Patents
Literature
109 results about "Lung volumes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
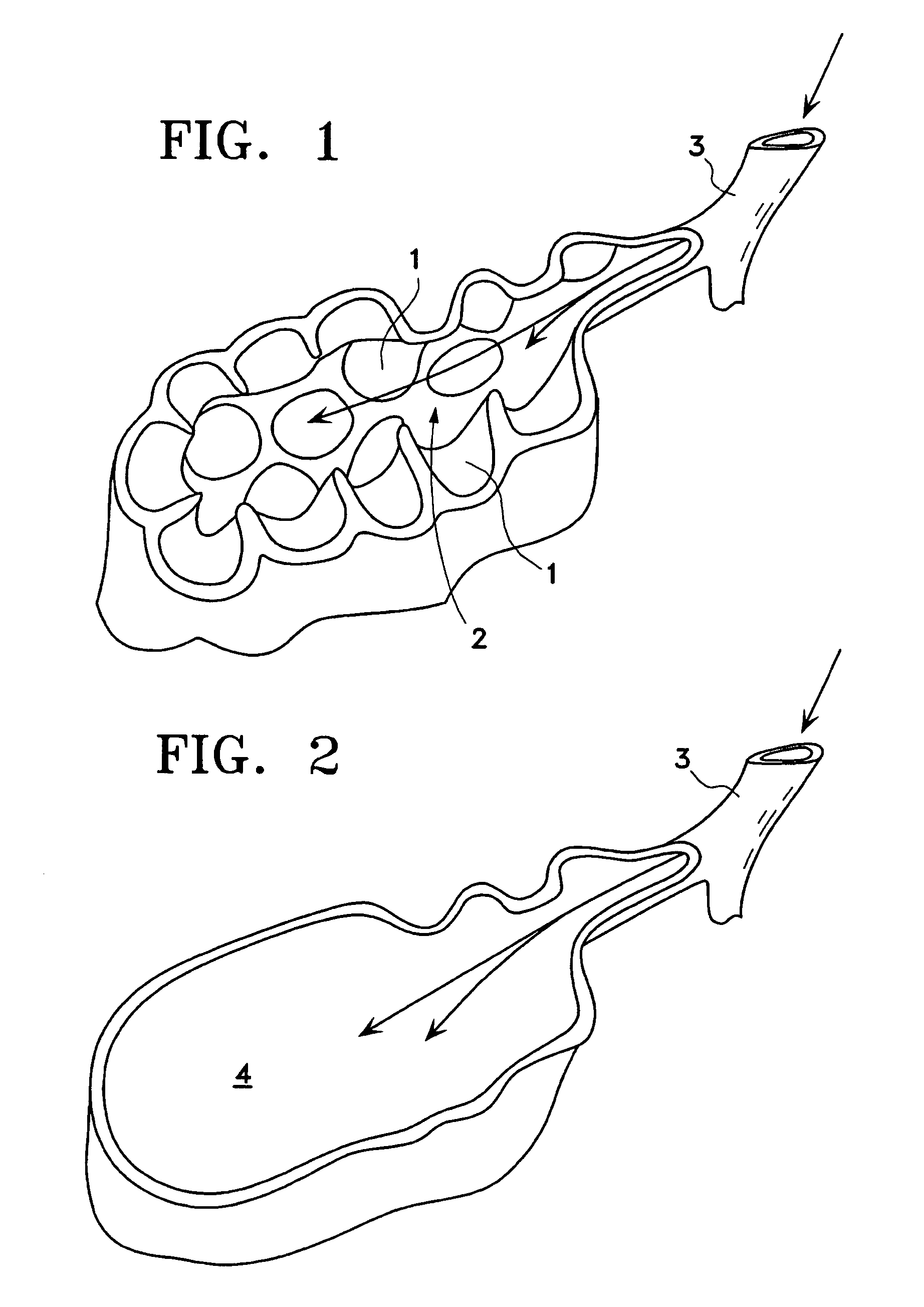
Lung volumes and lung capacities refer to the volume of air in the lungs at different phases of the respiratory cycle. The average total lung capacity of an adult human male is about 6 litres of air. Tidal breathing is normal, resting breathing; the tidal volume is the volume of air that is inhaled or exhaled in only a single such breath.
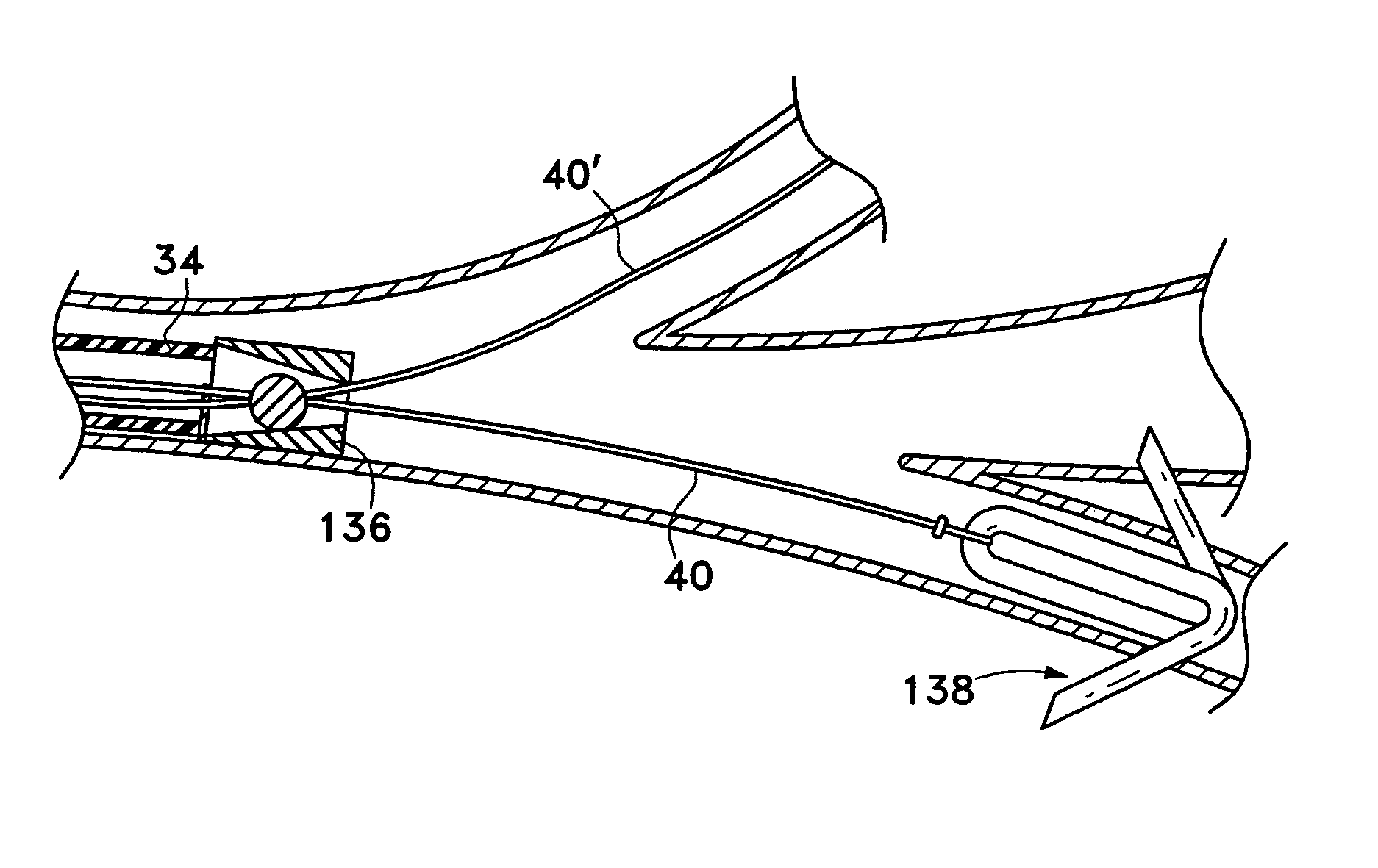
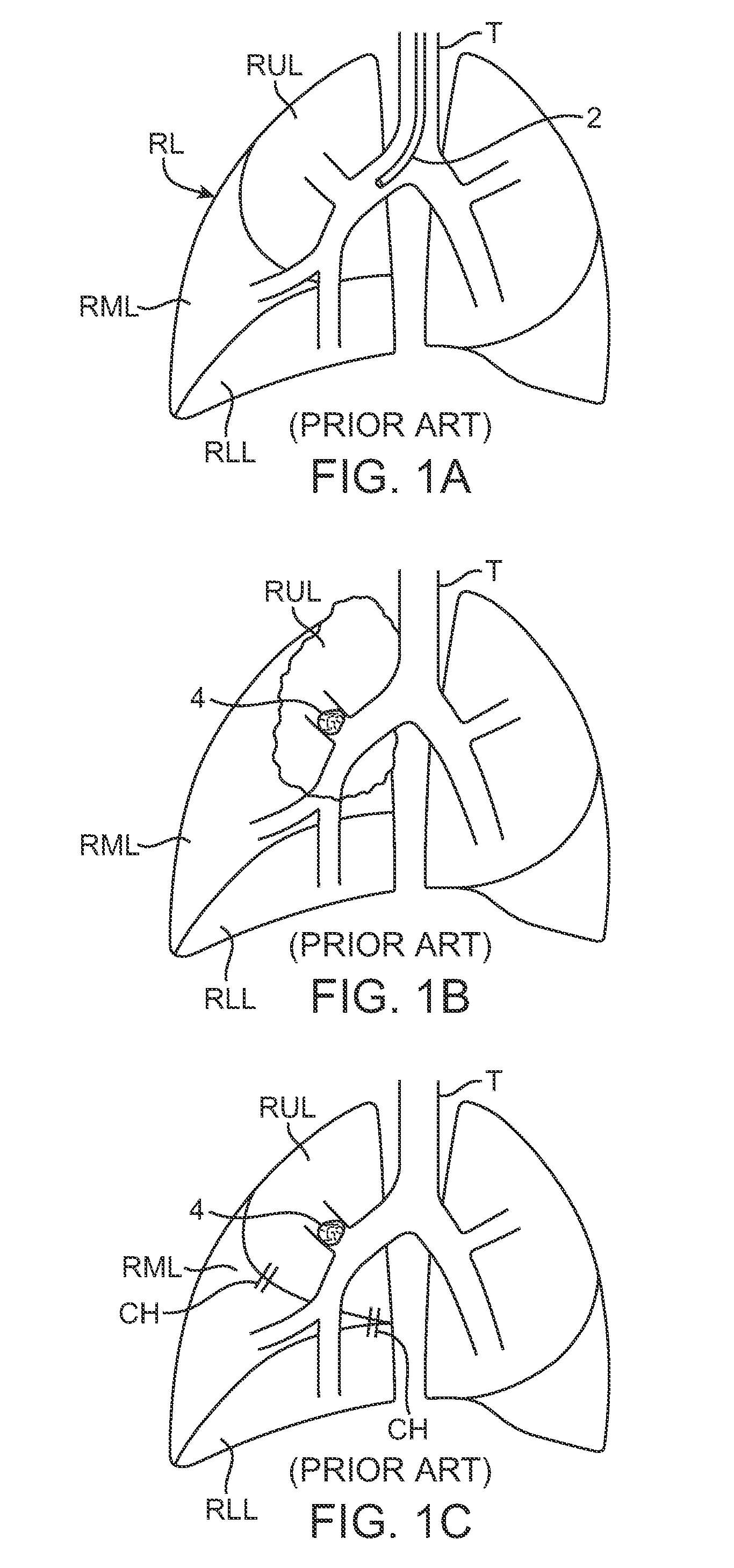
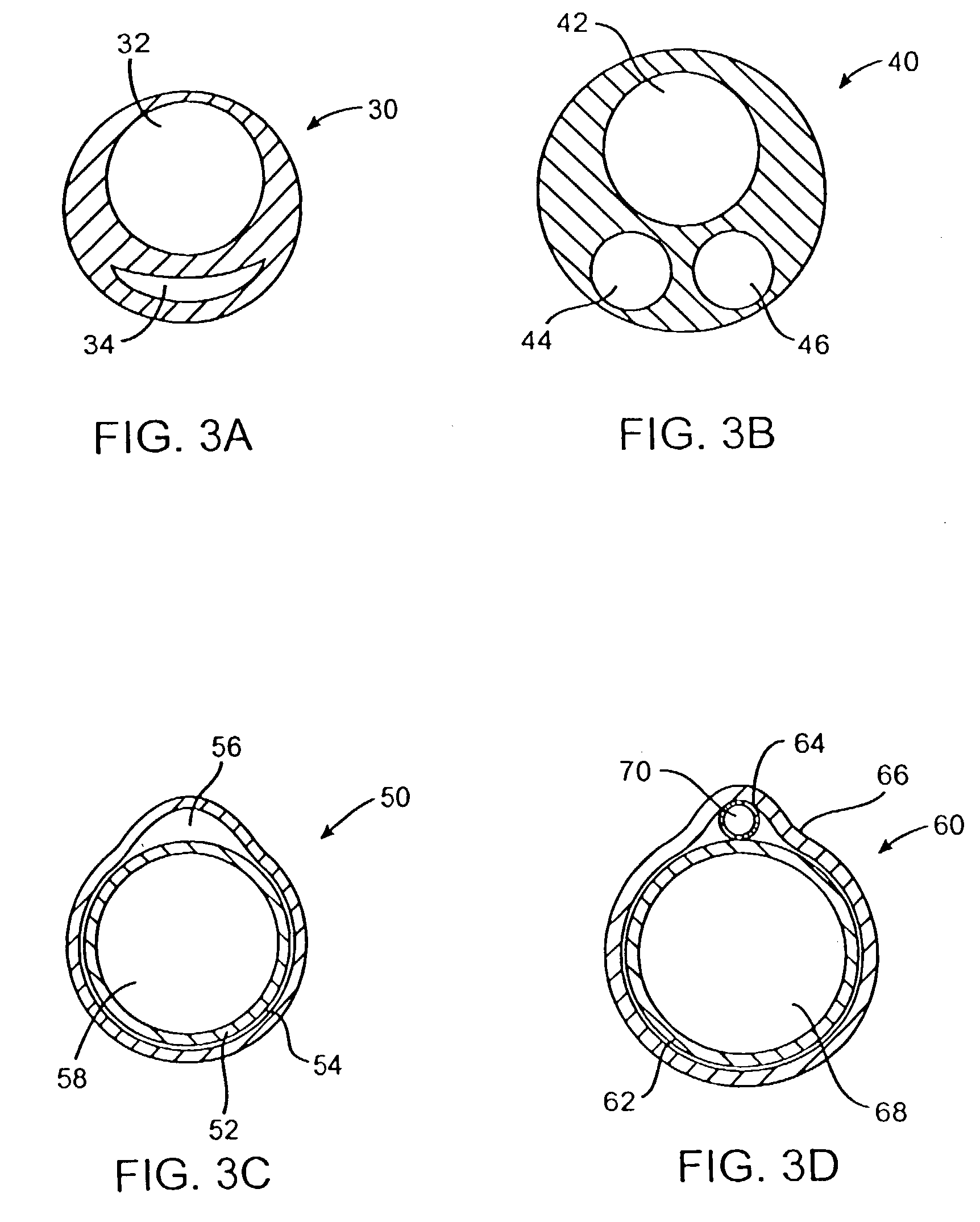
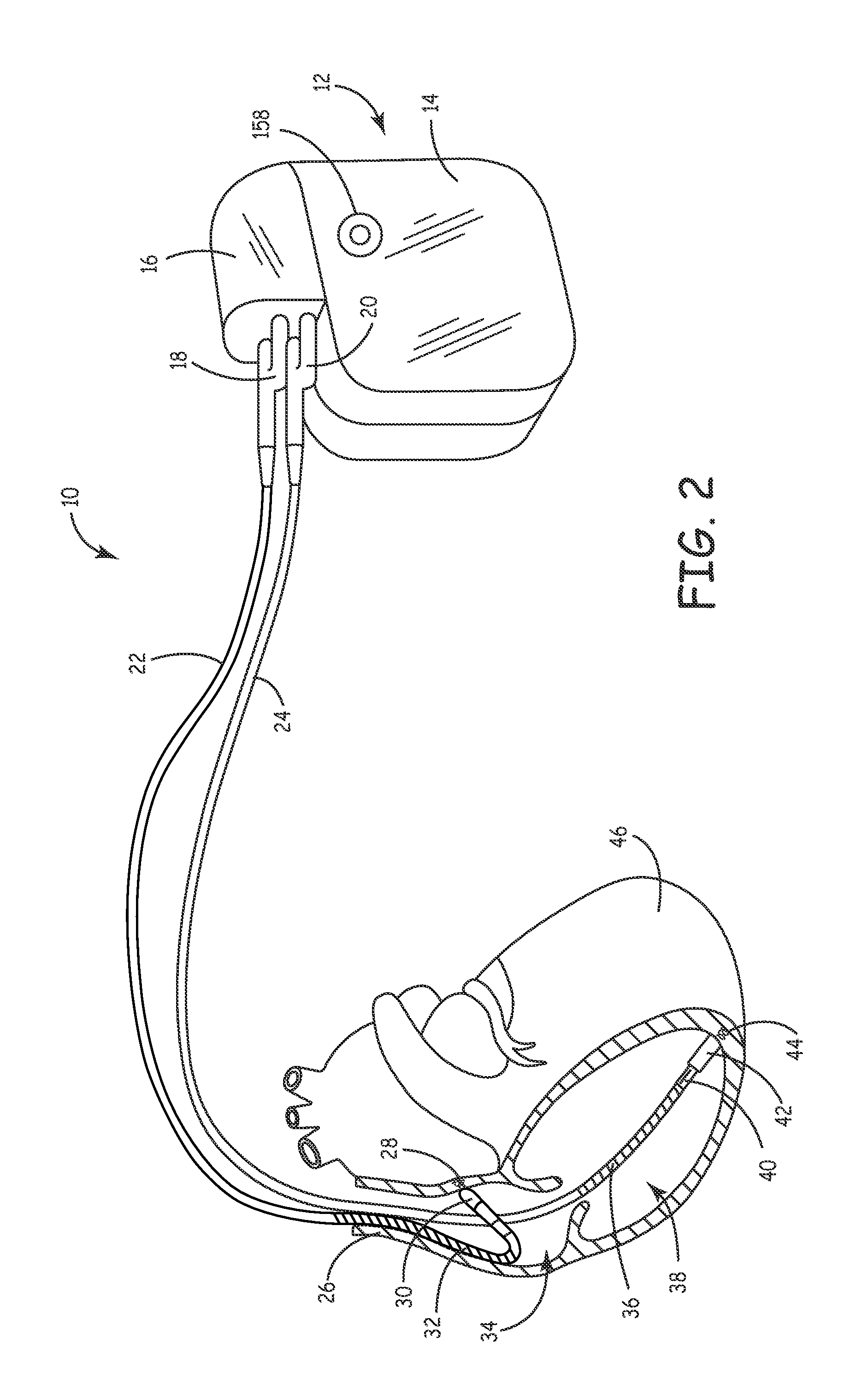
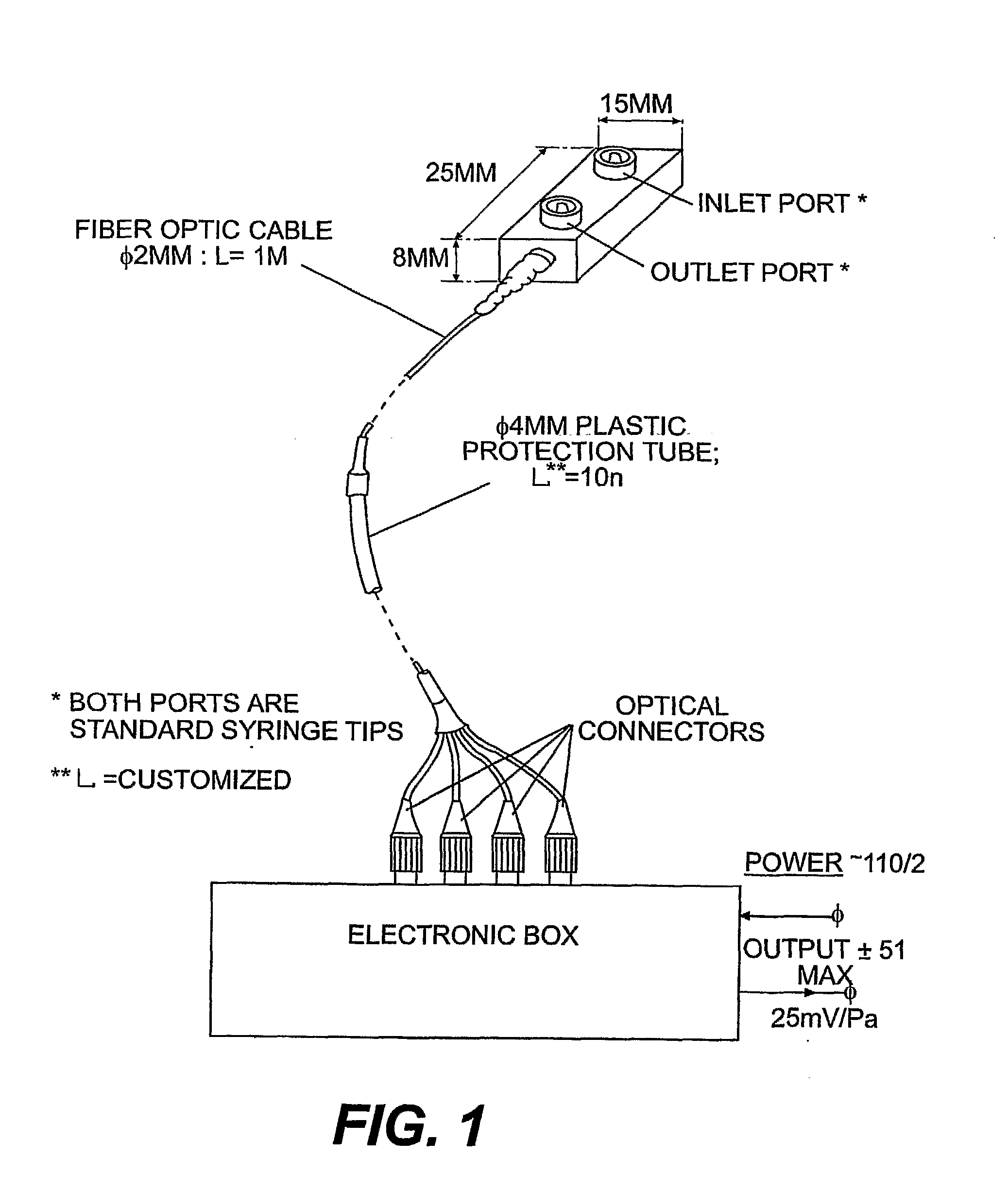
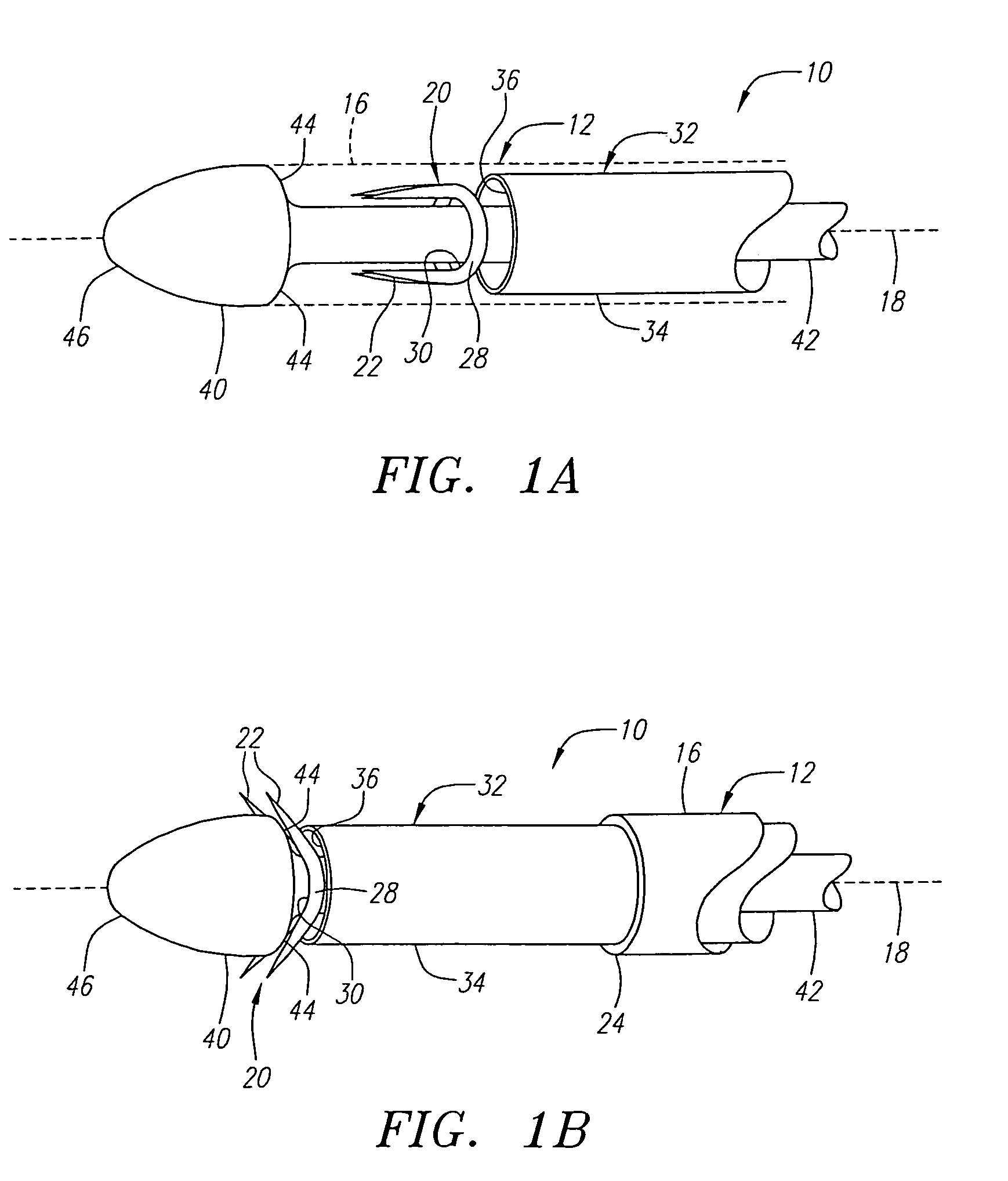
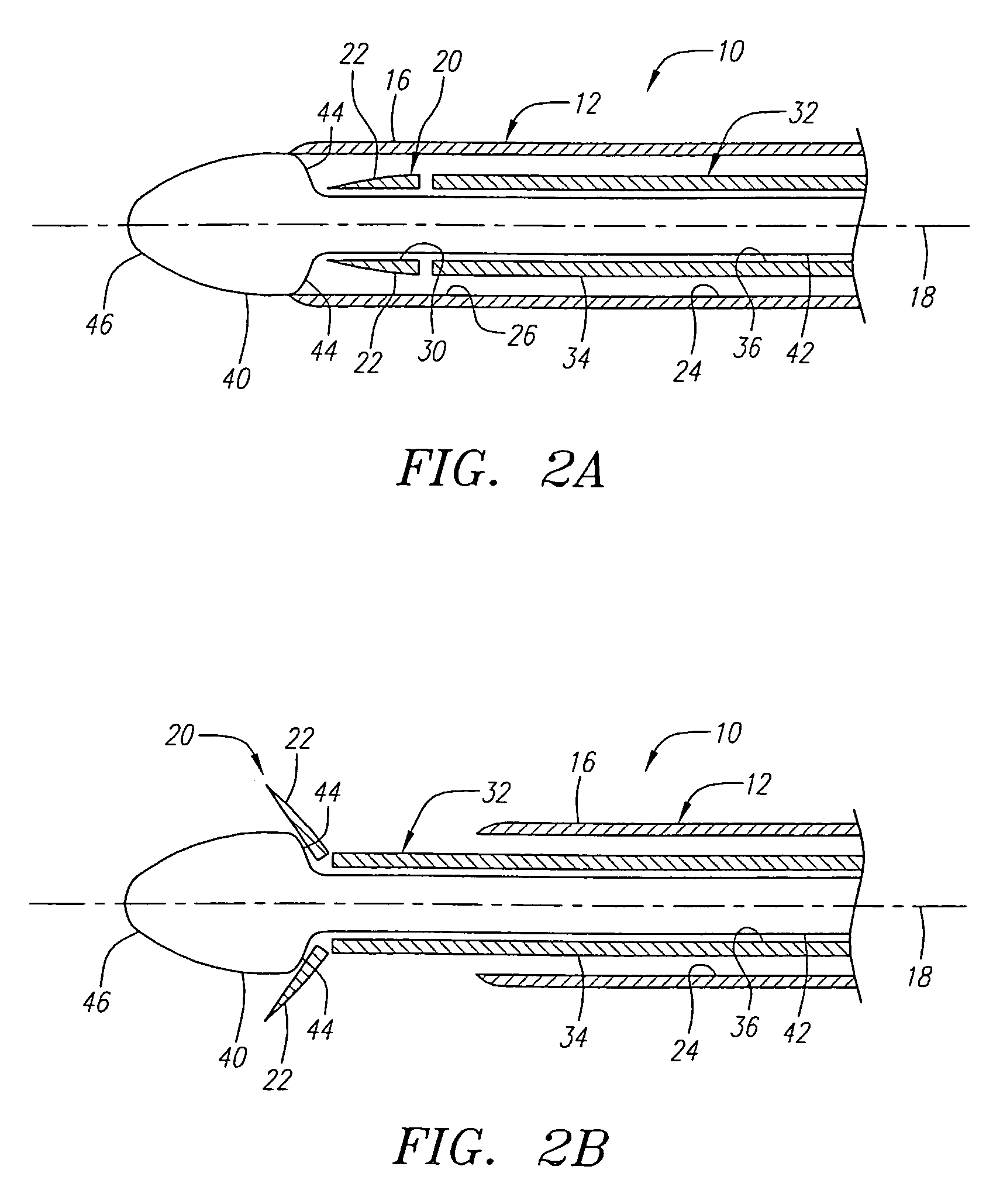
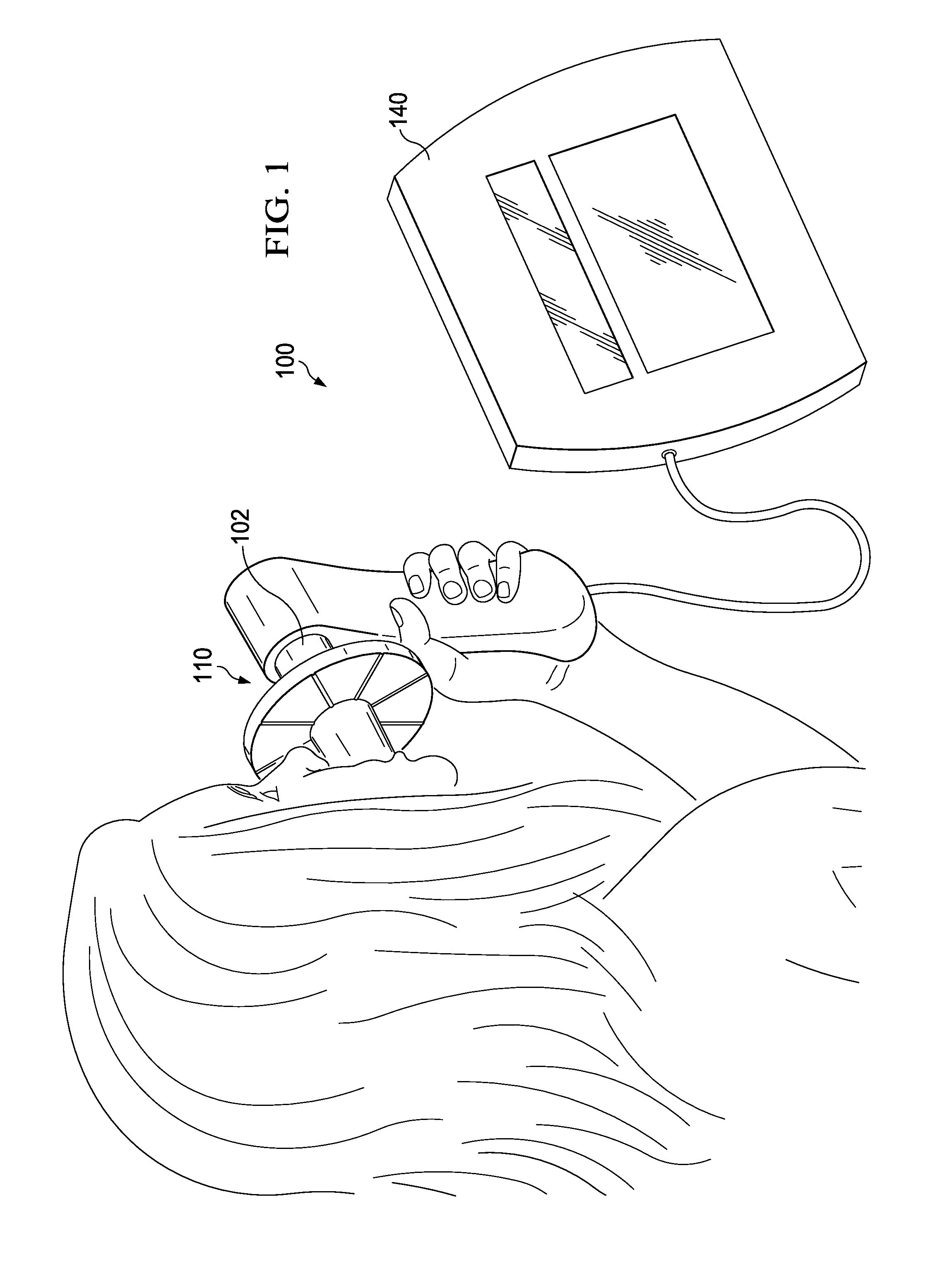
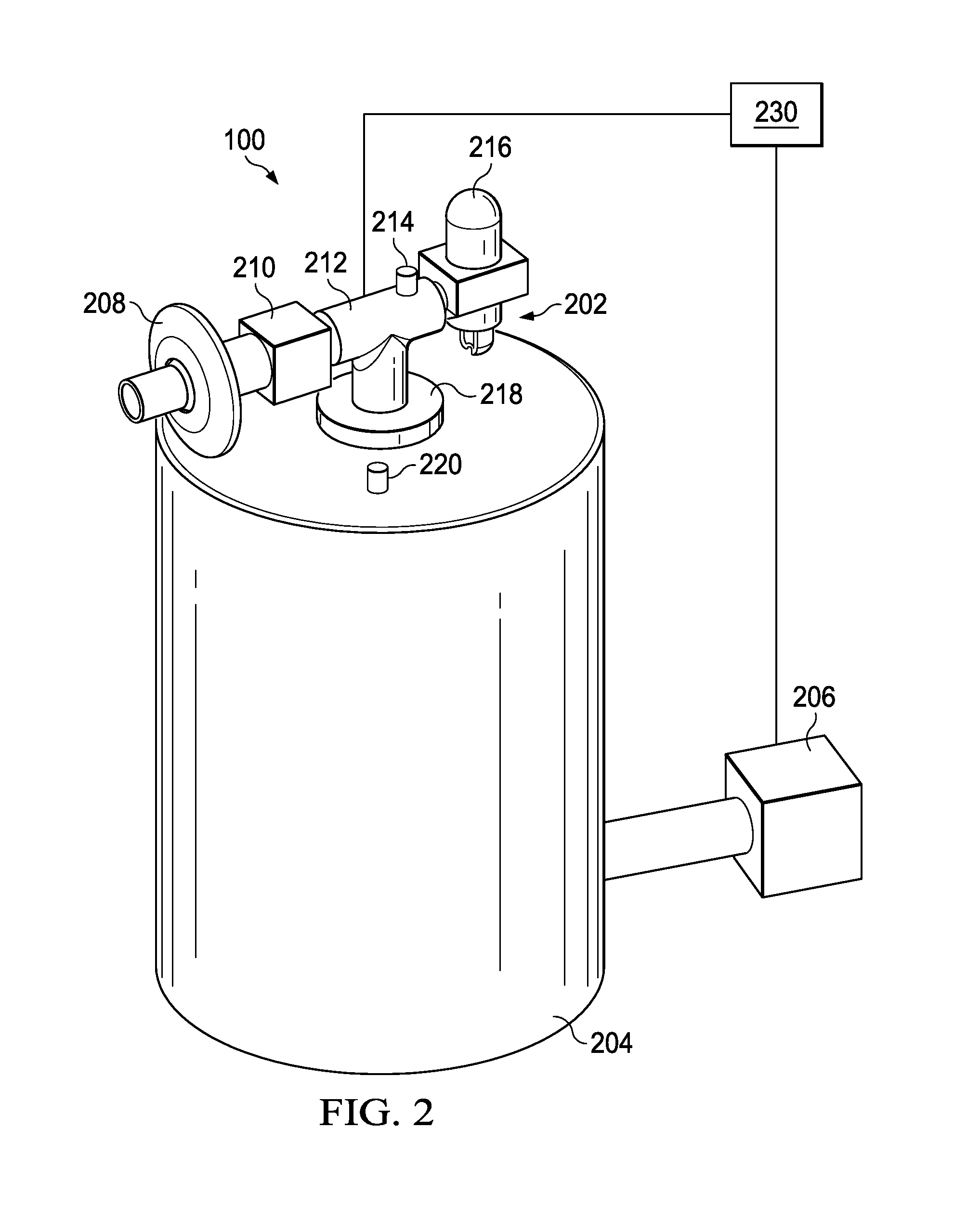
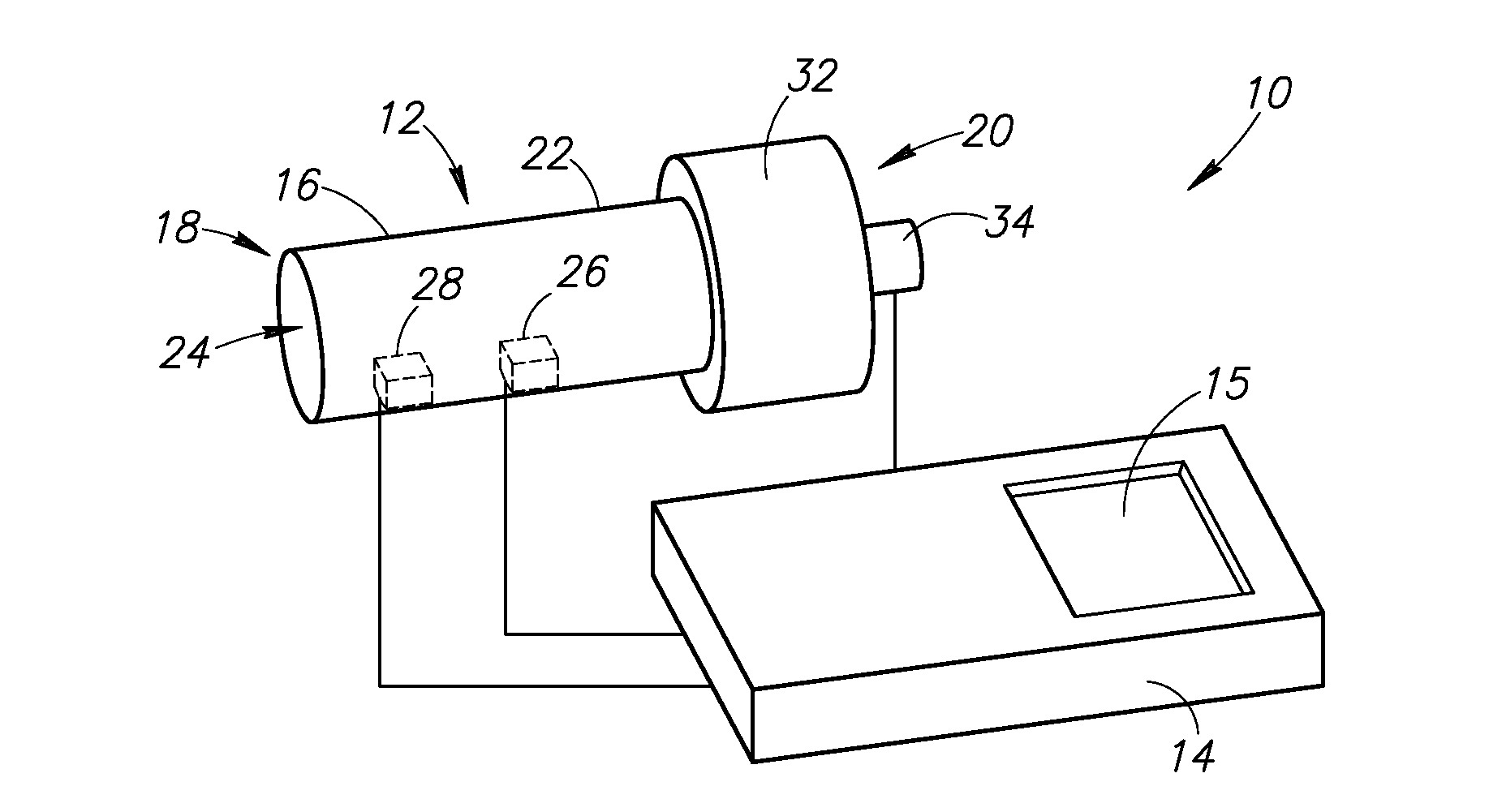
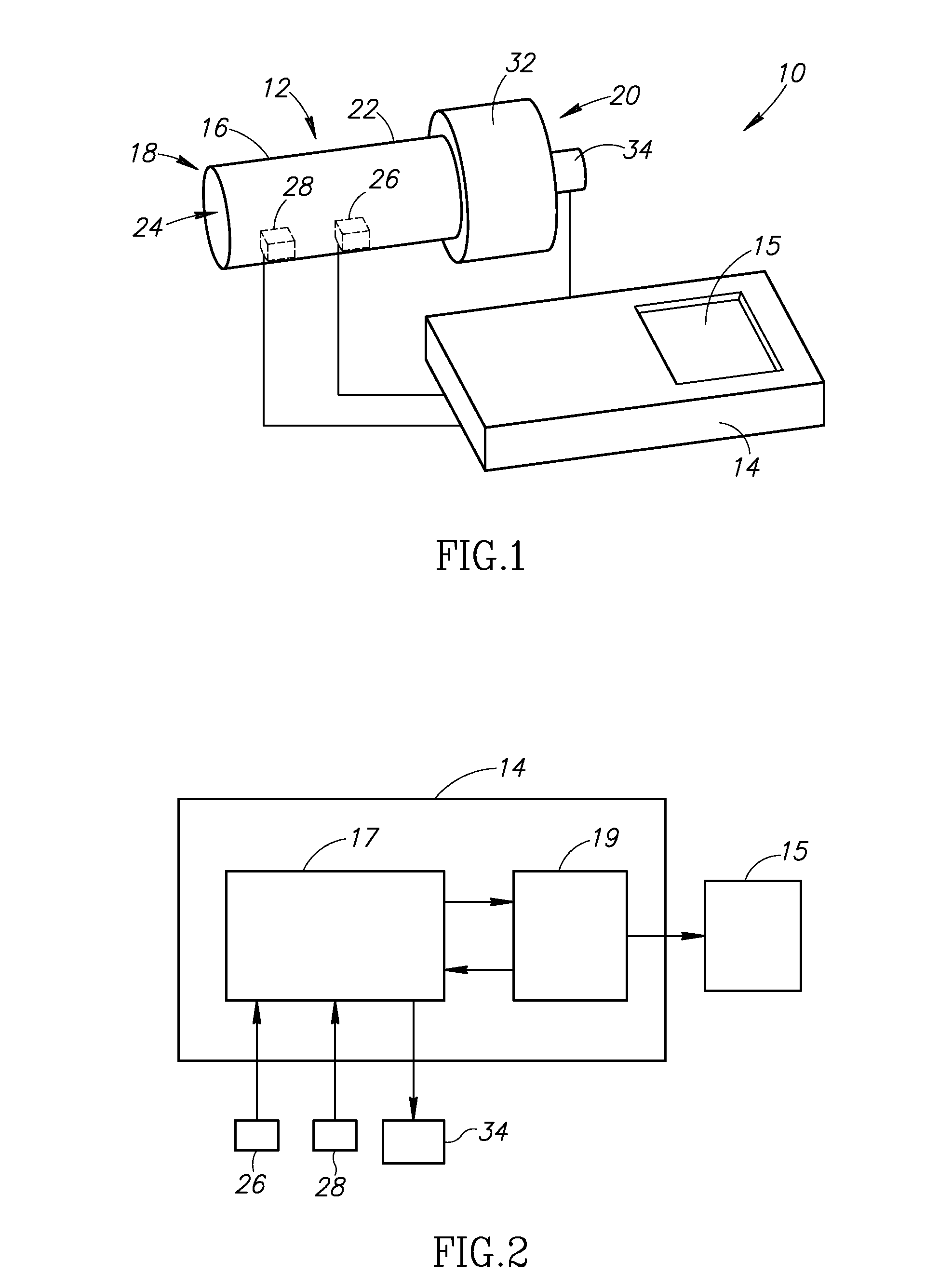
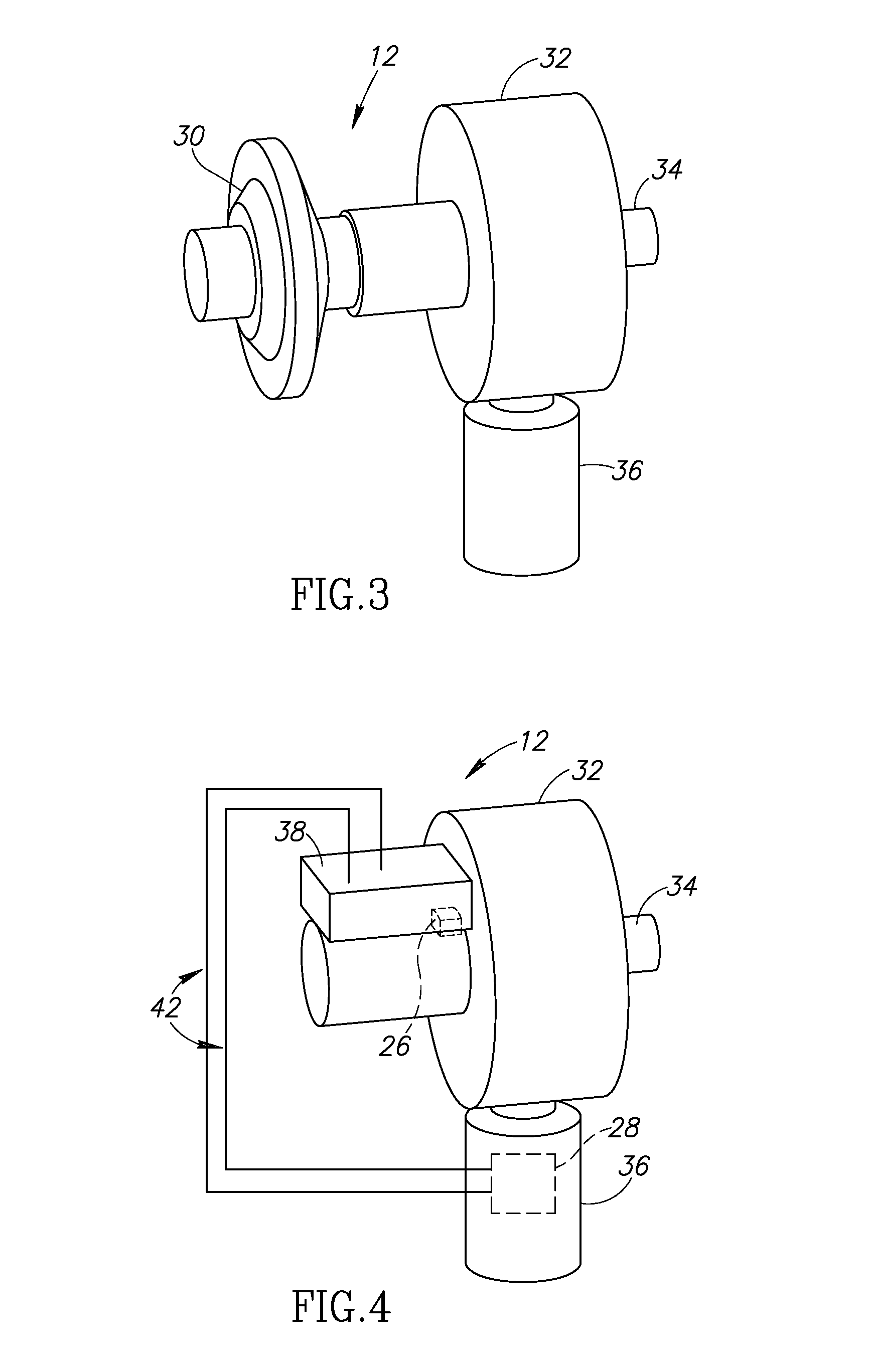
Methods and devices for obstructing and aspirating lung tissue segments
InactiveUS6527761B1Reduce the possibilityIncrease anchorageMedical devicesMedical applicatorsLung volumesObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
Methods, systems, devices and kits for performing lung volume reduction in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or other conditions using and comprising minimally invasive instruments introduced through the mouth (endotracheally) to isolate a target lung tissue segment from other regions of the lung and reduce lung volume. Isolation is achieved by deploying an obstructive device in a lung passageway leading to the target lung tissue segment. Once the obstructive device is anchored in place, the segment can be aspirated through the device. This may be achieved by a number of methods, including coupling an aspiration catheter to an inlet port on the obstruction device and aspirating through the port. Or, providing the port with a valve which allows outflow of gas from the isolated lung tissue segment during expiration of the respiratory cycle but prevents inflow of air during inspiration. In addition, a number of other methods may be used. The obstructive device may remain as an implant, to maintain isolation and optionally allow subsequent aspiration, or the device maybe removed at any time.
