Patents
Literature
236 results about "Respiratory support" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Respiratory support is a term that refers to the various medical procedures and equipment used by respiratory care providers and their patients to treat a chronic obstructive pulmonary disease ( COPD) such as asthma, emphysema and black lung. It also refers to the emergency respiratory care provided...
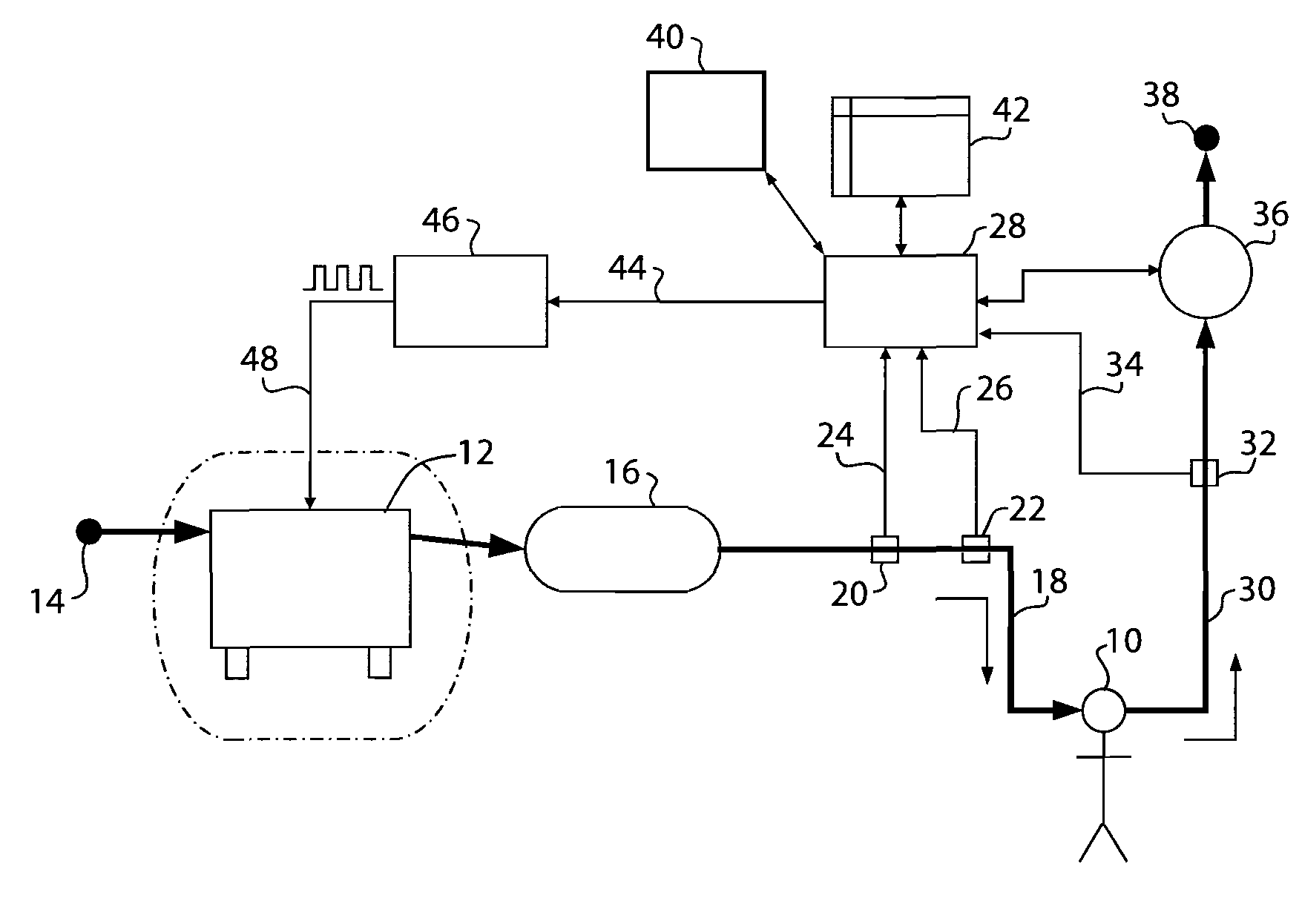
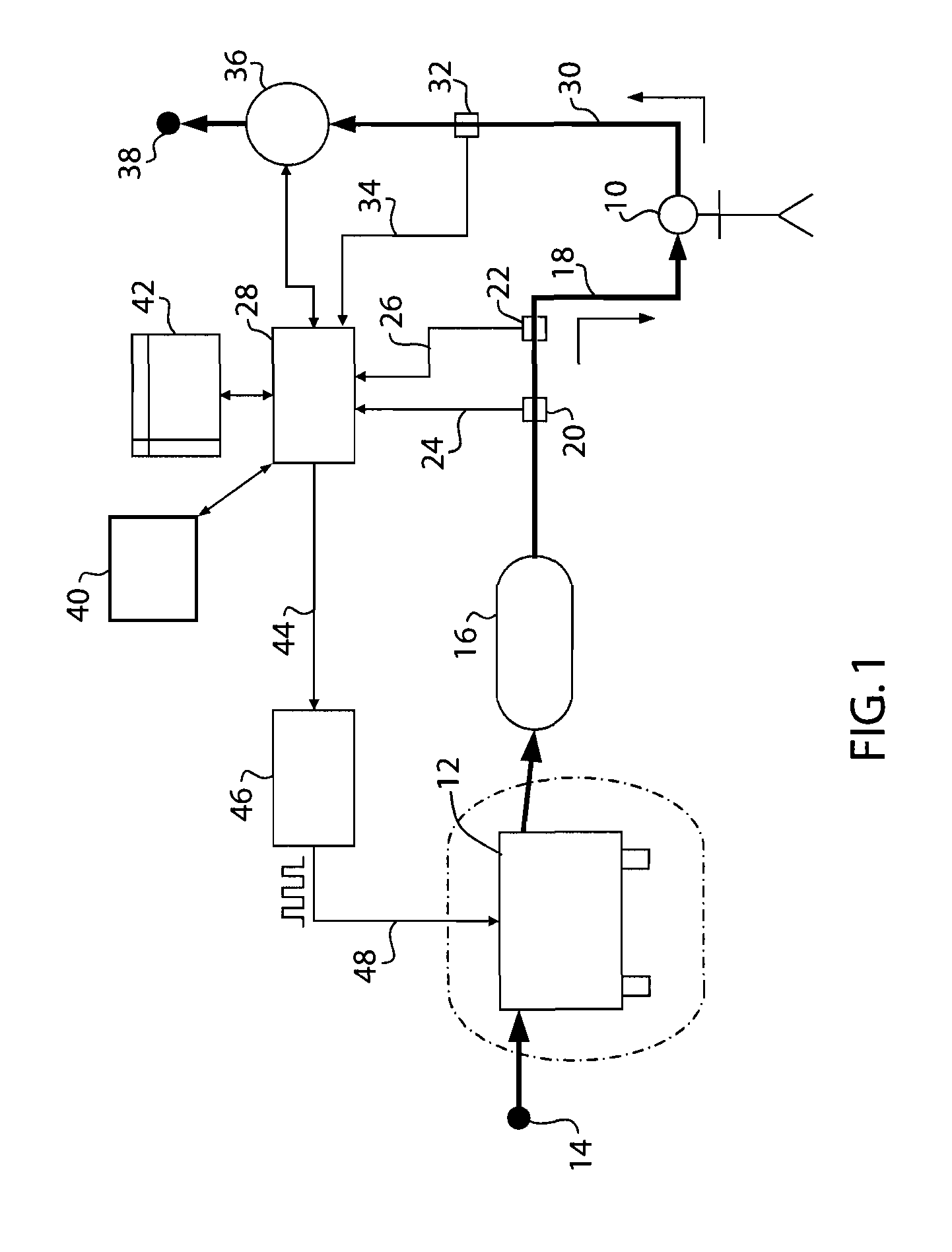
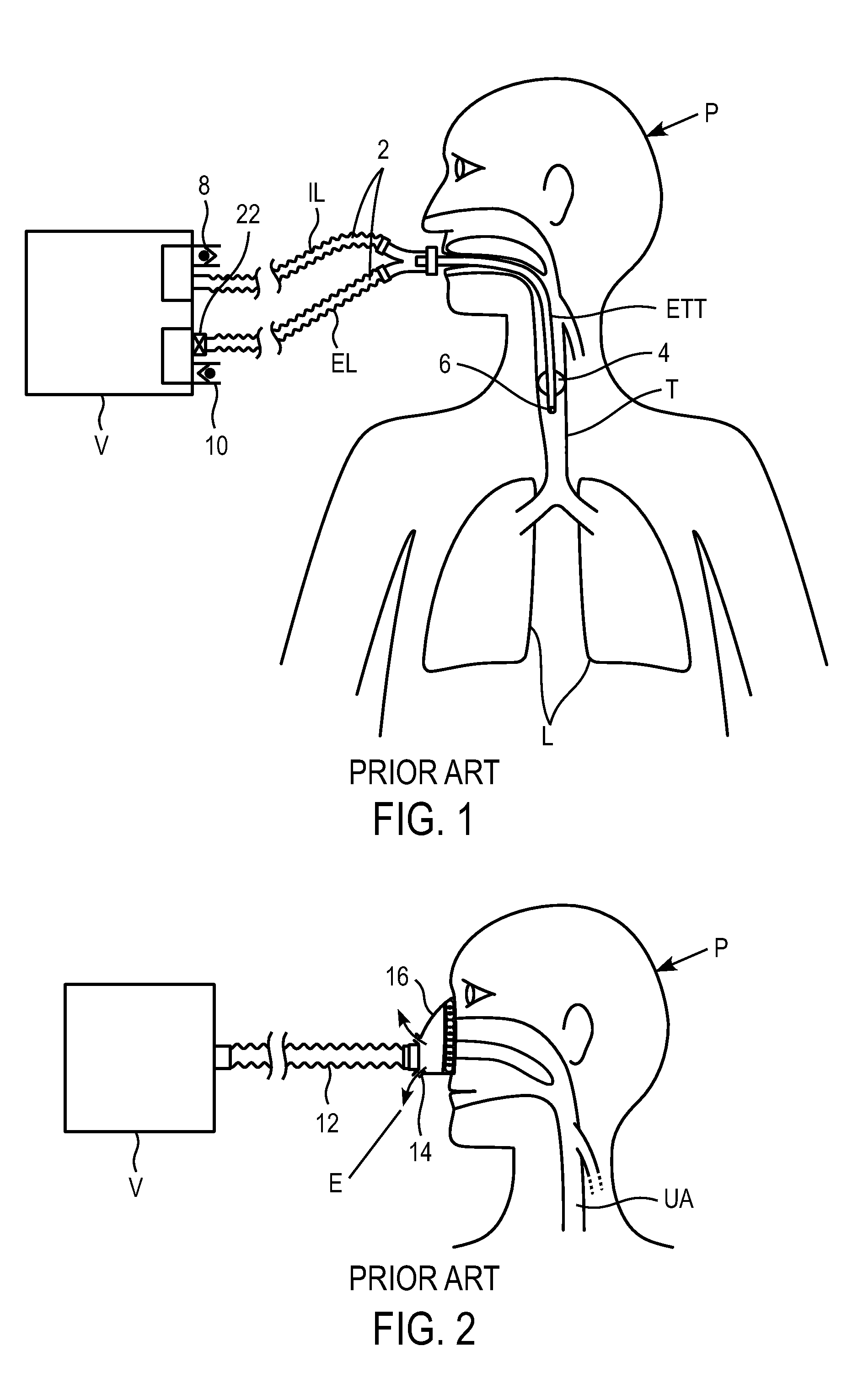
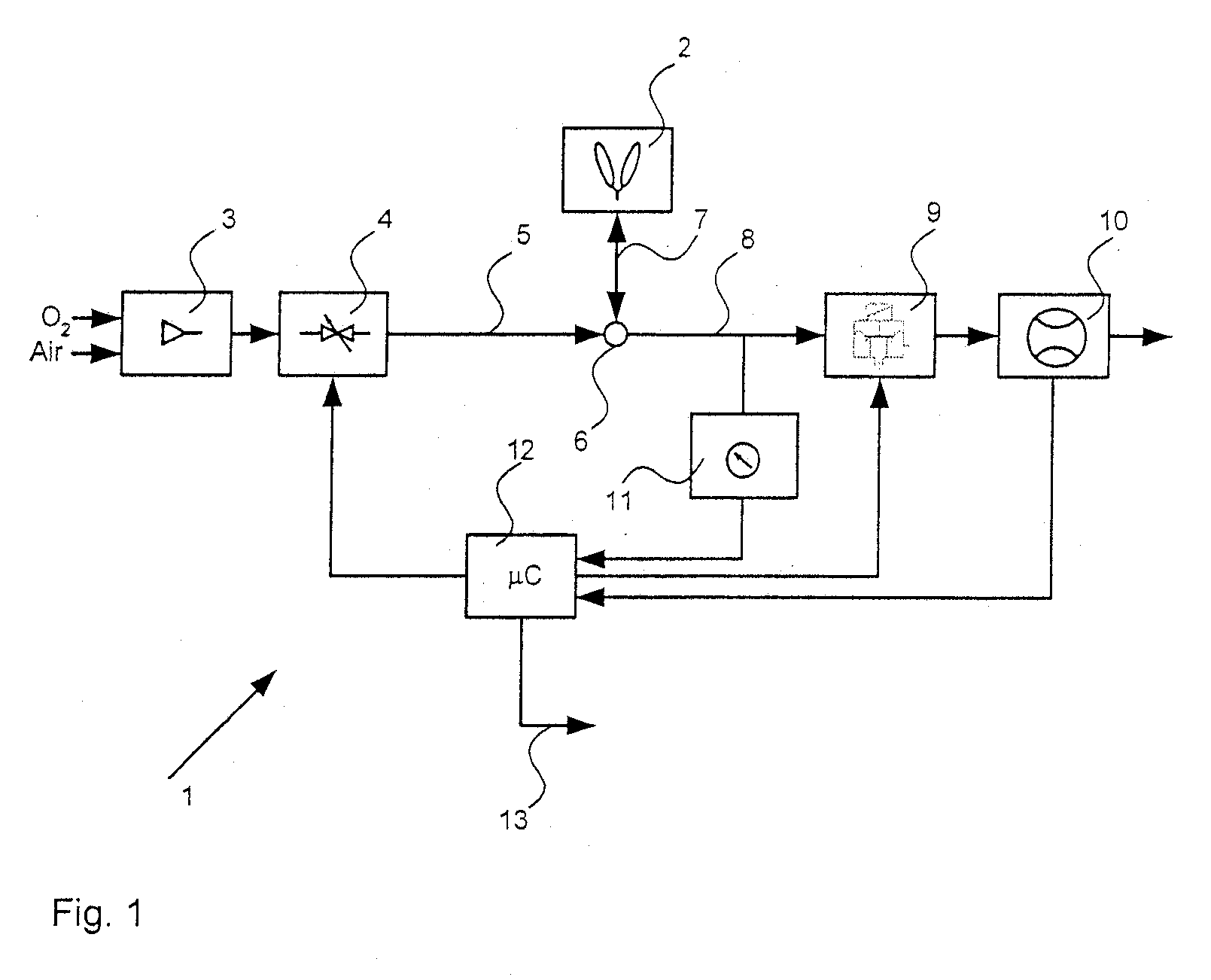
Methods and devices for minimally invasive respiratory support
ActiveUS20080135044A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationCatheter
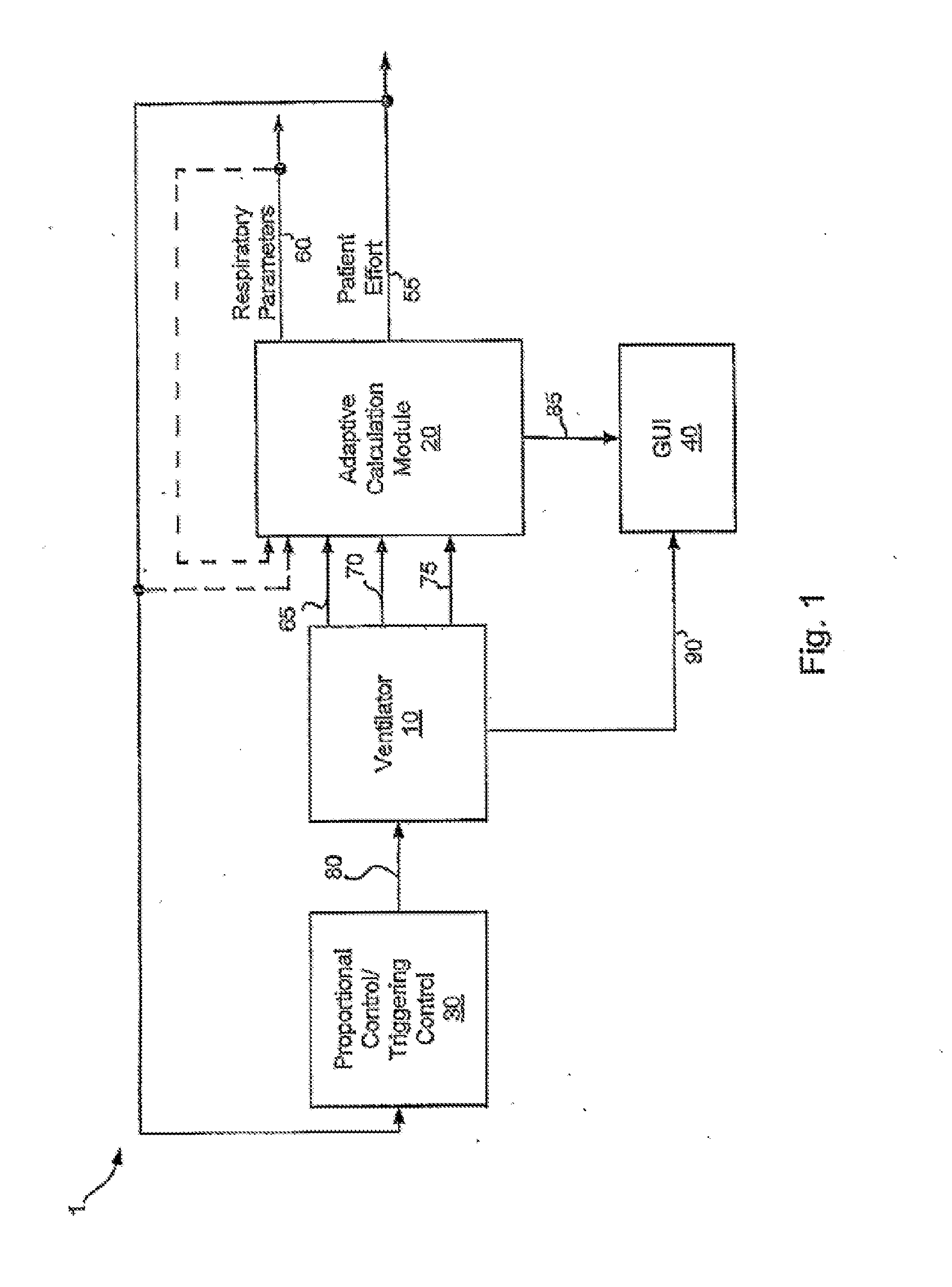
Modes, methods, systems and devices are described for providing assisted ventilation to a patient, including wearable ventilation systems with integral gas supplies, special gas supply features, ventilation catheters and access devices, and breath sensing techniques.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
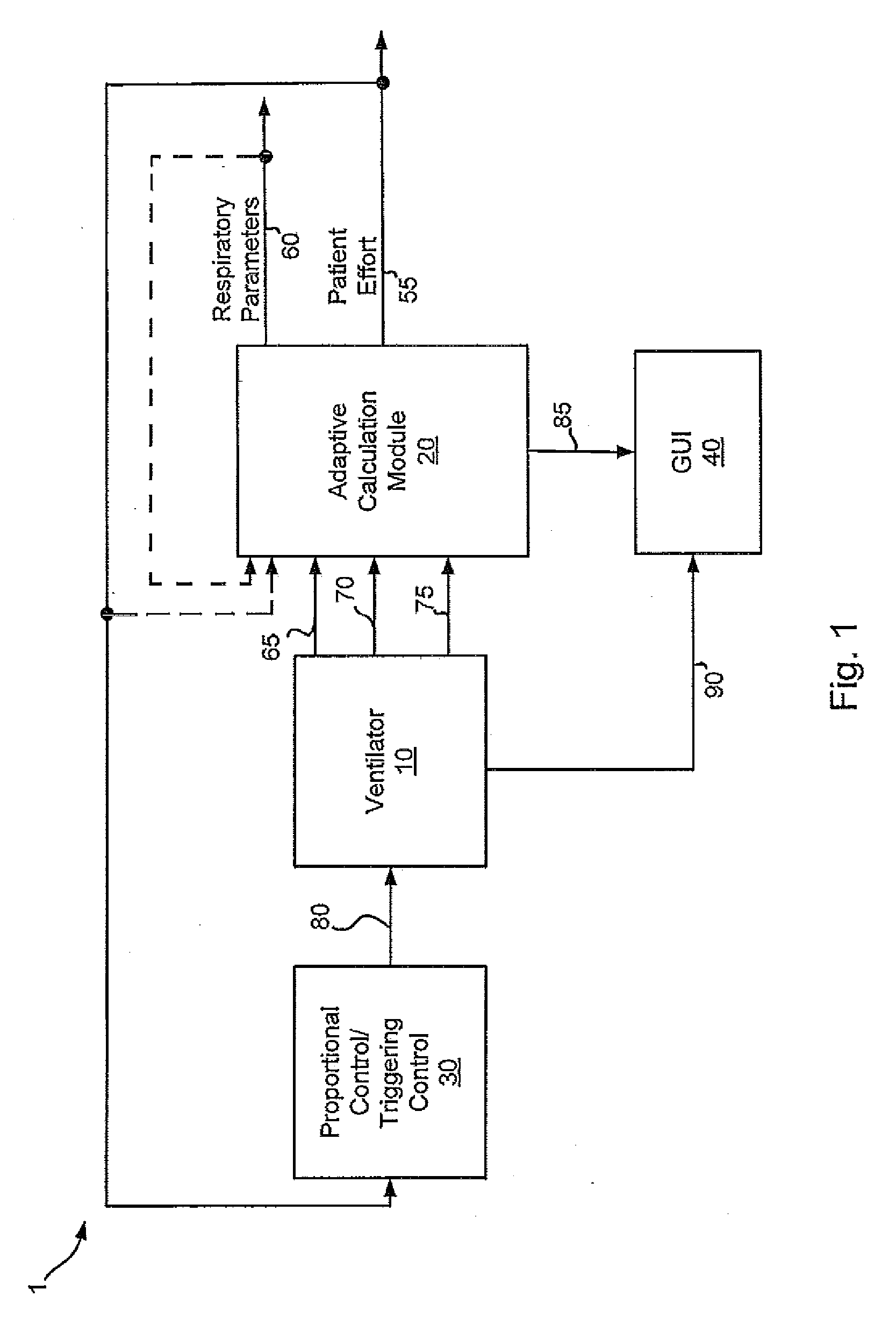
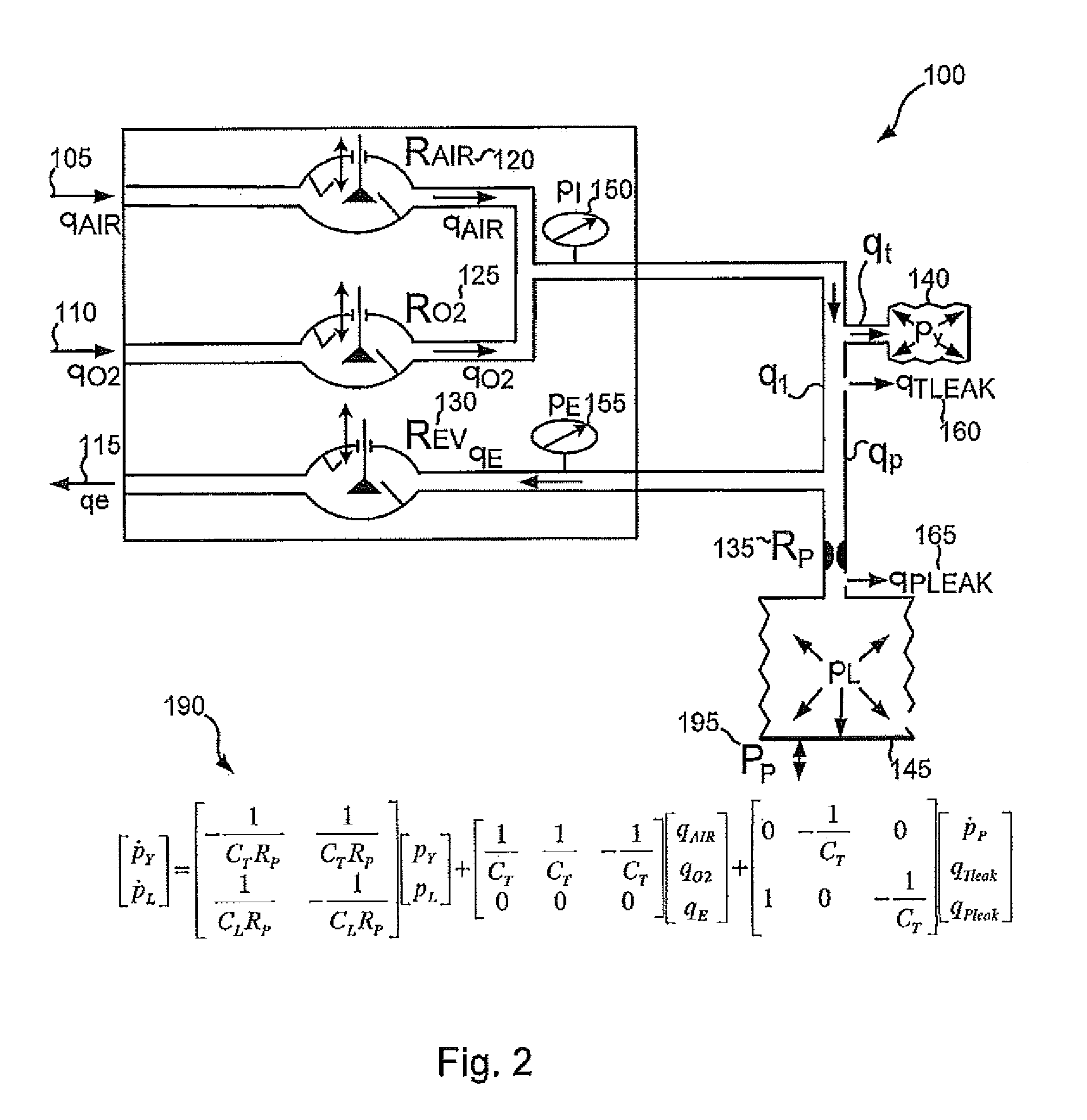
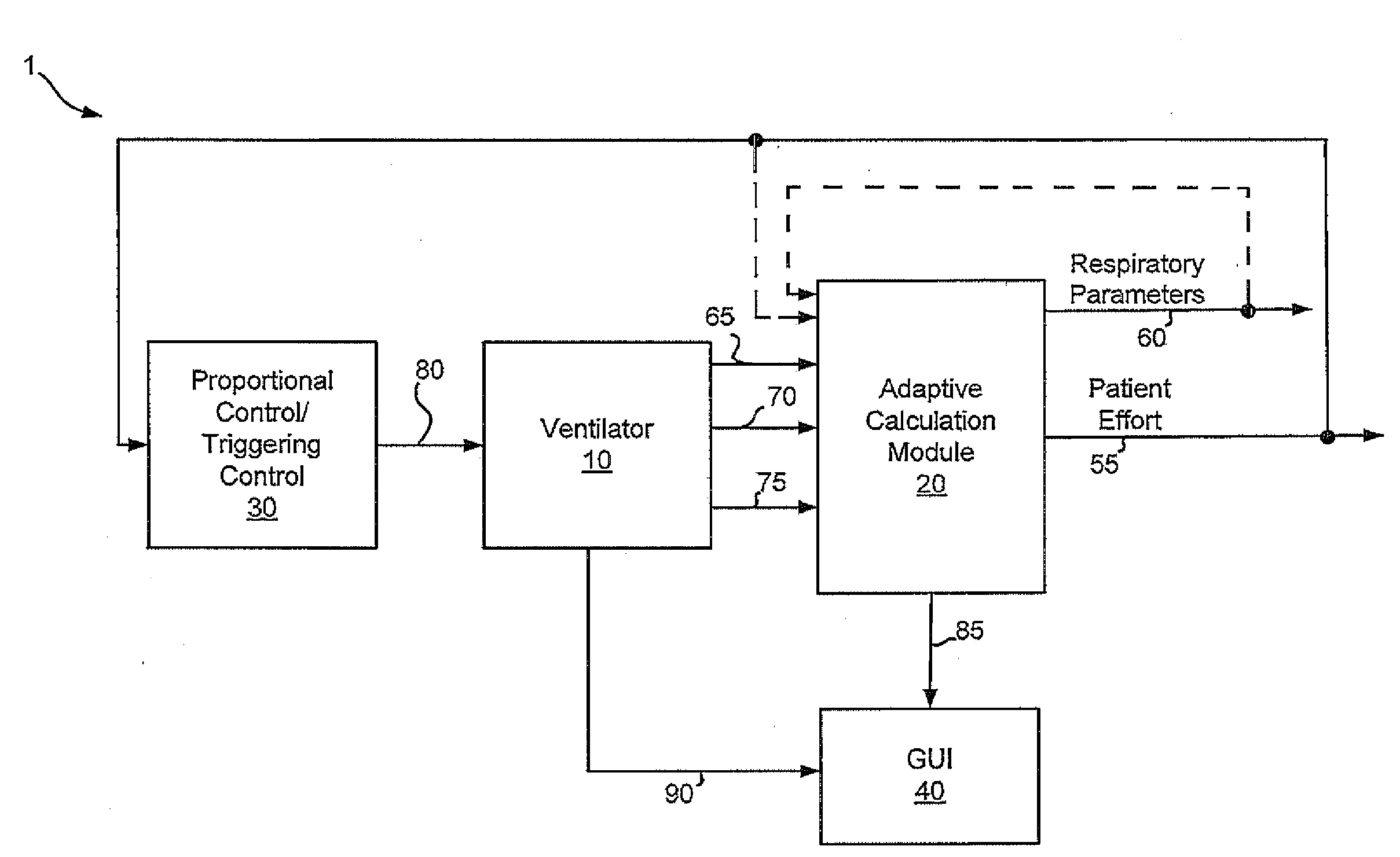
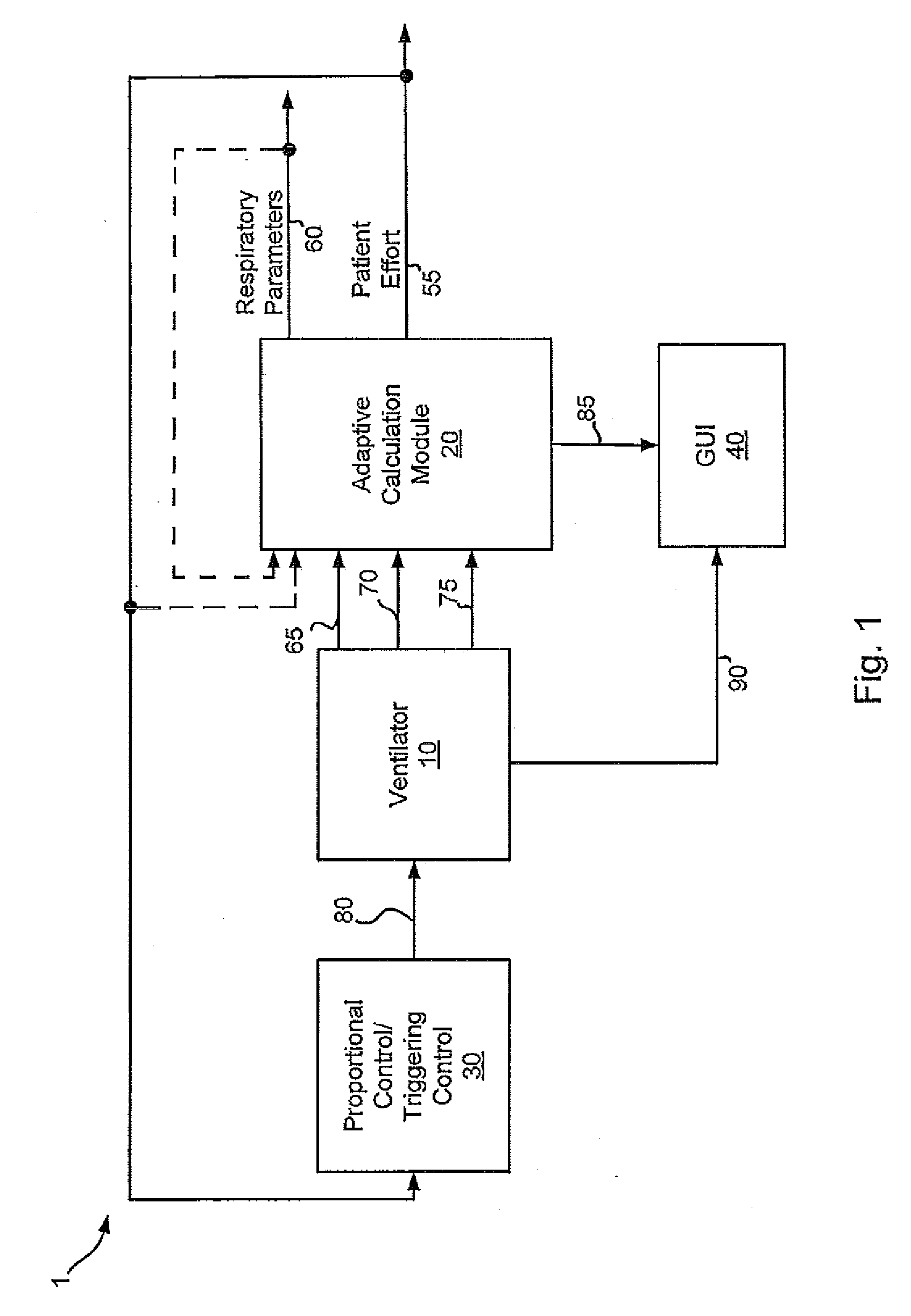
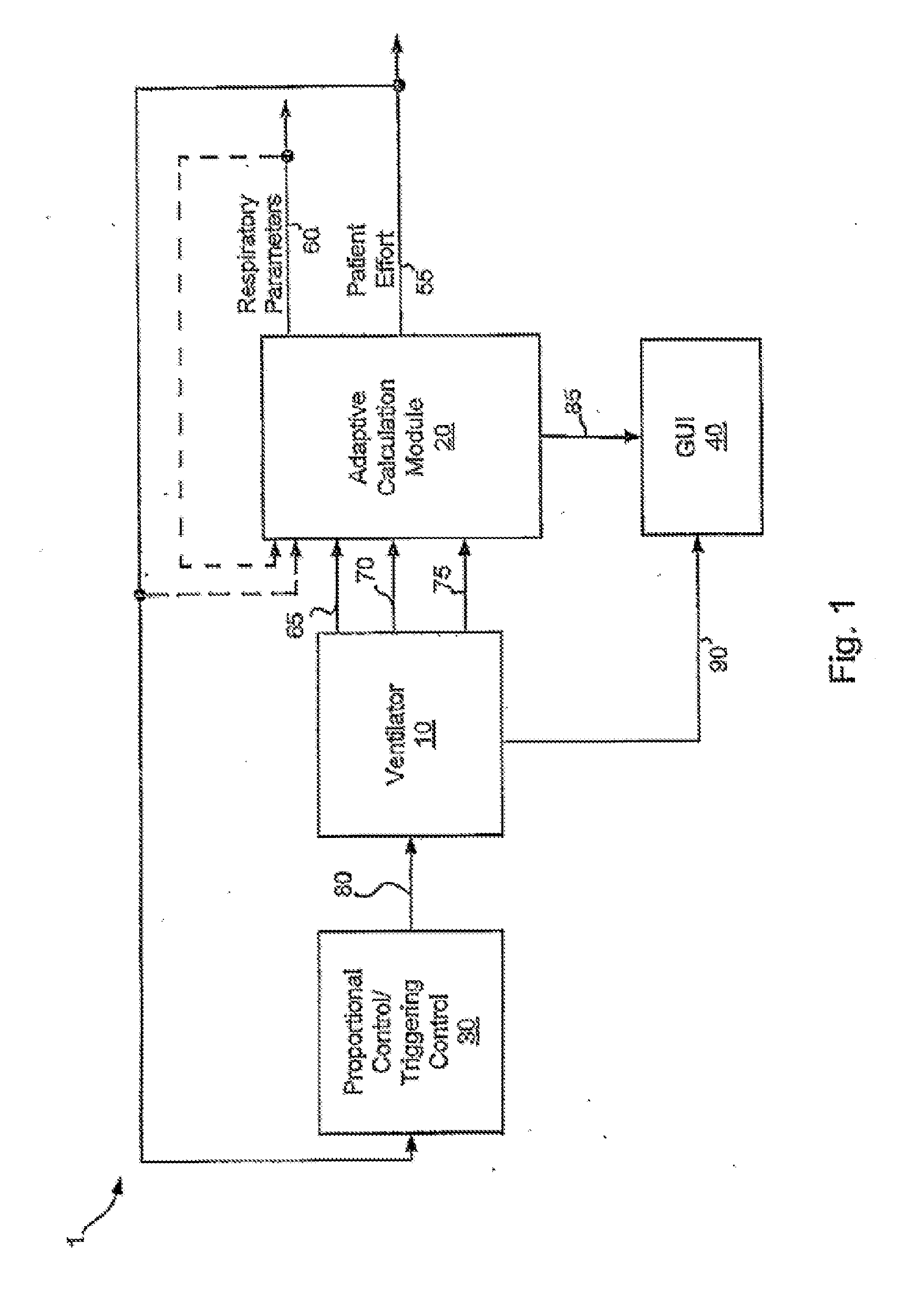
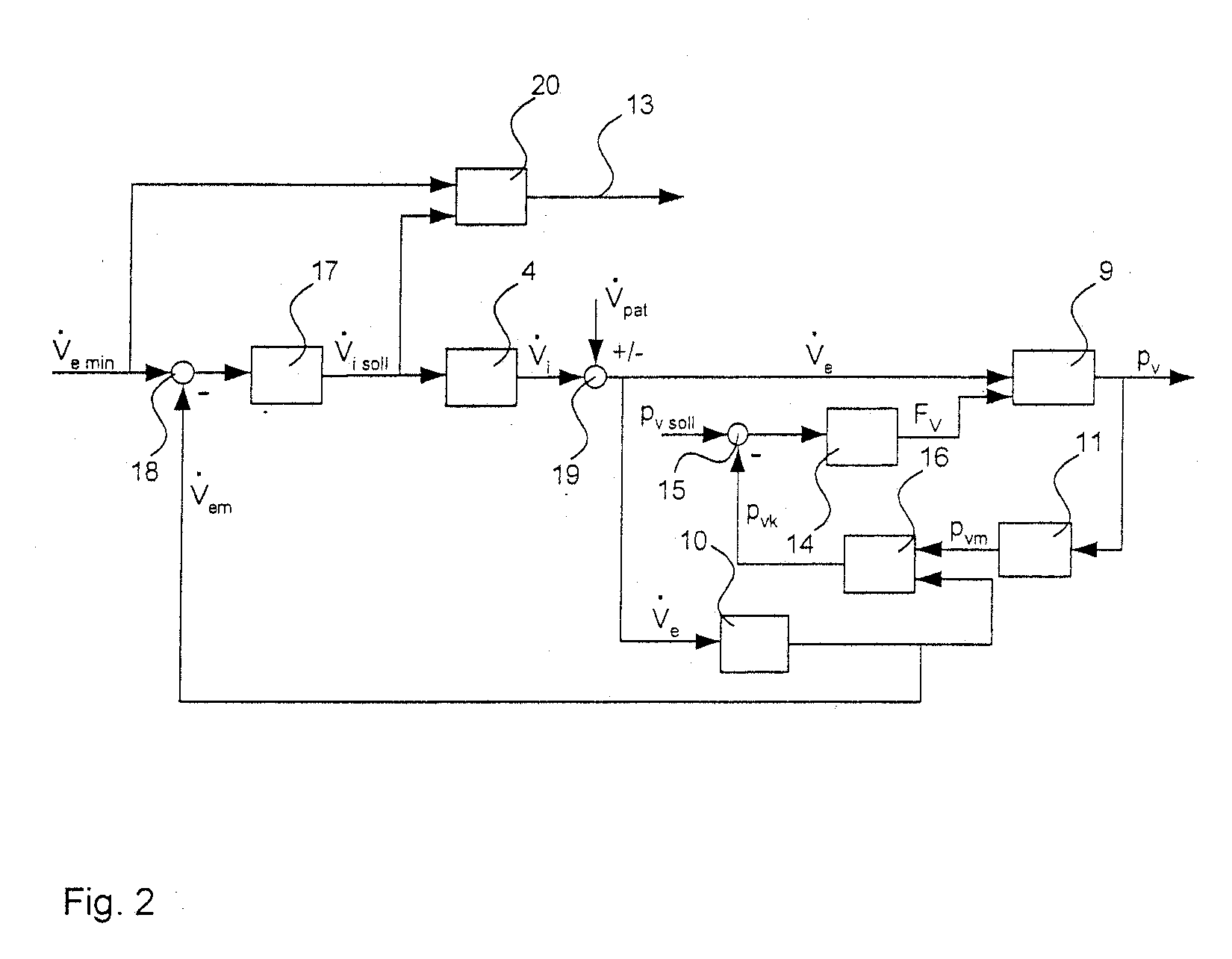
Systems and methods for triggering and cycling a ventilator based on reconstructed patient effort signal
ActiveUS20090301486A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory supportInlet flow
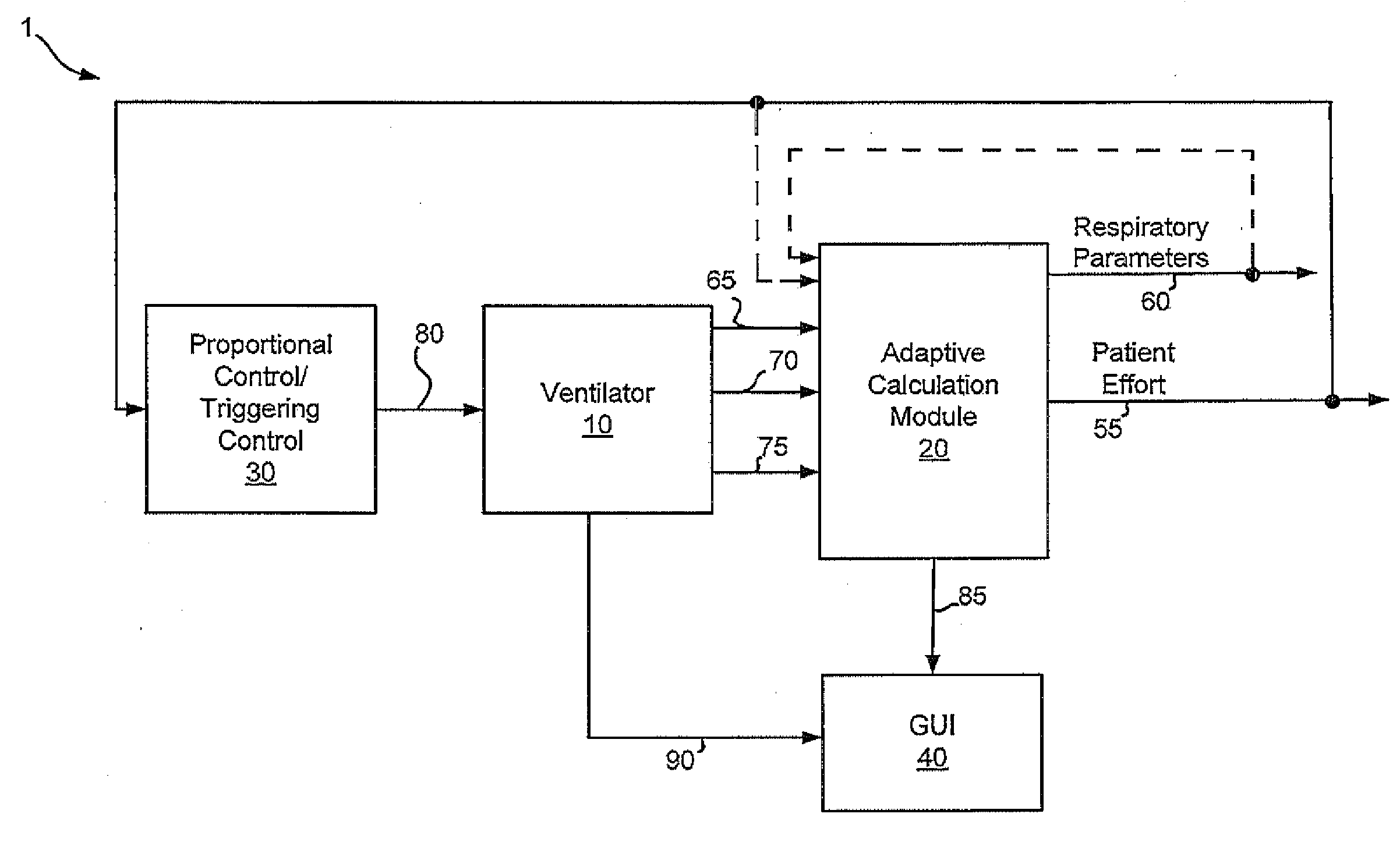
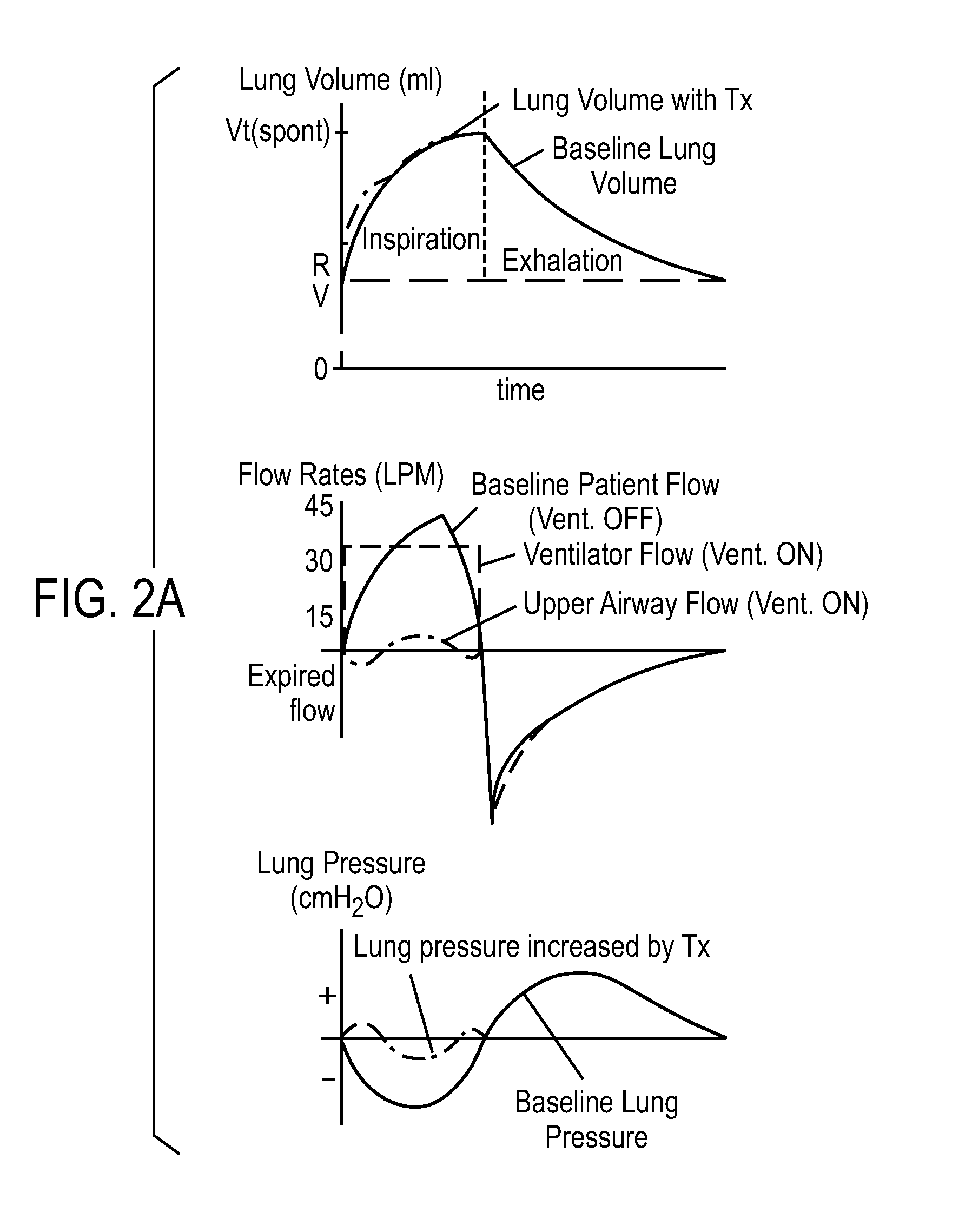
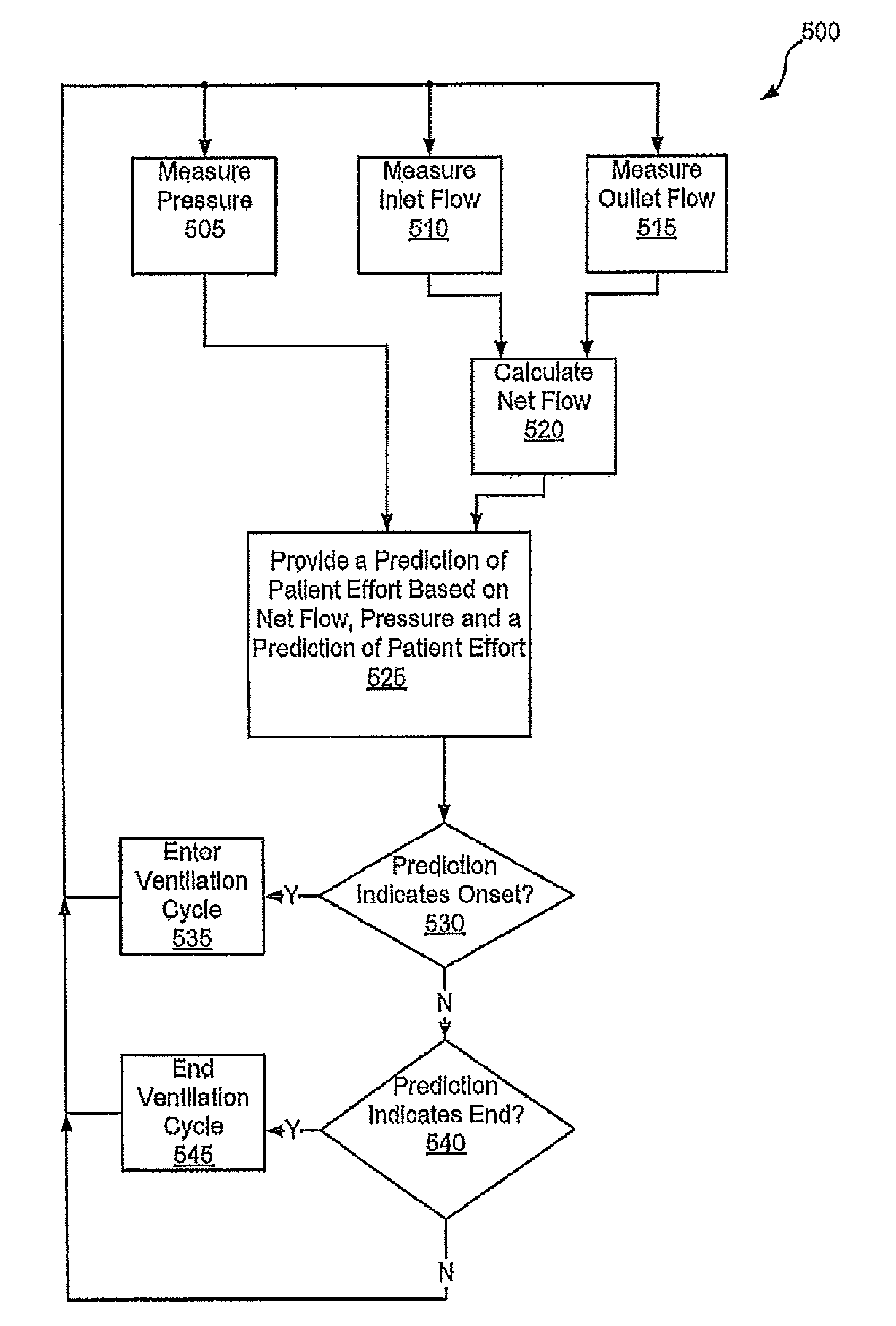
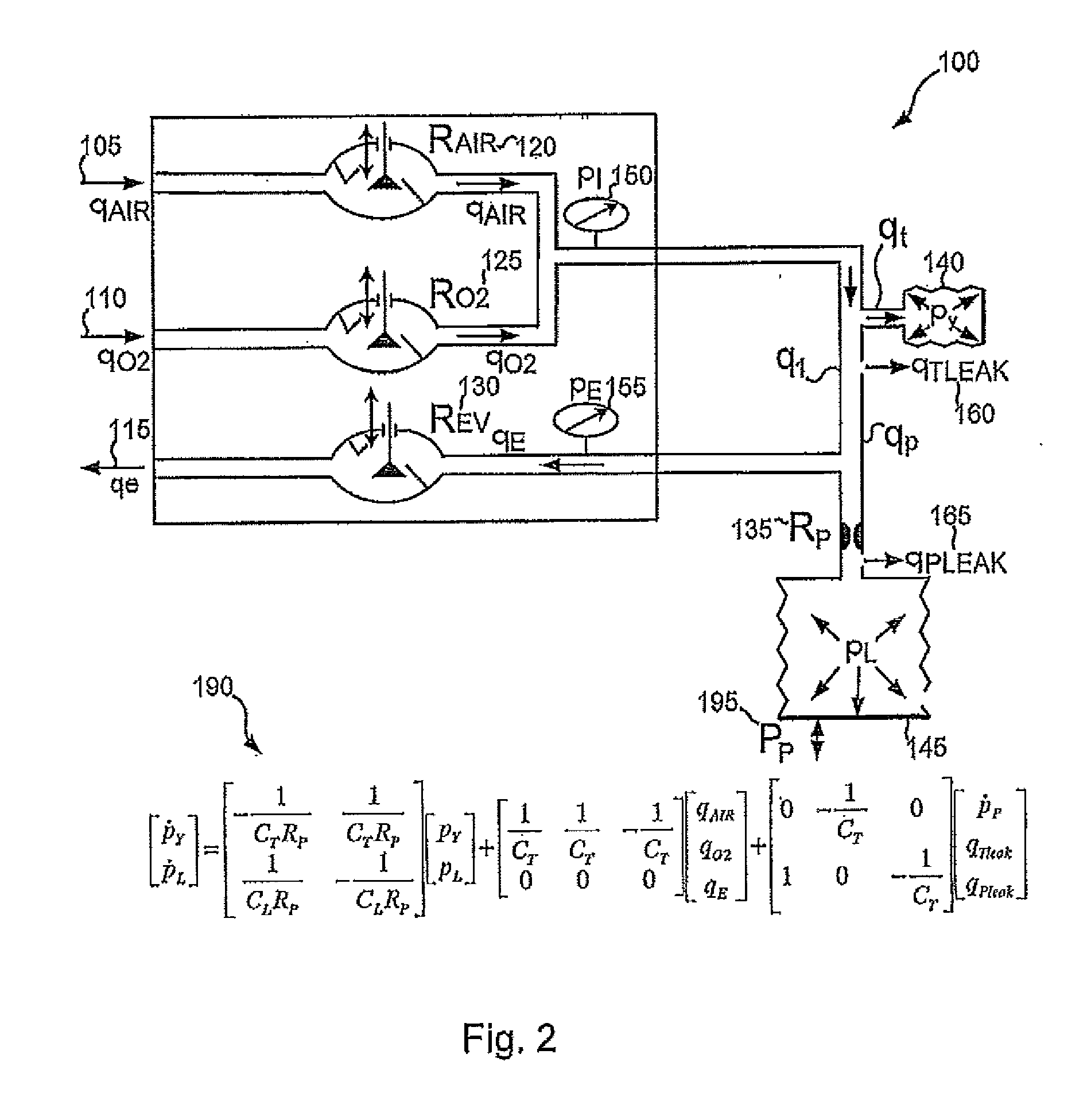
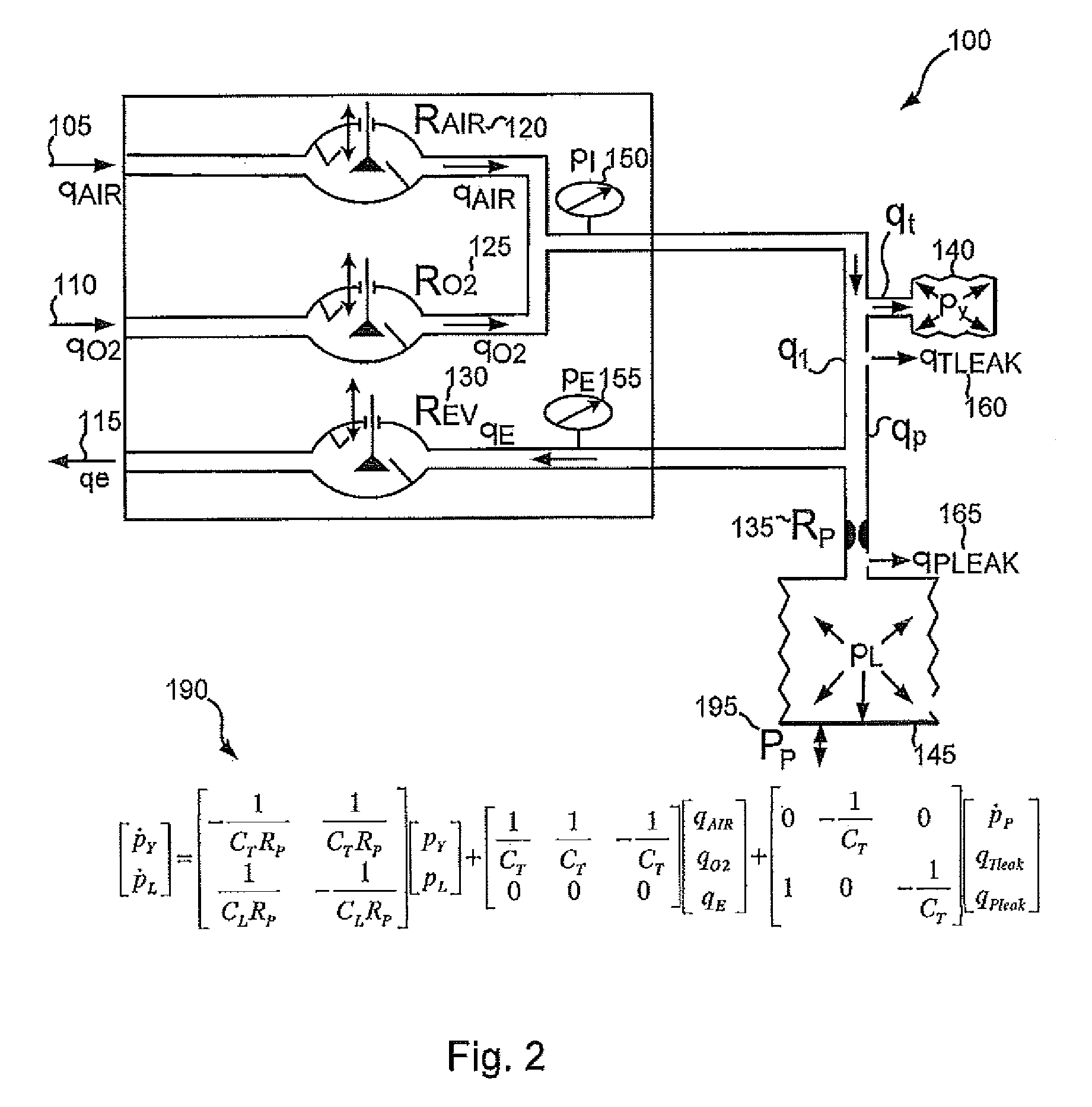
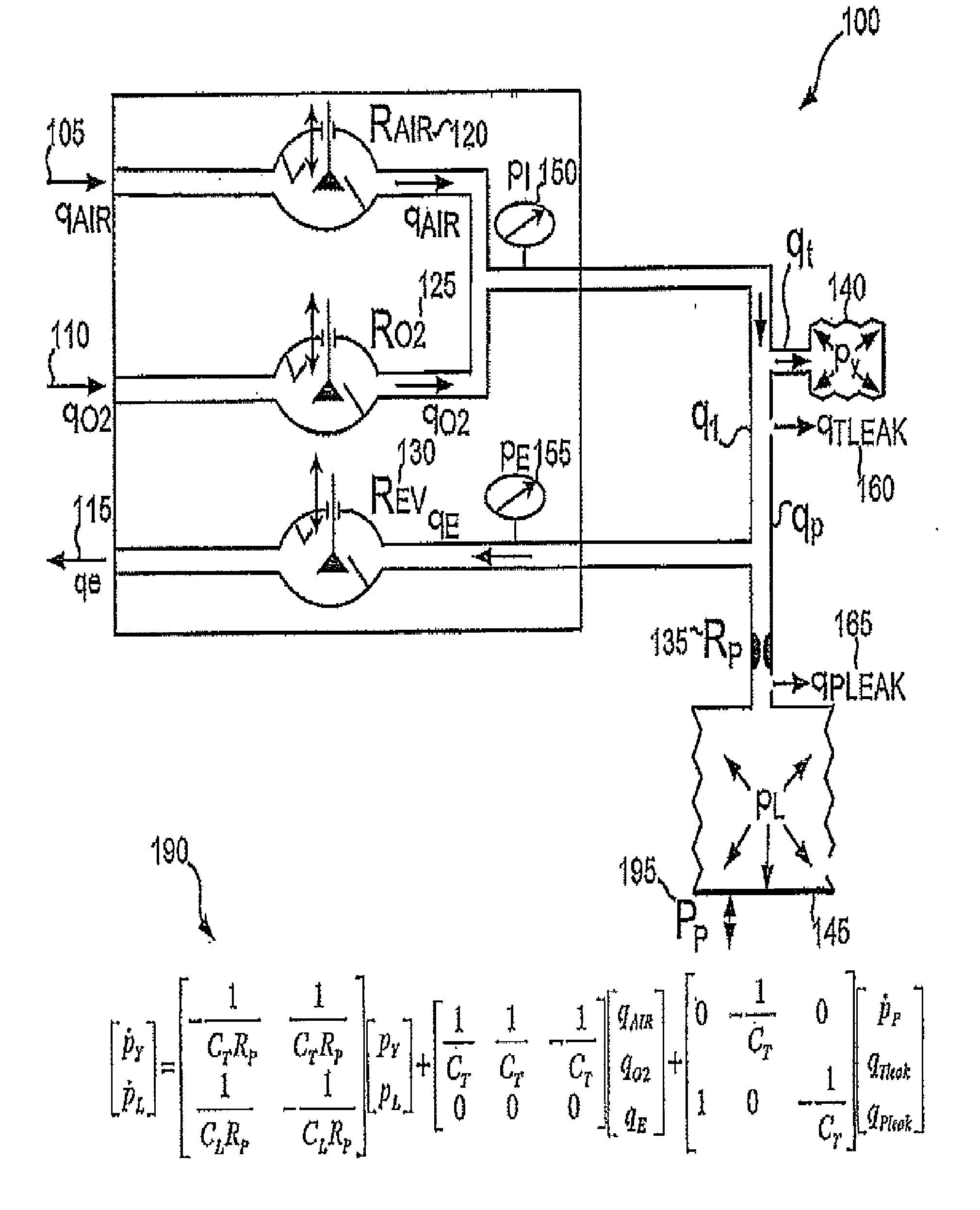
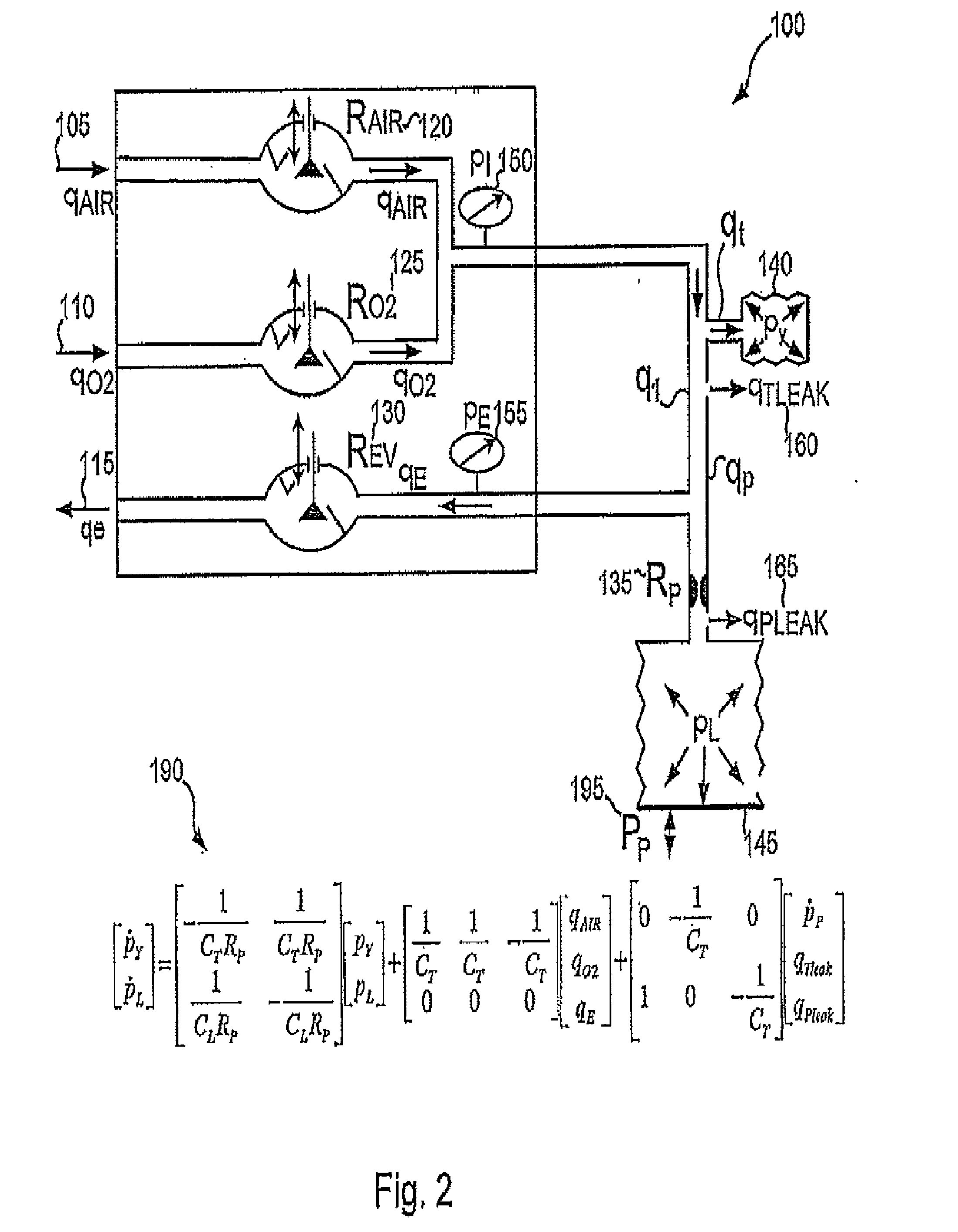
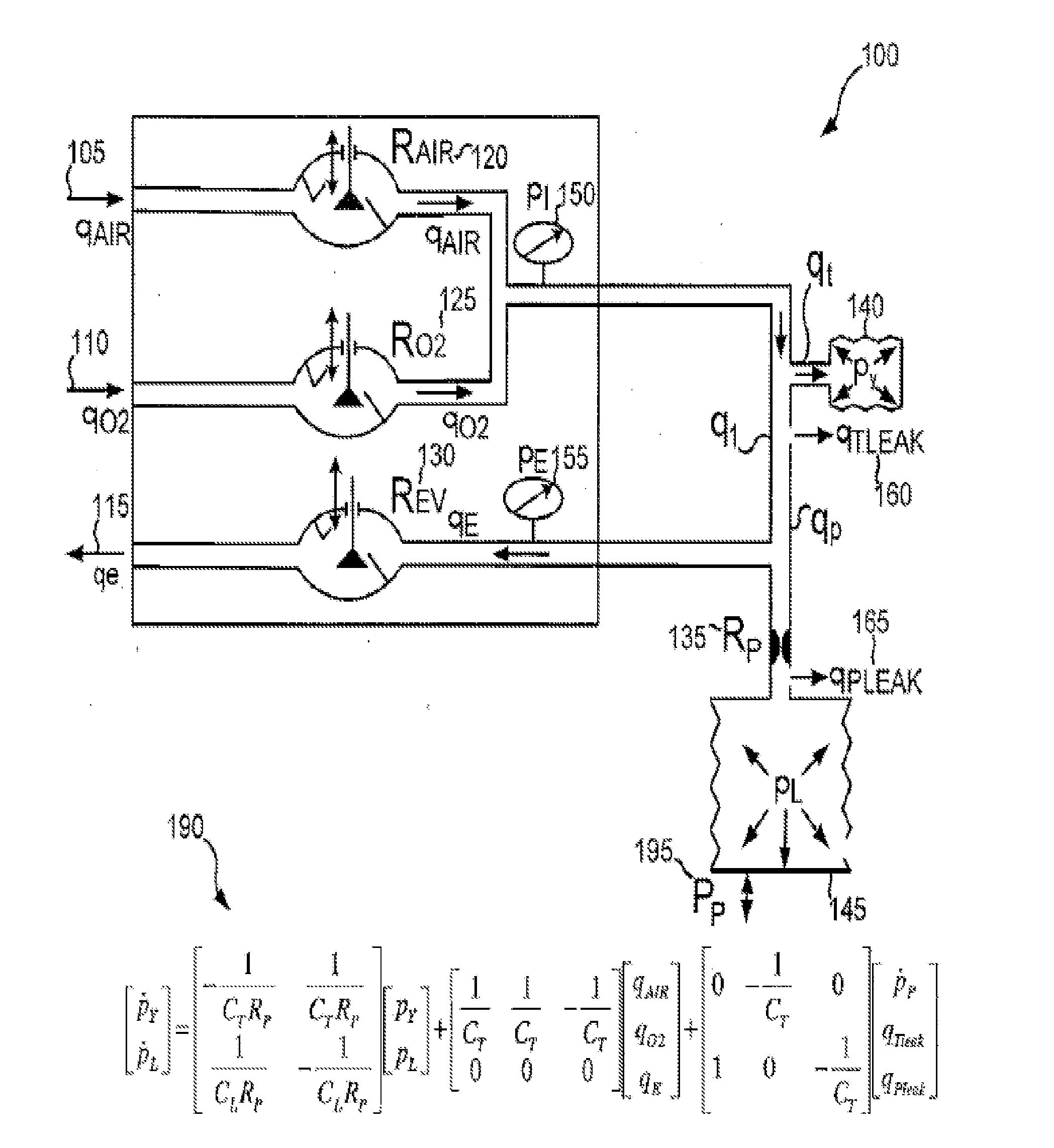
Various embodiments of the present disclosure provide systems, methods and devices for respiratory support. As one example, a method for respiratory support is described that includes providing a measured pressure, and calculating a net flow based on at least one measured inlet flow and measured outlet flow. A relationship between a first value related to the measured pressure, a second value related to the measured net flow and a third value related to patient effort is used to provide a prediction of patient effort. An interim value is updated based at least in part on the prediction of the patient effort, and used to help compute a patient effort. A ventilation cycle is initiated using the computed patient effort.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Ventilator with biofeedback monitoring and control for improving patient activity and health
