Patents
Literature
480 results about "Bend loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
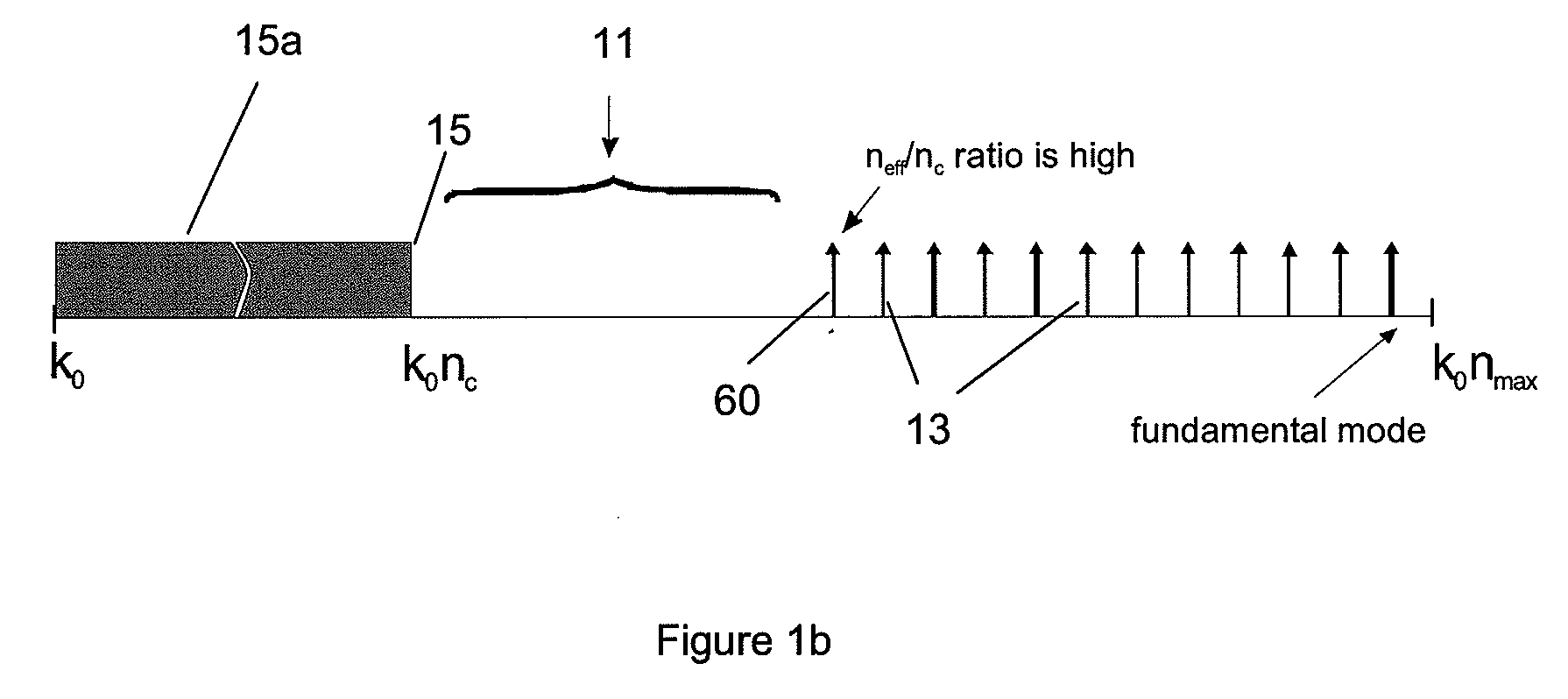
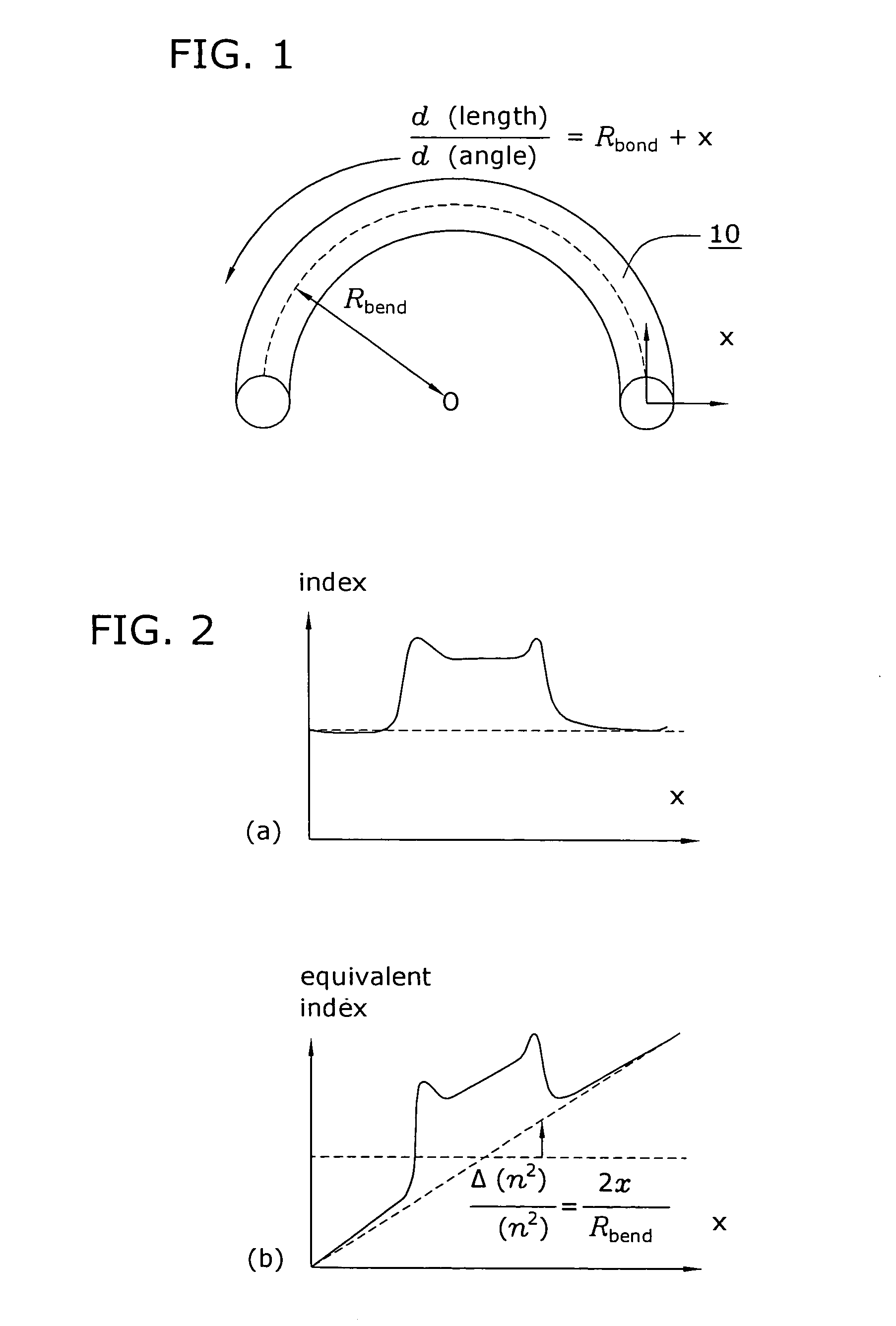
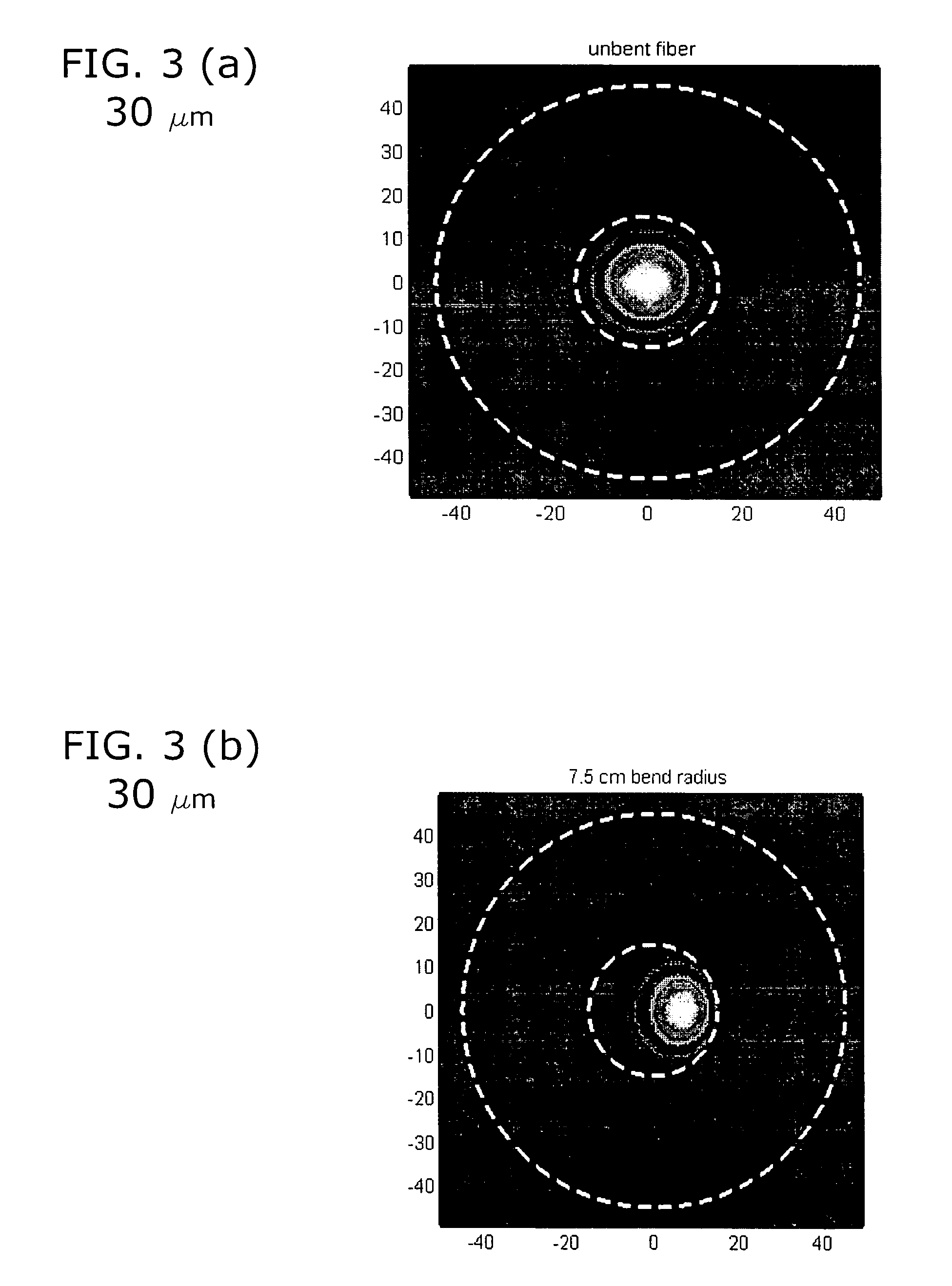
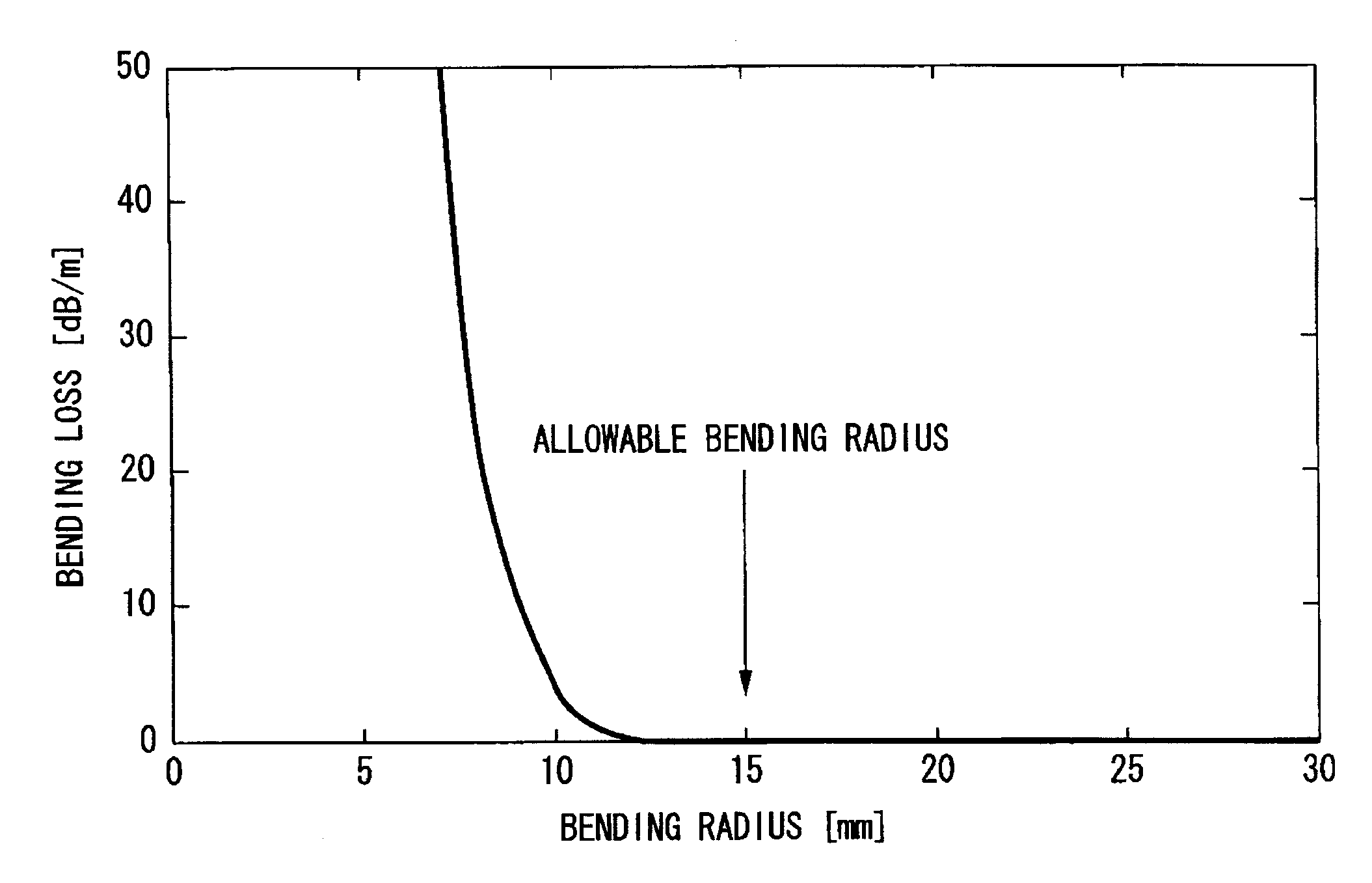
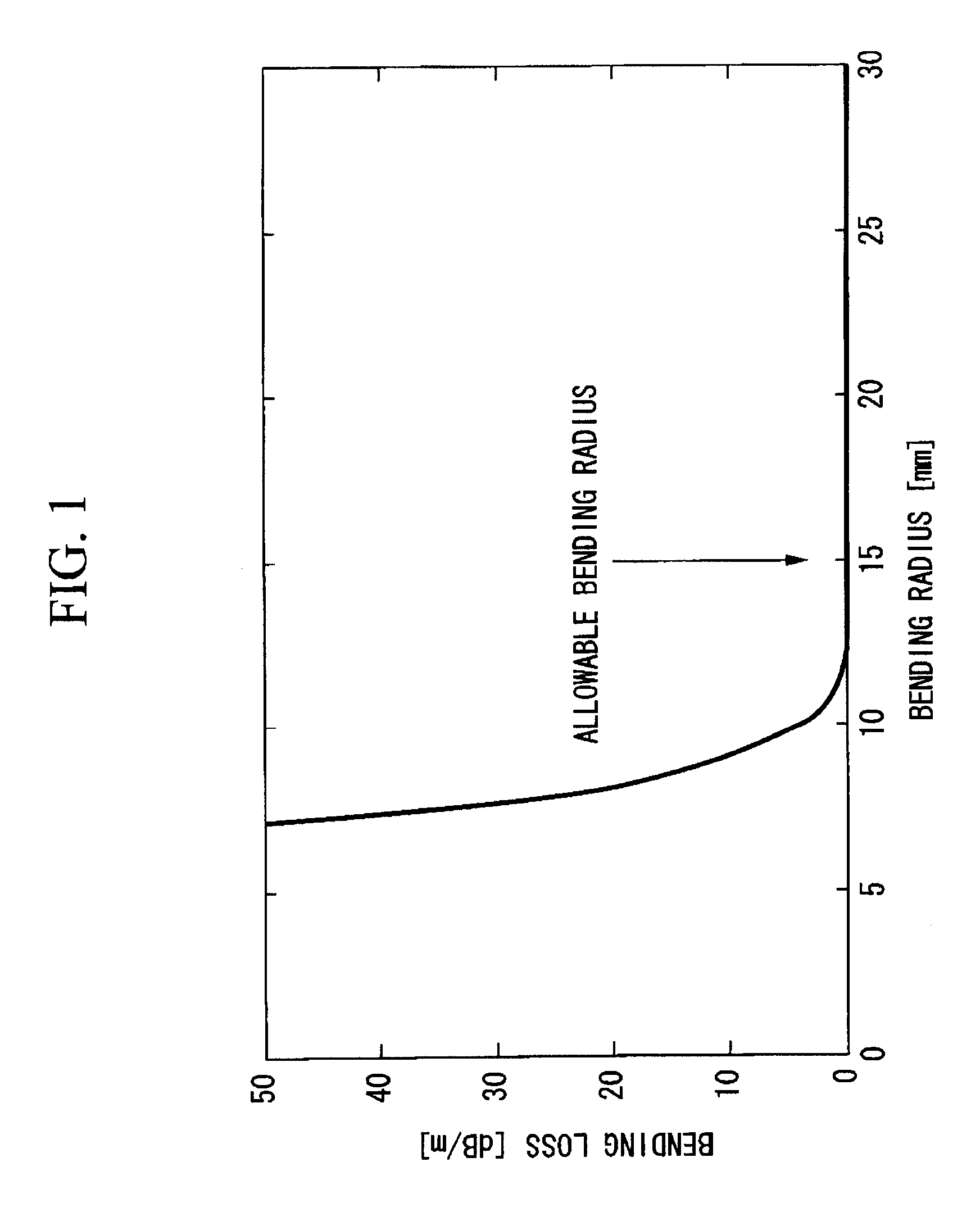
Macro-bending loss. Losses occur at bends as light at the bend tends to want to carry on in a straight line. When the bend diameter is on the order of a few tens of millimeters (the exact diameter range depends on the fiber design) the fiber can exhibit significant losses due to the bend disrupting the guidance of the fiber.
