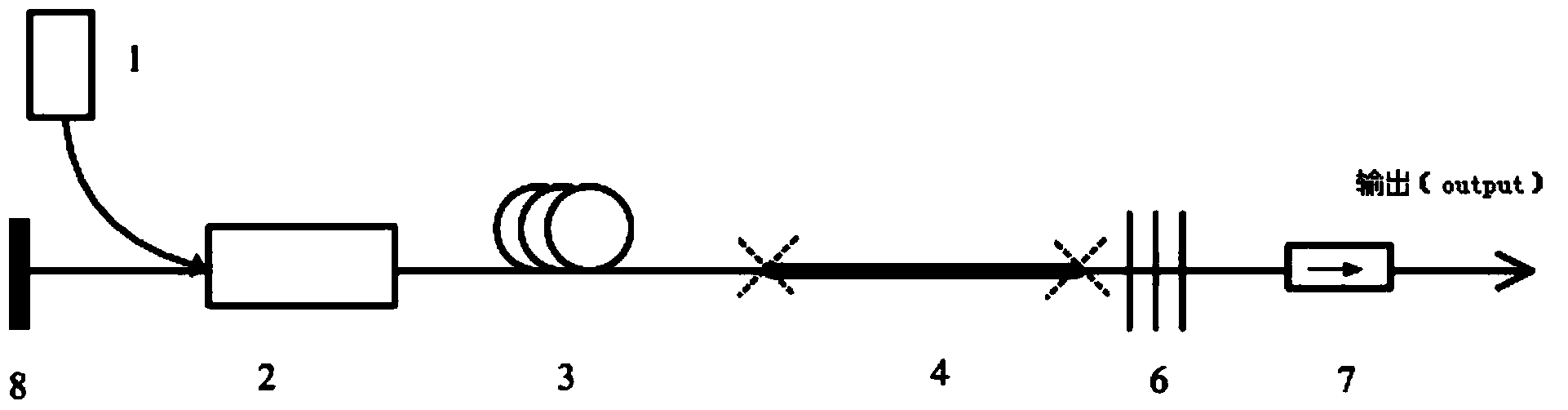Patents
Literature
697 results about "Mode-locking" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mode-locking