Patents
Literature
270 results about "Tidal volume" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
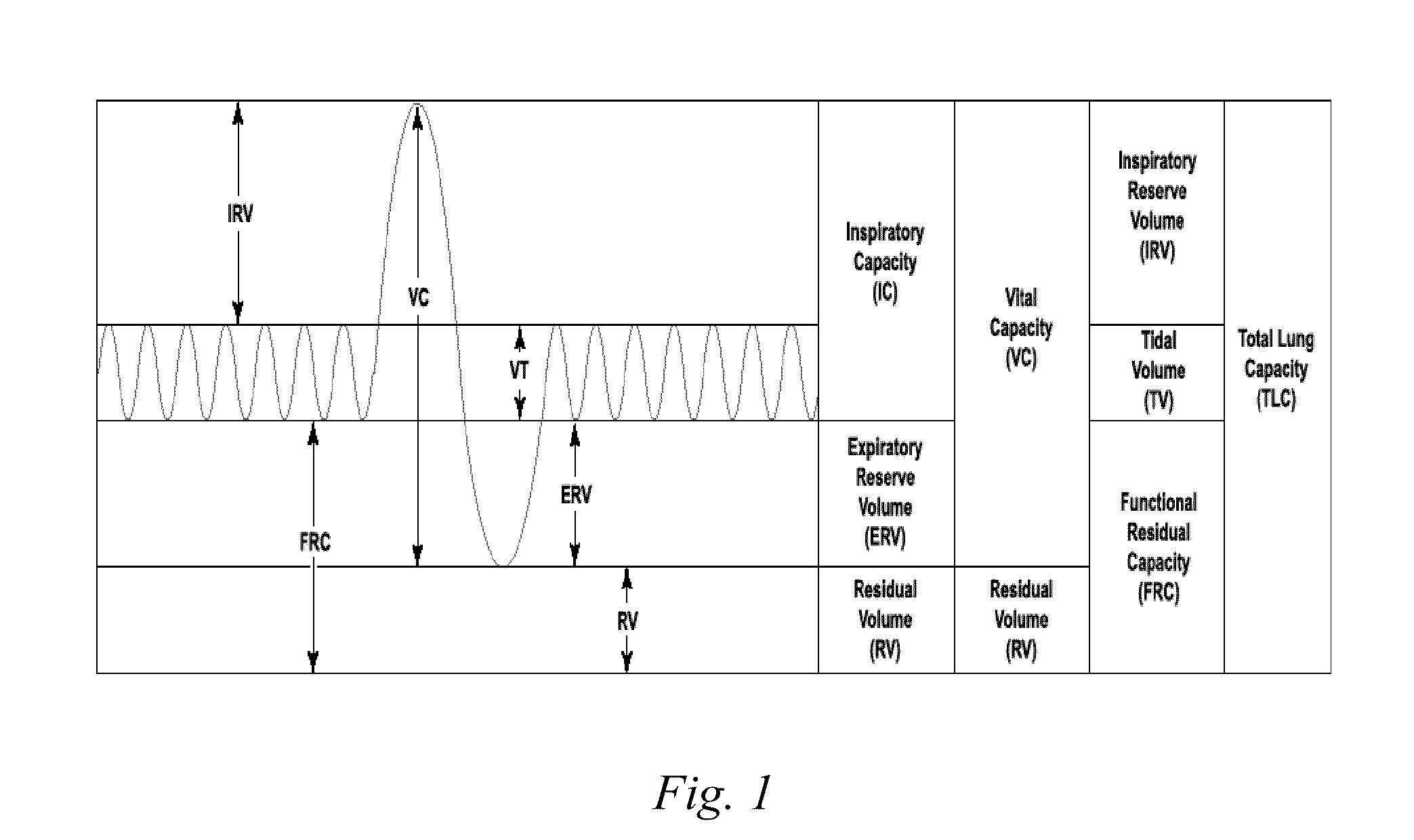
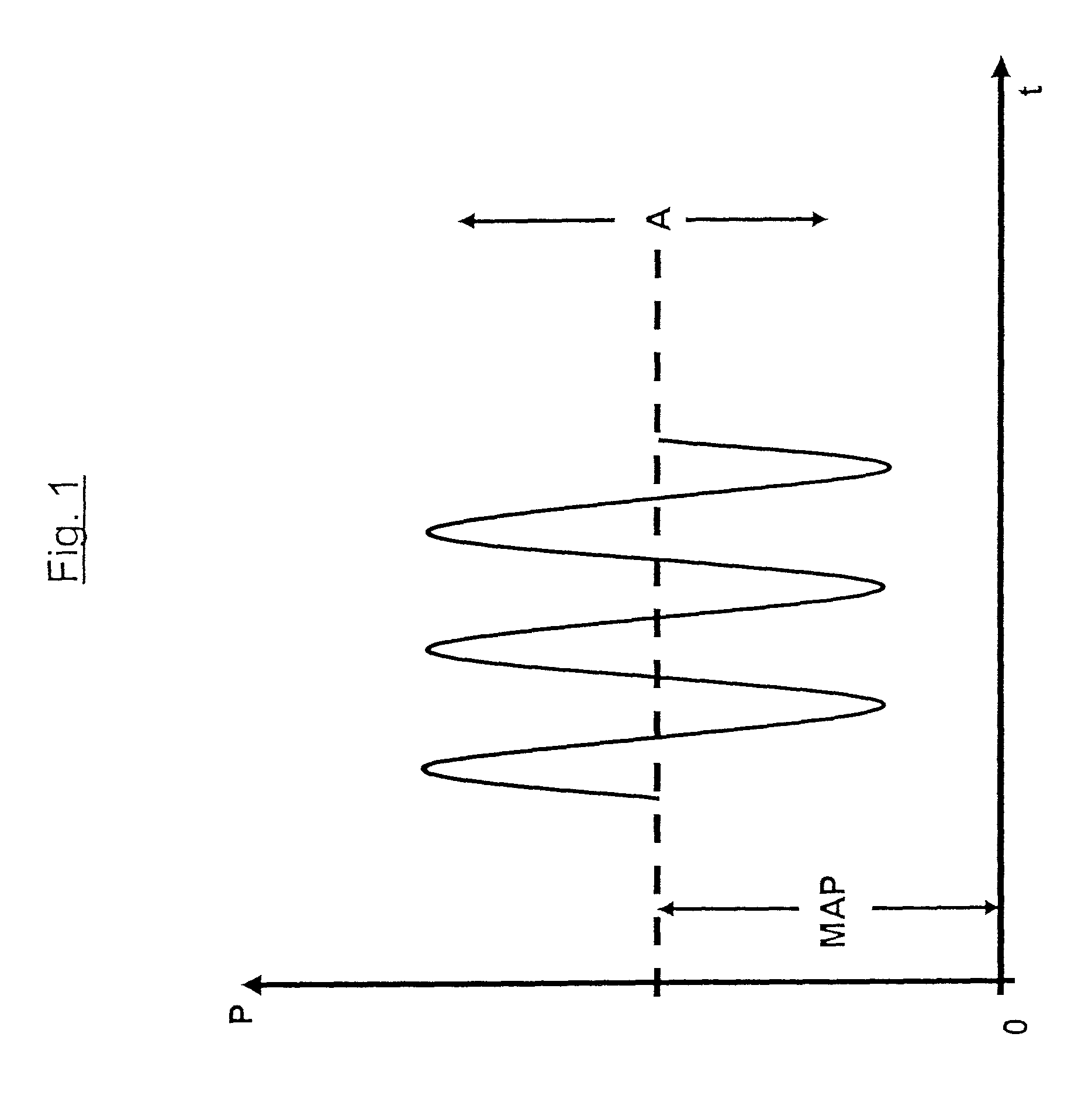
Tidal volume (symbol VT or TV) is the lung volume representing the normal volume of air displaced between normal inhalation and exhalation when extra effort is not applied. In a healthy, young human adult, tidal volume is approximately 500 mL per inspiration or 7 mL/kg of body mass.
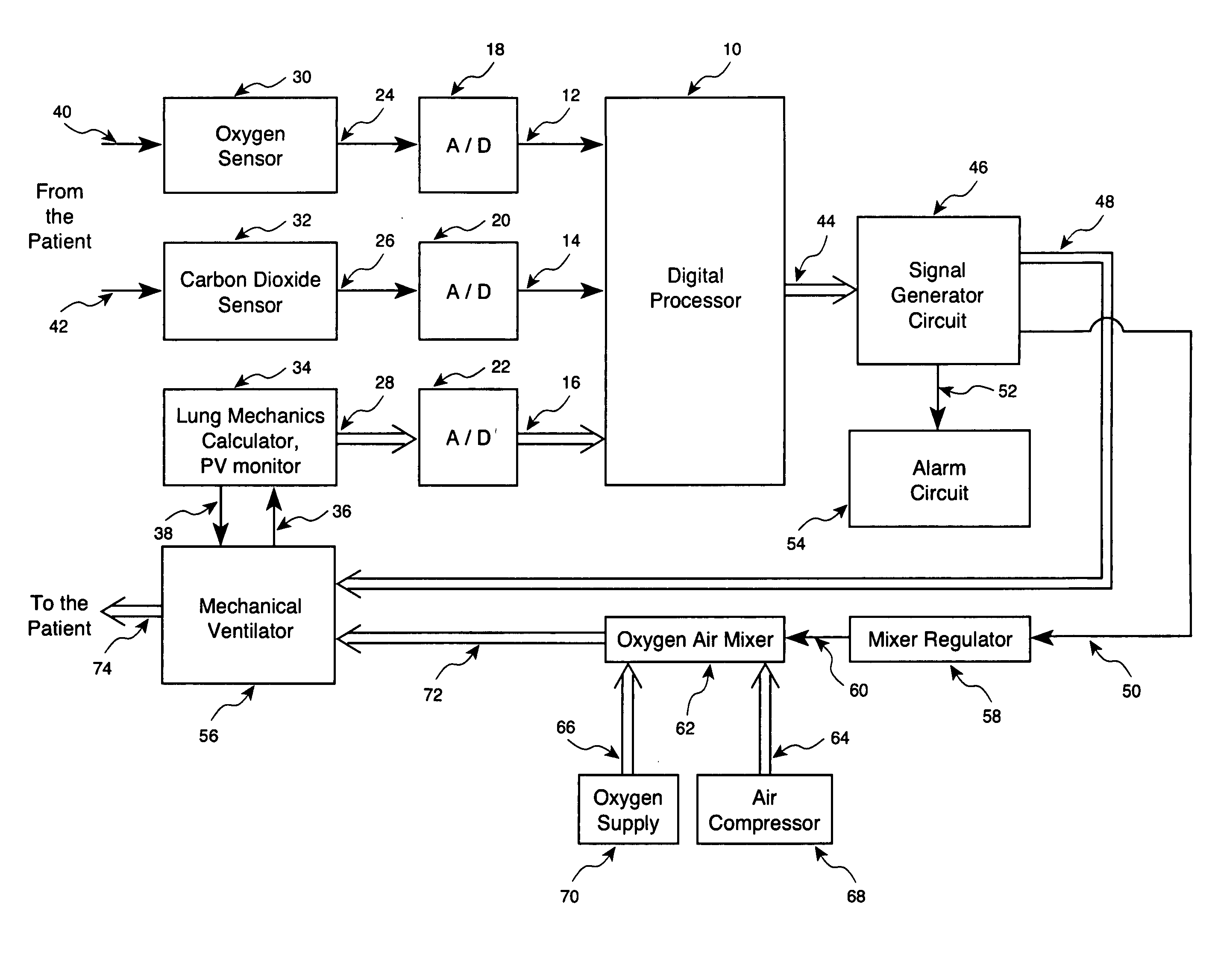
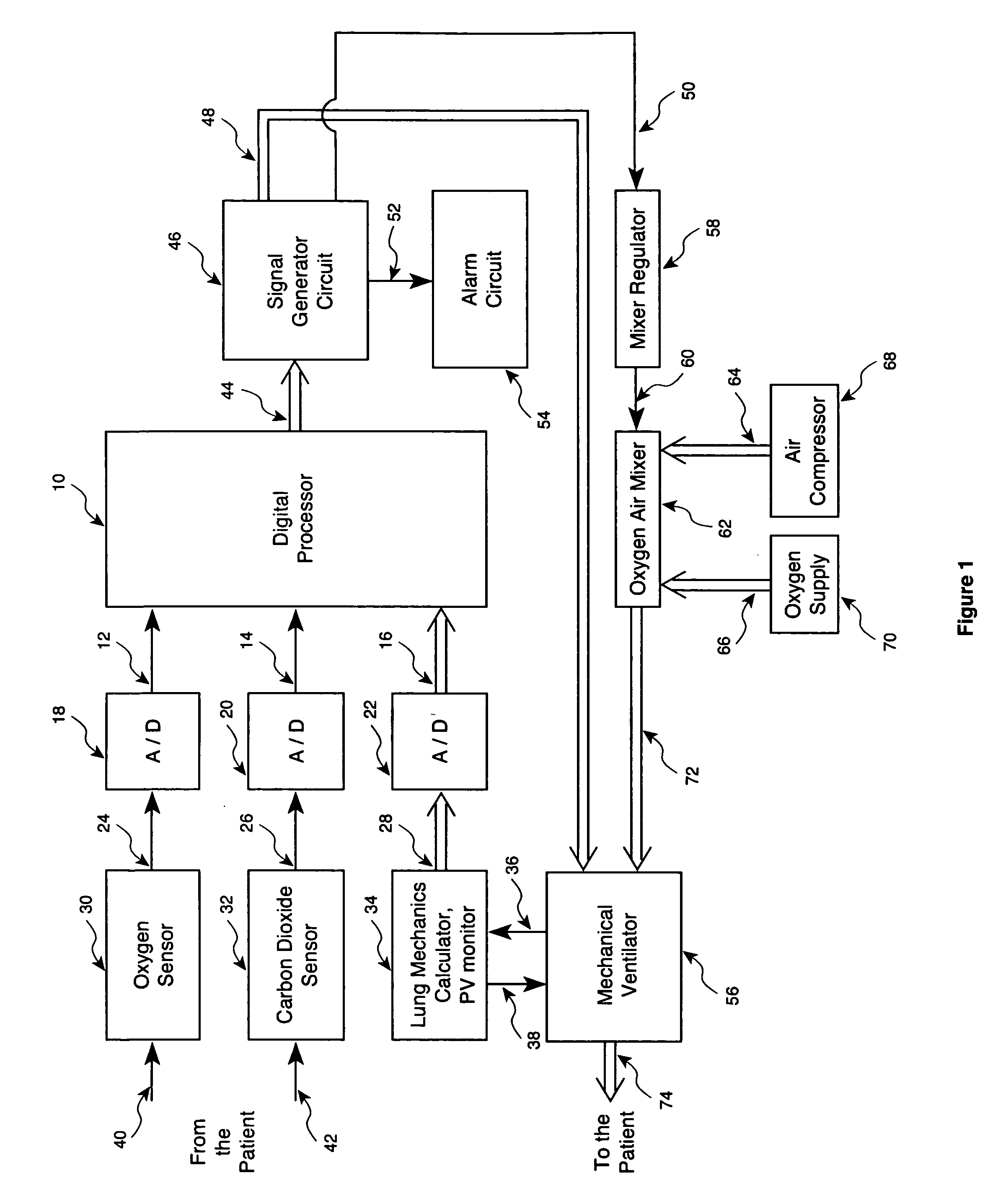
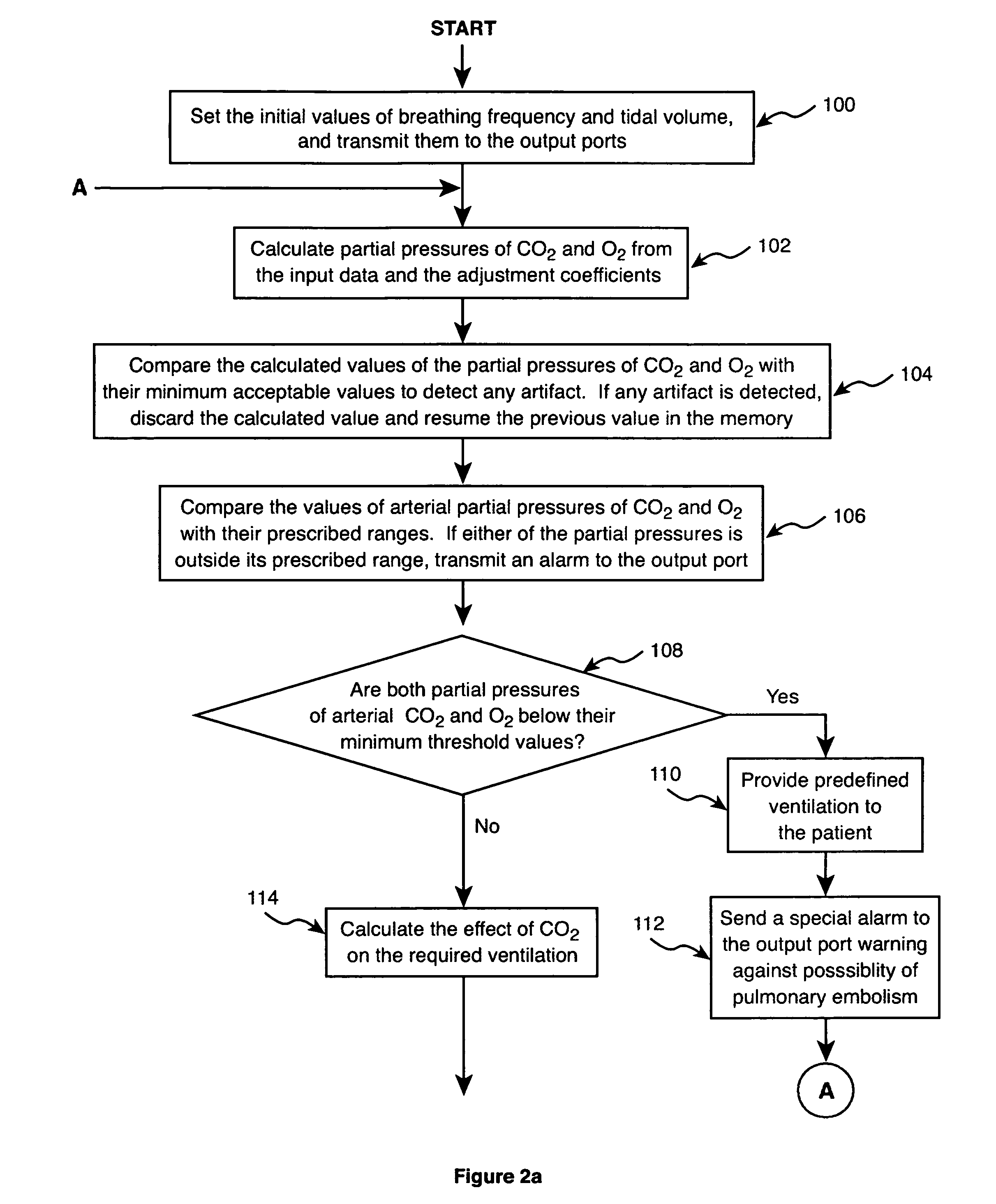
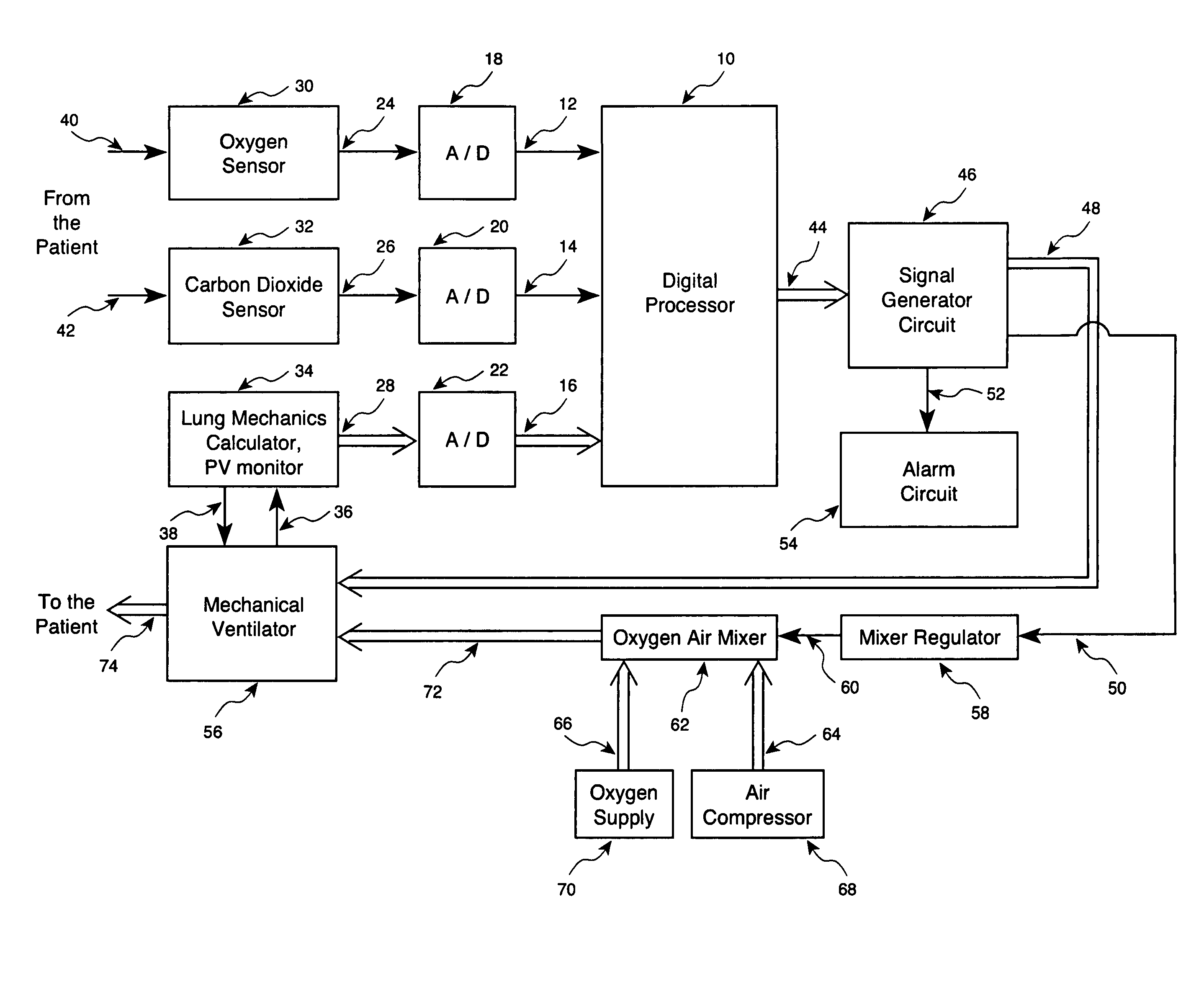
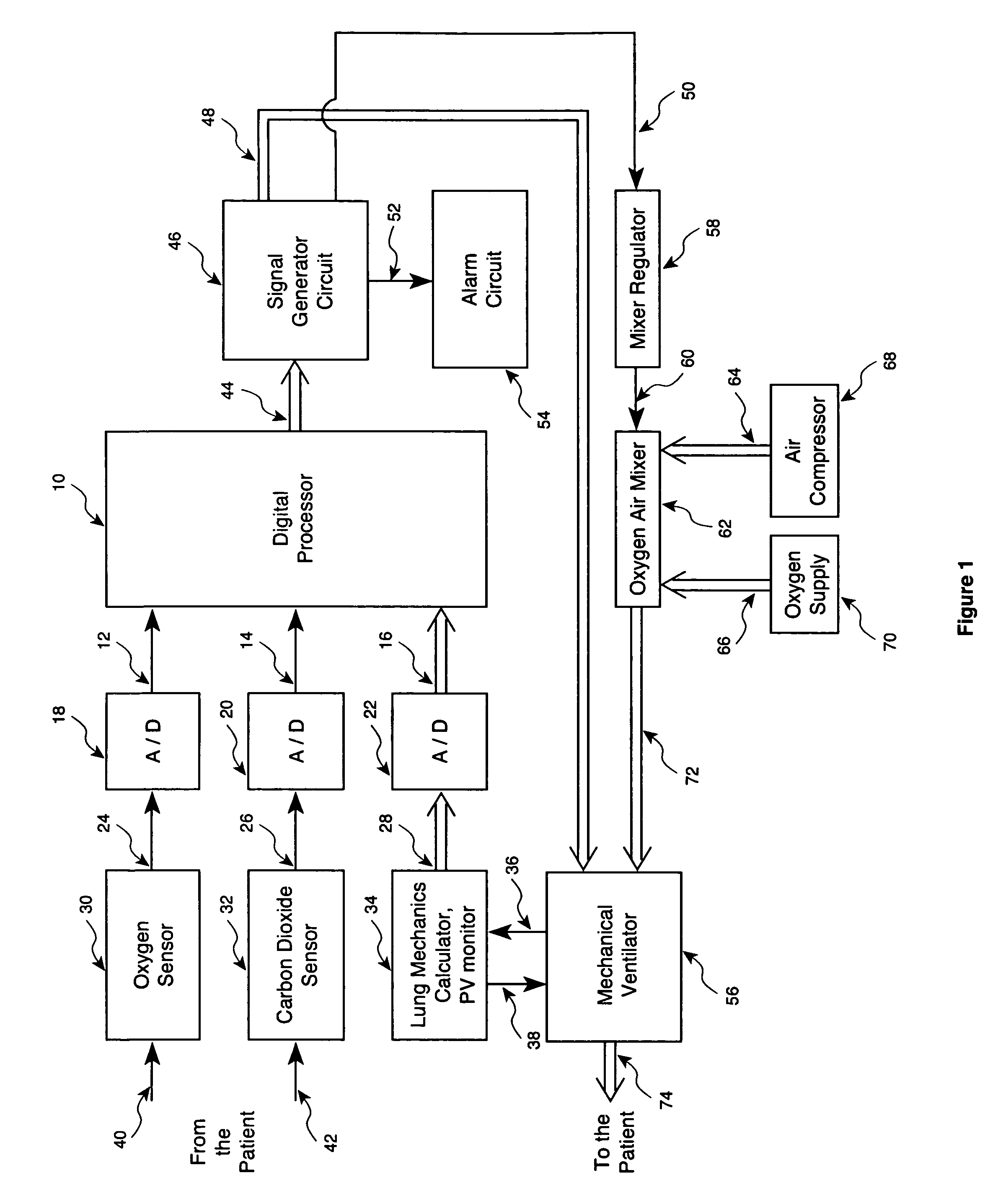
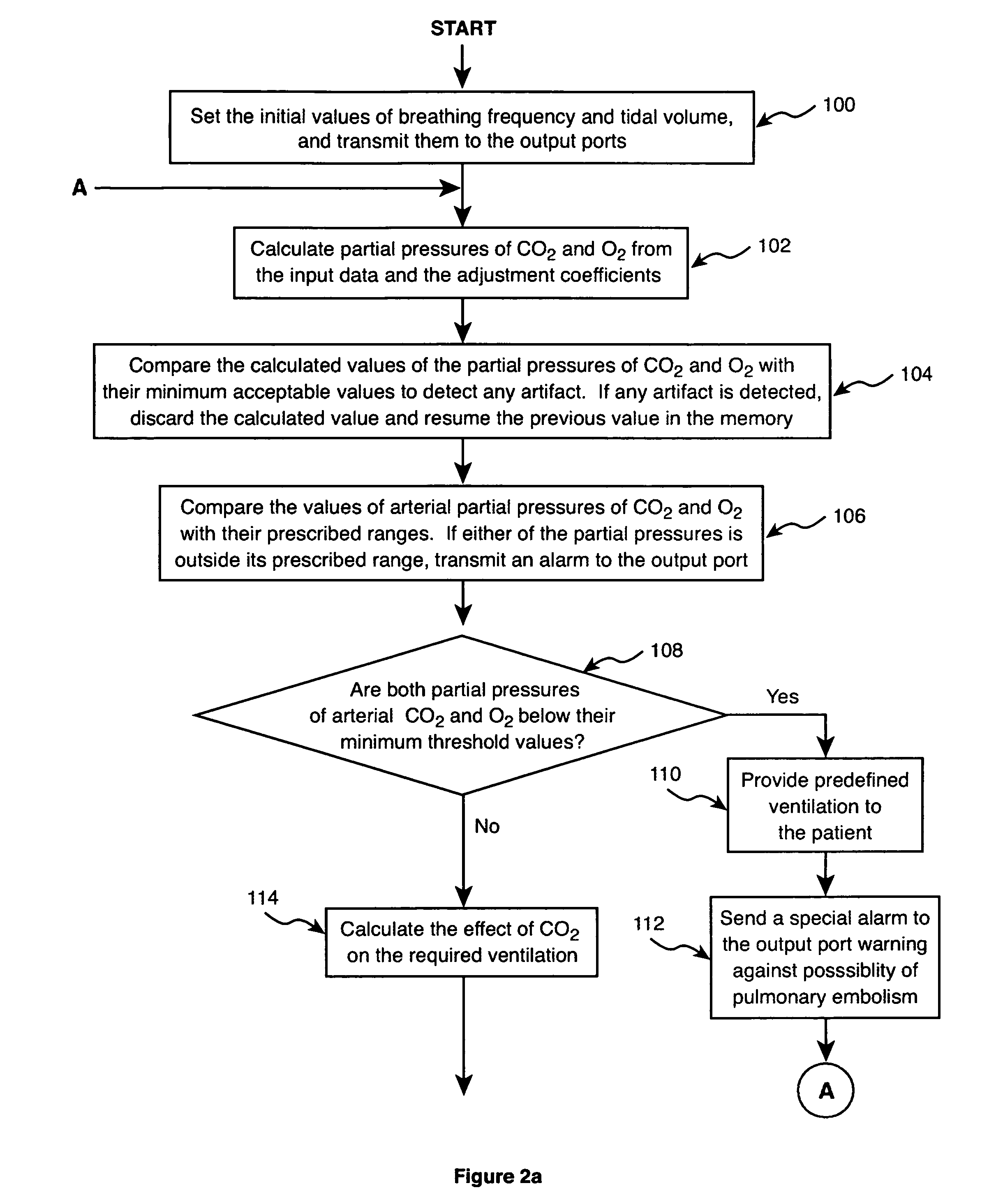
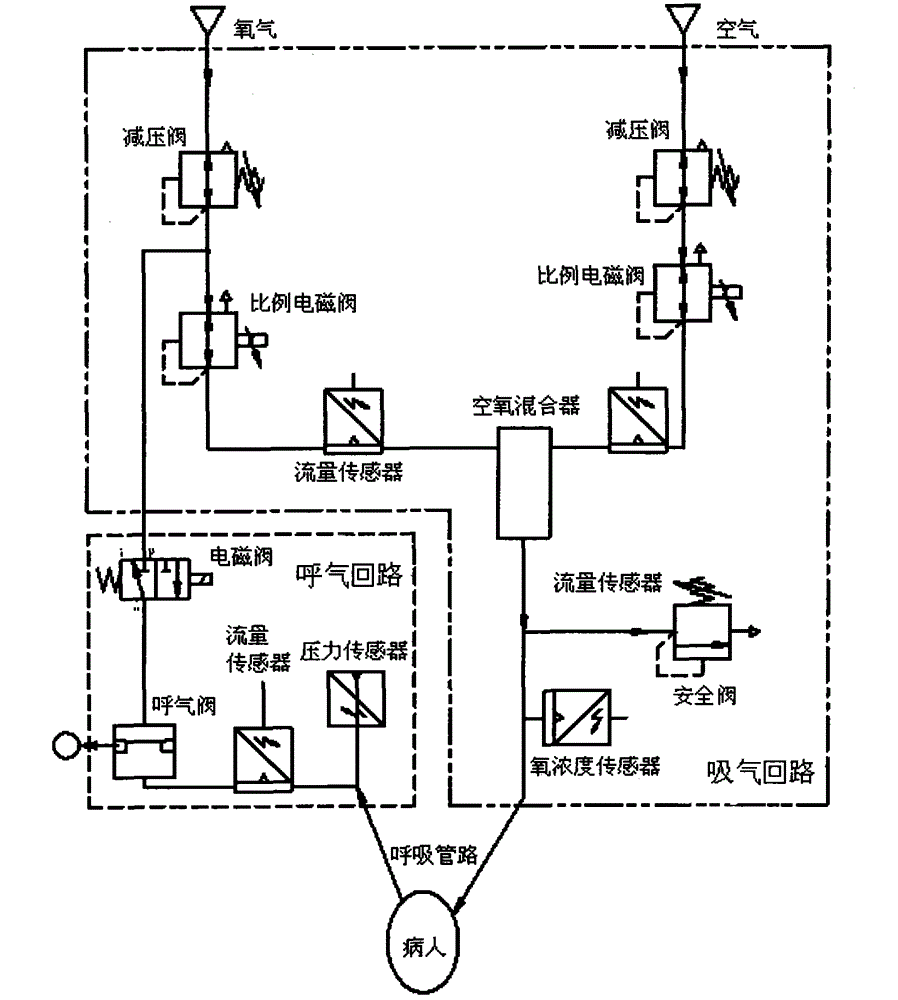
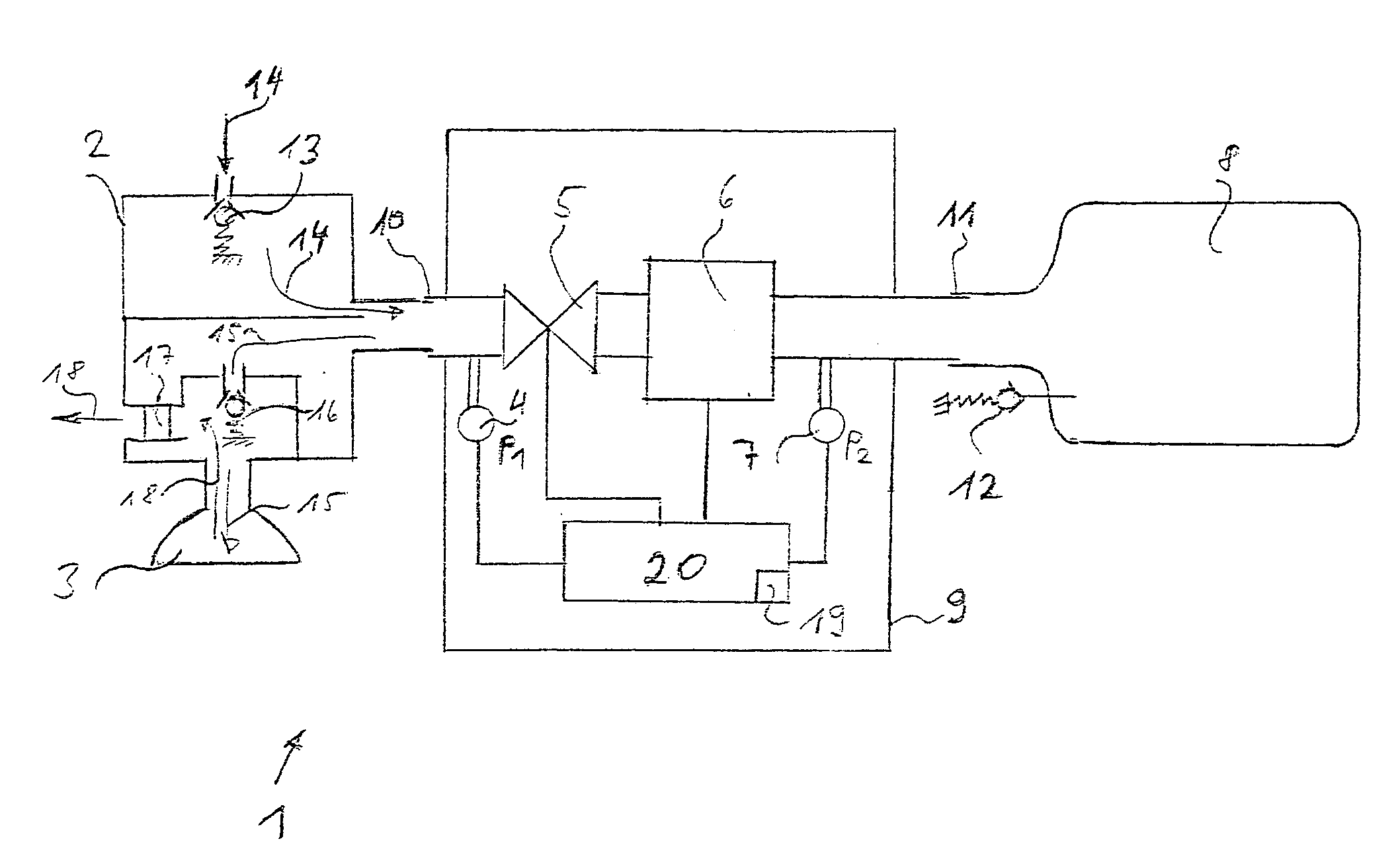
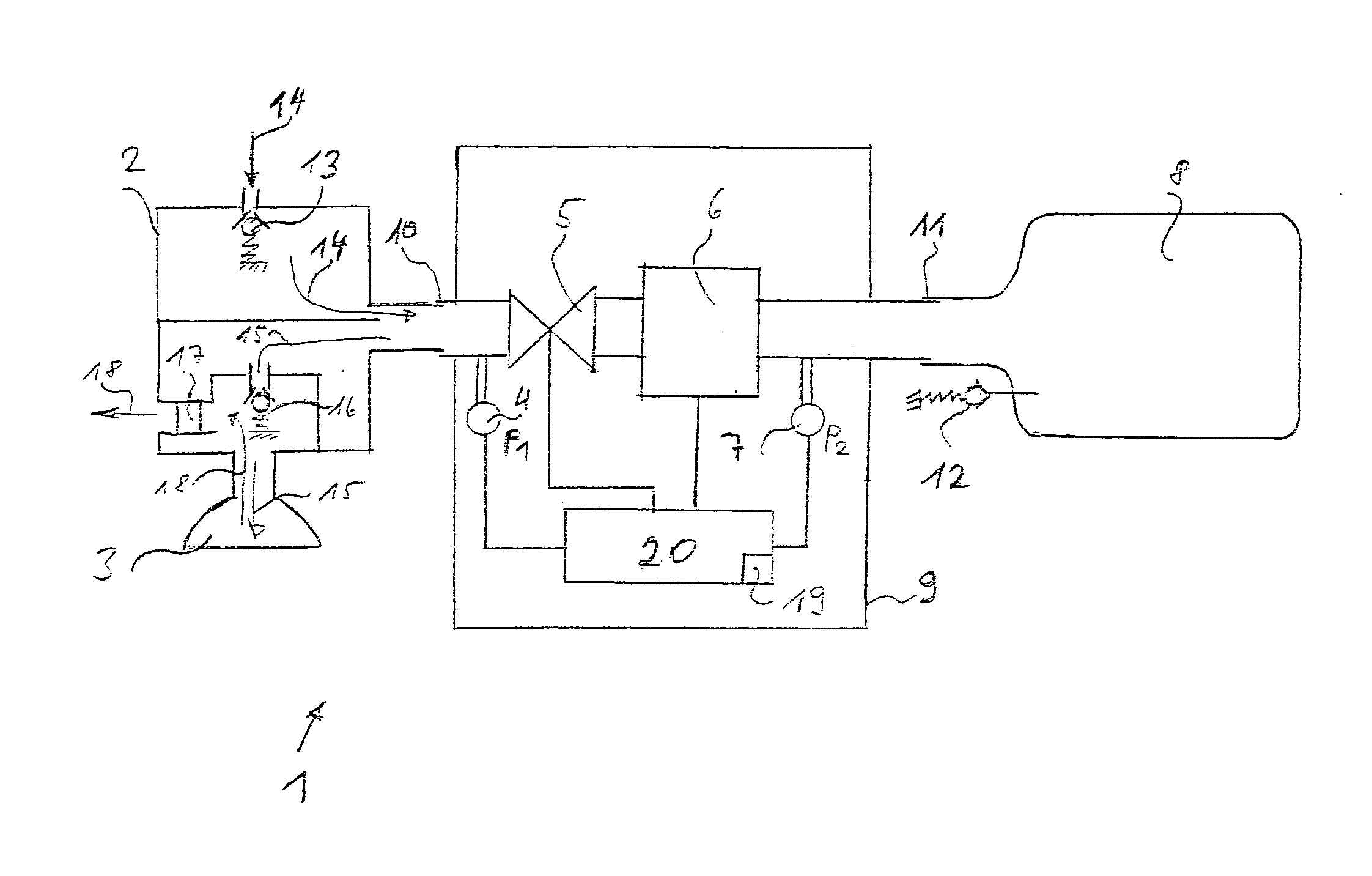
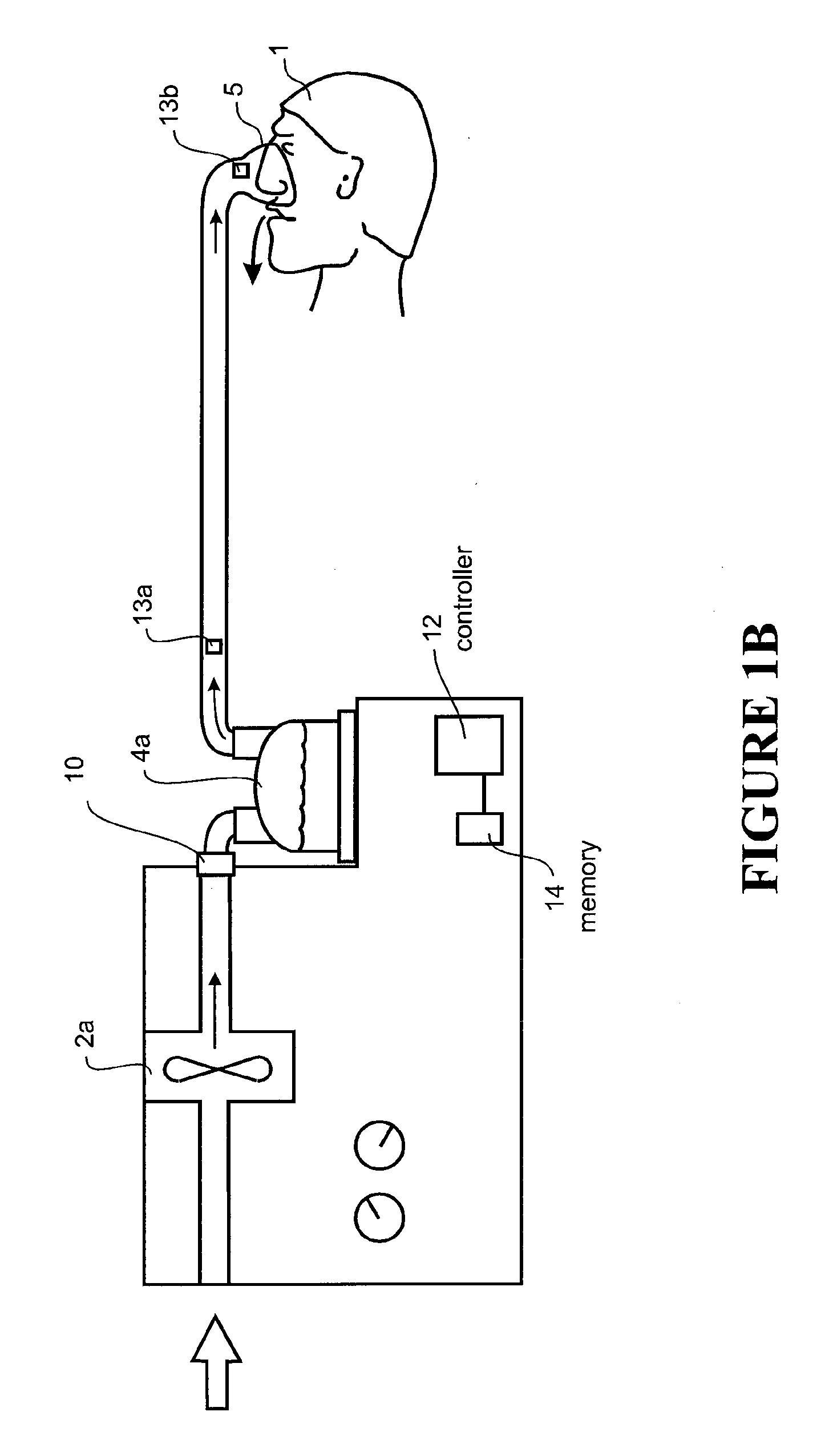
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator are described. The invention can be used to control mechanical ventilators as well as respiratory assist devices such as CPAP machines. The apparatus receives input data indicative of patient's oxygen level. A controller determines PEEP, or CPAP, and FIO2, on the basis of data indicative of the patient's oxygen level. In an alternative embodiment, the apparatus further receives input data indicative of patient's carbon dioxide levels, respiratory elastance and airway resistance, and barometric pressure. The controller further utilizes the said input data to determine the optimal values of tidal volume and breathing frequency for a next breath of the patient, and uses the respiratory elastance and airway resistance data to determine any necessary adjustments in the I:E ratio. The controller also applies safety rules, detects and corrects artifacts, and generates warning signals when needed.
Owner:TEHRANI FLEUR T
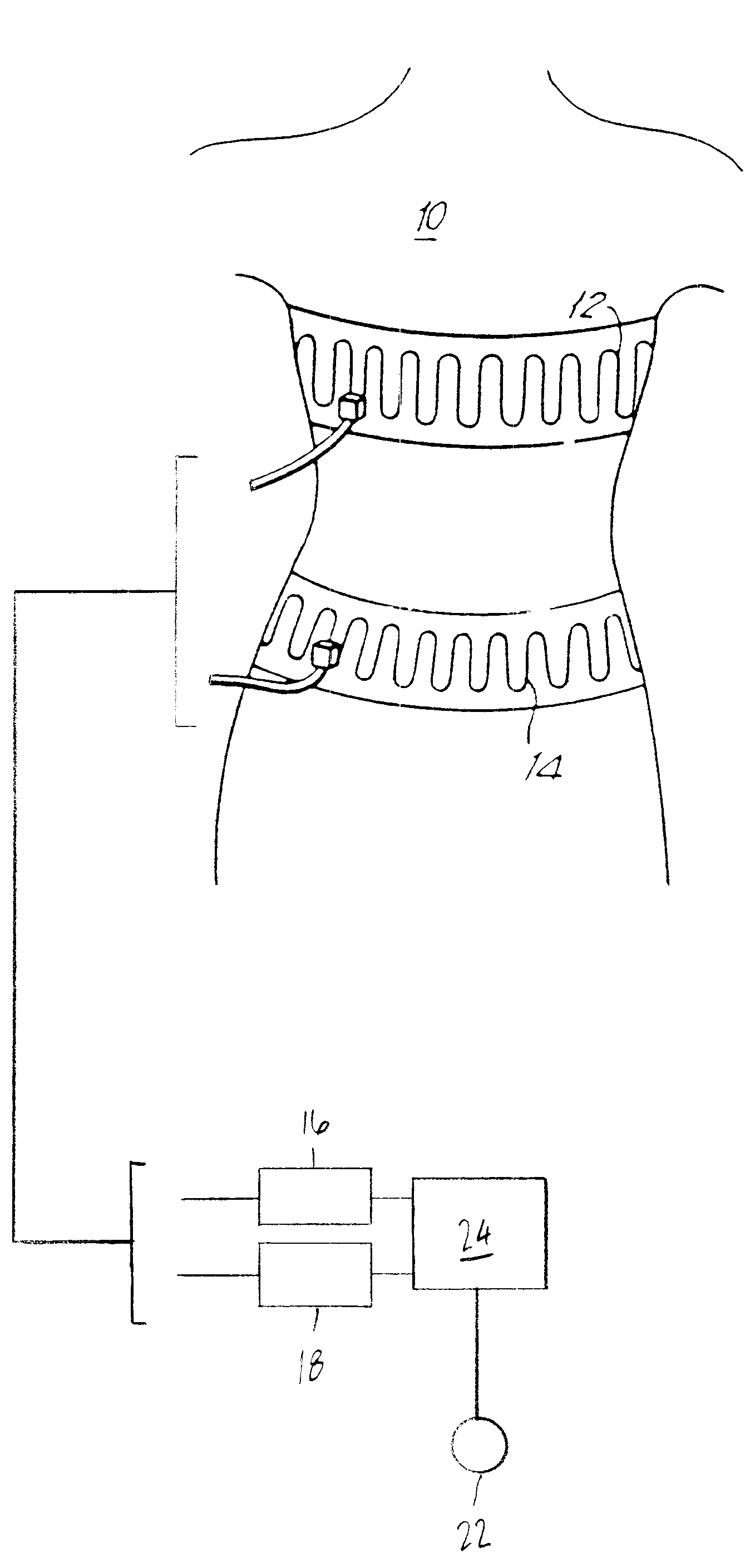
