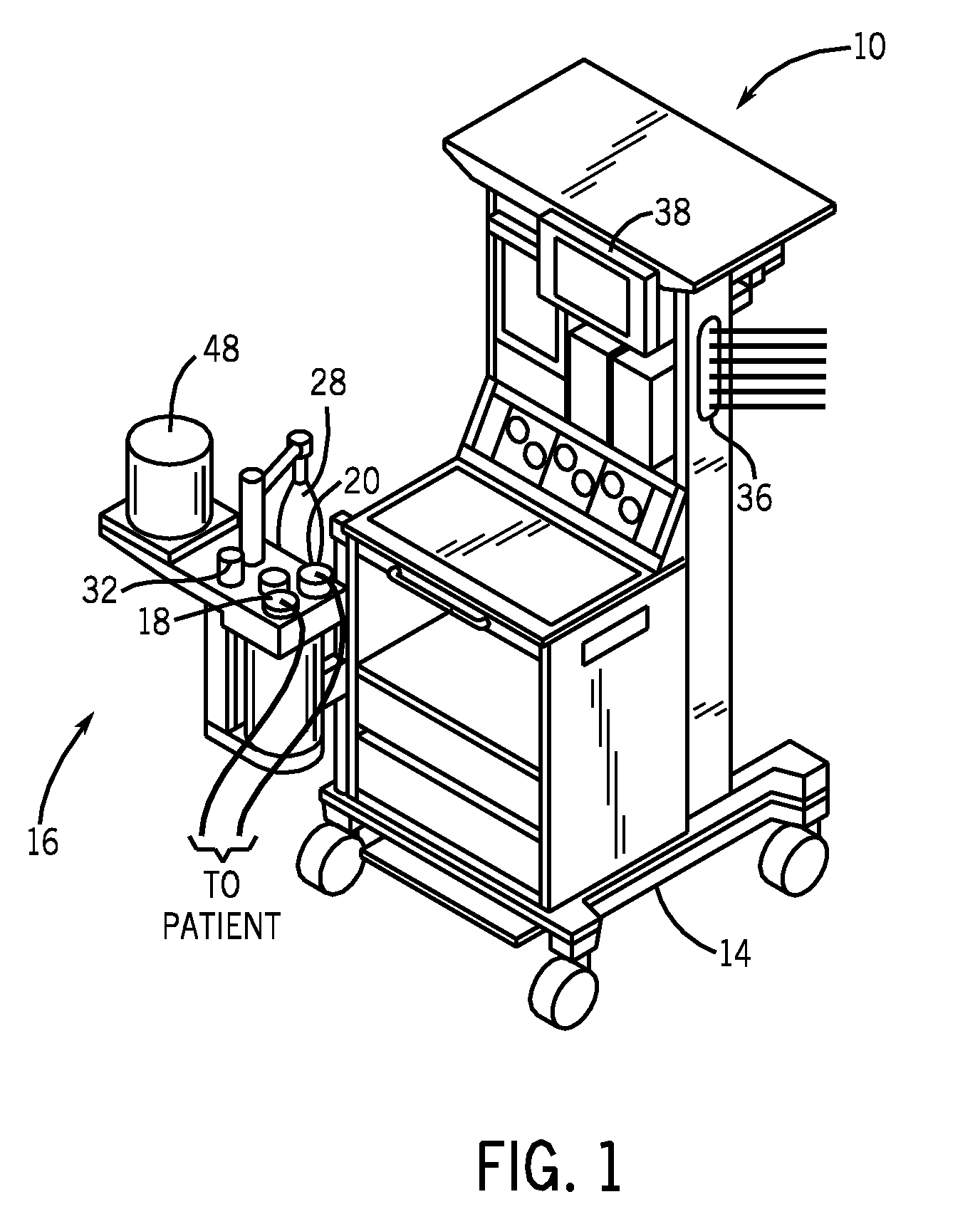
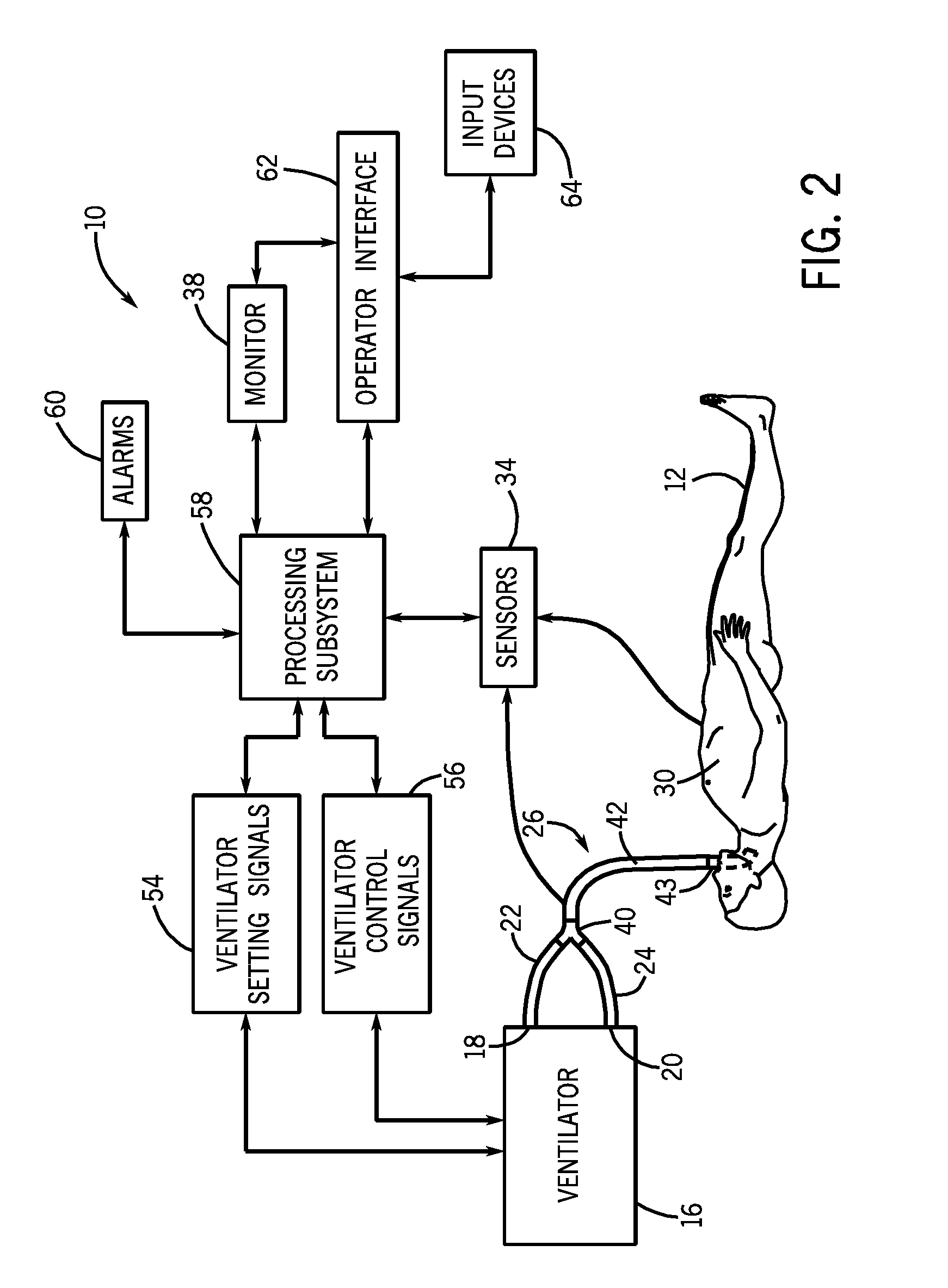
Patents
Literature
520 results about "Patient ventilated" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Respiratory therapist examining a mechanically ventilated patient on an Intensive Care Unit. Mechanical ventilation is indicated when the patient's spontaneous ventilation is inadequate to maintain life. It is also indicated as prophylaxis for imminent collapse of other physiologic functions, or ineffective gas exchange in the lungs.
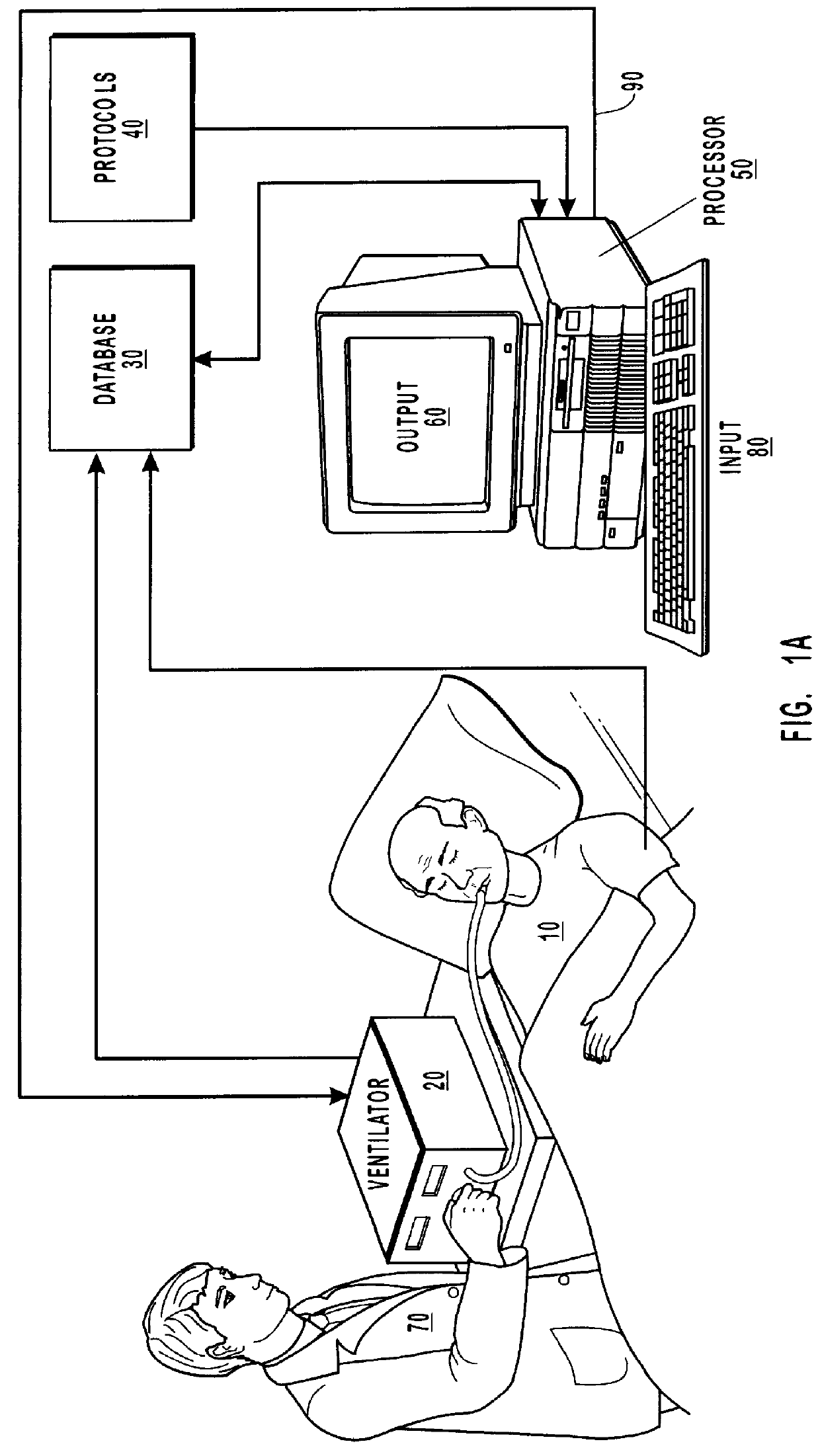
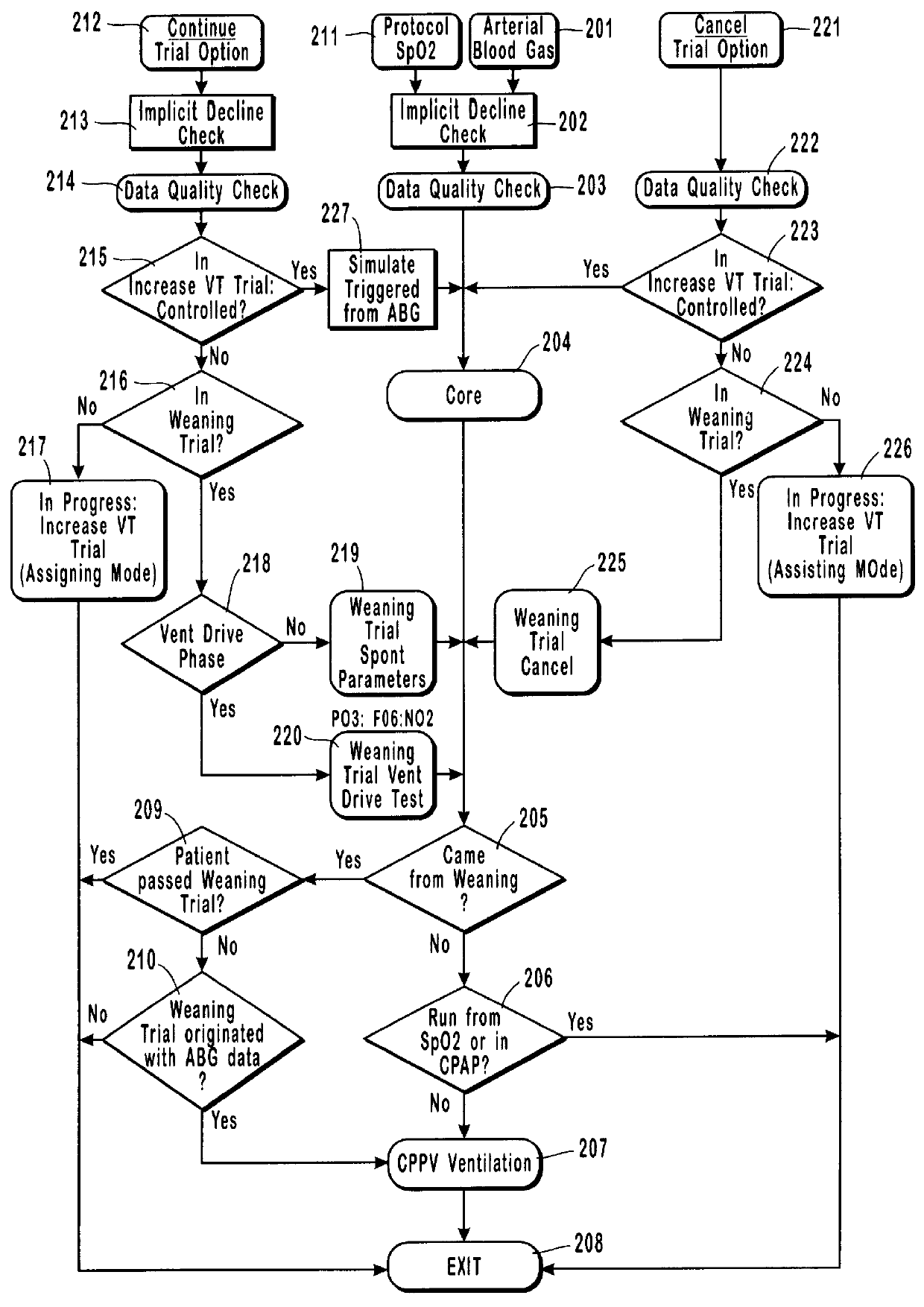
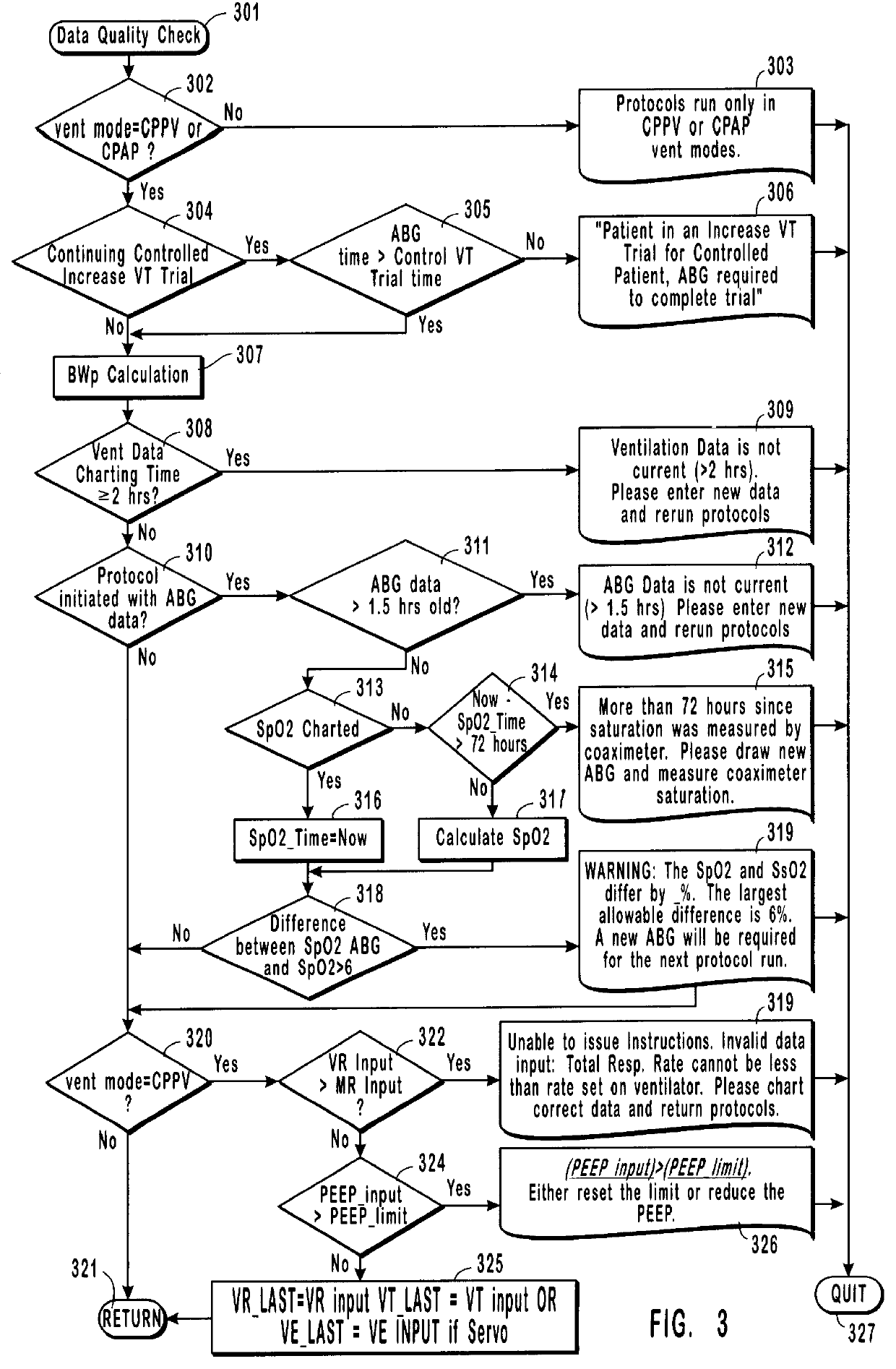
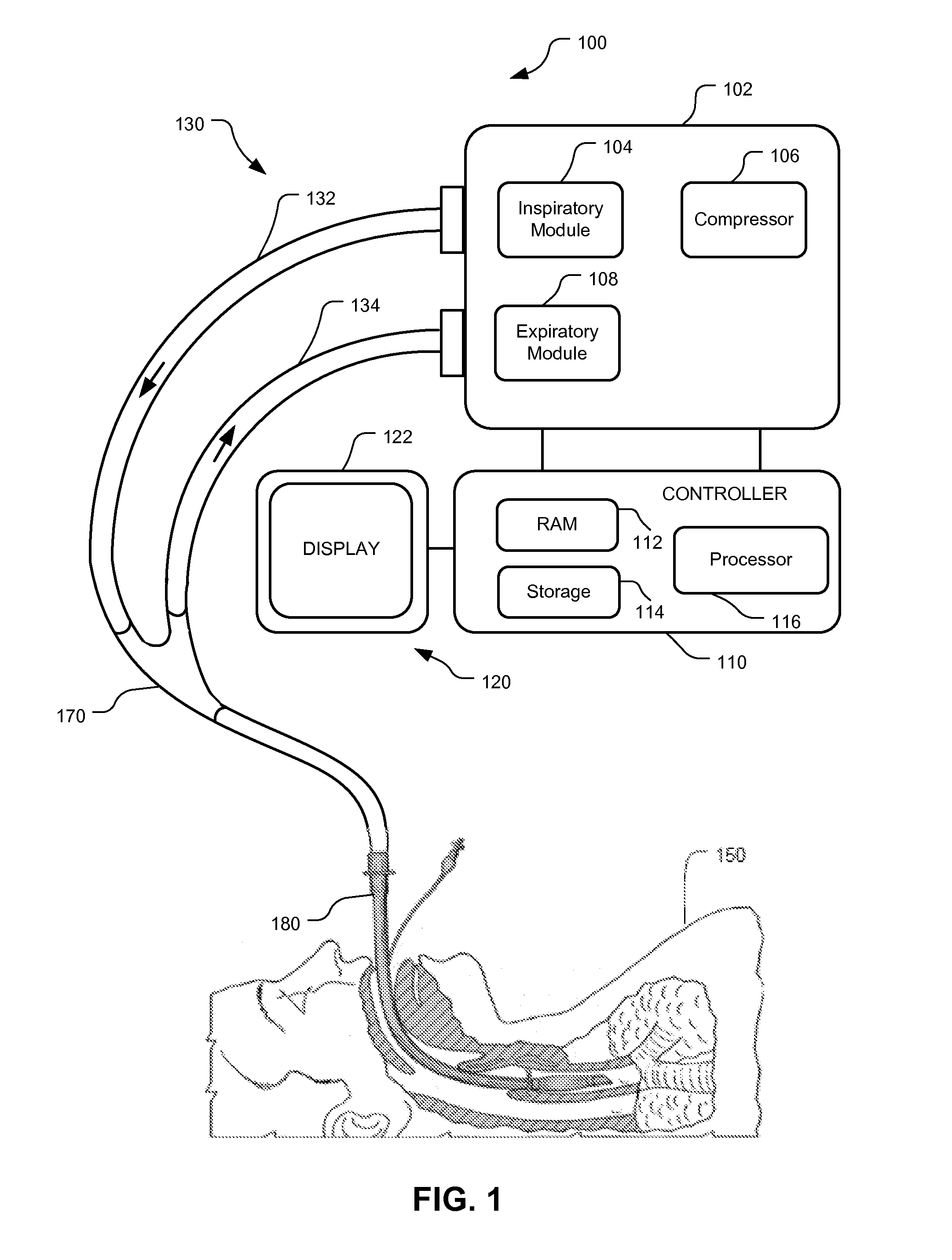
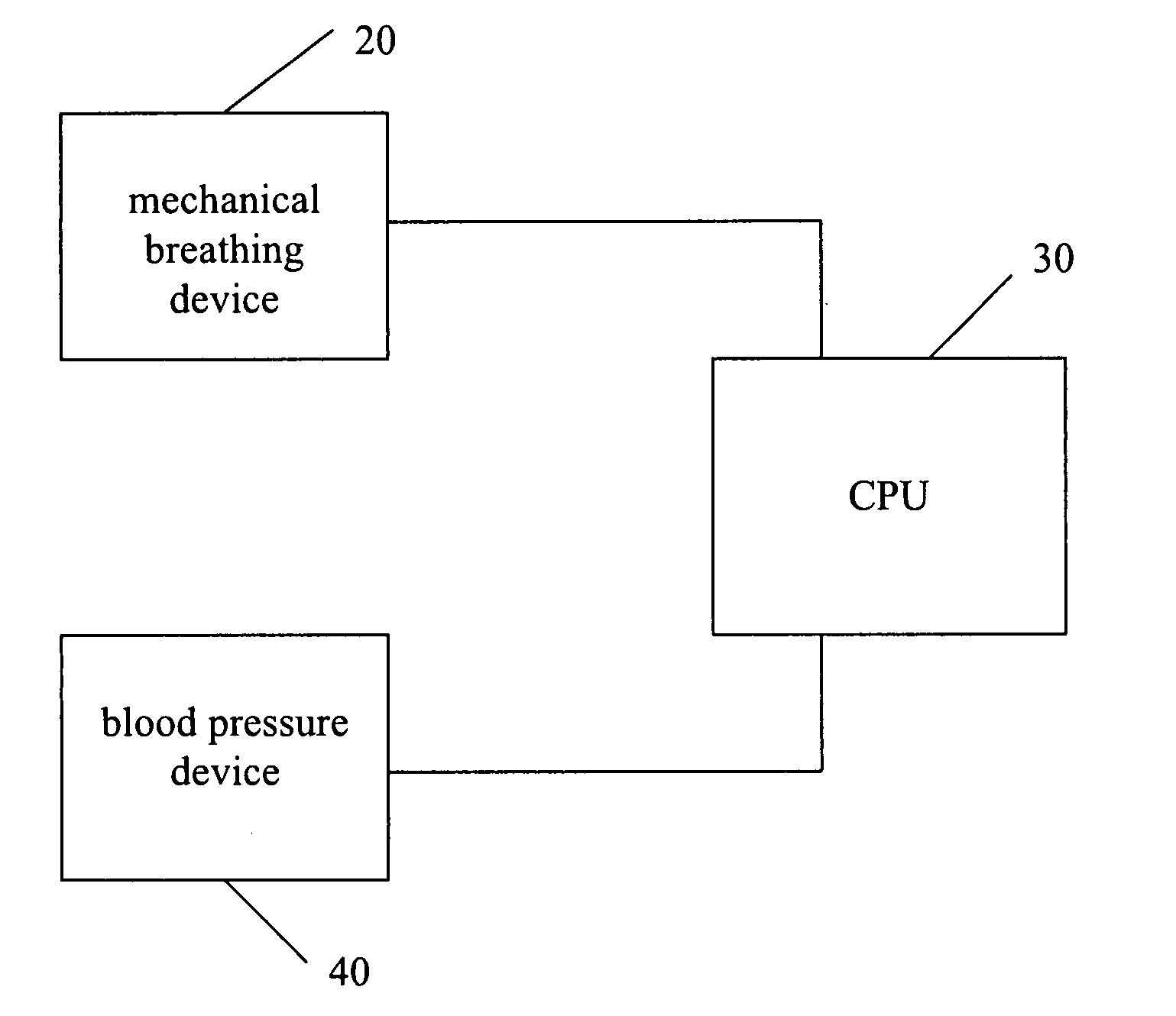
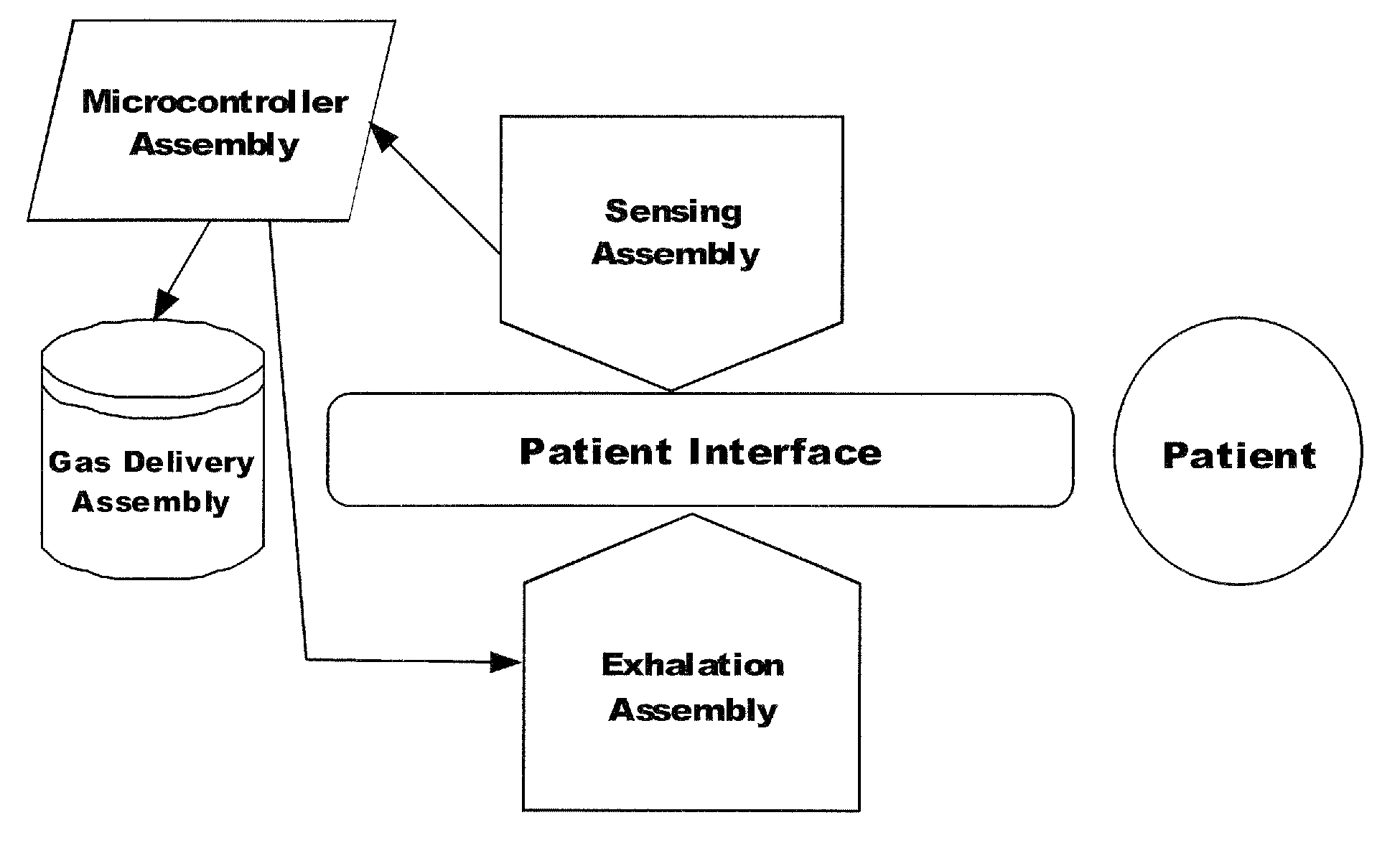
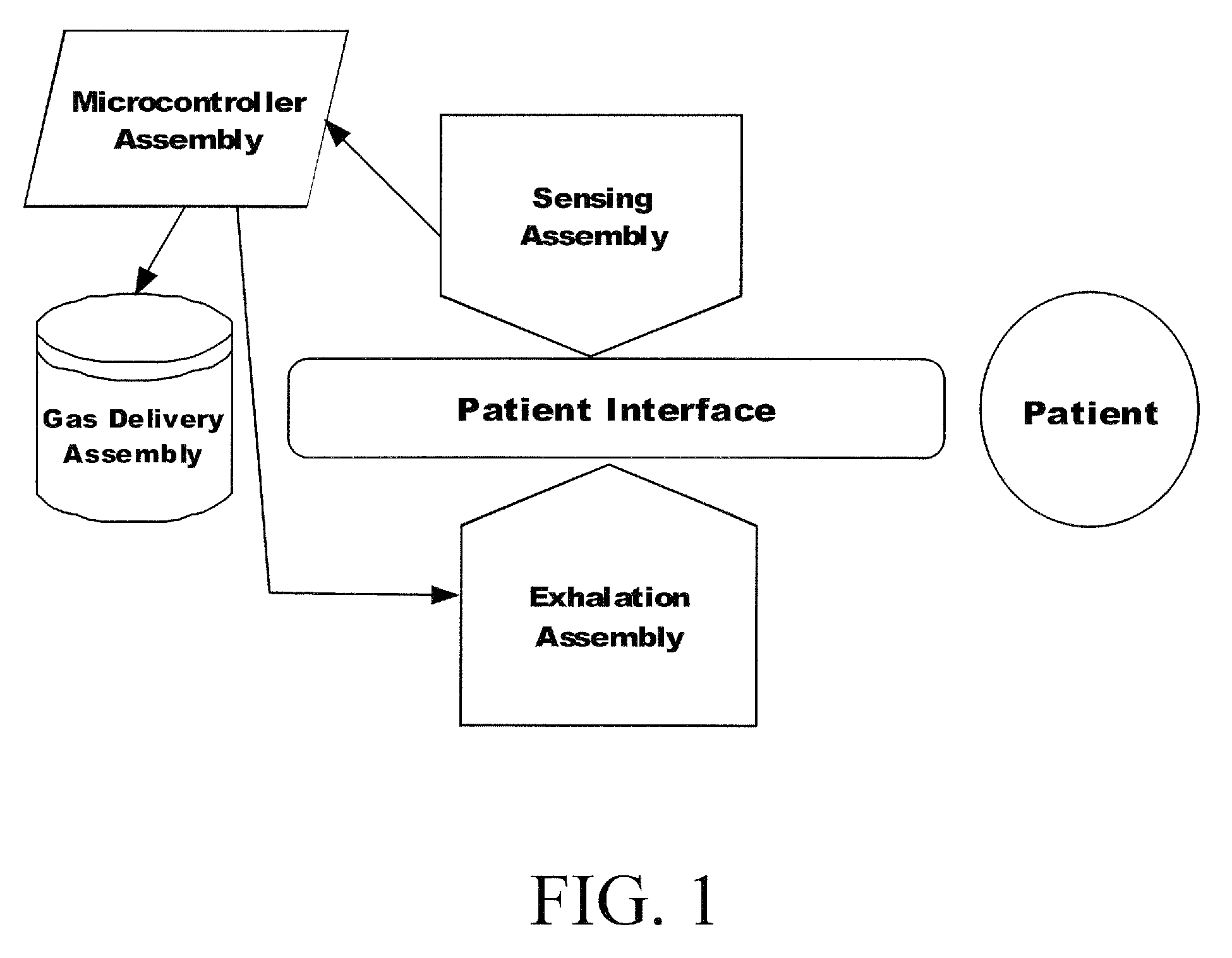
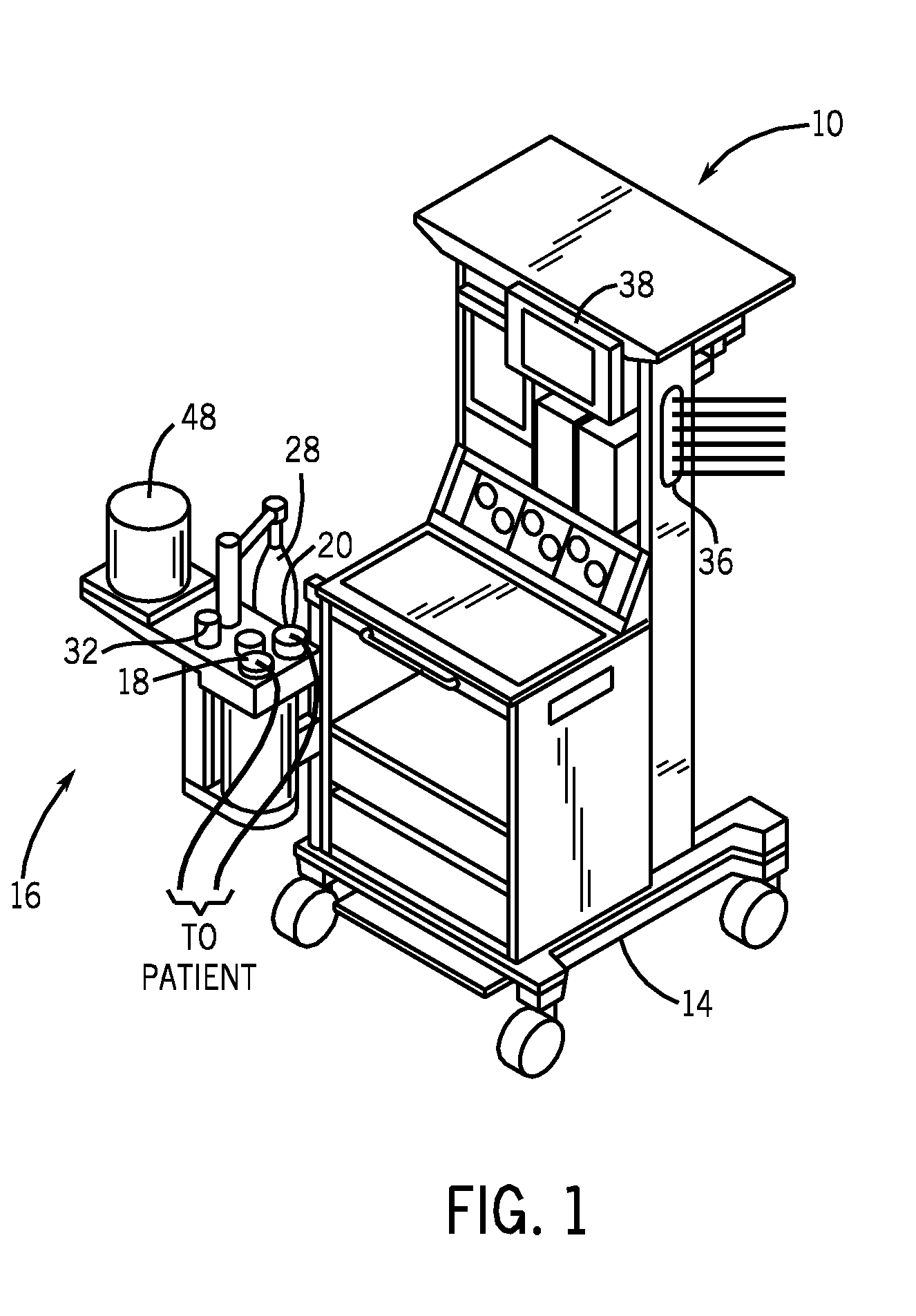
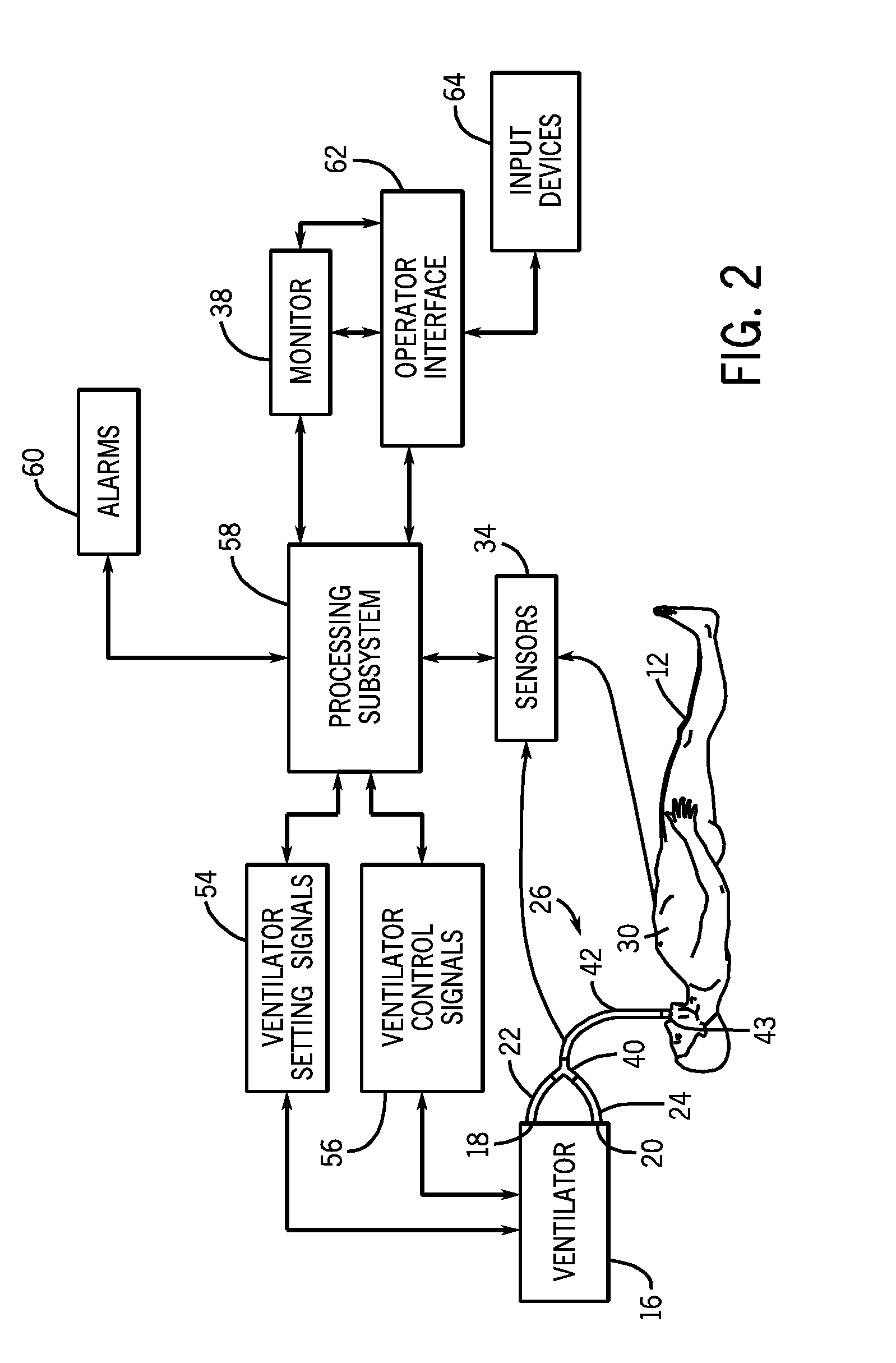
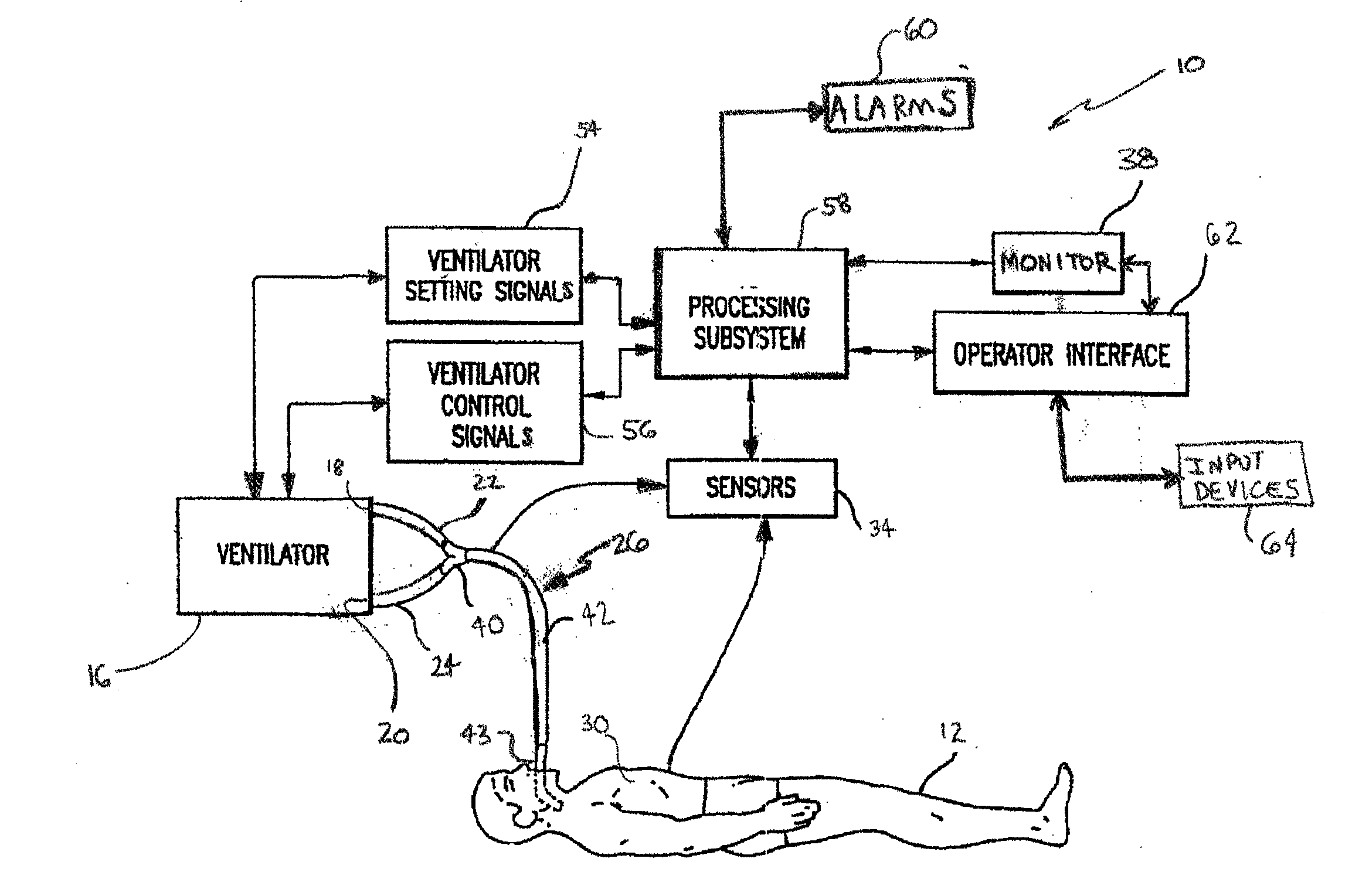
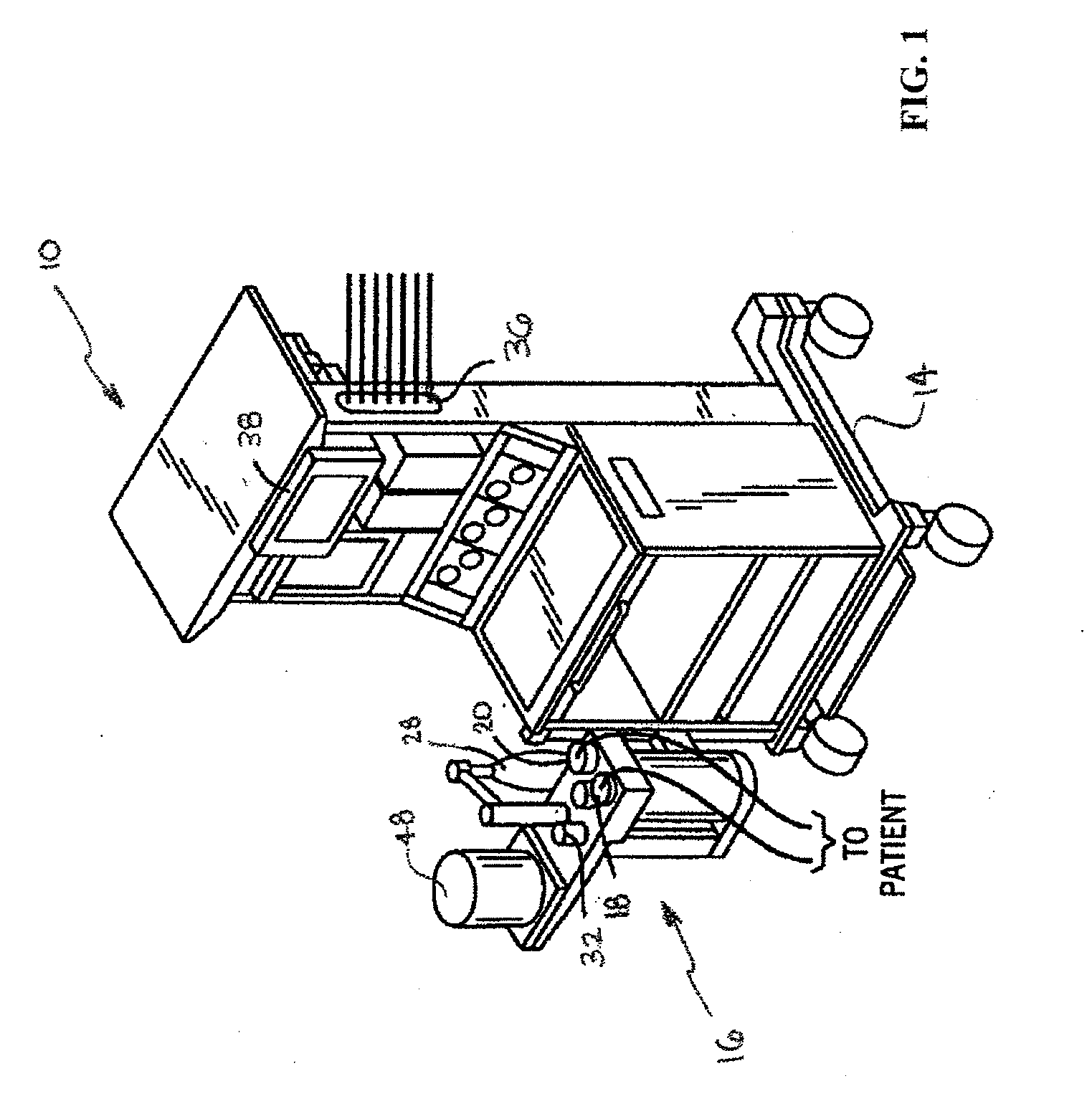
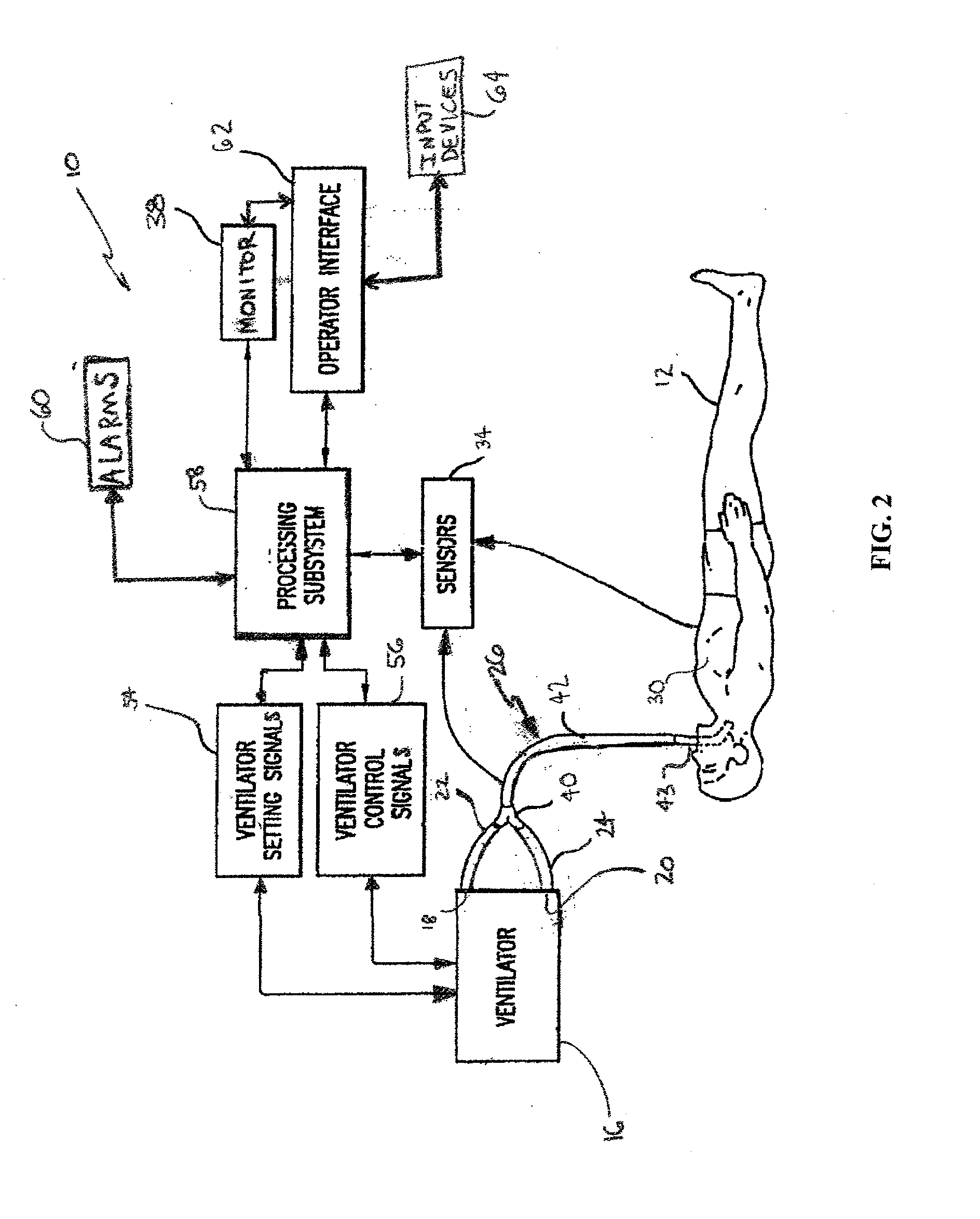
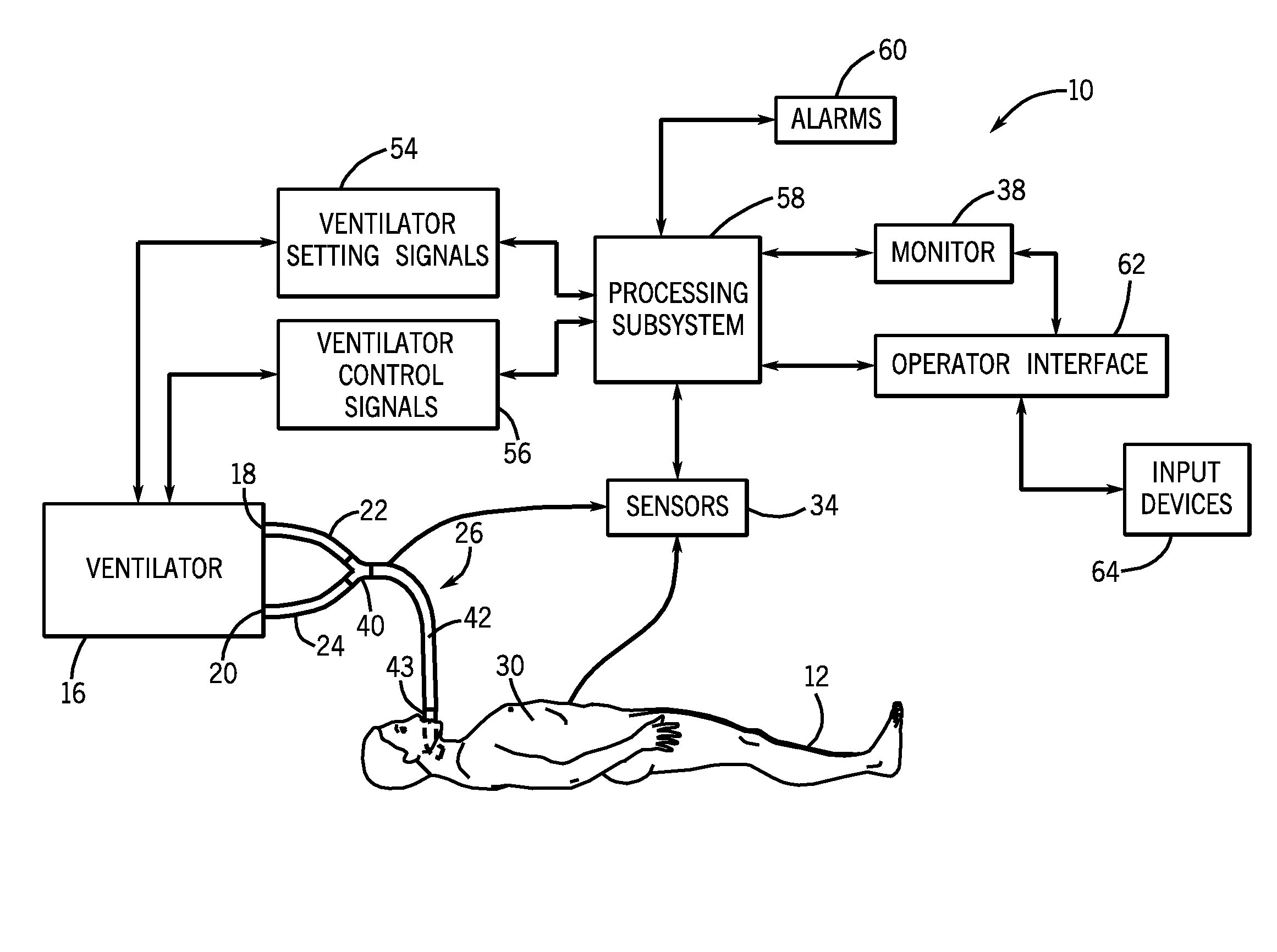
Method and system for patient monitoring and respiratory assistance control through mechanical ventilation by the use of deterministic protocols
InactiveUS6148814AReducing ventilator rateRelieve pressureRespiratorsBreathing masksDiseaseClinical staff
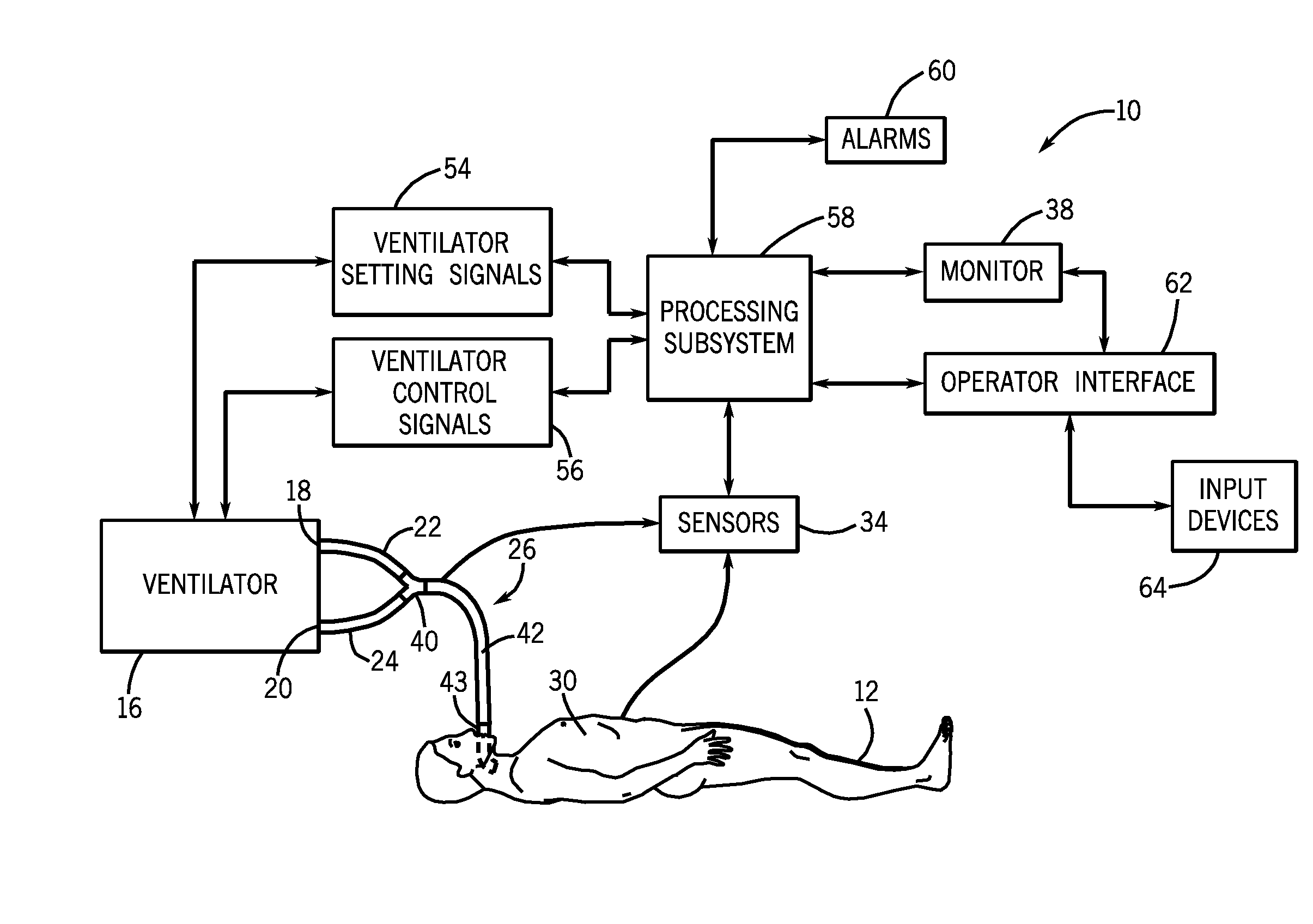
