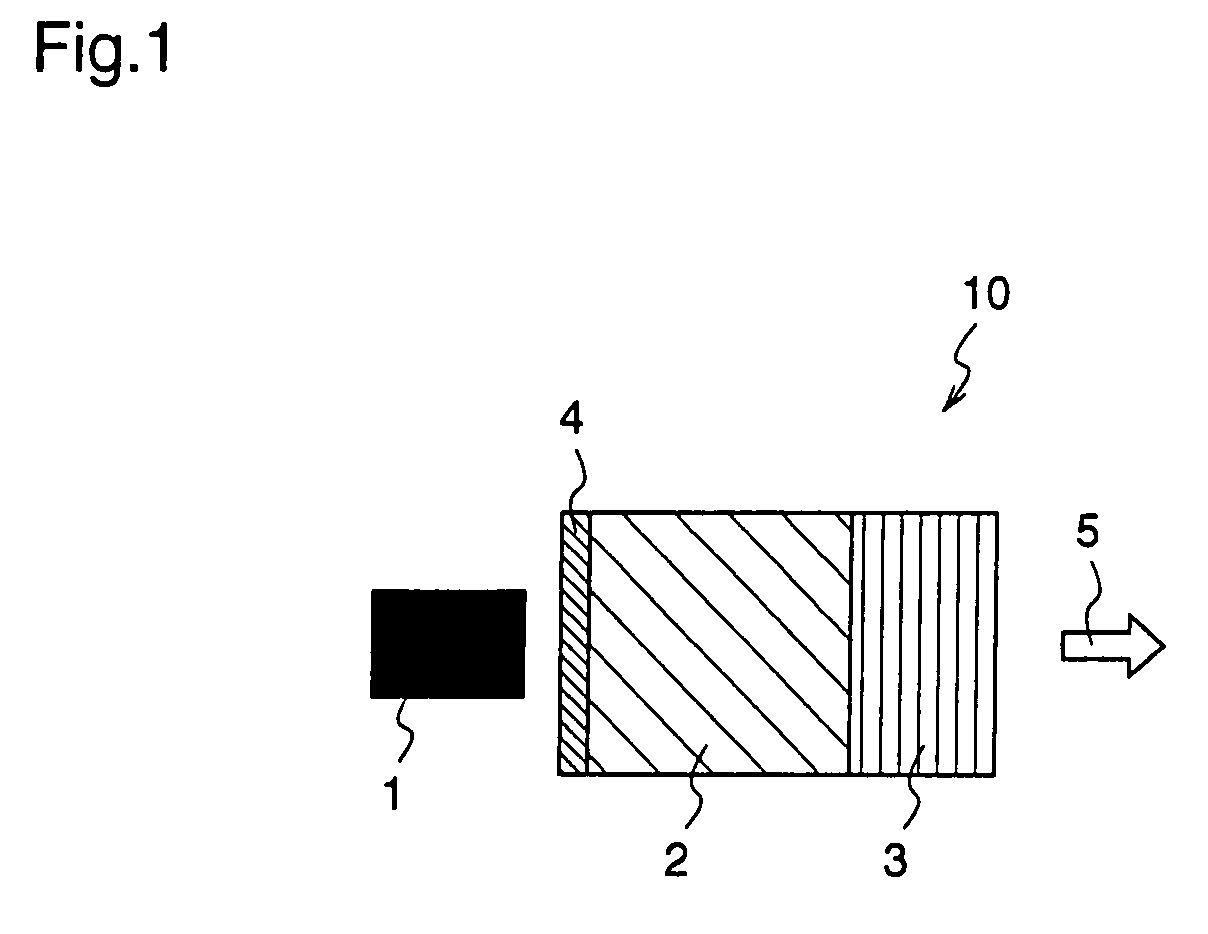
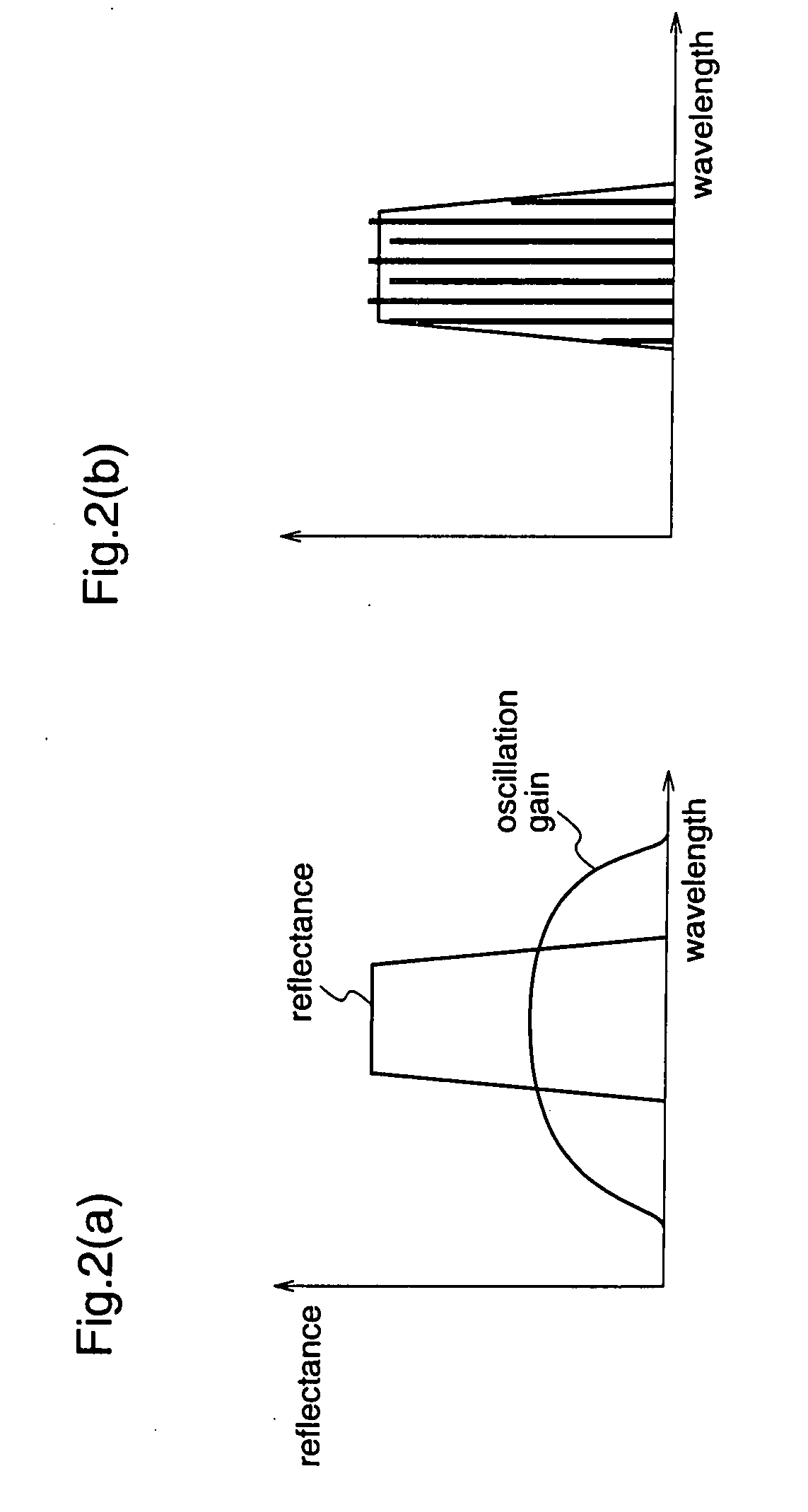
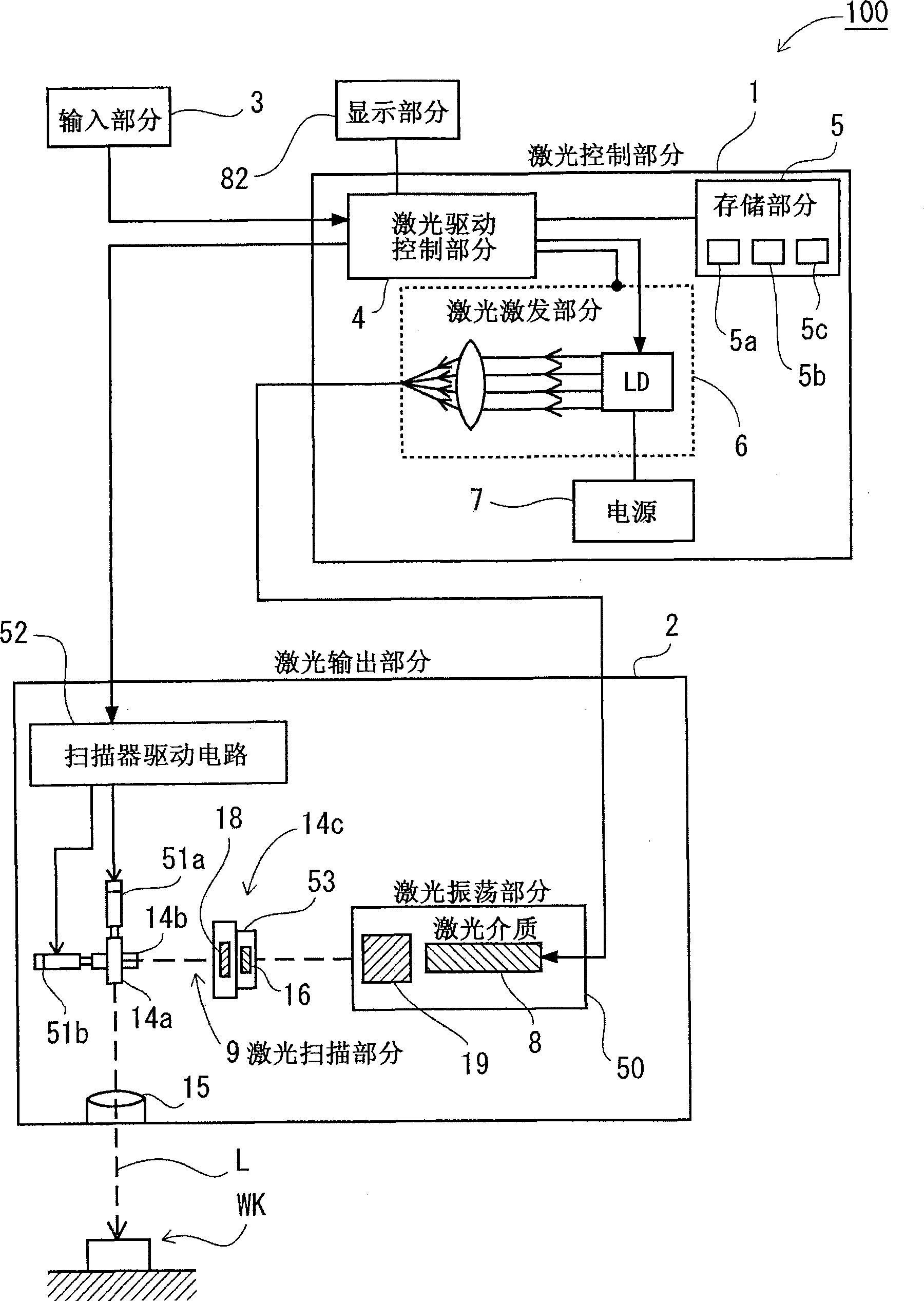
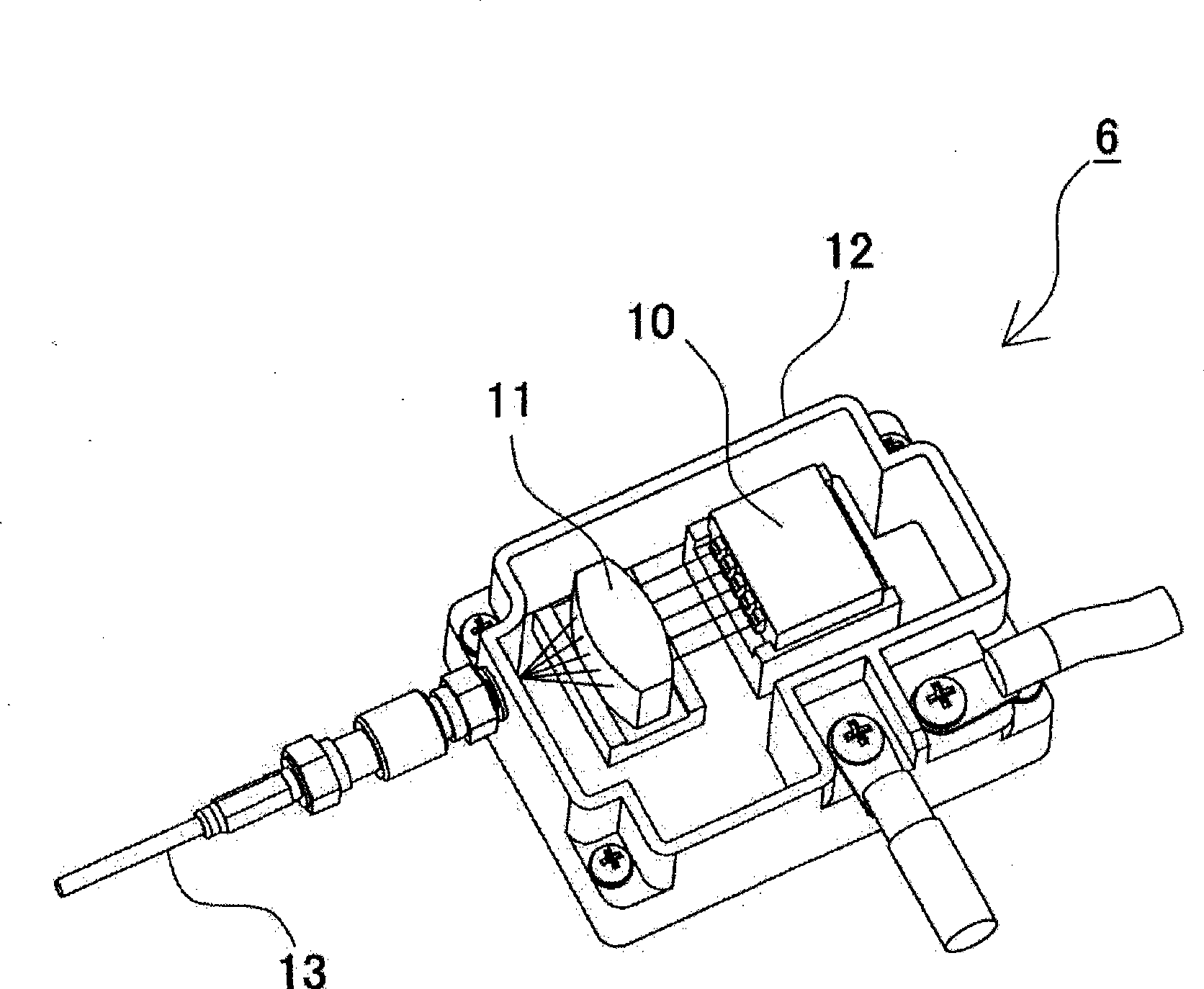
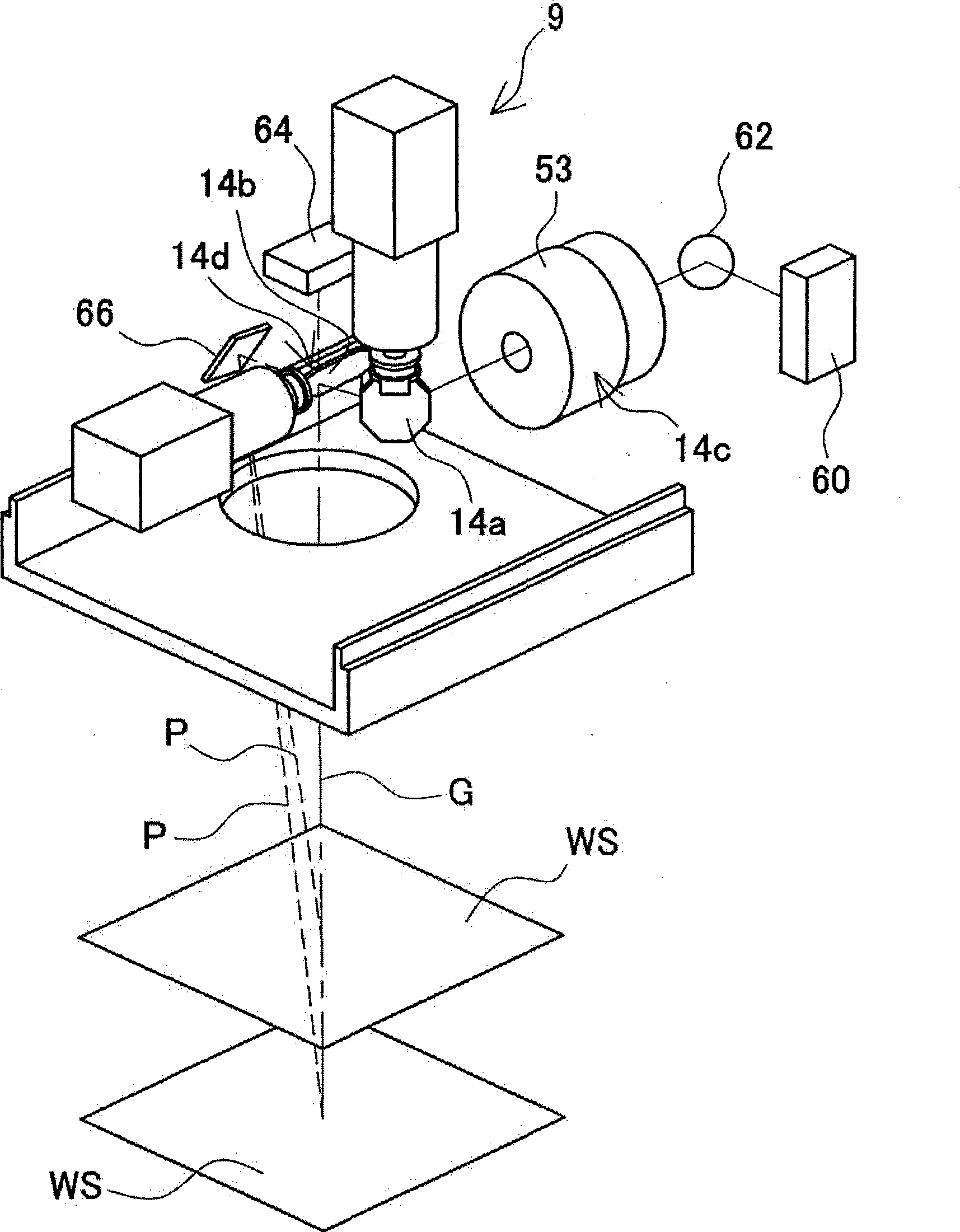
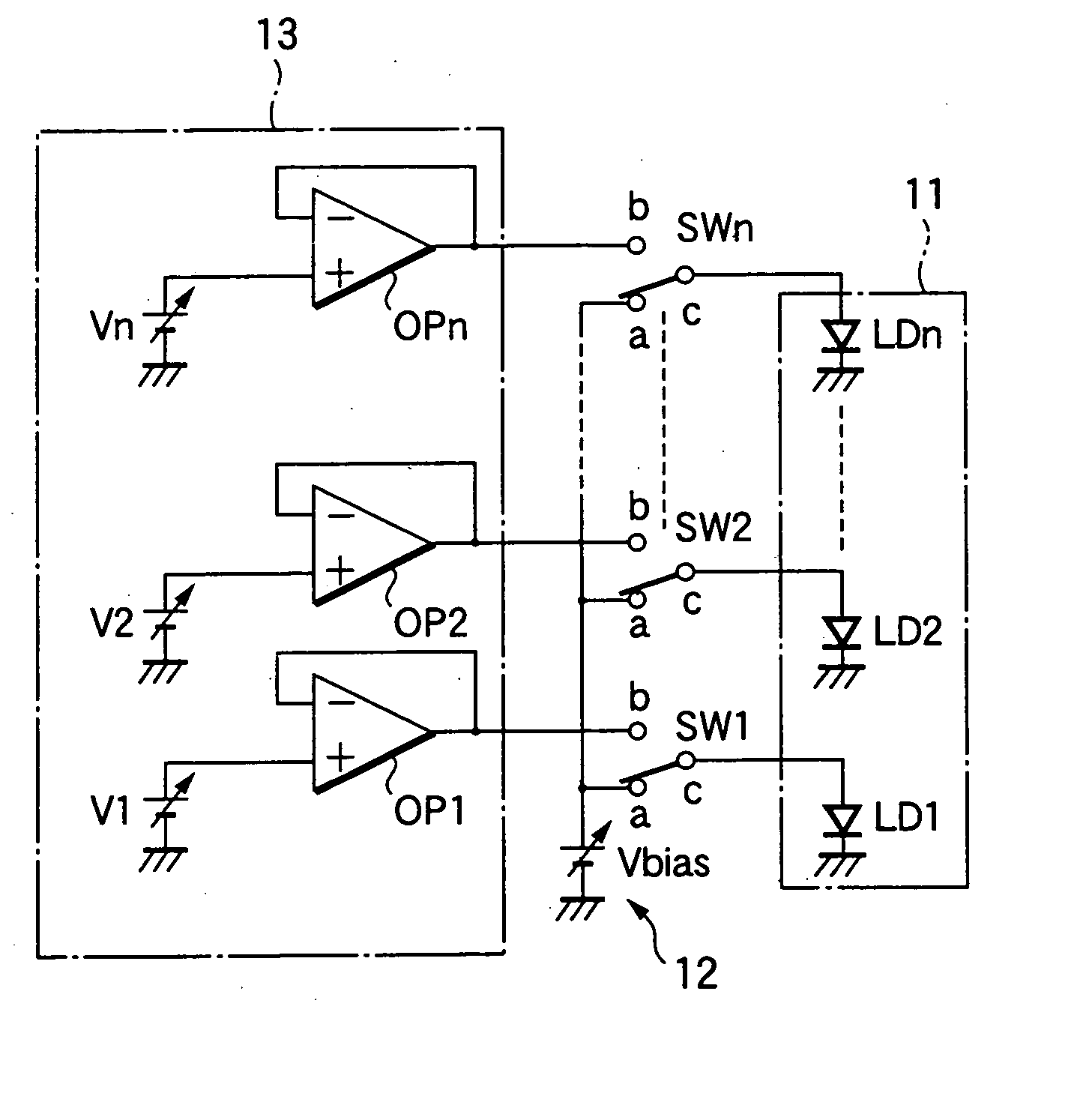
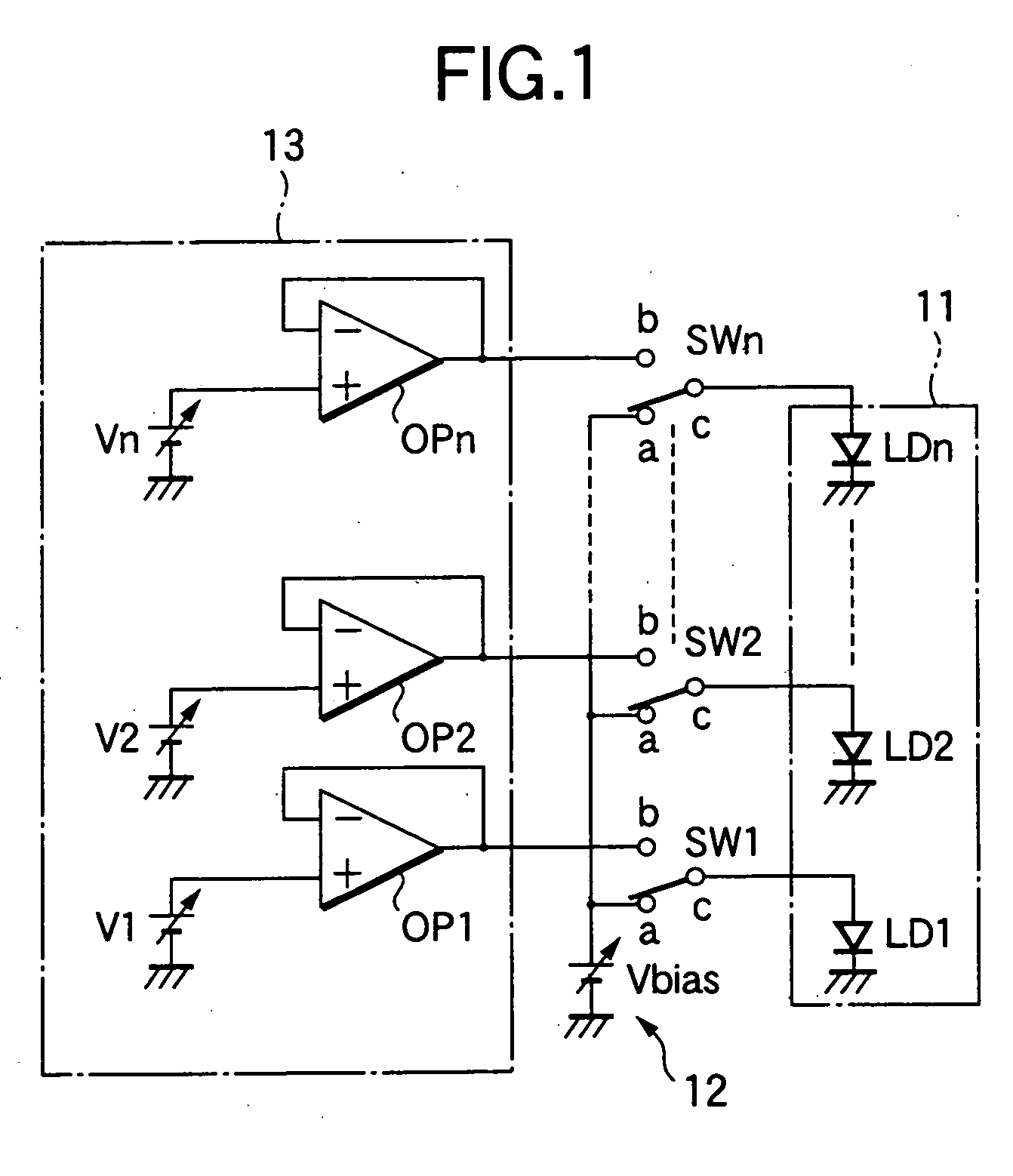
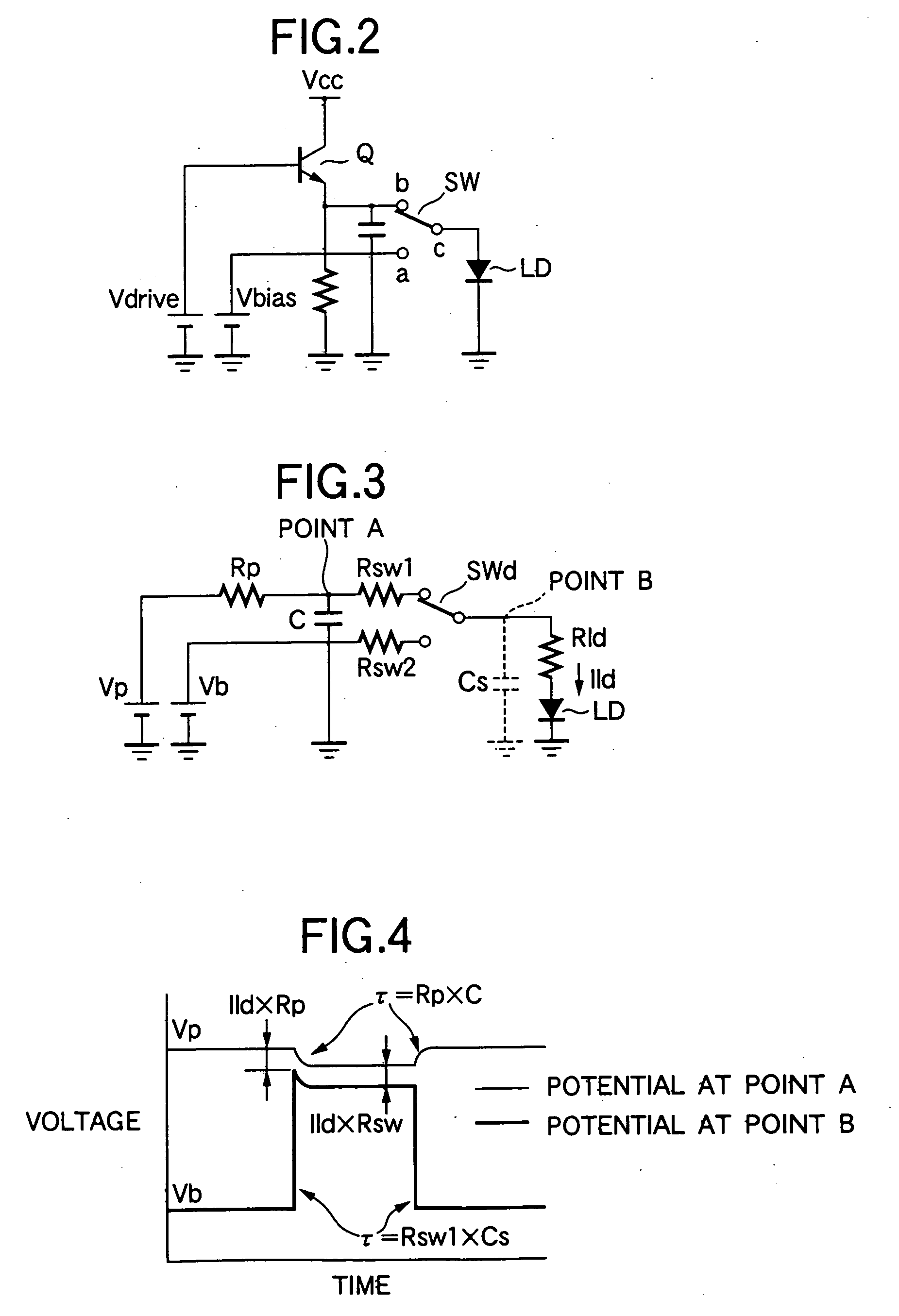
Patents
Literature
682 results about "Laser oscillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Laser Oscillation. The buildup of the coherent Wave between Laser Cavity end mirrors. In CW mode, the wave bounding back and forth between mirrors transmits a fraction of its Energy on each trip; in pulsed operation, Emission happens instantaneously. Related Terms Alignment Laser , Broad Area Laser Diodes , Burst Mode...
