Patents
Literature
279 results about "Airway pressures" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Device and method for nonclinical monitoring of breathing during sleep, control of CPAP treatment and preventing apnea
InactiveUS6398739B1Improve sound qualityQuality improvementElectrocardiographyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEmergency medicineAirway pressures
Owner:RESMED LTD
Apparatus and method for mask free delivery of an inspired gas mixture and gas sampling
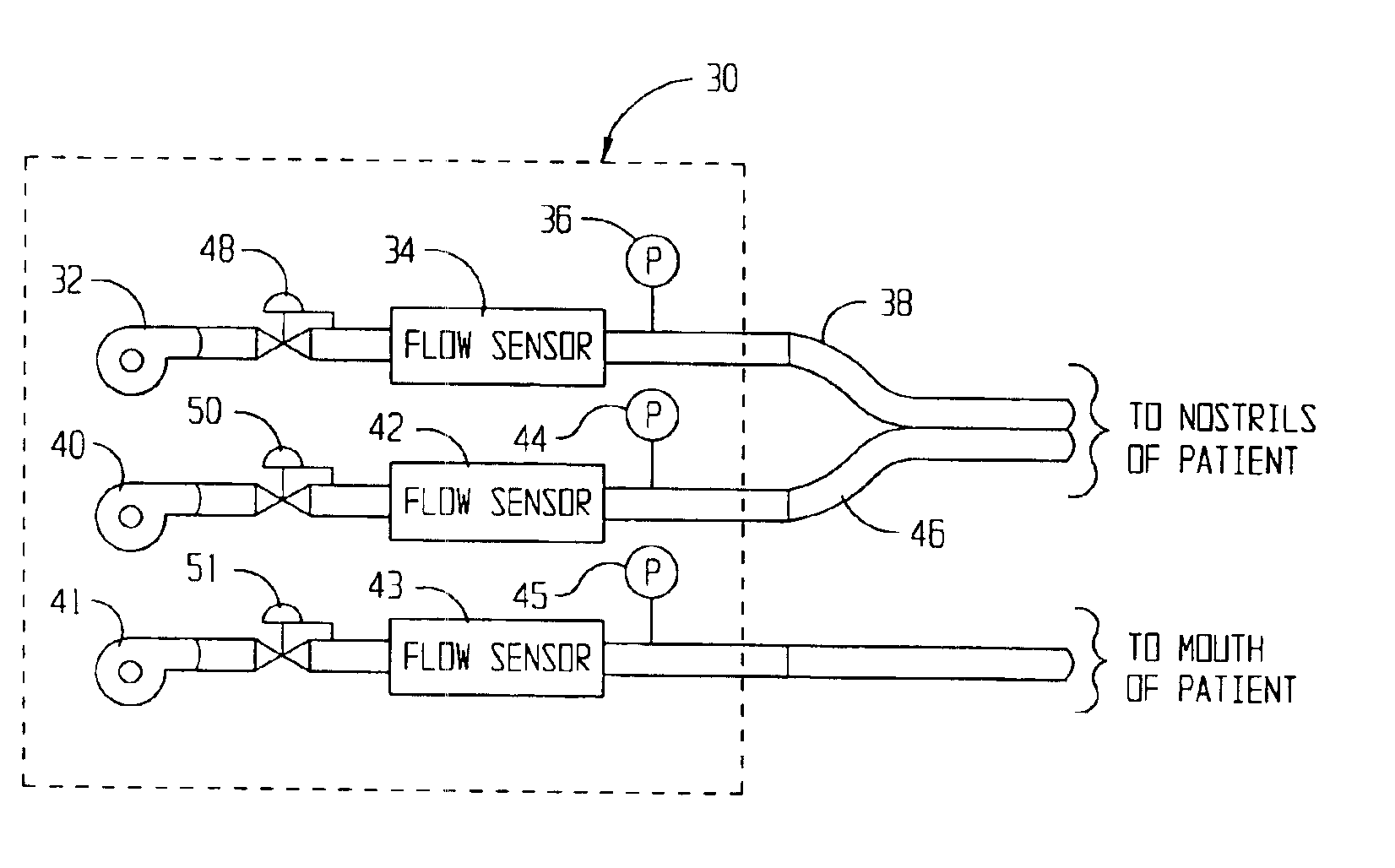
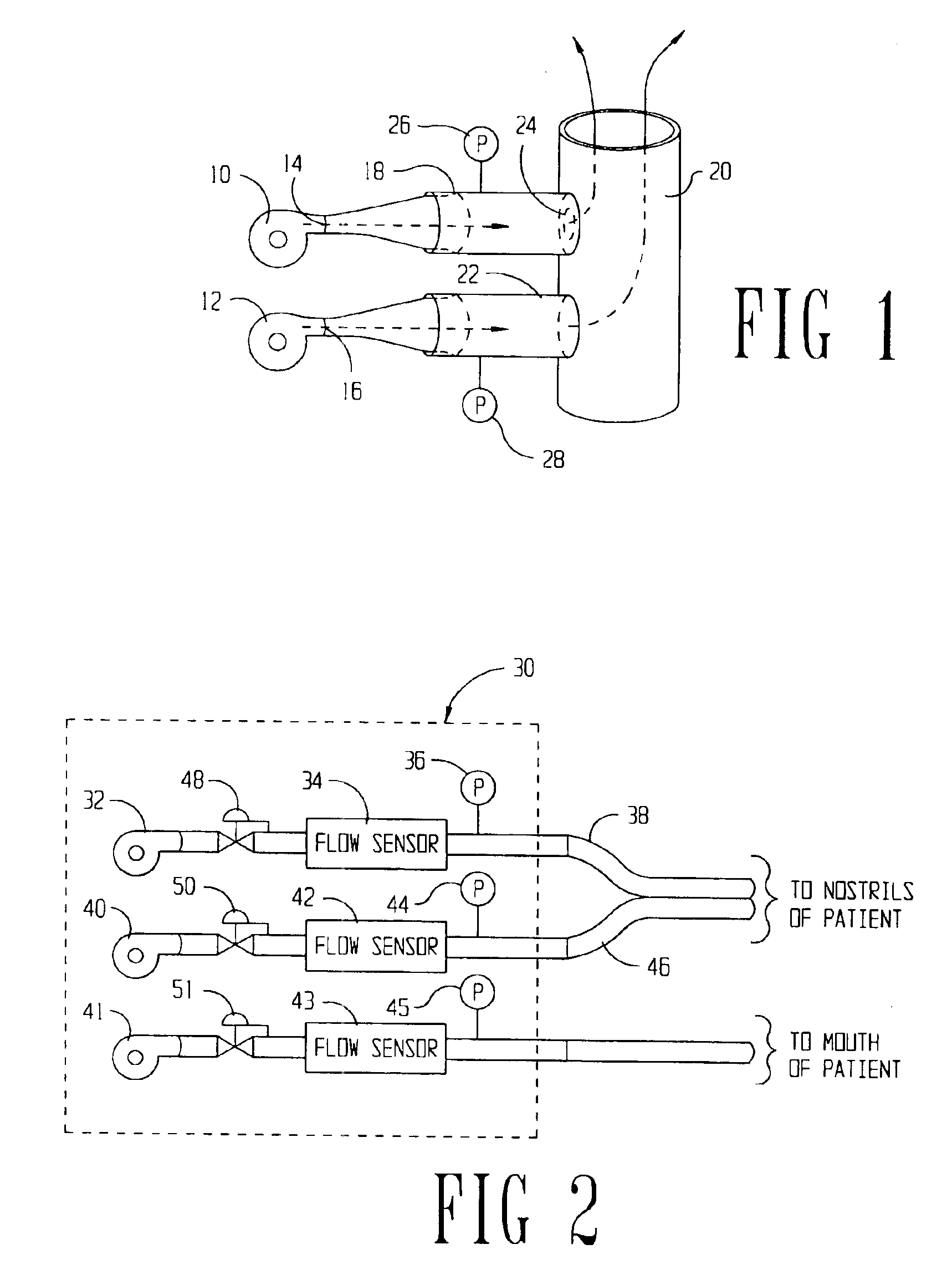
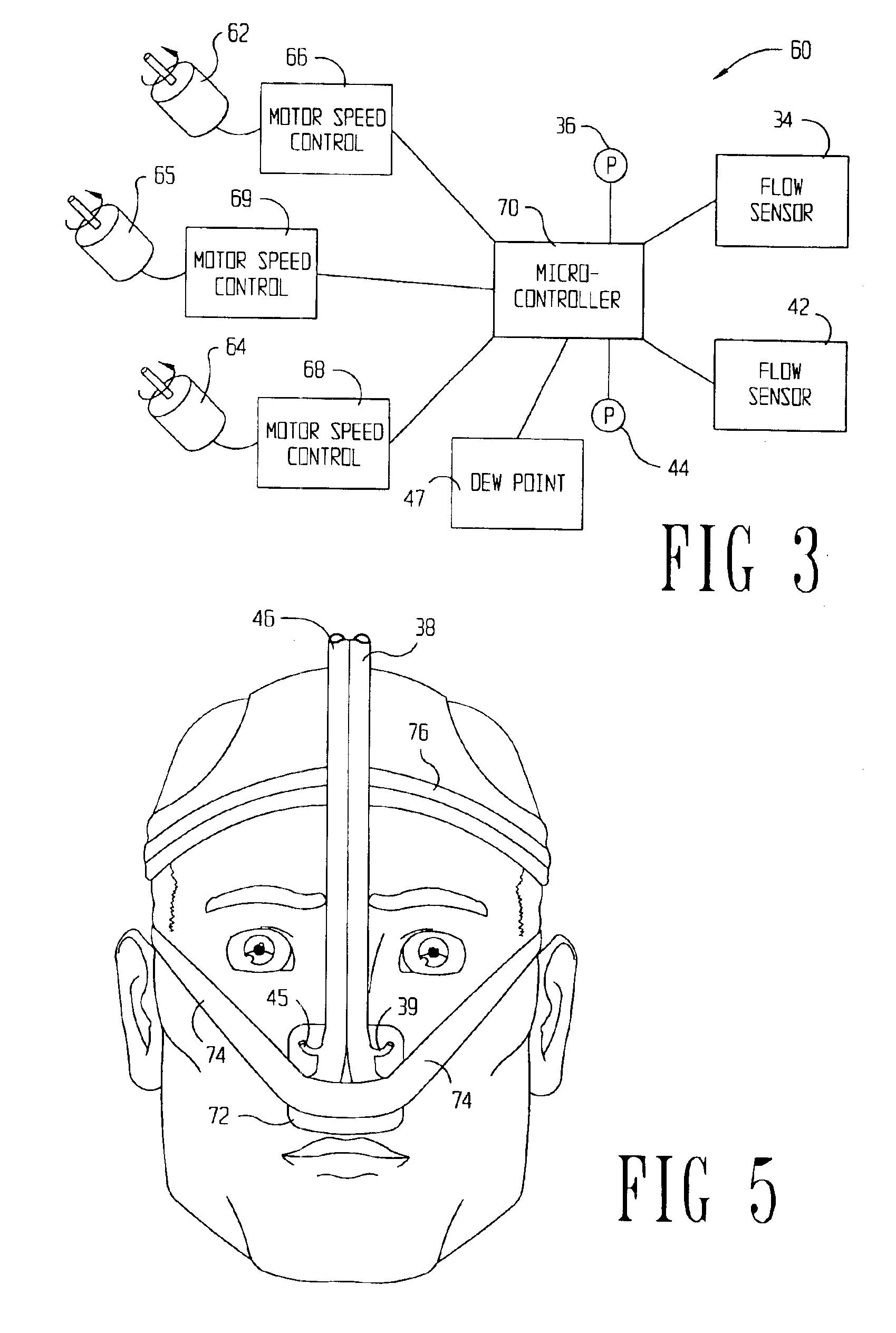
InactiveUS20020017300A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksOxygen deliveryInspired gas
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for the delivery of inspired gas, e.g., supplemental O2, to a person combined with gas sampling, including for the purpose of monitoring of the ventilation of the person. In the invention, the delivery of inspired gas and gas sampling are accomplished without the use of a sealed face mask. The apparatus of one embodiment of the present invention comprises an oxygen delivery device, nasal airway pressure sampling devices, optionally an oral airway pressure sampling device and at least one pressure analyzer connected to the sampling devices which determine the phase of the person's respiration cycle and the person's primary airway. The oxygen delivery device is connected to a controller such that it delivers a higher flow of oxygen to the person during the inhalation phase of the person's respiratory cycle. The invention thus increases end tidal oxygen concentrations. The invention further comprises carbon dioxide sampling tubes that continuously sample gas from two nasal sites and the mouth. The nasal sampling tubes are connected to a switching valve that is in turn connected to a capnometer which determines carbon dioxide concentration during exhalation. The oral gas sampling site is connected to a second capnometer.
Owner:SCOTT LAB
Method for controlling a ventilator, and system therefor
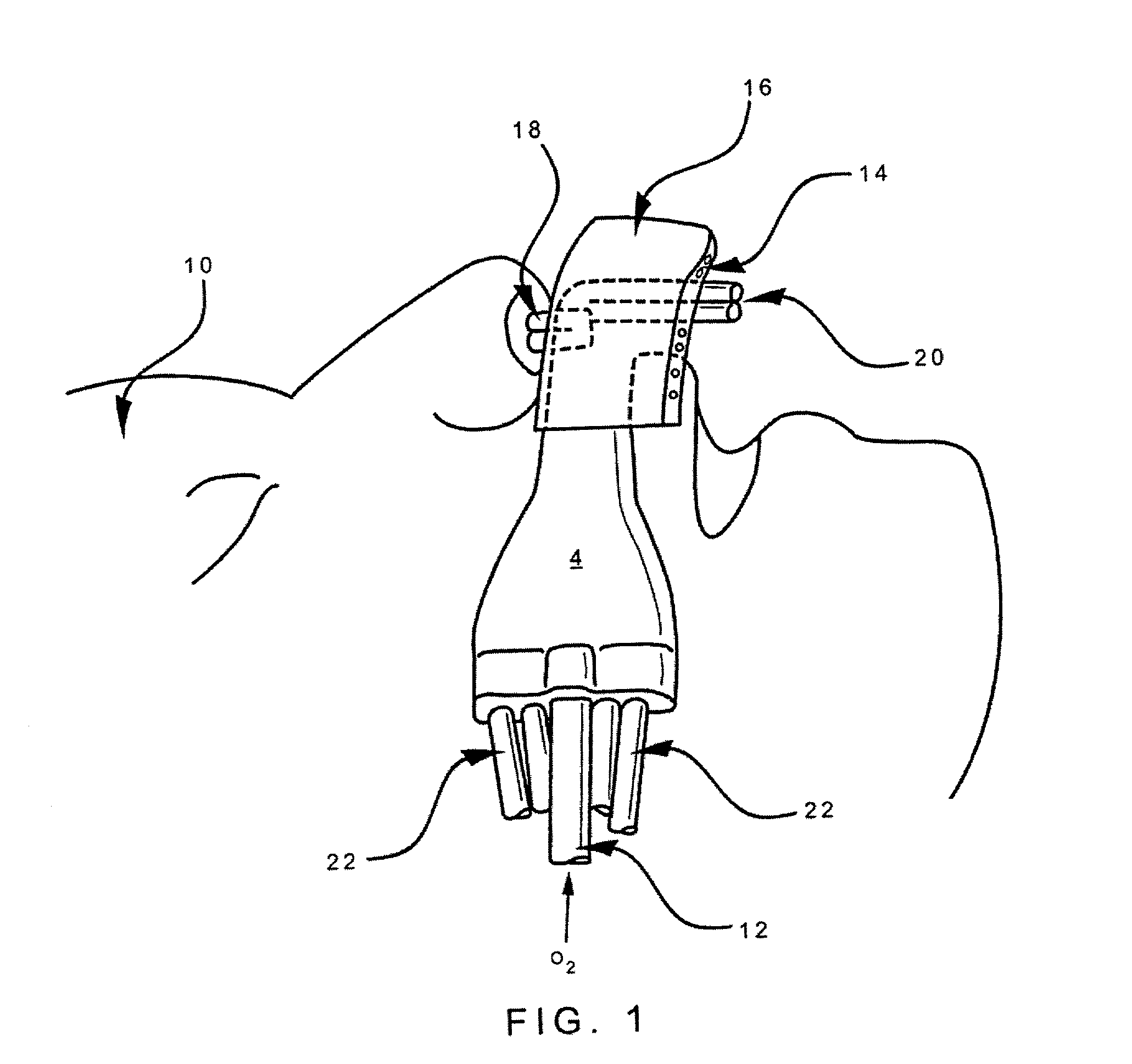
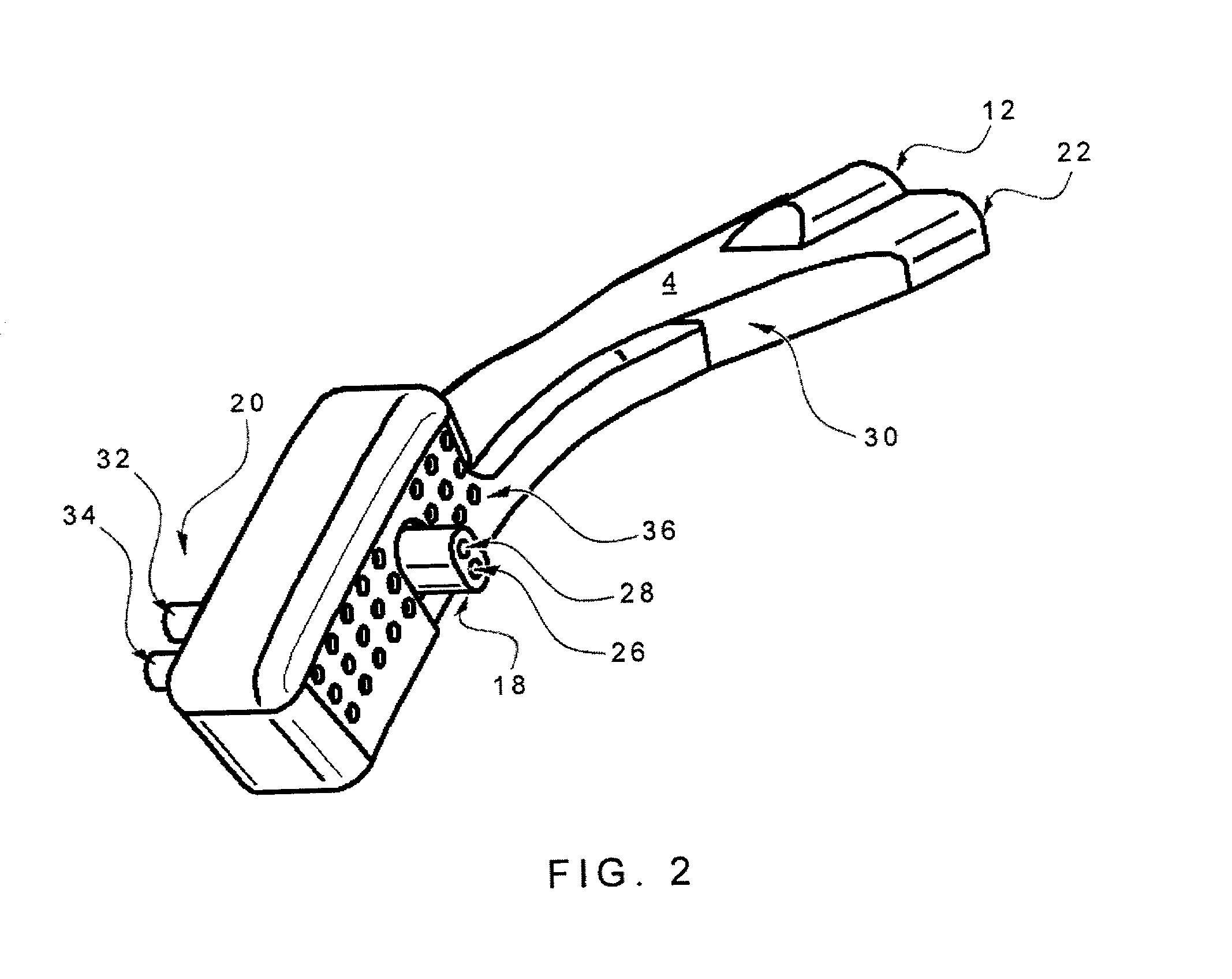
InactiveUS7040321B2Preventing situationEnhanced interactionTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesControlled breathingTracheal tube
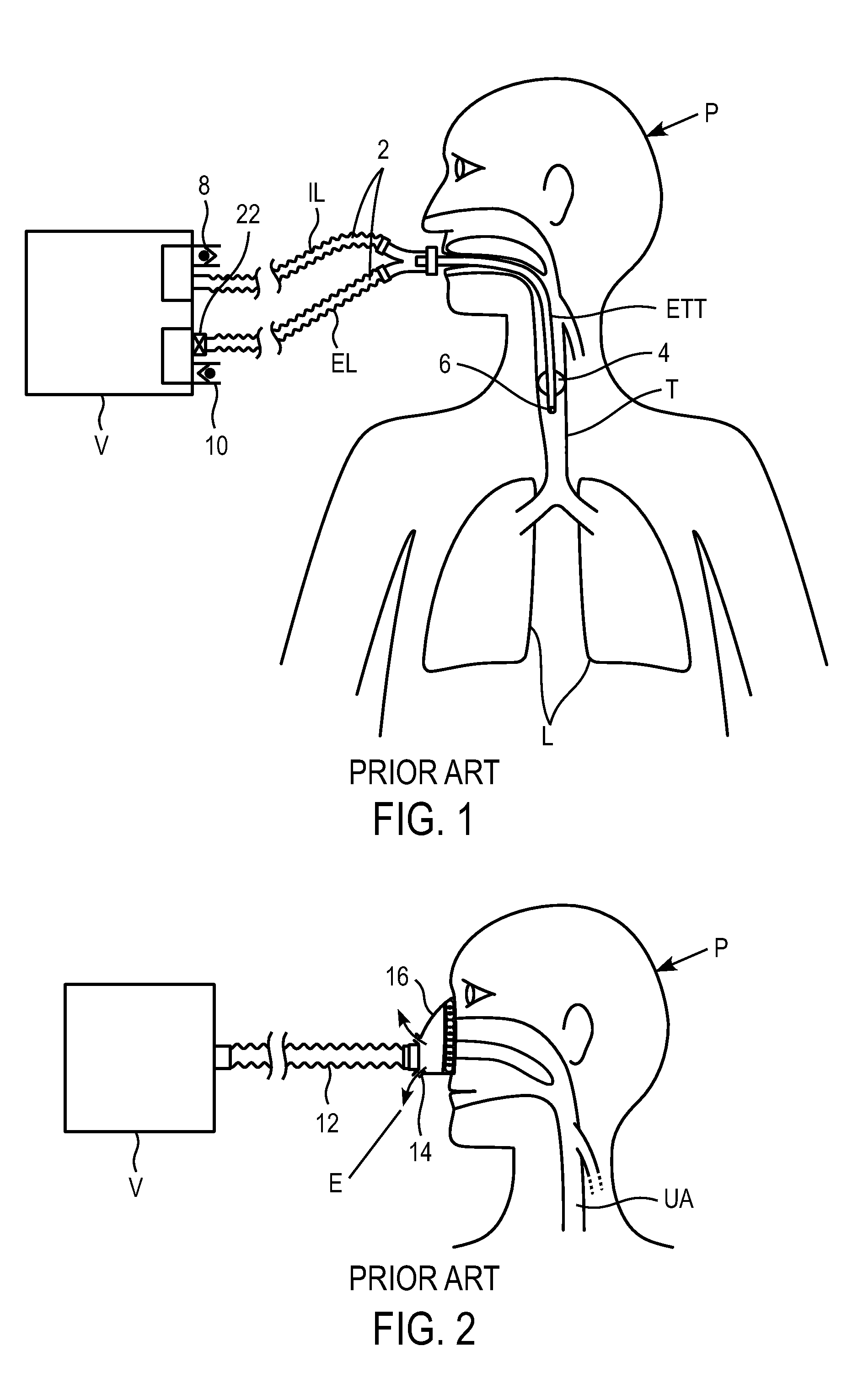
A method for controlling breathing gas flow of a ventilator for assisted or controlled ventilation of a patient as a function of a tracheobronchial airway pressure of the patient. A ventilator tube, such as a tracheal tube or tracheostomy tube, can be introduced into a trachea of the patient and subjected to the breathing gas, and has an inflatable cuff and at least one lumen that is continuous from a distal end of the tube to a proximal end of the tube. An apparatus detects an airway pressure, in which the tracheobronchial airway pressure is ascertained by continuous or intermittent detection and evaluation of an intra-cuff pressure prevailing in the cuff of the tube inserted into the trachea. The breathing gas flow of the ventilator is controlled as a function of the intra-cuff pressure detected.
