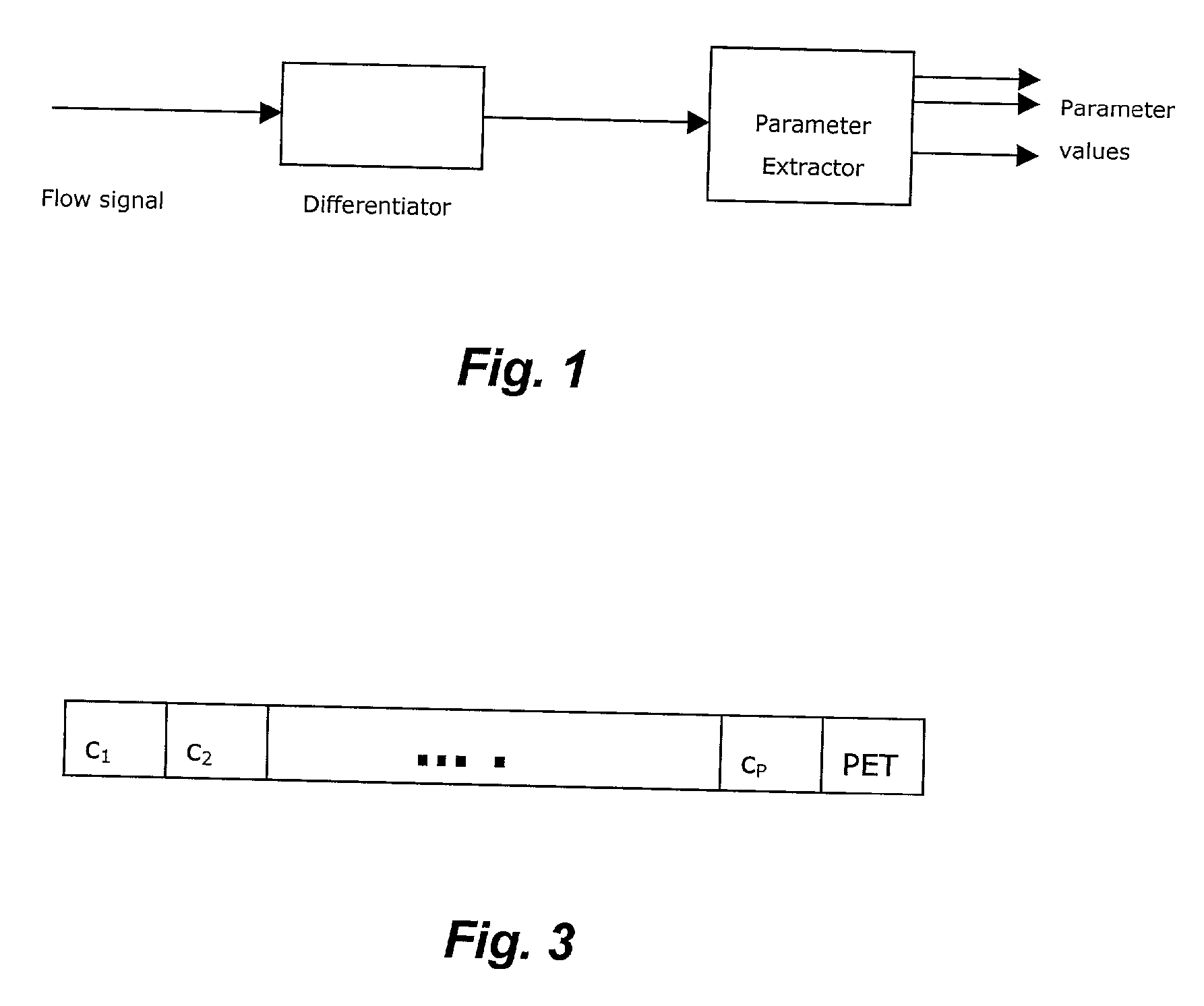
Patents
Literature
383 results about "Breathing circuits" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
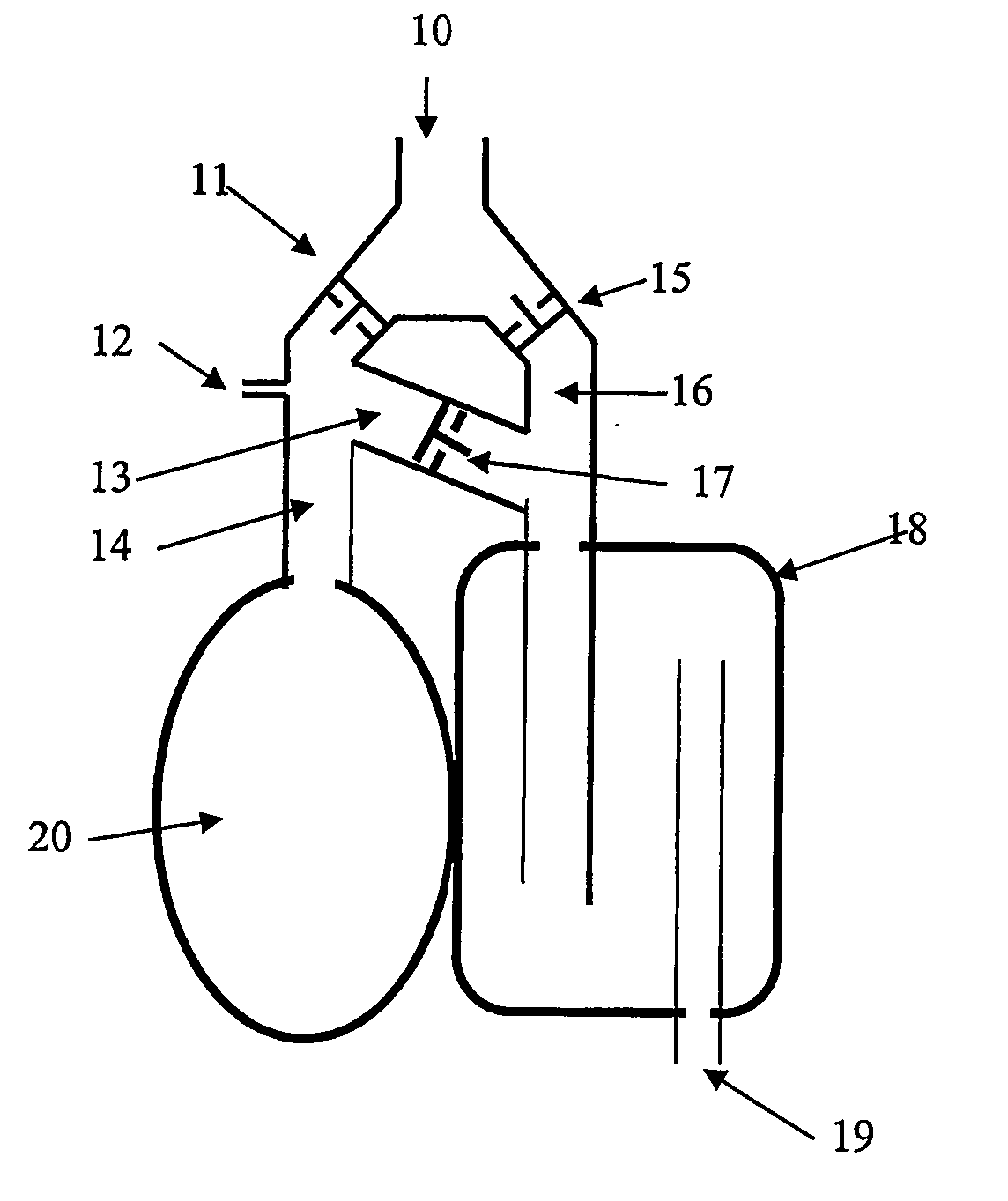
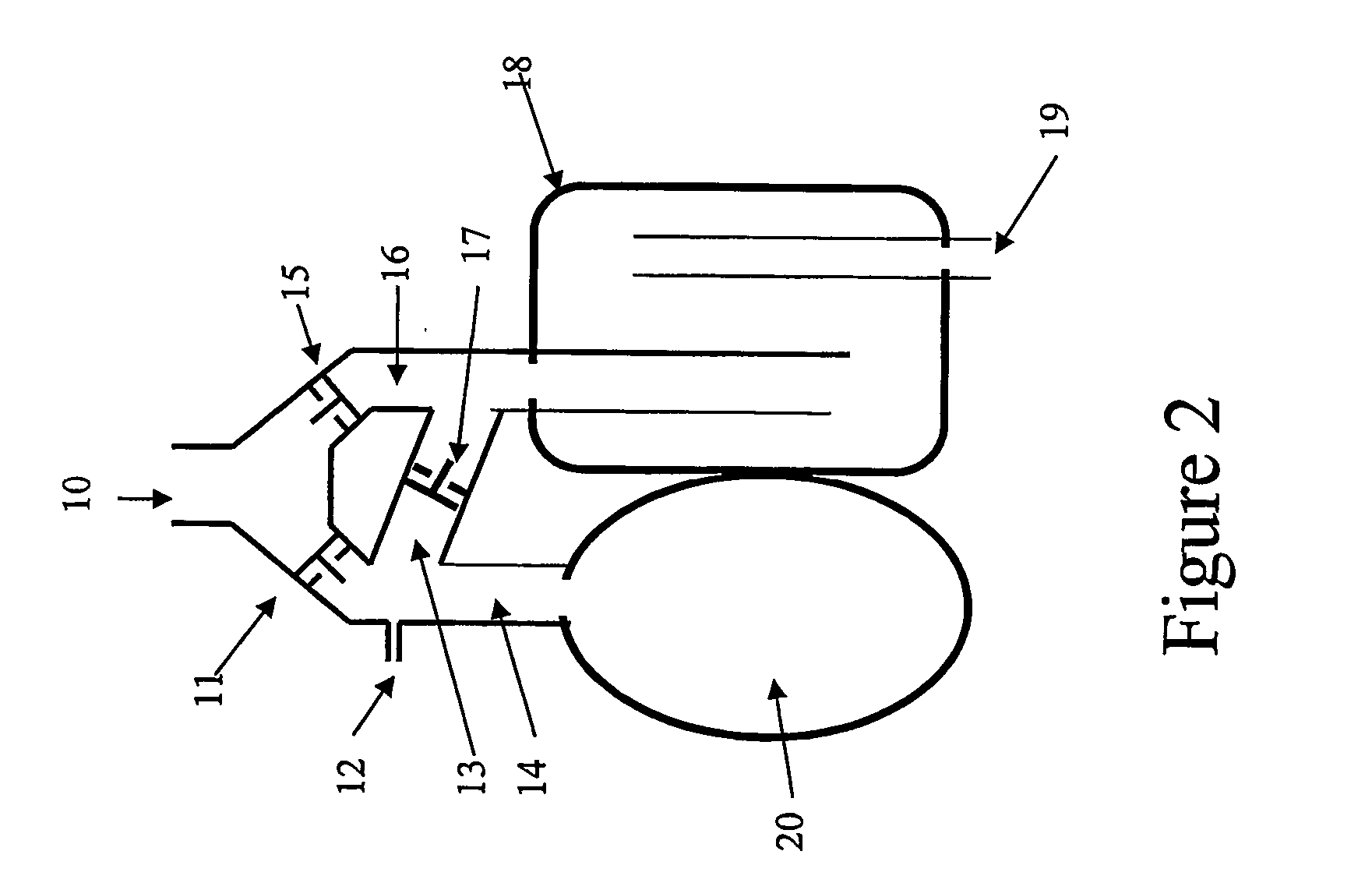
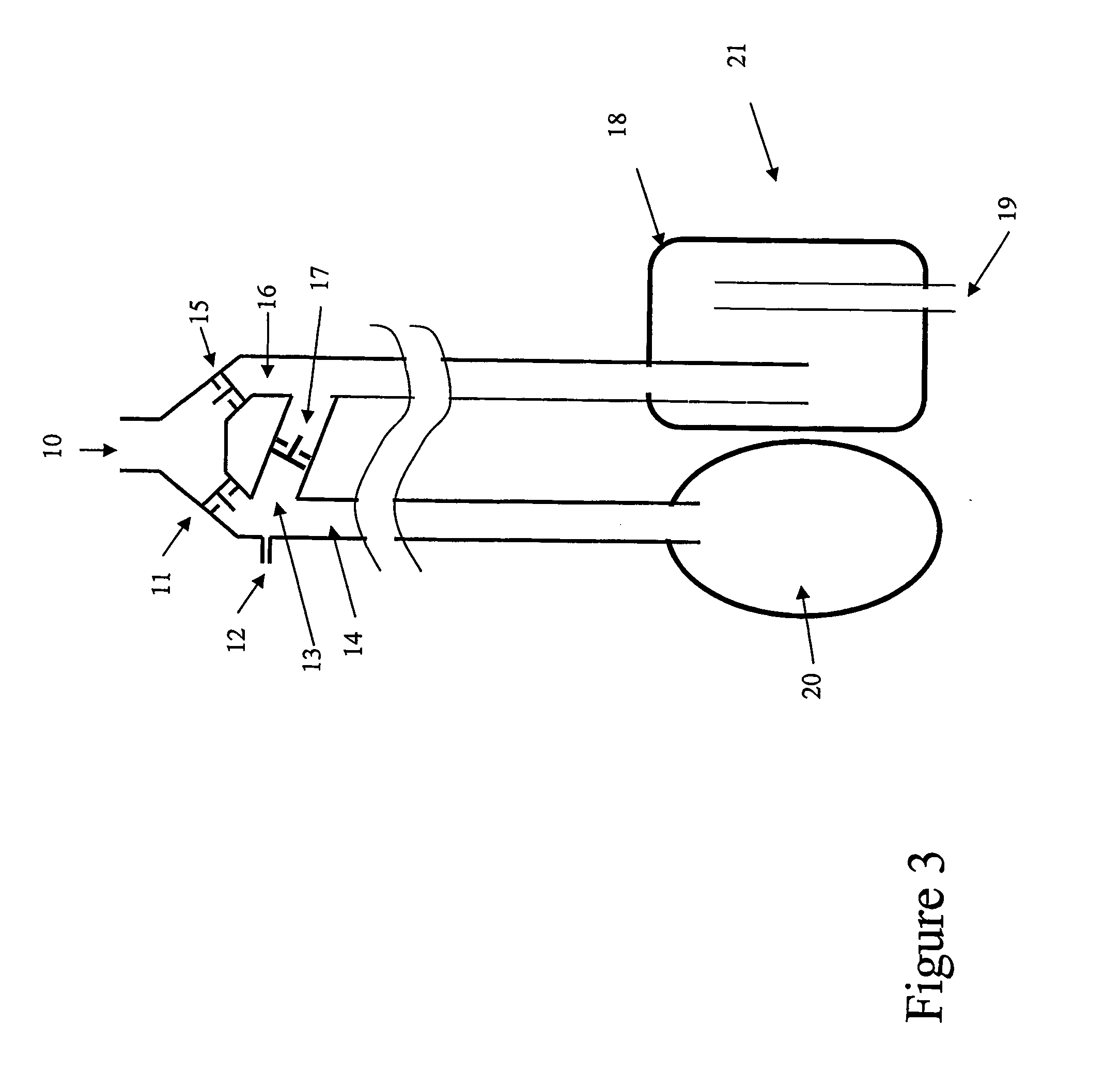
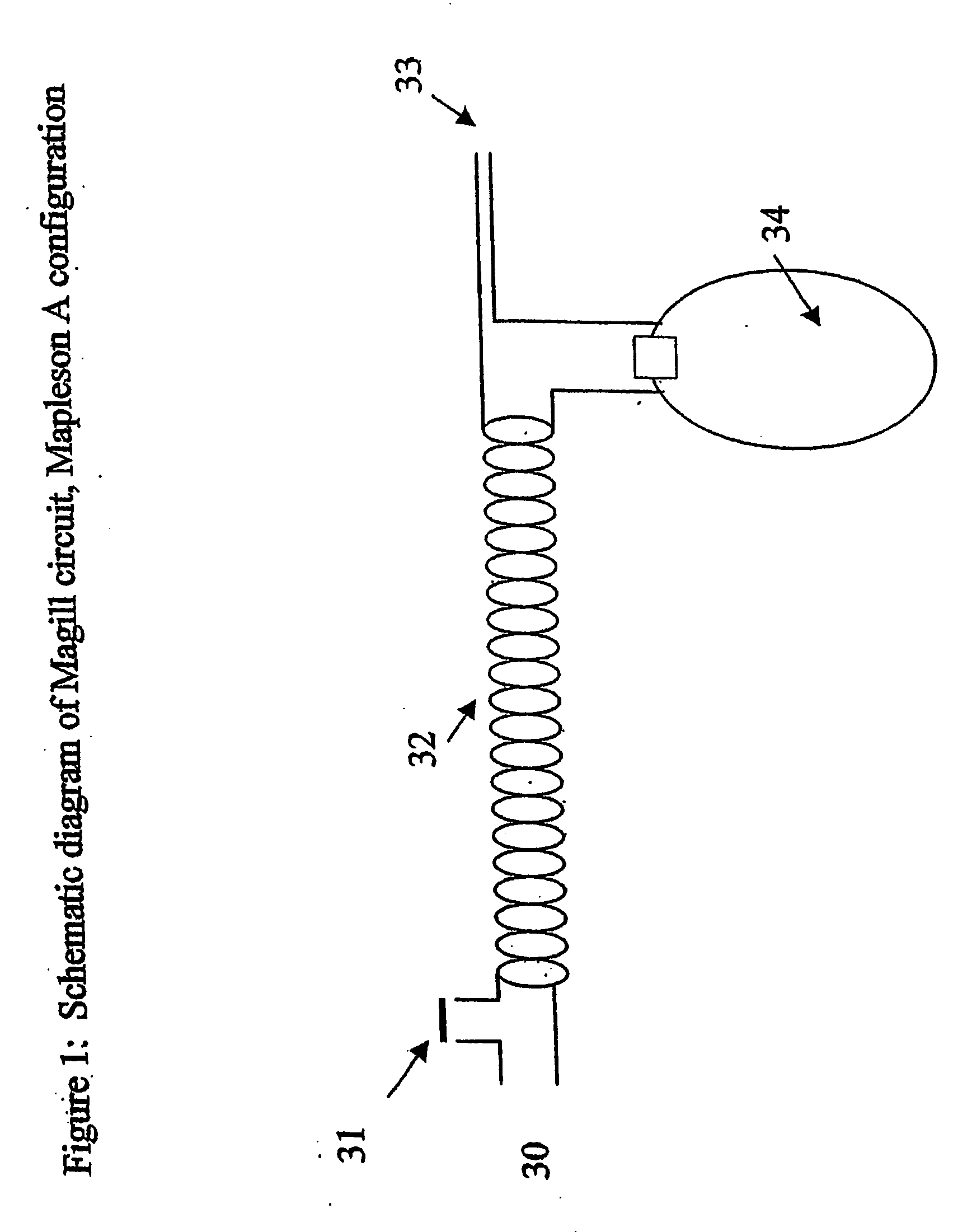
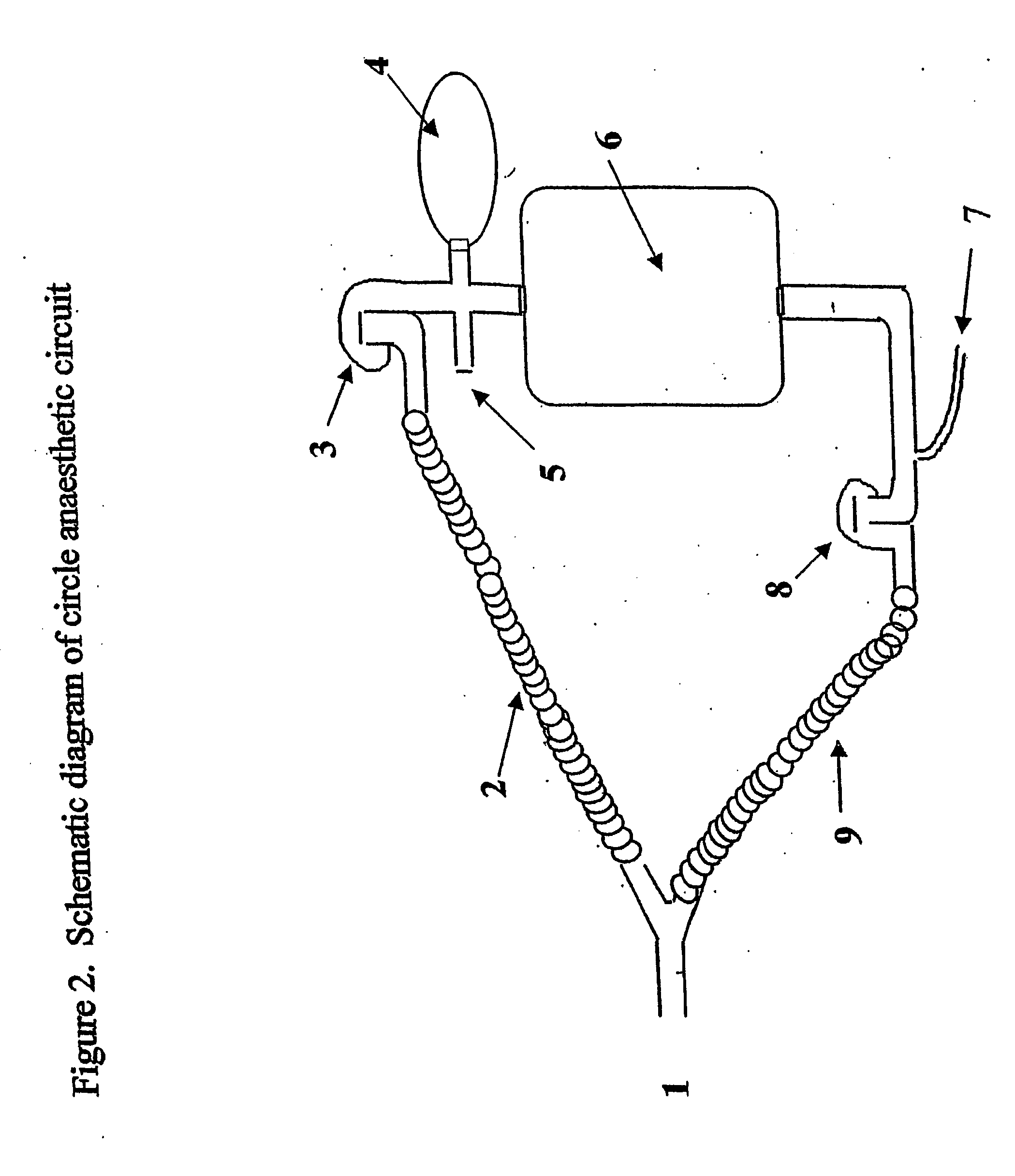
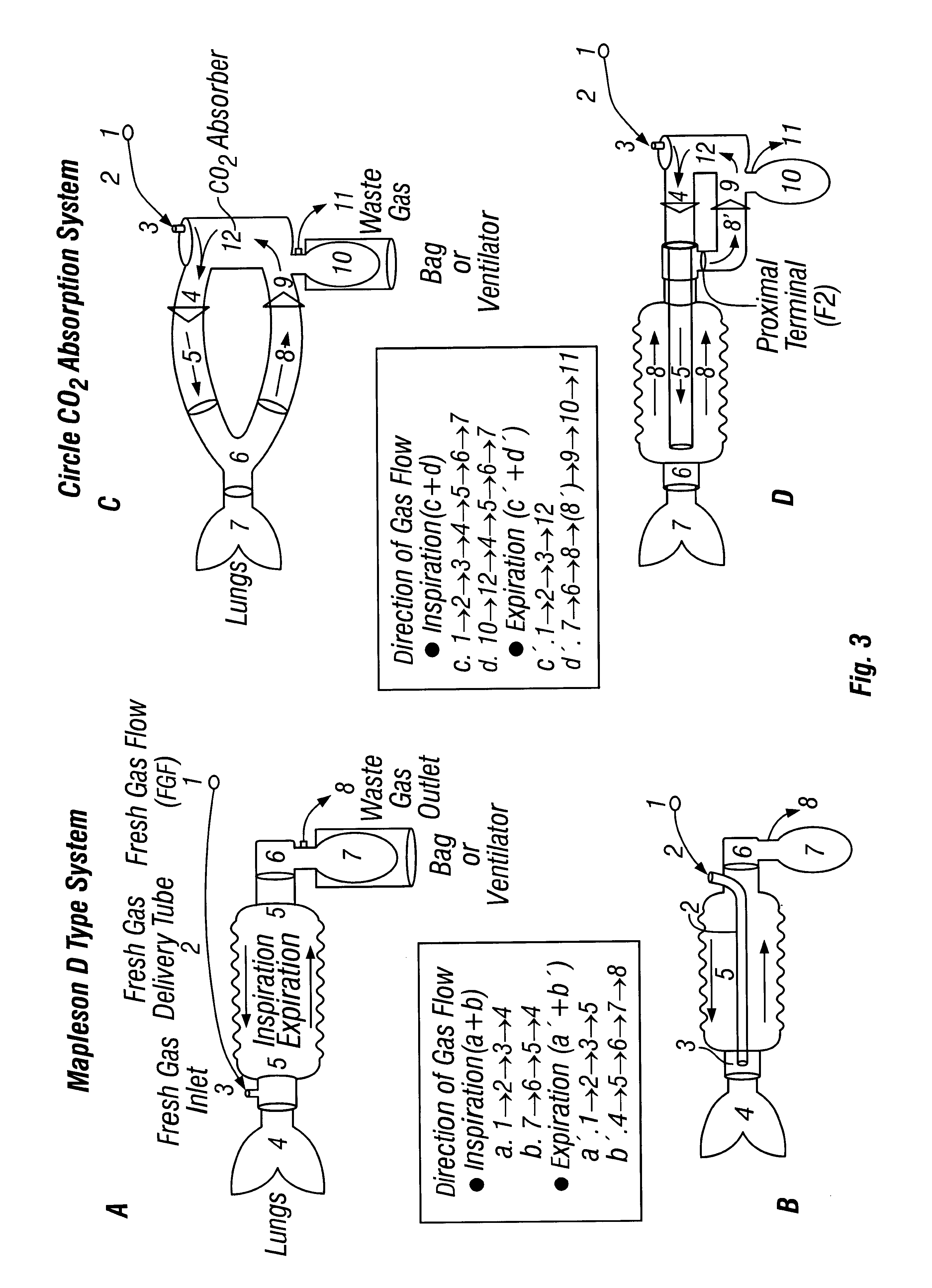
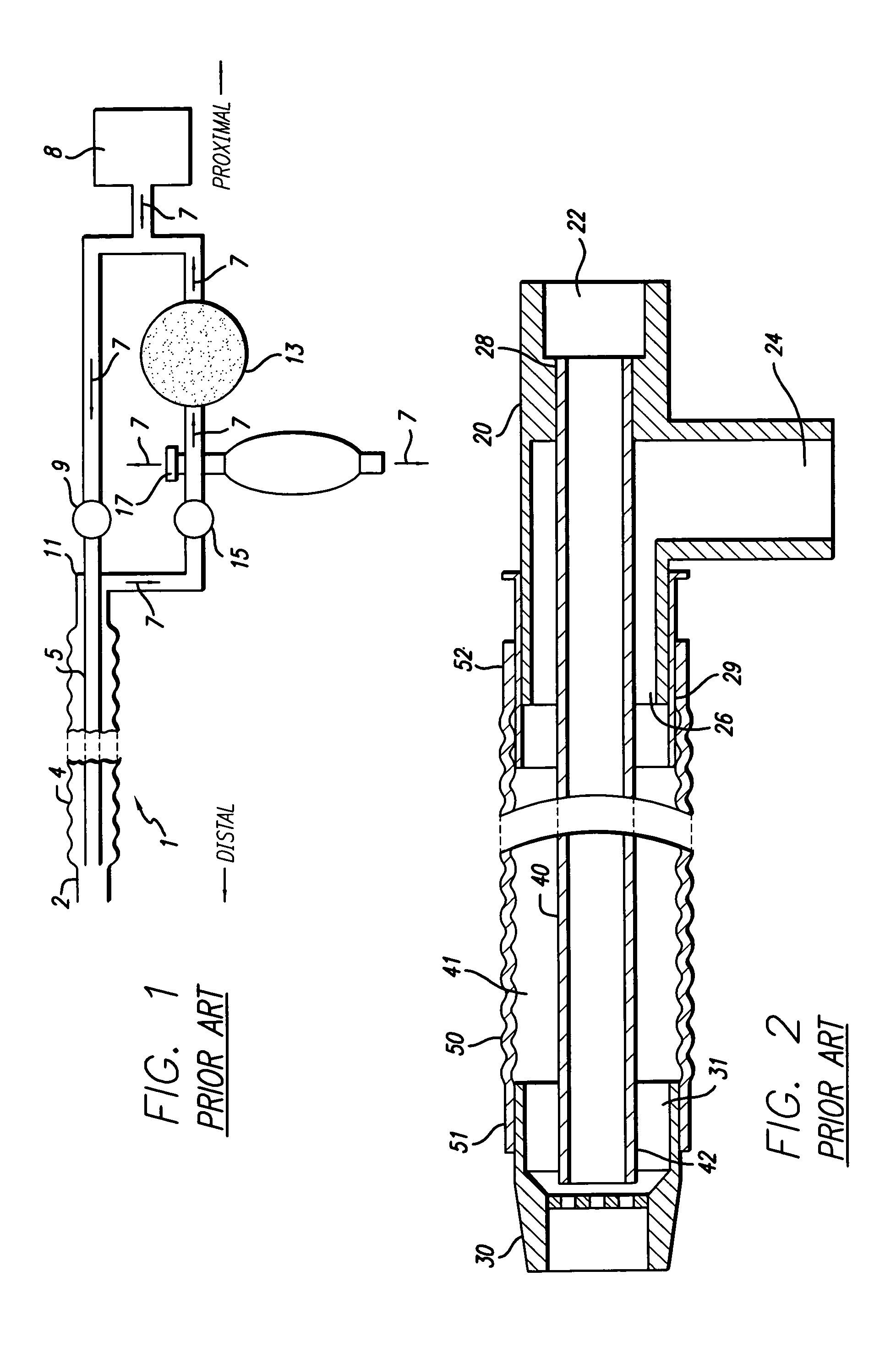
Circle breathing circuit. in an anesthetic machine; the flow of gases is directed by an inclusion in the system of two unidirectional valves, one in an expiratory and one in an inspiratory tube. The rebreathing bag and the canister of sodalime for CO2 absorption are located between the two tubes.
