Patents
Literature
138results about How to "Efficient evacuation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
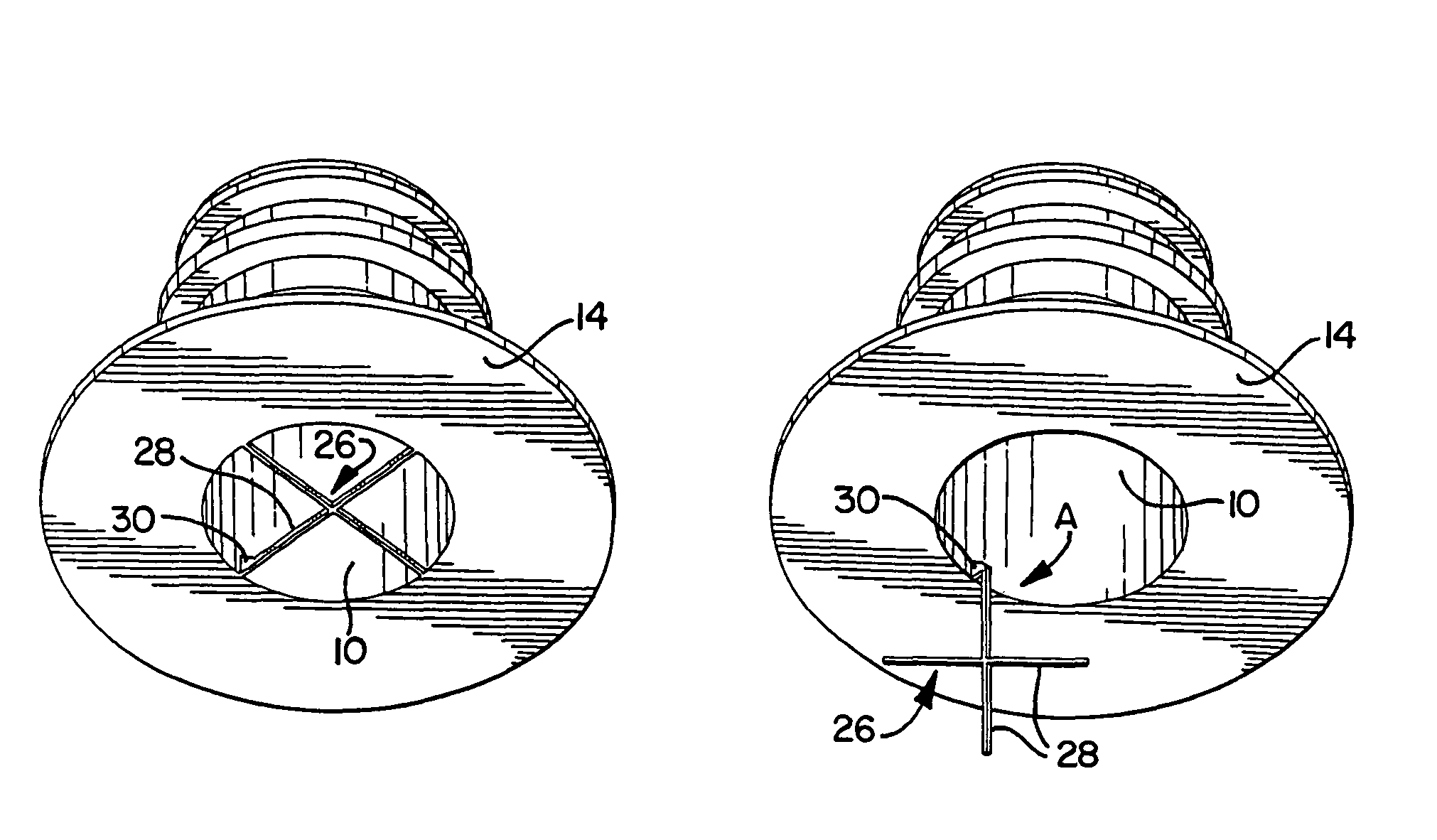
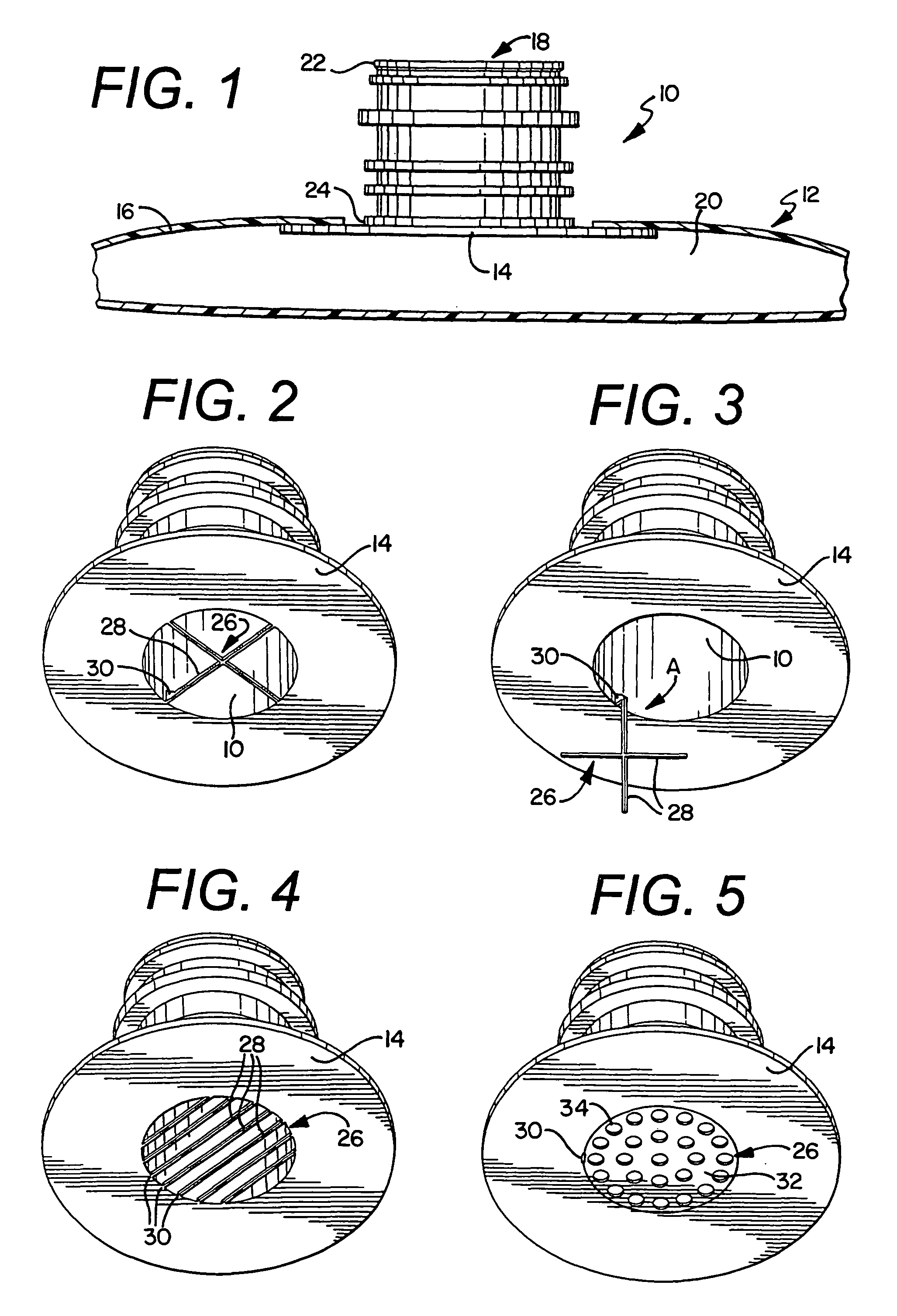
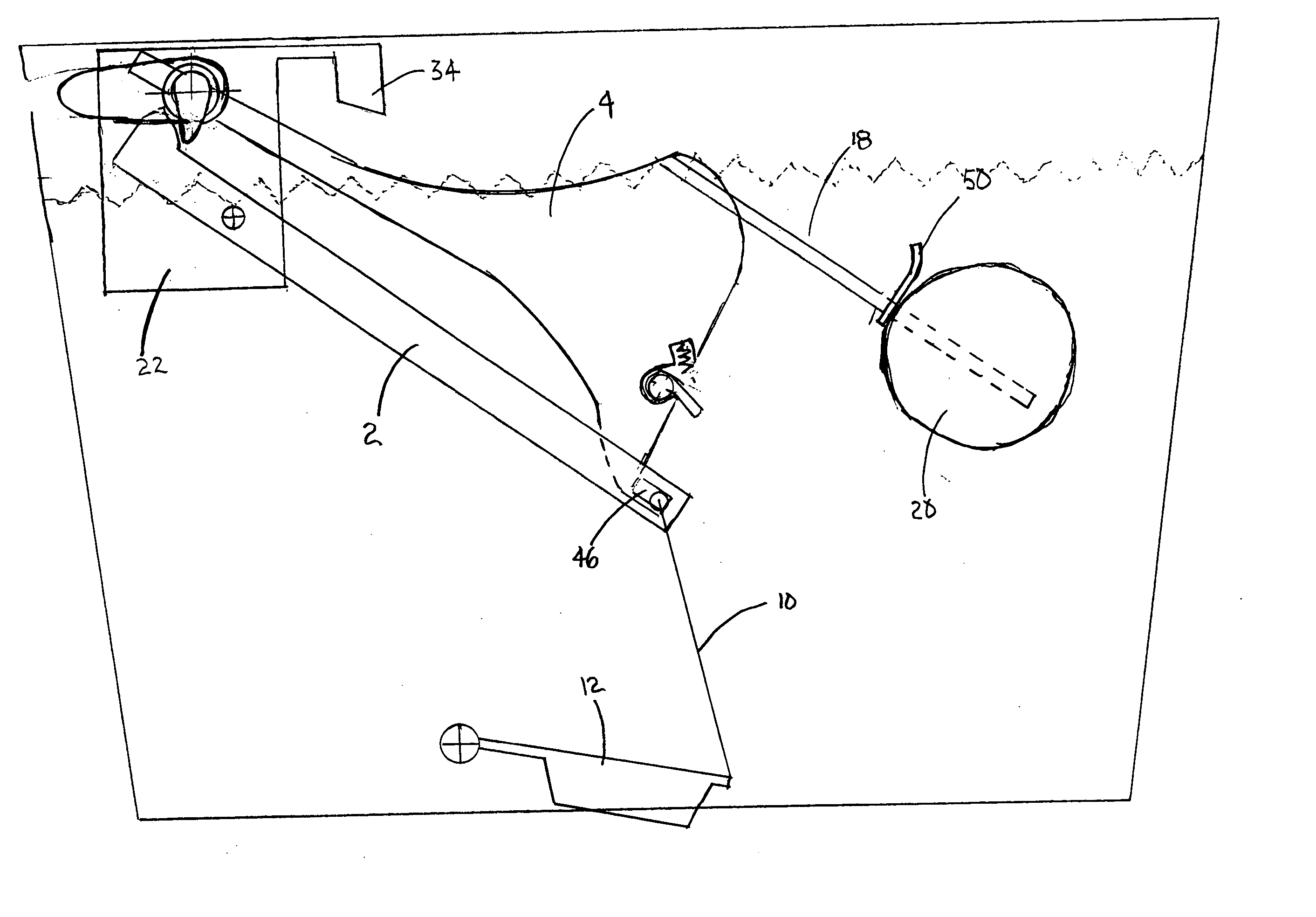
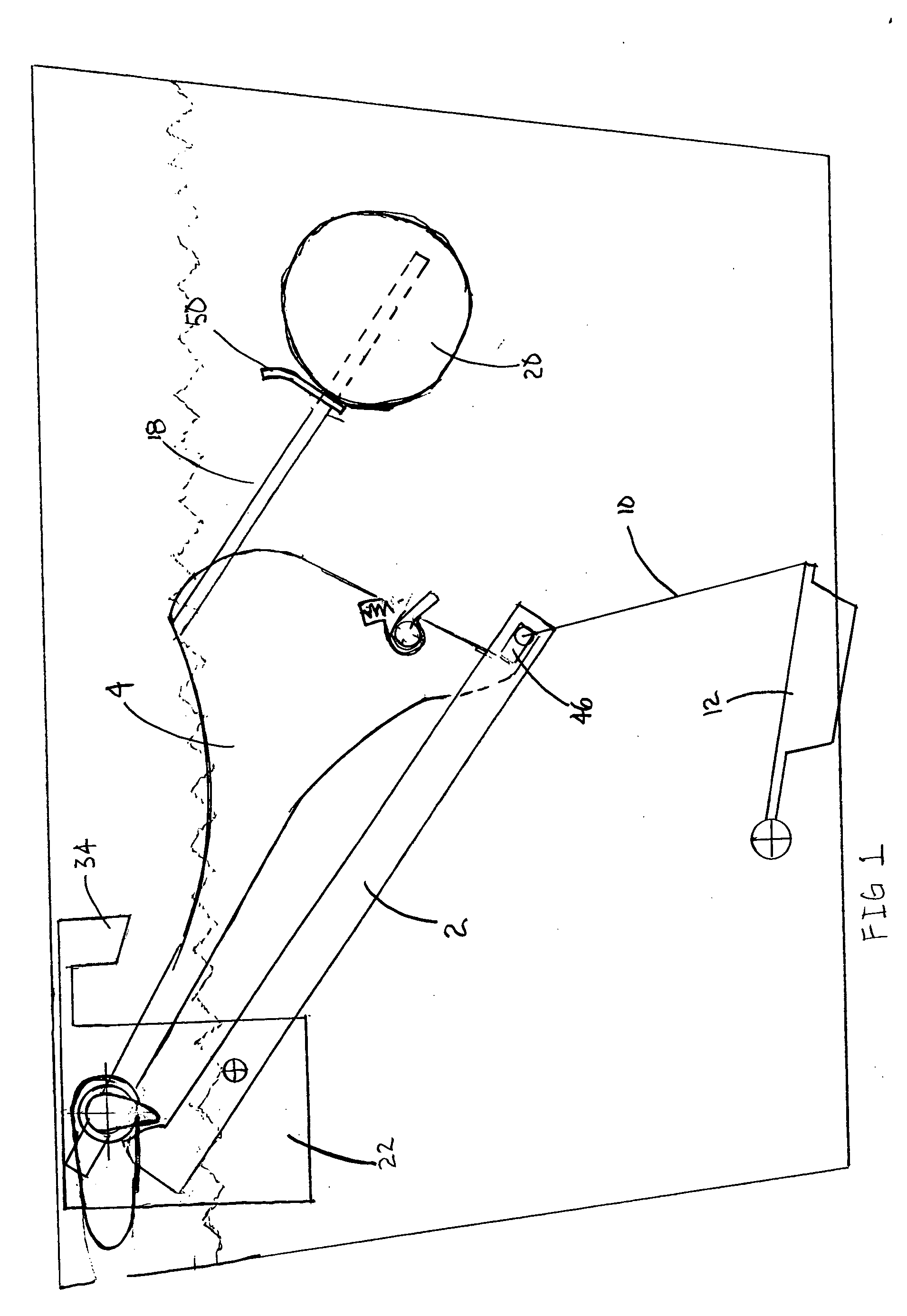
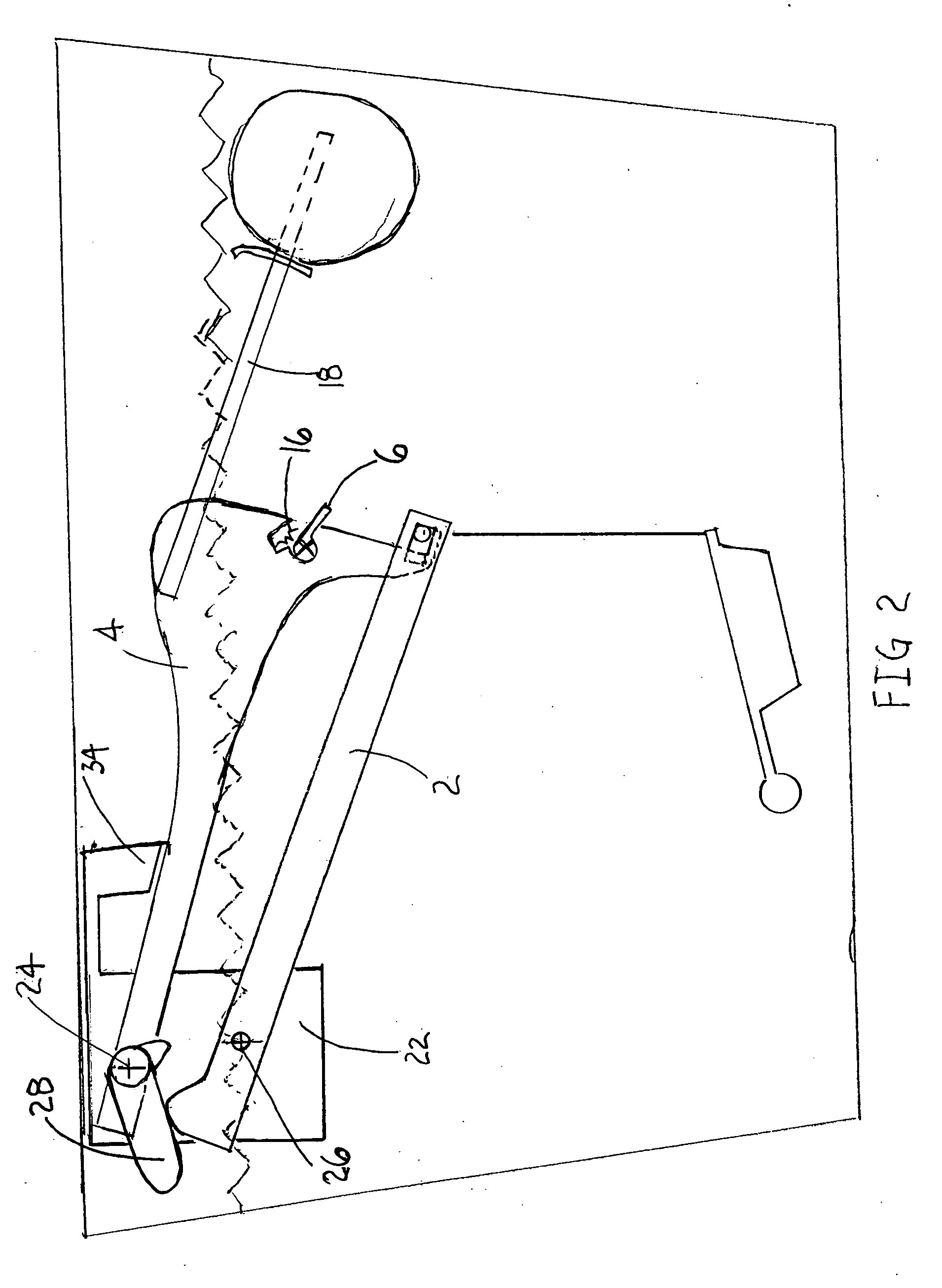
Device and a method for allowing performance of several separate treatments of a teat of an animal
InactiveUS7128020B2Quality improvementTreated differentlyCathetersOther apparatusInterior spaceEngineering
Owner:DELAVAL HLDG AB
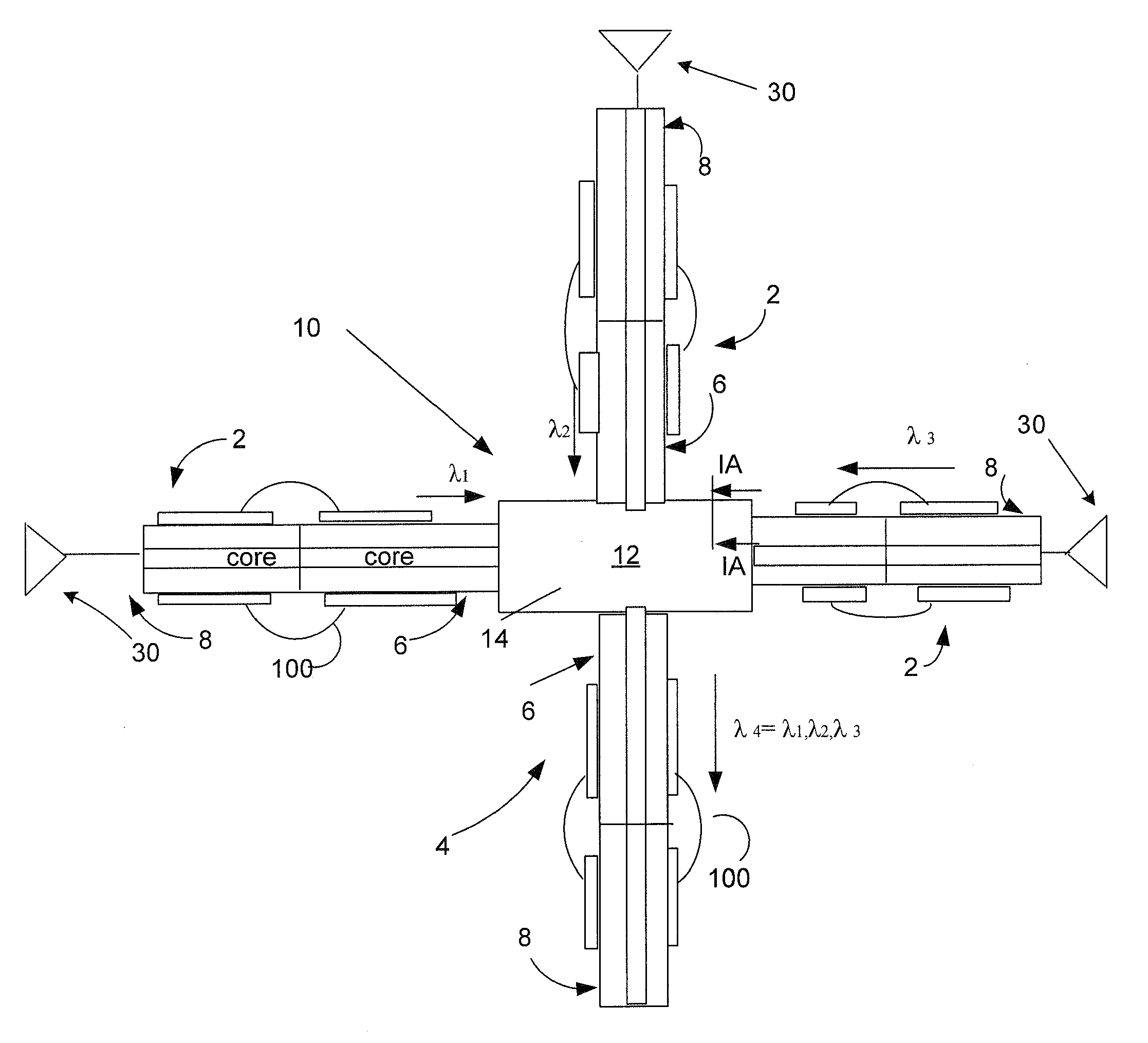
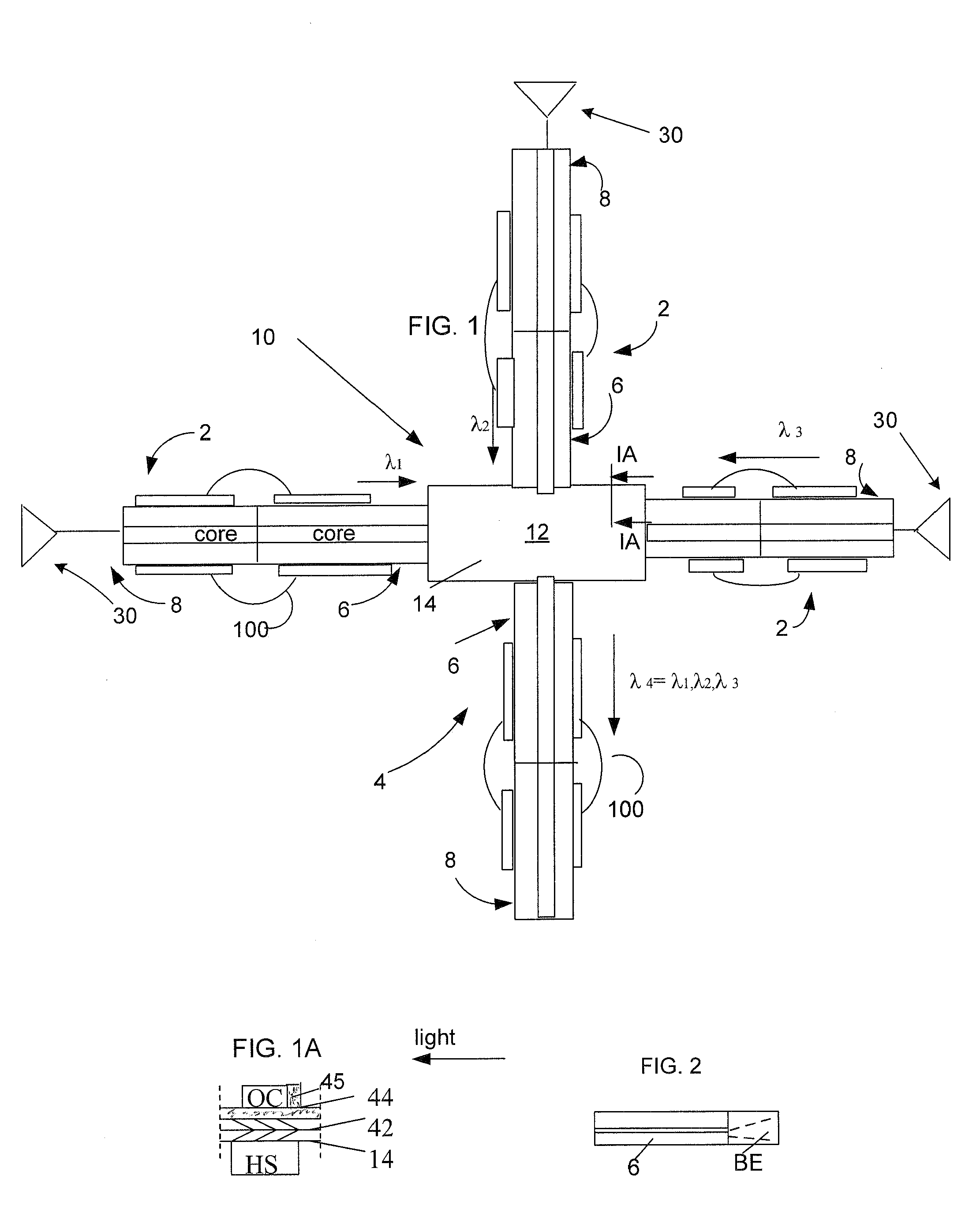
Led-based light engine
InactiveUS20100226139A1Efficient evacuationProduct's lifetimePoint-like light sourceLighting heating/cooling arrangementsEngineeringLight fixture
Owner:DIAMOND CREEK CAPITAL LLC
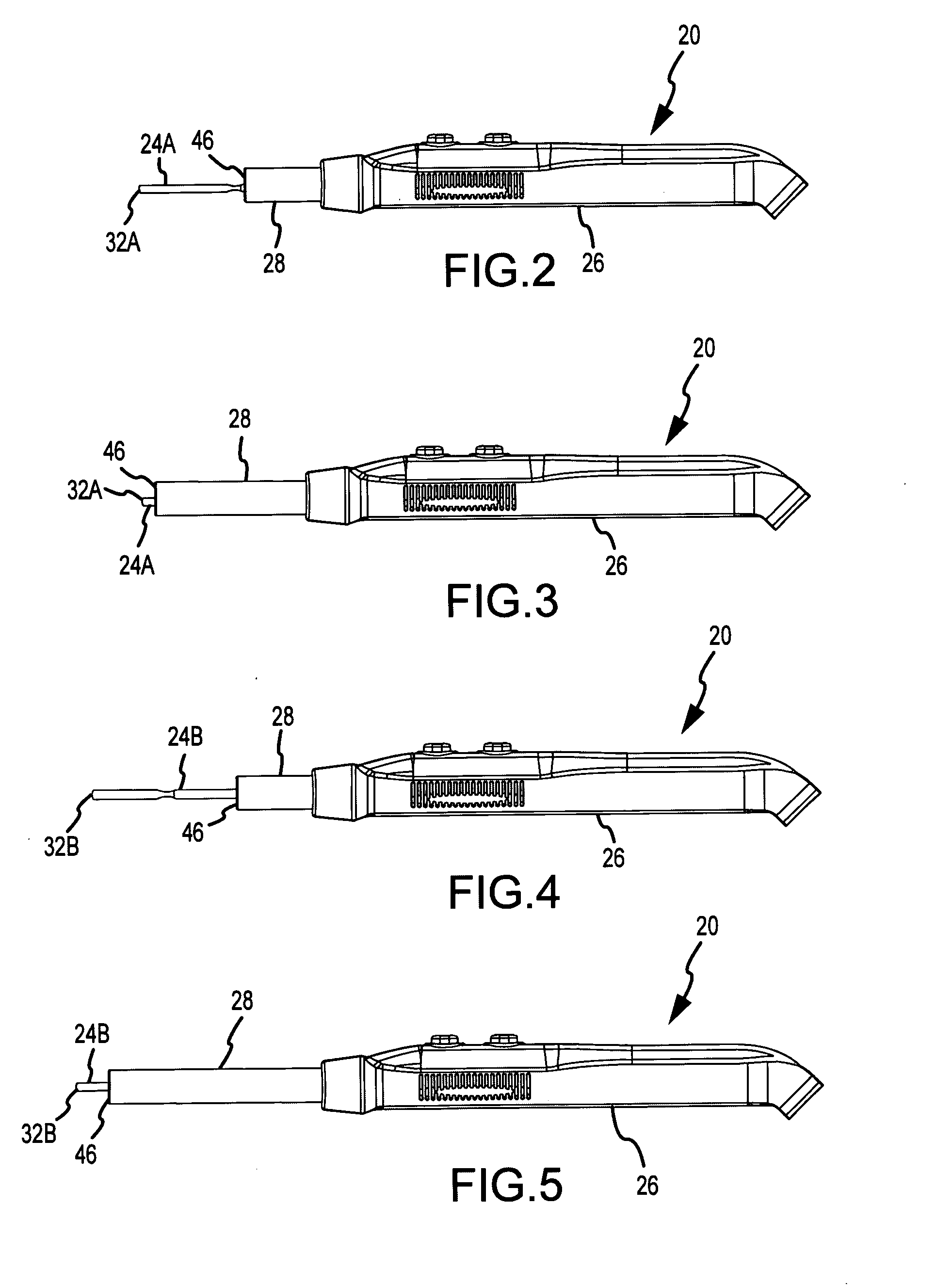
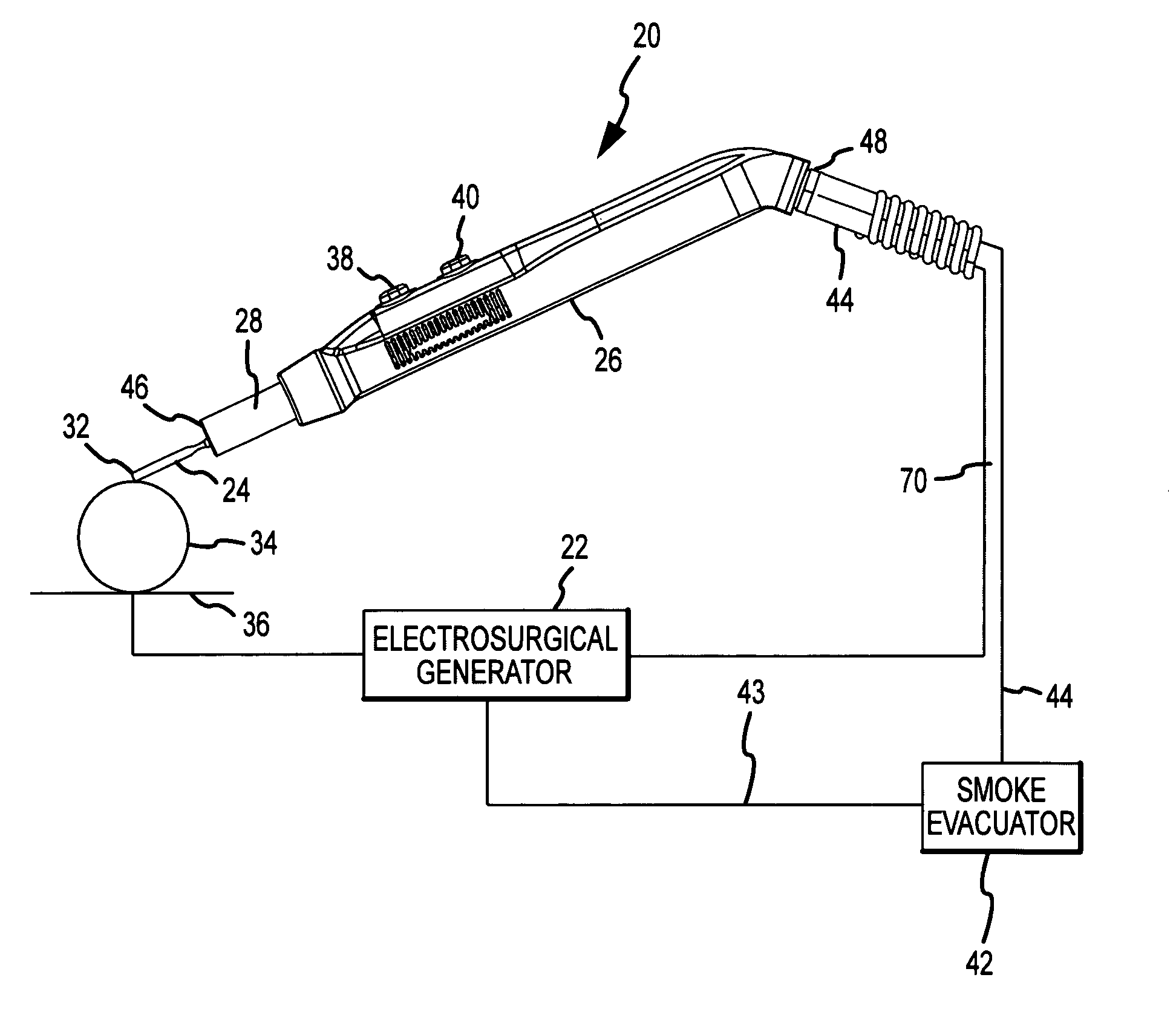
Integrated smoke evacuation electrosurgical pencil and method
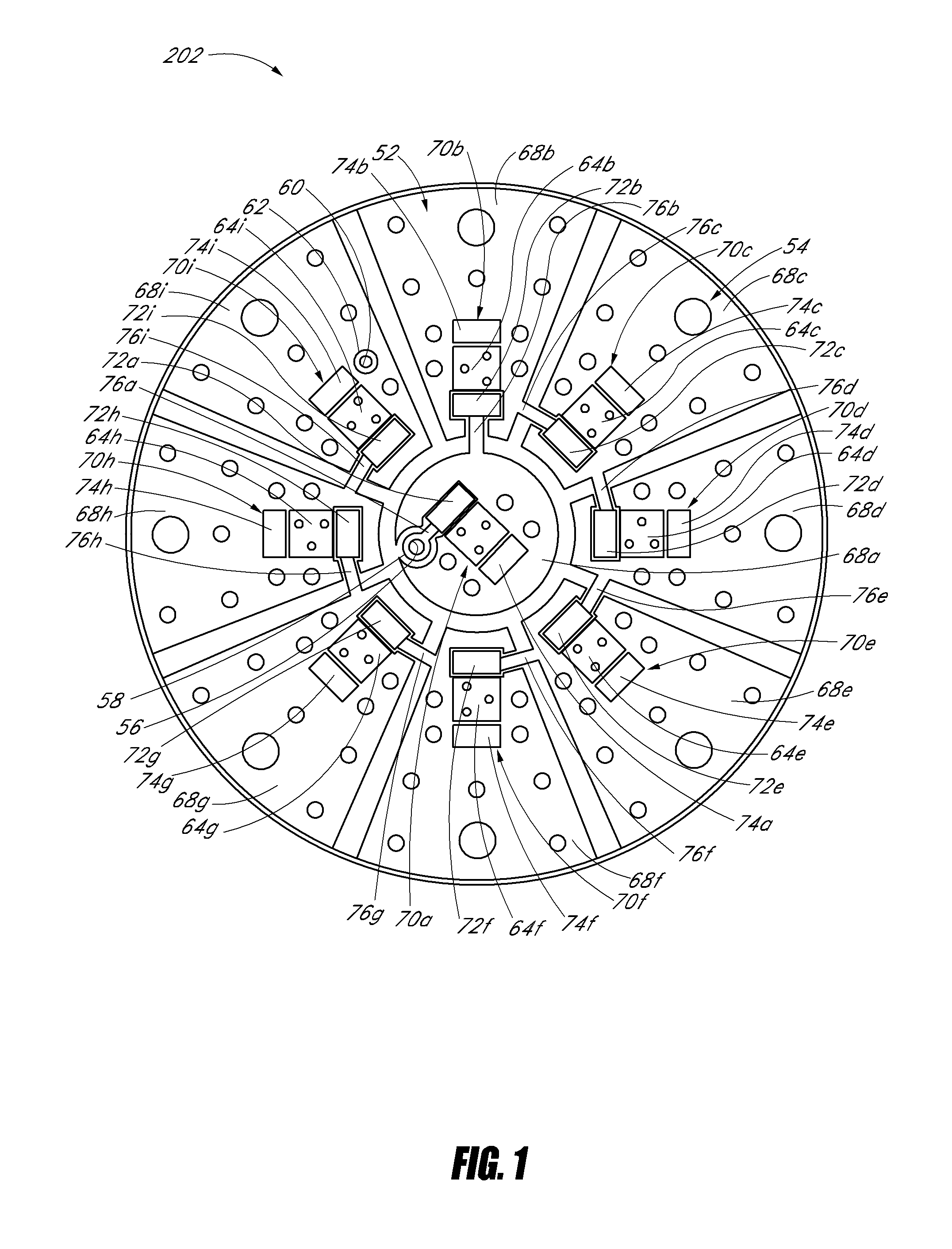
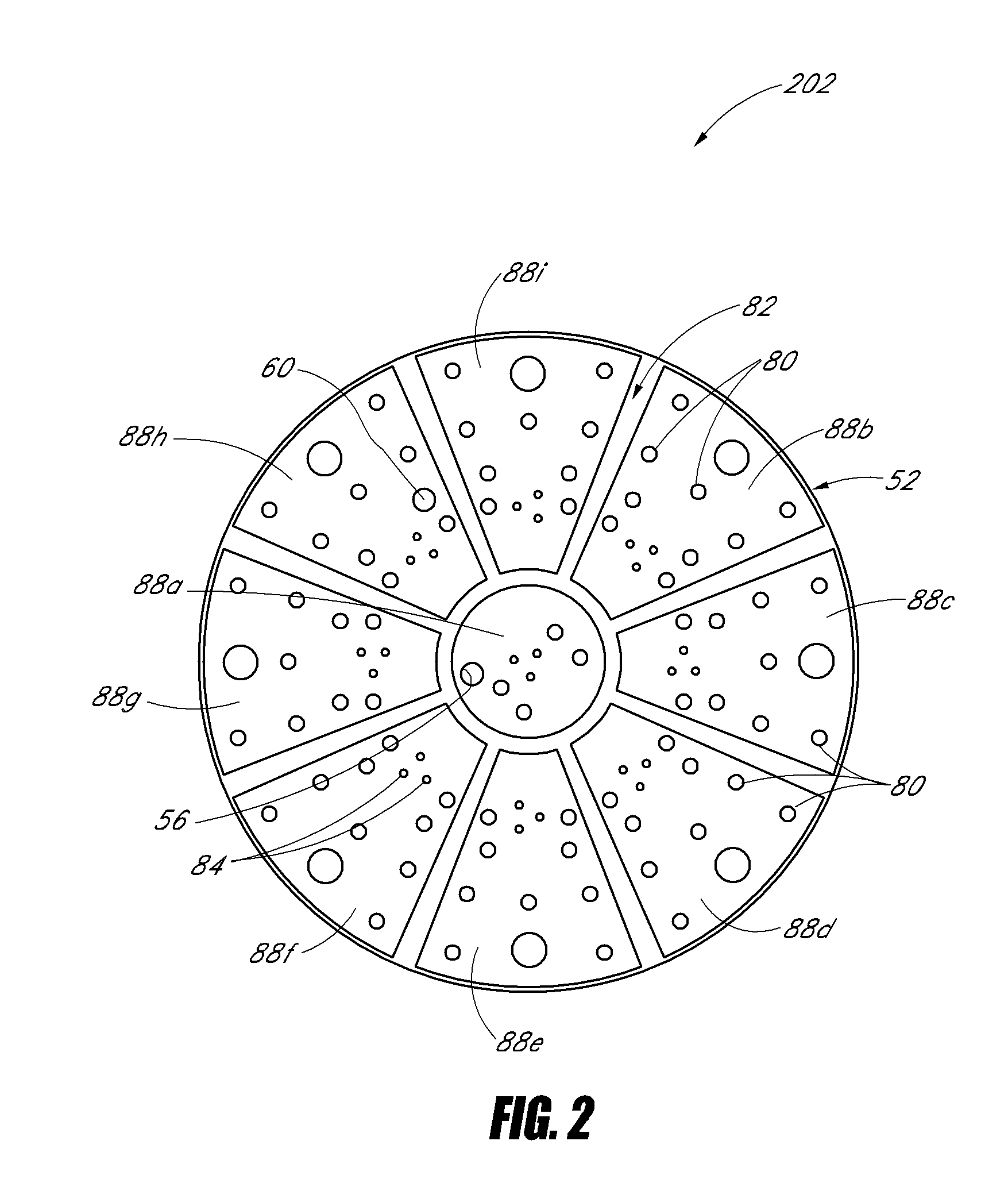
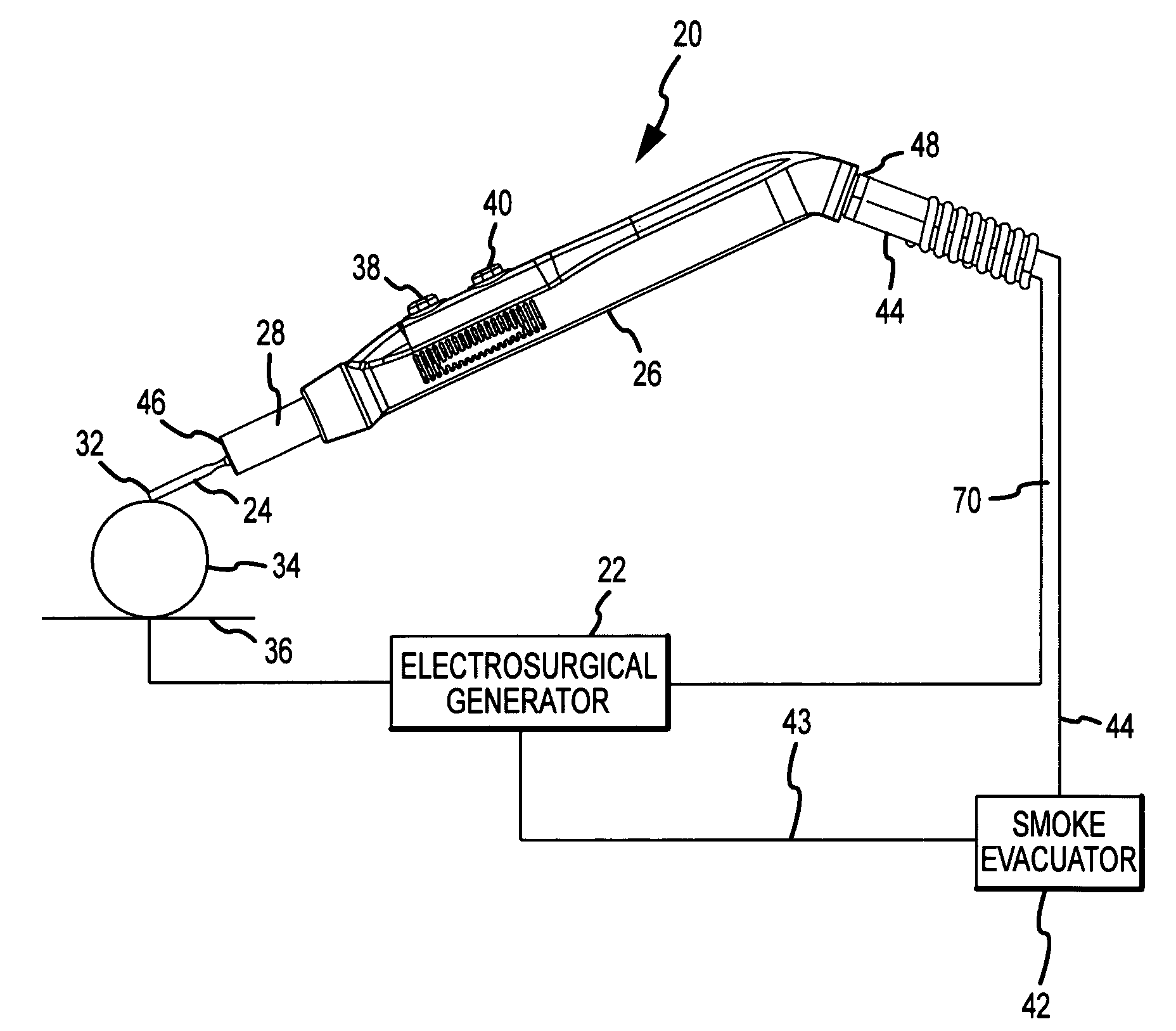
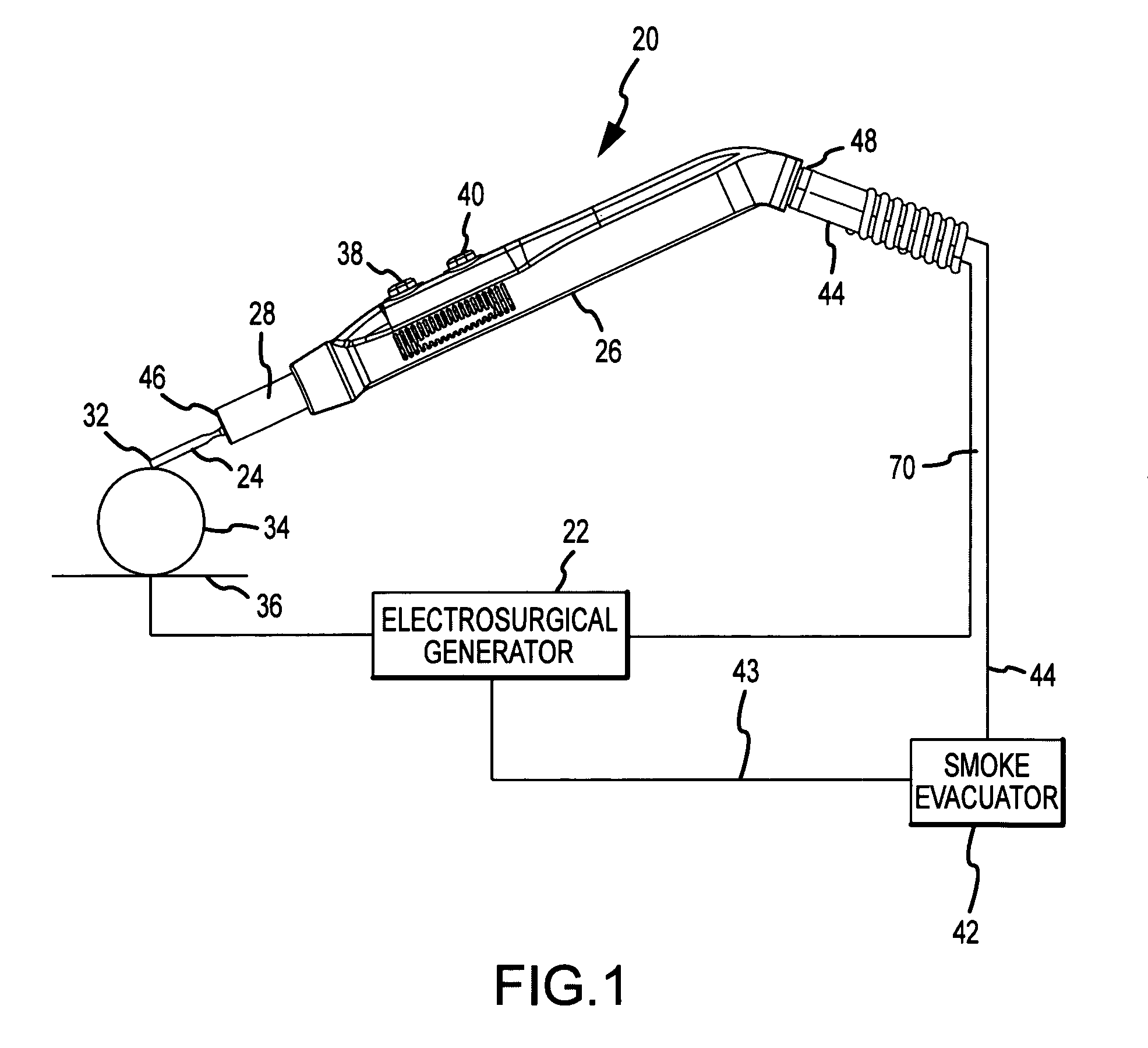
ActiveUS20090062791A1Effective positioningEfficient evacuationSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesEngineeringSmoke
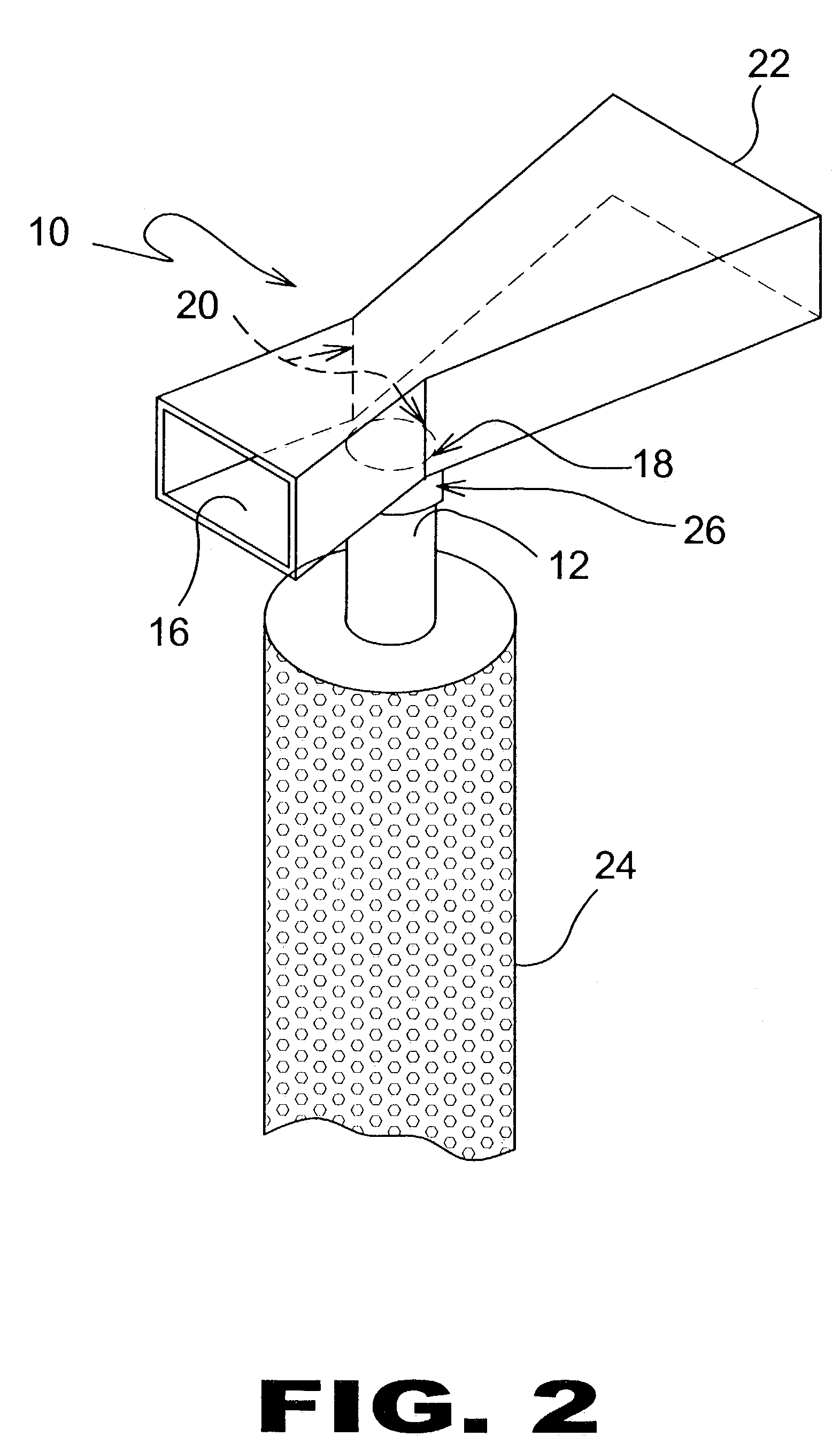
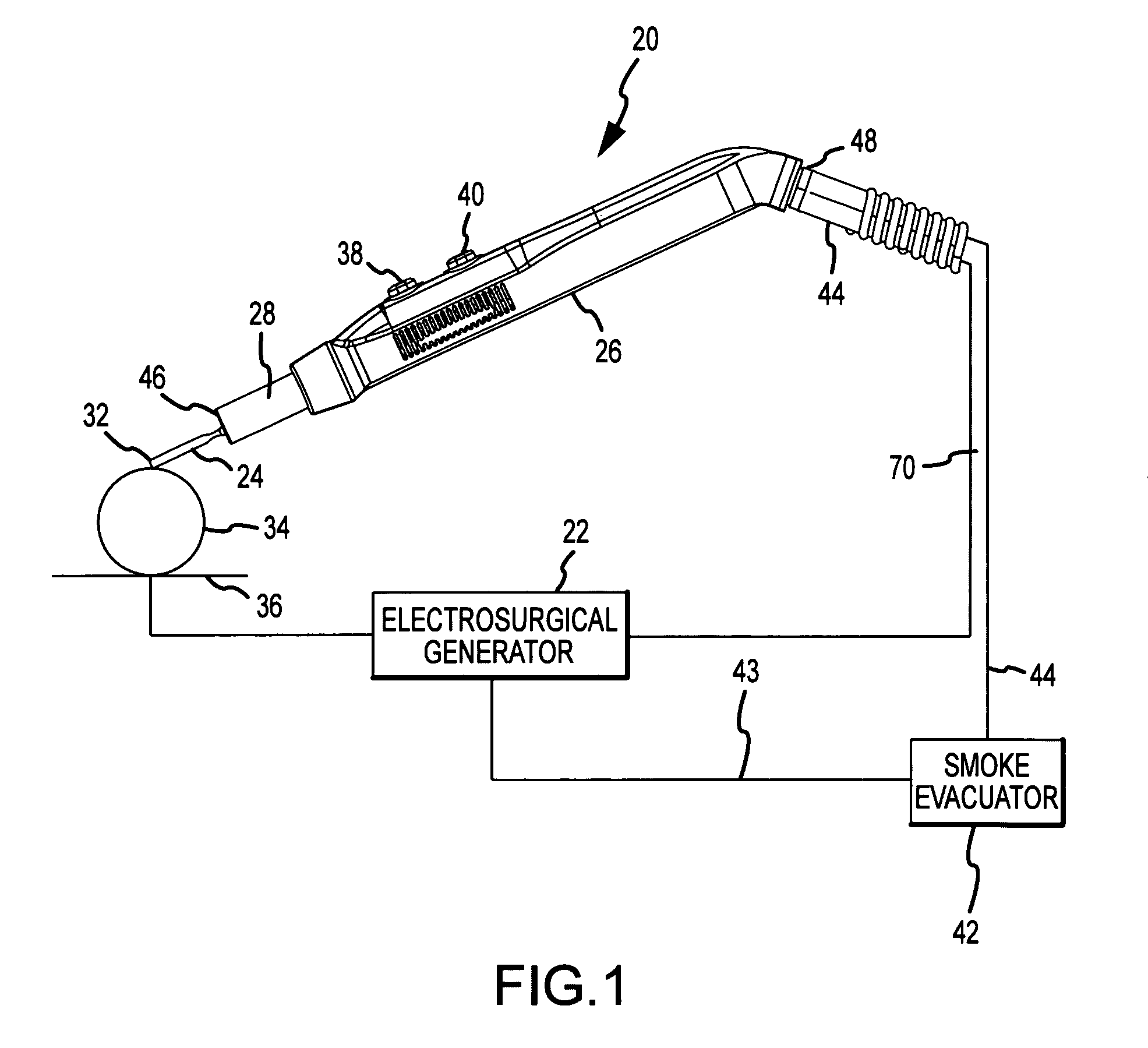
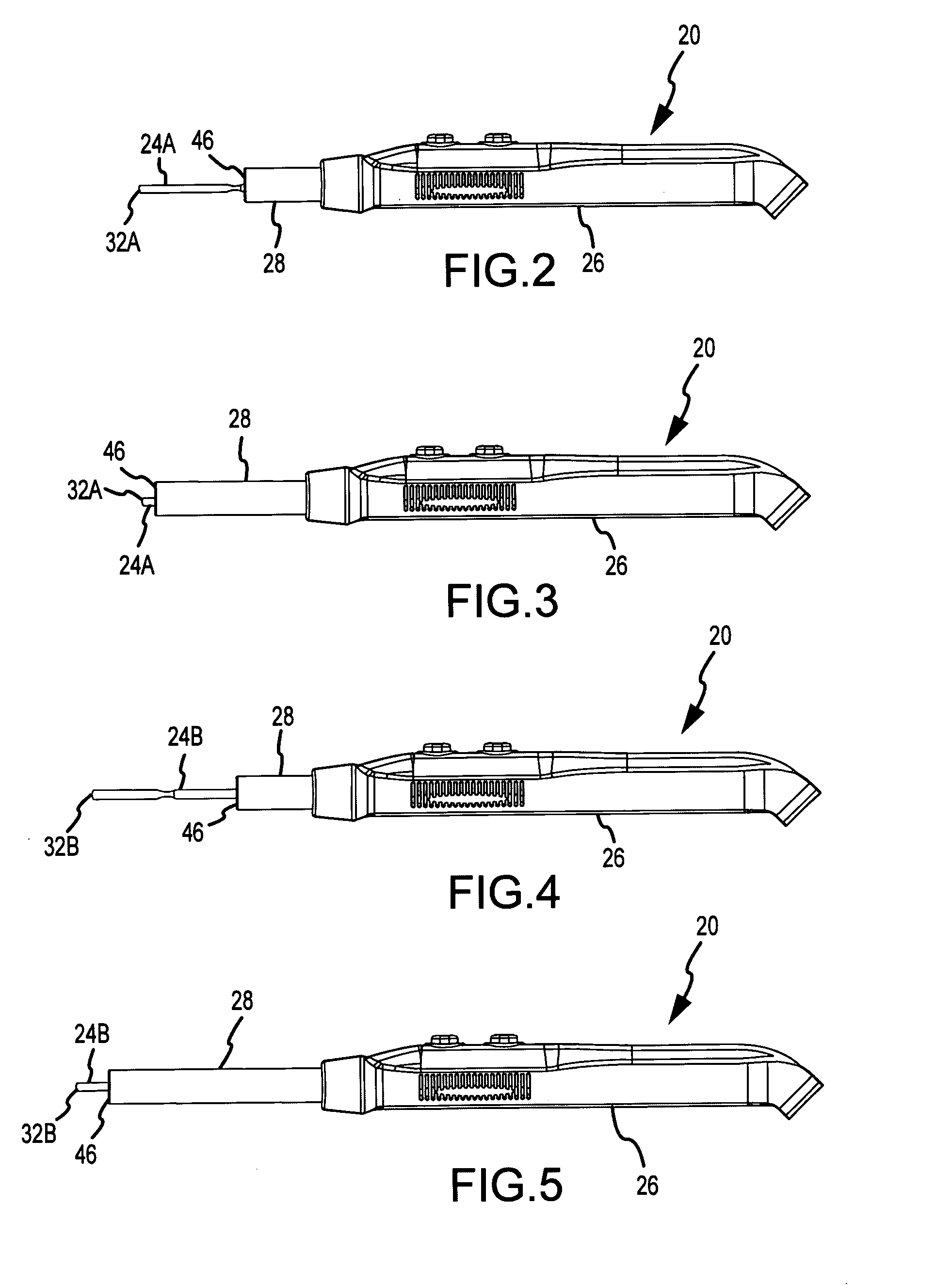
An electrosurgical pencil includes an adjustable-length suction tube which surrounds a stationary electrode to evacuate smoke and electrosurgical byproducts from a surgical site. An electrode anchor unit is located within the interior of the suction tube to allow relative movement of the suction tube relative to a stationarily-retained electrode, and to receive and connect to different lengths of the electrodes. Adjusting the length of the suction tube relative to the different lengths of the electrode achieves effective evacuation, among other things.
Owner:CONMED CORP
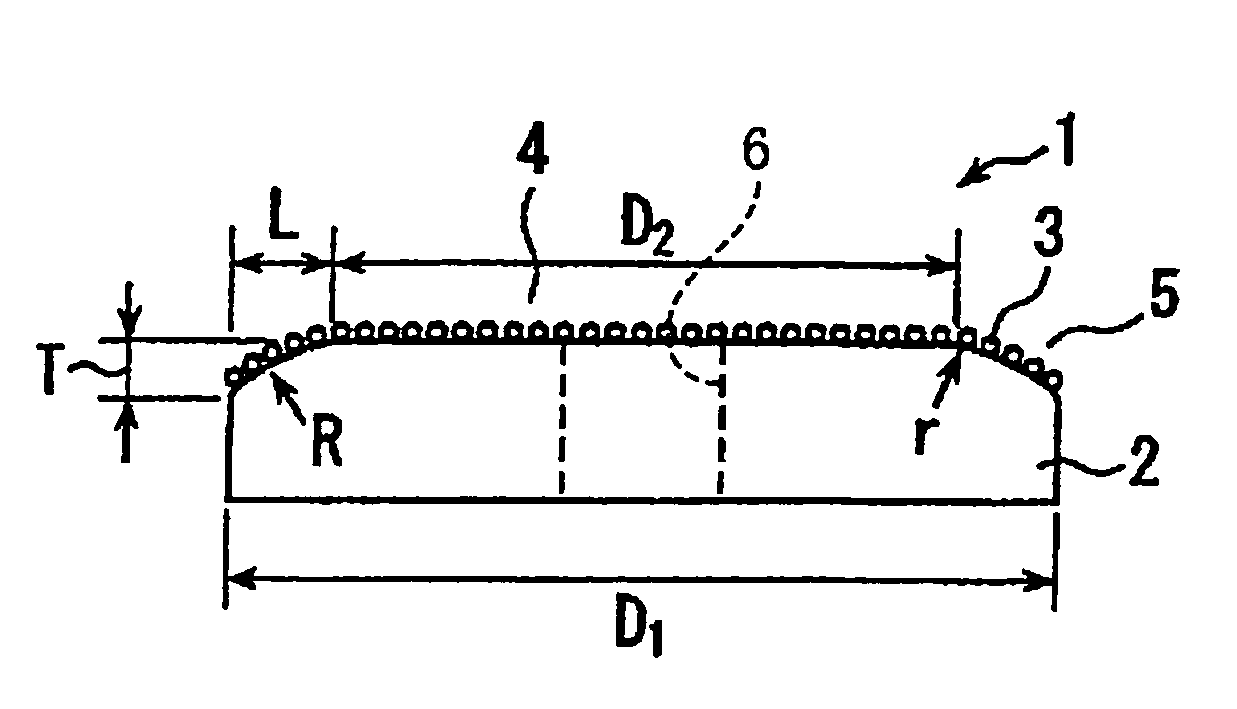
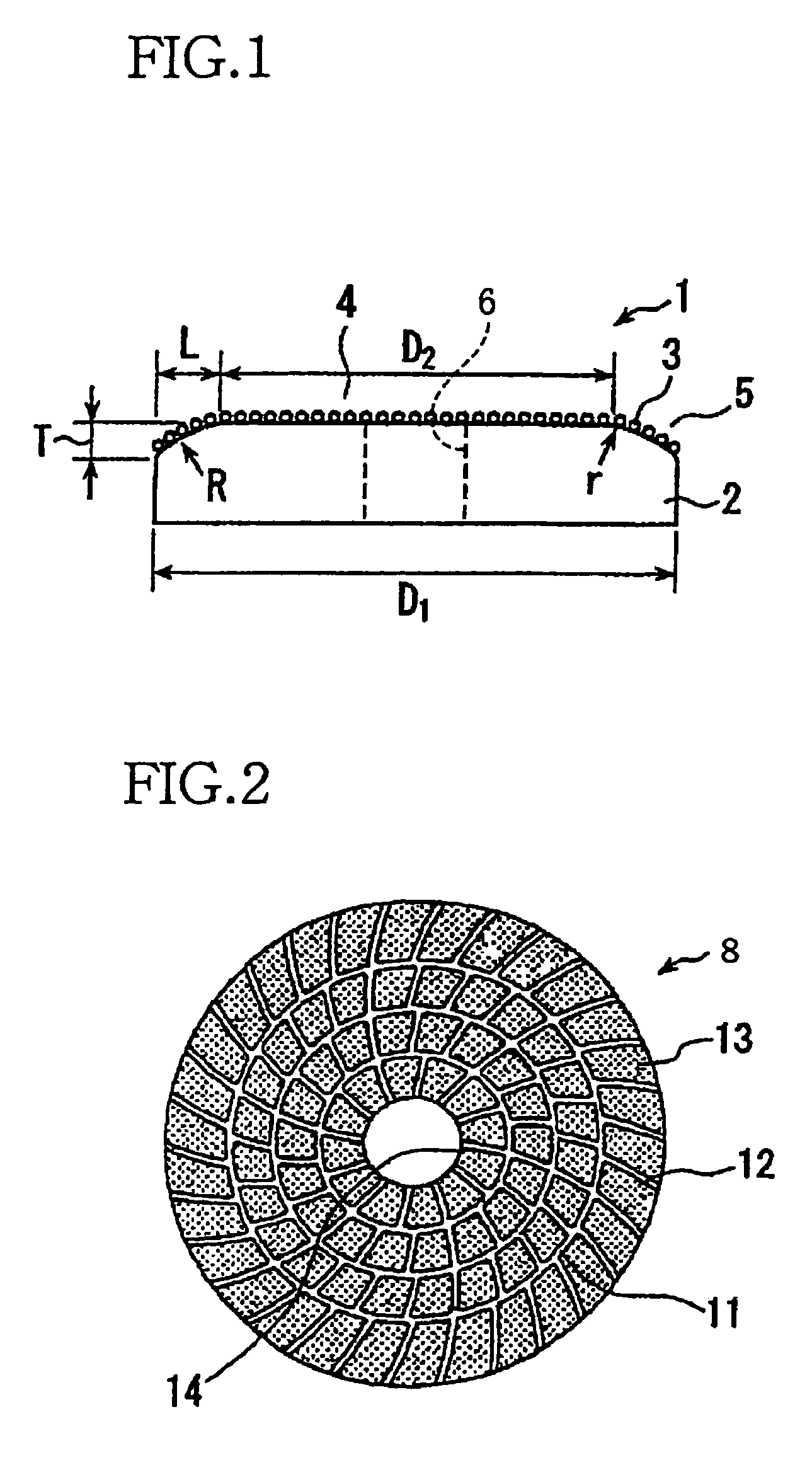