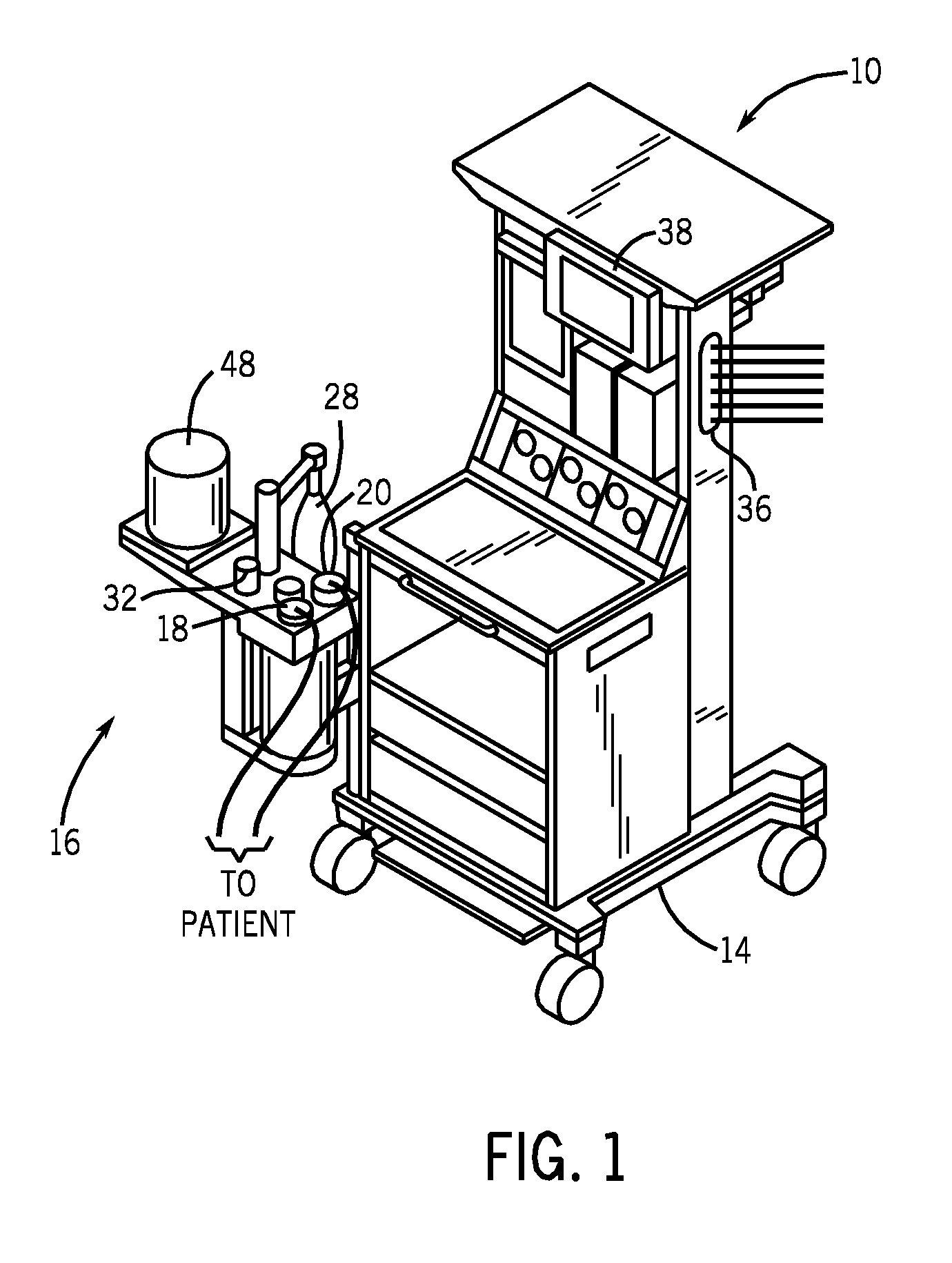
A method and system for managing mechanical ventilation of patients with respiratory disorders is described. The main objective of the system is to generate executable instructions for patient care which take into account a large number of parameters of patient condition and ventilation. Data regarding the state of the patient are stored in a database. Patient data are processed according to a set of protocols which contain rules for patient care decisions arranged in a logical sequence to generate detailed, executable instructions for patient care. Instructions are updated when new data are entered into the database. The data can be acquired in an automated fashion, or the clinician can be instructed to collect and enter new data into the clinical database. Likewise, patient care instructions can be carried out automatically or manually, but it is preferred that instructions are carried out manually as a safety check. The preferred embodiment of the invention includes a computer system, software for processing patient data, and a display device for presenting patient care instructions to the clinician. The system maintains a record of patient data, patient care instructions, whether instructions were followed by the clinical staff, and if not, a reason why.