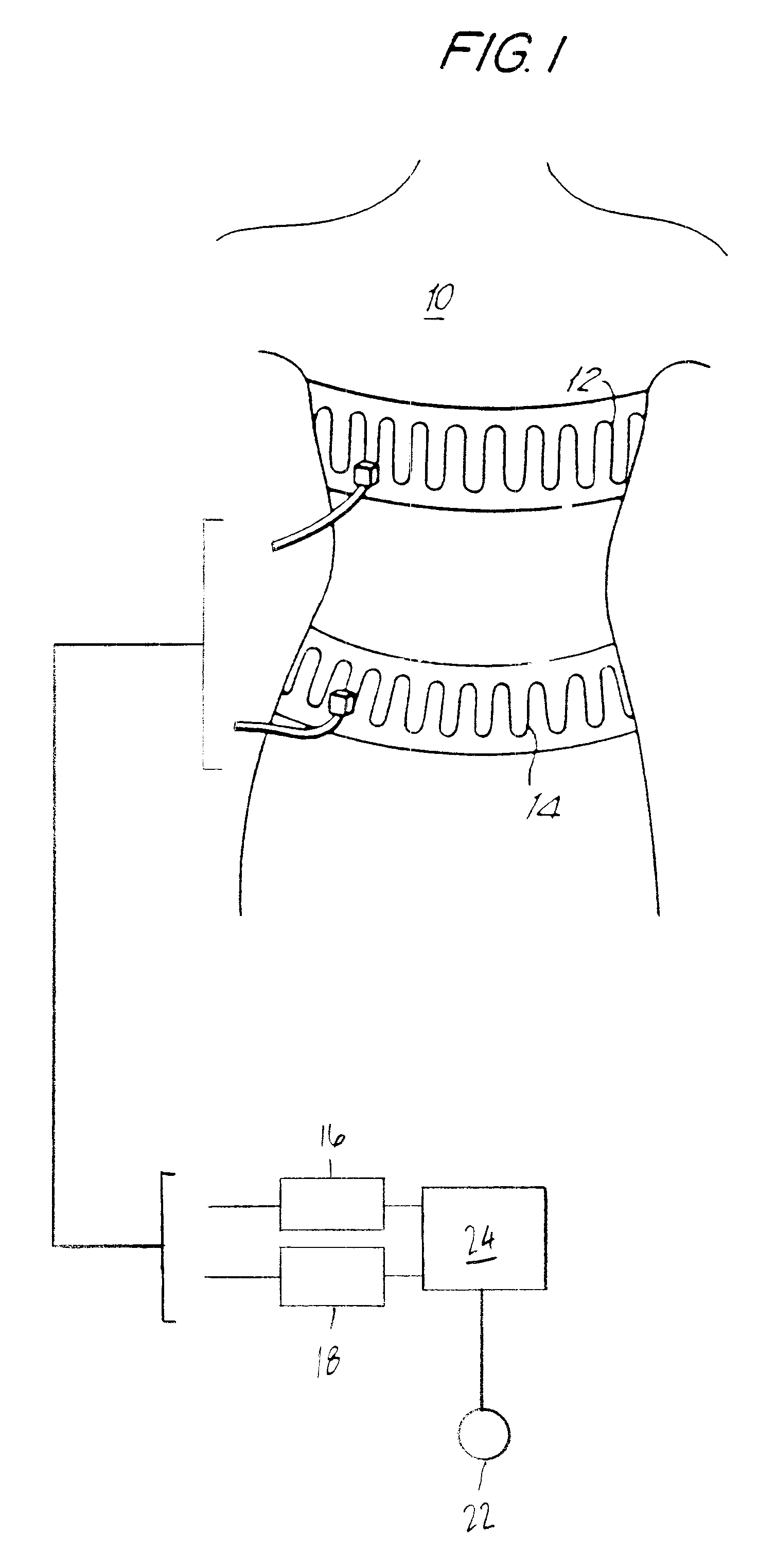
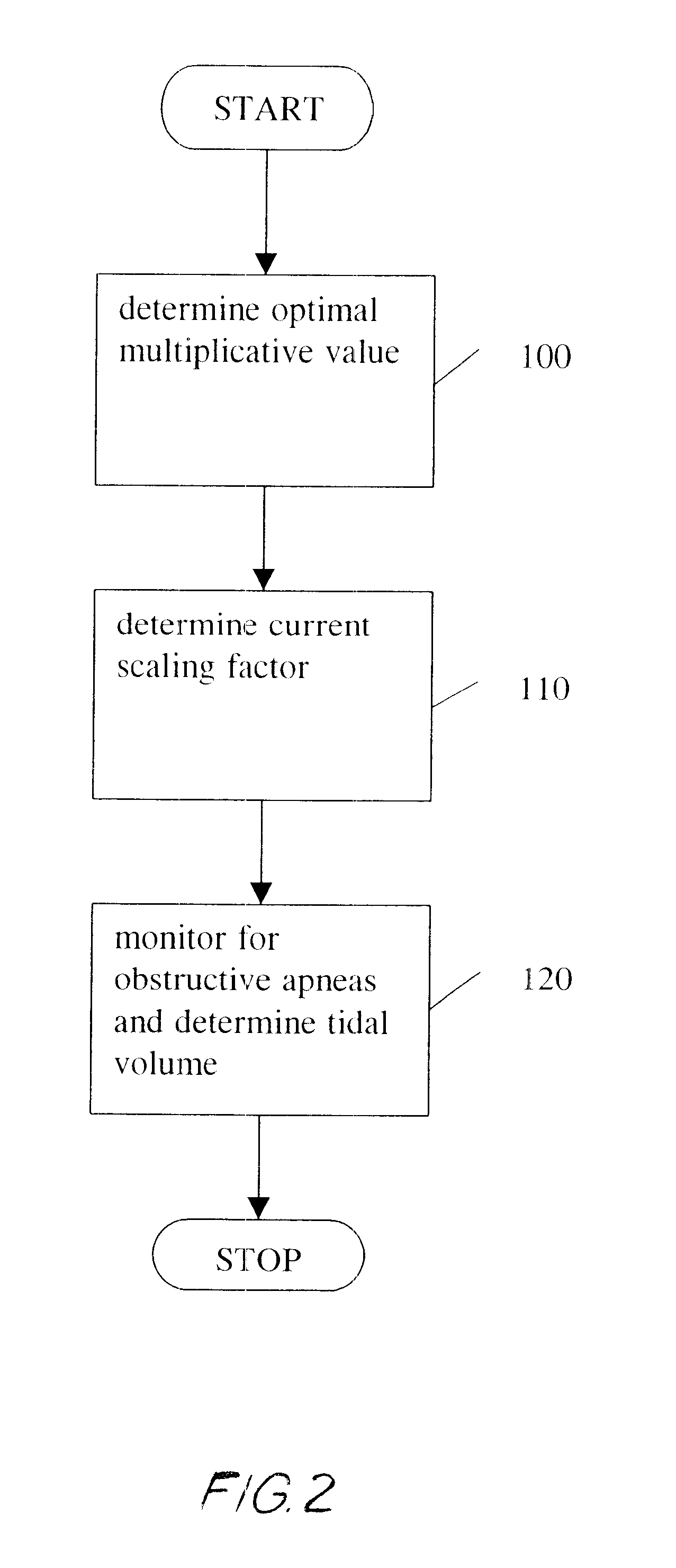
Quantitative calibration of breathing monitors with transducers placed on both rib cage and abdomen
A method for calibrating non-invasive breathing monitors with sensors placed on the rib-cage and abdomen of a subject includes determining an initial scaling factor and an optimal multiplicative factor for the readings of the rib-cage and abdomen sensors using one of a least squares, linear regression, or multi-linear regression techniques. A current scaling factor is determined on a periodic basis using qualitative device calibration techniques. The current scaling factor is used to monitor breathing and diagnose obstructive apneas. Furthermore, the optimal multiplicative and the current scaling factor are used to determine the current tidal volume.
Owner:ADIDAS +1
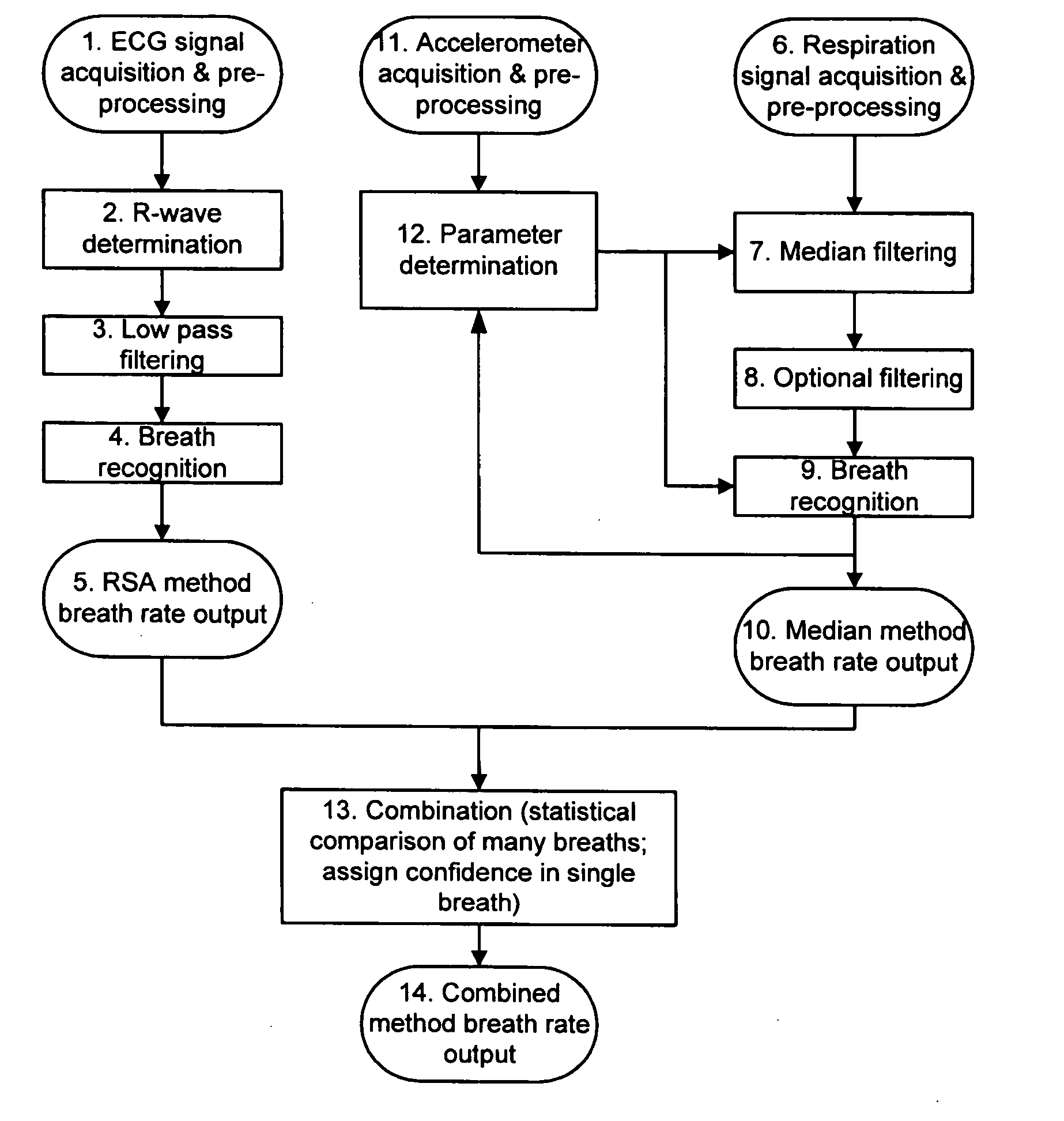
Methods and systems for real time breath rate determination with limited processor resources
InactiveUS20060178591A1Less durationElectrocardiographyInertial sensorsTidal volumeMonitoring system
A method for recognizing occurrences of breaths in respiratory signals. The method includes receiving digitized respiratory signals that includes tidal volume signals, filtering the received respiratory signals to limit artifacts having a duration less than a selected duration, and recognizing breaths in the filtered respiratory signals. A breath is recognized when amplitude deviations in filtered tidal volume signals exceed a selected fraction of an average of previously determined breaths. This invention also include methods for recognizing breathes from electrocardiogram R-waves; computer methods having code for performing the methods of this invention; monitoring systems that monitor a subject and include local or remote computers or other devices that perform the methods of this invention.
