Patents
Literature
76 results about "Mechanical ventilators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A mechanical ventilator is a machine that helps a patient breathe (ventilate) when he or she cannot breathe on his or her own for any reason.
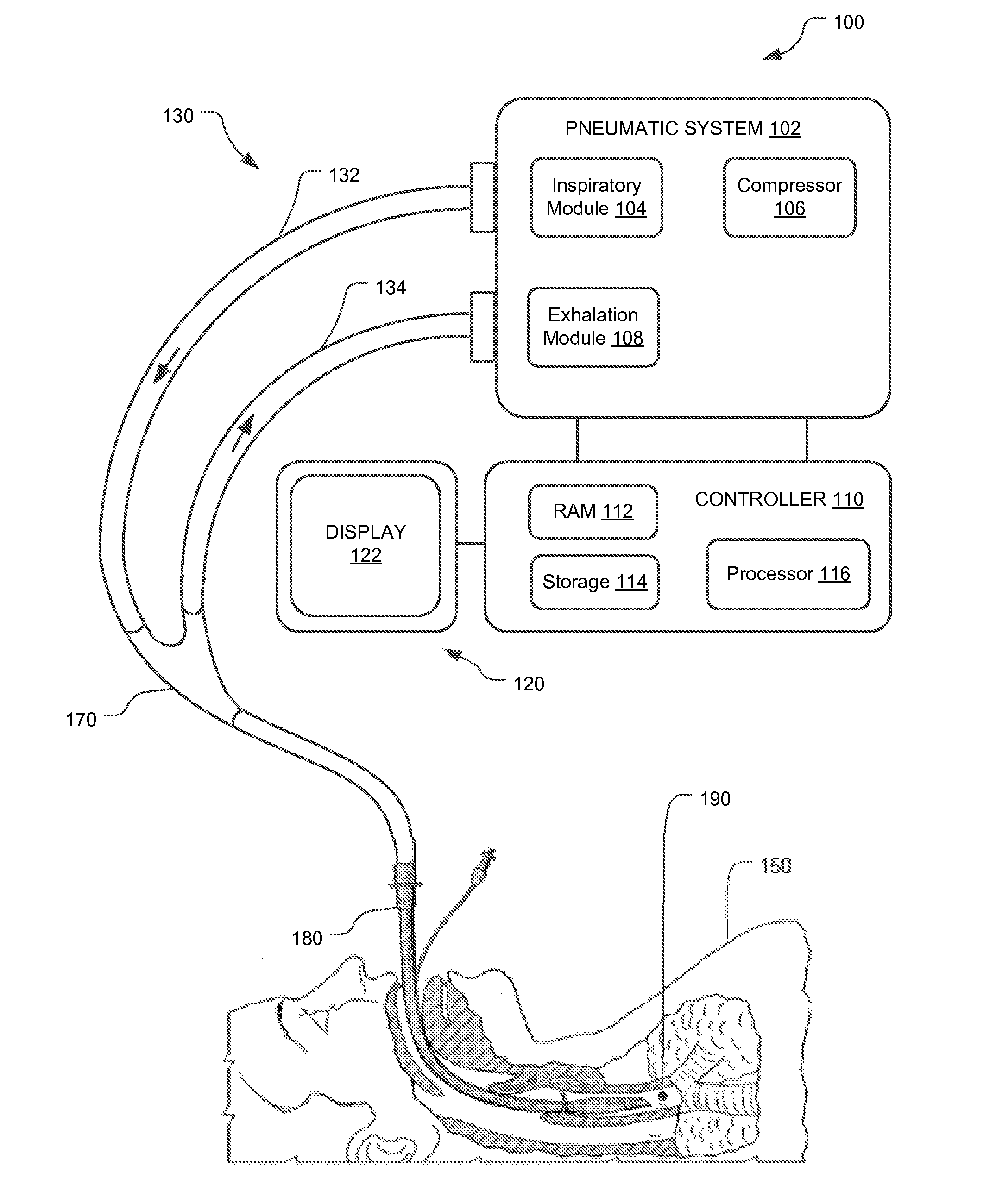
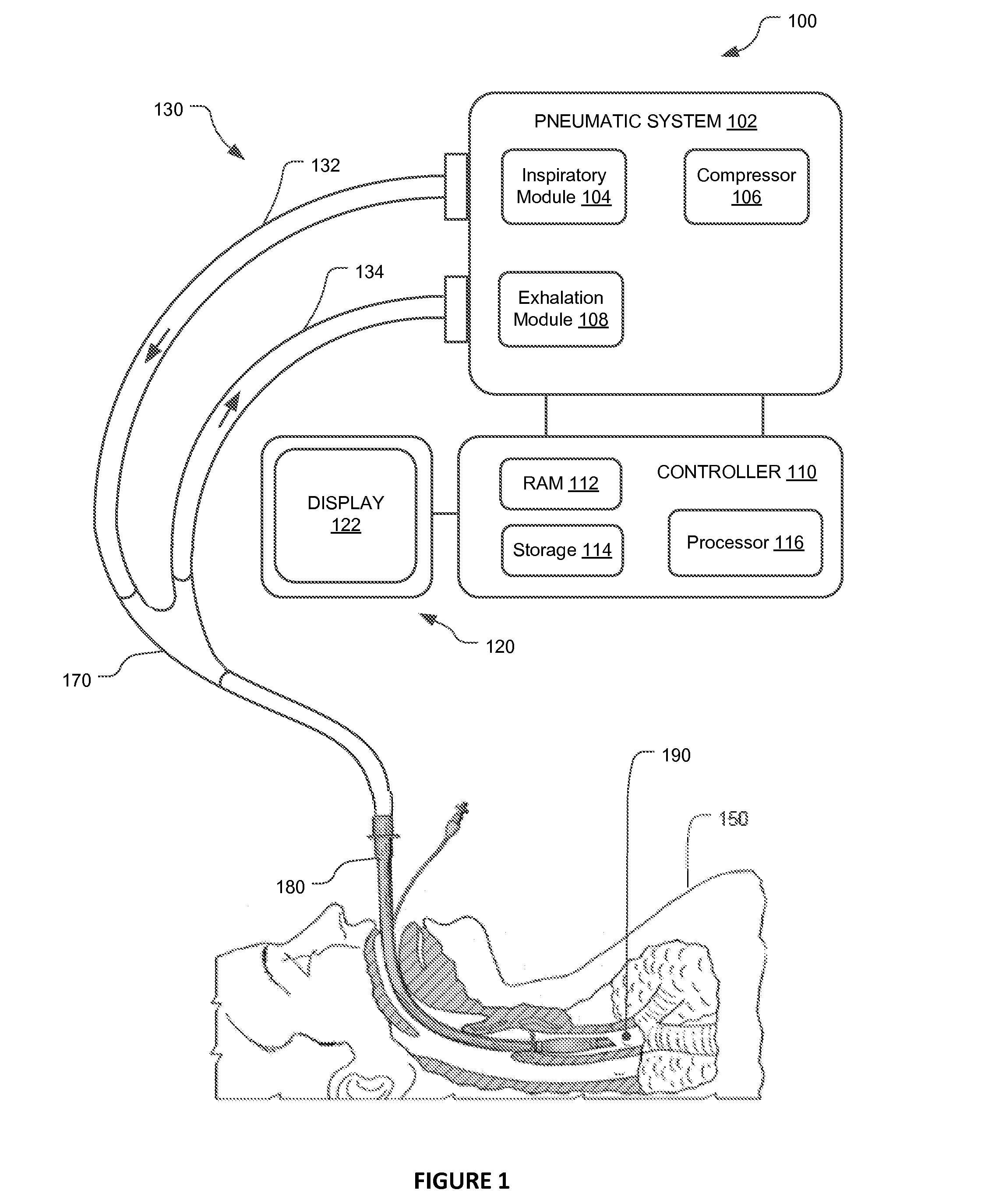
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator
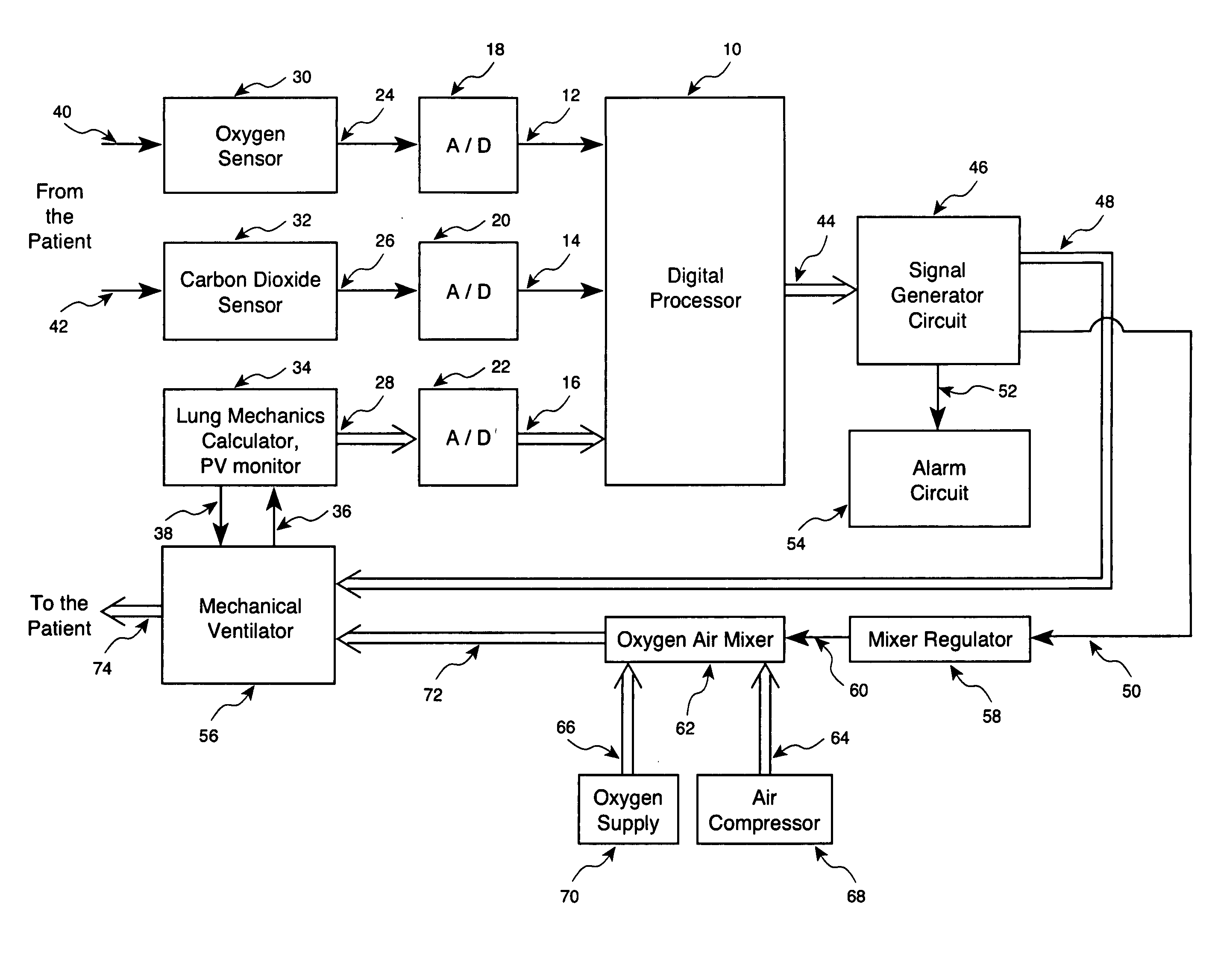
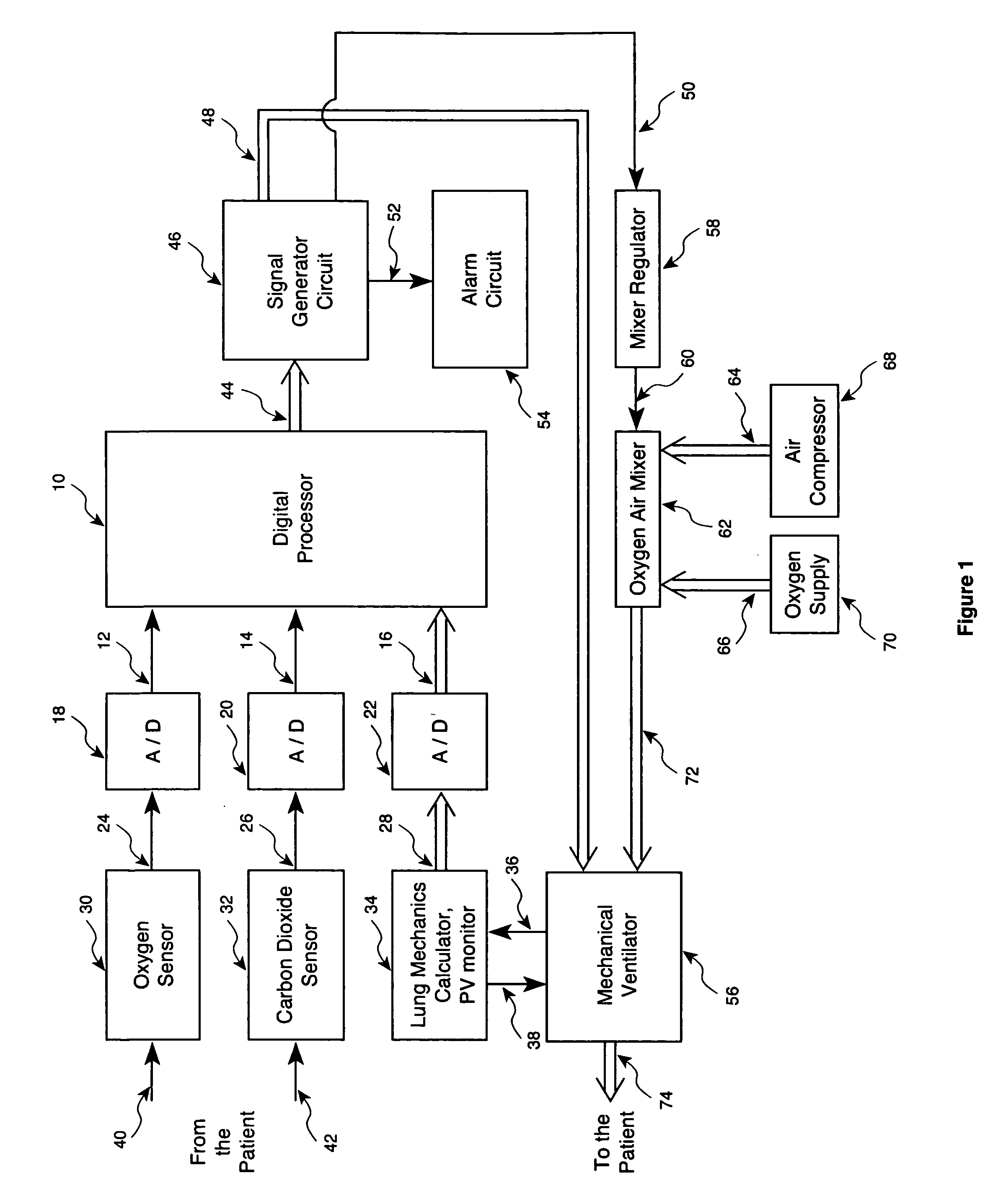
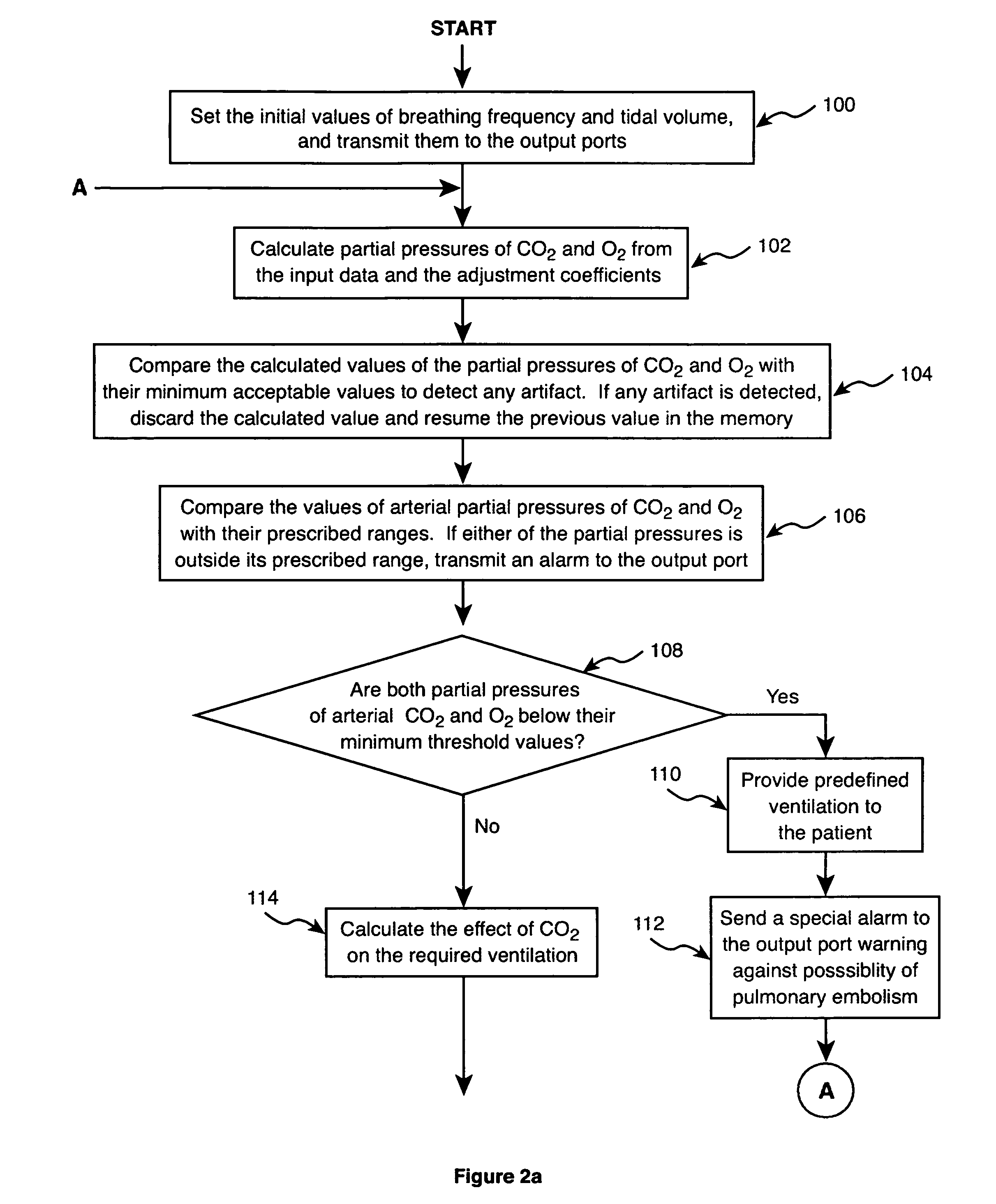
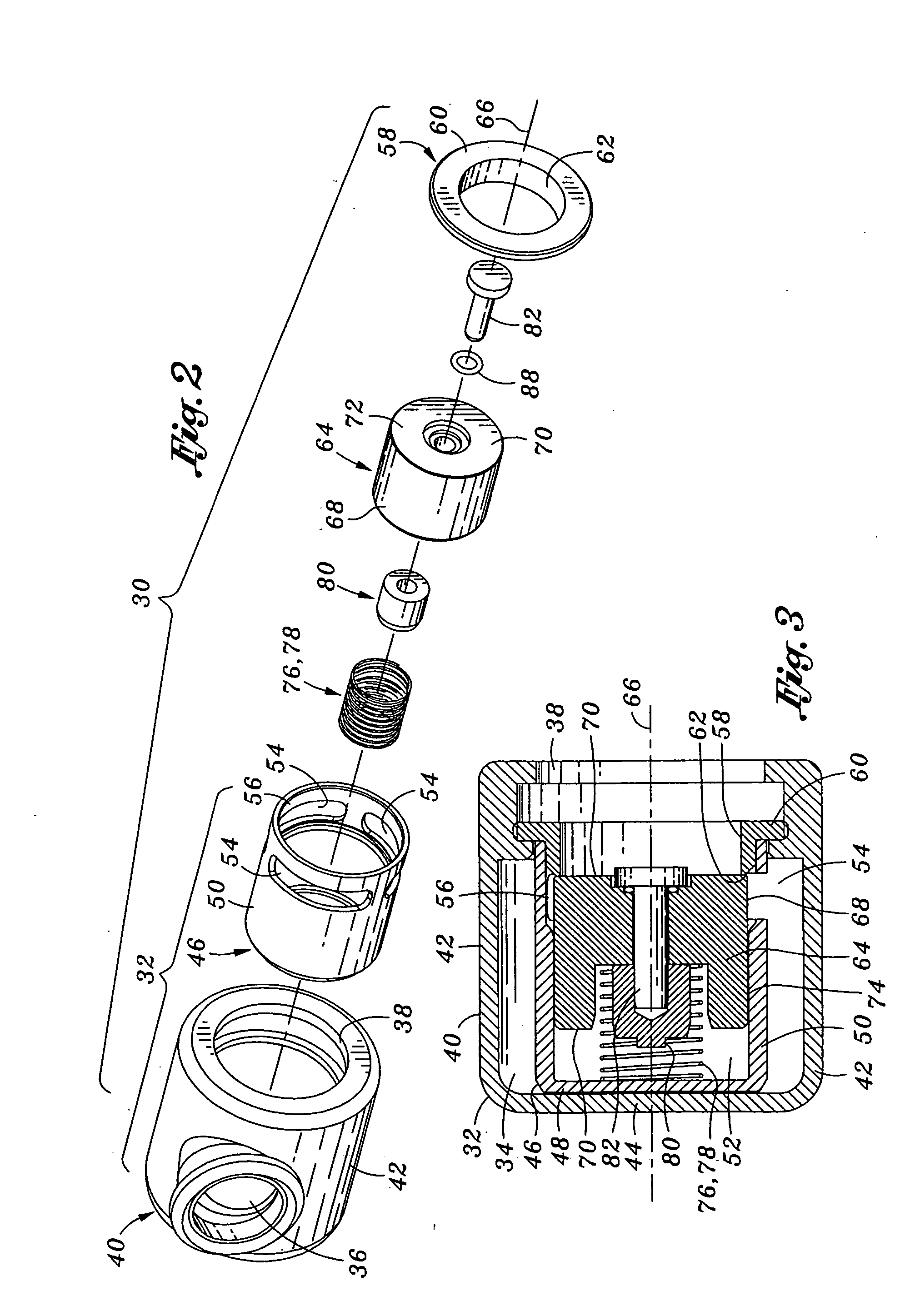
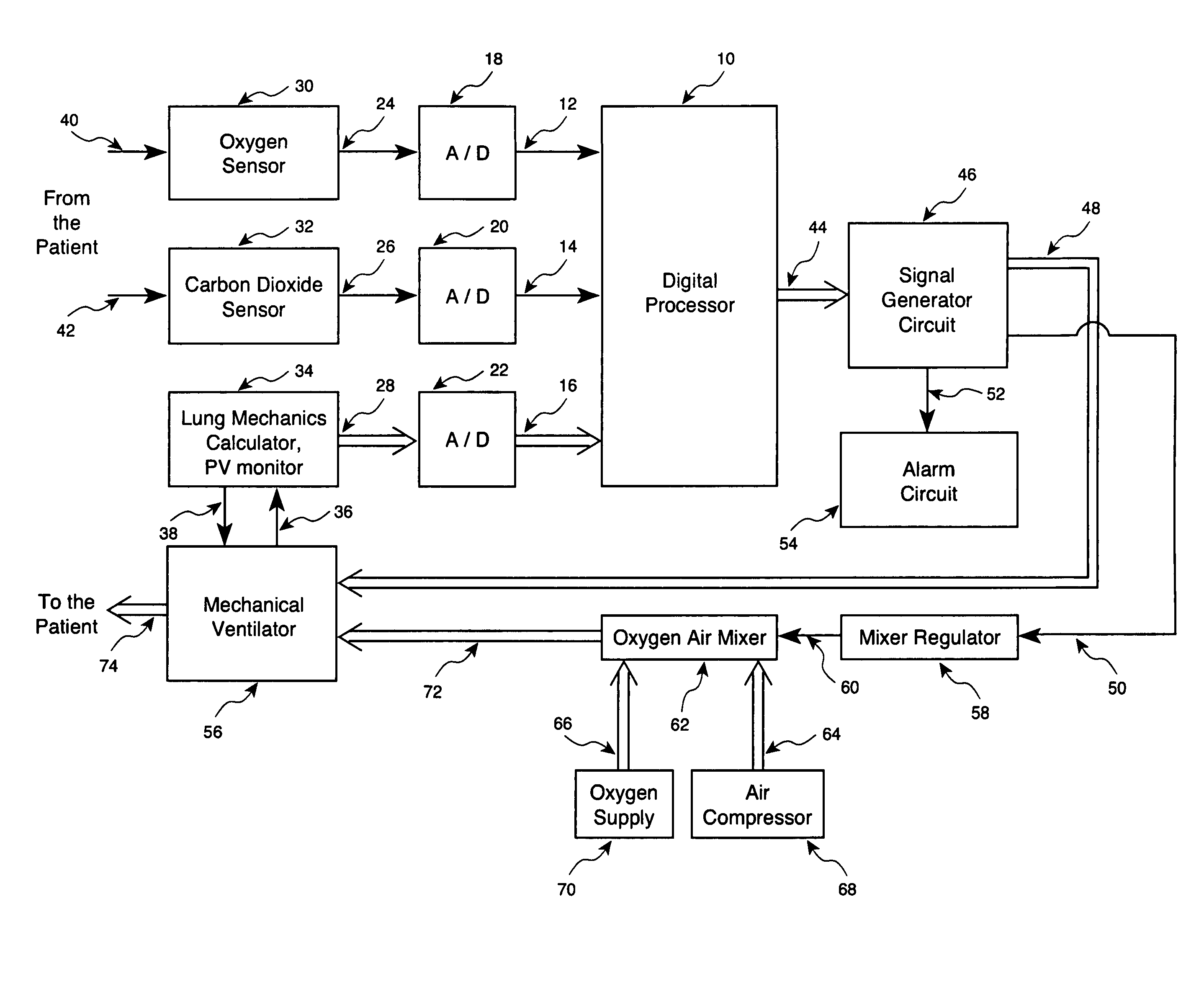
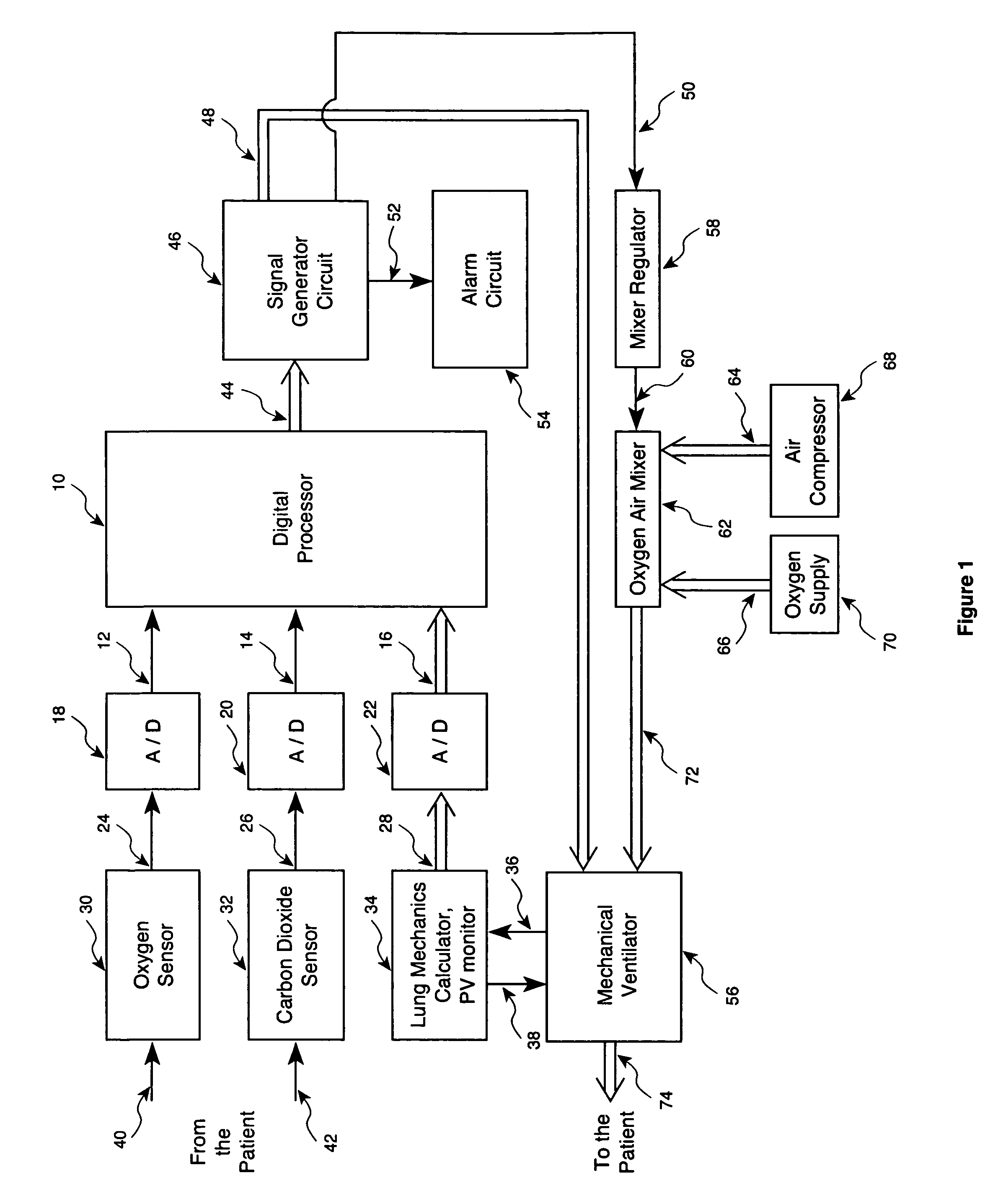
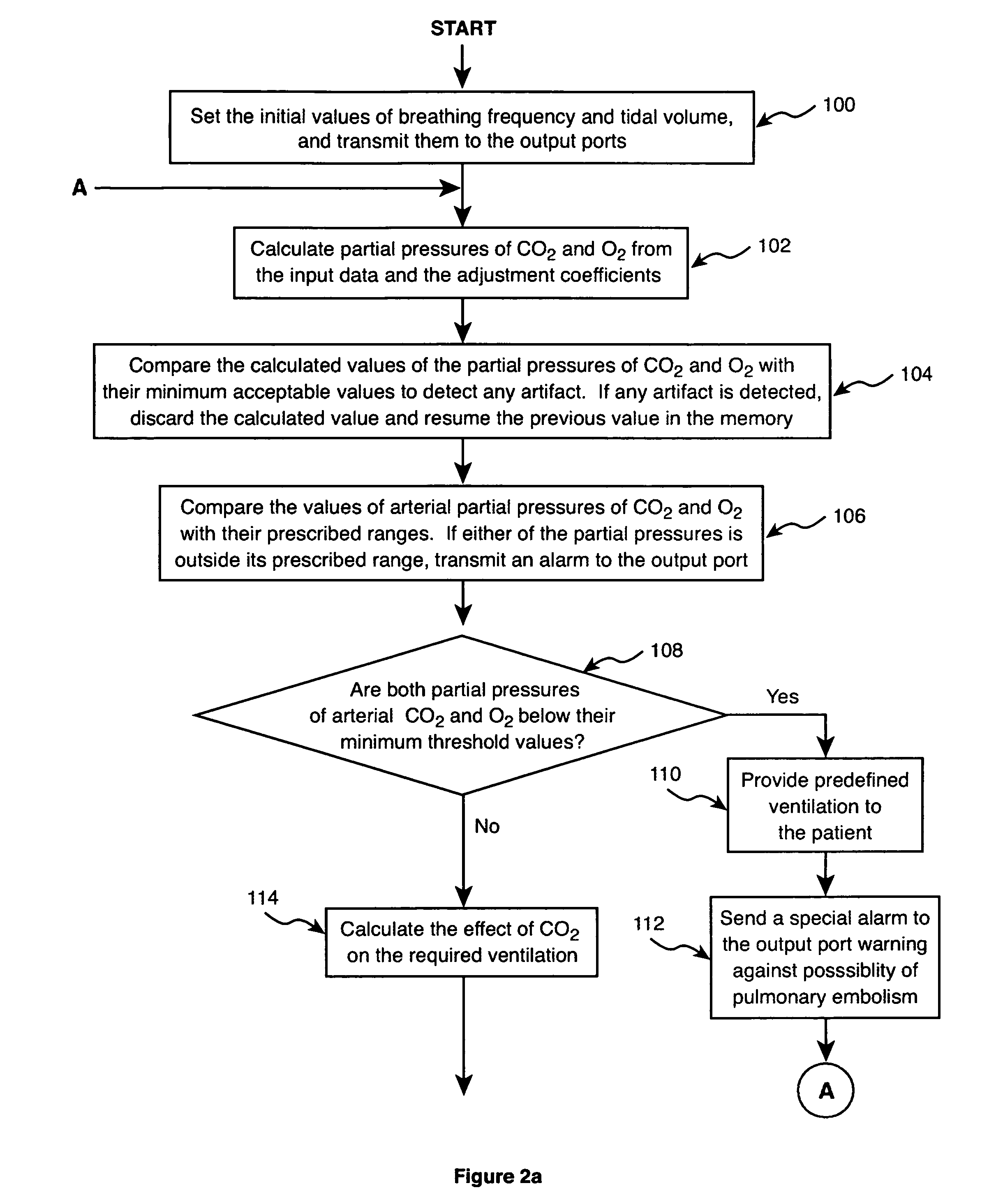
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator are described. The invention can be used to control mechanical ventilators as well as respiratory assist devices such as CPAP machines. The apparatus receives input data indicative of patient's oxygen level. A controller determines PEEP, or CPAP, and FIO2, on the basis of data indicative of the patient's oxygen level. In an alternative embodiment, the apparatus further receives input data indicative of patient's carbon dioxide levels, respiratory elastance and airway resistance, and barometric pressure. The controller further utilizes the said input data to determine the optimal values of tidal volume and breathing frequency for a next breath of the patient, and uses the respiratory elastance and airway resistance data to determine any necessary adjustments in the I:E ratio. The controller also applies safety rules, detects and corrects artifacts, and generates warning signals when needed.