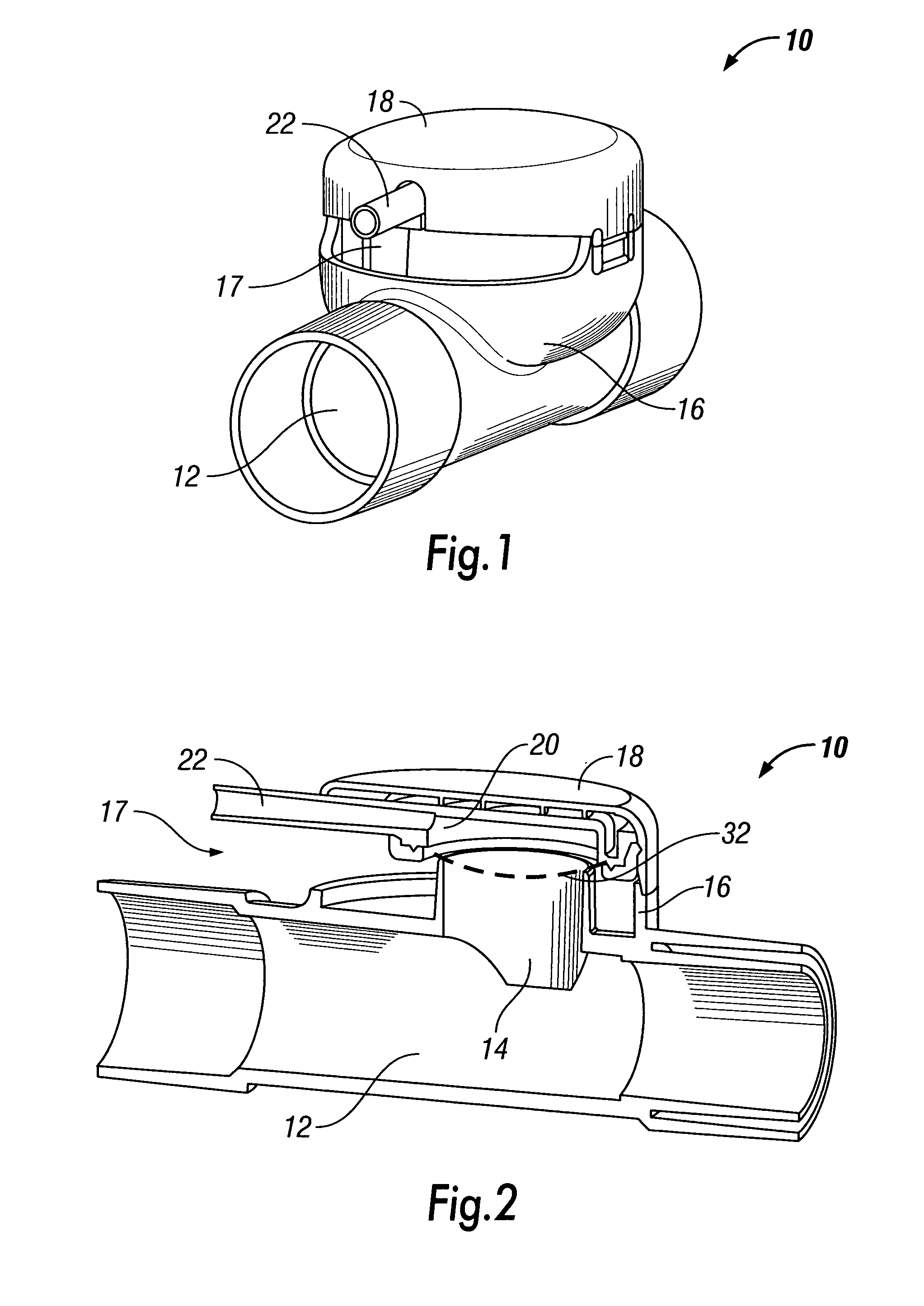
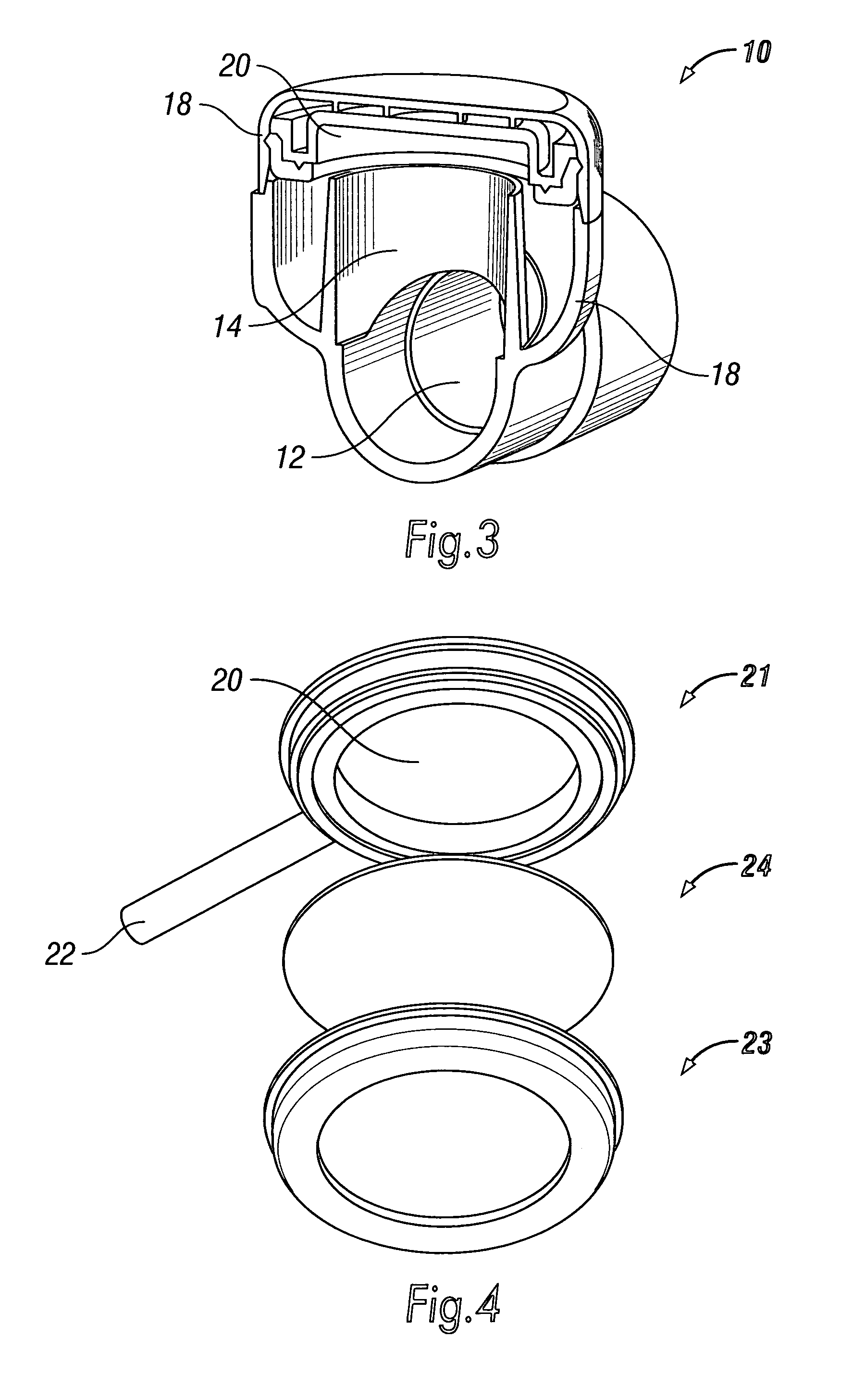
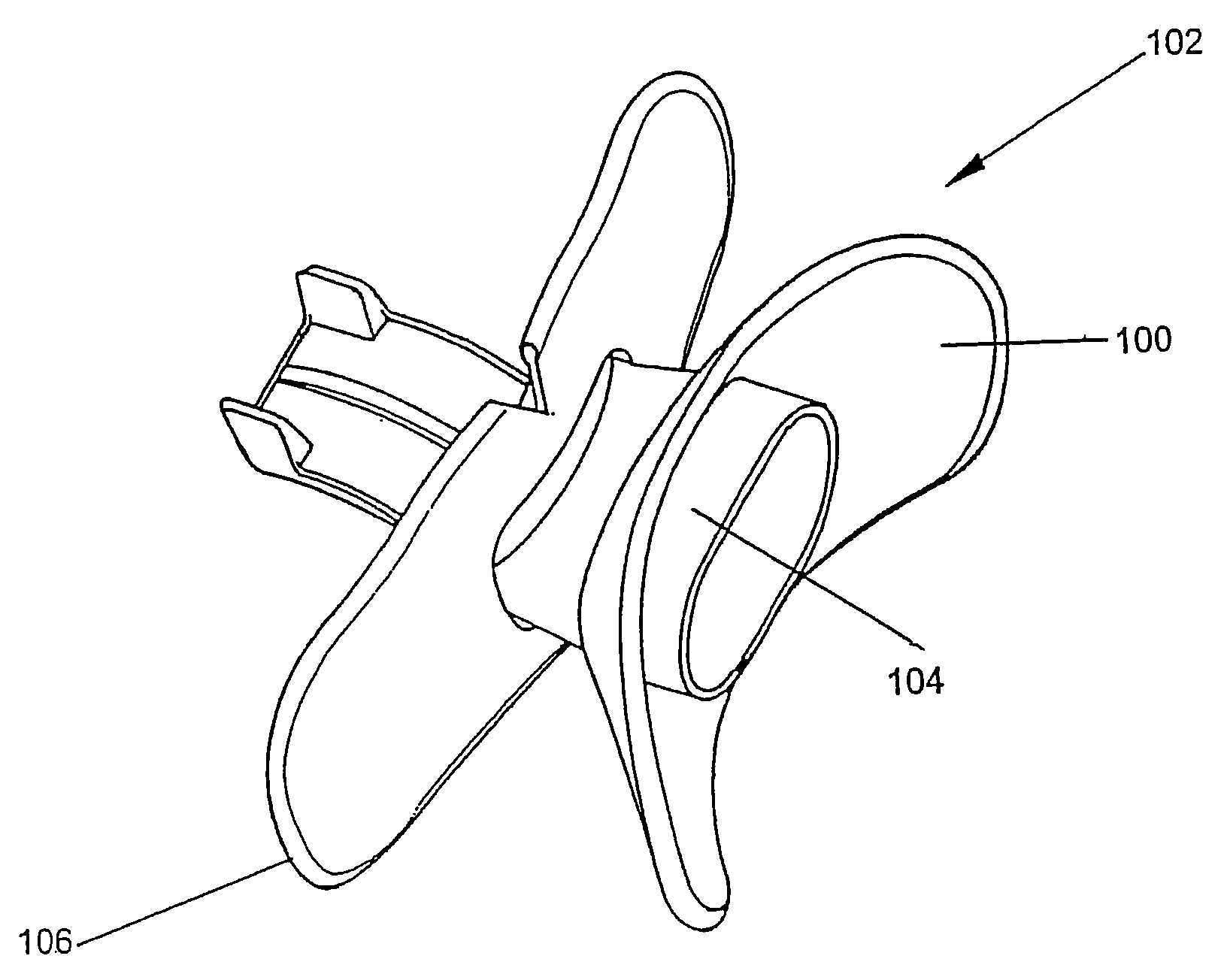
Disposable anesthesia face mask
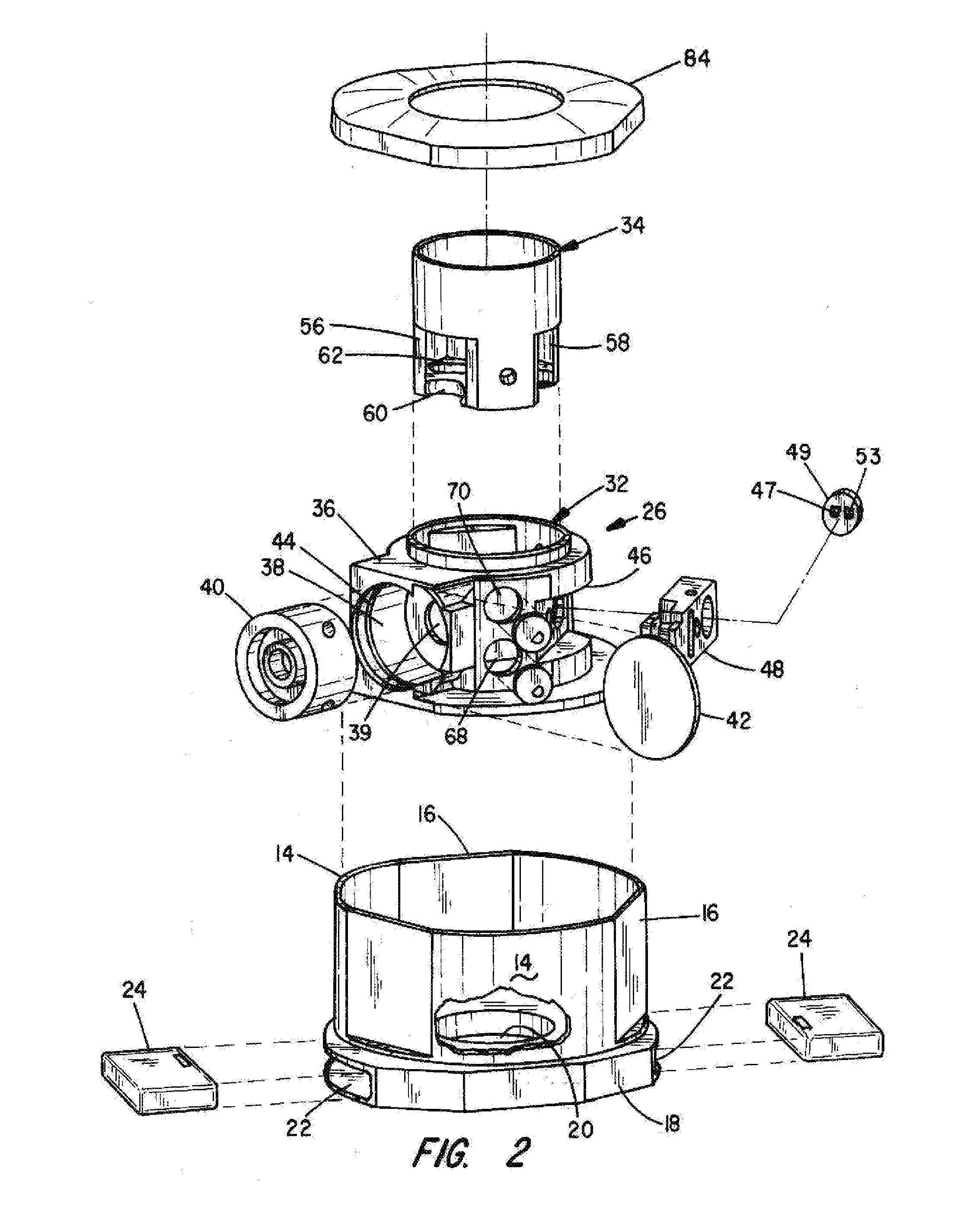
ActiveUS20070295335A1Durable and reliable constructionLower sales priceRespiratory masksBreathing masksChinNose
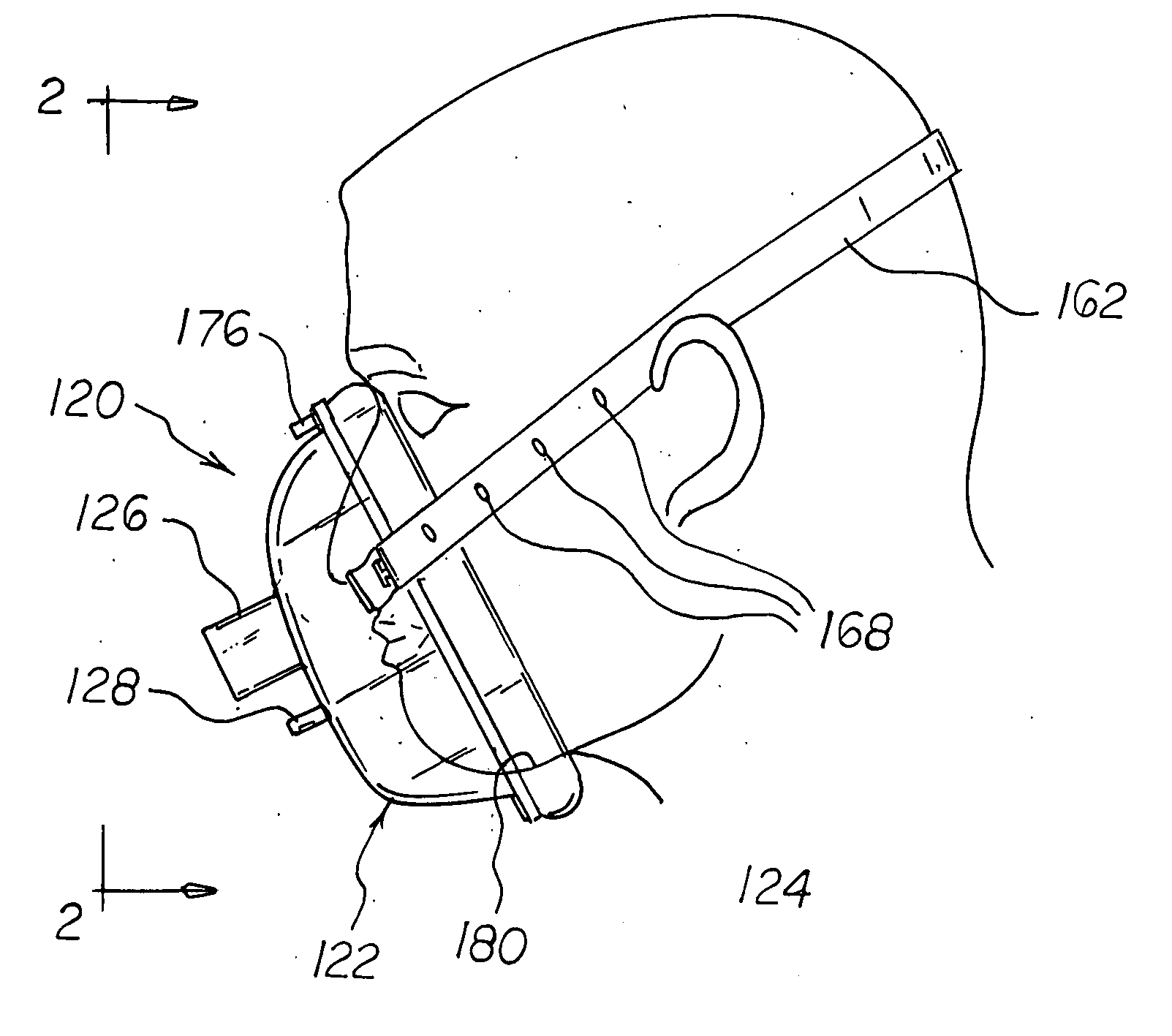
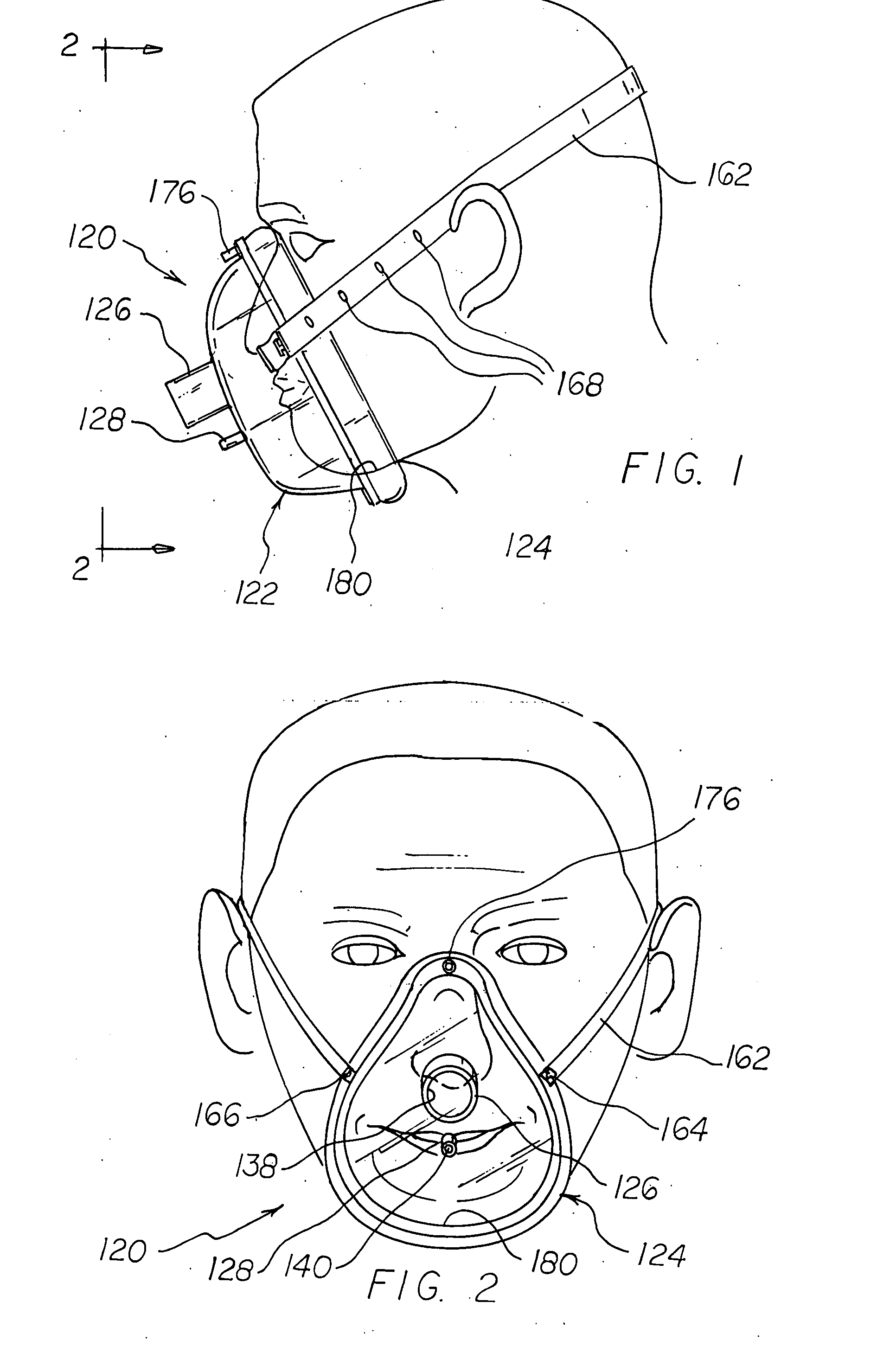
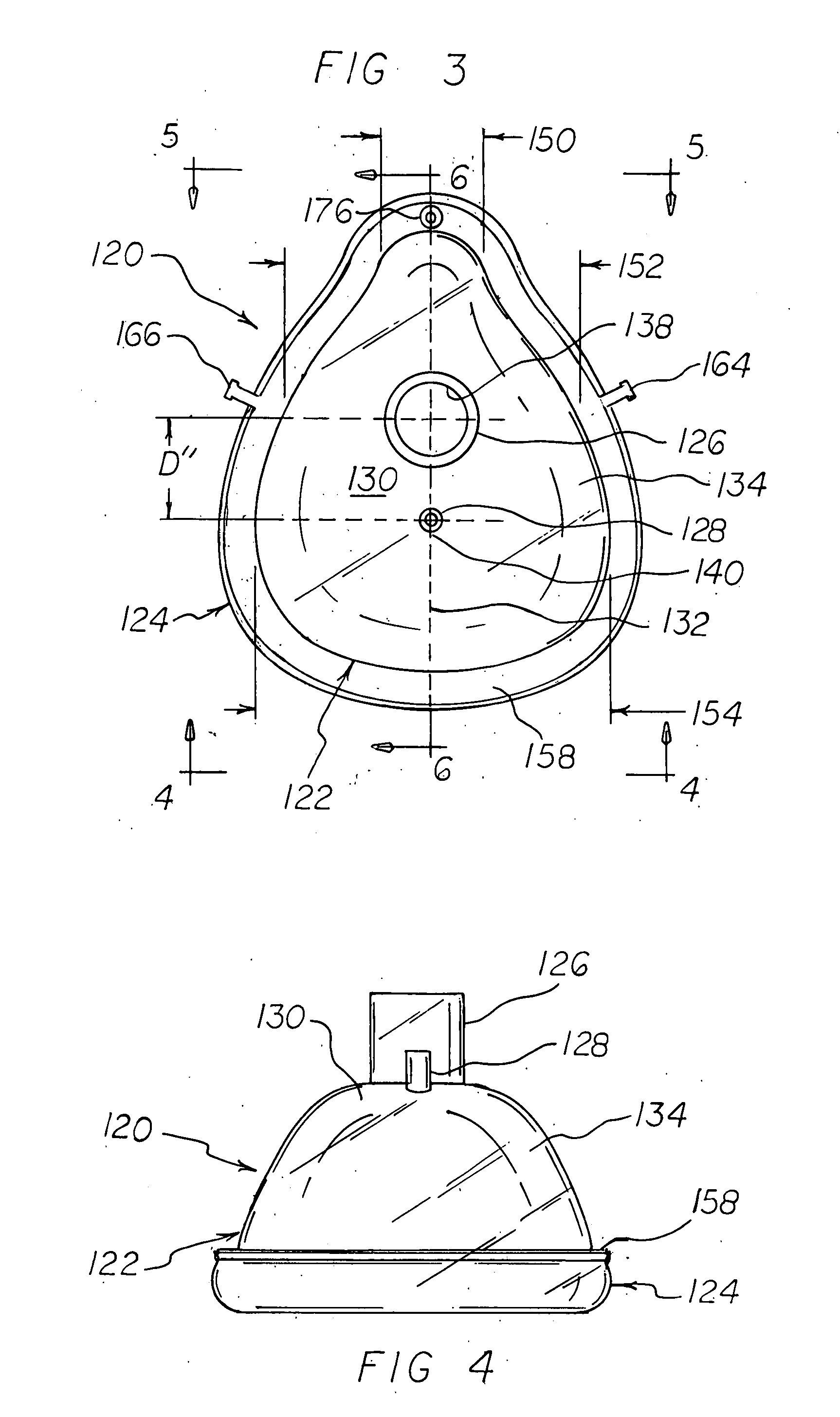
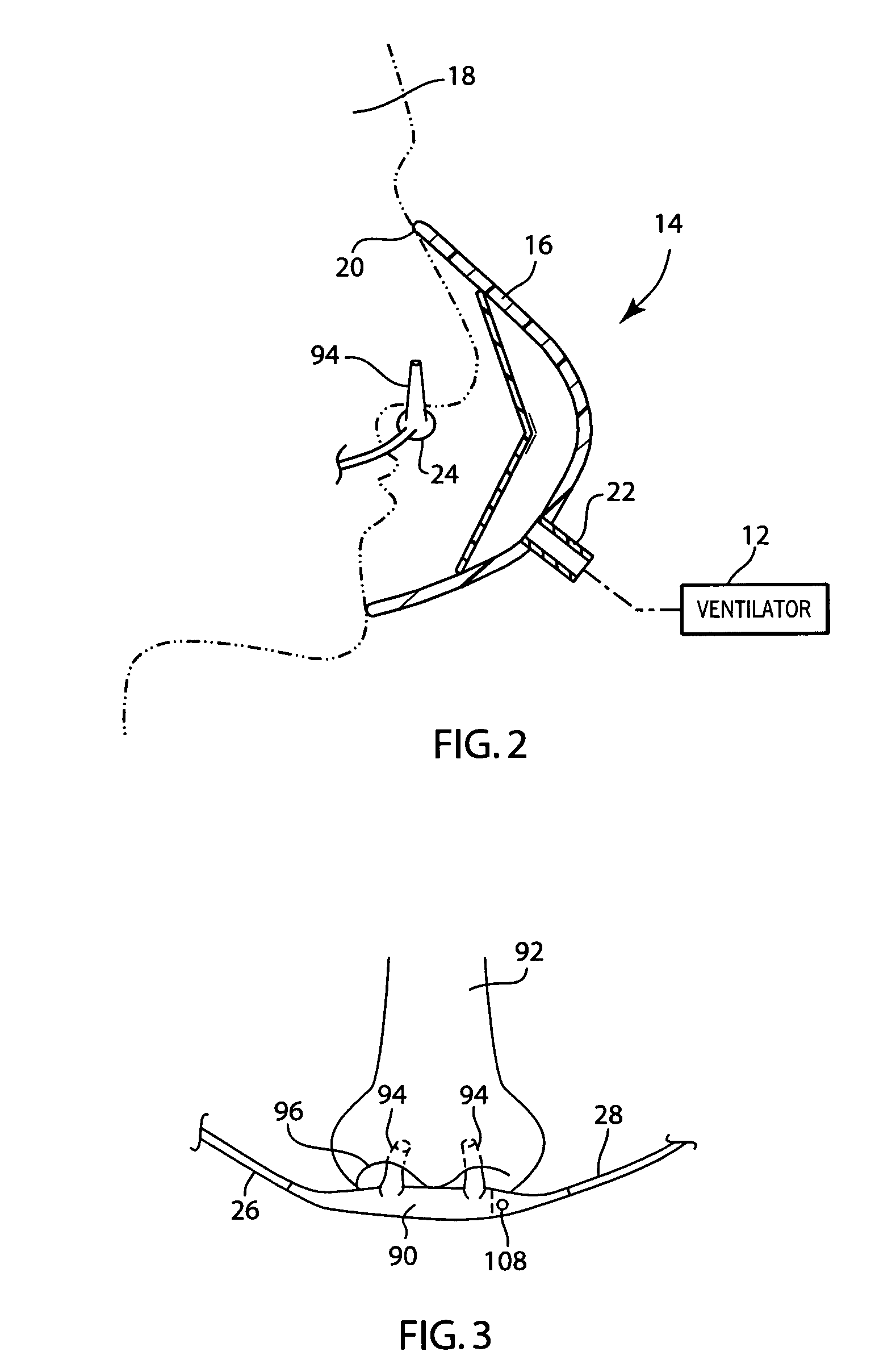
A disposable anesthesia face mask suitably sized and configured to engage the nose portion, mouth portion and chin portion of a patient's face comprises a cup-like shell or receptacle member and a flexible inflatable hollow sealing cushion attached to the shell member on a flange thereon and wherein the shell member includes first passageway means for coupling to a breathing circuit, and a second passageway for connection to a flexible tube which, in turn, is adapted to be connected to a CO2 monitoring machine or capnograph. The face mask shell nasal portion has a first width, the face mask shell mouth portion has a second width greater than the first width, and the face mask shell chin portion has a third width greater than the second width. The nasal, mouth and chin portions are continuous and form the cup-like extent of the shell or receptacle member giving it a characteristic “pear” shape. Lateral projections provided on the shell flange are intended to accommodate an elastic head strap that may adjustably be coupled to the projections to hold the mask in place on a patient's face and head.
Owner:NASHED RAMSES
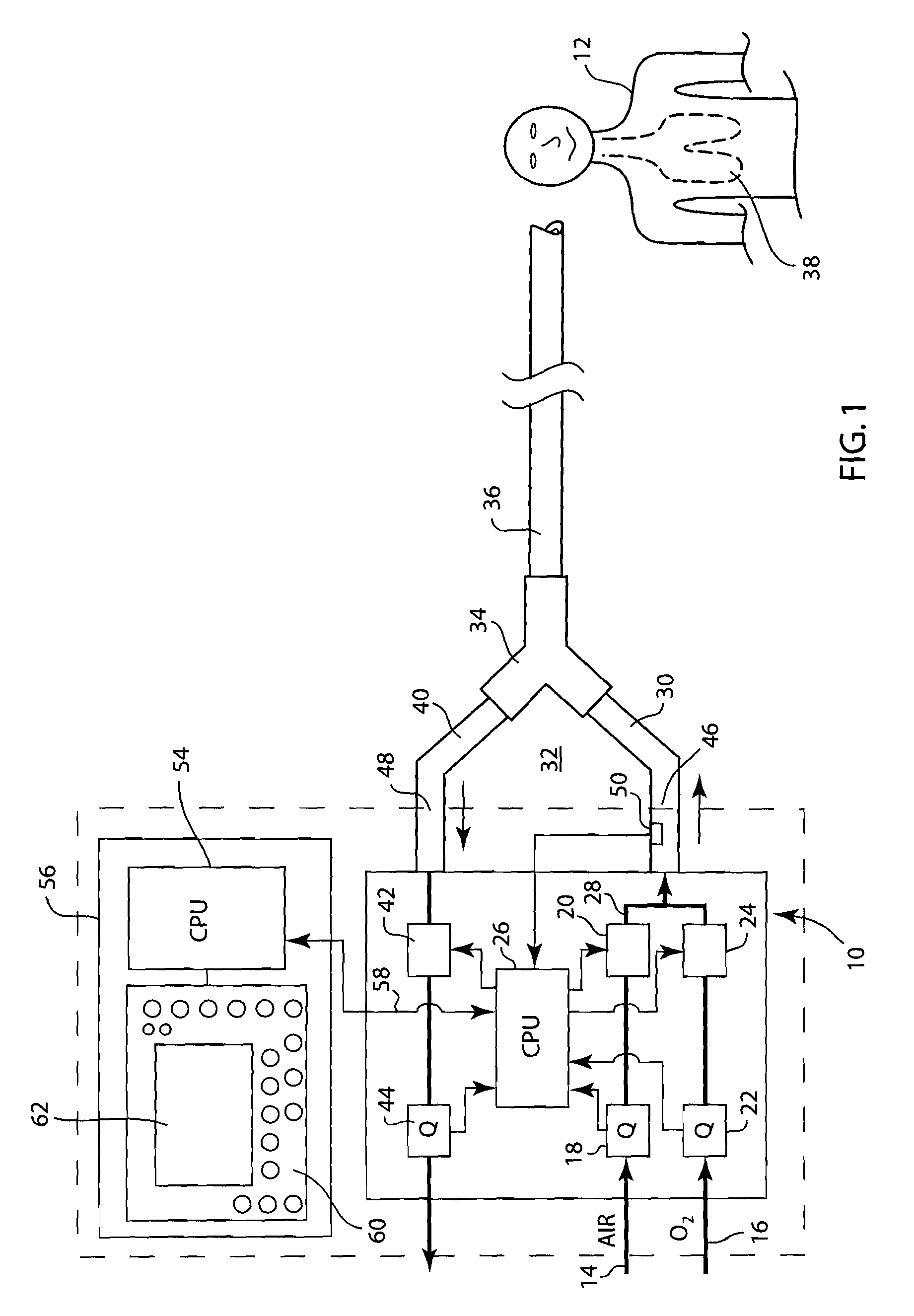
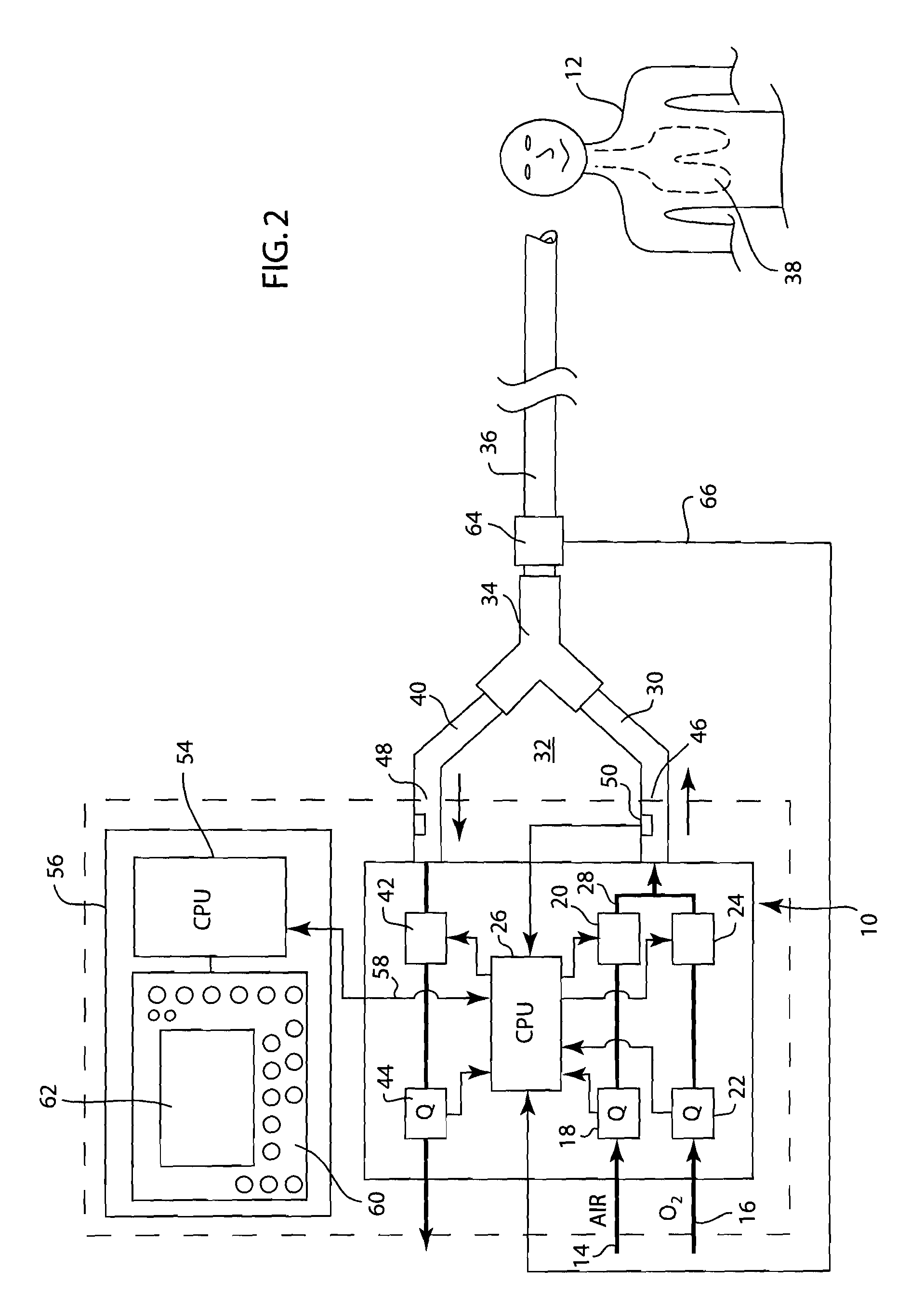
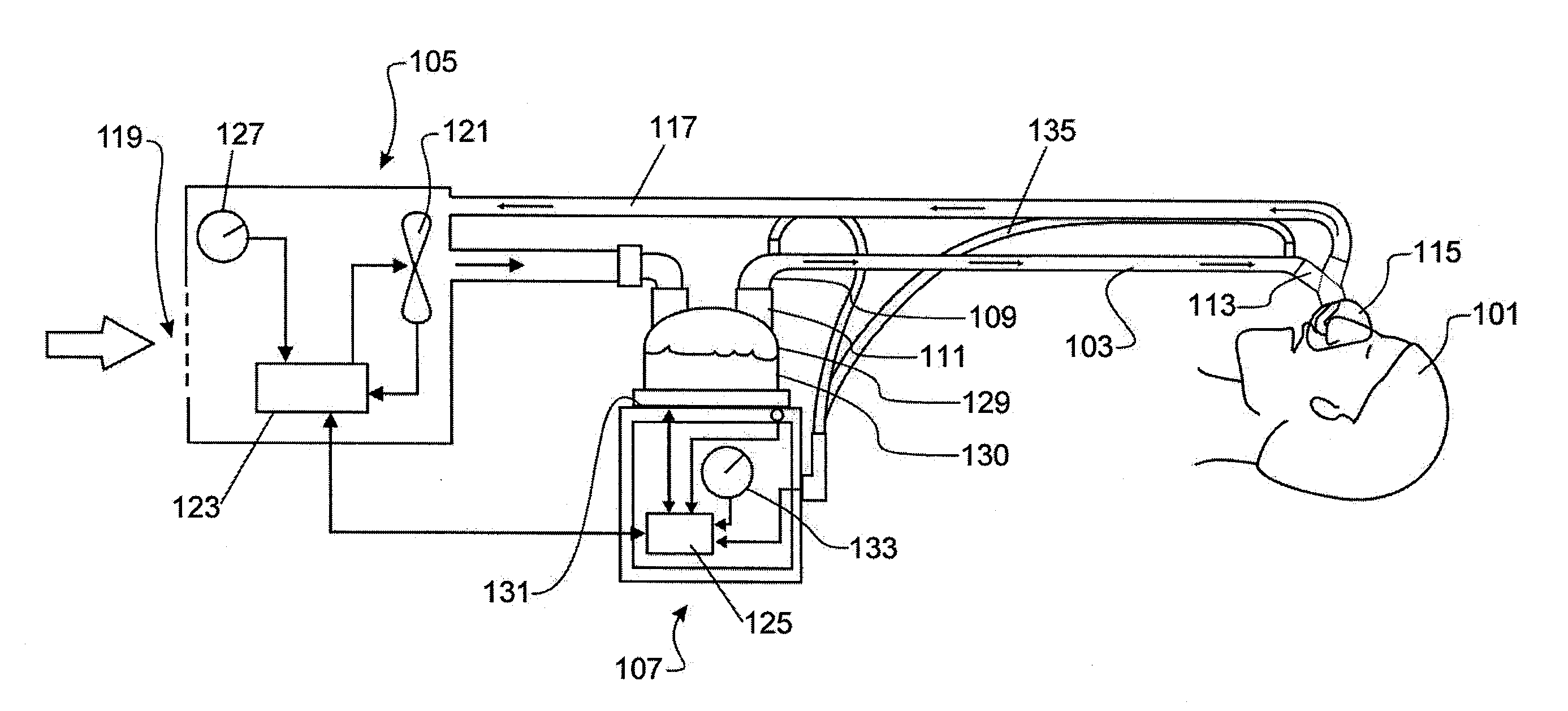
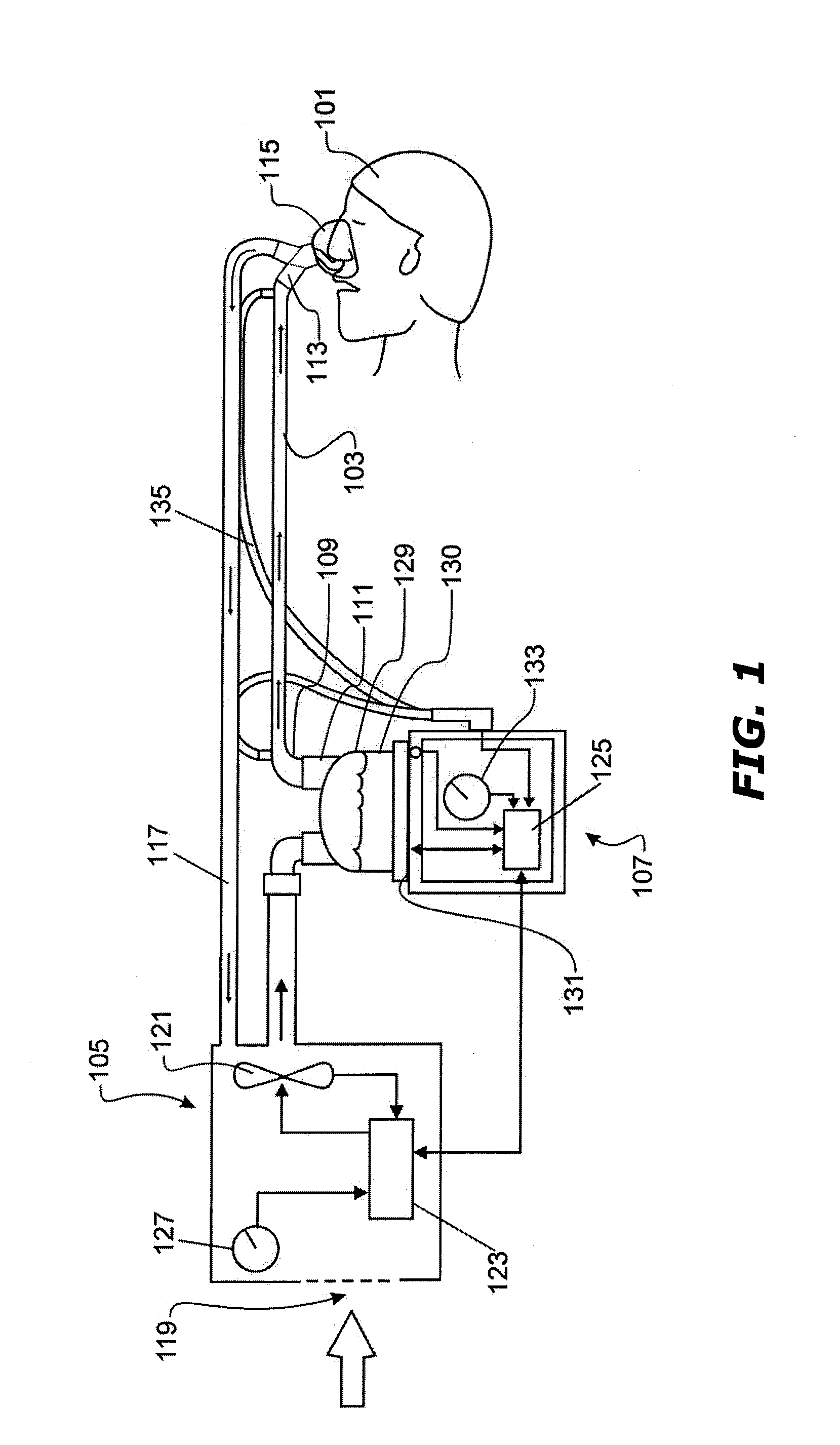
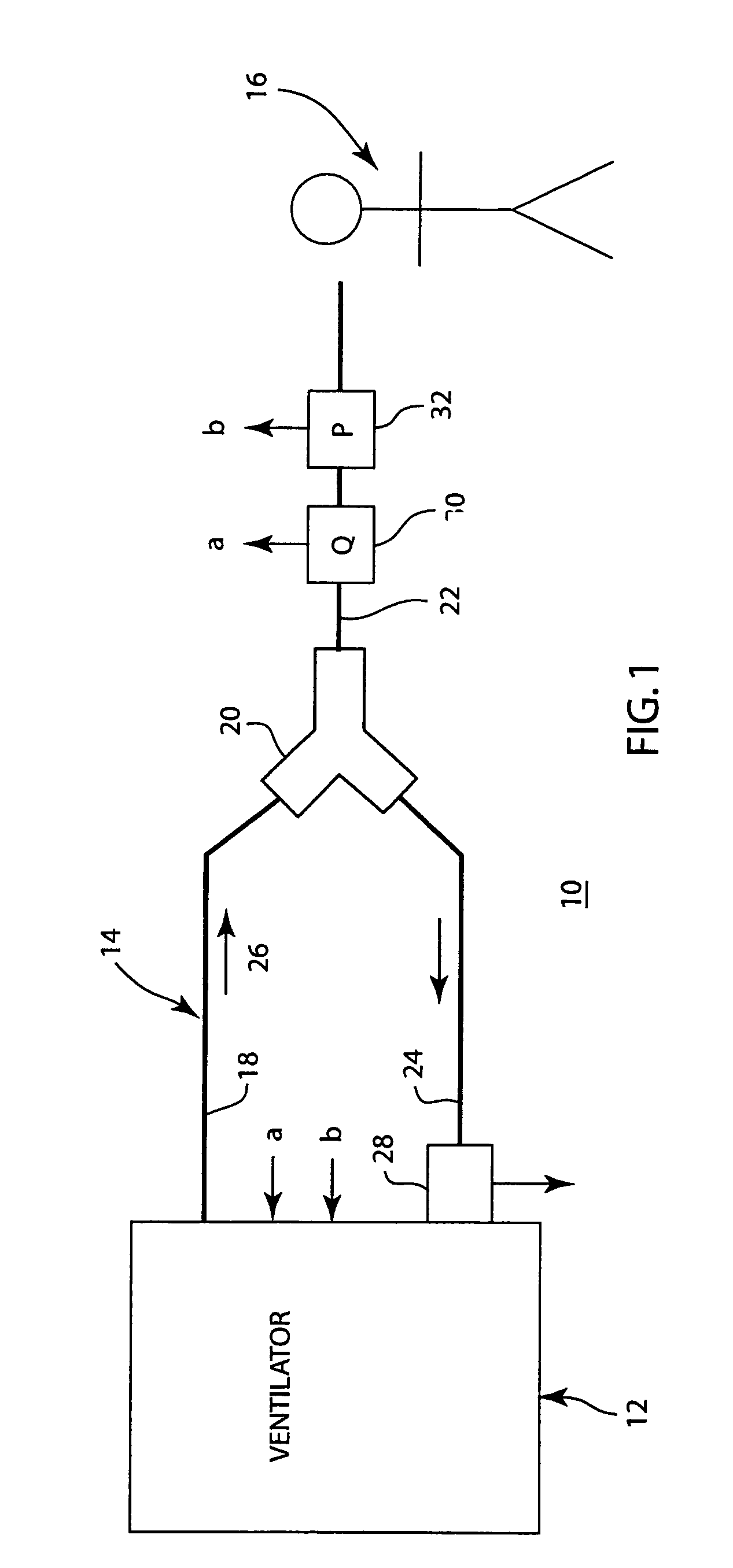
Method of measuring cardiac related parameters non-invasively via the lung during spontaneous and controlled ventilation
InactiveUS20070062531A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAnatomical dead spaceGas concentration
An apparatus to measure cardiac output (Q) and other parameters such as alveolar ventilation (VA), minute CO2 elimination from the lung (VCO2 ), minute oxygen consumption (VO2), oxygenated mixed venous partial pressure of CO2, (PvCO2-oxy), true mixed venous partial pressure of CO2(PvCO2), PaCO2, mixed venous oxygen saturation (SvO2), pulmonary shunt, and anatomical dead space, consisting of: a) a breathing circuit with characteristics that: i. on exhalation, exhaled gas is kept substantially separate from inhaled gas; ii. oninhalation, when VE is greater than FGS flow, the subject inhales FGS first and then inhales a gas that is substantially SGS, for the balance of inhalation; b) gas sensor means for monitoring gas concentrations at the patient-circuit interface c) a first gas set (FGS), and a second gas set (SGS), said second gas set which may comprise previously exhaled gases or exogenous gases or both d) a gas flow control means for controlling the rate of FGS flow into the breathing circuit e) means to identify phase of breathing, said means may consist of pressure sensors or analysis of signal generated by gas sensors or other means known to those skilled in the art; f) machine intelligence consisting of a computer or logic circuit capable of controlling the gas flow control means, receiving the output of the gas sensor means and means to identify phased of breathing, and performing the calculations for measuring cardiac output and other parameters as outlined in the disclosure.