Owner:VIVOMETRICS INC
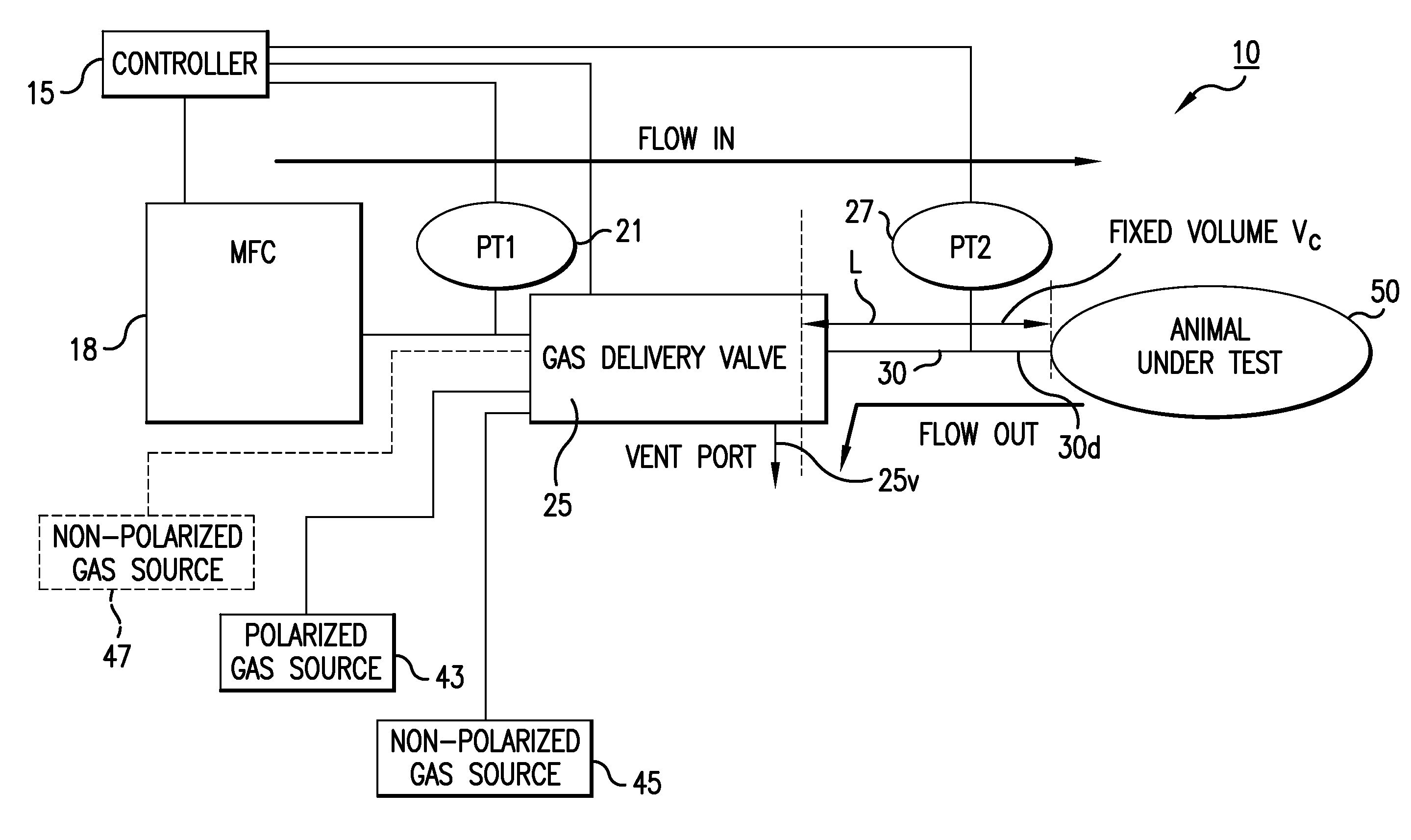
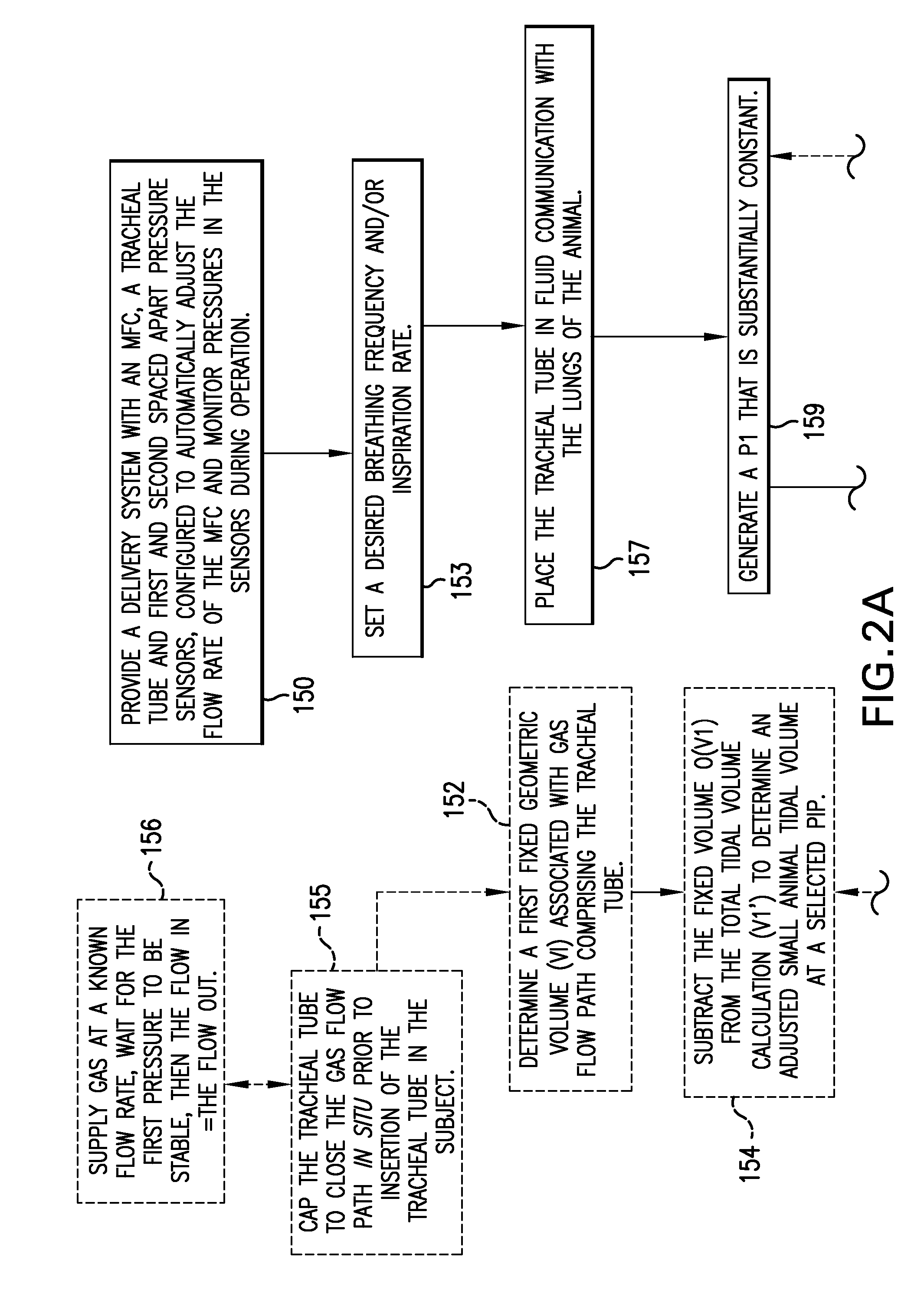
MRI/NMR-compatible, tidal volume control and measurement systems, methods, and devices for respiratory and hyperpolarized gas delivery
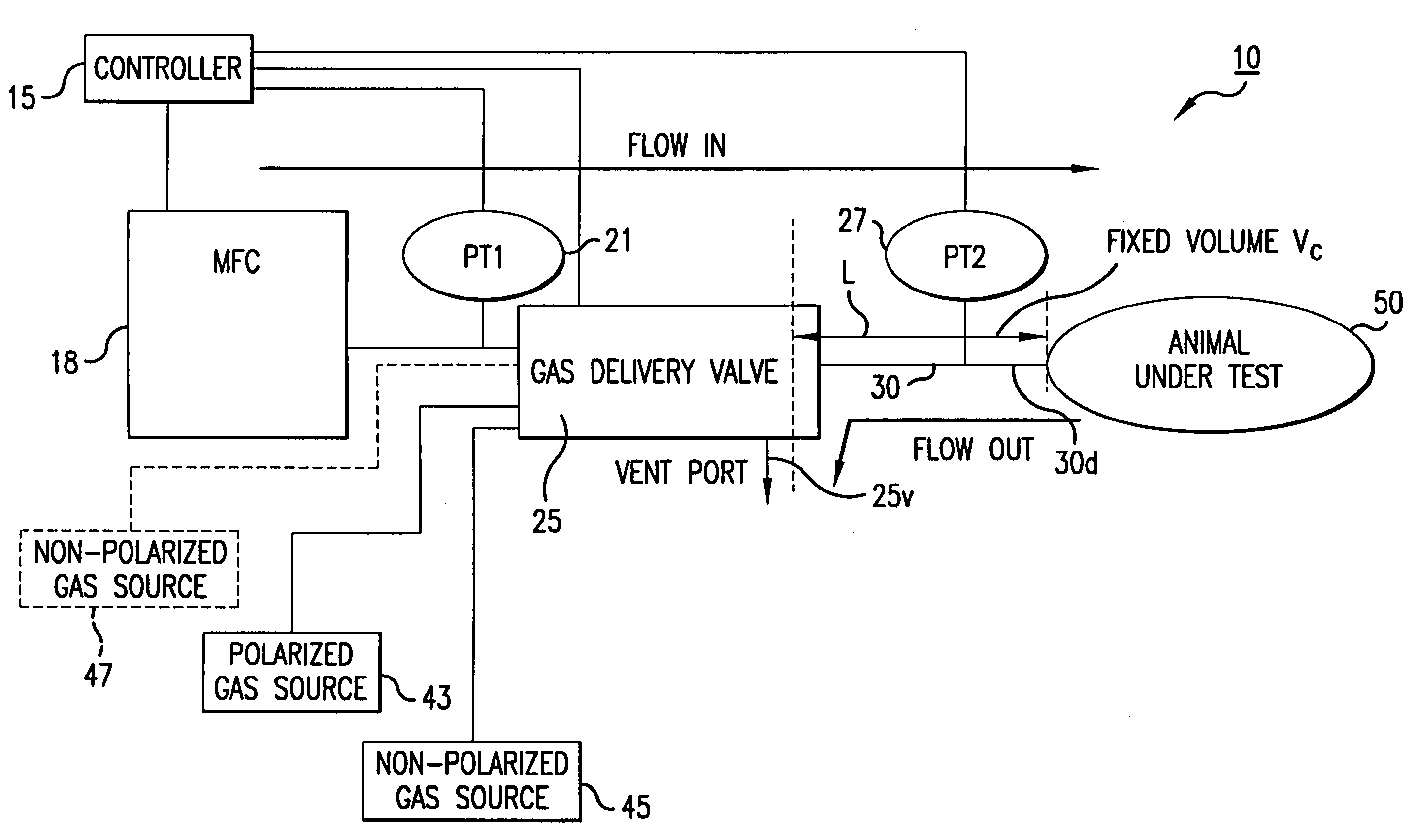
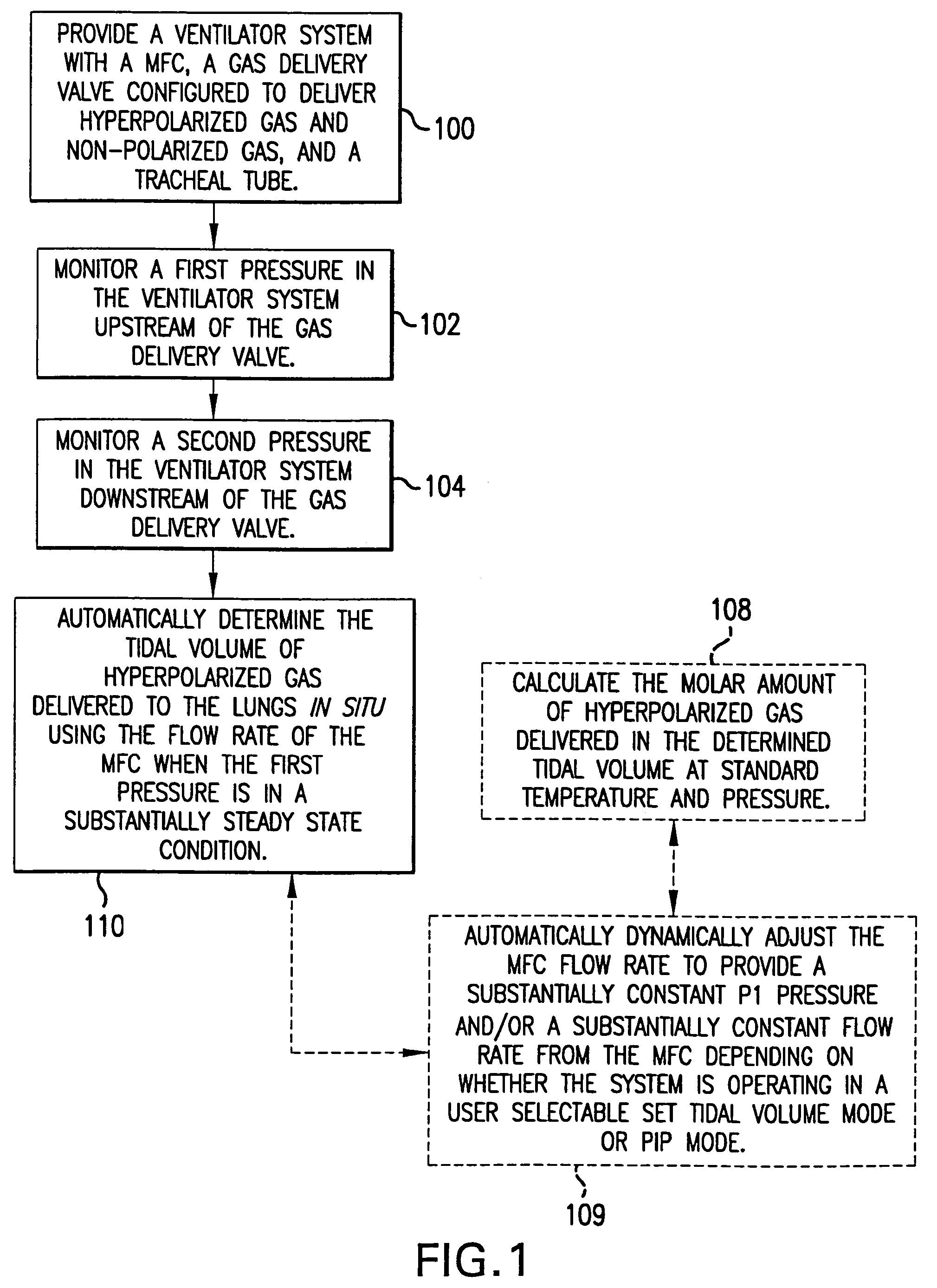
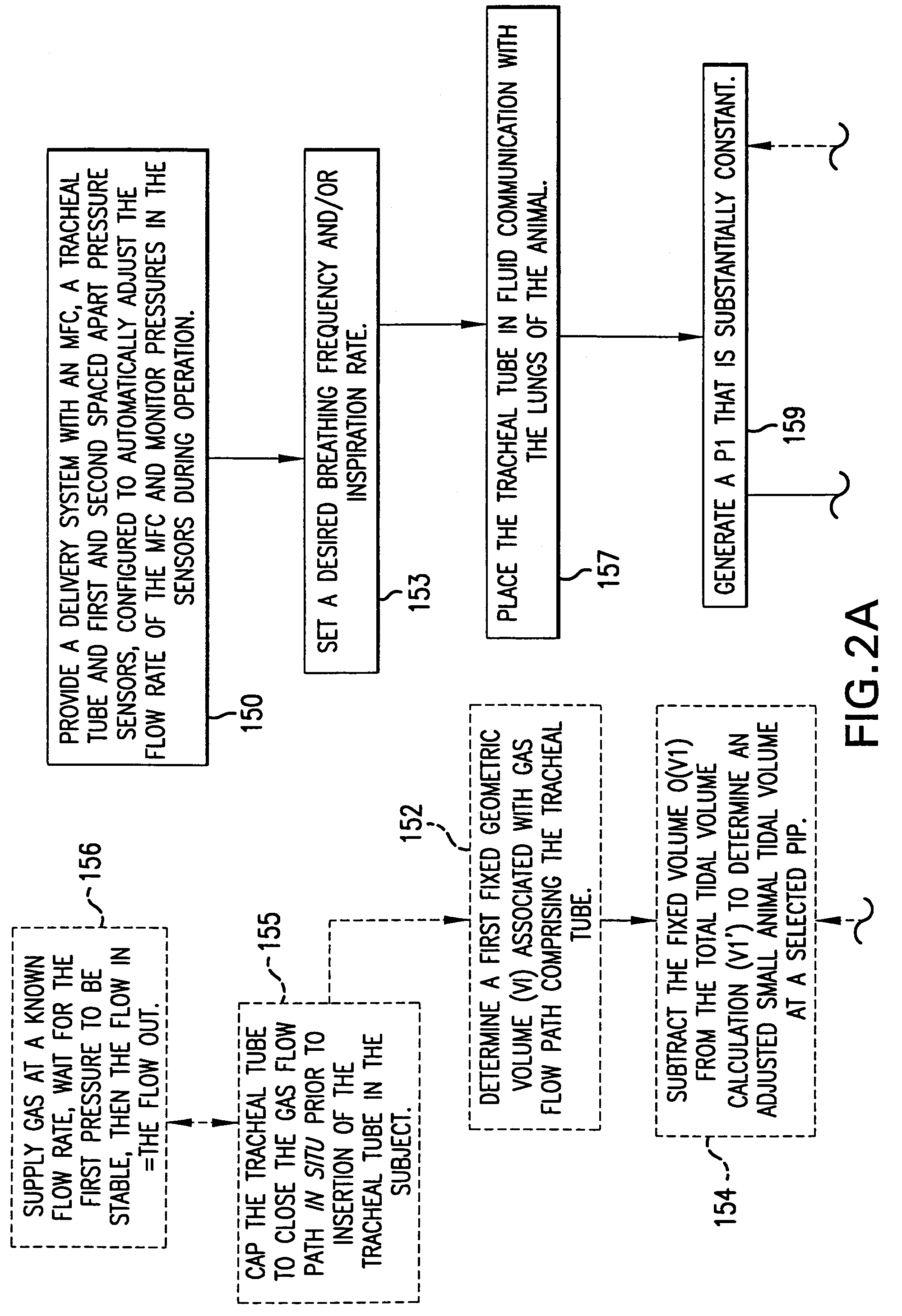
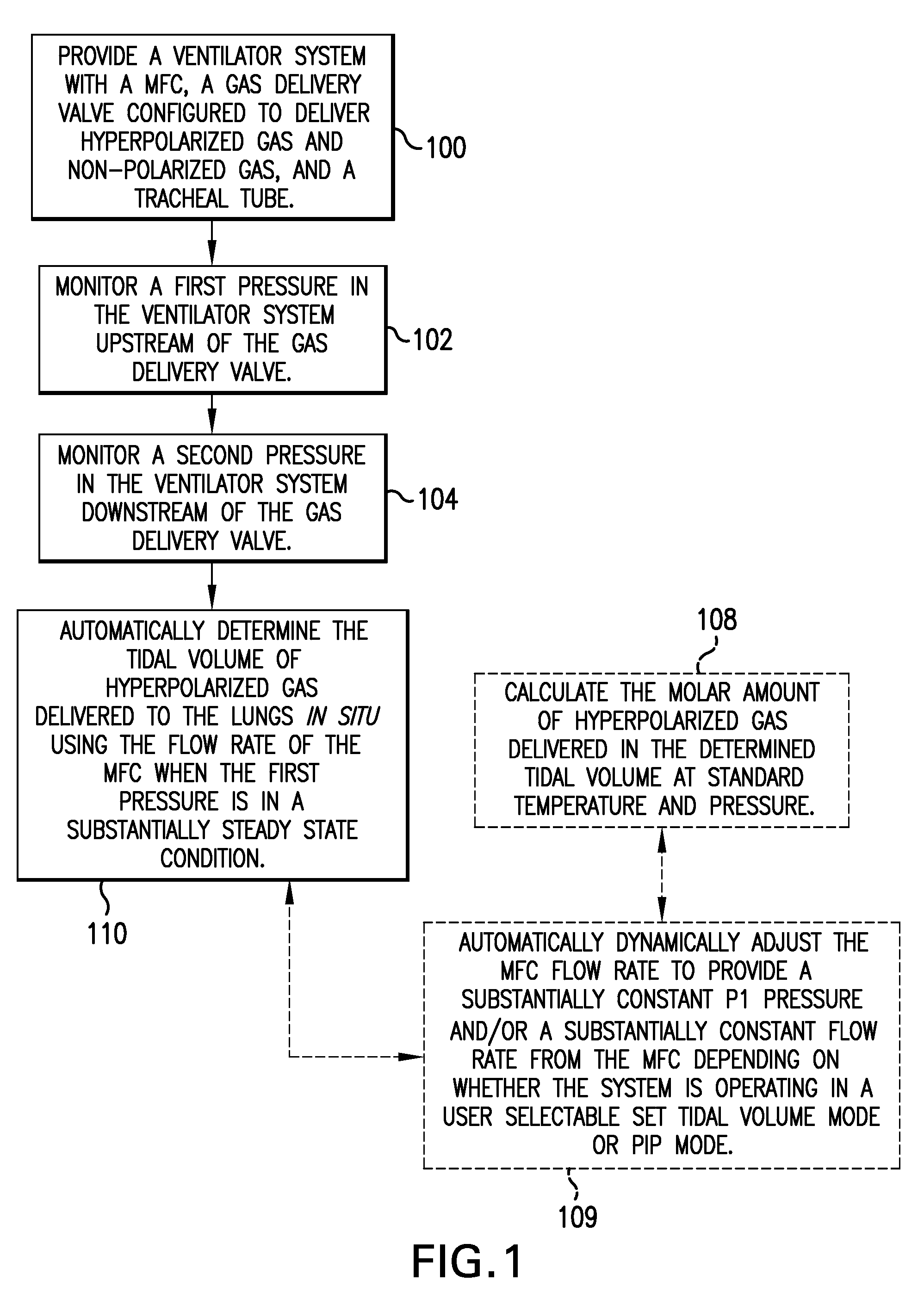
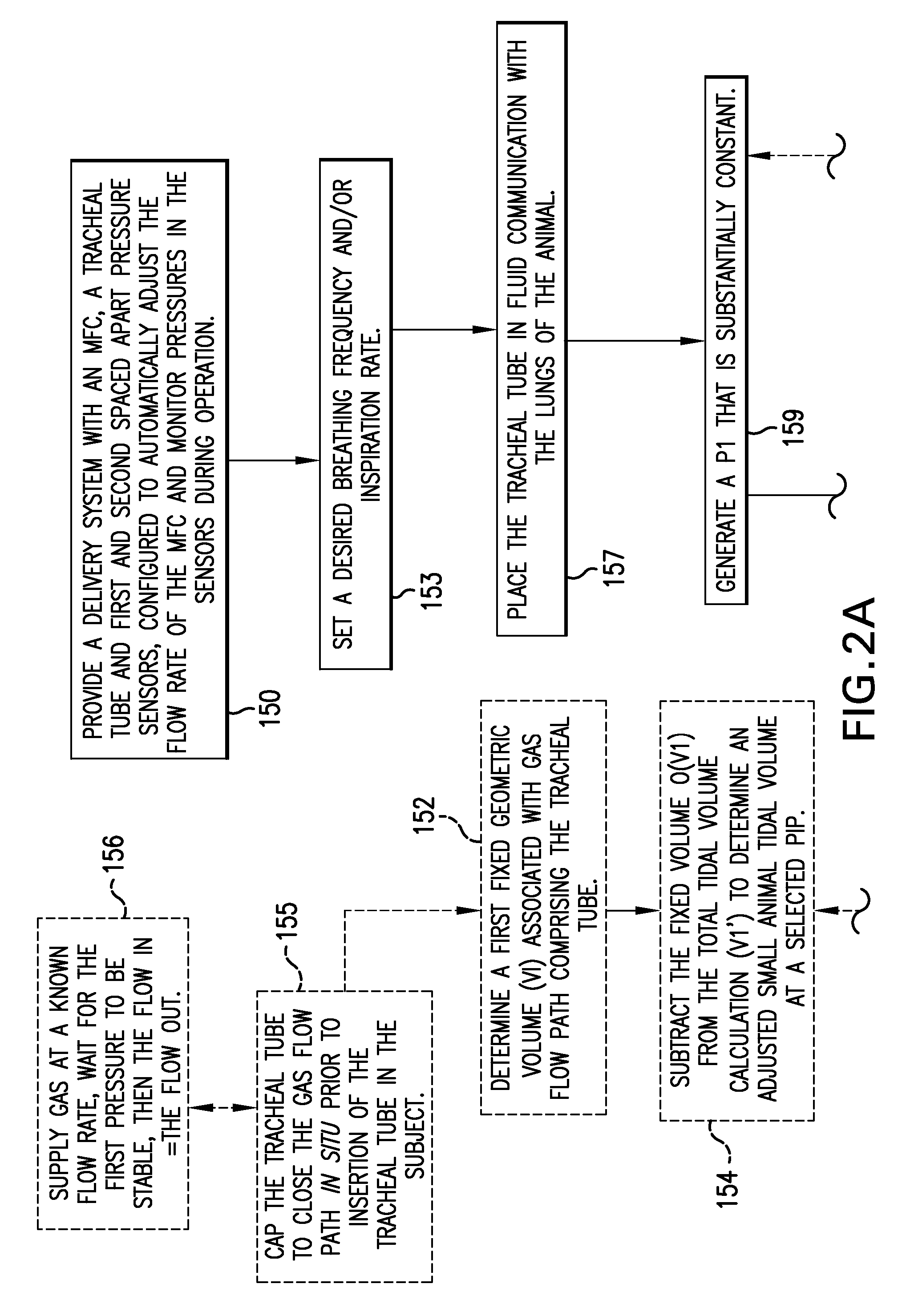
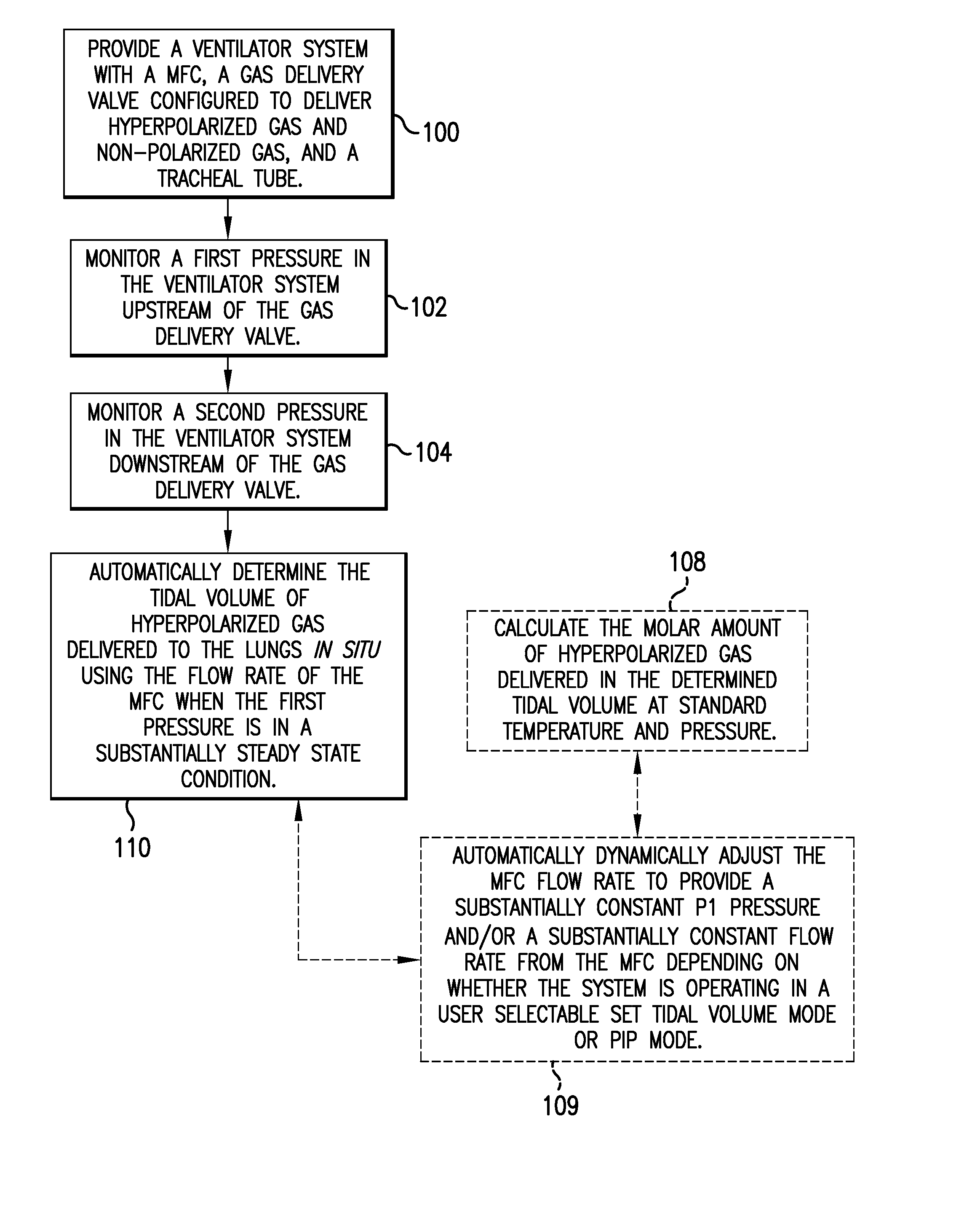
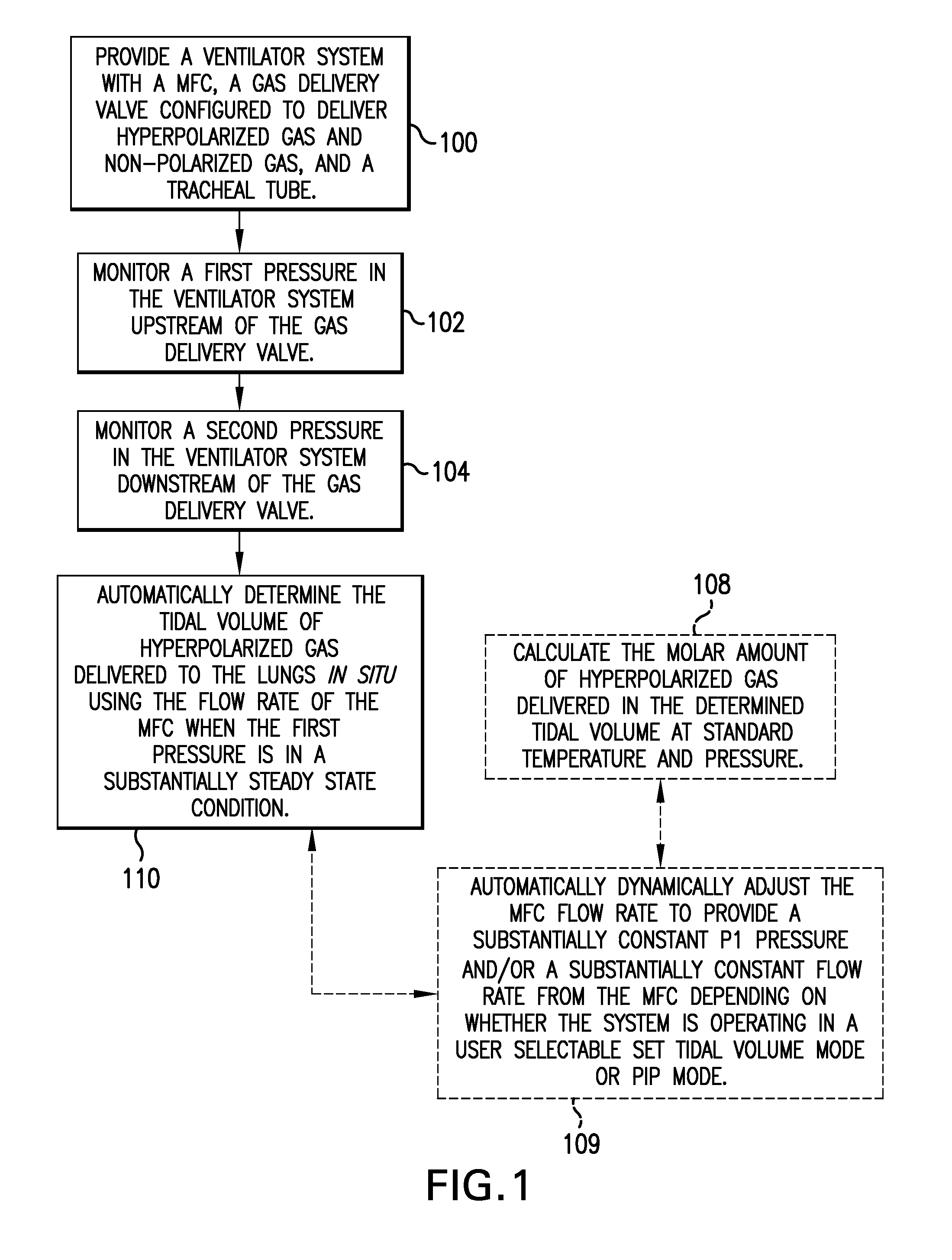
Ventilator systems include: (a) a mass flow controller; (b) a gas delivery valve in communication with the mass flow controller and configured to selectively dispense a plurality of different gases to a subject; (c) a first gas source in fluid communication with the gas delivery valve; (d) a second gas source in fluid communication with the gas delivery valve; (e) a first pressure sensor located upstream of the gas delivery valve; (f) a second pressure sensor located downstream of the gas delivery valve; and (g) a controller operatively associated with the first and second pressure sensors and the mass flow controller, the controller comprising computer program code that monitors the pressures measured by the first and second pressure sensors and automatically dynamically adjusts the flow rate of the mass flow controller.