Owner:TEHRANI FLEUR T
Portable drag compressor powered mechanical ventilator
InactiveUS6877511B2Accurate measurementMinimize fabrication inaccuracyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSolenoid valveEngineering
A ventilator device and system comprising a rotating compressor, preferably a drag compressor, which, at the beginning of each inspiratory ventilation phase, is accelerated to a sufficient speed to deliver the desired inspiratory gas flow, and is subsequently stopped or decelerated to a basal flow level to permit the expiratory ventilation phase to occur. The ventilator device is small and light weight enough to be utilized in portable applications. The ventilator device is power efficient enough to operate for extended periods of time on internal or external batteries. Also provided is an oxygen blending apparatus which utilizes solenoid valves having specific orifice sizes for blending desired amounts of oxygen into the inspiratory gas flow. Also provided is an exhalation valve having an exhalation flow transducer which incorporates a radio frequency data base to provide an attendant controller with specific calibration information for the exhalation flow transducer.
Owner:BIRD PRODS
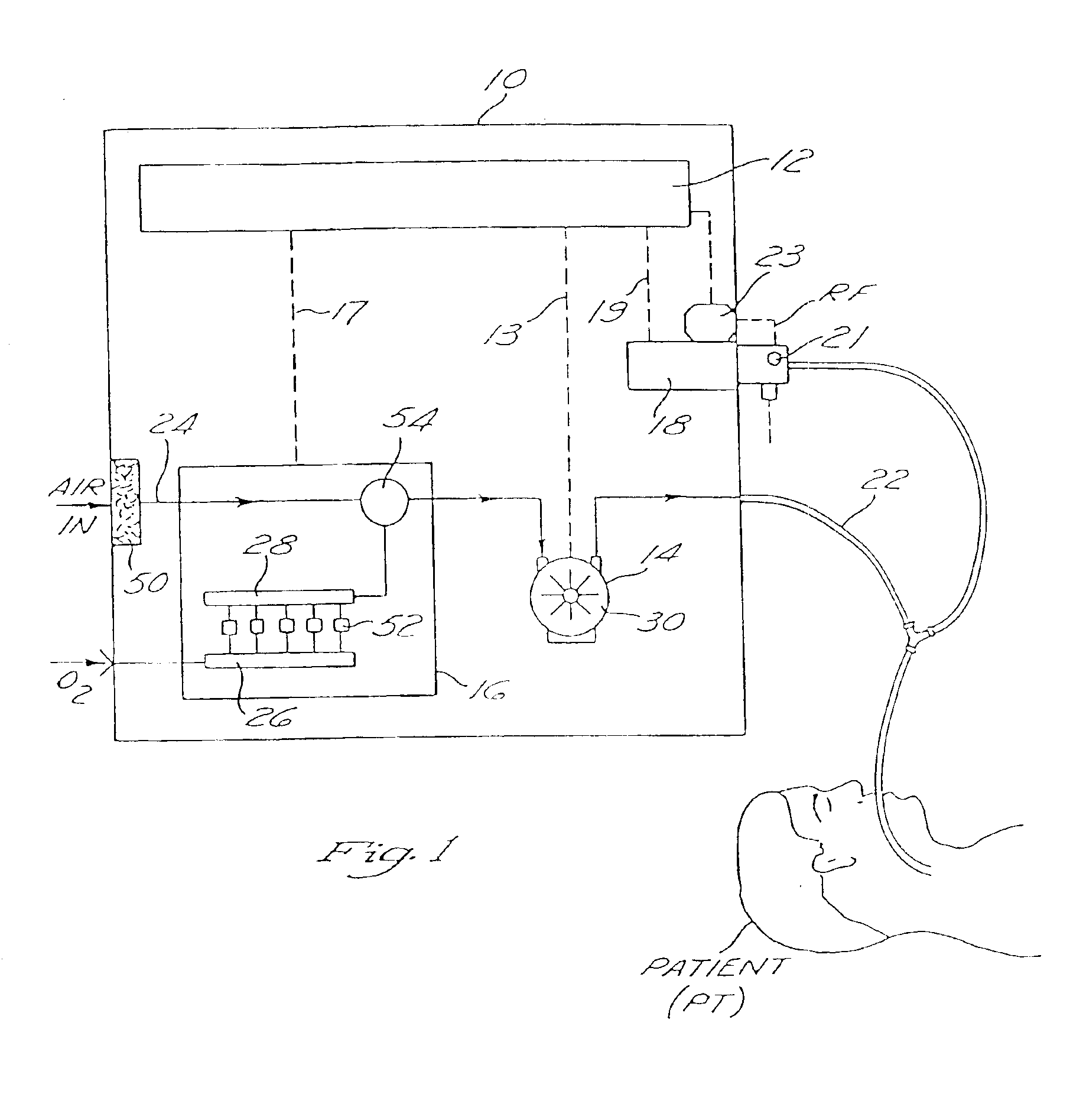
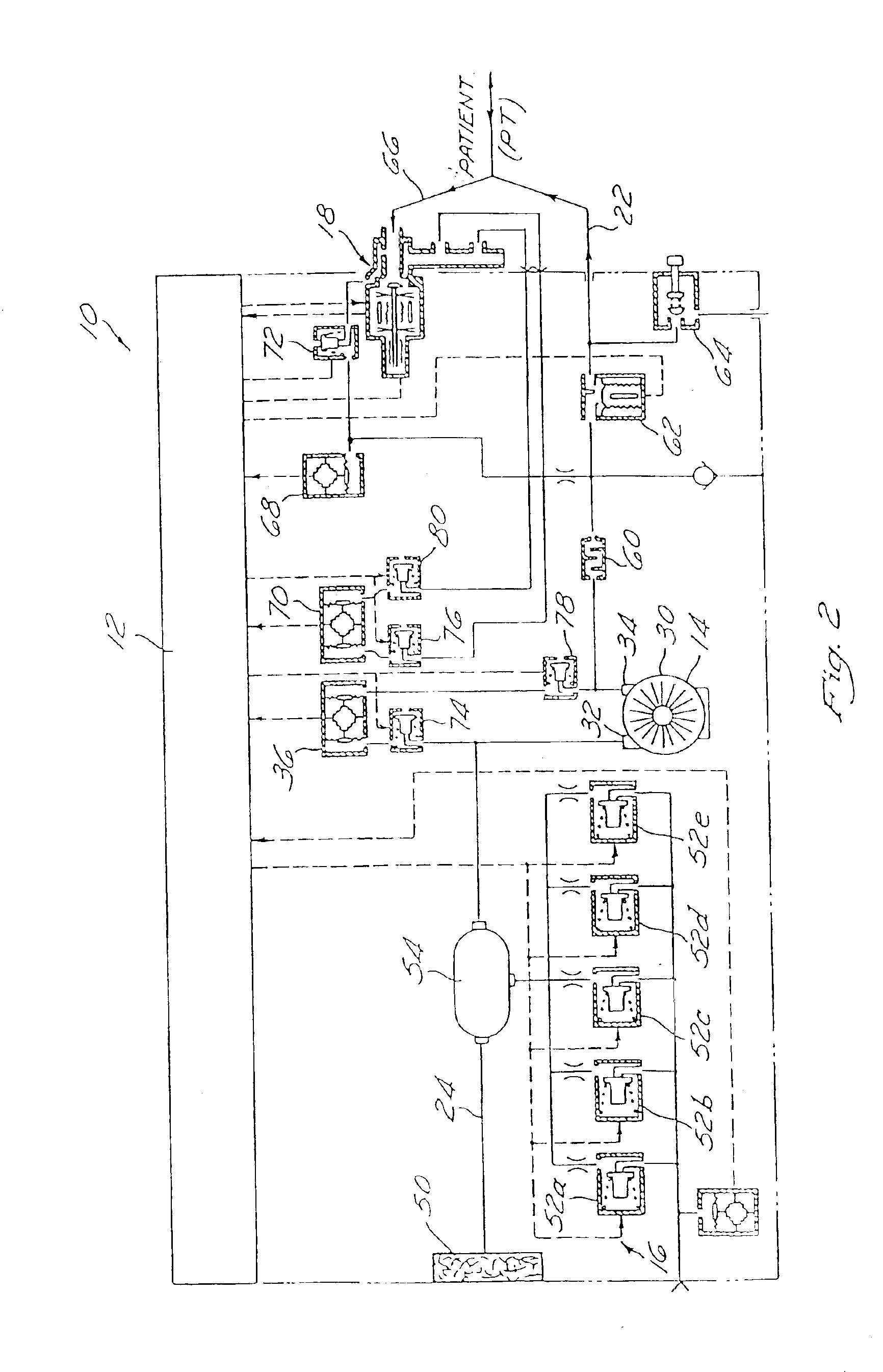
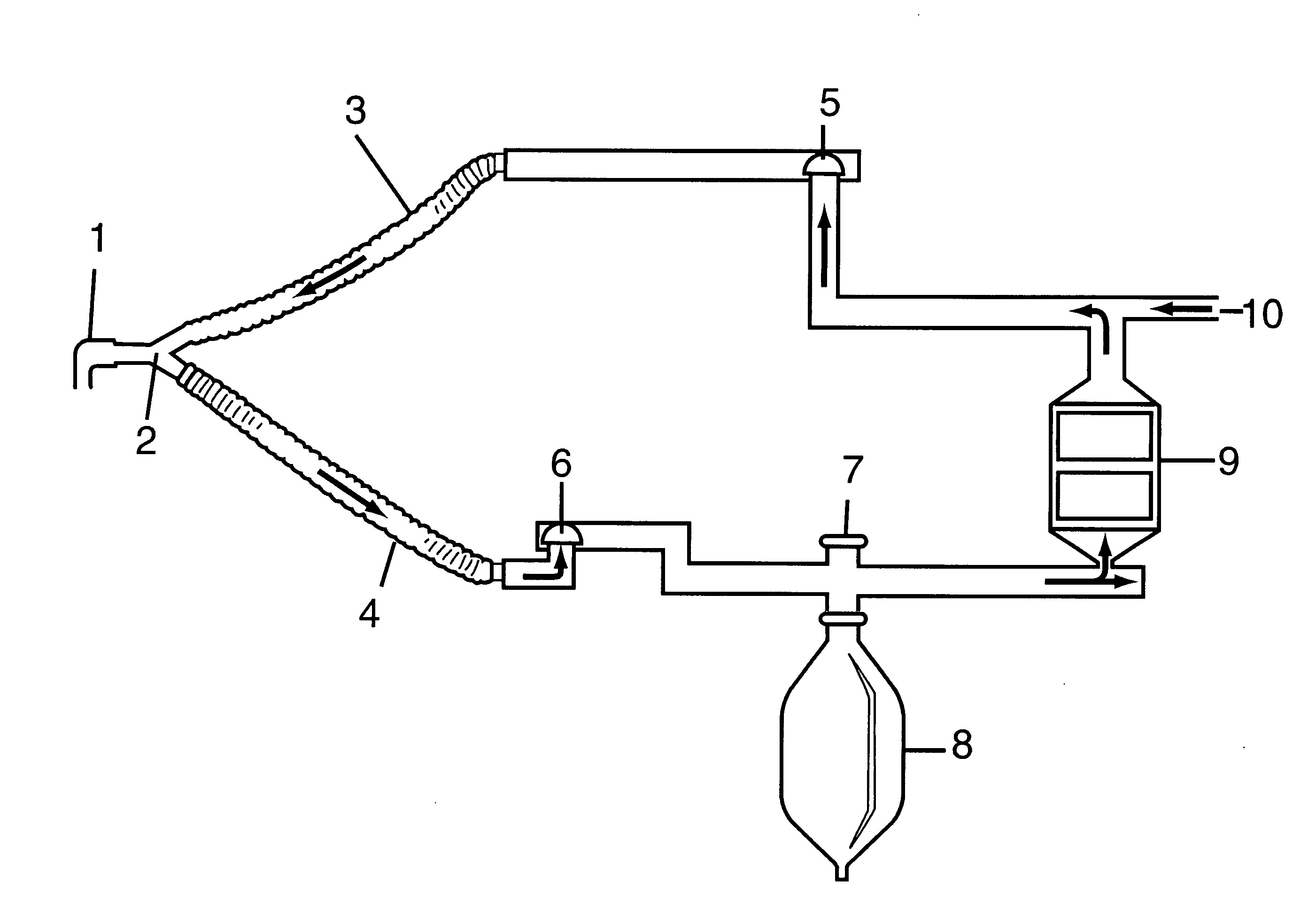
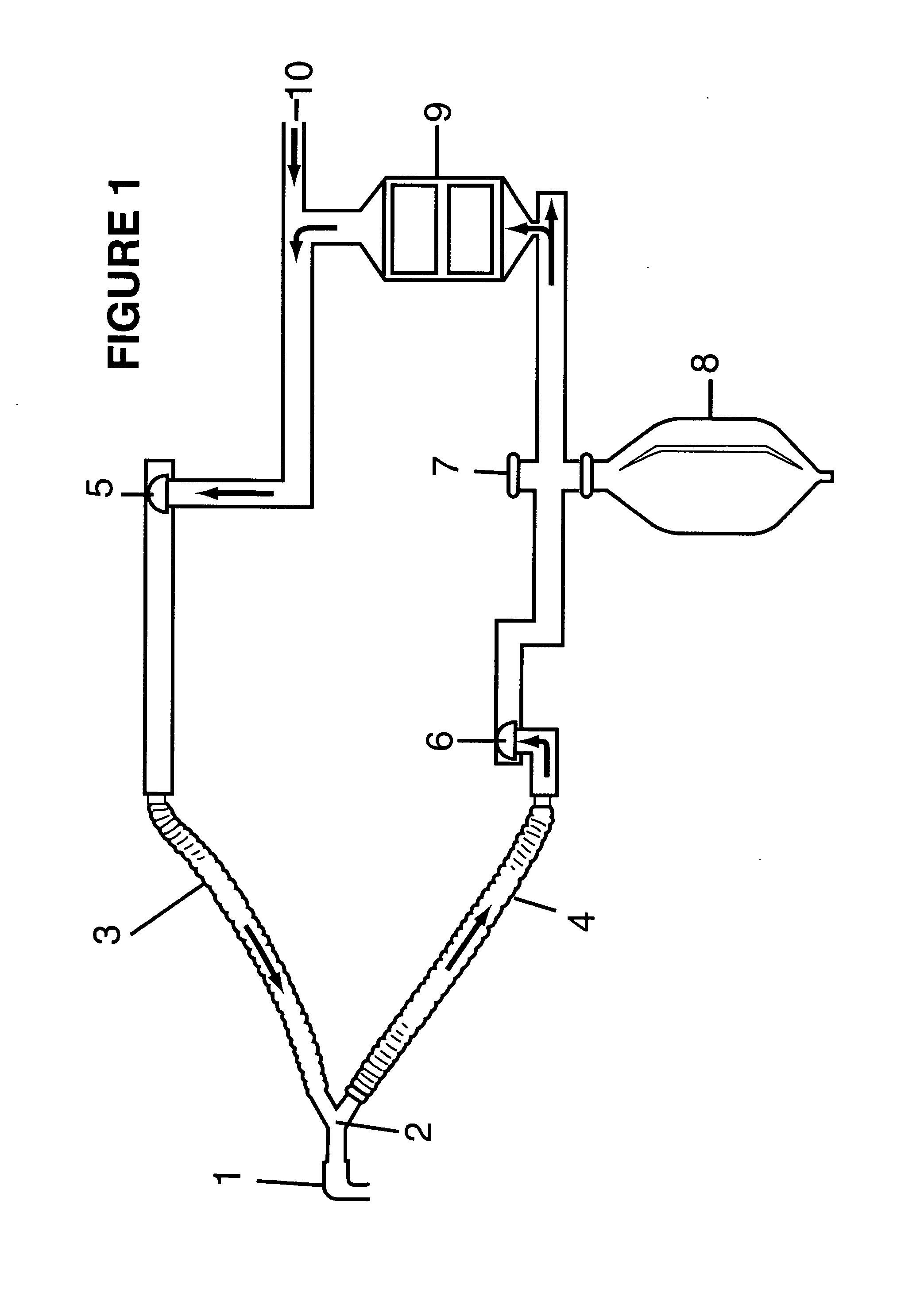
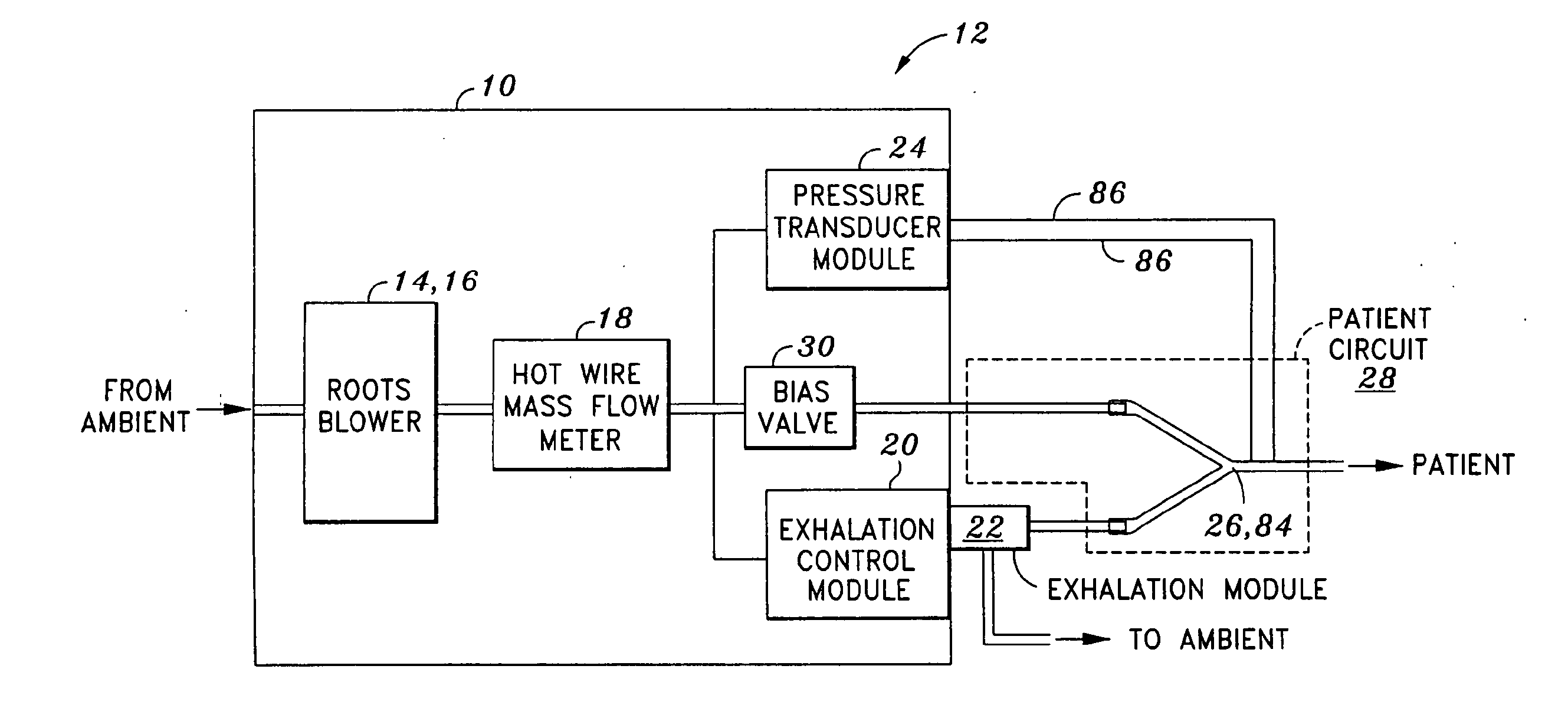
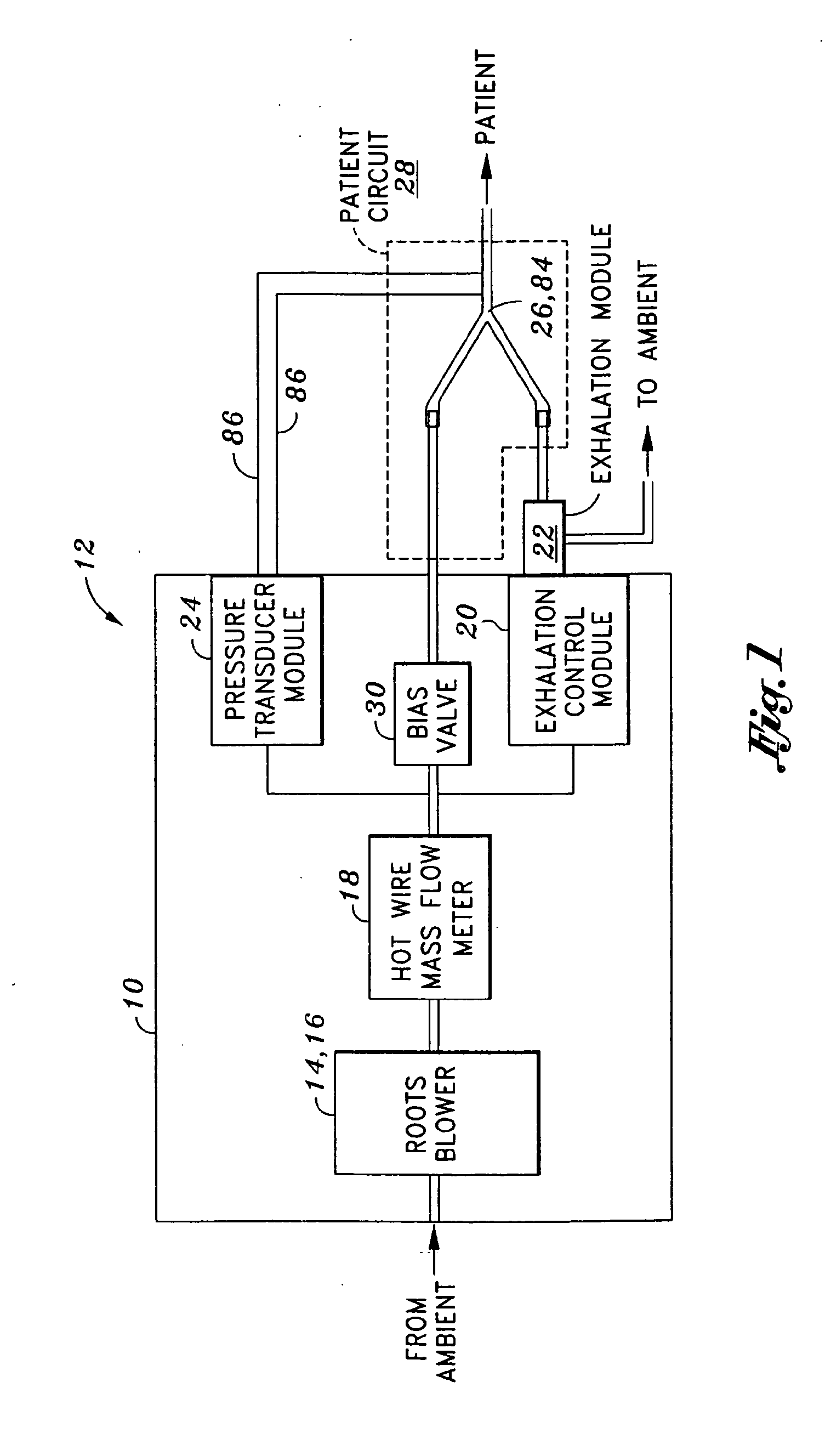
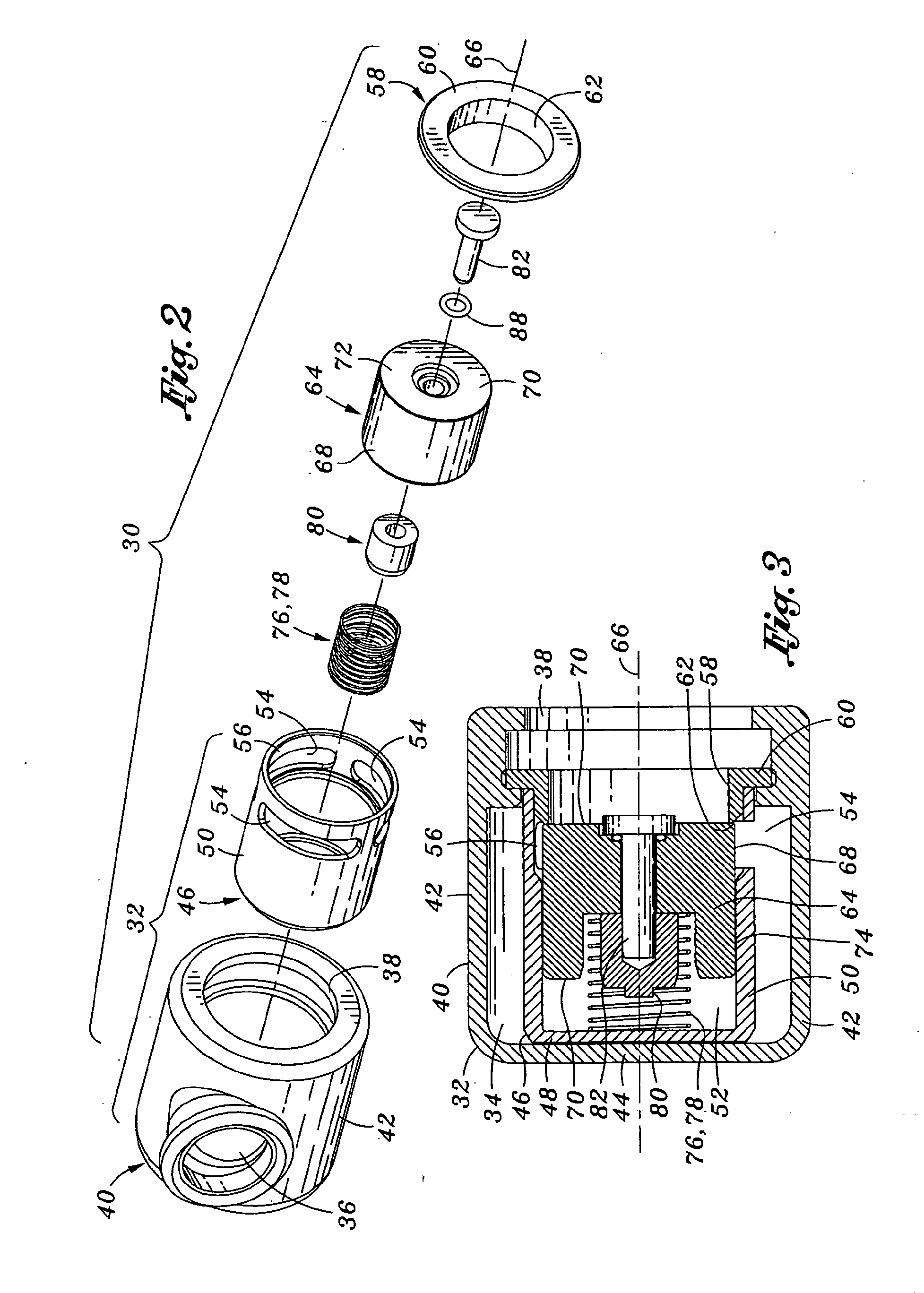
Mechanical ventilation system utilizing bias valve
ActiveUS20060249153A1Accurate measurementViscous dampingRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPositive pressureEngineering
A portable mechanical ventilator having a Roots blower is configured to provide a desired gas flow and pressure to a patient circuit. The mechanical ventilator includes a flow meter operative to measure gas flow produced by the Roots blower and an exhalation control module configured to operate an exhalation valve connected to the patient circuit. A bias valve connected between the Roots blower and the patient circuit is specifically configured to generate a bias pressure relative to the patient circuit pressure at the exhalation control module. The bias valve is further configured to attenuate pulsating gas flow produced by the Roots blower such that gas flowing to the mass flow meter exhibits a substantially constant pressure characteristic. The bias pressure facilitates closing of the exhalation valve at the start of inspiration, regulates positive end expiratory pressure during exhalation, and purges sense lines via a pressure transducer module.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 203 INC
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator
Method and apparatus for controlling a ventilator are described. The invention can be used to control mechanical ventilators as well as respiratory assist devices such as CPAP machines. The apparatus receives input data indicative of patient's oxygen level. A controller determines PEEP, or CPAP, and FIO2, on the basis of data indicative of the patient's oxygen level. In an alternative embodiment, the apparatus further receives input data indicative of patient's carbon dioxide levels, respiratory elastance and airway resistance, and barometric pressure. The controller further utilizes the said input data to determine the optimal values of tidal volume and breathing frequency for a next breath of the patient, and uses the respiratory elastance and airway resistance data to determine any necessary adjustments in the I:E ratio. The controller also applies safety rules, detects and corrects artifacts, and generates warning signals when needed.