Owner:THORNHILL SCI INC
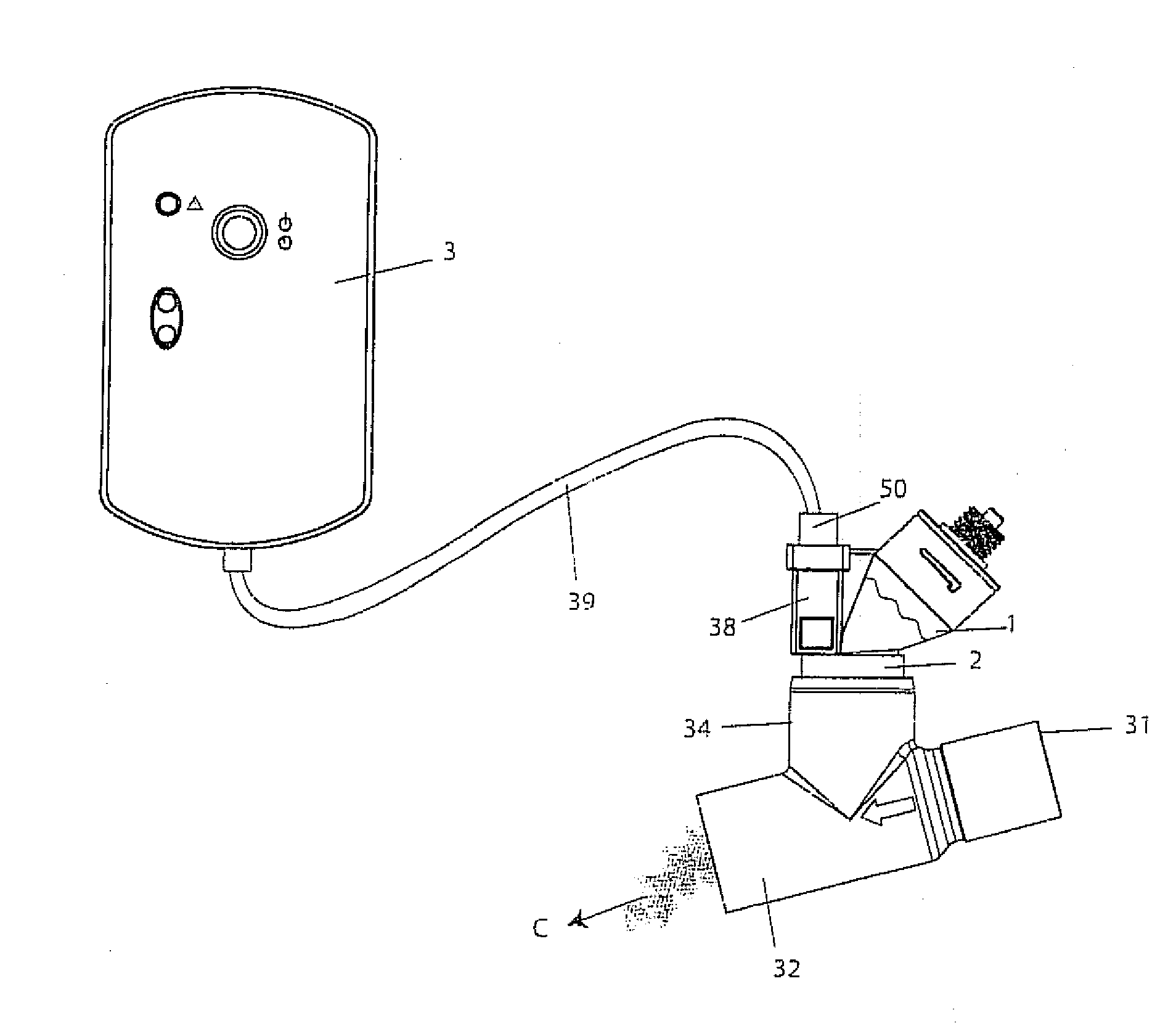
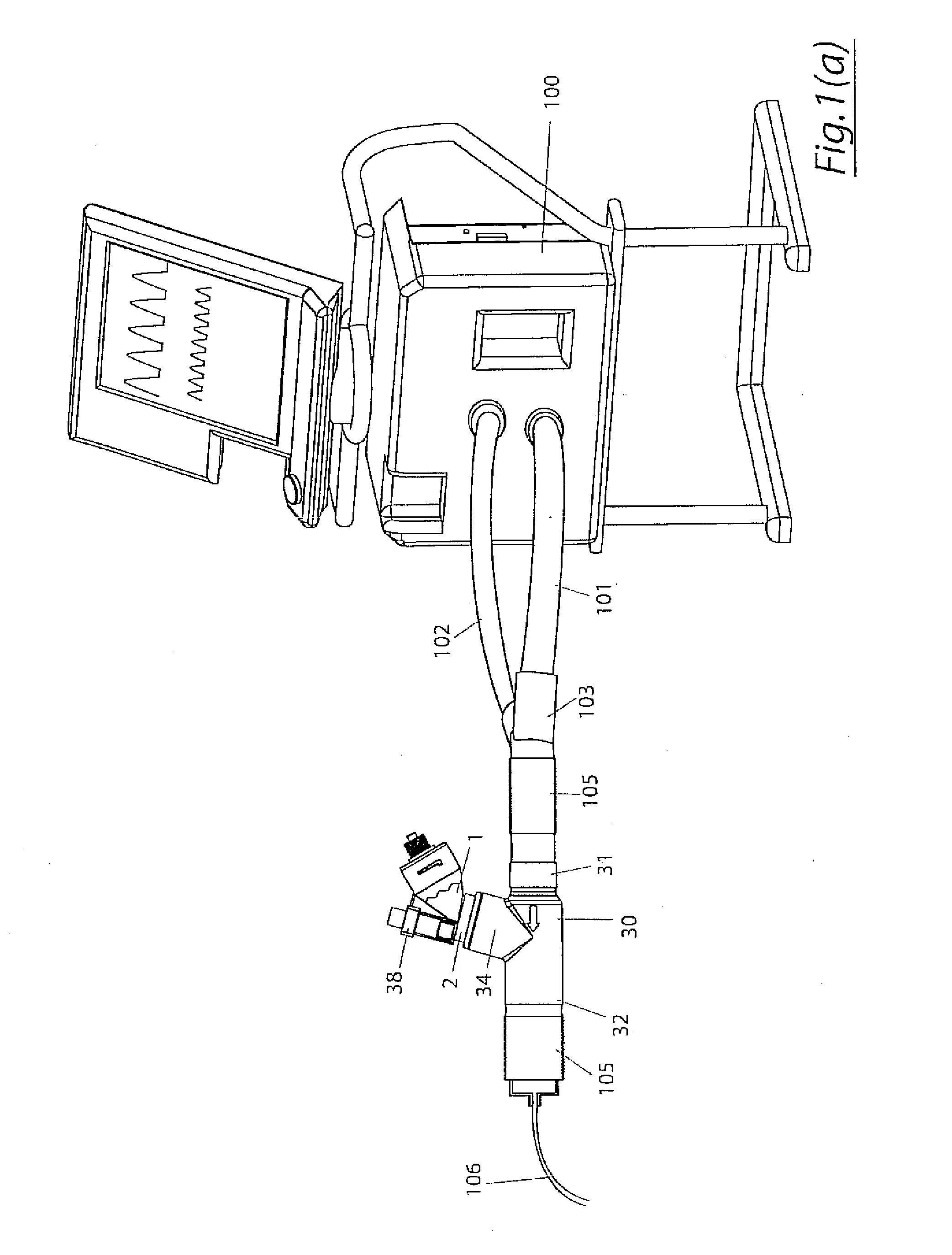
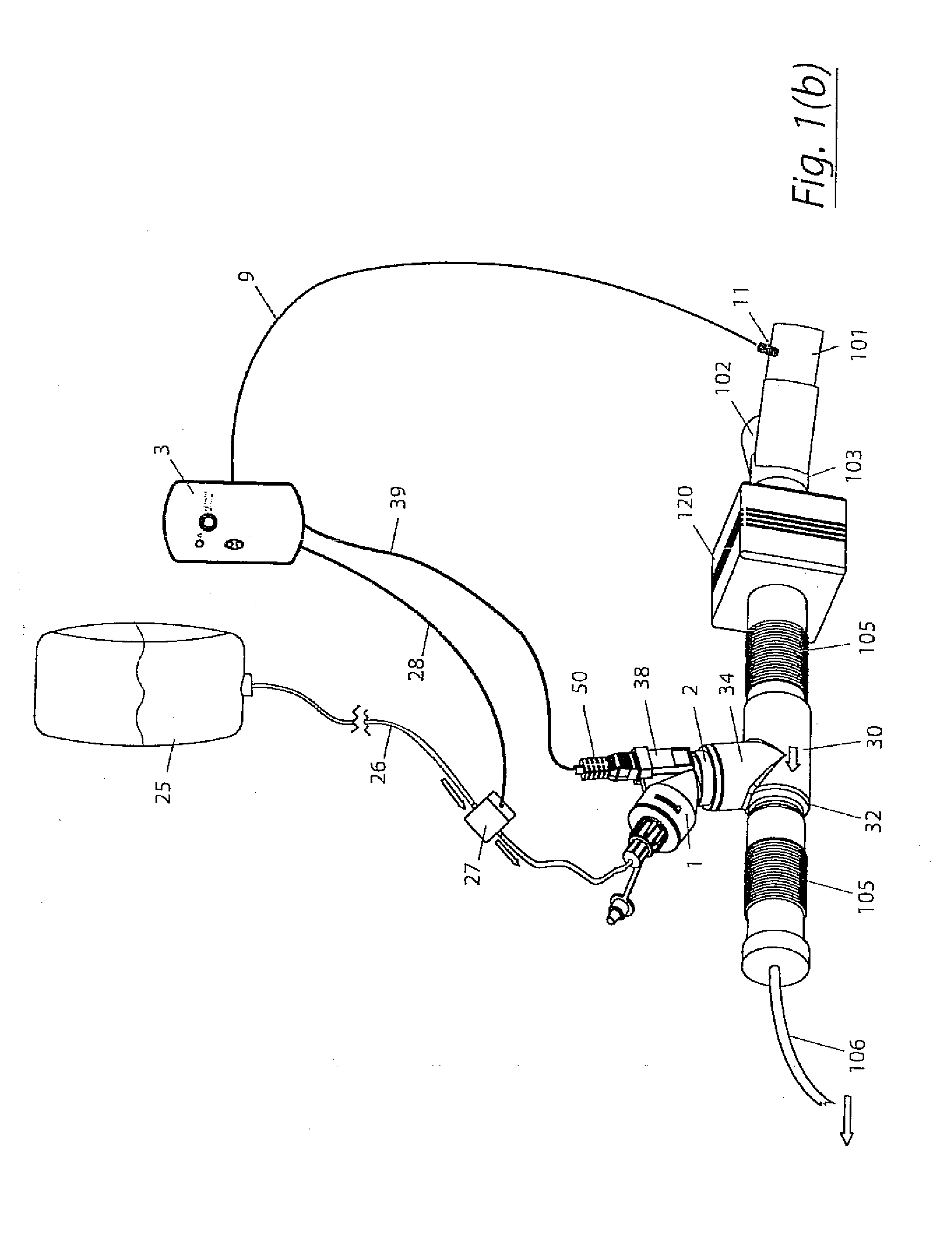
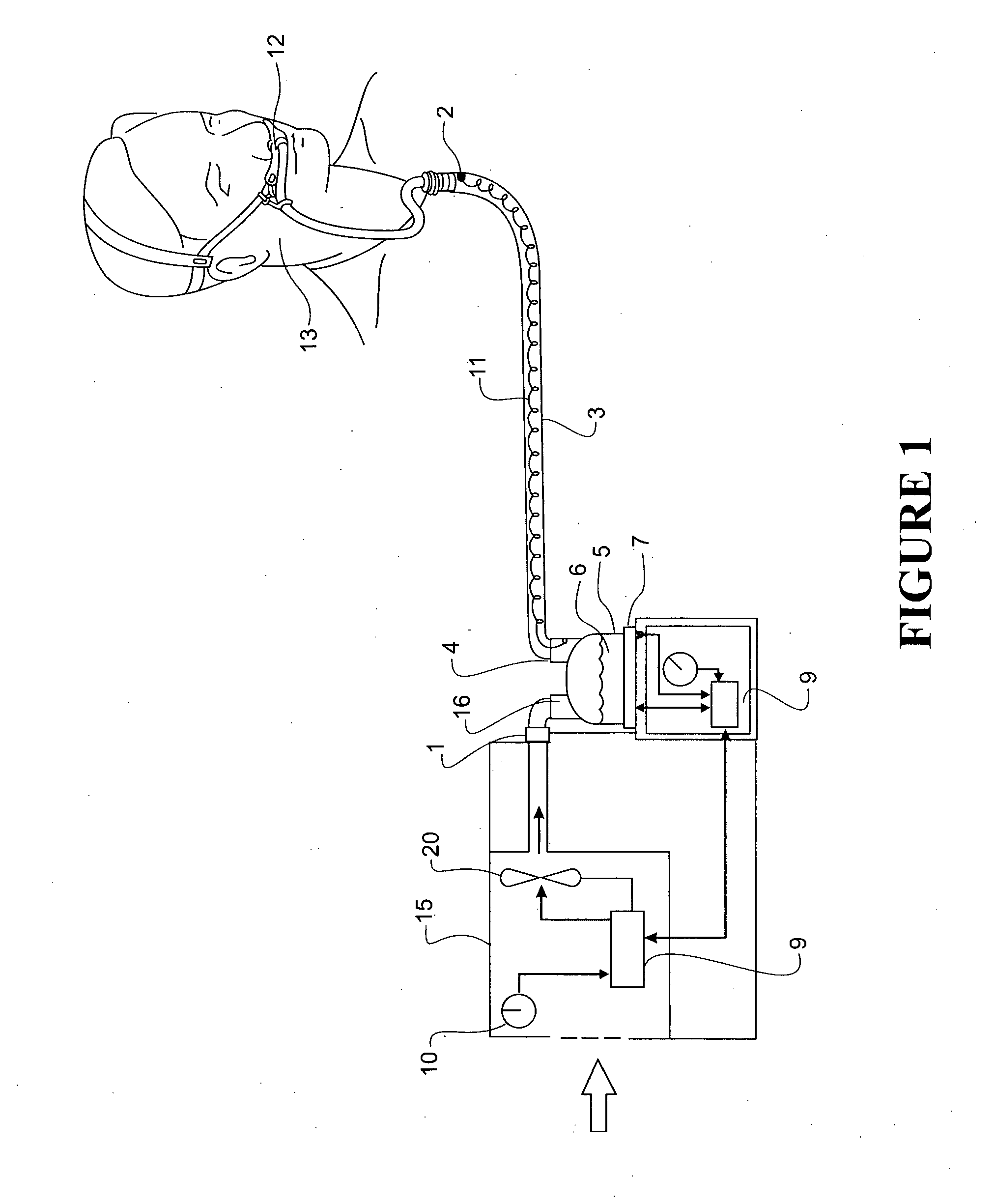
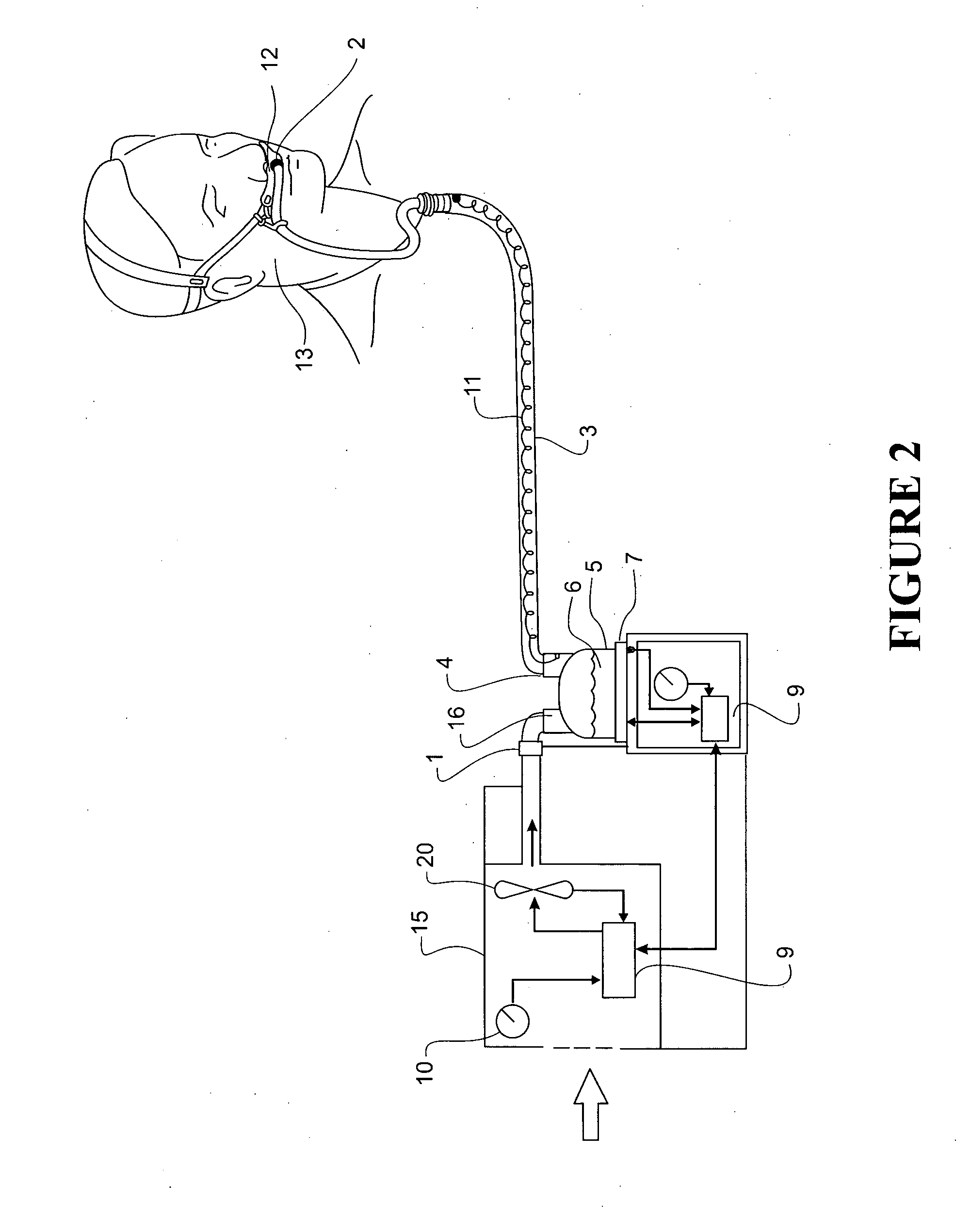
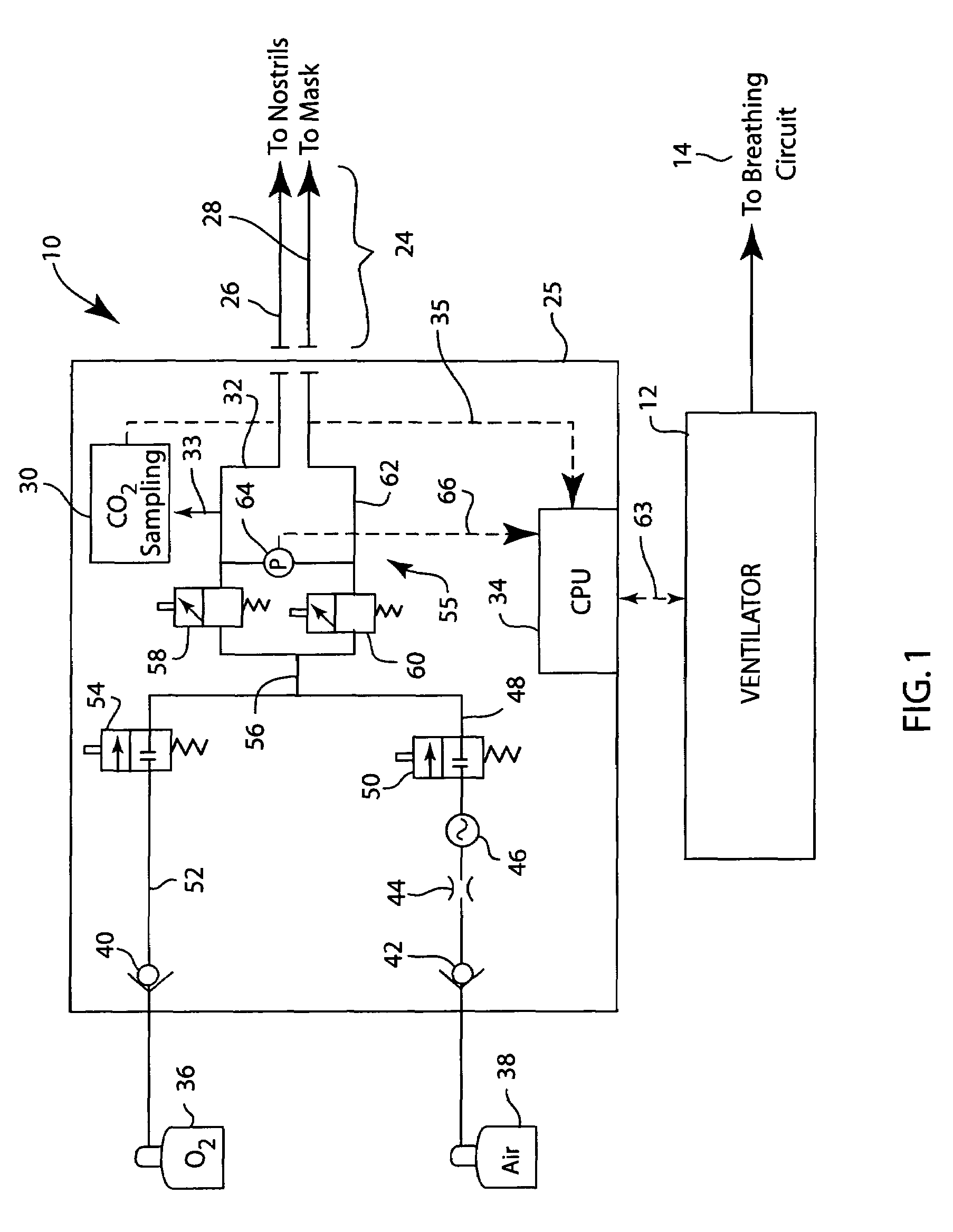
Humidification in breathing circuits
InactiveUS20090241948A1Accurate and repeatable changeEasy to controlRespiratorsSurgical needlesEngineeringVentilator circuit
A method for humidifying gas in a ventilator circuit 100, 101, 102, 105, 106 comprises aerosolising a humidifying agent such as water or saline using an aerosol generator 2 and delivering the aerosolised humidifying agent to the inspiration line 101 of the ventilator circuit coupled to the respiratory system of a patient. The aerosol generator 2 comprises a vibratable member 40 having a plurality of apertures extending between a first surface and a second surface. A controller 3 controls the operation of aerosol generator 2, for example in response to the flow of air in the inspiration line 101 as detected by a sensor 11.
Owner:CLANCY DERMOT JOSEPH +4
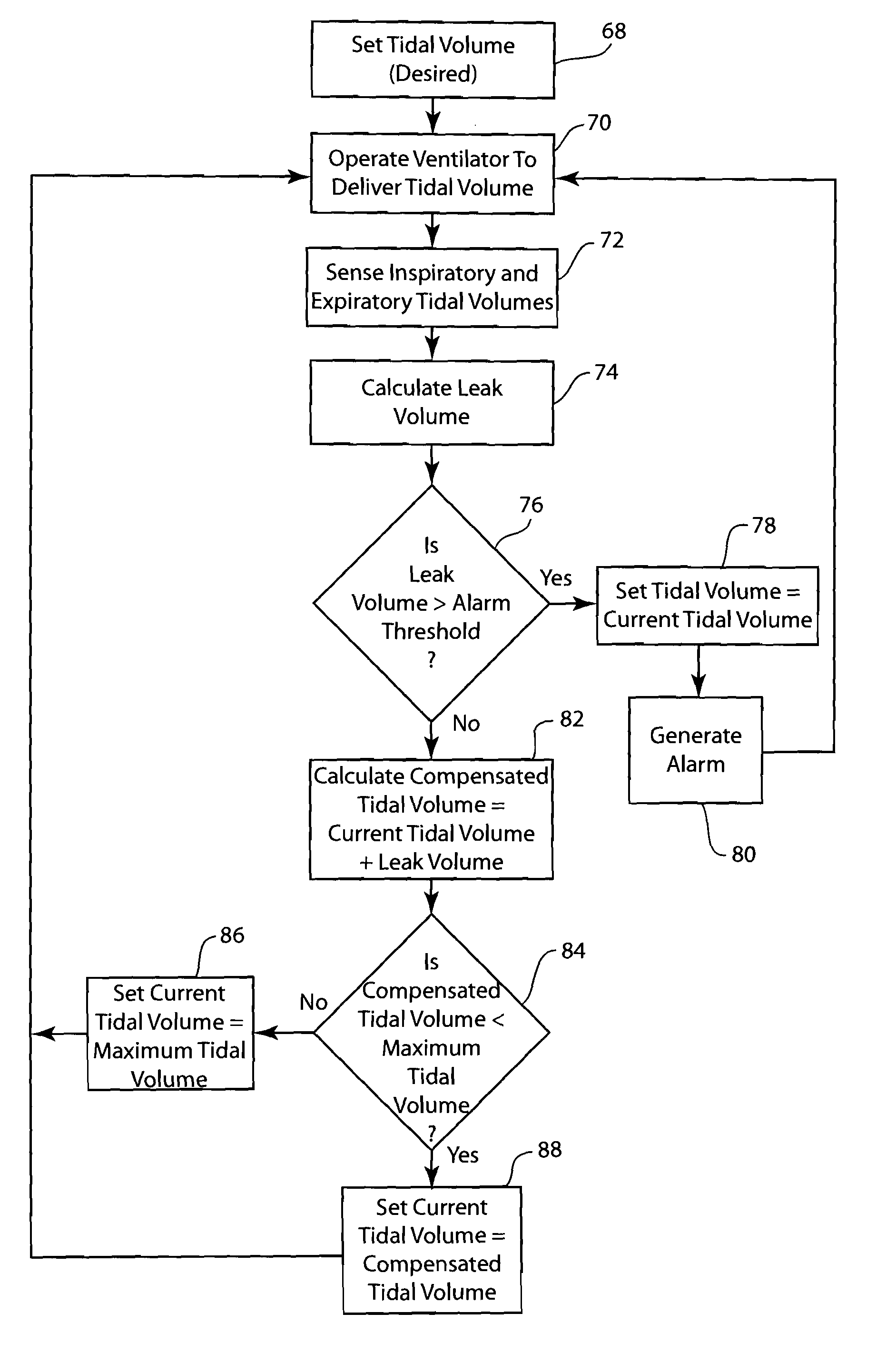
Method to limit leak compensation based on a breathing circuit leak alarm
InactiveUS20080295837A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBreathing gasIntensive care medicine
A method and system for ventilating a patient that compensates for leaks occurring within the patient breathing circuit while limiting the volume of breathing gas delivered to the patient. During the operation of a ventilator to supply breathing gases to a patient, the ventilator monitors for leak volumes occurring during the inspiratory phase and expiratory phase of the breathing cycle. Based upon the leak volumes sensed, the volume of breathing gas delivered by the ventilator is increased such that the tidal volume delivered to the patient is the desired tidal volume set by a clinician. The ventilator operates to generate a leak alarm when the leak volume exceeds an alarm threshold. If the leak alarm is generated, the tidal volume delivered to the patient is limited to the tidal volume being delivered prior to generation of the leak alarm. During compensation of the breathing gases delivered to the patient, the system and method determines whether the compensated tidal volume exceeds a maximum tidal volume threshold and limits the compensated tidal volume to the maximum tidal volume threshold.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Medical Ventilator System and Method Using Oxygen Concentrators
InactiveUS20100116270A1Save oxygenElectrocardiographyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesOxygen pulseIntensive care medicine
A medical ventilator system that allows the use of pulse flow of oxygen to gain higher FIO2 values and / or conserve oxygen is described. In one embodiment, the ventilator system includes an oxygen concentrator, a medical ventilator and a breathing circuit between the ventilator and a patient. In one embodiment, the oxygen concentrator includes a controller module that is configured to generate a trigger signal to initiate the distribution of one or more pulses of oxygen from the oxygen concentrator to the patient circuit at the onset of a ventilator supplied breath. A small flow of oxygen can be added in between pulses to aid in gaining higher FIO2.
Owner:CHART SEQUAL TECH
Method for continuous measurement of flux of gases in the lungs during breathing
ActiveUS20050217671A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingEngineering
A method of calculating the flux of any gas (x) in a CBC circuit for a ventilated or a spontaneous breathing subject, for example said gas(x) being; a) an anesthetic such as but limited to; i)N2O; ii) sevoflurane; iii) isoflurane; iv) halothane; v) desflurame; or the like b) Oxygen; c) Carbon dioxide; or the like utilizing the following relationships; Flux of gas(x)=SGF (FSX−FEX) wherein SGF=Source of gas flow into the breathing circuit (CBC circuit) in liters / minute as read from the gas flow meter as set by the anesthesiologist; FSX=Fractional concentration of gas X in the source gas (which is set by the anesthesiologist); FEX=Fractional concentration of gas X in the end expired gas as determined by a portable gas analyzer, or the like.
Owner:THORNHILL SCI INC
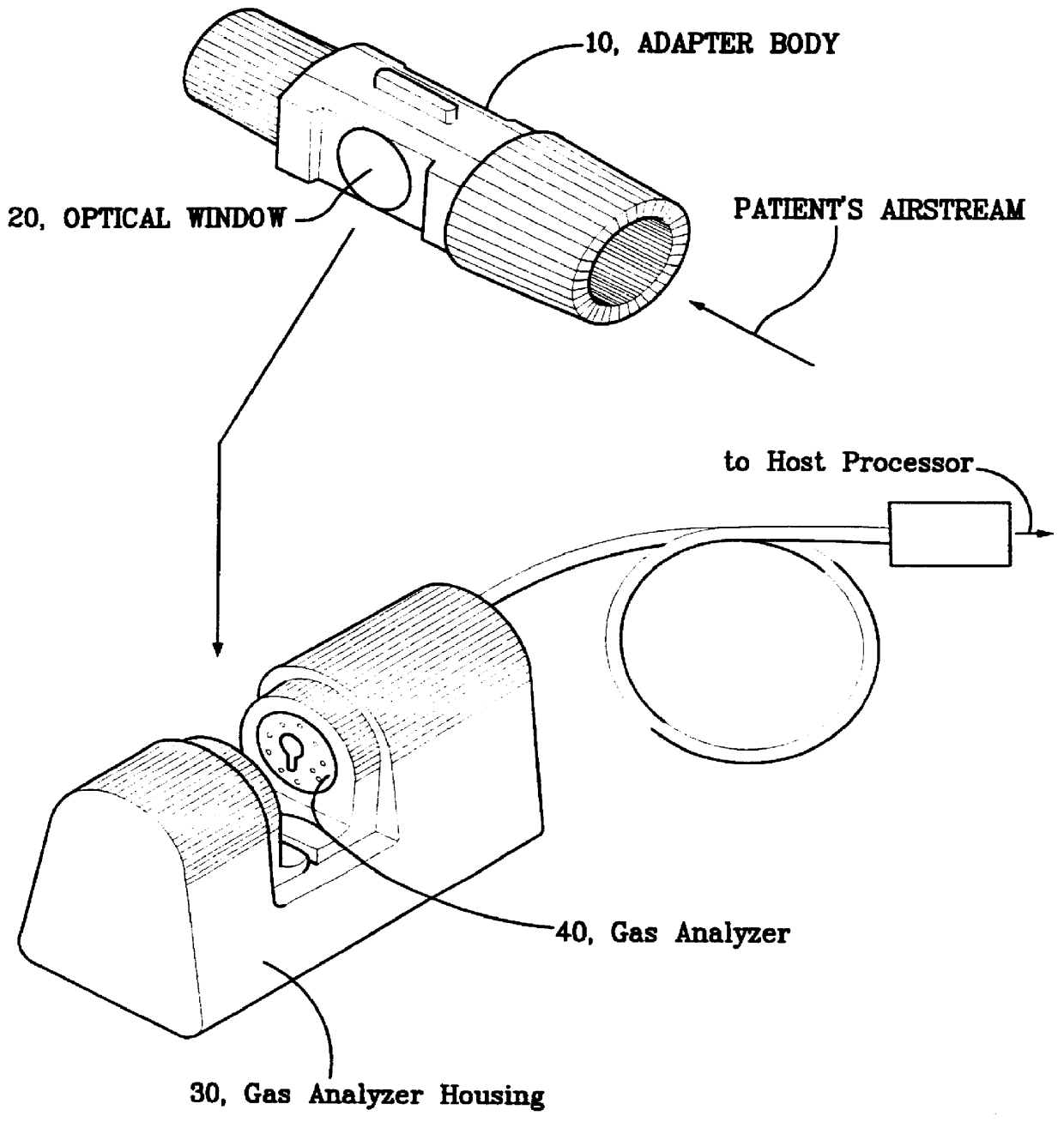
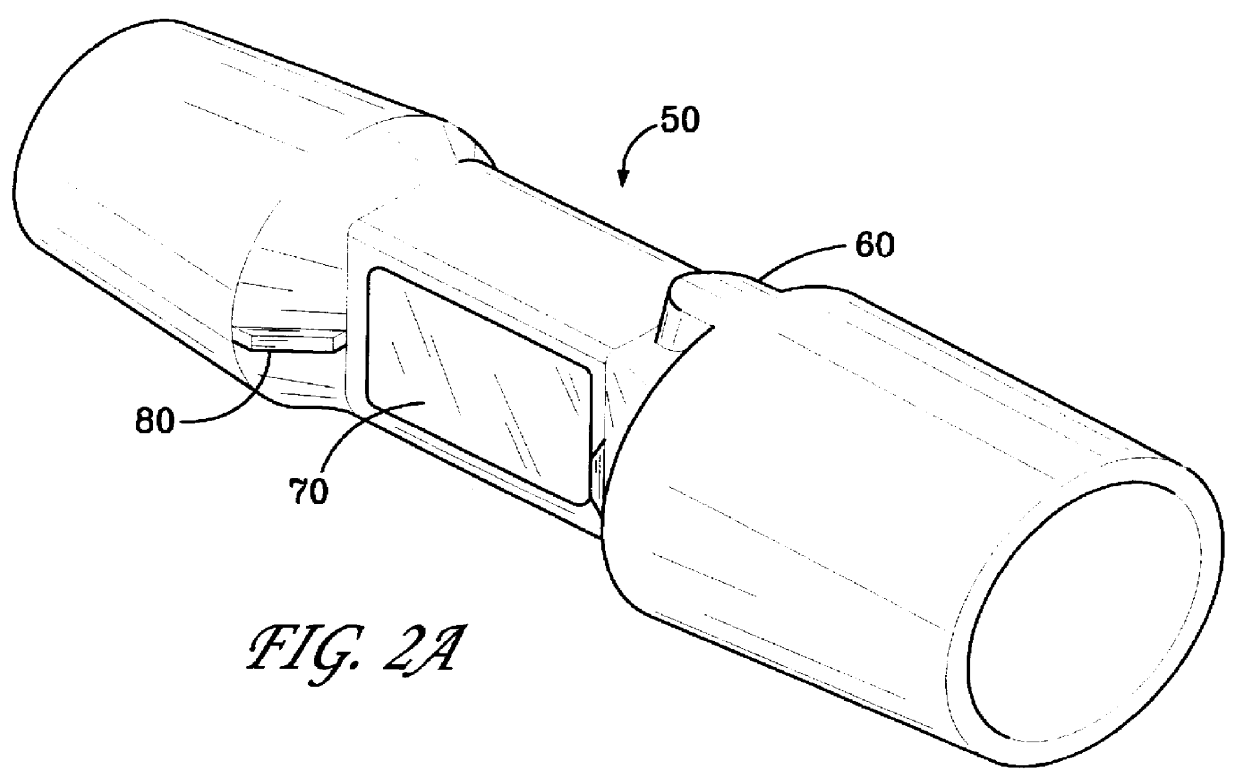
Disposable anti-fog airway adapter
InactiveUS6095986AImprove abilitiesOvercome problemsRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAirway adaptorHeat capacity
A disposable anti-fog airway adapter for use with a mainstream respiratory gas analyzer which provides a measurement of a patient's inhaled and exhaled gases. The airway adapter includes windows that are constructed of a thin, low heat capacity plastic that rapidly equilibrates to the temperature of the warm moist gases in the patient breathing circuit. In addition, the inside of the windows is also coated with an anti-fog surfactant either by laminating an anti-fog film with the window plastic prior to attaching the window to the airway adapter body or by first attaching the window to the airway adapter body and then applying the surfactant to the airway adapter after the window film is bonded in place so that the surfactant coats the entire inside of the adapter. The surfactant functions to increase the critical wetting tension of the surface it covers so that water on the window spreads into a uniform thin layer which does not absorb very much infrared energy and thus does not significantly reduce the signal strength. "Instant on" operation is accomplished because no heater and the like is necessary to warm up the windows to maintain them at an elevated temperature to prevent fogging. Numerous techniques are also provided for adhering the windows to the airway adapter body so that a substantially airtight seal may be obtained.
