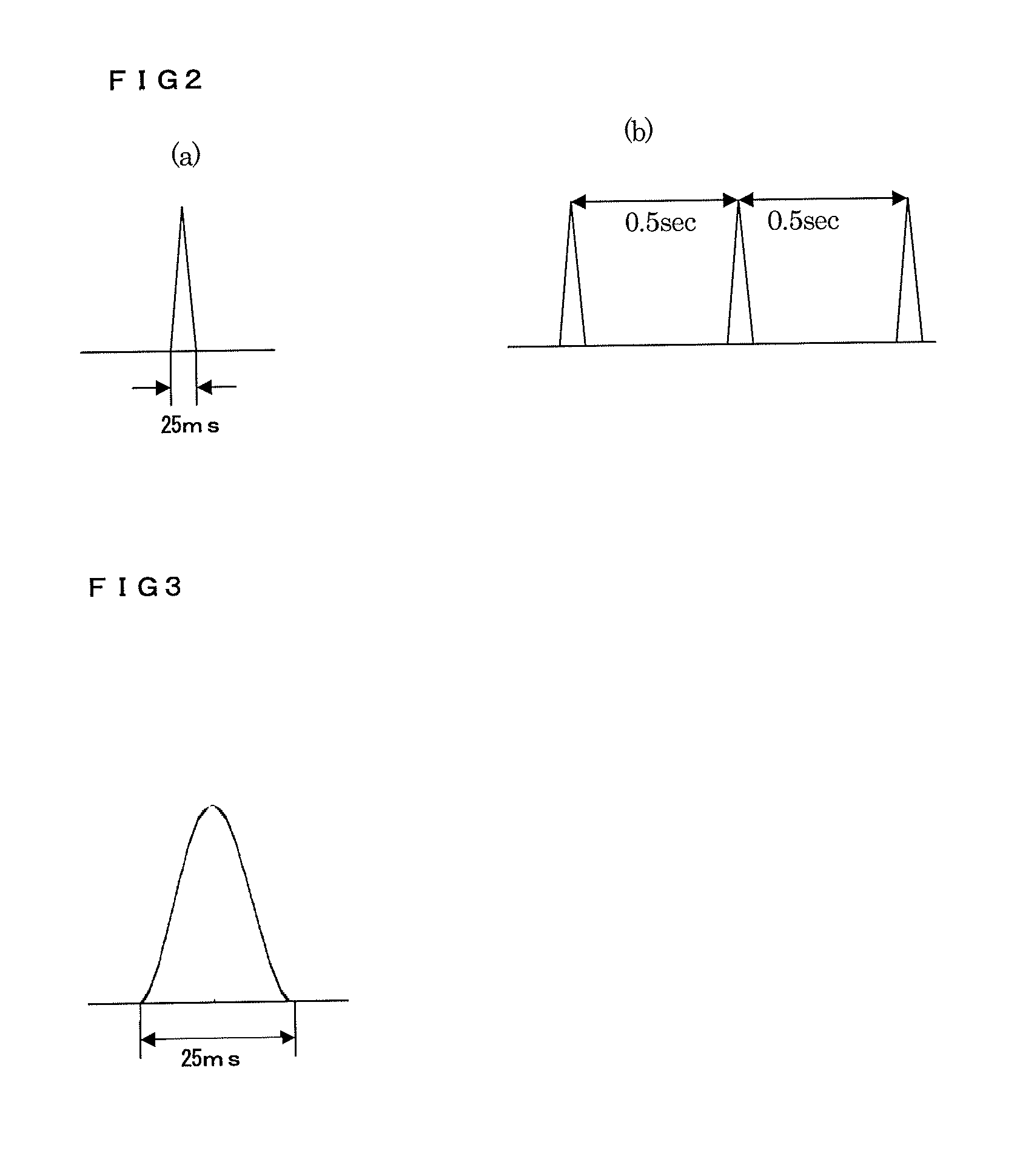Patents
Literature
31 results about "Expiratory Time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
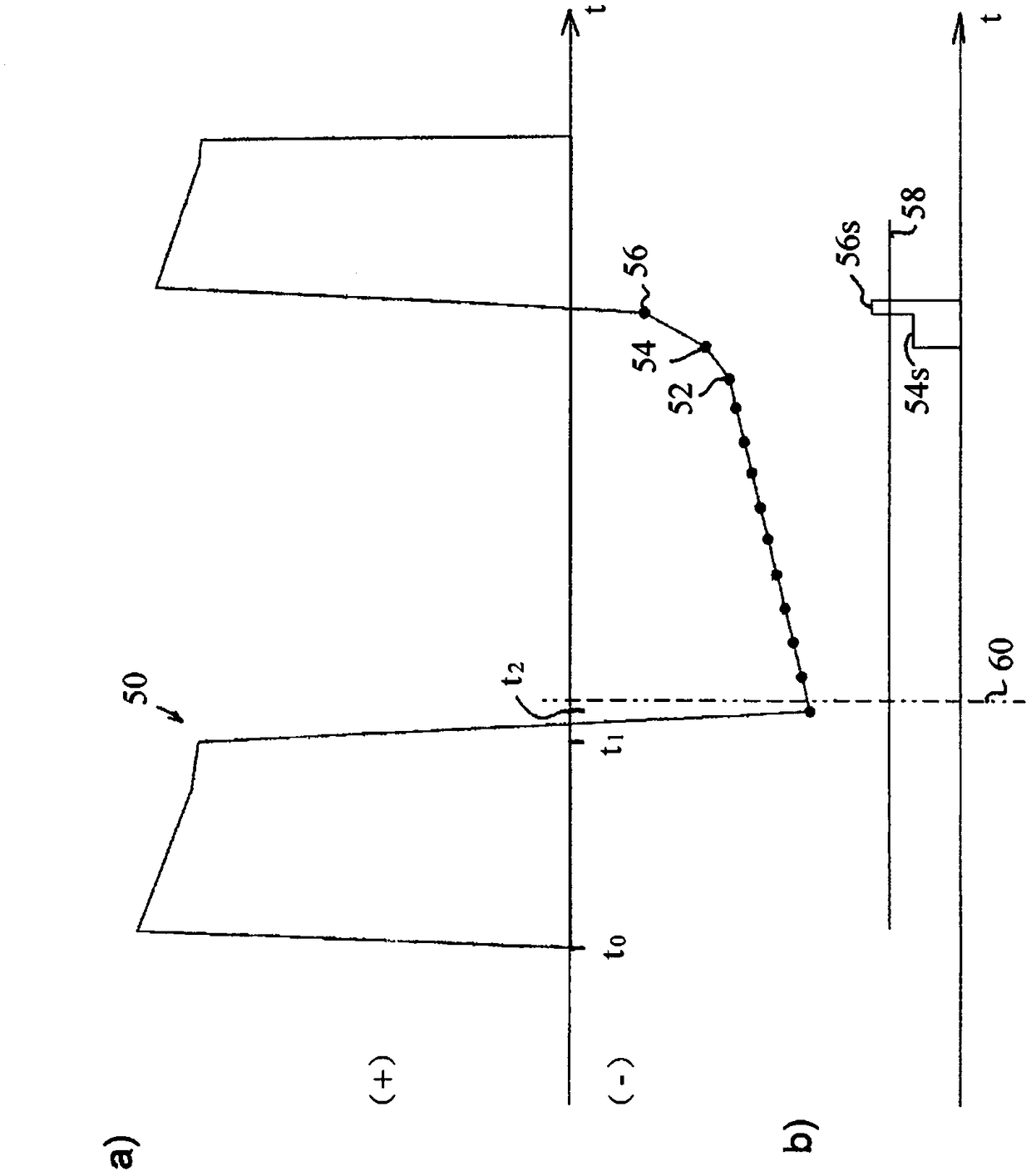
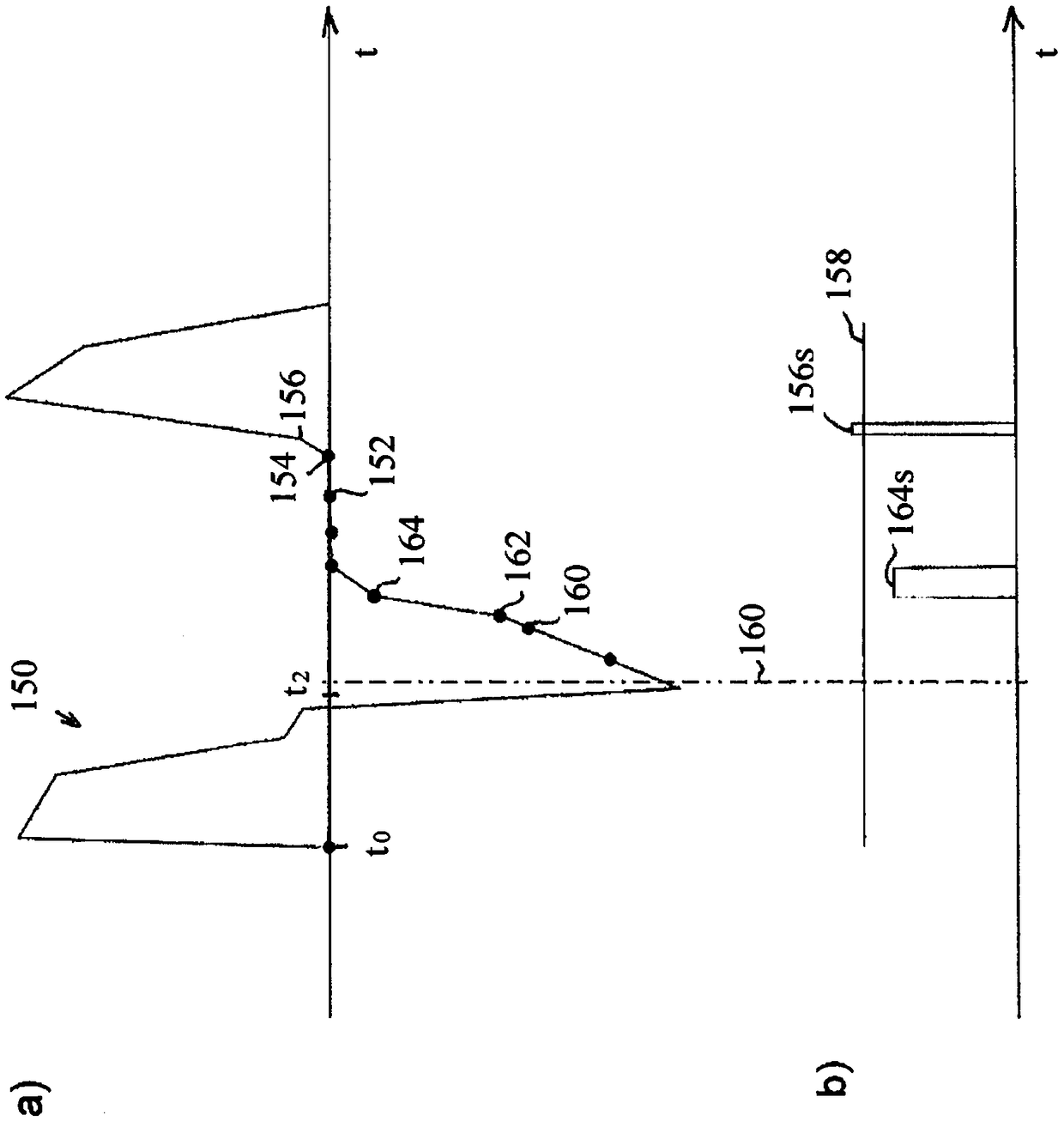
The recorded time interval between the initiation of exhalation and the time at which no further lung volume reduction occurs.
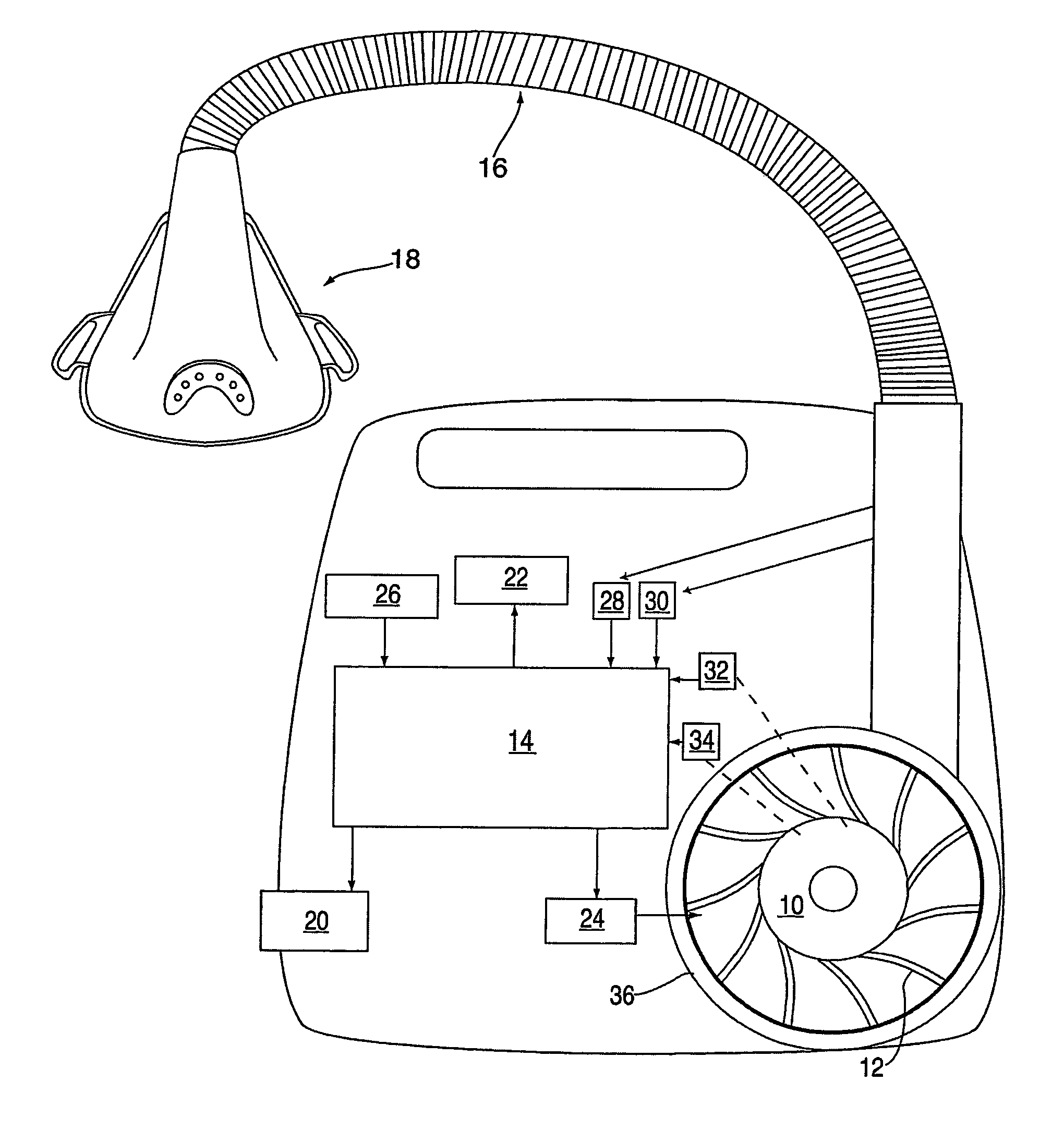
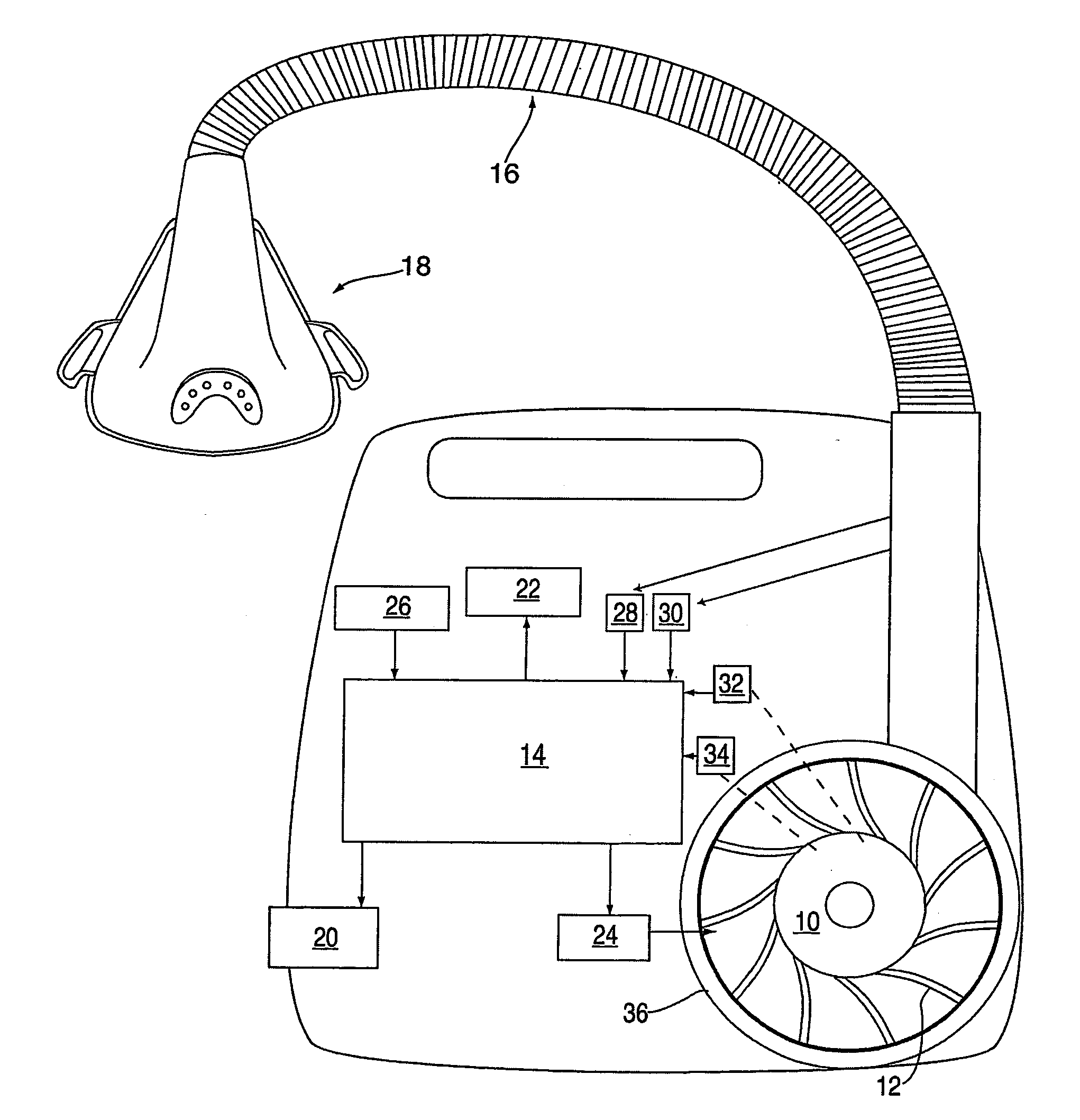
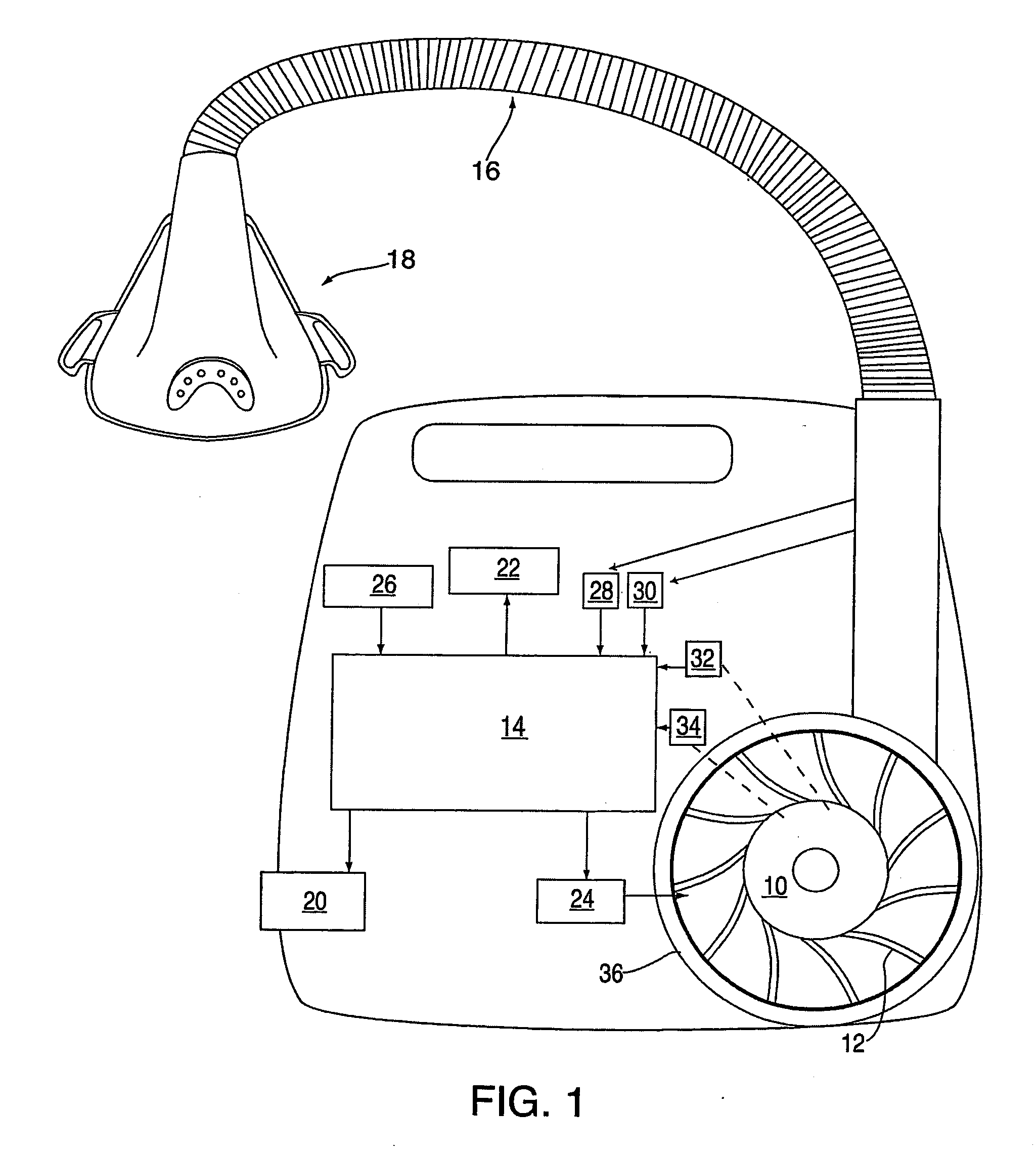
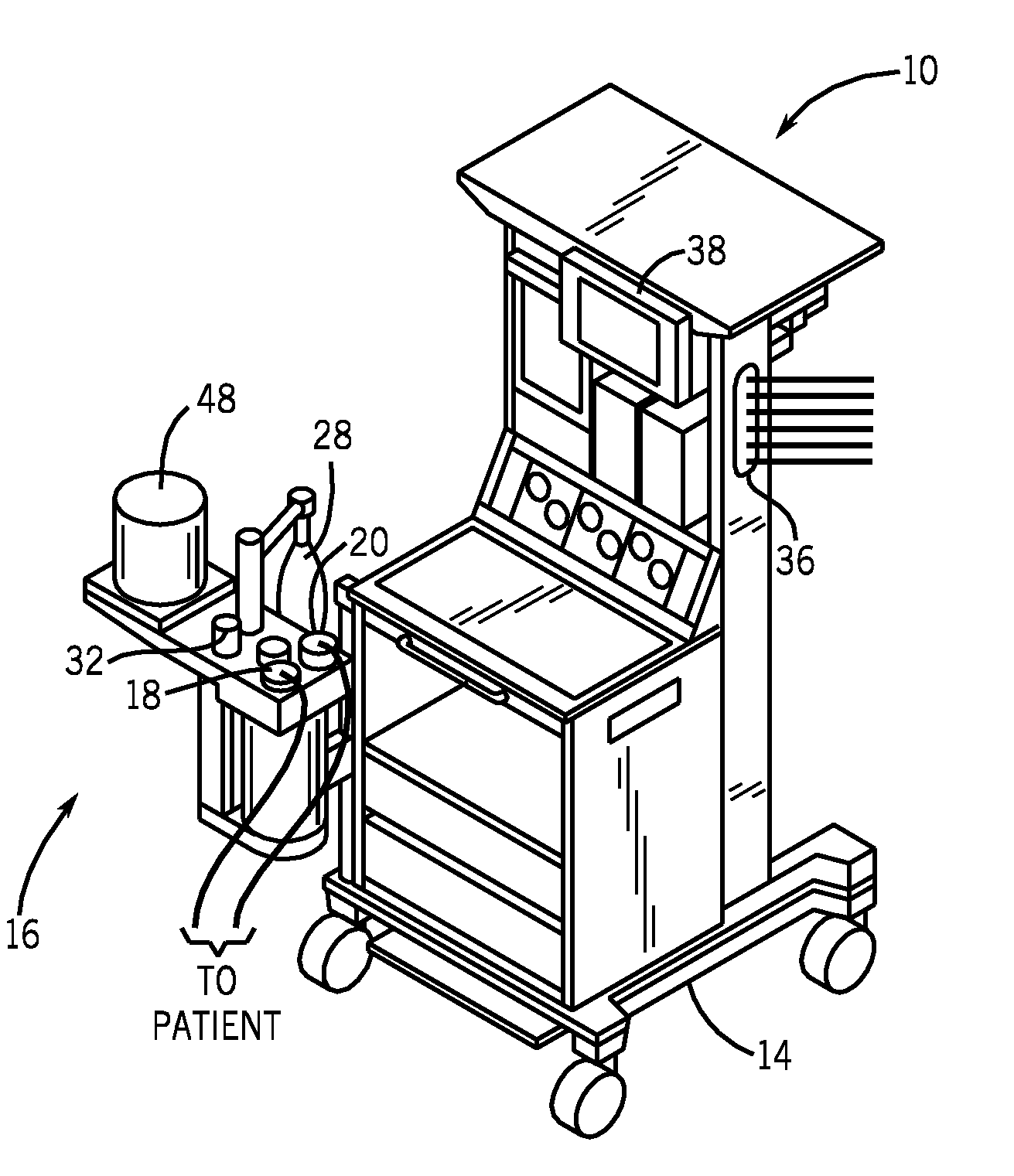
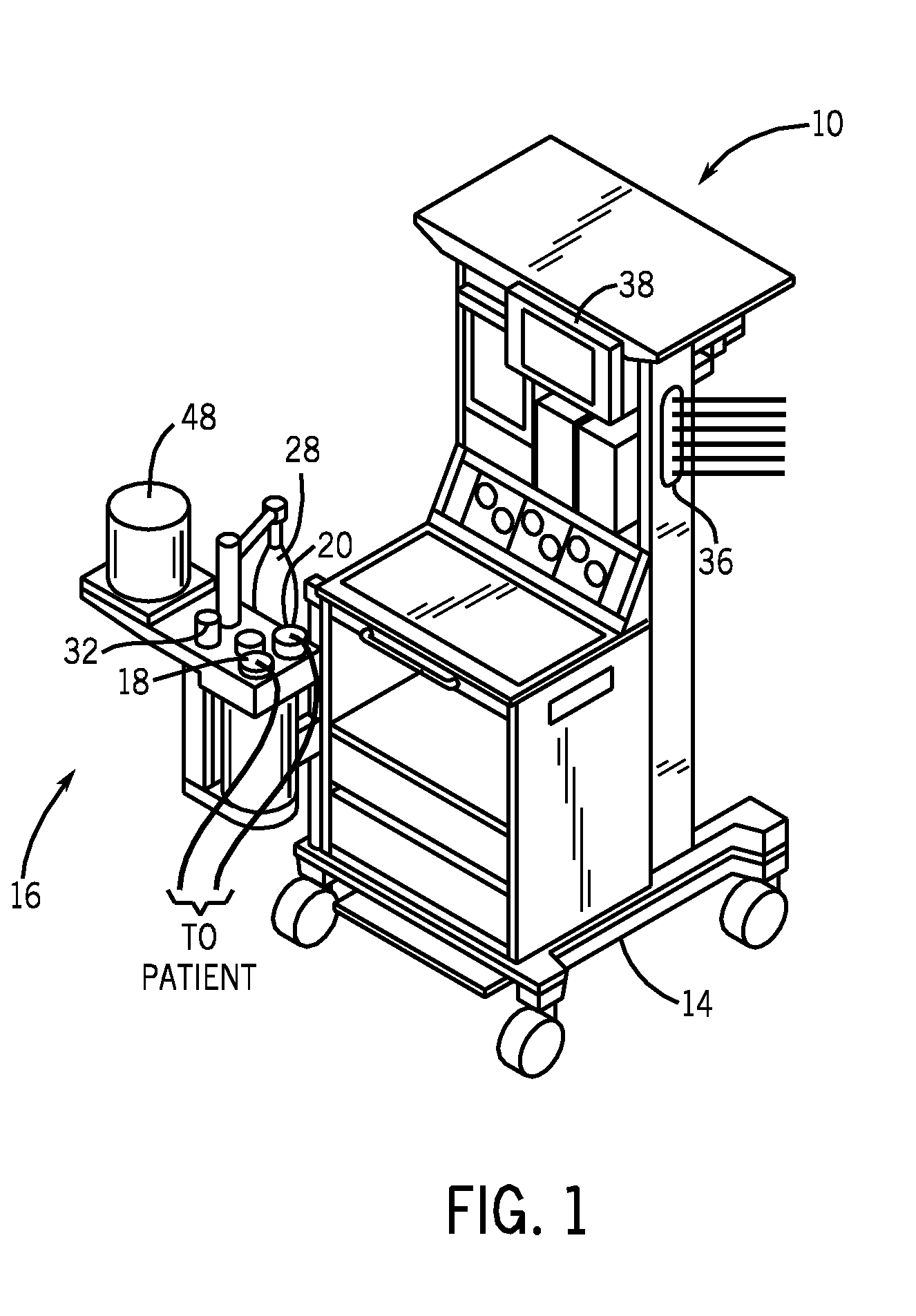
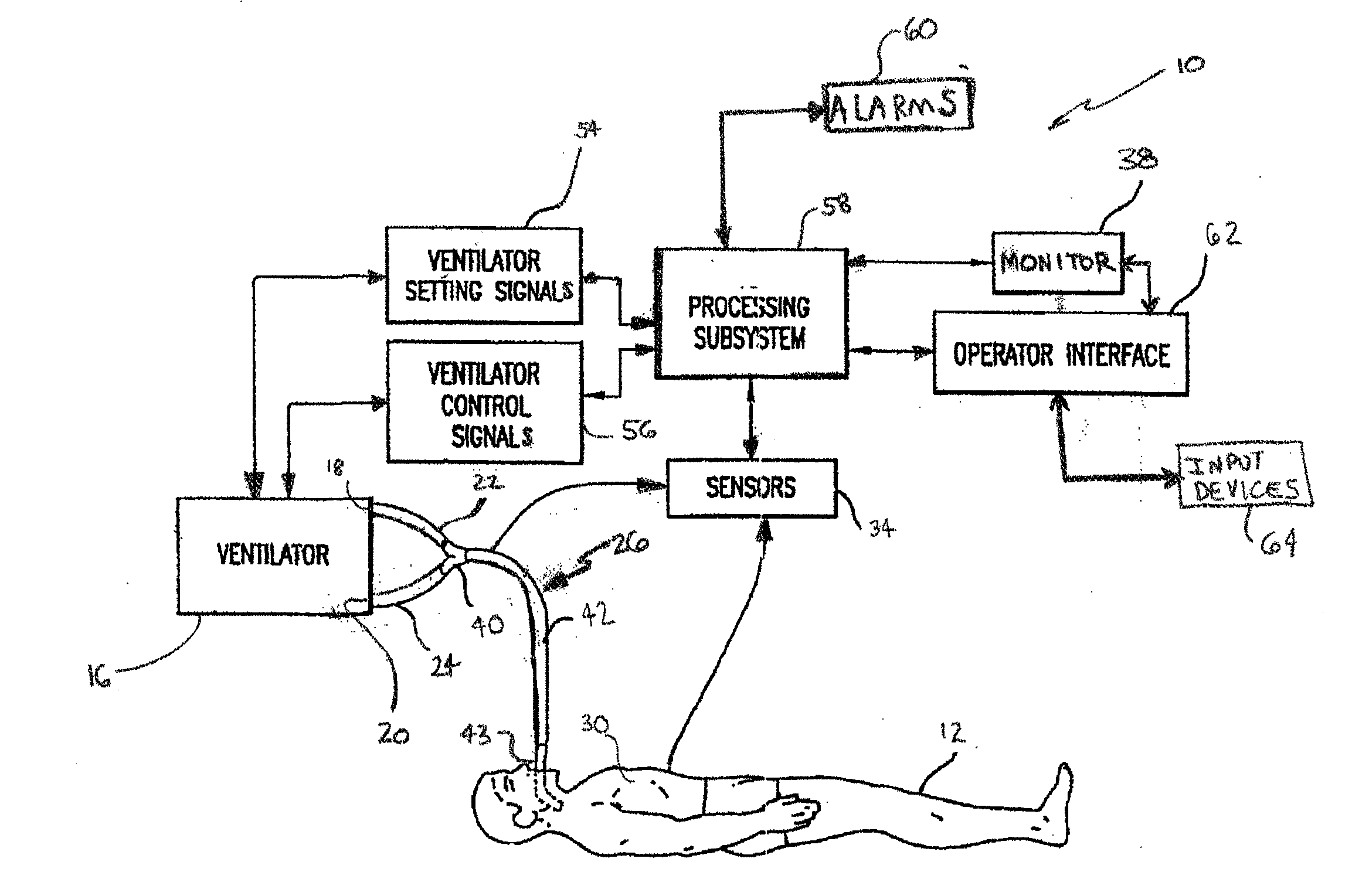
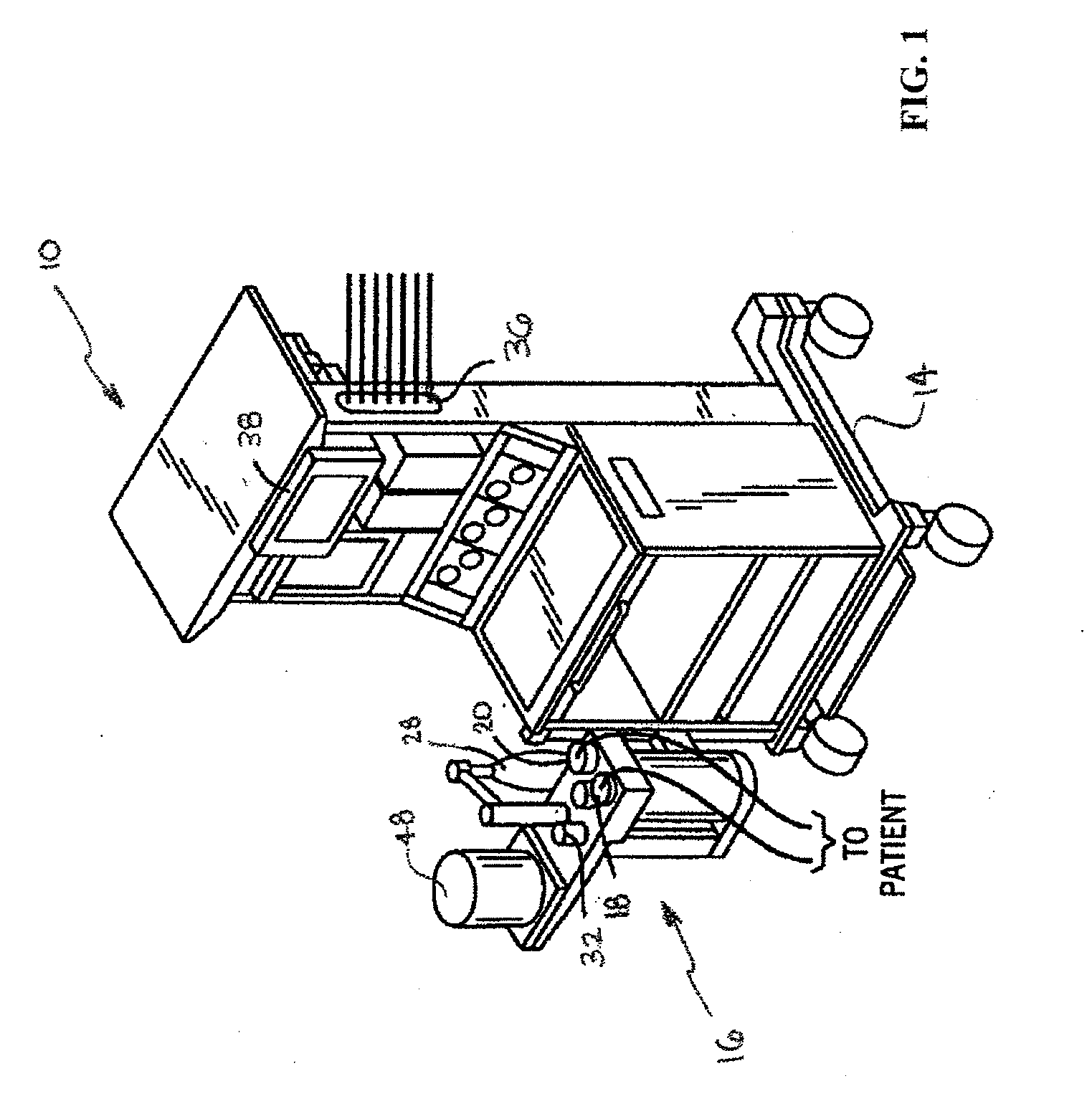
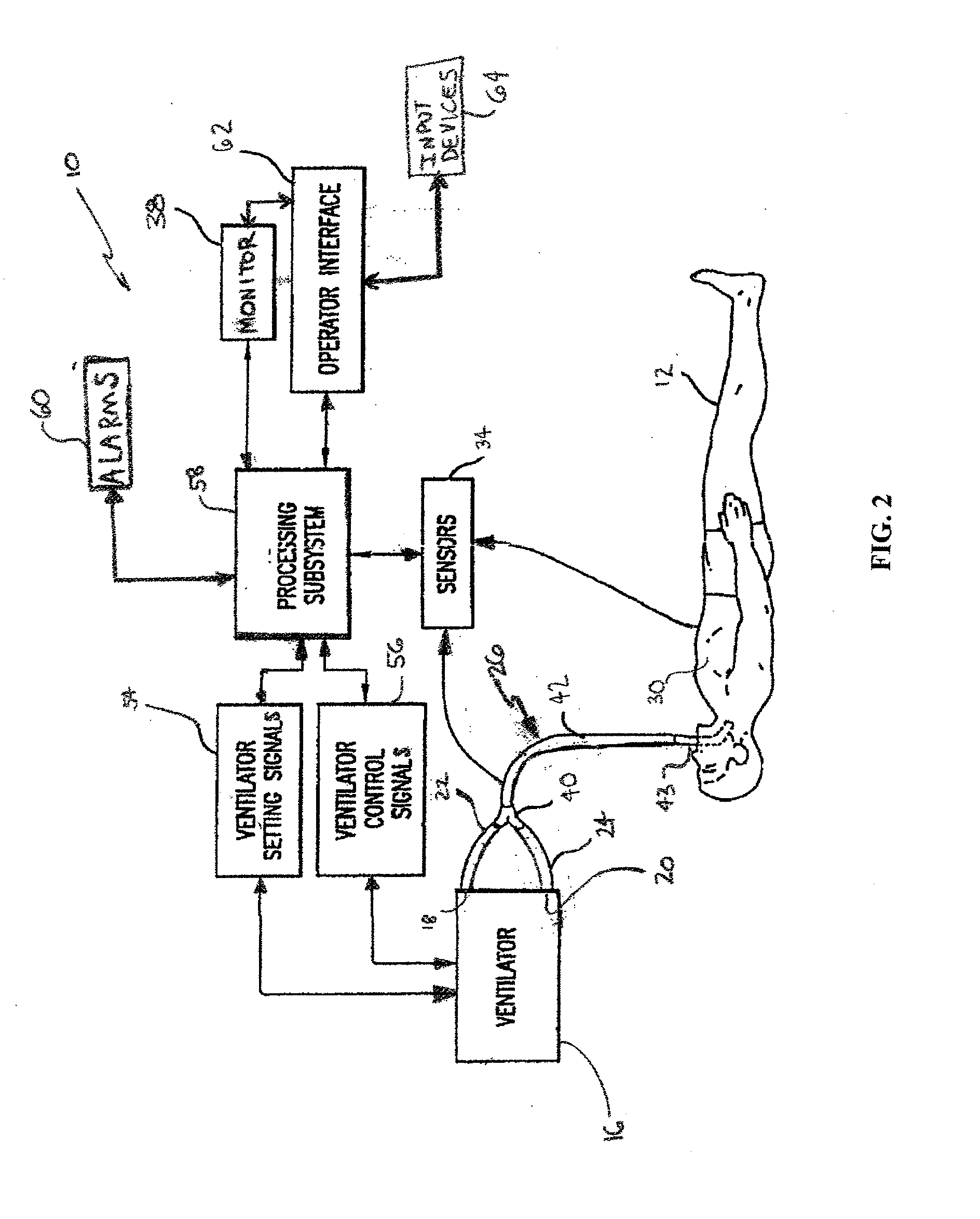
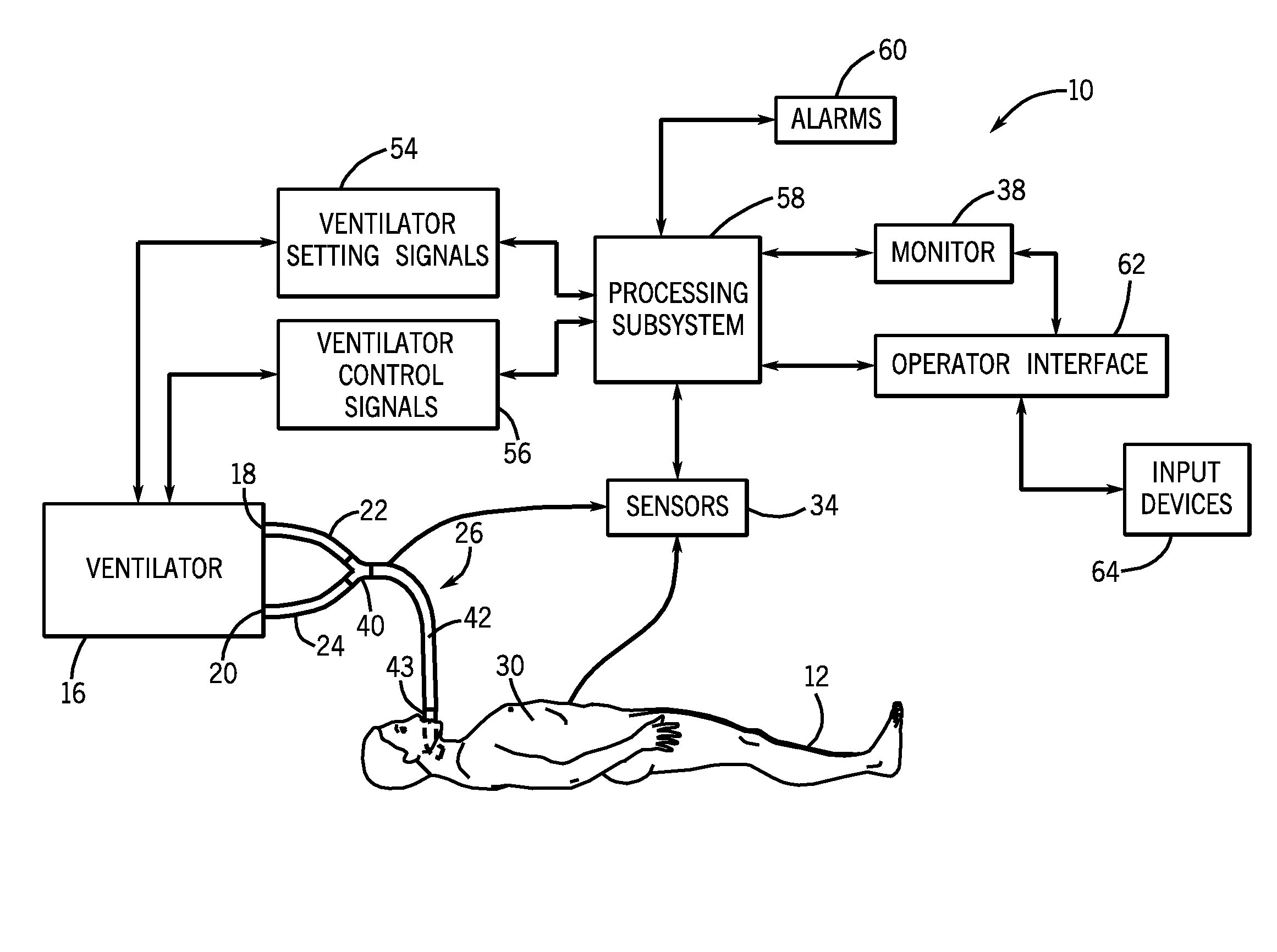
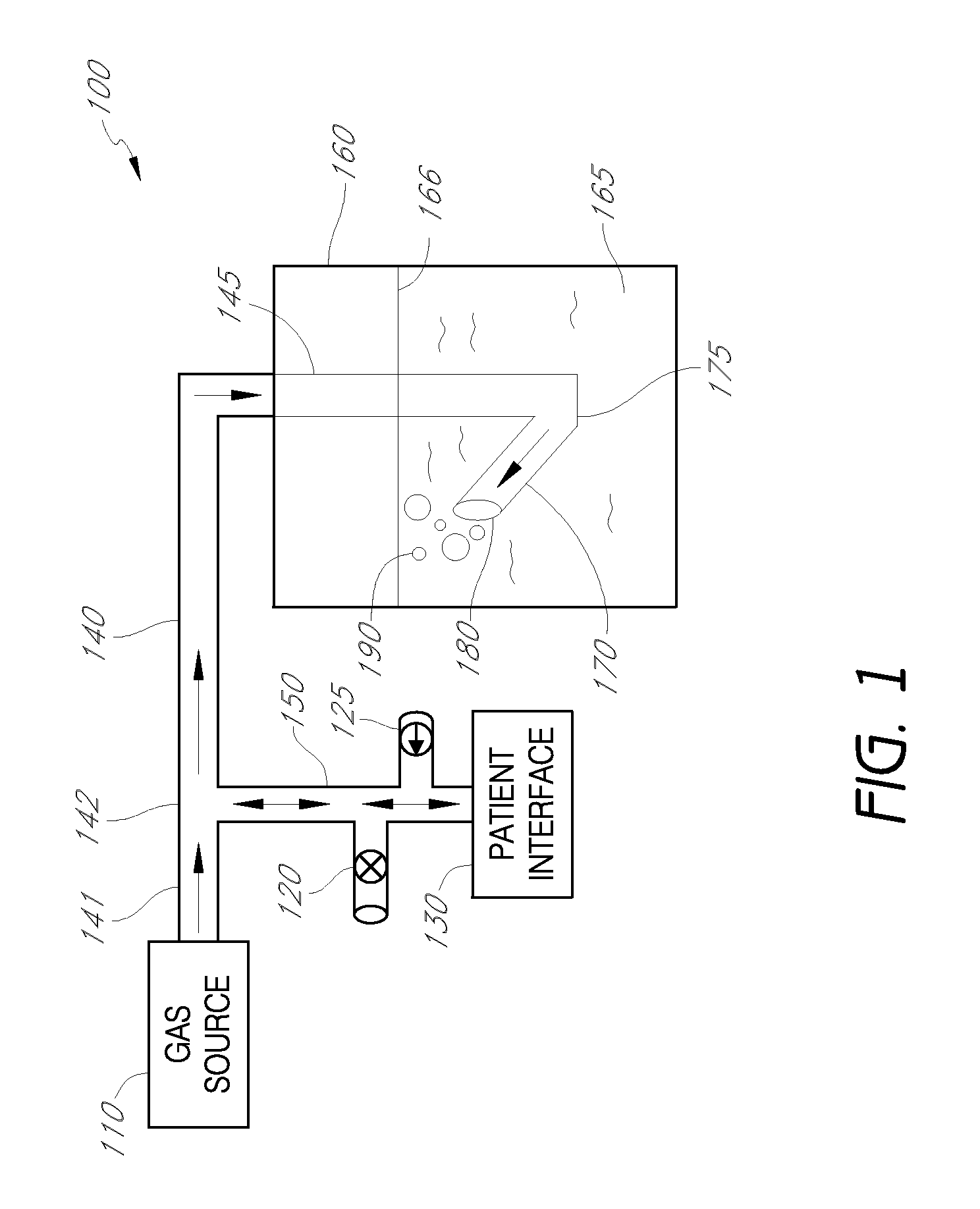
Methods for providing expiratory pressure relief in positive airway pressure therapy
InactiveUS7866318B2Stable changeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksRespiratory flowExpiration Time
Owner:RESMED LTD
Methods for providing expiratory pressure relief in positive airway pressure therapy
InactiveUS20090020121A1Stable changeOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksExpiration TimePositive airway pressure
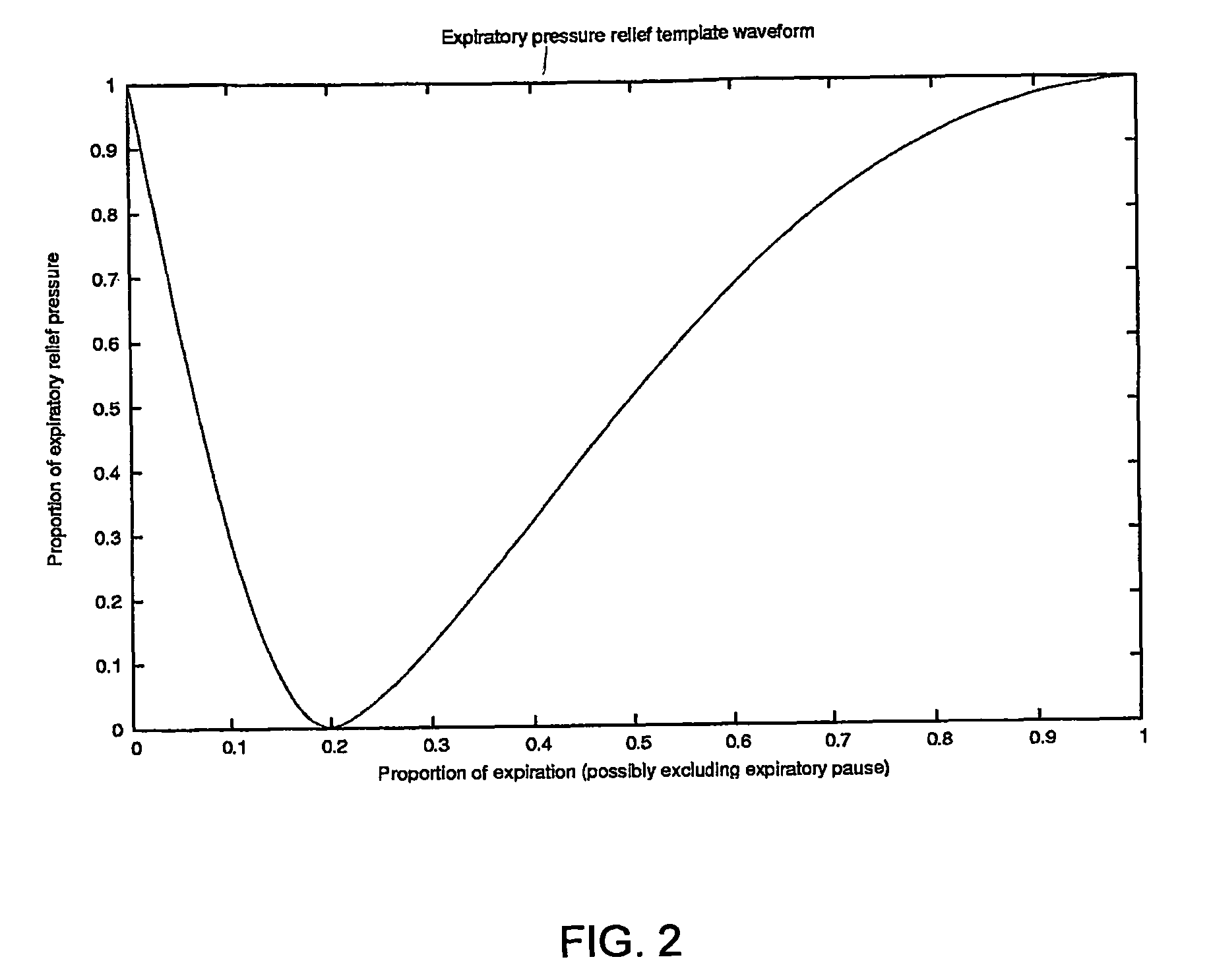
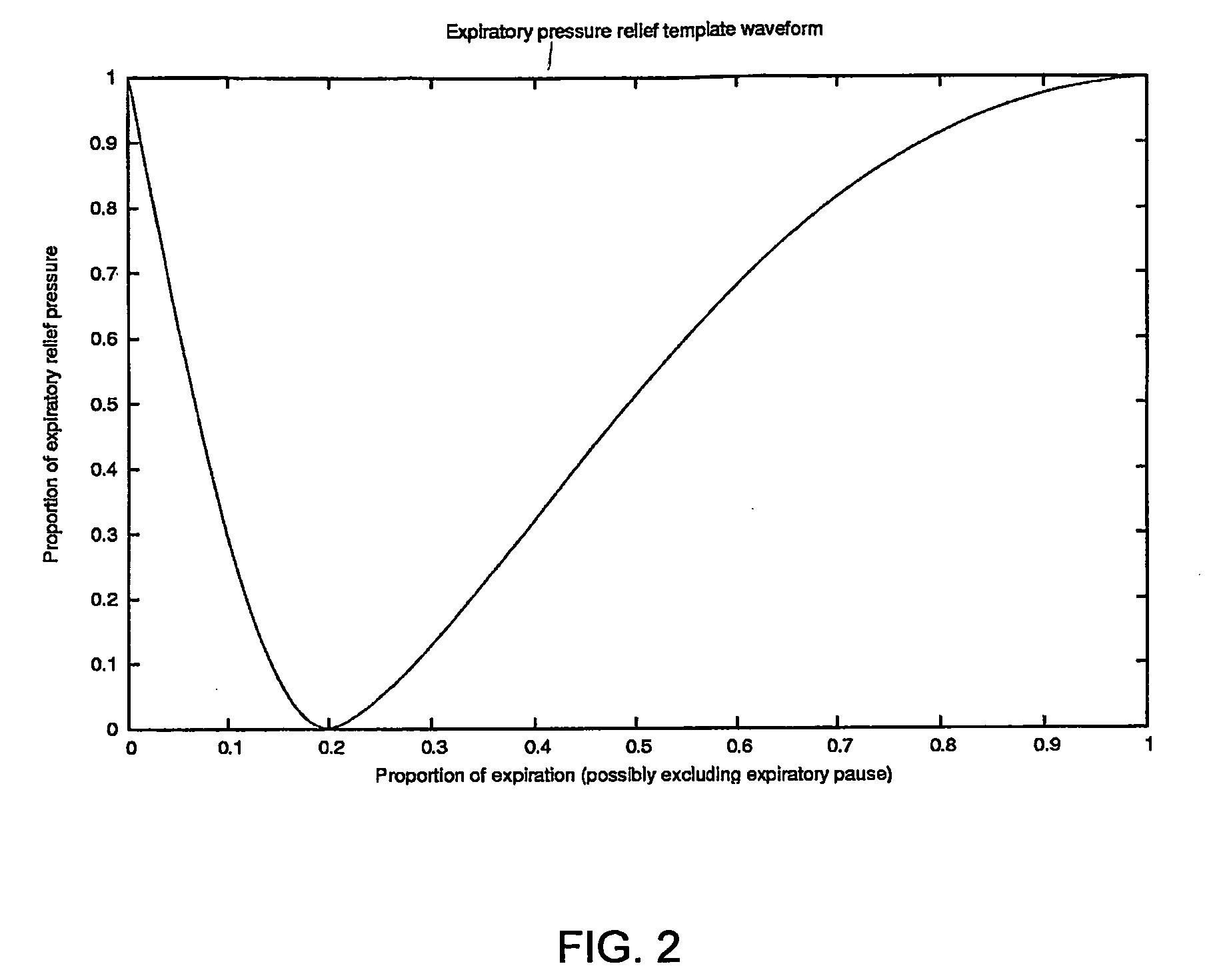
A method of operating a CPAP apparatus in which the interface pressure is controlled to rapidly drop at the start of expiration by an expiratory relief pressure (ERP) that is independent of instantaneous respiratory flow, following which the pressure rises to an inspiratory level at or shortly before the end of expiration, or at the onset of an expiratory pause, if any. The ERP is an increasing function of the inspiratory pressure. The expiratory pressure follows a template that is a function of the expected expiration time, the magnitude of the template being equal to the ERP. The current estimated proportion of expiration is determined by comparing the expiration time of the breath in progress to low-pass filtered expiratory durations measured for a number of the preceding breaths.
Owner:RESMED LTD
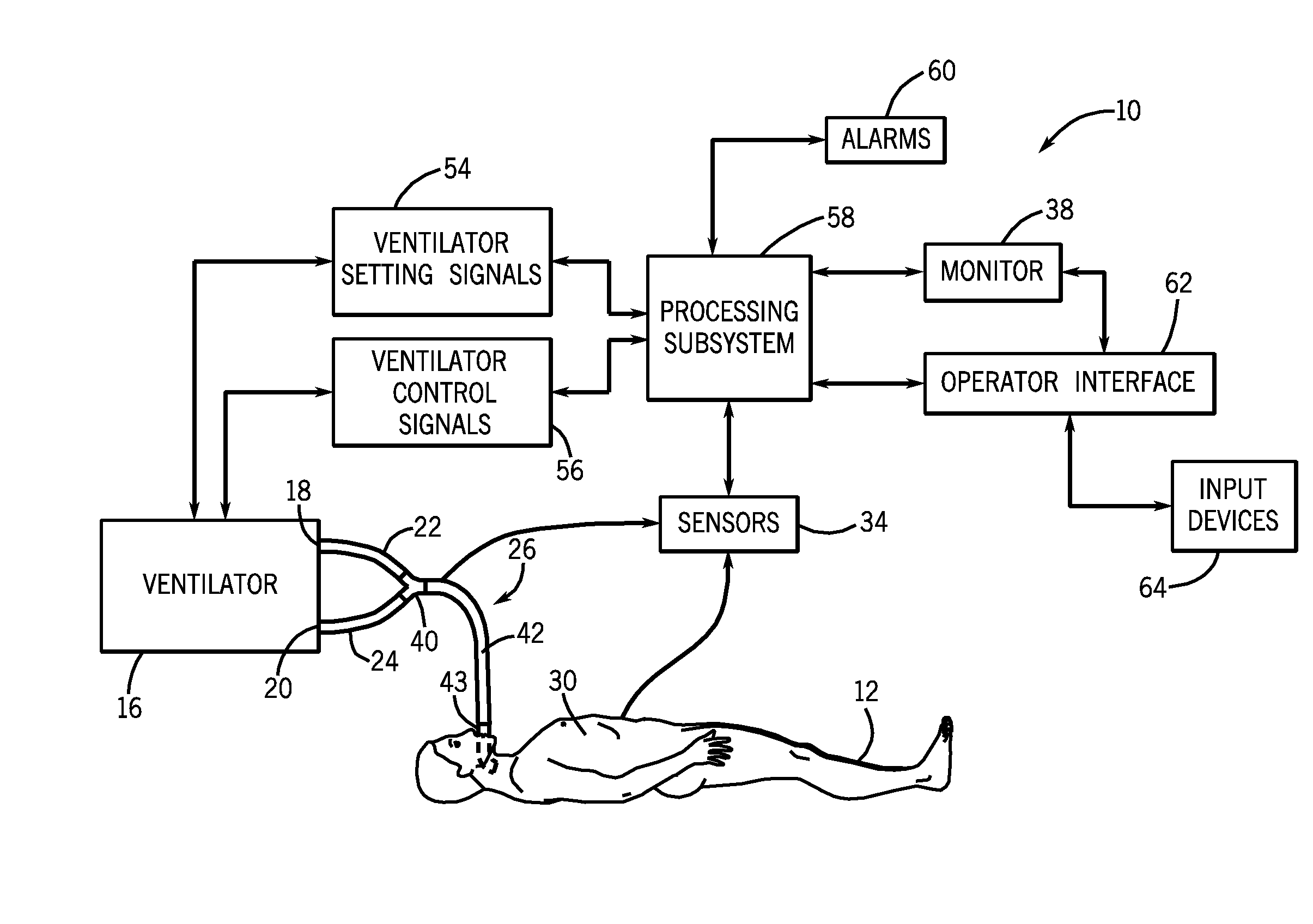
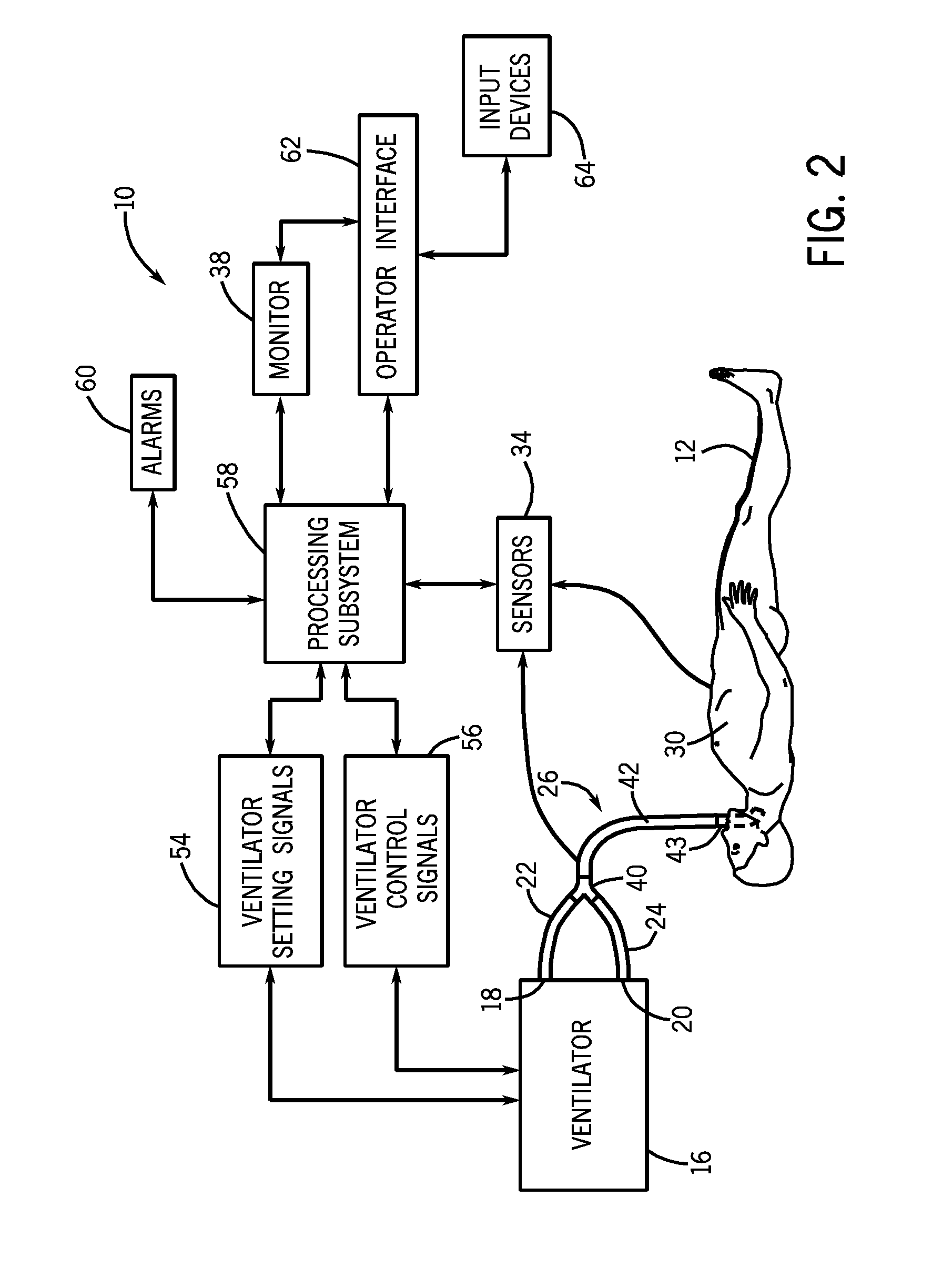
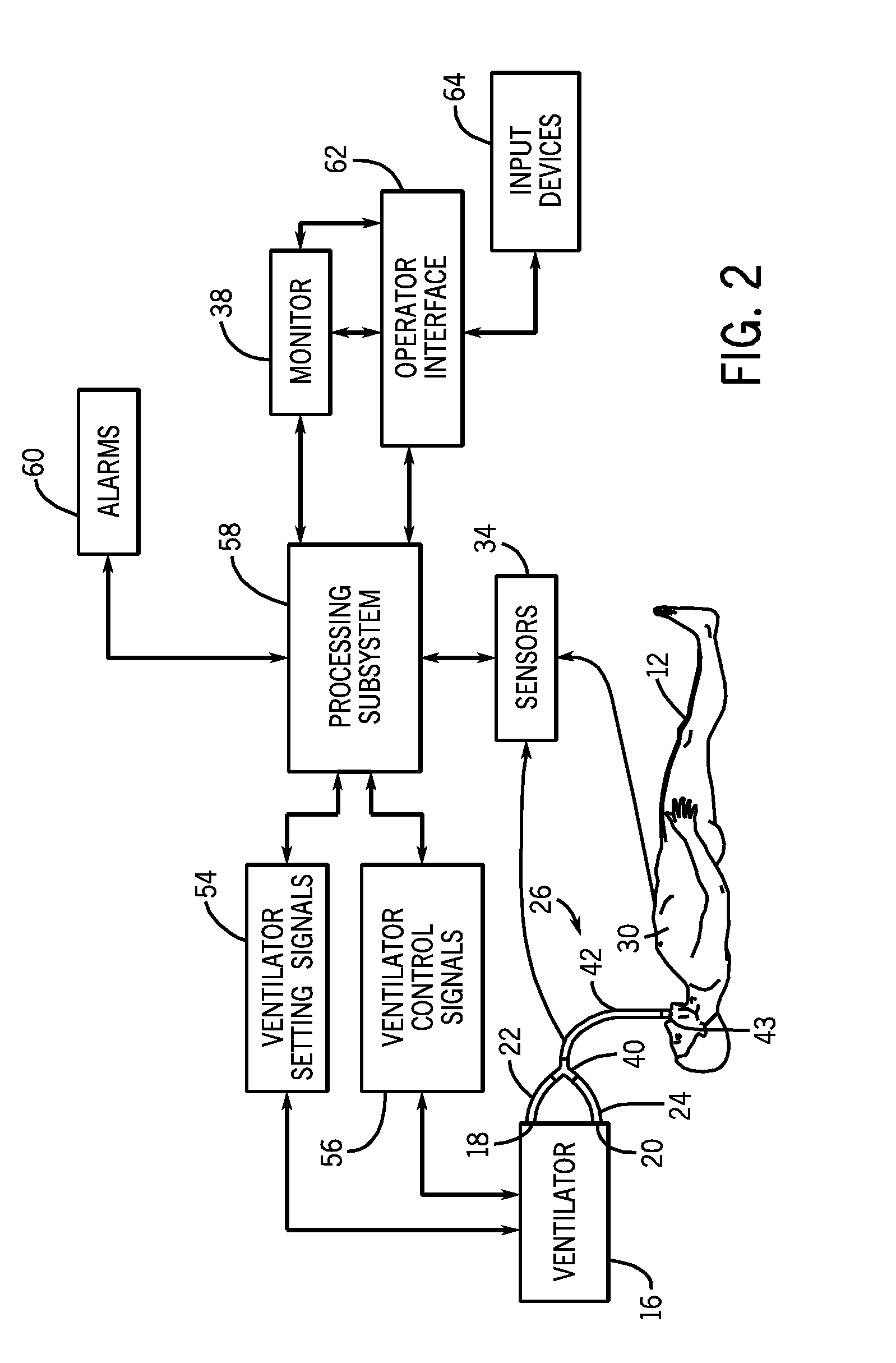
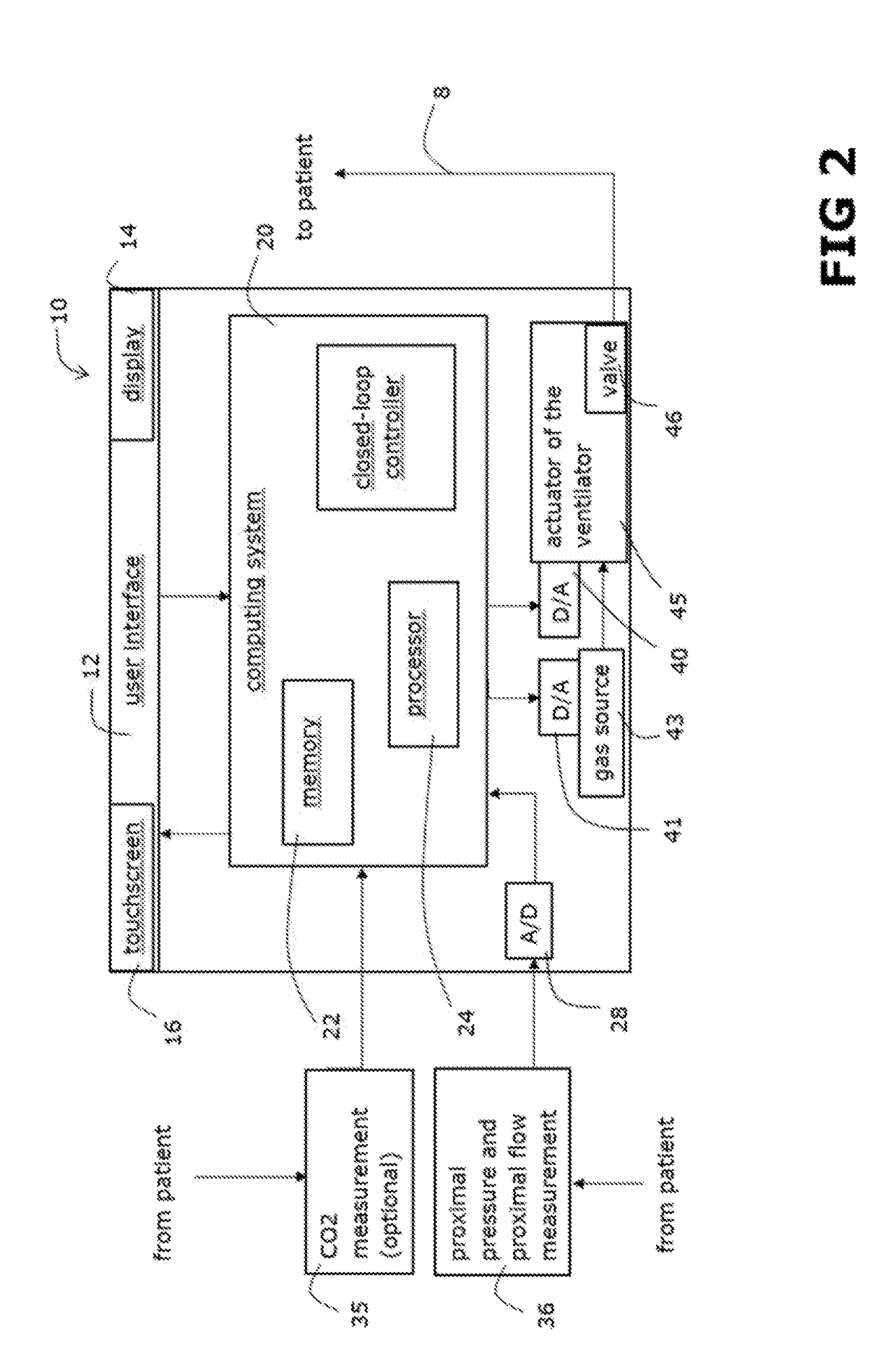
Setting mandatory mechanical ventilation parameters based on patient physiology
InactiveUS20080202525A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesExpiratory TimePhysical therapy
A method of setting inspiratory time, expiratory time, and a subject's breath size in controlled mechanical ventilation comprises: a) setting a subject's expiratory time; b) setting the subject's inspiratory time; and c) setting the subject's breath size, all based on various criteria.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Setting expiratory time in mandatory mechanical ventilation based on a deviation from a stable condition of exhaled gas volumes
