Patents
Literature
1182results about "Glass fibre products" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
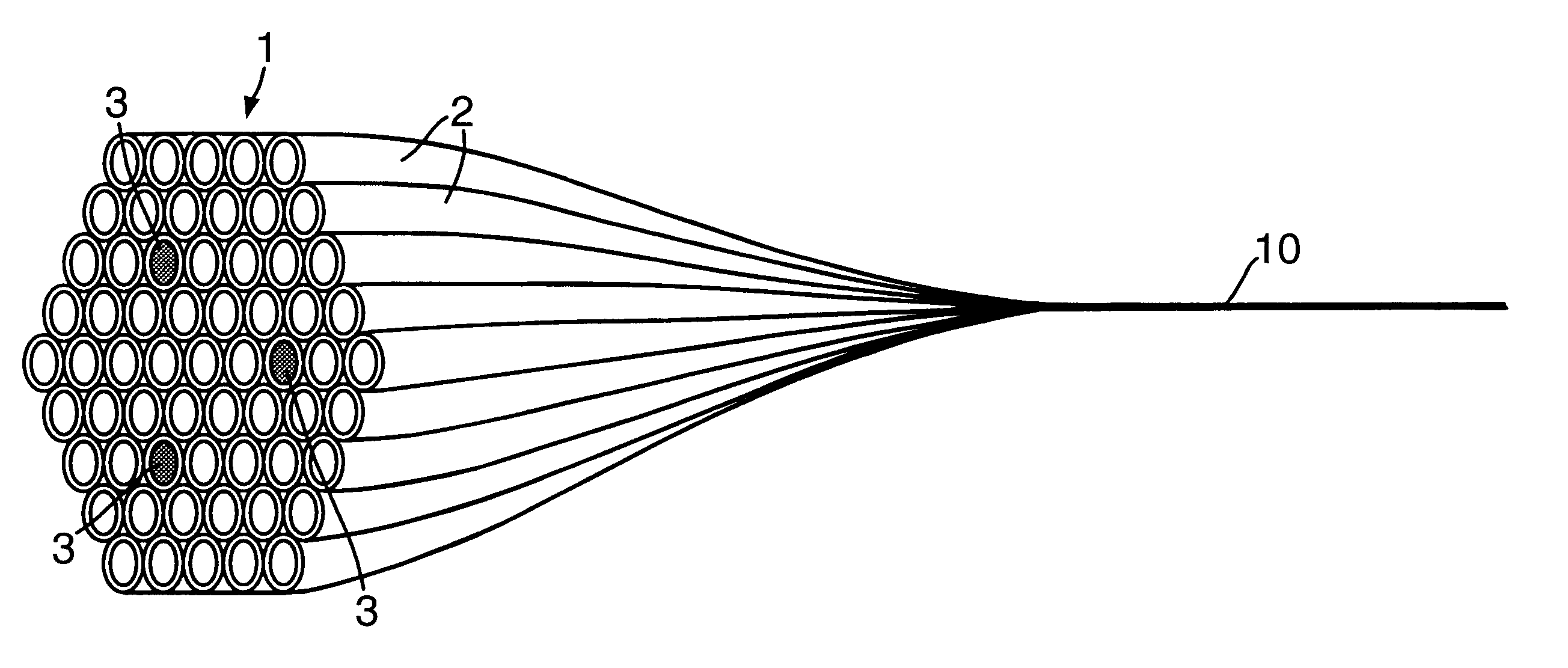
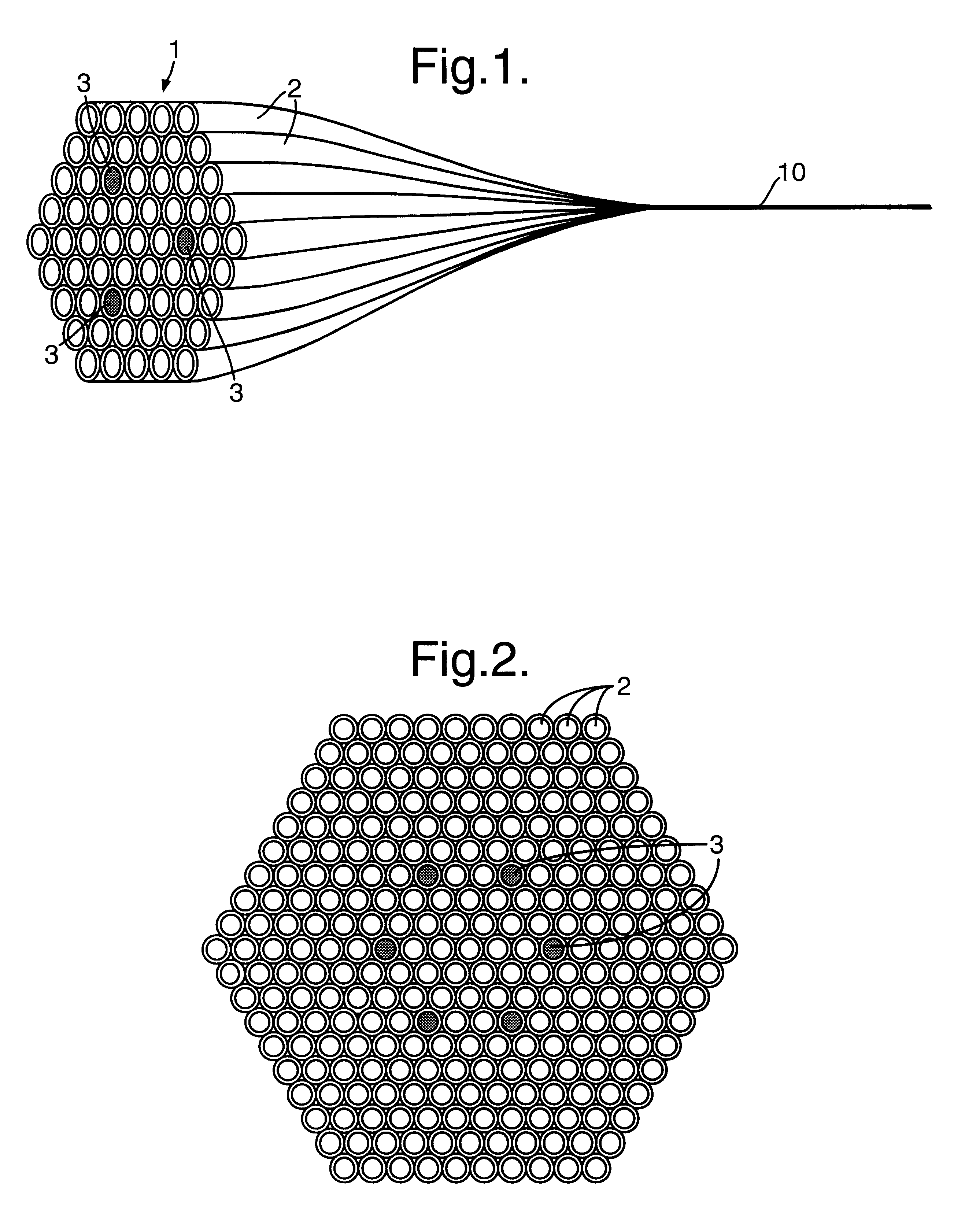
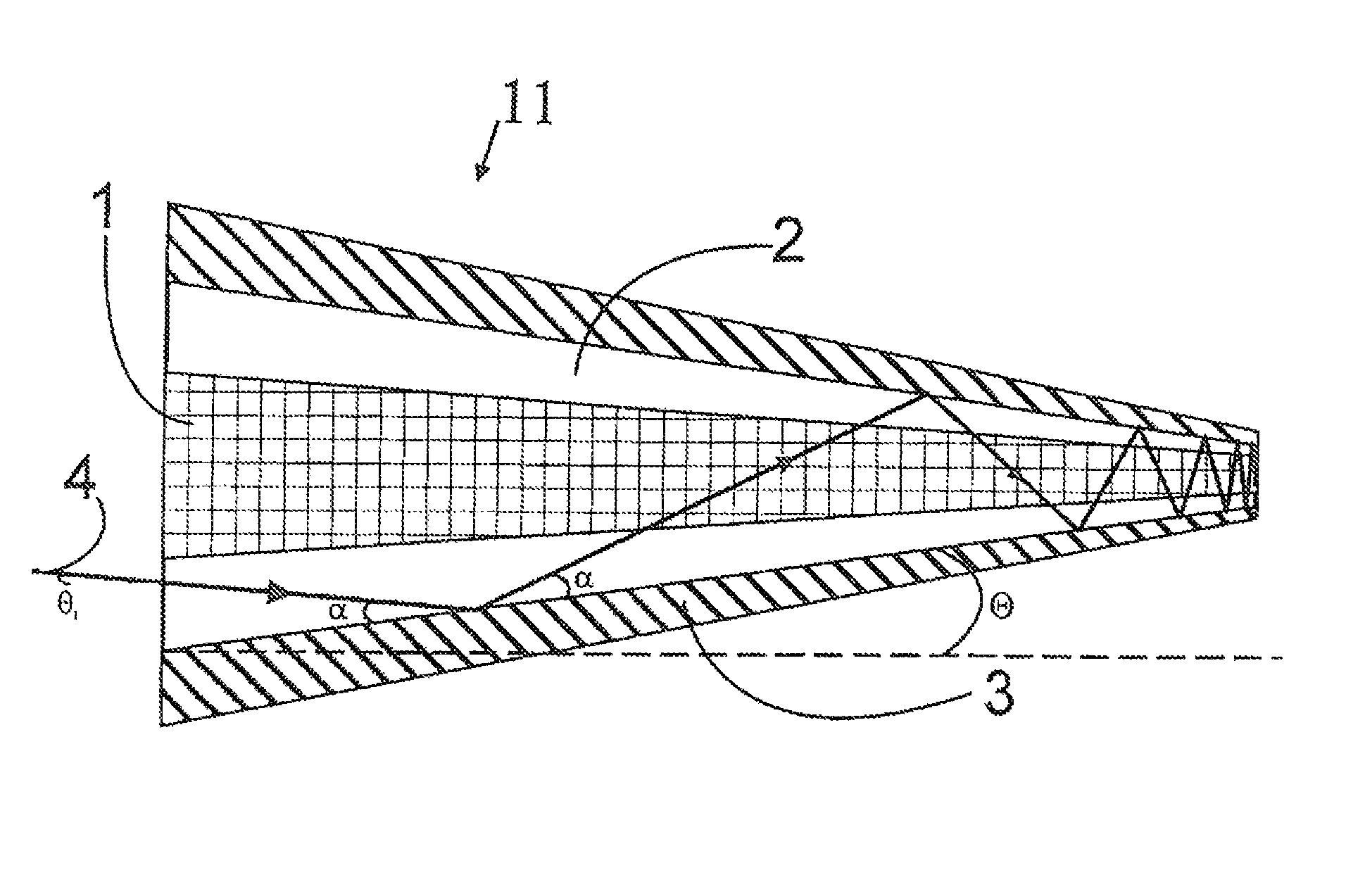
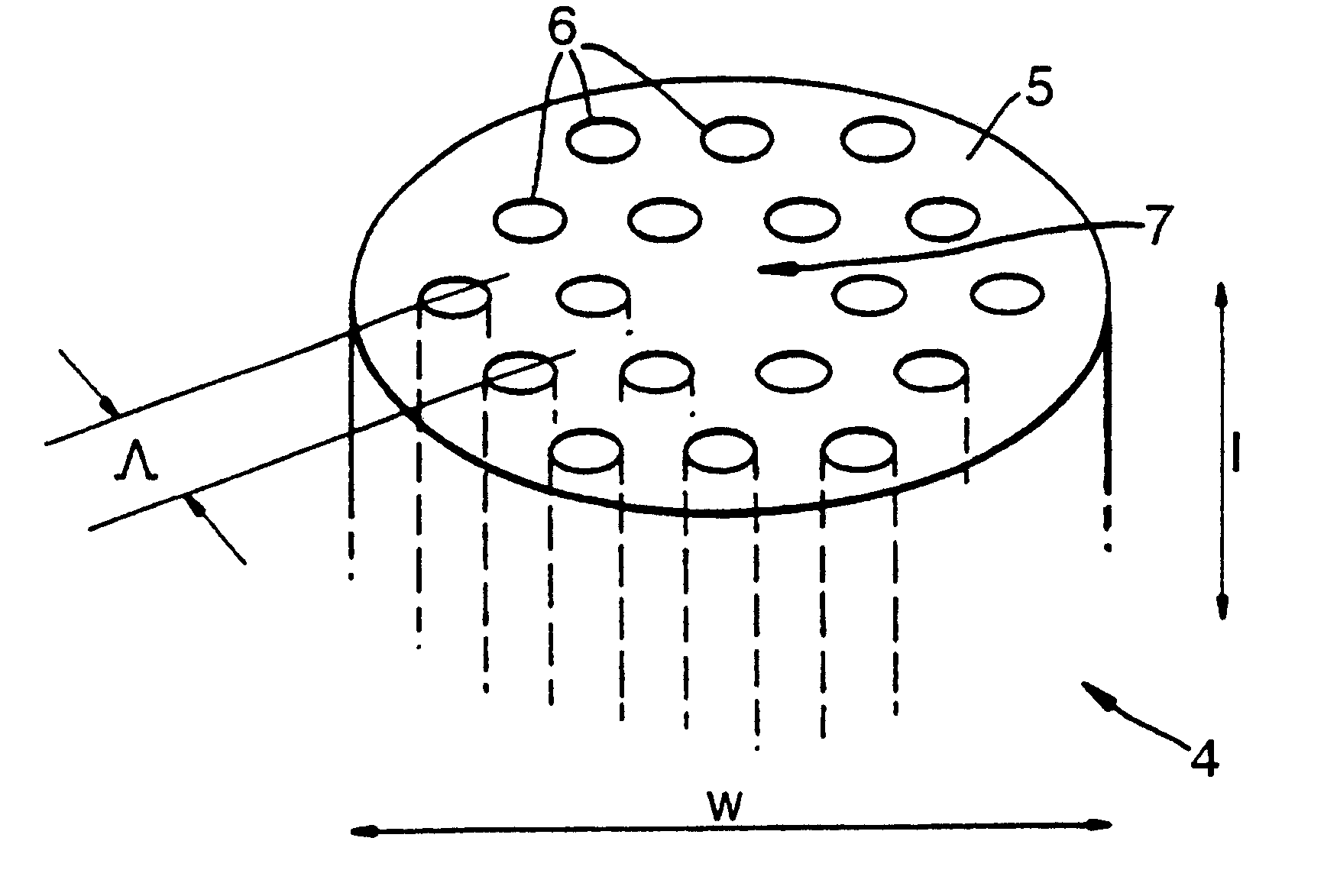
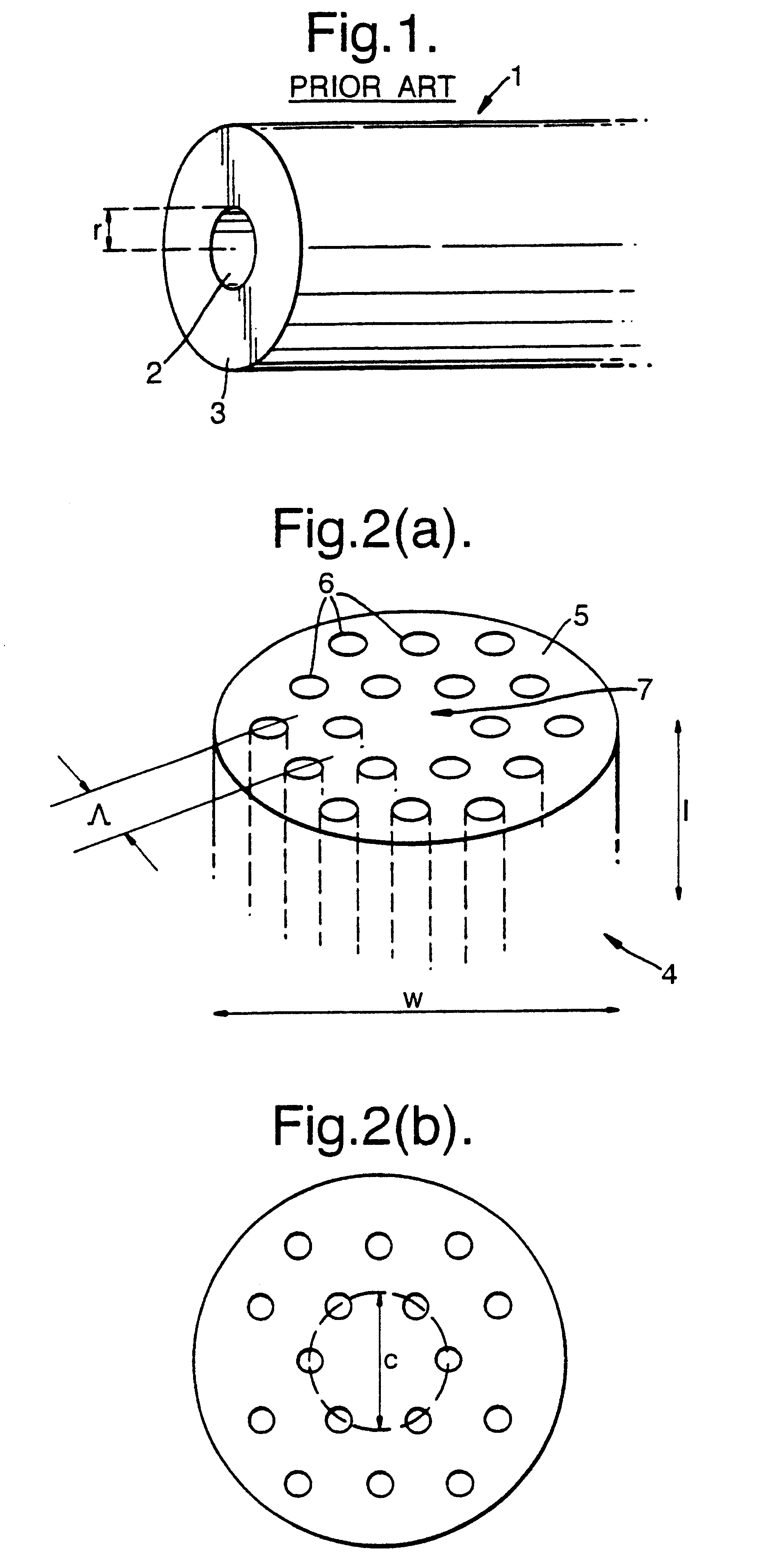
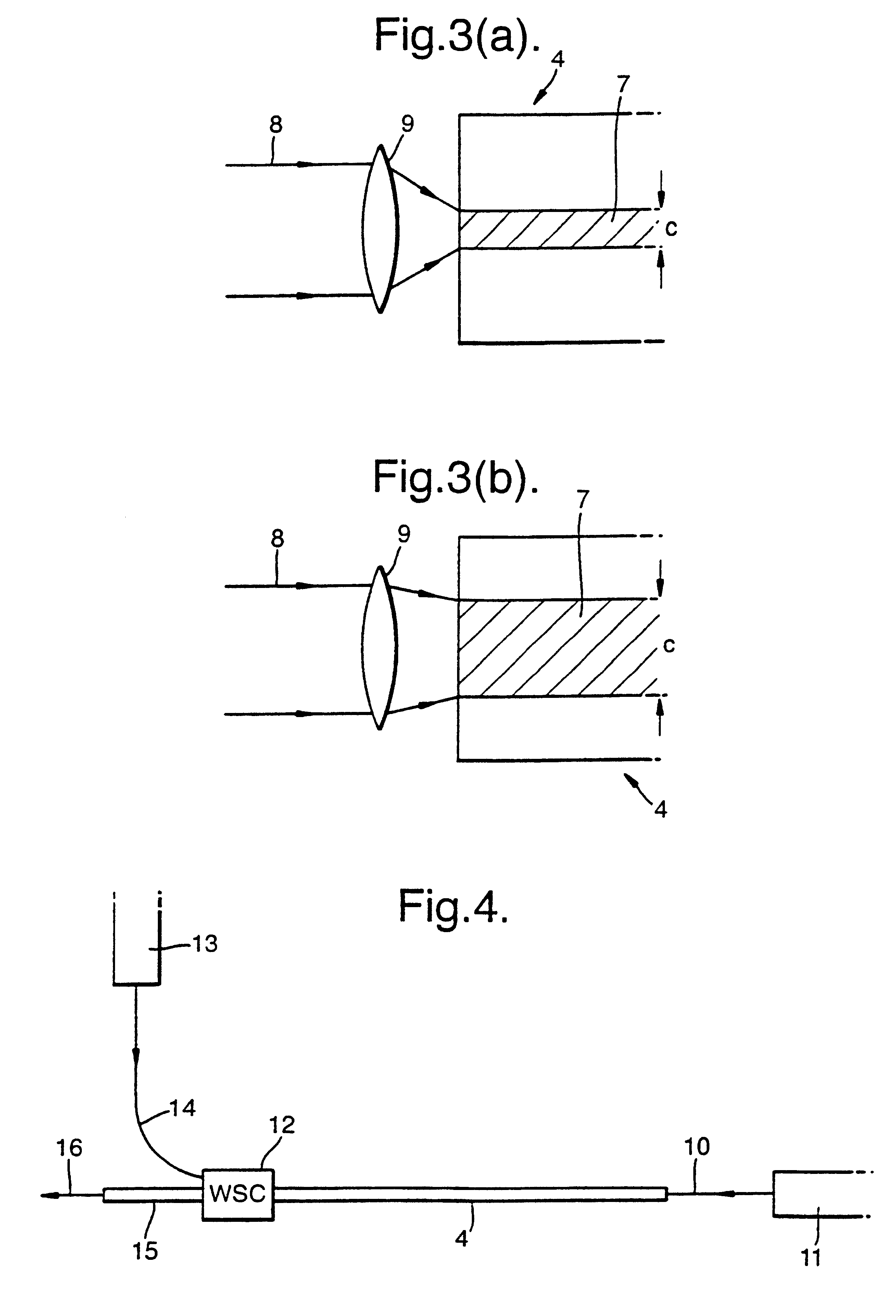
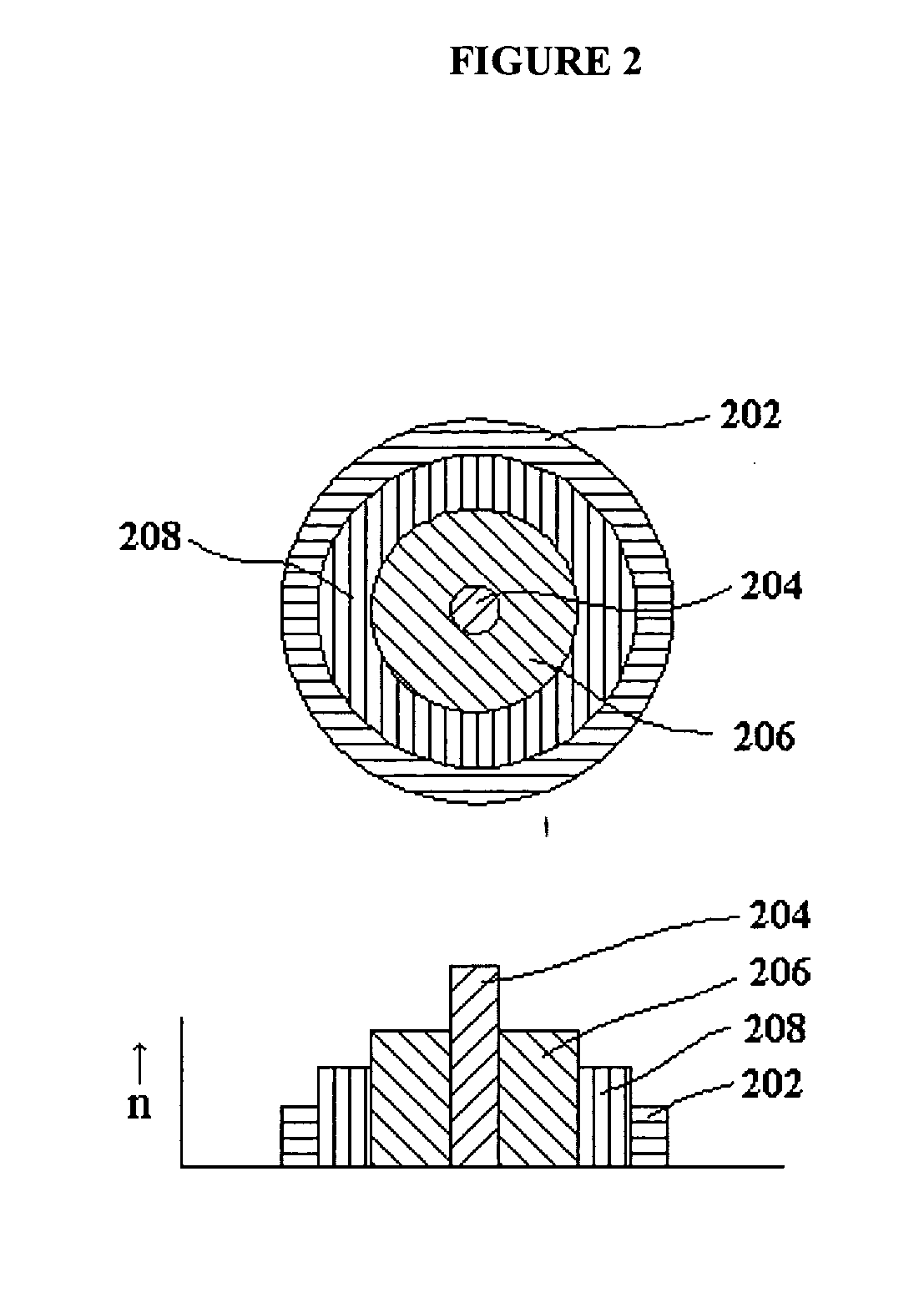
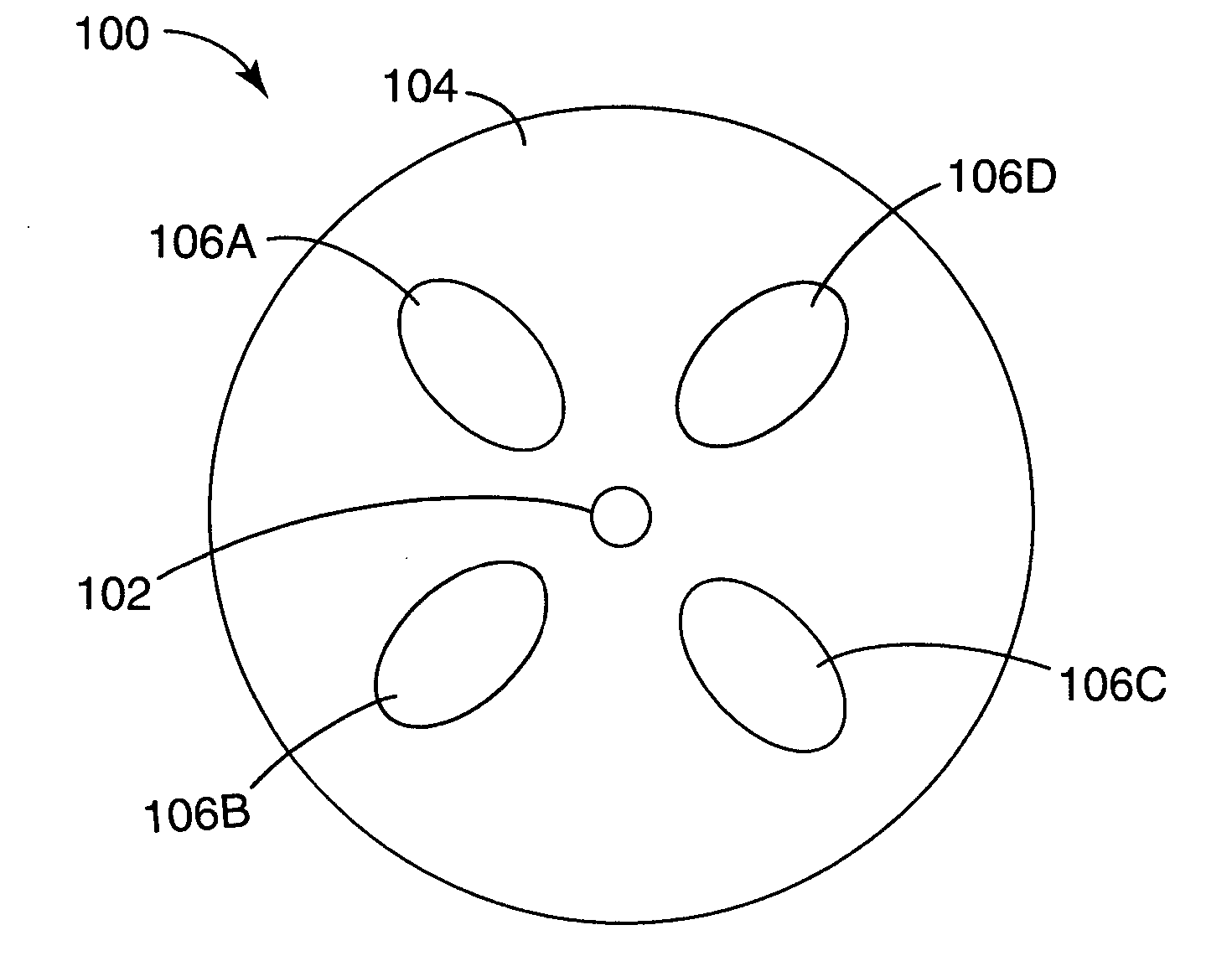
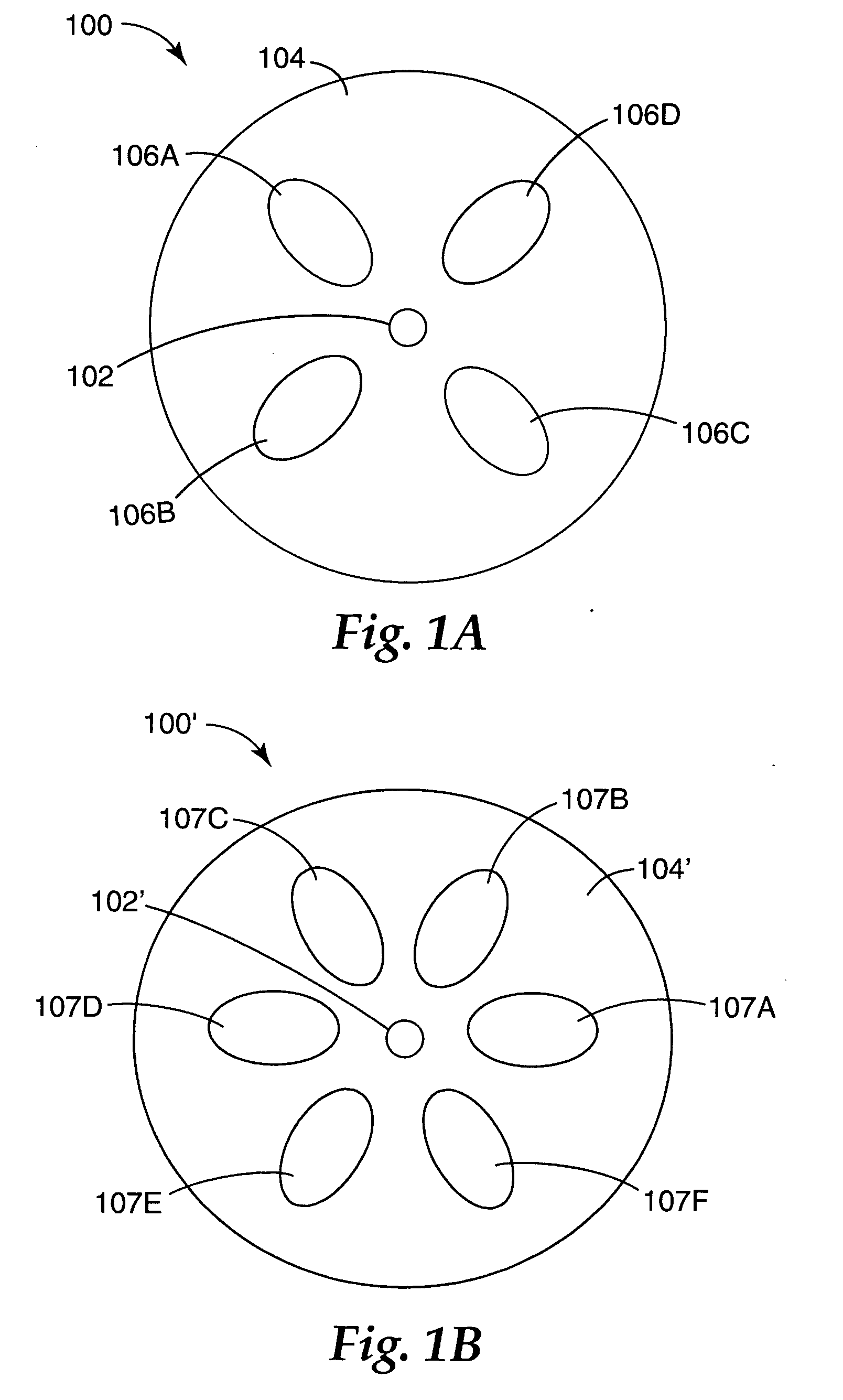
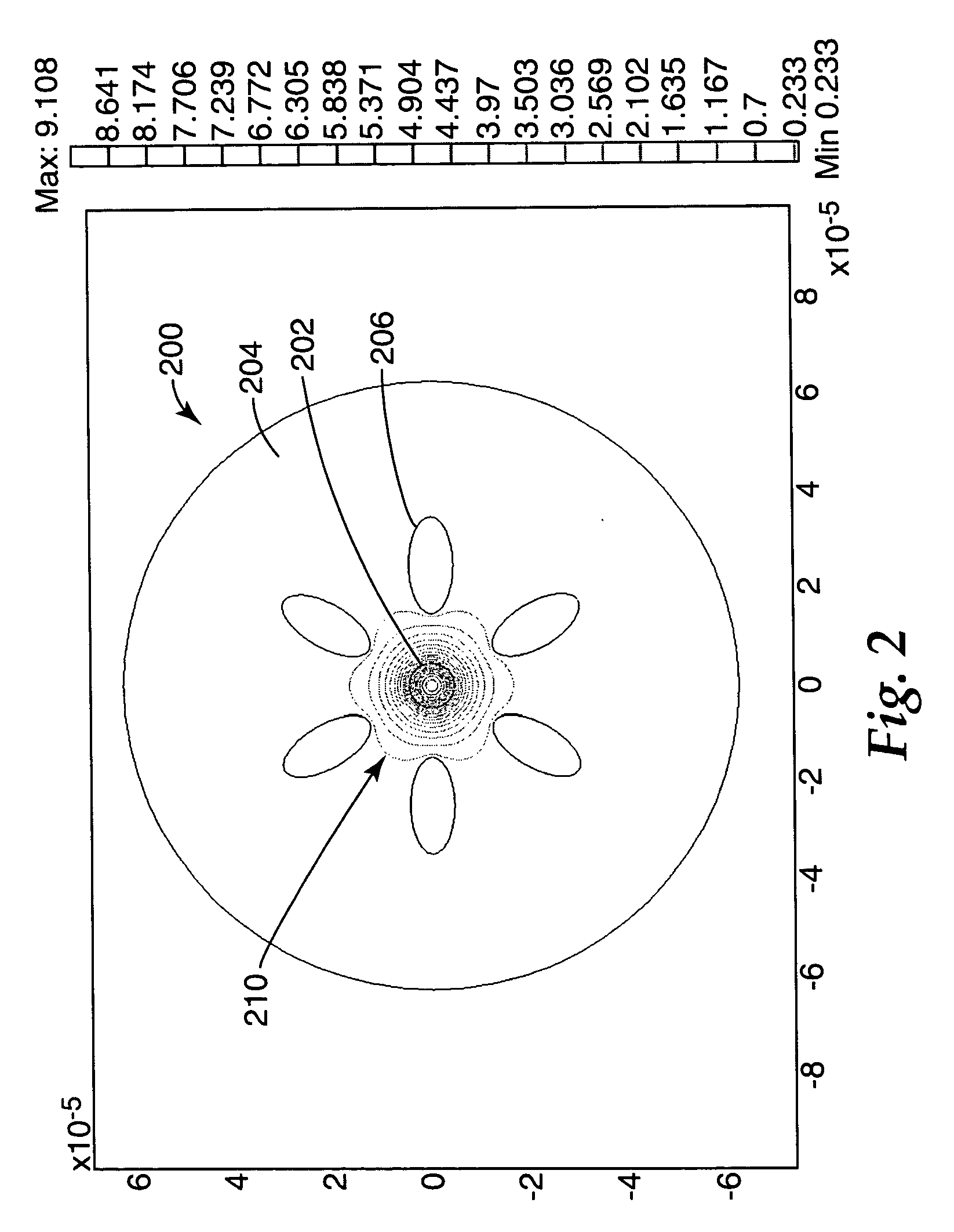
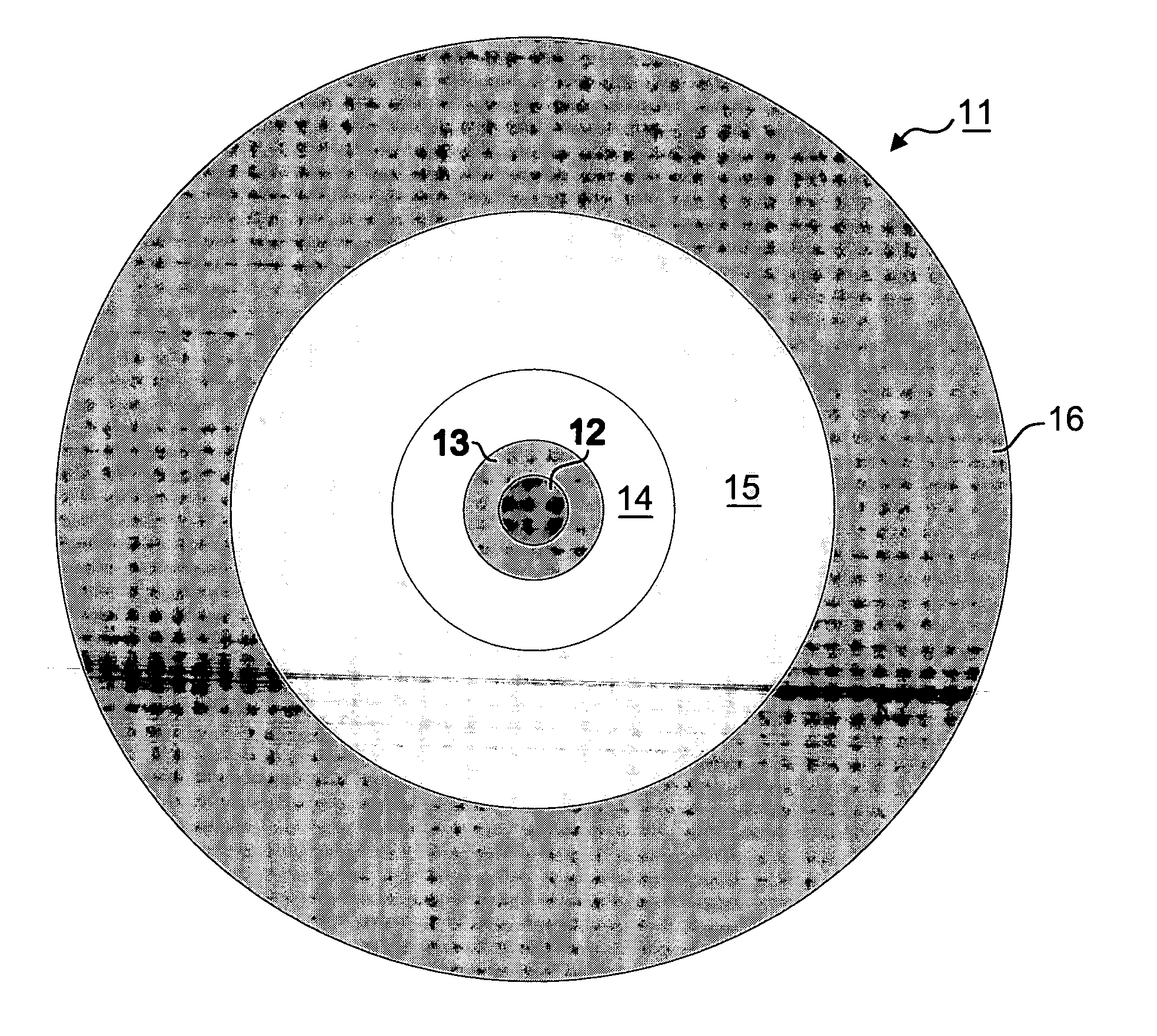
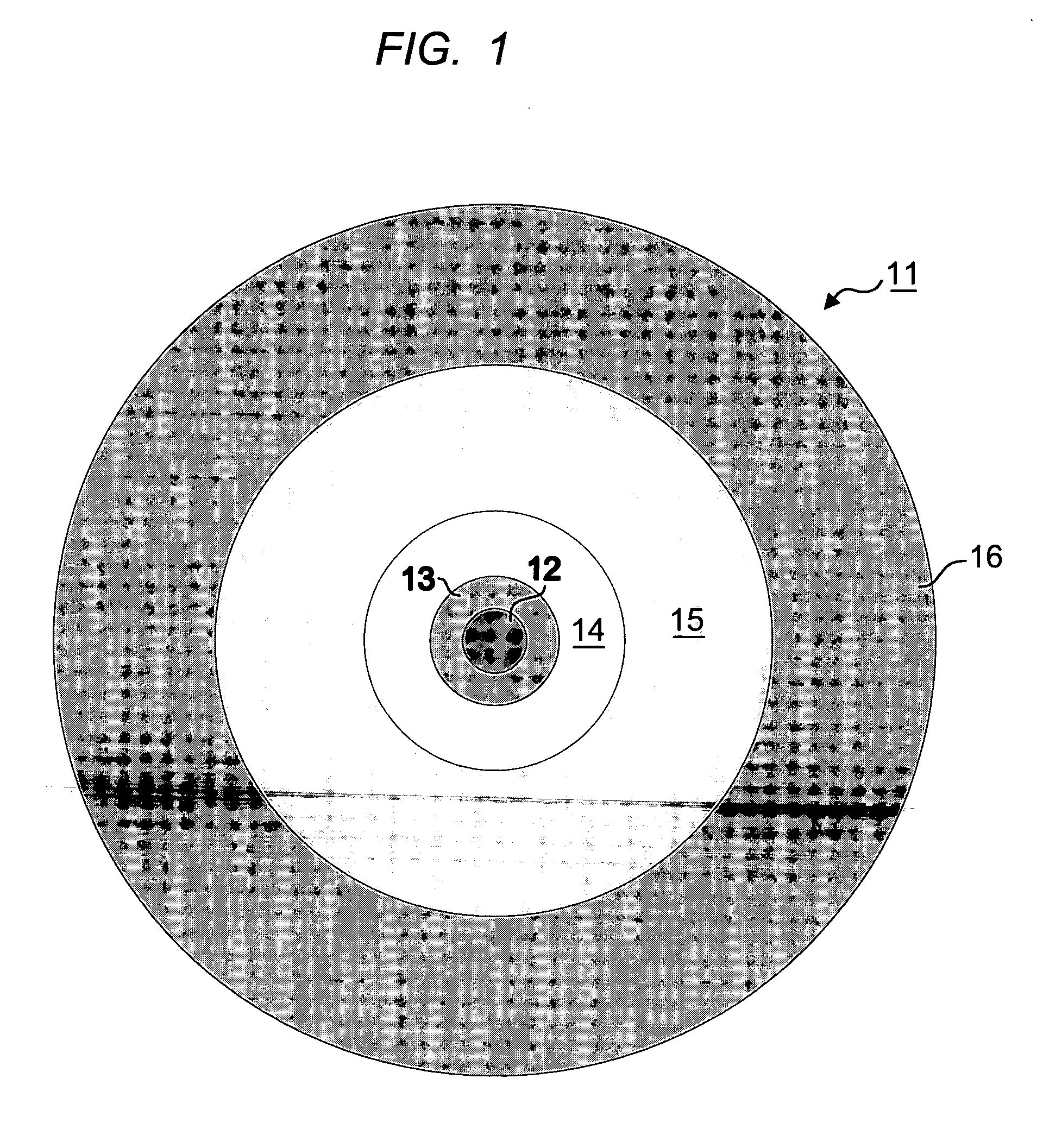
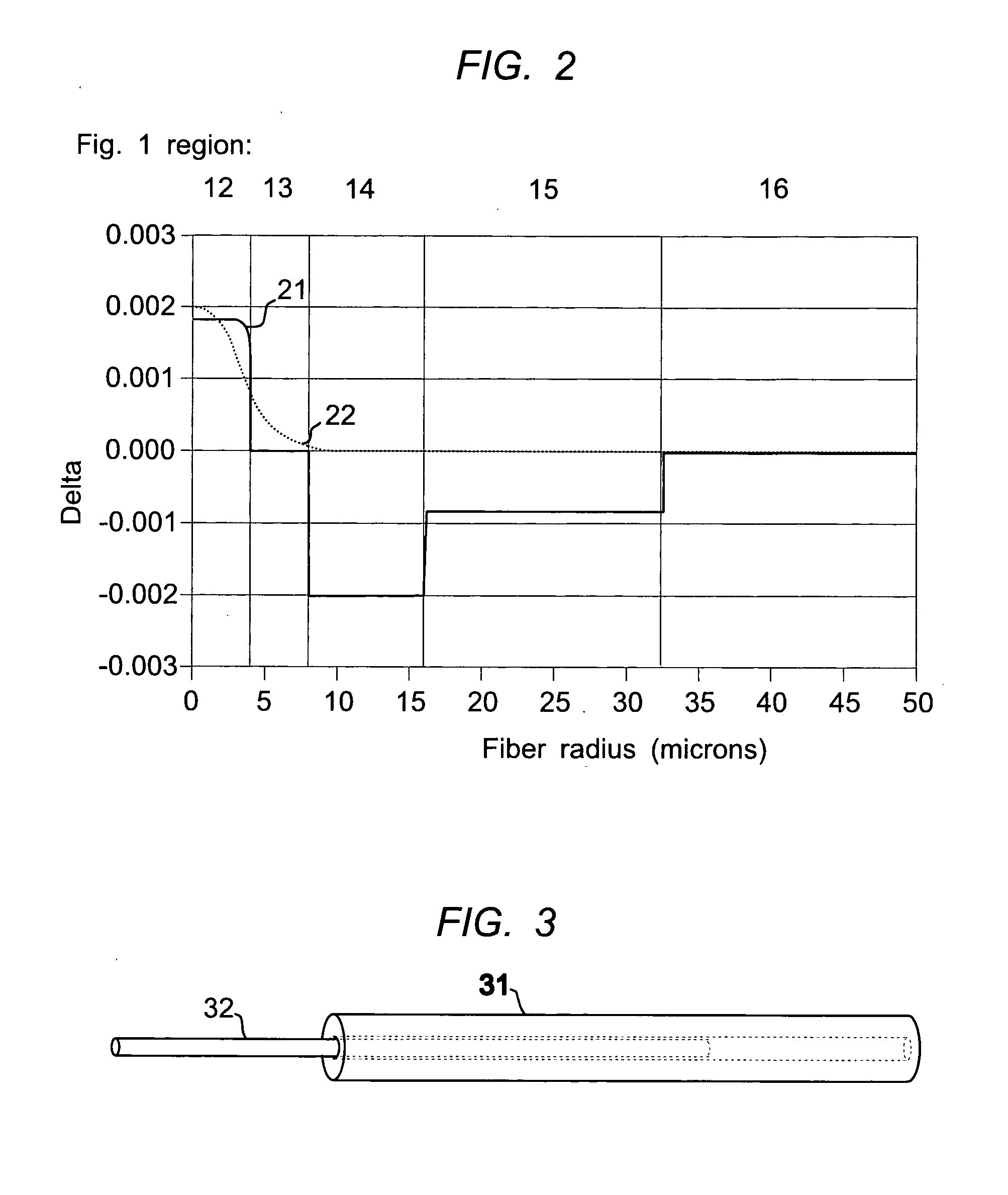
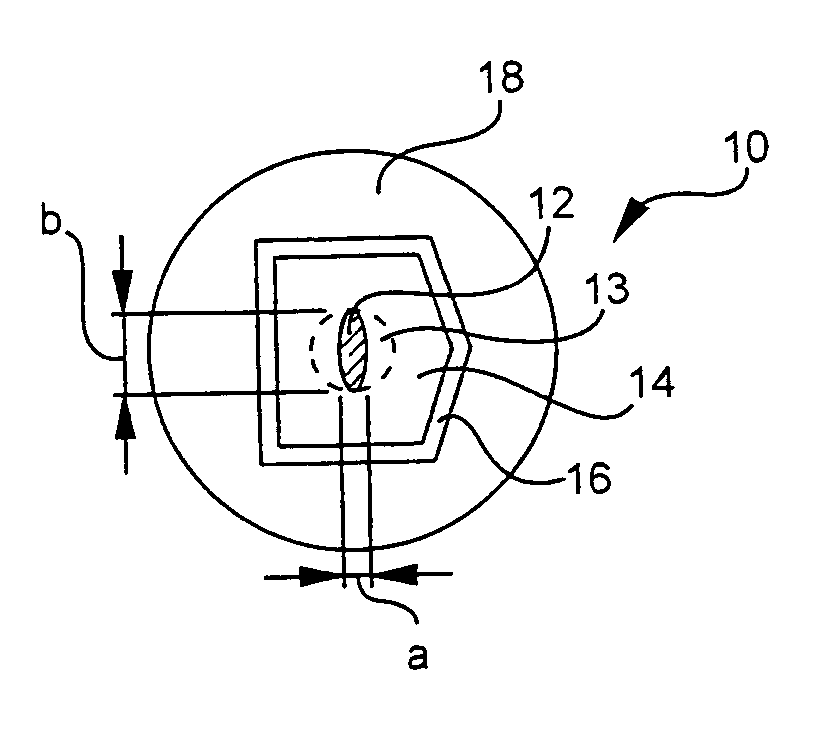
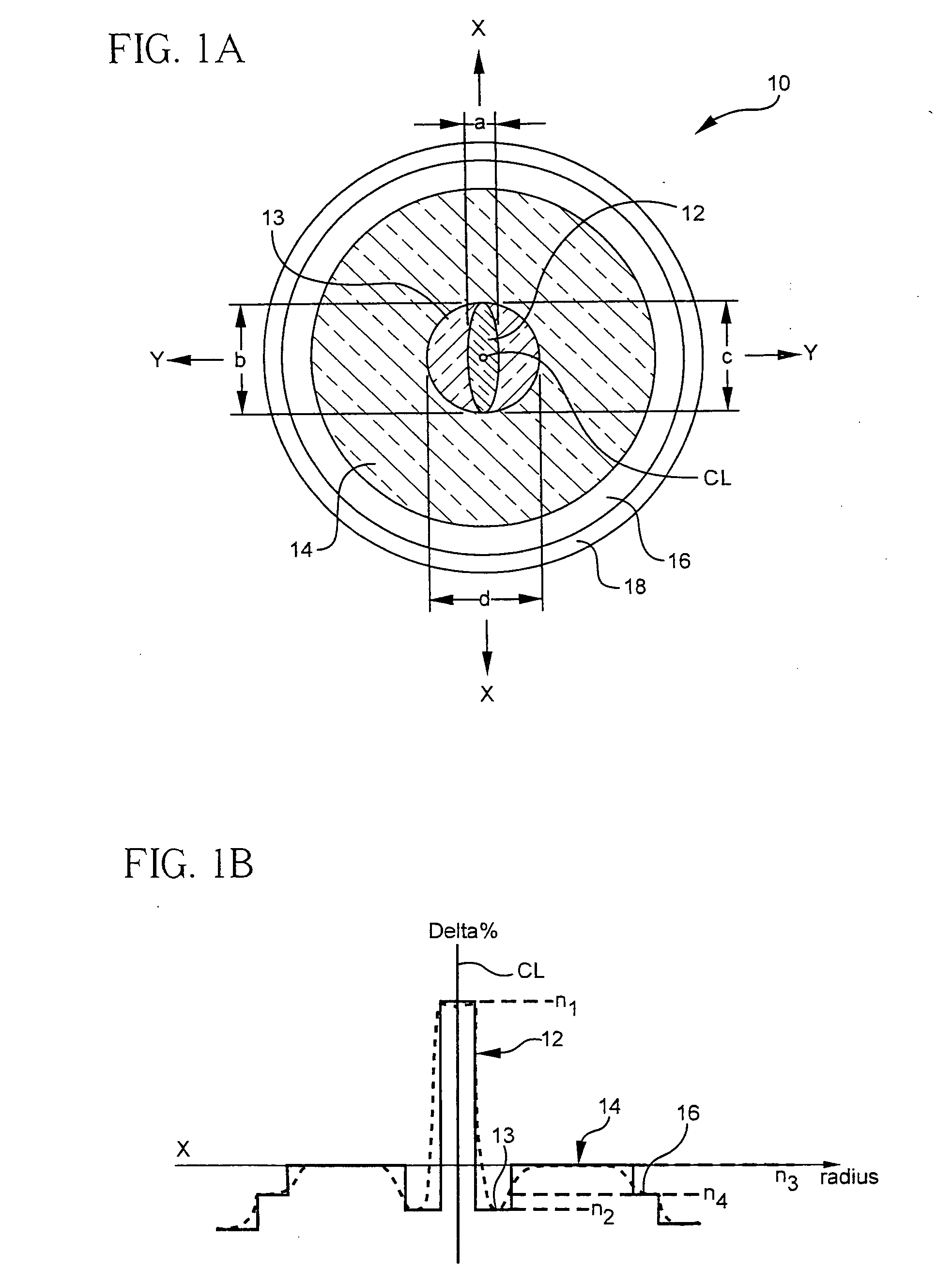
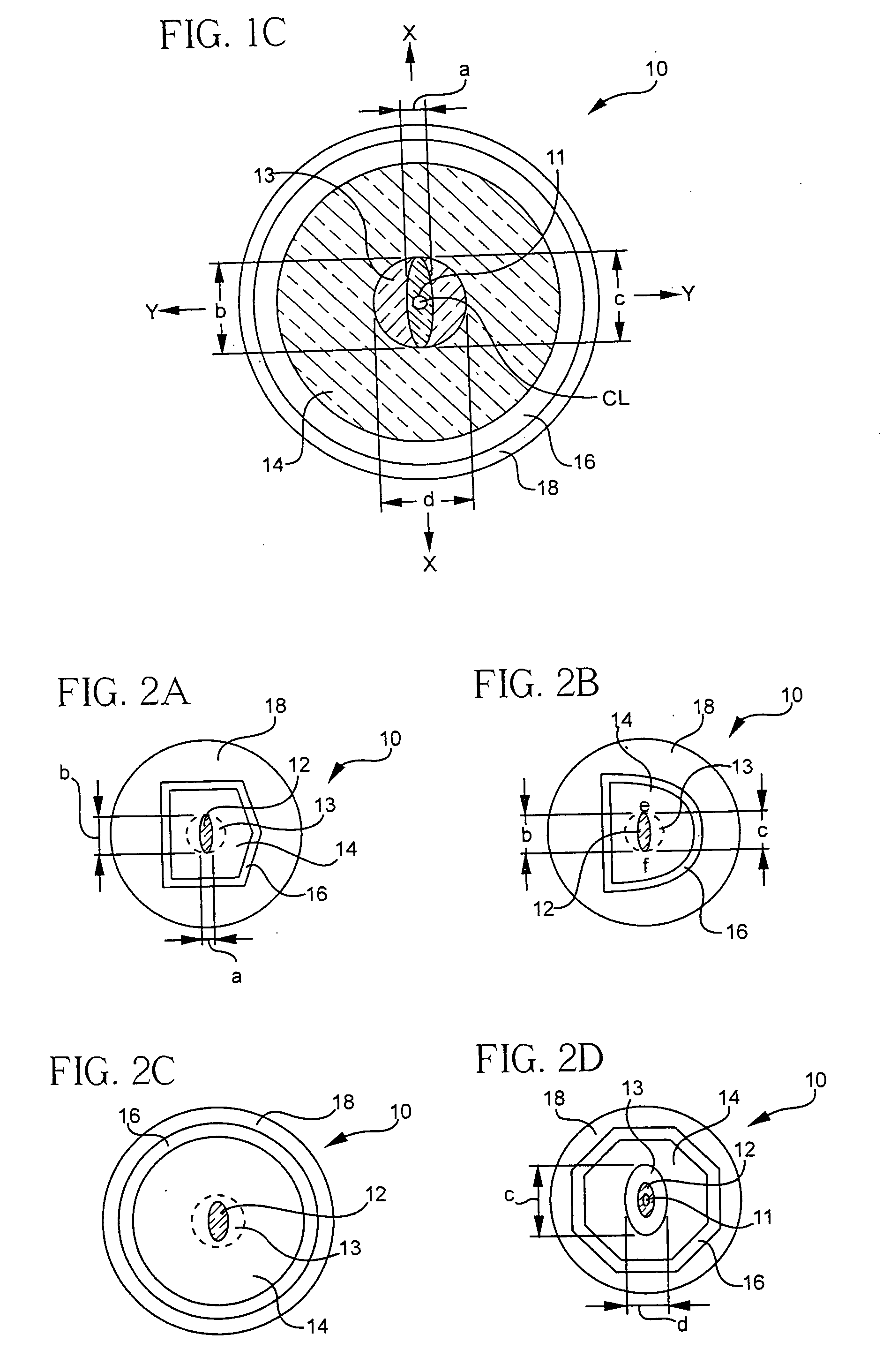
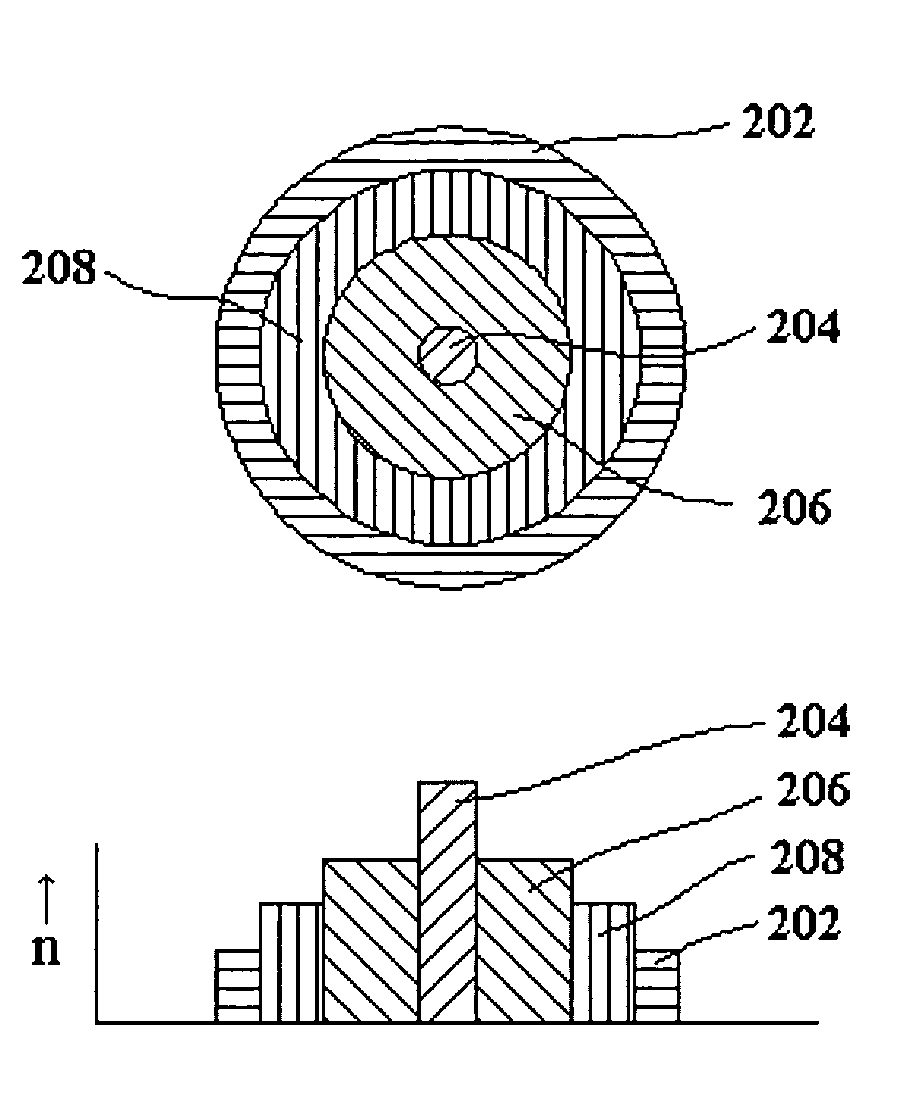
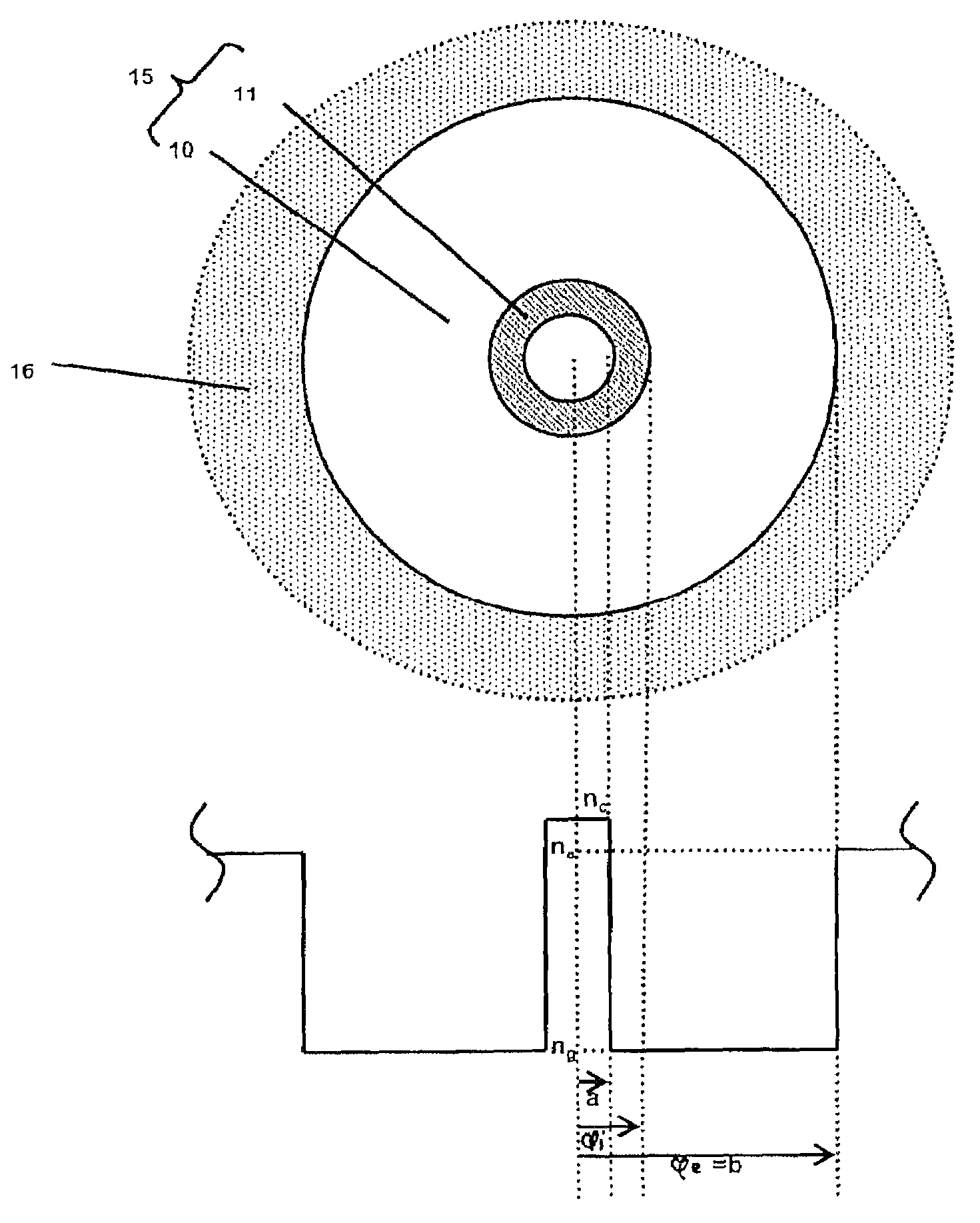
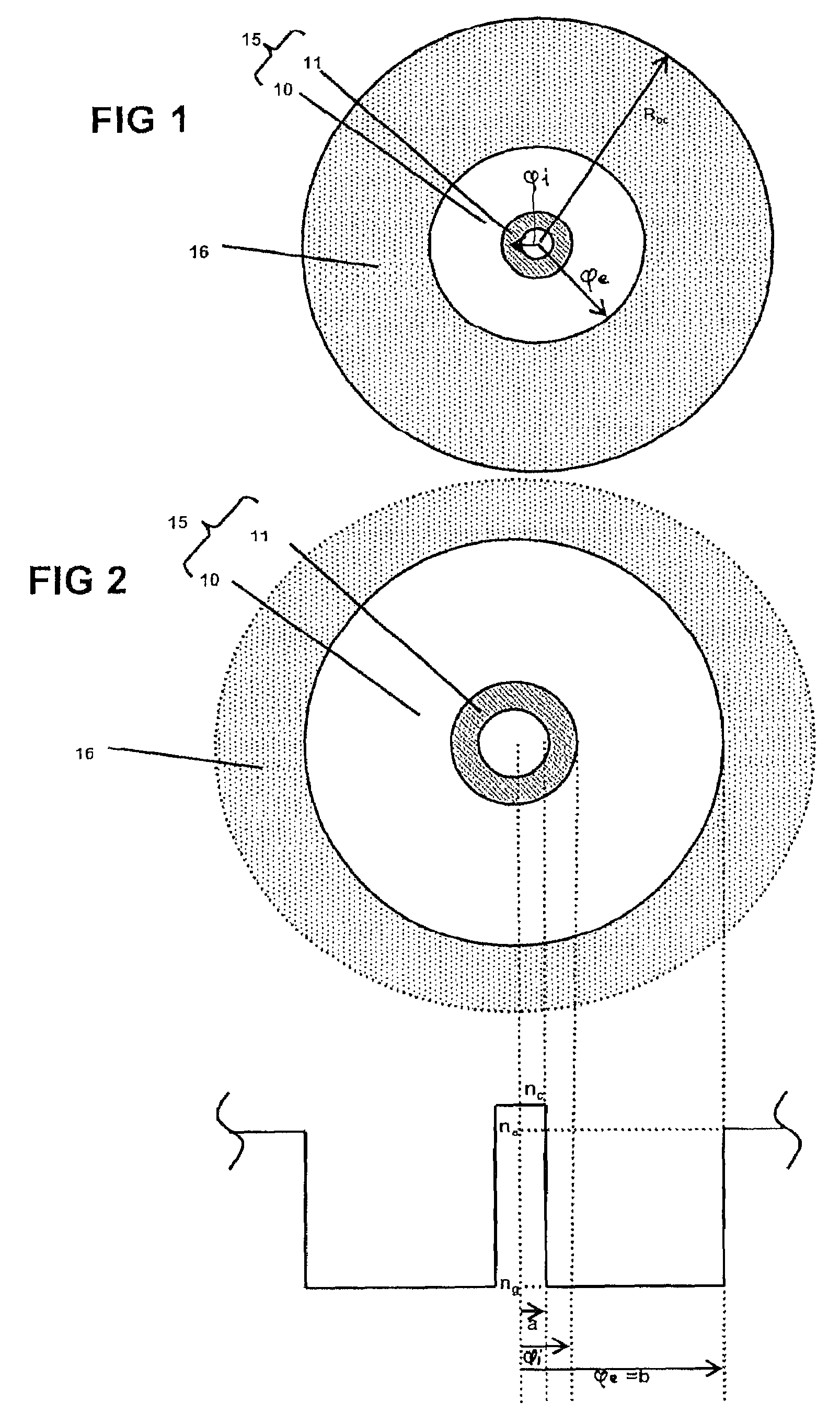
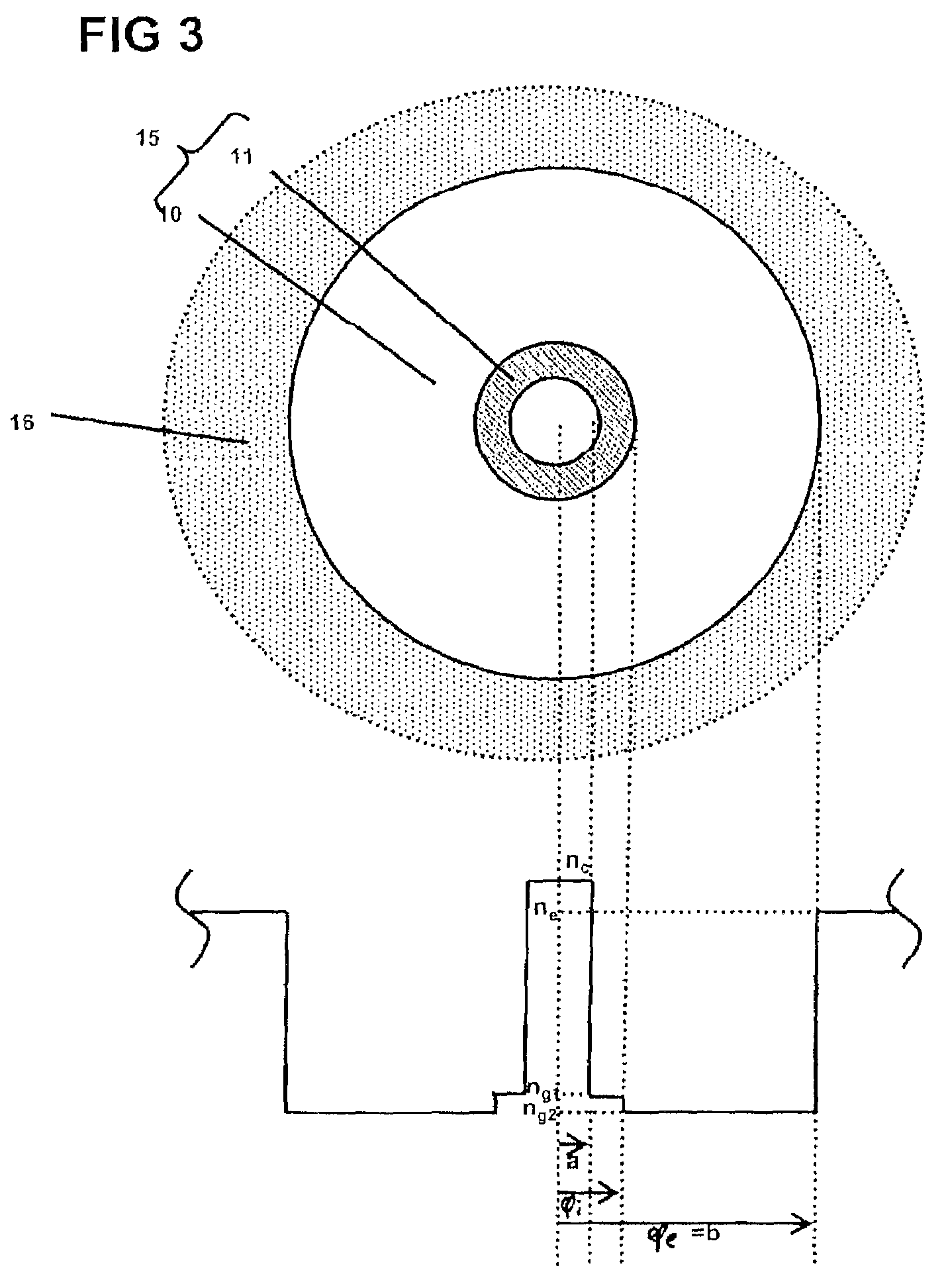
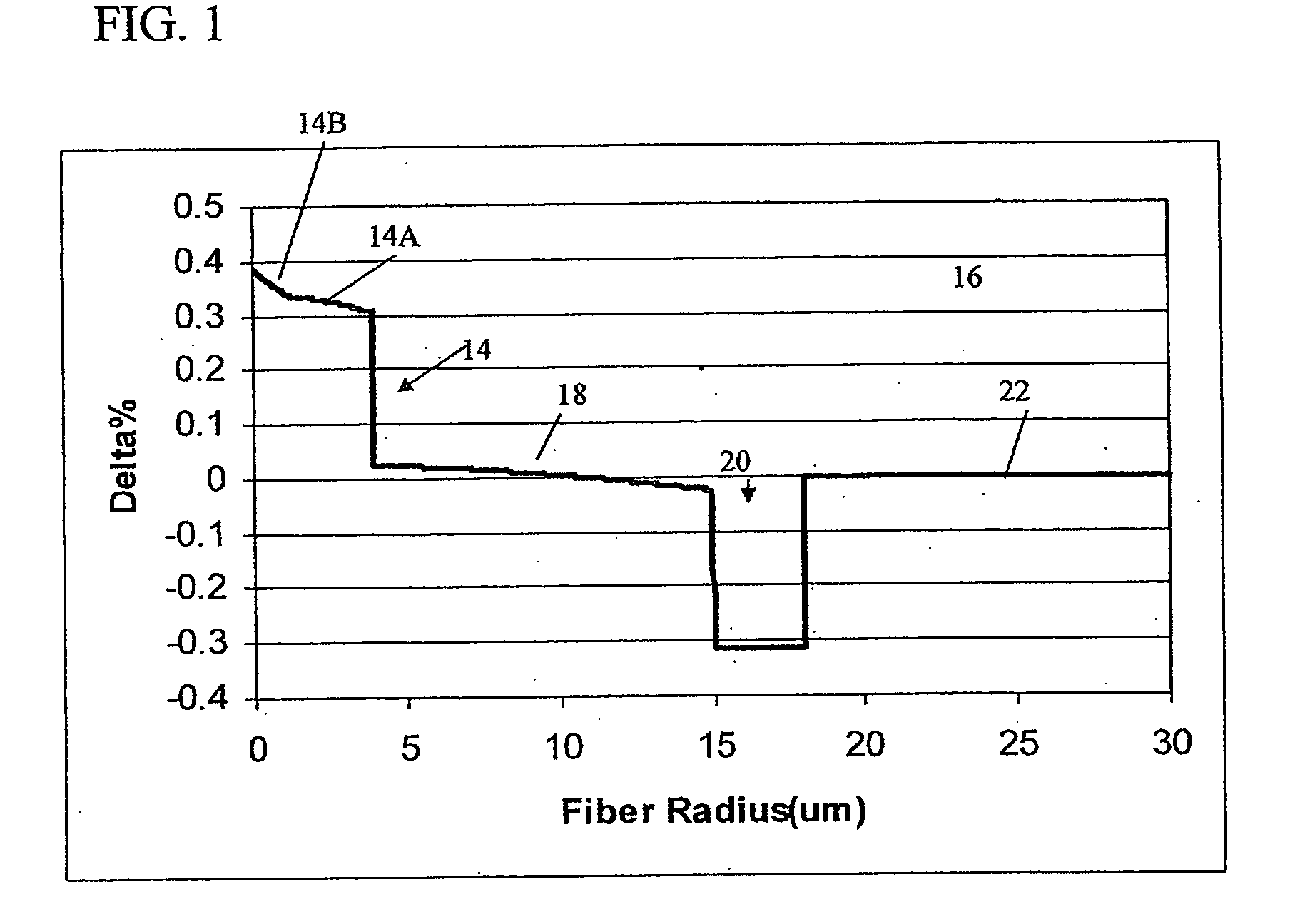
Multicore optical fibre
InactiveUS6301420B1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRefractive index
An optical fiber for transmitting radiation comprising two or more core regions, two or more core regions, each core region comprising a substantially transparent core material and having a core refractive index, a core length, and a core diameter, wherein said core regions are arranged within