ActiveUS20100083968A1Reducing and eliminating needEnable ambulationTracheal tubesMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesBiofeedback trainingQuality of life
A respiratory support ventilator apparatus is described that mechanically supports the work of respiration of a patient. The ventilator apparatus is highly portable and optionally wearable so as to promote mobility and physical activity of the patient, and to improve the overall health of the patient. The respiratory support ventilator may monitor a physical activity level and overall health status of the patient, and process this information. The information is used to track efficacy of the ventilation therapy relative to activity level and quality of life, and or to titrate or optimize the ventilation parameters to improve, maintain or optimize the physical activity level and overall health status of the patient.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Systems and methods for ventilation in proportion to patient effort
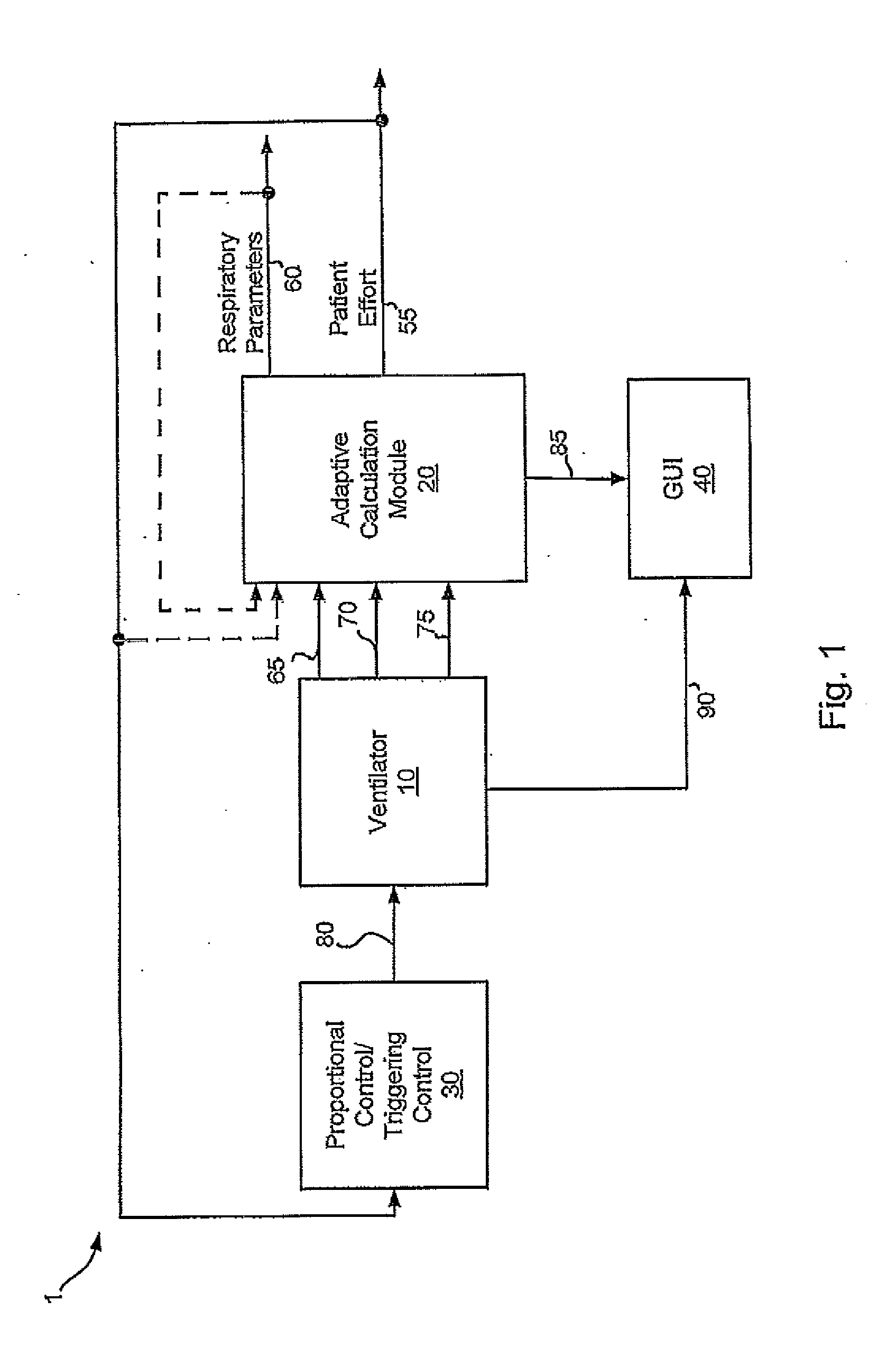
Various embodiments of the present disclosure provide systems, methods and devices for respiratory support. As one example, a ventilation system is disclosed that includes a computer readable medium including instructions executable by a processor to receive a measured pressure value and a net flow value. A patient effort value is calculated based on a relationship between patient effort, the measured pressure value and the net flow value. The instructions are further executable to calculate a gas delivery metric that varies as a function of the patient effort value. Gas is then caused to be delivered consistent with the gas delivery metric.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Systems and methods for monitoring and displaying respiratory information
ActiveUS20090301487A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGraphicsRespiratory support
Various embodiments of the present disclosure provide systems, methods and devices for respiratory support. As one example, a ventilation system is disclosed that includes a graphical display, a processor and a computer readable medium. The computer readable medium is communicably coupled to the processor and includes instructions executable by the processor to receive a measured pressure value, and receive a net flow value. The instructions are further executable to calculate a patient effort value based on a relationship between patient effort, the measured pressure value and the net flow value; and to plot the patient effort value to the graphical display.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