Owner:PULMONX
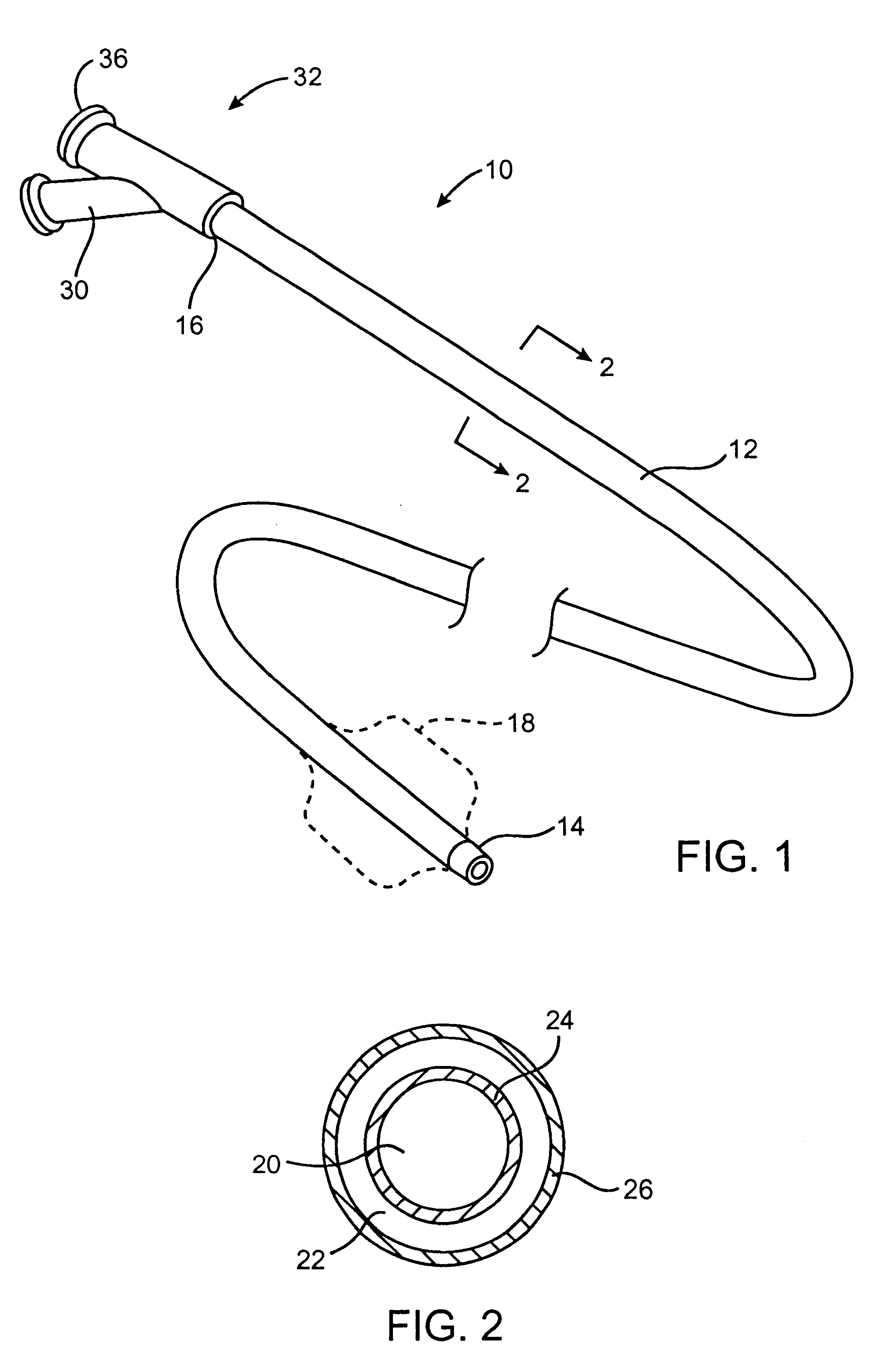
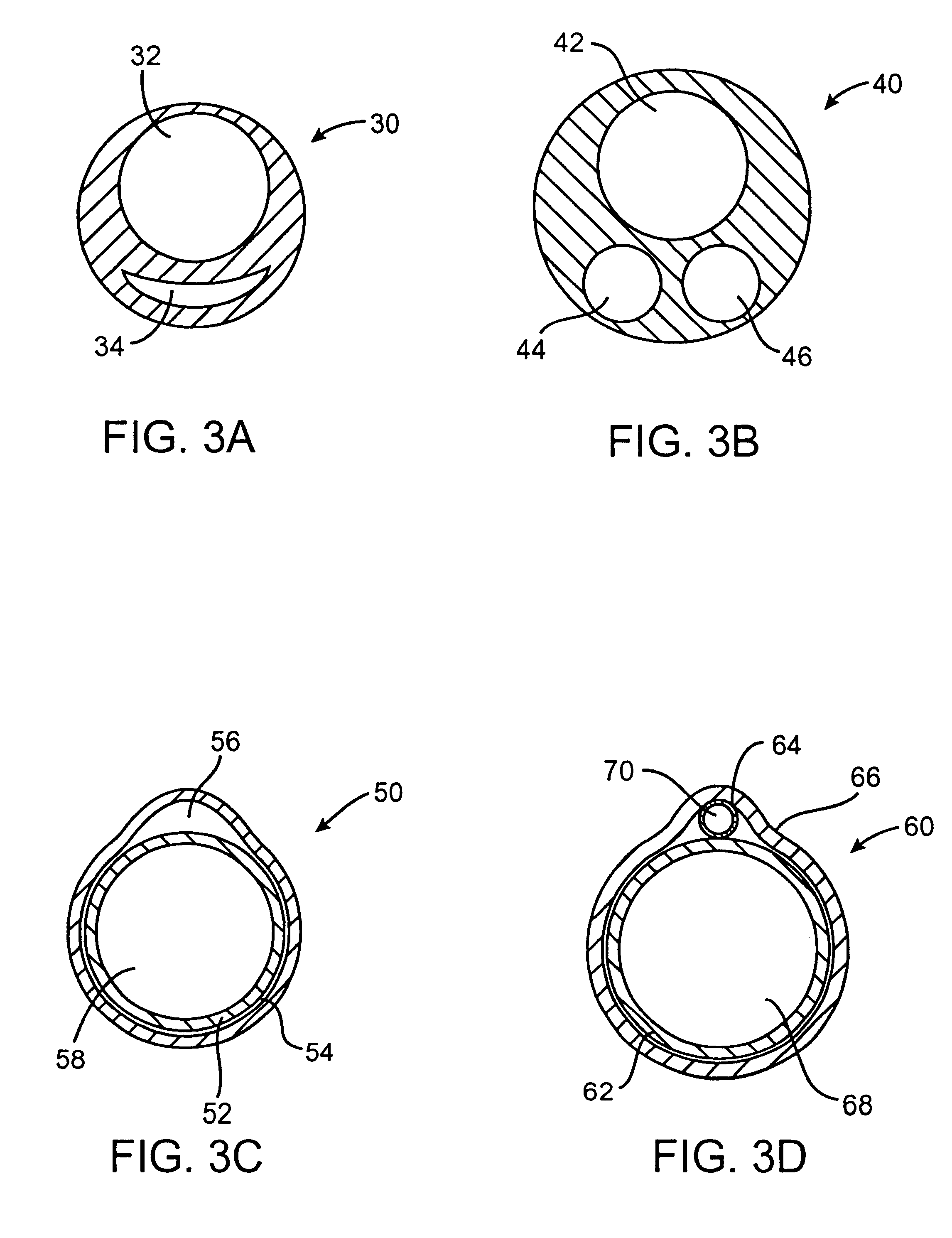
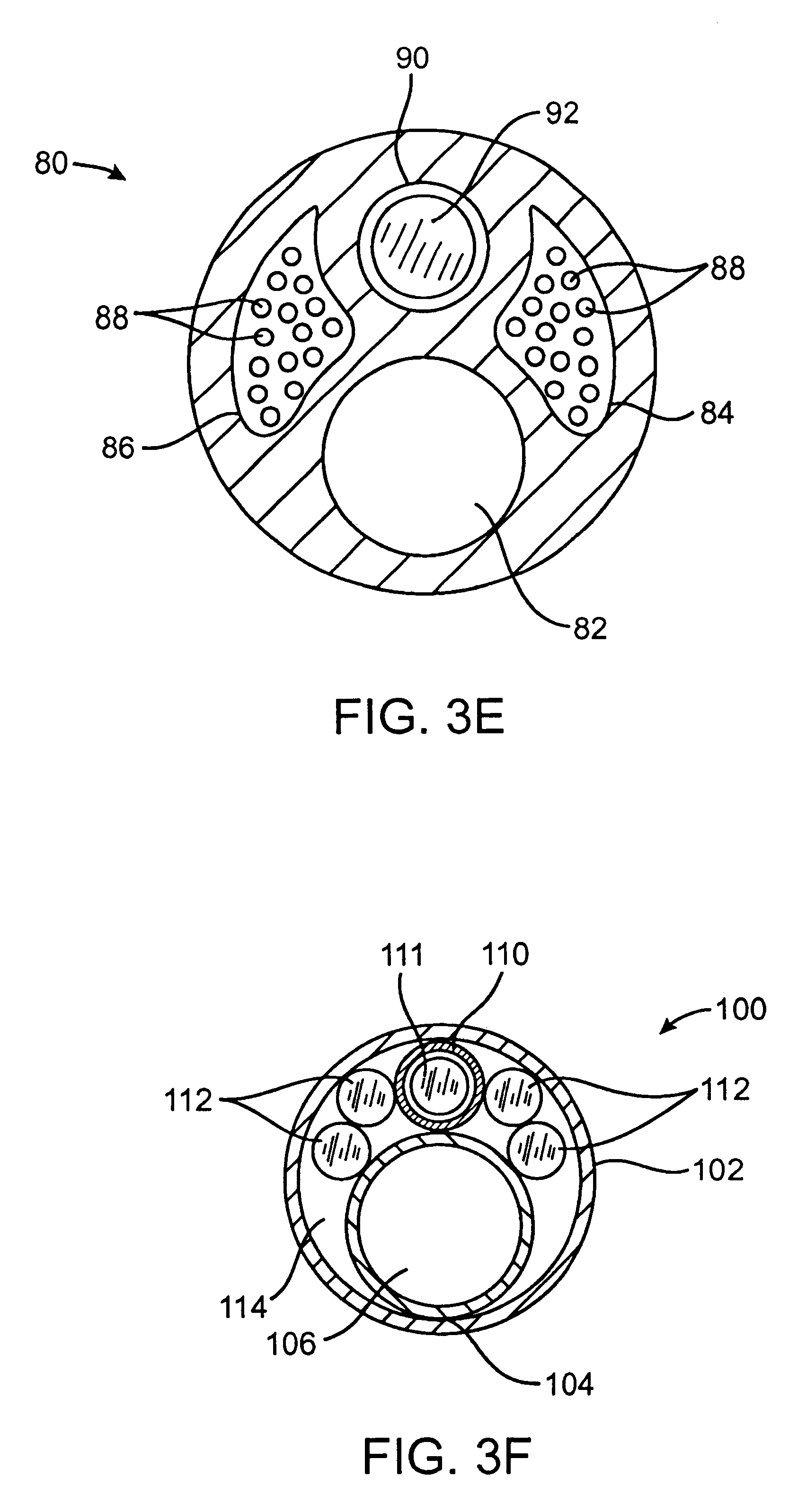
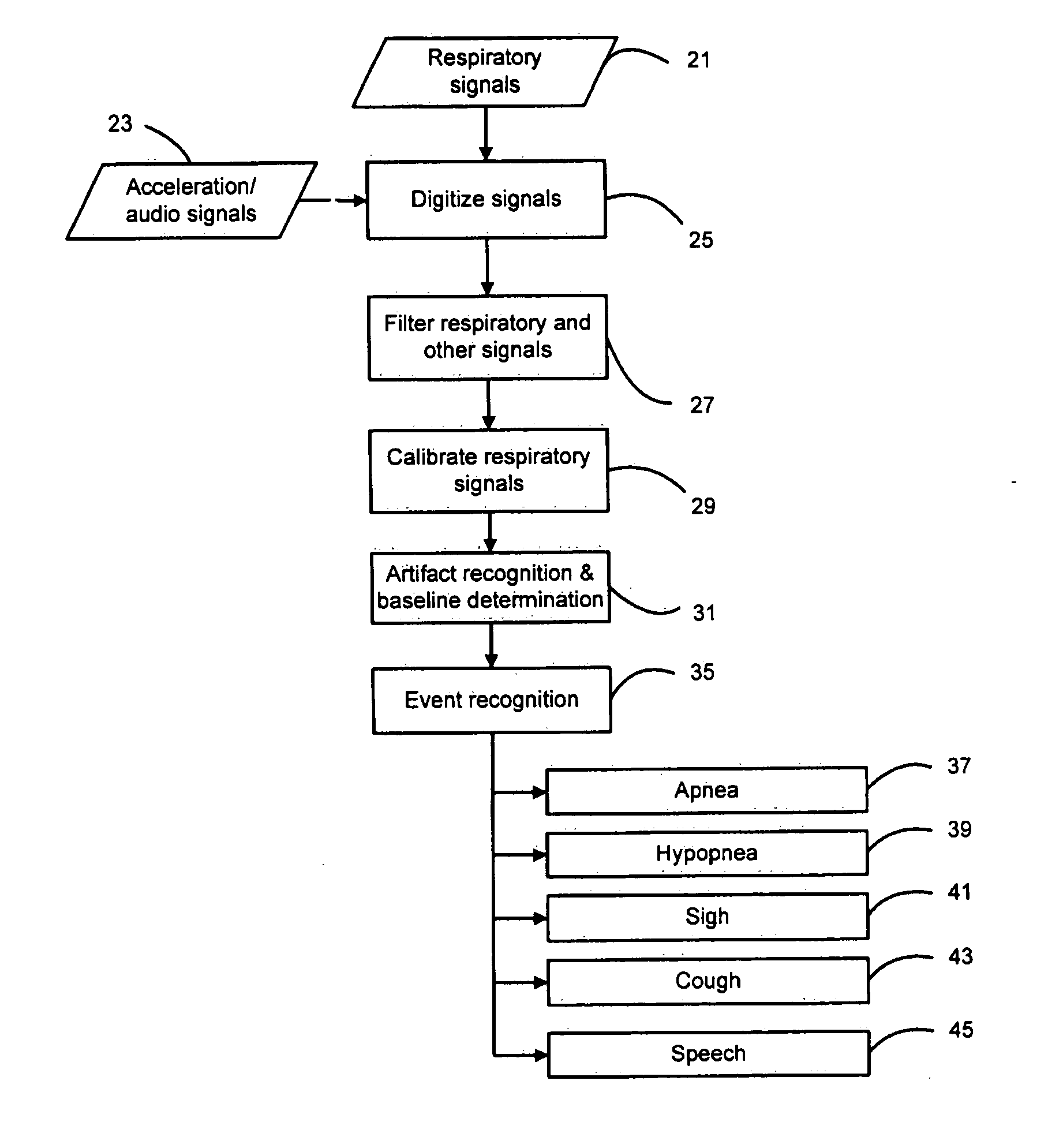
Systems and methods for respiratory event detection
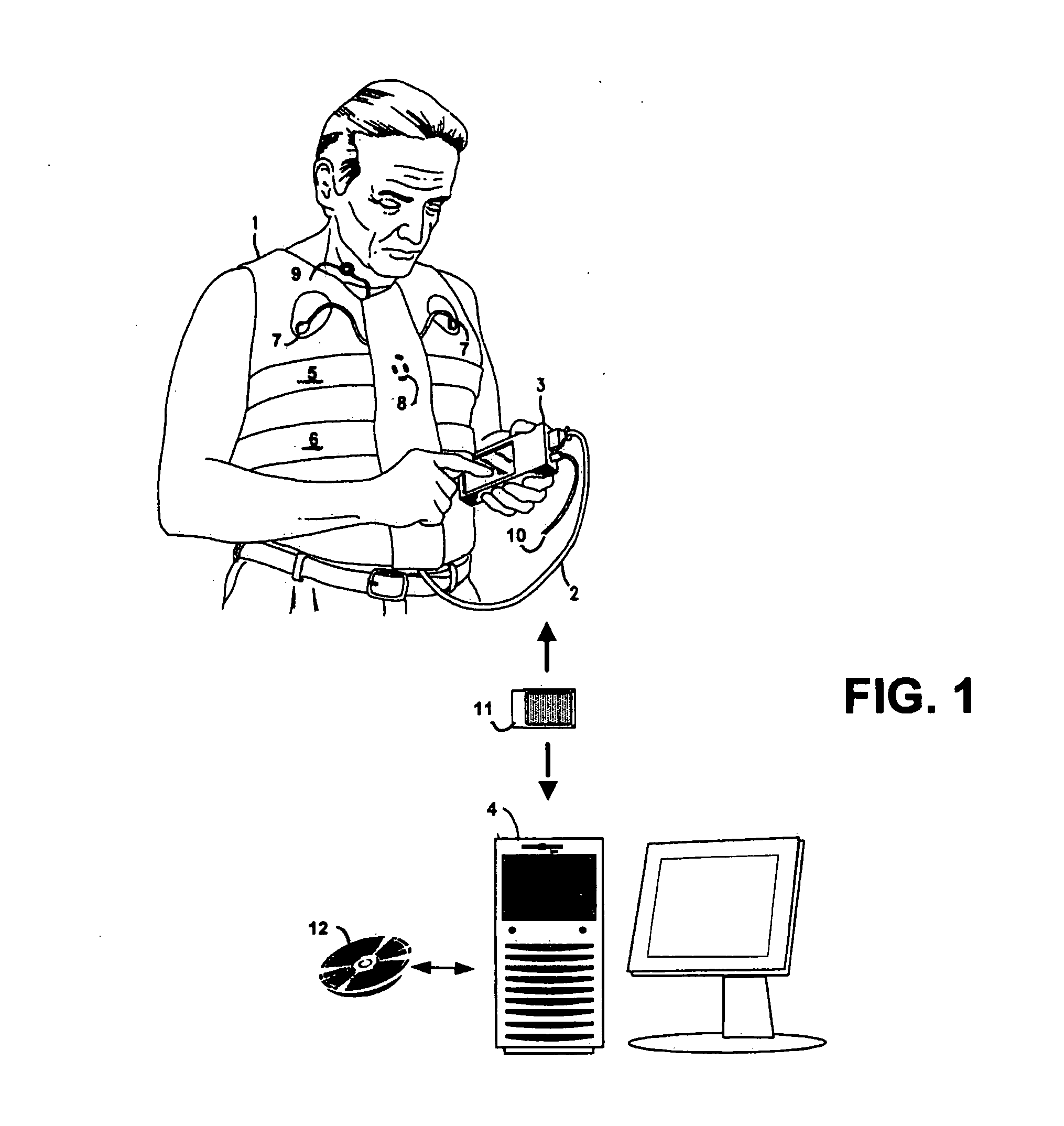
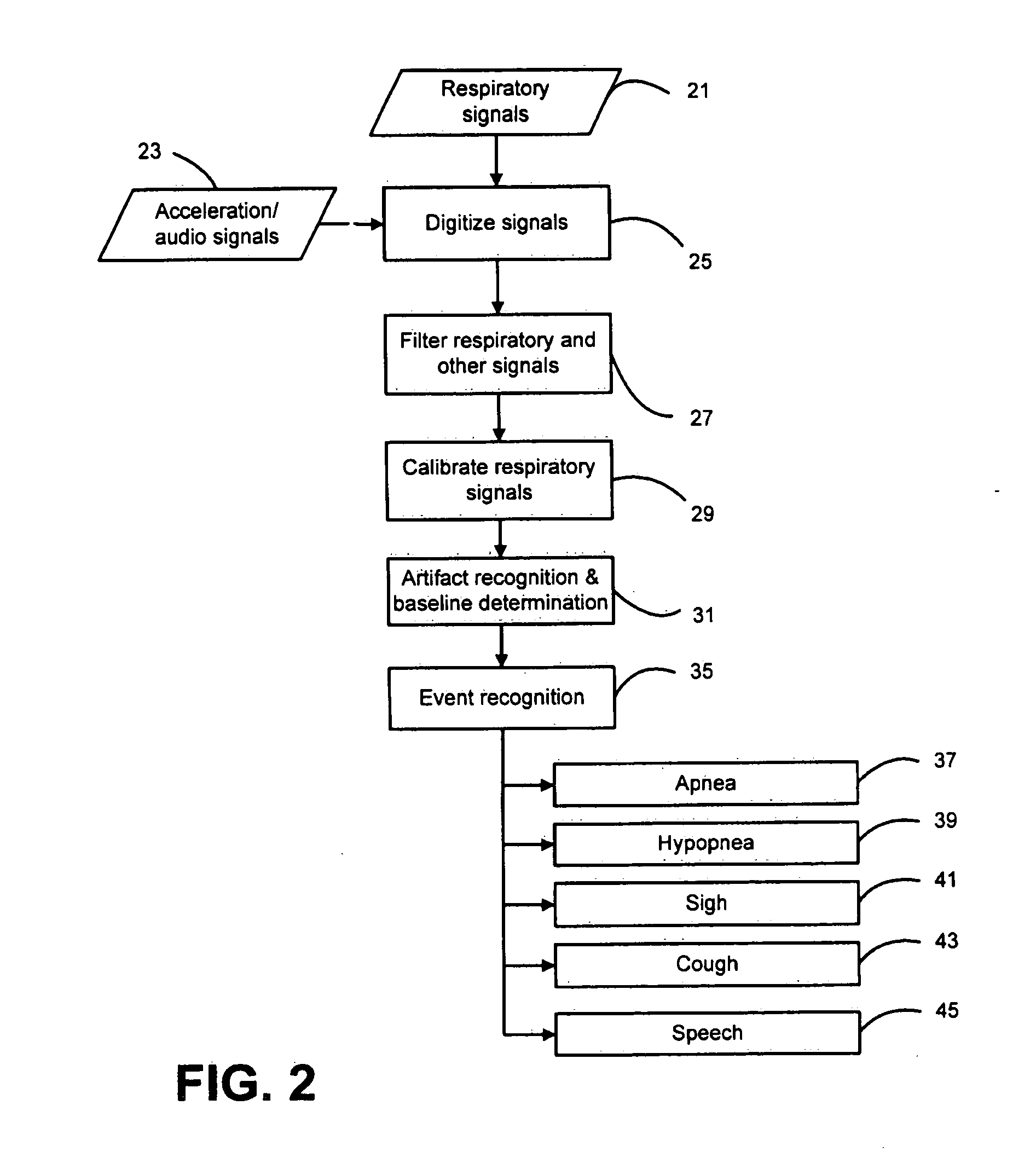
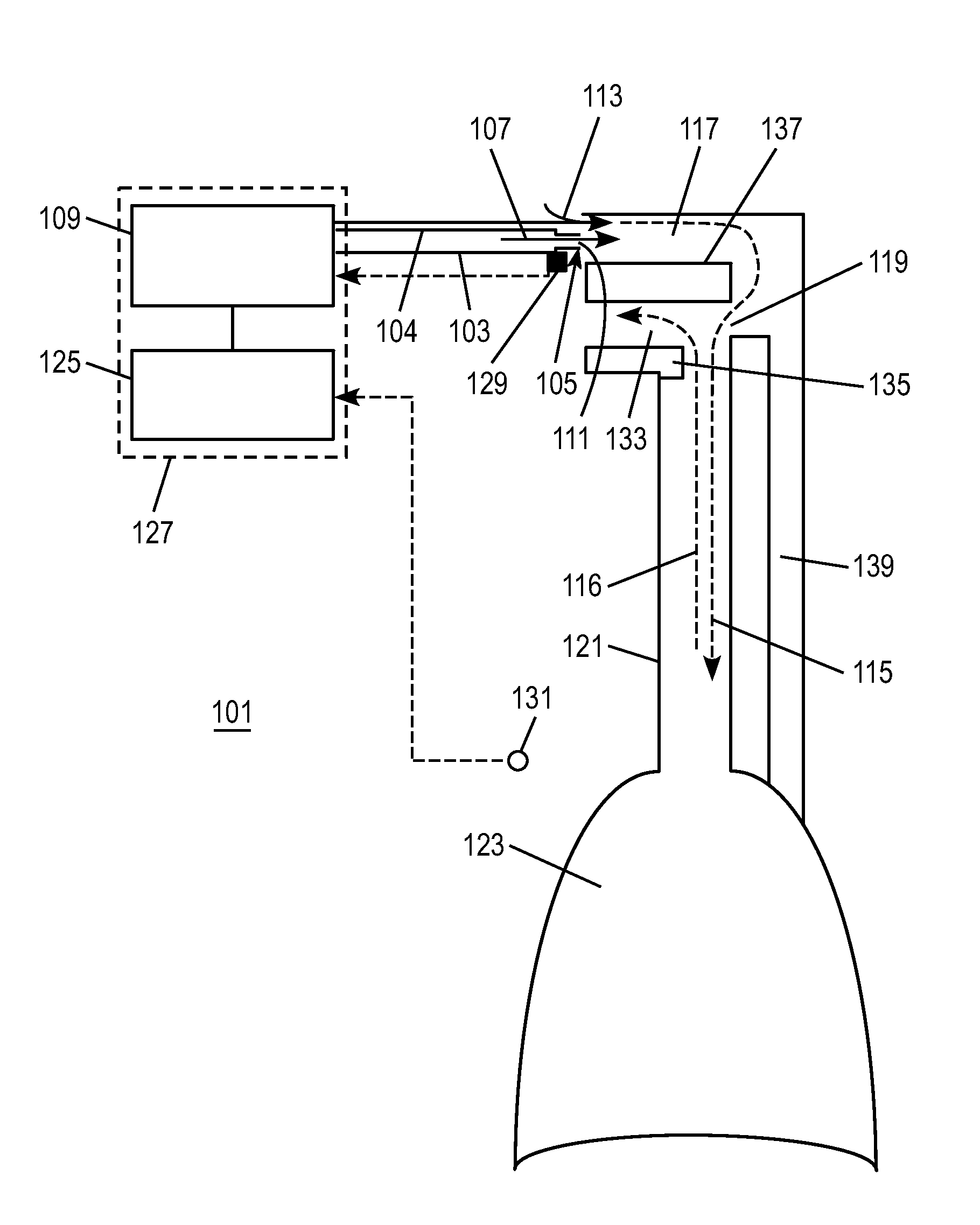
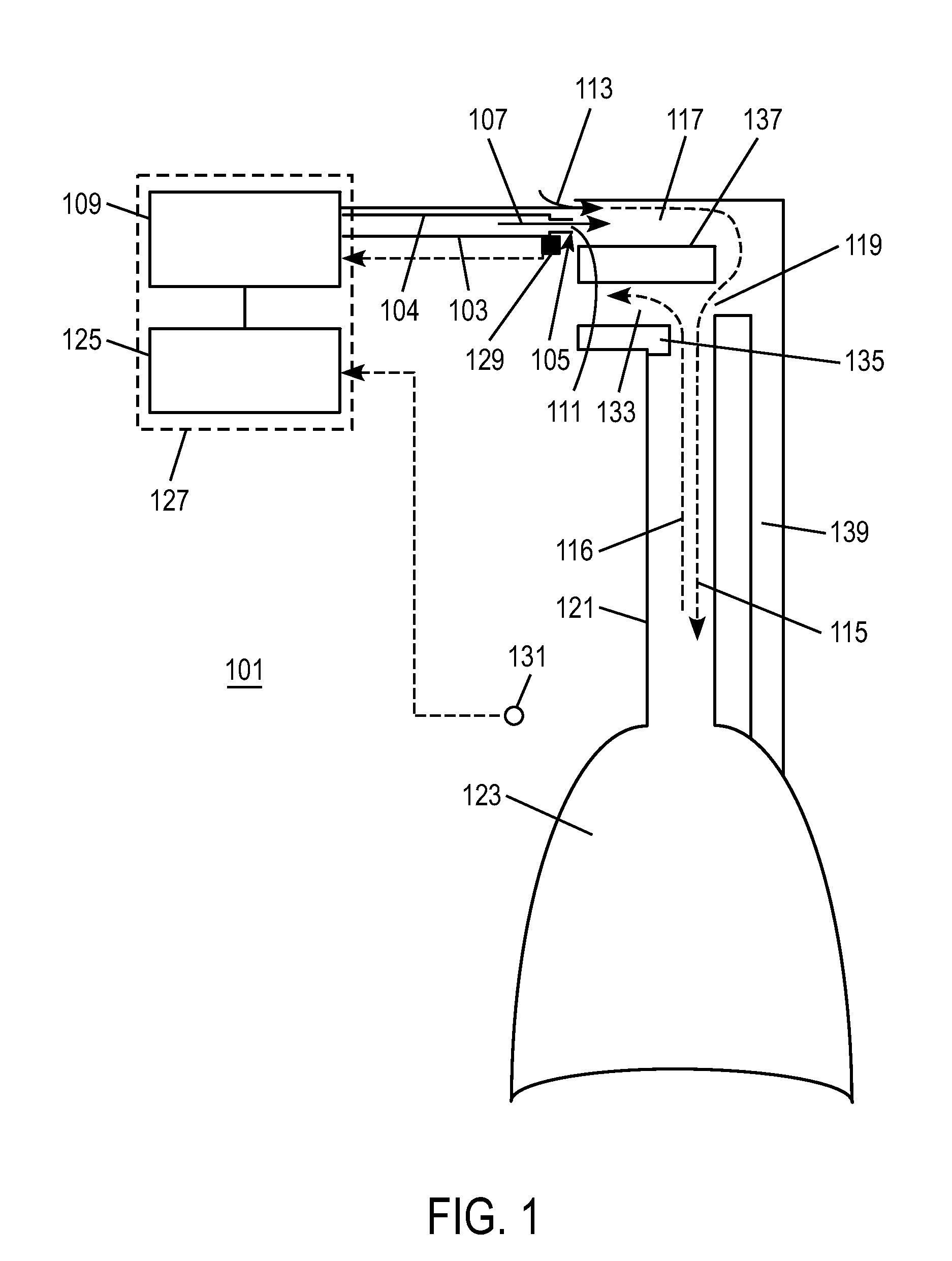
The present invention is directed to improved systems and methods for processing respiratory signals derived generally from respiratory plethysmography, and especially from respiratory inductive plethysmographic sensors mounted on a garment for ambulatory recording. The systems and methods provide improved signal filtering for artifact rejection, improved calibration of sensor data to produce outputs indicative of lung volumes. Further, this invention provides improved systems and methods directed to processing lung volume signals, however measured or derived, to provide improved determination of respiratory parameters and improved recognition of selected respiratory events.
Owner:ADIDAS
Method for lung volume reduction
InactiveUS6997189B2Prevent re-inflationLower the volumeSuture equipmentsDiagnosticsLung volumesLung volume reduction
Methods and assemblies for reducing the volume of a lung. A plurality of anchors are anchored at different positions in the lung. A cord is attached to each of the anchors. The anchors are drawn towards one another via the cords to cause the lung to collapse, thus compressing the tissue in the lung and establishing a reduction in lung volume.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Respiration responsive gating means and apparatus and methods using the same
InactiveUS6076005AReduce inaccuracyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryContinuous measurementLung volumes
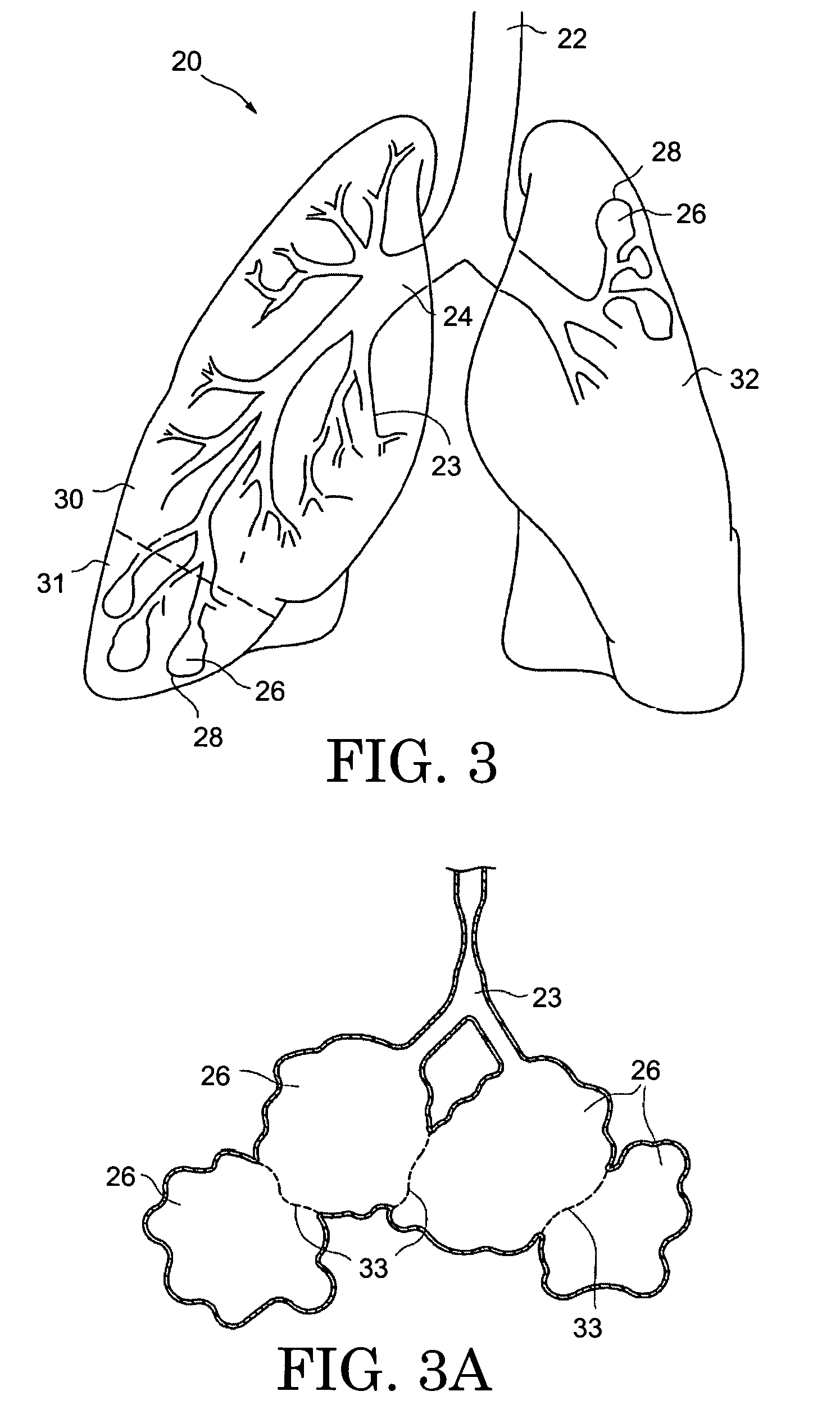
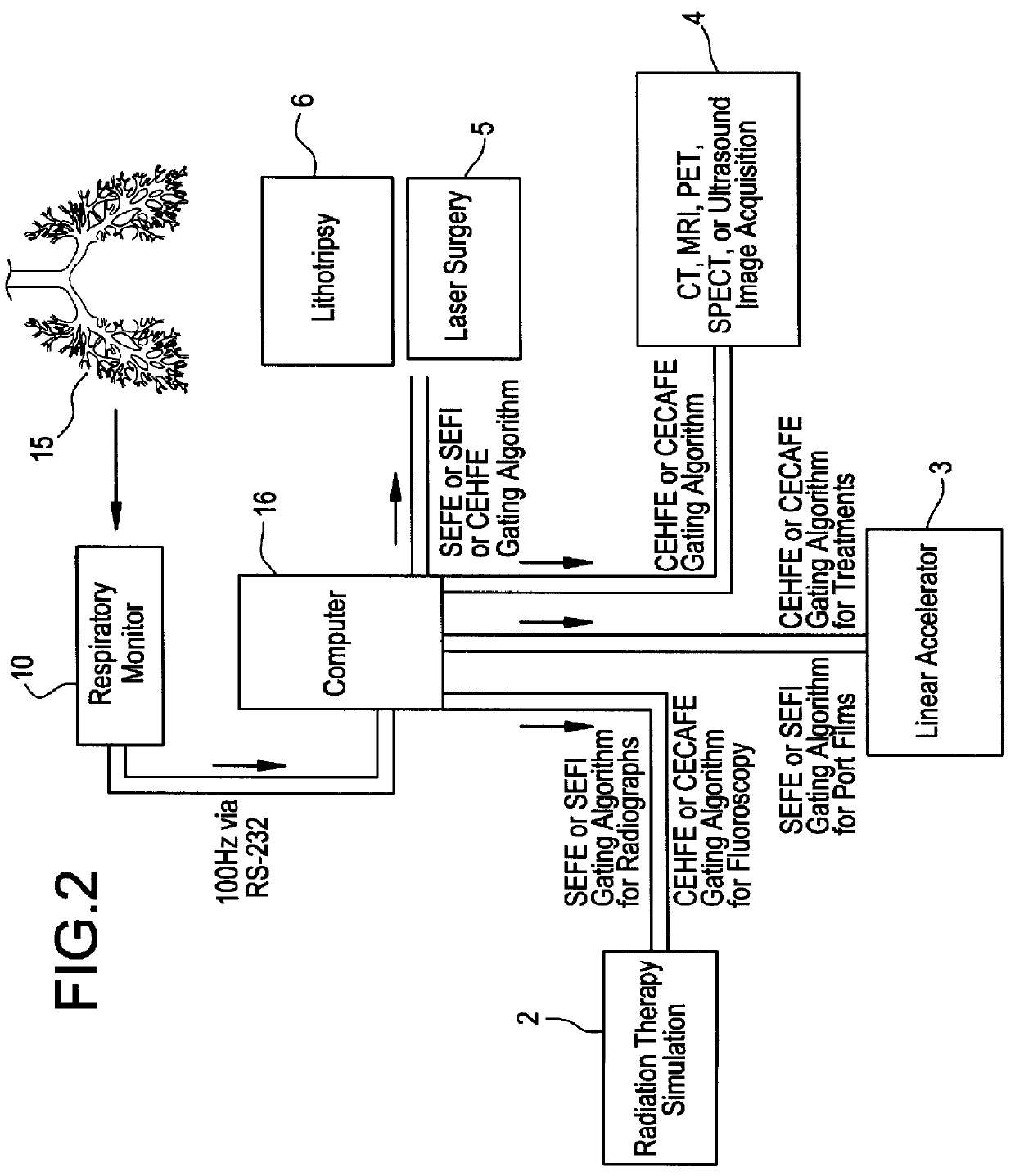
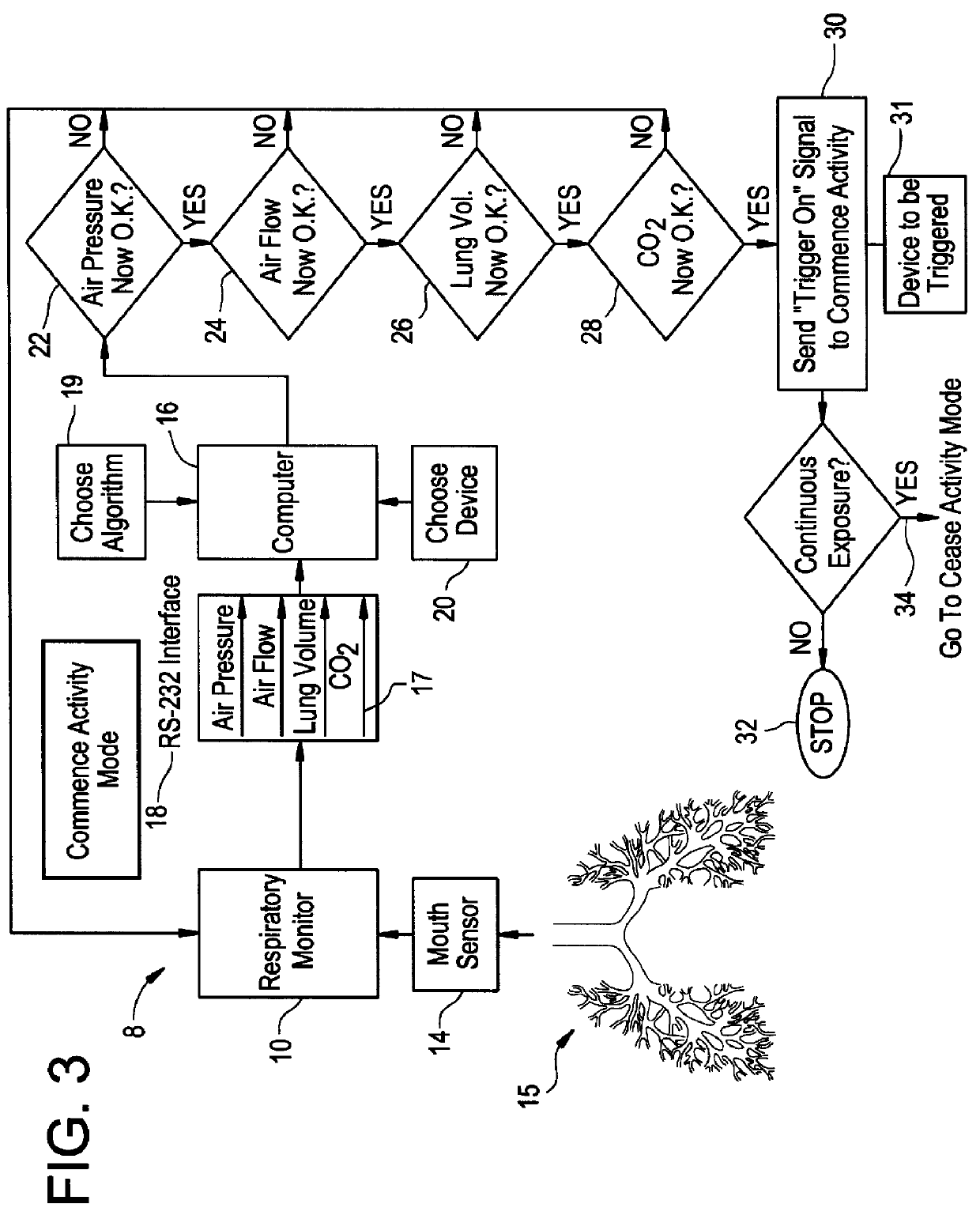
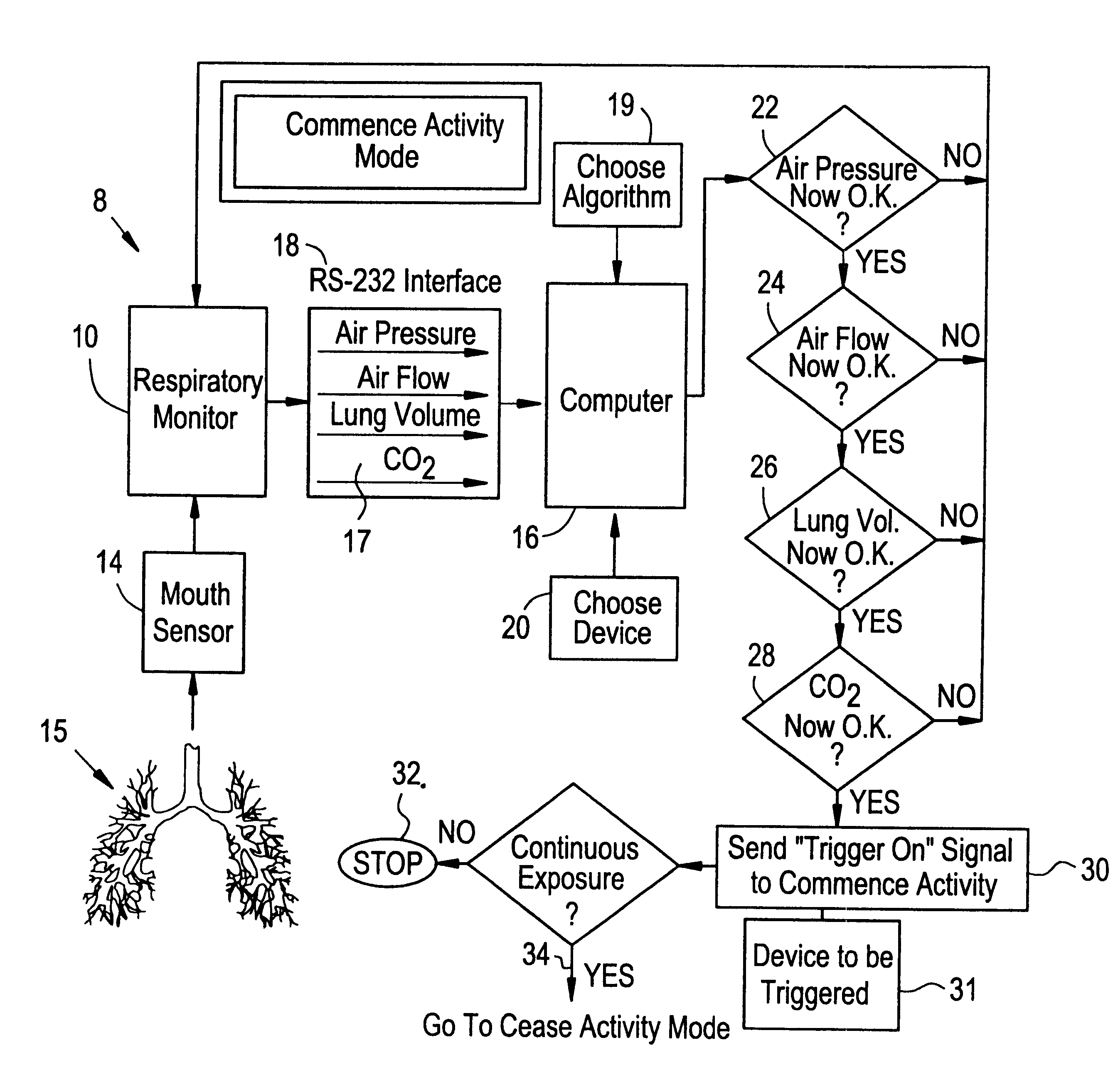