a cladding region, said cladding region comprising a length of first substantially transparent cladding material, having a first refractive index, wherein said first substantially transparent cladding material has an array of lengths of a second cladding material embedded along its length, wherein the second cladding material has a second refractive index which is less than said first refractive index, such that radiation input to said fiber propagates along at least one of said core regions. The cladding region and the core regions may be arranged such that radiation input to said optical fiber propagates along one or more said lengths of said core regions in a single mode of propagation. The optical fiber may be used as a bend sensor, a spectral filter or a directional coupler. The invention also relates to a method of manufacturing a multicore optical fiber.
Owner:NKT RES & INNOVATION
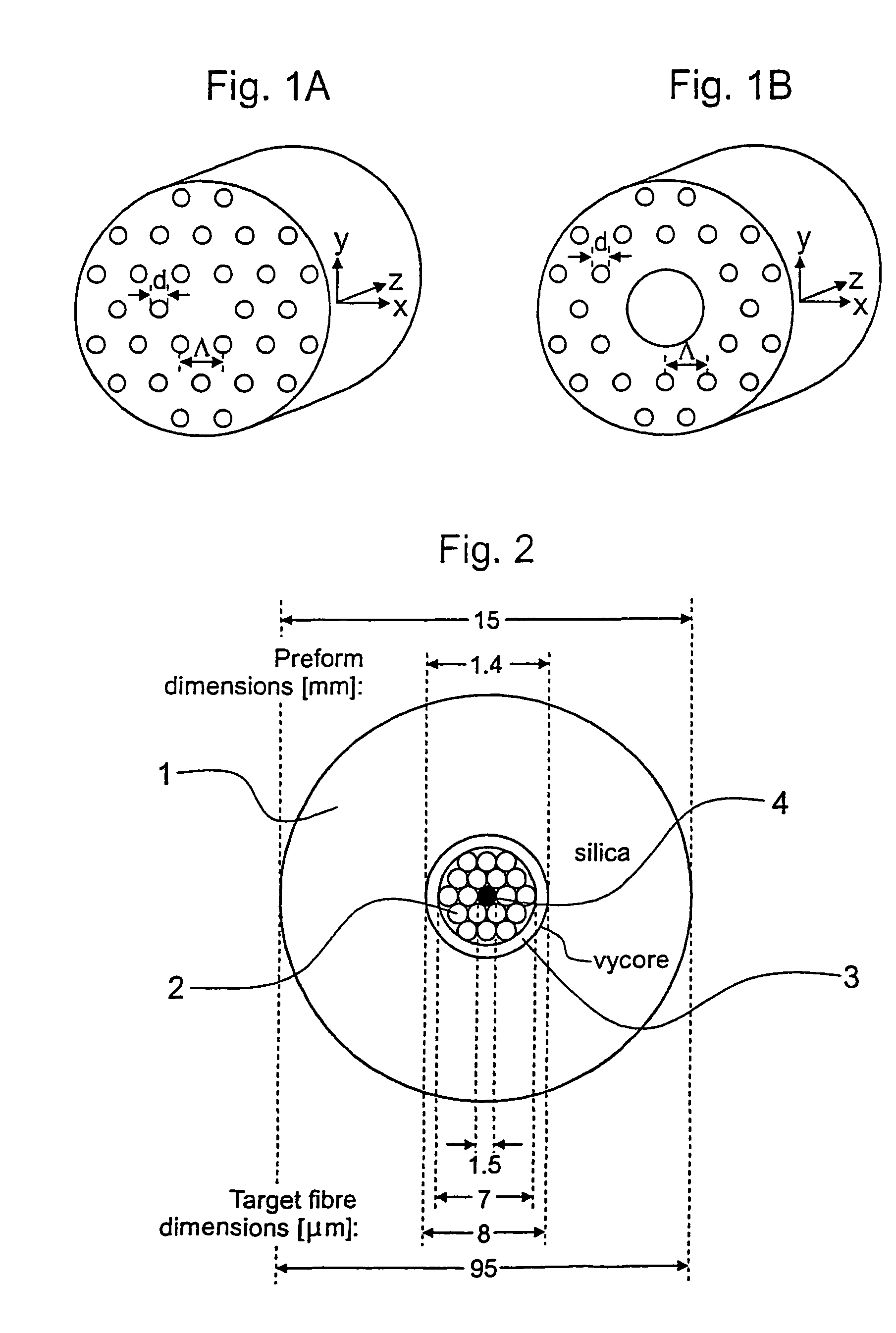
Holey optical fibres
An optical fiber structure having a holey fiber arranged in a holey outer support structure made up of holey tubes encased in a thin walled outer jacket. The holey fiber may have a solid core surrounded by a holey cladding having a plurality of rings of holes. With the invention it is possible to produce robust, coated and jacketed fibers with microstructured core features of micrometer size relatively easily using