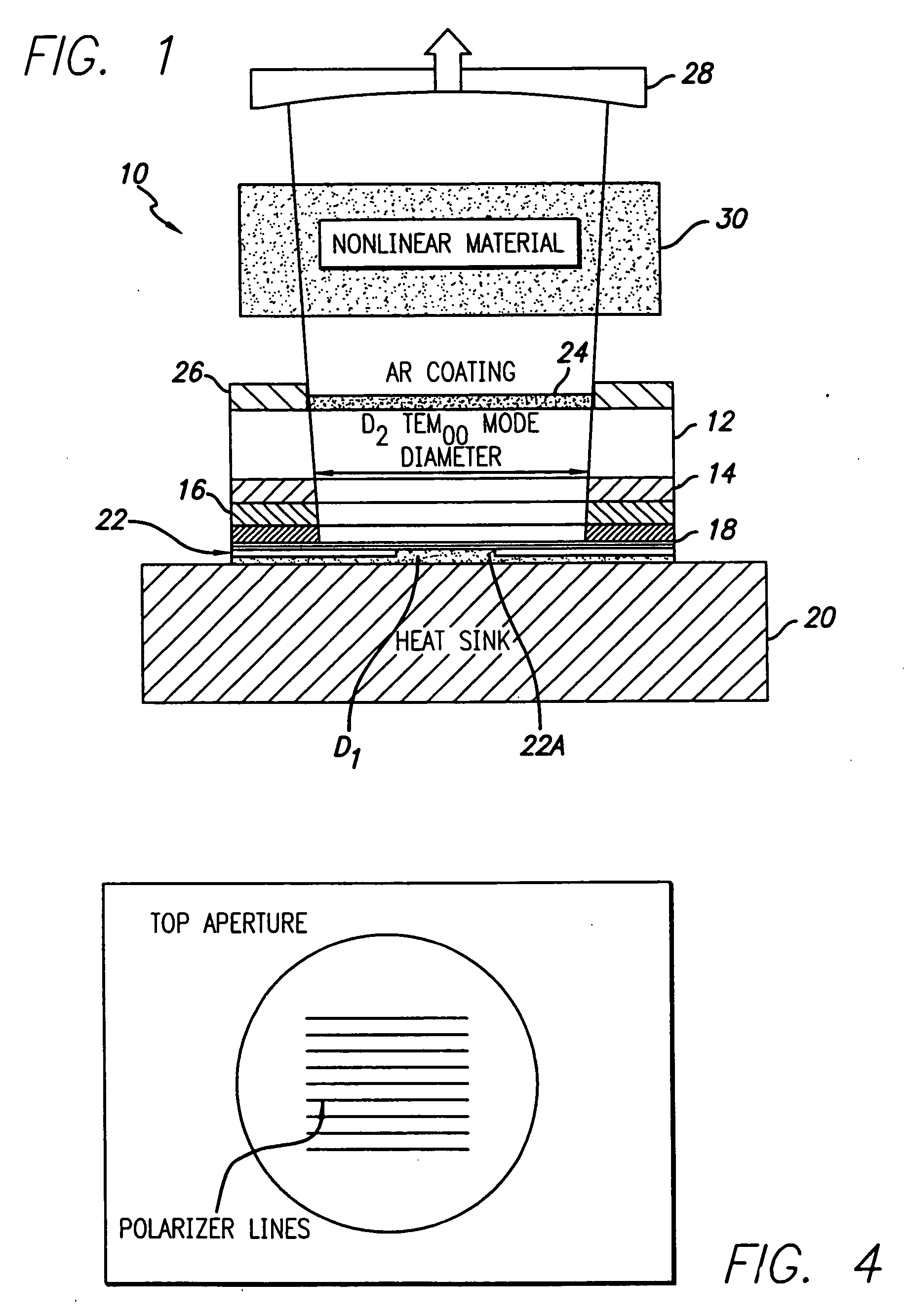
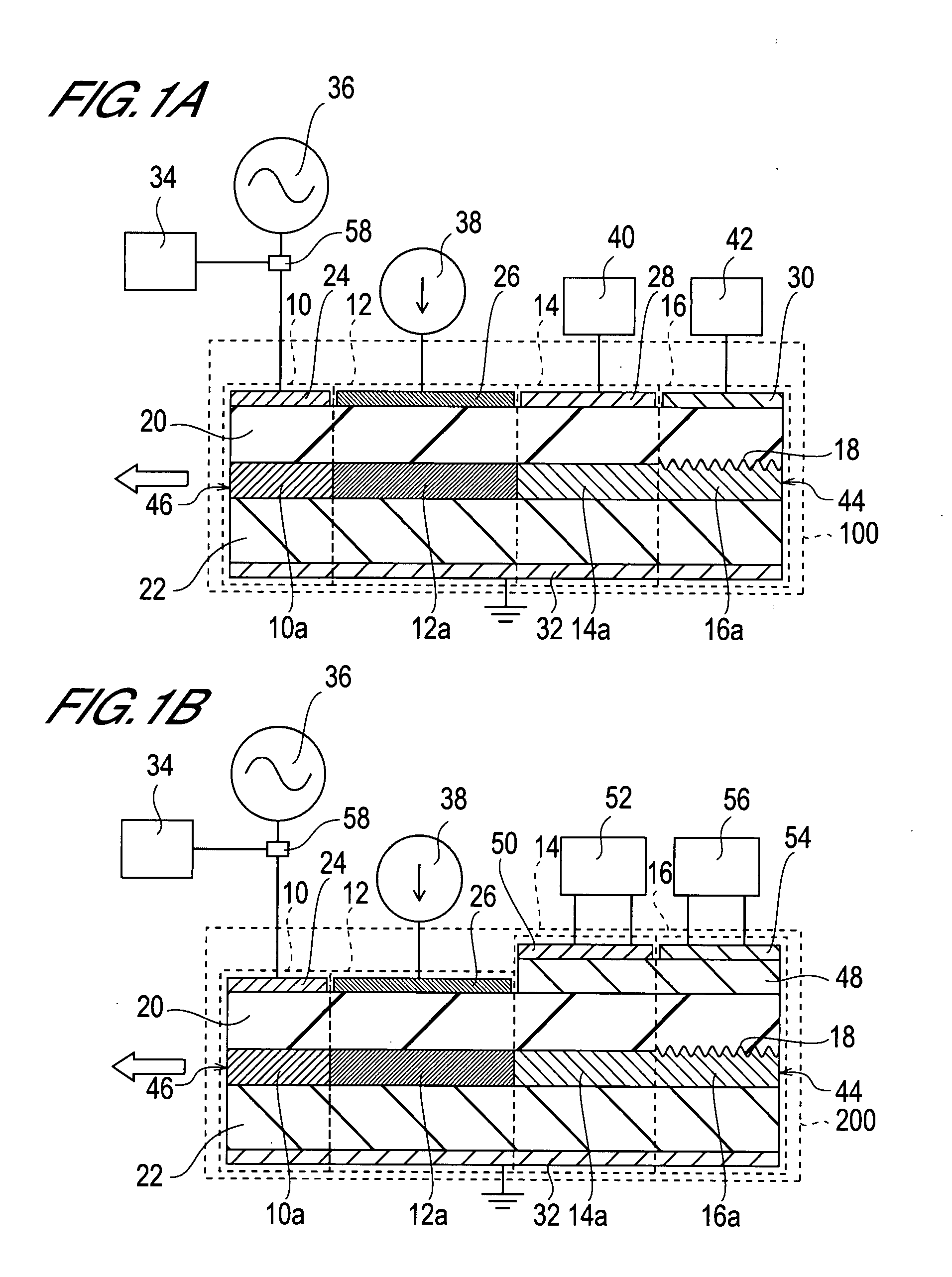
Tunable laser light source
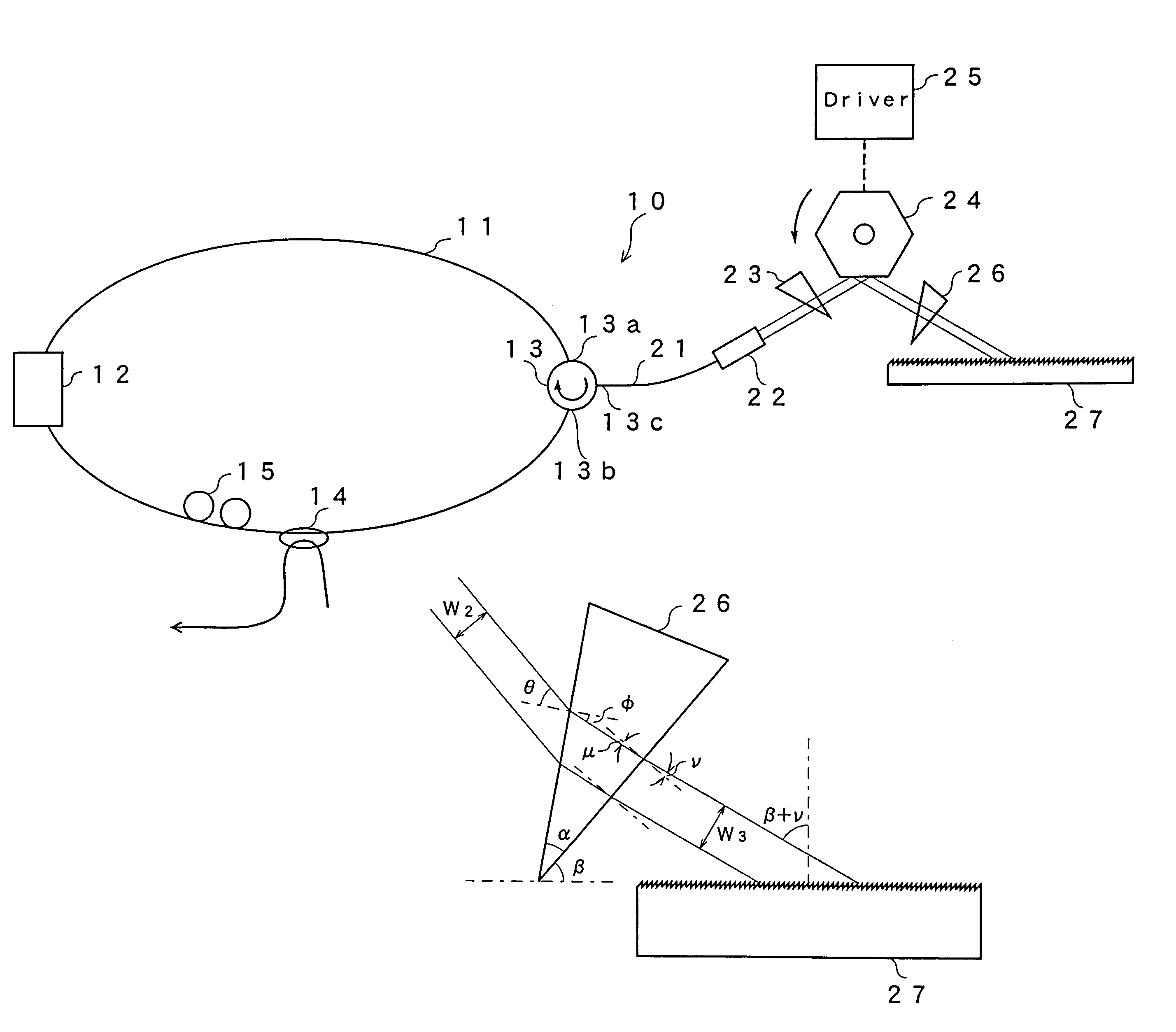
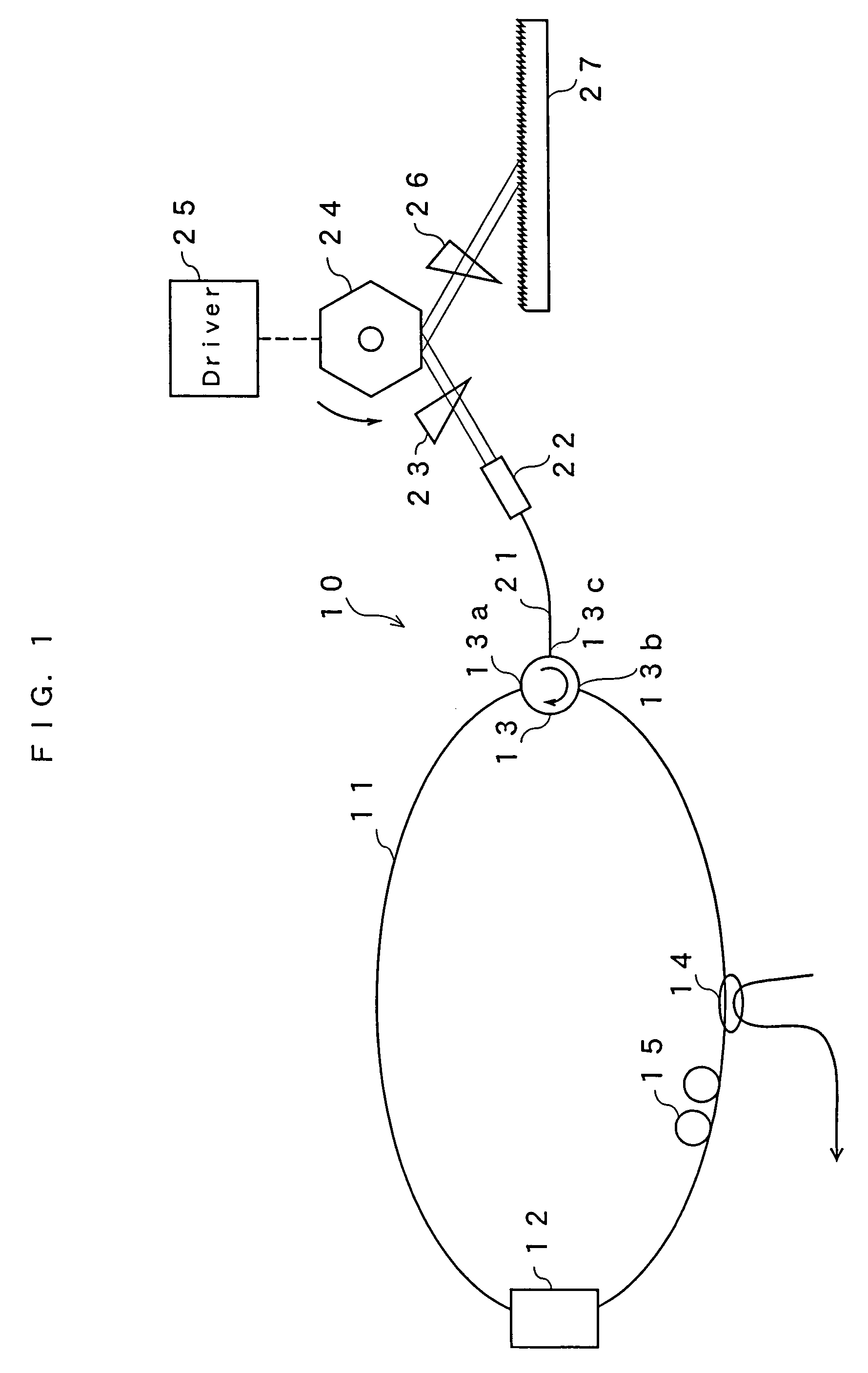
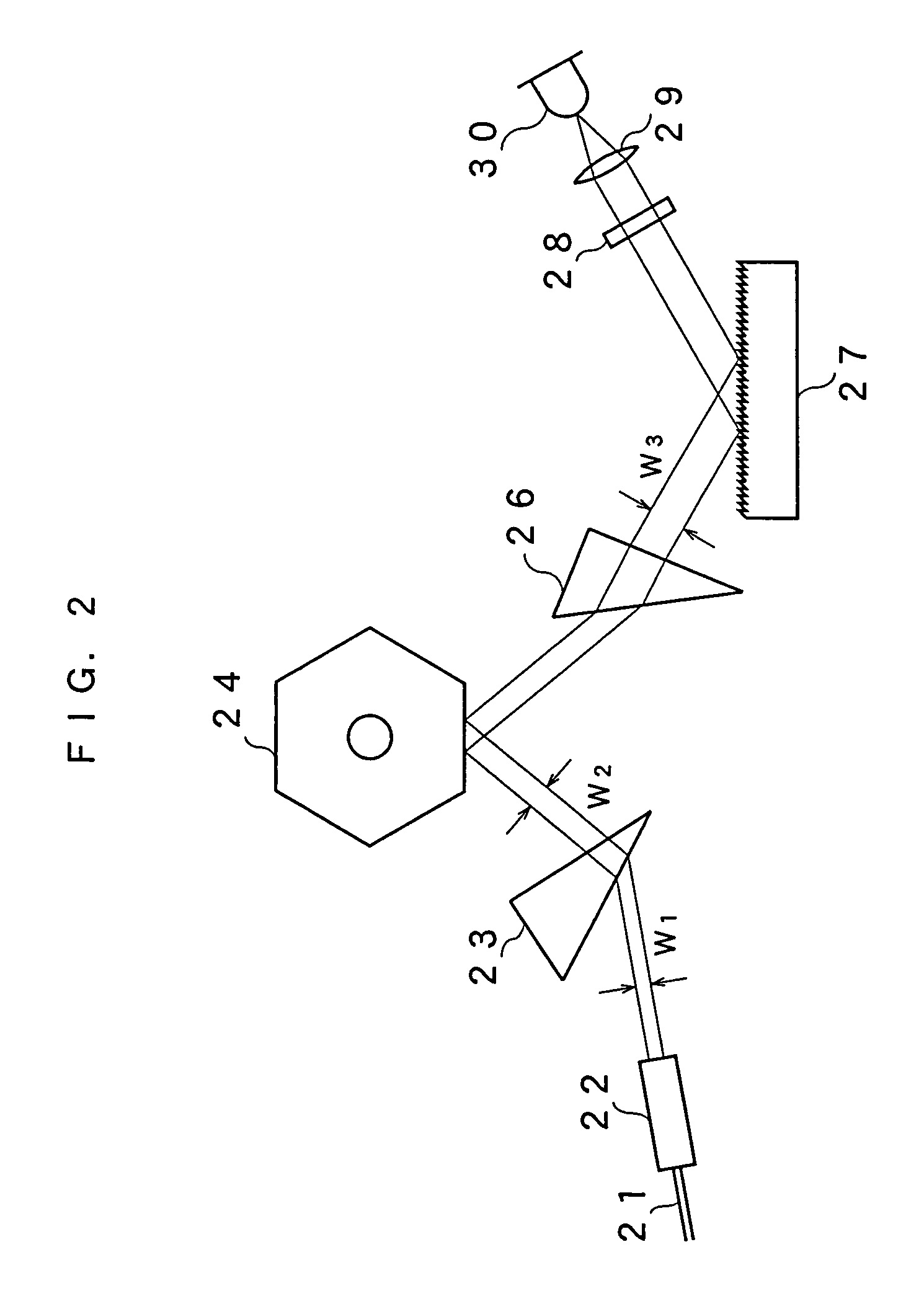
ActiveUS7099358B1Small distortionLittle noiseOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersLight beamPrism
A gain medium 12 and a tunable filter are provided in an optical path of laser oscillation. The tunable filter has an optical beam deflector for periodically changing an optical beam at a constant angular speed, a prism 26 on which deflected light is made incident, and a diffraction grating 27. Appropriate selection of the apex angle α of the prism 26 and an angle β formed by the prism 26 and the diffraction grating 27 can provide a tunable laser light source for changing the oscillation frequency at high speed and a constant variation rate.
Owner:SANTEC
Coupled cavity high power semiconductor laser
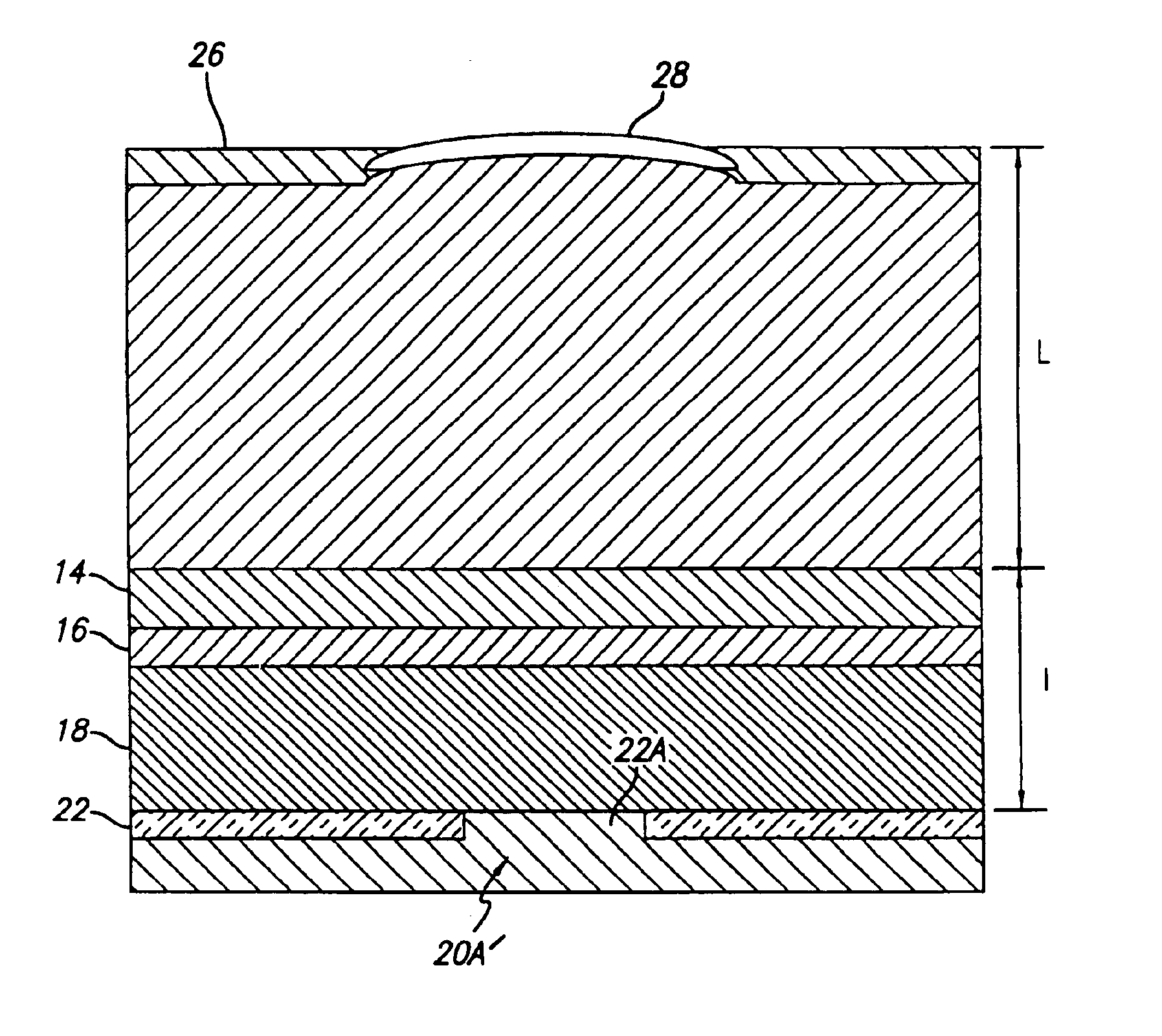
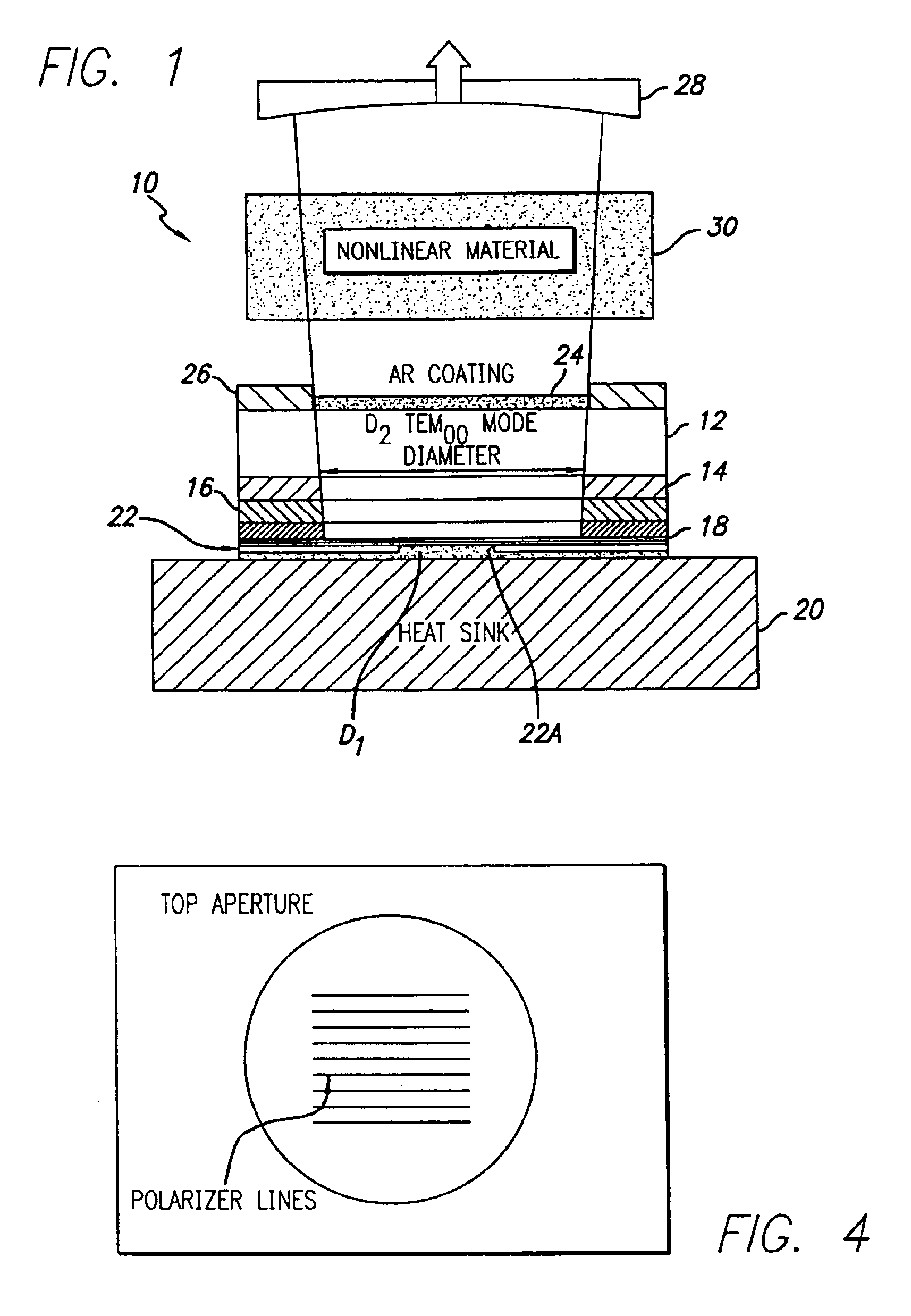
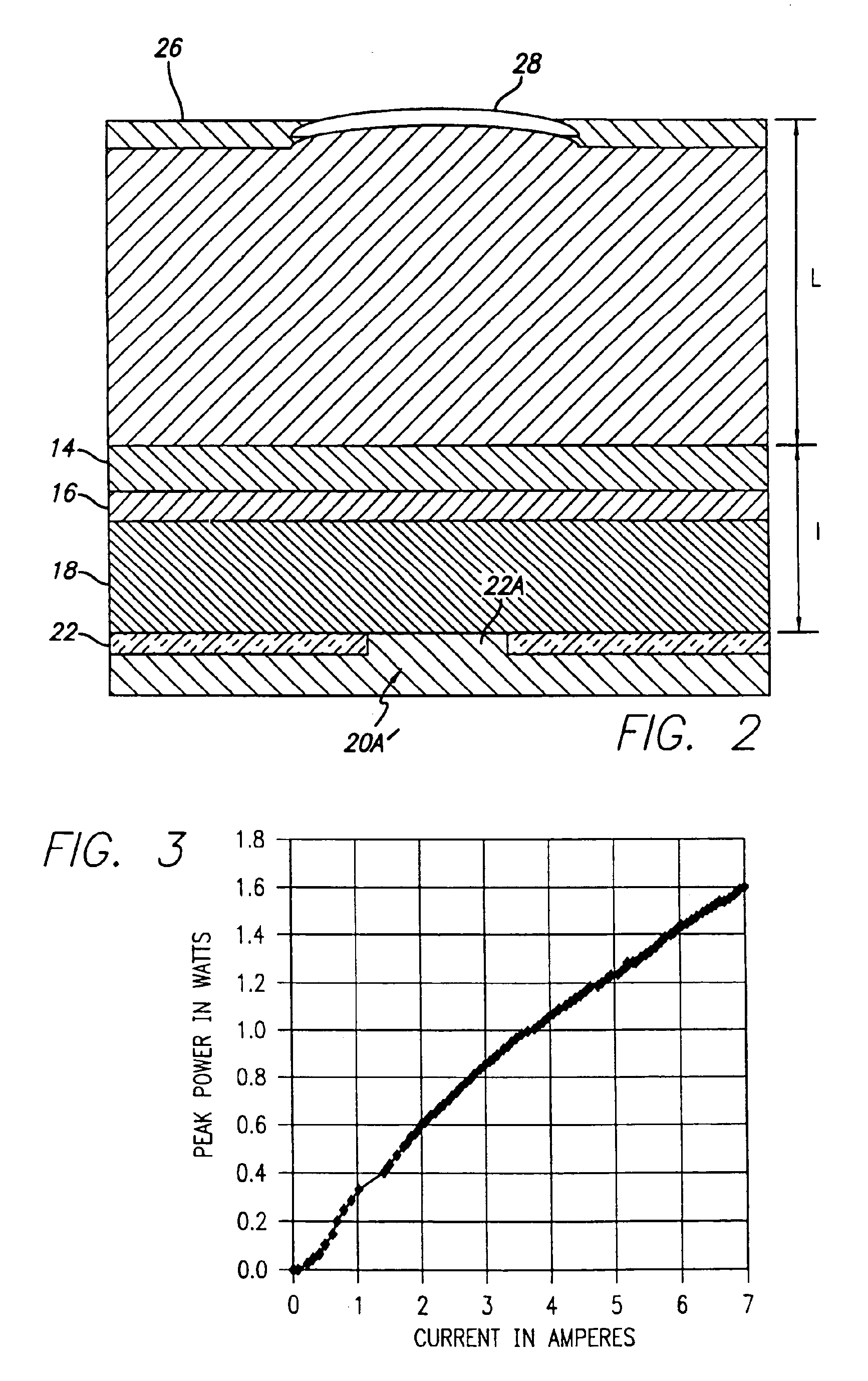
InactiveUS20060029120A1Maximize circulating fundamental laser powerConvenient registrationOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersFundamental frequencyPartial reflection
An active gain region sandwiched between a 100% reflective bottom Bragg mirror and an intermediate partially reflecting Bragg mirror is formed on a lower surface of a supporting substrate, to thereby provide the first (“active”) resonator cavity of a high power coupled cavity surface emitting laser device. The reflectivity of the intermediate mirror is kept low enough so that laser oscillation within the active gain region will not occur. The substrate is entirely outside the active cavity but is contained within a second (“passive”) resonator cavity defined by the intermediate mirror and a partially reflecting output mirror, where it is subjected to only a fraction of the light intensity that is circulating in the gain region. In one embodiment, non-linear optical material inside each passive cavity of an array converts an IR fundamental wavelength of each laser device to a corresponding visible harmonic wavelength, and the external output cavity mirror comprises a Volume Bragg grating (VBG) or other similar optical component that is substantially reflective at the fundamental frequency and substantially transmissive at the harmonic frequency. The VBG used in an array of such devices may be either flat, which simplifies registration and alignment during manufacture, or may be configured to narrow the IR spectrum fed back into the active resonant cavity and to shape the spatial mode distribution inside the cavity, thereby reducing the size of the mode and compensating for any deformations in the semiconductor array.