CMP pad conditioner having working surface inclined in radially outer portion
ActiveUS7021995B2Avoiding considerable damageExtended service lifeRevolution surface grinding machinesGrinding drivesMechanical engineeringEngineering
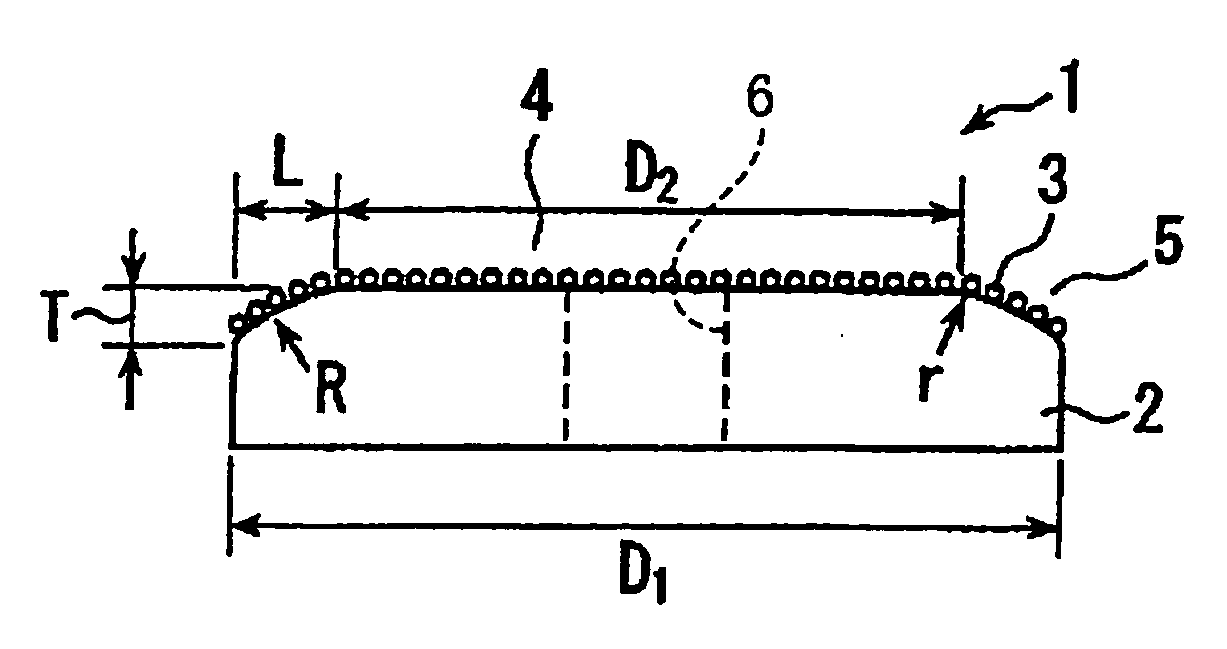
A CMP pad conditioner including: (a) a disk-shaped substrate having a working surface which is provided by one of its axially opposite end surfaces and which is to be brought into contact with the CMP pad; and (b) abrasive grains which are fixed to the working surface. The substrate includes a radially inner portion and a radially outer portion which is located radially outwardly of the radially inner portion. The working surface in the radially outer portion is inclined with respect to the working surface in the radially inner portion, such that a thickness of the radially outer portion as measured in an axial direction of the substrate is reduced as viewed in a direction away from an axis of the substrate toward a periphery of the substrate. A ratio of an outside diameter of the radially inner portion to an outside diameter of the substrate is 60–85%.
Owner:NORITAKE CO LTD +1
Photovoltaic Cell Module And Method Of Forming Same
InactiveUS20110061724A1Efficiently converted to electricityCost-effective and repeatable production of photovoltaicFinal product manufactureVacuum evaporation coatingEngineeringDepth of penetration
A photovoltaic cell module, a photovoltaic array including at least two modules, and a method of forming the module are provided. The photovoltaic cell module includes a substrate and a tie layer disposed on the substrate. The tie layer has a depth of penetration of from 1.1 to 100 mm and a tack value of less than −0.6 g·sec. The photovoltaic cell module also includes a photovoltaic cell disposed on the tie layer. The method of forming the photovoltaic cell module includes the steps of disposing the tie layer on the substrate and disposing the photovoltaic cell on the tie layer to form the photovoltaic cell module.
