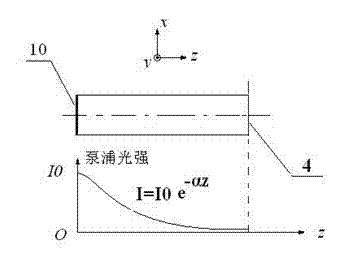
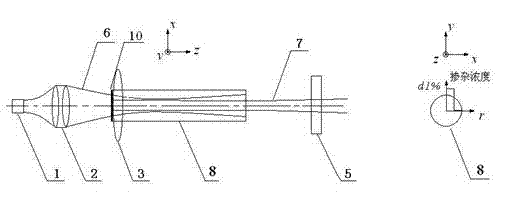
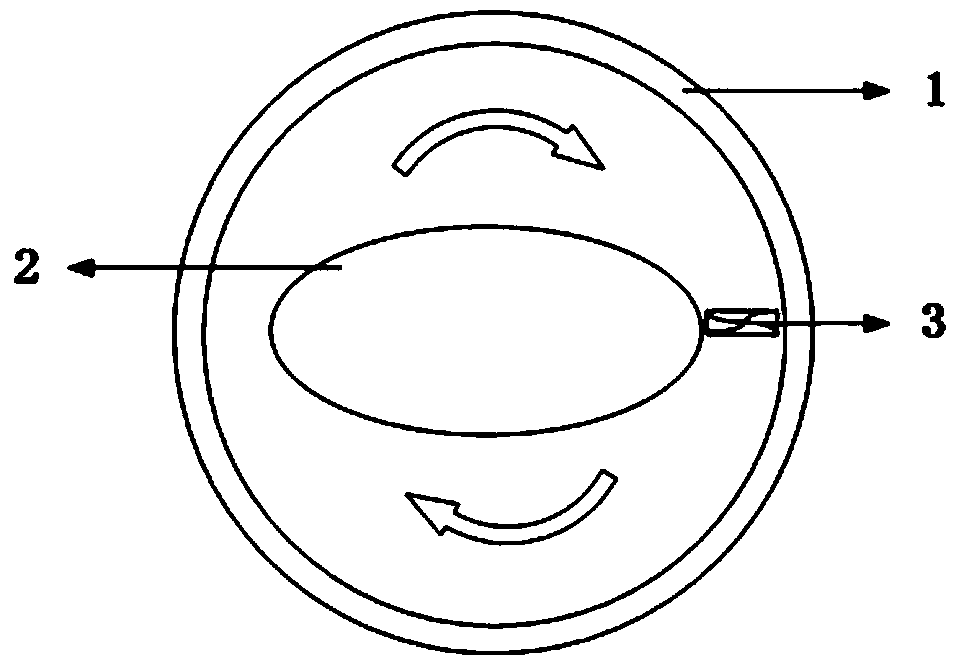
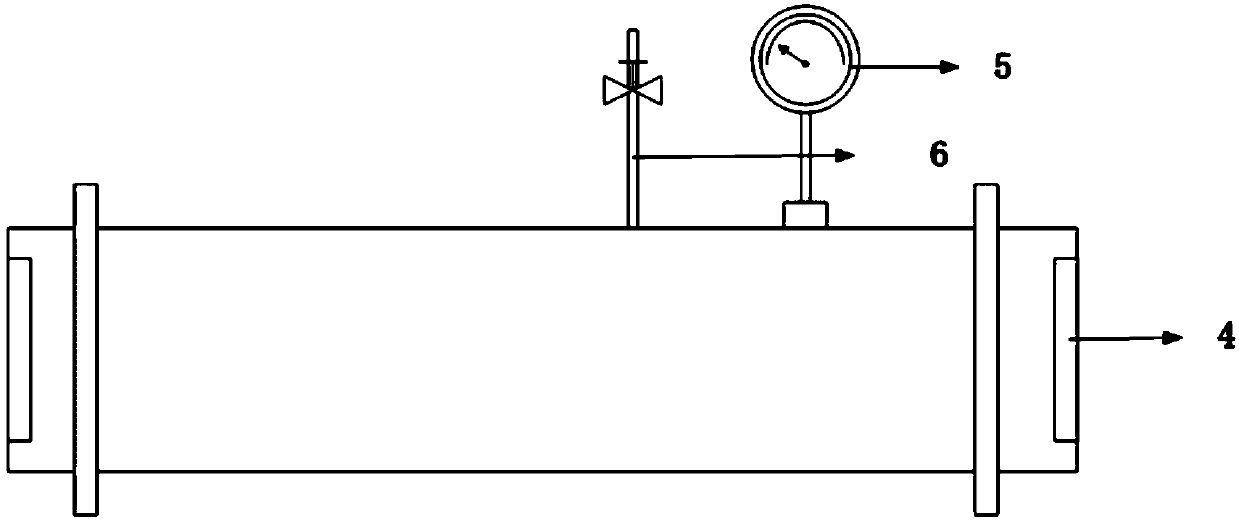
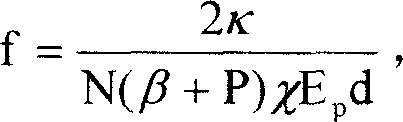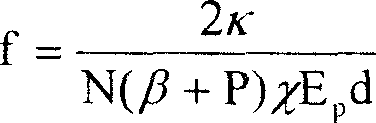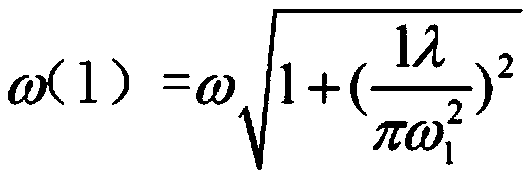Patents
Literature
102 results about "Thermal lensing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
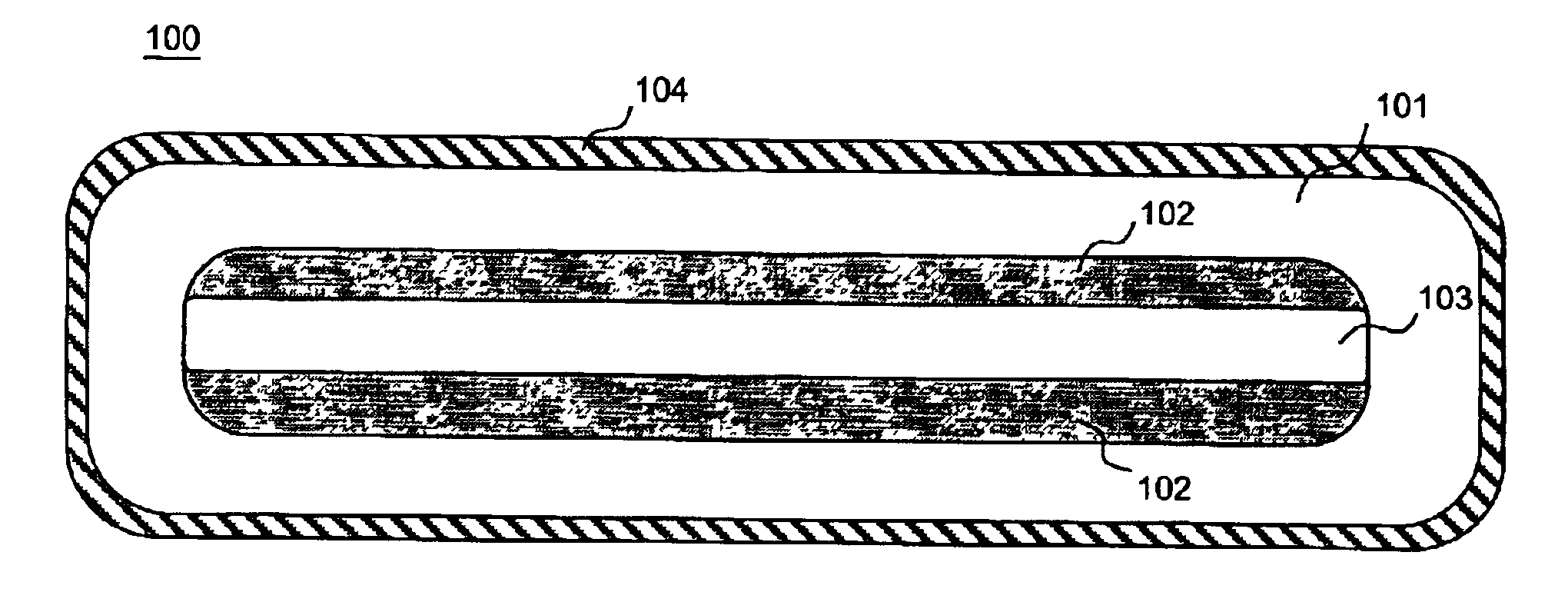
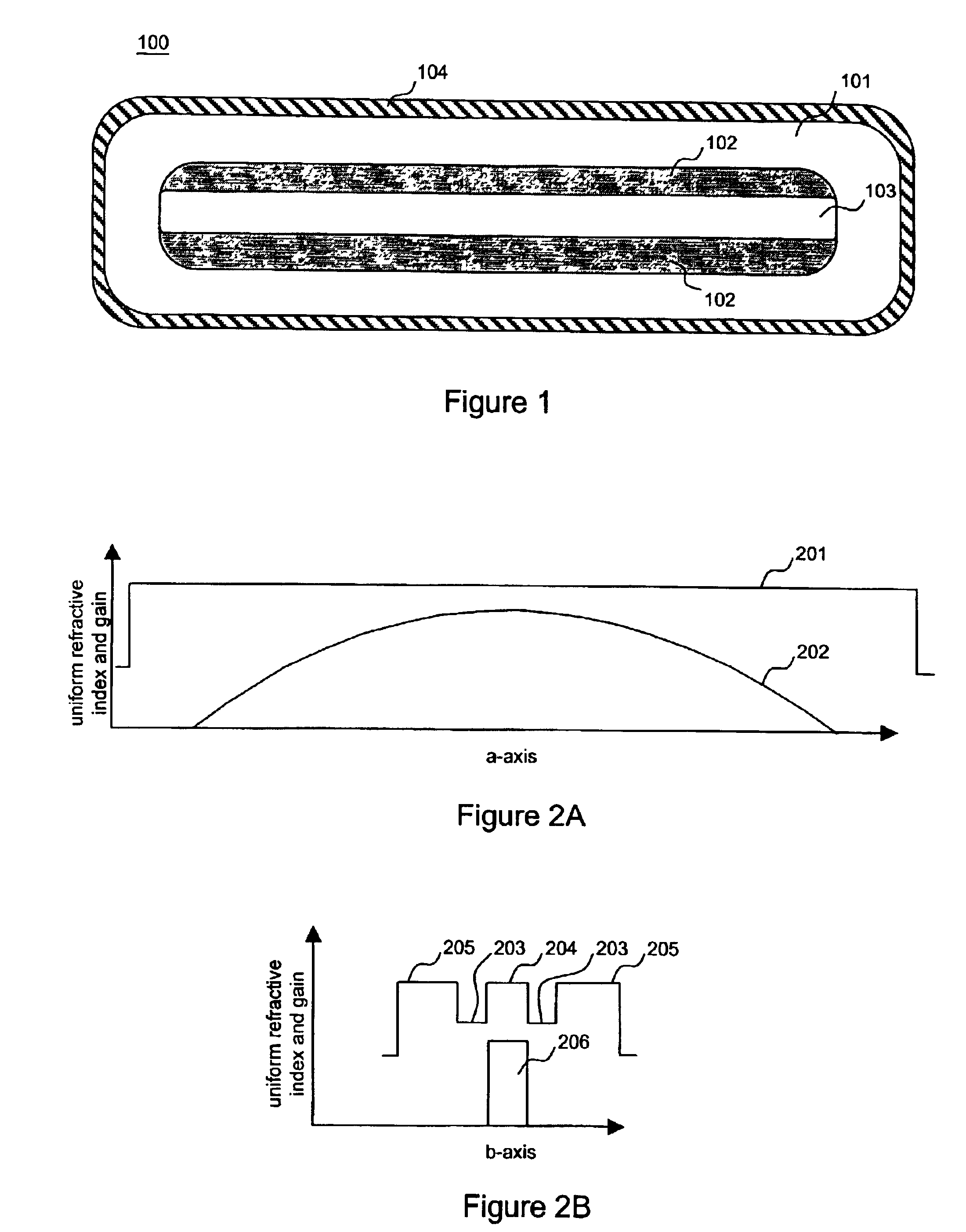
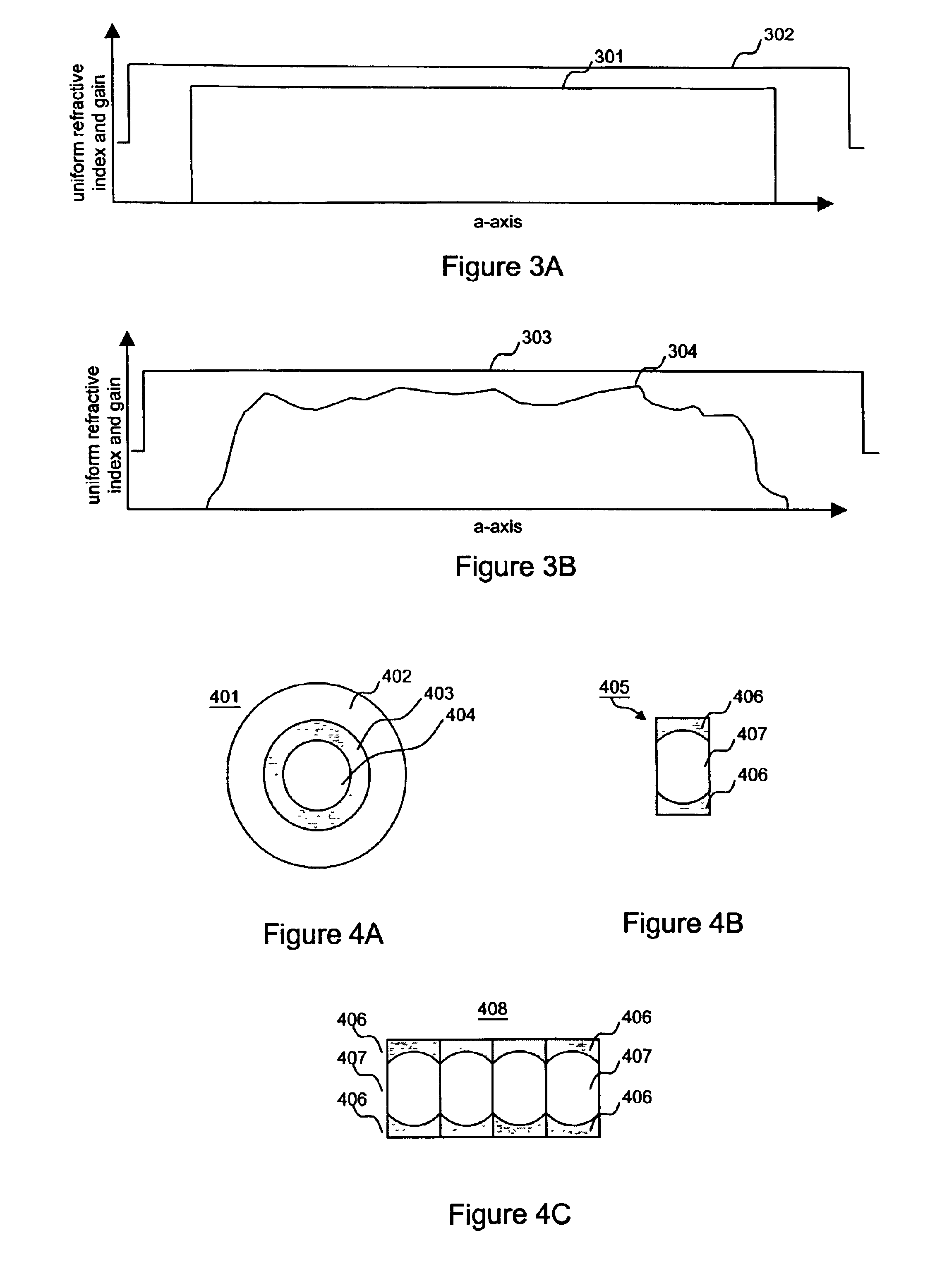
Ultra high-power continuous wave planar waveguide amplifiers and lasers
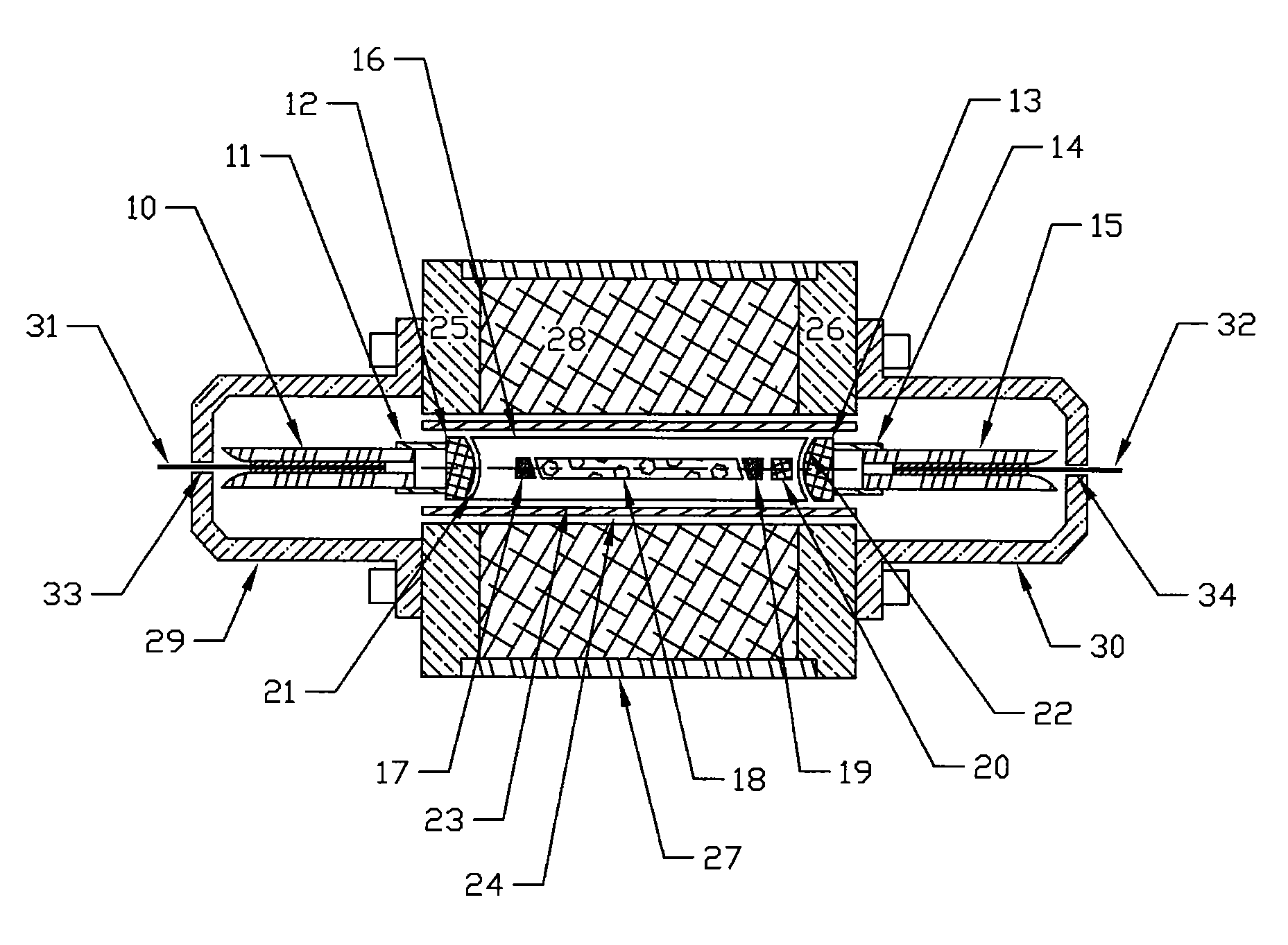
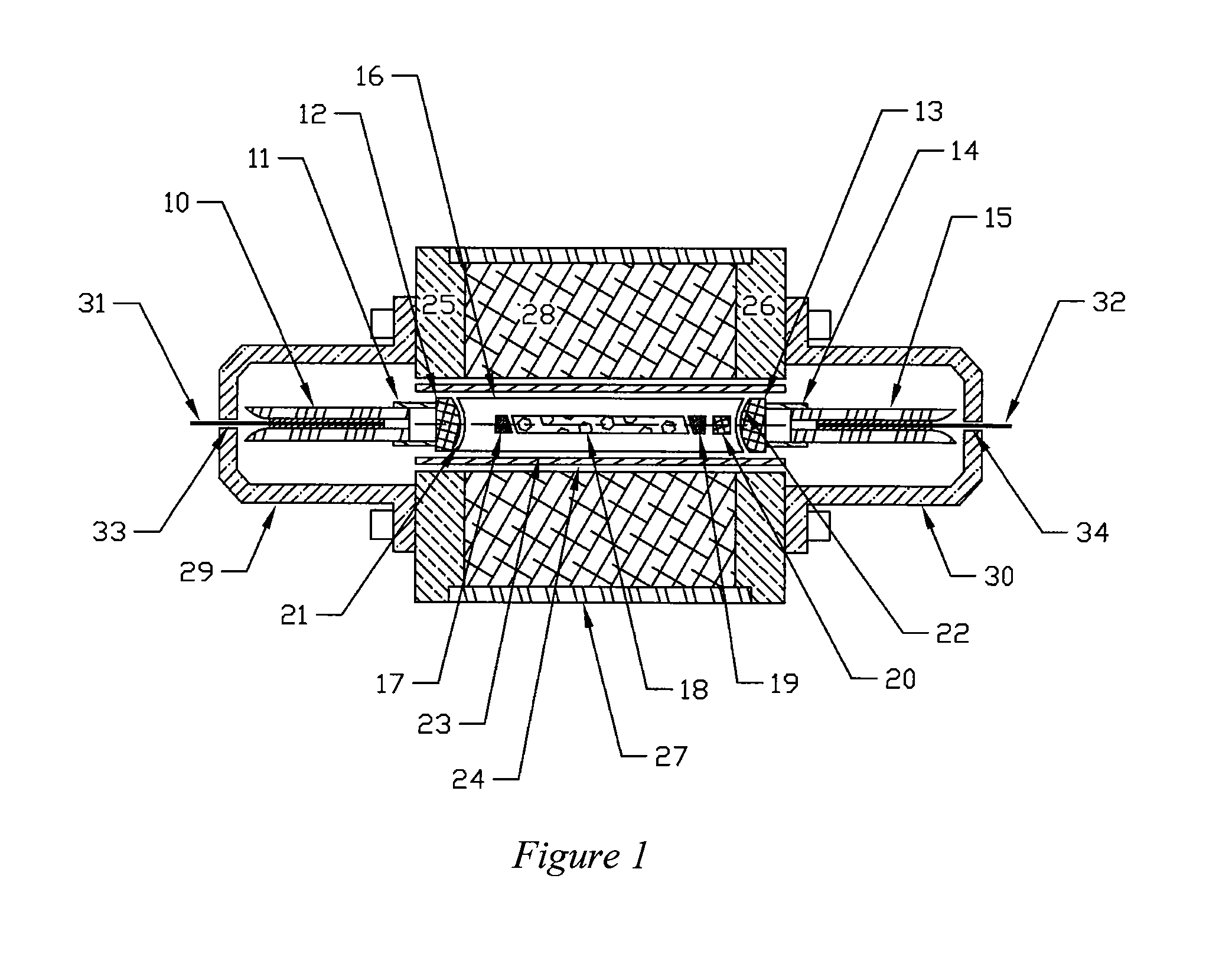
InactiveUS6904219B1Avoid bend lossesLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWaveguide amplifierHigh power diode laser
Double clad large mode area planar lasers or amplifiers comprising rare-earth or transition metal doped planar core regions are used to generate near-diffraction-limited optical beams of ultra-high power. The amplified light is guided in the core using different guiding mechanisms in two orthogonal axes inside the core. Waveguiding along a first long core axis is obtained substantially by gain-guiding or thermal lensing. Waveguiding along a second short core axis is obtained by index guiding. This is accomplished by surrounding the planar core region with regions of different refractive index. The long sides of the planar core region are surrounded with a depressed refractive index cladding region. The short sides of the planar core region are surrounded with a cladding region substantially index-matched to the core region. The whole structure is surrounded by an outer cladding region with a low refractive index to enable cladding pumping of the planar waveguide with high-power diode lasers. The rare-earth or transition metal doping level inside the planar core can be constant and can also vary substantially without negatively affecting the waveguiding properties. To avoid bend losses along the long axis of the planar waveguide, the planar core region and the planar waveguide are aligned parallel to each other and the planar waveguide is coiled with the long side of the planar waveguide mounted to a drum. The drum can also be used as a heat sink. A planar waveguide comprising a planar core region can be manufactured using conventional fiber fabrication methods.