A method of setting expiratory time in controlled mechanical ventilation varies a subject's expiratory times; determines gas volumes exhaled by the subject per breath associated with the expiratory times; establishes a stable condition of the gas volumes; and determines an optimal expiratory time based on a deviation from the stable condition. A device for use in controlled mechanical ventilation comprises means for the same.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Setting mandatory mechanical ventilation parameters based on patient physiology
InactiveUS20080202518A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFlow transducerExpiratory Time
A method of setting expiratory time in controlled mechanical ventilation sets a subject's expiratory time based on when the subject's natural exhalation flow ceases. Another method determines when the subject's natural exhalation flow ceases and sets the subject's expiratory time based on the determination. A device for use in controlled mechanical ventilation comprises a flow rate sensor configured to determine when a subject's natural exhalation flow ceases and bases the subject's expiratory time on the determination.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Setting madatory mechanical ventilation parameters based on patient physiology
InactiveUS20080202517A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesExpiratory TimeEmergency medicine
A method of setting expiratory time in controlled mechanical ventilation sets a subject's expiratory time based on the subject's natural exhalation time. Another method determines the subject's natural exhalation time and sets the subject's expiratory time based on the determination. A device for use in controlled mechanical ventilation comprises a flow rate sensor configured to determine a subject's natural exhalation time and base the subject's expiratory time on the determination.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
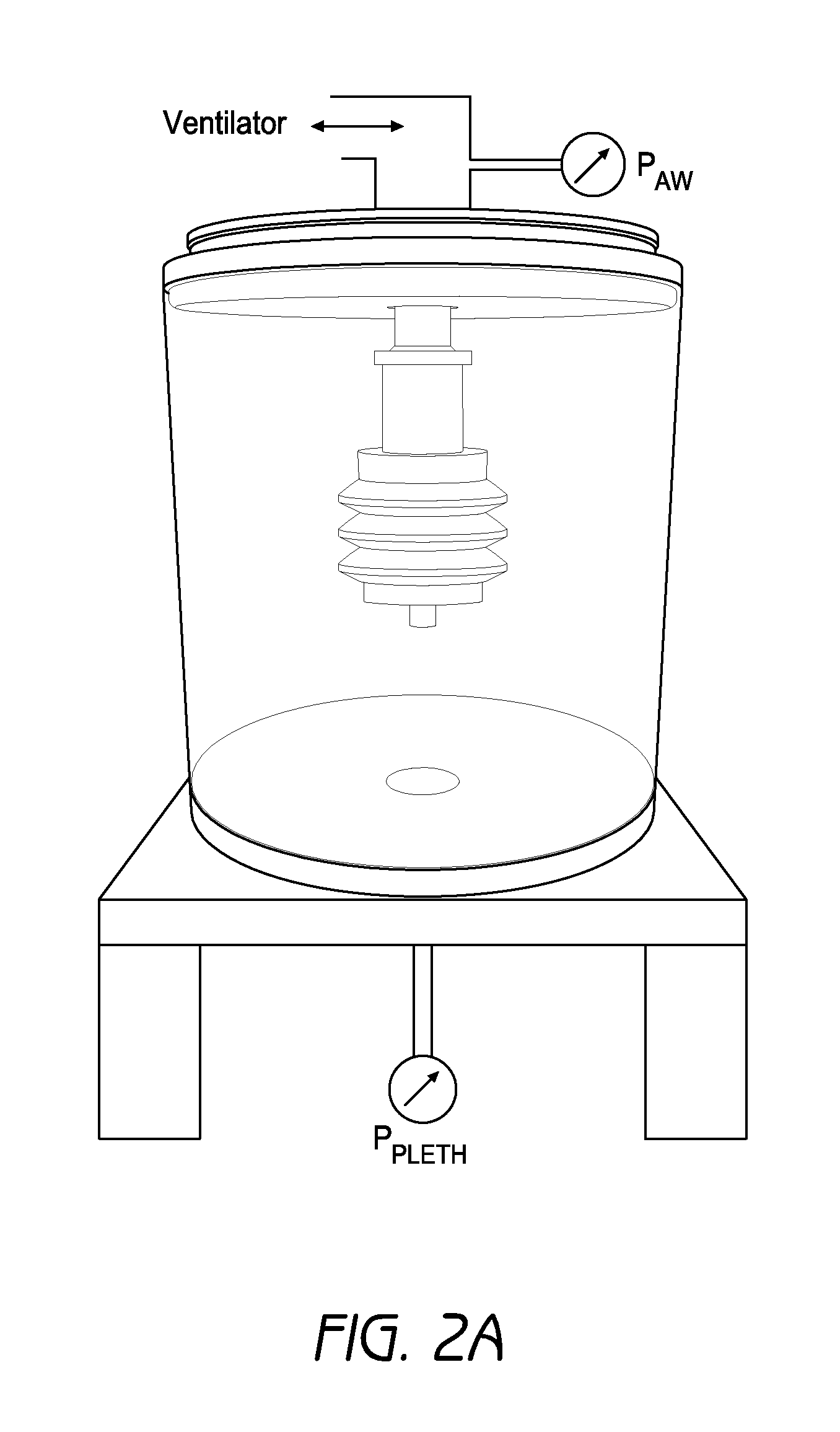
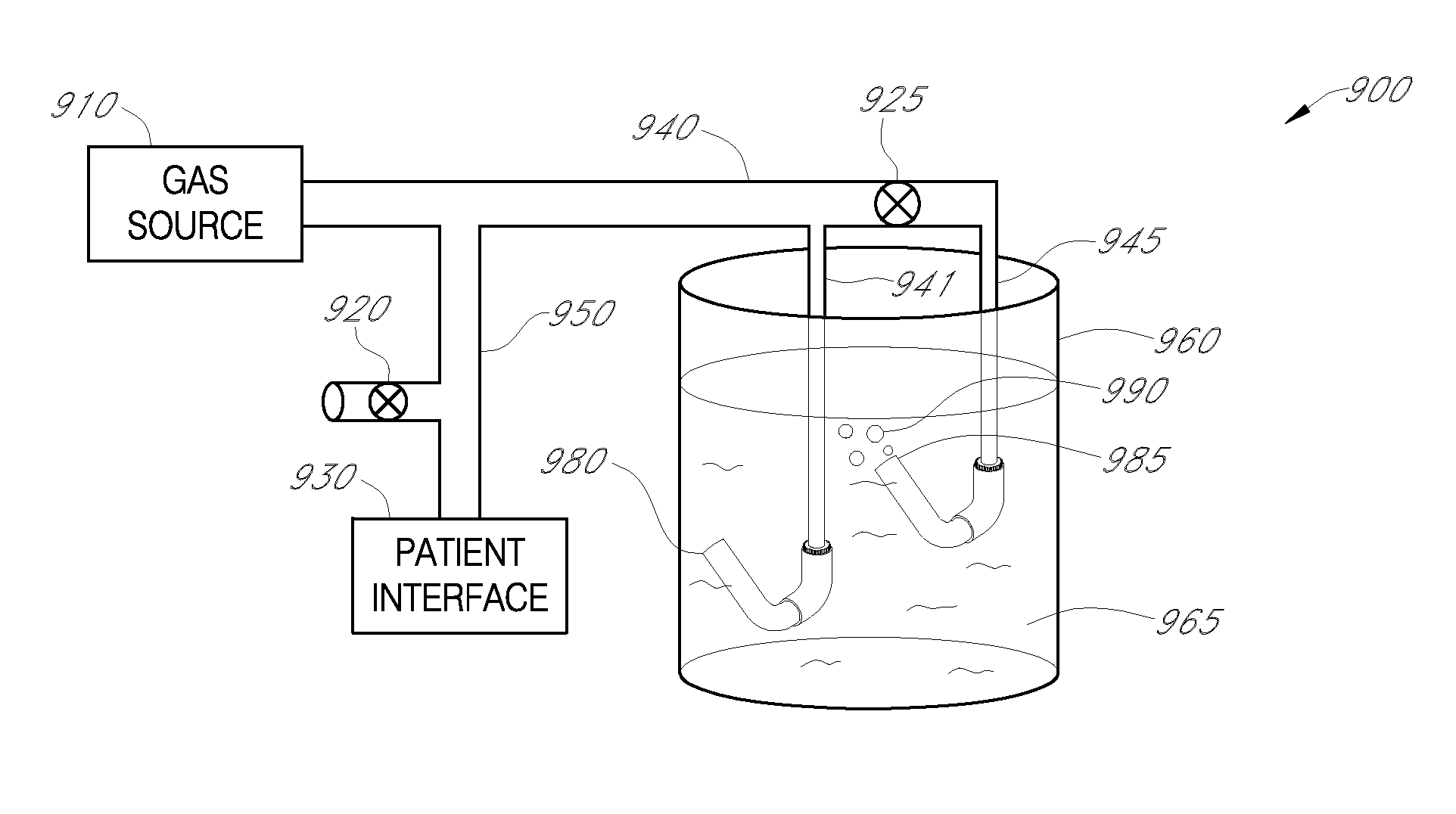
Broad-band, low frequency, high-amplitude, long time duration, oscillating airway pressure breathing apparatus and method utilizing bubbles
ActiveUS20110073112A1Stabilize lung volumeIncrease gas exchangeTracheal tubesRespiratory masksMeasurement deviceFrequency spectrum
It has been discovered that high amplitude, low frequency, broadband spectrum pressure oscillations of sufficient time duration can help stabilize lung volumes and improve gas exchange in a patient receiving ventilation assistance by helping to recruit and stabilize alveoli. A novel device is presented which can produce pressure oscillations having high amplitudes, a low broad-band frequency spectrum and long time duration. Additionally, the device can maintain a patient's mean airway pressure at one or more controlled levels. The device can control the oscillatory amplitude, frequency range and composition, time duration, and mean airway pressure levels by adjusting certain device parameters, such as the angle and depth of the device in