Owner:AVENT INC
Mask free delivery of oxygen and ventilatory monitoring
InactiveUS6938619B1Increase oxygen concentrationFast sensingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksOxygen deliveryAirway devices
Disclosed is an apparatus and method for the delivery of supplemental oxygen gas to a person combined with the monitoring of the ventilation of the person with both being accomplished without the use of a sealed face mask. Preferred embodiments of the present invention combine an oxygen delivery device, a nasal airway pressure sampling device, an oral airway pressure sampling device, and a pressure analyzer connected to the sampling devices to determine the phase of the person's respiration cycle and the person's primary airway. The oxygen delivery device is connected to a controller such that it delivers a higher flow of oxygen to the person during the inhalation phase of the person's respiratory cycle. The invention thus increases end tidal oxygen concentrations with improved efficiency comparative to known open airway devices. Embodiments of the invention can include carbon dioxide sampling tubes that continuously sample air from the nose and mouth to determine carbon dioxide concentration during exhalation.
Owner:SCOTT LAB
Method For Determining Hemodynamic Effects Of Positive Pressure Ventilation
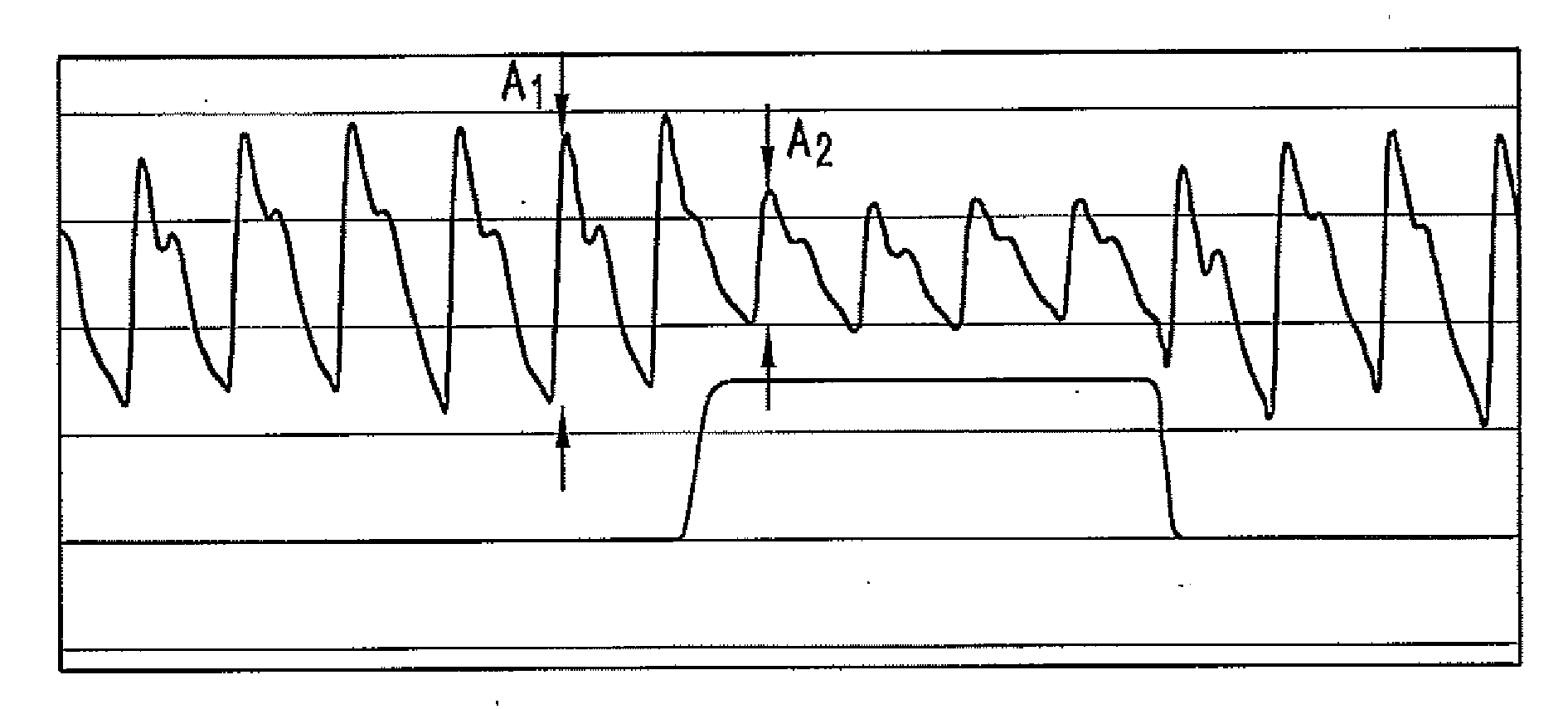
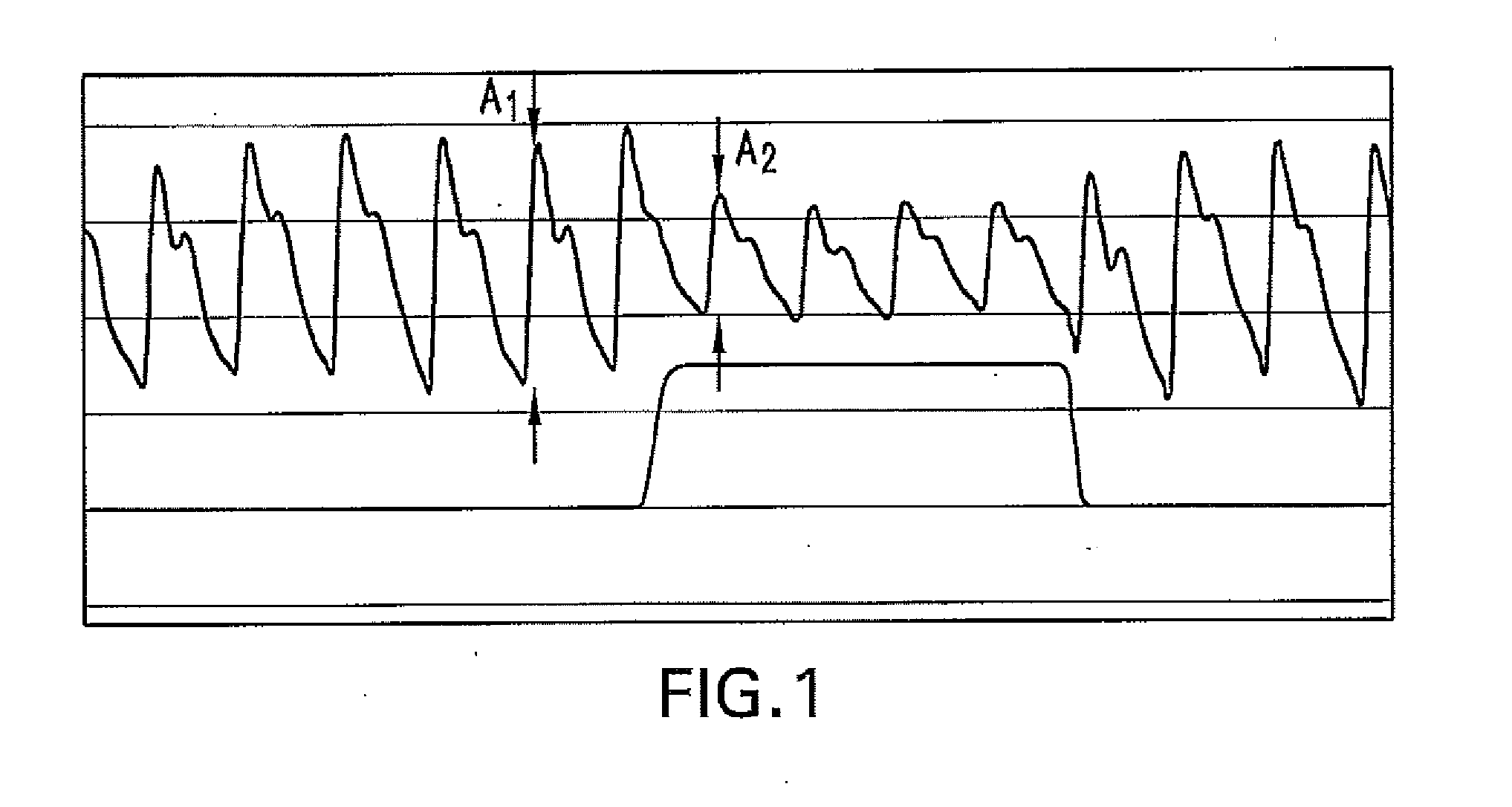
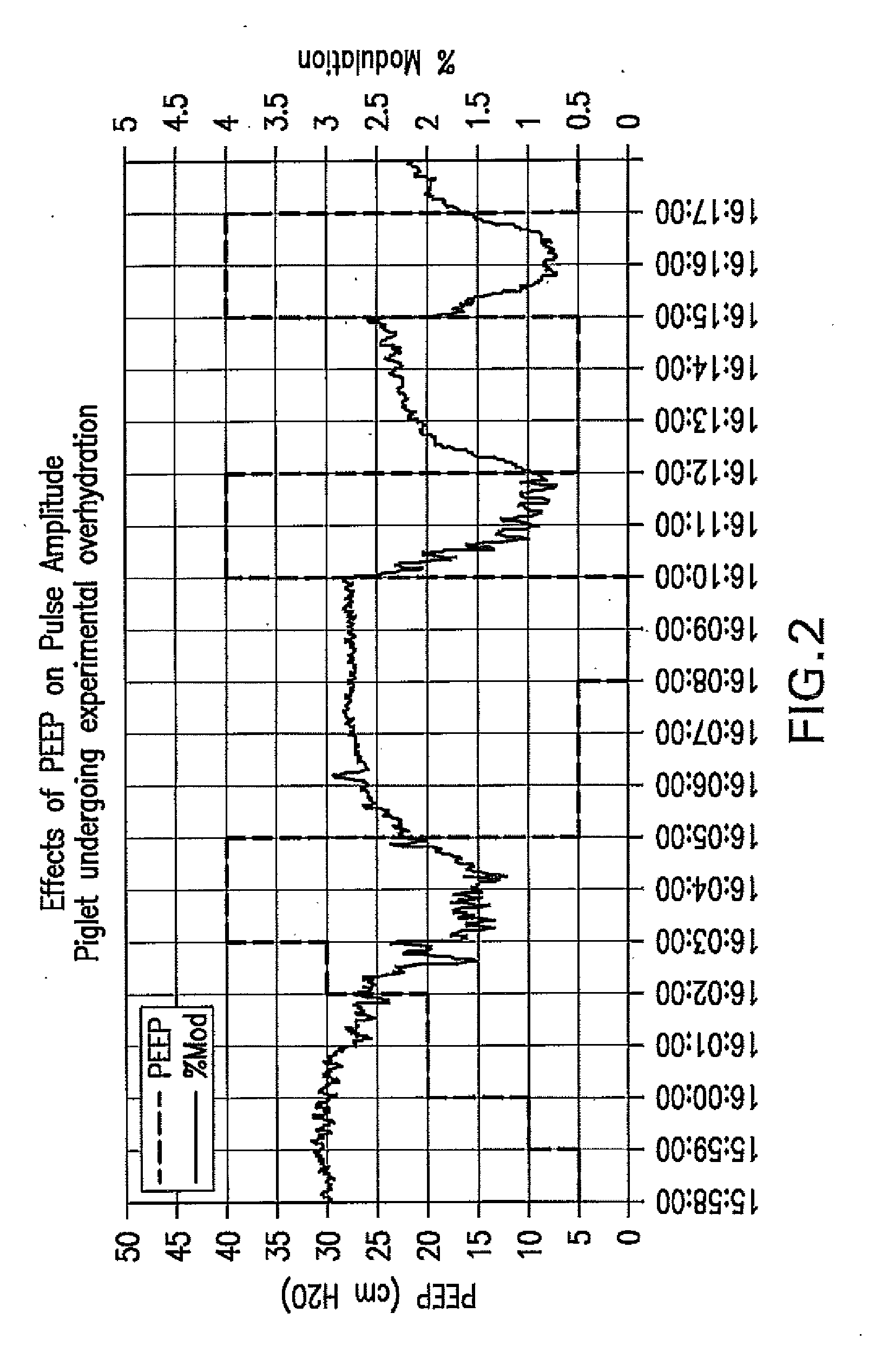
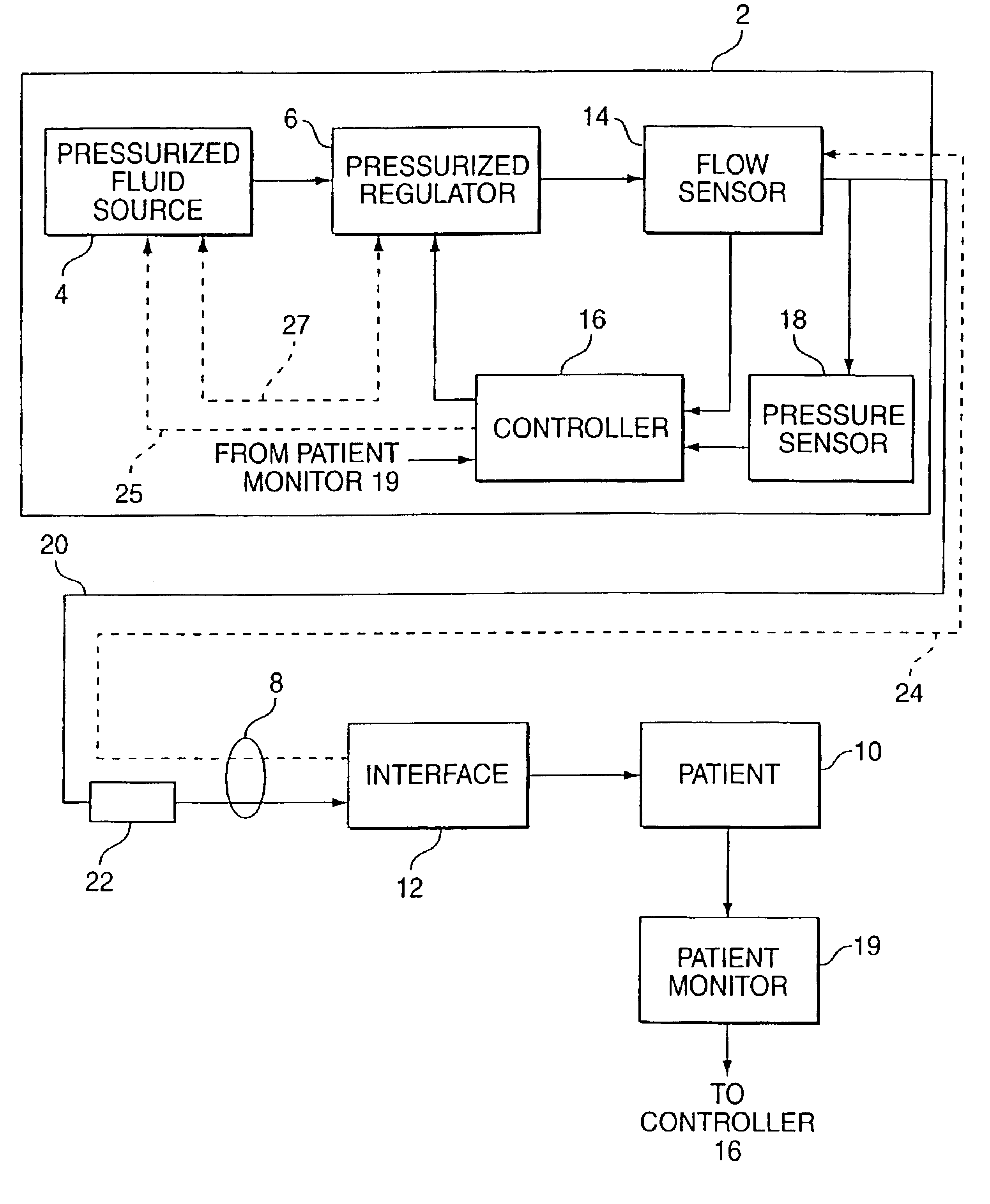
The present disclosure relates, in some embodiments, to devices, systems, and / or methods for collecting, processing, and / or displaying stroke volume and / or cardiac output data. For example, a device for assessing changes in cardiac output and / or stroke volume of a subject receiving airway support may comprise a processor; an airway sensor in communication with the processor, wherein the airway sensor is configured and arranged to sense pressure in the subject's airway, lungs, and / or intrapleural space over time; a blood volume sensor in communication with the processor, wherein the blood volume sensor is configured and arranged to sense pulsatile volume of blood in a tissue of the subject over time; and a display configured and arranged to display a representative of an airway pressure, a pulsatile blood volume, a photoplethysmogram, a photoplethysmogram ratio, the determined cardiac output and / or stroke volume, or combinations thereof. A method of assessing changes in cardiac output or stroke volume of a subject receiving airway support from a breathing assistance system may comprise sensing pressure in the subject's airway as a function of time, sensing pulsatile volume of blood in a tissue of the subject as a function of time, producing a photoplethysmogram from the sensed pulsatile volume, determining the ratio of the amplitude of the photoplethysmogram during inhalation to the amplitude of the photoplethysmogram during exhalation, and determining the change in cardiac output or stroke volume of the subject using the determined ratio.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Average volume ventilation
InactiveUS6920875B1Overcomes shortcomingRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPositive airway pressureMedicine
A ventilator supplies a plurality of volumes of fluid to a patient during a like plurality of inhalations by the patient. Each volume of fluid is supplied at an inspiratory positive airway pressure during a corresponding inhalation by the patient. A volume of fluid received by the patient is determined for each of the plurality of inhalations by the patient and an average volume of fluid received by the patient during each of the plurality of inhalations is determined. The average volume of fluid received by the patient during each inhalation is compared to a predetermined target volume and the inspiratory positive airway pressure each volume of fluid is supplied to the patient is adjusted as a function of the comparison.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Method and system of Individually controlling airway pressure of a patient's nares
InactiveUS20050011523A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksPositive airway pressurePhysical therapy
A method and system of individually controlling positive airway pressure of a patient's nares. Some exemplary embodiments may be a method comprising applying therapeutic gas pressure within a first naris of a patient during respiration, and applying therapeutic gas pressure within a second naris of the patient during the respiration. The therapeutic gas pressures applied to each naris are different.
