Patents
Literature
560results about "Fibre with gratings" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
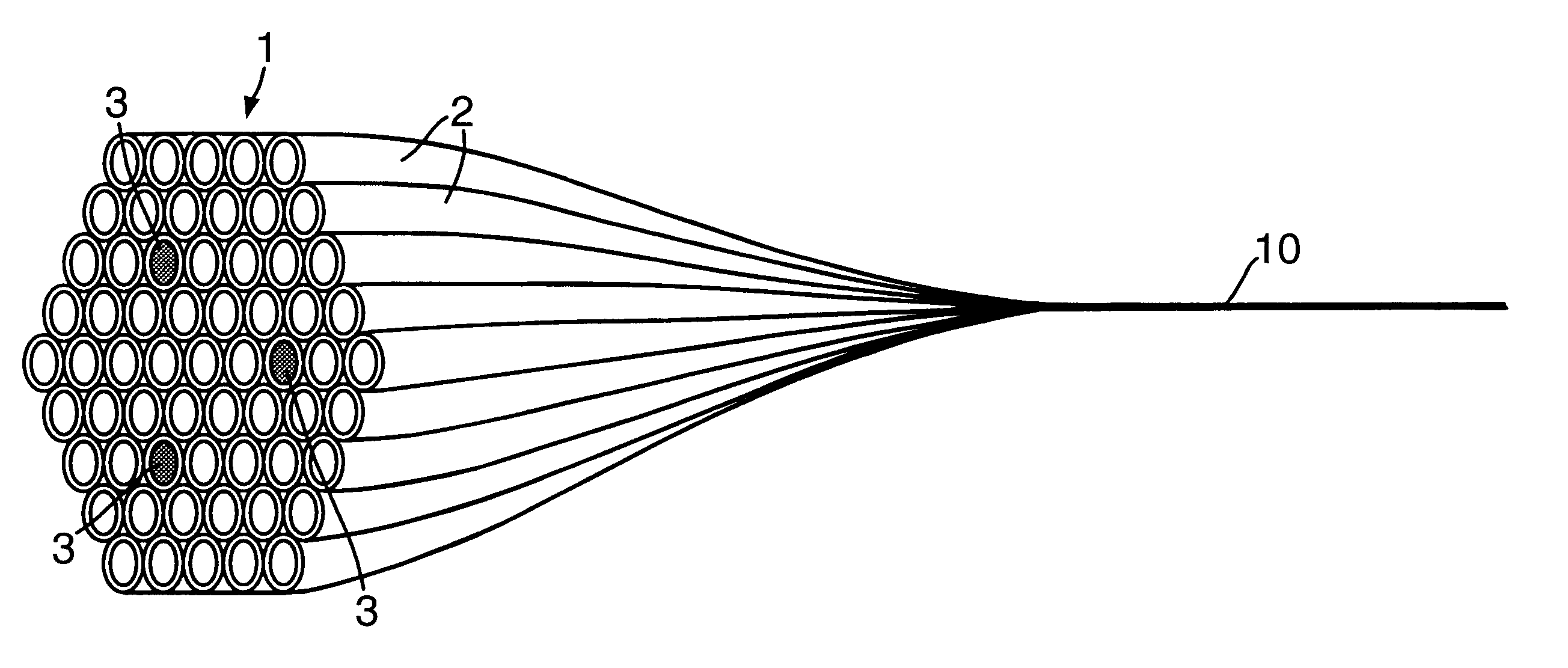
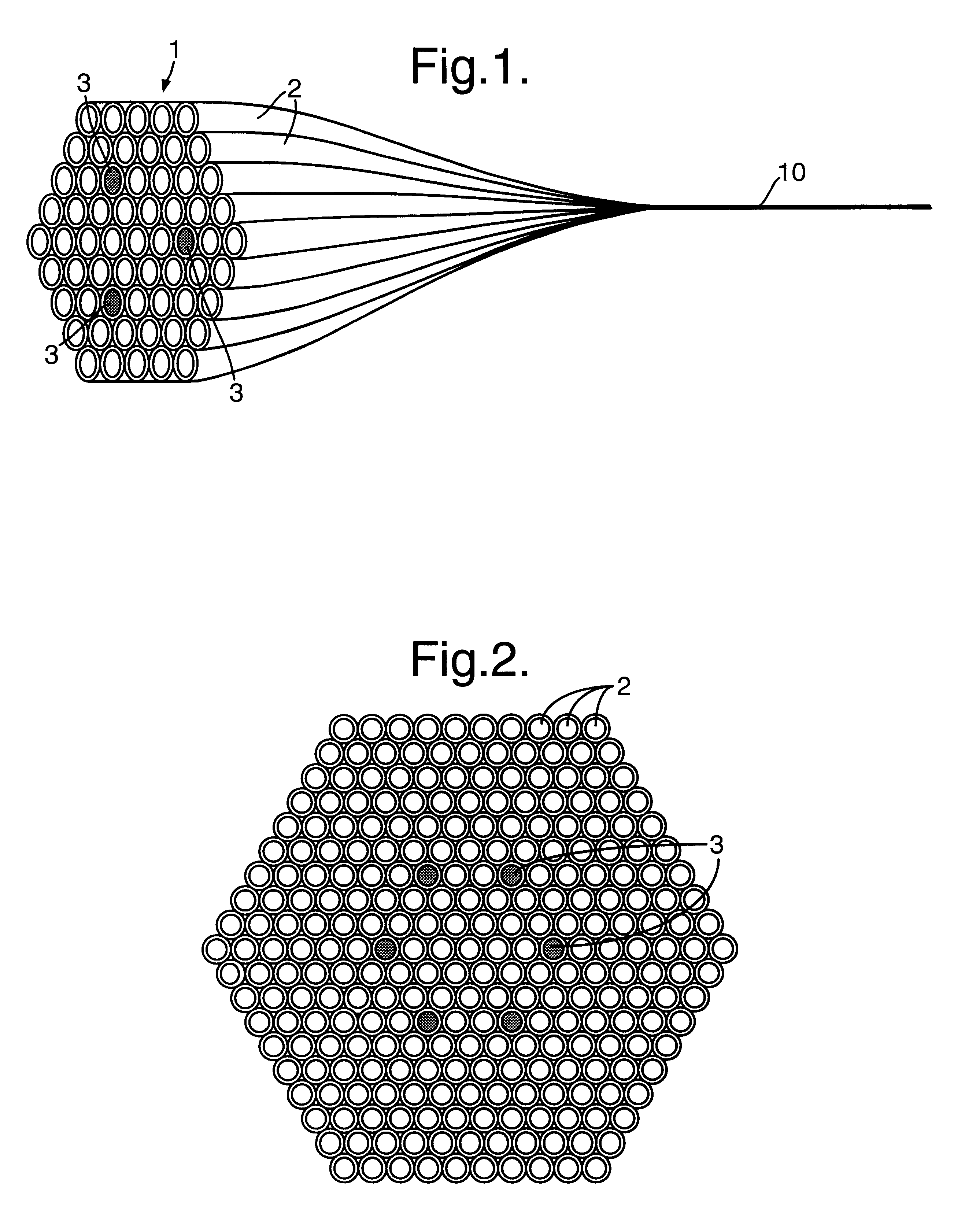
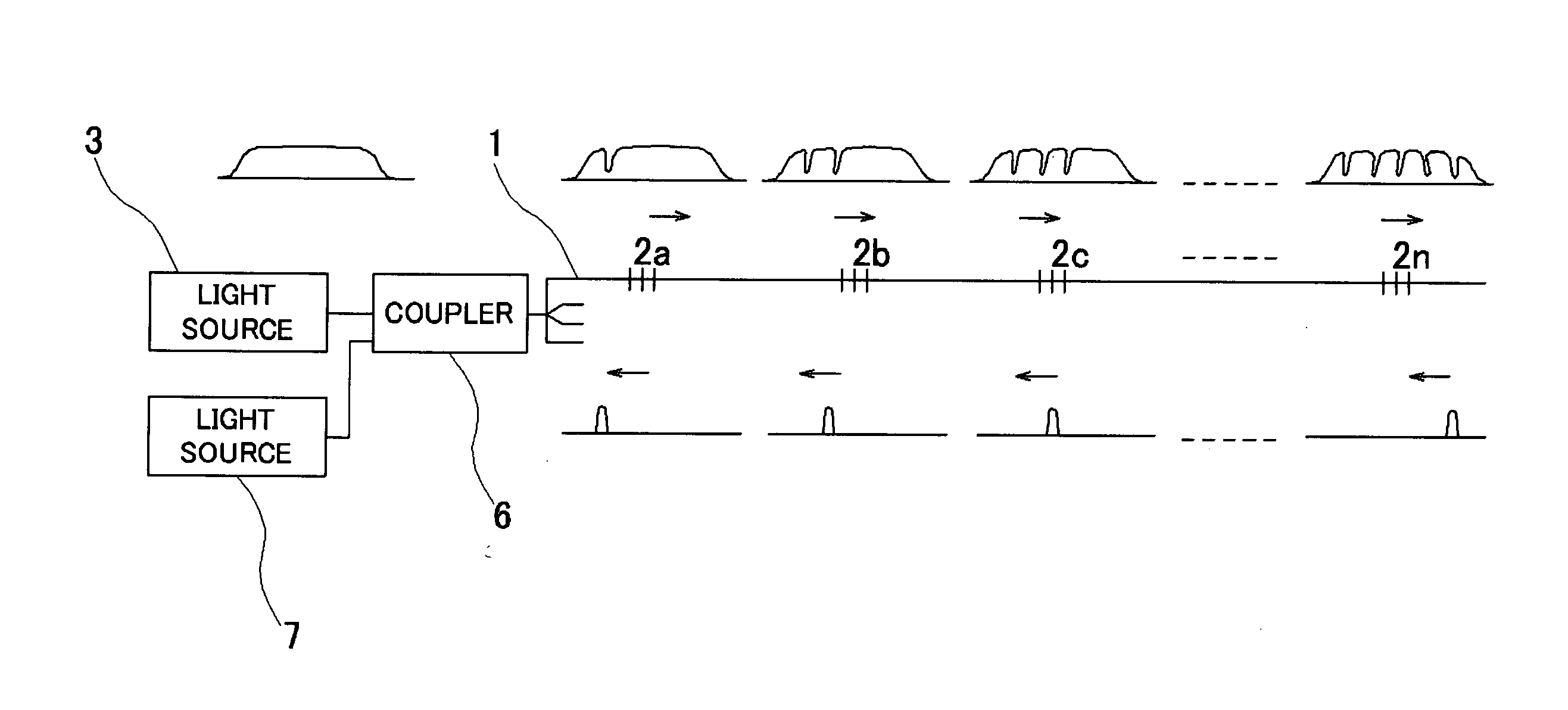
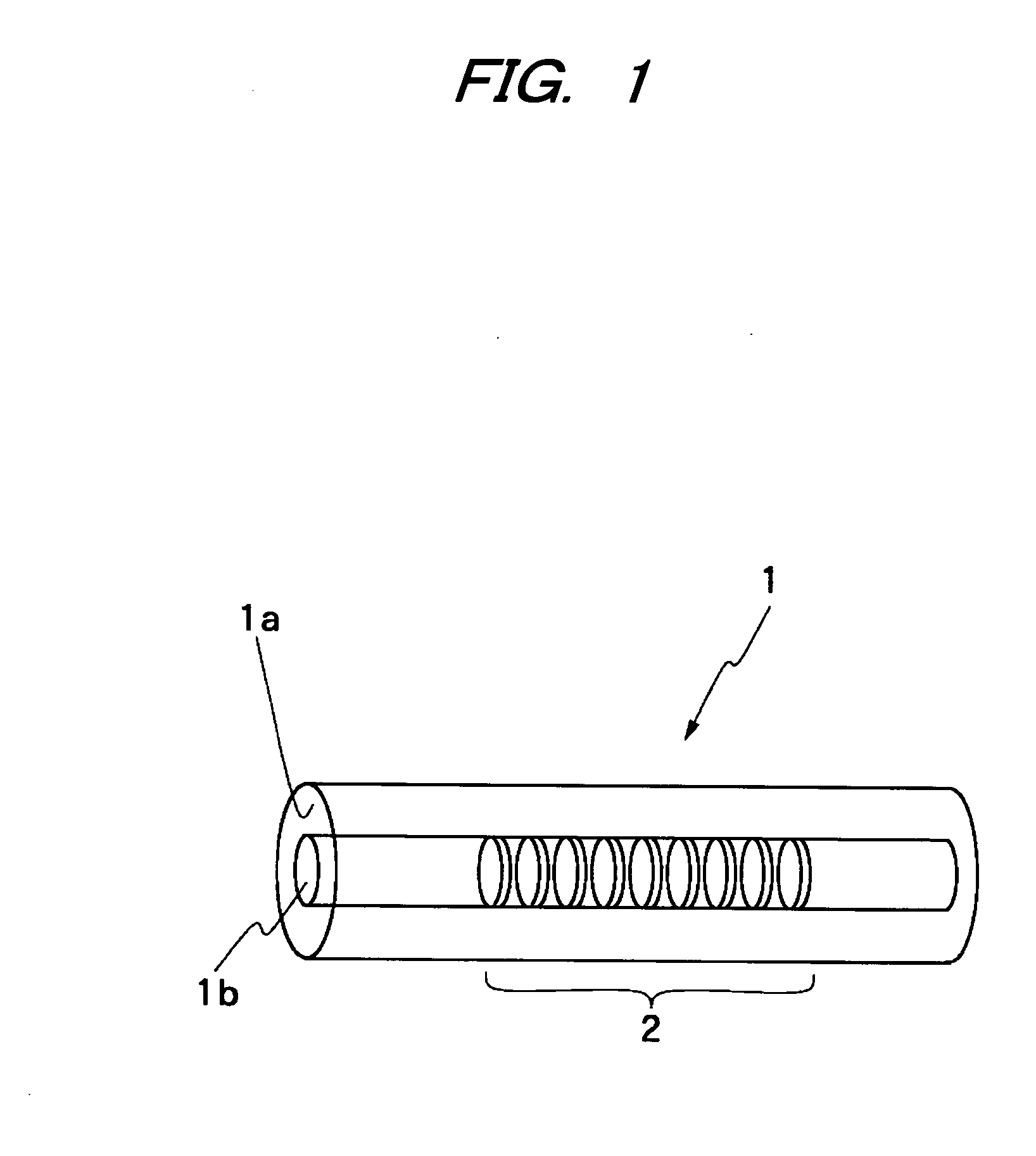
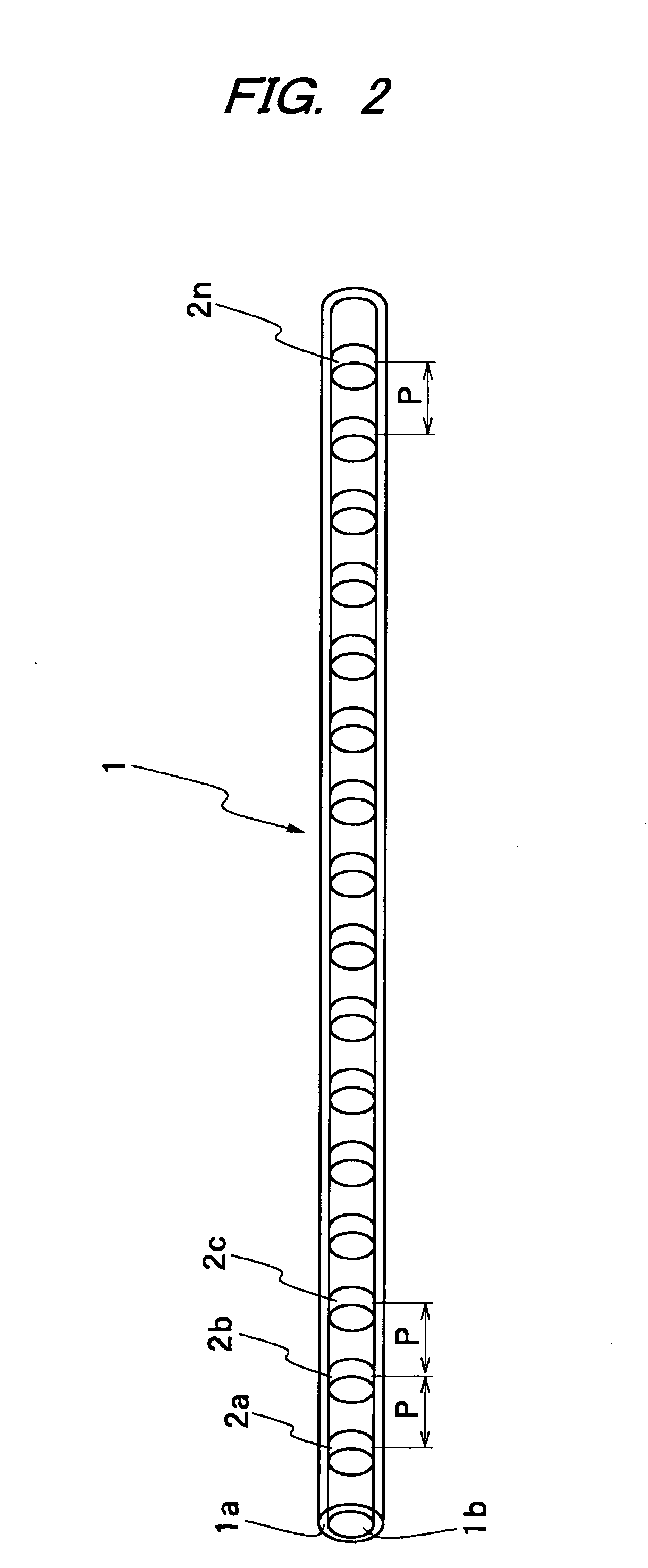
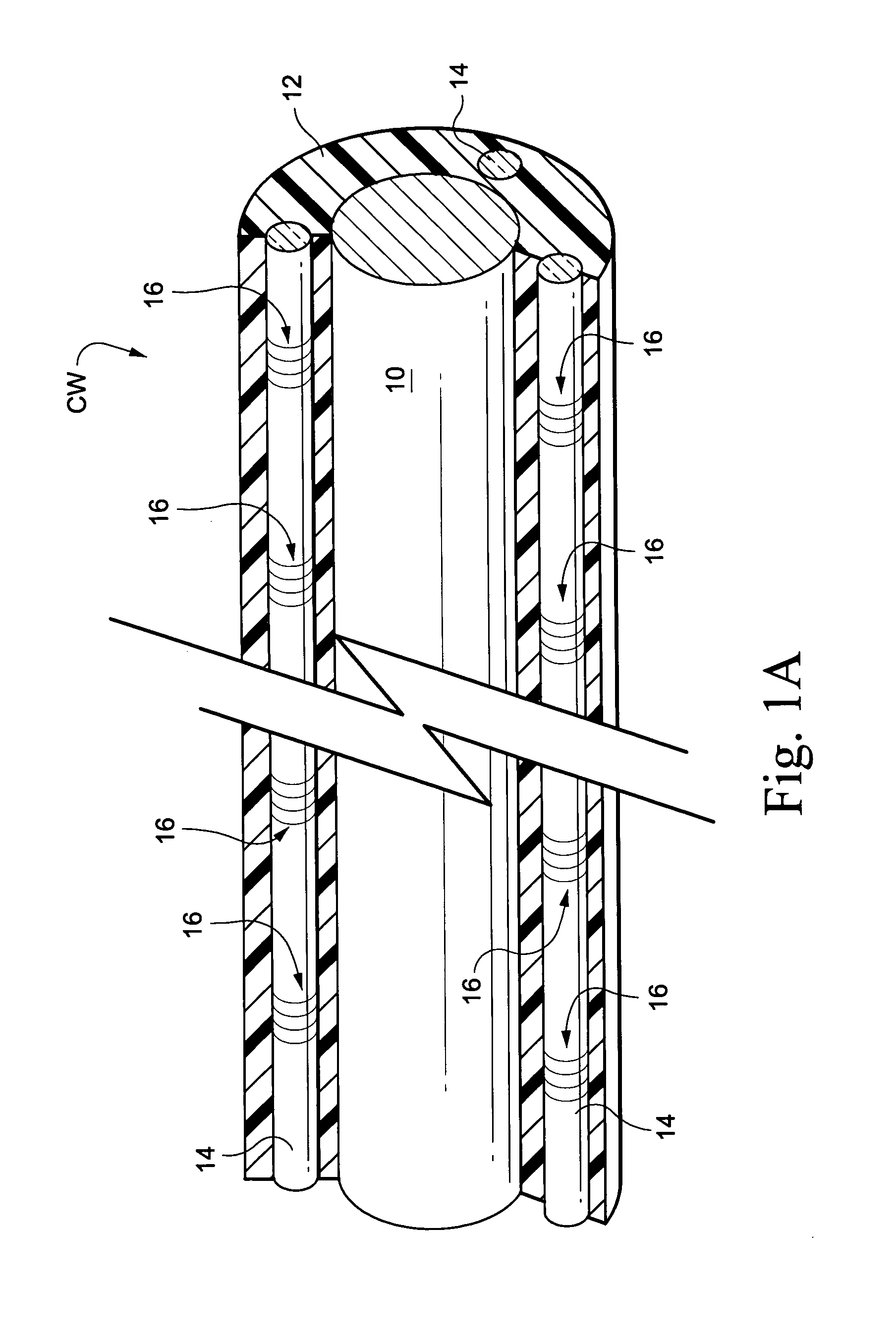
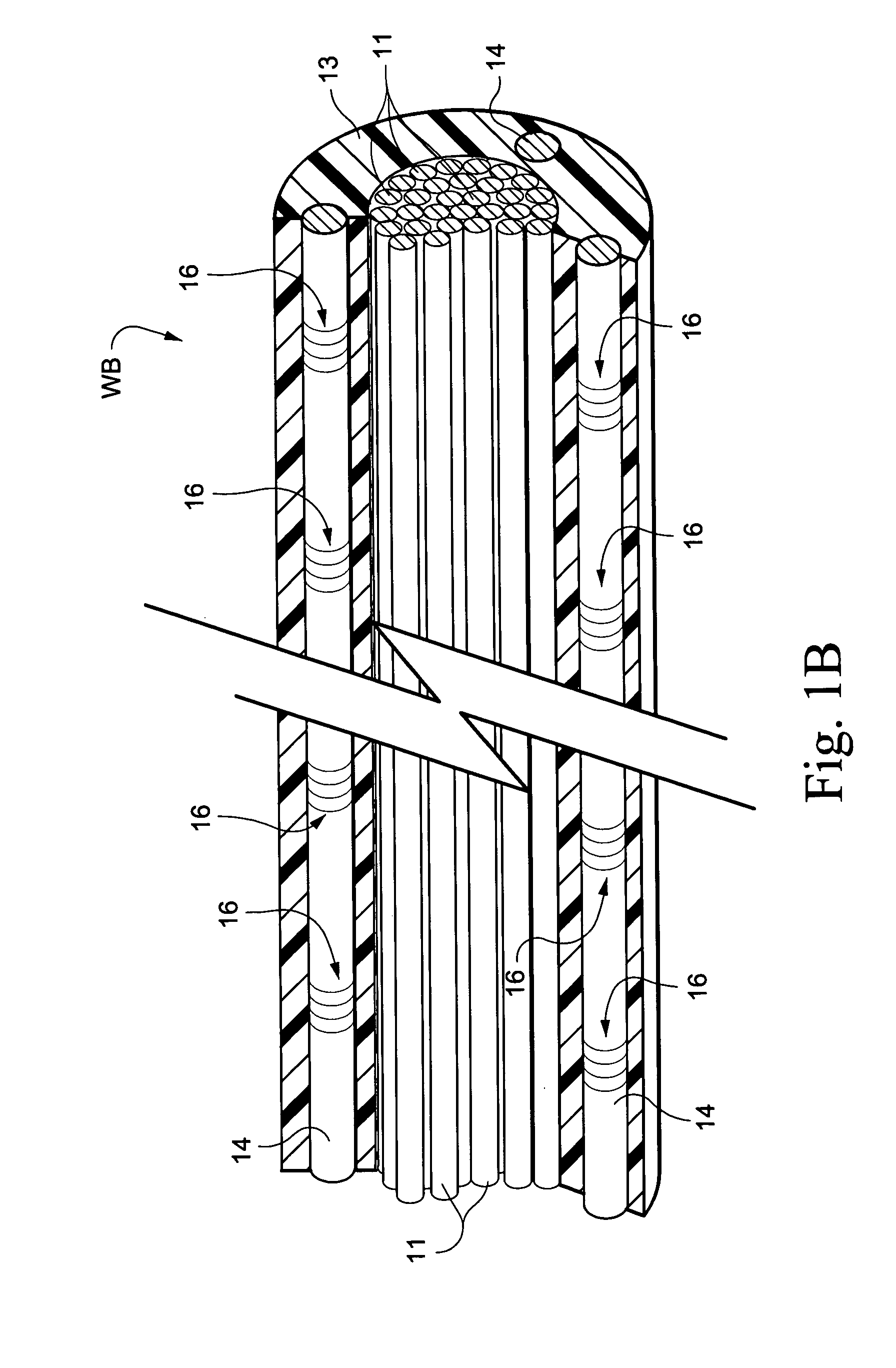
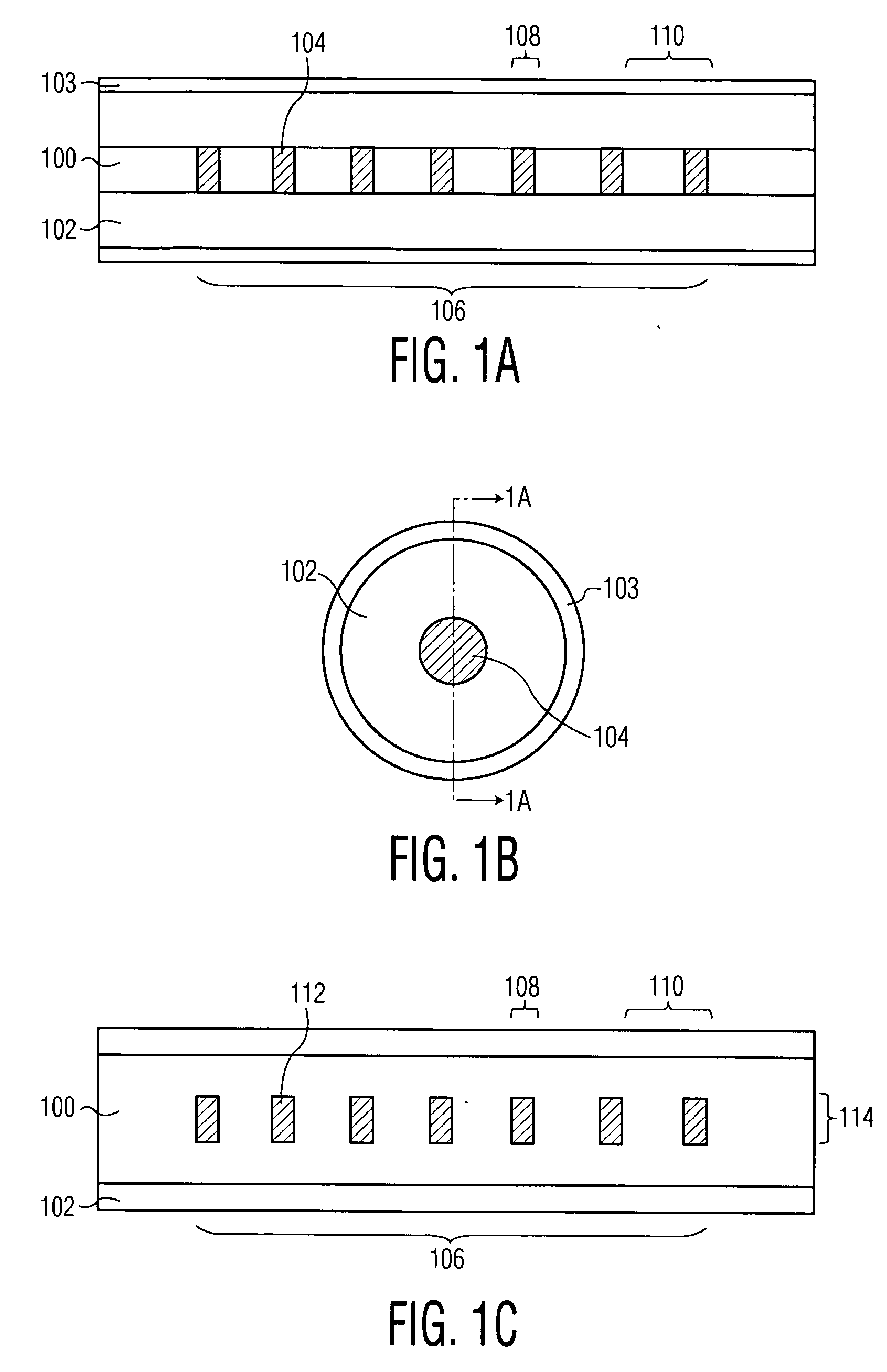
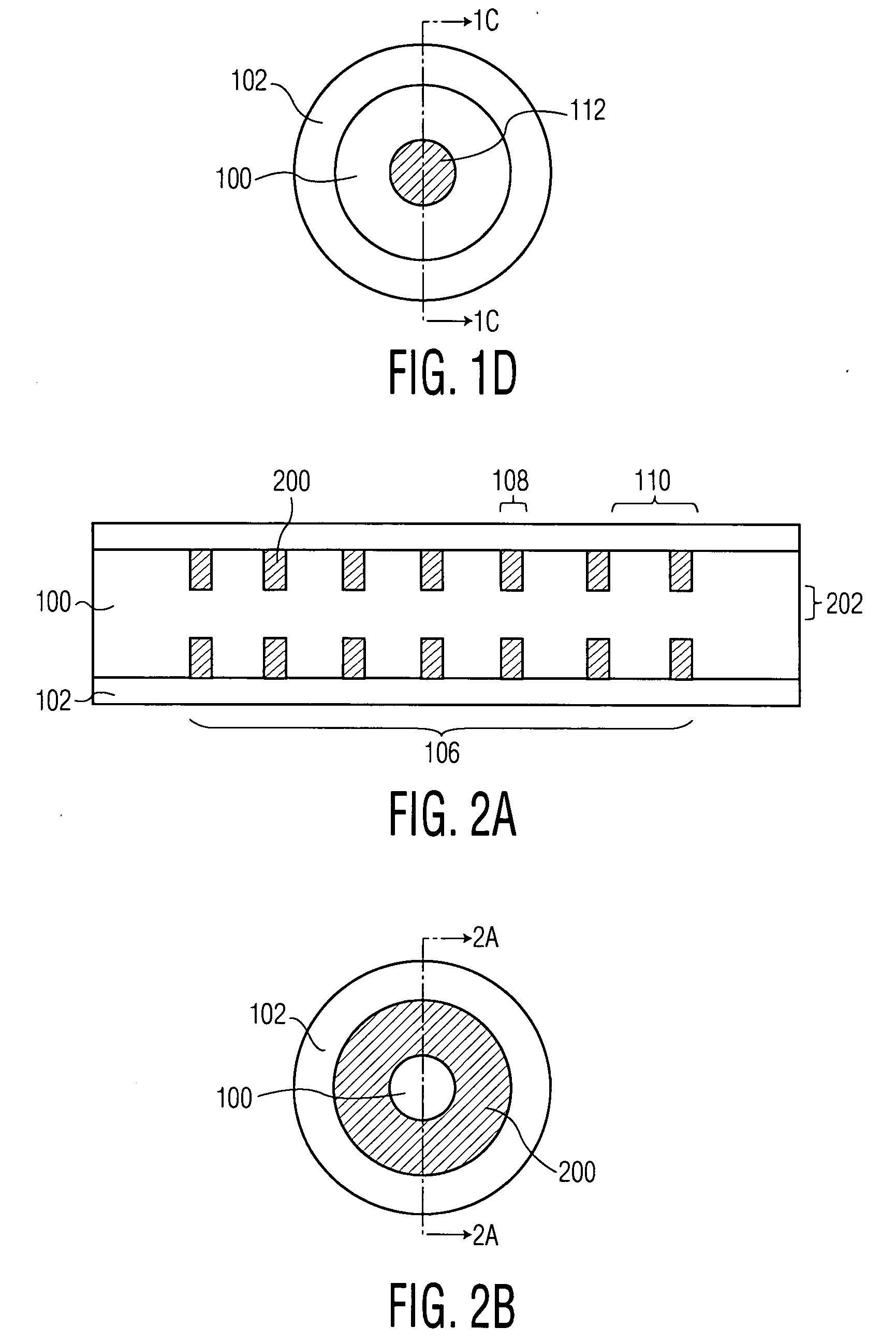
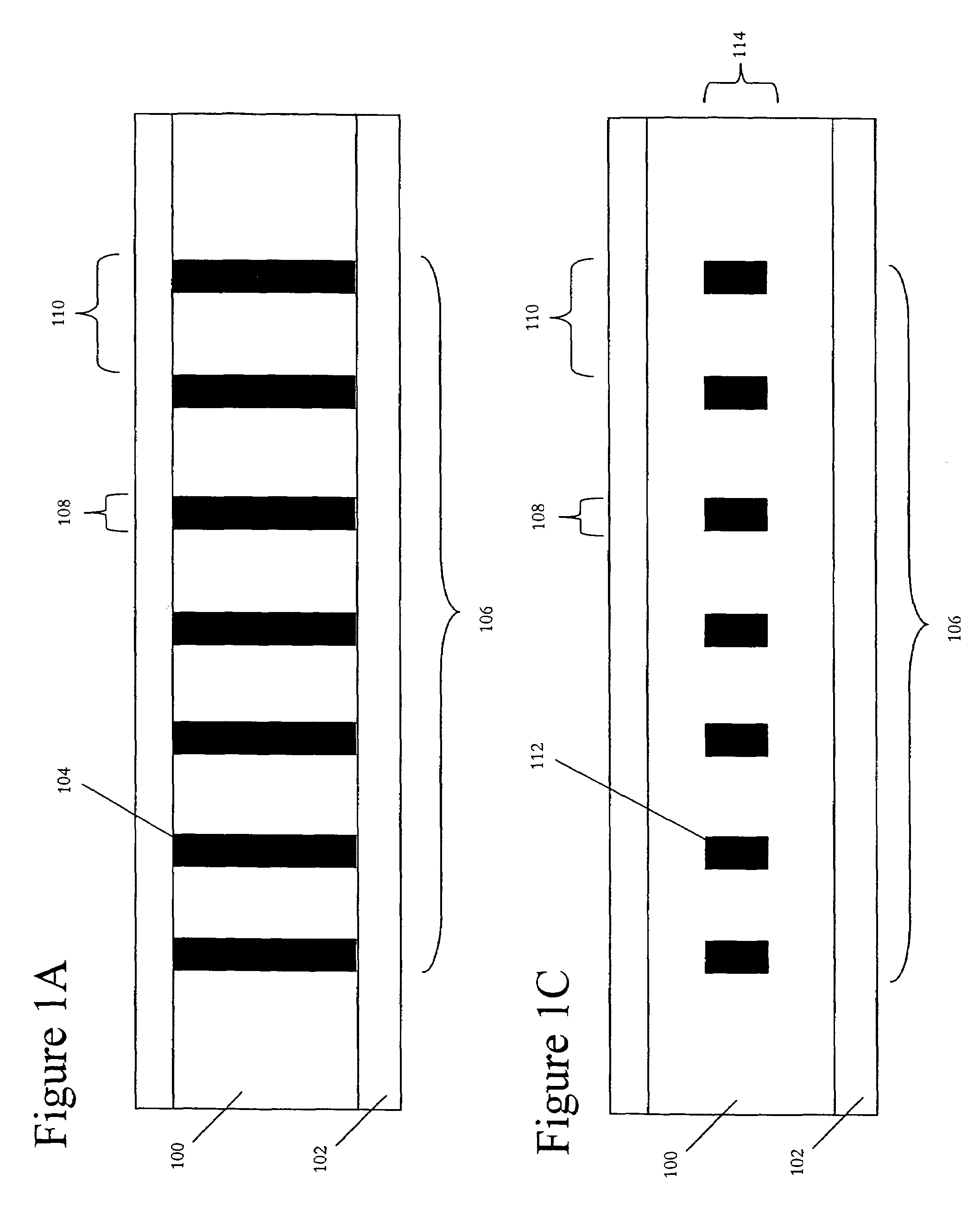
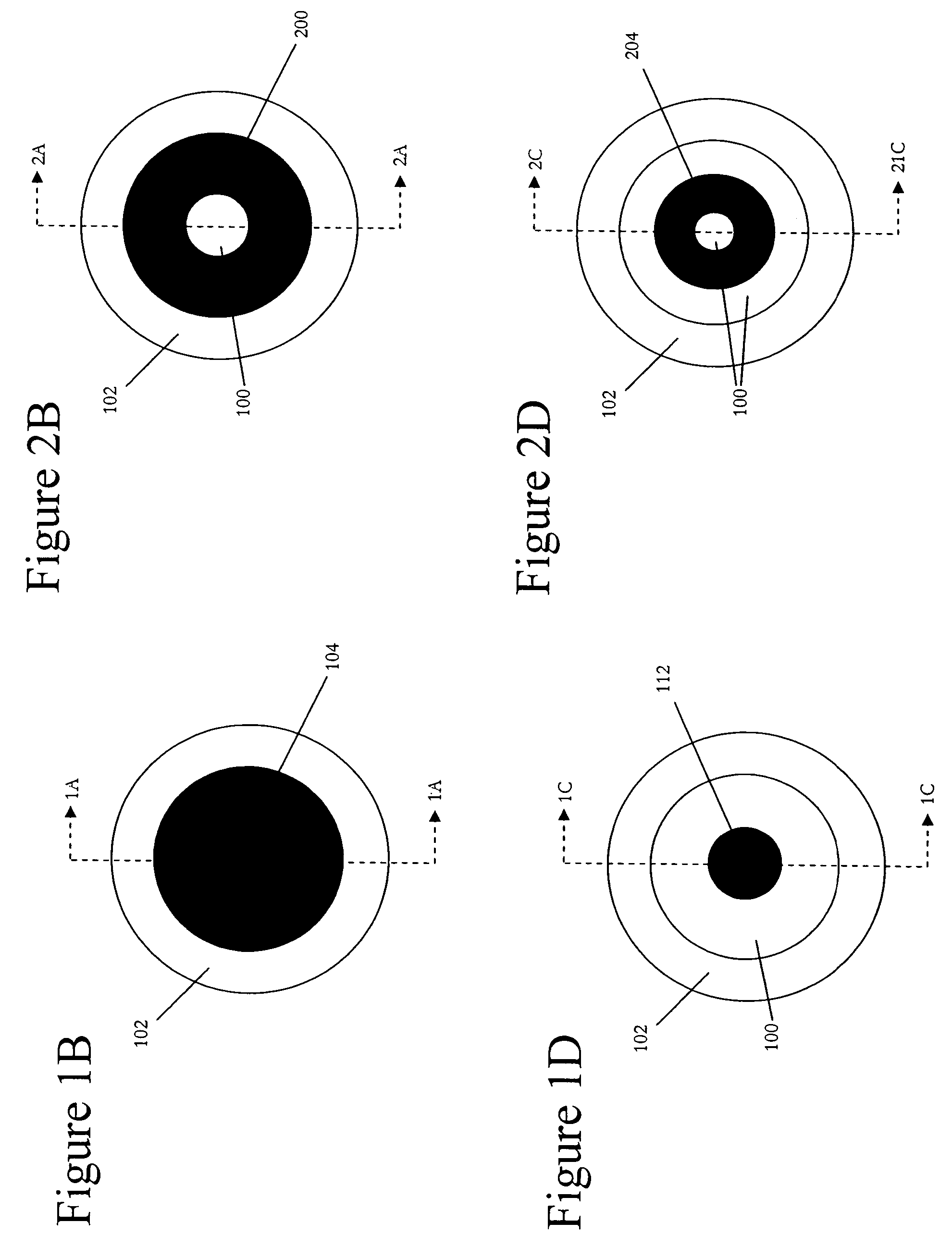
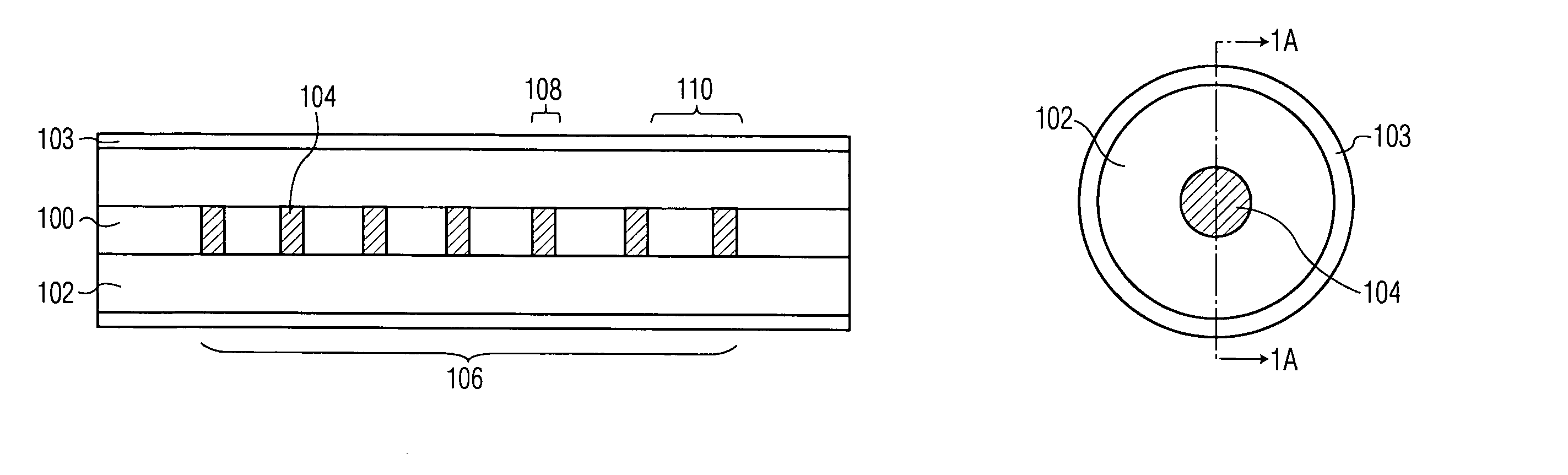
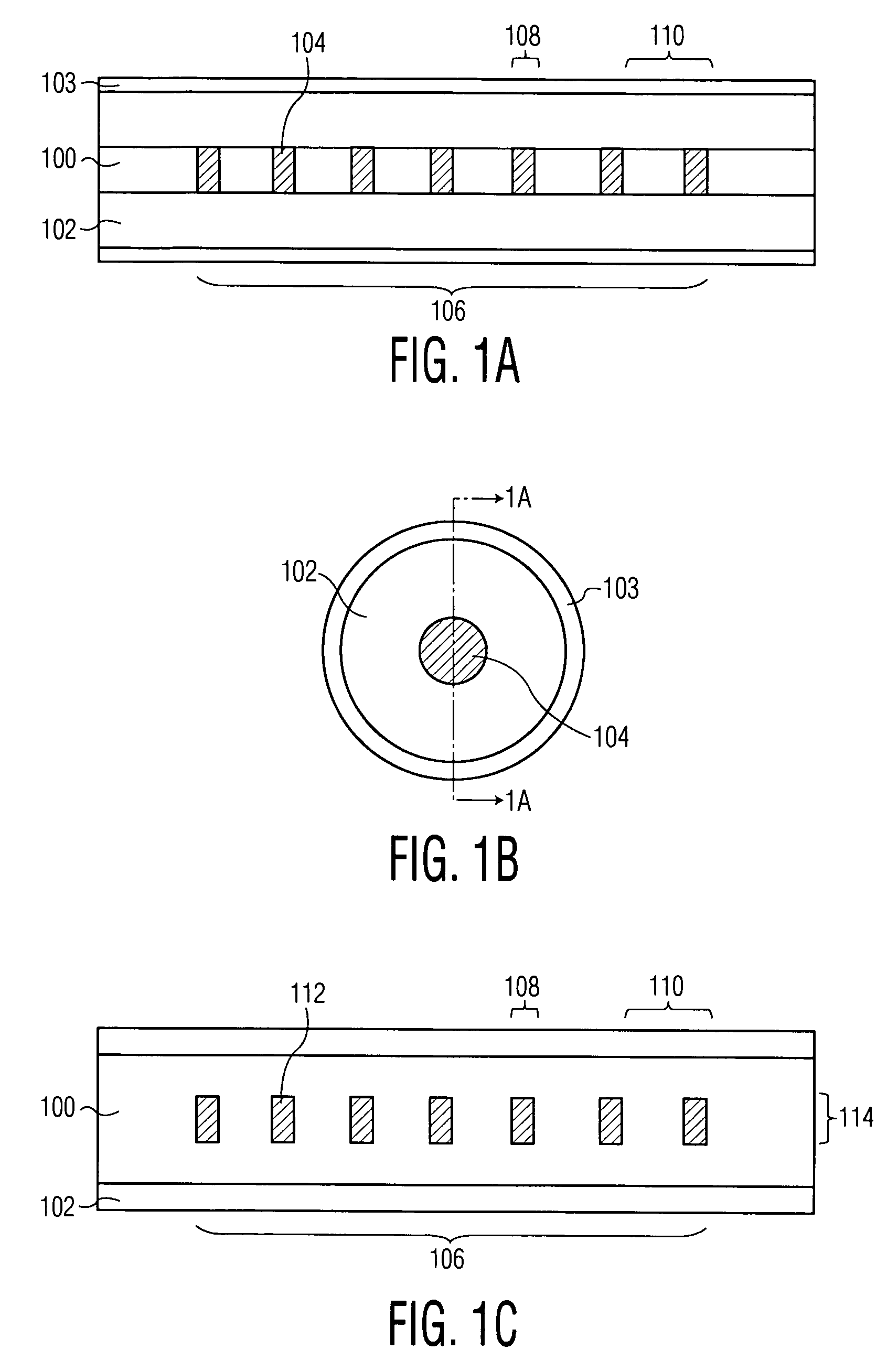
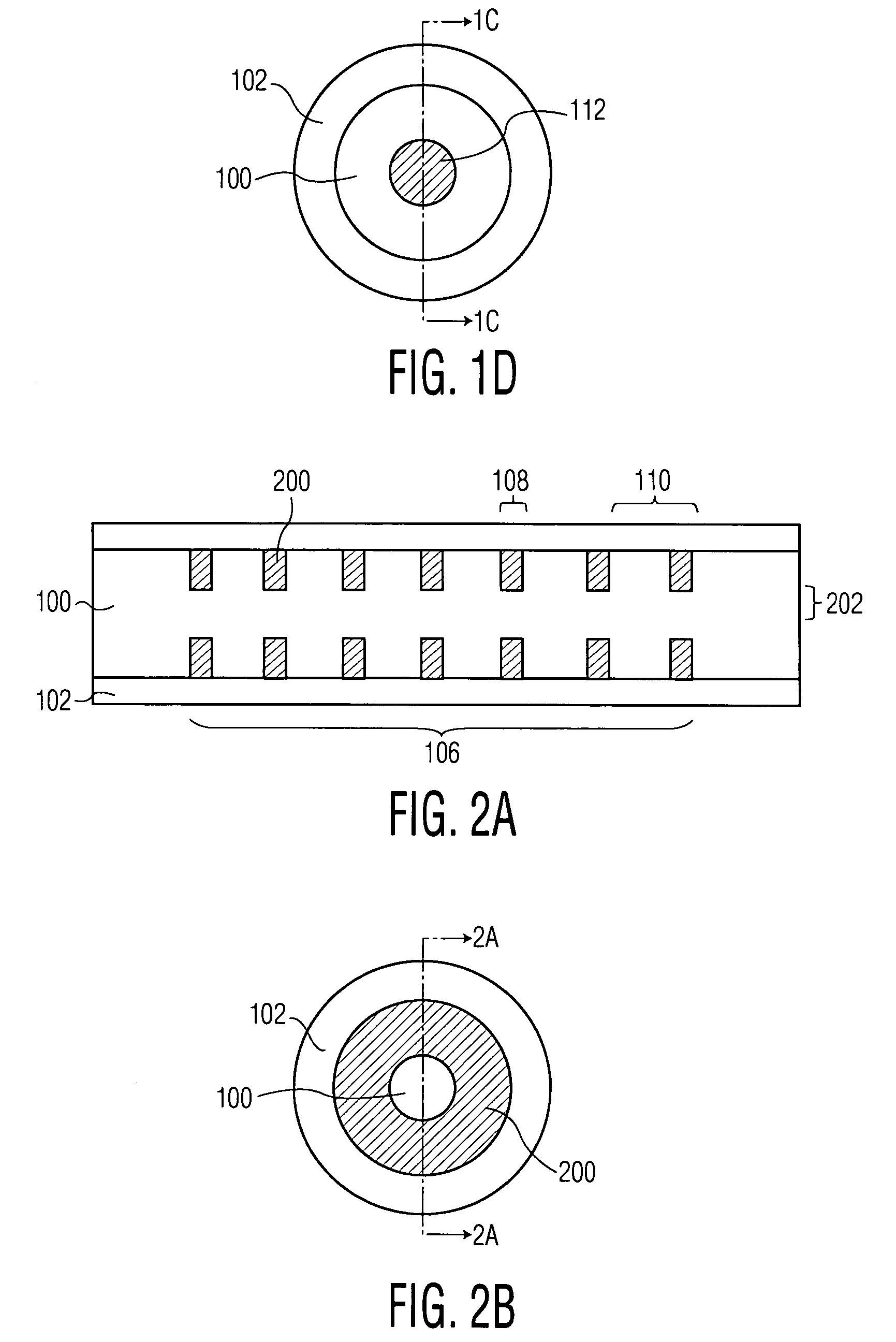
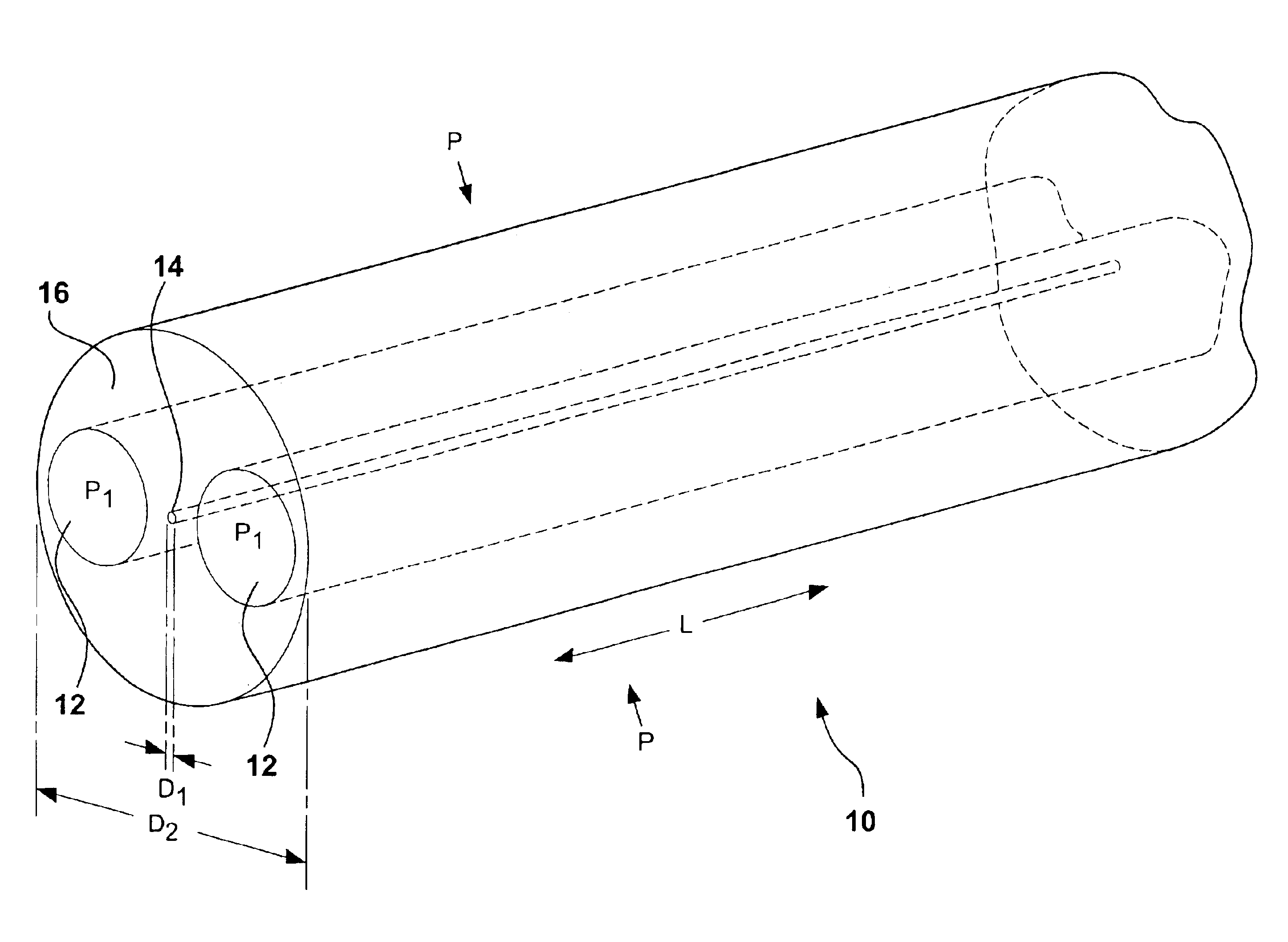
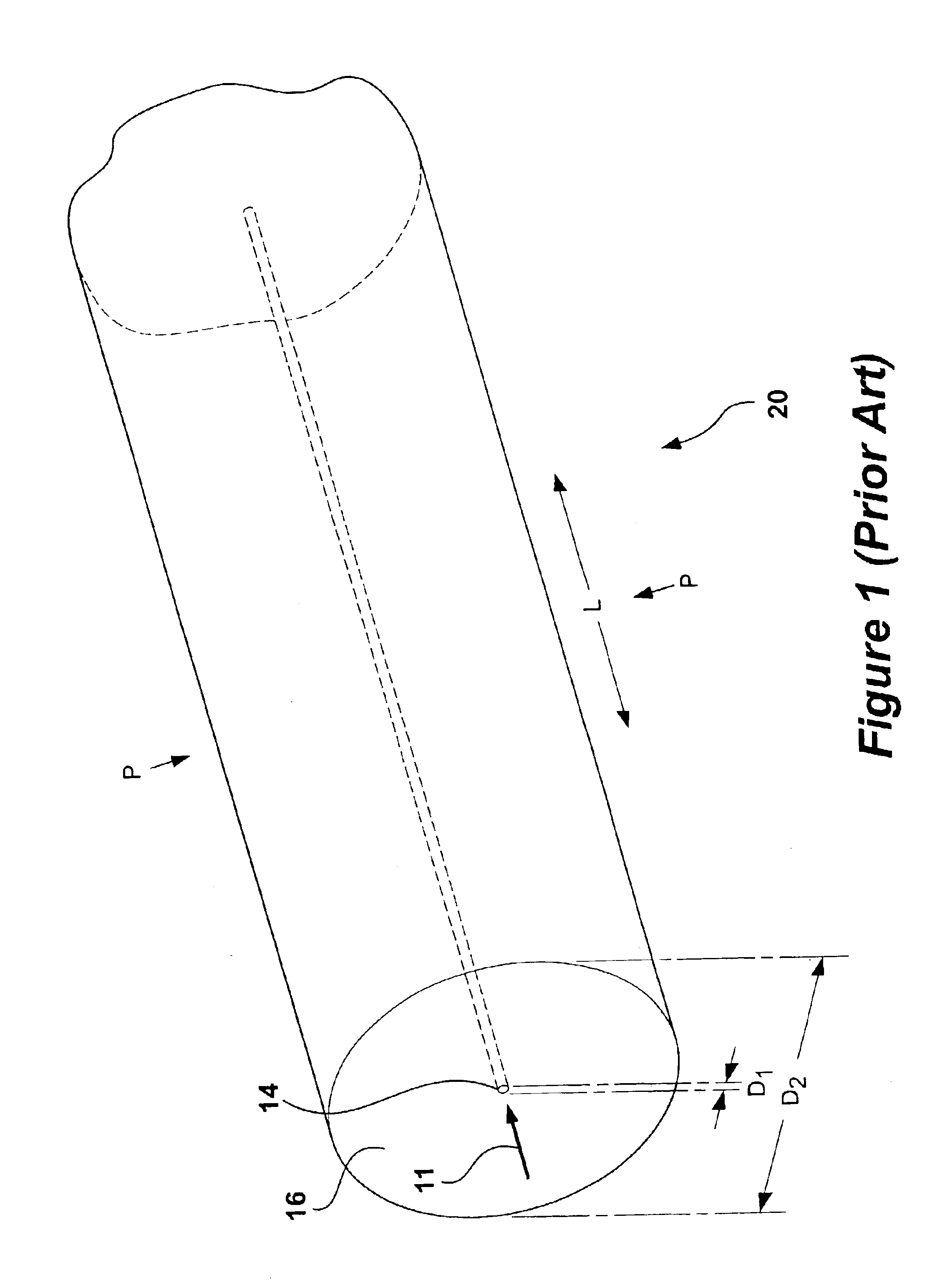