Large effective area fiber
ActiveUS7555187B2Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRelative refractive indexEngineering
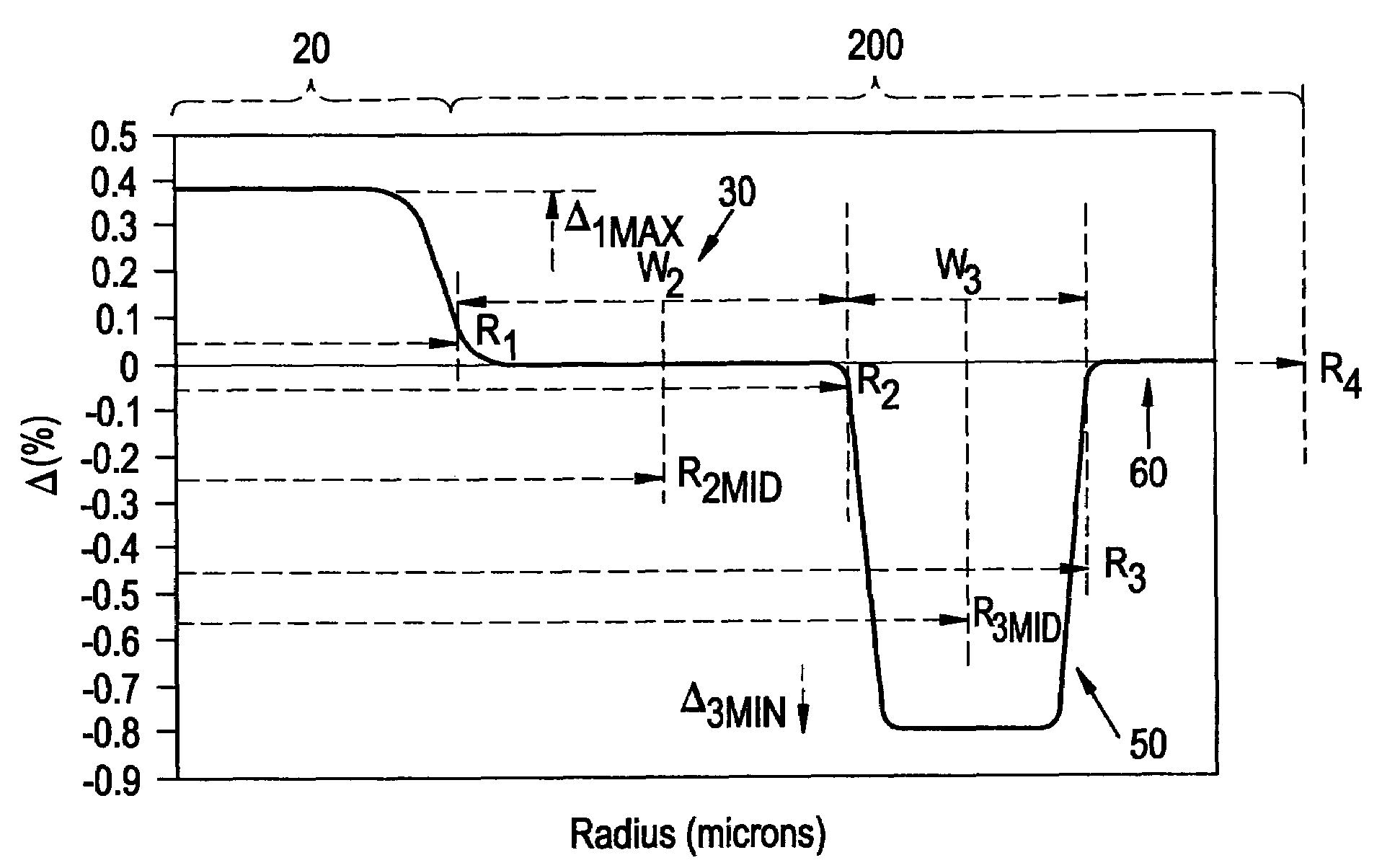
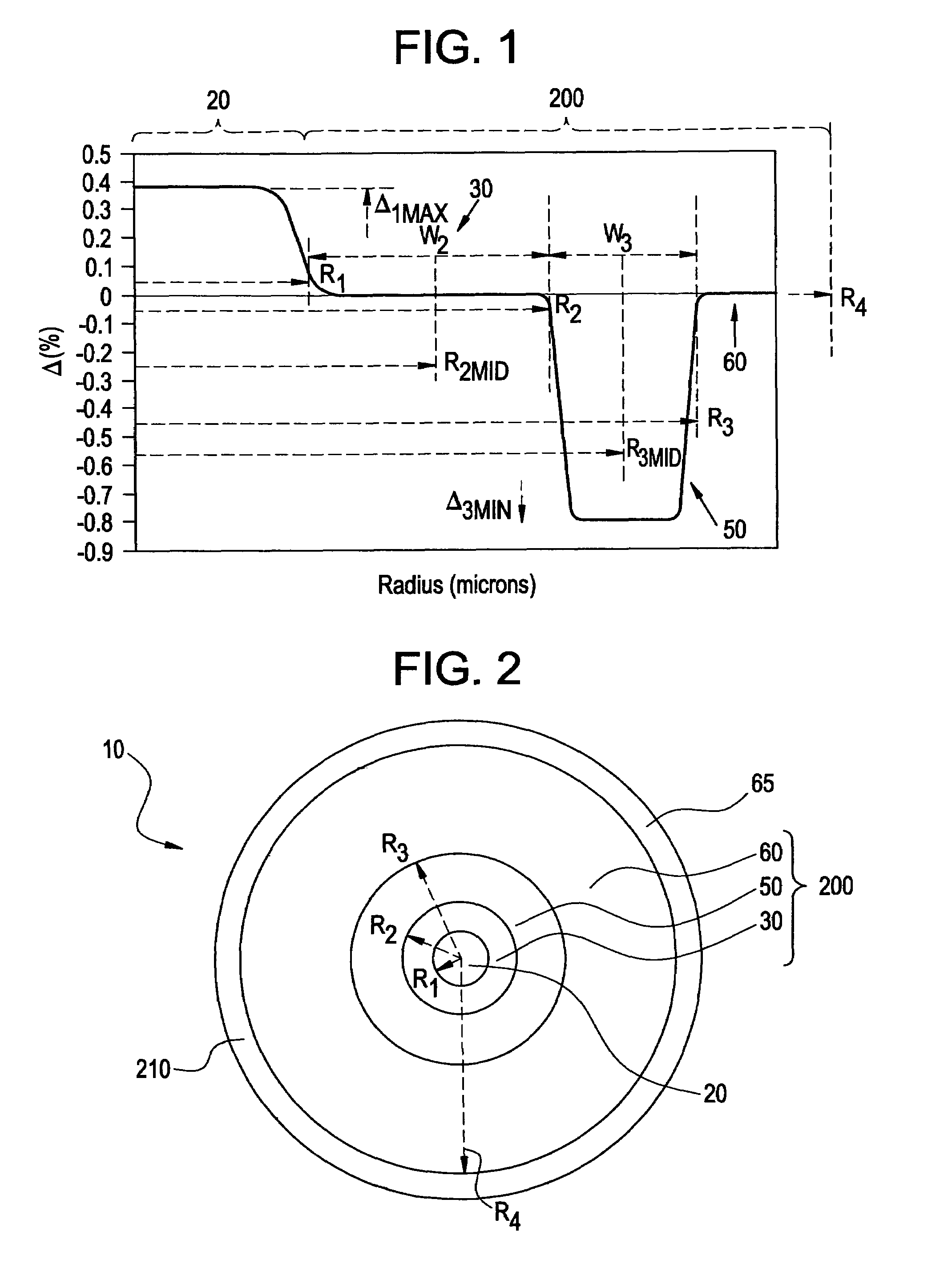
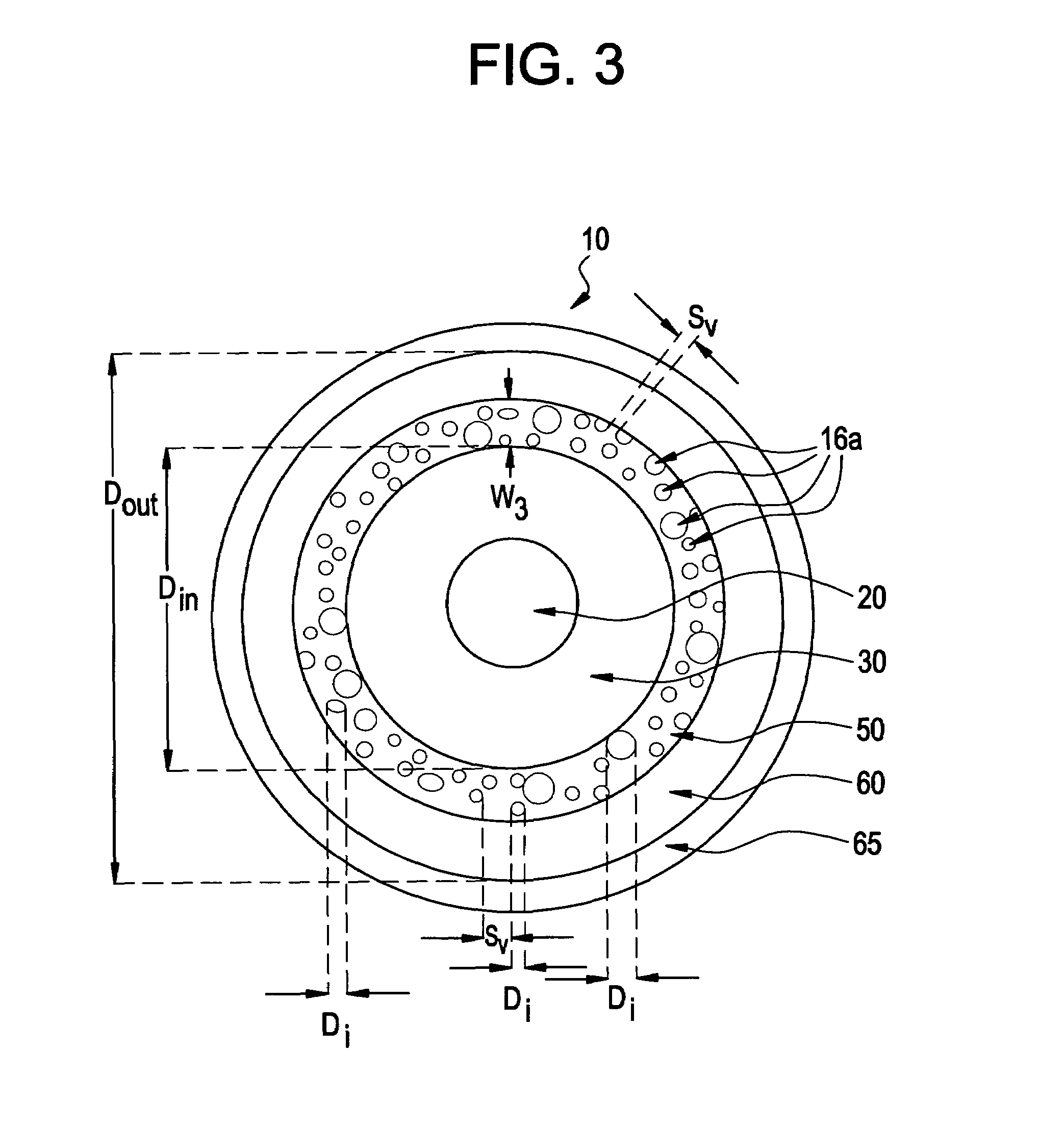
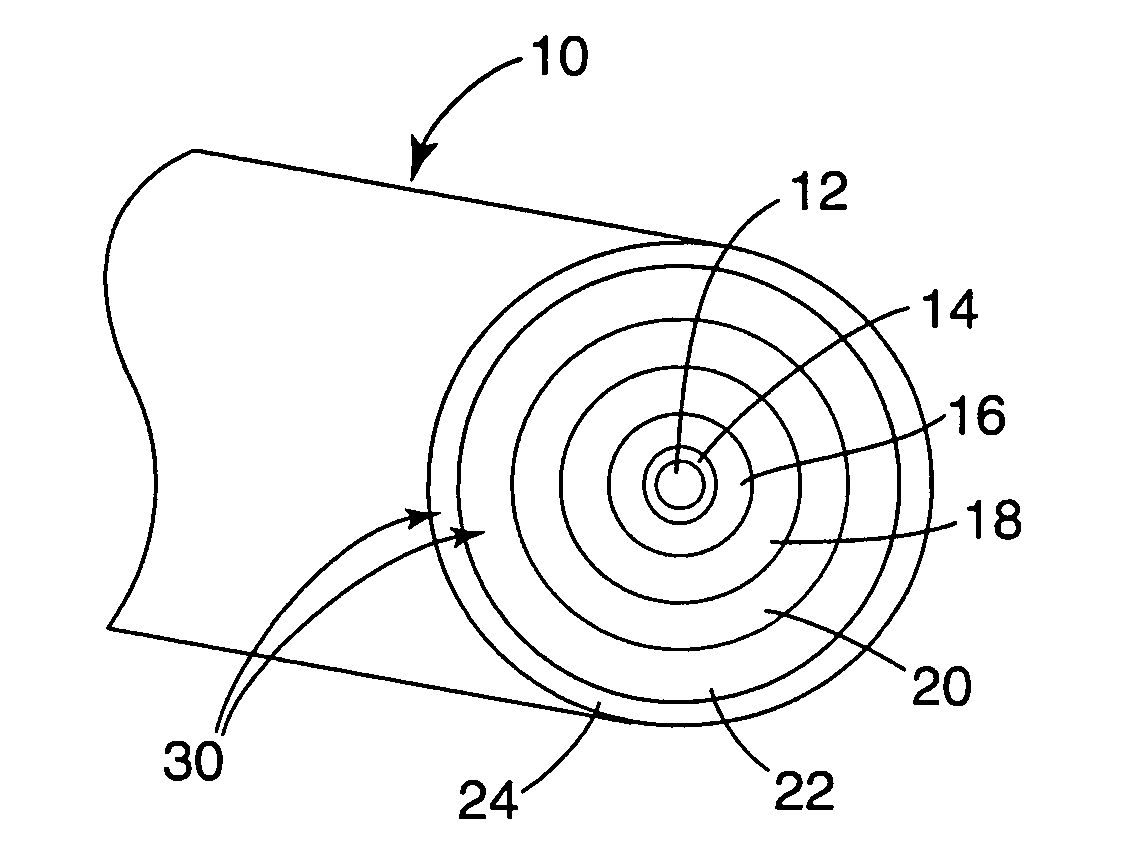
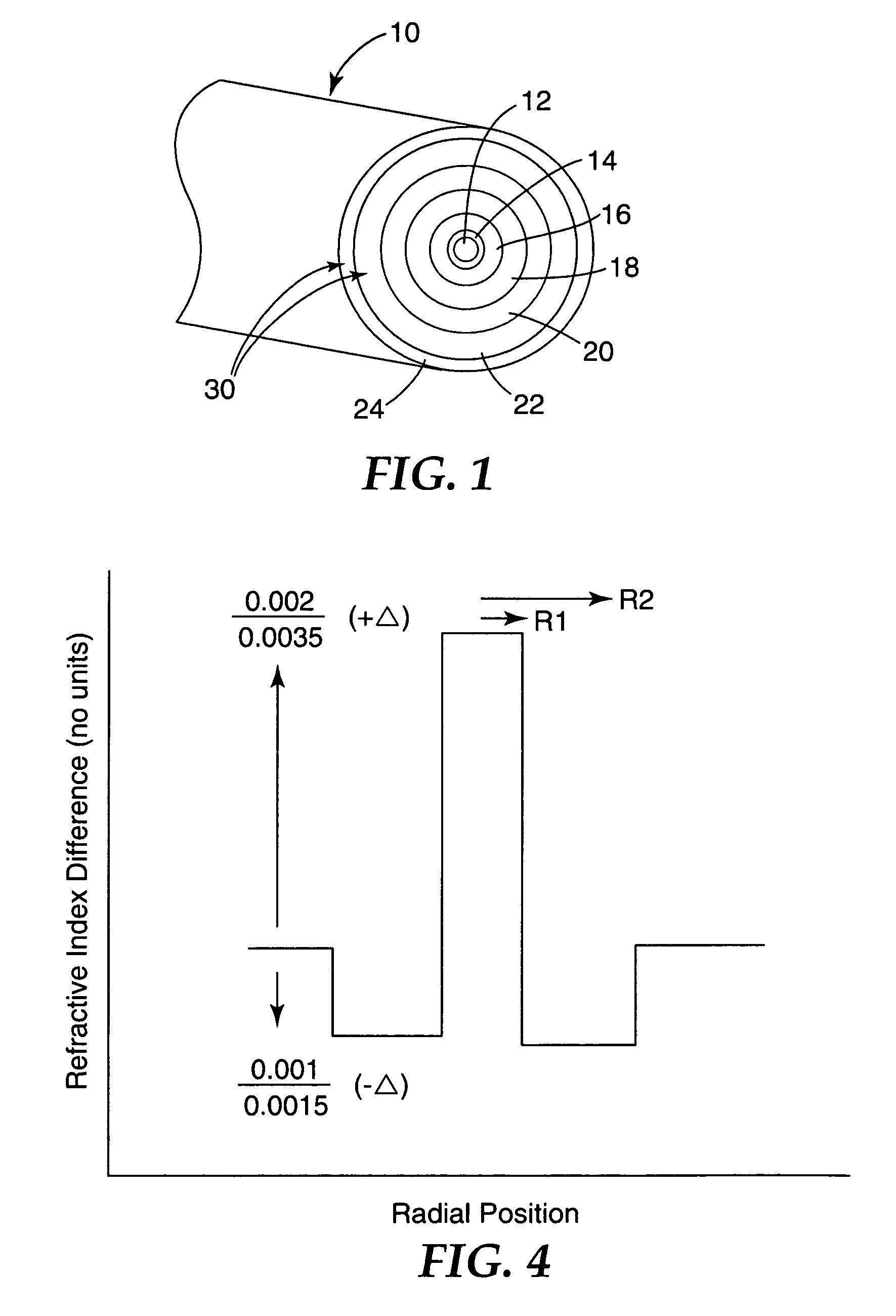
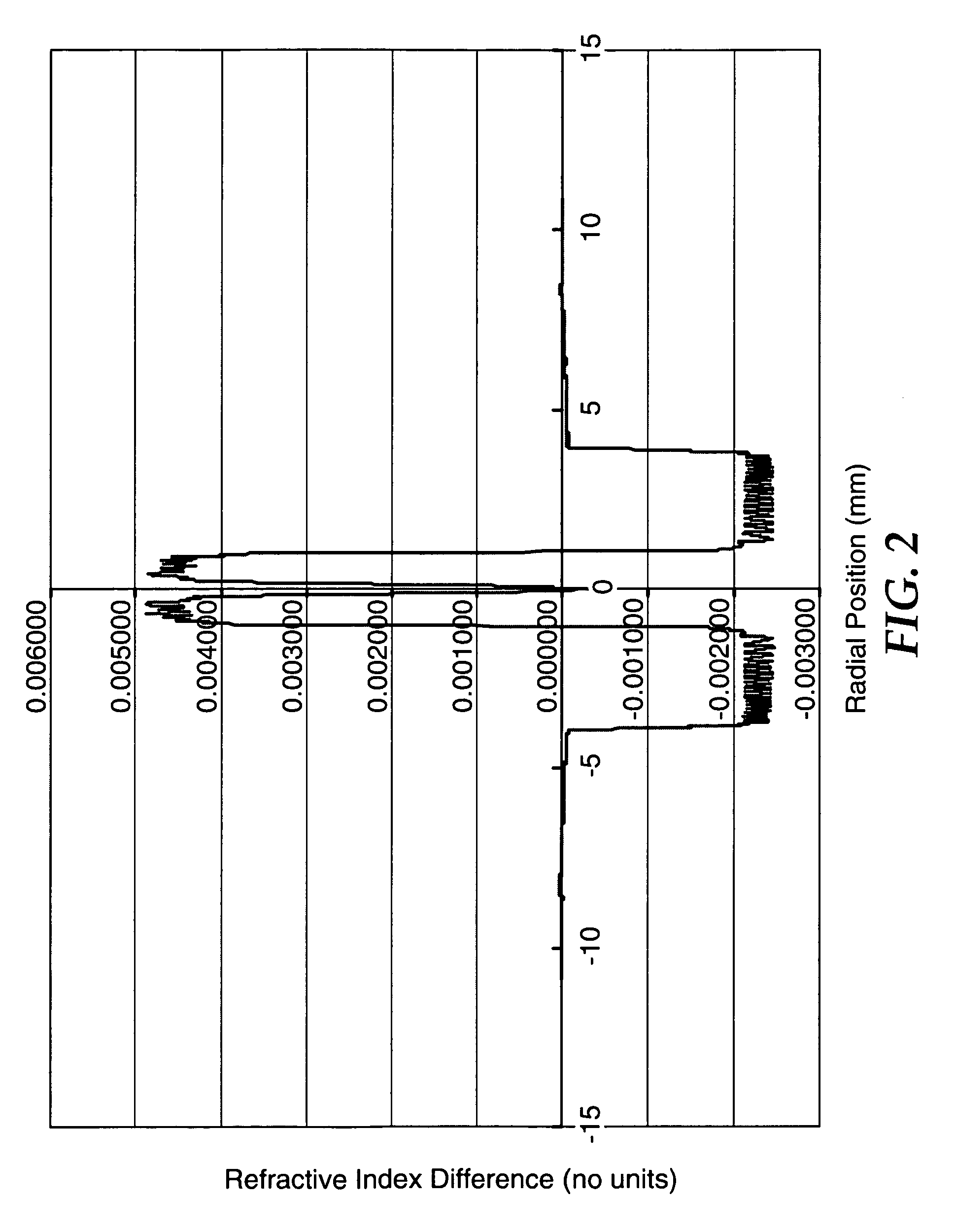
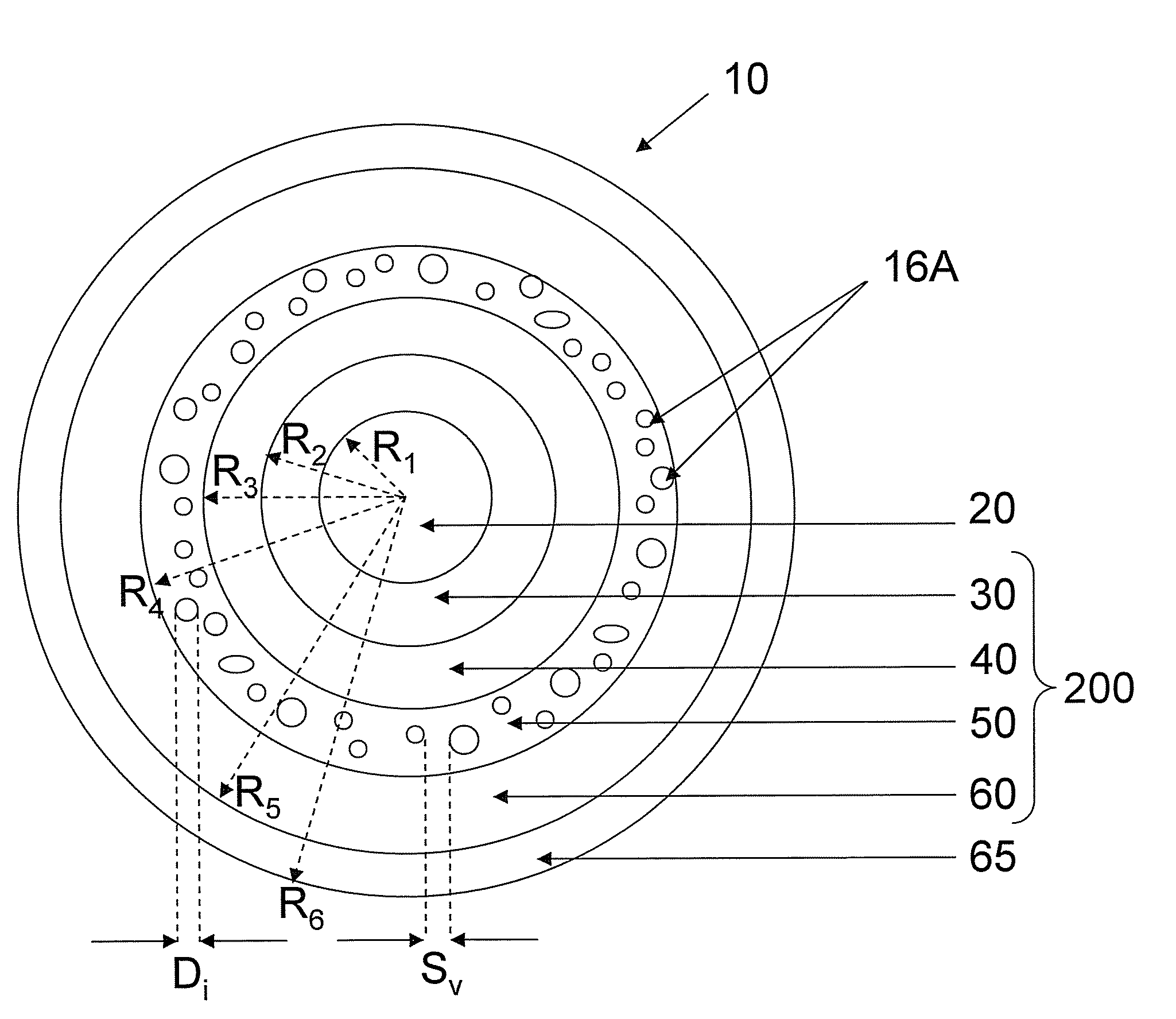
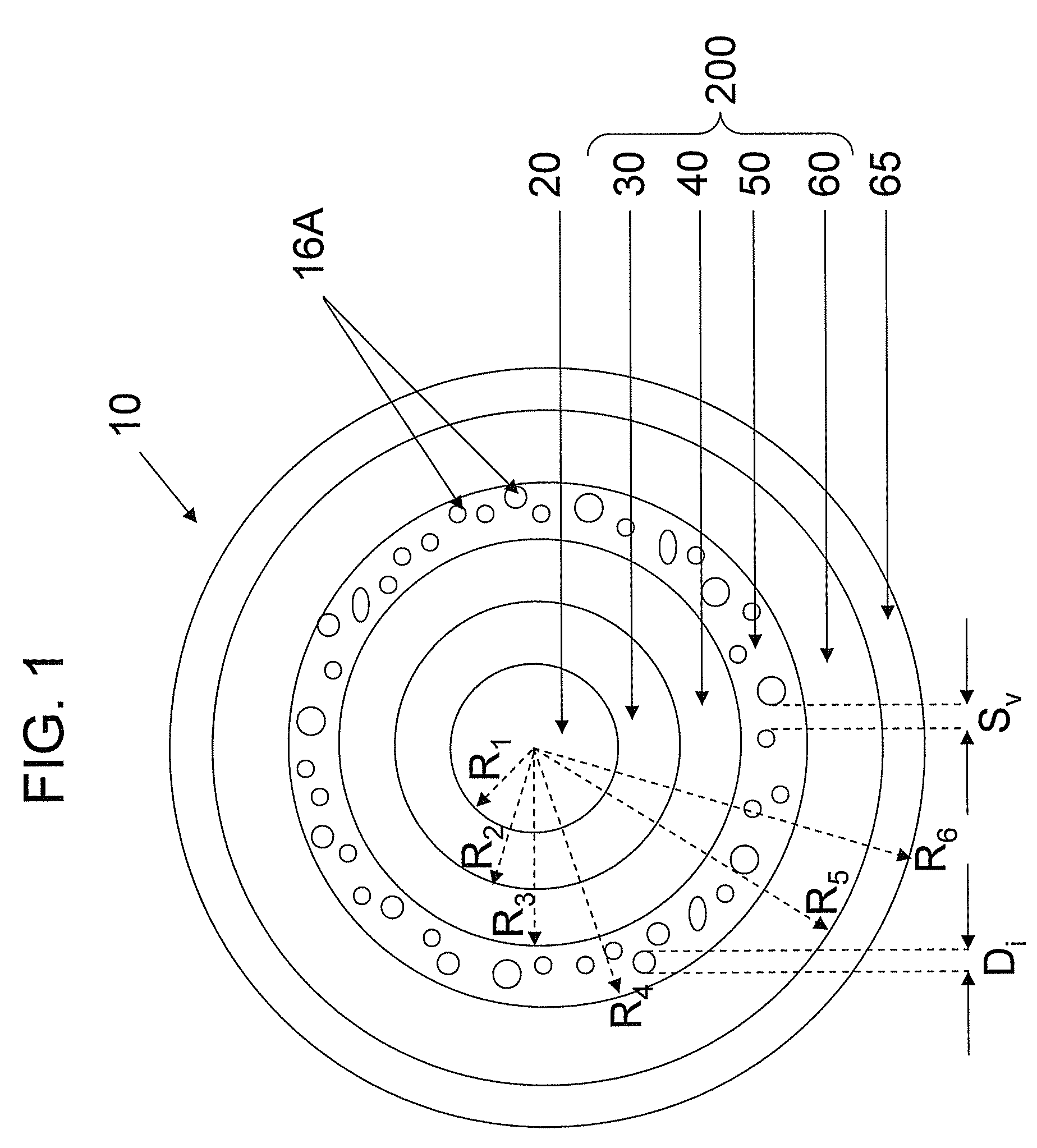
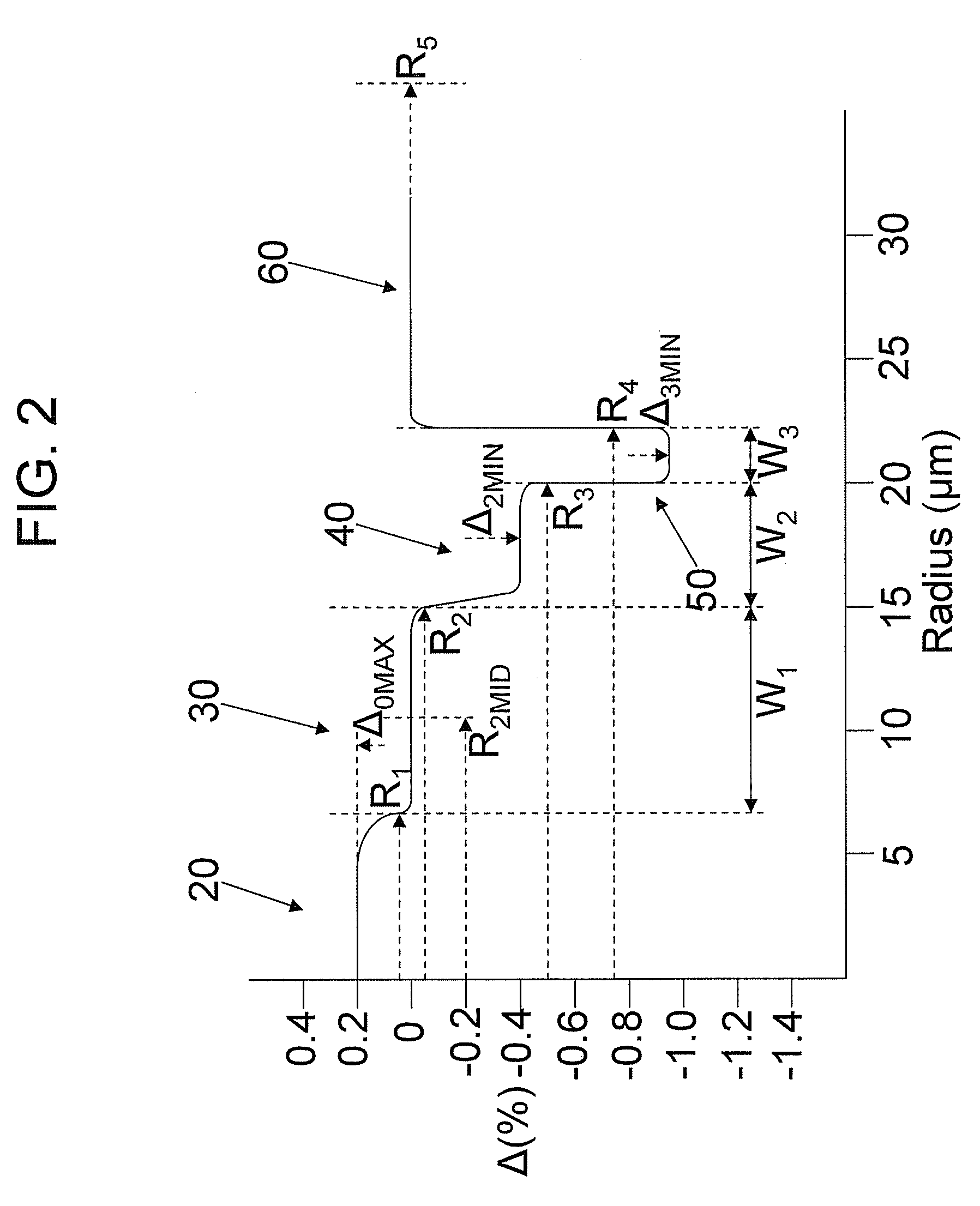
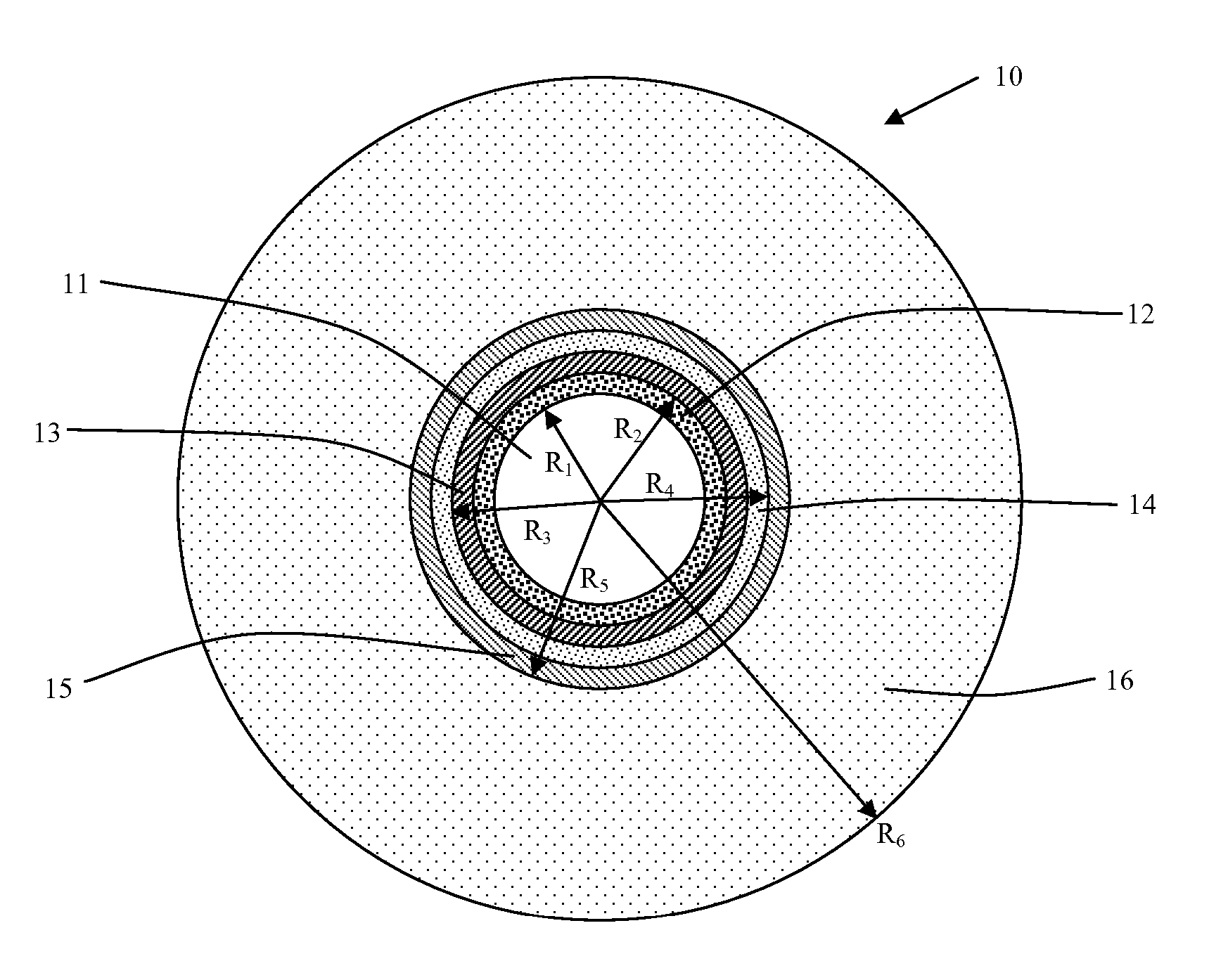
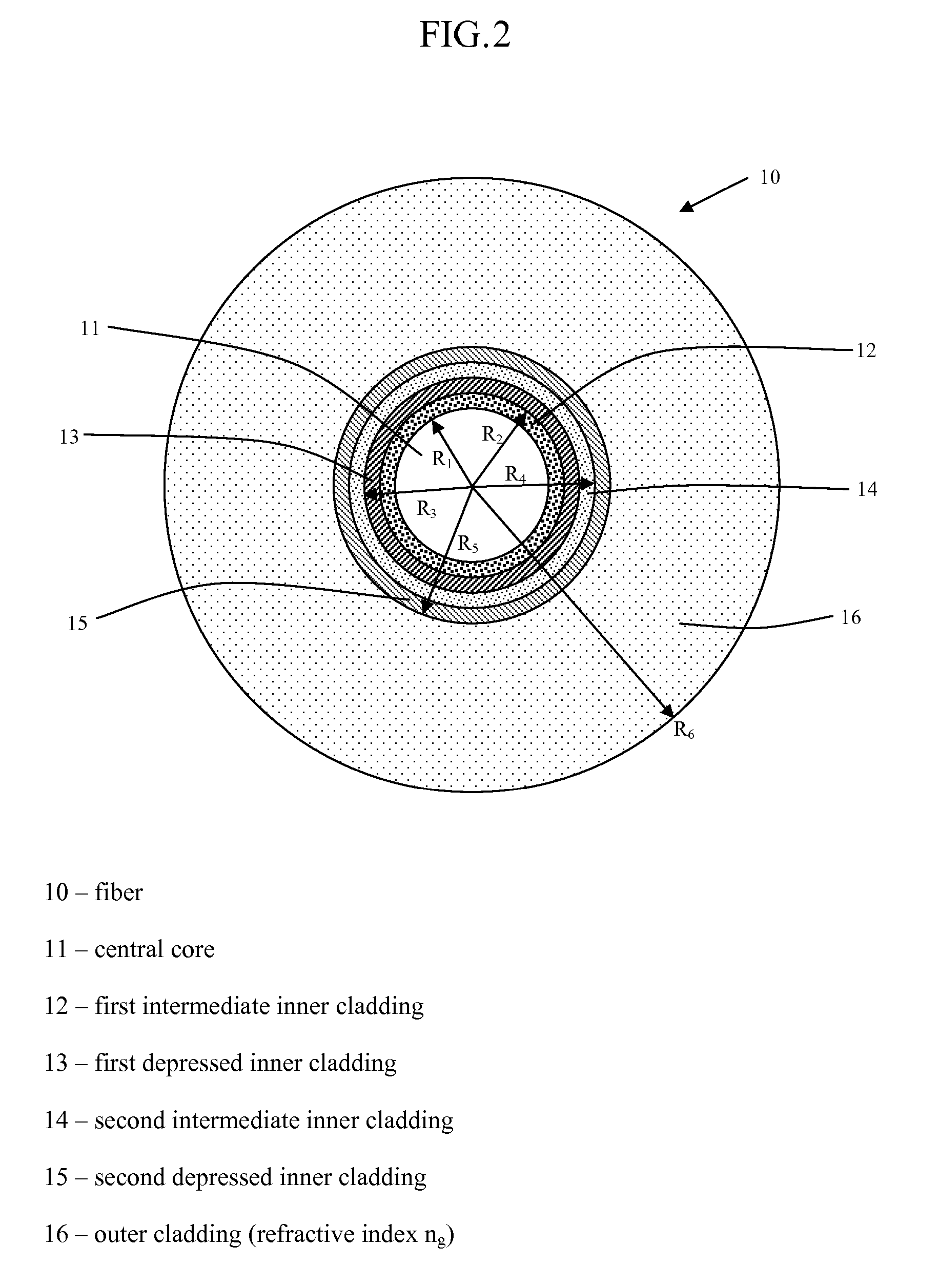
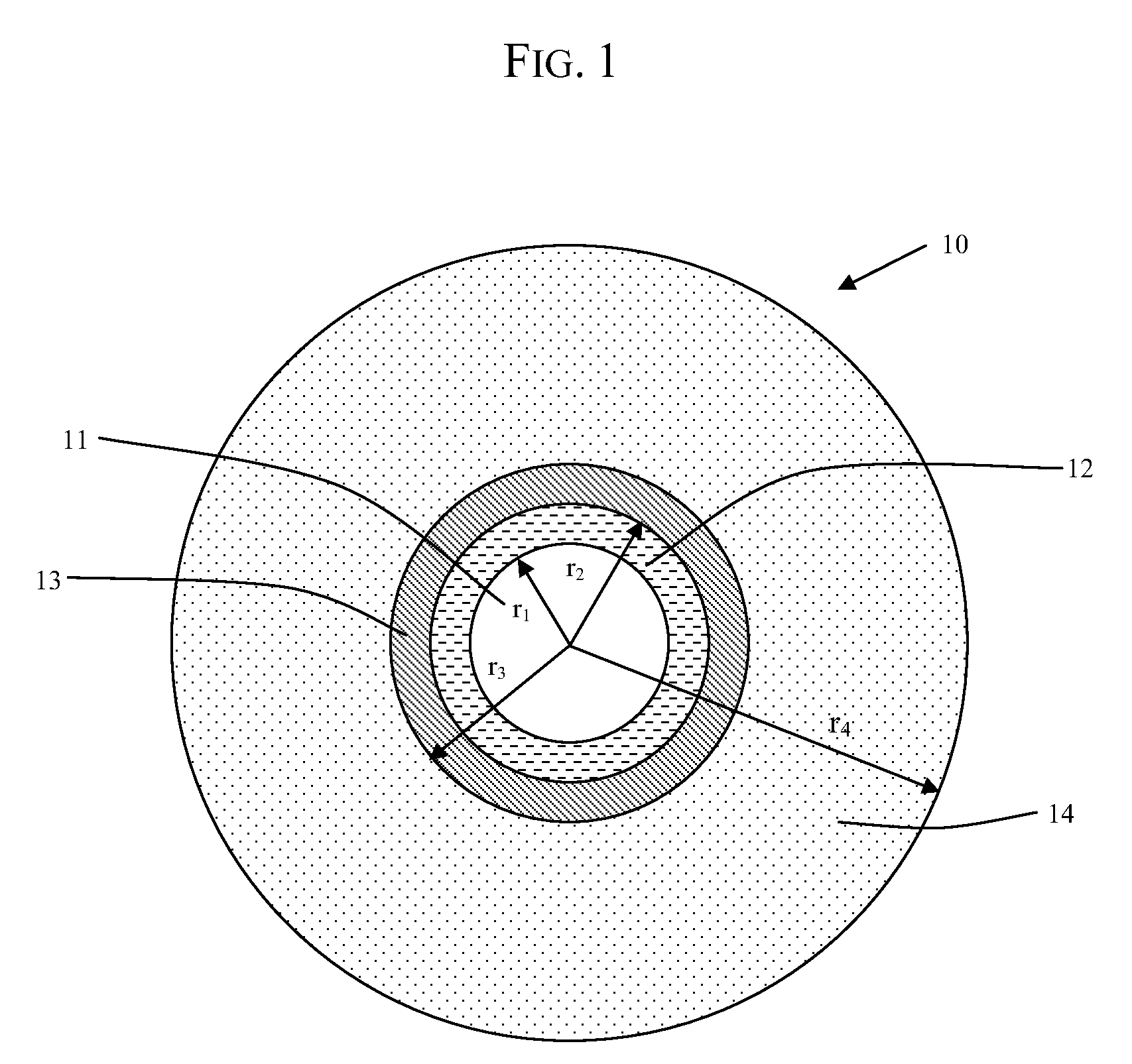
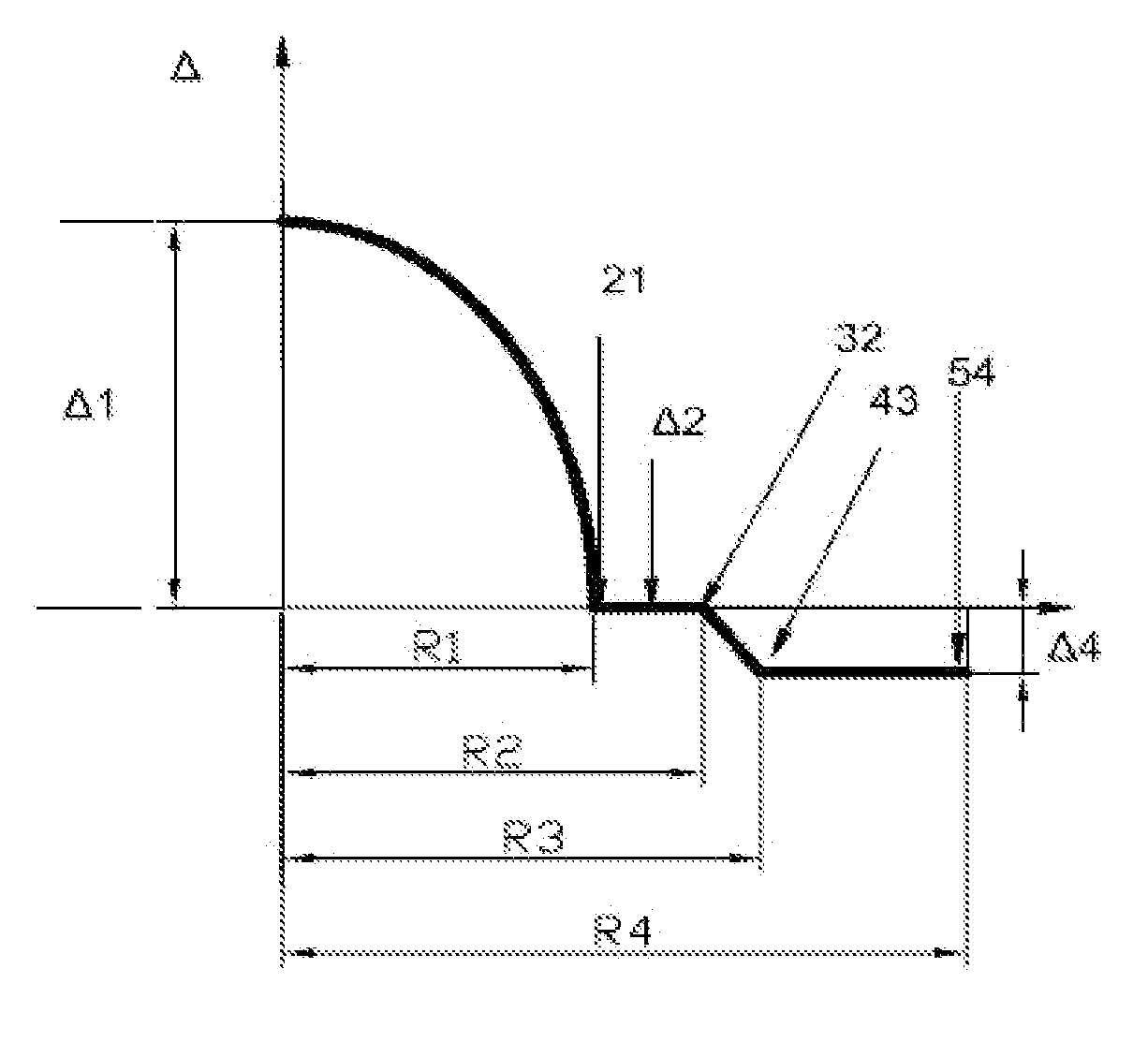
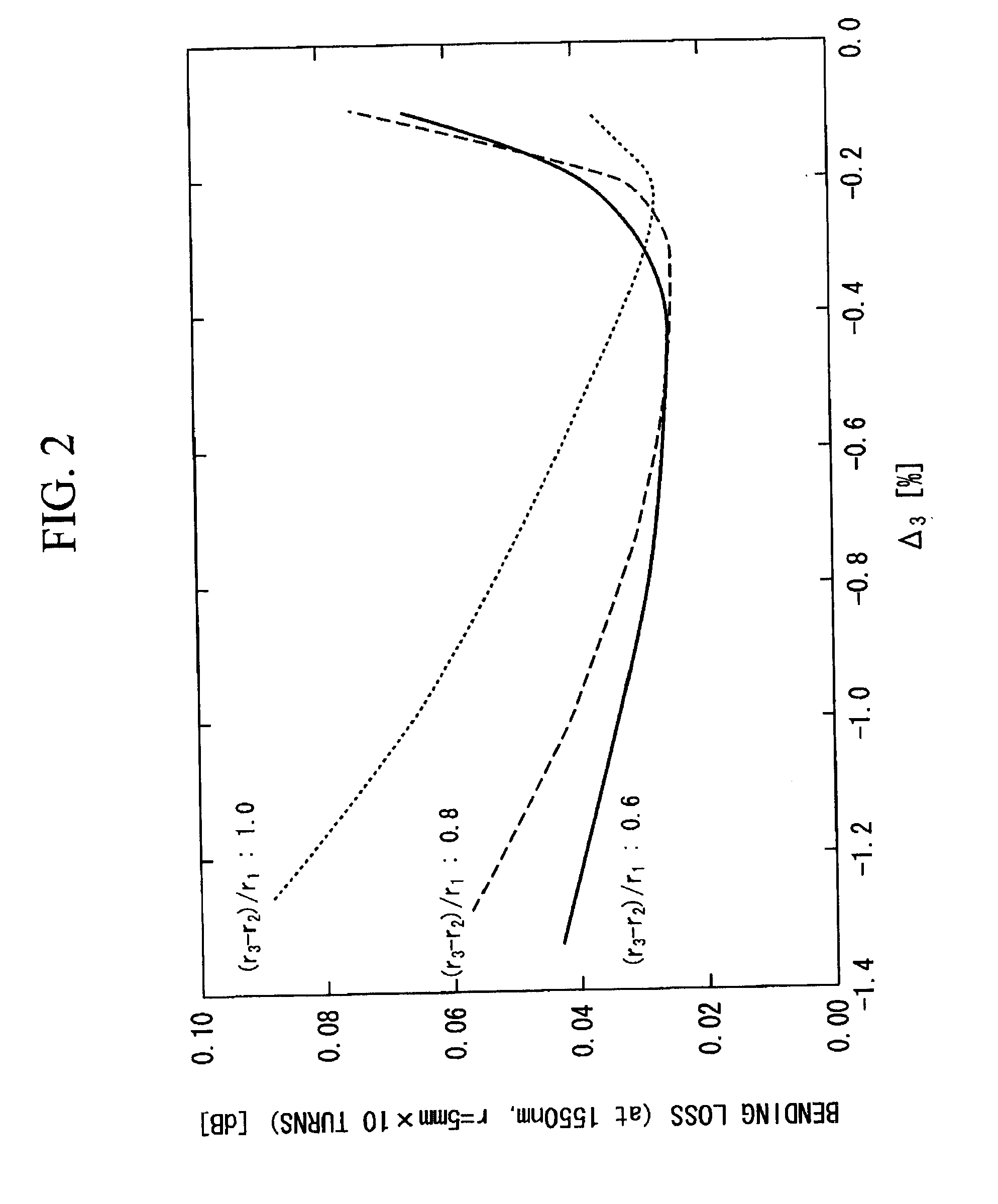
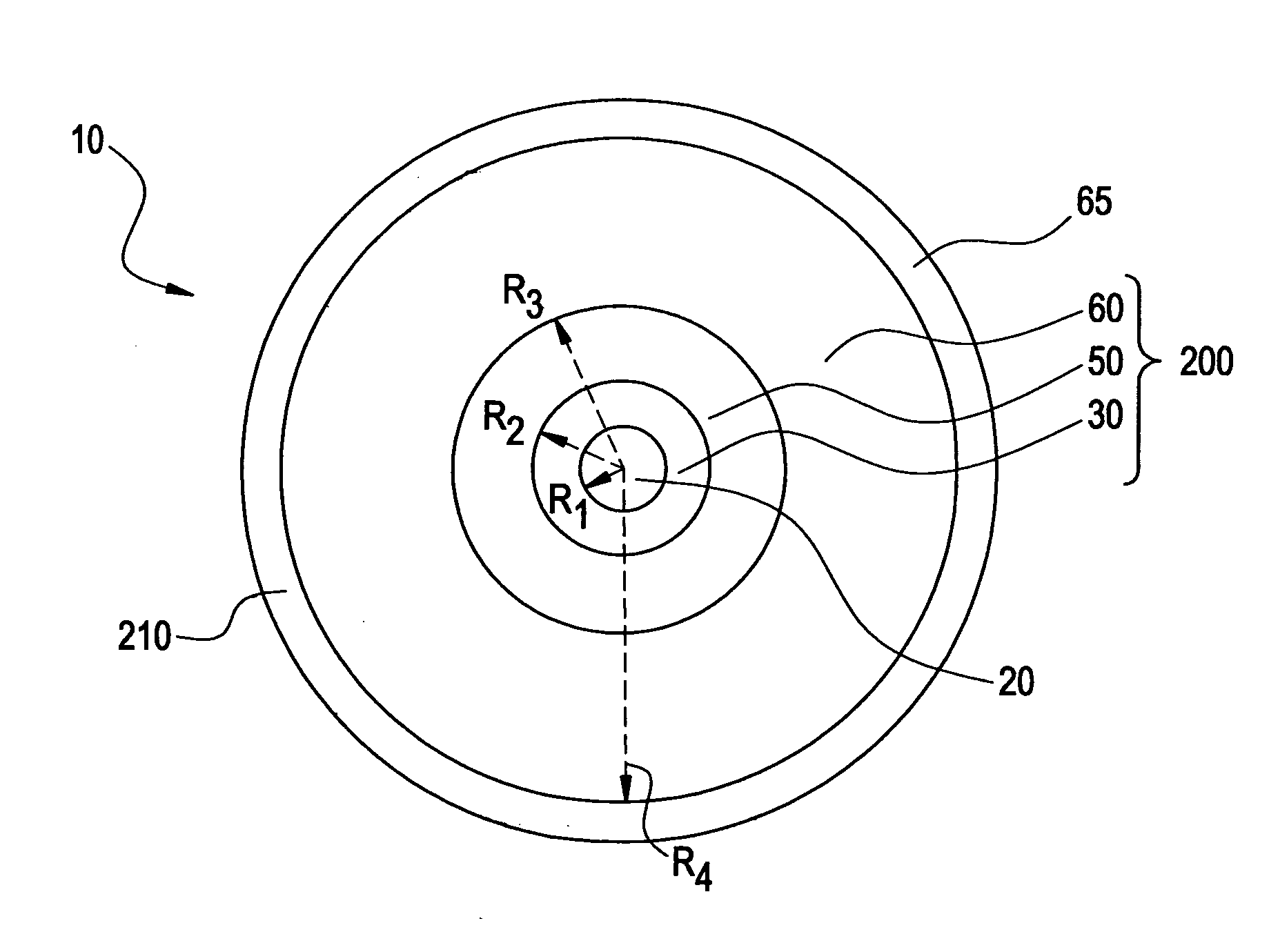
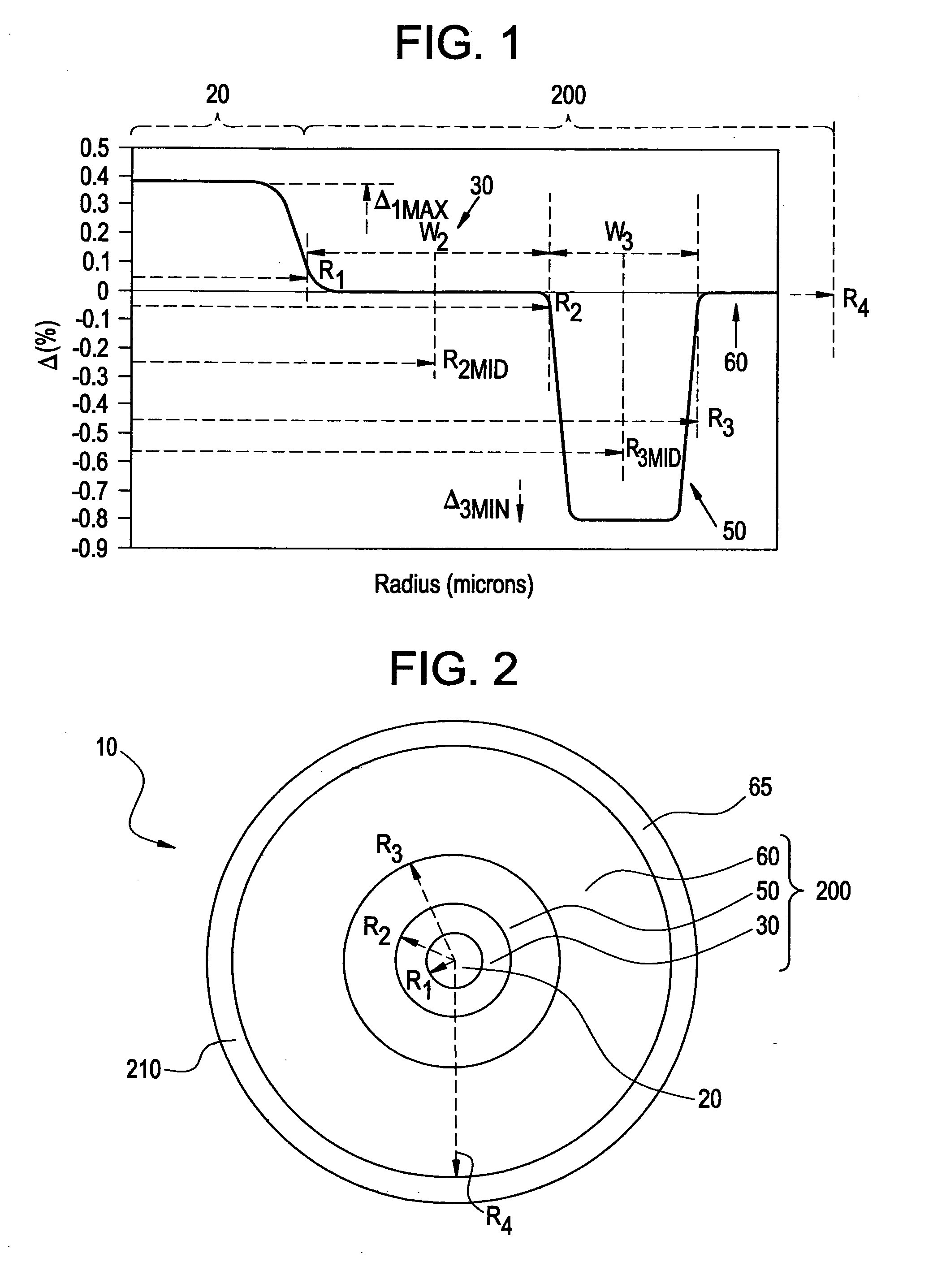
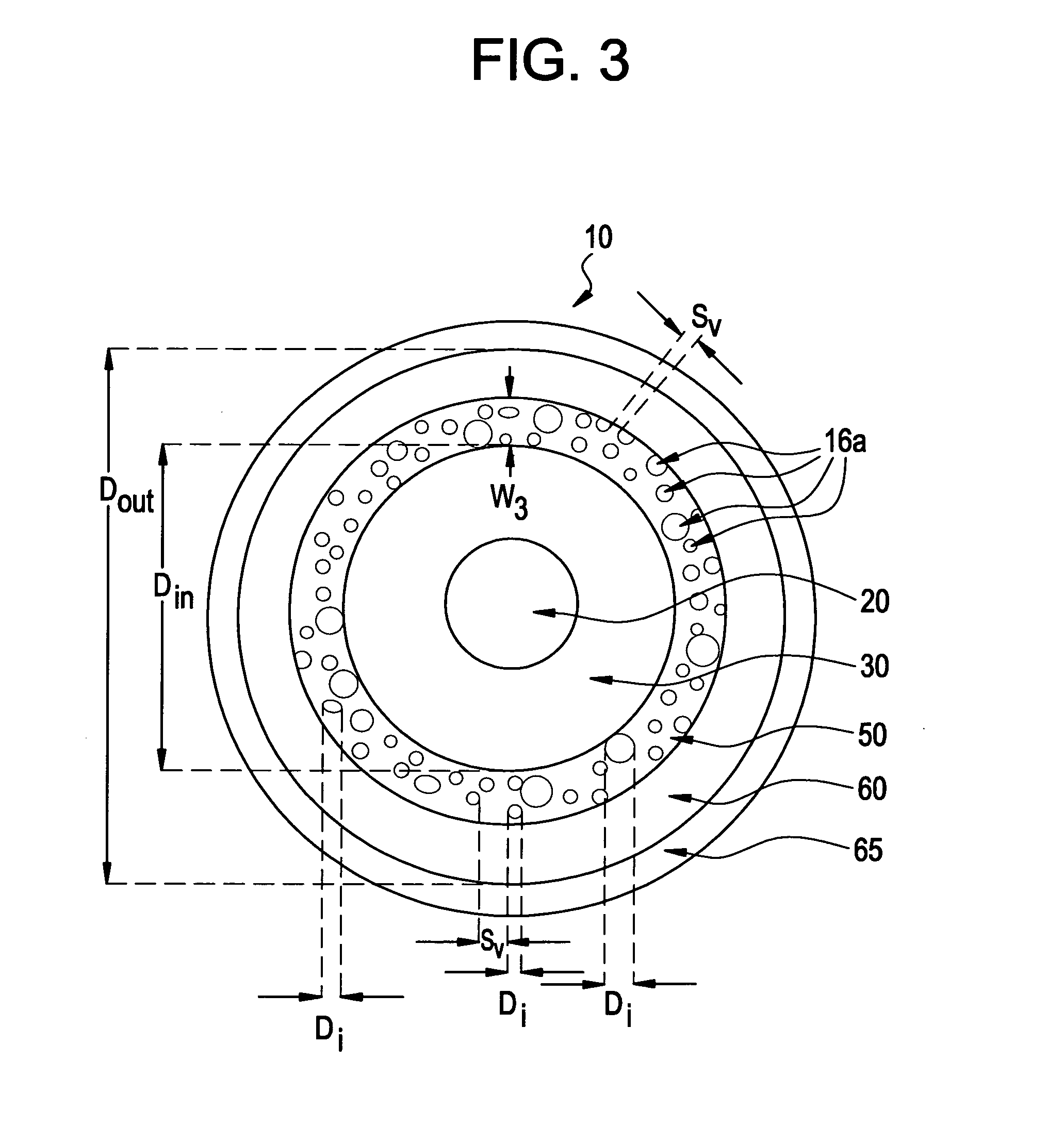
An optical fiber according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: a glass core extending from a centerline to a radius R1 wherein R1 is greater than about 5 μm; a glass cladding surrounding and in contact with the core, the cladding comprising: (i) a first annular region extending from the radius R1 to a radius R2, the first annular region comprising a radial width, W2=R2−R1, (ii) a second annular region extending from the radius R2 to a radius R3, and comprising a radial width, W3=R3−R2, and (iii) a third annular region surrounding the second annular region and extending from the radius R3 to an outermost glass radius R4; wherein the core comprises a maximum relative refractive index, Δ1MAX, relative to the third annular region, and wherein Δ1MAX is greater than about 0.1% and less than about 0.3%; the first annular region has a refractive index delta Δ2(r) is less than about 0.025%; wherein the second annular region comprises a minimum relative refractive index, Δ3MIN, relative to the third annular region;wherein Δ1MAX>Δ2MAX>Δ3MIN, and Δ2MIN>Δ3MIN<0; andwherein the core and the cladding provide a fiber with cable cutoff less than 1500 nm, and an effective area at 1550 nm greater than 95 μm2 and bend loss of ≦0.5 dB / turn on a 20 mm diameter mandrel.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical fiber cable and optical fiber ribbon
ActiveUS8548294B2Stable optical loss characteristicReduce warpageFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringBend radius
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Triple-band bend tolerant optical waveguide
ActiveUS7130516B2Minimal splice lossesGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingBand bendingLength wave
An optical waveguide comprises a core, an inner cladding laterally surrounding the core, and an outer cladding laterally surrounding the inner cladding, wherein the core, inner cladding, and outer cladding have a depressed well configuration. The waveguide operates in three or more wavelength bands, wherein a first wavelength band is centered at about 1300 nm, and wherein a second wavelength band is centered at about 1625 nm. The waveguide has bend losses that are less than or equal to 1.0 dB / turn when measured on a 5 mm radius bend at 1625 nm and bend losses that are less than or equal to 1.5 dB / turn when measured on a 5 mm radius bend at 1650 nm.
Owner:CORNING RES & DEV CORP
Large effective area low attenuation optical fiber
InactiveUS8218929B2Optical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideUltrasound attenuationBend loss
Optical waveguide fiber that has large effective area and low loss characteristics, such as low attenuation and low bend loss. The optical waveguide fiber includes a dual trench design wherein an annular region closer to the core is preferably doped with at least one downdopant such as fluorine, which annular region is surrounded by another annular region that preferably includes closed, randomly dispersed voids.