a fluid. A device and mechanical system for remotely adjusting and measuring the angle of the device in a fluid are also disclosed. Furthermore, a device and system are disclosed that can deliver pressure oscillations having high amplitudes, a low broad-band frequency spectrum, long time duration, and multiple mean airway inspiratory and expiratory pressure levels. The device and system also provide means for controlling respiration timing in a patient, including: breaths per minute, inspiratory time, and the ratio of inspiratory to expiratory time.
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
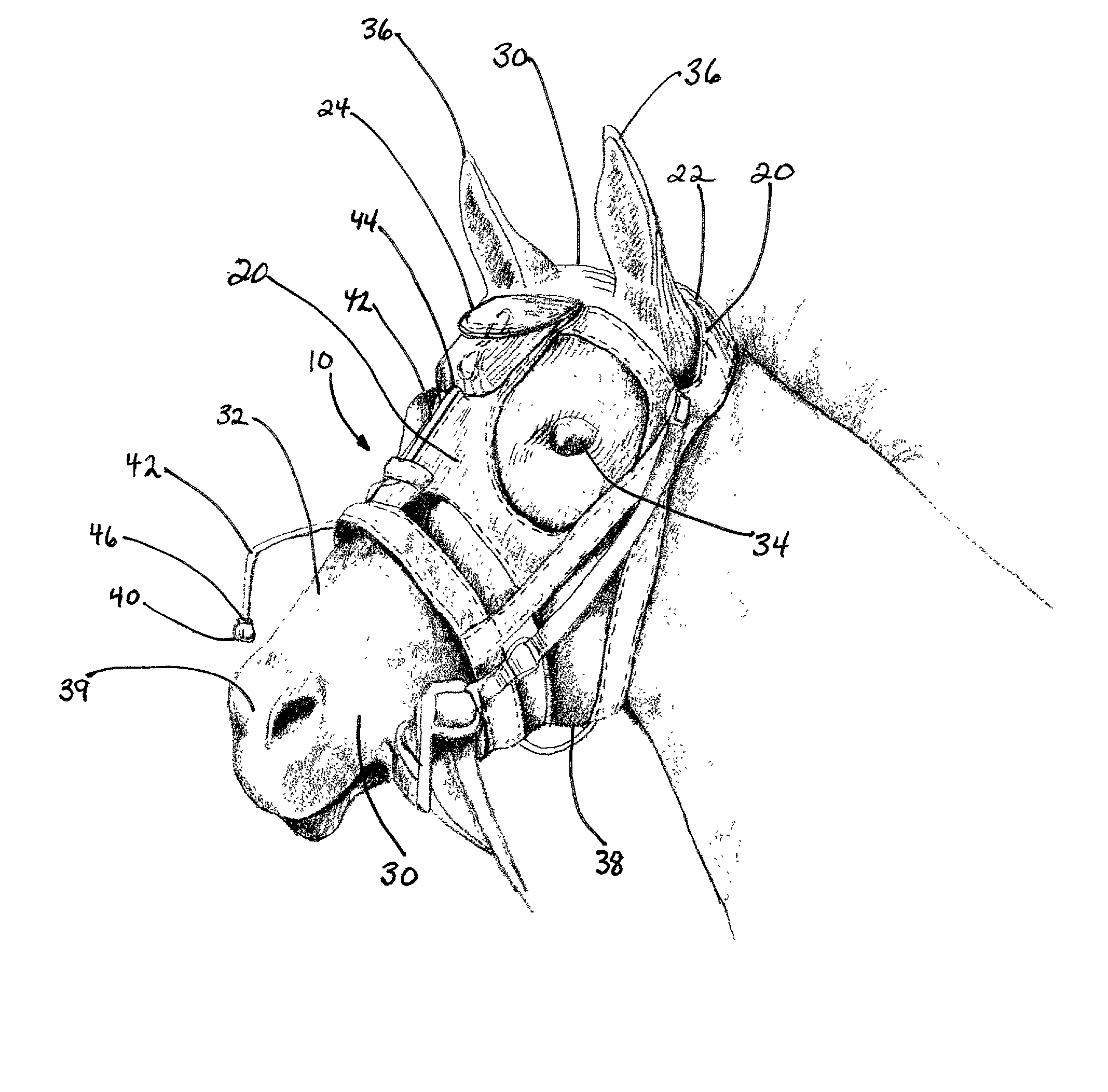
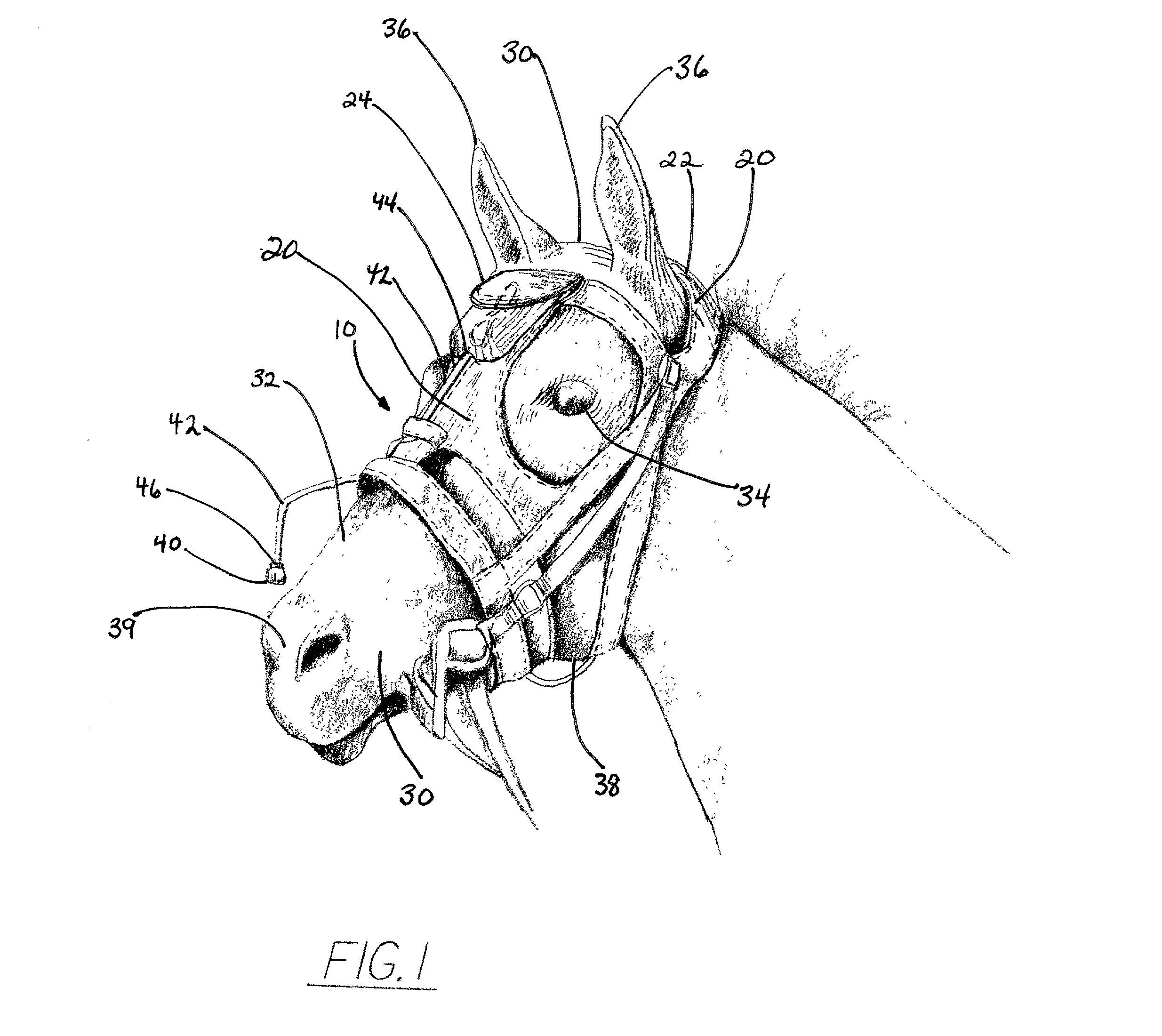
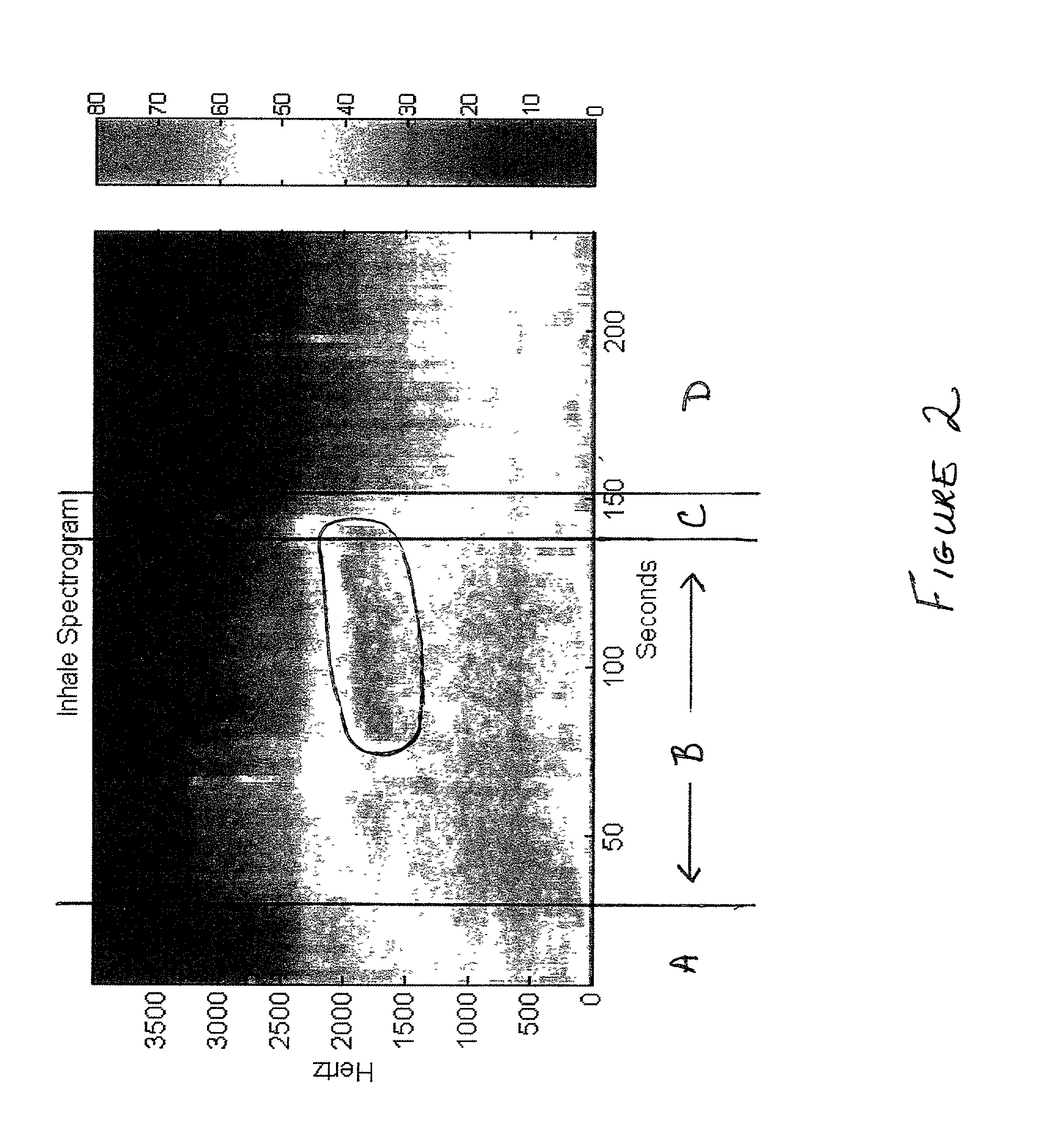
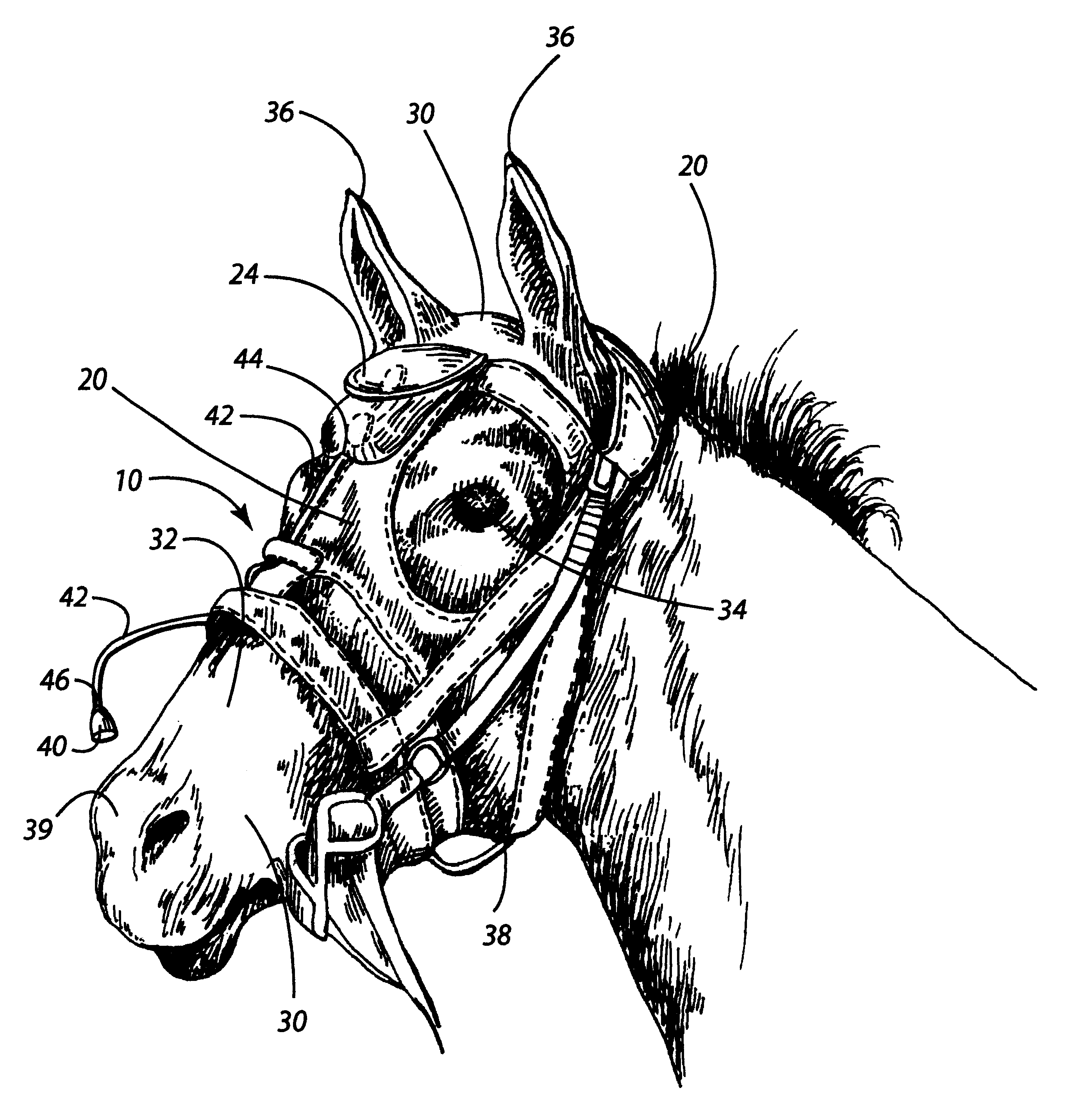
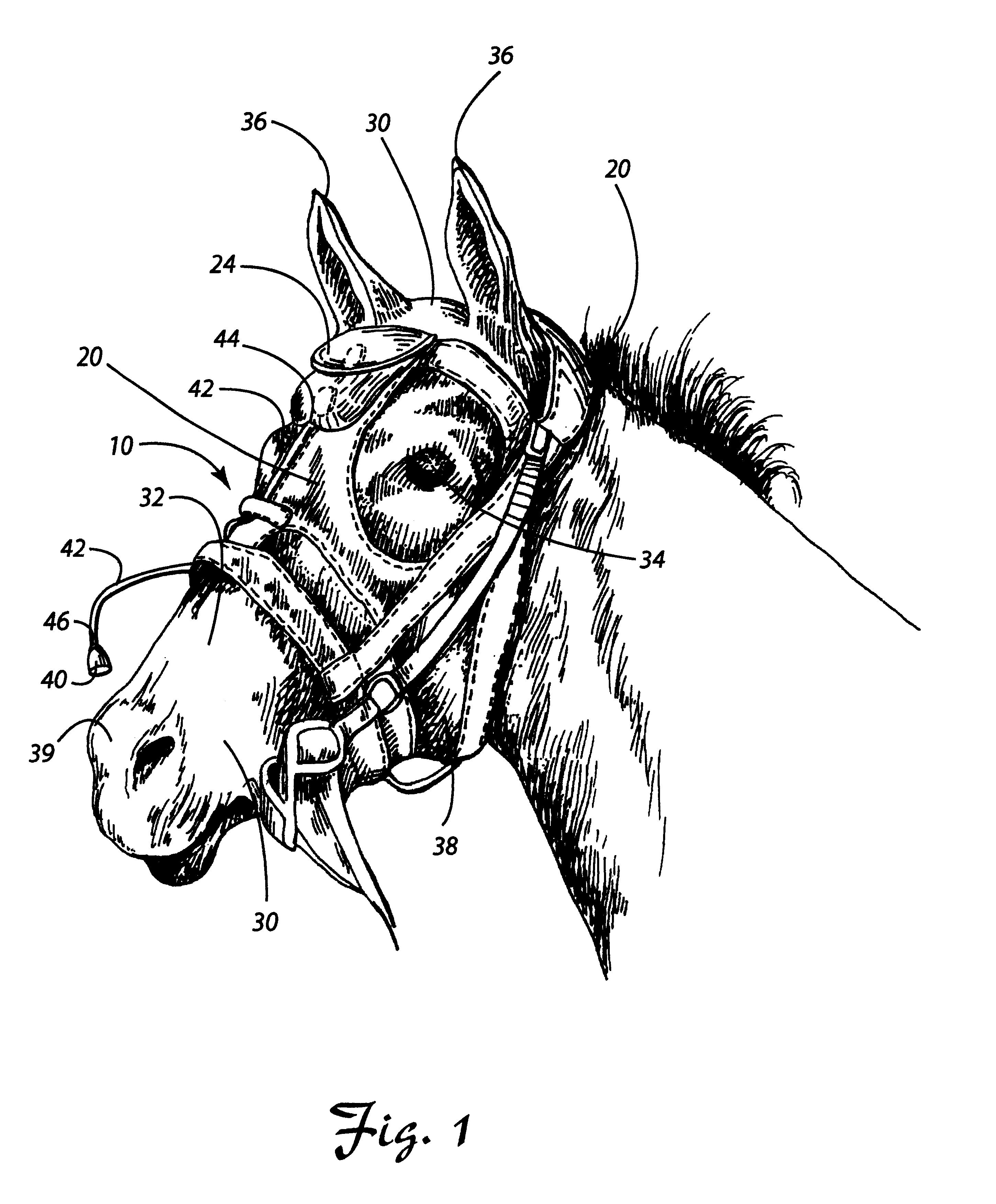
Method and device for analyzing athletic potential in horses
InactiveUS20020123699A1Accurately determineAccurately doneSurgeryAuscultation instrumentsMedicineExpiratory Time
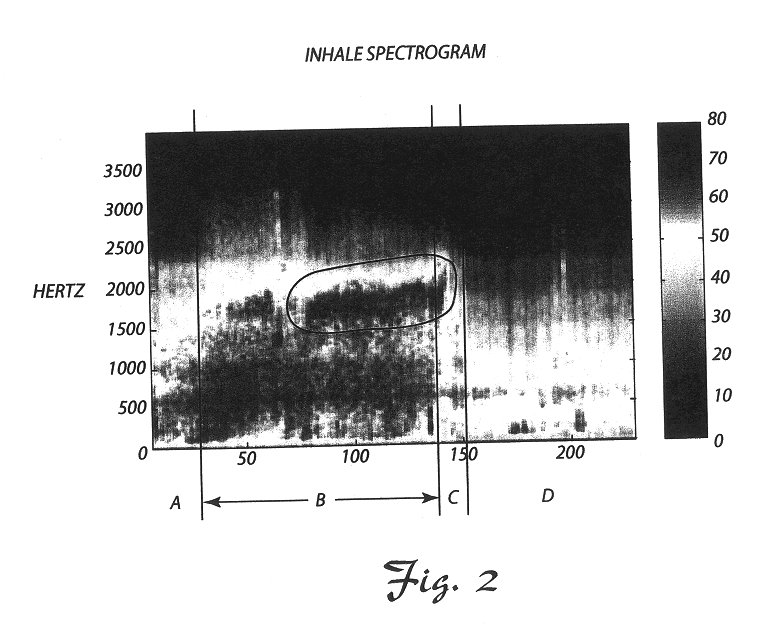
Provided is a device for attachment to the head of a horse to enable recording of respiratory sounds in the intensely exercising animal, e.g., in a breezing Thoroughbred racehorse. Also provided are methods for predicting racing performance in a horse, e.g., a Thoroughbred race horse, comprising measuring expiratory and / or inspiratory times for a subject horse during exercise and relating such information to anatomy, front leg stance times and / or front leg stance distances and / or to speed (velocity) to determine the animal's potential to sustain a superior rate of ground coverage for a desired amount of time and identify a maximum comfortable velocity for the animal. A presently preferred embodiment of the methods of the invention comprises predicting performance via identification of expiratory time determined directly from the analysis of recorded respiratory sound from the exercising animal.
Owner:AIRWAYS DYNAMICS
Method and device for analyzing athletic potential in horses
InactiveUS6602209B2Reduce fatigueAffect performanceSurgeryAuscultation instrumentsMedicineExpiratory Time
Provided is a device for attachment to the head of a horse to enable recording of respiratory sounds in the intensely exercising animal, e.g., in a breezing Thoroughbred racehorse. Also provided are methods for predicting racing performance in a horse, e.g., a Thoroughbred race horse, comprising measuring expiratory and / or inspiratory times for a subject horse during exercise and relating such information to anatomy, front leg stance times and / or front leg stance distances and / or to speed (velocity) to determine the animal's potential to sustain a superior rate of ground coverage for a desired amount of time and identify a maximum comfortable velocity for the animal. A presently preferred embodiment of the methods of the invention comprises predicting performance via identification of expiratory time determined directly from the analysis of recorded respiratory sound from the exercising animal.