Owner:POLAREAN
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator are described. The invention can be used to control mechanical ventilators as well as respiratory assist devices such as CPAP machines. The apparatus receives input data indicative of patient's oxygen level. A controller determines PEEP, or CPAP, and FIO2, on the basis of data indicative of the patient's oxygen level. In an alternative embodiment, the apparatus further receives input data indicative of patient's carbon dioxide levels, respiratory elastance and airway resistance, and barometric pressure. The controller further utilizes the said input data to determine the optimal values of tidal volume and breathing frequency for a next breath of the patient, and uses the respiratory elastance and airway resistance data to determine any necessary adjustments in the I:E ratio. The controller also applies safety rules, detects and corrects artifacts, and generates warning signals when needed.
Owner:TEHRANI FLEUR T
MRI/NMR-compatible, tidal volume control and measurement systems, methods, and devices for respiratory and hyperpolarized gas delivery
Ventilator systems include: (a) a mass flow controller; (b) a gas delivery valve in communication with the mass flow controller and configured to selectively dispense a plurality of different gases to a subject; (c) a first gas source in fluid communication with the gas delivery valve; (d) a second gas source in fluid communication with the gas delivery valve; (e) a first pressure sensor located upstream of the gas delivery valve; (f) a second pressure sensor located downstream of the gas delivery valve; and (g) a controller operatively associated with the first and second pressure sensors and the mass flow controller, the controller comprising computer program code that monitors the pressures measured by the first and second pressure sensors and automatically dynamically adjusts the flow rate of the mass flow controller.
Owner:POLAREAN
Mri/nmr-compatible, tidal volume control and measurement systems, methods, and devices for respiratory and hyperpolarized gas delivery
InactiveUS20080000471A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTidal volumeType ventilator
Ventilator systems include: (a) a mass flow controller; (b) a gas delivery valve in communication with the mass flow controller and configured to selectively dispense a plurality of different gases to a subject; (c) a first gas source in fluid communication with the gas delivery valve; (d) a second gas source in fluid communication with the gas delivery valve; (e) a first pressure sensor located upstream of the gas delivery valve; (f) a second pressure sensor located downstream of the gas delivery valve; and (g) a controller operatively associated with the first and second pressure sensors and the mass flow controller, the controller comprising computer program code that monitors the pressures measured by the first and second pressure sensors and automatically dynamically adjusts the flow rate of the mass flow controller.
Owner:POLAREAN
Monitoring and quantification of smoking behaviors
InactiveUS20070209669A1Limit, or improve their smoking behaviorsElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographySmoking behaviorTidal volume
The invention provides methods for characterizing a subject's overall smoking behavior and the subject's puff morphology in dependence on tidal volume information provided by ambulatory physiological monitoring. This invention also systems for executing the methods of this invention and computer-readable media having encoded the methods of this invention.
Owner:ADIDAS
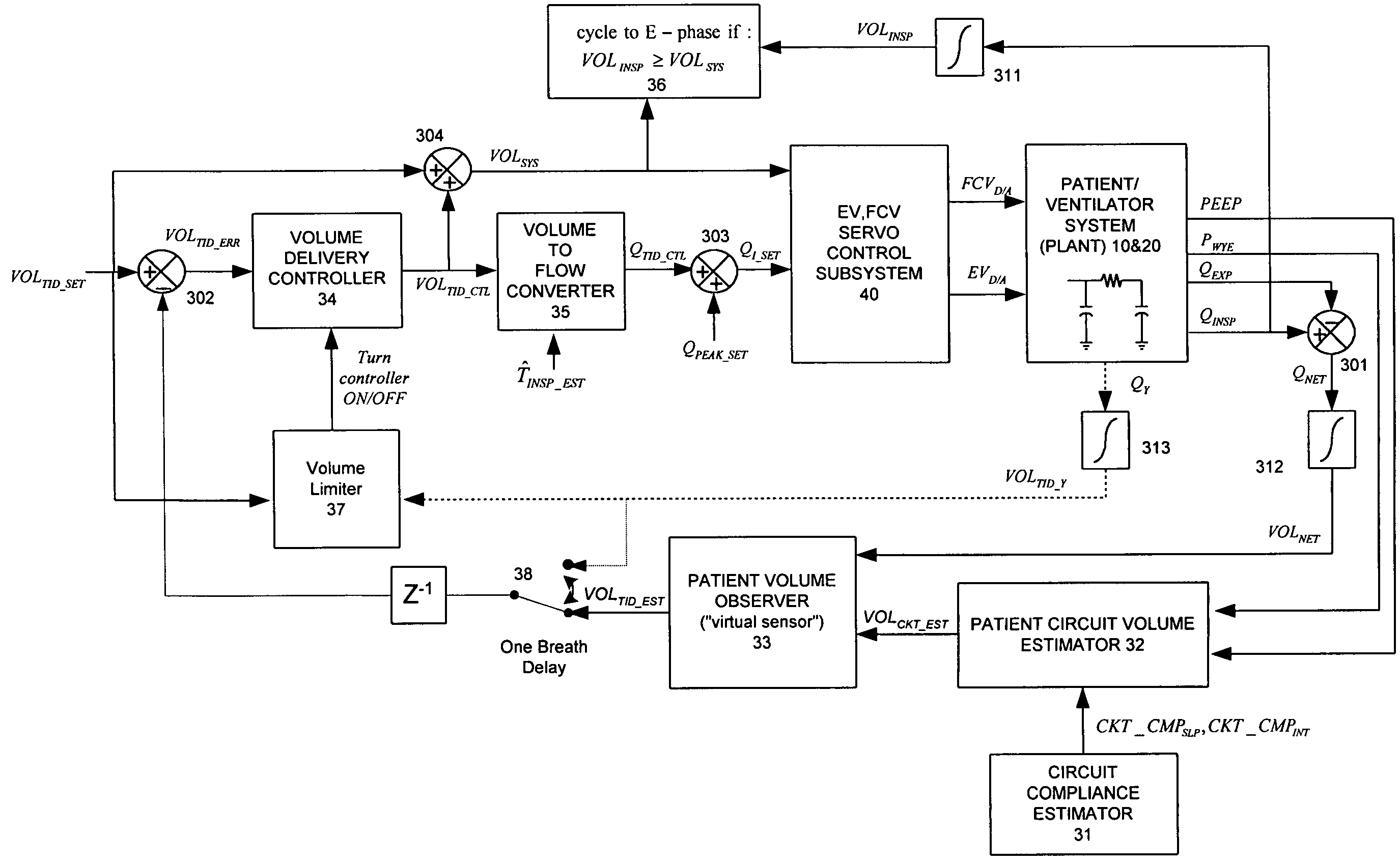
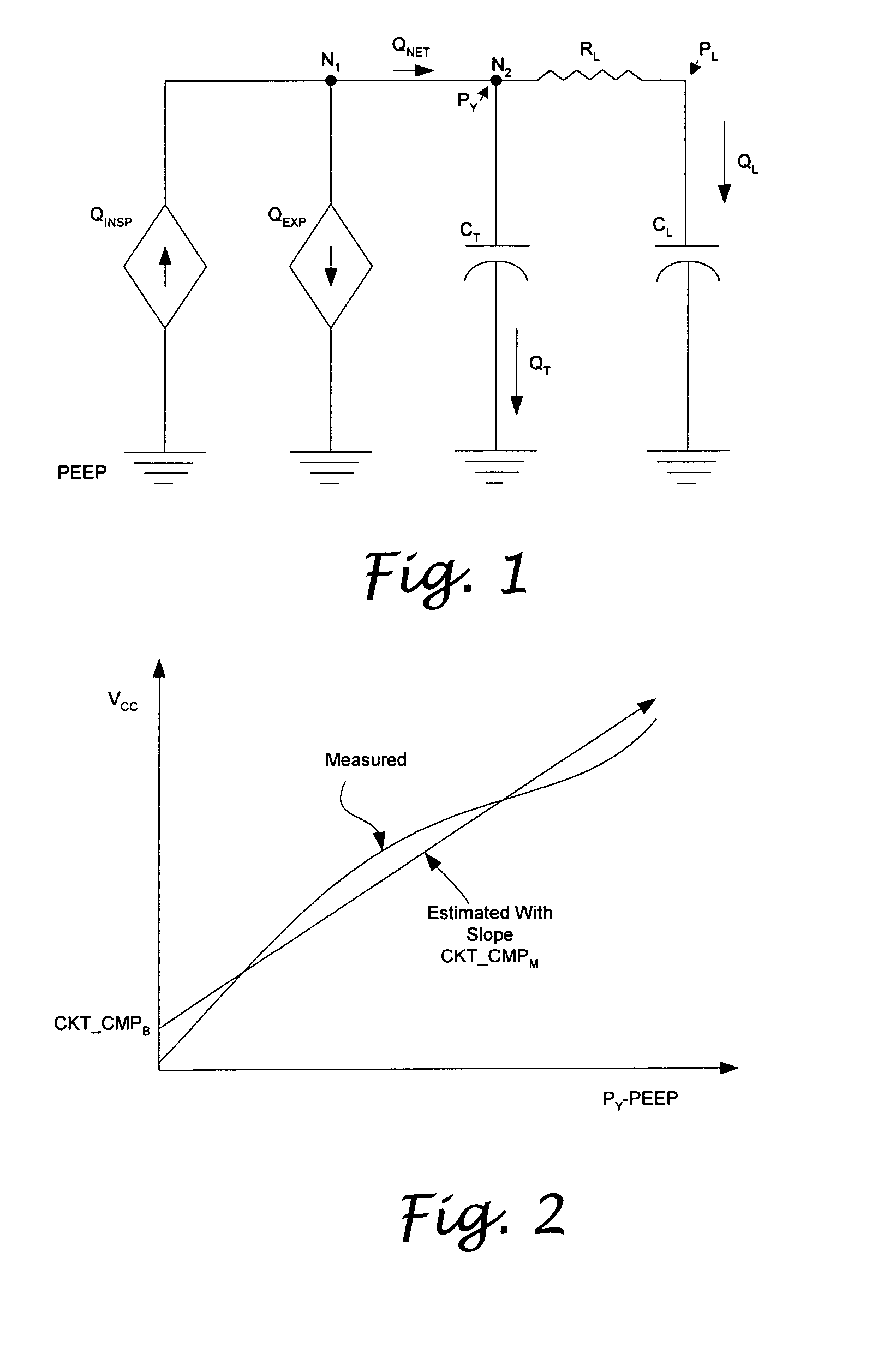
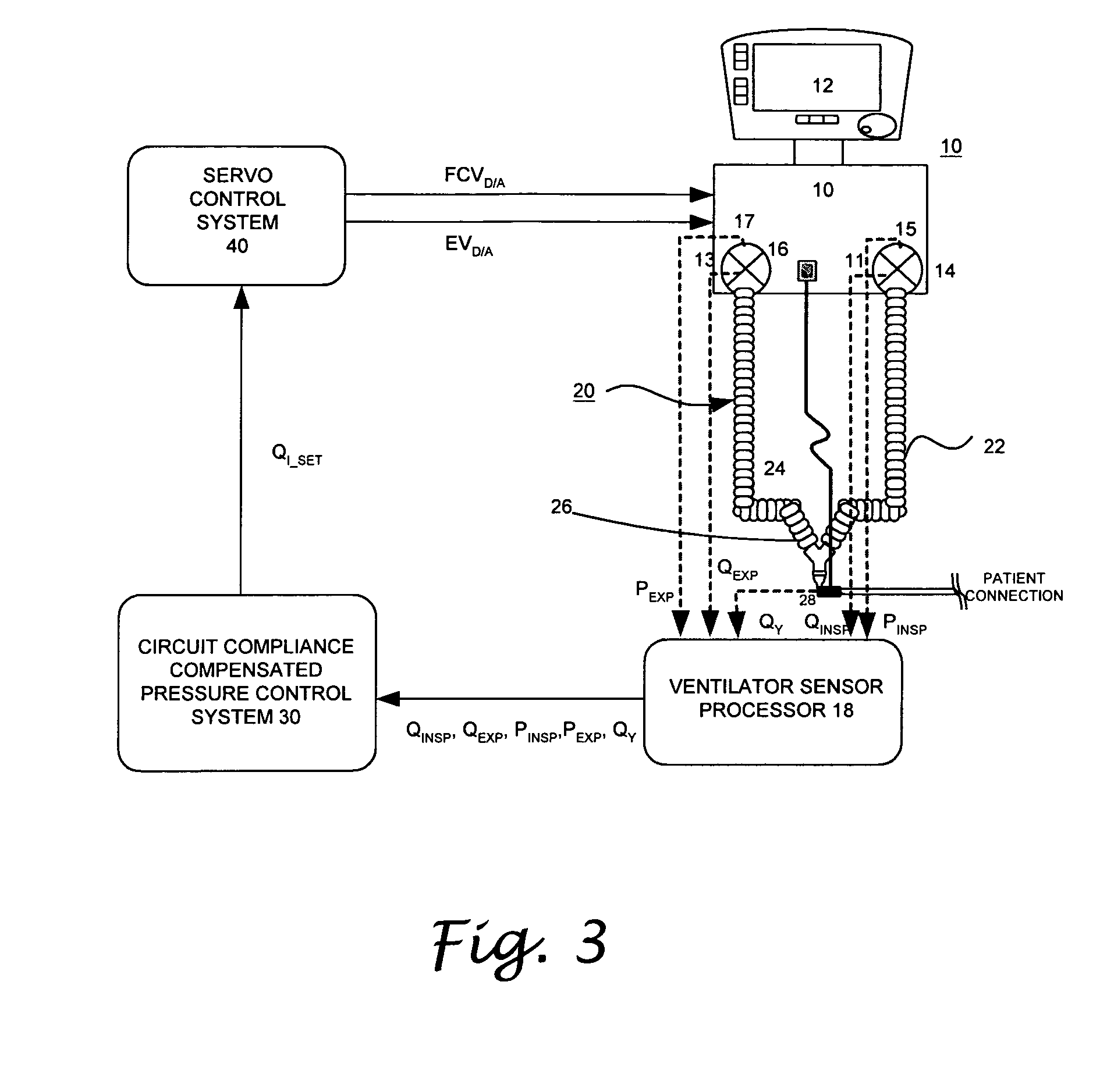
System and method for circuit compliance compensated volume control in a patient respiratory ventilator
ActiveUS7886739B2Accurate flowGas trapping and auto PEEP is preventedLevel controlInflated body pressure measurementDifferential pressureControl system
A circuit compliance compensated volume control system in a patient respiratory ventilation system and method, including: a circuit compliance estimator, to provide a relationship between a circuit volume and a differential pressure between a circuit pressure and a positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) of the respiratory circuit, a circuit volume estimator, operative to provide an estimated circuit volume based on the relationship between the circuit volume and the differential pressure, a patient volume observer, operative to provide an estimated patient volume by subtracting the estimated circuit volume from a measured machine delivered net volume, and a volume delivery controller, operative to update the machine delivered net volume based on the estimated patient volume and a set tidal volume.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 211 INC