Owner:CORNING INC
Single-mode optical fiber
ActiveUS7587111B2Reduce leakageEffectively reduce the bending lossesOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringMaterials science
Disclosed is an optical transmission fiber having reduced bending and microbending losses that is commercially usable in FTTH or FTTC transmission systems.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Single-Mode Optical Fiber Having Reduced Bending Losses
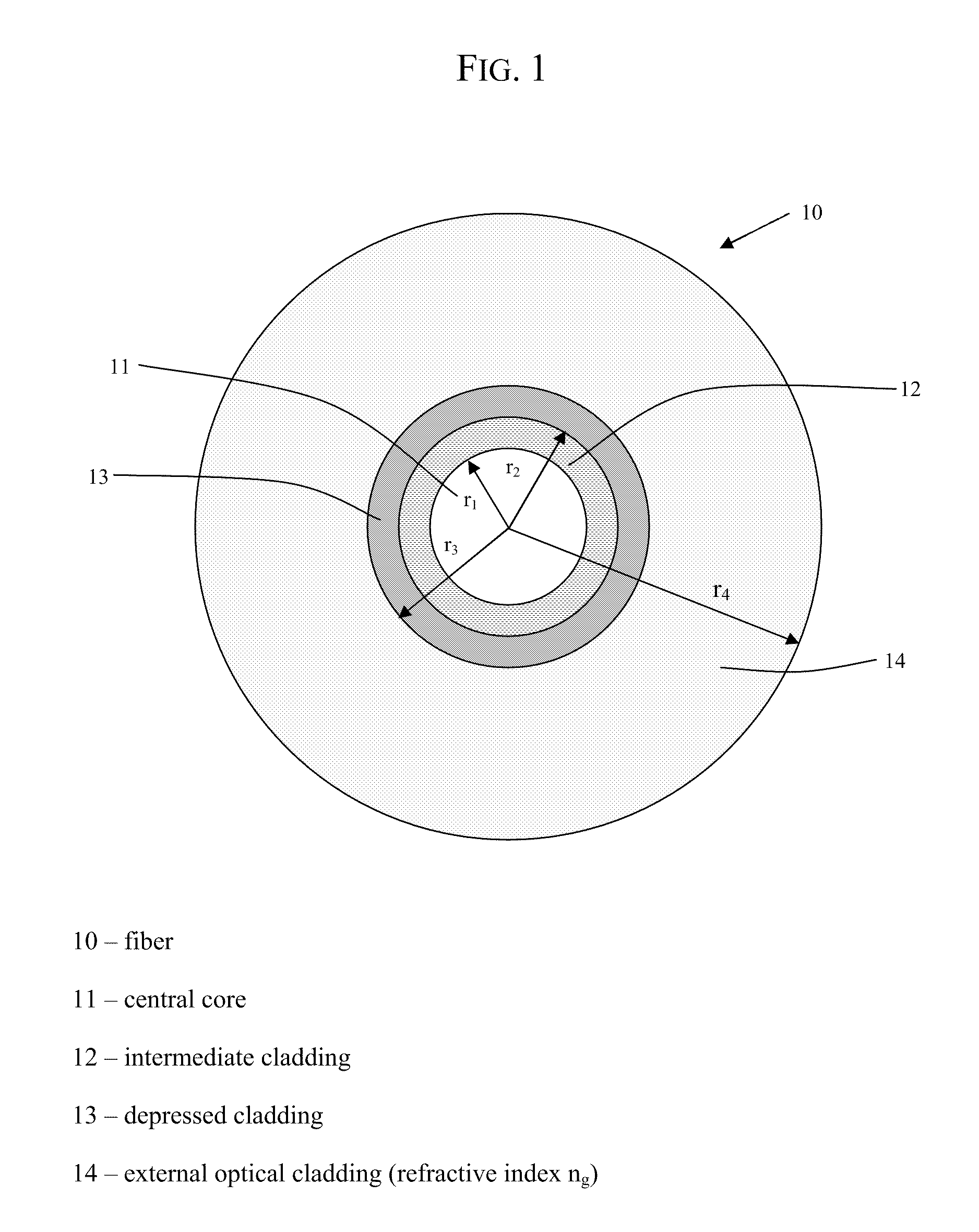
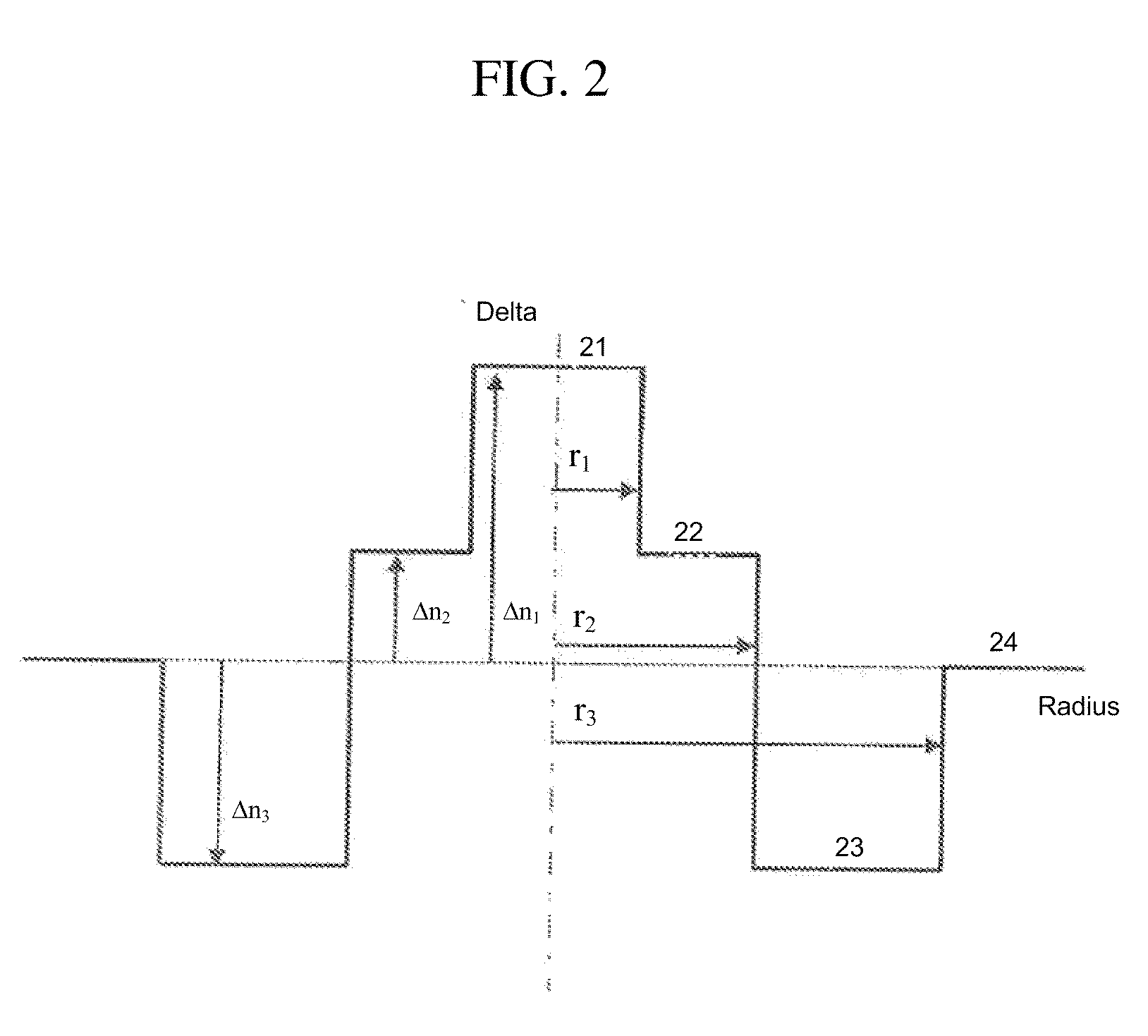
ActiveUS20090279835A1Improves bending lossSufficient attenuationGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingLength waveMode field diameter
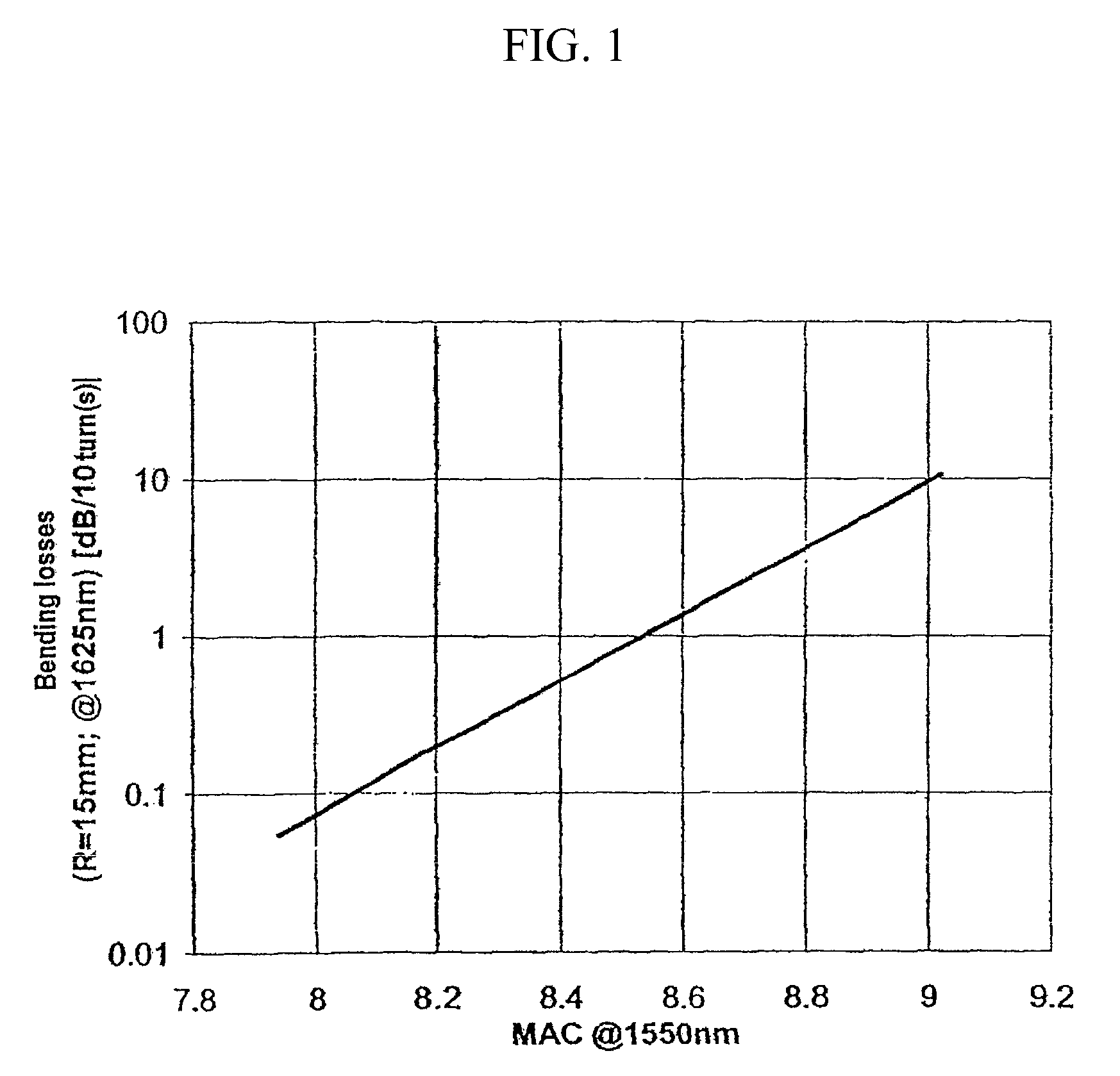
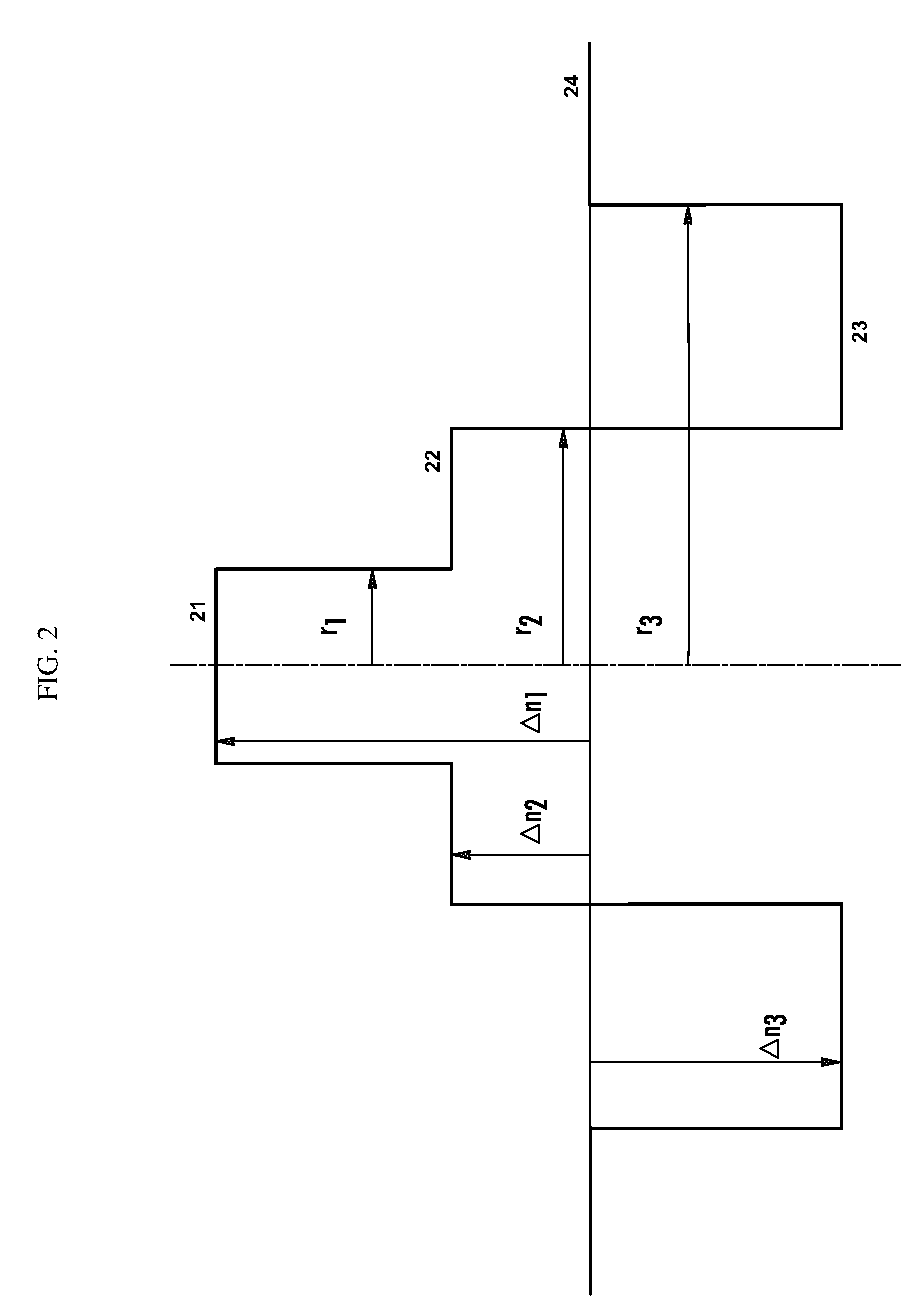
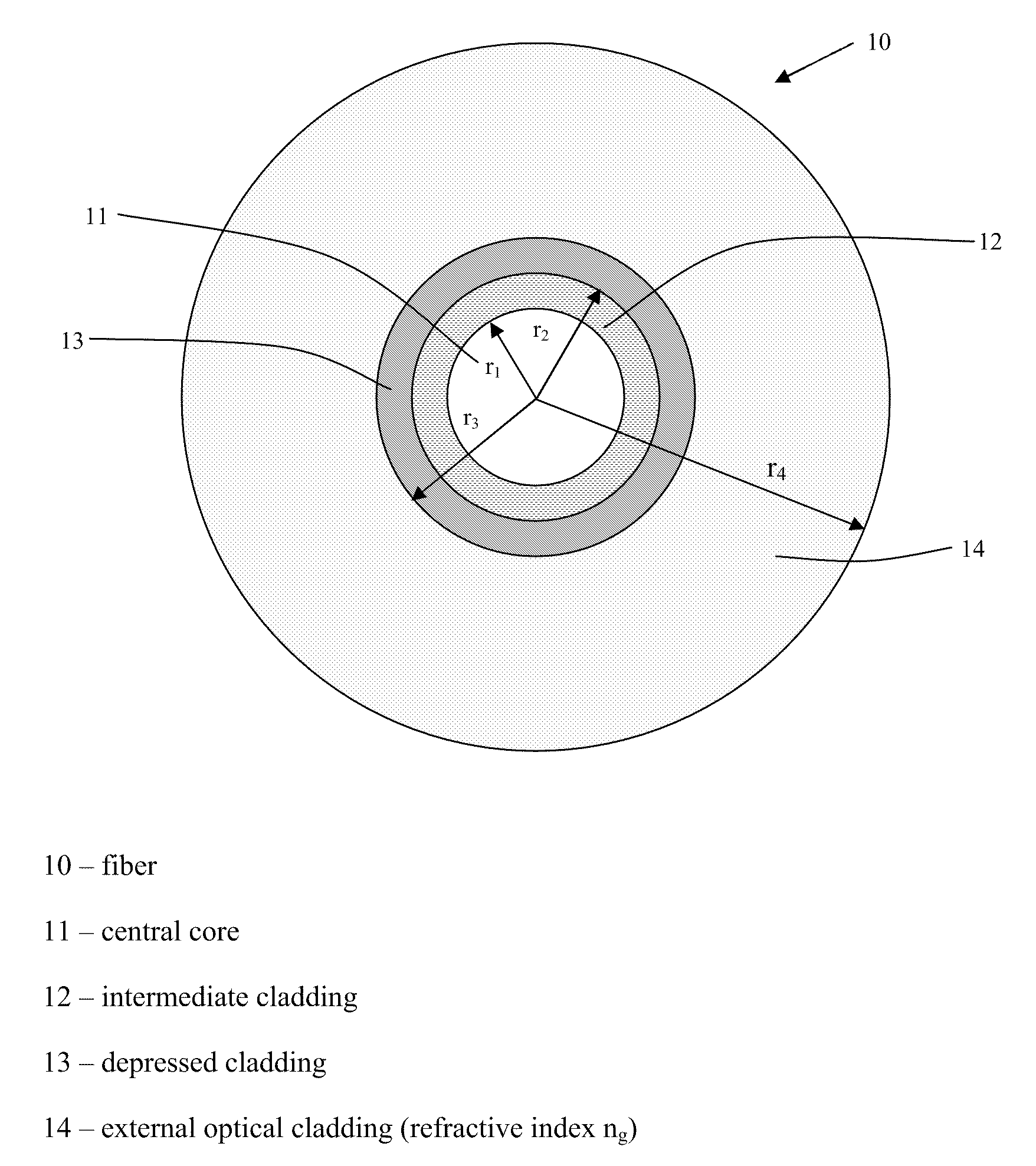
A single-mode optical fiber includes a central core, an intermediate cladding, a depressed trench, and an external optical cladding. The central core has a radius r1 and a positive refractive index difference Δn1 with the optical cladding. The intermediate cladding has a radius r2 and a positive refractive index difference Δn2 with the optical cladding, wherein Δn2 is less than Δn1. The depressed trench has a radius r3 and a negative index difference Δn3 with the optical cladding. At a wavelength of 1310 nanometers, the optical fiber has a mode field diameter (MFD) between 8.6 microns and 9.5 microns and, at a wavelength of 1550 nanometers, the optical fiber has bending losses less than about 0.25×10−3 dB / turn for a radius of curvature of 15 millimeters. At a wavelength of 1260 nanometers, attenuation of the LP11 mode to 19.3 dB is achieved over less than 90 meters of fiber.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Large core holey fibers
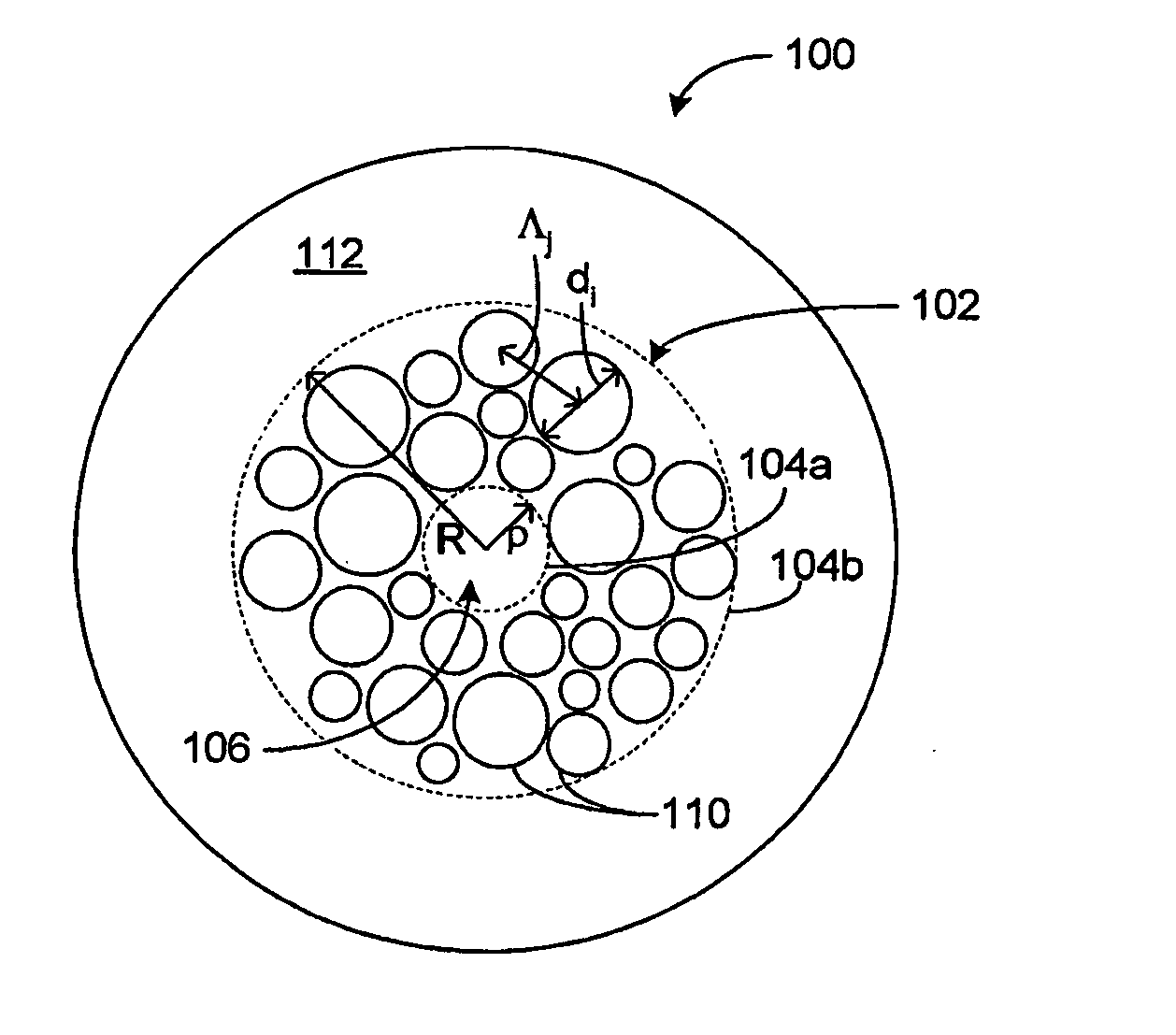
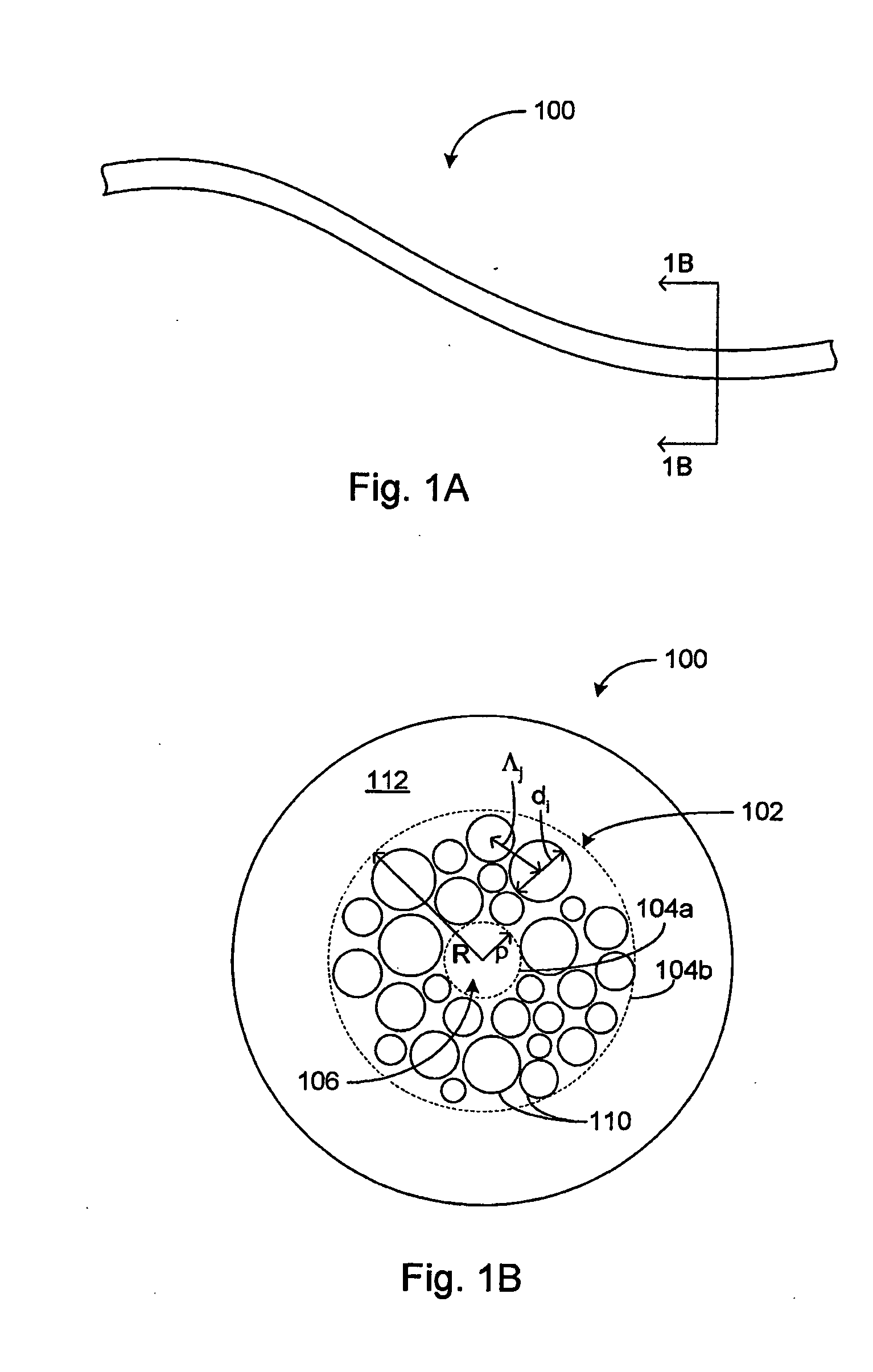
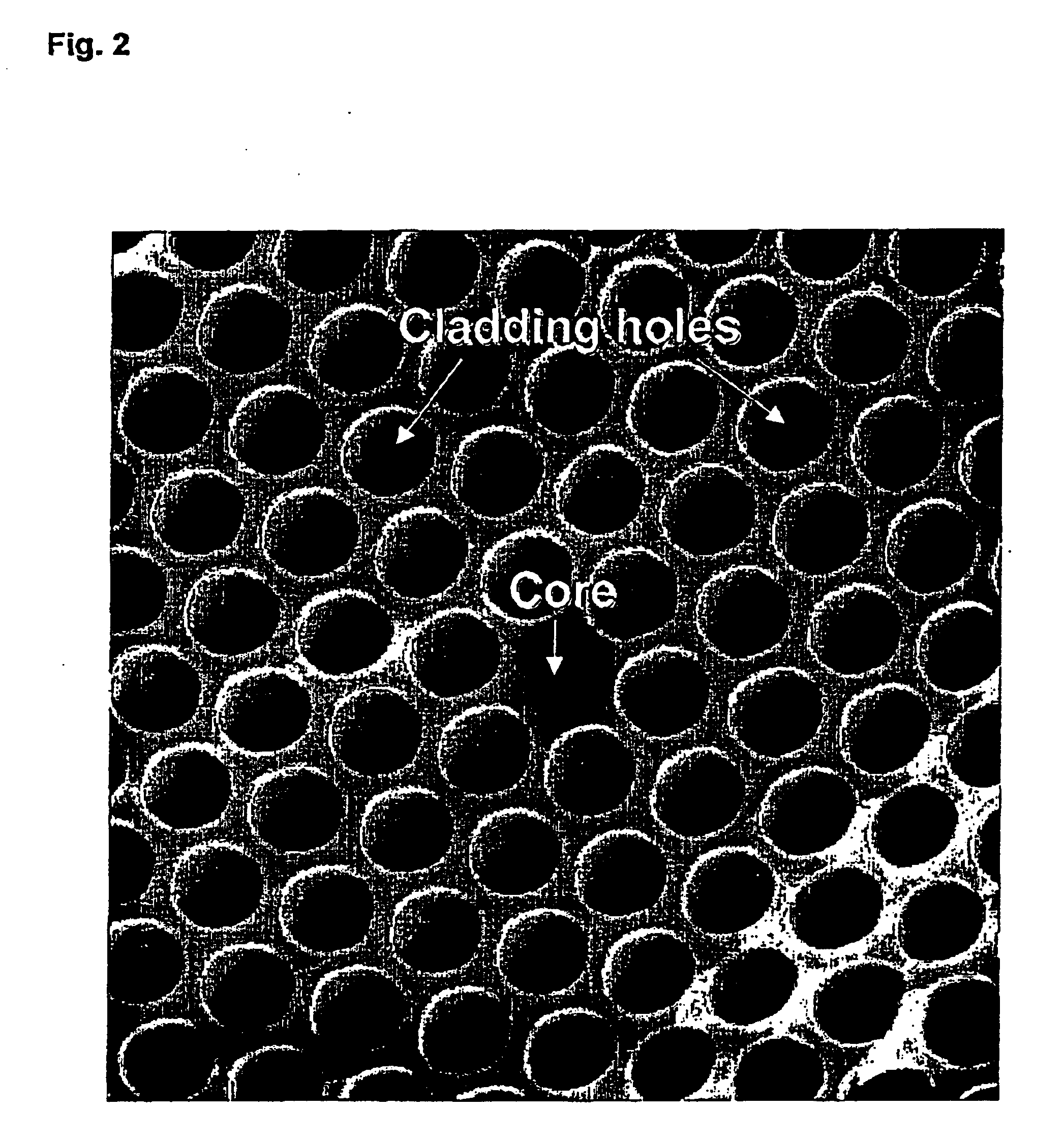
Various types of holey fiber provide optical propagation. In various embodiments, for example, a large core holey fiber comprises a cladding region formed by large holes arranged in few layers. The number of layers or rows of holes about the large core can be used to coarse tune the leakage losses of the fundamental and higher modes of a signal, thereby allowing the non-fundamental modes to be substantially eliminated by leakage over a given length of fiber. Fine tuning of leakage losses can be performed by adjusting the hole dimension and / or the hole spacing to yield a desired operation with a desired leakage loss of the fundamental mode. Resulting holely fibers have a large hole dimension and spacing, and thus a large core, when compared to traditional fibers and conventional fibers that propagate a single mode. Other loss mechanisms, such as bend loss and modal spacing can be utilized for selected modes of operation of holey fibers. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Single-mode Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20070280615A1Reduce leakageEffectively reduce the bending lossesOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringMaterials science
Disclosed is an optical transmission fiber having reduced bending and microbending losses that is commercially usable in FTTH or FTTC transmission systems.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Optical fiber cable and optical fiber ribbon
ActiveUS20110110635A1Stable optical loss characteristicReduce warpageFibre mechanical structuresEngineeringBend radius
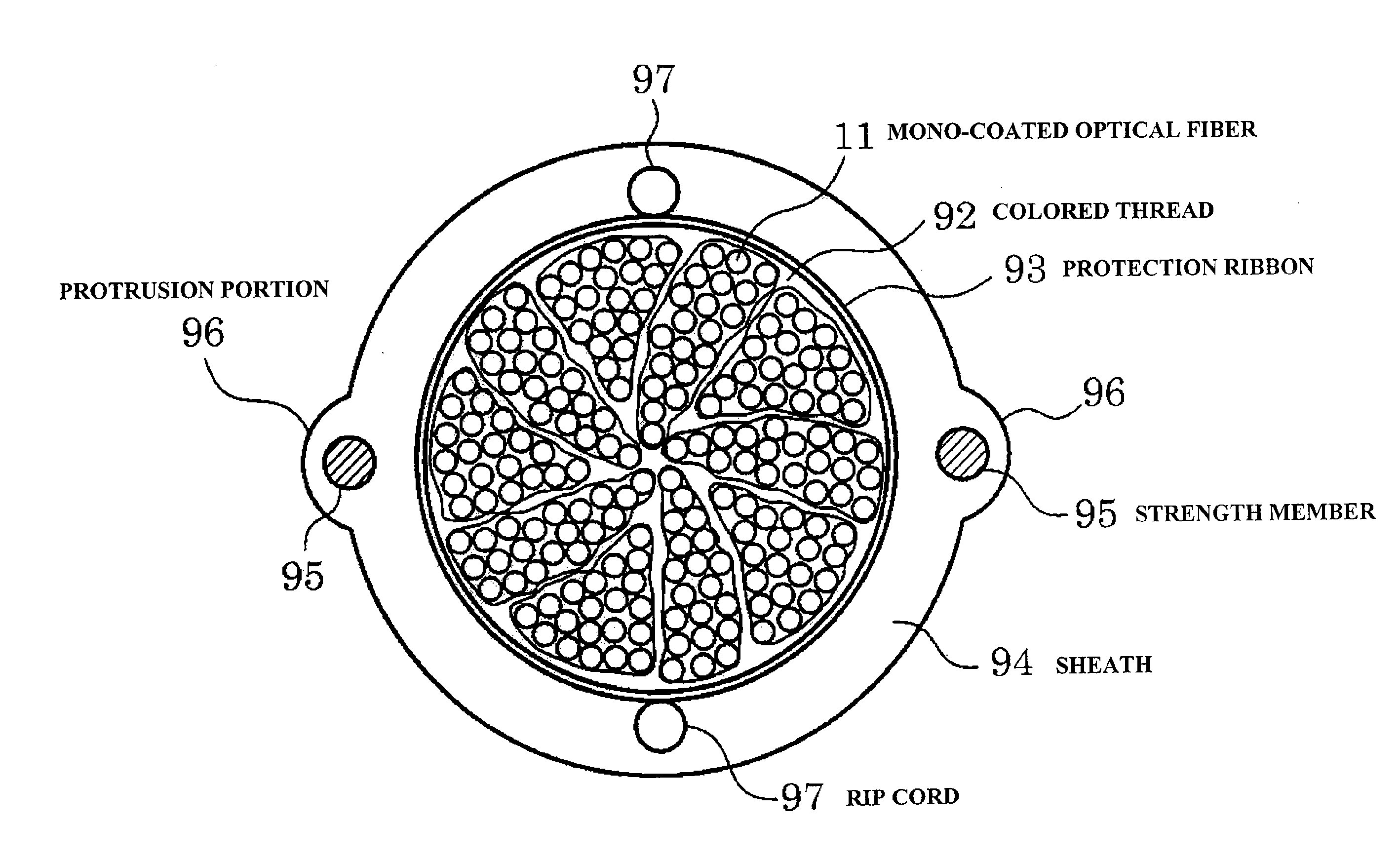
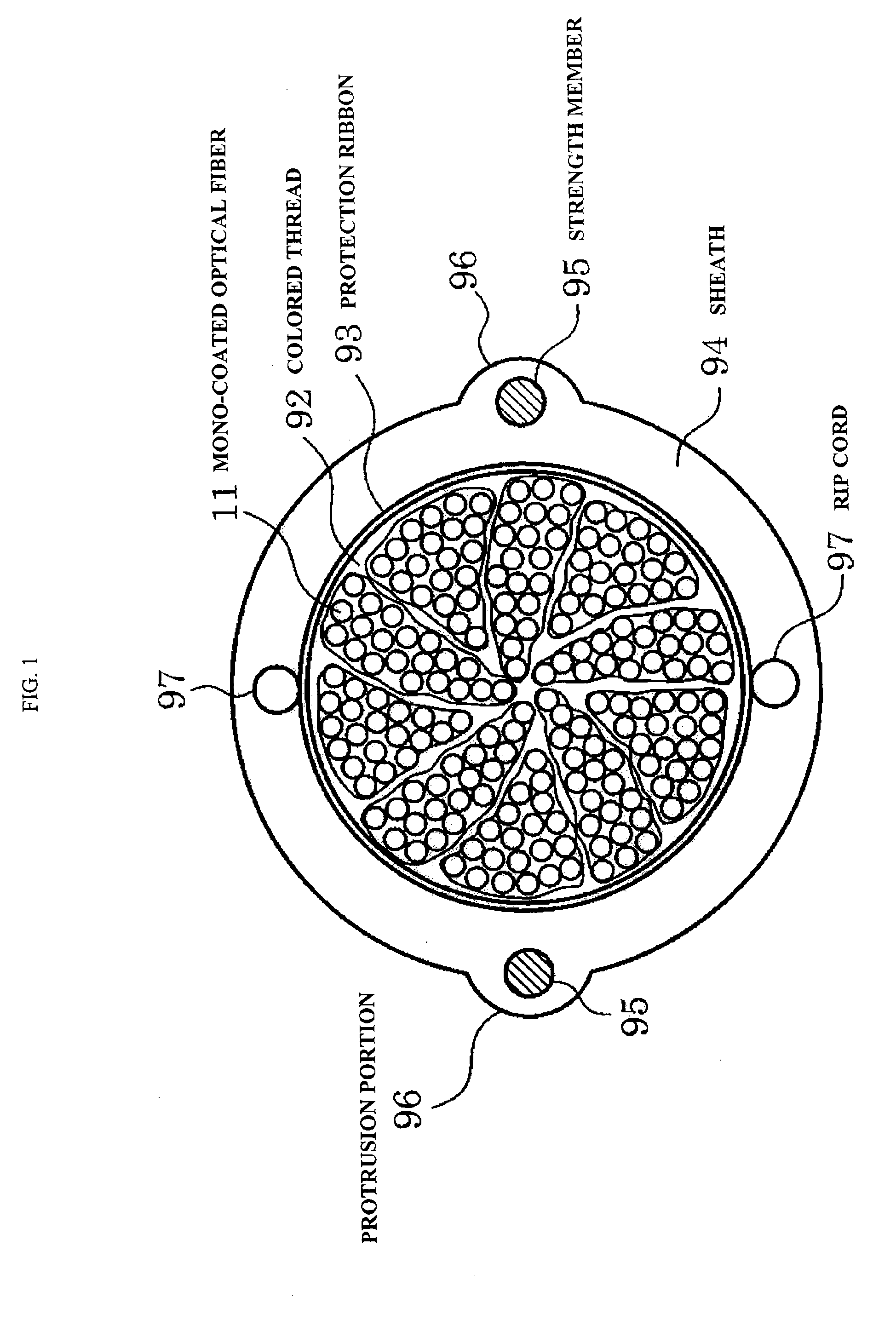
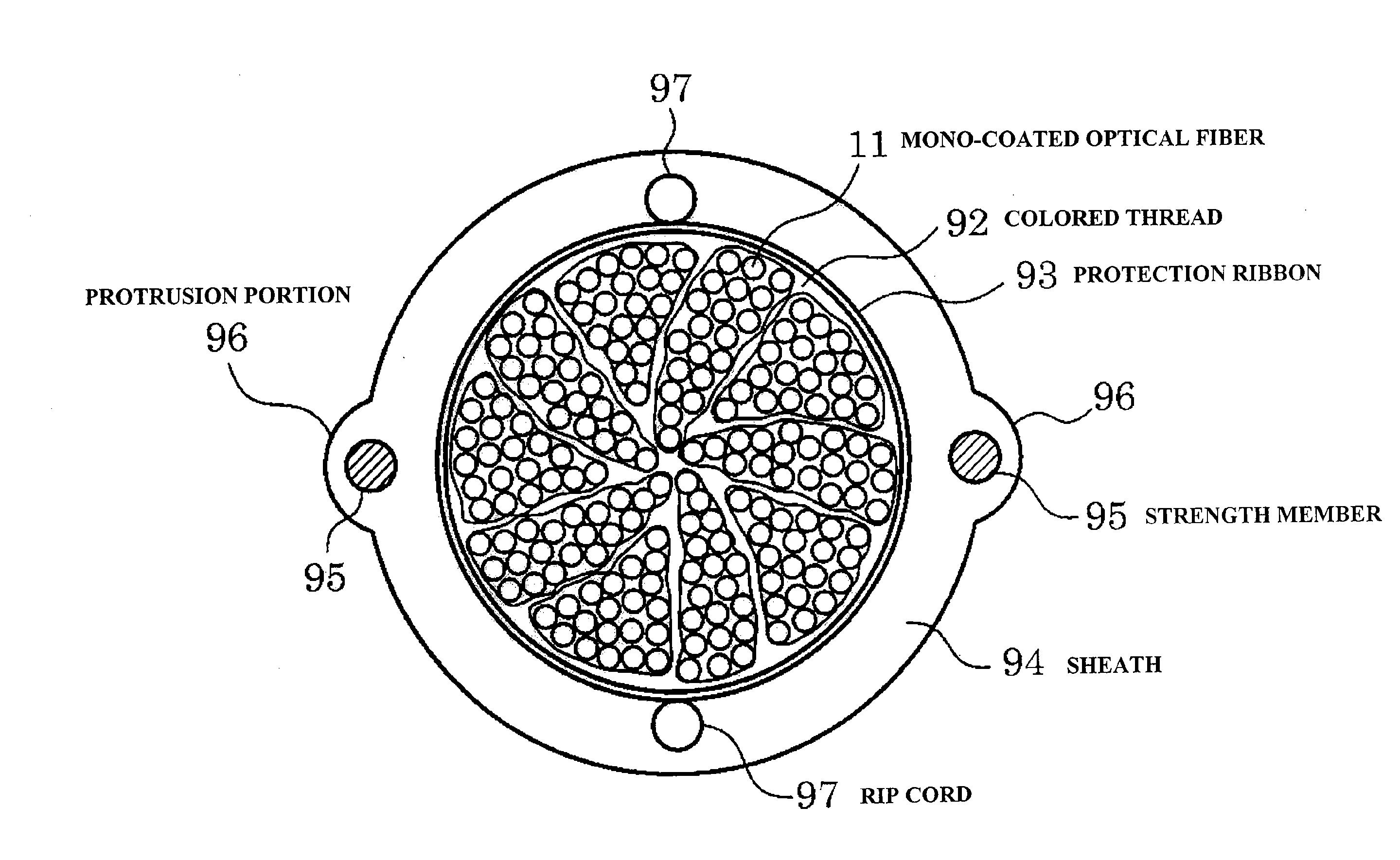
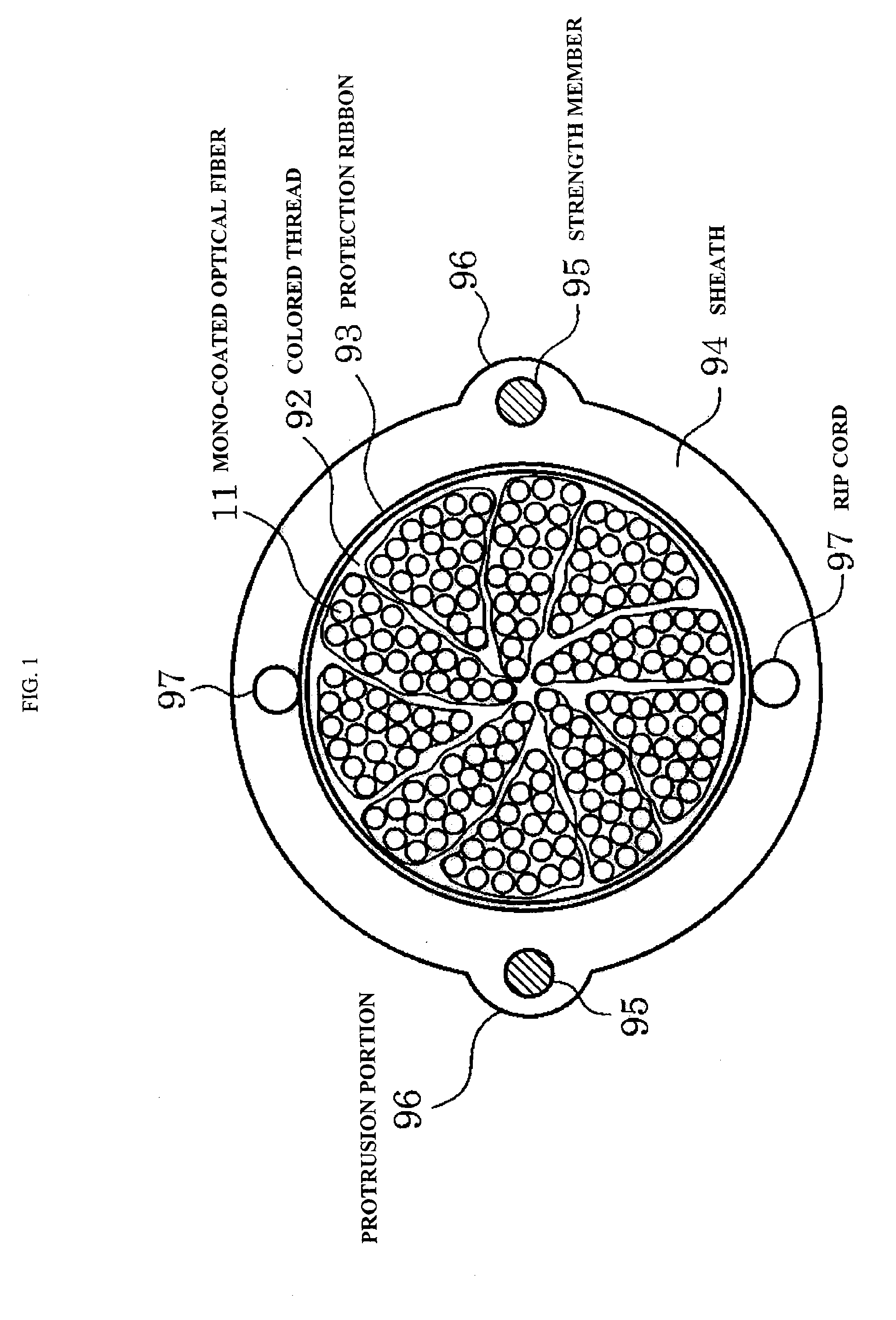
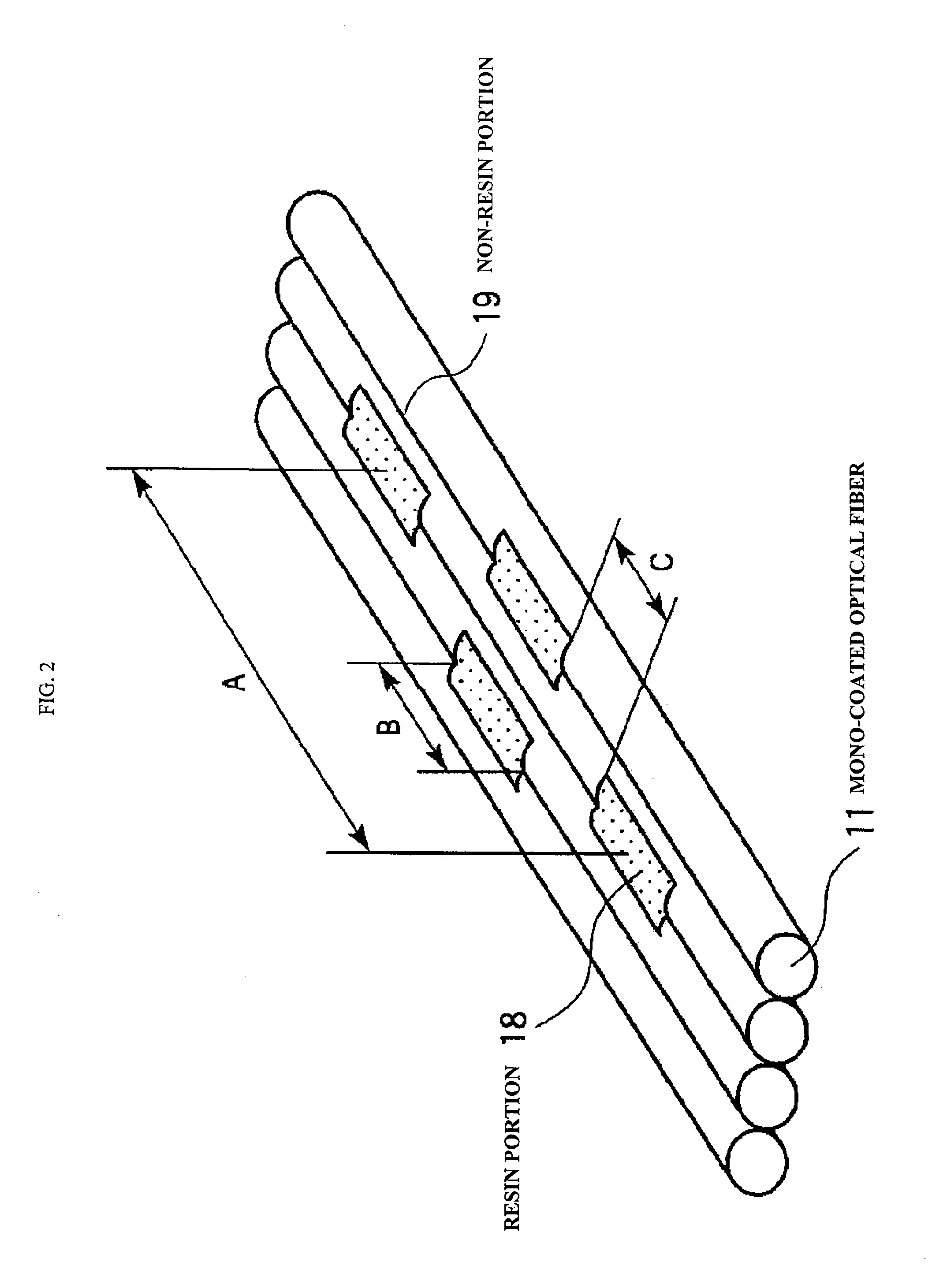