Owner:BOSTON LASER
Laser rod thermalization
InactiveUS6414980B1Additive manufacturing apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser processingOptical pumping
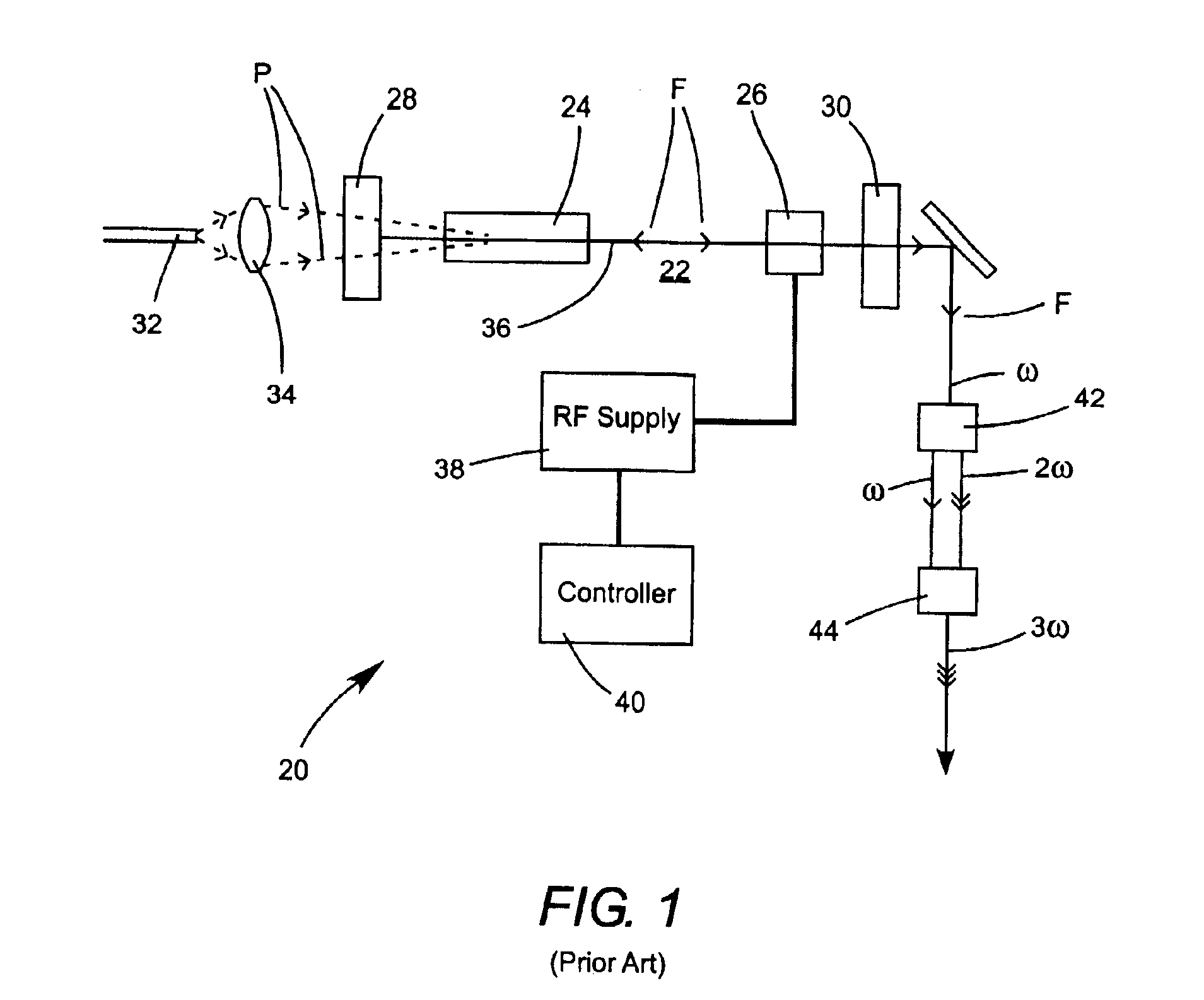
A method for operating an extracavity frequency-converted solid-state laser for performing a laser processing operation is disclosed. The laser has a laser-resonator including an optically-pumped gain-medium. The resonator is configured to compensate for a predetermined range of thermal lensing in the gain-medium. An optically-nonlinear crystal located outside the resonator converts fundamental laser radiation delivered by the resonator into frequency converted radiation. The laser processing operation is performed by a train of pulses of the frequency-converted radiation having sufficient power to perform the processing operation. The power of frequency-converted radiation is dependent on delivery parameters of the laser radiation from the laser-resonator. The laser is operated in a manner which provides that the resonator delivers effectively the same average power of fundamental laser radiation before and during the laser processing operation. This provides that thermal-lensing in the gain-medium is within the predetermined range before and during a laser processing operation. Delivery parameters of the laser radiation before and during the processing operation are varied such that power of frequency-converted radiation generated before the processing operating is insufficient to perform a laser processing operation.
Owner:COHERENT INC
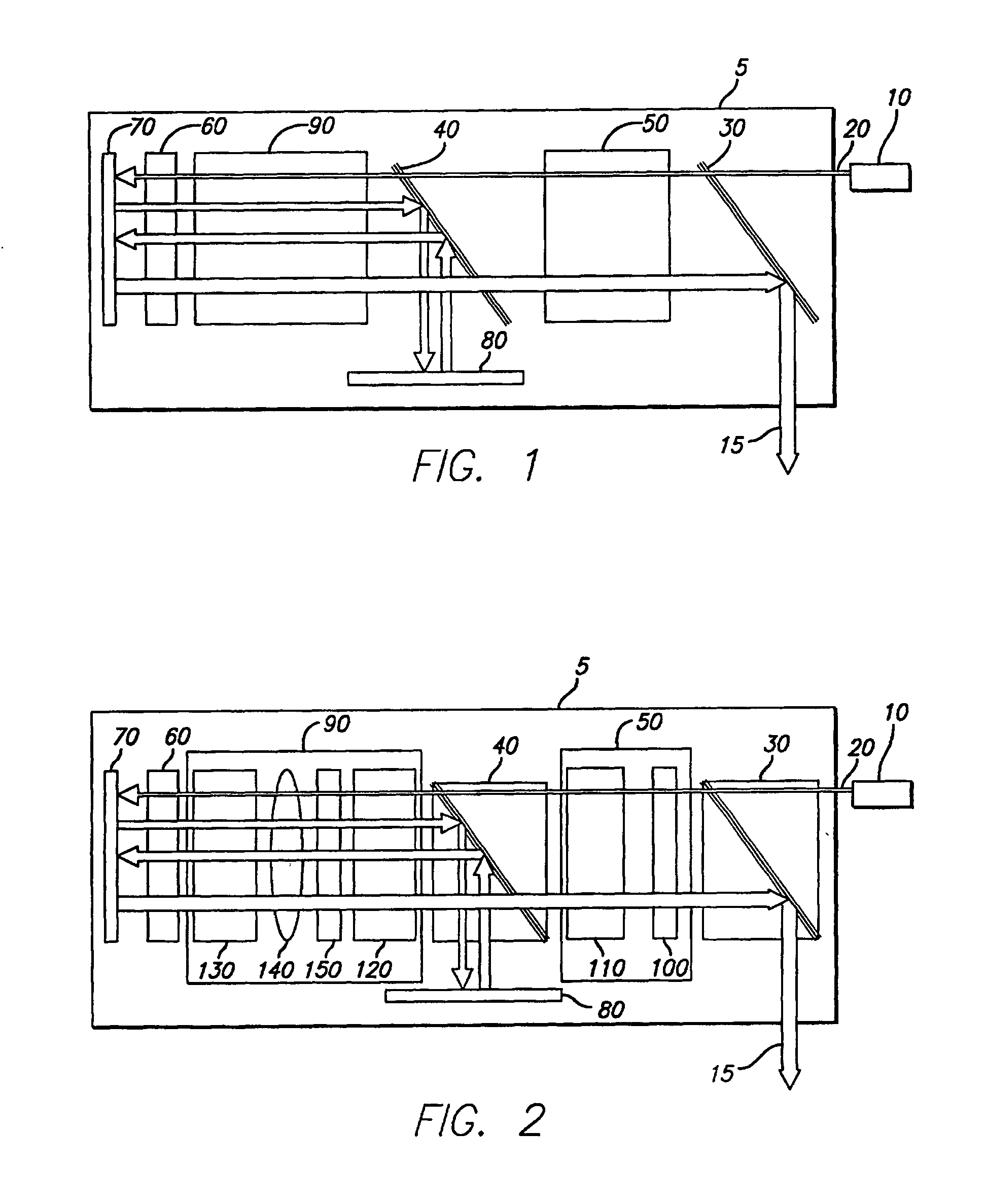
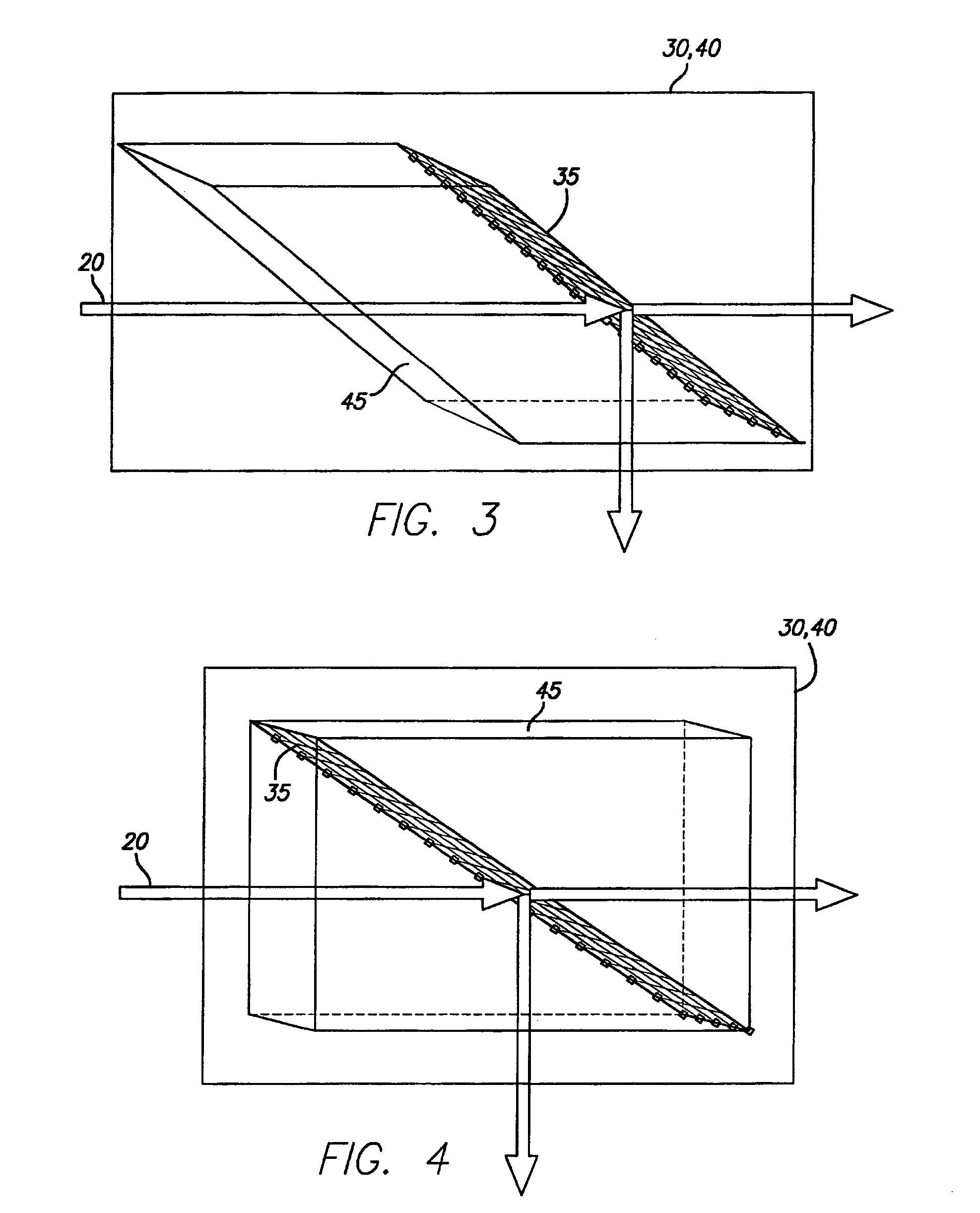
Optically controlled optical-path-switching apparatus, and method of switching optical paths
InactiveUS20070104417A1Increase speedIncreased durabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesDivergence angleLight beam
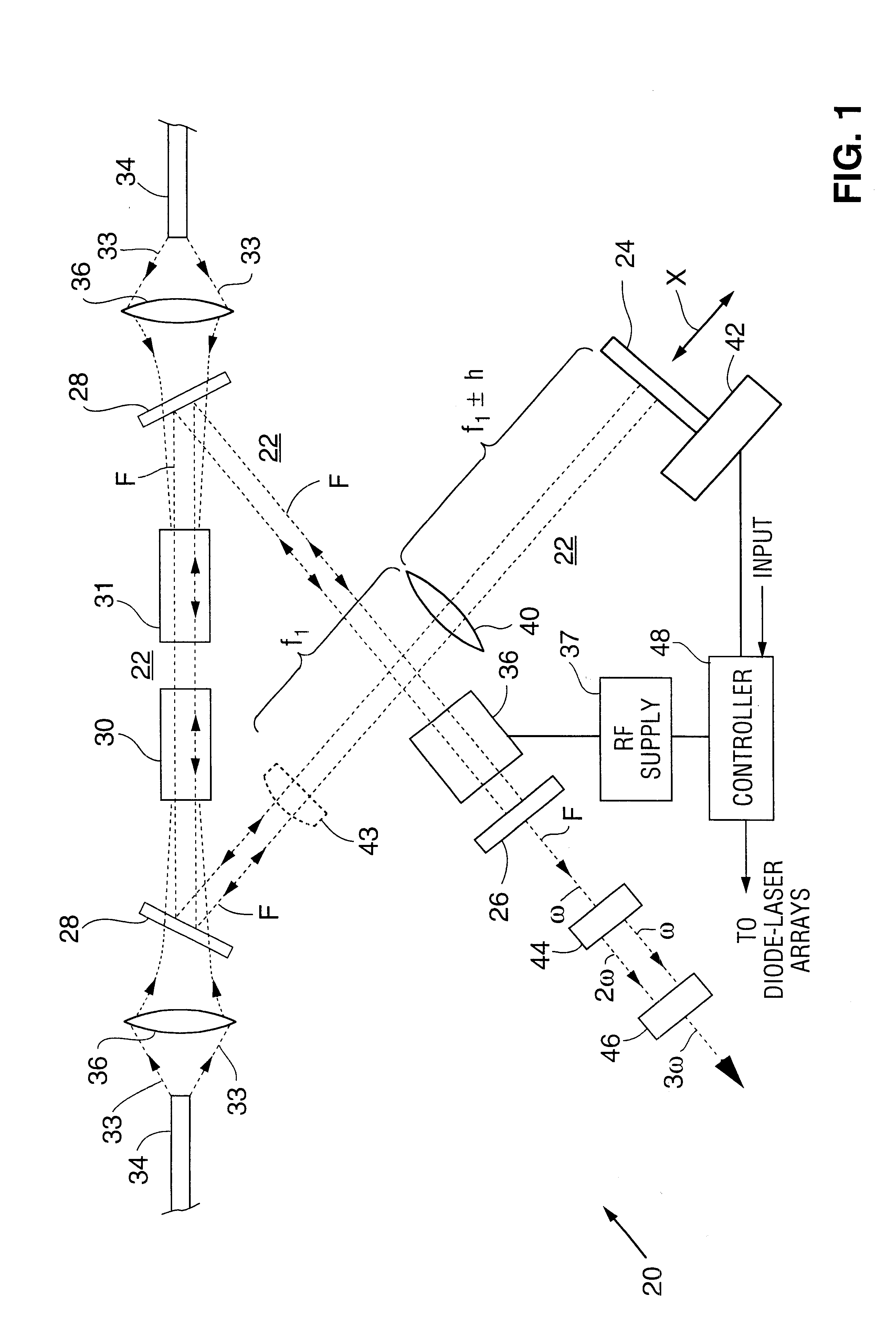
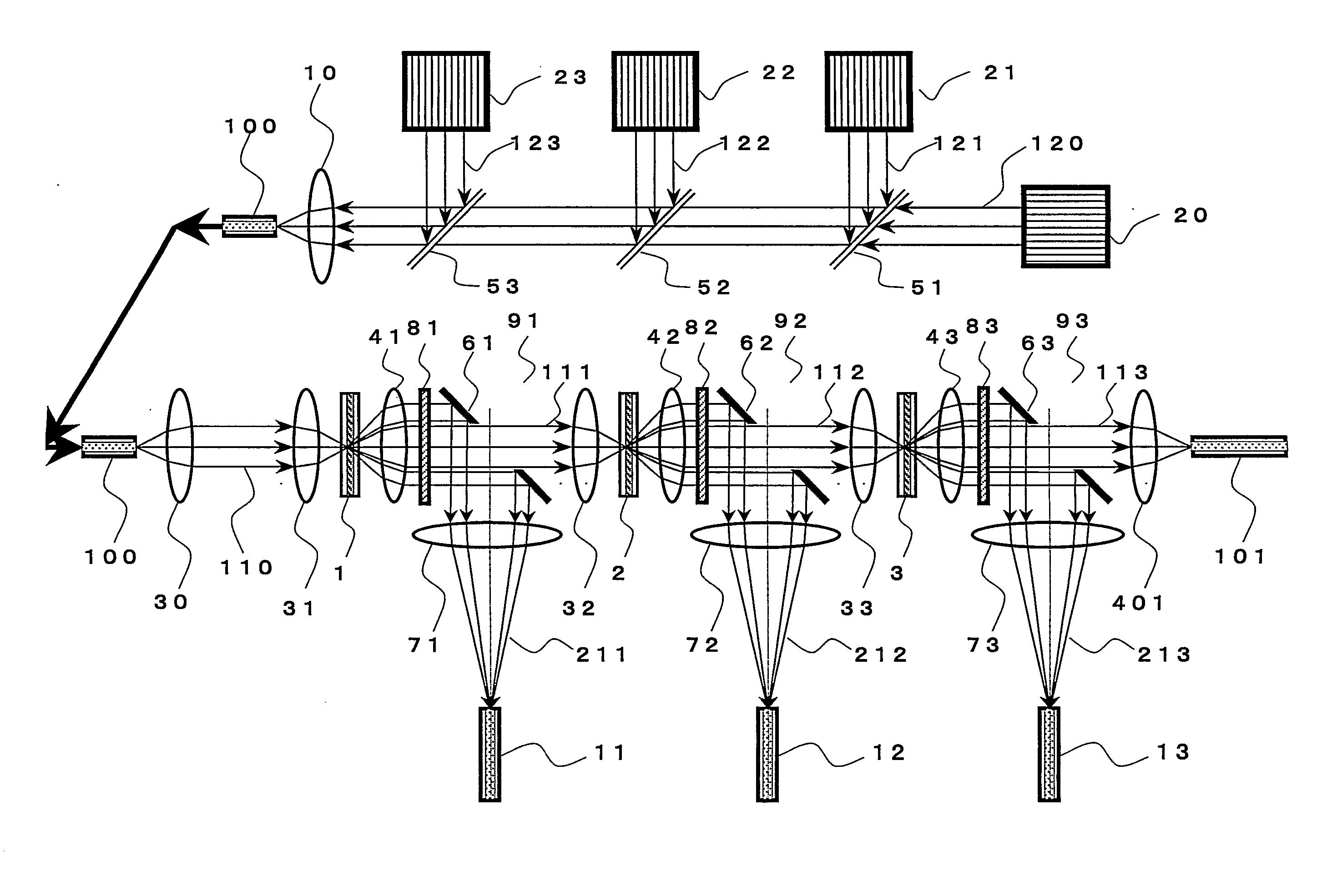
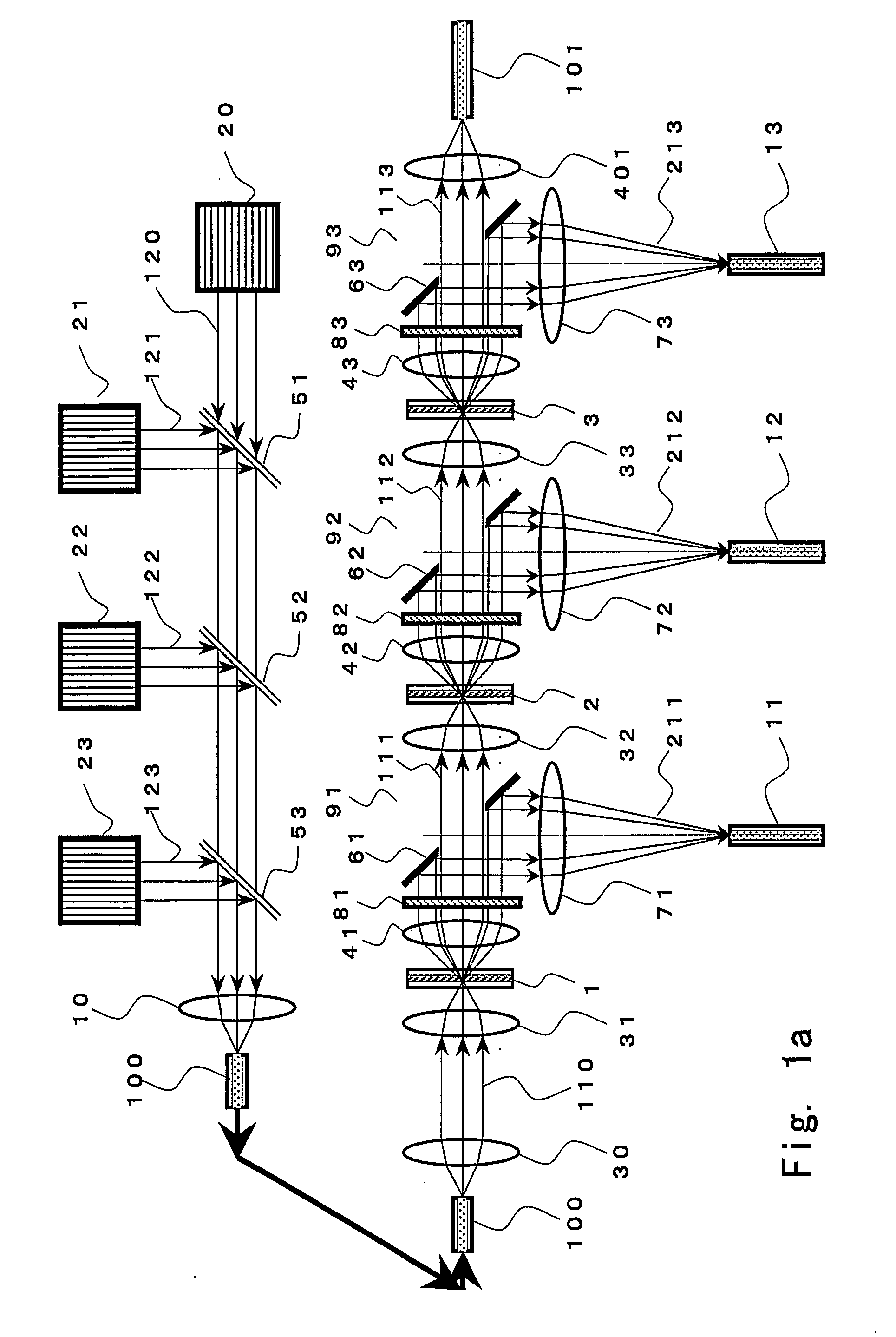
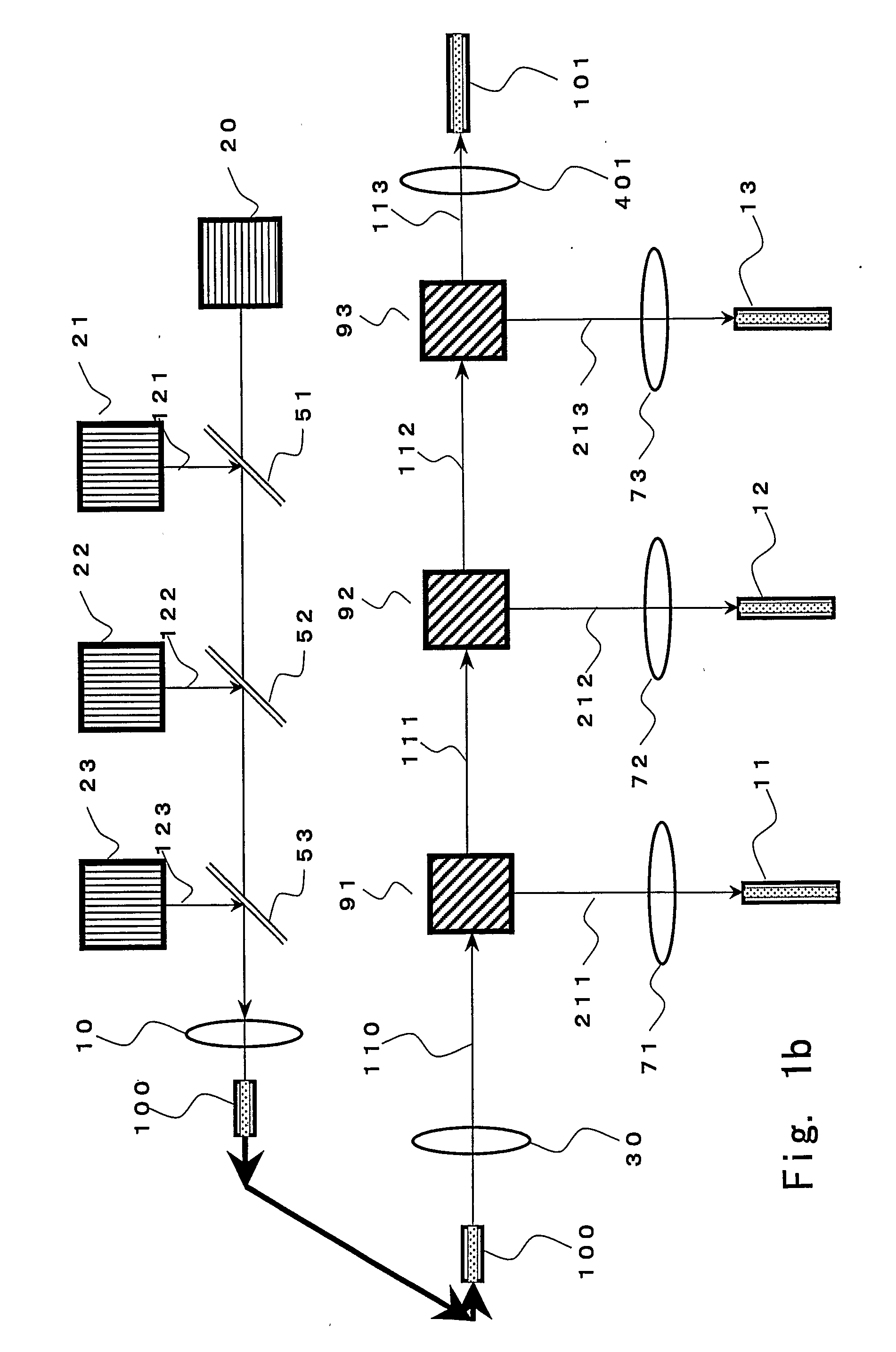
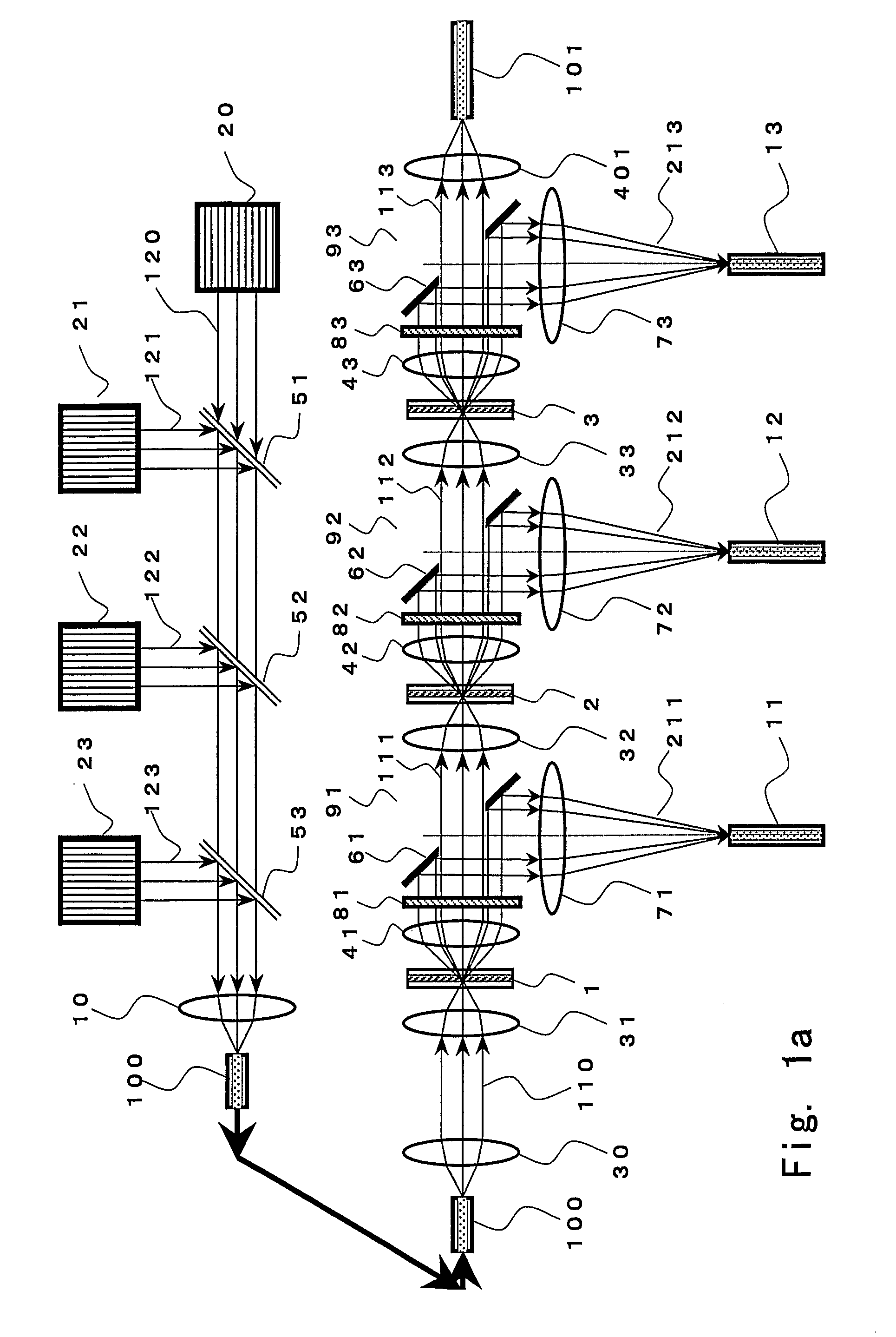
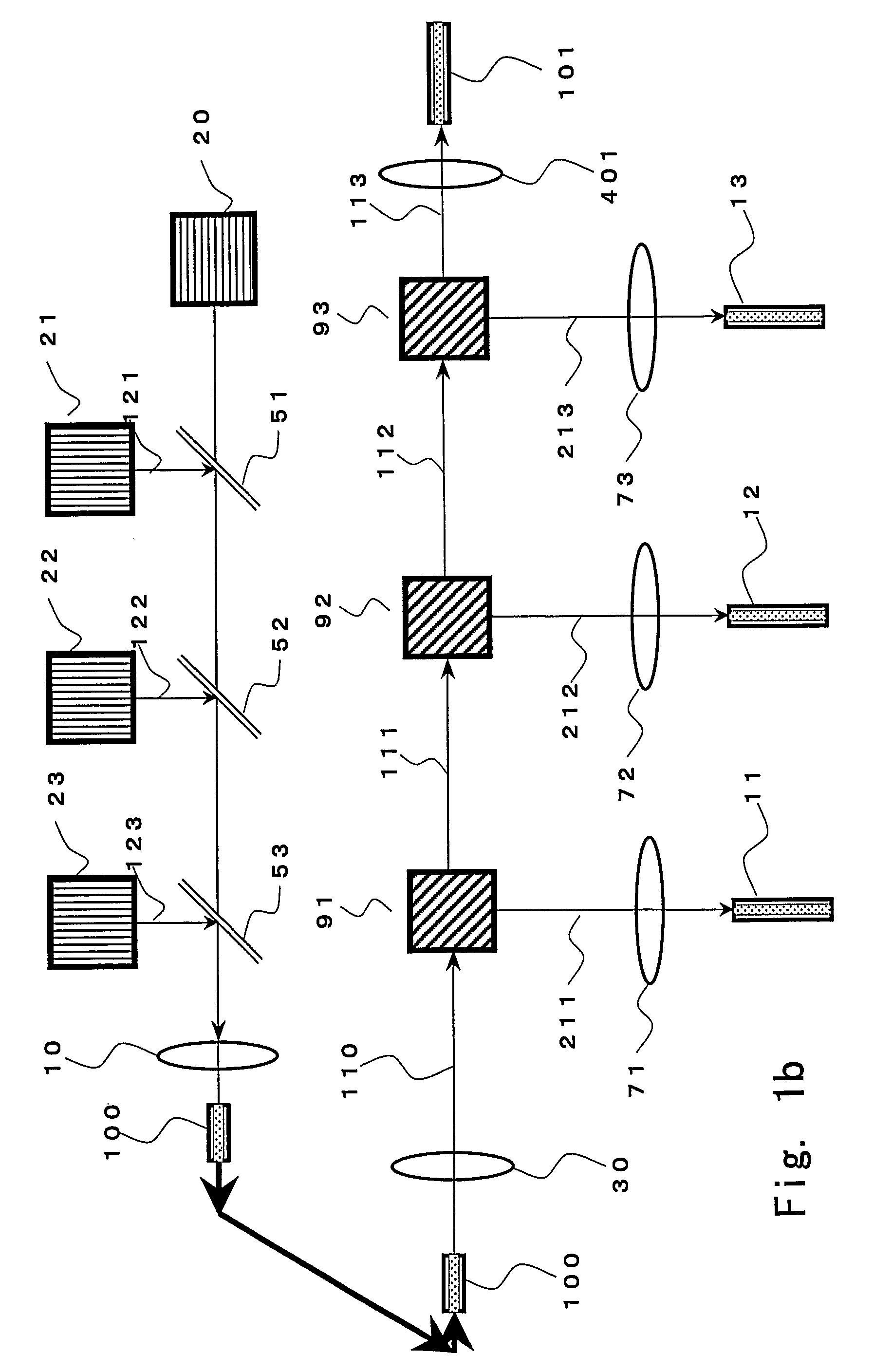
An optical signal optical path switching method comprising steps of using a thermal lens based on a distribution of refractive index produced reversibly caused by temperature increase generated in an area of the light-absorbing layer film of thermal lens forming devices 1, 2 and 3, that has absorbed control light beams 121, 122 and 123, and in the periphery thereof, causing the converged signal light beam to exit from the thermal lens forming device with an ordinary divergence angle when the control light beams 121, 122 and 123 have not been irradiated and no thermal lens has been formed, and causing the converged signal light beam to exit from the thermal lens forming device with a divergence