Owner:OSI OPTOELECTRONICS
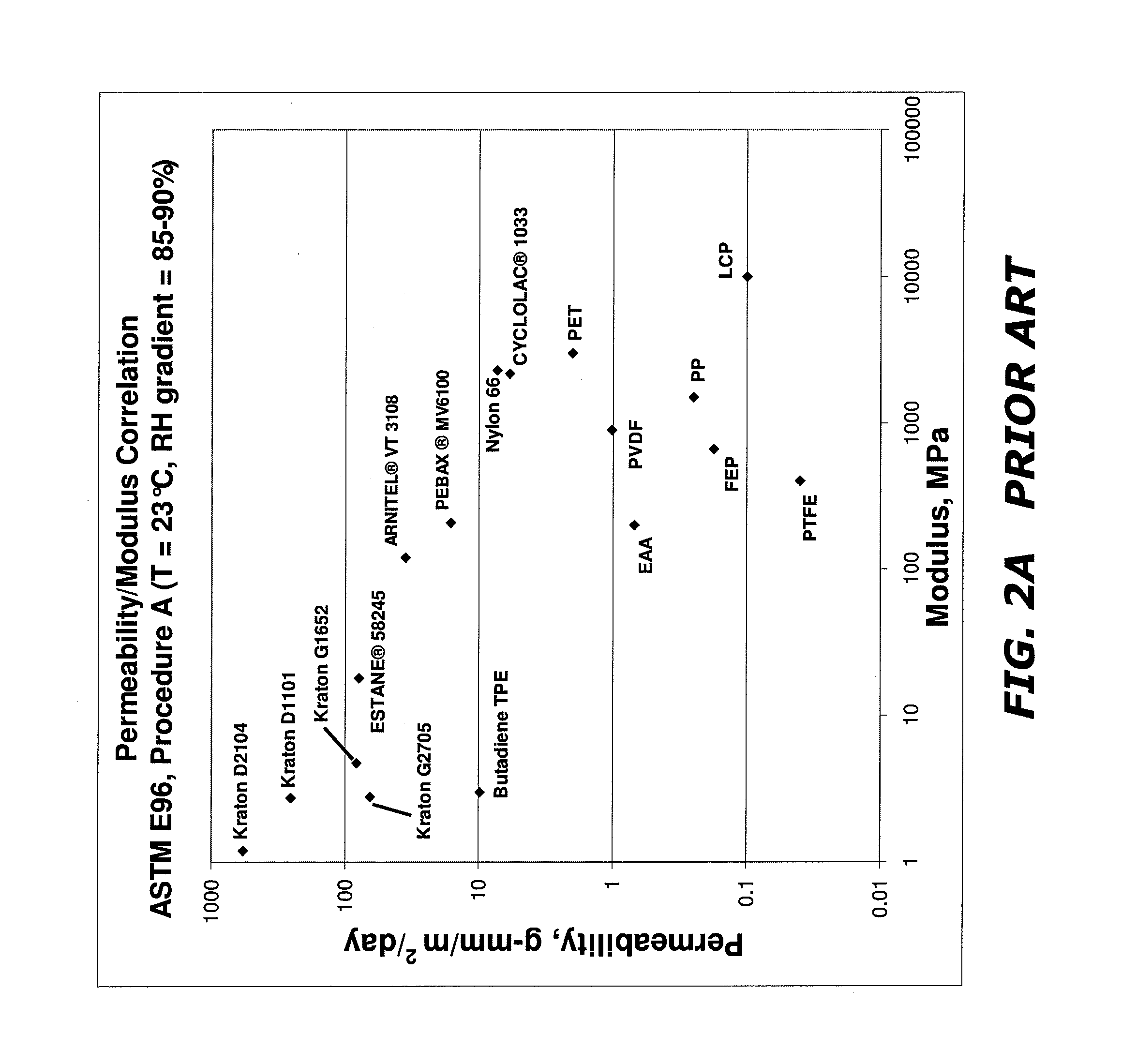
Components for medical circuits
ActiveUS20130098360A1Avoid spreadingRespiratory masksSynthetic resin layered productsWater vaporLiquid water
Breathable medical circuit components and materials and methods for forming these components are disclosed. These components incorporate breathable foamed materials that are permeable to water vapor and substantially impermeable to liquid water and the bulk flow of gases. The disclosed materials and methods can be incorporated into a variety of components, including tubes, Y-connectors, catheter mounts, and patient interfaces and are suitable for use in a variety of medical circuits, including insufflation, anesthesia, and breathing circuits.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
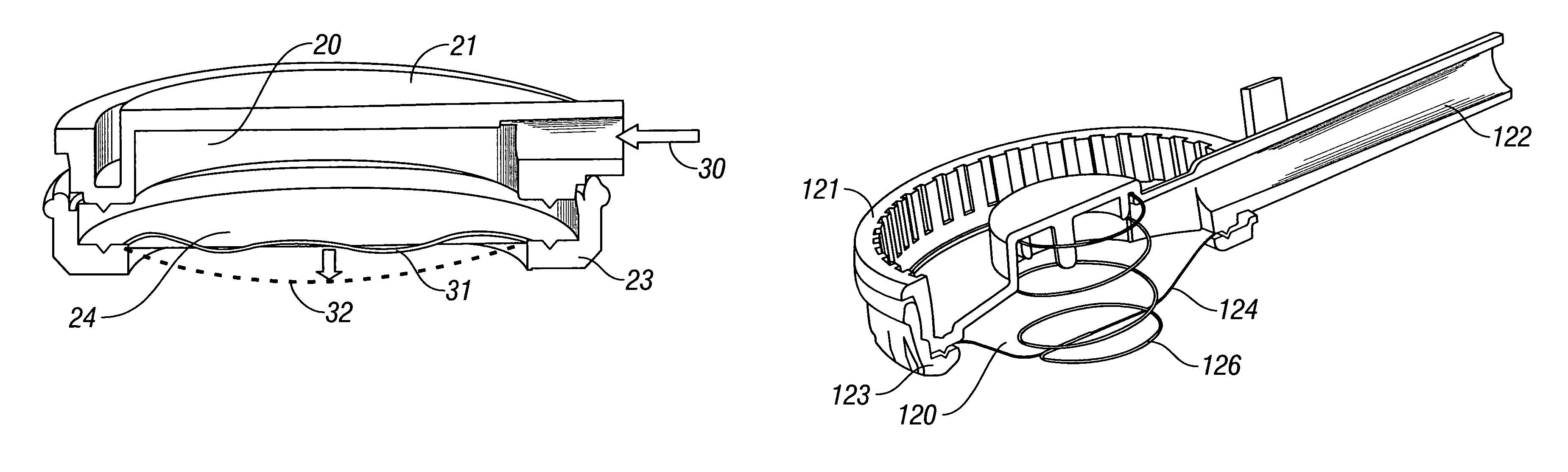
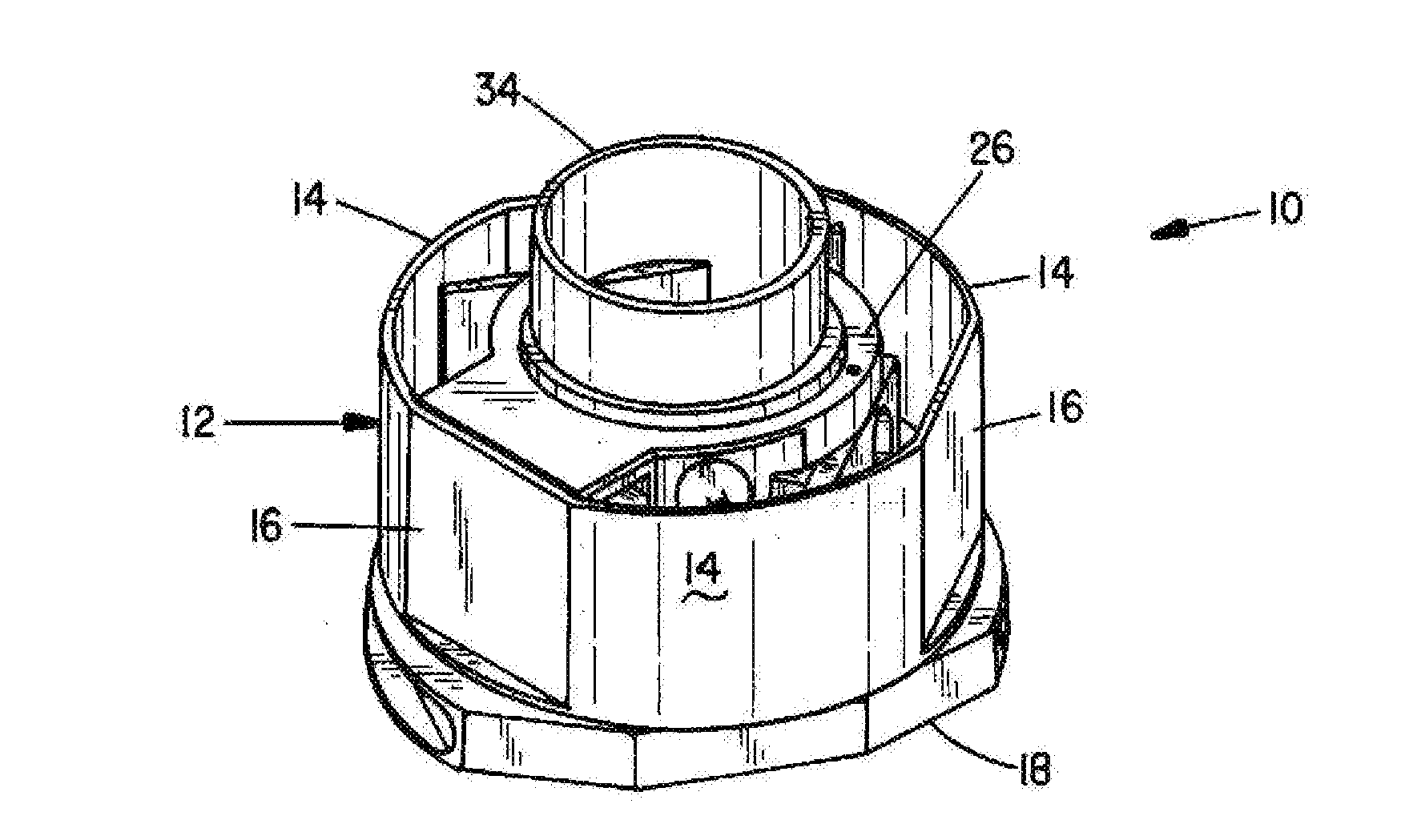
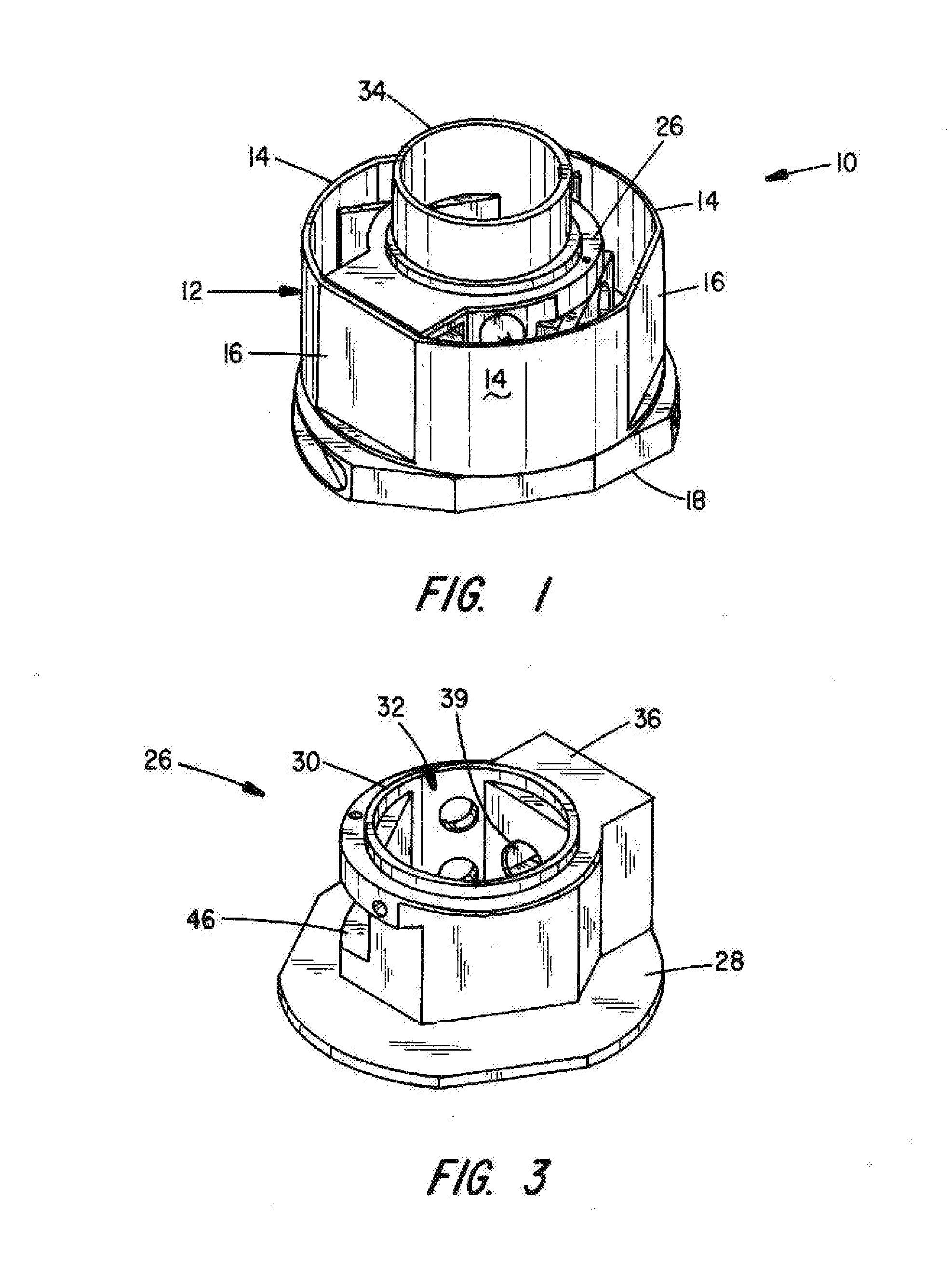
Exhalation valves
ActiveUS7066177B2Control flowReduce manufacturing costRespiratorsBreathing masksHermetic sealEngineering
An exhalation valve (10) is disclosed for use with an exhalation port (14) of a respiratory circuit. The exhalation valve comprises a hermetically sealed gas chamber (20,120), a gas inlet (22,122) for supplying gas to the gas chamber, and a membrane (24,124) of flexible material that defines at least part of a wall of the gas chamber. The membrane is deformable by a change in the pressure differential between the gas within the gas chamber and the gas within the exhalation port between an inoperative configuration and an operative configuration in which the membrane restricts the flow of gas from the exhalation port to a greater extent than in said inoperative configuration. The membrane is inherently planar but is mounted within the exhalation valve such that deformation of the membrane to its operative configuration occurs substantially without increase of the surface area of the membrane.
Owner:INTERSURGICAL AG
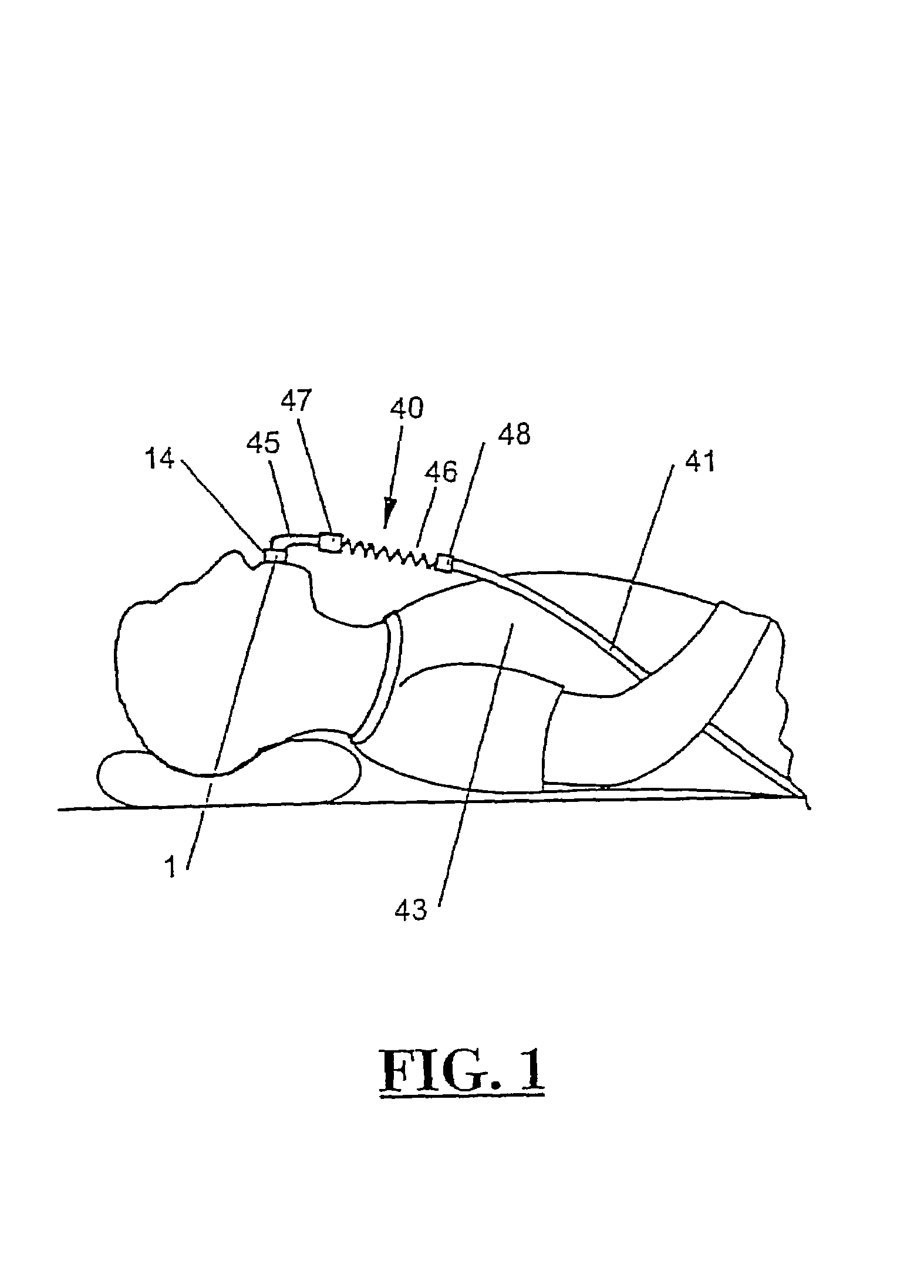
Breathing circuit disconnect warning system and method for using a disconnect system
InactiveUS6851427B1Easy and efficient to manufactureDurable and reliable constructionTracheal tubesSurgeryElectricityEndotrachial tubes
A breathing circuit disconnect warning system comprising an endotracheal tube, a breathing circuit supply tube with a pair of spaced electrically conductive strips, and a coupling tube. The coupling tube has an output end with a normally open switch including a first electrically conductive element and a spaced second electrically conductive element. The coupling tube also has an input end with a first electrically conductive ring and a second electrically conductive ring and lines coupling the rings and the elements. The rings are positionable in contact with the strips of the supply tube, whereby upon inserting the endotrachial tube into the output end, the switch will close and there will be an electrical connection across the switch and lines and rings and strips.
Owner:NASHED RAMSES
Metabolic analyzer transducer
A compact and wearable metabolic analyzer transducer comprising a housing containing a plurality of analog sensors, an A / D converter, a microcontroller, and a power source operatively coupled thereto where the microcontroller is programmed to compute minute ventilation, O2 uptake, and CO2 production of a subject. The transducer and its contents are of a size and weight that can either be easily supported from a facemask worn by a subject or incorporated in a respiratory circuit. The measured values can be wirelessly transmitted or transmitted, via a cable, to a remote personal computer, a personal digital assistant (PDA), or other display devices such as digital watches or image projectors.
Owner:MEDICAL GRAPHICS CORP A CORP OF MN
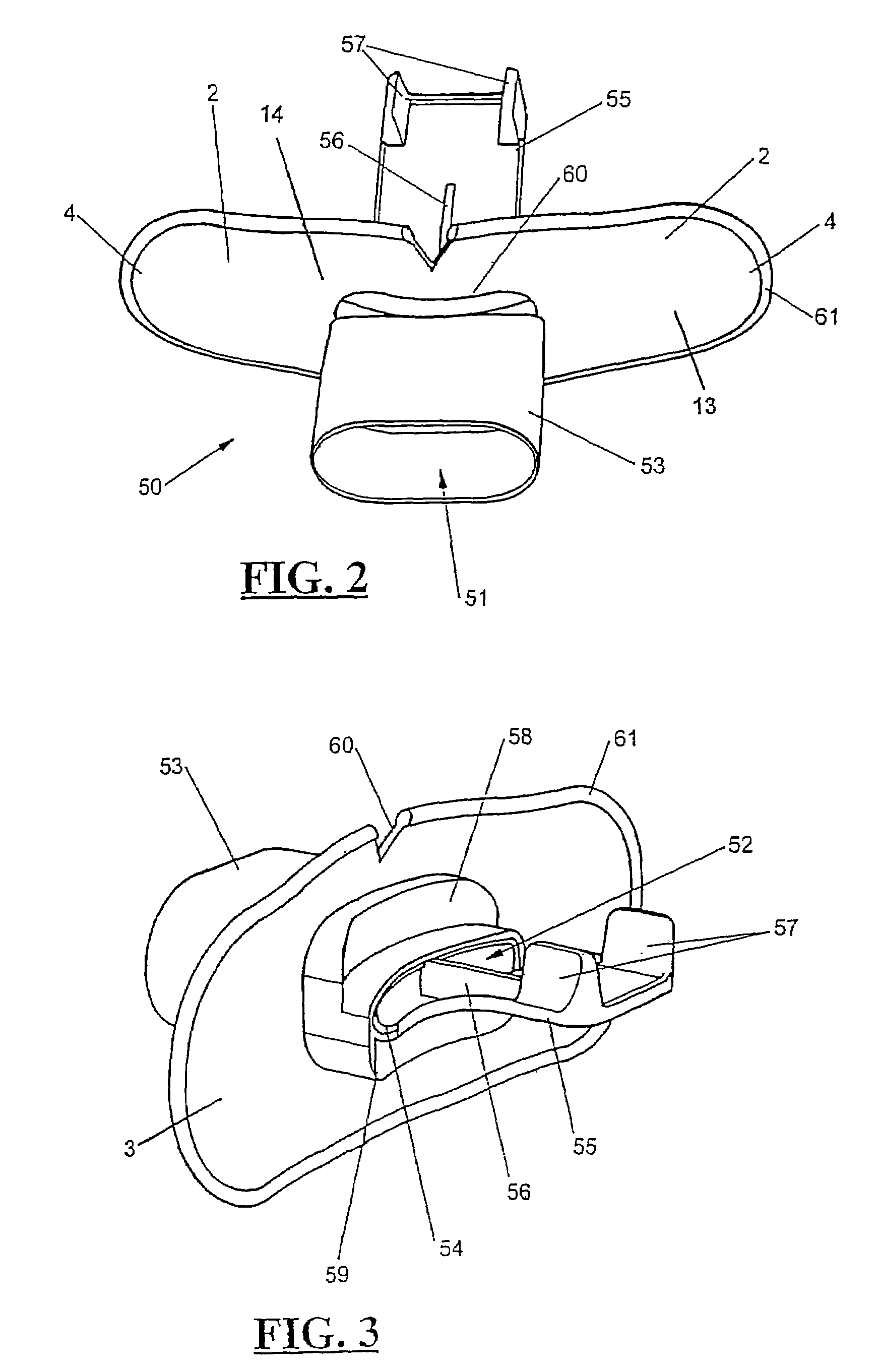
Adjustable length breathing circuit
Owner:KING SYST
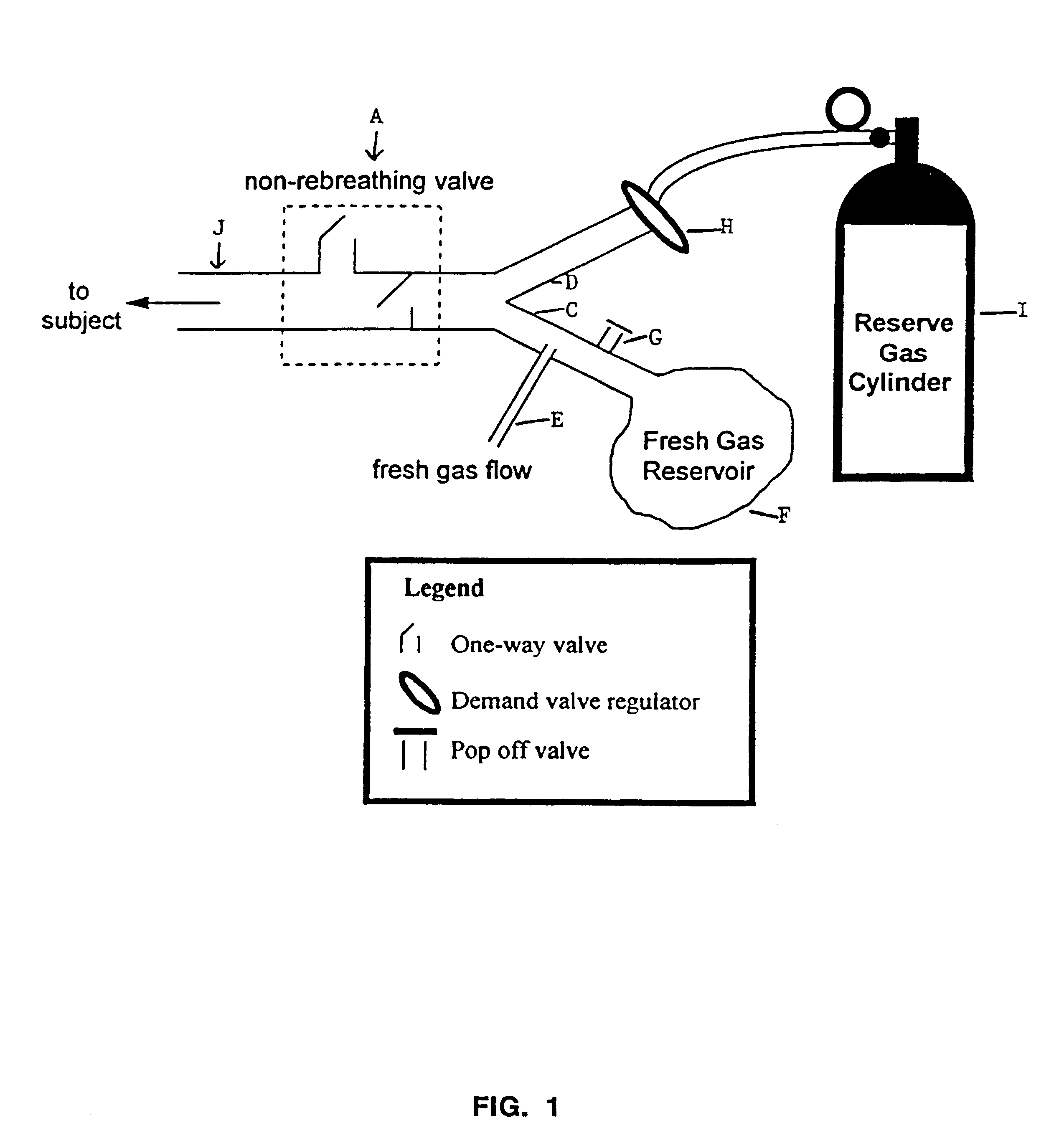
Self contained breathing apparatus control system for atmospheric use
InactiveUS7353824B1Facilitates assurance of system functionalityMinimize failureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAtmospheric airNormal functioning
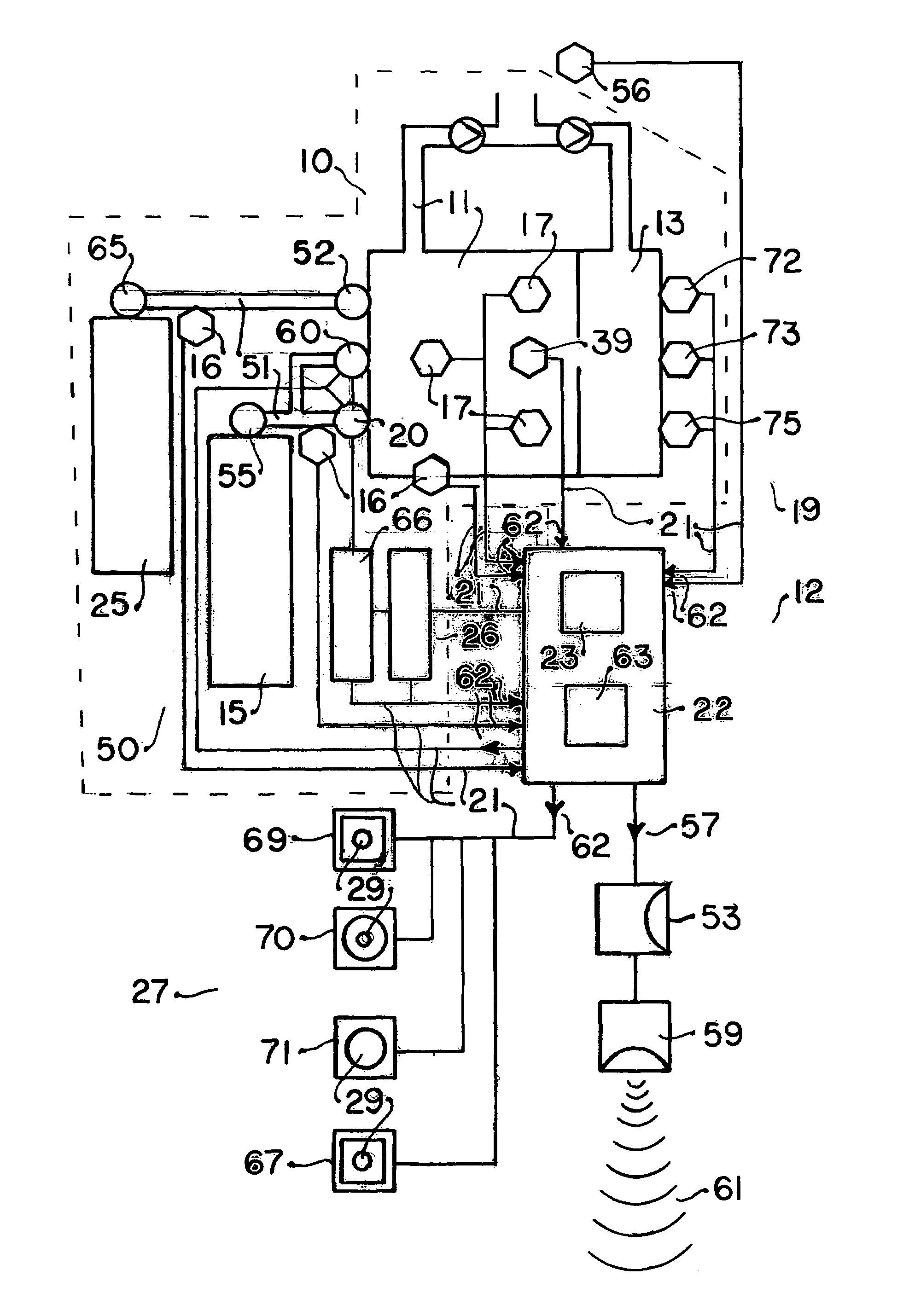
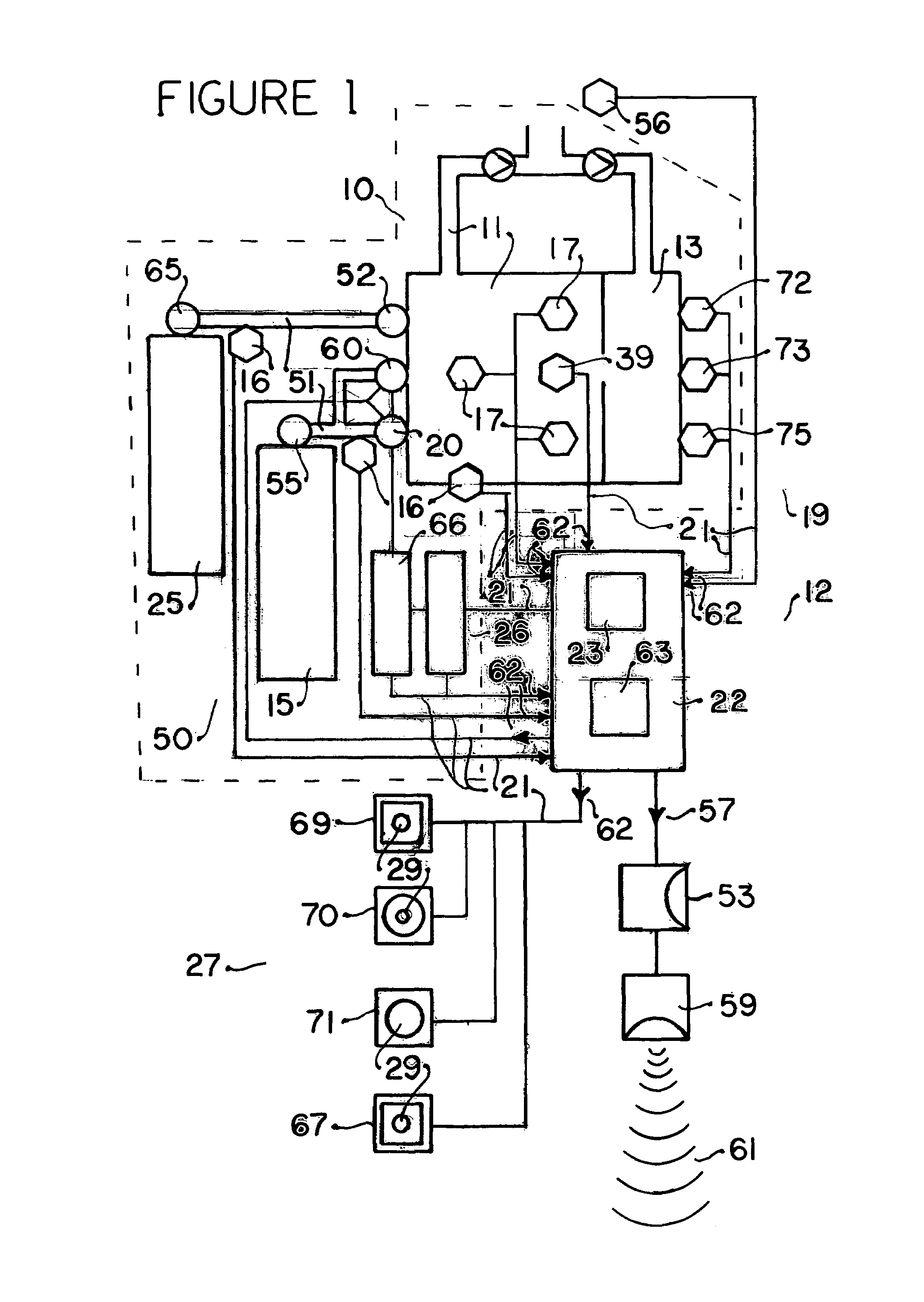
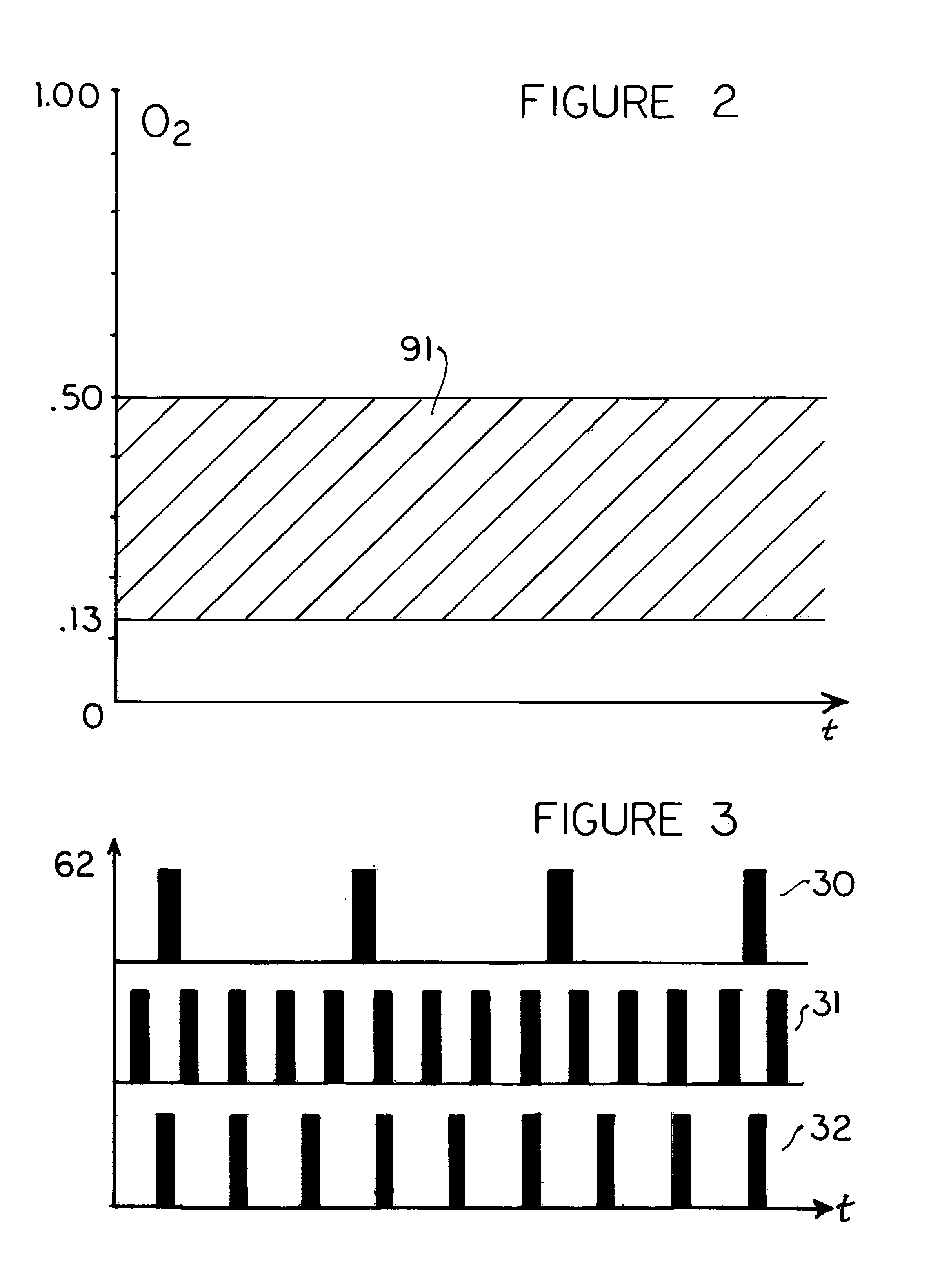
An electronic controller having at least one microprocessor controls the solenoid operated valve adding oxygen to the breathing loop of a closed circuit mixed gas rebreather with carbon dioxide scrubbing in maintenance of an oxygen set point in the rage of 0.13-0.50 without any need for monitoring or interpretation of signal data by the operator. The controller receives signals from at least one oxygen sensor located in the breathing loop and sends signals to an indicator: visual, aural, or tactile; during operation providing only intuitively understood normal functioning, limited time remaining, and bail out indications. Automatic diagnosis including oxygen sensor calibration, indication of actions required such as scrubber replacement, and confirmation of an action taken with signals from an action sensor are provided.