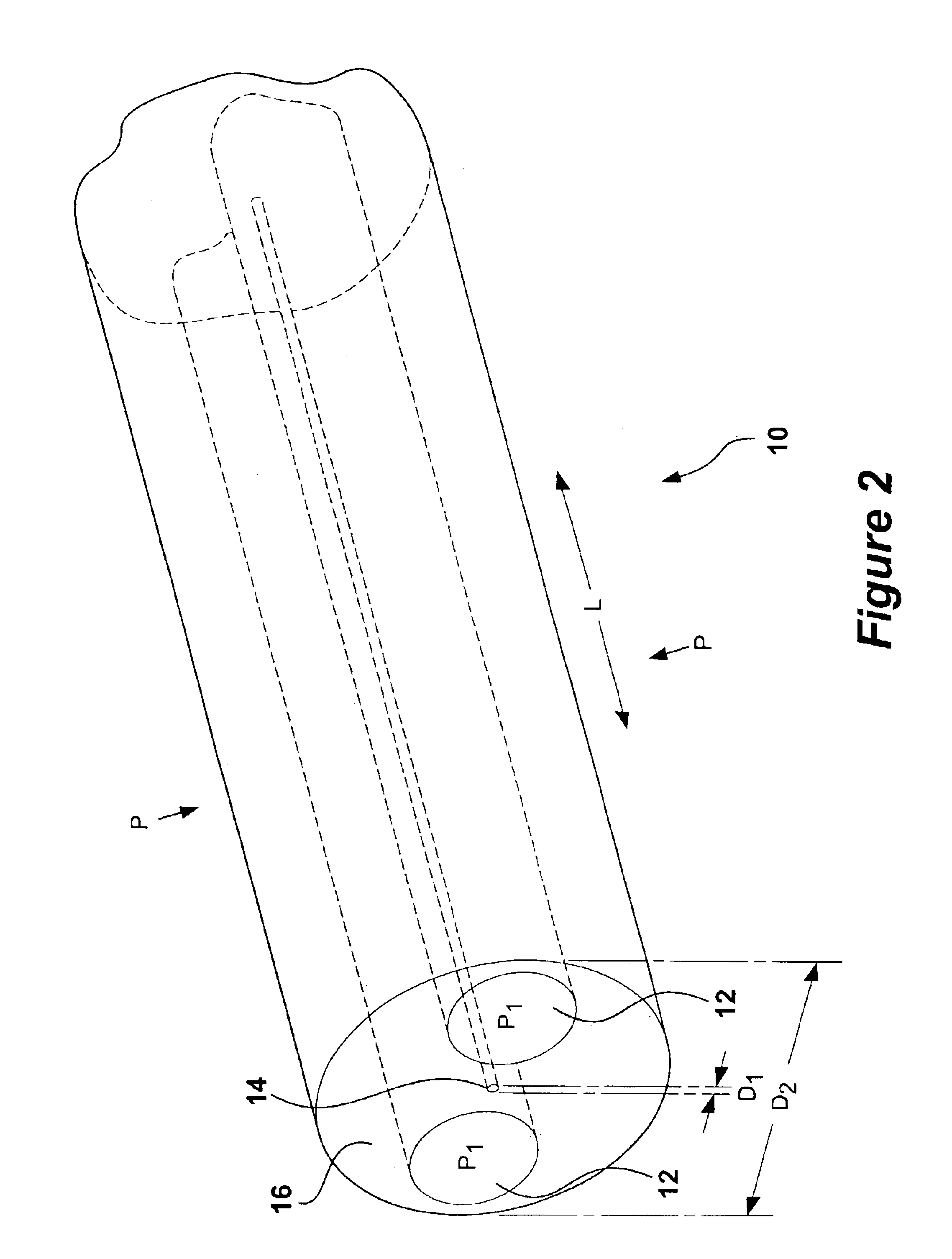
Multicore optical fibre
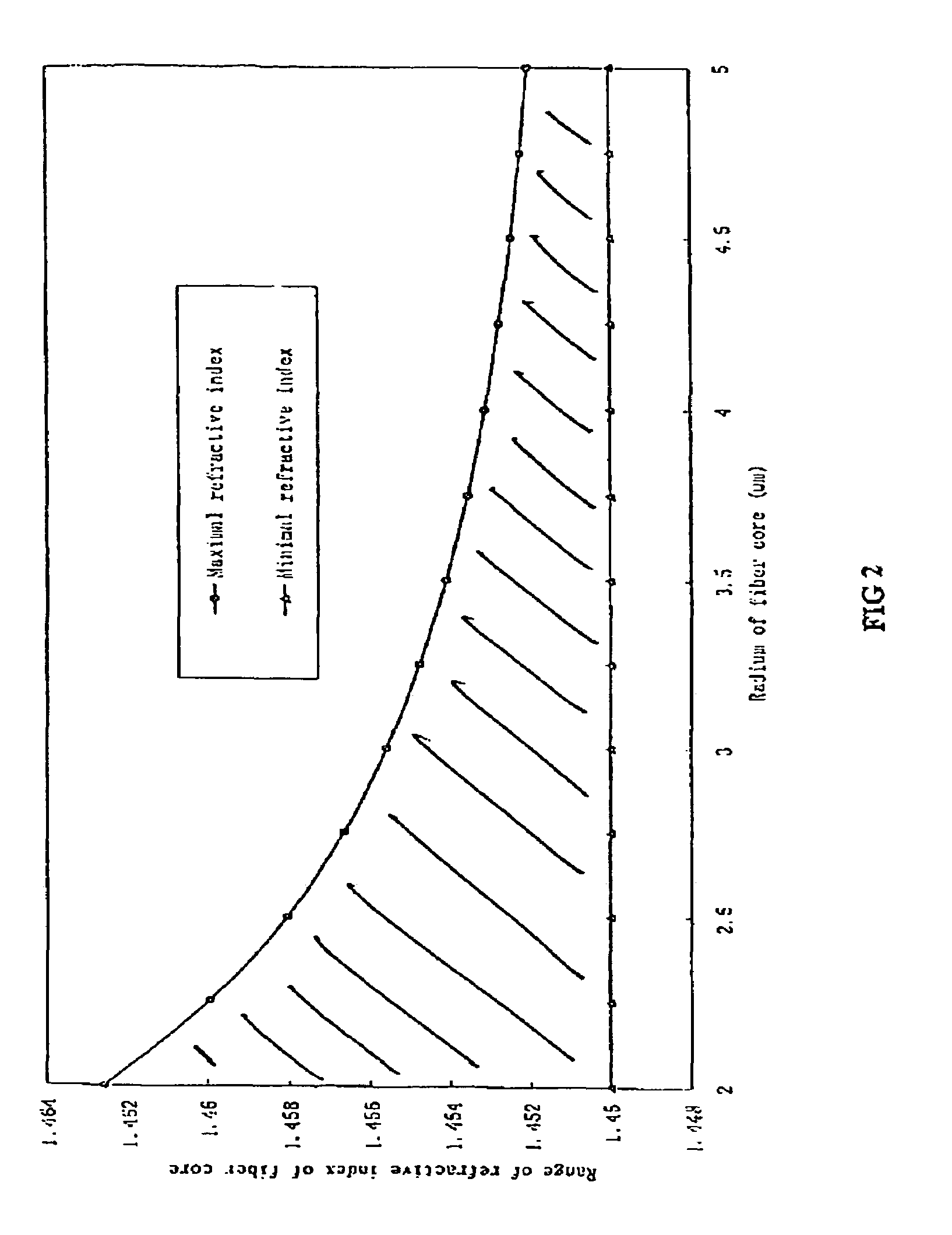
InactiveUS6301420B1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRefractive index
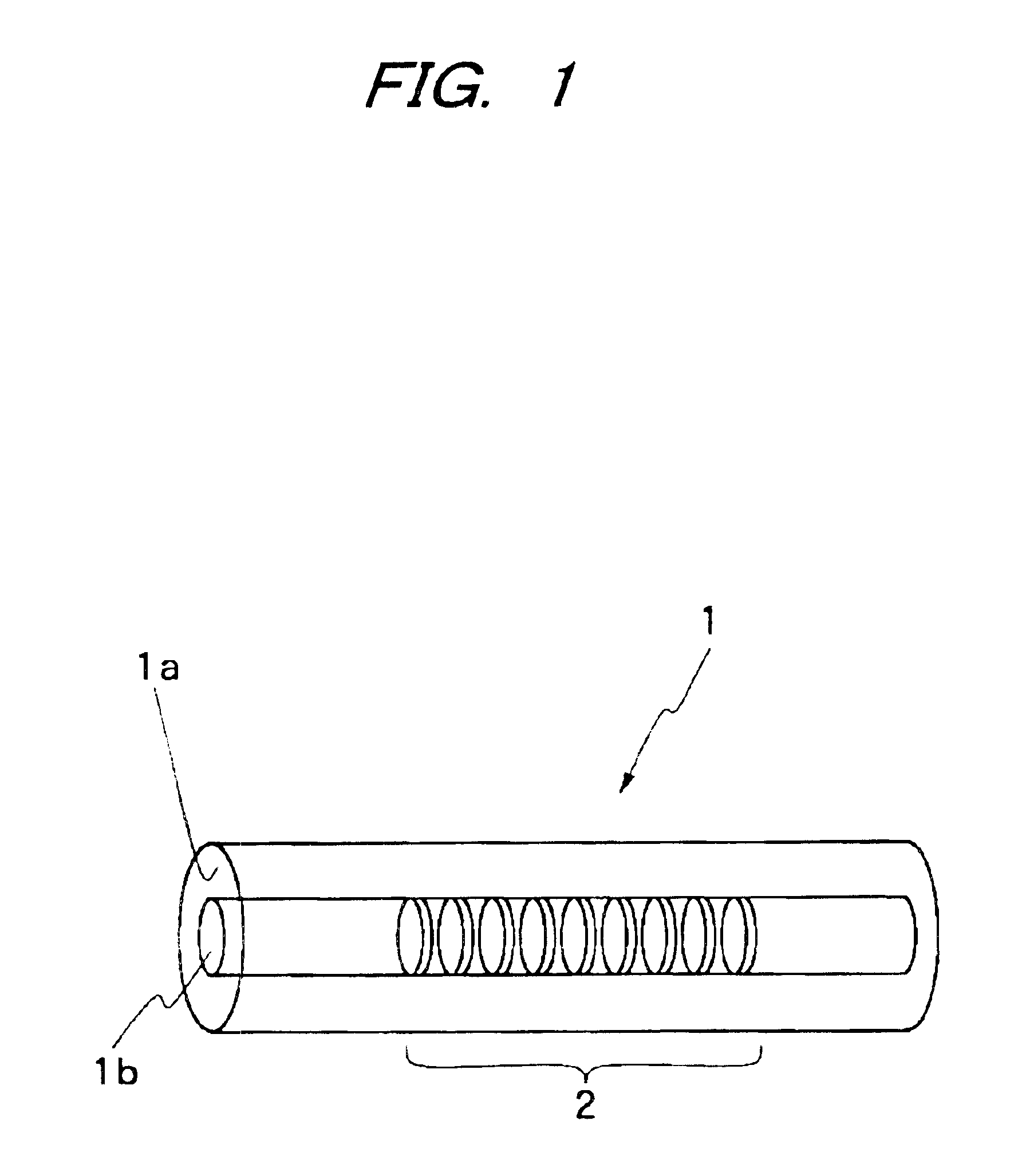
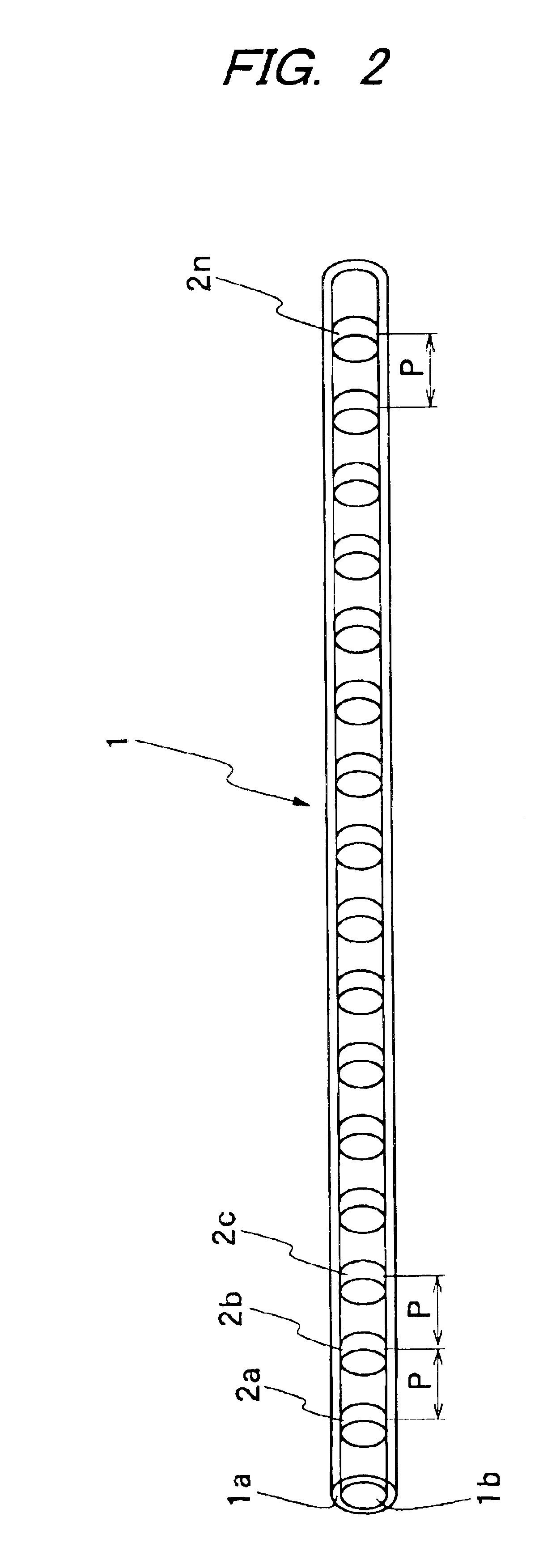
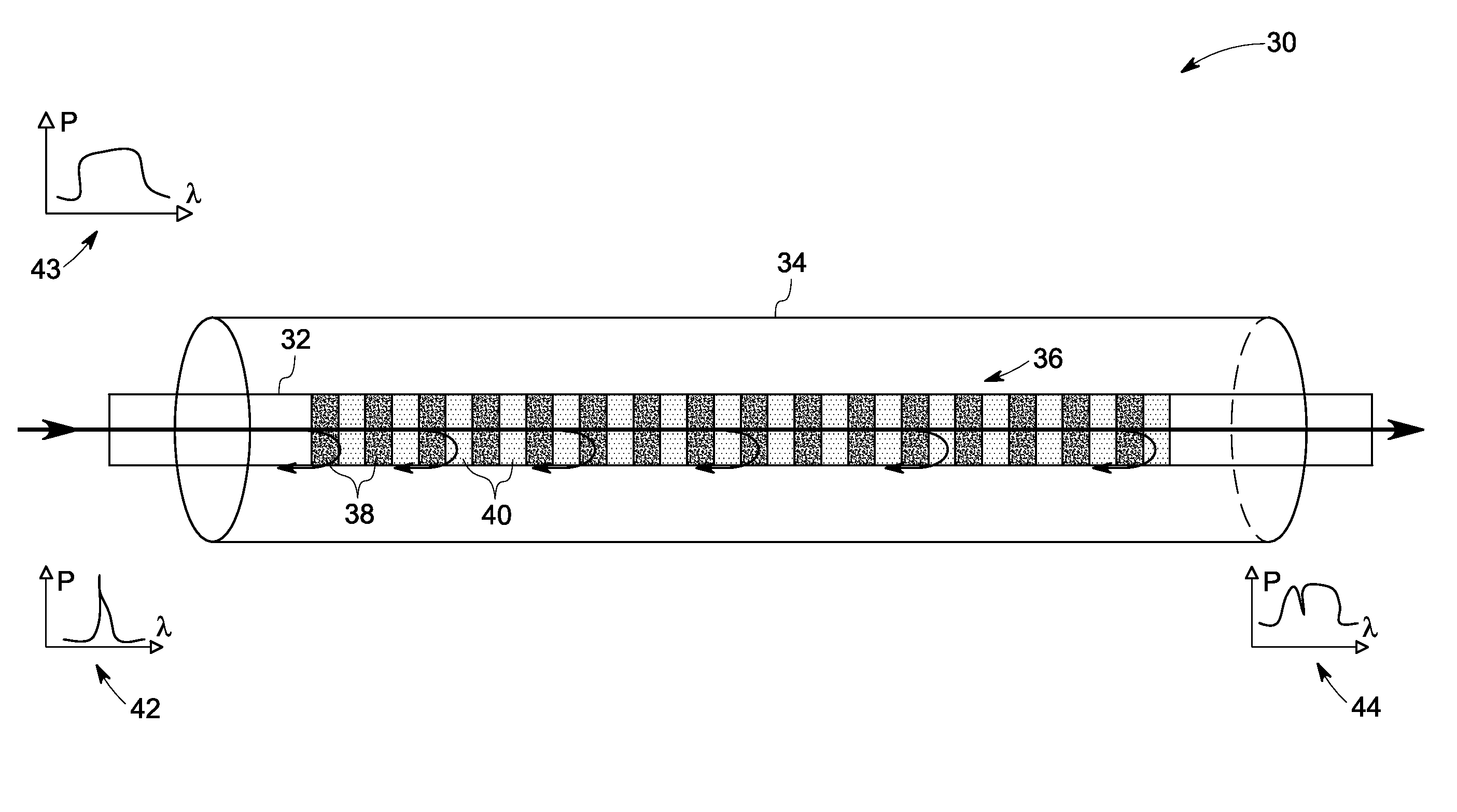
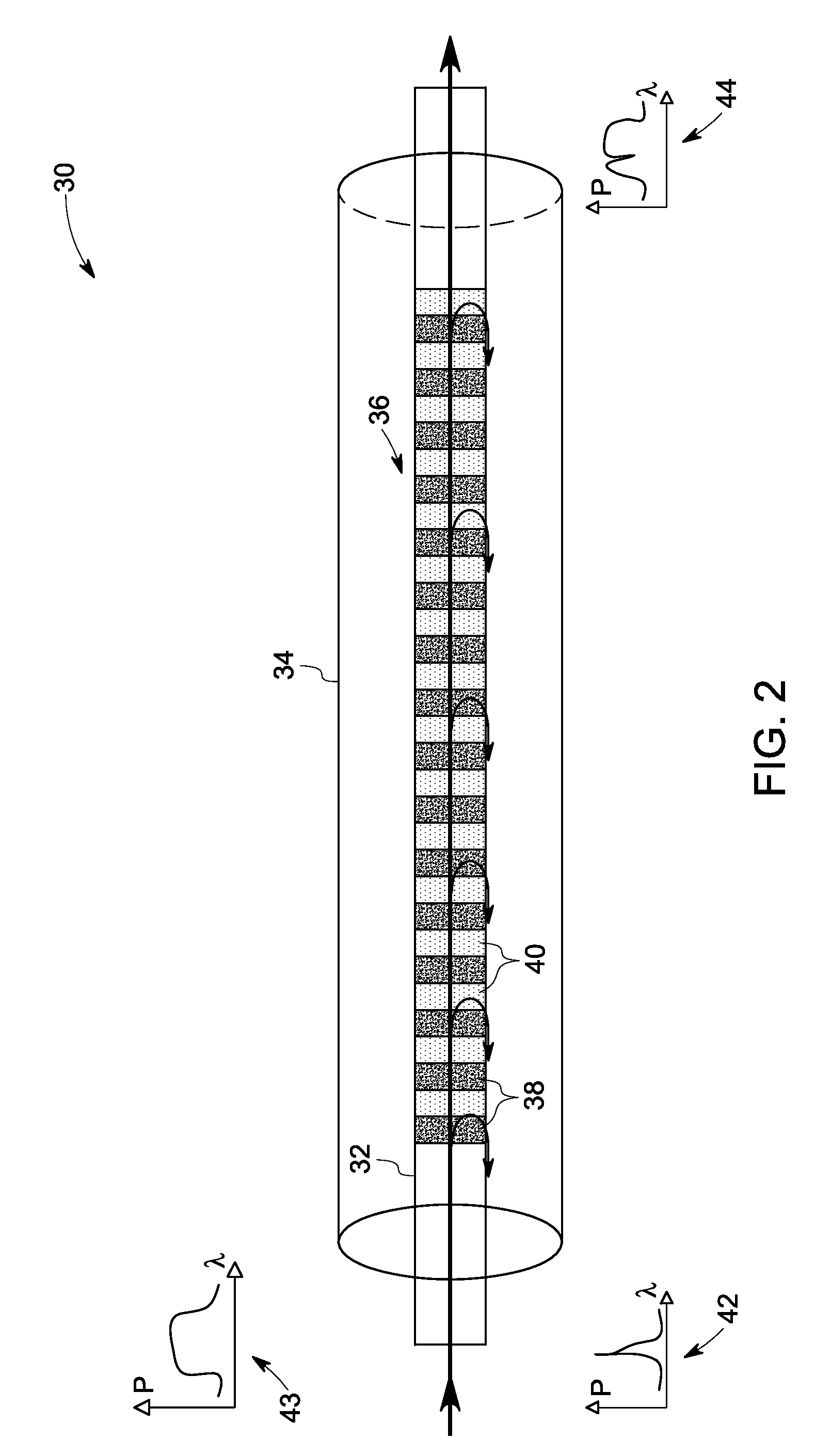
An optical fiber for transmitting radiation comprising two or more core regions, two or more core regions, each core region comprising a substantially transparent core material and having a core refractive index, a core length, and a core diameter, wherein said core regions are arranged within a cladding region, said cladding region comprising a length of first substantially transparent cladding material, having a first refractive index, wherein said first substantially transparent cladding material has an array of lengths of a second cladding material embedded along its length, wherein the second cladding material has a second refractive index which is less than said first refractive index, such that radiation input to said fiber propagates along at least one of said core regions. The cladding region and the core regions may be arranged such that radiation input to said optical fiber propagates along one or more said lengths of said core regions in a single mode of propagation. The optical fiber may be used as a bend sensor, a spectral filter or a directional coupler. The invention also relates to a method of manufacturing a multicore optical fiber.