Owner:INTERMOUNTAIN INTELLECTUAL ASSET MANAGEMENT LLC
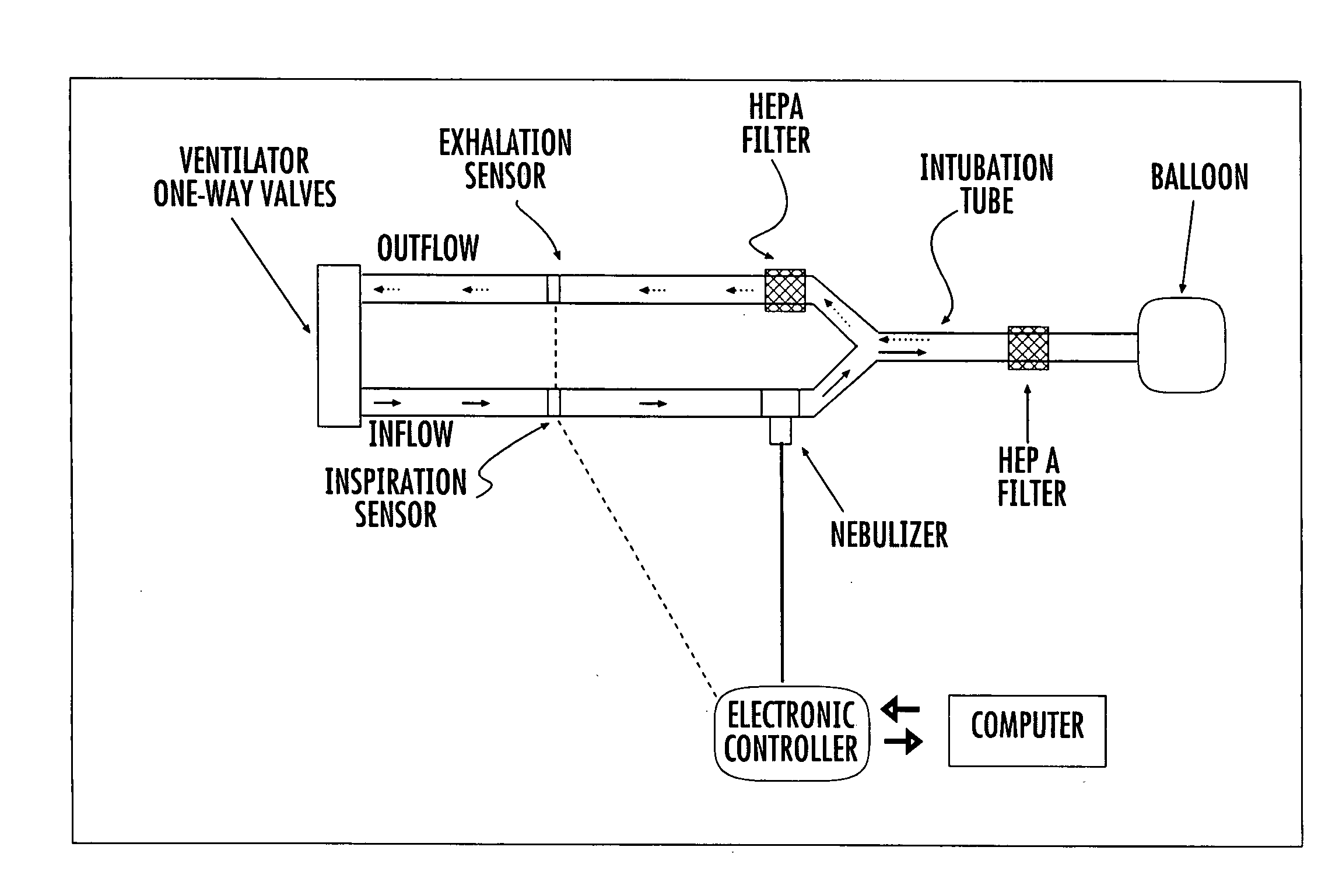
System and method for optimized delivery of an aerosol to the respiratory tract
InactiveUS20070157931A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingAerosol deposition
The present disclosure relates to systems, methods, and devices for controlling delivery of aerosolized formulations to patients in need of treatment, which optimizes aerosol deposition to the respiratory tract of the patient and can be adapted for use in spontaneously breathing patients or in those requiring mechanical ventilation.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Methods, systems and devices for improving ventilation in a lung area
ActiveUS7588033B2Effective and direct cannulationIncrease hyperinflationTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesDiseasePrimary bronchus
Methods, systems and devices are described for new modes of ventilation in which specific lung areas are ventilated with an indwelling trans-tracheobronchial catheter for the purpose of improving ventilation and reducing hyperinflation in that specific lung area, and for redistributing inspired air to other healthier lung areas, for treating respiratory disorders such as COPD, ARDS, SARS, CF, and TB. Trans-Tracheobronchial Segmental Ventilation (TTSV) is performed on either a naturally breathing or a mechanical ventilated patient by placing a uniquely configured indwelling catheter into a bronchus of a poorly ventilated specific lung area and providing direct ventilation to that area. The catheter can be left in place for extended periods without clinician attendance or vigilance. Ventilation includes delivery of respiratory gases, therapeutic gases or agents and evacuation of stagnant gases, mixed gases or waste fluids. Typically the catheter's distal tip is anchored without occluding the bronchus but optionally may intermittently or continuously occlude the bronchus. TTSV is optionally performed by insufflation only of the area, or by application of vacuum to the area, can include elevating or reducing the pressure in the targeted area to facilitate stagnant gas removal, or can include blocking the area to divert inspired gas to better functioning areas.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
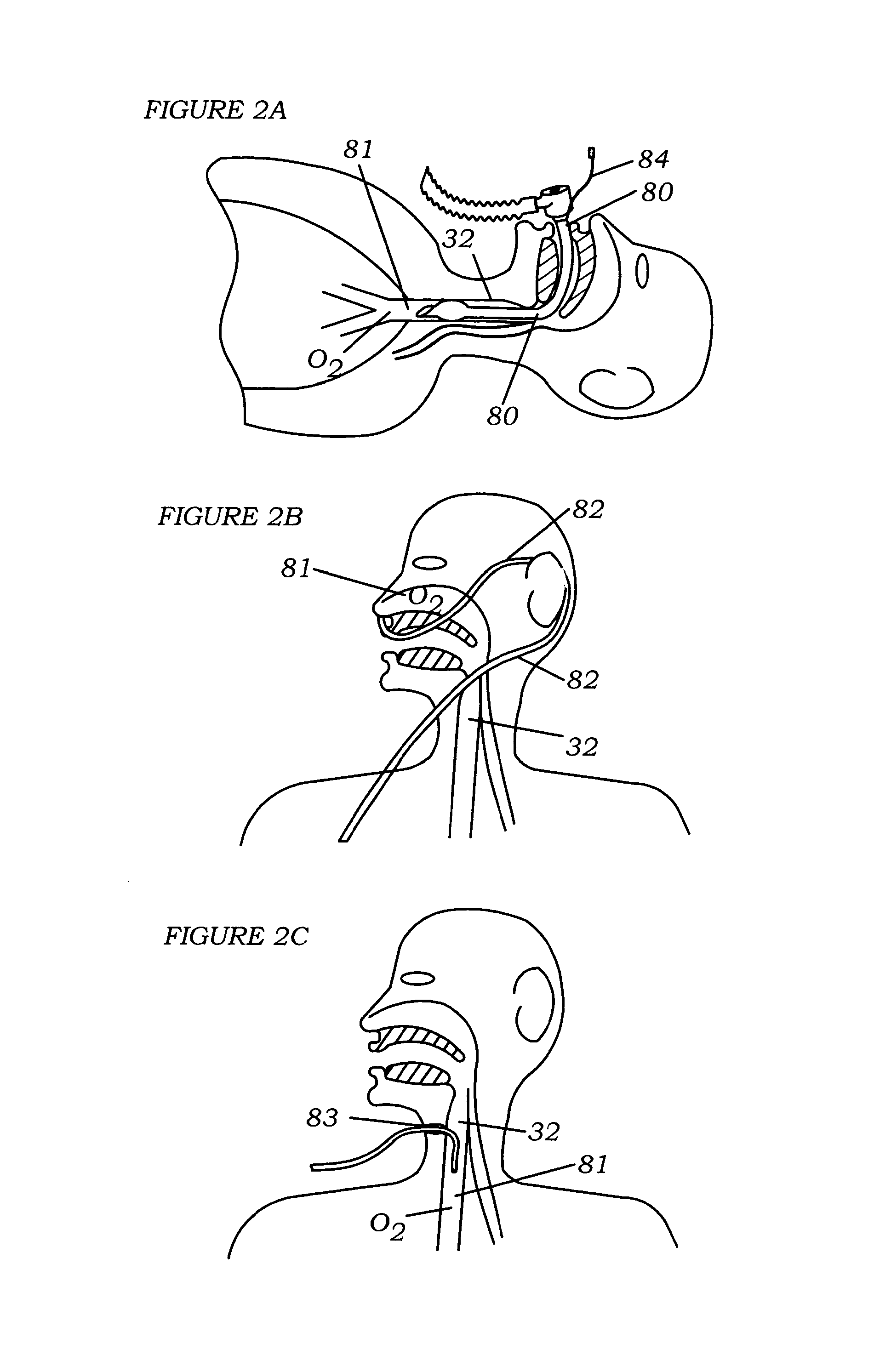
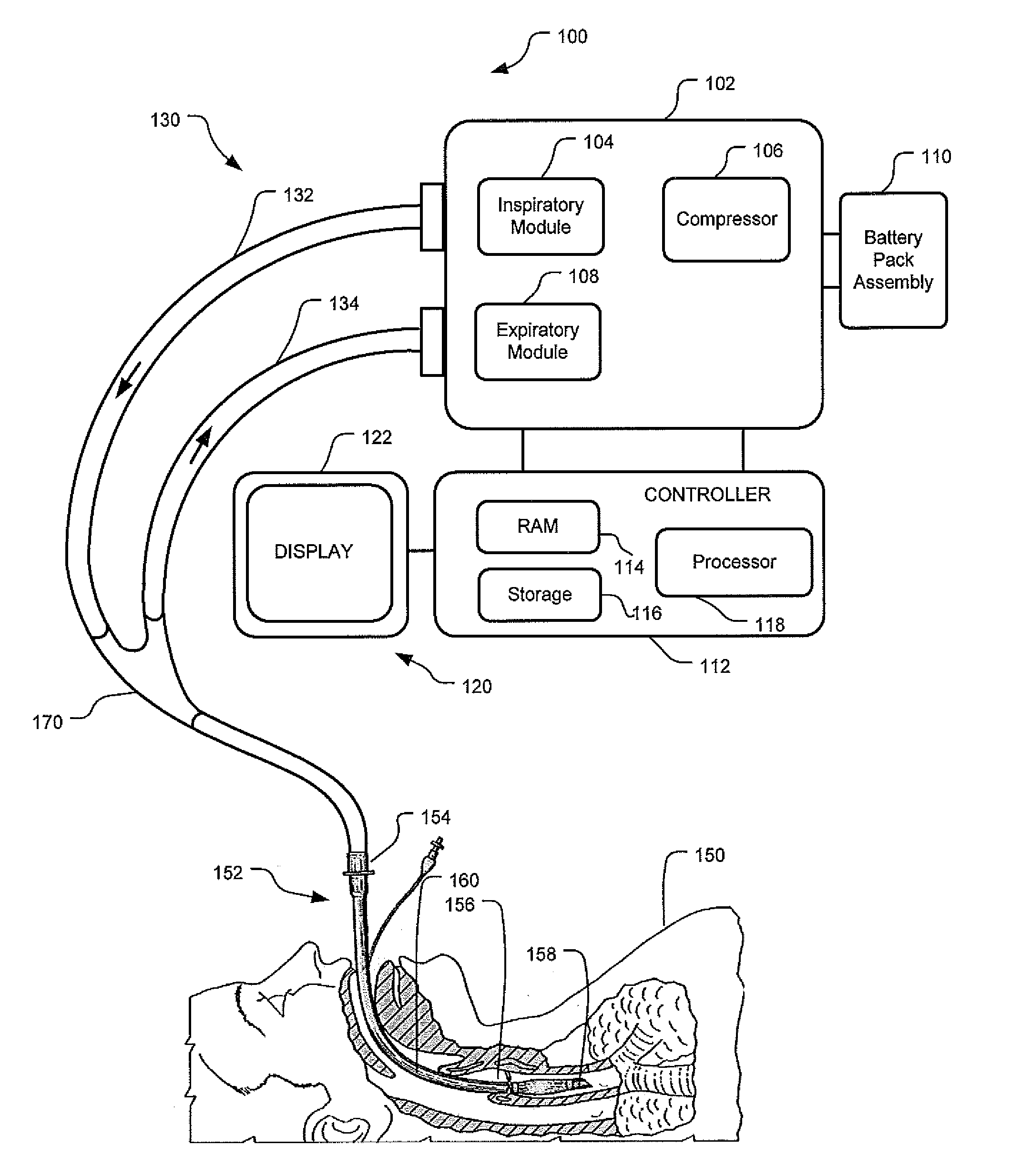
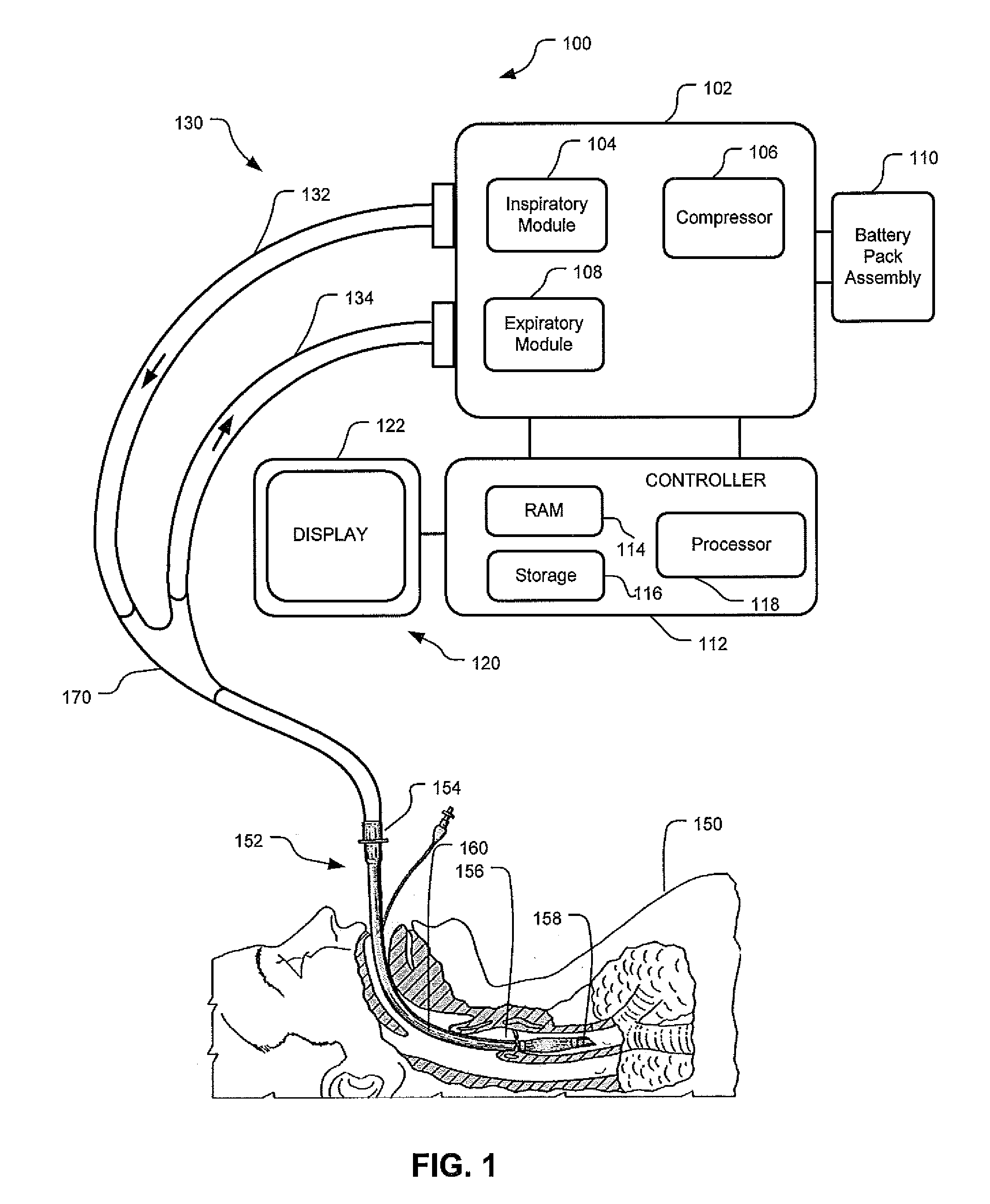
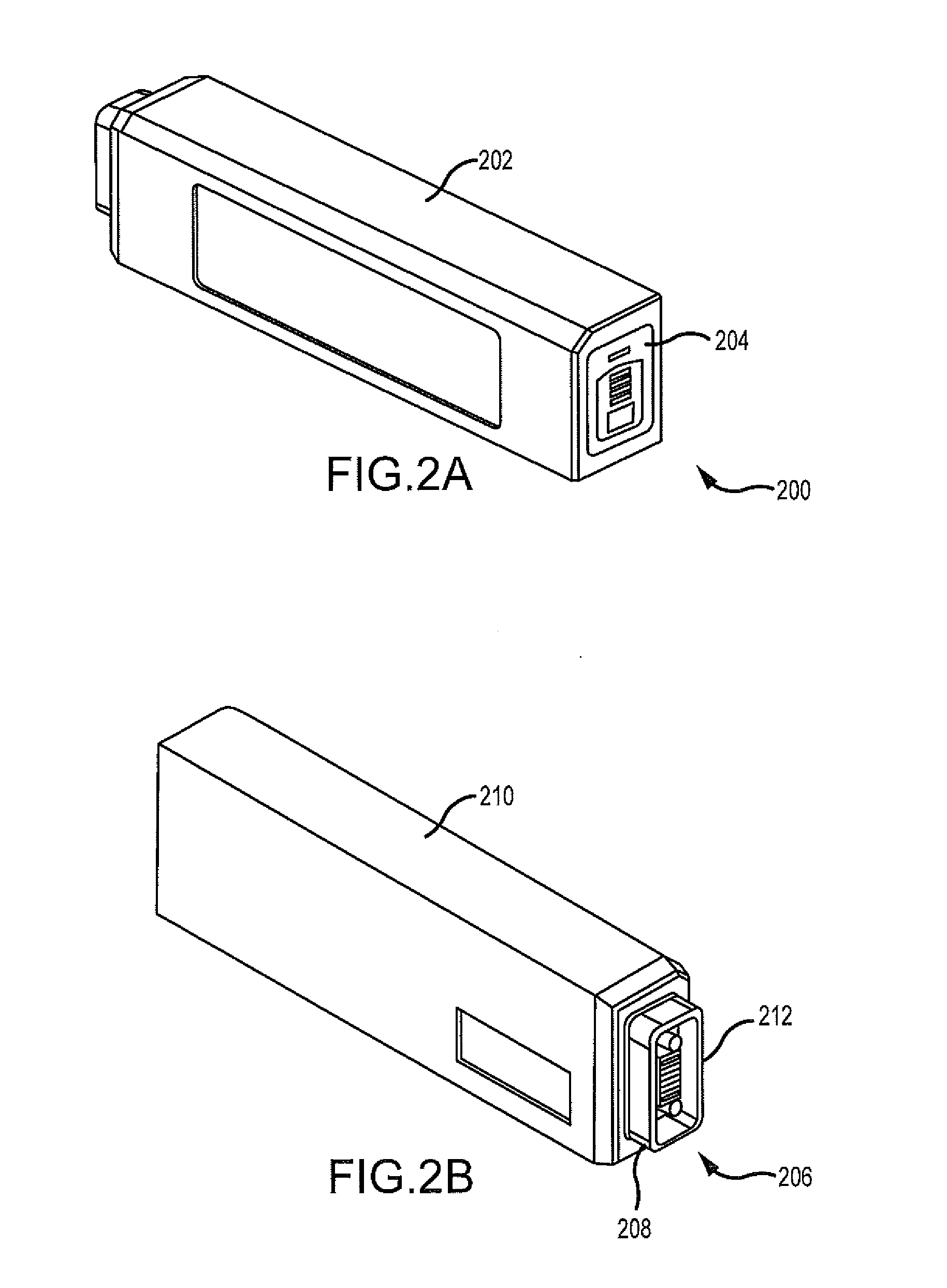
Apparatus And System For A Battery Pack Assembly Used During Mechanical Ventilation
This disclosure describes methods and apparatus for indicating battery cell status on a battery pack assembly used during mechanical ventilation. Embodiments described herein seek to provide methods for indicating battery cell status on the exposed exterior of a battery assembly pack both when the battery is in use and when the battery is not in use during mechanical ventilation. Embodiments utilize power from the ventilator as well as power from the battery pack itself to light the indicators during periods of battery use and non-use, respectively. Embodiments described herein further seek to provide an apparatus indicating battery cell status on the exposed exterior of the battery pack assembly during mechanical ventilation. Embodiments described herein further seek to provide an apparatus for a battery pack assembly used during mechanical ventilation. Embodiments described herein seek to provide a system for a ventilation system with an inserted battery pack assembly.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
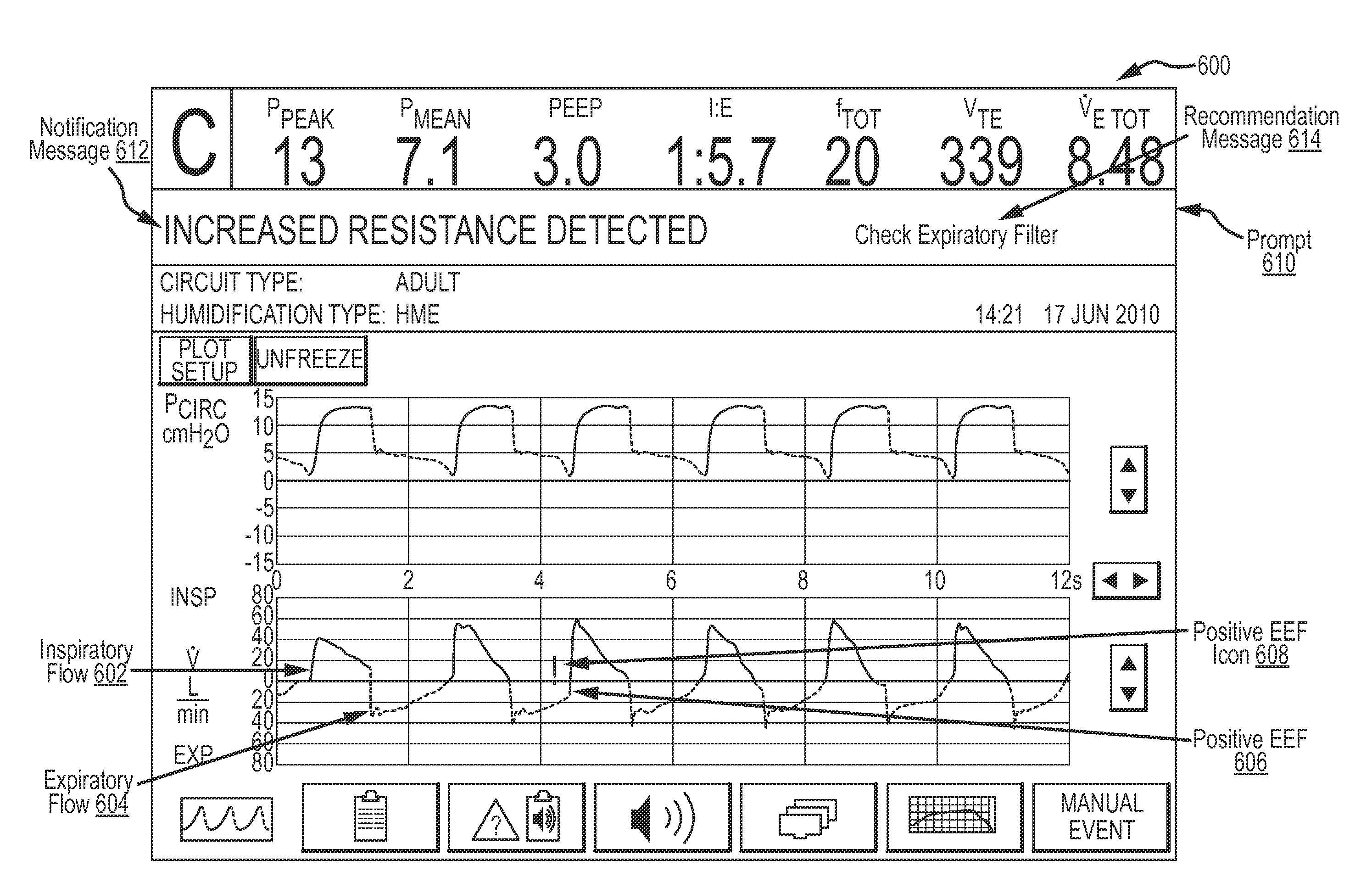
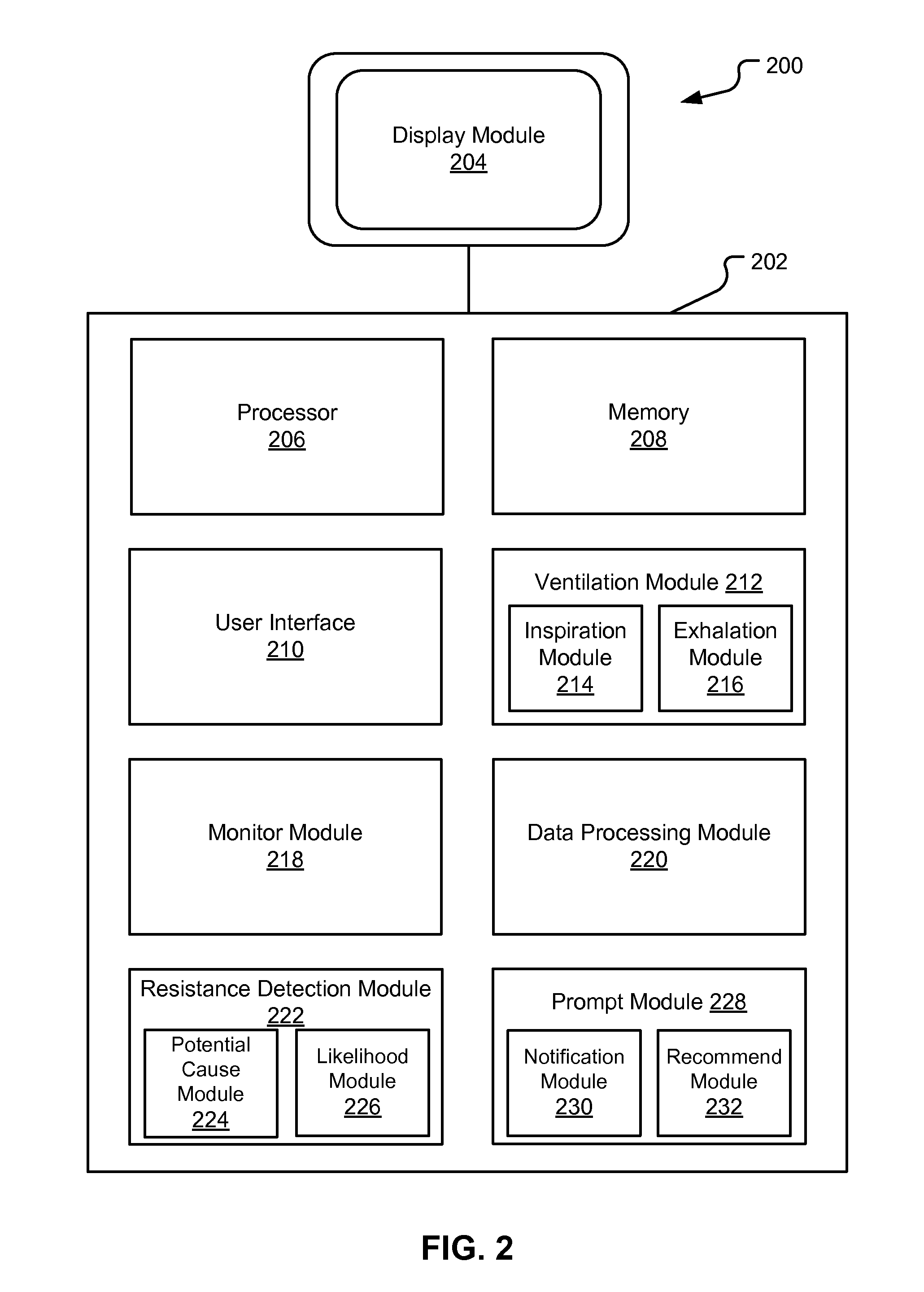
Ventilator-Initiated Prompt Regarding Detection Of Fluctuations In Resistance
This disclosure describes systems and methods for monitoring ventilatory parameters, analyzing ventilatory data associated with those parameters, and providing useful notifications and / or recommendations to clinicians. For example, many clinicians may not easily identify or recognize data patterns and correlations indicative of a fluctuation in resistance during mechanical ventilation of a patient. Furthermore, clinicians may not easily determine potential causes for the fluctuation in resistance and / or steps for mitigating the fluctuation in resistance. According to embodiments, a ventilator may be configured to monitor and evaluate diverse ventilatory parameters to detect fluctuations in resistance and may issue suitable notifications and recommendations to the clinician based on potential causes of the fluctuation, ventilatory and / or patient data, etc. The suitable notifications and recommendations may further be provided in a hierarchical format such that the clinician may selectively access information regarding the fluctuation in resistance.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
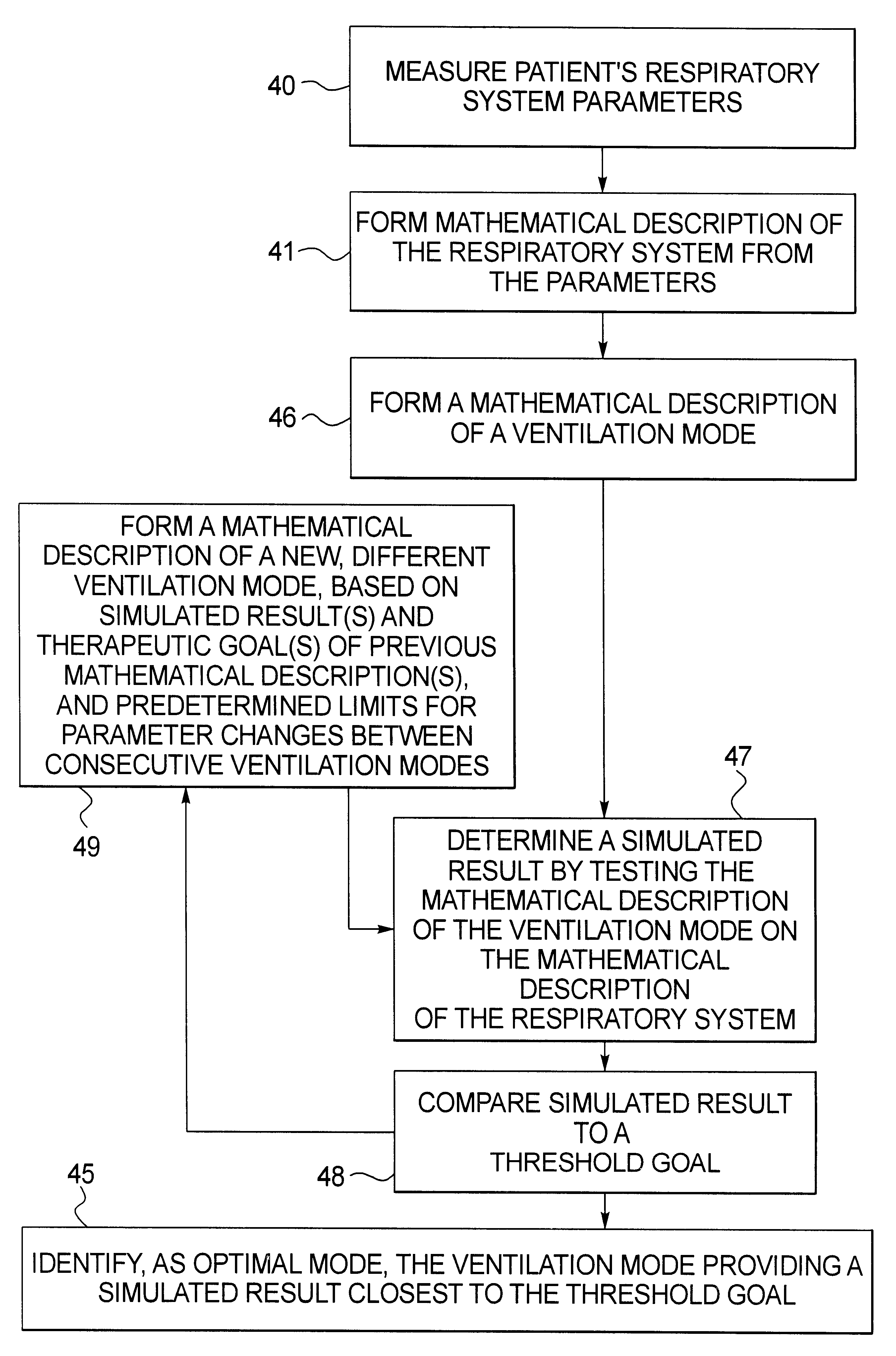
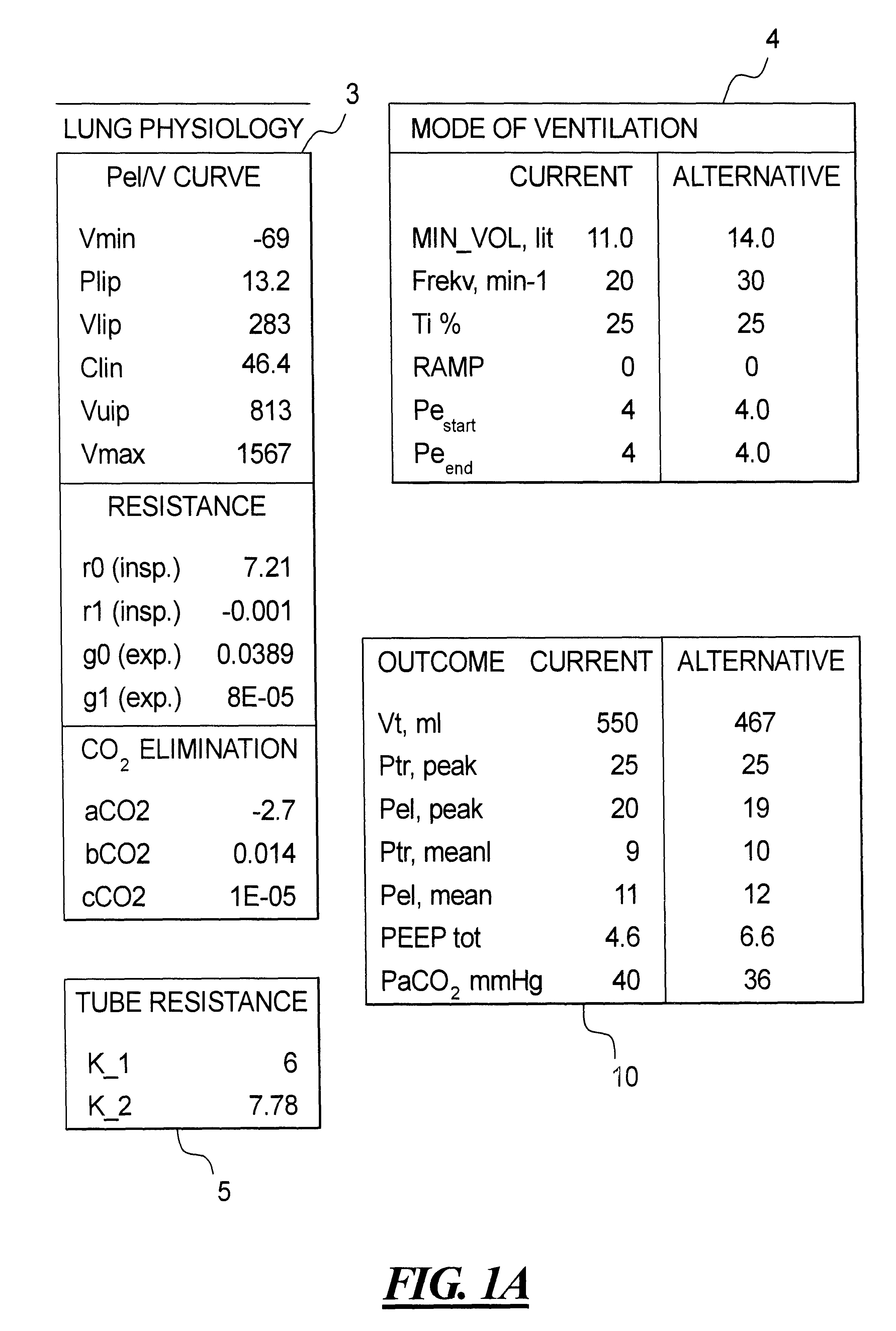
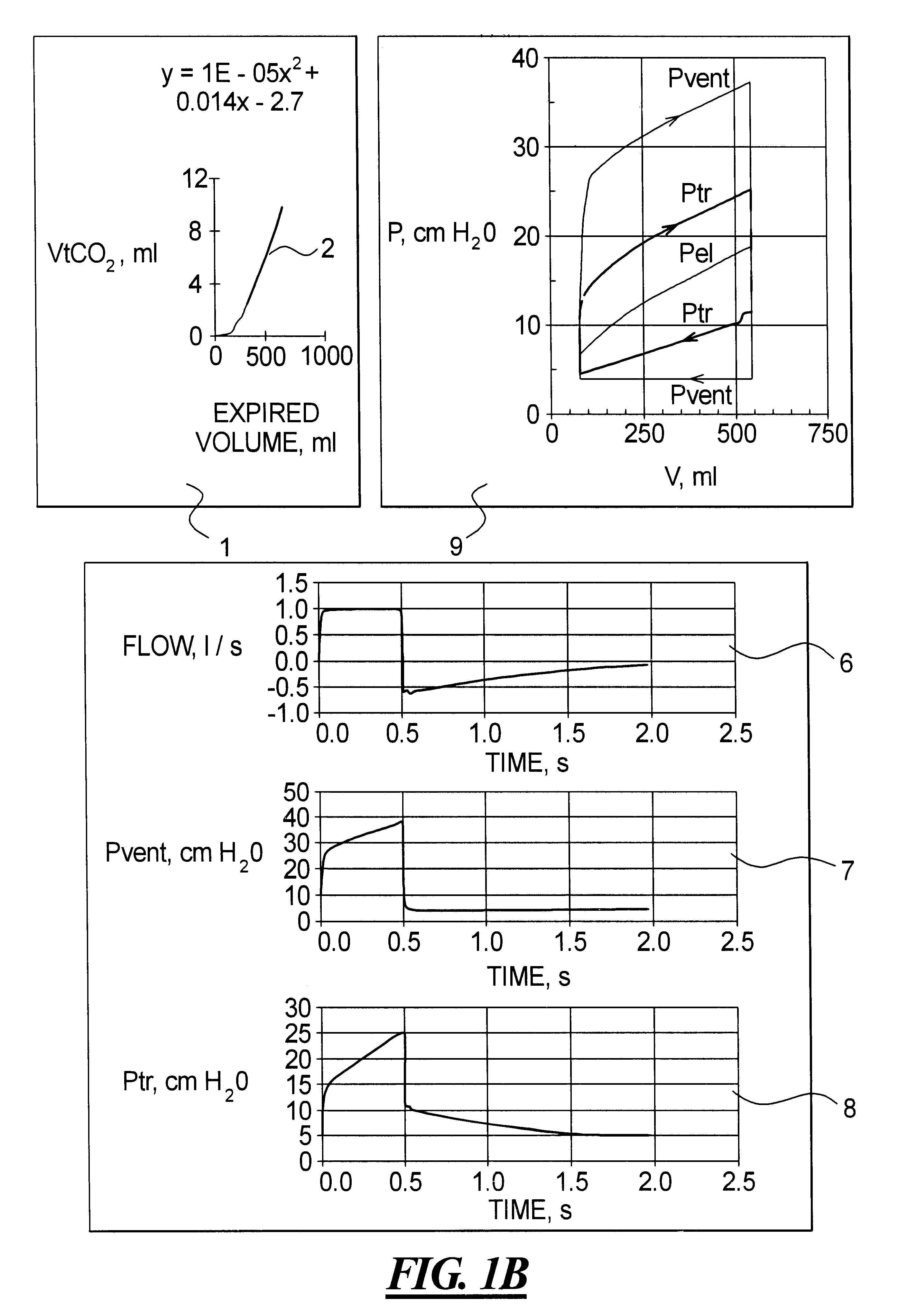
Method and apparatus for optimization of mechanical ventilation
InactiveUS6578575B1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesTherapeutic goalVentilation mode
In order to select an optimal ventilation mode for mechanically ventilating a patient, from among a number of ventilation modes, a mathematical description of the patient's respiratory system is produced in a computer from measured parameters related to properties of the respiratory system, and in the computer the mathematical descriptions for different modes of ventilation are tested on the mathematical description to obtain simulated results. An operator can selected a mode of ventilation to be analyzed by comparing the simulated results with a therapeutic goal, so that an optimal ventilation mode can be selected. Alternatively, the computer can iteratively test a number of modeled ventilation modes to identify the ventilation mode which comes closest to the therapeutic goal.