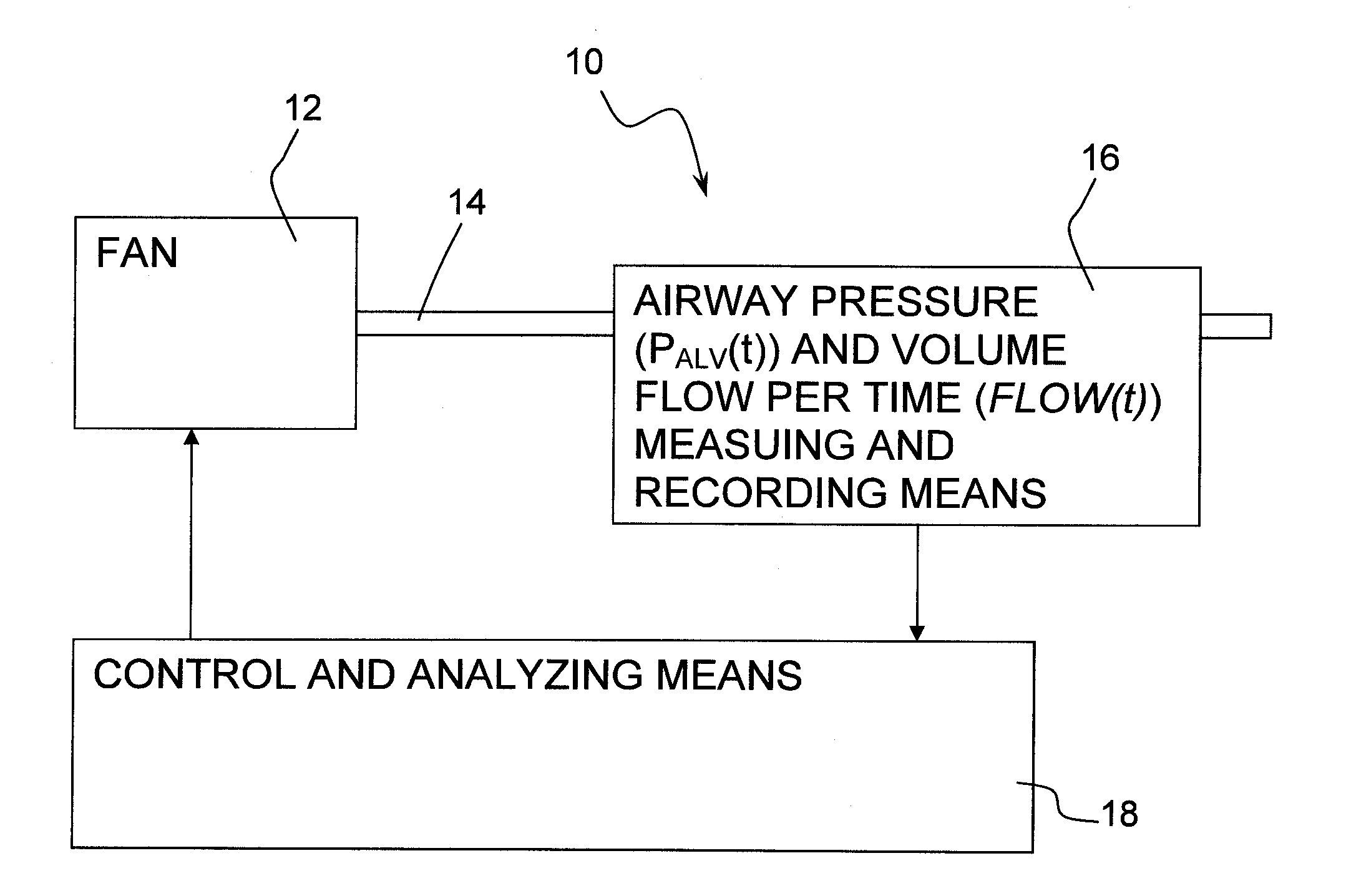
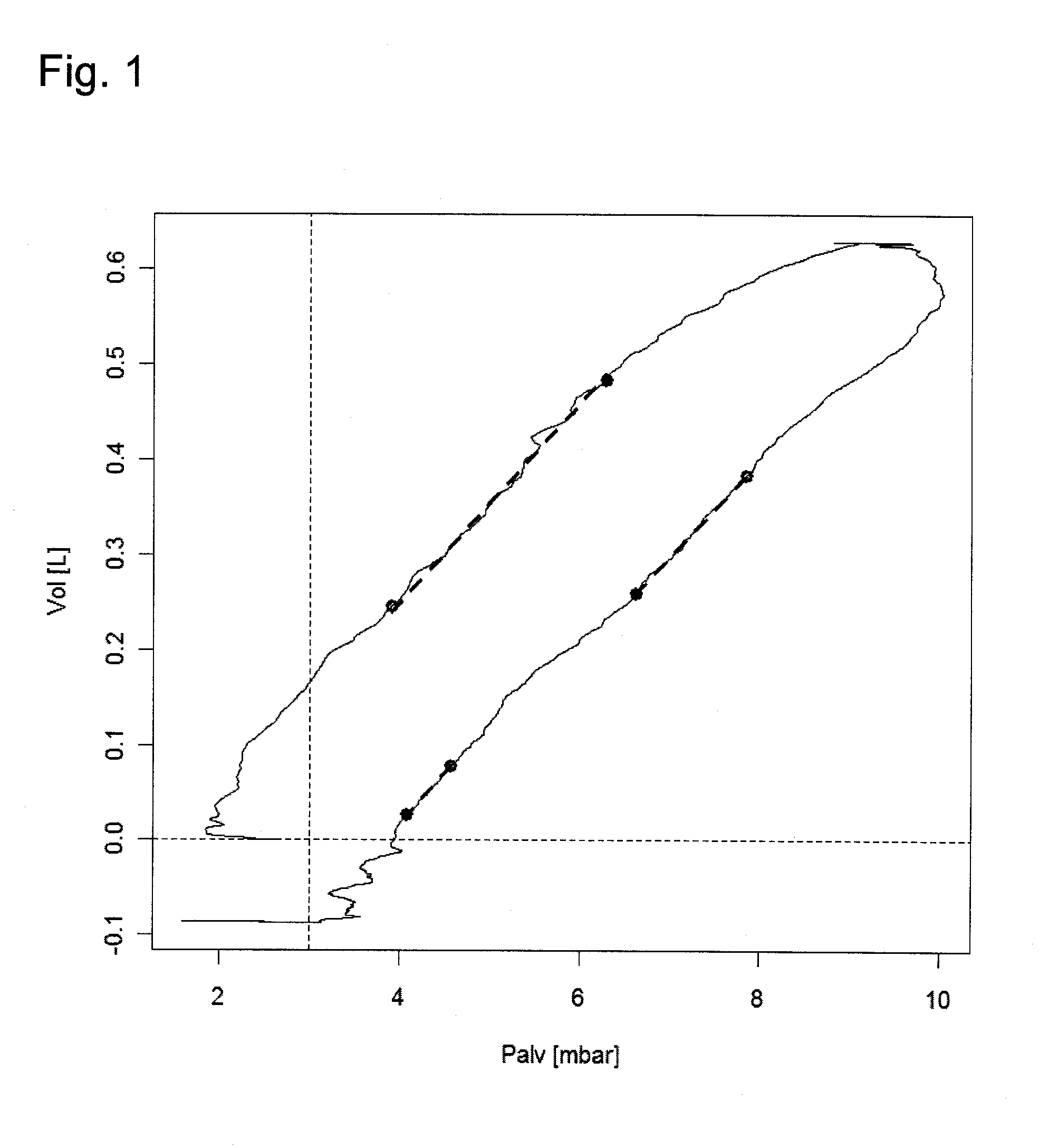
Respirator with automatically controlled pressure-assist respiration
InactiveUS20100307499A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrical resistance and conductanceAutomatic control
A respirator with an adjustable pressure or volume flow curve has a control and analyzing unit, which is set up to determine the resistance R and the alveolar pressure Palv(t). The control and analyzing unit checks the functional dependence of Palv(t) and of the tidal volume Vol(t) for time intervals in which an indicator of the quality of a linear functional dependence of Palv(t) and Vol(t) meets a preset threshold criterion and to determine the elastance E or compliance C from the rise of the alveolar pressure Palv(t) as a function of the volume Vol(t) only in the time intervals thus determined.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
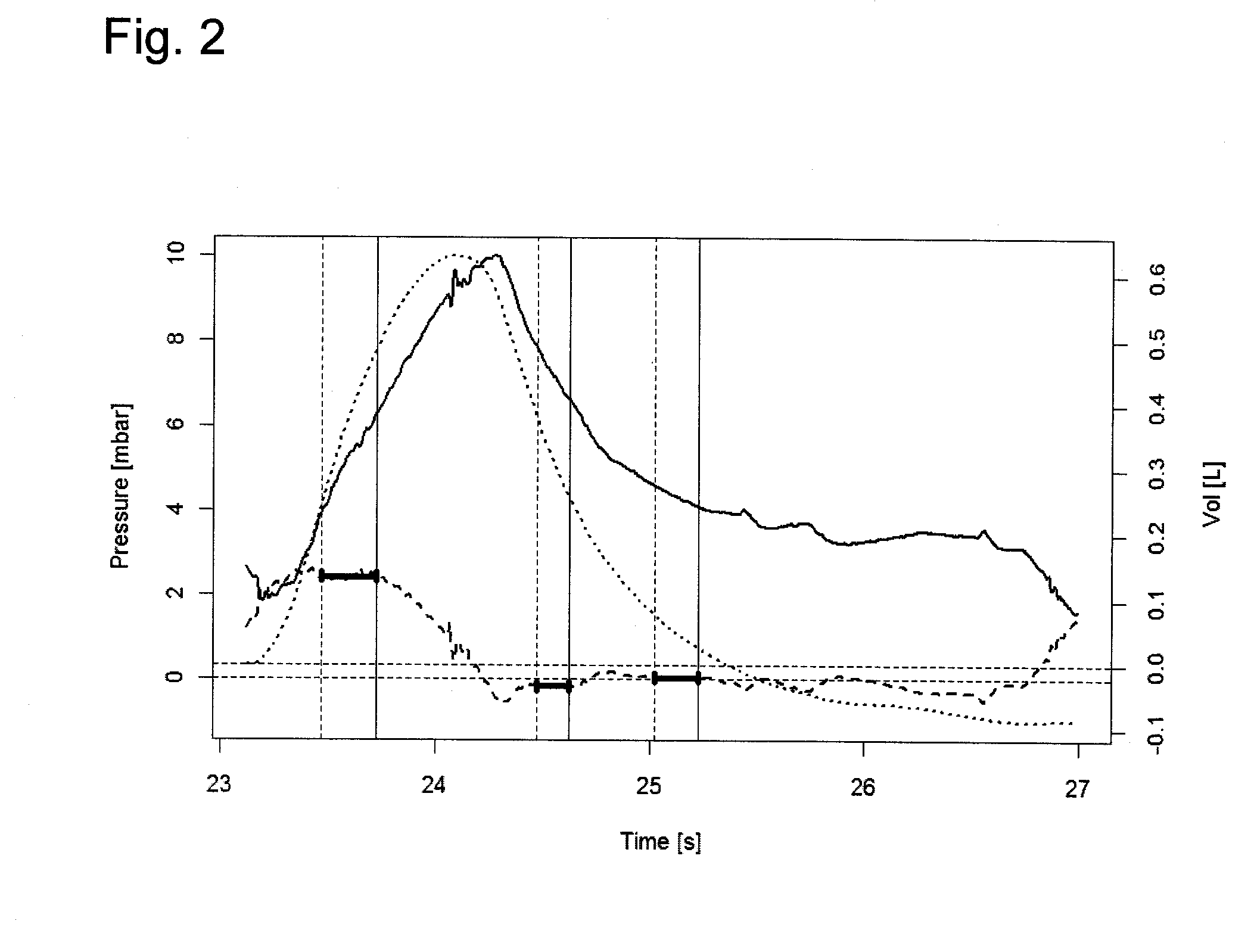
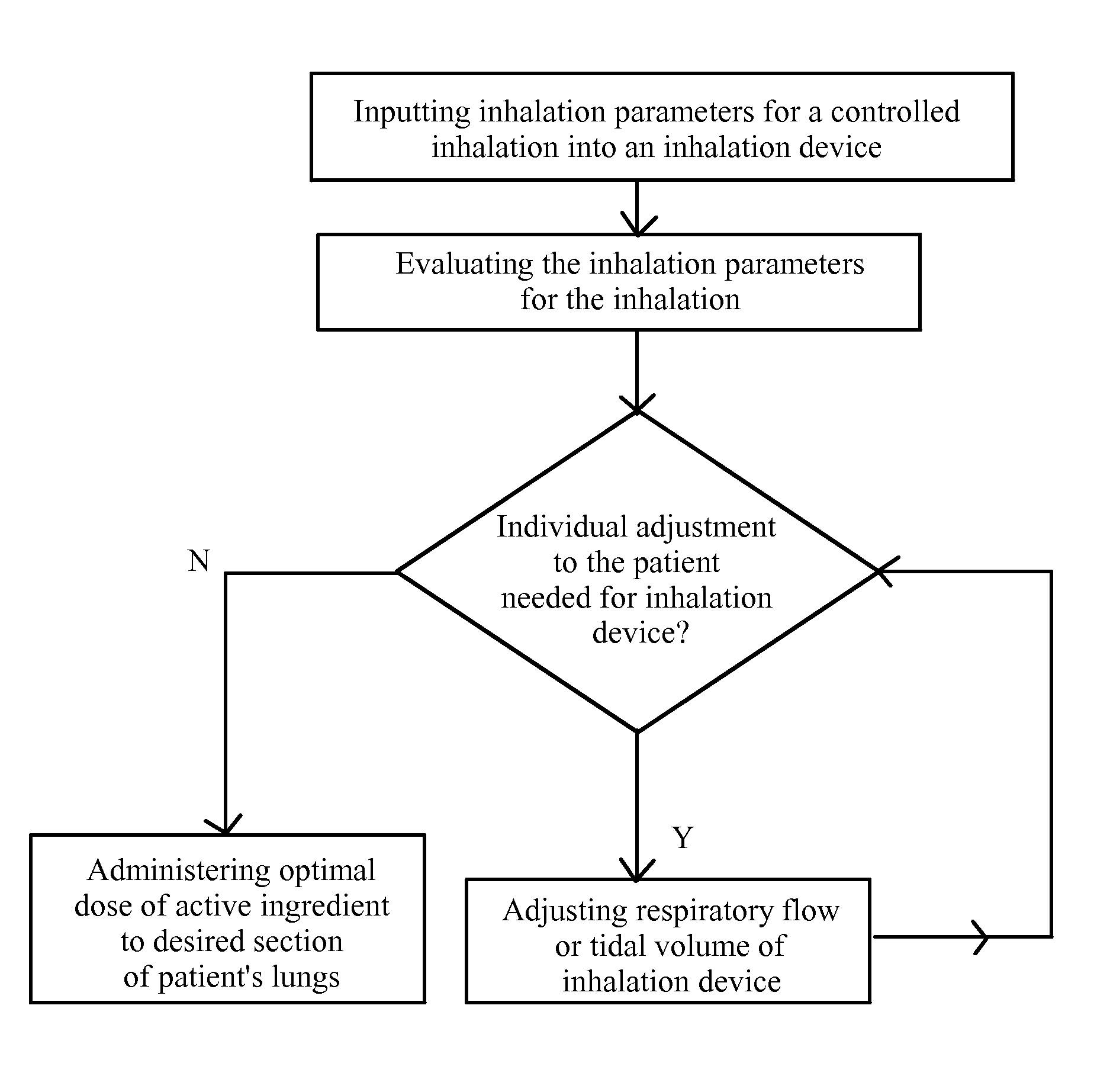
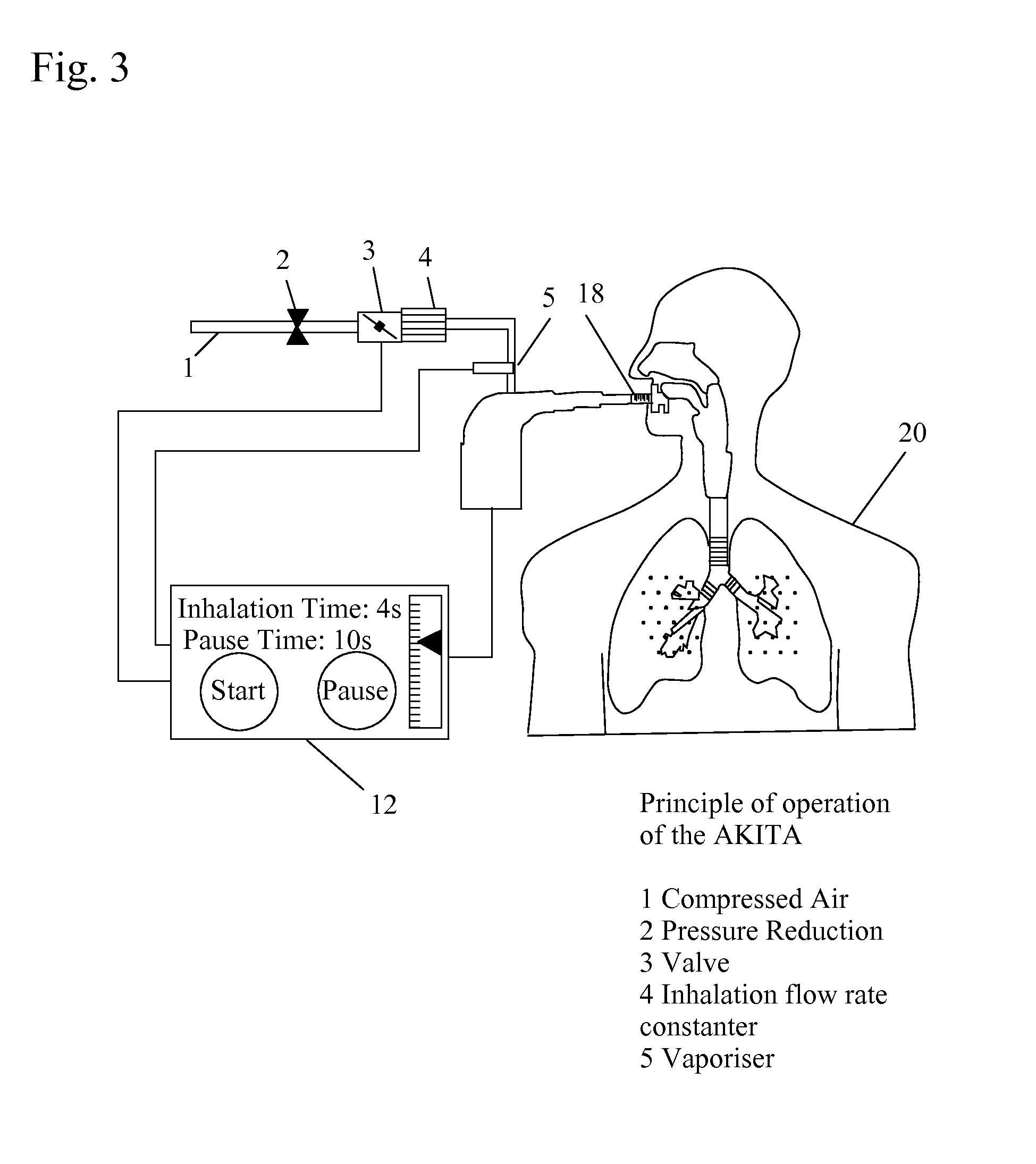
Device for the controlled inhalation of therapeutic aerosols
A device for the controlled inhalation of therapeutic aerosols comprises means providing individual patient parameters and / or aerosol parameters for the inhalation. The aerosol doses, such as the tidal volume and the respiratory flow, are individually adjusted on the basis of these individual parameters. Thus, the inhalation device may be individually adjusted to the patient to be treated.
Owner:VECTURA LTD
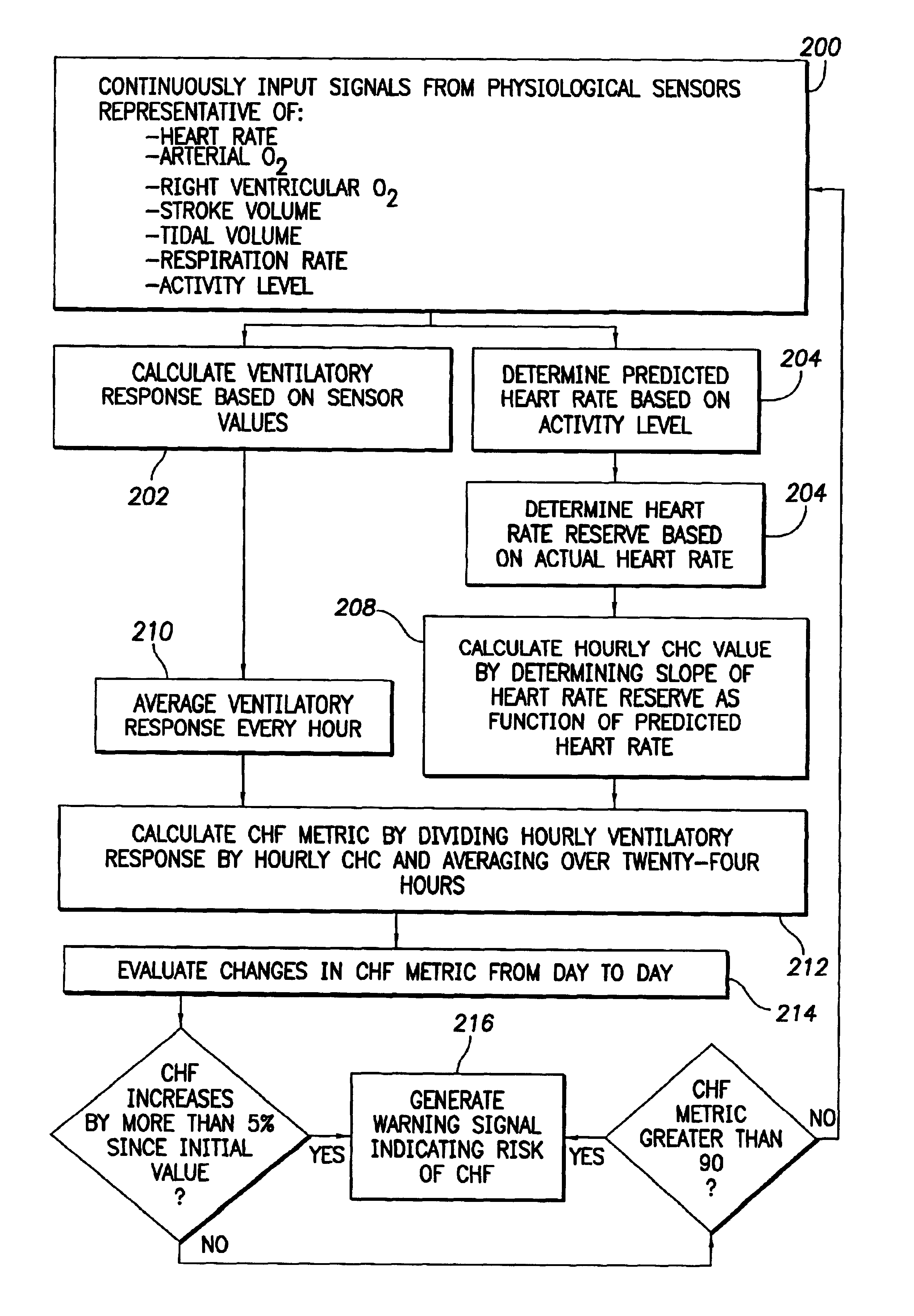
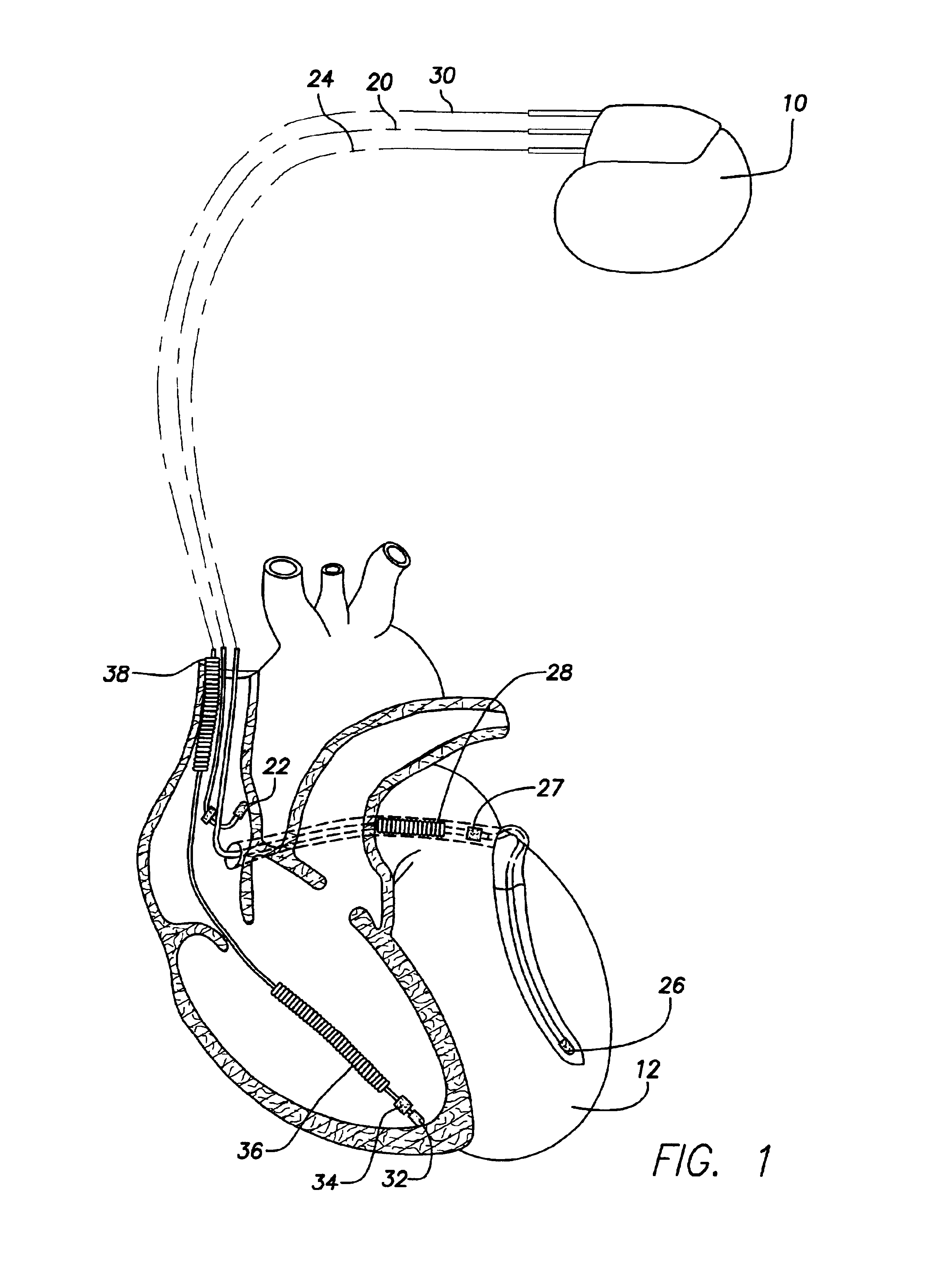
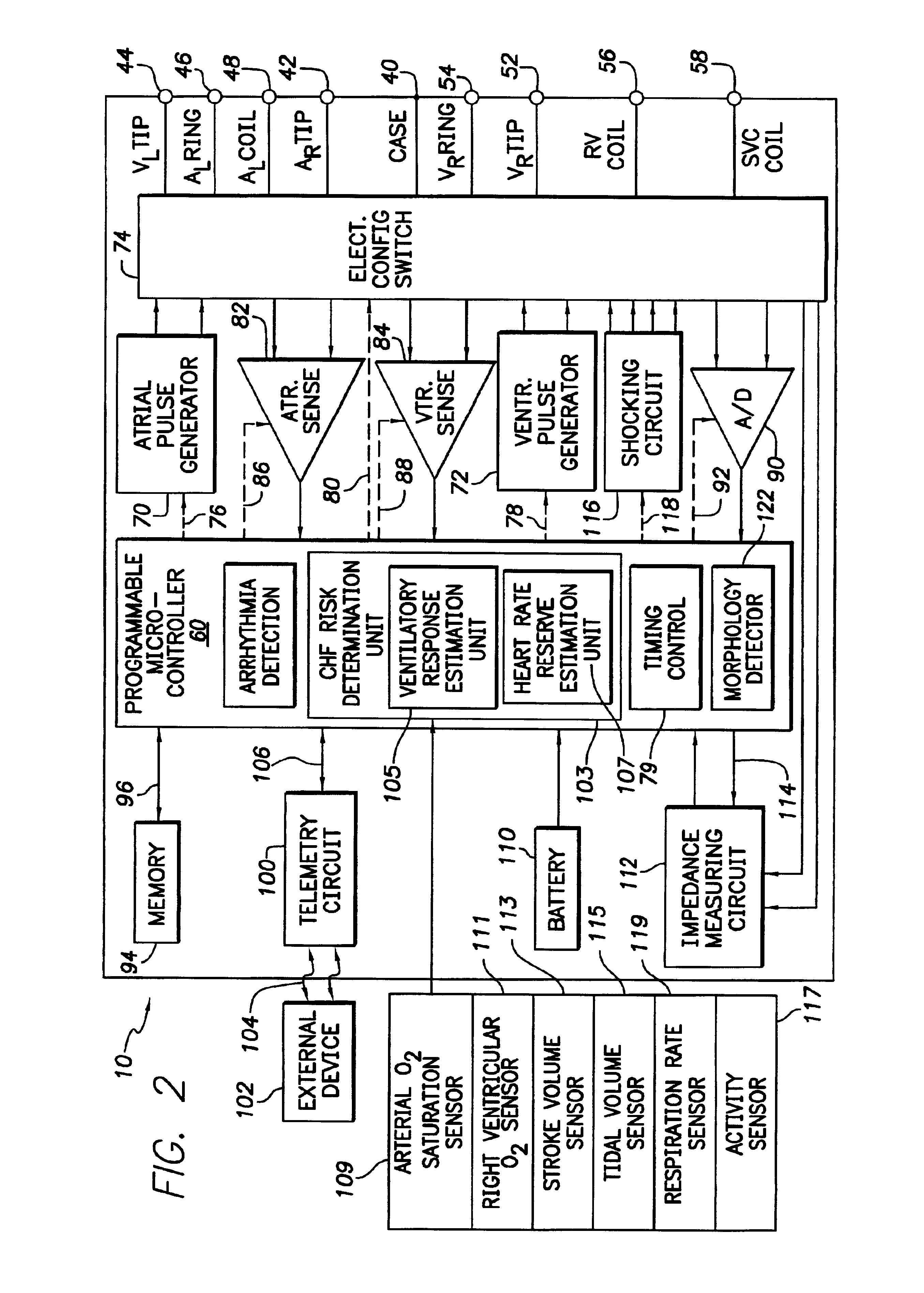
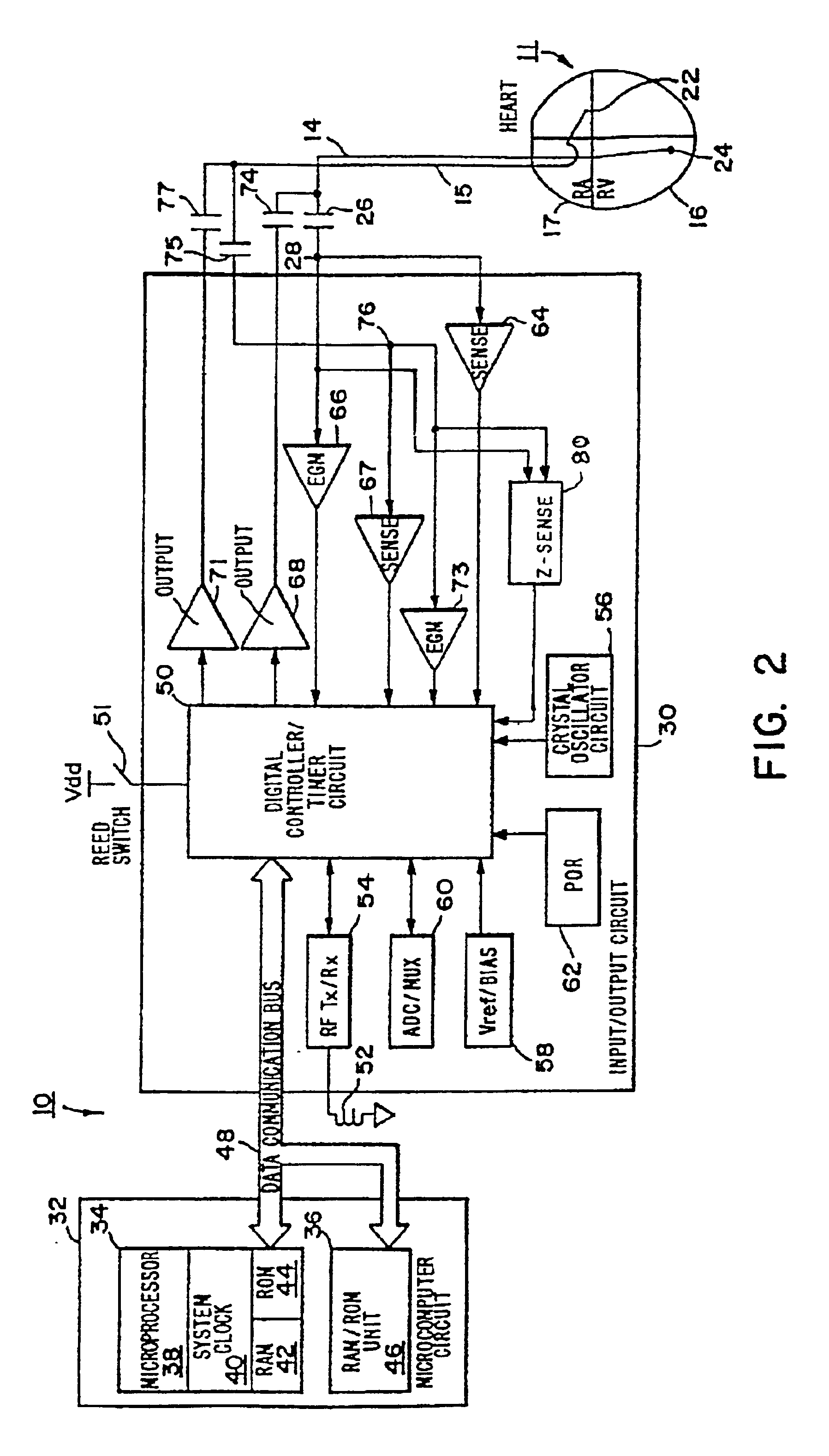
System and method for evaluating risk of mortality due to congestive heart failure using physiologic sensors
A congestive heart failure (CHF) mortality risk metric is automatically generated using an implantable medical device and, if it exceeds a predetermined threshold, a warning signal is issued indicating a significant risk of mortality due to CHF, perhaps necessitating more aggressive medical therapy. The CHF mortality risk metric is calculated based on a combination of estimated ventilatory response values and the slope of heart rate reserve as a function of predicted heart rates. Ventilatory response is estimated based on detected values of actual heart rate, arterial oxygen saturation, right ventricular O2, stroke volume, tidal volume, and respiration rate. Heart rate reserve values are derived from the actual heart rate along with patient age and rest heart rate. The predicted heart rates, which represent the heart rates the patient would achieve if healthy, are derived from activity sensor signals. The CHF mortality risk metric is then calculated as a ratio of ventilatory response and the slope of the heart rate reserve. If the CHF mortality risk metric exceeds a critical threshold value, such as 90, the warning signal is generated. Also described herein are various techniques for estimating ventilatory response.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Intelligent respirator and aerating method of using the respirator
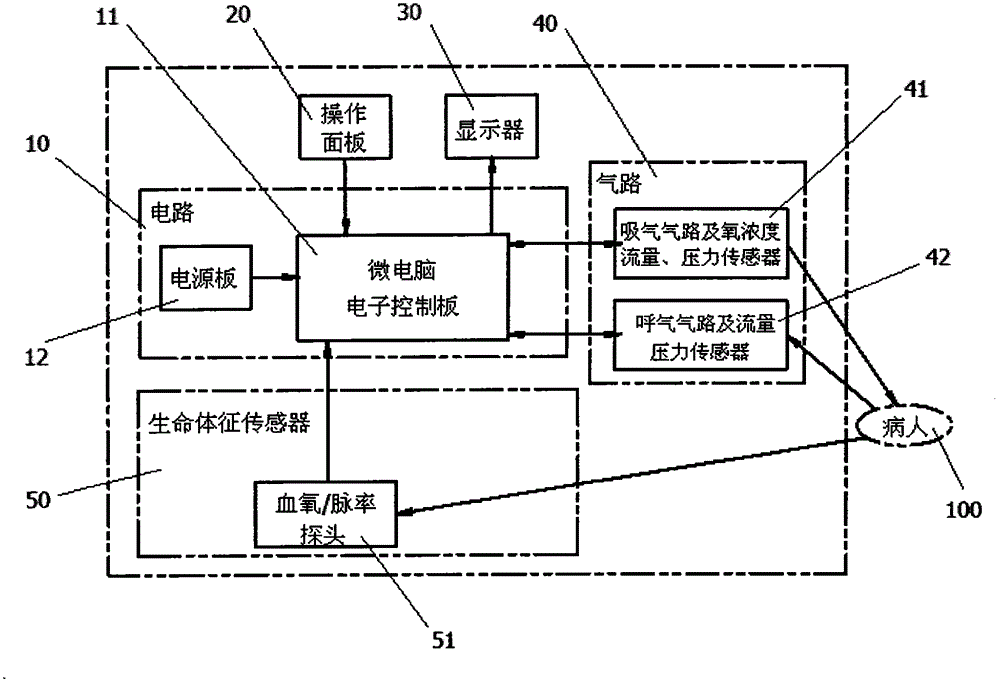
InactiveCN104399164AOperational intelligenceRespiratorsEvaluation of blood vesselsMicrocomputerEmergency treatment
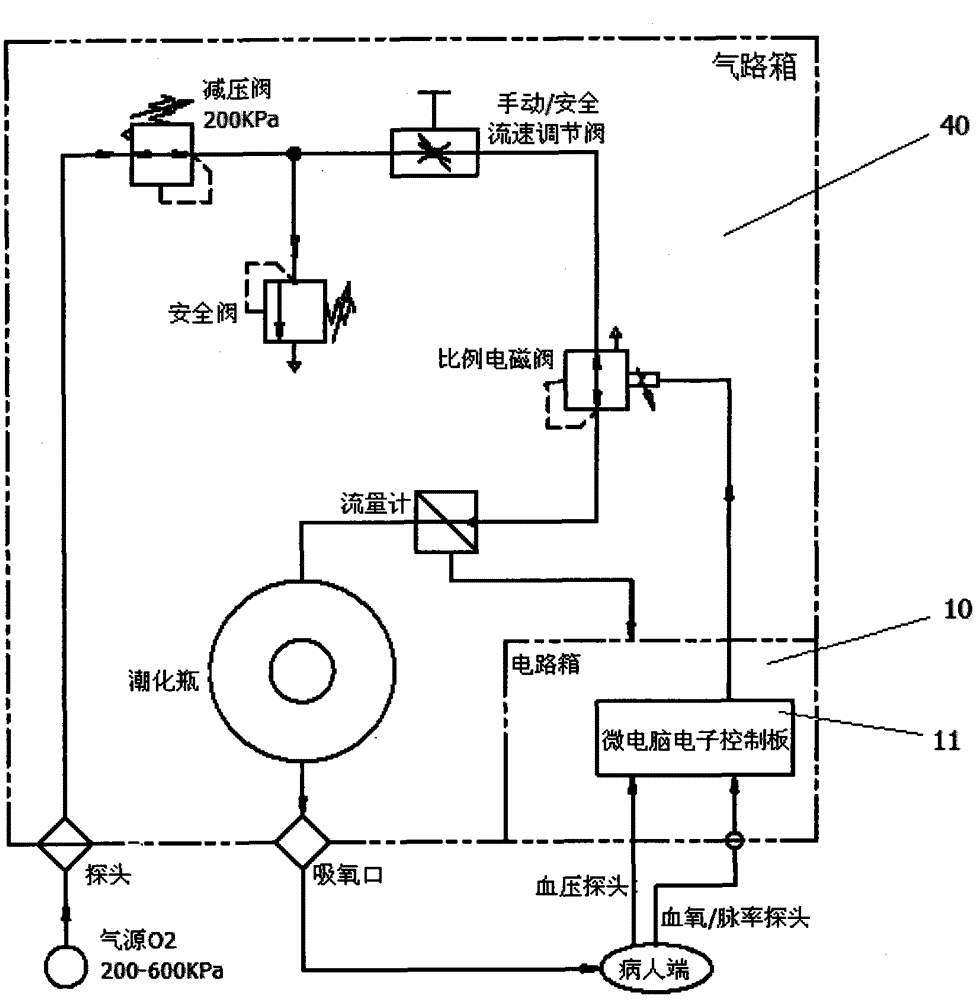
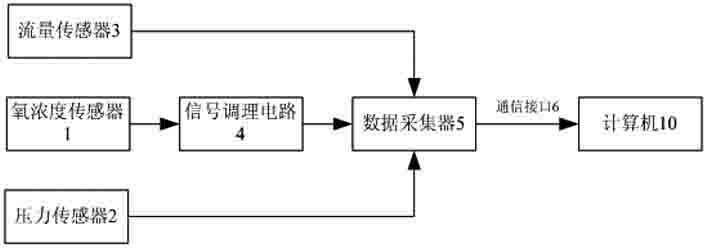
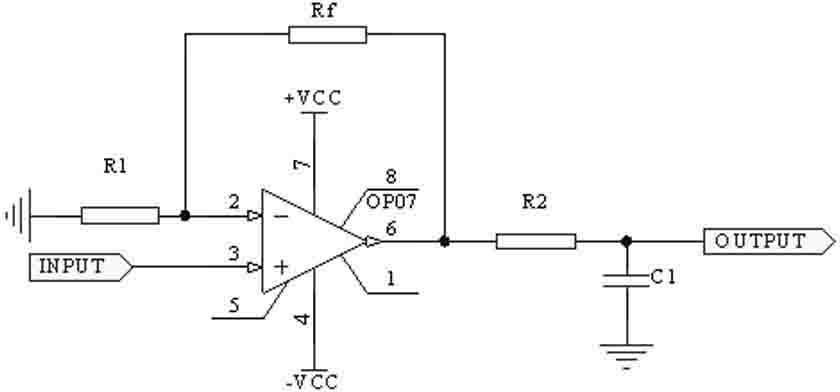
Provided is an intelligent respirator and aerating method of using the respirator, belonging to the technical field of medical instruments. The intelligent respirator comprises a circuit, an air channel, an operation panel, and a display; a flow meter and a transducer are installed inside the air channel; a power supply board is installed inside the circuit; the circuit further comprises a microcomputer electronic control panel and a vital sign transducer; the microcomputer electronic control panel is installed inside the circuit; the microcomputer electronic control panel is in communication connection respectively with the power supply board, the operation panel, the display, the air channel and the vital sign transducer. The aerating method of using the intelligent respirator comprises the following steps: collecting, by the microcomputer electronic control panel via the vital sign transducer, information changes of vital sign parameters, controlling the velocity ratio of air and oxygen in the air channel, and controlling a warning device, thereby achieving the intelligent adjustment to the oxygen concentration of the patient and sending out an alarm for emergency treatments. The intelligent respirator and aerating method of using the respirator can achieve the intelligent control, thus achieving the adjustment of oxygen concentration as in need and in time without changing the tidal volume.