Owner:NKT RES & INNOVATION
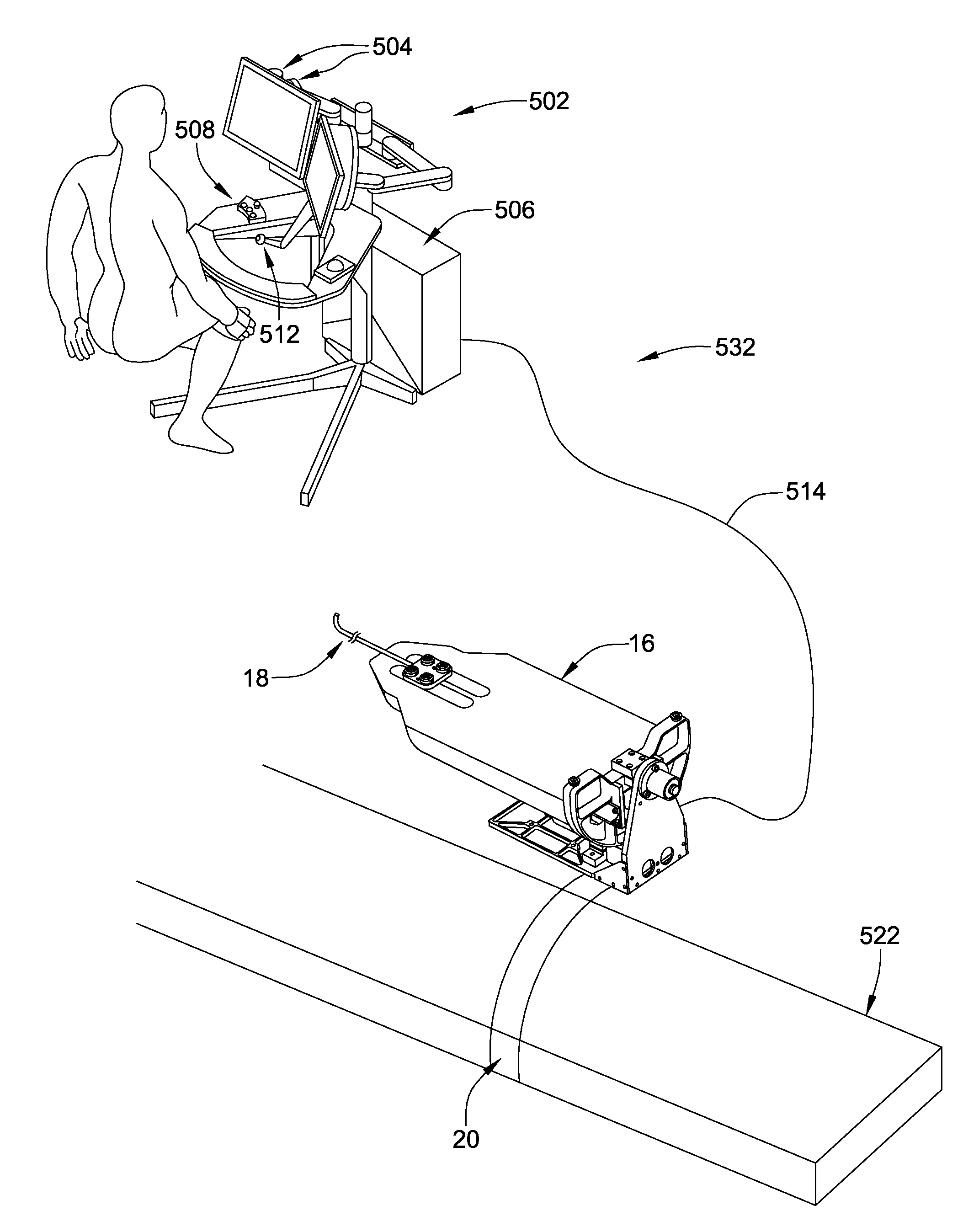
Fiber optic instrument sensing system
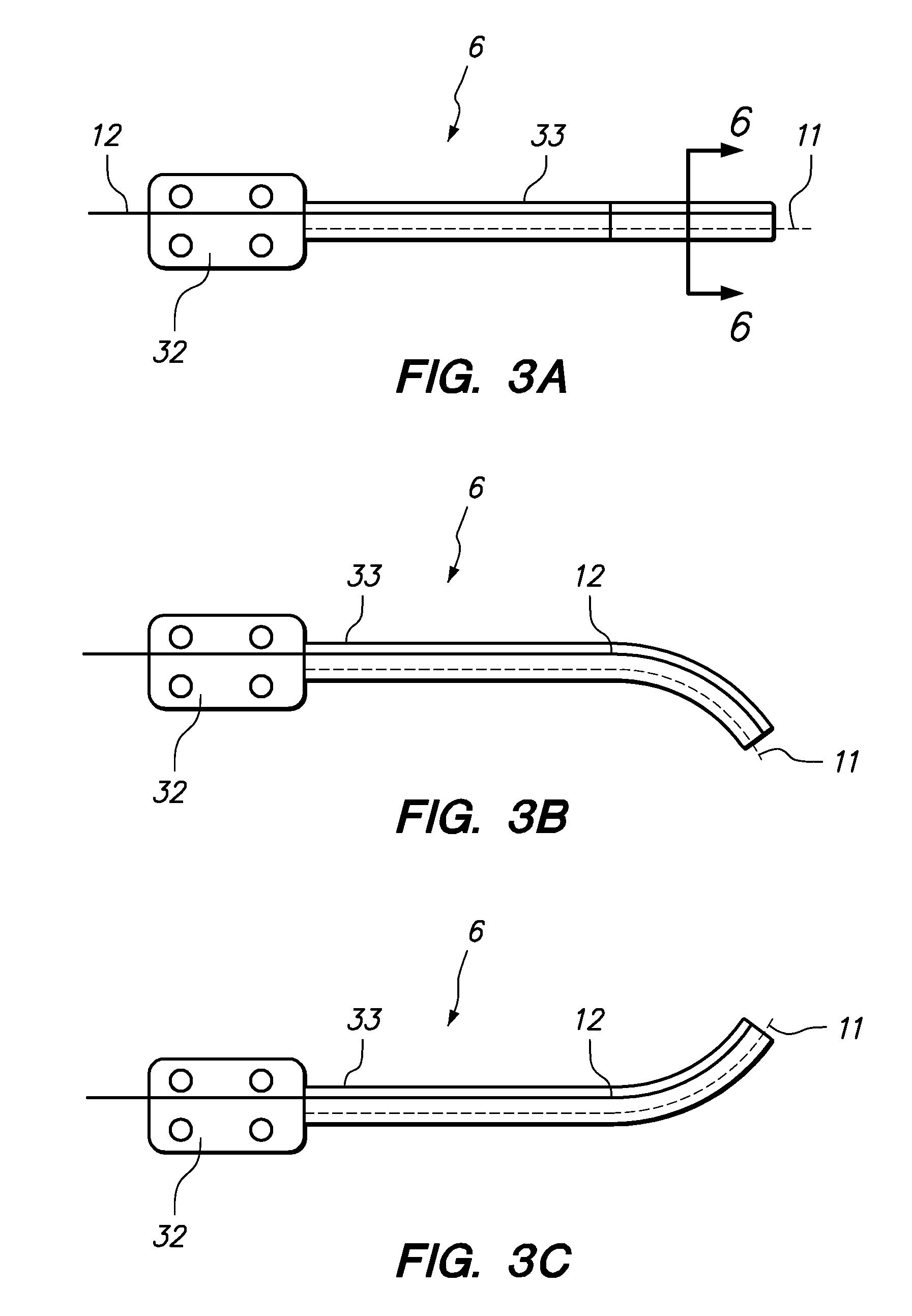
A medical instrument system comprises an elongate instrument body; an optical fiber coupled in a constrained manner to the elongate instrument body, the optical fiber including one or more Bragg gratings; a detector operably coupled to a proximal end of the optical fiber and configured to detect respective light signals reflected by the one or more Bragg gratings; and a controller operatively coupled to the detector, wherein the controller is configured to determine a geometric configuration of at least a portion of the elongate instrument body based on a spectral analysis of the detected reflected portions of the light signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Device for detecting three-dimensional shapes of elongated flexible body
InactiveUS6868195B2Simple and compact structureEndoscopesMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberRefractive index
For detecting three-dimensional shapes of an elongated flexible body, a sensor cable to be placed in a passage or channel which is formed axially and coextensively within the elongated flexible body. The sensor cable has two pairs of fiber Bragg grating strands within a tubular carrier casing. A signal light beam containing Bragg wavelength bands is projected from a light source to input same to refractive index change portions in the fiber Bragg grating strands. Reflection diffraction light signals from the refractive index change portions are received by a signal processor to measure the degree of strain at each one of the respective refractive index change portions by comparing wavelengths of the reflection diffraction light signals with reference wavelength.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Device for detecting three-dimensional shapes of elongated flexible body
For detecting three-dimensional shapes of an elongated flexible body, a sensor cable to be placed in a passage or channel which is formed axially and coextensively within the elongated flexible body. The sensor cable has two pairs of fiber Bragg grating strands within a tubular carrier casing. A signal light beam containing Bragg wavelength bands is projected from a light source to input same to refractive index change portions in the fiber Bragg grating strands. Reflection diffraction light signals from the refractive index change portions are received by a signal processor to measure the degree of strain at each one of the respective refractive index change portions by comparing wavelengths of the reflection diffraction light signals with reference wavelength.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
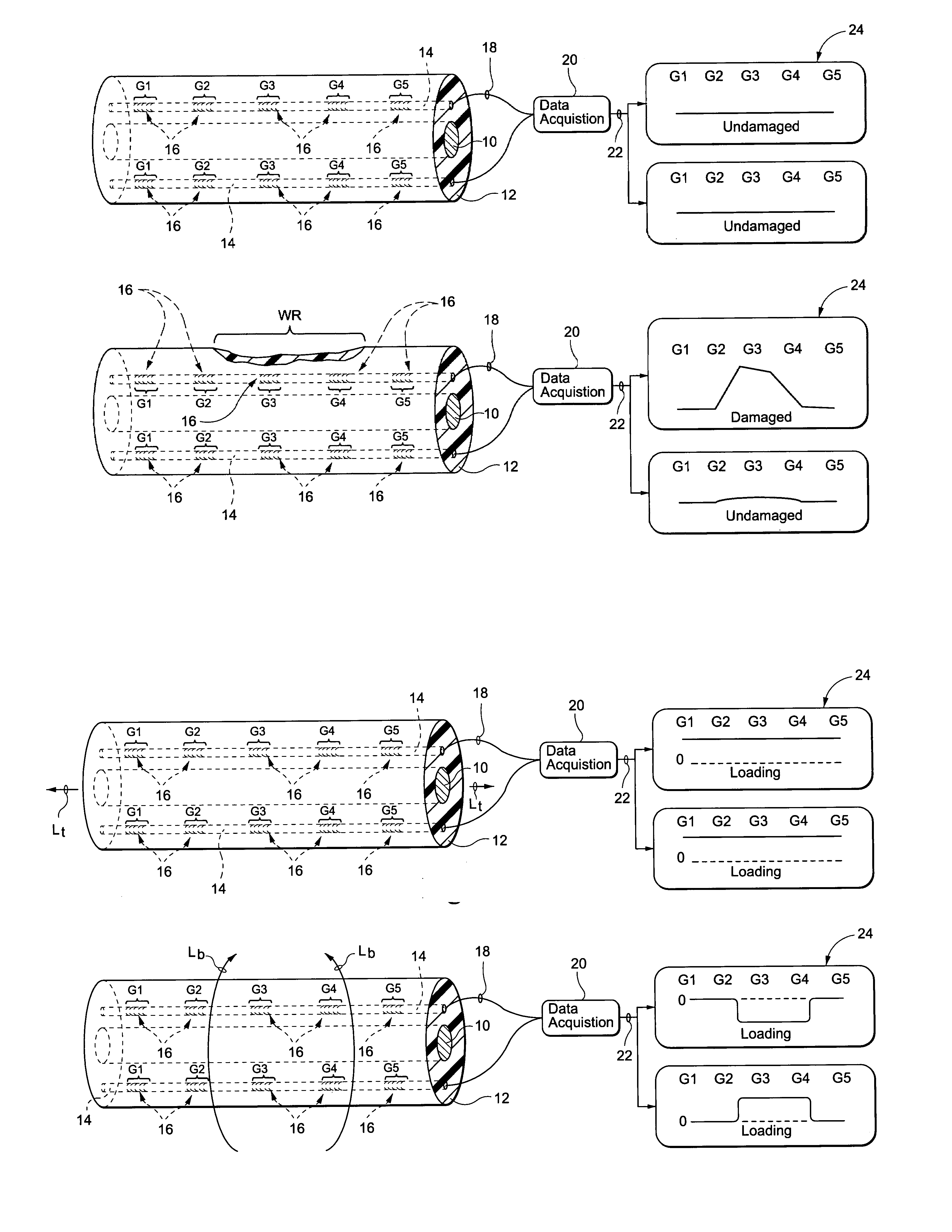
Composite structures, such as coated wiring assemblies, having integral fiber optic-based condition detectors and systems which employ the same
InactiveUS7154081B1Weakening rangeReducing compressive strainControlRadiation pyrometryElectrical conductorGrating
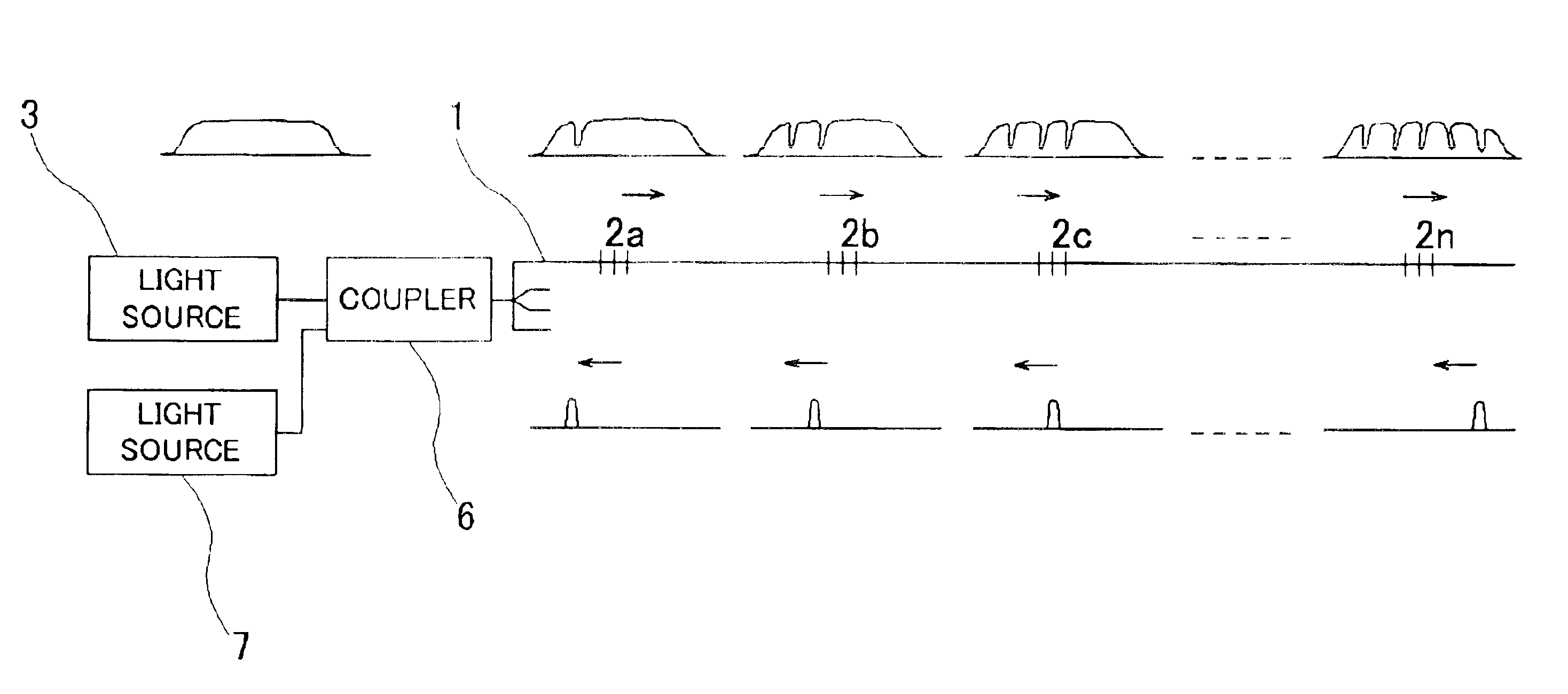
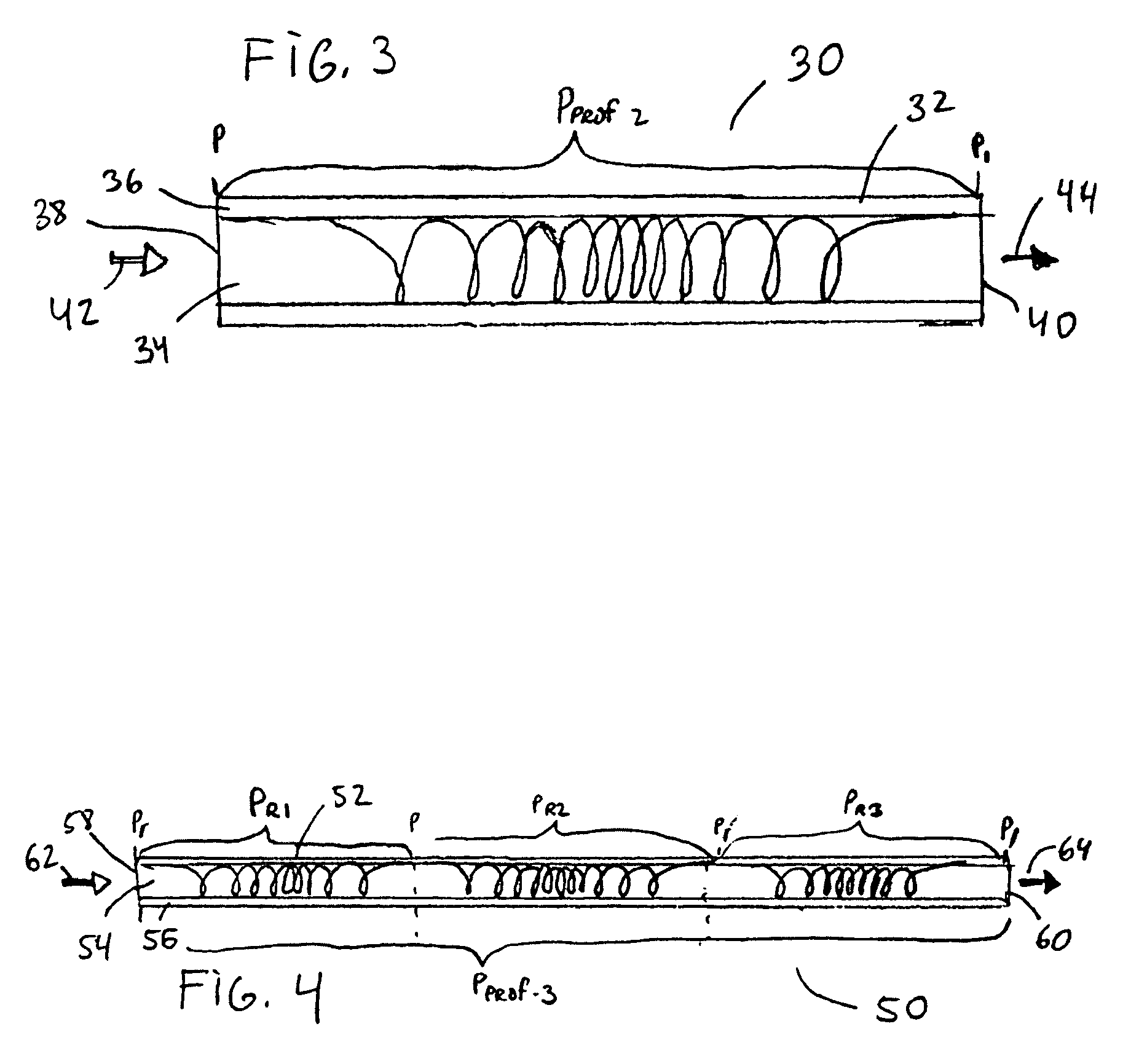
Integral fiber optic-based condition sensors detect conditions of a composite structure, e.g., a coated wire assembly so as to detect damage or conditions that may damage the same. Preferably, at least one optical fiber sensor having a plurality of Bragg gratings written into the fiber at spaced-apart locations along its axial length is integrated into the electrical insulator coating of a wire, wire bundle or wiring harness. The fiber optic sensor may thus be employed to measure the environmental loads on the electrical wiring including stresses from bending, axial loading, pinch points, high temperature excursions and chemical damage. The system is capable of detecting and locating transient conditions that might cause damage to a wiring system or permanent changes in state associated with damage events. The residual stress in the electrical insulator coating of a wire, wire bundle, or wiring harness are used to monitor the evolution of damage by wear or chaffing processes. Detected stress relief on one or more Bragg gratings will thus be indicative of damage to the insulator coating on the conductor. As such, the magnitude of such stress relief may be detected and used as an alert that the wire insulation is damaged to an unsafe extent.
Owner:LUNA INNOVATIONS
Fiber optic instrument sensing system
A medical instrument system comprises an elongate instrument body; an optical fiber coupled in a constrained manner to the elongate instrument body, the optical fiber including one or more Bragg gratings; a detector operably coupled to a proximal end of the optical fiber and configured to detect respective light signals reflected by the one or more Bragg gratings; and a controller operatively coupled to the detector, wherein the controller is configured to determine a geometric configuration of at least a portion of the elongate instrument body based on a spectral analysis of the detected reflected portions of the light signals.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Multimode long period fiber Bragg grating machined by ultrafast laser direct writing
InactiveUS20060093012A1Laser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingFiber Bragg grating
A multimode long period fiber Bragg grating (LPFBG) for a predetermined wavelength band. The LPFBG formed of a non-photosensitive material having an initial index of refraction. The multimode optical fiber core includes a substantially cylindrical surface, a longitudinal core axis, a core radius, and a number of index-altered portions having an altered index of refraction different from the initial cladding index of refraction. Each of the index-altered multimode optical fiber core has a first transmission surface and second transmission surface that is substantially parallel to the first transmission surface. Also, these index-altered portions are arranged within the non-photosensitive material of the multimode optical fiber core such that the first transmission surface of one portion of the plurality of index-altered portions is substantially parallel to the second transmission surface of a neighboring portion to form a long period Bragg grating structure.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
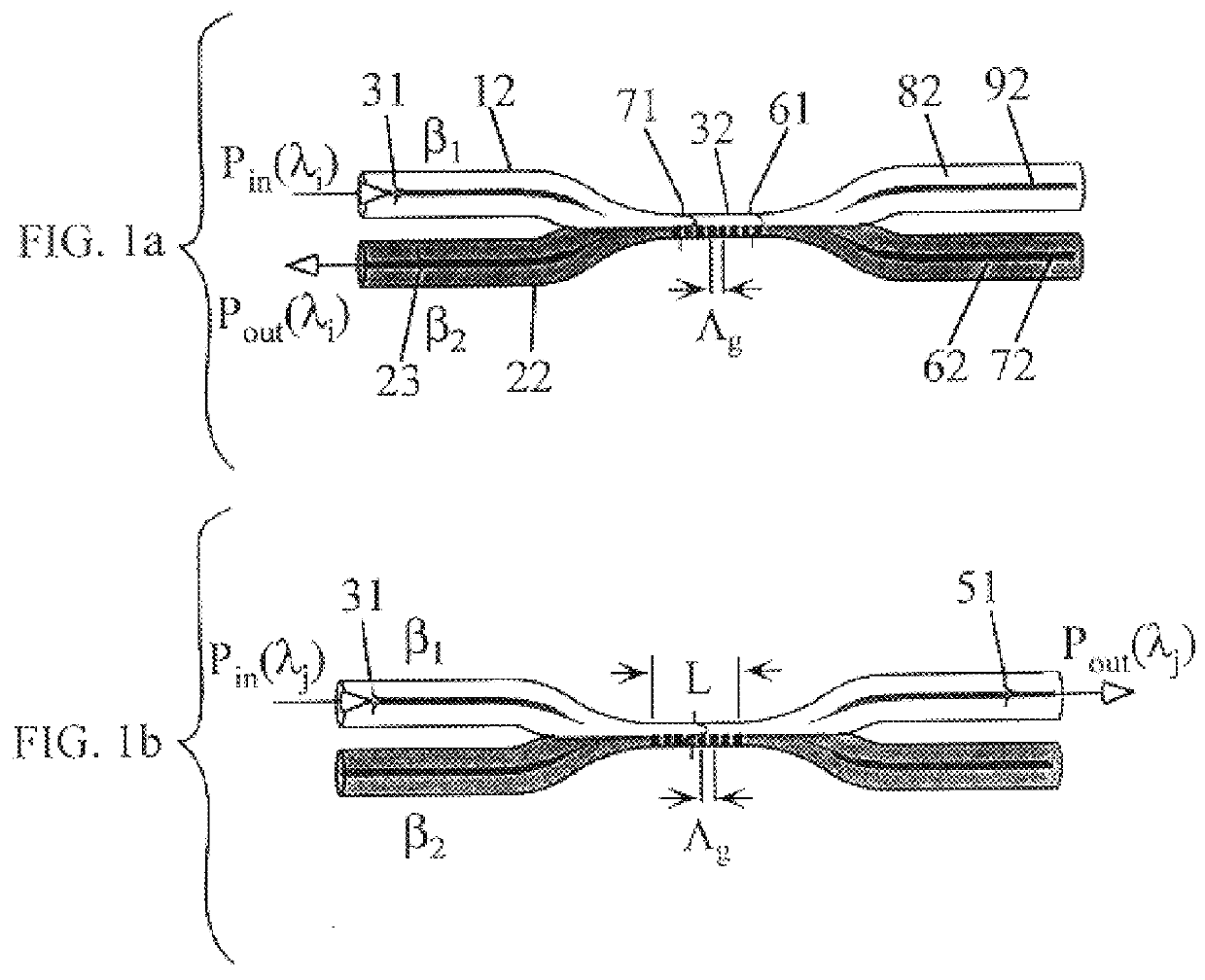
Wavelength selective optical routers
InactiveUS6201909B1Wide wavelength band to be manipulatedLow insertion lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesBandpass filteringFiber
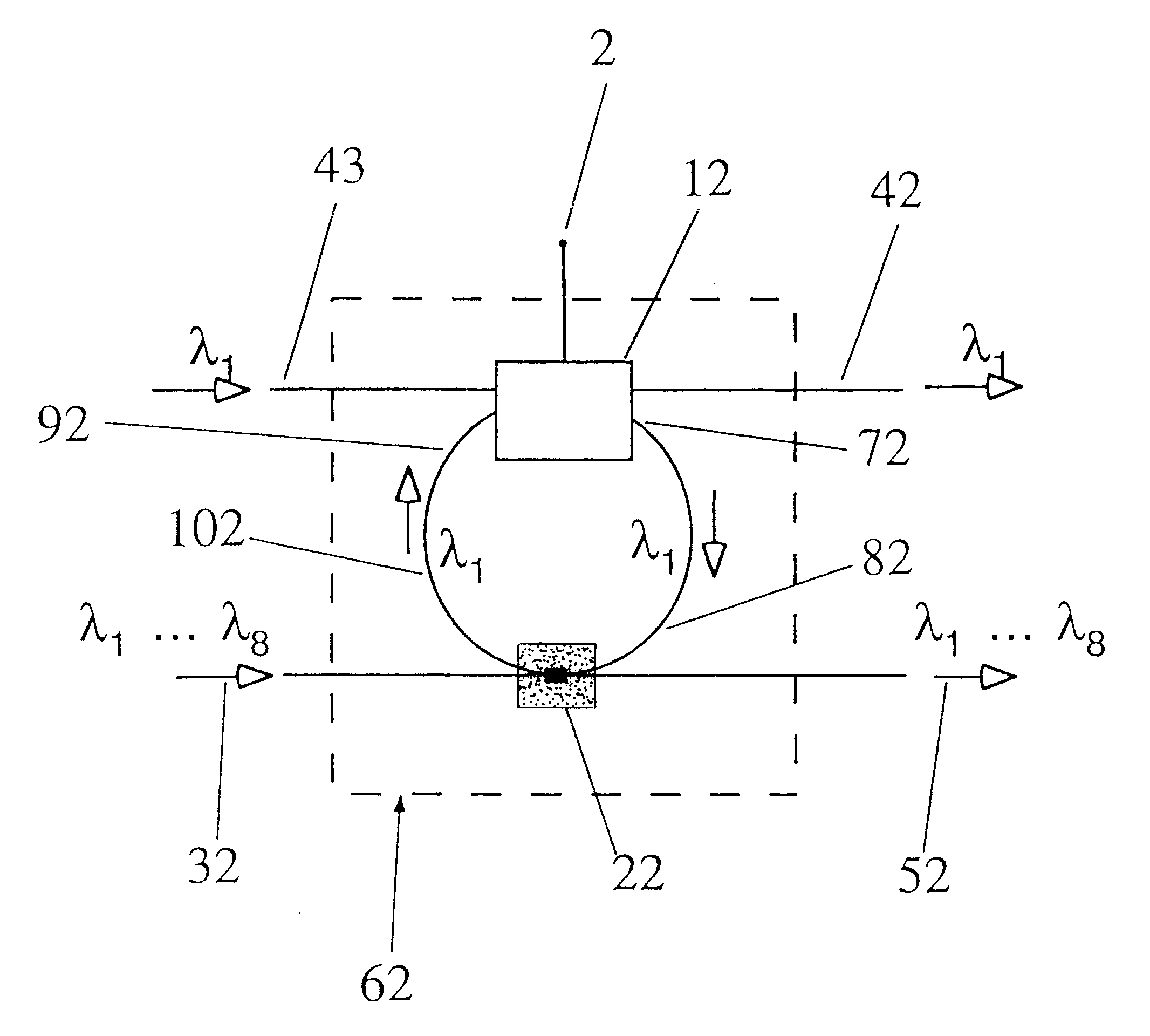
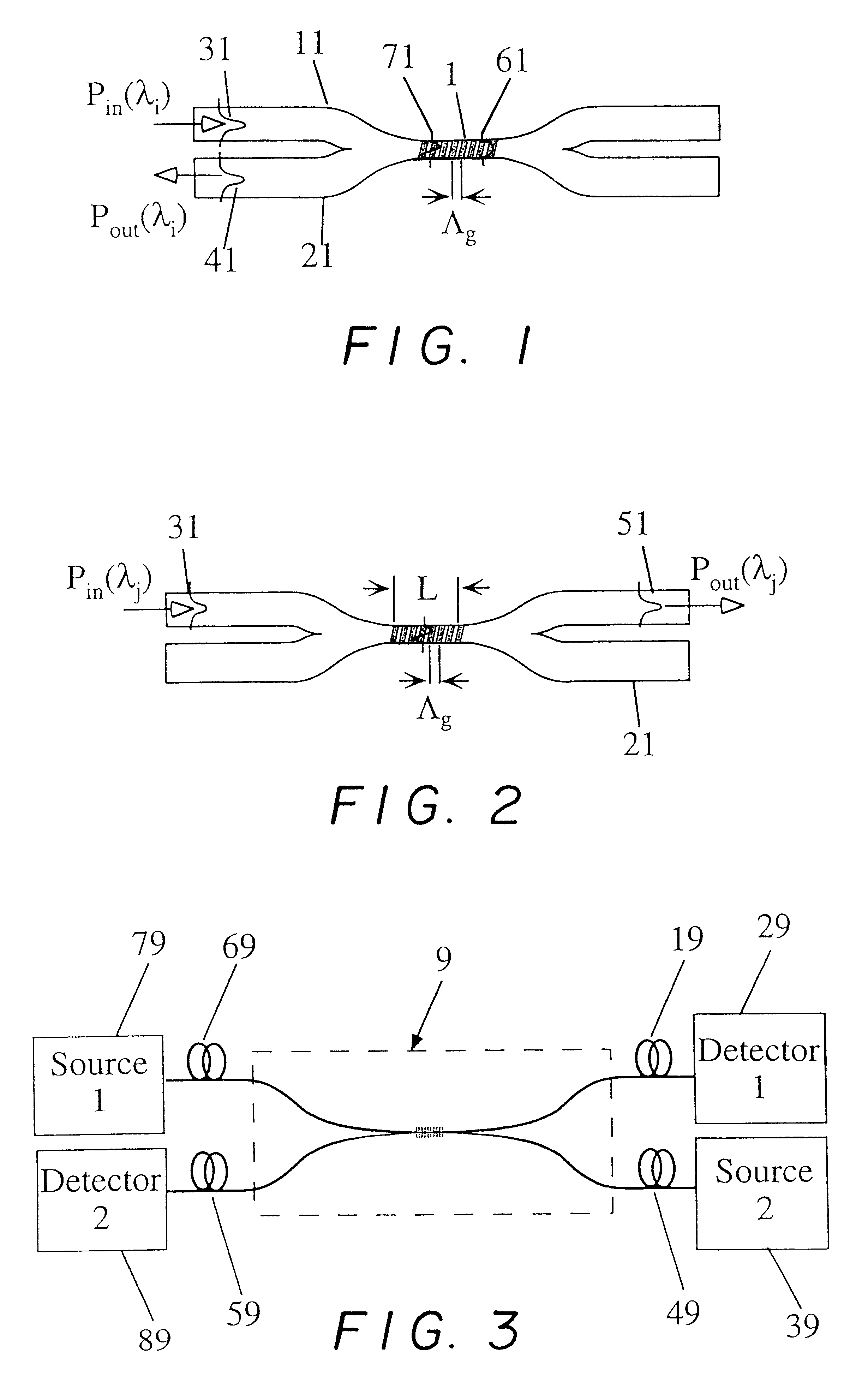
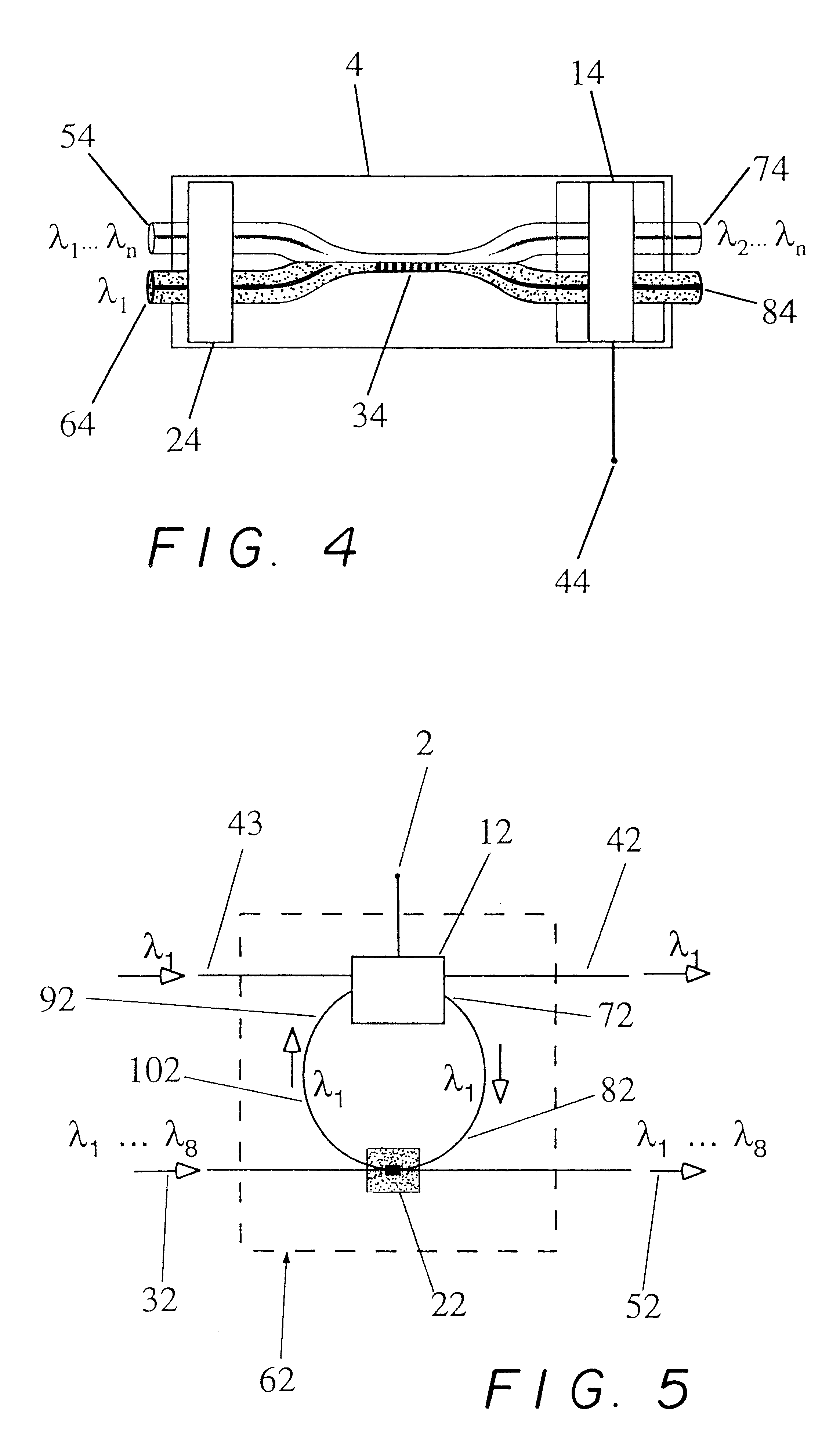
Using the wavelength selectivity and low loss characteristics of optical couplers, in which index of refraction gratings in a non-evanescent waveguide merged region reflect only a selected wavelength band, signal switching and control systems of novel characteristics are provided for multi-wavelength optical communication systems. In a router, for example, selected wavelengths or wavelength bands on an add / drop line can be added to or dropped from a main fiber, by cross switching between wavelength selective loops disposed sequentially in the lines. In a collector box, as another example, selected wavelength bundles can be routed from one fiber onto multiple fibers. In a bandpass filter a selected wavelength band is transmitted with low loss while those wavelengths outside the selected wavelength band are rejected with very high loss.