Amono-coated optical fiber that has a bending loss characteristic in which an optical loss increase at a bending radius 13 mm is 0.2 dB / 10 turn or less, an optical fiber ribbon that includes two-dimensionally disposed resin portions for bonding the adjacent 2-fiber mono-coated optical fibers in plural places, the resin portions being disposed apart from each other in the longitudinal direction of the optical fiber ribbon and an optical fiber cable that includes a cable core portion that stores twisting of plural units where the mono-coated optical fibers constituting the optical fiber ribbon are collected.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Bend-Insensitive Single-Mode Optical Fiber
ActiveUS20090279836A1Sufficient attenuationImproves the bending lossesGlass optical fibreOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingWavelengthLength wave
A single-mode optical fiber includes a central core, an intermediate cladding, a depressed trench, and an external optical cladding. The central core has a radius r1 and a positive refractive index difference Δn1 with the optical cladding. The intermediate cladding has a radius r2 and a refractive index difference Δn2 with the optical cladding, wherein Δn2 is less than the central core's refractive index difference Δn1. The depressed trench has a radius r3 and a negative index difference Δn3 with the optical cladding. The optical fiber has a nominal mode field diameter (MFD) between 8.6 microns and 9.5 microns at a wavelength of nanometers, and at a wavelength of 1550 nanometers, the optical fiber has bending losses less than 0.15 dB / turn for a radius of curvature of 5 millimeters and cable cut-off wavelengths of less than or equal to nanometers.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Dispersion-Shifted Optical Fiber
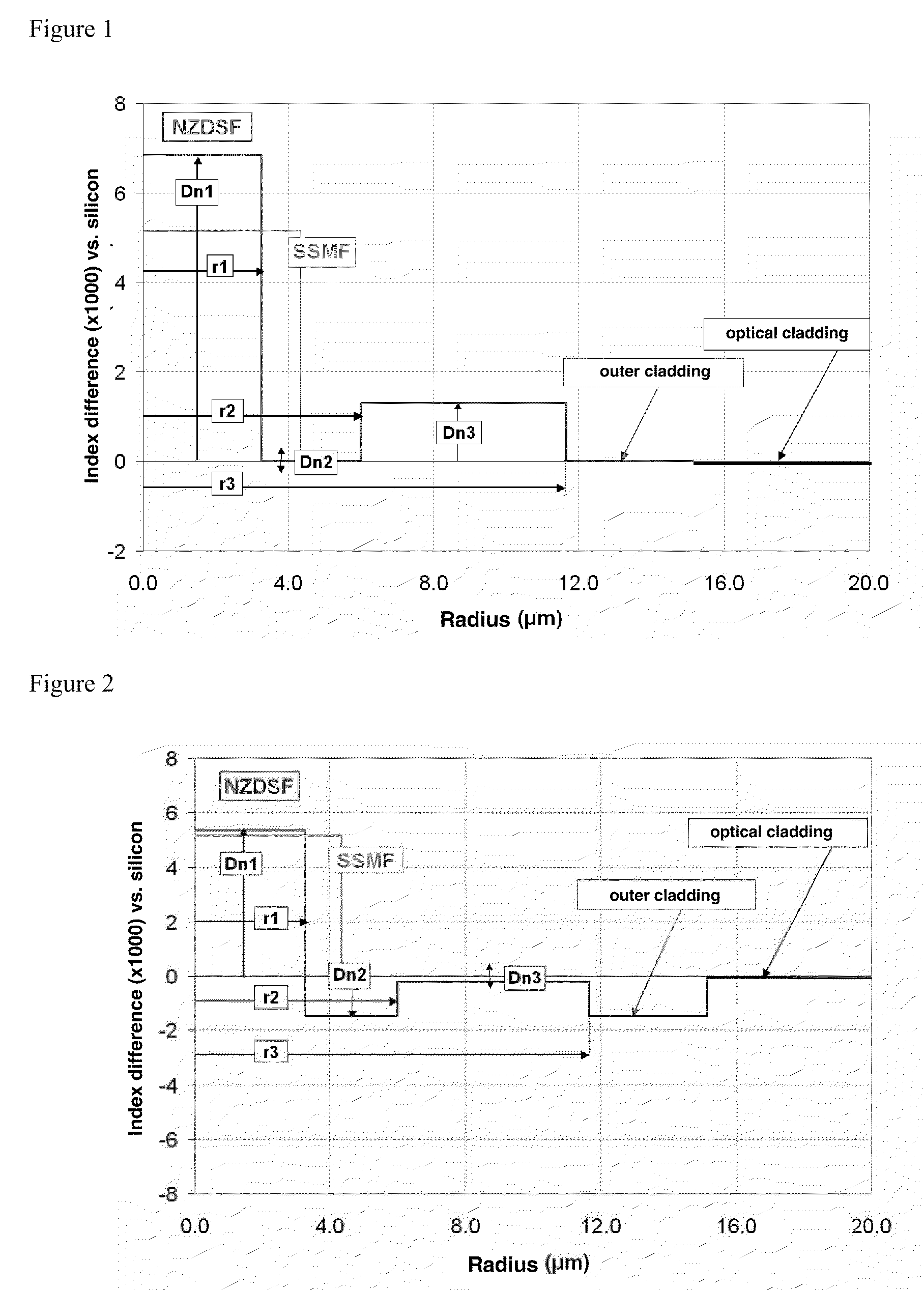
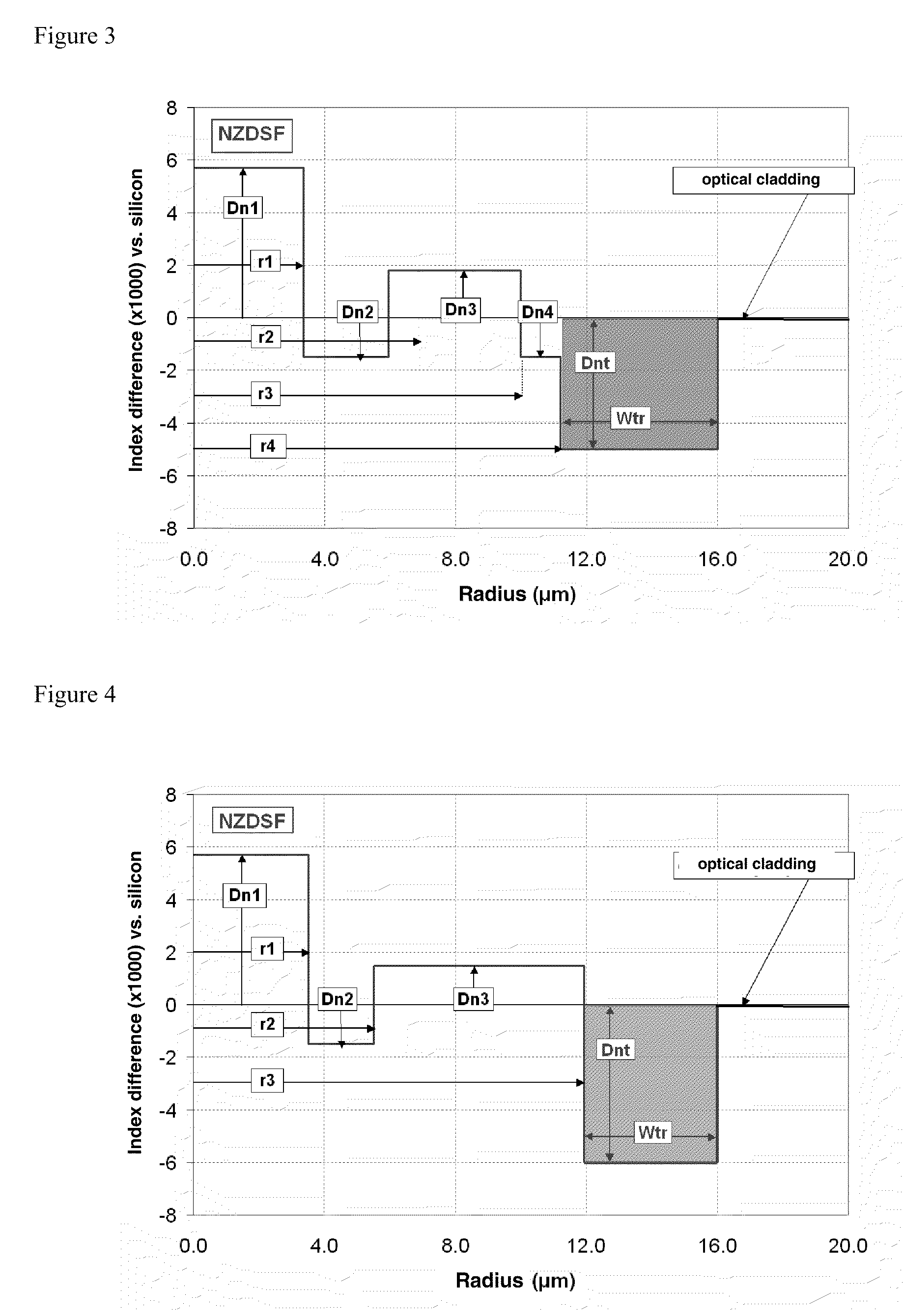
ActiveUS20090252469A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
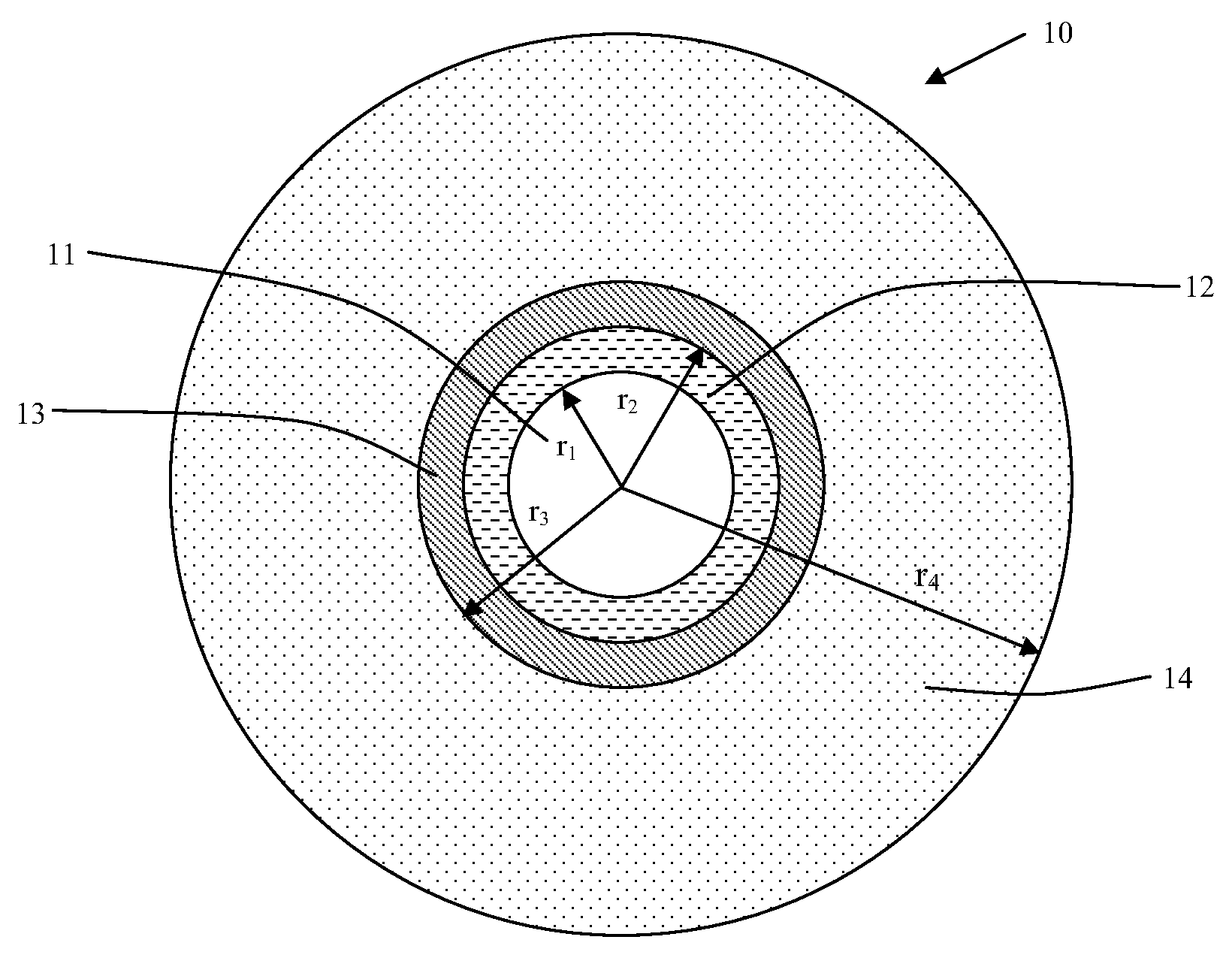
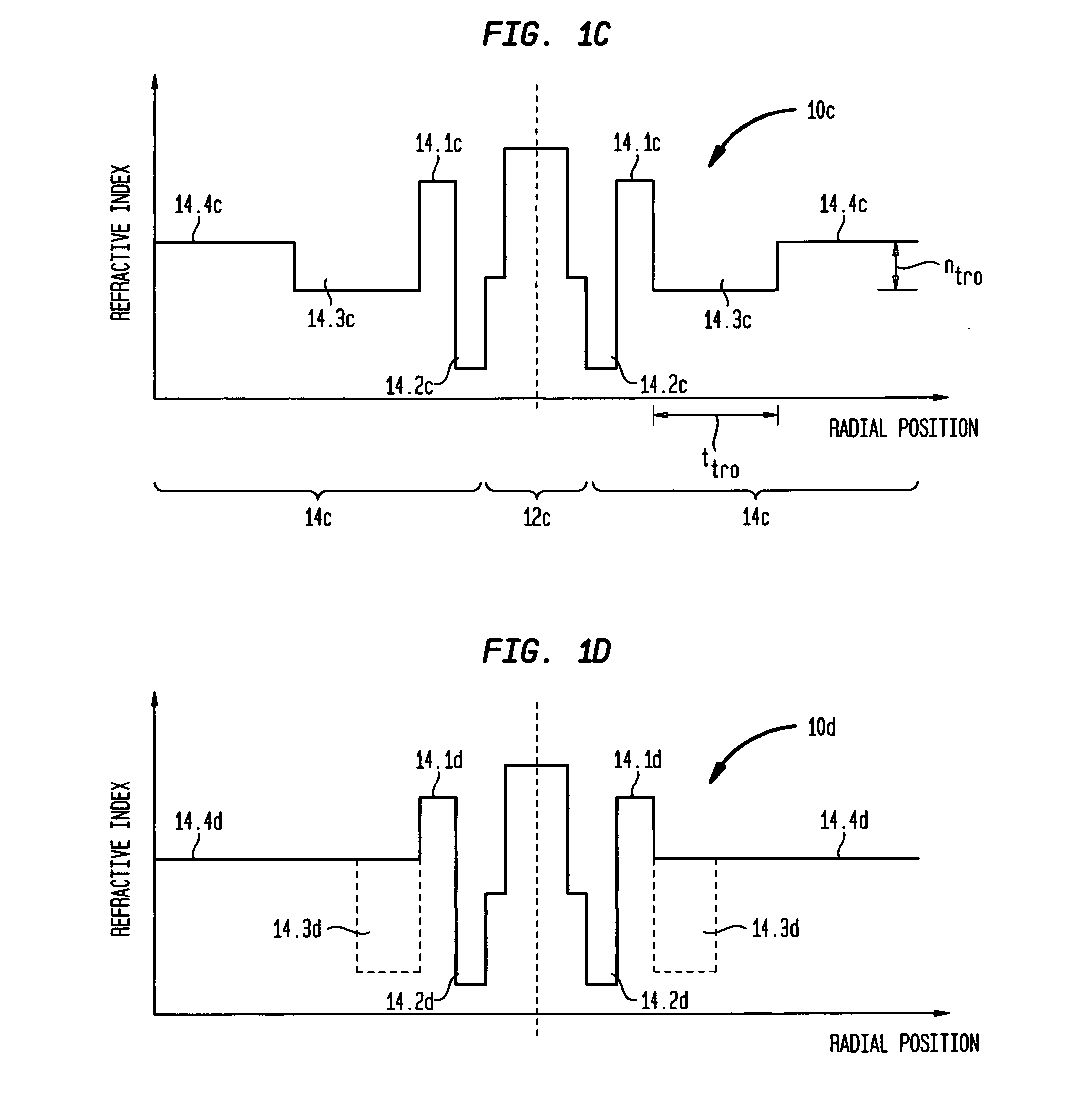
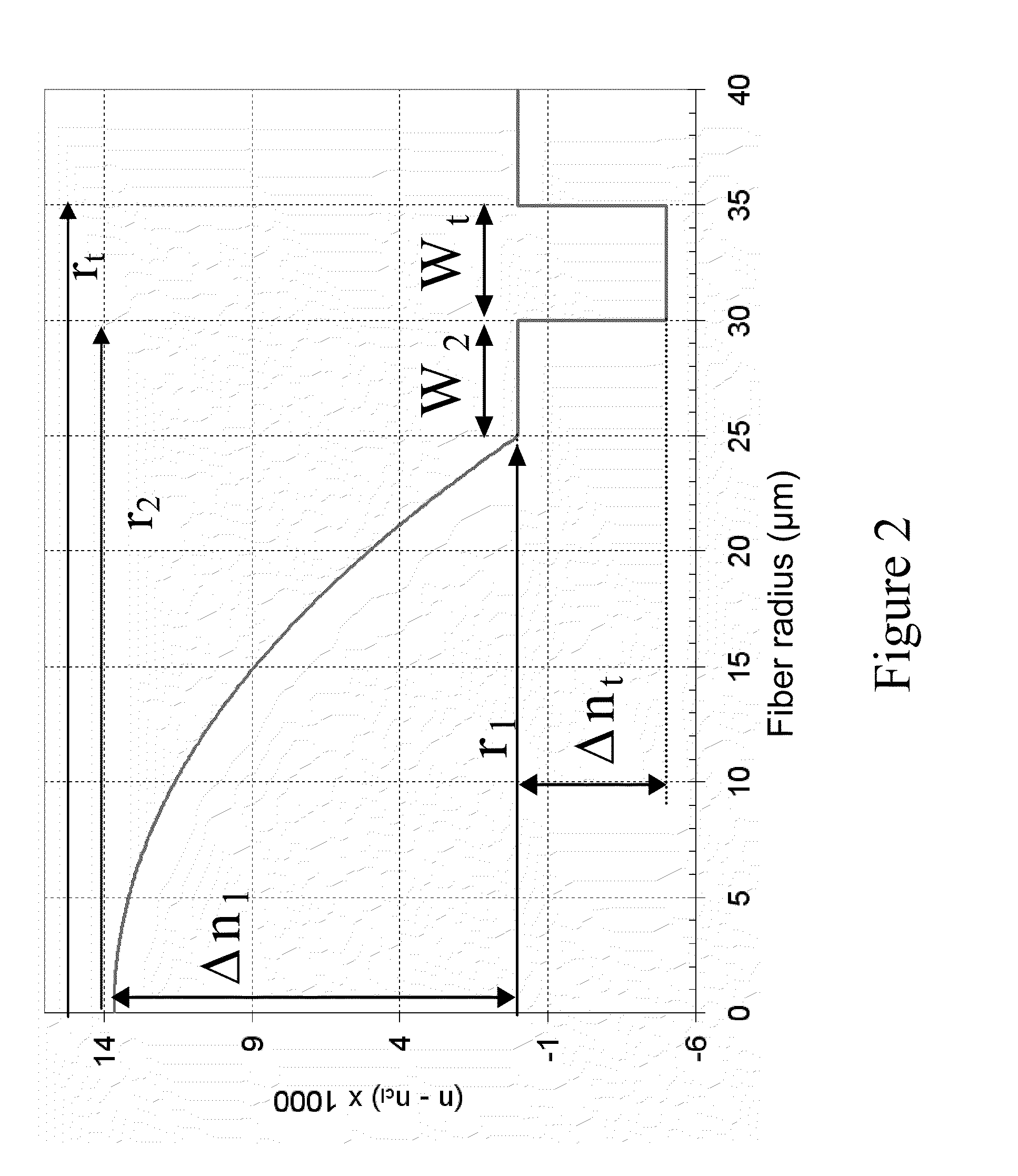
A dispersion-shifted optical fiber (NZDSF) includes a central core (r1, Dn1), an inner cladding having at least three zones with a first intermediate cladding zone (r2, Dn2), a second ring zone (r3, Dn3) and a third buried trench zone (Wtr, Dnt). The buried trench zone has an index difference (Dnt) with the optical cladding between −5·10−3 and −15·10−3 and has a width (Wtr) between 2.5 μm and 5.5 μm. The present optical fiber, at a wavelength of 1550 nm, has reduced Rayleigh scattering losses of less than 0.164 dB / km, with limited bending losses.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
Large-mode-area optical fibers with reduced bend distortion
ActiveUS20090059353A1Reduces effective transverse mode areaReduce interactionGlass making apparatusLaser using scattering effectsEngineeringBend radius
In a LMA optical fiber the index of the core region is graded (i.e., as viewed in a radial cross-section) and has a grading depth of Δng, as measured from a central maximum at or near the axis to a lower level that is not greater than the central maximum and not less than the index of the cladding region. When the fiber is to be bent at a bend radius, the grading depth, the radius of the core region, and the difference between the central maximum index and the cladding region index are configured to reduce bend distortion. They may also advantageously be configured to maximize the effective mode-field area of the fundamental mode, suppress higher order modes, and reduce bend loss. In a preferred embodiment, the core region includes a centralized gain region, which in turn includes a dark region that is no more than 30% of the area of the gain region. Also described is a method of making such LMA fibers.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Bend insensitivity in single mode optical fibers