Owner:AIRWAYS DYNAMICS
Broad-band, low frequency, high-amplitude, long time duration, oscillating airway pressure breathing apparatus and method utilizing bubbles
ActiveUS20110079222A1Increase gas exchangeVolume stabilityTracheal tubesRespiratory masksFrequency spectrumLung volumes
It has been discovered that high amplitude, low frequency, broadband spectrum pressure oscillations of sufficient time duration can help stabilize lung volumes and improve gas exchange in a patient receiving ventilation assistance by helping to recruit and stabilize alveoli. A novel device is presented which can produce pressure oscillations having high amplitudes, a low broad-band frequency spectrum and long time duration. Additionally, the device can maintain a patient's mean airway pressure at one or more controlled levels. The device can control the oscillatory amplitude, frequency range and composition, time duration, and mean airway pressure levels by adjusting certain device parameters, such as the angle and depth of the device in a fluid. A device and mechanical system for remotely adjusting and measuring the angle of the device in a fluid are also disclosed. Furthermore, a device and system are disclosed that can deliver pressure oscillations having high amplitudes, a low broad-band frequency spectrum, long time duration, and multiple mean airway inspiratory and expiratory pressure levels. The device and system also provide means for controlling respiration timing in a patient, including: breaths per minute, inspiratory time, and the ratio of inspiratory to expiratory time.
Owner:SEATTLE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Setting expiratory time in mandatory mechanical ventilation based on a deviation from a stable condition of end tidal gas concentrations
InactiveUS20080230061A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesExpiratory TimeGas concentration
A method of setting expiratory time in controlled mechanical ventilation varies a subject's expiratory times; determines end tidal gas concentrations associated with the expiratory times; establishes a stable condition of the gas concentrations; and determines an optimal expiratory time based on a deviation from the stable condition. A device for use in controlled mechanical ventilation comprises means for the same.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
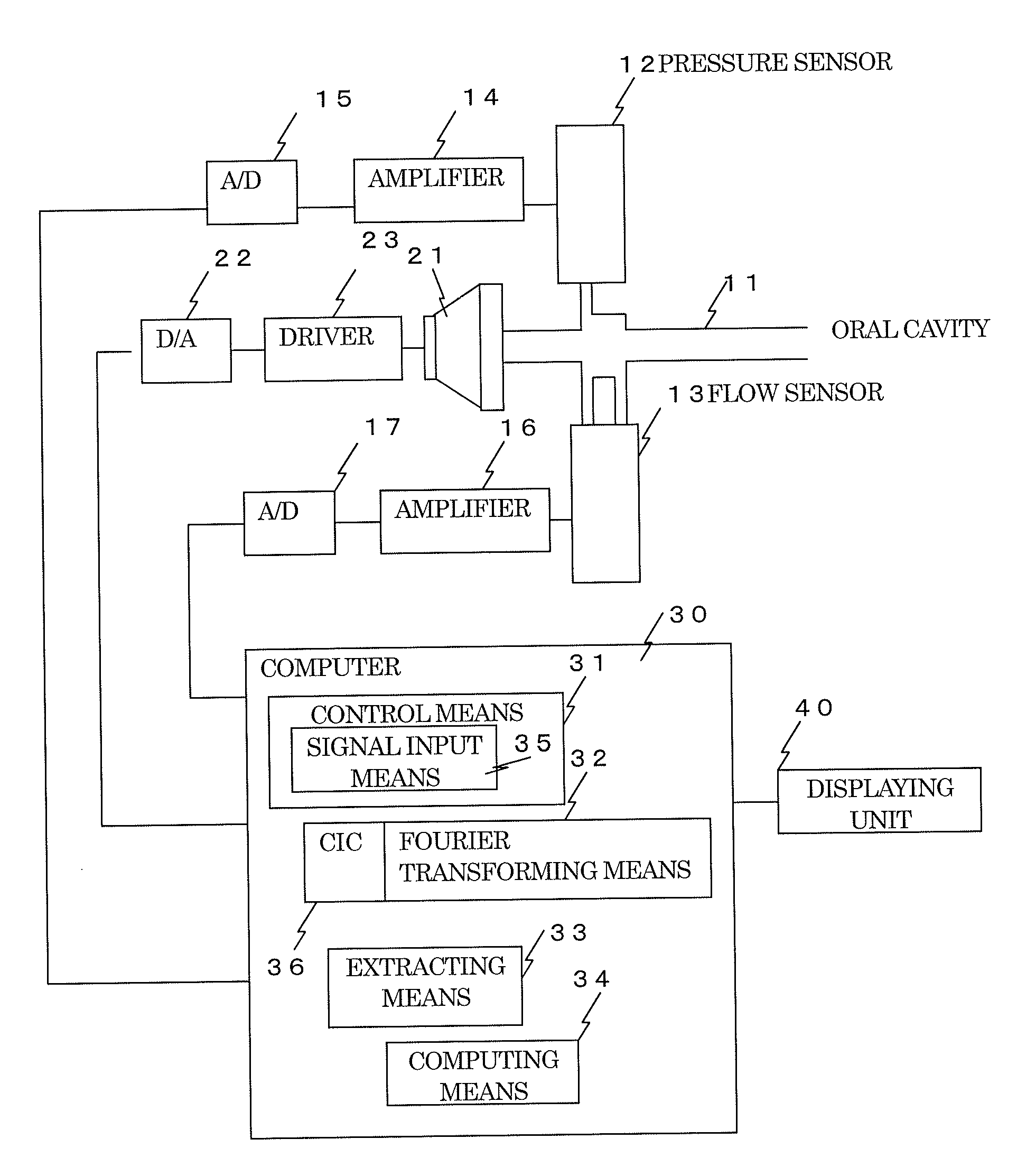
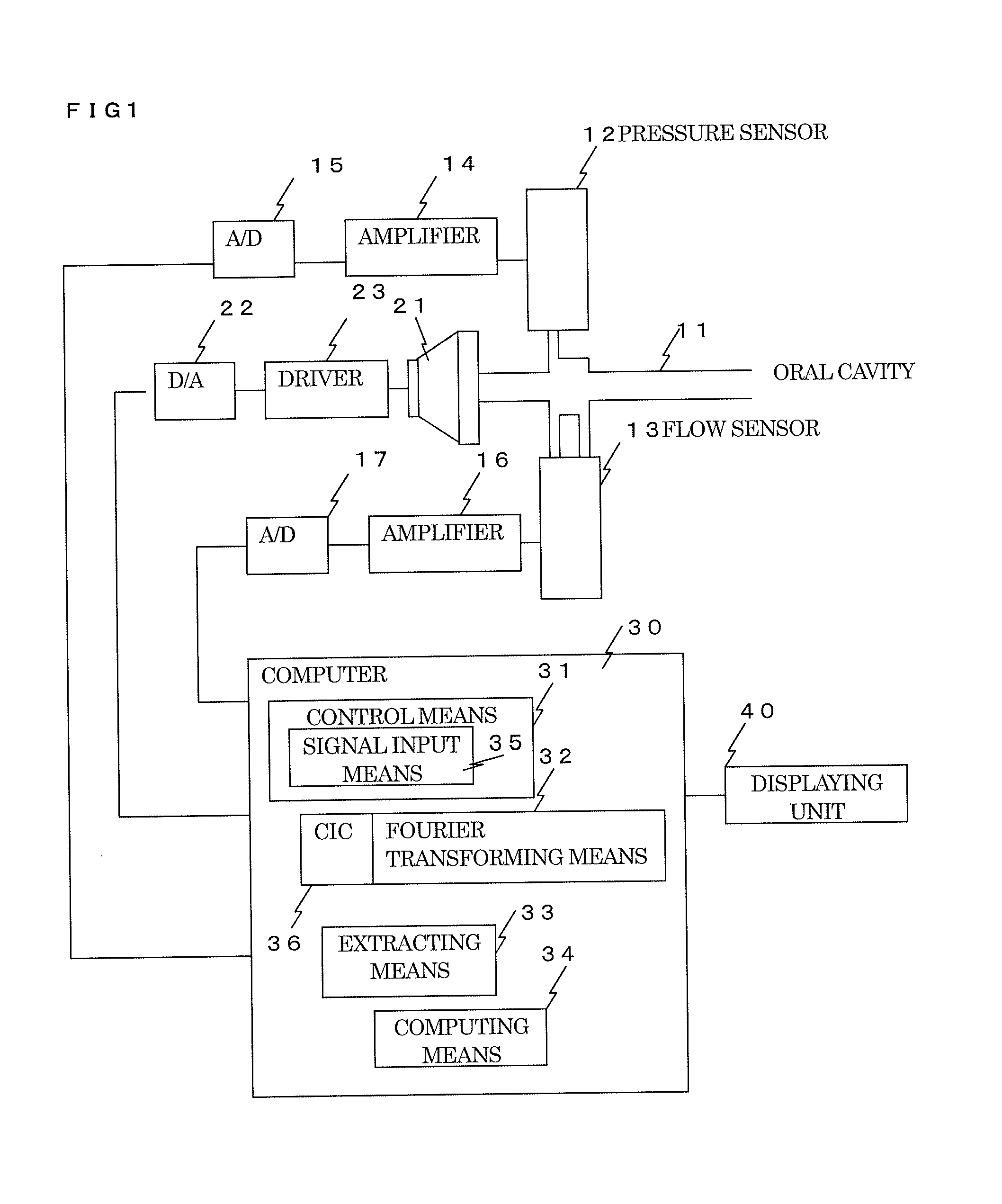
Respiration impedance measuring device and respiration impedance display method
ActiveUS20120101400A1Improve accuracyAccurate acquisitionMedical devicesRespiratory organ evaluationContinuous measurementFrequency spectrum
