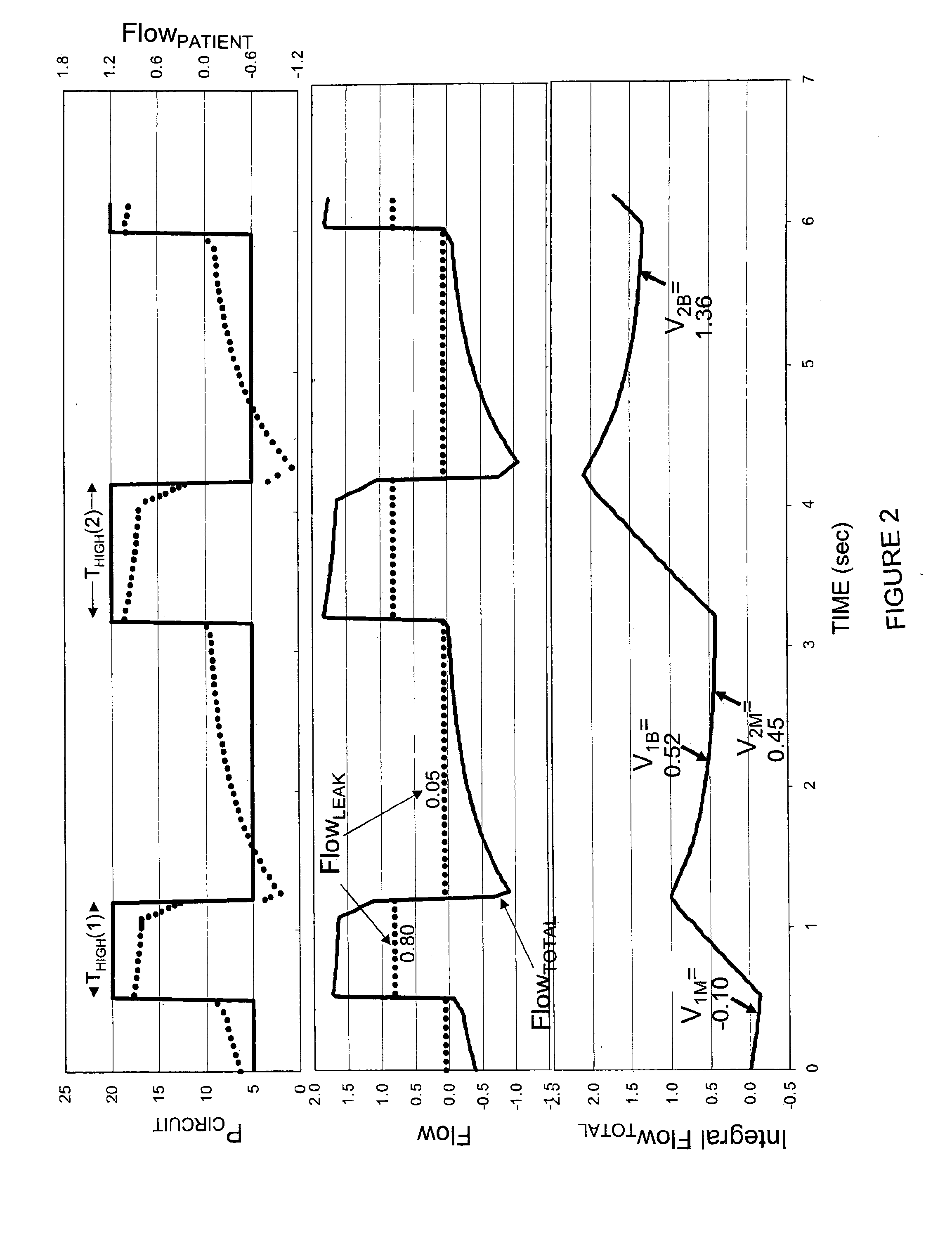
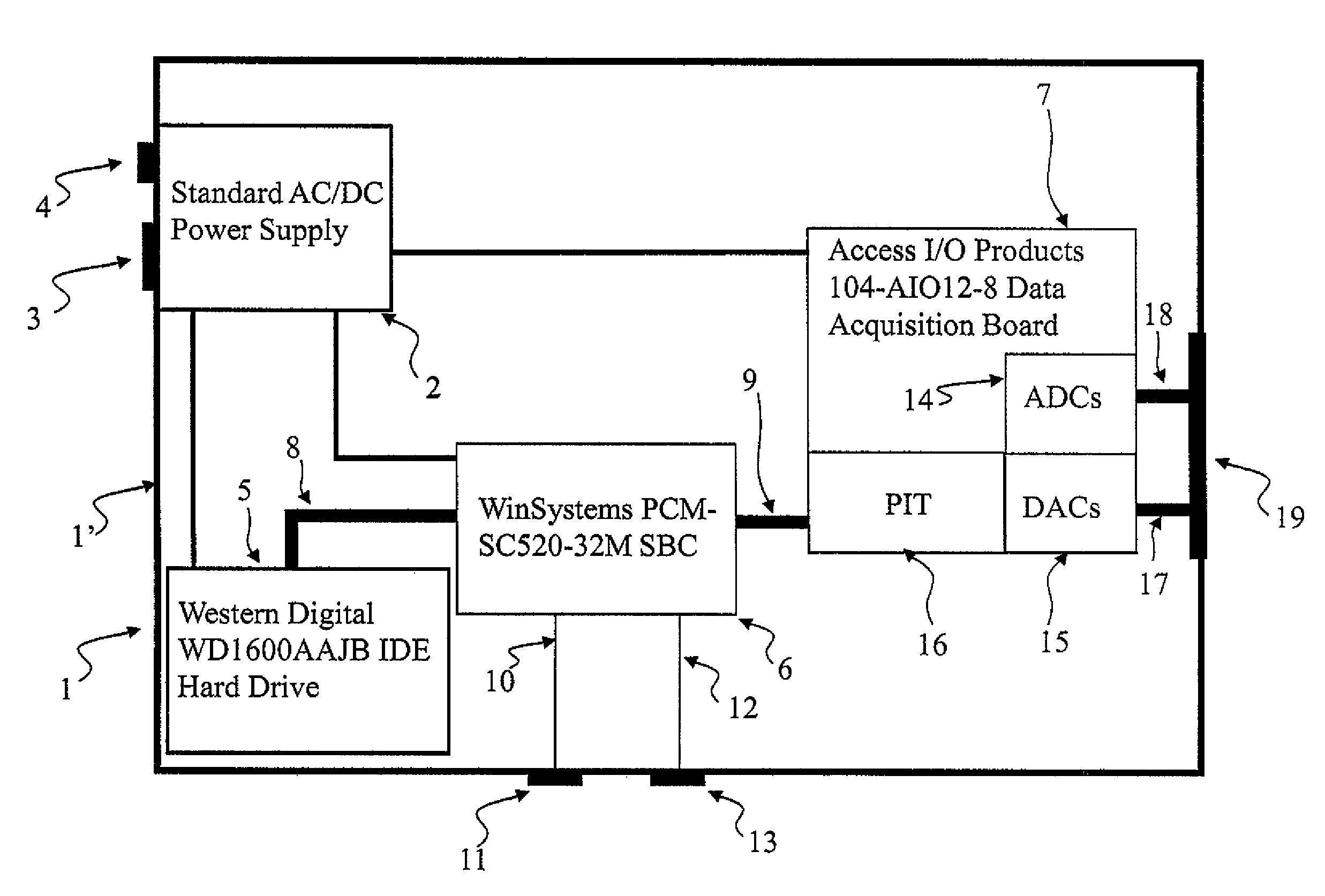
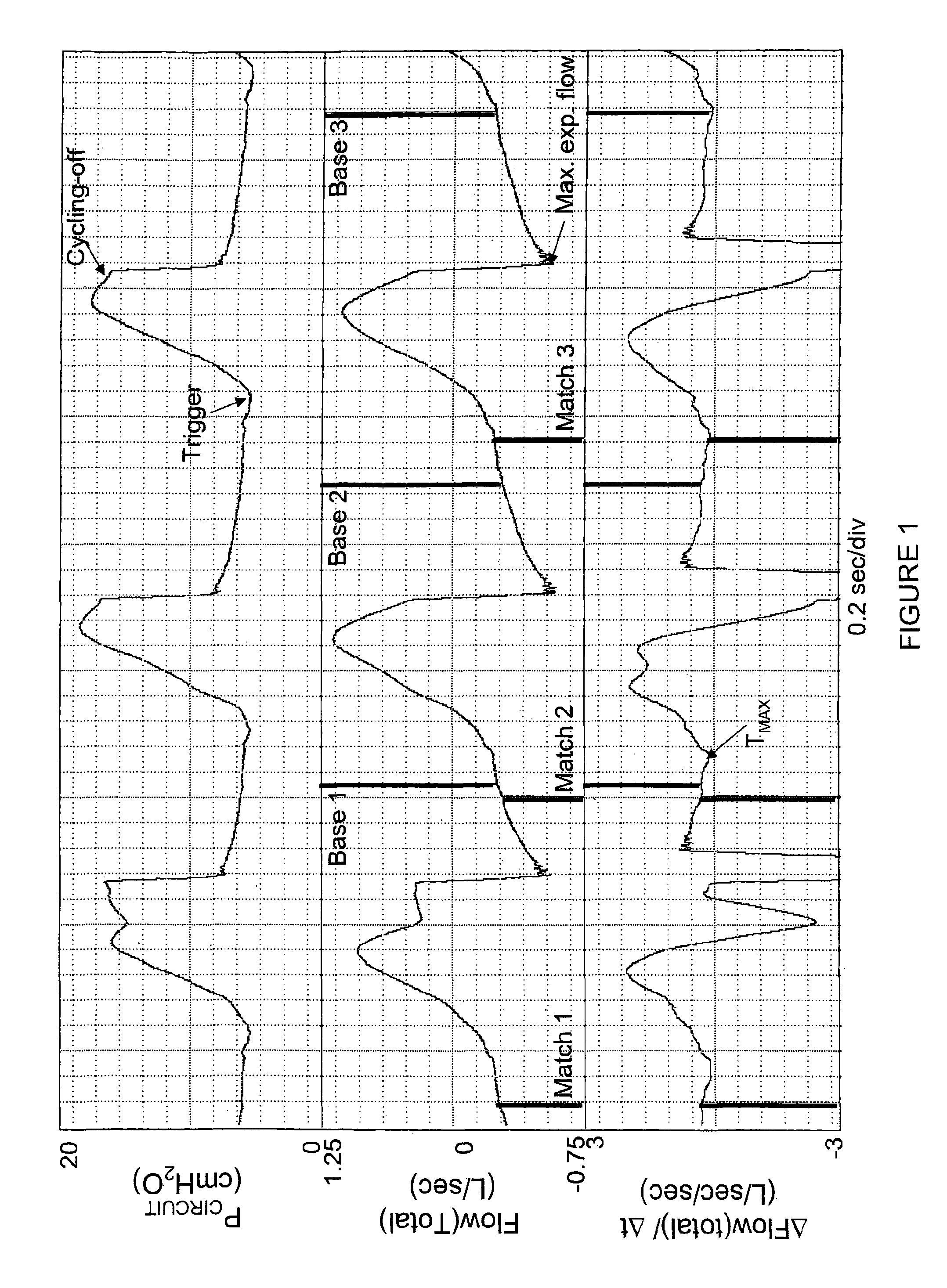
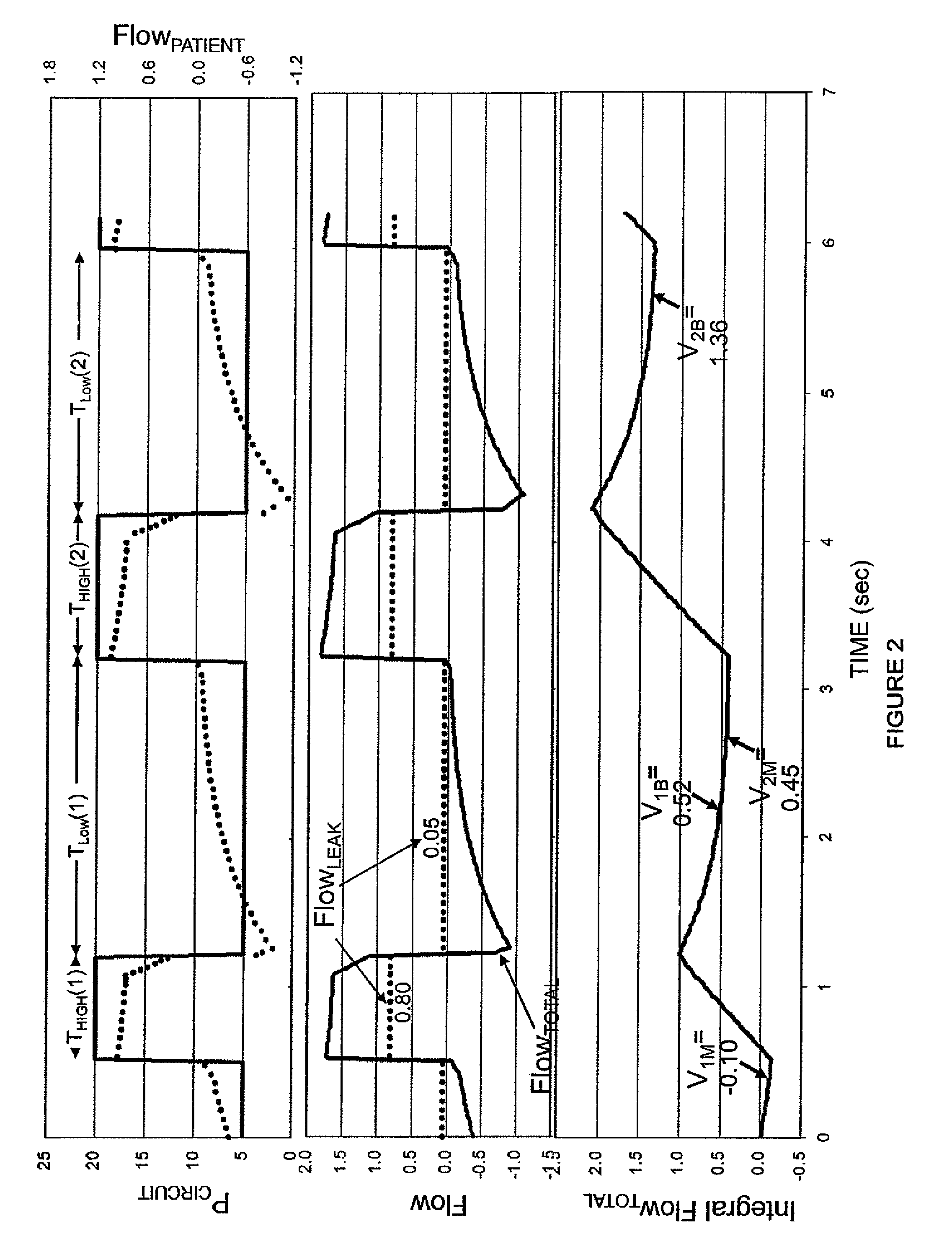
Gas leakage from a ventilator circuit and patient interface is estimated by a method that relies on breath-by-breath or time-to-time variability in the pattern of pressure delivery by the ventilator, comprising generating signals that correspond to pressure (PCIRCUIT) and flow rate (Flow) in the ventilator circuit, integrating flow (Integrated Flow), measuring the change in Integrated Flow (ΔV) over an INTERVAL extending from a selected point in the expiratory phase of a ventilator cycle to a selected point during the expiratory phase of a nearby ventilator cycle, repeating the measurement of ΔV for at least two said INTERVALS, processing PCIRCUIT to produce an index or indices that reflect(s) the pattern of pressure delivery by the ventilator during each of said INTERVALS, applying statistical methods to determine the relation between the differences in ΔV among INTERVALS and the corresponding differences in said index or indices of PCIRCUIT, and establishing from said relation the leak rate at specified PCIRCUIT values.