Owner:LAGUNA RES
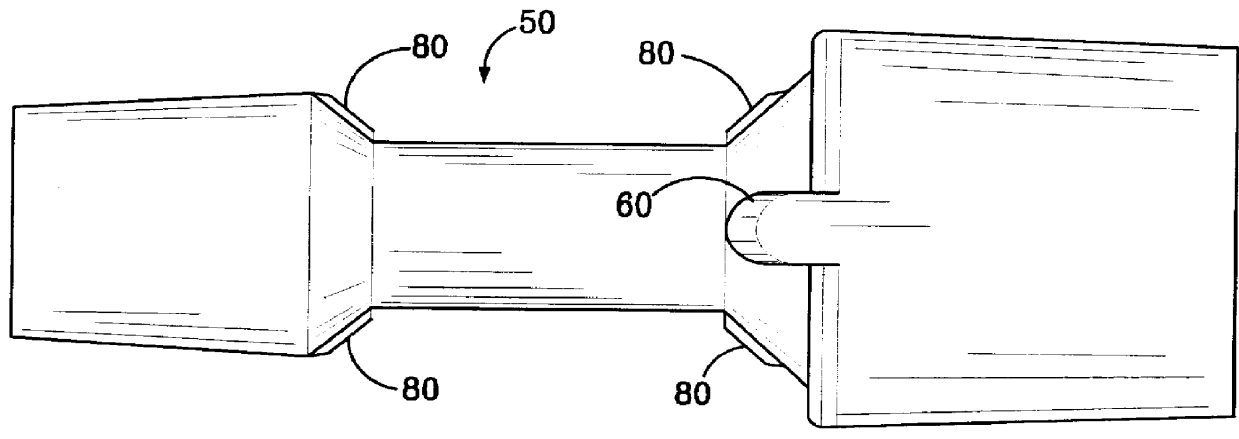
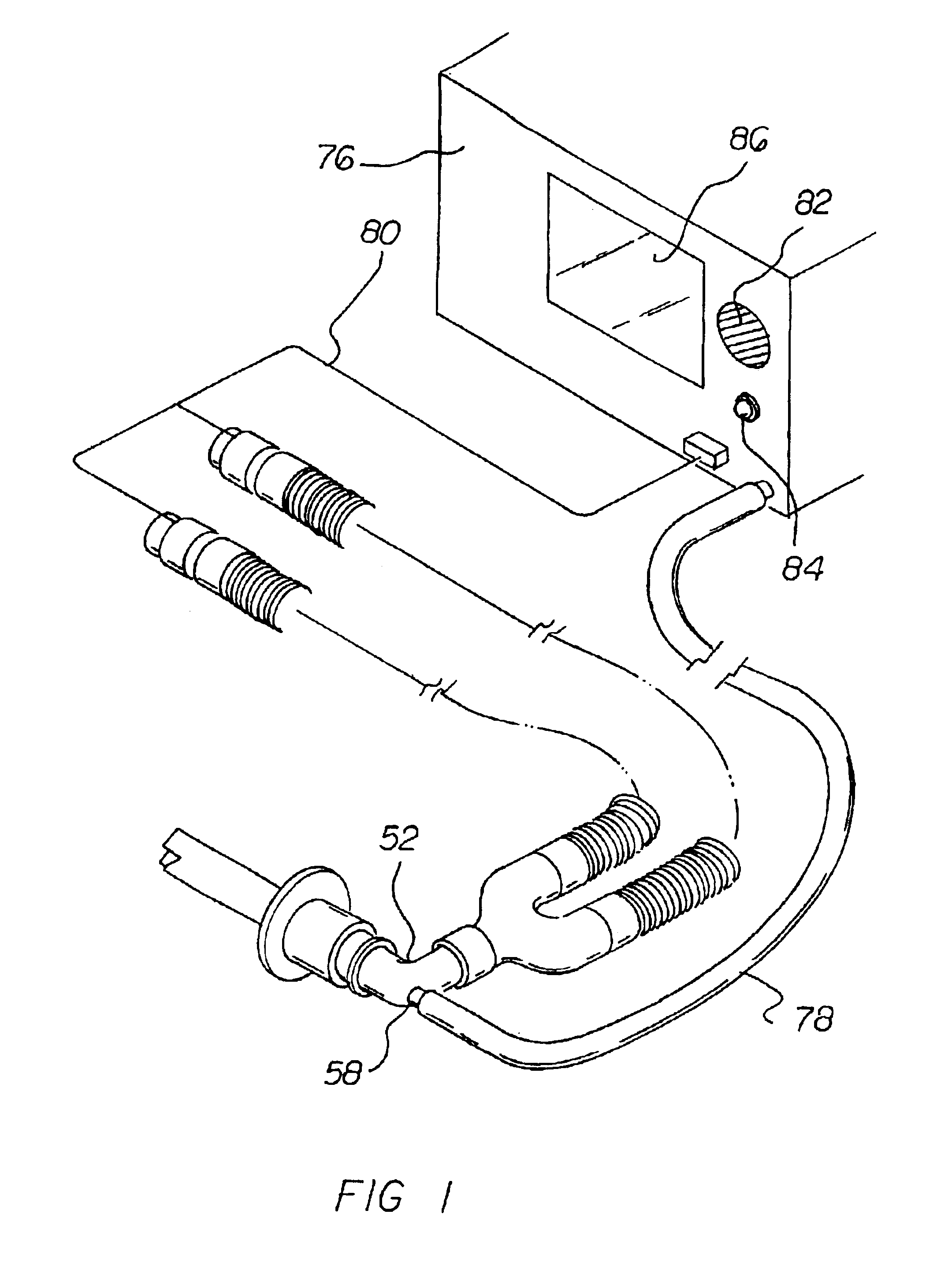
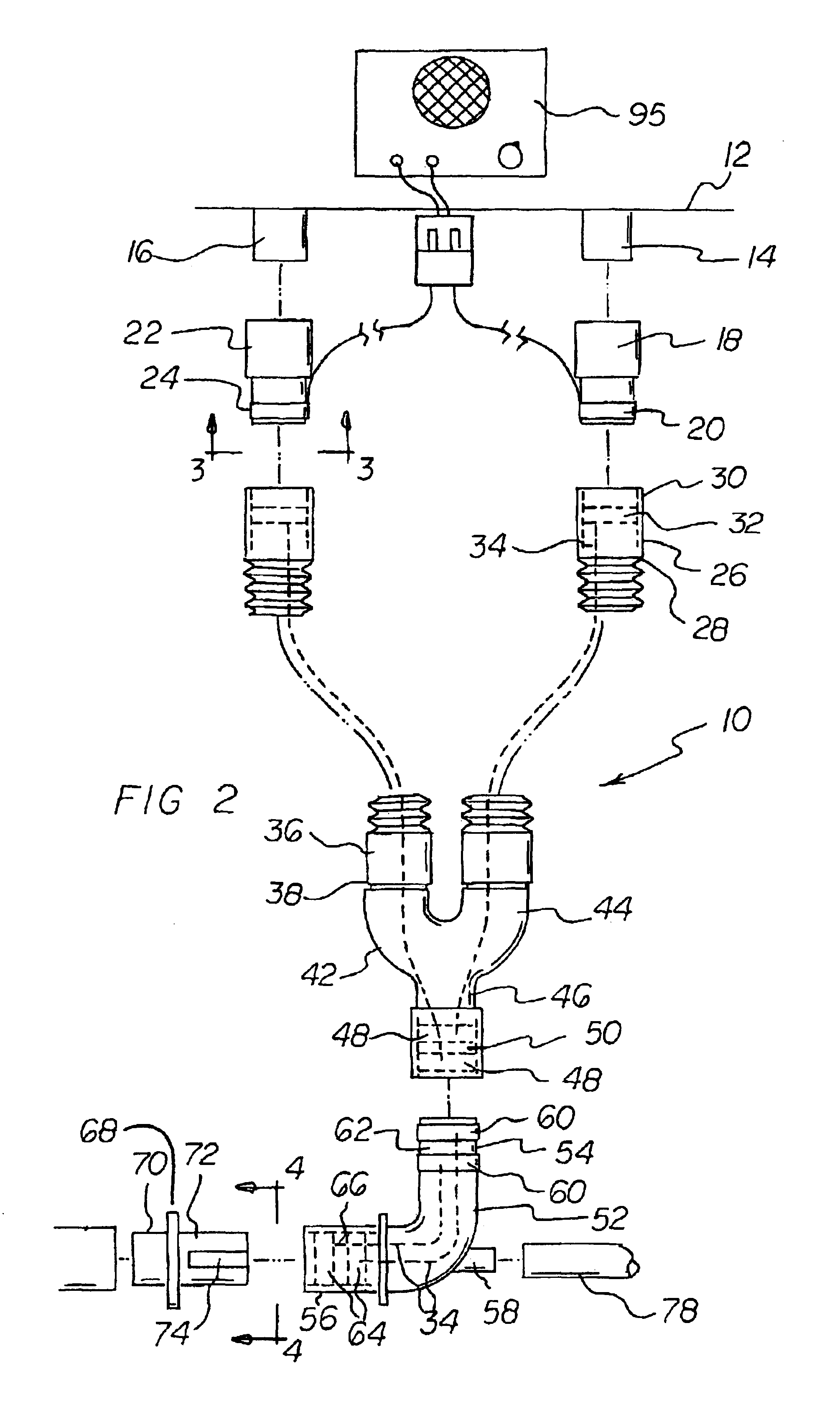
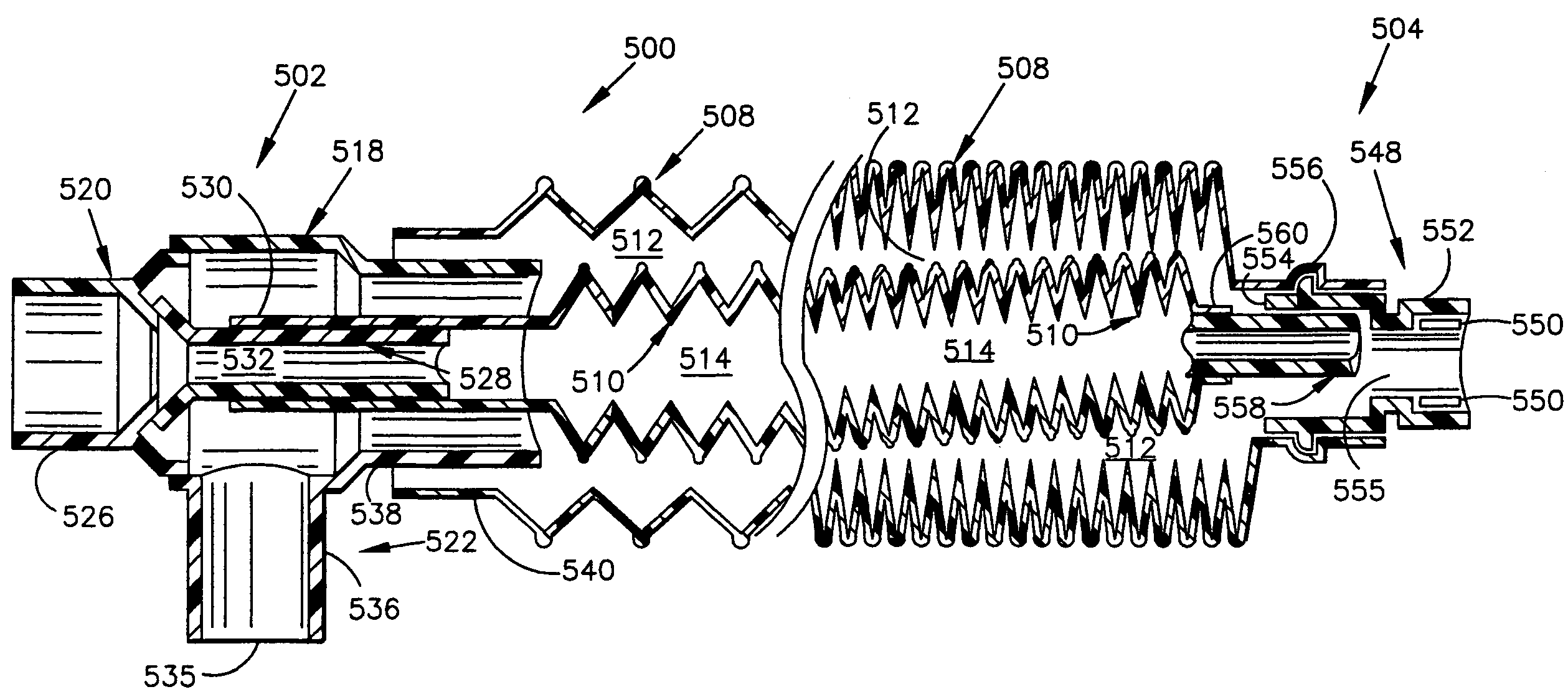
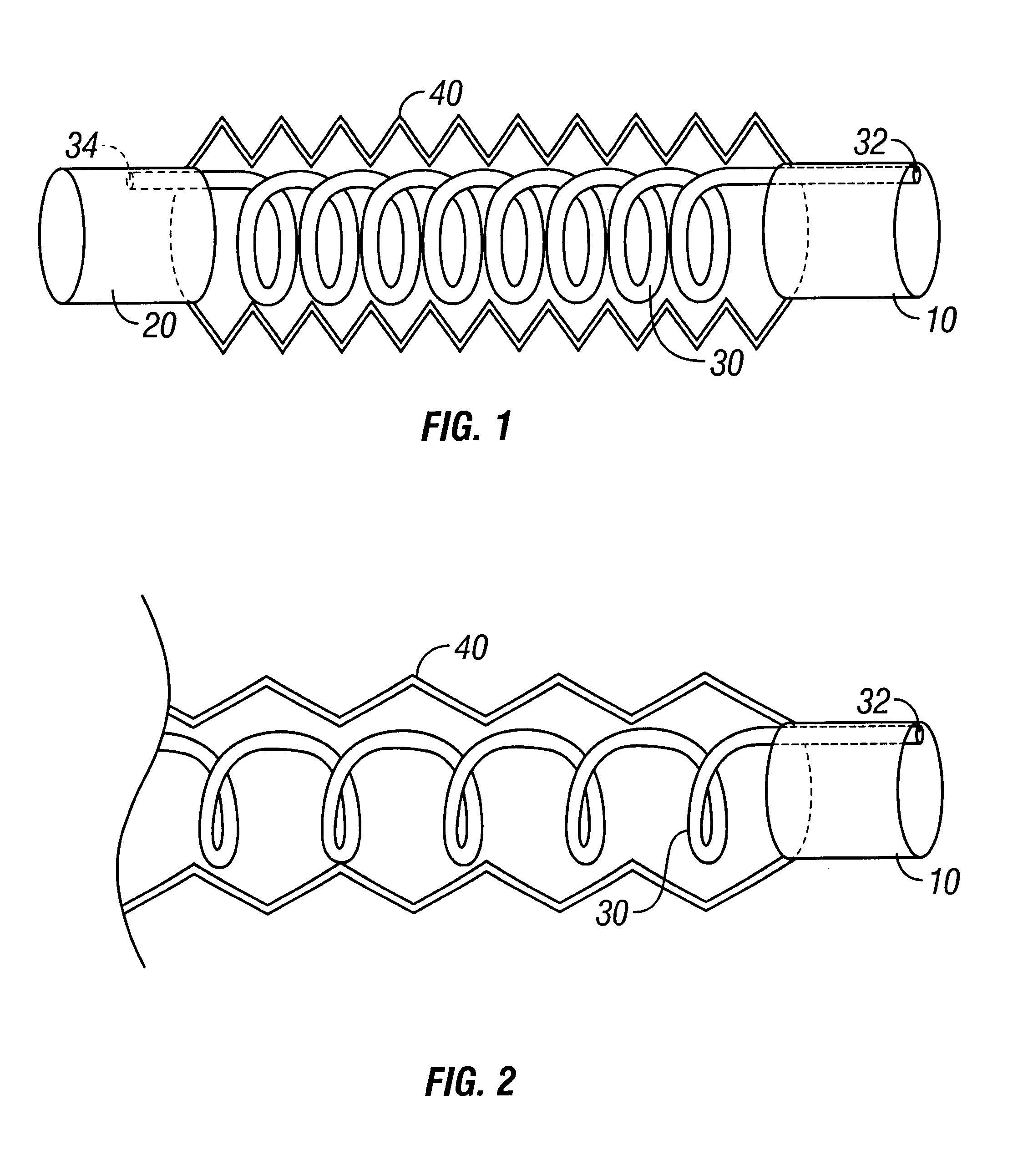
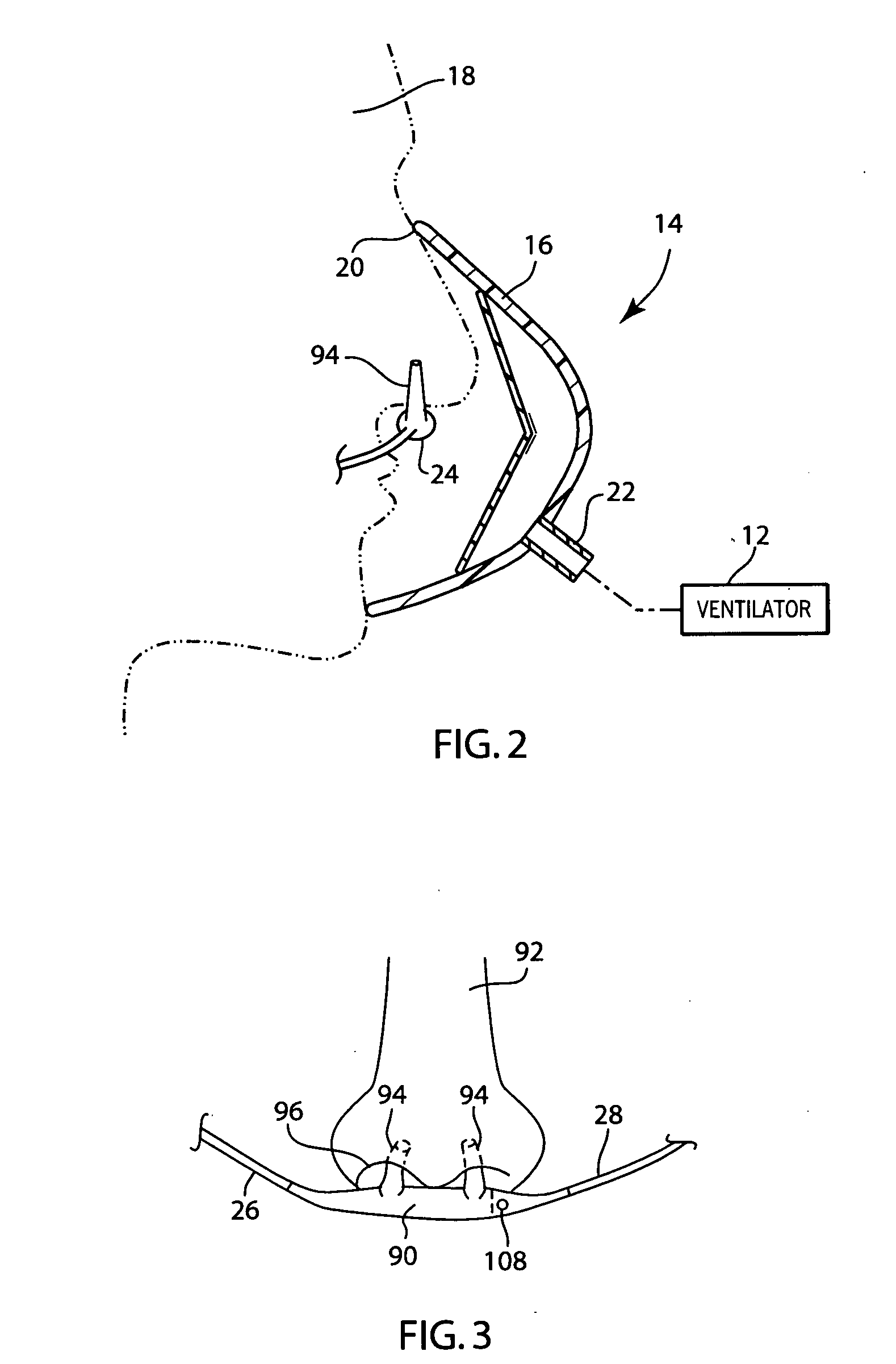
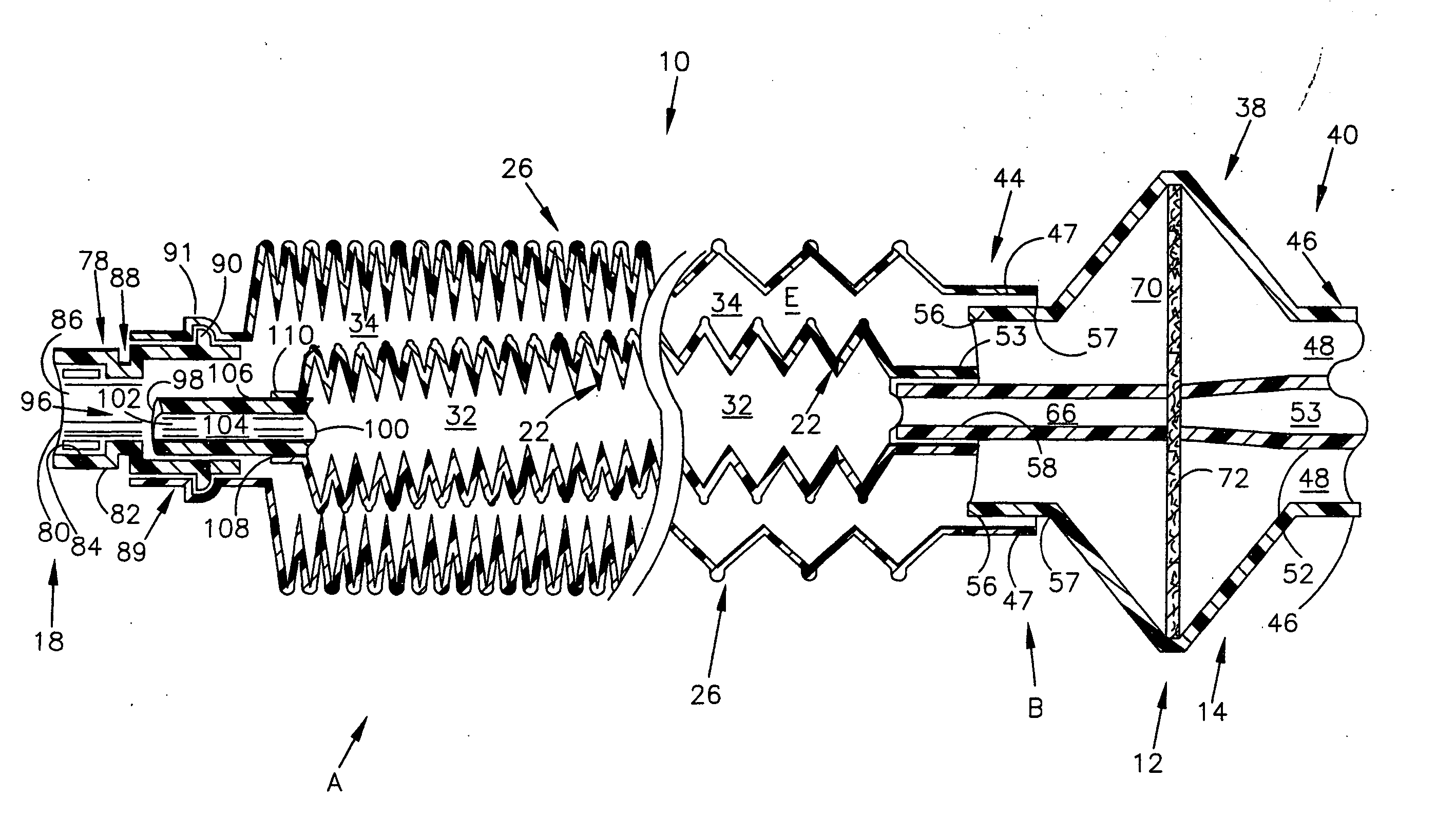
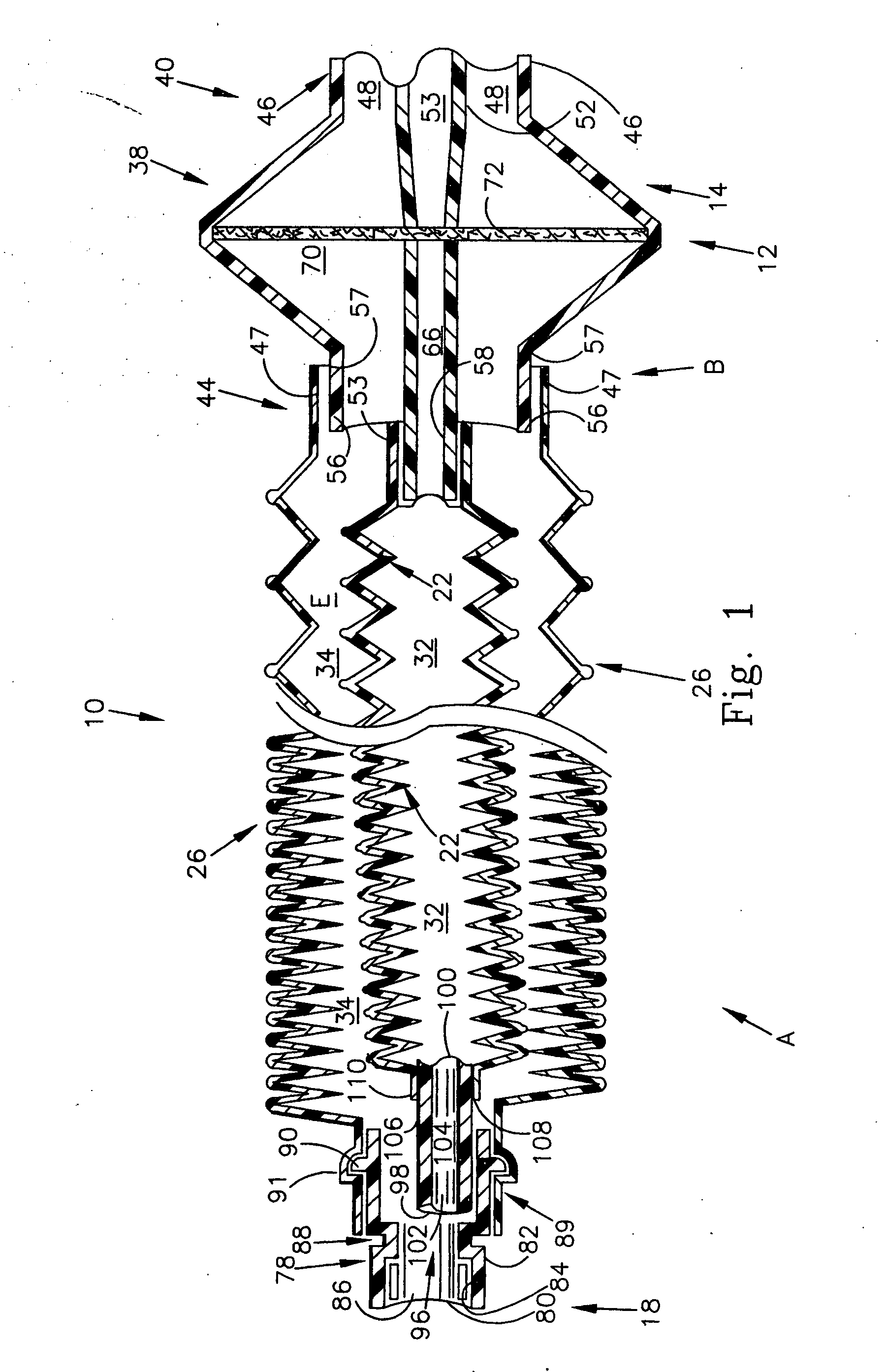
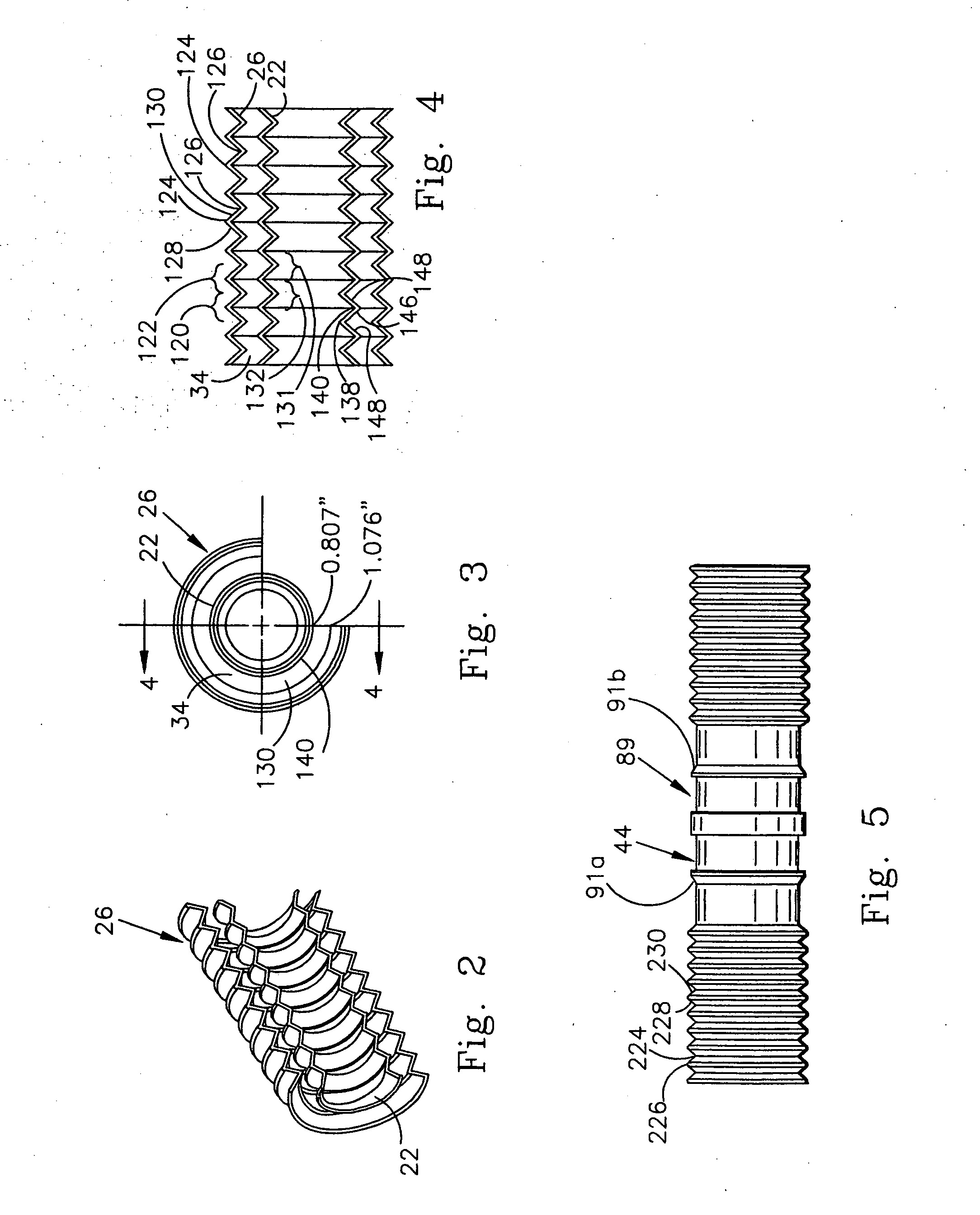
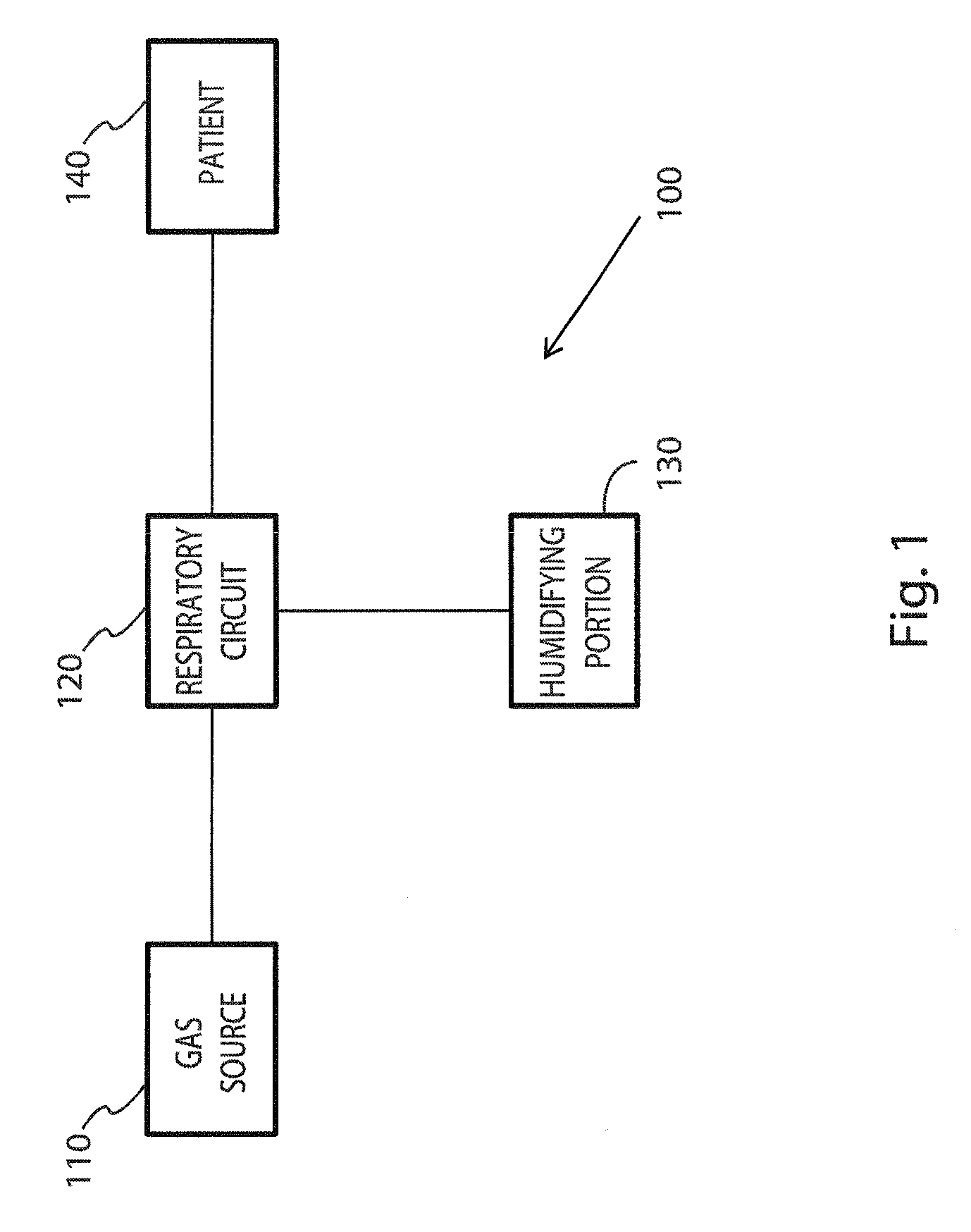
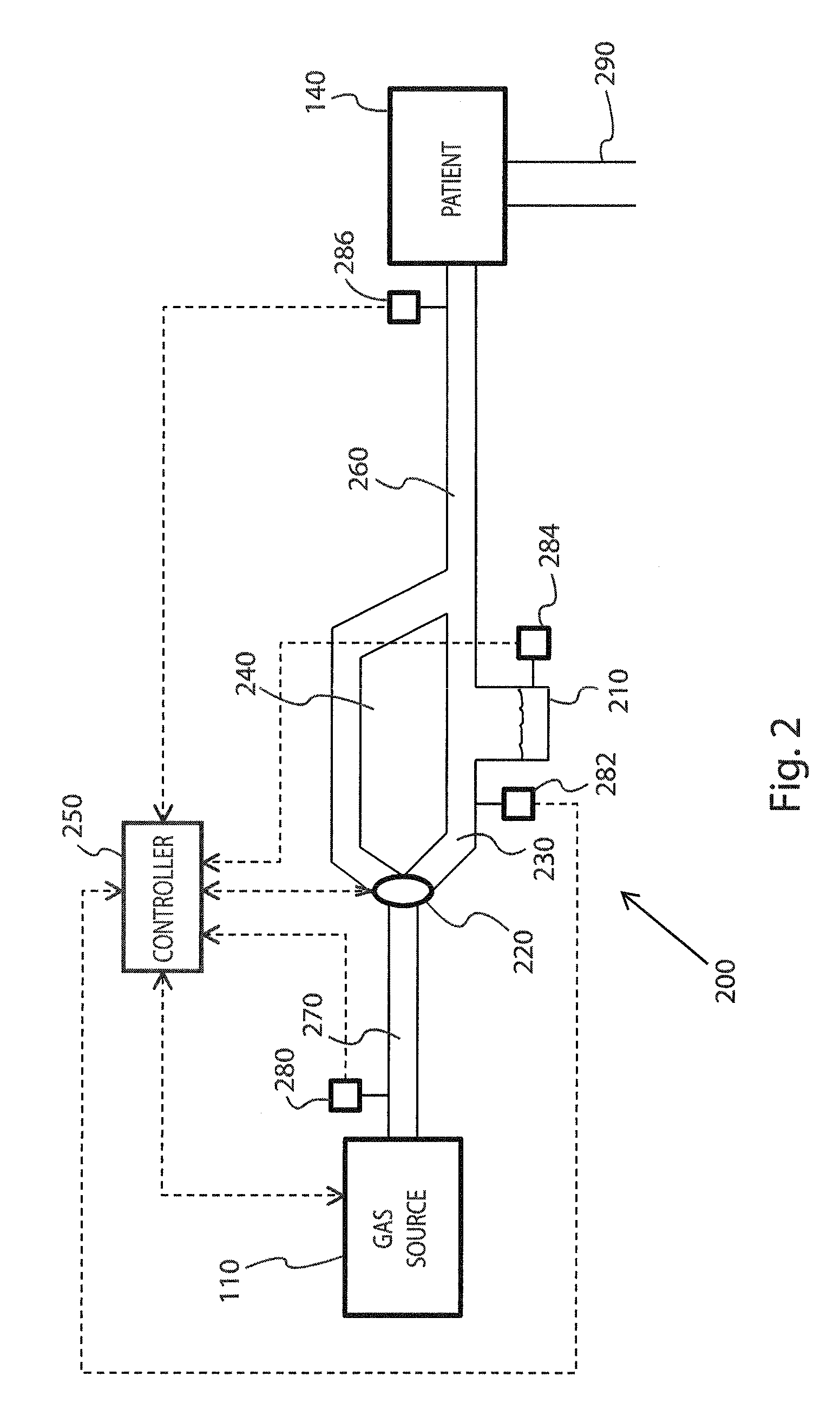
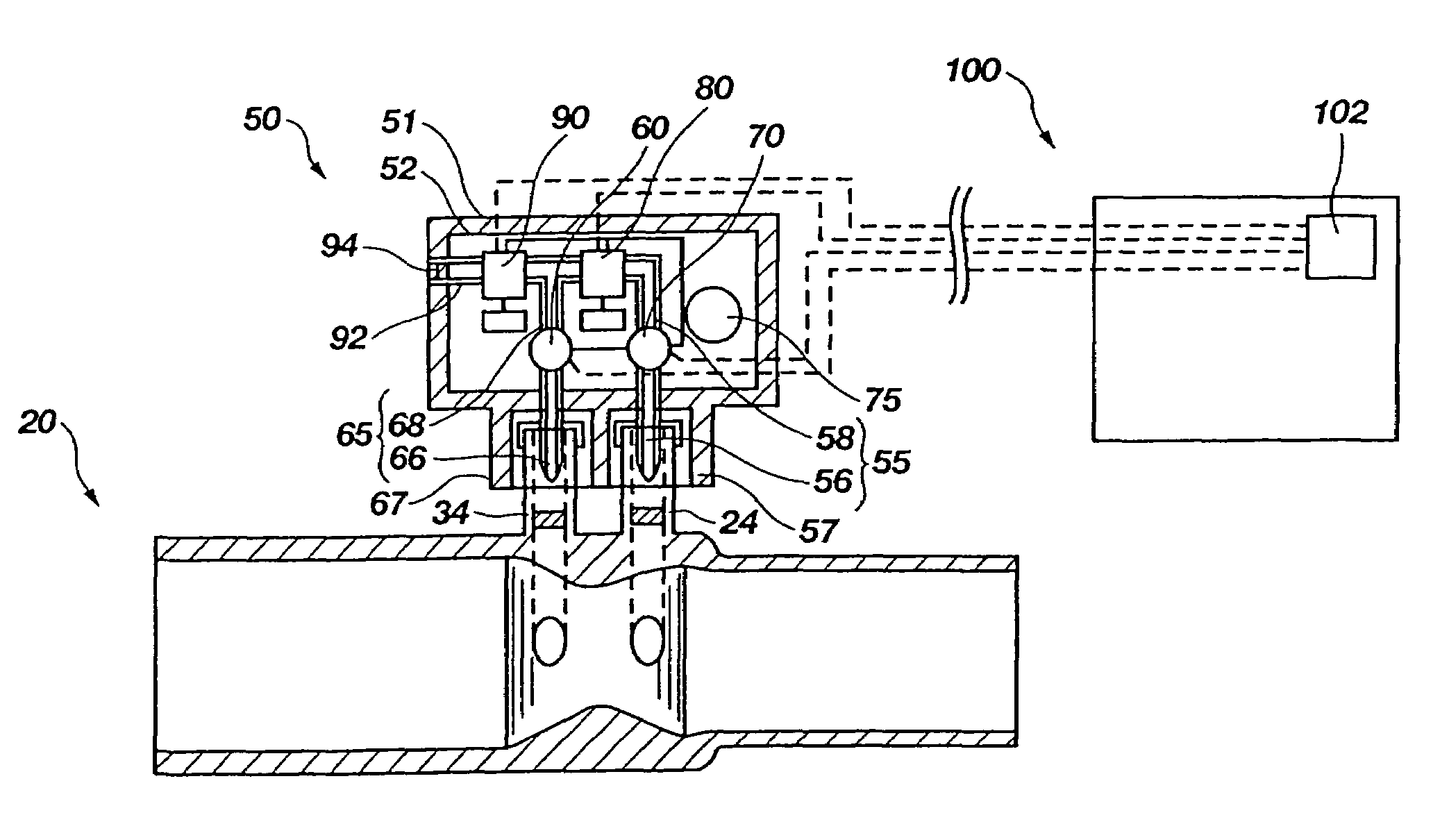
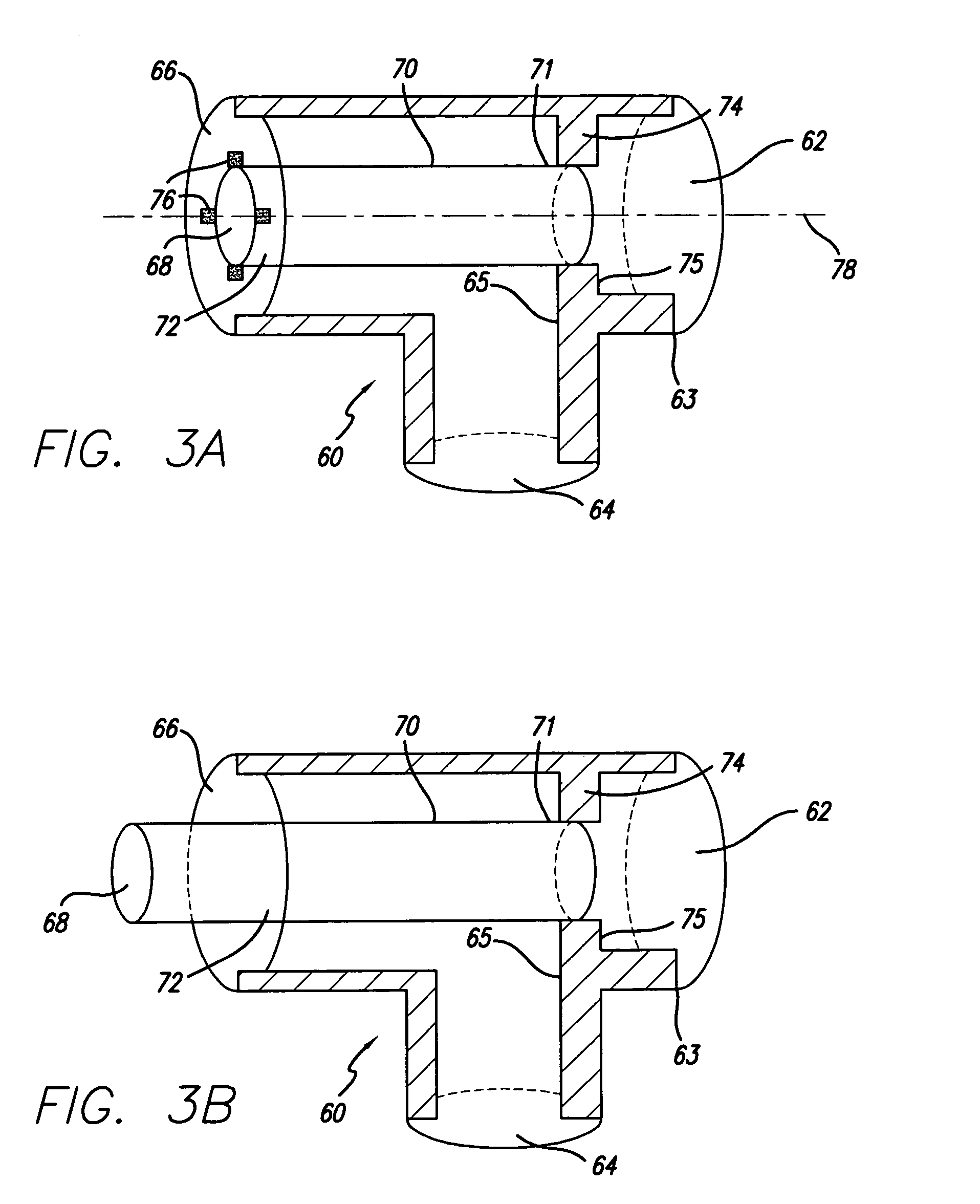
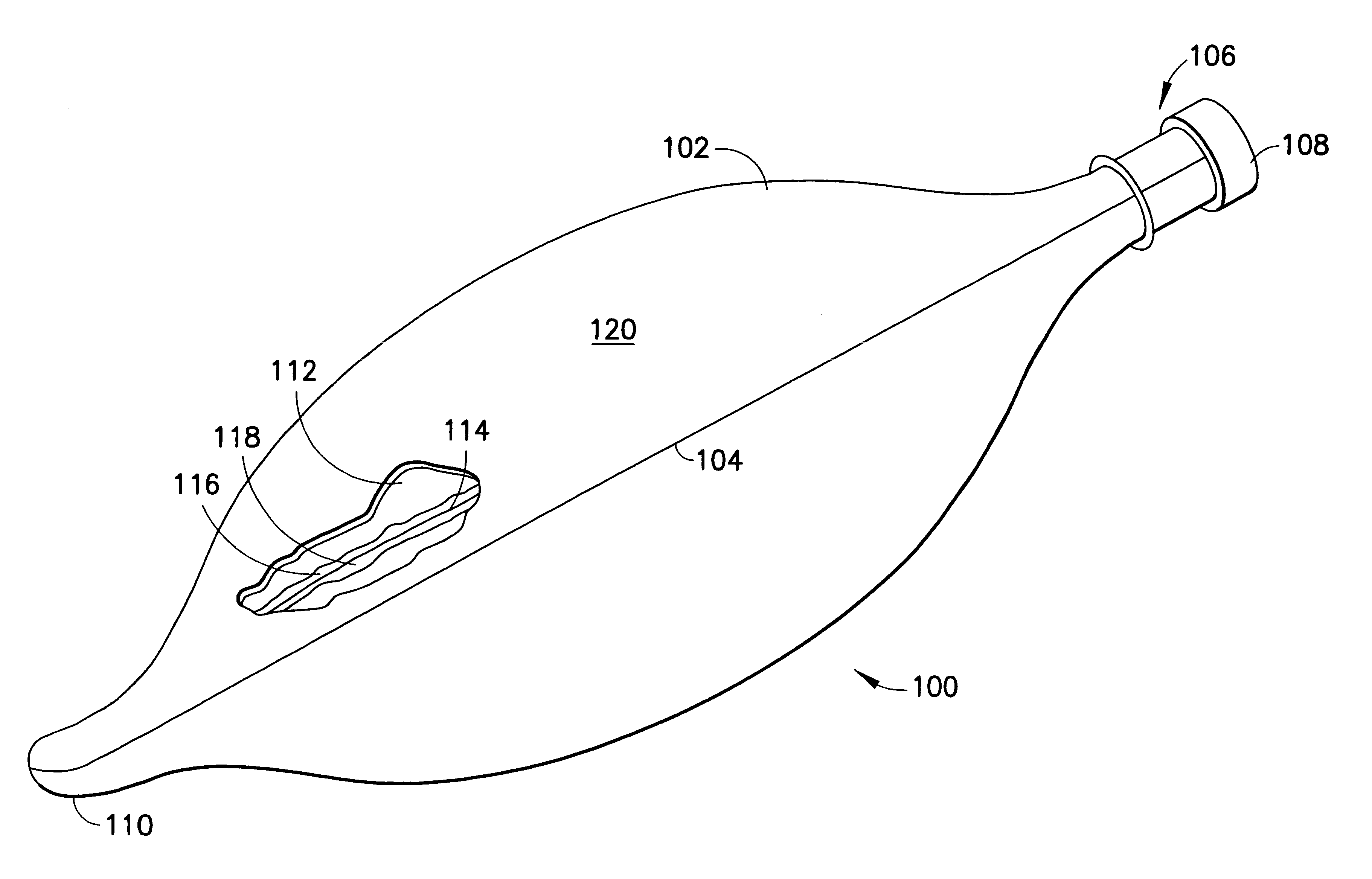
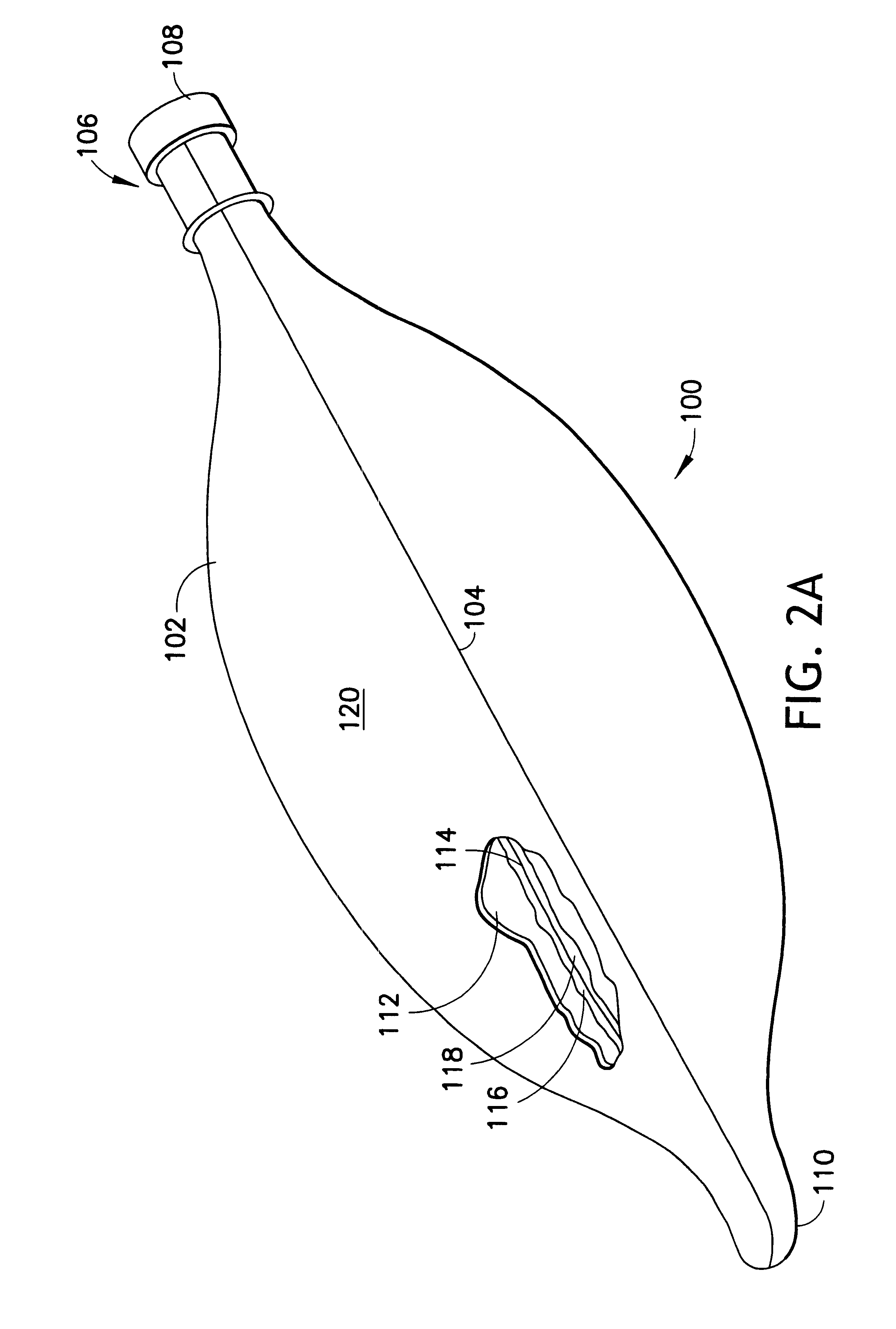
Breathing circuits having unconventional respiratory conduits and systems and methods for optimizing utilization of fresh gases
InactiveUS6874500B2Regulate securityOptimizing the utilization of anesthetic gasesRespiratorsSurgeryBreathing gasCatheter
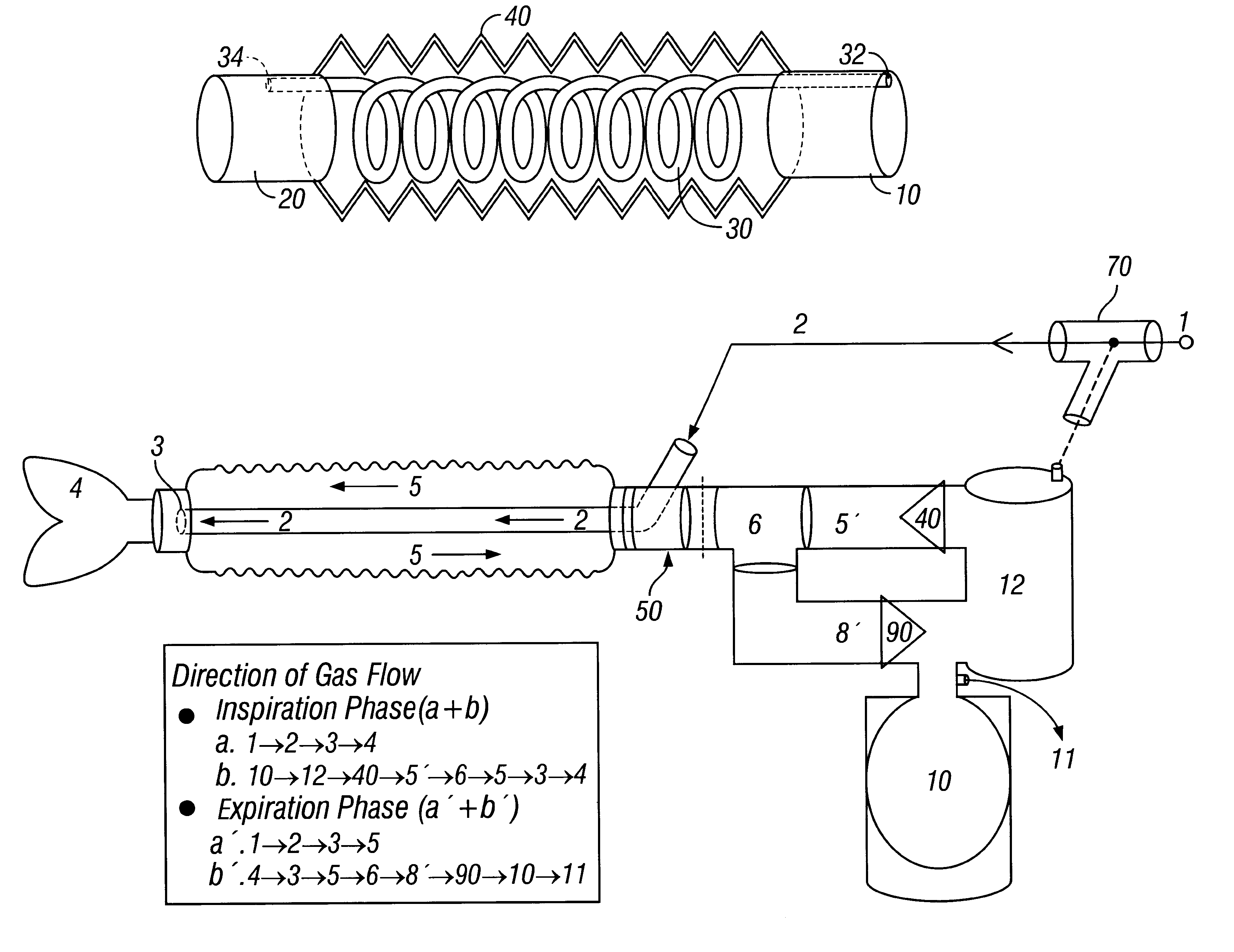
A breathing circuit comprising first and second conduits, wherein at least one of the conduits is a non-conventional conduit. In an embodiment, a multilumen unilimb breathing circuit has first and second conduits, wherein when the proximal ends of said first and second conduits are each connected to an inlet and outlet fitting, respectively, movement of the distal end of the first conduit causes a corresponding movement of the distal end of the second conduit. In an embodiment, at least one of said conduits is coiled. In another embodiment, a coiled conduit is contained within an outer flexible conduit that is axially extendable and compressible, forming a unilimb multilumen respiratory circuit. The outer flexible conduit may be pleated to provide for non-rebounding axial extension and contraction. The multilumen respiratory circuit can provide a variable rebreathing volume. In an embodiment, at least one tube in a multilumen respiratory conduit is radially collapsible and radially expandable to a maximum radius for carrying respiratory gases to and from a patient. The methods and systems can be used to administer anesthesia and for other purposes.
Owner:AMBU AS
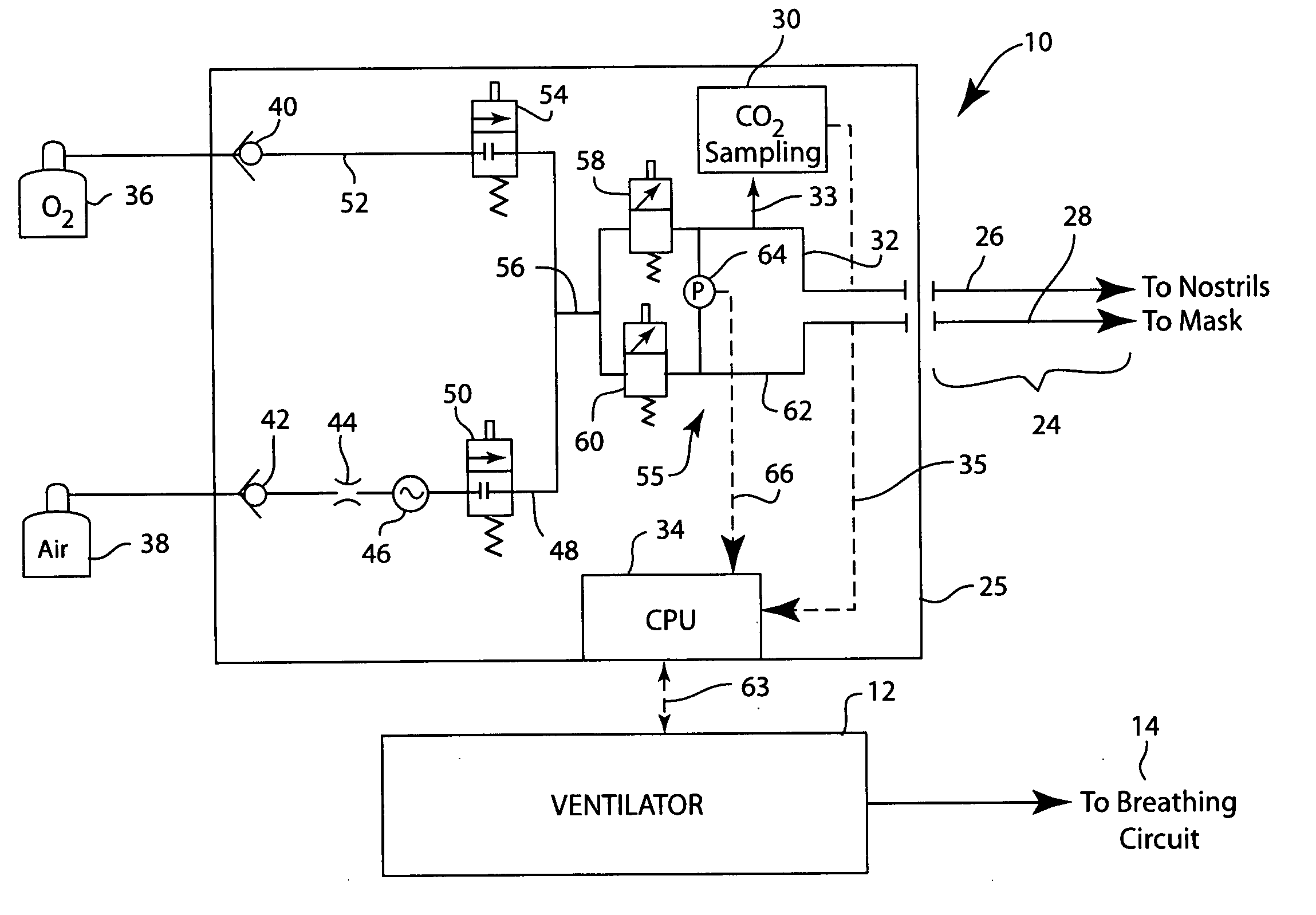