Owner:ARROYO OPTICS
Multicore optical fiber with integral diffractive elements machined by ultrafast laser direct writing
InactiveUS20060215976A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexMulticore fiber
A multicore optical fiber with an integral diffractive element. The multicore optical fiber includes: a first optical fiber core formed of a non-photosensitive material having an initial index of refraction; and a second optical fiber core including a second longitudinal core axis substantially parallel to the first longitudinal axis. The first optical fiber core includes: a first longitudinal core axis; and a number of index-altered portions having an altered index of refraction which is different from the initial index of refraction. The index-altered portions are arranged within the non-photosensitive material of the first optical fiber core to form a diffractive structure of the integral diffractive element.
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
Wavelength selective optical couplers
InactiveUS6289699B1Eliminate undesired leakageEasy to separateGlass making apparatusMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGratingOptical communication
A wavelength selective optical fiber coupler having various applications in the field of optical communications is disclosed. The coupler is composed of dissimilar waveguides in close proximity. A light induced, permanent index of refraction grating is recorded in the coupler waist The grating filters and transfers energy within a particular range of wavelengths from a first waveguide to a second waveguide. Transversely asymmetric gratings provide an efficient means of energy transfer. The coupler can be used to combine or multiplex a plurality of lasers operating at slightly different wavelengths into a single fiber. Other embodiments such as a dispersion compensator and gain flattening filter are disclosed.
Owner:ARROYO OPTICS
Fiber optic tracking system and method for tracking
ActiveUS20090314925A1Photometry using reference valueInstruments for comonautical navigationFiberEngineering
A fiber optic tracking system for tracking substantially rigid object(s) is described. The fiber optic tracking system includes a light source, an optical fiber having a sensing component configured to modify optical signals from the light source, the optical fiber being configured to attach to the substantially rigid object, a detection unit arranged to receive the modified optical signals from the sensing component, and a calculation unit configured to determine a pose of the substantially rigid object in six degrees of freedom based on the modified optical signals.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Fiber optic sensor for detecting multiple parameters in a harsh environment
A fiber optic sensor is provided. The fiber optic sensor includes a fiber core having a plurality of Bragg grating elements wherein, the grating elements comprise a periodic or a quasiperiodic modulated microcrystalline and rigid silicon dioxide tetrahedral structure and a cladding disposed about the fiber core.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Bragg grating and method of producing a Bragg grating using an ultrafast laser
A novel Bragg grating filter in optical waveguiding fiber with suppressed cladding mode coupling and method of producing same is disclosed. The novel grating structure is induced in both the core and the cladding of the optical fiber irrespective of the photosensitivity of the core or cladding to actinic radiation. Such core and cladding of the optical fiber need not be chemically doped to support the grating. The method incorporates an ultra short duration pulse laser source. Electromagnetic radiation provided from the laser propagates to a diffractive element positioned a specific distance to the target material such that the diffracted electromagnetic radiation forms a 2-beam interference pattern, the peaks of which are sufficiently intense to cause a change in index of refraction.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Wavelength-selective optical fiber components using cladding-mode assisted coupling
InactiveUS6850665B2High isolation between channelsIncrease light intensityWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesFiberGrating
A wavelength-selective optical device for coupling of light at predetermined wavelength from one optical fiber waveguide to another using at least two gratings and cladding-mode assisted coupling is disclosed. The transfer of light is performed using intermediate coupling to one or more cladding mode of the waveguides. In the case when the fibers have physically different cladding's, an arrangement for transfer of light from one cladding to another is required. The disclosed coupler has no back-reflection, small insertion loss, and very high channel isolation. The device can be used in wavelength-division multiplexing networks.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD +1
Optical fiber sensor and method
InactiveUS20070297712A1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingUsing optical meansGratingNeutral plane
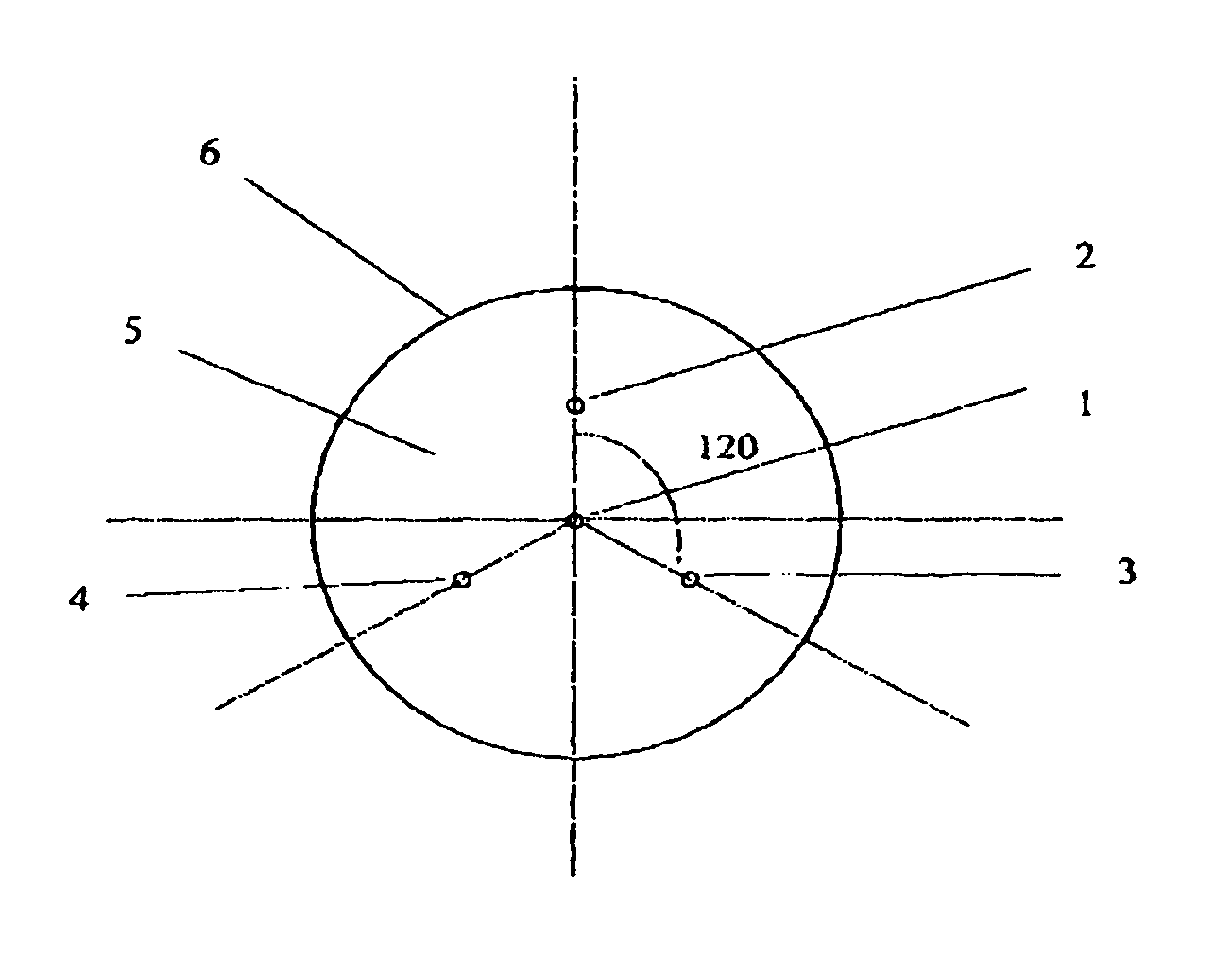
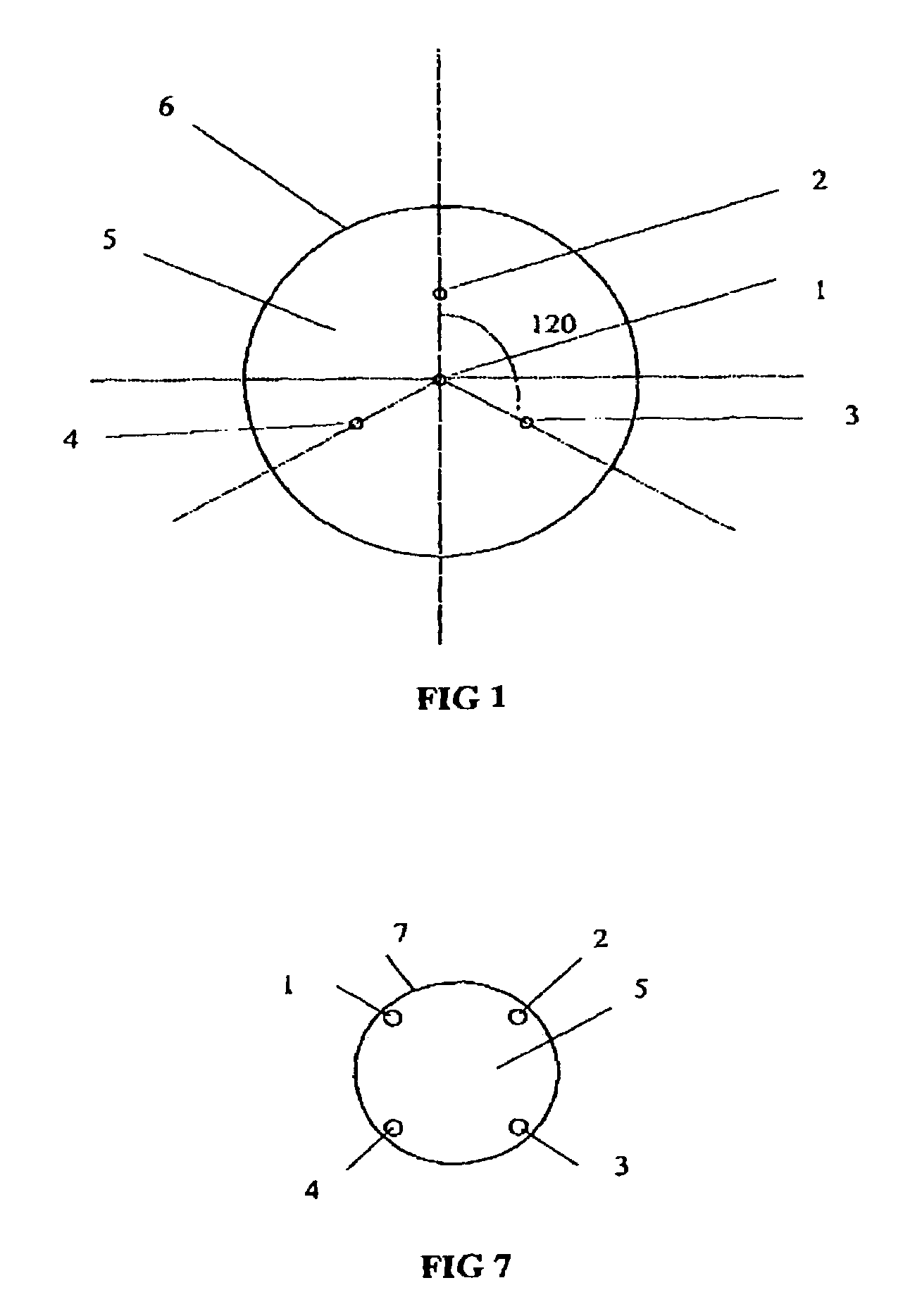
An optical fiber sensor for detecting curvature of a body / structure comprises a cladding having an outer periphery. A central core receives and transmits light. The central core has Bragg gratings and is positioned in neutral planes of the cladding. Peripheral cores receive and transmit light. The peripheral cores have Bragg gratings and are peripherally positioned in the cladding with respect to the neutral planes. A connection configuration is provided in the outer periphery of the cladding to attach the optical fiber sensor to a body / structure such that the central core and the peripheral cores are in a predetermined orientation with respect to the body / structure to measure curvature of the body / structure.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Ultra high-power continuous wave planar waveguide amplifiers and lasers
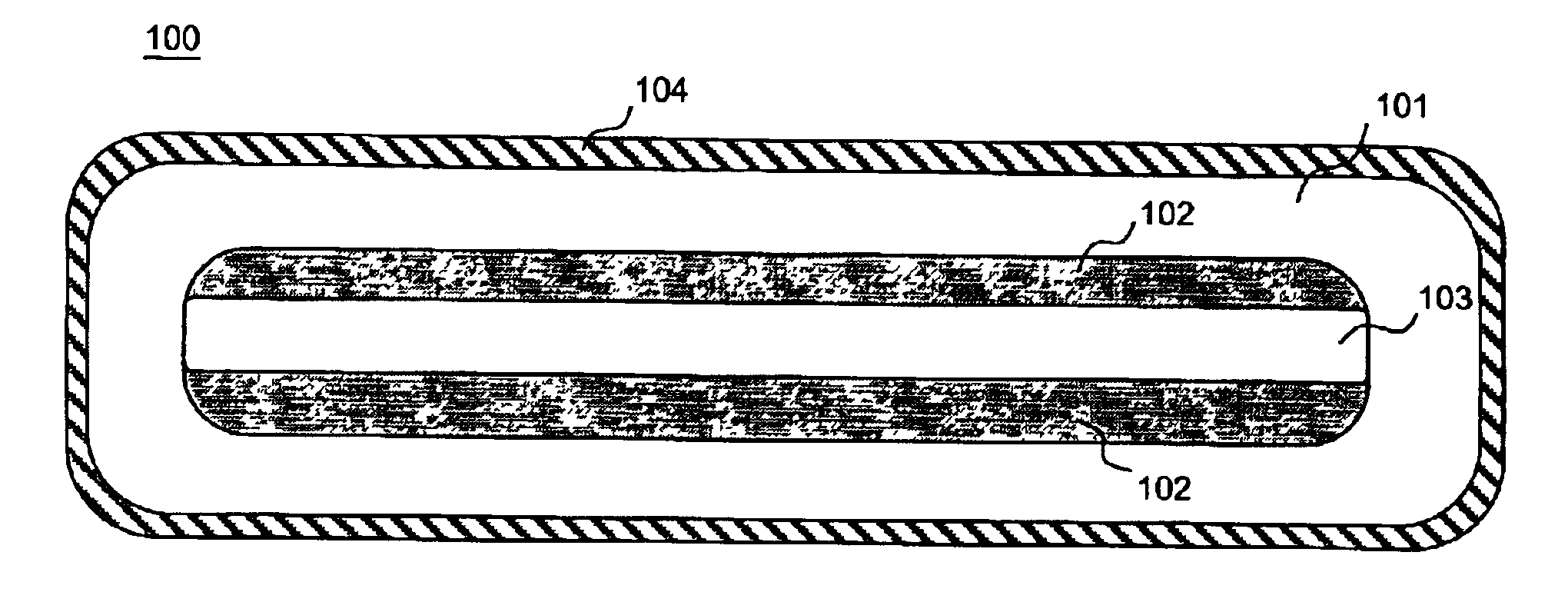
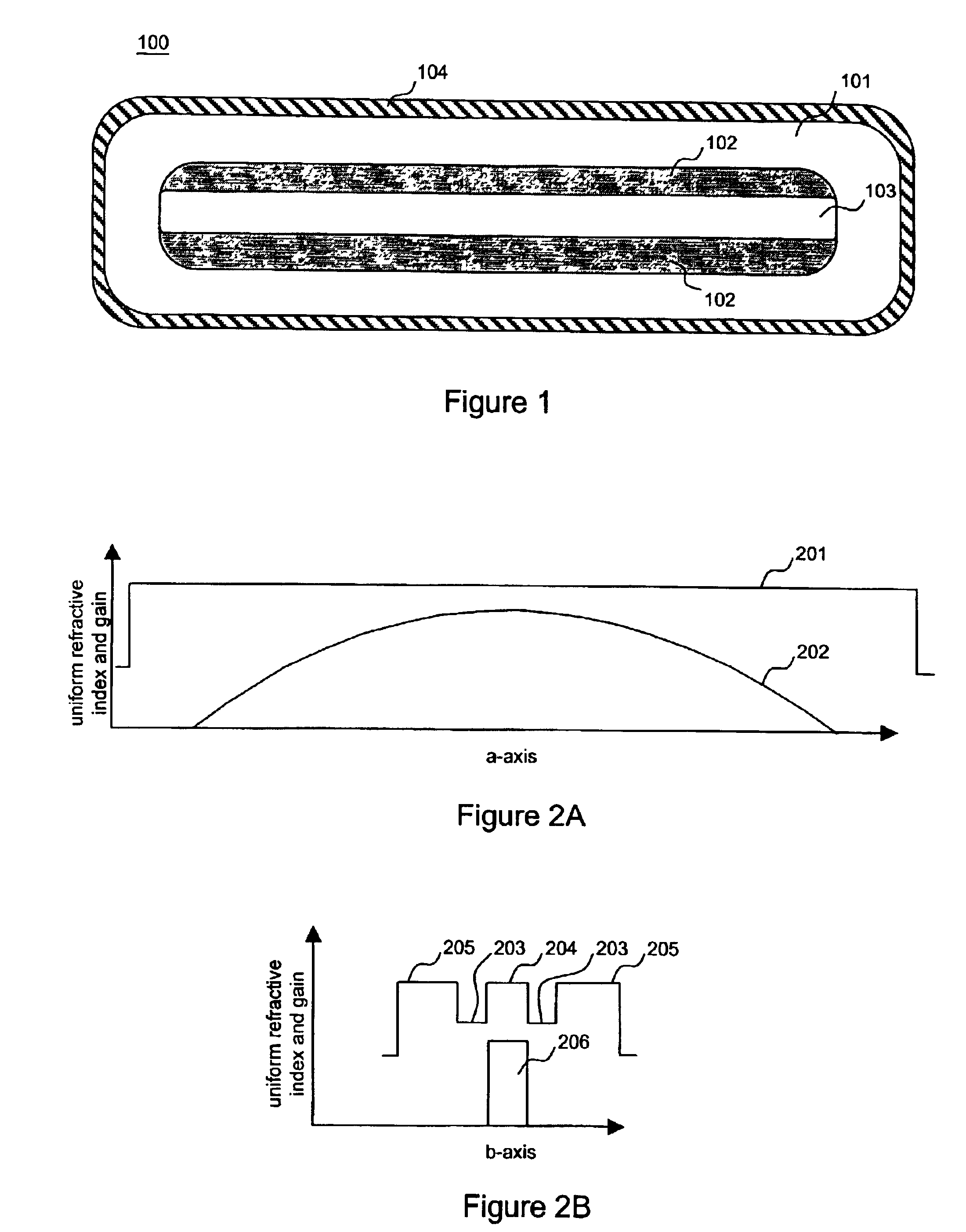
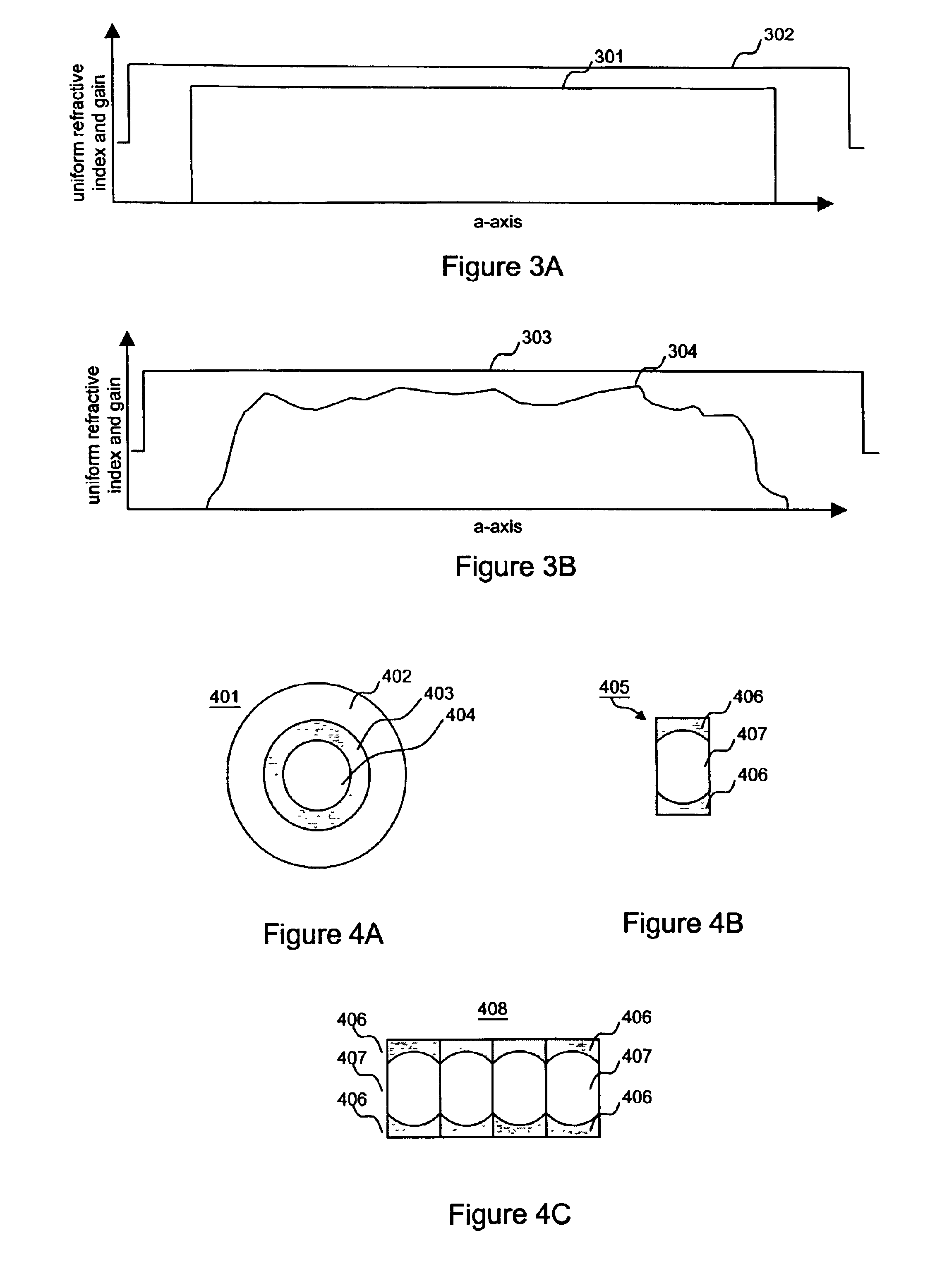
InactiveUS6904219B1Avoid bend lossesLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWaveguide amplifierHigh power diode laser
Double clad large mode area planar lasers or amplifiers comprising rare-earth or transition metal doped planar core regions are used to generate near-diffraction-limited optical beams of ultra-high power. The amplified light is guided in the core using different guiding mechanisms in two orthogonal axes inside the core. Waveguiding along a first long core axis is obtained substantially by gain-guiding or thermal lensing. Waveguiding along a second short core axis is obtained by index guiding. This is accomplished by surrounding the planar core region with regions of different refractive index. The long sides of the planar core region are surrounded with a depressed refractive index cladding region. The short sides of the planar core region are surrounded with a cladding region substantially index-matched to the core region. The whole structure is surrounded by an outer cladding region with a low refractive index to enable cladding pumping of the planar waveguide with high-power diode lasers. The rare-earth or transition metal doping level inside the planar core can be constant and can also vary substantially without negatively affecting the waveguiding properties. To avoid bend losses along the long axis of the planar waveguide, the planar core region and the planar waveguide are aligned parallel to each other and the planar waveguide is coiled with the long side of the planar waveguide mounted to a drum. The drum can also be used as a heat sink. A planar waveguide comprising a planar core region can be manufactured using conventional fiber fabrication methods.
Owner:BOSTON LASER
Multimode long period fiber bragg grating machined by ultrafast laser direct writing
A multimode long period fiber Bragg grating (LPFBG) for a predetermined wavelength band. The LPFBG formed of a non-photosensitive material having an initial index of refraction. The multimode optical fiber core includes a substantially cylindrical surface, a longitudinal core axis, a core radius, and a number of index-altered portions having an altered index of refraction different from the initial cladding index of refraction. Each of the index-altered multimode optical fiber core has a first transmission surface and second transmission surface that is substantially parallel to the first transmission surface. Also, these index-altered portions are arranged within the non-photosensitive material of the multimode optical fiber core such that the first transmission surface of one portion of the plurality of index-altered portions is substantially parallel to the second transmission surface of a neighboring portion to form a long period Bragg grating structure.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Multicore optical fiber with integral diffractive elements machined by ultrafast laser direct writing
InactiveUS7587110B2Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexPlastic optical fiber
A multicore optical fiber with an integral diffractive element. The multicore optical fiber includes: a first optical fiber core formed of a non-photosensitive material having an initial index of refraction; and a second optical fiber core including a second longitudinal core axis substantially parallel to the first longitudinal axis. The first optical fiber core includes: a first longitudinal core axis; and a number of index-altered portions having an altered index of refraction which is different from the initial index of refraction. The index-altered portions are arranged within the non-photosensitive material of the first optical fiber core to form a diffractive structure of the integral diffractive element.