A method and system for gating therapeutic or diagnostic energy to a tissue volume of a medical patient during a selected portion of the patient's respiratory cycle, to thereby diminish inaccuracies in the assumed spatial position of the tissue volume arising from displacements induced by the patient's respiration. The gases flowing to and from the patient's lungs are monitored to provide quasi-continuous measurements as a function of time, of (a) flow rate, (b) pressure, (c) patient lung volume and (d) carbon dioxide concentration. The measurements are utilized to trigger the time period during which the energy is gated on, at the beginning of the selected portion of the respiration cycle; and the time period during which the energy is gated on, is terminated at the end of the selected portion of the respiration cycle.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Respiration responsive gating means and apparatus and methods using the same
InactiveUS6298260B1Reduce inaccuracyImprove measurement reliabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryLung volumesMedical patient
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
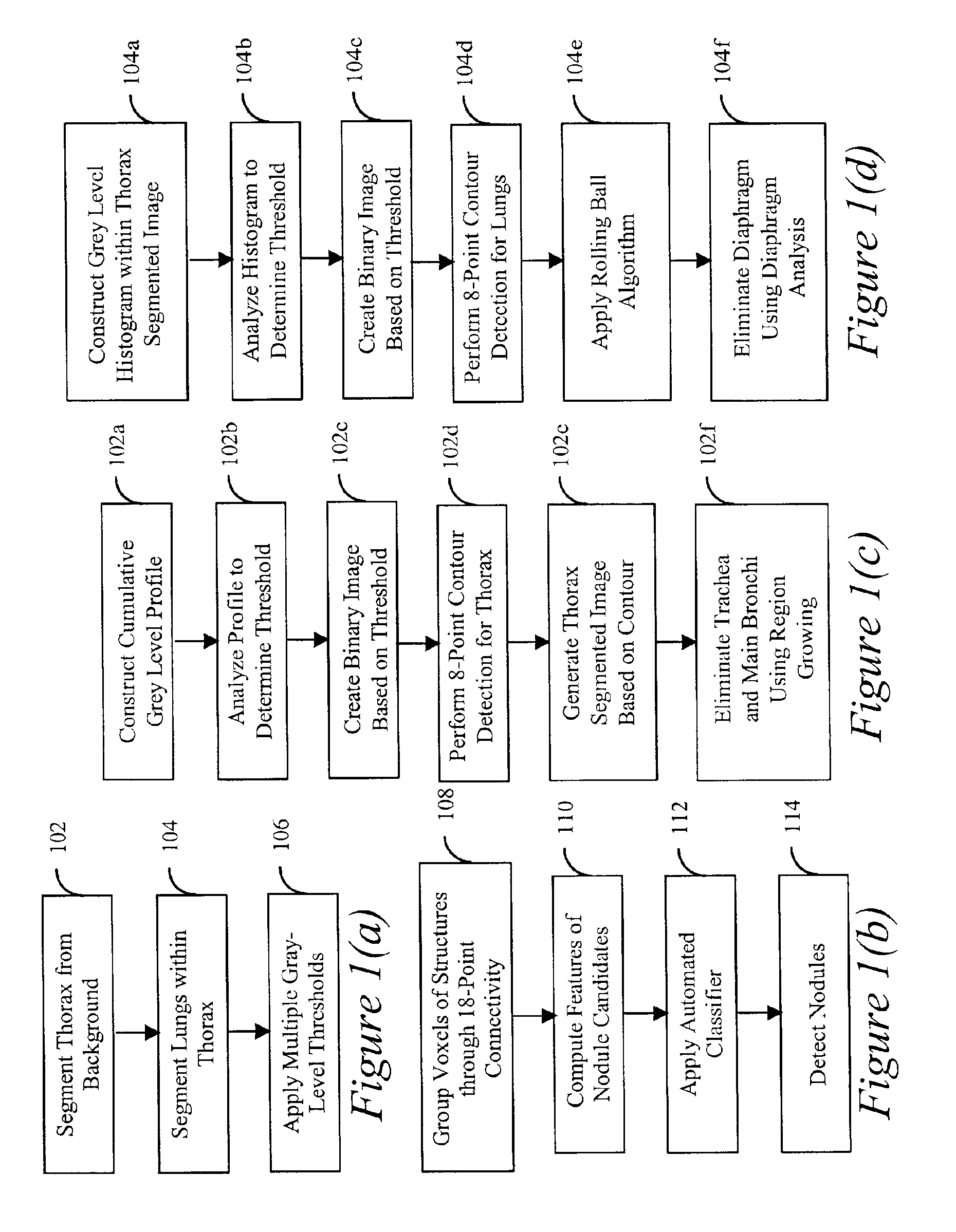
Method, system and computer readable medium for the two-dimensional and three-dimensional detection of lesions in computed tomography scans
InactiveUS6898303B2Significant comprehensive benefitsFocusImage enhancementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputed tomographyLung volumes
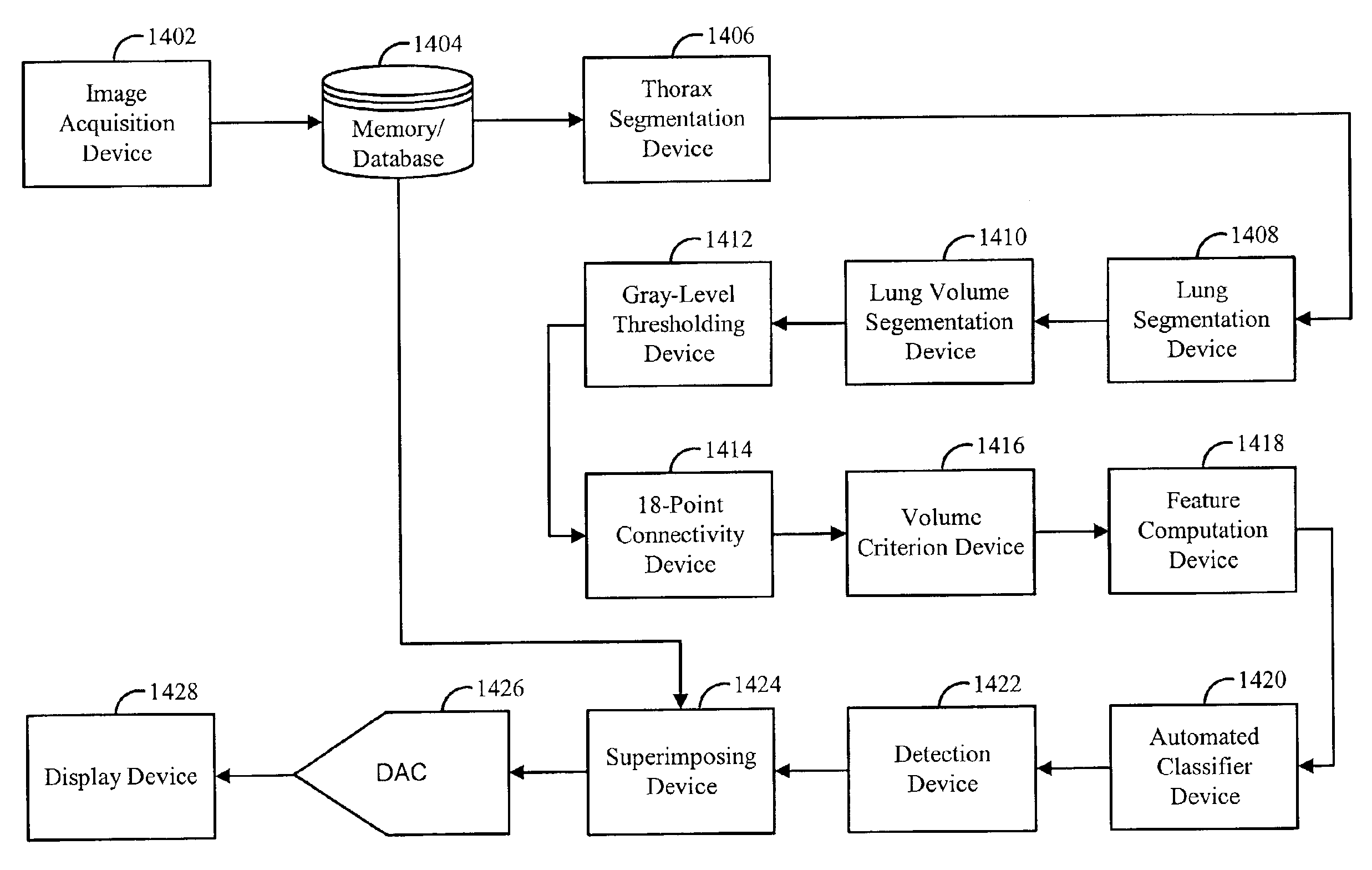
A method, system and computer readable medium for automated detection of lung nodules in computed tomography (CT) image scans, including generating two-dimensional segmented lung images by segmenting a plurality of two-dimensional CT image sections derived from the CT image scans; generating three-dimensional segmented lung volume images by combining the two-dimensional segmented lung images; determining three-dimensional lung nodule candidates from the three-dimensional segmented lung volume images, including, identifying structures within the three-dimensional segmented lung volume images that meet a volume criterion; deriving features from the lung nodule candidates; and detecting lung nodules by analyzing the features to eliminate false-positive nodule candidates from the nodule candidates.