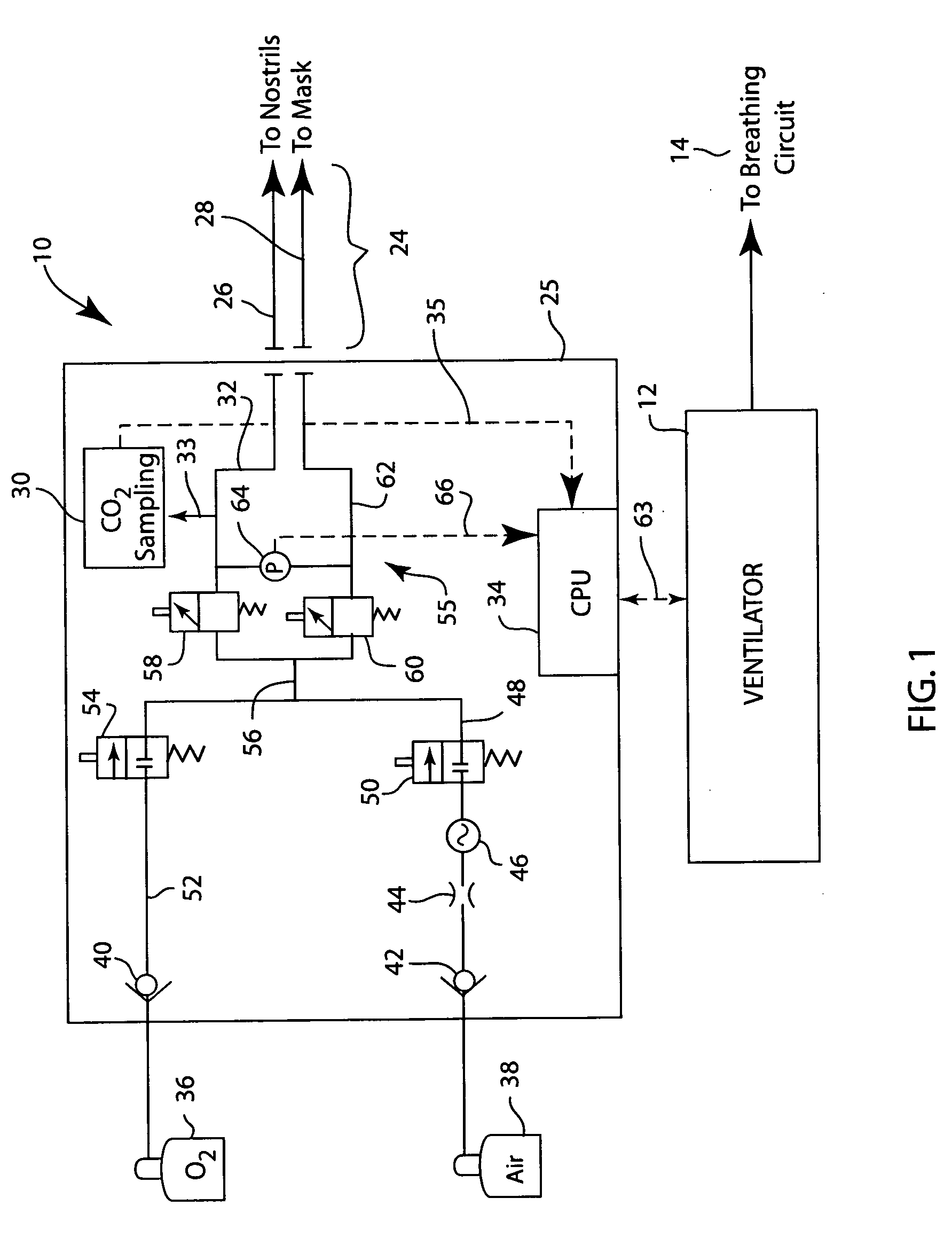
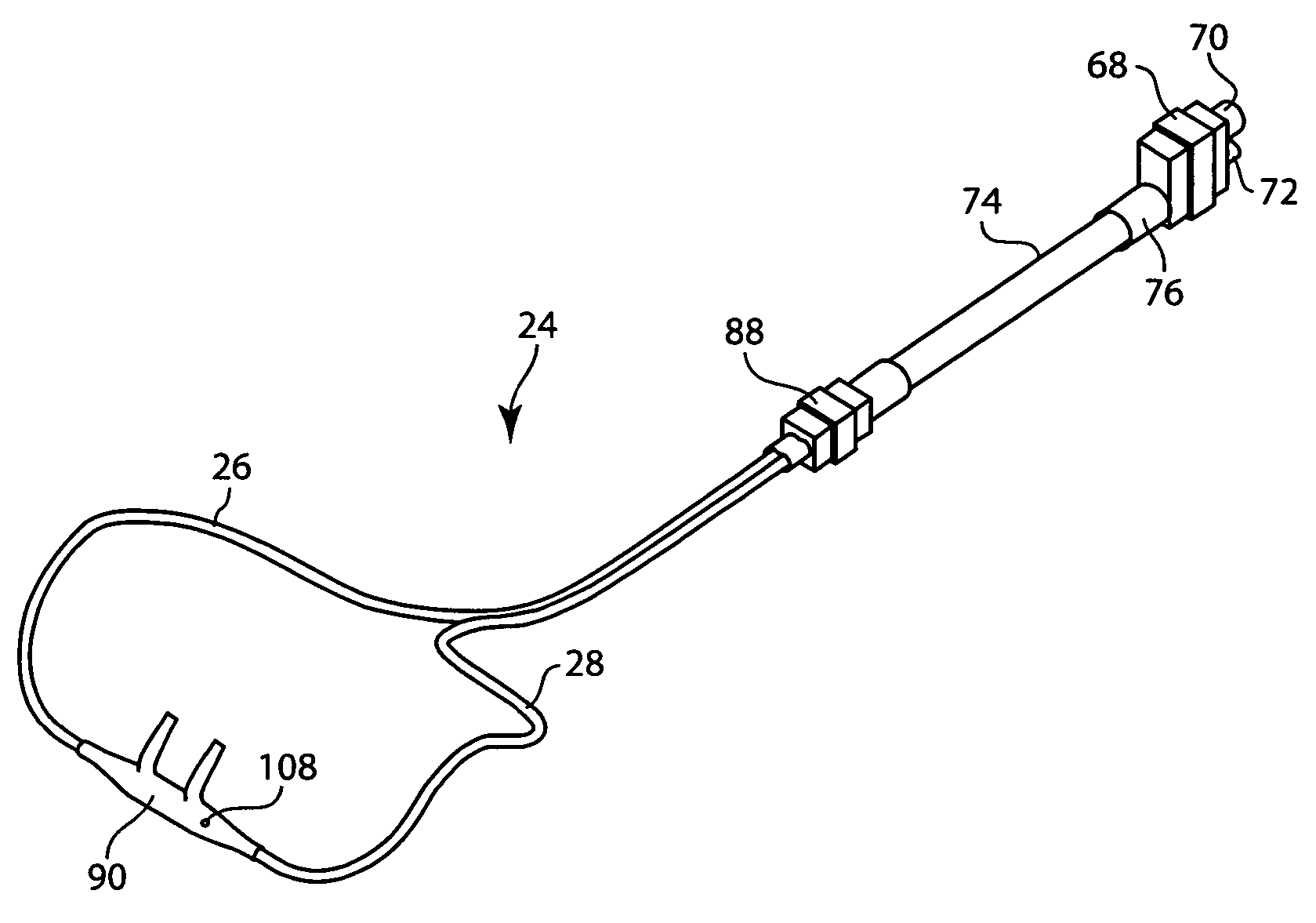
Integrated ventilator nasal trigger and gas monitoring system
ActiveUS20070144518A1Efficient combinationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksNostrilDifferential pressure
An arrangement and method for detecting spontaneous respiratory effort of a patient receiving ventilatory support by a breathing circuit. The nasal cannula control system includes a nasal cannula assembly having two distinct lumens. A different pressure sensor is positioned to detect the pressure difference between each of the two lumens, thereby determining the differential pressure from within the patient's nostrils and within a breathing mask. The nasal cannula control system includes a gas sampling system such that the amount of a monitored gas discharged or exhaled by the patient can be monitored using the same nasal cannula assembly used to generate the differential pressure signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
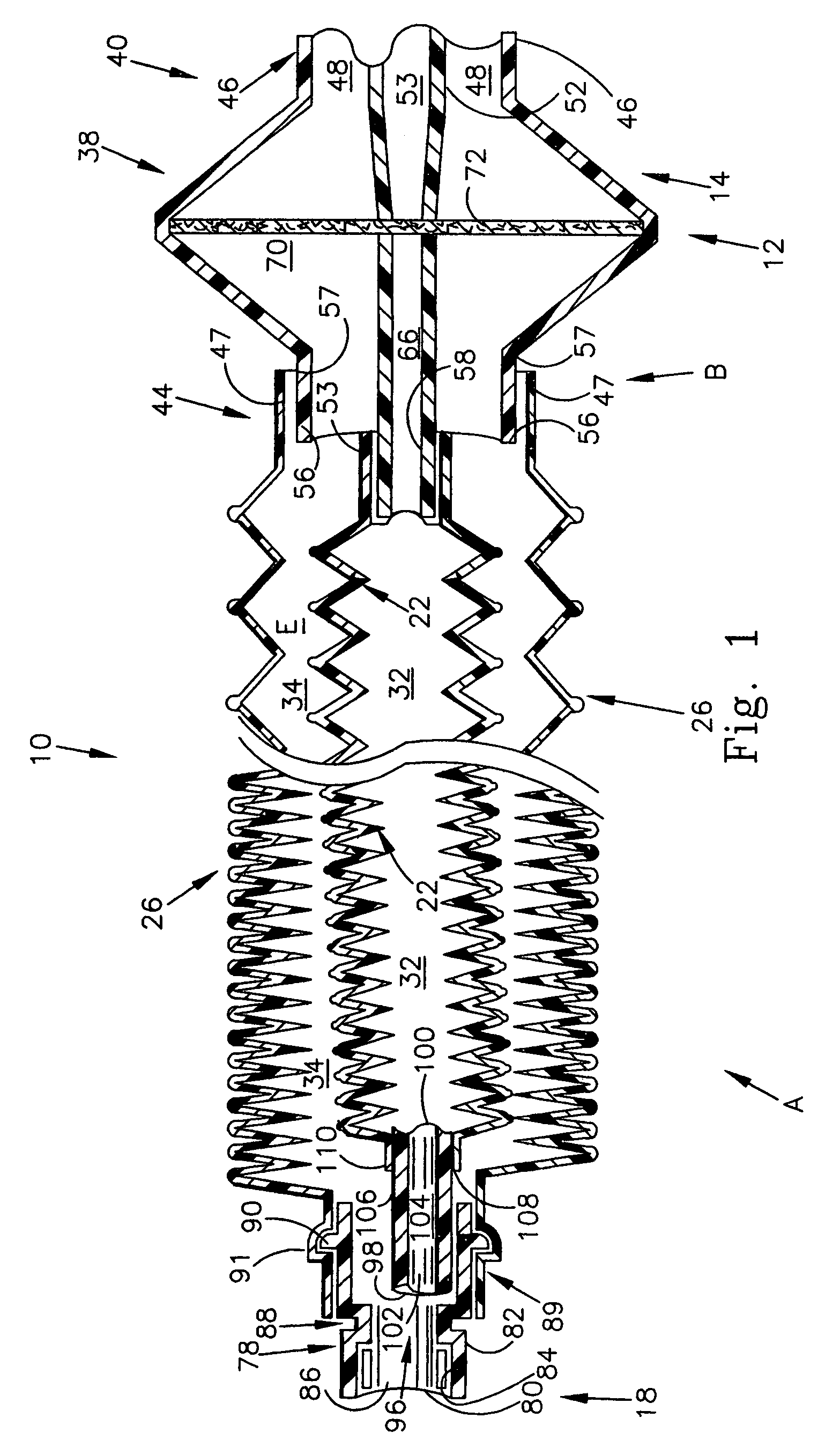
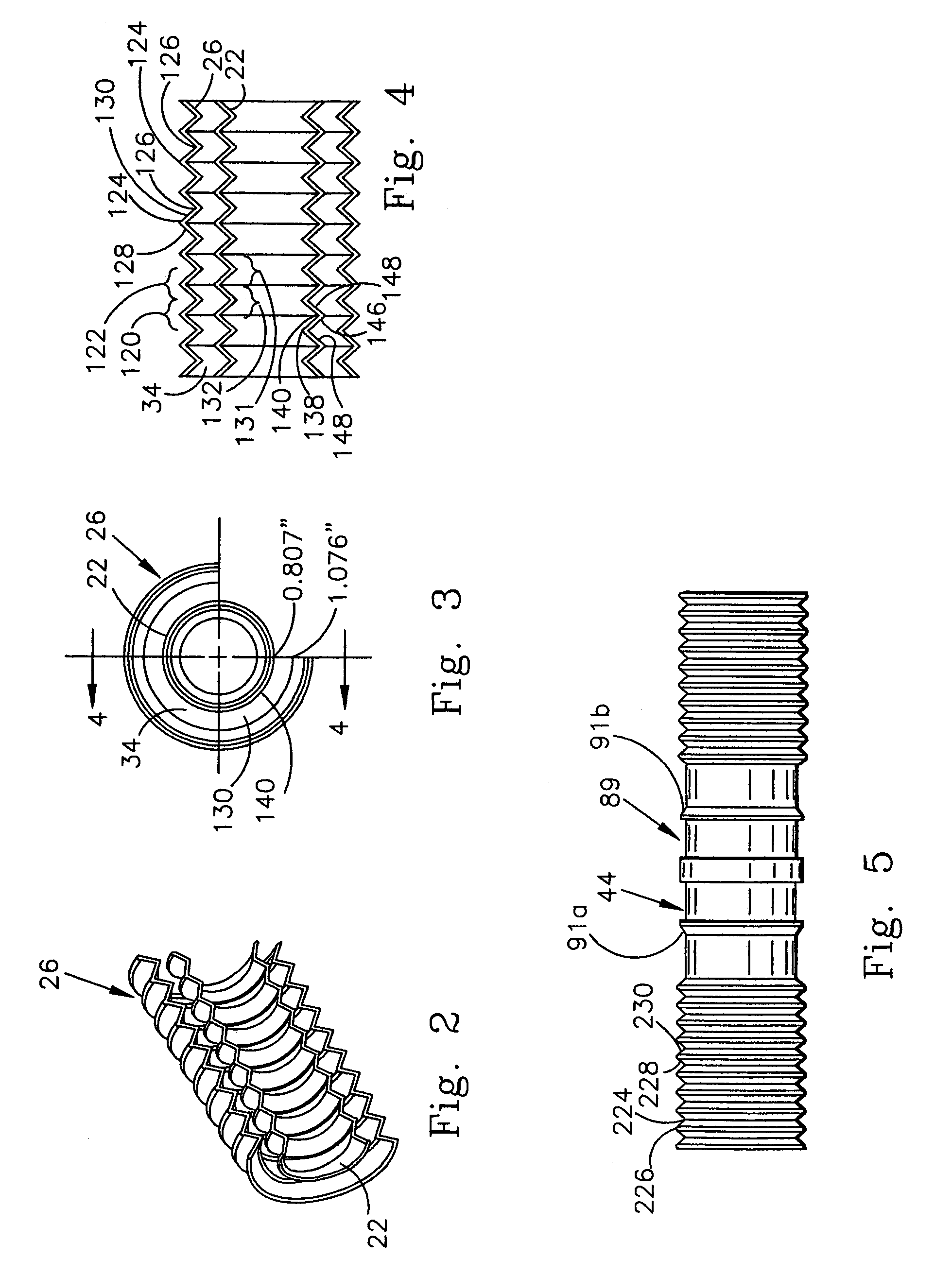
Adjustable length breathing circuit
A unilimb breathing circuit has a proximal end coupling member, a distal end coupling member, an expiratory tube extending between the proximal and distal end coupling members, and an inspiratory tube extending between the proximal and distal end coupling members. The expiratory tube is a corrugated expiratory tube that is expandable between a fully compressed rest position, and a fully expanded rest position, and has a plurality of intermediate rest positions. At the plurality of intermediate rest positions, the expiratory tube is capable of maintaining its rest length without the exertion of an external force. The inspiratory tube is a corrugated inspiratory tube having a length that is variable between a fully compressed rest position and a fully expanded rest position, and includes a plurality of intermediate rest positions between the fully expanded rest position and the fully compressed rest position. The inspiratory tube is also capable of maintaining these intermediate rest positions without the exertion of an external force.