Owner:北京神鹿腾飞医疗科技有限公司
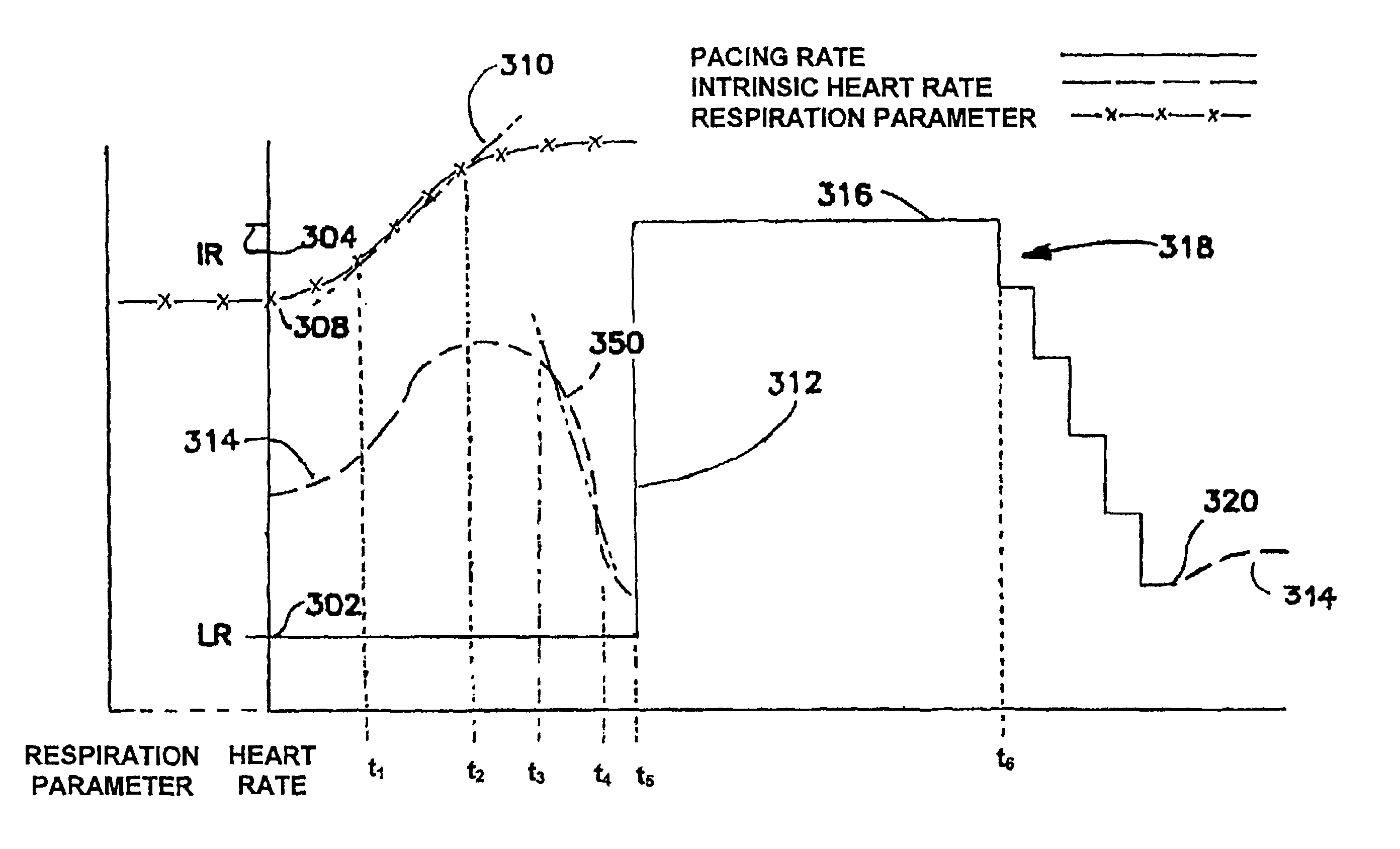
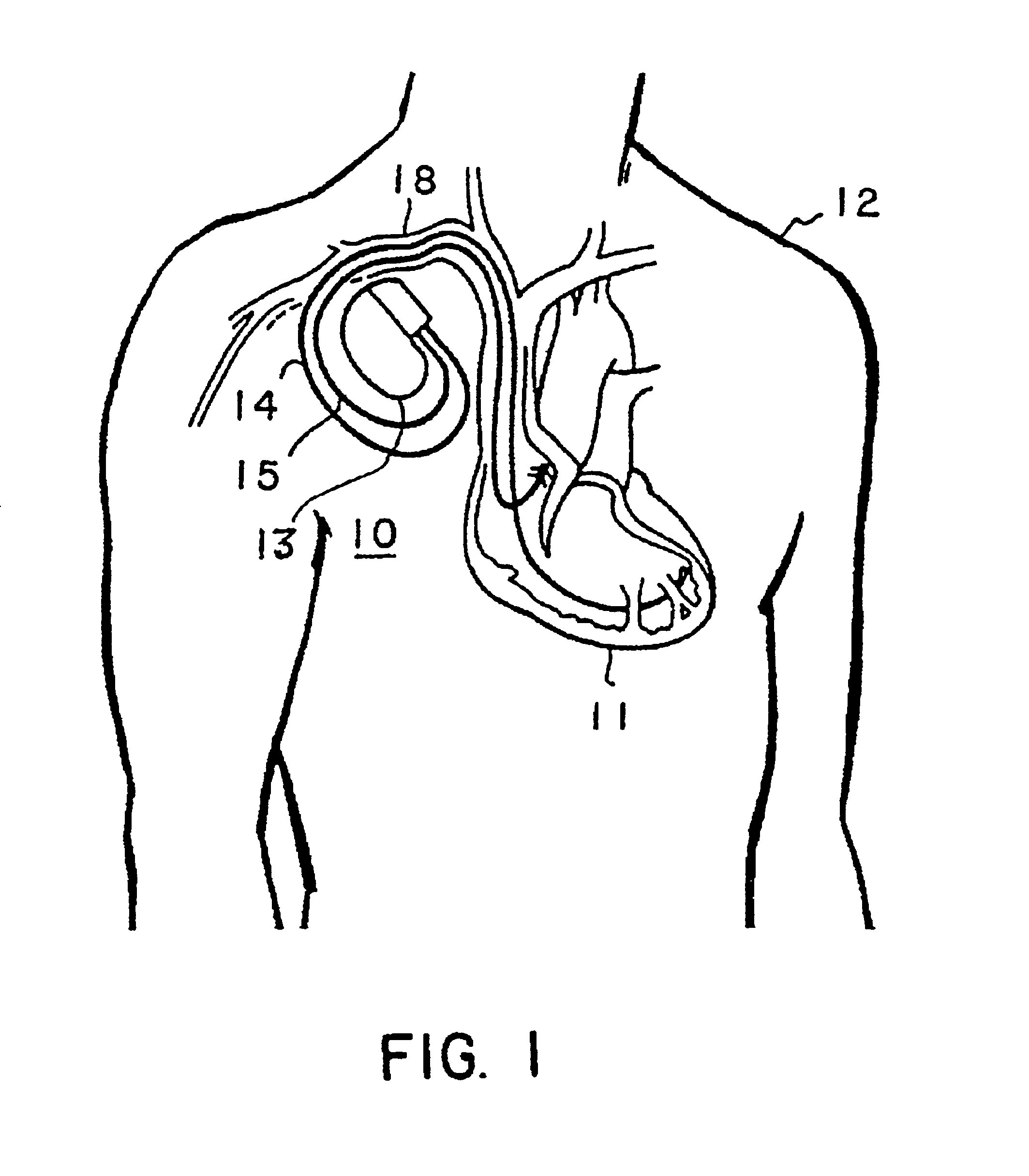
Methods and apparatus for detection and treatment of syncope
InactiveUS6895275B2Faster and robust detectionConfidenceHeart stimulatorsDiagnostic recording/measuringTidal volumePulse rate
The present invention relates to methods and apparatus for detection and treatment of syncope in an implantable medical device, and particularly to detection of syncope as a function of a predetermined increase in one or more respiration parameter and drop in heart rate and optionally delivering a pacing therapy in response thereto. The onset of a syncopal episode is declared when the patient's respiration rate and / or tidal volume and / or minute ventilation increases by a predetermined increment or threshold and a heart rate drops below a threshold heart rate drop. The threshold heart rate drop is preferably established as a function of the change in the respiration parameter.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
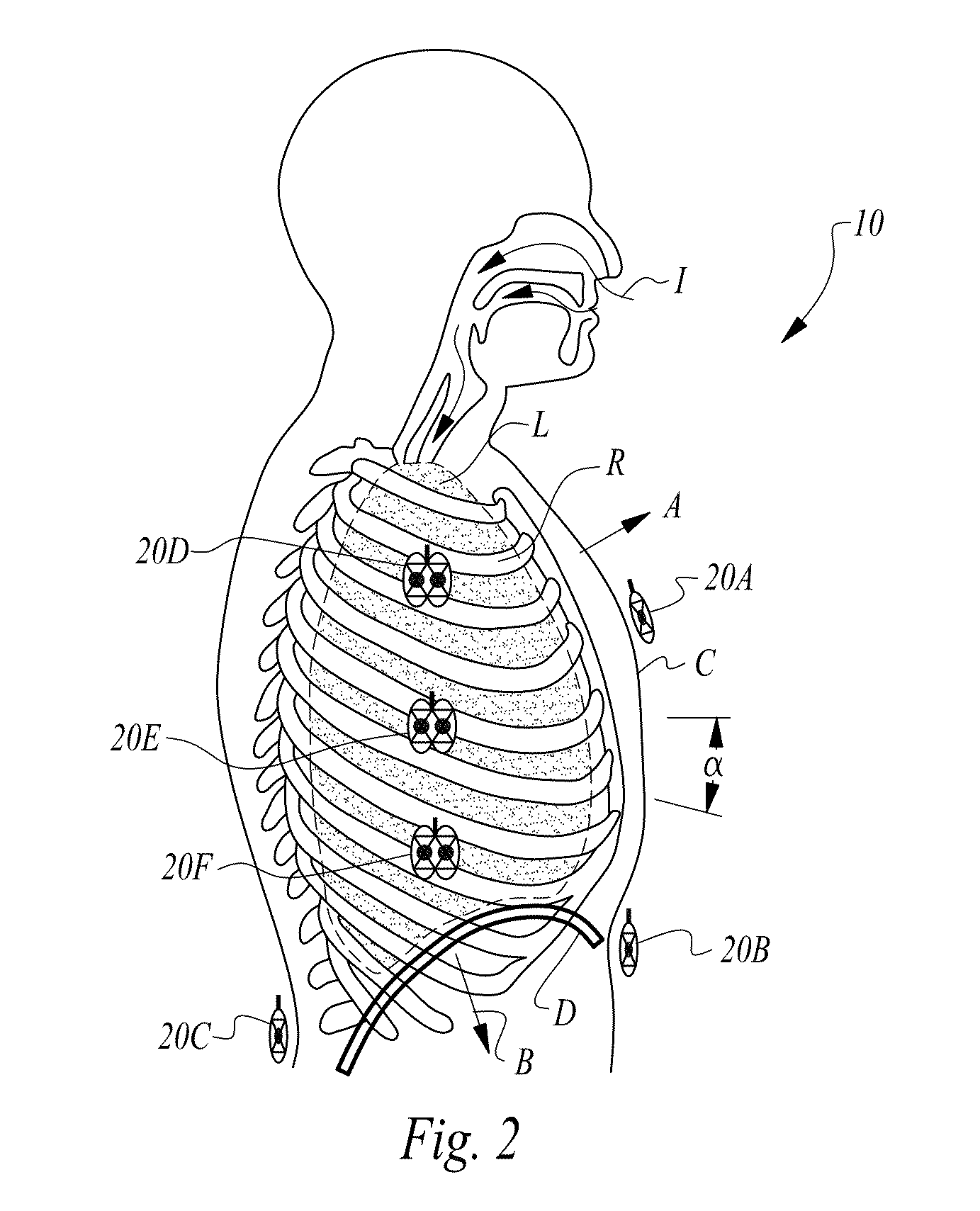
Apparatus and method for continuous noninvasive measurement of respiratory function and events
ActiveUS9002427B2Prevent corruptionNoise minimizationRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsContinuous measurementRadar systems
An apparatus and method for non-invasive and continuous measurement of respiratory chamber volume and associated parameters including respiratory rate, respiratory rhythm, tidal volume, dielectric variability and respiratory congestion. In particular, a non-invasive apparatus and method for determining dynamic and structural physiologic data from a living subject including a change in the spatial configuration of a respiratory chamber, a lung or a lobe of a lung to determine overall respiratory health comprising an ultra wide-band radar system having at least one transmitting and receiving antenna for applying ultra wide-band radio signals to a target area of the subject's anatomy wherein the receiving antenna collects and transmits signal returns from the target area.
Owner:LIFEWAVE BIOMEDICAL
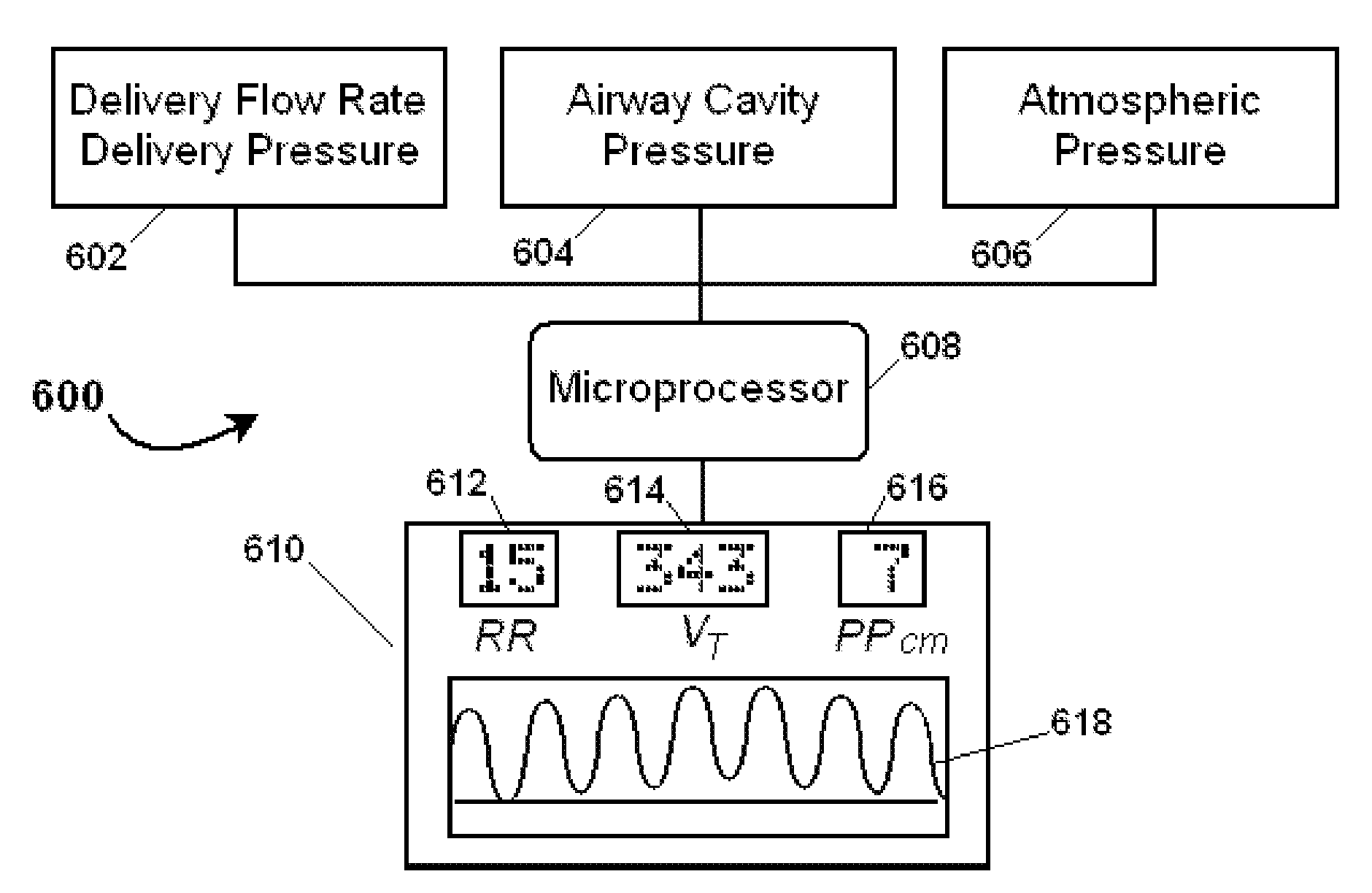
Clinical monitoring in open respiratory airways
A novel and non-obvious method, system and apparatus for determining respiratory volume flow rate of a subject and associated parameters such as tidal volume, minute volume, and respiratory rate. The method for determining respiratory volume flow rate of a subject can include selecting an airway cavity of the subject, measuring delivery volume flow rate of respiratory gas delivered to the airway cavity, measuring pressure within the airway cavity and calculating a respiratory volume flow rate of the subject using the measured delivery volume flow rate of respiratory gas delivered to the airway cavity and the measured pressure within the airway cavity. The method further can include generating a warning signal selected from the group consisting of an indicator that a respiratory volume flow value is outside of an expected value for the subject and an indicator that an airway cavity measurement value does not conform to an expected value.
Owner:MERGENET MEDICAL
Electric extrusion device of breathing bag
InactiveCN103495248AEnsure coordinationGuaranteed reliabilityRespiratorsTidal volumeThrough transmission
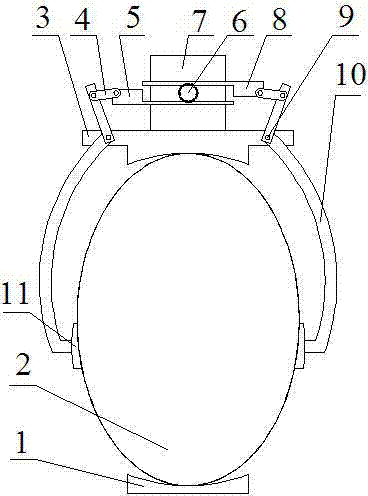
The invention discloses an electric extrusion device of a breathing bag. The extrusion device is fixed on the periphery of the breathing bag through an upper fixing block and a lower fixing block. The extrusion device comprises two mechanical arms which are symmetrically arranged on the two sides of the breathing bag and driven by a stepping motor. The two mechanical arms are both fixed to the upper fixing block through rotary shafts. The stepping motor simultaneously controls extrusion and expansion actions of the two mechanical arms through a gear rotating coaxially with the stepping motor. An upper rack and a lower rack which perform transmission in cooperation with the gear and opposite in transmission direction are arranged at the upper end and the lower end of the gear respectively. The end portion of the upper rack and the end portion of the lower rack are hinged to the end portions of the two mechanical arms through transmission rods, and the other end of each mechanical arm is provided with a manipulator matched with the peripheral face of the breathing bag in shape. The electric extrusion device of the breathing bag can replace human hands to press the breathing bag, is small in size and convenient to carry and facilitates implement of first-aid work. The mechanical operation can ensure the frequency of oxygen supply and stability of tidal volume, and thus quality of the first aid for a patient is improved.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and means of physiological monitoring using sonification
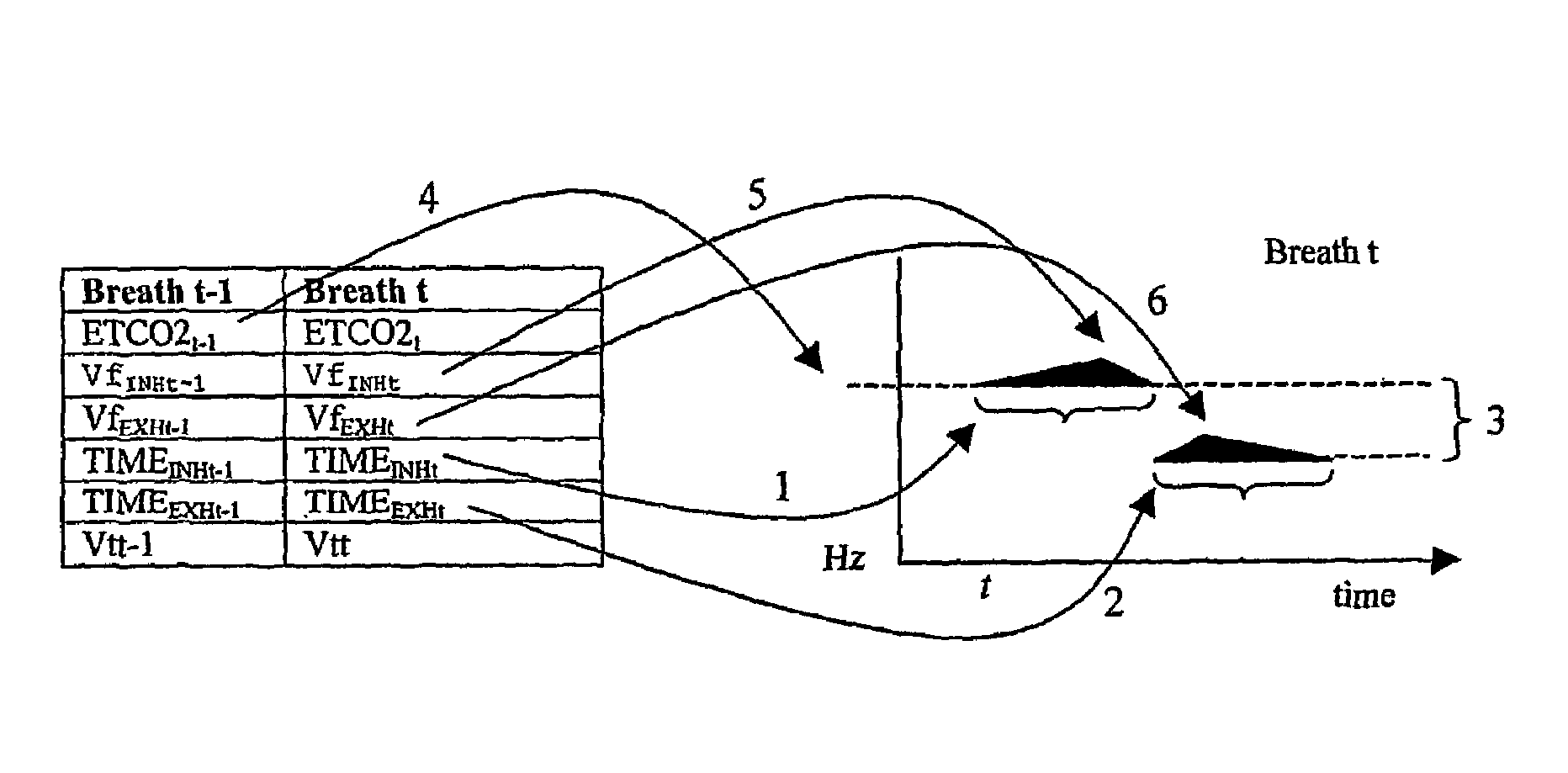
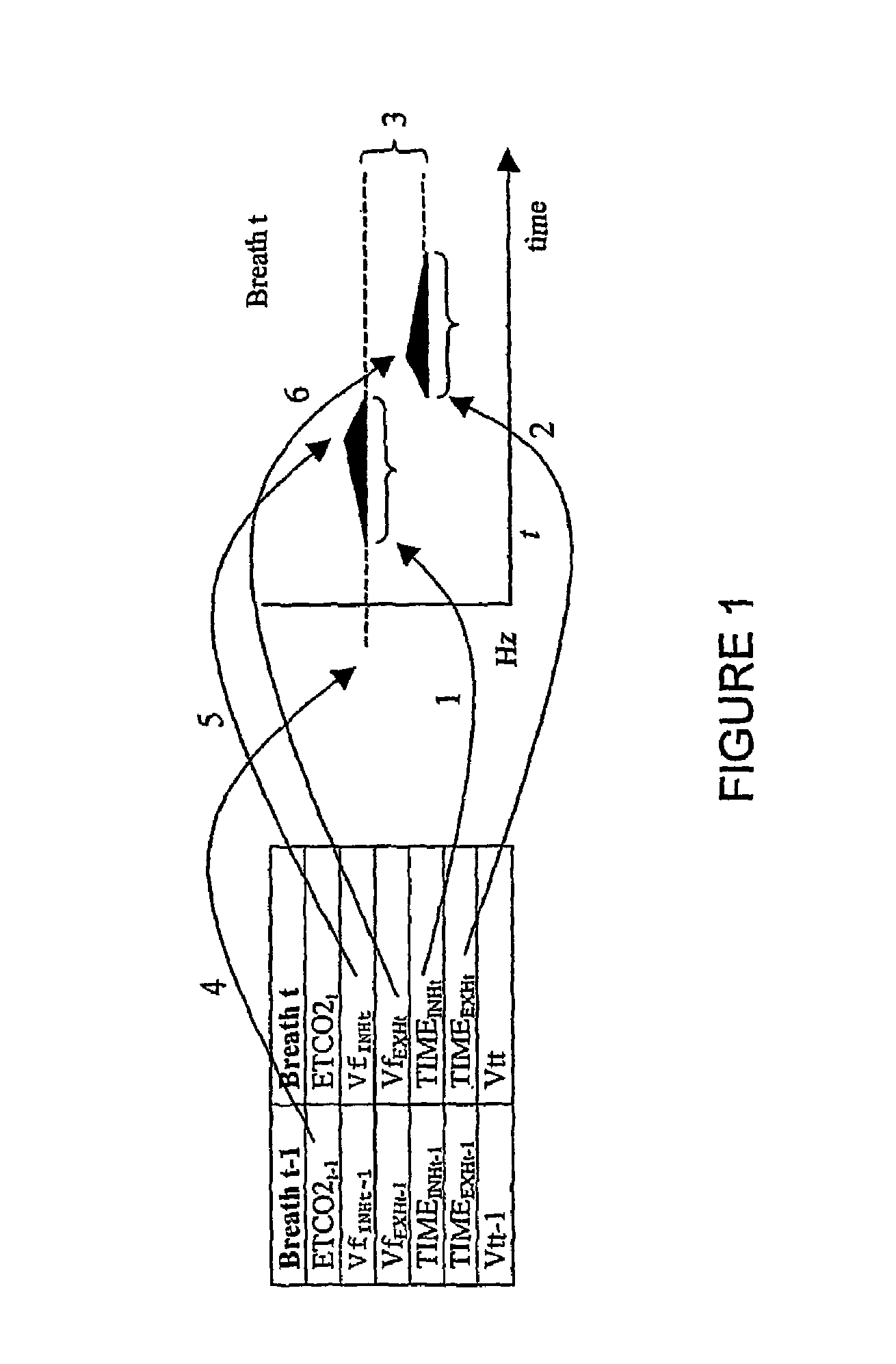
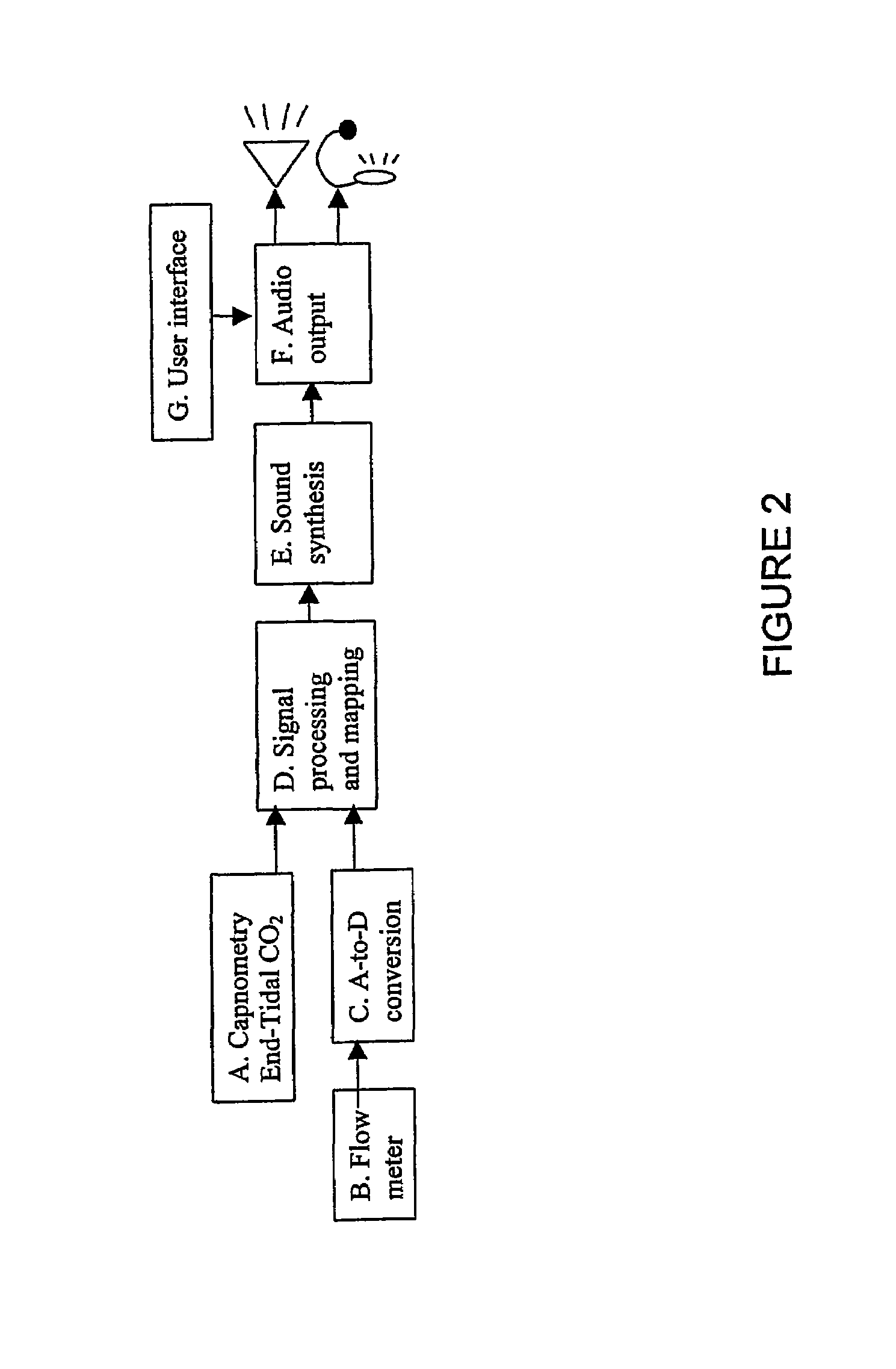
The invention resides in a respiratory sonification monitoring method and system for monitoring respiration in a subject including the use of capnometric means for measuring carbon dioxide concentrations, flowmeter means for measuring gas flow and volume of gas; means adapted to process into digital information, signal output from the capnometric means and the flowmeter means, sound synthesizer means adapted to convert the digital information into synthesised audio output, wherein, changes in respiratory flow during inhalation and exhalation, and changes in end tidal carbon dioxide concentrations (ETC02) and cumulative tidal volume (cumVt) of the subject can be represented as changes in synthesised sound heard through a loudspeaker, headphone or ear piece.