Owner:MAQUET CRITICAL CARE
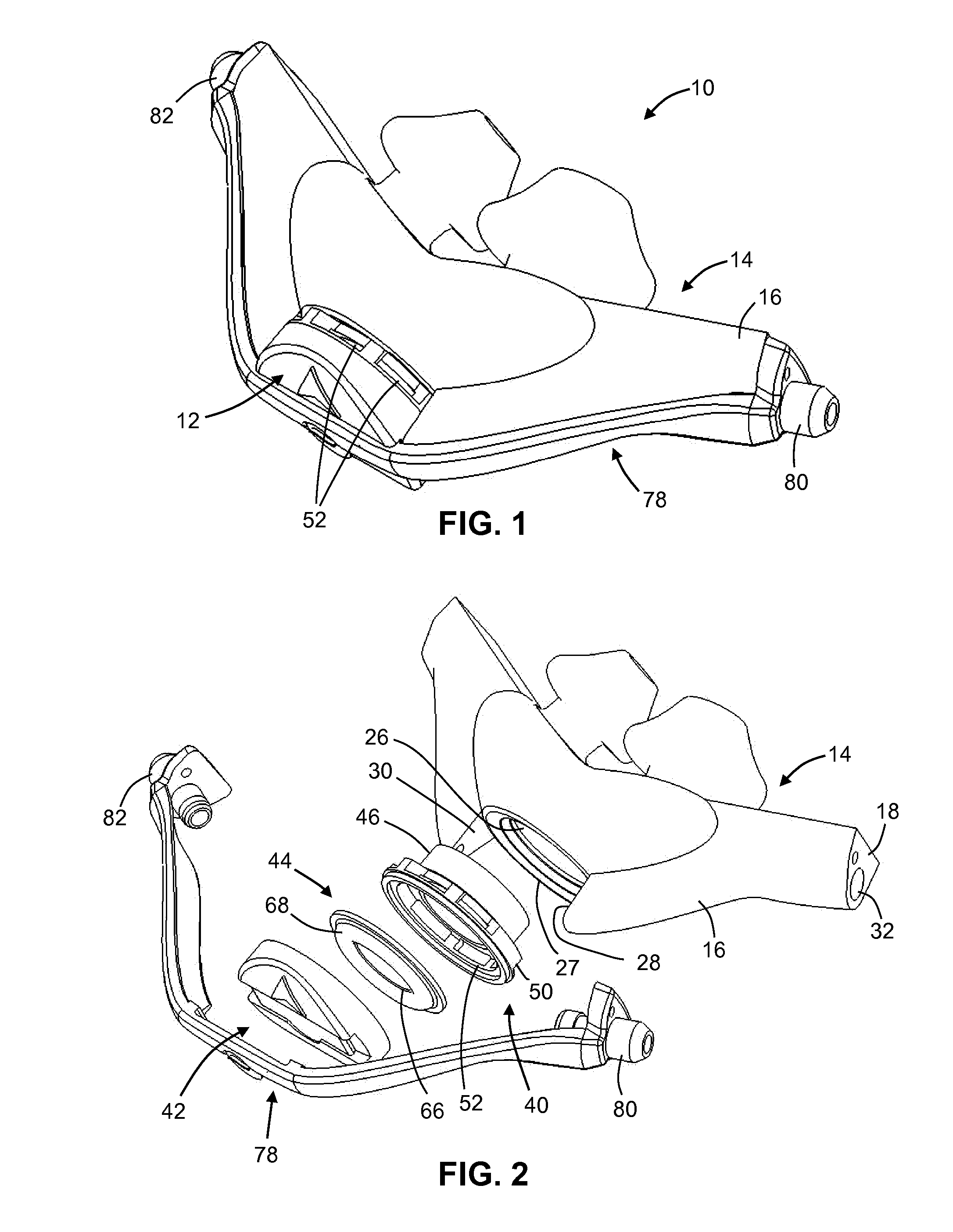
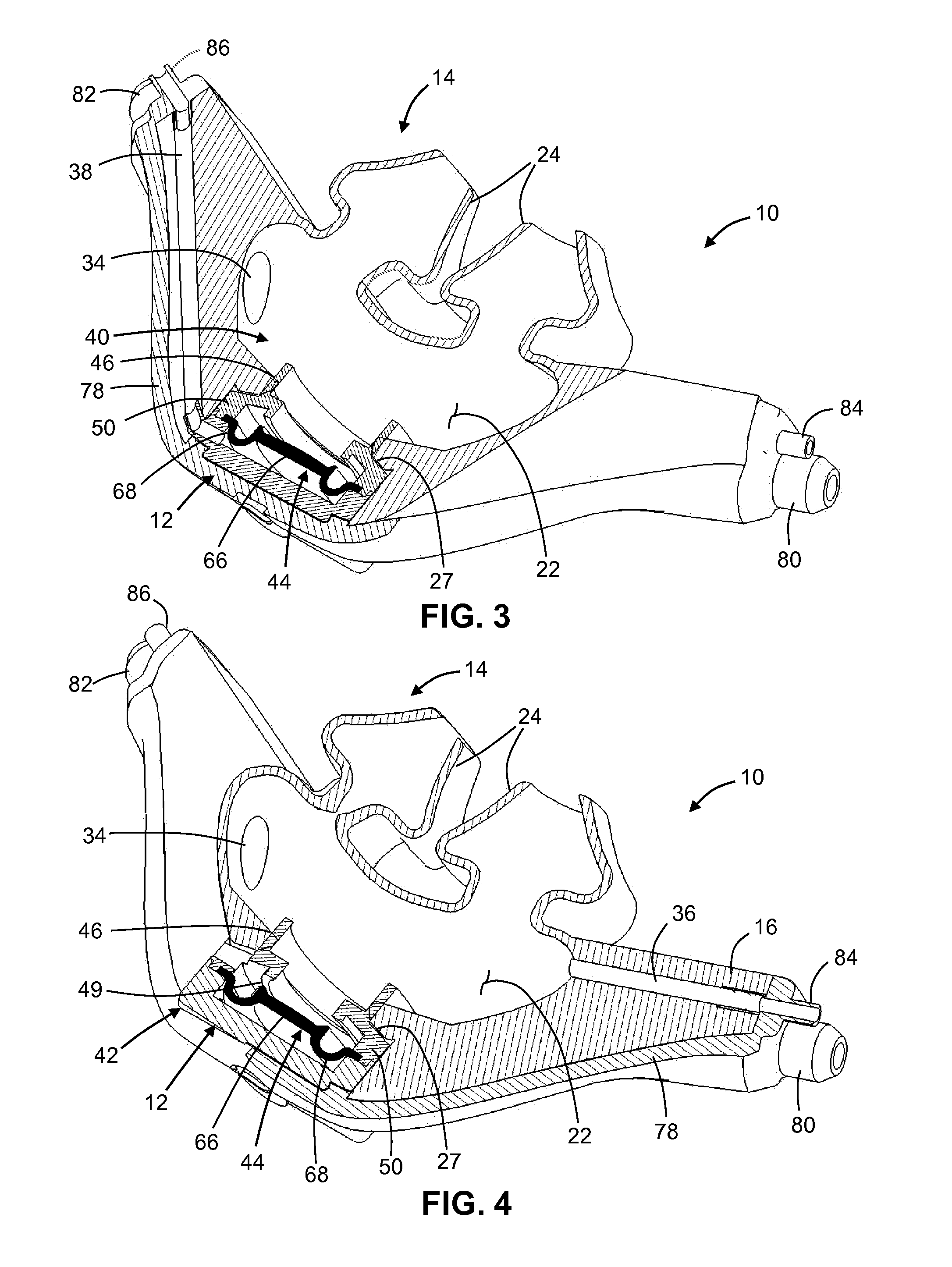
Methods and devices for providing mechanical ventilation with an open airway interface
ActiveUS20100071693A1Improve mobilityWork lessTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesIntensive care medicineAmbient air
Methods, systems and devices are described for providing mechanical ventilation support of a patient using an open airway patient interface. The system includes gas delivery circuit and patient interface configurations to optimize performance and efficiency of the ventilation system. A ventilation system may include a ventilator for supplying ventilation gas. A patient interface may include distal end in communication with a patient airway, a proximal end in communication with ambient air, and an airflow channel between the distal end and the proximal end. A gas delivery circuit may be adapted to attach to the patient interface without occluding the patient interface to allow ambient air to flow from outside the patient interface to the patient airway. The ventilation gas may entrain air from ambient and from the patient airway.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
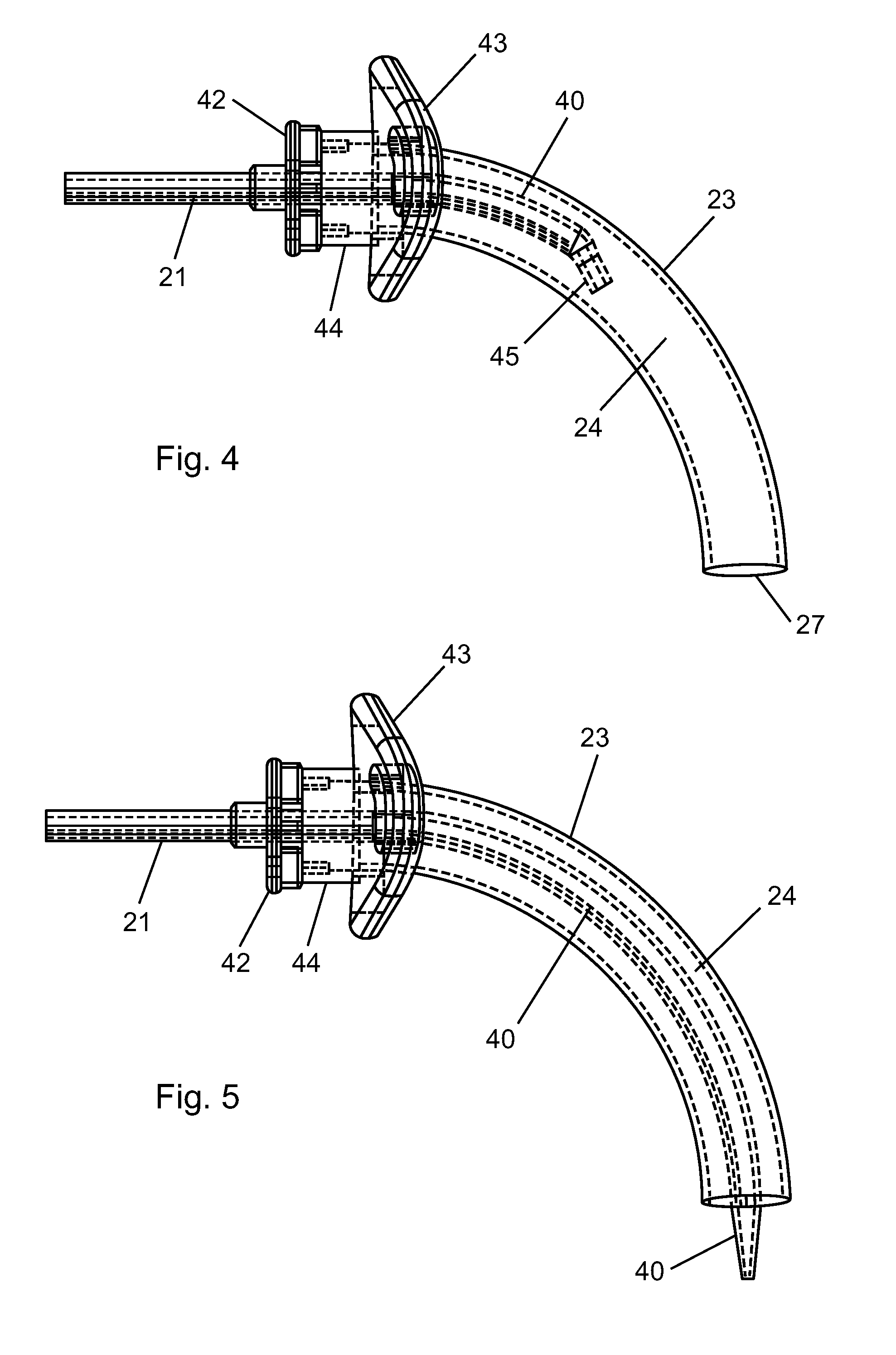
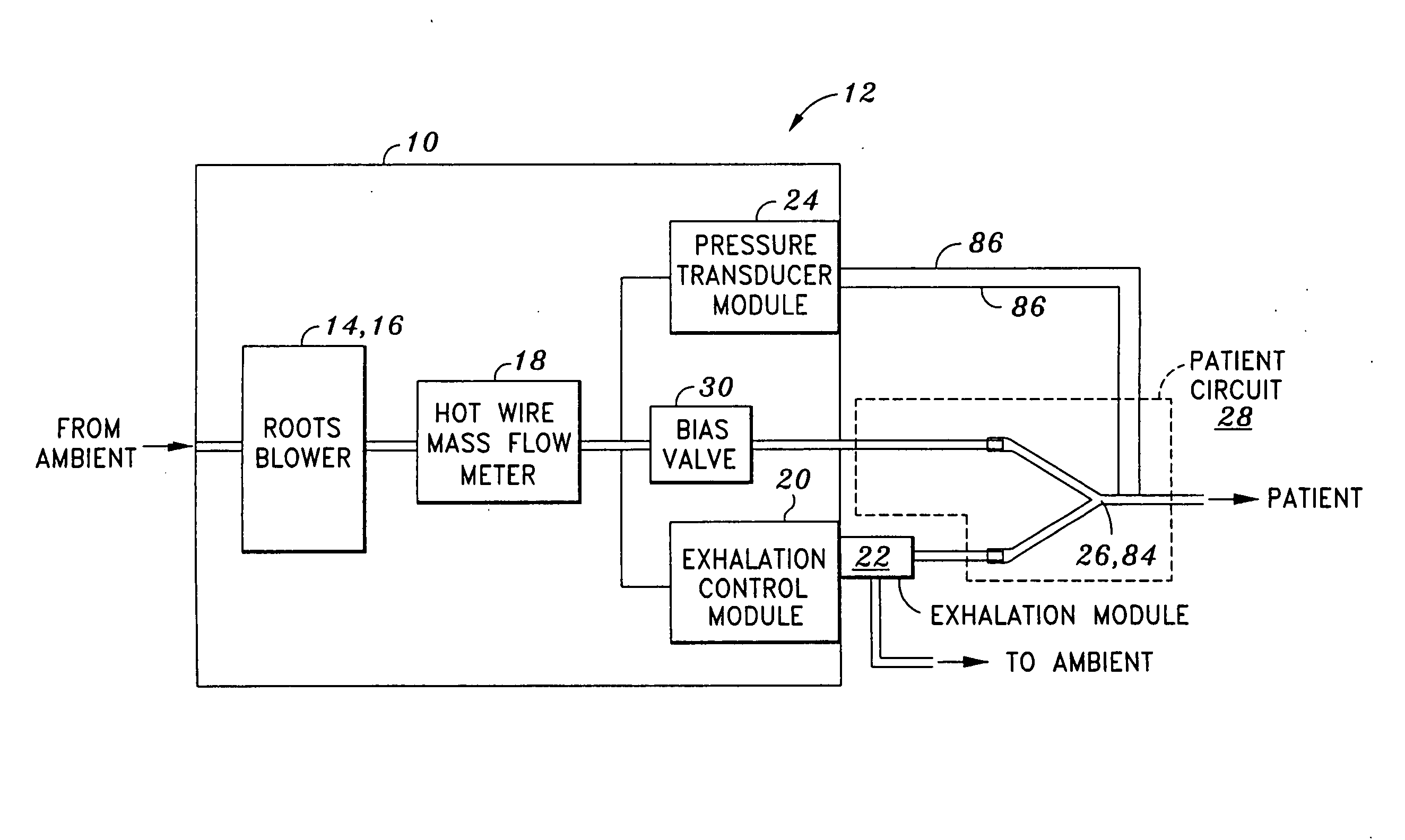
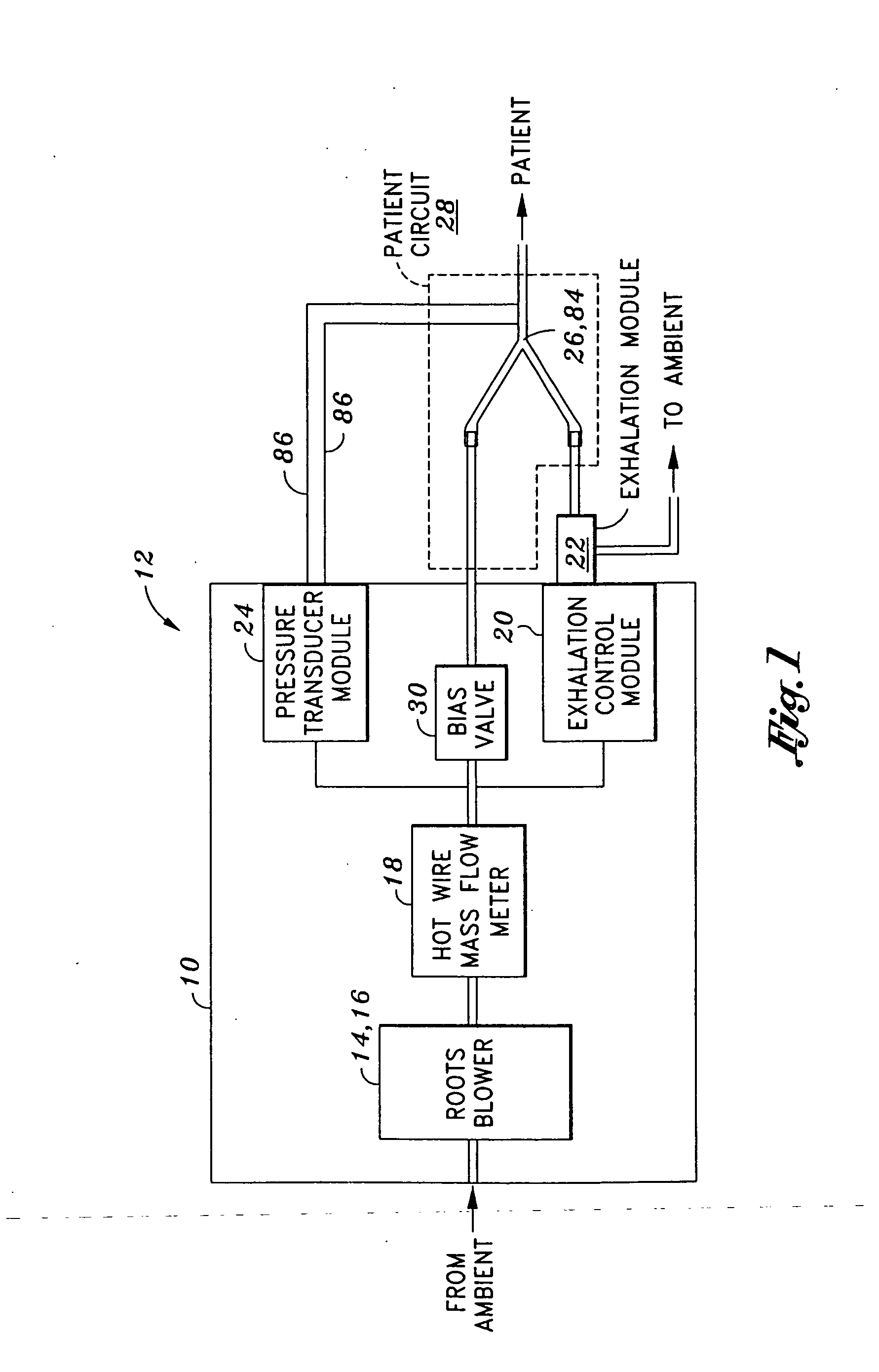
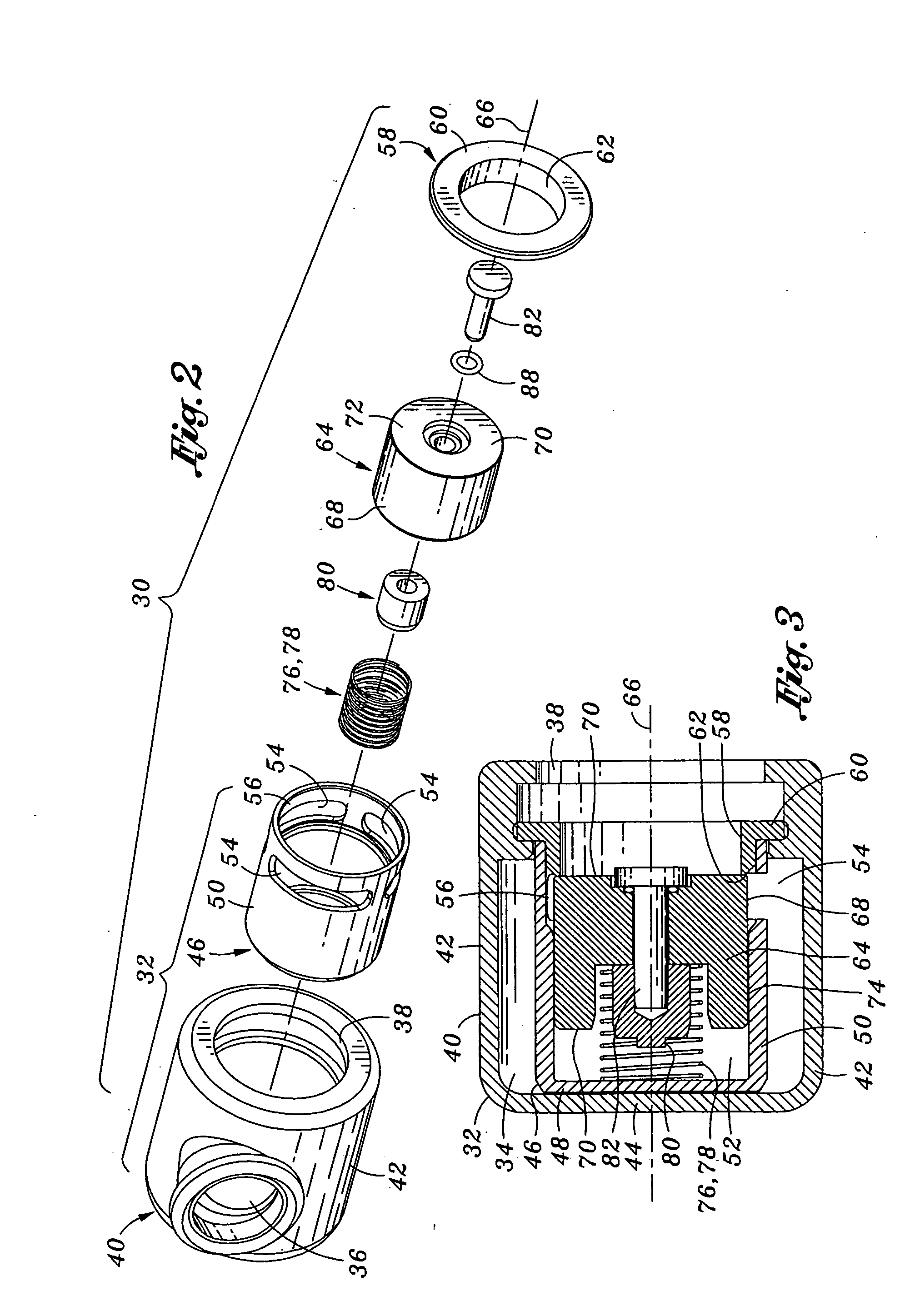
Mechanical ventilation system utilizing bias valve
ActiveUS20060249153A1Accurate measurementViscous dampingRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPositive pressureEngineering
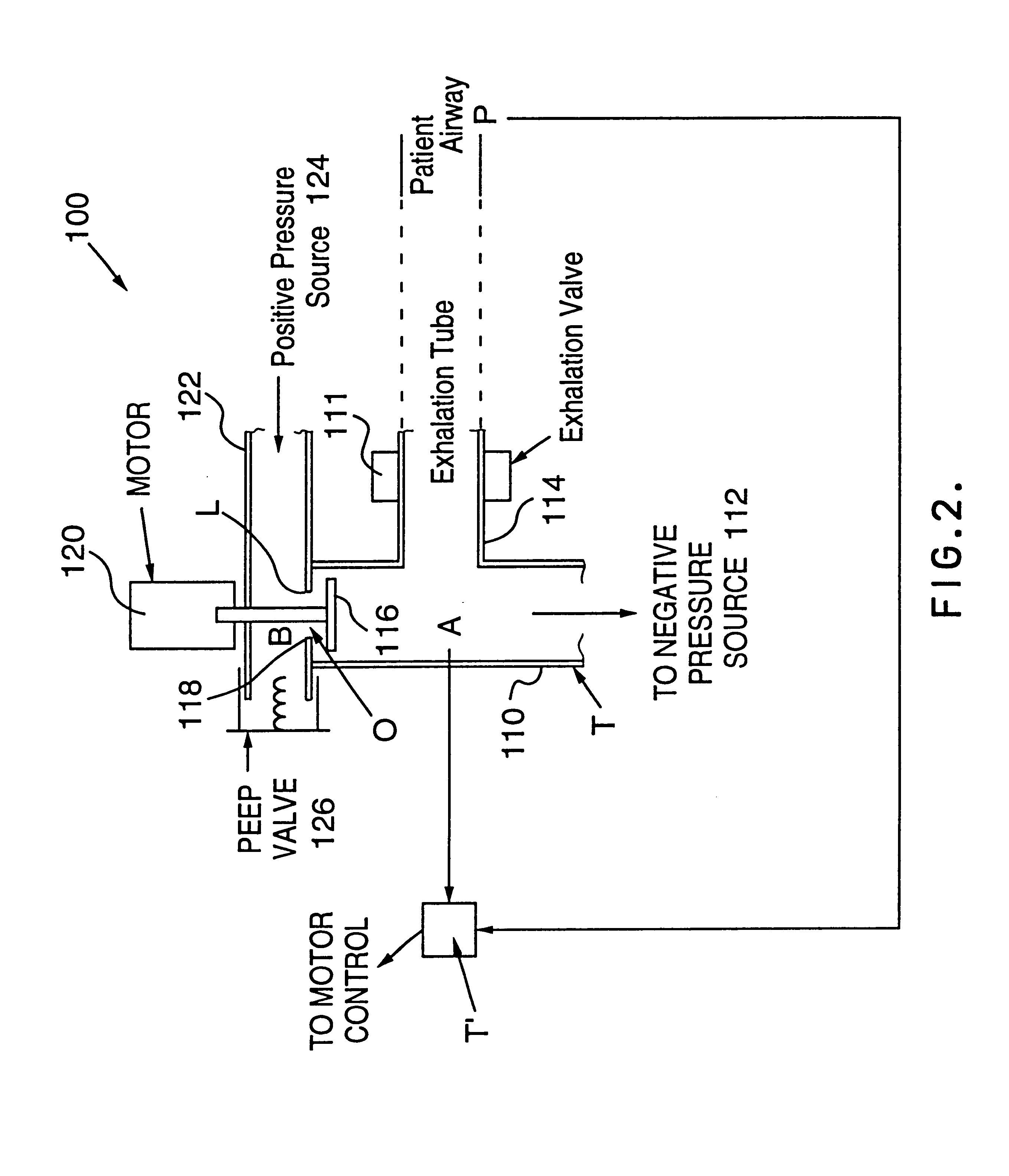
A portable mechanical ventilator having a Roots blower is configured to provide a desired gas flow and pressure to a patient circuit. The mechanical ventilator includes a flow meter operative to measure gas flow produced by the Roots blower and an exhalation control module configured to operate an exhalation valve connected to the patient circuit. A bias valve connected between the Roots blower and the patient circuit is specifically configured to generate a bias pressure relative to the patient circuit pressure at the exhalation control module. The bias valve is further configured to attenuate pulsating gas flow produced by the Roots blower such that gas flowing to the mass flow meter exhibits a substantially constant pressure characteristic. The bias pressure facilitates closing of the exhalation valve at the start of inspiration, regulates positive end expiratory pressure during exhalation, and purges sense lines via a pressure transducer module.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 203 INC
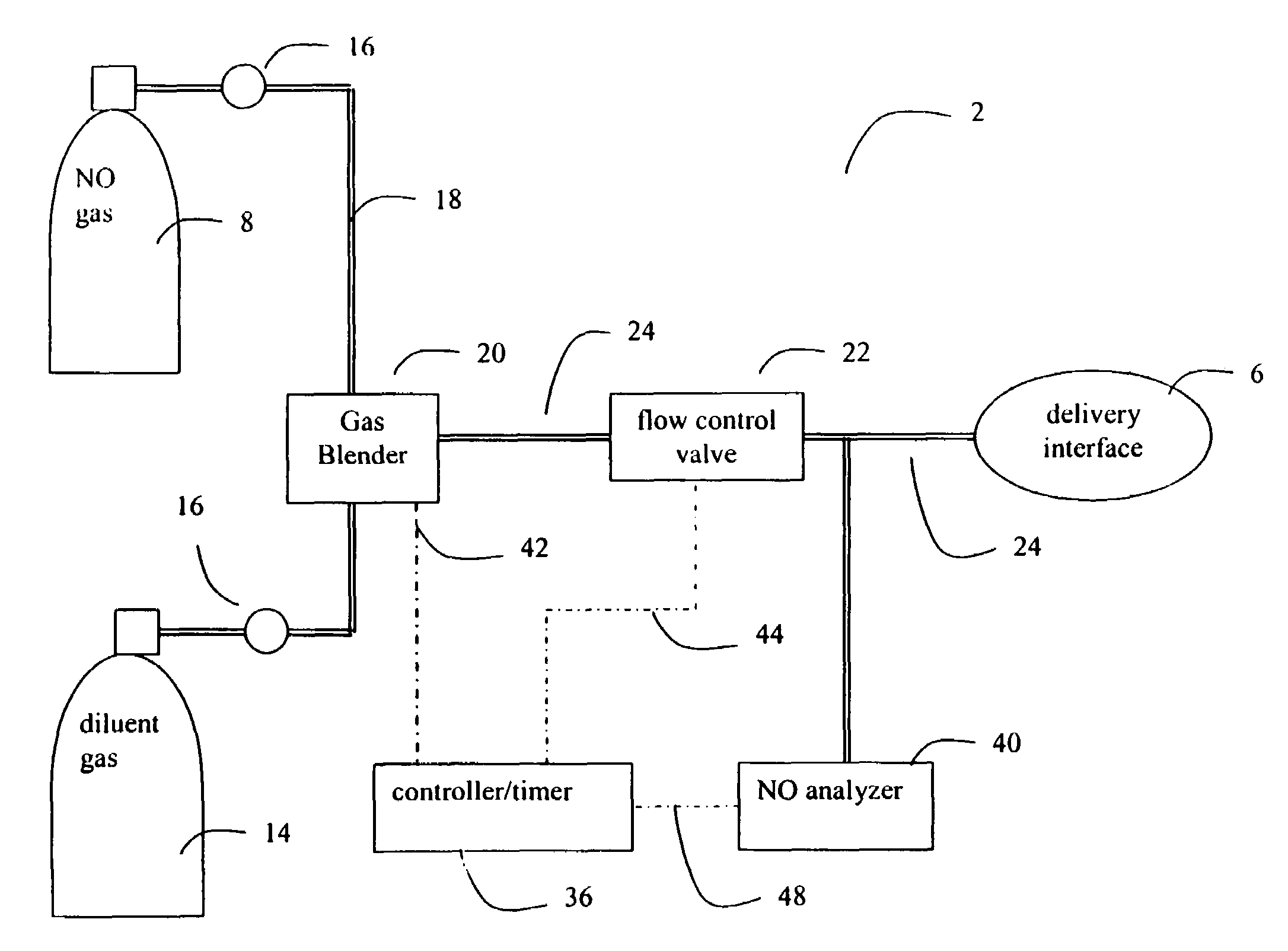
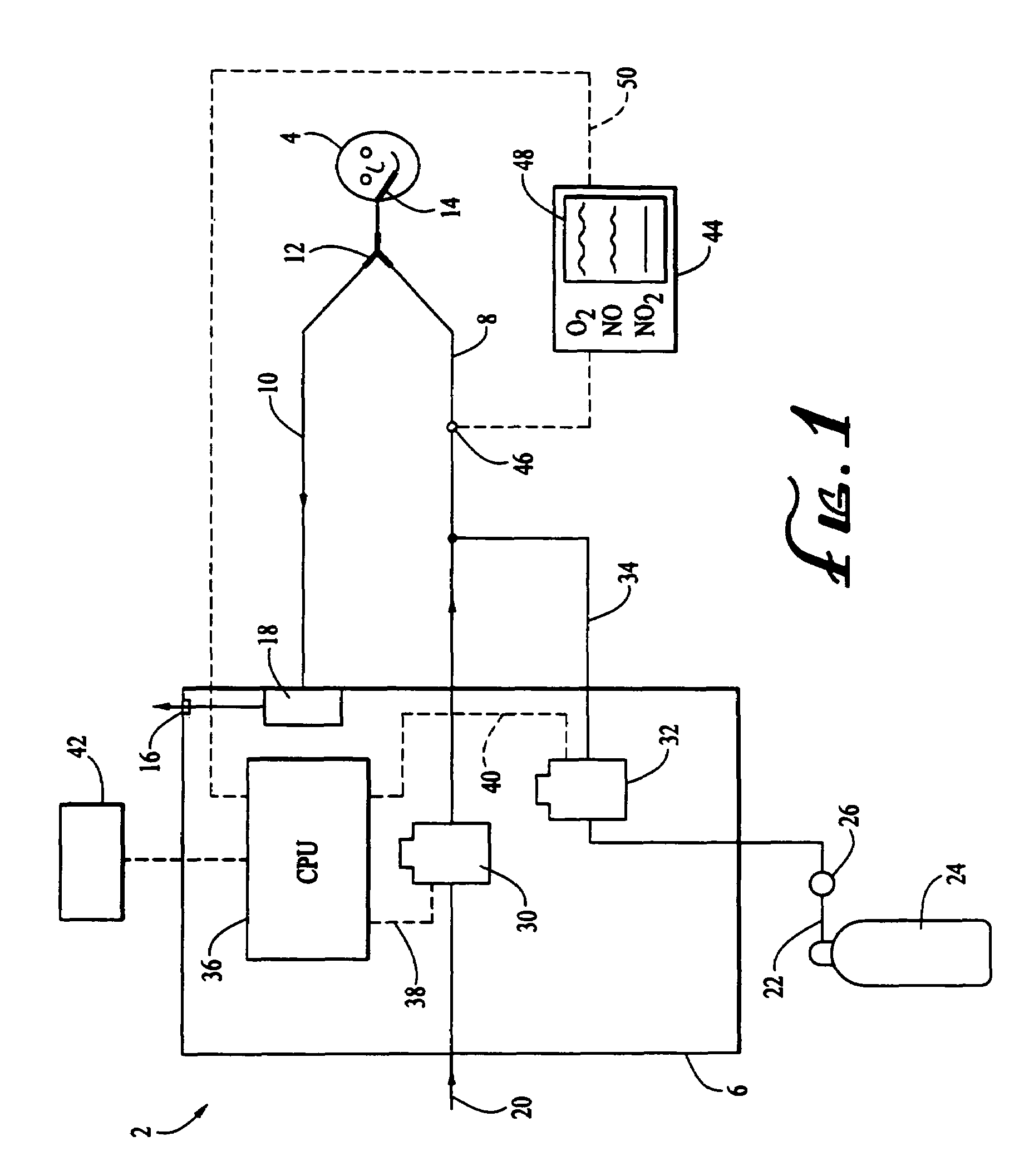
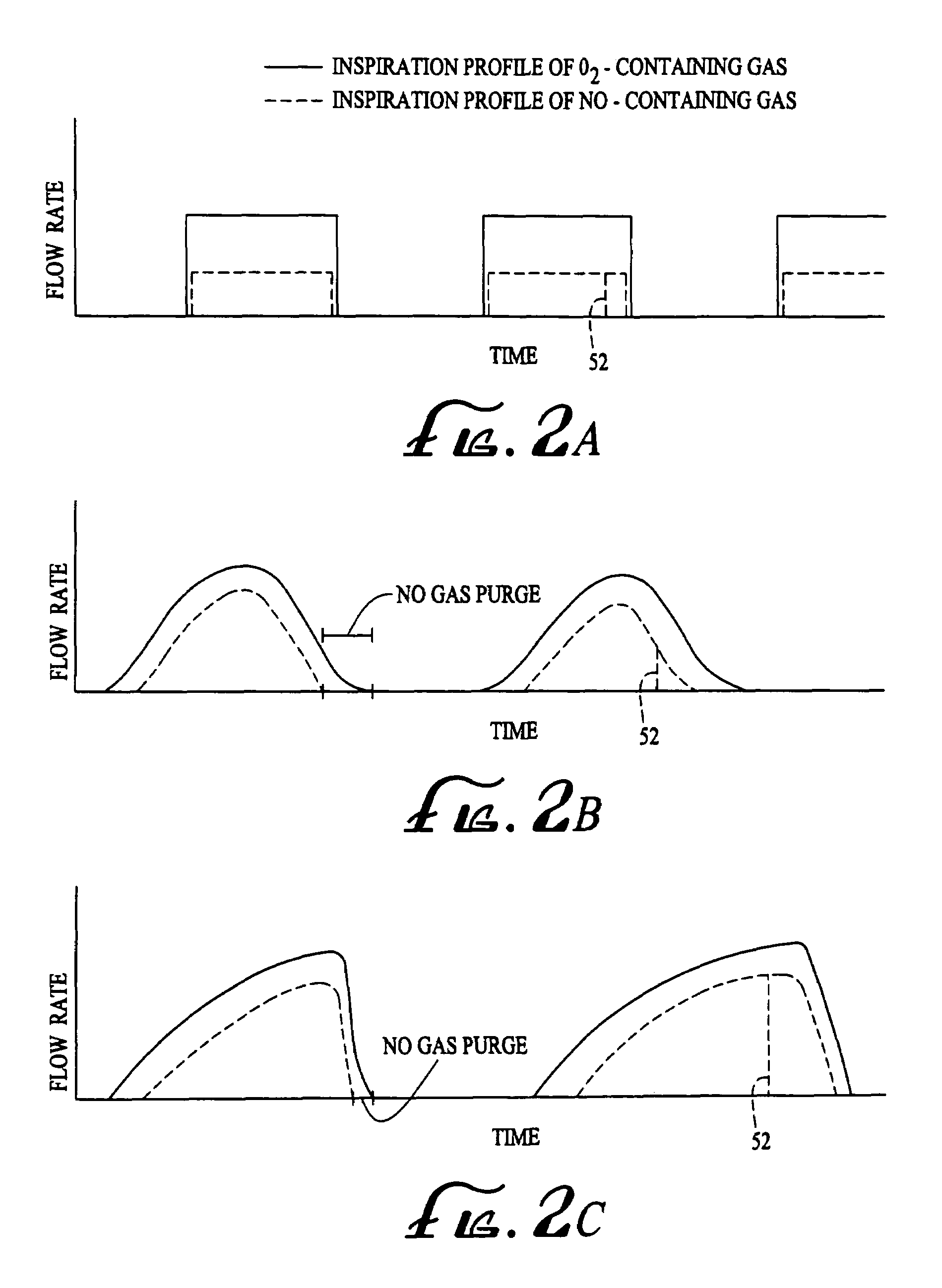
Method and apparatus for delivery of inhaled nitric oxide to spontaneous-breathing and mechanically-ventilated patients with intermittent dosing
InactiveUS7516742B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingNitric oxide
A device and method is disclosed for delivering NO to a patient. The device utilizes a single controller that controls two separate flow controllers to deliver an oxygen-containing gas and a NO-containing gas to the patient to provide NO-containing gas at a flow profile that is proportional or quasi-proportional to a flow profile of the oxygen-containing gas throughout patient inspiration. The controller further comprises logic for setting a nitric oxide delivery profile comprising at least two different concentrations of nitric oxide containing gas and for automatically switching between the at least two different concentrations of nitric oxide containing gas on a timed basis.