ActiveUS20090060437A1Enhance mode discriminationOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesTransverse modeBend loss
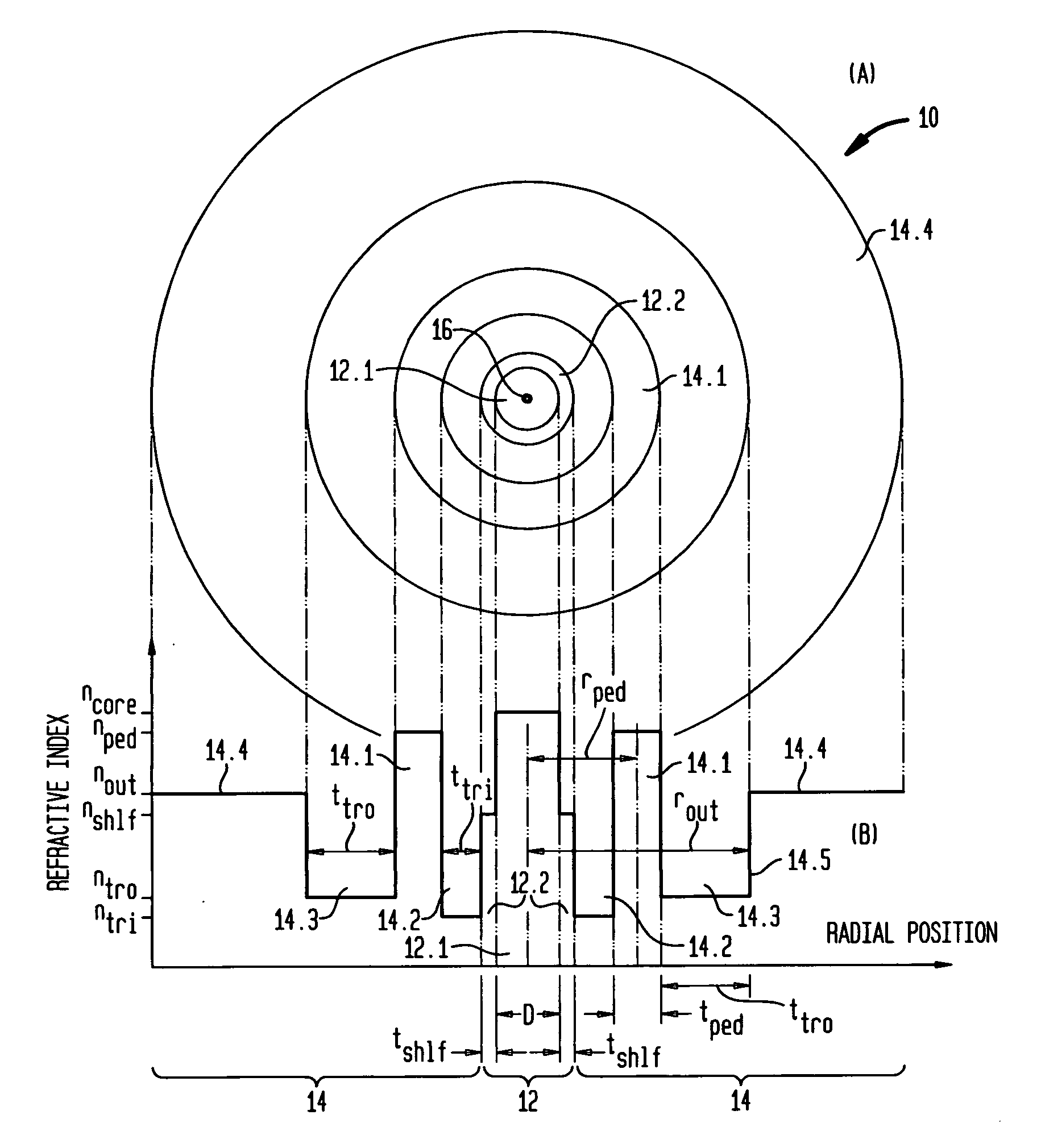
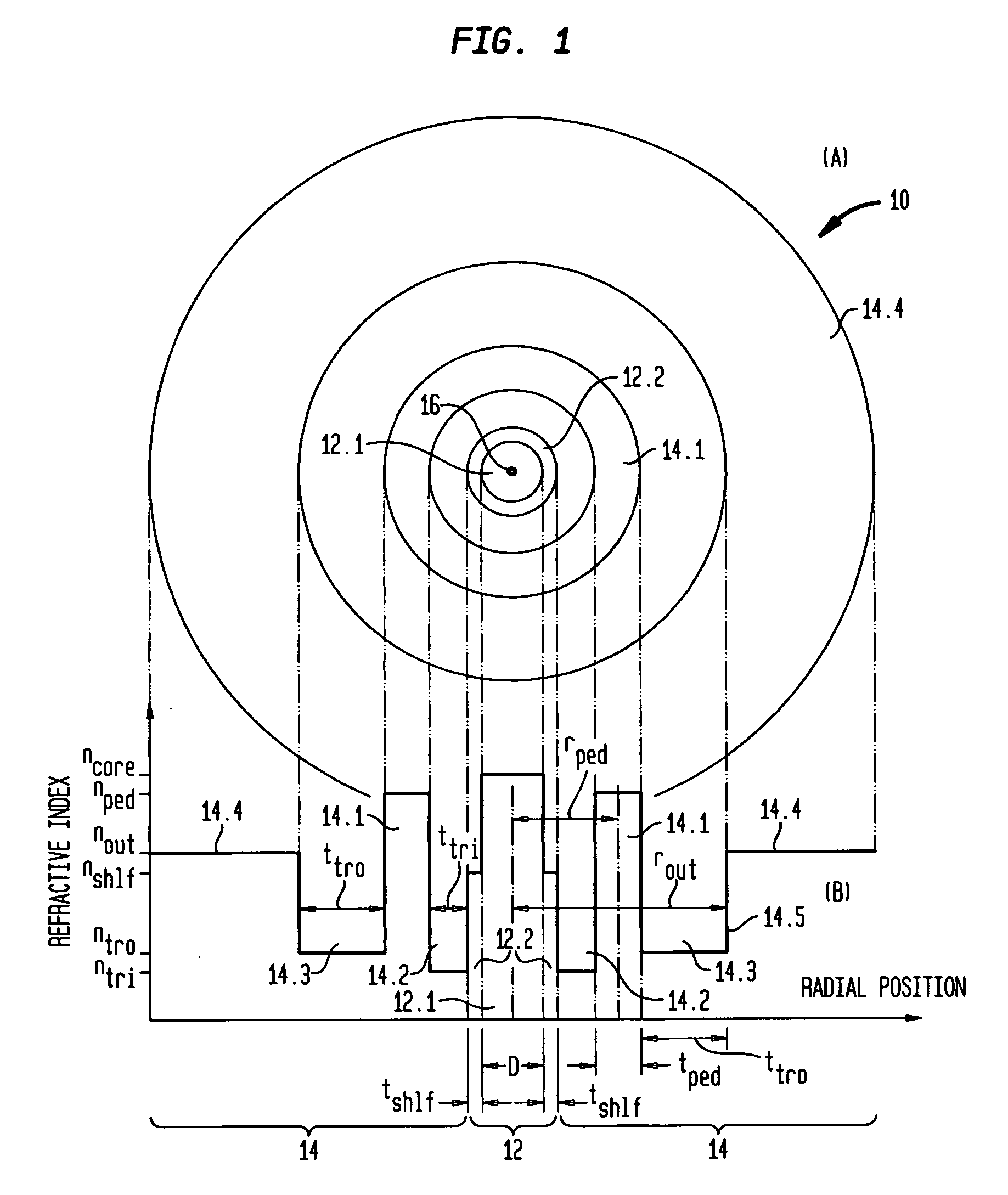
An optical fiber that is relatively insensitive to bend loss comprises a core region and a cladding region configured to support and guide the propagation of light in a fundamental transverse mode, the cladding region including (i) an outer cladding region having a refractive index less than that of the core region, (ii) an annular cladding pedestal region having a refractive index higher than that of the outer cladding region and comparable to that of the core region, and (iii) an annular cladding inner trench region disposed between the core region and the pedestal region, the inner trench region having a refractive index less than that of the outer cladding region. In one embodiment, the fiber also includes a (iv) an annular cladding outer trench region disposed between the pedestal region and the outer cladding region, the outer trench region having a refractive index less than that of the outer cladding region. In addition, to suppress HOMs the pedestal region is configured to resonantly couple at least one other transverse mode of the core region to at least one transverse mode of the pedestal region. Such fiber is advantageously used as access fiber, but may have other applications, such as sensor fiber.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Microstructured optical fiber
An optical fiber suitable for use in a single fiber or multifiber optical connector or array is structured with a core region and a cladding region surrounding the core region, and exhibits a bending loss of a fundamental mode of the fiber at a wavelength λ is lower than 0.1 dB / m at a diameter of 15 mm, a mode-field diameter of the fundamental mode at an end of the fiber at the wavelength λ is between 8.0 μm and 50 λ, and a bending loss of a first higher-order mode at the wavelength λ is higher than 1 dB / m at a diameter of 30 mm. The fiber may be multistructured, wherein the cladding region comprises a main medium and a plurality of sub medium regions therein to form a spatially uniform average refractive index.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Low bending loss multimode fiber transmission system
ActiveUS20090092365A1Low bend-lossOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical waveguide light guideEngineeringEffective refractive index
A bend-loss tolerant multimode fiber transmission system is provided. The system includes: a transmission fiber having a core and a cladding, and a mode-launching system for selectively exciting only a useful portion of the transmission modes, that portion corresponding to high effective refractive indices relative to a refractive index of the cladding the useful portion corresponding to a substantial number of modes. The mode-launching system may include a lead-in fiber, coupled to the transmission fiber, supporting a number of lead-in modes substantially corresponding to the number of transmission modes in the useful portion. The transmission fiber may have a refractive index profile, within a region of its core that is aligned with the lead-in fiber core, which has a shape that matches a refractive index profile shape in the lead-in fiber core. The transmission fiber core may have a graded refractive index profile that is parabolic or nearly parabolic or truncated.
Owner:LUMENTUM D O O OPTICNA VLAKNA
Multi-mode bending-resistant fiber and production method thereof
ActiveUS20110044596A1High mechanical reliabilityEasy to useOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical articlesMedicineRelative refractive index