Owner:ARCH DEVMENT
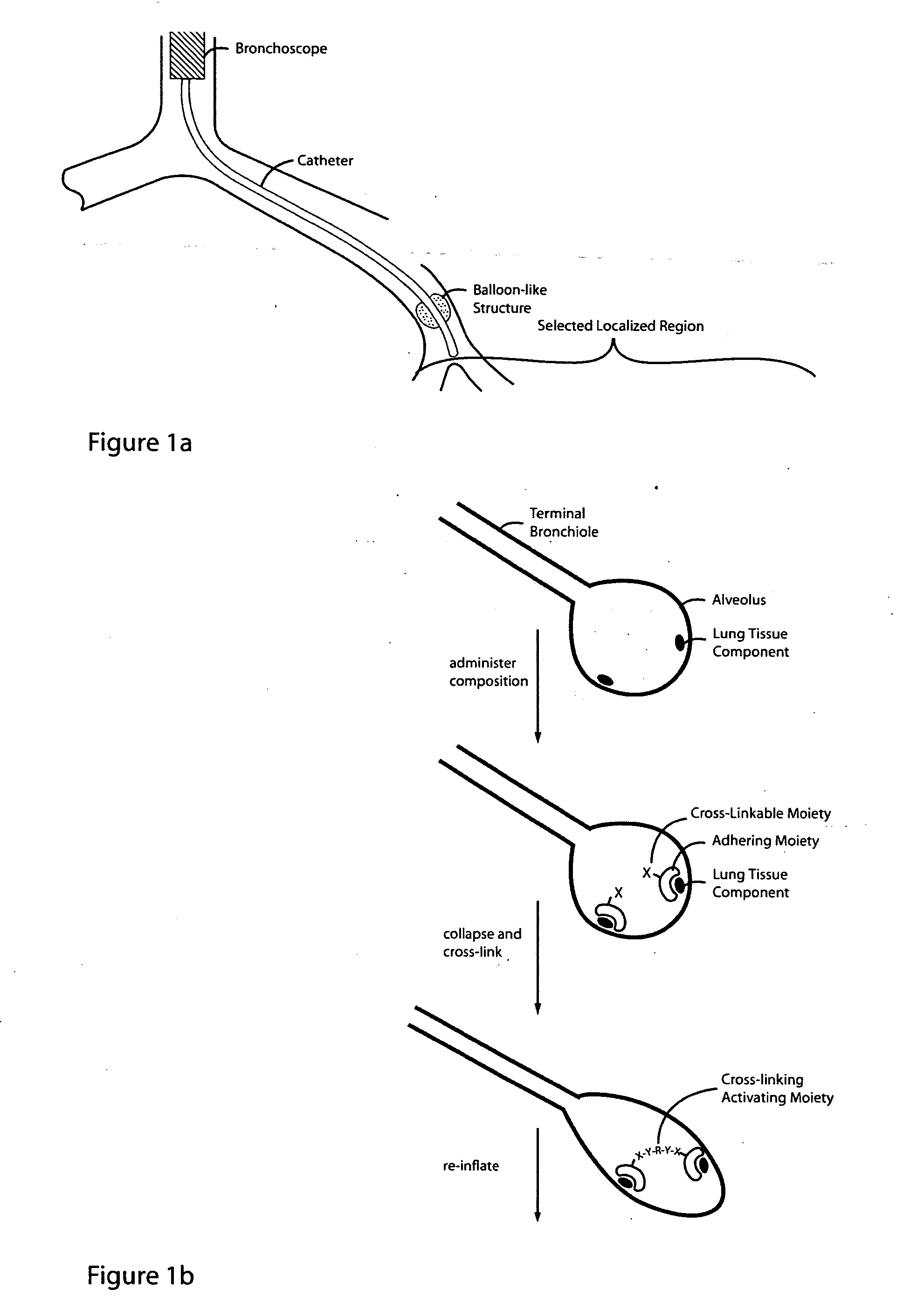
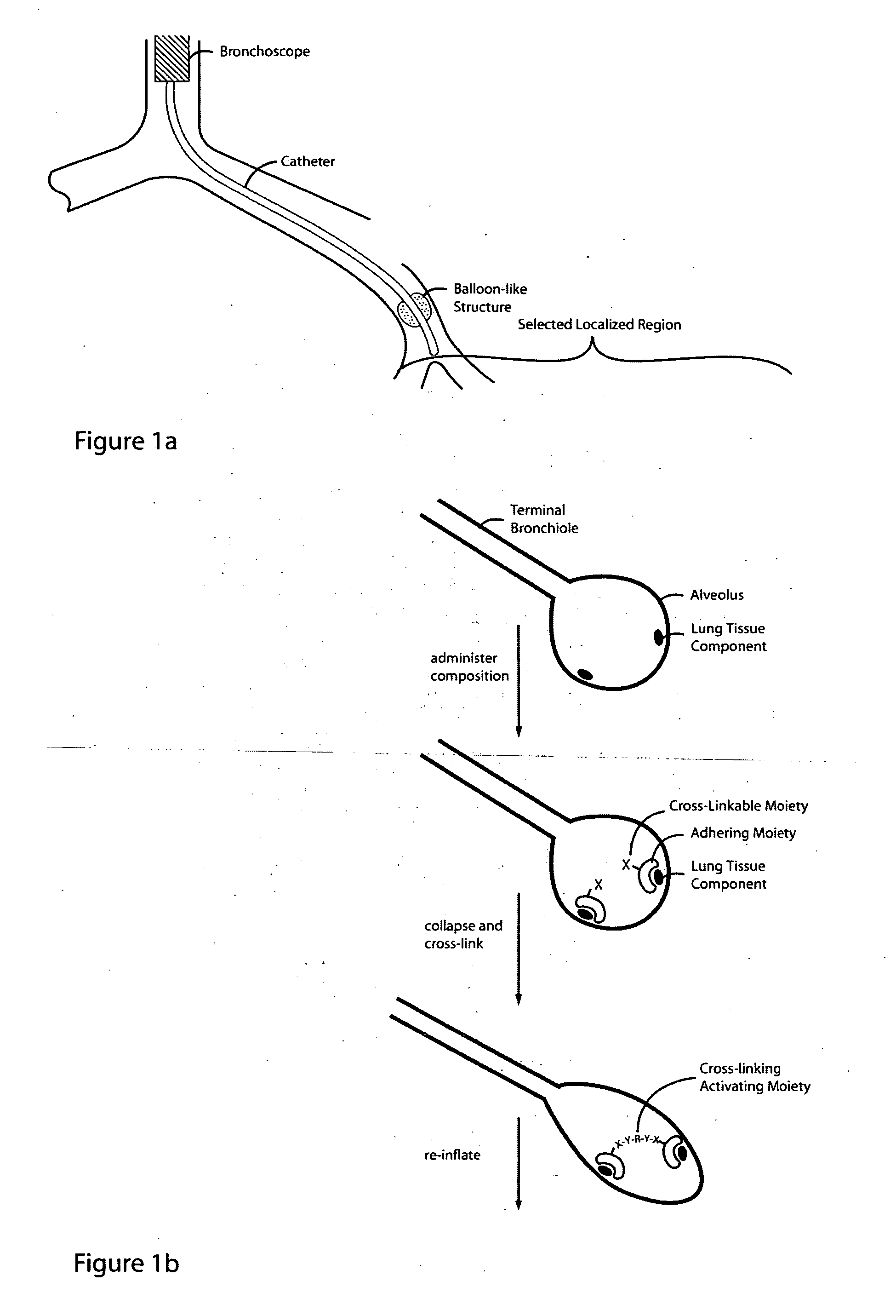
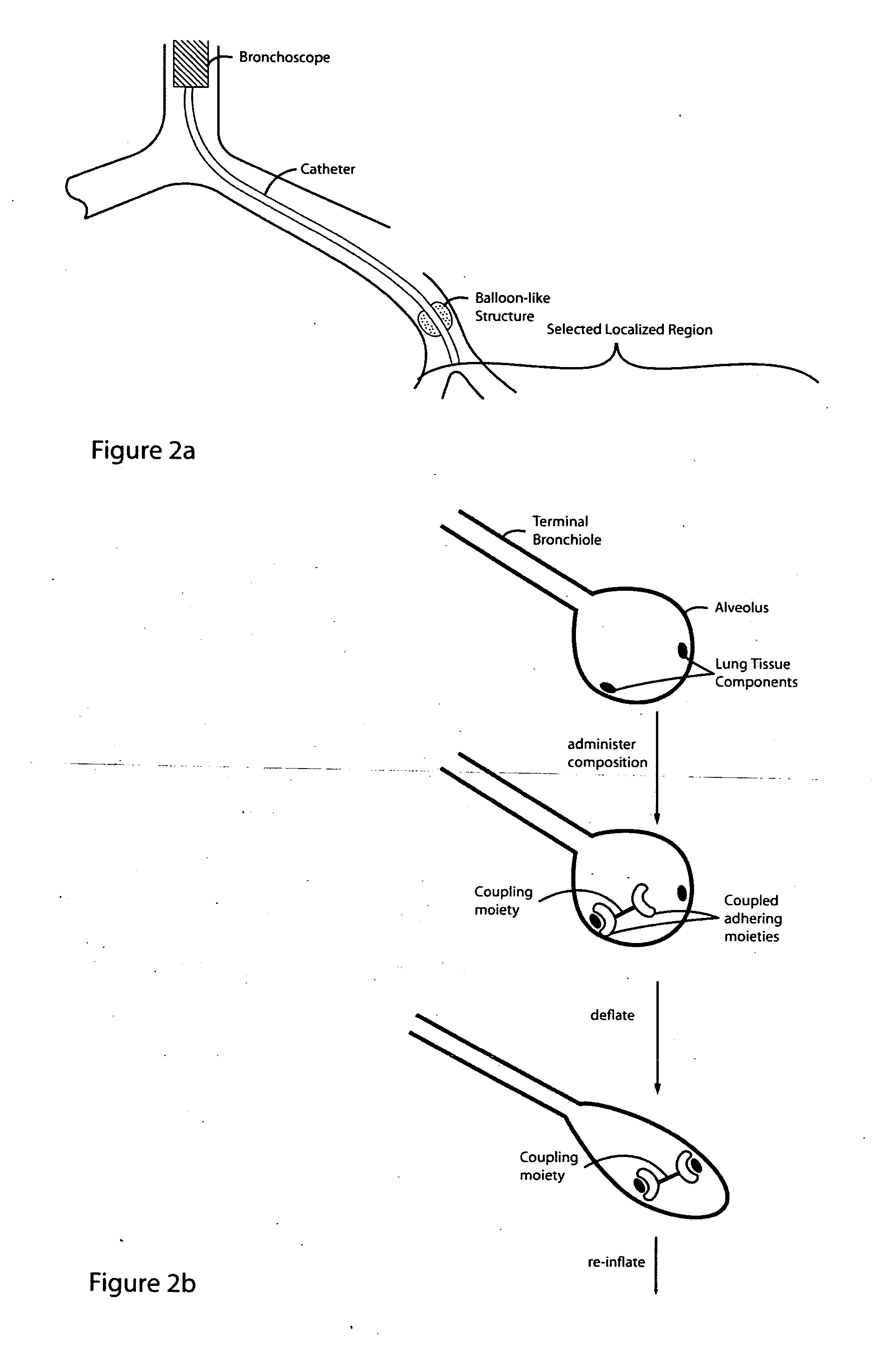
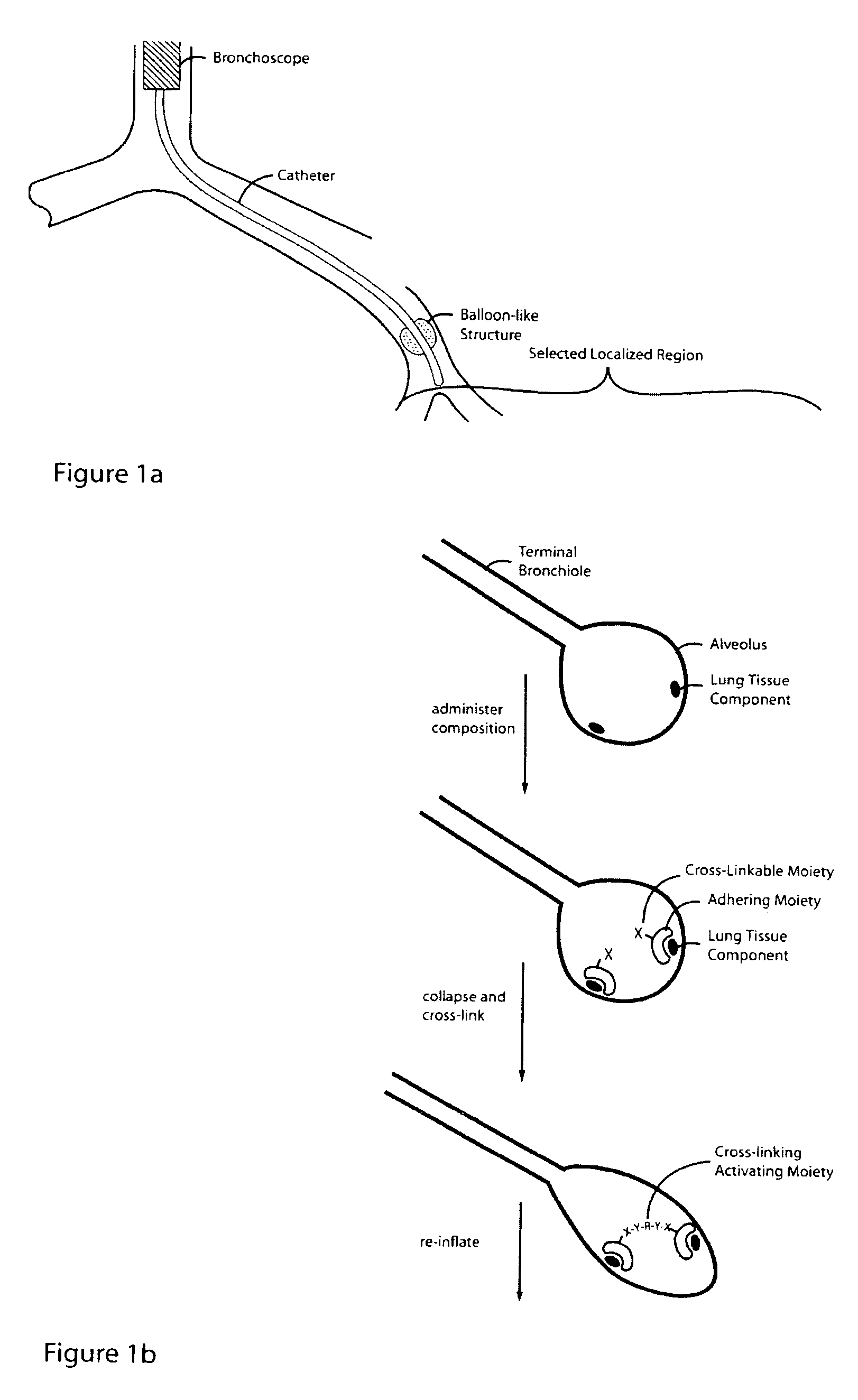
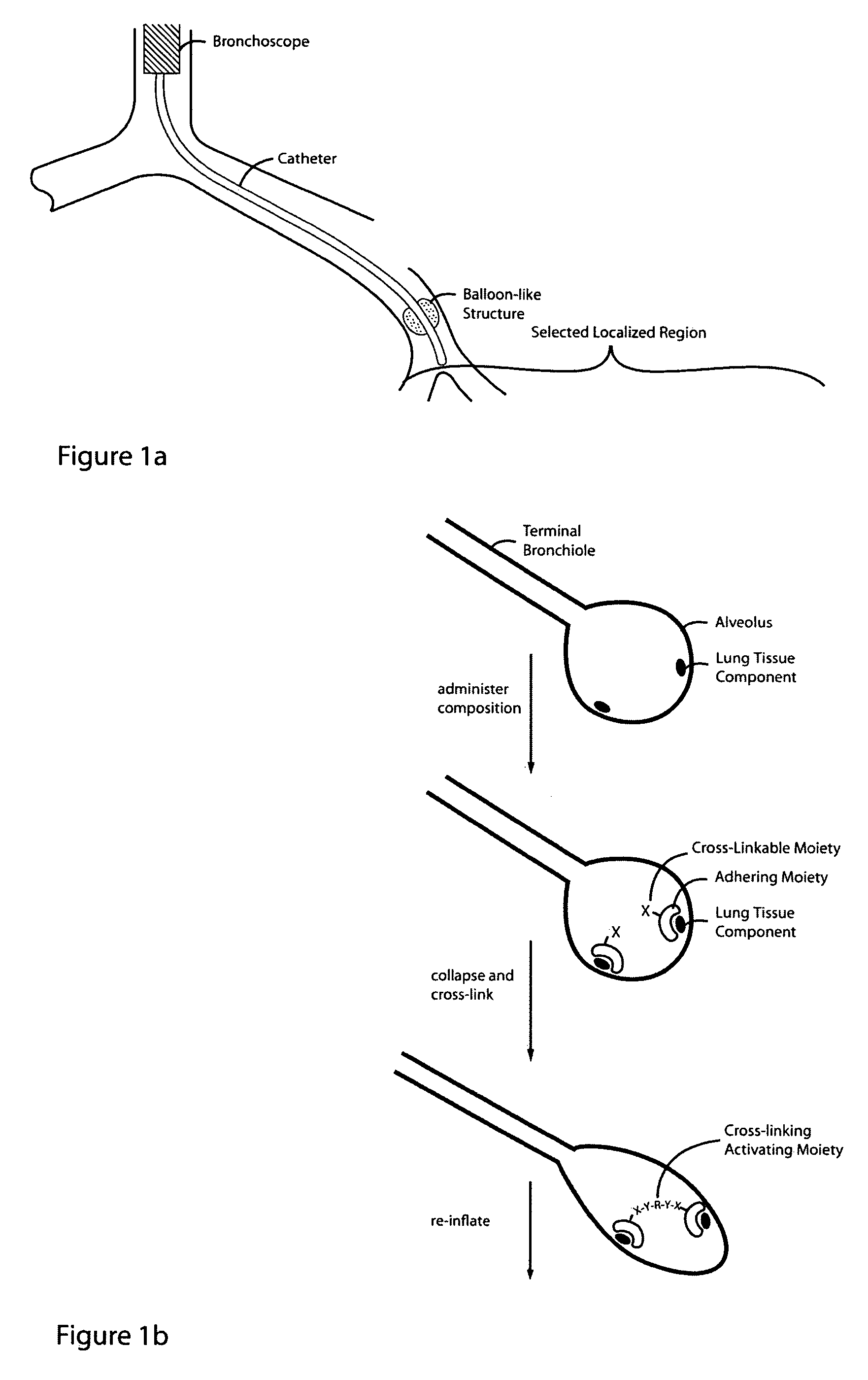
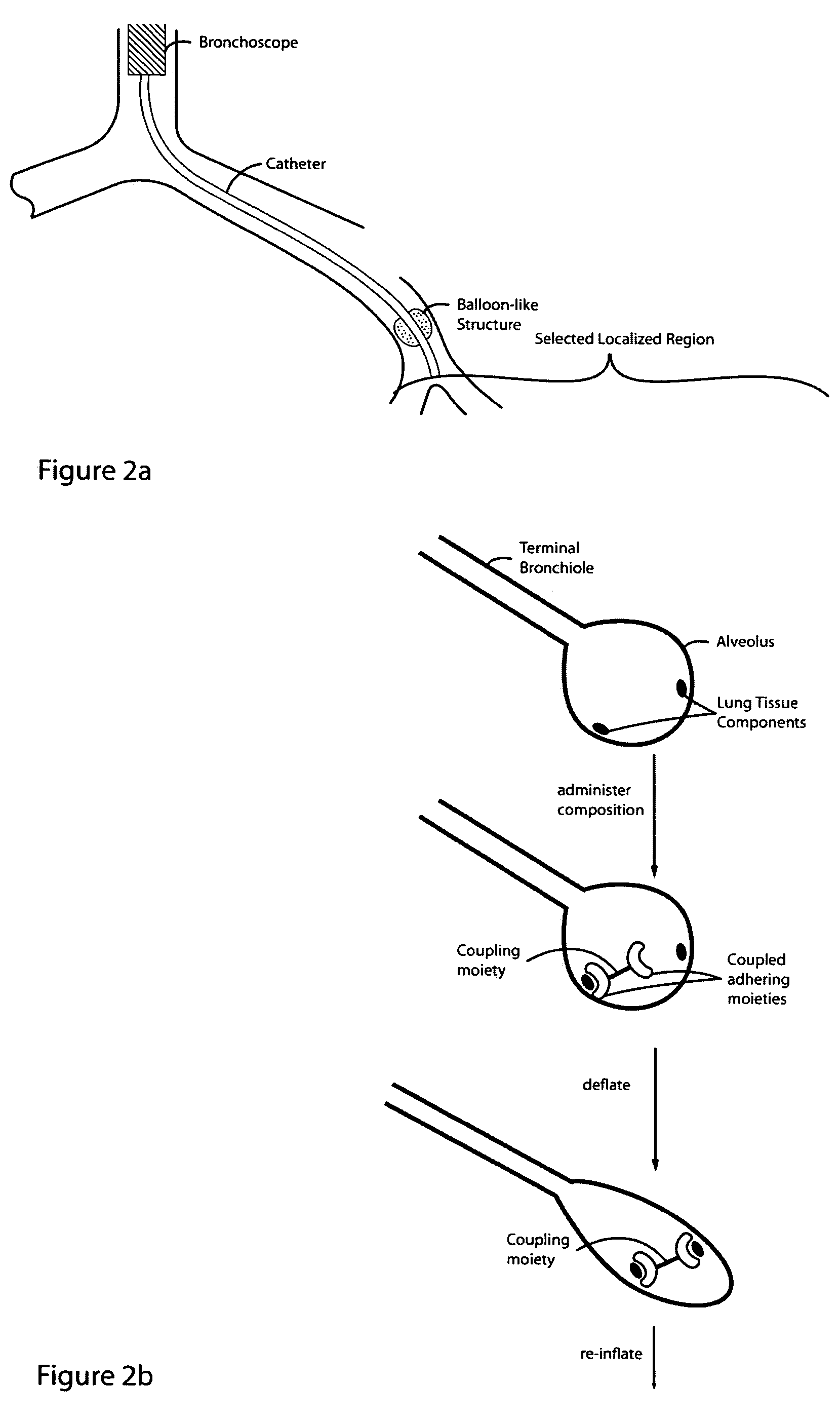
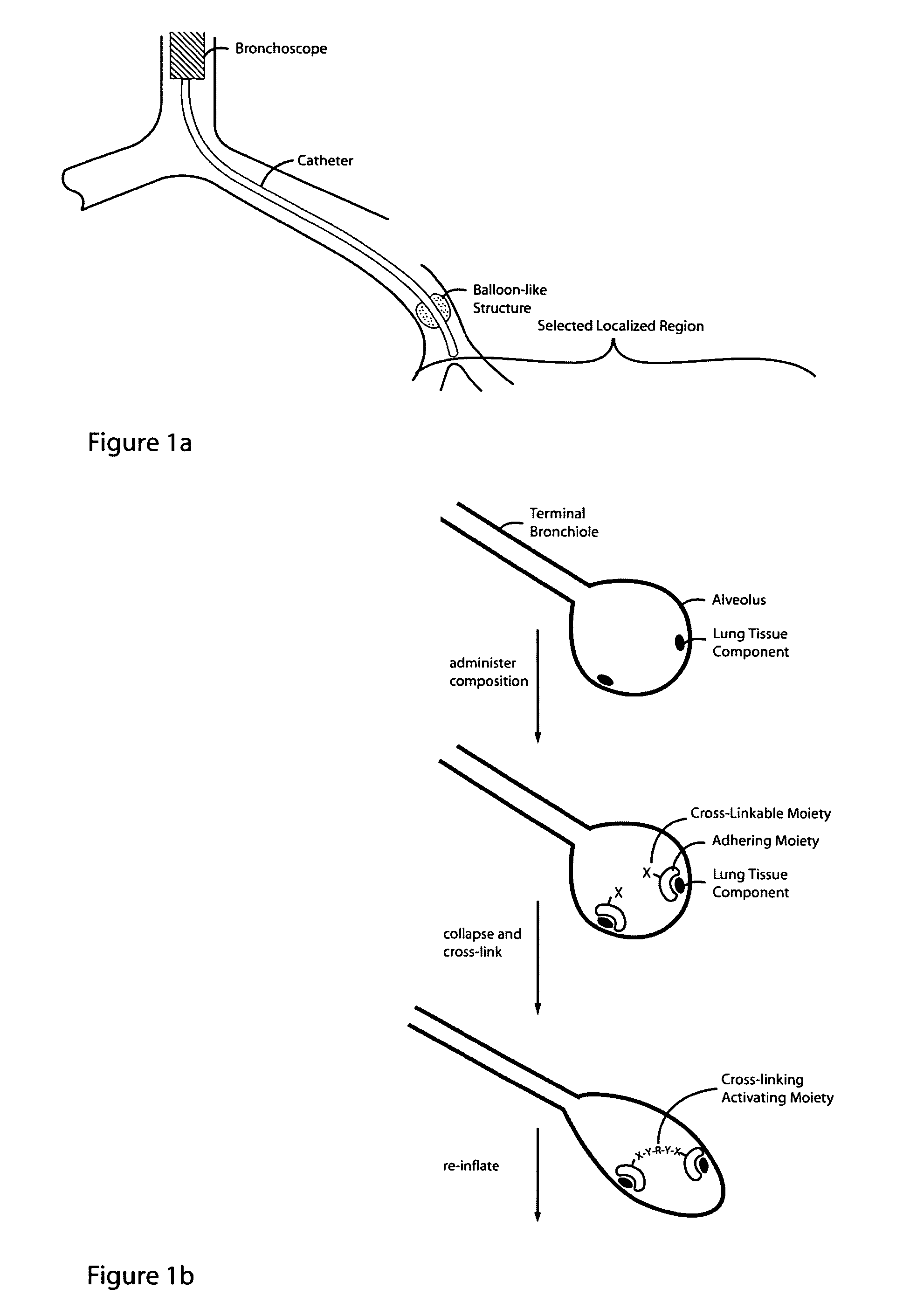
Lung volume reduction using glue composition
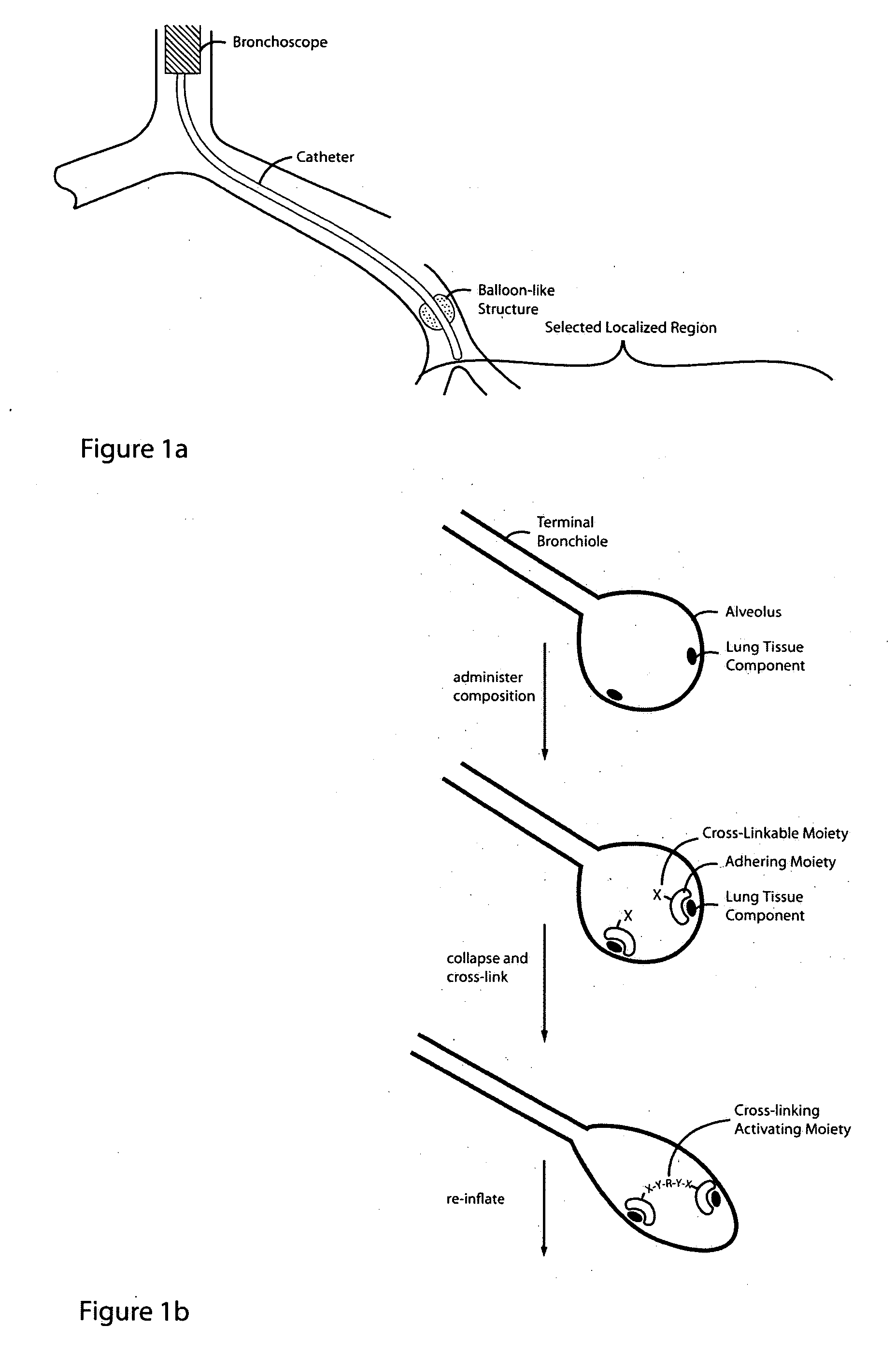
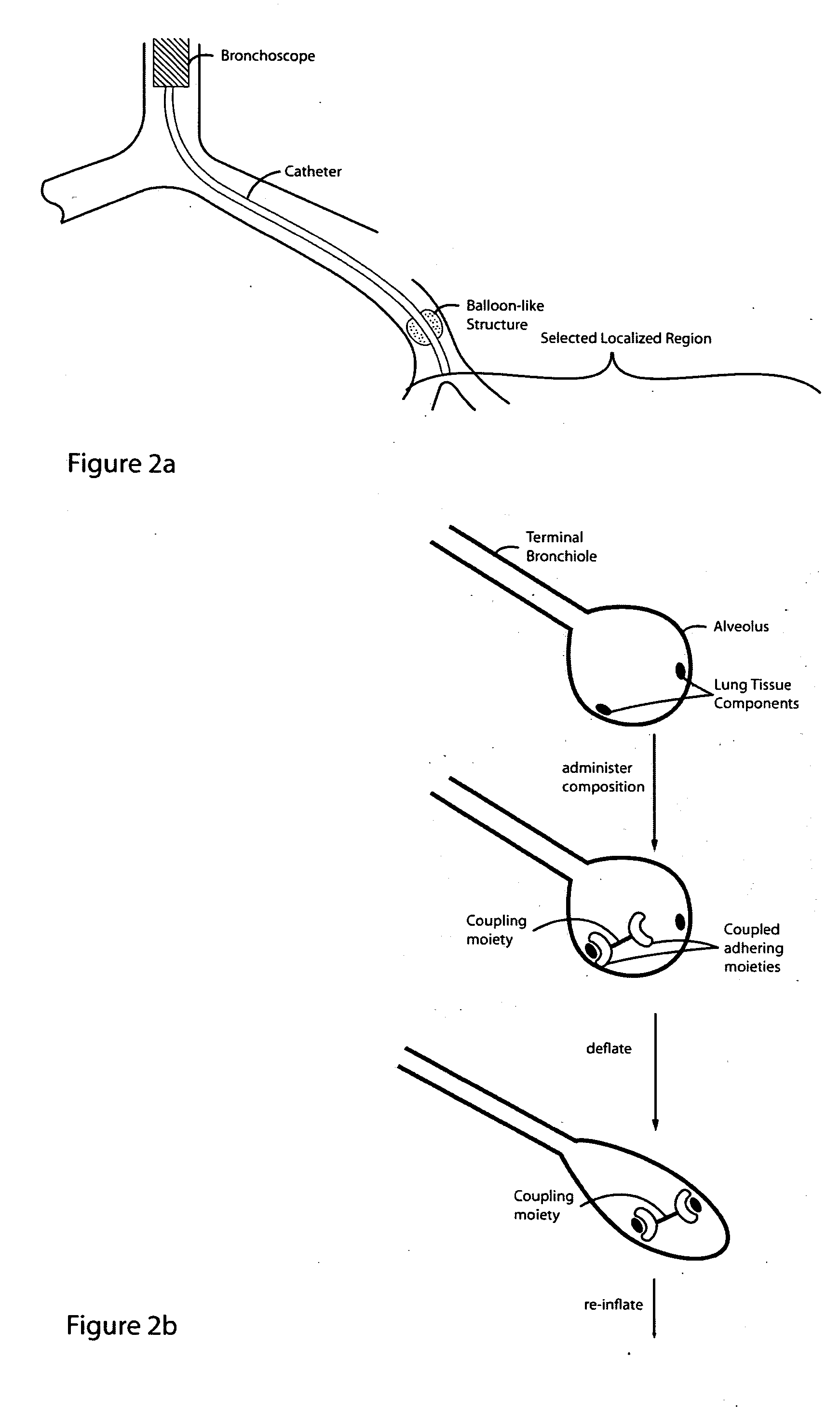
InactiveUS20050281802A1Reducing lung volumeSurgical adhesivesBacteria material medical ingredientsLung volumesLung tissue
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for sealing localized regions of damaged lung tissue to reduce overall lung volume. The glue compositions provide a glue featuring an adhering moiety coupled to one or more other moieties including, for example, a cross-linkable moiety and / or one other adhering moiety. The methods and compositions of the invention find use, for example, in treating pulmonary conditions, such as emphysema.