Owner:TEHRANI FLEUR T
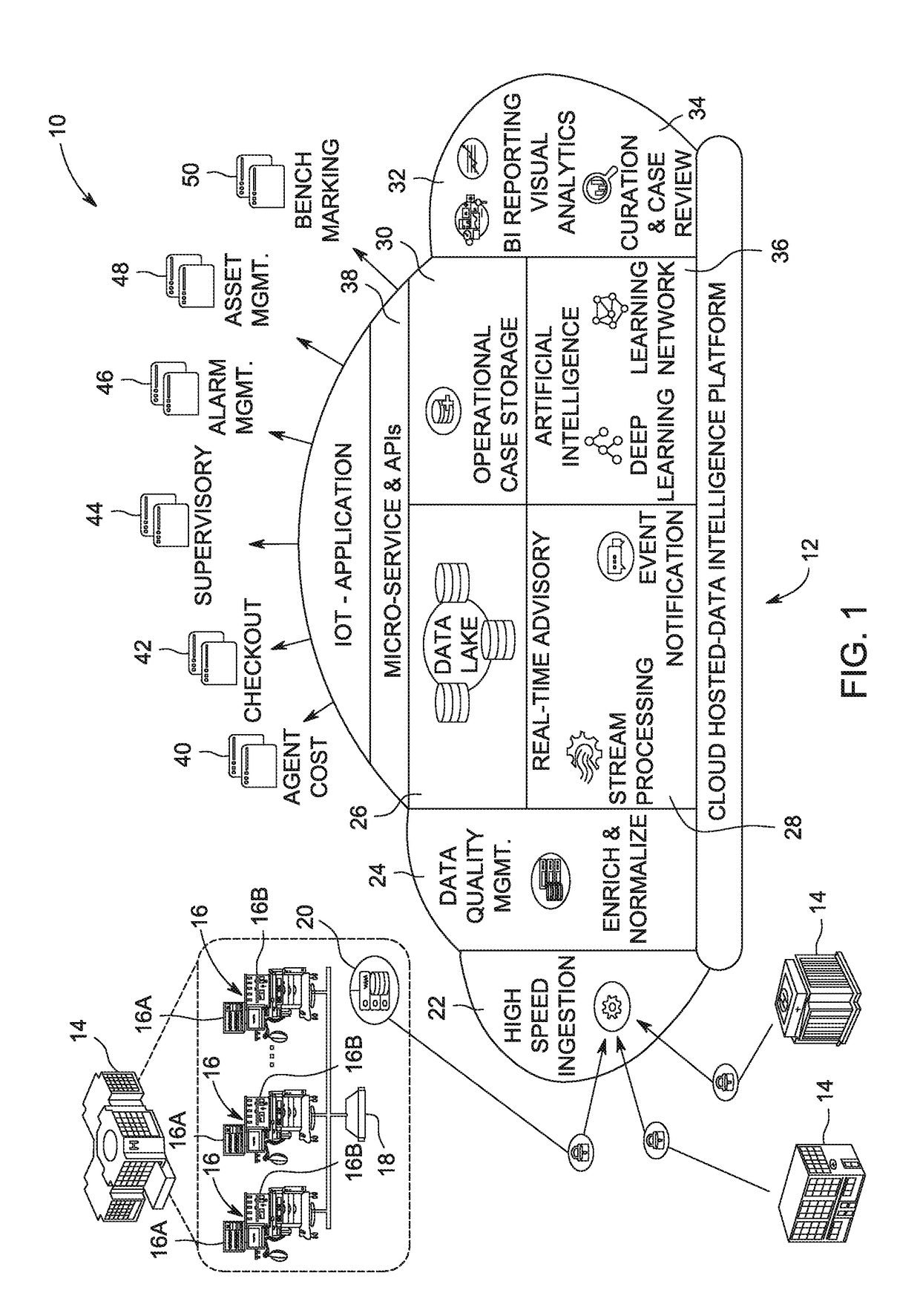
Lung protective ventilation control
ActiveUS20180193579A1RespiratorsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesMechanical ventilatorsControl system
Systems and methods of control of a mechanical ventilator include receiving machine data from a mechanical ventilator. A surgical event is detected in the received machine data. Clinical events within the surgical event are detected in the machine data. The machine data and the detected plurality of clinical events are evaluated for compliance with lung protective ventilation recommendations.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and system for reducing mechanical ventilator noise
InactiveUS20080127976A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsEngineering
A sound dampening apparatus to be disposed in pneumatic connection with a respiratory support system. The respiratory support system may comprise a source of medical gas, a plurality of pneumatic connections and a patient interface. The sound dampening apparatus comprises an inlet, an outlet, and an outer case which forms a sound dampening chamber. As the medical gas flows through the sound dampening apparatus, the noise energy associated with the flow of medical gas is reduced.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Compressor control system for a portable ventilator
ActiveUS20050031322A1Small and cost-efficient packageRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsPortable ventilators
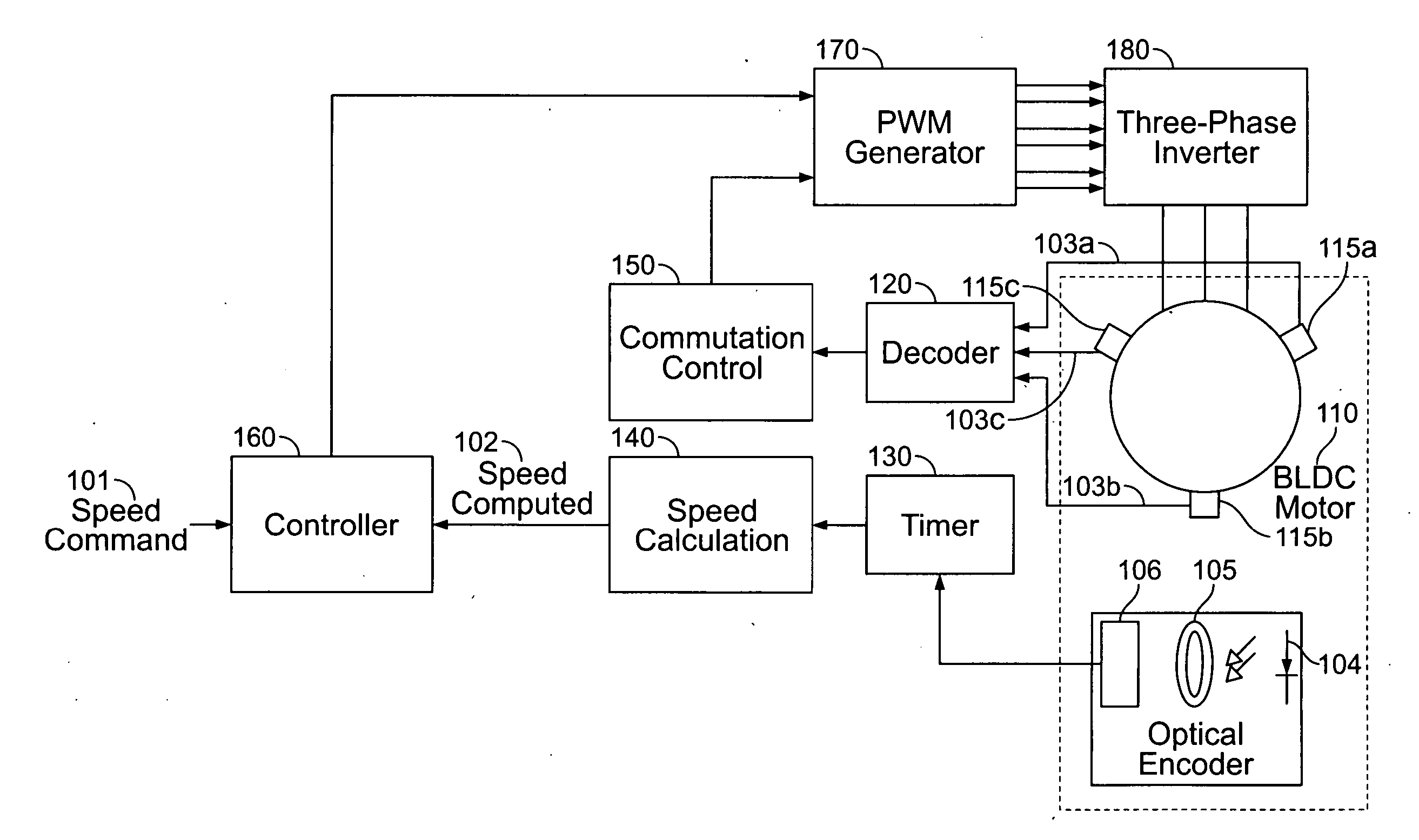
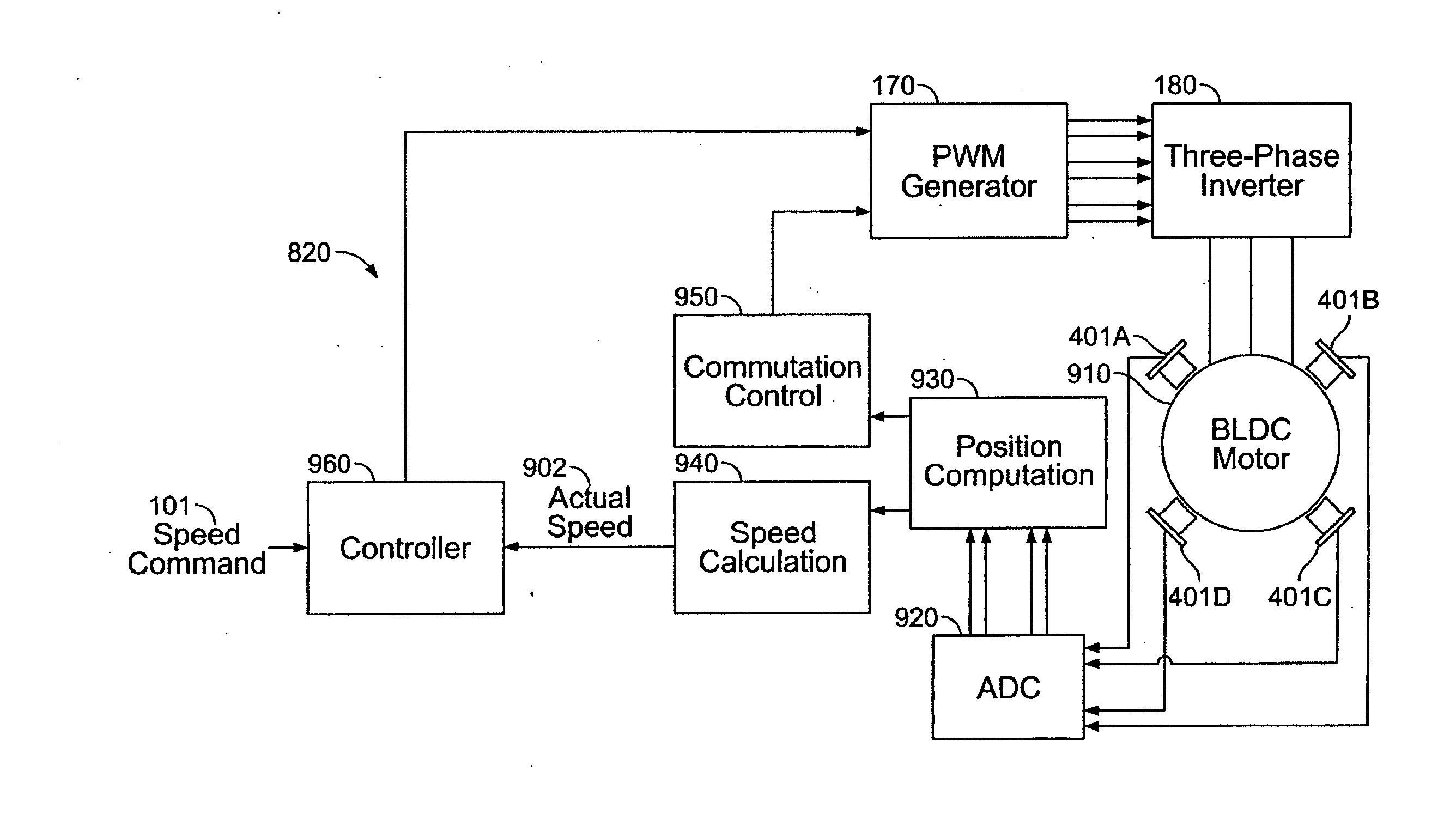
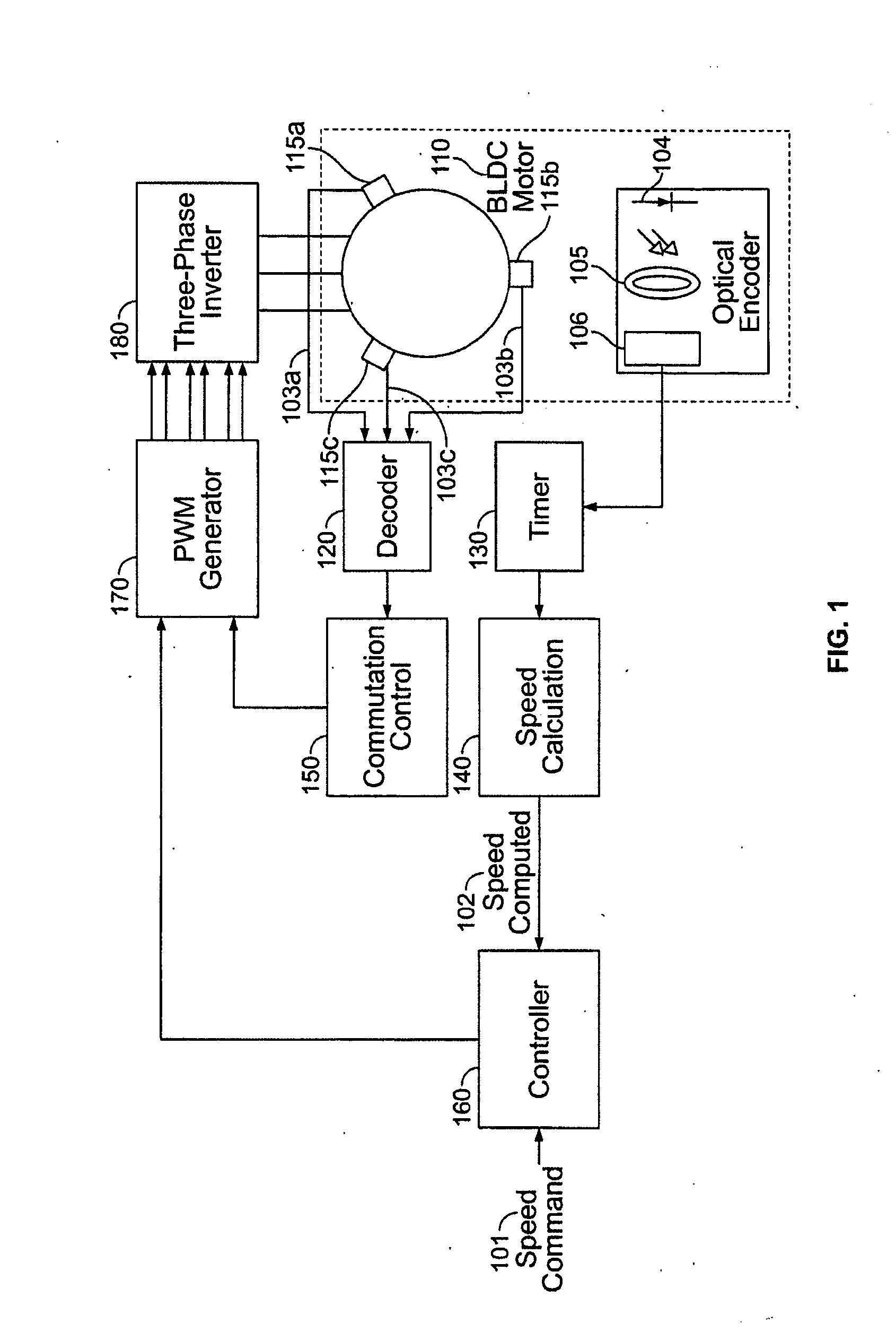
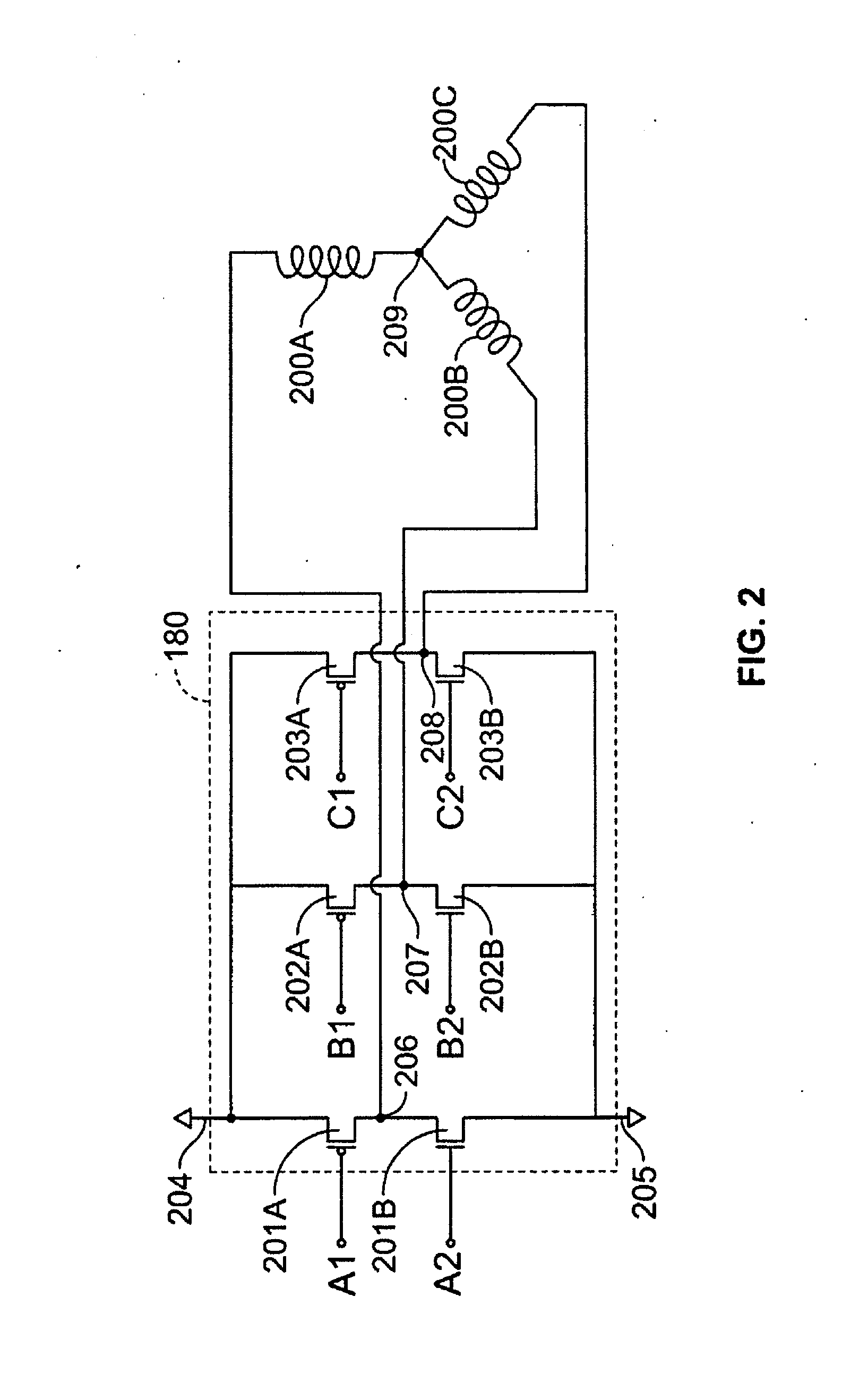
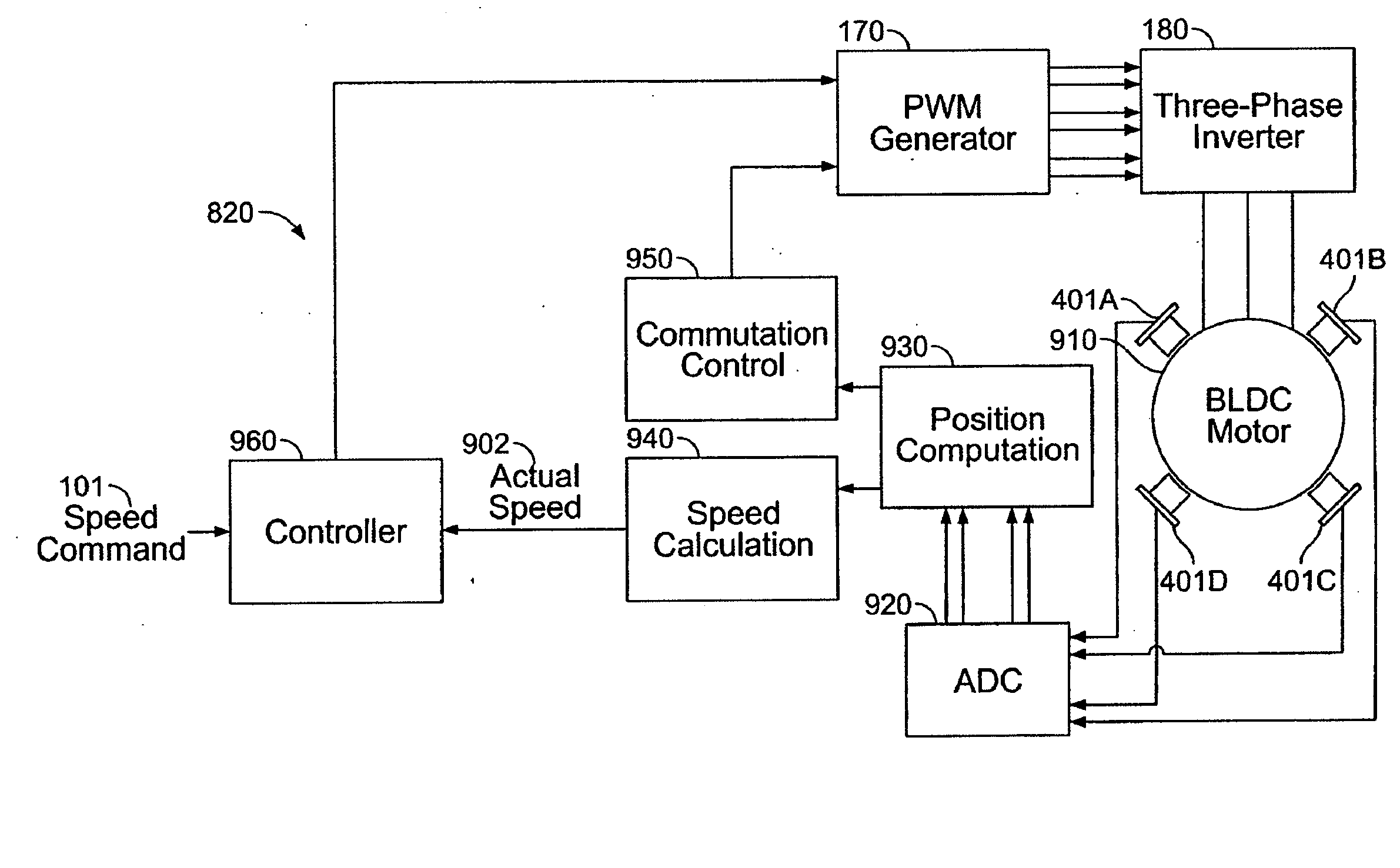
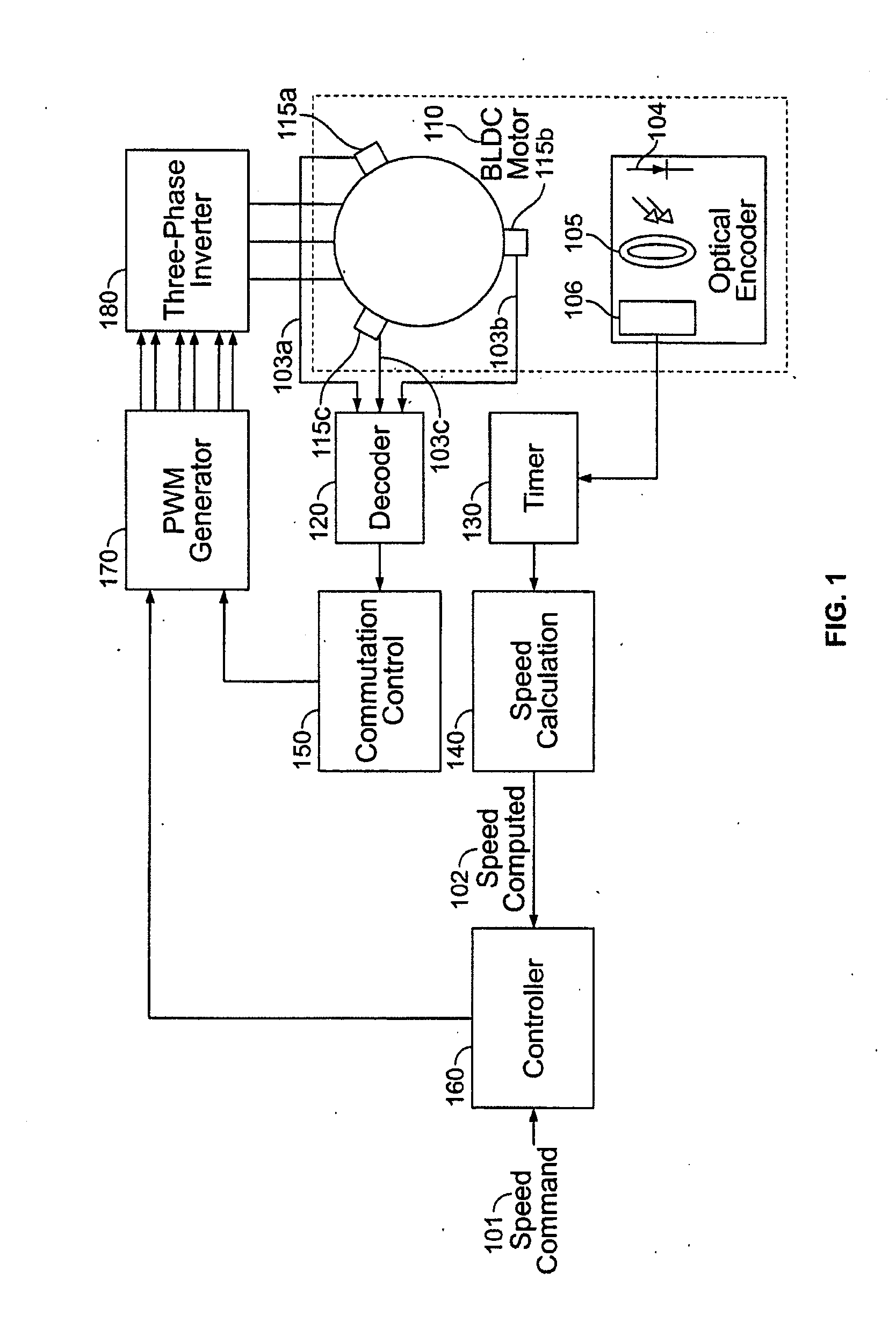
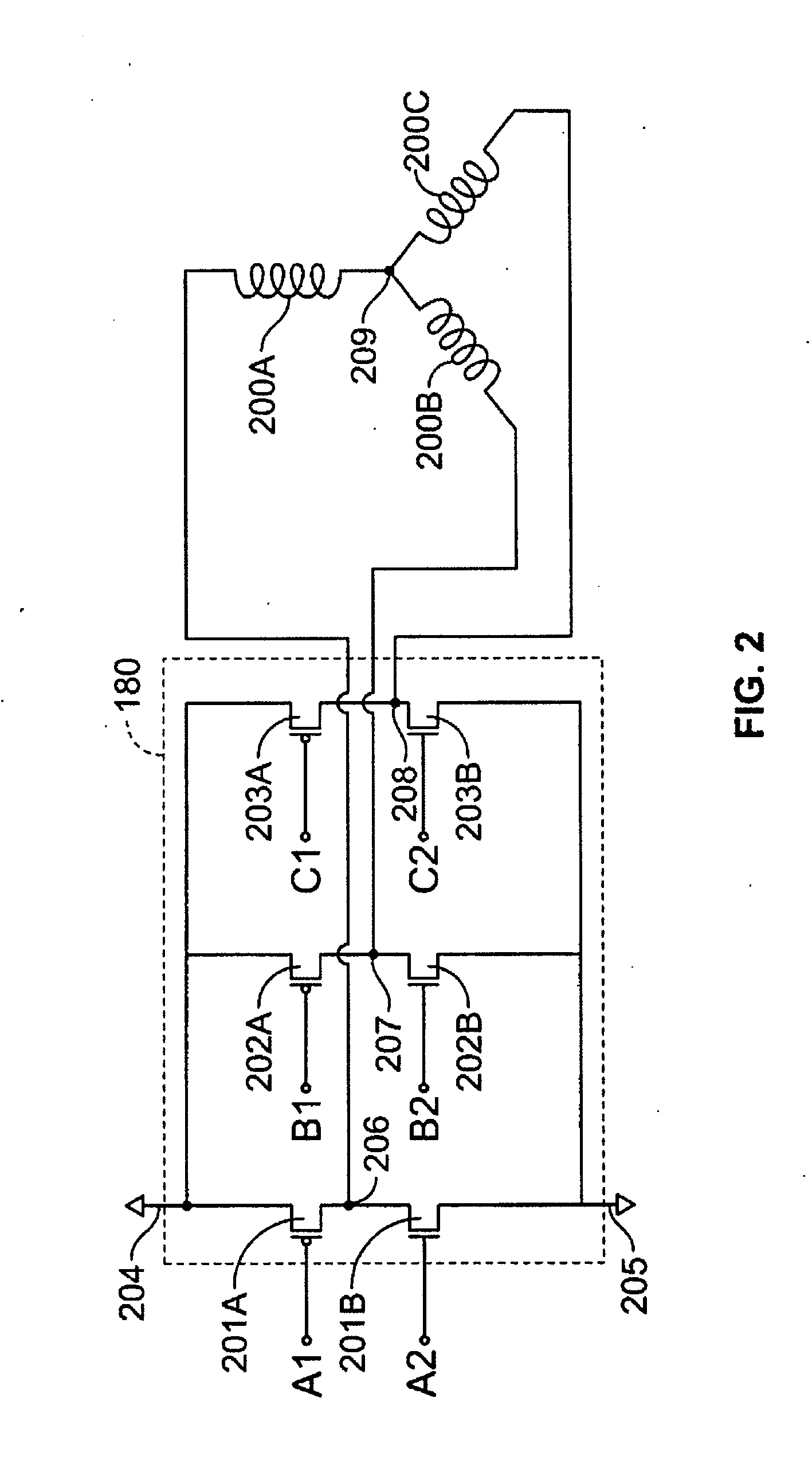
A method and apparatus for controlling a brushless DC (BLDC) motor over a wide range of angular speeds is presented. Analog magnetic sensors provide continuous signal measurements related to the rotor angular position at a sample rate independent of rotor angular speed. In one embodiment, analog signal measurements are subsequently processed using an arctangent function to obtain the rotor angular position. The arctangent may be computed using arithmetic computation, a small angle approximation, a polynomial evaluation approach, a table lookup approach, or a combination of various methods. In one embodiment, the BLDC rotor is used to drive a Roots blower used as a compressor in a portable mechanical ventilator system.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 203 INC
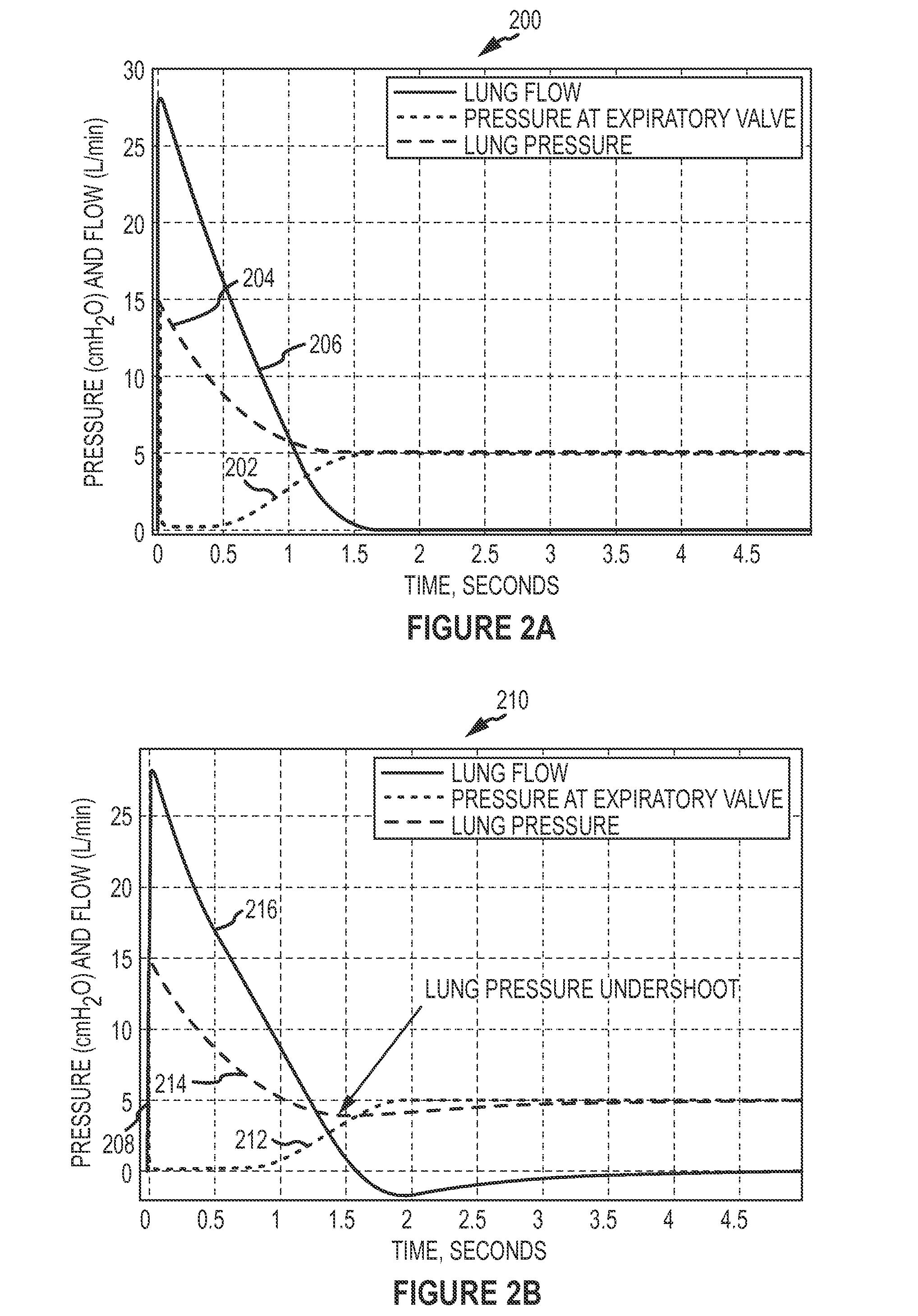
Energy relief control in a mechanical ventilator
ActiveUS20090188502A1Reduce positive pressureReduce anxietyElectrocardiographyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsPressure curve
The present invention relates to a solution for controlling the pressure / flow of breathing gas to a mechanical ventilator (4) by using an energy of breathing analysis and further to provide a pressure relief during exhalation and a trigger determination when to start the pressure relief using energy content of breathing in analysis for determining a pressure curve form during at least a portion of the expiration phase.
Owner:BREAS MEDICAL
Minimizing imposed expiratory resistance of mechanical ventilator by optimizing exhalation valve control
ActiveUS20130284177A1Promote exchangeReduce pressureTracheal tubesMedical devicesMechanical ventilatorsIntensive care medicine
This disclosure describes systems and methods for controlling an exhalation valve based on pressure and / or flow measurements during exhalation. The disclosure describes novel exhalation valve controls for ventilating a patient.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Delta Flow Pressure Regulation
InactiveUS20080276939A1Reduce dependenceLittle time differenceRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsIntensive care medicine
A method, system, apparatus, and computer program for detecting breathing pattern changes and controlling a mechanical ventilator in accordance to changes of breathing air flow thus reducing the work of breathing for the patient.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Inexsufflator
InactiveUS20070017523A1Clear secretionPreventing alveolar or airway collapseRespiratorsBuilding rescueMechanical ventilatorsSpool valve
A manual inexsufflator including a standard mechanical ventilator, a medical suction unit, and a piston-like sliding valve mechanism which connects a patient ventilation interface with either the ventilator or the suction unit. By sliding the valve mechanism in and out the user selectively connects the patient to either the ventilator, for purposes of insufflation, or the suction unit, for purposes of exsufflation. The ventilator may generate expiratory positive airway pressure between inexsufflation cycles.