Owner:VYAIRE MEDICAL 207 INC +1
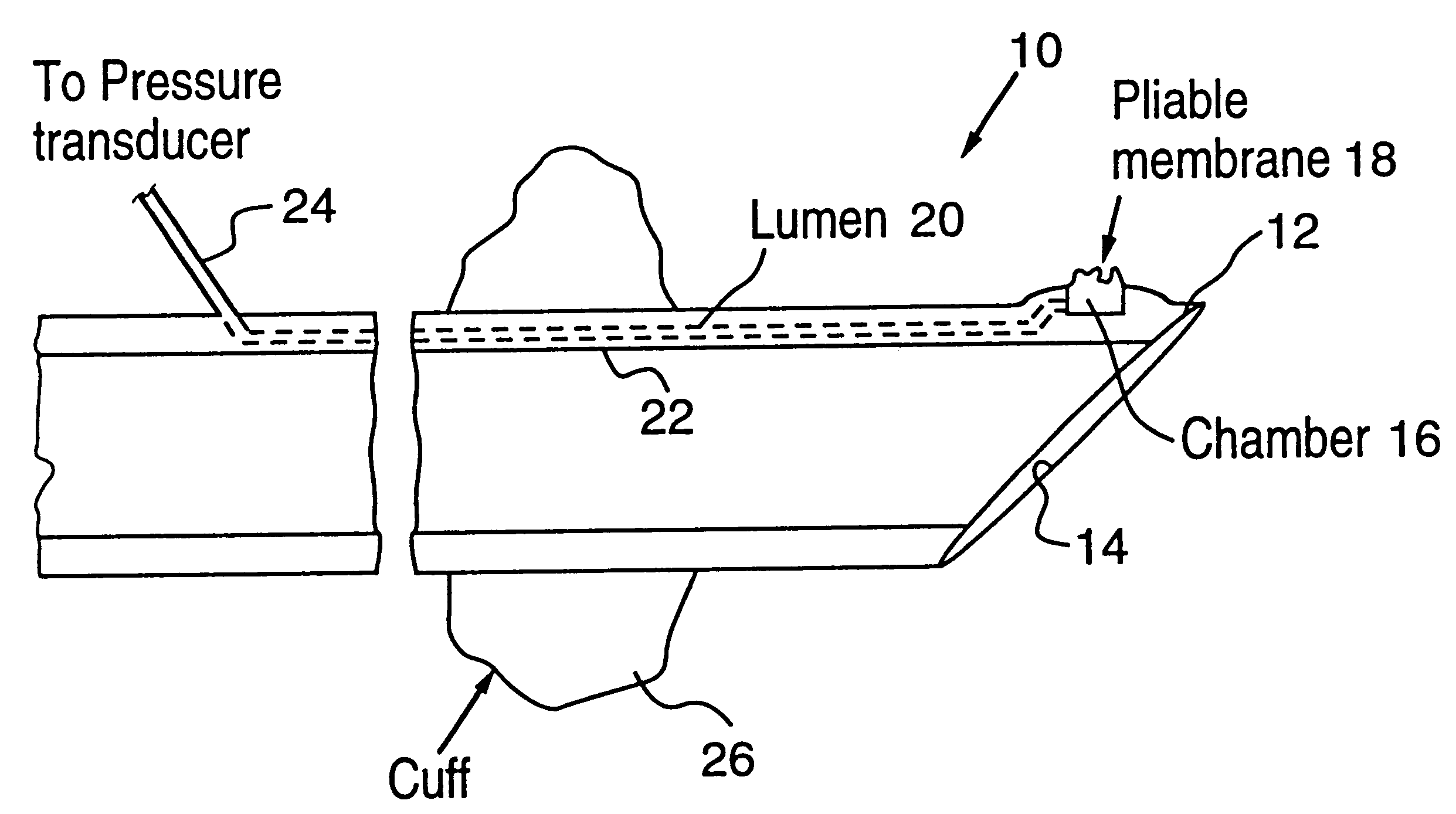
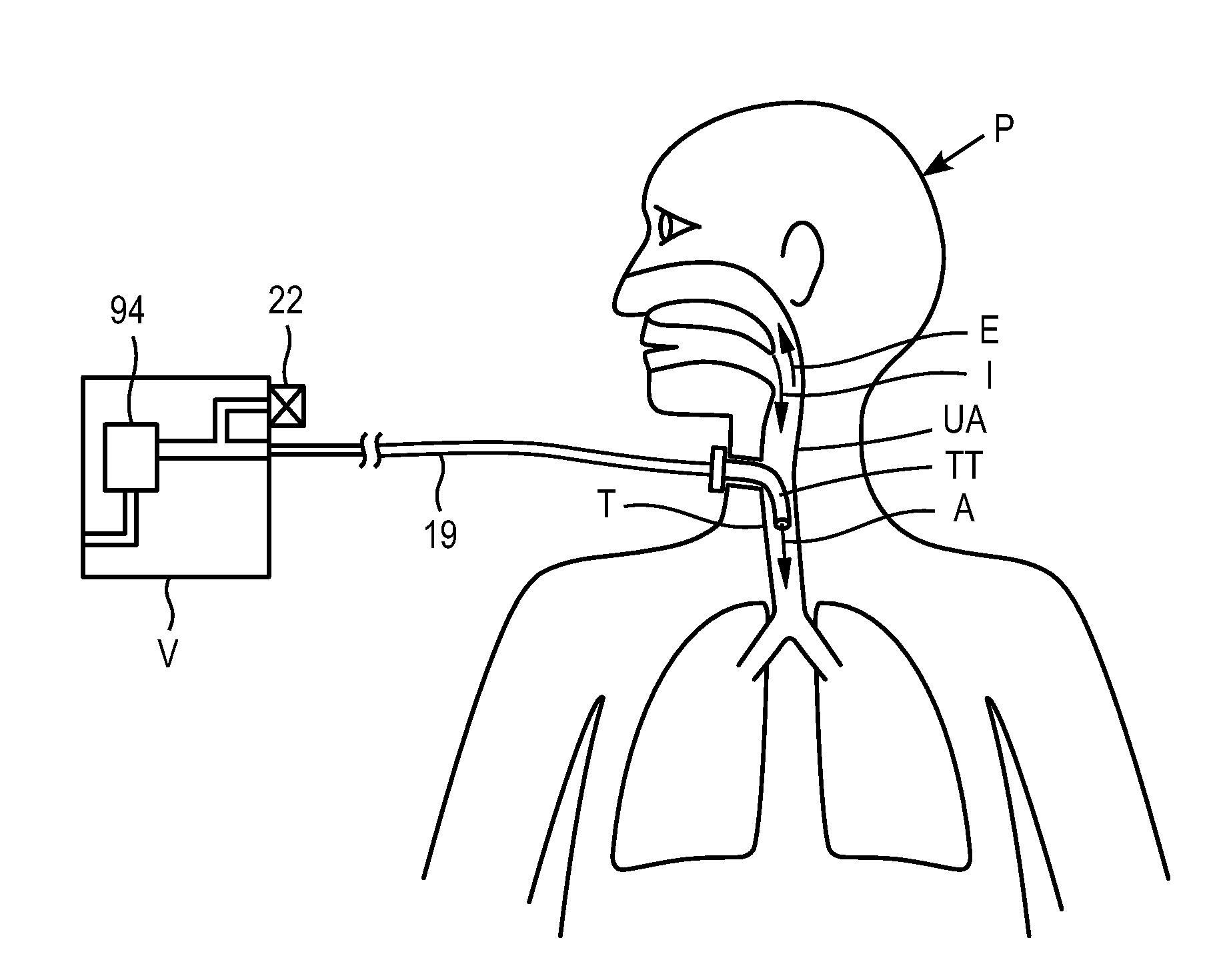
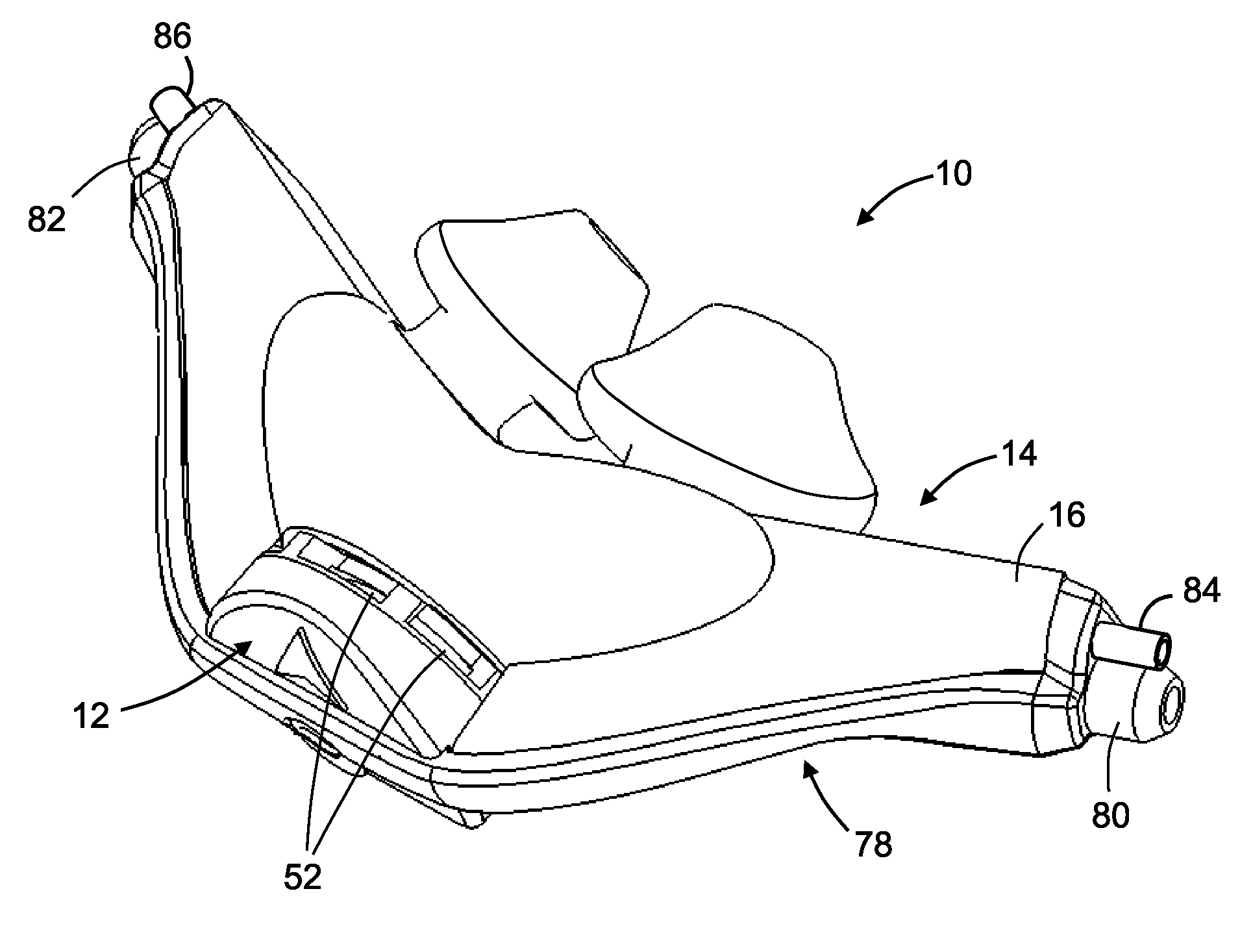
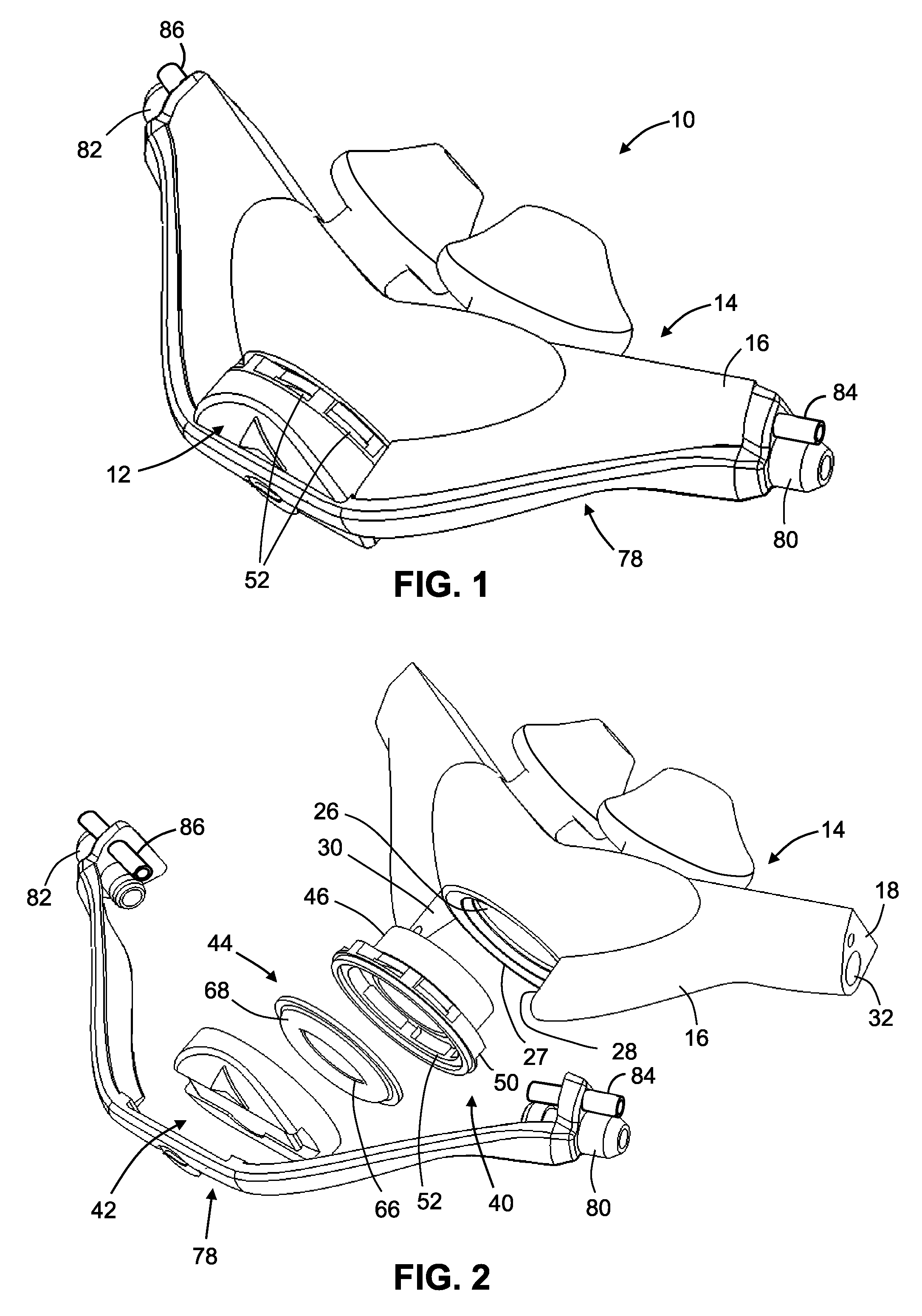
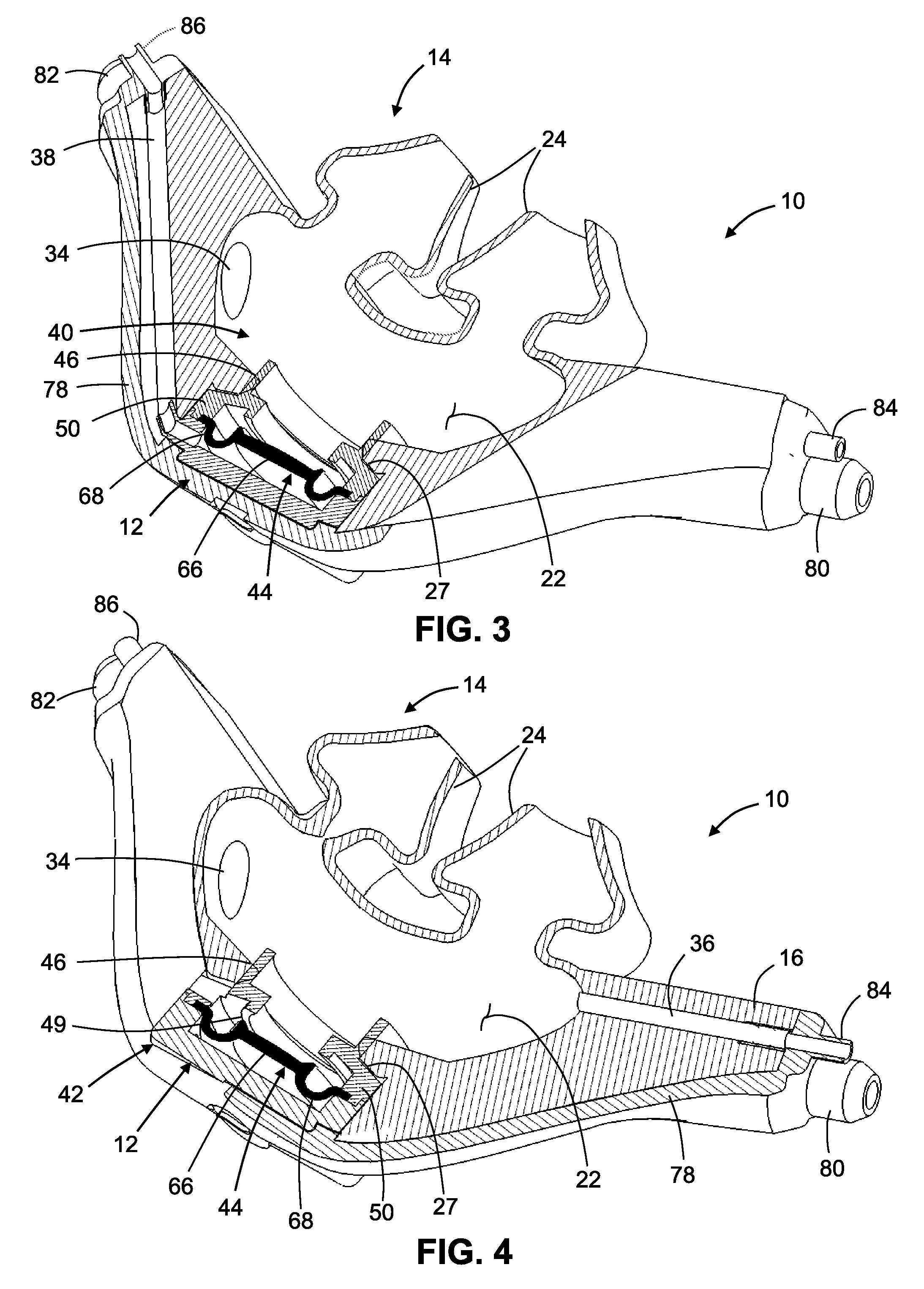
Control of airway pressure during mechanical ventilation
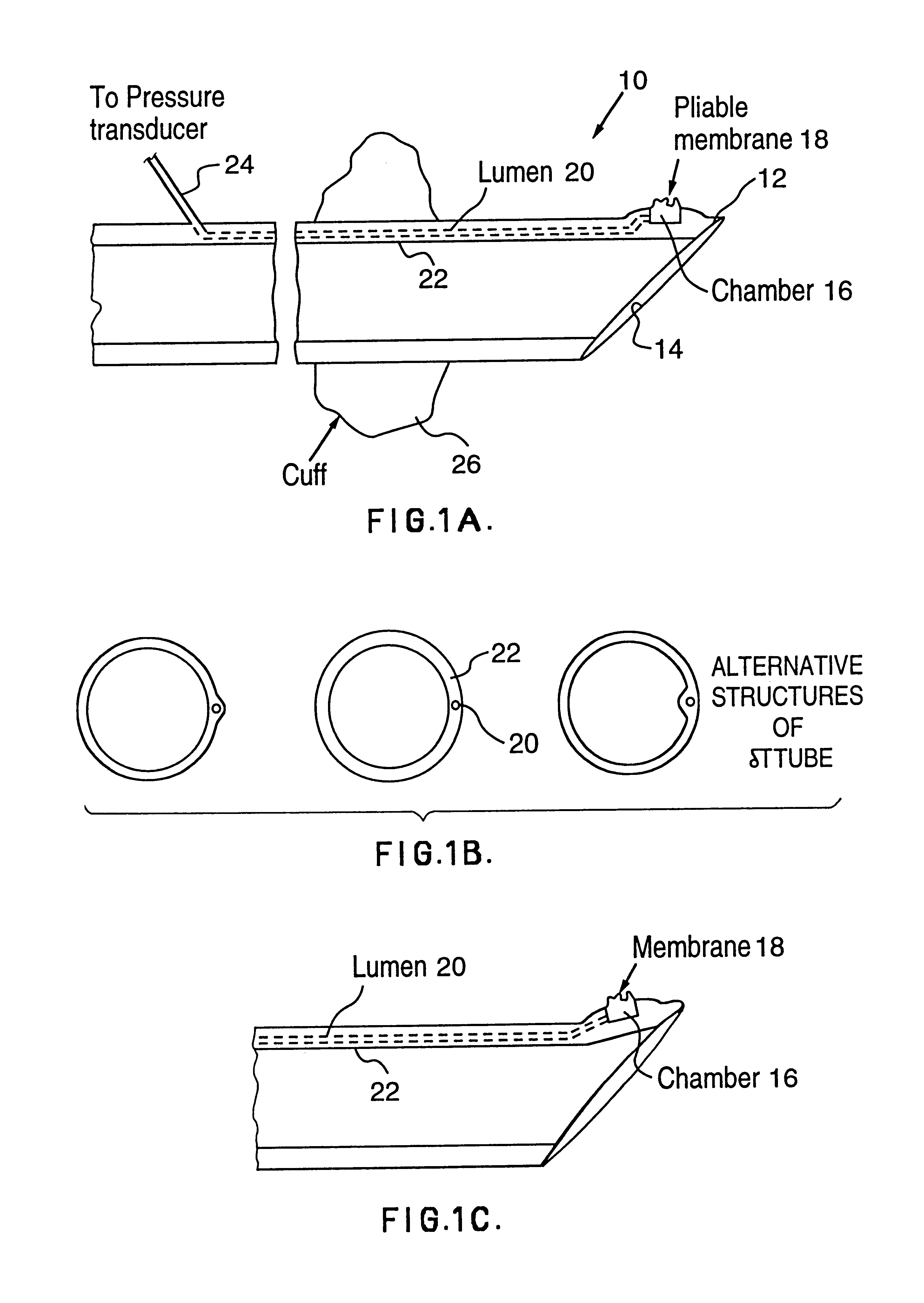
A endotracheal tube for patient ventilation is modified to permit measurement of pressure at the patient trachea by providing a chamber in the end of the ET tube to be located in the patient, airway. This chamber has a highly pliant external wall with a degree of redundancy and is connected to a pressure measuring device exterior of the patient by a lumen in the wall of the ET tube. In addition, apparatus for controlling airway pressure during exhalation comprises valve means connected via a first inlet to an exhalation tube from a patient airway, connected to a source of negative pressure through an outlet and having a second inlet with a variable flow control means for controlling the flow of gas therethrough. Gas pressure is controlled within the valve by varying the pressure gradient between the upstream and downstream sides of the second inlet so that it equals the pressure gradient between the patient airway and the downstream side of the second inlet.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA
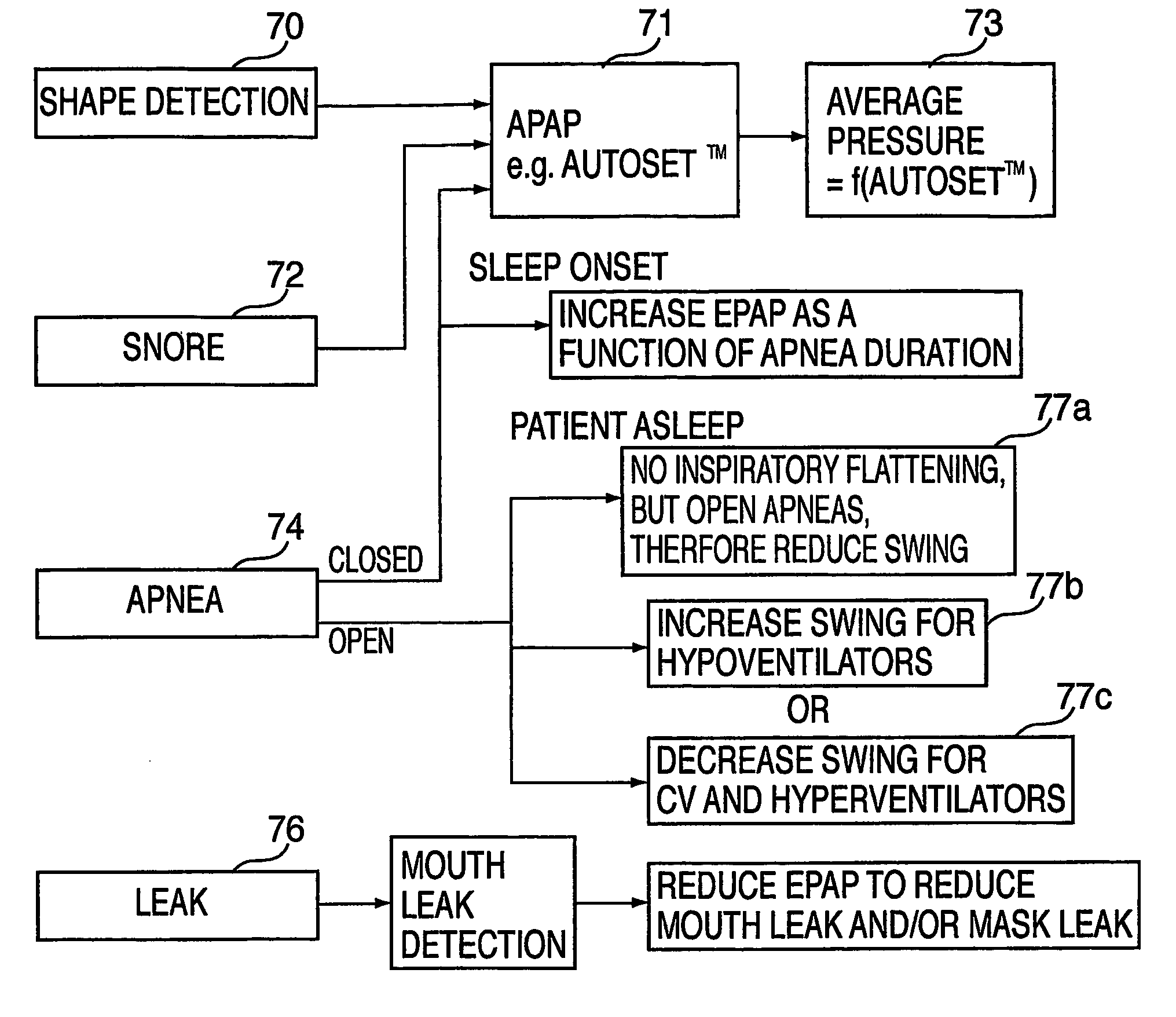
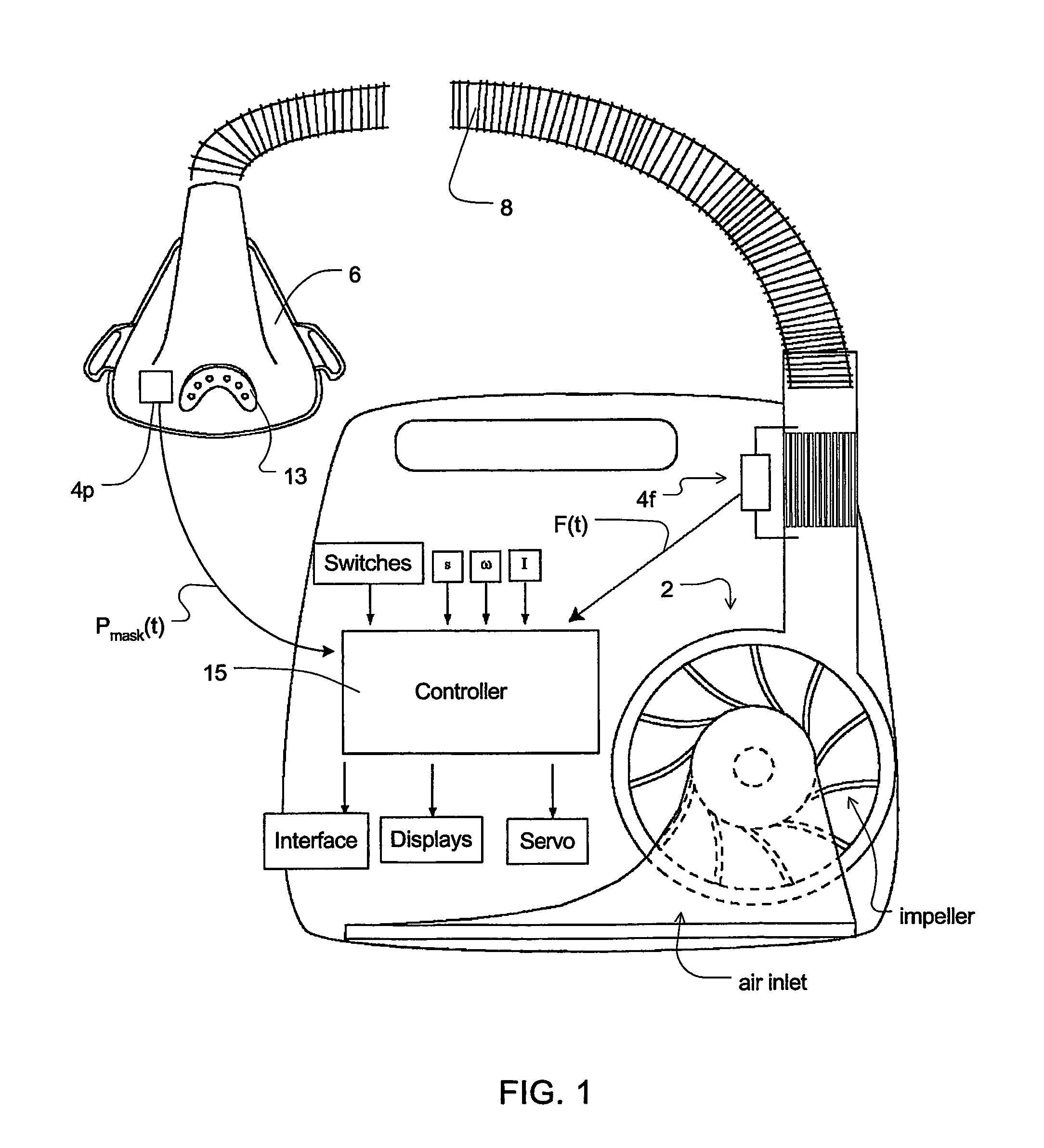
Mechanical ventilation in the presence of sleep disordered breathing
ActiveUS20070215146A1Operating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksHypopneaSleep disordered breathing
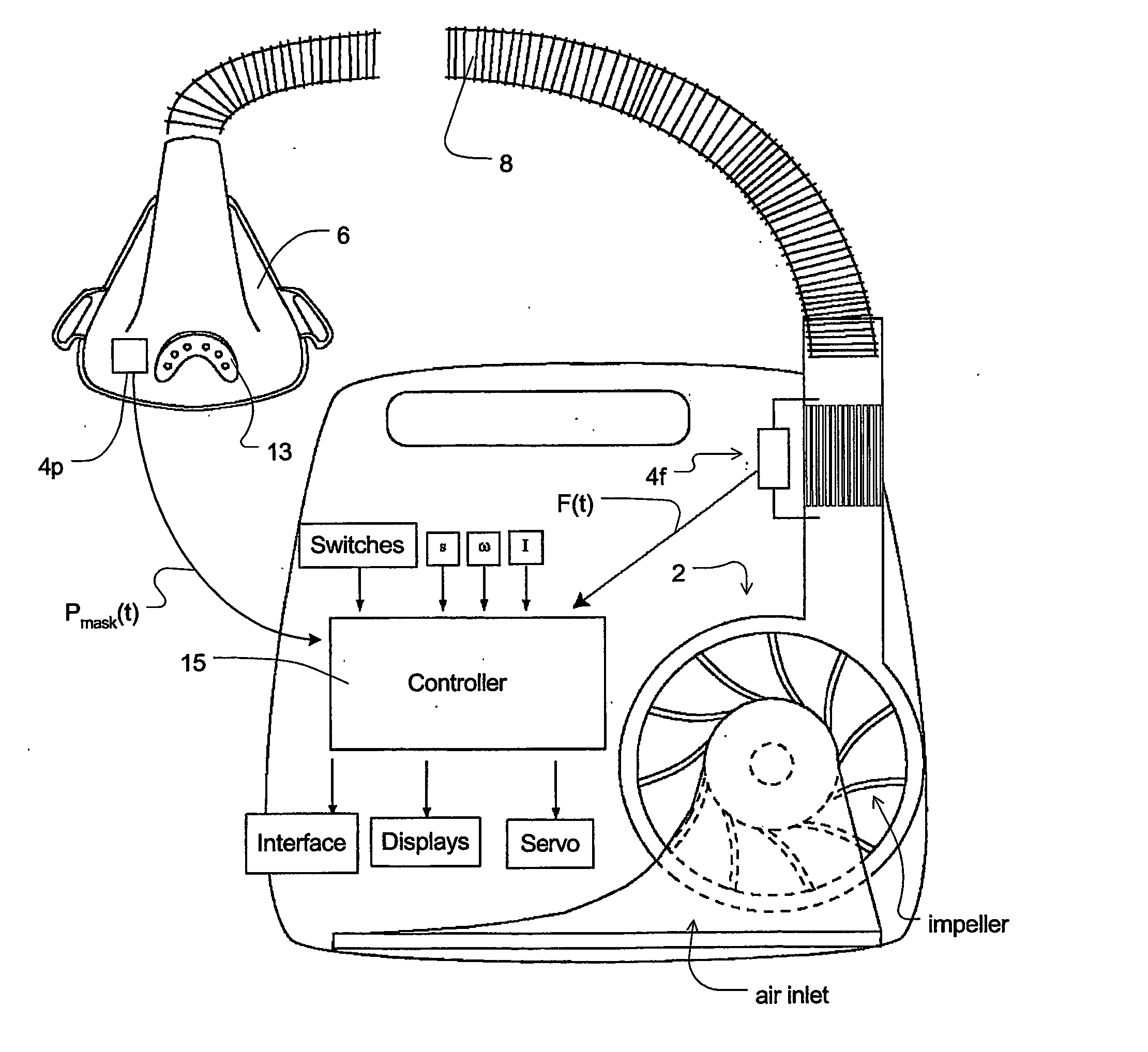
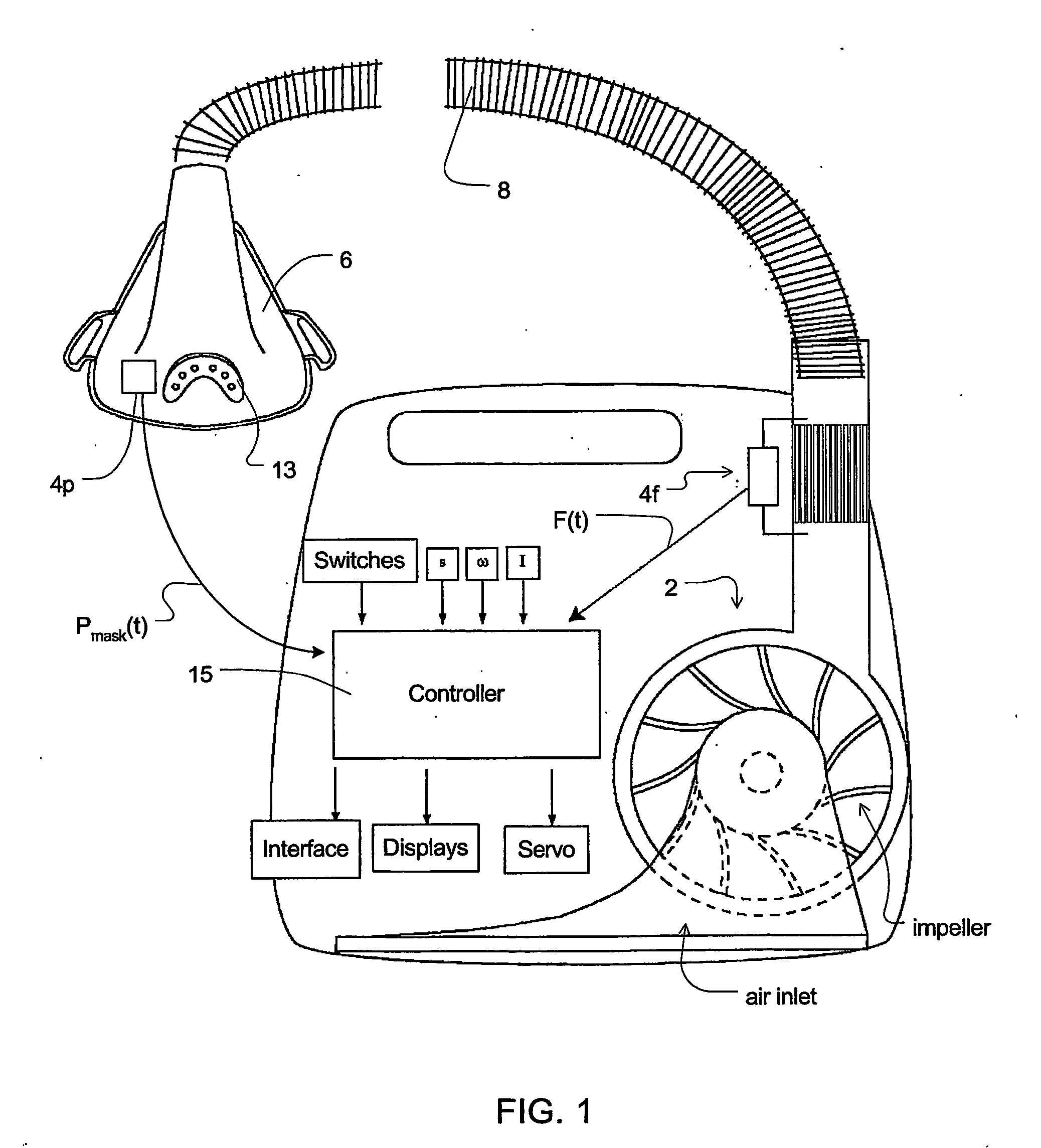
A method for controlling operation of a CPAP apparatus. The apparatus has a blower (2), a patient interface (6), an air delivery conduit (8) for delivering air from the blower (2) to the patient interface (6), a sensor (4p) for determining the pressure in the patient interface (6), and a control mechanism (15) that causes air to be delivered at a desired pressure to the patient interface (6) and that detects transitions between inhalation and exhalation of a respiratory cycle of a patient in order to synchronise the blower output with the patient's efforts. In one form the CPAP apparatus provides pressure in accordance with a bi-level waveform with at least one characterising parameter of the waveform being automatically adjusted in accordance with indications of sleep disordered breathing. The indications of sleep disordered breathing can be one or more of snoring, apnea, hypopnea, and flow limitation.