Owner:ARASOR ACQUISITION +1
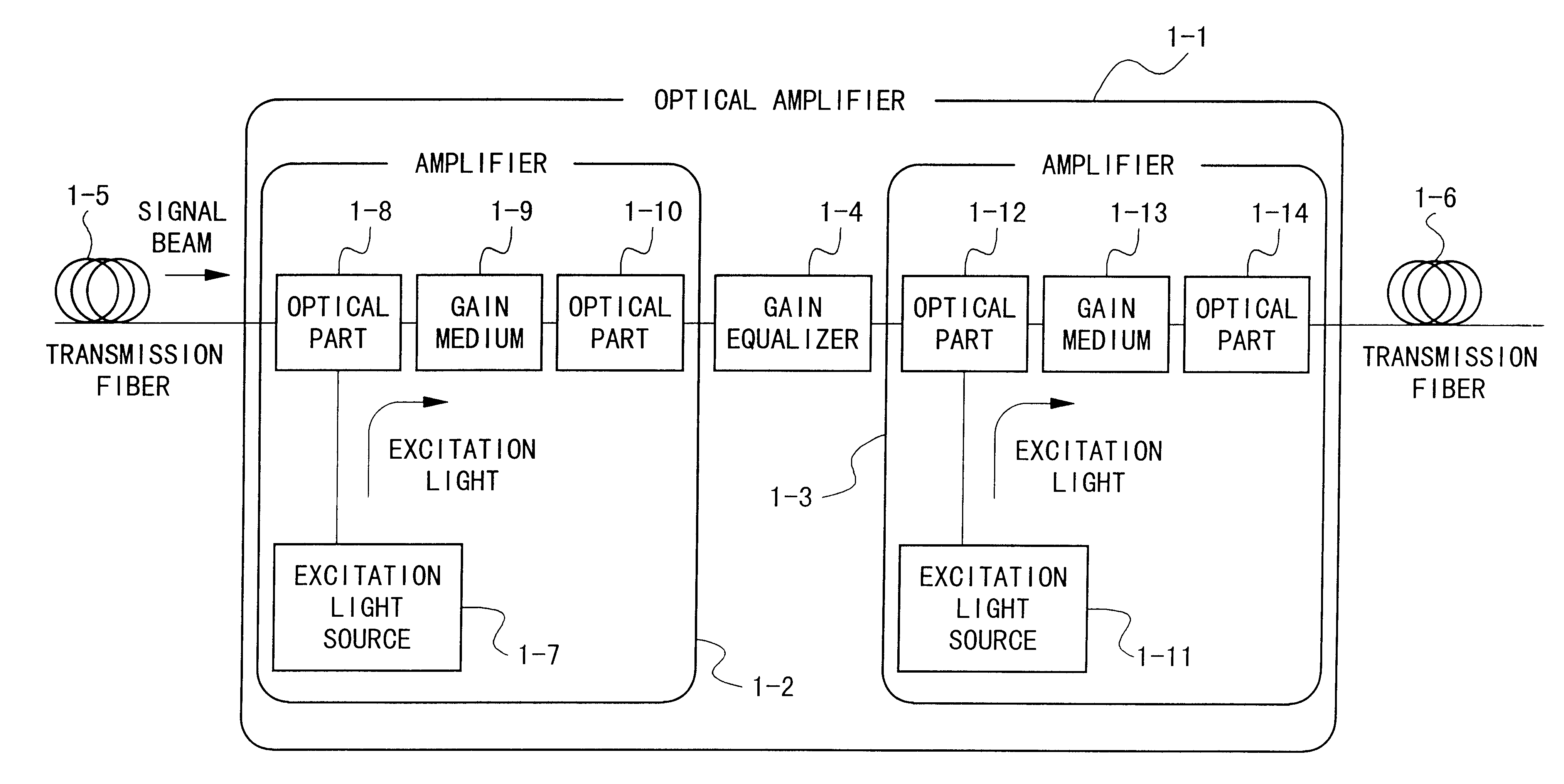
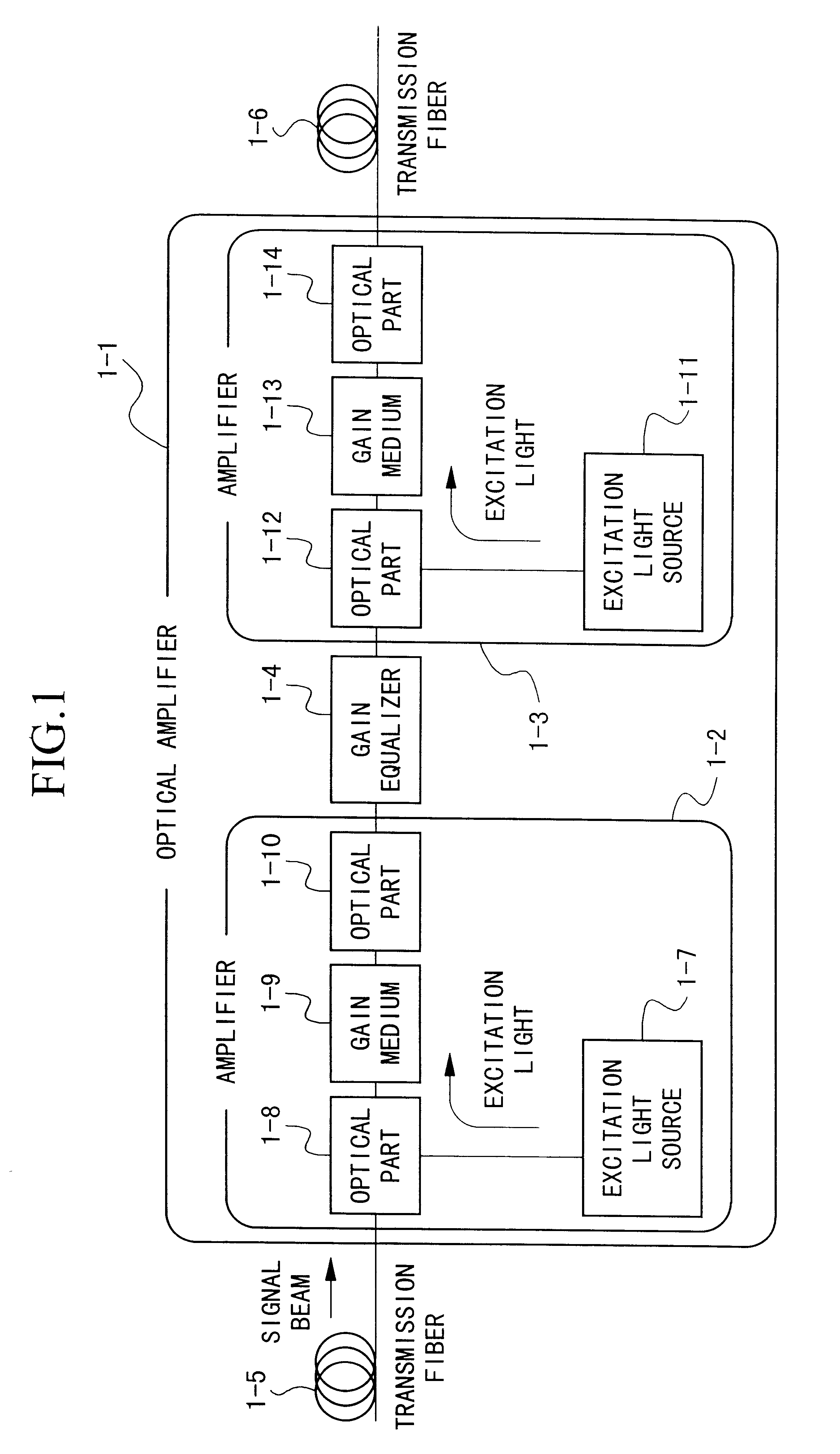
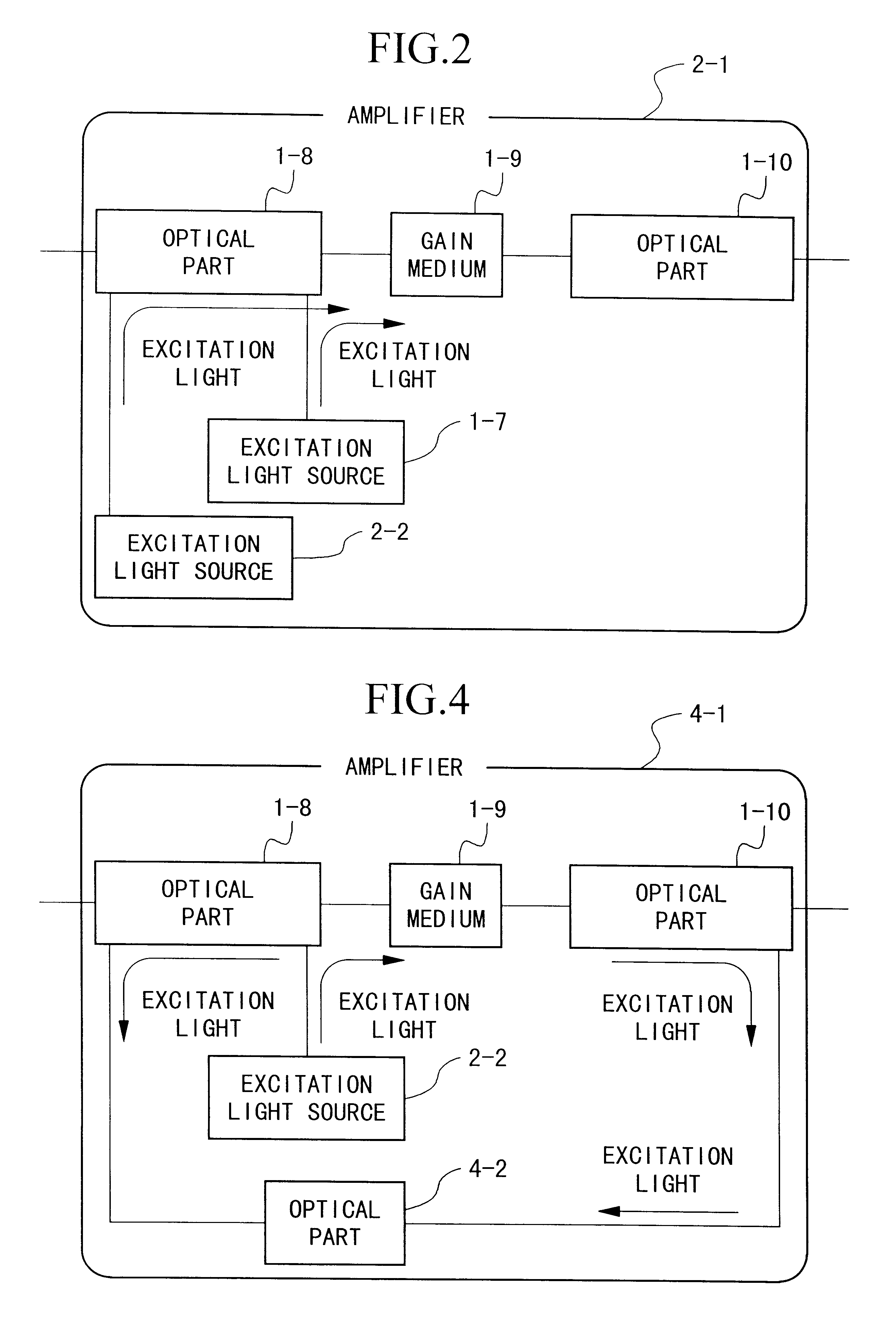
Optical amplifier and transmission system using the same
InactiveUS6172803B1Laser using scattering effectsOptical transmission with multiple stagesFiberErbium doping
An optical amplifier having a two-stage construction using an erbium doped fiber (EDF) as a gain medium. The erbium dopant concentration is 1000 ppm, and the unsaturated absorption coefficient of the signal beam at 1550 nm is 1 dB / m. The length of the EDF 14-8 is 10 m, and the length of the EDF 14-12 is 70 m. The excitation light sources 14-6 and 14-10 are semiconductor lasers of 1.53 mum, and the excitation light power is 100 mW. Multiplexers 14-7 and 14-11 are inductive multi-layer film filters, and the gain equalizer 14-4 is a Fourier filter. The peak loss of the Fourier filter is 17 dB. The gain of the EDF 14-8 is 25 dB, and the gain of the EDF 14-12 is 15 dB. Two optical isolators are installed on a pre-stage amplifier, and one on a post-stage amplifier in order to prevent laser oscillation.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
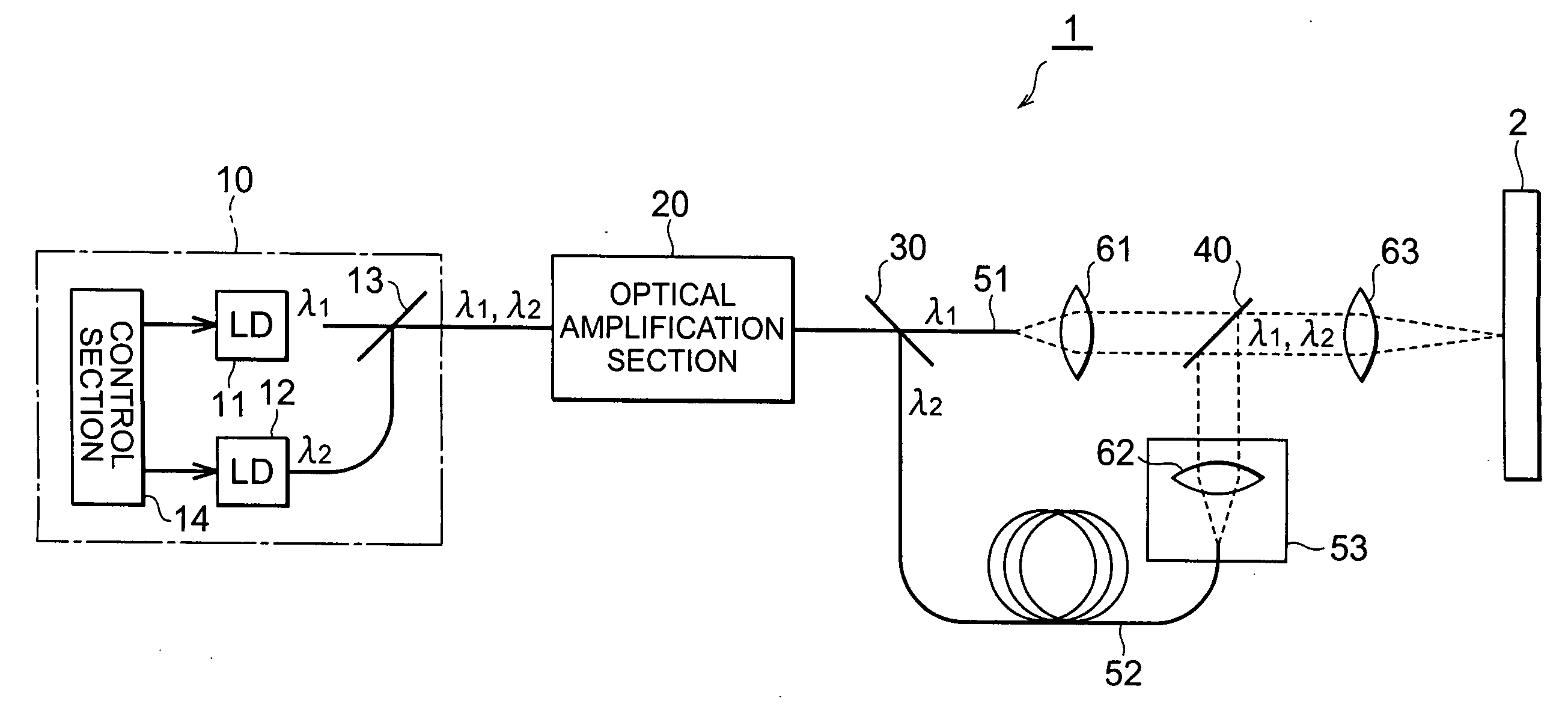
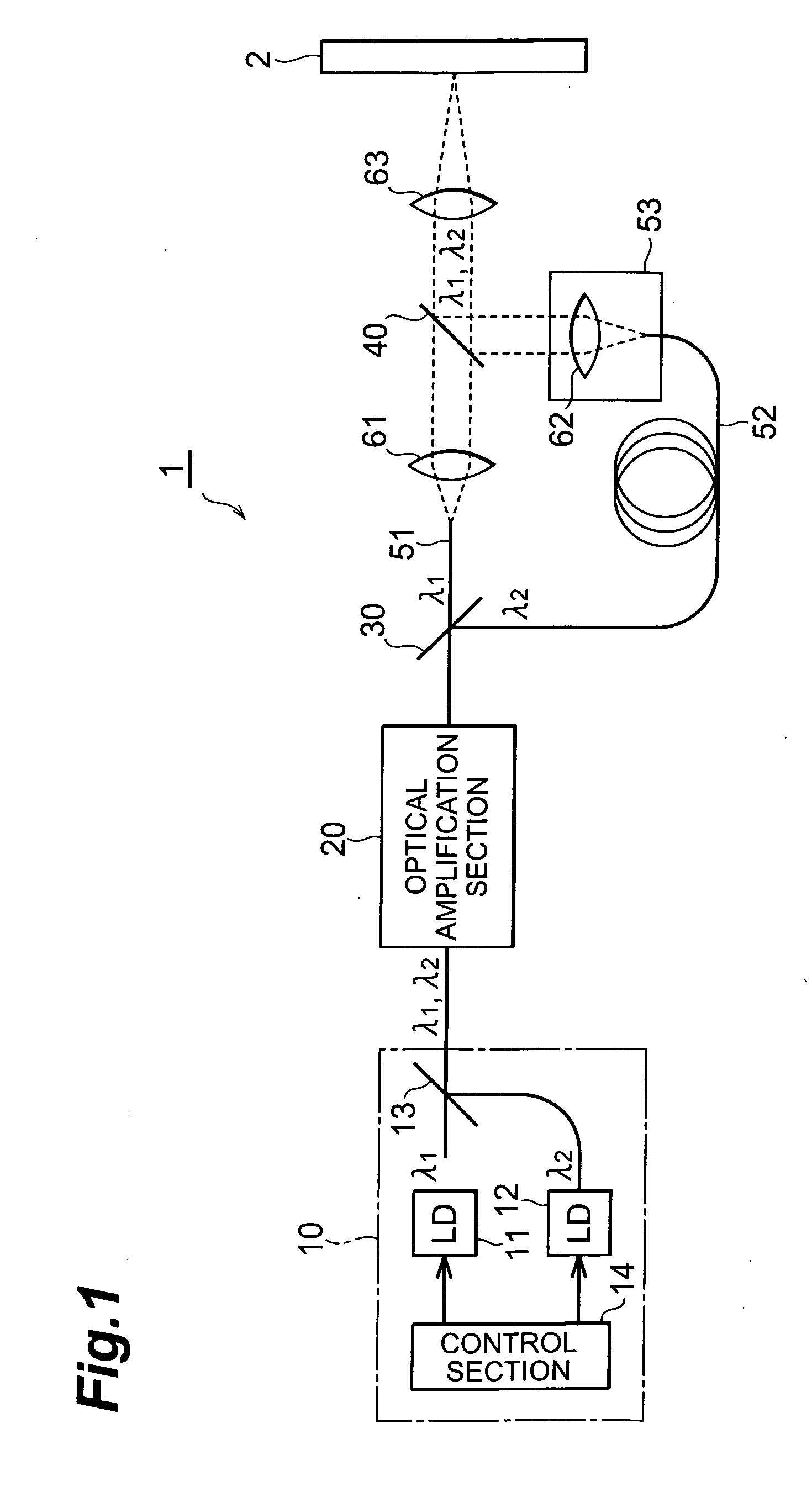
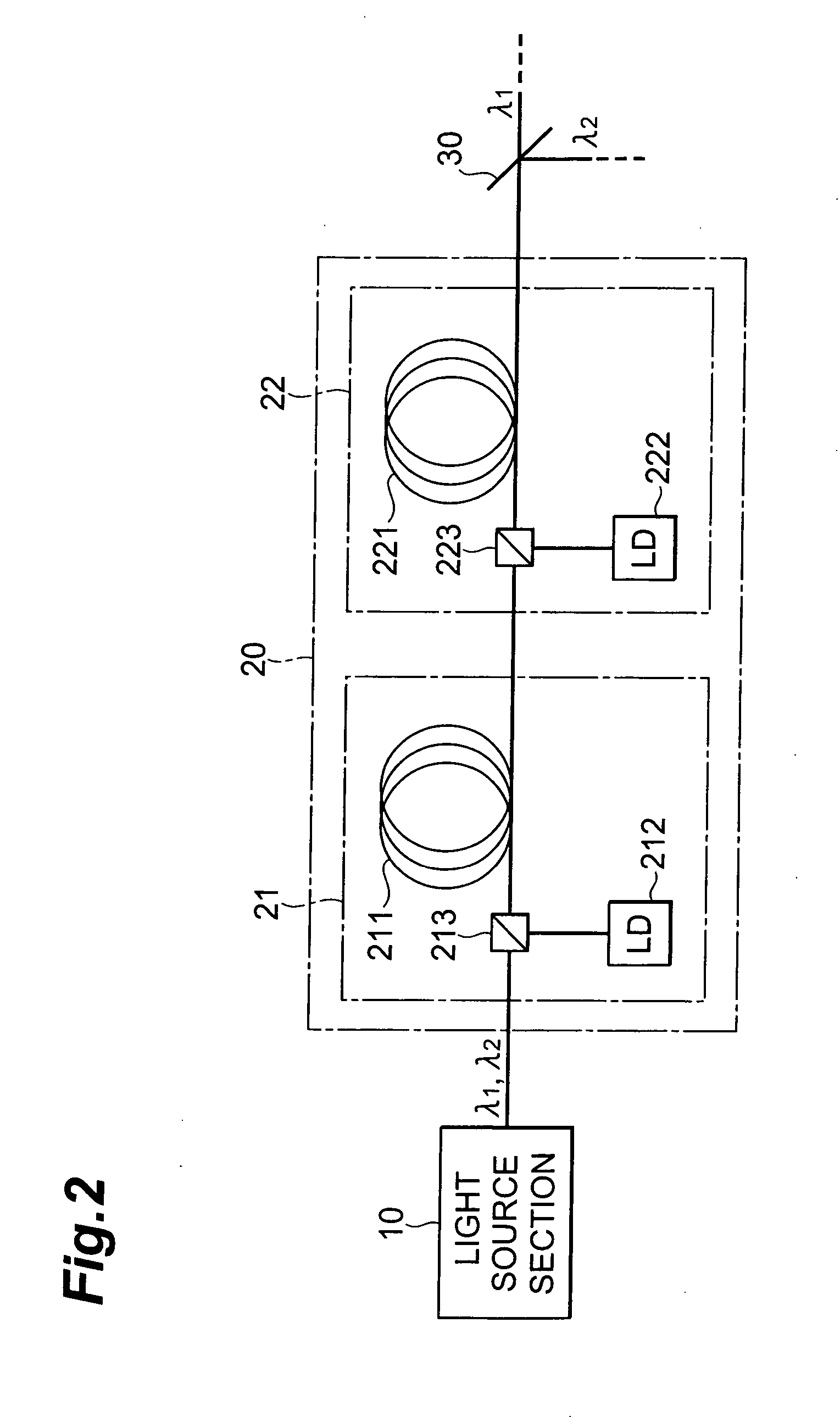
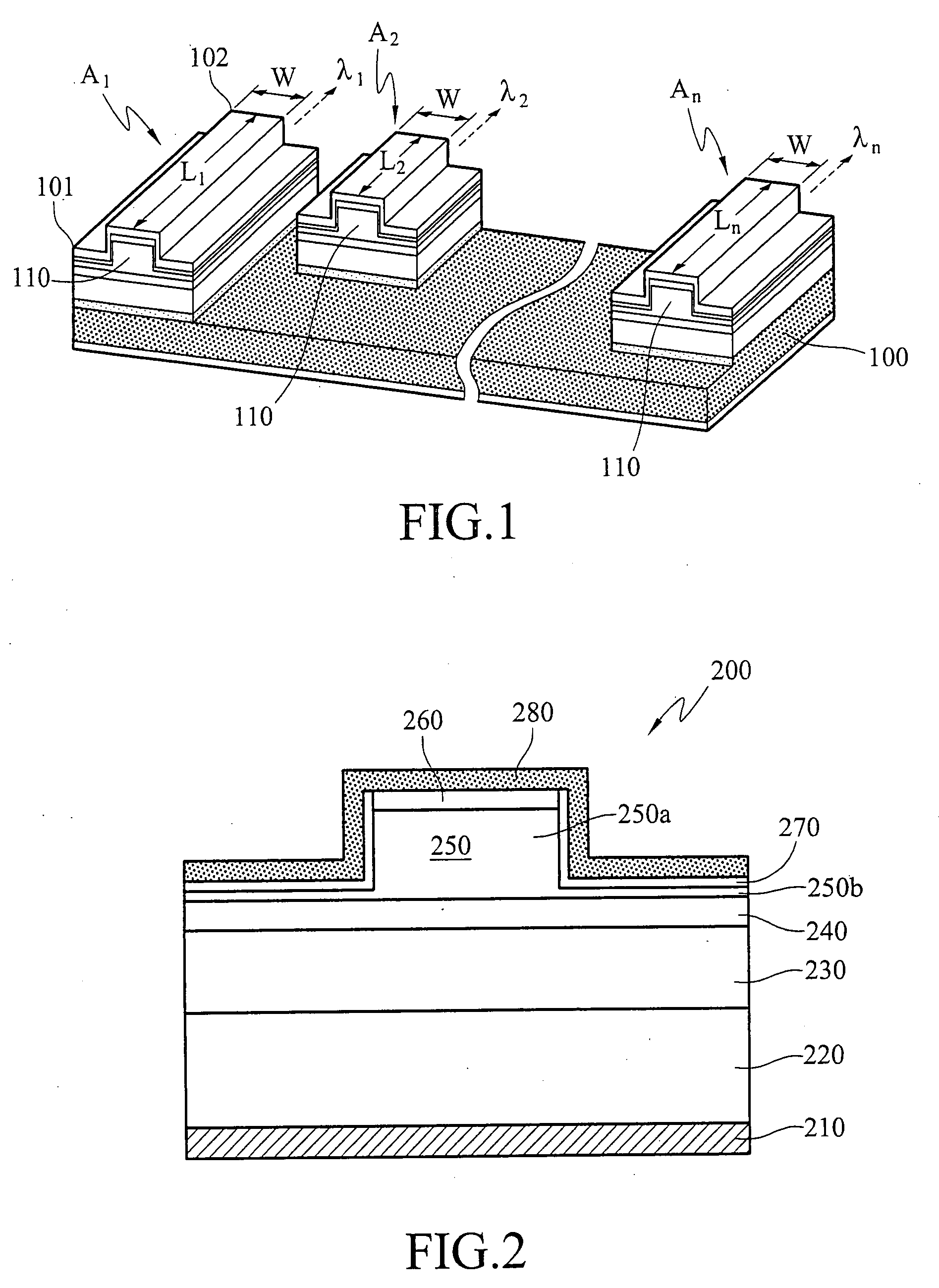
Laser light source, method of laser oscillation, and method of laser processing
InactiveUS20060257150A1Precise processingGuaranteed uptimeLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingLaser processing
A laser light source includes a light source section for outputting pulse laser light λ1, λ2 with a mutually identical repetition frequency, an optical amplification section for amplifying and outputting the pulse laser light λ1, λ2 output from the above light source section by means of a common optical amplification medium, an optical demultiplexing section for mutually demultiplexing pulse laser light λ1, λ2, an optical multiplexing section for multiplexing and outputting the pulse laser light λ1, λ2 demultiplexed in the above optical demultiplexing section, and an optical path length difference setting section for adjusting an optical path length difference between the pulse laser light λ1, λ2 in between the optical demultiplexing section and the optical multiplexing section.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Coupled cavity high power semiconductor laser
InactiveUS6898225B2Reduce lossesConveniently formedLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsElectricityThermal contact
An active gain region sandwiched between a 100% reflective bottom Bragg mirror and an intermediate partially reflecting Bragg mirror is formed on a lower surface of a supporting substrate, to thereby provide the first (“active”) resonator cavity of a high power coupled cavity surface emitting laser device. The bottom mirror is preferably in direct thermal contact with an external heat sink for maximum heat removal effectiveness. The reflectivity of the intermediate mirror is kept low enough so that laser oscillation within the active gain region will not occur. The substrate is entirely outside the active cavity but is contained within a second (“passive”) resonator cavity defined by the intermediate mirror and a partially reflecting output mirror, where it is subjected to only a fraction of the light intensity that is circulating in the gain region. The active gain region is preferably electrically excited, with a circular bottom electrode formed by an oxide current aperture between the bottom mirror and the heat sink, and with an annular top electrode formed on an upper surface of the substrate.