Owner:EKOS CORP
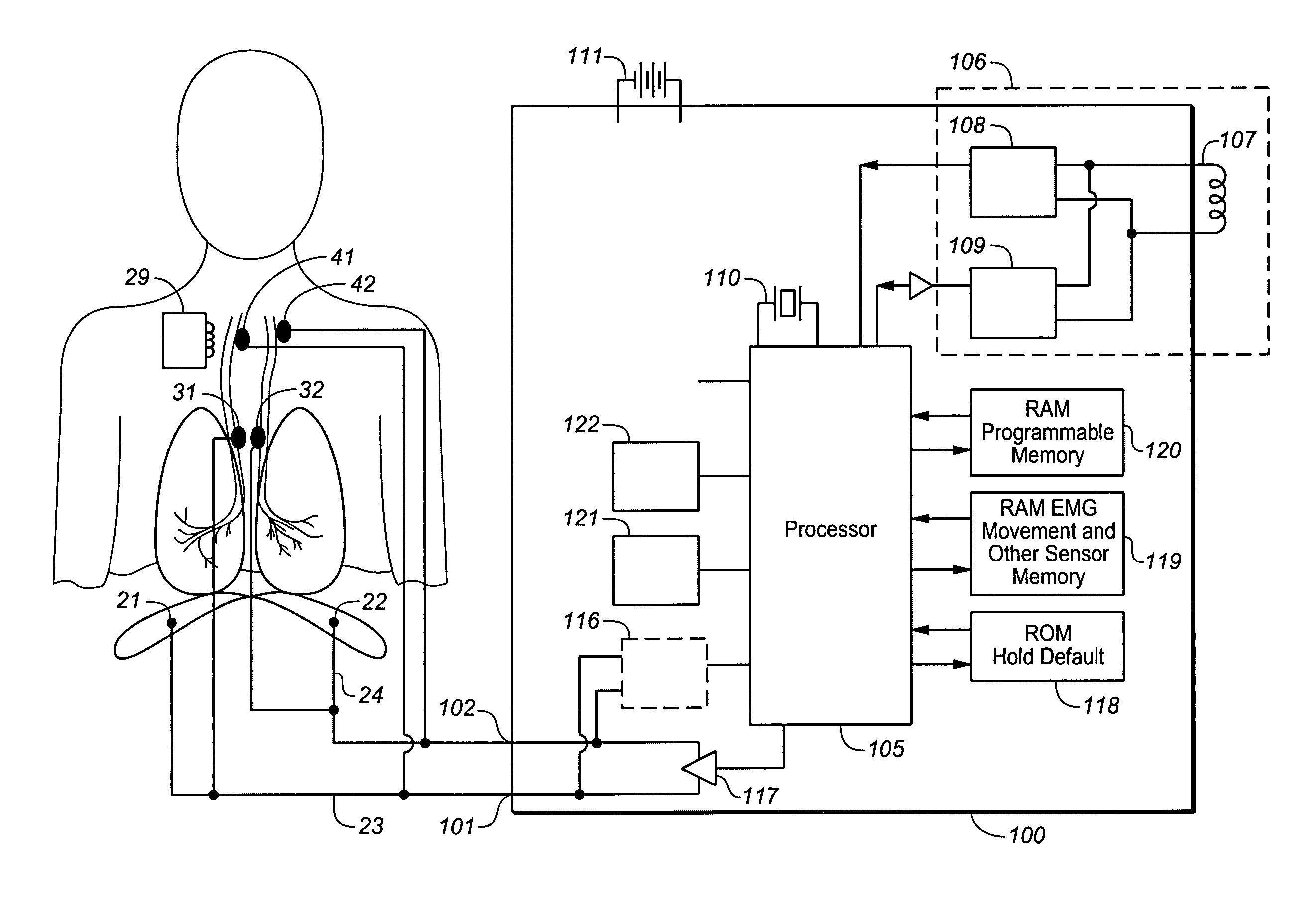
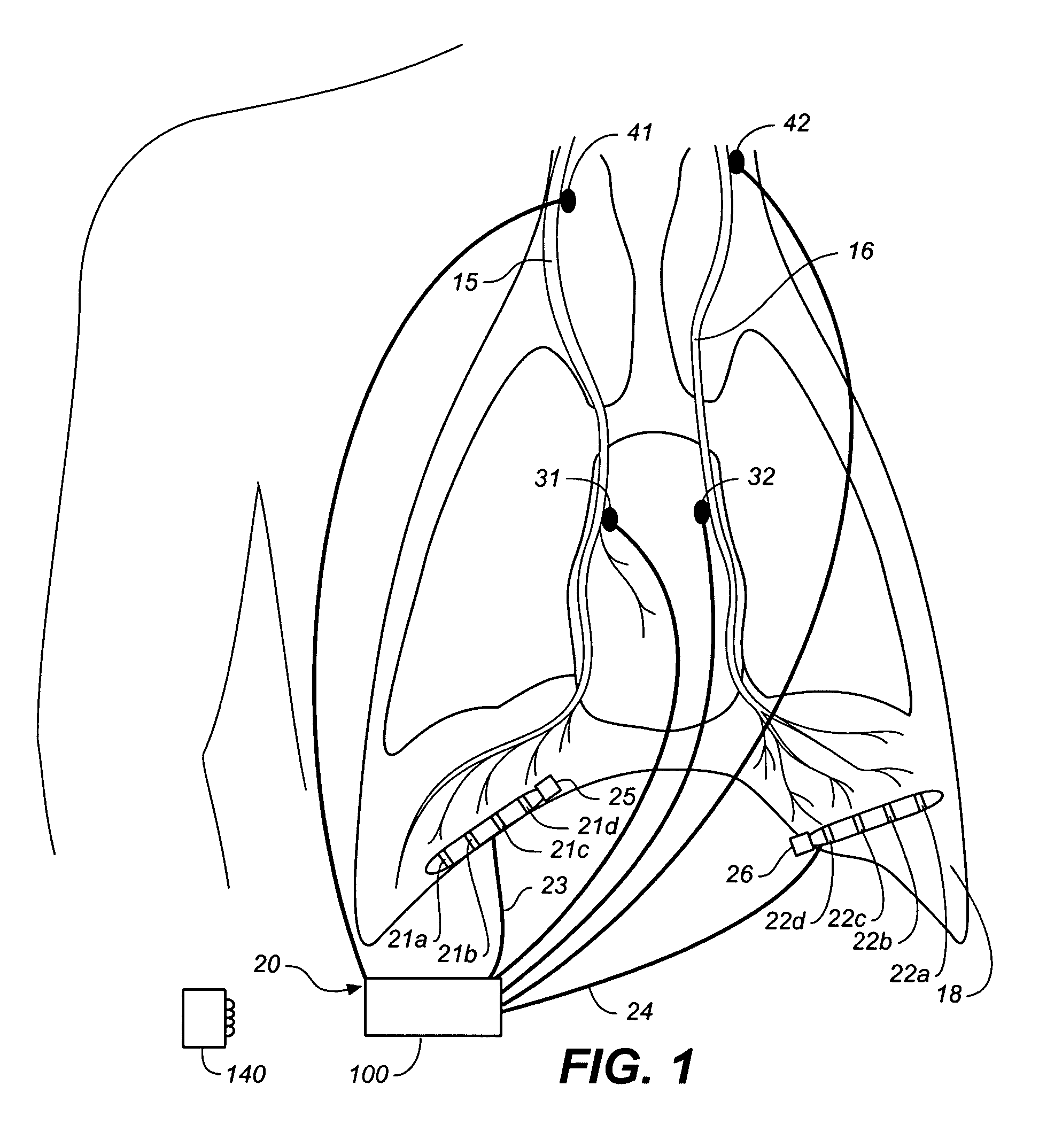
Device and method for biasing lung volume
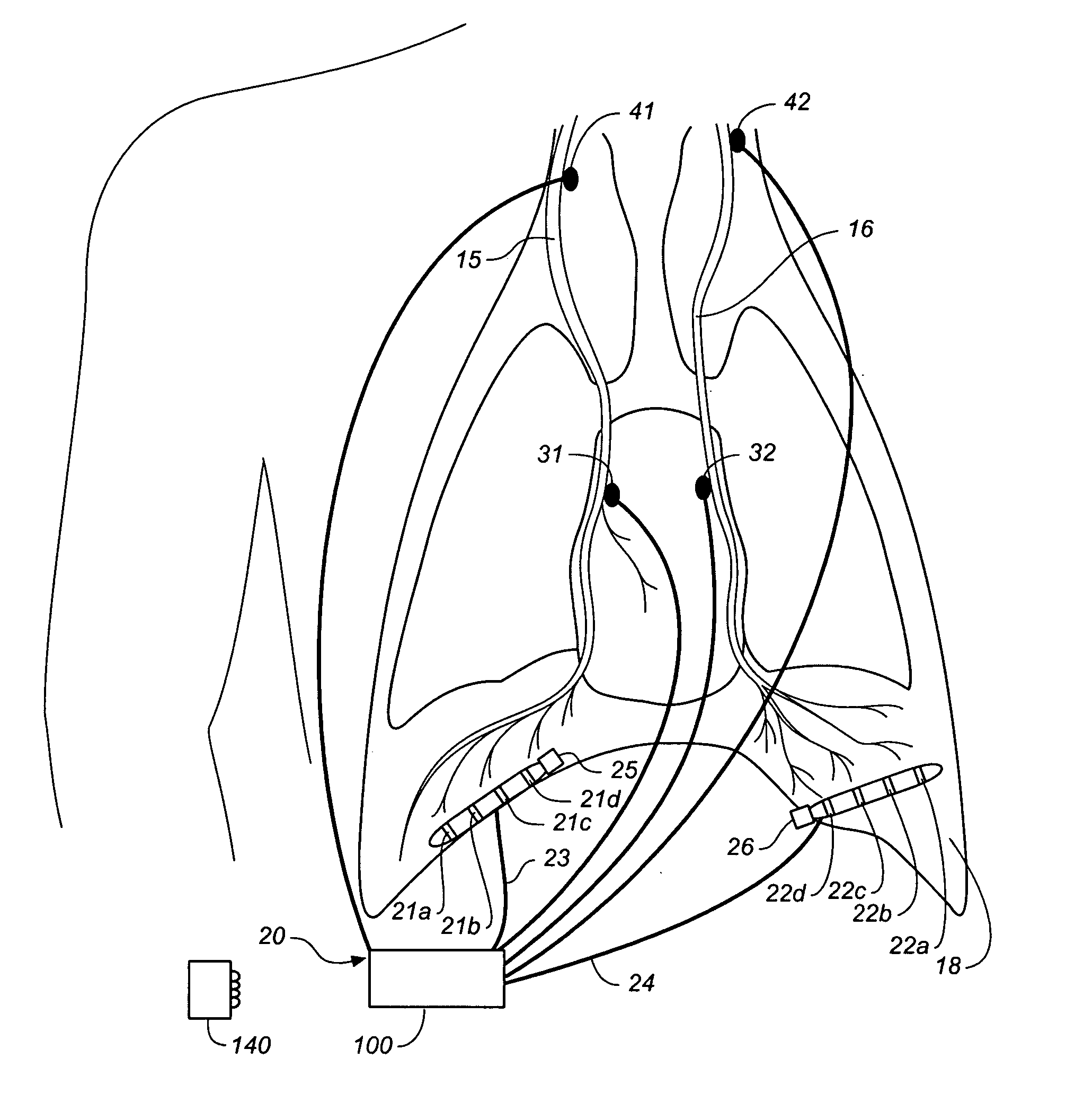
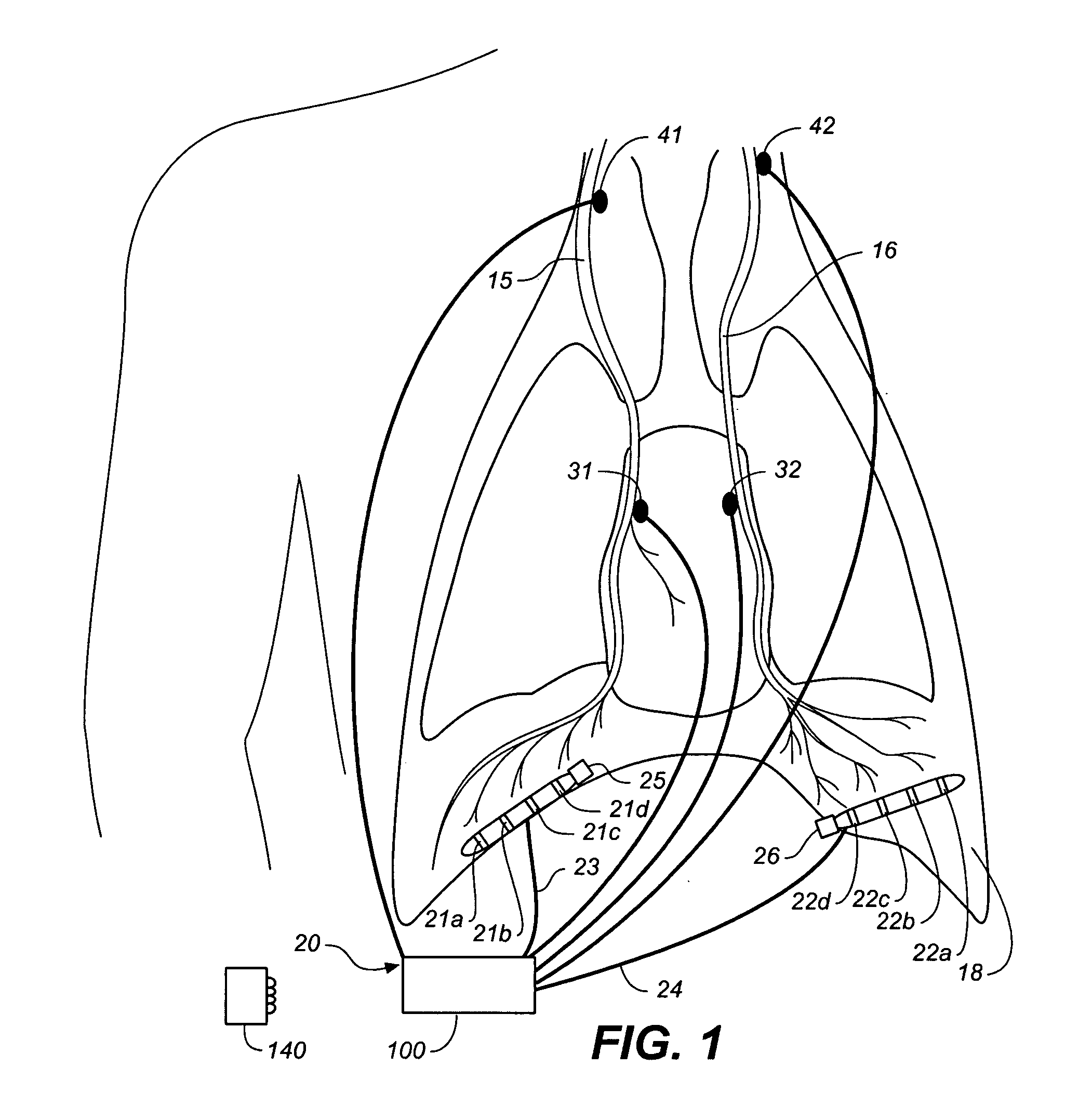
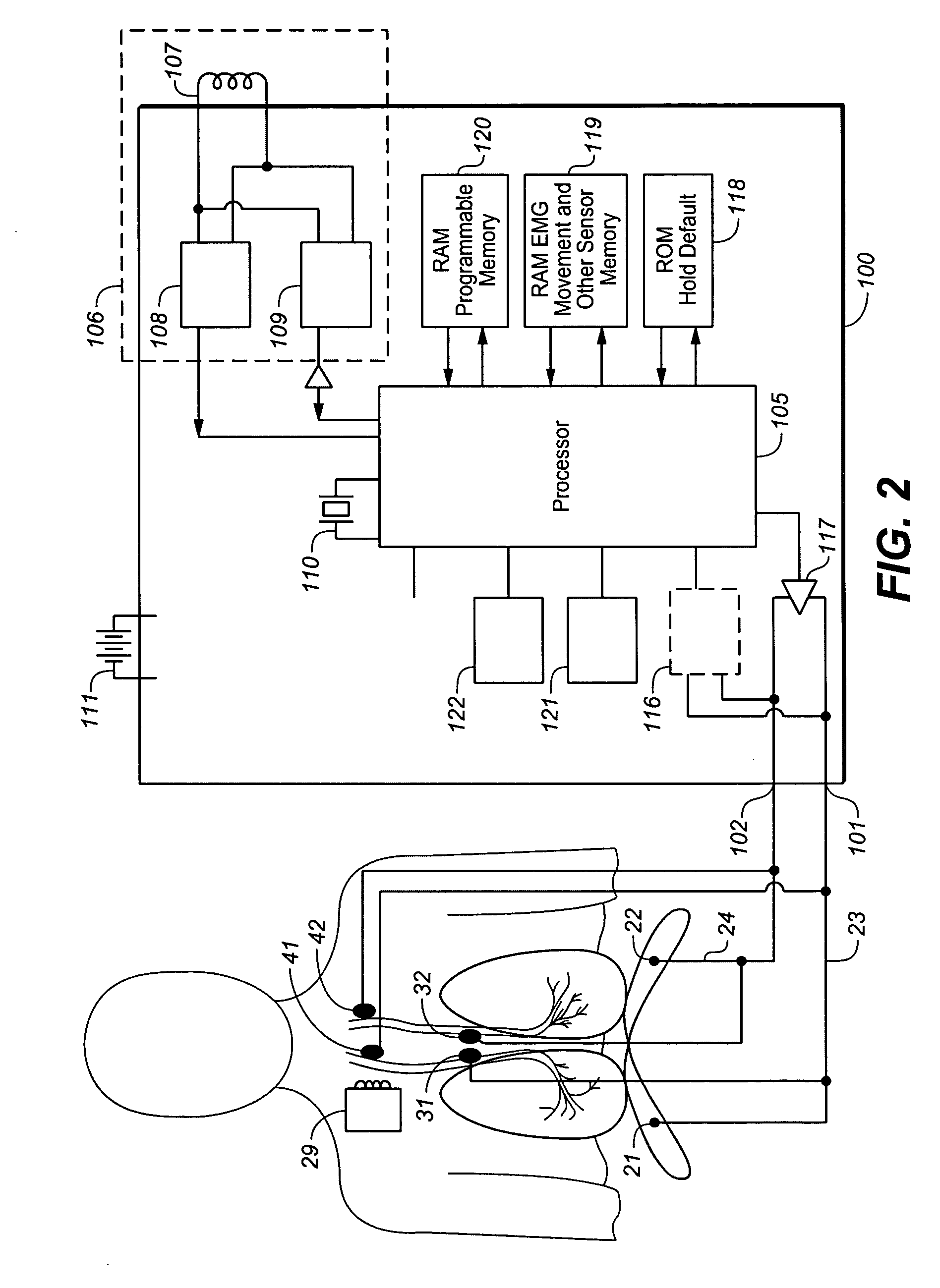
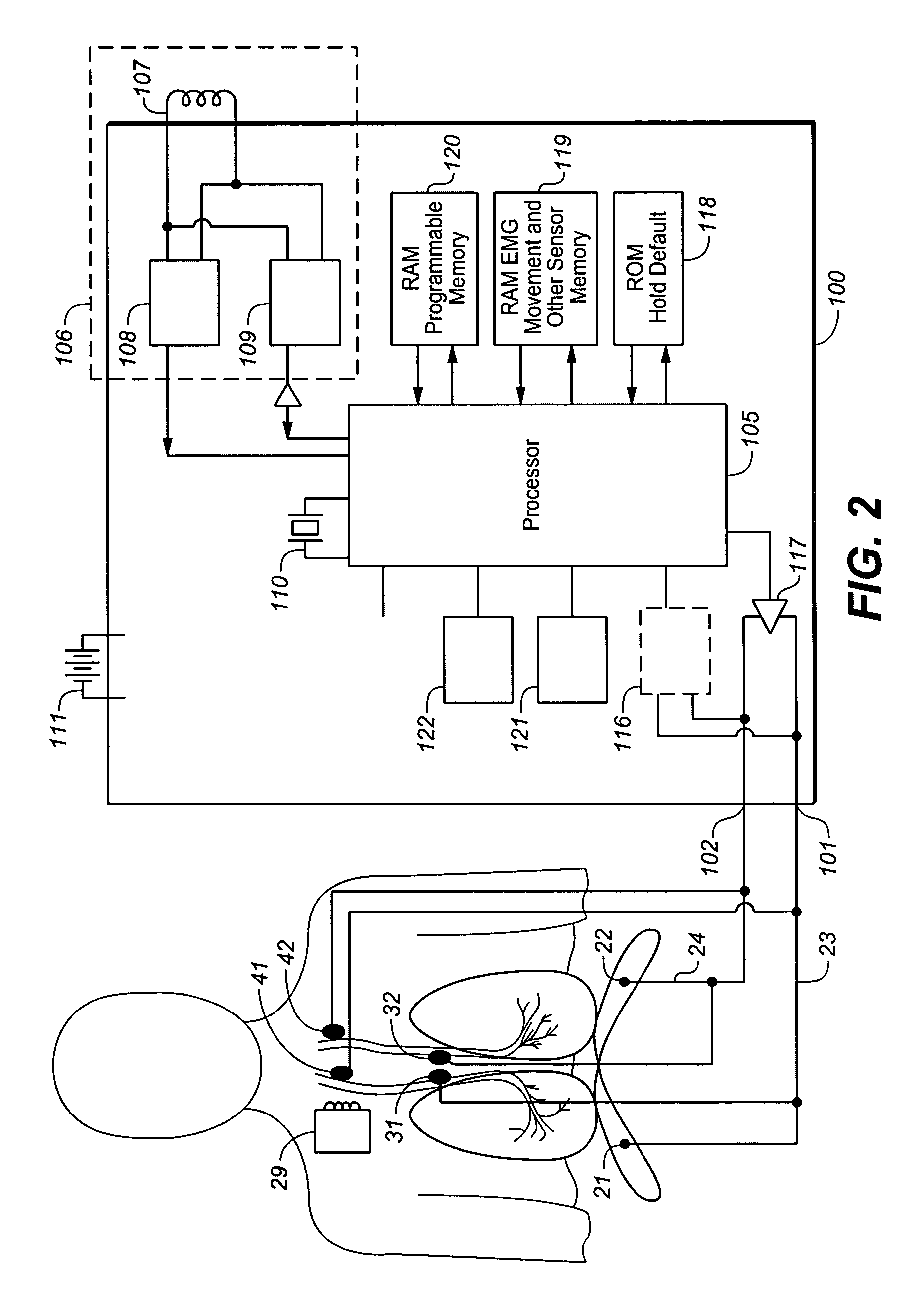
ActiveUS20060155341A1Reduce generationIncreasing functional residual capacityElectrotherapyElectromyographyLung volumesRadiology
A device and method is provided for biasing lung volume by electrically stimulating tissue associated with the diaphragm or phrenic nerve at a low level.
Owner:RMX
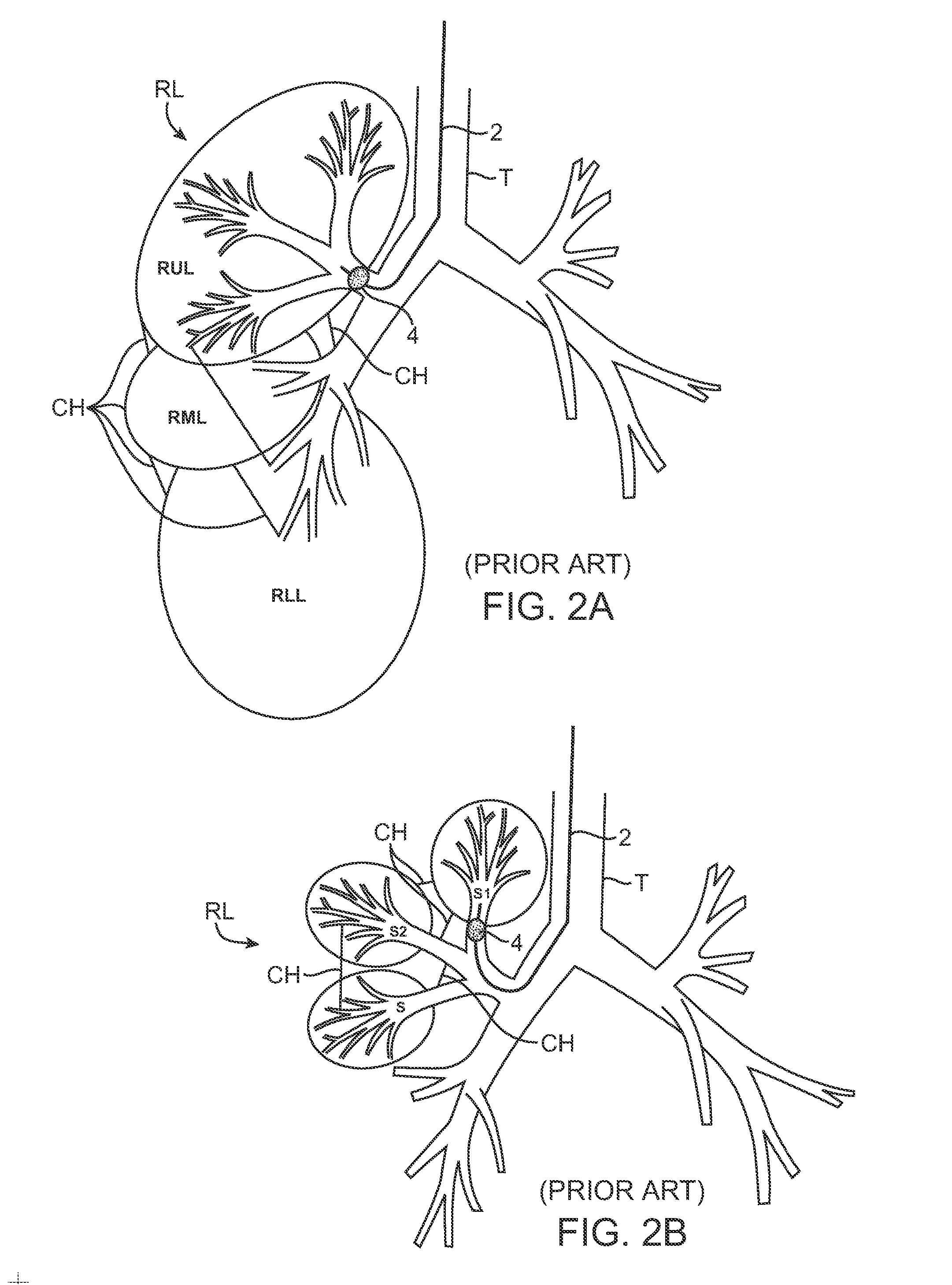
Methods and systems for segmental lung diagnostics
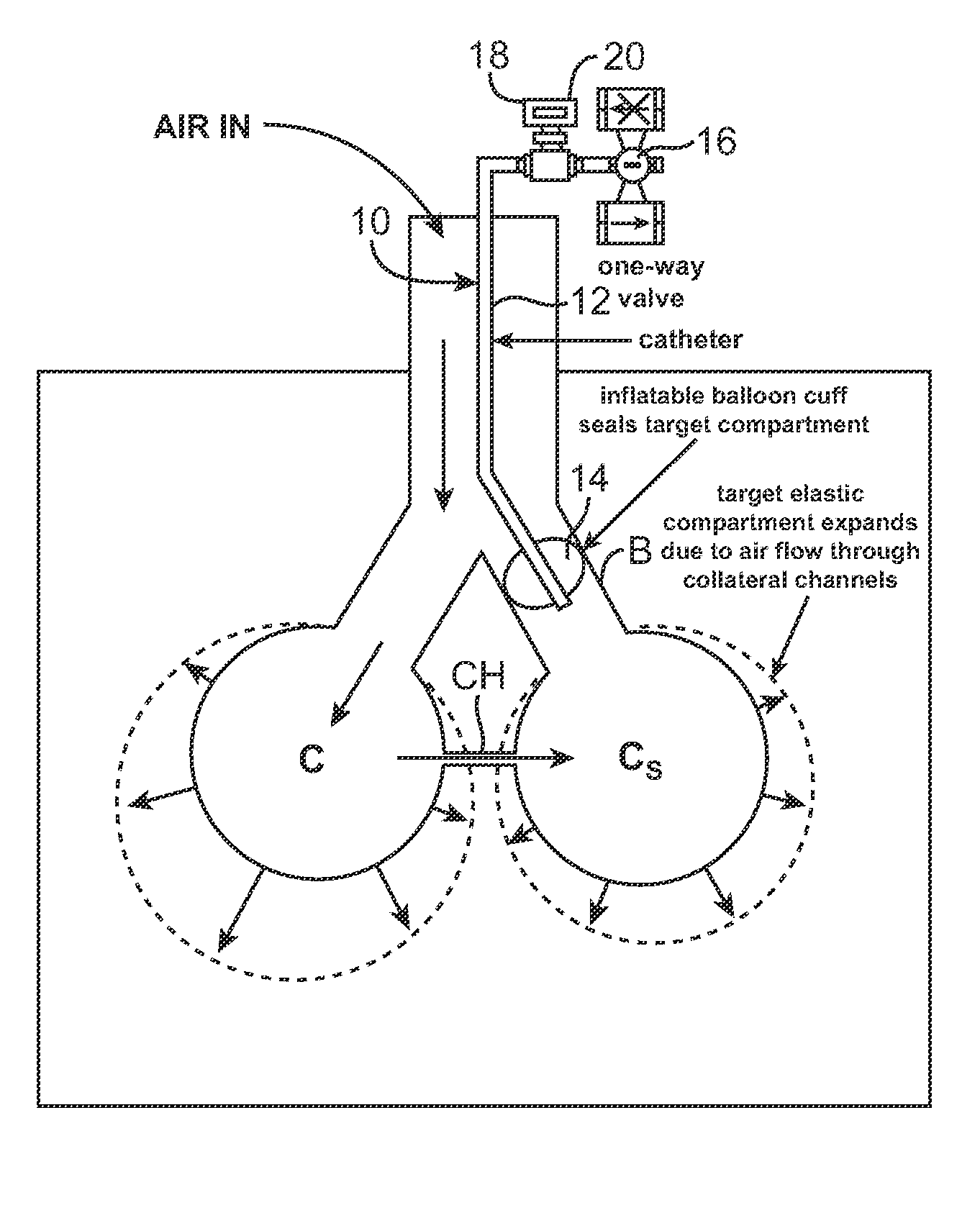
InactiveUS20070142742A1Least riskRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsCollateral ventilationLung volumes
Minimally invasive systems and methods are provided for diagnosing conditions in target lung compartments. Using catheters capable of isolating the target lung compartments and measuring one or more of collateral ventilation, pressure, flow rate, and volume, conditions such as hyperinflation, compliance, gas exchange including oxygen uptake, directionality of collateral channels, blood flow, and blood flow per unit lung volume may be assessed.