Owner:ALYN WOLDENBERG FAMILY HOSPITAL
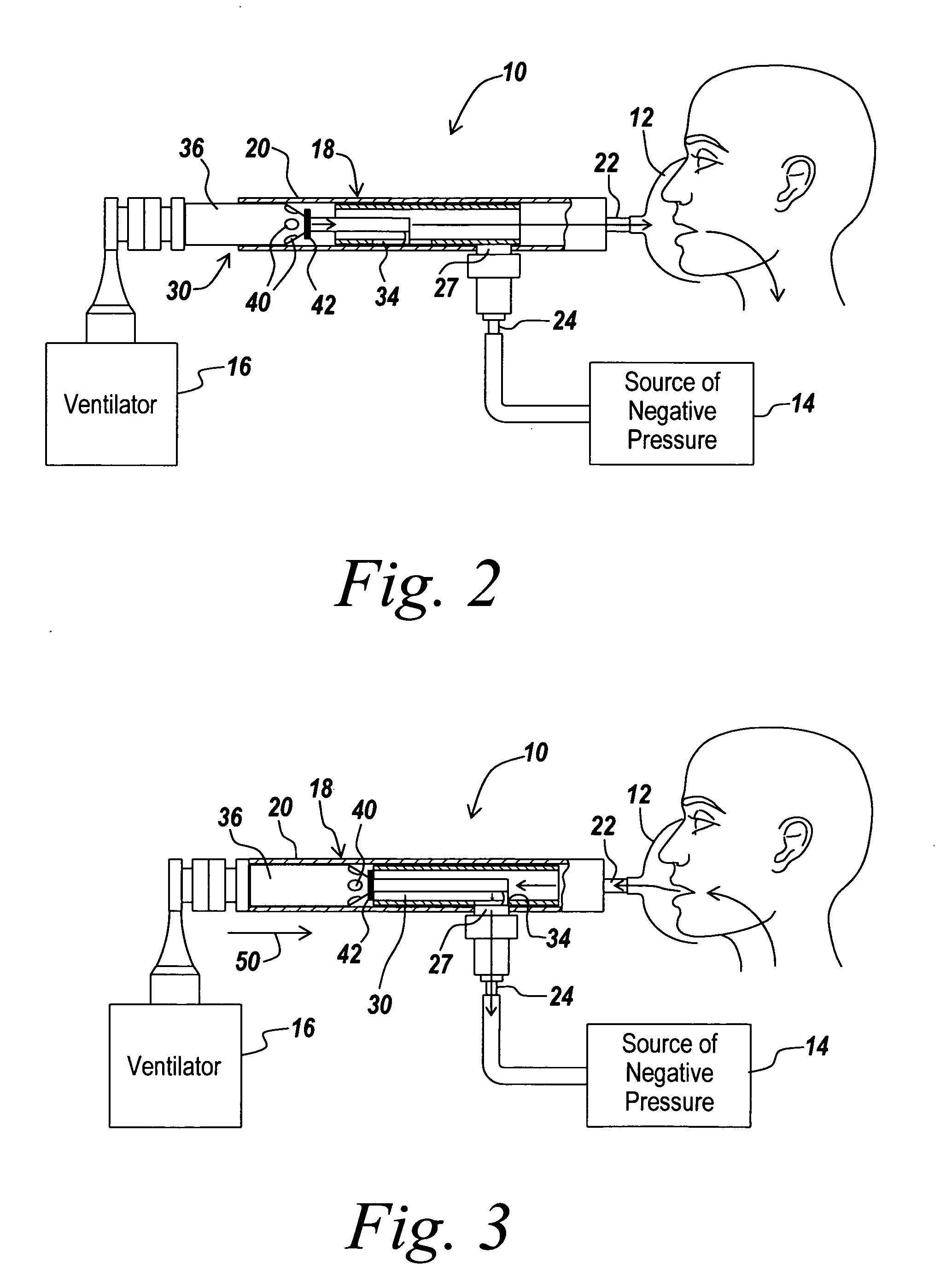
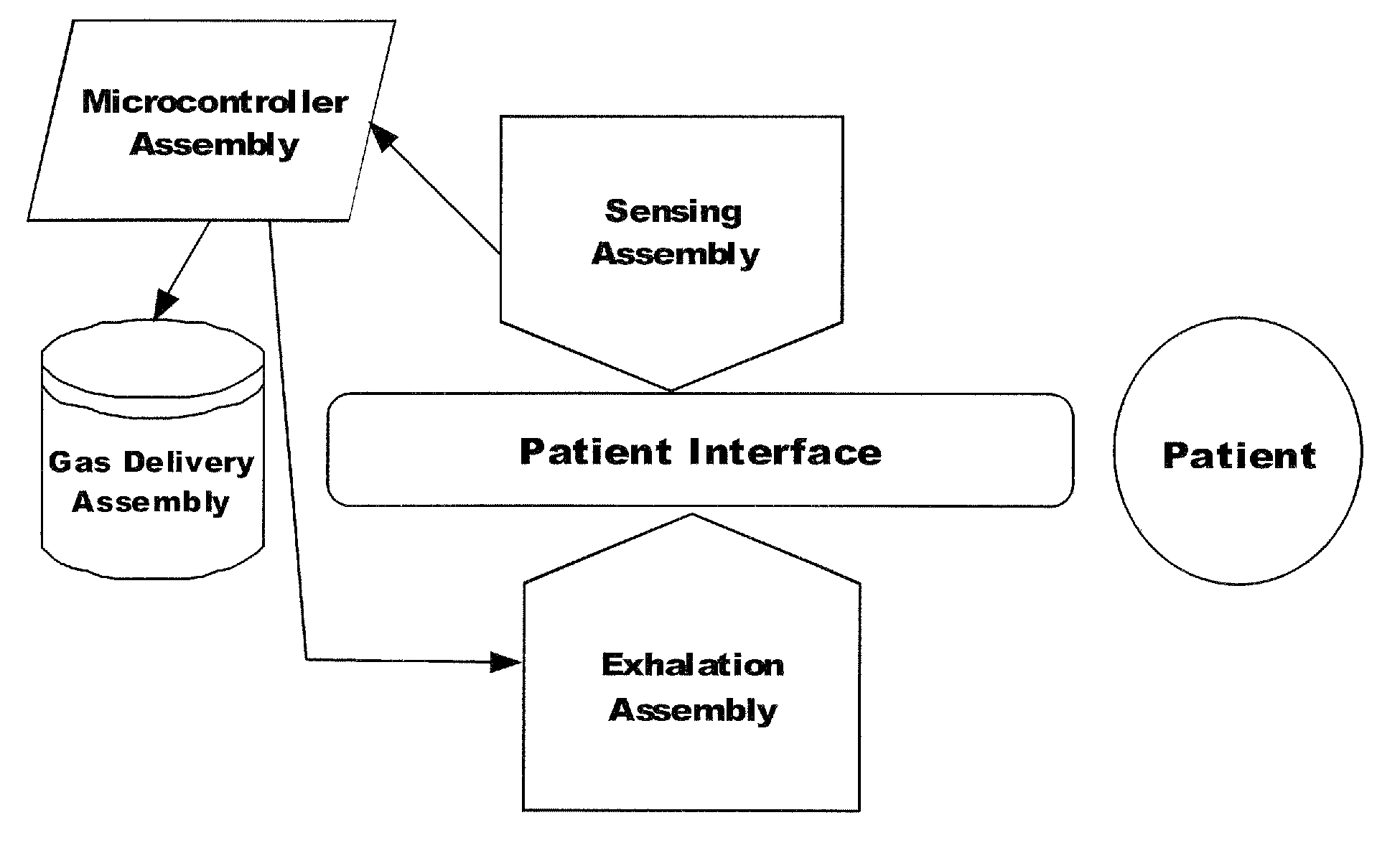
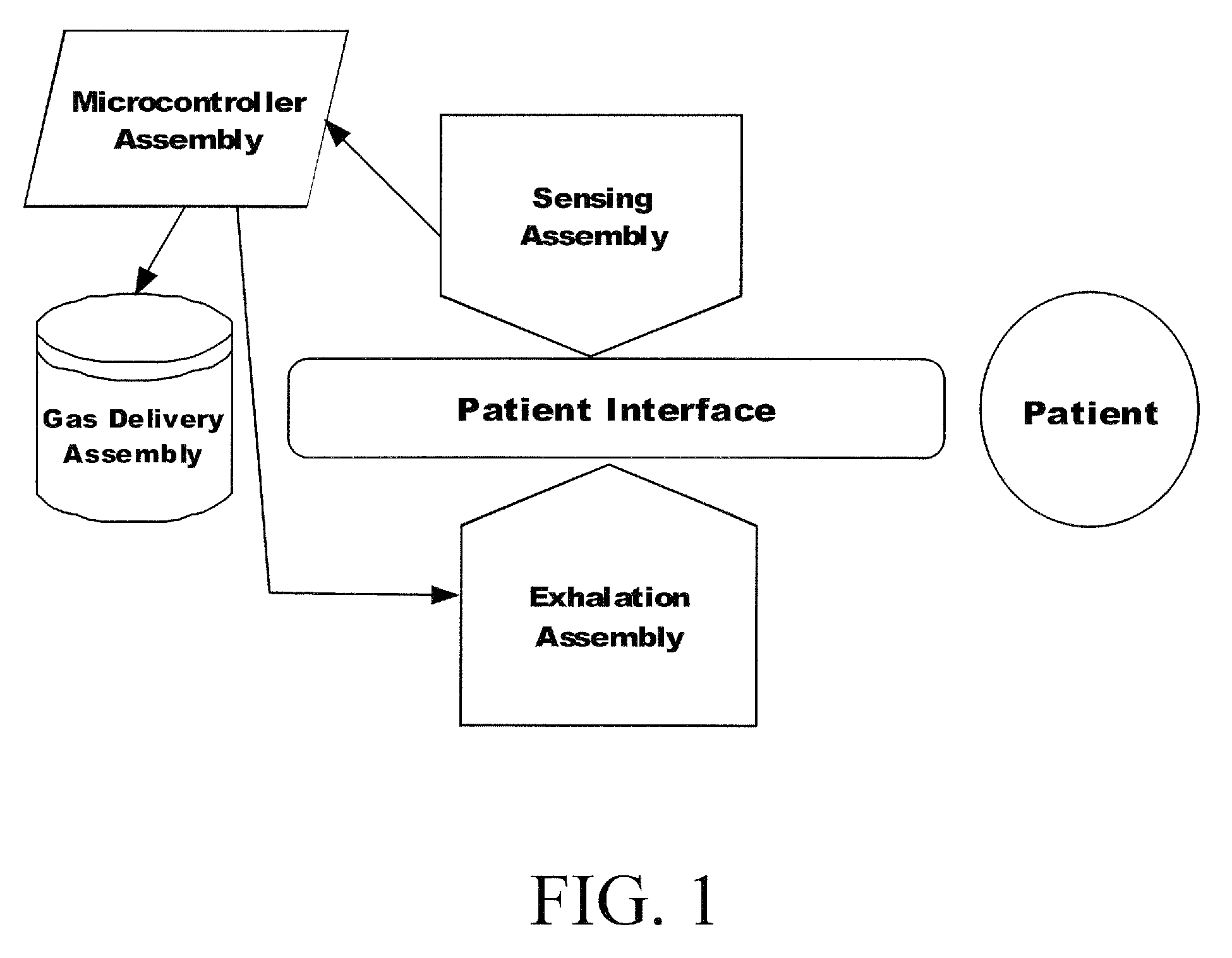
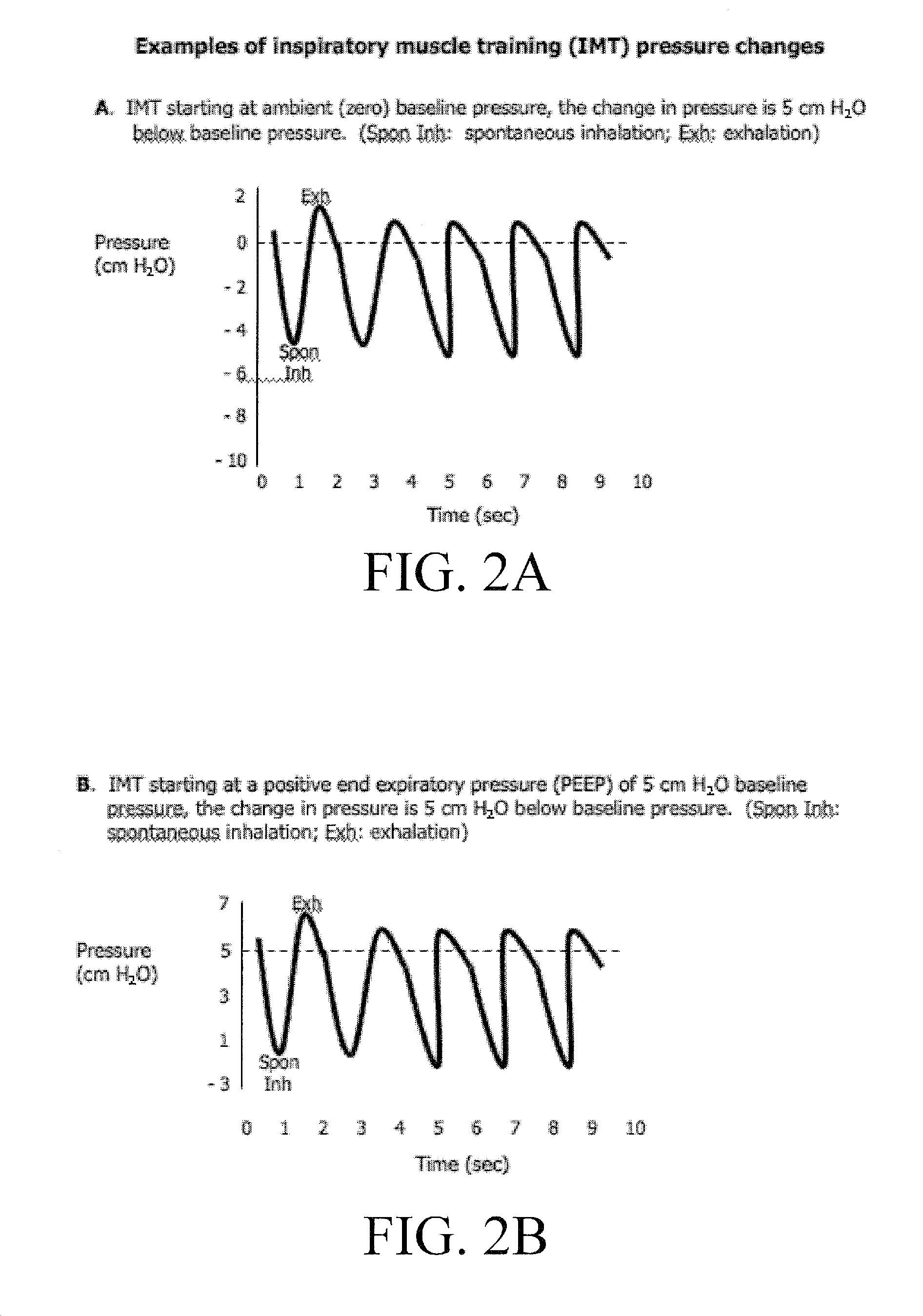
Automated Inspiratory Muscle Training for Patients Receiving Mechanical Ventilation
ActiveUS20090229611A1Improve coordinationIncrease powerRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsHigh pressure
A system and method for automated inspiratory muscle strength exercise includes software for setting a mechanical ventilator for a pressure regulated breath with an initial pressure target that is at the highest pressure setting a patient can tolerate and increasing the pressure target as tolerated.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and apparatus for airway compensation control
ActiveUS20110087123A9RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsTracheal tube
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
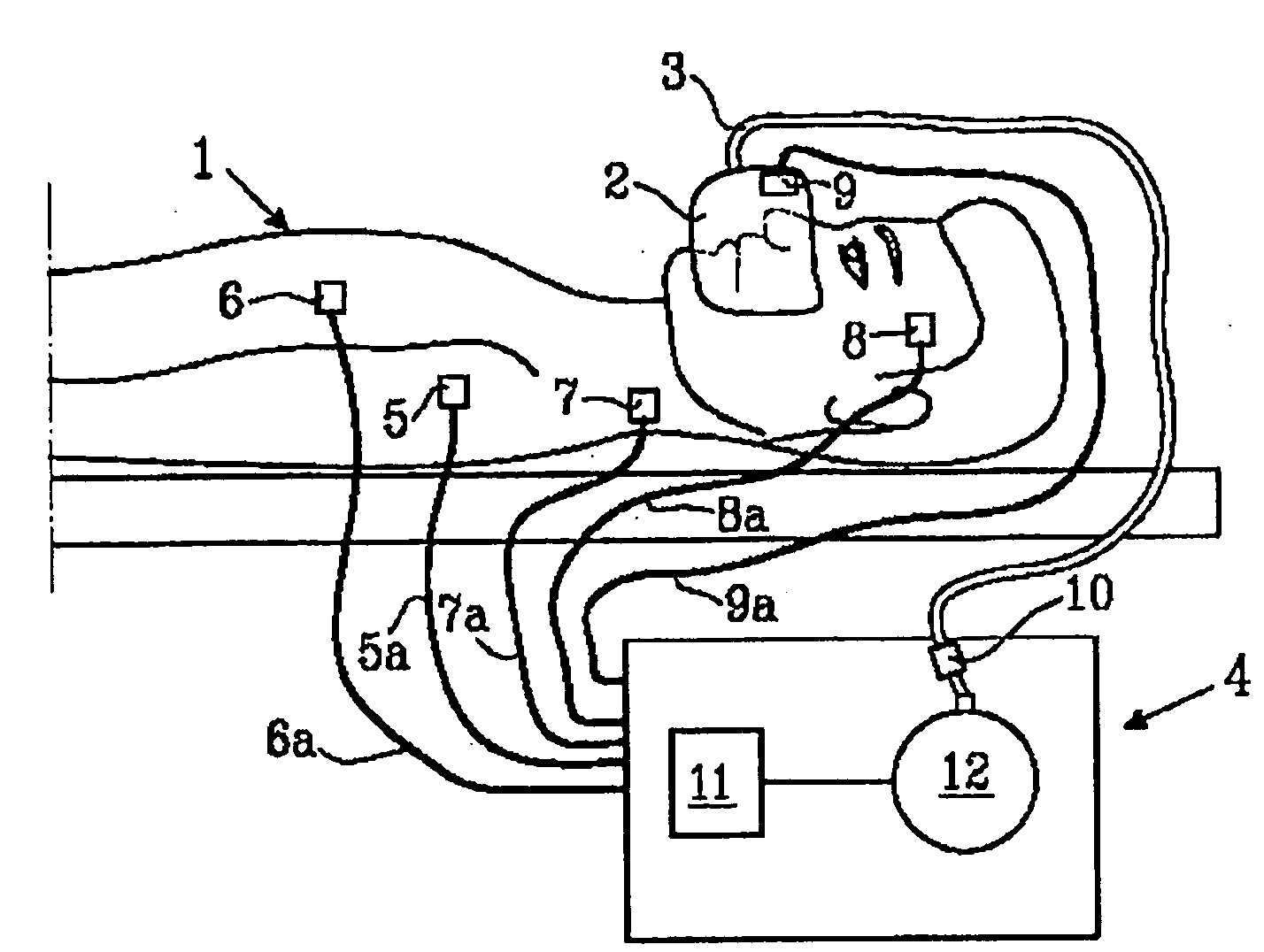
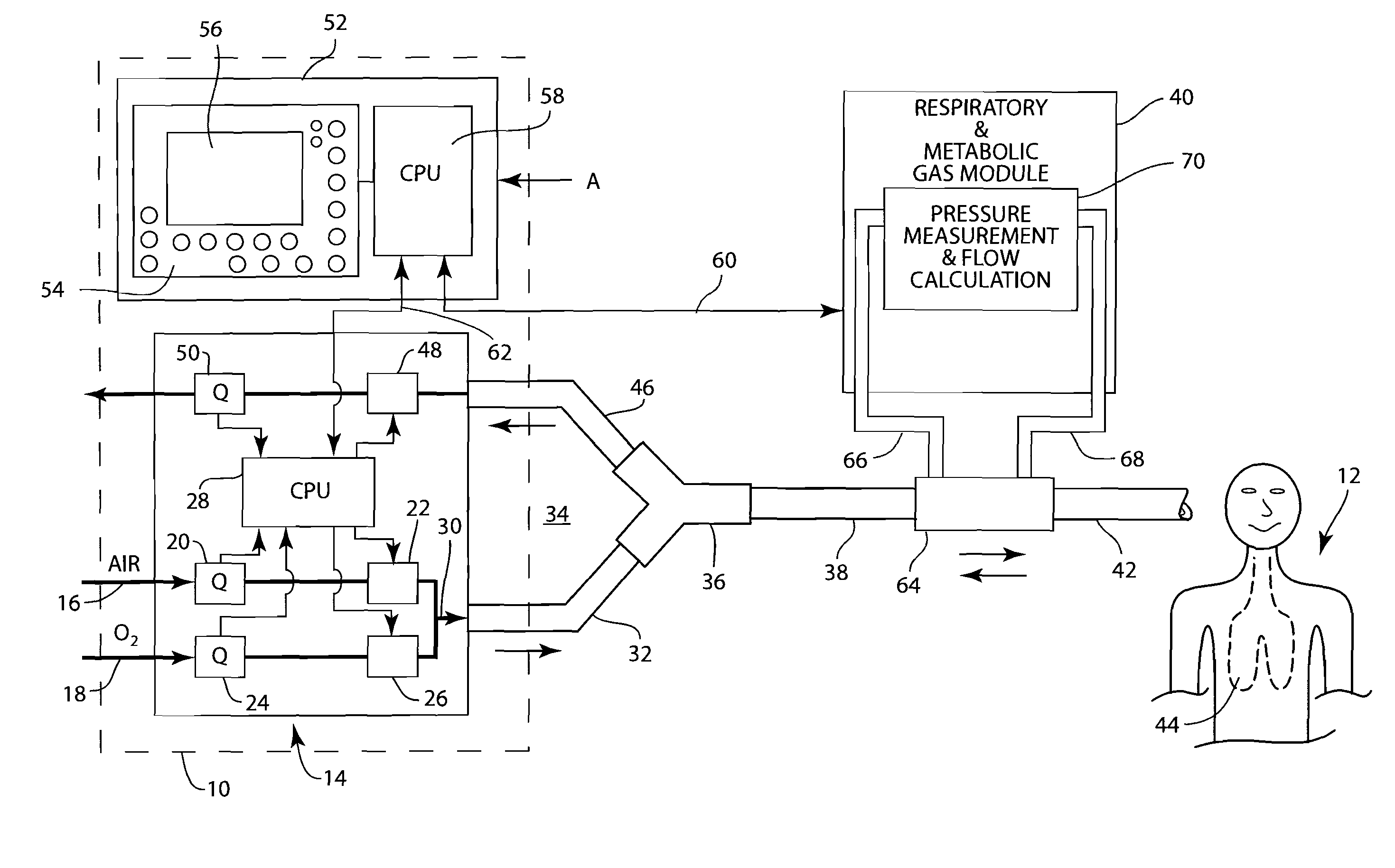
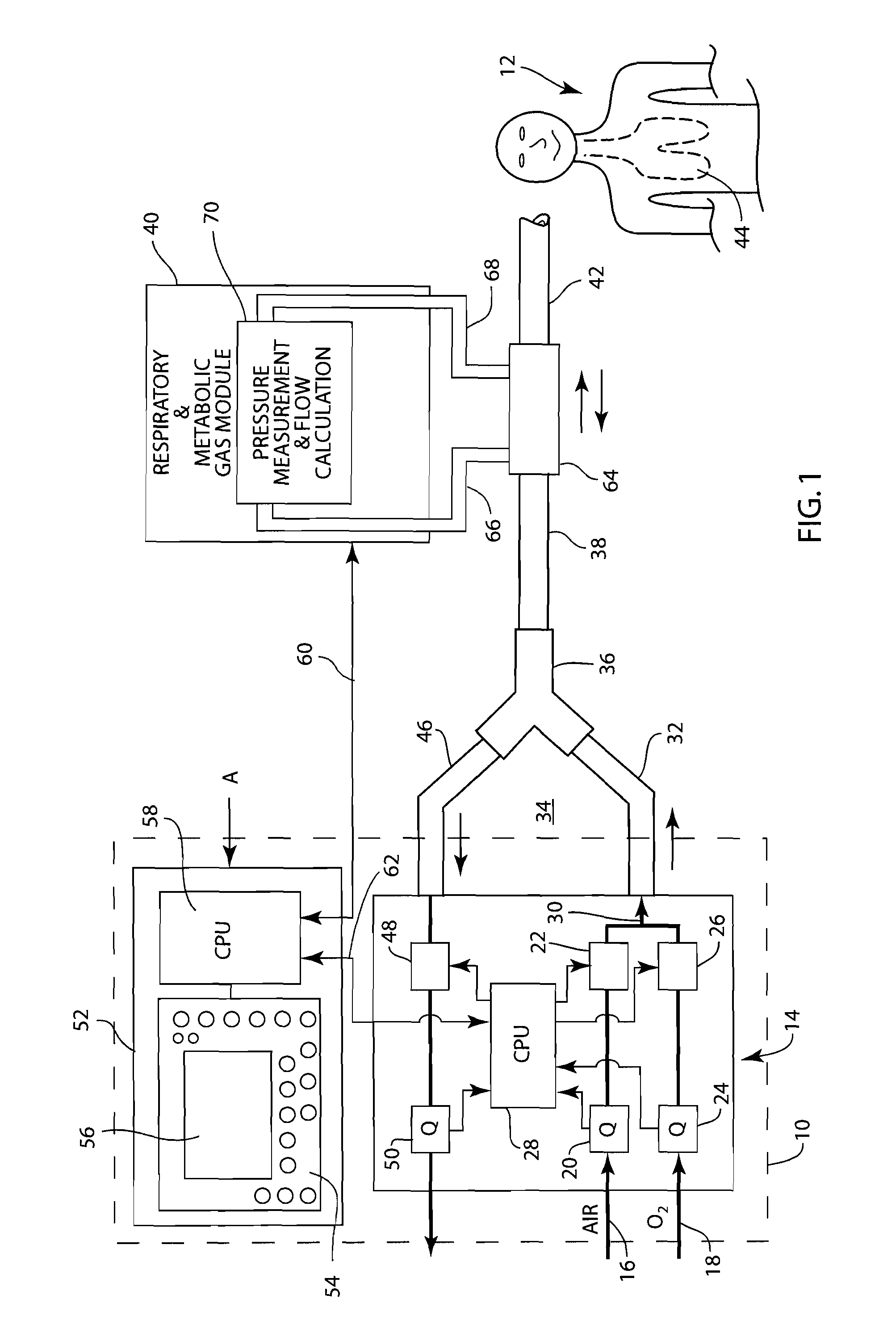
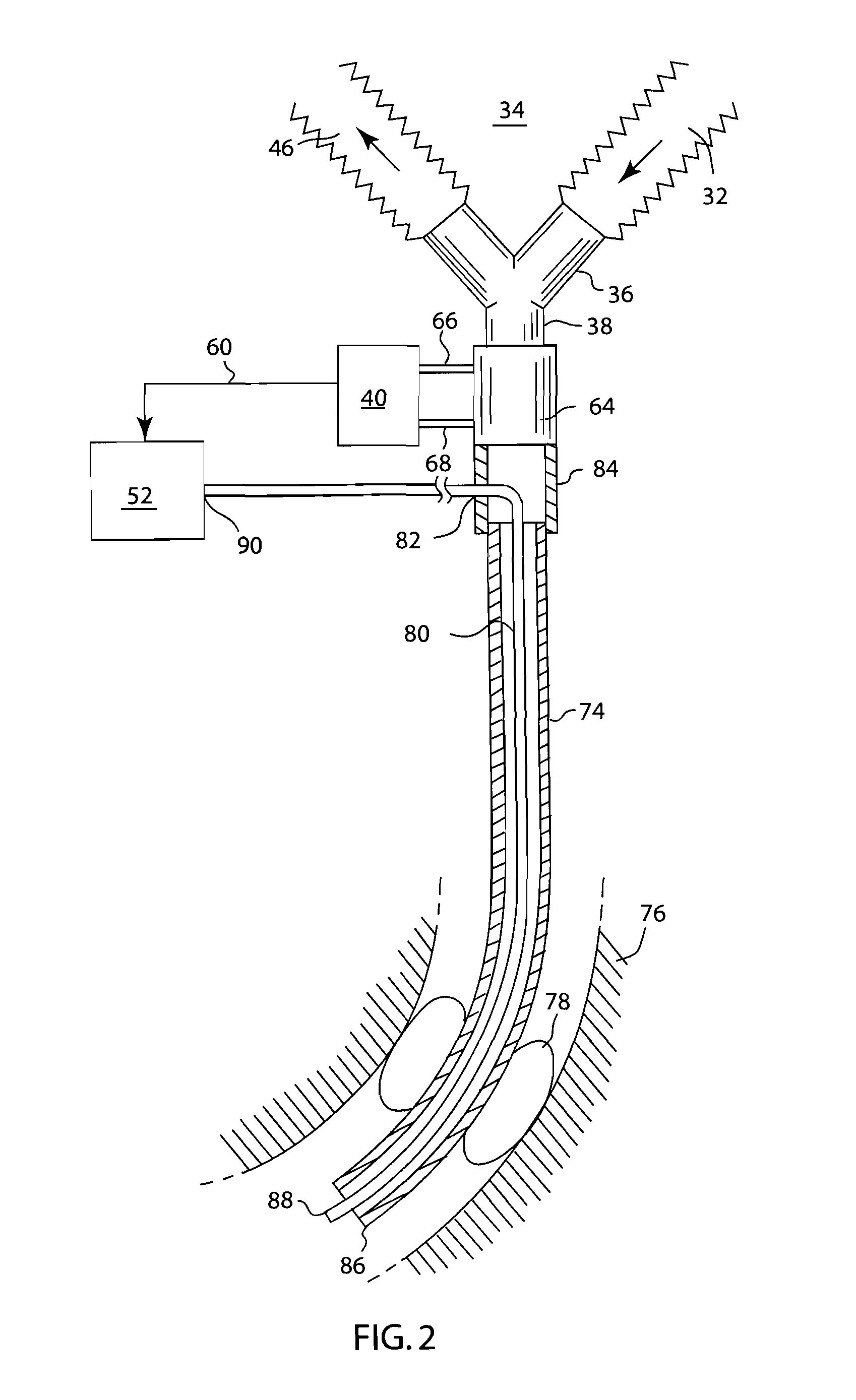
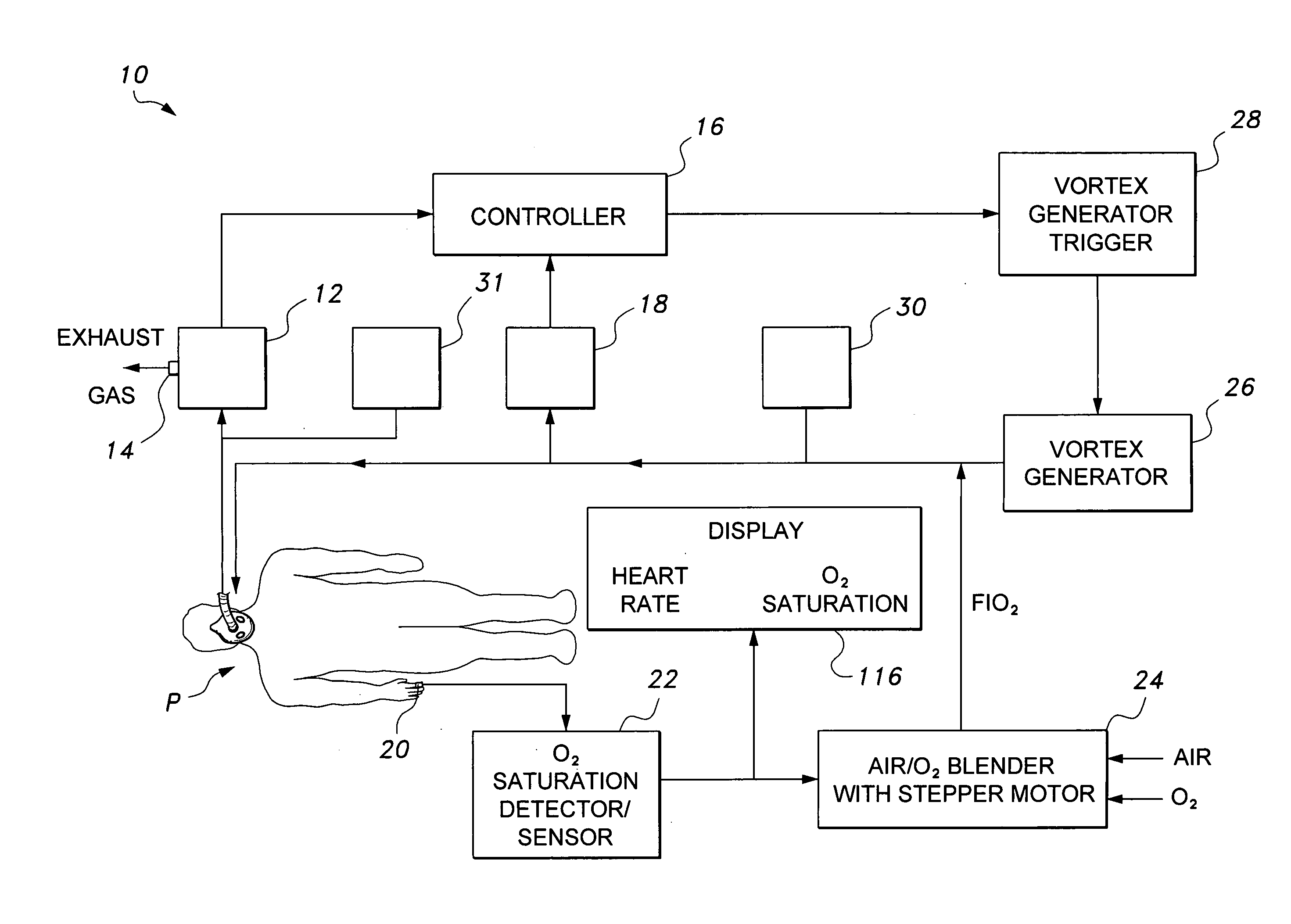
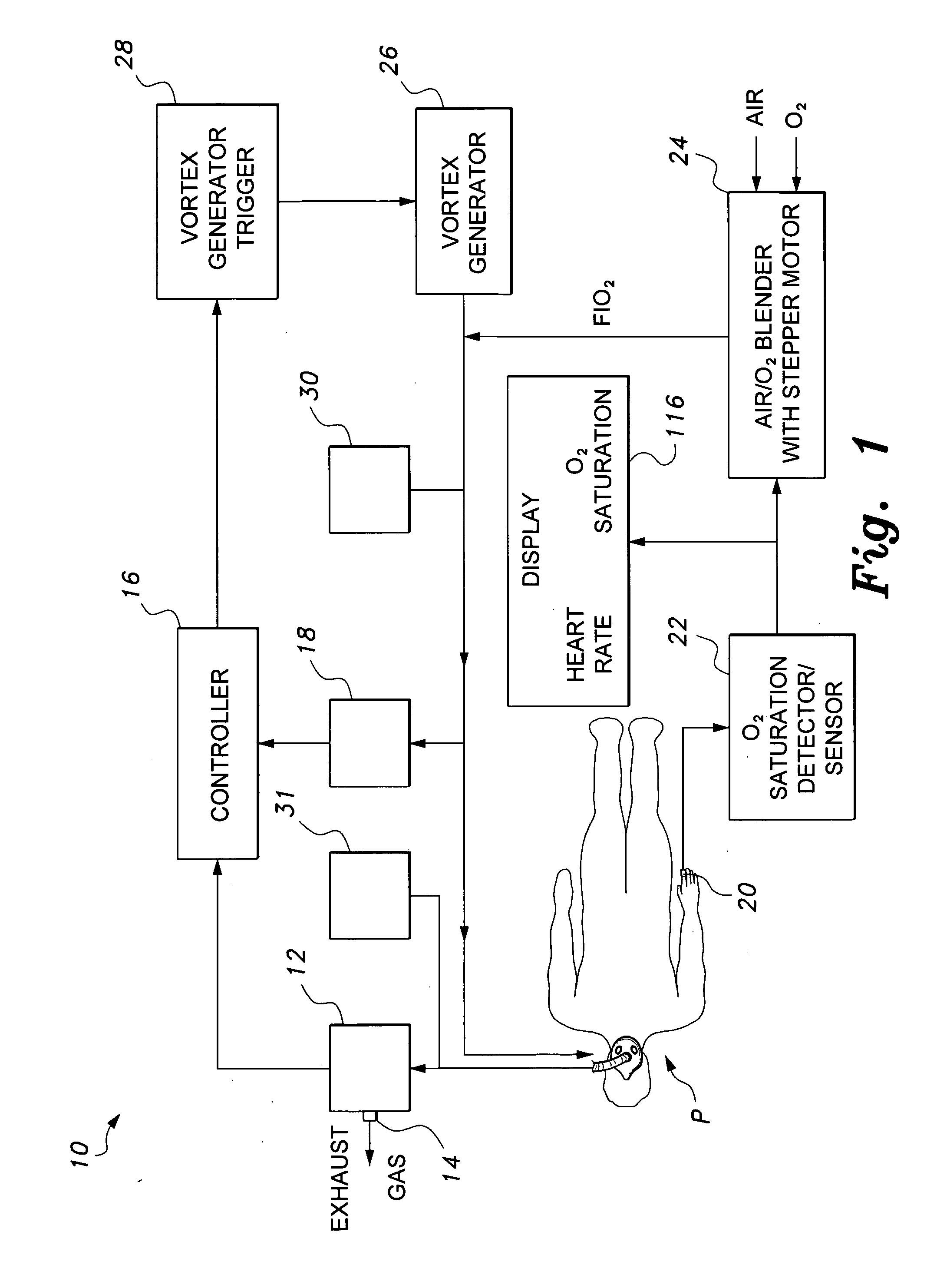
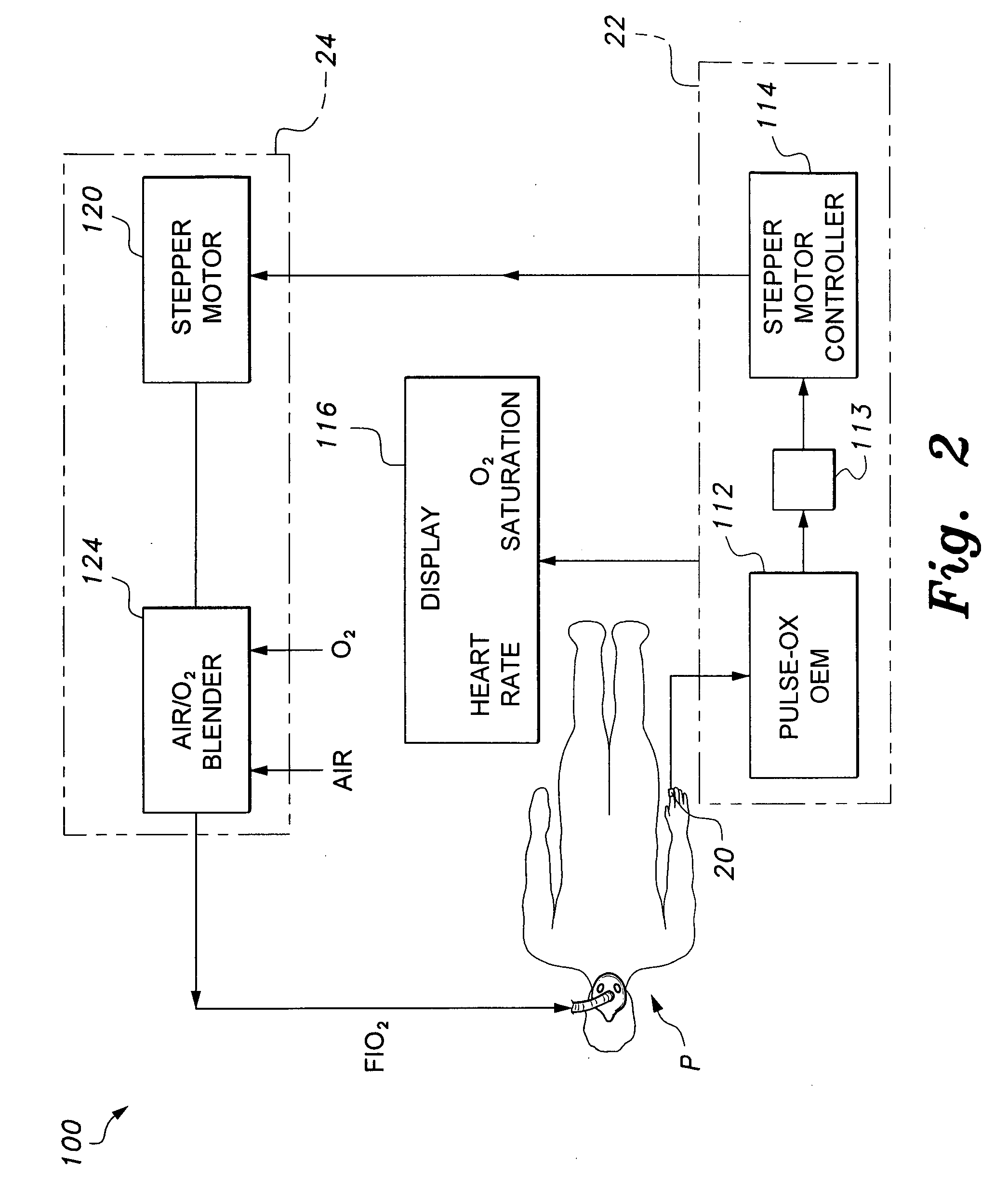
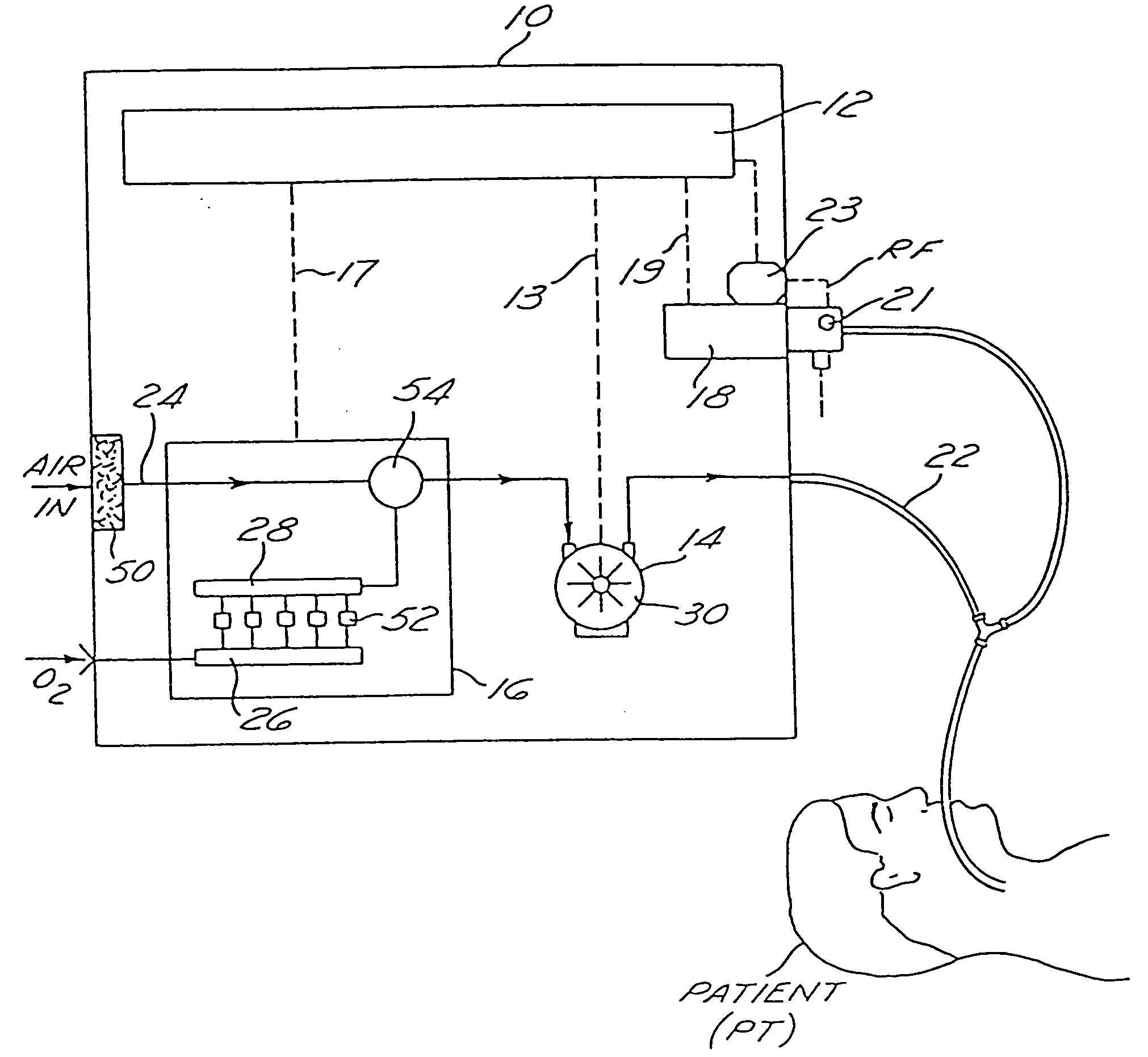
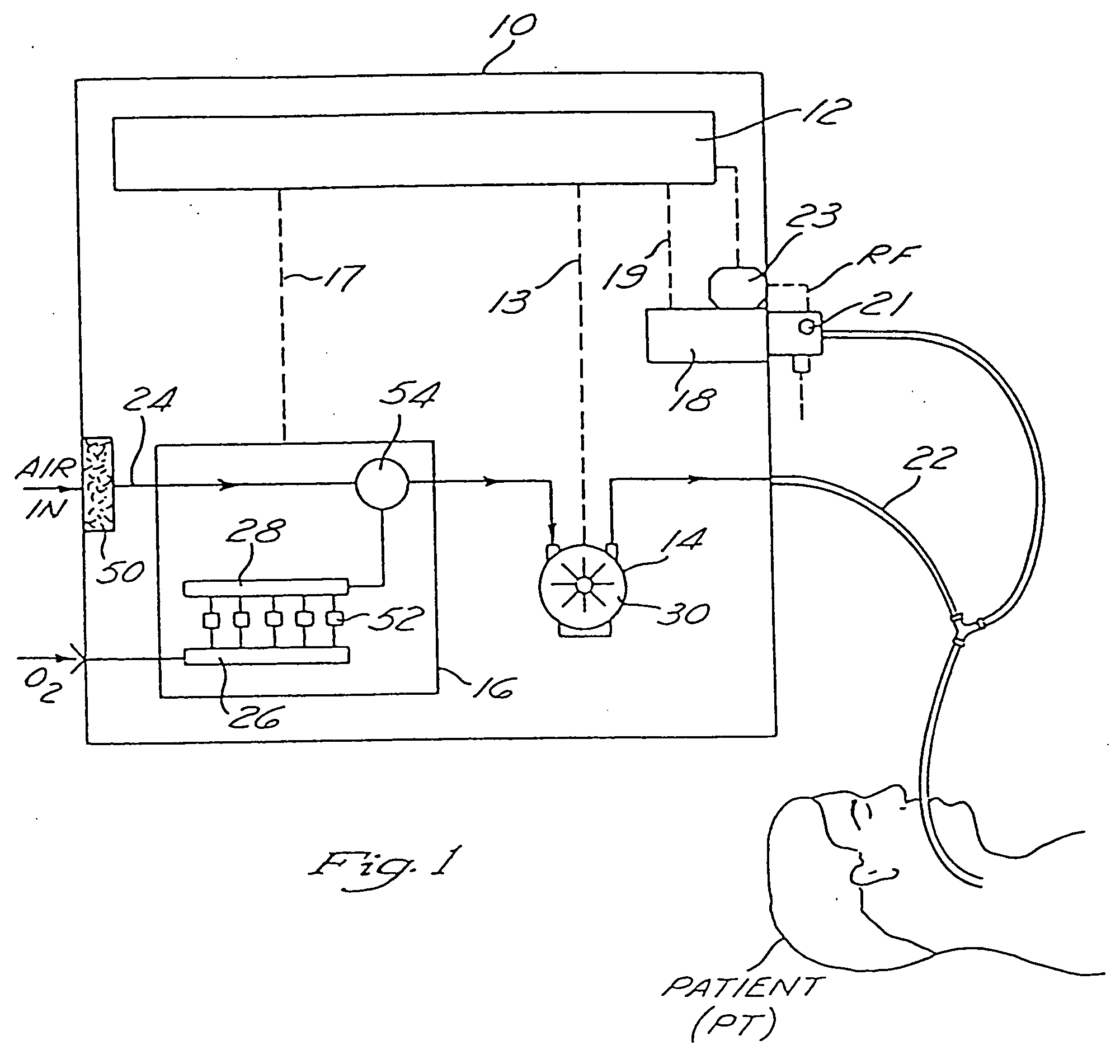
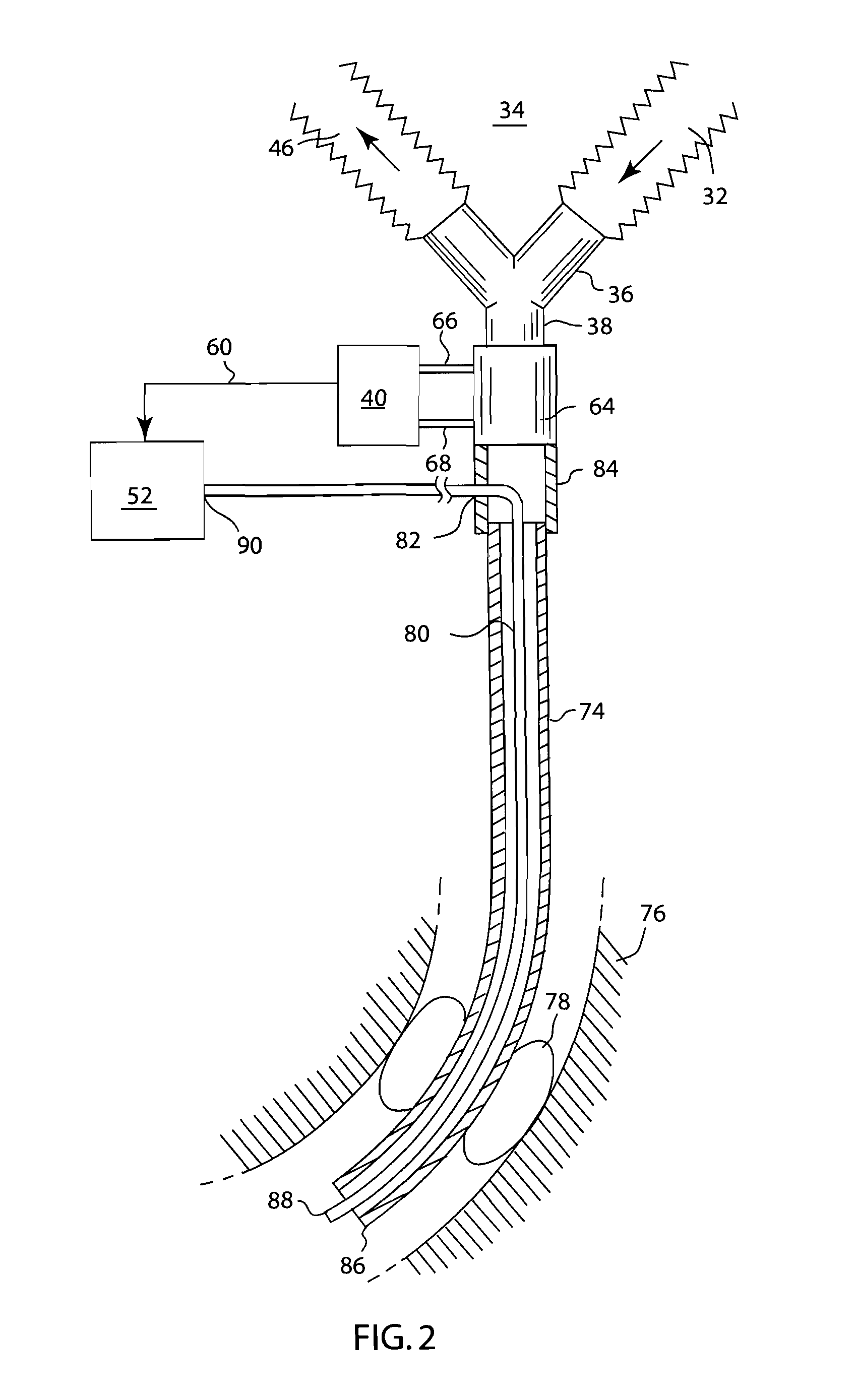
Mechanical ventilator system
The mechanical ventilator system is a compact and portable artificial respiration system. A negative pressure vortex generator delivers an FiO2 mix from an air-oxygen blender to the patient during the patient's inhalations, but remains idle during the patient's exhalations. Exhaust gases generated by the patient are released through an exhaust gas valve. During operation, the patient's oxygen saturation level is measured by an infrared pulse-oxygen probe, and an FiO2 autoregulator is in communication with the probe to receive oxygen saturation level signals. The FiO2 autoregulator is coupled with the air-oxygen blender to control the oxygen proportion of the FiO2 mix. An automatic pressure flow sensor is fluidly coupled with the patient's airway to control actuation of the negative pressure vortex generator. The automatic flow sensor is coupled with a controller, which actuates a vortex generator trigger circuit in communication with the vortex generator.
Owner:RAO CHAMKURKISHTIAH P +1
Energy Trigger