Owner:NECSEL INTPROP +1
Laser Light Source and Optical Device
InactiveUS20090067453A1Highly-efficient monochrome light generationReduce coherenceCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsTransverse modeLaser light
A laser light source is provided with a pump light source (1) comprising a semiconductor laser, a solid laser medium (2) which is excited by the semiconductor laser, and multi-mode means for changing at least either a longitudinal mode or a transverse mode of laser oscillation of the solid laser. The oscillation light of the laser medium excited by the light outputted from the pump light source is changed by the multi-mode means into output light (5) having a plurality of oscillation spectra and is outputted, thereby a small, high power, and highly efficient low coherent light source can be realized, and a laser light source having reduced speckle noises can be provided.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Laser processing apparatus, laser processing method, and method for making settings for laser processing apparatus
Owner:KEYENCE
Apparatus for driving light emitting element and system for driving light emitting element
InactiveUS20060133435A1High modulation speedSuppress power consumptionLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionEngineeringThreshold voltage
In case of driving each of light emitting parts of a surface emitting laser, each of light emitting parts is made to be in forward-bias state and switches appropriately change bias voltage, which is lower than laser oscillation threshold voltage, and drive voltages, which are not less than the laser oscillation threshold voltage to directly apply the changed voltage to each of drive ends of the light emitting parts. Whereby, each of light emitting parts is driven.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
Semiconductor laser apparatus and optical amplifier apparatus
A method of bonding a compound semiconductor on a silicon waveguide is used for attaining a laser above a silicon substrate. While it is essential to attain laser oscillation by injection of a current, since amorphous is formed at the bonding surface of a silicon compound semiconductor, it is difficult to directly inject the current through the silicon waveguide to the compound semiconductor. Further, even when an electrode is formed near the waveguide and the current is injected, since the current is not injected near the silicon waveguide, laser oscillation through the silicon waveguide can not be attained. The problem is solved by forming a structure of laterally injecting a current to the silicon waveguide and concentrating the current near the silicon waveguide in a compound semiconductor. Specific methods includes the following two methods, that is, a method of forming a tunneling junction structure in the compound semiconductor and another method of laterally forming a P-I-N junction to the compound semiconductor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Rare earth-doped core optical fiber
InactiveUS20100067860A1Lower refractive indexSufficient powerLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRefractive indexRare earth
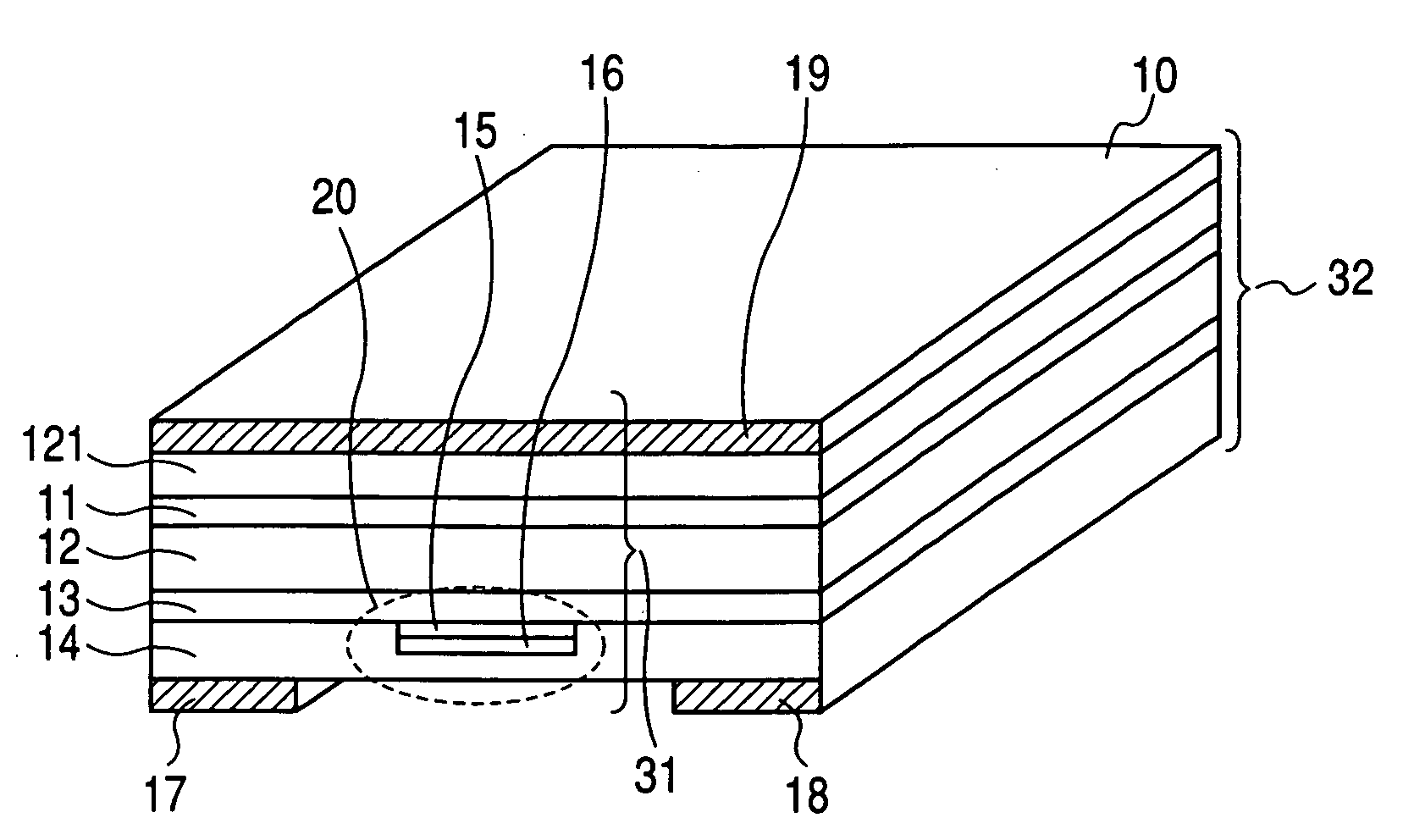
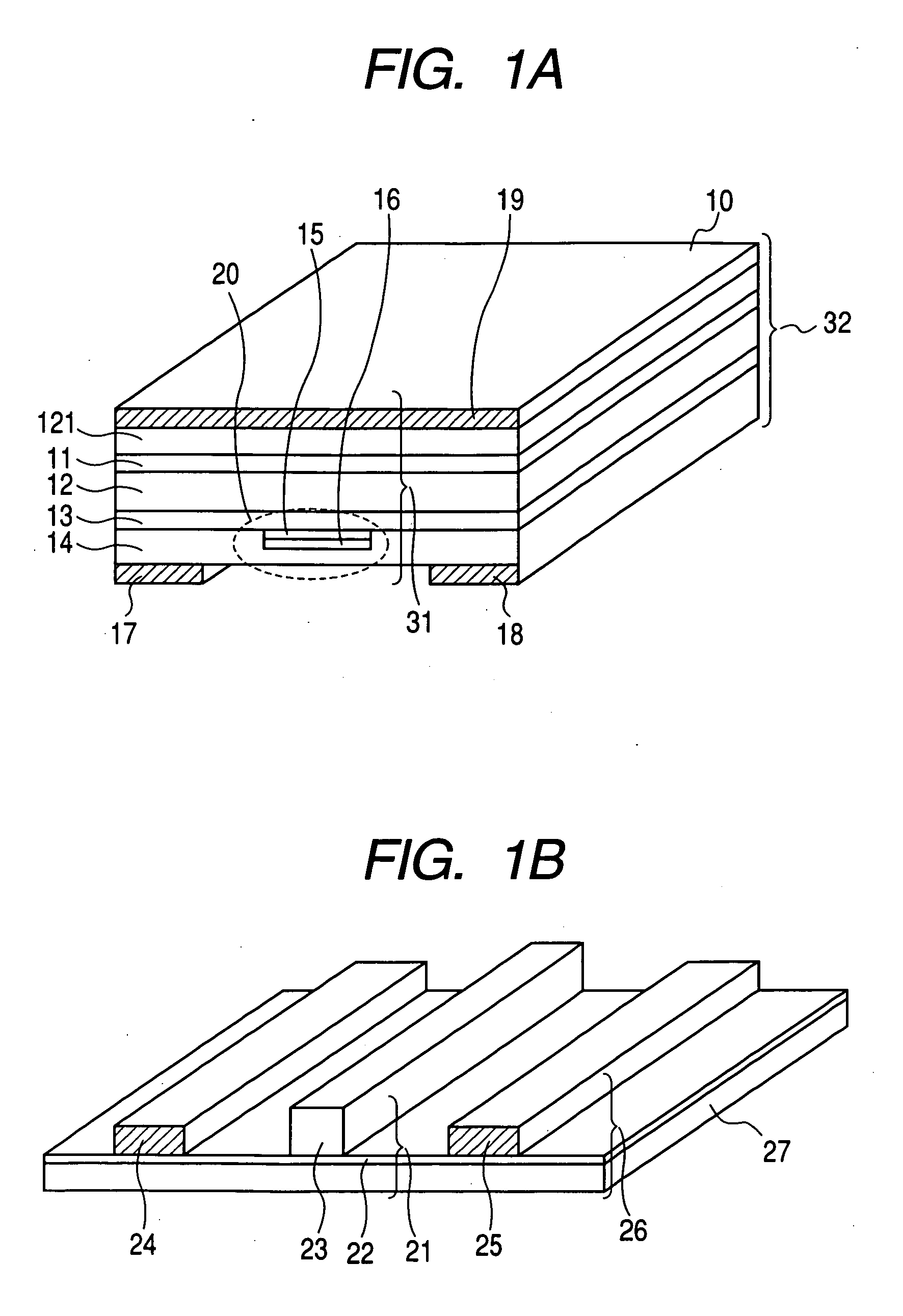
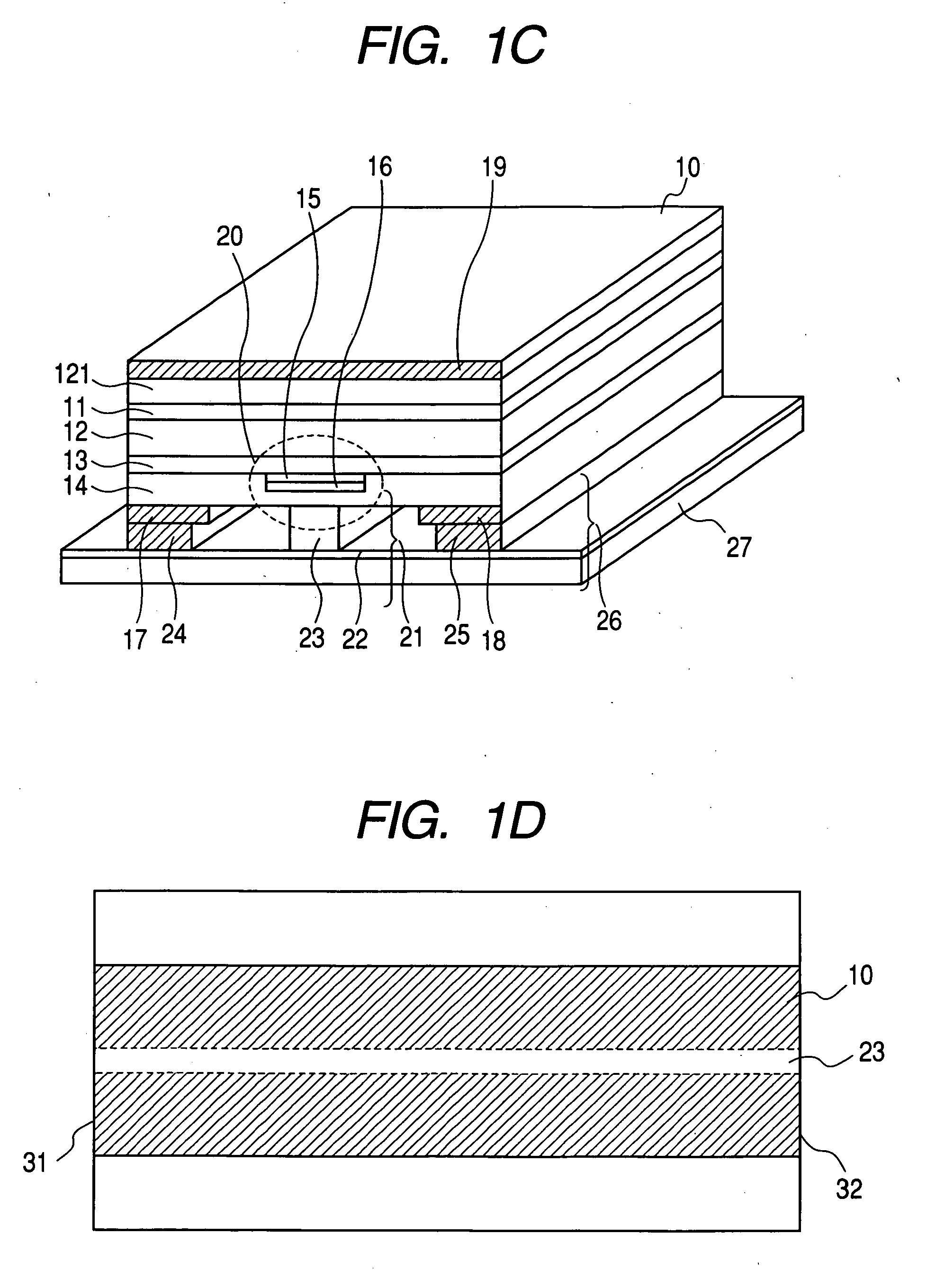
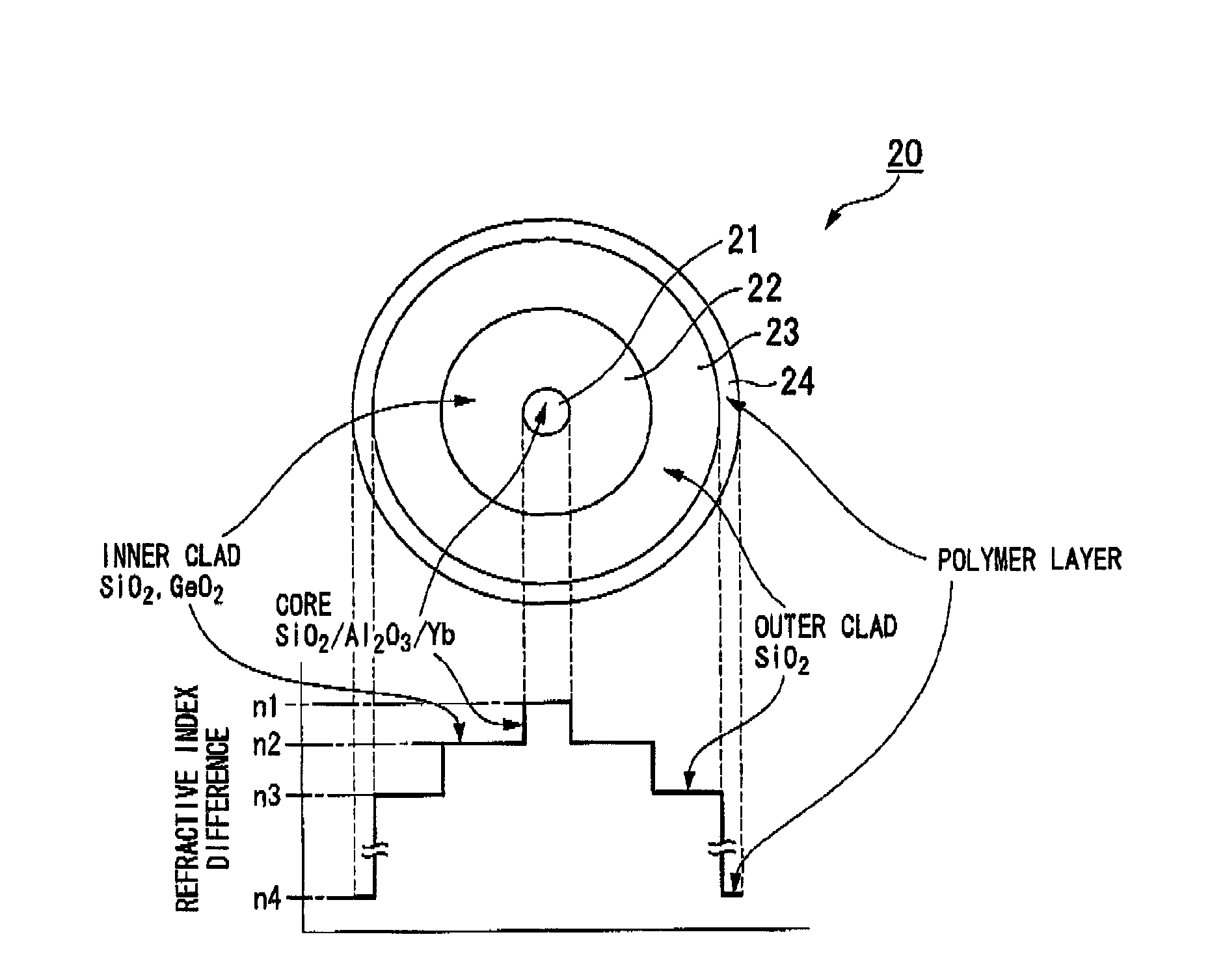
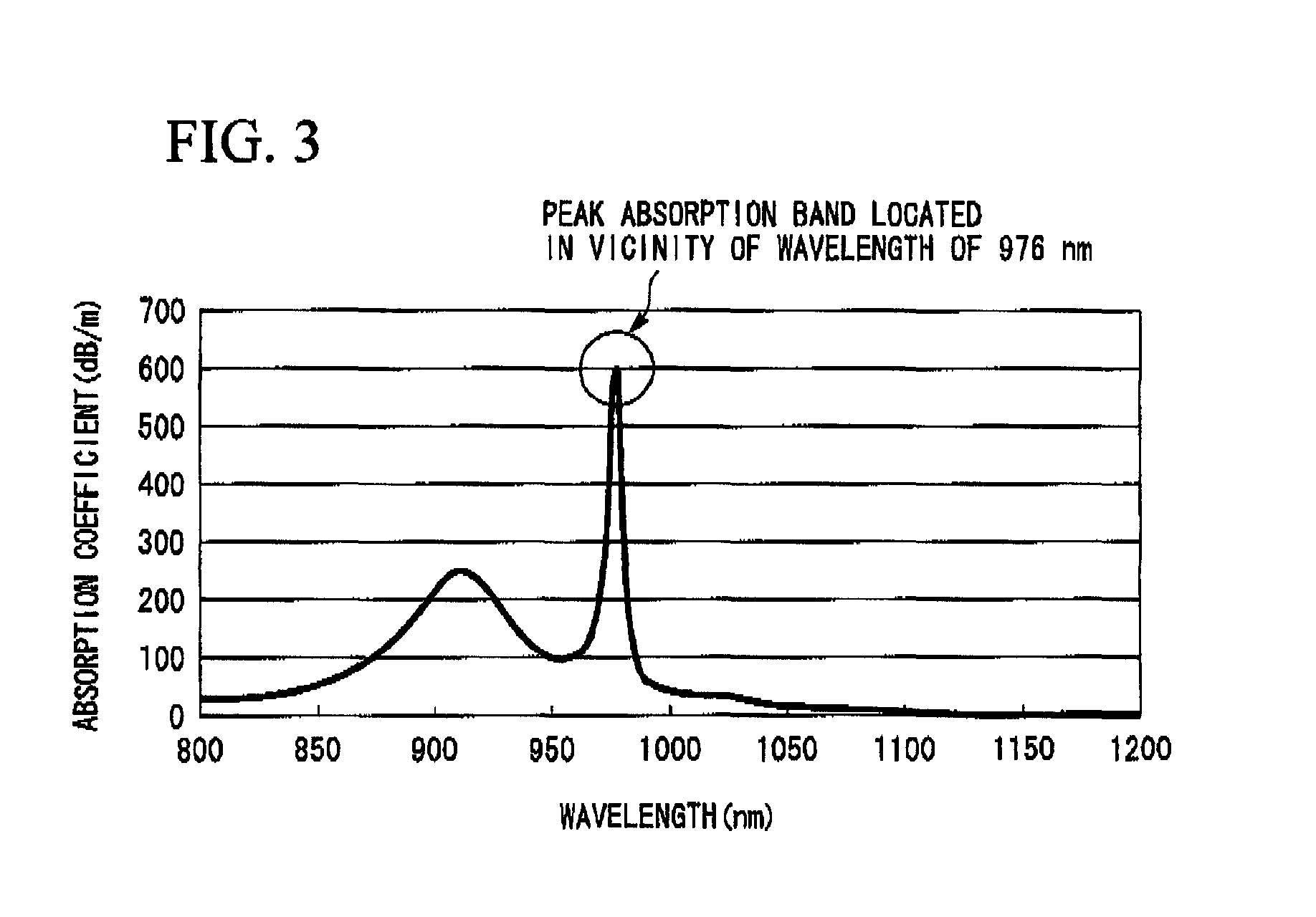
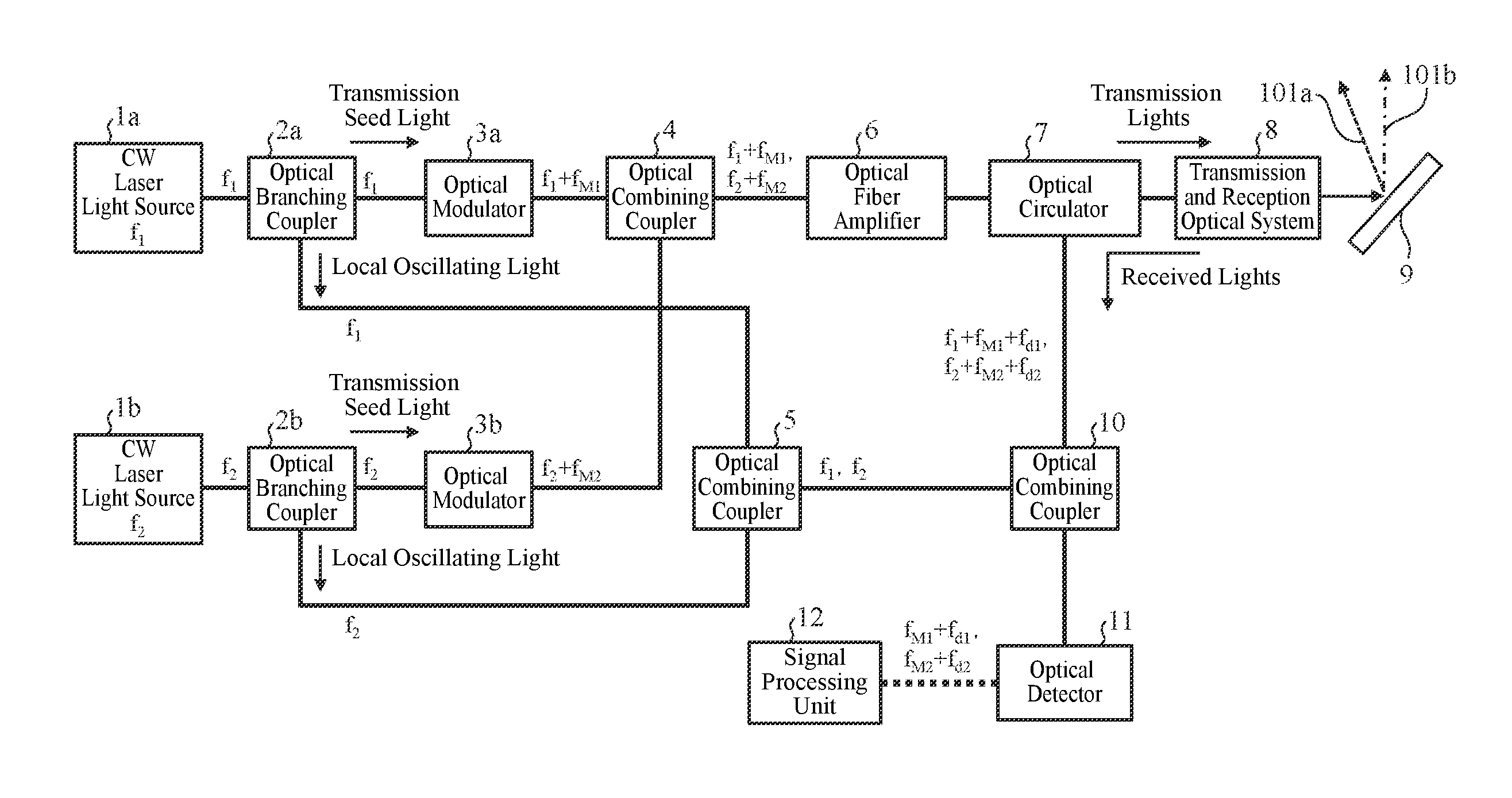
A rare earth-doped core optical fiber includes a core comprising a silica glass containing at least aluminum and ytterbium, a clad provided around the core and comprising a silica glass having a lower refraction index than that of the core, and a polymer layer provided on the outer circumference of the clad and having a lower refractive index than that of the clad, wherein aluminum and ytterbium are doped into the core such that a loss increase by photodarkening, TPD, satisfies the following inequality (A). By this rare earth-doped core optical fiber, it is possible to manufacture an optical fiber laser capable of maintaining a sufficient laser oscillation output even when used for a long period of time.TPD≧10{−0.655*(D<sub2>Al< / sub2>)−4.304*exp{−0.00343*(A<sub2>Yb< / sub2>)}+1.274} (A)
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD
Laser radar device
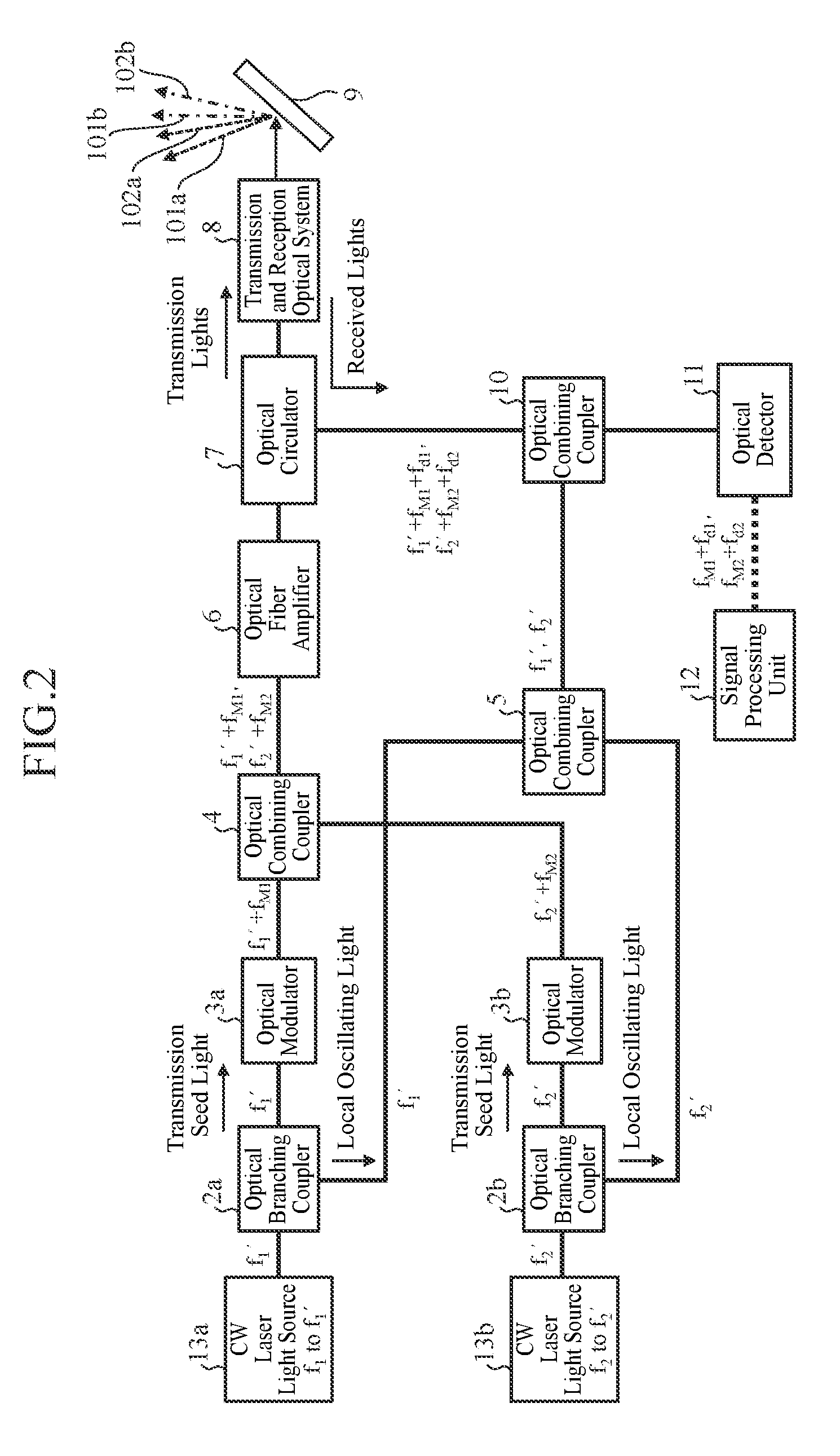
InactiveUS20160291137A1Simple and low-cost configurationLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsRadarLaser light
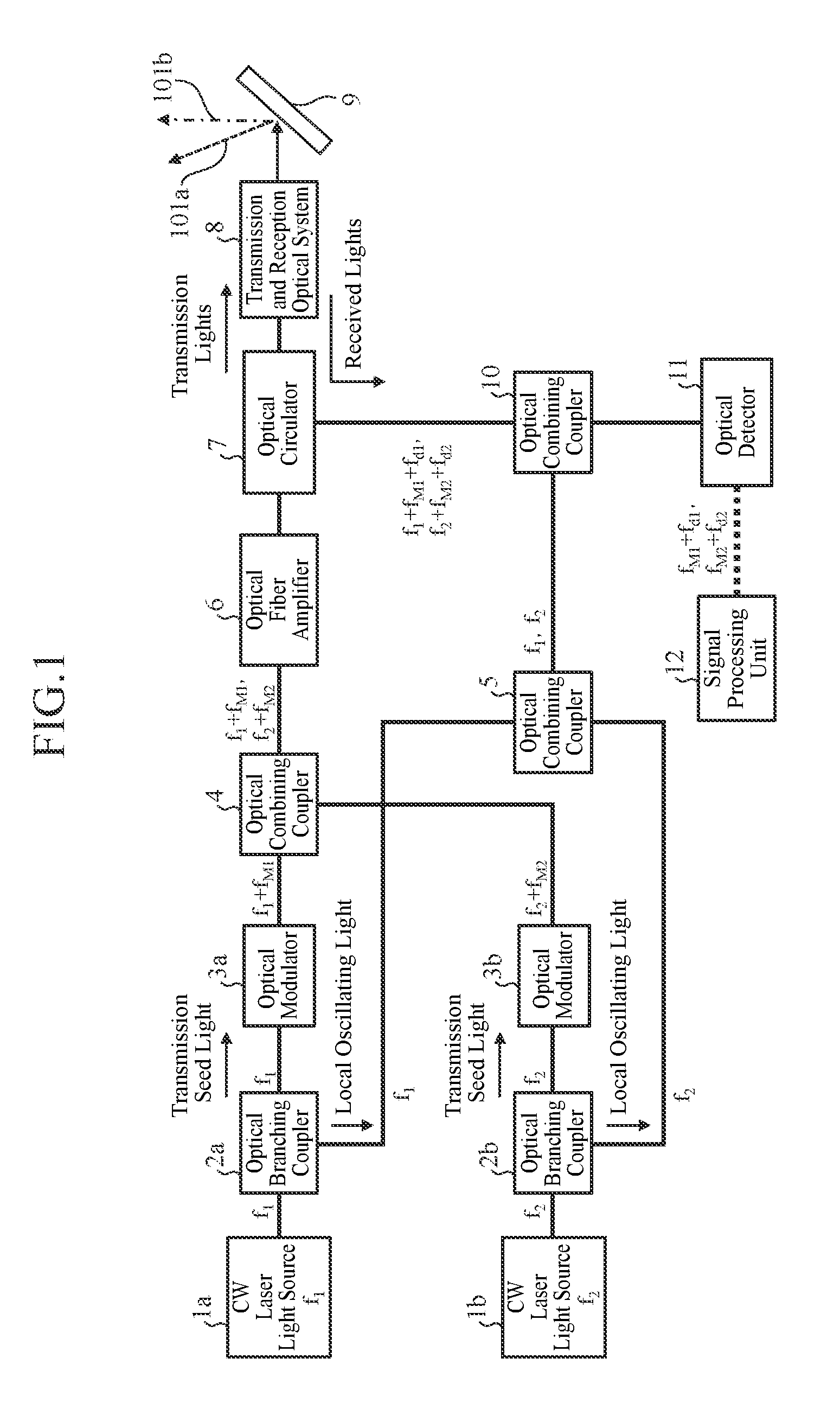
Disclosed is a laser radar device including optical branching couplers each of that branches a laser light oscillated, optical modulators each of that modulates a laser light after being branched, an optical combining coupler that combines laser lights modulated by the optical modulators, an optical combining coupler that combines other laser lights after being branched, an optical system that emits a composite light from the optical combining coupler, and receives lights scattered by a target, an optical combining coupler that combines the scattered lights and a composite light from the optical combining coupler, an optical detector that detects beat signals from a composite light from the optical combining coupler, a signal processing unit that extracts information about the target from the beat signals, and a diffraction grating that emits a light incident thereupon toward a specific direction according to the angle and the frequency of the incident light.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
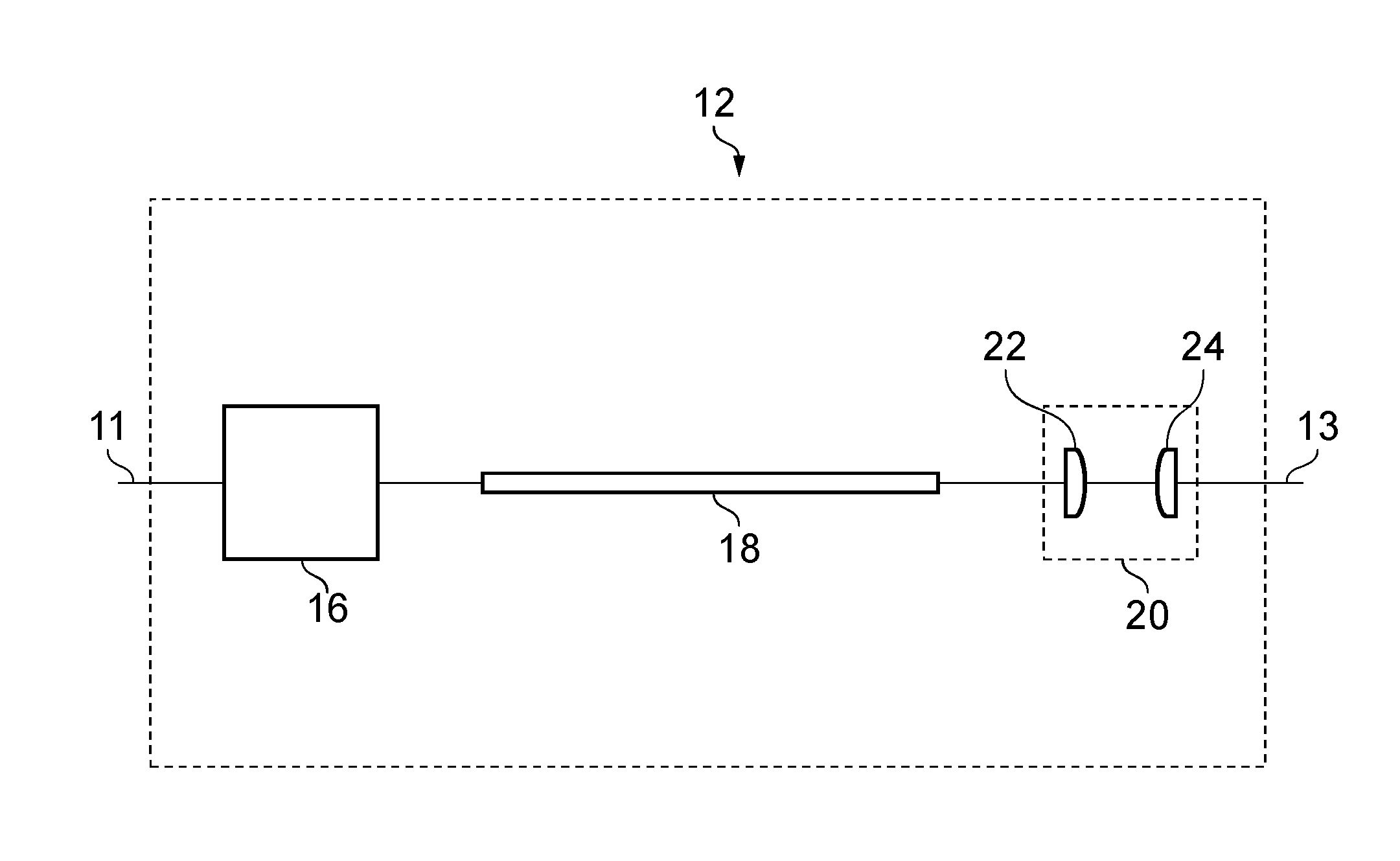
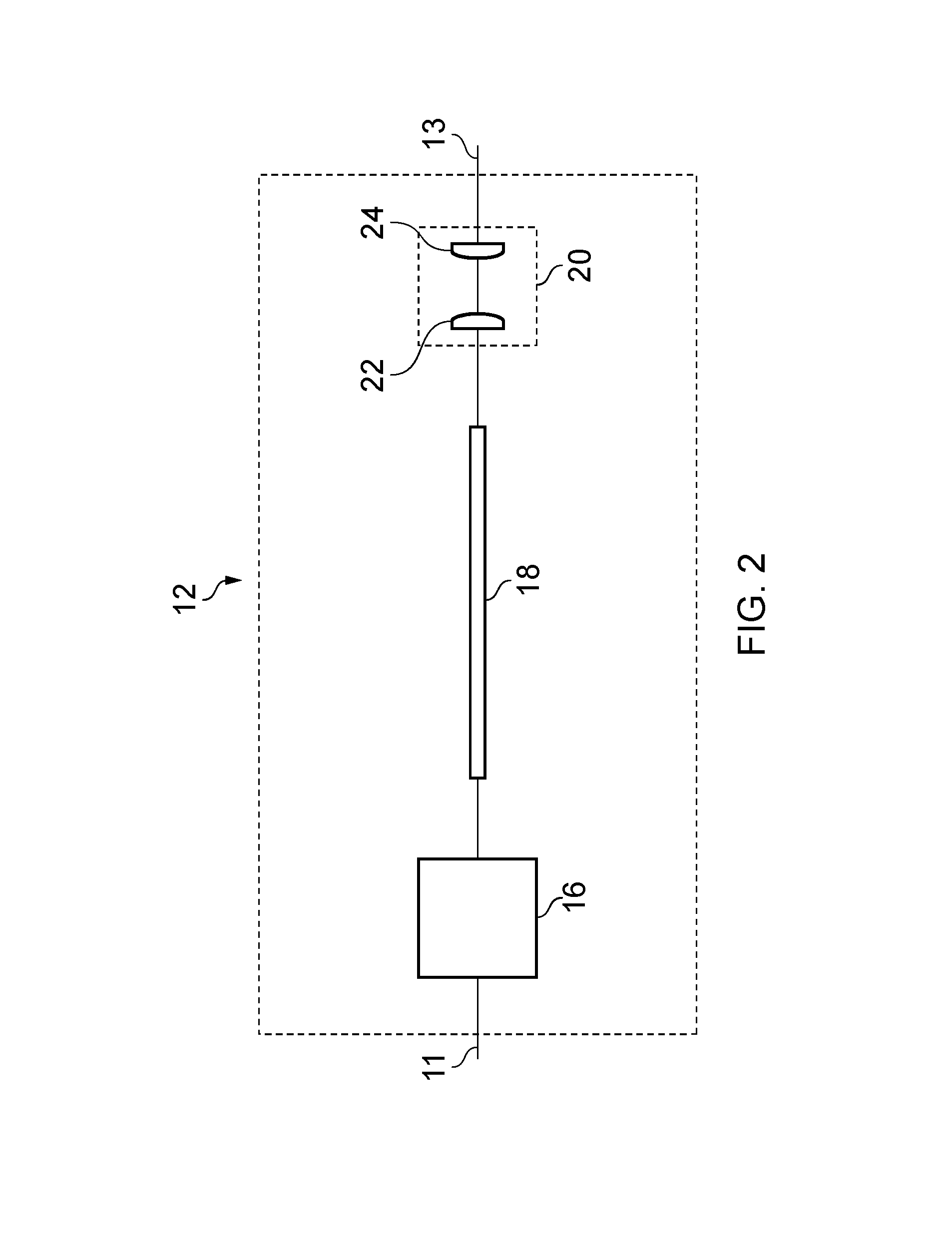
Laser with a tailored axially symmetric pump beam profile by mode conversion a waveguide
InactiveUS20140044143A1Fibre with gratingsOptical devices for laserResonant cavityUltimate tensile strength
A laser device comprising a pump source (10) operable to generate a pump beam (11) for a resonant cavity in which a laser medium (74) is arranged. A beam-shaping waveguide element (18) is arranged between the pump source and the resonant cavity. Shaping of the pump beam is achieved by tailoring the refractive index profile of the waveguide element (18) so that it yields an intensity distribution which spatially overlaps a desired ring-shaped Laguerre-Gaussian mode of the resonant cavity sufficiently well to achieve laser oscillation on said desired Laguerre-Gaussian mode. A ring-shaped or doughnut-shaped laser beam profile can thus be generated. It is further possible to design the refractive index profile (76) so that the pump beam's intensity distribution also spatially overlaps the fundamental mode of the resonant cavity sufficiently well to achieve laser oscillation also on said fundamental mode. The laser will then lase on both the fundamental mode and the selected Laguerre-Gaussian mode. This is useful for producing a variety of beam profiles based on mixing a Gaussian profile with a ring-shaped profile. A top-hat beam profile can be achieved by such mixing.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Laser apparatus, laser irradiation method, manufacturing method for a semiconductor device, semiconductor device and electronic equipment