Owner:SANDERSON PENELOPE MARGARET +1
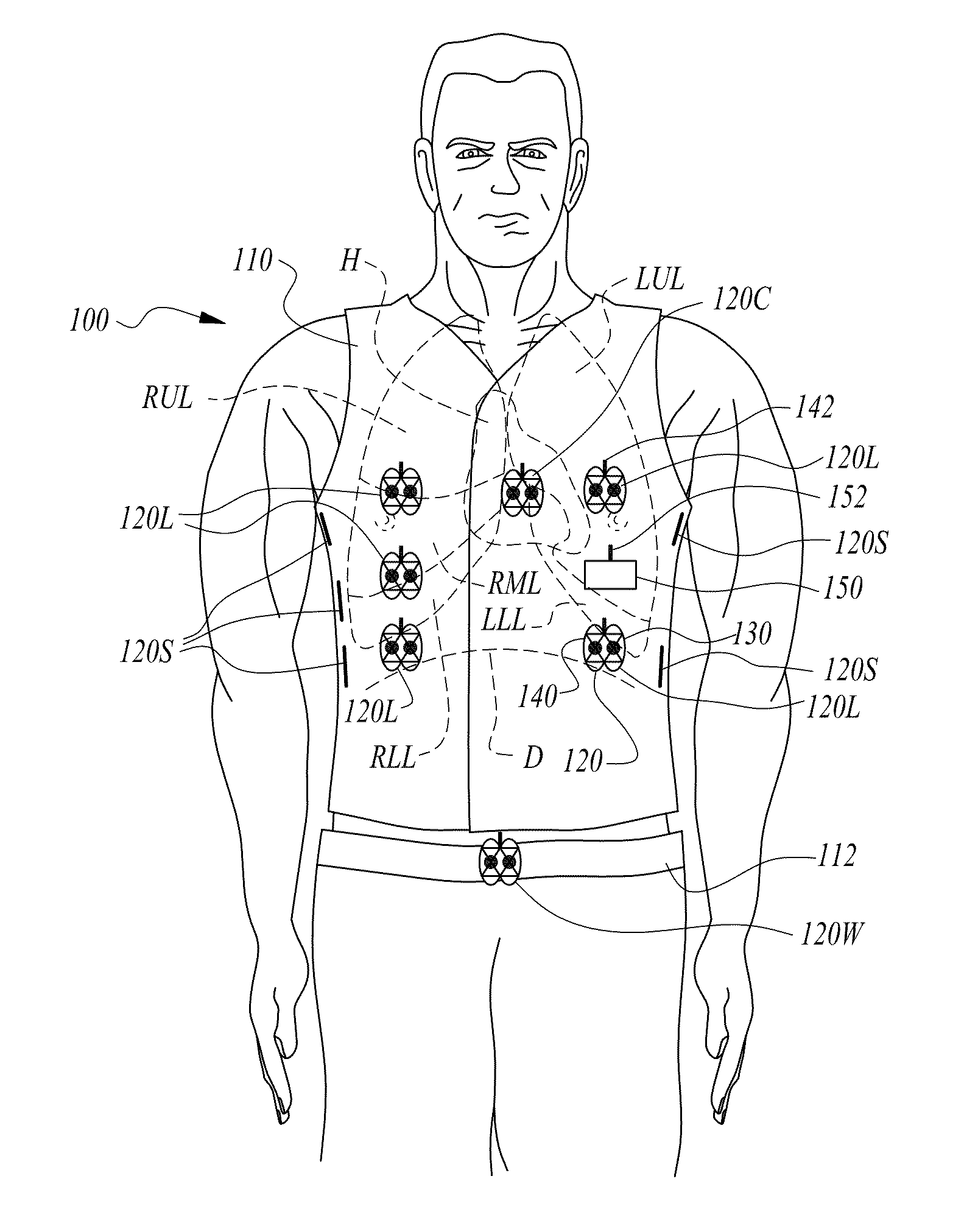
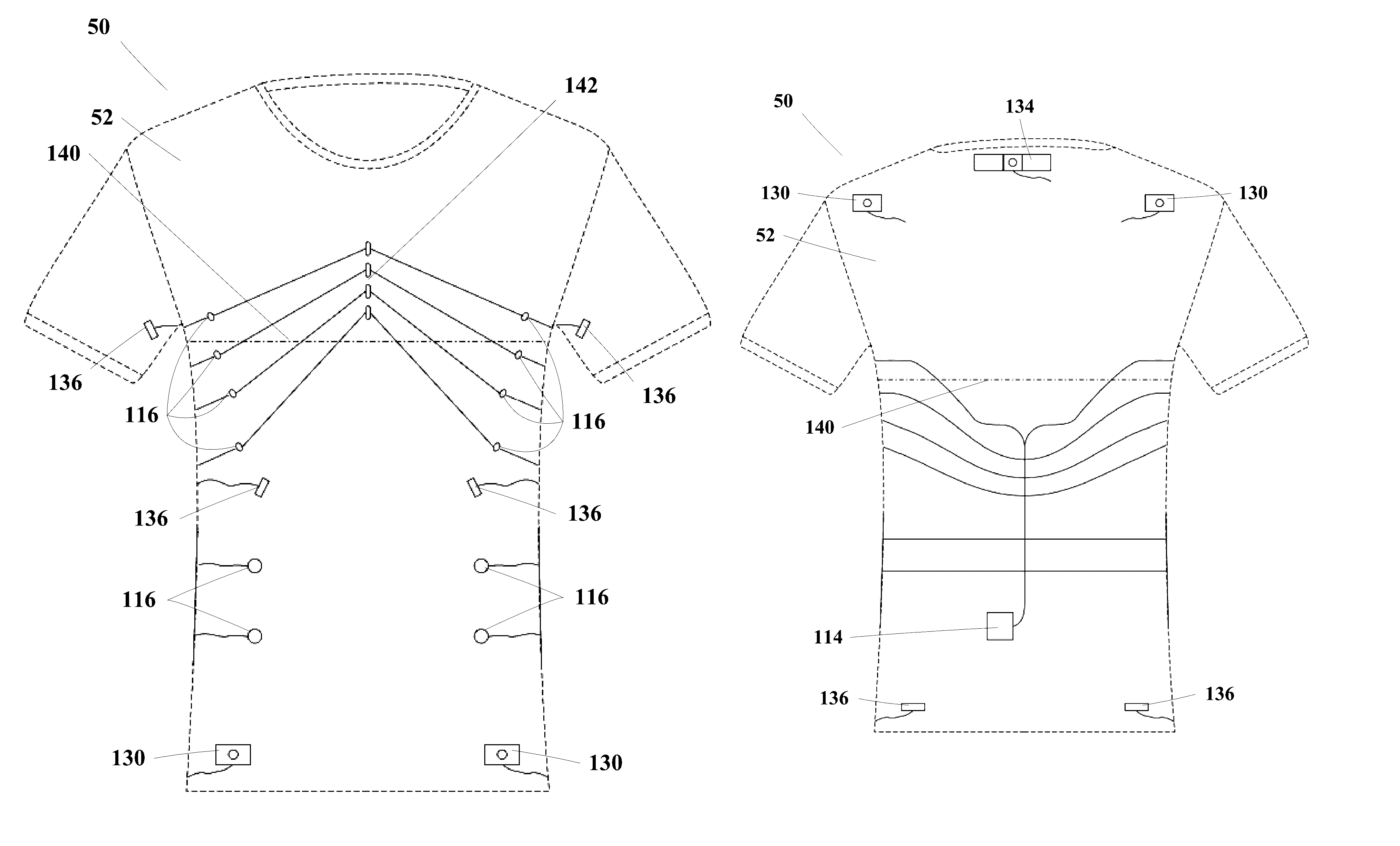
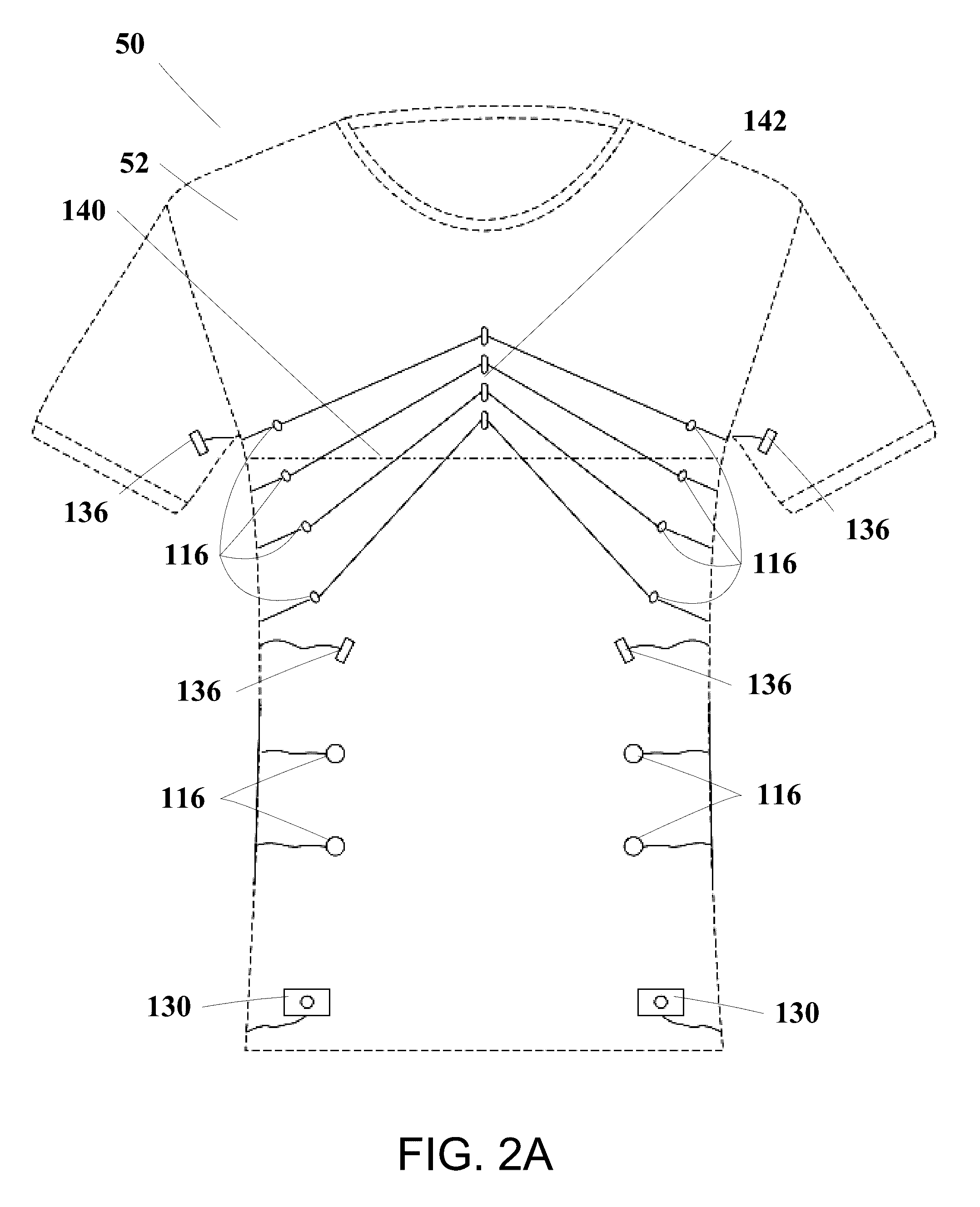
Garment System With Electronic Components and Associated Methods
ActiveUS20160120470A1Improve the measurement effectElectric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsAbdominal movementsBiometric data
The disclosure provides a wireless biometric monitoring system that may be capable of acquiring, compiling, analyzing, and transmitting biometric data in near real time / real time. The system may utilize either the most up-to-date Bluetooth protocol (currently Bluetooth Smart) or a similar wireless protocol. The system may further integrate through this wireless protocol with peripheral devices to expand the measurement capacity of the system.In embodiments, the system may be capable of monitoring multiple biometric responses including, but not limited to: skin temperature, core temperature, respirations, heart rate, predicted tidal volume, chest wall movement, abdominal movement in conjunction with inspiration, abdominal movement in conjunction with expiration, HRR (heart rate reserve), HRV (heart rate variability), body position relevant to perpendicular, shoulder position relevant to hip position, general body posture, up time, down time, and malfunctions.
Owner:CIPHER SKIN
Device and method for respirating a patient by means of high-frequency ventilation
ActiveUS7770580B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTidal volumeEmergency medicine
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Patient cassette with variable patient circuit volume
ActiveUS20100307490A1Maximize rebreathingDifferent typeRespiratorsMedical devicesTidal volumeIntensive care medicine
A flexible patient cassette that can be optimized for different types of breathing circuits, different drive circuits and different patient categories has a first inlet arranged to be connected to a drive circuit, and at least a second inlet arranged to be connected to a patient connector, the first and second inlets being pneumatically connected with each other through a gas conducting passage constituting a patient circuit having a certain volume. The patient cassette has a volume-varying arrangement for varying the patient circuit volume to allow that volume to be varied in dependence of at least one of the type of breathing circuit in which the patient cassette is used; the type of drive circuit to which the patient cassette is connected; the tidal volume of a patient connected to the patient connector.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
Device and method for respirating a patient by means of high-frequency ventilation
ActiveUS20080087284A1Accurate measurementReduce formationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTidal volumeEmergency medicine
A device is provided for respirating a patient by means of high-frequency ventilation, which has at least one device for setting a desired tidal volume by a user, and which has at least one regulating device for regulating an amplitude of the respiration pressure and / or at least one regulating device for regulating the oscillation frequency on the basis of the tidal volume determined. A corresponding method is provided for regulating a device for respirating a patient by high-frequency ventilation and a method is provided for respirating a patient.
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Device and process for metering breathing gas
ActiveUS6929006B2Accurate measurementSimple wayRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTidal volumeRespirator
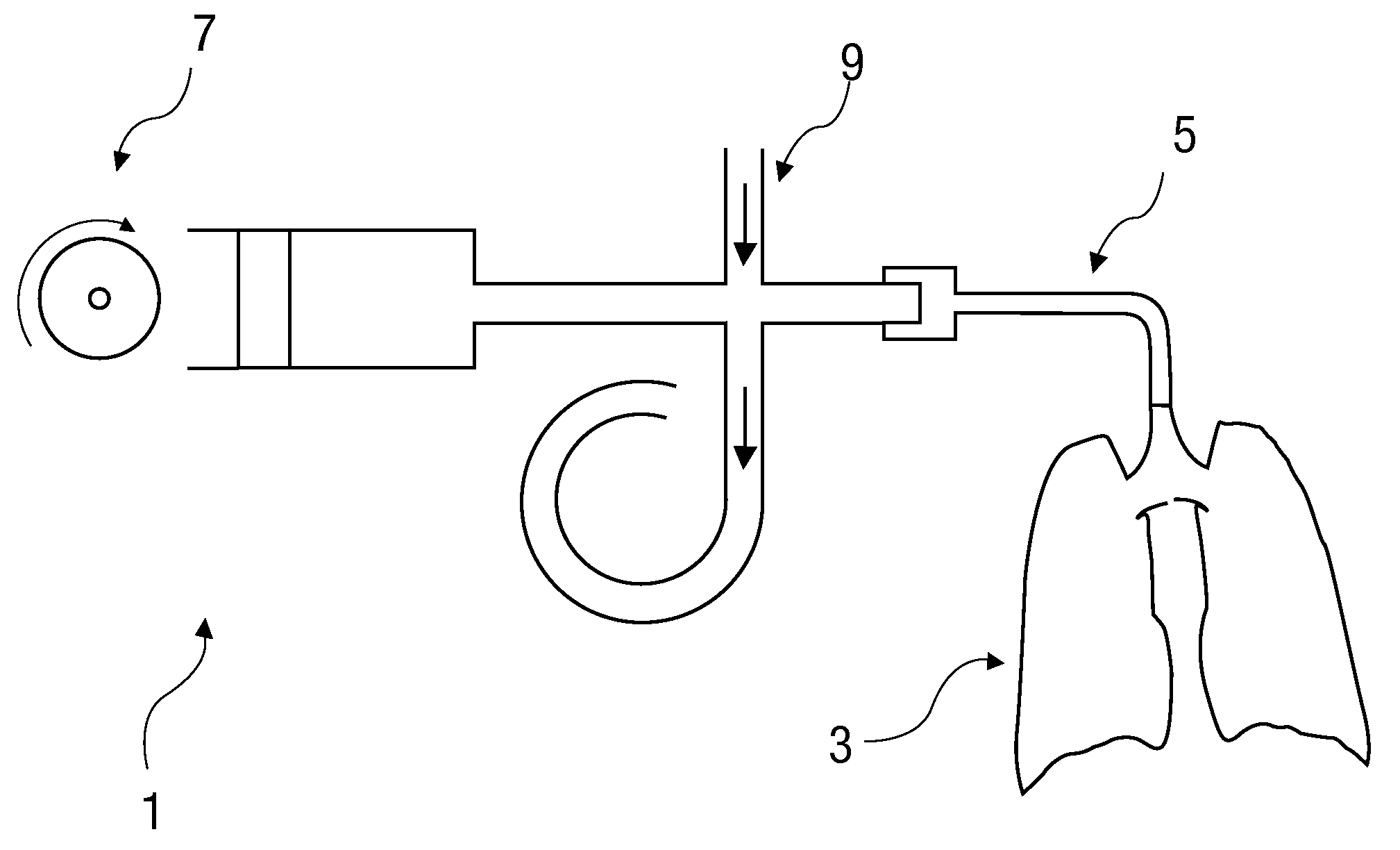
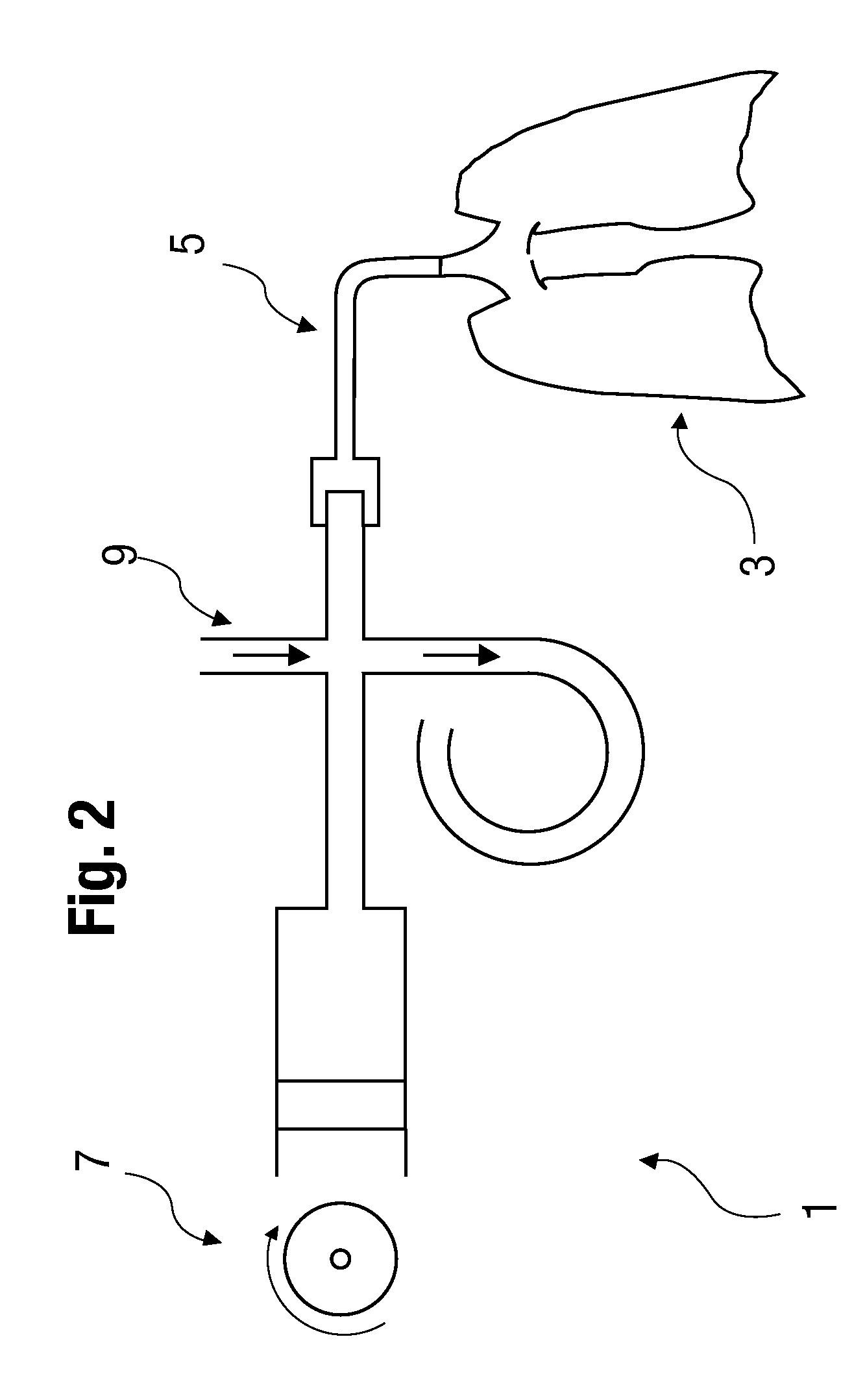
A respirator with a tidal volume-measuring device (6) between a respiration bag (8) and a patient adapter (2) provides accurate metering of the tidal volume. The device includes a first pressure-measuring device (4) and a breathing gas interruptor (5) in series sequence between the patient adapter (2) and the tidal volume-measuring device (6). A second pressure-measuring device (7) is provided between the tidal volume-measuring device (6) and the respiration bag (8). A control unit (20) is connected with the tidal volume-measuring device (6) and the pressure-measuring devices (4, 7) and sends control signals in such a way that when a predetermined tidal volume is reached, the breathing gas interrupter (5) is switched to the closed position, and that the closed position is eliminated when the pressure p2 measured with the second pressure-measuring means (7) has dropped below the pressure p1 determined with the first pressure-measuring means (4).
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Resuscitator device
ActiveUS20140318544A1Reduce riskInflation difficultRespiratory masksMedical devicesTidal volumePositive pressure
A manually actuated, self-inflating bag valve mask provides users with a positive pressure ventilation device that reliably provides a proper tidal volume to the patient and controls the rate of ventilation of the patient. The bag valve mask is lightweight, compact, durable, and quickly deployable in the field. The device is preferably operable with one hand and can be configured for use in low-light environments.