Owner:KING SYST
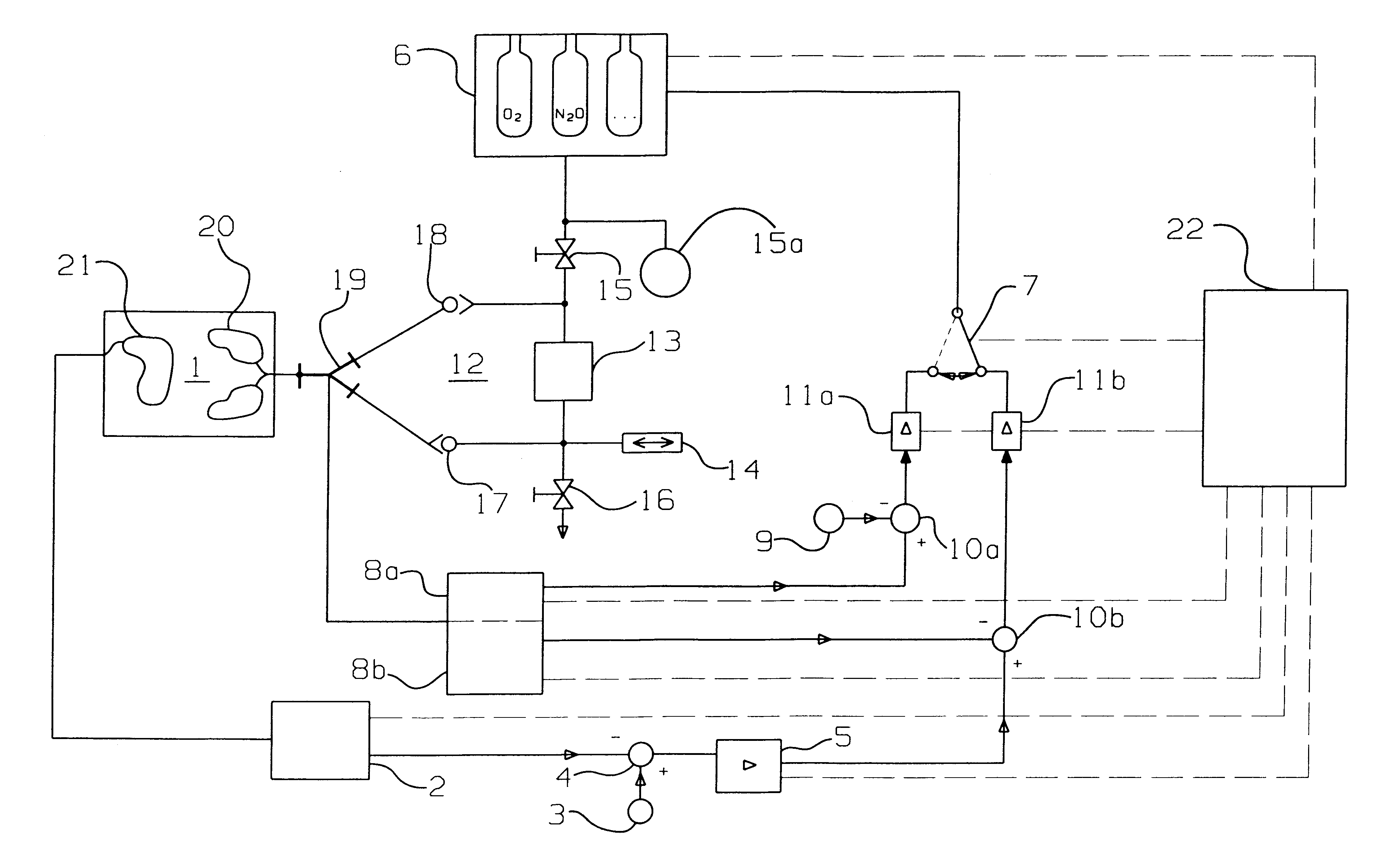
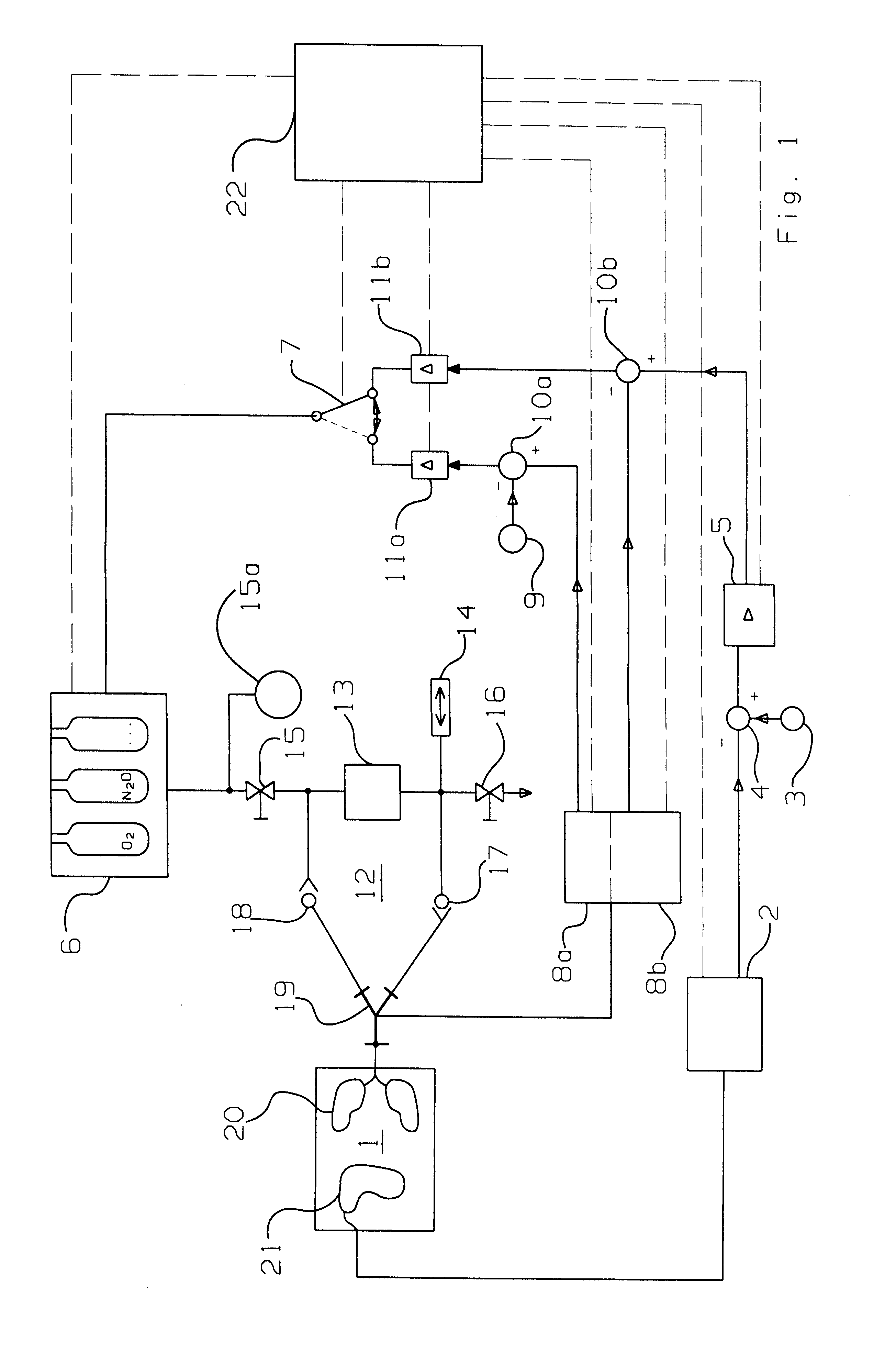
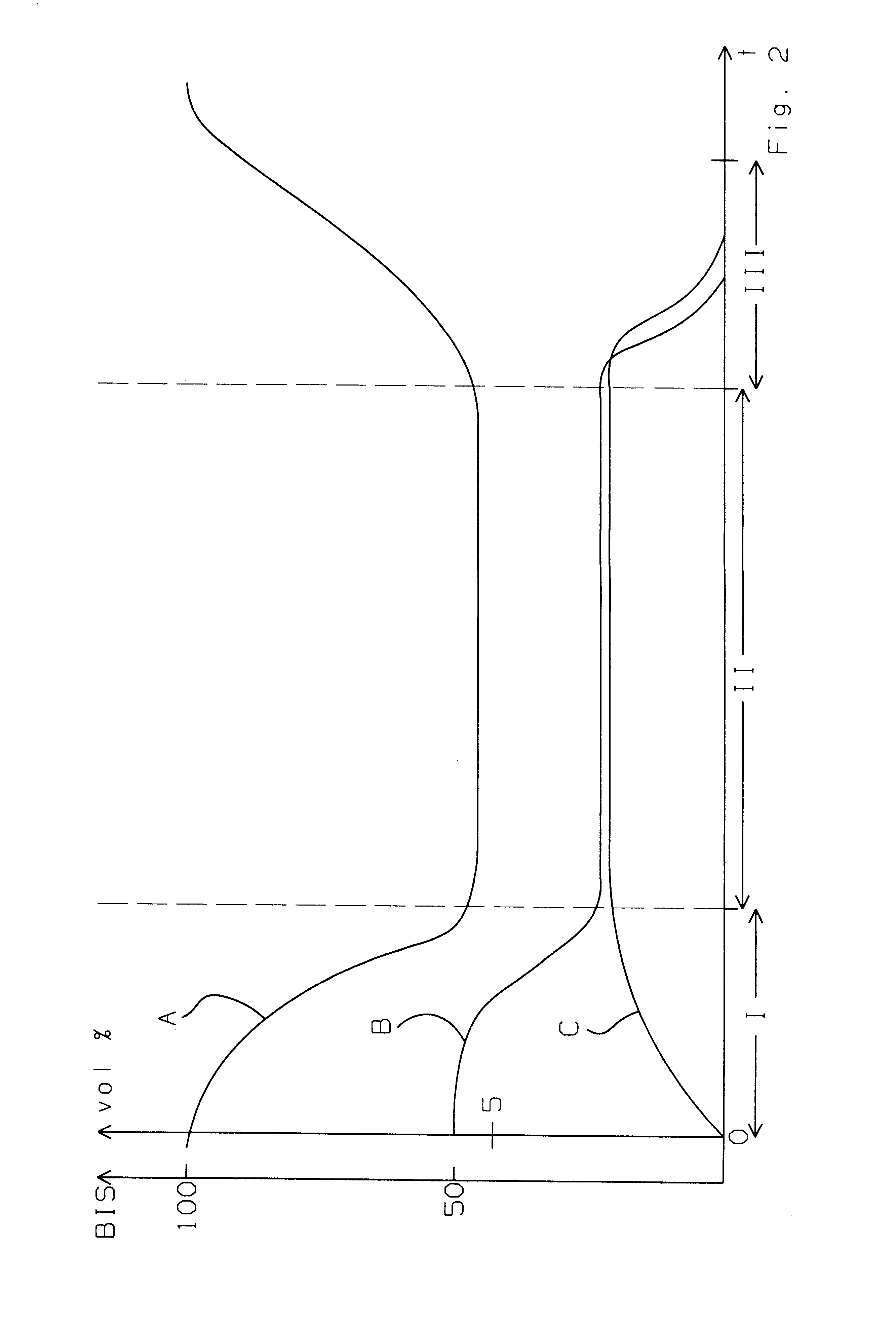
Arrangement and process for controlling a numerical value for patient respiration
An arrangement with a control circuit for controlling a numerical value for patient respiration as well as to a process for controlling the numerical value. The numerical value is controlled on the basis of an evaluation of the EEG (electroencephalogram) of the patient (1) by an EEG sensor (2), e.g., by determining the so-called BIS (bispectral index). A control of the inspiratory gaseous anesthetic concentrations is cascaded to the control of the EEG value in the manner of a cascade circuit. This has the advantage that a metering device (6) belonging to the arrangement meters a gaseous anesthetic mixture directly according to the patient's needs. As an alternative, the control of the numerical value is performed on the basis of an evaluation of the expiratory gaseous anesthetic concentrations resolved for individual breaths at the Y-piece (19) of the respiration circuit (12) by a gaseous anesthetic sensor (8a), preferably an infrared optical gas sensor.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
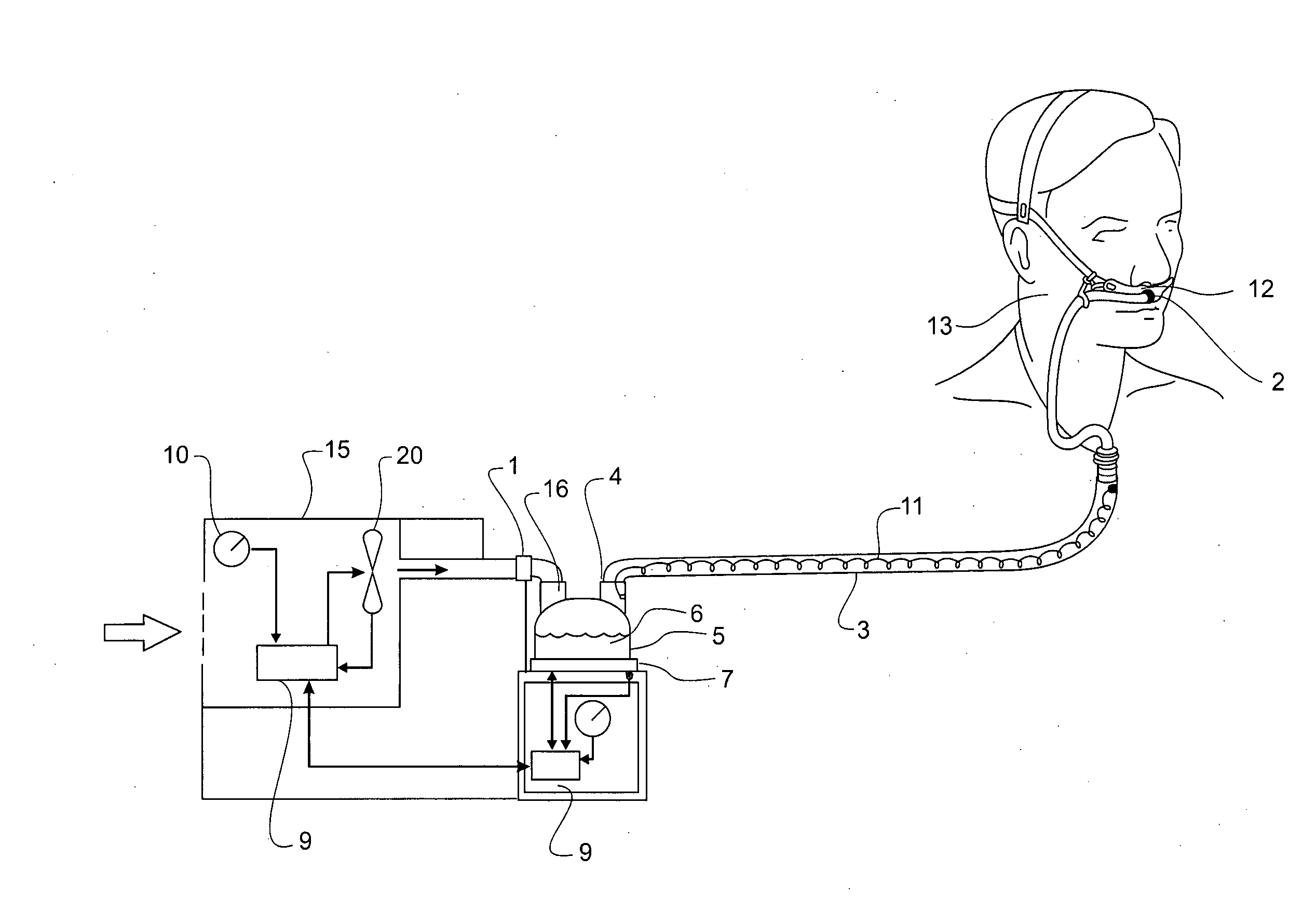
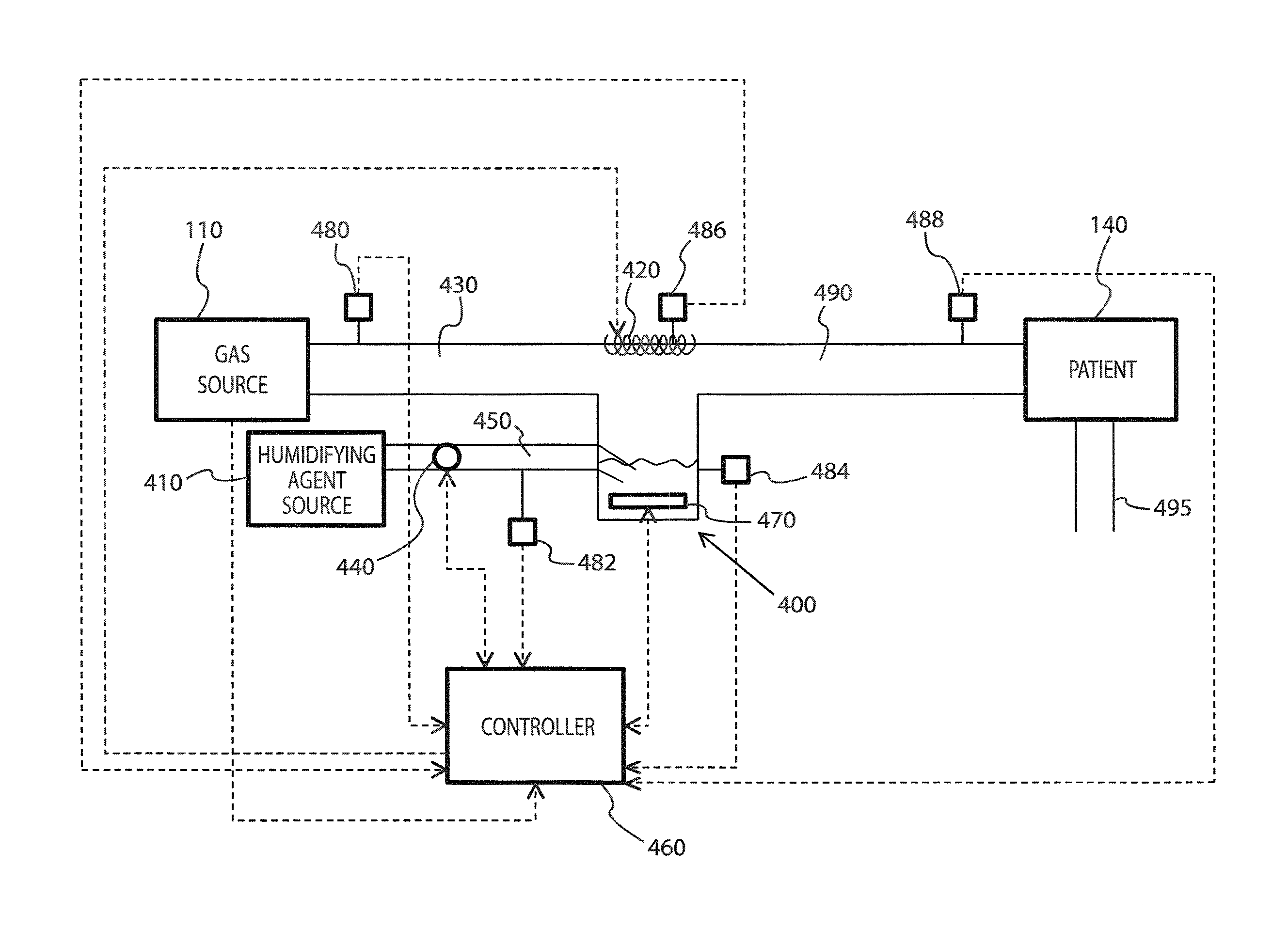
Humidification apparatus having RFID tag sensor at patient end of gas pathway
A breathing circuit for delivering heated, humidified gases to a patient for medical purposes is described, comprising a humidifier chamber holding a quantity of water, a blower unit that delivers a pressurised gases stream to the chamber inlet, and a control system that adjusts output parameters of the breathing circuit, the circuit including a heater plate which heats the water in the chamber so that gases flowing through the chamber become heated and humidified, the circuit also including a gases transportation pathway and patient interface to convey heated humidified gases to a patient, the gases transportation pathway including an RFID tag located at the patient end which senses a parameter of the gases passing through the pathway, the control system including an RFID interrogator interrogating and receiving data relating to the sensed parameter from the RFID tag in real time, and adjusting the output parameters of the breathing circuit accordingly.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
Humidification system
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for reducing condensed humidifying agent in a humidification system by pulsing a delivery of humidifying agent into a respiratory circuit. During a non-pulsed interval, gas flowing through the respiratory circuit will evaporate the condensed humidifying agent present in the respiratory circuit. The present invention also provides a method and apparatus for delivering humidified gas to a patient, wherein the delivery avoids the problems associated with a stationary water humidifier. In the method, the delivery of humidifying agent is precisely controlled to deliver a flow of humidifying agent to a volume of gas.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL CONSUMABLES LLC
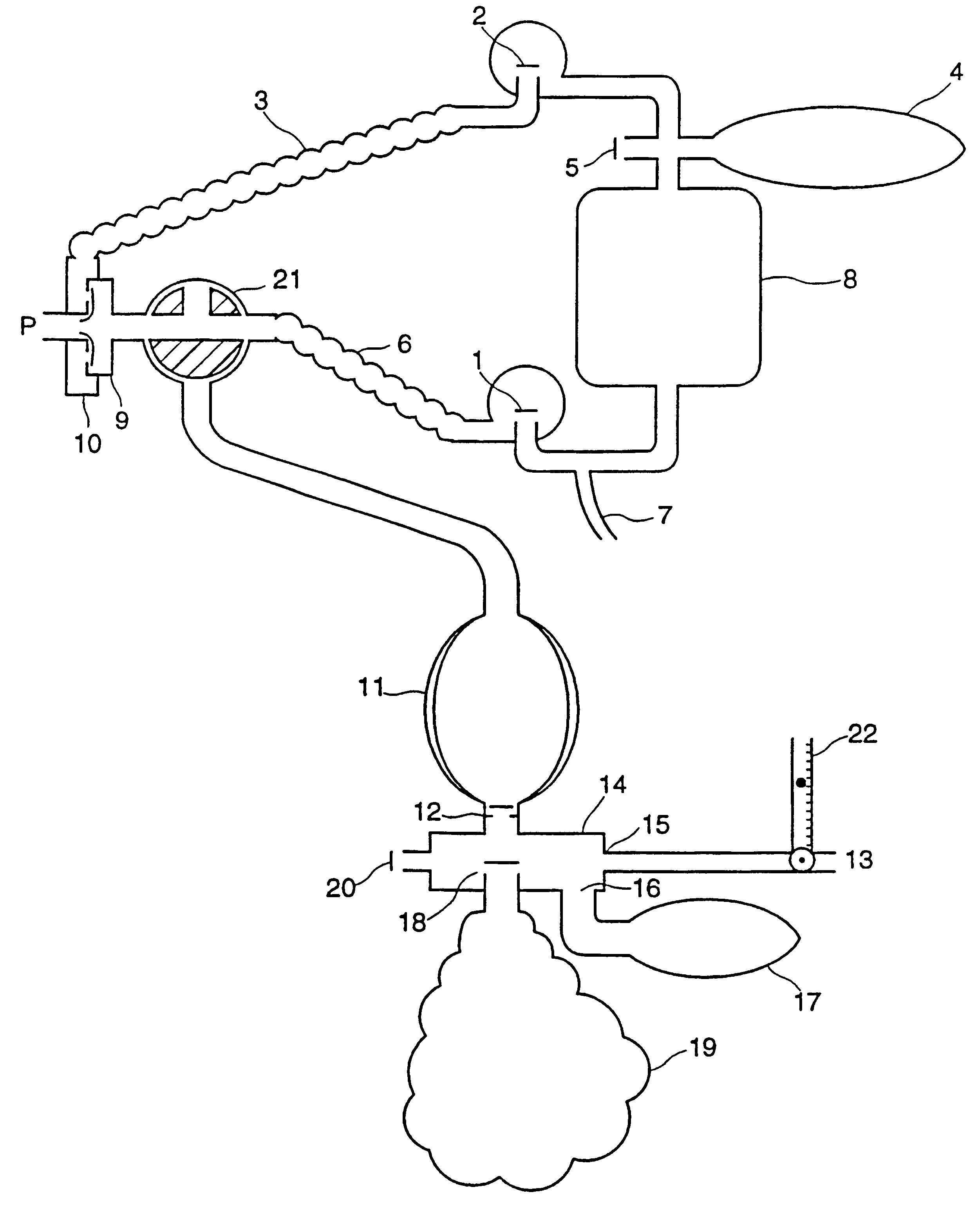
Elimination of vapour anaesthetics from patients after surgical procedures
InactiveUS6354292B1Preventing any perturbationPromote recoveryRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSurgical departmentBreathing circuits
A simple breathing circuit is designed to be added to a standard anesthetic circuit to hasten recovery of patients administered vapor anesthetic prior to an operation and also to method of treatments of a patient to hasten recovery from administration of vapor anesthetic prior to surgical procedures.
Owner:FISHER JOSEPH A
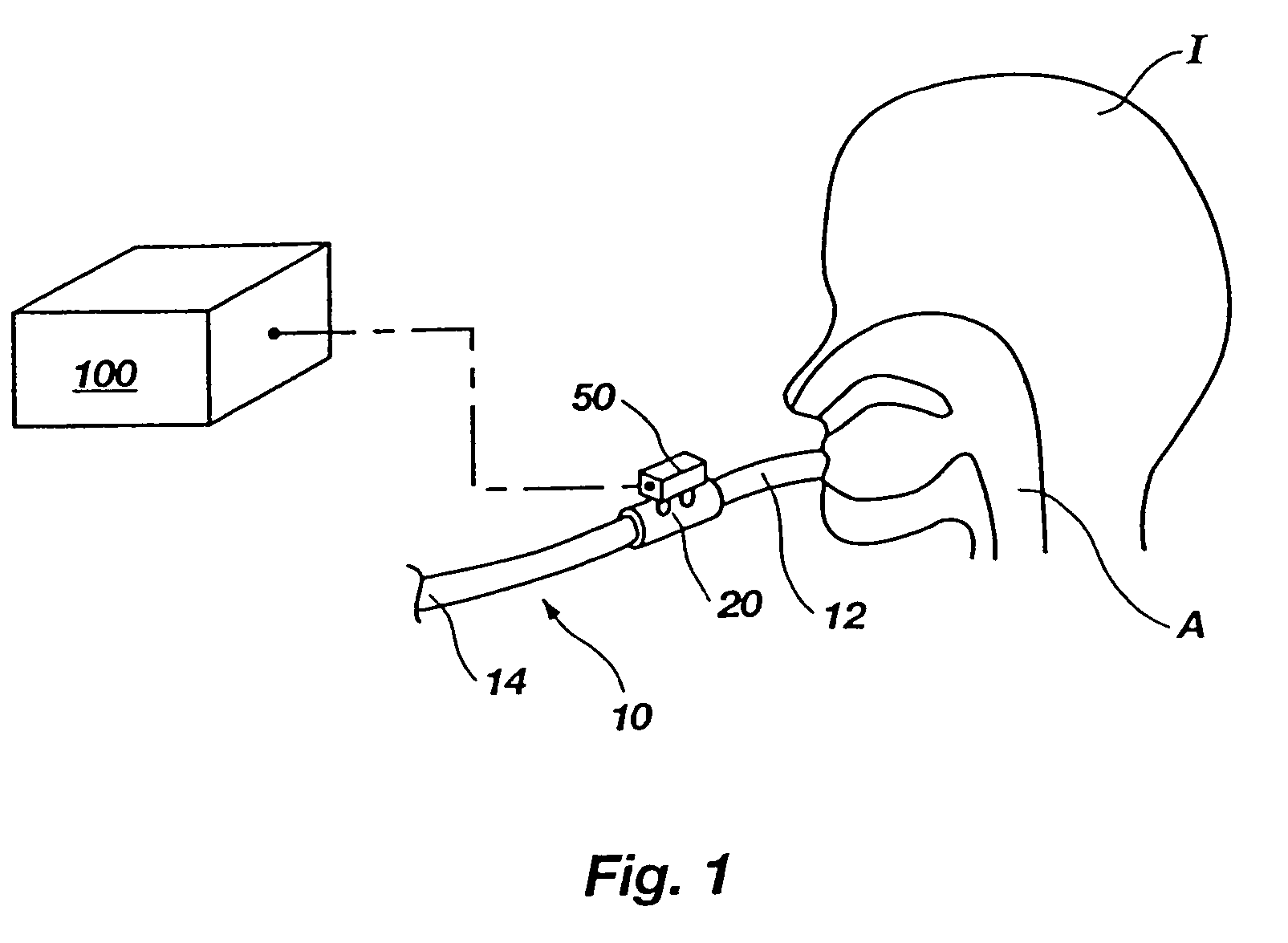
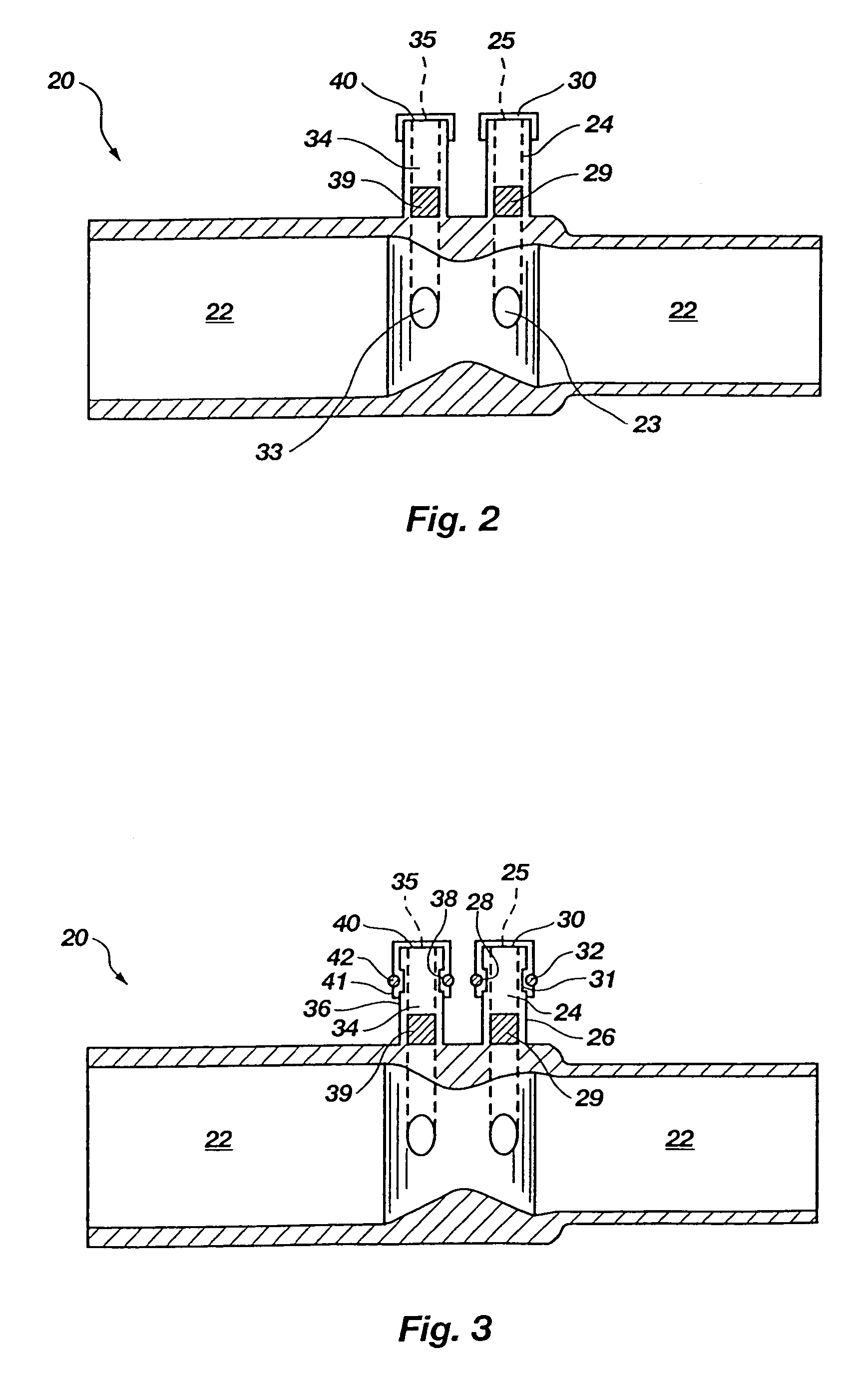
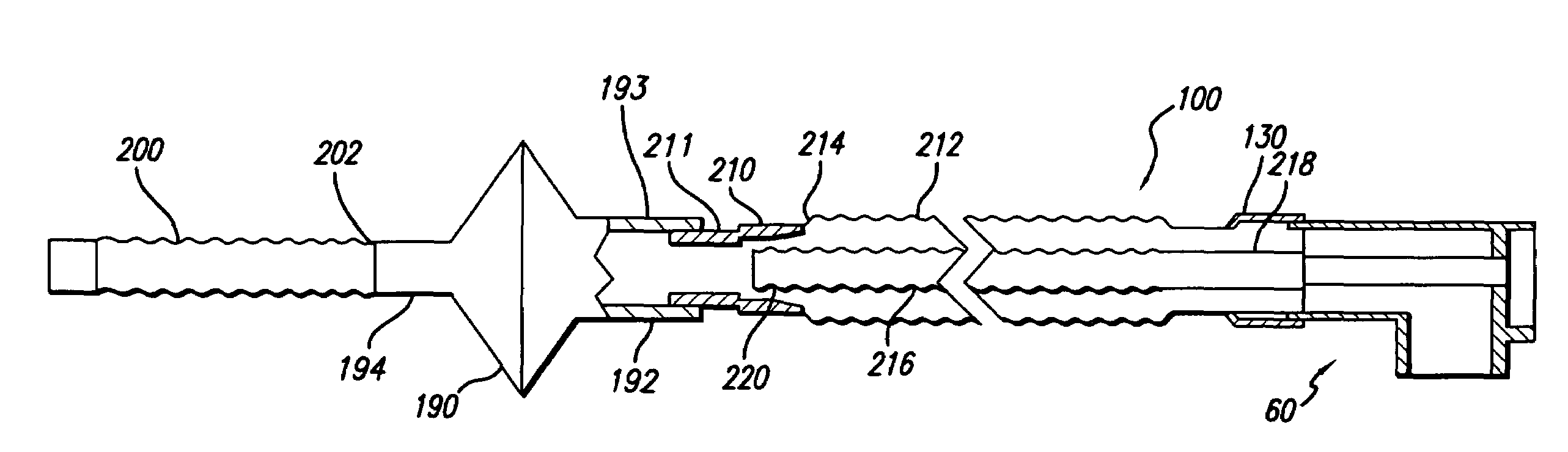
Portable pressure transducer, pneumotach for use therewith, and associated methods
InactiveUS7174789B2Facilitate formation and maintenanceLow costRespiratory organ evaluationFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsAirway adaptorTransducer
A system for sensing respiratory pressure includes a portable pressure transducer configured to be carried by or proximate to a respiratory conduit, such as a breathing circuit or a nasal canula. The portable pressure transducer may removably couple with a pneumotach, in the form of an airway adapter, disposed along the respiratory conduit. The pneumotach may include two pressure ports positioned at opposite sides of an obstruction, which partially blocks flow through a primary conduit of the pneumotach. Corresponding sample conduits of the portable pressure transducer removably couple with the pressure ports. The pressure ports may have sealing elements which are configured to seal against piercing members of the sample conduits upon introduction of the piercing members therethrough. Upon removal of the piercing members, the sealing elements substantially reseal. Methods for using the system are also disclosed.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
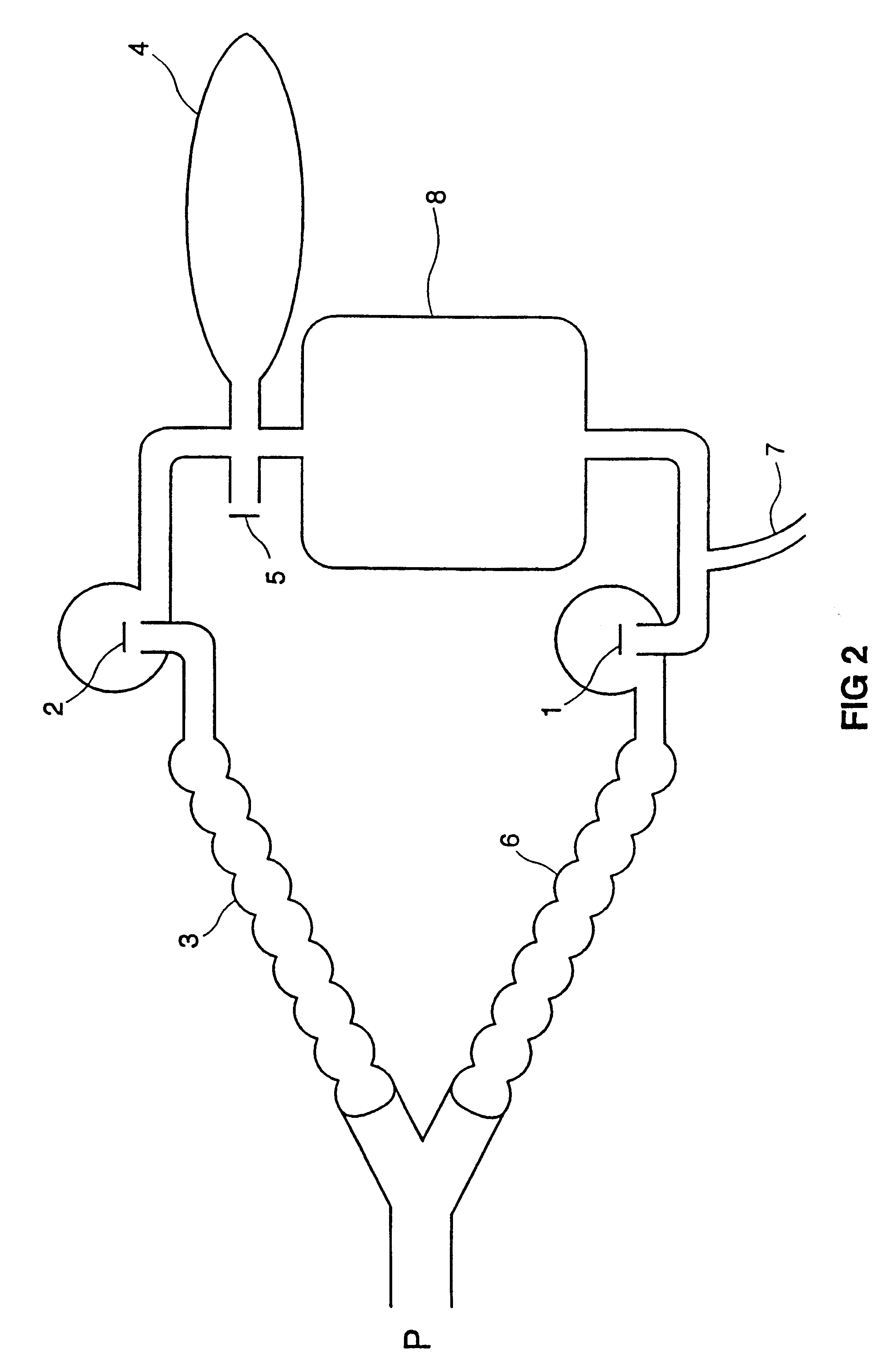
Multilumen unilimb breathing circuit with detachable proximal fitting
InactiveUS7418965B2Avoids hypocapnia and hypoxiaReadily attachableRespiratorsSurgeryAssisted ventilationBreathing circuit tube
Owner:AMBU AS
Integrated ventilator nasal trigger and gas monitoring system
ActiveUS7305988B2Efficient combinationOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksNostrilDifferential pressure
An arrangement and method for detecting spontaneous respiratory effort of a patient receiving ventilatory support by a breathing circuit. The nasal cannula control system includes a nasal cannula assembly having two distinct lumens. A different pressure sensor is positioned to detect the pressure difference between each of the two lumens, thereby determining the differential pressure from within the patient's nostrils and within a breathing mask. The nasal cannula control system includes a gas sampling system such that the amount of a monitored gas discharged or exhaled by the patient can be monitored using the same nasal cannula assembly used to generate the differential pressure signal.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Limb for breathing circuit
A limb for a breathing circuit manufactured from very thin walled polymer materials has an elongate axial reinforcing spine lying freely inside the conduit and fixed to each end connector. The spine is laterally compliant but axially stiff. The spine provides resistance to tensile and compressive loads on the conduit, including that induced by prevailing internal pressures.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
Film welded reservoir bag for breathing circuit and method of making the same
A pulmonarily sized bag formed of a non-latex material, including a bag body formed of panels of resin film material welded to one another along a weld line defining a seam of the bag body bounding an interior volume of the bag. The seam includes an interior seam portion in the interior volume, and an exterior seam portion at an exterior surface of the bag. One of the interior seam portion and exterior seam portion comprises free edges of the seam, and the other one of such seam portions is devoid of free edges. The bag is formable by various techniques, including radio frequency welding, impulse heating, solvent bonding, etc., and is usefully employed in a breathing circuit to obviate the necessity of using latex breathing bags.