InactiveUS6844523B2Improve processing efficiencyAvoid intensityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPower semiconductor deviceCentre of rotation
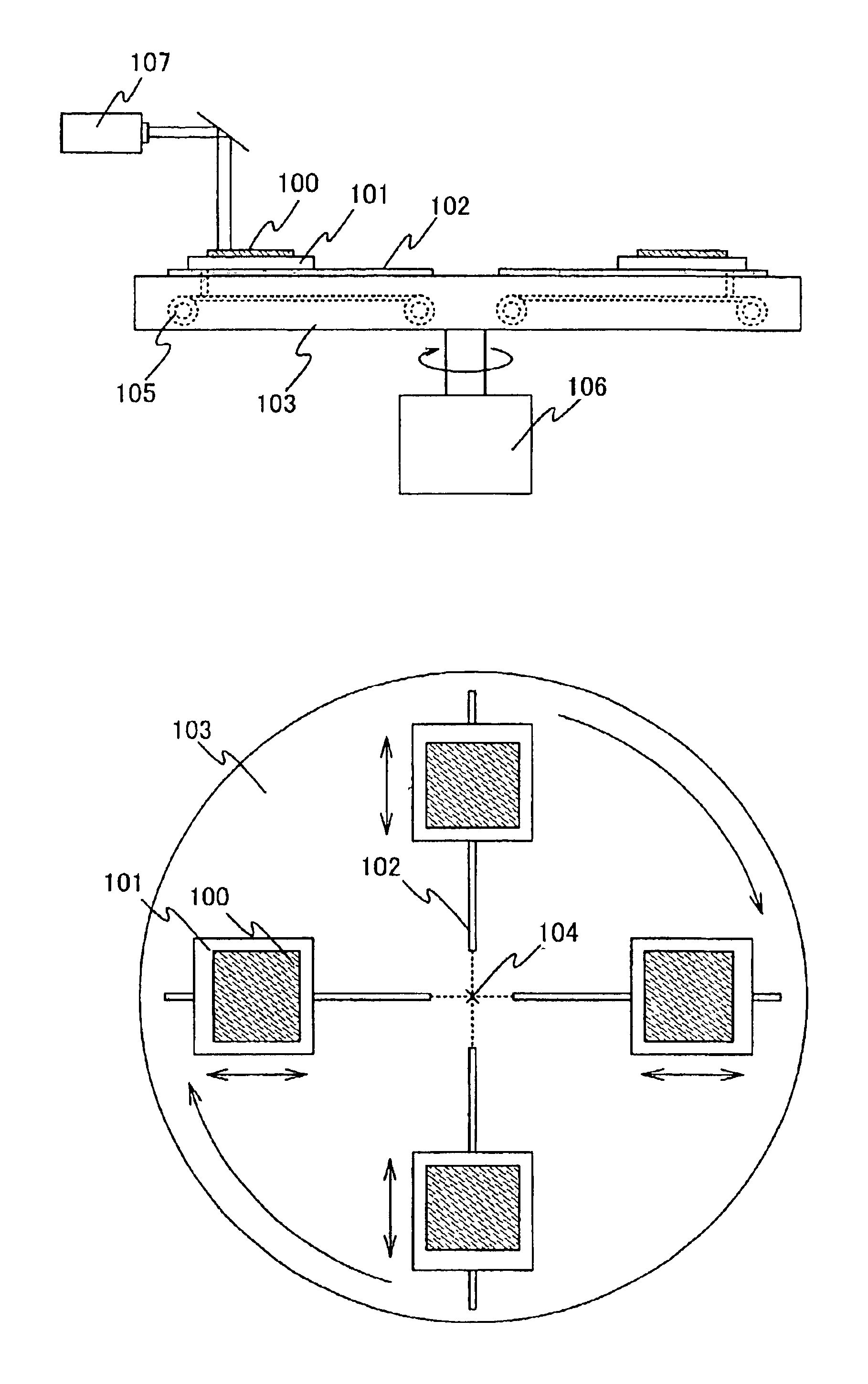
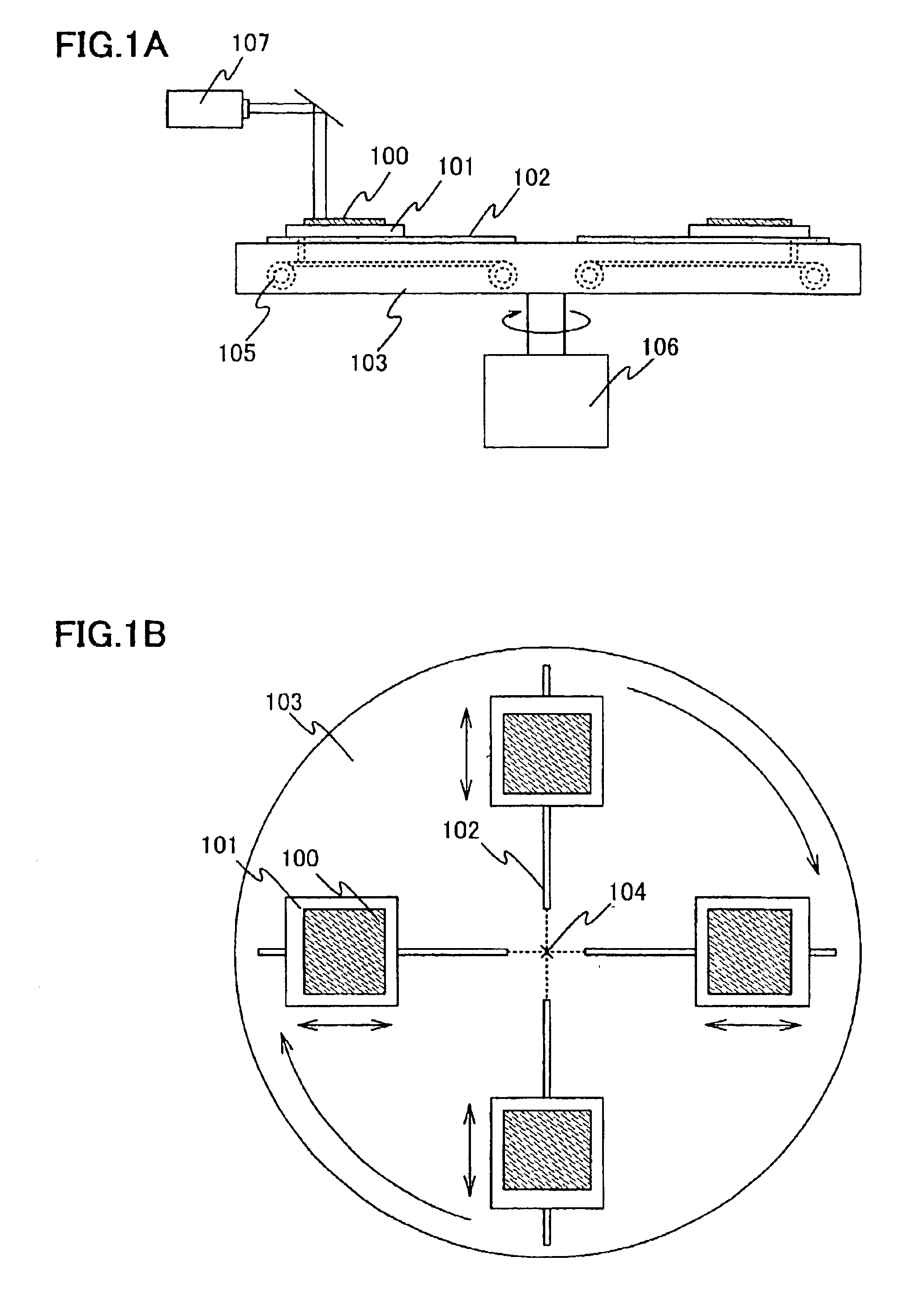
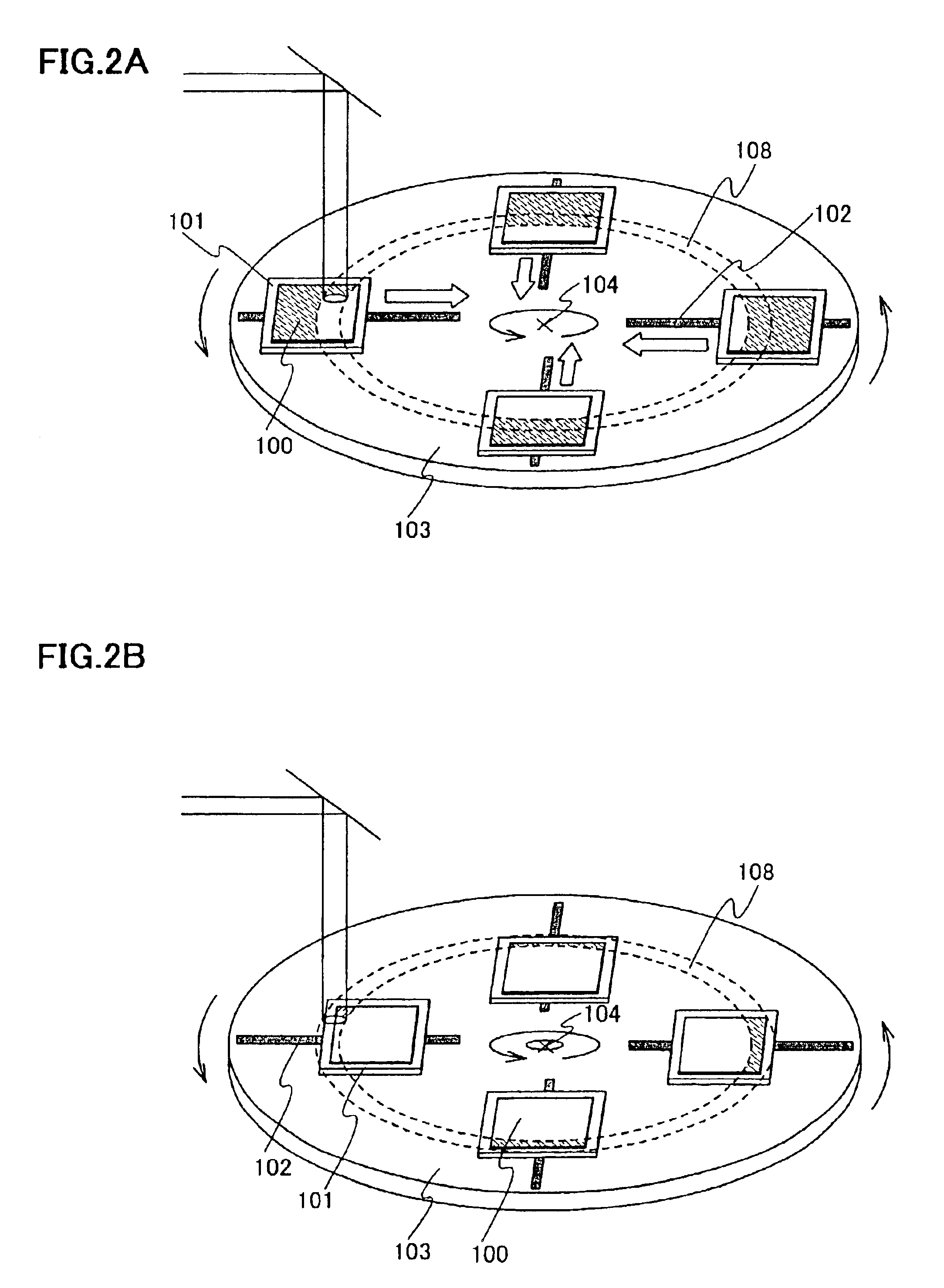
To provide a continuous oscillation laser apparatus, and a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device using the continuous oscillation laser apparatus, which can enhance processing efficiency. A laser apparatus according to the present invention includes: a laser oscillation apparatus; a unit for rotating an object to be processed; a unit for moving the object to be processed toward a center of the rotation or toward an outside from the center; and an optical system for processing a laser light outputted from the laser oscillation apparatus and irradiating the processed laser light to a definite region in a moving range of the object to be processed, in which, while the object to be processed is rotated, the object to be processed is moved toward the center of the rotation or toward the outside from the center to move a position where the definite region and the object to be processed overlap.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
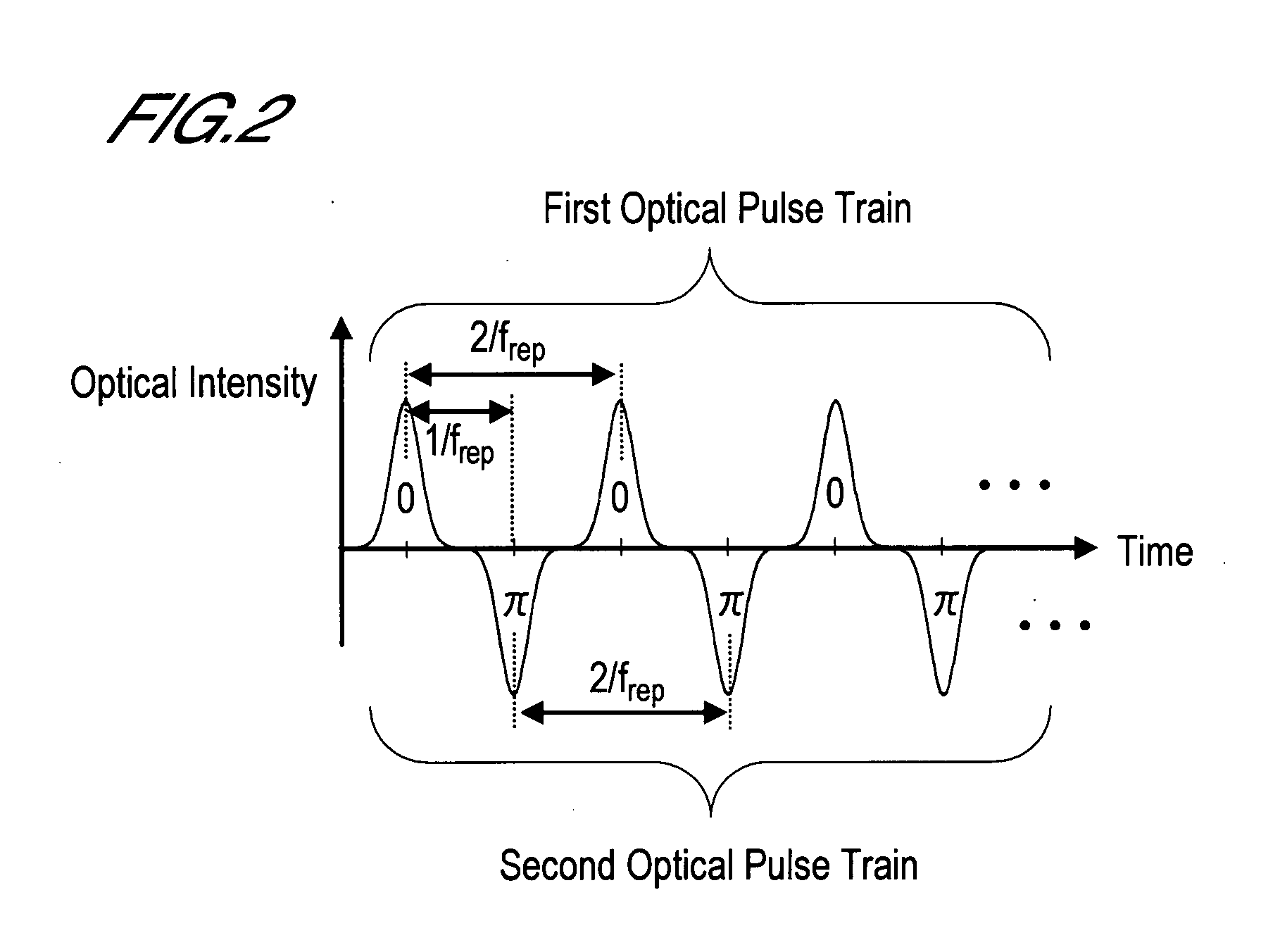
Carrier-suppressed optical pulse train generation method and mode-locked semiconductor laser diode for realizing this method
InactiveUS20080025358A1Small sizePrevented from reachingOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersMode-lockingCarrier signal
A CS optical pulse train generation method, which is able to change the half width of an optical pulse constituting a CS optical pulse train, and which is compact and has low power consumption. A distributed Bragg reflector semiconductor laser utilized in this method is one which is constituted comprising an optical modulation region, a gain region, a phase control region, and a distributed Bragg reflector region. Current is injected into the gain region by way of a p-side electrode and a n-side common electrode by a constant current source, forming the population inversion required for laser oscillation. Optical modulation required to manifest mode locking is carried out in the optical modulation region. A diffraction grating is formed in the distributed Bragg reflector region. A CS optical pulse train with a repetitive frequency of frep is generated by adjusting the effective indices of both the phase control region and the distributed Bragg reflector region such that, of the longitudinal modes of the mode-locked semiconductor laser diode, the two longitudinal modes close to the frequency f0, which is the Bragg wavelength of the distributed Bragg reflector region converted to a frequency, become f0+(frep / 2) and f0−(frep / 2).
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
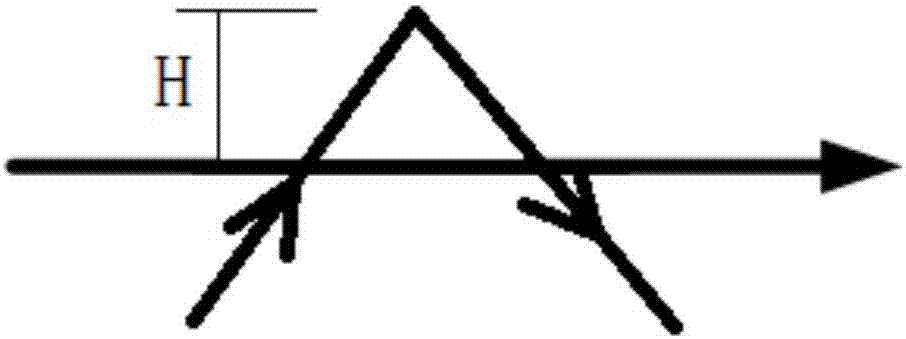
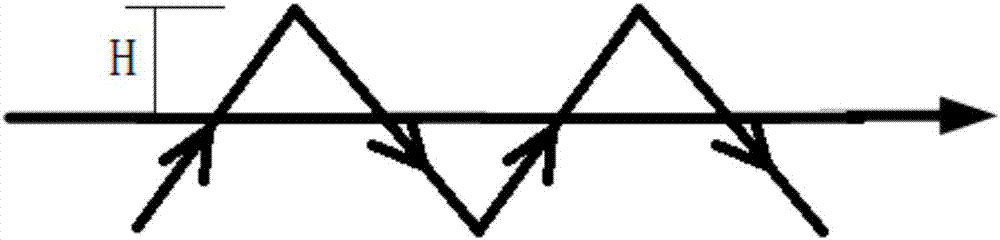
Aluminum alloy laser oscillation welding method
InactiveCN107442935AAvoid crackingAvoid stomatal defectsWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusClassical mechanicsMechanical property
The invention discloses an aluminum alloy laser swing welding process method, which belongs to the technical field of welding. The method includes welding with an oscillating laser beam, wherein during welding, the oscillating laser beam advances along an axis parallel to the welding direction, and while advancing, the oscillating laser beam is in the direction of the axis. Both sides oscillate back and forth to form a zigzag motion path, and the motion path has the same swing amplitude on both sides of the shaft, and the motion path is formed by repeatedly arranging a plurality of motion path units. The invention can effectively avoid the occurrence of internal cracks and porosity defects in the laser welding seam of the aluminum alloy, the welding seam formed by welding is excessively smooth, and the comprehensive mechanical properties of the welding seam are excellent.
Owner:BEIJING HANGXING MACHINERY MFG CO LTD
Semiconductor light-emitting device, surface-emission laser diode, and production apparatus thereof, production method, optical module and optical telecommunication system
InactiveUS20060261352A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical ModuleNitrogen
A semiconductor light-emitting device has a semiconductor layer containing Al between a substrate and an active layer containing nitrogen, wherein Al and oxygen are removed from a growth chamber before growing said active layer and a concentration of oxygen incorporated into said active layer together with Al is set to a level such that said semiconductor light-emitting device can perform a continuous laser oscillation at room temperature.
Owner:RICOH KK
Wavelength tunable laser diode using double coupled ring resonator
InactiveUS20090154505A1Improve output characteristicsRapid wavelength tunabilityLaser detailsOptical light guidesProduction rateLength wave
A wavelength tunable laser diode using a double coupled ring resonator is provided. A new double coupled ring resonator structure is formed by a connection of two ring resonators having different radii so that stable laser oscillation occurs only in a resonant wavelength at which the two ring resonators are simultaneously resonated, and the effective refractive index of the two ring resonators is properly controlled differently for tunable laser oscillation wavelengths. The reproducibility of the optical coupling characteristics of the passive waveguides and the ring resonator can be assured by multi-mode couplers. This results in improved manufacturing productivity of the wavelength tunable laser diode. It is possible to amplify and output an output light without having an effect on oscillation wavelength characteristic by means of an optical amplifier integrated in an output end.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
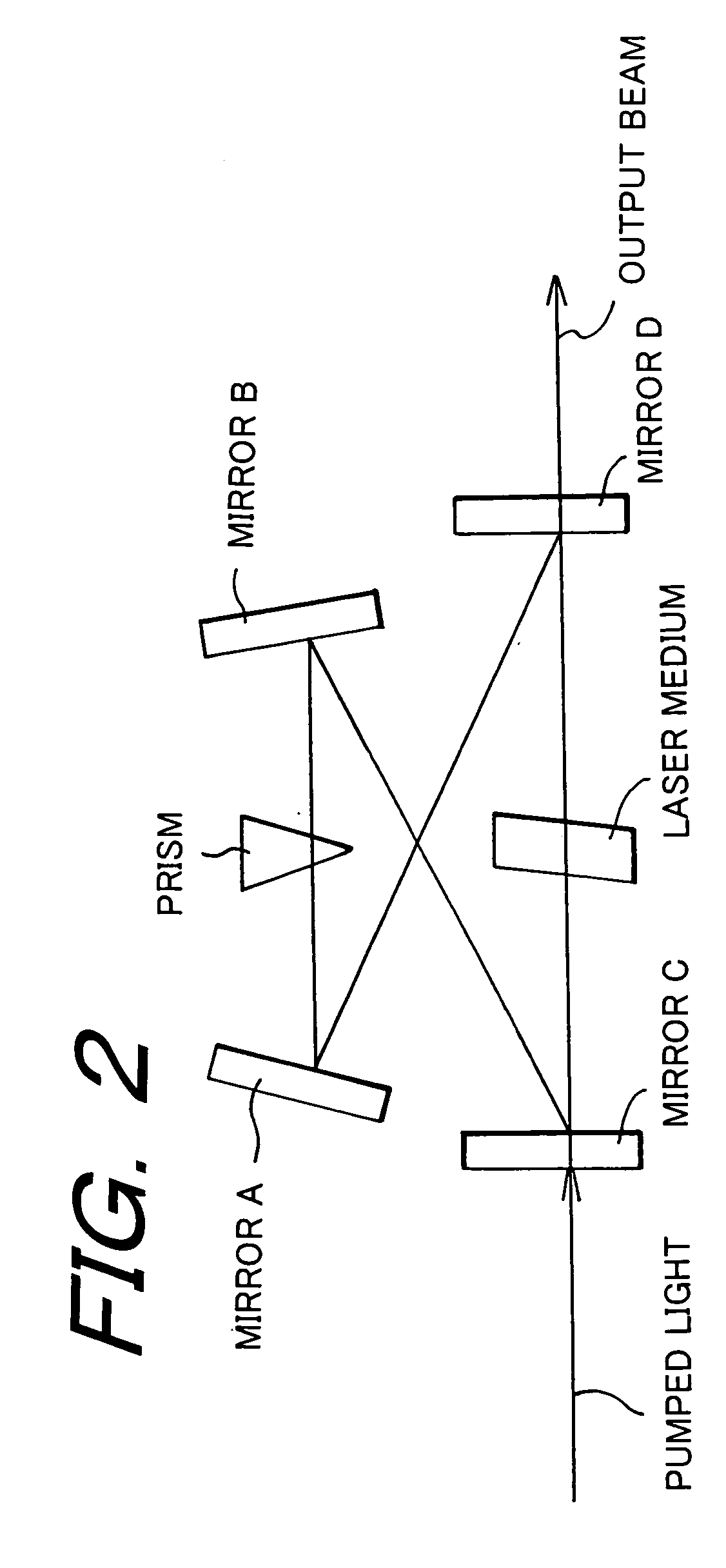
Composite Laser Element and Laser Oscillator Employing It
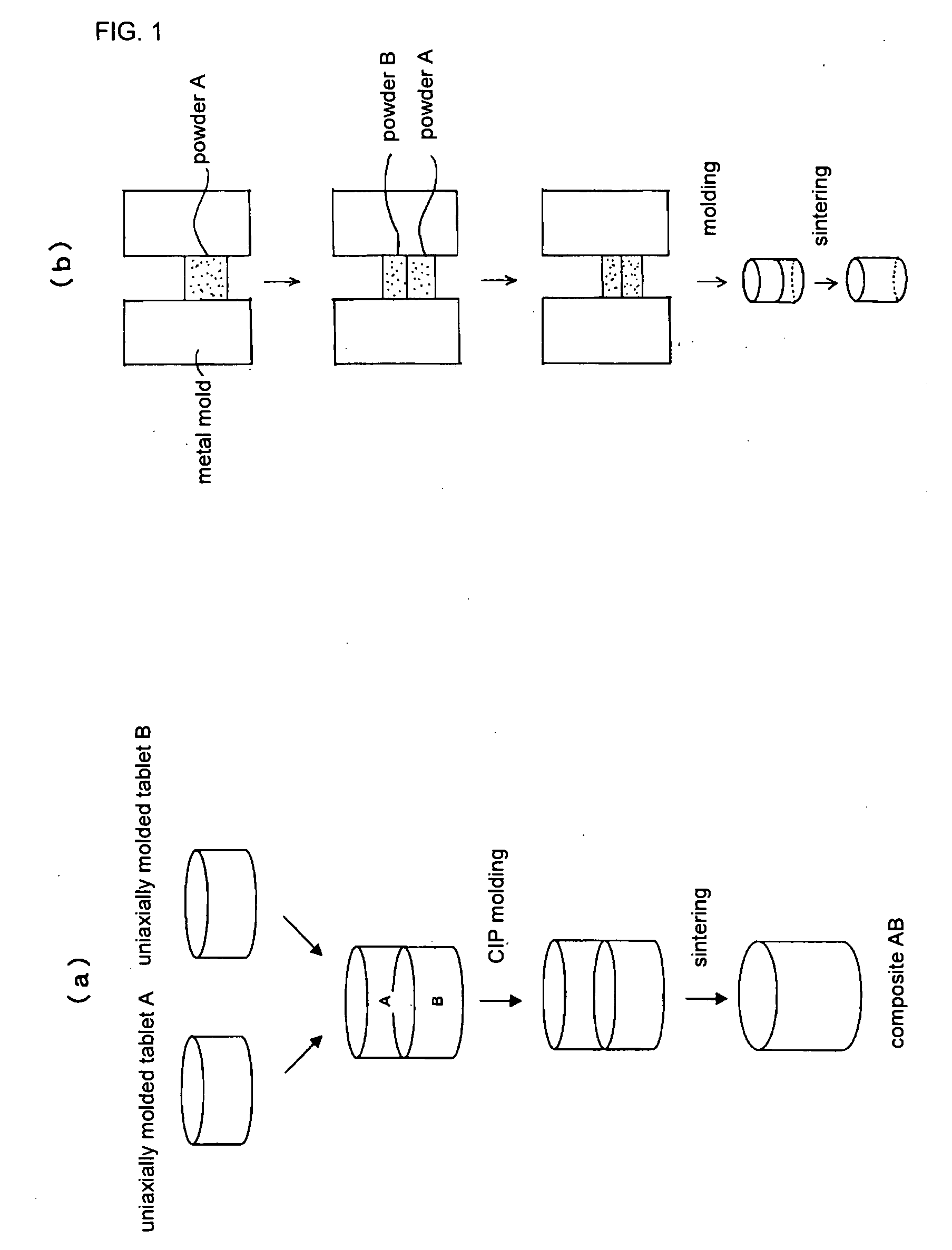
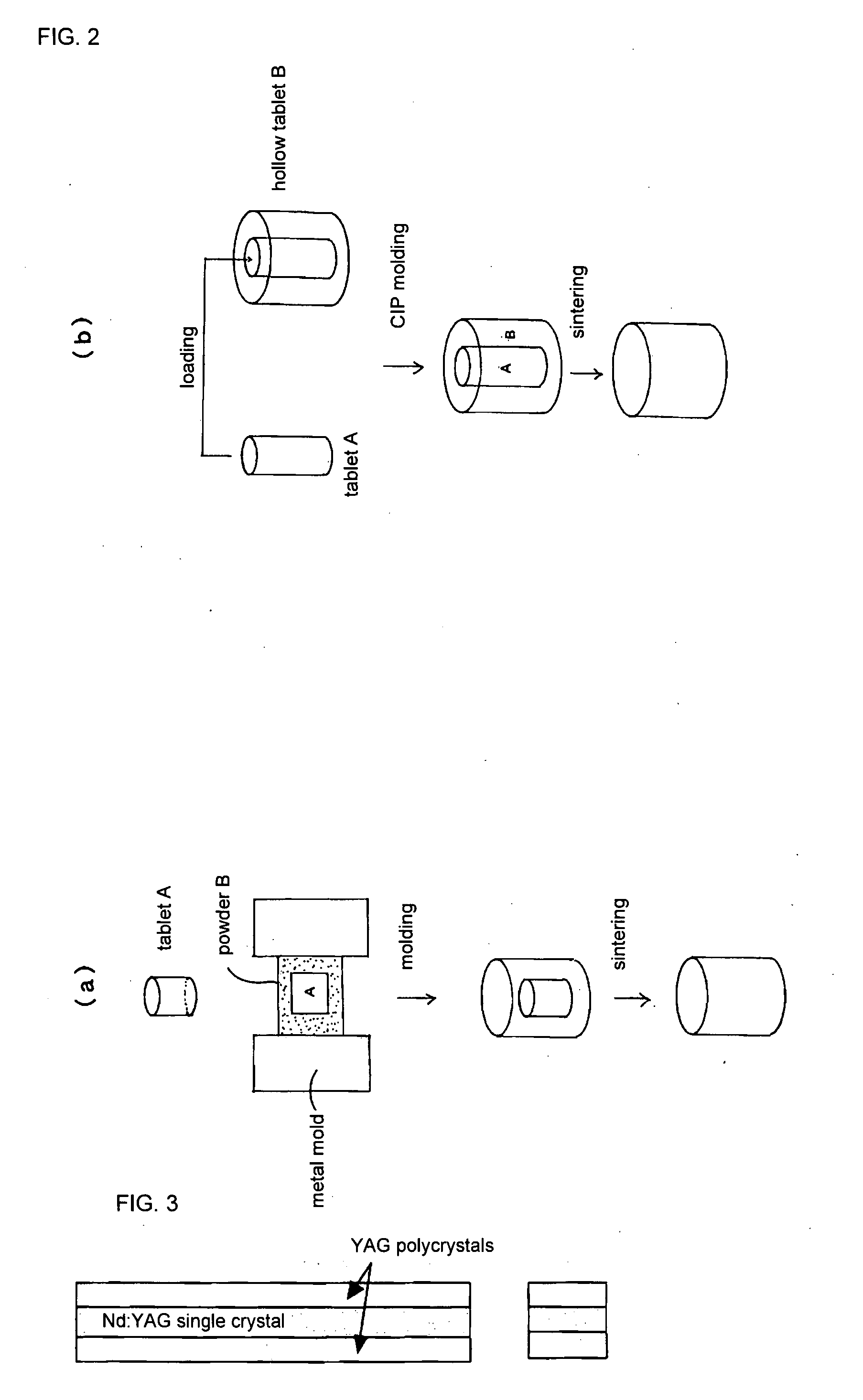
The present invention provides a composite laser element that solves the problems encountered with a conventional laser medium composed of an Nd:YAG single crystal or polycrystal, and exhibits excellent performance as a laser medium. The invention relates to a laser element in which two or more crystal materials are joined, wherein (1) at least one of the crystal materials is a transparent crystal material capable of laser oscillation, including a laser active element in a matrix crystal, and (2) the transparent crystal material capable of laser oscillation and / or a second crystal body joined thereto is a polycrystal.