Owner:PULMONX
Methods and devices for obstructing and aspirating lung tissue segments
InactiveUS20040073191A1Reduce the possibilityIncrease anchorageMedical devicesOcculdersLung volumesObstructive Pulmonary Diseases
The present invention provides improved methods, systems, devices and kits for performing lung volume reduction in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or other conditions where isolation of a lung segment or reduction of lung volume is desired. The methods are minimally invasive with instruments being introduced through the mouth (endotracheally) and rely on isolating the target lung tissue segment from other regions of the lung. Isolation is achieved by deploying an obstructive device in a lung passageway leading to the target lung tissue segment. Once the obstructive device is anchored in place, the segment can be aspirated through the device. This may be achieved by a number of methods, including coupling an aspiration catheter to an inlet port on the obstruction device and aspirating through the port. Or, providing the port with a valve which allows outflow of gas from the isolated lung tissue segment during expiration of the respiratory cycle but prevents inflow of air during inspiration. In addition, a number of other methods may be used. The obstructive device may remain as an implant, to maintain isolation and optionally allow subsequent aspiration, or the device may be removed at any time.
Owner:PULMONX
Method and apparatus for impedance signal localizations from implanted devices
A patient monitoring system including an implantable medical device for monitoring a plurality of physiological factors contributing to physiological conditions of a patient's heart by measuring a first impedance affected by the plurality of physiological factors, across one of a plurality of vectors, and a second impedance affected by the plurality of physiological factors, across a second one of the plurality of vectors subsequent to determining the first impedance. A change in impedance is determined based upon the first impedance and the second impedance measurements. Using an equation ΔZVX=αAVX*QA+αBVX*QB, where QA is a fractional resistivity change of a first contributing physiological impedance factor, QB is a fractional resistivity change of a second physiological impedance factor, αAVX is an impedance sensitivity factor for physiological impedance factor QA, and αBVX is an impedance sensitivity factor for physiological impedance factor QB, the value of one of the contributing physiological impedance factors is determined. The contributing physiological impedance factors may include lung resistivity, blood resistivity, heart muscle resistivity, skeletal muscle resistivity, heart volume and lung volume.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
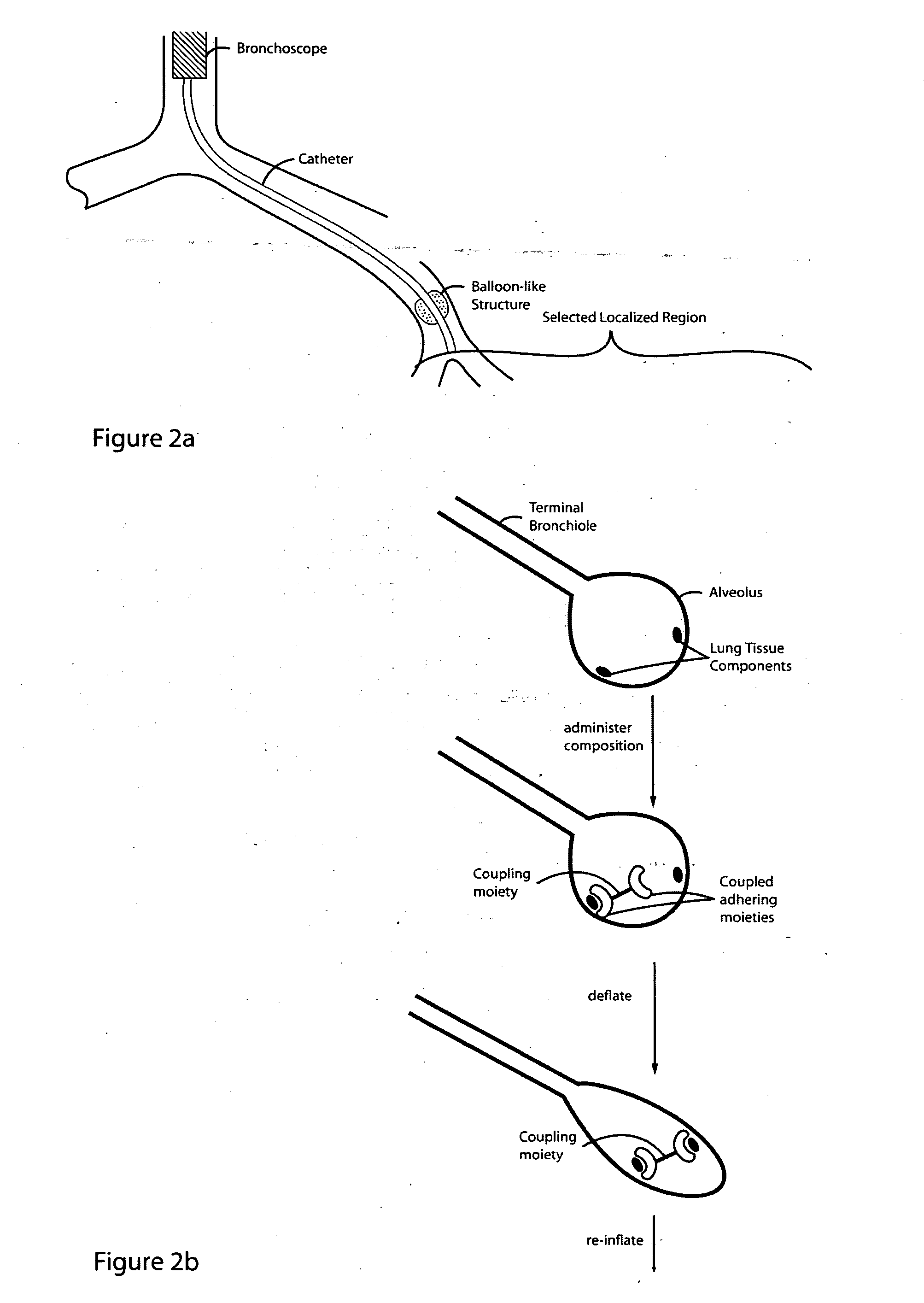
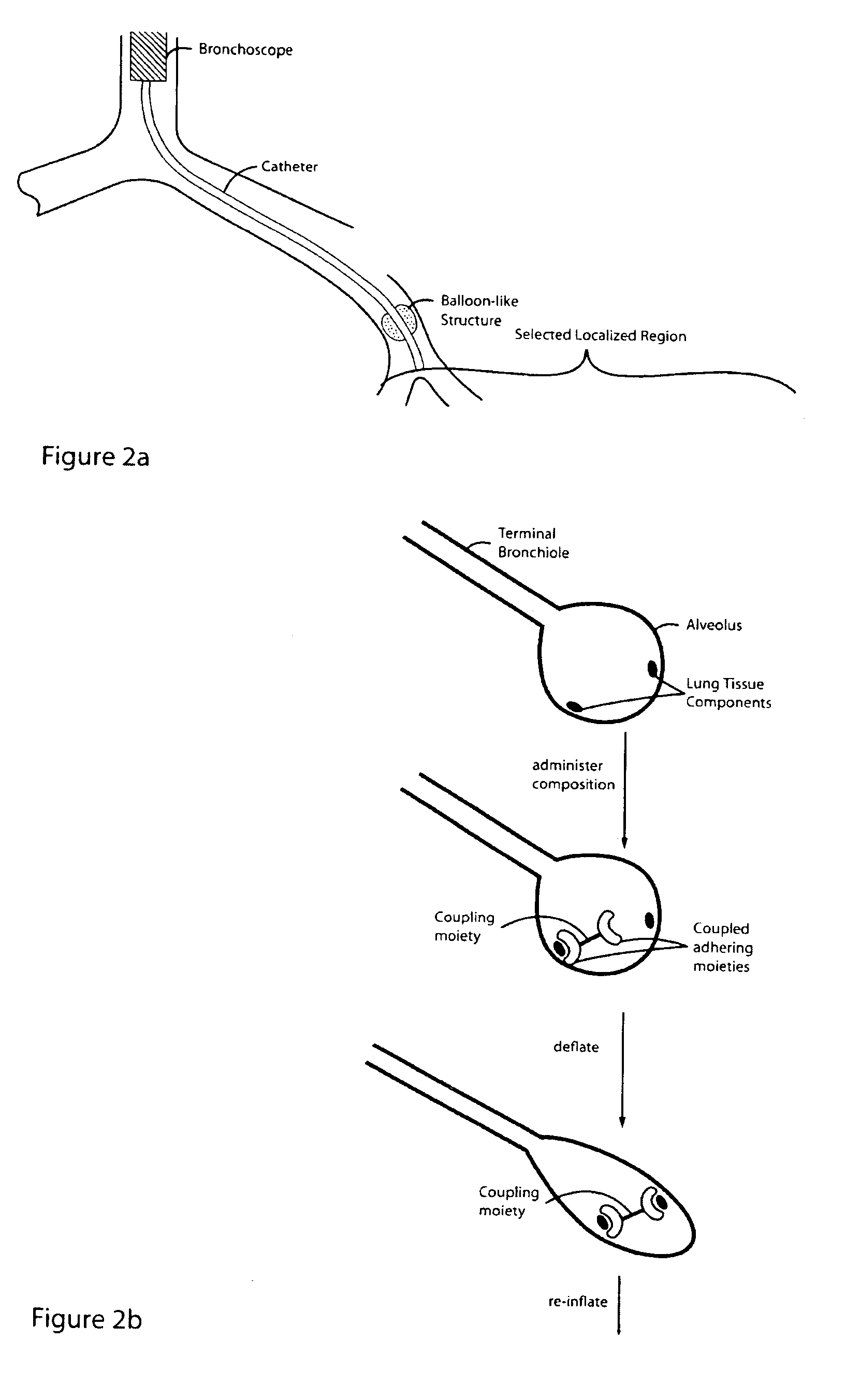
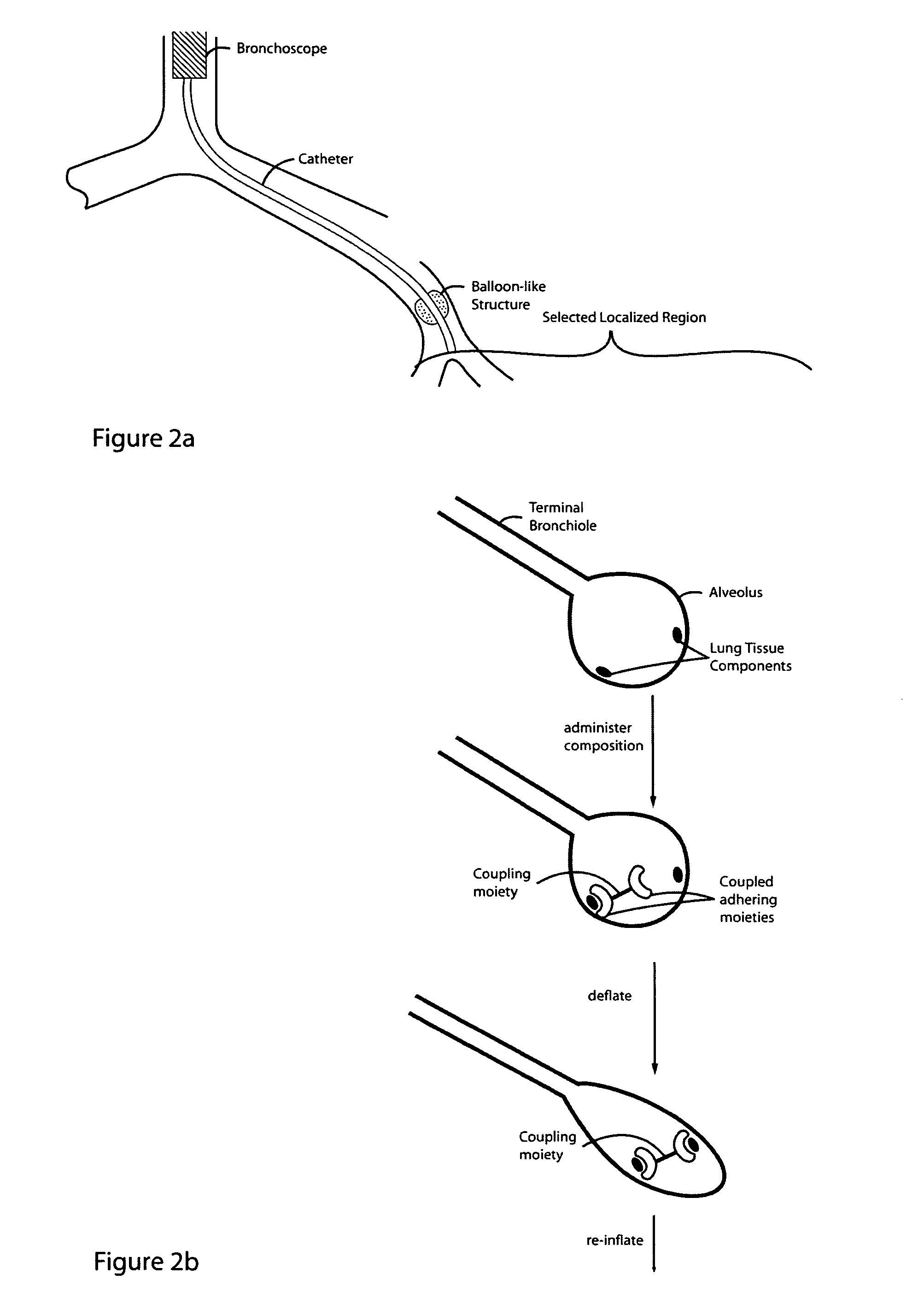
Lung volume reduction using glue compositions
InactiveUS20050281797A1Reducing lung volumeHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideLung volumesPneumatocele
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for sealing localized regions of damaged lung tissue to reduce overall lung volume. The glue compositions provide a glue featuring an adhering moiety coupled to one or more other moieties including, for example, a cross-linkable moiety and / or one other adhering moiety. The methods and compositions of the invention find use, for example, in treating pulmonary conditions, such as emphysema.
Owner:EKOS CORP
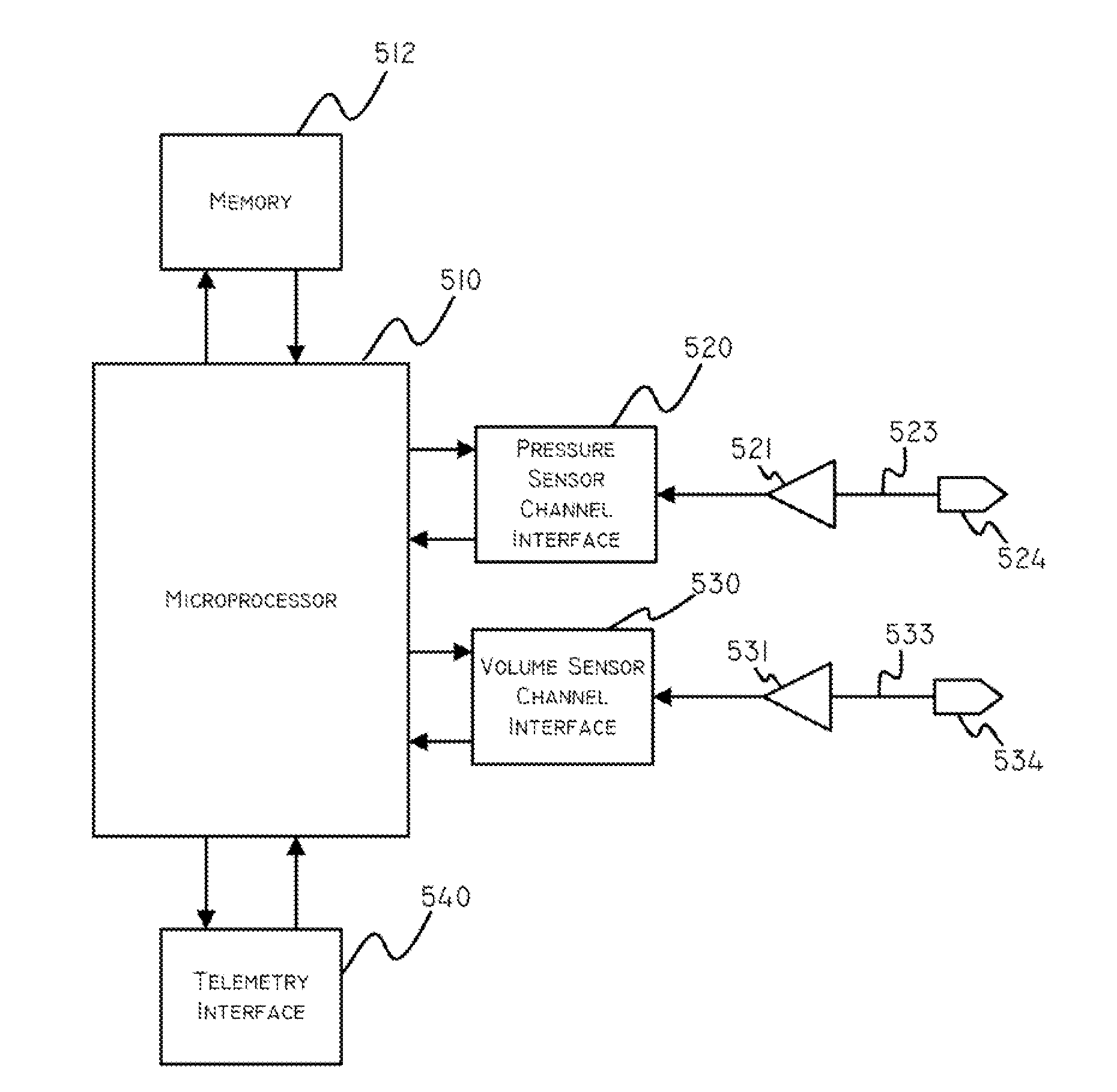
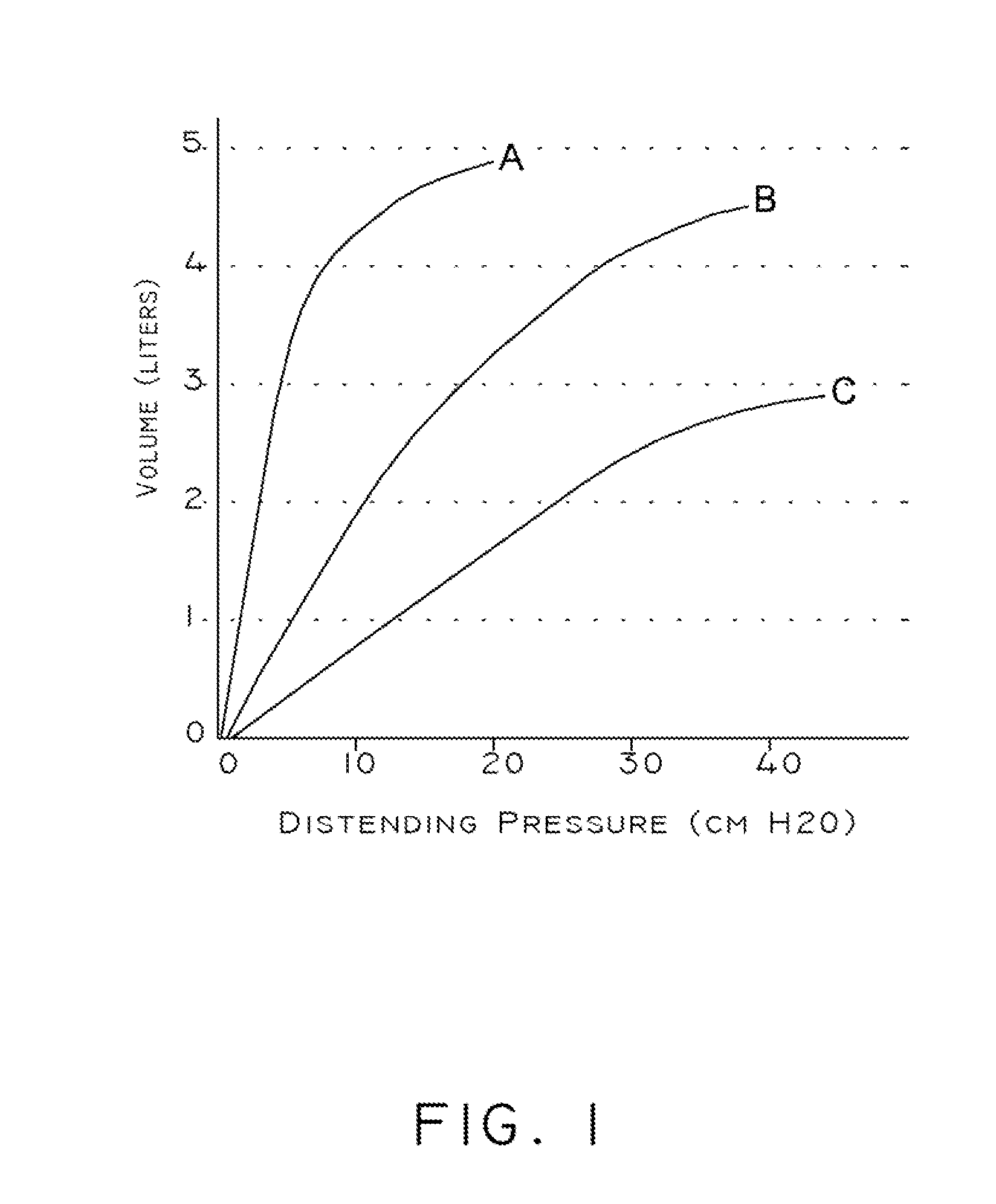
Devices and methods for disease detection, monitoring and/or management
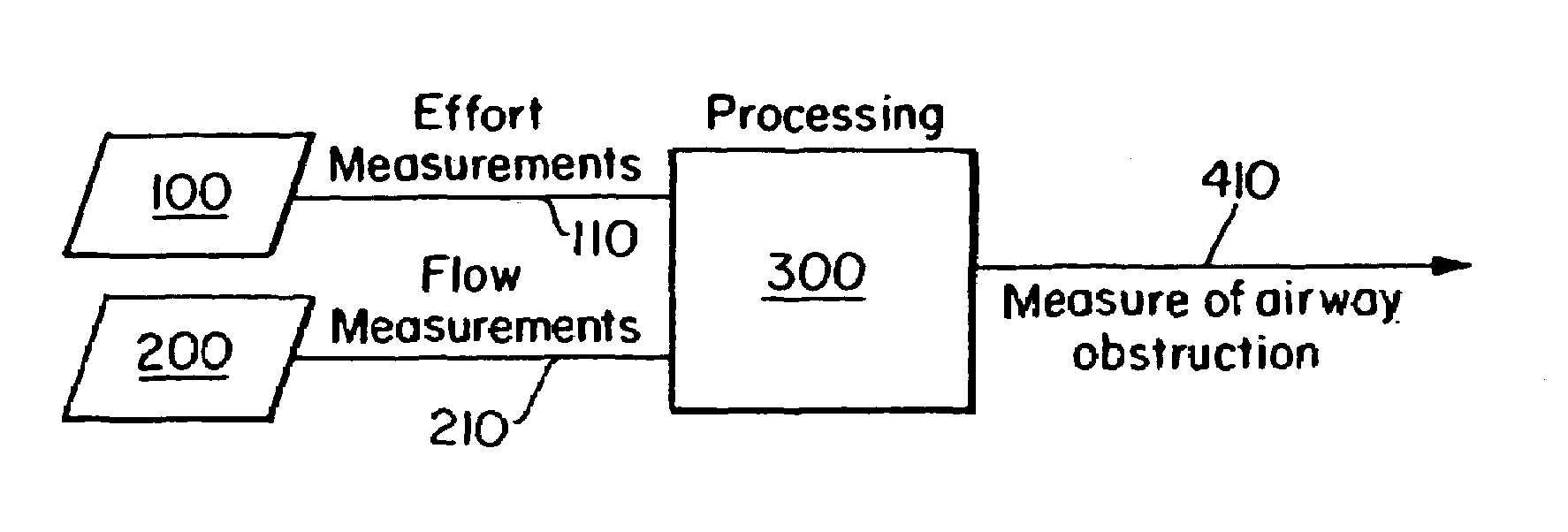
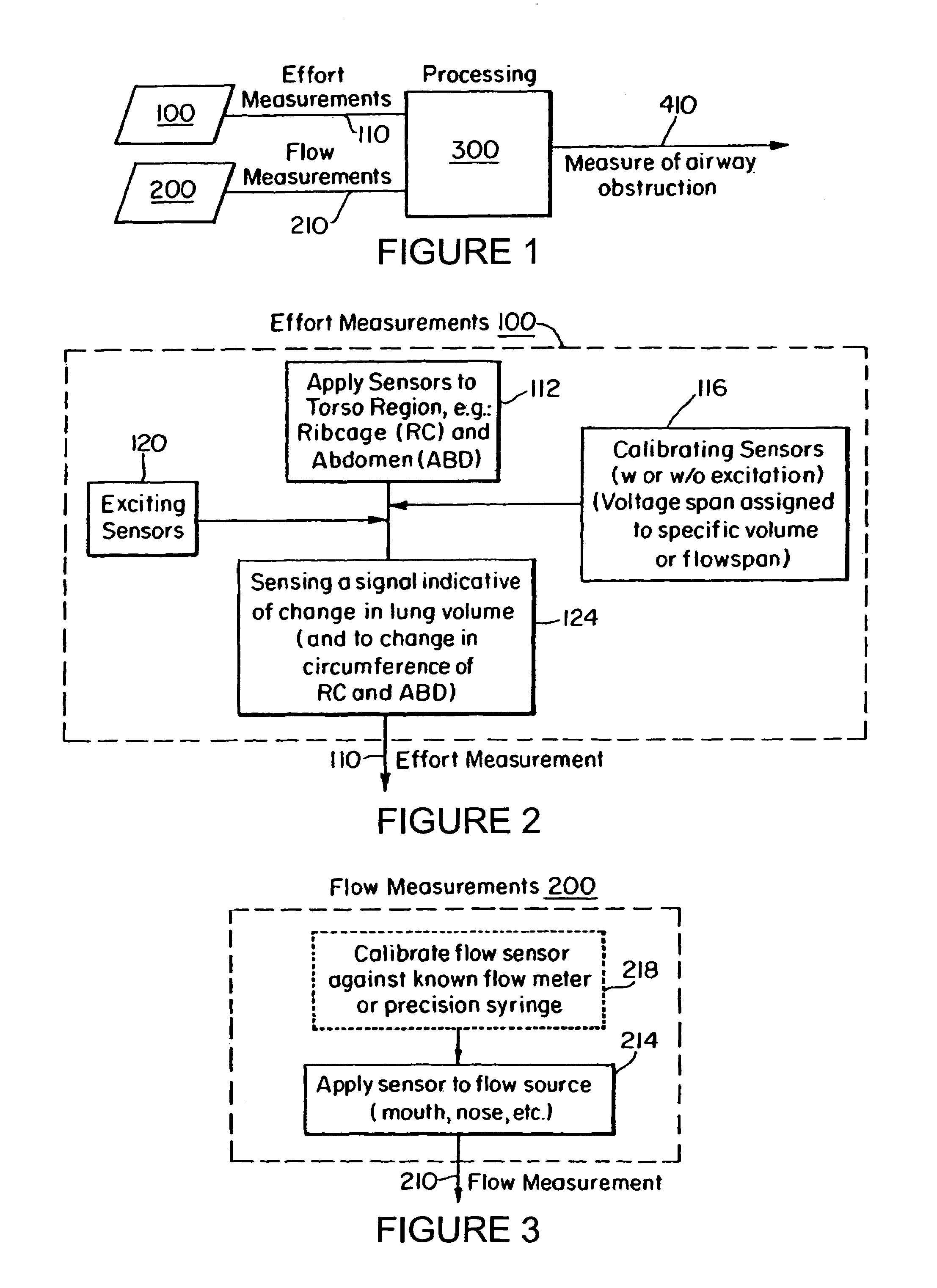
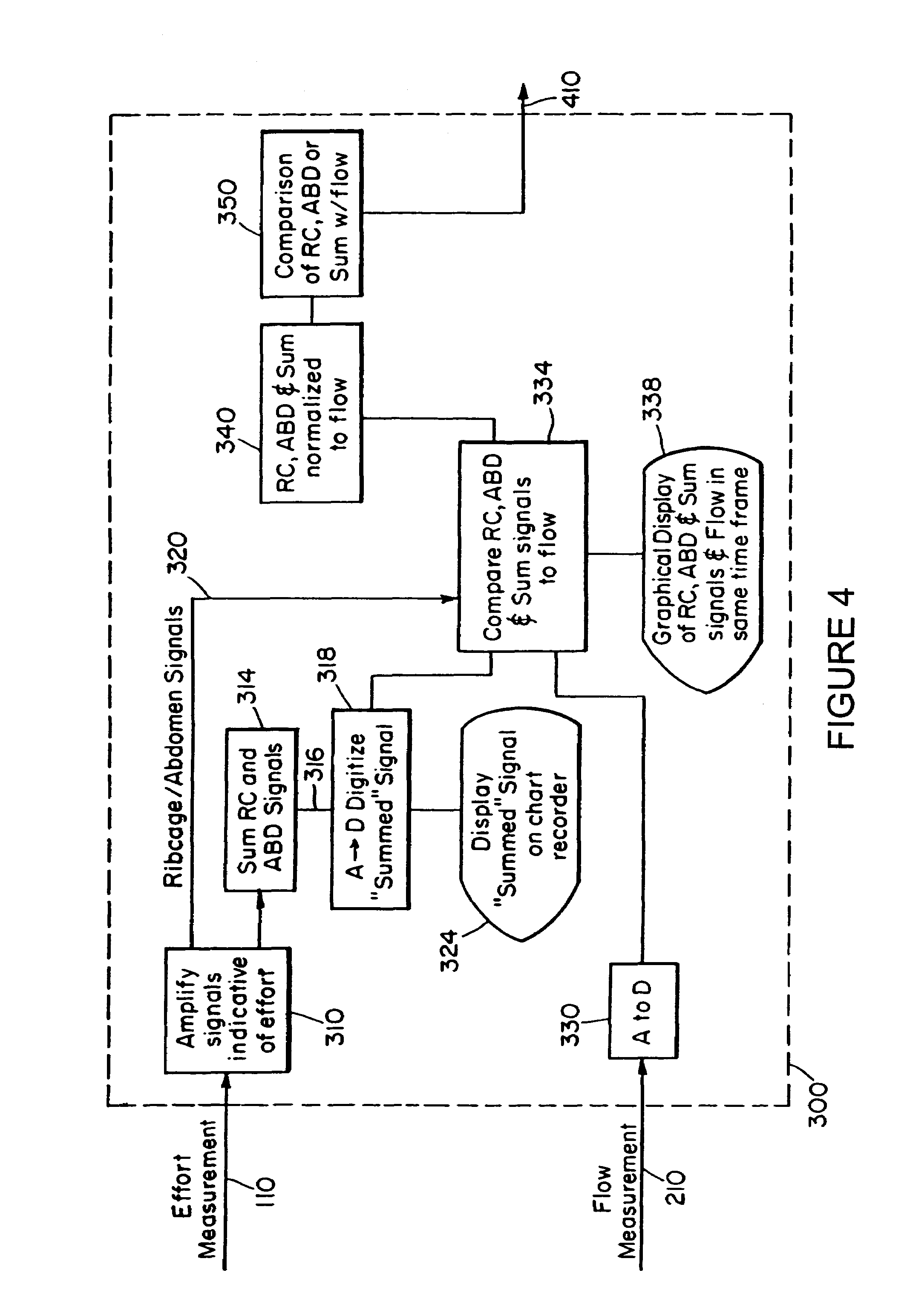
Embodiments of the invention are related to methods and devices for respiratory or cardiac disease detection, monitoring, and / or management. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method of calculating a pulmonary function parameter of a subject. The method can include obtaining a first signal indicative of lung volume change during breathing from a first sensor, obtaining a second signal indicative of distending pressure from a second sensor, and calculating the pulmonary function parameter based on the first signal and the second signal. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method of monitoring pulmonary or cardiac disease status. In an embodiment, the invention includes an implantable medical device. The implantable medical device can include a first sensor configured to produce a first signal indicative of lung volume change during breathing, a second sensor configured to produce a second signal indicative of intrapleural pressure, and a processor configured to calculate lung compliance or pulmonary resistance based on the first signal and the second signal. Other aspects and embodiments are provided herein.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