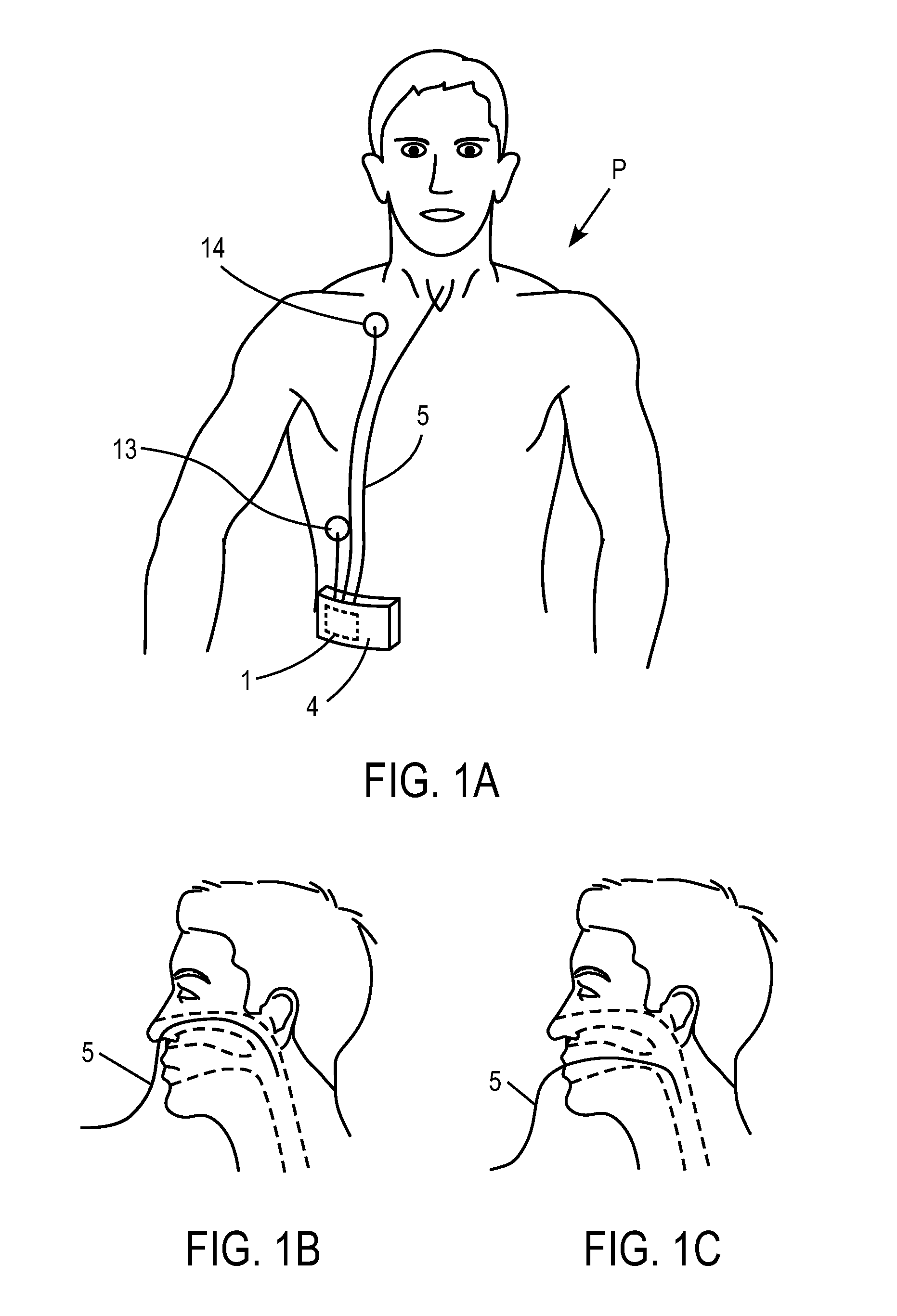
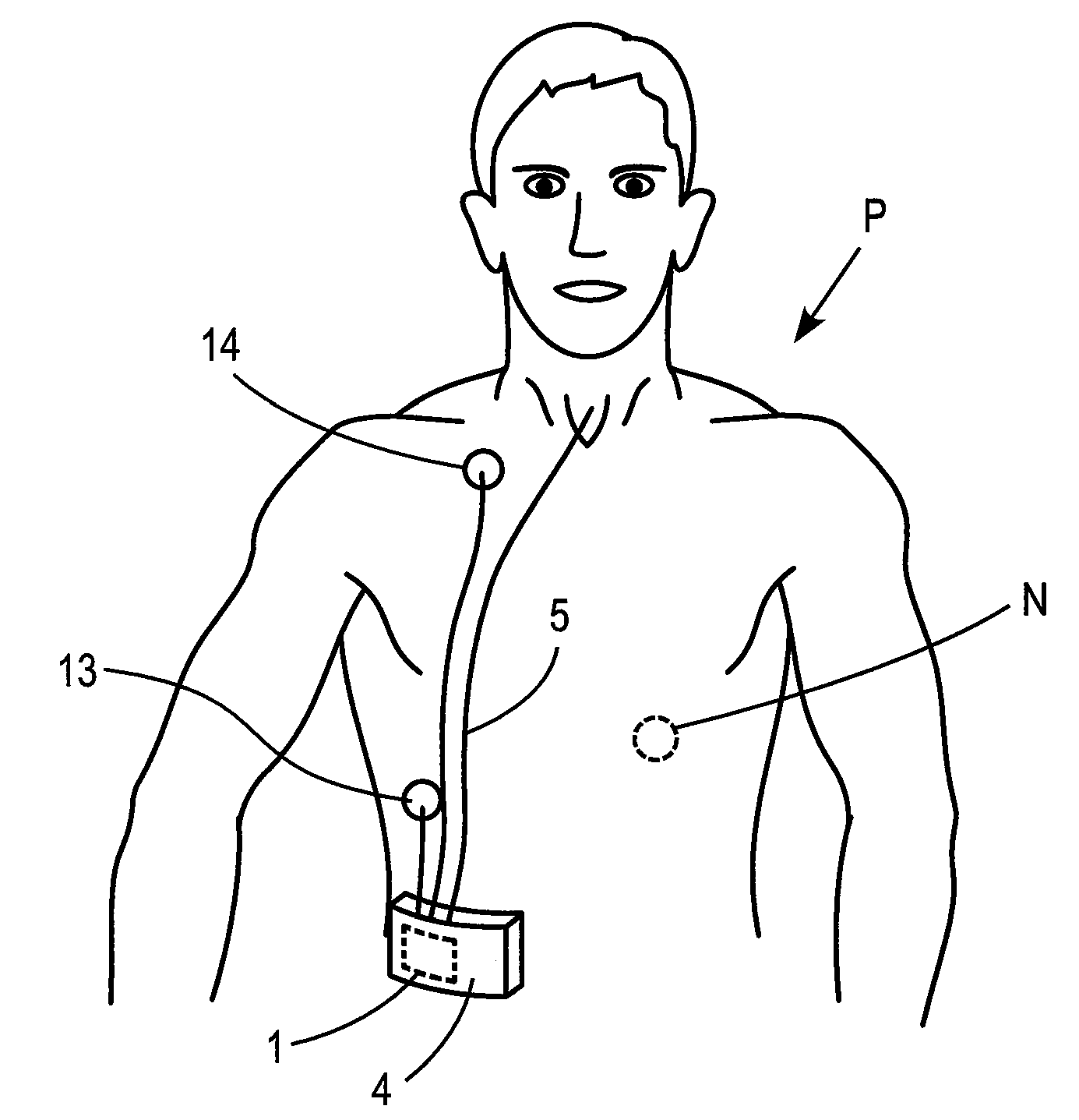
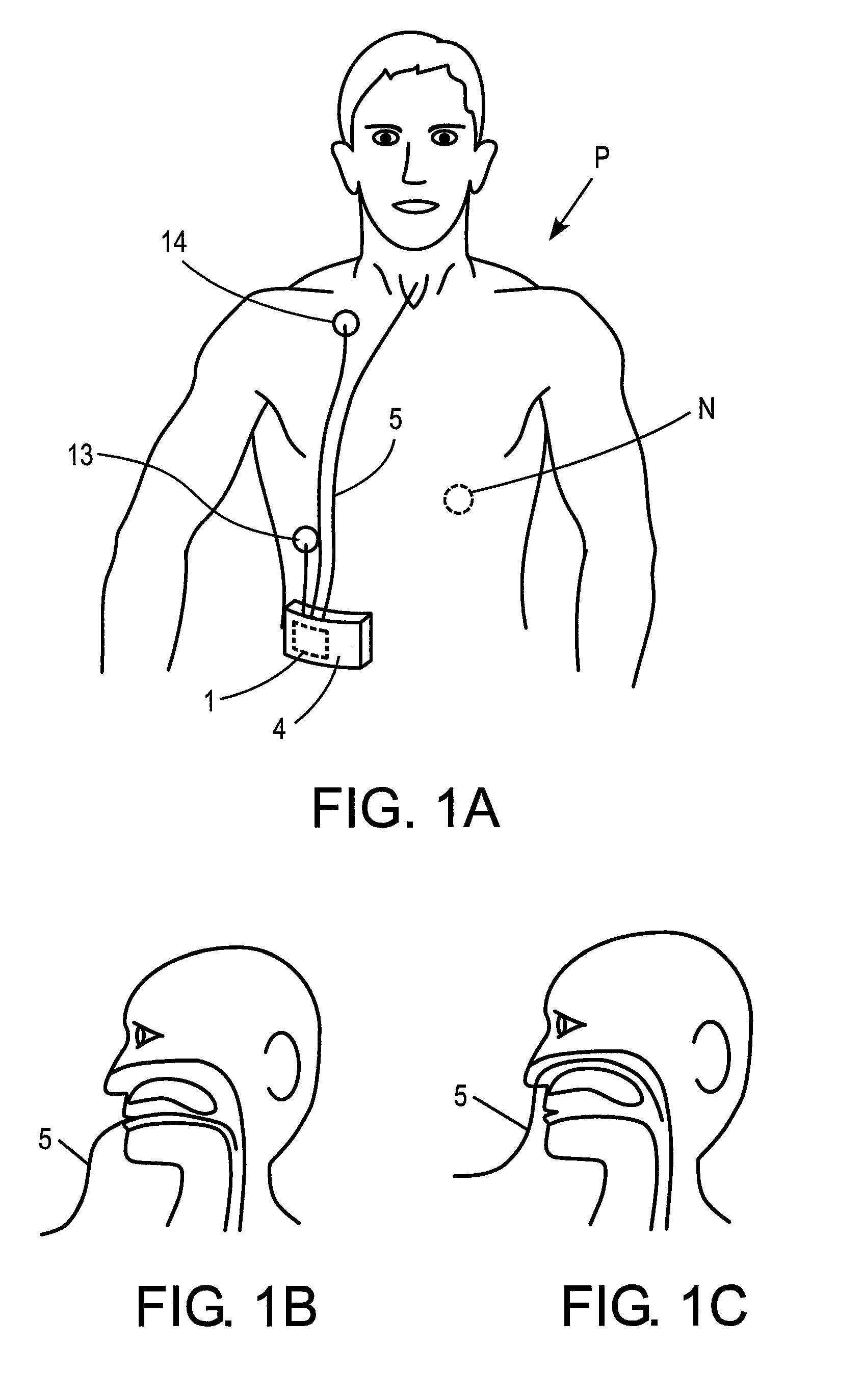
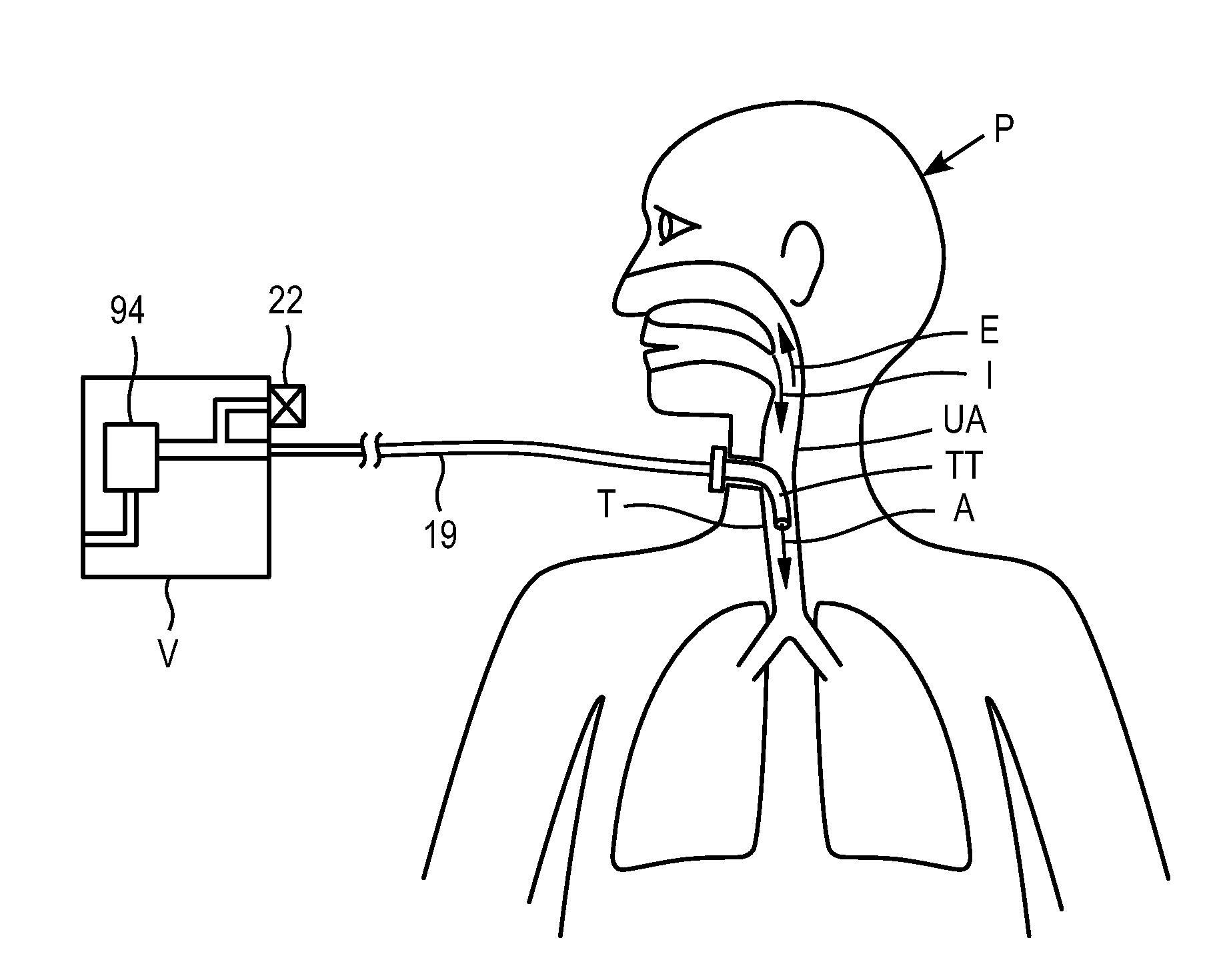
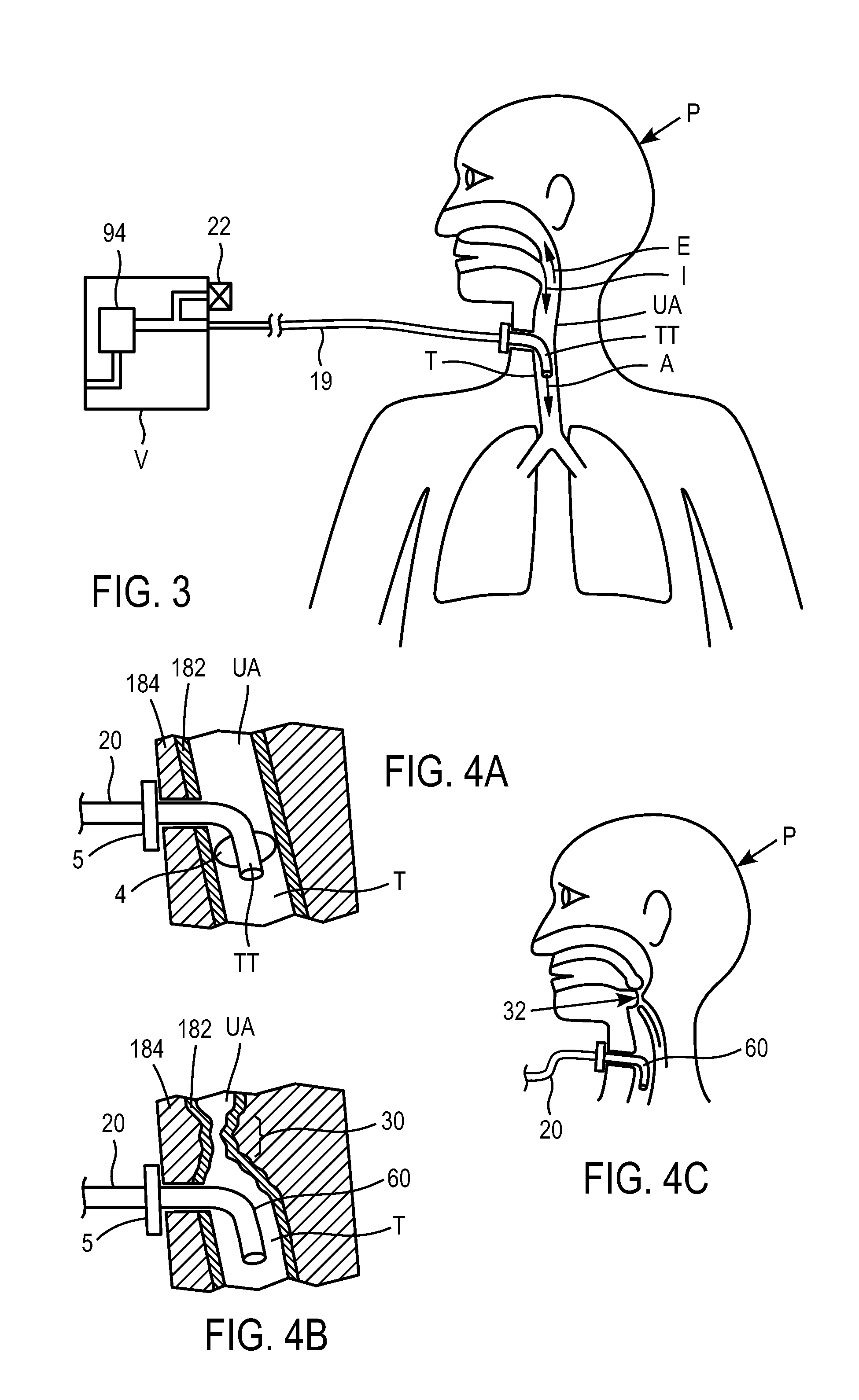
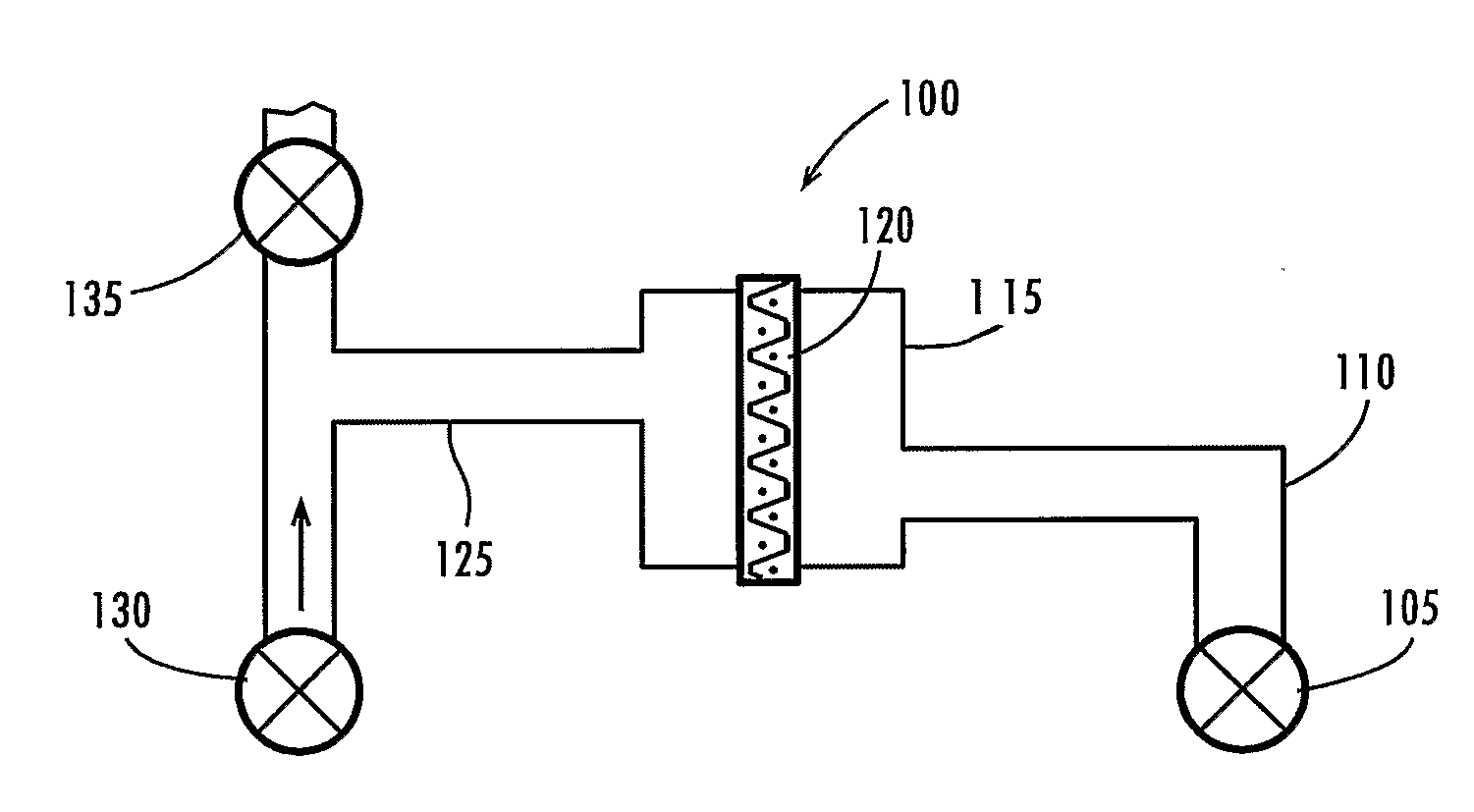
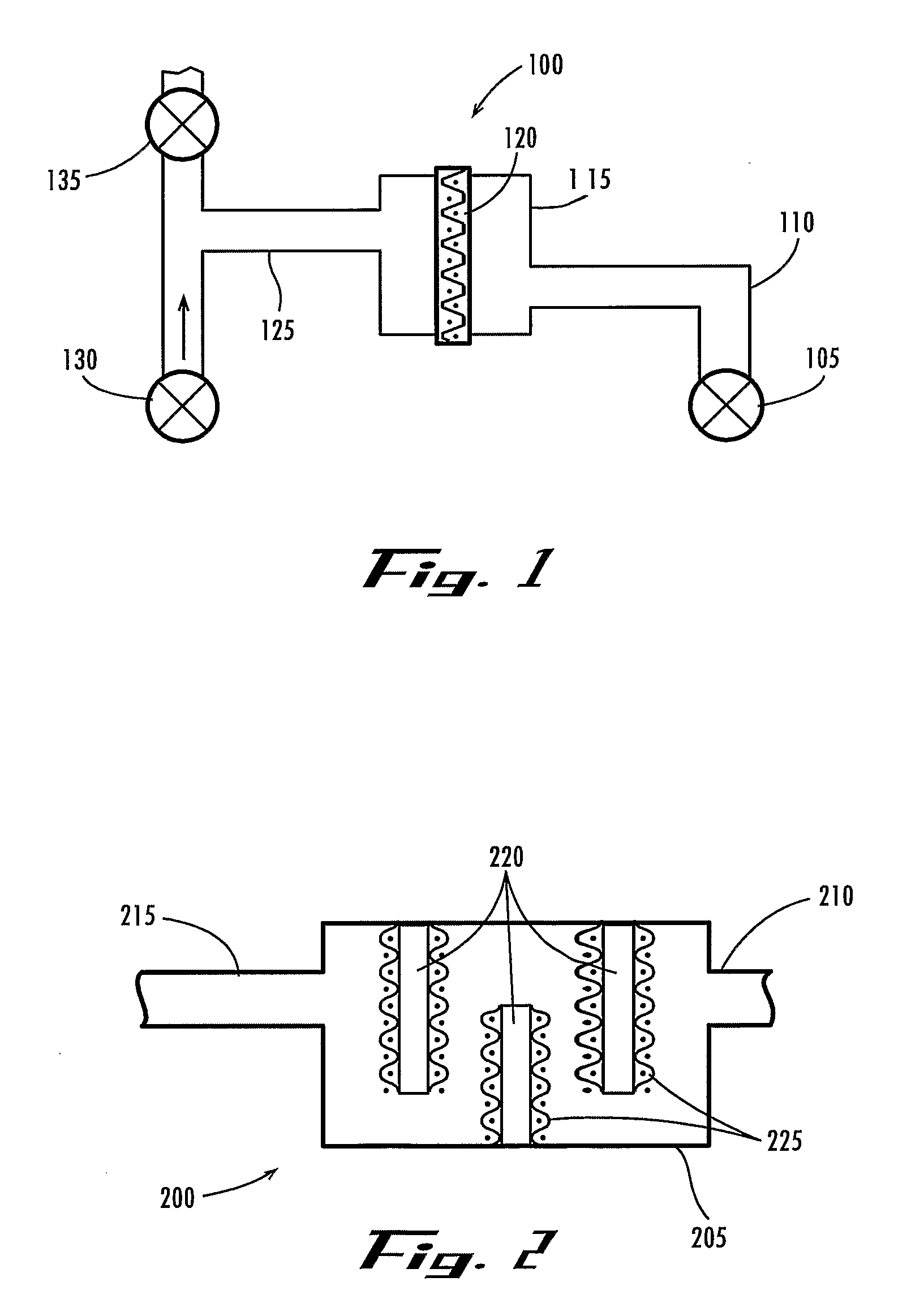
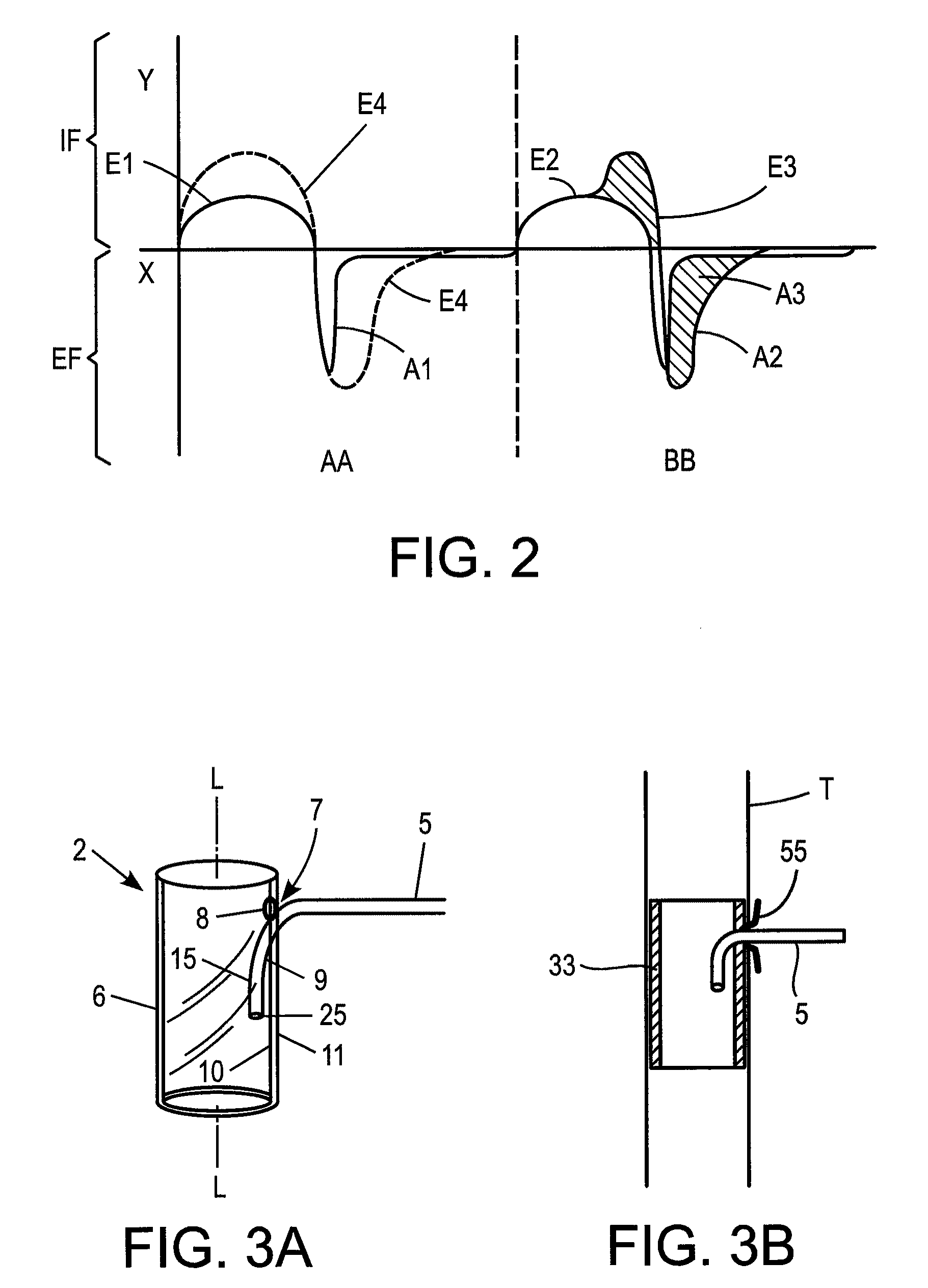
Tracheal catheter and prosthesis and method of respiratory support of a patient
ActiveUS7487778B2Improve the quality of lifeEfficient methodTracheal tubesMedical devicesEndotracheal tubeDuring expiration
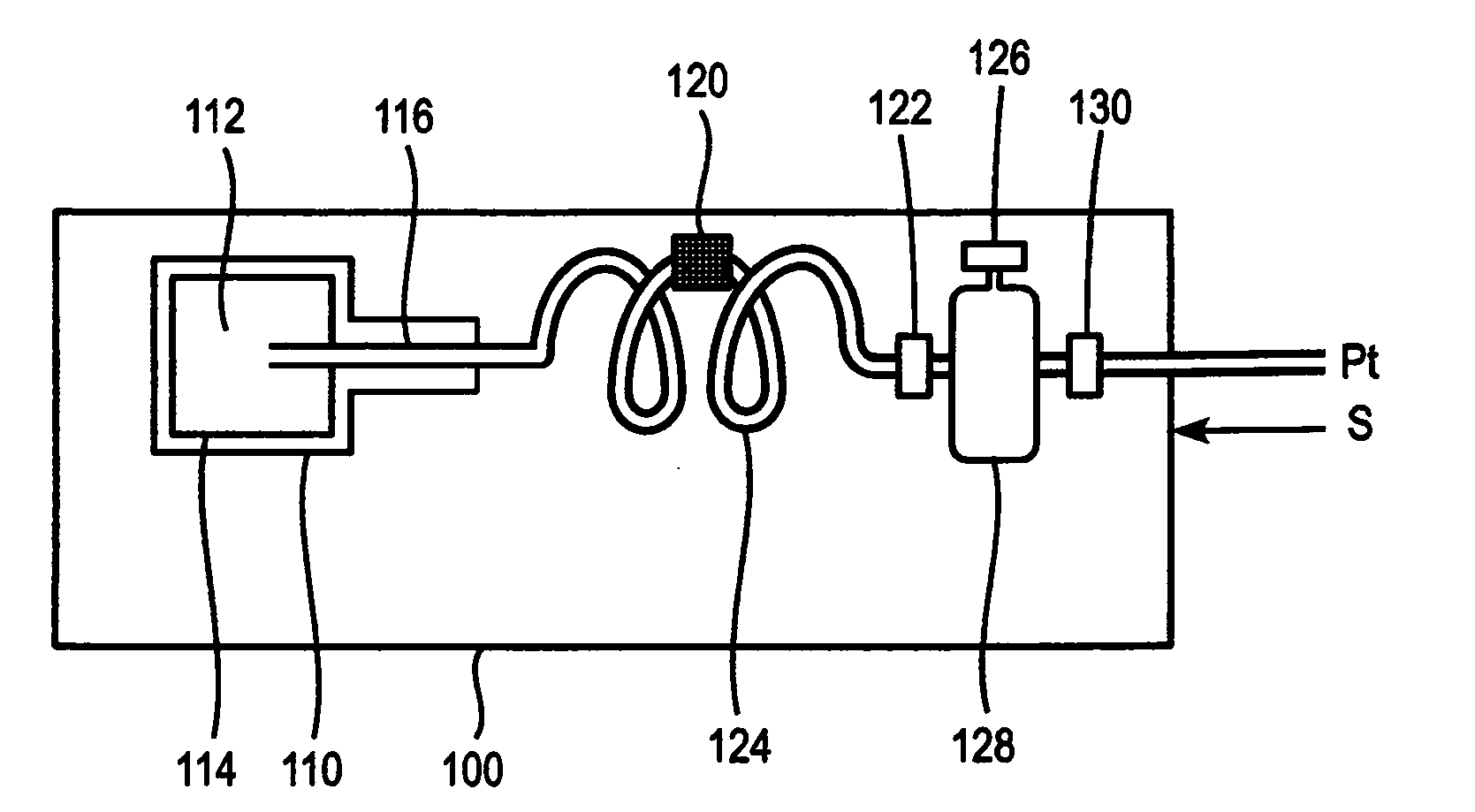
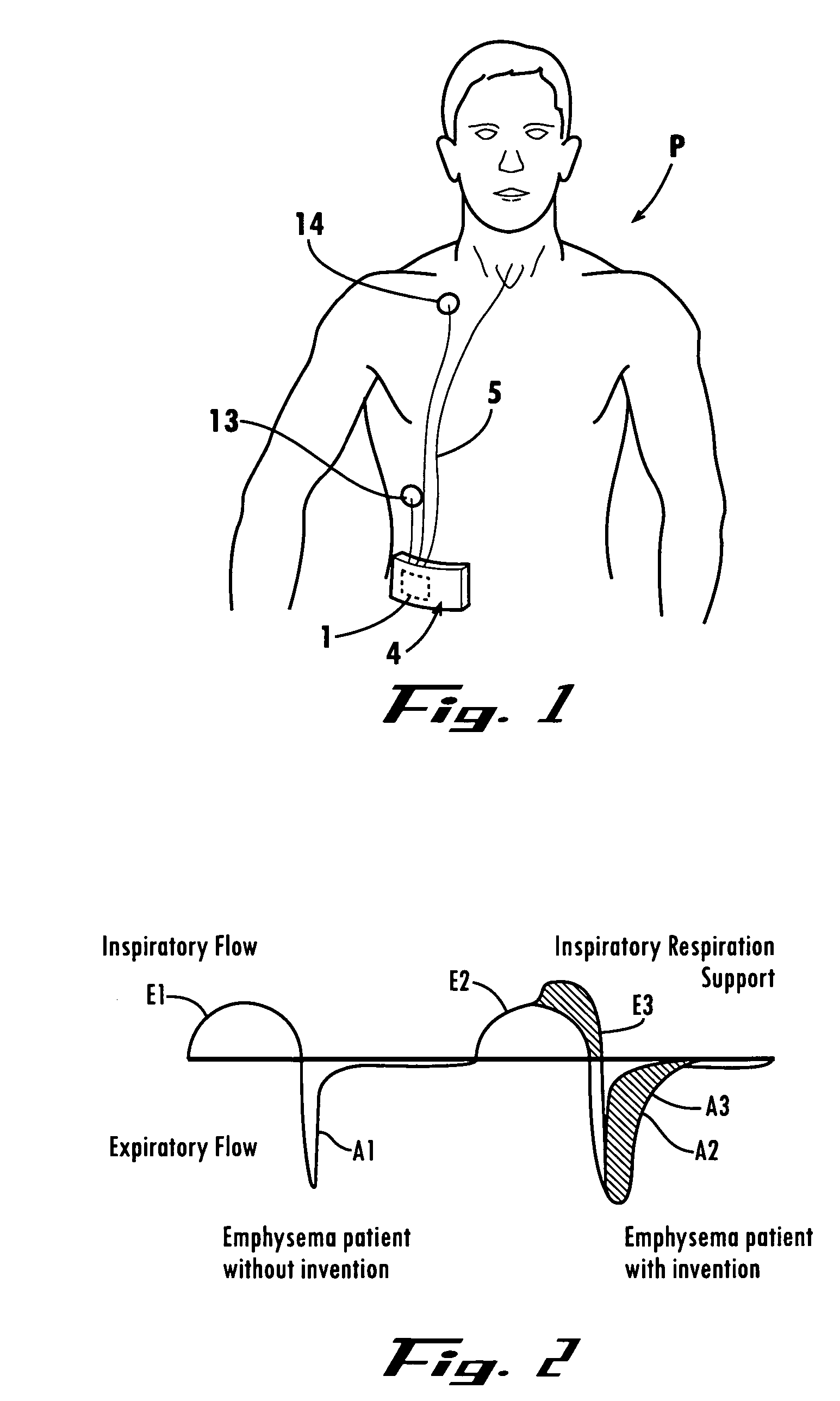
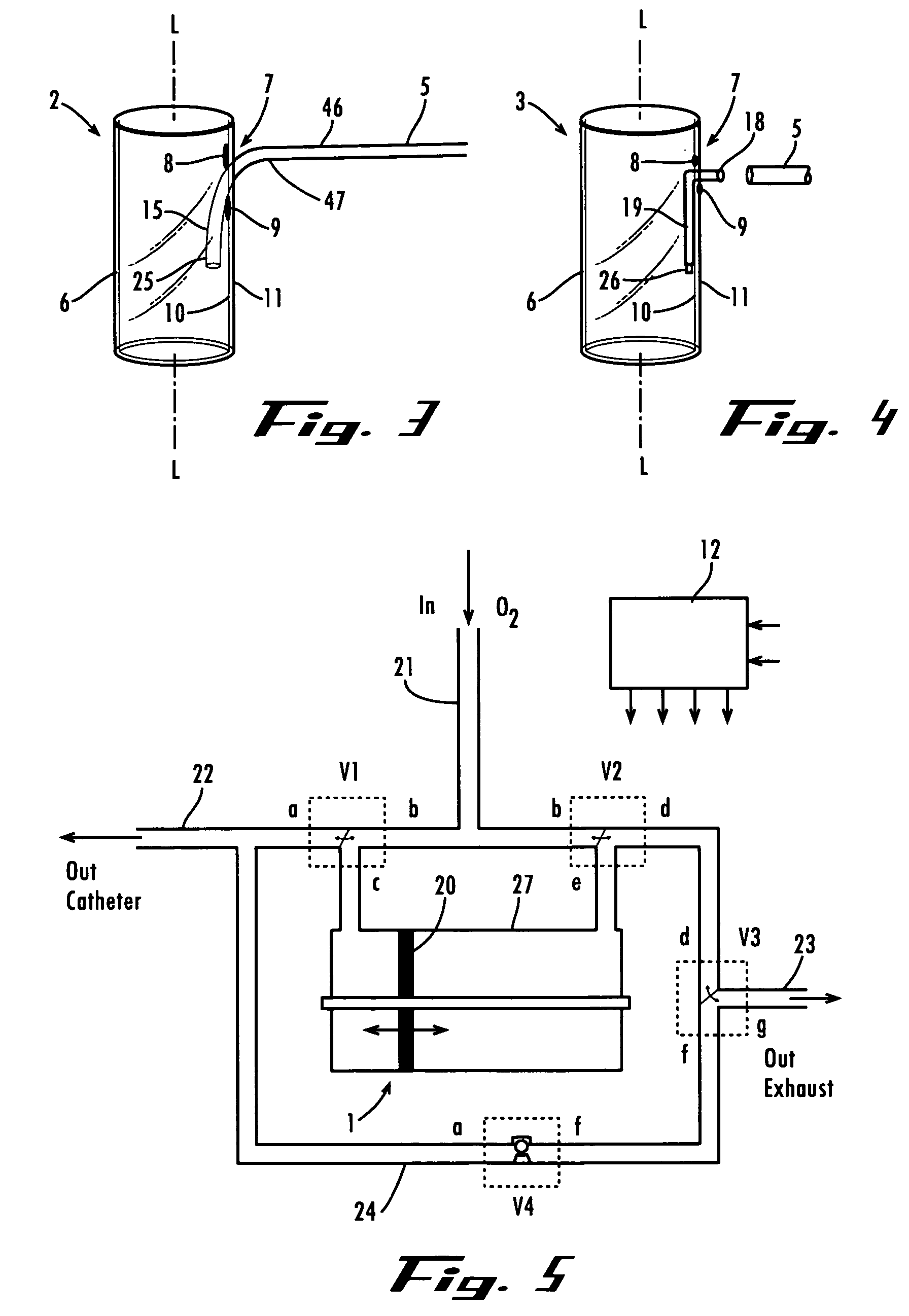
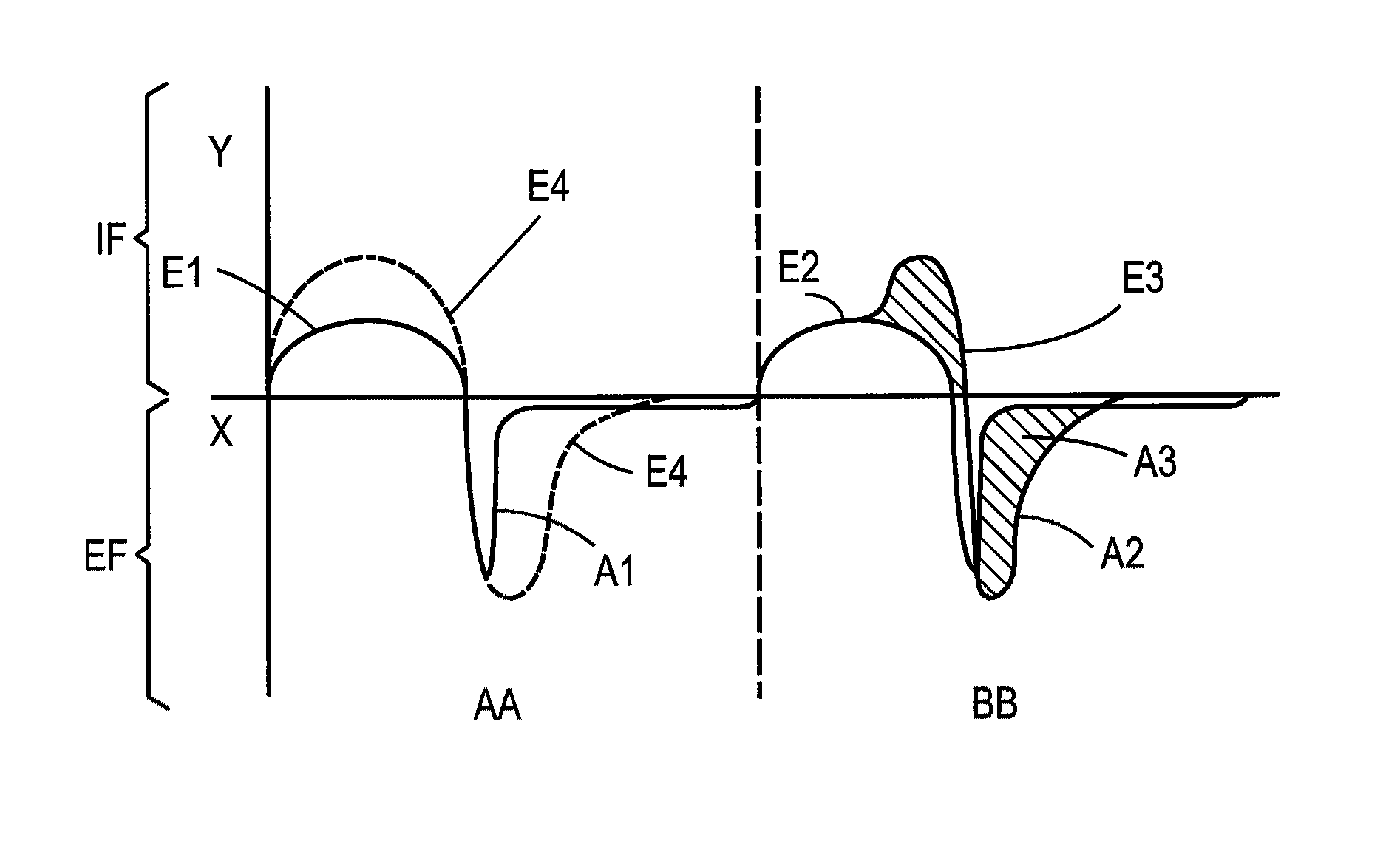
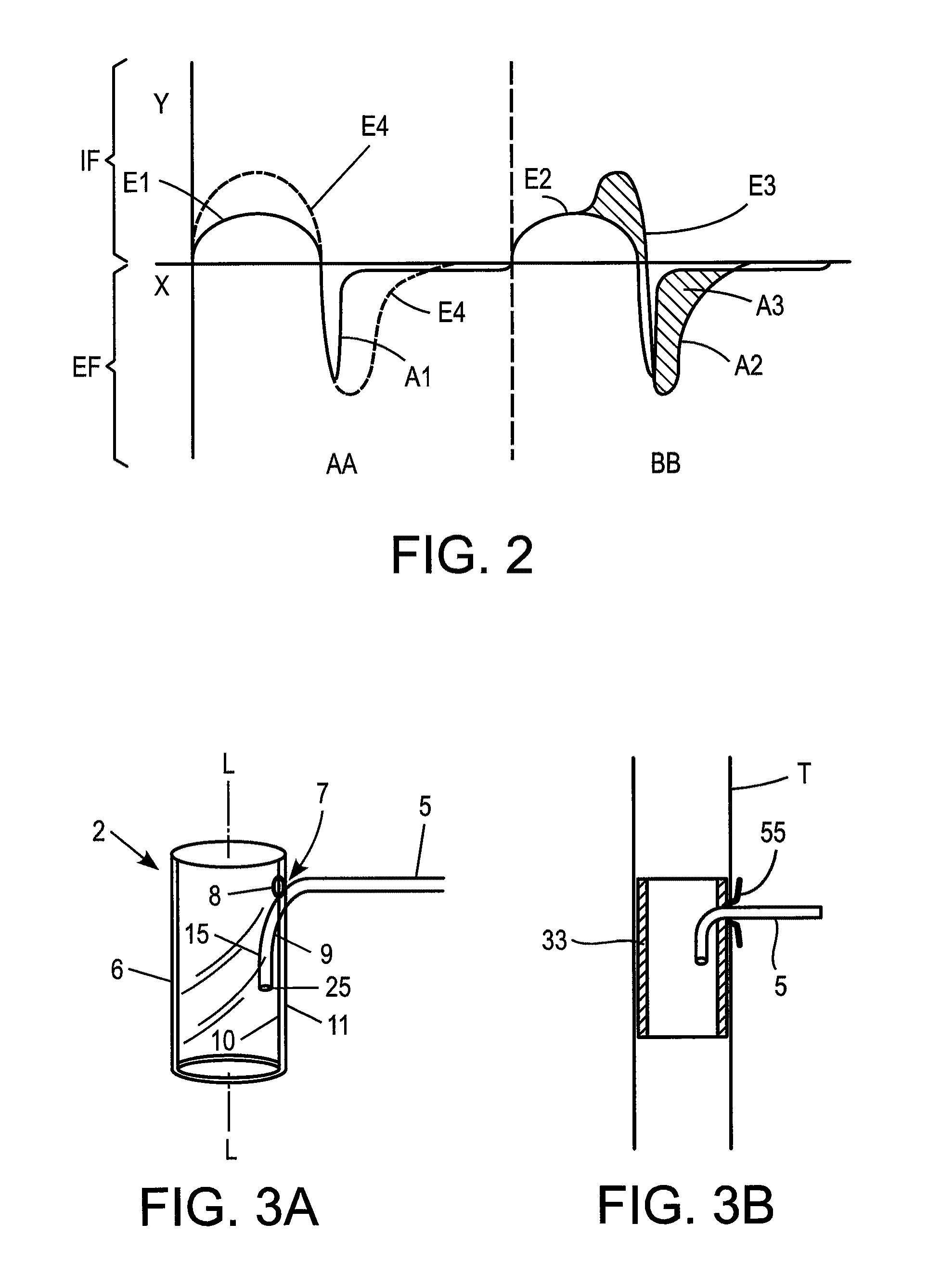
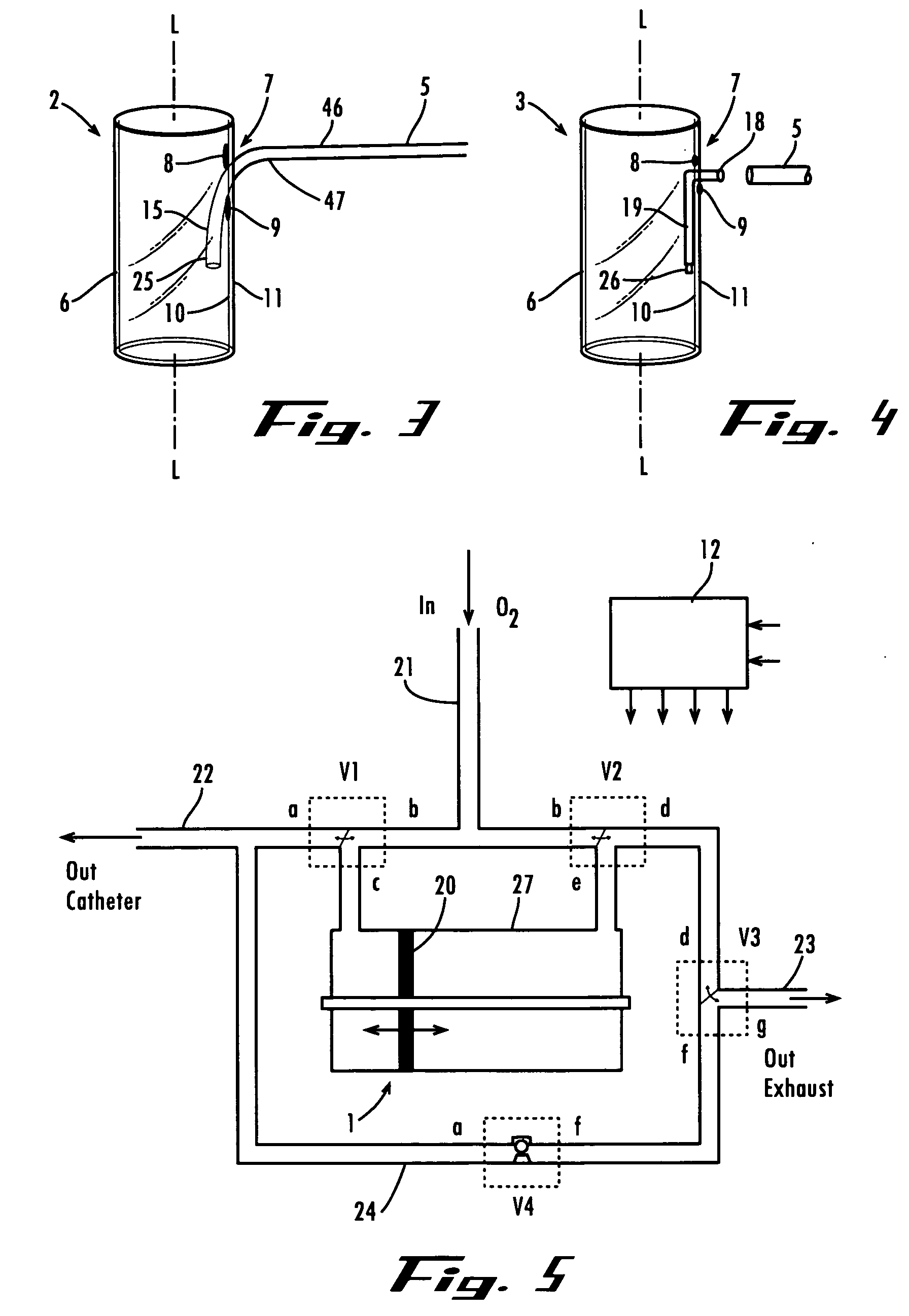
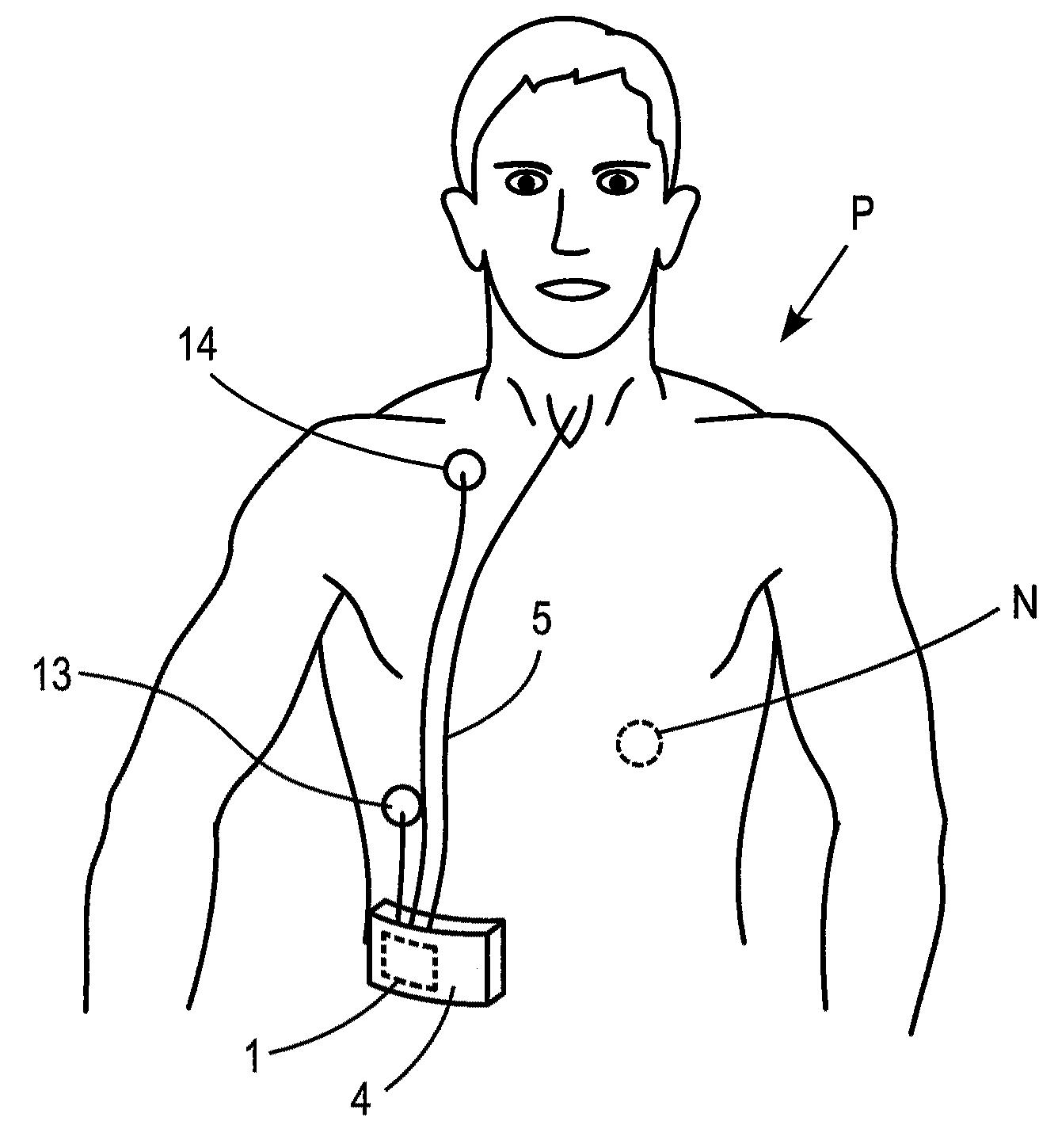
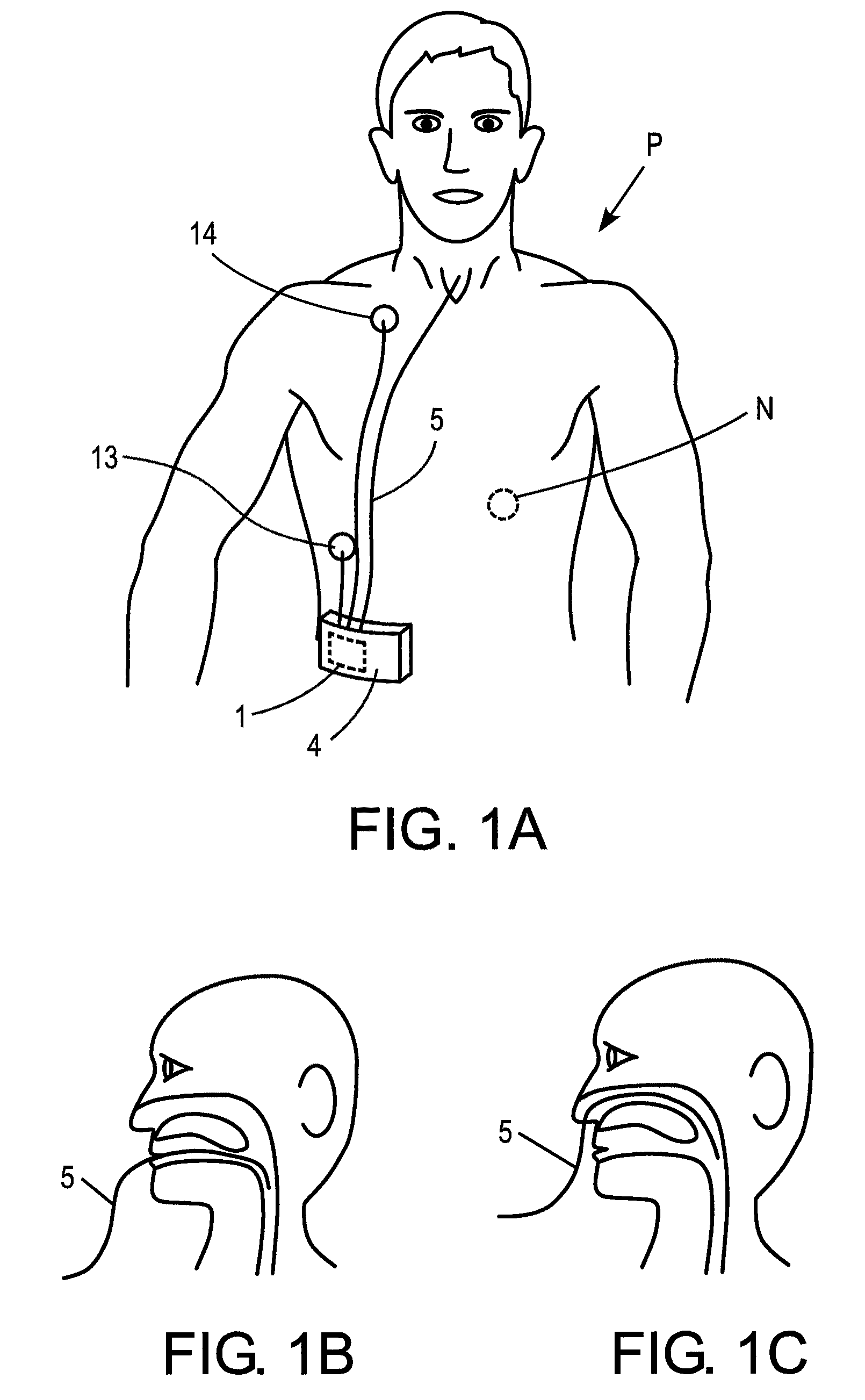
A method and apparatus is described for supporting the respiration of a patient. The spontaneous respiration of a patient can be detected by sensors and during inhalation an additional amount of oxygen can be administered to the lungs via a jet gas current. If required, during exhalation a countercurrent can be administered to avoid collapse of the respiration paths. This therapy can be realized by an apparatus including a transtracheal catheter, an oxygen pump connected to an oxygen source, spontaneous respiration sensor(s) connected to a control unit for activating the oxygen pump and, if needed, a tracheal prosthesis. The tracheal prosthesis may include a connection for the catheter and the breath sensor(s). The tracheal prosthesis, if used, and the catheter can be dimensioned so the patient can freely breathe, cough, swallow and speak without restriction, and the system can be wearable to promote mobility.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
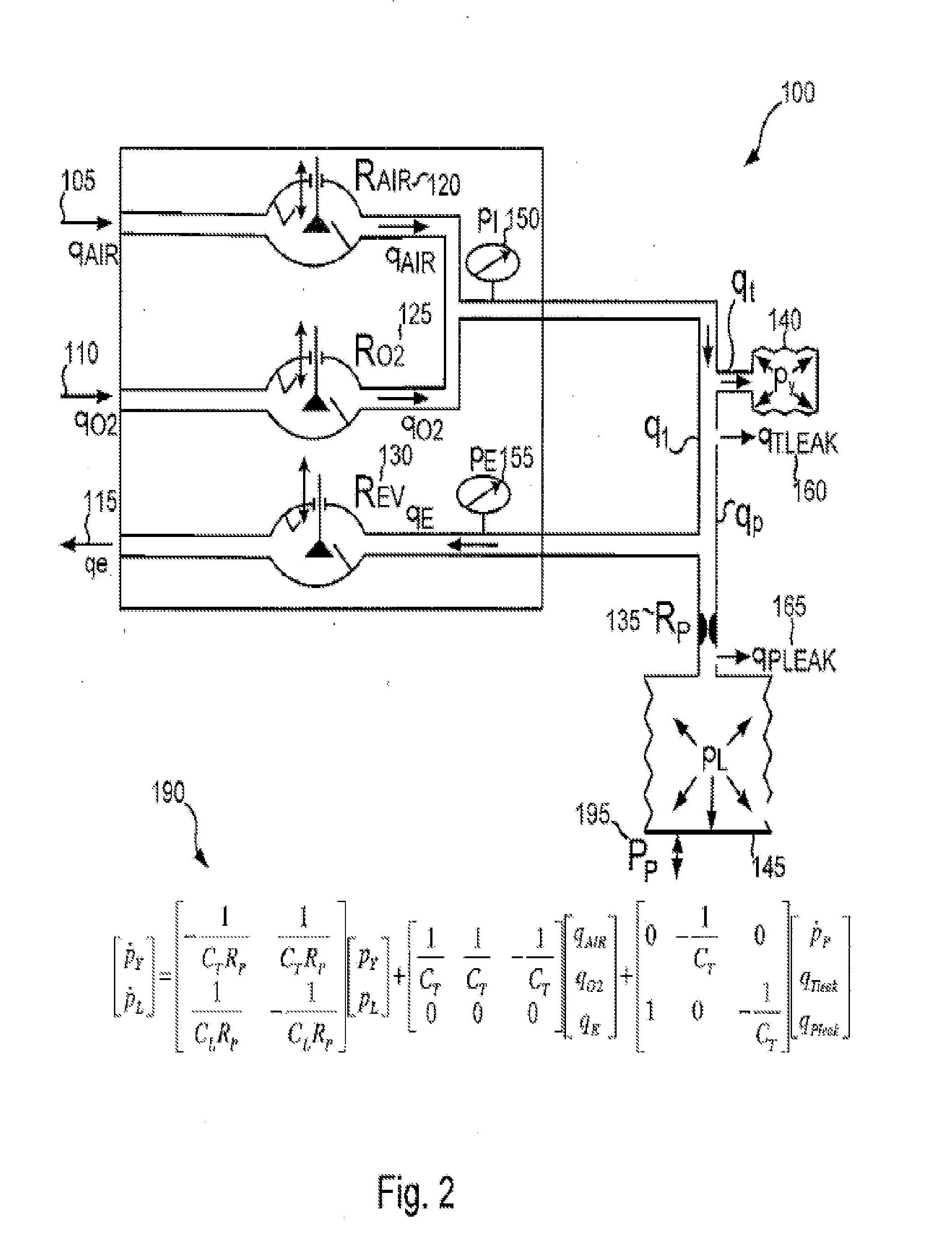
Systems and methods for determining patient effort and/or respiratory parameters in a ventilation system
ActiveUS20090301490A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory supportInlet flow
Various embodiments of the present disclosure provide systems, methods and devices for respiratory support. As one example, a method for respiratory support is described that includes measuring a pressure, providing a measured pressure, measuring an inlet flow and an outlet flow, and providing a measured net flow. A relationship between a first value related to the measured pressure, a second value related to the measured net flow and a third value related to patient effort is used to provide a prediction of patient effort. An interim value is updated based at least in part on the prediction of the patient effort.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Systems And Methods For Automatic Adjustment Of Ventilator Settings