Owner:IKESUE AKIO
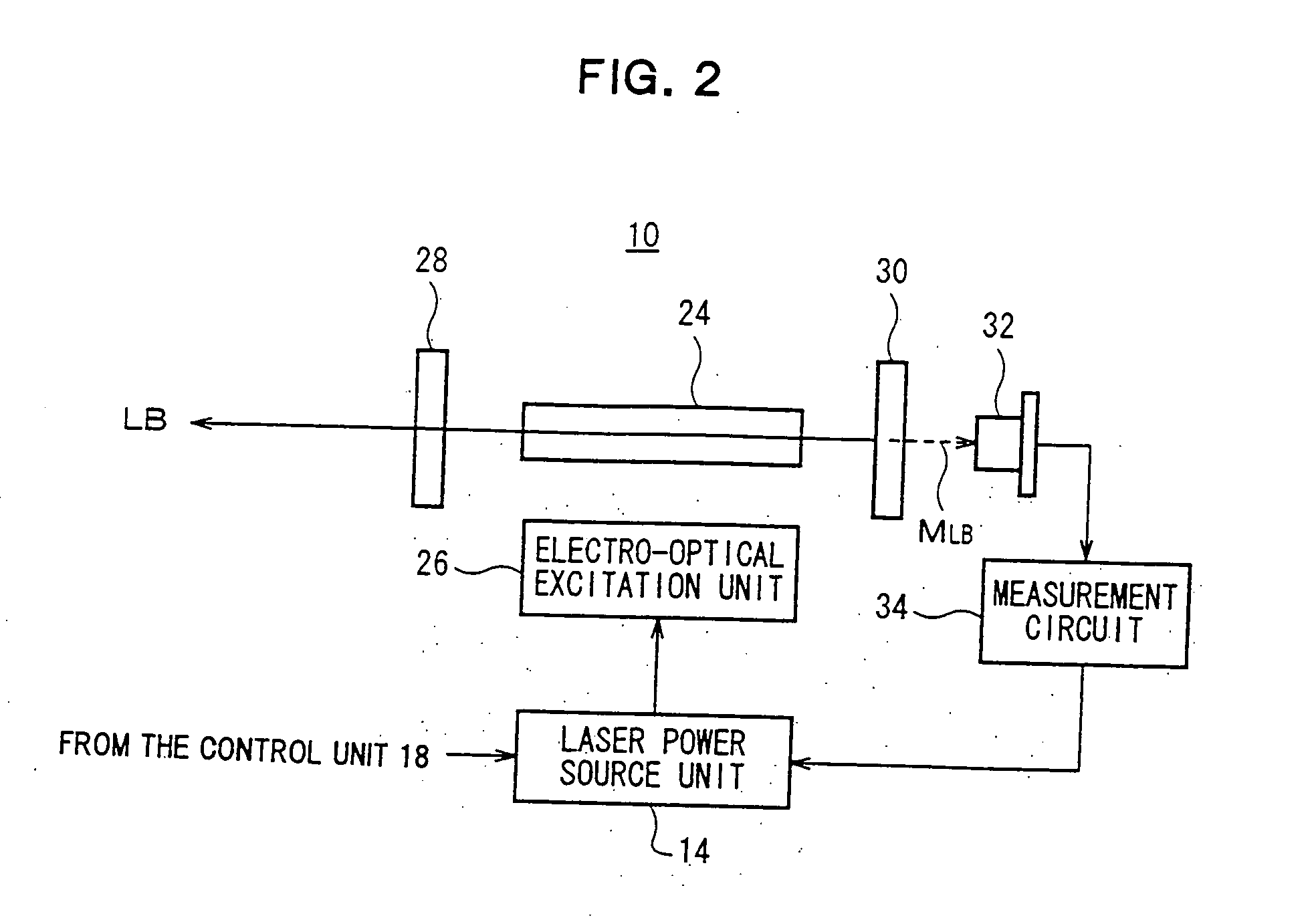
Method of stabilizing laser beam, and laser beam generation system
InactiveUS20050018723A1Constant characteristicVariation in characteristicActive medium materialExcitation beamLight beam
A laser beam generation system comprises a solid state laser oscillator excited by an excitation beam, and a Q switch for pulsating laser oscillation by use of a saturable absorber, wherein the optical path length of a laser resonator is variable. The pulse of a laser beam generated from the laser beam generation system is detected, and variation of the optical path length of the laser resonator is controlled based on a characteristic of the detected pulse, to thereby stabilize the laser beam. The laser beam generation system may further comprise resonator length regulation element for varying the optical path length of the laser resonator, and detection element for detecting the pulse laser beam outputted, wherein the optical path length of the laser resonator is regulated by the resonator length regulation element based on a characteristic of the pulse detected by the detection element.
Owner:SONY CORP
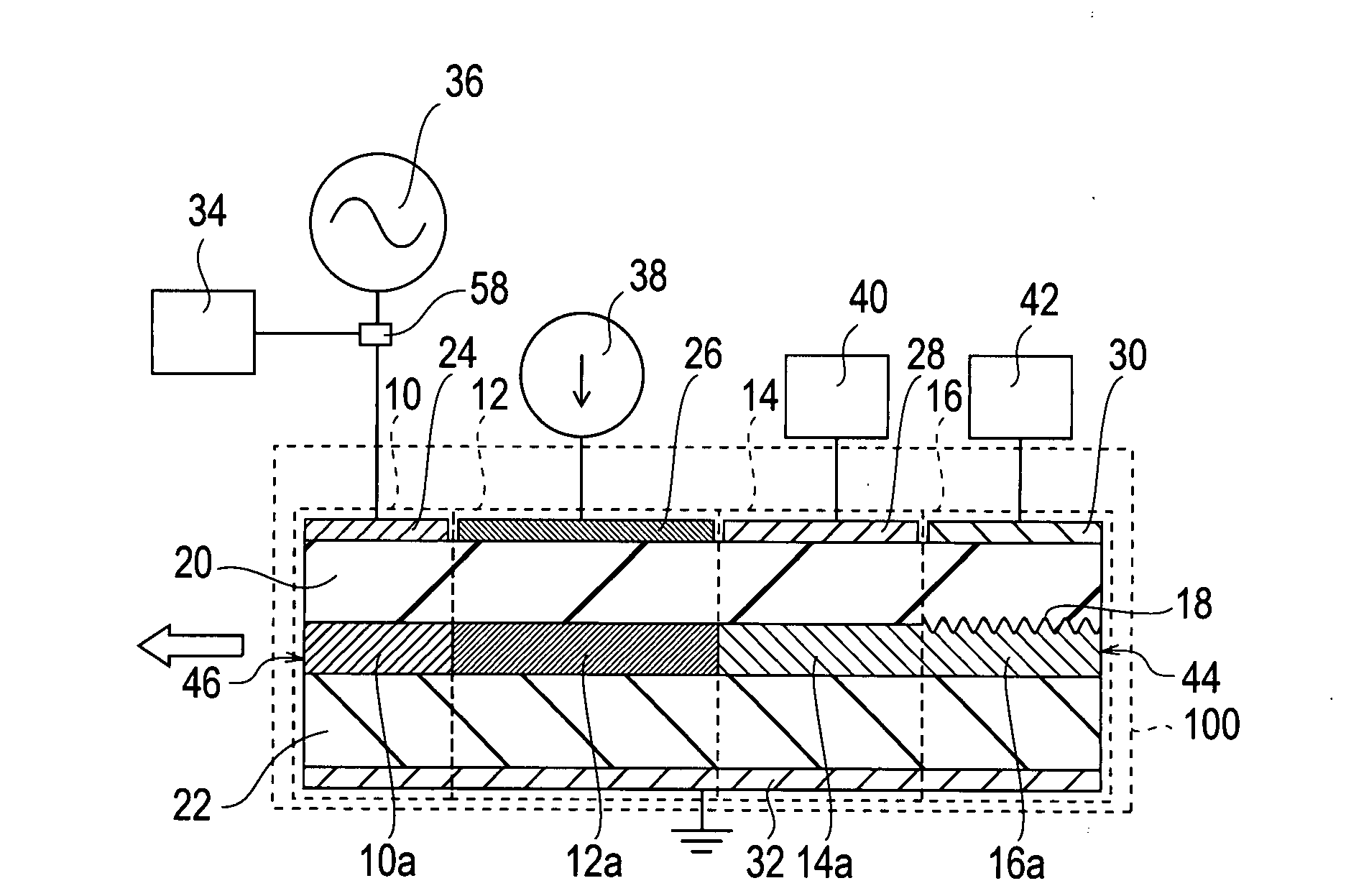
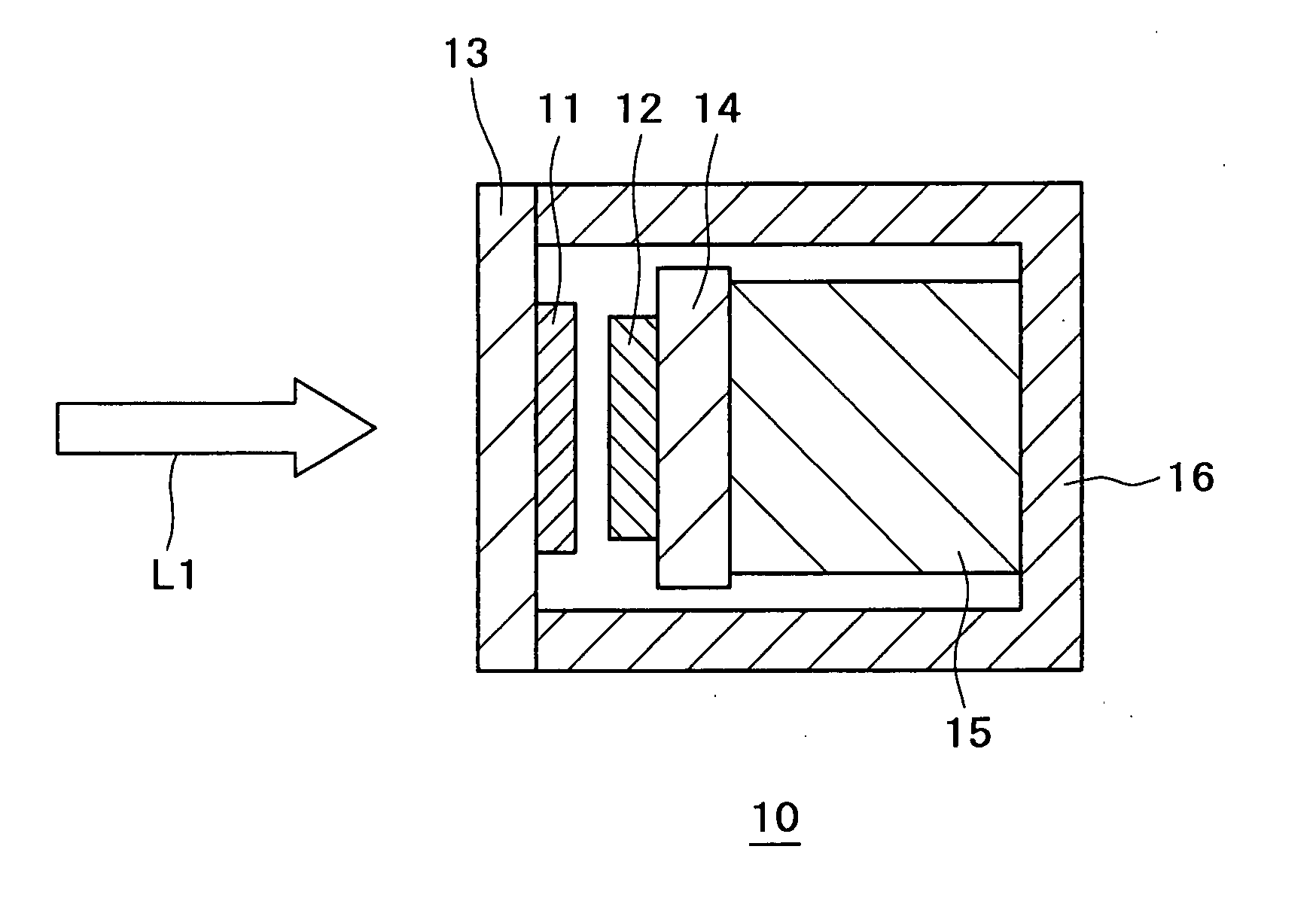
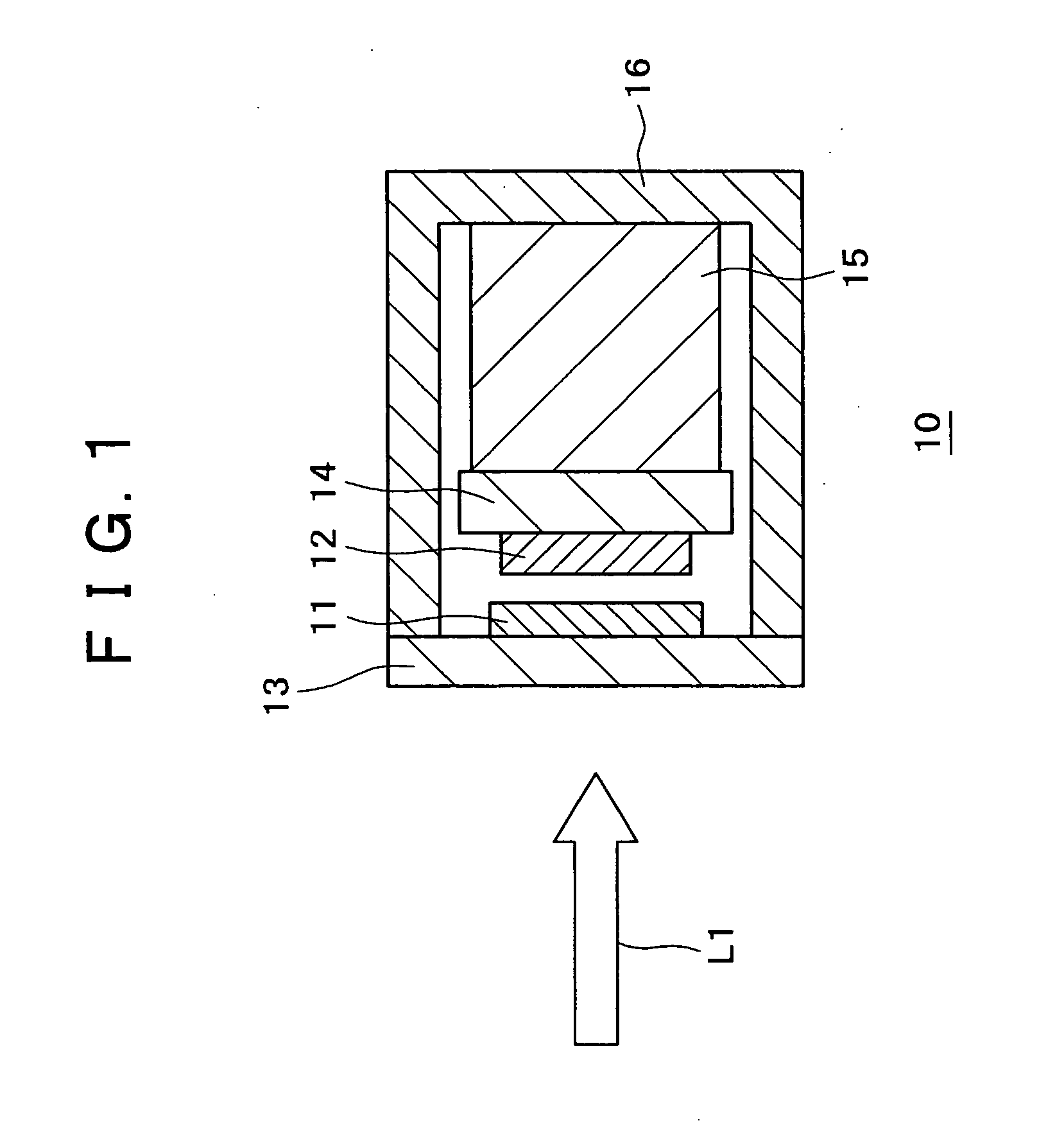
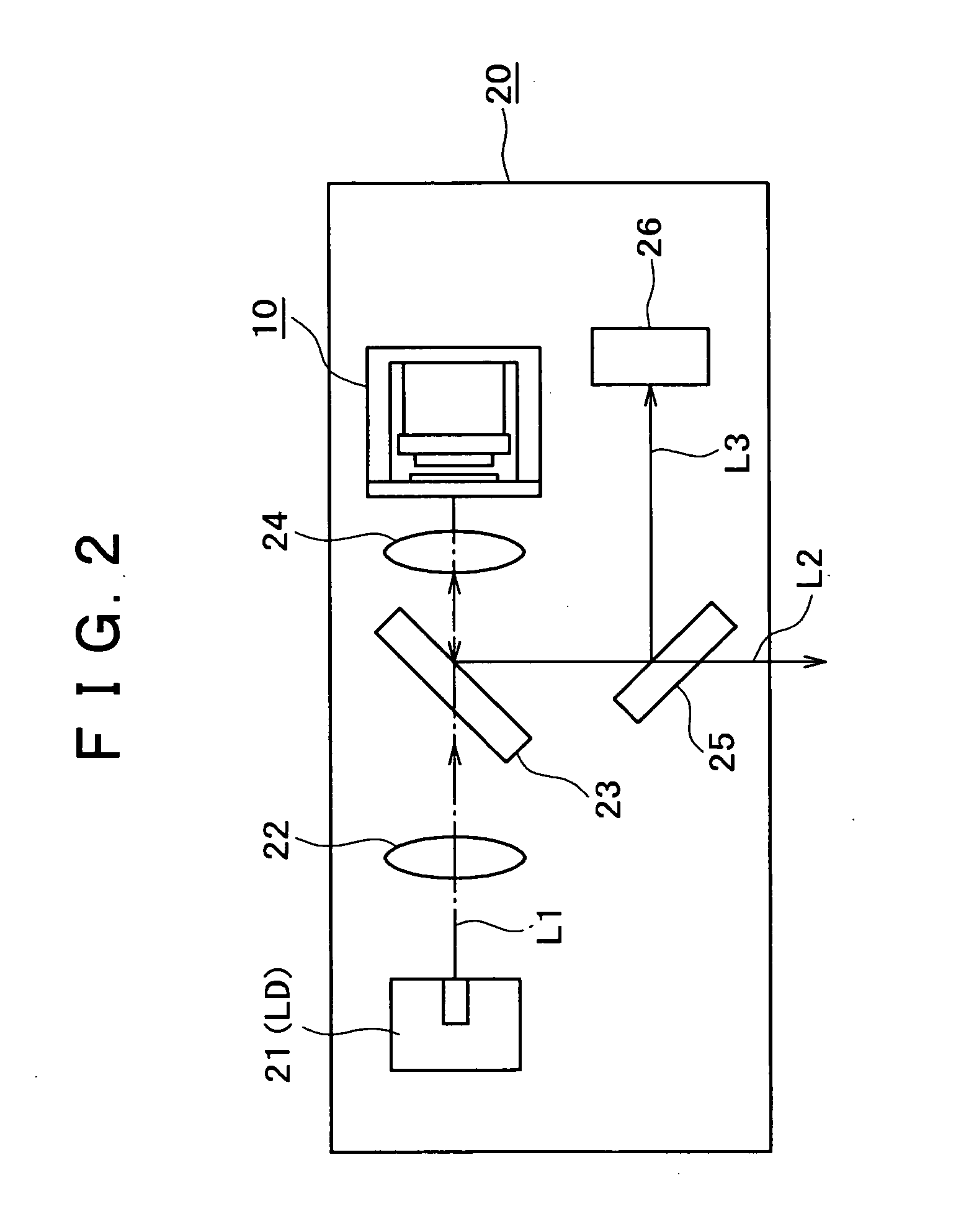
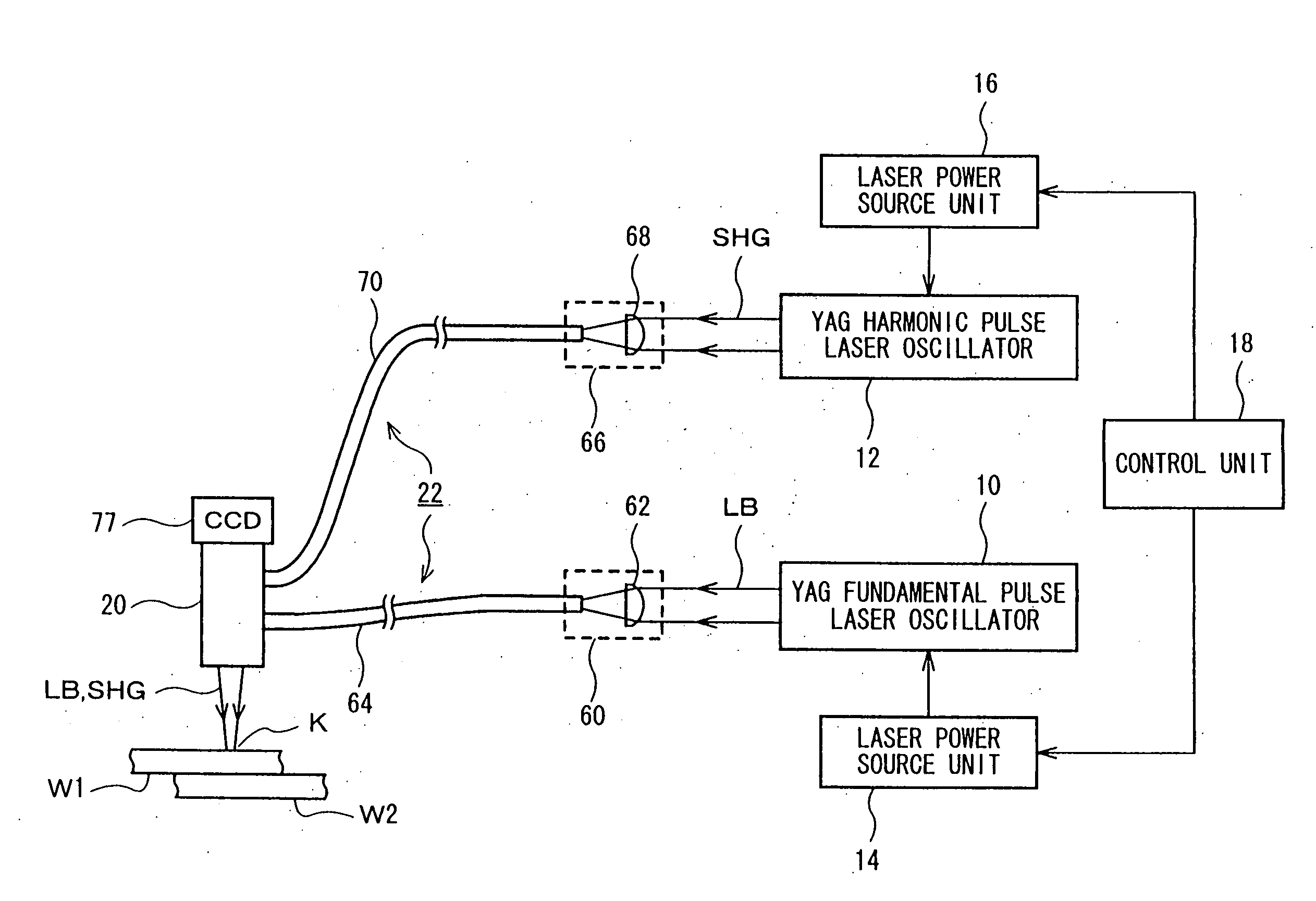
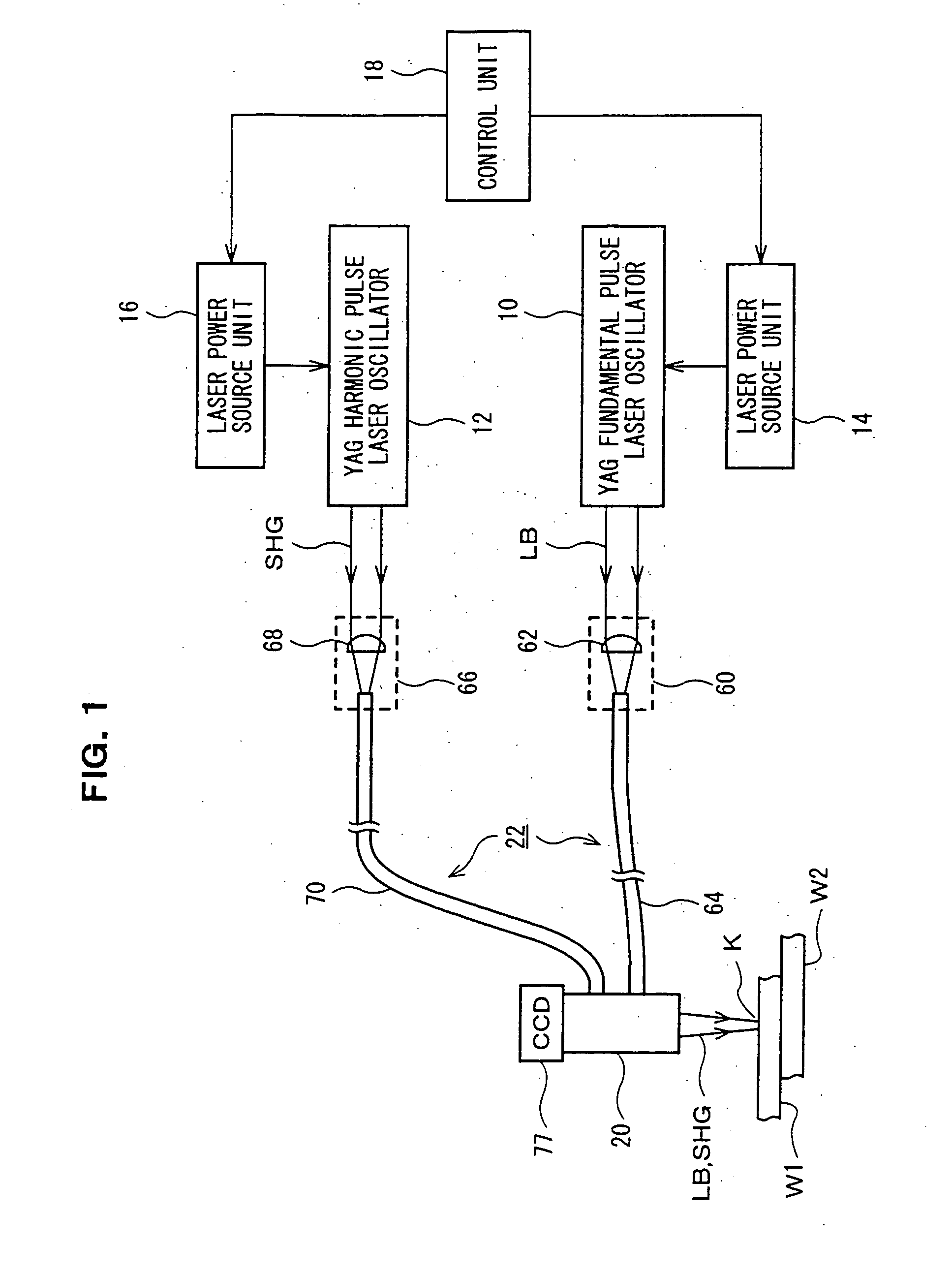
Laser welding method and laser welding apparatus
ActiveUS20060237402A1Large caliberFlat surfaceWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusHarmonicOptical axis
A YAG pulse laser oscillator 10 oscillates / outputs pulse width-variable YAG fundamental pulse laser light LB, and a YAG pulse laser oscillator 12 oscillates / outputs pulse width-variable YAG second harmonic pulse laser light SHG. An emission unit 20 superposes the pulse laser light LB and the pulse laser light SHG on the same optical axis and focuses, and irradiates a welding point K on welding pieces (W1 and W2) with, the pulse laser light LB and the pulse laser light SHG. A control unit 18 controls the laser oscillation operation of the laser oscillators 10 and 12 so that the point in time when the laser output of the YAG second harmonic pulse laser light SHG reaches its peak is slightly earlier than the point in time when the laser output of the YAG fundamental pulse laser light LB reaches its peak.