Owner:ACOBA LLC
Nasal gas delivery system and method for use thereof
A gas administering method for administering gas to an airway of a patient having a nasal vestibule and for use with a gas administering apparatus comprises a primary gas source that is operable to provide gas and a nasal vestibular portion arranged so as to receive the gas from the primary gas source. Further, the nasal vestibular portion is capable of releasing the primary gas into the nasal vestibule. The method comprises inserting the nasal vestibular portion into the nasal vestibule, forming a seal between the nasal vestibular portion and an inner surface of the nasal vestibule, administering an amount of a gas from the primary gas source at a constant flow rate into the nasal vestibule via the nasal vestibular portion, and administering an anesthetic to the patient. The anesthetic induces depression of a portion of the nervous system of the patient. Furthermore, the seal promotes airway pressure buildup that is sufficient to prevent obstruction of the airway during depression of at least a portion of the nervous system and prevents escape of the gas from between the nasal vestibule and the nasal vestibular portion.
Owner:NOBLE LINDA
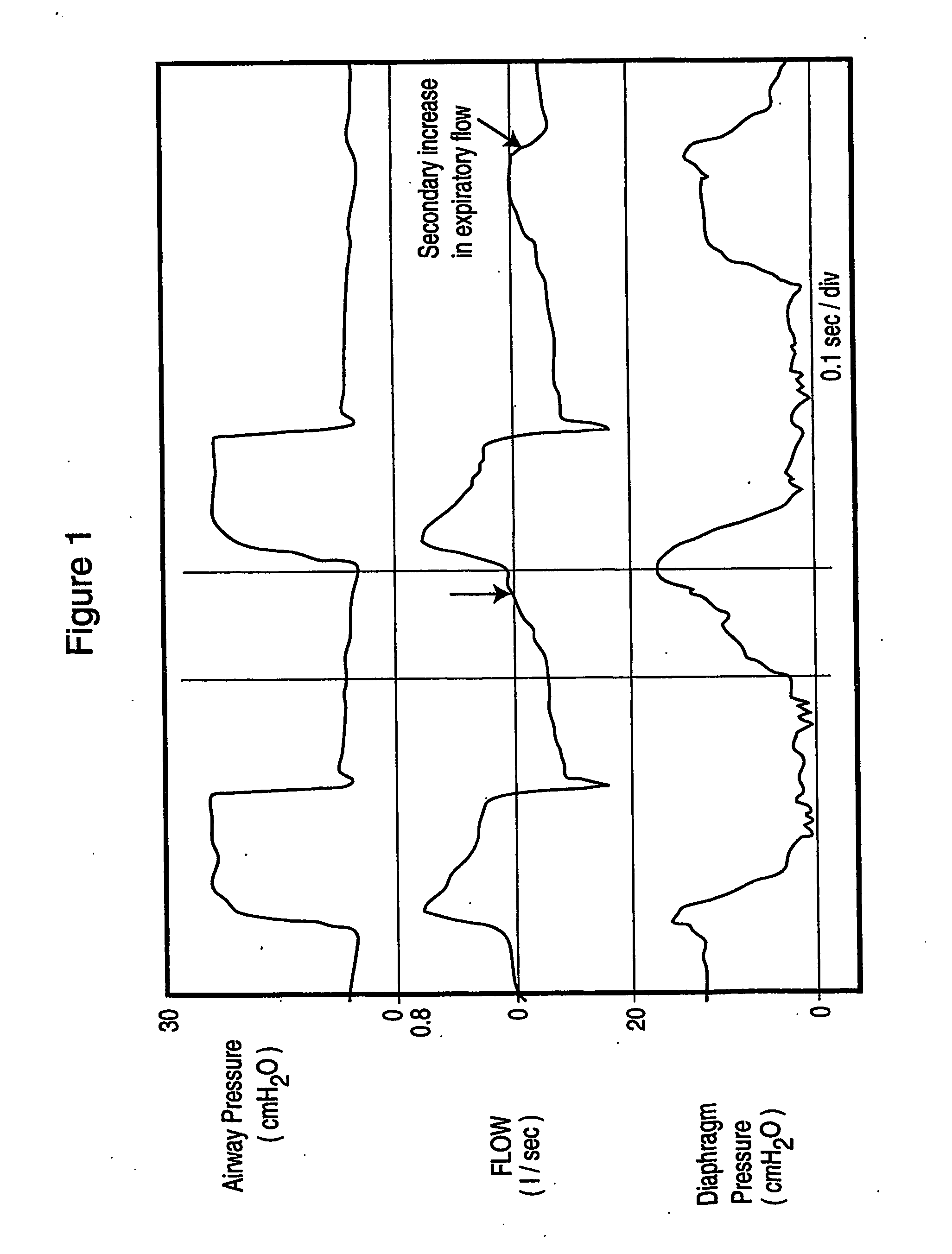
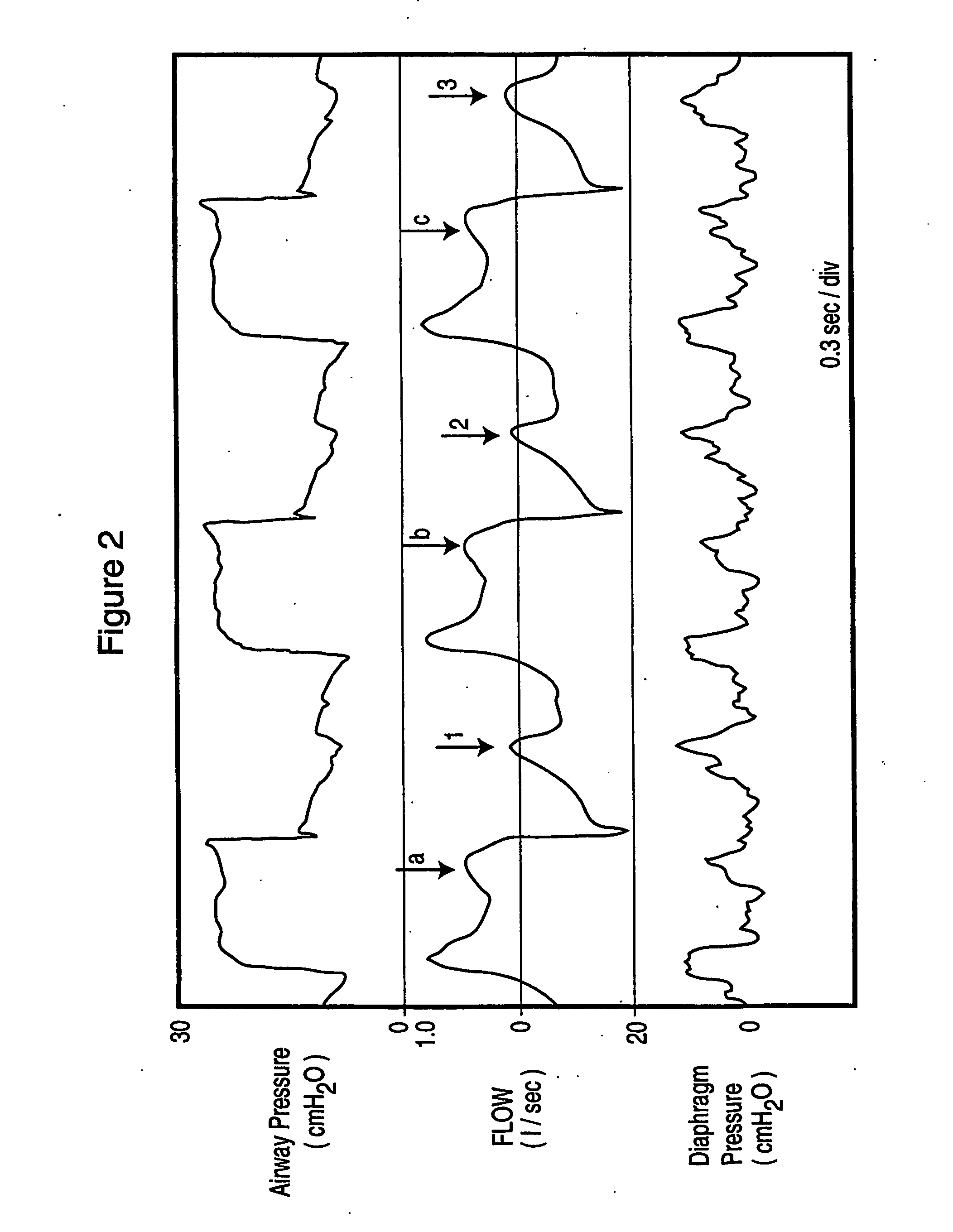
Method and device for monitoring and improving patient-ventilator interaction
InactiveUS20040050387A1Increase uncertaintySharp changeRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringAirway pressures
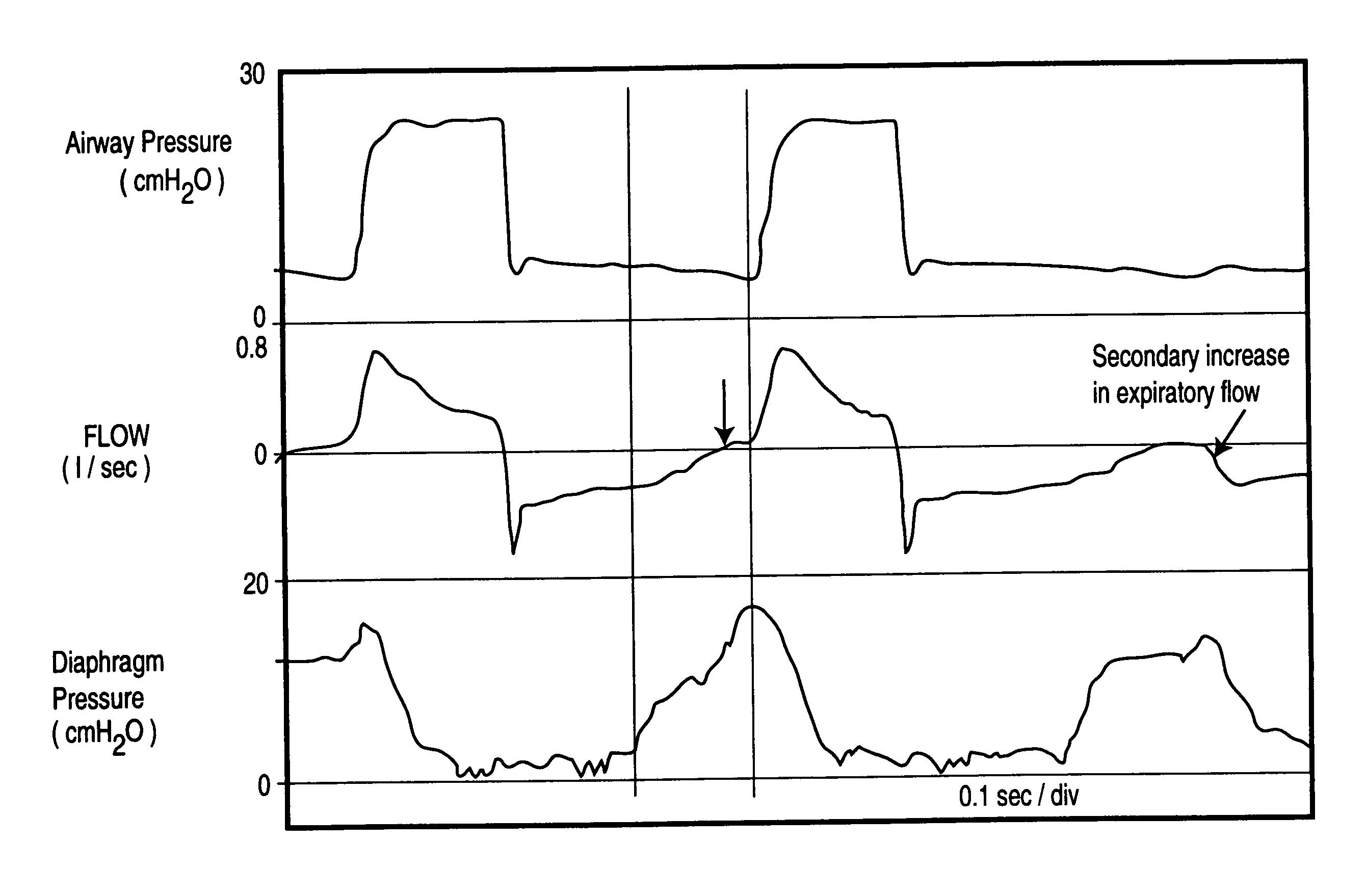
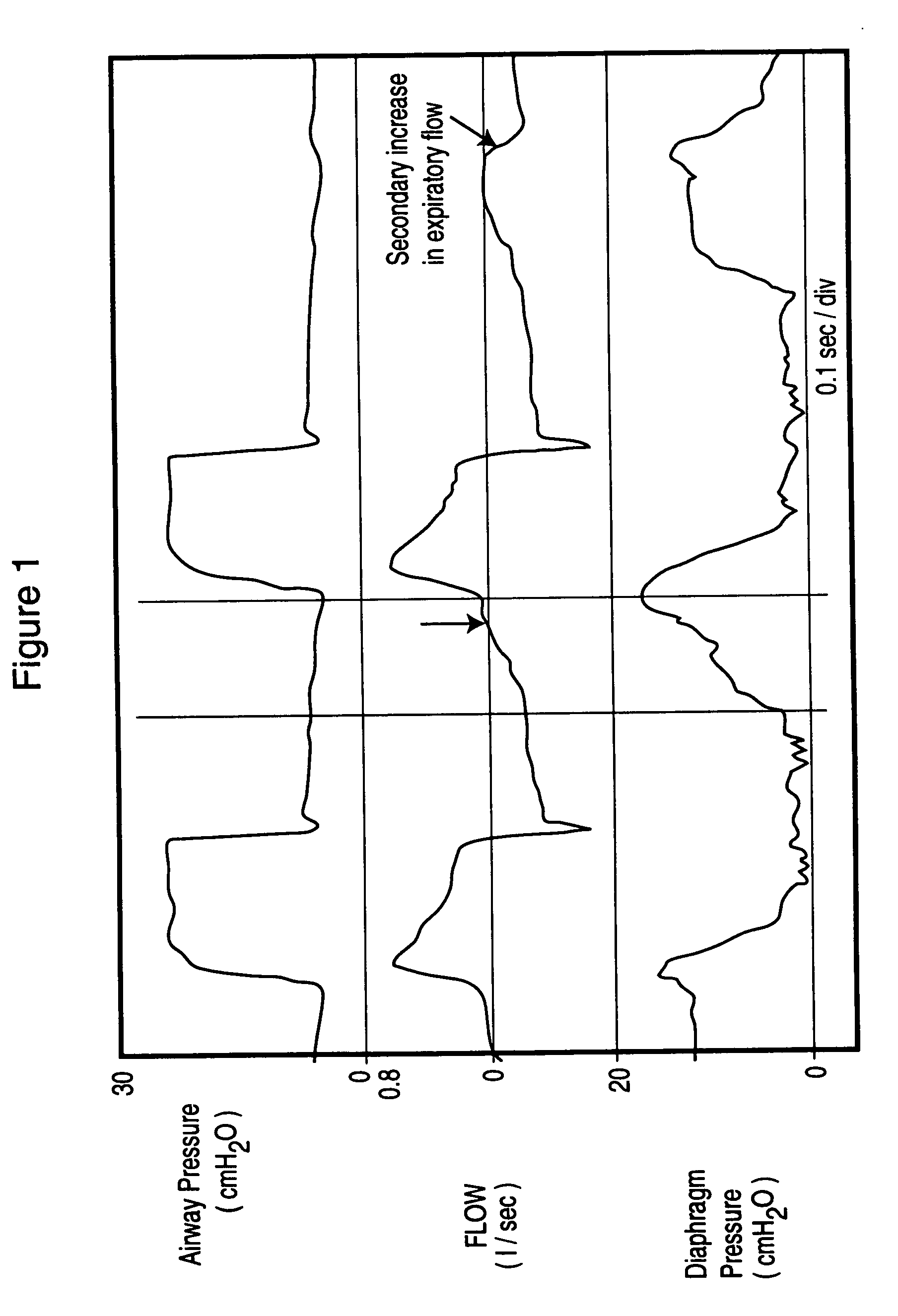
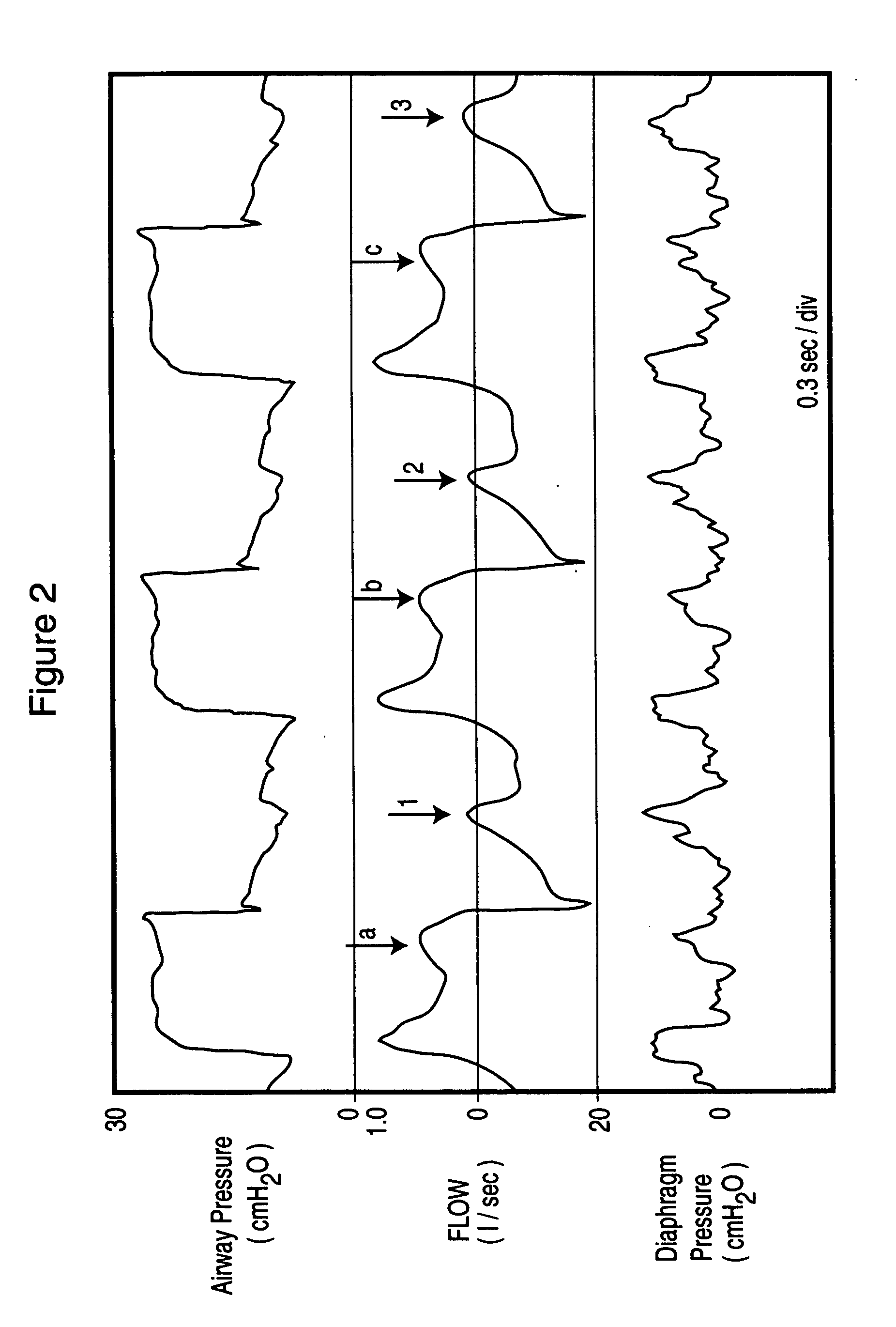
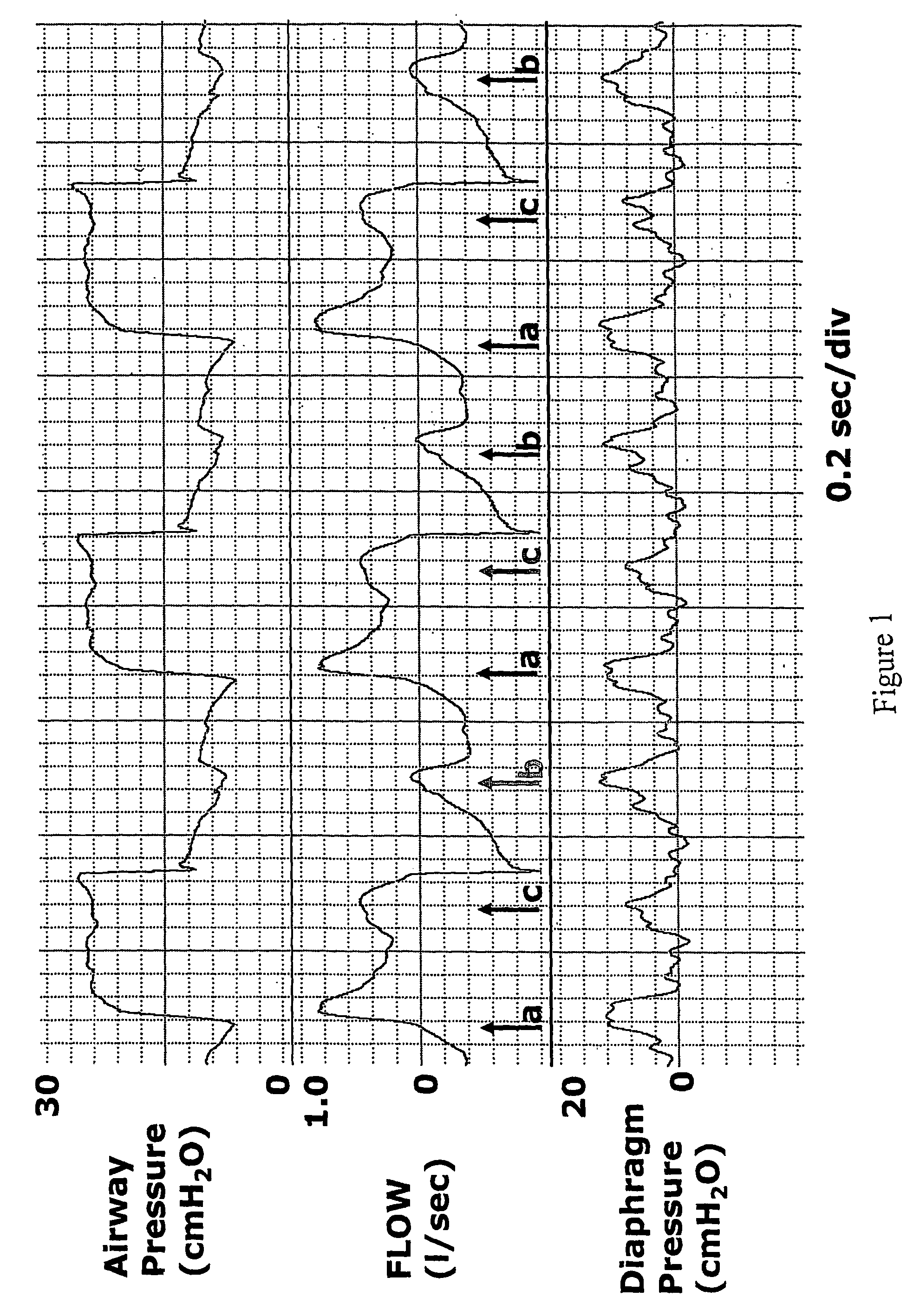
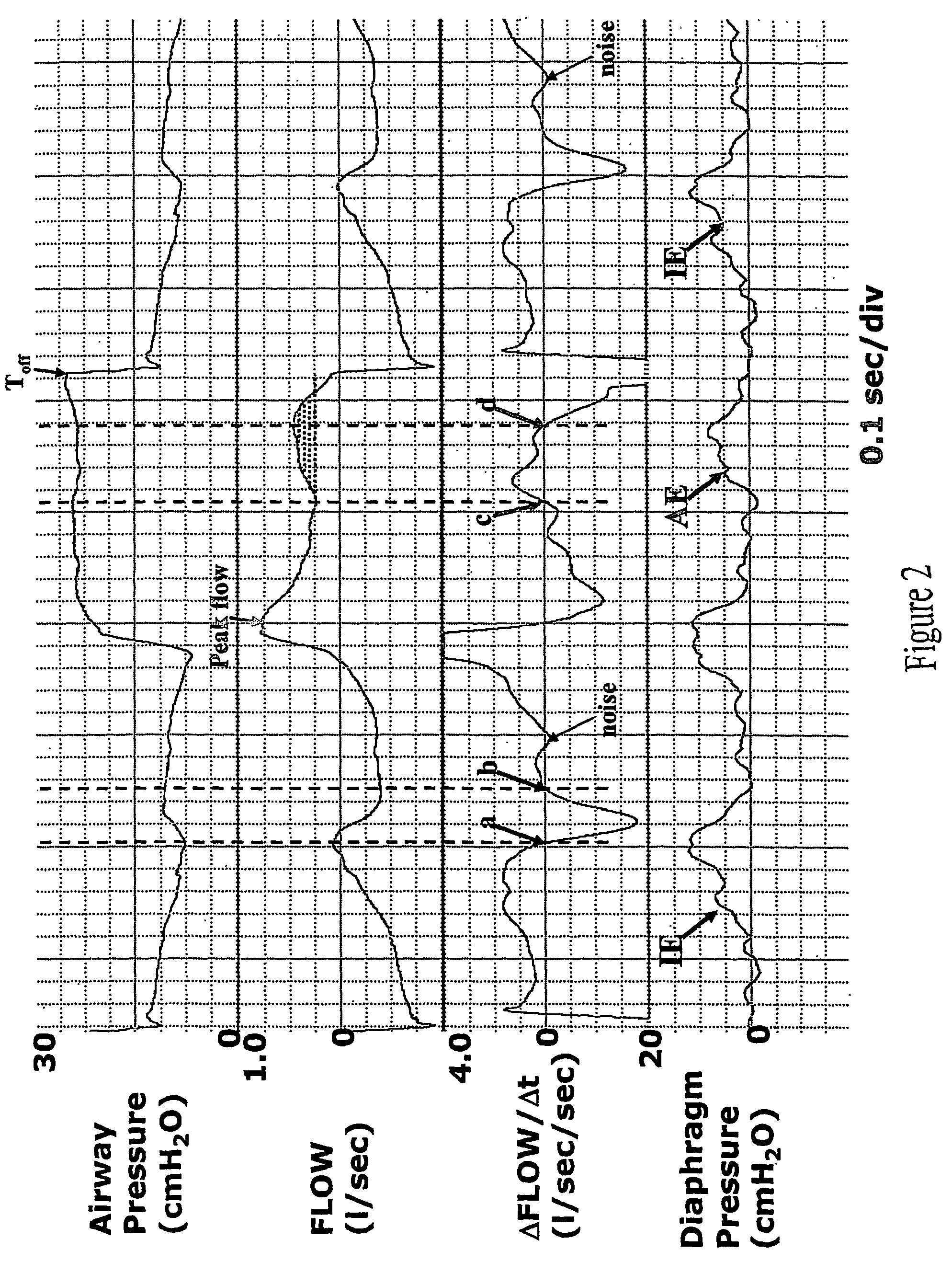
Method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the time onset (Tonset) and end (Tend) of patient inspiratory efforts. A composite pressure signal is generated comprising the sum of an airway pressure signal, a gas flow pressure signal obtained by applying a gain factor (Kf) to a signal representing gas flow rate and a gas volume pressure signal obtained by applying a gain factor (Kv) to a signal representing volume of gas flow. Kf and Kv values are adjusted to result in a desired linear trajectory of composite pressure signal baseline in the latter part of the exhalation phase. The current composite pressure signal is compared with (i) selected earlier composite pressure signal values and / or (ii) value expected at current time based on extrapolation of composite pressure signal trajectory at specified earlier times and / or (iii) the current rate of change in the composite pressure signal with a selected earlier rates of change. The differences obtained by the comparison are compared with selected threshold values. Tonset is identified when at least one of the differences exceeds the threshold values.