Owner:PANASONIC HEALTHCARE HLDG CO LTD
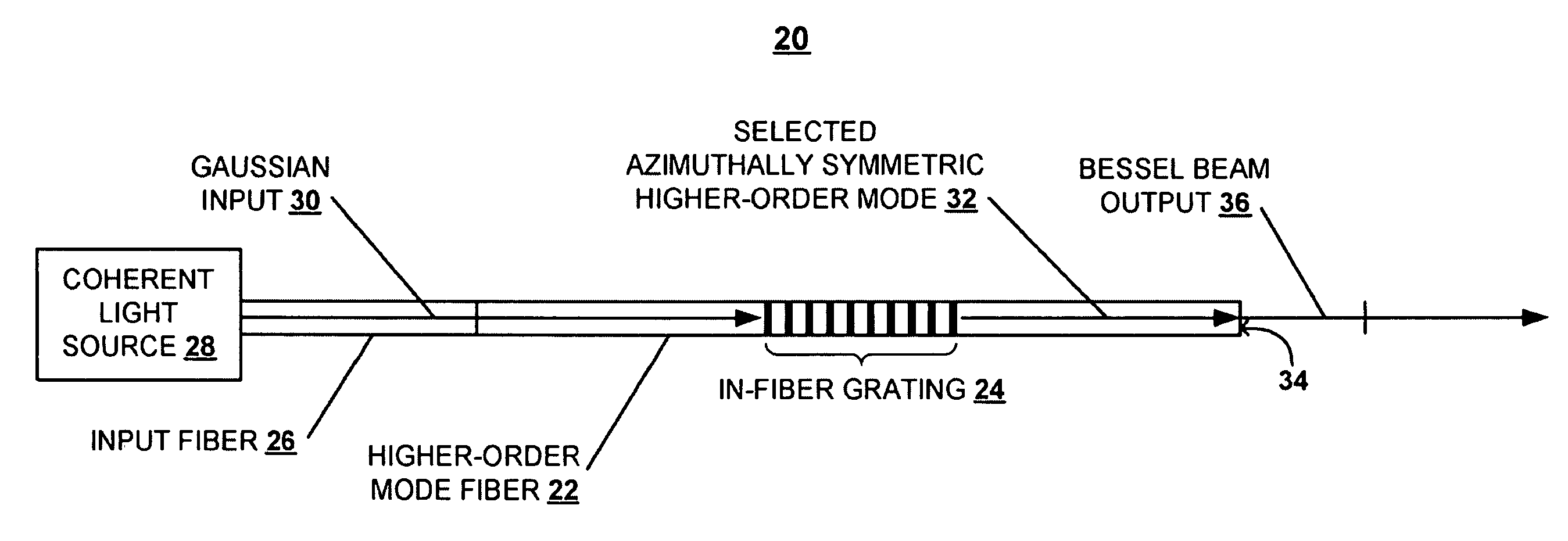
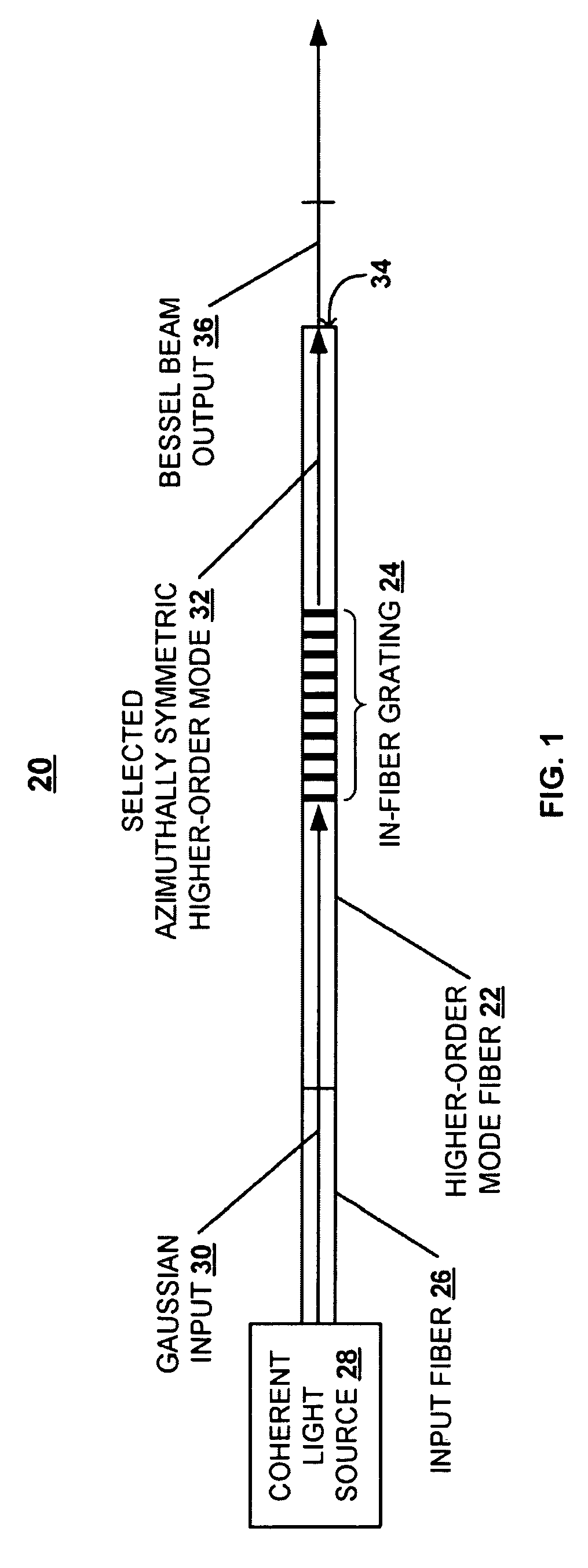
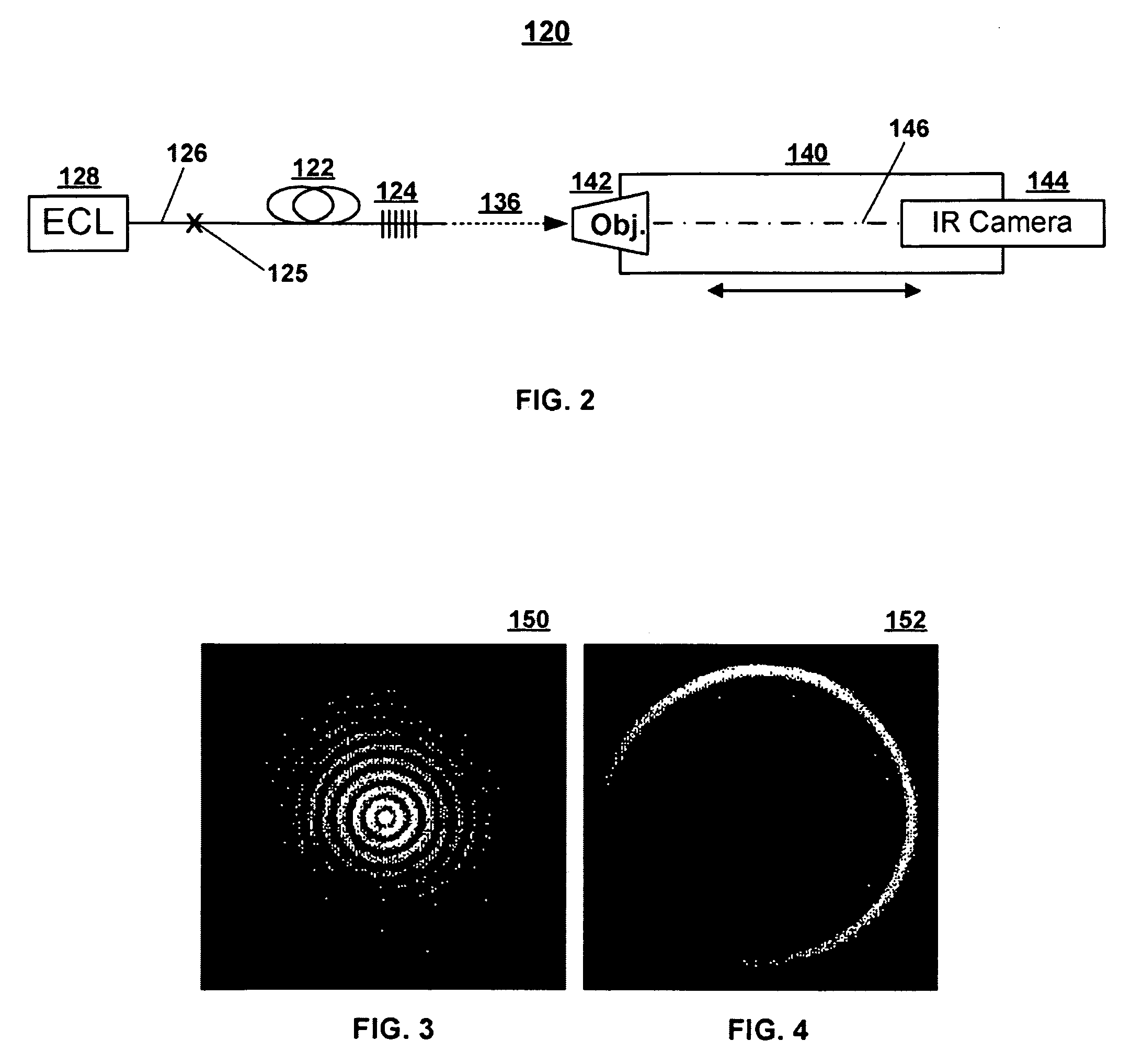
Systems and techniques for generating Bessel beams
A technique is described for generating a Bessel beam. An input optical fiber is provided that supports propagation in the fundamental mode. The input fiber is connected to a fiber mode converting device that provides phase matching, at a predetermined excitation wavelength, between the fundamental mode and a selected azimuthally symmetric higher-order mode. As an input to the fiber mode converting device, a coherent light beam is fed through the input optical fiber to provide a fundamental mode input at the excitation wavelength. The fiber mode converting device resonantly excites the selected azimuthally symmetric mode. The azimuthally symmetric mode is provided as a beam output from an endface of the fiber mode converting device to approximate a Bessel beam.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Chiral fiber grating
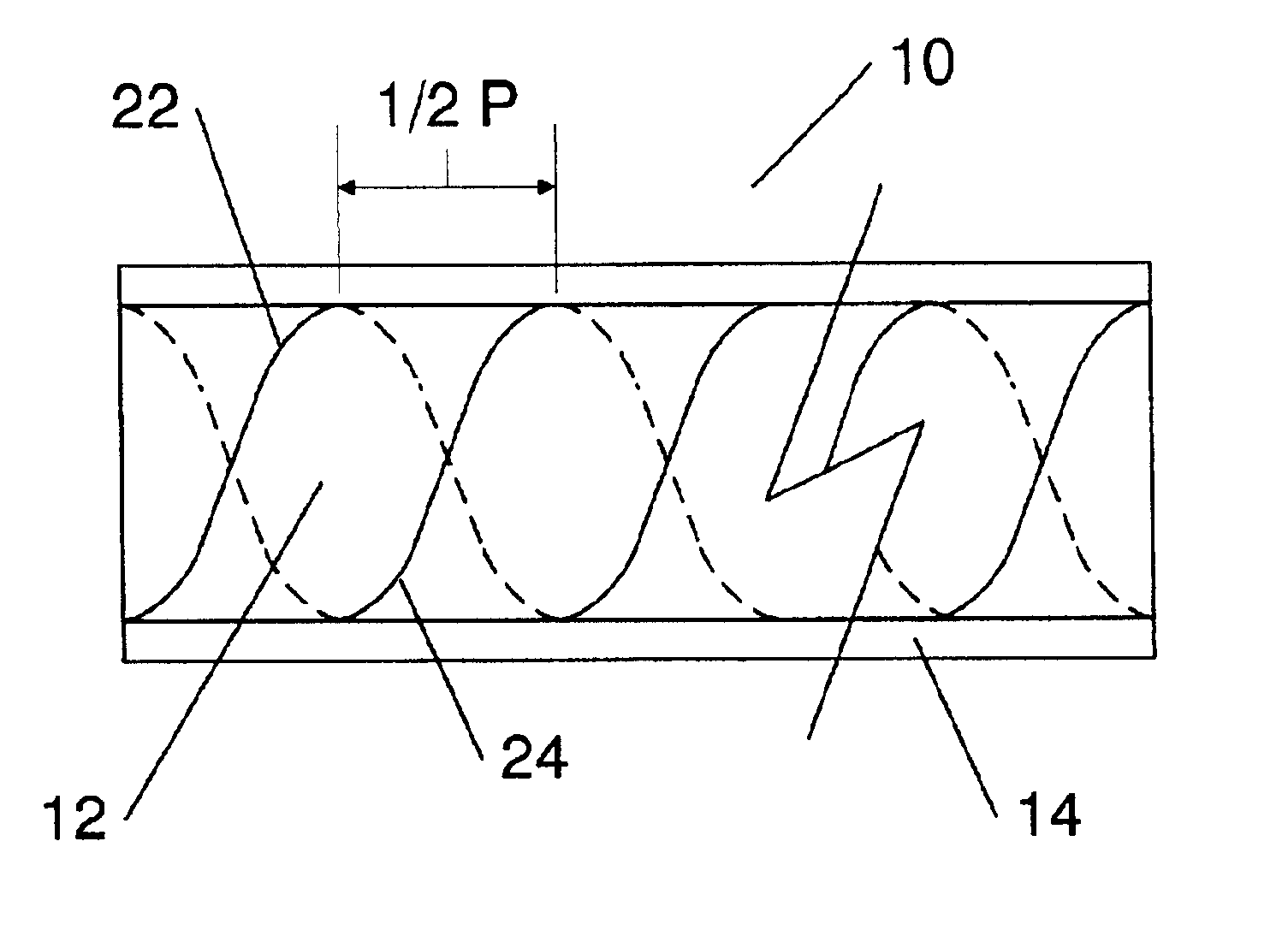
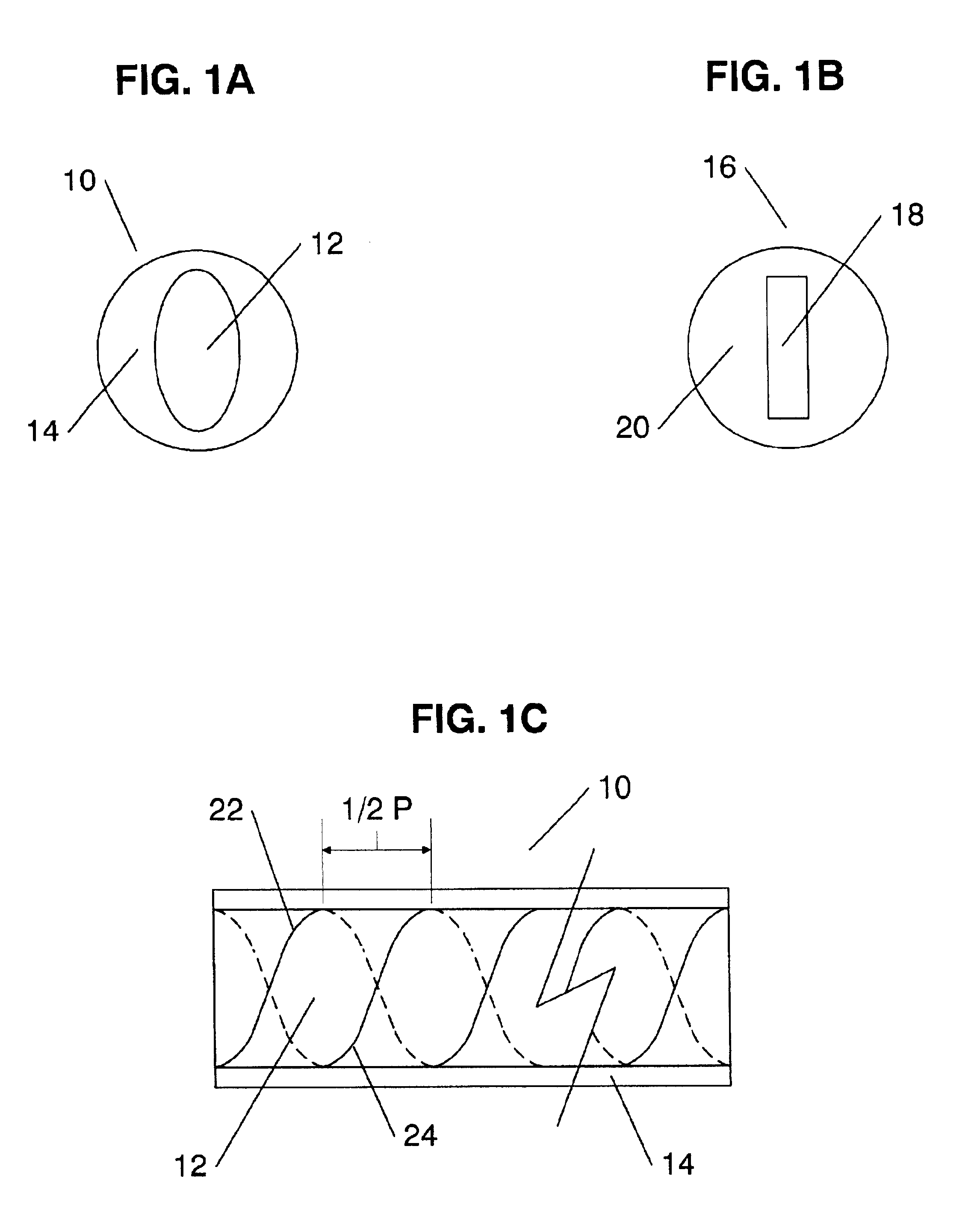
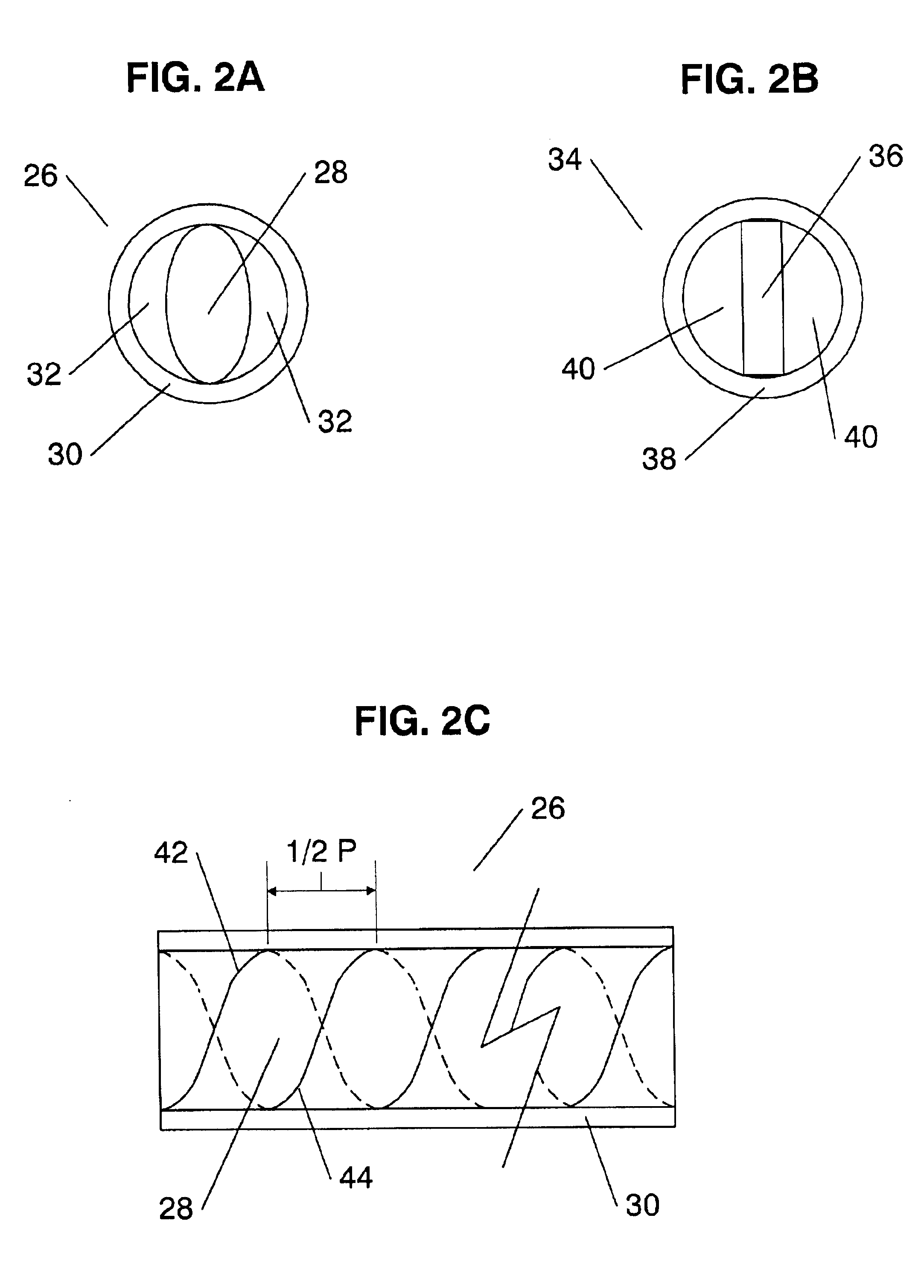
InactiveUS6839486B2Different optical propertyOptical fibre with polarisationCoupling light guidesFiberGrating
A a chiral fiber grating mimicking a cholesteric liquid crystal structure to achieve fiber Bragg grating properties, is provided. The chiral fiber grating includes a first and a second helical structures disposed along its central longitudinal axis, where the second helical structure is identical in orientation to the first helical structure but is shifted by one half of the structure's pitch forward. In another embodiment of the invention, only a single helical structure is disposed along the fiber to create an optically resonant chiral fiber.
Owner:CHIRAL PHOTONICS
Compensation apparatus and method utilising sampled bragg gratings
Dispersion compensation devices are described which comprise waveguides including sampled Bragg gratings which exhibit comb-like reflectance characteristics. The profile of effective refractive index along the length of the grating is controlled to adjust the position of the teeth and / or to control the dispersion exhibited by the device (i.e. to control the chirp of the grating). The devices can thus be used to provide dispersion compensation to any one of a number of wavelength channels in a WDM system. In preferred arrangements, the effective refractive index distribution is set by a applying a temperature distribution along the length of the grating, or by setting an applied electric field.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Method for analyzing strain data
ActiveUS20090254280A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingDigital computer detailsPosition dependentEngineering
A method for estimating a shape, the method including: selecting a structure comprising a plurality of strain sensors inoperable communication with the structure, each strain sensor configured to provide a strain measurement; placing the structure in a borehole; receiving the strain measurements from the plurality of strain sensors; creating a mesh grid having nodes, each node related to a location of one strain sensor and assigned a strain value measured by the one strain sensor; creating an additional node for the mesh grid wherein a strain value assigned to the additional node is derived from the strain value corresponding to at least one adjacent node; and performing an inverse finite method using the mesh grid with the assigned strain values to estimate the shape.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
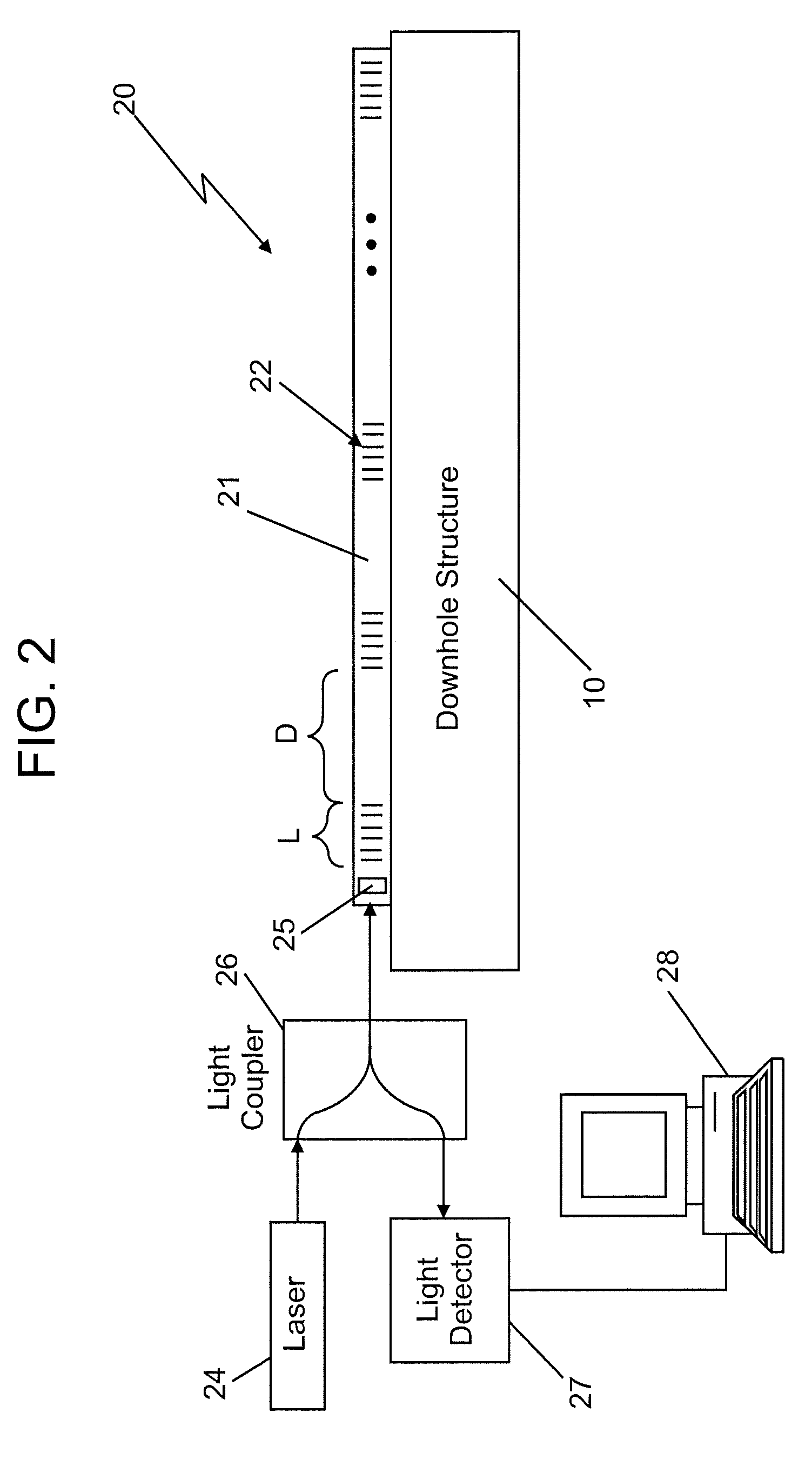
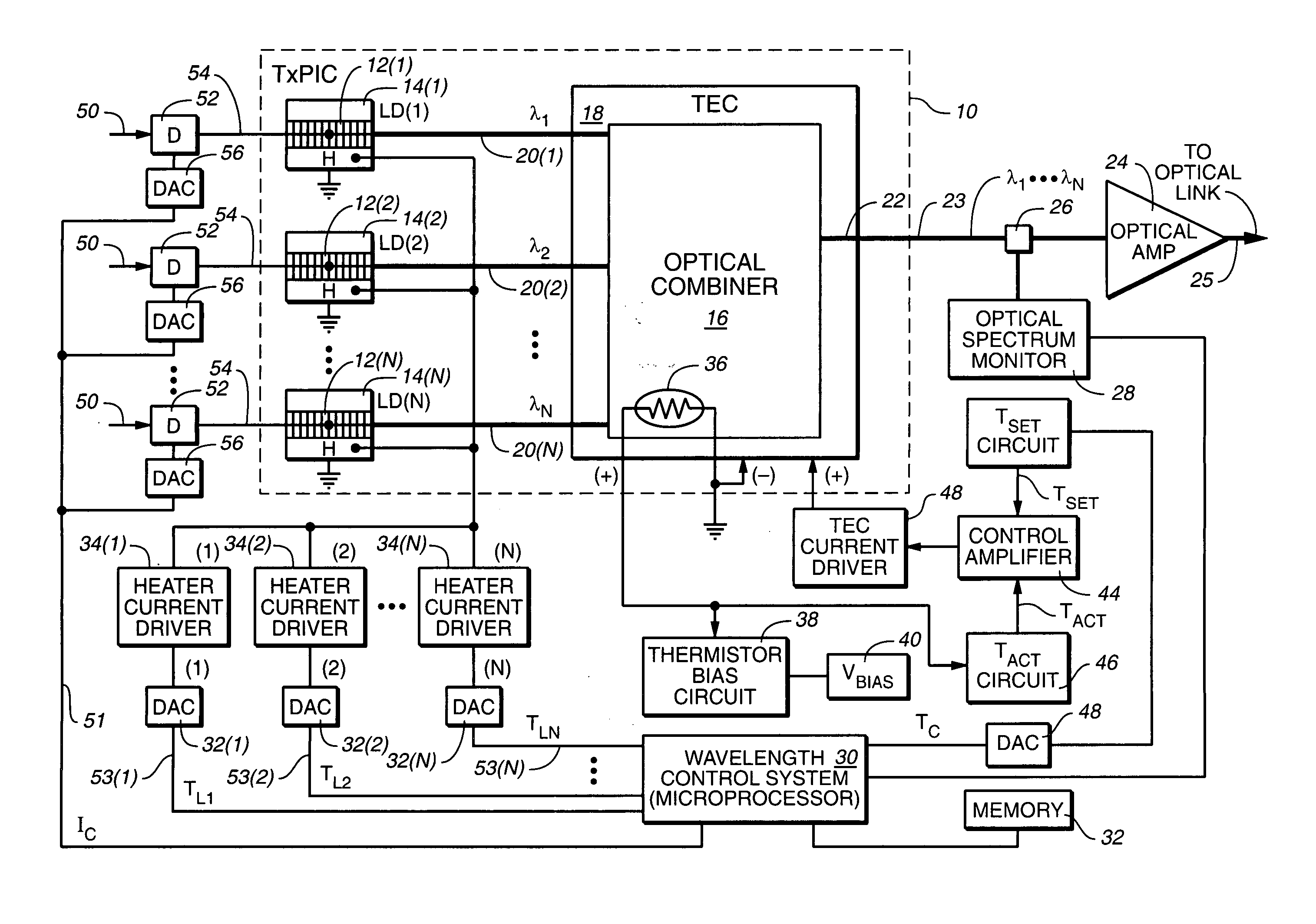
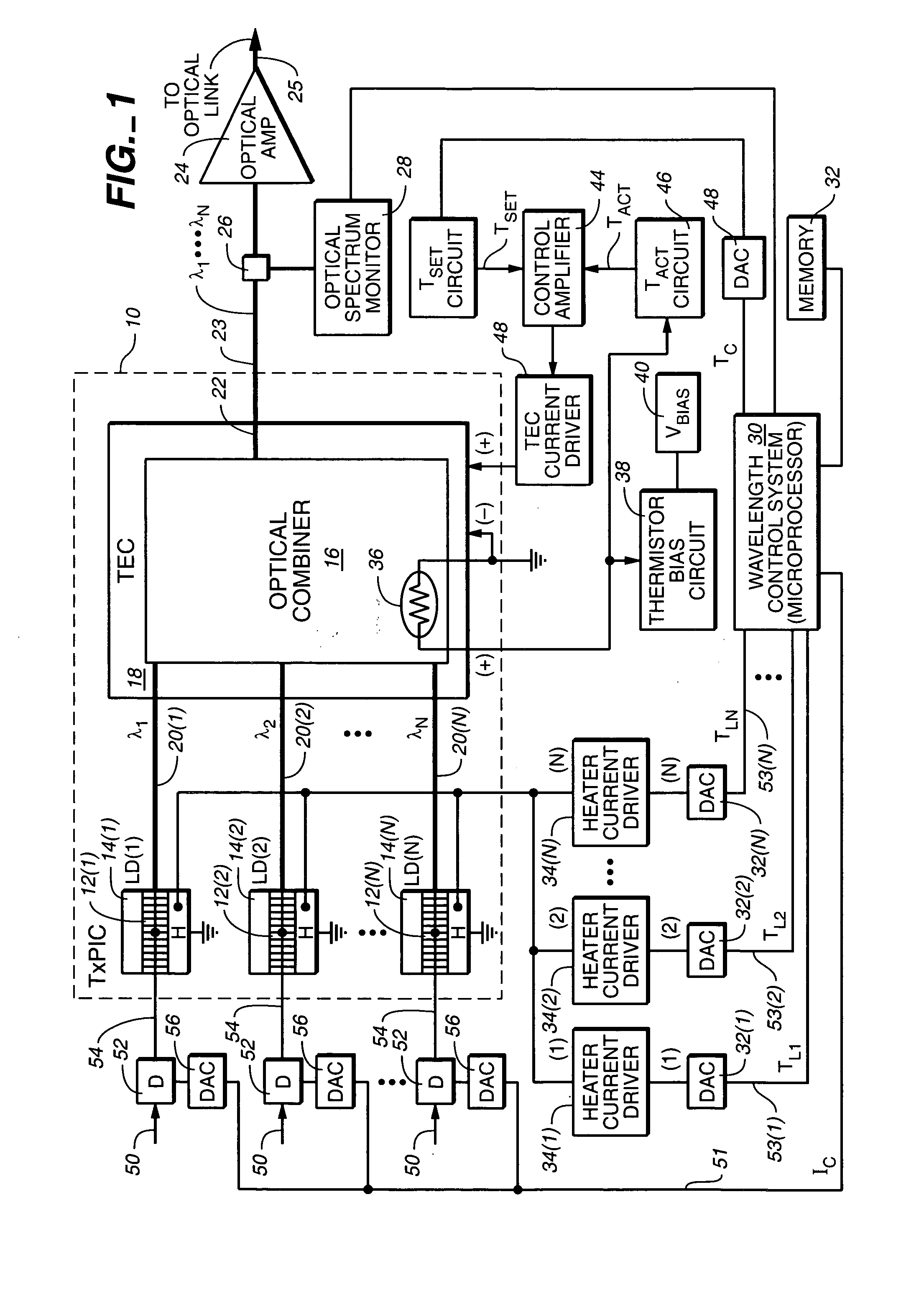
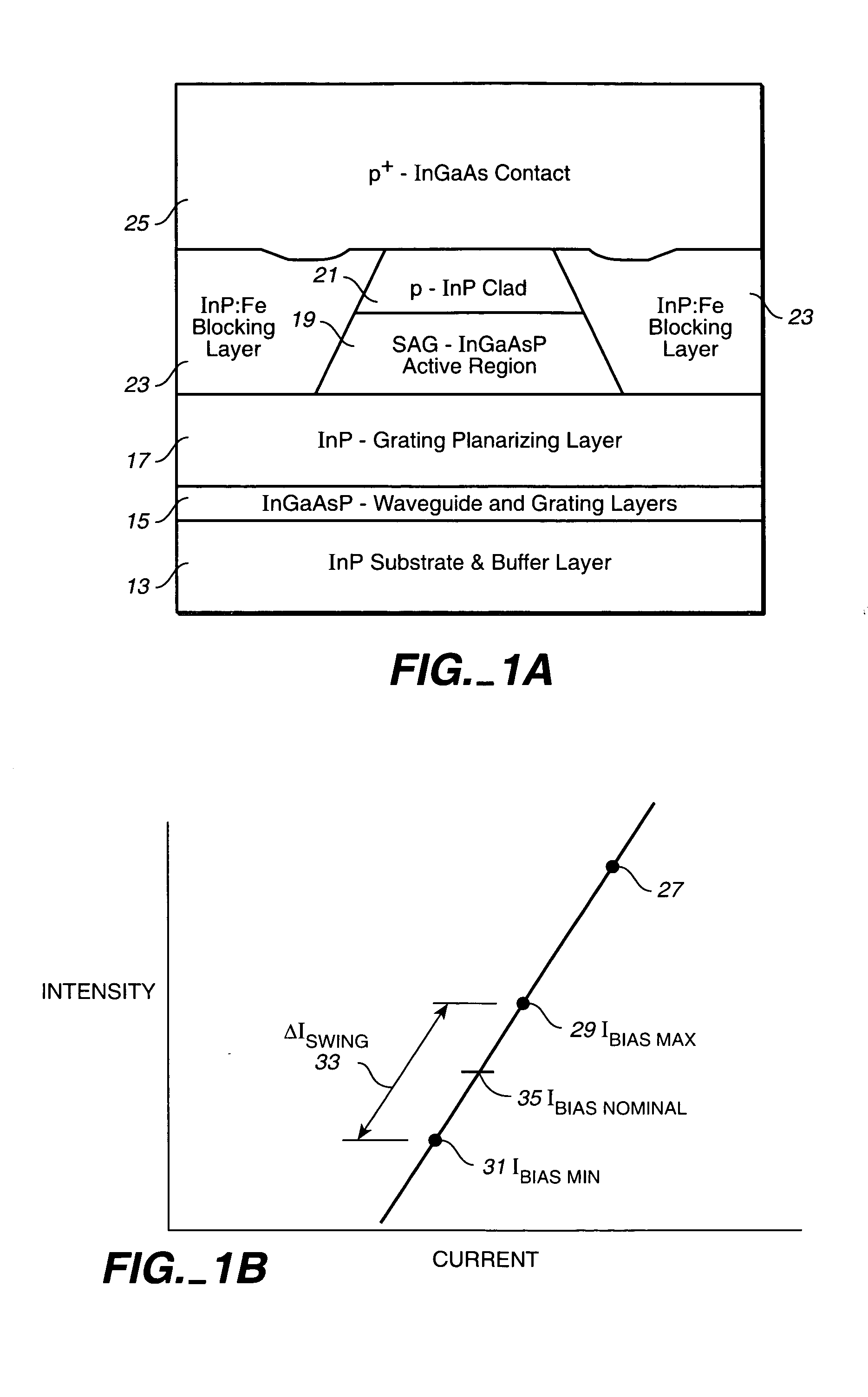
Method of operating an array of laser sources integrated in a monolithic chip or in a photonic integrated circuit (PIC)
A method of operating an array of laser sources integrated as an array in a single monolithic chip where the steps include designing the laser sources to have different target emission wavelengths so that together they form a spectral emission wavelength grid, coupling outputs from the laser sources to an array of gain / loss elements also integrated on the single monolithic chip, one each receiving the output from a respective laser source; and adjusting the outputs with the gain / loss elements so that the power levels of the laser source array across are substantially uniform.