ActiveUS20120247471A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesVentilator settingsRespiratory support
Various embodiments of the present disclosure provide systems, methods and devices for respiratory support. As one example, a ventilation system is disclosed that includes a computer readable medium including instructions for operating in a hybrid mode. These instructions include measuring patient effort during a spontaneous breath type and deriving a neural inspiratory time from the measurements of patient effort. This neural inspiratory time is then set as the inspiratory for a breath of a mandatory breath type. If new patient effort measurements are received by the ventilator, the neural inspiratory time may be adjusted.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Systems, methods and apparatus for respiratory support of a patient
ActiveUS7533670B1Improve the quality of lifeEfficient way of supporting the respiration of a patientTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCounter flowOxygen
Spontaneous respiration is detected by sensors. An additional amount of oxygen is administered to the lungs via a jet gas current at the end of an inhalation procedure. Breathing volume, absorption of oxygen during inhalation, and clearance of carbon dioxide during exhalation are improved. If required, the exhalation procedure of the patient can be arrested or slowed by a countercurrent to avoid a collapse of the respiration paths. An apparatus including an oxygen pump can be connected to an oxygen source and includes a tracheal prosthesis that can be connected via a catheter. The respiration detections sensors are connected to a control unit for activating the oxygen pump. The tracheal prosthesis includes a tubular support body with a connection for the catheter, and the sensors are associated with the support body. The tracheal prosthesis and jet catheter are dimensioned so the patient can freely breathe and speak without restriction.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Systems And Methods For Ventilation To Obtain A Predetermined Patient Effort
InactiveUS20120167885A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory supportComputer science
Various embodiments of the present disclosure provide systems, methods and devices for respiratory support. As one example, a ventilation system is disclosed that includes a computer readable medium including instructions executable by a processor to receive a measured pressure value and a net flow value. A patient effort value is calculated based on a relationship between patient effort, the measured pressure value and the net flow value. The instructions are further executable to calculate a gas delivery metric based on the computed patient effort to obtain a predetermined patient effort. Gas is then caused to be delivered consistent with the gas delivery metric.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