Continuous measurement of breathing impedance with extremely high precision is enabled by executing noise elimination. A loudspeaker 21 applies an air vibration pressure by an oscillation wave to an oral cavity, the oscillation wave being obtained by frequency-culling so executed that the oscillation wave has only the frequency component that is left after the culling is executed from a plurality of different frequencies and being generated by a pulse signal for pulse drive with pulses made positive and negative separately in correspondence to the time of exhalation and the time of inhalation. A pressure inside the oral cavity is detected and a breathing flow is detected, and a signal obtained by the detection is Fourier-transformed by a Fourier transforming means 32 to obtain a spectrum. A breathing high frequency component that contributes as a noise is obtained by an extracting means 33, using a spectrum that corresponds to a frequency component culled from the result of the Fourier transformation. This breathing high frequency component is subtracted from a spectrum that corresponds to a frequency component left by the culling to extract an oscillation wave component. Computing of dividing a pressure component by a flow component for each of frequencies for the result of this extraction is executed by a computing means 34 to obtain breathing impedance.
Owner:CHEST CORP +1
Storage medium having stored thereon respiratory instruction program, respiratory instruction apparatus, respiratory instruction system, and respiratory instruction processing method
ActiveUS20110306024A1Easy to identifyVideo gamesElectrical appliancesExpiratory TimeComputer science
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD +1
Respirator having improved synchronicity during the transition from expiratory to inspiratory operation
InactiveCN109069780AShort expiratory time constantPromote resultsRespiratorsMedical devicesRespiratorBreathing gas
The invention relates to a respirator (10) for the at least supportive respiration of living beings (12), wherein the respirator comprises the following: a connection formation for connection to a breathing gas supply; a breathing gas conduit arrangement (30); a pressure change arrangement (16) for changing the pressure in the breathing gas conduit arrangement (30); a flow sensor (44), which provides a flow signal (50) representing a breathing gas volume flow in the breathing gas conduit arrangement (30), a control unit (18) controlling the operation of the respirator (10). Said control unit is designed to trigger a transition from an expiratory to an inspiratory operation of the respirator (10), whenever an increase in the steepness of a flow signal curve (50) exceeds a steepness change threshold value (58). According to the invention, the control unit (18) is configured to detect the steepness change threshold value (58) depending on an expiratory time constant of the respective patient (12) to be ventilated, and to trigger the transition from an expiratory to an inspiratory operation of the respirator (10), whenever the increase in the steepness of the flow signal curve (50) exceeds the steepness change threshold value (58) determined in accordance with the expiratory time constant.