Owner:YRT
Aerosolisation system
Owner:STAMFORD DEVICES LTD
Tracheal tube anti-disconnect device
Owner:WILSON ELOUISE +1
Methods, devices and formulations for targeted endobronchial therapy
ActiveUS7334580B2Mortality rate is decreasedReduce morbidityTracheal tubesBreathing masksTracheobronchitisTreatment effect
The present invention provides an improved method and novel devices for treating tracheobronchitis, bronchiectasis and pneumonia in the intubated patient, preferably with aerosolized anti gram-positive and anti-gram negative antibiotics administered in combination or in seriatim in reliably sufficient amounts for therapeutic effect. In one aspect, the invention assures this result when aerosol is delivered into the ventilator circuit. In one embodiment the result is achieved mechanically. In another embodiment, the result is achieved by aerosol formulation. In another aspect, the invention assures the result when aerosol is delivered directly to the airways distal of the ventilator circuit. The devices eliminate the dosage variability that ventilator systems engender when aerosols are introduced via the ventilator circuit. The treatment also concentrates the therapeutic agent specifically at affected sites in the lung such that therapeutic levels of administrated drug are achieved without significant systemic exposure of the patient to the drug. The invention further provides a dose control device to govern this specialized regimen.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
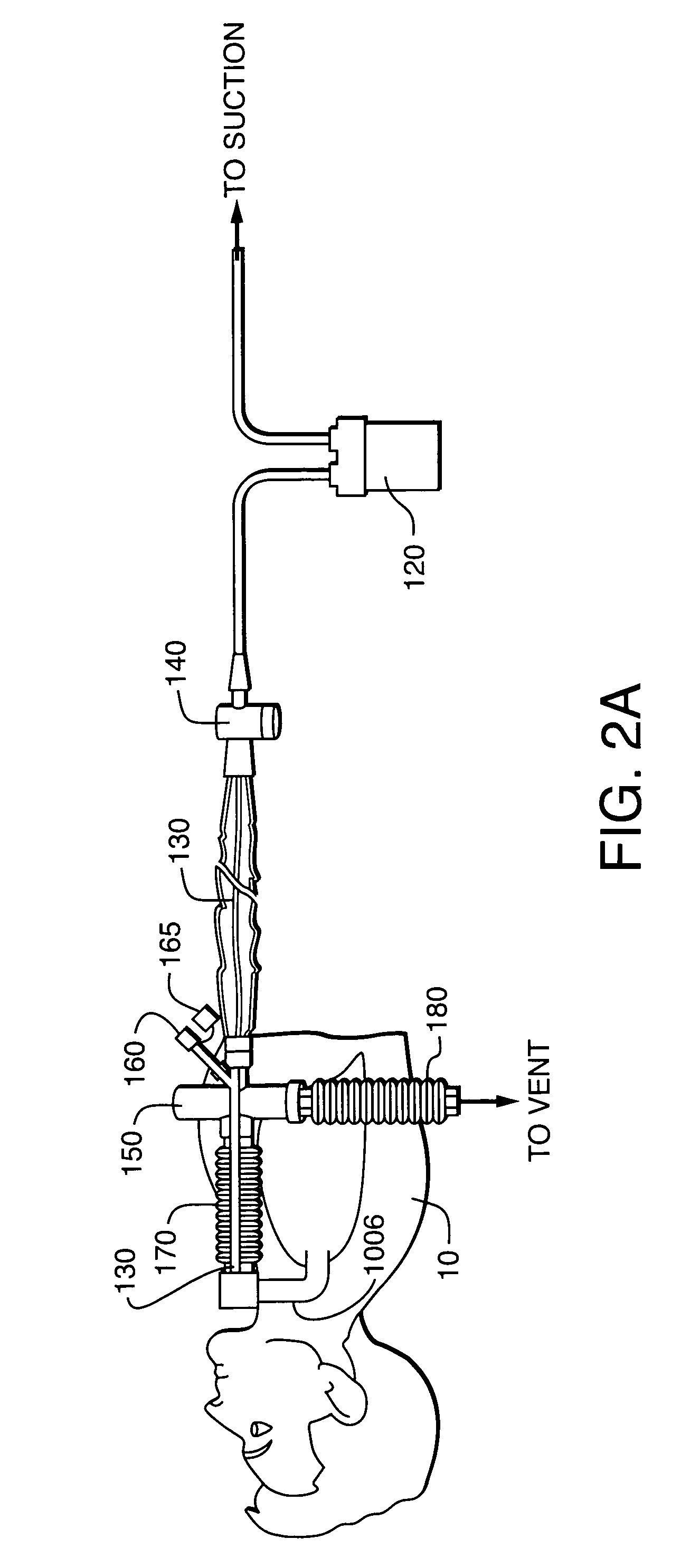
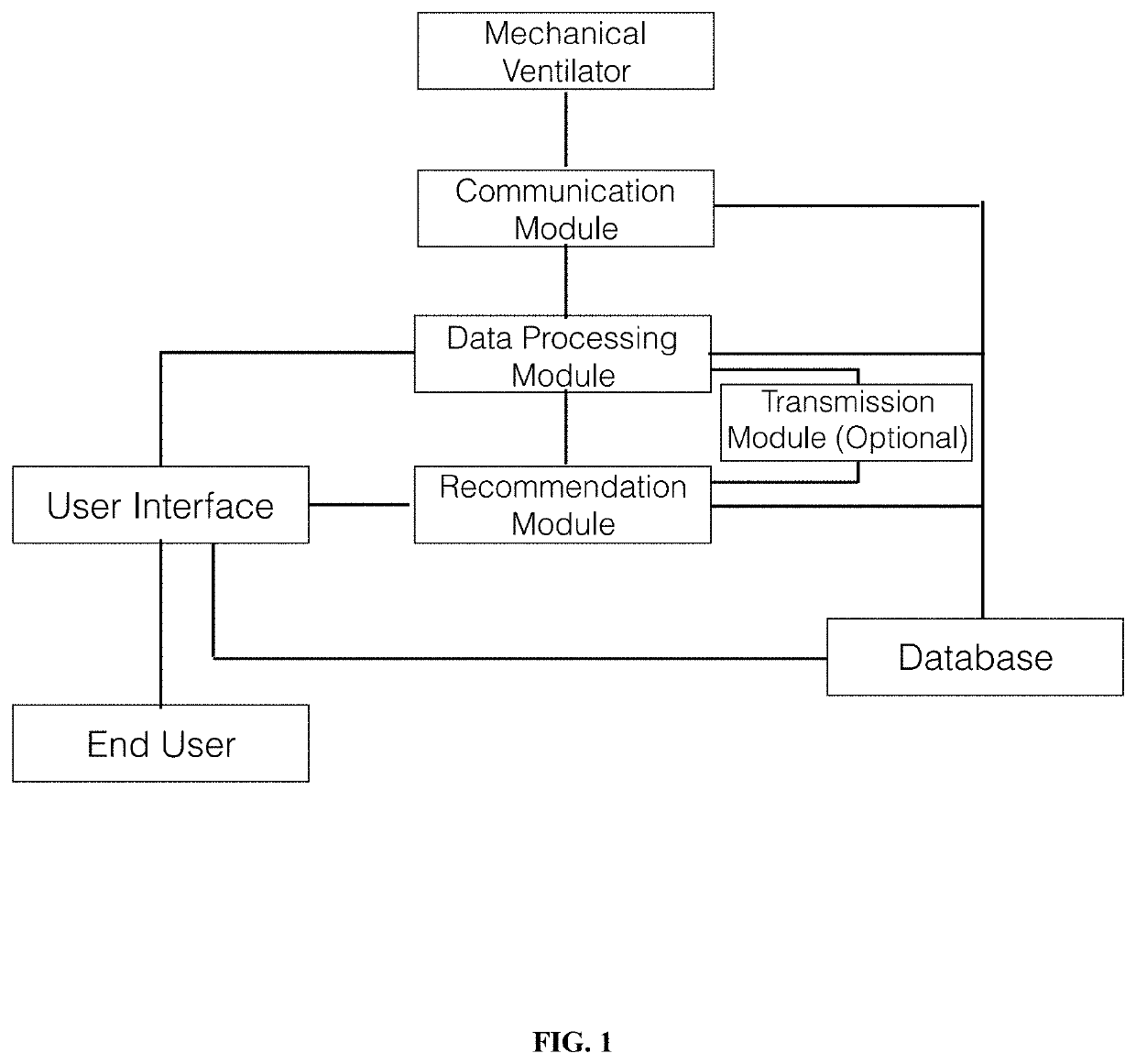