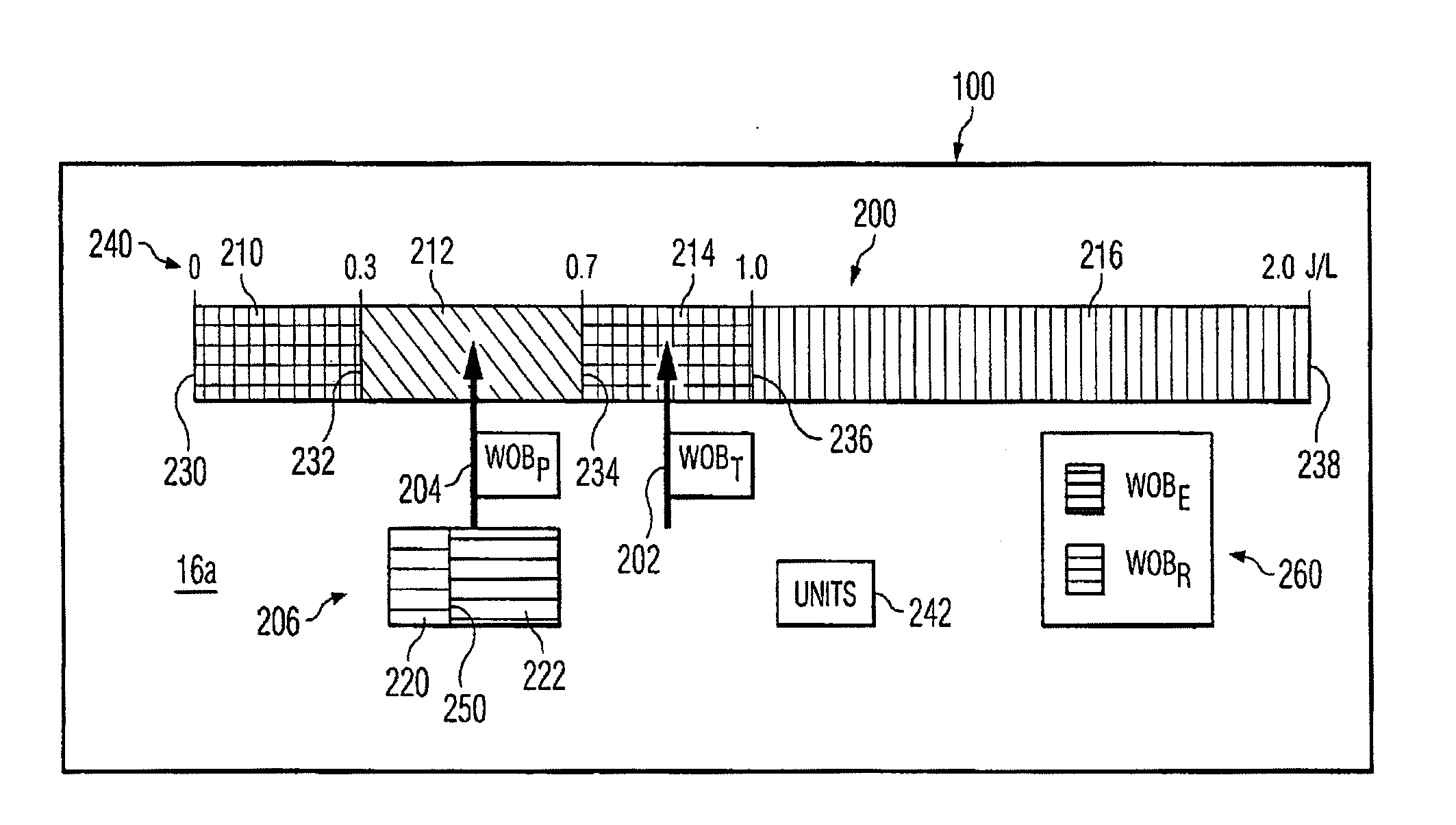
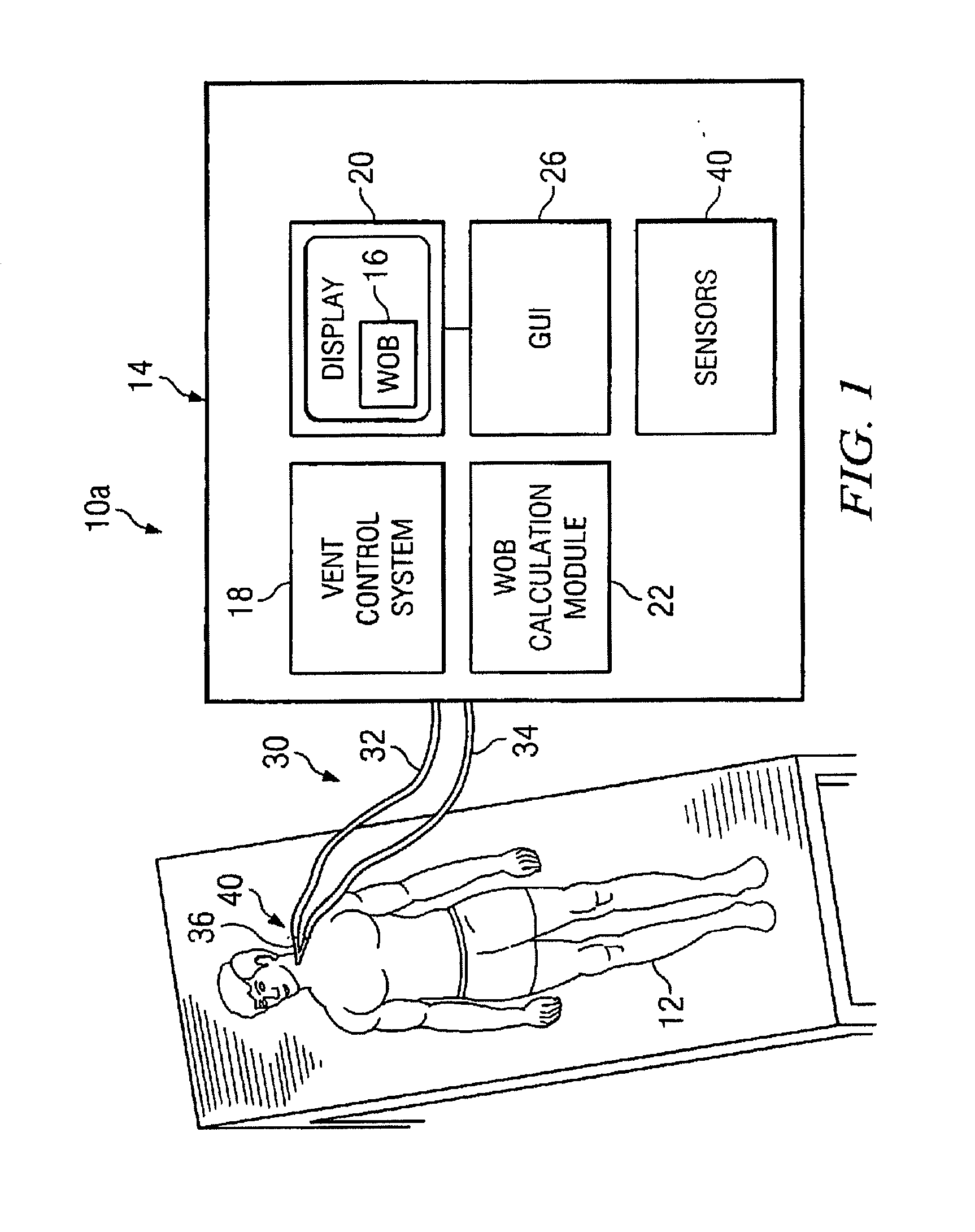
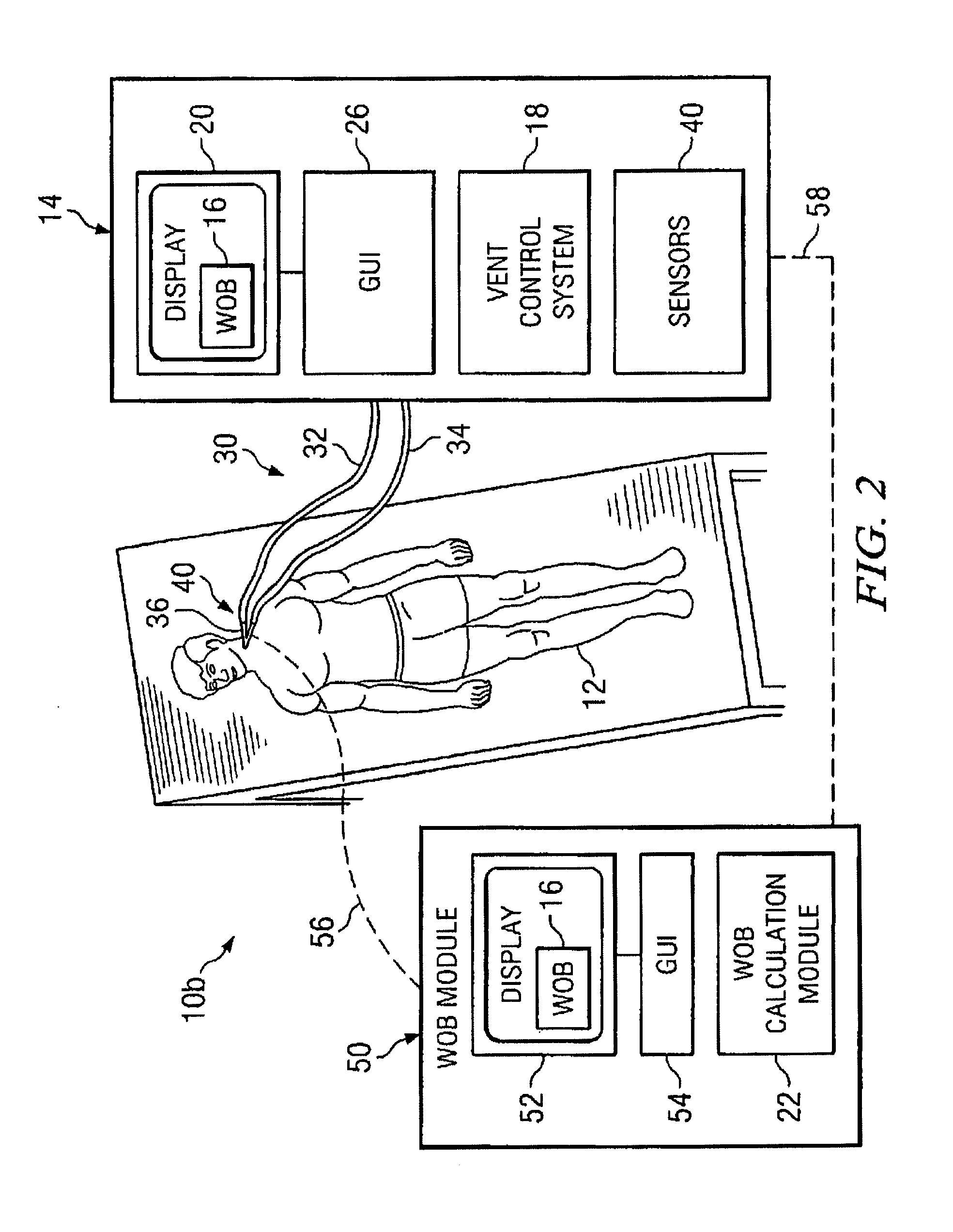
Work of breathing display for a ventilation system
ActiveUS20110230780A1Simple processEffectively “ drive ”RespiratorsMedical devicesSupporting systemDisplay device
A breathing support system is provided. The system may include a breathing support device configured to deliver gas to a patient and a display device associated with the breathing support device. The display device may be configured to display a graphic indicating one or more measures regarding the patient's work of breathing.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Apparatus and system for reducing mechanical ventilator noise
InactiveUS20080127976A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsEngineering
A sound dampening apparatus to be disposed in pneumatic connection with a respiratory support system. The respiratory support system may comprise a source of medical gas, a plurality of pneumatic connections and a patient interface. The sound dampening apparatus comprises an inlet, an outlet, and an outer case which forms a sound dampening chamber. As the medical gas flows through the sound dampening apparatus, the noise energy associated with the flow of medical gas is reduced.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
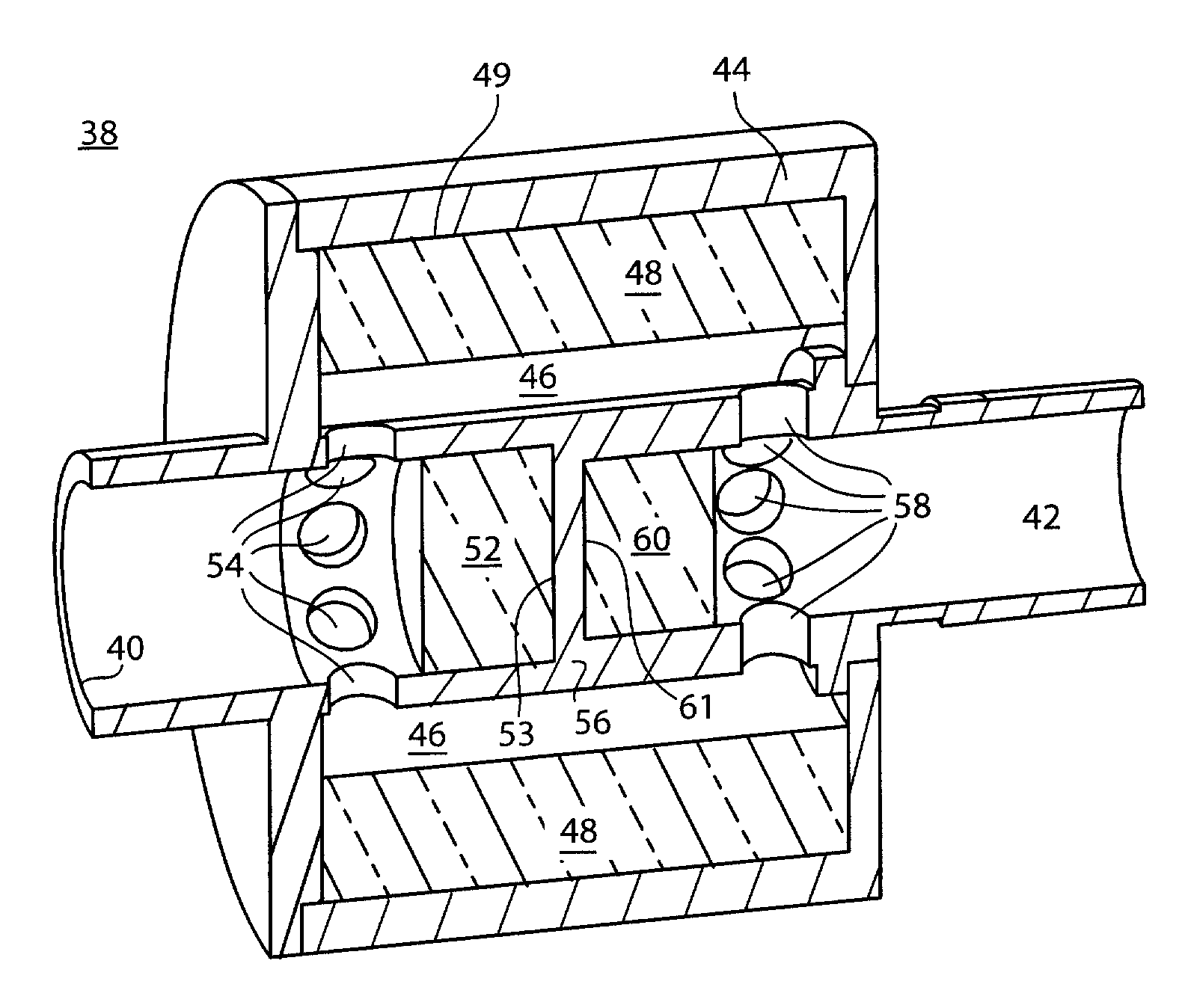
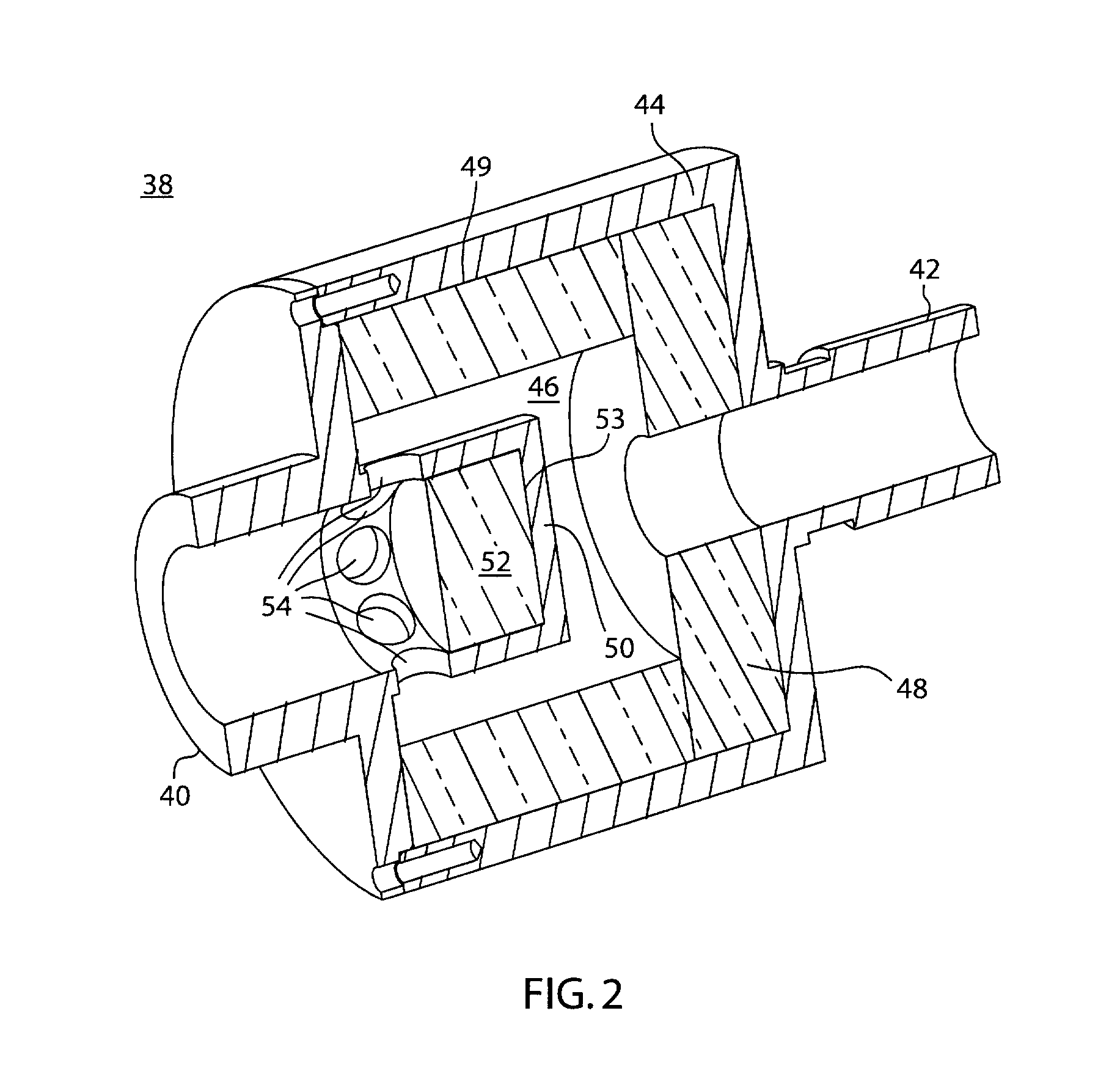
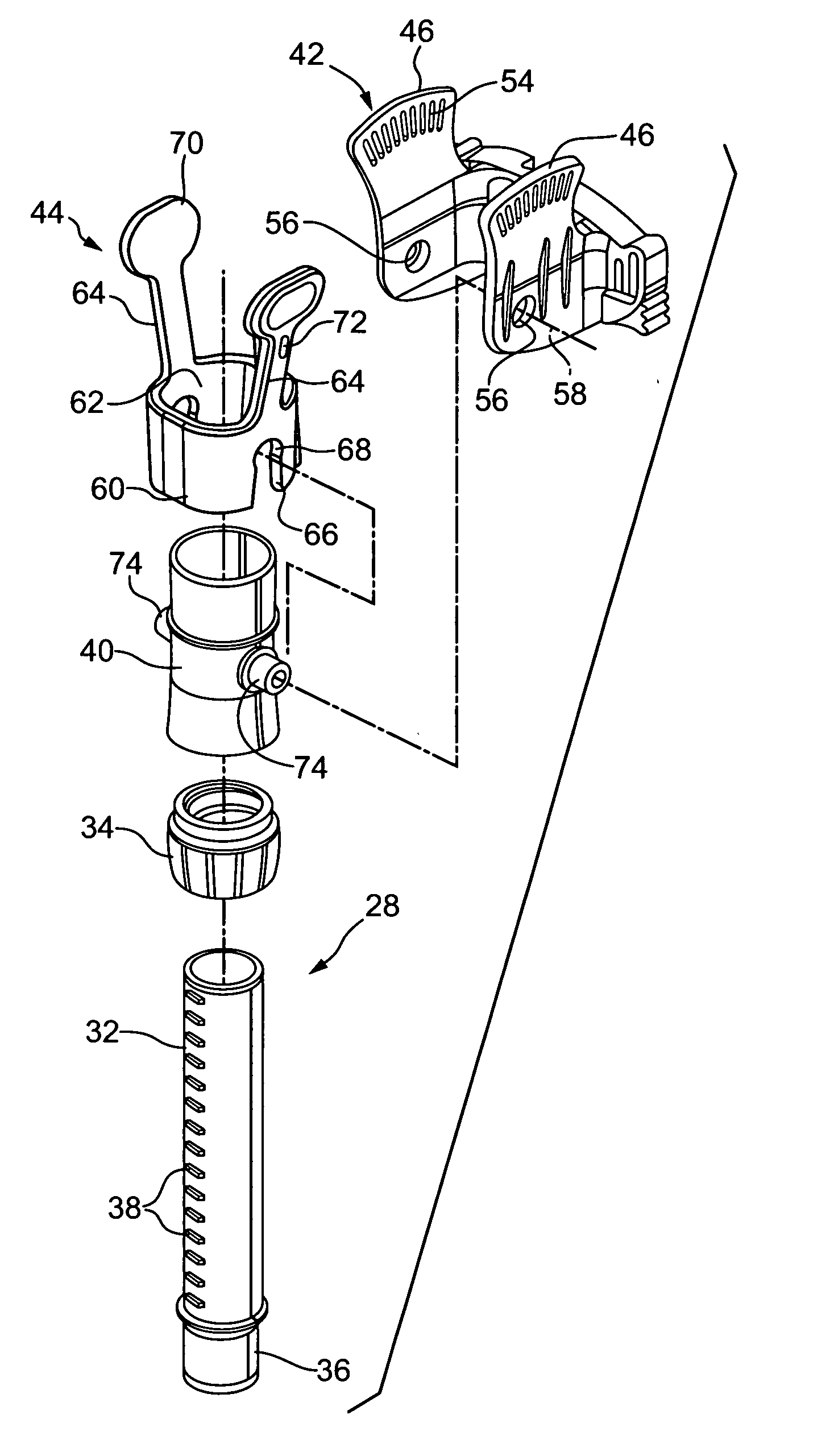
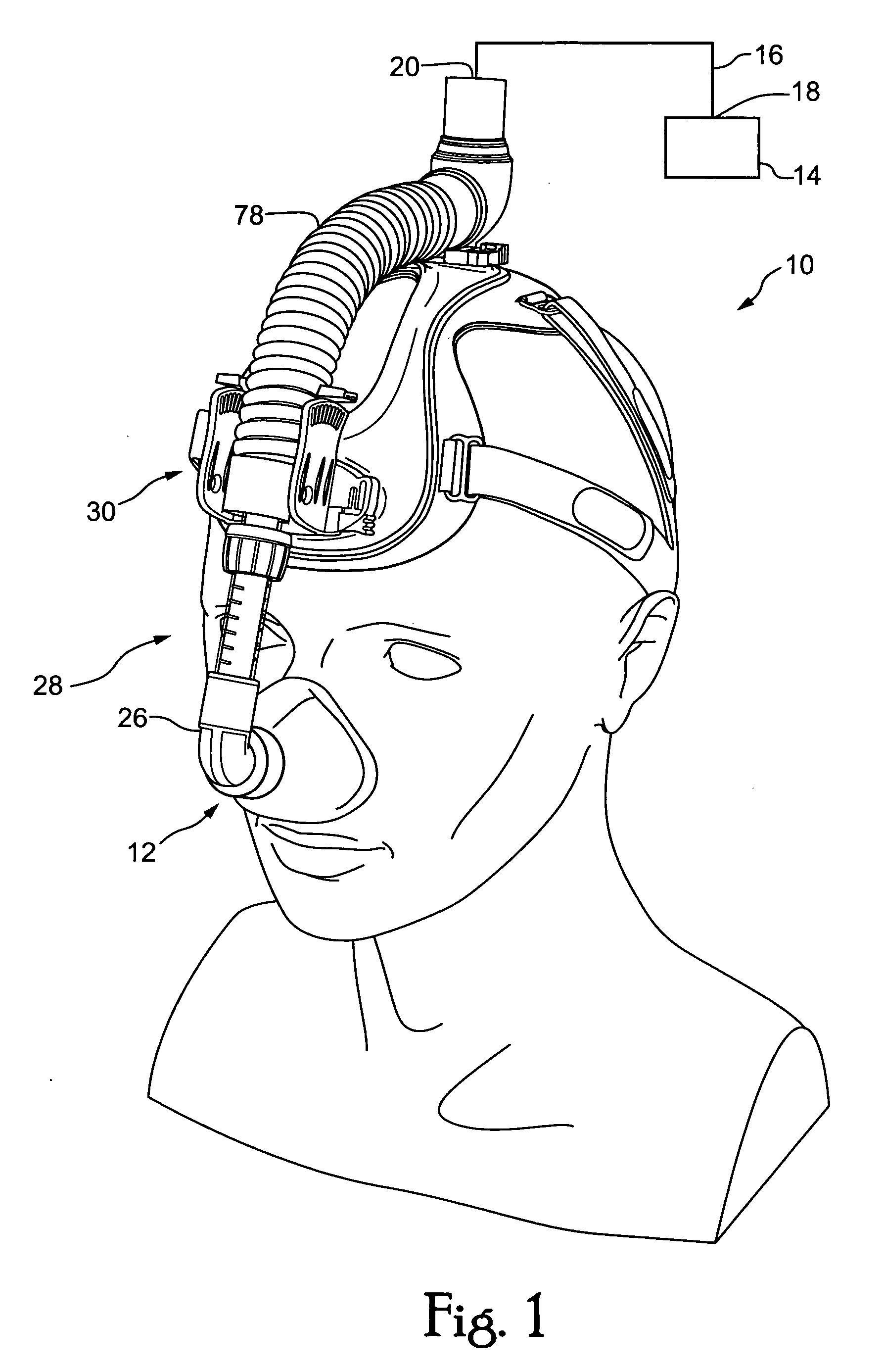
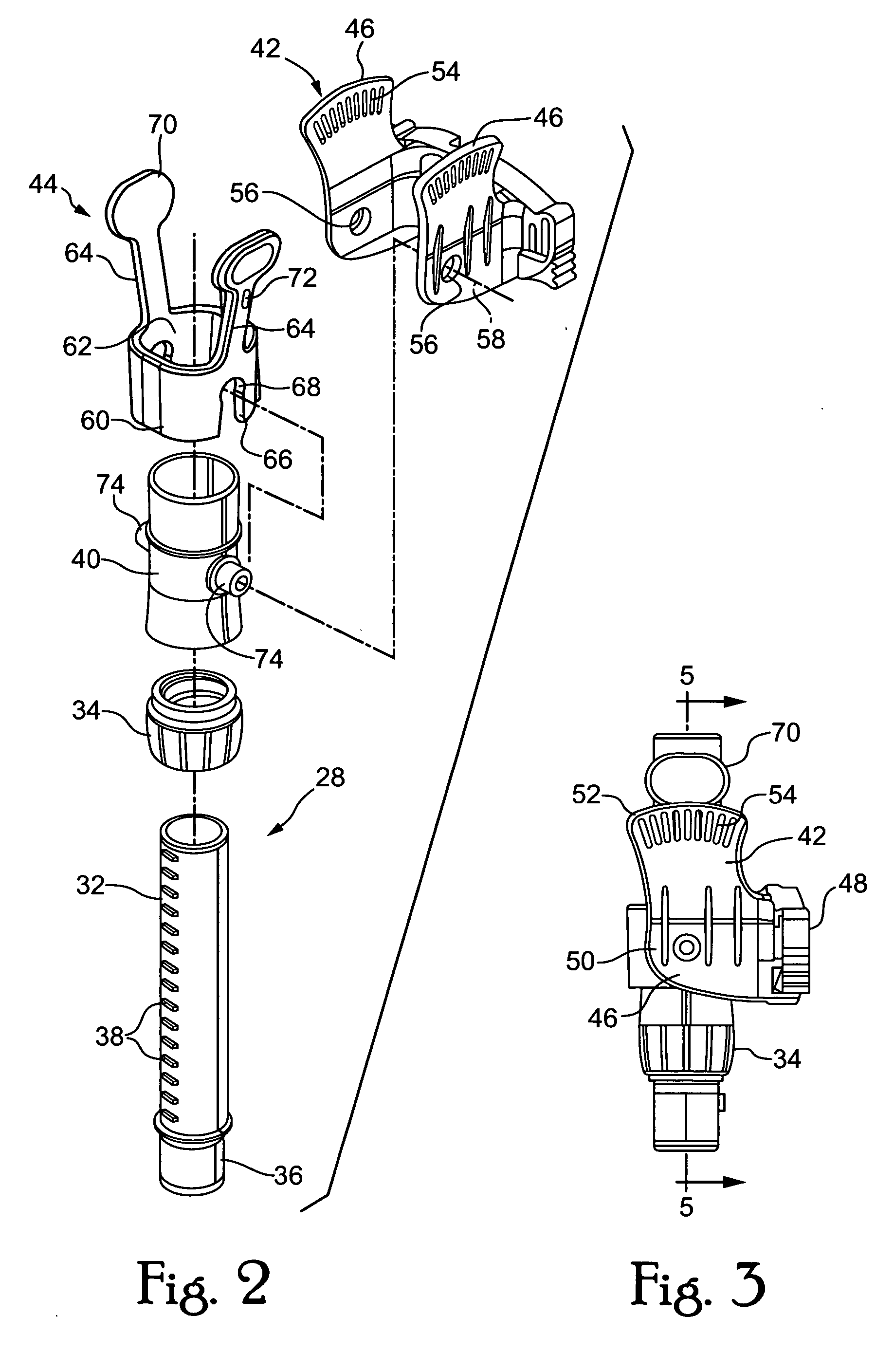
Ventilator to tracheotomy tube coupling
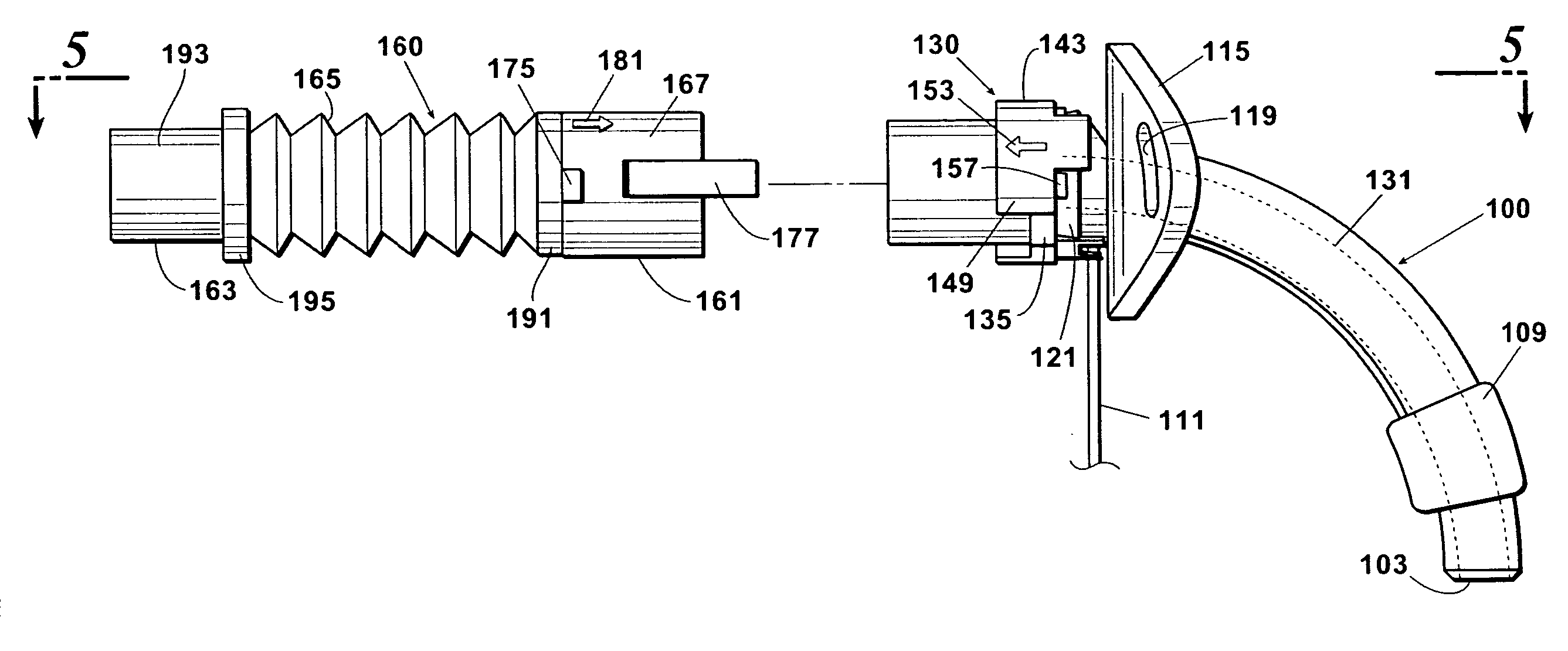
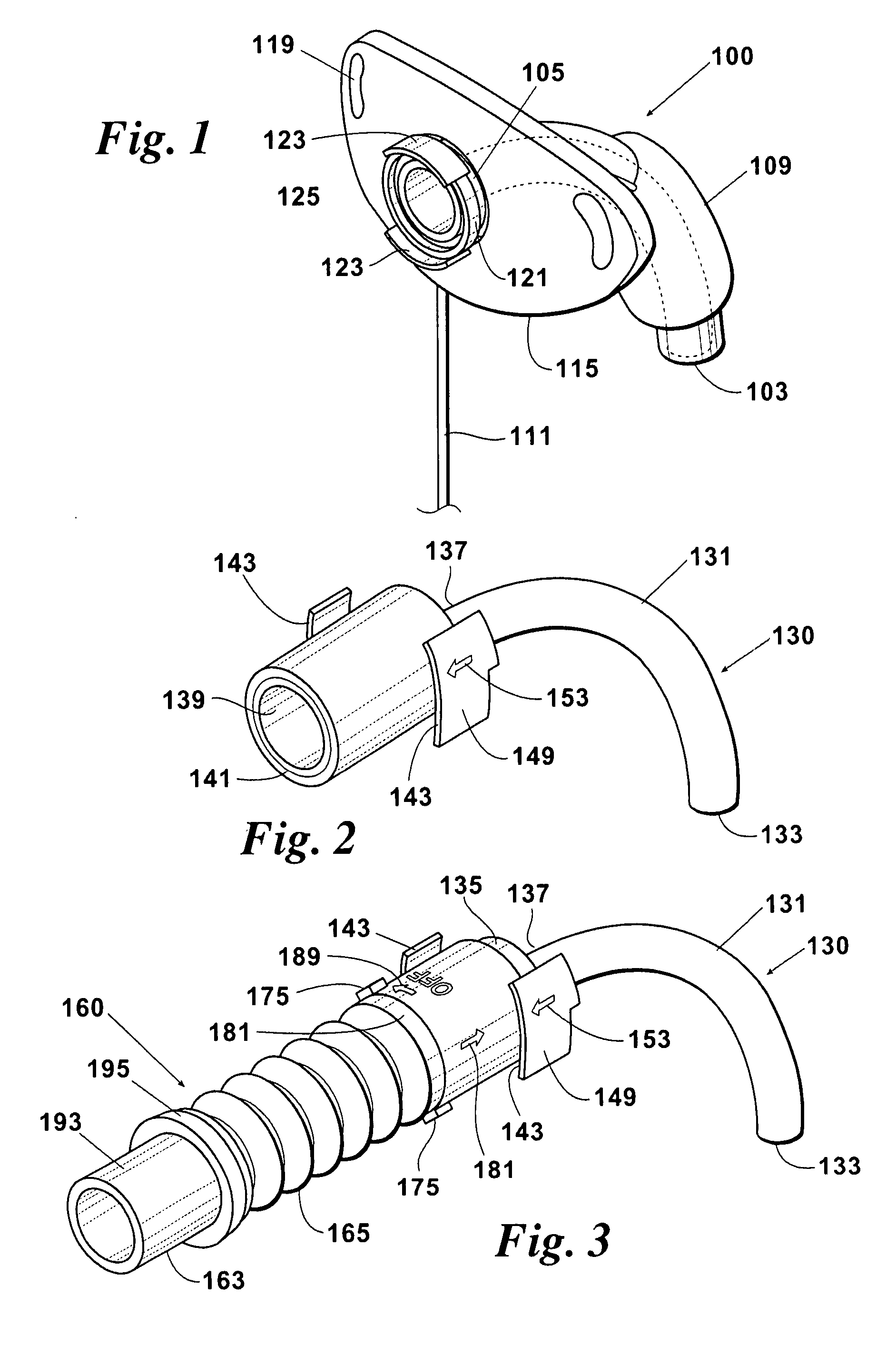
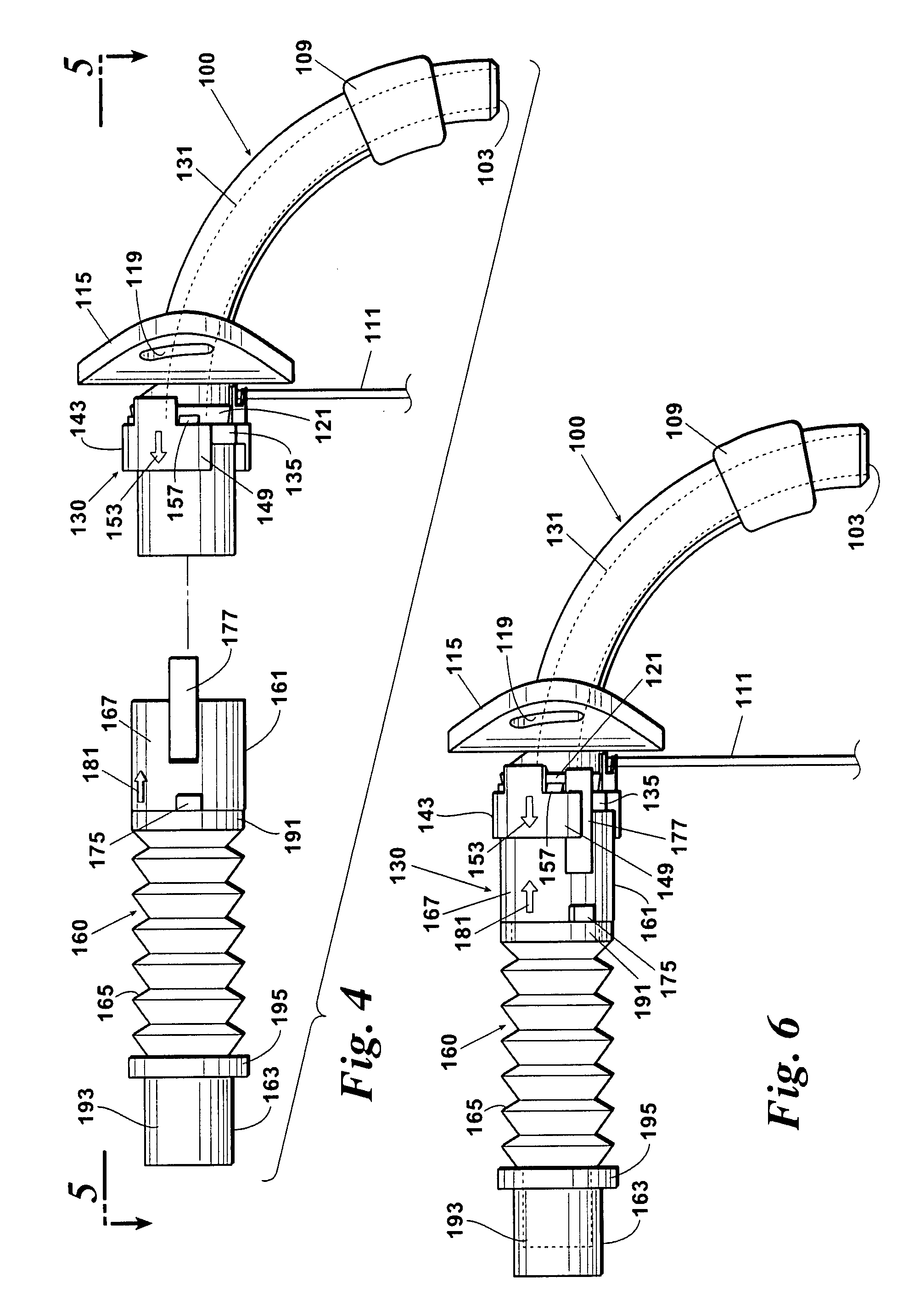
ActiveUS20080041391A1Avoid displacementReduce the possibilityRespiratorsRespiratory apparatusTracheotomyCoupling
A coupling for connecting an air supply to a respiratory support device has a latching mechanism which prevents the coupling from inadvertently axially displacing from the respiratory support device after they have been mated in a pneumatically discrete path. Non-axial forces are used to disengage the coupling from the respiratory support device. The coupling may include a trailing end adapter which permits rotation of the coupling relative to the air supply rather than to the respiratory support device.