Owner:DOW CORNING CORP
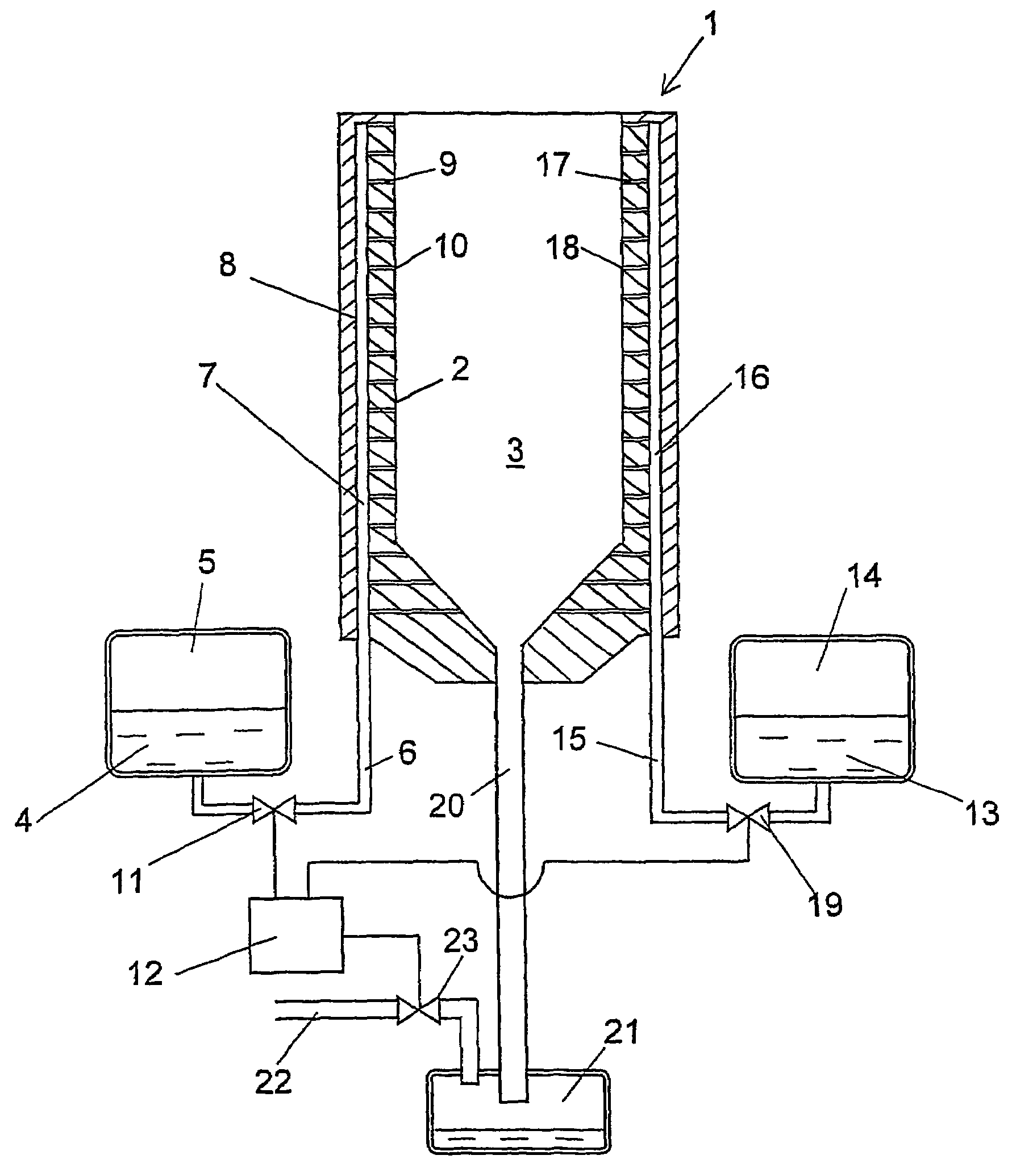
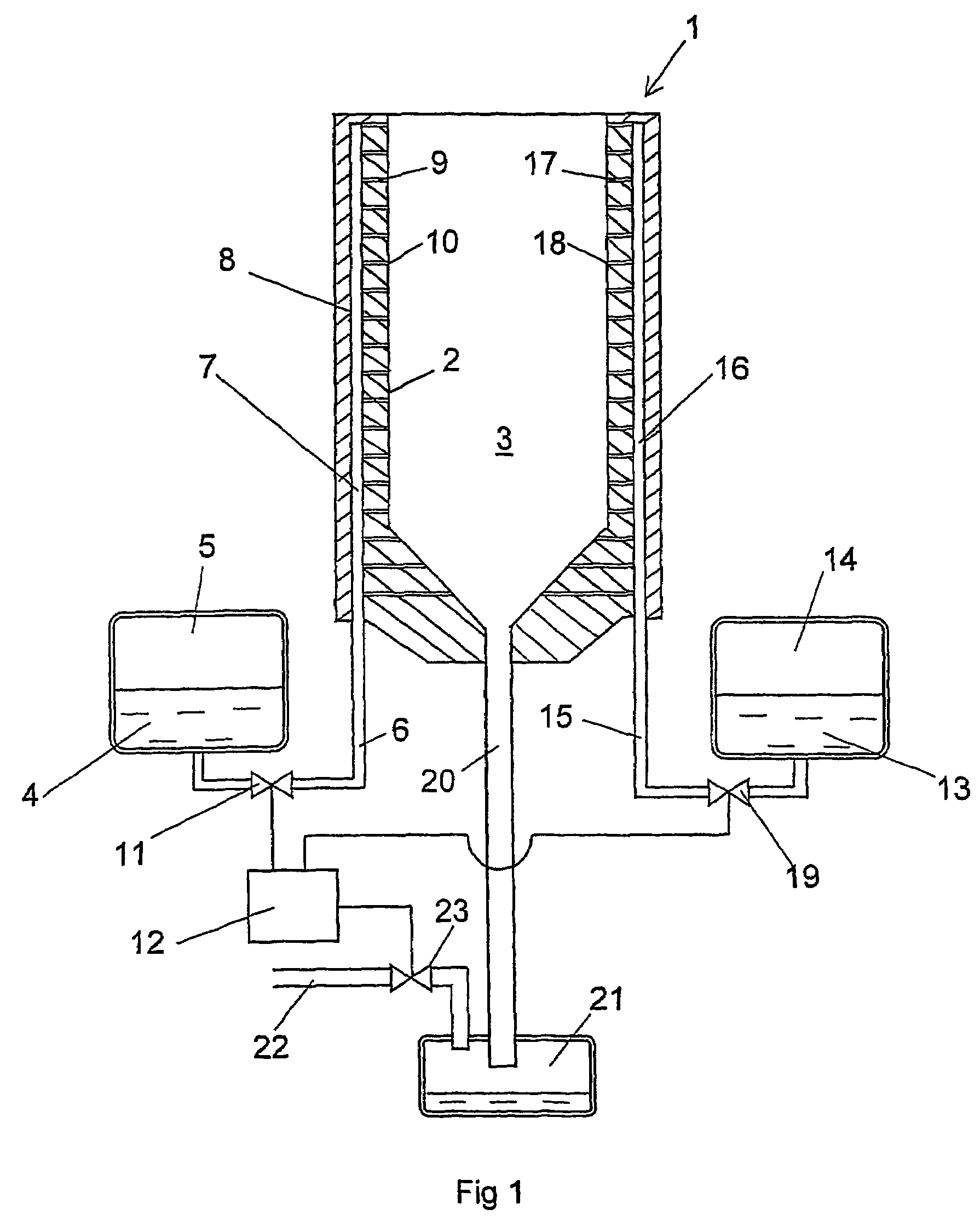
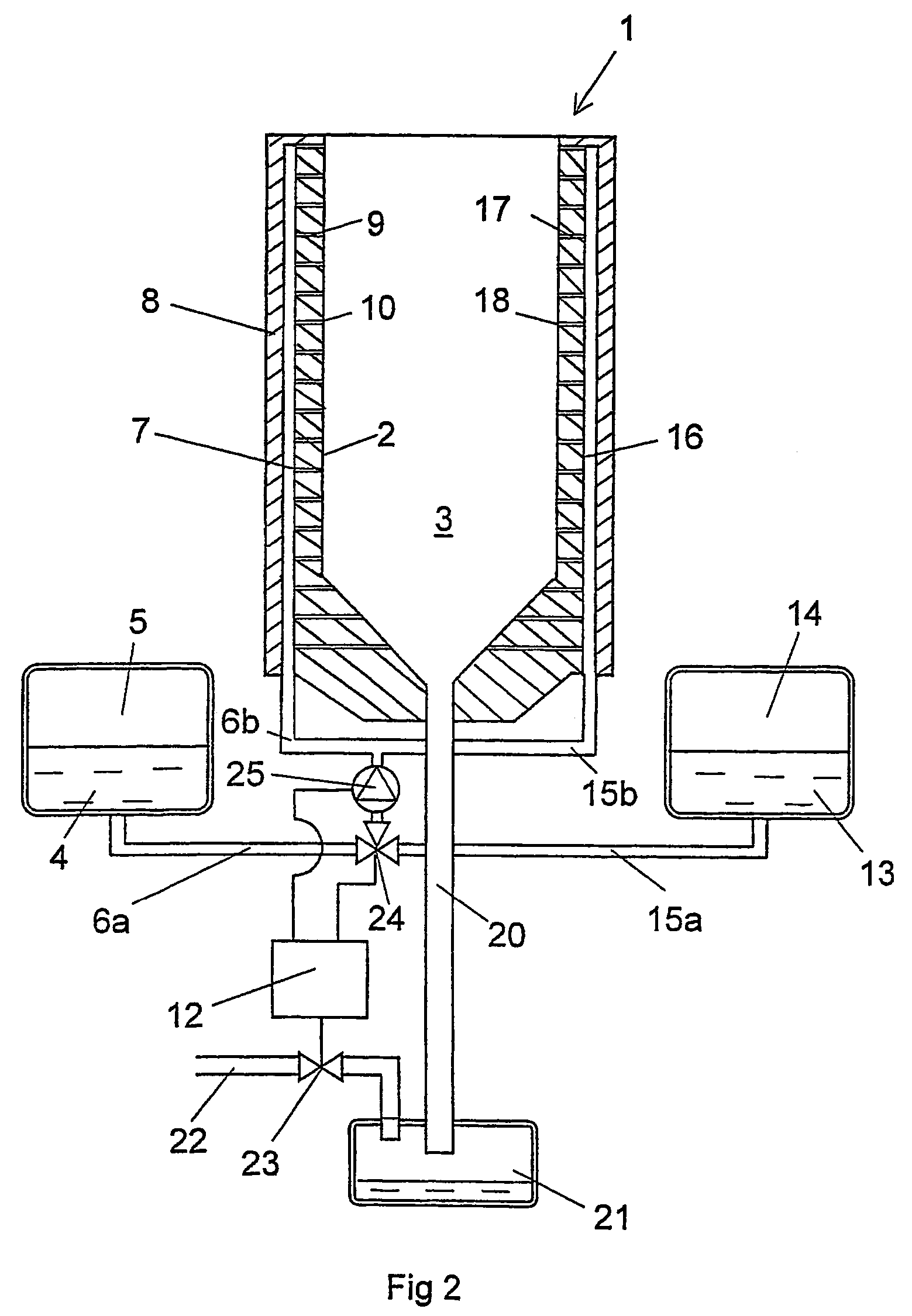
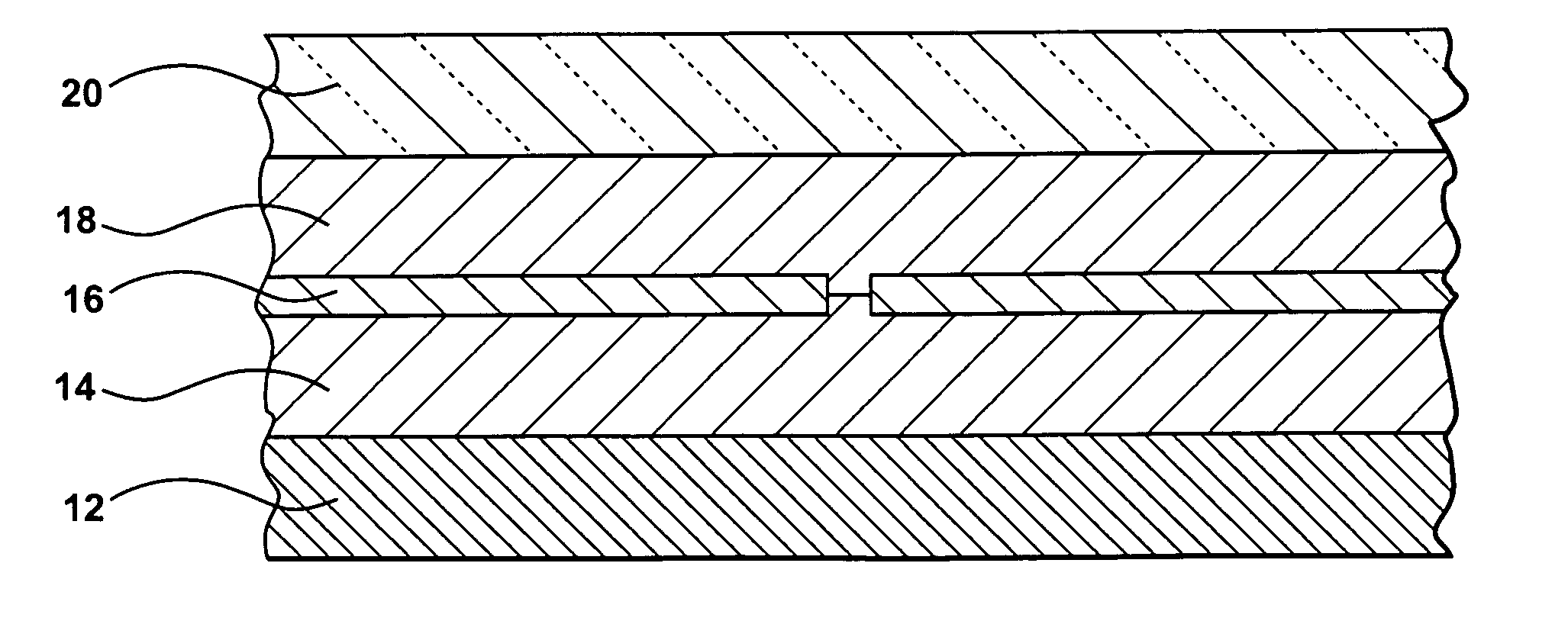
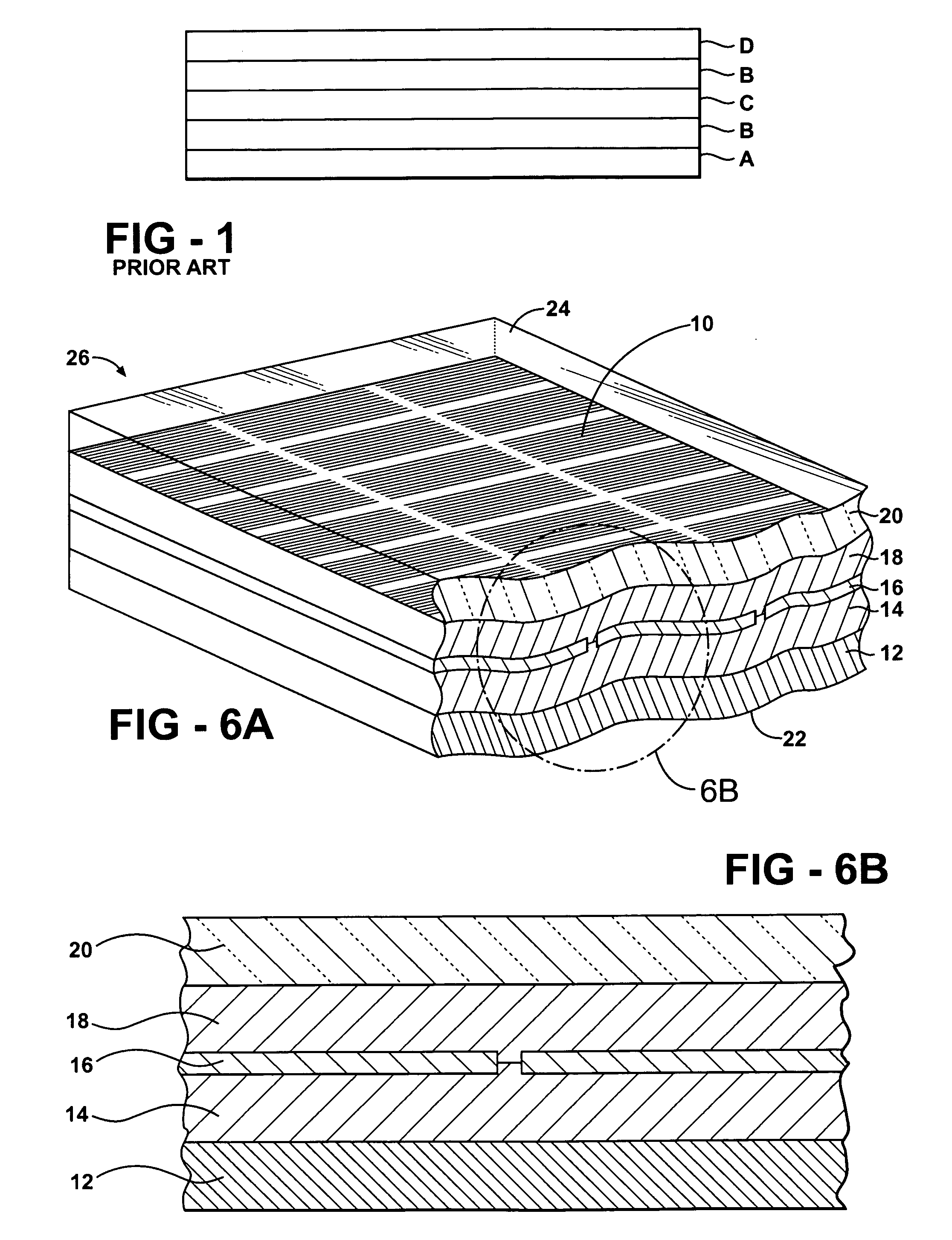
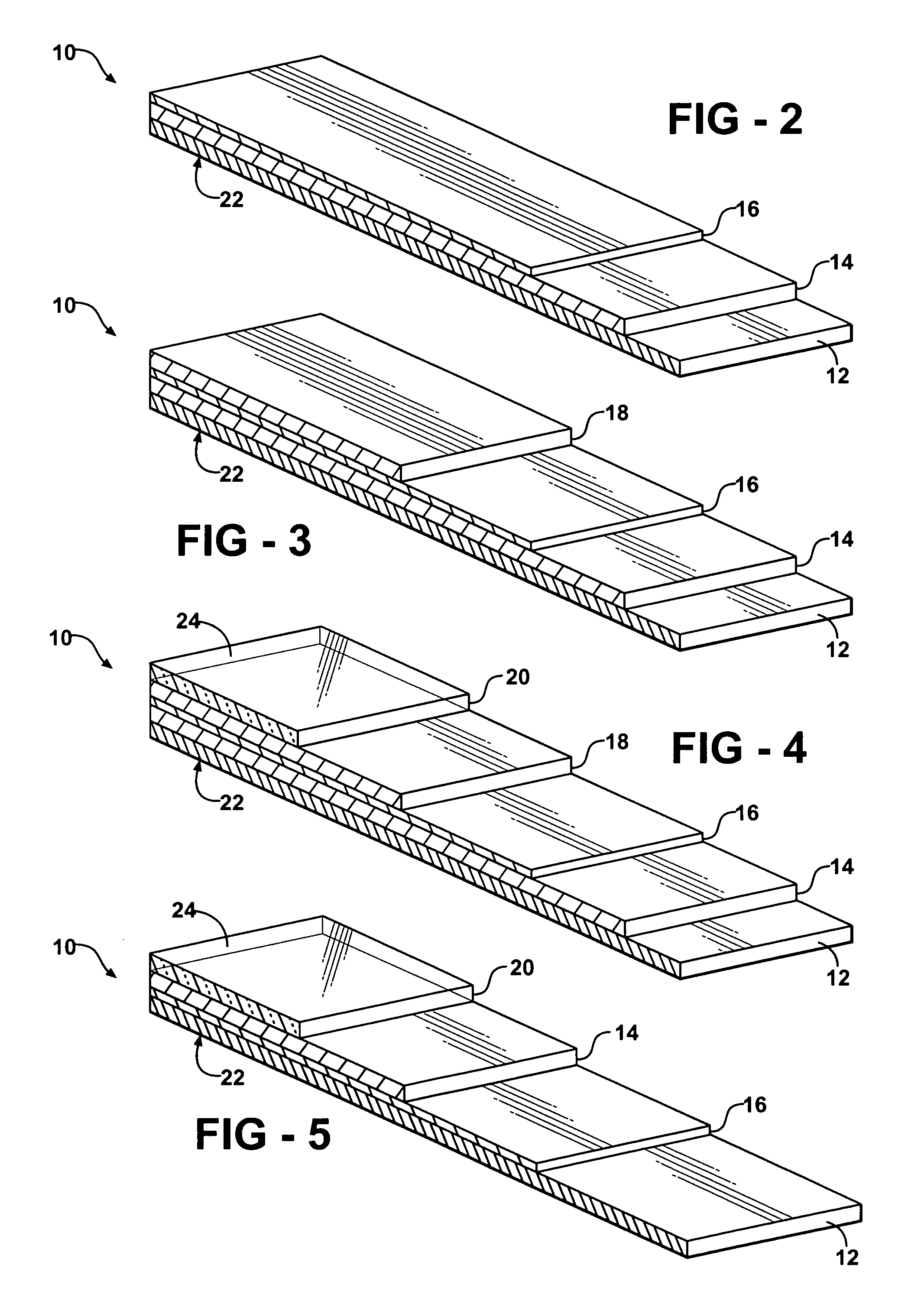
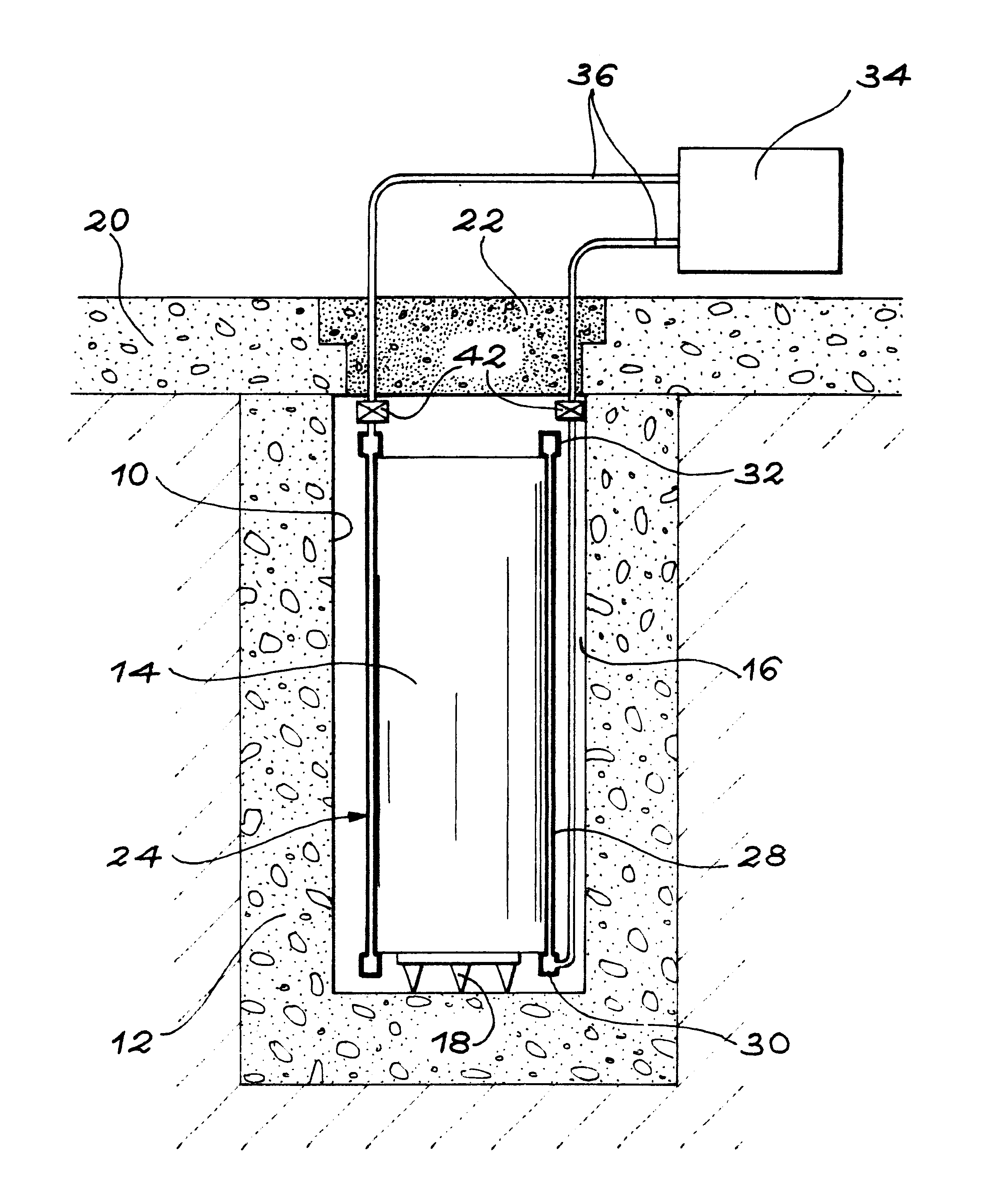
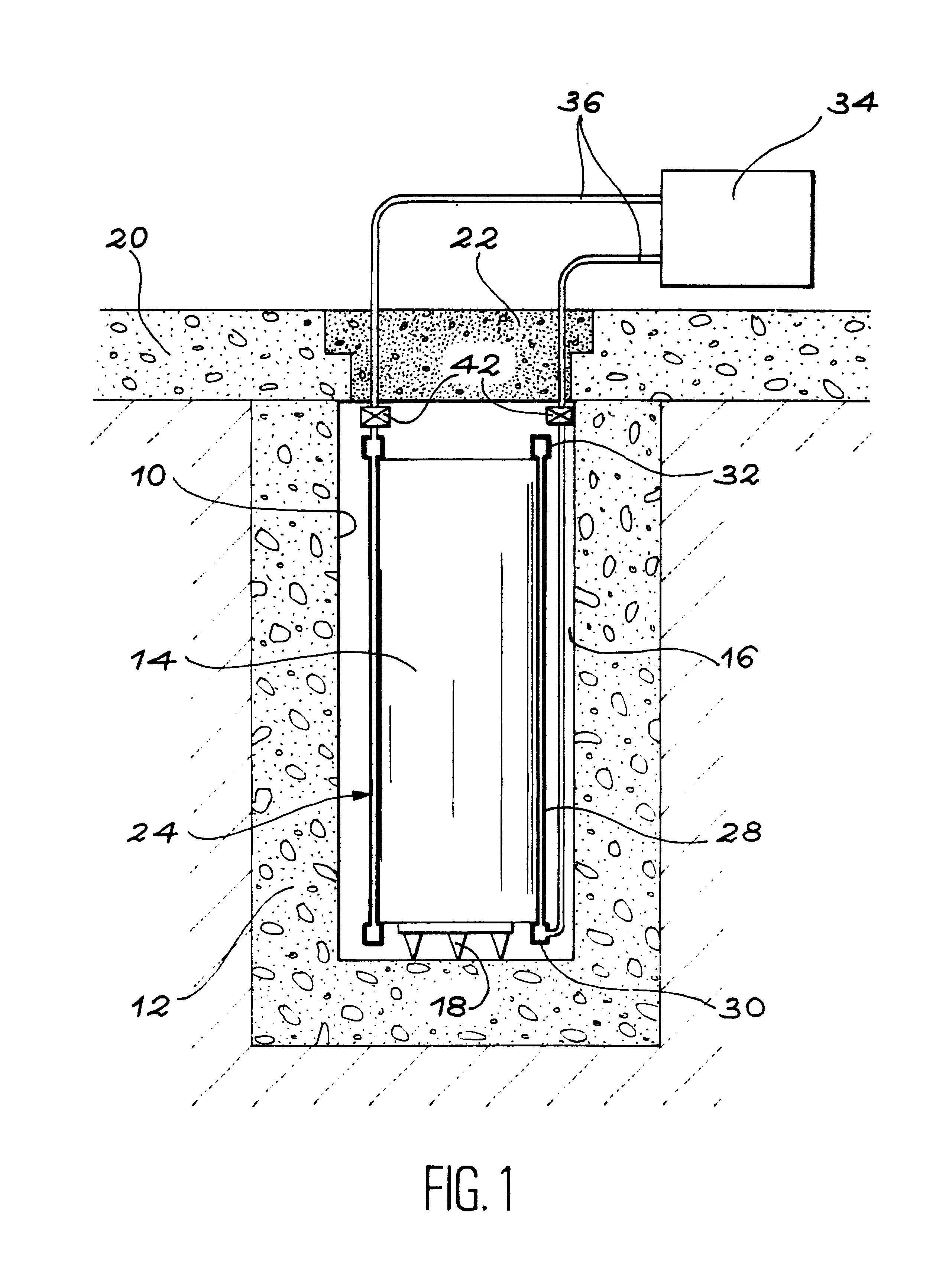
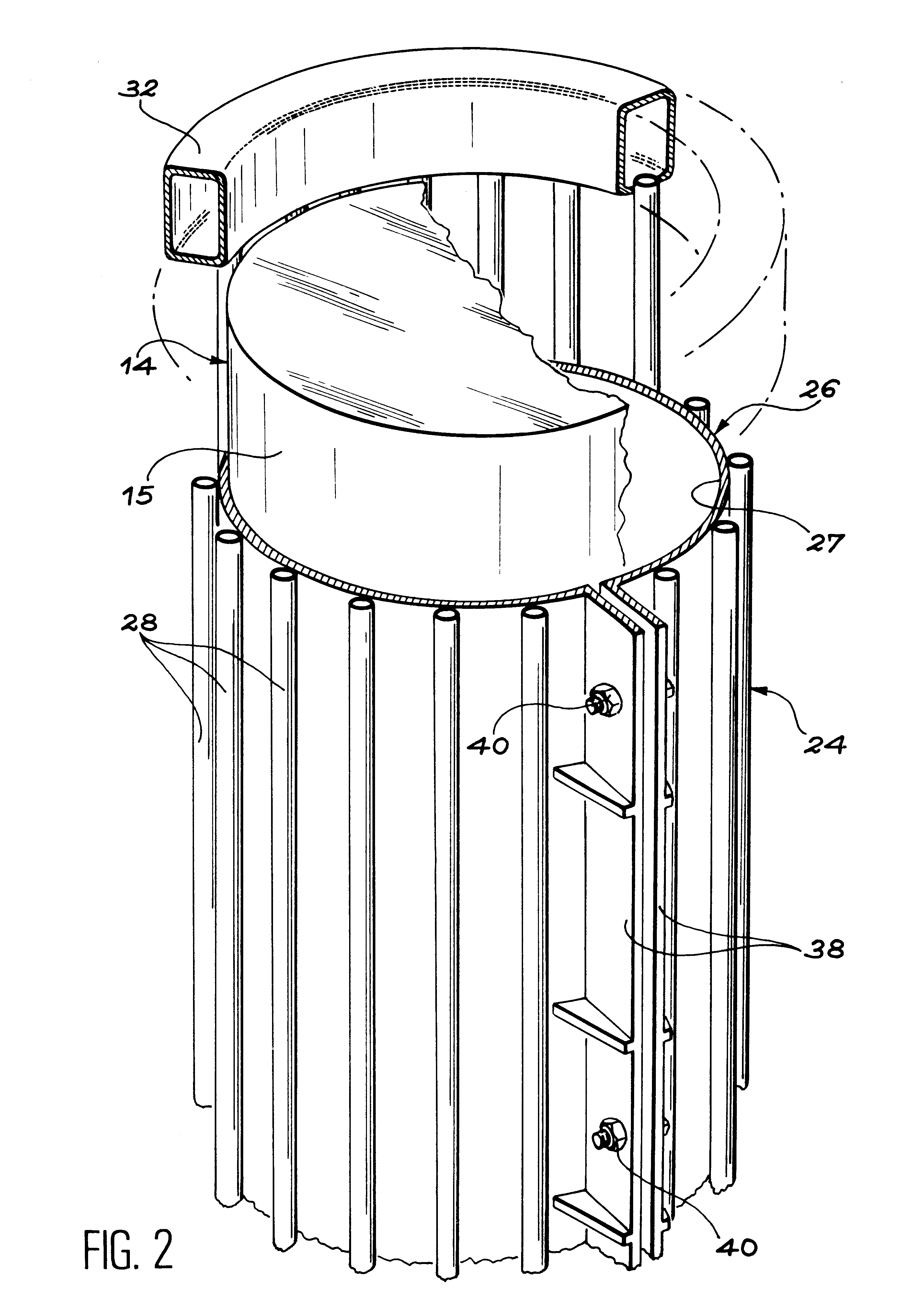
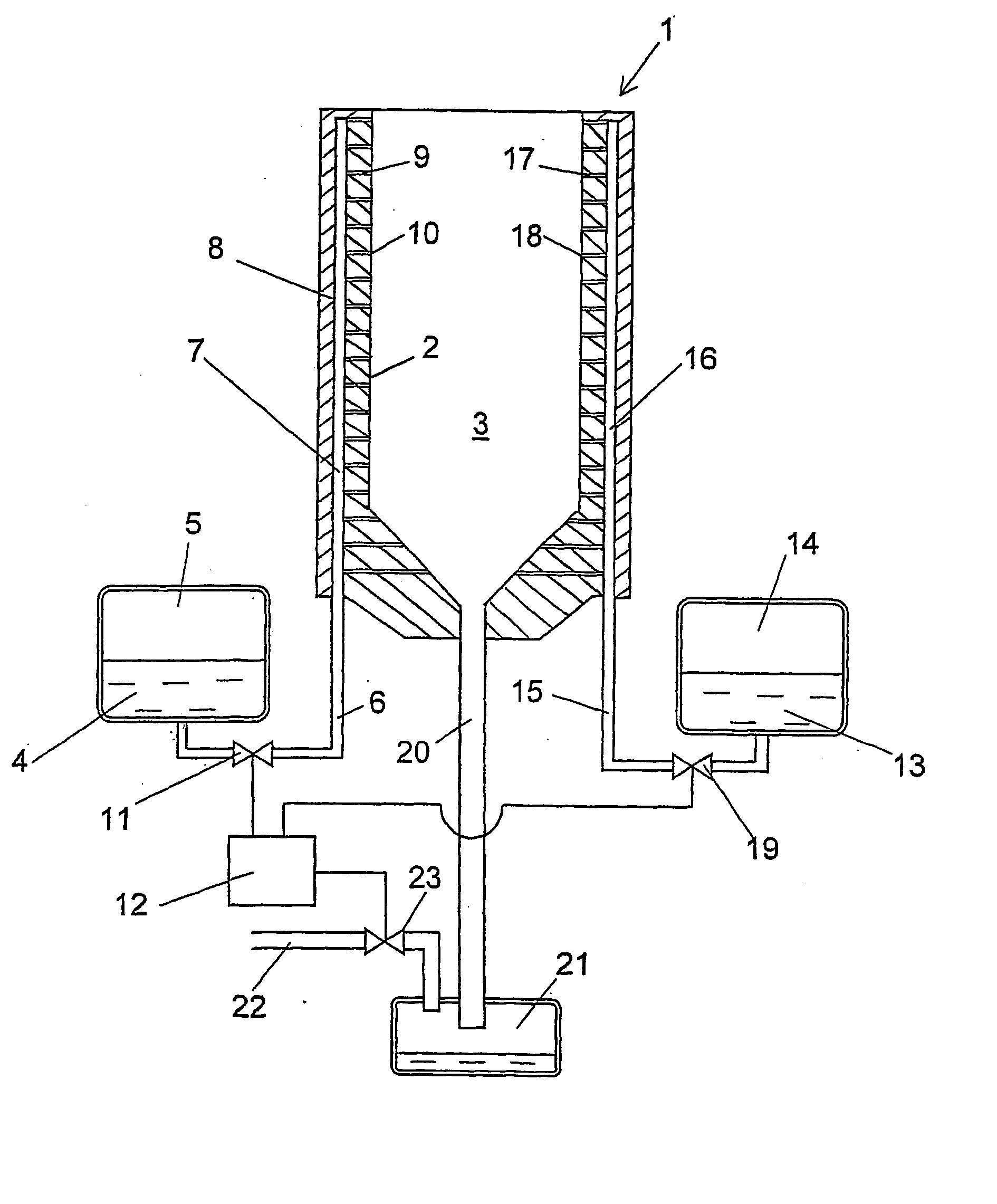
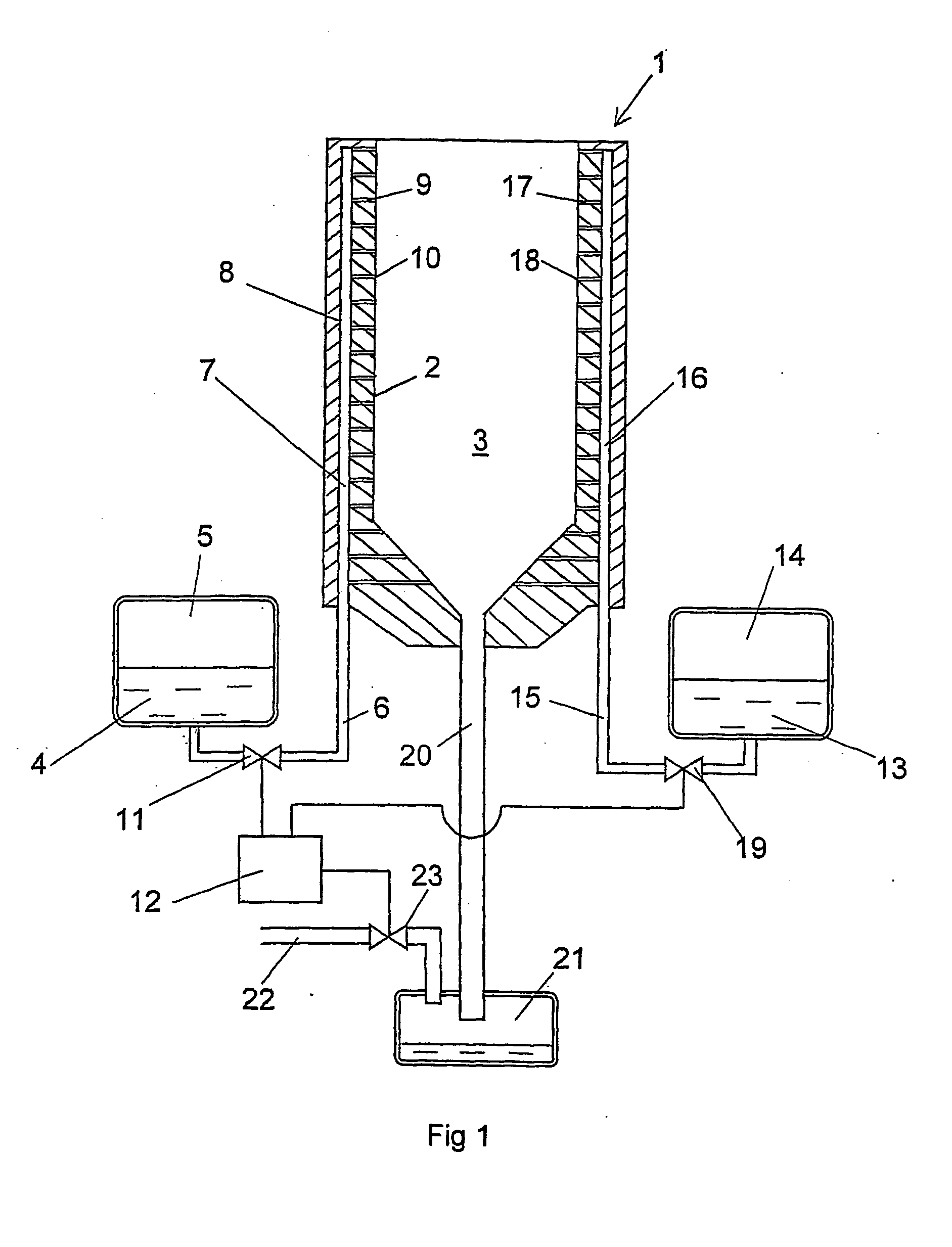
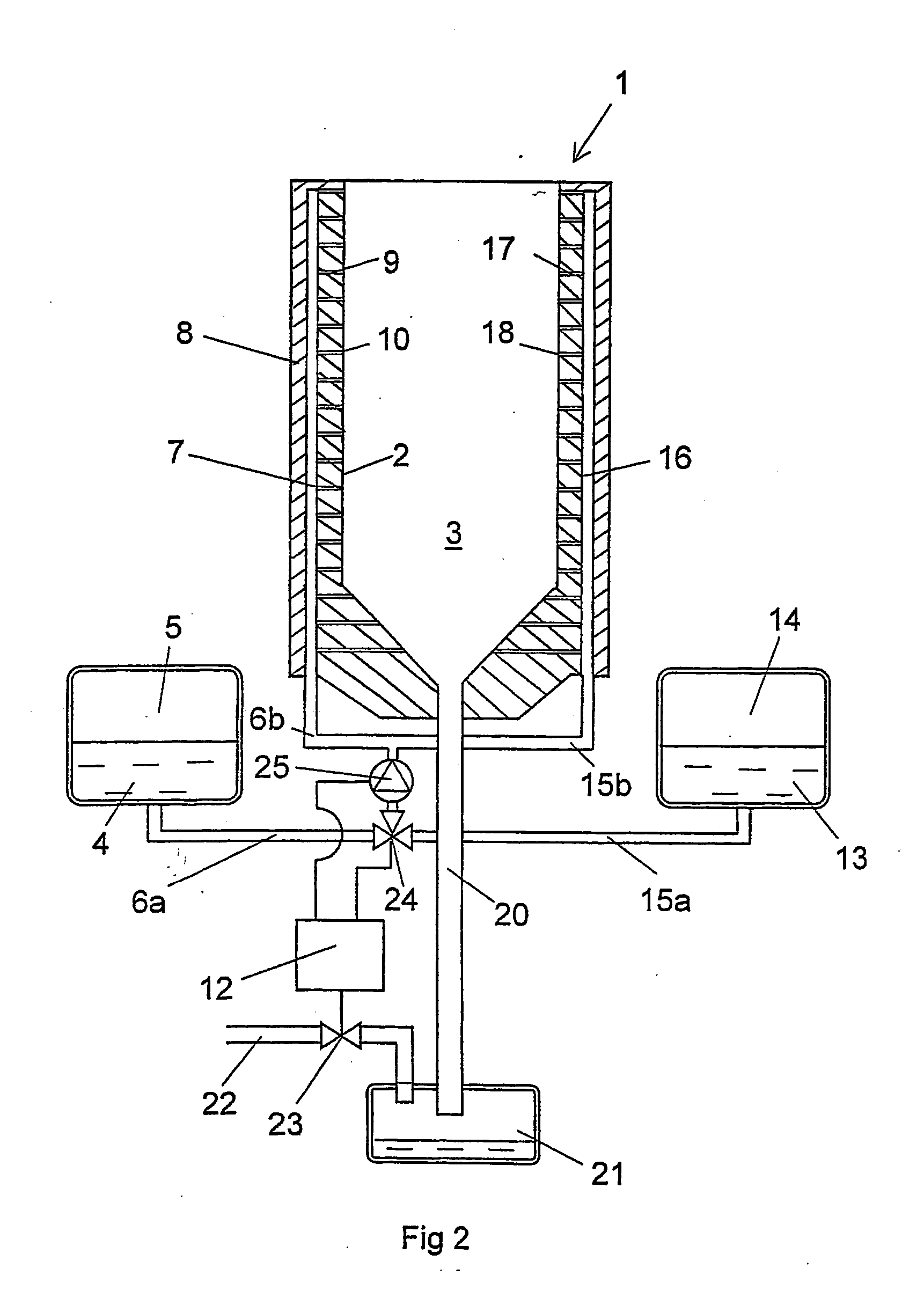
Installation for very long term storage of heat-generating products such as nuclear waste
InactiveUS6802671B1Efficient evacuationRisking dispersionSolid waste disposalProtective foundationEngineeringClosed cavity
A very long term storage installation for calorific products such as nuclear waste, comprises at least one closed cavity (10), in which at least one product confinement container is housed (14). To evacuate the heat released by the stored products, each container (14) is surrounded by a jacket (26) associated with a thermosiphon (24) whose cold source is formed of an air condenser provided above a slab (20) sealing the top part of the cavity. The jacket (26) is preferably interchangeable and tightly surrounds the container (14).