angle larger than the ordinary divergence angle when the control light beams have been irradiated and a thermal lens has been formed, and causing the signal light beam to travel straight through holes 61, 62 and 63 of mirrors provided with the holes for the signal light beam to pass through when the control light beams have not been irradiated and no thermal lens has been formed, and changing the optical path by reflecting the signal light beam using the hole-provided mirror when the control light beams have been irradiated and a thermal lens has been formed.
Owner:DAINICHISEIKA COLOR & CHEM MFG CO LTD +1
Q-switching method for pulse train generation
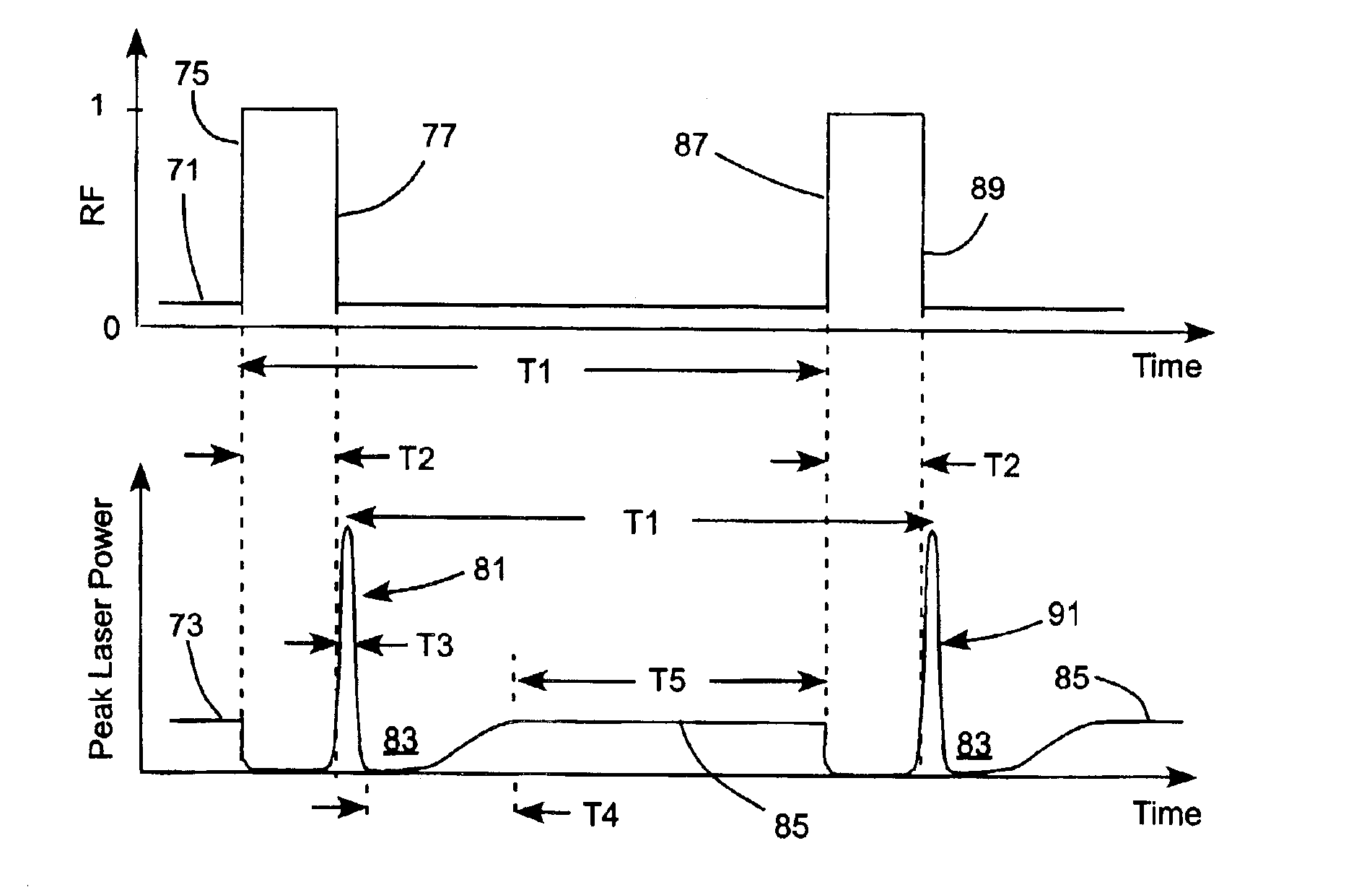
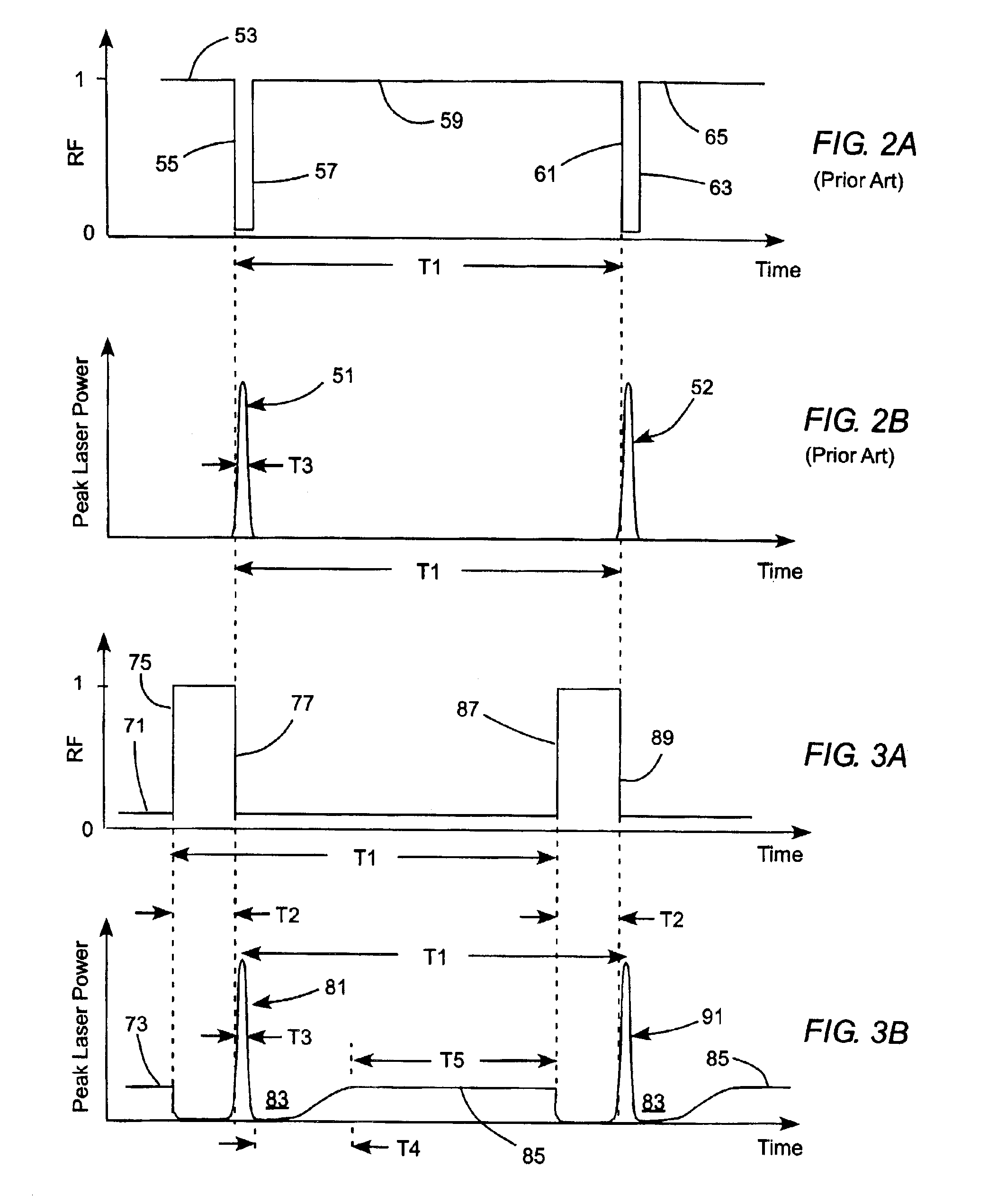
ActiveUS6931035B2Constant effectAdditive manufacturing apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionOptoelectronicsCw laser
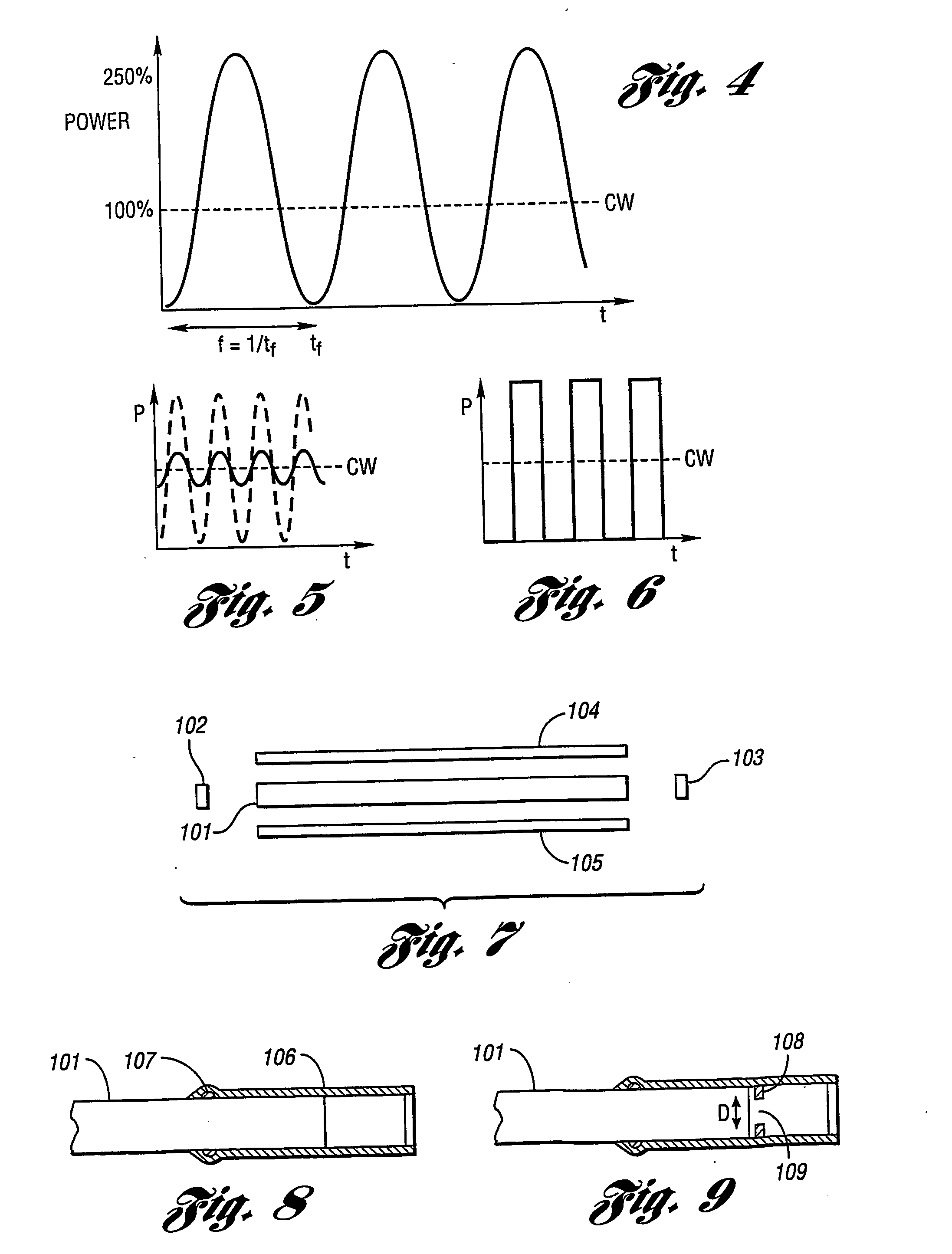
A method of operating a continuously pumped, Q-switched laser to provide trains of pulses for laser operations is disclosed. The laser includes a solid-state gain-medium that exhibits a thermal-lensing effect on being optically pumped. Pulse delivery is controlled by a Q-switch that is in a normally-open state when the laser is not delivering pulses. This allows the laser to deliver CW laser radiation when pulses are not being delivered. A train of pulses is delivered by repeatedly interrupting the CW operation by closing then reopening the Q-switch. When the Q-switch reopens after the interruption, the laser delivers a pulse of laser radiation, then resumes delivery of CW operation until the next interruption. The interruption periods may be varied to provide pulses of different peak power in a pulse train.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Compact, high power, fiber pigtailed faraday isolators
Faraday rotator or isolator with mode stripping ferrules and collimators having fiber pigtailed mode stripping components. An example is a compact Faraday Isolator module employing mode stripping ferrules and mode stripping collimators at the input and / or at the output of a fiber pigtailed Faraday Isolator. Two basic isolator types are a Polarization Independent Faraday isolator and a Polarization Maintaining Faraday isolator. The device is substantially immune to damage due to back-reflection, thermal lensing, energy leakage and absorption. Mode stripped optical energy propagating in the reverse direction is diverted onto a heat absorbing and heat sinking structure, as for example at the input of a compact birefringent wedge-based PI isolator. Alternatively, the optical energy propagating in the reverse direction is angularly refracted away from the forward incident beam path and is coupled into the energy dispersive cladding of the input fiber or the ferrule itself.