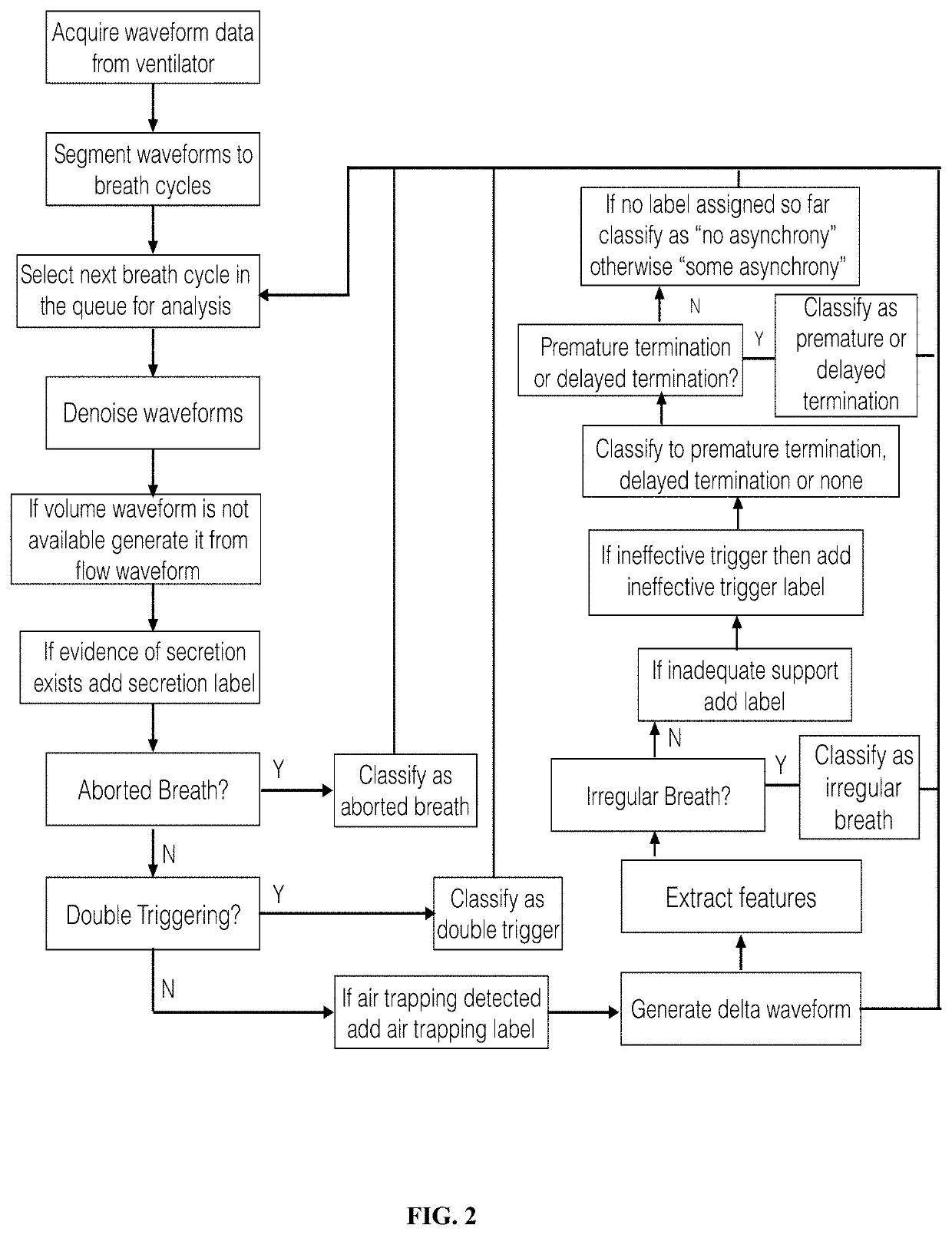
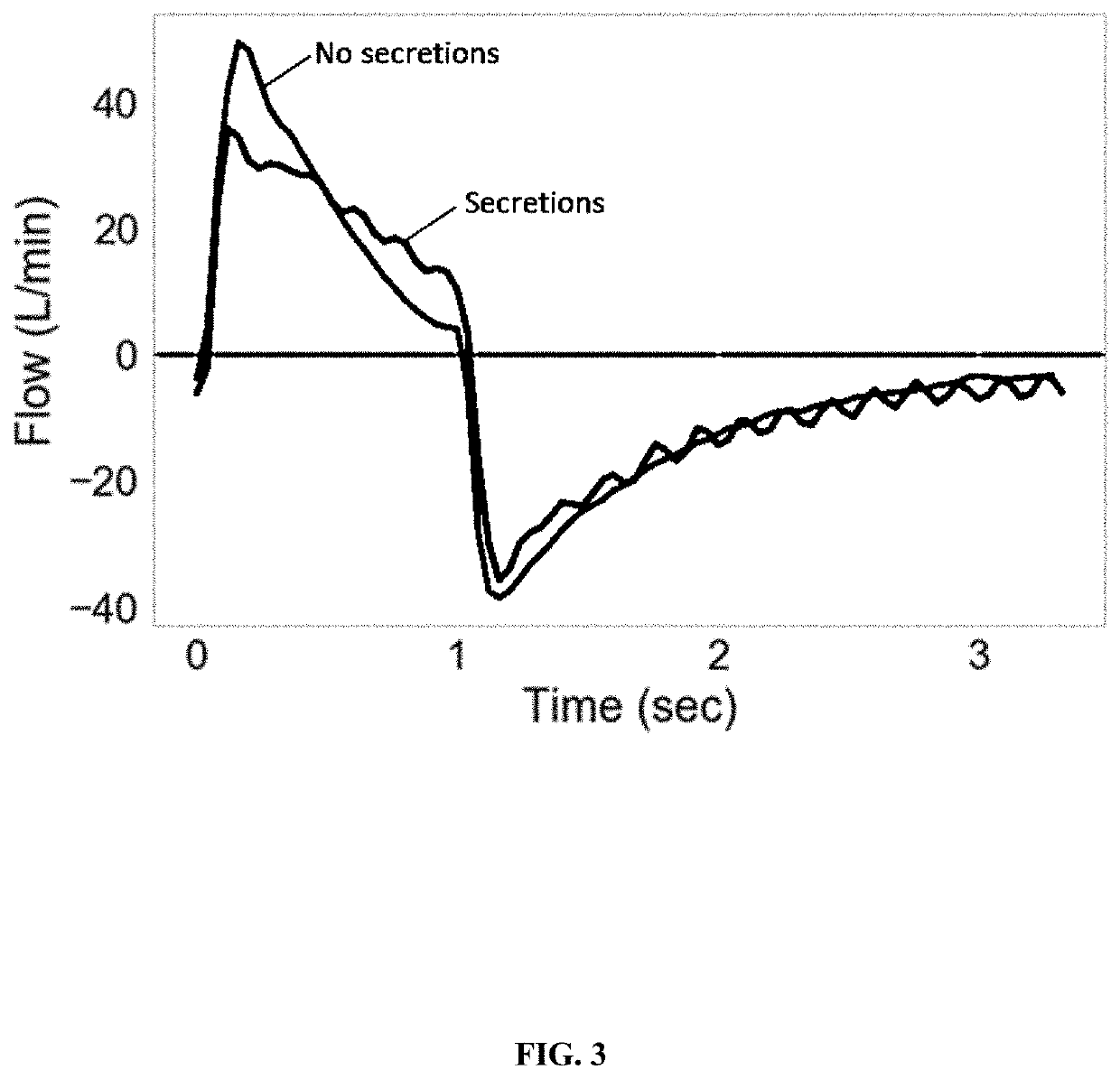
Clinical Decision Support System for Patient-Ventilator Asynchrony Detection and Management
The present disclosure describes a system that automatically detects patient-ventilator asynchrony and trends in patient-ventilator asynchrony. The present disclosure describes a framework that uses pressure, flow, and volume waveforms to detect patient-ventilator asynchrony and the presence of secretions in the ventilator circuit.
Owner:AUTONOMOUS HEALTHCARE INC
Portable Fluid Warming System
The present invention relates to a portable apparatus for warming biocompatible fluids for use in the treatment of injured patients and a method of heating a biocompatible fluid to treat a patient experiencing hypothermia. The present invention may be used to warm intravenous fluids for trauma resuscitation or to warm air from a ventilator circuit. The portable nature of the present invention makes it highly suitable for field applications, such as a forward surgical hospital near a combat zone.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Portable fluid warming system
The present invention relates to a portable apparatus for warming biocompatible fluids for use in the treatment of injured patients. The present invention may be used to warm intravenous fluids for trauma resuscitation or to warm air from a ventilator circuit. The portable nature of the present invention makes it highly suitable for field applications, such as a forward surgical hospital near a combat zone.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com