Owner:HAMILTON MEDICAL AG
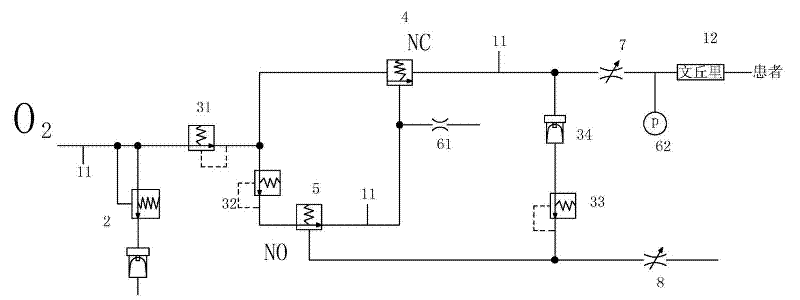
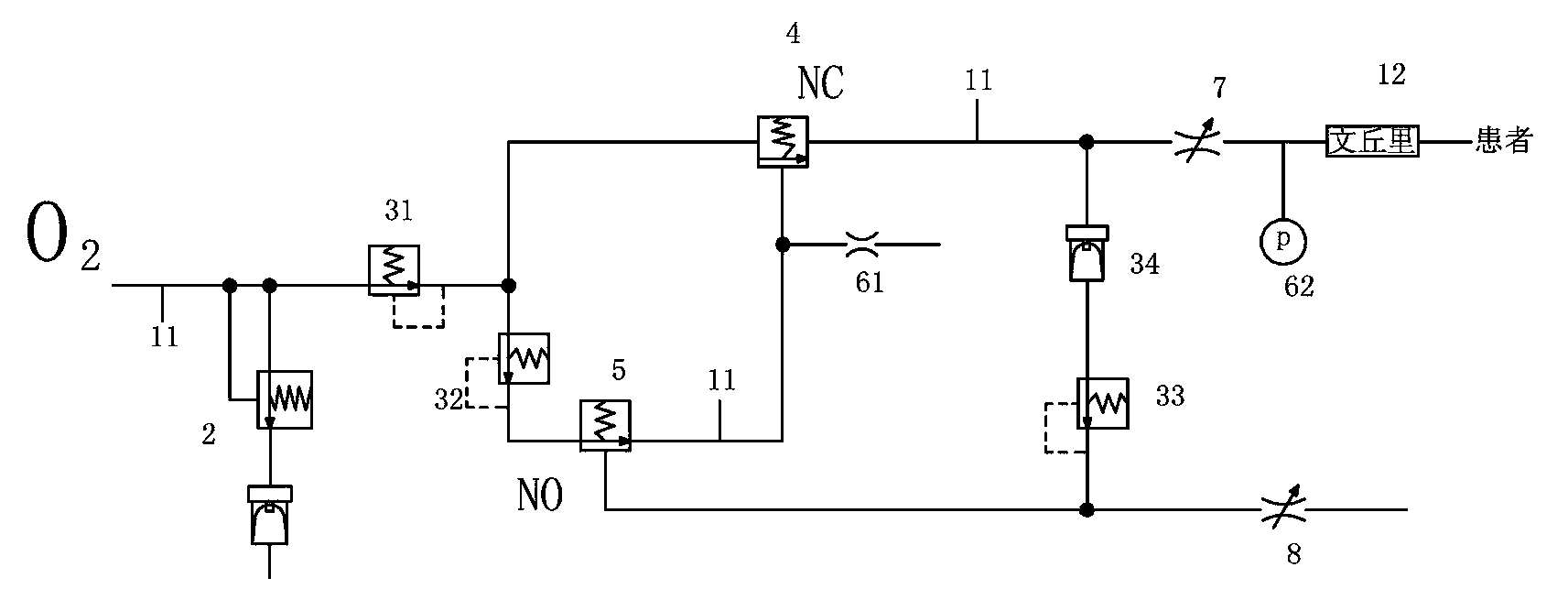
Pneumatic gas-controlled breathing machine
The invention relates to a pneumatic gas-controlled breathing machine which takes gas as a power source. High-pressure gas forms periodic operation through a pneumatic valve so as to supply a proper tidal volume and breathing frequency for a patient. The pneumatic gas-controlled breathing machine only needs to be connected with the gas source so as to supply the proper tidal volume and breathing frequency for the patient through a reducing valve and a control valve of the pneumatic gas-controlled breathing machine self, and the control valve of the pneumatic gas-controlled breathing machine can adjust the breathing frequency and the tidal volume. A normally open valve is closed when the normally open valve controls the pressure of a gas cavity body to rise to a set value, control gas in the gas cavity body is controlled by a normally closed valve and is discharged from an air-resistor simultaneously when the normally open valve is closed, and the normally closed valve recovers to be in the closed state, so that gas supply at the rear end of the normally closed valve is stopped, the time slot from the moment to the next time of ventilation of the normally closed valve is the time for the patient to breathe, and then the process from inhaling to exhaling of the patient is finished. The pneumatic gas-controlled breathing machine works repeatedly in the way.
Owner:于邦仲
Setting mandatory mechanical ventilation parameters based on patient physiology
InactiveUS20080202520A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTidal volumeExpiratory Time
A method sets a subject's expiratory time based on the subject's natural exhalation time, when the subject's natural exhalation flow ceases, and / or when the subject's tidal volume is expired. Another determines the subject's natural exhalation time, when the subject's natural exhalation flow ceases, and / or when the subject's tidal volume is expired, and sets the subject's expiratory time based on the determination. In addition, a flow rate sensor determines the subject's natural exhalation time, when the subject's natural exhalation flow ceases, and / or when the subject's tidal volume is expired, and bases the subject's expiratory time on the determination.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
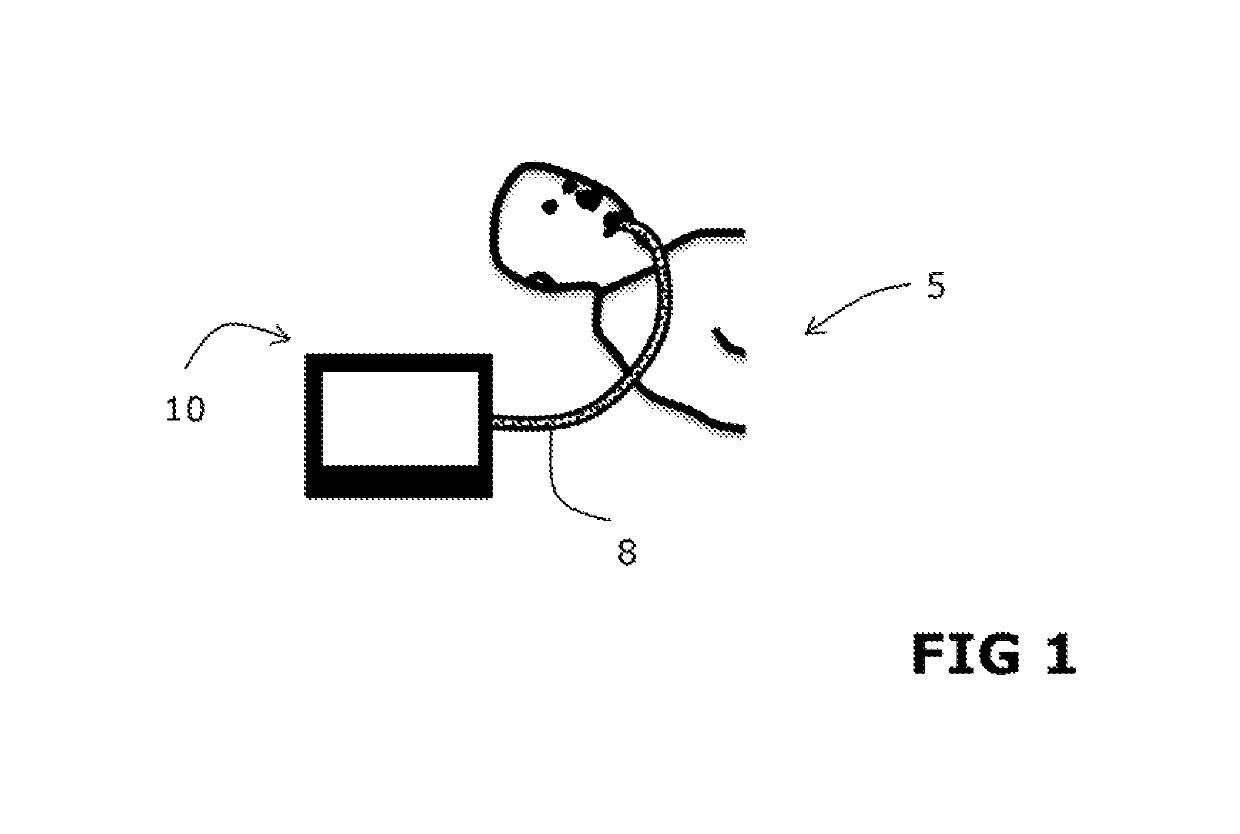
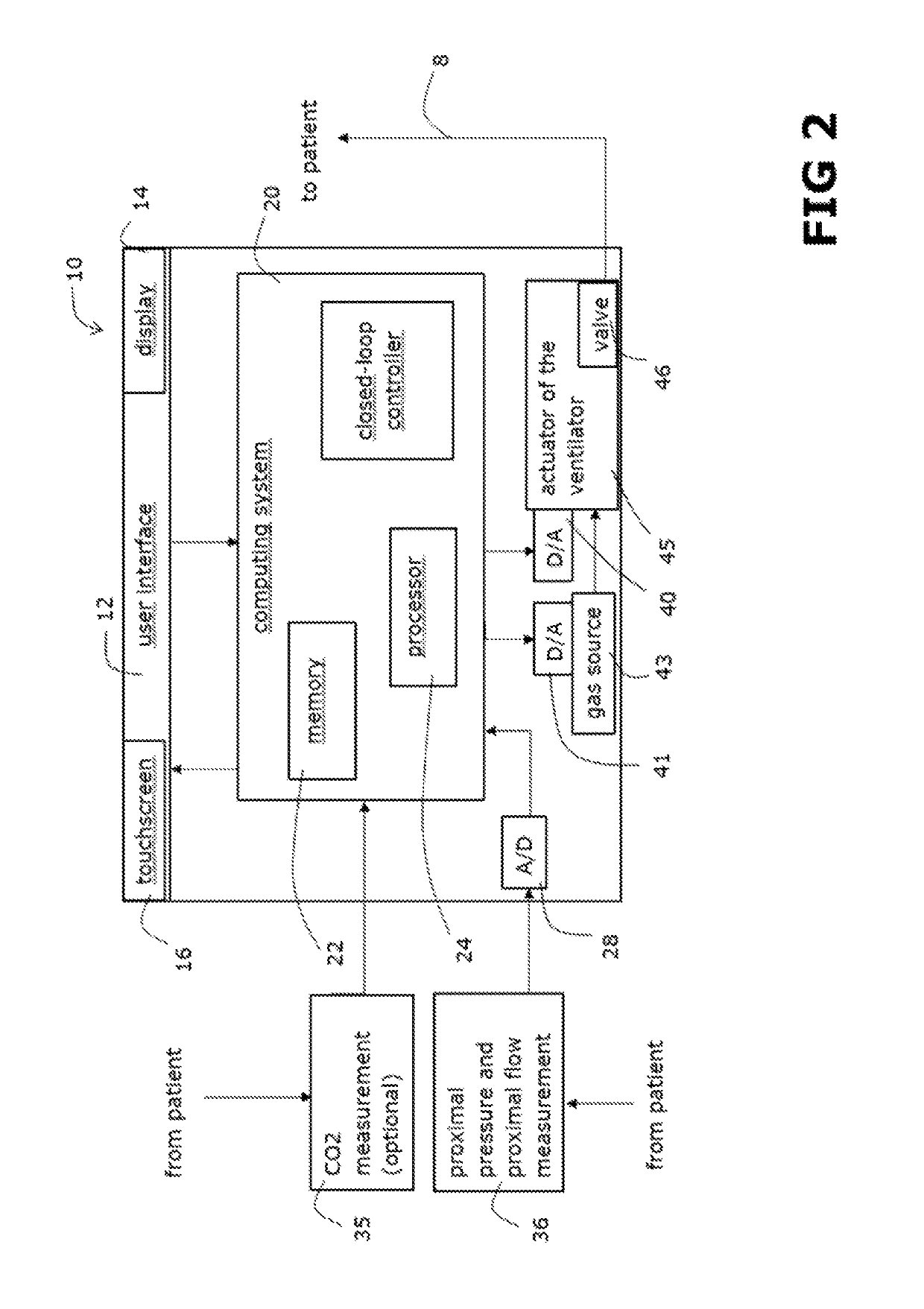
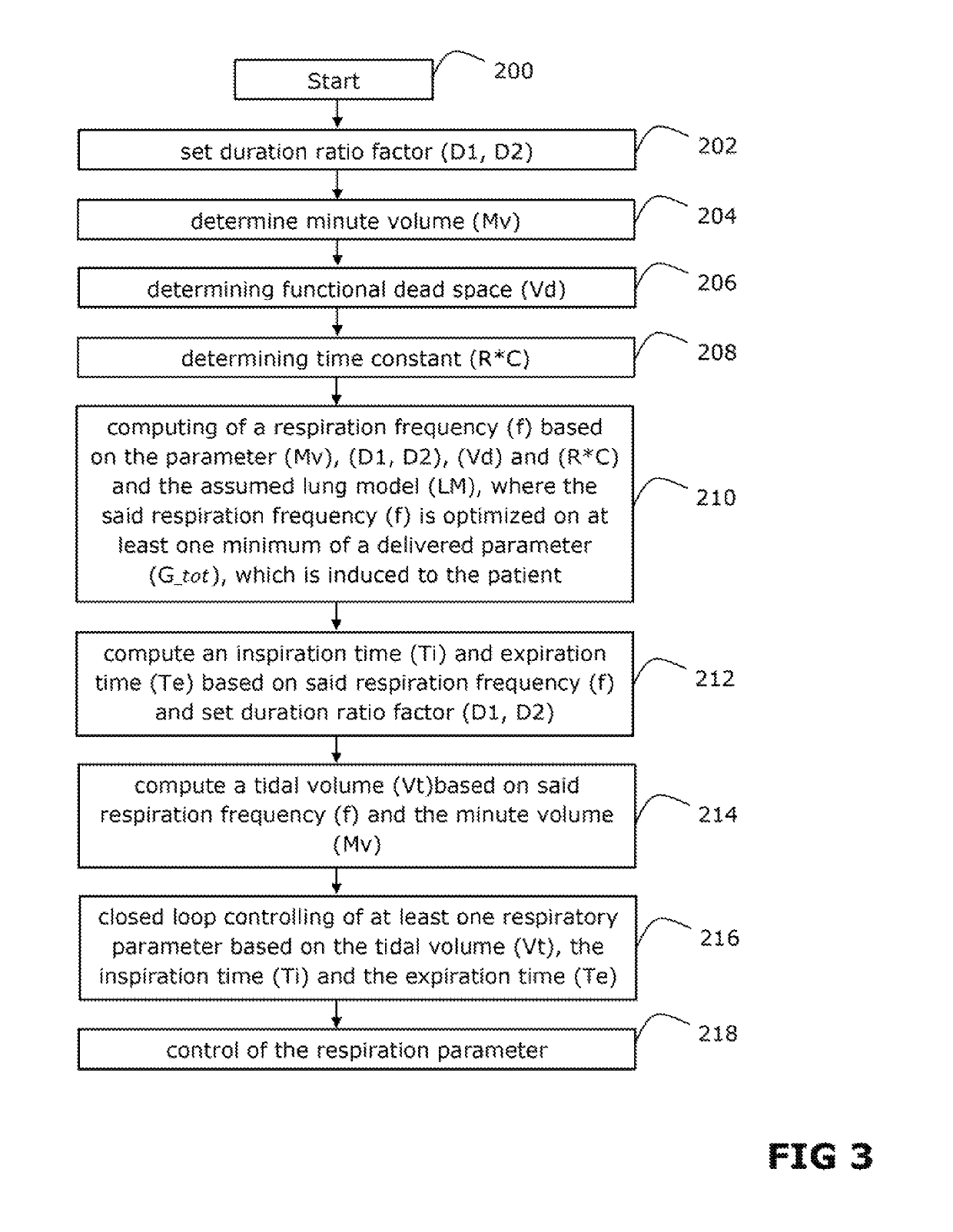
Ventilator apparatus and method for operating a ventilator in said ventilator apparatus
ActiveUS20180154095A1Easy to controlPromote breathingMedical simulationRespiratorsTidal volumeExpiratory Time
The invention comprises a ventilation apparatus and method for operating a ventilator of a ventilator apparatus, wherein in the method at least one duration ratio factor is set in a computing system of the ventilator apparatus; at least one minute volume, at least one functional dead space volume and at least one time constant are determined; a respiration frequency is computed, based on a previously defined lung model, depending on said determined parameters, where said computed respiration frequency is optimized on at least one minimum of a delivered parameter, which is induced to a patient using said ventilator; an inspiratory time and an expiratory time are determined based on said computed respiration frequency and said duration ratio factor; at least one tidal volume based on said previously computed respiration frequency and said determined minute volume is computed; and a delivered respiratory parameter of the ventilator is closed loop controlled.
Owner:IMTMEDICAL
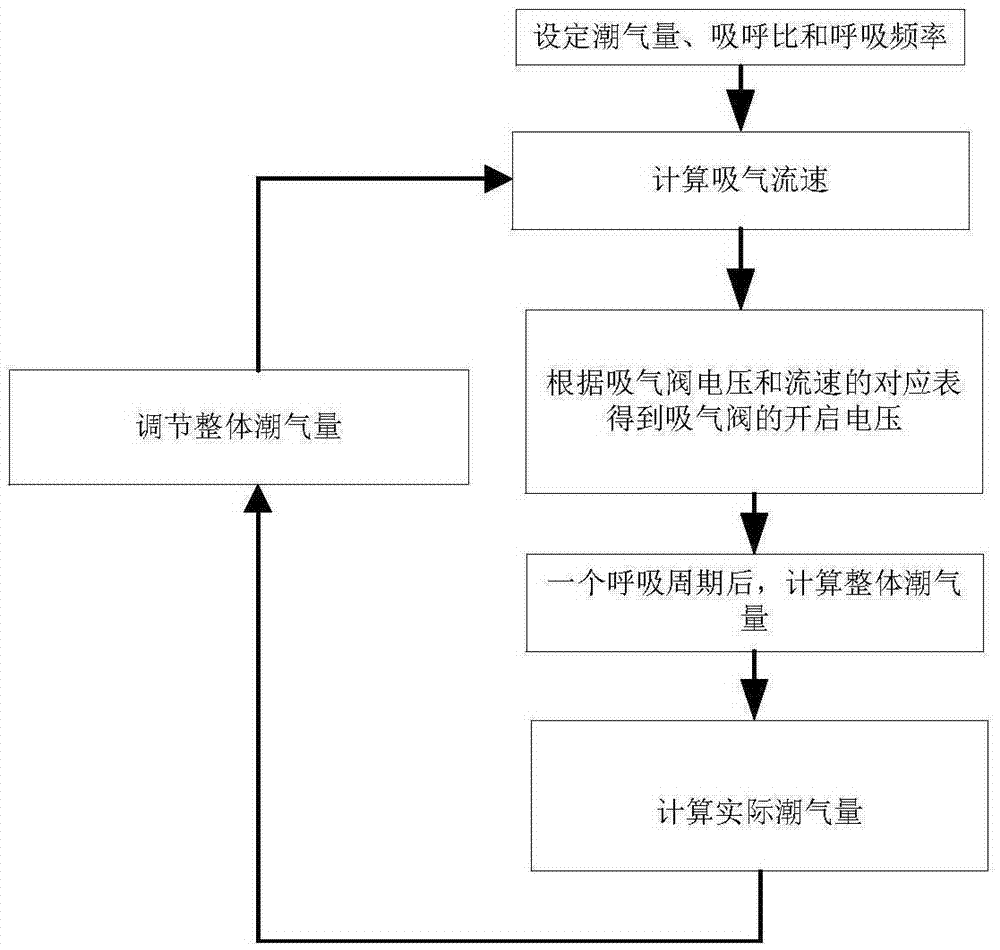
Method for adjusting tidal volume under IPPV mode
The invention discloses a method for adjusting tidal volume under an IPPV mode. The method comprises the following steps: 1) setting tidal volume, inspiration and expiration ratio, and respiratory frequency, according to the following formula, calculating inspiratory flow of an inhalation valve, inspiratory flow = set tidal volume / inspiratory time, inspiratory time=60 / respiratory frequency x (inspiratory time / (inspiratory time + expiratory time)); 2) through the inspiratory flow, according to a corresponding table of inhalation valve voltage and flow velocity, obtaining threshold voltage of the inhalation valve, after an expiration period, according to the following formula, calculating overall tidal volume, overall tidal volume = system compliance / (system compliance - pipeline compliance) x set tidal volume; 3) according to the following formula, calculating actual tidal volume, actual tidal volume = overall tidal volume - tidal volume consumed by a pipeline; 4) according to the difference value of the set tidal volume and the actual tidal volume, through adjusting inspiratory flow, adjusting the threshold voltage of the inhalation valve, so as to adjust the overall tidal volume. The method is simple and feasible.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
Ventilator apparatus and method for operating a ventilator in said ventilator apparatus
ActiveUS10357624B2Easy to controlPromote breathingRespiratorsMedical simulationTidal volumeClosed loop
The invention comprises a ventilation apparatus and method for operating a ventilator of a ventilator apparatus, wherein in the method at least one duration ratio factor is set in a computing system of the ventilator apparatus; at least one minute volume, at least one functional dead space volume and at least one time constant are determined; a respiration frequency is computed, based on a previously defined lung model, depending on said determined parameters, where said computed respiration frequency is optimized on at least one minimum of a delivered parameter, which is induced to a patient using said ventilator; an inspiratory time and an expiratory time are determined based on said computed respiration frequency and said duration ratio factor; at least one tidal volume based on said previously computed respiration frequency and said determined minute volume is computed; and a delivered respiratory parameter of the ventilator is closed loop controlled.