Owner:POLYZEN INC
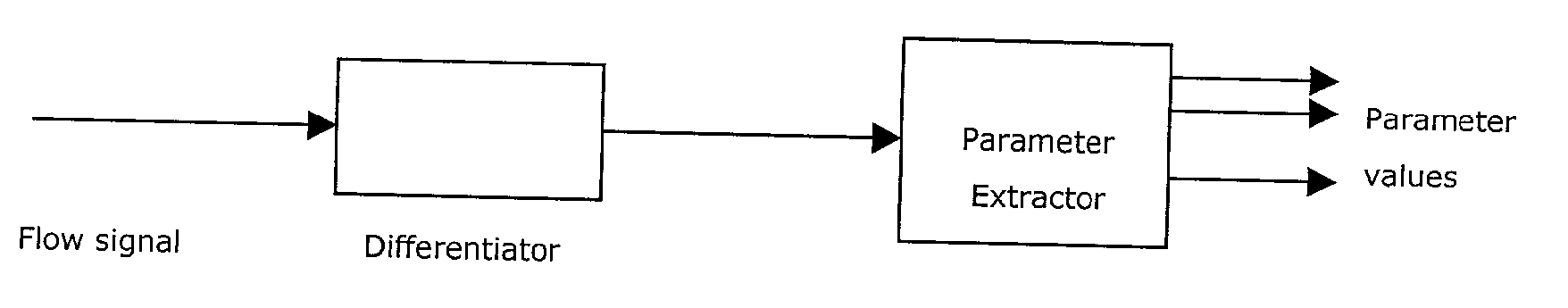
Auto CPAP
InactiveUS20030000528A1Simple methodRespiratorsMedical data miningSleep disordered breathingBreathing gas
A method for the detection and treatment of disordered breathing during sleep employs an artificial neural network (ANN) in which data related to breathing gas flow are analyzed. A respiratory circuit is established by connecting the patient to a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) system with pressurized breathing gas supply, the gas flow in the circuit is periodically sampled, one or several cepstrum parameters distinctive of various breathing patterns are periodically calculated; the parameter values are periodically fed to an ANN trained to recognize breathing patterns characteristic of sleep disordered breathing and are analyzed in the network, the CPAP pressurized breathing gas supply is controlled in response to the ANN output. Also disclosed is a corresponding apparatus.
Owner:BREAS MEDICAL
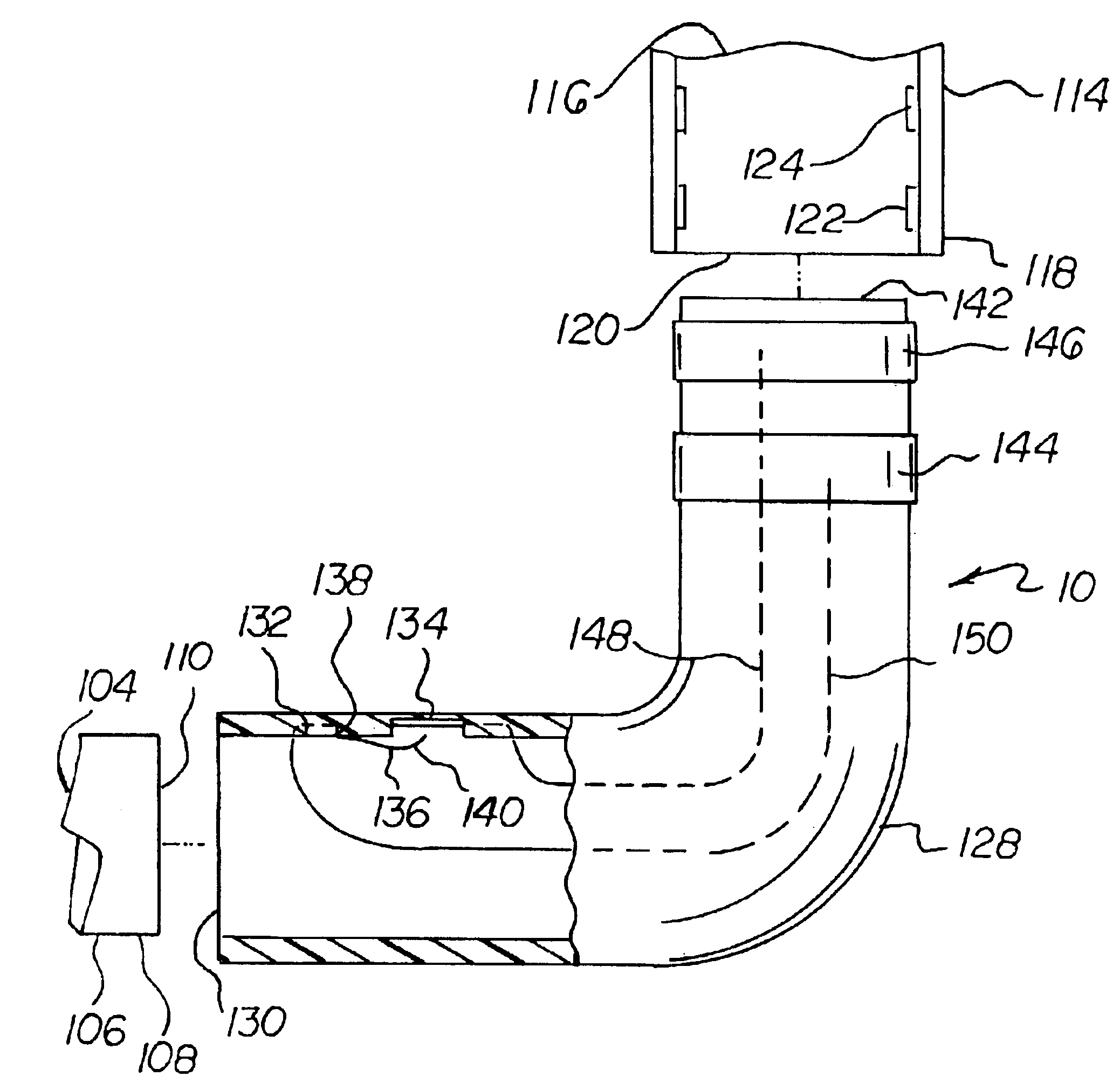
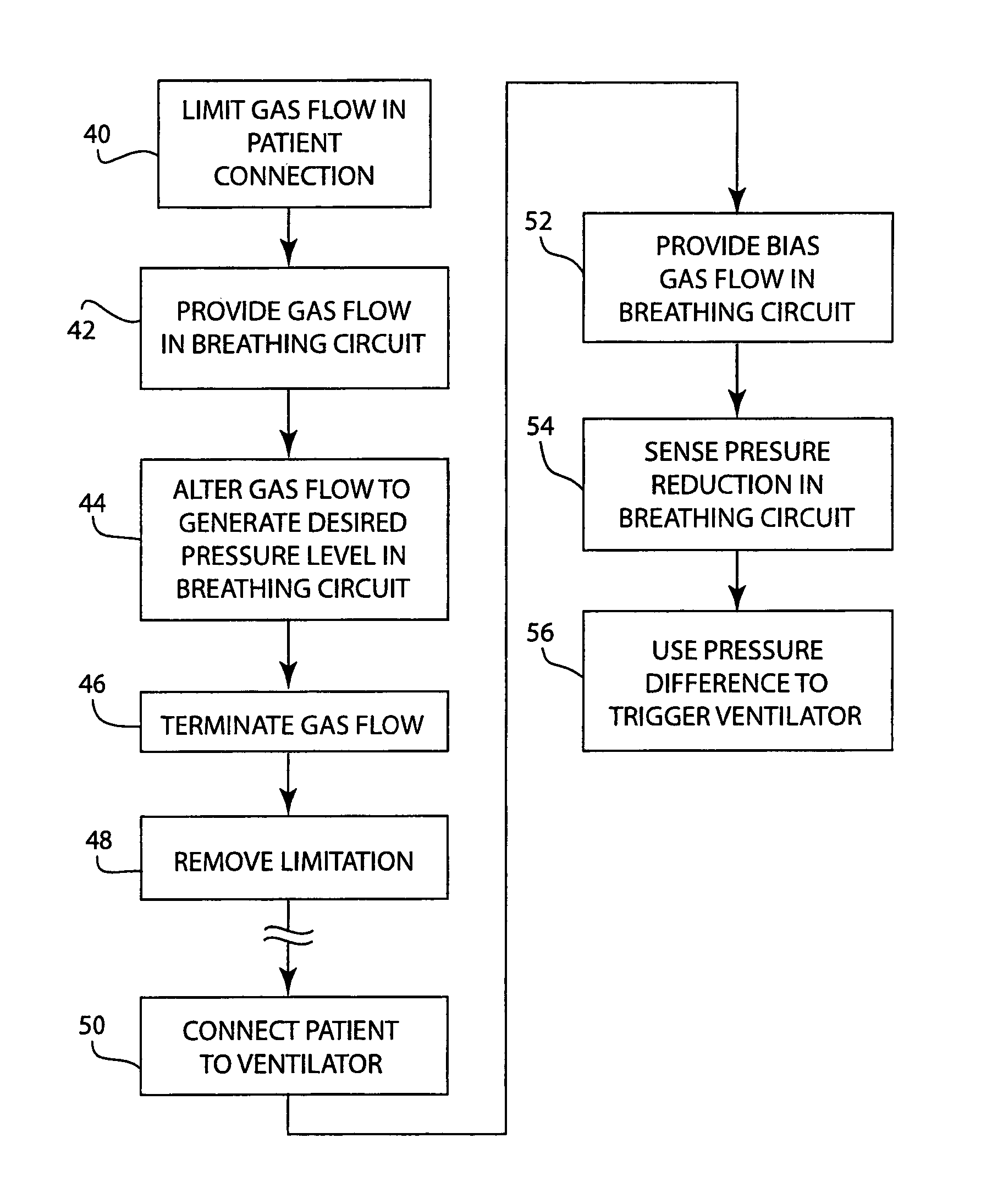
Method for use with the pressure triggering of medical ventilators
ActiveUS7347205B2High sensitivityDesign economyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInhalationAssisted breathing
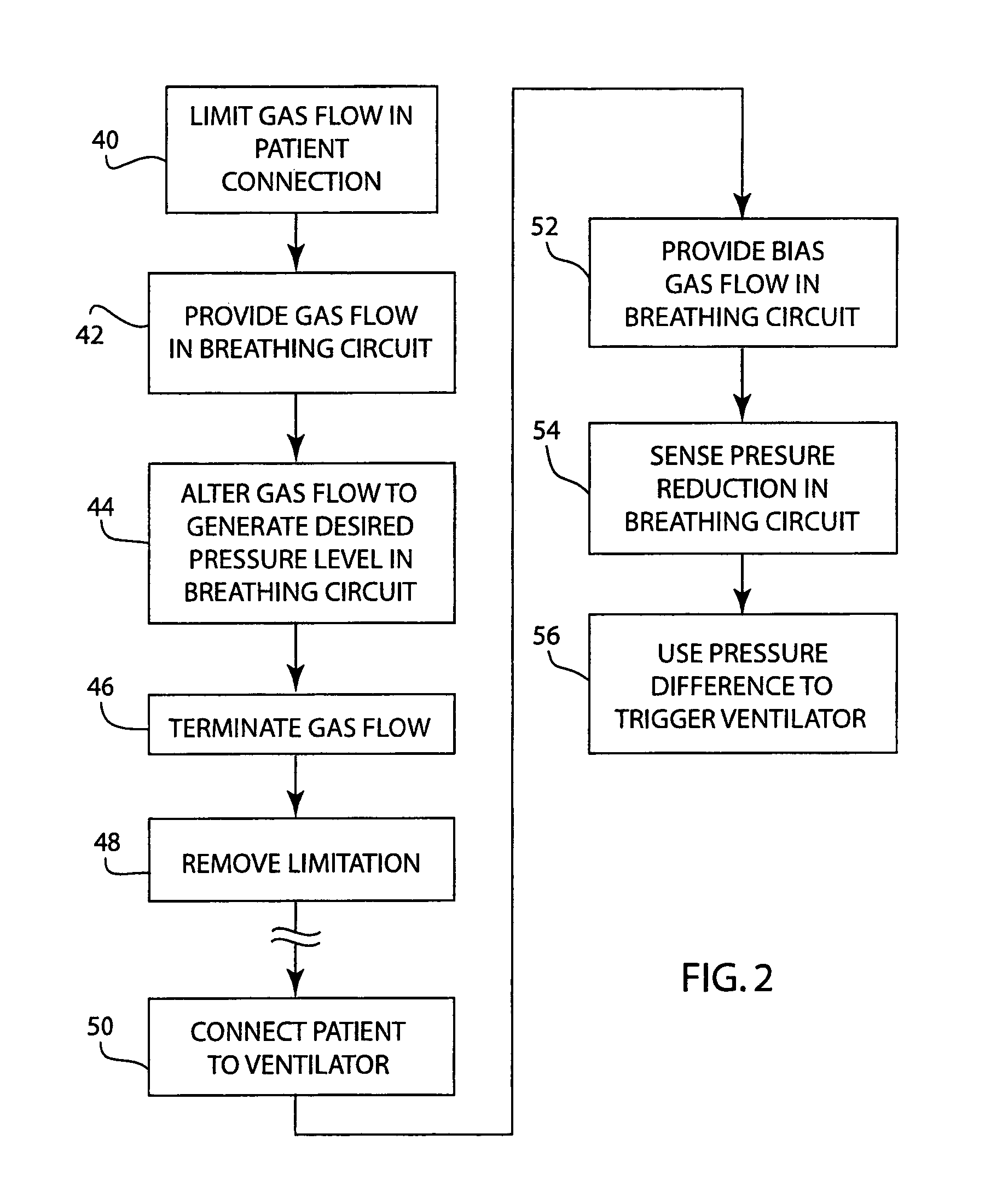
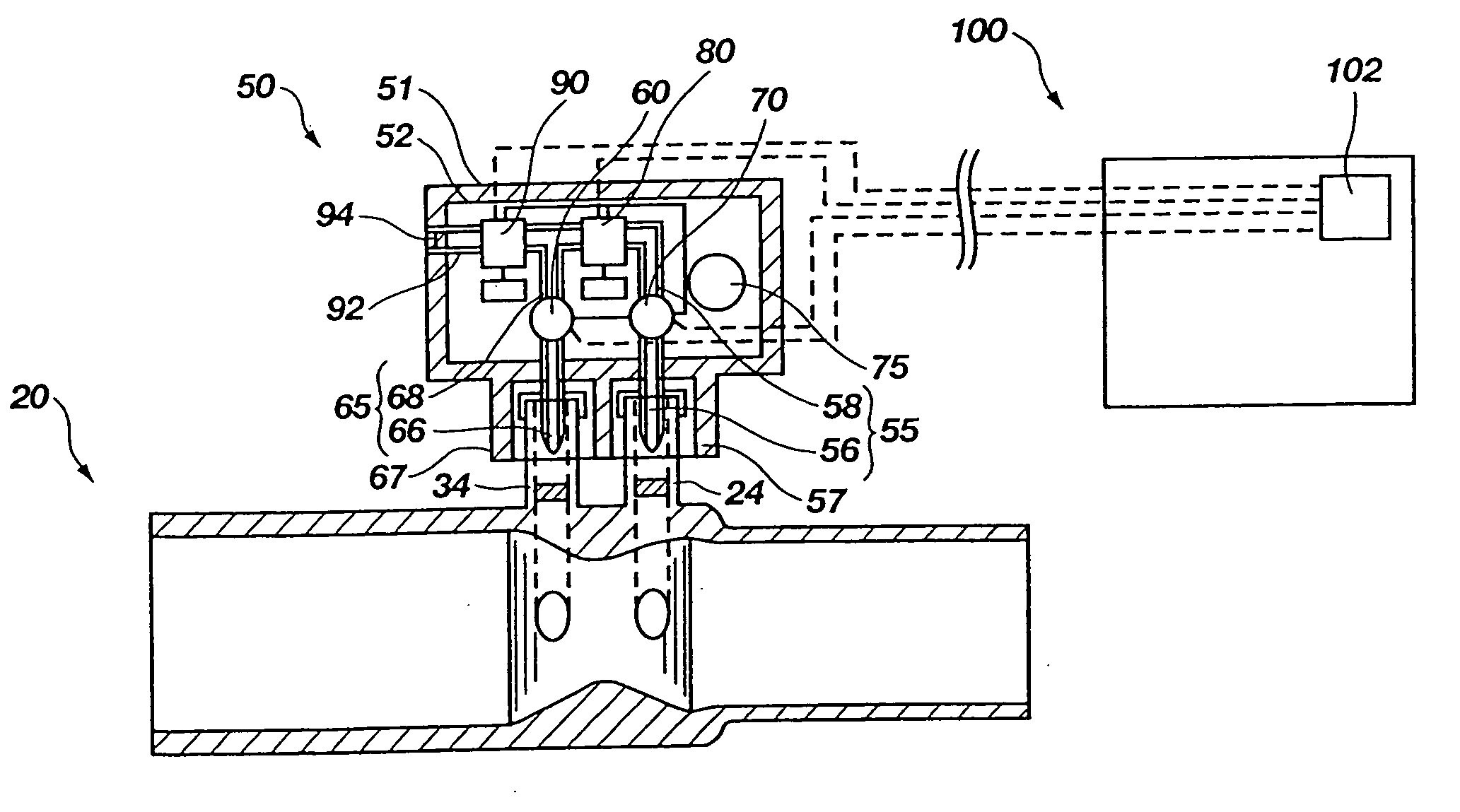
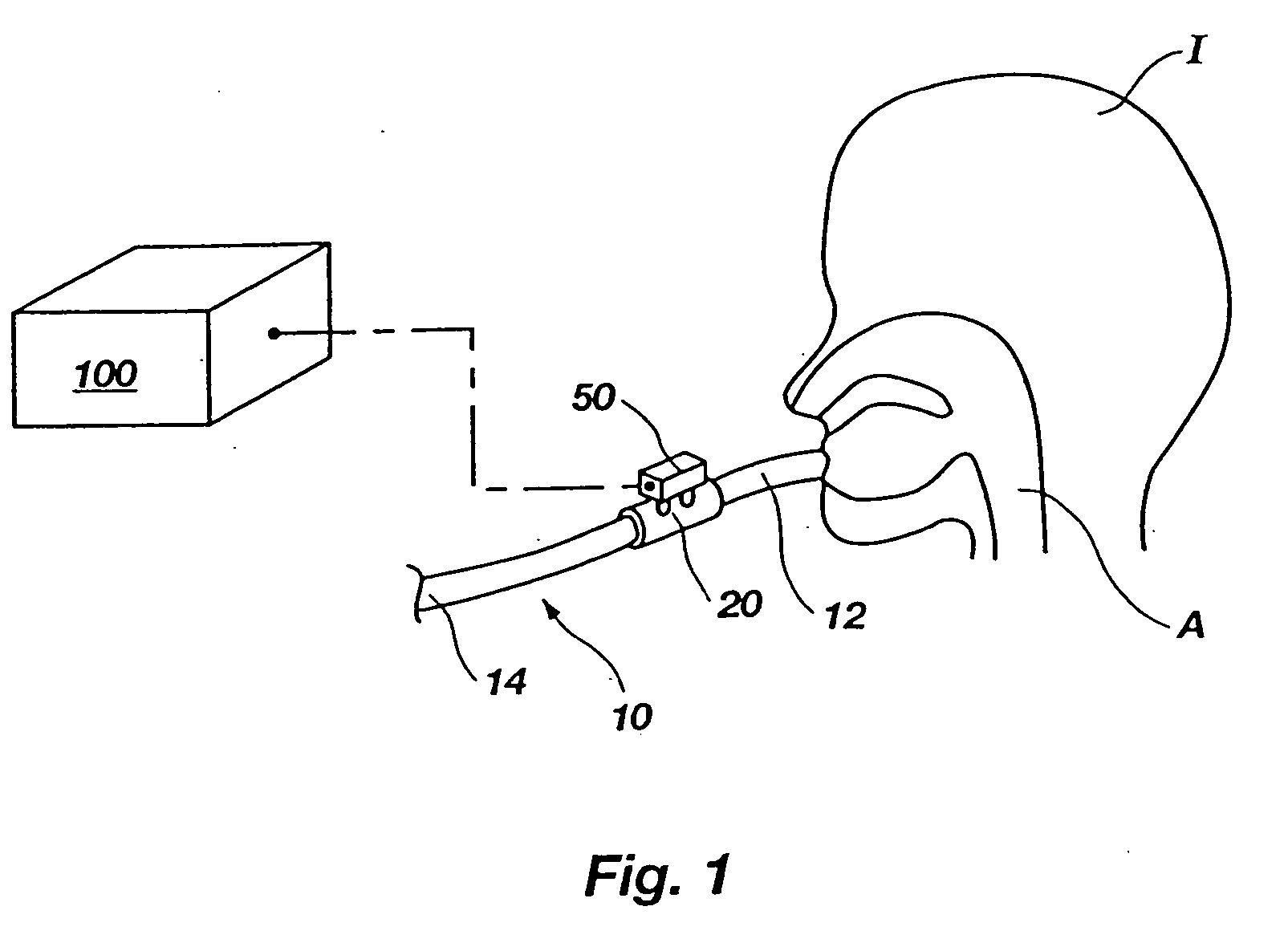
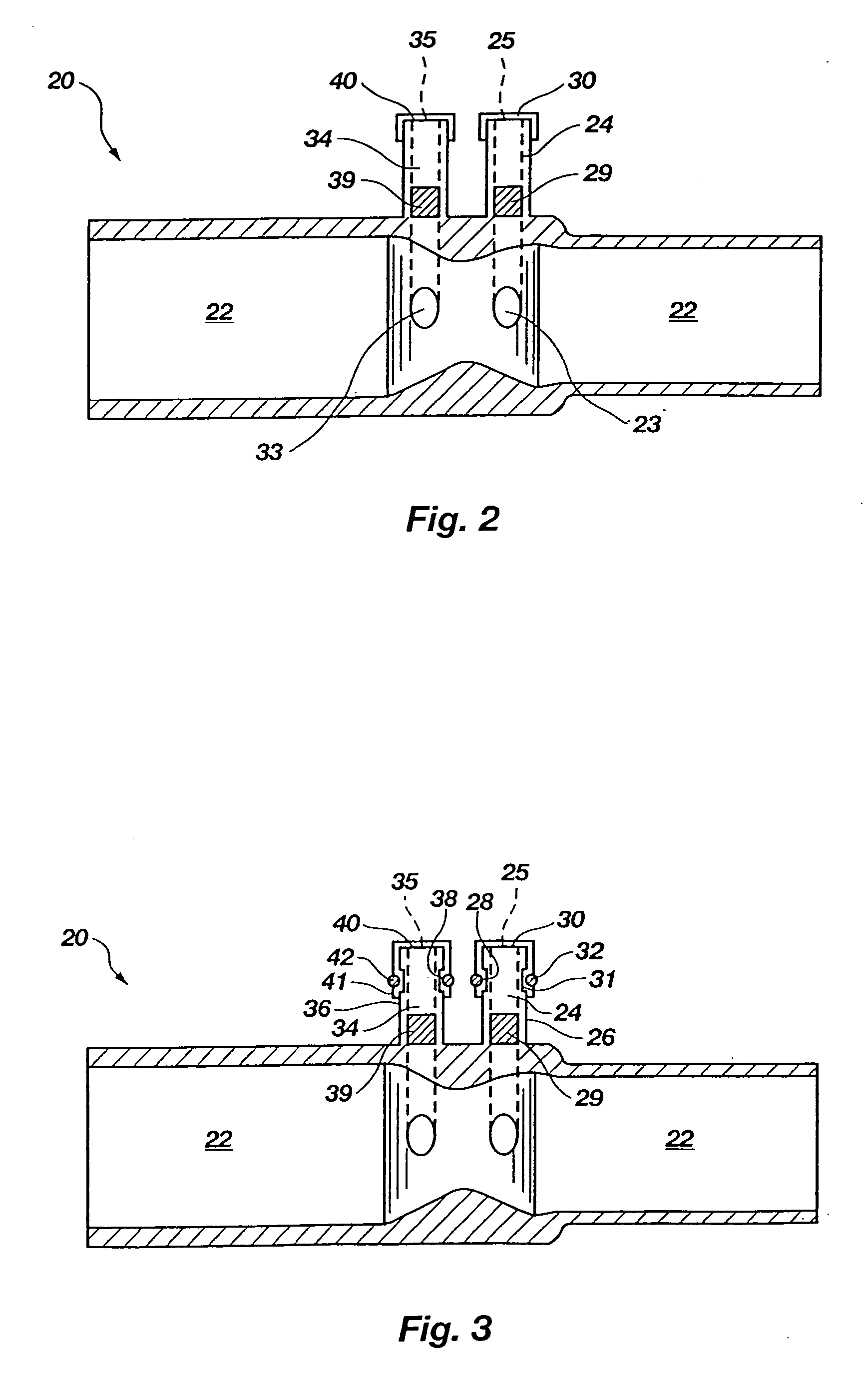
A method for providing a pressure reference level for pressure triggering a ventilator responsive to a spontaneous breathing attempt by a patient. In the method, the patient connection of the breathing circuit is capped or plugged. A gas flow is then provided through the breathing circuit and is altered to an amount that causes the flow resistance properties of the breathing circuit to generate a desired gas pressure in the breathing circuit suitable for use as a reference pressure by the ventilator for pressure responsive triggering. During the operation of the ventilator, gas flow in a corresponding amount serves as a bias flow in the breathing circuit to assist breathing by the patient. The bias flow also generates the reference pressure level in the breathing circuit. A reduction in pressure from the pressure level resulting from inhalation by the patient triggers the operation of the ventilator.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Portable pressure transducer, pneumotach for use therewith, and associated methods
InactiveUS20060117856A1Facilitate formation and maintenanceLow costRespiratory organ evaluationFluid pressure measurement by mechanical elementsAirway adaptorTransducer
A system for sensing respiratory pressure includes a portable pressure transducer configured to be carried by or proximate to a respiratory conduit, such as a breathing circuit or a nasal canula. The portable pressure transducer may removably couple with a pneumotach, in the form of an airway adapter, disposed along the respiratory conduit. The pneumotach may include two pressure ports positioned at opposite sides of an obstruction, which partially blocks flow through a primary conduit of the pneumotach. Corresponding sample conduits of the portable pressure transducer removably couple with the pressure ports. The pressure ports may have sealing elements which are configured to seal against piercing members of the sample conduits upon introduction of the piercing members therethrough. Upon removal of the piercing members, the sealing elements substantially reseal. Methods for using the system are also disclosed.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Breathing assistance apparatus
A mouthpiece for oral delivery for oral delivery of CPAP treatment has a vestibular shield for location between the teeth and lips / cheeks of a wearer. The vestibular shield is formed from a very supple material and is dimensioned to extend laterally into the buccal vestibule and vertically to overlap the gums. A gases pathway is provided through the vestibular shield and may include a hard plastic insert through the shield. A connection for connecting the mouthpiece to a breathing circuit is provided which reduces the transfer of forces caused by movement therebetween.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
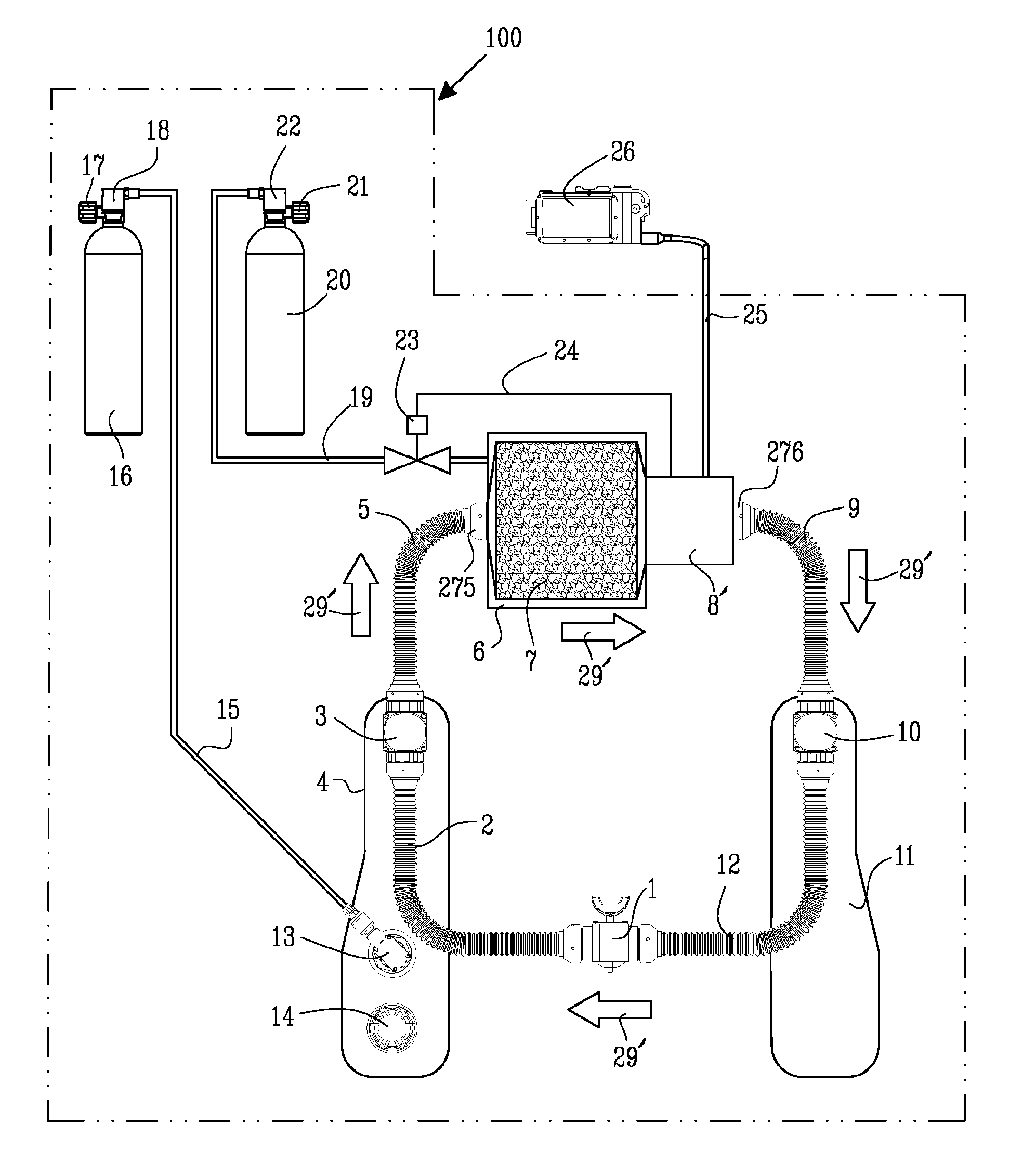
Oxygen control in breathing apparatus
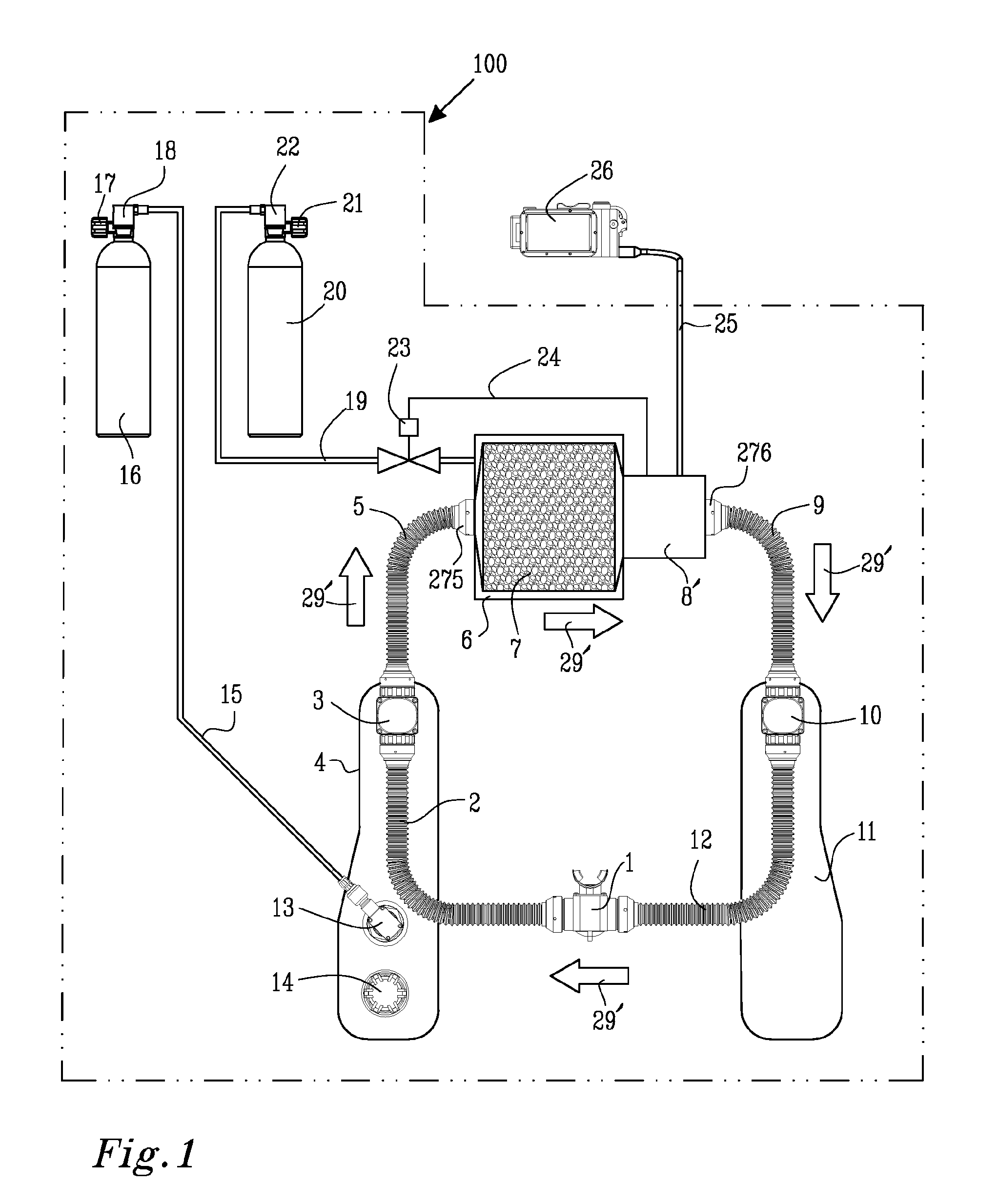
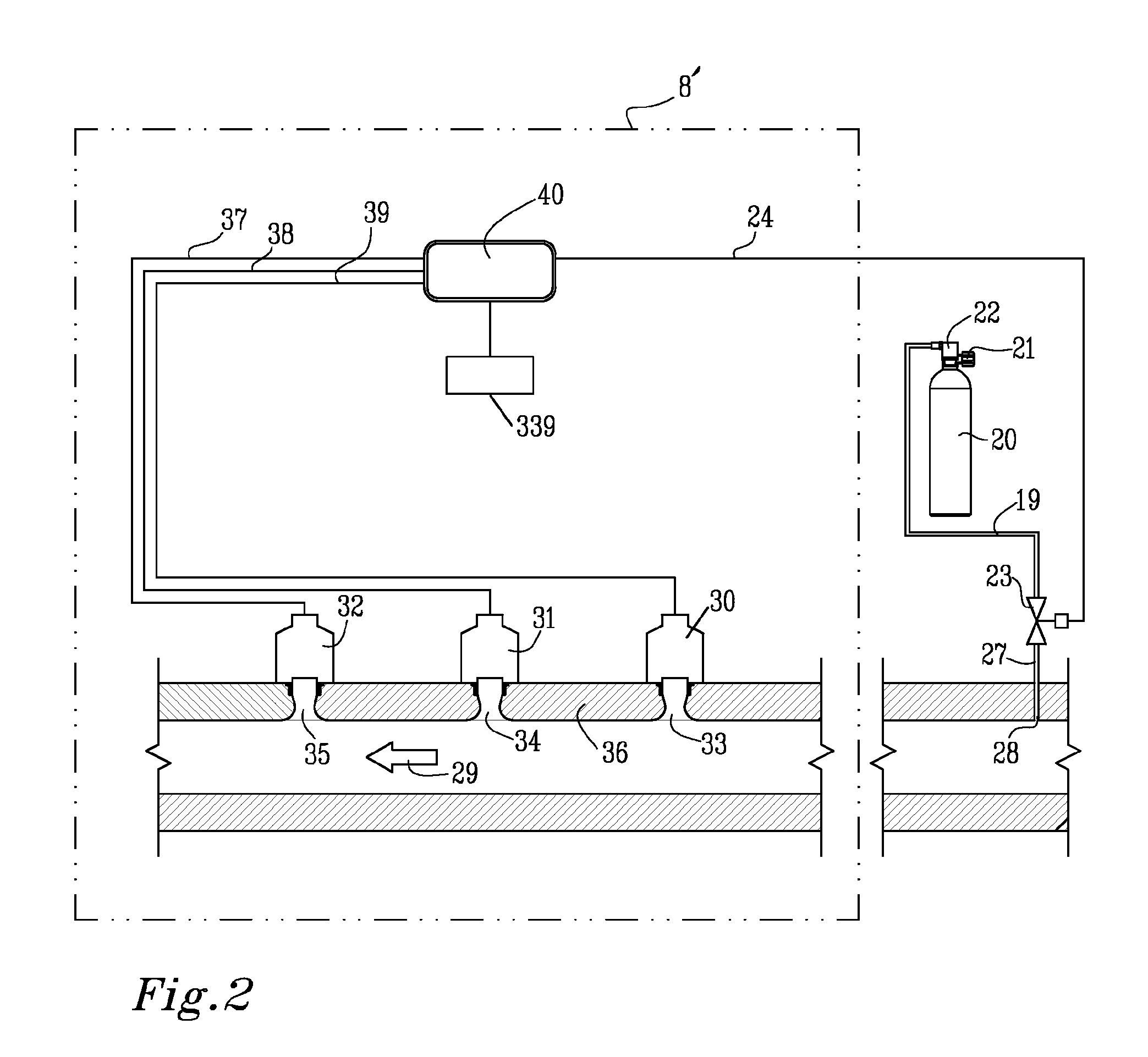
ActiveUS20110041848A1Poor condensation purgeNegligible impactRespiratorsMedical devicesTest channelOxygen sensor
The invention is directed to an oxygen sensor arrangement 8 for sensing the oxygen in a breathing loop 29 of a breathing apparatus 100. The sensor arrangement 8 comprises at least one primary oxygen sensor 30 arranged to operatively measure the oxygen in the breathing loop 29, and a control arrangement 40 for obtaining measures from said oxygen sensor. A test channel arrangement 15, 362 is adapted to operatively provide a first gas having a first fraction of oxygen from a first supply 20 to said primary oxygen sensor 30 at a position 267 adjacent to or directly adjacent to said primary oxygen sensor. A first test valve arrangement 41 is arranged to operatively open and close the flow of said first gas through said test channel arrangement 15, 362. Said a control arrangement 40 is arranged to operatively actuate said first test valve arrangement 41 so as to provide an amount of said first gas to said primary oxygen sensor 30 via said test channel arrangement 15, 362.
Owner:POSEIDON DIVING SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com