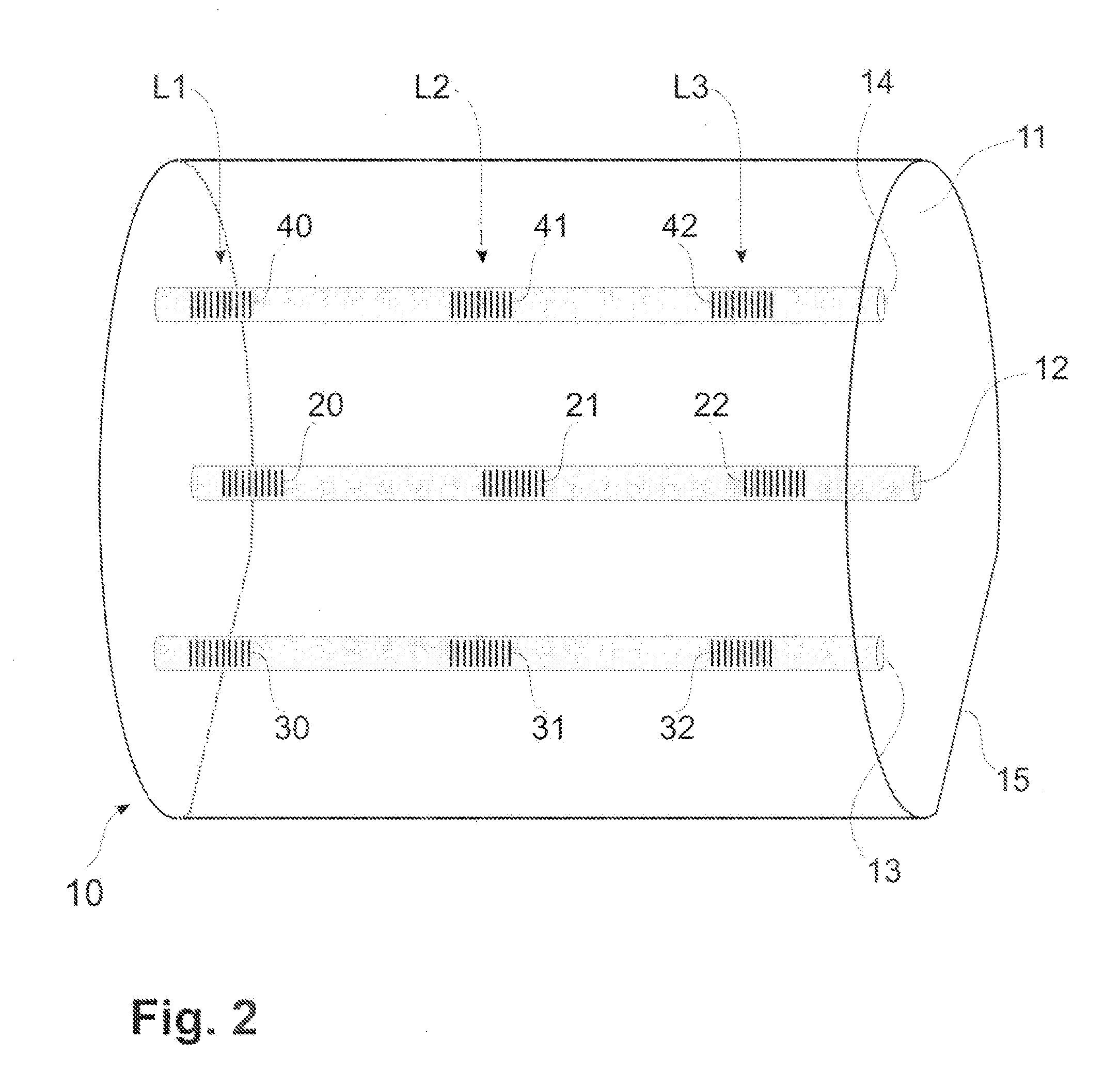Optical fiber sensor and method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
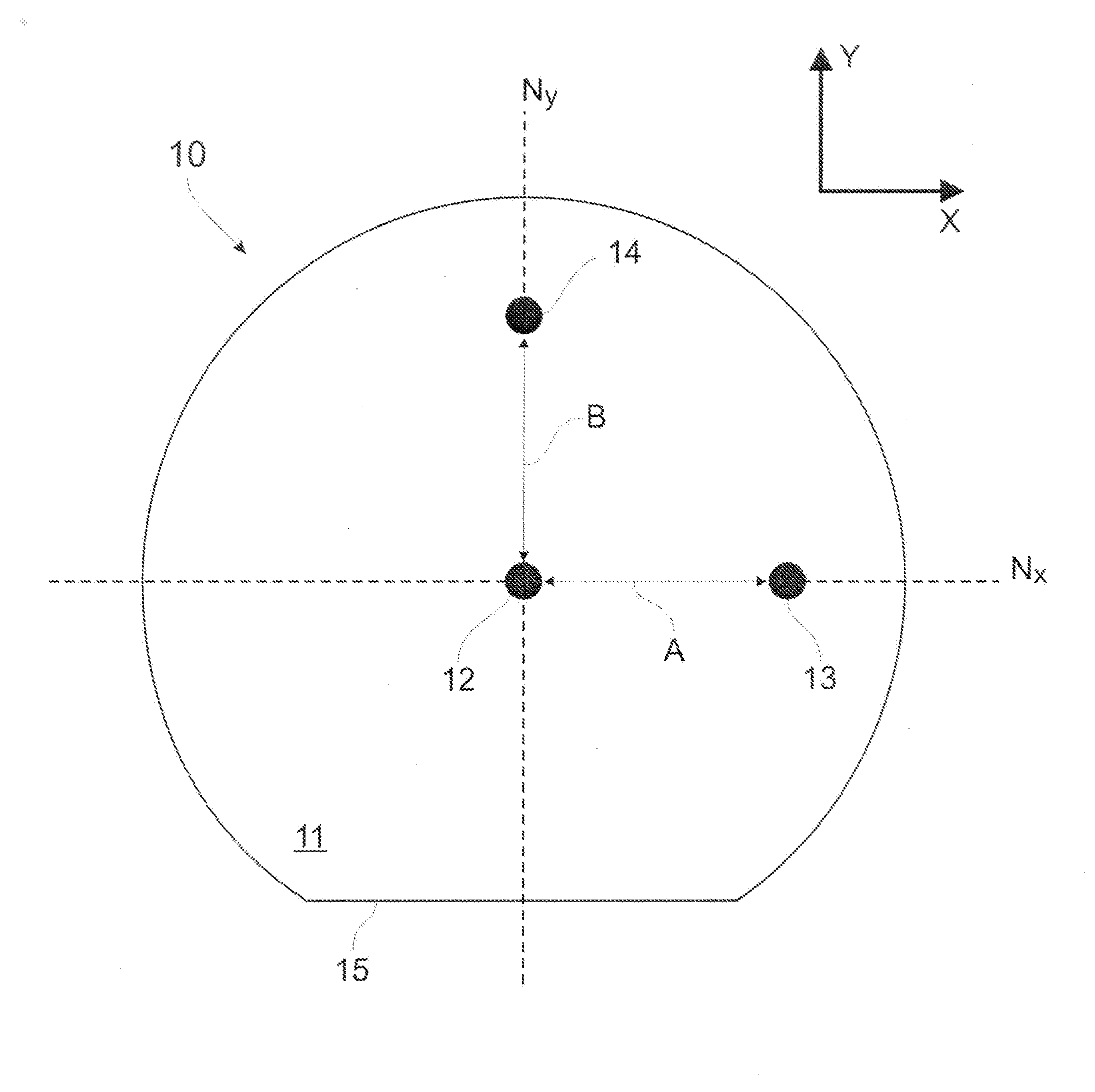
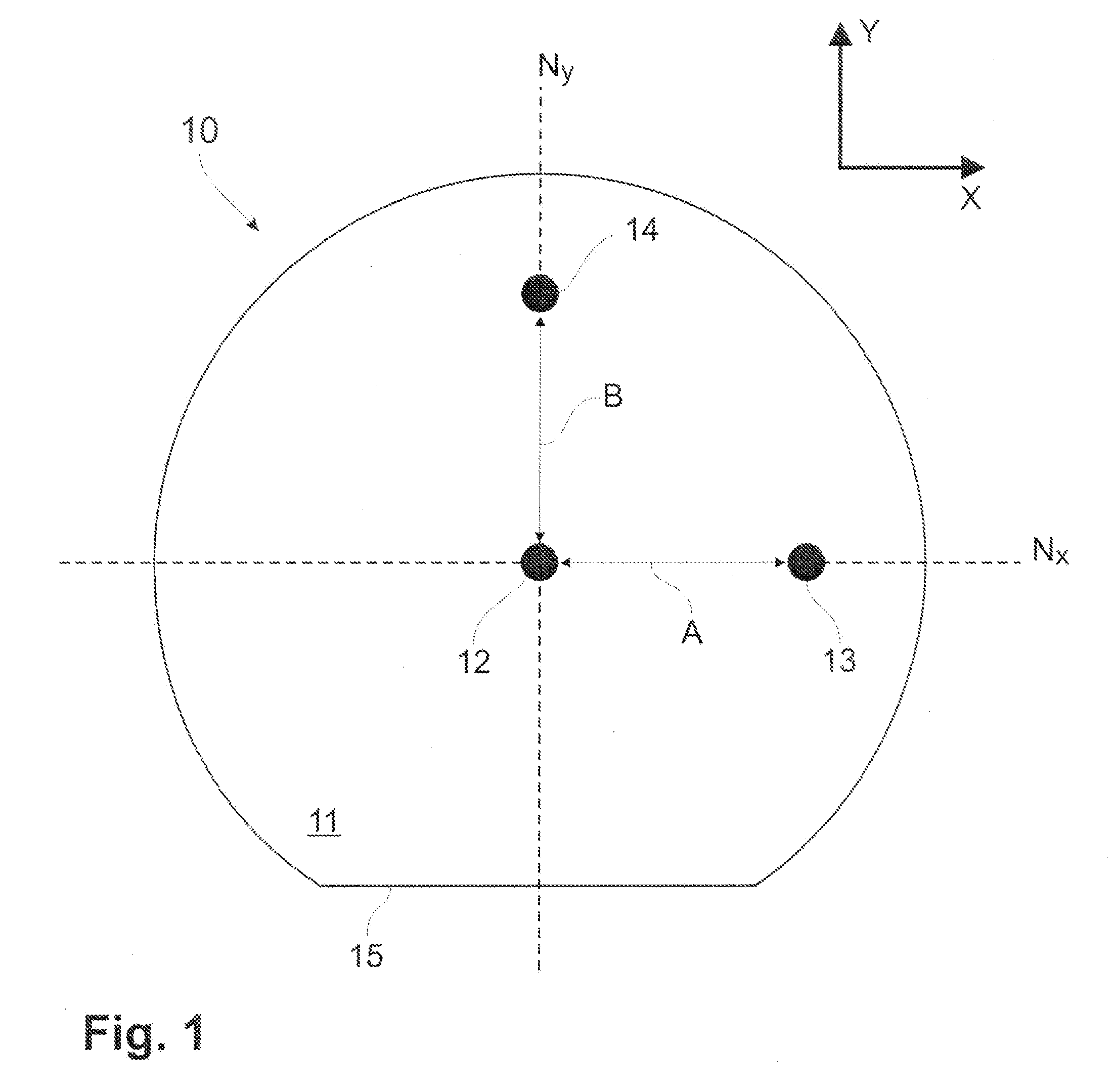
[0020]Referring now to the drawings and, more particularly, to FIG. 1, an optical fiber sensor in accordance with a first embodiment is generally shown at 10. The optical fiber sensor 10 is an optical fiber having a cladding 11, a central core 12, and peripheral cores 13 and 14.
[0021]The cladding 11 has a generally circular section, but has a flat edge, defining a flat surface 15 on the full length of the cladding 11. The cladding 11 is made of a material having an effective index of refraction smaller than that of the cores 12, 13 and 14.
[0022]The central core 12 is generally centrally positioned within the cladding 11, as is visible in FIG. 1.
[0023]The peripheral cores 13 and 14 are respectively spaced apart from the central core 12 by distances A and B. In the first embodiment of FIGS. 1 and 2, the central core 12 and the peripheral core 13 lie in a first neutral plane Nx generally parallel to the flat surface 15. The central core 12 and the peripheral core 14 lie in a second neu...