Owner:ELECTRO OPTICS TECH
A compensation method for laser bar thermal lens effect
InactiveCN101017951AIncrease lossDoes not affect conversion efficiencyOptical resonator shape and constructionMotor driveOptical axis
The disclosed thermal-lensing compensation method for laser rod comprises: setting the holophote with a step-motor driving movable mechanism in optical resonator of laser as raised convex mirror toward the laser rod; controlling the step motor by a computer to make the distance from mirror to rod as a = f - R / 2 - d / 2n. Wherein, R for curvature radius of the mirror, d for rod length, n for refractive index of rod, and f for lens focus. This invention simplifies system structure, affects no energy conversion efficiency, and applies computer to control laser frequency N and pumping energy density Ep for complete automatic compensation.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Methods and systems for laser processing a workpiece and methods and apparatus for controlling beam quality therein
InactiveUS20050094684A1Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionHigh power lasersLaser processing
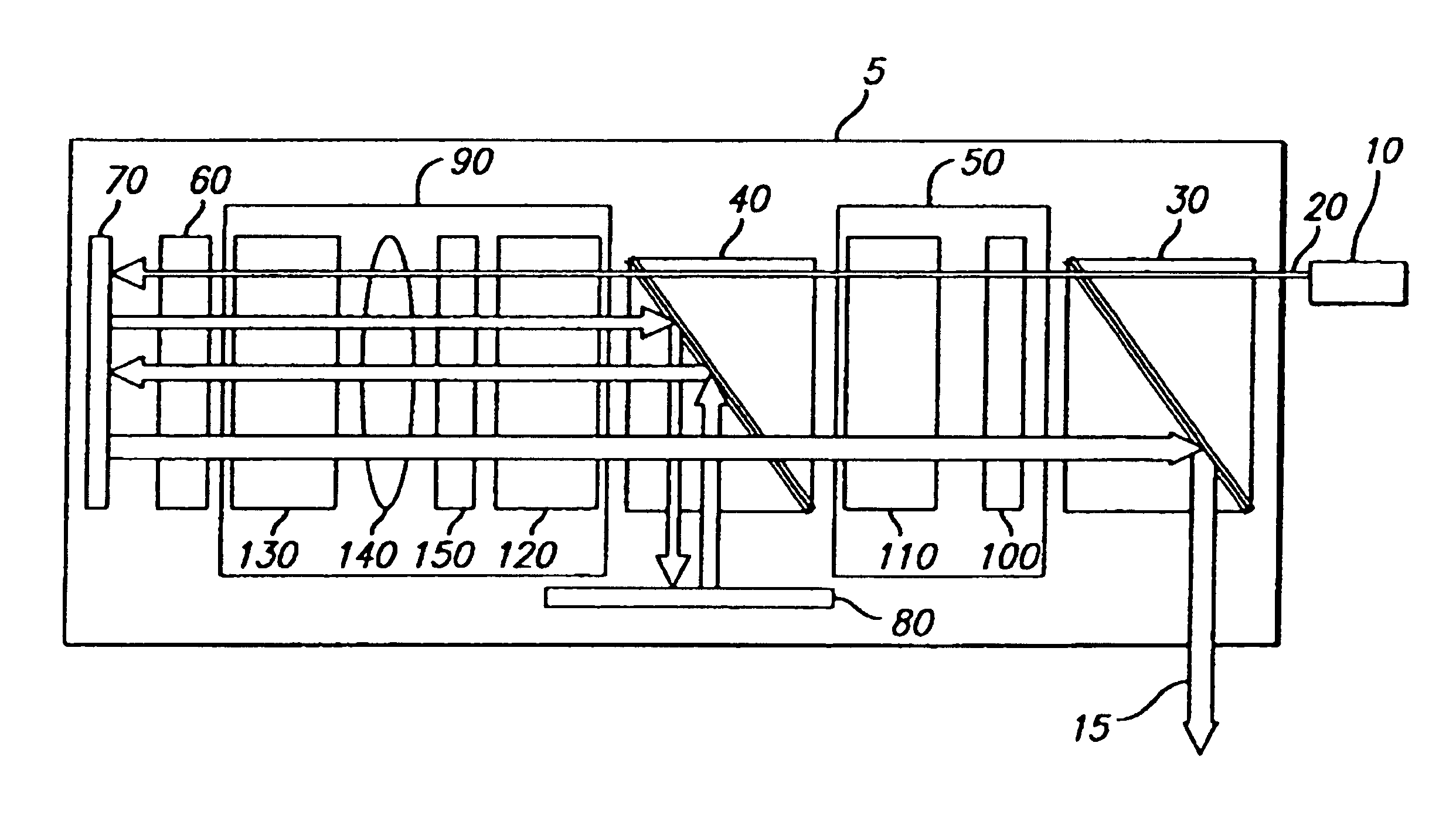
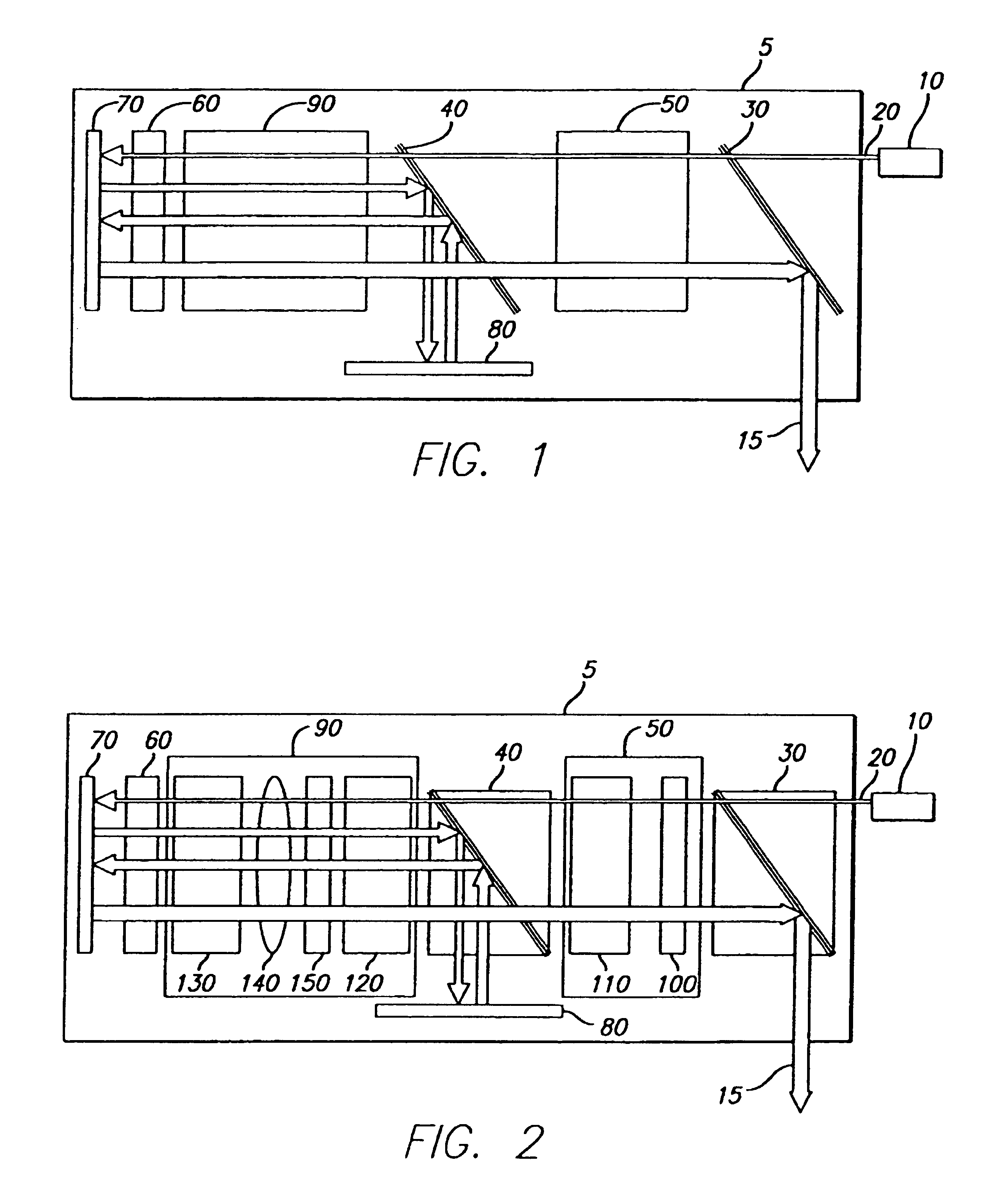
Laser processing methods, systems and apparatus having a super-modulating power supply (6) or pumping subsystem (5) and high beam quality (i.e., brightness) are disclosed. The methods, systems and apparatus have significant benefits, improved operation characteristics and material processing capability over currently available methods, systems and apparatus. In at least one embodiment, the beam quality of a high power solid state laser (2) is improved in the presence of thermal lensing. High power laser cutting, scribing, and welding results are improved with a combination of modulation and high beam quality while providing for improved processing speeds.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS LTD
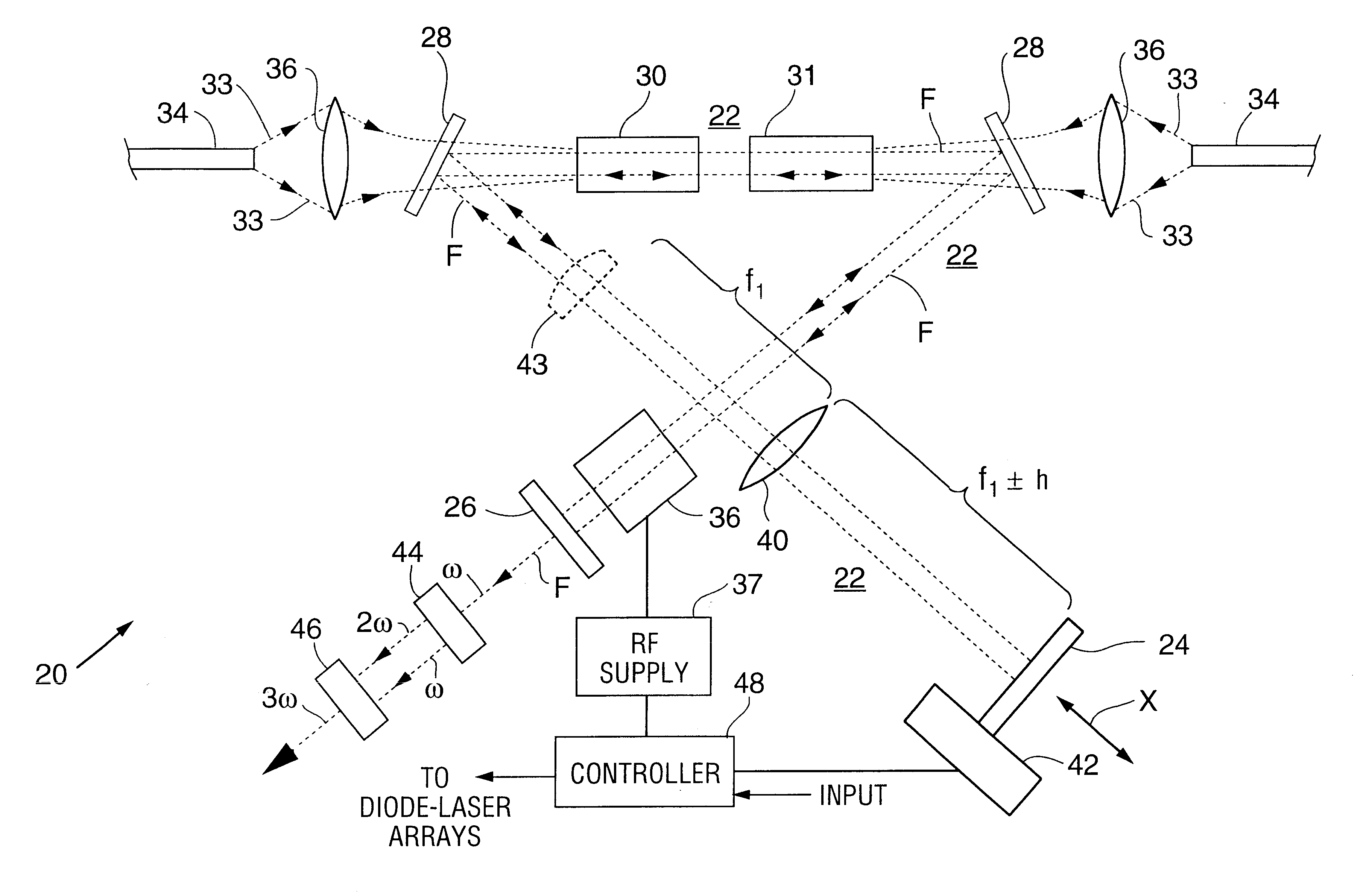
High intensity and high power solid state laser amplifying system and method
InactiveUS6999491B2Increase intensityIncrease powerExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionAudio power amplifierOptoelectronics
Systems and methods are provided for achieving high power and high intensity laser amplification. In a four-pass optical amplifying system, a linear polarized optical beam is directed by various optical elements four times through an optical amplifier. The optical amplifier is transversely pumped by a pumping energy source that includes laser diode arrays. The pumping module and the other optical components are provided to counteract thermal lensing effects, induced thermal birefringence effects and to achieve enhanced amplification and efficiencies.
Owner:JMAR RES
Methods and systems for changing a refractive property of an implantable intraocular lens
A method of altering a refractive property of a crosslinked acrylic polymer material by irradiating the material with a high energy pulsed laser beam to change its refractive index. The method is used to alter the refractive property, and hence the optical power, of an implantable intraocular lens after implantation in the patient's eye. In some examples, the wavelength of the laser beam is in the far red and near IR range and the light is absorbed by the crosslinked acrylic polymer via two-photon absorption at high laser pulse energy. The method also includes designing laser beam scan patterns that compensate for effects of multiphone absorption such as a shift in the depth of the laser pulse absorption location, and compensate for effects caused by high laser pulse energy such as thermal lensing. The method can be used to form a Fresnel lens in the optical zone.
Owner:AMO DEVMENT
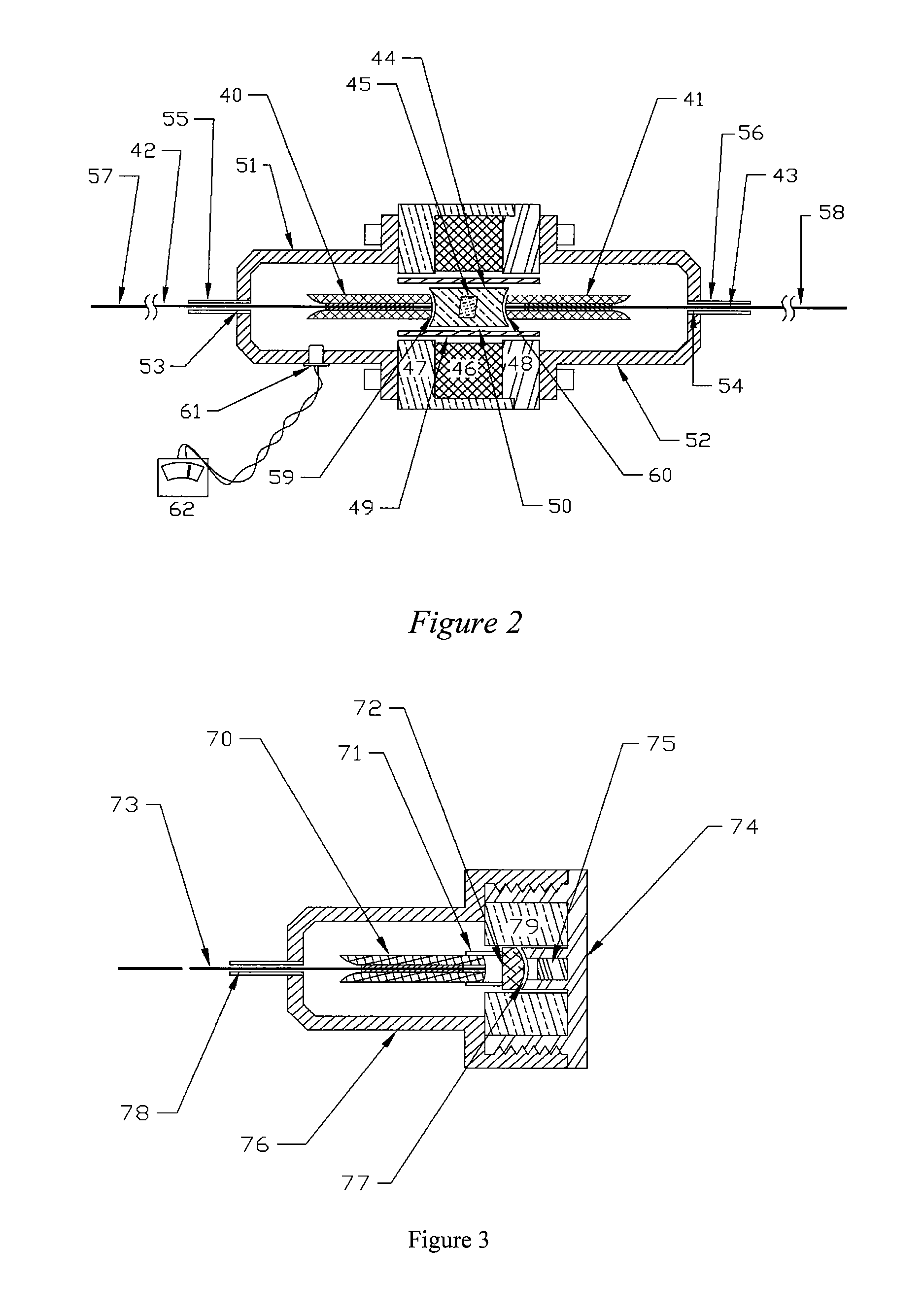
Device for measuring the focal distance of a thermal lens
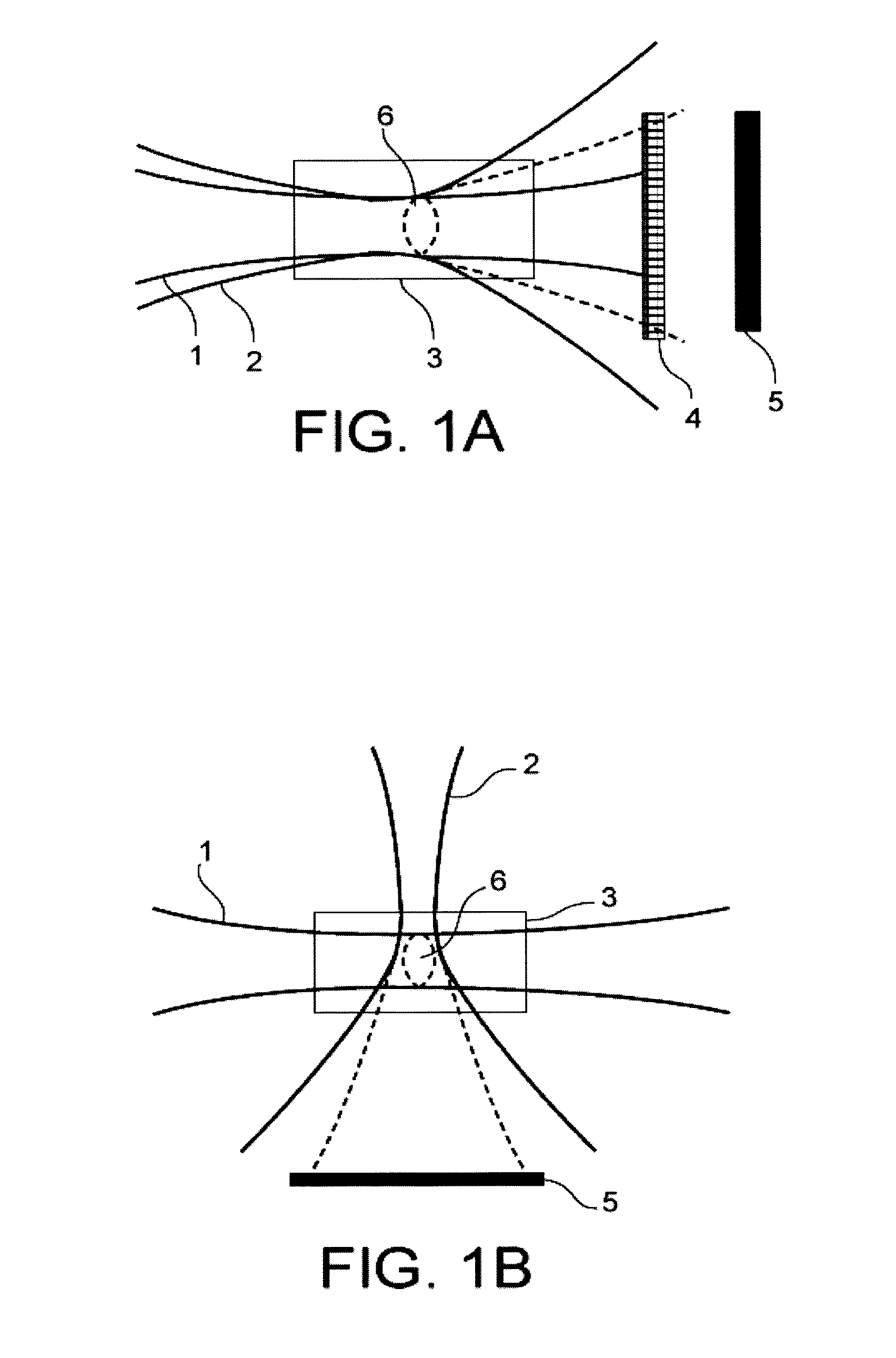
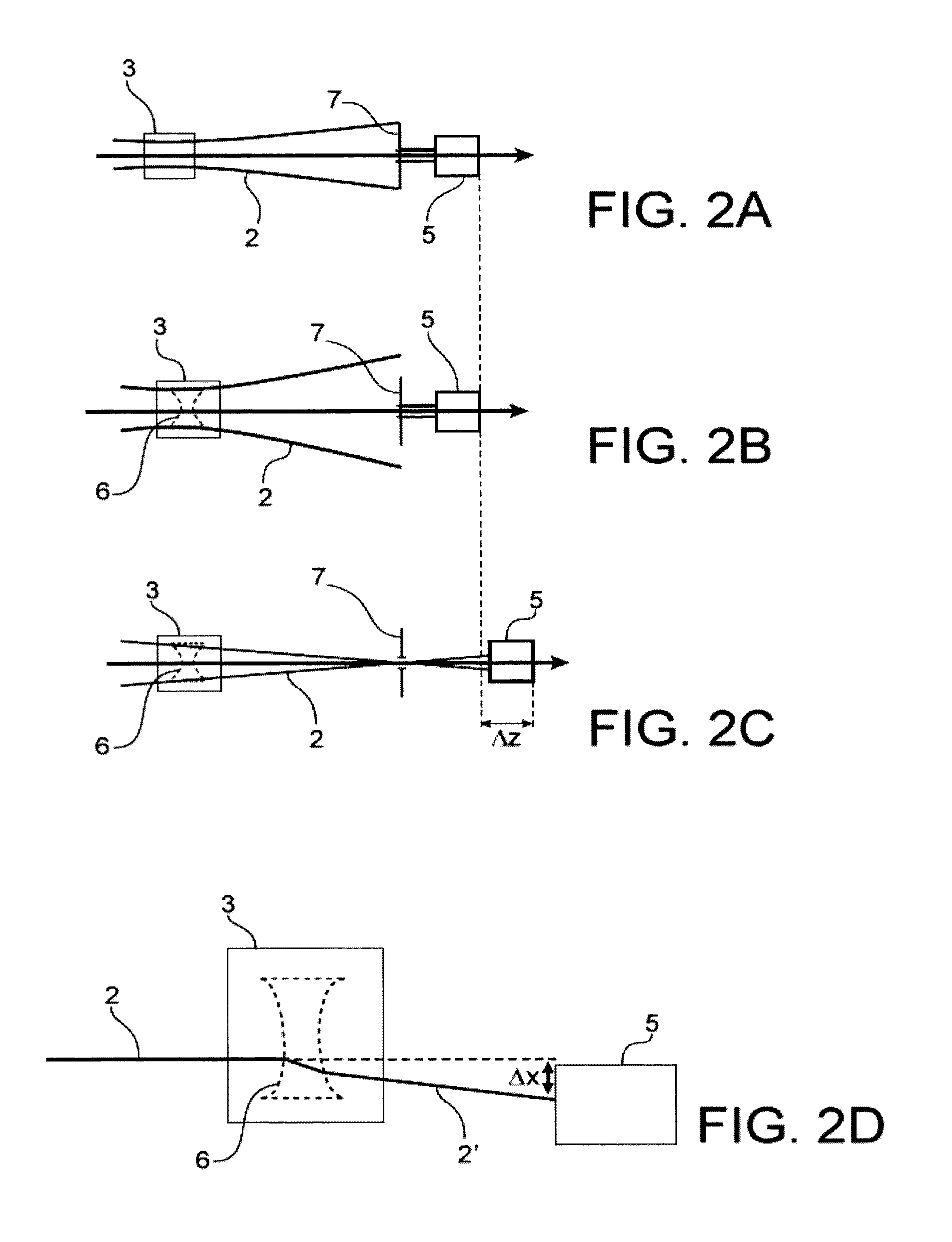
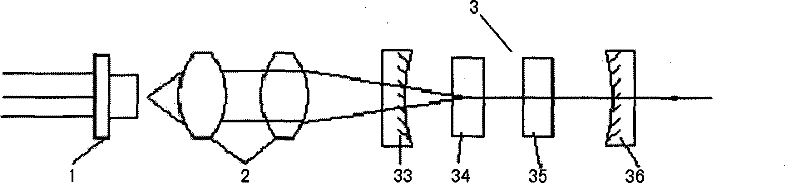
ActiveUS20120026485A1Small sizePhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansOpticsExcitation beam
A method for measuring focal distance of a thermal lens located in an analyte, the method including: providing an exciting optical beam passing through the analyte and creating the thermal lens therein; emitting a coherent probe optical beam passing through the analyte and being propagated substantially perpendicular to the exciting optical beam; intercepting the probe optical beam by a detector after passing through the analyte; focusing the probe optical beam upstream or downstream of the thermal lens such that only a fraction of the probe optical beam passes through the thermal lens; acquiring an interference image by the detector; and processing the interference image to calculate the focal distance of the thermal lens. Such a method may find application in physico-chemical analysis of the analyte.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
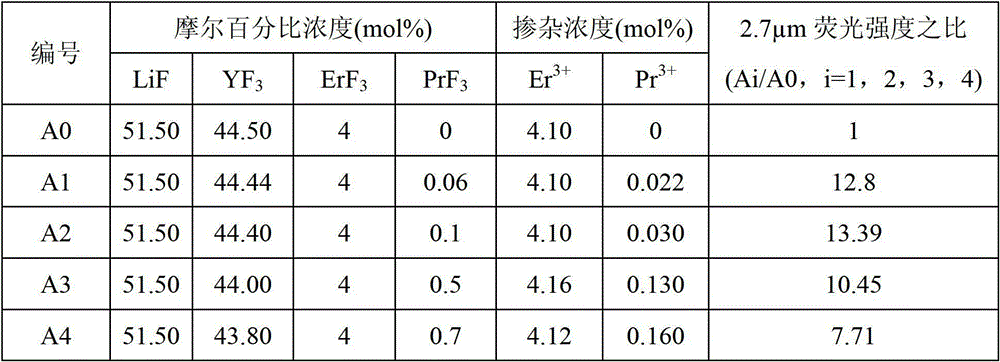
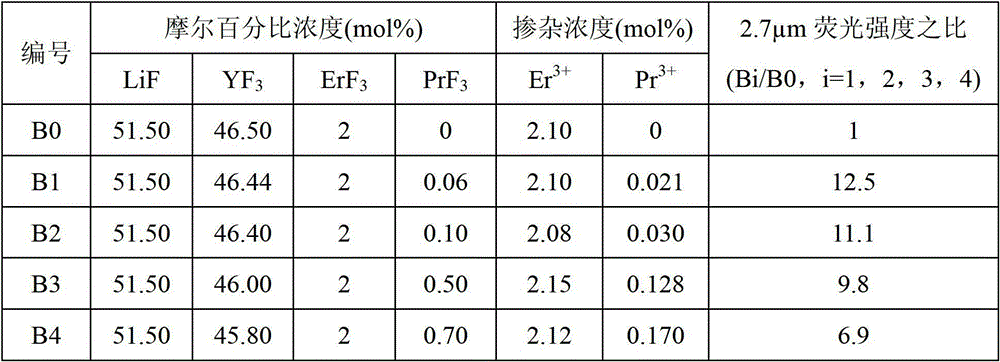
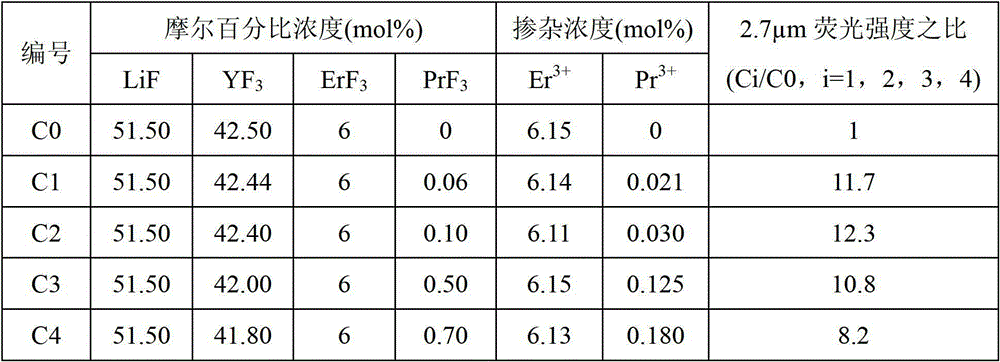
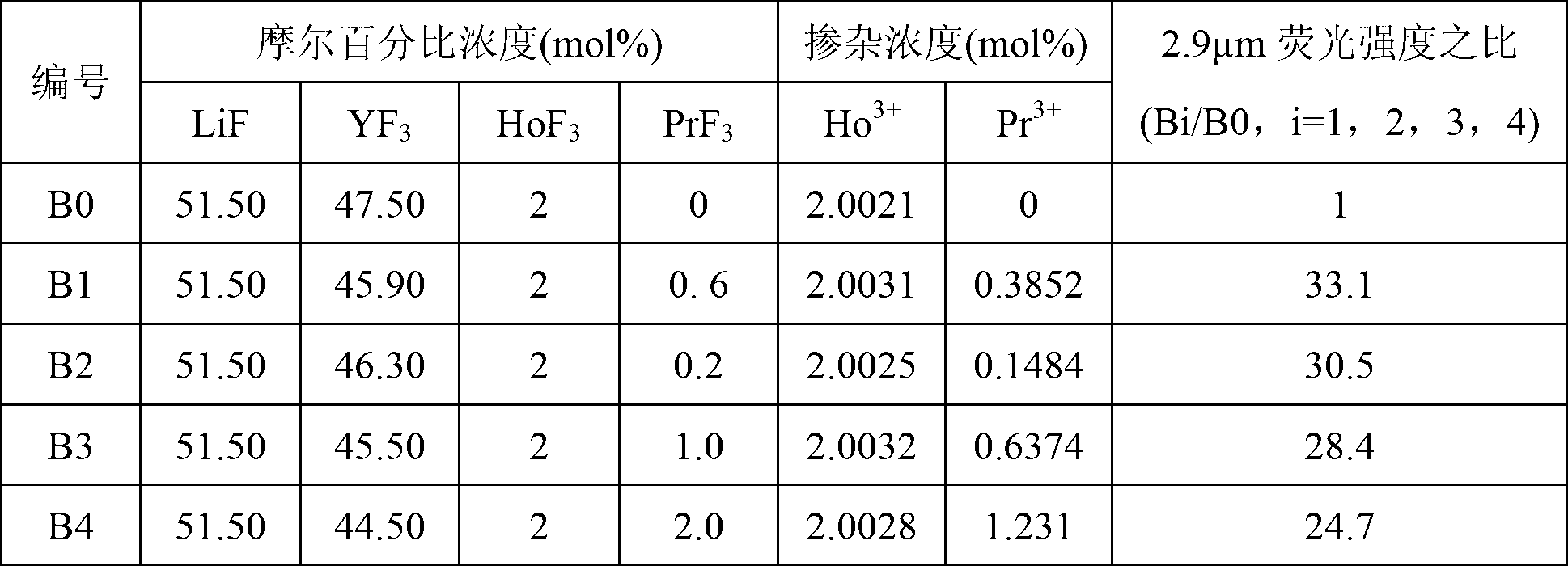
Er<3+>/Pr<3+> co-doped yttrium lithium fluoride monocrystal and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102978700ASensitizationEfficient transferPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsFluorescenceWater vapor
The invention discloses an Er<3+> / Pr<3+> co-doped yttrium lithium fluoride monocrystal and a preparation method thereof. The yttrium lithium fluoride monocrystal is a rare earth ion Er<3+> / Pr<3+> co-doped monocrystal; and the molecular formula is LiY(1-x-y)ErxPryF4, wherein x is greater than or equal to 0.010 and less than or equal to 0.085, and y is greater than or equal to 0.0001 and less than or equal to 0.008. The yttrium lithium fluoride monocrystal has the advantages of high emission efficiency of fluorescence of 2.7 microns and high transmittance in intermediate infrared ray, has better thermal, mechanical and chemical stabilities than those of glass state materials and has the characteristics of low phonon energy, high optical transmittance of wavebands with width of 300-5500nm, less color center forming amount, low thermal lens effect and the like, thereby being more easily processed and more suitably used in laser devices. In the preparation method disclosed by the invention, a sealing crucible falling technology is used, so that the operation is simple; the raw material is fluorated at high temperature in a sealed water-free and oxygen-free environment, so that the crystal is isolated from air and water vapor during the growth; and therefore, the high-quality Er<3+> / Pr<3+> co-doped LiYF4 monocrystal containing little OH<-> ion and oxide is obtained.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Cooling method for gain medium in solid laser and low interior heat solid laser
InactiveCN101505030AReduce the temperatureExcellent refrigeration efficiencyActive medium materialSequence signalFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for cooling a gain medium in a solid laser and a solid laser having lower internal heat. A laser pump light source and a refrigerating pump light source which can adjust light intensity, pulse width and repetition rate respectively are arranged. The gain medium corresponding to the laser pump light source and a refrigerating medium corresponding to the refrigerating pump light source are the same block of crystal mixed with rare earth ions. Two physical processes of laser refrigeration and laser oscillation are controlled to alternatively or synchronously operate by a sequence signal circuit and a gain switch so as to approximately counteract the refrigerating capacity of superradiance on the media and the heat generated by the laser oscillation, to make the laser in a laser resonance cavity transmitted along the crystal 'apyrexia' direction, and to reduce the thermal lens effect caused by a residual temperature gradient in the crystal . The method converts waste heat in the gain medium into an anti-Stocks scattering photon which has fast radiation and small residual temperature gradient. A main pump light beam and an auxiliary pump light beam (pulse) are used for inducing the crystal to emit the superradiance. The refrigerating efficiency of the superradiance is better than that of fluorescence in the prior laser refrigerators.