Owner:SAFEGUARD MEDICAL HOLDCO LLC
Back-silting simulation method for basin channel of force tide firth artificial island operating area
ActiveCN108256137ADesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityMathematical model
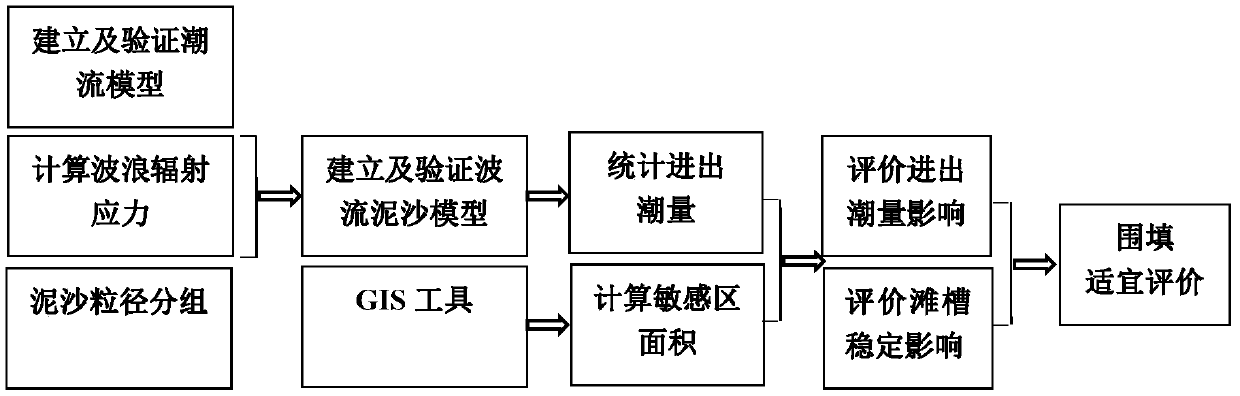
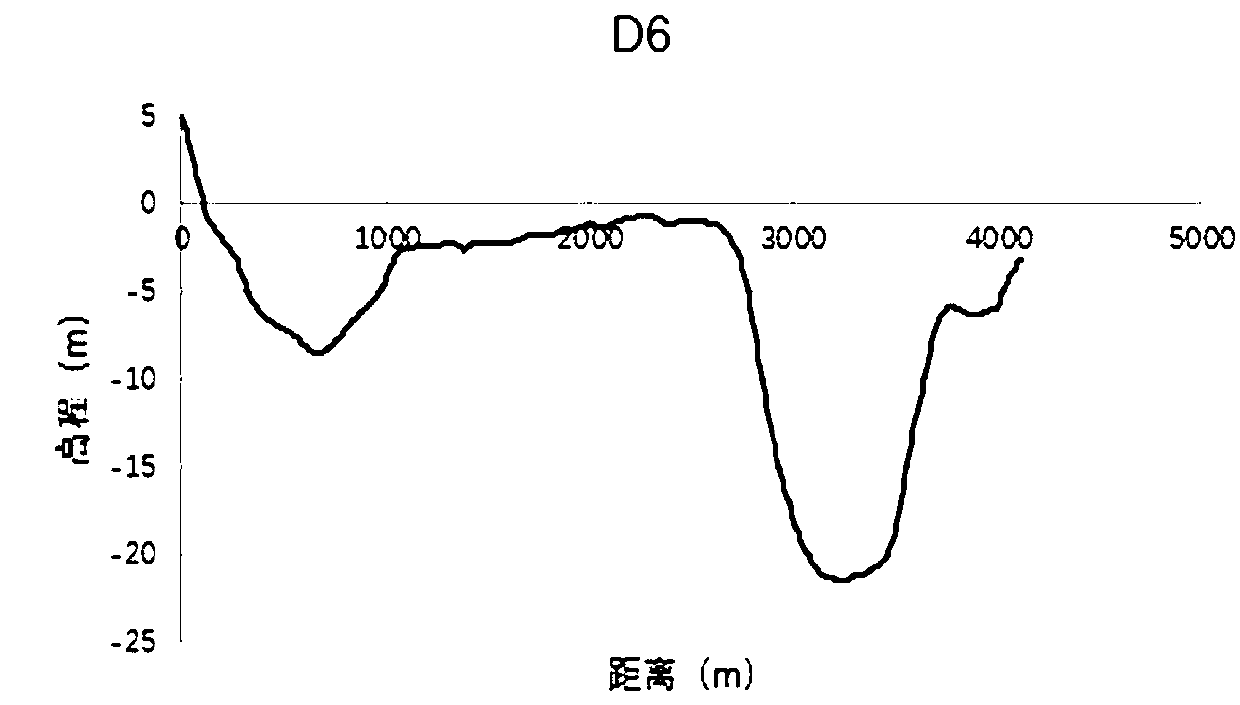
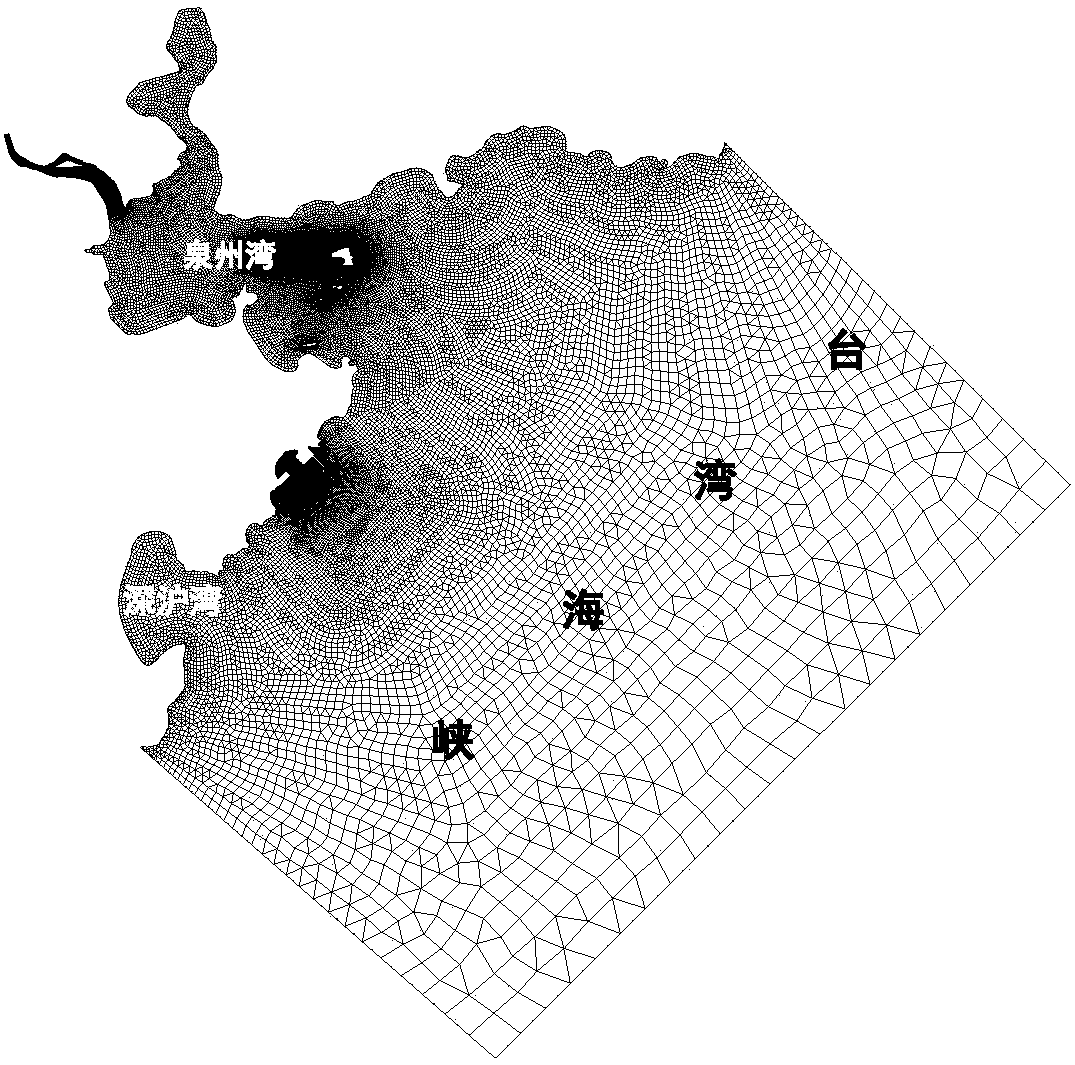
The invention discloses a method for simulating back-silting of a basin channel of a force tide firth artificial island operating area. The method comprises the steps of establishing a water flow mathematical model by use of a water flow sediment mutual feedback calculation mode and variable roughness factors changing with geomorphology and tide levels; calculating representative wave radiation stresses at different tide levels; optimizing an artificial island plane modality; performing wave, tide and runoff and sediment discharge coupling fitting; and finally, counting aback-silting amount. According to the method, in a wave current sediment mathematical model construction process, the requirement of basin channel back silting simulation of force tide firth artificial island operating areas with different geomorphologic shapes can be adapted and satisfied for the unique dynamic geomorphology characteristics of irregular coastlines of a semi-closed force tide firth offshore artificialisland, large tidal volume of inflow and outflow of force tides, wide tidal flat and complex geomorphology, strong tidal current under the action of rotary current, high influence of waves and combined action of sediment movements affected by wave currents in consideration of the variable roughness factors changing with the geomorphology and the tide levels.
Owner:NANJING HYDRAULIC RES INST +1
Plethysmograph
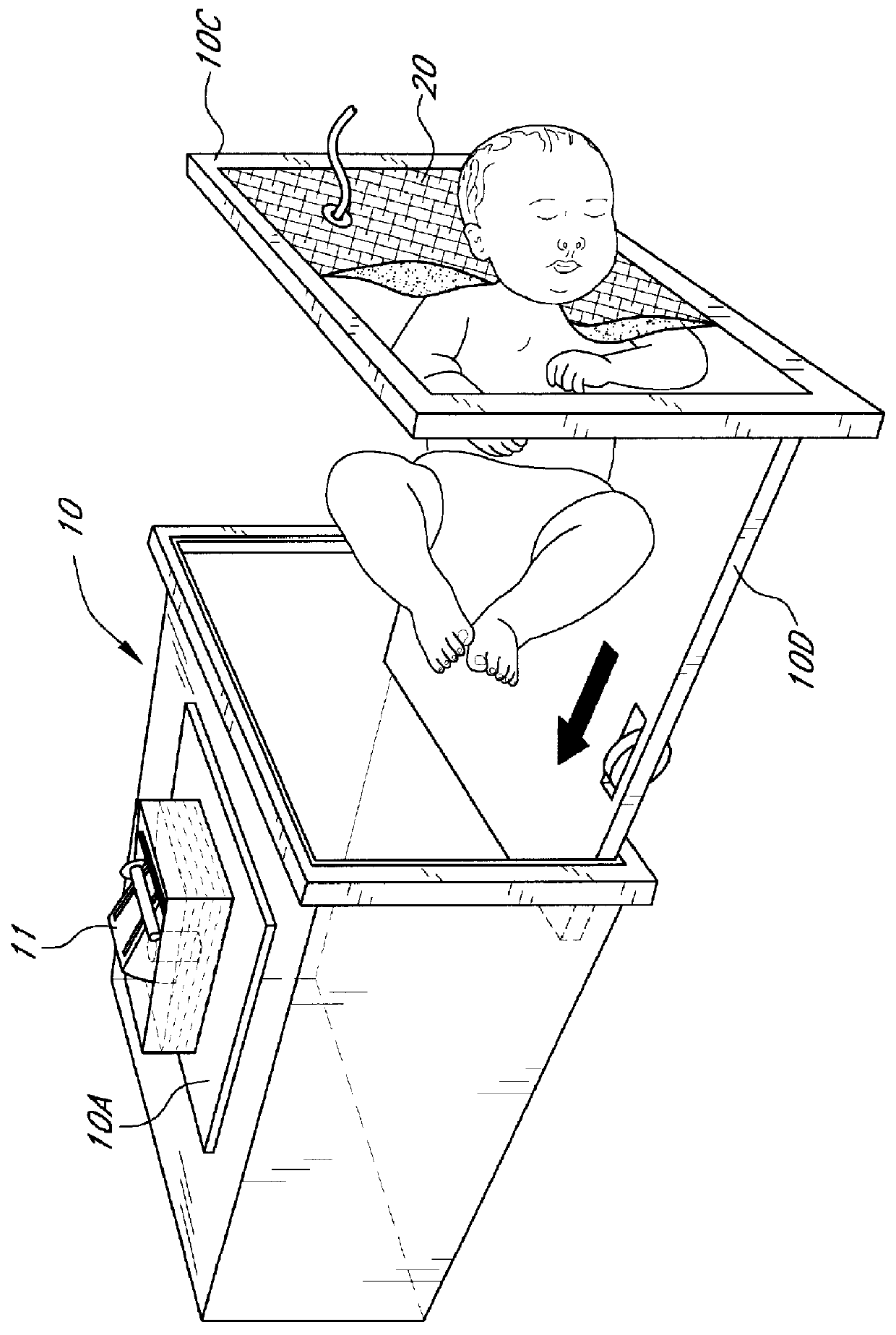
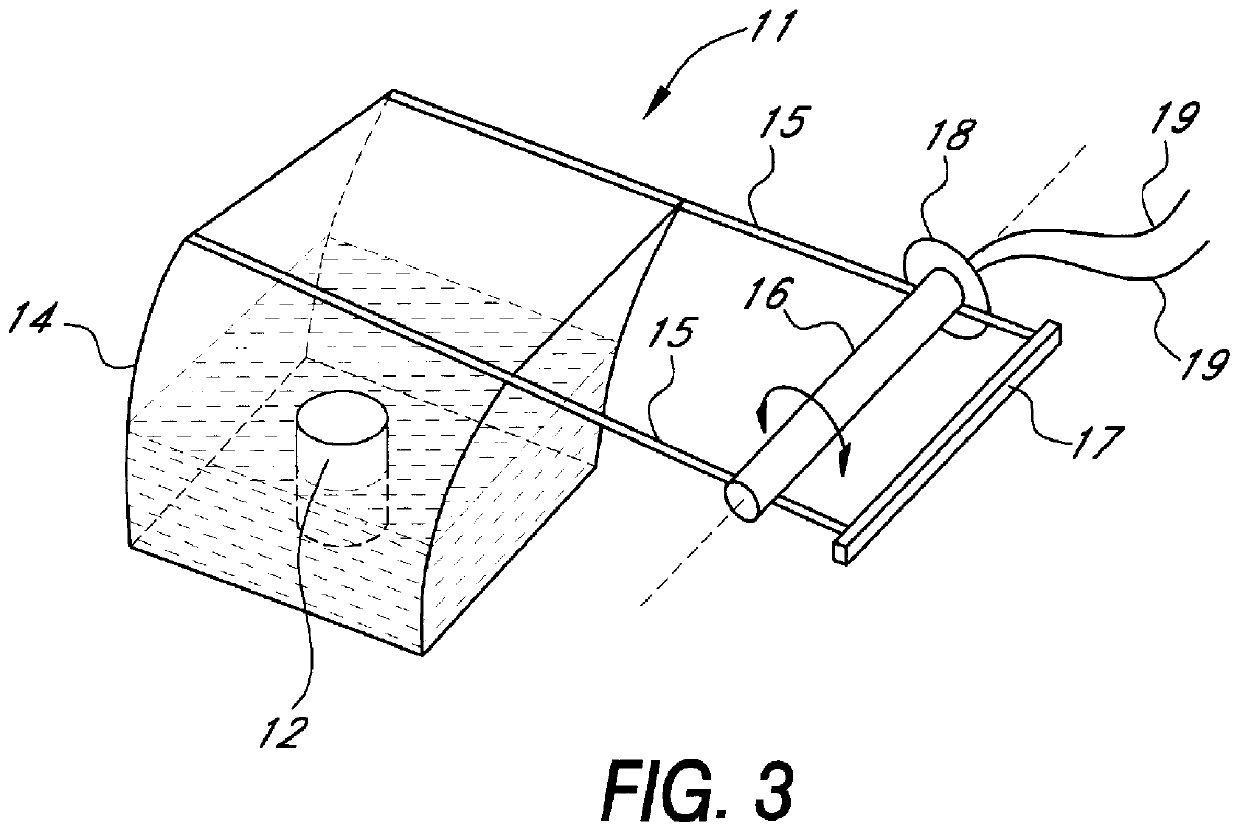
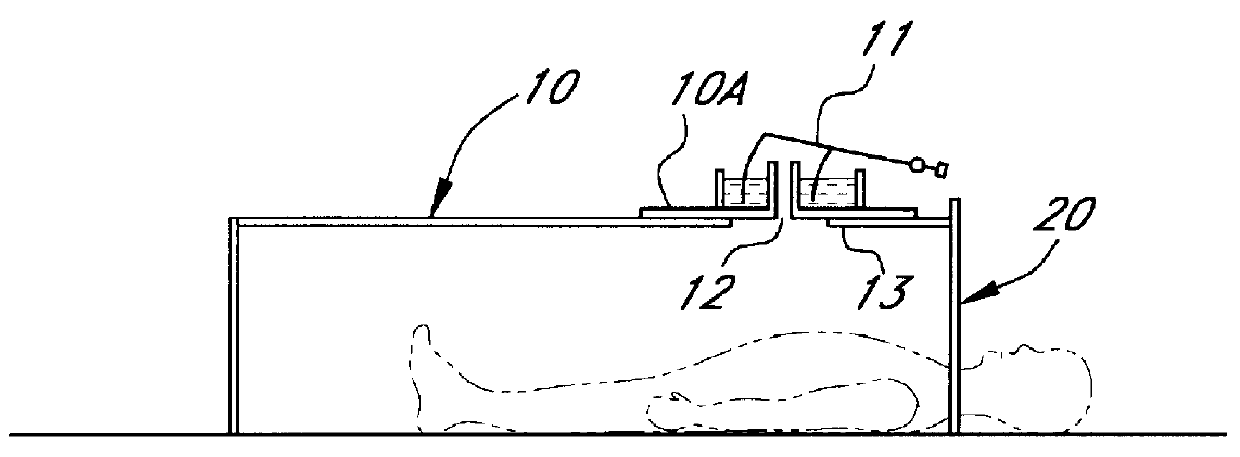
InactiveUS6113550ACheap constructionBreathe freelyBaby-incubatorsRespiratory organ evaluationTidal volumeNon invasive
Non invasive measurement of infant lung function during unsedated sleep is achieved by a plethysmograph which comprises of a rigid acrylic box (10) with integral water sealed spirometer (11) and a vacuum-actuated neck seal (20) allowing "head out" monitoring. The neck seal comprises particulate material entrapped in the space between two layers of rubber, which become rigid when a vacuum is applied to the space. Tidal volume, respiratory rate and changes in functional residual capacity (FRC) are able to be recorded during unsedated REM and NREM sleep whilst monitoring with conventional polysomnographic methods. The head out configuration allows additional instrumentation to be used, avoids facial stimulation and allows unimpeded access to the upper airway.
Owner:QUEENSLAND UNIV OF THE
Apparatus for actively simulating autonomous respiration of human body in vitro and gas analyzing method employing the same
The invention, which belongs to the psychological research filed of respiratory medicine, relates to an apparatus for actively simulating autonomous respiration of a human body in vitro and a gas analyzing method employing the same. The apparatus includes a circulating gas circuit formed by a driving respirator, a dual-cavity simulation lung device and a head dead space model; and the output end of the dual-cavity simulation lung device is connected with the head dead space model by a gas analyzing device. The gas analyzing method comprises the following steps that: data are collected; integration is carried out on results by multiplication of obtained real-time oxygen concentration inside the apparatus and inspiration / expiration flow rates so as to obtain oxygen fluxes and tidal volumes of expiration / inspiration in each respiratory cycle; and division operation is carried out on the oxygen fluxes and tidal volumes to obtain mean effective inspired oxygen concentration in inspiratory / expiratory phases. According to the invention, the apparatus having a compact structure can be applied to scientific research and training of various ventilation modes; and the applied gas analyzing method enables a detection result to be accurate and to approach a real one.
Owner:THE FIRST HOSPITAL OF CHINA MEDICIAL UNIV +1
Control of flow and/or pressure provided by breathing apparatus
ActiveUS20150128942A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksTidal volumeEngineering
The invention comprises a method of operating a breathing apparatus comprising measuring a baseline breath flow parameter being respiratory rate and / or tidal volume or a parameter derived therefrom, varying the flow rate provided by the breathing apparatus, measuring a current breath flow parameter being respiratory rate and / or tidal volume or a parameter derived therefrom, comparing the baseline and current breath flow parameters, and altering operation of the breathing apparatus based on the comparison. The invention also comprises a breathing apparatus that implements the above method.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
Garment system with electronic components and associated methods
ActiveUS9566033B2Improve the measurement effectElectric signal transmission systemsTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsBiometric dataAbdominal movements
The disclosure provides a wireless biometric monitoring system that may be capable of acquiring, compiling, analyzing, and transmitting biometric data in near real time / real time. The system may utilize either the most up-to-date Bluetooth protocol (currently Bluetooth Smart) or a similar wireless protocol. The system may further integrate through this wireless protocol with peripheral devices to expand the measurement capacity of the system.In embodiments, the system may be capable of monitoring multiple biometric responses including, but not limited to: skin temperature, core temperature, respirations, heart rate, predicted tidal volume, chest wall movement, abdominal movement in conjunction with inspiration, abdominal movement in conjunction with expiration, HRR (heart rate reserve), HRV (heart rate variability), body position relevant to perpendicular, shoulder position relevant to hip position, general body posture, up time, down time, and malfunctions.
Owner:CIPHER SKIN
Human-body respiratory training device and respiratory training feedback method
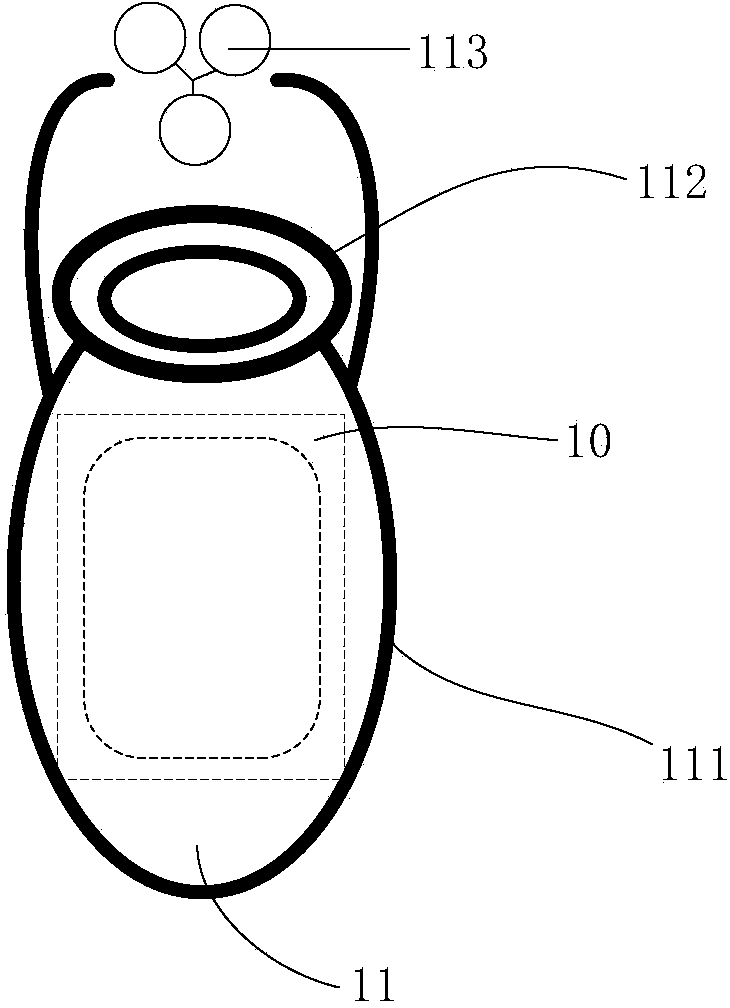
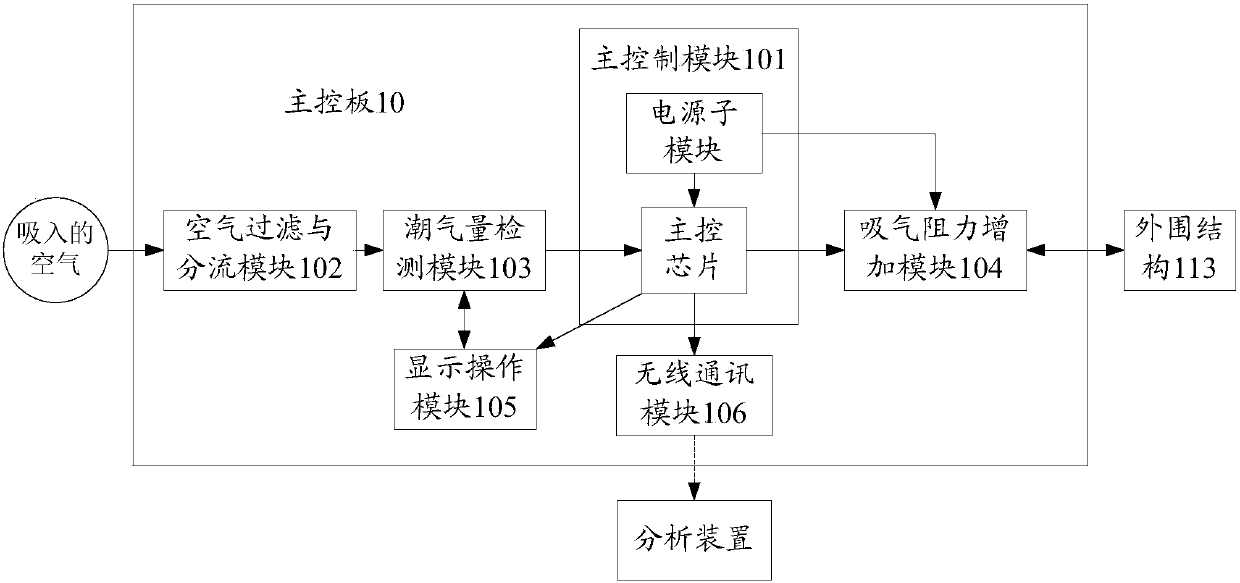
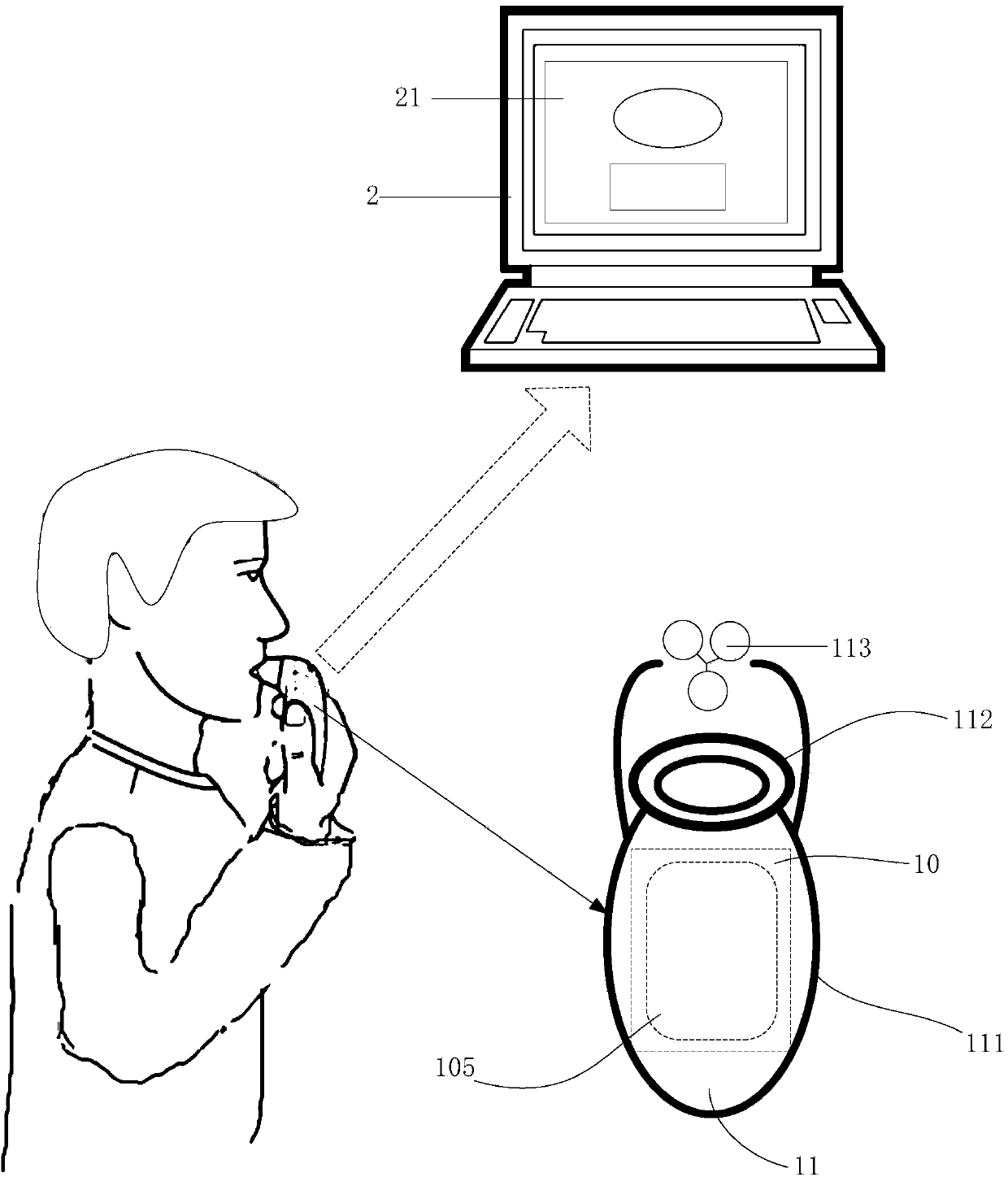
ActiveCN103736256AImprove experienceOvercome the lack of feedback mechanismGymnastic exercisingRespiratory organ evaluationAir filtrationHuman body
The invention discloses a human-body respiratory training device and a respiratory training feedback method. The human-body respiratory training device comprises a main control board and a portable device. The main control board comprises an air filtering and distributing module, a tidal volume detection module, a main control module, an inspiratory resistance increasing module and a communication module. A user breathes in air by holding the portable device, the breathed-in air is purified to be clean air through the air filtering and distributing module, the air is distributed into small-flow airflows, the tidal volume detection module detects the tidal volume in the small-flow airflows and converts the flowing-in airflow into electric signals, the main control module is used for collecting, detecting, analyzing and processing the electric signals, the inspiratory resistance increasing module is controlled to change inspiratory resistance according to the processed data, a peripheral structure of the portable device is used for reflecting the inspiratory resistance, and an operation display module can be used for regulating the strength and speed of inspiration and feeding back a training effect in real time. The human-body respiratory training device is simple in structure, convenient to carry, high in efficiency, low in cost, and high in practicability.
Owner:HUMANEOTEC EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS EQUIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com