Owner:MIYACHI TECHNOS CORP
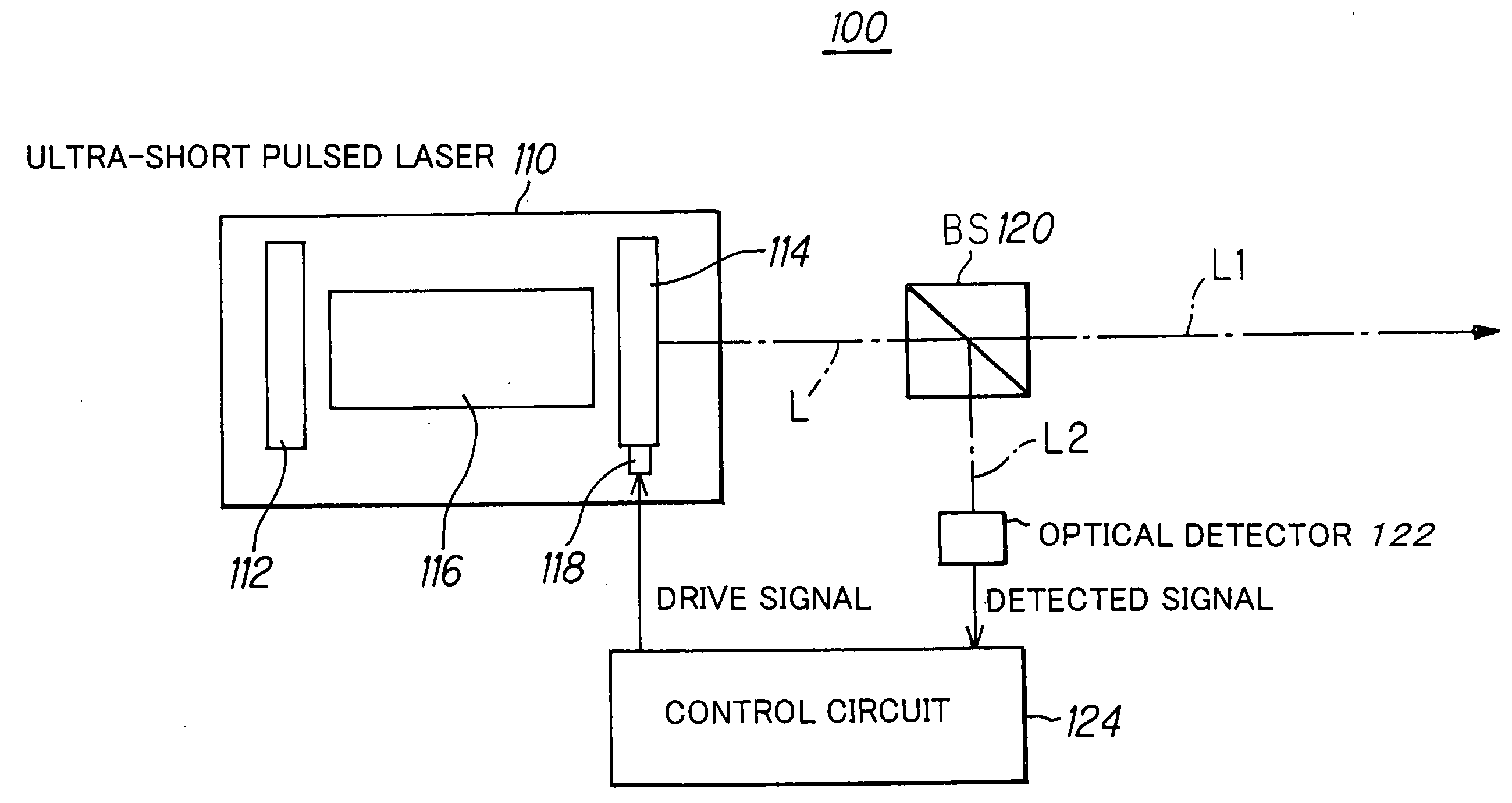
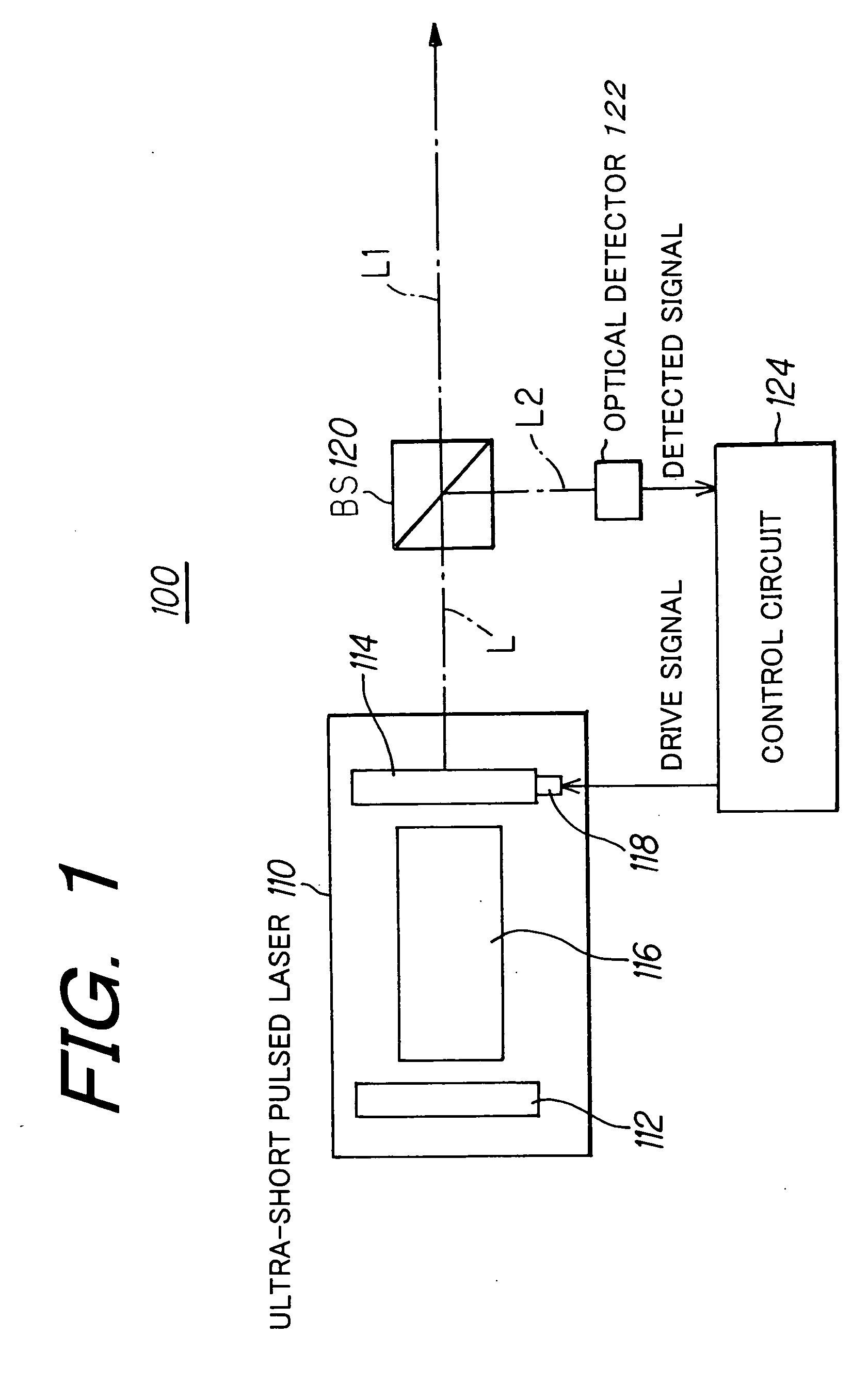
Method of controlling laser oscillation of pulsed laser and pulsed laser system
InactiveUS20060182154A1Improve accuracyGood effectLaser detailsLaser beam welding apparatusPicosecond laserOptical processing
In order to perform positional control of a condensing spot of pulsed laser beam highly accurately when performing optical modeling, optical recording or the like in optical machining technology, optical recording technology or the like which uses various kinds of pulsed laser, which are ultra-short pulsed lasers such as a femtosecond laser and short pulsed laser such as a picosecond laser and a sub-picosecond laser, as a light source, a pulsed laser system detects an output beam from a pulsed laser, controls laser oscillation of the pulsed laser based on the detection result such the output beam contains CW laser beam together with pulsed laser beam, and allows the pulsed laser to output the pulsed laser beam and the CW laser beam simultaneously as the output beam from the pulsed laser.
Owner:RIKEN
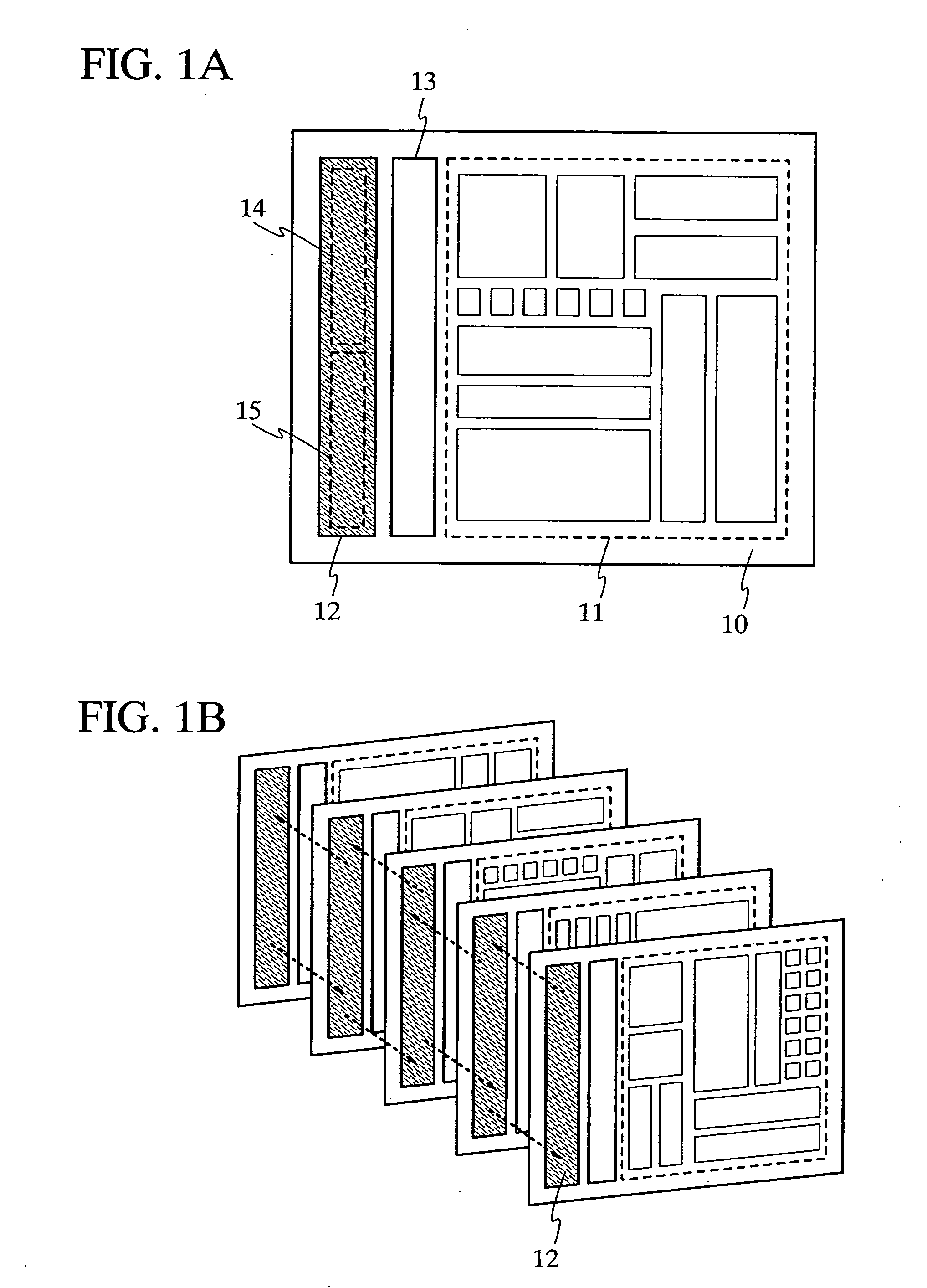
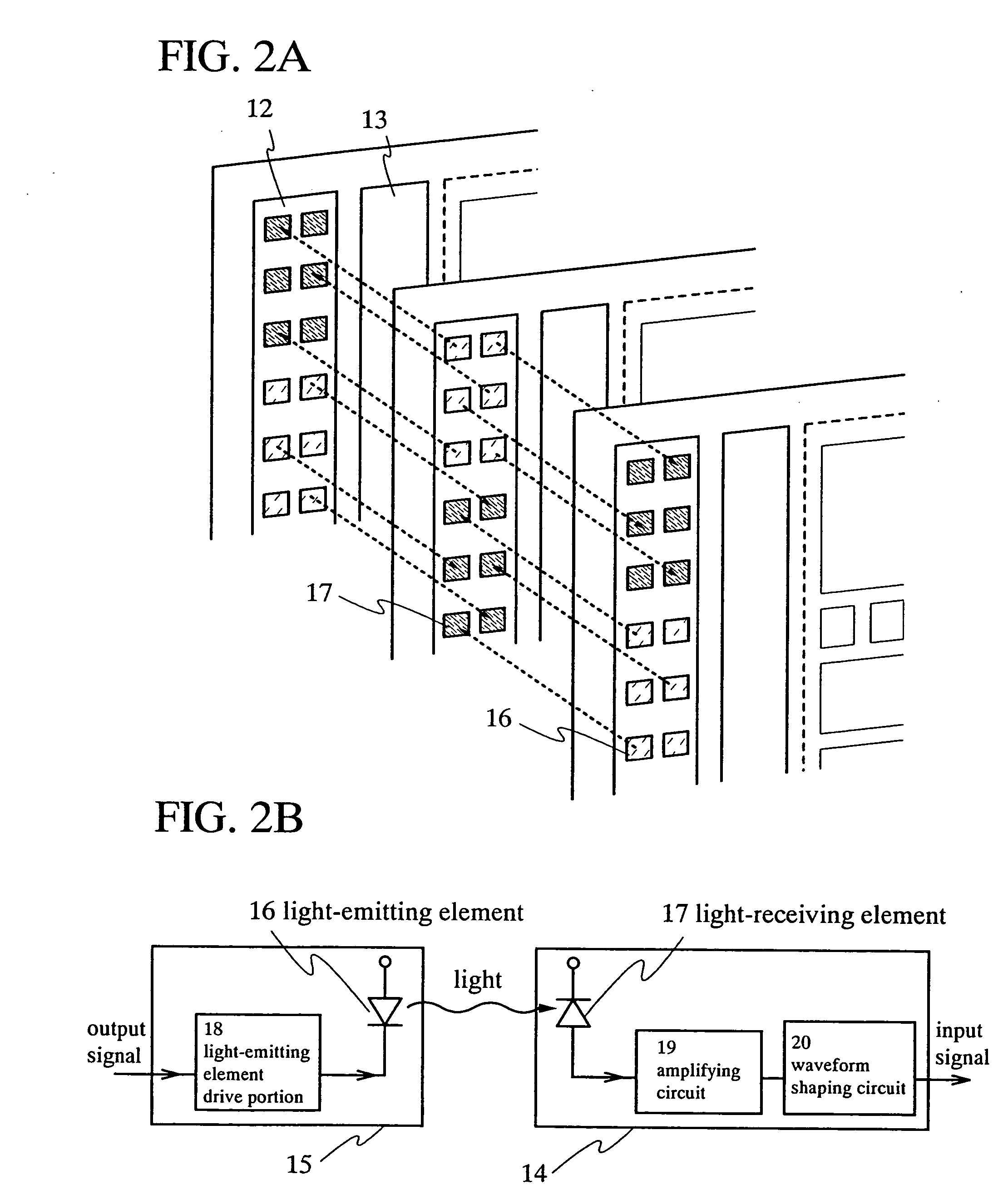
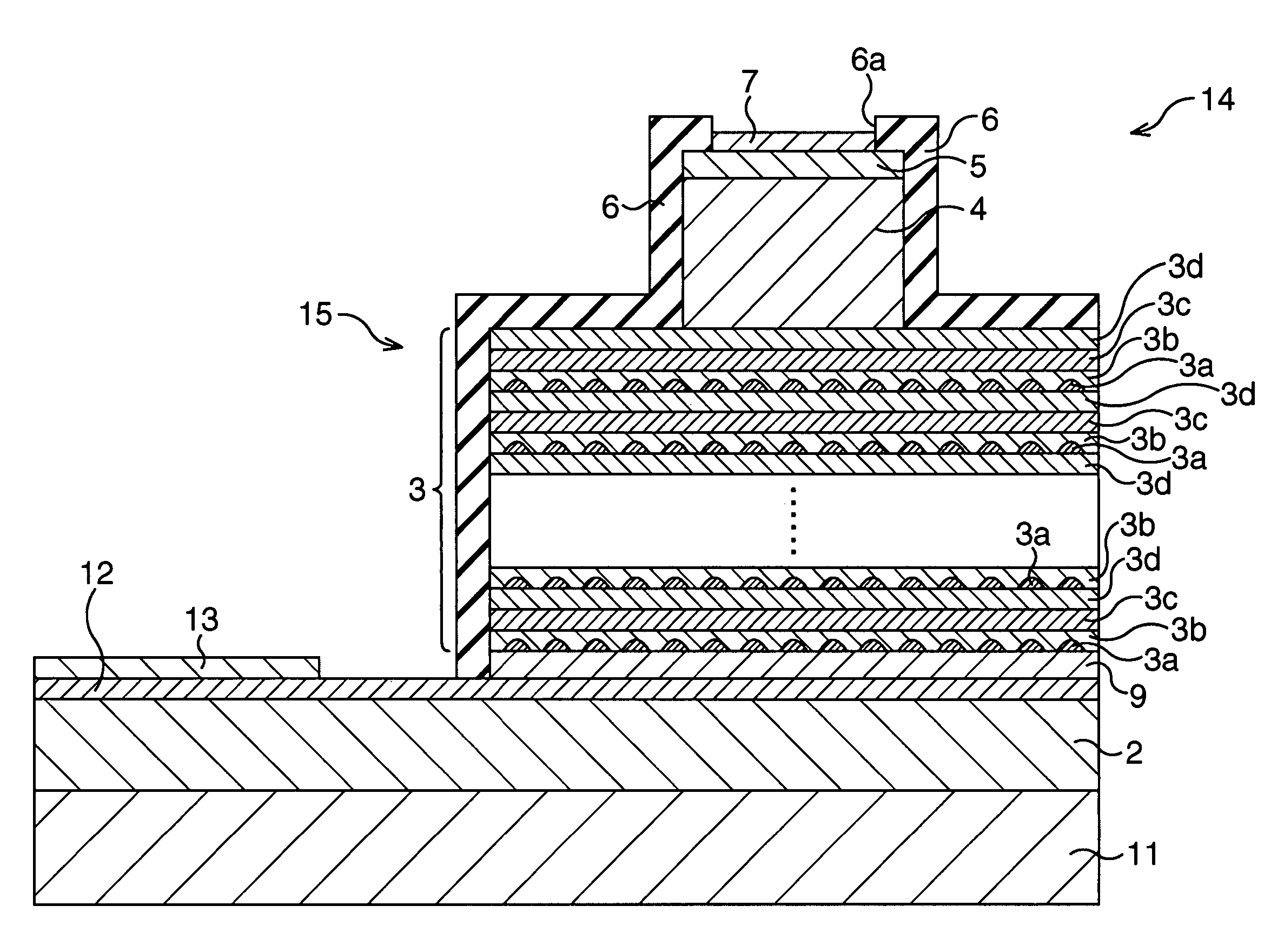
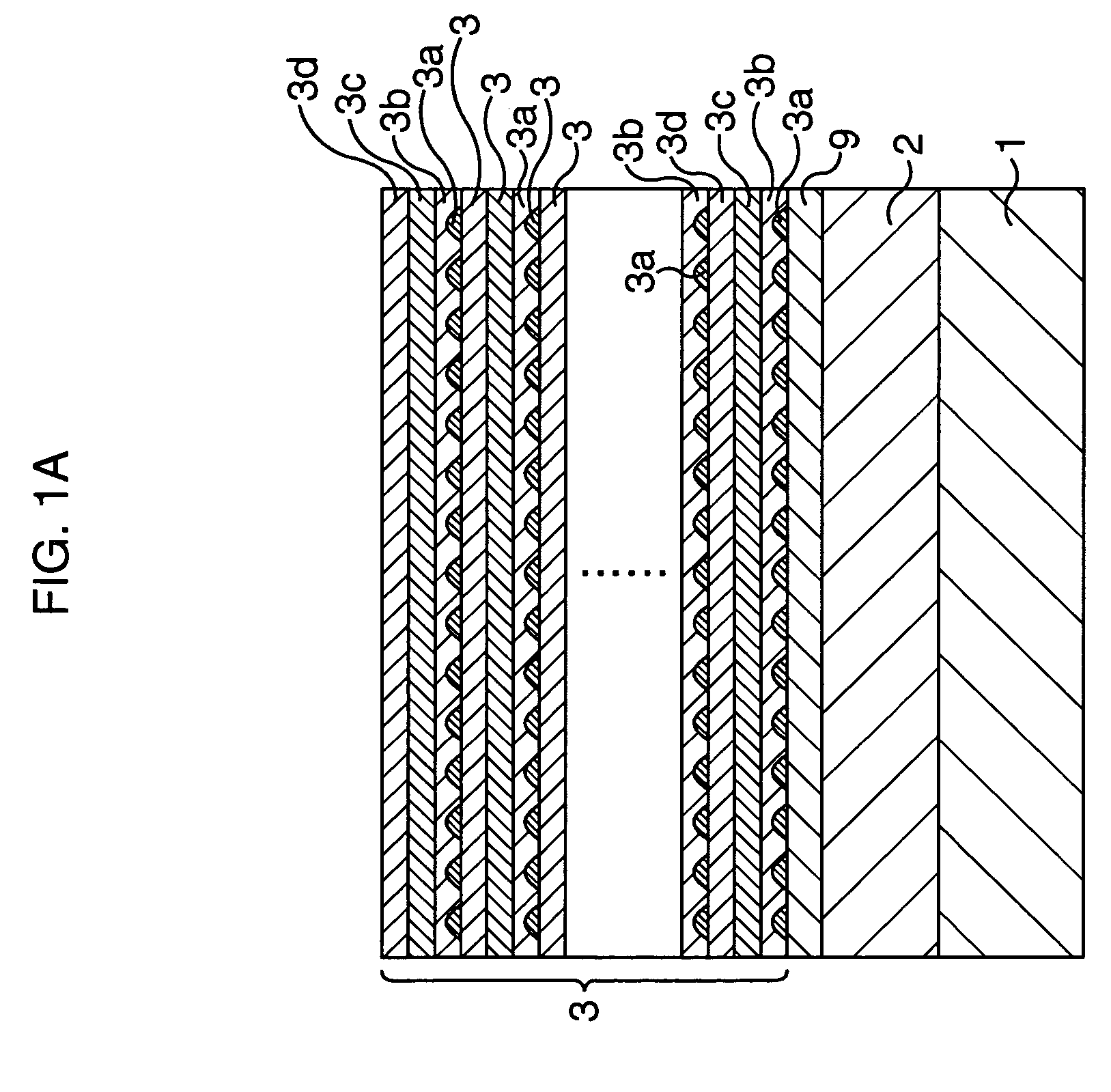
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20050006648A1Low costImprove performanceLaser active region structureSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
The present invention provides a semiconductor device having an integrated circuit formed by a low cost glass substrate, which can respond to the increase of an amount of information, and which offers high performance at high speed. A semiconductor device comprises a plurality of glass substrates respectively provided with a circuit including a semiconductor element, in which each of the plurality of glass substrates has both or either of a light-emitting element and / or a light-receiving element; wherein the light-emitting element is formed to have an electroluminescent layer interposed between a pair of electrodes, in which the electroluminescent layer is formed by stacking a plurality of layers capable of emitting light each other so that laser light is oscillated upon applying current to the electroluminescent layer; and a signal is transmitted among circuits formed over the plurality of glass substrates by generating a light signal using the laser light oscillated from the light-emitting element and converting the light signal into an electrical signal in the light-receiving element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
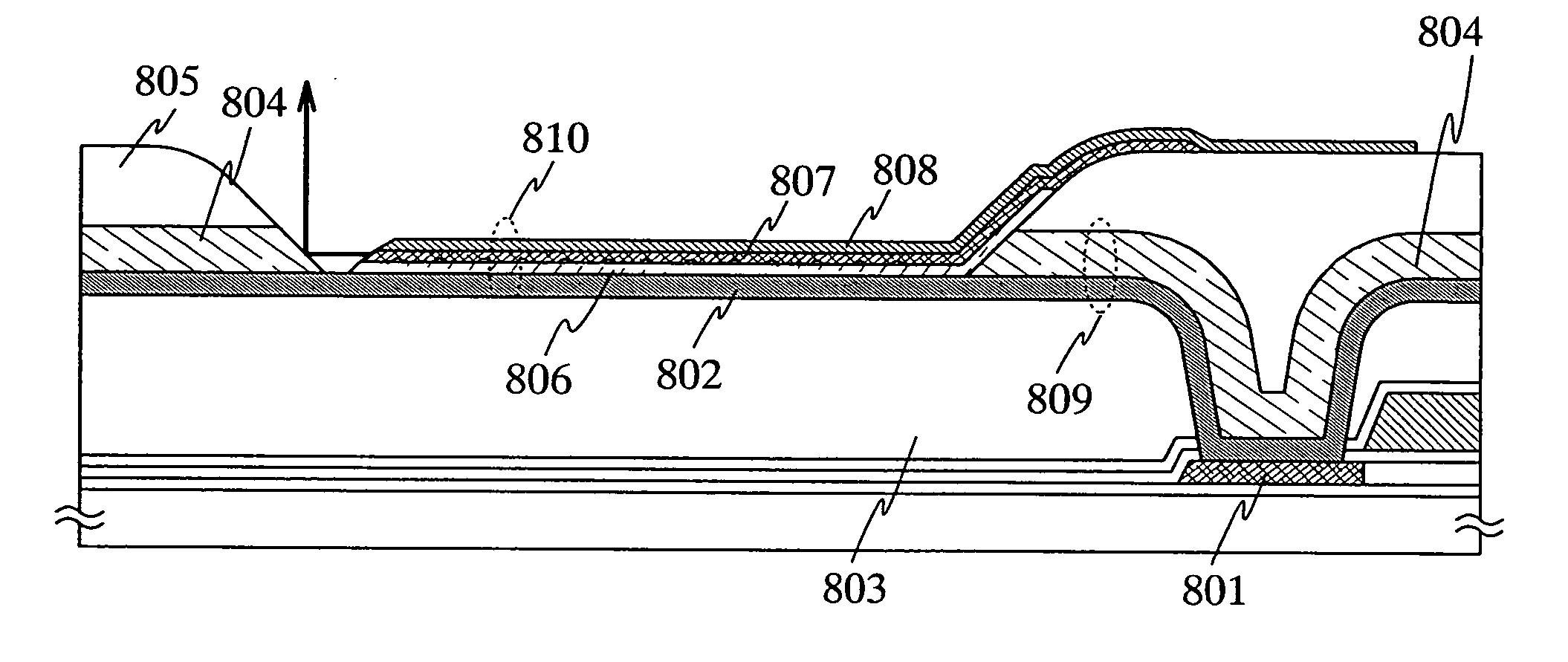
Semiconductor laser and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS7522647B2Improve reliabilityRun at high speedOptical wave guidanceNanoinformaticsQuantum dotSemiconductor package
An intrinsic GaAs waveguide layer is formed on a p-type AlGaAs cladding layer, a quantum dot active layer is formed further thereon. An n-type AlGaAs cladding layer is formed on the center portion of the quantum dot active layer. Thus-configured semiconductor laser is allowed to successfully suppress the area of the p-n junction plane to a small level, and to obtain a high level of reliability, because there is no need of processing the center portion of the quantum dot active layer, contributive to laser oscillation.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
Semiconductor laser element
InactiveUS7103082B2Easy to getInhibition releaseOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsSemiconductor packageActive layer
To provide a semiconductor laser device which has no ripple and can afford better FFP having a pattern near a Gaussian distribution upon operation at the high output, the semiconductor laser comprising a laminate structure in which a first conductive type semiconductor layer, an active layer and a second conductive type semiconductor layer different from the first conductive type are laminated in this order, the laminate structure having a waveguide region to guide a light and resonator planes for laser oscillation on both ends, characterized in that the laminate structure has a non-resonator plane on one end side and the non-resonator plane is covered with a shading layer.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Semiconductor light-emitting device, surface-emission laser diode, and production apparatus thereof, production method, optical module and optical telecommunication system
InactiveUS20090286342A1Polycrystalline material growthLaser detailsCommunications systemOptical Module
A semiconductor light-emitting device has a semiconductor layer containing Al between a substrate and an active layer containing nitrogen, wherein Al and oxygen are removed from a growth chamber before growing said active layer and a concentration of oxygen incorporated into said active layer together with Al is set to a level such that said semiconductor light-emitting device can perform a continuous laser oscillation at room temperature.