Owner:LAZARUS MEDICAL
Systems, methods and apparatus for respiratory support of a patient
ActiveUS20090255533A1Improve the quality of lifeEfficient way of supporting the respiration of a patientTracheal tubesLiquid surface applicatorsOxygenBreathing process
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
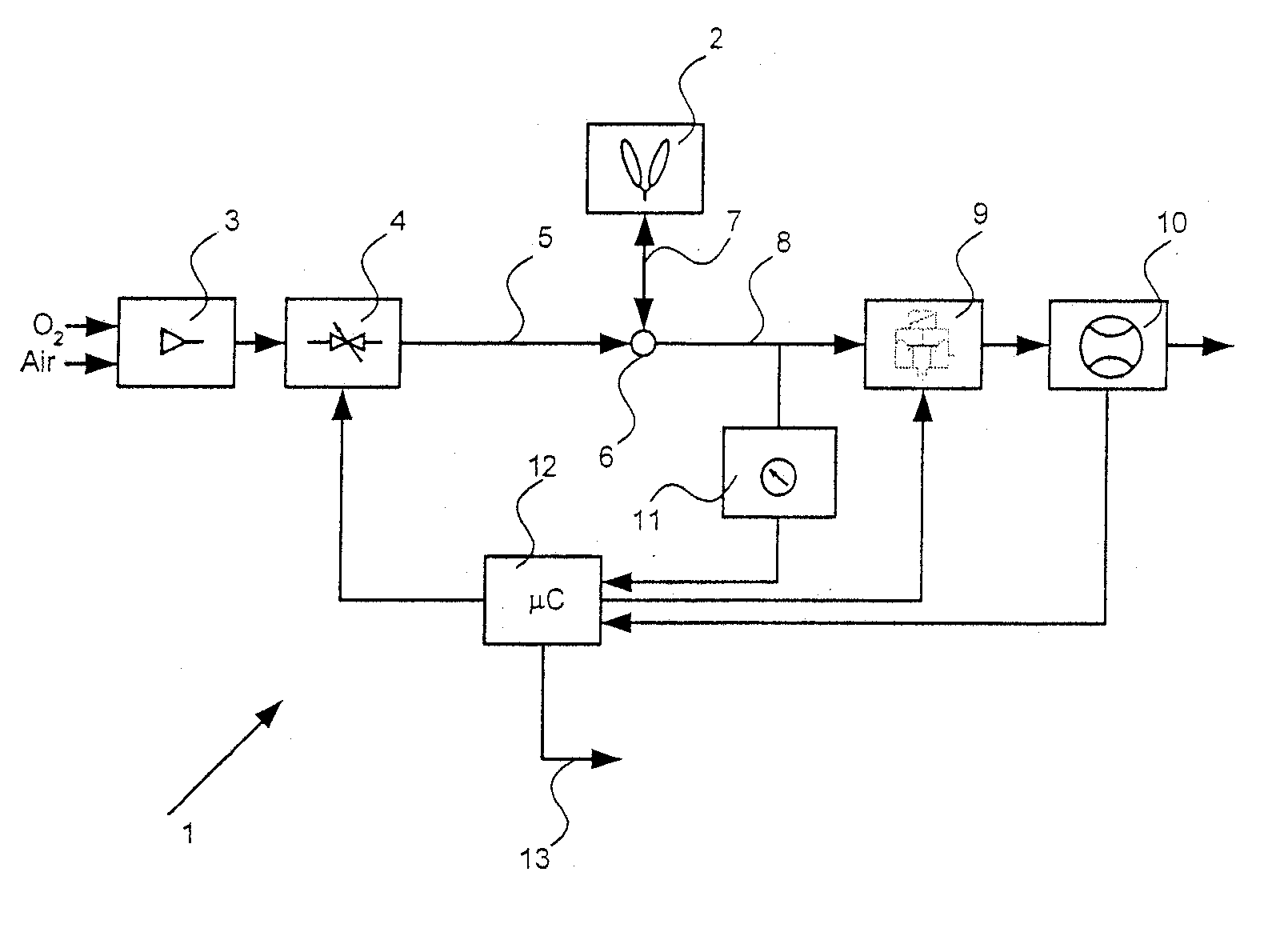
Pressure targeted ventilator using an oscillating pump
InactiveUS20080029096A1Fast response timeSave electricityRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory supportAmbient air
A respiratory support system for providing respiratory support to a patient comprising an oscillating pump. The oscillating pump pressurizes ambient air to a pressure suitable for delivery to the patient for respiratory support. The system further comprises a sensor and a microprocessor to control the oscillating pump in response to patient breath attempts.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
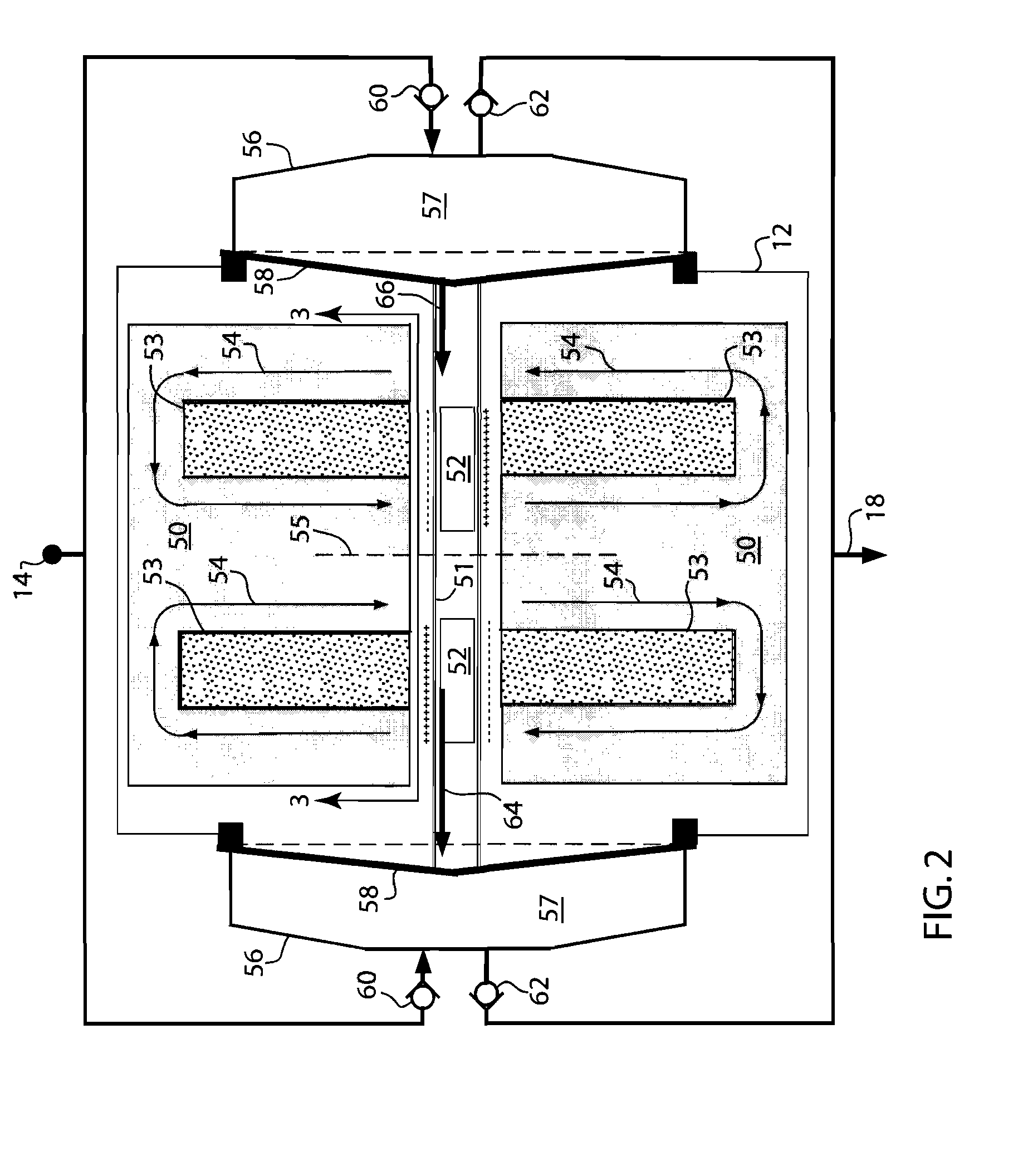
Headgear assembly for a respiratory support system
InactiveUS20060213521A1Accurate locationBreathing filtersBreathing masksEngineeringRespiratory support
A respiratory support system having a patient interface attached to a headgear assembly for delivering a gas to a patient is disclosed. The headgear provides a rigid member and a pad held in place on the patient's head by straps. The rigid member functions to prevent creep of the straps, distribute the strapping forces, and minimized tangential strap forces that otherwise squeeze the sides of the patient's head.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
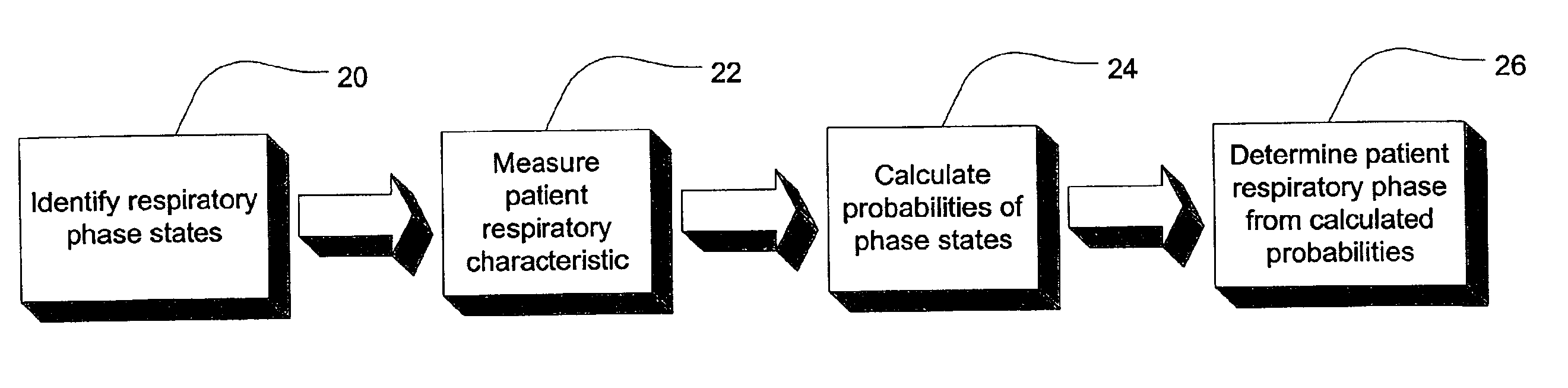
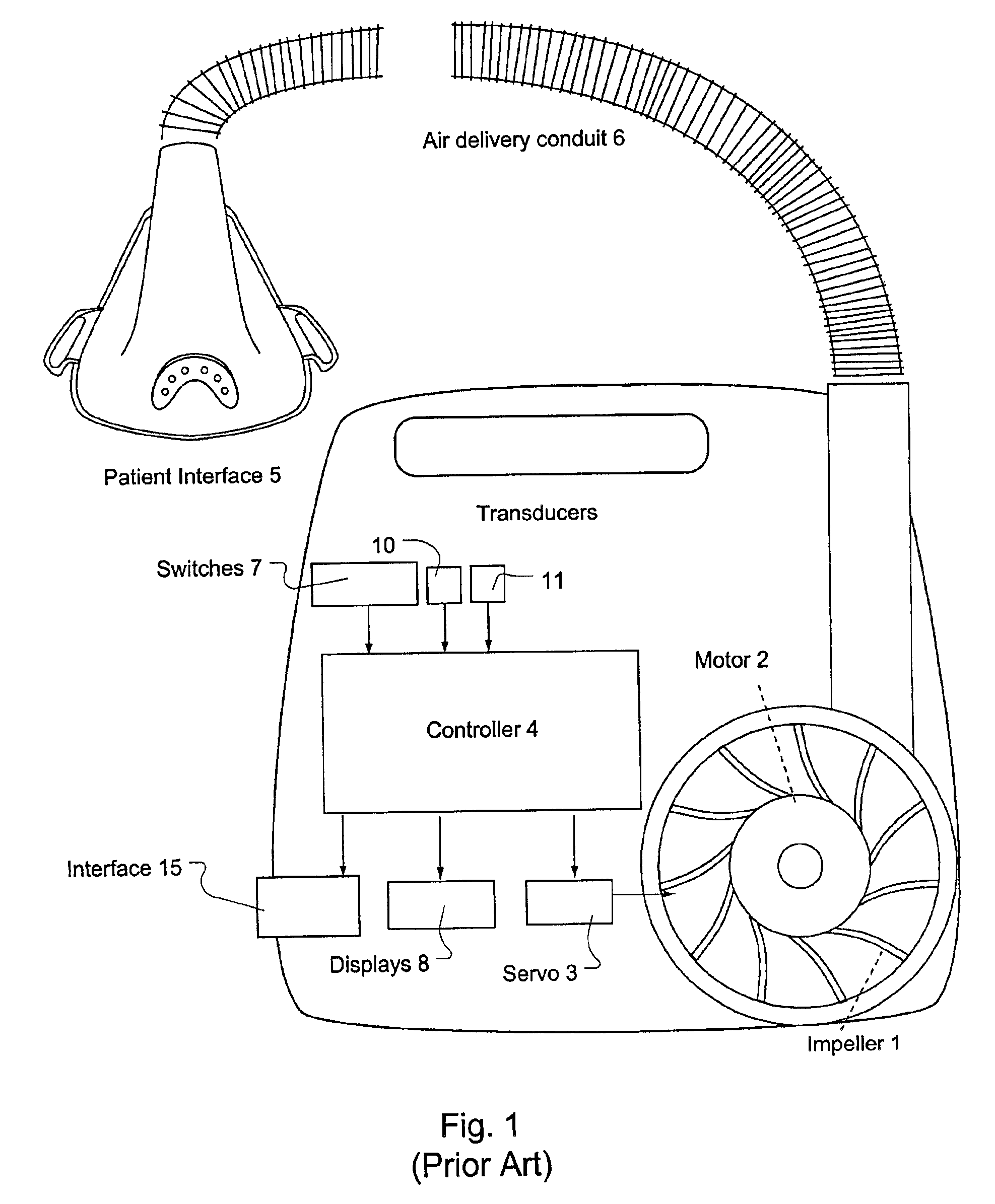
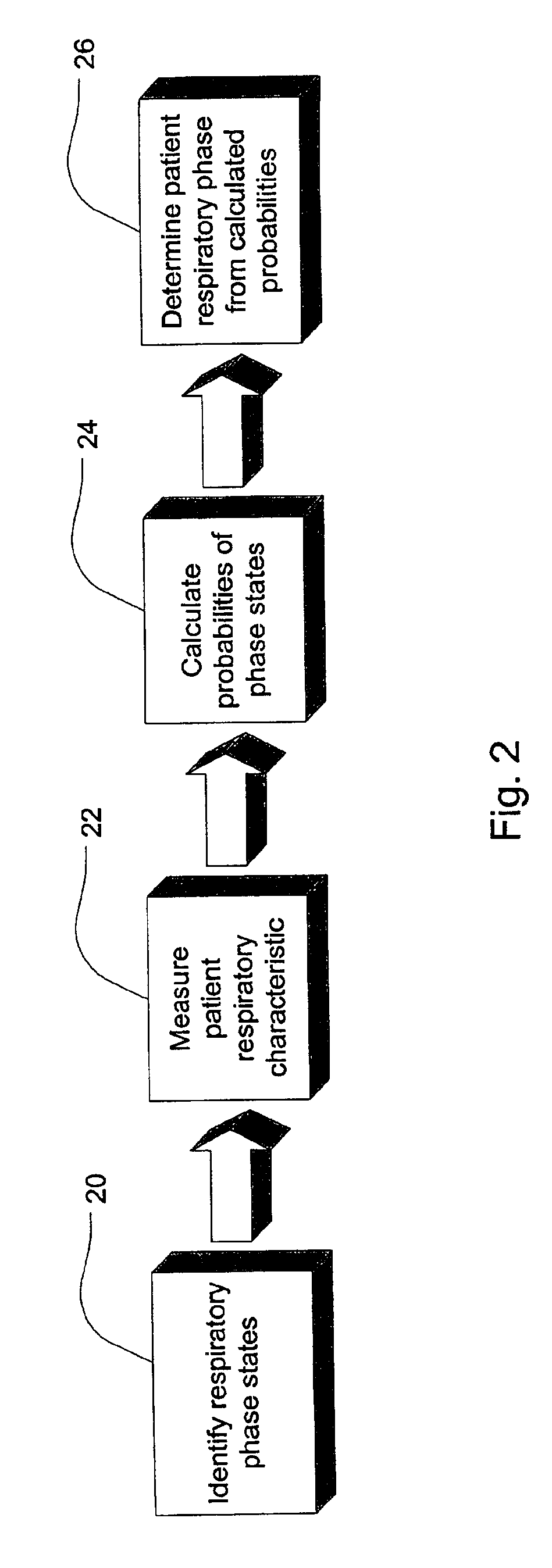
Ventilator patient synchronization
InactiveUS6860858B2Improve reliabilityImprove accuracyRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory phasePhase state
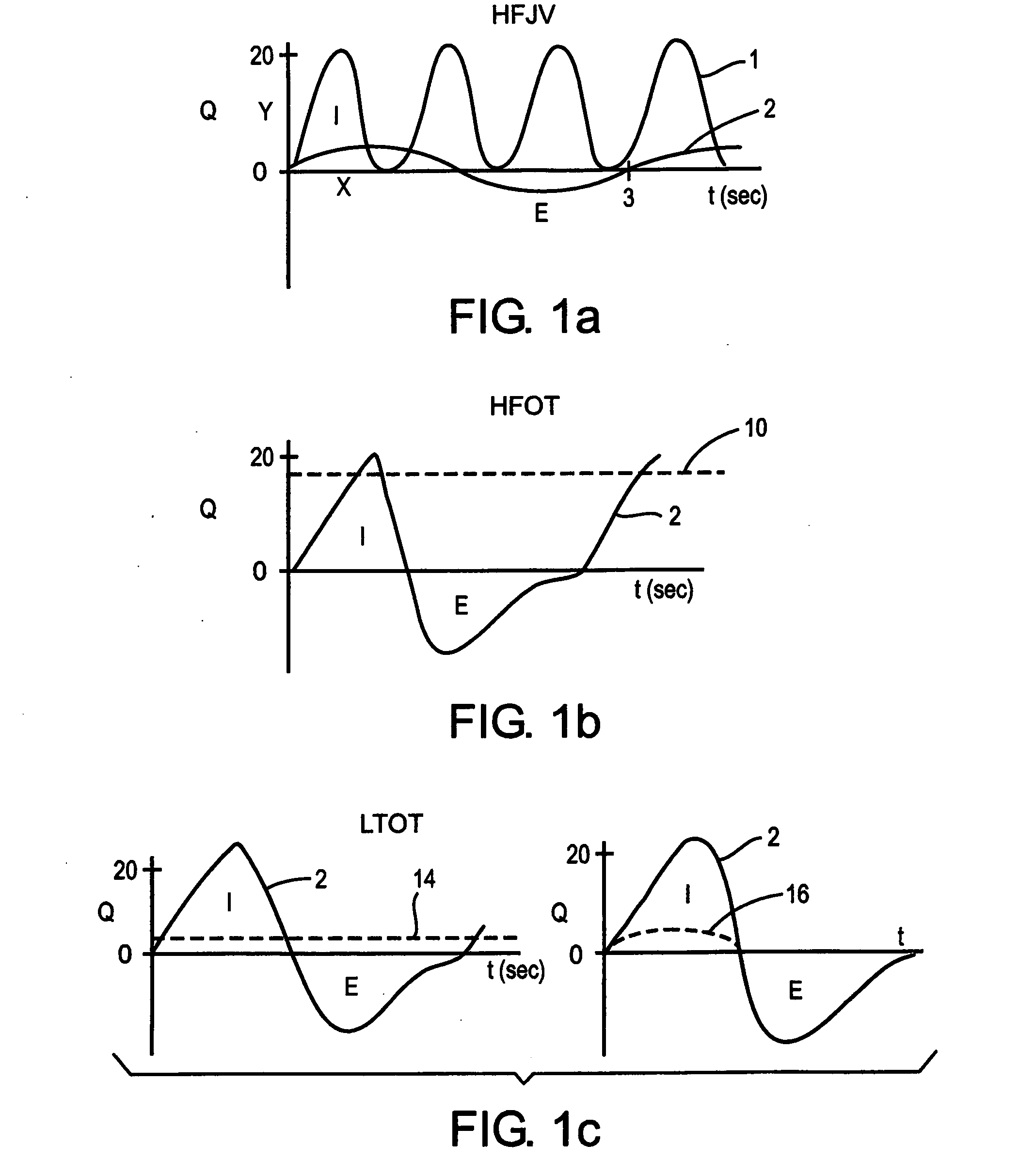
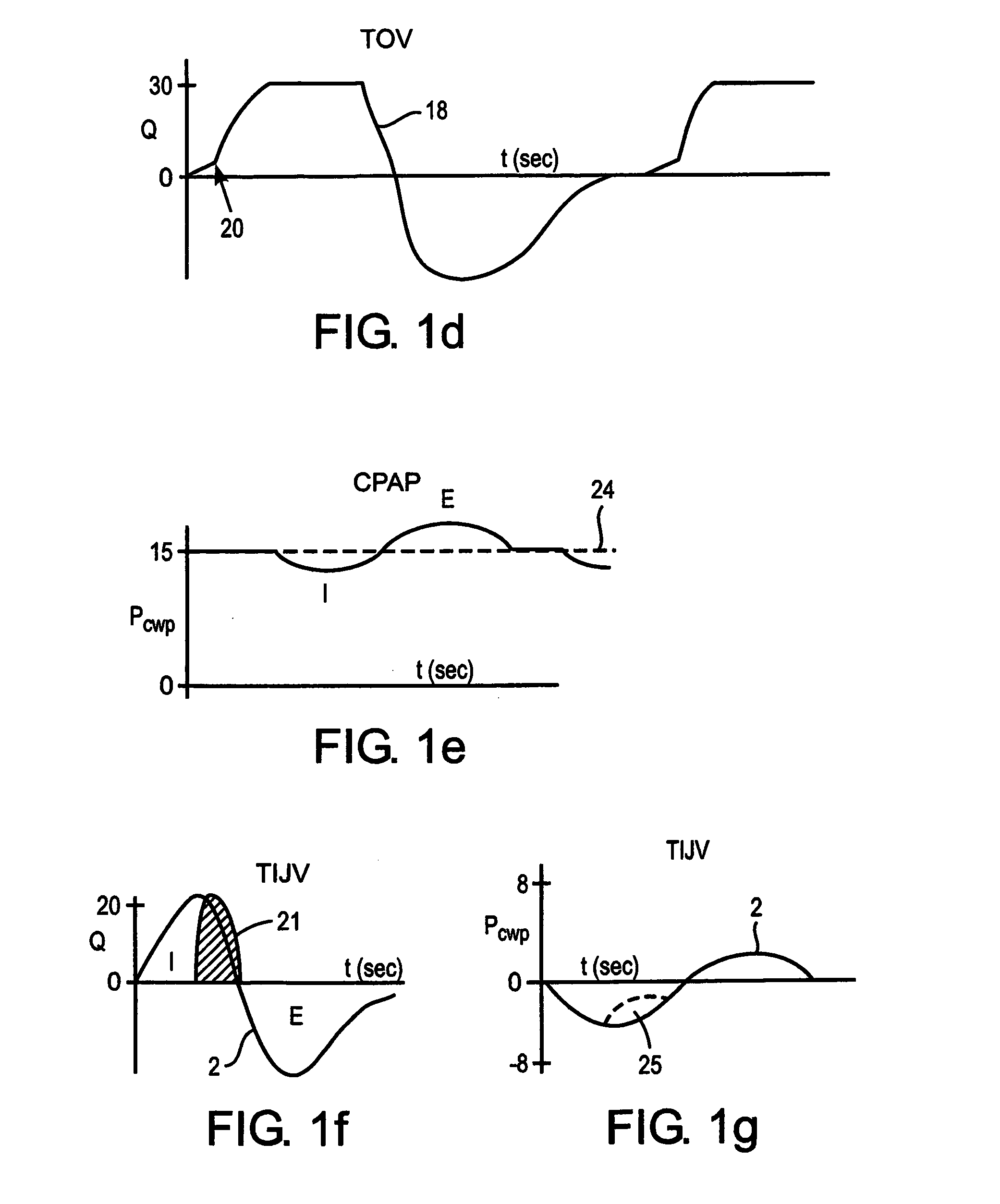
A method and apparatus that provides an expert system for determining respiratory phase during ventilatory support of a subject. Discrete phase states are partitioned and prior probability functions and observed probability functions for each state are defined. The probability functions are based upon relative duration of each state as well as the flow characteristics of each state. These functions are combined to determine phase probabilities for each state using Bayes' theorem. The calculated probabilities for the states may then be compared to determine which state the subject is experiencing. A ventilator may then conform respiratory support in accordance with the most probable phase. To provide a learning feature, the probability functions may be adjusted during use to provide a more subject specific response that accounts for changing respiratory characteristics.