A method and apparatus for facilitating breathing using a mechanical breathing gas ventilator is presented. The patient effort is deduced from a measured flow signal and analyzed with respect to the energy in the breathing system comprising the mechanical ventilator and the patient. When a predetermined energy threshold has been reached the ventilator responds to the breathing pattern change.
Owner:BREAS MEDICAL
Portable drag compressor powered mechanical ventilator
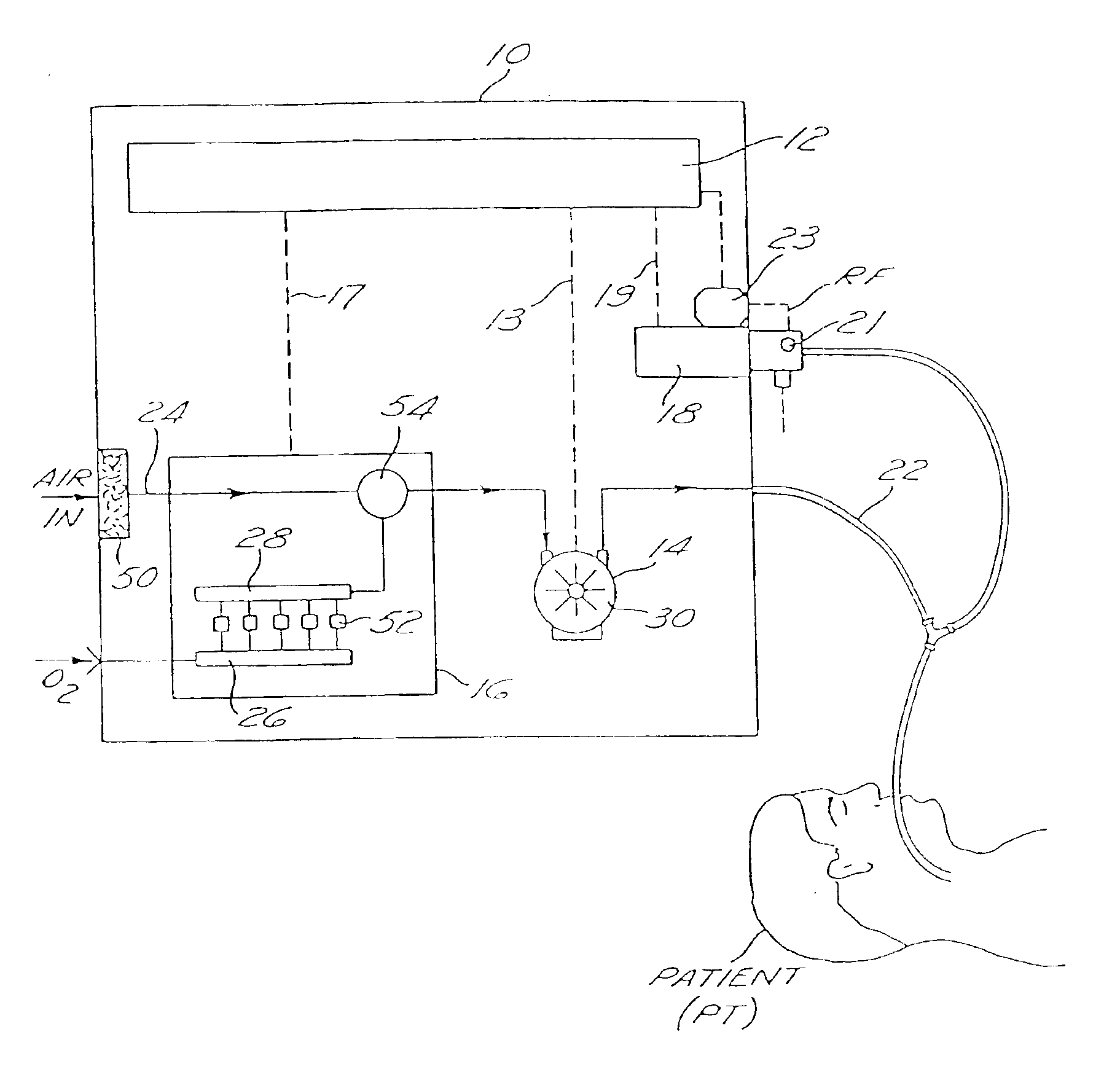
InactiveUS20050150494A1Accurate measurementMinimize inaccuracyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSolenoid valveEngineering
A ventilator device and system comprising a rotating compressor, preferably a drag compressor, which, at the beginning of each inspiratory ventilation phase, is accelerated to a sufficient speed to deliver the desired inspiratory gas flow, and is subsequently stopped or decelerated to a basal flow level to permit the expiratory ventilation phase to occur. The ventilator device is small and light weight enough to be utilized in portable applications. The ventilator device is power efficient enough to operate for extended periods of time on internal or external batteries. Also provided is an oxygen blending apparatus which utilizes solenoid valves having specific orifice sizes for blending desired amounts of oxygen into the inspiratory gas flow. Also provided is an exhalation valve having an exhalation flow transducer which incorporates a radio frequency data base to provide an attendant controller with specific calibration information for the exhalation flow transducer.
Owner:BIRD PRODS
Compressor control system for a portable ventilator
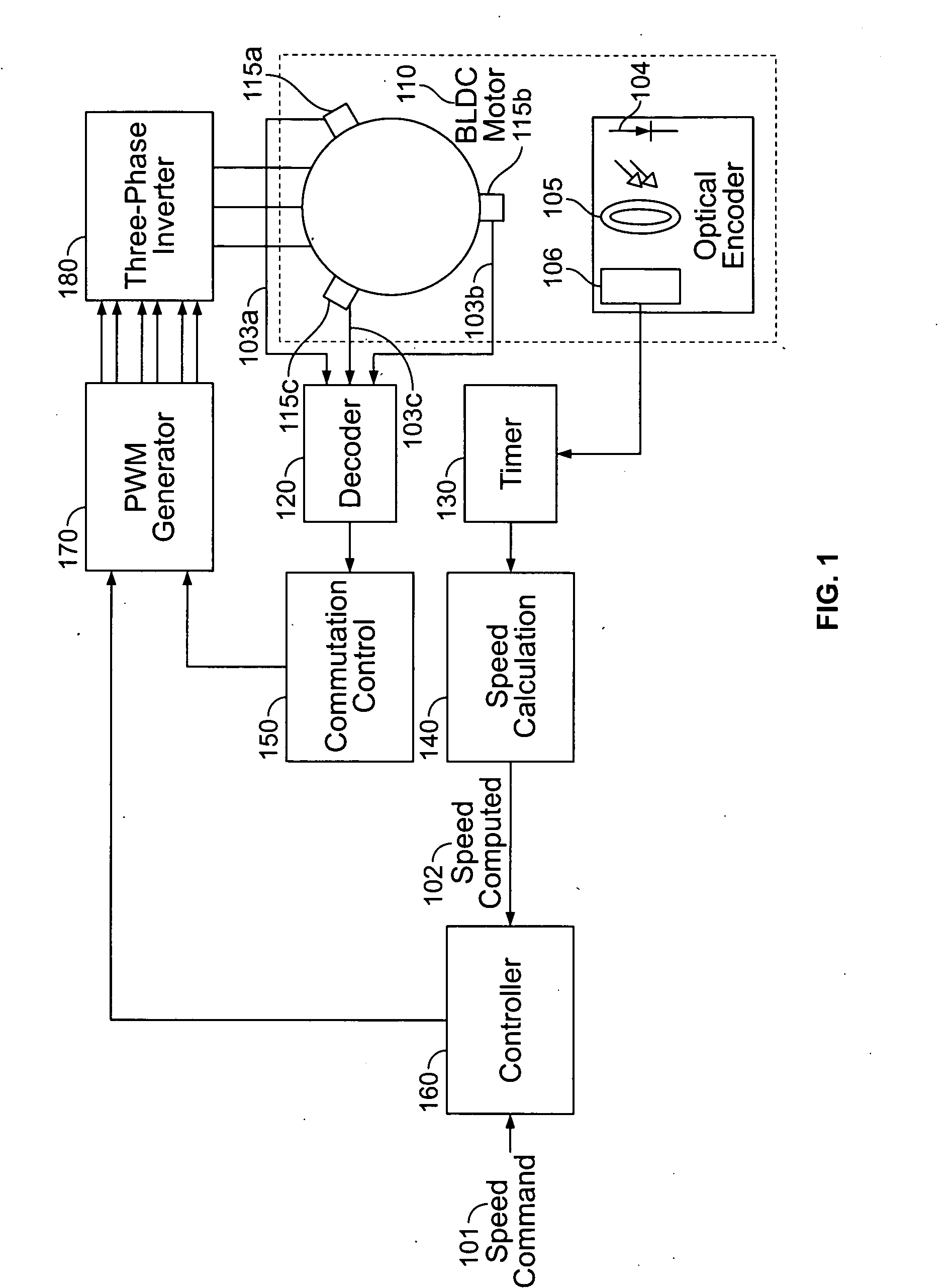
InactiveUS20080092893A1RespiratorsDC motor speed/torque controlMechanical ventilatorsPortable ventilators
A method and apparatus for controlling a brushless DC (BLDC) motor over a wide range of angular speeds is presented. Analog magnetic sensors provide continuous signal measurements related to the rotor angular position at a sample rate independent of rotor angular speed. In one embodiment, analog signal measurements are subsequently processed using an arctangent function to obtain the rotor angular position. The arctangent may be computed using arithmetic computation, a small angle approximation, a polynomial evaluation approach, a table lookup approach, or a combination of various methods. In one embodiment, the BLDC rotor is used to drive a Roots blower used as a compressor in a portable mechanical ventilator system.