Owner:YRT
Breathing assistance apparatus
InactiveUS7063086B2Eliminate disadvantagesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksInhalationEmergency medicine
A valve for use in a CPAP system or any stem at a pressure above ambient which vents the pressurised gases from the blower during expiration. Due to the pressure-flow characteristics of the blower this results in the patient having a much lower airway pressure during expiration making breathing easier. The valve includes a movable member which blocks flow from the blower to the patient during exhalation and vents externally. During inhalation gases flow normally from the blower to the patient. Also disclosed is a further application as an antiasphyxia.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
Sleep apnea treatment apparatus
InactiveUS7013892B2Reduce pressureEasy to operateRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesSleep researchClinical study
Improved methodology and apparatus for the clinical study and treatment of sleep apnea which incorporates one or more of the following features: (1) application of mono-level, alternating high and low level, or variable positive airway pressure generally within the airway of the patient with the mono-level, high and low level, or variable airway pressure generally being coordinated with and / or responsive to the spontaneous respiration of the patient, (2) usage of adjustably programmable pressure ramp circuitry capable of producing multiple pressure ramp cycles of predetermined duration and pattern whereby the ramp cycles may be customized to accommodate the specific needs of an individual sleep apnea patient so as to ease the patient's transition from wakefulness to sleep, (3) remote control or patient-sensed operation of the apparatus, (4) employment of safety circuitry, reset circuitry and minimum system leak assurance circuitry, controls and methods, and (5) utilization of clinical control circuitry whereby sleep disorder data may be compiled and appropriate therapy implemented during a one-night sleep study.
Owner:RIC INVESTMENTS LLC
Ventilation method and control of a ventilator based on same
InactiveUS7246618B2Prevents de-recruitmentLower Level RequirementsRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAirway pressuresIntensive care medicine
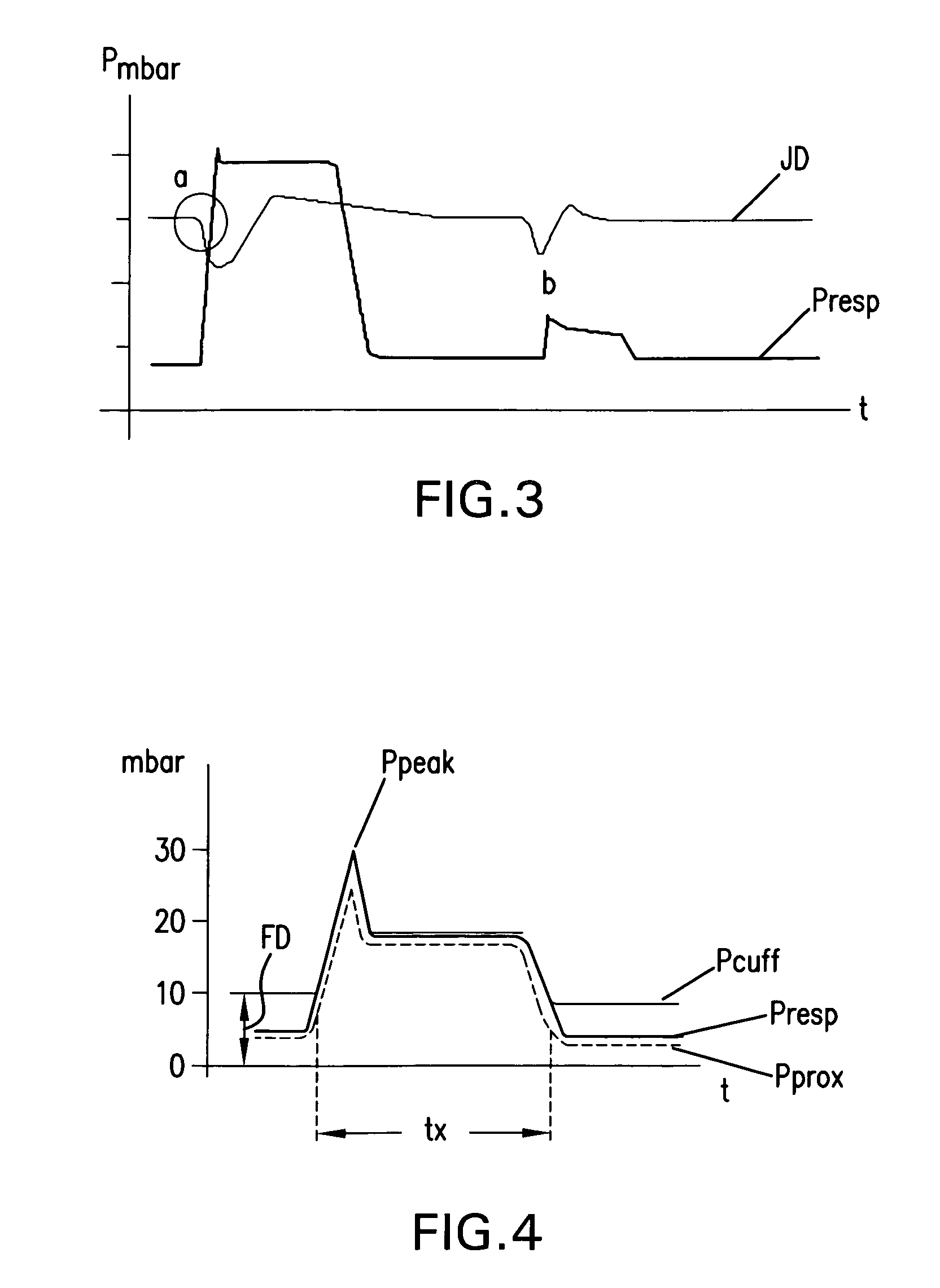
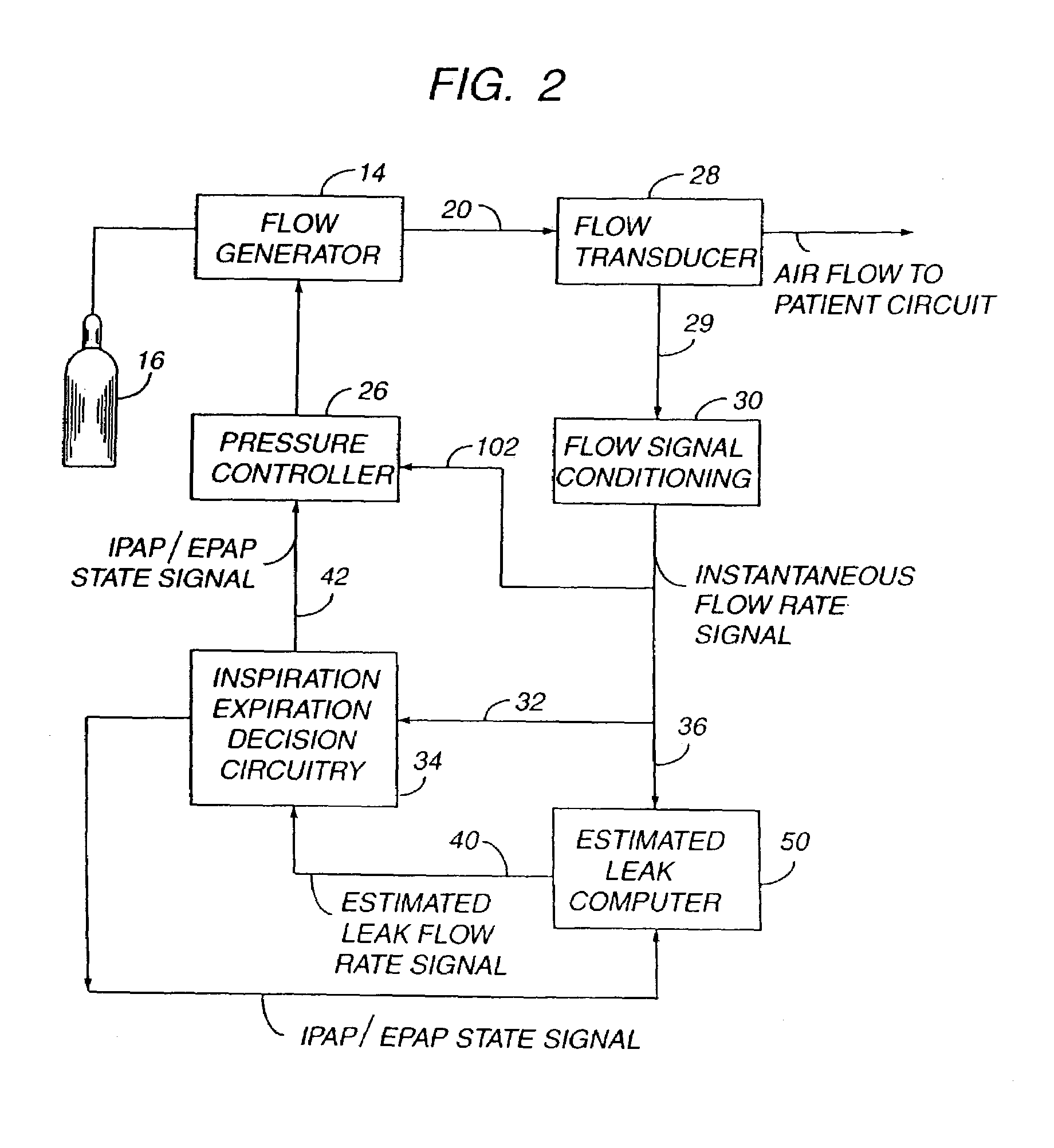
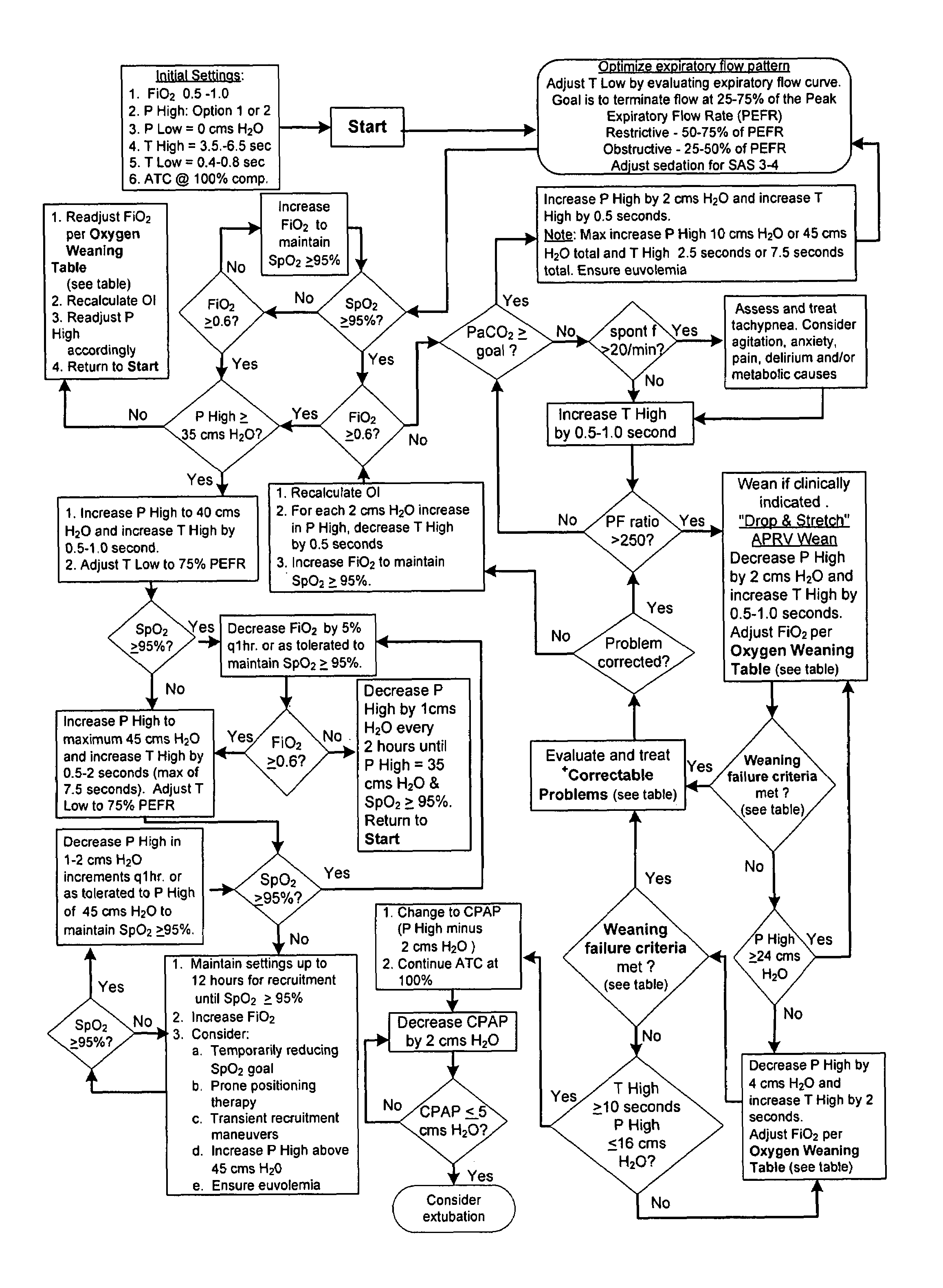
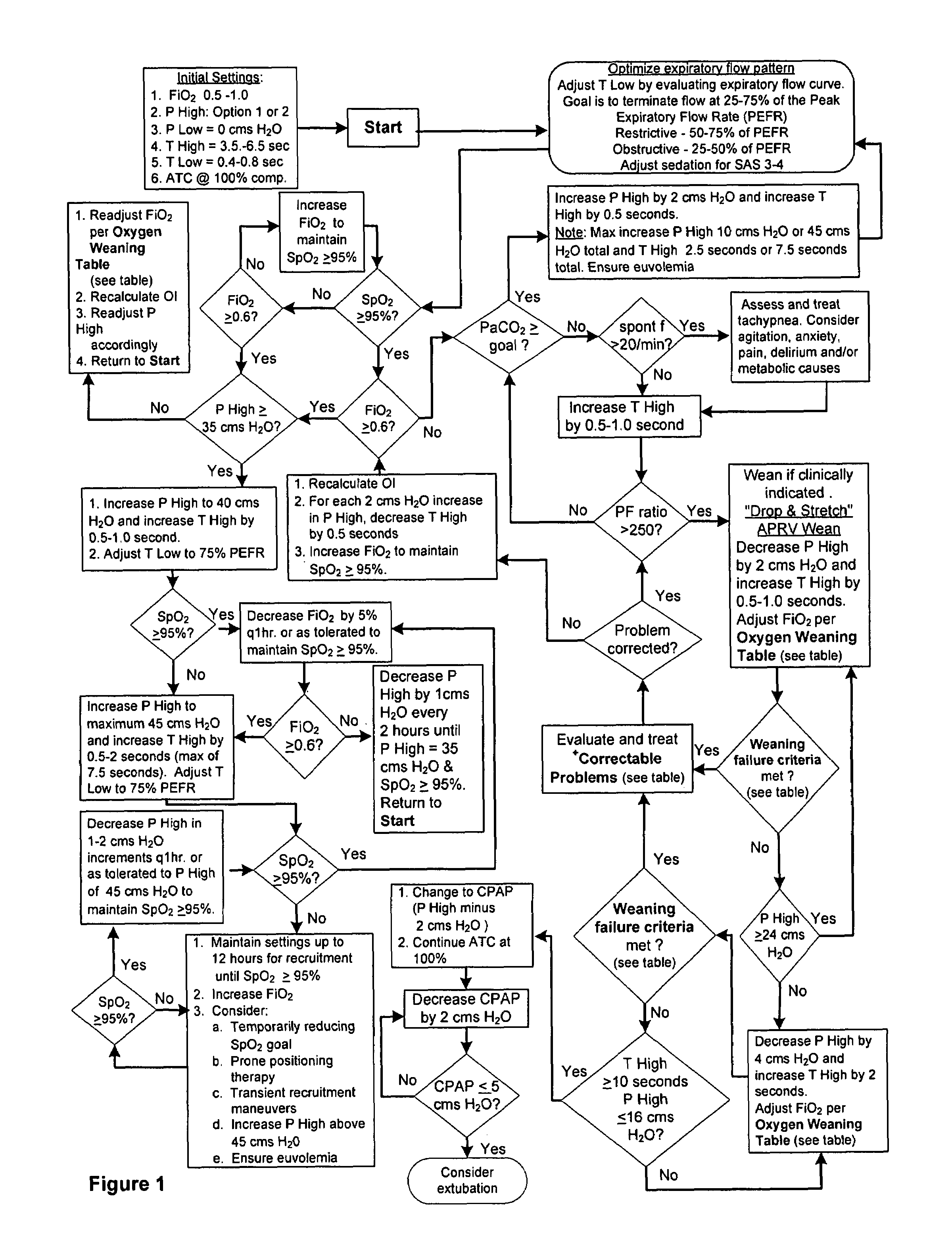
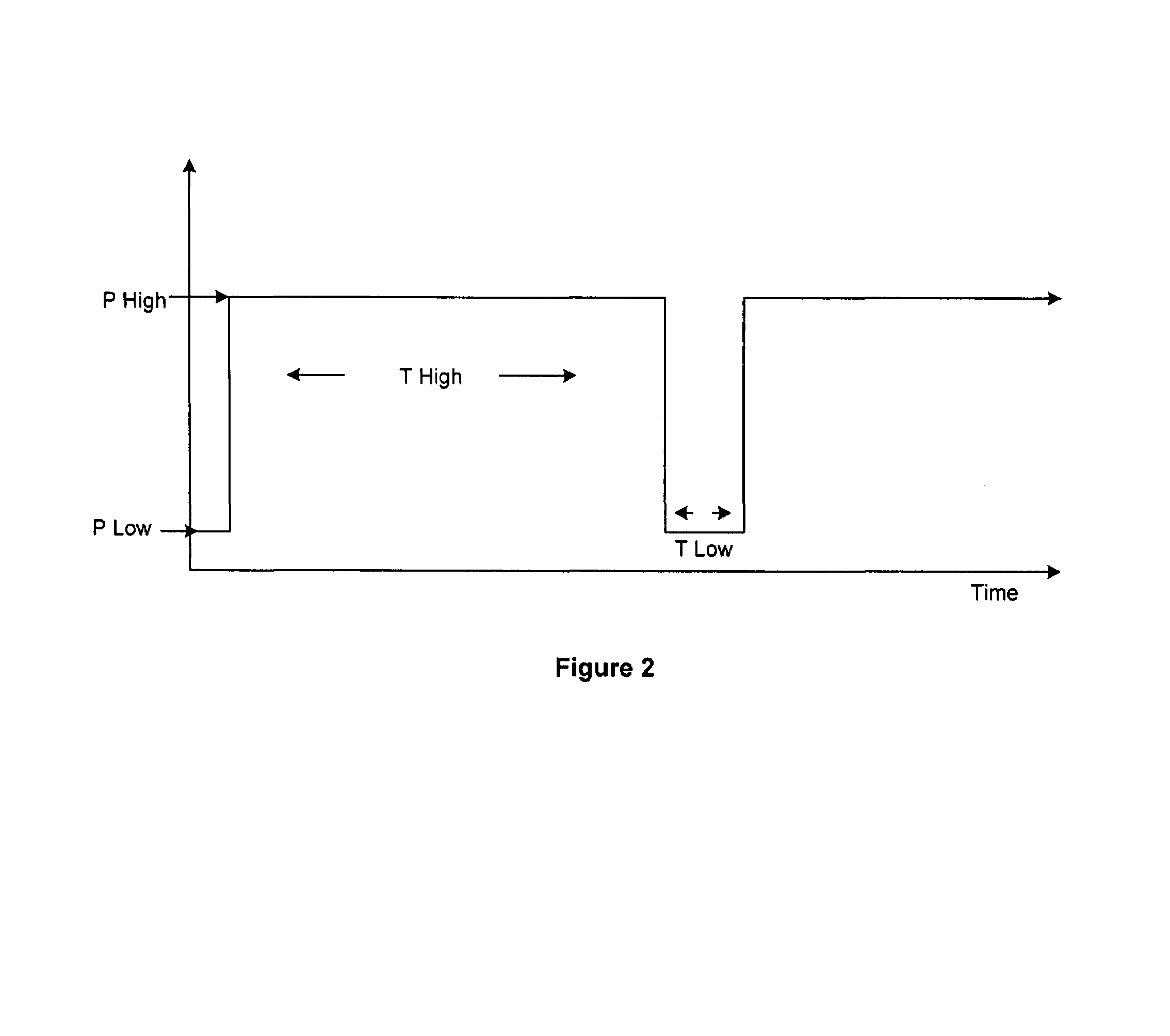
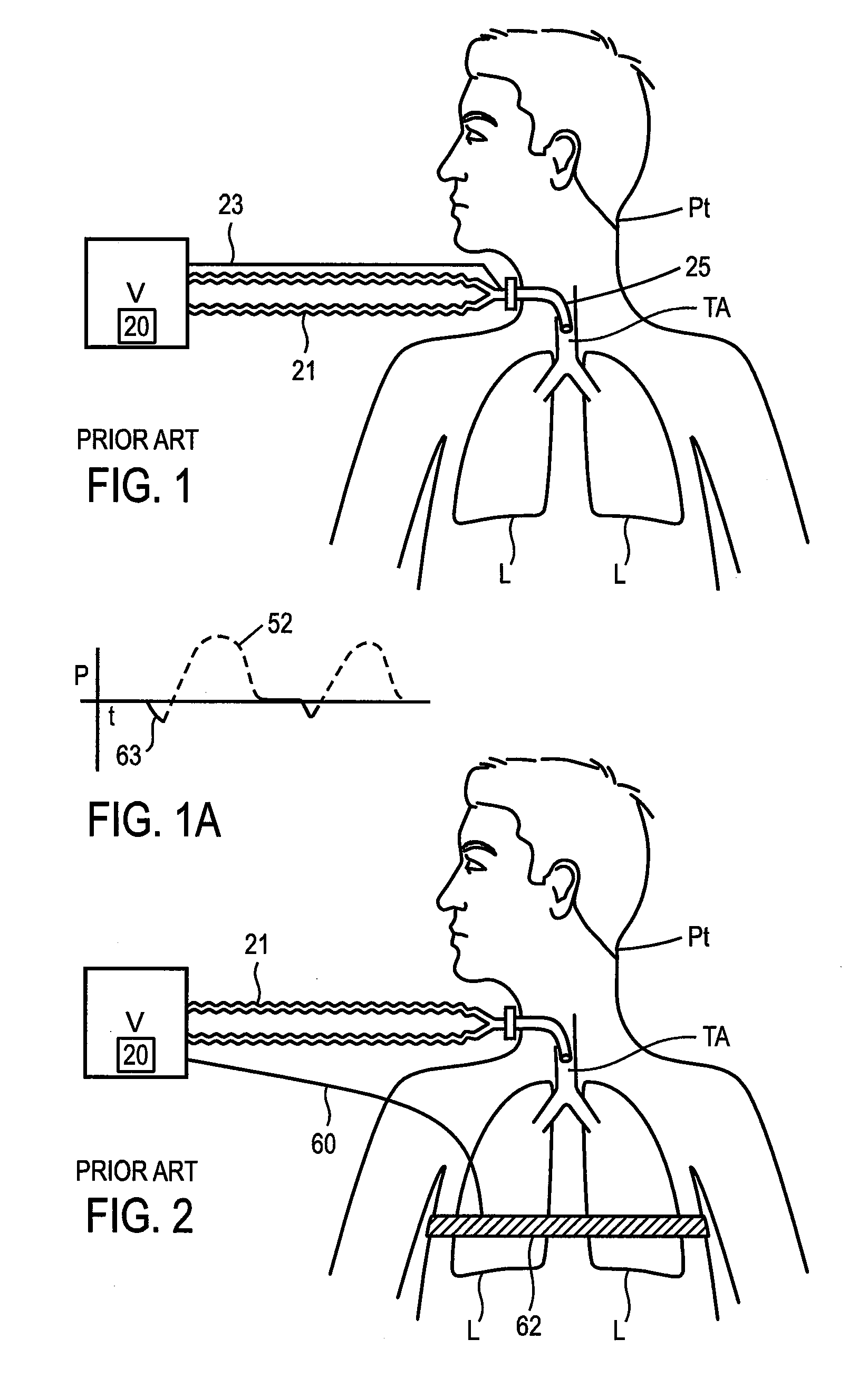
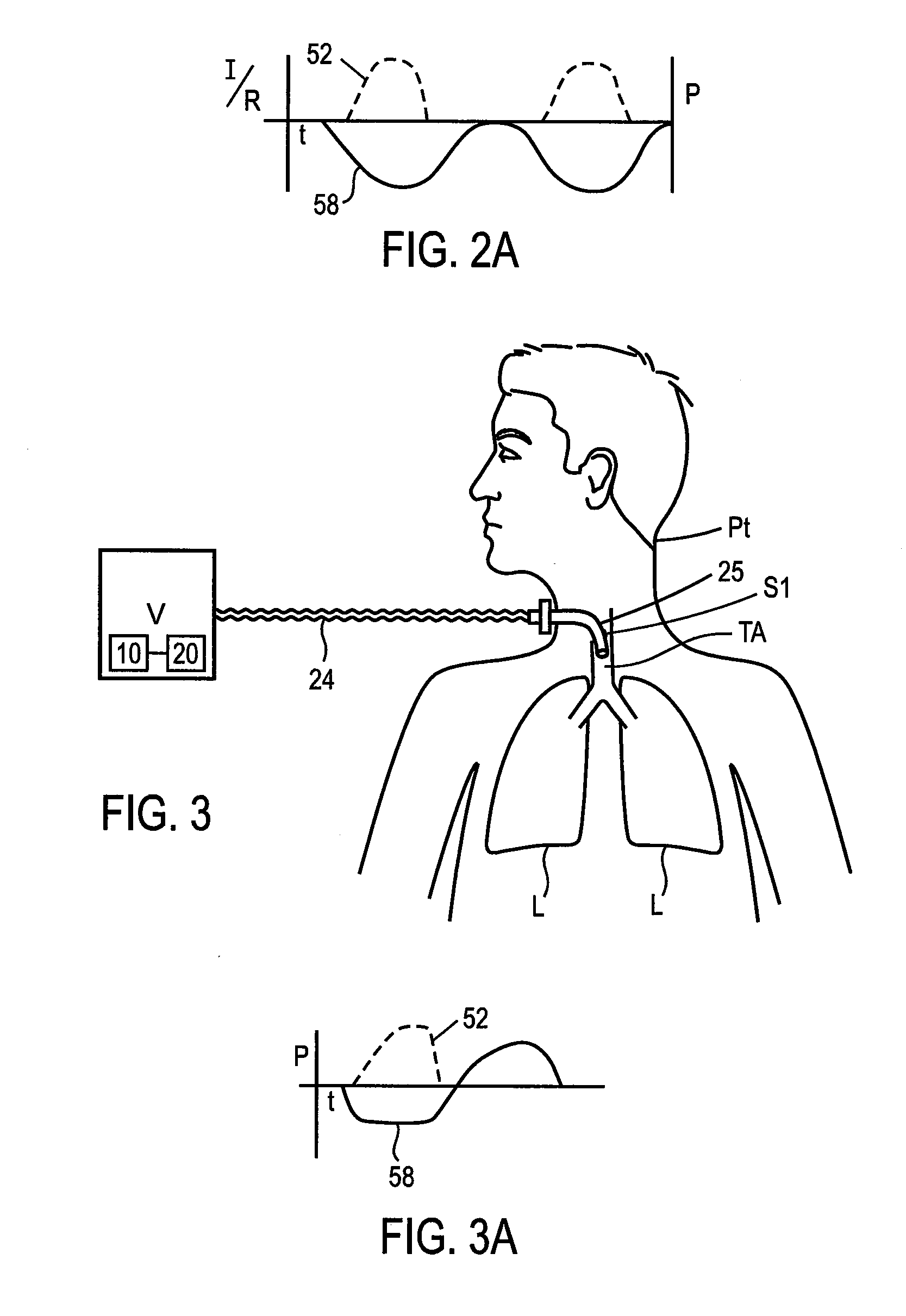
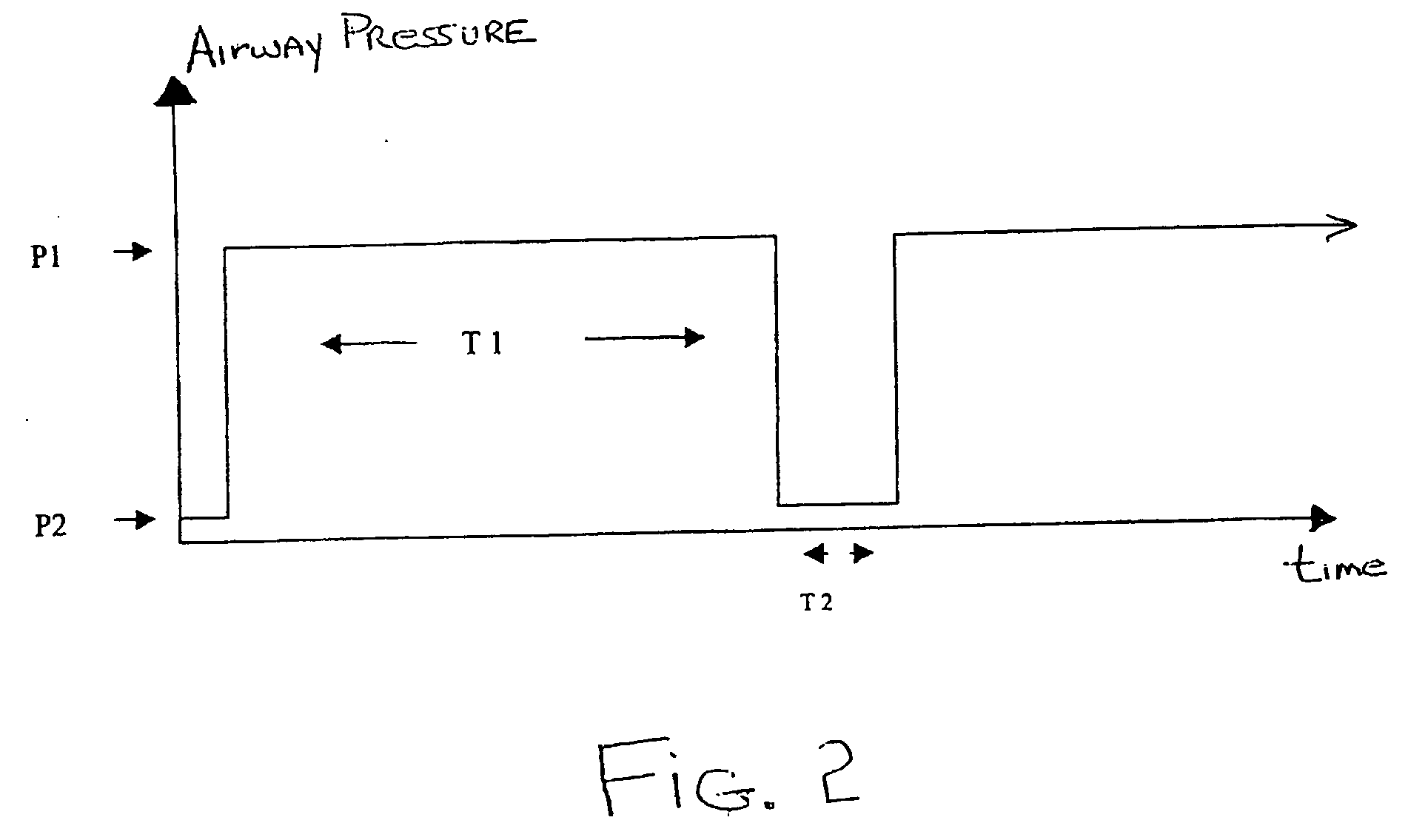
The invention provides an improved ventilation method and method for controlling a ventilator apparatus in accordance with same. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method of controlling a ventilator apparatus comprising the steps of placing a ventilator in a mode capable of adjusting airway pressure (P) and time (T), monitoring expiratory gas flow, analyzing the expiratory gas flow over time (T) to establish an expiratory gas flow pattern, and setting and / or adjusting a low time (T2) based on the expiratory gas flow pattern. Alternatively, the present invention relates to a method of controlling a ventilator apparatus comprising the steps of placing a ventilator in a mode capable of adjusting airway pressure (P) and time (T), and setting a low airway pressure (P2) of substantially zero cmH2O.
Owner:HABASHI NADER M
Method and system of individually controlling airway pressure of a patient's nares
InactiveUS7114497B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksPositive airway pressureAirway pressures
A method and system of individually controlling positive airway pressure of a patient's nares. Some exemplary embodiments may be a method comprising applying therapeutic gas pressure within a first naris of a patient during respiration, and applying therapeutic gas pressure within a second naris of the patient during the respiration. The therapeutic gas pressures applied to each naris are different.
Owner:ACOBA LLC
Nasal gas delivery system and method for use thereof