Owner:RESMED LTD
Out flow resistance switching ventilator and its core methods
InactiveUS20080011301A1Ensure ventilation safetyIncrease spaceRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesAutonomous breathingFlow resistivity
An out flow resistance switching ventilator and its methodology for providing mechanical ventilation support to the respiratory failure patient are claimed. Based on the continuous out flow impounding ventilation mechanism, the apparatus provides ventilation by switching flow resistance between two different levels at a continuous gas flow system outlet valve controlled by patient's spontaneous breathing or preset mandatory parameters, resulting in airway pressure levels switching, and therefore creating lung volume switching, which is totally different from either volume ventilation or pressure ventilation mechanism utilized in the current conventional ventilators.
Owner:QIAN YUANCHENG
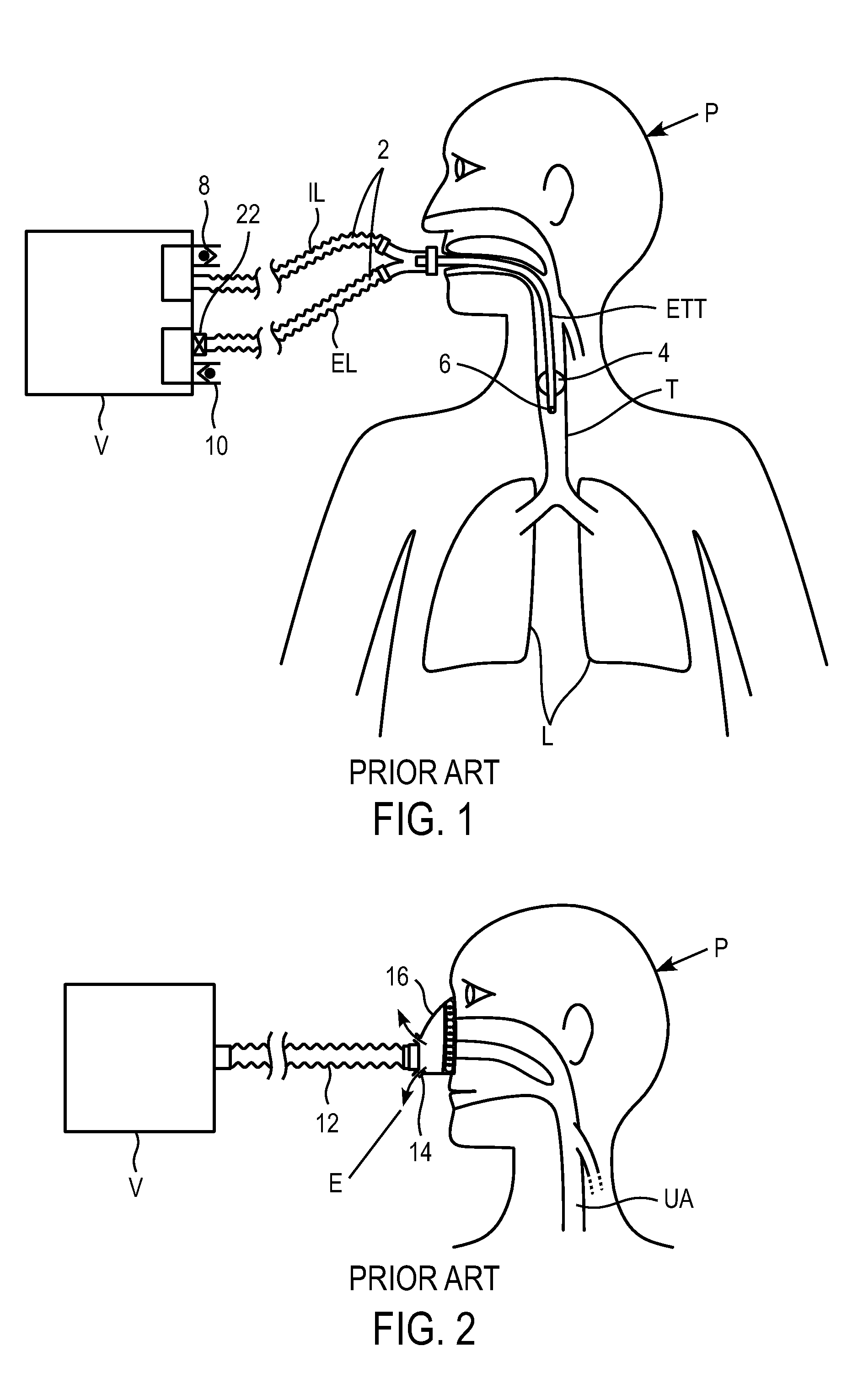
Endotracheal Tube and Intubation System Including Same
ActiveUS20090038620A1Reduce chanceEfficient evacuationTracheal tubesMedical devicesTracheal tubeSubglottic area
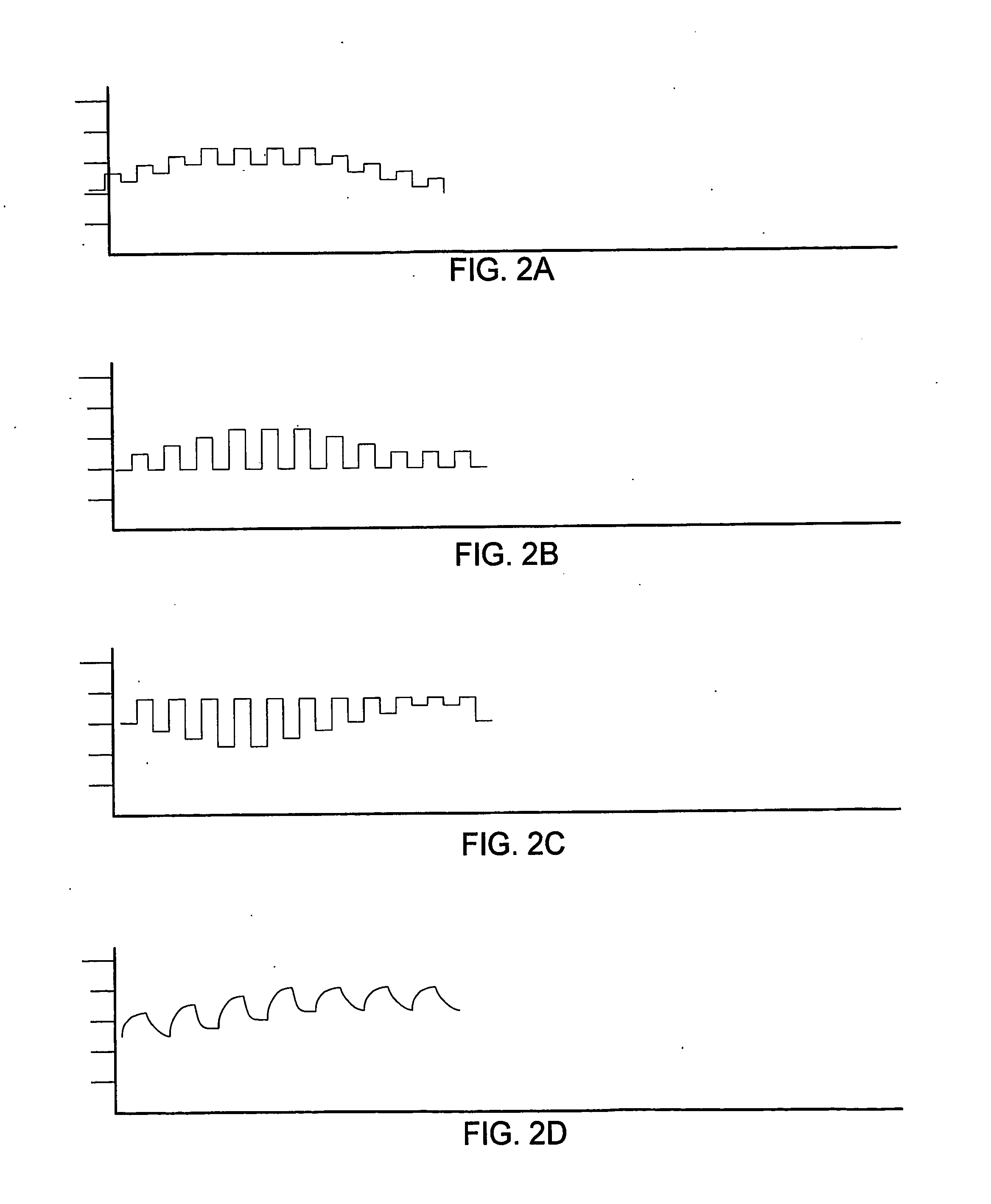
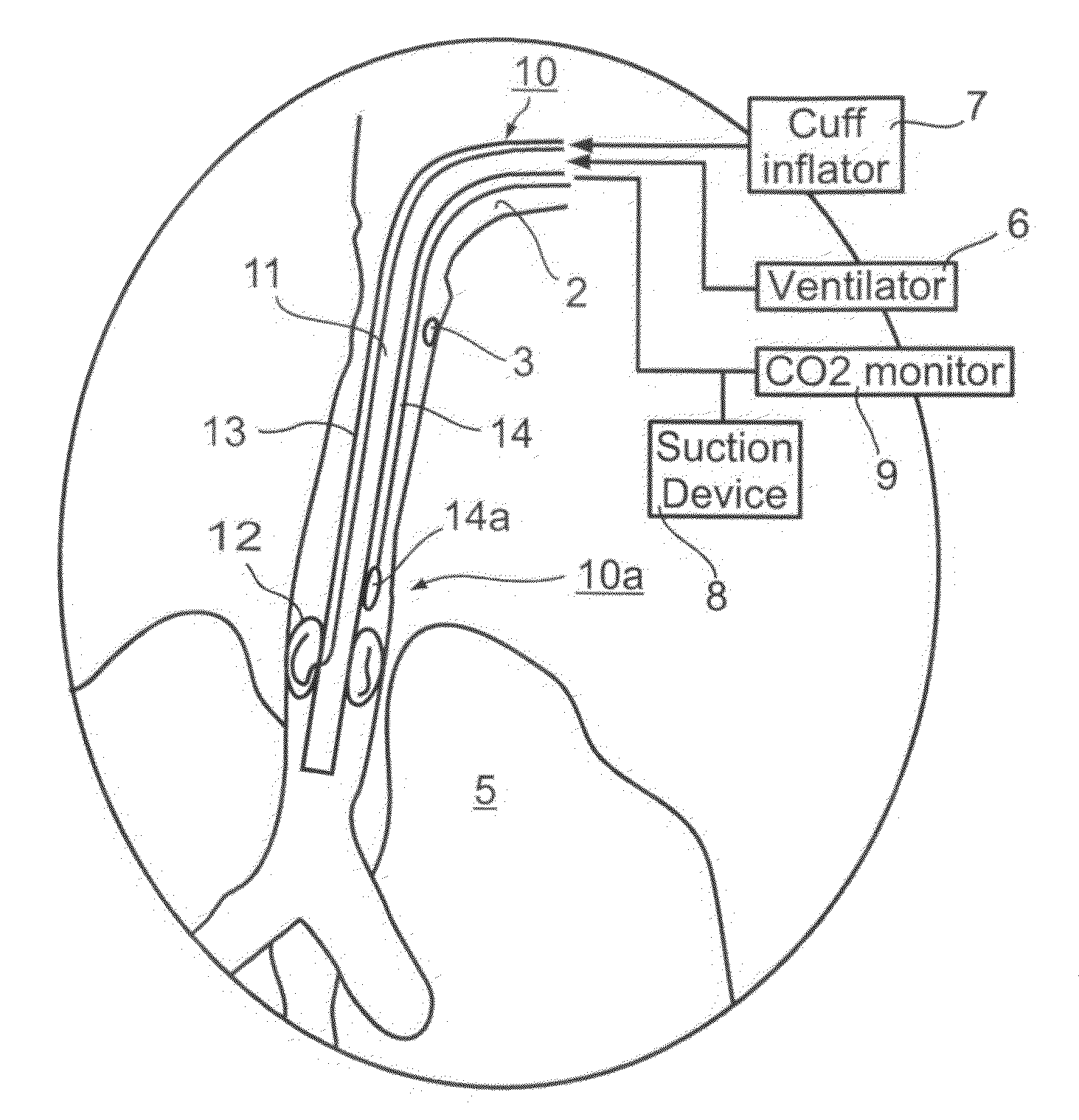
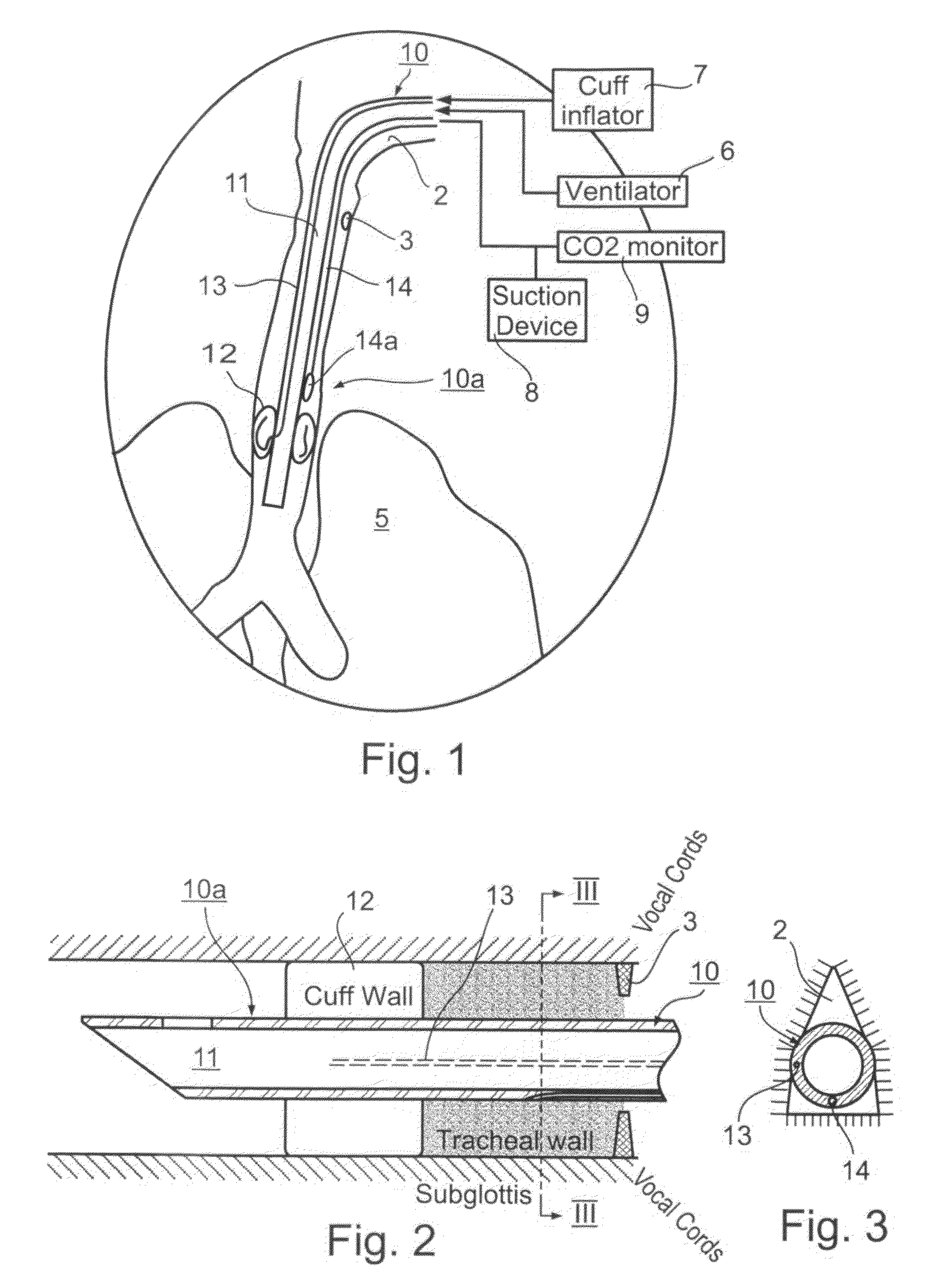
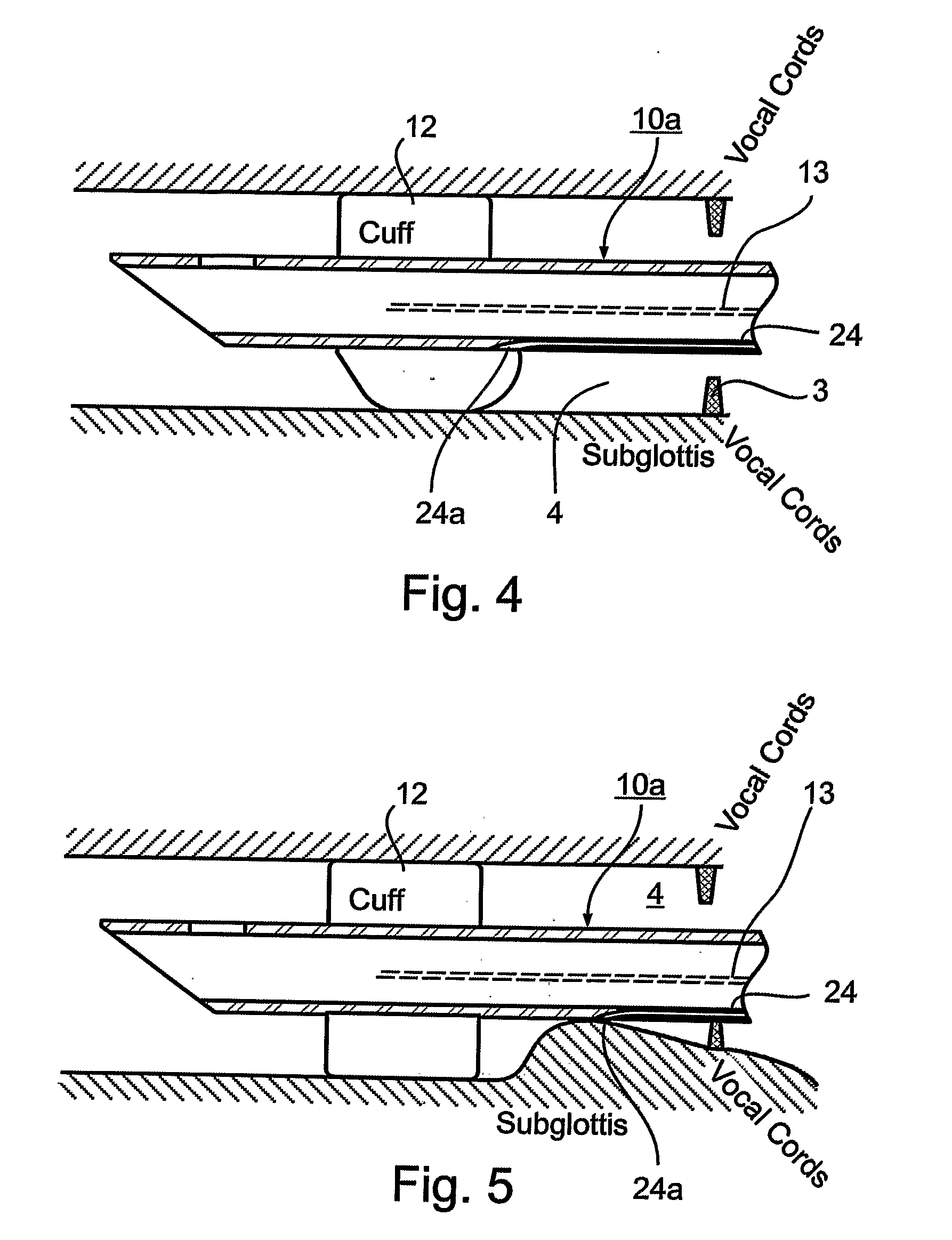
An endotracheal tube for mechanically ventilating patients is disclosed. The endotracheal tube comprises a distal end for insertion into the patient's airway, past the vocal chords, through the subglottal region, and into the patient's lung; and a proximal end for connection to a mechanical ventilator. The endotracheal tube further comprises a cuff at the distal end of the endotracheal tube to be located in the subglottal region of the patient below the vocal chords, an inflating lumen for inflating the cuff, and a suction lumen having a suction inlet port leading from the outer surface of the endotracheal tube, and to be located in the subglottal region, for evacuating secretions and / or rinsing fluid from the subglottal region during the mechanical ventilation of the patient. The distal end of the endotracheal tube is formed with an outer surface configuration effective to prevent blockage of the suction inlet port by the cuff or by tracheal mucosal tissue of the patient during a negative pressure condition in the suction lumen.
Owner:HOSPITECH RESPIRATION
Apparatus and computer program for determining a patient's volemic status represented by cardiopulmonary blood volume
InactiveUS20080045845A1The implementation process is simpleLess laborRespiratorsCatheterAutonomous breathingNormal blood volume
An apparatus for determining a patient's volemic status can make use of a physiological heart-lung interaction during spontaneous breathing or mechanical ventilation. Further, a computer program for determining the patient's volemic status has instructions for carrying out the steps of generating data of a physiological heart-lung interaction during spontaneous breathing or mechanical ventilation, and determining the patient's volemic status when making use of the data of the physiological heart-lung interaction, when run on a computer.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCE IPRM AG
Ventilation mask with integrated piloted exalation valve
ActiveUS20120325205A1High functional dead spaceReduce trafficRespiratory masksBreathing masksExhaust valvePositive pressure
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a mask for achieving positive pressure mechanical ventilation (inclusive of CPAP, ventilator support, critical care ventilation, emergency applications), and a method for a operating a ventilation system including such mask. The mask of the present invention includes a piloted exhalation valve that is used to achieve the target pressures / flows to the patient. The pilot for the valve may be pneumatic and driven from the gas supply tubing from the ventilator. The pilot may also be a preset pressure derived in the mask, a separate pneumatic line from the ventilator, or an electro-mechanical control. The mask of the present invention may further include a heat and moisture exchanger (HME) which is integrated therein.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
Methods and devices for providing inspiratory and expiratory flow relief during ventilation therapy
ActiveUS20090151724A1Breathe freelyUndesirable pressureRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory supportAirway pressures
Respiratory support and / or controlled mechanical ventilation of a patient are provided. A ventilation apparatus may include a ventilator, a transtracheal prosthesis, and a respiratory relief device. The transtracheal prostheses and ventilation catheter may be arranged such that the patient can breathe freely through the upper airway and / or the tracheal prostheses. Respiratory sensors may measure a breathing rate, lung pressure, airway pressure, or a combination thereof. Pulses of gas may be provided to the patient through the ventilation catheter during inspiration. The pulses may have a first volume while the patient breathes normal and a second volume when the sensors detect a cessation of breathing or reduction in breathing volume. The second volume may be provided at 1-5 times the normal breathing rate, with a volume 25-500% times the first volume, or both.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
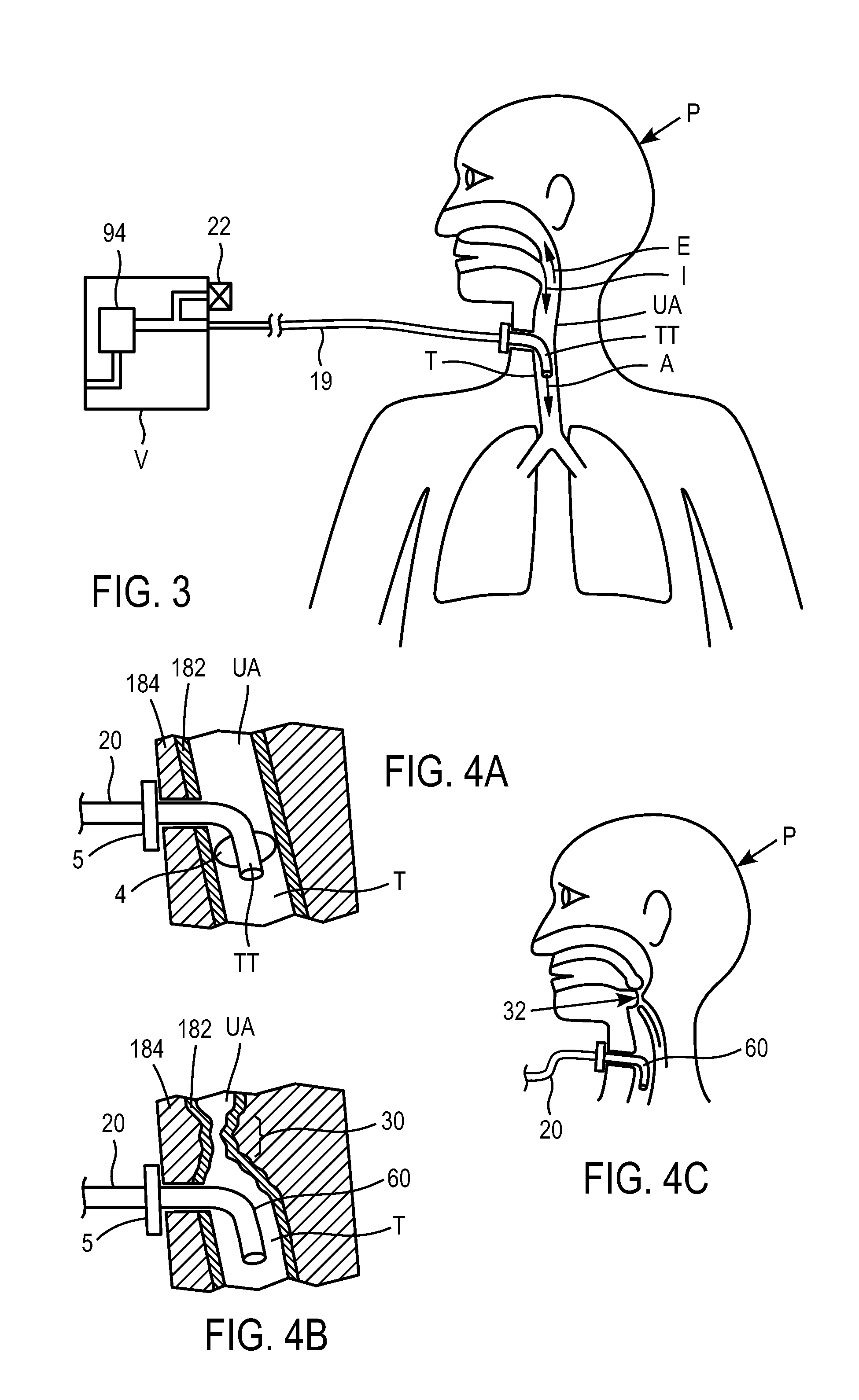
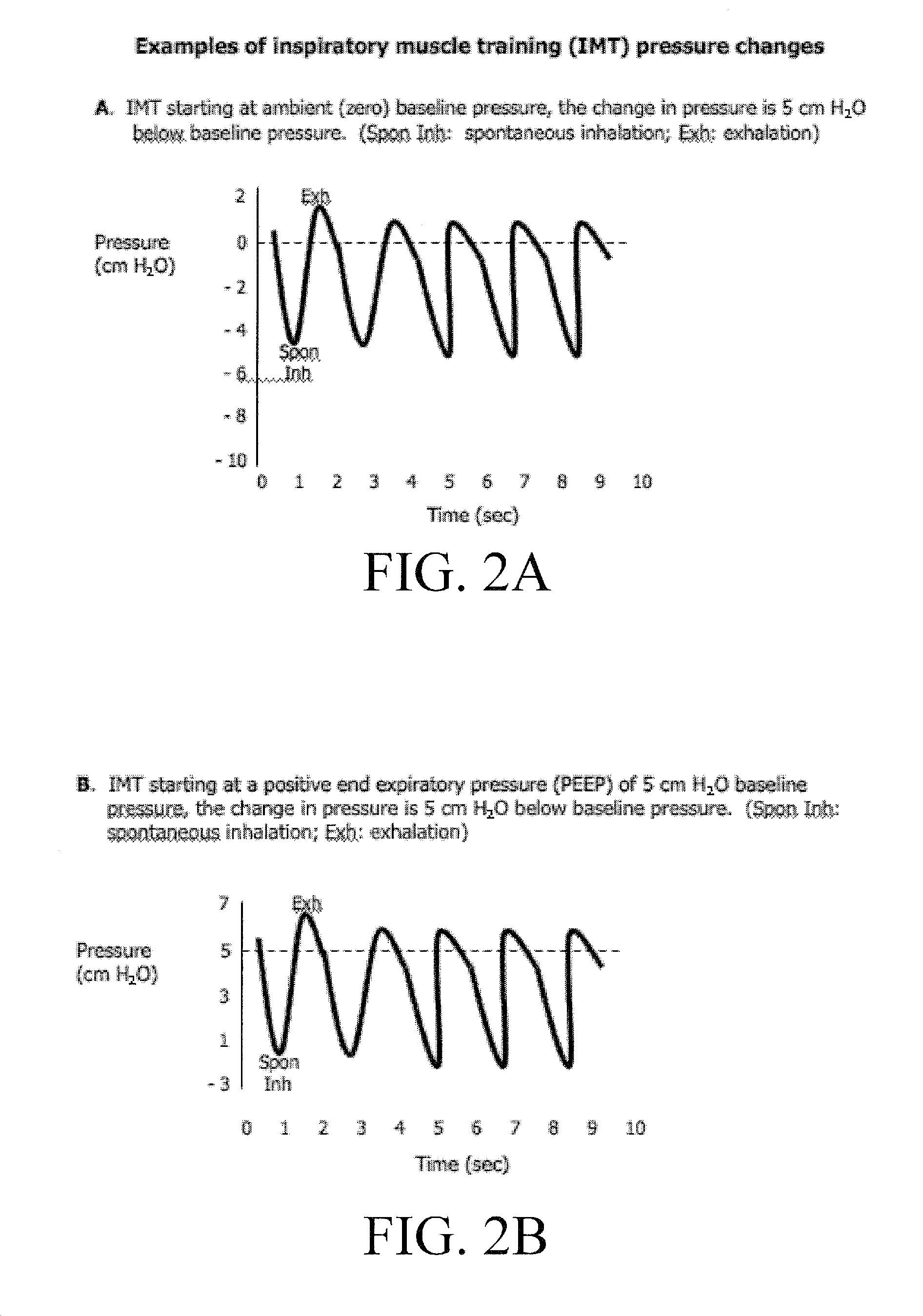
Automated Inspiratory Muscle Training for Patients Receiving Mechanical Ventilation
ActiveUS20090229611A1Improve coordinationIncrease powerRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesMechanical ventilatorsHigh pressure
A system and method for automated inspiratory muscle strength exercise includes software for setting a mechanical ventilator for a pressure regulated breath with an initial pressure target that is at the highest pressure setting a patient can tolerate and increasing the pressure target as tolerated.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Ventilation mask with integrated piloted exhalation valve
ActiveUS20120325218A1High functional dead spaceReduce trafficRespiratory masksBreathing masksPositive pressureHeat and moisture exchanger
In accordance with the present invention, there is provided a mask for achieving positive pressure mechanical ventilation (inclusive of CPAP, ventilator support, critical care ventilation, emergency applications), and a method for a operating a ventilation system including such mask. The mask of the present invention includes a piloted exhalation valve that is used to achieve the target pressures / flows to the patient. The pilot for the valve may be pneumatic and driven from the gas supply tubing from the ventilator. The pilot may also be a preset pressure derived in the mask, a separate pneumatic line from the ventilator, or an electro-mechanical control. The mask of the present invention may further include a heat and moisture exchanger (HME) which is integrated therein.