Owner:CAREFUSION 207 INC
Compressor Control System for a Portable Ventilator
ActiveUS20080092892A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPortable ventilatorsMechanical ventilators
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 203 INC
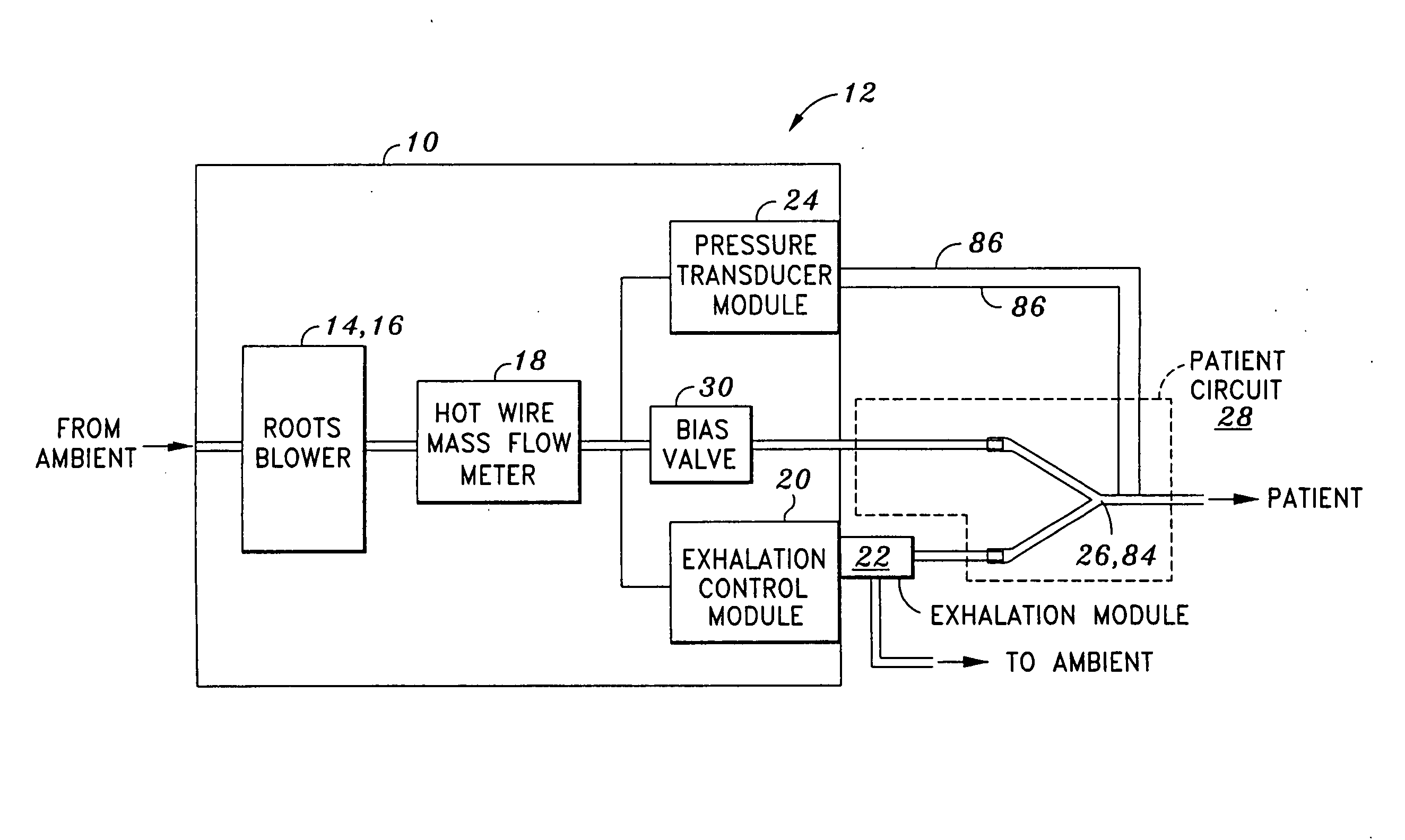
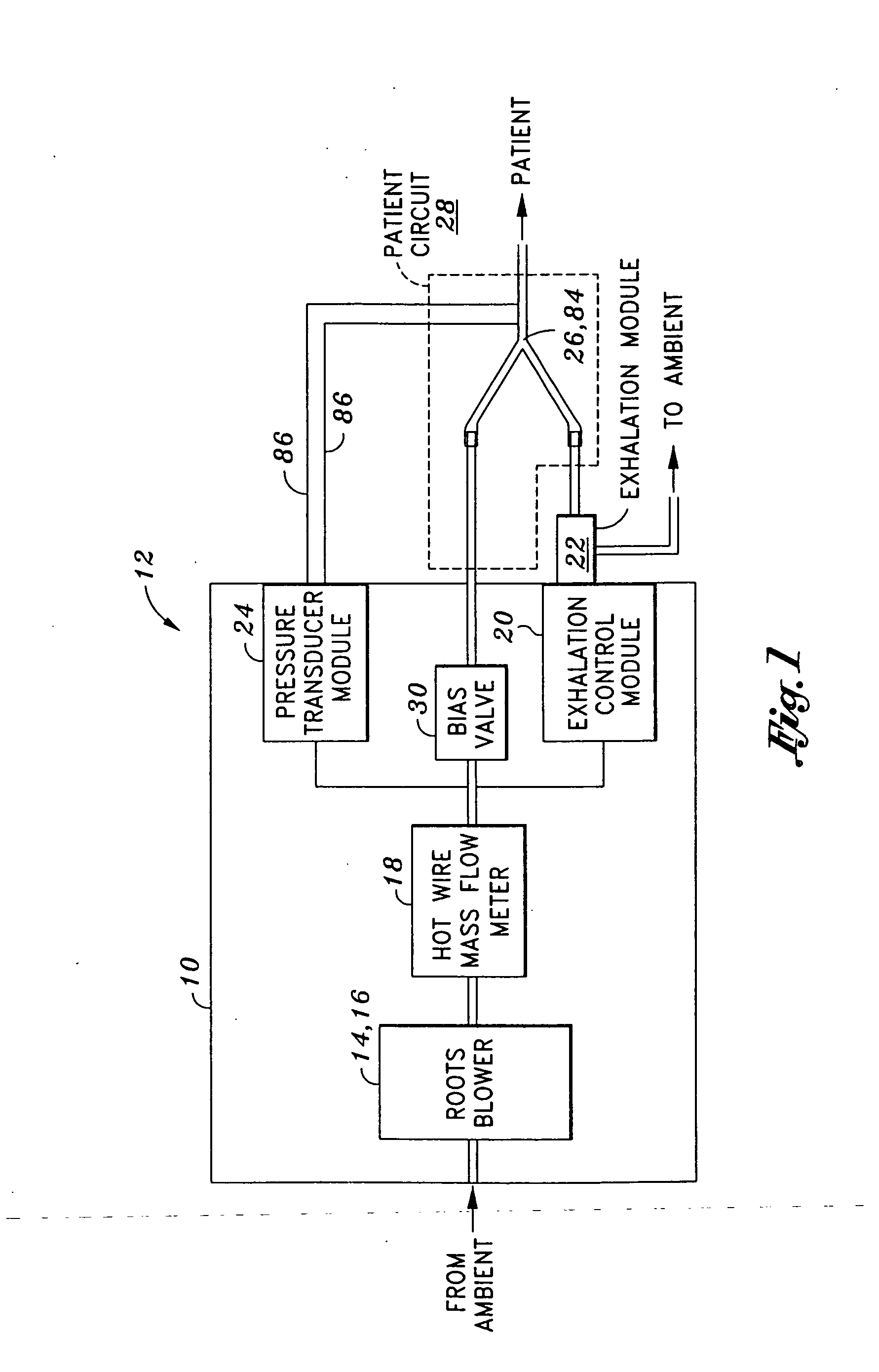
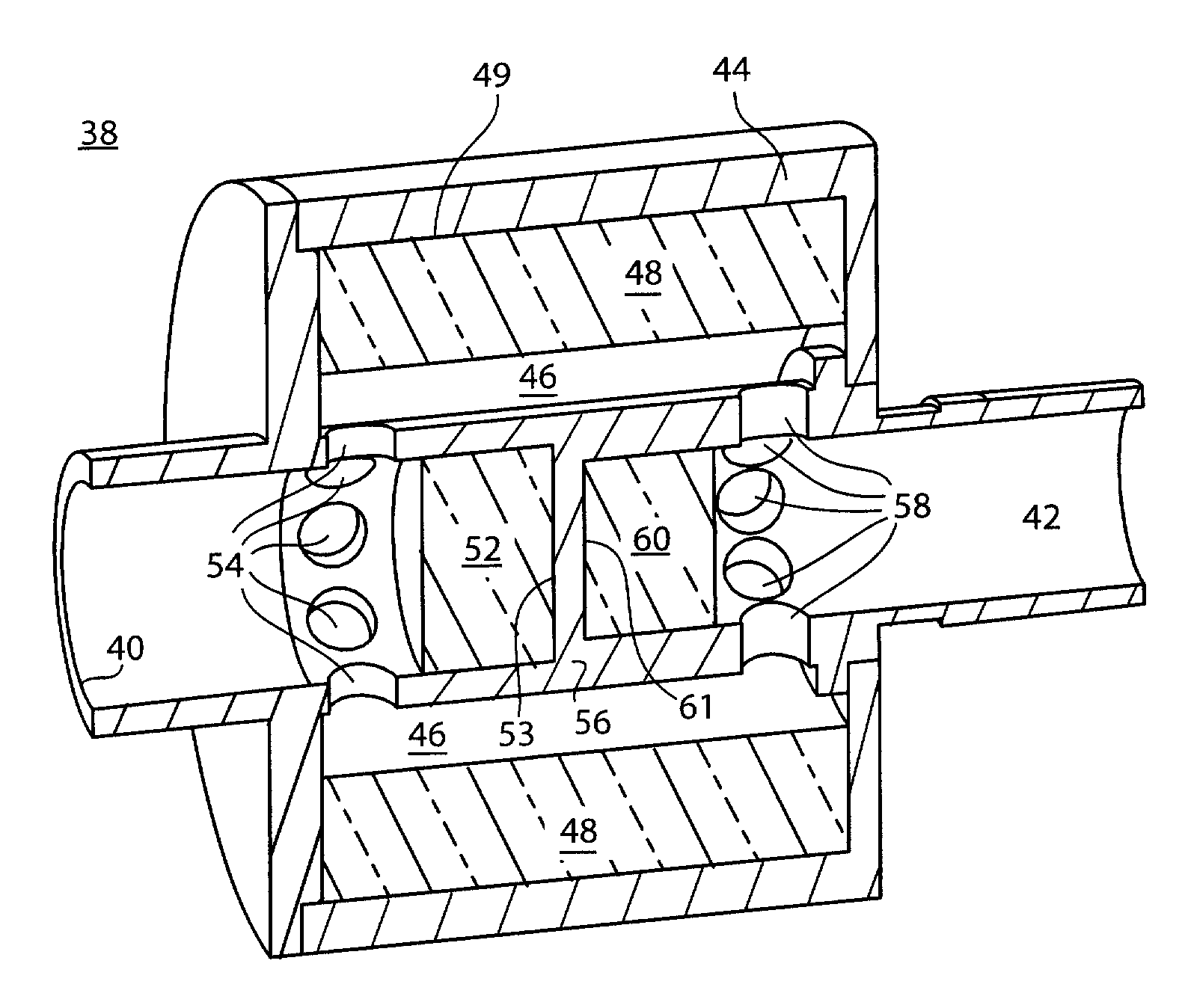
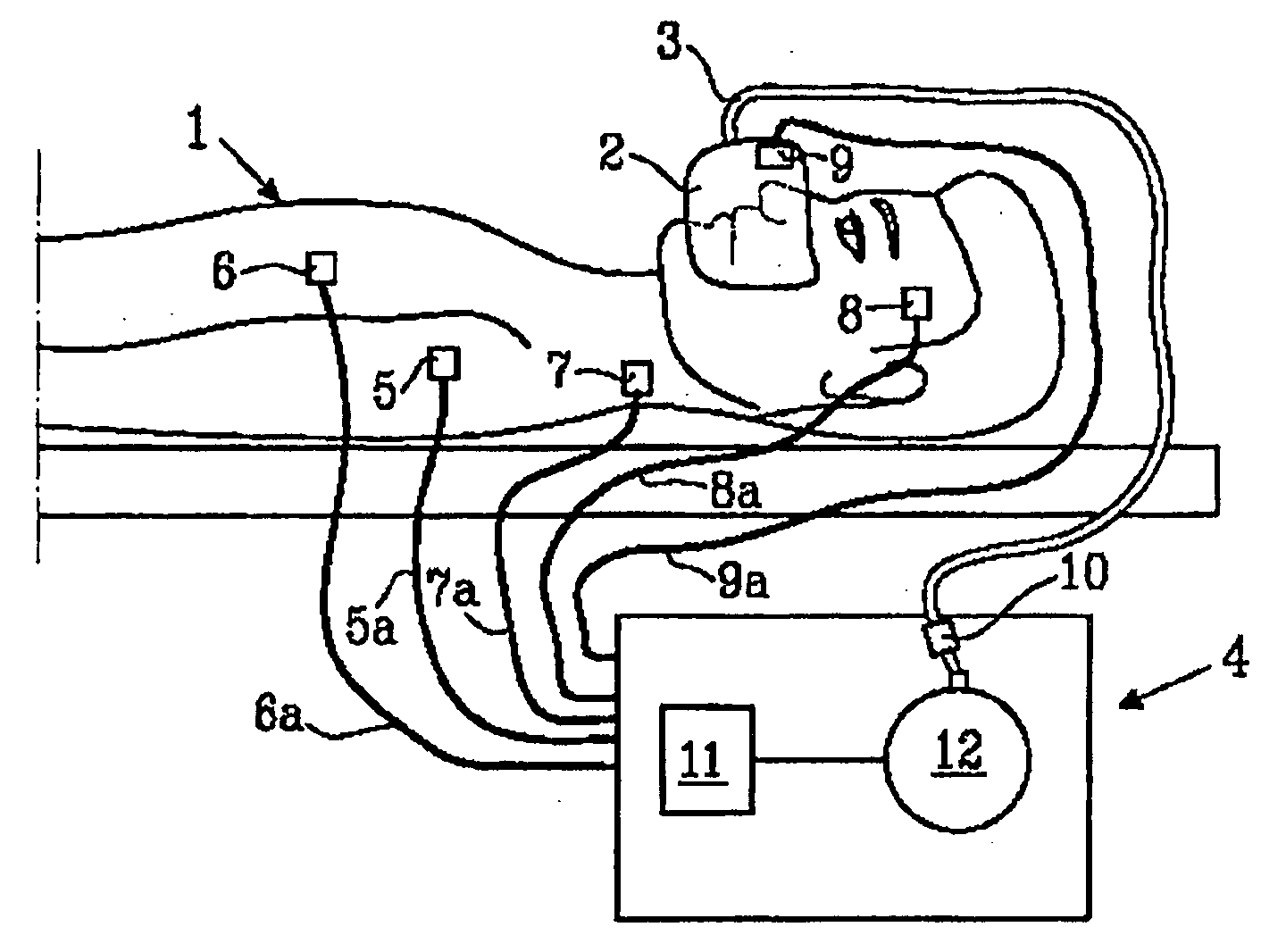
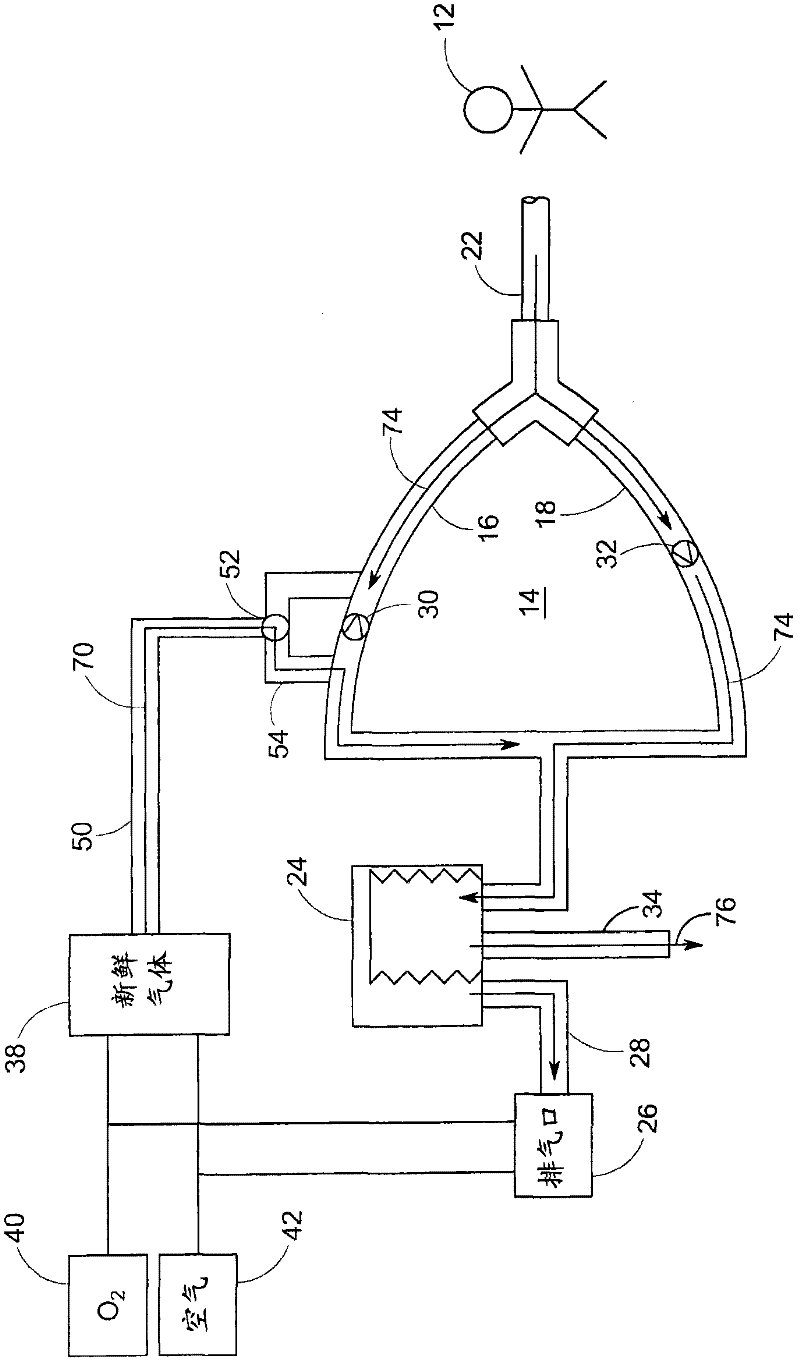
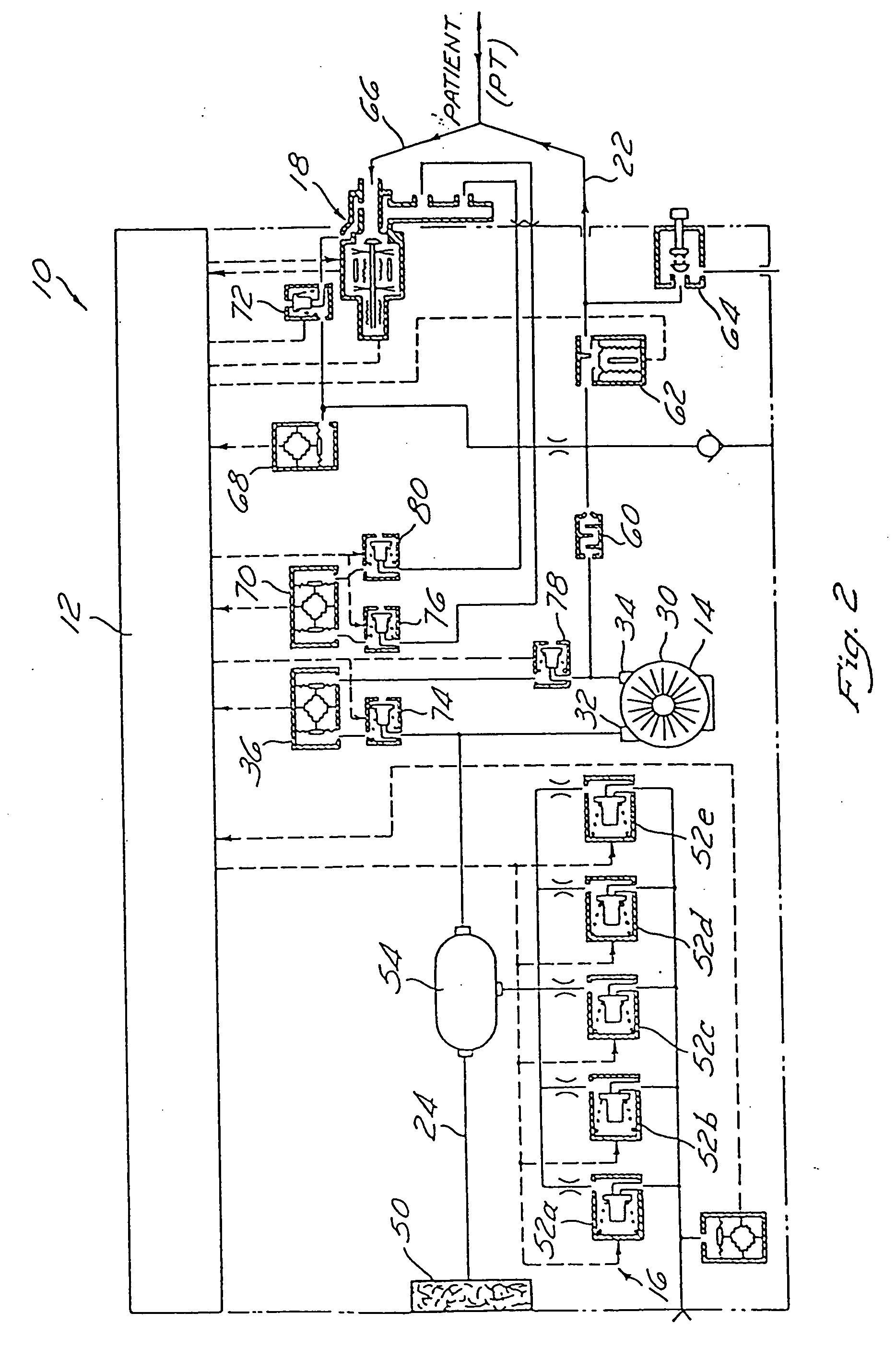
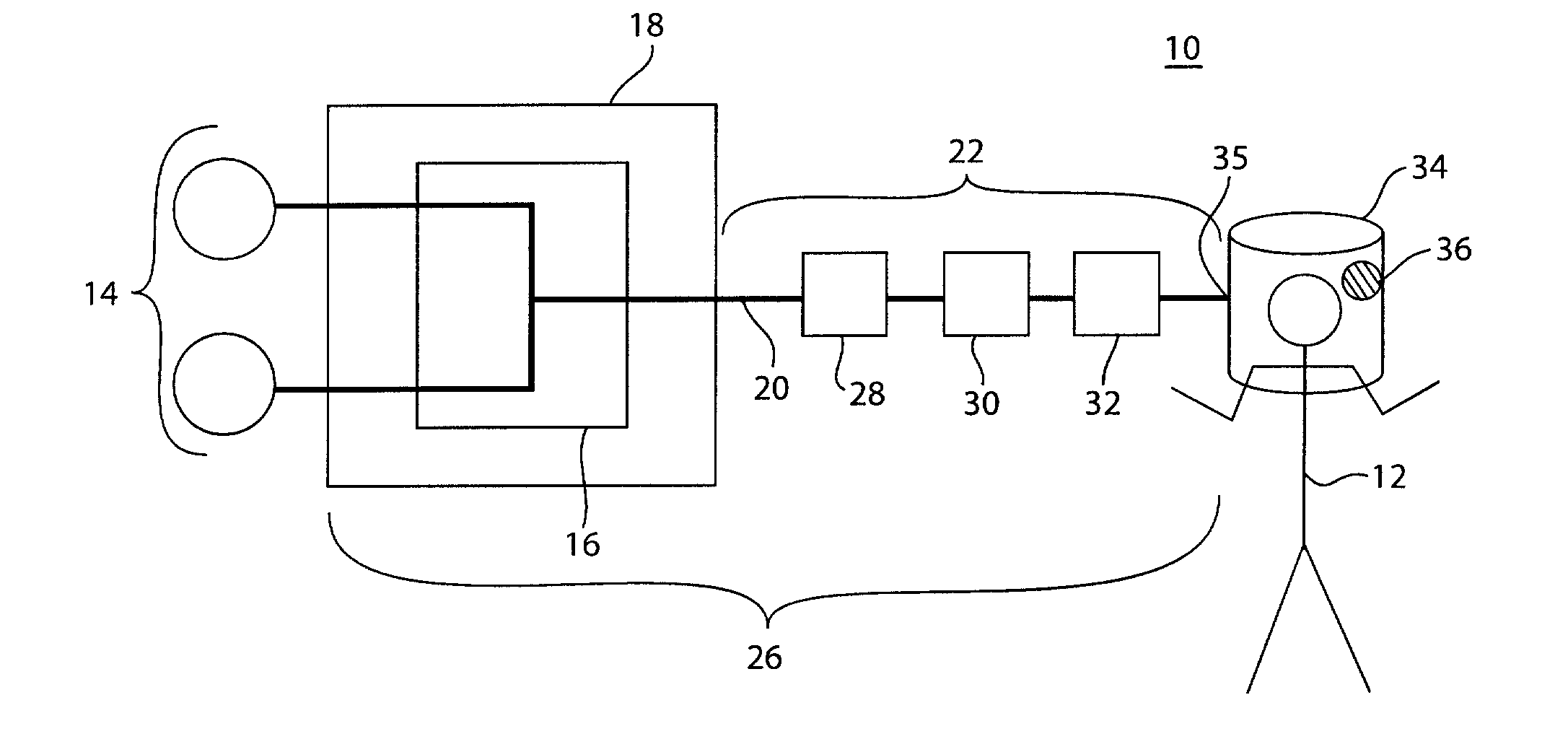
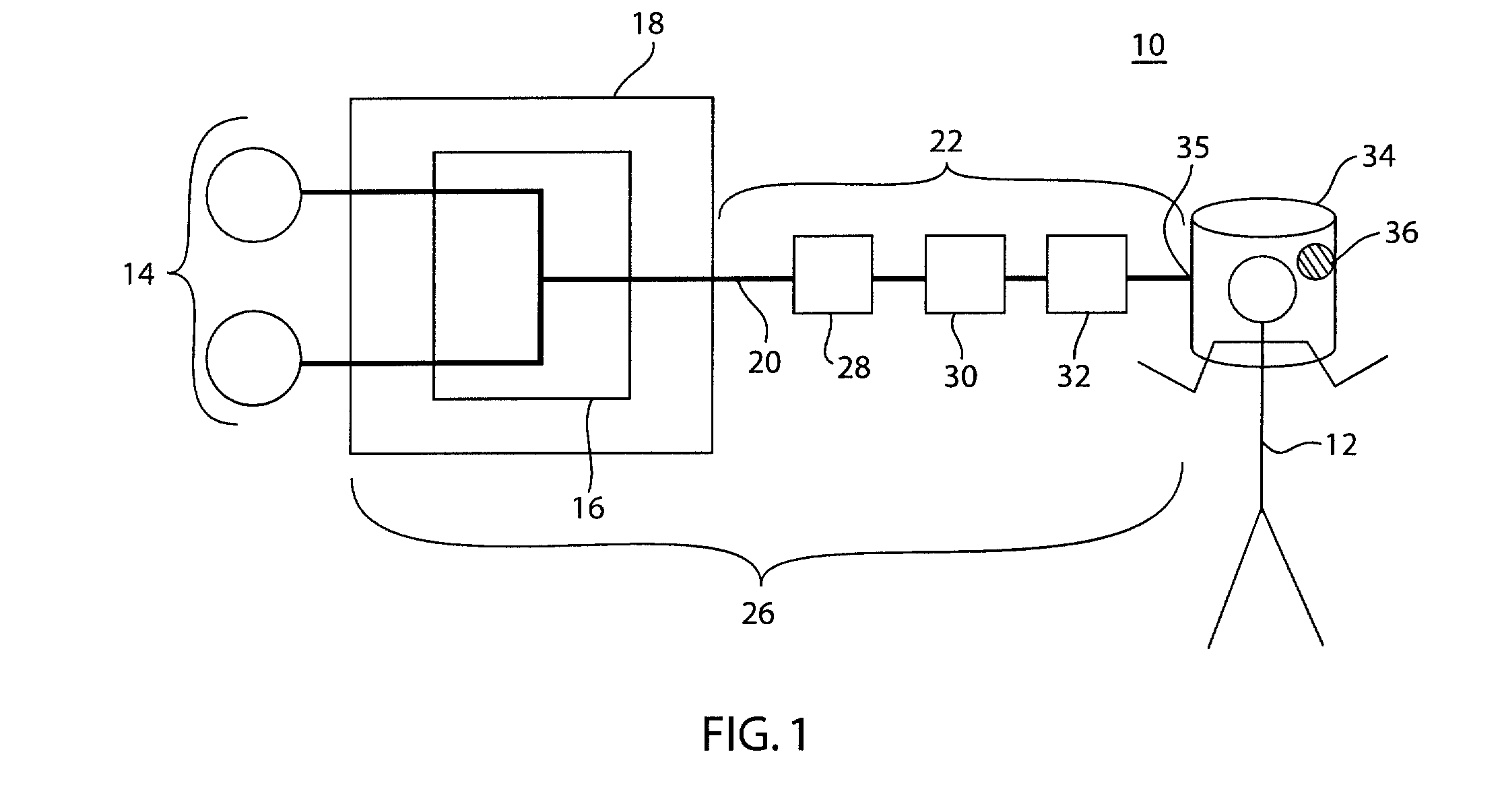
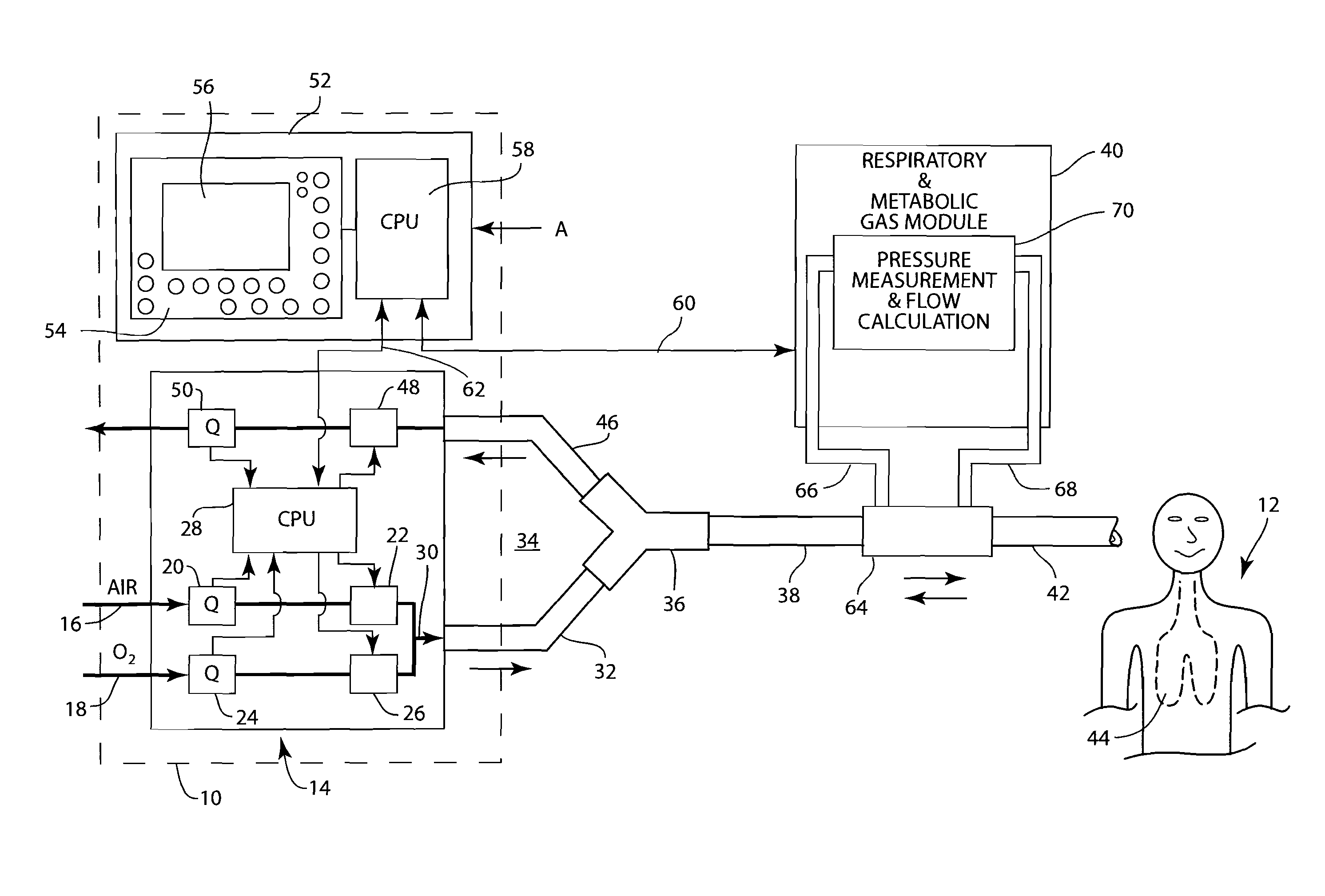
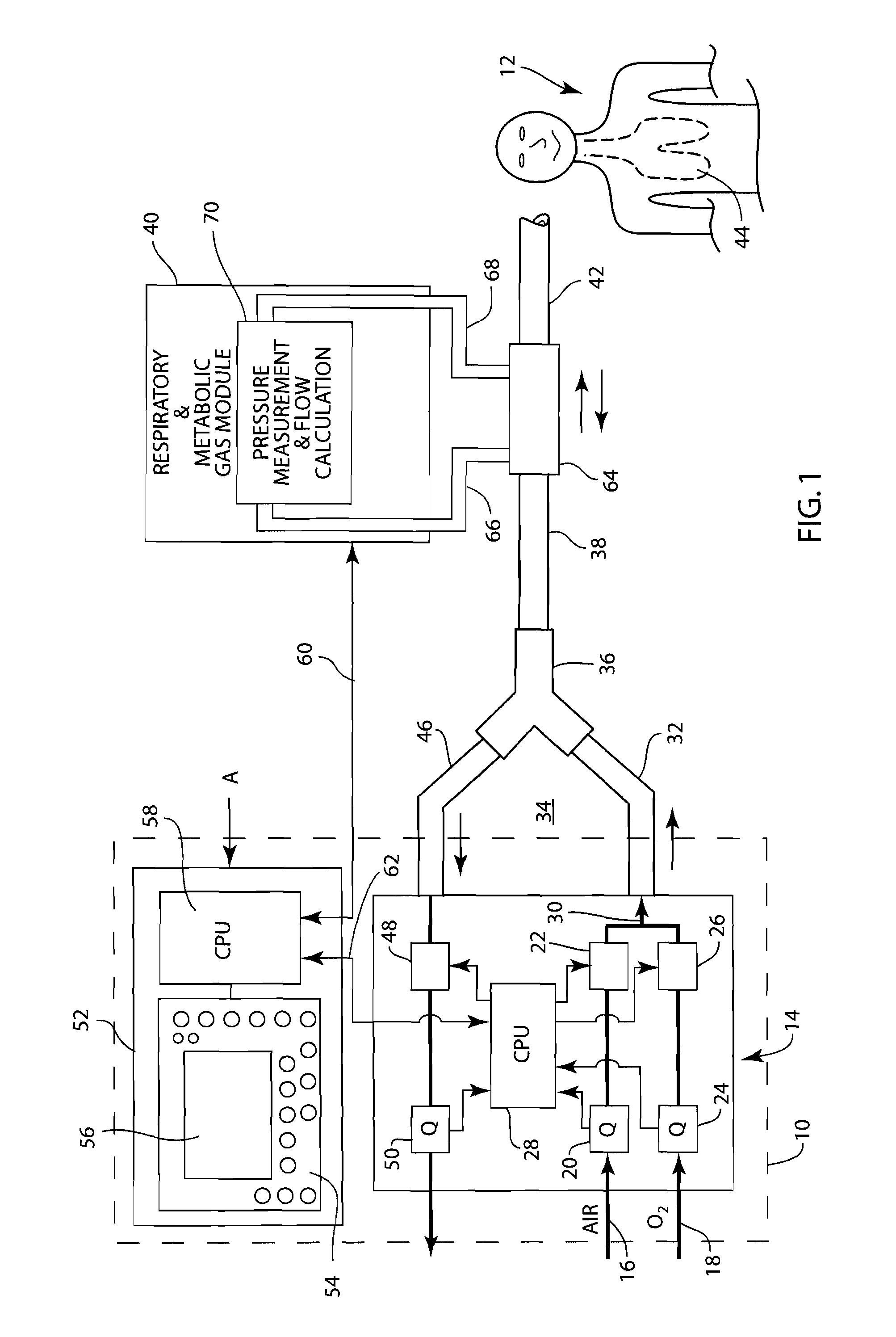
System and method for providing mechanical ventilation support to a patient
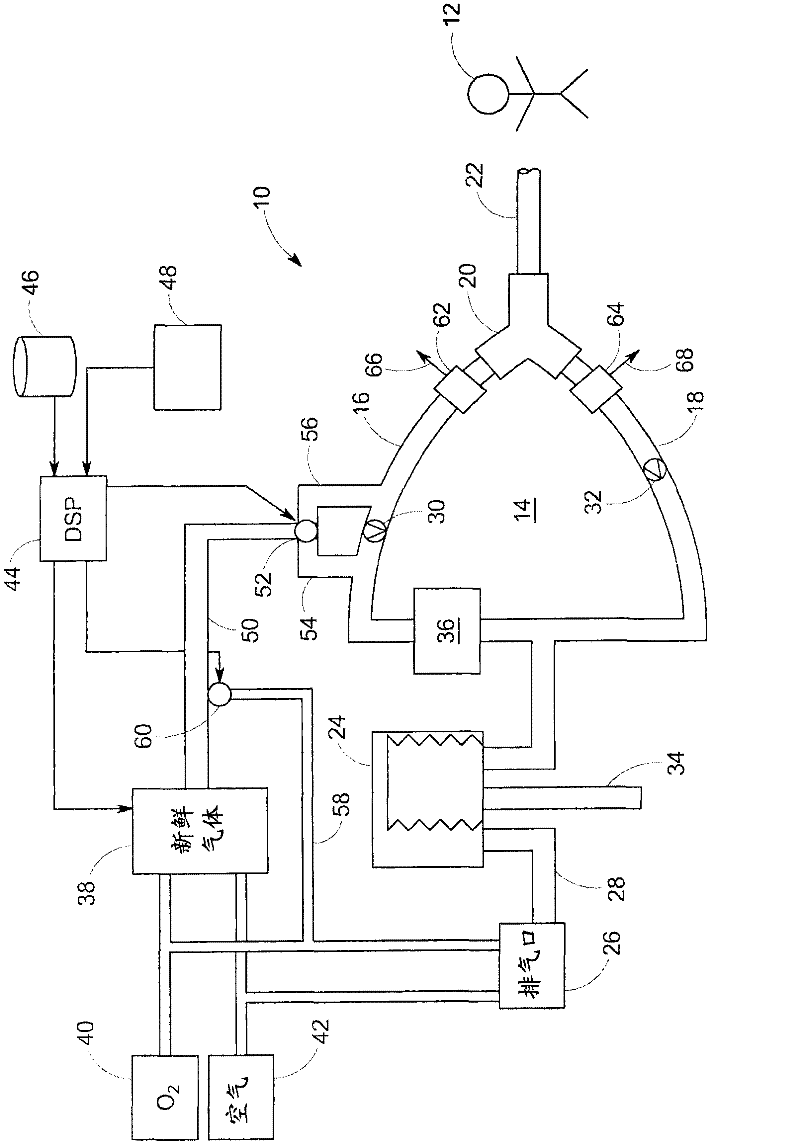
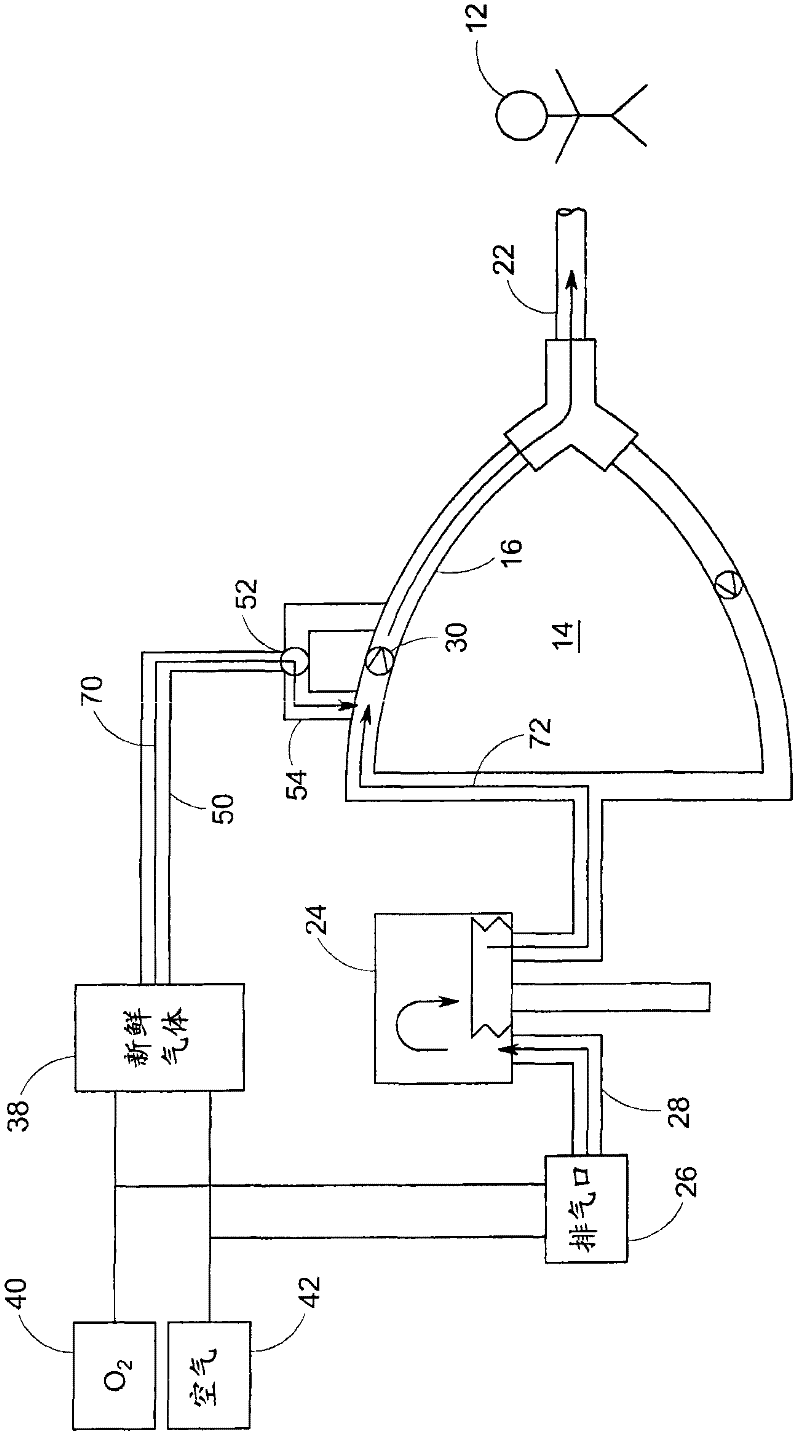
The present invention relates to a system and a method for providing mechanical ventilation support to a patient. The system for providing mechanical ventilation support to a patient and includes a mechanical ventilator (26). A breathing circuit (14) is pneumatically connected between the mechanical ventilator (26) and a patient connection (22). An inspiratory check valve (30) is disposed within an inspiratory limb (16) of the breathing circuit (14). A fresh gas manifold (38) provides fresh gas to the breathing circuit (14) for delivery to the patient. A fresh gas valve (52) is disposed between the fresh gas manifold (38) and the breathing circuit (14). The fresh gas valve (52) is operable between a first position which directs fresh gas upstream of the inspiratory check valve (30) and a second position that directs fresh gas downstream of the inspiratory check valve (30). A digital signal processor (44) operates the fresh gas valve (52) selectively between the first position and the second position. A method of ventilating a patient includes introducing a flow of fresh gas into an inspiratory limb (16) of the breathing circuit (14). A ventilatory support value is sensed with at least one sensor (62, 64) disposed within the breathing circuit (14). An operational condition of the breathing circuit (14) is identified with a digital signal processor (44). A fresh gas valve (52) is operated with the digital processor (44) between a first position that directs fresh gas to the inspiratory limb (16) upstream from the inspiratory check valve (30) and a second position that directs the fresh gas downstream from the inspiratory check valve (30).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
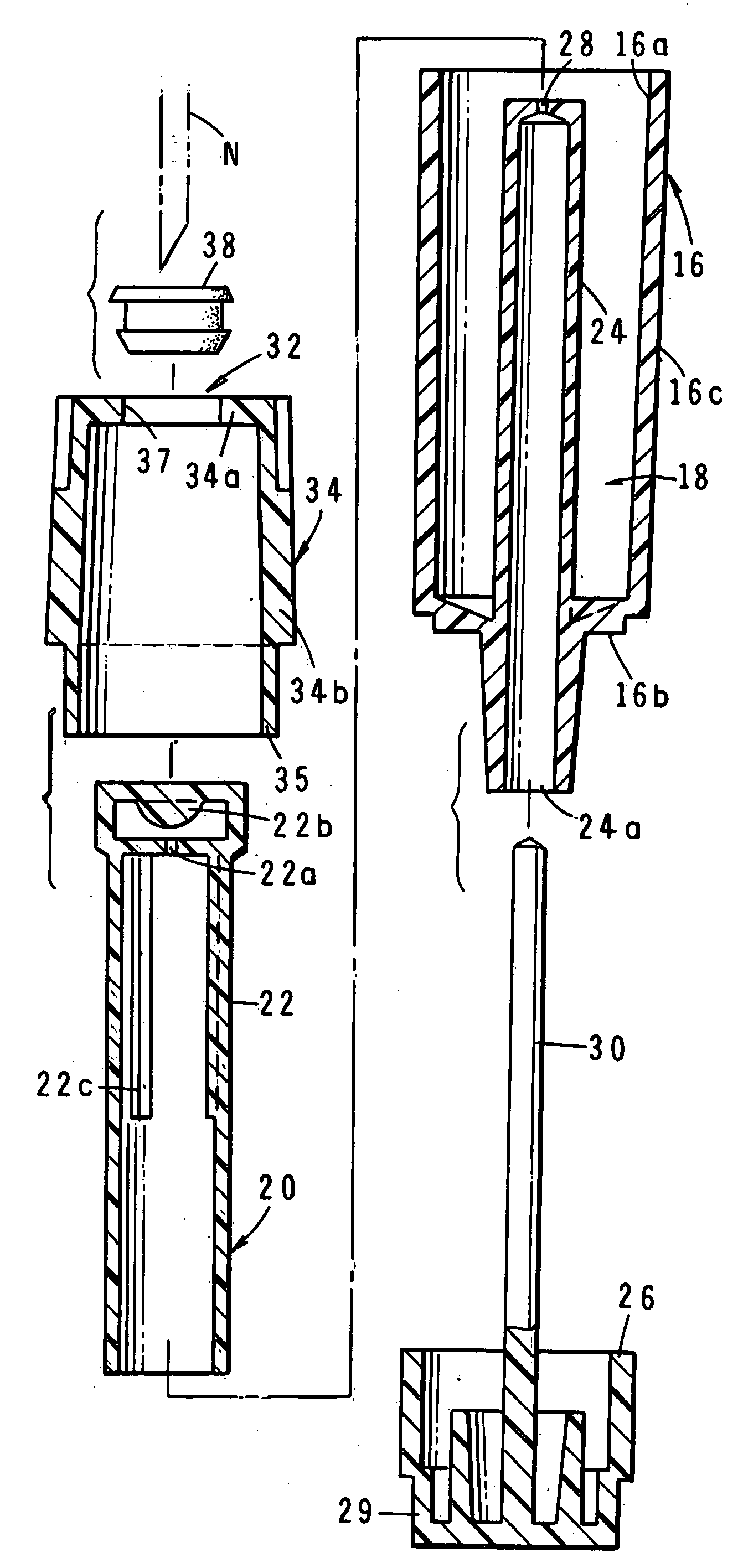
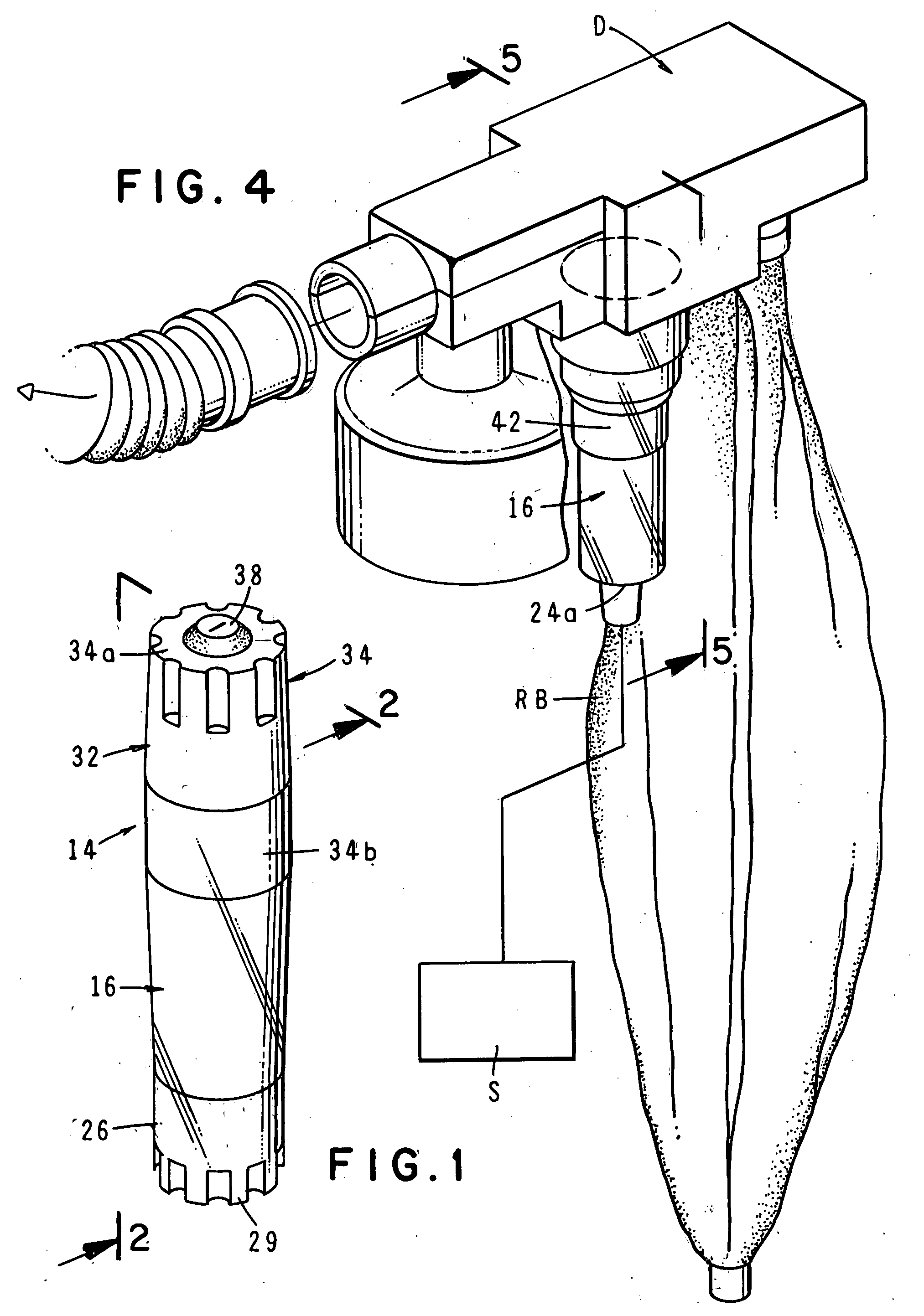
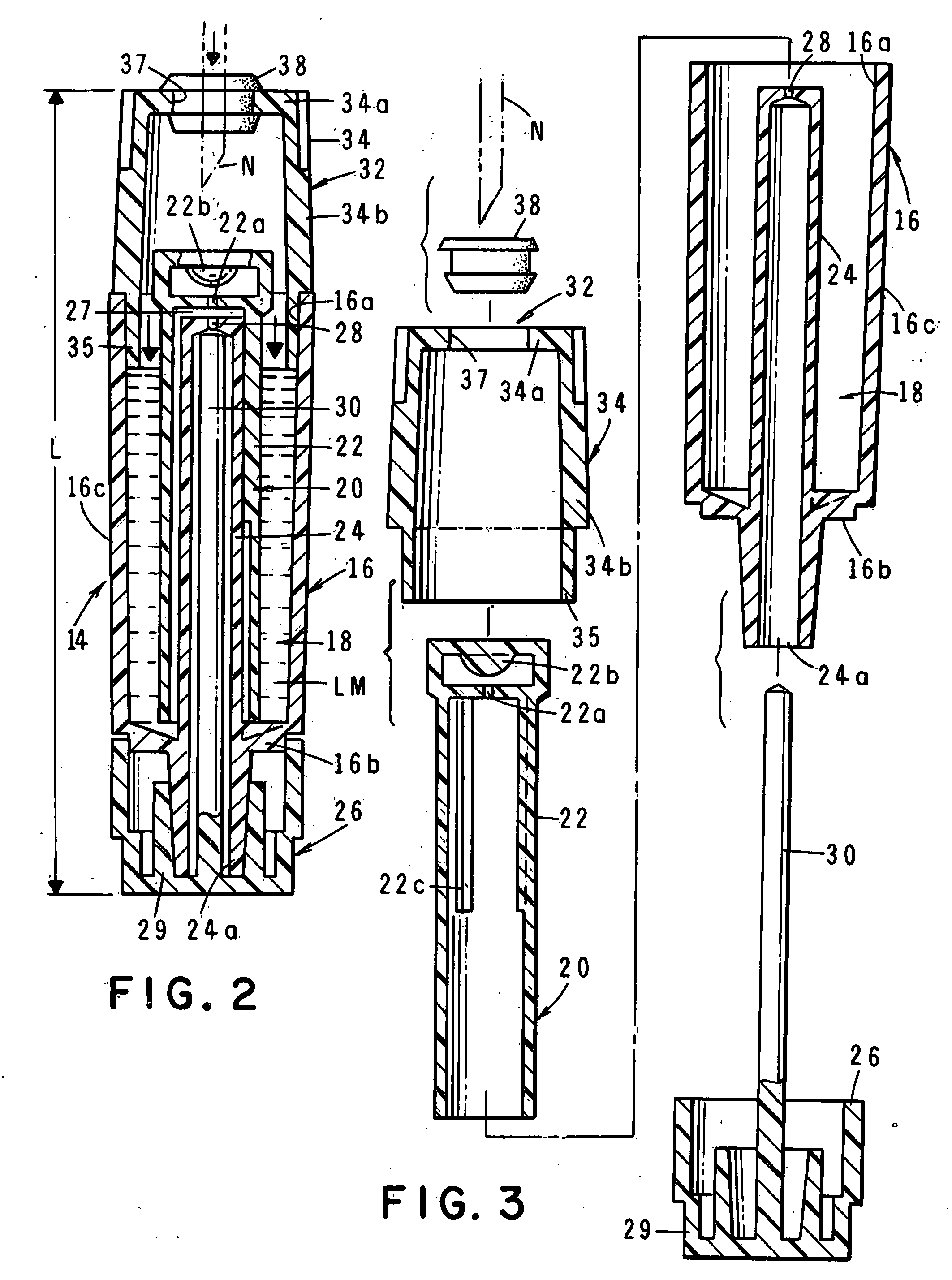
Pre-filled, single-use, disposable small volume medication nebulizer
InactiveUS20090050141A1Easy to useEffectively mitigates against possibilityMedical devicesSpray nozzlesMechanical ventilatorsNebulizer
A miniaturized pre-filled, single-use, disposable, small volume medication nebulizer unit for medicinal use that delivers a mist of properly sized aerosol particles of medicament to the patient with a very high level of efficiency. The nebulizer can be effectively used in conjunction with conventional tee and mouthpiece patient interface devices as well as with more sophisticated interface devices such as dosimetric / reservoir systems, or mechanical ventilator systems.
Owner:KING RUSSELL WAYNE +1
Multi-lumen breathing tube device
InactiveUS20140276178A1Increase respiratory rateDiminished tidal volumeTracheal tubesRespiratory organ evaluationLaryngeal airwayMechanical ventilators
A multi-lumen breathing tube device providing for separate and bidirectional gas flow for expired and inspired gas during ventilation of a lung. Embodiments of the multi-lumen breathing tube include an improved laryngeal mask airway device and an improved endotracheal tube. The invention is compatible with a circle breathing circuit system used with many mechanical ventilators including those used in conjunction with anesthesia machines.