Owner:谭吉春
Method for rapid imaging of absorption defect distribution on surface of large-diameter optical element
ActiveCN109444166AHigh sensitivityFast imagingMaterial heat developmentOptically investigating flaws/contaminationRapid imagingHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for rapid imaging of absorption defect distribution on the surface of a large-diameter optical element. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out collimation and beam expanding of high-energy pulse laser to form a large-size excitation light spot for radiation heating on an optical element, enabling absorption defects on the surface and the subsurfaceof the optical element to be at transient temperature distribution and refractive index distribution; after certain time delay, carrying out collimation and beam expanding of another beam of high-energy pulse laser to form a large-size detection light spot which penetrates through an identical area radiated by the optical element, and recording diffraction light field distribution of the light spot by using a CCD; controlling time delay between excitation and detection laser pulses and analyzing characteristics of diffraction light field images recorded by using the CCD, thereby confirming whether the radiated area of the optical element has absorption defects or not and corresponding characteristics. By adopting the method, advantages that a conventional optical-thermal lens technique ishigh in detection sensitivity, high in resolution ratio, and the like are retained, a single-time detection area can be greatly increased, and rapid detection on absorption defect distribution of large-diameter optical elements is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONIC SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method of distribution of absorption of laser crystal radial-direction non-uniform doping control pump light
InactiveCN103490278AAvoid the risk of falling off or even end face burstingImprove conversion efficiencyLaser output parameters controlActive medium materialPlane mirrorThin lens
The invention relates to a method of distribution of absorption of laser crystal radial-direction non-uniform doping control pump light. The method is characterized in that after the pump light output by an optical fiber coupling laser diode optical fiber output end is gathered by a coupling system, the light field of the pump light is distributed in a Gaussian mode or flat Gaussian mode; a pump light anti-reflection film and an oscillating high-reflection film are plated on the pump end face of a radial-direction non-uniform doping crystal, an output mirror is a plane mirror, and the output mirror and the oscillating light high-reflection film on the pump end face of the crystal form a flat resonant cavity; in the working process, a thermal lens formed in the crystal can be simply equivalent to a thin lens on the pump end face of the radial-direction non-uniform doping crystal, and the resonant cavity becomes a stable cavity through the gather effect of the thermal lens; under the condition that a pump light distribution area and an oscillating light distribution area are determined, the spatial overlapping of the pump light distribution area and the oscillating light distribution area are achieved through the radial-direction non-uniform doping optimization design of the laser crystal. According to the method, ideal space coupling efficiency and ideal beam quality can be achieved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Fan-type gas circulation high repetition frequency Raman cell
InactiveCN110600987AReduce CooldownWide range of choicesLaser using scattering effectsLaser cooling arrangementsLight beamCell wall
The invention discloses a novel Raman cell capable of reducing the thermal lens effect of high repetition frequency pump light during a gaseous medium propagation process. In the design, the outermostRaman cell wall is made of stainless steel, and a three-dimensional filler is disposed in the Raman cell. Gaps between the outer wall of the Raman cell and the built-in filler can be filled with a high-pressure gas, and have inconsistent widths. A fan unit is placed in one of narrow gaps. One of the remaining narrow gaps is selected as a light passage of the pump light. When high repetition frequency pump light is configured to pump a gaseous medium, the heat in the vicinity of the pump light gradually accumulates and generates a thermal lens effect to affect the beam quality of the output light. After an electric fan operates, the high-pressure gaseous medium in the gaps flows in a fixed direction, takes away the heat in the vicinity of the pump light, reduces the thermal lens effect inthe Raman cell so as to improve the conversion efficiency of Raman light. The novel Raman cell improves the Raman light conversion efficiency and beam quality by reducing the thermal effect, and has bright application prospects.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser with highly efficient gain medium
InactiveUS7720121B2Increase pump powerLess thermal lensingActive medium materialSemiconductor lasersHigh energyVanadate
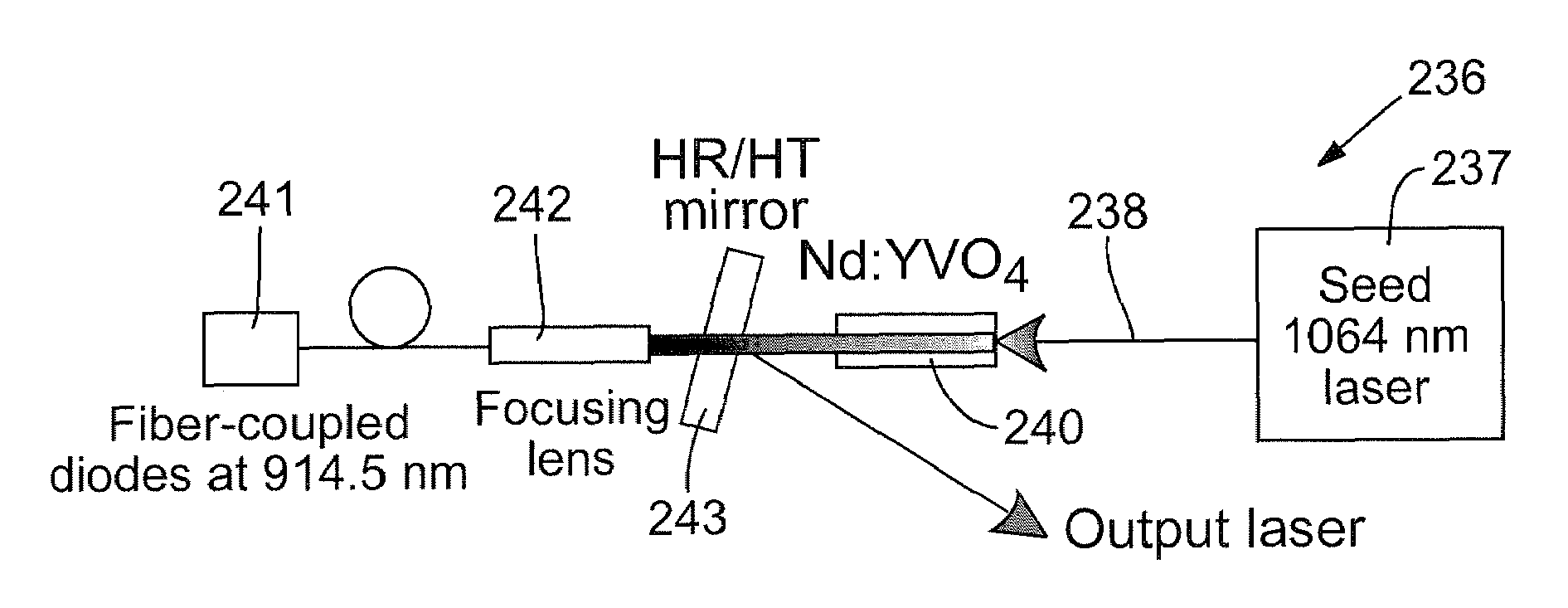
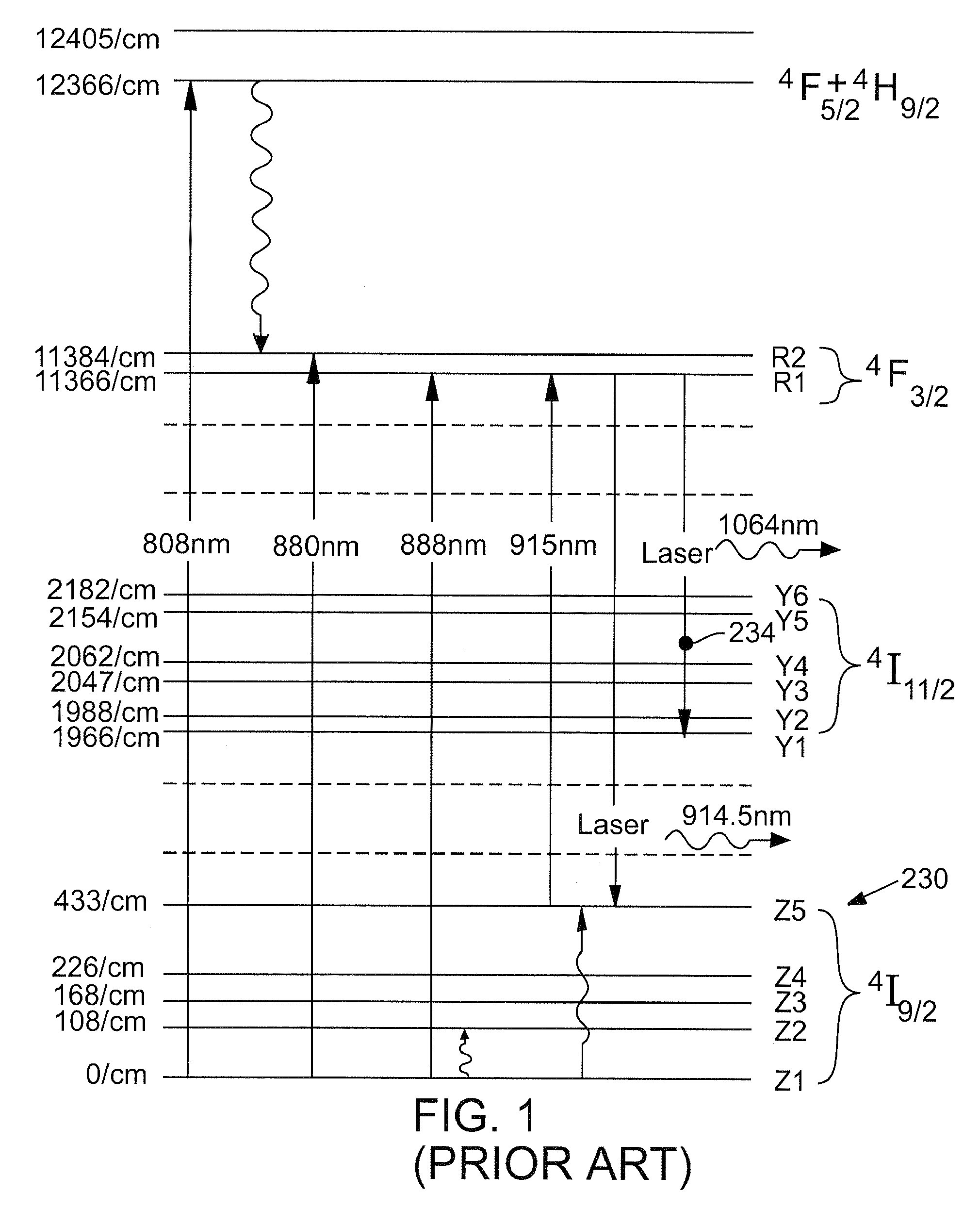
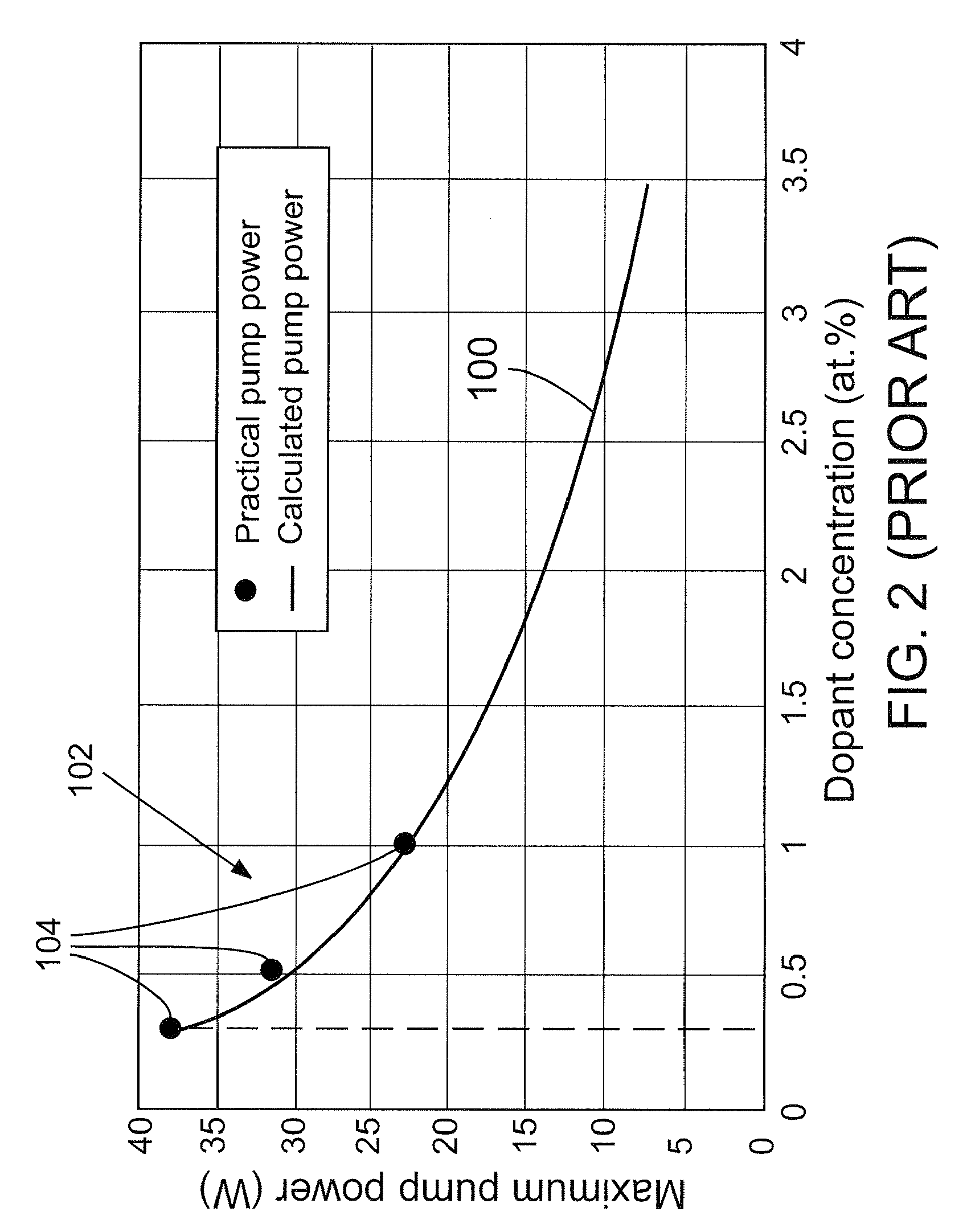
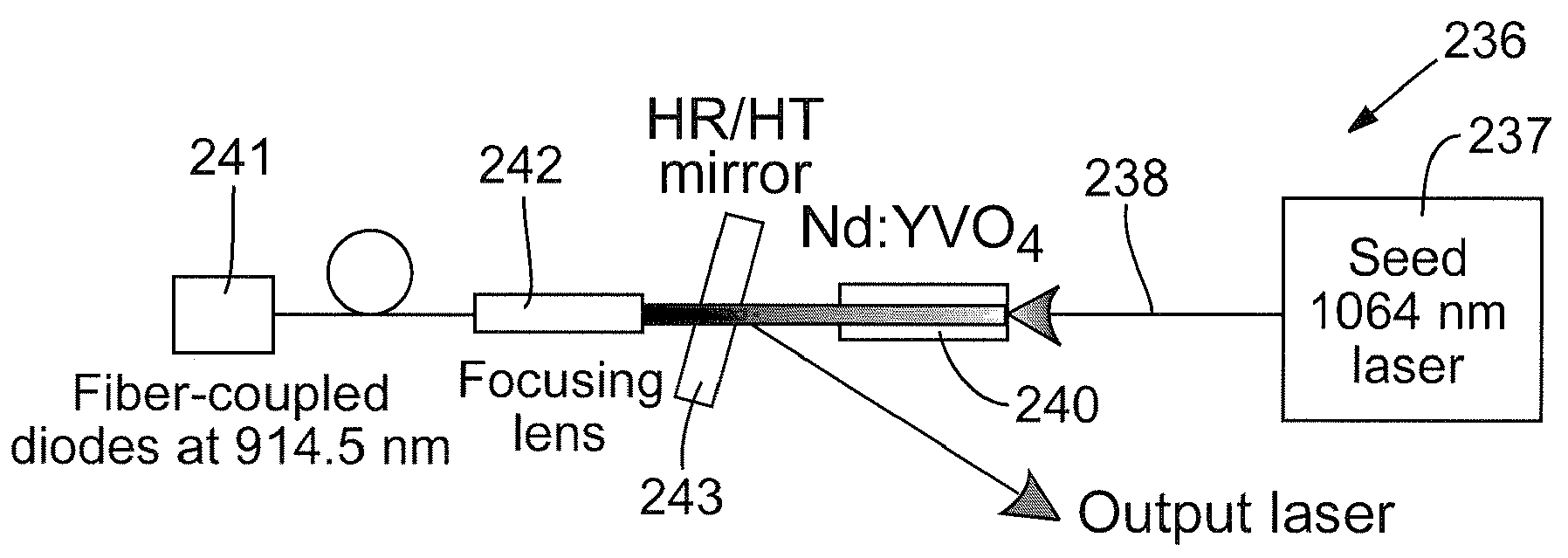
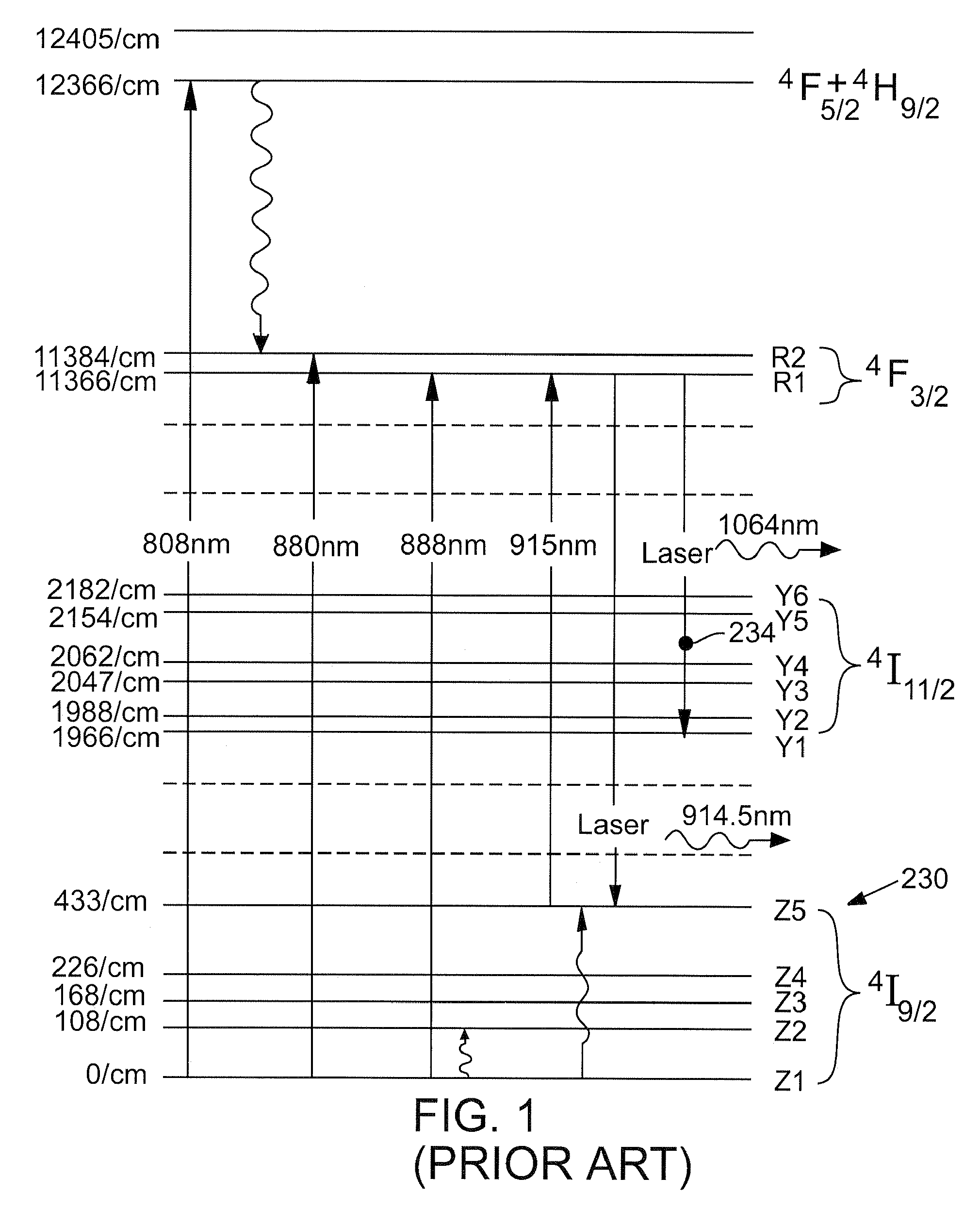