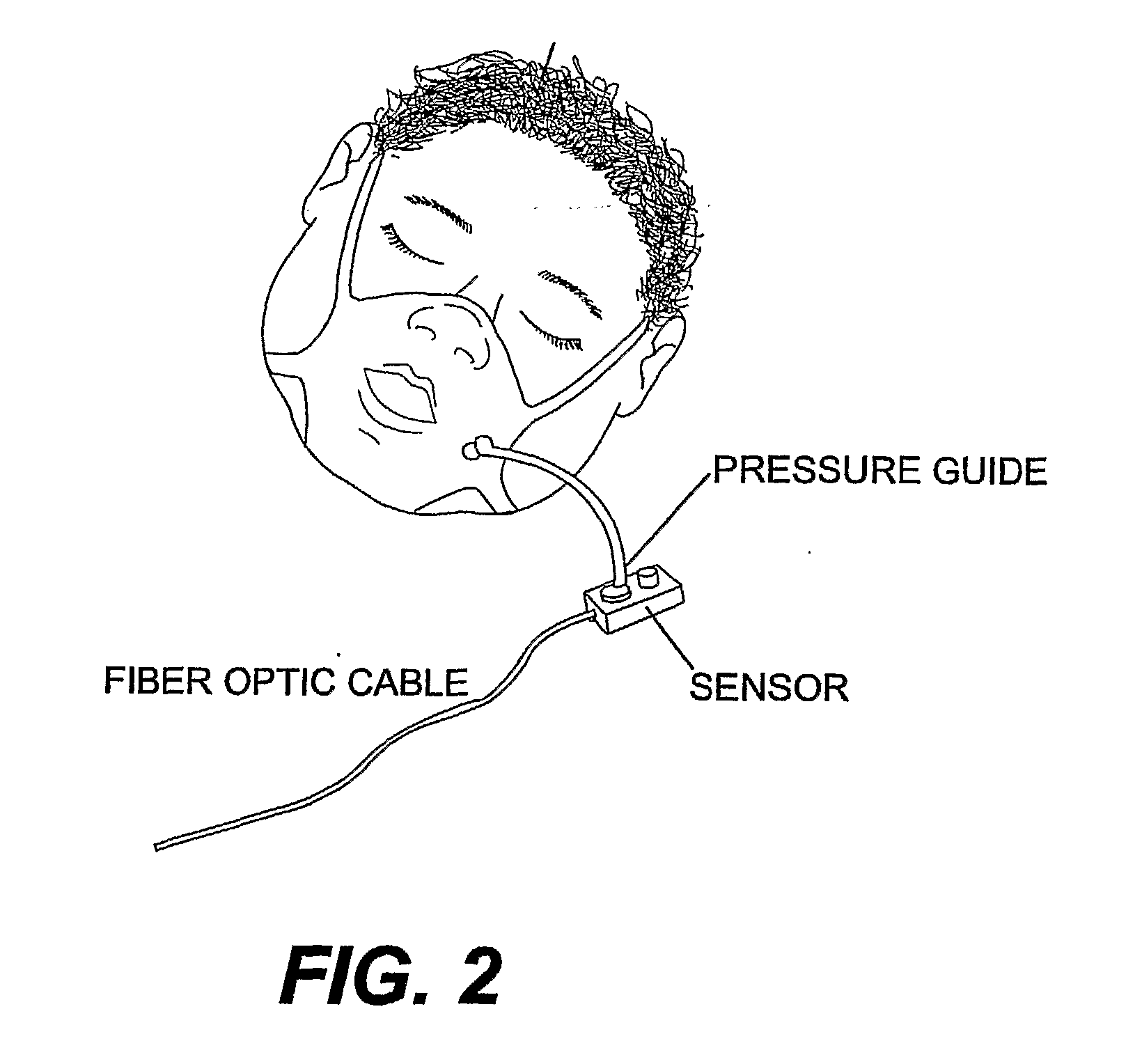
System for measuring respiratory function
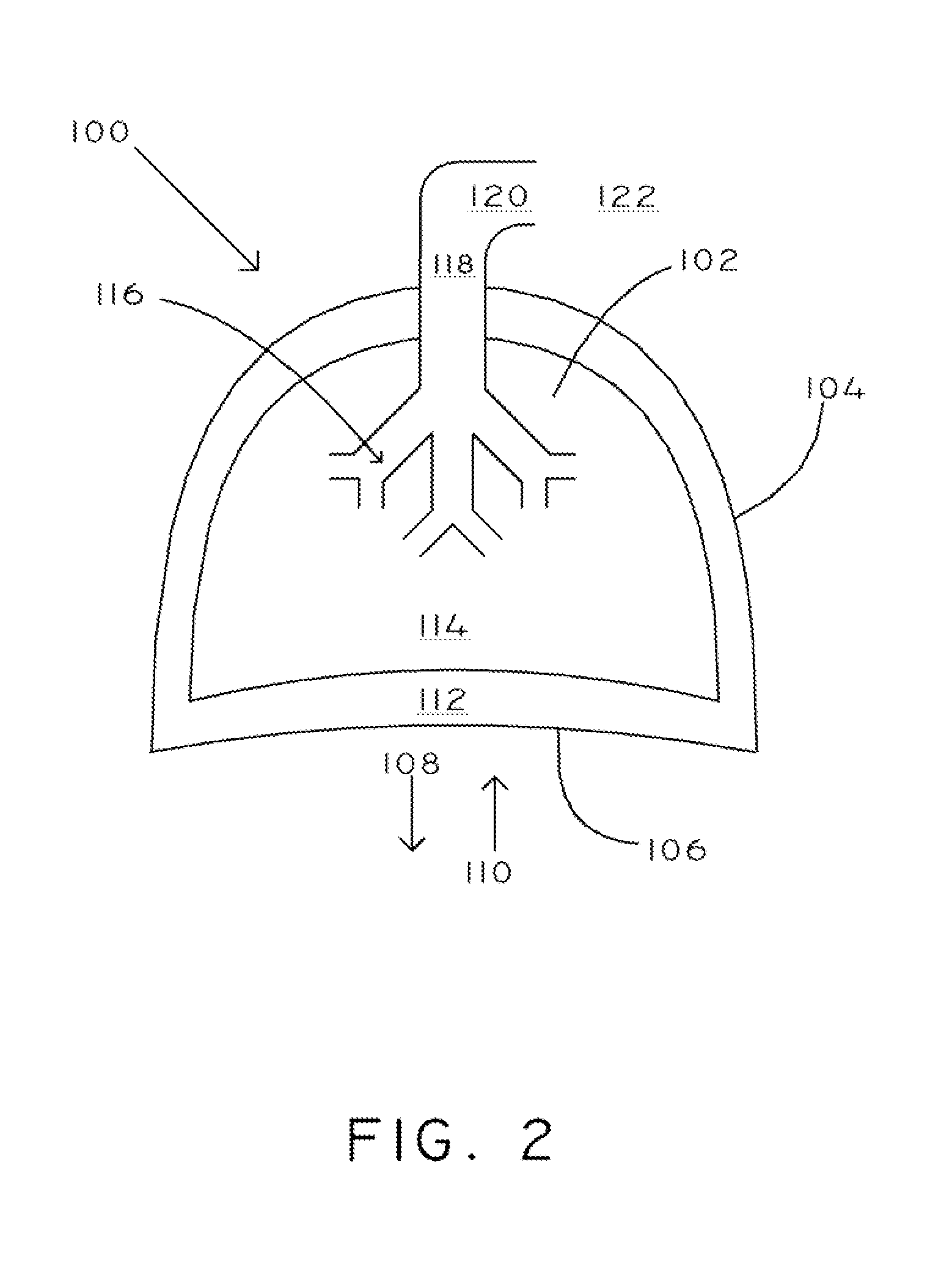
InactiveUS7094206B2Easy to carryEasy to transportMedical automated diagnosisRespiratory organ evaluationBiological bodyAirway responsiveness
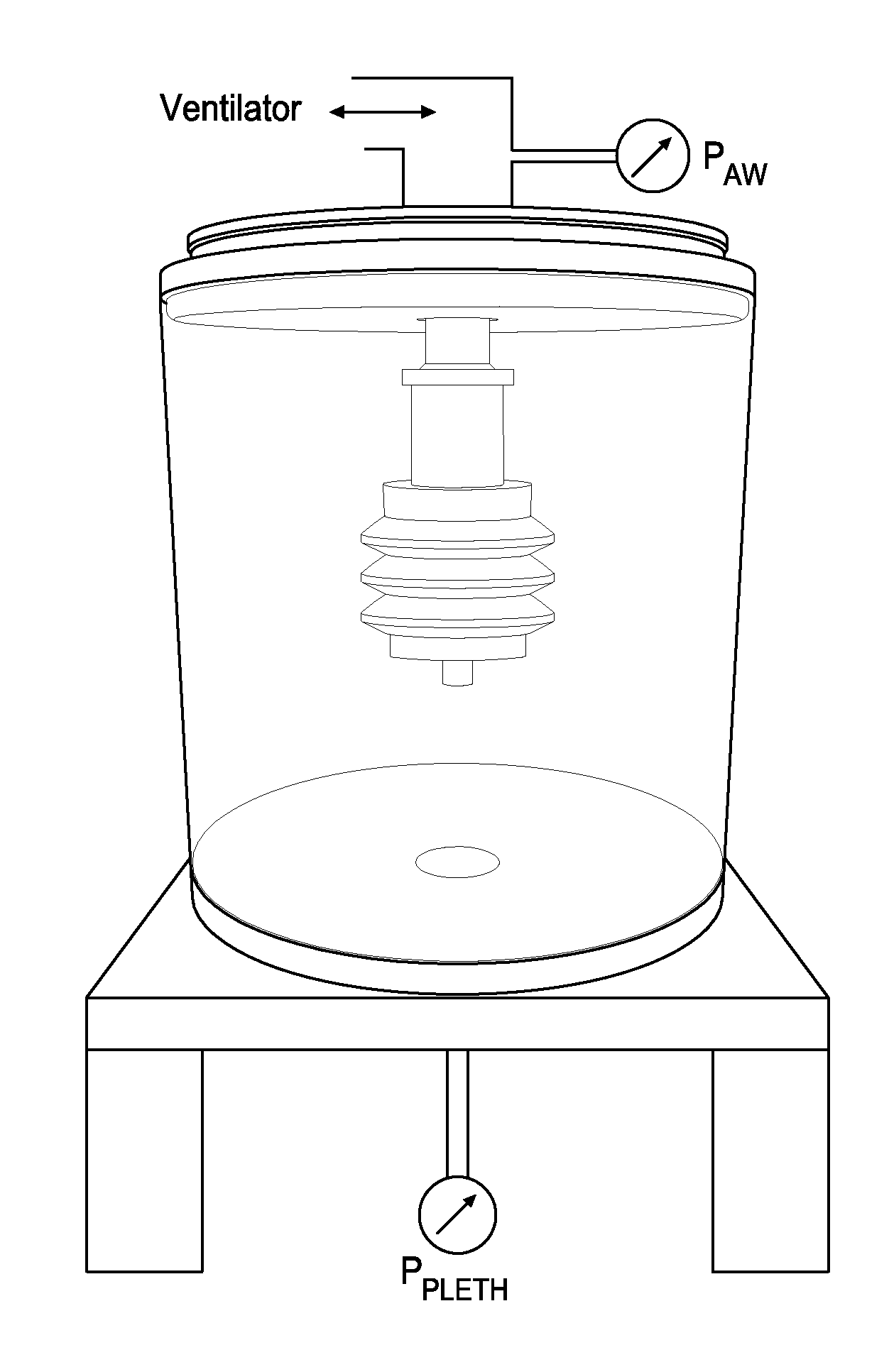
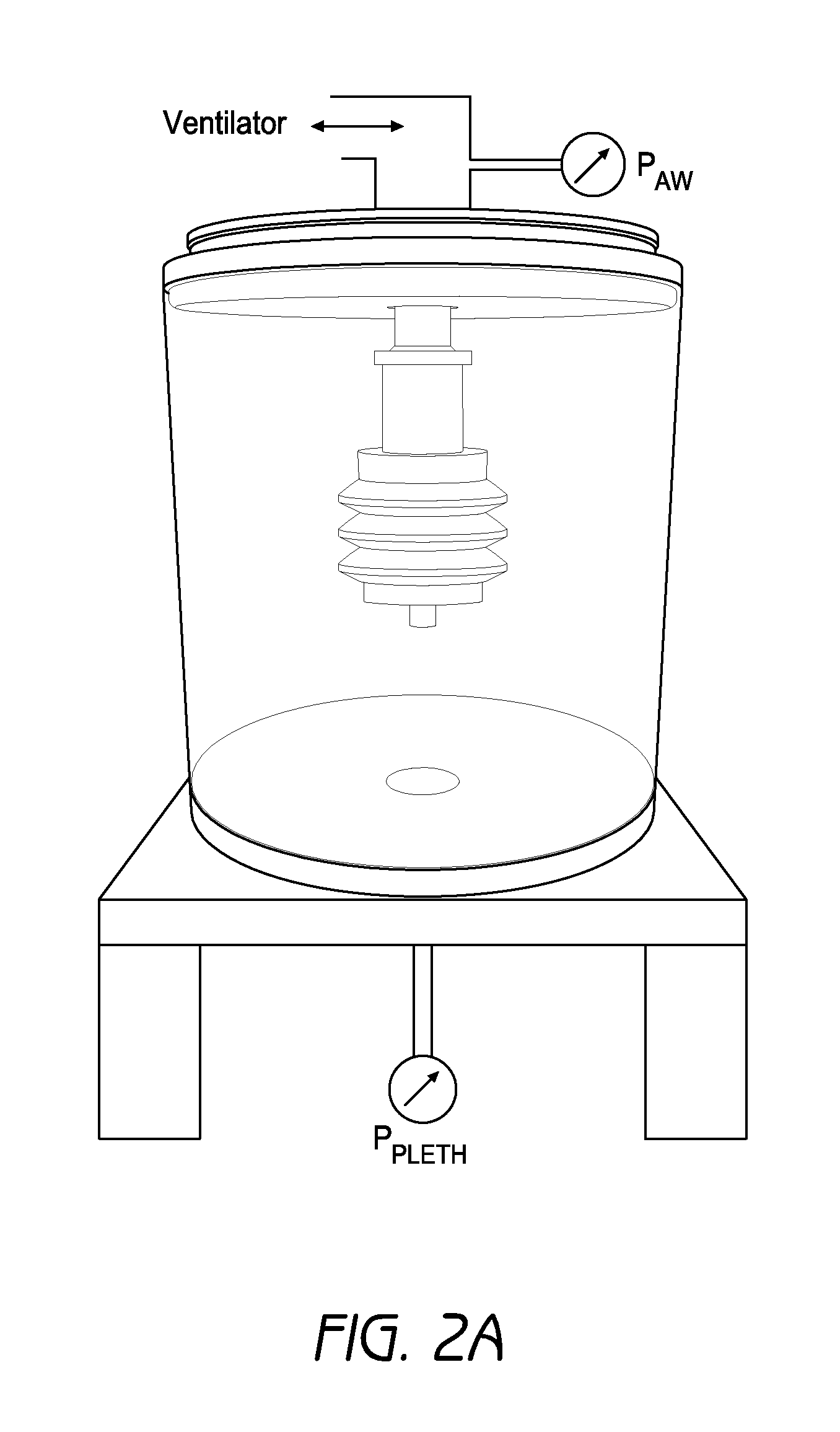
The present invention relates to a system for measuring respiratory function of living organisms. More particularly, signals indicative of the change in lung volume, defined as active and passive work, required to breathe and the airflow through the respiratory system of the living organism are obtained and processed as waveforms to provide a signal indicative of the respiratory restriction. The methods of the present invention measure clinical forms of airway obstruction, airway reactivity and lung volume and may be used to continuously or intermittently monitor patients with compromised respiratory function. In a preferred embodiment, a head-out, breath in respiratory plethysmograph system provides the signals indicative of change in lung volume as related to pressure changes in a chamber. Further, flowmetric variables are generated that provide a characterization of airway obstructions.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGETHE
Glue composition for lung volume reduction
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for sealing localized regions of damaged lung tissue to reduce overall lung volume. The glue compositions provide a glue featuring an adhering moiety coupled to one or more other moieties including, for example, a cross-linkable moiety and / or one other adhering moiety. The methods and compositions of the invention find use, for example, in treating pulmonary conditions, such as emphysema.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Device and method for biasing lung volume
ActiveUS7970475B2Prevent obstructive respiratory eventsReduce generationElectrotherapyElectromyographyLung volumesRadiology
A device and method is provided for biasing lung volume by electrically stimulating tissue associated with the diaphragm or phrenic nerve at a low level.
Owner:RMX
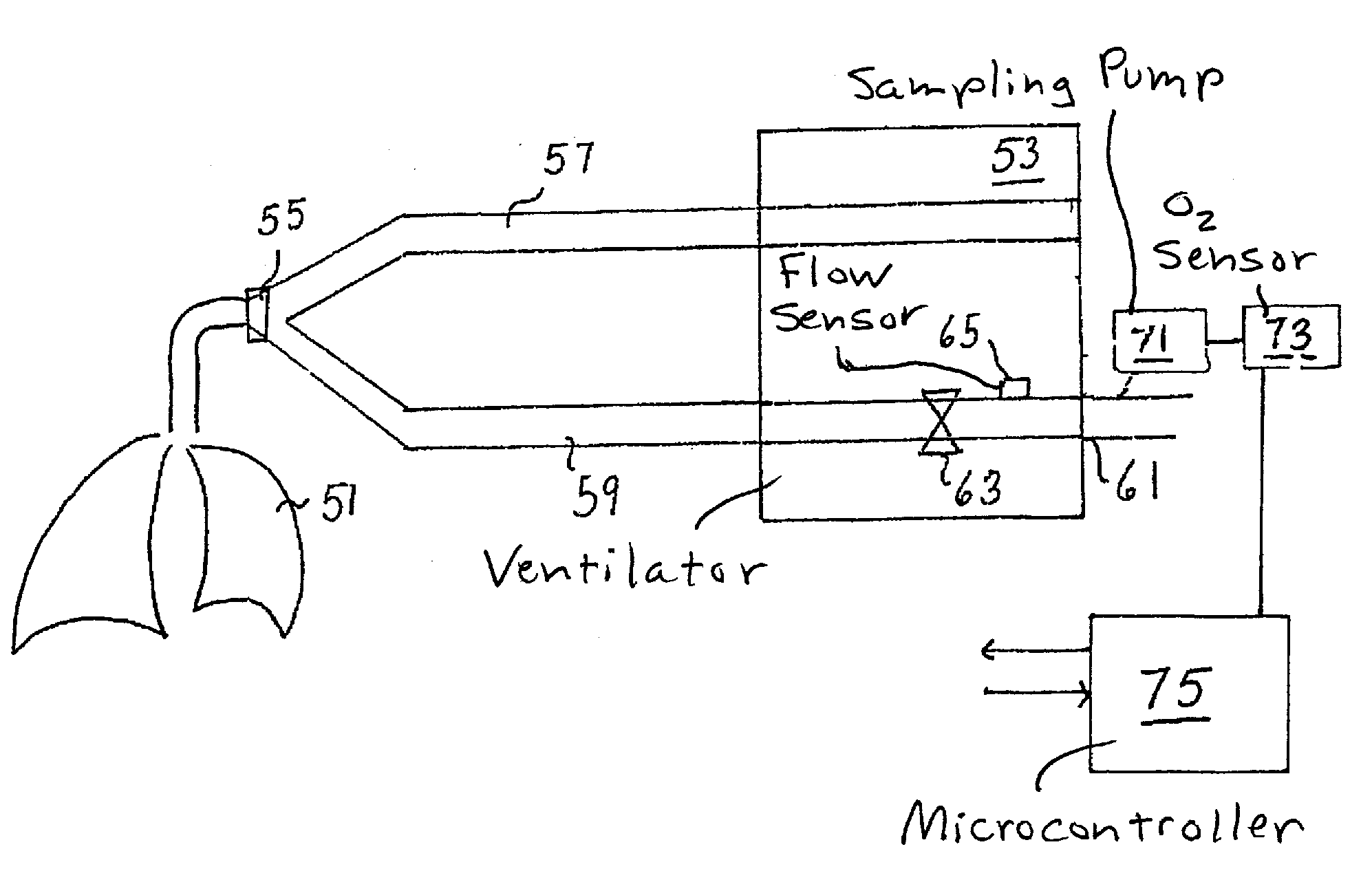
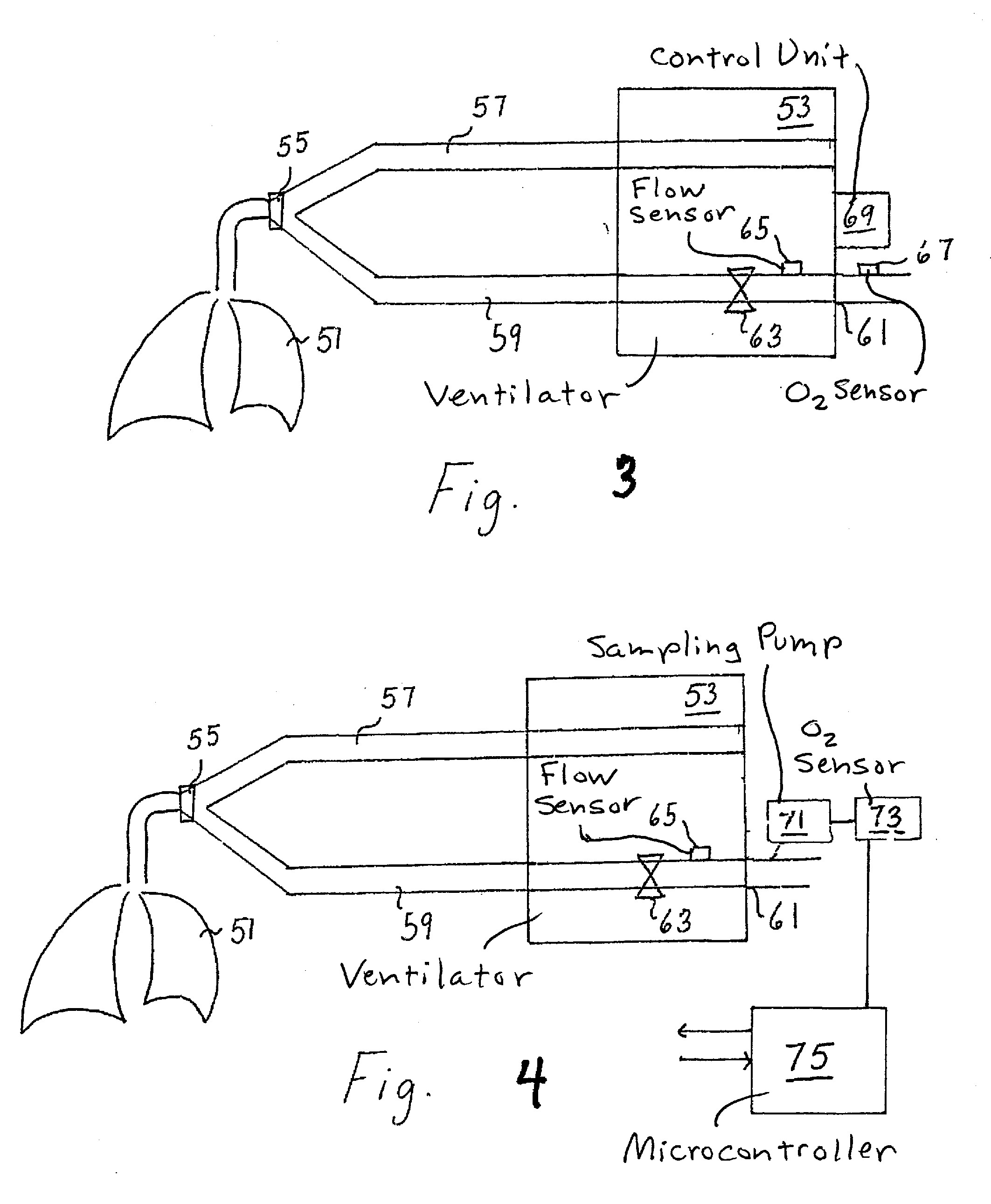
Methods, systems and devices for non-invasive open ventilation for providing ventilation support
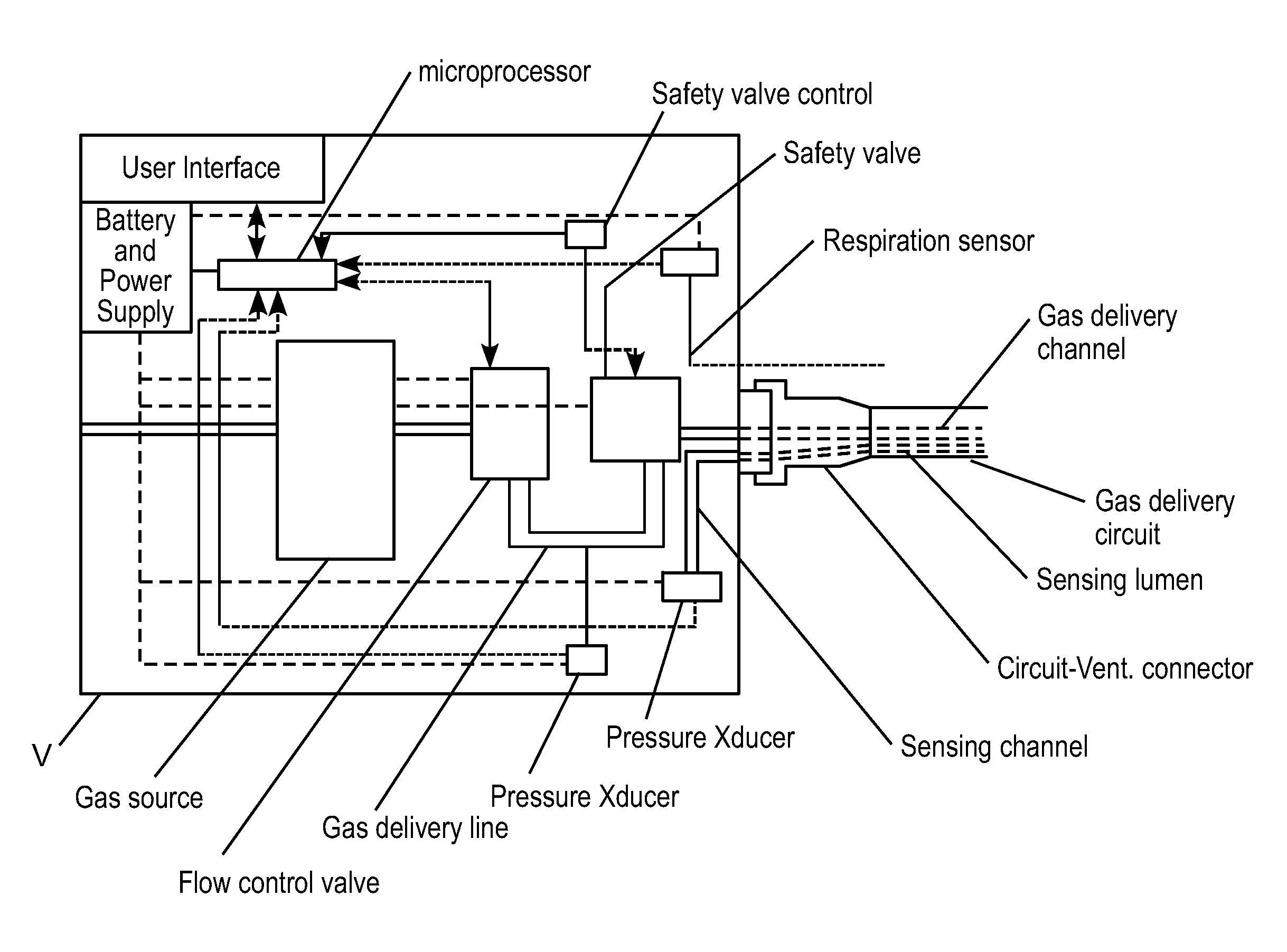
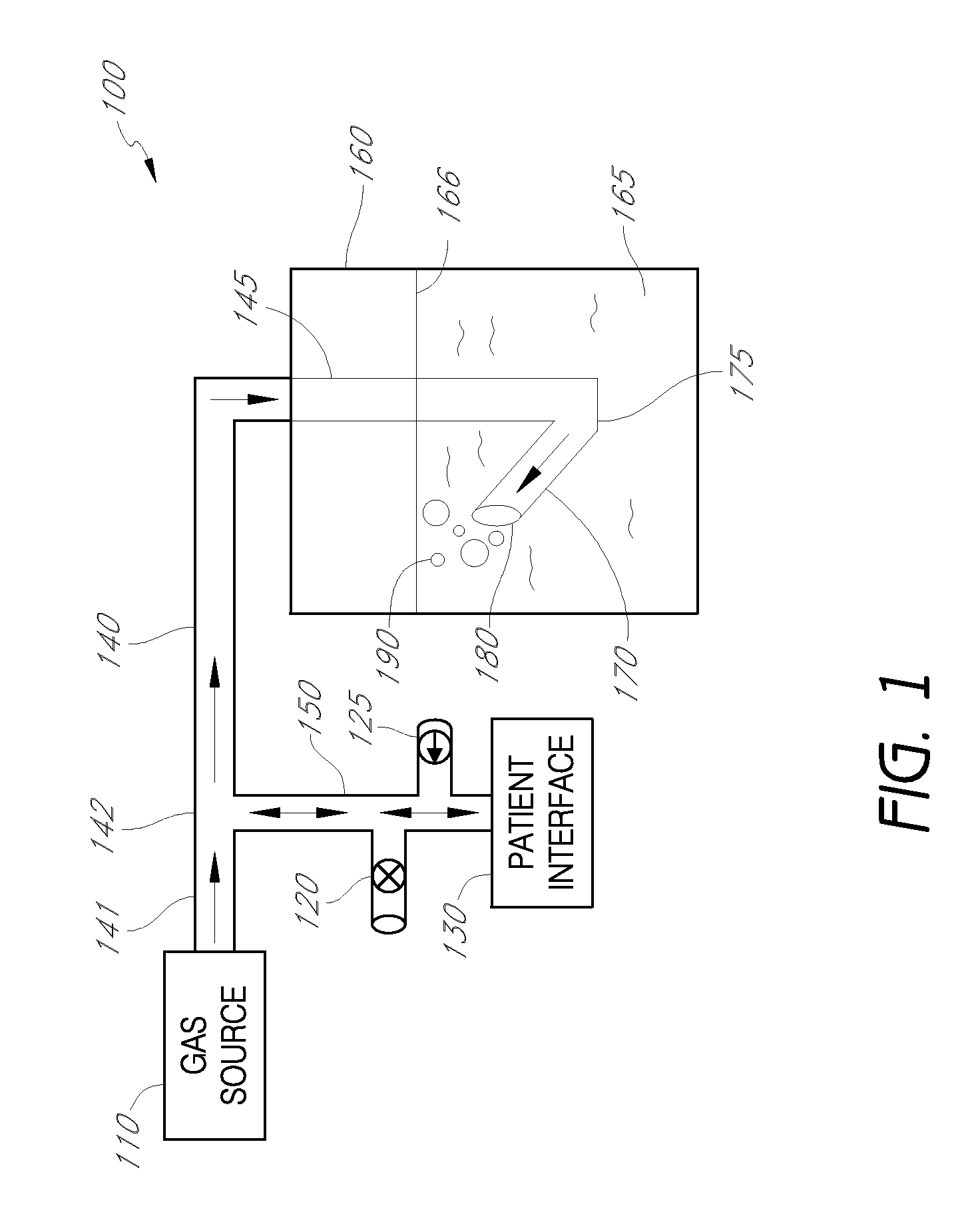
ActiveUS20100252041A1Work lessIncrease airway pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesLung volumesNon invasive
A system for providing ventilation support to a patient may include a ventilator, a control unit, a gas delivery circuit with a proximal end in fluid communication with the ventilator and a distal end in fluid communication with a nasal interface, and a nasal interface. The nasal interface may include at least one jet nozzle at the distal end of the gas delivery circuit; and at least one spontaneous respiration sensor for detecting respiration in communication with the control unit. The system may be open to ambient. The control unit may receive signals from the at least one spontaneous respiration sensor and determine gas delivery requirements. The ventilator may deliver gas at a velocity to entrain ambient air and increase lung volume or lung pressure above spontaneously breathing levels to assist in work of breathing, and deliver ventilation gas in a cyclical delivery pattern synchronized with a spontaneous breathing pattern.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Out flow resistance switching ventilator and its core methods
InactiveUS20080011301A1Ensure ventilation safetyIncrease spaceRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingFlow resistivity
An out flow resistance switching ventilator and its methodology for providing mechanical ventilation support to the respiratory failure patient are claimed. Based on the continuous out flow impounding ventilation mechanism, the apparatus provides ventilation by switching flow resistance between two different levels at a continuous gas flow system outlet valve controlled by patient's spontaneous breathing or preset mandatory parameters, resulting in airway pressure levels switching, and therefore creating lung volume switching, which is totally different from either volume ventilation or pressure ventilation mechanism utilized in the current conventional ventilators.