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Venturi device
InactiveUS7051524B1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusAtmospheric pressurePressure difference
The present invention 10 discloses a venturi that is installed perpendicularly to the end of the exhaust pipe 12 of a truck or like vehicle 14 thus resulting in the air flow through the venturi being at a 90 degree angle relative to the exhaust gases exiting the exhaust pipe. The present invention 10 seeks to increase the performance and efficiency of an engine of a vehicle 14 by overcoming the backpressure in the engine exhaust system created by the muffler baffles. The present invention 10 may also be installed on automobiles and other motor vehicles 14 having appropriately modified exhaust systems. A front aperture 16 for air intake tapers in width to the back pressure relief port or nozzle 20 being slightly greater than the exhaust port 18 on the bottom portion thereof and then widens to form an air discharge port 22 on the rear portion thereof that is substantially wider and longer than the air intake port 16 thereby creating an air pressure differential wherein the reduced pressure in the back pressure relief port 20 serves to create a vortex to draw exhaust gases from the exhaust pipe 12 toward the discharge port 22.
Owner:KRAFT BERNARD A
CMP pad conditioner having working surface inclined in radially outer portion
ActiveUS20050215188A1Facilitates evacuationEfficient evacuationRevolution surface grinding machinesGrinding drivesEngineeringMechanical engineering
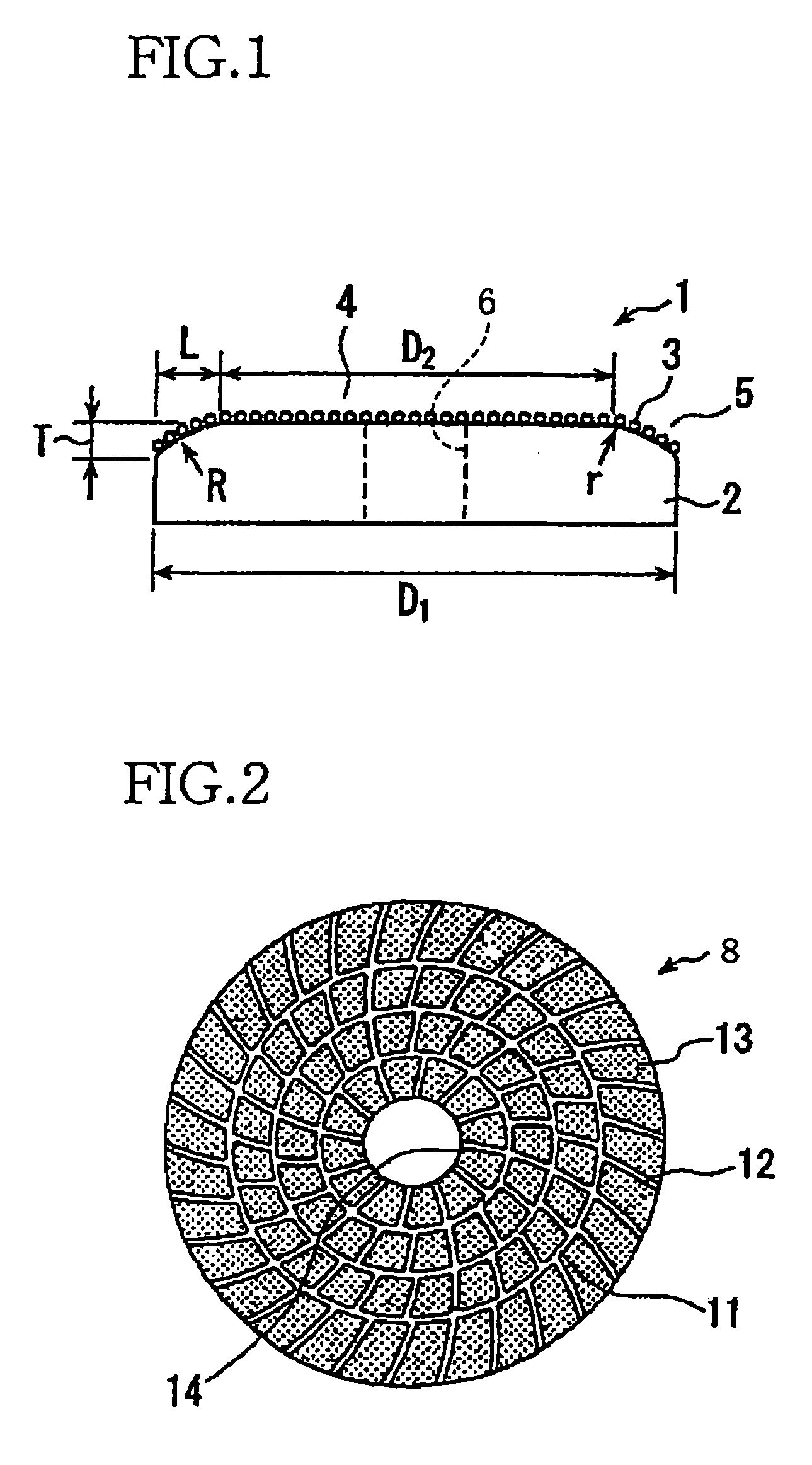
A CMP pad conditioner including: (a) a disk-shaped substrate having a working surface which is provided by one of its axially opposite end surfaces and which is to be brought into contact with the CMP pad; and (b) abrasive grains which are fixed to the working surface. The substrate includes a radially inner portion and a radially outer portion which is located radially outwardly of the radially inner portion. The working surface in the radially outer portion is inclined with respect to the working surface in the radially inner portion, such that a thickness of the radially outer portion as measured in an axial direction of the substrate is reduced as viewed in a direction away from an axis of the substrate toward a periphery of the substrate. A ratio of an outside diameter of the radially inner portion to an outside diameter of the substrate is 60-85%.
Owner:NORITAKE CO LTD +1
High Power Laser System with Multiport Circulator
ActiveUS20140086526A1High powerEffectively heatCoupling light guidesFibre with gratingsHigh power lasersEngineering
Owner:IPG PHOTONICS CORP
Integrated smoke evacuation electrosurgical pencil and method
ActiveUS8057470B2Effective positioningEfficient evacuationSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments for aspiration of substancesElectrosurgerySurgical site
Owner:CONMED CORP
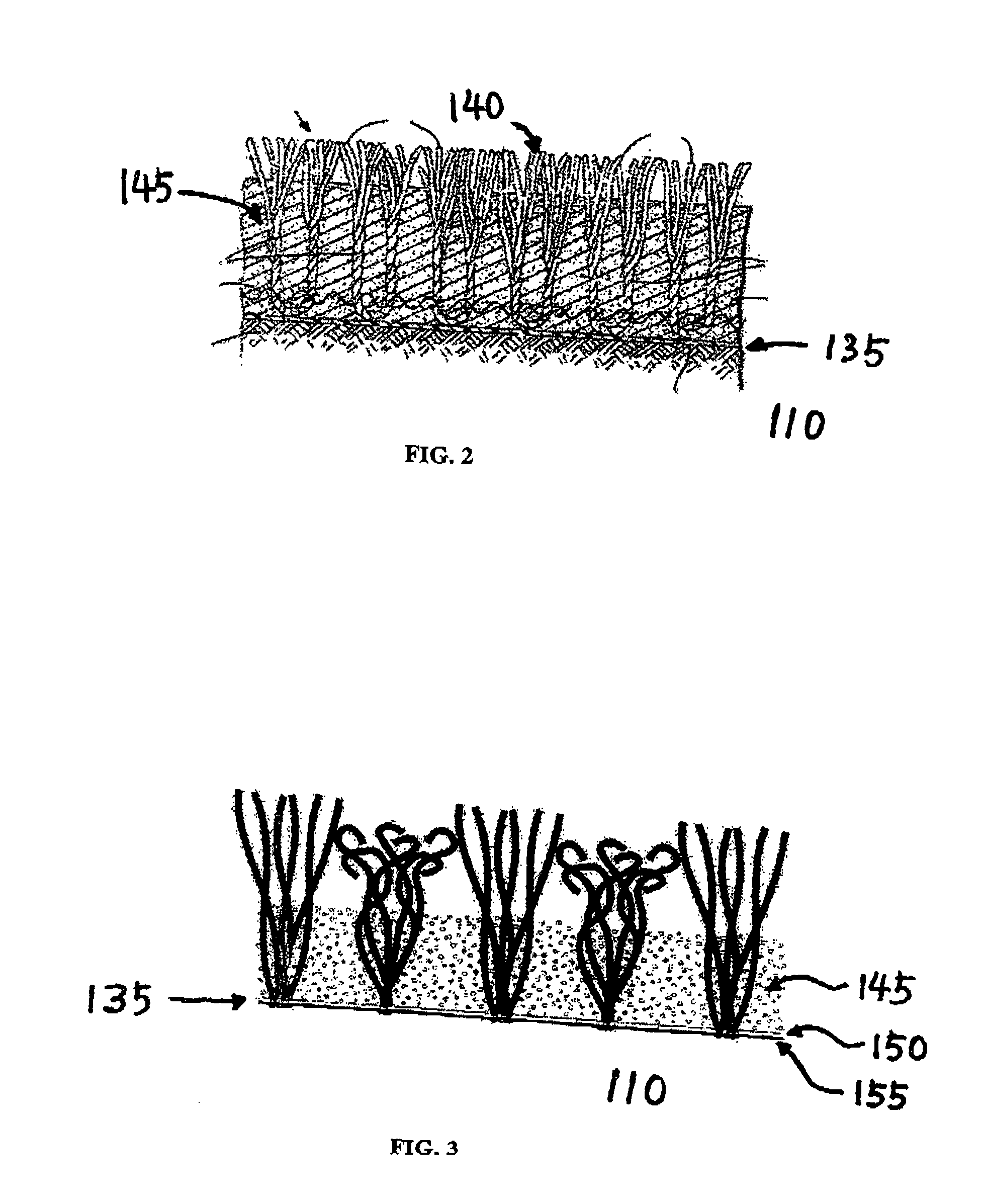
Horizontally draining artificial turf system
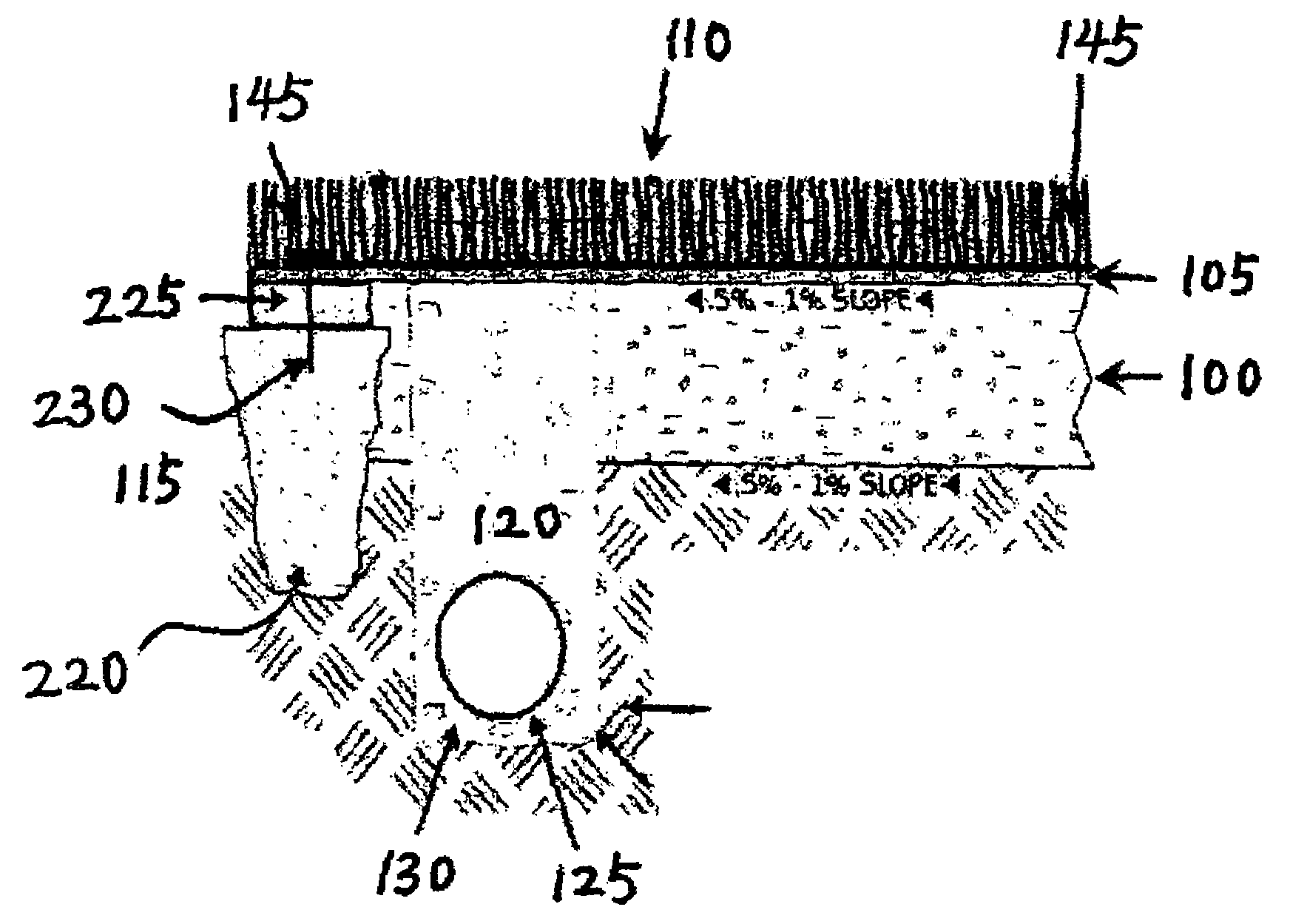
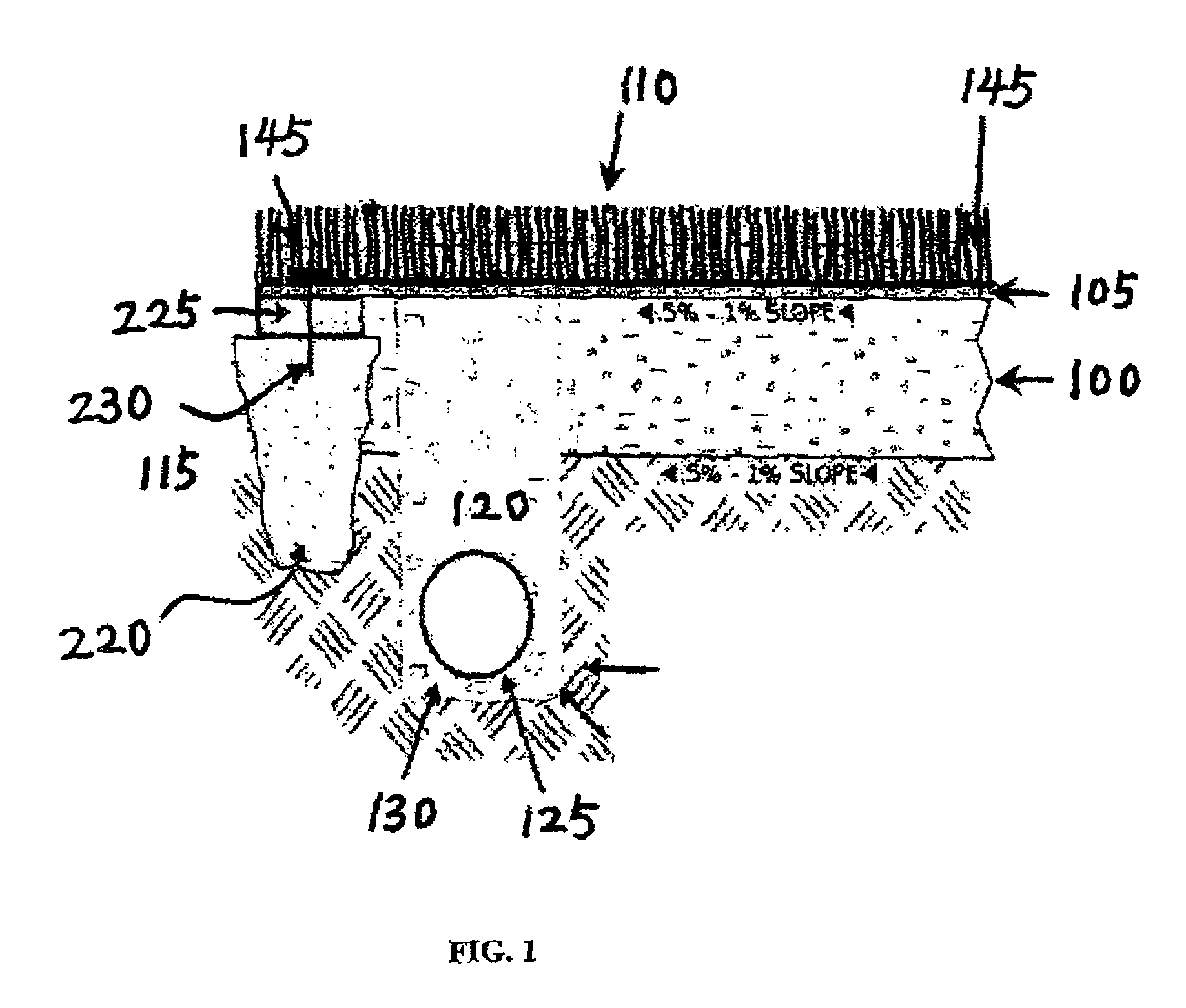
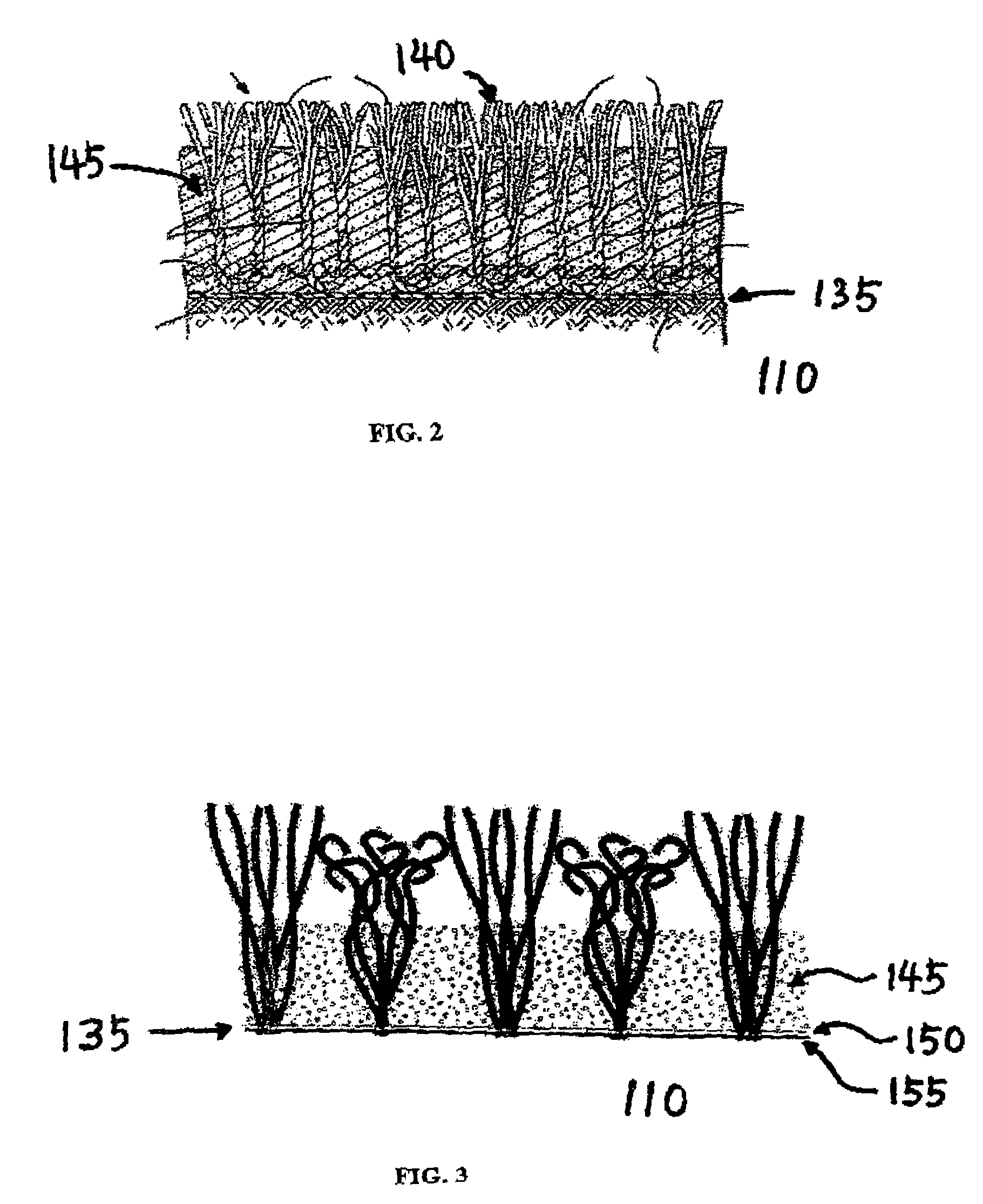
ActiveUS20050238433A1Improve stabilityEfficient evacuationSoil drainageIrrigation ditchesArtificial turfEngineering
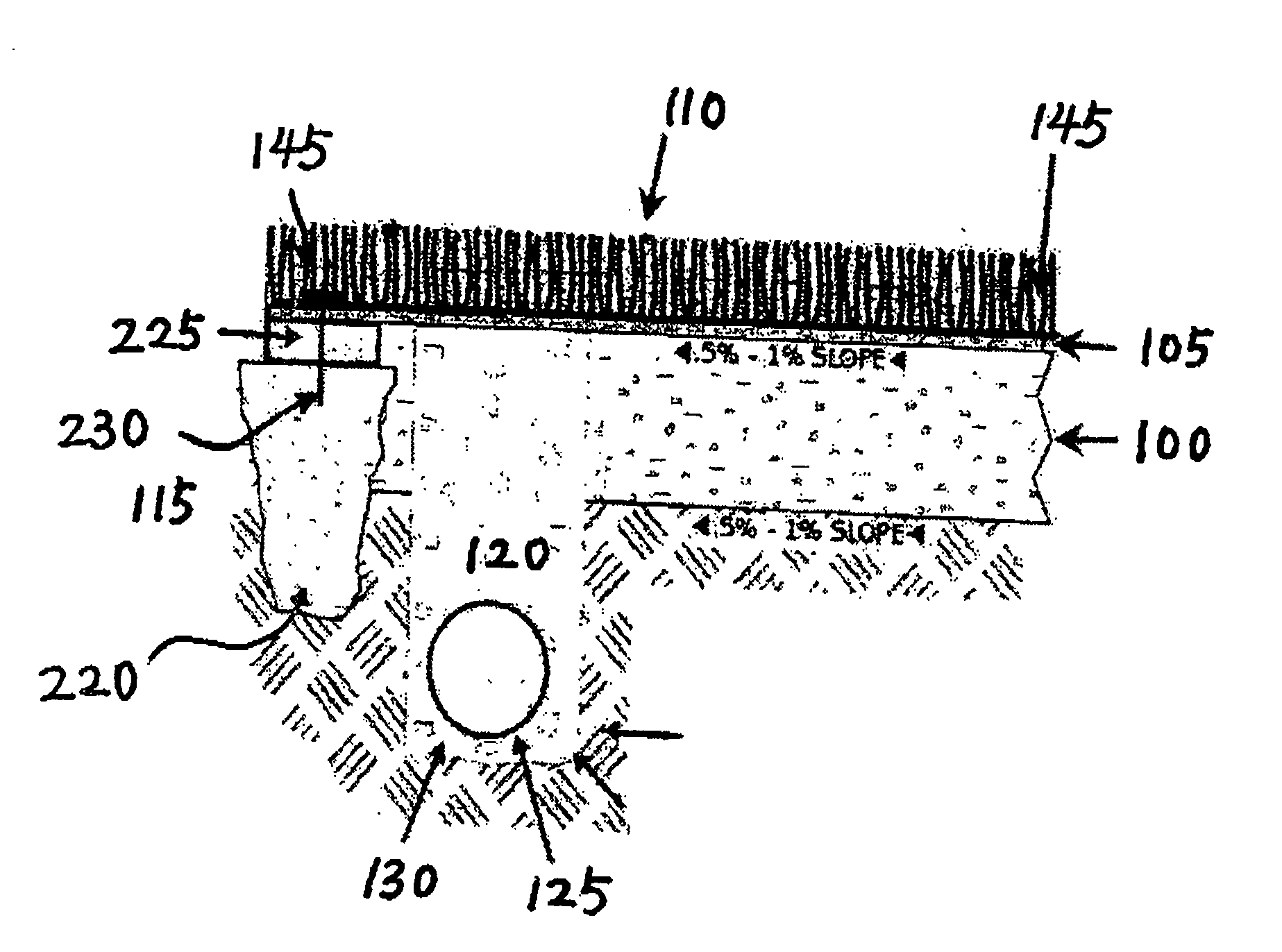
A horizontally draining artificial turf system comprises an impervious base at proper slope, an impermeable layer or drainage blanket over the base at a corresponding slope for guiding water horizontally, an artificial turf at top of the impermeable layer, and a perforated pipe near the lower edge of the base for receiving water for evacuation. Rainwater over the artificial turf first drains vertically onto the impermeable layer and then flows along the impermeable layer to reach the perforated pipe, without infiltrating into the base. Alternatively, a partially pervious drainage blanket is provided in lieu of the impermeable layer where the base is partially pervious. Backup rainwater runs off the drainage blanket horizontally after it saturates the soils of the base.