High-power, diode-pumped solid state (DPSS) pulsed lasers are preferred for applications such as micromachining, via drilling of integrated circuits, and ultraviolet (UV) conversion. Nd:YVO4 (vanadate) lasers are good candidates for high power applications because they feature a high energy absorption coefficient over a wide bandwidth of pumping wavelengths. However, vanadate has poor thermo-mechanical properties, in that the material is stiff and fractures easily when thermally stressed. By optimizing laser parameters and selecting pumping wavelengths and doping a concentration of the gain medium to control the absorption coefficient less than 2 cm−1 such as the pumping wavelength between about 910 nm and about 920 nm, a doped vanadate laser may be enhanced to produce as much as 100 W of output power without fracturing the crystal material, while delivering a 40% reduction in thermal lensing.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
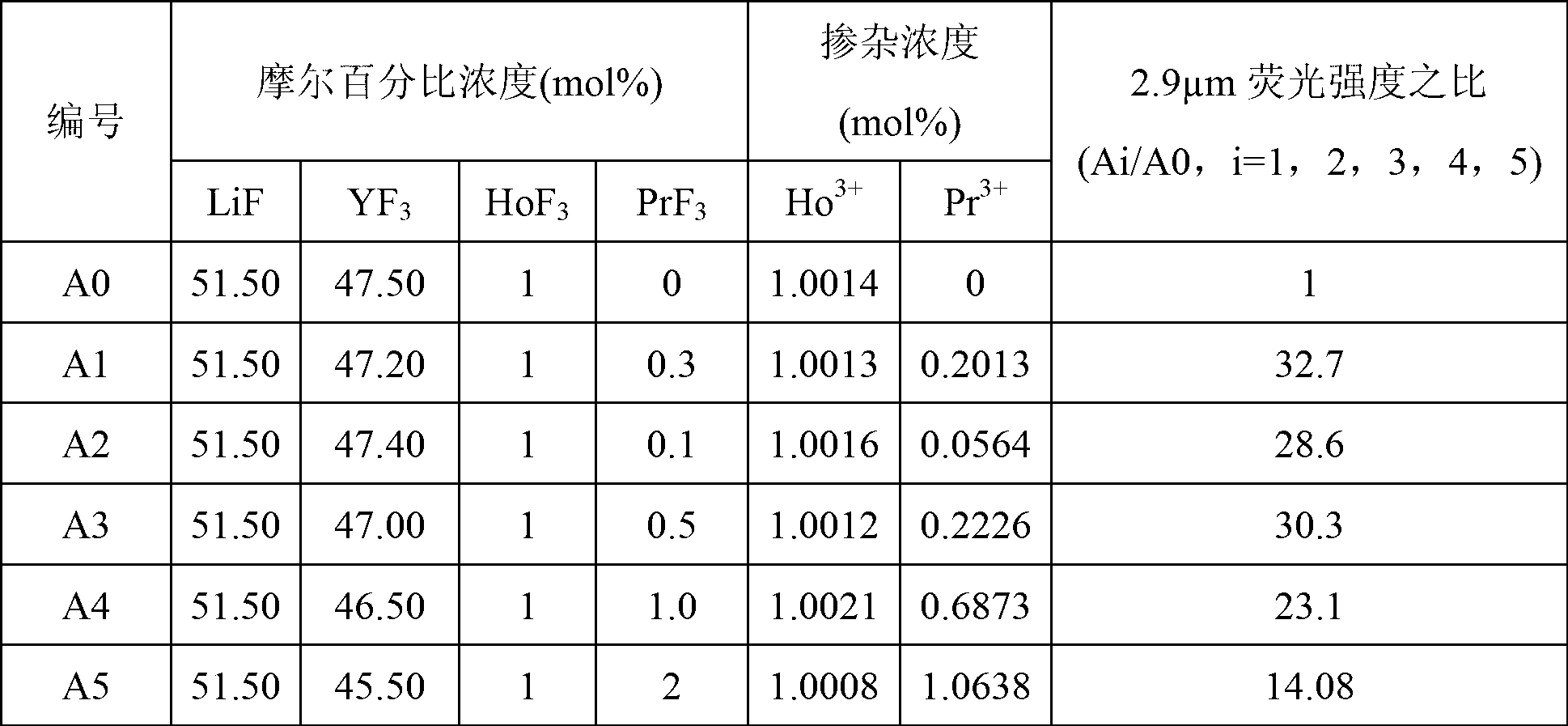
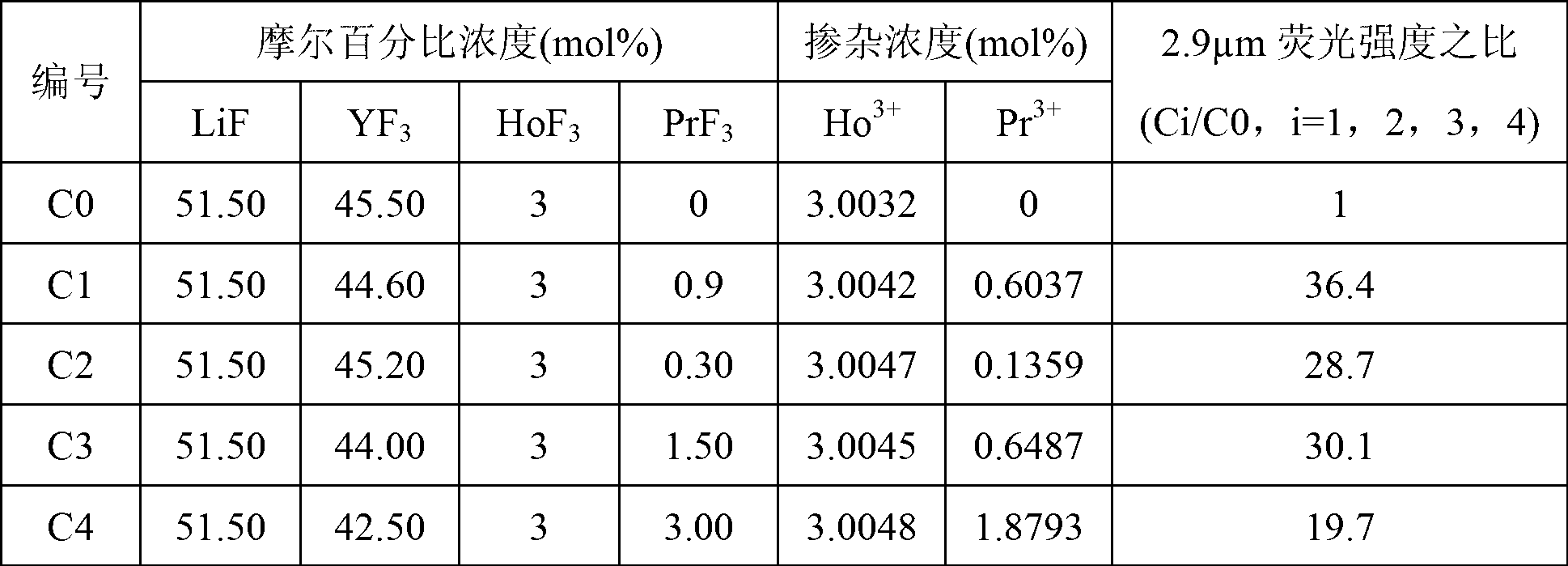
Ho<3+>/Pr<3+> codoping lithium yttrium fluoride monocrystal and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103014854AHigh phonon energyHigh optical transmittancePolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsFluorescenceChemical stability
The invention discloses a Ho<3+> / Pr<3+> codoping lithium yttrium fluoride monocrystal and a preparation method thereof. The lithium yttrium fluoride monocrystal is a rare-earth iron Ho<3+> / Pr<3+> codoping monocrystal; the molecular formula of the lithium yttrium fluoride monocrystal is LiY(1-x-y)HoxPryF4, wherein x is more than and equal to 0.004 or less than and equal to 0.08, and y is more than and equal to 0.0002 or less than and equal to 0.01. The lithium yttrium fluoride monocrystal disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high efficiency of 2.9 mu m fluorescence emission, high intermediate-infrared transmittance, more excellent thermotic, mechanical and chemical stability compared with those of a glass-state material, low phonon energy, high optical transmissibility at a 300-5500 nanometer broadband, small color center forming amount, low thermal lens effect, and the like, and is easier to process and more suitable for a laser device. The preparation method disclosed by the invention adopts a sealing crucible descent method technology, is easy to operate, carries out high-temperature fluorination treatment on a raw material and obtains the high-quality Ho<3+> / Pr<3+> codoping LiYF4 monocrystal almost without -OH ions or oxides by insulating the monocrystal from air and vapors in the growing process by adopting a water-insulated oxygen-insulated sealing environment.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Magnetooptical material, manufacturing method therefor, and magnetooptical device
ActiveCN105531619ANo deterioration in qualityPolycrystalline material growthFrom solid stateFiberLaser light
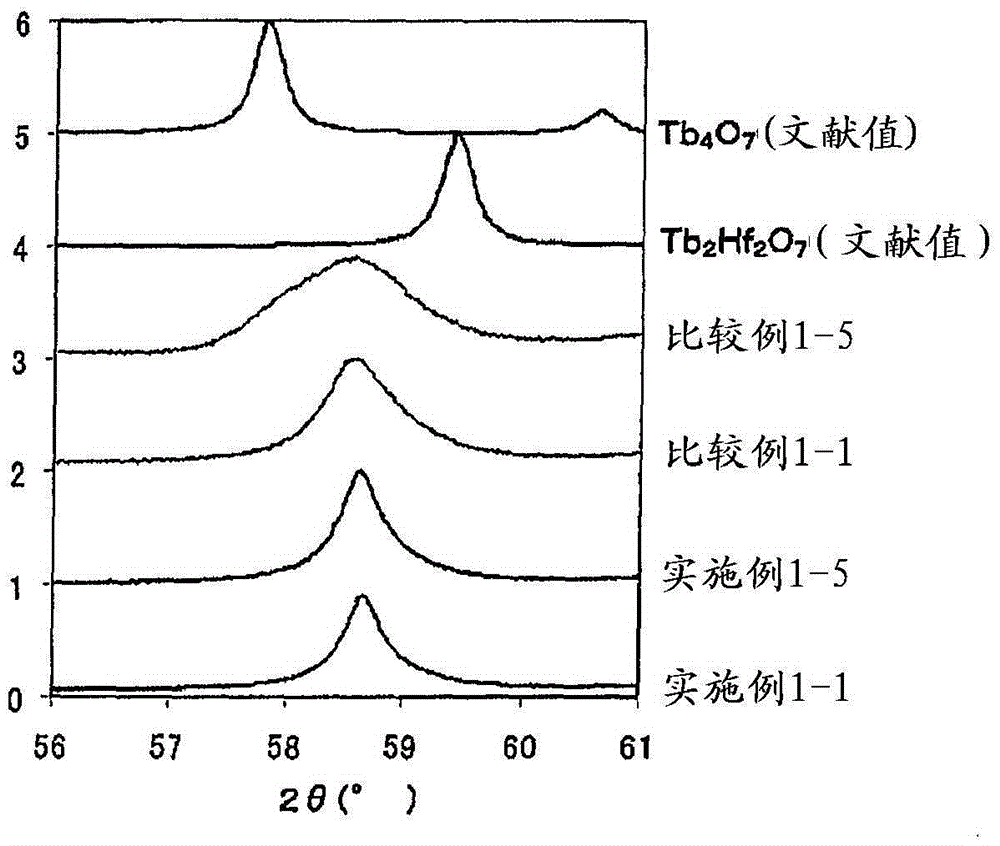
This invention provides a transparent magnetooptical material that is suitable for use in a magnetooptical device such as an optical isolator. Said magnetooptical material comprises either a transparent ceramic consisting primarily of a complex oxide that can be represented by formula (1) or a single crystal of such a complex oxide. Said magnetooptical material does not absorb fiber-laser light in the 0.9-1.1 mum wavelength range, does not cause heat lensing, and has a higher Verdet constant than TGG crystals, with a Verdet constant of at least 0.14 min / (Oe.cm) at a wavelength of 1,064 nm. (1) Tb2R2O7 (In formula (1), R represents one or more elements selected from among the group consisting of silicon, germanium, titanium, tantalum, tin, hafnium, and zirconium (but not silicon only, germanium only, or tantalum only)).
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM CO LTD
NONLINEAR OPTICAL CdSiP2 CRYSTAL AND PRODUCING METHOD AND DEVICES THEREFROM
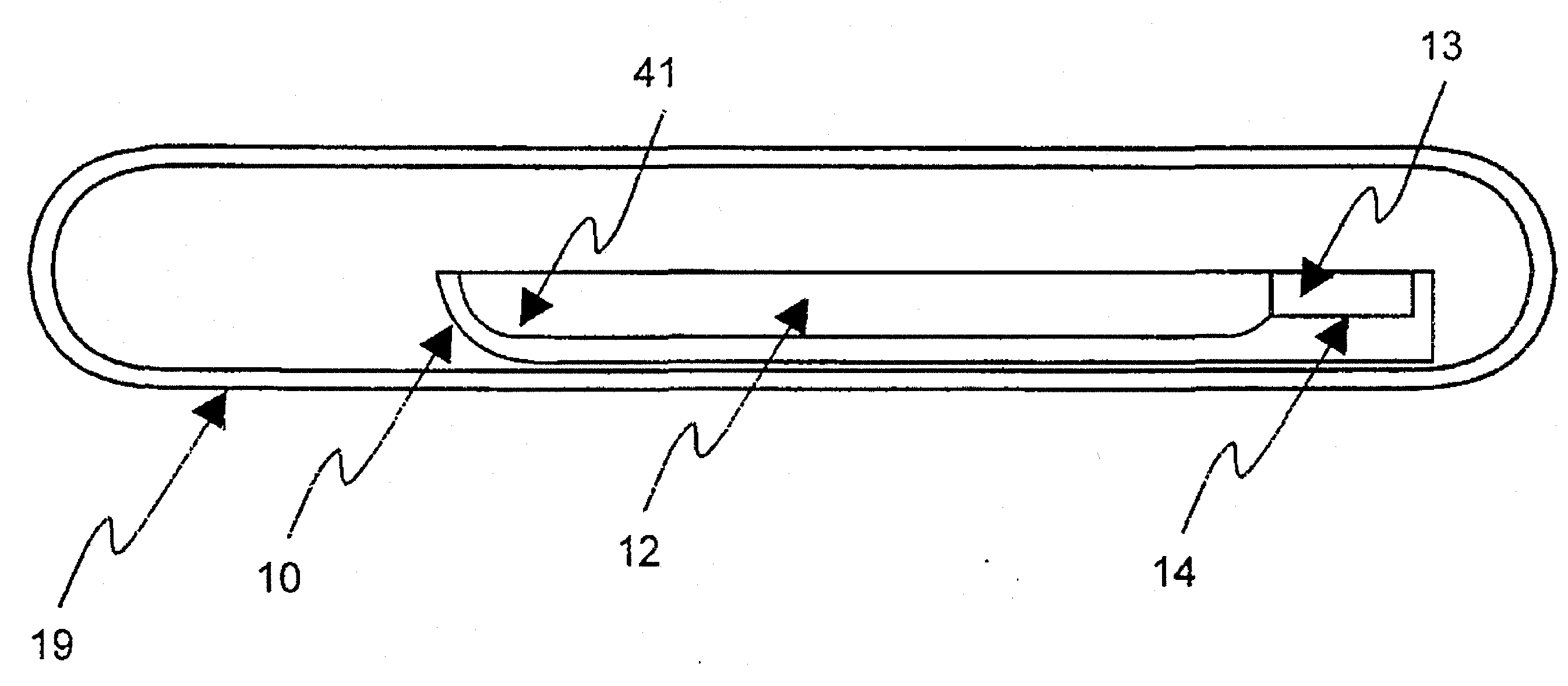
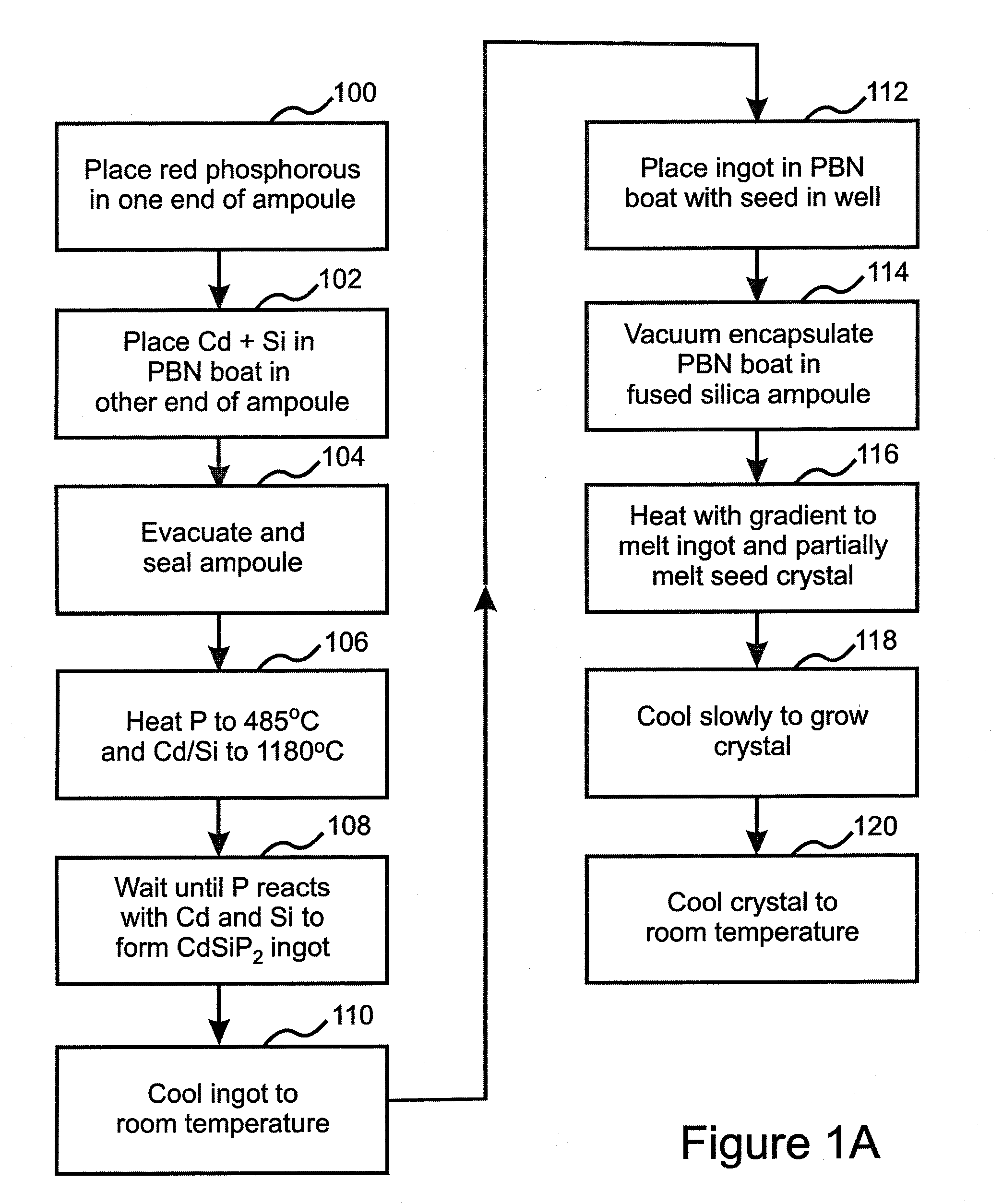
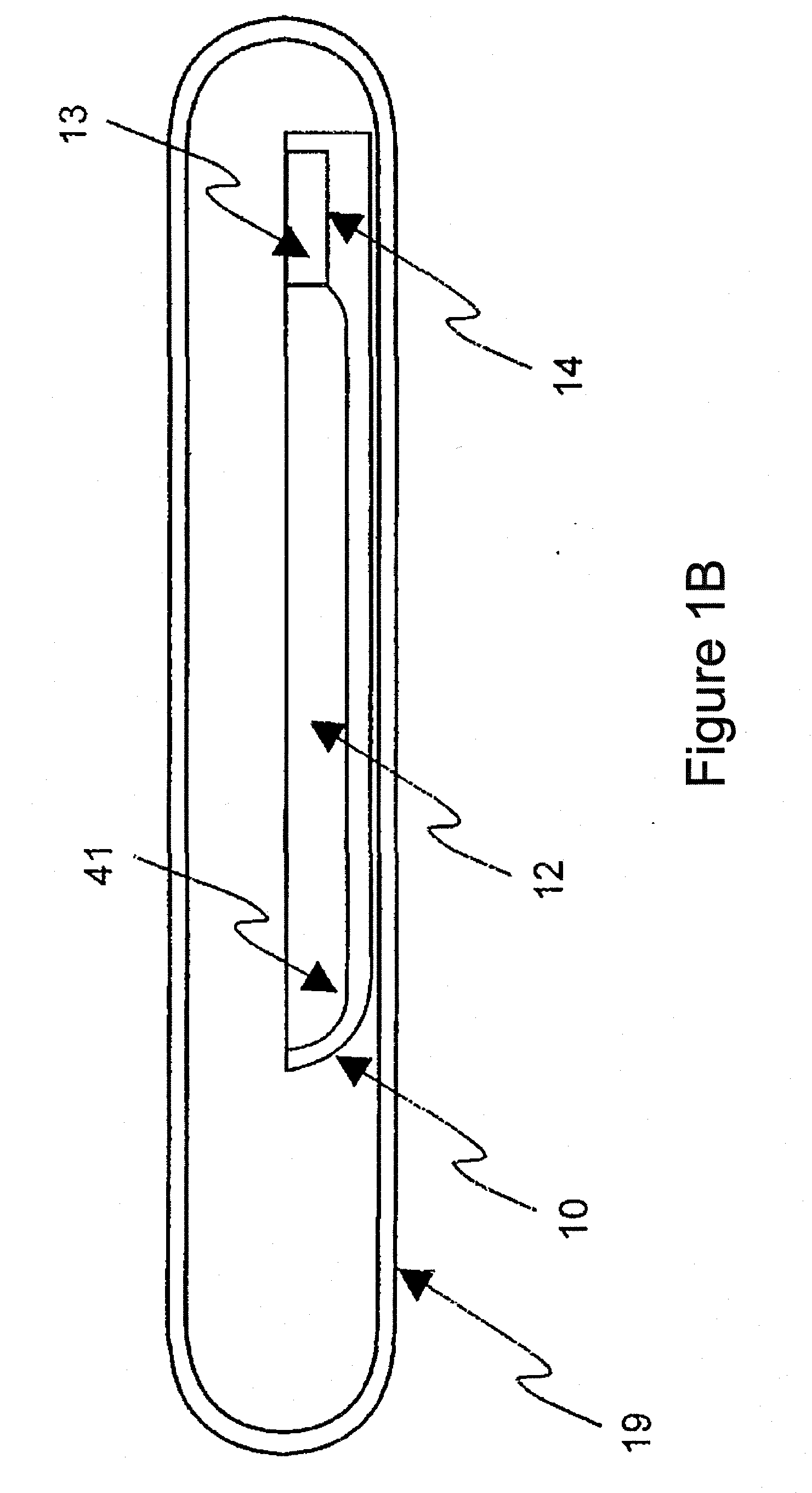
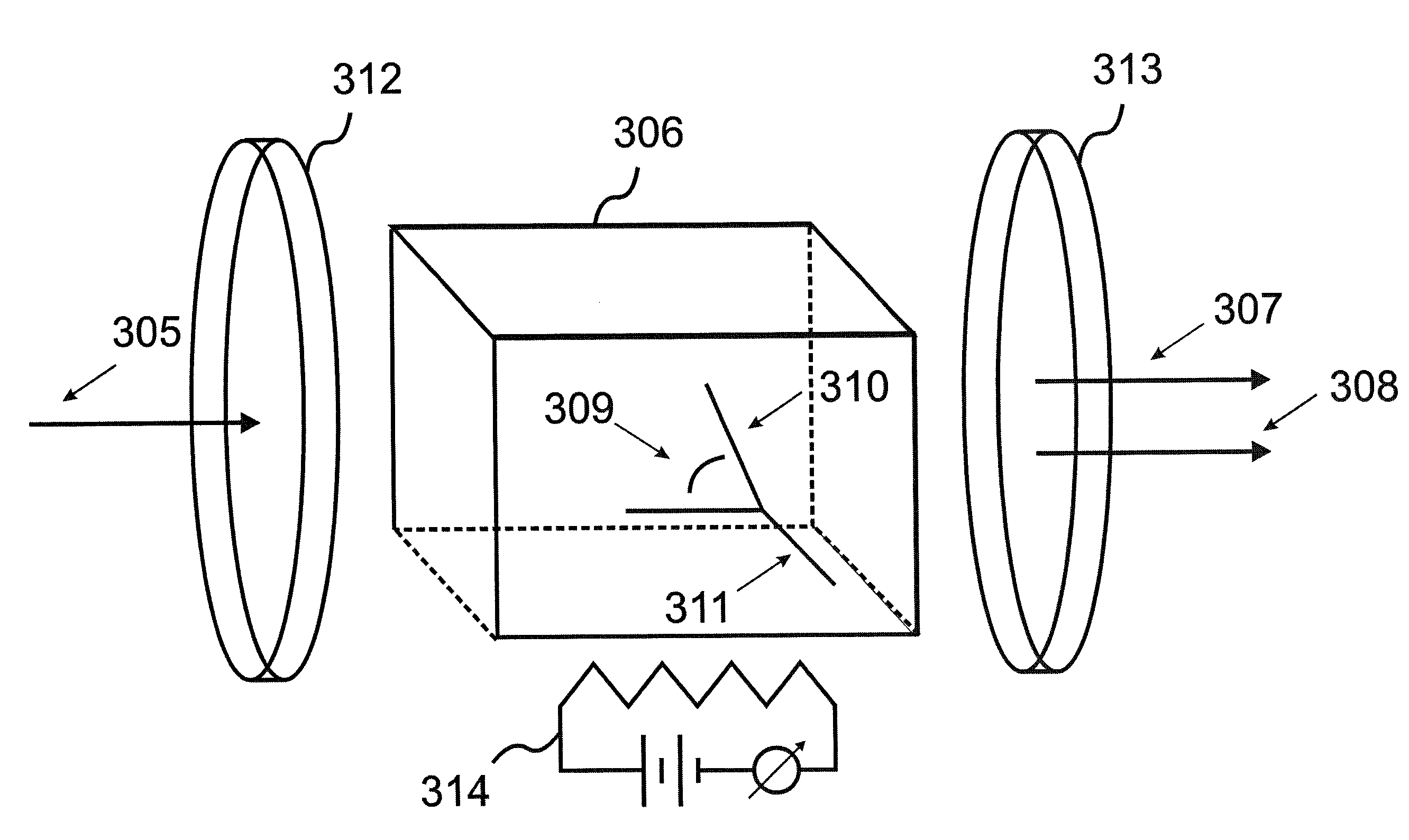
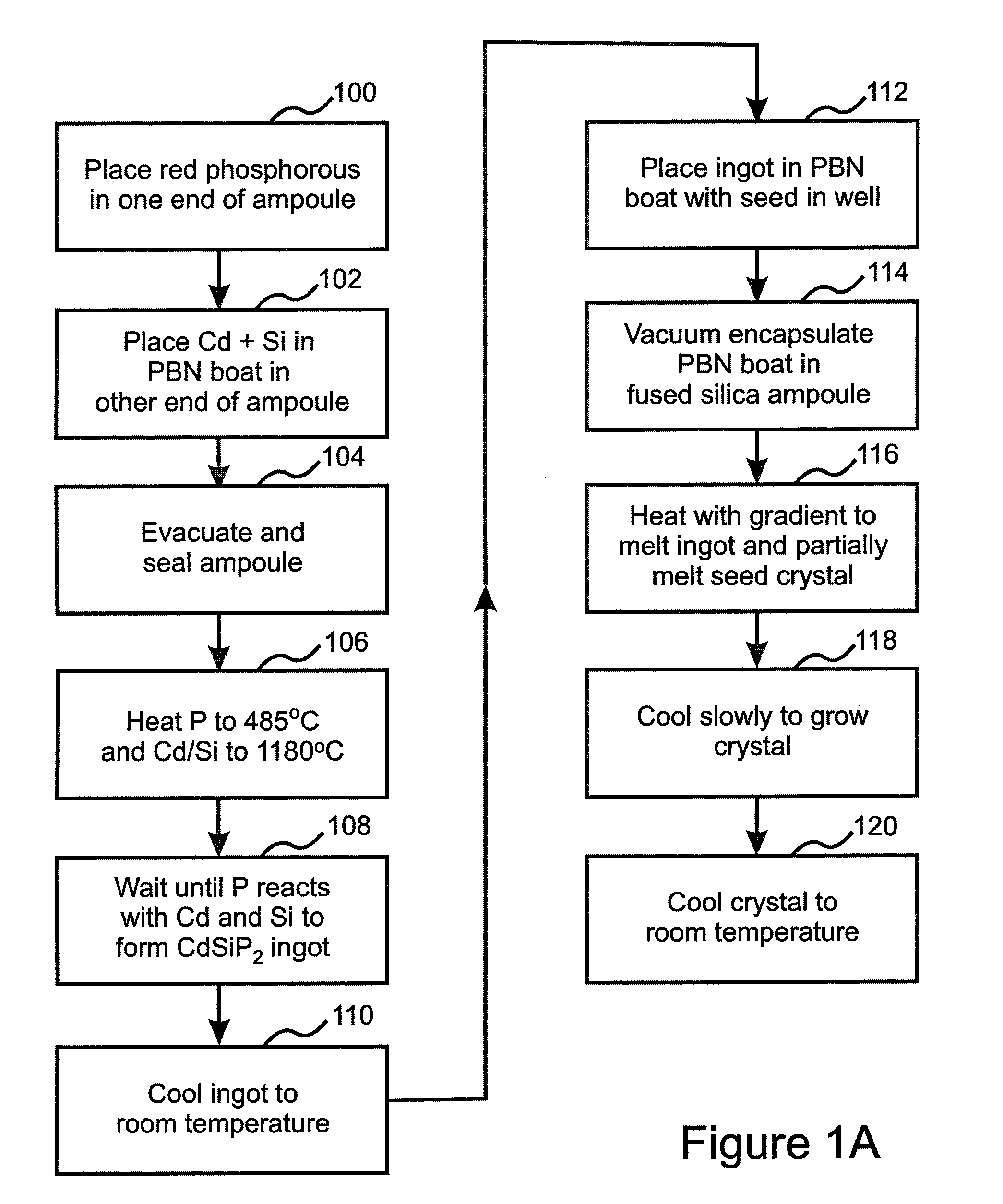
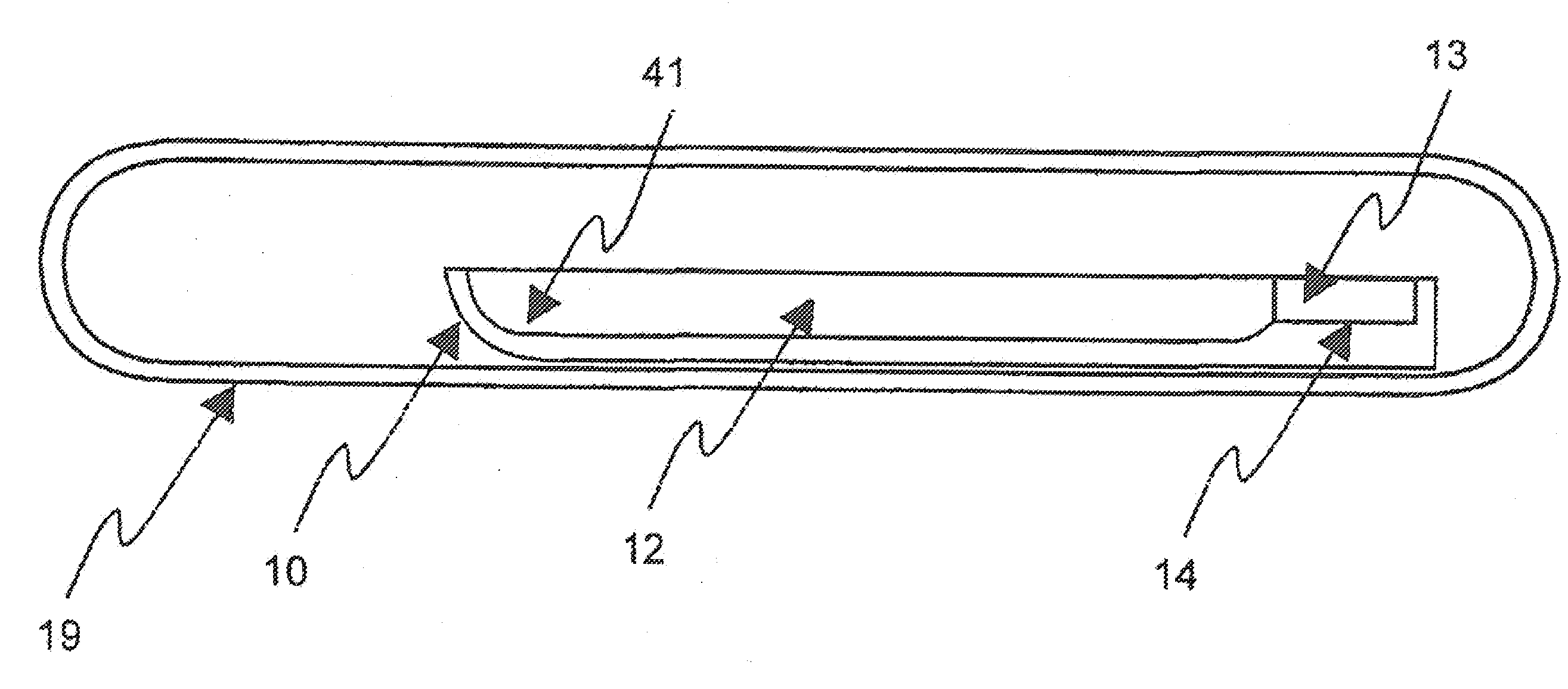
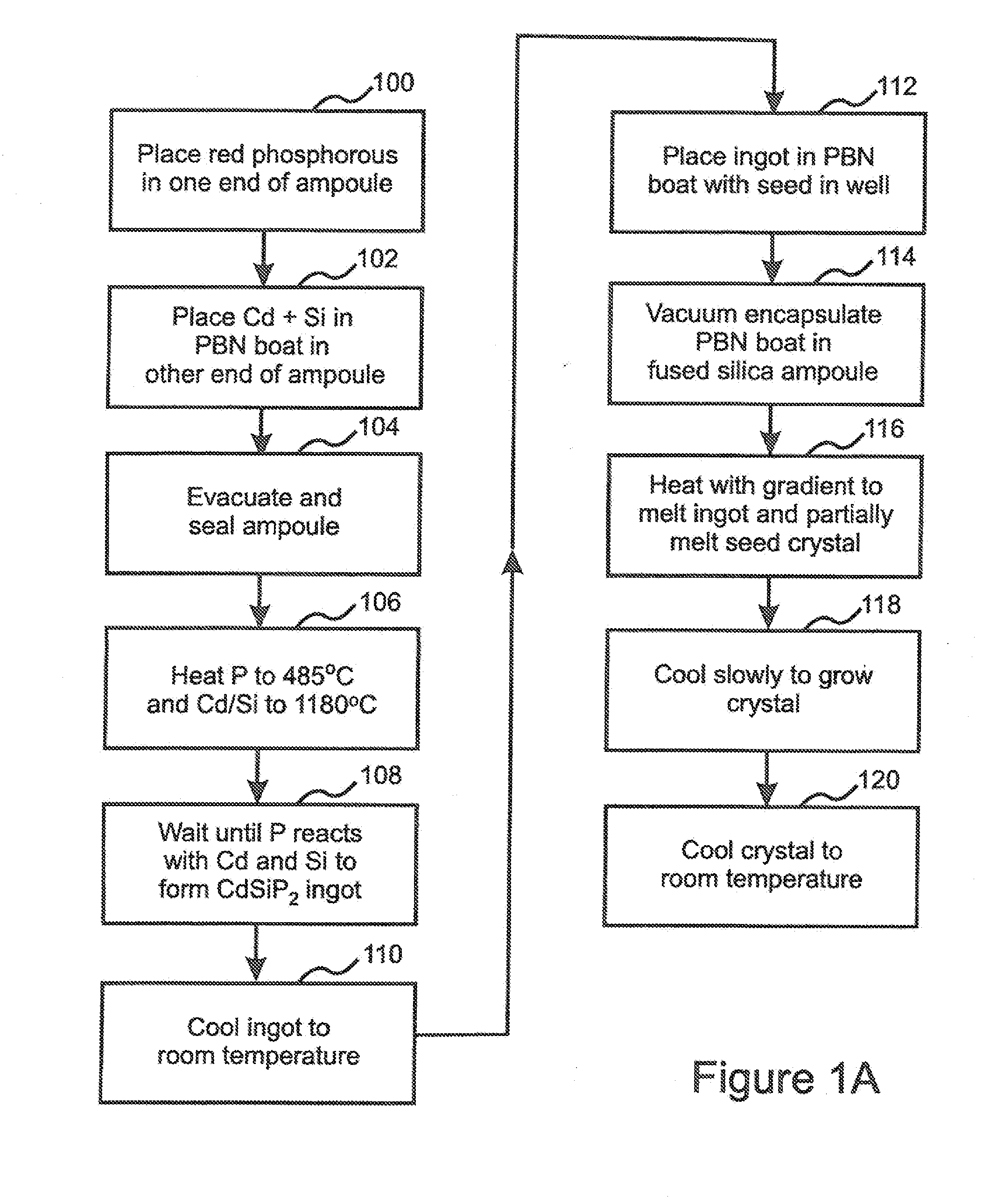
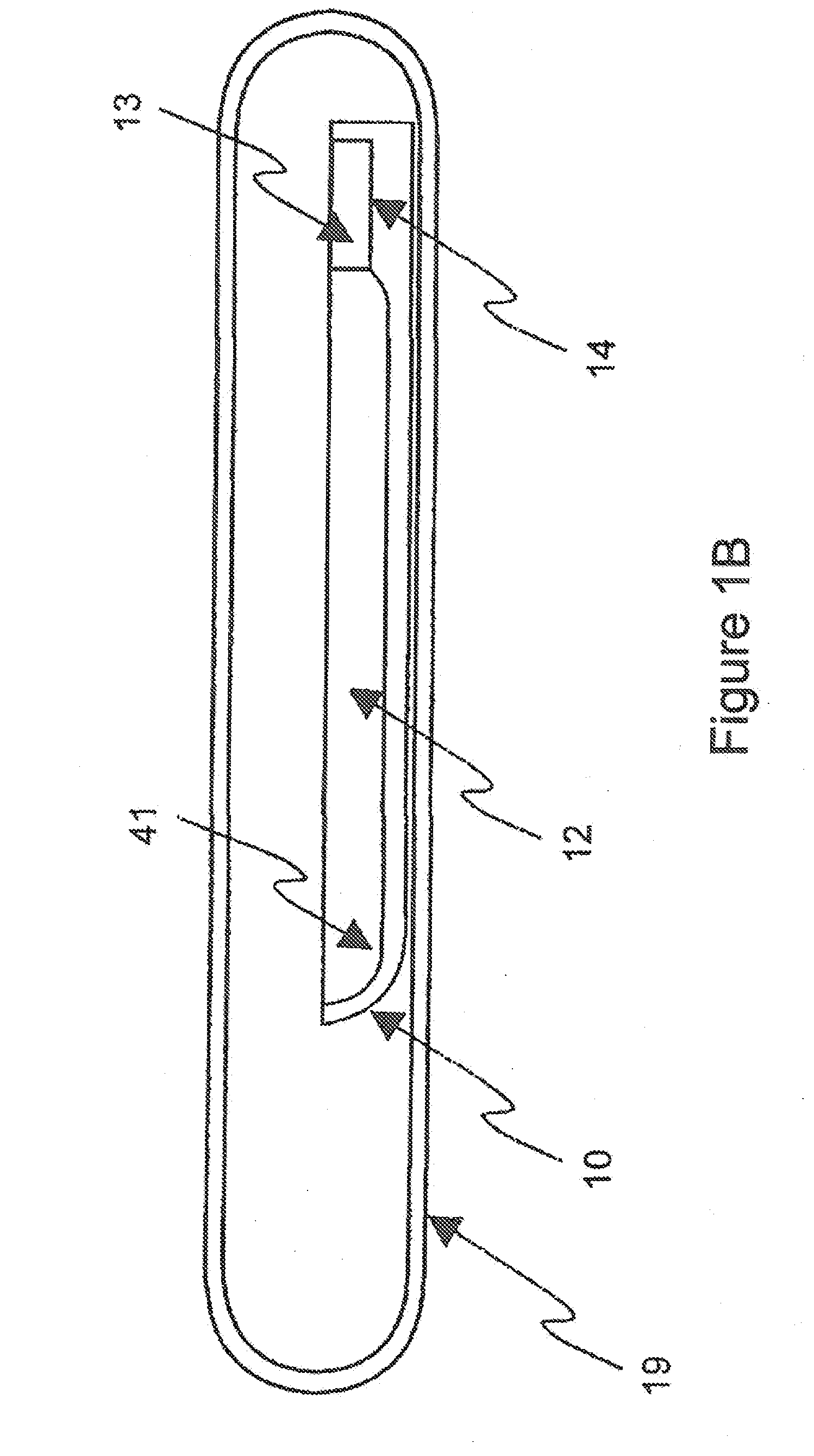
ActiveUS20110054451A1Improve optical qualitySufficient optical qualityLaser detailsSurgical instrument detailsLaser scalpelNd:YAG laser
CdSiP2 crystals with sizes and optical quality suitable for use as nonlinear optical devices are disclosed, as well as NLO devices based thereupon. A method of growing the crystals by directional solidification from a stoichiometric melt is also disclosed. The disclosed NLO crystals have a higher nonlinear coefficient than prior art crystals that can be pumped by solid state lasers, and are particularly useful for frequency shifting 1.06 μm, 1.55 μm, and 2 μm lasers to wavelengths between 2 μm and 10 μm. Due to the high thermal conductivity and low losses of the claimed CdSiP2 crystals, average output power can exceed 10 W without severe thermal lensing. A 6.45 μm laser source for use as a medical laser scalpel is also disclosed, in which a CdSiP2 crystal is configured for non-critical phase matching, pumped by a 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser, and temperature-tuned to produce output at 6.45 μm.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Nonlinear optical CdSiP2 crystal and producing method and devices therefrom
ActiveUS8379296B2Increase heightQuality improvementLaser detailsSurgical instrument detailsLaser scalpelNd:YAG laser