existing fiber fabrication technology. This improvement is a result of the outer holey structure which reduces the thermal mass of the supporting structure and makes it possible to reliably and controllably retain small hole features during the fiber fabrication process.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
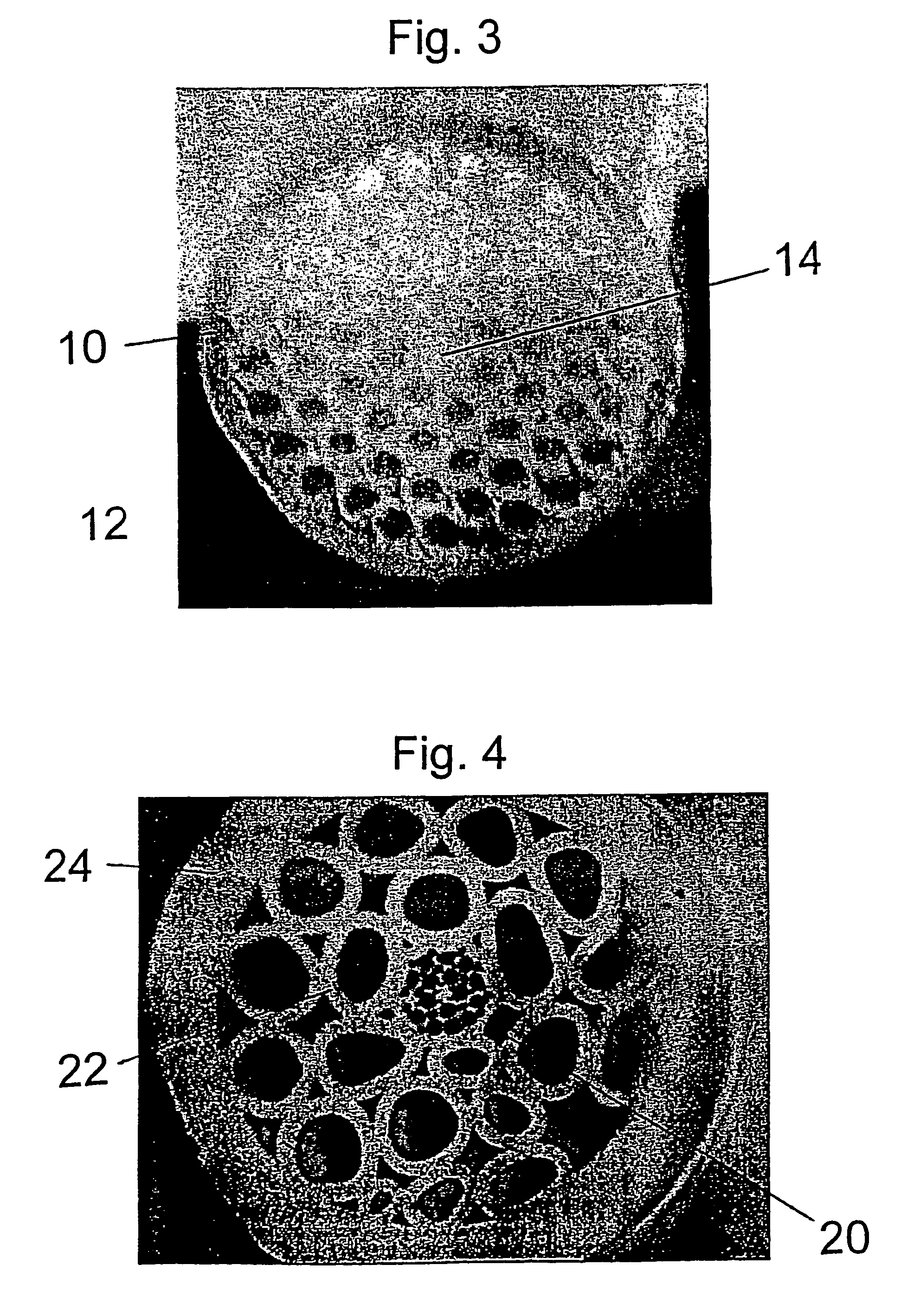
Active optical fiber and method for fabricating an active optical fiber
ActiveUS8433168B2Reduce the overall diameterLarge volumeLaser detailsMetal rolling stand detailsFiberActive core
A section of active optical fiber (11) which comprises an active core (1), an inner cladding layer (2) and an outer cladding layer (3). The diameter of said core 1) and the thickness of said inner cladding (2) change gradually along the length of said section of active optical fiber (11). This forms tapered longitudinal profile enabling a continuous mode conversion process along the length of the section of fiber (11). The method for fabricating a section of tapered active optical fiber comprises the steps of fabricating a preform for drawing active optical fiber from said preform, installing said preform into a drawing tower, drawing optical fiber in said drawing tower and altering at least one of the two parameters including the take-off preform speed and the take-up fiber speed during drawing of the optical fiber.