Owner:DAWSON HLDG L L C
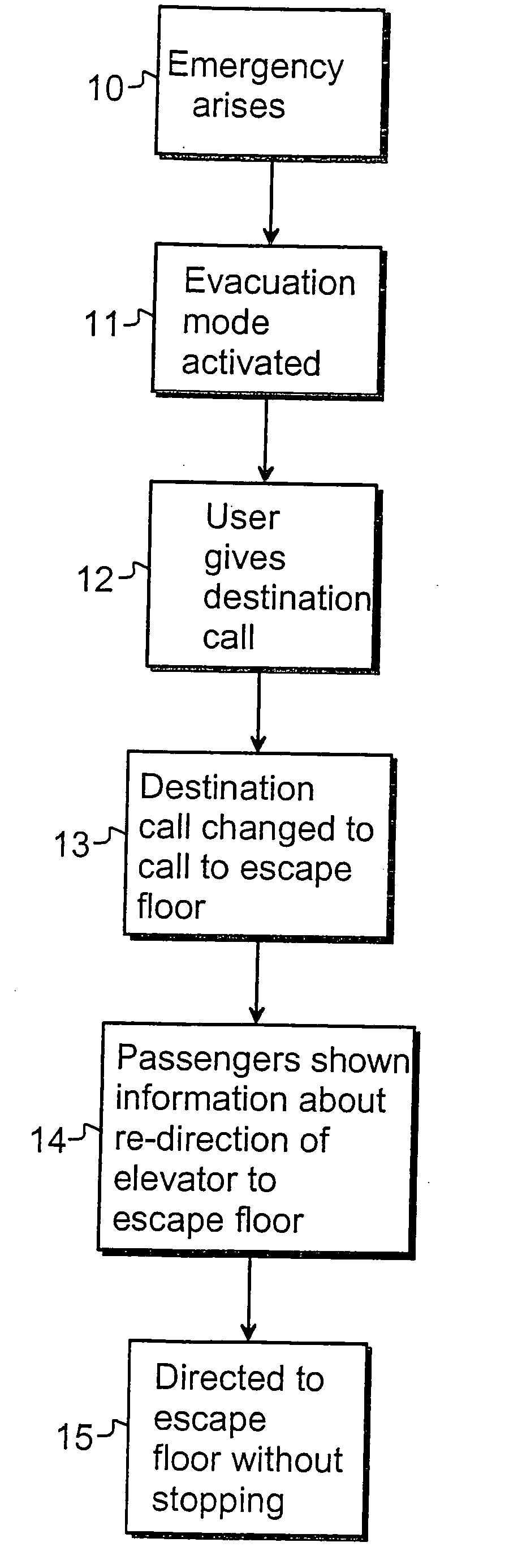
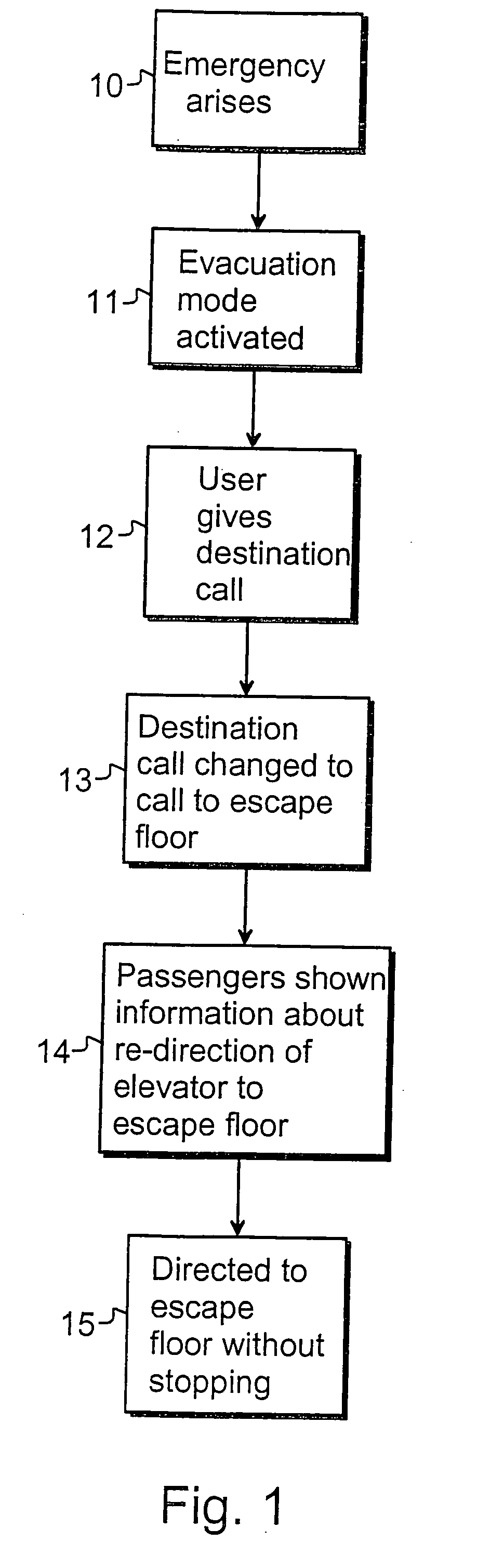
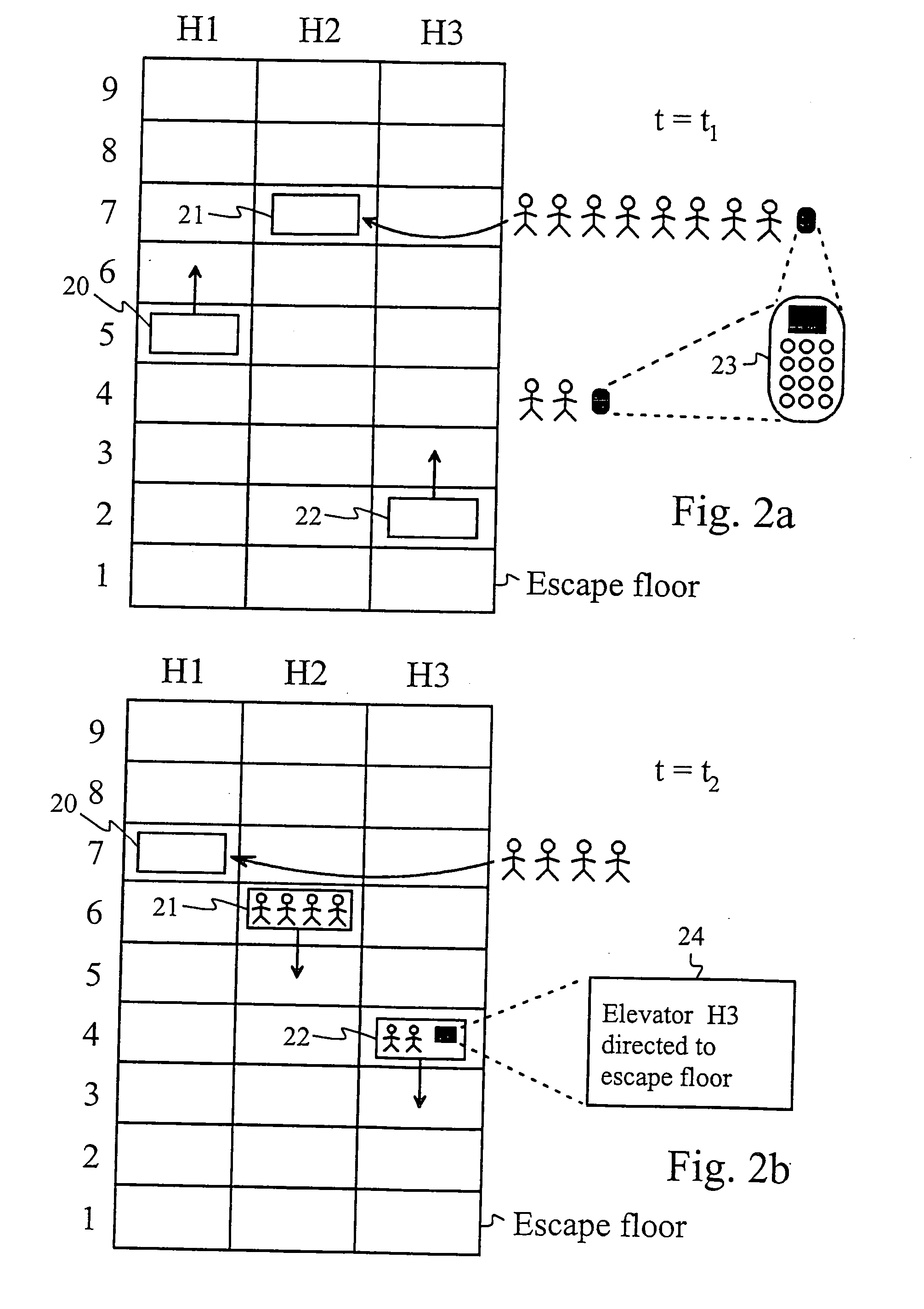
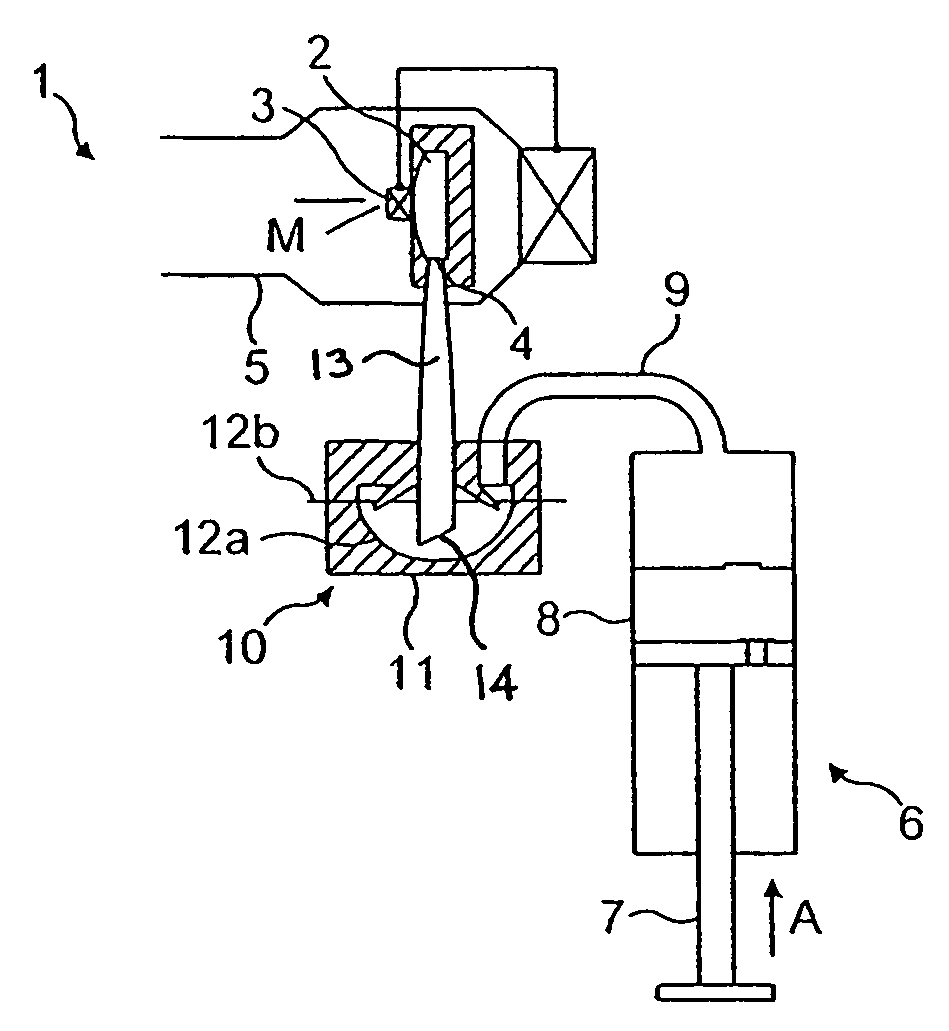
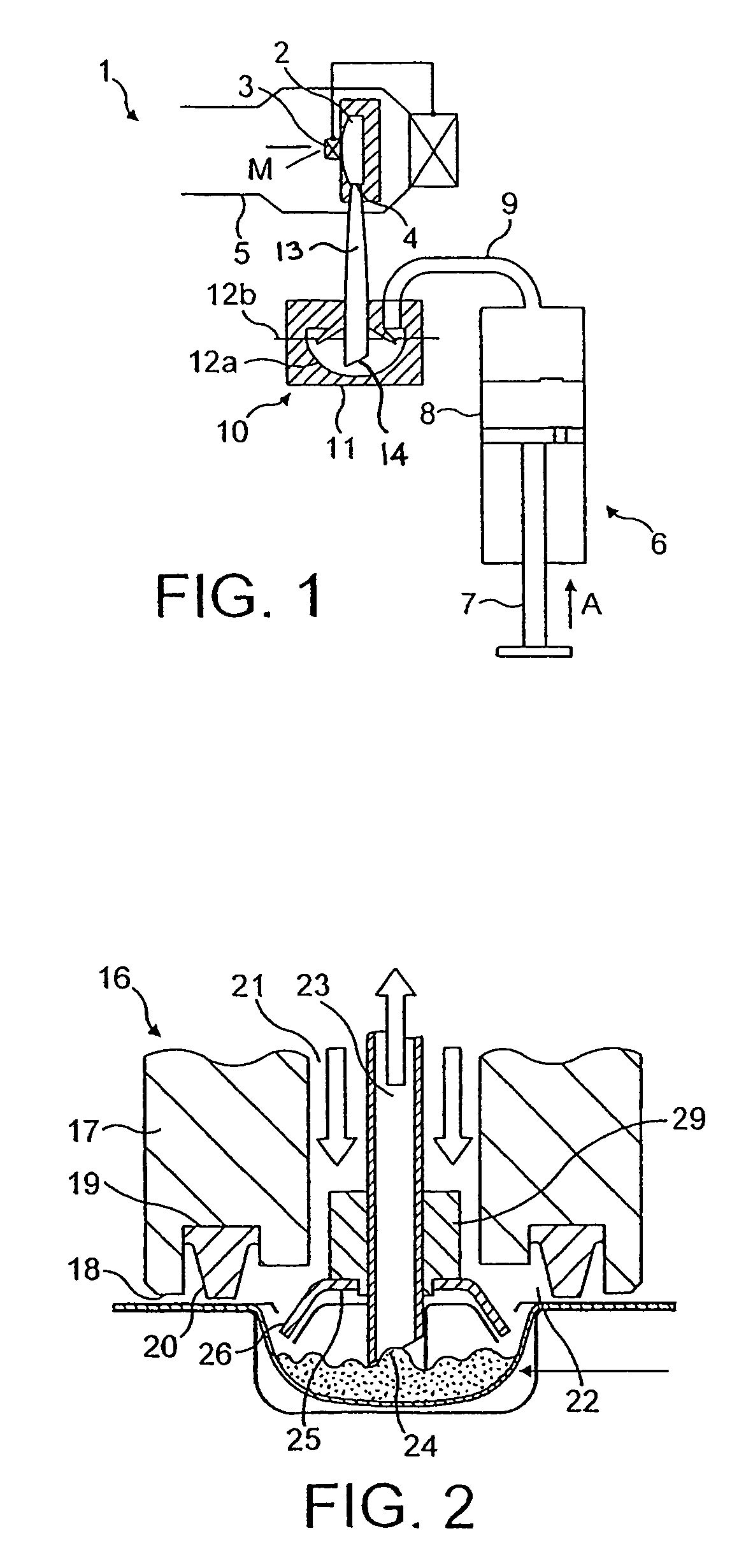
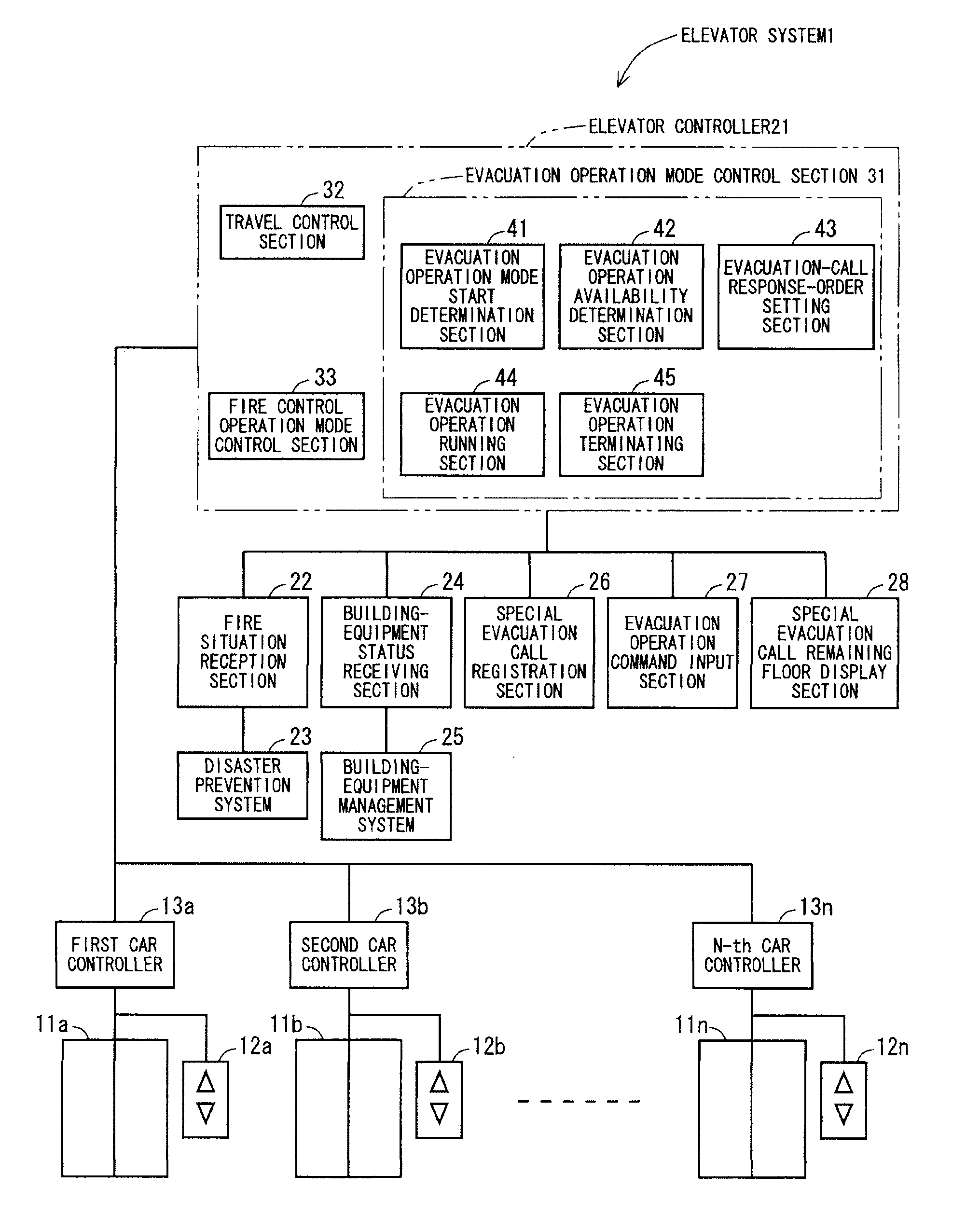
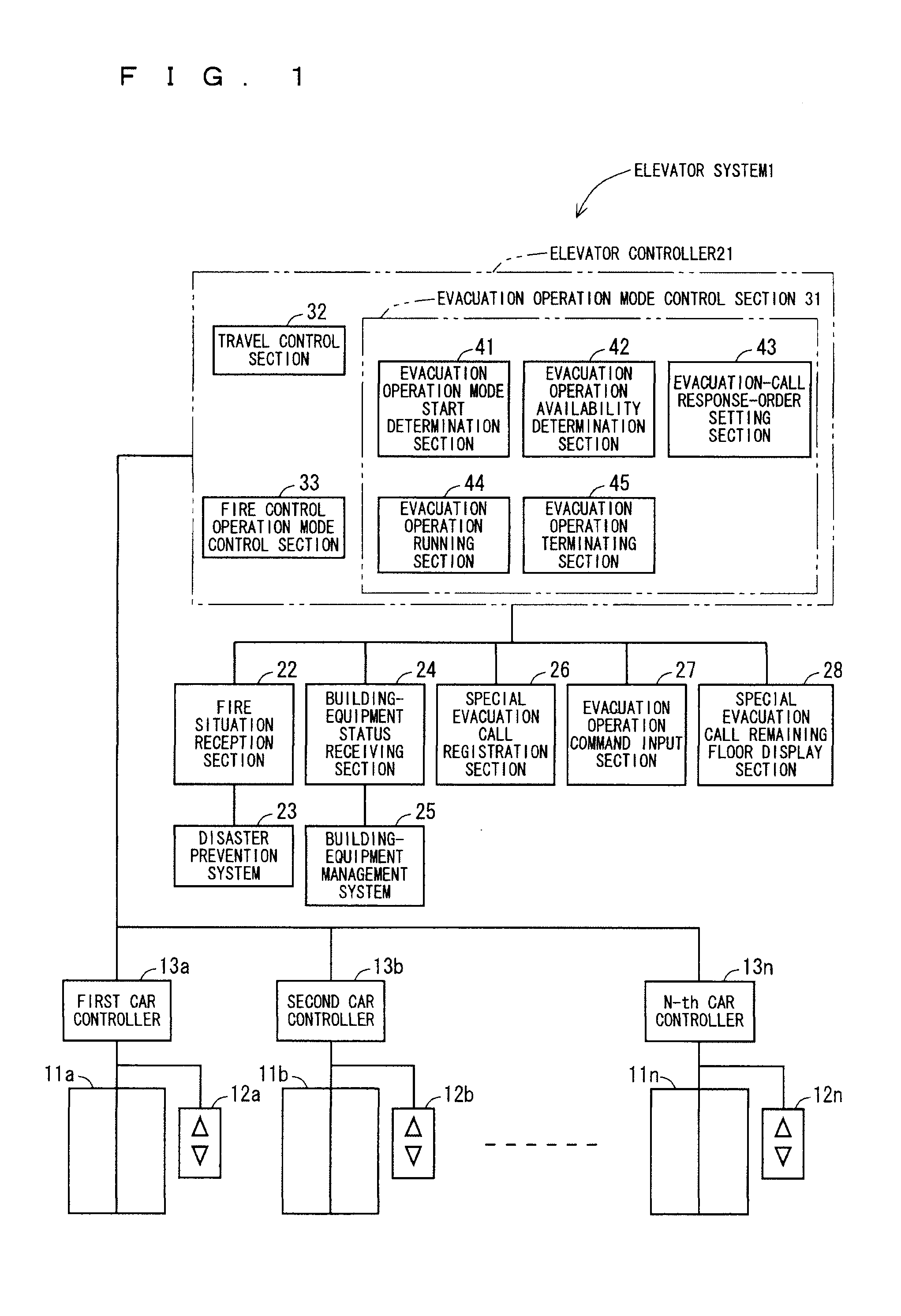
Elevator system
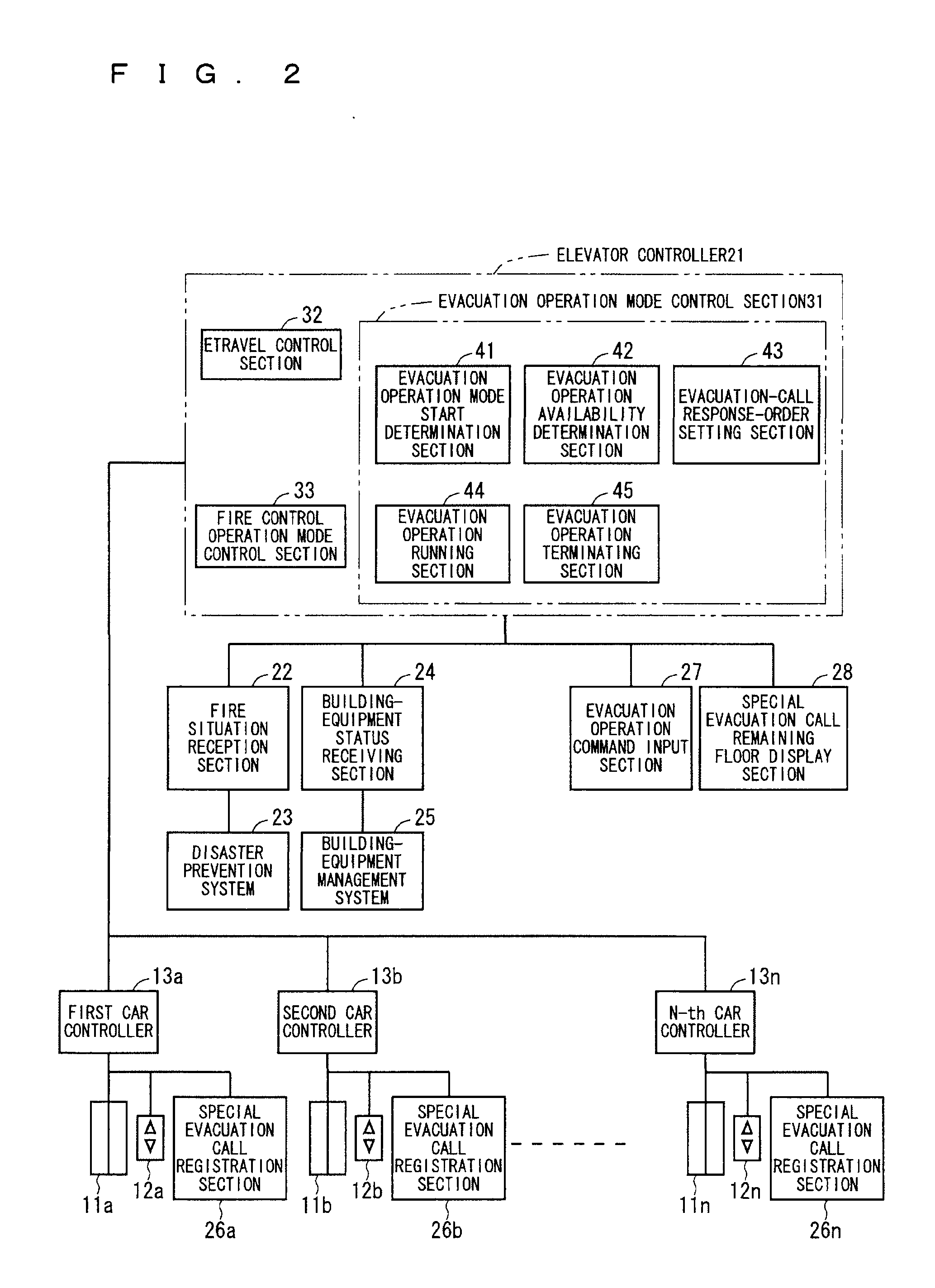
ActiveUS20080196978A1Safe and effectiveEfficient evacuationAlarmsElevatorsElevator systemDisplay device
In the method of the present invention an evacuation mode is presented in an elevator system, which receives destination calls i.e. operates in accordance with so-called destination control. In the method the destination floor calls given on the evacuation floors of the building are changed in the event of an exceptional incident such that the destination floor becomes an exit floor of the building. In the method the elevator car is filled as full as possible on one floor and the travel time to the exit floor is minimized by directing the elevator car to the escape floor without intermediate stops. The passengers to be evacuated are shown information relating to the evacuation on a display located on the destination call panel and / or inside the car of the evacuation elevator.