CdSiP2 crystals with sizes and optical quality suitable for use as nonlinear optical devices are disclosed, as well as NLO devices based thereupon. A method of growing the crystals by directional solidification from a stoichiometric melt is also disclosed. The disclosed NLO crystals have a higher nonlinear coefficient than prior art crystals that can be pumped by solid state lasers, and are particularly useful for frequency shifting 1.06 μm, 1.55 μm, and 2 μm lasers to wavelengths between 2 μm and 10 μm. Due to the high thermal conductivity and low losses of the claimed CdSiP2 crystals, average output power can exceed 10 W without severe thermal lensing. A 6.45 μm laser source for use as a medical laser scalpel is also disclosed, in which a CdSiP2 crystal is configured for non-critical phase matching, pumped by a 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser, and temperature-tuned to produce output at 6.45 μm.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
High intensity and high power solid state laser amplifying system and method
InactiveUS20050271111A1Increase powerEffective coolingExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionLight beamOptoelectronics
Systems and methods are provided for achieving high power and high intensity laser amplification. In a four-pass optical amplifying system, a linear polarized optical beam is directed by various optical elements four times through an optical amplifier. The optical amplifier is transversely pumped by a pumping energy source that includes laser diode arrays. The pumping module and the other optical components are provided to counteract thermal lensing effects, induced thermal birefringence effects and to achieve enhanced amplification and efficiencies.
Owner:JMAR LLC A DELAWARE LLC
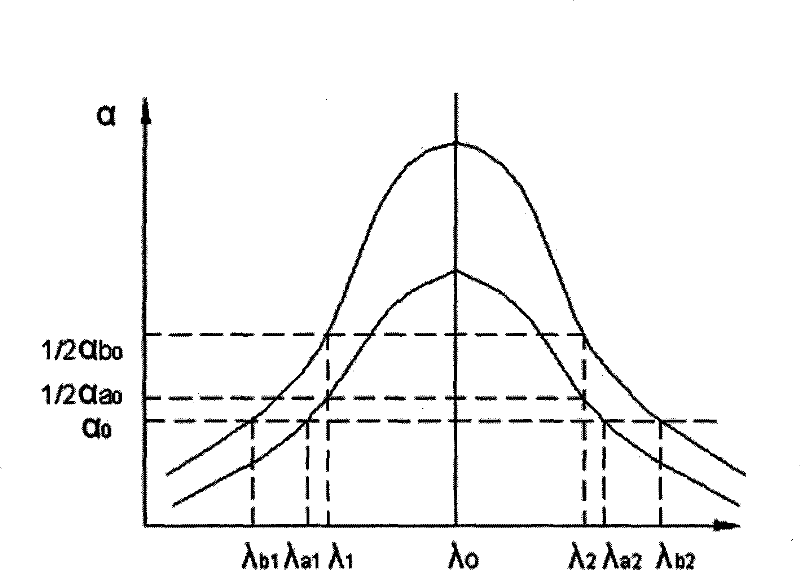
Frequency-doubling crystal temperature gradient compensation method temperature control apparatus
InactiveCN1972037AImprove frequency doubling efficiencyImprove output stabilityLaser detailsTemperature control using electric meansTemperature controlThermodynamics
This invention relates to one temperature control device for high power solid laser double frequency transistor temperature gradient compensation, which forms one dimension temperature gradient from top to down in different temperature point by combining control element transistor and forms temperature gradient different from top to down at double frequency transistor poison through adjusting laser work base wave to achieve the whole work temperature evenness.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optically controlled optical-path-switching apparatus, and method of switching optical paths
InactiveUS7301686B2Increase speedIncreased durabilityMultiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesLight beamDivergence angle
An optical signal optical path switching method comprising steps of using a thermal lens based on a distribution of refractive index produced reversibly caused by temperature increase generated in an area of the light-absorbing layer film of thermal lens forming devices 1, 2 and 3, that has absorbed control light beams 121, 122 and 123, and in the periphery thereof, causing the converged signal light beam to exit from the thermal lens forming device with an ordinary divergence angle when the control light beams 121, 122 and 123 have not been irradiated and no thermal lens has been formed, and causing the converged signal light beam to exit from the thermal lens forming device with a divergence angle larger than the ordinary divergence angle when the control light beams have been irradiated and a thermal lens has been formed, and causing the signal light beam to travel straight through holes 61, 62 and 63 of mirrors provided with the holes for the signal light beam to pass through when the control light beams have not been irradiated and no thermal lens has been formed, and changing the optical path by reflecting the signal light beam using the hole-provided mirror when the control light beams have been irradiated and a thermal lens has been formed.
Owner:DAINICHISEIKA COLOR & CHEM MFG CO LTD +1
Laser with highly efficient gain medium
InactiveUS20090245317A1Increase pump powerLess thermal lensingActive medium materialLaser detailsHigh energyVanadate
High-power, diode-pumped solid state (DPSS) pulsed lasers are preferred for applications such as micromachining, via drilling of integrated circuits, and ultraviolet (UV) conversion. Nd:YVO4 (vanadate) lasers are good candidates for high power applications because they feature a high energy absorption coefficient over a wide bandwidth of pumping wavelengths. However, vanadate has poor thermo-mechanical properties, in that the material is stiff and fractures easily when thermally stressed. By optimizing laser parameters and selecting pumping wavelengths and doping a concentration of the gain medium to control the absorption coefficient less than 2 cm−1 such as the pumping wavelength between about 910 nm and about 920 nm, a doped vanadate laser may be enhanced to produce as much as 100 W of output power without fracturing the crystal material, while delivering a 40% reduction in thermal lensing.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Methods and systems for laser processing a workpiece and methods and apparatus for controlling beam quality therein
InactiveUS7054341B2Optical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionHigh power lasersLaser processing
Laser processing methods, systems and apparatus having a super-modulating power supply (6) or pumping subsystem (5) and high beam quality (i.e., brightness) are disclosed. The methods, systems and apparatus have significant benefits, improved operation characteristics and material processing capability over currently available methods, systems and apparatus. In at least one embodiment, the beam quality of a high power solid state laser (2) is improved in the presence of thermal lensing. High power laser cutting, scribing, and welding results are improved with a combination of modulation and high beam quality while providing for improved processing speeds.