Owner:AMPLICONYX OY
Optical fiber and method for making such fiber
ActiveUS7313312B2Coupling efficiency is highIncrease optical powerOptical fibre with polarisationOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRare earth
According to one example of the invention an optical fiber comprises: (i) silica based, rare earth doped core having a first index of refraction n1; (ii) at least one silica based cladding surrounding the core and having a second index of refraction n2, such that n1>n2; wherein at least one of the core or cladding is doped with Al2O3, such that the ratio of max wt % to min wt % of Al2O3 concentration is less than 2:1.
Owner:CORNING INC
Manufacture method for polarization maintaining fiber and polarization maintaining fiber
InactiveCN102351415AImprove the finishImprove processing efficiencyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with polarisationSurface finishPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
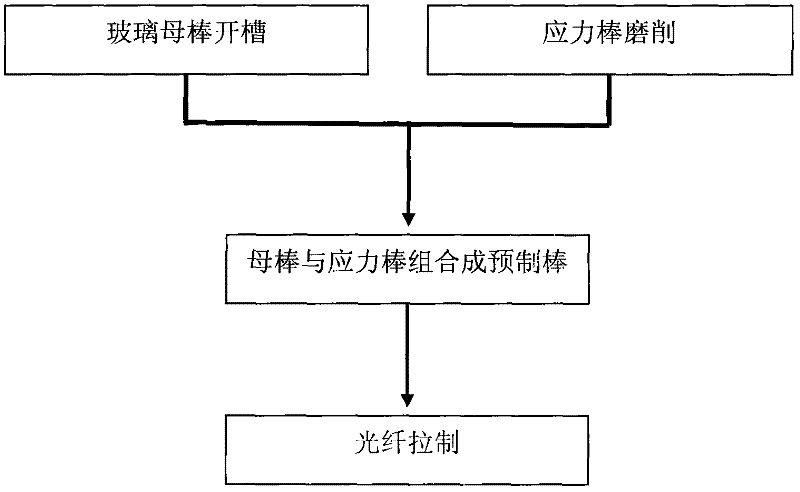
The invention provides a manufacture method for polarization maintaining fiber and a polarization maintaining fiber, and relates to optical waveguide fibers in the field of fiber-optical communication and fiber optical sensors. The method comprises the following steps that: (1) two oppositely arranged open slots with a same shape are inwardly provided at a side surface of a glass mother rod, stress rods are machined to obtain a shape matching the open slots, and the centers of the cross sections of the two open slots and the center of circle in the cross section of the glass mother rod are in a same line; (2) the stress rods are respectively inserted into each open slot on the glass mother rod, and the assembled glass mother rod and stress rods are put in a cannula to form a preformed rod of the polarization maintaining fiber; (3) the preformed rod of the polarization maintaining fiber is drew to form the polarization maintaining fiber. According to the invention, the glass mother rod is provided with the open slots, and the stress rods are embedded in the open slots, thereby obtaining high process repeatability; inner surfaces of the open slots have high fineness, and the open slots have good symmetry, thereby improving processing efficiency; therefore, the optical performance and reliability of the polarization maintaining fiber are substantially improved.
Owner:RUIGUANG TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
Polarization-maintaining optical fiber, method of manufacturing polarization-maintaining optical-fiber connecting portion, and polarization-maintaining optical-fiber connecting portion
InactiveUS7809223B2Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with polarisationShortest distancePolarization-maintaining optical fiber
A polarization-maintaining optical fiber includes a core region and a cladding region formed around the core region. The cladding region has a refractive index lower than a refractive index of the core region. A refractive index profile of the core region is either one of a step shaped or a concave shaped. The cladding region includes two holes formed in such a manner that a shortest distance from the core region is virtually zero at locations in opposite to each other across the core region.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Single mode optical fiber
InactiveUS6334019B1High refractive indexGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexFiber disk laser
A large core photonic crystal fiber for transmitting radiation having a core comprising a substantially transparent core material and having a core diameter of at least 5 mu. The fiber also comprises a cladding region surrounding the length of core material, wherein the cladding region comprises a first substantially transparent cladding material, having a first refractive index, and wherein the first substantially transparent cladding material has embedded along its length a substantially periodic array of holes, wherein the holes are filled with a second cladding material having a second refractive index less than the first refractive index, such that radiation input to the optical fiber is transmitted along the length of the core material in a single mode of propagation. In a preferred embodiment, the core diameter may be at least 20 mu, and may be as large as 50 mu. The fiber is capable of transmitting higher power radiation than conventional fibres, whilst maintaining propagation in a single mode. The core material may be doped with a material capable of providing amplification under the action of pump radiation input to the fiber. The invention also relates to a fiber amplifier and a fiber laser comprising a doped large core photonic crystal fiber. The fiber may also be used in a system for transmitting radiation comprising a plurality of lengths of large core photonic crystal fiber, separated by large core photonic crystal fiber amplifiers, such that the power of radiation transmitted through the system is maintained above a predetermined threshold power.
Owner:NKT RES & INNOVATION
Microstructured optical fibers and methods
InactiveUS7450806B2Improve bending performanceLower refractive indexGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingNitrogenNitrogen gas
Microstructured optical fiber and method of making. Glass soot is deposited and then consolidated under conditions which are effective to trap a portion of the consolidation gases in the glass to thereby produce a non-periodic array of voids which may then be used to form a void containing cladding region in an optical fiber. Preferred void producing consolidation gases include nitrogen, argon, CO2, oxygen, chlorine, CF4, CO, SO2 and mixtures thereof.
Owner:CORNING INC
Methods and apparatus for forming heat treated optical fiber
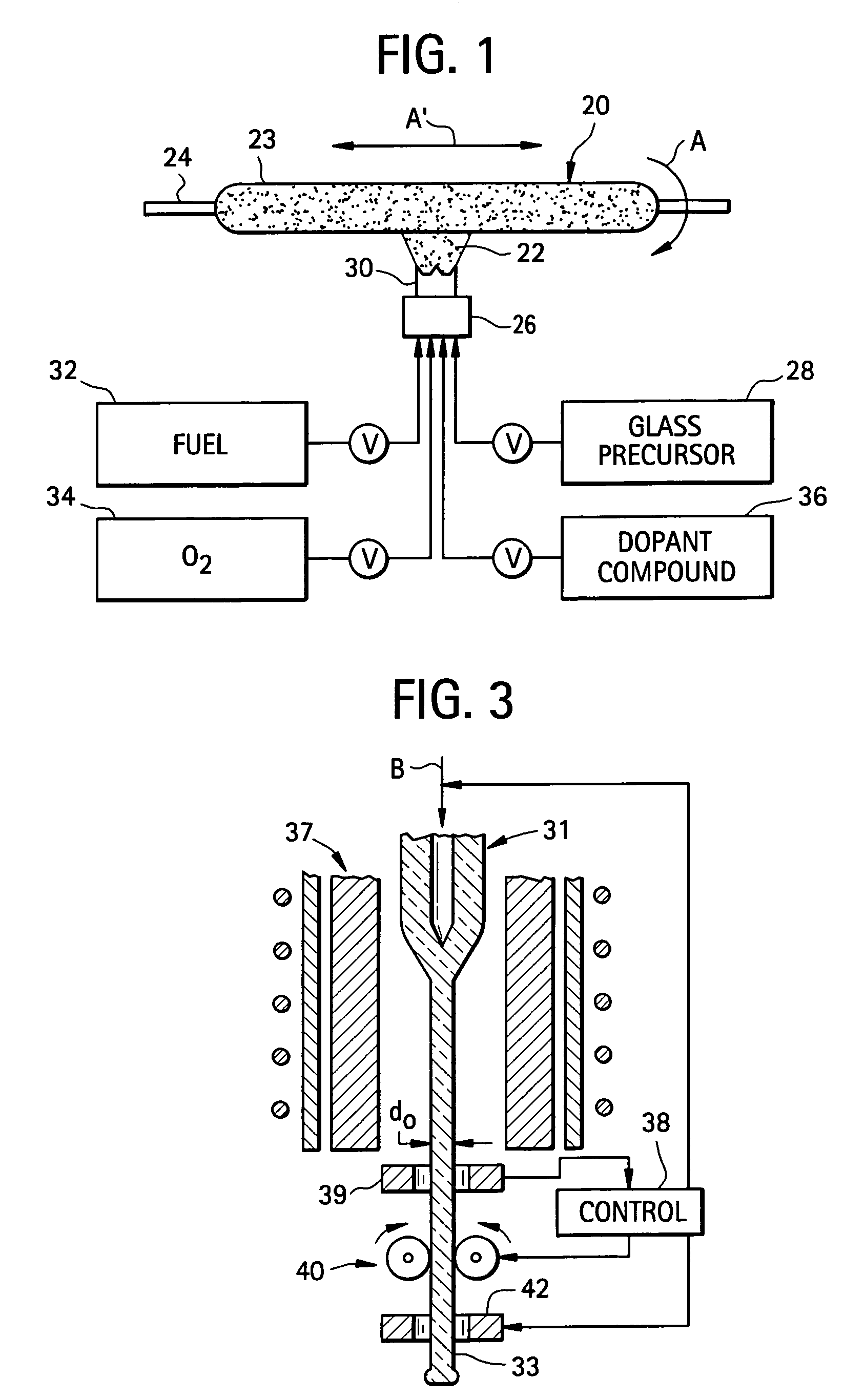
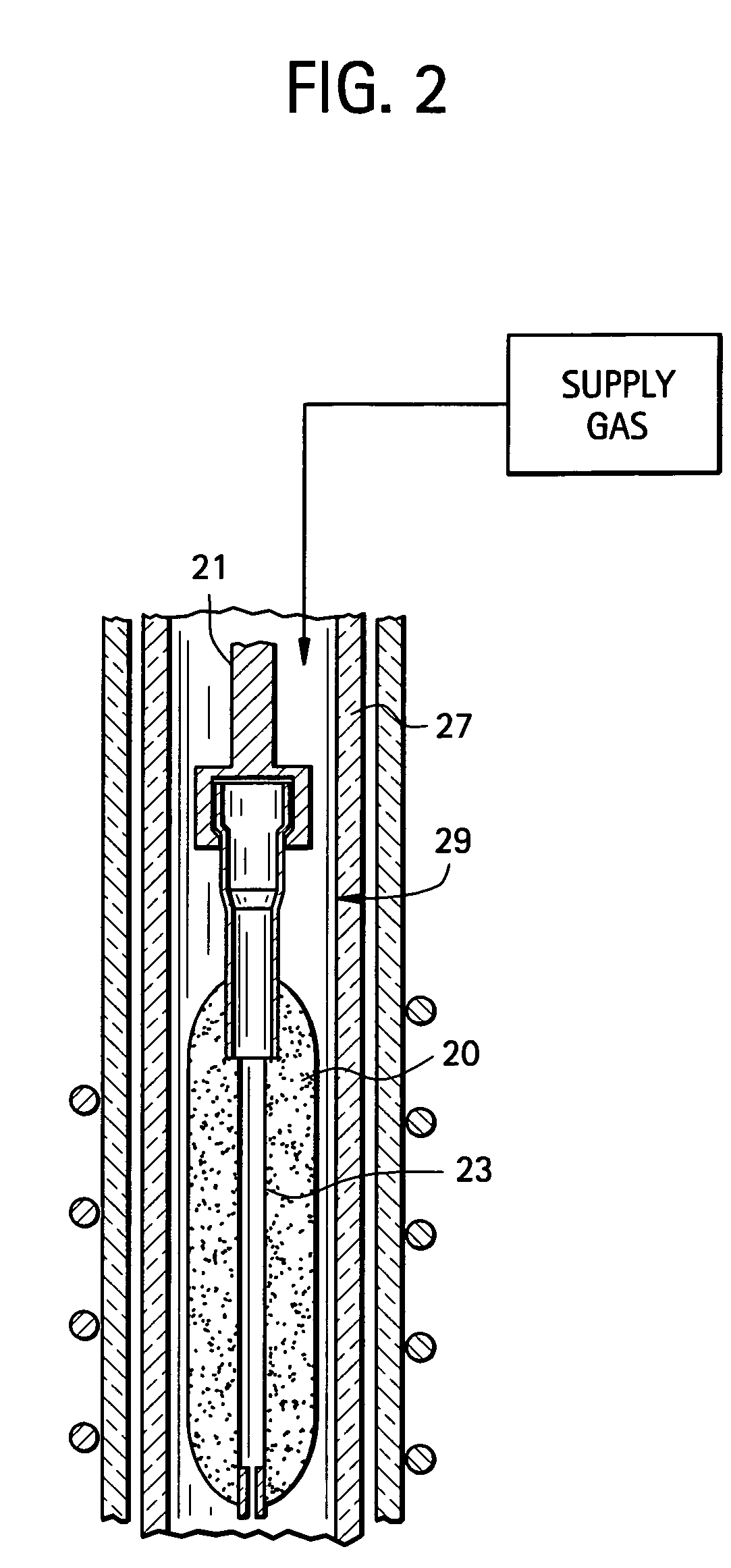
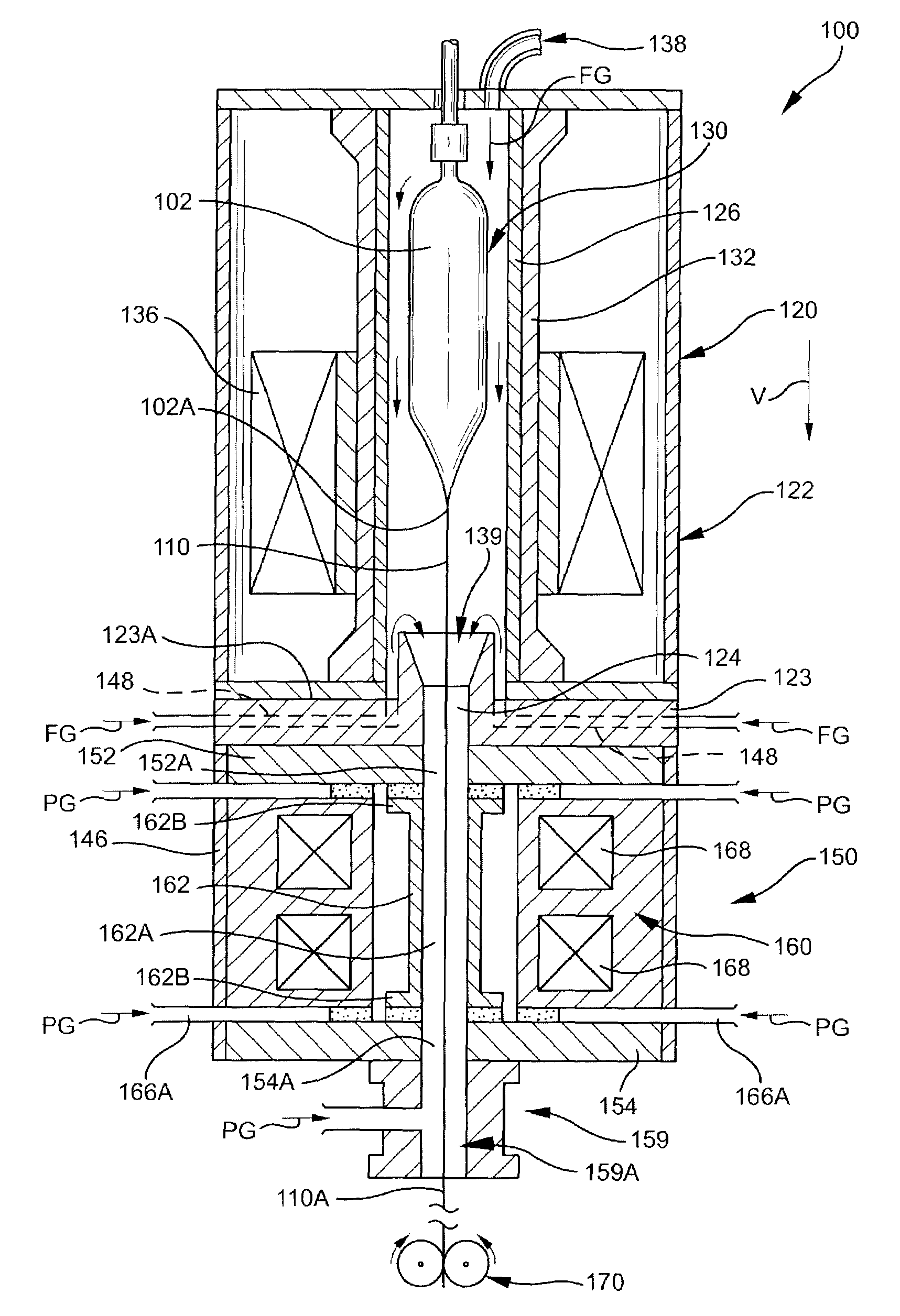
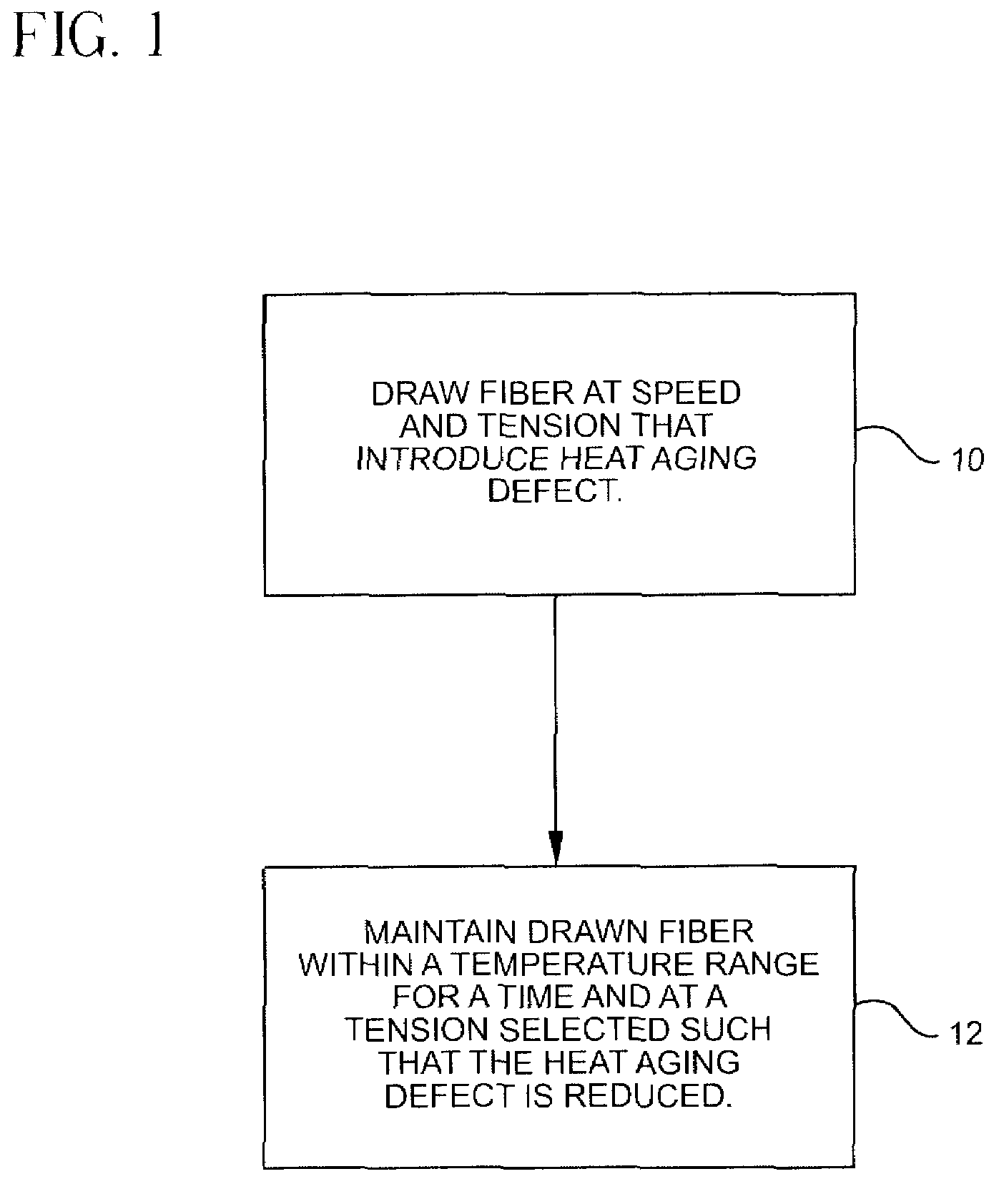
InactiveUS7565820B2Trend downDecreases micro-density variationGlass fibre drawing apparatusNon-linear opticsUltrasound attenuationRayleigh scattering
A method for forming an optical fiber includes drawing the optical fiber from a glass supply and treating the fiber by maintaining the optical fiber within a treatment temperature range for a treatment time. Preferably also, the fiber is cooled at a specified cooling rate. The optical fiber treatment reduces the tendency of the optical fiber to increase in attenuation due to Rayleigh scattering, and / or over time following formation of the optical fiber due to heat aging. Apparatus are also provided.