Owner:SIMON DAVID LEW
Mechanical ventilation system utilizing bias valve
A portable mechanical ventilator having a Roots blower is configured to provide a desired gas flow and pressure to a patient circuit. The mechanical ventilator includes a flow meter operative to measure gas flow produced by the Roots blower and an exhalation control module configured to operate an exhalation valve connected to the patient circuit. A bias valve connected between the Roots blower and the patient circuit is specifically configured to generate a bias pressure relative to the patient circuit pressure at the exhalation control module. The bias valve is further configured to attenuate pulsating gas flow produced by the Roots blower such that gas flowing to the mass flow meter exhibits a substantially constant pressure characteristic. The bias pressure facilitates closing of the exhalation valve at the start of inspiration, regulates positive end expiratory pressure during exhalation, and purges sense lines via a pressure transducer module.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 203 INC
Portable drag compressor powered mechanical ventilator
InactiveUS20050115564A1Accurate measurementMinimize inaccuracyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSolenoid valveEngineering
A ventilator device and system comprising a rotating compressor, preferably a drag compressor, which, at the beginning of each inspiratory ventilation phase, is accelerated to a sufficient speed to deliver the desired inspiratory gas flow, and is subsequently stopped or decelerated to a basal flow level to permit the expiratory ventilation phase to occur. The ventilator device is small and light weight enough to be utilized in portable applications. The ventilator device is power efficient enough to operate for extended periods of time on internal or external batteries. Also provided is an oxygen blending apparatus which utilizes solenoid valves having specific orifice sizes for blending desired amounts of oxygen into the inspiratory gas flow. Also provided is an exhalation valve having an exhalation flow transducer which incorporates a radio frequency data base to provide an attendant controller with specific calibration information for the exhalation flow transducer.
Owner:BIRD PRODS
Apparatus and system for reducing mechanical ventilator noise
InactiveUS8028695B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsEngineering
A sound dampening apparatus to be disposed in pneumatic connection with a respiratory support system. The respiratory support system may comprise a source of medical gas, a plurality of pneumatic connections and a patient interface. The sound dampening apparatus comprises an inlet, an outlet, and an outer case which forms a sound dampening chamber. As the medical gas flows through the sound dampening apparatus, the noise energy associated with the flow of medical gas is reduced.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
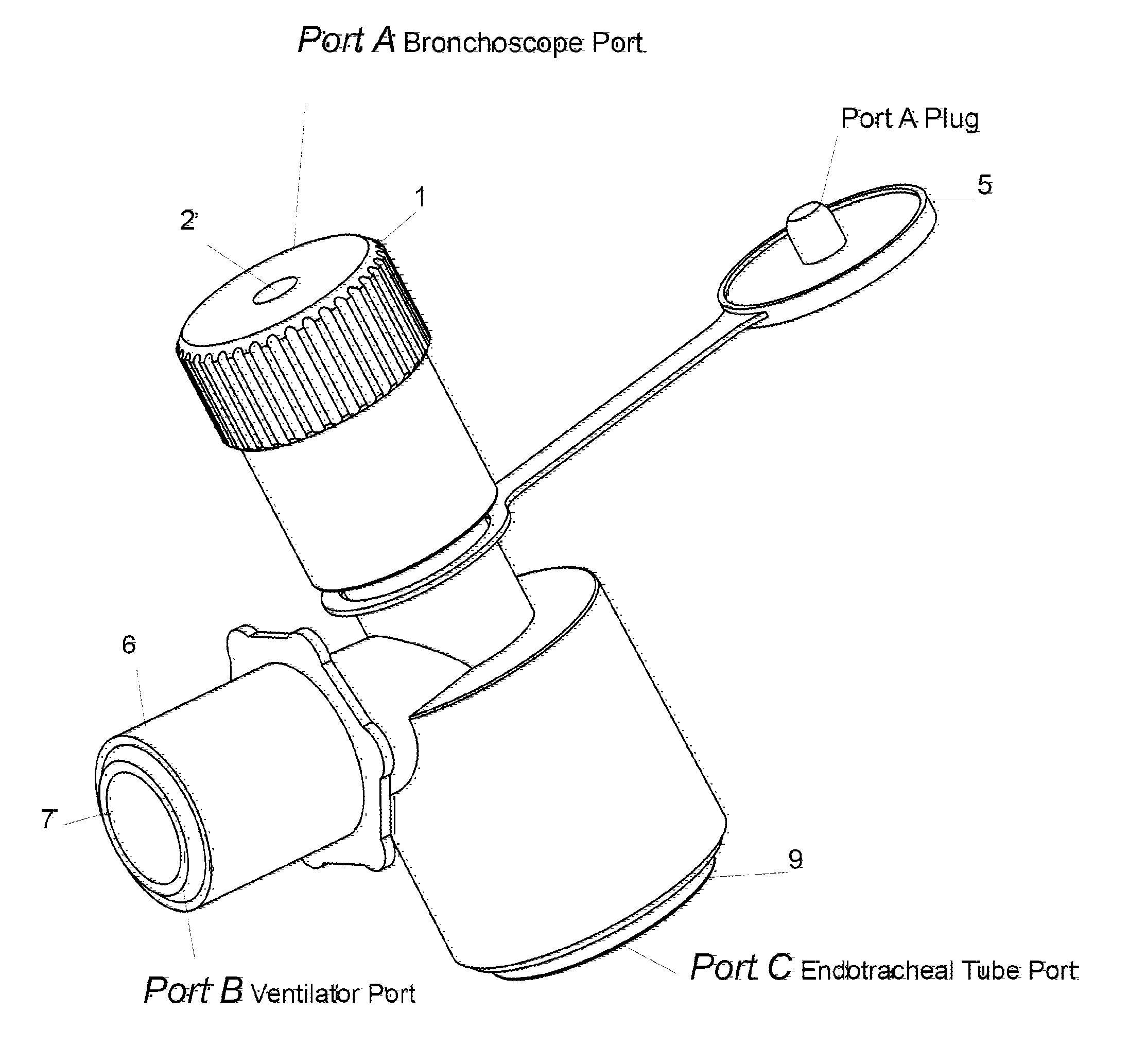
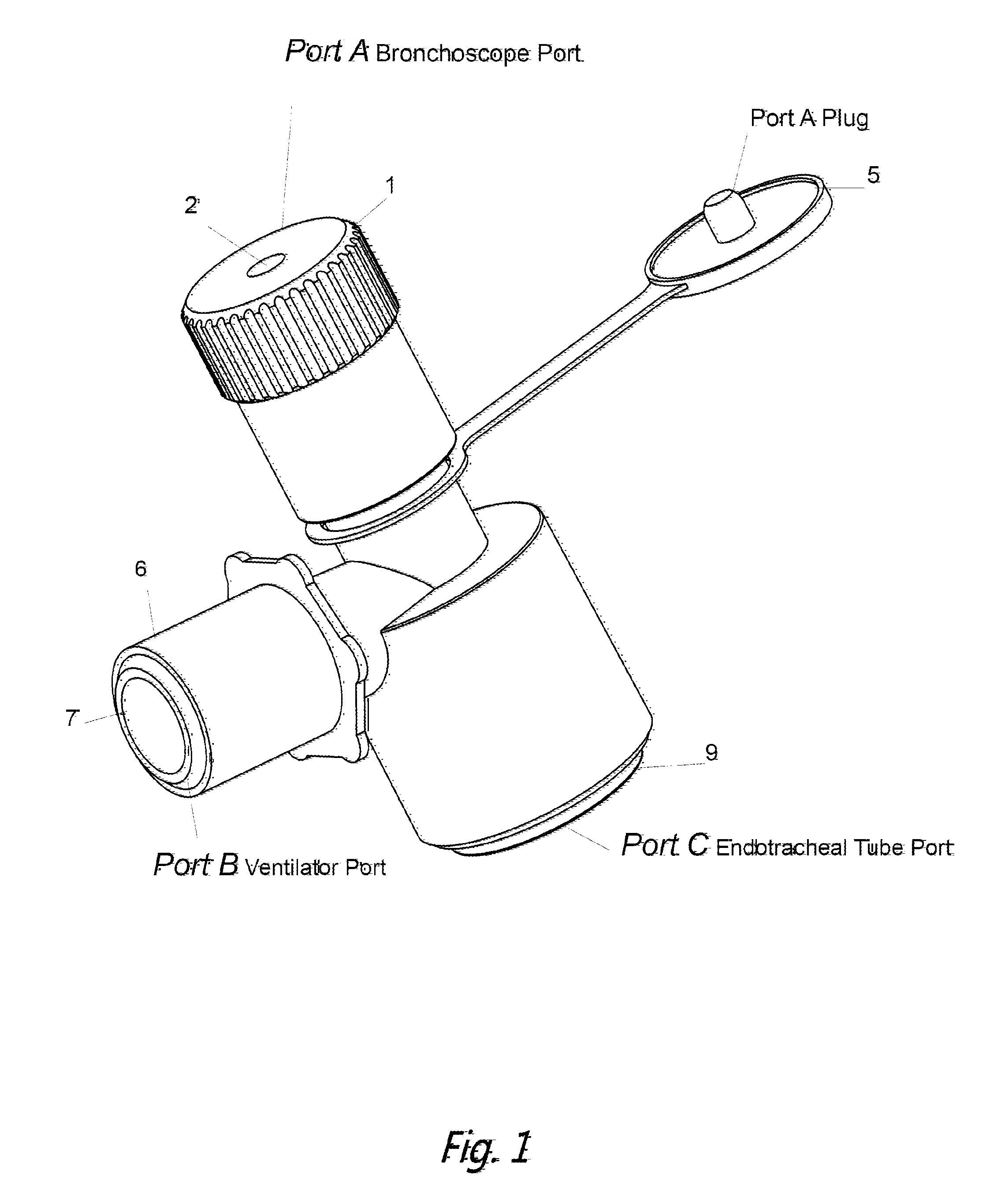
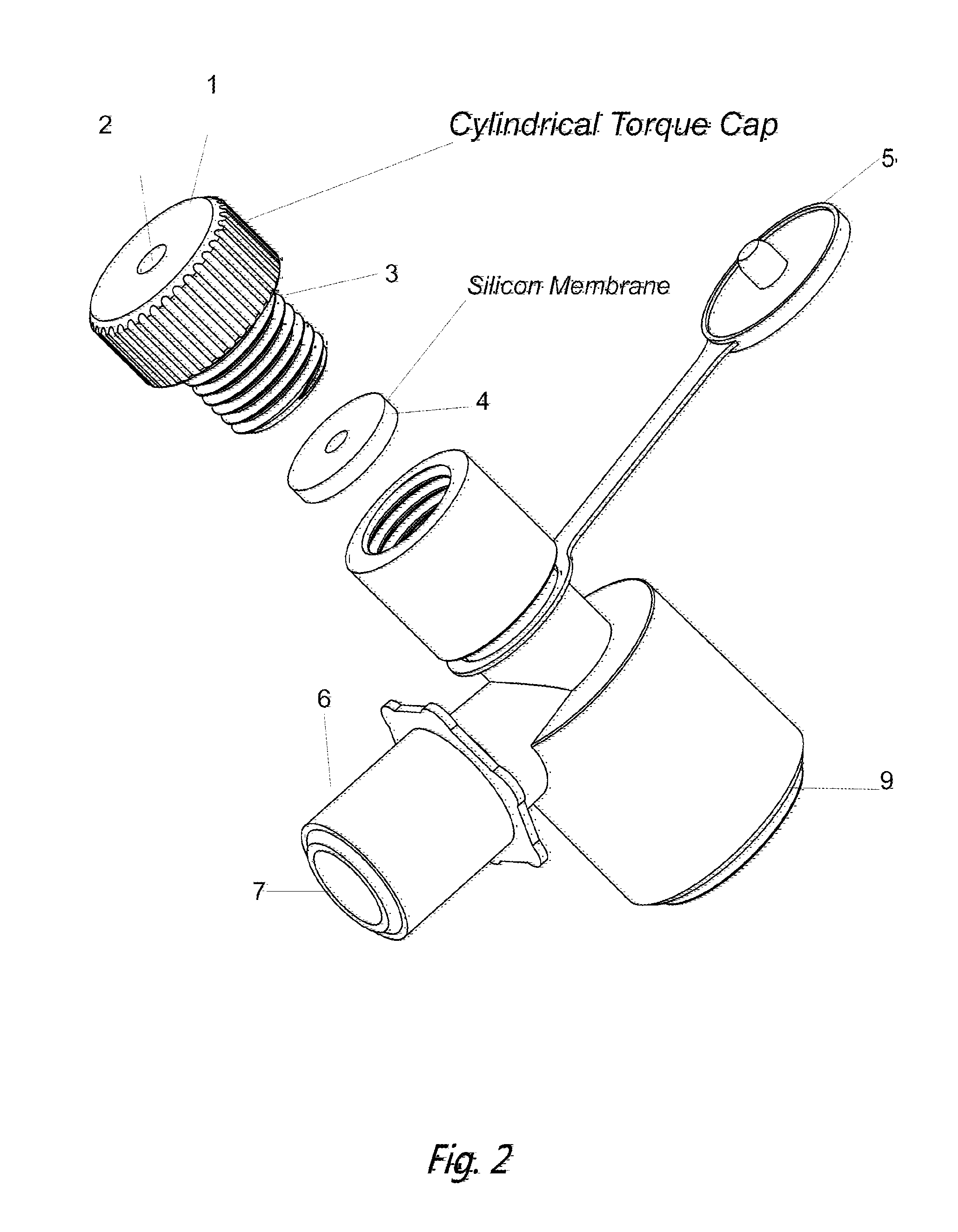
Bronchoscope Adapter and Methods for Using the Same
ActiveUS20150335228A1Reduce decreaseFacilitate and secure lockingBronchoscopesTracheal tubesMechanical ventilatorsEngineering
Bronchoscope adapters and methods of using the same are provided. Aspects of the adaptors include a body having a passageway, a mechanical ventilator access port, a bronchoscope access port configured to receive a bronchoscope into the passageway, and an exit port. The bronchoscope access port comprises a reversibly adjustable inner diameter component that provides locking of the bronchoscope at desired position. The adaptors find use in a variety of different applications.