Owner:KONE CORP
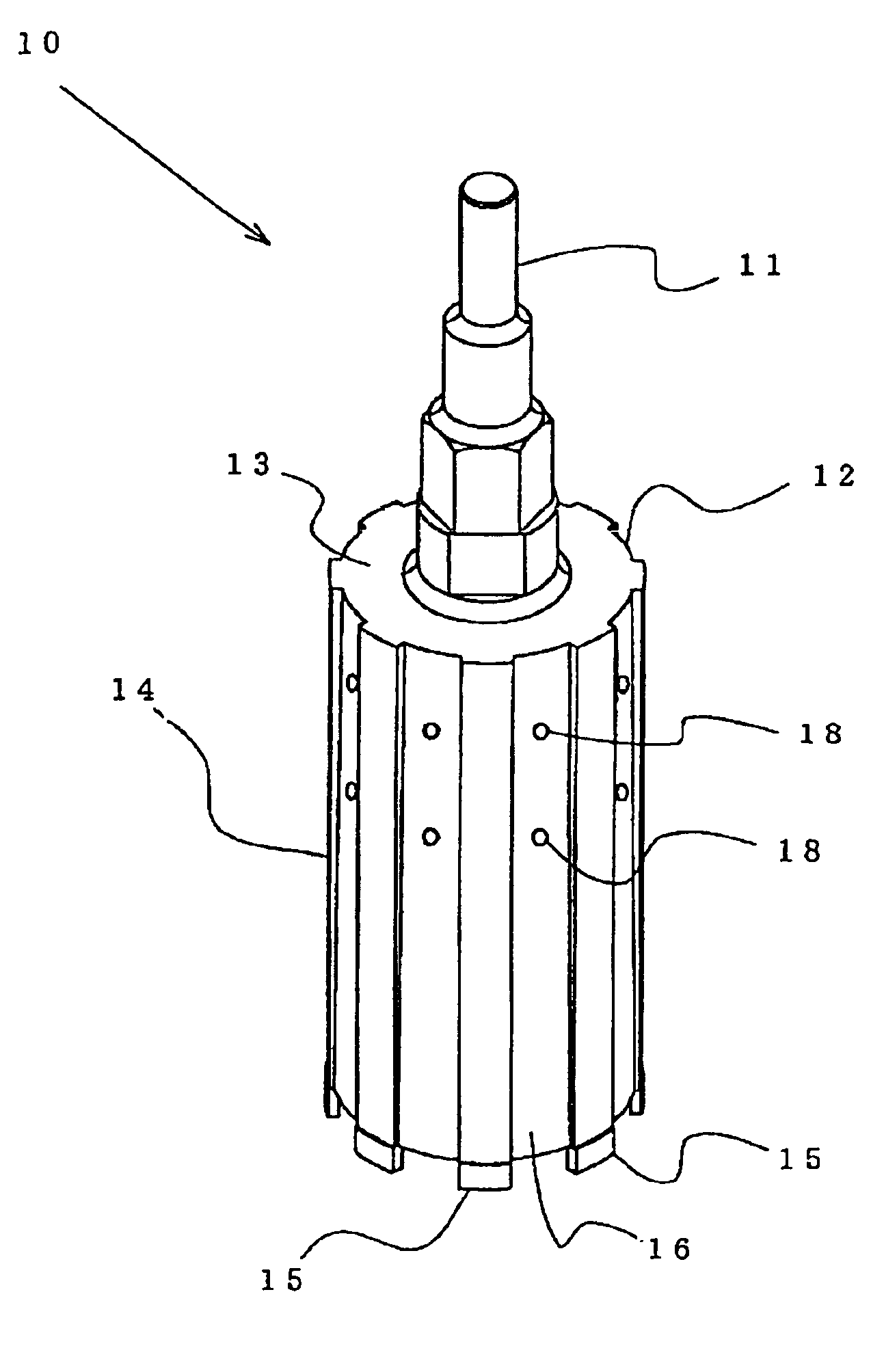
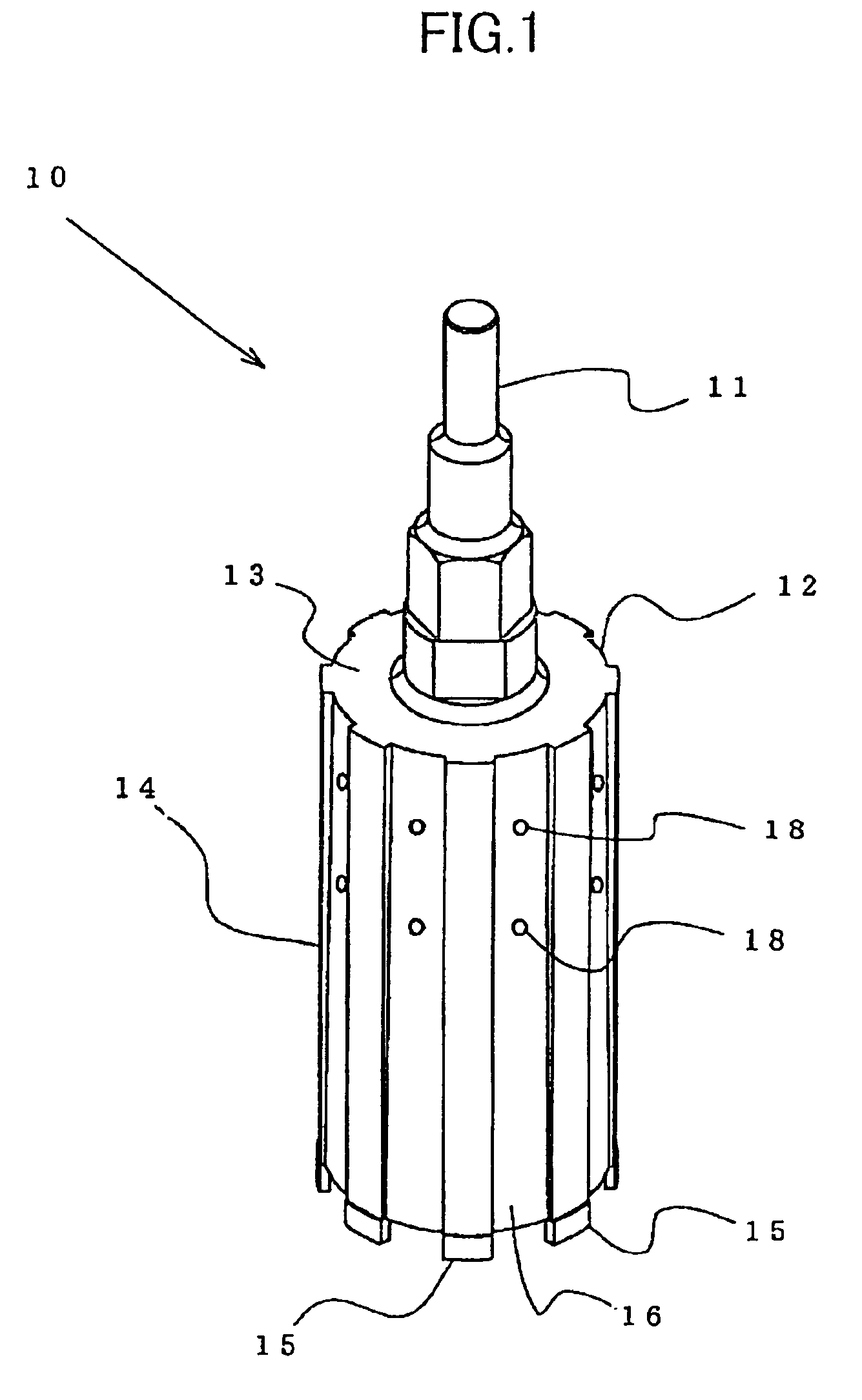
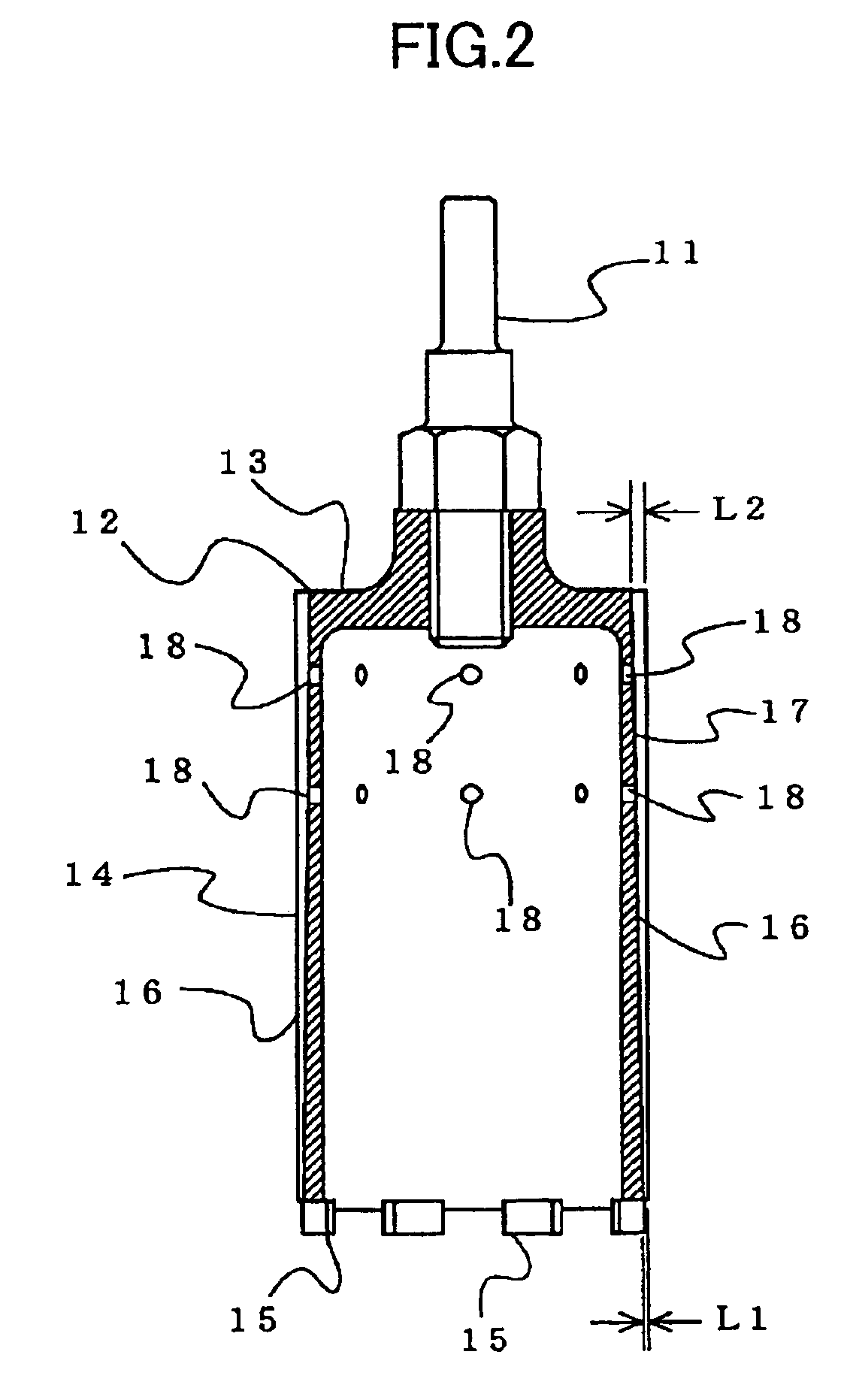
Device and a method for allowing performance of several separate treatments of a teat of an animal
InactiveUS20040231603A1Quality improvementTreated differentlyCathetersAnimal feeding devicesInterior spaceEngineering
Owner:DELAVAL HLDG AB
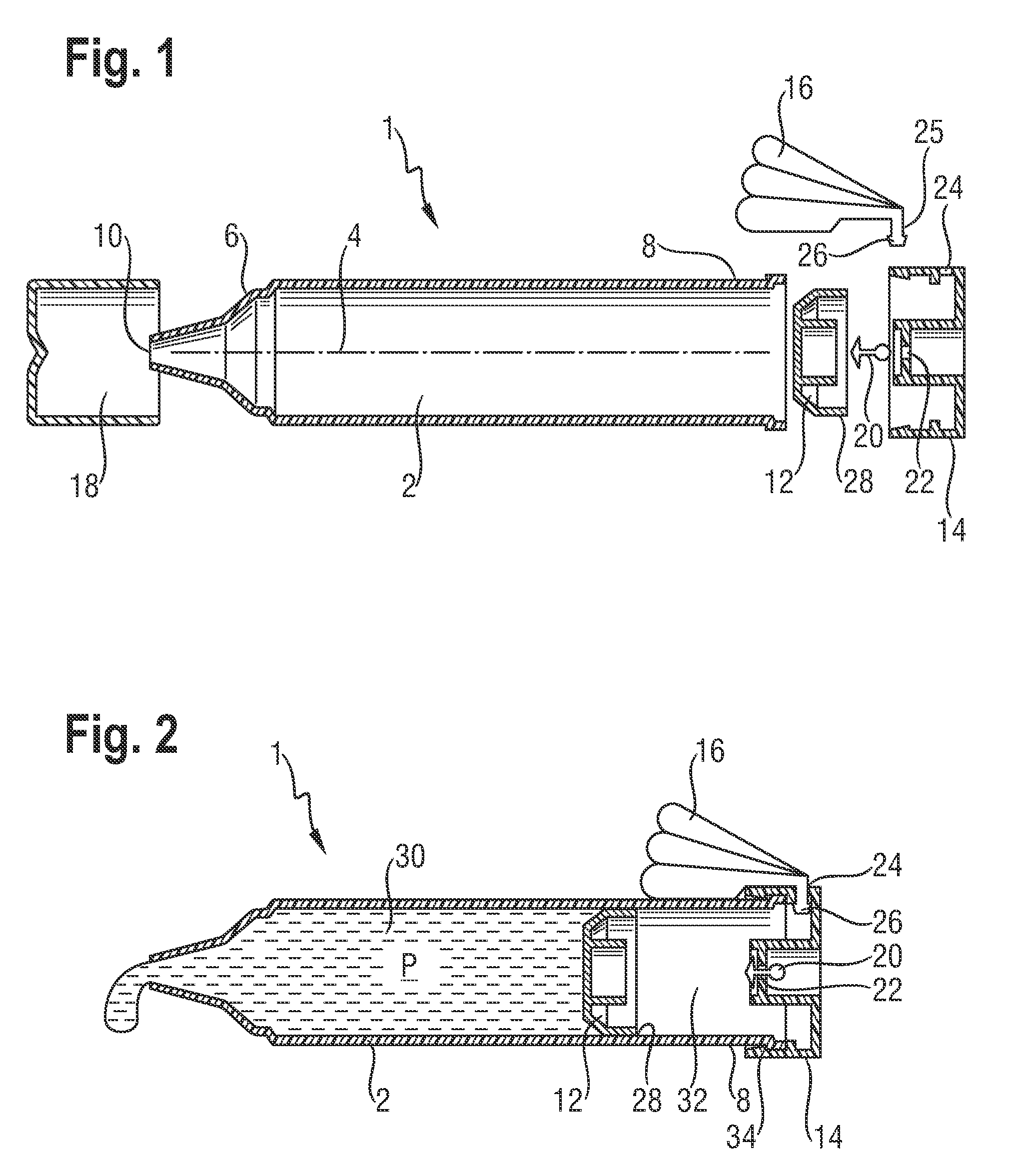
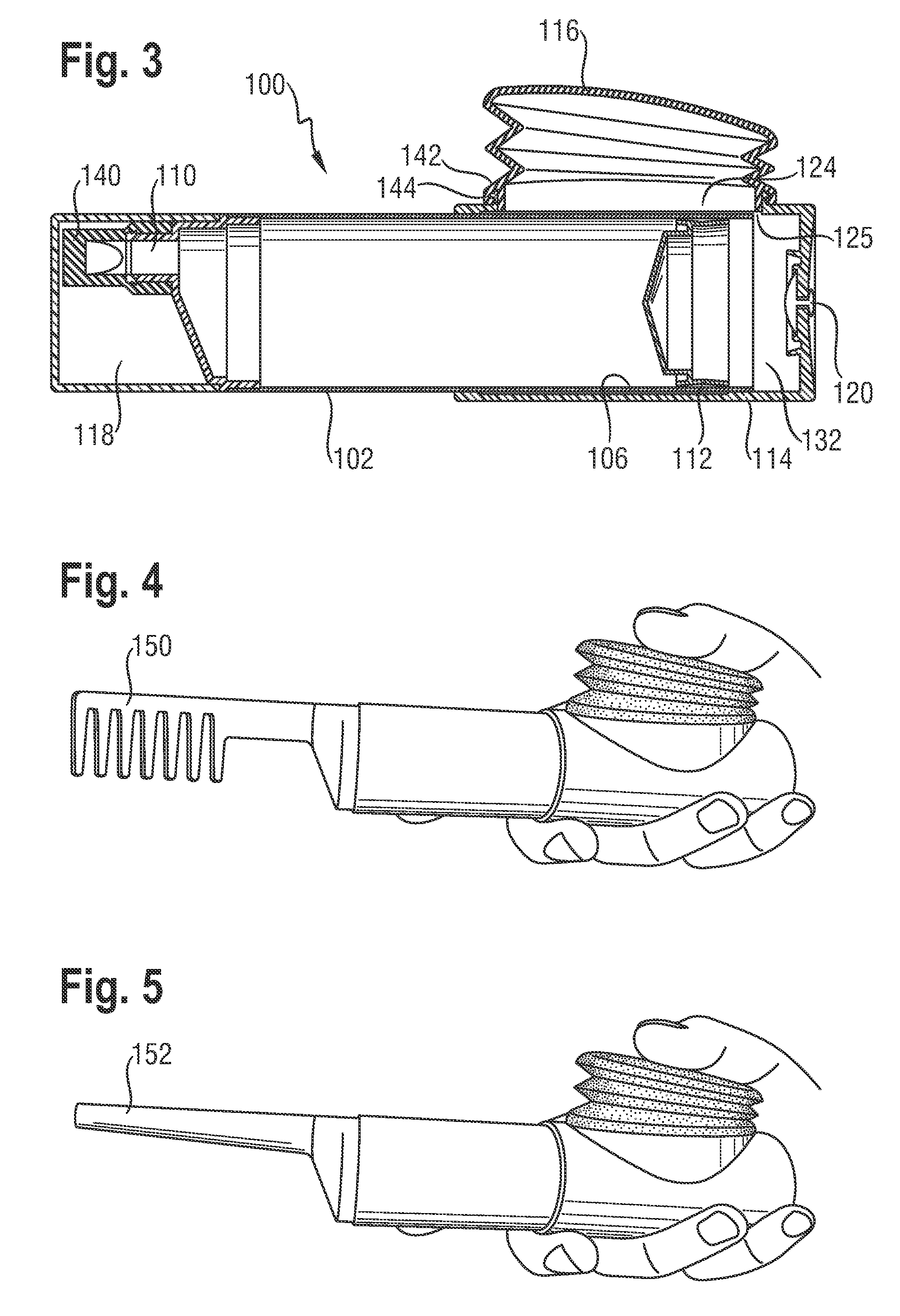
Dispensing device for viscous materials
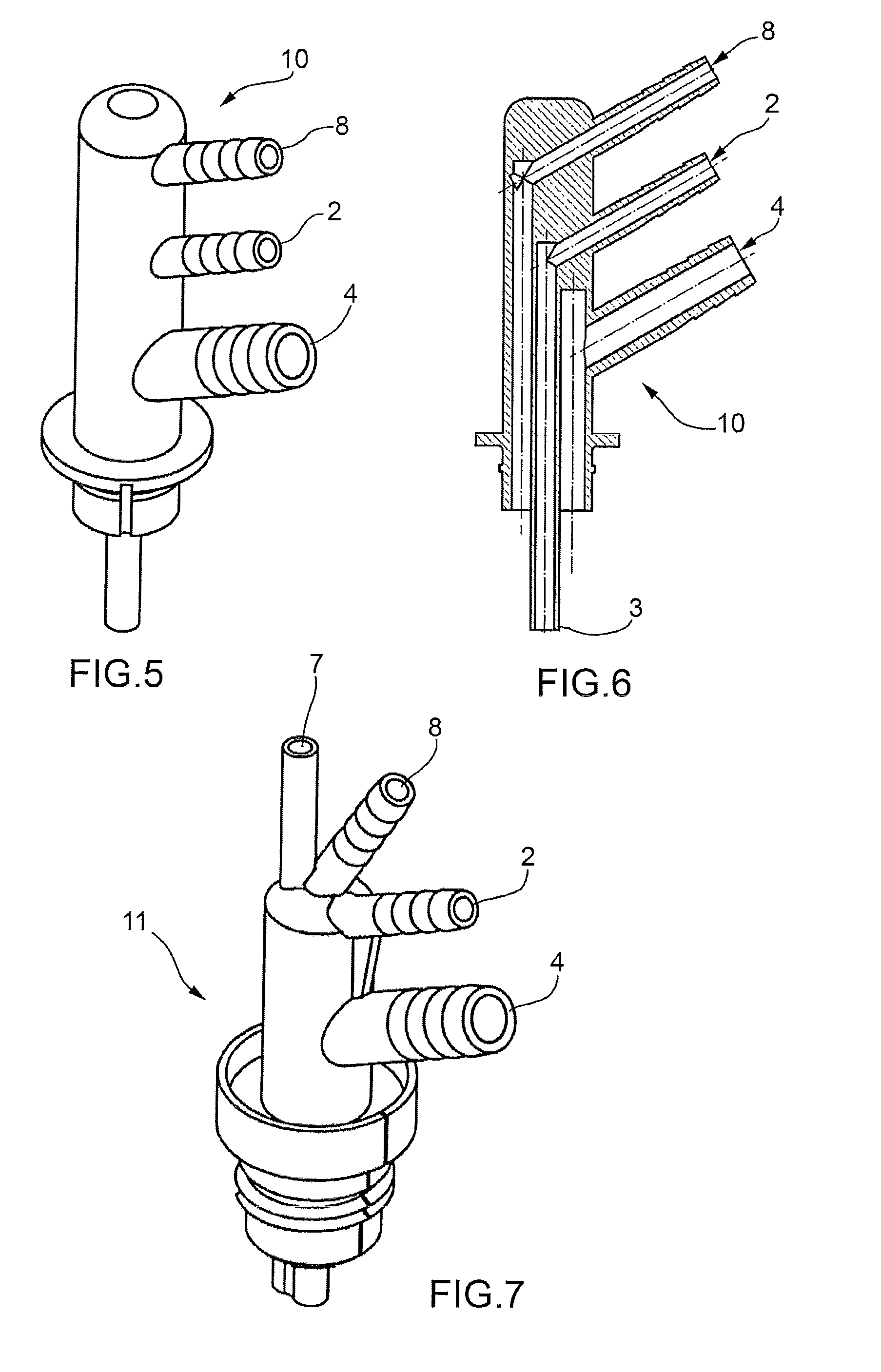
ActiveUS20100155431A1Conveniently heldLower the volumeLiquid surface applicatorsLiquid transferring devicesEngineeringViscous material
A dispenser for viscous materials has a housing with a moveable wall that divides the interior volume of the housing into a distal product chamber and a proximal pressure chamber. An outlet from the product chamber is located adjacent to the distal end of the housing and an air inlet is provided to allow air to enter the pressure chamber. Displacement of the product occurs when accumulated excess air pressure in the pressure chamber acts on the back of the movable wall. The excess air pressure is built up by a bellows assembly arranged in fluid communication with the pressure chamber. On actuation, the bellows can be reduced in volume and subsequently recover by entry of air through the inlet. The direction of force application is preferably perpendicular to the housing axis and the location of the bellows is preferably distant from the product outlet.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
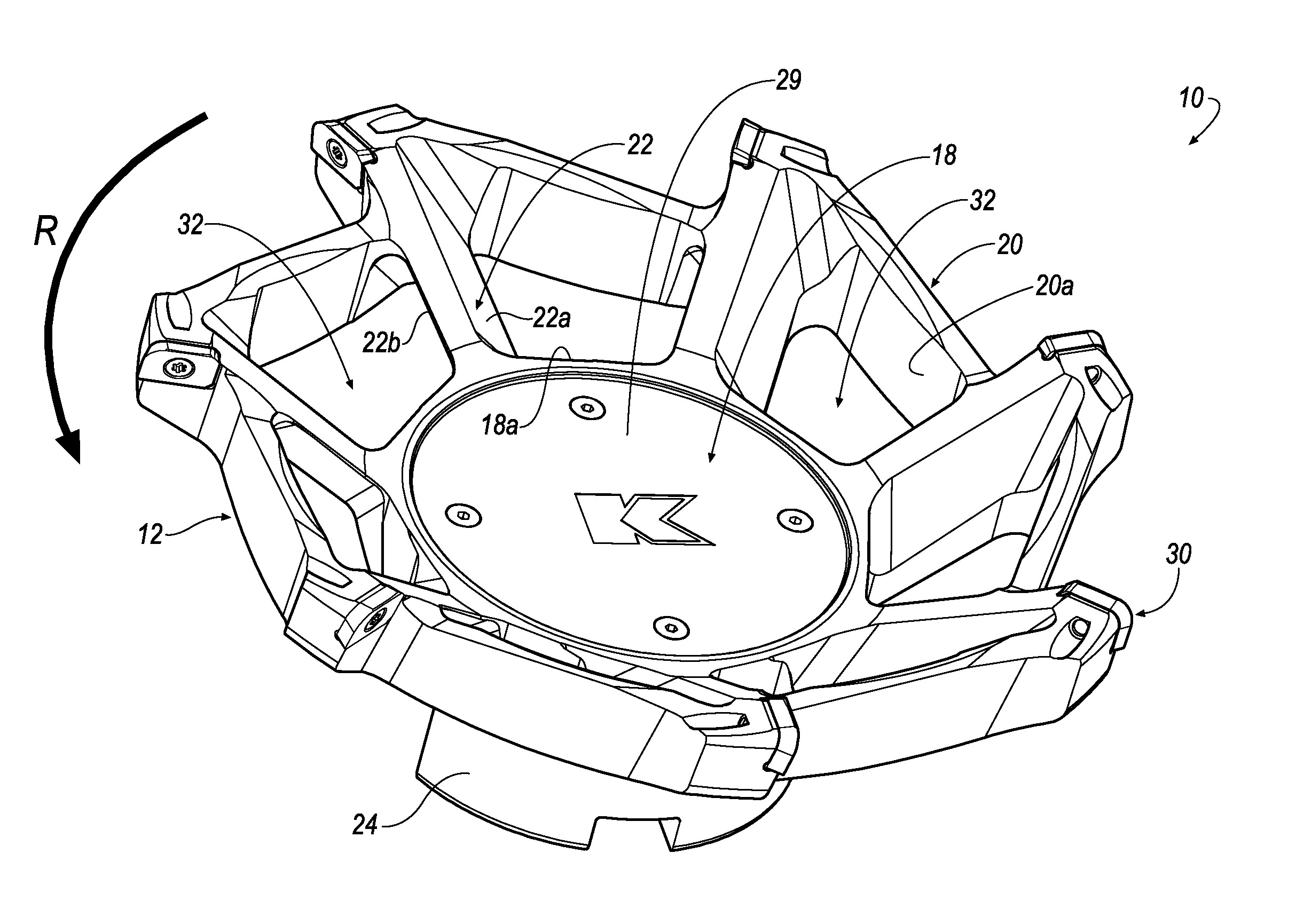
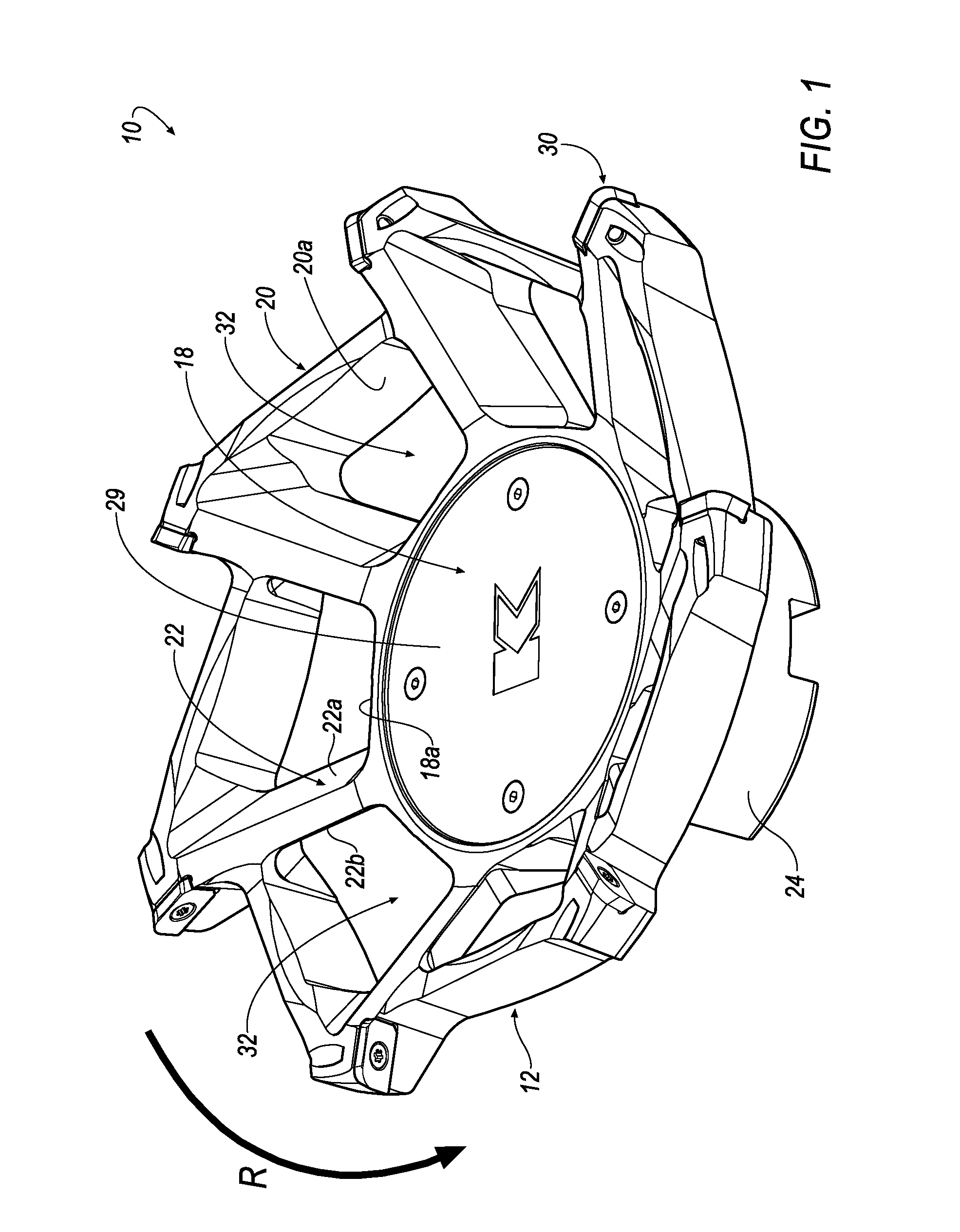
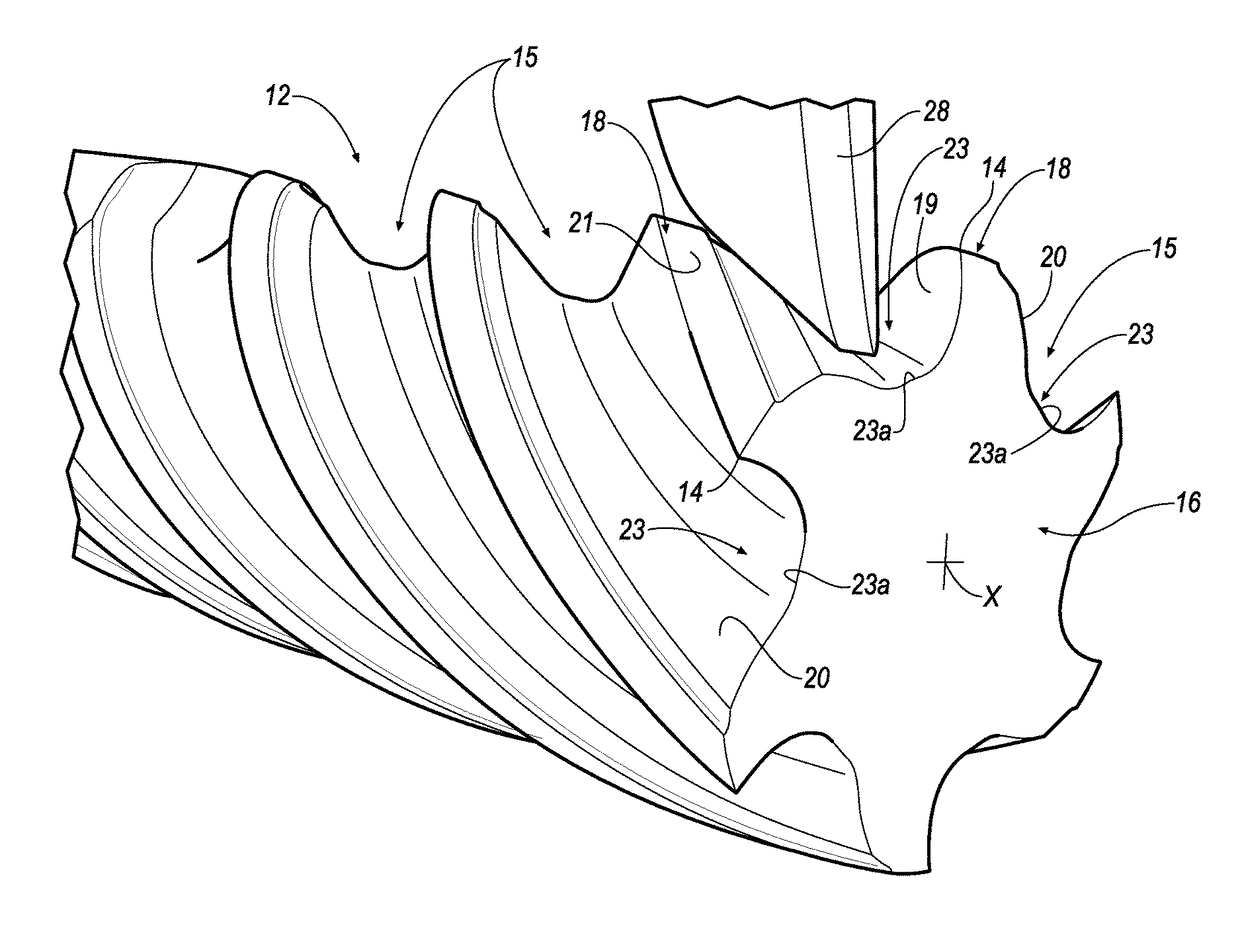
Rotary cutting tool with effective chip evacuation
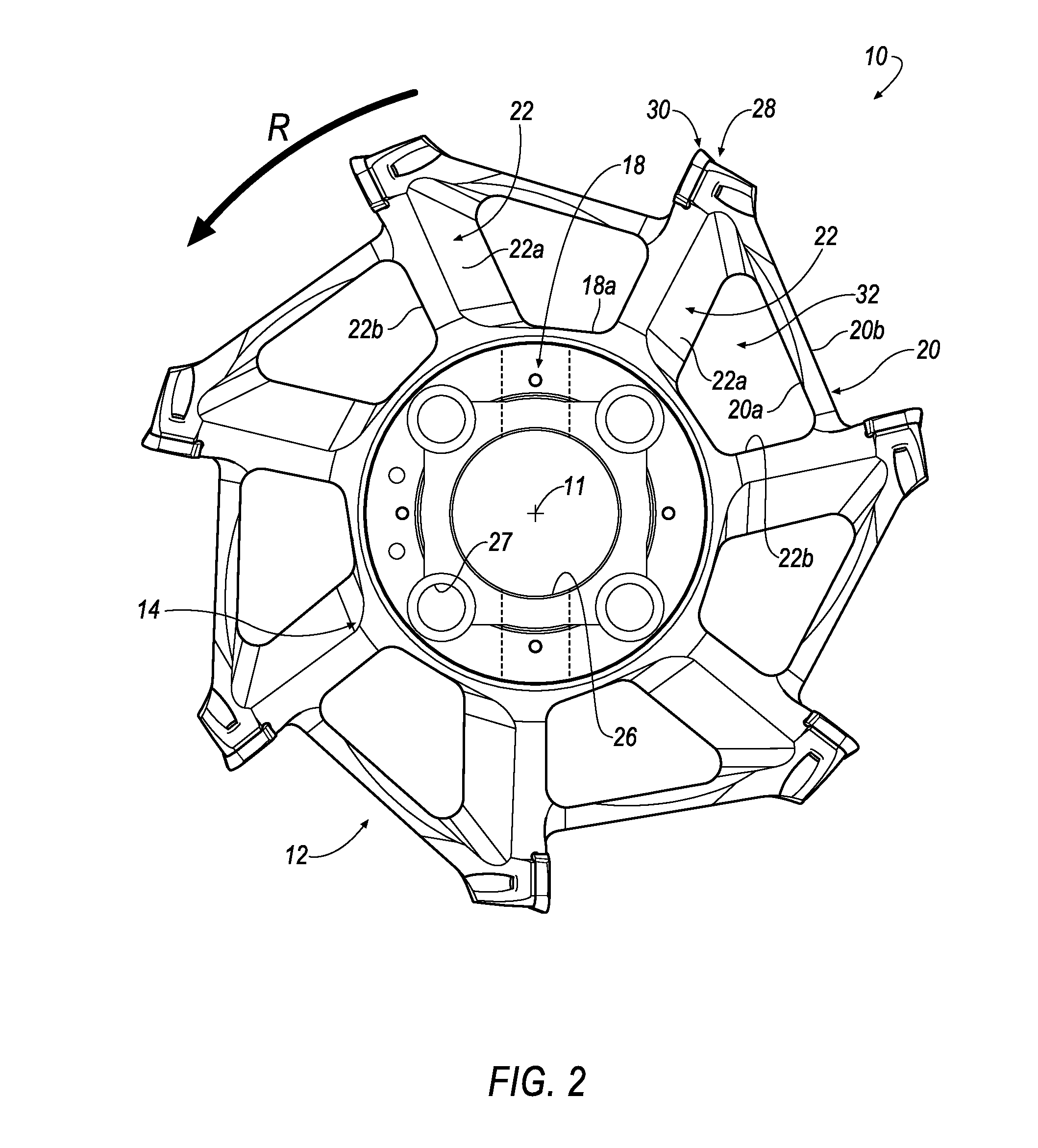
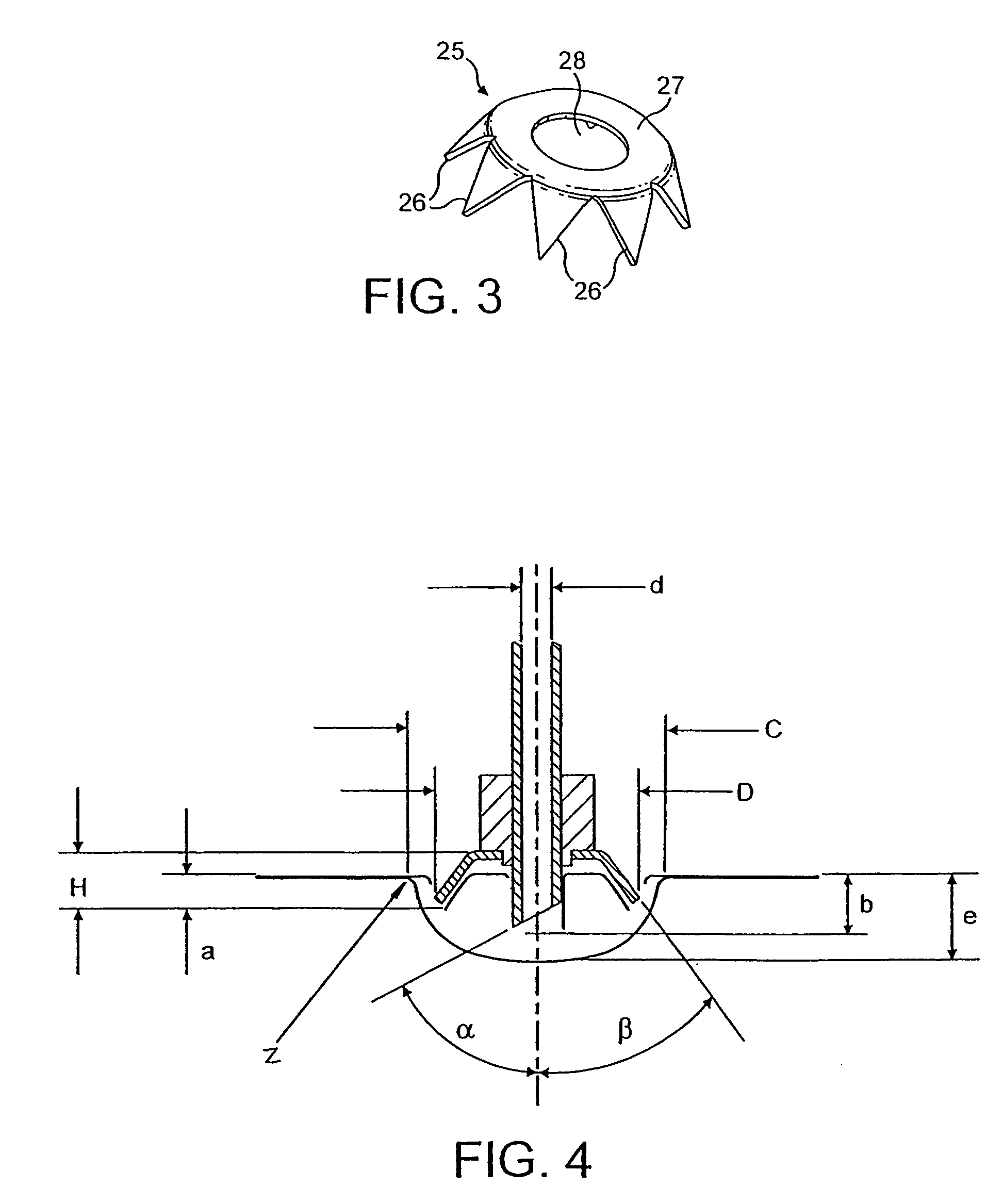
ActiveUS20140161543A1Effective chip evacuationEfficient evacuationMilling cuttersShaping cuttersMilling cutterMaterial removal
A rotary cutting tool, such as a milling cutter (10) includes a central hub (12), a cutting rim (14) and a plurality of spokes (22) connecting the central hub (12) to the cutting rim (14). Each spoke (22) is separated by an opening (32) and polygonal in cross-sectional shape formed by two side walls (22a, 22b), two front walls (22c, 22d) and a rear wall (22e). One of the side walls (22a) of each spoke (22) is formed at a pitch angle (42) with respect to a central axis (11) of the cutting tool (10) that is sufficient to cause lift of chips through the opening (32), thereby providing effective chip evacuation during a material removal operation.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Method for producing metal foams and furnace for producing same
InactiveUS20040074338A1Reduce manufacturing costEliminate riskFurnace componentsElectrode carriers/collectorsHot zonePolymer substrate
A method for producing a metal structure comprising the following steps: providing a metal-coated polymer substrate; heating the metal-coated polymer substrate in a hot zone, in which a temperature of at least 600° C. prevails and in which an atmosphere essentially composed of water vapor or of a mixture of water vapor and neutral gas is maintained, so as to remove the polymer substrate and form a metal structure; and cooling the metal structure in a cooling zone.