Owner:GSI LUMONICS LTD
Plasma suppression method for high-power laser welding
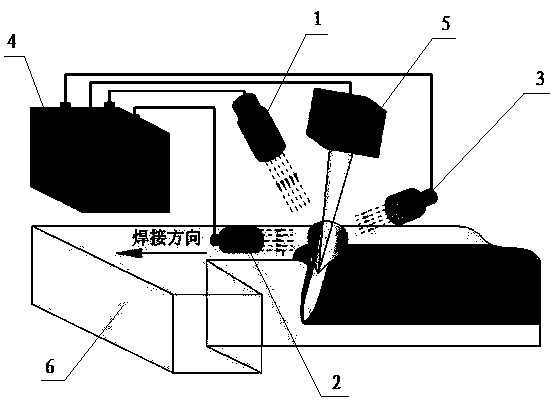
PendingCN111482699ANumber of suppressed clustersGood welding stabilityLaser beam welding apparatusShielding gasLight beam
The invention discloses a plasma suppression method for high-power laser welding. In existing laser welding, a high-temperature plasma cluster reversely jetted from the welding position of a plate exists in the light path transmission direction, the cluster can cause a thermal lens effect to affect the focusing position of a laser beam and the energy density of the laser beam, a laser protection lens is stained, and the welding quality and the service life are affected. The component of the laser welding plasma suppression method comprises a controller (4), the upper end of the controller is connected with a laser generator (5), an air injection device A (1), an air injection device B (2) and an air suction device (3), the air injection device A injects air in the laser beam conduction direction and is coaxial or paraxial with the laser beam, protective gas is continuously provided in the welding process, the air injection device B is arranged in the lateral direction of the plasma cluster, gas is injected in the lateral direction, and the air suction device is distributed on the opposite side of the air injection device B and is mainly used for absorbing the plasma cluster. The method is used for the plasma suppression method for high-power laser welding.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
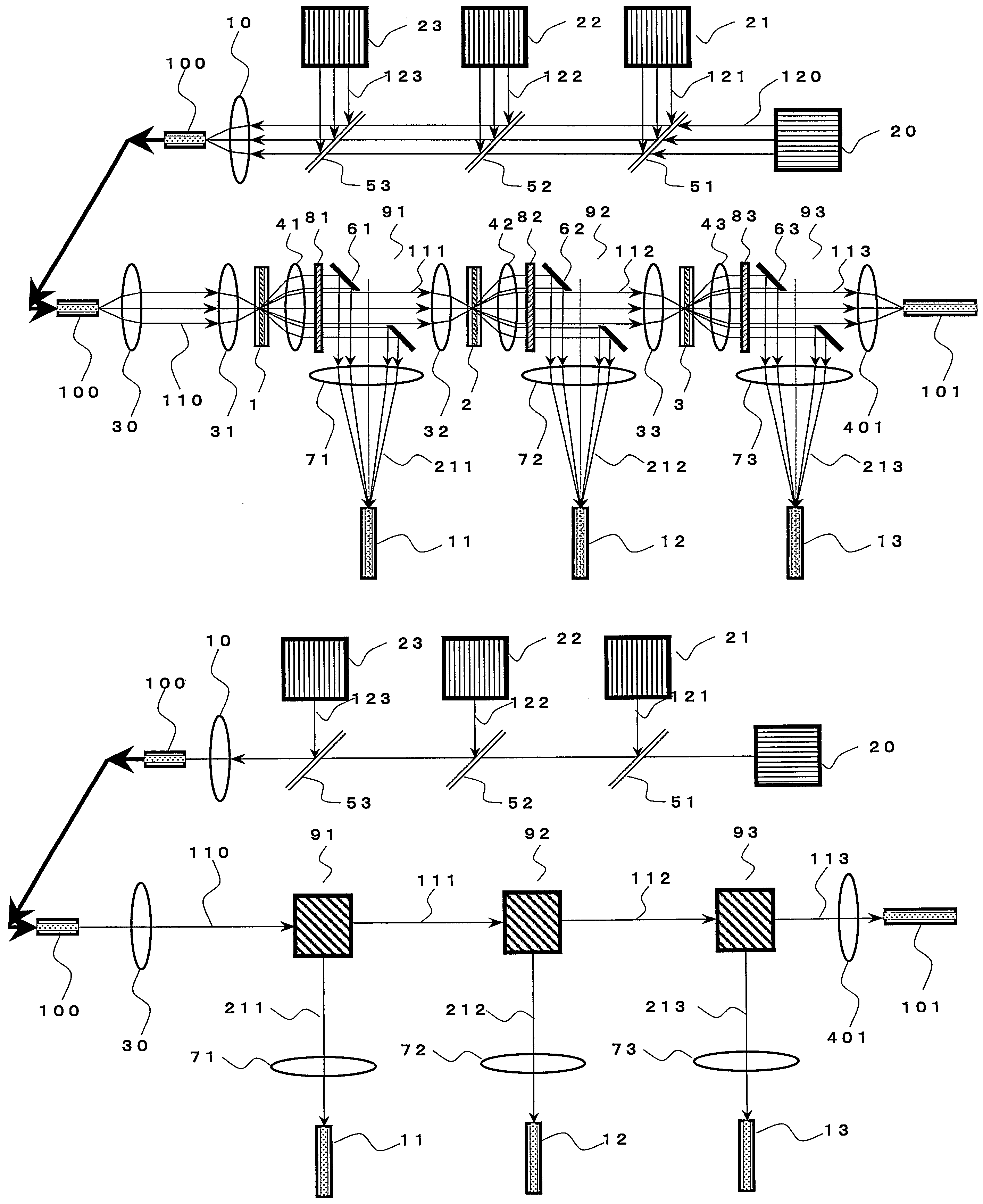
Laser amplifier
PendingCN113193469AAmplify laser powerSmall structure sizeOptical resonator shape and constructionLight beamEngineering
The invention discloses a laser amplifier. The laser amplifier comprises a pump light path and a laser amplification light path; and the pump light path and the laser amplification light path also comprise a laser gain medium together. A folding light path in the laser amplifier enables the overall structural size of the amplifier to be reduced, and installation and use are convenient. The pump light passes through the laser gain medium twice, so that the utilization rate of the pump light is improved. In addition, a thermal lens imaging system is introduced into the laser amplifier, so that the wavefront distortion influence introduced by the device is reduced, and the beam quality of output laser is improved.
Owner:北京盛镭科技有限公司 +1
A semiconductor pump laser
InactiveCN101247019BPromote absorptionReduce Thermal LensingOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialIon laserWorking temperature
The invention discloses a semiconductor pump laser, which includes a semiconductor laser pump source, an optical coupling system and a laser cavity. The laser cavity includes front and rear cavity plates, a laser gain medium, and optical elements other than the laser gain medium, wherein the laser gain The medium is composed of two or more laser gain media with different doping ion concentrations or different absorption coefficients. Different laser gain media are arranged in ascending order of doping ion concentration or absorption coefficient along the incident direction of pump light. The laser gain medium with low impurity ion concentration absorbs part of the pump light, and the other part of the pump light passes through the low-doped laser gain medium and is pumped and absorbed by the laser gain medium with high dopant ion concentration, reducing the The thermal lens effect of the laser gain medium can enhance the absorption of pump light at the same time, so as to obtain a semiconductor-pumped laser suitable for wide pump wavelength range and wide temperature operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI BRANCH FUZHOU GAOYI COMM CO LTD
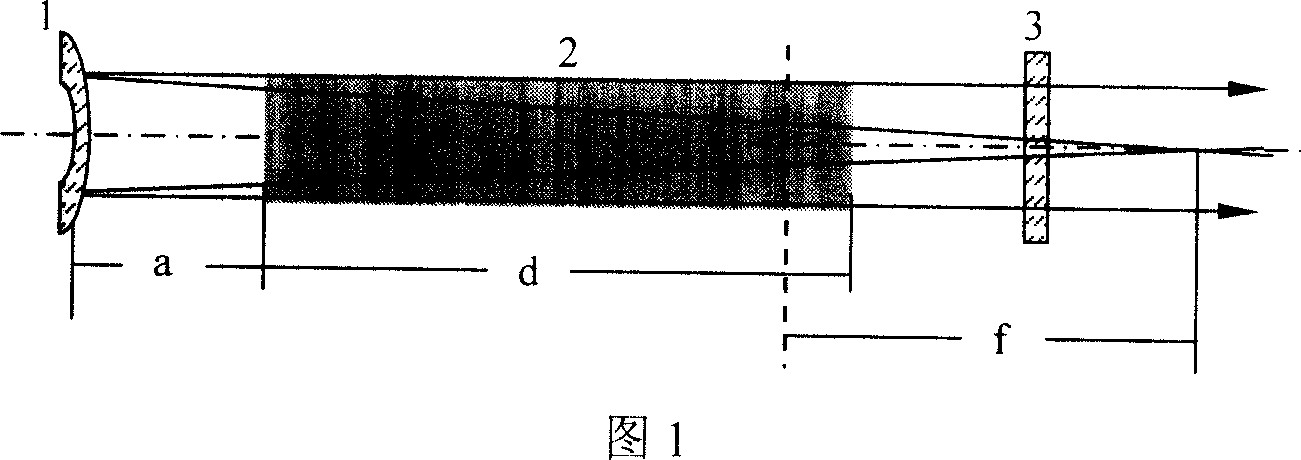
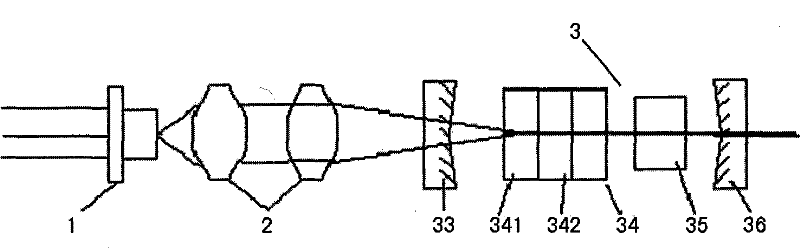
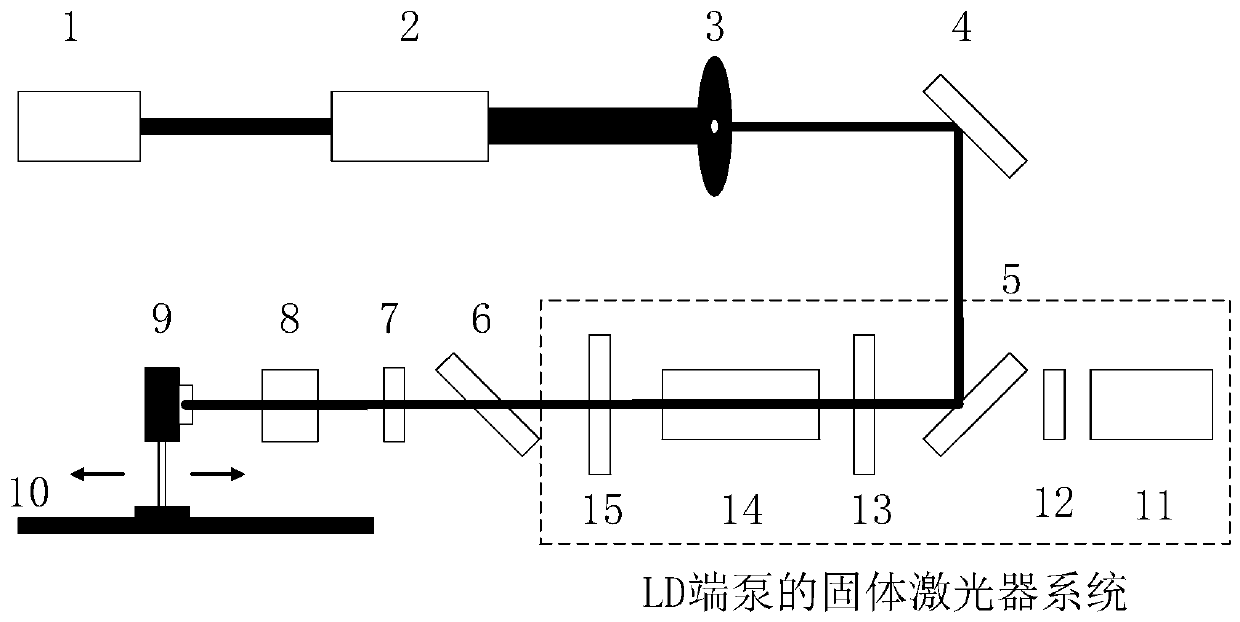
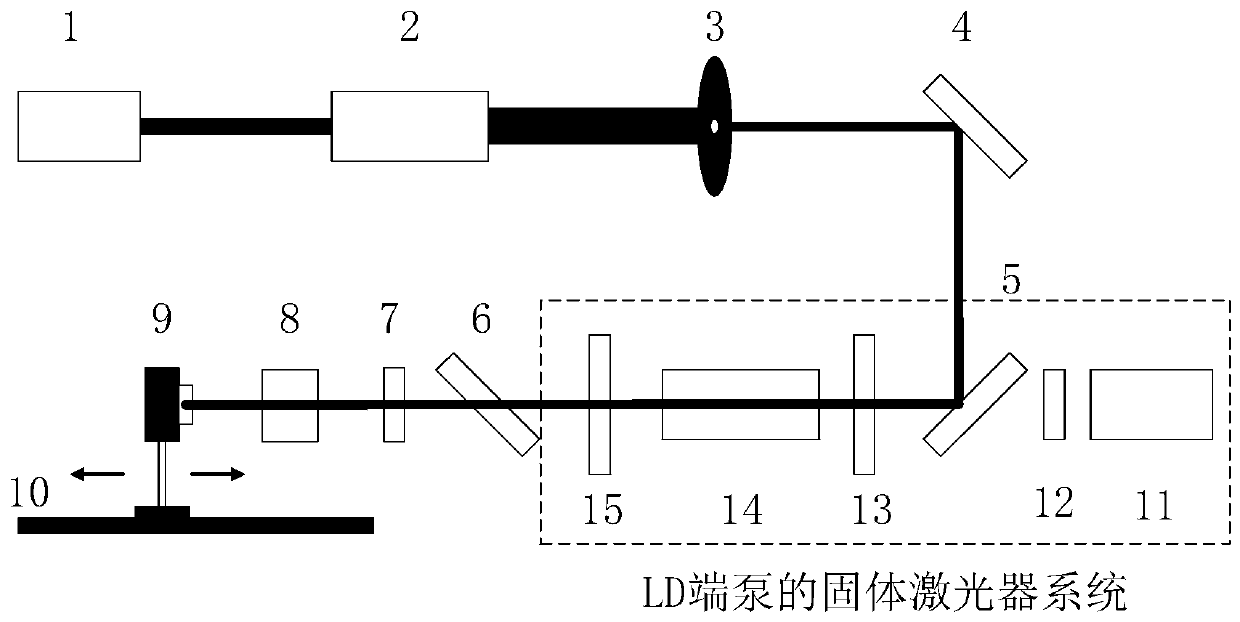
Laser crystal thermal lens focal length online real-time measurement device and method
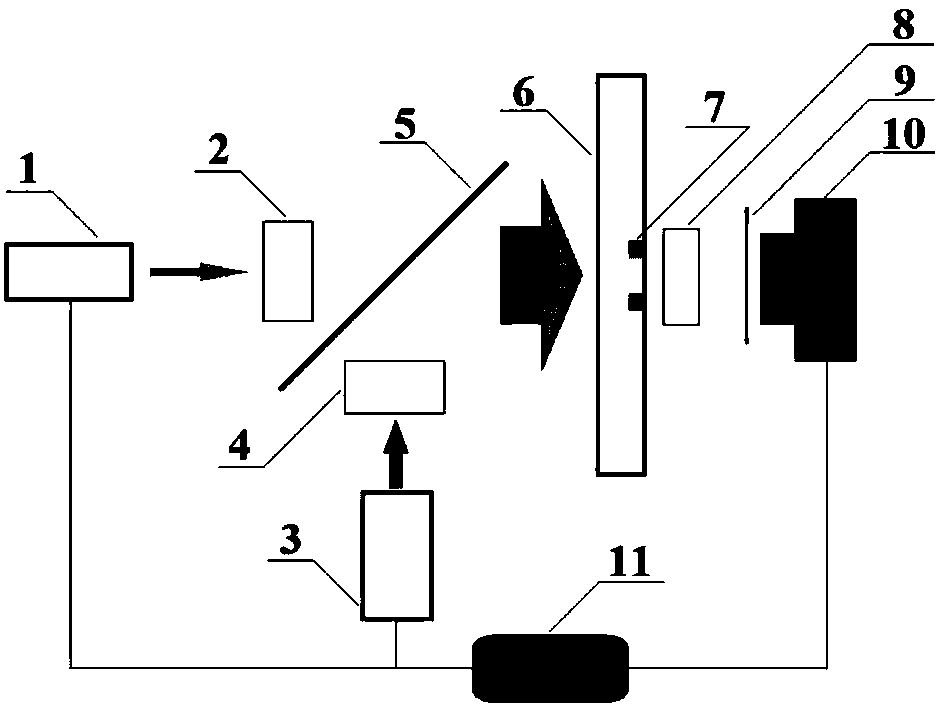
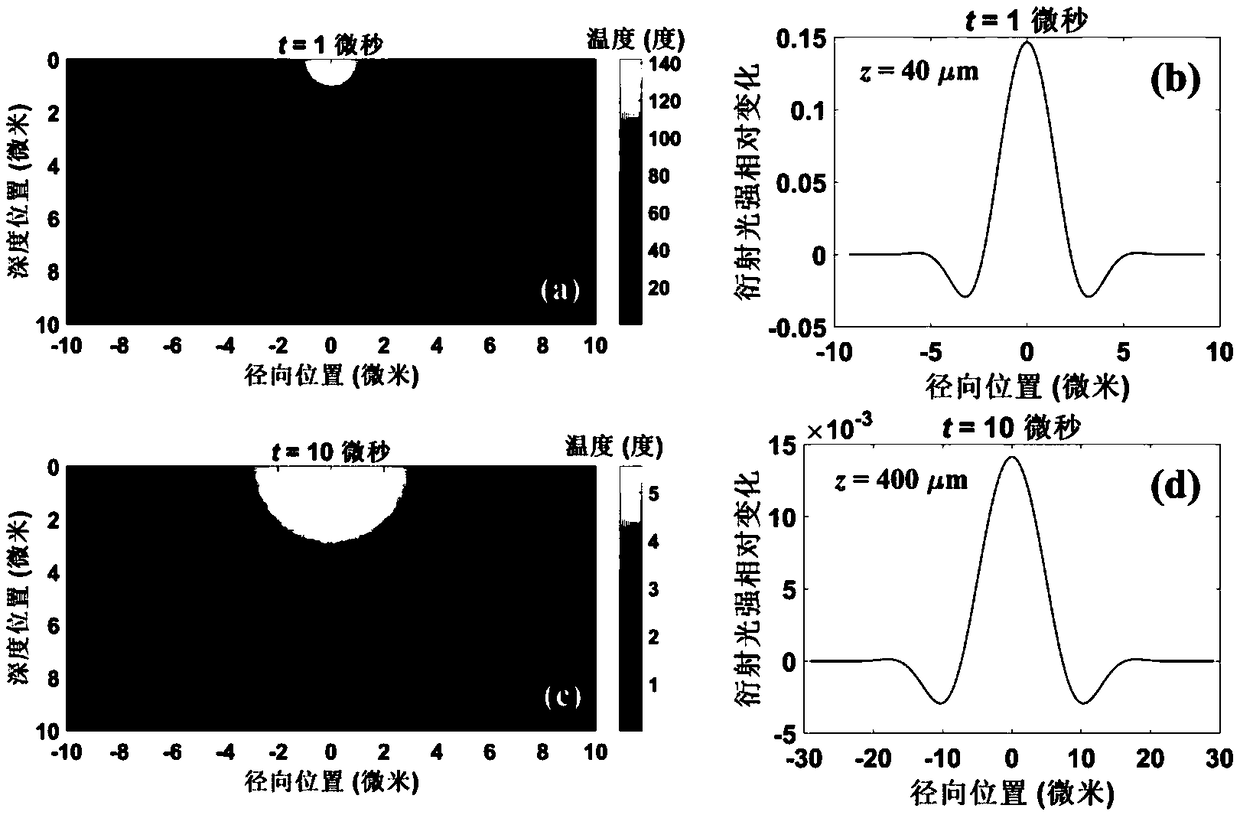
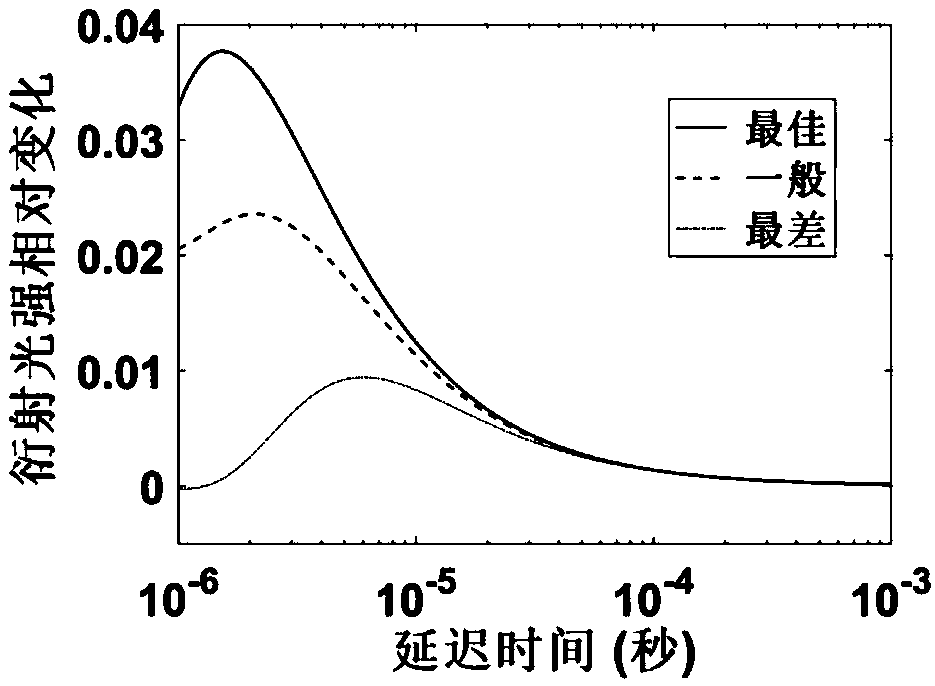
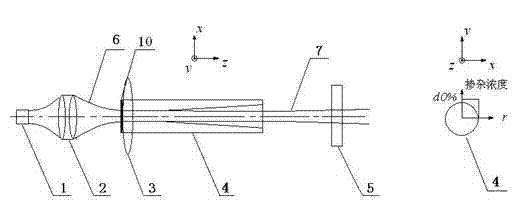
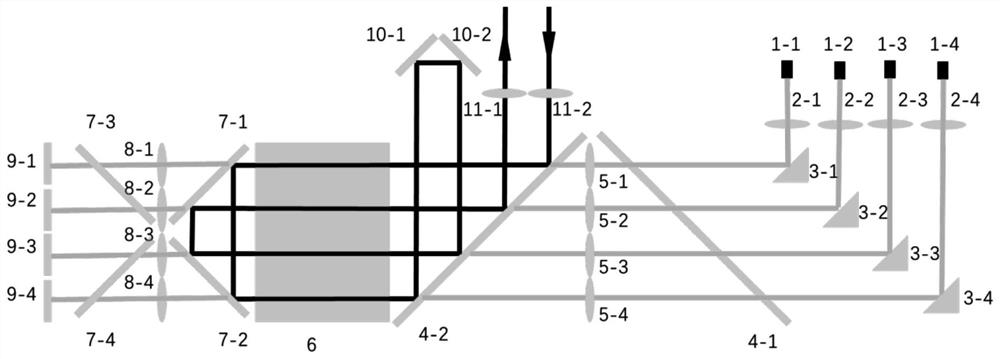
InactiveCN111175023AEnables Thermal Focal Length MeasurementsAccurate measurementTesting optical propertiesBeam splittingOptical axis
The invention discloses a laser crystal thermal lens focal length online real-time measurement device and method for an LD end-pumped solid laser. The device comprises a He-Ne laser (1), a 5-10-time first beam expanding system (2), a variable aperture diaphragm (3), a 45-degree 632.8 nm high-reflectivity mirror (4), a beam splitting cube (5), a 45-degree dichroic mirror (6), an attenuation slice group (7), a 2-5-time second beam expanding system (8), a camera (9) and a guide rail (10). The He-Ne light and the laser pump light are adjusted to be strictly transmitted on the same optical axis byutilizing the high-reflectivity mirror (4) and the beam splitting cube (5); and the He-Ne imaging light spot on the camera (9) is as large as possible through the second beam expanding system (8), butcannot exceed the imaging surface element of the camera (9). The device is accurate in measurement result and can quickly achieve the measurement of the thermal focal length of the laser crystal under different pumping powers and provides a powerful guarantee for the compensation design of the laser.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH +2
NONLINEAR OPTICAL CdSiP2 CRYSTAL FOR USE IN SURGICAL LASER
ActiveUS20130158528A1Increase heightQuality improvementSurgical instrument detailsNon-linear opticsLaser scalpelNd:YAG laser
CdSiP2 crystals with sizes and optical quality suitable for use as nonlinear optical devices are disclosed, as well as NLO devices based thereupon. A method of growing the crystals by directional solidification from a stoichiometric melt is also disclosed. The disclosed NLO crystals have a higher nonlinear coefficient than prior art crystals that can be pumped by solid state lasers, and are particularly useful for frequency shifting 1.06 μm, 1.55 μm, and 2 μm lasers to wavelengths between 2 μm and 10 μm. Due to the high thermal conductivity and low losses of the claimed CdSiP2 crystals, average output power can exceed 10 W without severe thermal lensing. A 6.45 μm laser source for use as a medical laser scalpel is also disclosed, in which a CdSiP2 crystal is configured for non-critical phase matching, pumped by a 1064 nm Nd:YAG laser, and temperature-tuned to produce output at 6.45 μm.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTEGRATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com