Owner:CORNING INC
Suppression of stimulated Brillouin scattering in optical fiber
InactiveUS6542683B1Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusFiberDopant
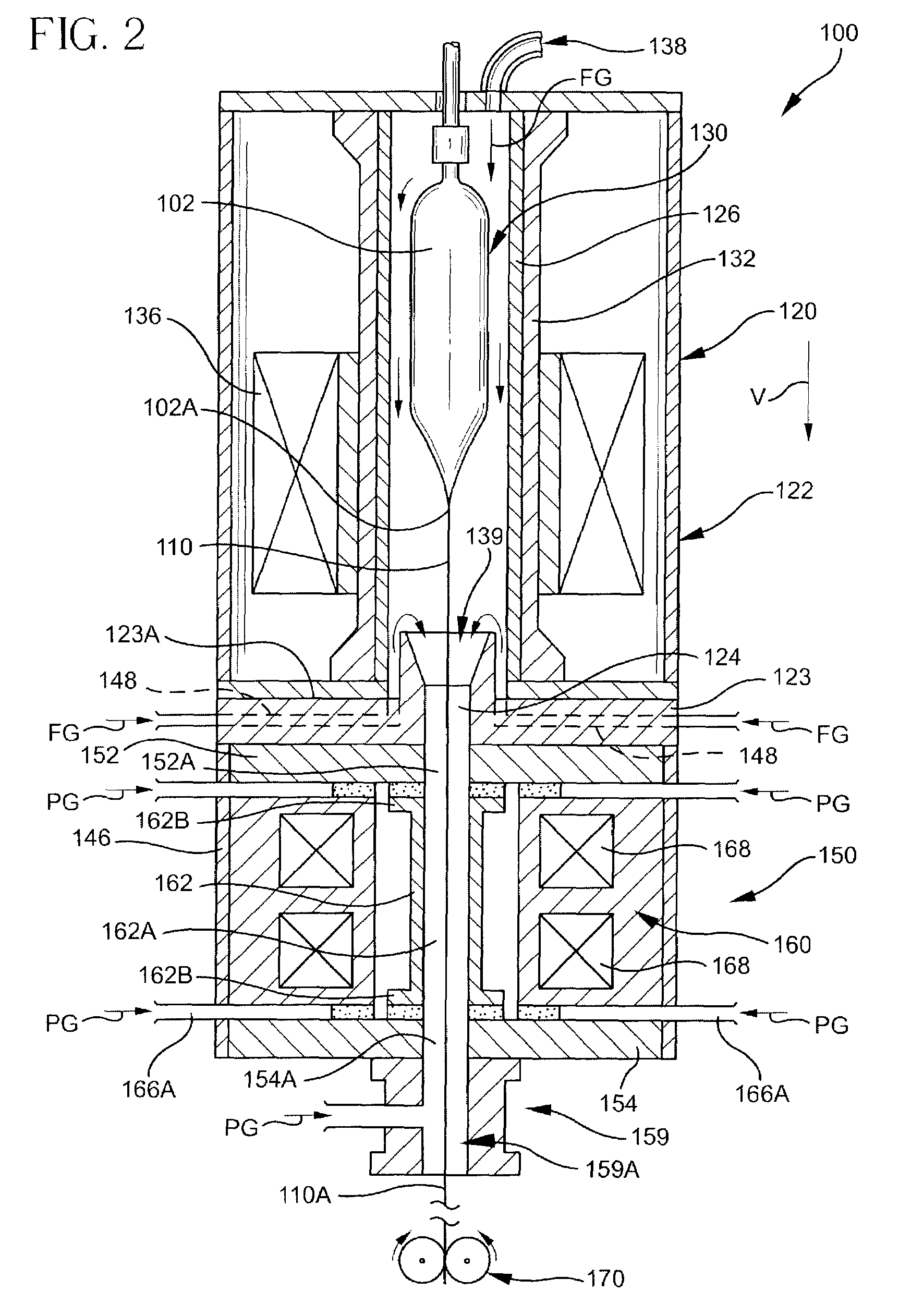
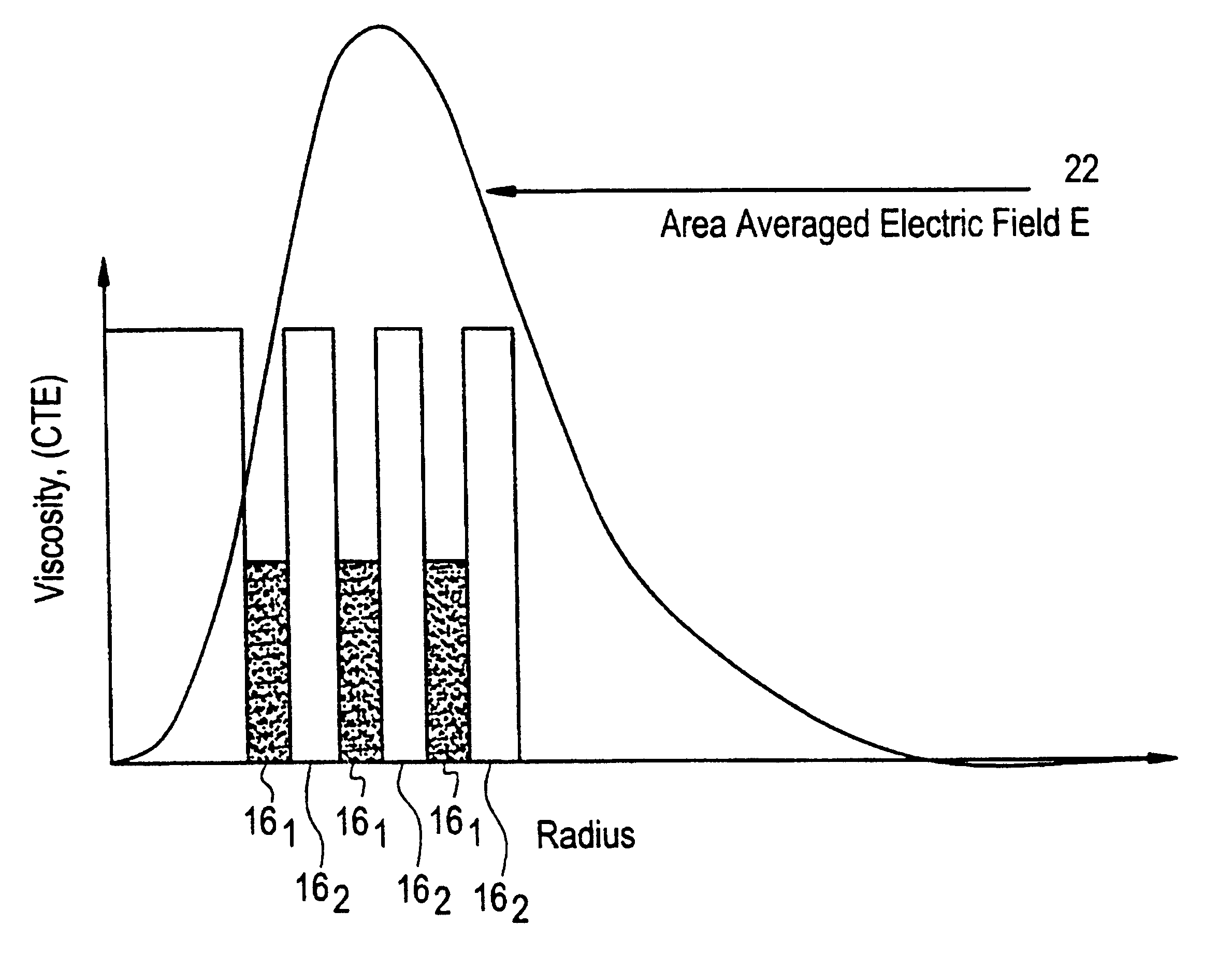
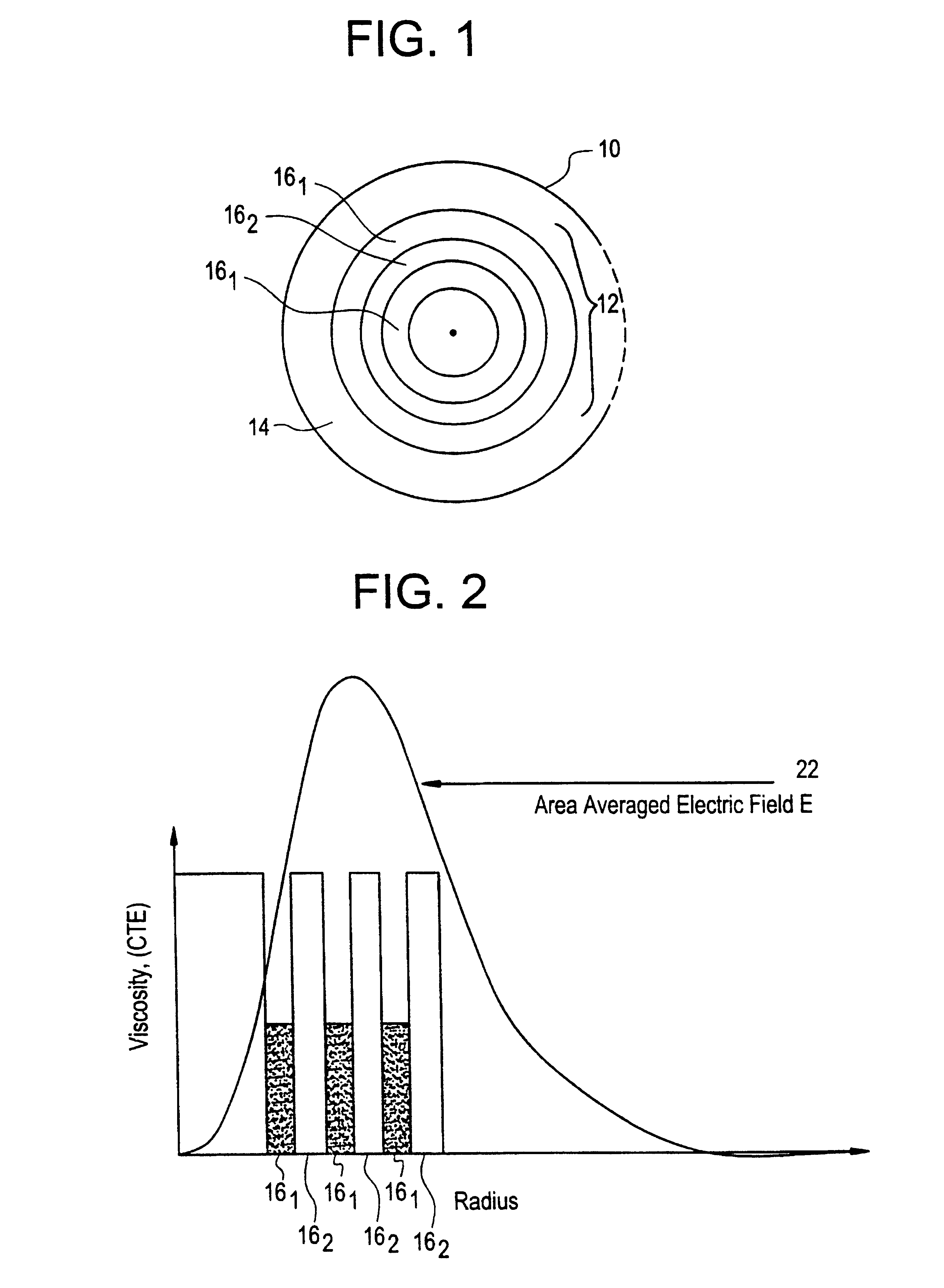
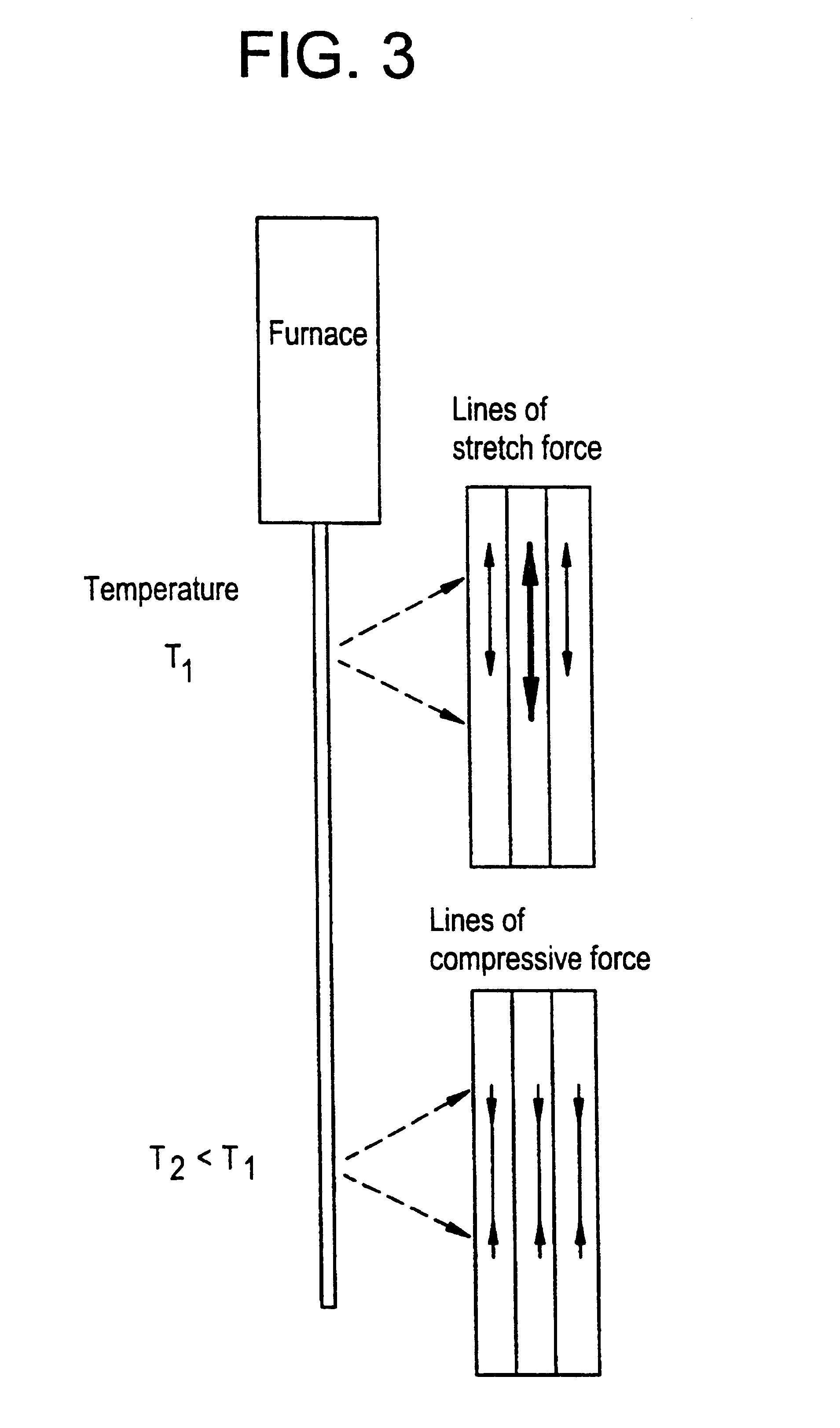
Suppression of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) by broadening the energy spectrum of participating SBS photons and / or phonons is achieved in an optical fiber having a core with both radially nonuniform viscosity and CTE profiles provided by alternating layers of glass modifying dopants such as phosphorous and fluorine. The nonuniform thermal expansion and viscosity profiles impart a residual, permanent, nonuniform stress in the fiber. The SBS suppressing effect provided by the nonuniform stress can be controlled and enhanced by applying a uniform or nonuniform tensile force to the fiber as it is being drawn. A preform for the fiber is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNING INC
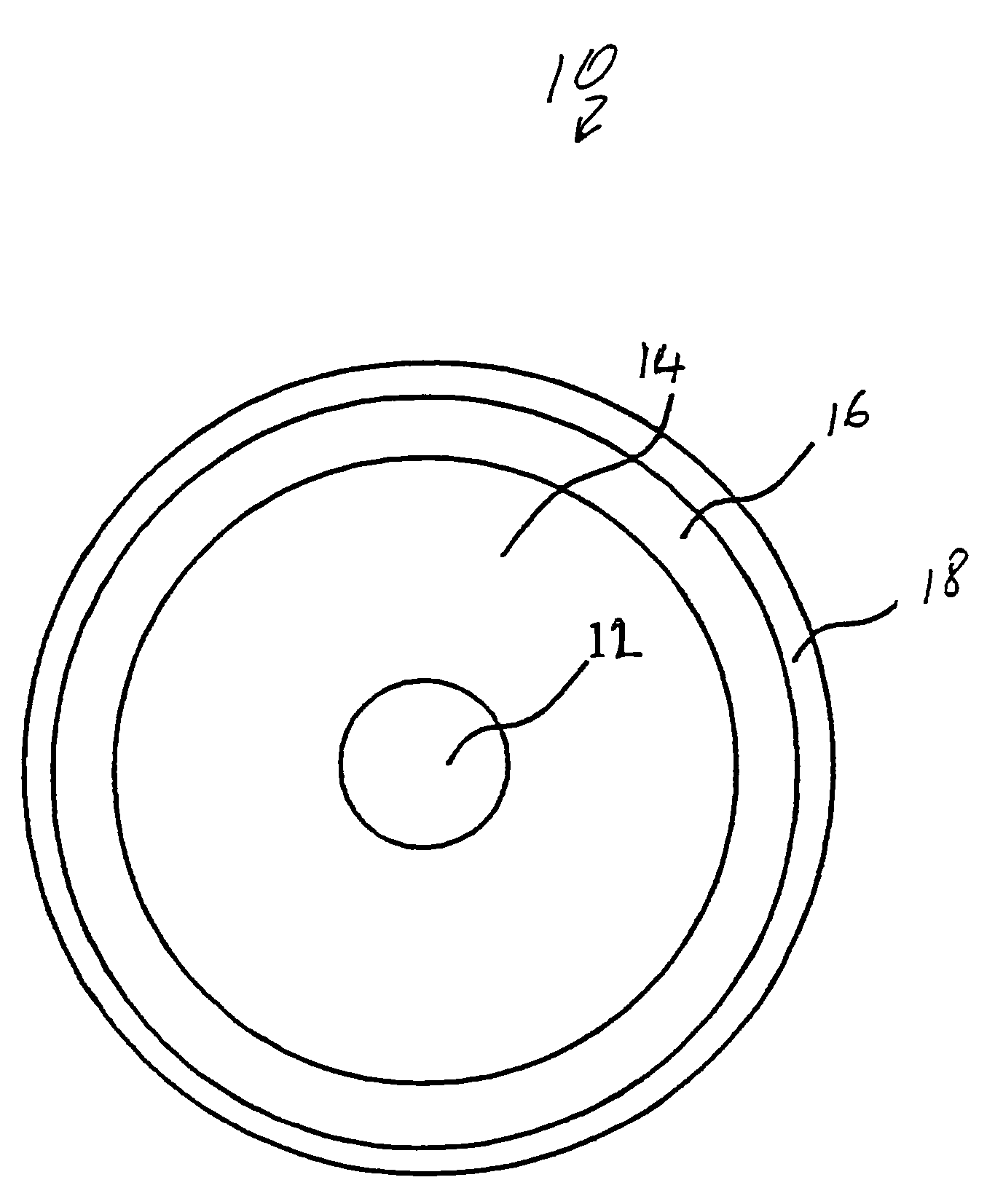
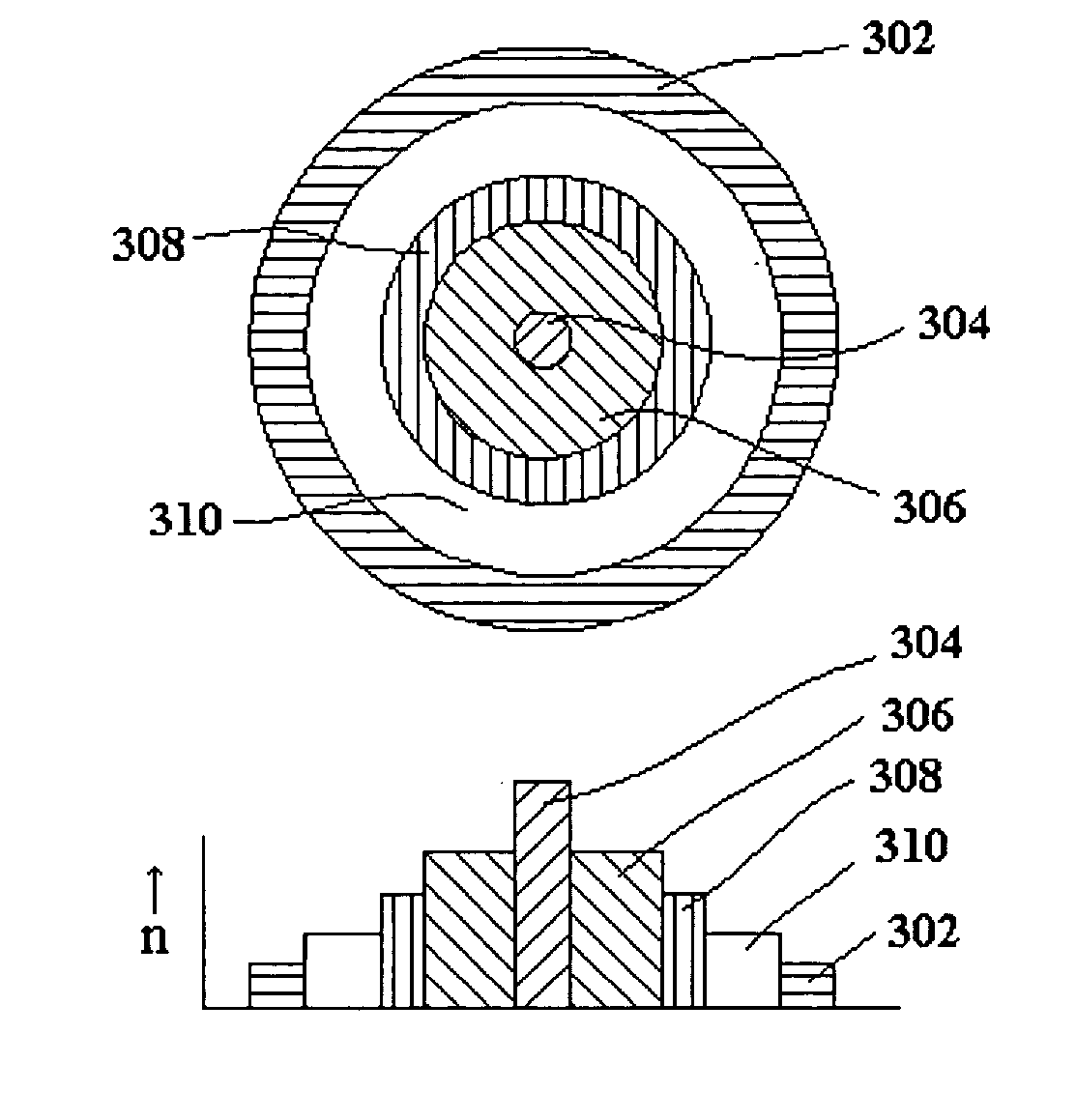
Optical fiber with irregularities at cladding boundary
InactiveUS6411762B1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCouplingOptical fiber cable
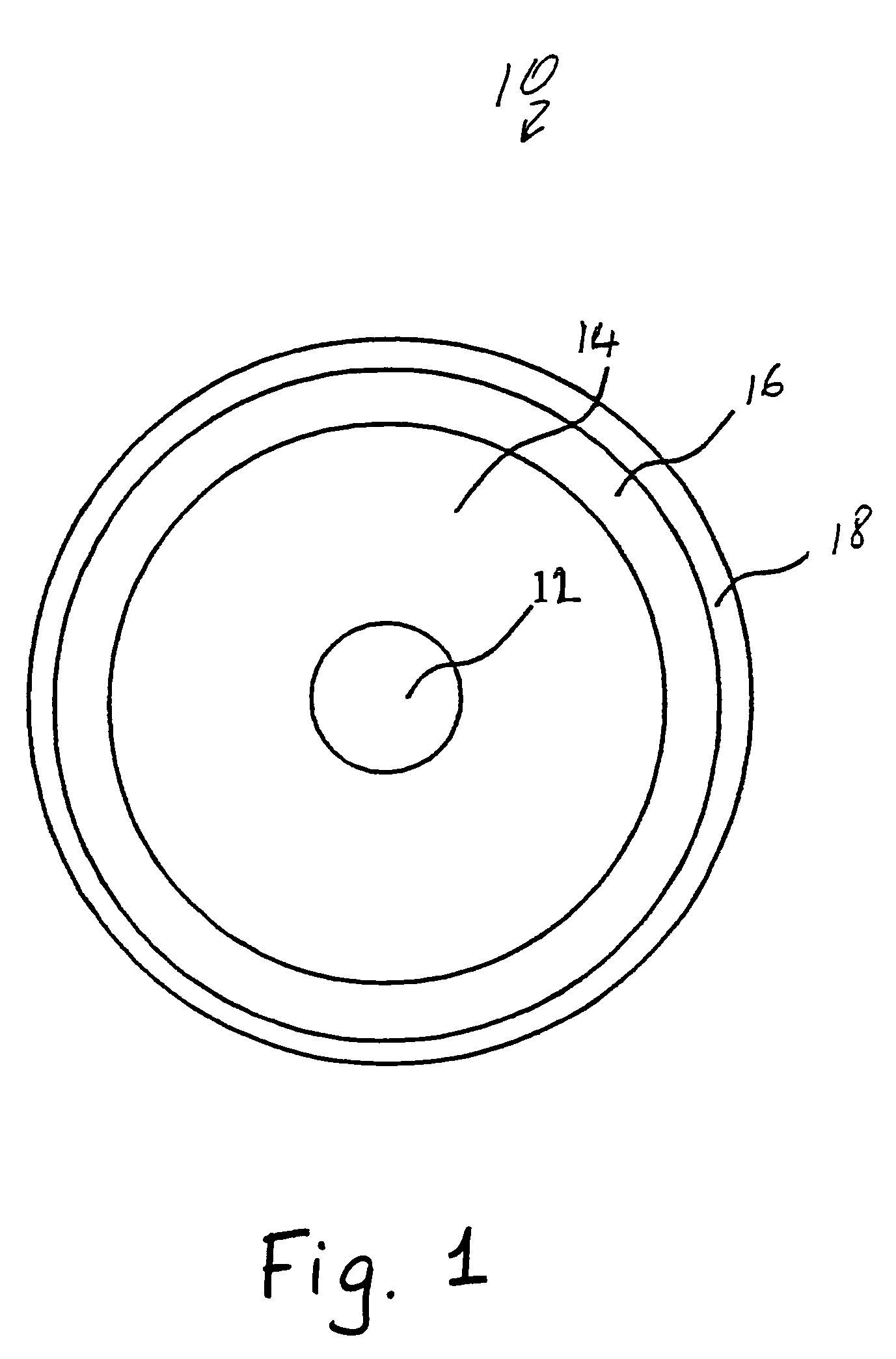
An optical fiber (10) made with a central core (12), a first cladding layer (16), and a second cladding layer (18) having a series of perturbations or irregularities formed into the otherwise generally circular outer boundary of the first cladding layer (16). The irregularities in the first cladding layer (16) interrupt the propagation of skew rays and encourage coupling into the core (12).