InactiveUS20060174889A1Convenient and continuous operation of C-PAPReduce riskRespiratorsBreathing filtersNasal vestibuleNervous system
A gas administering method for administering gas to an airway of a patient having a nasal vestibule and for use with a gas administering apparatus comprises a primary gas source that is operable to provide gas and a nasal vestibular portion arranged so as to receive the gas from the primary gas source. Further, the nasal vestibular portion is capable of releasing the primary gas into the nasal vestibule. The method comprises inserting the nasal vestibular portion into the nasal vestibule, forming a seal between the nasal vestibular portion and an inner surface of the nasal vestibule, administering an amount of a gas from the primary gas source at a constant flow rate into the nasal vestibule via the nasal vestibular portion, and administering an anesthetic to the patient. The anesthetic induces depression of a portion of the nervous system of the patient. Furthermore, the seal promotes airway pressure buildup that is sufficient to prevent obstruction of the airway during depression of at least a portion of the nervous system and prevents escape of the gas from between the nasal vestibule and the nasal vestibular portion.
Owner:NOBLE LINDA
Methods, systems and devices for non-invasive ventilation including a non-sealing ventilation interface with an entrainment port and/or pressure feature
ActiveUS20110214676A1Avoid airway obstructionRespiratorsMedical devicesGas delivery sourceAirway pressures
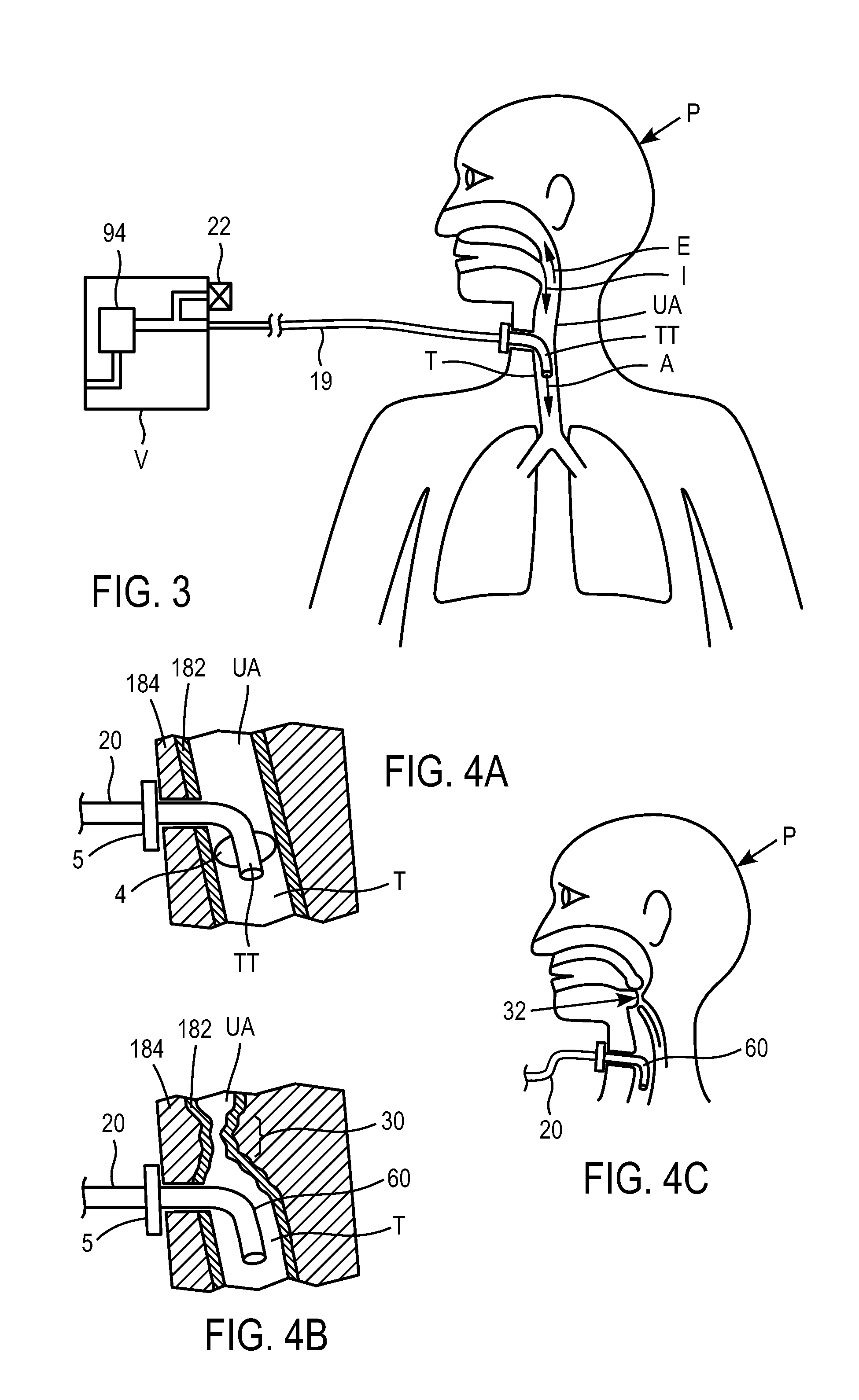
Systems and methods may include a gas source, a gas delivery circuit, and a nasal interface allowing breathing ambient air through the nasal interface. A gas flow path through the nasal interface may have a distal gas flow path opening. A nozzle may be associated with a proximal end of the nasal interface a distance from the distal end gas flow path opening. At least a portion of an entrainment port may be between the nozzle and the distal end gas flow opening. The nozzle may deliver gas into the nasal interface to create a negative pressure area in the gas flow path at the entrainment port. The nasal interface and the nozzle may create a positive pressure area between the entrainment port and the distal end gas flow path opening. Gas from the gas delivery source and air entrained through the entrainment port may increase airway pressure or lung pressure or provide ventilatory support.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Method and apparatus useful in the diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea of a patient
InactiveUS20020124848A1Improve sound qualityQuality improvementOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrocardiographyAirway pressuresBiomedical engineering
Owner:RESMED LTD
Method and device for monitoring and improving patient-ventilator interaction
InactiveUS20060249148A1Error minimizationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAirway pressuresIntensive care medicine
Method and apparatus for non-invasively determining the time onset (Tonset) and end (Tend) of patient inspiratory efforts. A composite pressure signal is generated comprising the sum of an airway pressure signal, a gas flow pressure signal obtained by applying a gain factor (Kf) to a signal representing gas flow rate and a gas volume pressure signal obtained by applying a gain factor (Kv) to a signal representing volume of gas flow. Kf and Kv values are adjusted to result in a desired linear trajectory of composite pressure signal baseline in the latter part of the exhalation phase. The current composite pressure signal is compared with (i) selected earlier composite pressure signal values and / or (ii) value expected at current time based on extrapolation of composite pressure signal trajectory at specified earlier times and / or (iii) the current rate of change in the composite pressure signal with a selected earlier rates of change. The differences obtained by the comparison are compared with selected threshold values. Tonset is identified when at least one of the differences exceeds the threshold values.