Owner:LEI THOMAS DINGHUA +2
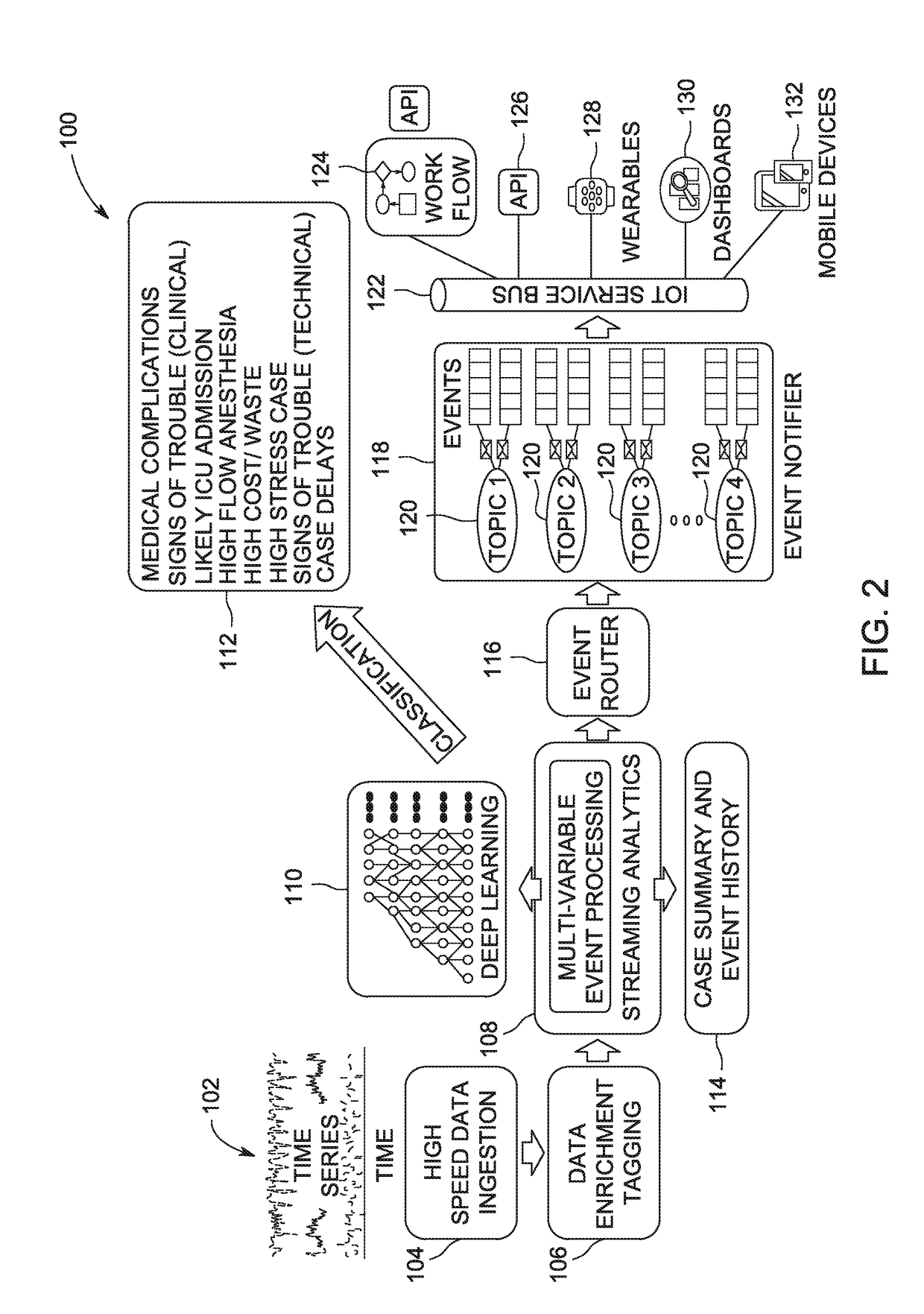
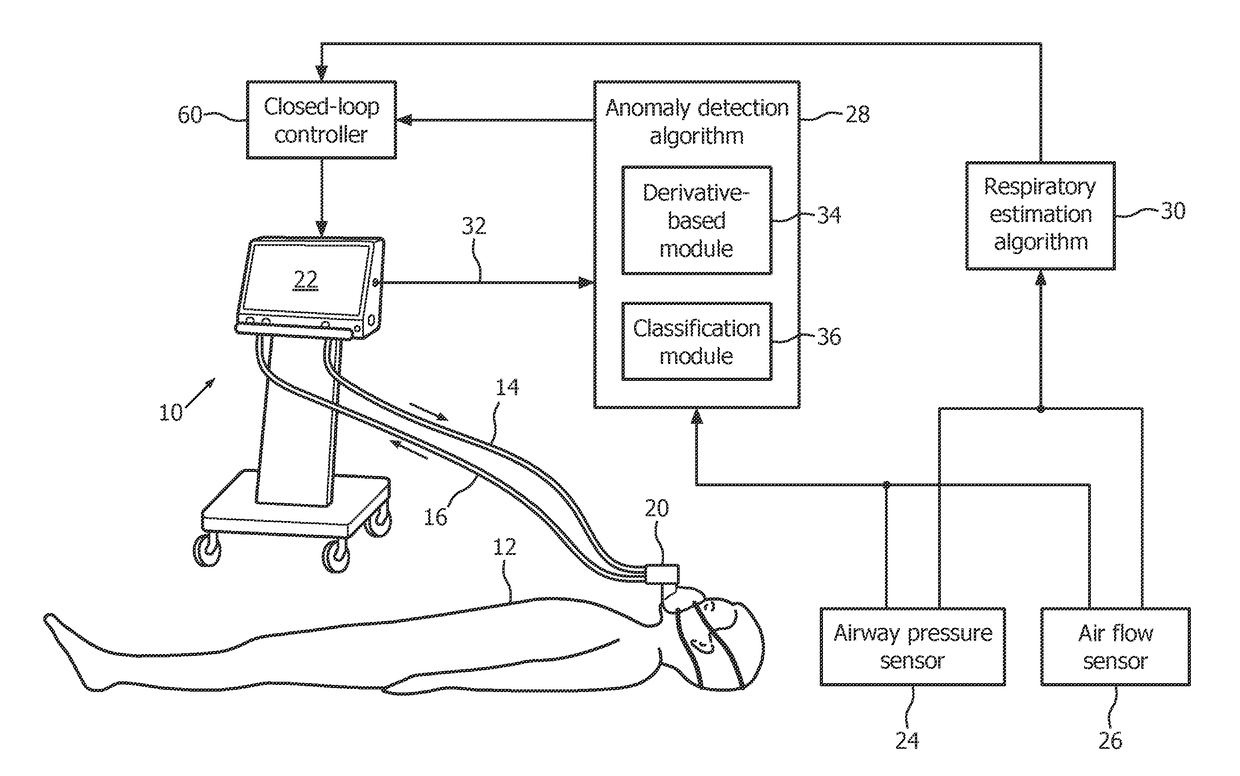
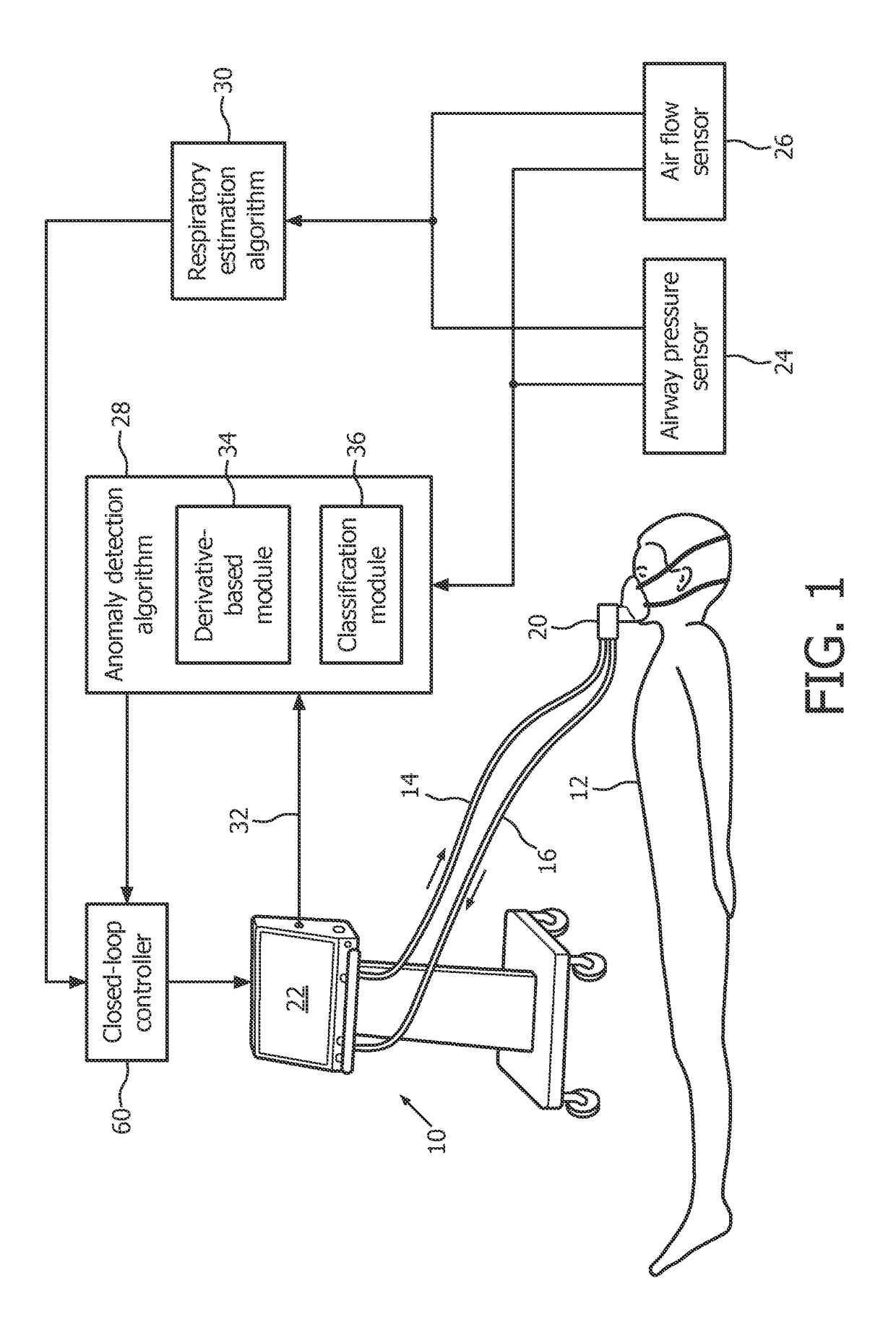
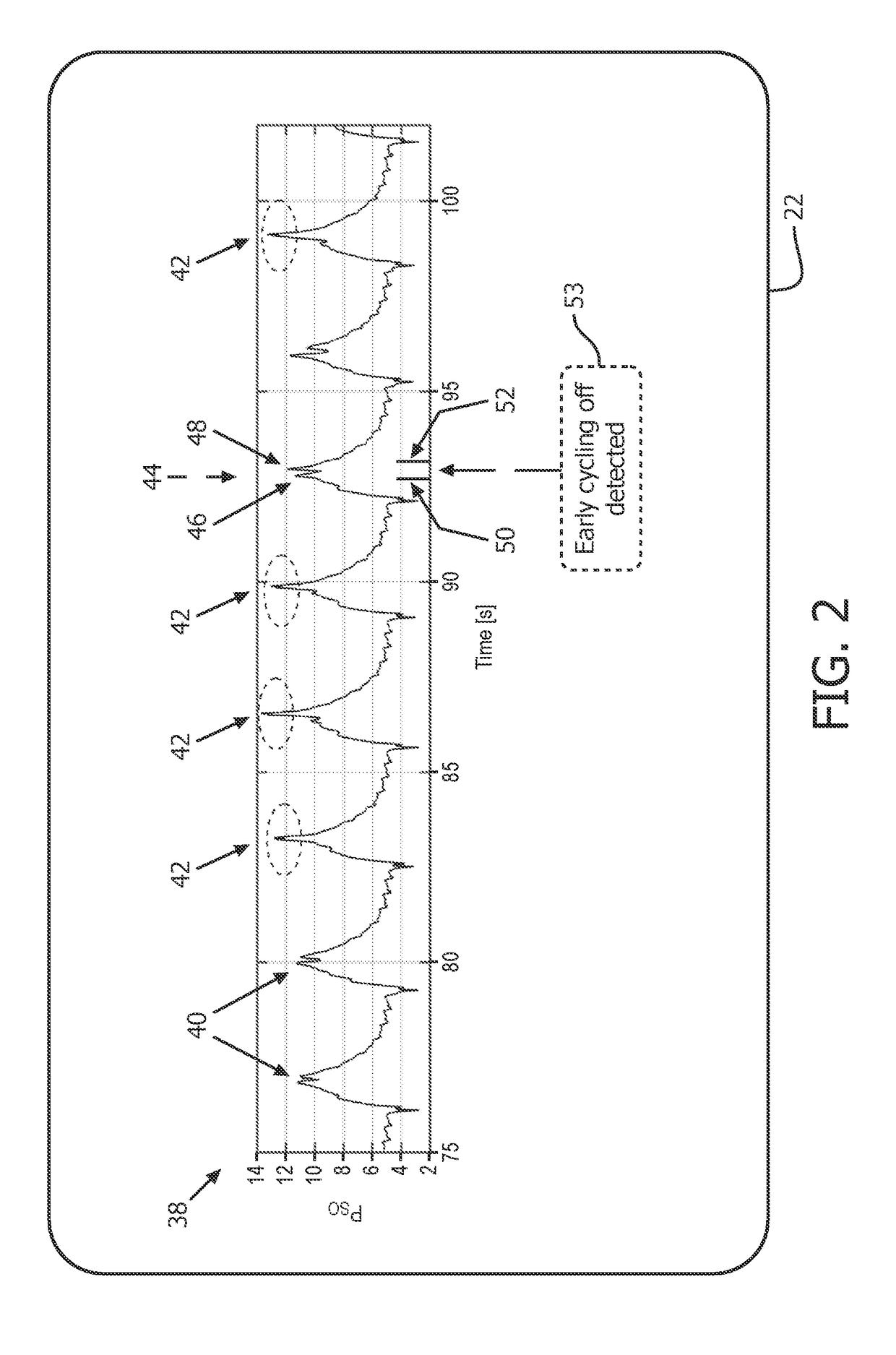
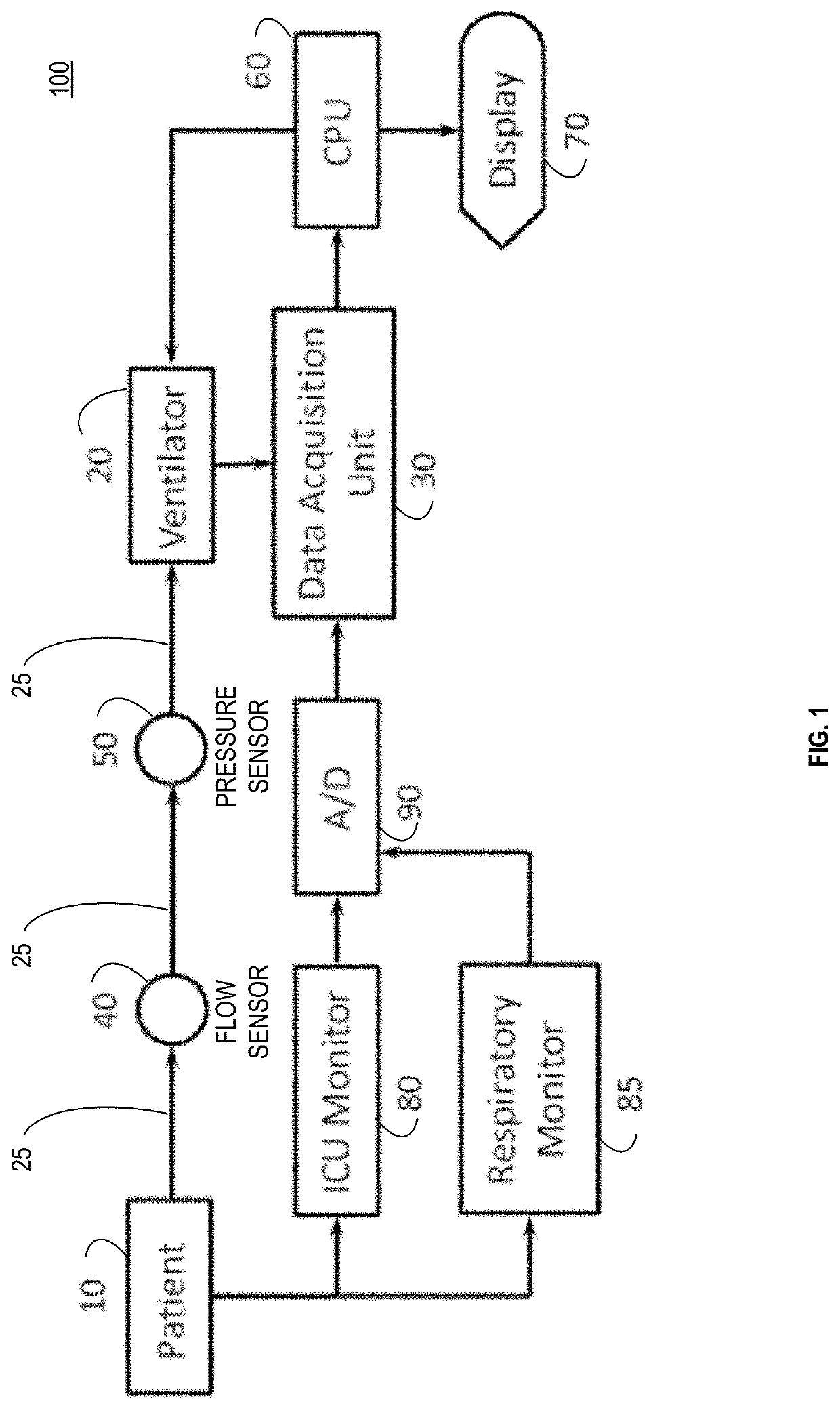
Anomaly detection device and method for respiratory mechanics parameter estimation
ActiveUS20180304034A1Easy to monitorAdjustment of settingRespiratorsElectrocardiographyRespiratory muscleAnomaly detection
A mechanical ventilation device (10) includes a mechanical ventilator. At least one airway sensor (24, 26) is configured to measure at least one of airway pressure and airway air flow as a function of time for a patient on the mechanical ventilator. At least one microprocessor (28, 30) is programmed to analyze at least one of airway pressure and airway air flow measured by the airway sensor to detect a spontaneous respiration anomaly in respiratory muscle pressure as a function of time generated by a patient on the mechanical ventilator. A display component (22) is configured to display an indication of a spontaneous respiration anomaly detected by the anomaly detection component.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and apparatus for airway compensation control
ActiveUS8312879B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsTracheal tube
A method for controlling a mechanical ventilator that is supplying medical gas to a patient via an endotracheal tube. A pressure is measured from a patient end of an endotracheal tube. The pressure at the patient end of the endotracheal tube is used to create an improved endotracheal tube resistance model such that the medical gas supplied by the mechanical ventilator may be compensated for the resistance of the endotracheal tube thereby providing increased control over the medical gas that is delivered to the patient's lungs. Additionally, if an obstruction in the patient's airway is detected, the location of the obstruction may be targeted such that the proper remedial treatment or procedure is selected by a clinician.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Energy trigger
A method and apparatus for facilitating breathing using a mechanical breathing gas ventilator is presented. The patient effort is deduced from a measured flow signal and analyzed with respect to the energy in the breathing system comprising the mechanical ventilator and the patient. When a predetermined energy threshold has been reached the ventilator responds to the breathing pattern change.
Owner:BREAS MEDICAL
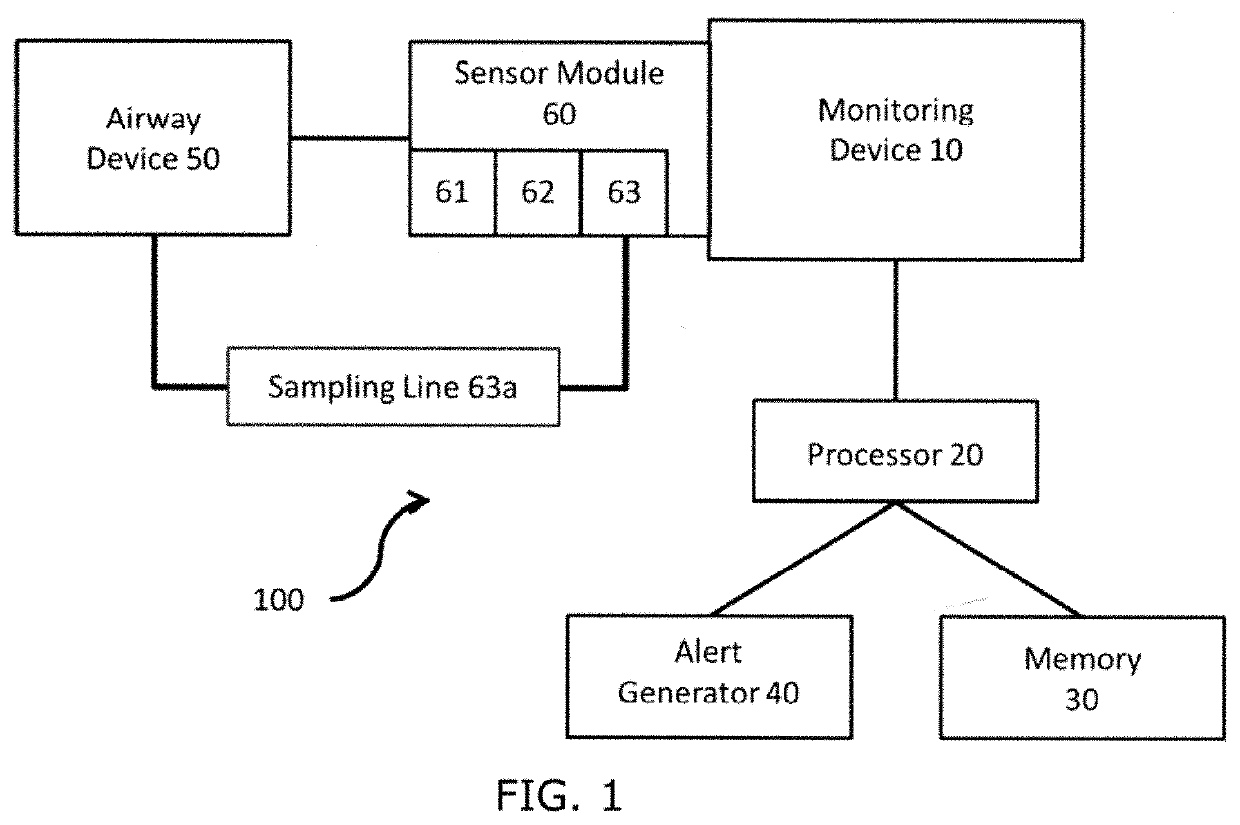
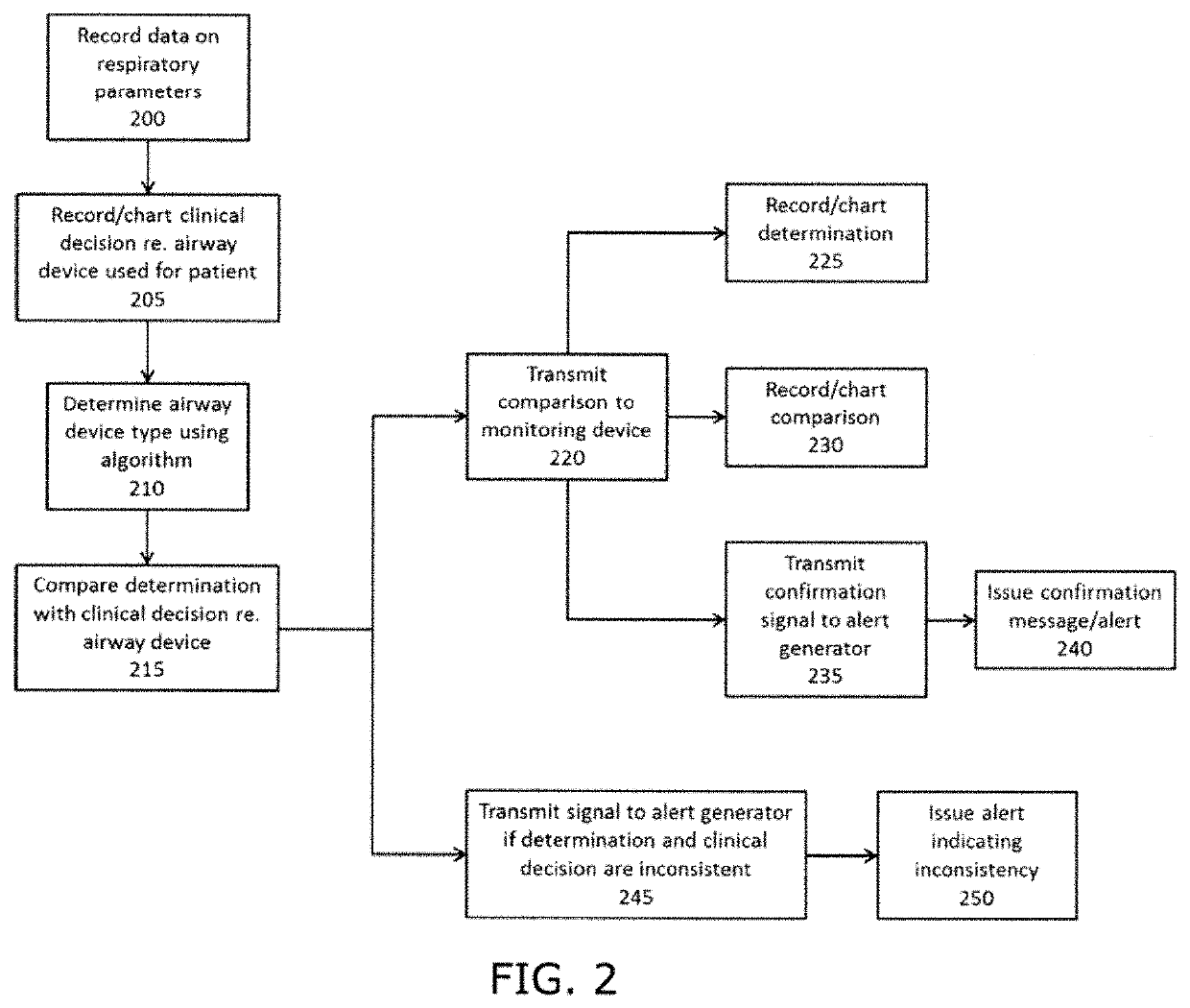
Automatic detection of airway device, endotracheal intubation, and tube misplacement in children during the anesthesia procedure
ActiveUS20200261675A1High-precision detectionLengthy time delayTracheal tubesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesPeak inspiratory pressureEndotracheal tube
Algorithms for detecting endotracheal intubation and / or misplacement of endotracheal tubes in child patients during anesthesia for use with anesthesia machines, mechanical ventilators, and / or respiratory function monitors. An algorithm uses end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO2), and tidal volume (TV) or peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) to detect exact intubation time. Another algorithm uses respiratory parameters to identify and / or confirm the type of airway device used during mechanical ventilation, and to detect if and when an issue has arisen with use of a specific airway device to provide real-time decision support to attending medical care professionals.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
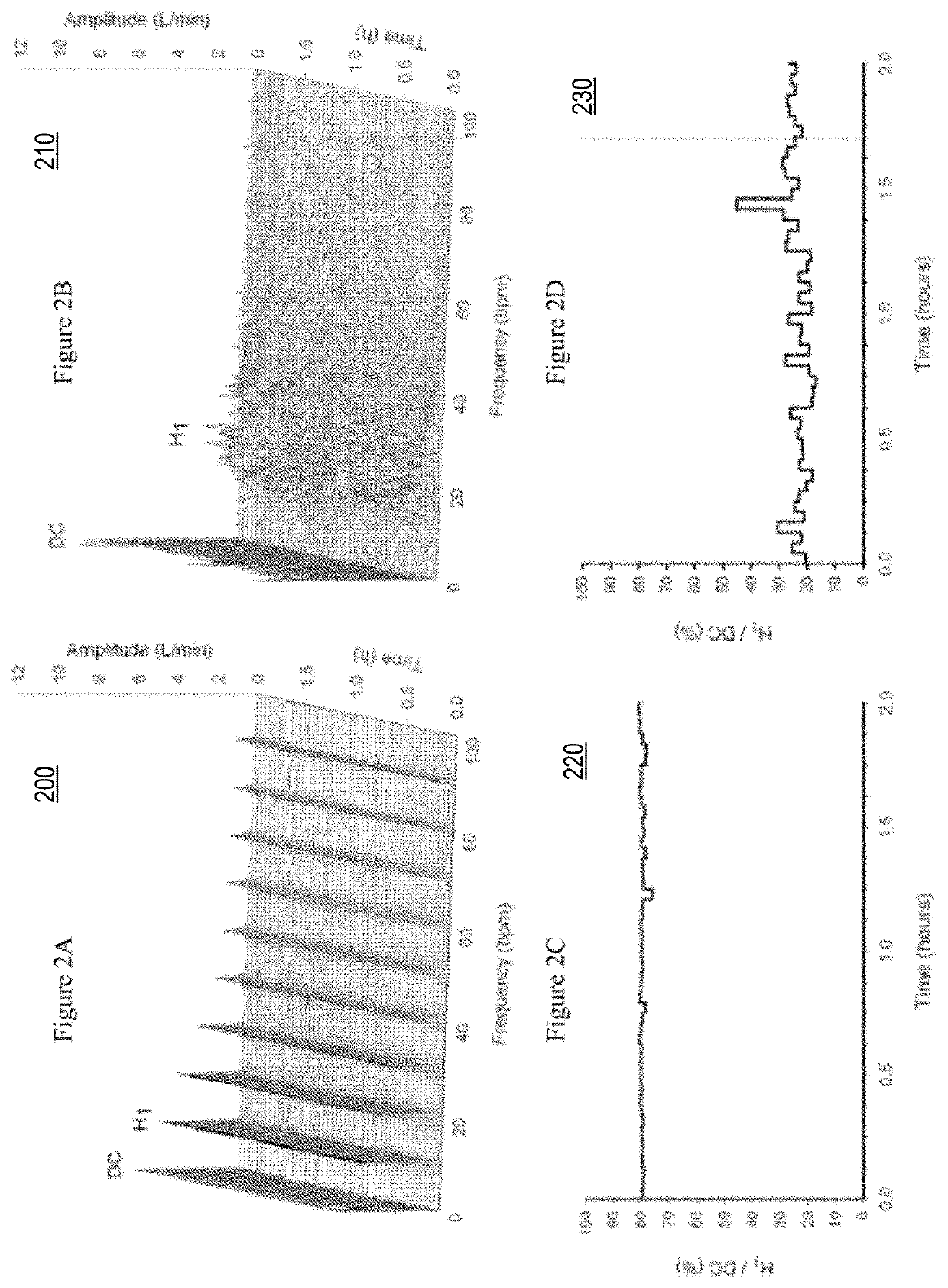
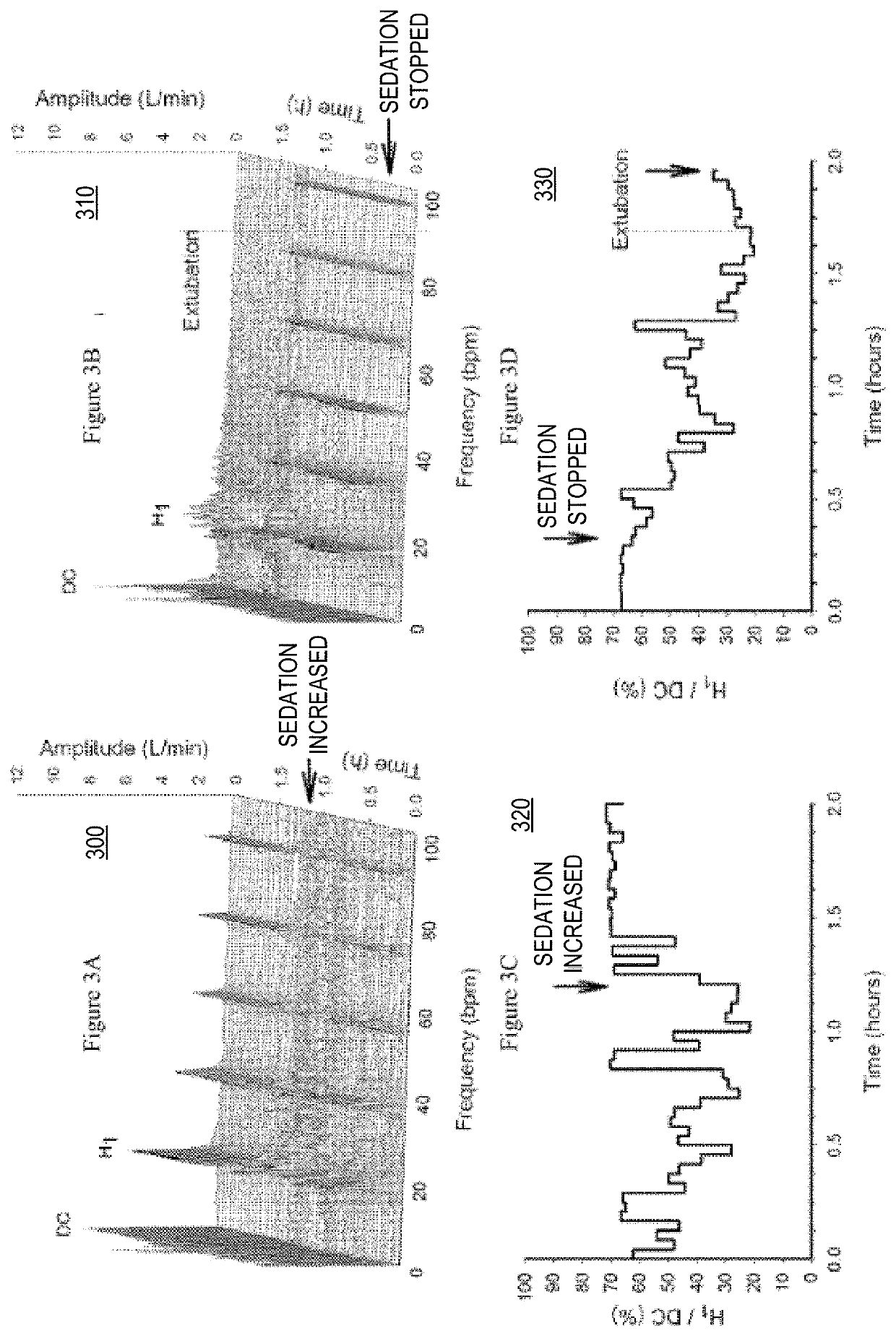
Detection and Display of Respiratory Rate Variability, Mechanical Ventilation Machine Learning, and Double Booking of Clinic Slots, System, Method, and Computer Program Product
A noninvasive of detecting patient-ventilator asynchrony that is easily adaptable to existing ventilator monitoring systems and provides timely and actionable information on the degree of patient asynchrony both during invasive and non-invasive ventilation. Capture, analysis or display of, frequency spectra and the use of a measure of spectral organization, such as H1 / DC, allows for both manual and automatic adjustment of a ventilators to prevent or correct patient-ventilator asynchrony via interventions. Embodiments use artificial intelligence or machine learning to predict interventions predicted to result in positive outcomes, based on analysis of a large number of epochs, captured by an electronic monitor of a mechanical ventilator, where the monitor continuously monitors, captures and transfers, epochs of data for aggregated machine learning analysis, of such epochs associated with positive outcomes. Scheduling processes that seek to overbook or double book to overcome negative effects of no shows, on clinician productivity in a medical setting.
Owner:RESPIVAR LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com