Owner:FIBERCORE INC
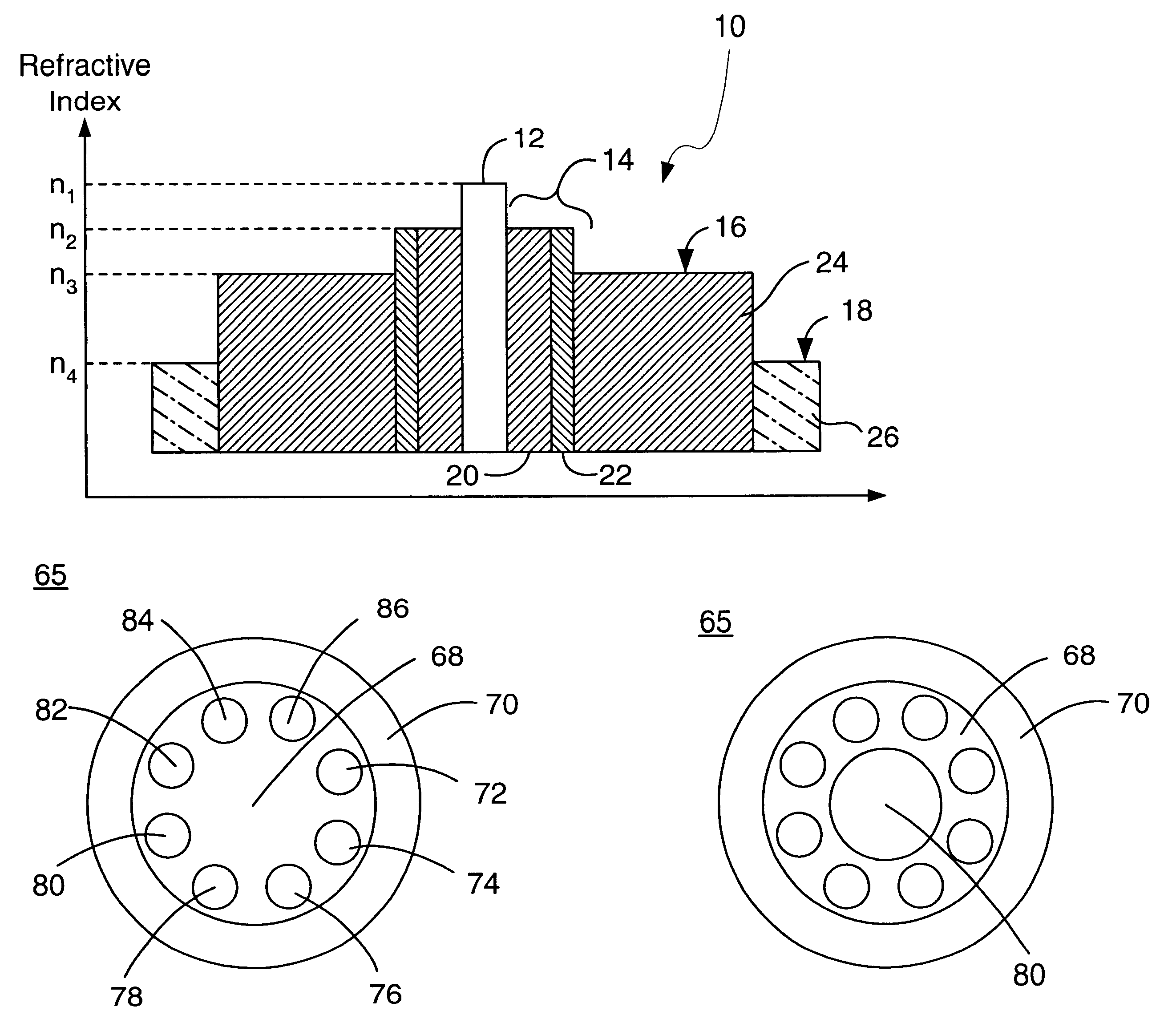
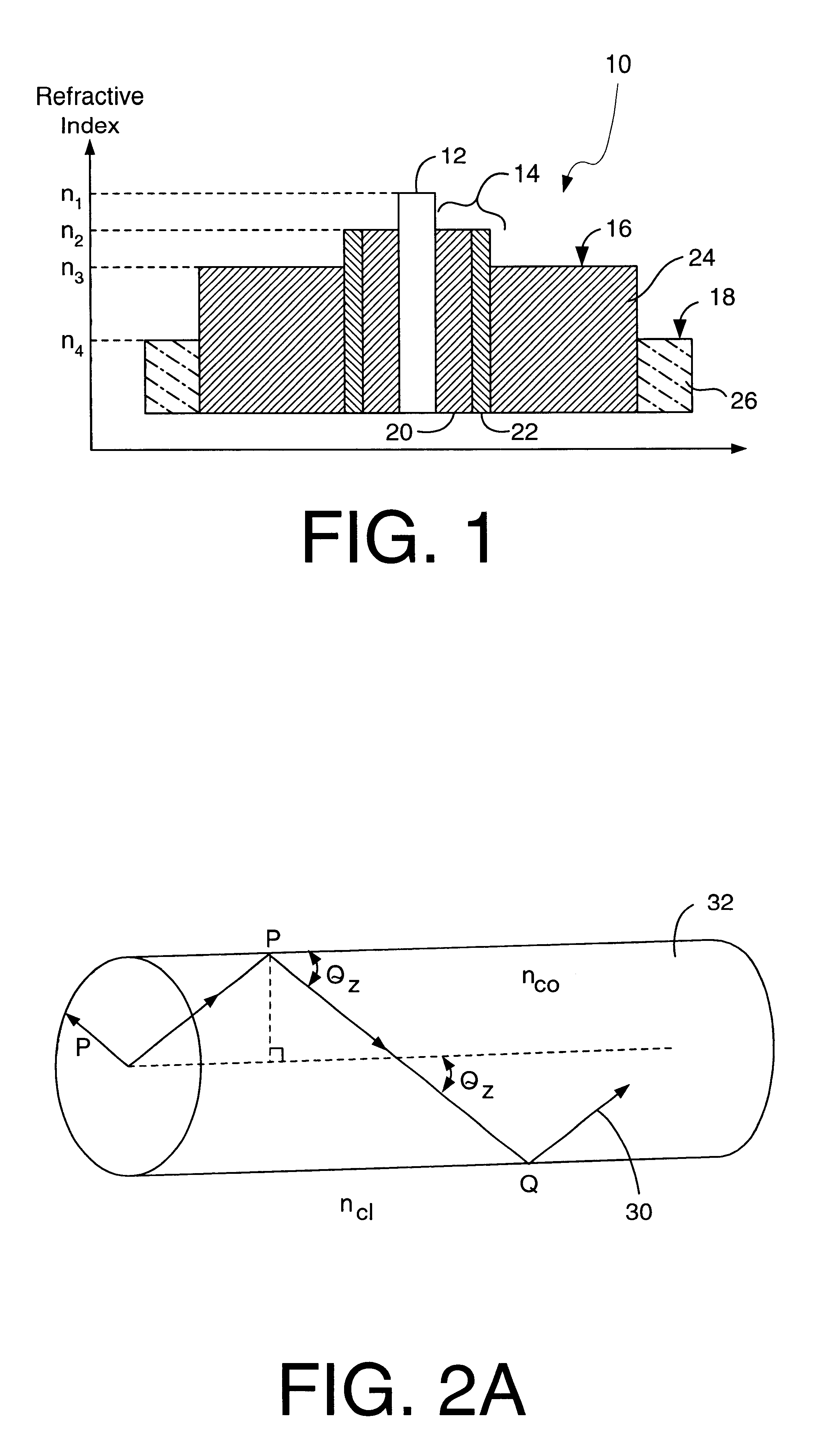
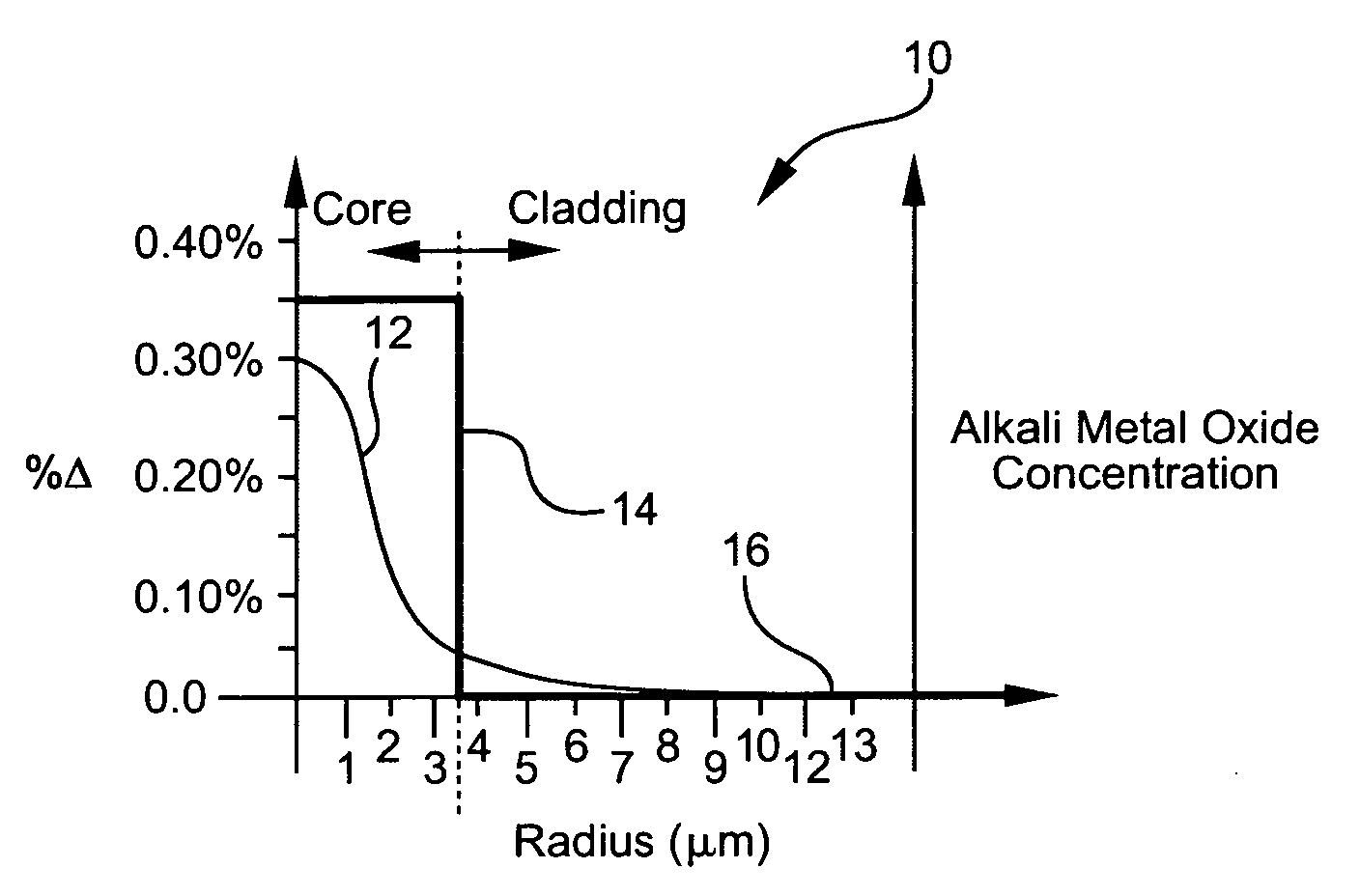
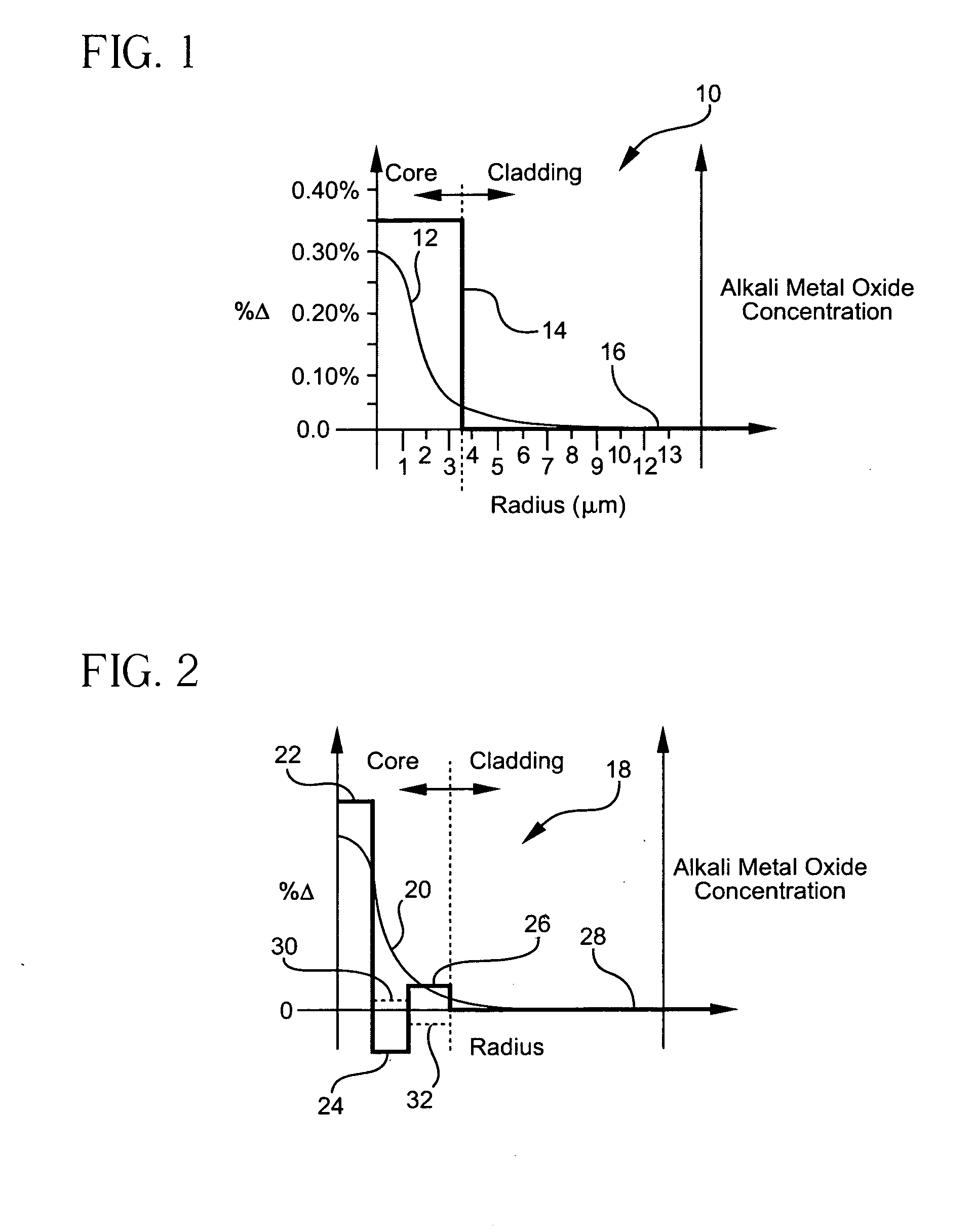
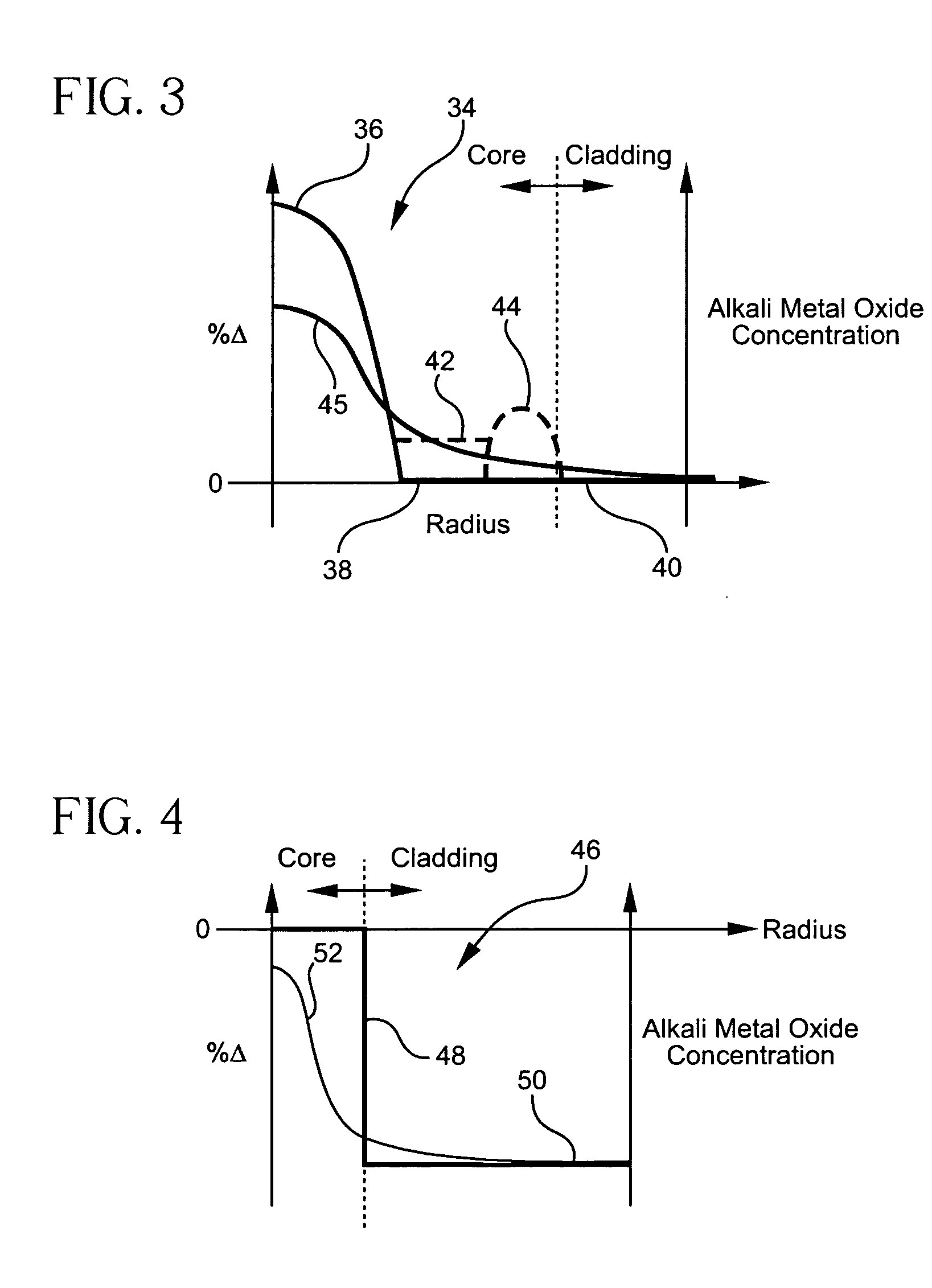
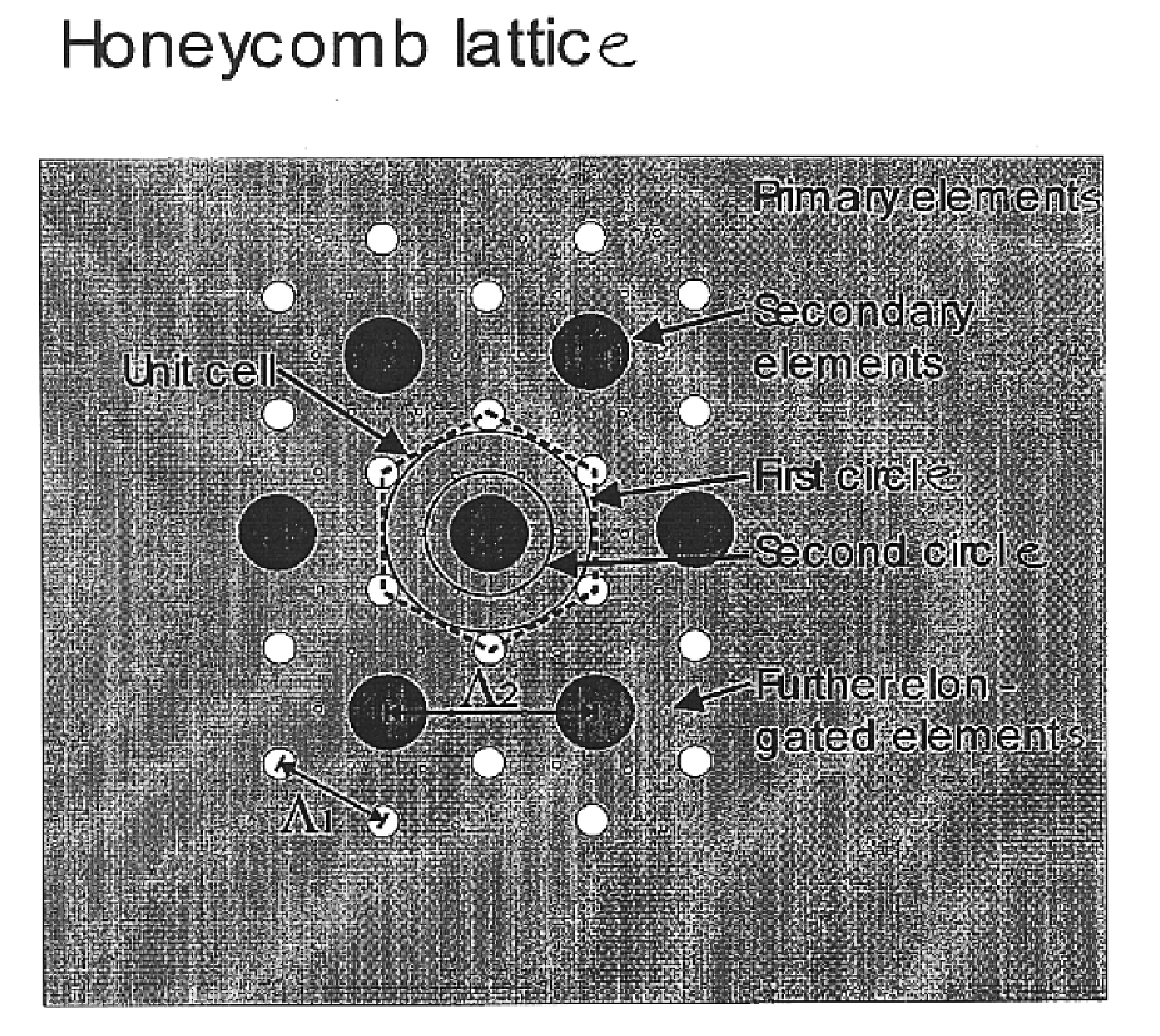
Optical fiber containing an alkali metal oxide and methods and apparatus for manufacturing same
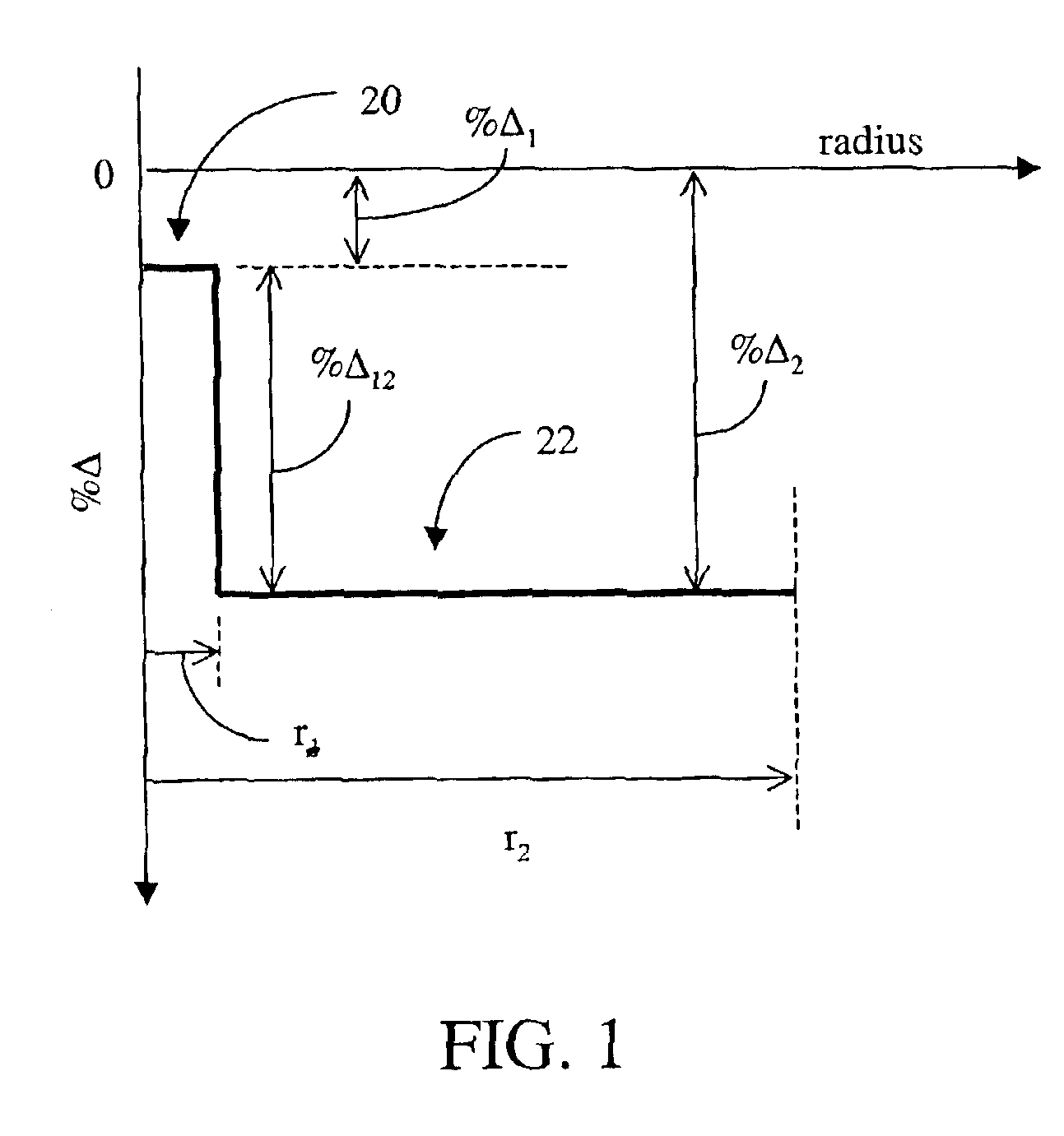
ActiveUS20050063663A1Increase radiusReduce doping concentrationOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantAlkali metal oxide
Disclosed is an optical fiber having a core with an alkali metal oxide dopant in an peak amount greater than about 0.002 wt. % and less than about 0.1 wt. %. The alkali metal oxide concentration varies with a radius of the optical fiber. By appropriately selecting the concentration of alkali metal oxide dopant in the core and the cladding, a low loss optical fiber may be obtained. Also disclosed are several methods of making the optical fiber including the steps of forming an alkali metal oxide-doped rod, and adding additional glass to form a draw perform. Preferably, the draw preform has a final outer dimension (d2), wherein an outer dimension (d1) of the rod is less than or equal to 0.06 times the final outer dimension (d2). In a preferred embodiment, the alkali metal oxide-doped rod is inserted into the centerline hole of a preform to form an assembly.