Owner:INFINERA CORP
Enhanced supercontinuum generation in highly nonlinear fibers using post-fabrication processing
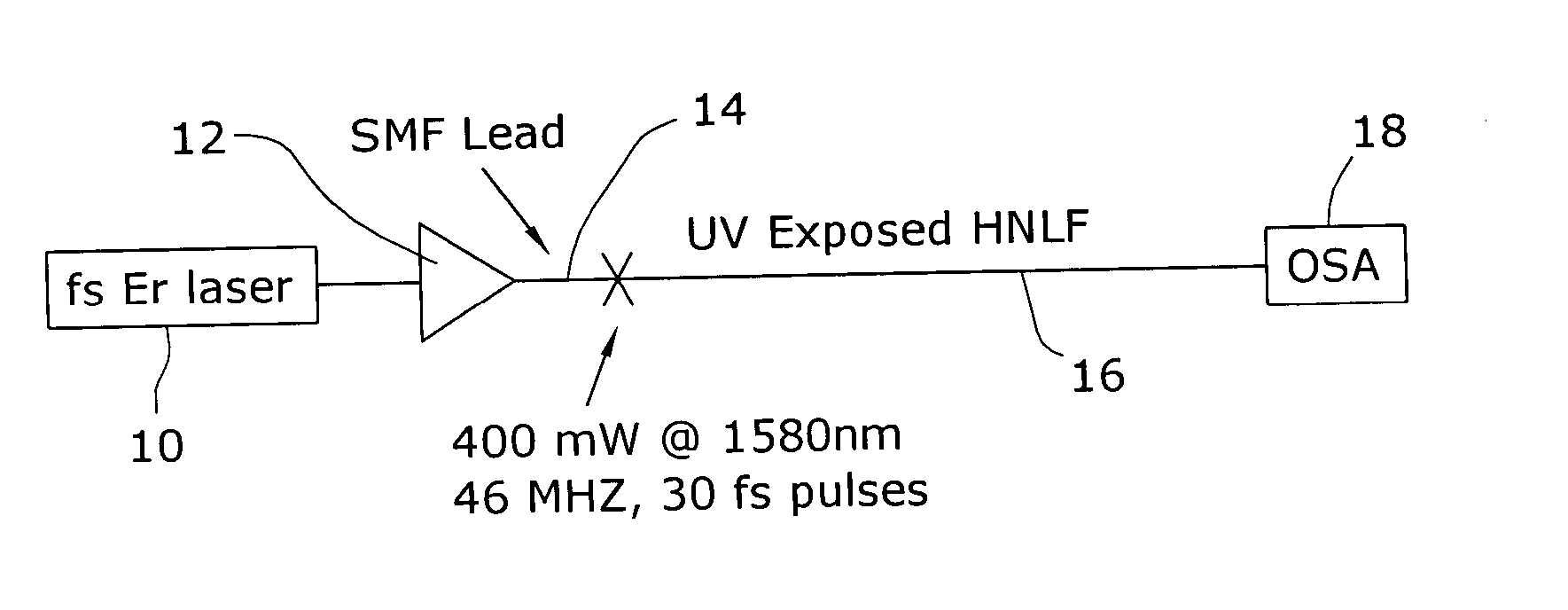
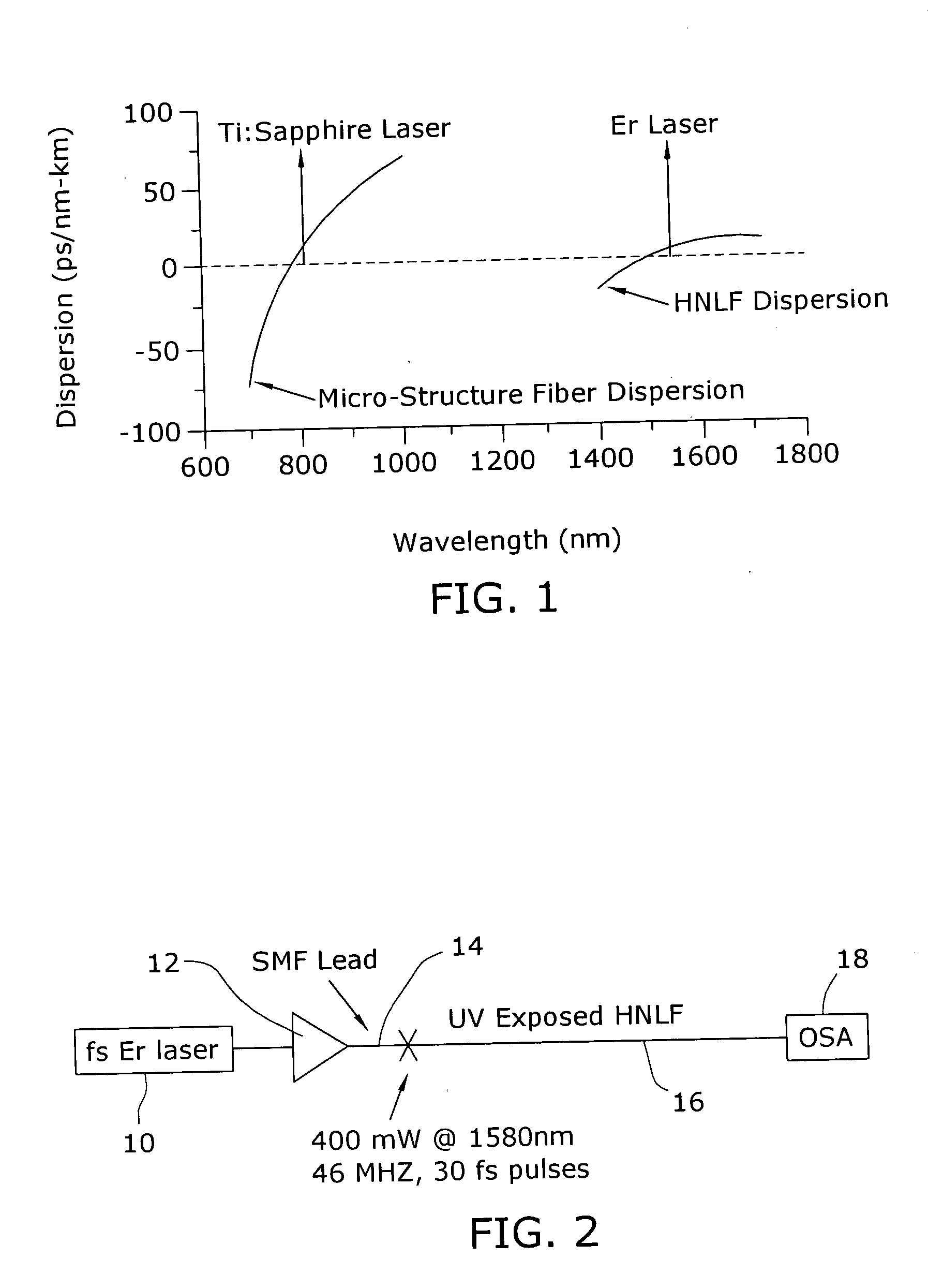
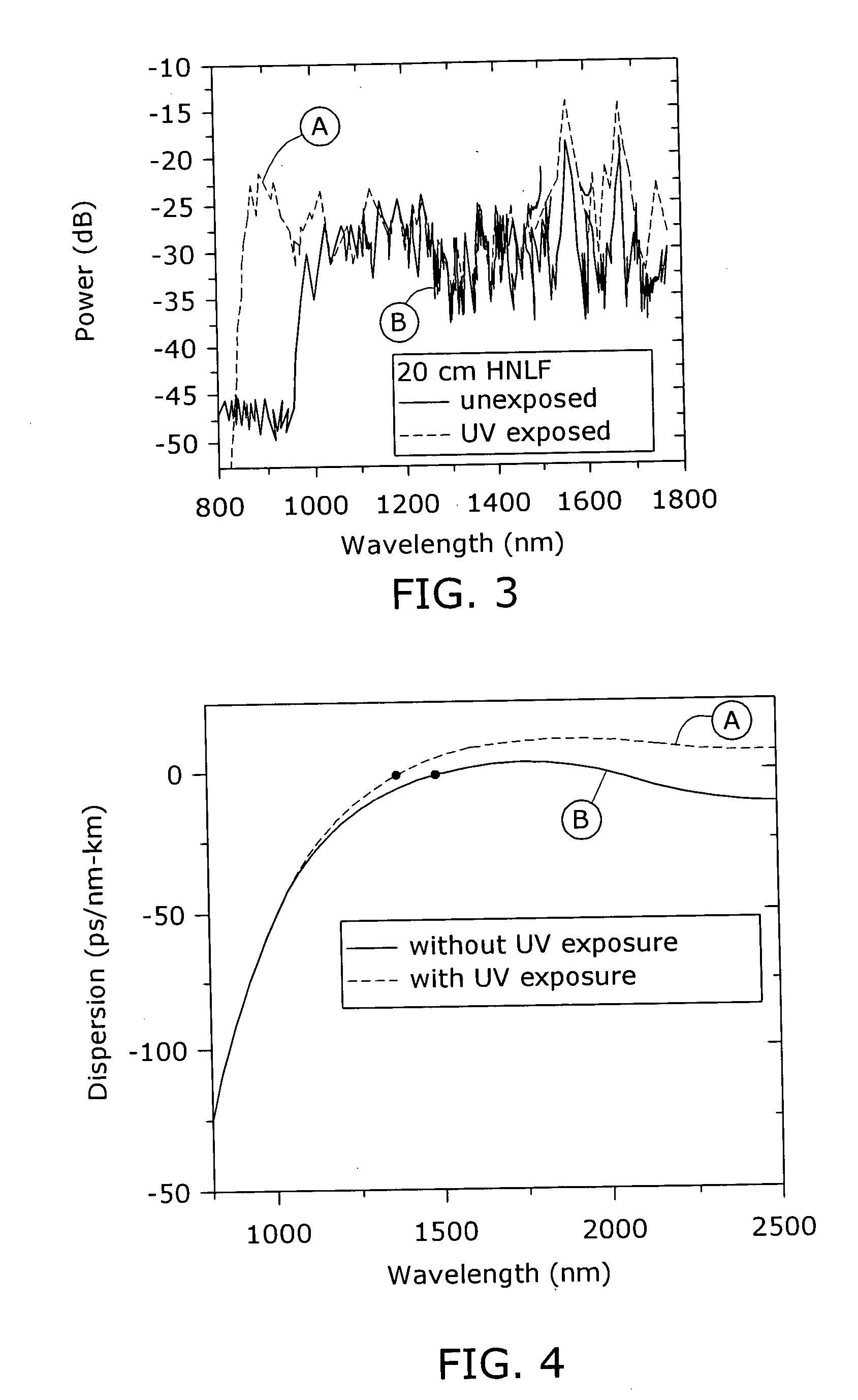
ActiveUS20050226576A1Alteration in dispersionAlteration in effective areaLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsEngineeringNonlinear fiber
Enhancement of the supercontinuum generation performance of a highly-nonlinear optical fiber (HNLF) is accomplished by performing at least one post-processing treatment on the HNLF. Particularly, UV exposure of the HNLF will modify its dispersion and effective area characteristics so as to increase its supercontinuum bandwidth, without resorting to techniques such as tapering or introducing unwanted reflections into the HNLF. The UV exposure can be uniform, slowly varying or aperiodic along the length of the HNLF, where the radiation will modify the nonlinear properties of the HNLF. Various other methods of altering these properties may be used. The output from the HNLF can be monitored and used to control the post-processing operation in order to achieve a set of desired features in the enhanced supercontinuum spectrum.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Active in-fiber optic components powered by in-fiber light
ActiveUS20050163424A1Reduce manufacturing costEliminates any additional electrical cablingVolume/mass flow measurementMachines/enginesFiberSignal light
An optical fiber system that includes an in-fiber optic component powered by in-fiber light includes an optical fiber having a core, wherein the optical fiber propagates a sensing / signal light and a power light, with the sensing / signal light being propagated in the core. An optical transducing element, such as a layer of light absorbing material, is located in proximity to the in-fiber optic component. An optical tap region is provided in the optical fiber in proximity to the optical transducing element, and enables the power light to leak from the optical fiber and be absorbed by the optical transducing element. The optical transducing element converts the absorbed power light into a second energy form, such as heat, which is used to tune the in-fiber optic component.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Chiral in-fiber polarizer apparatus and method
ActiveUS7095911B2Eliminating undesirable polarization componentRaise the ratioCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guidePitch variationRefractive index
A chiral in-fiber polarizer implemented in a chiral fiber structure having a core and a cladding surrounding the core, is provided. The chiral polarizer includes an entry end for receiving incident light and an exit end for outputting polarized light, as well as a pitch variation along its length between the entry and exit ends in accordance with a predetermined desirable pitch profile, wherein in one embodiment of the inventive polarizer, the inverse value of the chiral structure's pitch at the exit end is less than at the entry end, and preferably substantially equal to zero. The pitch profile may be advantageously selected to correspond to one or more predetermined pitch configurations, may be determined in accordance with one or more mathematical functions, or may be random. In accordance with the present invention, at least one of various parameters of the chiral structure, including, but not limited to, the core and cladding refractive indices and sizes, and the pitch profile, may be configured and selected to substantially eliminate the undesirable polarization component of the incident light by achieving an optimized extinction ratio within a desired spectral range. In another embodiment of the inventive chiral polarizer, the pitch profile is selected and configured such that the inverse value of the chiral structure's pitch at the entry end of the chiral structure is also zero. This arrangement enables significant reduction of insertion loss of the incident light entering the entry end of the inventive polarizer.
Owner:CHIRAL PHOTONICS
Optical fiber and optical fiber sensors
InactiveUS7027699B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical articlesGratingThermal expansion
An optical fiber device has at least two cores within the same cladding having different characteristics. The characteristics include including strain optic coefficient, thermo-optic coefficient, thermal expansion coefficient, photo-sensitivity and refractive index. One or more cores can have a Bragg grating.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Side-hole cane waveguide sensor
A side-hole optical cane for measuring pressure and / or temperature is disclosed. The side-hole cane has a light guiding core containing a sensor and a cladding containing symmetrical side-holes extending substantially parallel to the core. The side-holes cause an asymmetric stress across the core of the sensor creating a birefringent sensor. The sensor, preferably a Bragg grating, reflects a first and second wavelength each associated with orthogonal polarization vectors, wherein the degree of separation between the two is proportional to the pressure exerted on the core. The side-hole cane structure self-compensates and is insensitive to temperature variations when used as a pressure sensor, because temperature induces an equal shift in both the first and second wavelengths. Furthermore, the magnitude of these shifts can be monitored to deduce temperature, hence providing the side-hole cane additional temperature sensing capability that is unaffected by pressure. Additionally, the side-hole cane can be used to measure a differential pressure between a first pressure ported to the side-holes and a second external pressure.