Owner:YRT
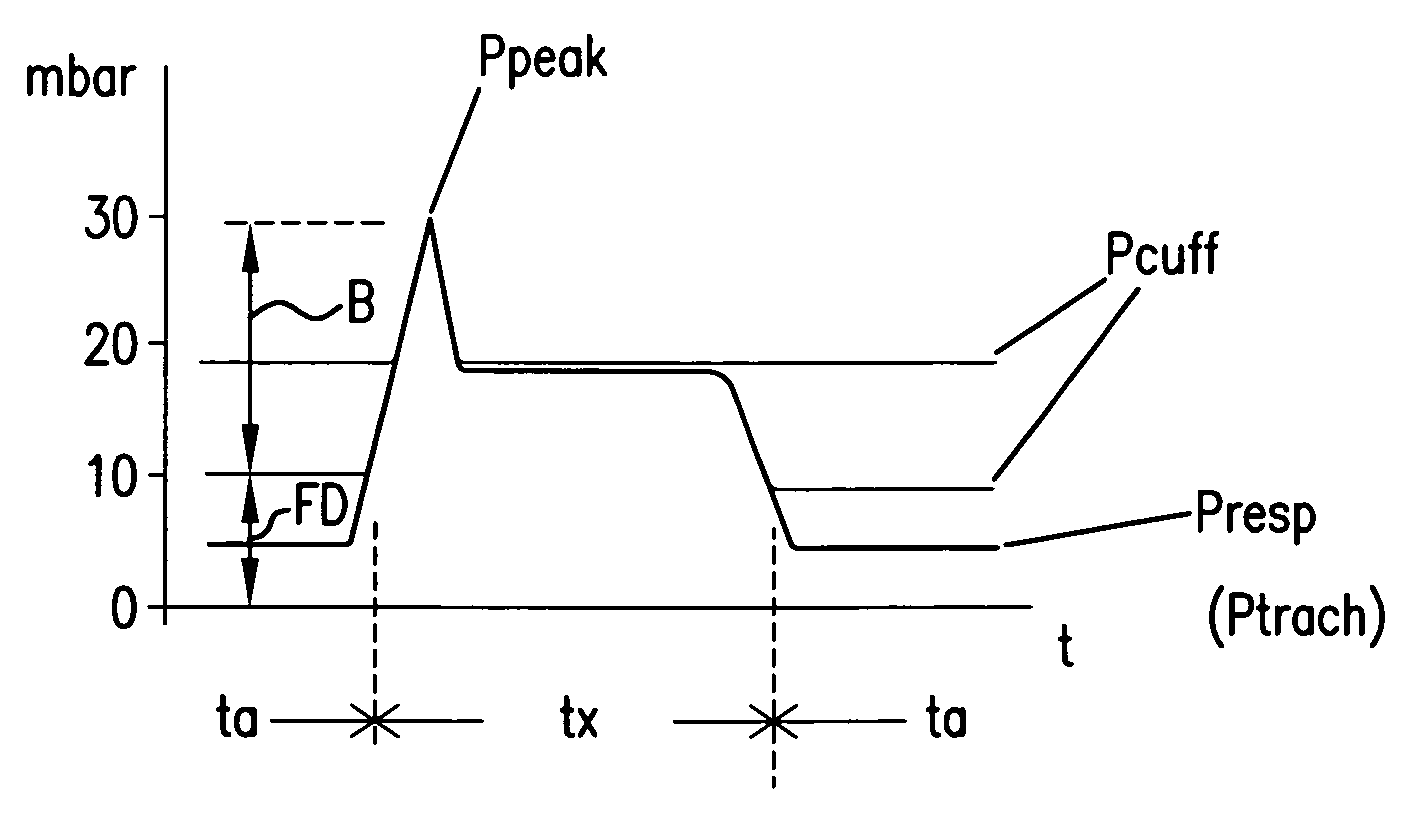
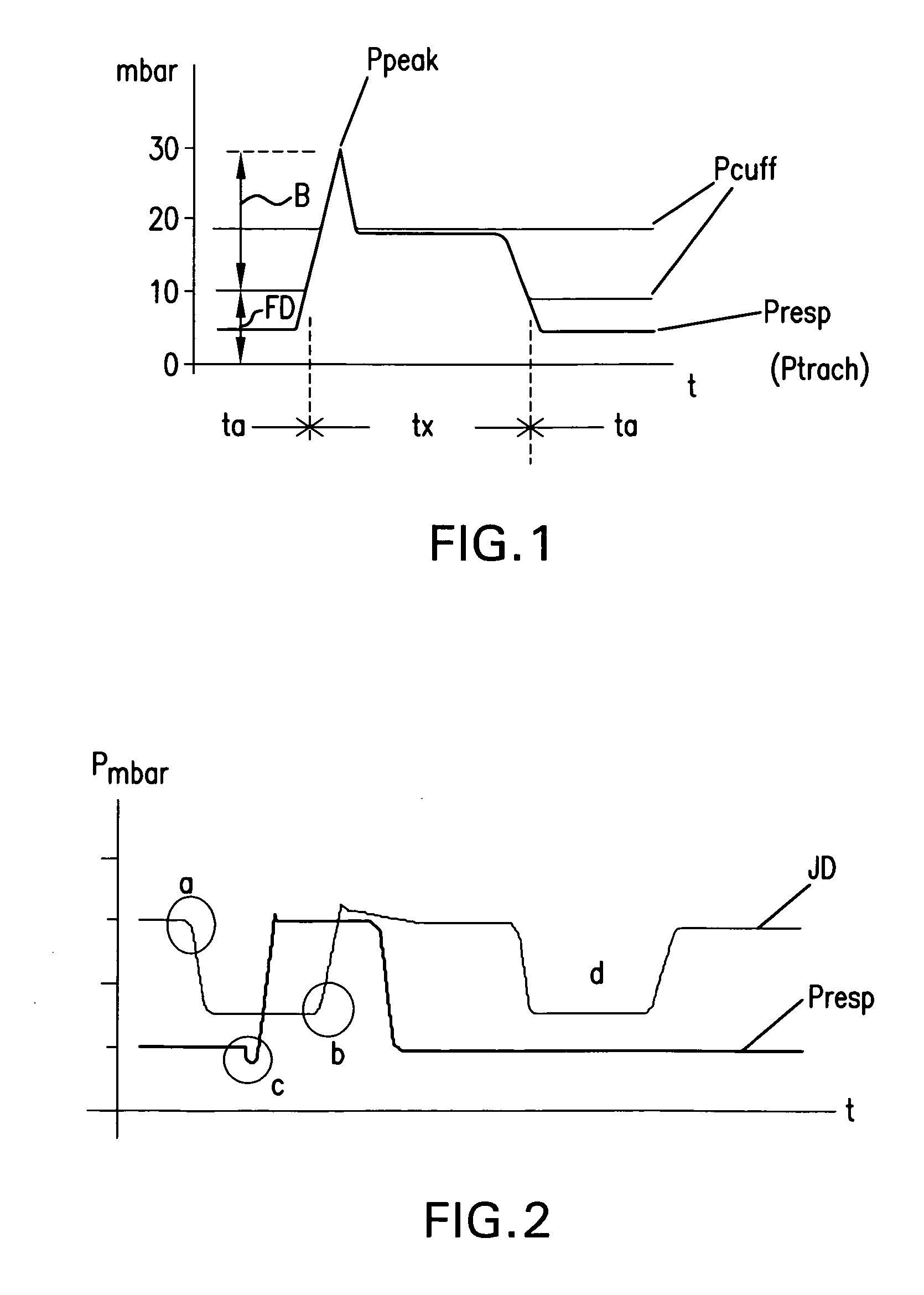
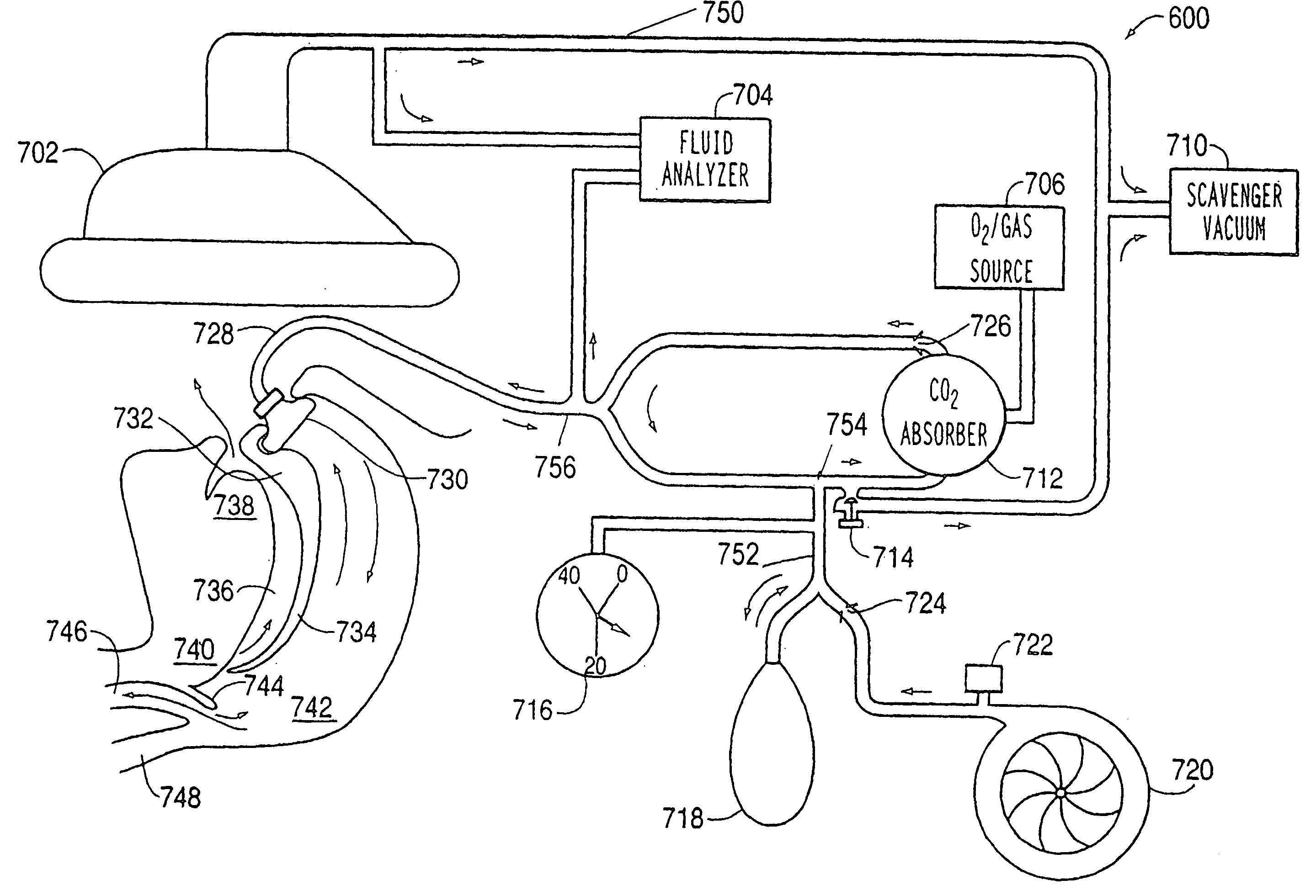
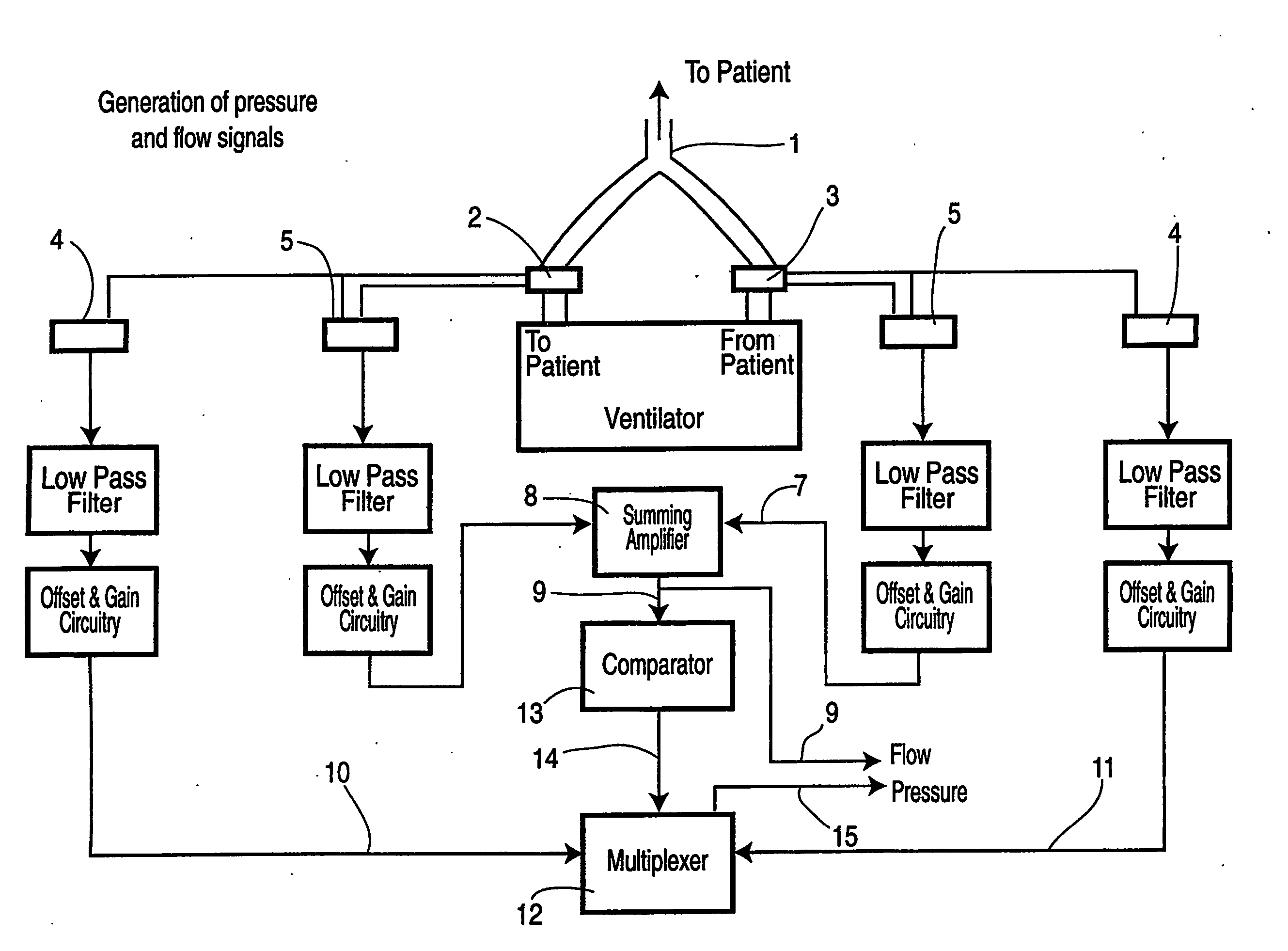
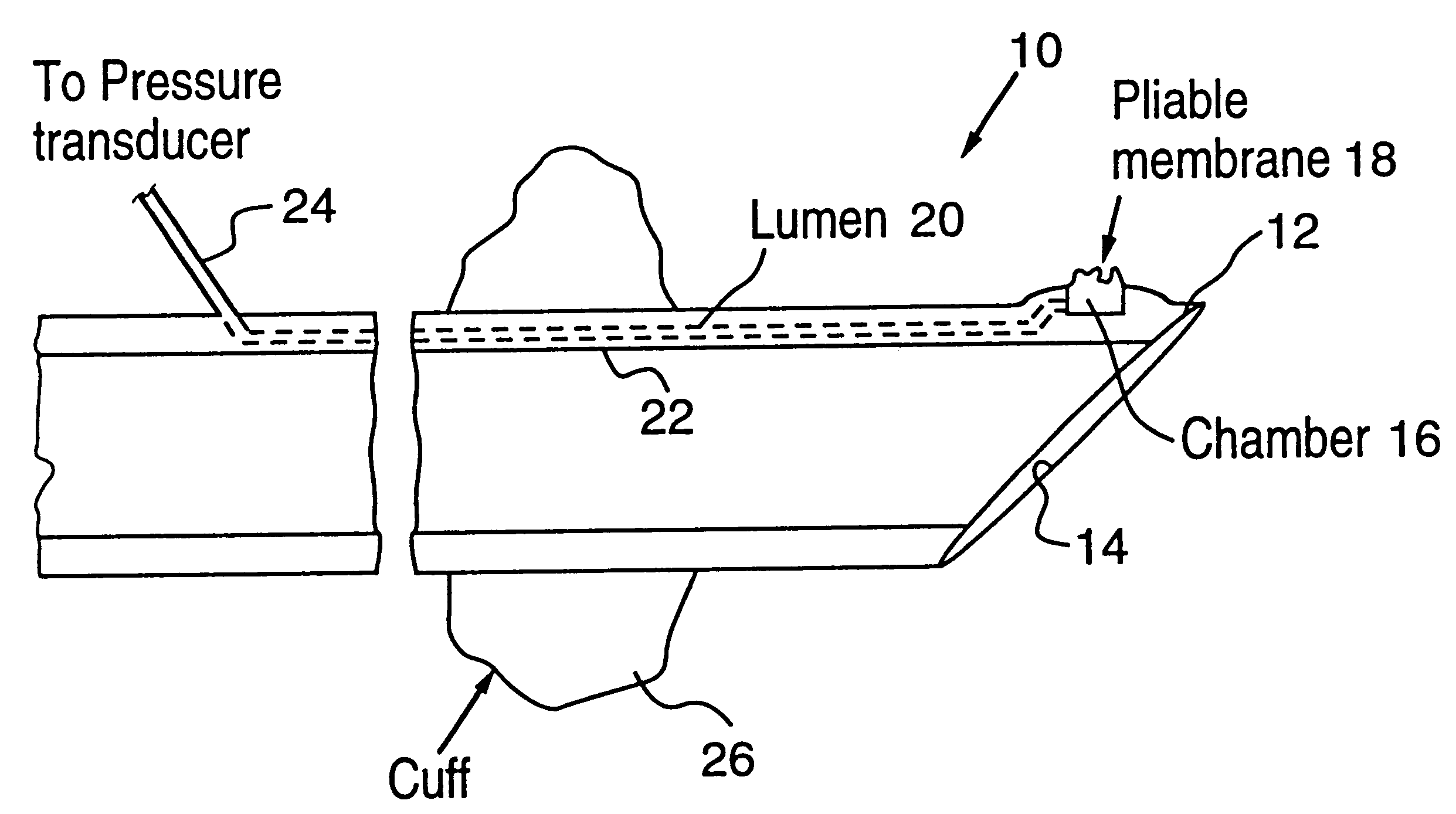
Control of airway pressure during mechanical ventilation
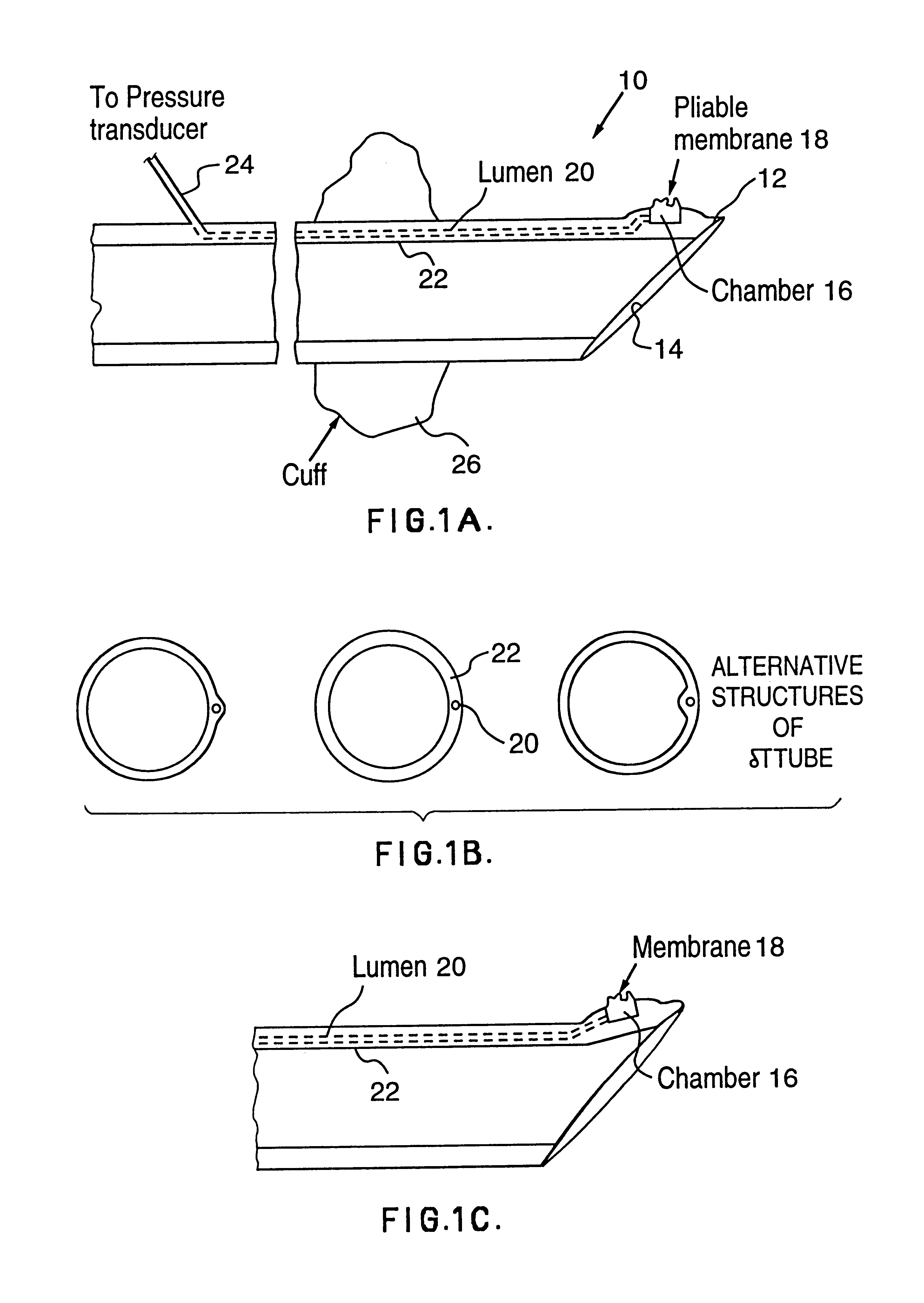
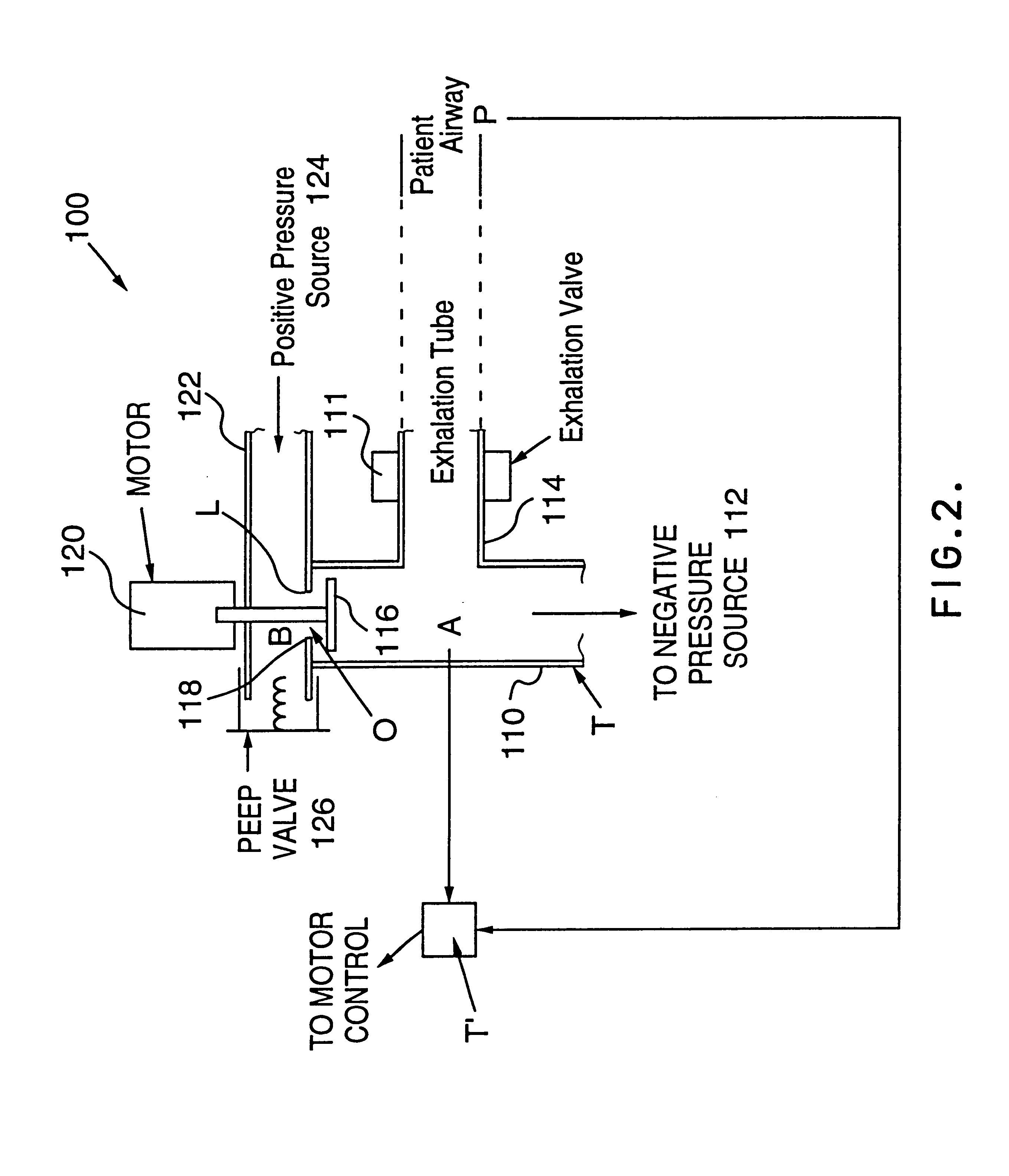
A endotracheal tube for patient ventilation is modified to permit measurement of pressure at the patient trachea by providing a chamber in the end of the ET tube to be located in the patient, airway. This chamber has a highly pliant external wall with a degree of redundancy and is connected to a pressure measuring device exterior of the patient by a lumen in the wall of the ET tube. In addition, apparatus for controlling airway pressure during exhalation comprises valve means connected via a first inlet to an exhalation tube from a patient airway, connected to a source of negative pressure through an outlet and having a second inlet with a variable flow control means for controlling the flow of gas therethrough. Gas pressure is controlled within the valve by varying the pressure gradient between the upstream and downstream sides of the second inlet so that it equals the pressure gradient between the patient airway and the downstream side of the second inlet.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
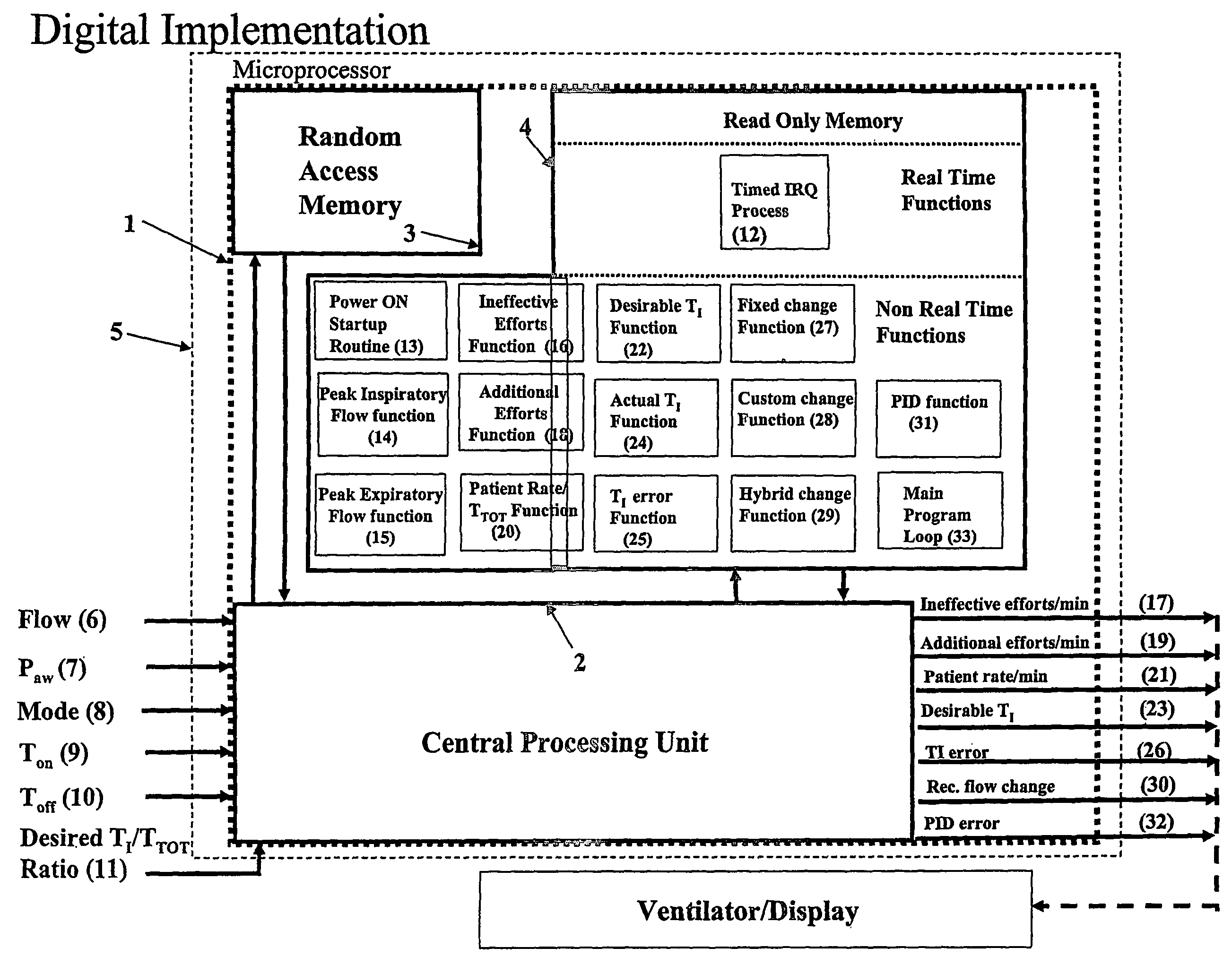
Synchrony between end of ventilator cycles and end of patient efforts during assisted ventilation
InactiveUS7819815B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAssisted ventilationInhalation
Automatic ongoing adjustment of the cycling-off time of ventilator inflation phase during assisted ventilation in accordance with true respiratory rate of a patient. Electrical signals are generated corresponding to the gas flow exchanged between patient and ventilator (flow) and / or to airway pressure (Paw) and the true respiratory rate of the patient (patient RR) is determined on an ongoing basis from the flow and / or Paw. The current average cycle duration of patient respiratory efforts (current patient TTOT) is estimated from patient RR. A current desirable duration of the inhalation phase (desirable TI) is calculated from the product of current patient TTOT a TI / TTOT ratio chosen to be in the physiological range, usually 0.25 to 0.50. The ventilator phase is caused to terminate in accordance with the desirable TI.
Owner:YRT
Nasal gas delivery system and method for use thereof
InactiveUS7047969B2Reduce riskOperating means/releasing devices for valvesBreathing filtersNasal vestibuleNervous system
Owner:NOBLE LINDA
Method and apparatus for predicting work of breathing
ActiveUS7425201B2Non-invasively predicting (estimatingAvoid muscle fatigueRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingMathematical model
A method of creating a non-invasive predictor of both physiologic and imposed patient effort from airway pressure and flow sensors attached to the patient using an adaptive mathematical model. The patient effort is commonly measured via work of breathing, power of breathing, or pressure-time product of esophageal pressure and is important for properly adjusting ventilatory support for spontaneously breathing patients. The method of calculating this non-invasive predictor is based on linear or non-linear calculations using multiple parameters derived from the above-mentioned sensors.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