Owner:BREATHE TECHNOLOGIES INC
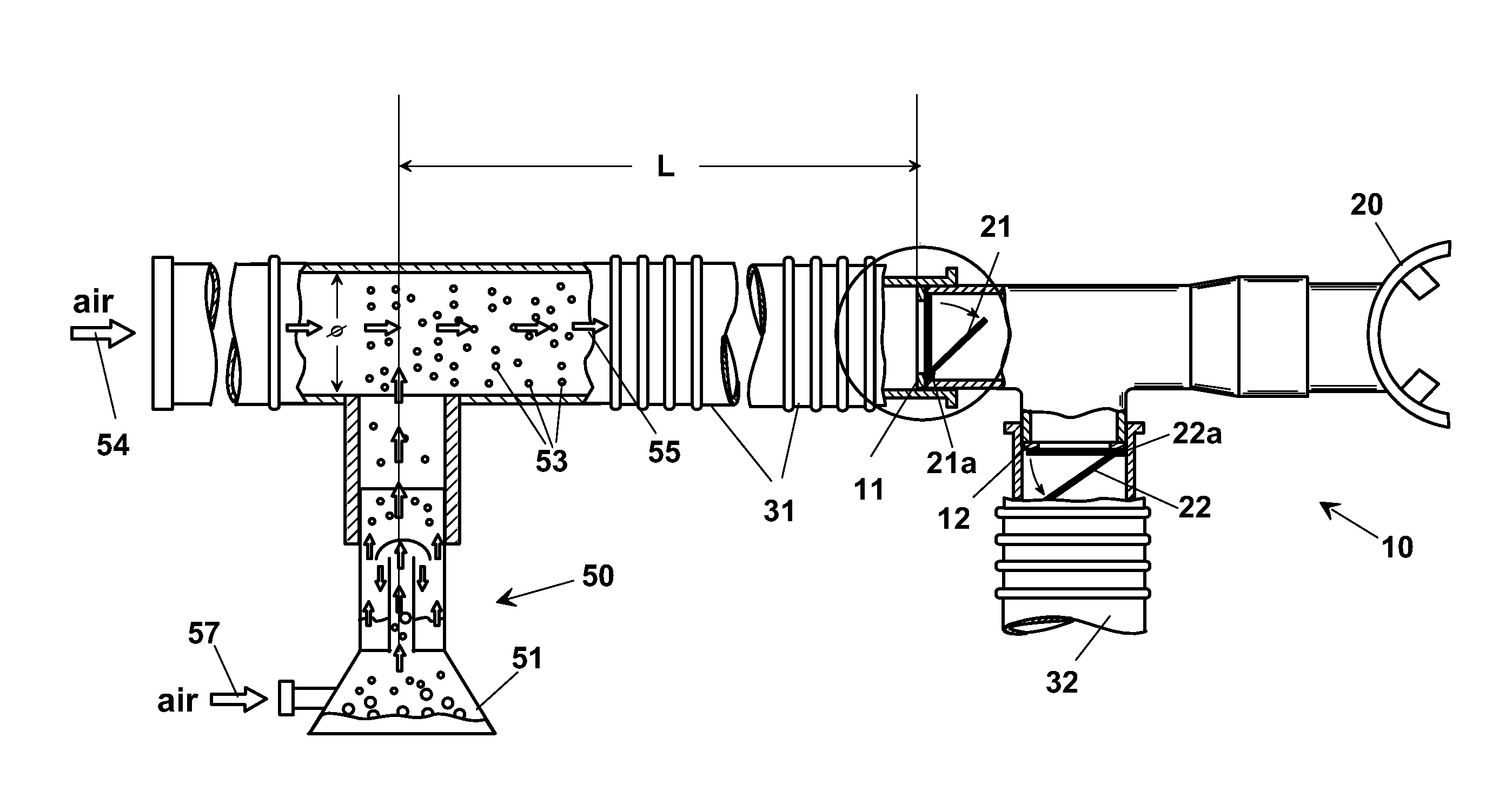
Ventilation apparatus for pulmonary scintigraphy
InactiveUS20100249584A1Quality improvementReduce impactRespiratory masksDiagnostic recording/measuringNon invasiveVALVE PORT
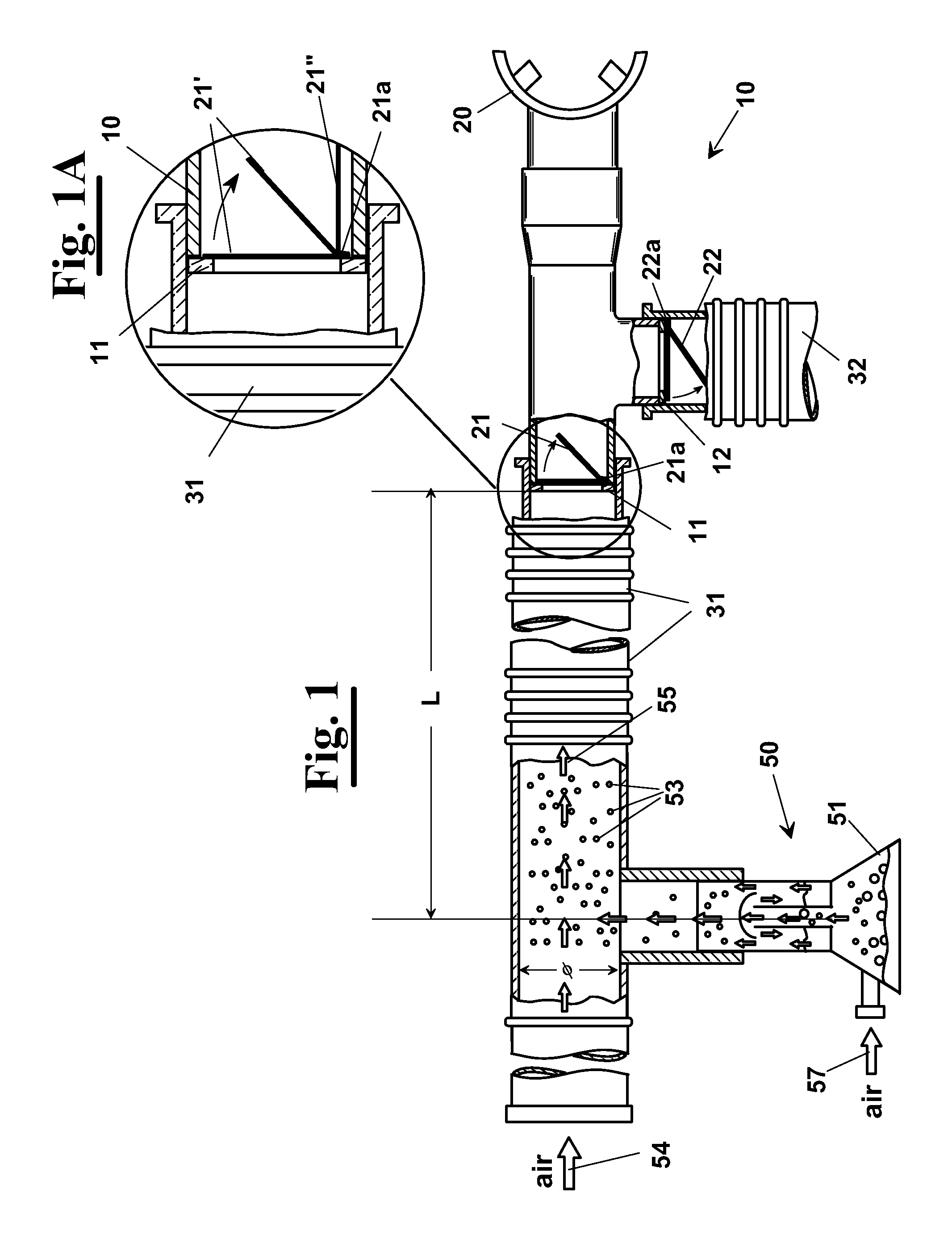
A ventilation apparatus (1) for pulmonary scintigraphy, having an inhalation collector (10) to which an element of inhalation (20), a feed duct (31), defining a flow of marked aerosol (55), and an outlet duct (32), for disposal of exhaled flow and any aerosol surplus, are connected. The feeding air may be of bi-level type, whereby the air flow rate when breathing out is low, even if always positive. The collector (10) has a first interposition element (21) located at the connection with the air feeding tube (31) that only allows inlet flow towards the patient. A second interposition element (22) is located at the connection with outlet duct (32). The presence of one-way valve(s) (21, 22) allows breathing of the marked aerosol in the bronchial branches of the patient (20) in a completely natural manner following physiologic respiration and avoiding hyper-accumulation of marker in the largest bronchial branches. Scintigraphy is also allowed during non-invasive mechanical ventilation, carried out through the ventilation apparatus (1).
Owner:AZIENDA OSPEDALIERO UNIVRIA PISANA
Setting mandatory mechanical ventilation parameters based on patient physiology
InactiveUS20080202525A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesExpiratory TimePhysical therapy
A method of setting inspiratory time, expiratory time, and a subject's breath size in controlled mechanical ventilation comprises: a) setting a subject's expiratory time; b) setting the subject's inspiratory time; and c) setting the subject's breath size, all based on various criteria.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
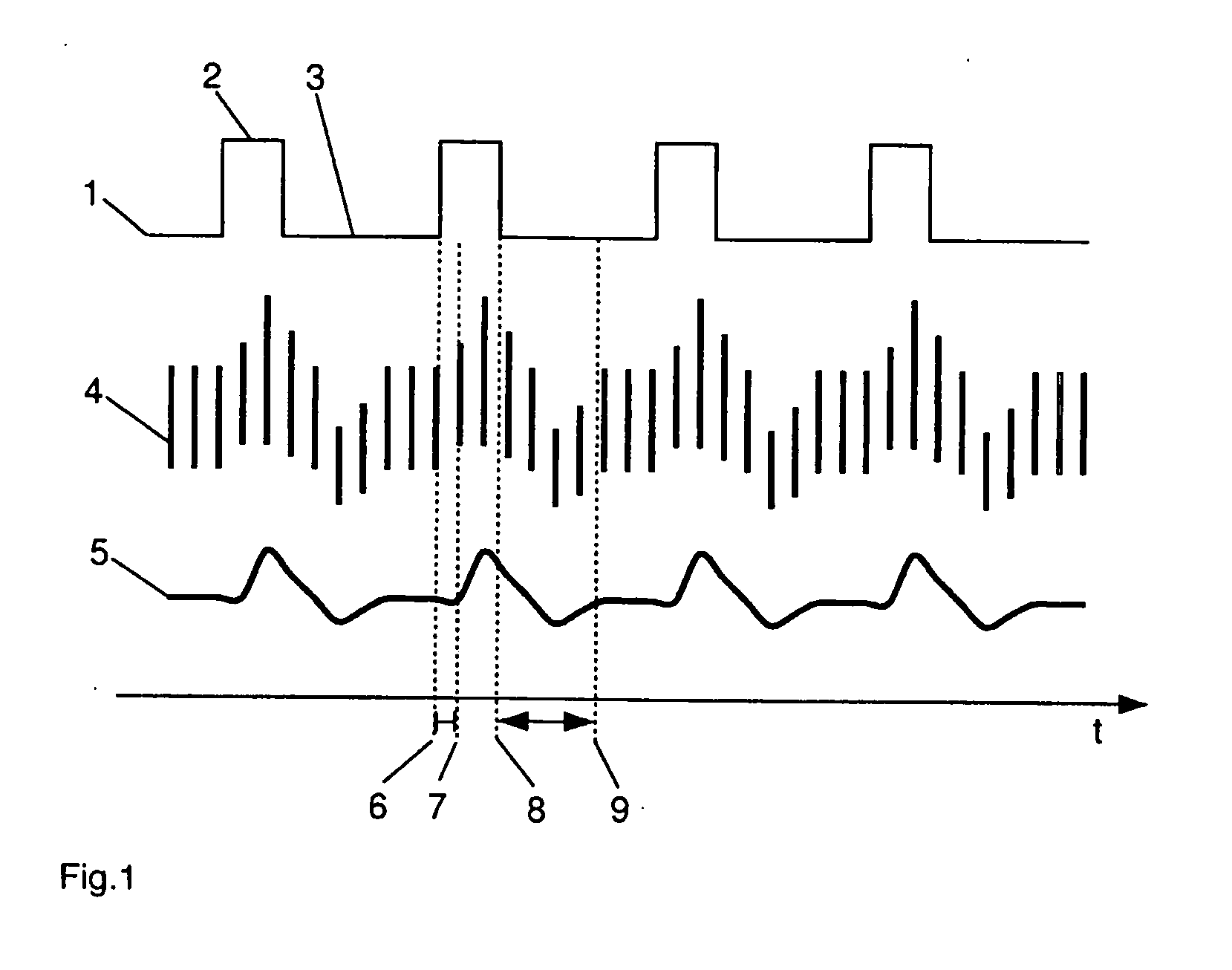
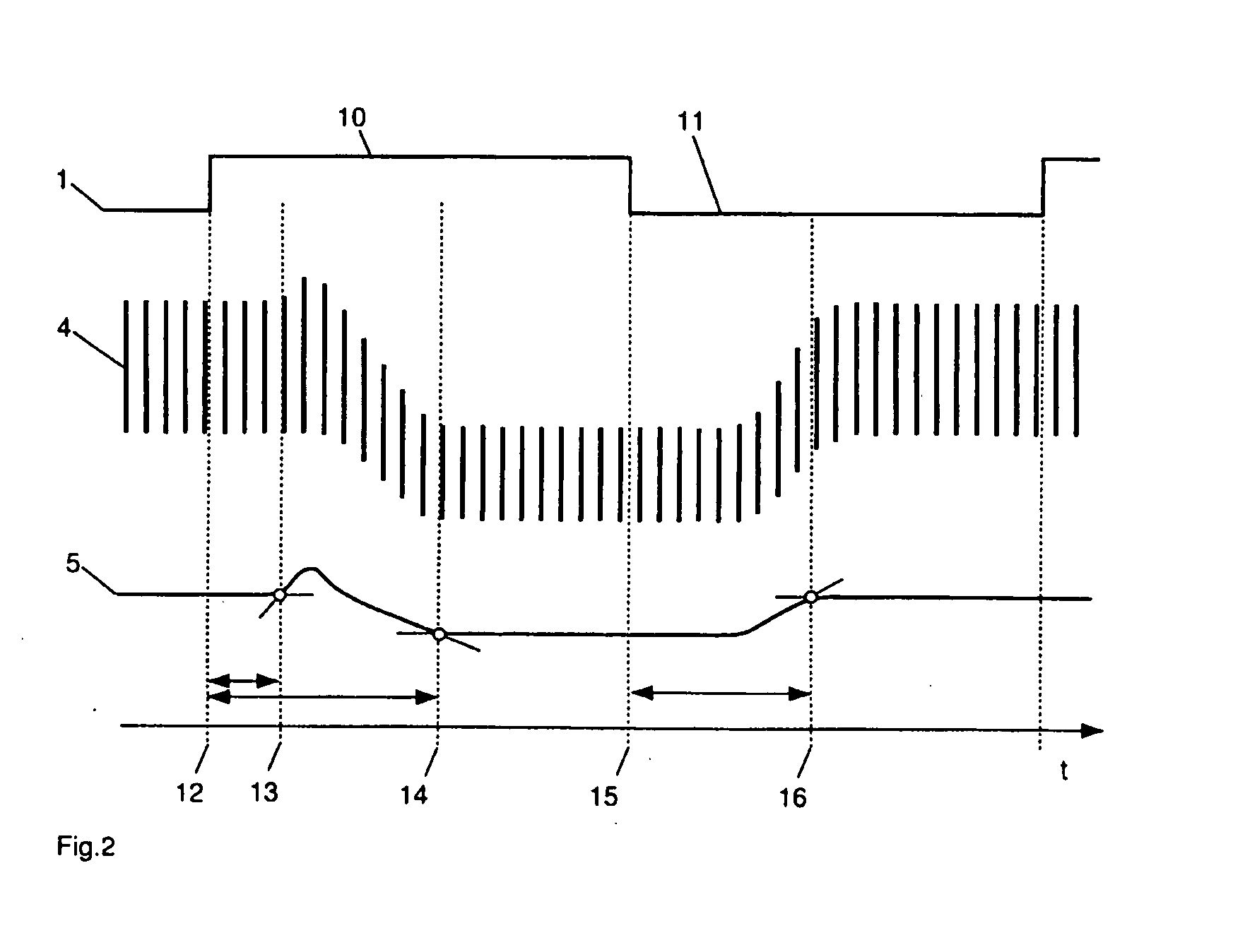
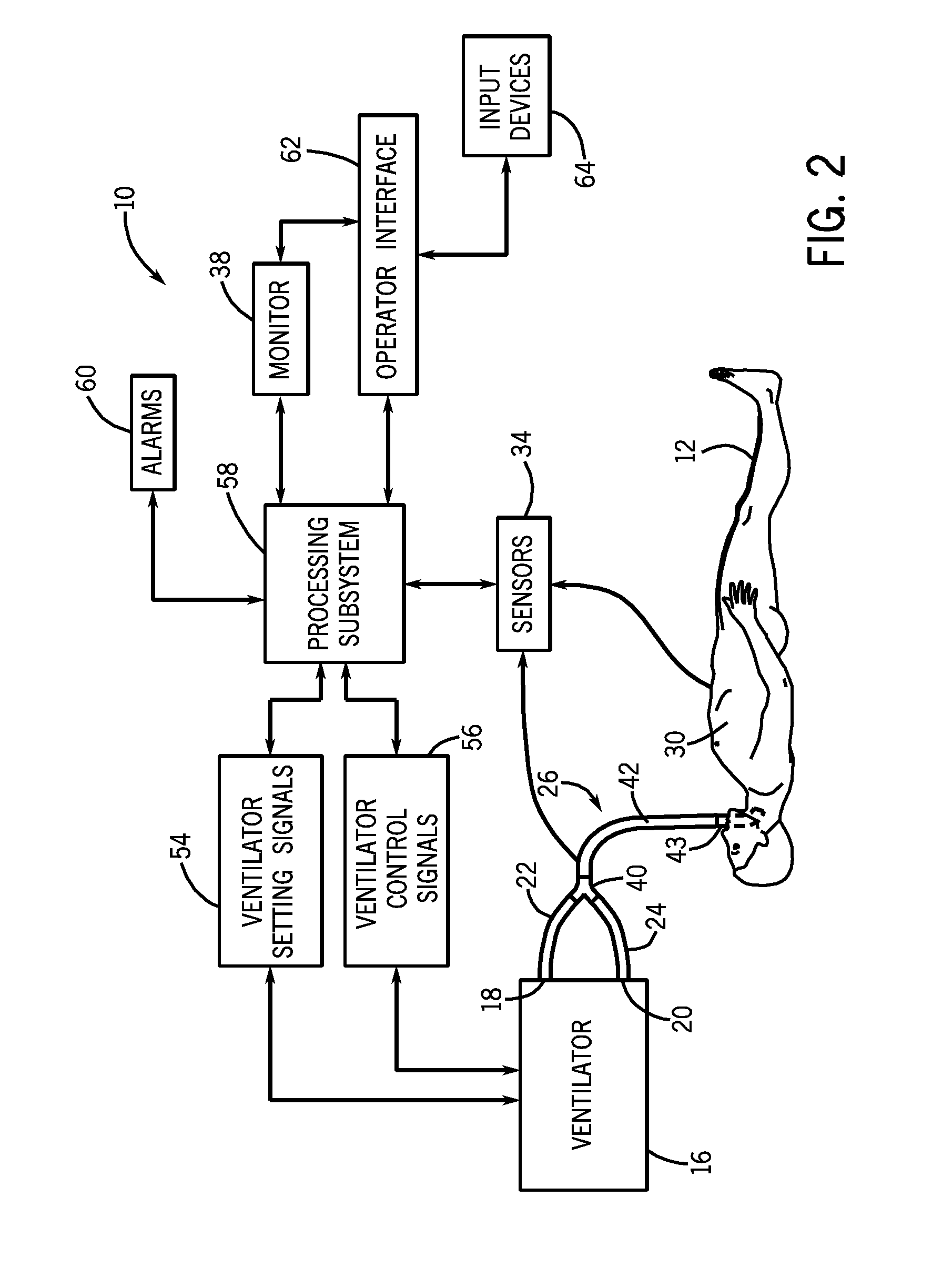
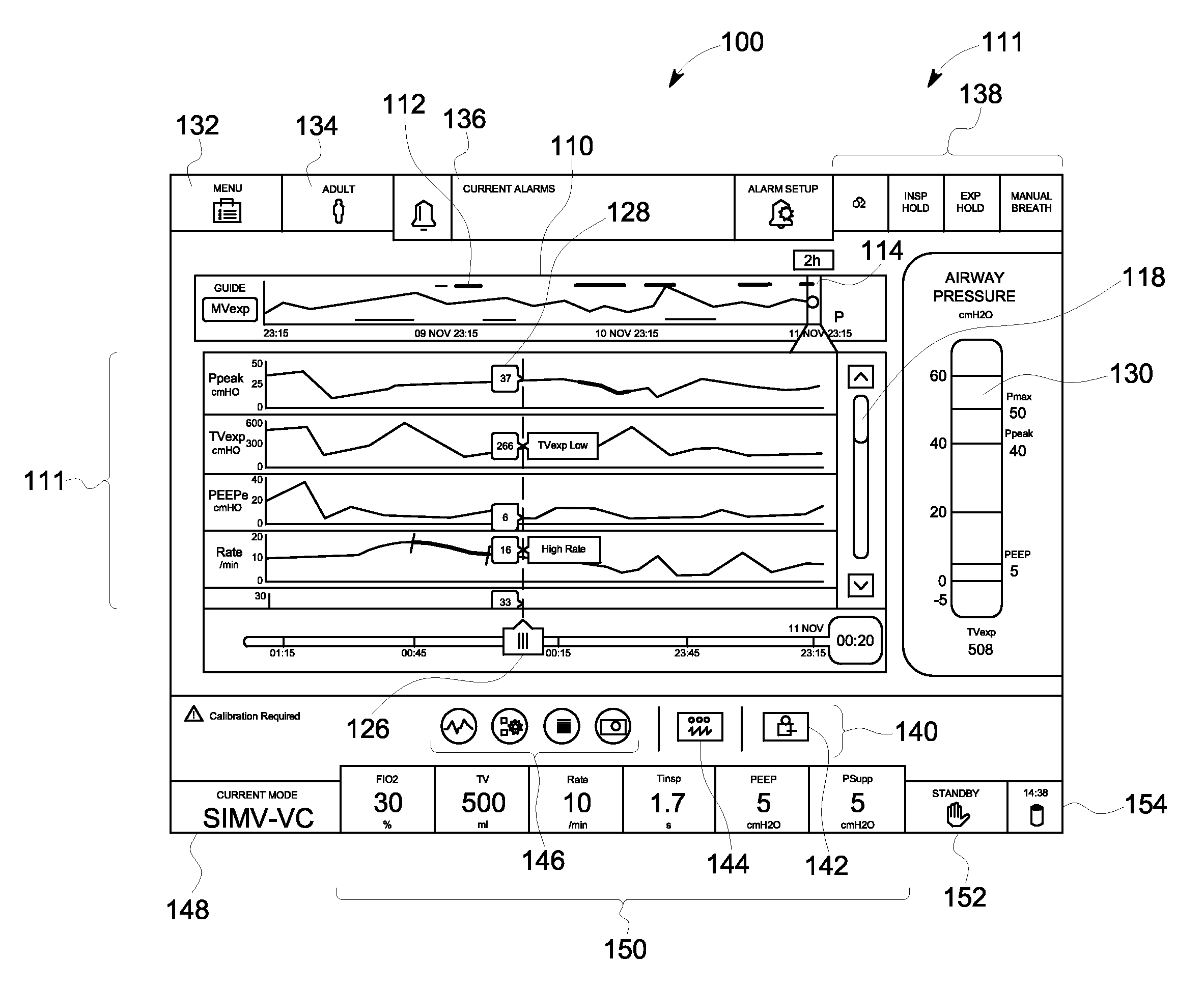
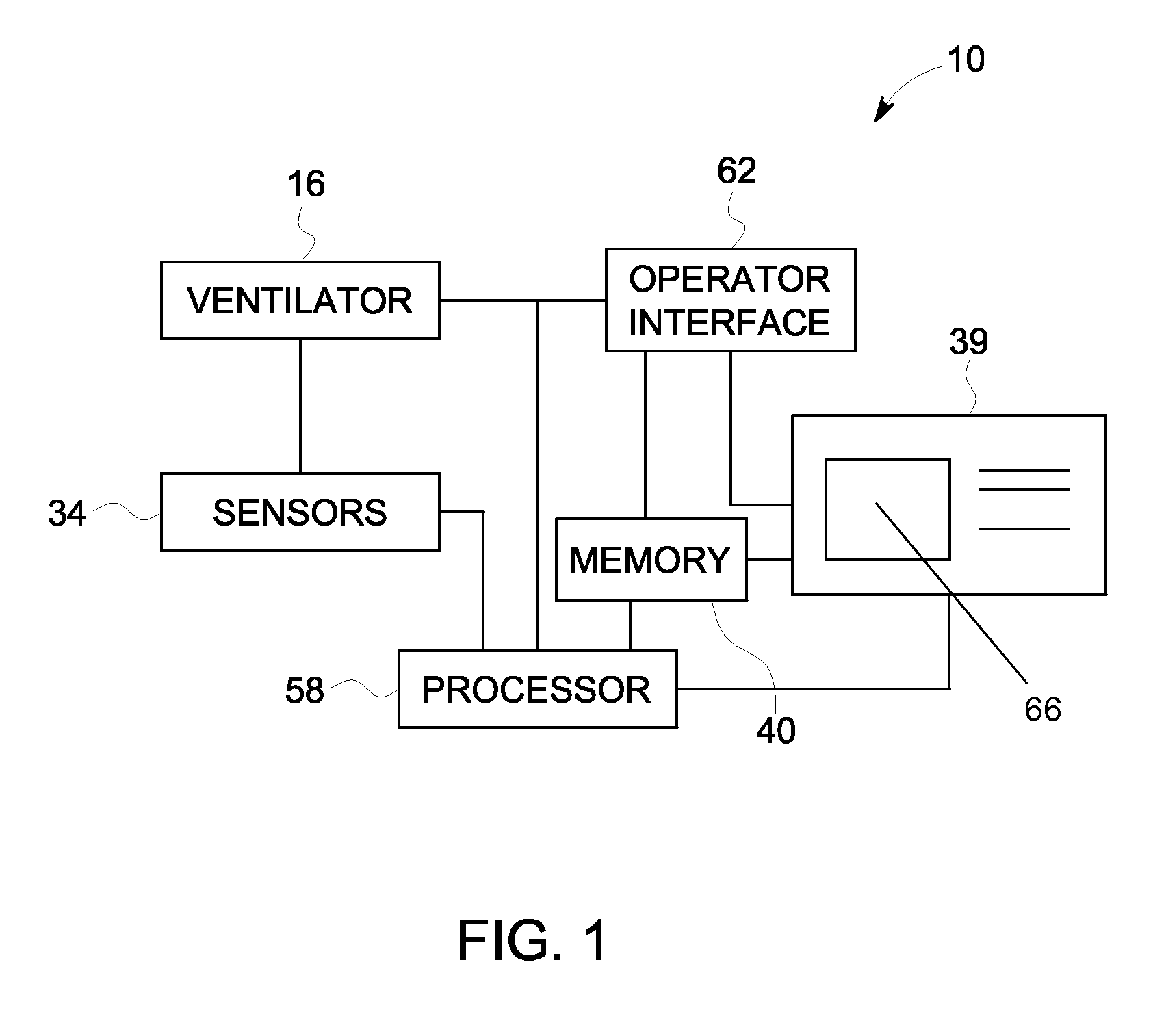
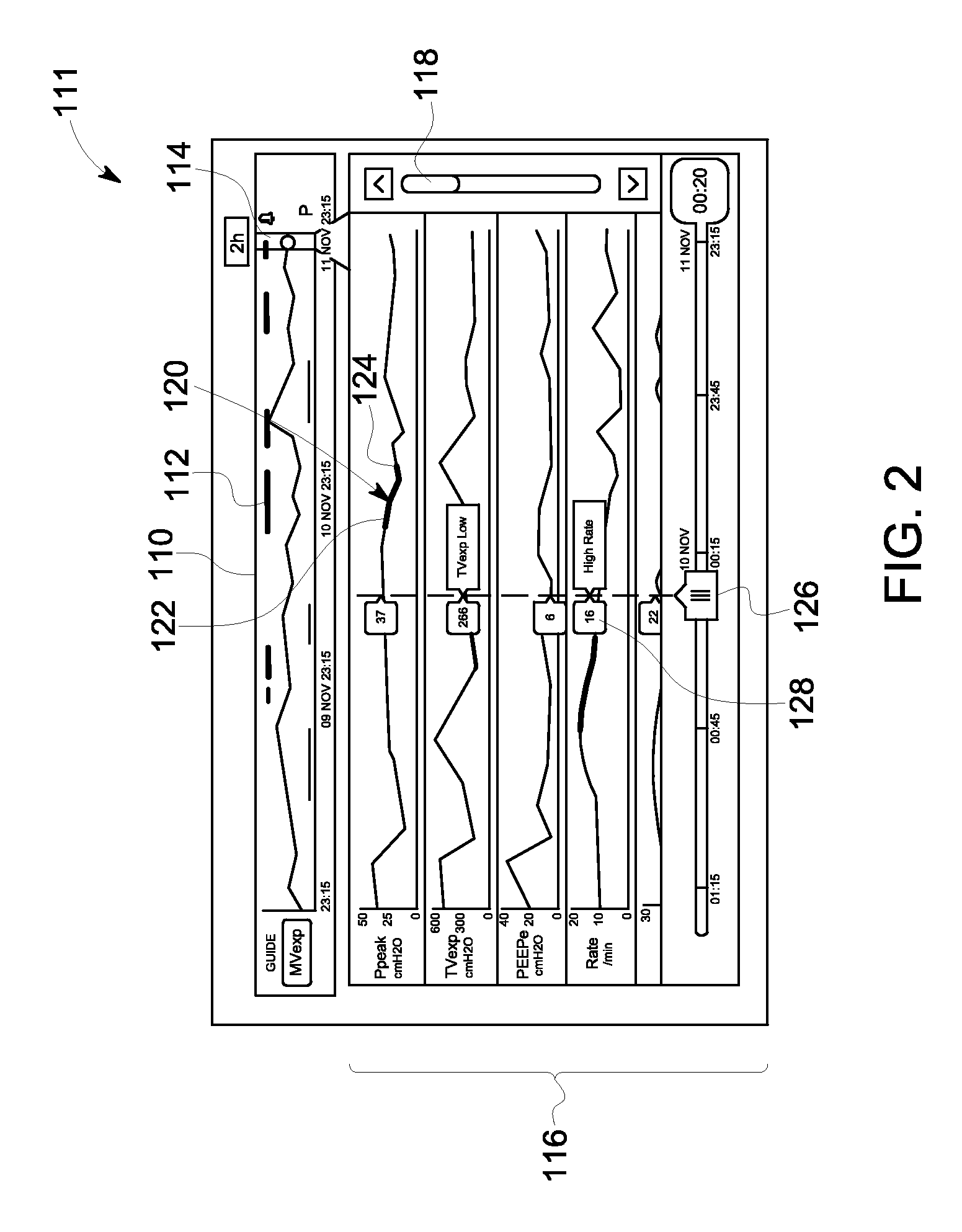
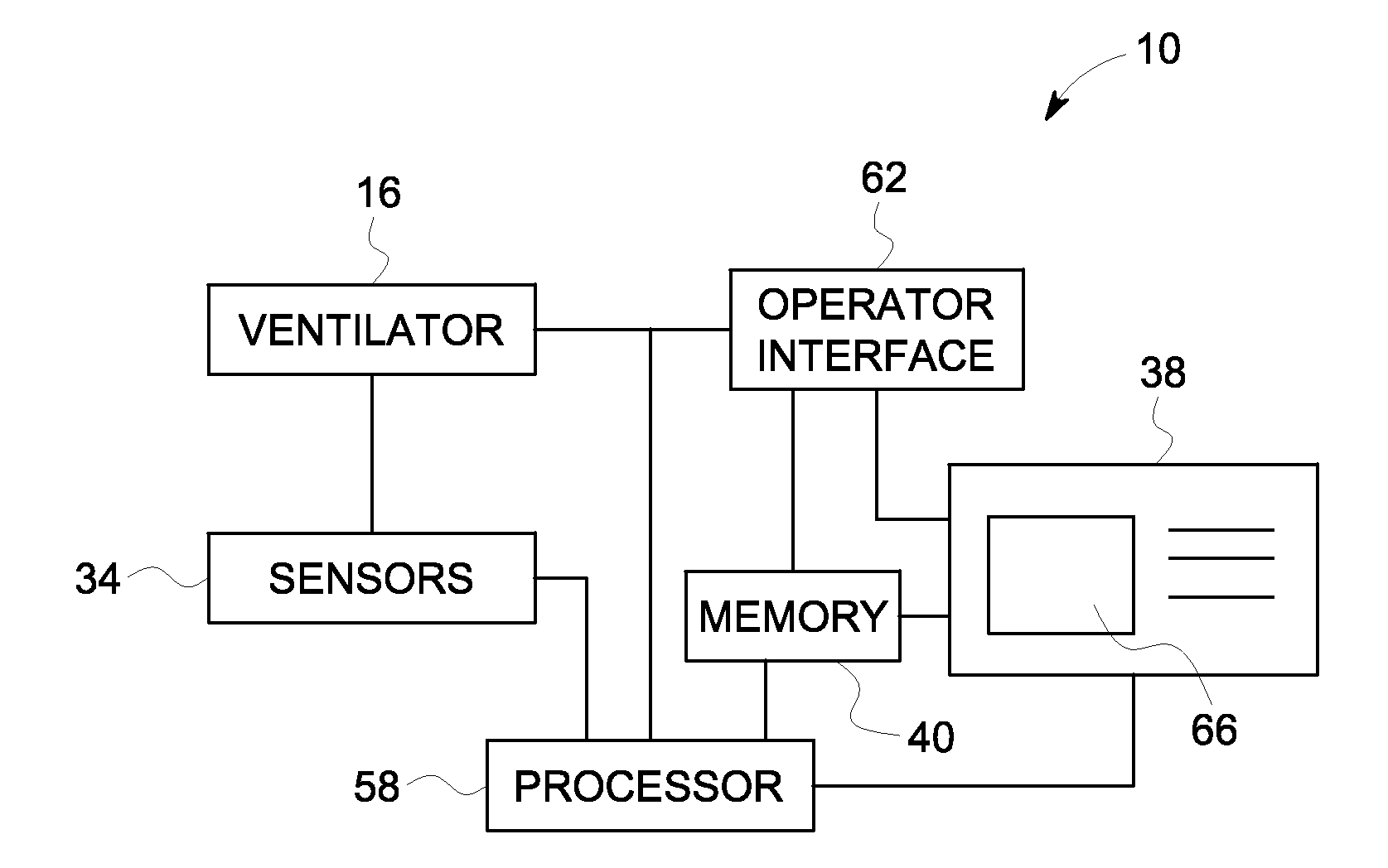
Method and system for visualizing mechanical ventilation information
A medical system having a ventilator is provided. The medical system includes a memory storing data related to patient and ventilator parameters. A processor is programmed to organize, in time, the data related to the patient and ventilator parameters. A viewer displays the patient and ventilator parameters for an overall monitoring time period on a timeline. A reference marker is displayed on the timeline to select a segment of the patient and ventilator parameters corresponding to a past monitoring time, wherein the segment selected represents a time segment within the overall monitoring time period. The patient and ventilator parameters corresponding to the time segment are displayed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Setting expiratory time in mandatory mechanical ventilation based on a deviation from a stable condition of exhaled gas volumes
A method of setting expiratory time in controlled mechanical ventilation varies a subject's expiratory times; determines gas volumes exhaled by the subject per breath associated with the expiratory times; establishes a stable condition of the gas volumes; and determines an optimal expiratory time based on a deviation from the stable condition. A device for use in controlled mechanical ventilation comprises means for the same.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
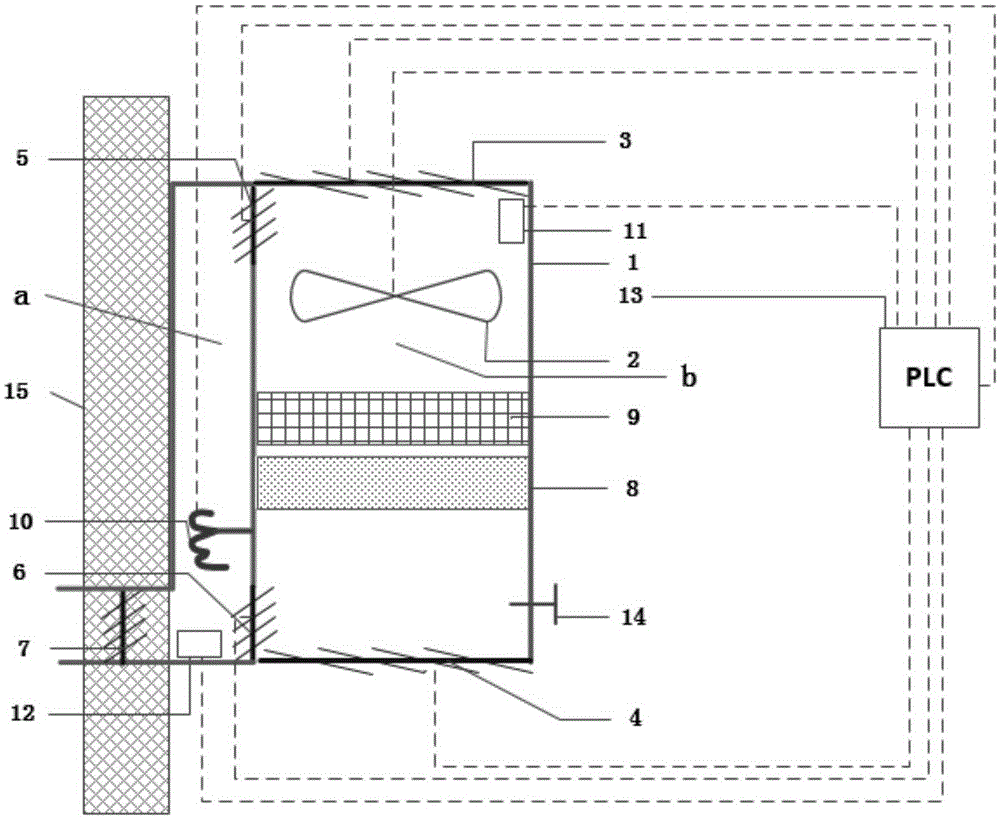
Wall-mounted type air purifier based on thermal regeneration and purification method thereof
ActiveCN105371383AGood removal effectQuick removalMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsPurification methodsFresh air
The invention belongs to the field of indoor air purification and relates to a wall-mounted type air purifier based on thermal regeneration and a purification method thereof. The purifier comprises a sealed cabin, a draught fan, an air channel body which is composed of a plurality of air valves, a low efficient filter, efficient reproducible volatile organic compounds (VOCs) absorption module, a formaldehyde absorption module, a heating wire, a VOCs sensor, a temperature sensor, and a programmable logic controller; the sealed cabin of the air purifier comprises an air purification chamber and a heating regeneration chamber; the low efficient filter, the efficient reproducible VOCs absorption module, the formaldehyde absorption module, the draught fan and the VOCs sensor are installed in the air purification chamber of the sealed cabin from bottom to top; the heating wire and the temperature sensor are installed in the heating regeneration chamber from top to bottom; the programmable logic controller is connected with the draught fan, the temperature sensor, the VOCs sensor and circuits of the multiple air valves. The purification method comprises four modes of purifying, thermal regenerating, pollution discharging and fresh air, and further comprises two functions of indoor purification and mechanical ventilation. According to the wall-mounted type air purifier based on thermal regeneration and the purification method thereof, indoor VOCs and indoor formaldehyde can be purified quickly, continuously and effectively, and the service life of the wall-mounted type air purifier is prolonged.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and system for visualizing mechanical ventilation information
InactiveUS20130032149A1Medical devicesRespiratory organ evaluationIntensive care medicineVisualization methods
