Apparatus for actively simulating autonomous respiration of human body in vitro and gas analyzing method employing the same
A technology of spontaneous breathing and gas analysis, applied in the field of respiratory medical physiology research, can solve the lack of gas flow and gas composition measurement and analysis functions flowing through the simulated lung, the artificial simulated lung does not have the function of simulating the spontaneous breathing of the human body, and cannot satisfy the auxiliary type Ventilation mode research needs and other issues, to achieve the effect of compact structure, convenient disassembly and assembly, and fast concentration response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] specific implementation plan
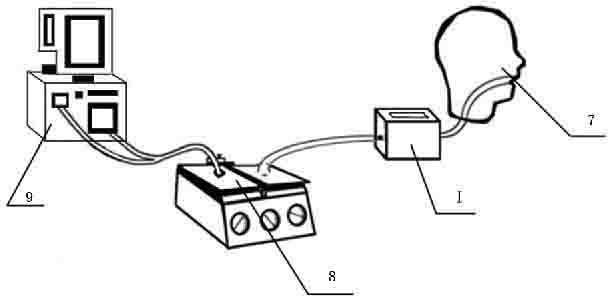
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown: the gas circuit part of the device of the present invention includes a driving ventilator 9, a double-chamber simulated lung 8 and a head dead space model 7, and the driving ventilator 9 is connected with a chamber (as a driving chamber) of the double-chamber simulated lung 8, Another chamber (as a test chamber) is connected with the head dead space model 7 . Drive the ventilator 9 to work according to the set parameters, and drive the volume of the driving chamber of the double-chamber simulated lung 8 to change regularly. The driving chamber and the test chamber are connected by a metal connecting rod, so that the airflow between the test chamber and the driving chamber is synchronized. Conduction, simulating the spontaneous breathing of the human body.
[0026] Among them, the driving ventilator is produced by NEWPORT Company, model: Niubang HT50. The double-chamber simulated lung 8 is a commercially...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com