Out flow resistance switching ventilator and its core methods
InactiveUS20080011301A1Ensure ventilation safetyIncrease spaceRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingFlow resistivity
An out flow resistance switching ventilator and its methodology for providing mechanical ventilation support to the respiratory failure patient are claimed. Based on the continuous out flow impounding ventilation mechanism, the apparatus provides ventilation by switching flow resistance between two different levels at a continuous gas flow system outlet valve controlled by patient's spontaneous breathing or preset mandatory parameters, resulting in airway pressure levels switching, and therefore creating lung volume switching, which is totally different from either volume ventilation or pressure ventilation mechanism utilized in the current conventional ventilators.
Owner:QIAN YUANCHENG
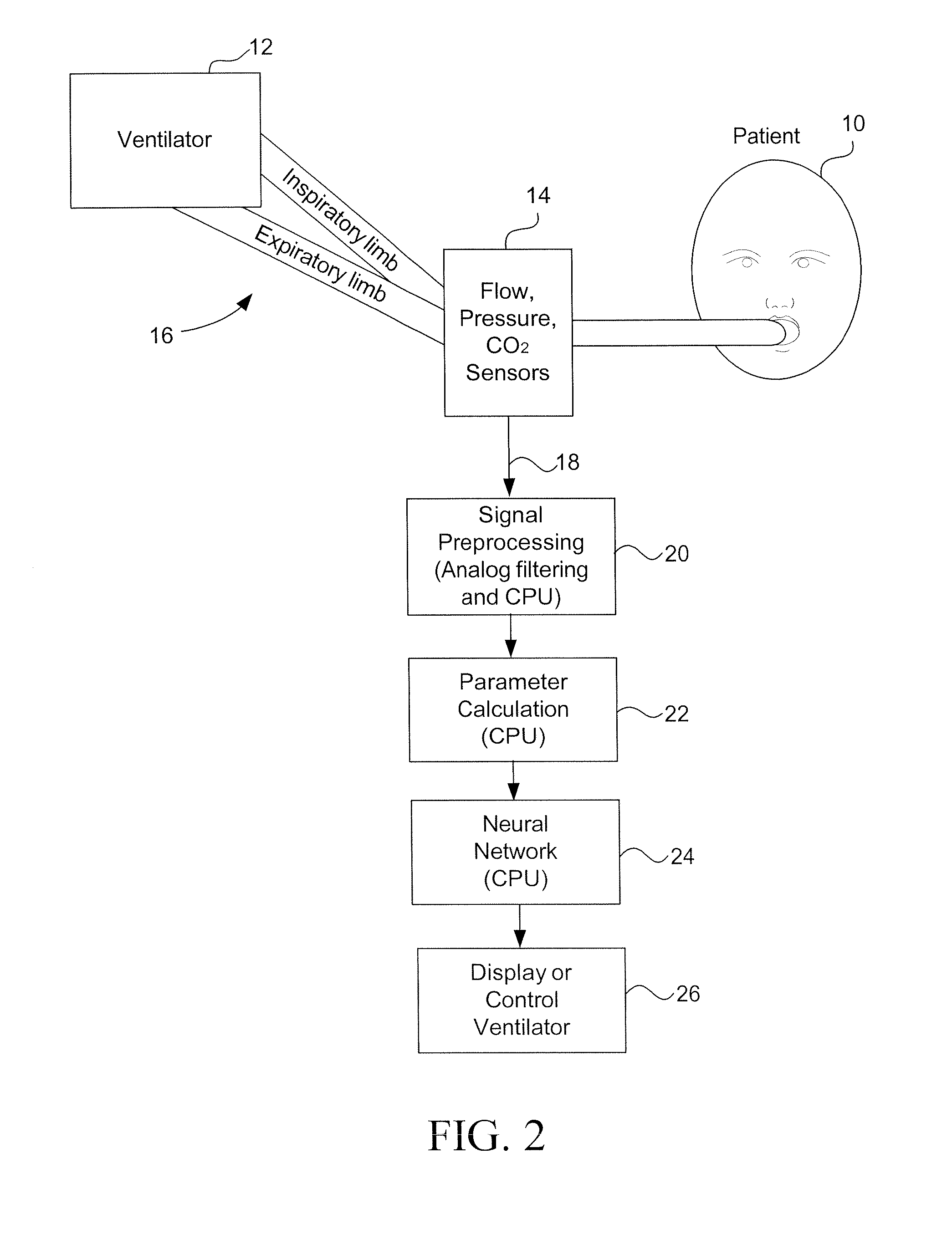
Methods and devices for sensing respiration and controlling ventilator functions
ActiveUS20110197885A1Tracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesVentilation tubeTransducer
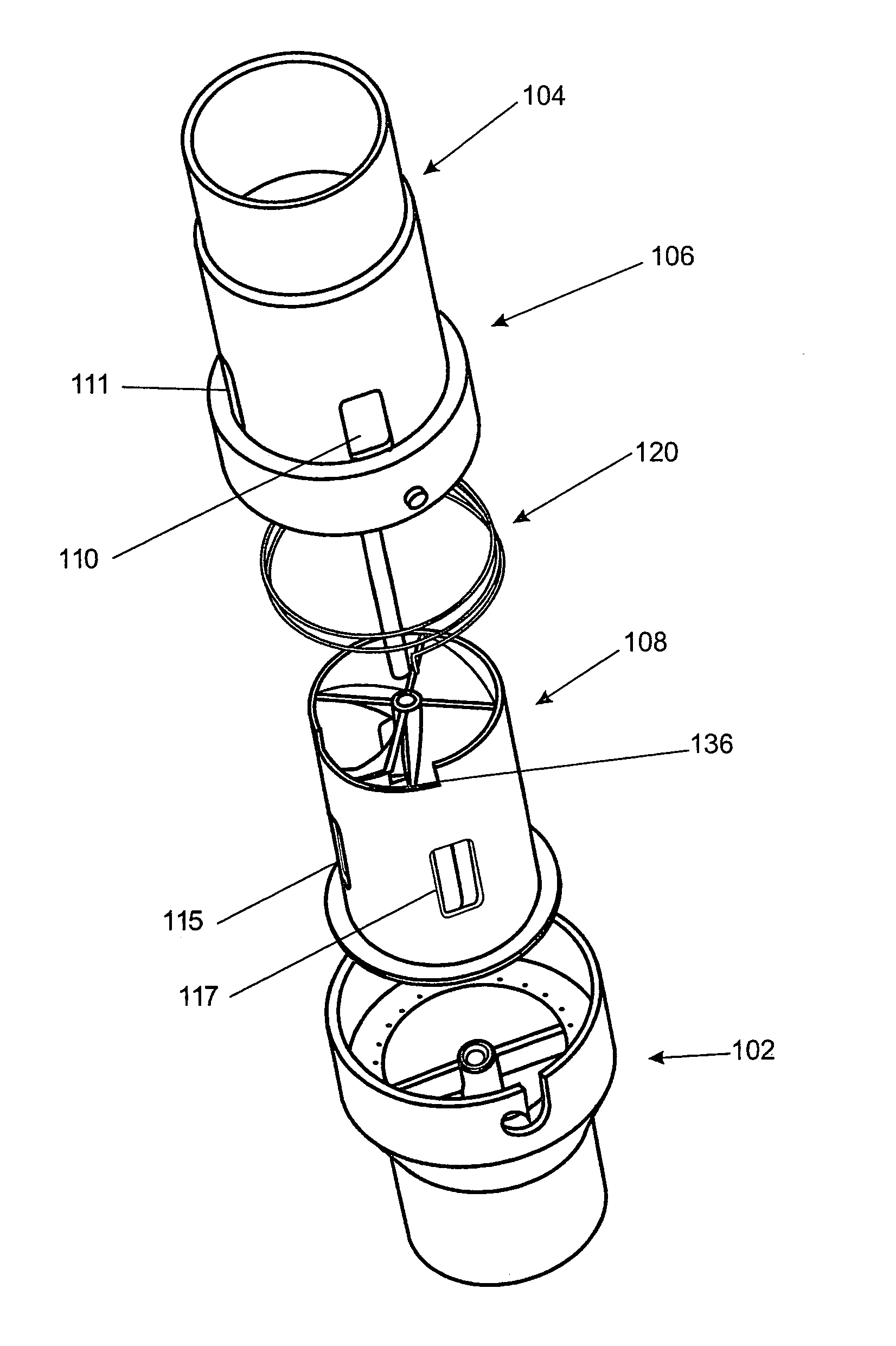
Improved methods and devices are described for sensing the respiration pattern of a patient and controlling ventilator functions, particularly for use in an open ventilation system. A ventilation and breath sensing apparatus may include a ventilation gas delivery circuit and a ventilation tube coupled to the ventilation gas delivery circuit. A plurality of pressure sensing elements may be separated by a distance and may produce independent signals. The signals may be used to detect pressure differentials between the plurality of pressure sensing elements. Sensing ports may be located in an airway, and connected to transducers that are valved to optimize sensitivity and overpressure protection. Airway pressure and flow can both be obtained and used to optimize ventilator synchronization and therapy.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Ventilation method and control of a ventilator based on same
InactiveUS20060174884A1Increase in vent free dayDrug costRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAirway pressuresIntensive care medicine
The invention provides an improved ventilation method and method for controlling a ventilator apparatus in accordance with same. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method of controlling a ventilator apparatus comprising the steps of placing a ventilator in a mode capable of adjusting airway pressure (P) and time (T), monitoring expiratory gas flow, analyzing the expiratory gas flow over time (T) to establish an expiratory gas flow pattern, and setting and / or adjusting a low time (T2) based on the expiratory gas flow pattern. Alternatively, the present invention relates to a method of controlling a ventilator apparatus comprising the steps of placing a ventilator in a mode capable of adjusting airway pressure (P) and time (T), and setting a low airway pressure (P2) of substantially zero cmH2O.