Owner:RICOH KK
Multiwavelength semiconductor laser array and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20080151950A1Simplify the manufacturing processAvoid complex processOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionManufacturing technologyLaser array
A multiwavelength semiconductor laser array and a method of fabricating the same are provided. Laser resonators having stacked quantum dot active regions of different emission wavelengths are utilized together with a fabricating process to change the length of each laser resonator or that of an upper electrode layer to generate different laser oscillation conditions, such that each of the laser resonators generates a single-wavelength band laser in a specific quantum dot active region, thereby achieving a multiwavelength semiconductor laser array capable of generating multiple laser wavelengths.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Light source apparatus and projector
InactiveUS20100238966A1Low costIncrease brightnessProjectorsOptical resonator shape and constructionResonant cavityLength wave
A light source apparatus includes: a light emitter; a pair of electrodes for driving the light emitter; and an external resonant cavity that reflects part of the light emitted from a light-exiting end surface of the light emitter. The light emitter includes an active layer that generates light, an internal resonant cavity, and a diffractive optical layer that diffracts light having a predetermined wavelength. The external resonant cavity includes an external mirror that reflects the light having the predetermined wavelength. The internal resonant cavity, the external resonant cavity, and the diffractive optical layer form a laser resonant cavity that allows the light generated in the active layer to achieve laser oscillation.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Optical fiber for fiber laser, fiber laser, and laser oscillation method
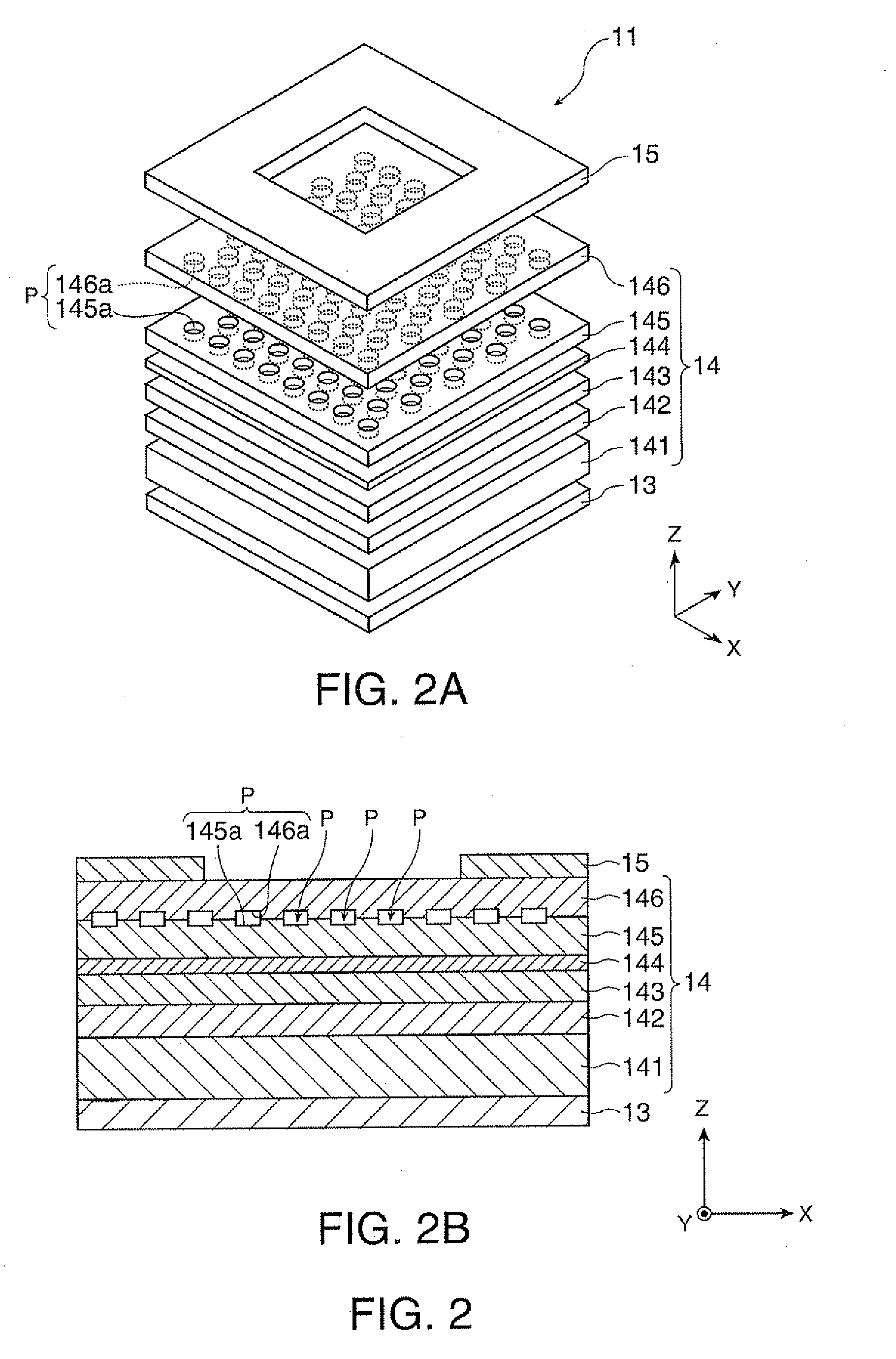
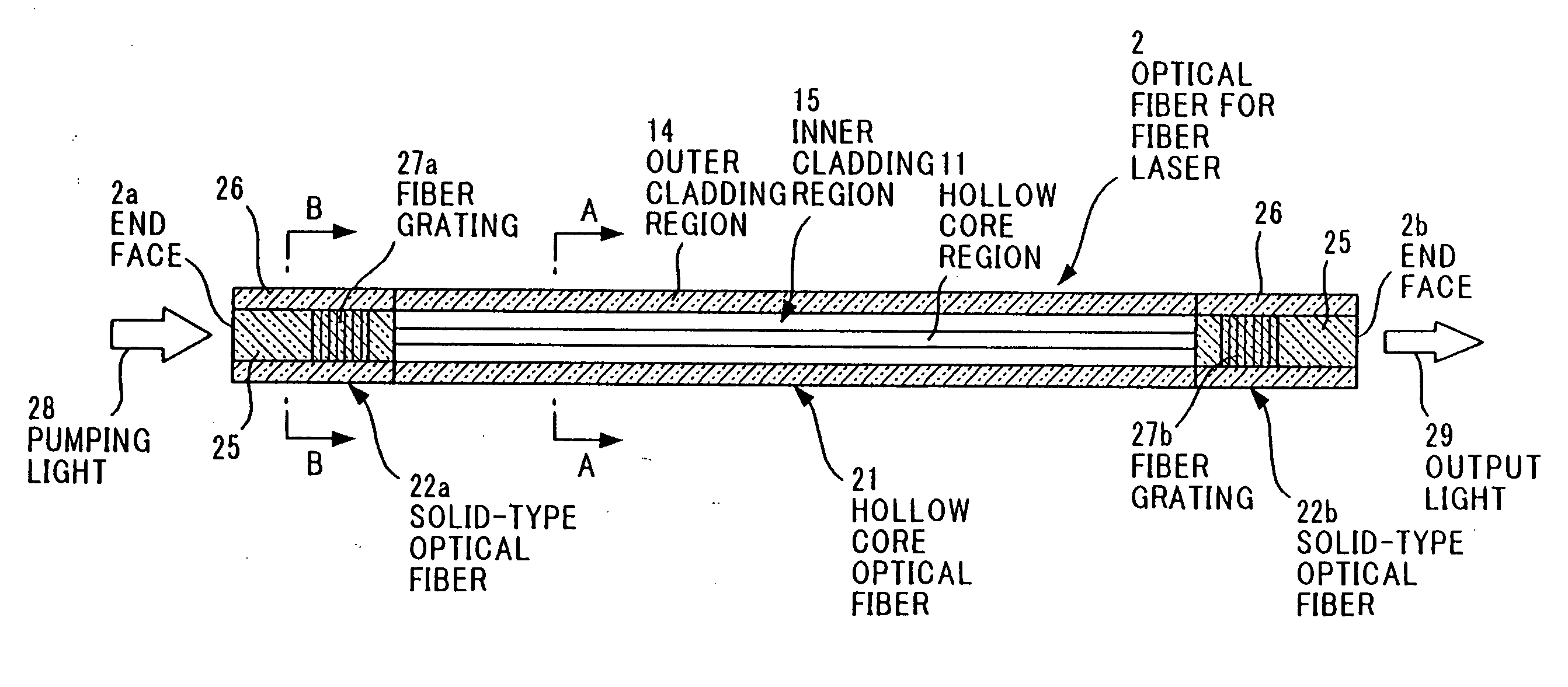
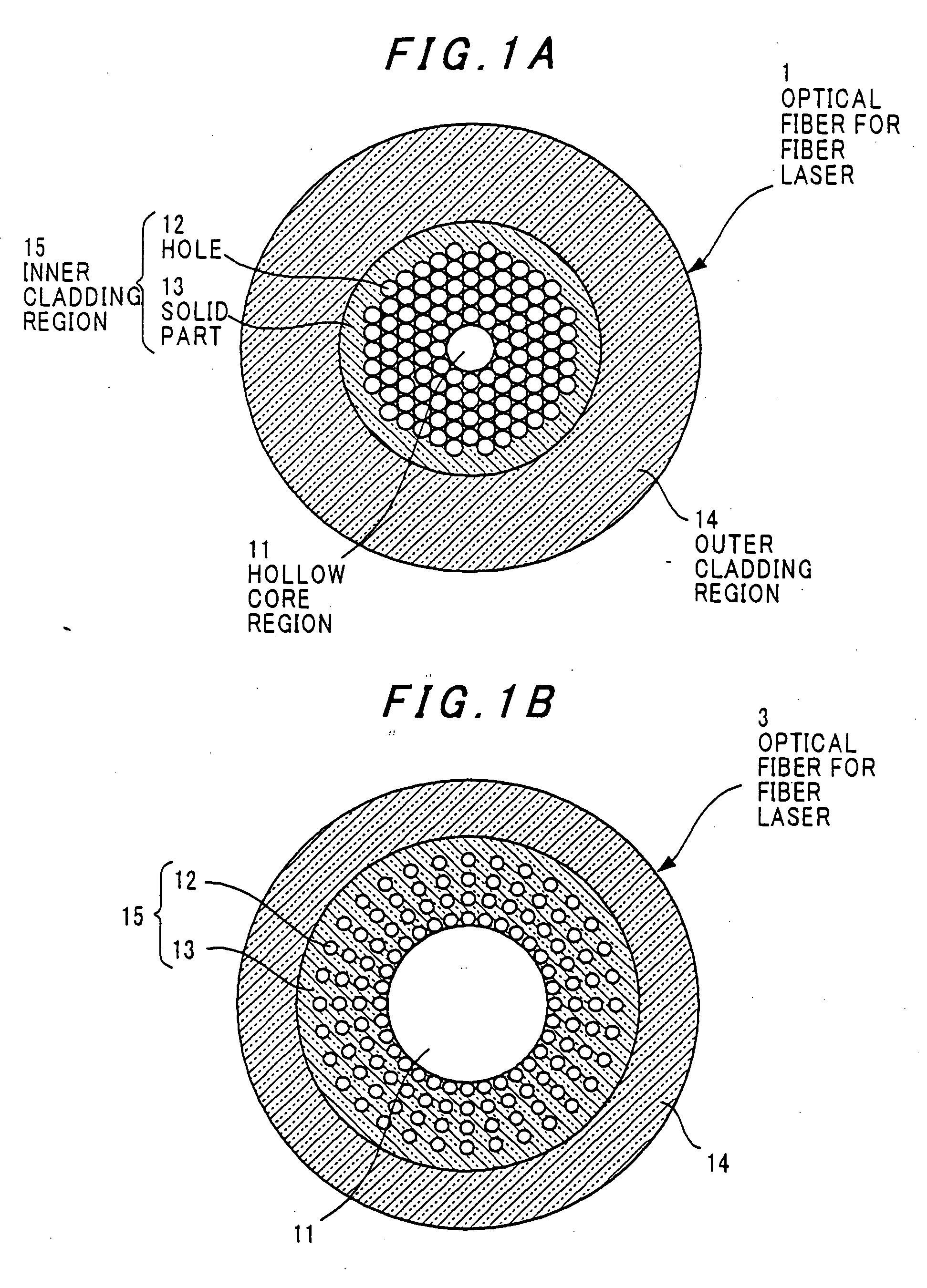
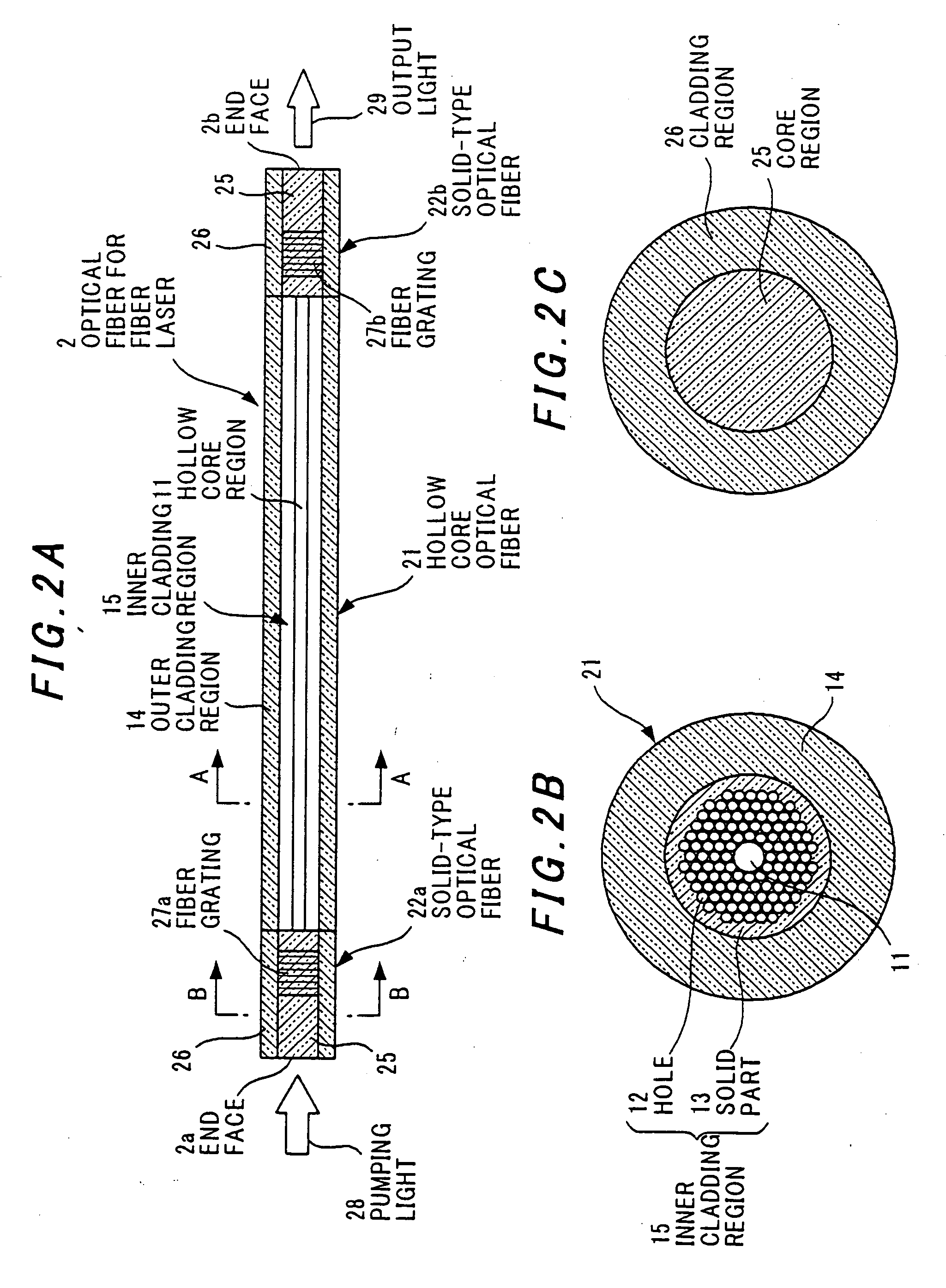
InactiveUS20060098694A1Selectively oscillateQuality improvementCladded optical fibreLaser using scattering effectsRare-earth elementRefractive index
An optical fiber for a fiber laser has: a hollow core region; an inner cladding region having a plurality of holes that extend in a longitudinal direction of the optical fiber and surround the hollow core region; and an outer cladding region that surrounds the inner cladding region. The inner cladding region has a solid part that is made of a glass material into a part or all of which a rare earth element is doped, and the outer cladding region has a refractive index lower than that of the solid part of the inner cladding region.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
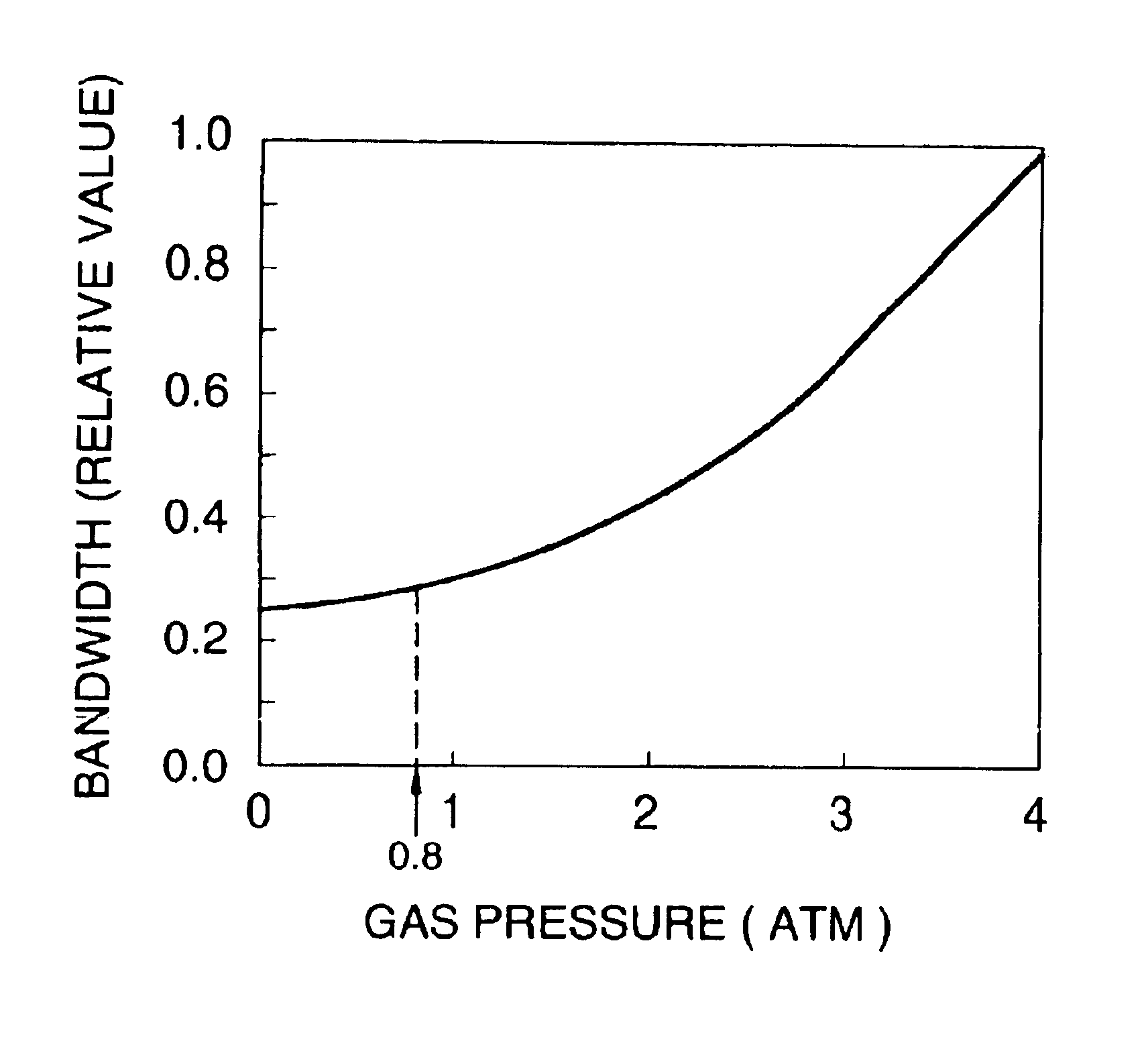
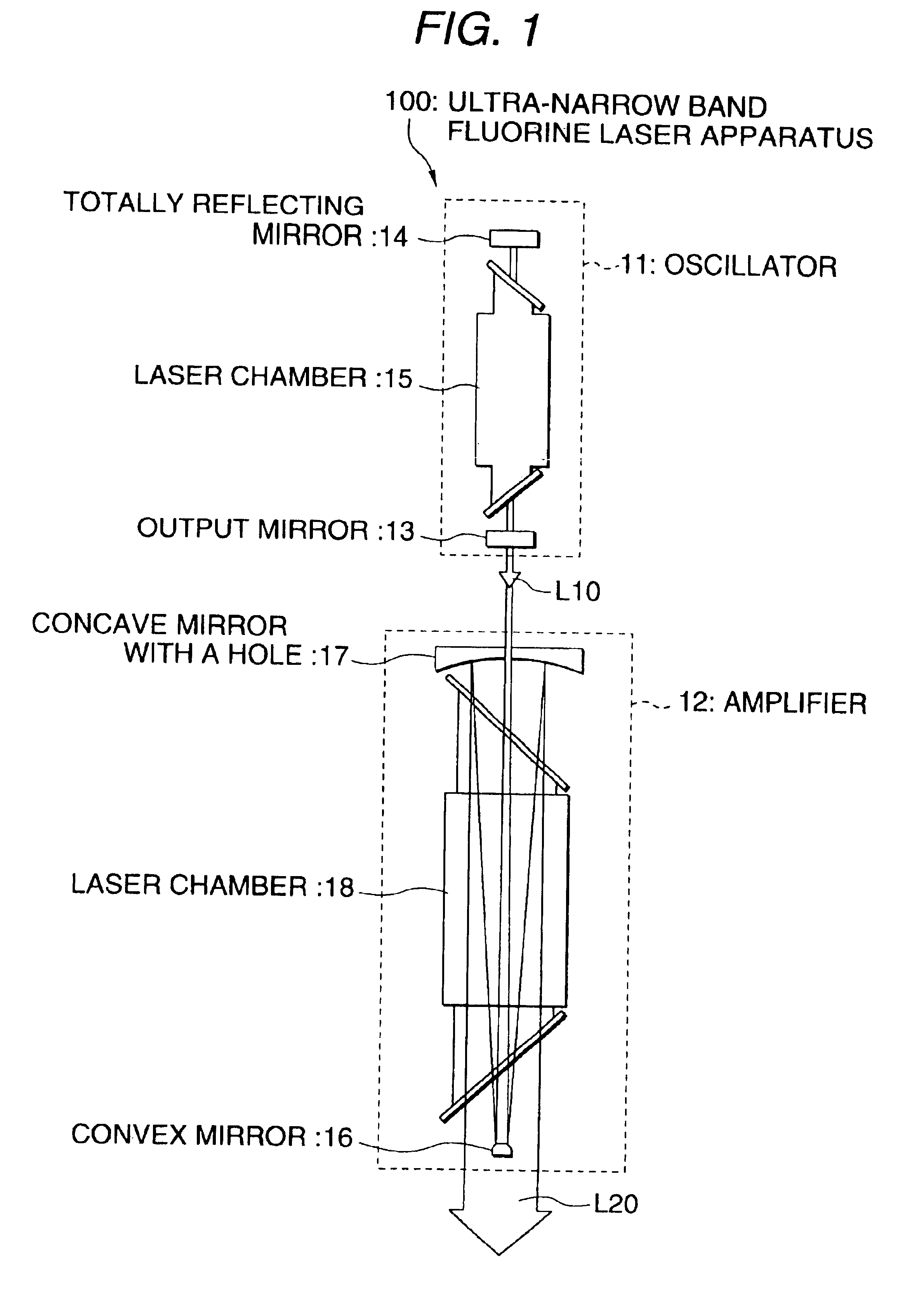
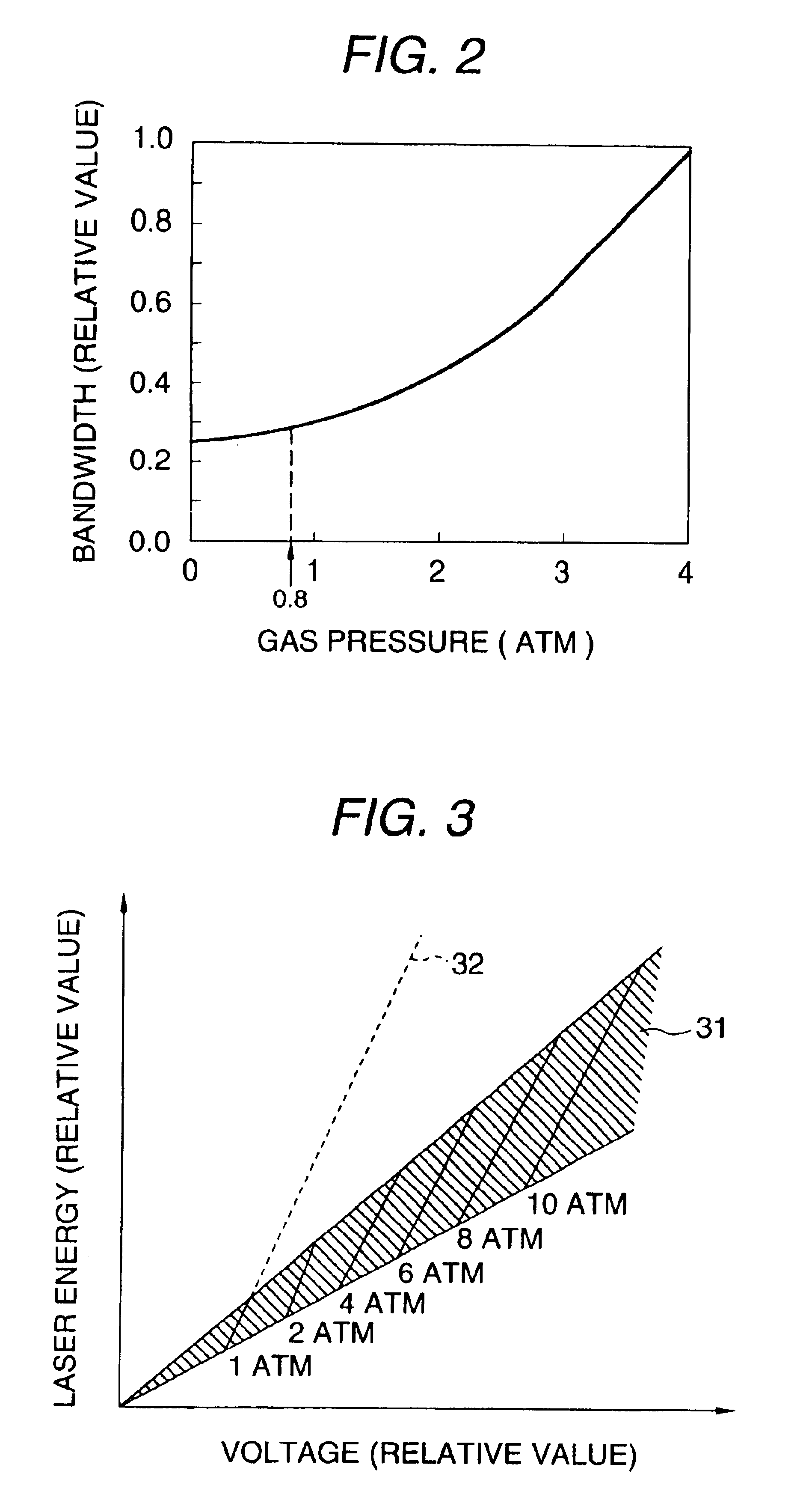
Ultra-narrow band flourine laser apparatus
InactiveUS6839373B1Attenuation bandwidthNarrowing bandOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser arrangementsLine widthLaser light
An ultra-narrow band fluorine laser apparatus is provided in which a line width of a fluorine laser can be narrowed to about 0.2 to 0.3 pm without using any band-narrowing element such as an etalon. In an oscillator 11, a laser chamber 15 is provided in a stable type resonator constituted by an output mirror 13 and a totally reflecting mirror 14. The laser chamber 15 is filled with a laser gas at about 0.8 atm. As a result, when discharge is caused in the laser chamber 15 to cause laser oscillation, laser light L10 in a bandwidth of about 0.3 pm is provided. The power of the laser light L10 is increased by an amplifier 12. The amplifier 12 emits laser light L20 in a bandwidth of about 0.3 pm having laser energy of 10 mJ or more.
Owner:GIGAPHOTON
Semiconductor laser diode device and method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS8477819B2Satisfied with stabilityAdvantageousSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical resonator shape and constructionRefractive indexOptical power
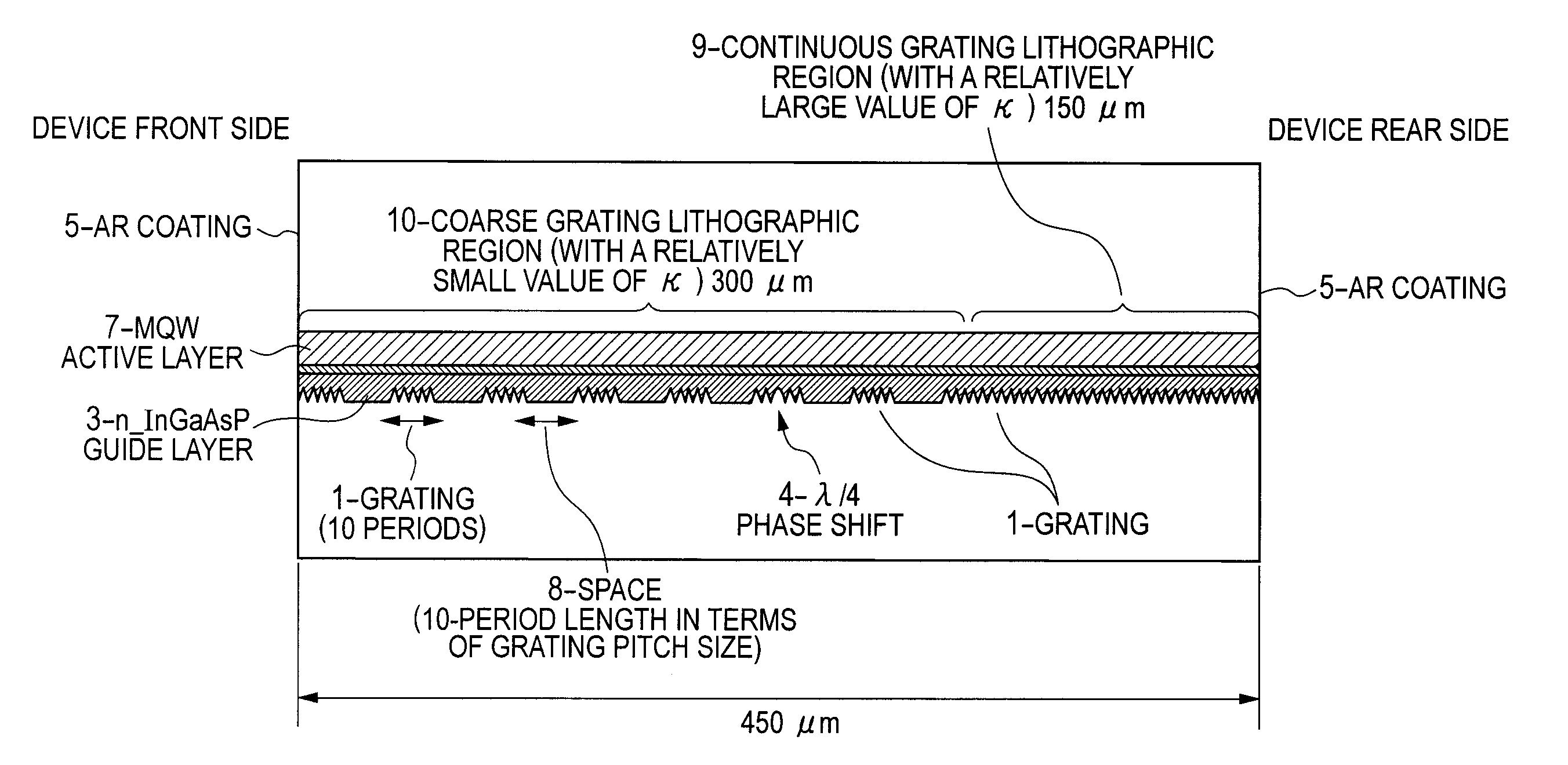
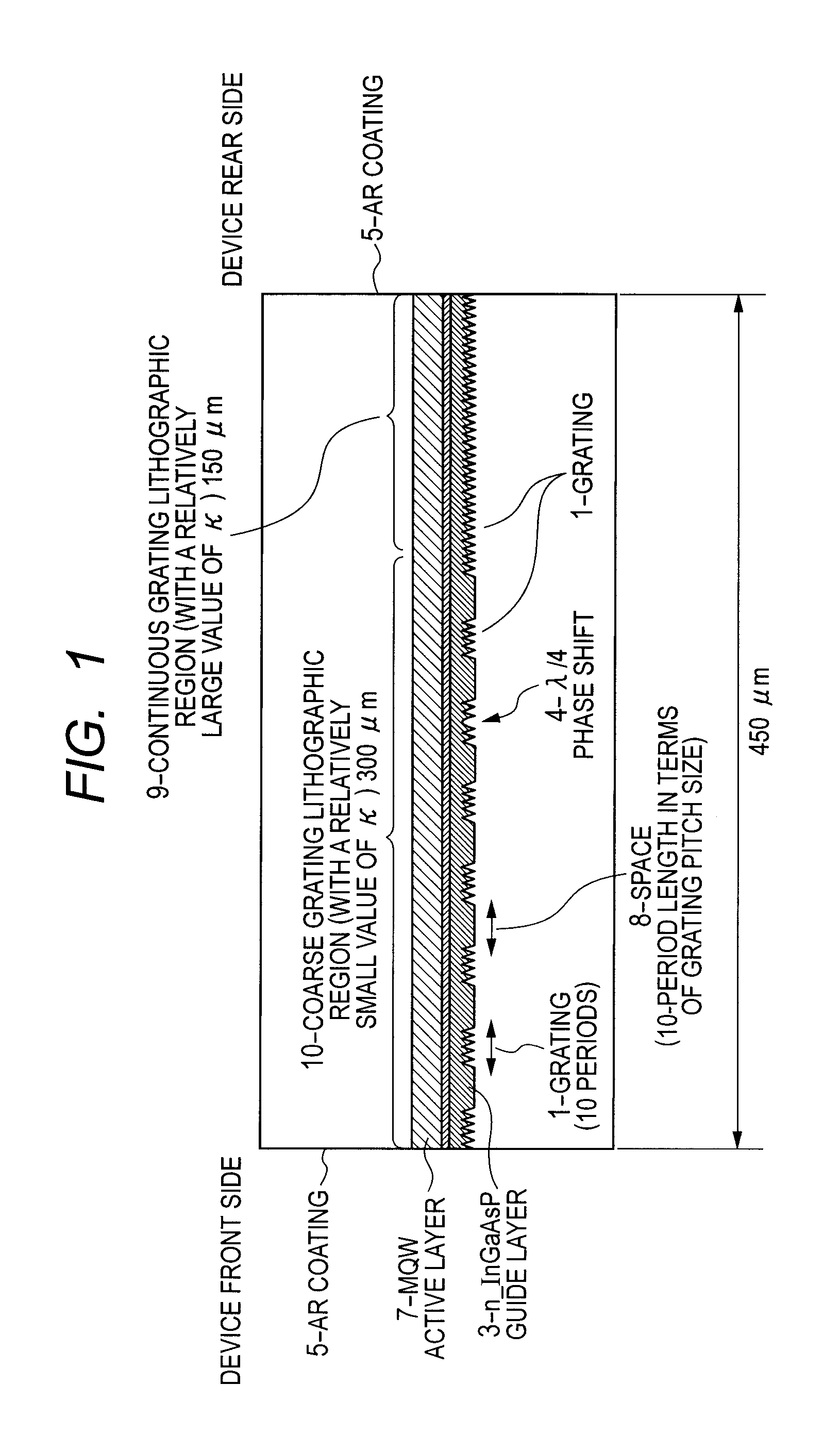
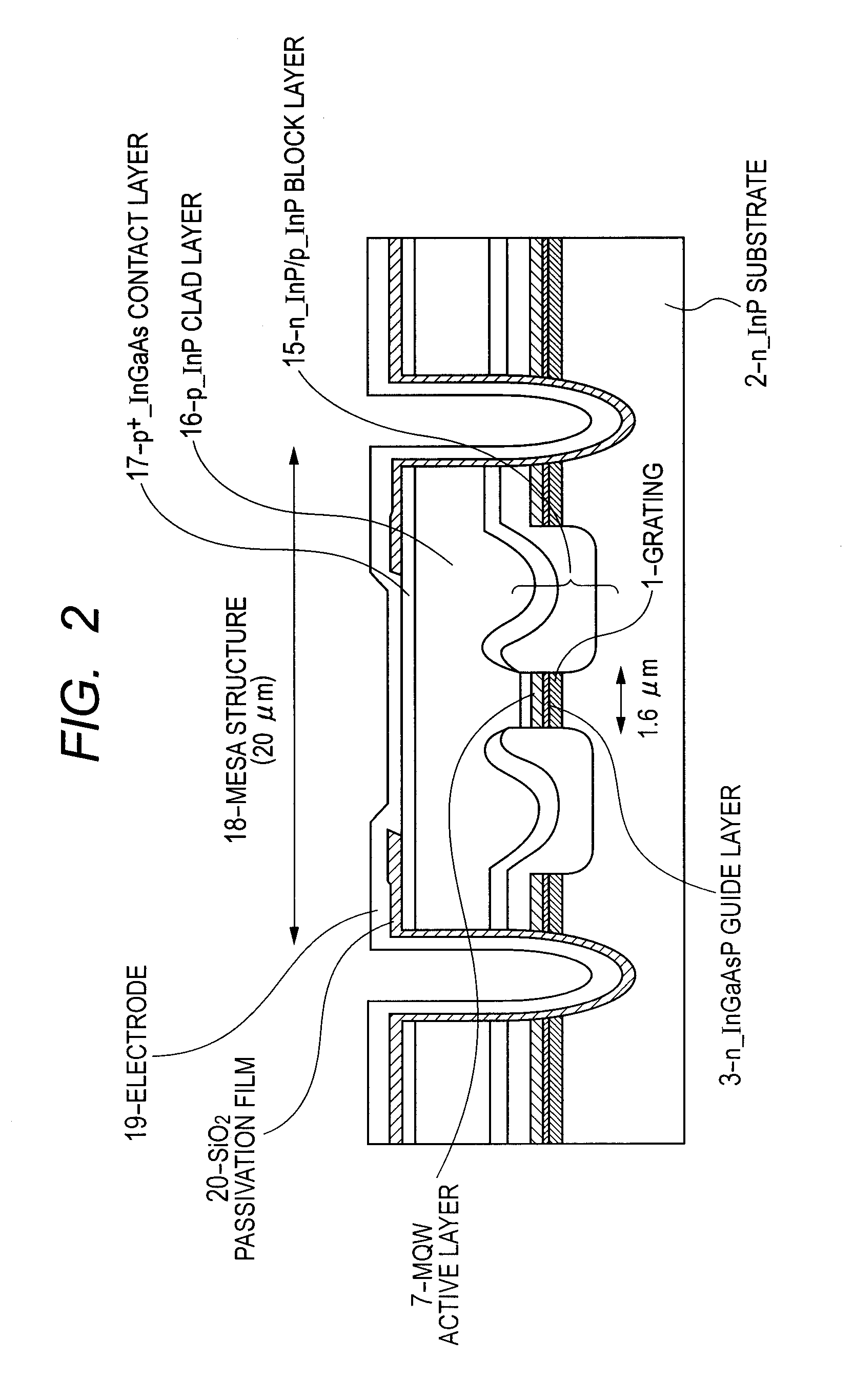
Disclosed is a distributed feedback semiconductor laser diode device capable of operating at a high output ratio of forward / backward optical power while ensuring satisfactory stability of single-mode oscillation. The distributed feedback semiconductor laser diode device is configured to include a diffraction grating formed in an optical waveguide thereof. In a partial region of the optical waveguide, there is formed an alternately repetitive pattern of a grating part possessing a distributive refractivity characteristic and a no-grating space part possessing a uniform refractivity characteristic. The no-grating space part possessing a uniform refractivity characteristic has an optical path length that is half an integral multiple of a wavelength of laser oscillation, and the grating part possessing a distributive refractivity characteristic includes at least five grating periods.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com