Owner:IMTMEDICAL
Device for assisting respiration aerosol gas and method for regulating respiration aerosol gas
ActiveCN104436386ABreathe fullyFully absorbedMedical atomisersAssisted breathingMechanical engineering
The invention discloses a device for assisting respiration aerosol gas and a method for regulating the respiration aerosol gas. When the device is used for inhalation, atomizing gas is triggered to be generated, and the atomizing gas and absorbed air enter the respiratory tract synchronously. A one-way exhalation valve is arranged on an exhalation opening, exhalation resistance is regulated through the one-way exhalation valve, positive end-expiratory pressure is generated, exhalation time is prolonged, the time of the aerosol gas in the respiratory tract is guaranteed, the aerosol gas can be absorbed, and meanwhile gas of the lung can be fully exhaled. An inhalation flow limiter is arranged on a gas inlet connecter, the ratio of the sprayed aerosol gas to non-aerosol gas is regulated through the inhalation flow limiter, proper inhalation flow speed and enough long inhalation time are guaranteed, it is guaranteed that aerosol medicine is fully inhaled into the lung, and the curative effect is achieved.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF GUANGZHOU MEDICAL UNIV (GUANGZHOU RESPIRATORY CENT) +1
Intelligent adjustable one-way exhaust device
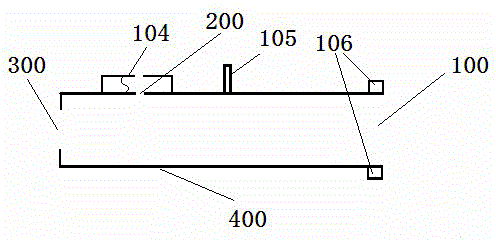
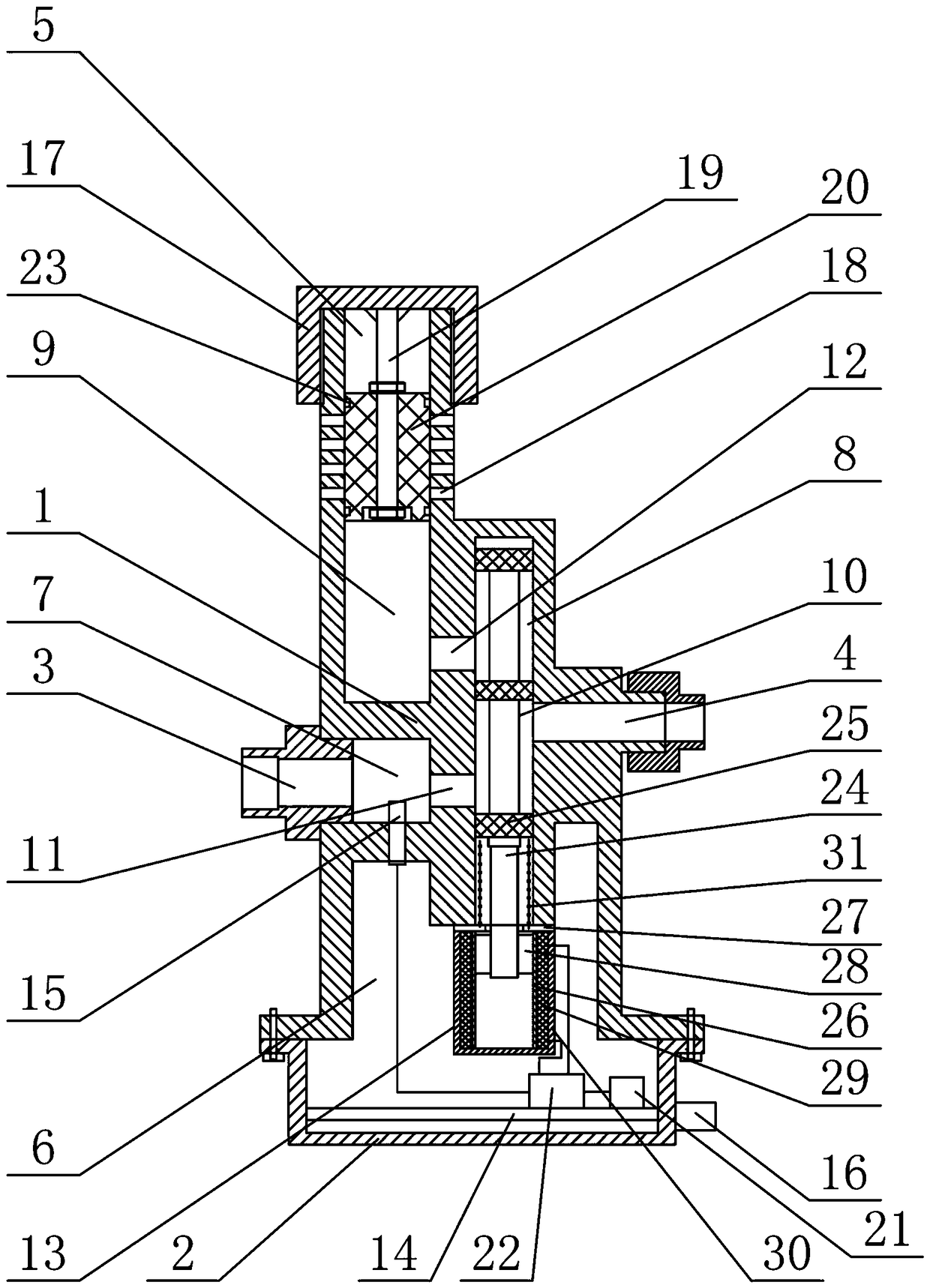
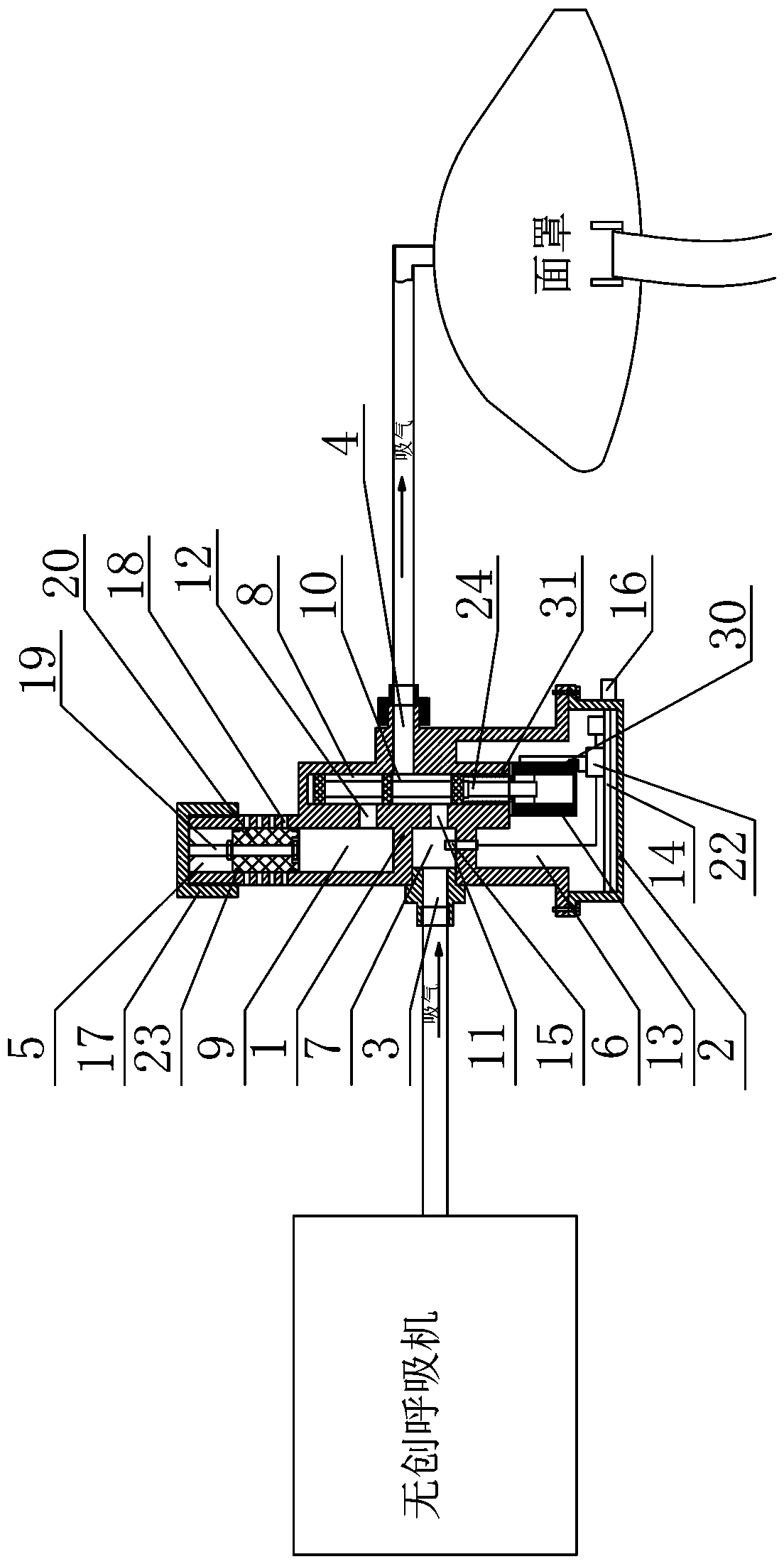
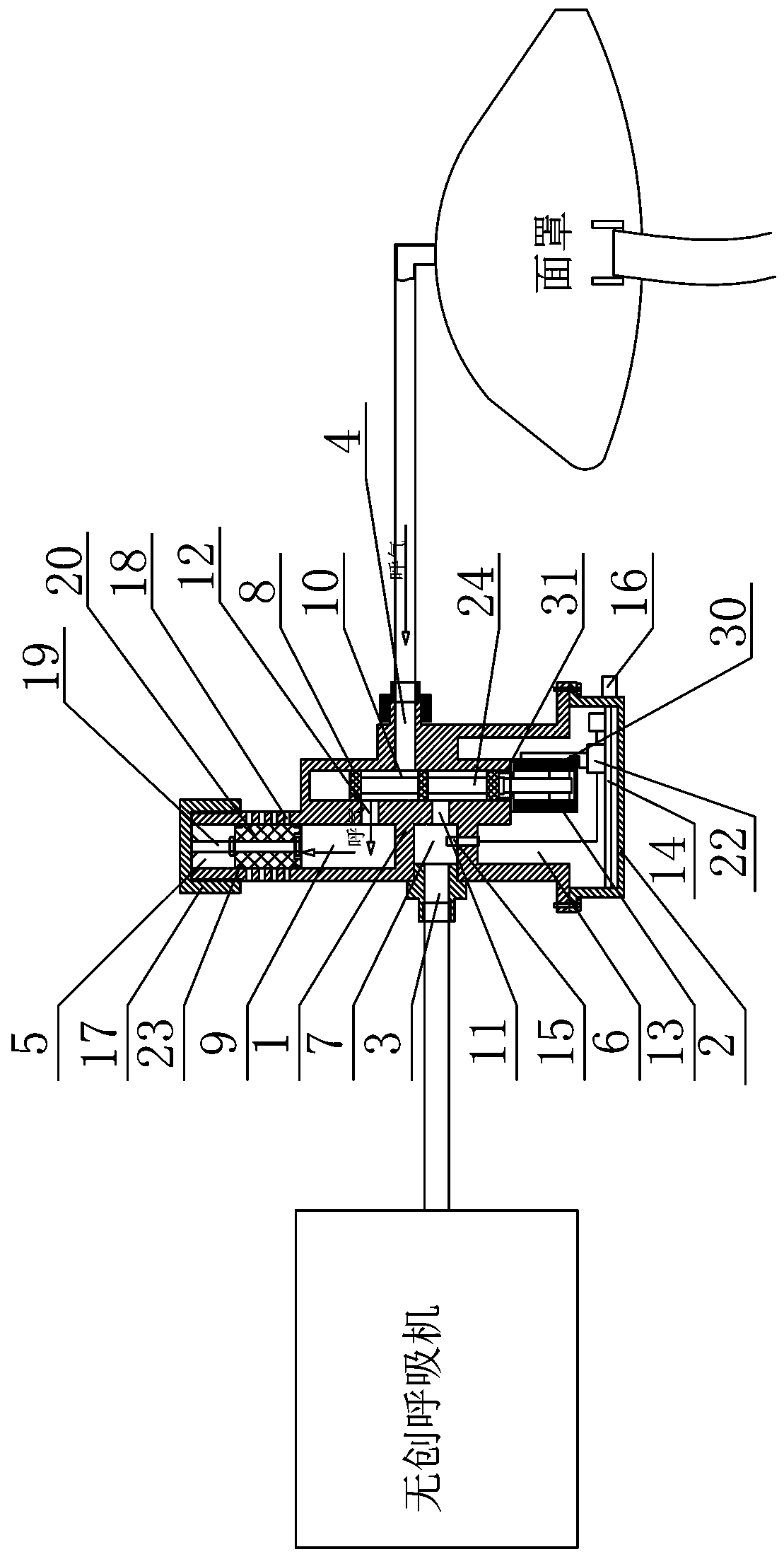
PendingCN109172978AAvoid a collapse situationGuaranteed to open normallyRespiratorsMedical devicesExpiratory TimeNon invasive
The invention relates to an intelligent adjustable one-way exhaust device, which includes a valve body, a valve cover, an air inlet, an outlet, an exhaust, a control chamber, a reversing chamber, an exhaust chamber and a reversing spool. The invention provides a reversible pressure breathing valve between a non-invasive ventilator and a face mask; when the patient inhales, the ventilator providespositive pressure gas to the patient, Guaranteeing patient airway openness, so that that patient is smoothly inhale, patient expiratory time, At that same time, an air outlet with adjustable open sizeis arranged on the breathe valve, so as to maintain a certain pressure in the respiratory tract of the patient by adjusting the size of the air outlet, thereby avoiding the occurrence of respiratorytract collapse, so that the non-invasive ventilator with single-loop air supply can meet the needs of the patient with lung problems.
Owner:马利军 +2
Respiratory support method capable of dynamically adjusting flow and respiratory support equipment
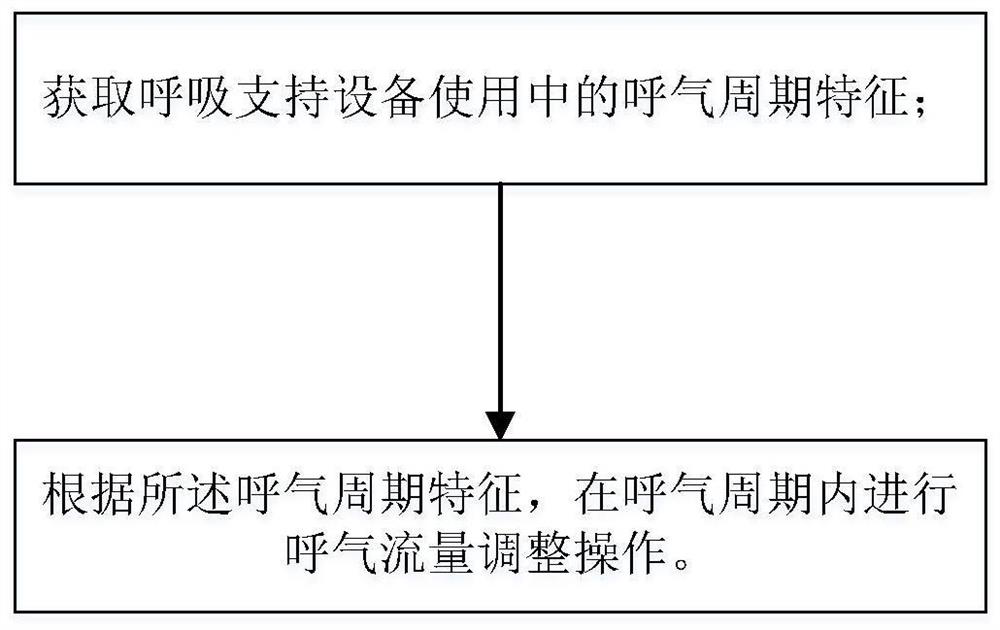
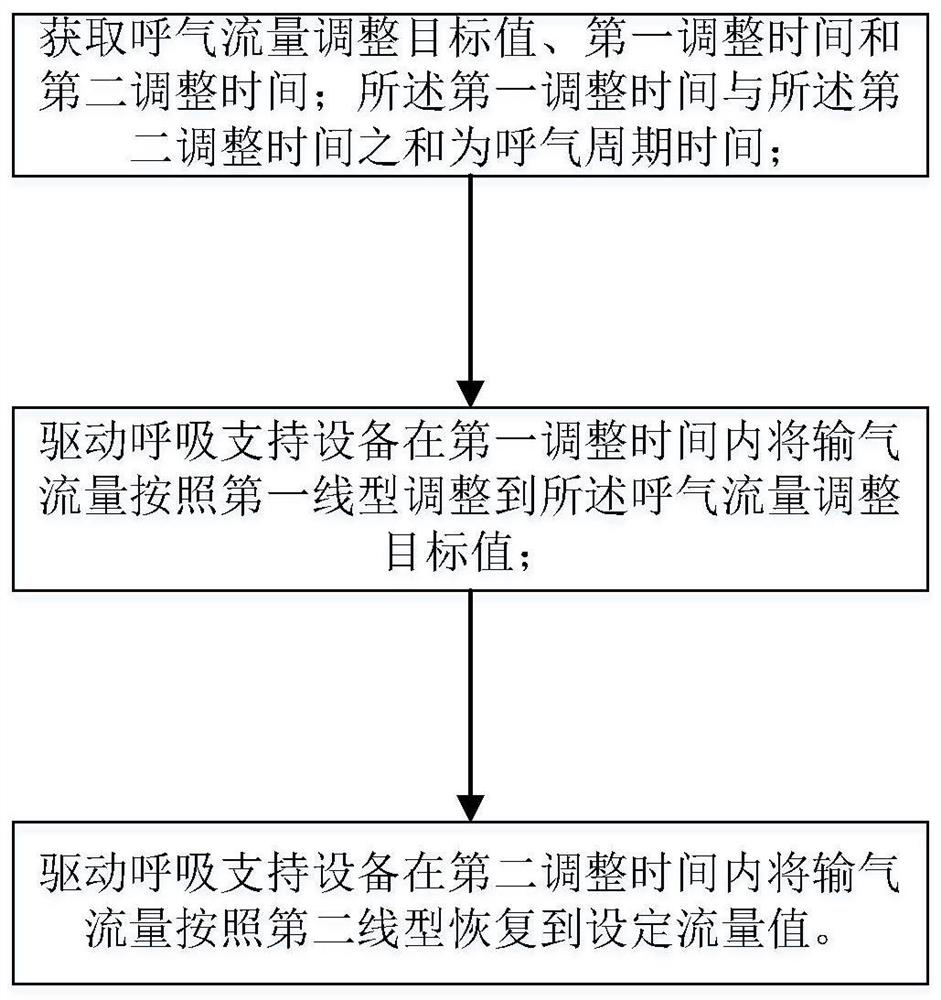
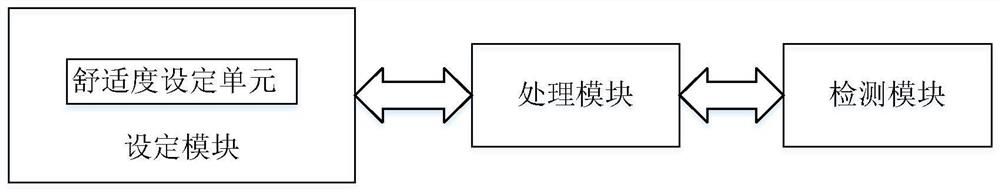
PendingCN112274740AImprove comfortReal-time controlRespiratorsMedical devicesExpiratory TimeEngineering
The invention relates to a respiratory support method capable of dynamically adjusting flow and respiratory support equipment. The respiratory support method capable of dynamically adjusting flow comprises the following steps: acquiring expiration period characteristics of the respiratory support equipment in use; and according to the expiration period characteristics, carrying out expiration flowadjustment operation is in the expiration period. According to the respiratory support method provided by the invention, through a flow control mode capable of setting comfort, when the expiration ofthe patient is detected, the expiration flow is dynamically adjusted, so that the use comfort of a user is improved; and the flow is reduced according to the set comfort level, and then the flow is controlled in real time according to the detected expiration time of the patient, so that the use comfort of the patient is improved and the tolerance is improved under the condition that the use requirements of the patient are met.
Owner:HUNAN MICOME ZHONGJIN MEDICAL SCI & TECH DEV CO LTD
Pneumatic gas-controlled breathing machine
The invention relates to a pneumatic air-controlled ventilator. The pneumatic air-controlled ventilator uses gas as the power source, and the high-pressure gas forms periodic work through the pneumatic valve to supply the patient with an appropriate tidal volume and respiratory rate. The pneumatic air-controlled ventilator only needs to be connected to the air source, and the patient's appropriate respiratory rate and tidal volume can be supplied through the pressure reducing valve and control valve of the pneumatic air-controlled ventilator itself. The control valve of the pneumatic air-controlled ventilator can control the respiratory frequency and tidal volume adjustment. When the pressure of the normally open valve control air chamber rises to the set value, close the normally open valve, and the control gas in the normally closed valve control air chamber is discharged from the air resistance at the same time as the normally open valve is closed, and the normally closed valve resumes closing state, then stop the air supply at the rear end of the normally closed valve, the time period from this moment to the next normally closed valve ventilation is the patient’s exhalation time, and the process from inhalation to exhalation is completed, and the pneumatic air-controlled ventilator works in a cycle like this.