A multimode fiber including a core and a cladding. The core has a radius (R1) of 24-26 μm, the refractive index profile thereof is a parabola, and the maximum relative refractive index difference (Δ1) is 0.9-1.1%. The cladding surrounds the core and includes from inside to outside an inner cladding, a middle cladding, and an outer cladding; a radius (R2) of the inner cladding is 1.04-1.6 times that of the core, and a relative refractive index difference (Δ2) thereof is −0.01-0.01%; the middle cladding is a graded refractive index cladding whose radius (R3) is 1.06-1.8 times that of the core, and a relative refractive index difference thereof is decreased from Δ2 to Δ4; and a radius (R4) of the outer cladding is 2.38-2.63 times that of the core, and a relative refractive index difference (Δ4) thereof is between −0.20 and −0.40%. The invention reduces the additional bending loss of the fiber, improves the bending resistance and mechanical properties, basically eliminates the internal stress, and ensures the service life even working for a long term under the condition of low radius. The method for producing the fiber is simple, effective, and suitable for mass production.
Owner:YANGTZE OPTICAL FIBRE & CABLE CO LTD
Micro-structured fiber profiles for mitigation of bend-loss and/or mode distortion in LMA fiber amplifiers, including dual-core embodiments
ActiveUS7924500B1Improved amplification characteristicReduce numerical apertureOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingFibre transmissionMicro structureDual core
An apparatus and method for compensating for mode-profile distortions caused by bending optical fibers having large mode areas. In various embodiments, the invention micro-structures the index of refraction in the core and surrounding areas of the inner cladding from the inner bend radius to the outer bend radius in a manner that compensates for the index changes that are otherwise induced in the index profile by the geometry and / or stresses to the fiber caused by the bending.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Optical fiber with specialized index profile to compensate for bend-induced distortions
InactiveUS20070147751A1Minimize impactLaser detailsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingPhotonic bandgapEngineering
An optical fiber that exhibits reduced mode distortions as the fiber is bent is formed by properly defining its refractive index profile during fabrication. The as-fabricated profile is defined as a “pre-distorted” profile that takes into account the gradient introduced by bending the fiber. A parabolic index profile is one exemplary bend-resistant profile that exhibits a quadratic form. A raised-cone index is another profile that may be used as the “as-fabricated” profile. In any properly configured form, factors such as bend loss and mode distortion are significantly reduced, since the profile undergoes a shift of essentially constant gradient as a bend is introduced. The resultant effective area of the inventive fiber is substantially improved over state-of-the-art fiber that is subjected to bending during installation. The as-fabricated profile may be incorporated into various types of fibers (birefringent, photonic bandgap, etc.), and is particularly well-suited for use in a fiber amplifier arrangement.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Hollow anti-resonance optical fiber
InactiveCN105807363AImprove efficiencyHigh sensitivityCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideTransmission lossElectron