Owner:RESMED LTD
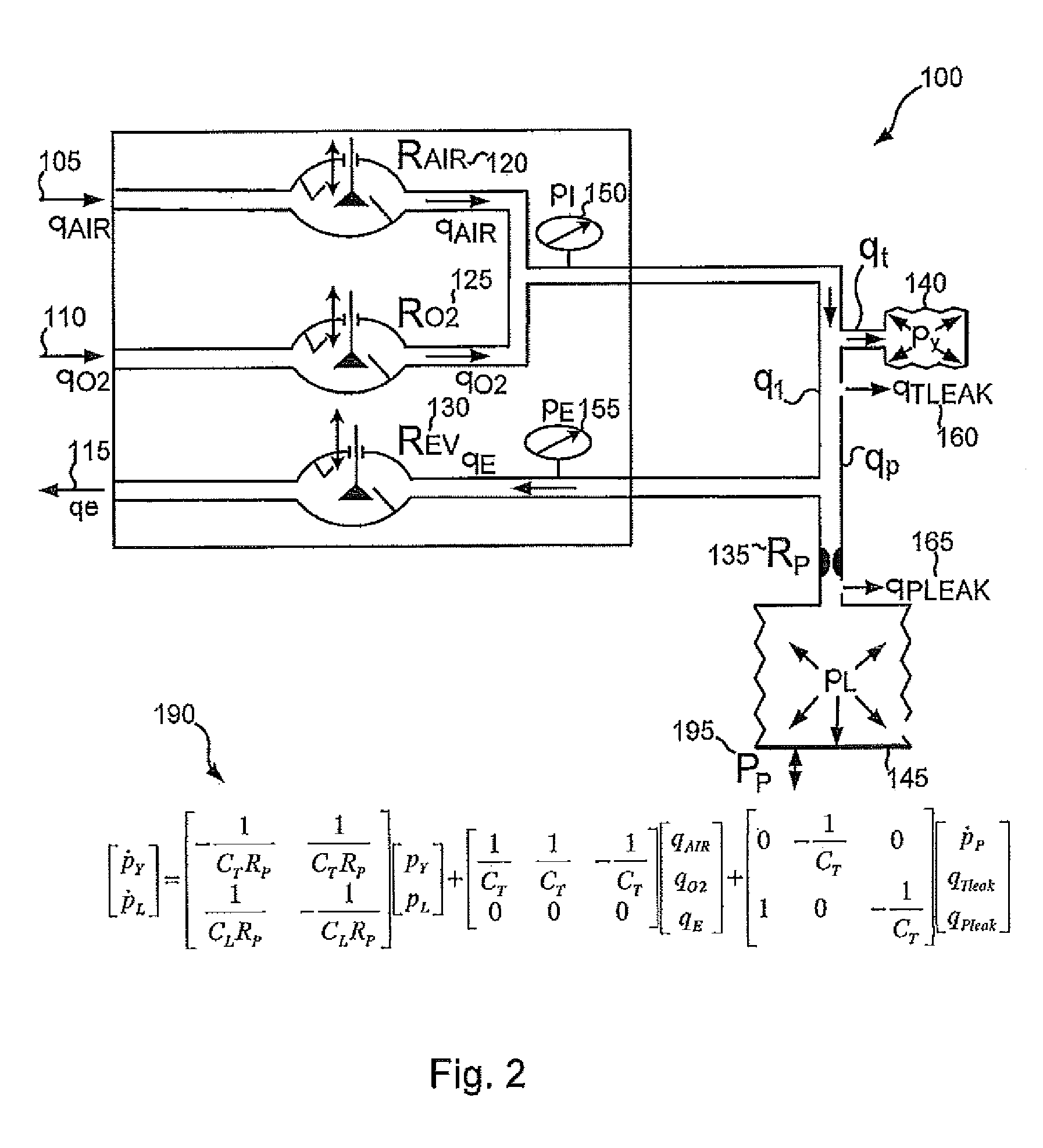
Methods and devices for providing inspiratory and expiratory flow relief during ventilation therapy
ActiveUS20090151724A1Breathe freelyUndesirable pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory supportAirway pressures
Respiratory support and / or controlled mechanical ventilation of a patient are provided. A ventilation apparatus may include a ventilator, a transtracheal prosthesis, and a respiratory relief device. The transtracheal prostheses and ventilation catheter may be arranged such that the patient can breathe freely through the upper airway and / or the tracheal prostheses. Respiratory sensors may measure a breathing rate, lung pressure, airway pressure, or a combination thereof. Pulses of gas may be provided to the patient through the ventilation catheter during inspiration. The pulses may have a first volume while the patient breathes normal and a second volume when the sensors detect a cessation of breathing or reduction in breathing volume. The second volume may be provided at 1-5 times the normal breathing rate, with a volume 25-500% times the first volume, or both.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Tracheal catheter and prosthesis and method of respiratory support of a patient
ActiveUS20050034721A1Improve the quality of lifeEfficient methodTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingOxygen
The invention is relative to a method and an apparatus for supporting the respiration of a patient and to a tracheal prosthesis. According to the invention the spontaneous respiration of a patient is detected by sensors and at the end of an inhalation procedure an additional amount of oxygen is administered to the lungs via a jet gas current. This improves the absorption of oxygen during inhalation. If required, the exhalation procedure of the patient can be arrested or slowed by a countercurrent in order to avoid a collapse of the respiration paths in this manner. This procedure is realized by an apparatus comprising an oxygen pump that can be connected to an oxygen source and comprising a tracheal prosthesis that can be connected via a catheter. The spontaneous respiration of the patient is detected by sensors connected to a control unit for activating the oxygen pump. The tracheal prosthesis comprises a tubular support body with a connection for the catheter and two of the sensors are associated with the support body. The tracheal prosthesis and the jet catheter that is integrated or can be introduced are dimensioned so that the patient can freely breath and speak without restriction.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Methods and devices for minimally invasive respiratory support
ActiveUS8381729B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationAssisting ventilation
Modes, methods, systems and devices are described for providing assisted ventilation to a patient, including wearable ventilation systems with integral gas supplies, special gas supply features, ventilation catheters and access devices, and breath sensing techniques.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
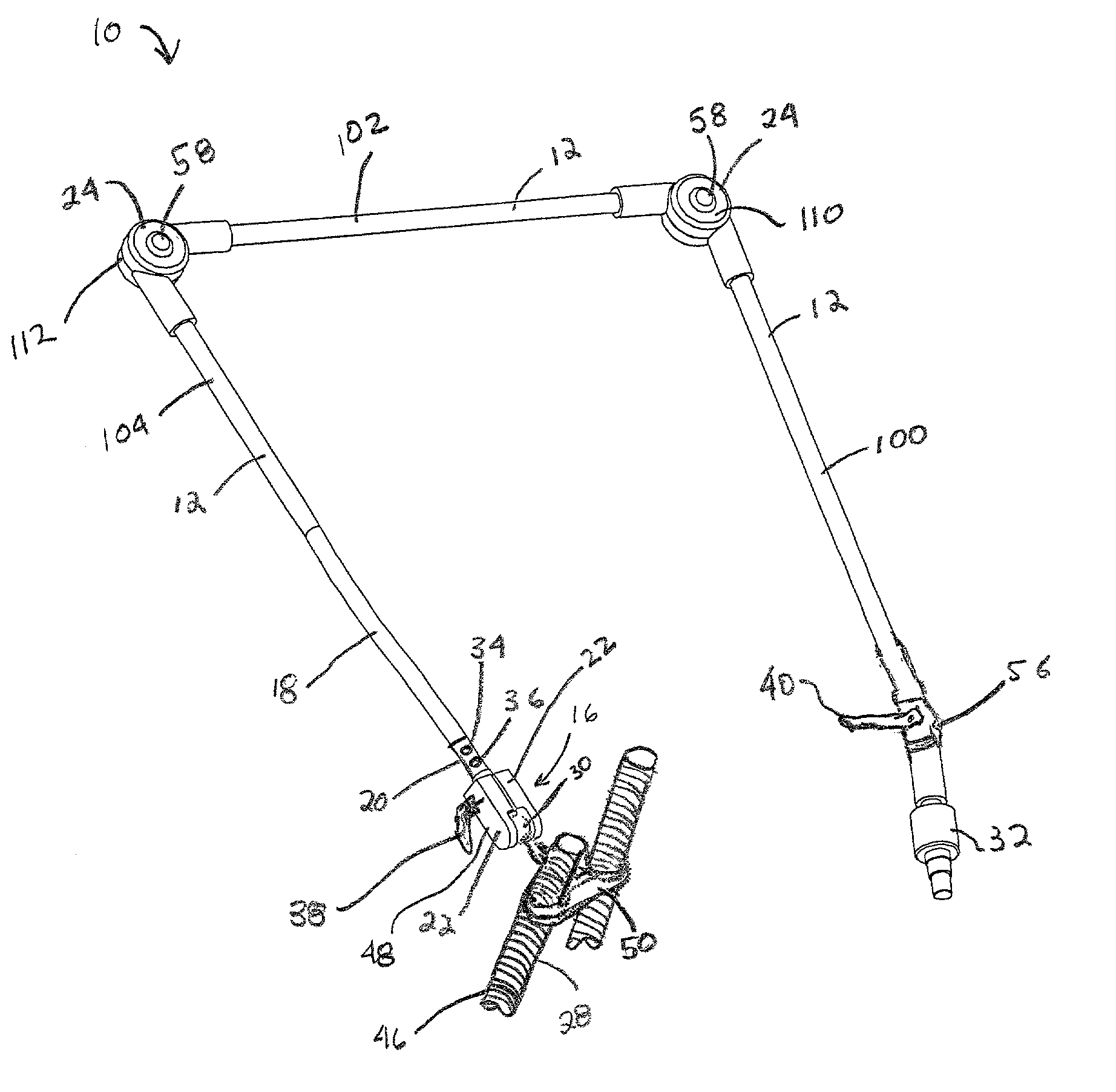
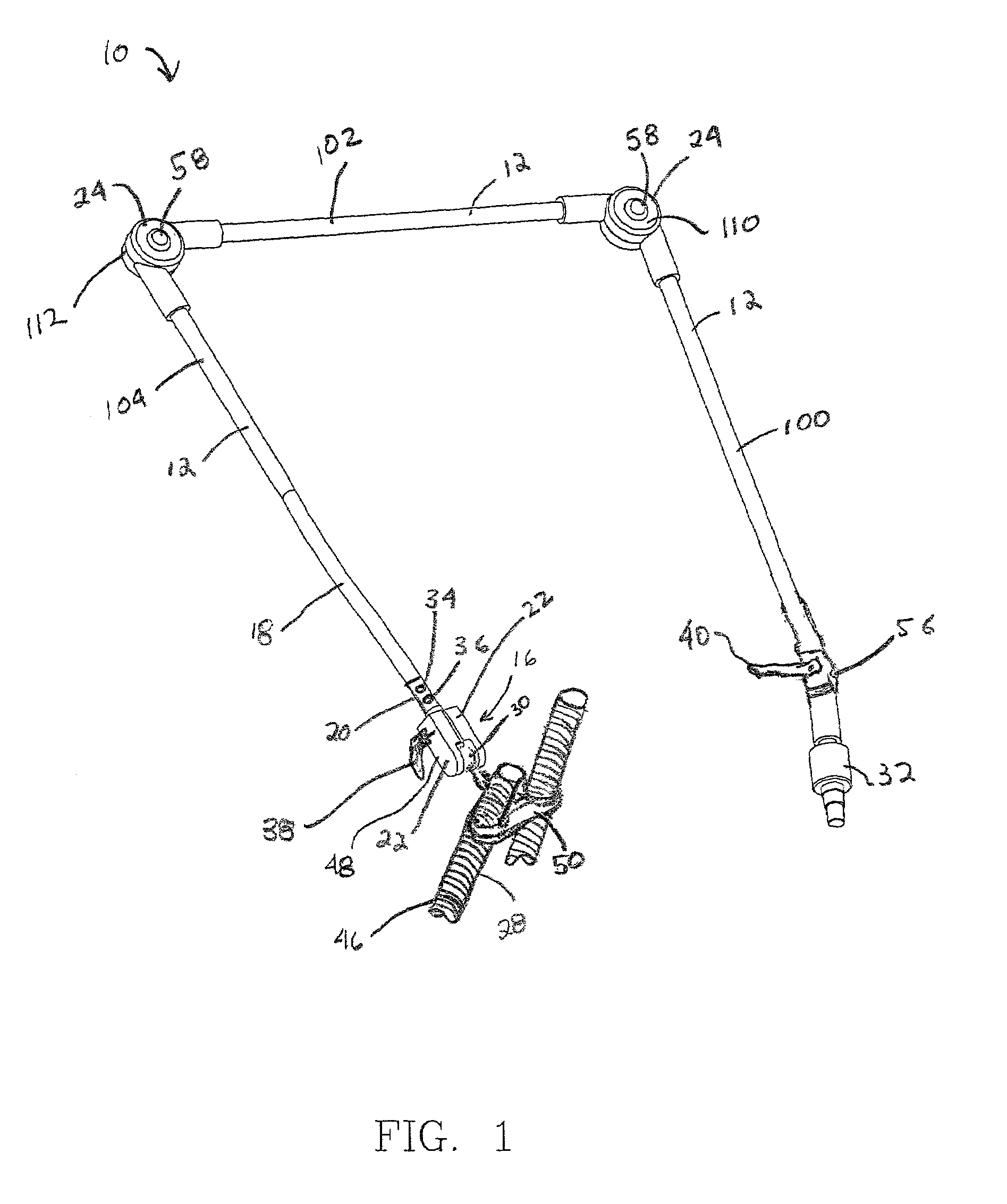
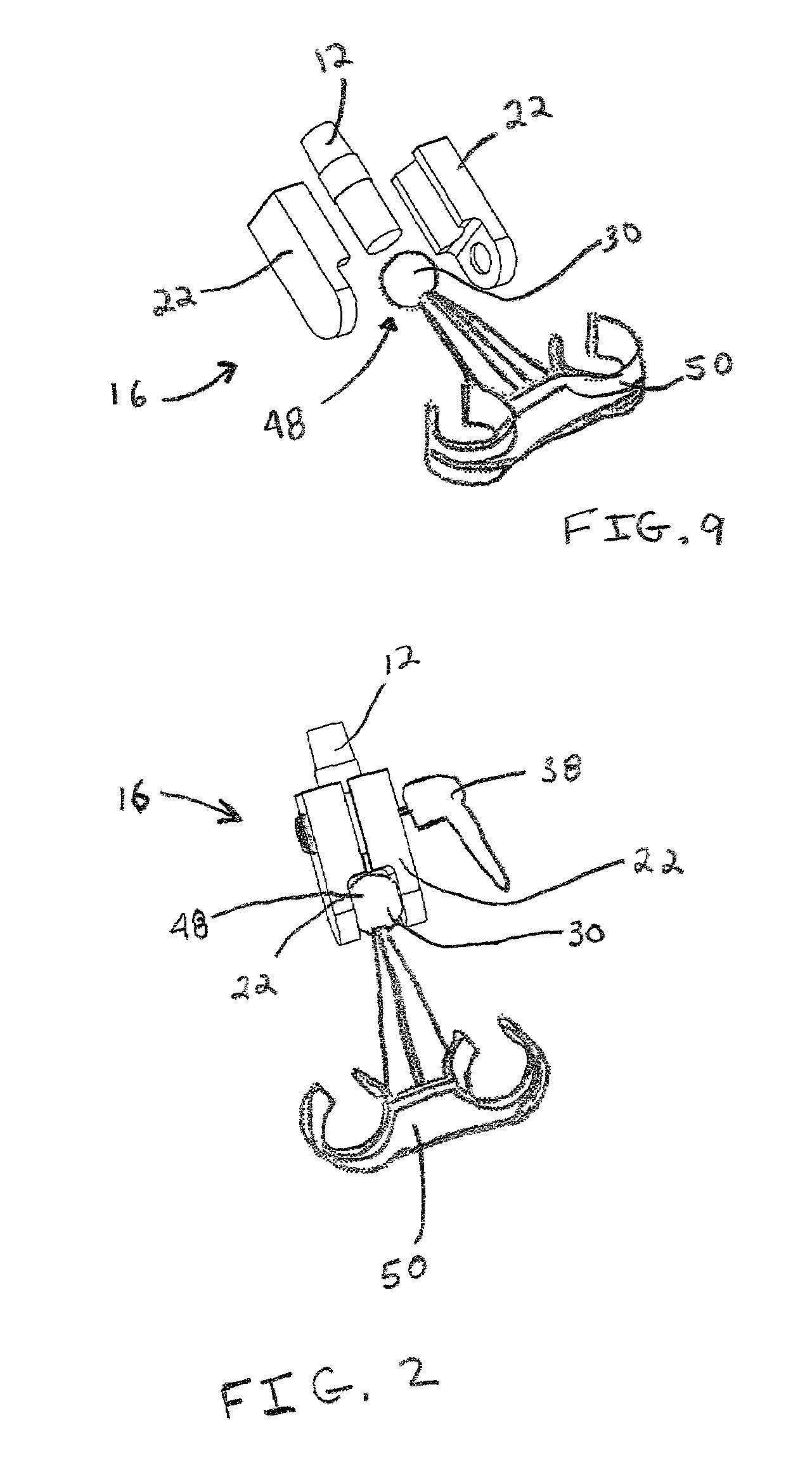
Respiratory circuit support arm
ActiveUS7124755B2“locking” effectAvoid adjustmentPicture framesOperating chairsEngineeringRespiratory support
A support arm for use in a respiratory circuit is provided. The support arm includes a plurality of arm segments that are movably connected with one another such that the arm segments are adjustable with respect to another. At least one inflatable bladder is provided. The bladder is operably disposed at a point of connection between at least two of the arm segments. The arm segments are locked into position with respect to one another upon inflation of the bladder. The arm segments are released and positionable with respect to one another upon deflation of the bladder. Also, a respiratory support member is attached to one of the arm segments. The respiratory support member is configured for engaging the respiratory circuit to support the respiratory circuit.
Owner:AVENT INC
Device and process for breath-supporting respiration
InactiveUS20070062530A1Measurement is compromisedClosing pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratorEmergency medicine
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Filter Device for Administration of Stored Gases
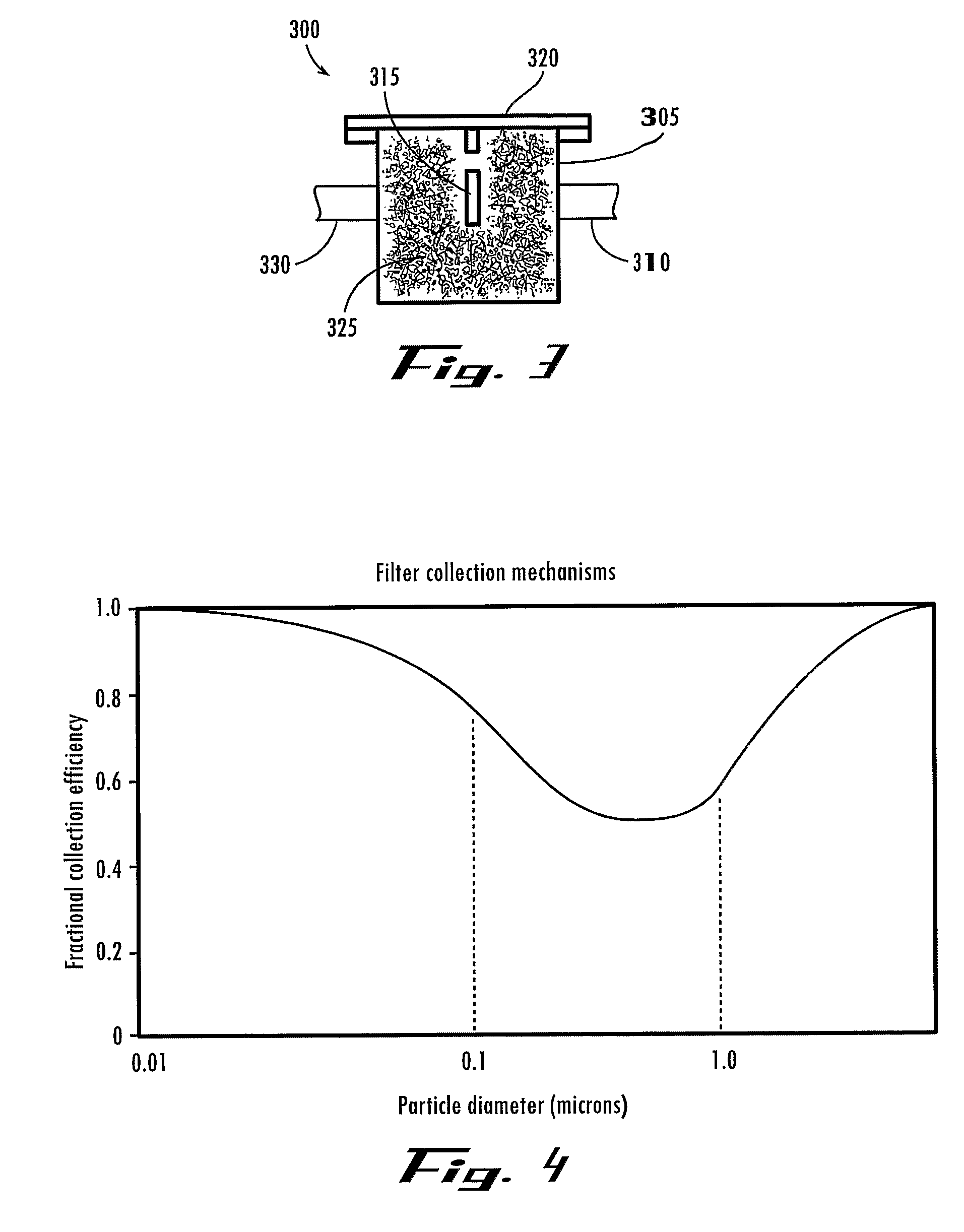
InactiveUS20080034967A1Prevent inadvertent transmissionFor quick replacementRespiratorsGas treatmentProduct gasRespiratory support
This invention relates to the field of connectors used to connect gas sources to apparatus for the administration or other use of gas or mixtures of gases, and more specifically to filters used to remove biological contaminants that might be colonized with the pressurized containers used in gas administration for respiratory support of a user or patient or other applications where biological contamination is not desired.
Owner:BOC GRP INC
Headgear assembly for a respiratory support system
InactiveUS7665465B2Accurate locationBreathing filtersRespiratory masksEngineeringRespiratory support
A respiratory support system having a patient interface attached to a headgear assembly for delivering a gas to a patient is disclosed. The headgear provides a rigid member and a pad held in place on the patient's head by straps. The rigid member functions to prevent creep of the straps, distribute the strapping forces, and minimized tangential strap forces that otherwise squeeze the sides of the patient's head.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