Owner:EFOAM
Horizontally draining artificial turf system
ActiveUS7128497B2Improve stabilityEfficient evacuationSoil drainageIrrigation ditchesArtificial turfEngineering
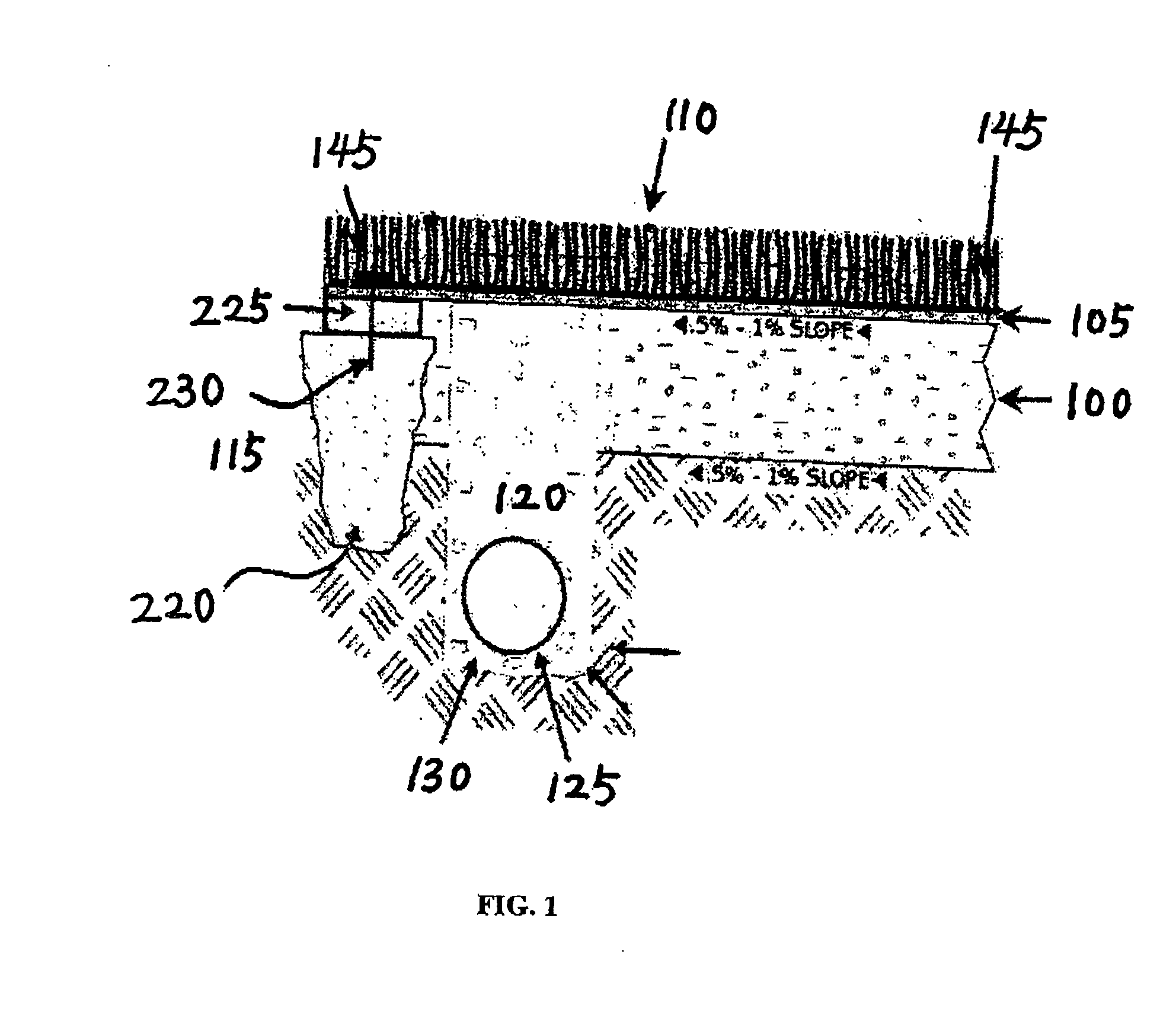
A horizontally draining artificial turf system comprises an impervious base at proper slope, an impermeable layer or drainage blanket over the base at a corresponding slope for guiding water horizontally, an artificial turf at top of the impermeable layer, and a perforated pipe near the lower edge of the base for receiving water for evacuation. Rainwater over the artificial turf first drains vertically onto the impermeable layer and then flows along the impermeable layer to reach the perforated pipe, without infiltrating into the base. Alternatively, a partially pervious drainage blanket is provided in lieu of the impermeable layer where the base is partially pervious. Backup rainwater runs off the drainage blanket horizontally after it saturates the soils of the base.
Owner:DAWSON HLDG L L C
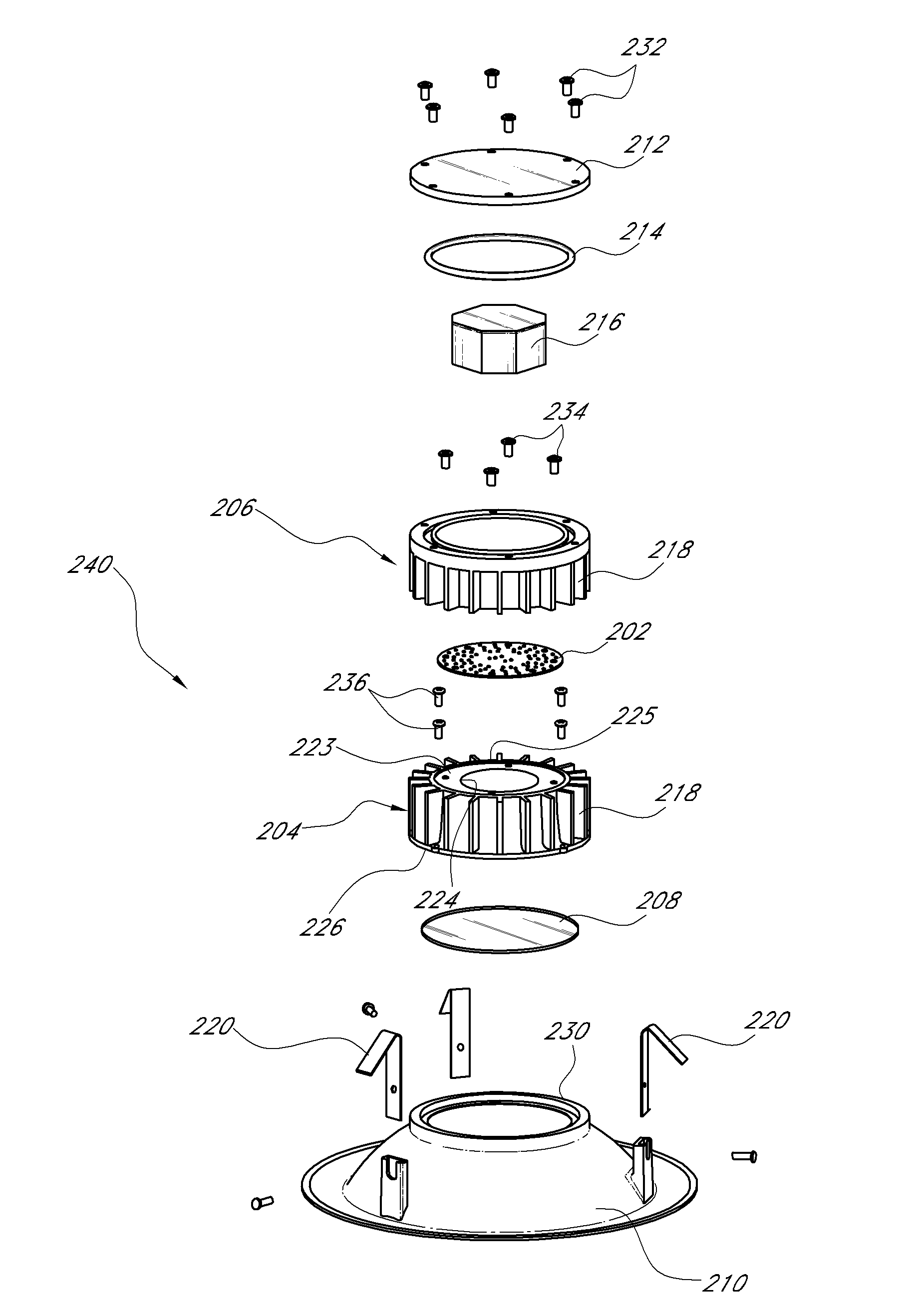
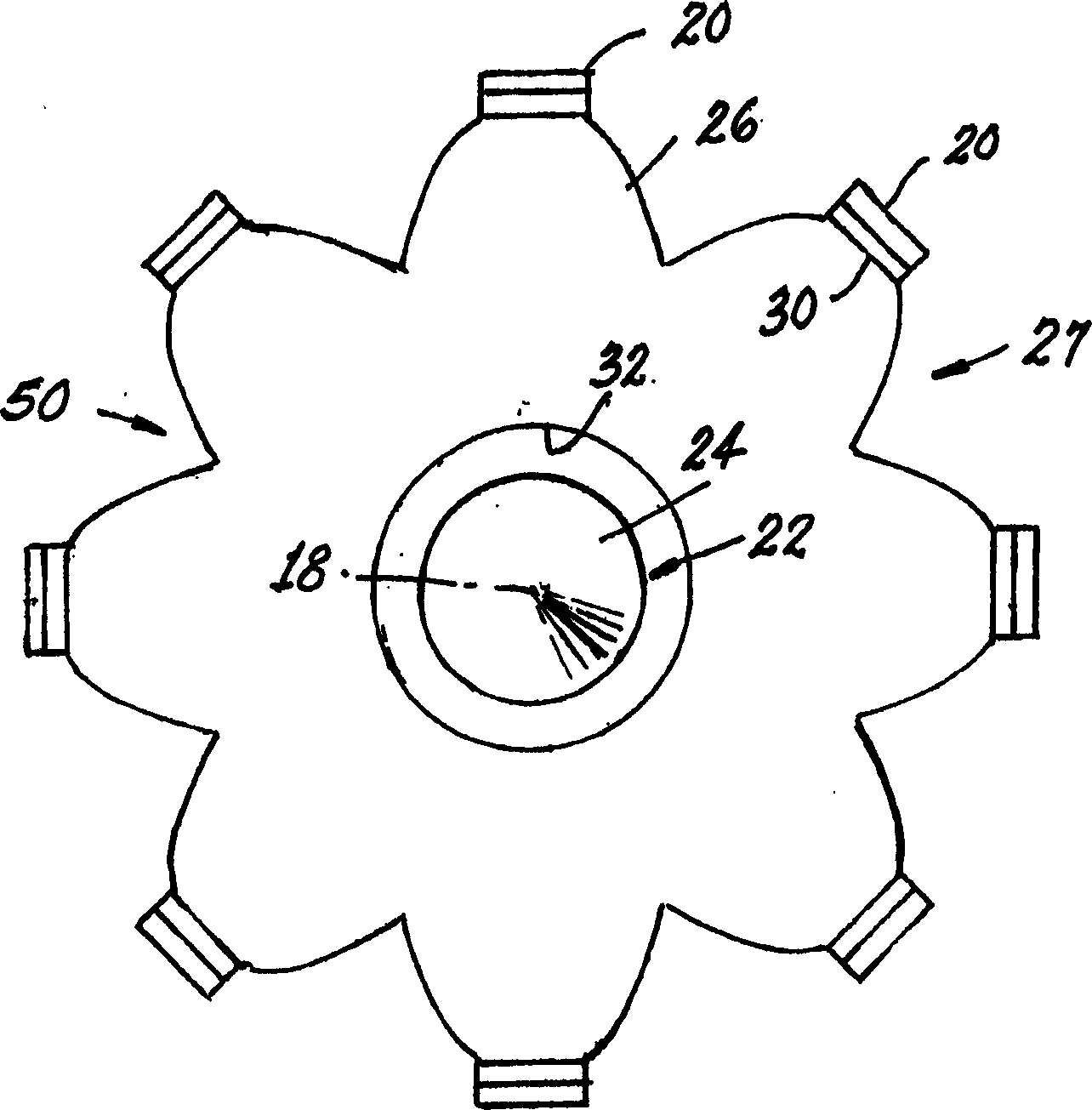
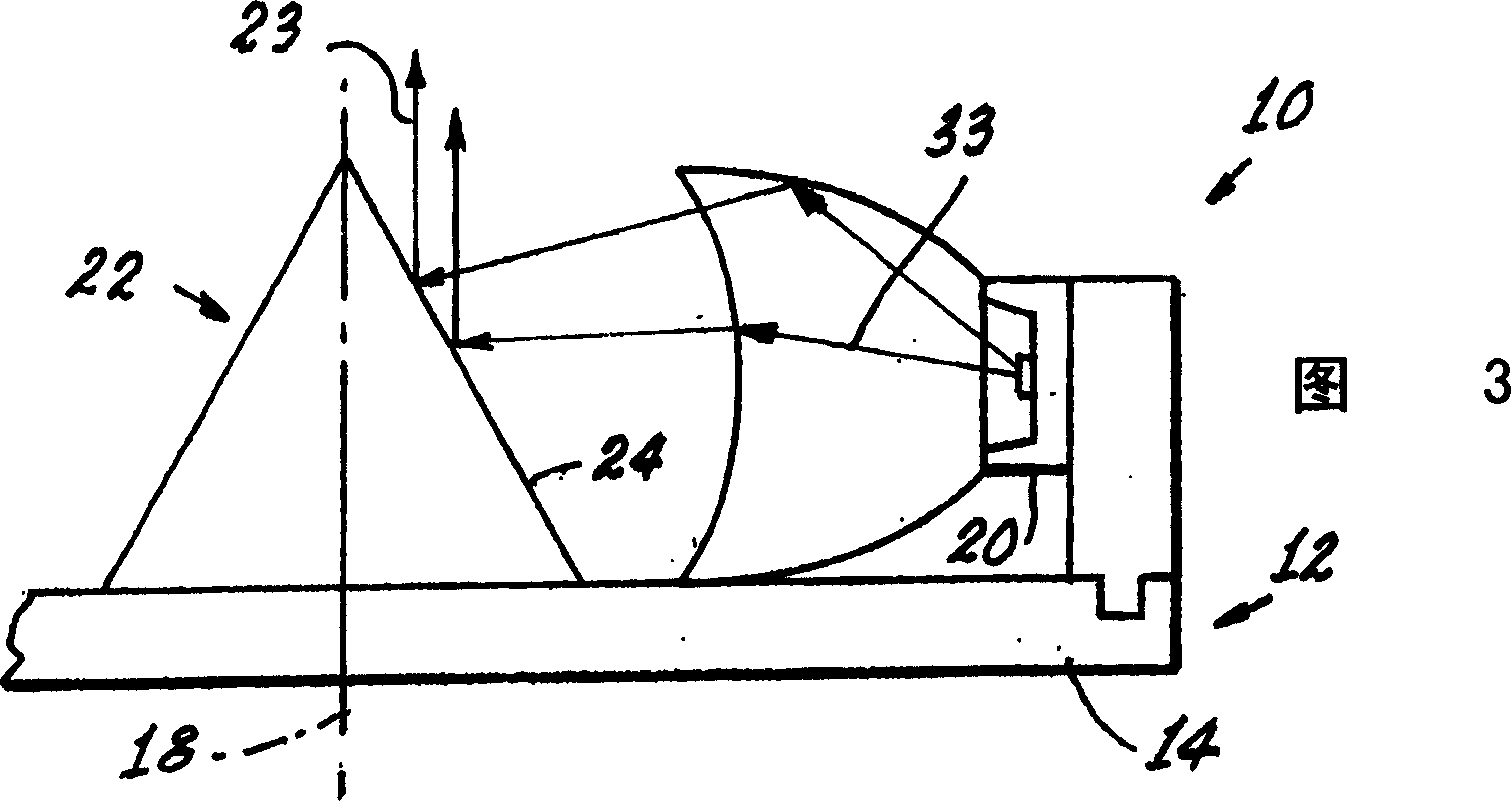
Light emitting diode lamp with conically focused light guides
A lamp component comprising: a support having a base surrounded by an inner wall defining a cavity with a central axis; a plurality of light emitting diodes supported on the inner wall and generally aligned such that light is directed toward the central axis; and a central piece having a first reflective surface shaped and positioned to facilitate intercepting light received from the light emitting diode and causing the received light to generally lie along a direction parallel to the axis direction reflection.
Owner:OSRAM SYLVANIA INC
Dry powder inhaler
InactiveUS7810494B2Enhanced entrainmentShorten speedRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsInhalationMedicine
An Inhaler for delivering an aerosolized dose of a powdered drug for inhalation by a user is disclosed. The inhaler comprises a drug entrainment device vice to a receive a package having a piercable lid containing a dose to be delivered, the device including a drug outlet tube terminating with a primary piercing element to pierce an opening in said lid when a package is located in the inhaler, a secondary piercing member to pierce a plurality of peripheral openings in said lid and, an airflow path to enable the supply of a charge of gas into the package via said peripheral openings to scour the interior of a pierced package such that all or substantially all of the dose is entrained in the gas and flows out of the package via the drug outlet tube. A medicament pack is also disclosed.
Owner:VECTURA DELIVERY DEVICES
Kingdon mass spectrometer with cylindrical electrodes
ActiveUS8319180B2Efficient evacuationOptimize the durationStability-of-path spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsPotential wellParabolic potential
The invention relates to measuring devices of an electrostatic Fourier transform mass spectrometer and measurement methods for the acquisition of mass spectra with high mass resolution. The measuring device includes electrostatic measuring cells according to the Kingdon principle, in which ions can, when appropriate voltages are applied, orbit on circular trajectories around the cylinder axis between two concentric cylindrical surfaces, which are composed of specially shaped sheath electrodes, insulated from each other by parabolic gaps, and can harmonically oscillate in the axial direction, independently of their orbiting motion. In the longitudinal direction, the two cylindrical surfaces of the measuring cell are divided by the parabolic separating gaps into different types of double-angled and tetragonal sheath electrode segments. Appropriate voltages at the sheath electrode segments generate a potential distribution between the two concentric cylindrical surfaces which forms a parabolic potential well in the axial direction for orbiting ions. The ion clouds oscillating harmonically in the axial direction in this potential well induce image currents in suitable electrodes, from which the oscillation frequencies can be determined by Fourier analyses.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
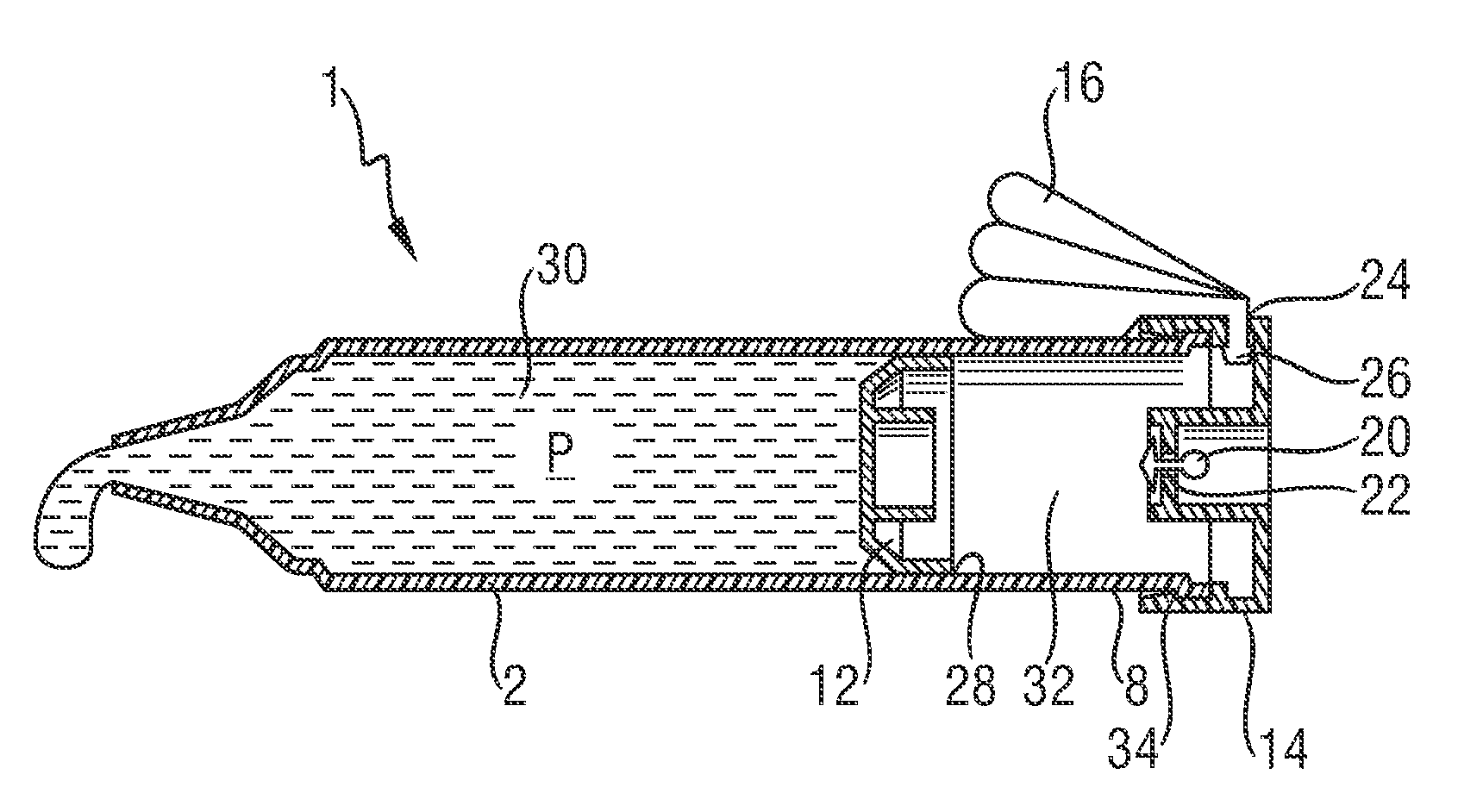
Spout for ensuring evacuation of a flexible container
Owner:RAPAK INC
Elevator system
An elevator system capable of an efficient evacuation using an elevator in case of a fire, and capable of confirming an evacuee remaining status in a case that an evacuation operation using the elevator is discontinued. An evacuation-call response-order setting section sets a priority order of a response to an evacuation special call registered in an evacuation special call registration section, based on fire occurrence information received by a fire situation reception section. A responding floor is selected based on the priority order. The evacuation operation running section controls an operation of the elevator so as to direct a car to the responding floor selected in this manner. In a case that the evacuation operation availability determination section determines that the evacuation operation is not available, the evacuation operation terminating section causes an evacuation special call remaining floor display section to display a remaining evacuation special call registration floor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Footer track with moisture vent
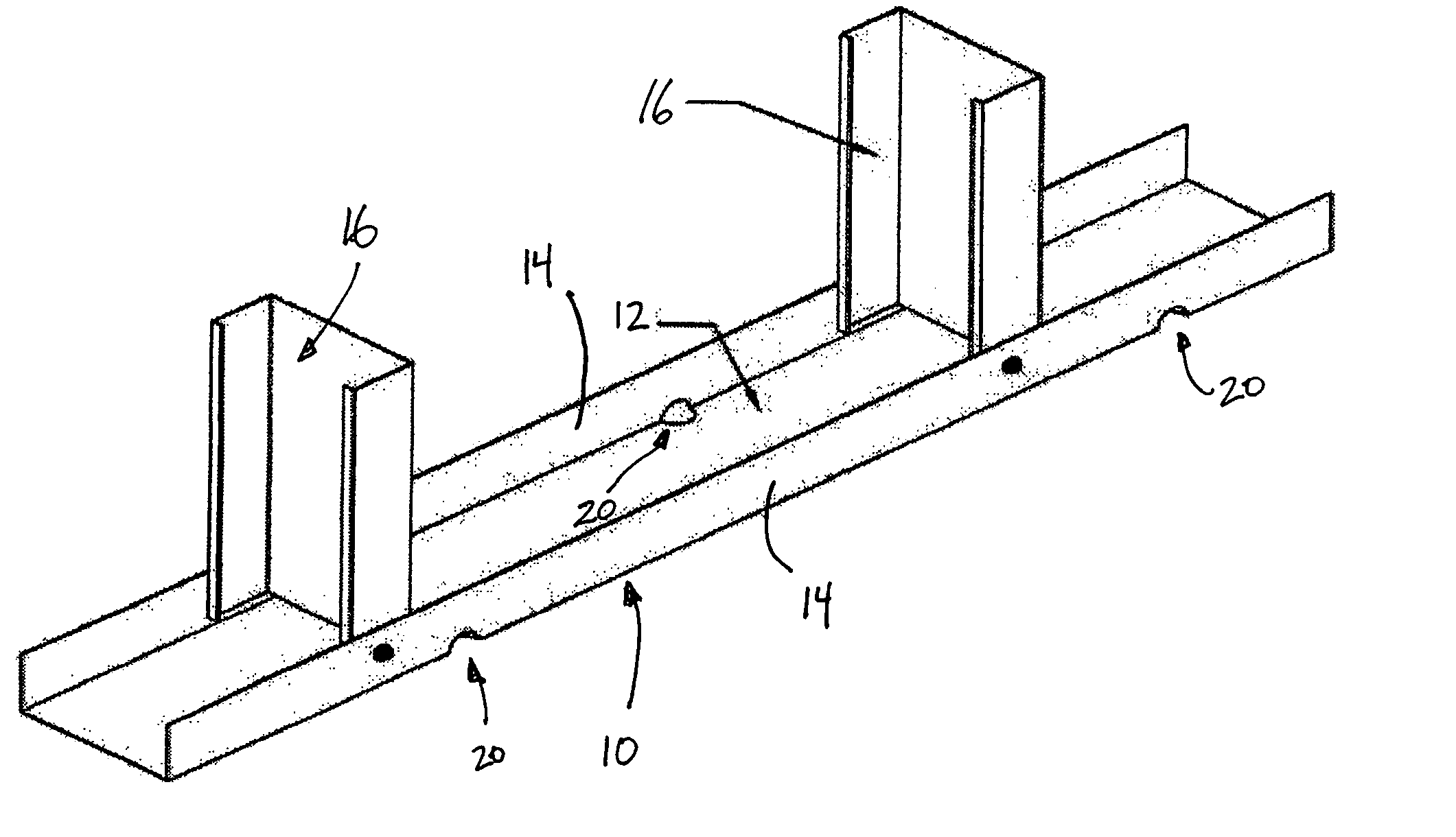
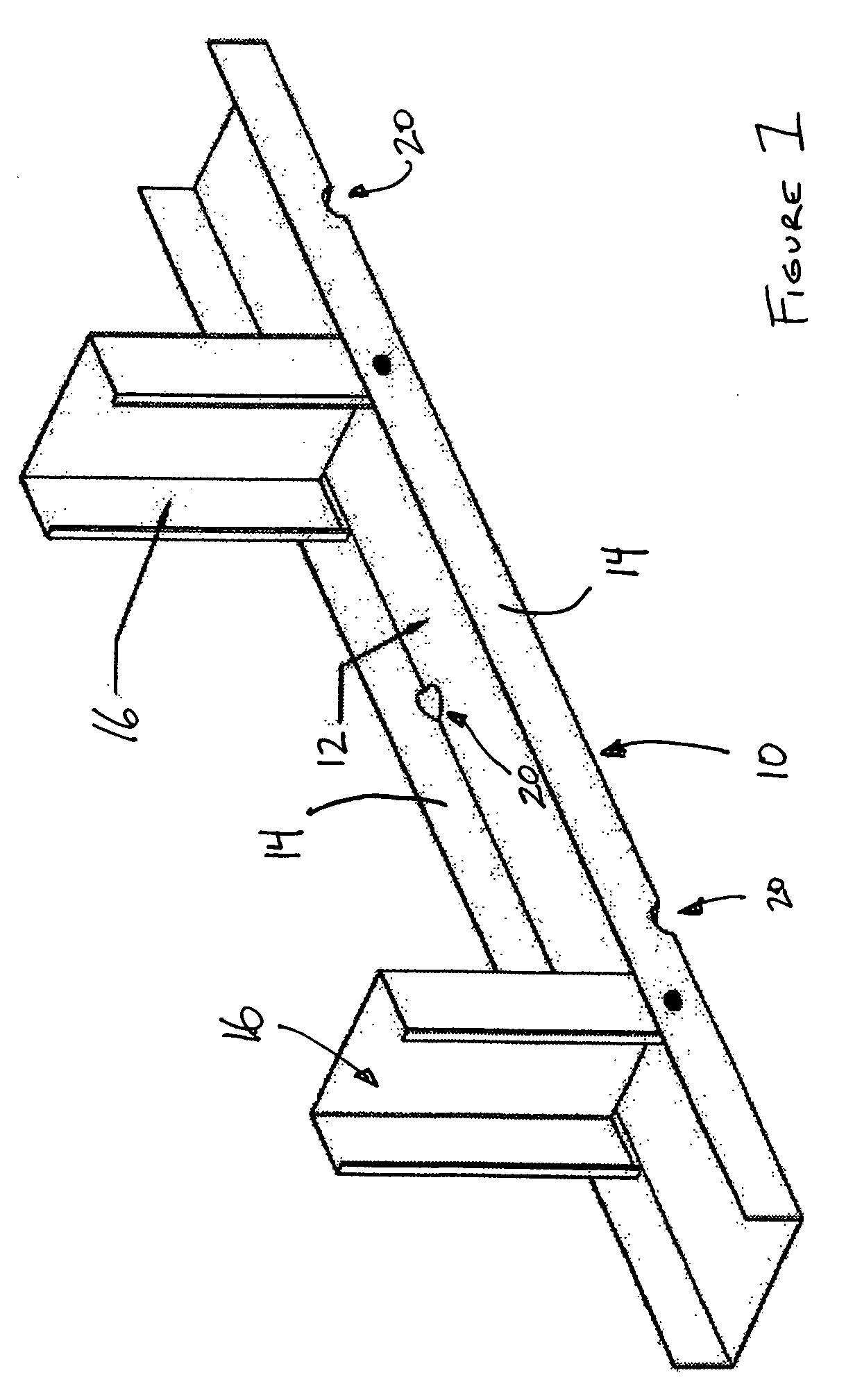
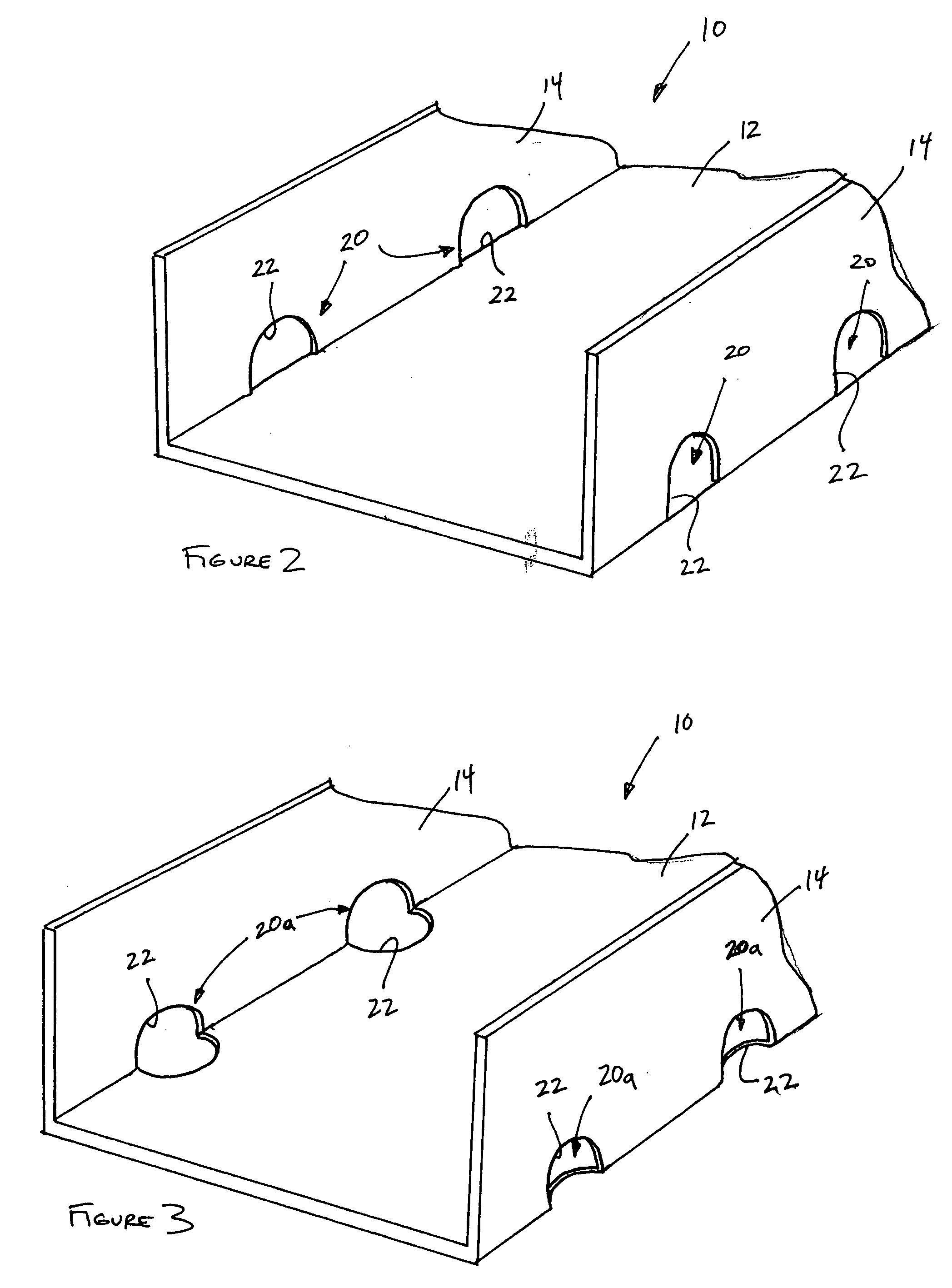
InactiveUS20060026911A1Efficient evacuationPromote escapeWallsFoundation engineeringWall studEngineering
A footer track for supporting a plurality of wall studs, and a method for making a footer track, including a web and a pair of legs extending from opposing sides of the web. The pair of legs are spaced from one another a distance sufficient to accommodate a wall stud therebetween. The footer track defines a plurality of drain openings spaced along a length of the footer track. Preferably, each of the plurality of drain openings has a boundary defined by both of the web and one of the pairs of legs. In one arrangement, each drain opening extends a distance into the web such that the opening, itself, is defined by both the web and leg.
Owner:SUTTON ADAM F
Core drill
InactiveUS6945339B2Reduce frictional resistanceLow costDrill bitsDrilling rodsRotational axisEngineering
A plurality of chip evacuating grooves (16, 26, 36, 46a, 46b) in a vertical direction in parallel with a rotational axis of a core main body (14) are formed at an outer peripheral face of the core main body (14) in a circumferential direction from a lower end portion to an upper end portion of the core main body (14) in a cylindrical shape provided with a drilling blade (15) at a lower end edge thereof. Further, a sectional area of the chip evacuating groove (16) is formed to gradually increase from a lower end to an upper end of the core main body (14). Further, a number of projections (52, 62, 70, 72) are formed at the outer peripheral face of the core main body (14) between the chip evacuating grooves.