second embodiment
[0031]Referring to FIG. 4, an optical fiber sensor in accordance with a second embodiment is generally shown at 10′. The optical fiber sensor 10′ is generally similar to the optical fiber sensor 10 (FIG. 1), in that it has a cladding 11, a central core 12, and peripheral cores 13 and 14. The optical fiber sensor 10′ additionally has peripheral cores 13′ and 14′, diametrically opposed to the peripheral cores 13 and 14, respectively.
[0032]The peripheral cores 13′ and 14′ are provided to increase the sensitivity of the optical fiber sensor 10′. More specifically, the longitudinally aligned sets of gratings of the peripheral cores 13′ and 14′ are respectively combined with that of the peripheral cores 13 and 14, to provide two gratings per axis of curvature (e.g., axes X and Y of FIG. 1). For example, when the grating in the peripheral core 13 is compressed, the corresponding grating in the peripheral core 13′ is elongated, giving twice the total spectral shift, in opposite directions, ...
third embodiment
[0052]Referring to FIG. 7, an optical fiber sensor in accordance with a third embodiment is generally shown at 10″. The optical fiber sensor 10″ is similar to the optical fiber sensor 10′ of FIG. 4, whereby like reference numerals will designate like elements.
[0053]The cladding 11 of the optical fiber sensor 10″ has a generally circular section, but with a pair of flat edges, defining flat surfaces 15 and 15′ on the full length of the cladding 11. Advantageously, the fiber sensor 10″ is symmetrical along both the X- and Y-axes. The planes of symmetry are therefore coplanar with the first neutral plane Nx and the second neutral plane Ny. The presence of a pair of flat surfaces 15 and 15′ facilitates the securing of the optical fiber sensor 10″ in a desired orientation, and ensures that the central core 12 is n the neutral planes for both axes.
[0054]Amongst contemplated uses for the optical fiber sensors 10 / 10′ / 10″ and the optical fiber sensor system 100 are posture detection (e.g., h...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com