The invention discloses a hollow anti-resonance optical fiber, and belongs to the technical field of optics and laser photoelectrons.The basic structure of the hollow anti-resonance optical fiber comprises a fiber core area with low refraction rate and a wrapping layer area with high refraction rate.The wrapping layer area with high refraction rate is divided into an inner wrapping layer region and an outer wrapping layer region.The inner wrapping layer region is composed of one or two layers of micro capillary pipes.The fiber core area with low refraction rate is wrapped by the inner wrapping layer region.Compared with a traditional band gap type hollow-core photonic crystal fiber, the hollow anti-resonance optical fiber has the advantages of being large in spectral bandwidth, small in bending loss, low in transmission loss, high in damage threshold and capable of keeping single-modulus transmission.A high-efficiency and high-sensitivity ideal platform is created for nonlinear frequency conversion, trace gas / liquid detection, high-power pulse compression and other foremost application.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Large core holey fibers
Various types of holey fiber provide optical propagation. In various embodiments, for example, a large core holey fiber comprises a cladding region formed by large holes arranged in few layers. The number of layers or rows of holes about the large core can be used to coarse tune the leakage losses of the fundamental and higher modes of a signal, thereby allowing the non-fundamental modes to be substantially eliminated by leakage over a given length of fiber. Fine tuning of leakage losses can be performed by adjusting the hole dimension and / or the hole spacing to yield a desired operation with a desired leakage loss of the fundamental mode. Resulting holey fibers have a large hole dimension and spacing, and thus a large core, when compared to traditional fibers and conventional fibers that propagate a single mode. Other loss mechanisms, such as bend loss and modal spacing can be utilized for selected modes of operation of holey fibers. Other embodiments are also provided.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Large-mode-area optical fibers with reduced bend distortion
ActiveUS7783149B2Reduces effective transverse mode areaReduce interactionLaser using scattering effectsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEngineeringBend radius
In a LMA optical fiber the index of the core region is graded (i.e., as viewed in a radial cross-section) and has a grading depth of Δng, as measured from a central maximum at or near the axis to a lower level that is not greater than the central maximum and not less than the index of the cladding region. When the fiber is to be bent at a bend radius, the grading depth, the radius of the core region, and the difference between the central maximum index and the cladding region index are configured to reduce bend distortion. They may also advantageously be configured to maximize the effective mode-field area of the fundamental mode, suppress higher order modes, and reduce bend loss. In a preferred embodiment, the core region includes a centralized gain region, which in turn includes a dark region that is no more than 30% of the area of the gain region. Also described is a method of making such LMA fibers.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
High-Bandwidth Multimode Optical Fiber with Reduced Cladding Effect
ActiveUS20110123161A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingHigh bandwidthHigh data rate
The present invention embraces an optical fiber that includes a central core having an alpha refractive index profile with respect to an outer cladding. The optical fiber also includes an inner cladding, a depressed trench, and an outer cladding. The optical fiber achieves reduced bending losses and a high bandwidth with a reduced cladding effect for high-data-rate applications.