Owner:WEATHERFORD TECH HLDG LLC
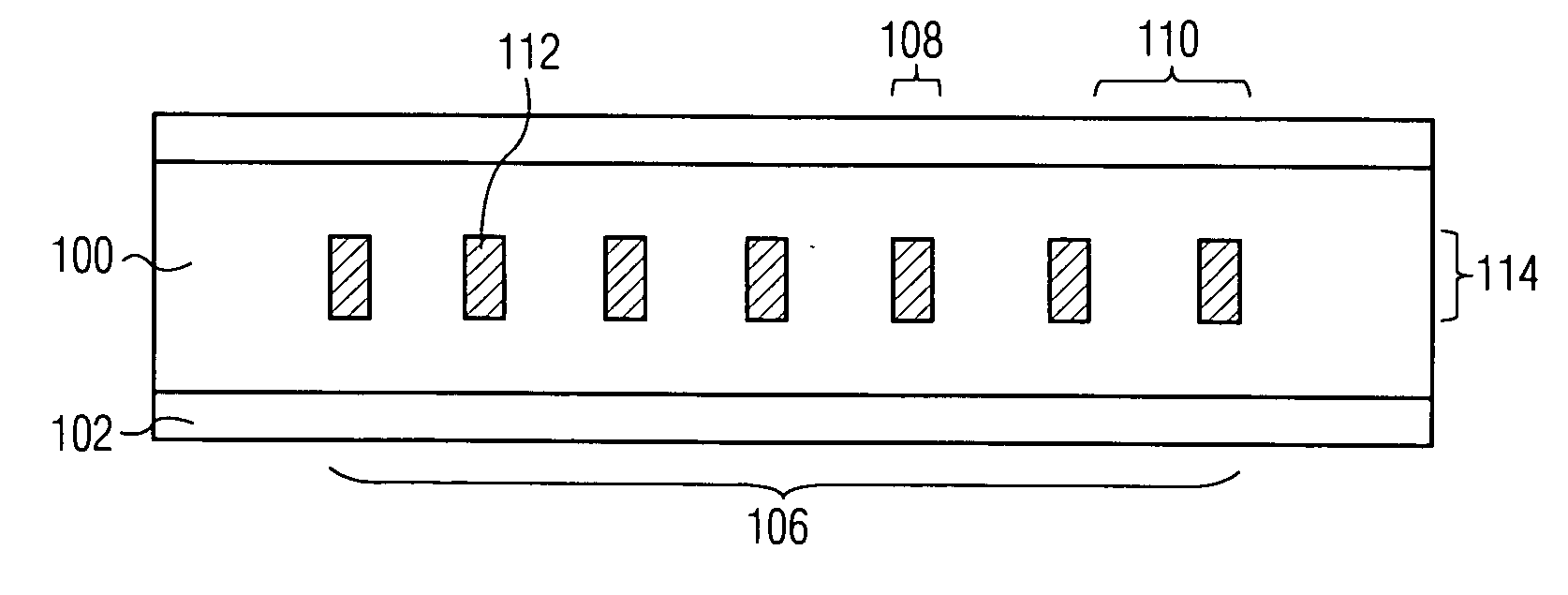
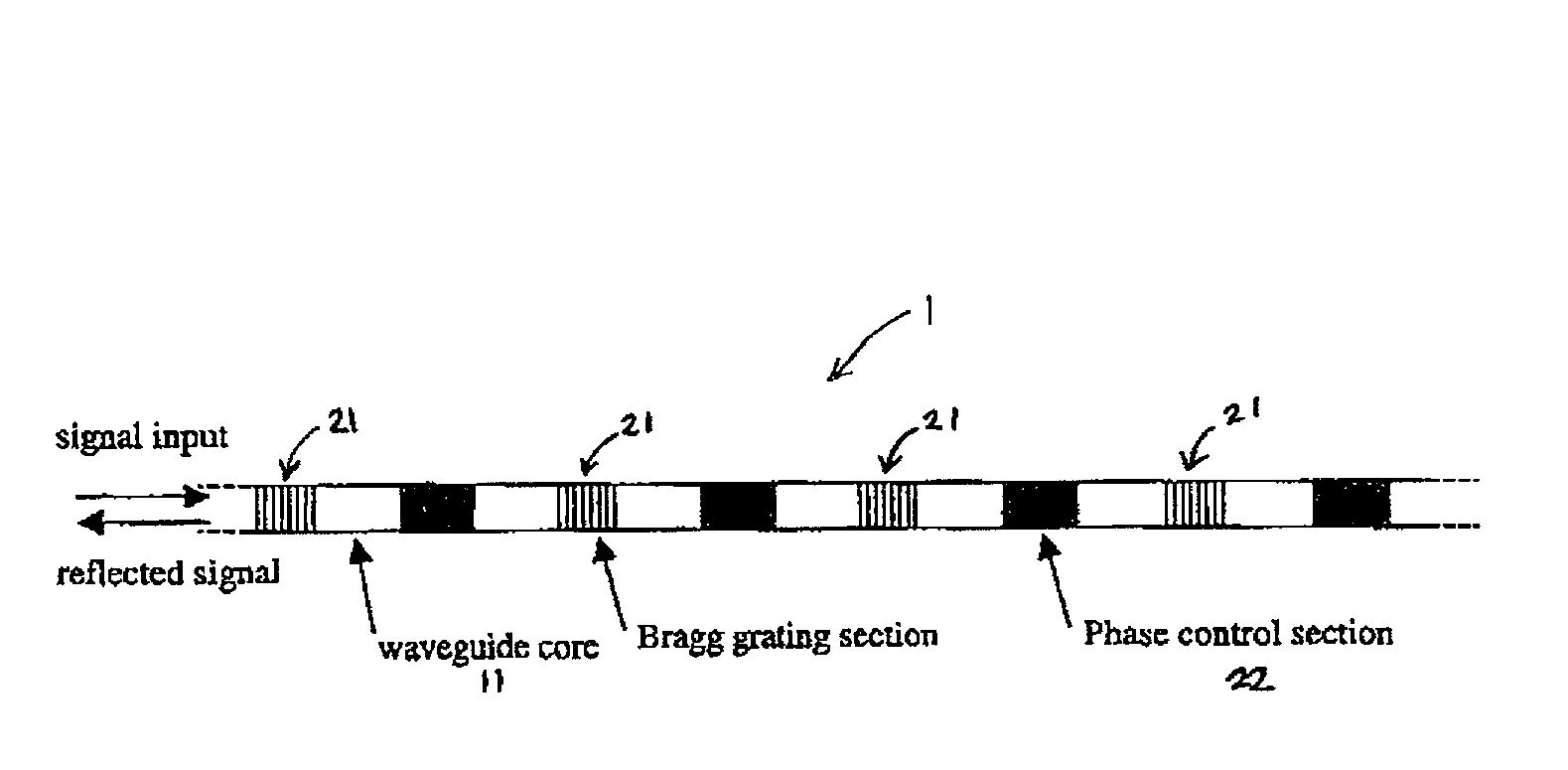
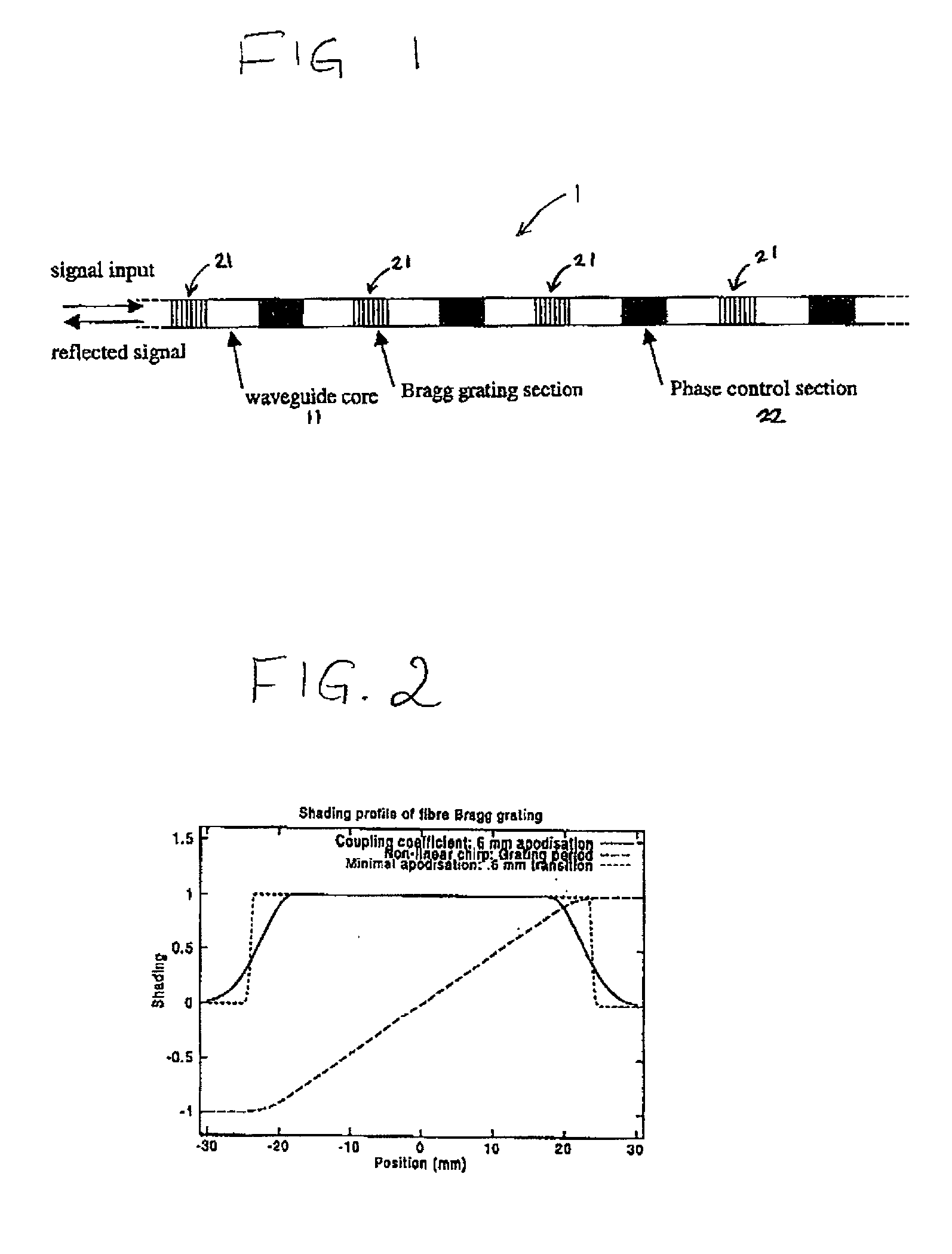
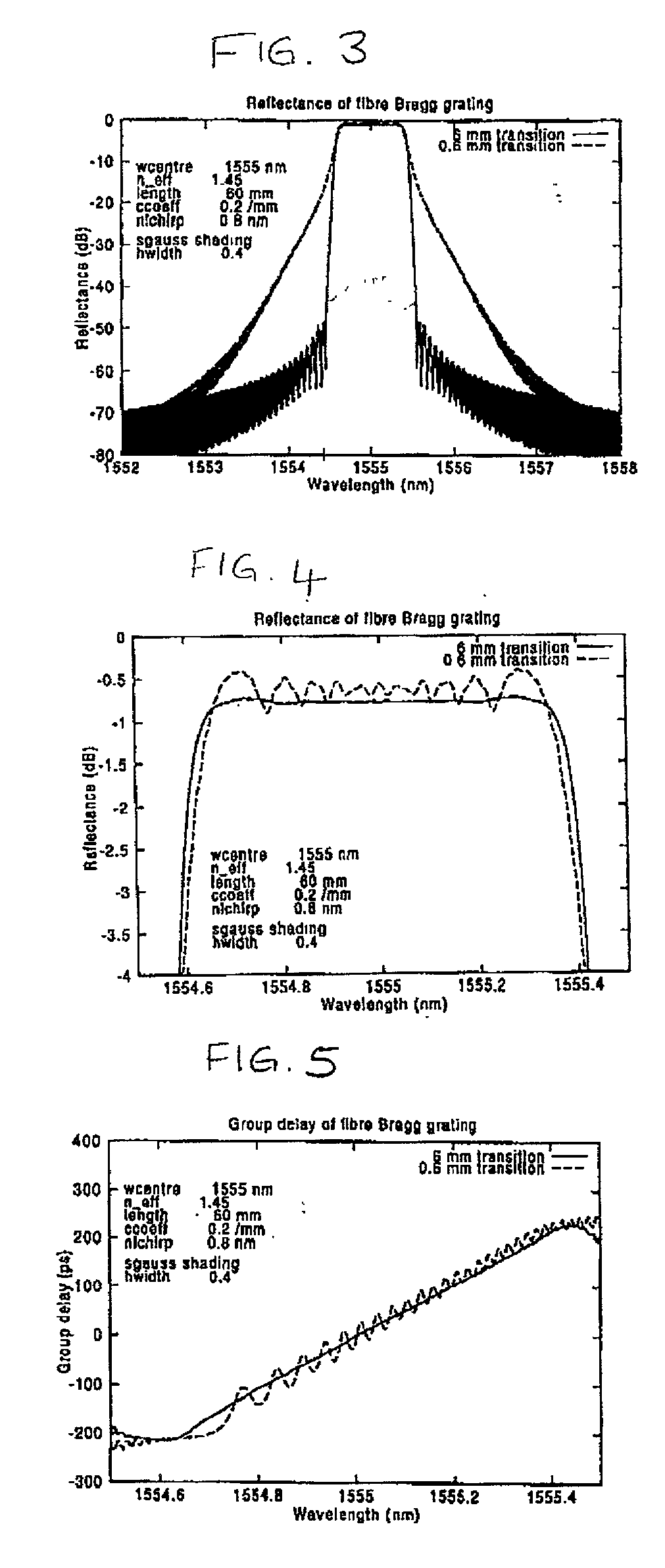
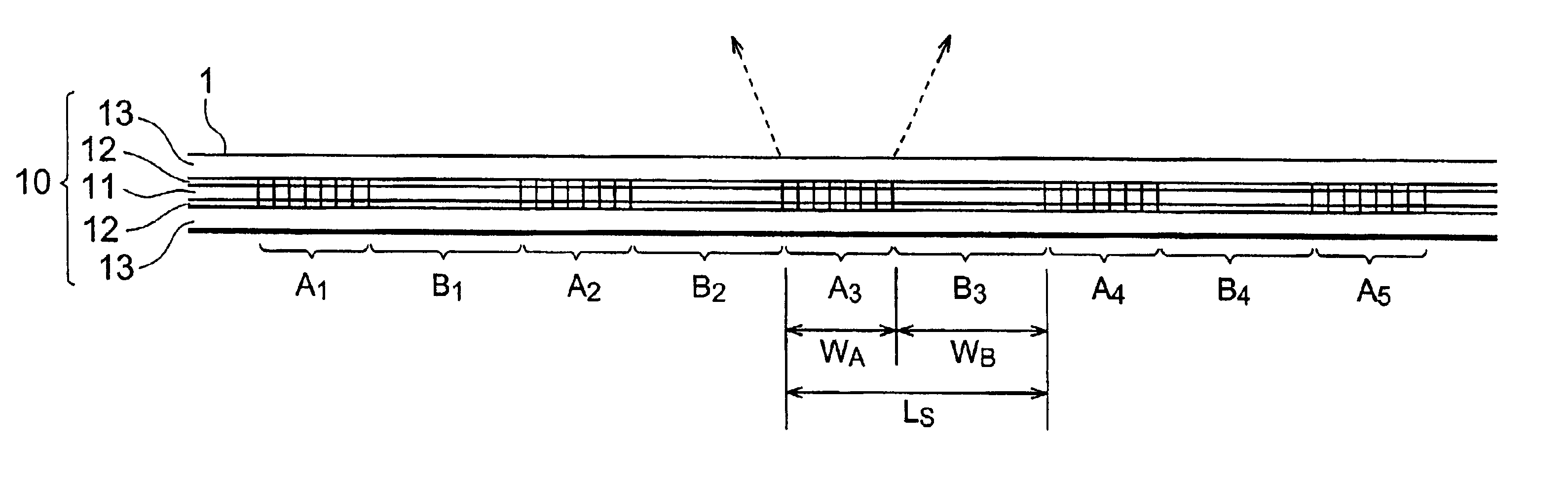
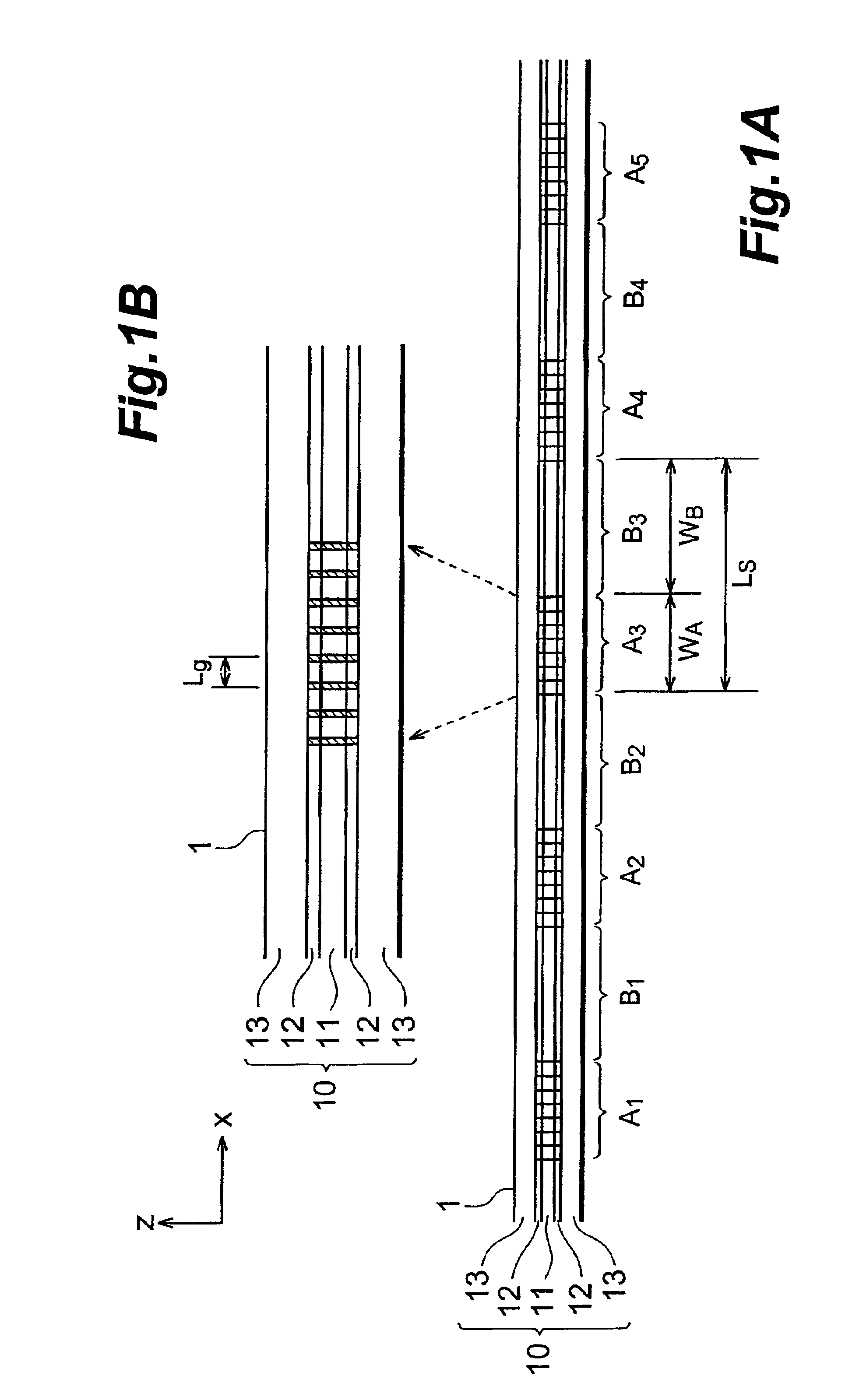
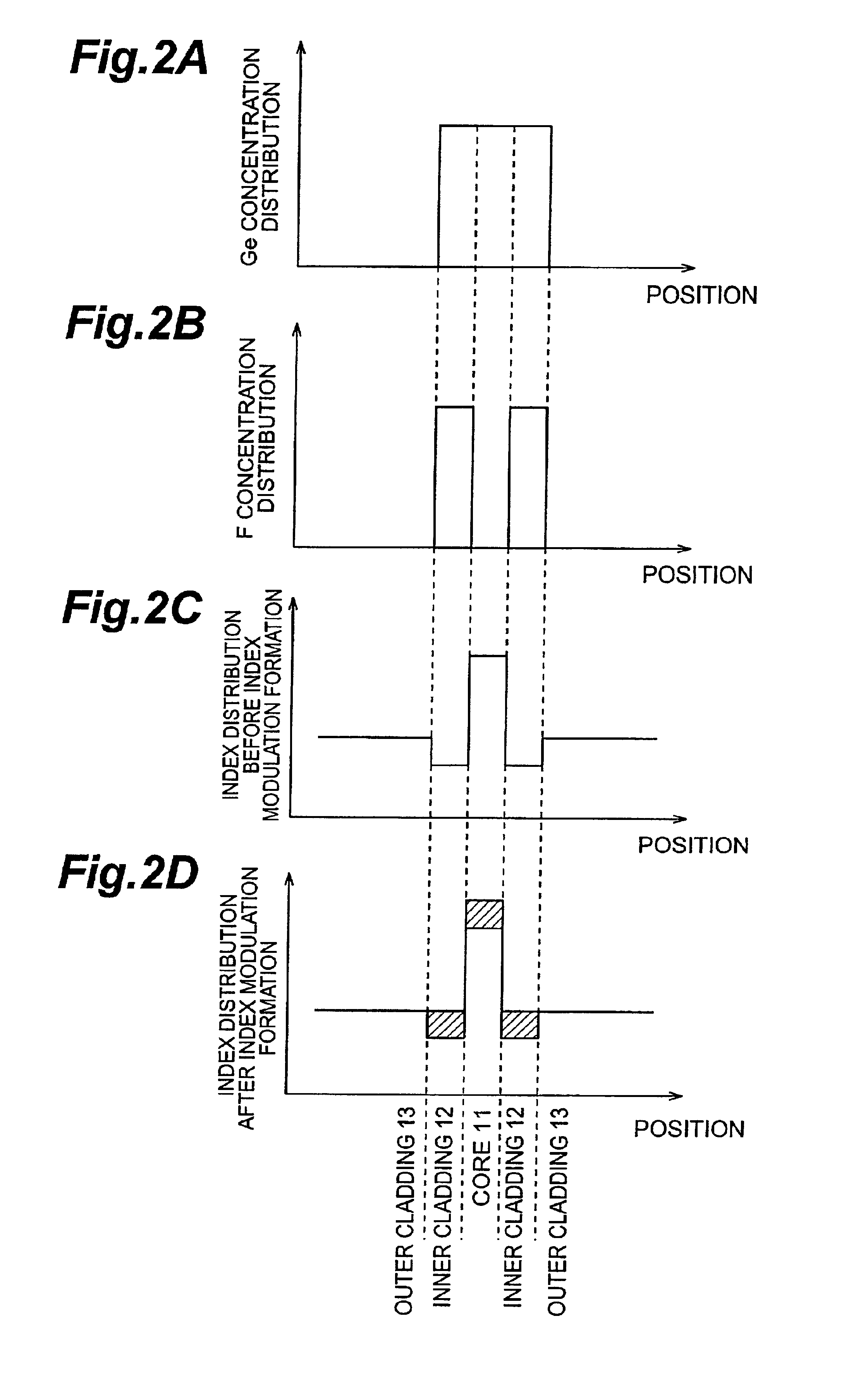
Diffraction grating device
InactiveUS6876791B2Longitudinal length can be shortenedIncrease amplitudeCoupling light guidesOptical waveguide light guideOptical axisRefractive index
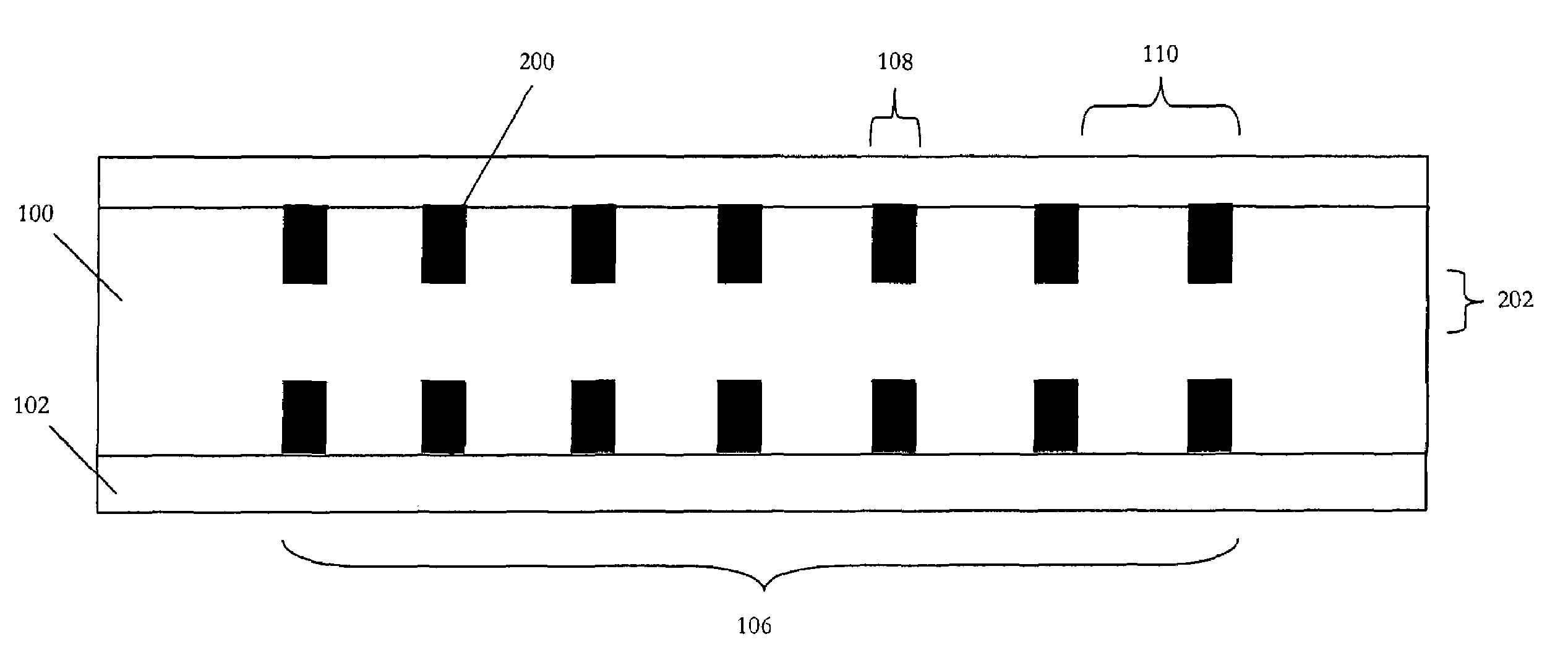
In a diffraction grating device (1), index modulations are formed along the longitudinal direction of an optical fiber (10) serving as an optical waveguide. The optical fiber (10) has a core region (11), an inner cladding region (12), and an outer cladding region (13) sequentially from the optical axis center. Index modulations are formed in both the core region (11) and the inner cladding region (12) of the optical fiber (10) in each of a plurality of regions A1 to AN (N is an integer; N≧2) separated from each other along the longitudinal direction of the optical fiber (10). In the diffraction grating device (1), regions An (n=1 to N) in which index modulations are formed in both the core region (11) and the inner cladding region (12) and regions Bn (n=1 to N−1) in which no index modulations are formed alternately exist along the longitudinal direction.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Multimode optical fiber with a higher order mode removing function
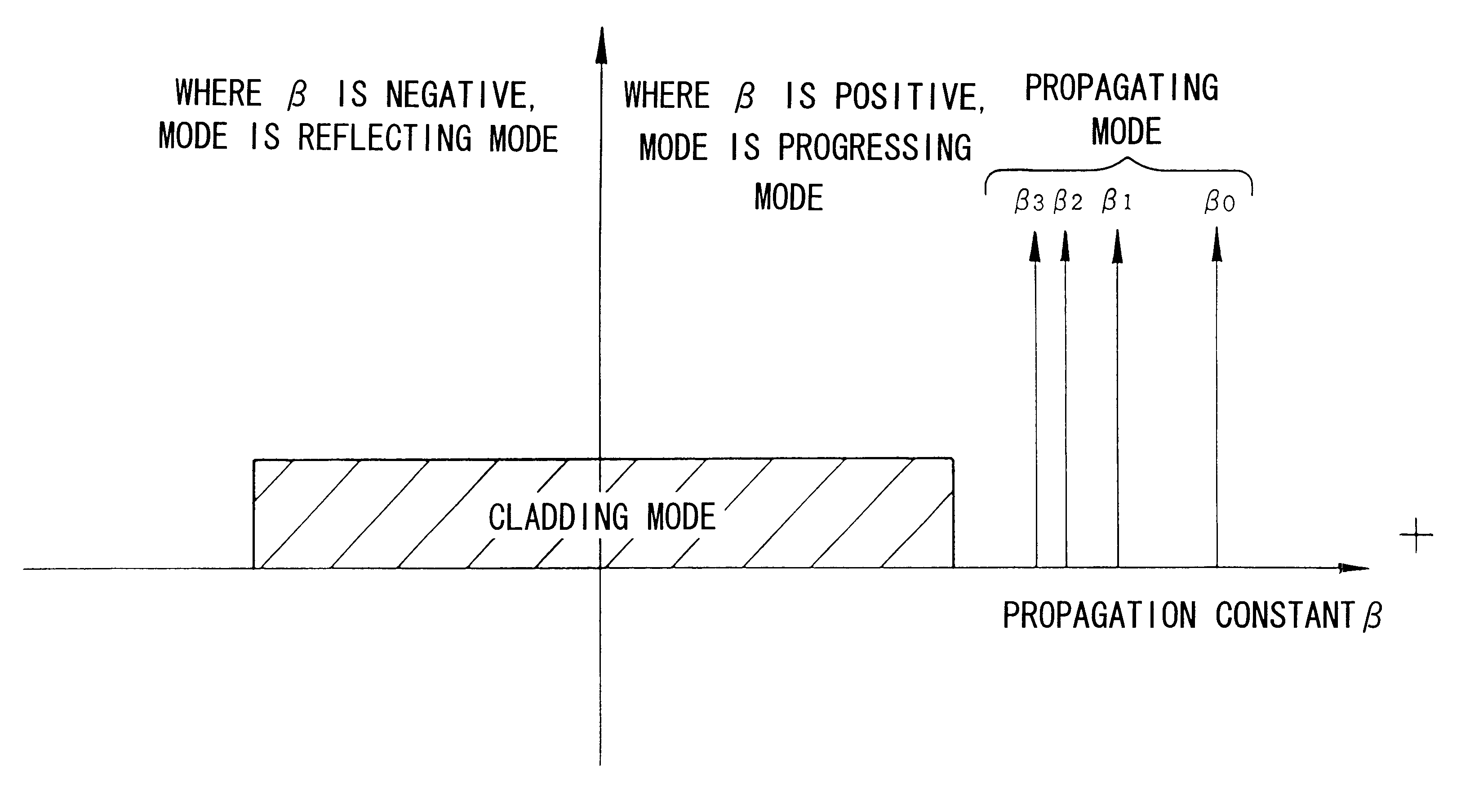
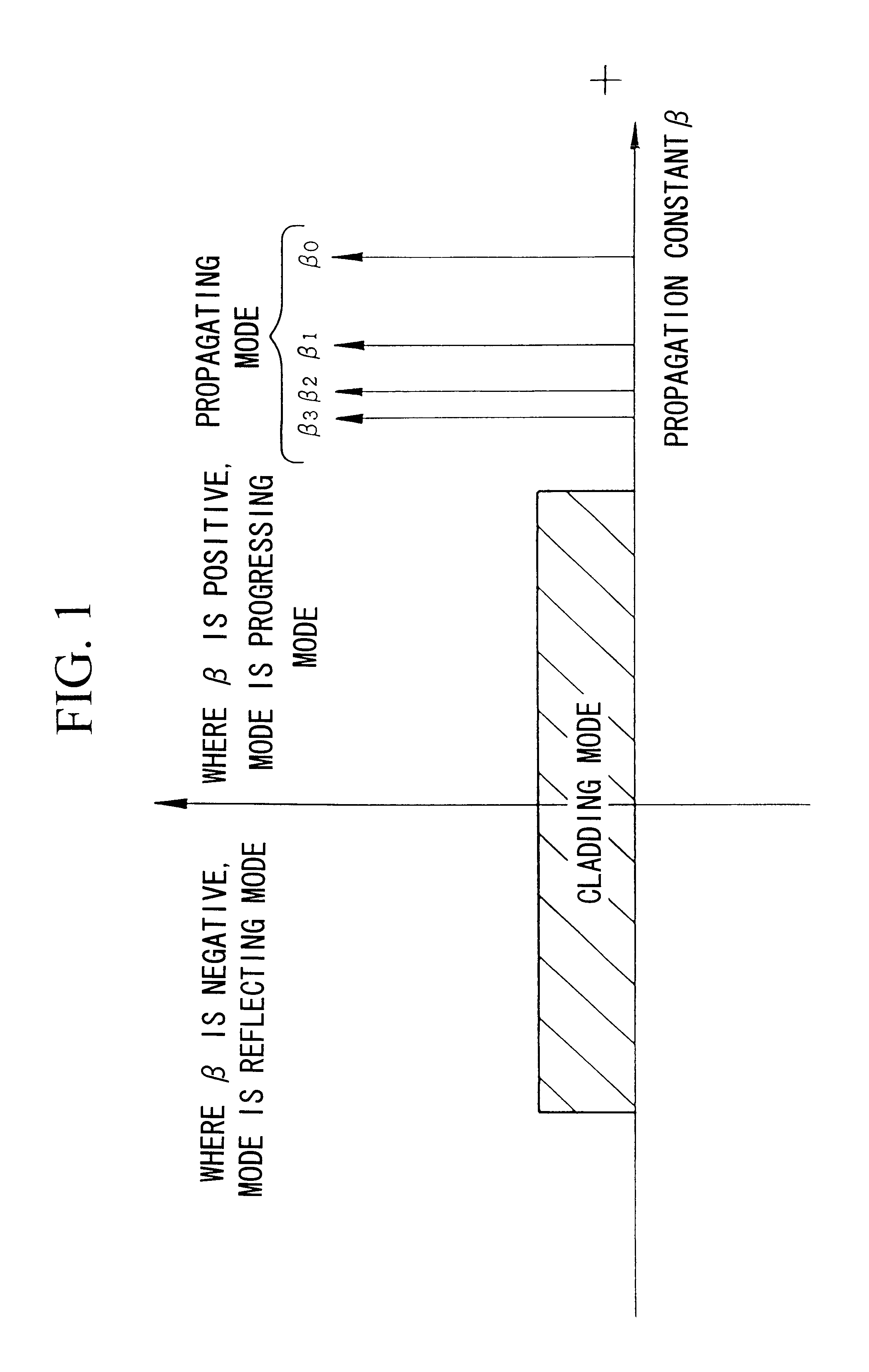
InactiveUS6535678B1Reduce lossLoss of sensitivityOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberClassical mechanics
The present invention's multimode optical fiber is characterized in that the propagating modes include a mode the lowest and second or higher order modes; and the difference between the propagation constants of the lowest order mode and the second order mode is 2-fold or more than the difference between the propagation constants of adjacent modes that are second order or higher order modes. Due to this design, single mode propagation becomes possible once the modes have propagated over a specific distance. As a result, it is possible to relax the conventional single mode conditions, enabling the fiber parameters to be set relatively freely.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com