Owner:CORNING INC
Photonic band gap fiber
InactiveUS6845204B1Lower areaHigh refractive indexGlass making apparatusLaser optical resonator constructionFiberMulti method
An optical fiber having a periodical cladding structure providing an photonic band gap structure with superior qualities. The periodical structure being one wherein high index areas are defined and wherein these are separated using a number of methods. One such method is the introduction of additional low index elements, another method is providing elongated elements deformed in relation to a circular cross section. Also described is a cladding structure comprising elongated elements of a material having an index of refraction higher than that of the material adjacent thereto. Using this additional material, prior art structures may obtain much better qualities.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Optical fiber for transmitting ultraviolet ray, optical fiber probe, and method of manufacturing the optical fiber probe
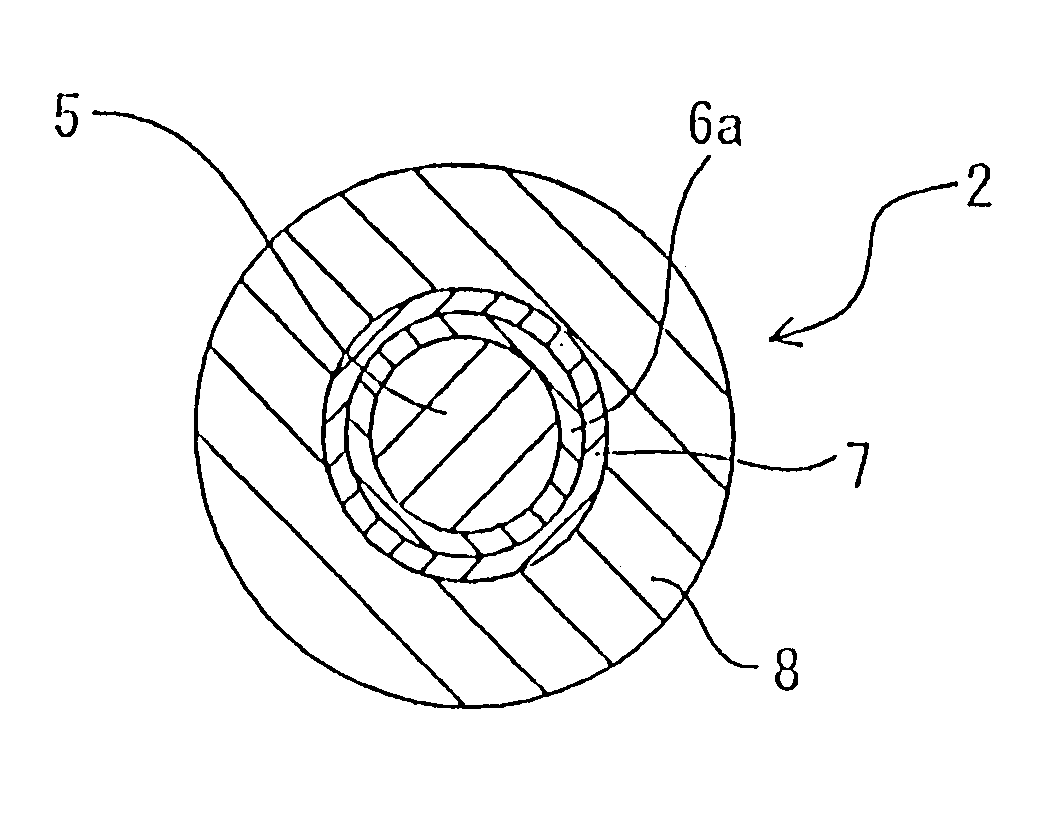
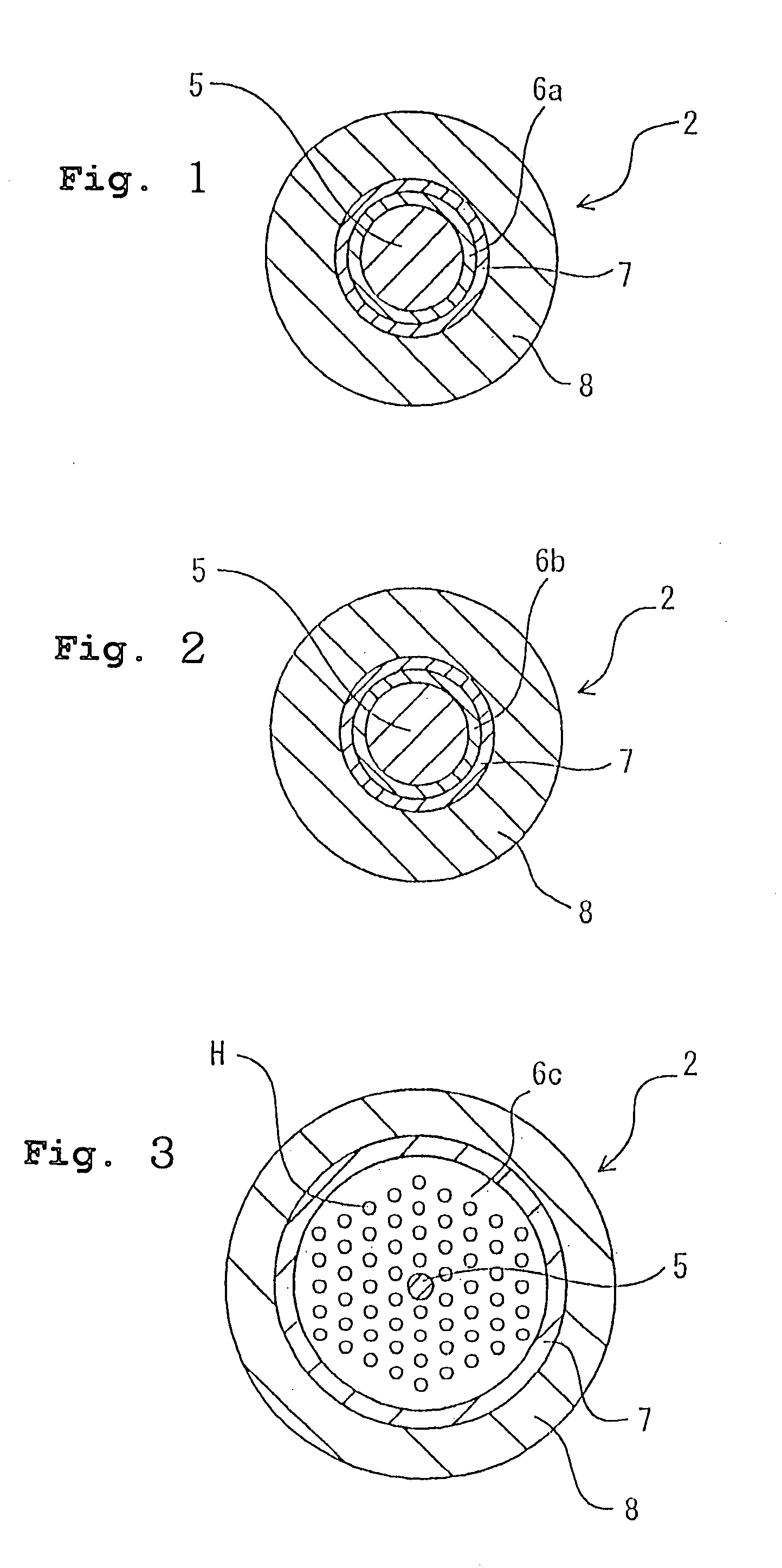
InactiveUS6944380B1High light transmittanceResistant to deteriorationGlass optical fibreGlass making apparatusFiberHydrogen
It is an object of the present invention to provide an optical fiber for transmitting ultraviolet ray which has an improve transmittance and is prevented from deterioration by ultraviolet ray with which it is irradiated. It is another object of the present invention to provide an optical fiber probe which can propagate vacuum ultraviolet ray and deep ultraviolet ray at a high transmittance, is deteriorated only to a limited extent when irradiated with ultraviolet ray and can be etched to have a desired shape of the sharpened section at the fiber end.The present invention provides the optical fiber for transmitting ultraviolet ray which has a core 5 of silica glass containing a given content of fluorine and a clad 6a of silica glass containing a given content of fluorine or boron, a clad 6b of a resin which transmits ultraviolet ray or a clad 6c having air holes H. The clad may be coated with a protective layer and further with a covered layer for protection. In particular, the core, clad and protective layer have a high transmittance for ultraviolet ray and resistance to ultraviolet ray with which they are irradiated, when treated with hydrogen.An optical fiber probe 1 has an optical fiber 2 provided with a sharpened section 3 at the end, which is sharpened with an etchant solution, the sharpened section 3 being coated with a light-shielding metallic film 4.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
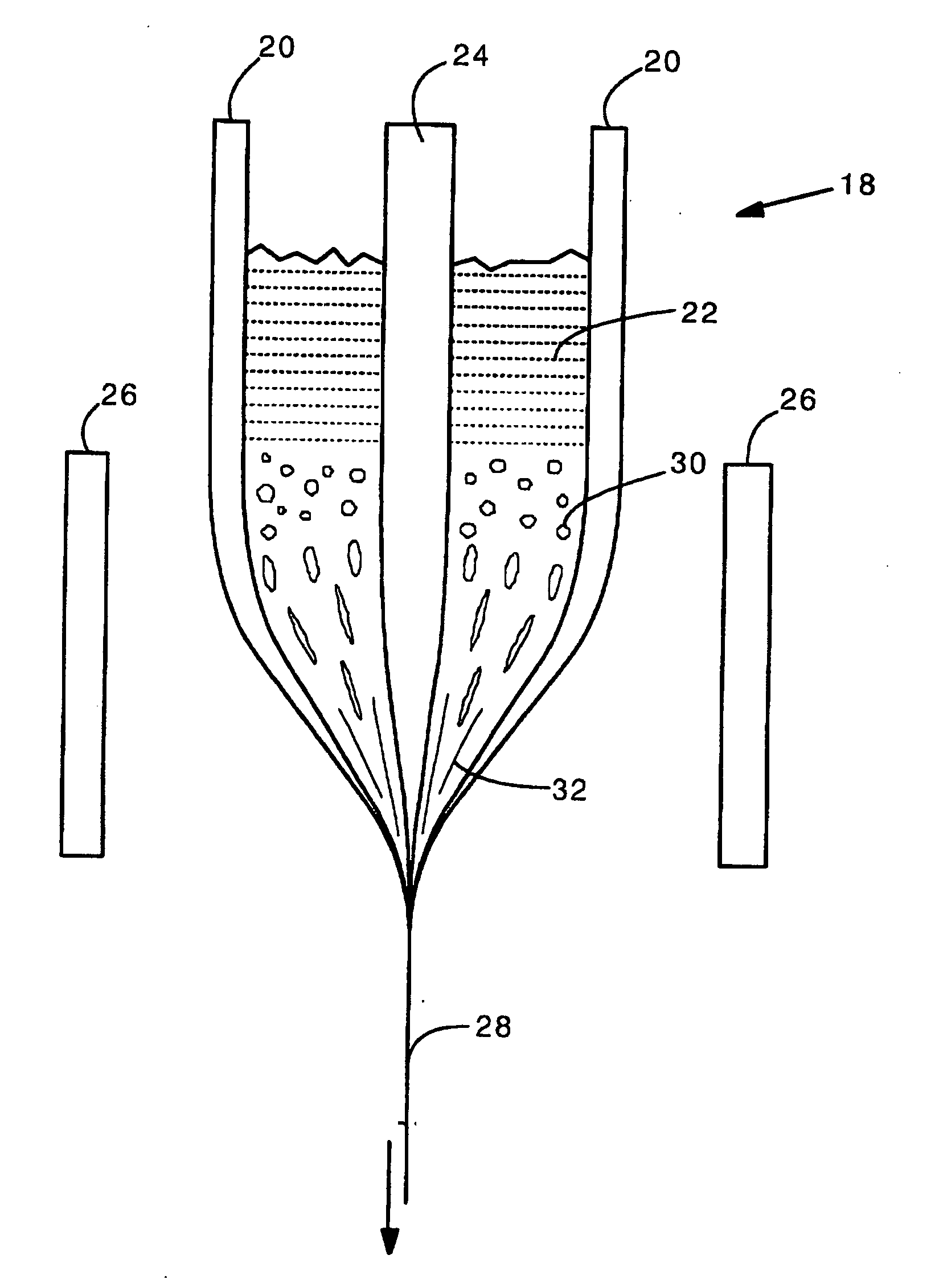
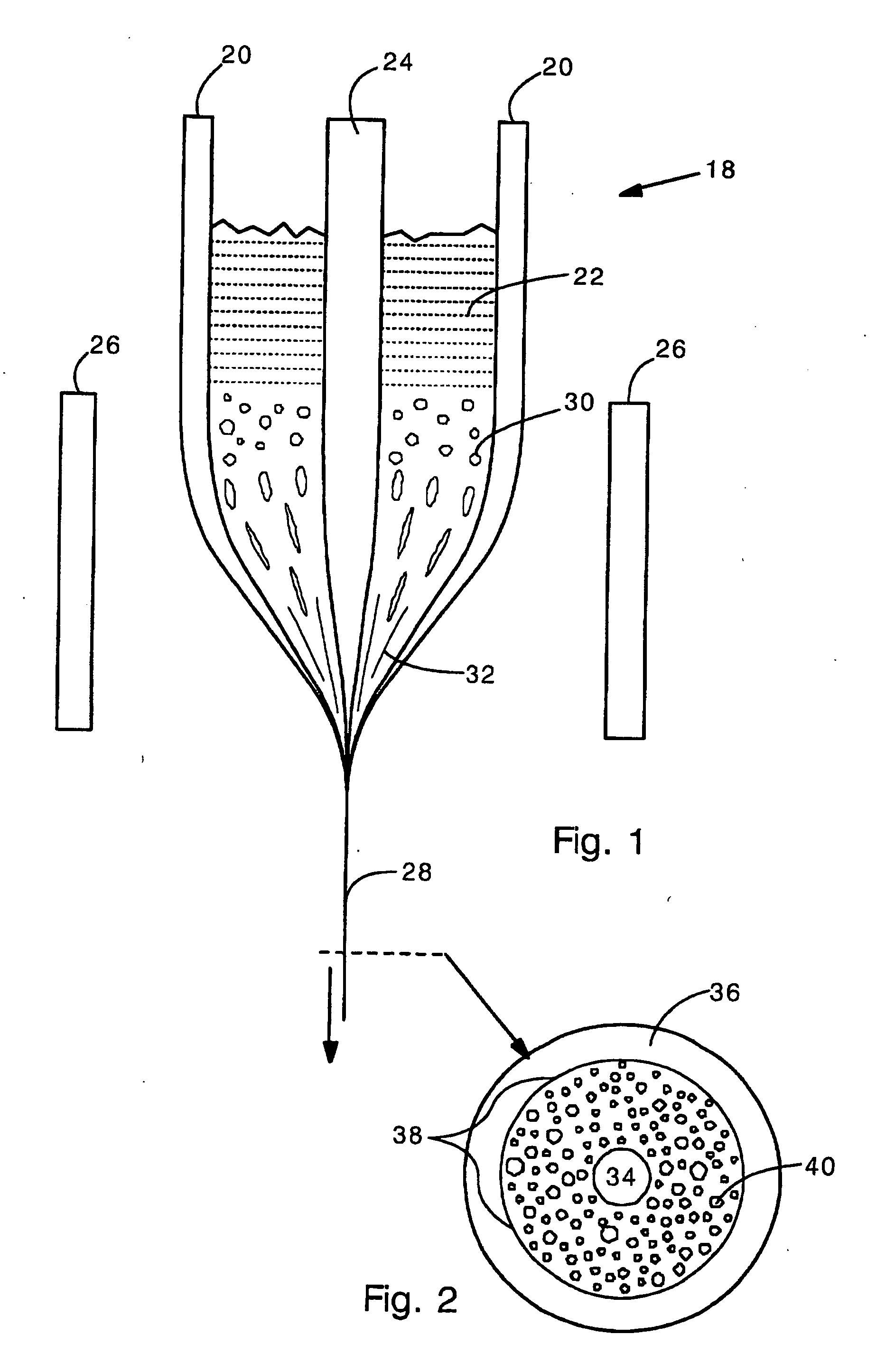
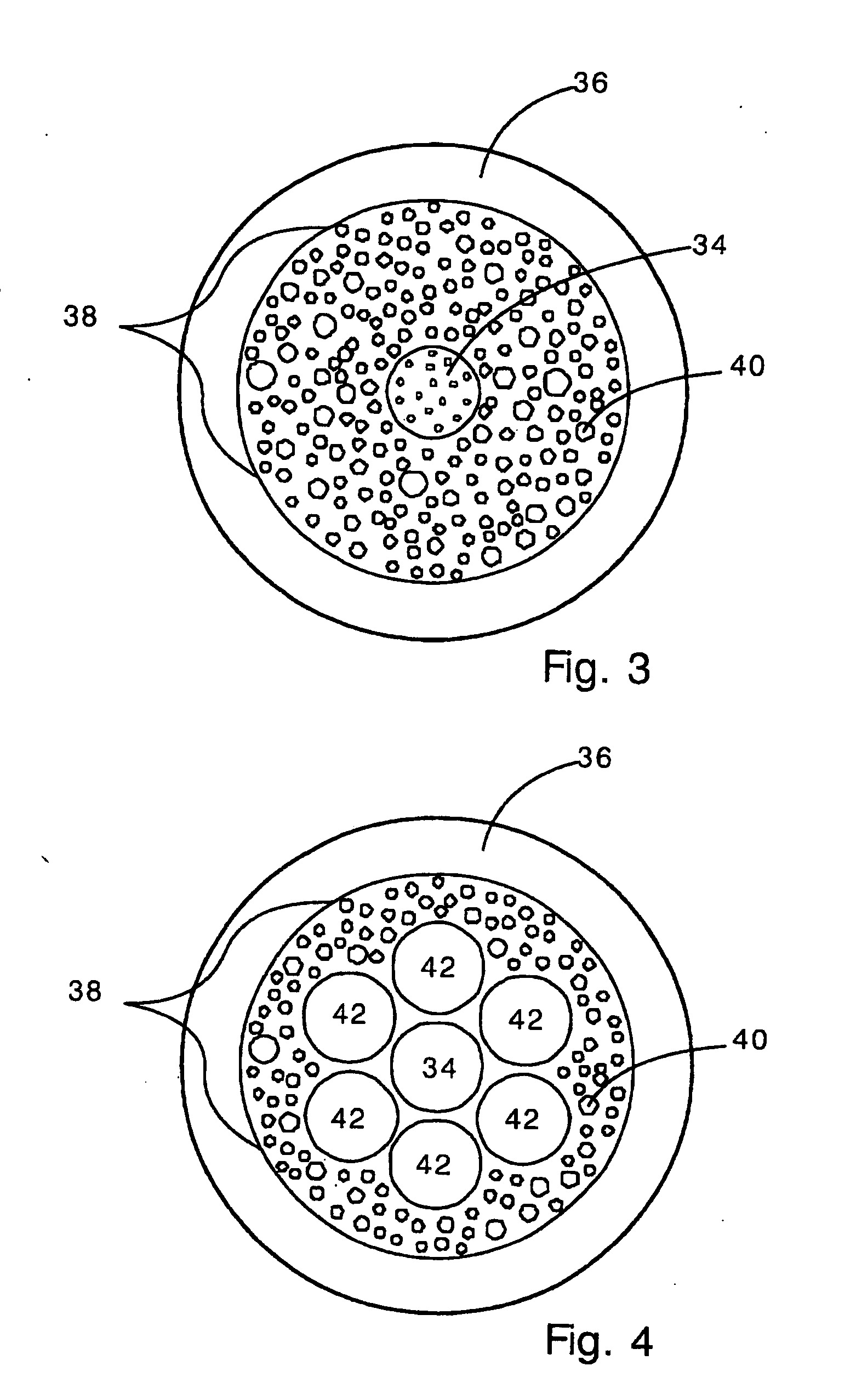
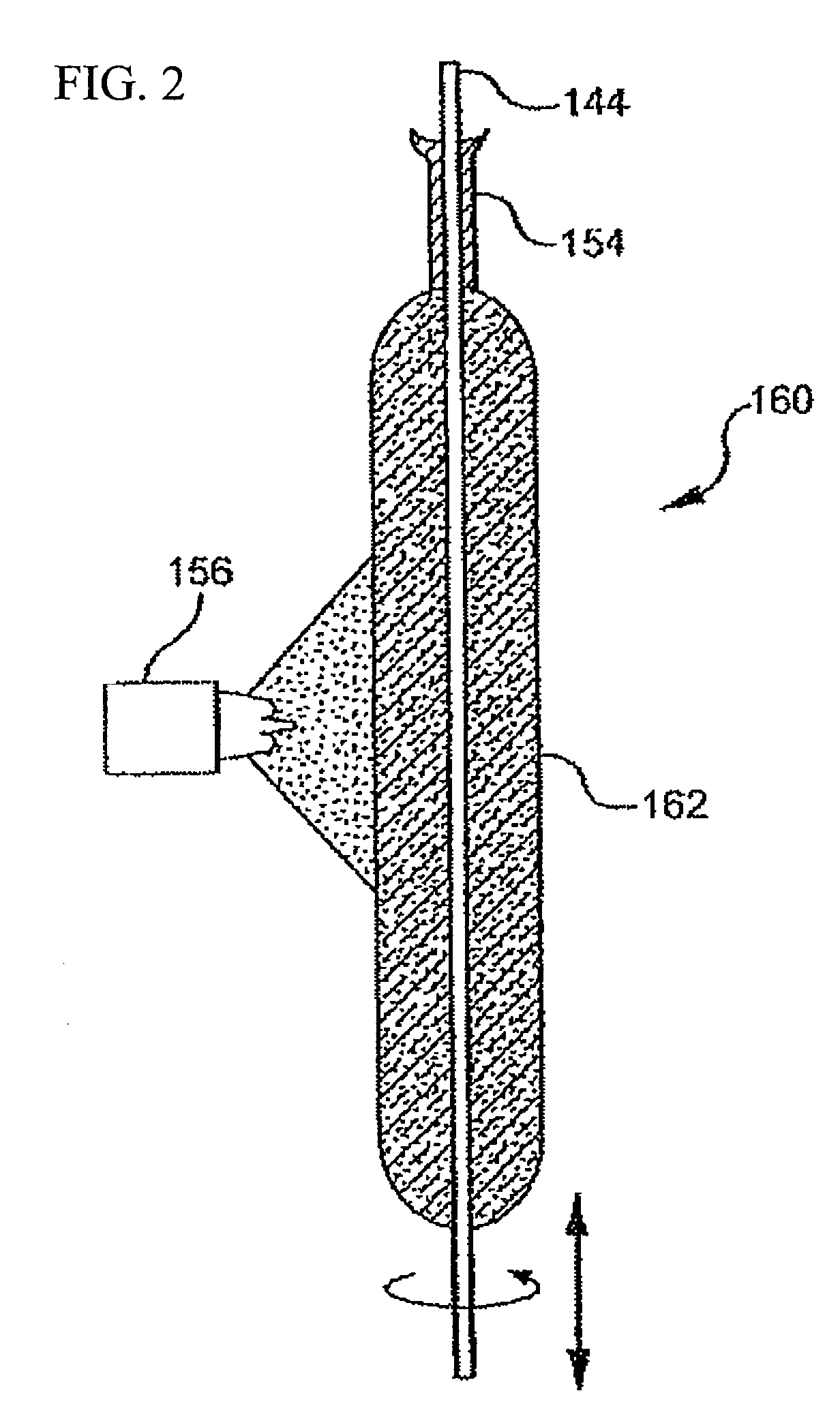
Side-emitting step index fiber
ActiveUS20110103757A1Produced economicallyImprove scalabilityOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingGlass fibre drawing apparatusCouplingRefractive index
Side-emitting step index fibers. Between core and cladding, the side-emitting step index fibers have scattering centers that ensure the coupling out of light from the fiber. The side-emitting step index fibers are produced by preforms that contain inlay rods, in which the scattering centers are embedded and which are applied to the outer region of the fiber core during fiber drawing. Alternatively, at least one inlay tube can be used.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Optical fiber having reduced viscosity mismatch
InactiveUS6917740B2Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingVitrificationRefractive index
An optical fiber is disclosed in which the core region of the optical fiber is doped with Cl and F in order to reduce the viscosity mismatch between the core region and the adjacent cladding region. In one embodiment of the invention, the optical fiber is a single-mode step index optical fiber having a core region doped with Cl and F in an amount effective to produce a difference in temperature between the glass transition temperature of the core region and the glass transition temperature of the adjacent cladding region of less than about 200° C.
Owner:CORNING INC
Multi-clad optical fiber lasers and their manufacture
ActiveUS20040156401A1Low refractive indexProtection from damageGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreRare earthRefractive index
An optical fiber is disclosed that can be used as an active medium in fiber lasers and / or fiber amplifiers, featuring a preferably rare-earth-doped silica active core surrounded by a pure or doped silica cladding layer ("pump core"). The pump core is surrounded by a doped or pure silica inner cladding for guiding pumping radiation within the pump core. Thus, the refractive index of the inner cladding is lower than that of the pump core. The fiber is surrounded by a protective coating made of polymeric material. One or more additional outer cladding layers, having refractive indexes lower than said inner cladding, may optionally be placed between the inner cladding and the protective coating to further protect the polymer coating from damage. Unlike the prior art, the protective coating does not serve as the only cladding, but is assisted by the inner cladding and optional outer cladding(s). The resultant fiber restricts radiation mainly to silica layers, thereby increasing the damage threshold and the applicable maximum pump power of the fiber.
Owner:BIOLITEC UNTERNEHMENSBETEILLIGUNGS II AG +1
Holey optical fiber with random pattern of holes and method for making same
ActiveUS20050094954A1Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingSilicon dioxideAir bubble
A random array of holes is created in an optical fiber by gas generated during fiber drawing. The gas forms bubbles which are drawn into long, microscopic holes. The gas is created by a gas generating material such as silicon nitride. Silicon nitride oxidizes to produce nitrogen oxides when heated. The gas generating material can alternatively be silicon carbide or other nitrides or carbides. The random holes can provide cladding for optical confinement when located around a fiber core. The random holes can also be present in the fiber core. The fibers can be made of silica. The present random hole fibers are particularly useful as pressure sensors since they experience a large wavelength dependant increase in optical loss when pressure or force is applied.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Photonic bandgap fibers
InactiveUS20060193583A1Reduce transmission lossWide transmission bandAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhotonic bandgapRefractive index
Included among the many structures described herein are photonic bandgap fibers designed to provide a desired dispersion spectrum. Additionally, designs for achieving wide transmission bands and lower transmission loss are also discussed. For example, in some fiber designs, smaller dimensions of high index material in the cladding and large core size provide small flat dispersion over a wide spectral range. In other examples, the thickness of the high index ring-shaped region closest to the core has sufficiently large dimensions to provide negative dispersion or zero dispersion at a desired wavelength. Additionally, low index cladding features distributed along concentric rings or circles may be used for achieving wide bandgaps.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
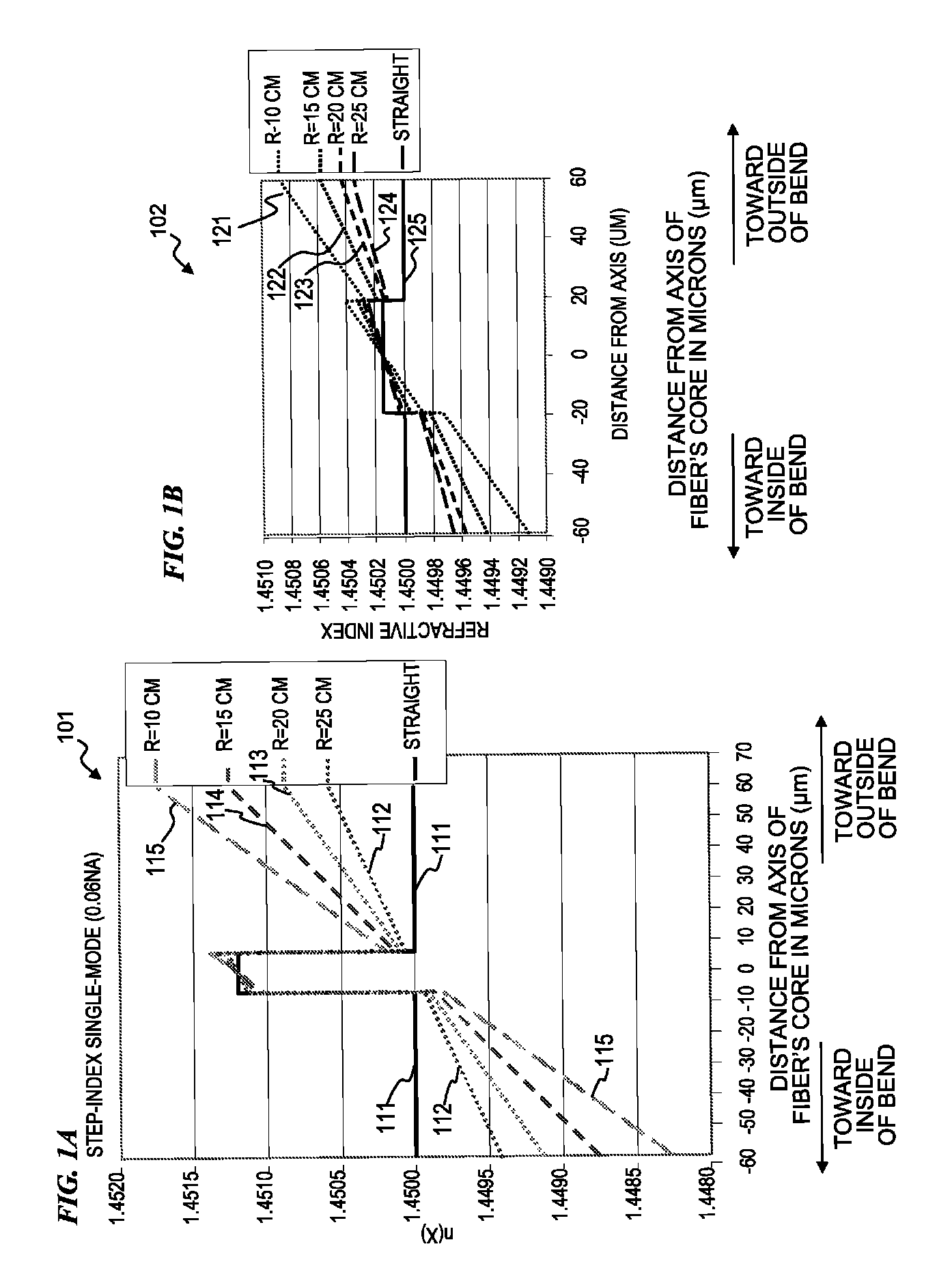
Apparatus and method for compensating for and using mode-profile distortions caused by bending optical fibers
An apparatus and method for compensating for mode-profile distortions caused by bending optical fibers having large mode areas. In various embodiments, the invention micro-structures the index of refraction in the core and surrounding areas of the inner cladding from the inner bend radius to the outer bend radius in a manner that compensates for the index changes that are otherwise induced in the index profile by the geometry and / or stresses to the fiber caused by the bending. Some embodiments of an apparatus and method include a fiber having a plurality of substantially parallel cores, the fiber including a straight section and a curved section; guiding signal light primarily in a second core in the straight section; guiding the signal light from the second core into a first core between the straight section and the curved section; and guiding the signal light primarily in the first core in the curved section.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
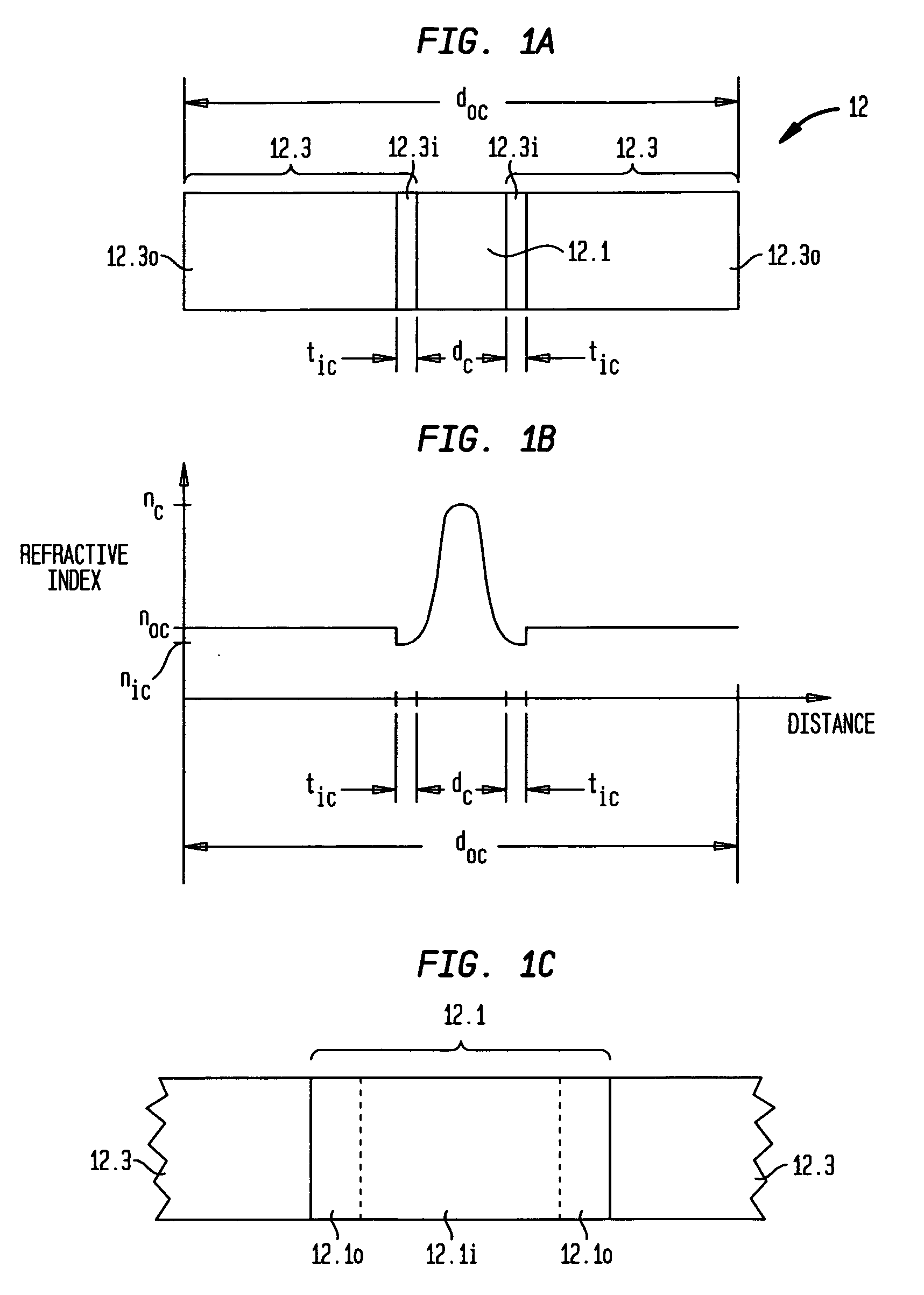
Hole assisted fiber device and fiber preform
A hole-assisted fiber comprises a core region and a cladding region, where the cladding region includes multiple substantially elliptical holes spaced apart from each other to surround the core region. The holes are filled with one of a gas and a liquid to form a low refractive index portion of the cladding region.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Low loss optical fiber designs and methods for their manufacture
InactiveUS20070003198A1Lower Level RequirementsOptimize composite loss characteristicGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreFiberRefractive index
The specification describes an improved optical fiber produced by a hybrid VAD / MCVD process. The core of the fiber is produced using VAD and the inner cladding layer has a depressed index and is produced using MCVD. In preferred embodiments, the optical power envelope is essentially entirely contained in VAD produced core material and the MCVD produced depressed index cladding material. Optical loss is minimized by confining most of the optical power to the VAD core where OH presence is low, as well as by maximizing the optical power in the un-doped silica region. The MCVD substrate tube material is essentially devoid of optical power.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Rare earth doped single polarization double clad optical fiber and a method for making such fiber
ActiveUS20060088261A1Produced in advanceLarge amount of processingLaser detailsOptical fibre with polarisationFiberRefractive index
An optical fiber, comprising: (i) a rare earth doped silica based elongated core with a first refractive index (n1) with an aspect ratio of 1:5 to 1; (ii) a silica based moat abutting and at least substantially surrounding the core, the moat having a refractive index n2, wherein n2<n1; (iii) a silica based inner cladding surrounding the moat, the inner cladding having a third refractive index (n3), wherein n1>n3; and n3>n2; (iv) a silica based outer cladding surrounding said inner cladding, the outer cladding having a fourth refractive index (n4), such that n4<n3; the optical fiber exhibits single polarization at the operating wavelength band.