Owner:QIAN YUANCHENG
Methods, systems and devices for non-invasive open ventilation with gas delivery nozzles in free space
ActiveUS20100252039A1Work lessIncrease airway pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesNoseLung volumes
A non-invasive ventilation system may include an interface. The interface may include at least one gas delivery jet nozzle adapted to be positioned in free space and aligned to directly deliver ventilation gas into an entrance of a nose. The at least one gas delivery jet nozzle may be connected to a pressurized gas supply. The ventilation gas may entrain ambient air to elevate lung pressure, elevate lung volume, decrease the work of breathing or increase airway pressure, and wherein the ventilation gas is delivered in synchrony with phases of breathing. A support for the at least one gas delivery jet nozzle may be provided. A breath sensor may be in close proximity to the entrance of the nose. A patient may spontaneous breathe ambient air through the nose without being impeded by the interface.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Respiratory Volume/Flow Gating, Monitoring, and Spirometry System for Mri
InactiveUS20080077038A1Improve accuracyHigh precisionMagnetic measurementsRespiratory organ evaluationForced expiratory vital capacityLung volumes
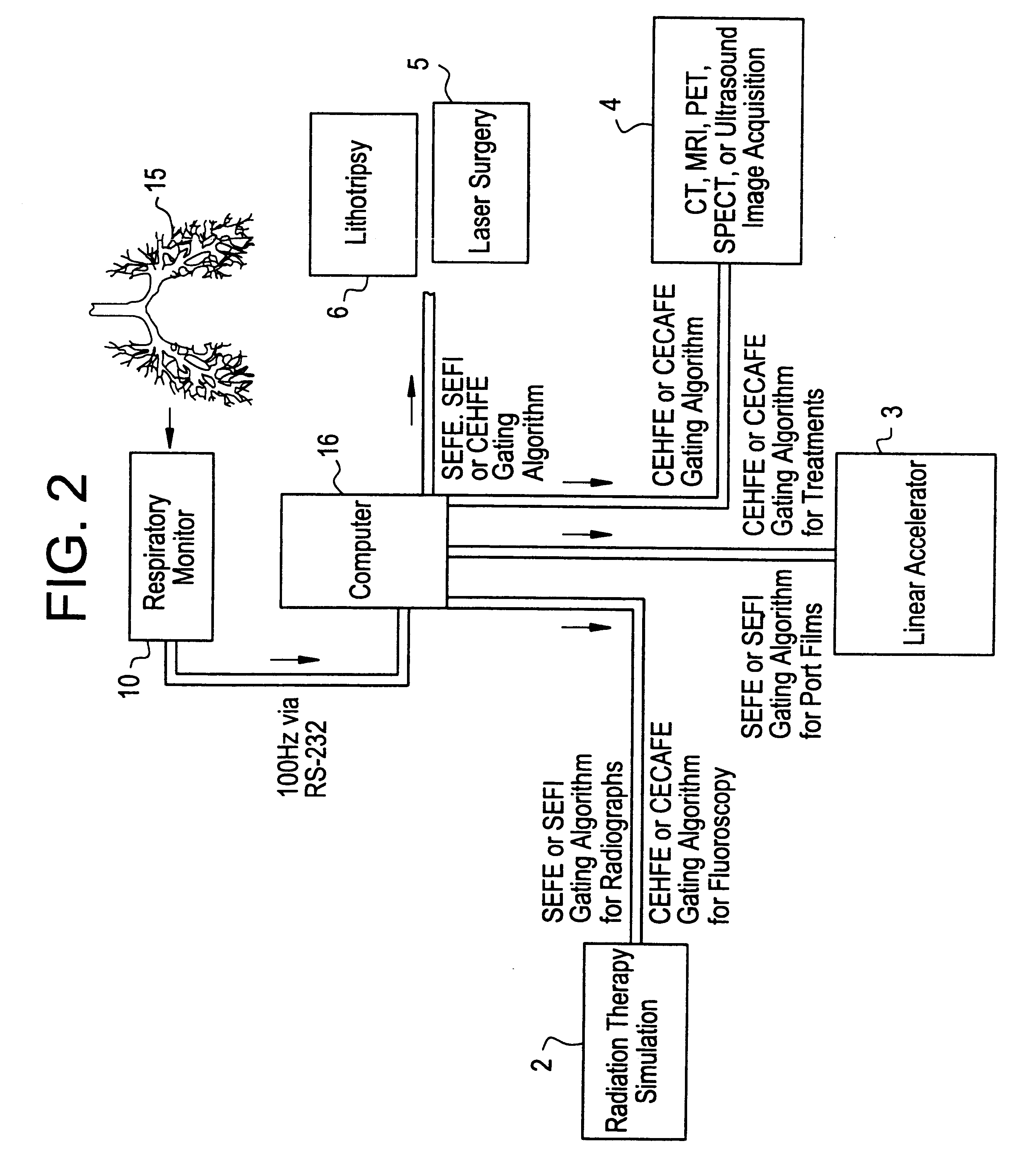
A respiratory volume / flow monitoring system, including a pneumotach that measures micromovements of a membrane in a MRI environment, gates (triggers) a MRI machine to start image acquisition at specific lung volumes or airflow rates during the breathing cycle or other breathing maneuvers of a patient. The system provides breathing motion artifact suppression for any imaging test susceptible to breathing motion artifact, allows respiratory monitoring of the subject during an MRI procedure, and provides the capability to perform spirometric testing while the subject is in the MRI environment. Embodiments of the invention are also applicable for patients undergoing CT imaging or any other imaging modality that allows external triggering.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Lung volume reduction using glue compositions
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for sealing localized regions of damaged lung tissue to reduce overall lung volume. The glue compositions provide a glue featuring an adhering moiety coupled to one or more other moieties including, for example, a cross-linkable moiety and / or one other adhering moiety. The methods and compositions of the invention find use, for example, in treating pulmonary conditions, such as emphysema.
Owner:EKOS CORP
Broad-band, low frequency, high-amplitude, long time duration, oscillating airway pressure breathing apparatus and method utilizing bubbles
ActiveUS20110073112A1Stabilize lung volumeIncrease gas exchangeTracheal tubesRespiratory masksMeasurement deviceFrequency spectrum
It has been discovered that high amplitude, low frequency, broadband spectrum pressure oscillations of sufficient time duration can help stabilize lung volumes and improve gas exchange in a patient receiving ventilation assistance by helping to recruit and stabilize alveoli. A novel device is presented which can produce pressure oscillations having high amplitudes, a low broad-band frequency spectrum and long time duration. Additionally, the device can maintain a patient's mean airway pressure at one or more controlled levels. The device can control the oscillatory amplitude, frequency range and composition, time duration, and mean airway pressure levels by adjusting certain device parameters, such as the angle and depth of the device in a fluid. A device and mechanical system for remotely adjusting and measuring the angle of the device in a fluid are also disclosed. Furthermore, a device and system are disclosed that can deliver pressure oscillations having high amplitudes, a low broad-band frequency spectrum, long time duration, and multiple mean airway inspiratory and expiratory pressure levels. The device and system also provide means for controlling respiration timing in a patient, including: breaths per minute, inspiratory time, and the ratio of inspiratory to expiratory time.
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Apparatus and methods for reducing lung volume
InactiveUS7128747B2Increase engagementImprove the situationSuture equipmentsEar treatmentLung volumesBronchial tube
Apparatus and methods are provided for reducing the volume of a lung using a clip including a plurality of tines. The clip is advanced along an interior of a bronchial passage to a predetermined location with the tines in a contracted condition. The tines are expanded outwardly to engage surrounding tissue, and then collapsed towards the contracted condition, thereby drawing the surrounding tissue inwardly to substantially close the bronchial passage from air flow therethrough. Optionally, electrical energy may be applied to the surrounding tissue after collapsing the tines to the contracted condition, thereby fusing the surrounding tissue together. The clip is then released within or removed from the passage.
Owner:GATEWAY MEDICAL
Glue composition for lung volume reduction
Owner:EKOS CORP
CT lung nodule detection system based on 3D-Unet
ActiveCN108648172AImplement automatic detectionSolve the workloadImage enhancementImage analysisLung volumesResidual Blocks
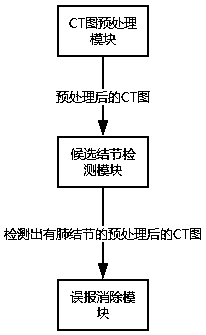
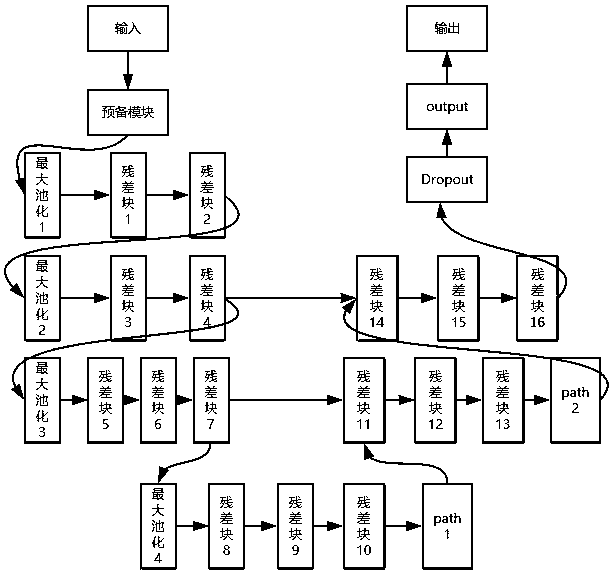
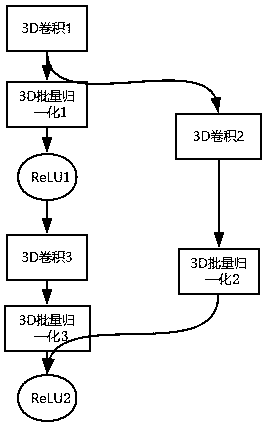
The invention discloses a CT lung nodule detection system based on 3D-Unet. The system includes a CT image input and preprocessing module, a candidate nodule detection module and a false-reporting elimination module which are sequentially connected. The CT image input and preprocessing module is used for reading a chest CT graph, obtaining spacing and origin information of the CT graph, and carrying out lung volume segmentation on the CT graph. The candidate nodule detection module is used for inputting the image, of which preprocesing is completed, into a Unet network, and obtaining a location of a candidate lung nodule. The Unet network includes sixteen residual blocks, two path units, four maximum-pooling units, one preparation unit, one probabilistic neuron failure unit and one outputunit. According to the system, automatic detection of the lung nodule is realized, problems of high doctor workloads and high misdiagnosis rates in lung nodule diagnosis are solved, an effect of detecting the lung nodule by the 3D-Unet is realized, more contextual semantic information in the CT image is utilized, and detection accuracy is higher.
Owner:四川元匠科技有限公司
Determining respiratory parameters
InactiveUS20160106341A1Computerised tomographsRespiratory organ evaluationMeasurement deviceLung volumes
A pulmonary measurement system includes a pulmonary measurement device that includes a mouthpiece with an airflow path and a sensor positioned in the airflow path; and a controller communicably coupled to the sensor. The controller includes a processor and instructions stored in memory and is operable to execute the instructions with the processor to perform operations including identifying a measurement from the sensor; identifying a particular equation stored in the memory, the particular equation developed using data analytics and including an input parameter that is based on the identified measurement; and based on the identified measurement and the particular equation, determining a value of absolute lung volume.
Owner:PULMONE ADVANCED MEDICAL DEVICES
Lung volume reduction using glue composition
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for sealing localized regions of damaged lung tissue to reduce overall lung volume. The glue compositions provide a glue featuring an adhering moiety coupled to one or more other moieties including, for example, a cross-linkable moiety and / or one other adhering moiety. The methods and compositions of the invention find use, for example, in treating pulmonary conditions, such as emphysema.
Owner:EKOS CORP
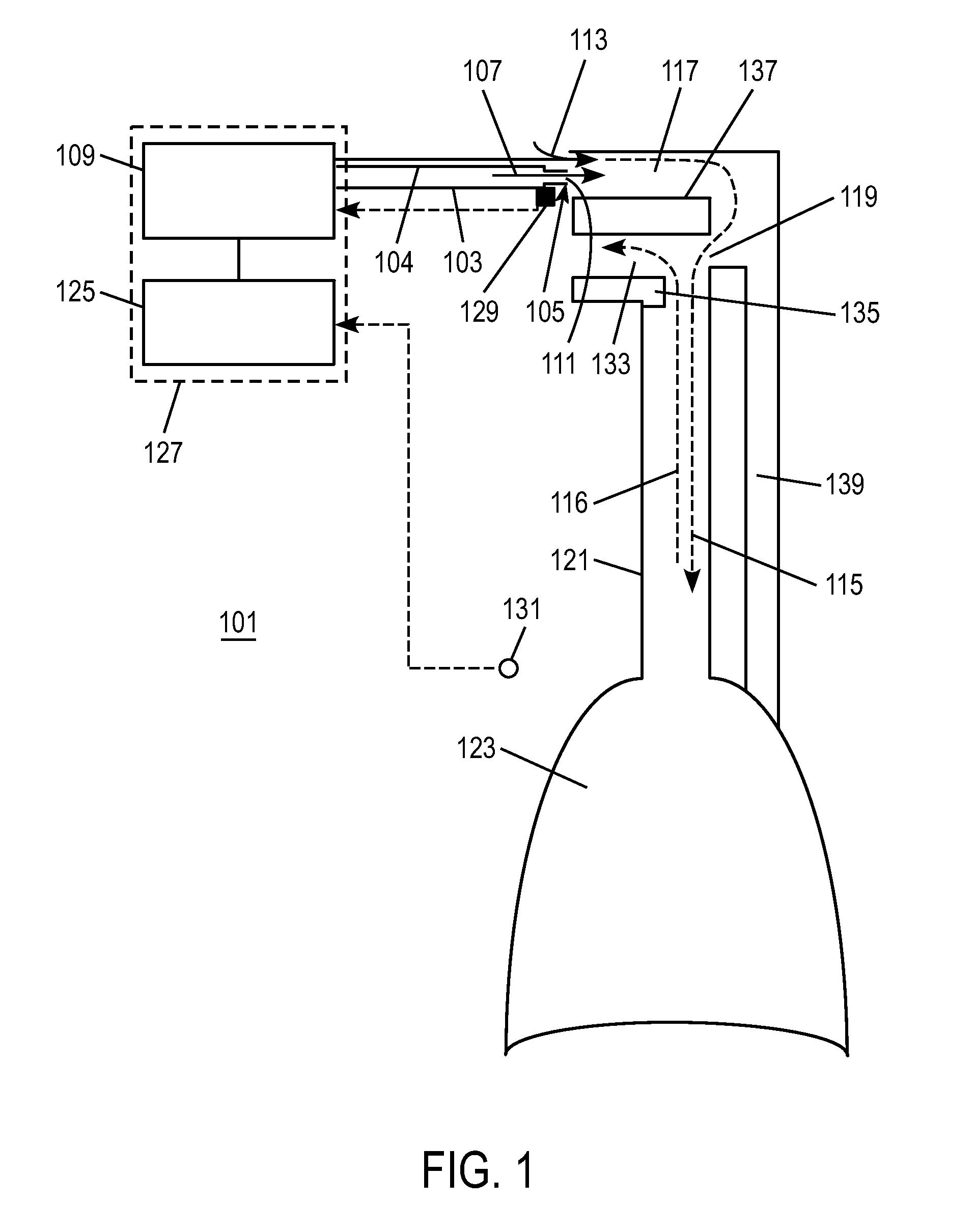
System and Methods for the Measurement of Lung Volumes
ActiveUS20100286548A1Increase volumeLower the volumeRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsAir volumeDensity of air
A method for determining a pulmonary volume change includes: receiving a respiration event from a subject in an airflow chamber; interrupting the respiration event by an occlusion of the airflow chamber initiated at a first time instant and terminated at a second time instant subsequent to the first time instant; taking a plurality of measurements of airflow rate through the airflow chamber between the second time instant and a third time instant subsequent to the second time instant; and determining a pulmonary volume change substantially equal to a reduction of a pulmonary air volume by a pulmonary response air volume and a normal air volume, wherein the pulmonary volume change is related to a change in density of air in the airflow chamber.
Owner:PULMONE ADVANCED MEDICAL DEVICES
Method and Apparatus for Lung Volume Estimation
ActiveUS20080289628A1Reliably determinedThe result is accurateRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesGas compositionLung volumes
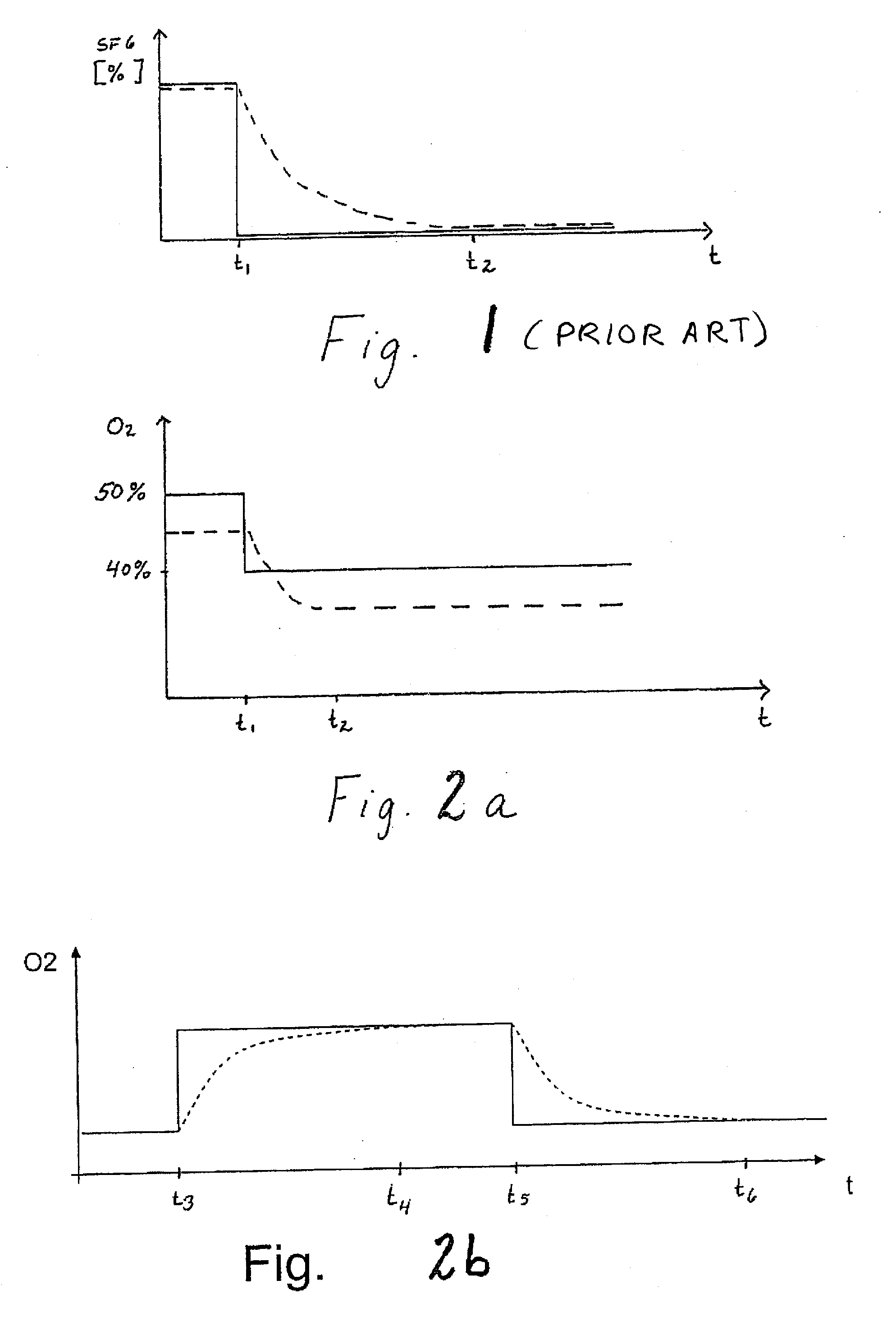
In a method, ventilator and ventilator control unit for determining an end-expertorial lung volume (EELV) for a mechanically ventilated patient, a breathing gas is provided to the patient that has a first fixed N2 / O2 gas composition, at least until the N2 / O2 gas composition in air expired from the patient is constant. At least once, at a first predetermined point in time, the N2 / O2 gas composition in the breathing gas is changed to a second fixed composition. The change in the N2 / O2 gas composition exhaled by the patient for each breath is measured until a second point in time at which the level of expired O2 in at least two subsequent breadths is substantially stable. The measurement is made downstream of the expiratory tube of the ventilator. The total gas volume is determined for each breath, and the EELV of the patient's lungs is determined based on the change in O2 level between the first and second points in time.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
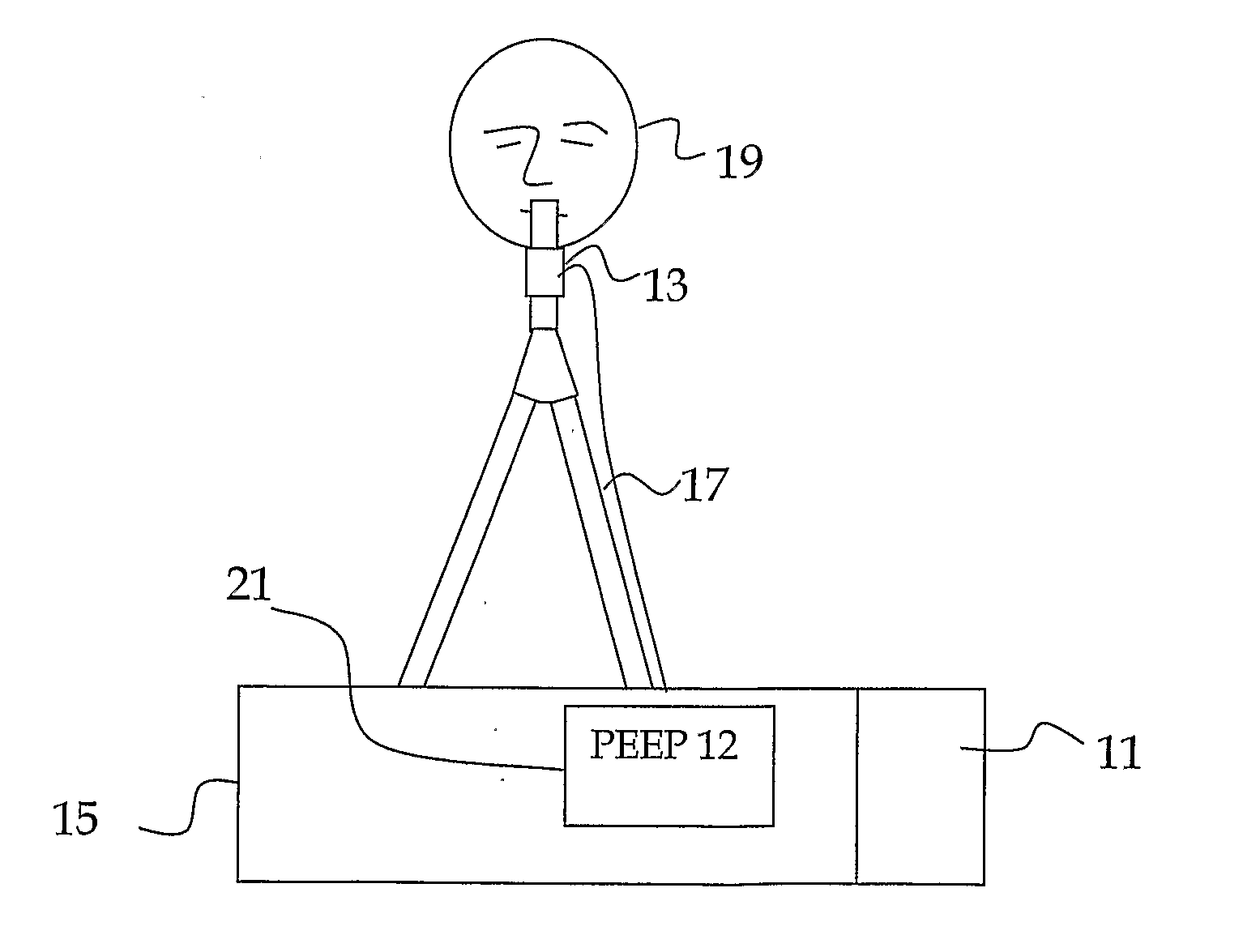
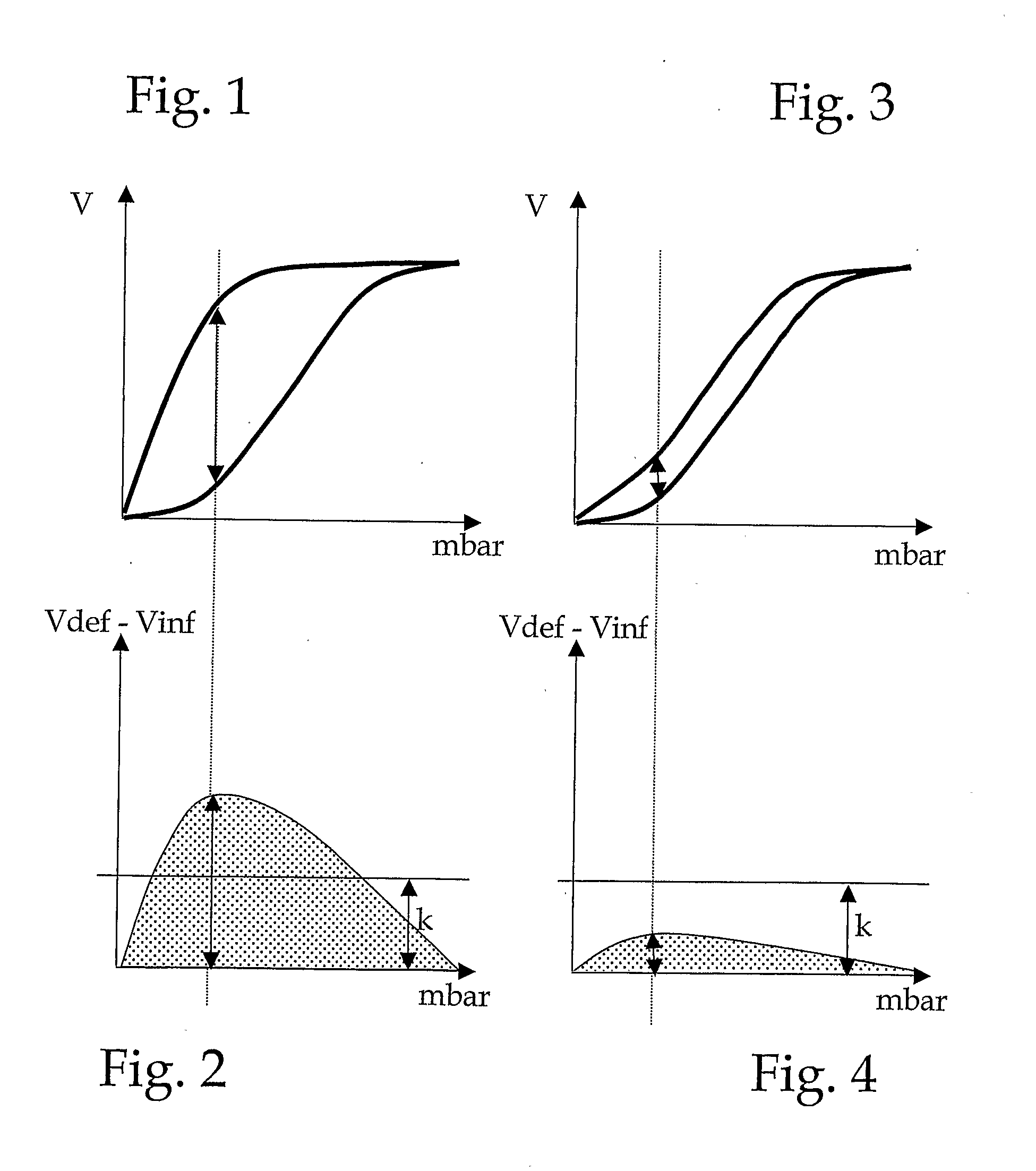
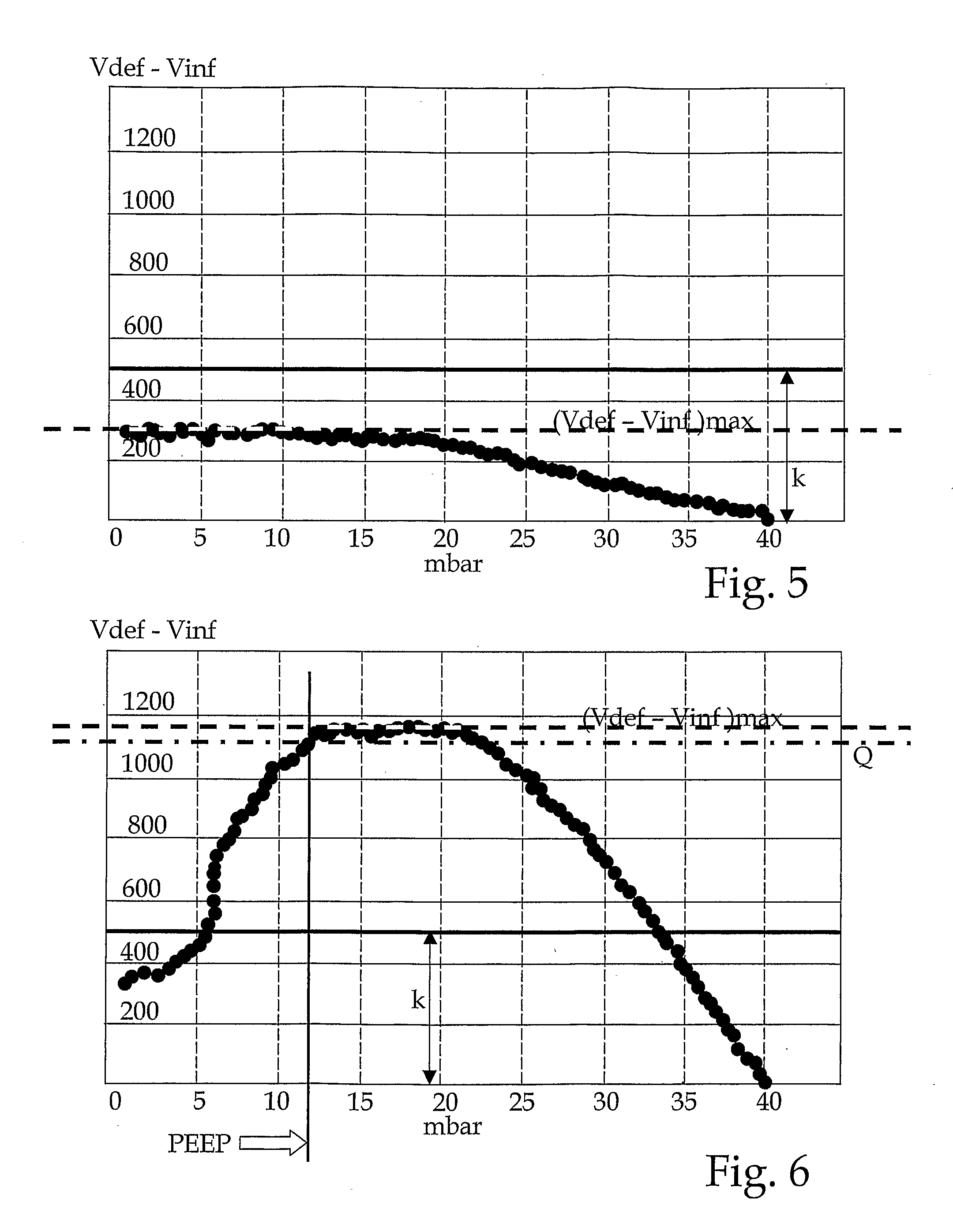
Method and device for determining the peep during the respiration of a patient
ActiveUS20090301492A1Low PEEPReduction in PEEPRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectronic systemsInhalation
The invention relates to a device for the automated determination of the PEEP of a patient. Said device comprises sensors and a suitable electronic system for determining a pressure-volume characteristic curve during a P / V manoeuvre. The electronic system is designed in such a way as to generate, specifically in terms of breathing pressure, the difference between “lung volume during exhalation (Vdef)” and “lung volume during inhalation (Vinf)”, and to determine the maximum value of said difference. The breathing pressure is then determined, for which the volume difference has a value defined in relation to the maximum value of the volume difference. The device calculates a PEEP value on the basis of said determined breathing pressure value.
Owner:HAMILTON MEDICAL AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com