is a technique in optics by which a laser can be made to produce pulses of light of extremely short duration, on the order of picoseconds (10⁻¹² s) or femtoseconds (10⁻¹⁵ s). A laser operated in this way is sometimes referred to as a femtosecond laser, for example in modern refractive surgery. The basis of the technique is to induce a fixed-phase relationship between the longitudinal modes of the laser's resonant cavity. Constructive interference between these modes can cause the laser light to be produced as a train of pulses. The laser is then said to be 'phase-locked' or 'mode-locked'.
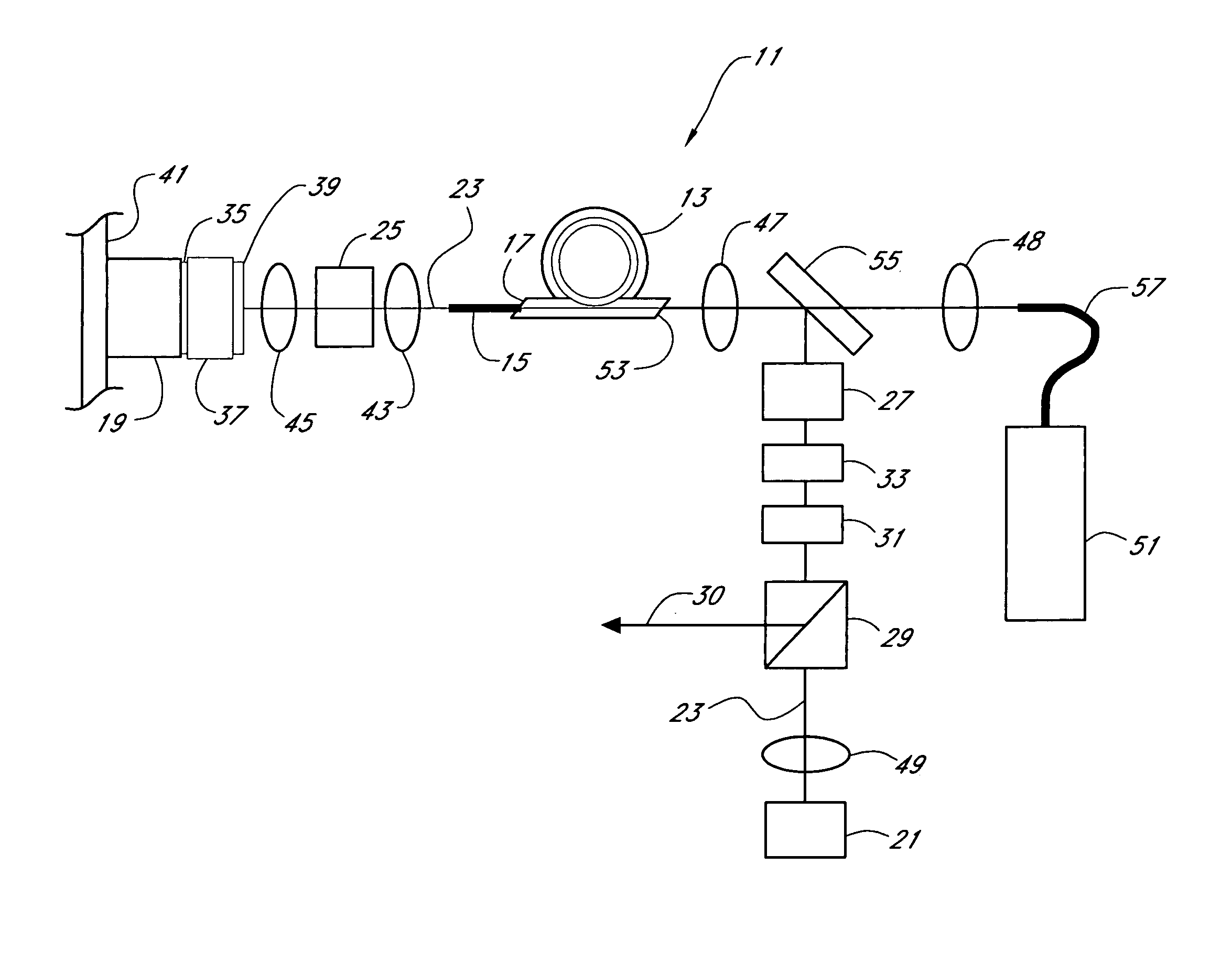
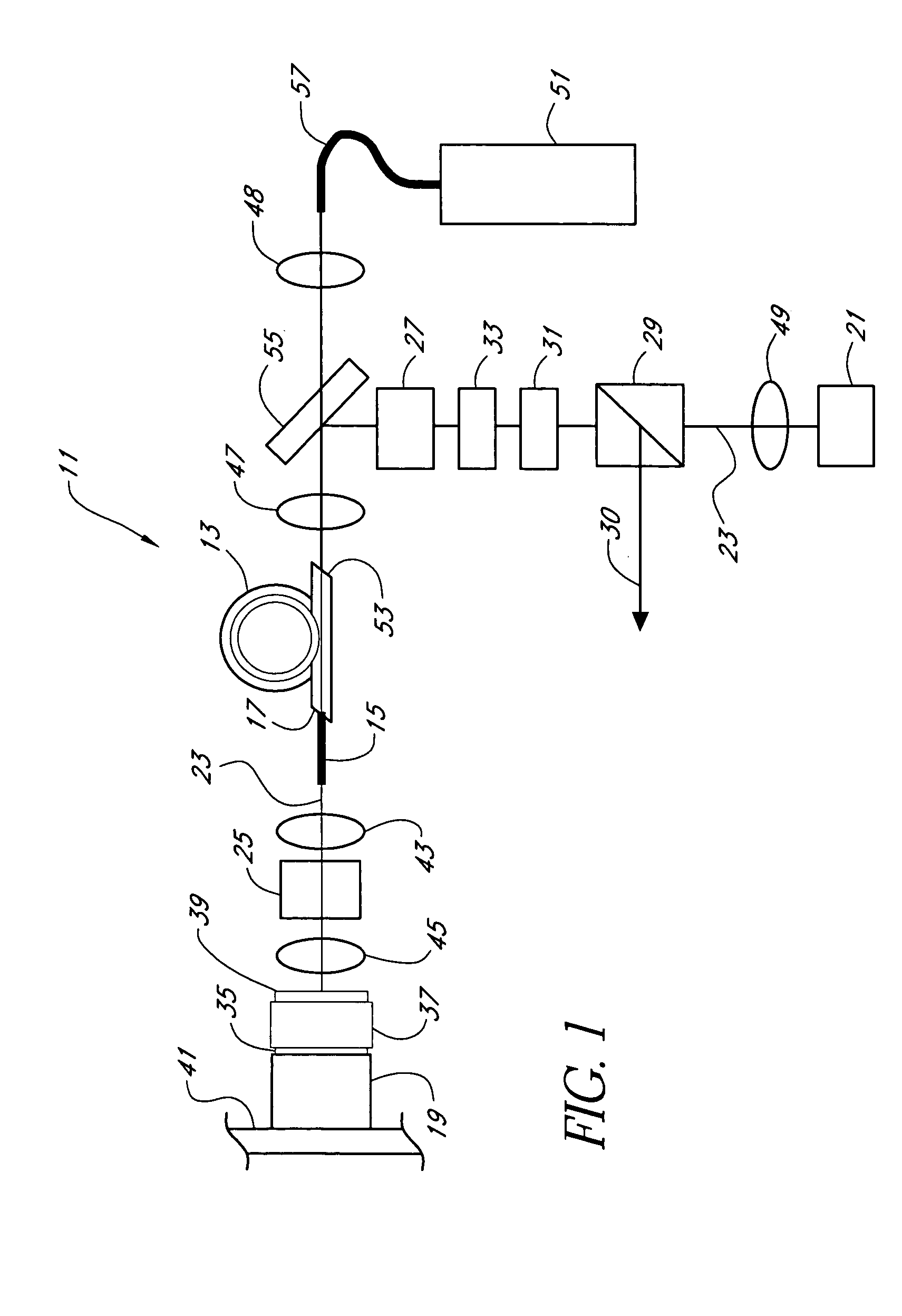
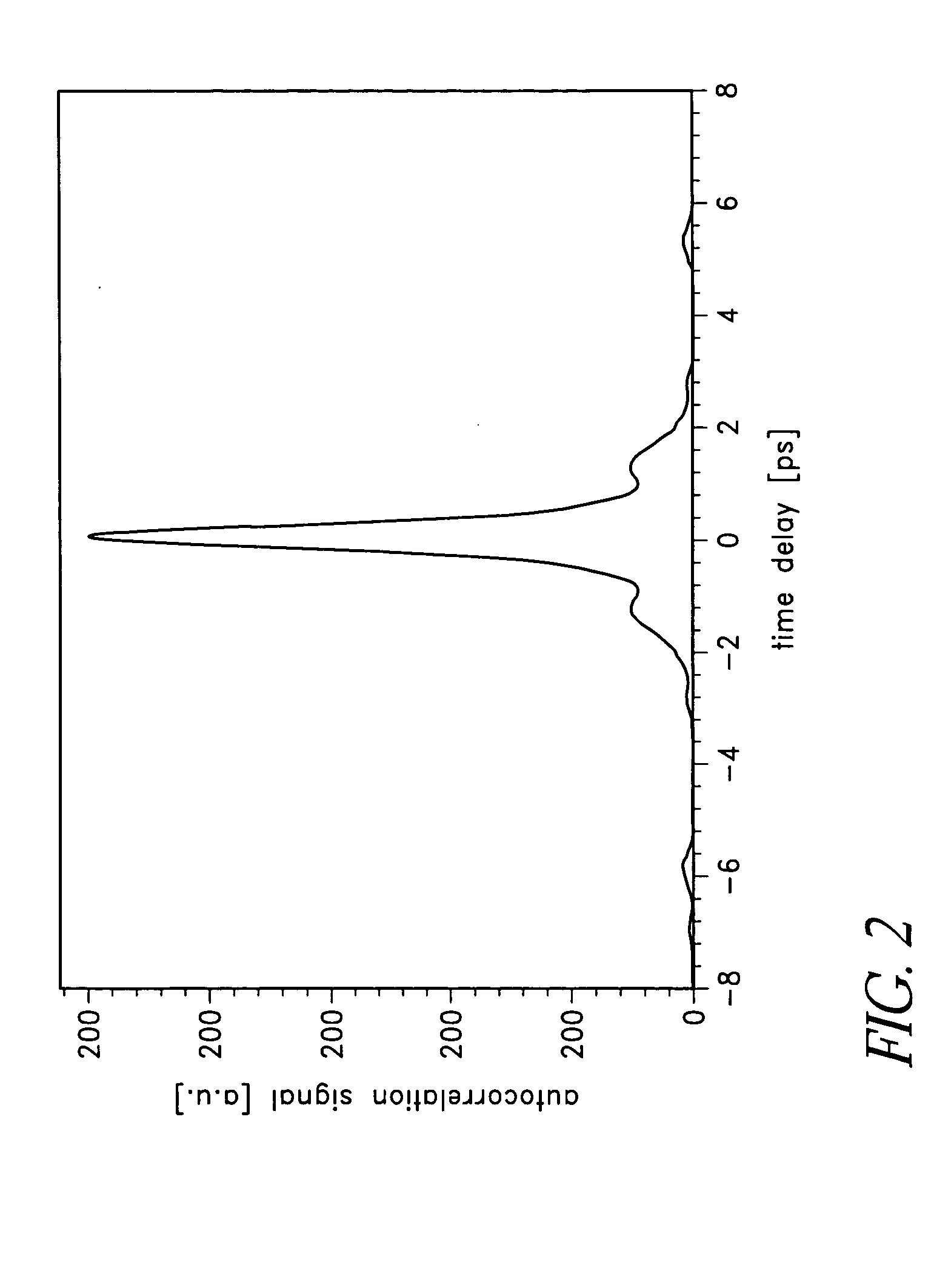