Owner:MAX CO LTD
Horizontally positionable vertical wine press
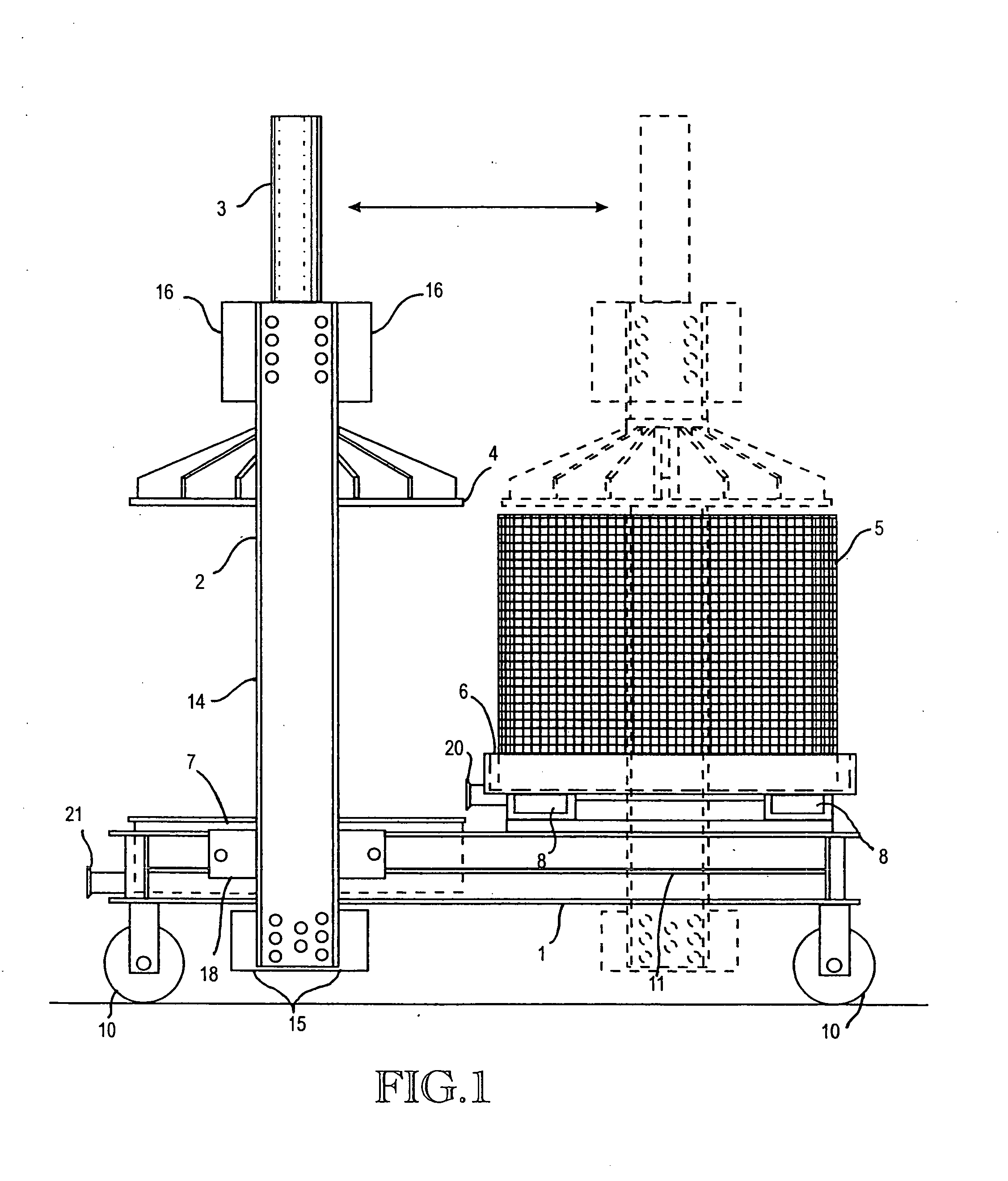
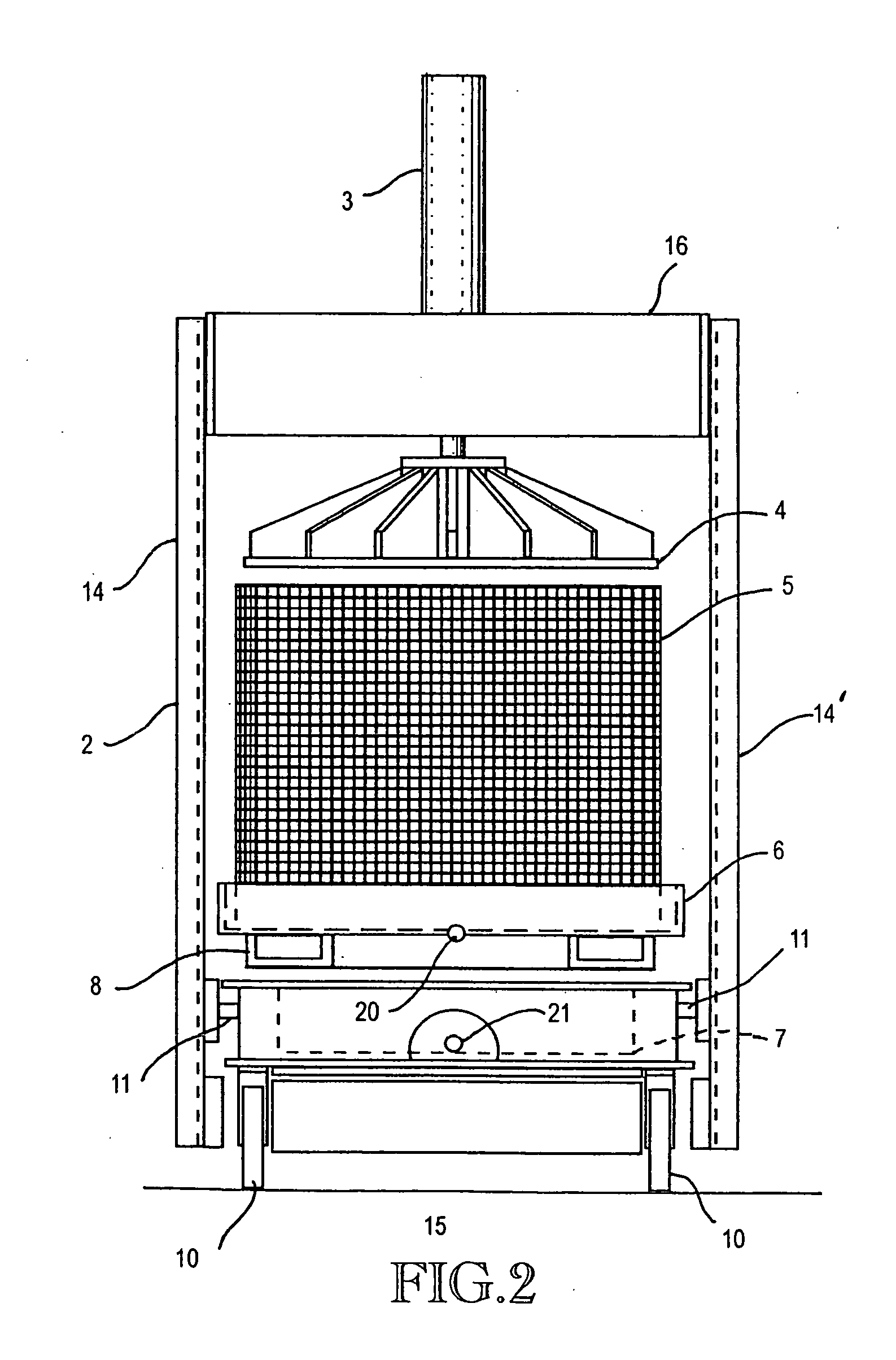
InactiveUS20050139093A1Minimize possibility for overflowImprove efficiencyWine preparationRoasters/grillsSludgeEngineering
A juice press as used in the production of wine for removing liquids from solids, having a horizontally positionable press frame that allows a vertical press mechanism to be rolled to a first position for interference-free loading of a press basket with material to be pressed, and then rolled to a second operating position located over the press basket. The press basket has a liquid channeling plate having an arrangement of holes and channels that creates a perimeter seal along a circumference at the bottom of a loaded press basket. The liquid channeling plate traps naturally occurring sludge along the circumference bottom and allows for efficient evacuation of extracted juice from the bottom of the basket as the press mechanism is operated. In one embodiment, the press frame is configured with a hydraulic press basket lift that raises and holds the press basket after a press operation is completed and allows the press mechanism to be used to eject a disk of compressed solids from the bottom of the raised press basket.
Owner:AMERICAN BASKET PRESS
Plant for electrochemical forming of lead-acid batteries
ActiveUS20090314383A1Shorten the timeFast formingPrimary cellsElectrode carriers/collectorsCombustible gasEngineering
The present invention concerns a plant for the forming of lead-acid battery cells, comprising plugs to be fitted to the openings of the cells, each plug comprising a first inlet duct, a second outlet duct to set up a circulation of electrolyte inside the cell and supply and balancing elements to dilute with air the inflammable gases formed in the cell and to favor the balancing of the pressure inside the cell with the external atmospheric pressure; the supply and balancing elements comprise a third supply and balancing duct connecting the upper part of the plug with a part of the supply tank at atmospheric pressure which introduces the electrolyte into the cell; the plant comprises a fan which forms a vacuum in the suction header, drawing the electrolyte and the inflammable gases from the cells and, through the third duct, ventilating the cells without forming a vacuum inside them.
Owner:SOVEMA
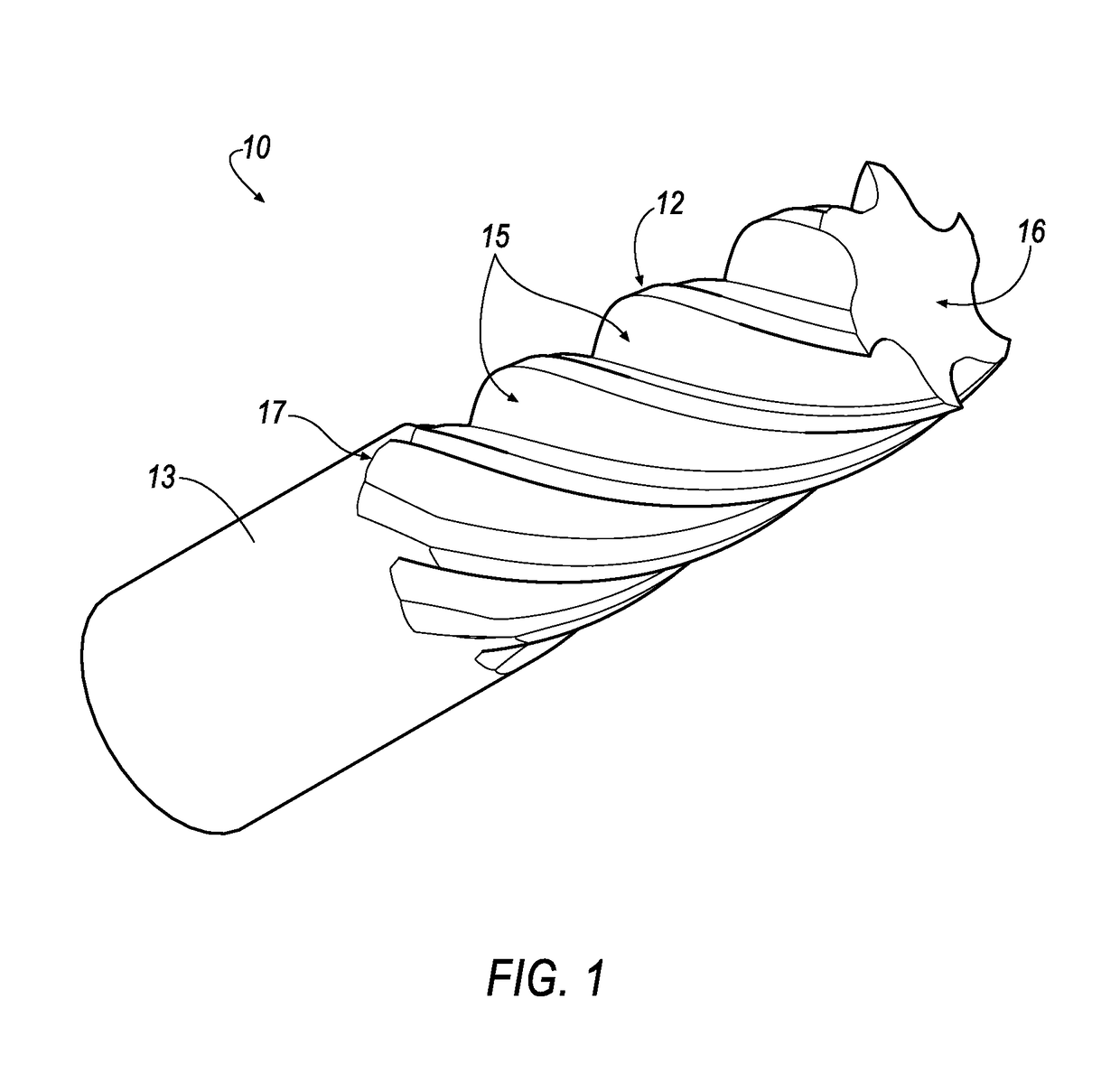
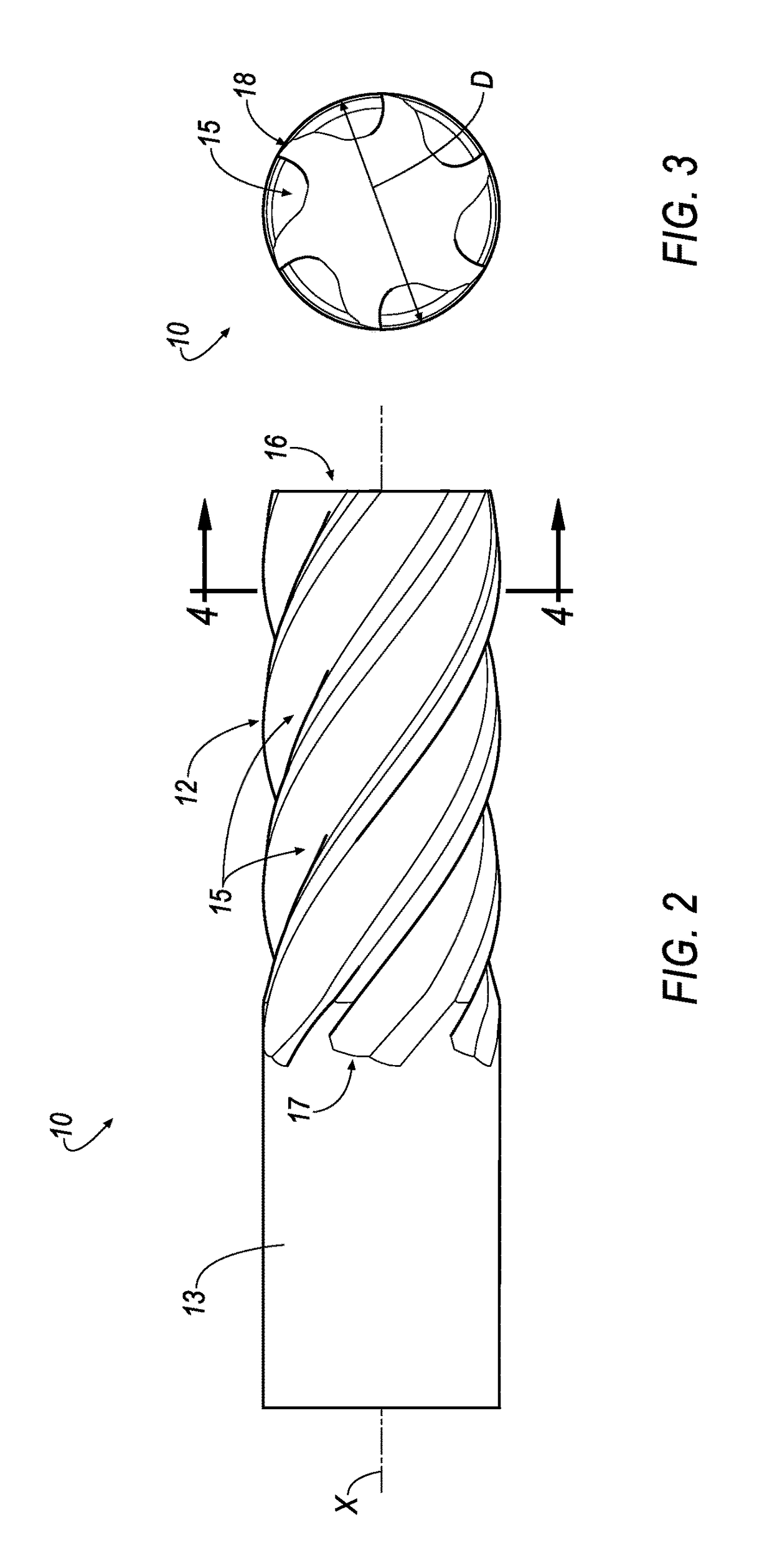
Cutting tool with enhanced chip evacuation capability and method of making same
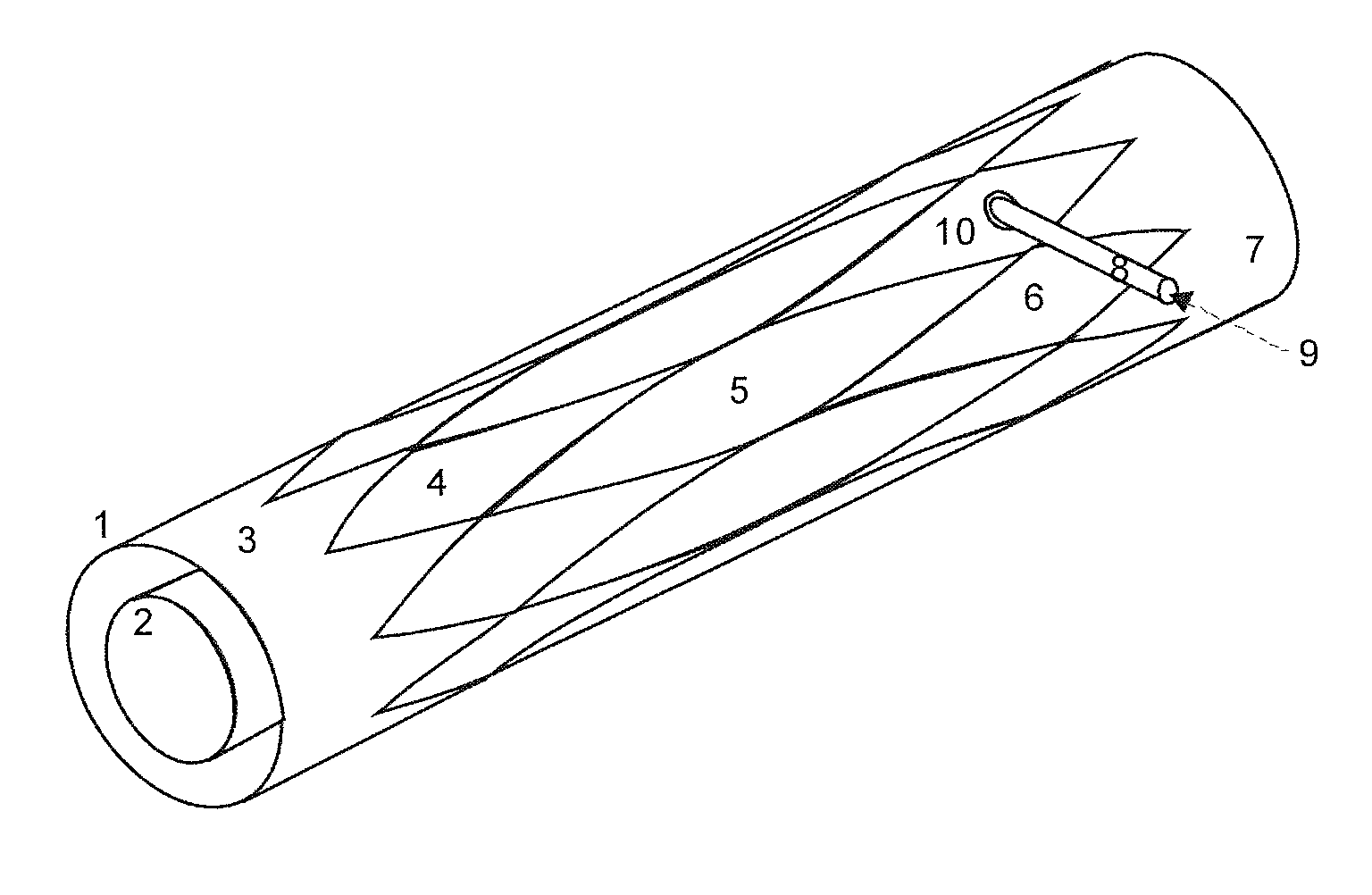
ActiveUS9878379B2Increase volumeEfficient evacuationMilling cuttersGrinding machinesRotational axisMilling cutter
A milling cutter includes a shank and a cutting head attached to the shank. The cutting head has a plurality of helical teeth, each tooth including a cutting tip, a leading face and a rear face. A flute is defined between the leading face of a trailing tooth, and a rear face of an immediately preceding tooth. A gully of the flute has a flute base with a portion that is planar or convex in profile to provide additional volume for effective chip evacuation. A method for manufacturing the milling cutter includes rotating a cylindrical blank about its own longitudinal axis, rotating a disc-shaped flute grinding wheel) about a rotational axis of a flute wheel and moving the grinding wheel in a longitudinal direction so as to form the helical flute with the gully having the flute base with the planar or convex portion in profile.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Water saving toilet device
InactiveUS20050050625A1Avoid difficult choicesEfficient evacuationWater resource protectionFlushing devicesWater savingEngineering
A water saving toilet device is provided which allows the user to select one of two flush modes at the time of use. A low volume flush mode is selected by turning the handle counter clockwise and a high volume flush mode is selected by turning the handle clockwise. The device can be retrofitted to accommodate existing toilets.
Owner:BAYER SETH
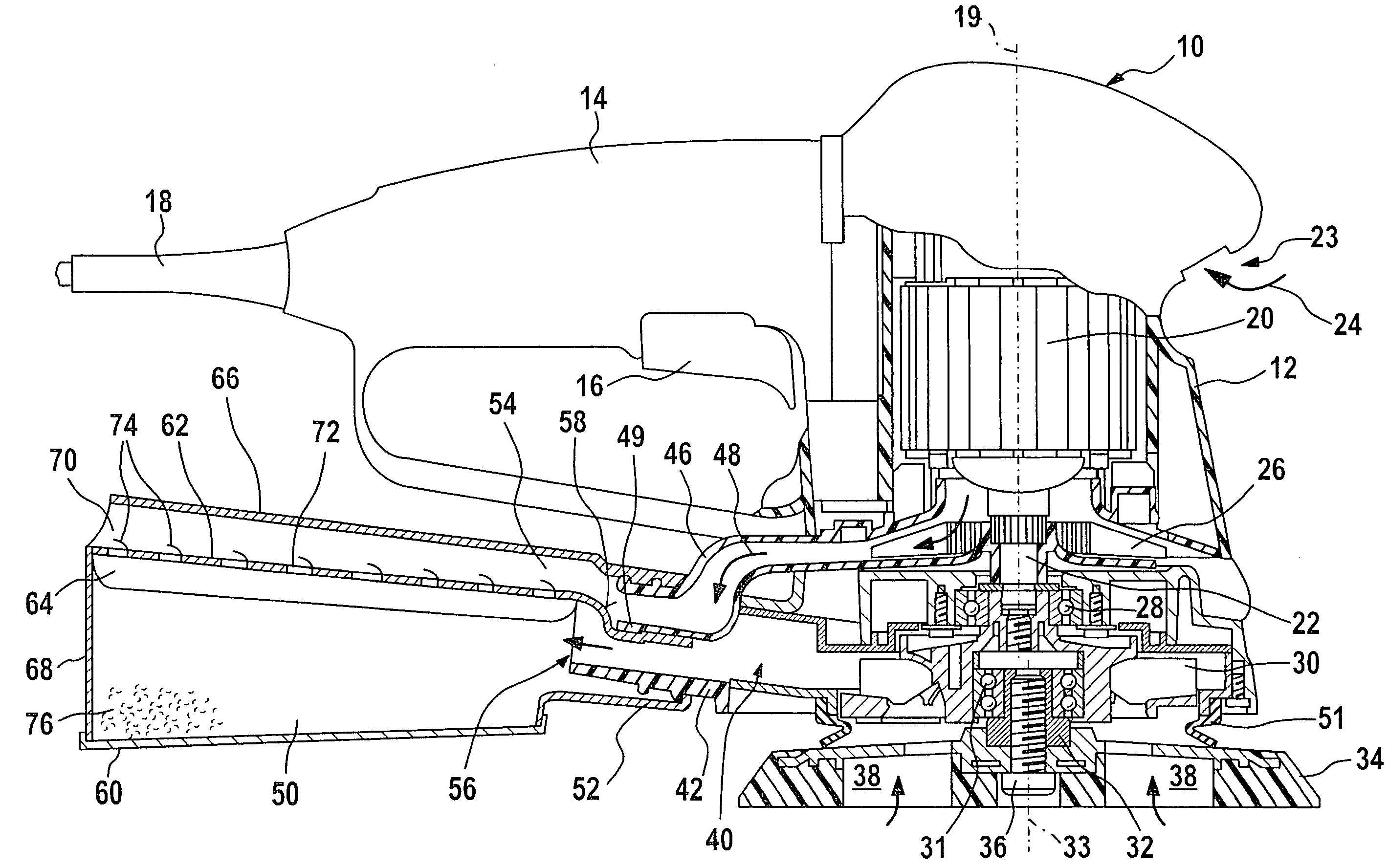
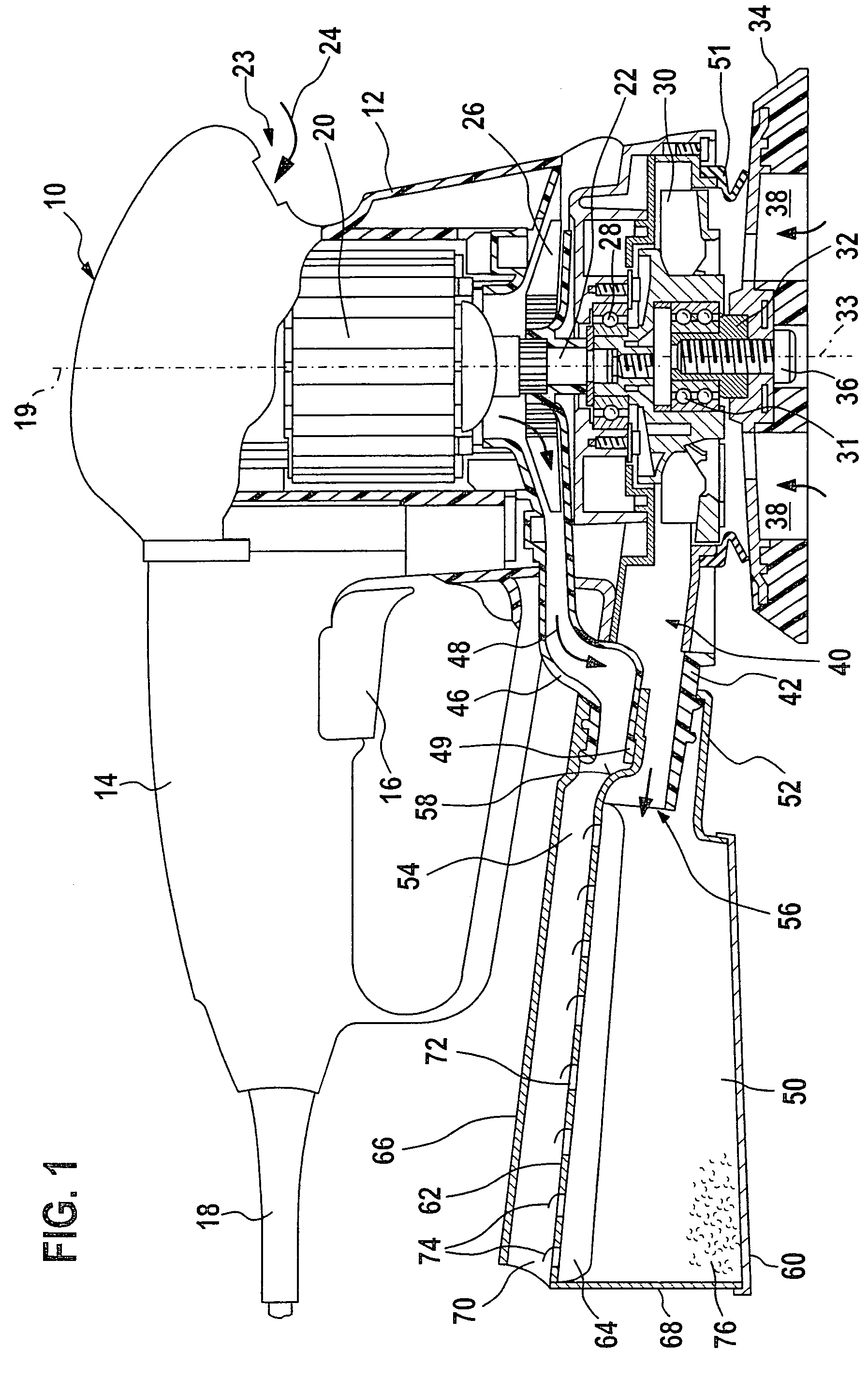
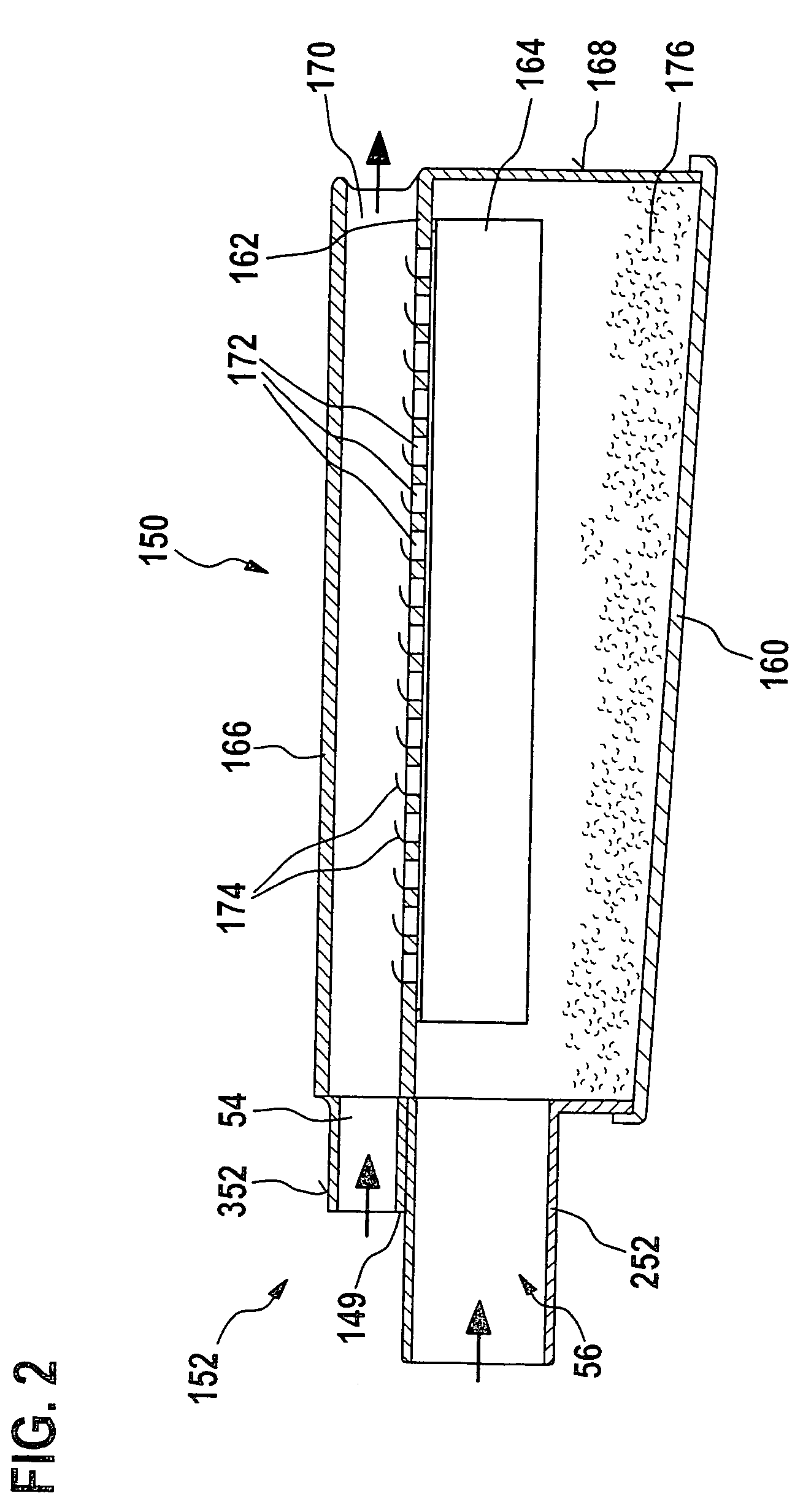
Hand-held machine tool comprising a dust box
A power tool (10) with a housing (12) that includes a dust box (50, 150) and a motor (20) with air cooling, and a cooling exhaust-air duct (44, 46) and a chip suctioning duct (40) which guides a chip-suctioning flow can be used with improved performance and in an environmentally friendlier manner due to the fact that the cooling air flows across the dust box (50, 150) under favorable flow conditions, whereby the evacuation of dust into the dust box (50, 150) is improved and whirls of dust caused by cooling air in the tool region are prevented from forming.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
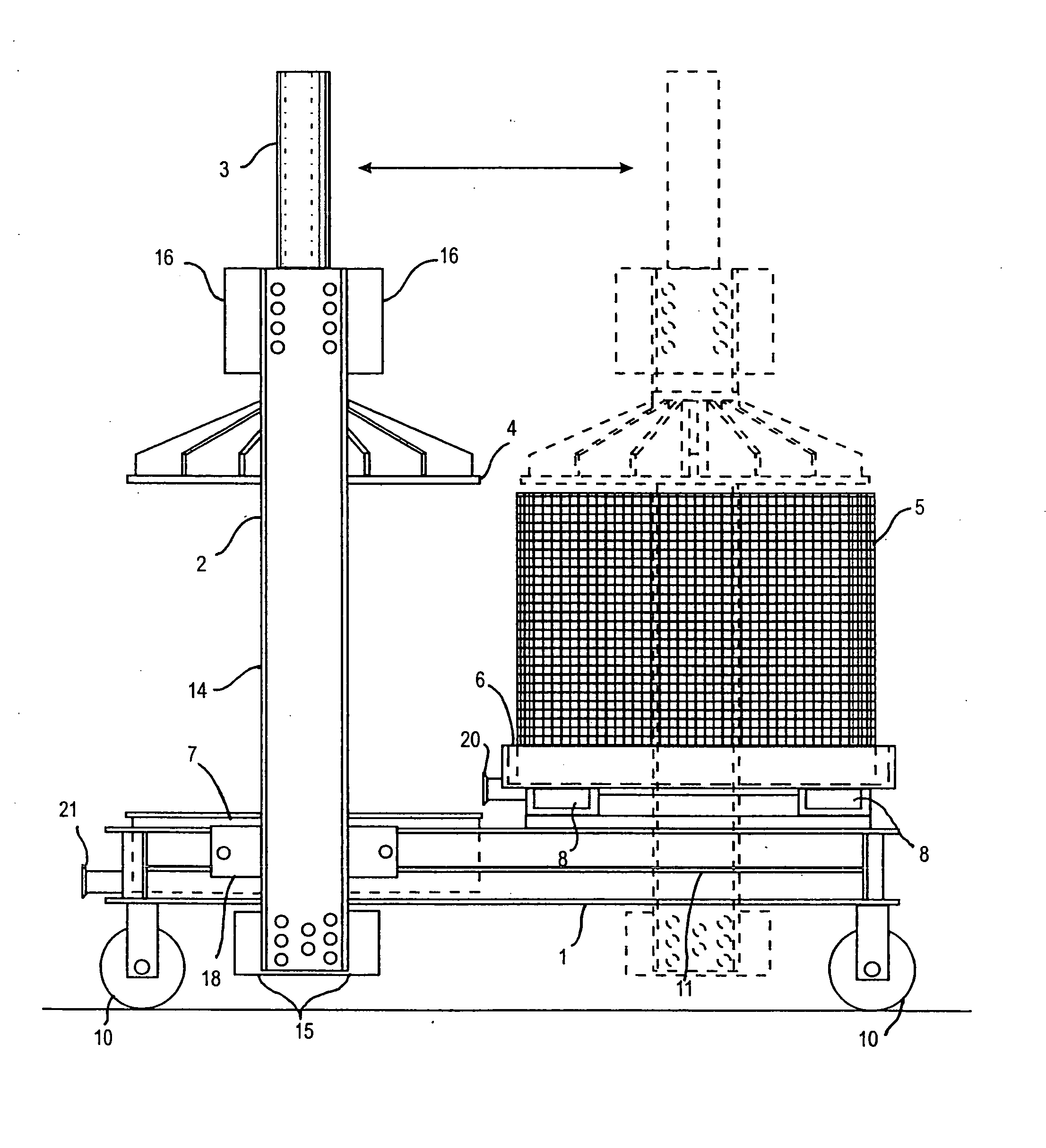
Unmanned aerial vehicle for evacuating people from skyscraper and managing method for the same
InactiveUS20170197719A1Efficient evacuationReduced controllabilityAircraft navigation controlAnchoring installationsPropellerEngineering
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com