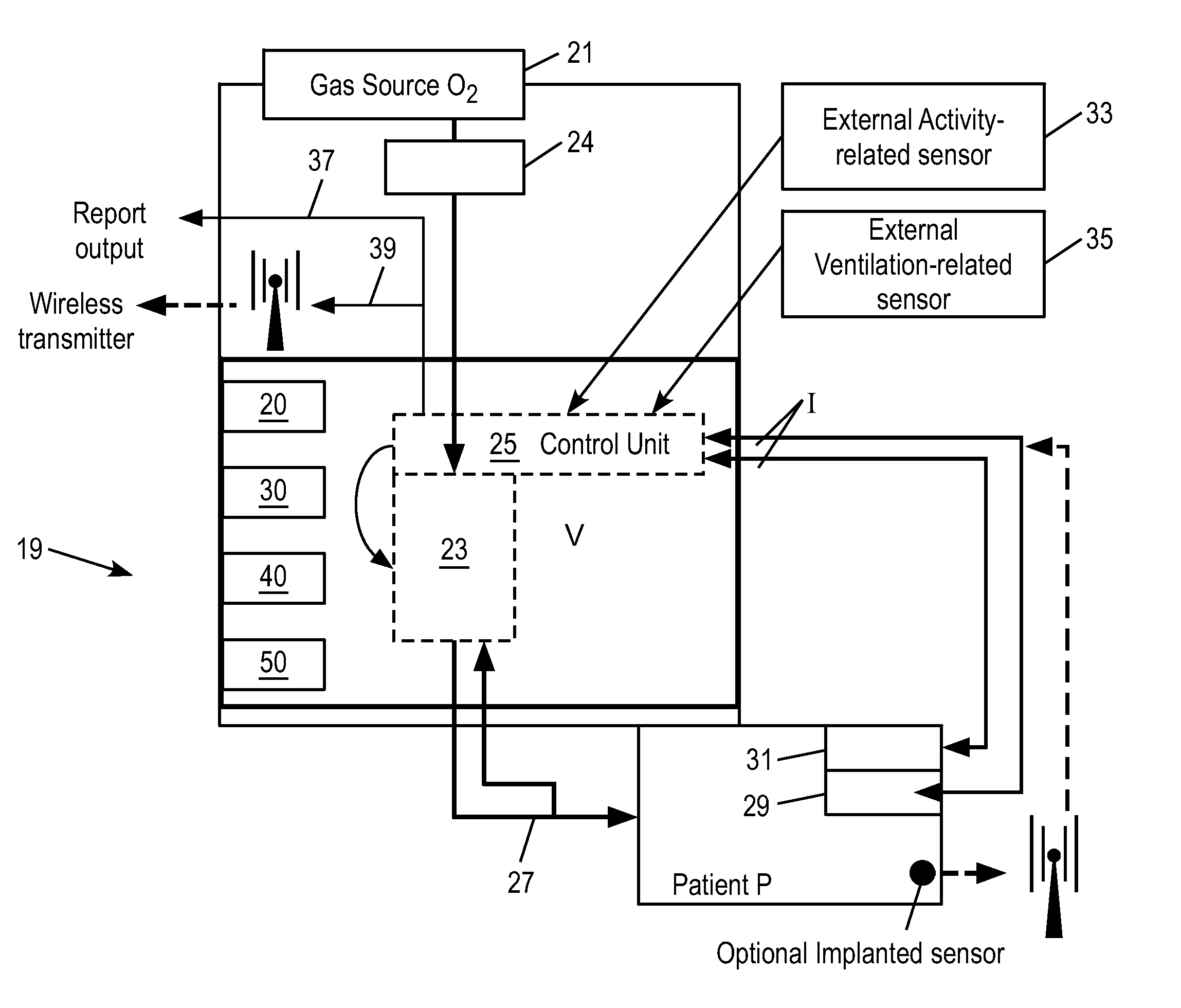
Closed loop respiratory support device with dynamic adaptability
ActiveUS20110290252A1Improve system performanceNovel featuresRespiratorsElectrocardiographyClosed loopRespiratory support
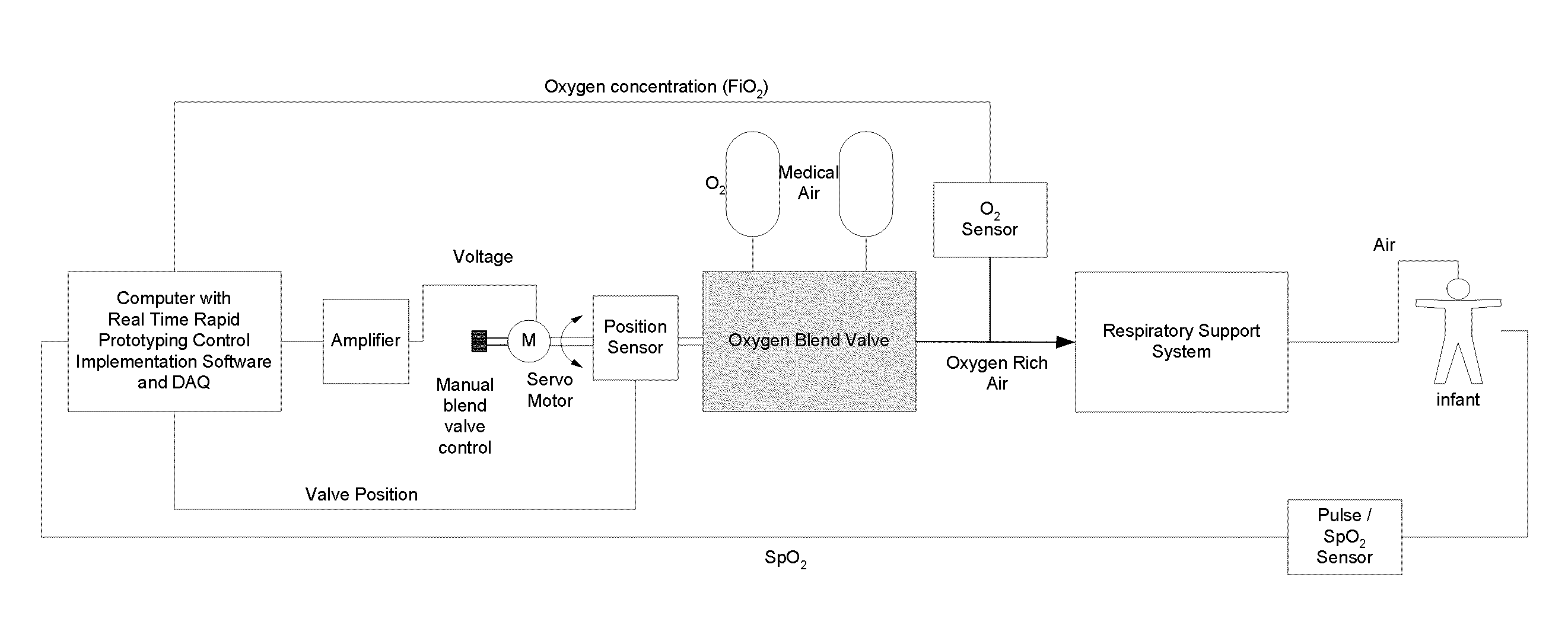
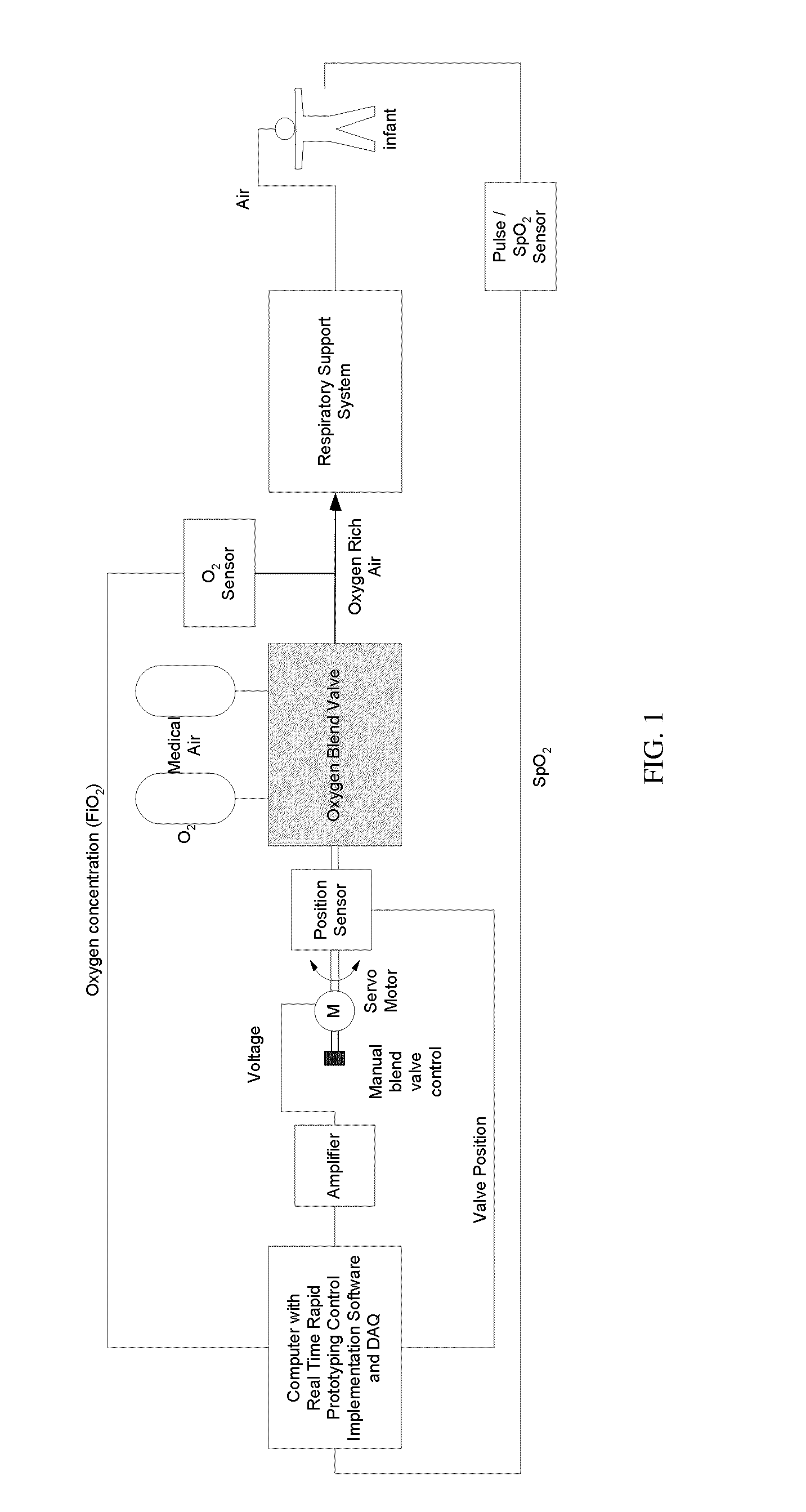
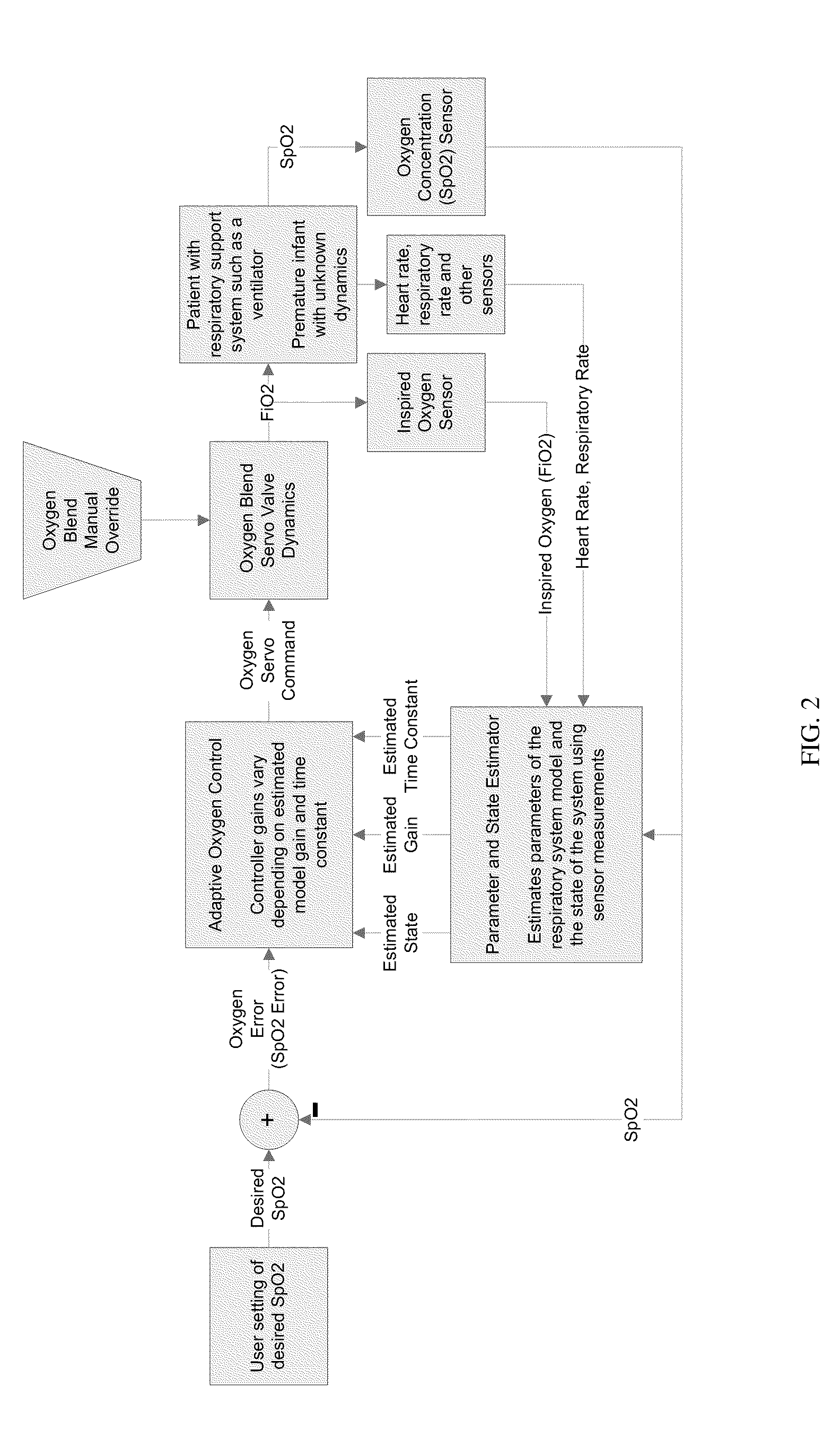
The invention provides an automatic system based on the dynamic adaptability strategy for controlling oxygen concentration in blood of patients with fluctuating oxygen needs. The inventive system monitors patient's clinical measurement data and updates the system continuously, which provides changes in FiO2 and gas flow that are more patient specific and reduce the patient's unnecessary oxygen exposure.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
Arrangement and method for controlling operational characteristics of medical equipment
ActiveUS7207331B2Freedom of movementImprove abilitiesRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMedical equipmentPressure sense
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems, methods and apparatus for respiratory support of a patient
ActiveUS20090107494A1Improve the quality of lifeIncrease oxygenTracheal tubesBalloon catheterCounter flowOxygen
Spontaneous respiration is detected by sensors. An additional amount of oxygen is administered to the lungs via a jet gas current at the end of an inhalation procedure. Breathing volume, absorption of oxygen during inhalation, and clearance of carbon dioxide during exhalation are improved. If required, the exhalation procedure of the patient can be arrested or slowed by a countercurrent to avoid a collapse of the respiration paths. An apparatus including an oxygen pump can be connected to an oxygen source and includes a tracheal prosthesis that can be connected via a catheter. The respiration detections sensors are connected to a control unit for activating the oxygen pump. The tracheal prosthesis includes a tubular support body with a connection for the catheter, and the sensors are associated with the support body. The tracheal prosthesis and jet catheter are dimensioned so the patient can freely breathe and speak without restriction.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
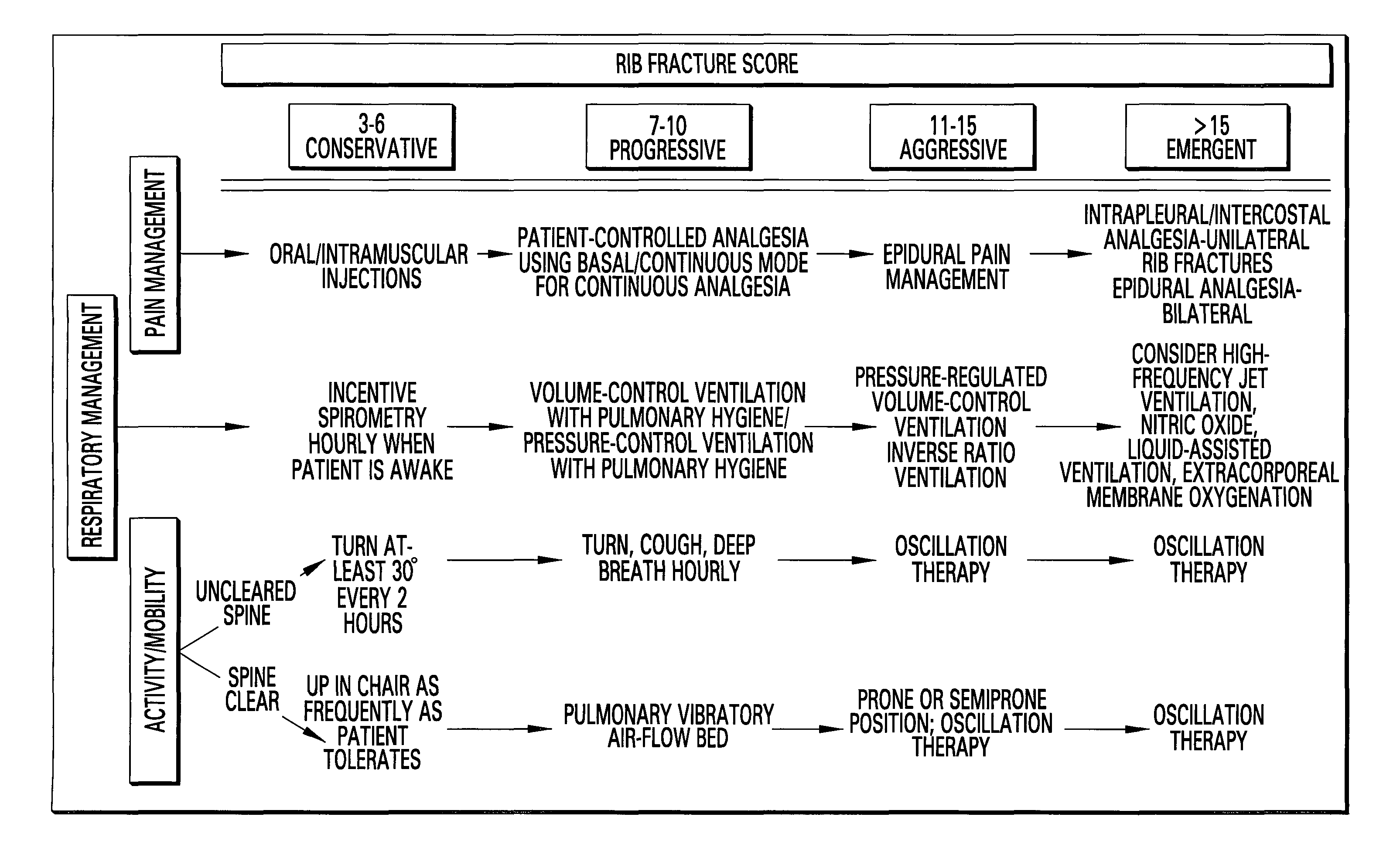
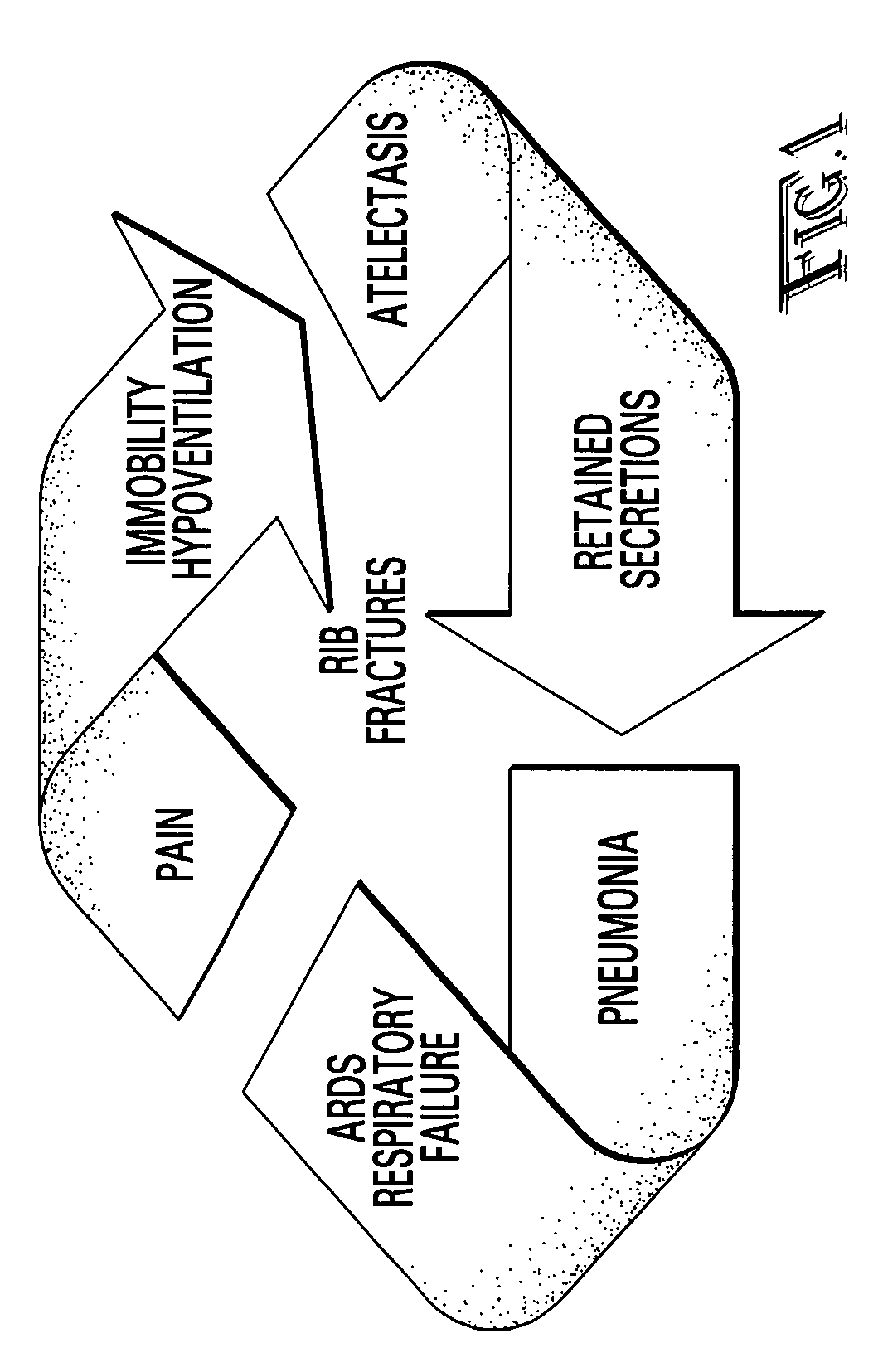
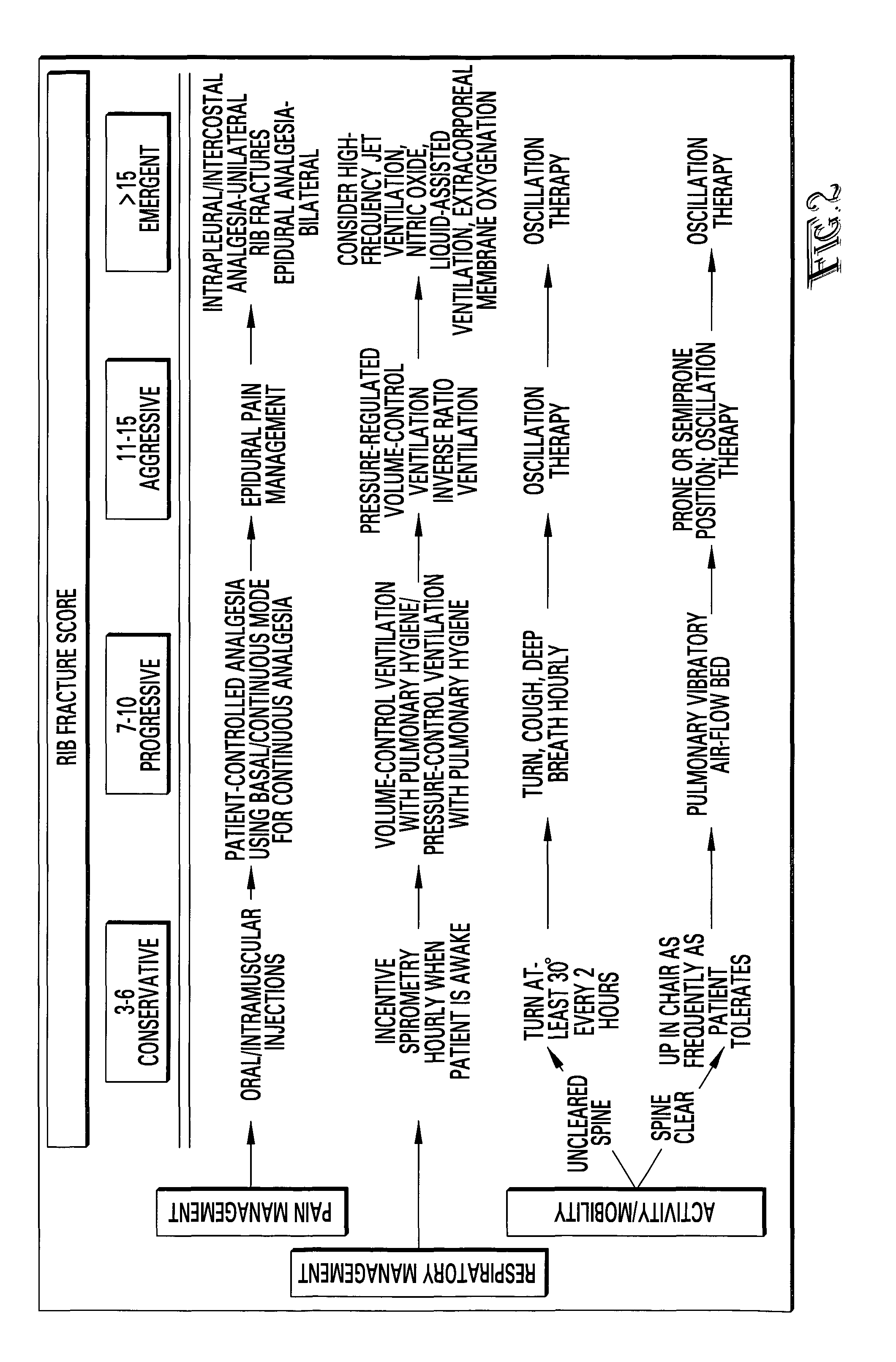
Rib fracture score and protocol
InactiveUS7225813B2Promote recoverySurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringRespiratory careMortality rate
Multiple rib fractures in trauma patients are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Delayed morbidity for patients with rib fractures is often a result of hypoventilation leading to atelectasis, pneumonia and respiratory failure. Pain management was first recognized as an important factor in preventing complications in these patients. Later, management of the respiratory system became more widely recognized as a major factor in, patients' care. It is now known that patients with multiple rib fractures benefit most from adequate pain control, rapid mobilization, and meticulous respiratory care to prevent complications. A rib fracture score and protocol based on a synthesis of the existing literature is developed. The protocol is directed to decisions about rapid mobilization, respiratory support, and pain management interventions to decrease the length of patients' stay in intensive care units.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
Apparatus and system for reducing mechanical ventilator noise
InactiveUS8028695B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsEngineering
A sound dampening apparatus to be disposed in pneumatic connection with a respiratory support system. The respiratory support system may comprise a source of medical gas, a plurality of pneumatic connections and a patient interface. The sound dampening apparatus comprises an inlet, an outlet, and an outer case which forms a sound dampening chamber. As the medical gas flows through the sound dampening apparatus, the noise energy associated with the flow of medical gas is reduced.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Arrangement and method for controlling operational characteristics of medical equipment
ActiveUS20060213517A1Freedom of movementImprove abilitiesRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPressure senseEngineering
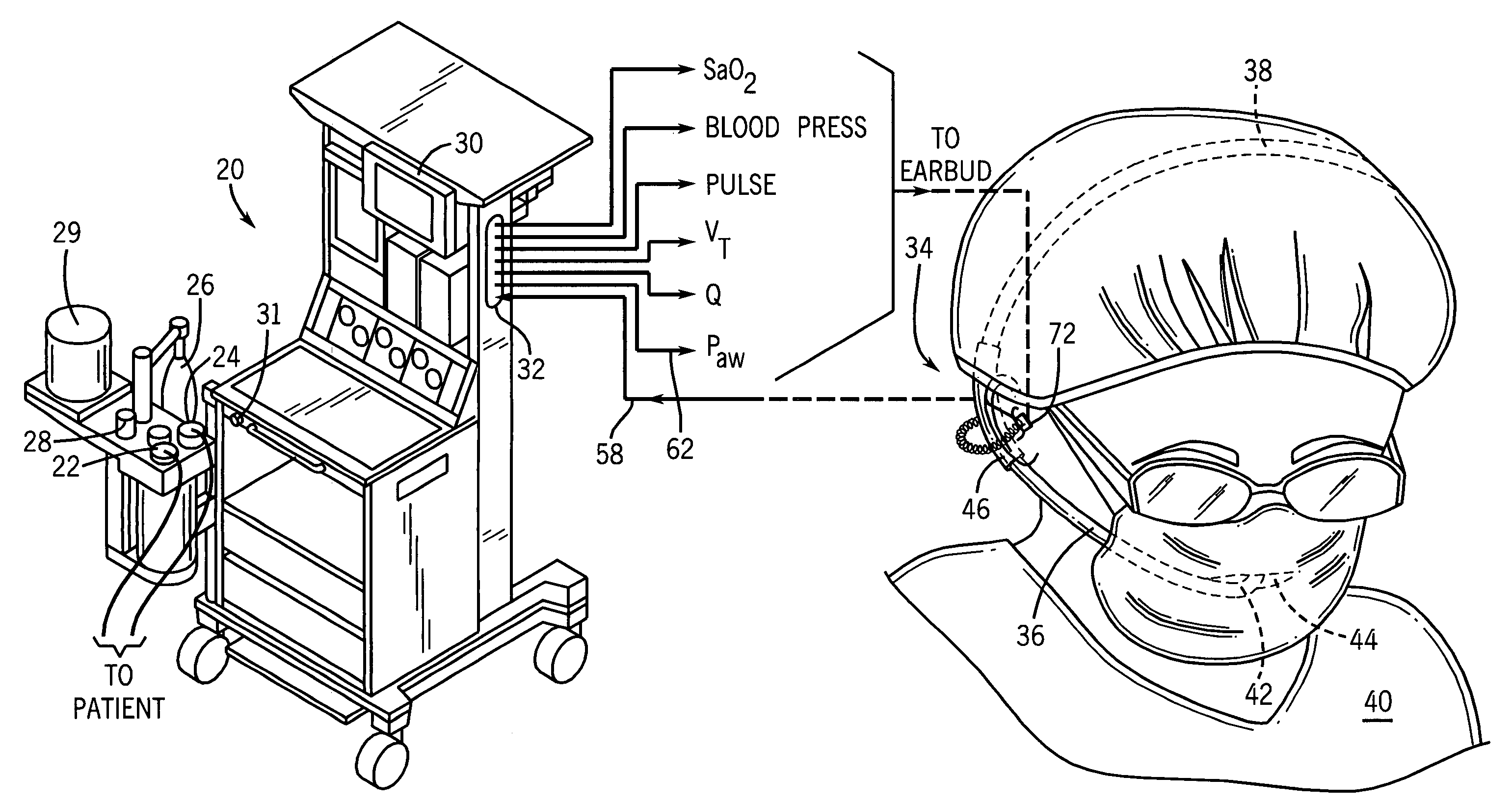
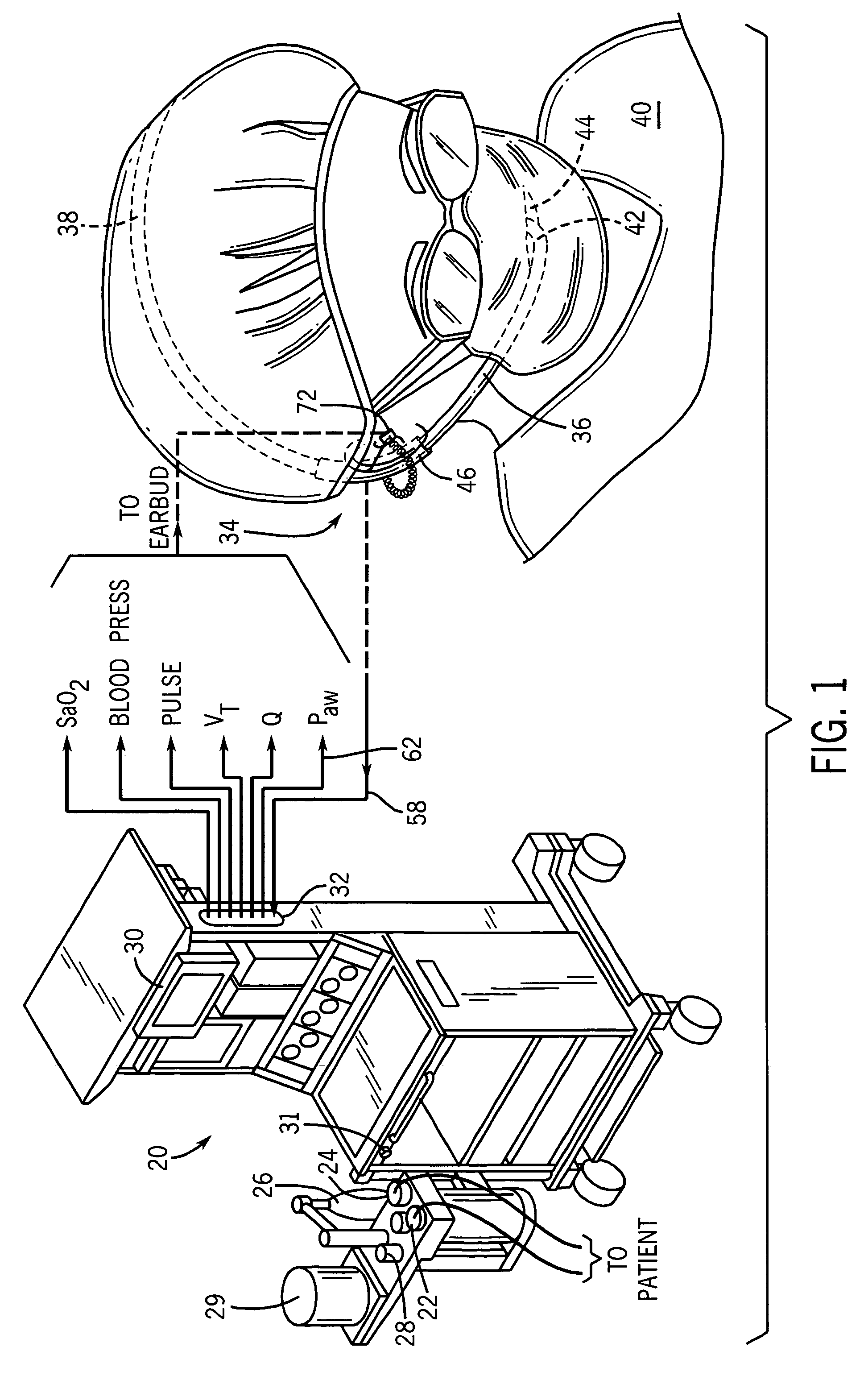
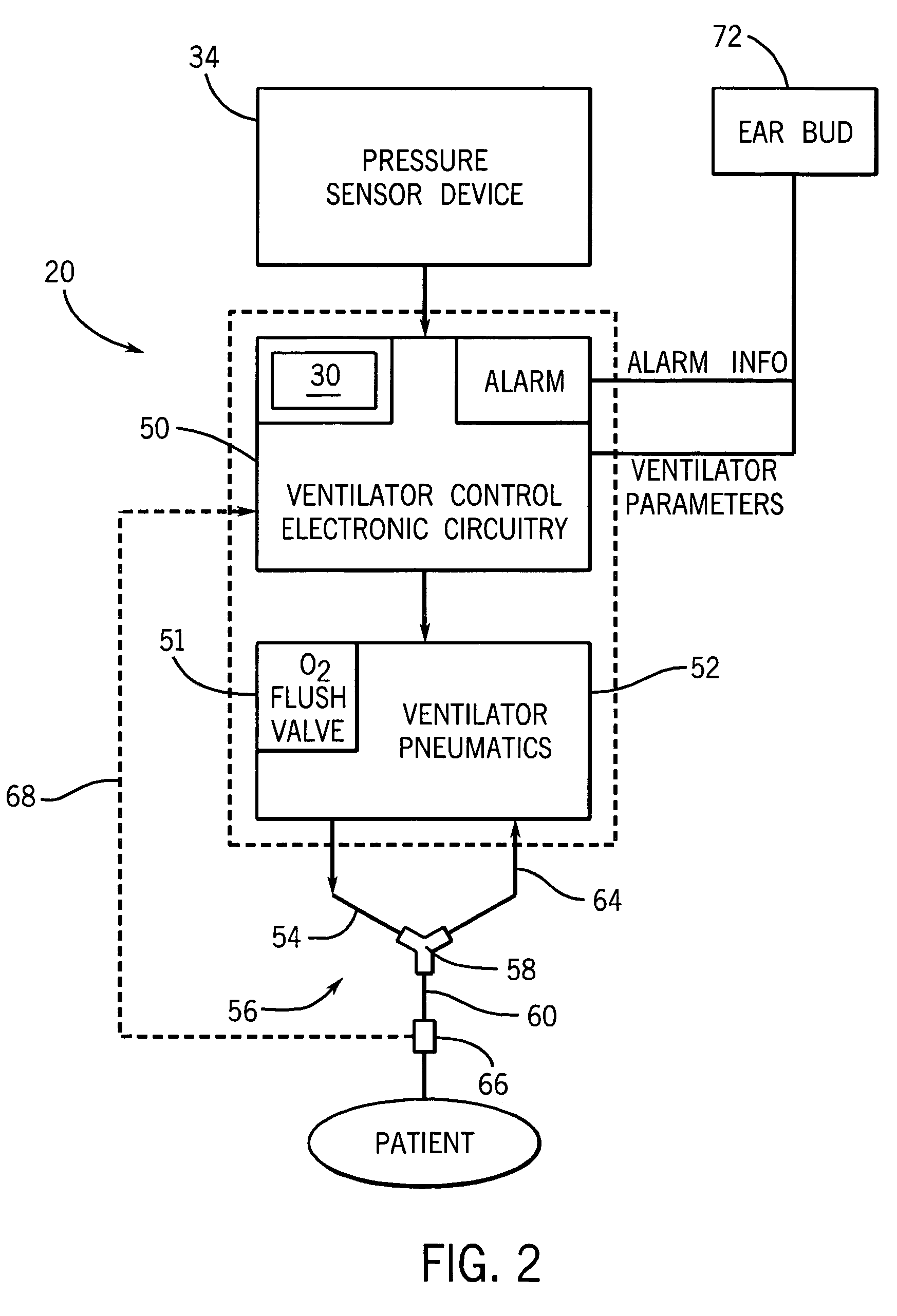
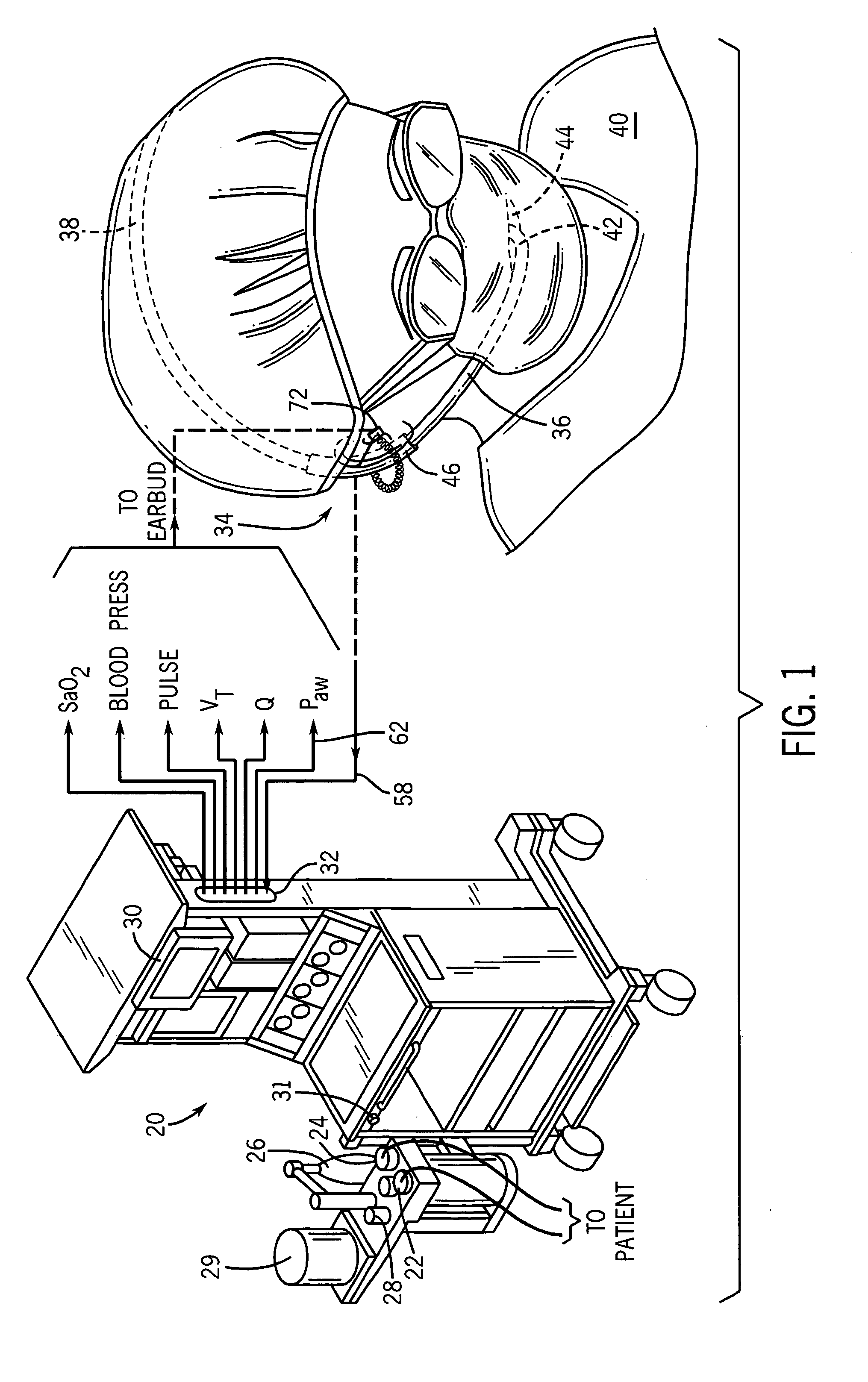
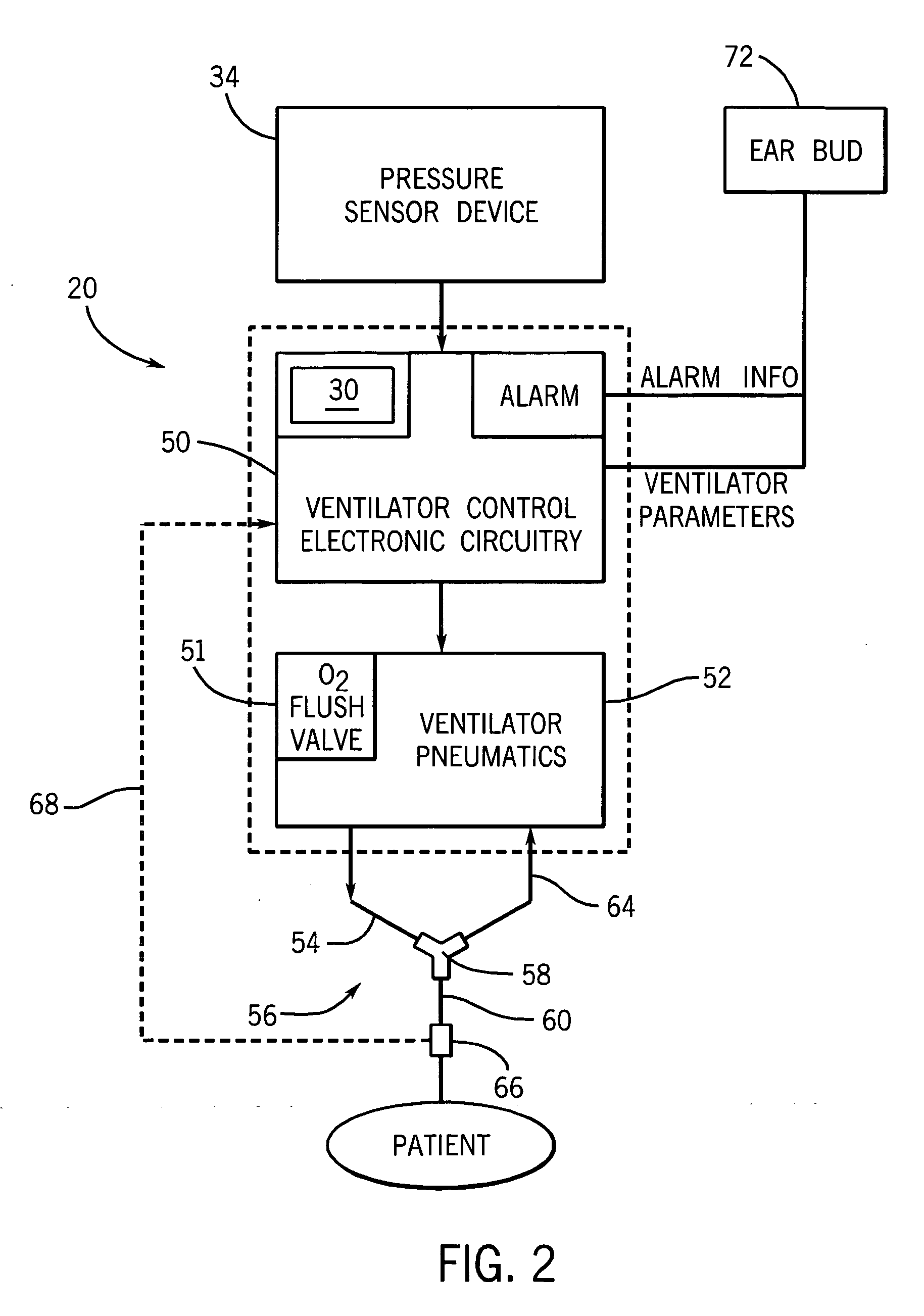
An arrangement and method is provided for controlling operational characteristics of medical equipment. A pressure sensor associated with the caregiver is arranged to sense changes in air pressure that correspond to breathing activity of the caregiver. The pressure sensor may comprise a neckband, headset, or the like. In the arrangement shown, a headset that is worn by the caregiver includes a disposable tube connected to a pressure transducer such that the pressure sensor senses changes in air pressure in the tube. An open end of the tube is positioned near the mouth of the caregiver to receive changes in airflow from the caregiver's mouth. The pressure sensor is in communication with a controller associated with the ventilator. The controller is arranged to control at least one operational parameter of the ventilator, such as the delivery of respiratory support to the patient or actuation of an oxygen flush valve on the ventilator, based upon the changes in air pressure sensed by the pressure sensor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com