Owner:DRAKA COMTEQ BV
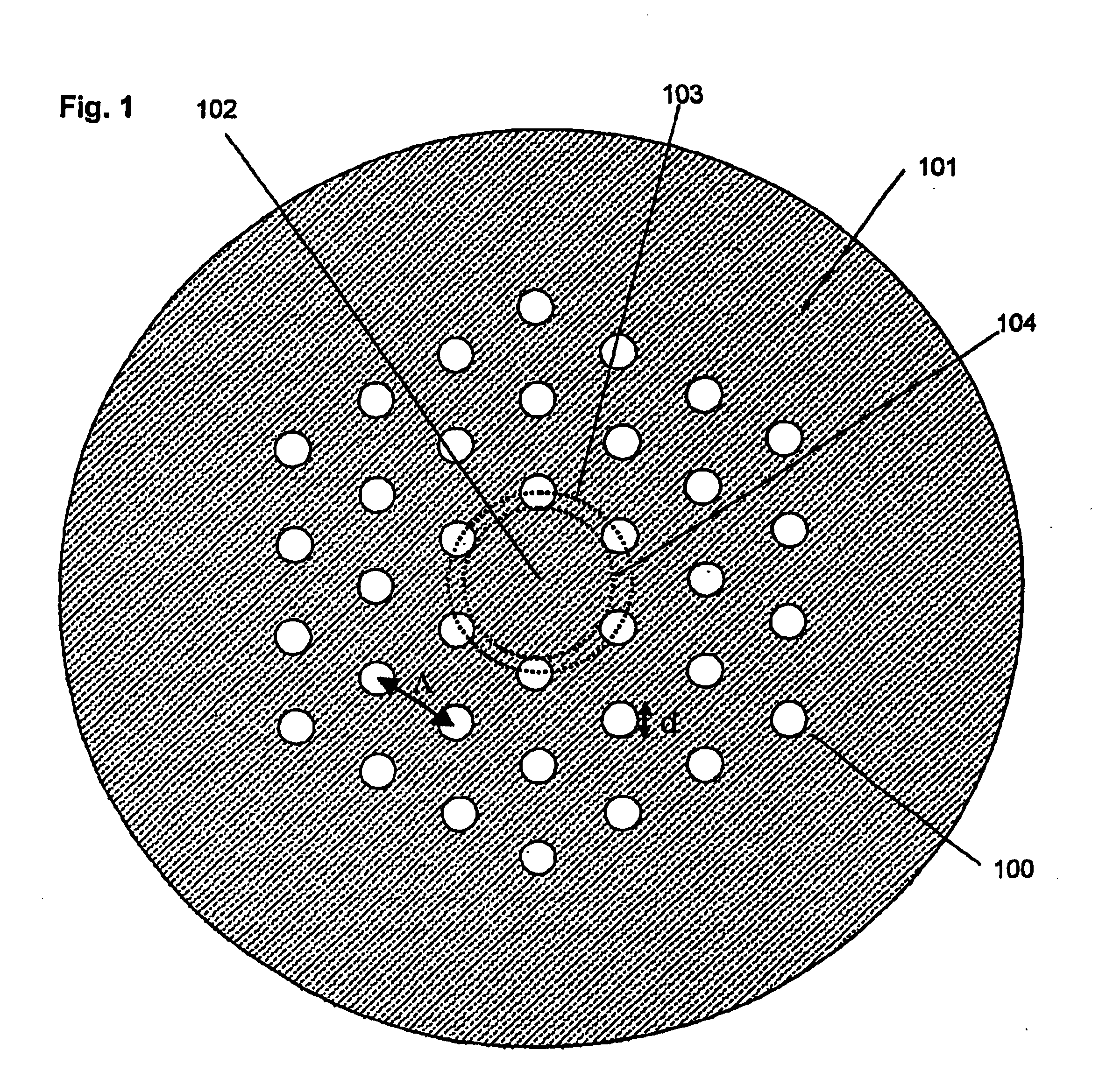
Microstructured transmission optical fiber
InactiveUS7505660B2Improve bending abilityReduce decreaseGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingEngineeringOptical fiber cable
Microstructured optical fiber for single-moded transmission of optical signals, the optical fiber including a core region and a cladding region, the cladding region including an annular hole-containing region that contains non-periodically disposed holes. The optical fiber provides single mode transmission and low bend loss.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical fibres with special bending and dispersion properties
InactiveUS6856742B2Improve the cutoff effectGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with polarisationEngineeringEquilateral polygon
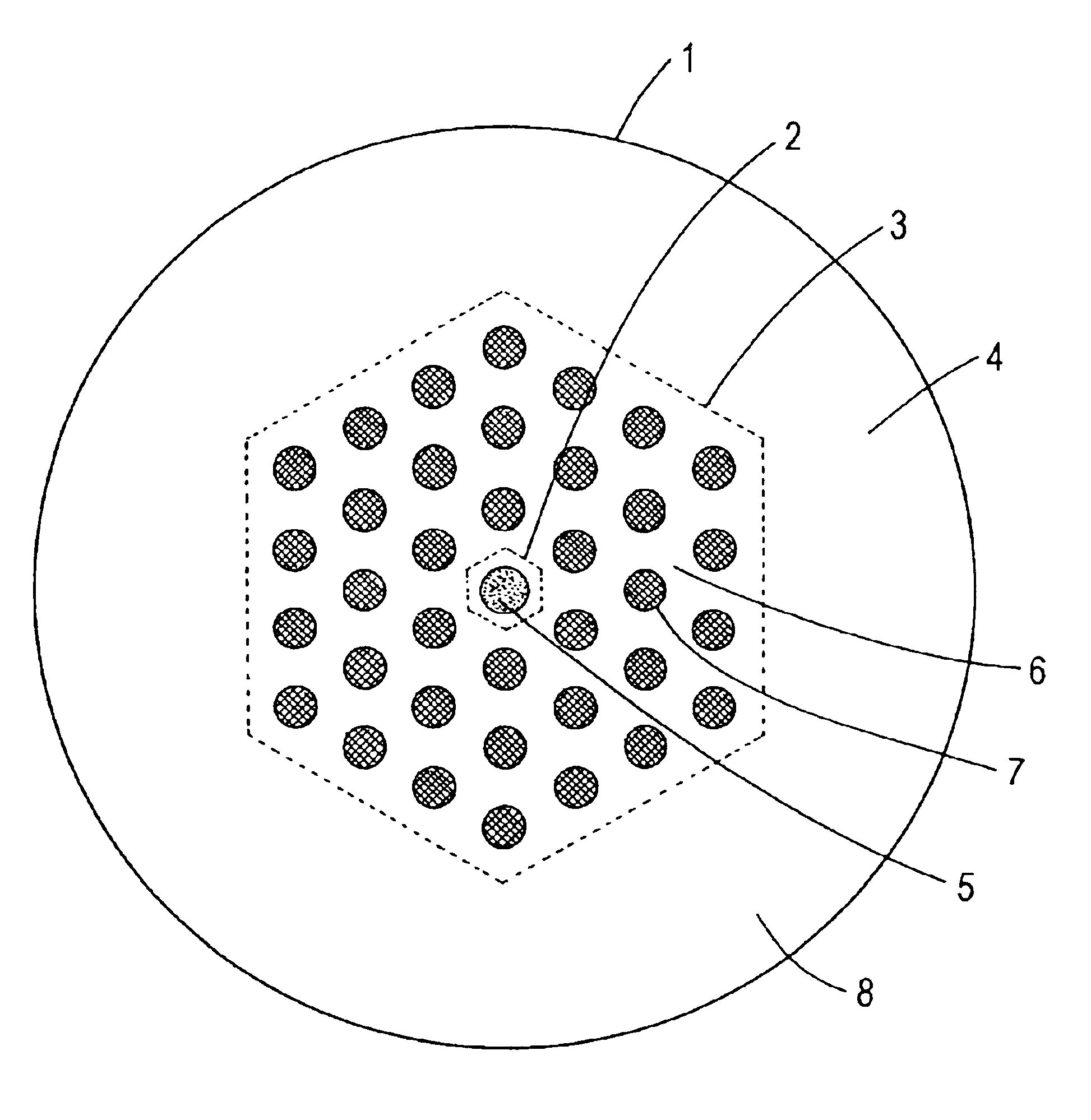
A microstructured optical fiber having a specially designed cladding to provide single mode waveguidance and low sensitivity to bending losses. In one aspect the optical fiber has an inner and an outer cladding each comprising elongated features. The inner cladding features have normalized dimensions in the range from 0.35 to 0.50 and the outer cladding features have normalized dimensions in the range from 0.5 to 0.9, where the normalization factor is a typical feature spacing. The fiber is further characterized by a feature spacing of the inner cladding larger than 2.0 micron. In a second aspect, the fiber has a special non-circular and non-equilateral-polygonial outer cross-sectional shape to mechanically ensure bending in predetermined directions that are favourable with respect to low bending losses. The present invention provides fibers, which are less sensitive to macro-bending losses than presently known single-mode fibers with similar sized mode areas, and provides robust, single-mode, large-mode area fibers for long-distance optical transmission and fibers with special dispersion properties.
Owner:CRYSTAL FIBRE AS
Ultra high-power continuous wave planar waveguide amplifiers and lasers
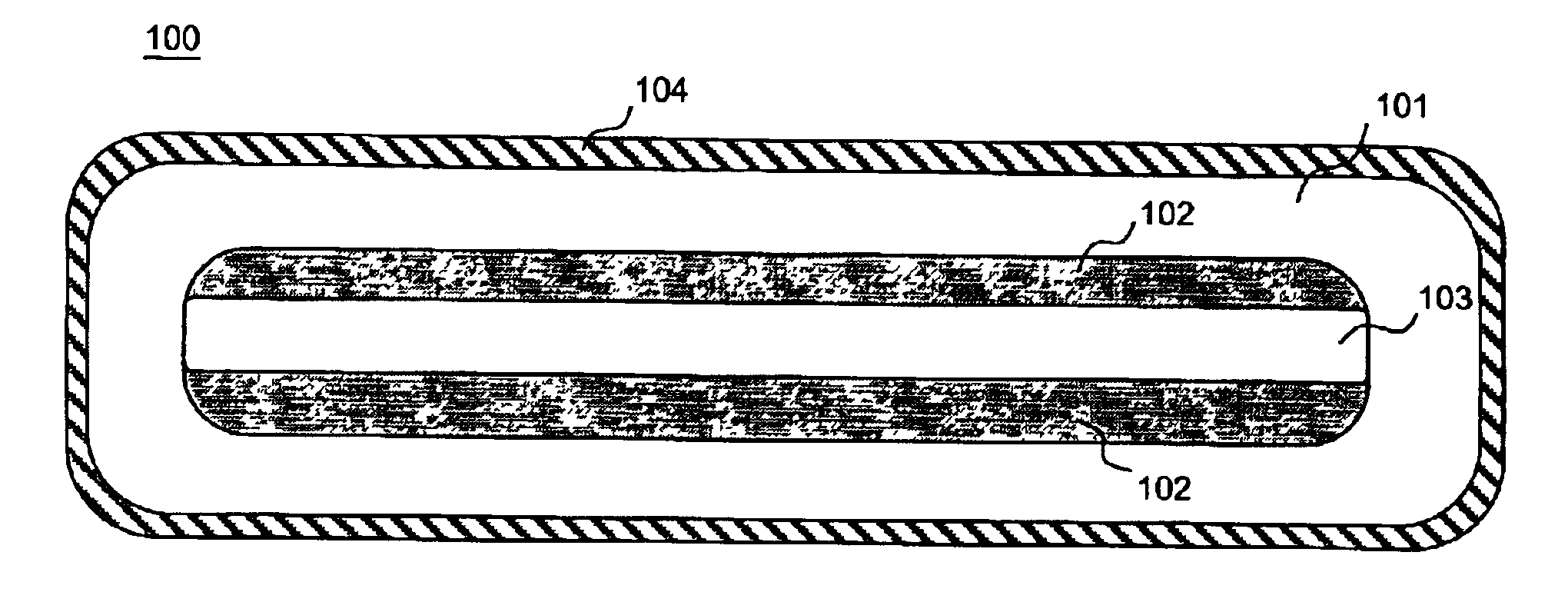
InactiveUS6904219B1Avoid bend lossesLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWaveguide amplifierHigh power diode laser
Double clad large mode area planar lasers or amplifiers comprising rare-earth or transition metal doped planar core regions are used to generate near-diffraction-limited optical beams of ultra-high power. The amplified light is guided in the core using different guiding mechanisms in two orthogonal axes inside the core. Waveguiding along a first long core axis is obtained substantially by gain-guiding or thermal lensing. Waveguiding along a second short core axis is obtained by index guiding. This is accomplished by surrounding the planar core region with regions of different refractive index. The long sides of the planar core region are surrounded with a depressed refractive index cladding region. The short sides of the planar core region are surrounded with a cladding region substantially index-matched to the core region. The whole structure is surrounded by an outer cladding region with a low refractive index to enable cladding pumping of the planar waveguide with high-power diode lasers. The rare-earth or transition metal doping level inside the planar core can be constant and can also vary substantially without negatively affecting the waveguiding properties. To avoid bend losses along the long axis of the planar waveguide, the planar core region and the planar waveguide are aligned parallel to each other and the planar waveguide is coiled with the long side of the planar waveguide mounted to a drum. The drum can also be used as a heat sink. A planar waveguide comprising a planar core region can be manufactured using conventional fiber fabrication methods.
Owner:BOSTON LASER
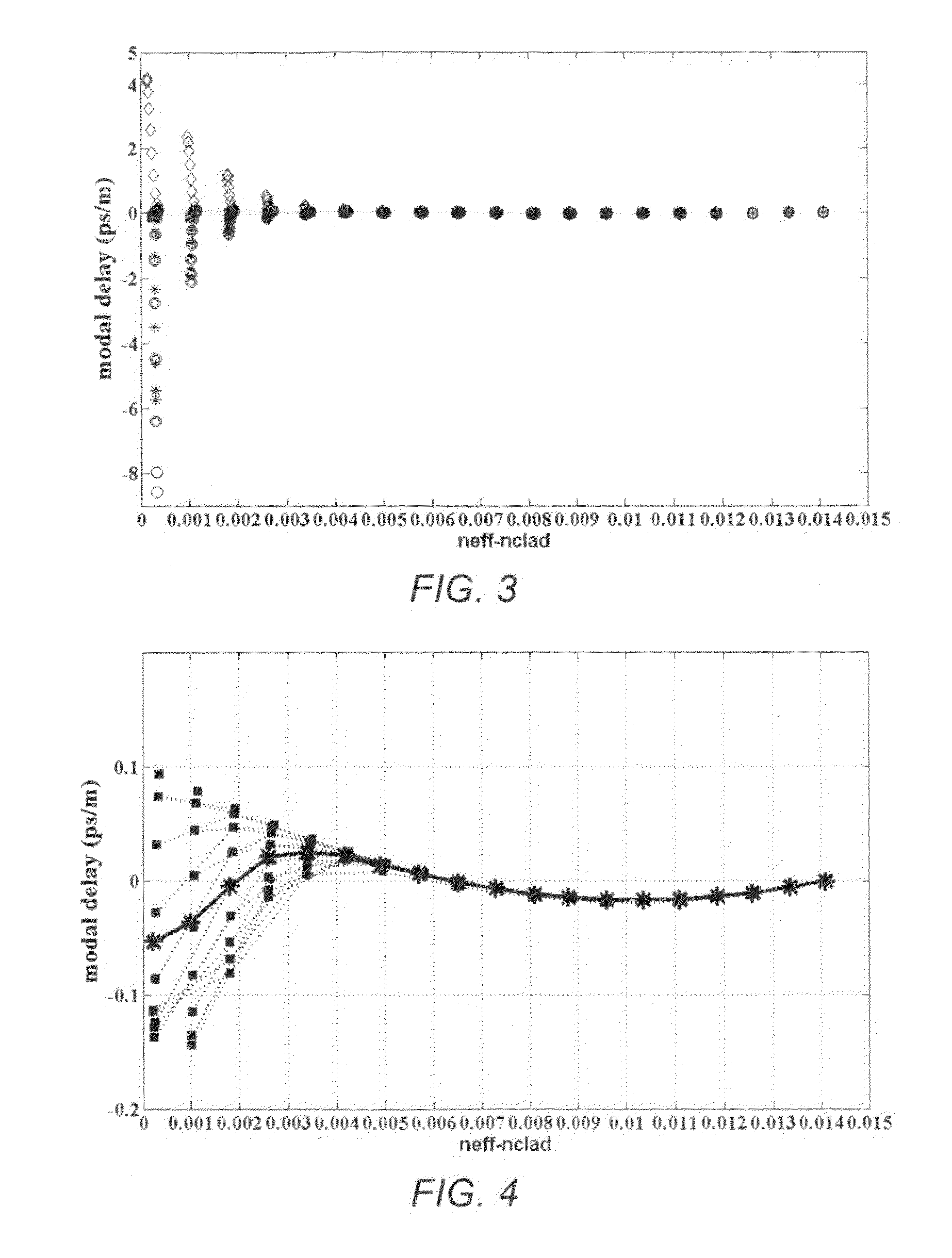
Equalizing modal delay of high order modes in bend insensitive multimode fiber
ActiveUS7865050B1RelaxingReducing bend lossOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingHigh bandwidthEngineering
Described are multimode optical fibers in which the differential in the mode delay for higher order modes is reduced for bending insensitive MMF. The result is preservation of low differential mode delay and high bandwidth while low bend loss is achieved. The designs are based on choosing a combination of a core profile and a cladding structure with a negative trench positioned at a radius related to the core profile. A feature of the preferred embodiments is a core with a hybrid refractive index profile. The hybrid refractive index profile is essentially a combination of a standard alpha profile and a step profile at the outer edge of the alpha profile.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
Hole-assisted holey fiber and low bending loss multimode holey fiber
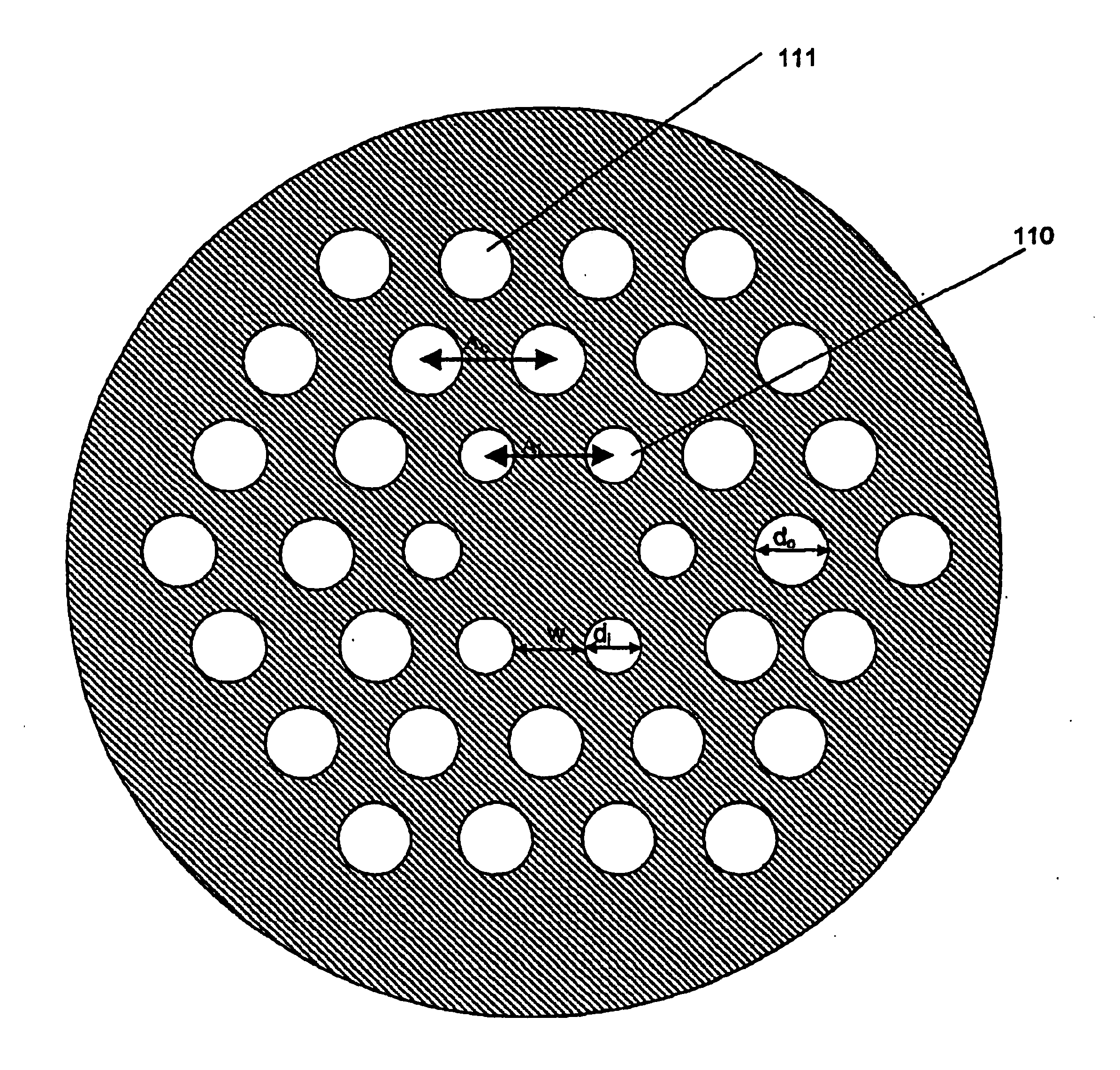
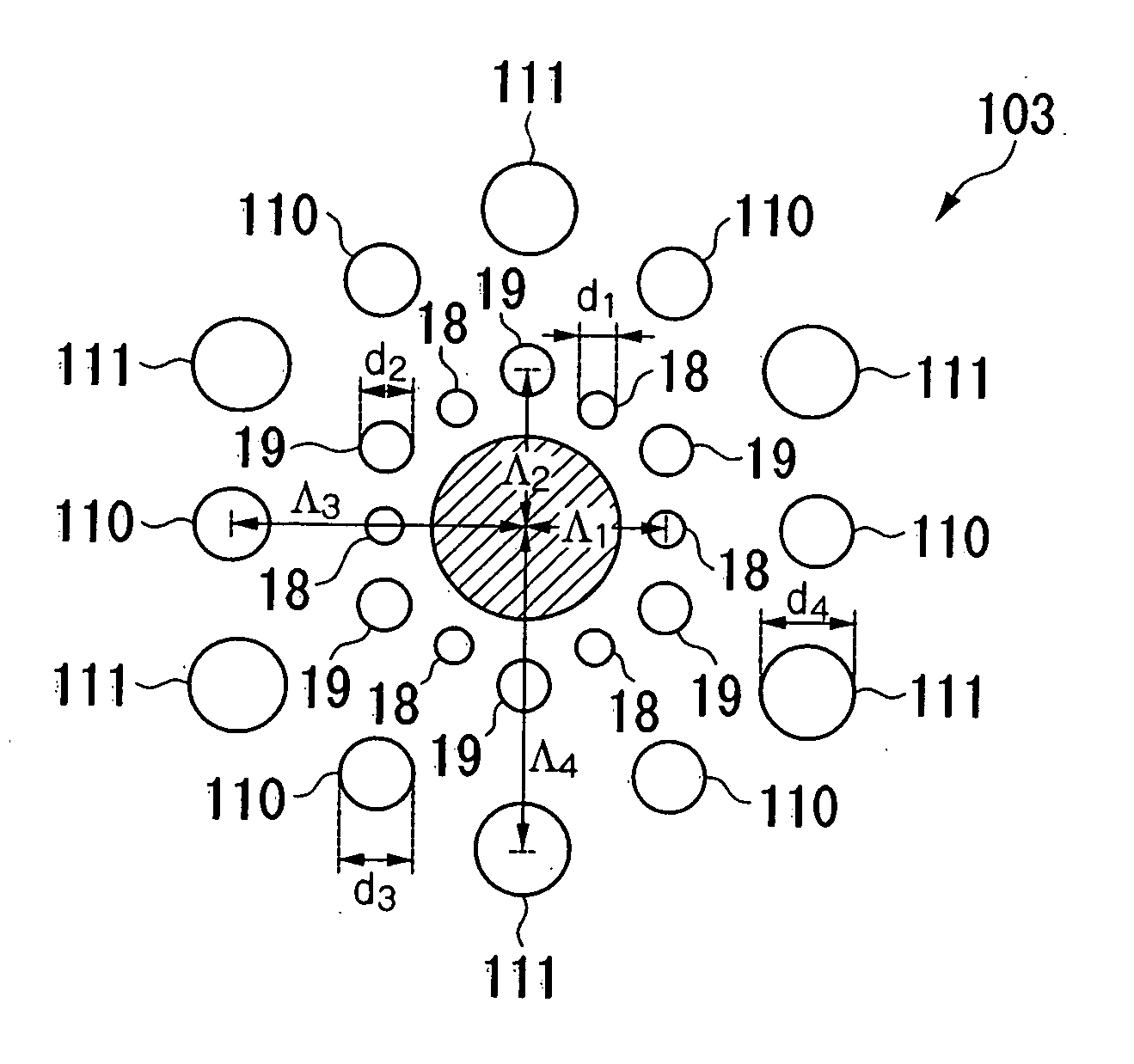
A hole-assisted holey fiber is provided. The holey fiber includes a core region; a cladding region around the core region, and a plurality of holes in the cladding region around the core region. The core region has a higher refractive index than that of the cladding region. The holes form an inner hole layer and an outer hole layer, and the inner hole layer has the same number of holes as the number of the holes in the outer hole layer. The outer layer holes are provided in locations in which inner holes are absent when viewed from the center of the core region, and holes defining the same layer have the same diameter. A distance Λ1 from a center of the core region to a center of an inner hole and a distance Λ2 from the center of the core region to a center of an outer hole satisfy the relationship Λ1<Λ2, and a diameter d1 of an inner hole and a diameter d2 of an outer hole satisfy the relationship d1≦d2.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Optical fiber having a lower bending loss
ActiveUS6901196B2Bending lossSuppressing transmission loss increaseGlass optical fibreGlass making apparatusHydrogenRelative refractive index
An optical fiber includes a first core having a relative refractive index difference of larger than 0.36%, and a cladding. The optical fiber has fiber cut-off wavelength λc of more than 1350 nm, cable cut-off wavelength λcc of less than 1285 nm, bending loss at a wavelength of 1625 nm of not more than 10 dB / km when wound at a diameter of 20 mm, transmission loss at a wavelength range of 1285 to 1625 nm of not more than 0.40 dB / km, transmission loss at a wavelength of 1383 nm less than transmission loss at a wavelength of 1310 nm, and difference in transmission loss at a wavelength of 1383 nm of not more than 0.04 dB / km before and after exposure to hydrogen. The lower bending loss of the optical fiber provides an optical fiber cable for use in a WDM transmission in wavelength range of 1285 to 1625 nm.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Single-mode optical fiber
ActiveUS20070147756A1Small bending lossOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingZero-dispersion wavelengthLength wave
A single-mode optical fiber has a cut-off wavelength of 1260 nm or less, a zero-dispersion wavelength in the range of 1300 nm to 1324 nm, a zero-dispersion slope of 0.093 ps / nm2 / km or less, a mode field diameter at a wavelength of 1310 nm in the range of 5.5 μm to 7.9 μm, and a bending loss of 0.5 dB or less at a wavelength of 1550 nm, the bending loss being produced when the fiber is wound around a 10-mm radius for 10 turns.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Large effective area fiber
ActiveUS20080279517A1Optical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRelative refractive indexEngineering
An optical fiber according to an embodiment of the present invention comprises: a glass core extending from a centerline to a radius R1 wherein R1 is greater than about 5 μm; a glass cladding surrounding and in contact with the core, the cladding comprising: (i) a first annular region extending from the radius R1 to a radius R2, the first annular region comprising a radial width, W2=R2−R1, (ii) a second annular region extending from the radius R2 to a radius R3, and comprising a radial width, W3=R3−R2, and (iii) a third annular region surrounding the second annular region and extending from the radius R3 to an outermost glass radius R4; wherein the core comprises a maximum relative refractive index, Δ1MAX, relative to the third annular region, and wherein Δ1MAX is greater than about 0.1% and less than about 0.3%; the first annular region has a refractive index delta Δ2(r) is less than about 0.025%; wherein the second annular region comprises a minimum relative refractive index, Δ3MIN, relative to the third annular region;wherein Δ1MAX>Δ2MAX>Δ3MIN, and Δ2MIN>Δ3MIN<0; andwherein the core and the cladding provide a fiber with cable cutoff less than 1500 nm, and an effective area at 1550 nm greater than 95 μm2 and bend loss of ≦0.5 dB / turn on a 20 mm diameter mandrel.
Owner:CORNING INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com