Owner:HABASHI NADER M
Method of automatically controlling a respiration system and a corresponding respirator
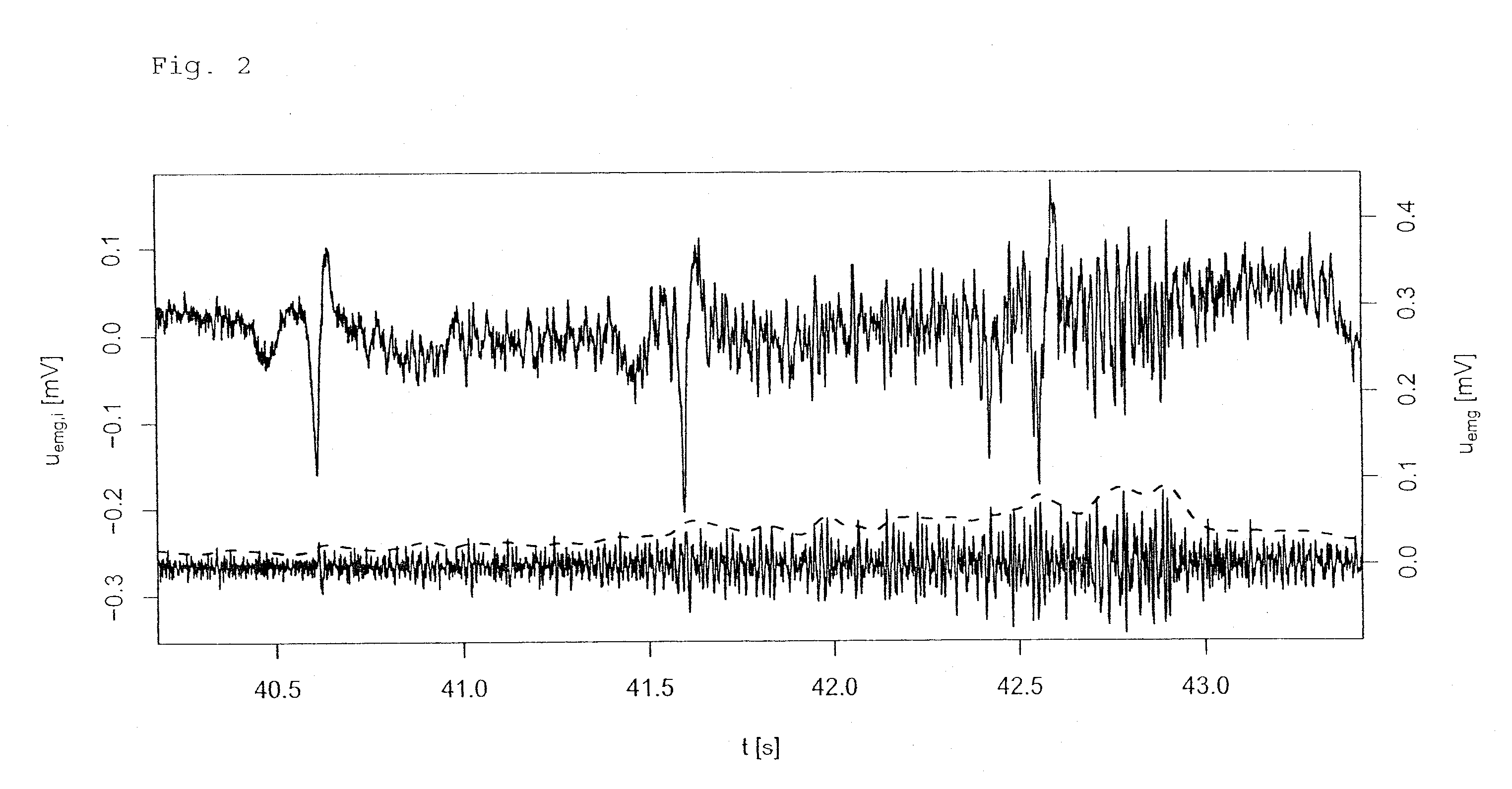
ActiveUS20090159082A1Convenient for patientAccurate operationRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutomatic controlProportional Assist Ventilation
A method of automatically controlling a respiration system for proportional assist ventilation with a control device and with a ventilator. An electrical signal is recorded by electromyography with electrodes on the chest in order to obtain a signal uemg(t) representing the breathing activity. The respiratory muscle pressure pmus(t) is determined by calculating it in the control unit from measured values for the airway pressure and the volume flow Flow(t) as well as the patient's lung mechanical parameters. The breathing activity signal uemg(t) is transformed by means of a preset transformation rule into a pressure signal pemg(uemg)(t)) such that the mean deviation of the resulting transformed pressure signal pemg(t) from the respiratory muscle pressure pmus(t) is minimized. The respiratory effort pressure ppat(t) is determined as a weighted mean according to ppat(t)=a·pmus(t)+(1−a)·pemg(t), where a is a parameter selected under the boundary condition 0≦a≦1. The airway pressure paw(t) to be delivered is calculated as a function of preselected degrees of assist VA (Volume Assist) and FA (Flow Assist) by sliding adaptation aspaw(ti)=k0+∑j=1nkj·paw(ti-j)+∑j=0nhj·ppat(ti-j)wherein ti is a current point in time and ti−j, wherein j=1, . . . , n, are previous points in time of a periodical time-discrete sampling, and kj and hj, wherein j=1, . . . , n are parameters dependent on resistance (R), elastance (E), positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP), intrinsic PEEP (iPEEP), Volume Assist (VA) and Flow Assist (FA) and the sampling time Δt, and the ventilator is set by the control unit so as to provide this airway pressure paw(ti)
Owner:DRAGERWERK AG
Methods, systems and devices for non-invasive open ventilation with gas delivery nozzles in free space
ActiveUS20100252039A1Work lessIncrease airway pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesNoseLung volumes
A non-invasive ventilation system may include an interface. The interface may include at least one gas delivery jet nozzle adapted to be positioned in free space and aligned to directly deliver ventilation gas into an entrance of a nose. The at least one gas delivery jet nozzle may be connected to a pressurized gas supply. The ventilation gas may entrain ambient air to elevate lung pressure, elevate lung volume, decrease the work of breathing or increase airway pressure, and wherein the ventilation gas is delivered in synchrony with phases of breathing. A support for the at least one gas delivery jet nozzle may be provided. A breath sensor may be in close proximity to the entrance of the nose. A patient may spontaneous breathe ambient air through the nose without being impeded by the interface.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Methods and devices for providing inspiratory and expiratory flow relief during ventilation therapy
ActiveUS20090151724A1Breathe freelyUndesirable pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory supportAirway pressures
Respiratory support and / or controlled mechanical ventilation of a patient are provided. A ventilation apparatus may include a ventilator, a transtracheal prosthesis, and a respiratory relief device. The transtracheal prostheses and ventilation catheter may be arranged such that the patient can breathe freely through the upper airway and / or the tracheal prostheses. Respiratory sensors may measure a breathing rate, lung pressure, airway pressure, or a combination thereof. Pulses of gas may be provided to the patient through the ventilation catheter during inspiration. The pulses may have a first volume while the patient breathes normal and a second volume when the sensors detect a cessation of breathing or reduction in breathing volume. The second volume may be provided at 1-5 times the normal breathing rate, with a volume 25-500% times the first volume, or both.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
System and method for circuit compliance compensated pressure-regulated volume control in a patient respiratory ventilator
ActiveUS20070101992A1Prolonging inspiratory timeAccurate pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPeak valueAirway pressures
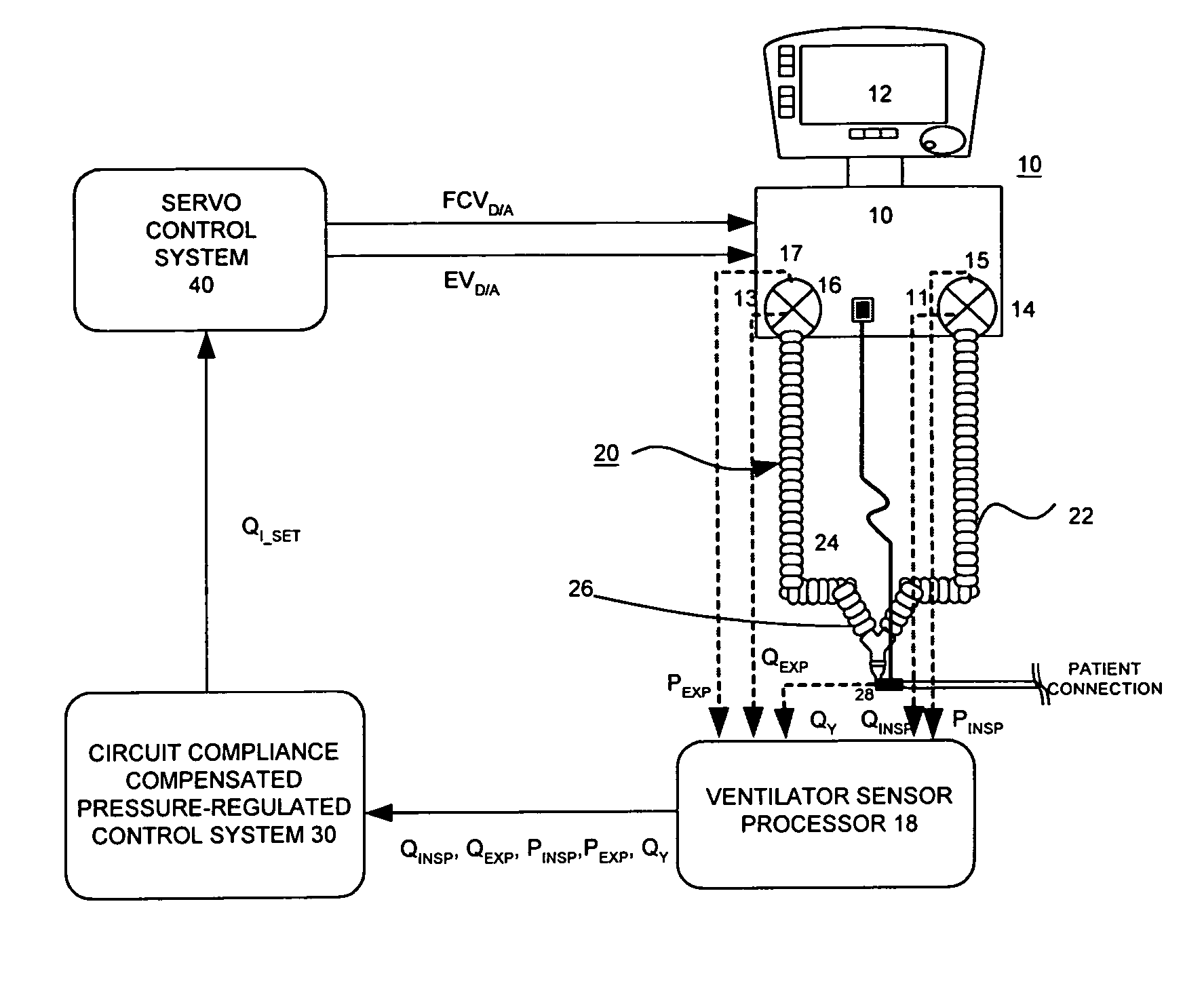
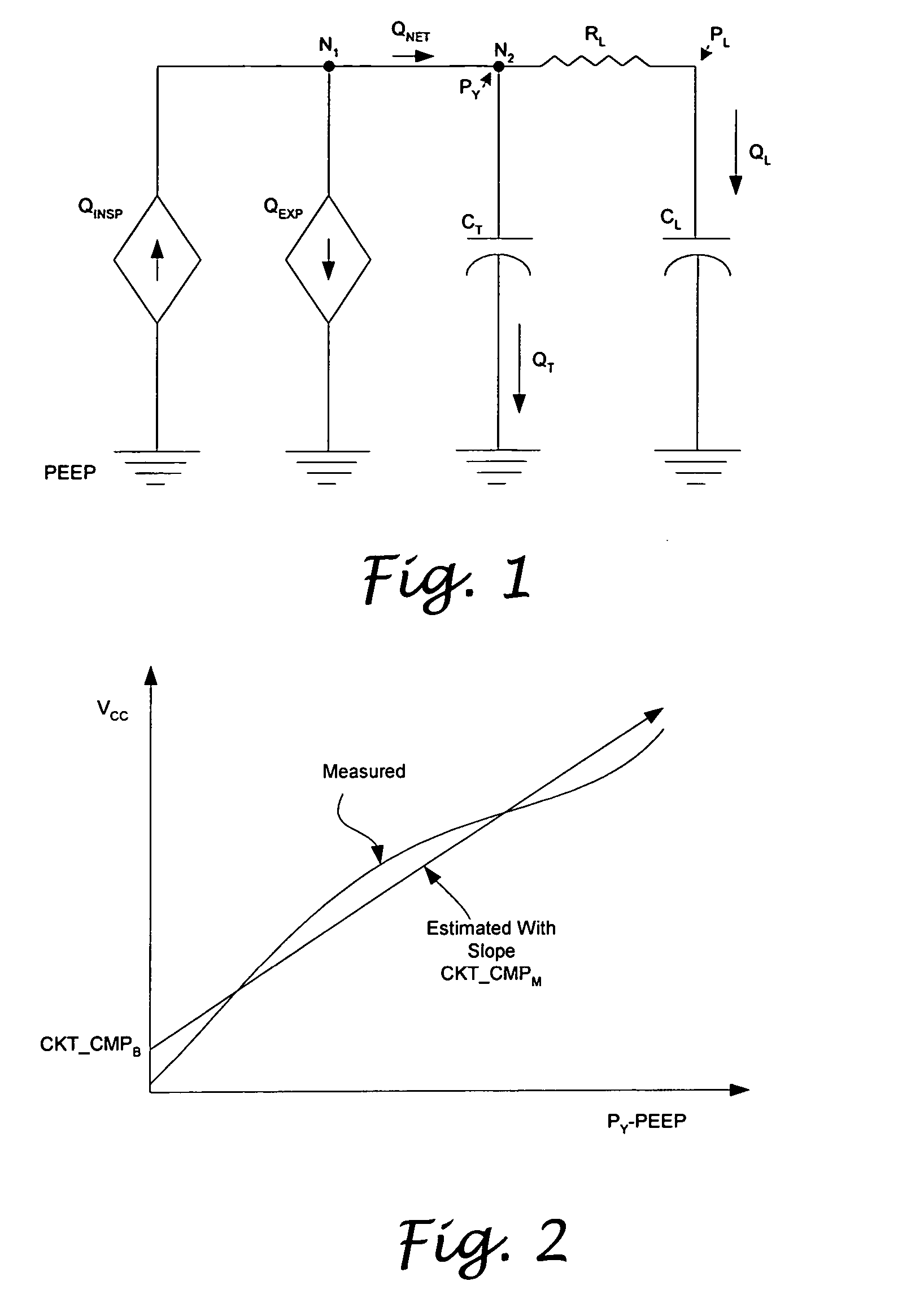
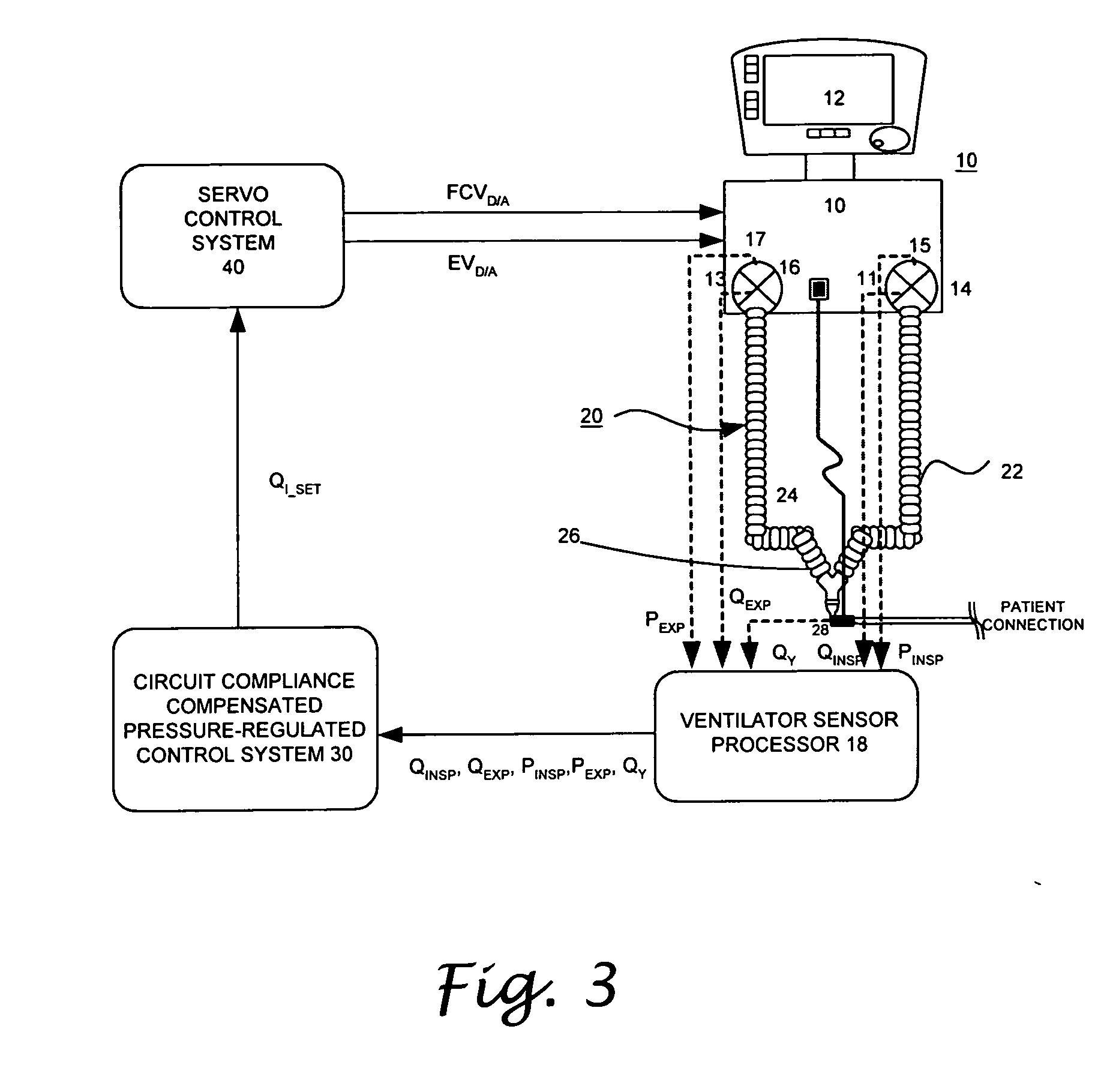
A system and a method for circuit compliance compensated pressure control in a patient respiratory ventilation system, having a pressure regulated feedback servo control loop, a pressure-regulated volume controller, and a patient volume observer. The patient volume observer is operative to estimate a patient volume, that is, the volume actually delivered to the patient by accounting for volume deviation or loss caused by patient circuit leakage and valve dynamics. Based on the difference between the estimated patient volume and a set tidal volume, the pressure-regulated volume controller is operative to generate and update a circuit compliance pressure compensation factor. The pressure regulated feedback servo control loop is operative to modulate the peak airway pressure based on the circuit compliance pressure compensation factor, so as to achieve the set tidal volume while maintaining a constant inspiratory time and a constant I:E ratio.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 211 INC
Method and Apparatus for Predicting Work of Breathing
ActiveUS20070232951A1Avoids respiratory muscle fatigue respiratory muscleAvoids respiratory muscle respiratory muscle deconditioningRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFlow transducerMathematical model
A method of creating a non-invasive predictor of both physiologic and imposed patient effort from airway pressure and flow sensors attached to the patient using an adaptive mathematical model. The patient effort is commonly measured via work of breathing, power of breathing, or pressure-time product of esophageal pressure and is important for properly adjusting ventilatory support for spontaneously breathing patients. The method of calculating this non-invasive predictor is based on linear or non-linear calculations using multiple parameters derived from the above-mentioned sensors.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method of triggering a ventilator
InactiveUS20090120439A1Patient weaning acceleratedMinimize workTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesNoseEndotracheal tube
There is provided a method for controlling breathing gas flow of a ventilator for assisted or controlled ventilation of a patient as a function of a intra-thoracic airway pressure of the patient using a tracheal tube or naso-gastric tube. The intra-thoracic pressure is transmitted to a controller and the information detected is used to control a valve to vent gas from the inhalation tubing of the ventilator, thus triggering an inhalation cycle in the ventilator.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com