Owner:DARPA
Multi-clad optical fiber lasers and their manufacture
ActiveUS6959022B2Easily damagedIncrease powerGlass making apparatusLaser using scattering effectsRare earthRefractive index
An optical fiber is disclosed that can be used as an active medium in fiber lasers and / or fiber amplifiers, featuring a preferably rare-earth-doped silica active core surrounded by a pure or doped silica cladding layer (“pump core”). The pump core is surrounded by a doped or pure silica inner cladding for guiding pumping radiation within the pump core. Thus, the refractive index of the inner cladding is lower than that of the pump core. The fiber is surrounded by a protective coating made of polymeric material. One or more additional outer cladding layers, having refractive indexes lower than said inner cladding, may optionally be placed between the inner cladding and the protective coating to further protect the polymer coating from damage. Unlike the prior art, the protective coating does not serve as the only cladding, but is assisted by the inner cladding and optional outer cladding(s). The resultant fiber restricts radiation mainly to silica layers, thereby increasing the damage threshold and the applicable maximum pump power of the fiber.
Owner:BIOLITEC UNTERNEHMENSBETEILLIGUNGS II AG +1
Microstructured transmission optical fiber
InactiveUS7505660B2Improve bending abilityReduce decreaseGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringOptical fiber cable
Microstructured optical fiber for single-moded transmission of optical signals, the optical fiber including a core region and a cladding region, the cladding region including an annular hole-containing region that contains non-periodically disposed holes. The optical fiber provides single mode transmission and low bend loss.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method for manufacturing an optical fiber preform
ActiveUS7702204B2Glass making apparatusOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingTransmission lossSilicon dioxide
A method for manufacturing a final optical fiber preform via overcladding of a primary preform having a cross section area is disclosed. The method includes at least one manufacturing step of the primary preform by deposit of an inner cladding and of a central core inside a tube of fluorine-doped silica, the tube being chosen such that it has a cross section area that is maximally about 15% less than the cross section area of the primary preform. With the method of the invention it is possible to manufacture a preform of large capacity at reduced cost which allows the drawing of an optical fiber having reduced transmission losses.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Optical fiber containing alkali metal oxide
InactiveUS20080279515A1Bending loss can be improvedGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingDopantZero-dispersion wavelength
Disclosed is an optical fiber having a silica-based core comprising an alkali metal oxide a silica-based core, said core comprising an alkali metal oxide selected from the group consisting of K2O, Na2O, LiO2, Rb2O, Cs2O and mixtures thereof in an average concentration in said core between about 10 and 10000 ppm by weight, and a silica-based cladding surrounding and directly adjacent the core, the cladding including a region having a lower index of refraction than the remainder of such cladding. By appropriately selecting the concentration of alkali metal oxide dopant in the core and the cladding, a low loss optical fiber may be obtained which exhibits a cable cutoff less than 1400 nm chromatic dispersion at 1550 nm between about 13 and 19 ps / nm / km, and a zero dispersion wavelength less than about 1324 nm.
Owner:CORNING INC
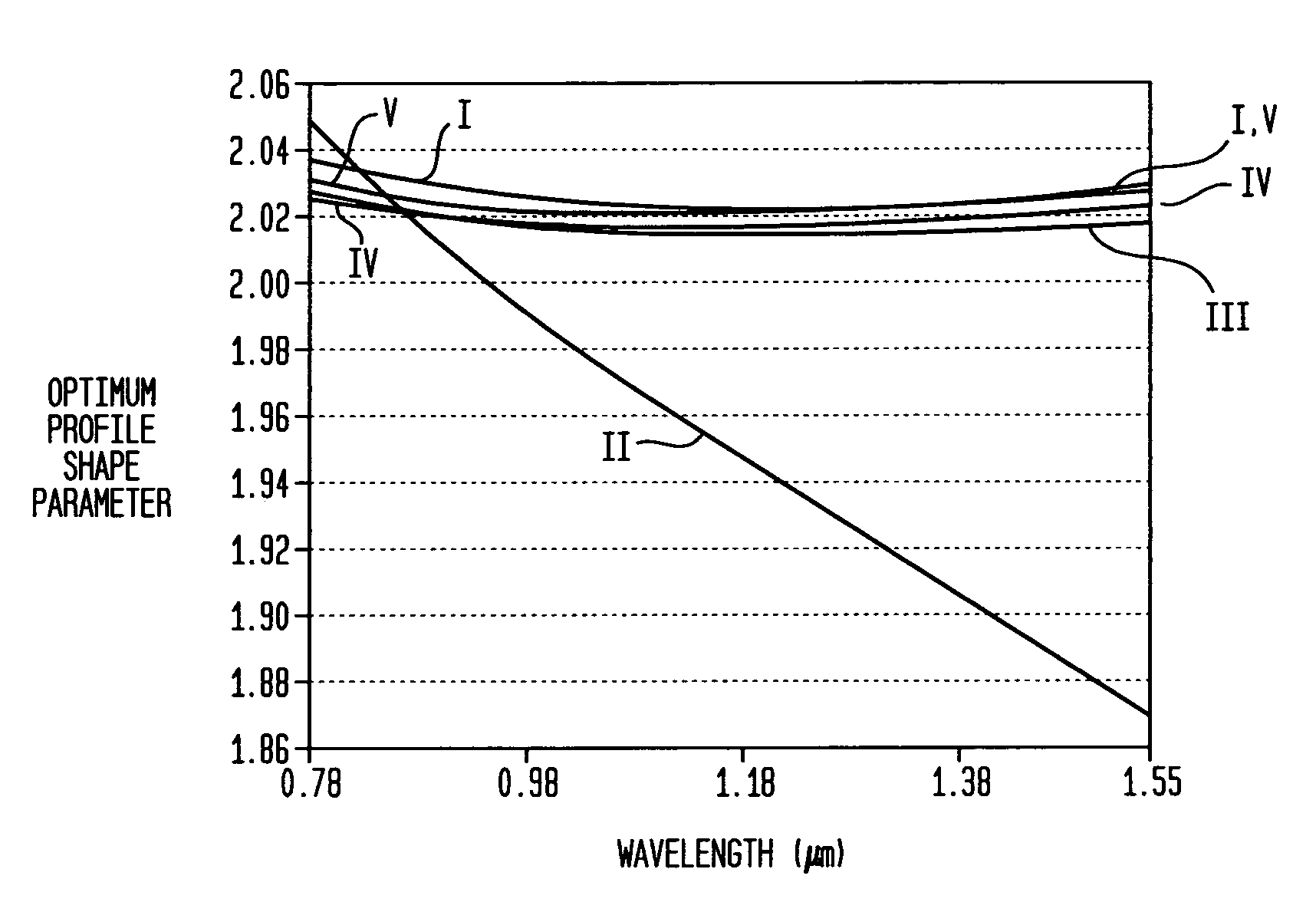
Multi-wavelength, multimode optical fibers
ActiveUS7421174B2Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideFiberRefractive index
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Hollow-core optical fiber and method of making same
InactiveUS20050185908A1Increase surface tensionReduce surface tensionGlass making apparatusCladded optical fibreFiberSurface roughness
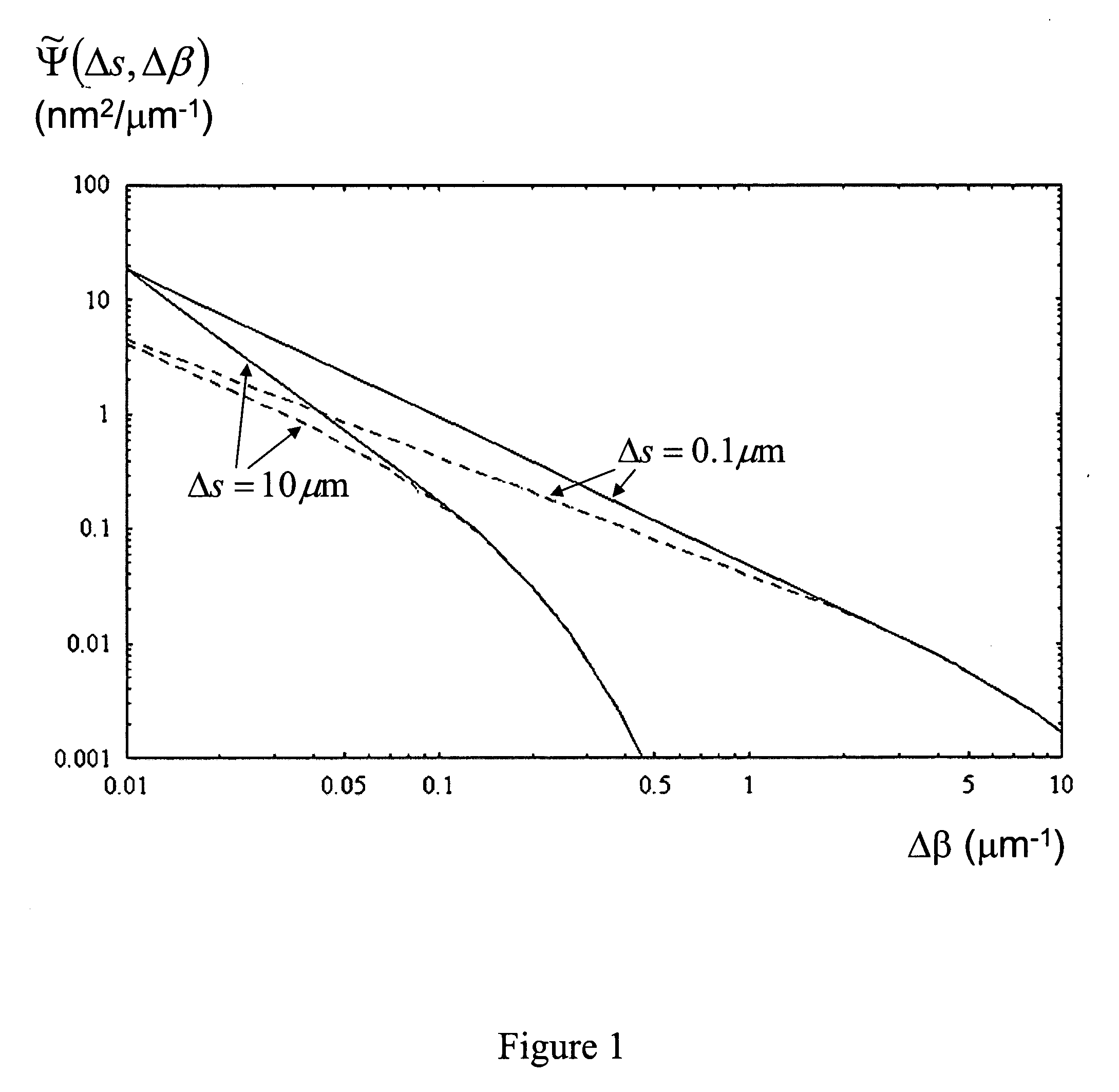
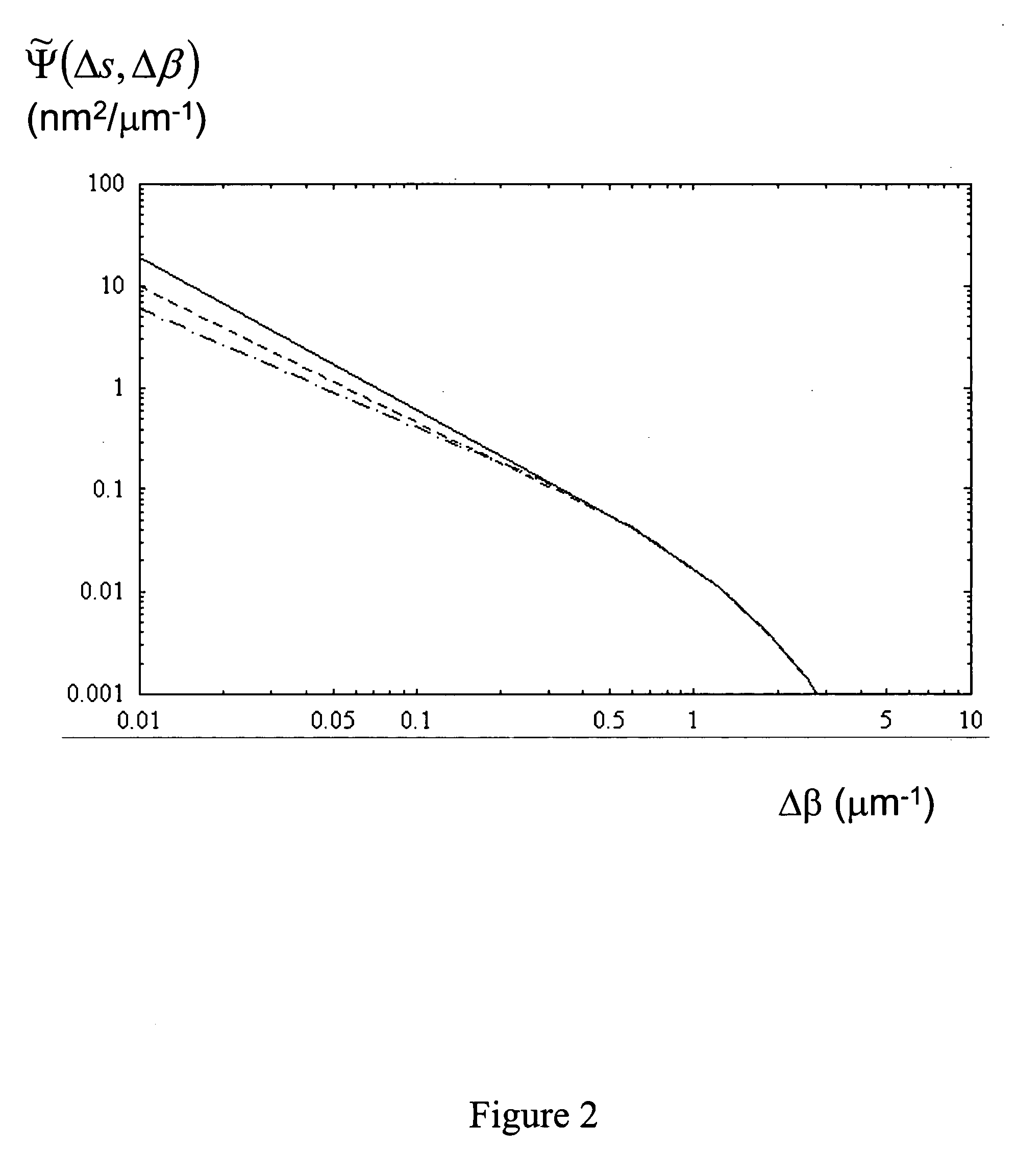
An optical fiber having a cladding region surrounding a core region having an elongate core hole, the inner or outer surface of the core hole having a surface roughness with a spatial period equal to or less than 5 μm by a spectral power below 0.0017 nm2μm−1. A method of making an optical fiber including a cladding region having an arrangement of elongate cladding holes in a matrix material, surrounding an elongate core region having an elongate core hole, the method including the step of increasing the surface tension of the matrix material prior to or during the step of heating and drawing the fiber.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Anti-bending multimode fiber and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN101634728AReduce bend add-on attenuationImprove bending resistanceGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingUltrasound attenuationRelative refractive index
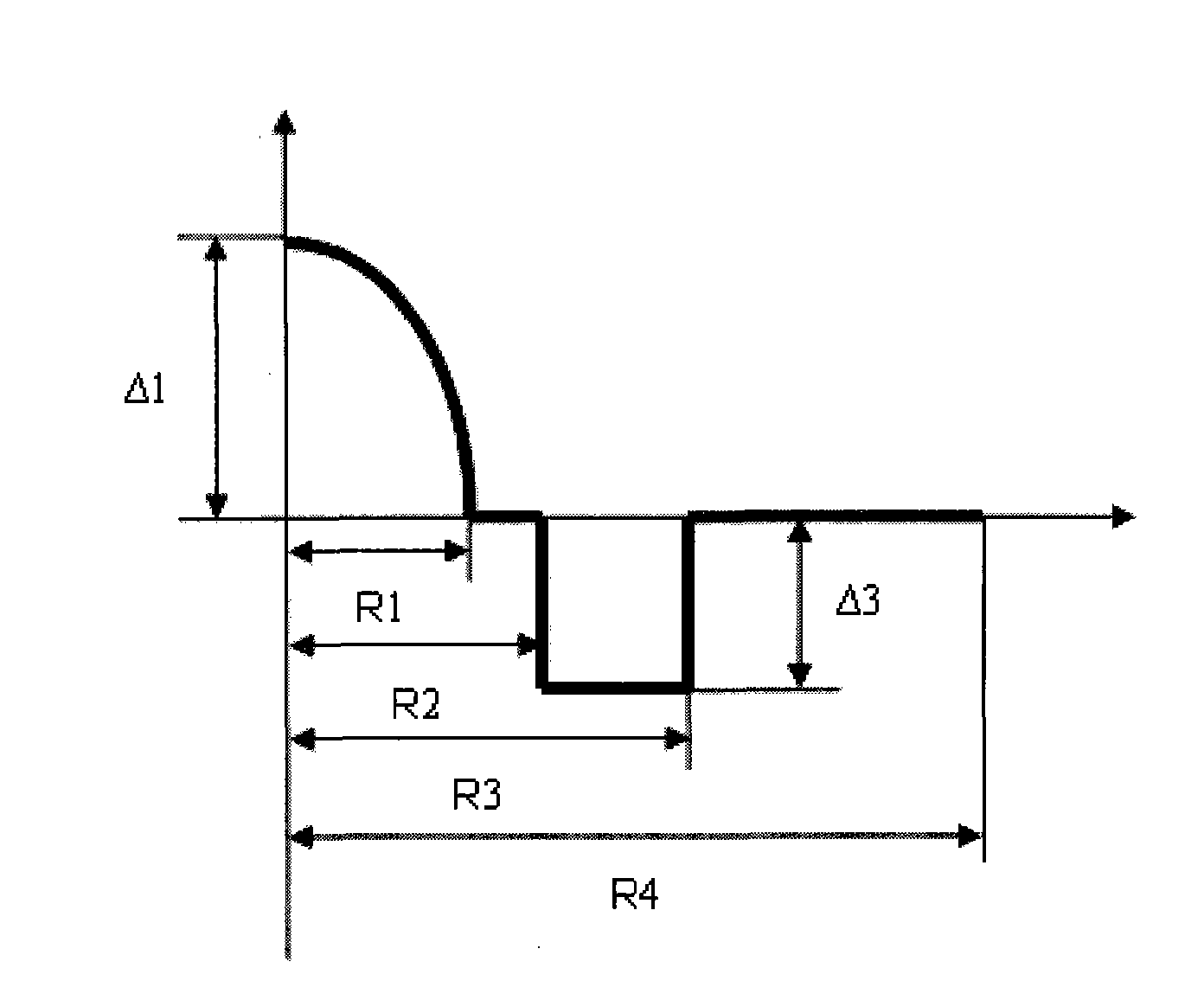
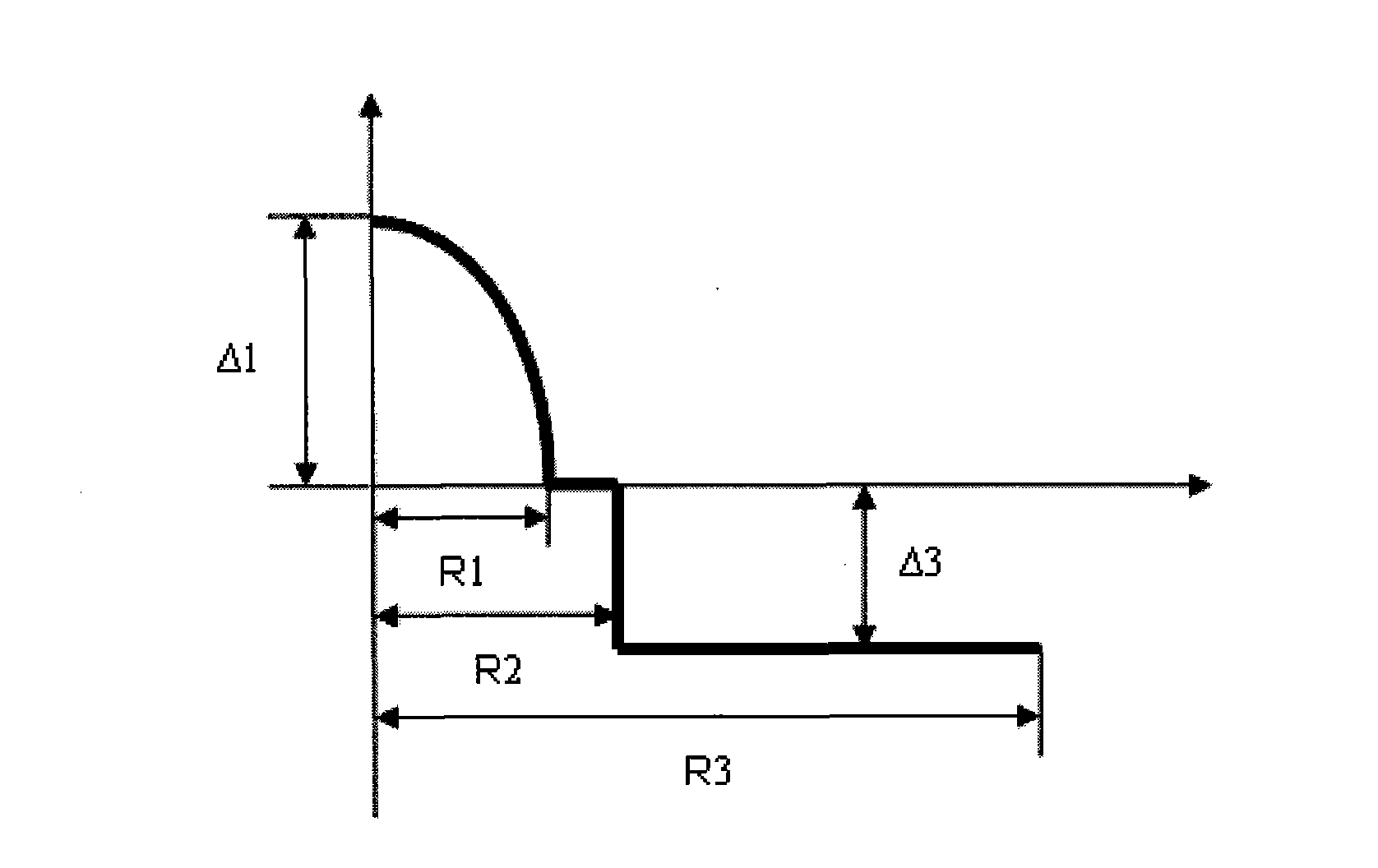
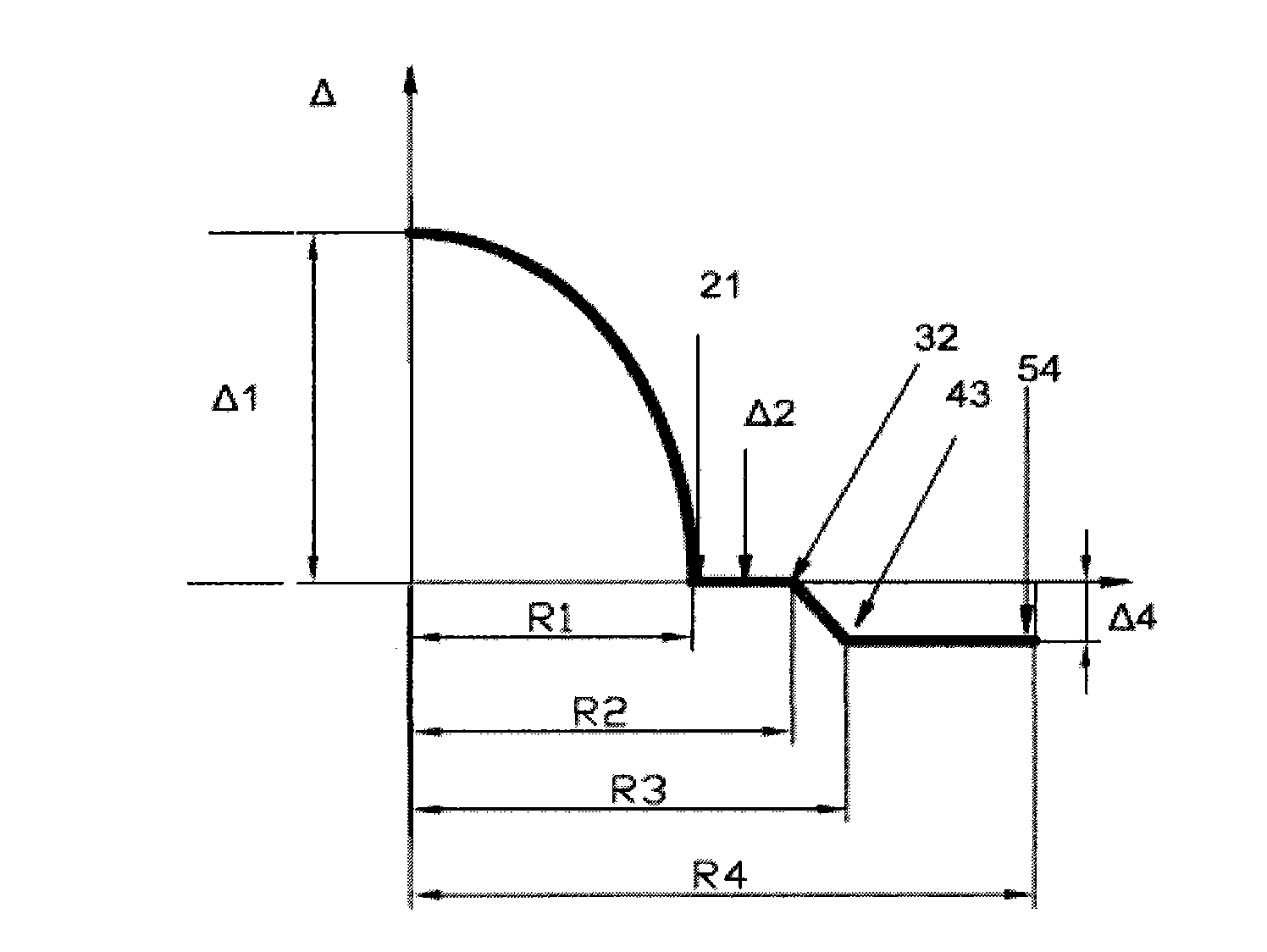
The invention relates to an anti-bending multimode fiber and manufacturing method thereof. The fiber comprises a core and a cladding and is characterized in that the radius of core R1 is 24-26 microns, refractive index section of the core is like a parabola, refractivity maximum delta1 is 0.9-1.1%, the cladding outside the core is composed of three parts, the radius of inner cladding R2 is 1.04-1.6 times of the radius of core R1, delta2 is minus 0.01-0.01%, intermediate cladding is gradually changed in refractive index, the radius of intermediate cladding R3 is 1.06-1.8 times of R1, refractivity is gradually changed into delta4 from delta2, the radius of outer cladding R4 is 2.38-2.63 times of R1, and delta4 is minus 0.20% to minus 0.40%. The invention reduces fiber bending additional attenuation and improves anti-bending performance of fiber but also basically eliminates inner stress of fiber, greatly improves mechanical properties of fiber, and service life of fiber operating in minor radius for a long time also can be guaranteed. The manufacturing method of the invention is simple, convenient and effective and is applicable to mass production.
Owner:EVERPRO TECH COMPANY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com