A medical system having a ventilator is provided. The medical system includes a memory for storing one or more patient and ventilation parameters. A processor is programmed to organize the one or more patient parameters into at least one of past patient and ventilation parameters, present patient and ventilation parameters, or future patient and ventilation parameters. A viewer displays at least one of the past patient or ventilation parameters, the present patient or ventilation parameters, or the future patient or ventilation parameters. The past patient and ventilation parameters, the present patient and ventilation parameters, and the future patient and ventilation parameters are selectable on the viewer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus for non-invasive mechanical ventilation
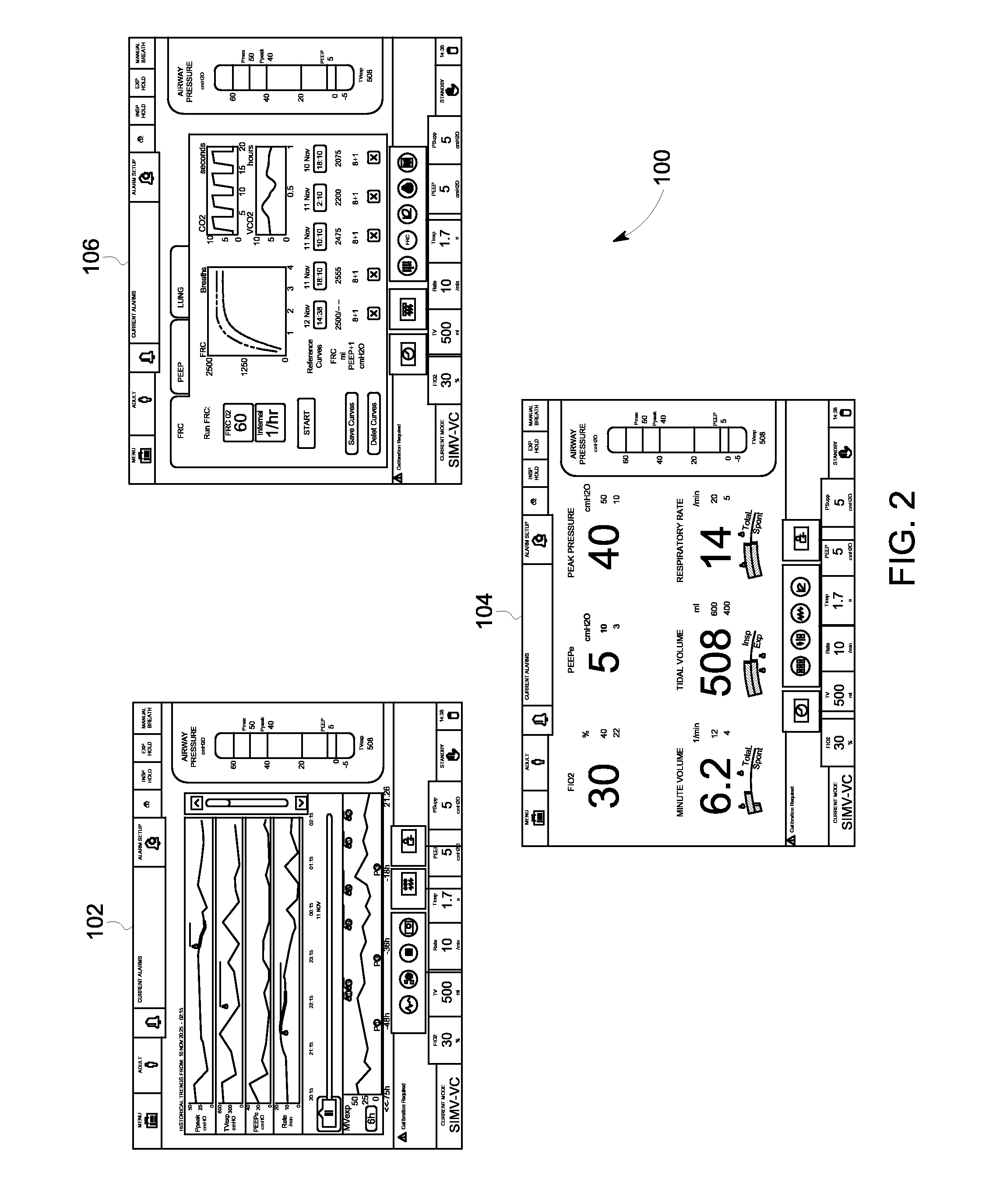
InactiveUS20060283451A1Facilitates gas exchangeShorten the construction periodOperating means/releasing devices for valvesRespiratory masksPressure decreaseEngineering
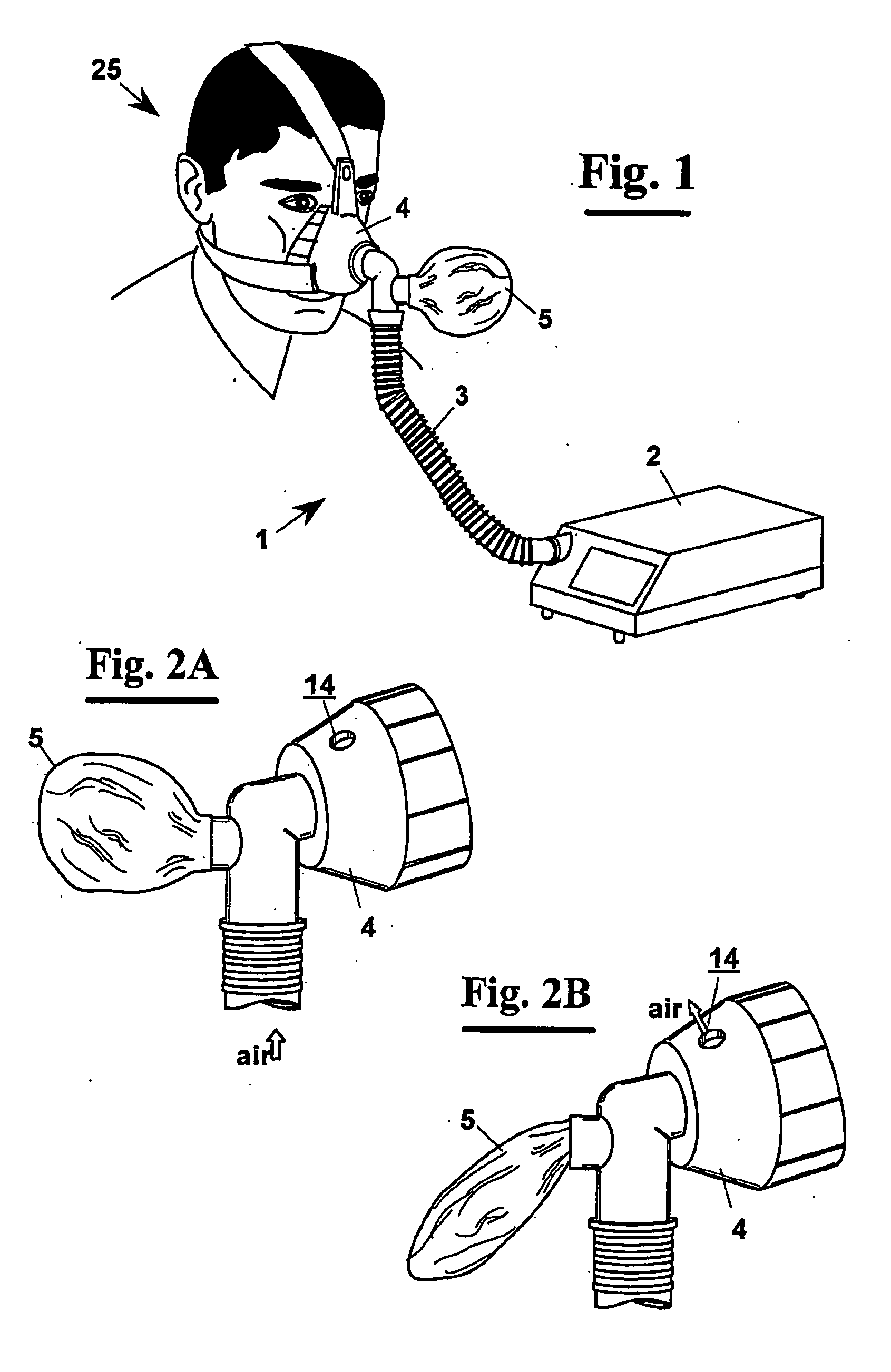
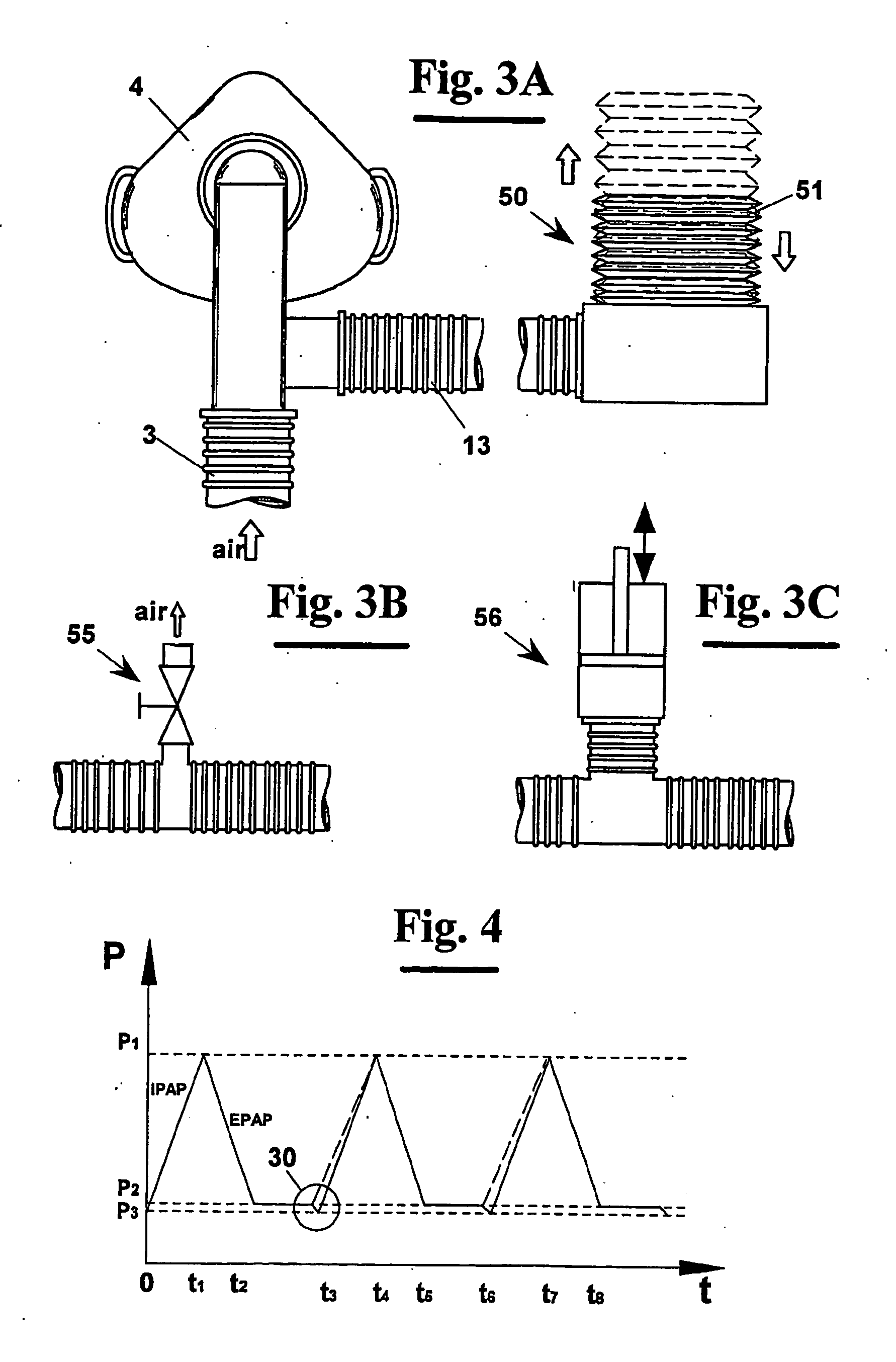
An apparatus (1) for non-invasive mechanical ventilation comprises a fan (2) of Bi-level type, or BiPAP, for generating an air flow according to a succession of inspiration steps, or IPAP, and exhalation steps, or EPAP. The flow is conveyed in the aerial ducts of a patient (25) by means of a flexible tube (3) connected to a nasal mask (4). A flexible air reservoir (5) is provided pneumatically connected to the duct (3) and the nasal mask (4) in order to subtract from the inspiration flow a certain air amount before that it reaches the patient (25) at the beginning of an IPAP step. During the exhalation EPAP step, since the air flow pressure decreases automatically, there is the emptying at least partial of the flexible air reservoir (5), whereas the air exhaled by the patient exits through an opening (14) made on the nasal mask (4). This way an air exchange occurs also in the most peripheral patient's aerial ducts and the amount of gaseous exchanges is increased, reducing at the same time the duration of the treatment.
Owner:AZIENDA OSPEDALIERA PISANA
Automatic Control System For Mechanical Ventilation For Active Or Passive Subjects
ActiveUS20110017214A1Avoid fatiguePrevent dyspneaRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesElectrical resistance and conductanceAutomatic control
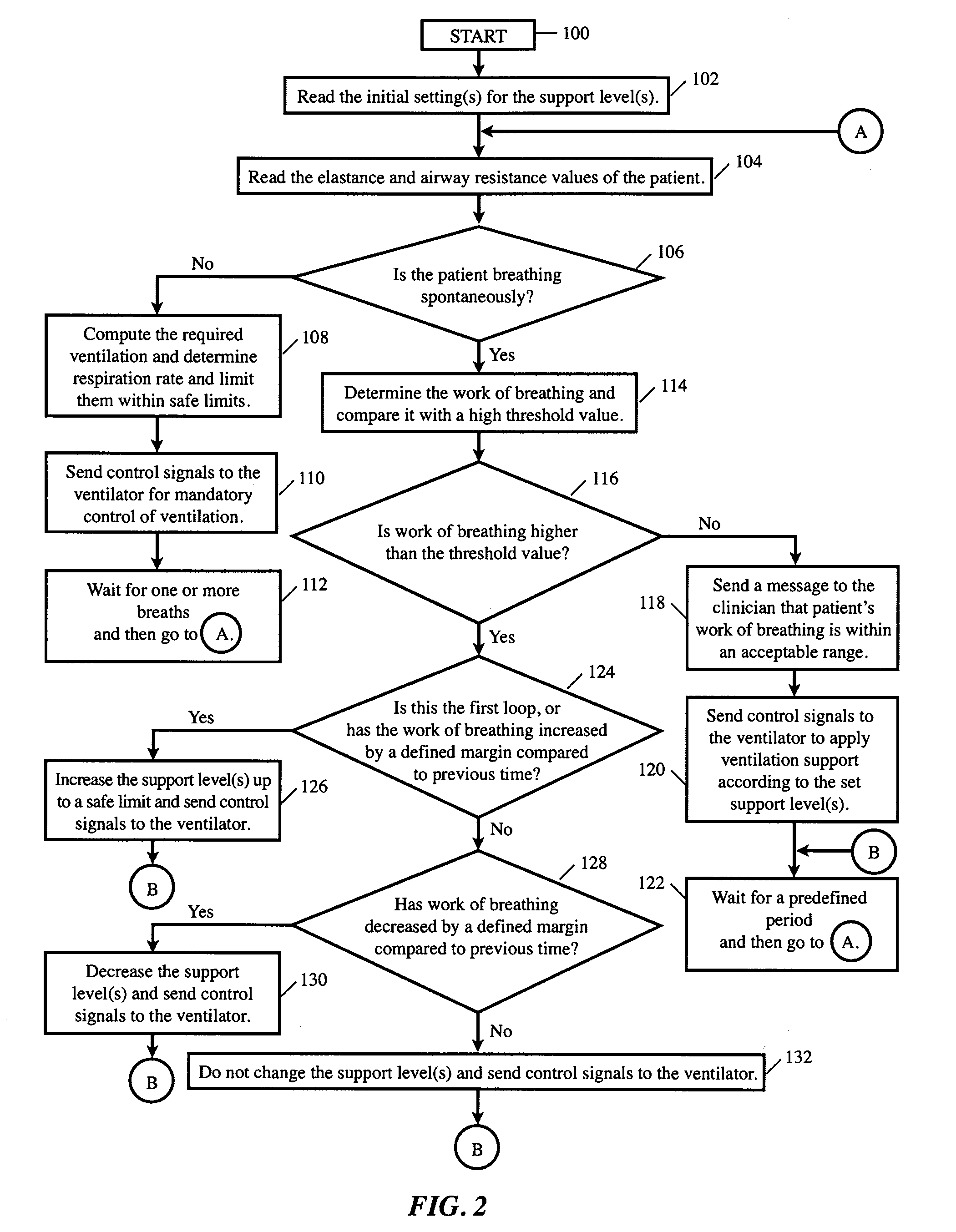
A method and an apparatus for controlling a ventilator to automatically adjust ventilation assistance to an active or passive subject. The method includes determining volume and flow rate of gas to the patient during inspiration on an ongoing basis, and generating control signals in proportion to the volume and flow rate of gas to the patient wherein proportionality factors, and support levels for the elastic and resistive components of pressure are automatically adjusted by the ventilator. The ongoing pressure applied by the ventilator is a sum of elastic and resistive pressures that are automatically controlled by the system. When the patient breathes spontaneously, the support levels are automatically adjusted based on the patient's requirements. If the patient does not breathe spontaneously, the ventilator provides ventilation at an optimal level and rate. The method may be used in weaning or in a management phase of ventilation.
Owner:TEHRANI FLEUR T
Residential integrated ventilation energy controller
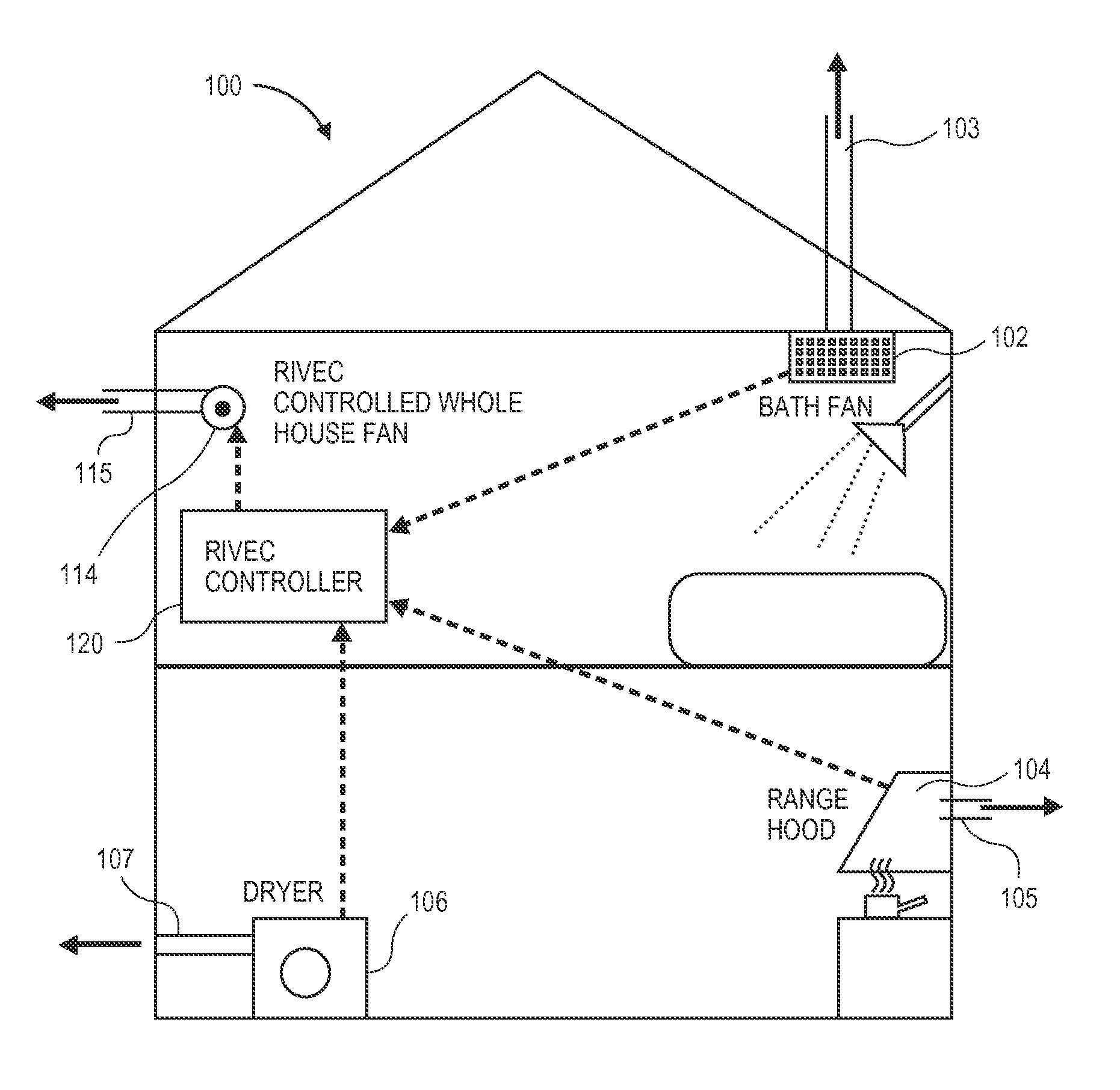
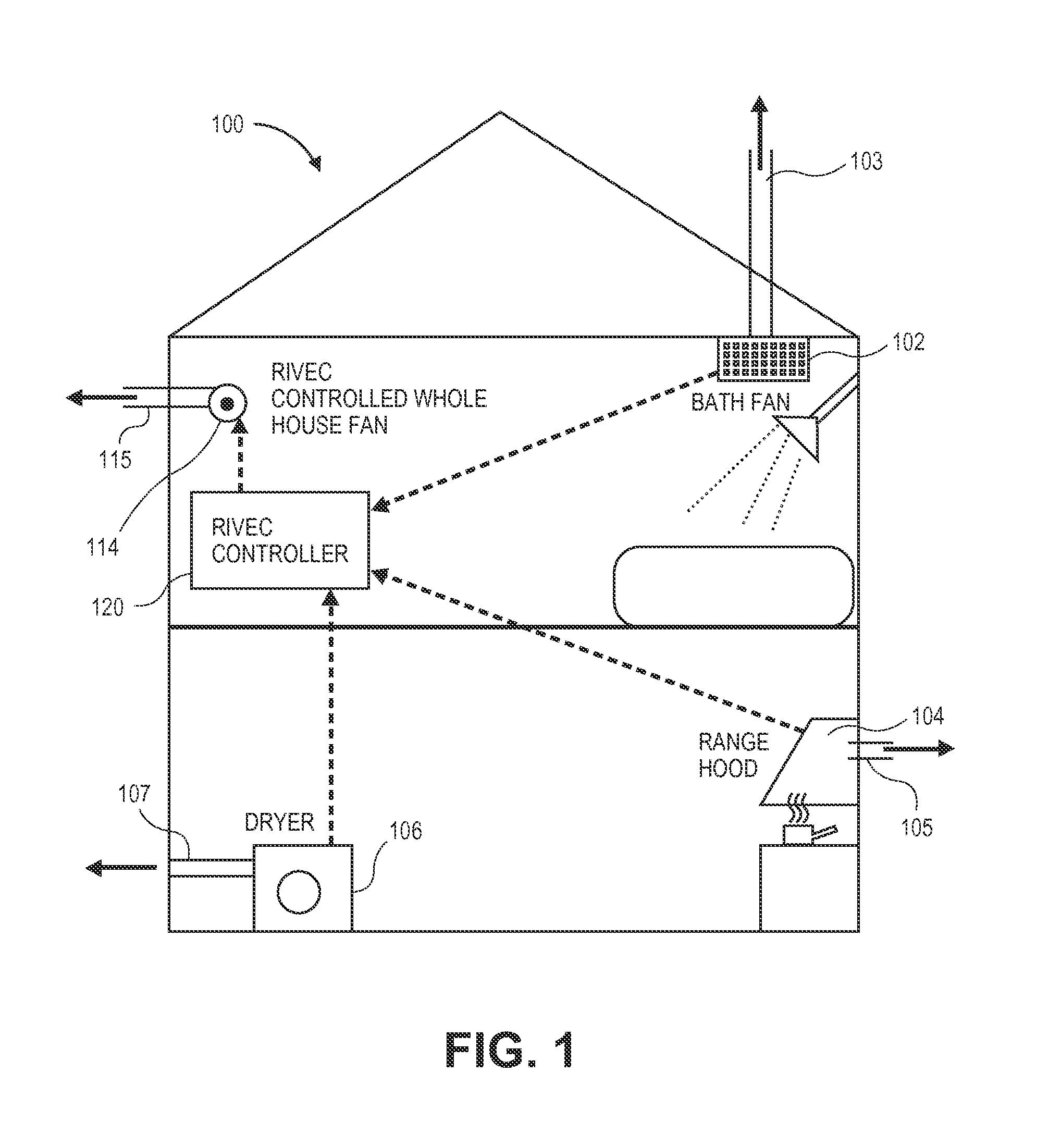
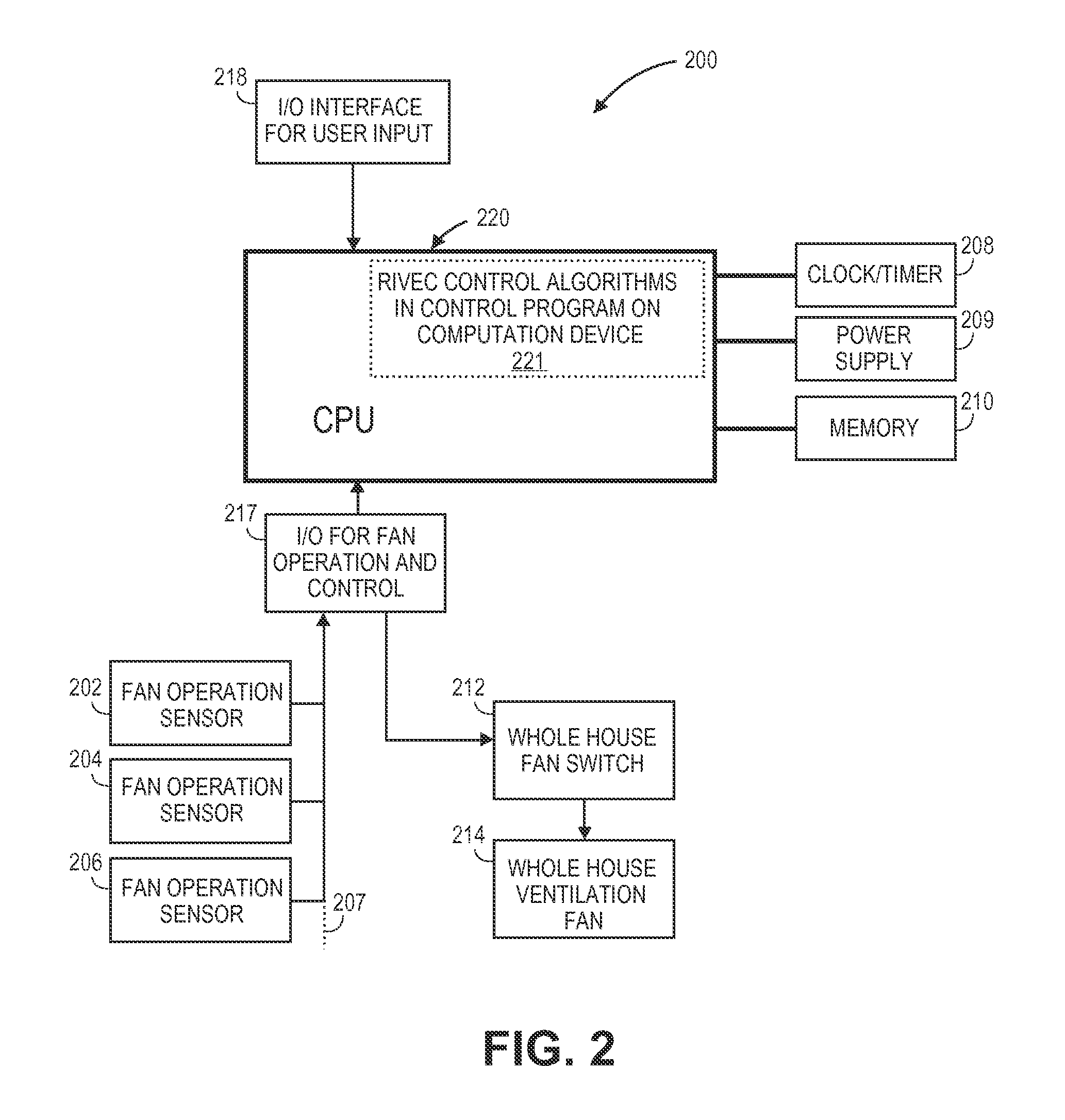
InactiveUS20110151766A1Weaken energyReduce peak powerMechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsEngineeringLoad following power plant
A residential controller is described which is used to manage the mechanical ventilation systems of a home, installed to meet whole-house ventilation requirements, at the same time reducing energy costs. This is achieved in part by shifting the ventilation load of the whole-house system to off peak hours and by taking into account exogenous mechanical ventilation induced by other systems. The controller is linked by wire or wirelessly to other house ventilation systems using any one of a number of communication protocols, sensing the on-off status of such exogenous systems. An operational algorithm preloaded and / or modified at the point of use is used to control the on-off status or fan speed of a whole-house ventilation fan which forms a part of the home ventilation system, the operating status of the whole-house fan in part responsive to the status of other home ventilation systems, and in part based on time of day.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Setting mandatory mechanical ventilation parameters based on patient physiology
InactiveUS20080202518A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesFlow transducerExpiratory Time
A method of setting expiratory time in controlled mechanical ventilation sets a subject's expiratory time based on when the subject's natural exhalation flow ceases. Another method determines when the subject's natural exhalation flow ceases and sets the subject's expiratory time based on the determination. A device for use in controlled mechanical ventilation comprises a flow rate sensor configured to determine when a subject's natural exhalation flow ceases and bases the subject's expiratory time on the determination.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Setting madatory mechanical ventilation parameters based on patient physiology
InactiveUS20080202517A1RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesExpiratory TimeEmergency medicine
A method of setting expiratory time in controlled mechanical ventilation sets a subject's expiratory time based on the subject's natural exhalation time. Another method determines the subject's natural exhalation time and sets the subject's expiratory time based on the determination. A device for use in controlled mechanical ventilation comprises a flow rate sensor configured to determine a subject's natural exhalation time and base the subject's expiratory time on the determination.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com