Owner:于邦仲
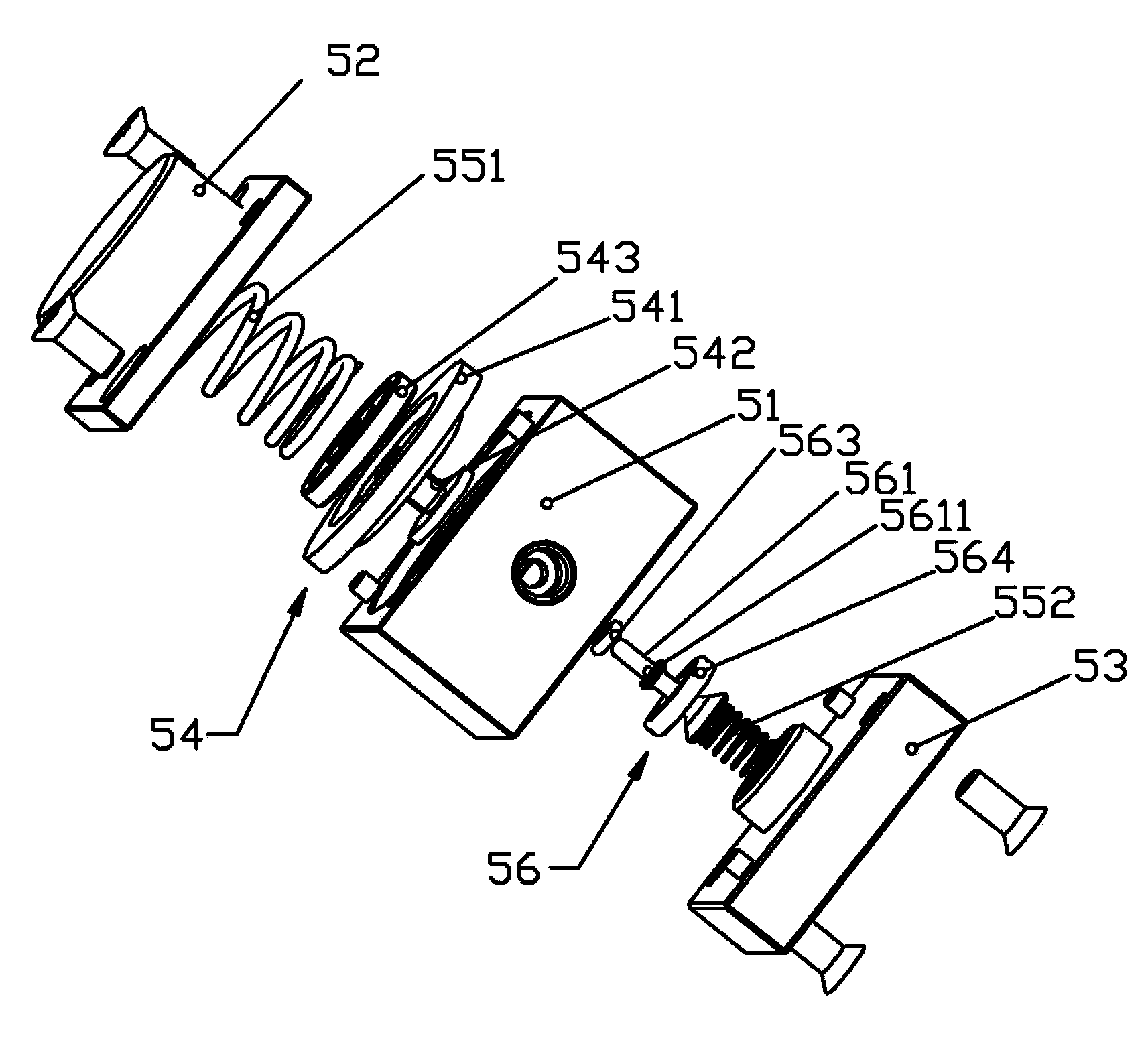
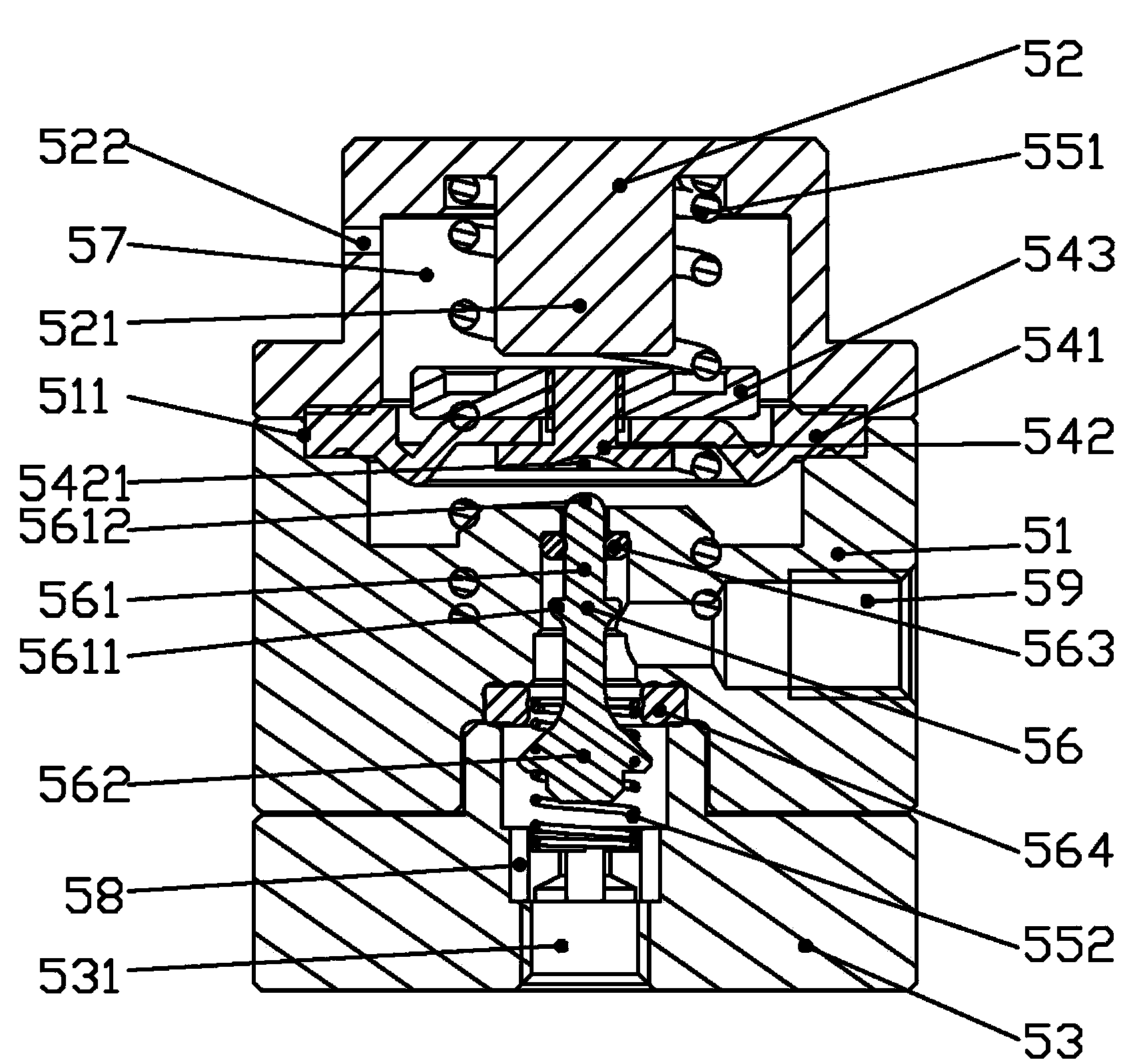
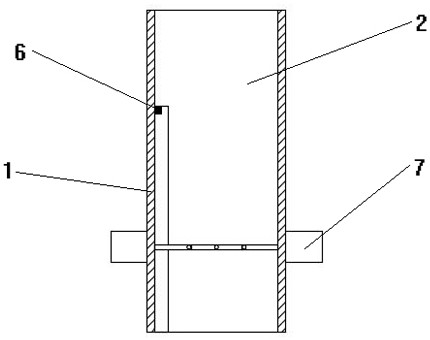
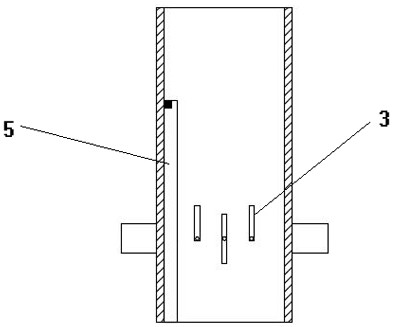
Mechanical PEEP valve of medical first-aid breathing machine
PendingCN111729172AReduce trafficIncrease oxygenation timeRespiratorsMedical devicesPhysical medicine and rehabilitationExpiratory Time
The invention relates to a mechanical PEEP valve of a medical first-aid breathing machine. The mechanical PEEP valve comprises a valve body, a movable blocking piece mechanism and a control mechanism,wherein the movable blocking piece mechanism comprises a round blocking piece; the blocking piece is arranged in an expiration channel of the valve body through a rotating shaft in the radial direction of the blocking piece; the blocking piece is driven by the control mechanism to be switched between the initial state and the turnover state; in the initial state, the blocking piece is parallel tothe axis direction of the expiration channel; in the turnover state, the blocking piece is perpendicular to the axis direction of the expiration channel; the control mechanism comprises a power source, a signal induction assembly and a transmission assembly; an airflow sensor is electrically connected with the power source through a control line; and the power source is in transmission connectionwith a rotating shaft in the movable blocking piece assembly through the transmission assembly. By means of the mechanical PEEP valve, smooth exhausting can be achieved without obstruction at the initial expiration stage of a patient, the flow of the expiration channel can be reduced at the later expiration stage, and therefore resistance is applied to expiration of the patient, the expiration time is prolonged, the oxygenation time is prolonged, and the oxygenation state is improved.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
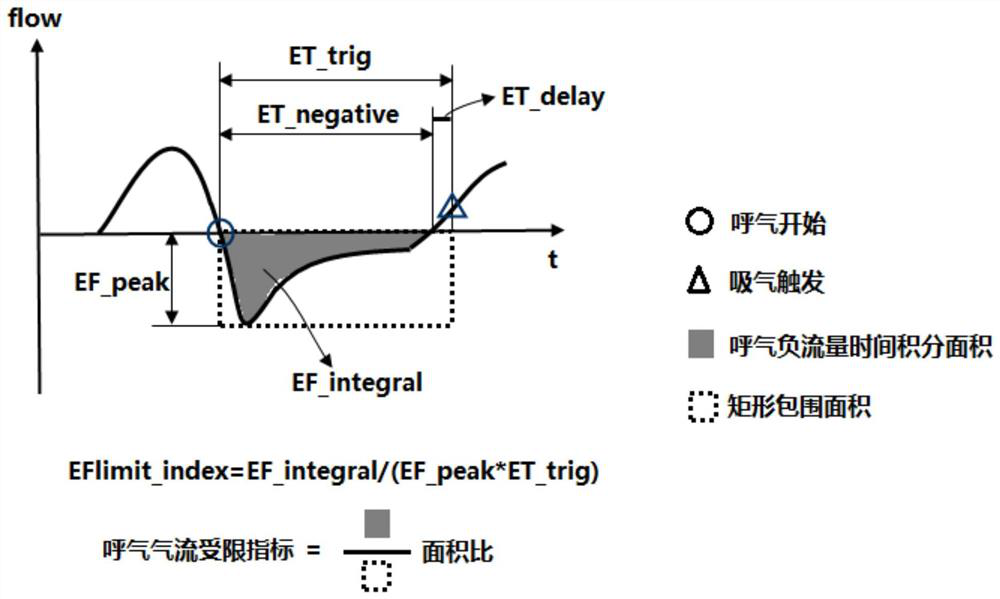
Expiratory pressure automatic titration method and system based on expiratory flow limited index
ActiveCN112827030ASimple calculationLow costRespiratorsDiagnostic recording/measuringExpiratory AirflowExpiratory Time
The invention discloses an expiration pressure automatic titration method and system based on an expiration flow limited index; the method comprises the steps: in a maintenance stage, when a preset maintenance time is reached, calculating a current expiration flow limited index according to a negative expiration flow, an expiration peak flow and expiration time which are monitored in real time, and entering a regulation stage; determining whether the current expiratory flow limited index is smaller than the expiratory flow limited index at the end moment of the previous adjustment stage or not, and if yes, increasing the positive end expiratory pressure; if not, carrying out the operation of lowering the positive end expiratory pressure; and when the positive end expiratory pressure increasing operation or the positive end expiratory pressure decreasing operation is ended, recording the expiratory flow limitation index when the adjusting stage is ended. The exhaled air flow limitation index provided by the invention has vivid description significance and can be used as an indication of the actual exhaled air flow limitation degree; the method is relatively simple in calculation, does not need hardware support with high complexity requirements, and reduces the product cost.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
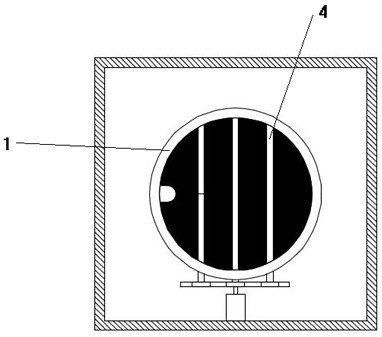
Mechanical PEEP valve and emergency ventilator with PEEP valve
PendingCN111729173AReduce trafficIncrease oxygenation timeRespiratorsMechanical energy handlingPhysical medicine and rehabilitationMedicine
The invention relates to a mechanical PEEP valve and an emergency ventilator with the PEEP valve. The mechanical PEEP valve comprises a valve body, a movable separation blade mechanism and a control mechanism. The movable separation blade mechanism comprises at least two separation blades, the separation blades are arranged in an expiration channel of the valve body through rotating shafts, the separation blades are driven by the control mechanism to be switched between an initial state and an overturning state, the separation blades and the axial direction of the expiration channel are parallel to each other in the initial state, and the separation blades and the axial directions of the expiration channel are perpendicular to each other in the overturning state; the control mechanism comprises a driving motor, a signal induction assembly and an adjustable transmission assembly. The driving motor can drive all or part of the rotating shafts to rotate through the adjustable transmissionassembly. The mechanical PEEP valve can make a patient have a smooth expiration without obstruction in the initial stage of expiration, and can reduce the flow of the expiration channel in the laterstage of expiration, so that resistance is applied to the expiration of the patient, expiration time is prolonged, oxygenation time is prolonged, and an oxygenation state is improved.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
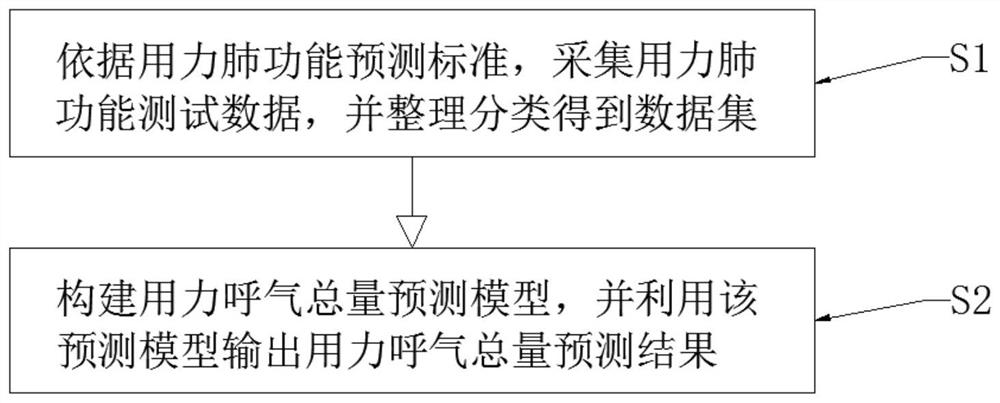
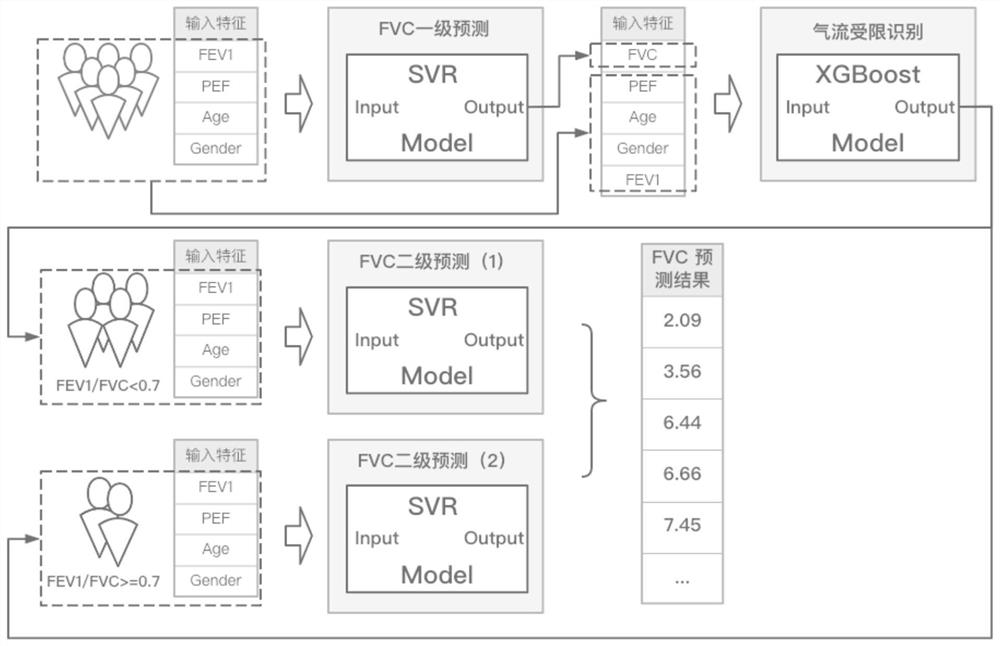
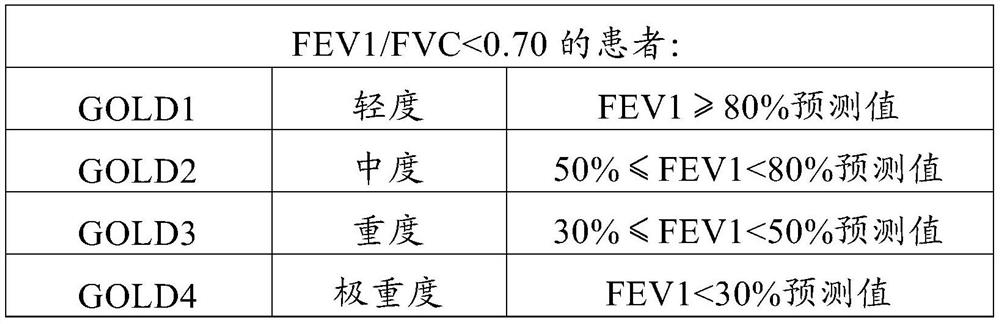
Forced expiration total amount prediction method
PendingCN113469227ASolve the resultAddress issues that affect its diagnostic effectivenessCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringData setForced expiration
The invention discloses a forced expiration total amount prediction method, which comprises the following steps: S1, according to a forced lung function prediction standard, collecting forced lung function test data, and sorting and classifying the data to obtain a data set; and S2, constructing a forced expiration total amount prediction model, and outputting a forced expiration total amount prediction result by using the prediction model. The method has the beneficial effects that by providing the forced expiration total amount prediction method, a tester can still obtain an FVC value under the condition that the whole test is not completed, so that the problem that the diagnosis effect is influenced due to the fact that an FVC detection result does not meet the acceptability because it is difficult for the tester to insist in expiration time long enough is effectively solved.
Owner:RES INST OF NANJING RUNNAN MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
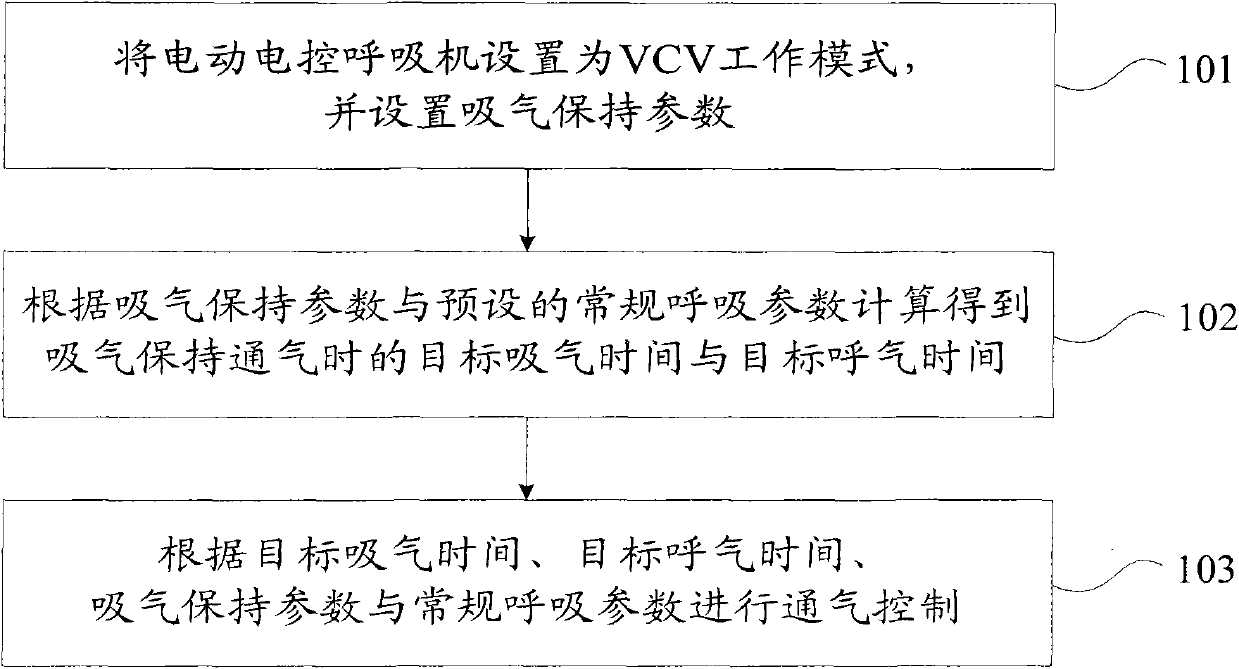
Inhaling holding method for electrically powered electrically controlled ventilator
ActiveCN102114284BOvercoming problems that can adversely affect healthEasy to operate manuallyRespiratorsVentilator settingsType ventilator
The invention provides an inhaling holding method for an electrically powered electrically controlled ventilator. The method comprises the following steps of: setting the electrically powered electrically controlled ventilator into a volume controlled ventilation working mode, and setting inhaling holding parameters; obtaining target inhaling time and target exhaling time during the ventilation of inhaling holding according to the inhaling holding parameters and the preset conventional respiratory parameters; and performing ventilation control according to the target inhaling time, the targetexhaling time, the inhaling holding parameters and the conventional respiratory parameters. The inhaling holding method is applicable to the situation that the ventilator is in transit and has no compressed air sources, does not need medical staff to stay for operation, simplifies the manual operation of realizing an inhaling holding function, and ensures that the medical staff who perform lung function radiography are free from physical injury caused by high-intensity radiation, so the inhaling holding method solves the problems that a pneumatically powered electrically controlled ventilatorin the prior art fails to be used under the condition of transit or no compressed air sources and has adverse effect on the health of the medical staff who perform lung function radiography.
Owner:BEIJING AEONMED
Ventilator pressure control method and ventilator based on breathing conversion
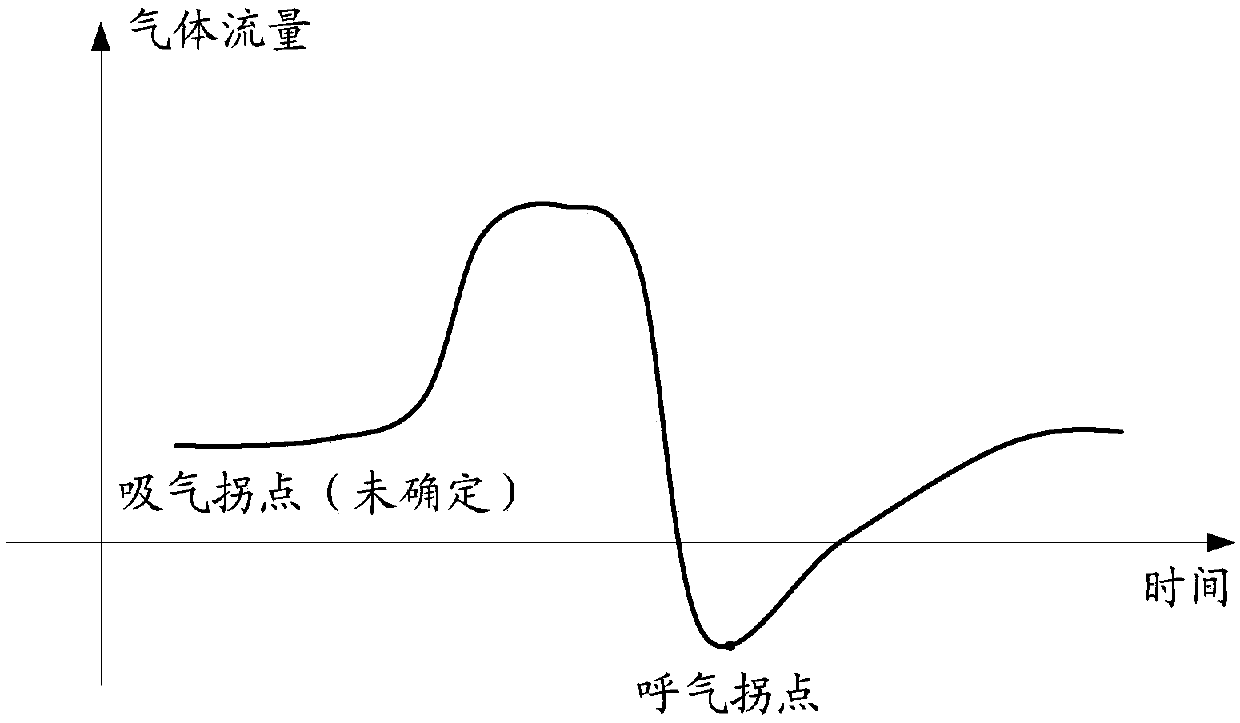
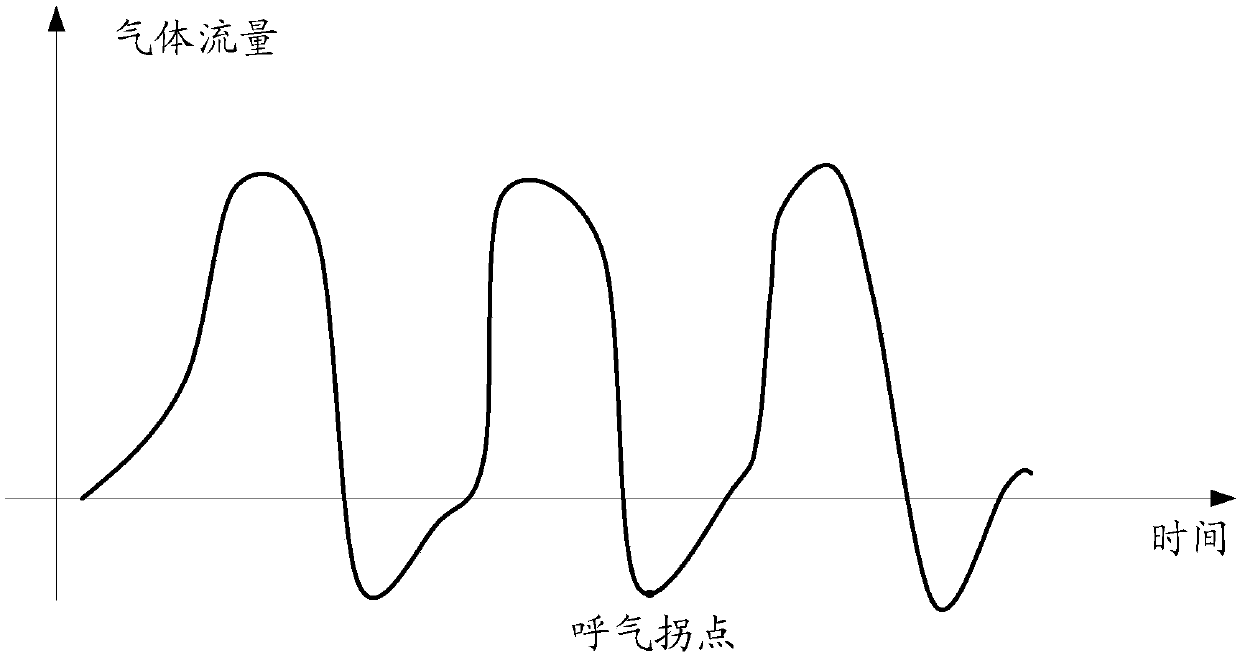
ActiveCN106362257BControl pressureAvoid discomfortRespiratorsMedical devicesExpiration TimeRapid respirations
The invention relates to a breathing switching based breathing machine pressure control method and a breathing machine. The breathing switching based breathing machine pressure control method comprises the steps that gas flow data of the breathing machine is acquired, an expiration time point corresponding to an expiration inflection point of a user during expiration in each expiration period is determined according to the acquired gas flow data; whether a breathing state of the user is rapid breathing or normal breathing is judged based on the gas flow data corresponding after the expiration time point within the same expiration period, and whether an inspiration time point when the user begin to inspire corresponding in a breathing period is determined according to a judgement result; a breathing machine pressure is controlled based on the gas flow data corresponding to the expiration time point in each breathing period and the gas flow data corresponding to the inspiration time point. The breathing switching can accurately control the breathing machine pressure, discomfort brought to the user in the using process is avoided, and the usage experience of the user is improved.
Owner:HUNAN MICOME ZHONGJIN MEDICAL SCI & TECH DEV CO LTD
Setting mandatory mechanical ventilation parameters based on patient physiology
InactiveUS20080202519A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTidal volumeExpiratory Time
A method of setting expiratory time in controlled mechanical ventilation sets a subject's expiratory time based on when the subject's tidal volume expires. Another method determines when the subject's tidal volume expires and sets the subject's expiratory time based on the determination. A device for use in controlled mechanical ventilation comprises a flow rate sensor configured to determine when a subject's tidal volume expires and bases the subject's expiratory time on the determination.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com