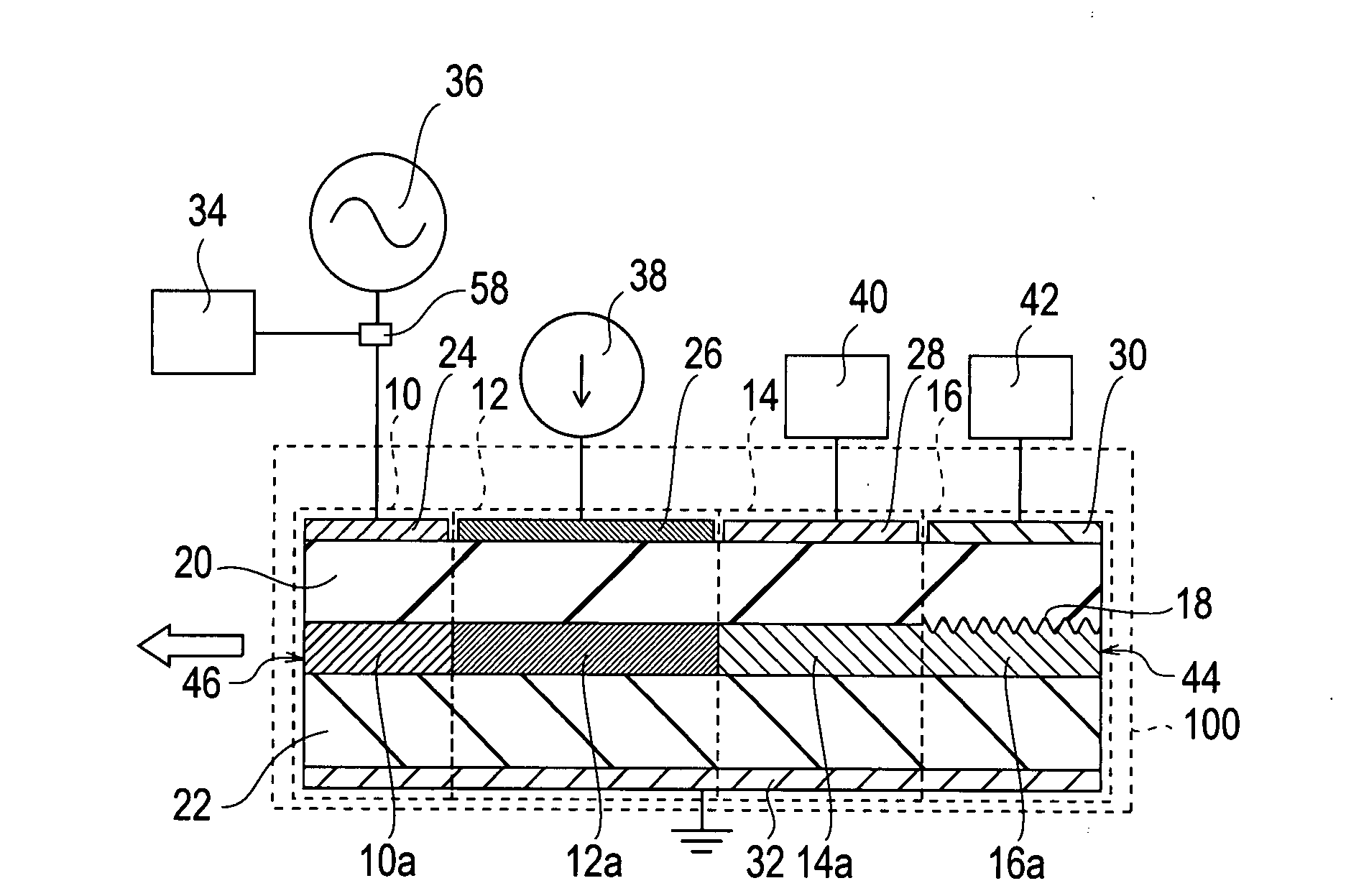
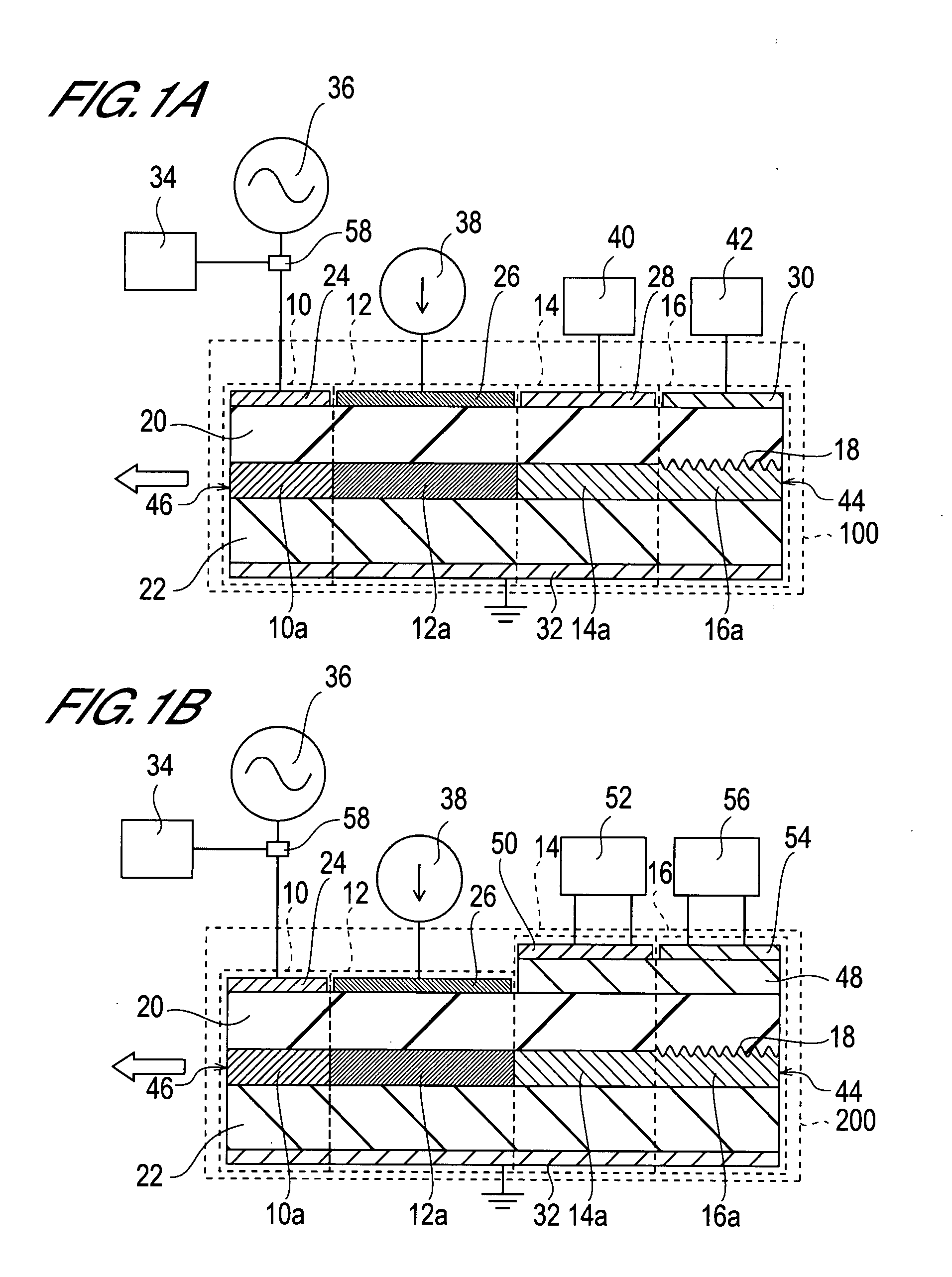
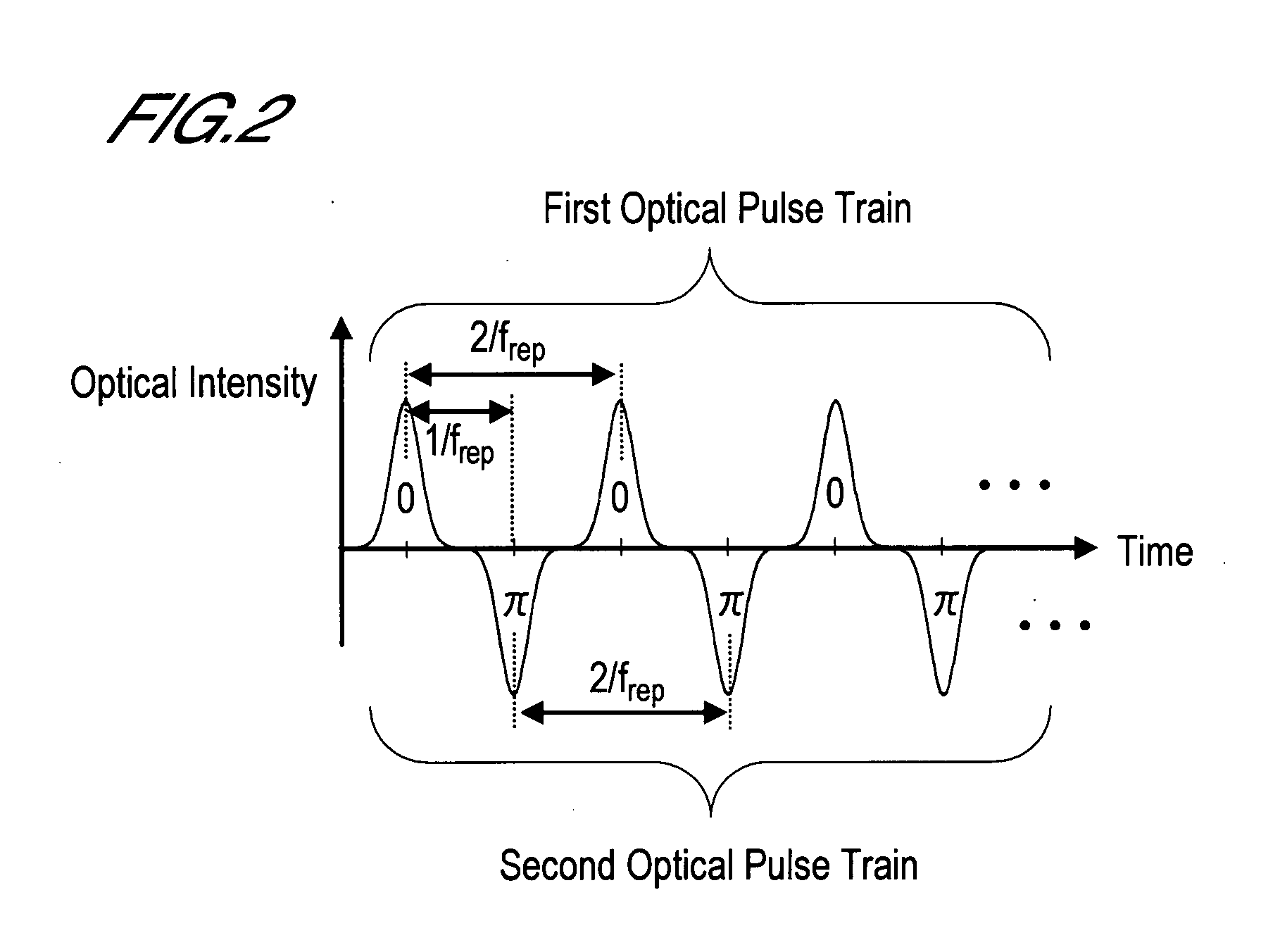
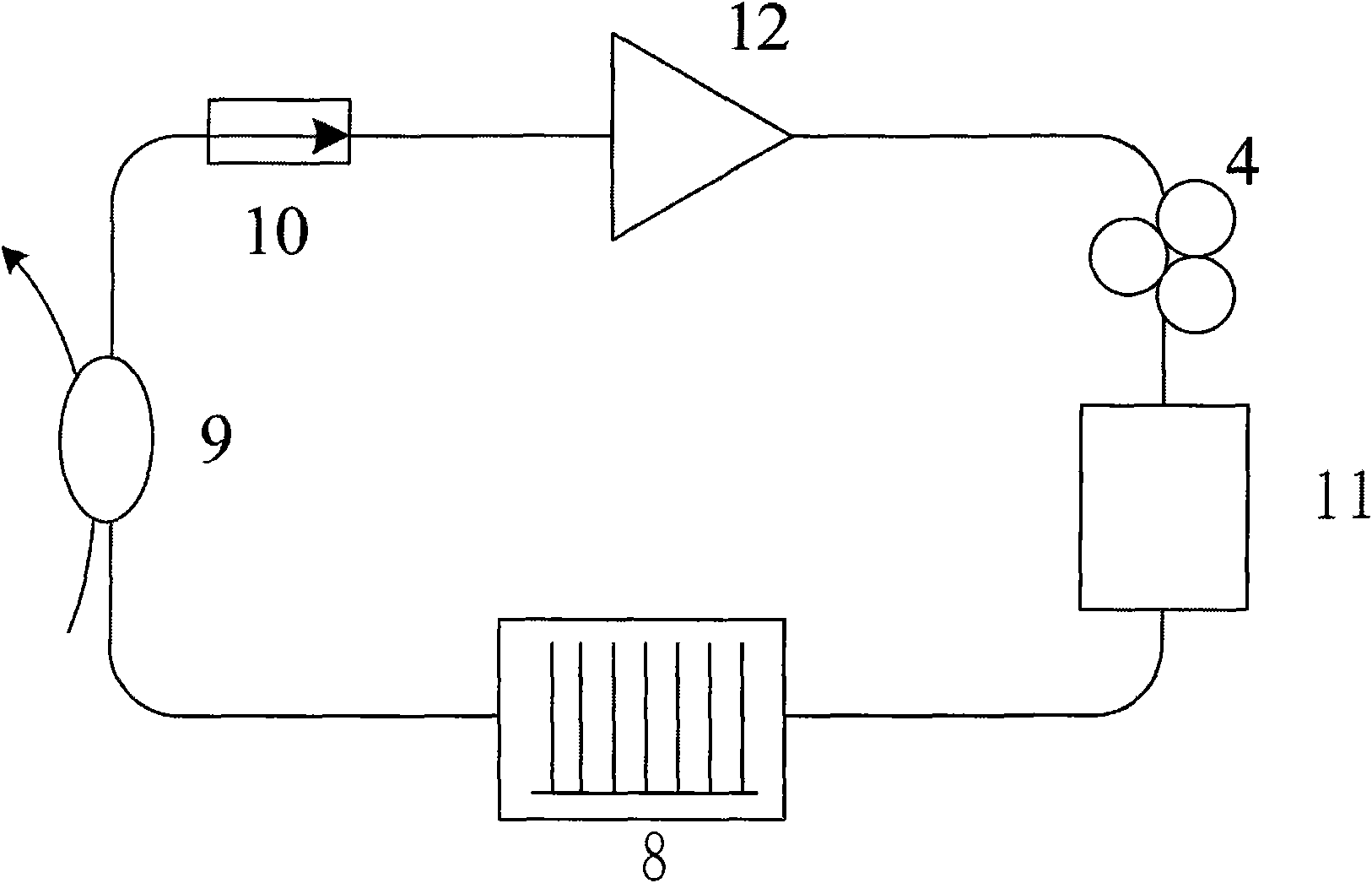
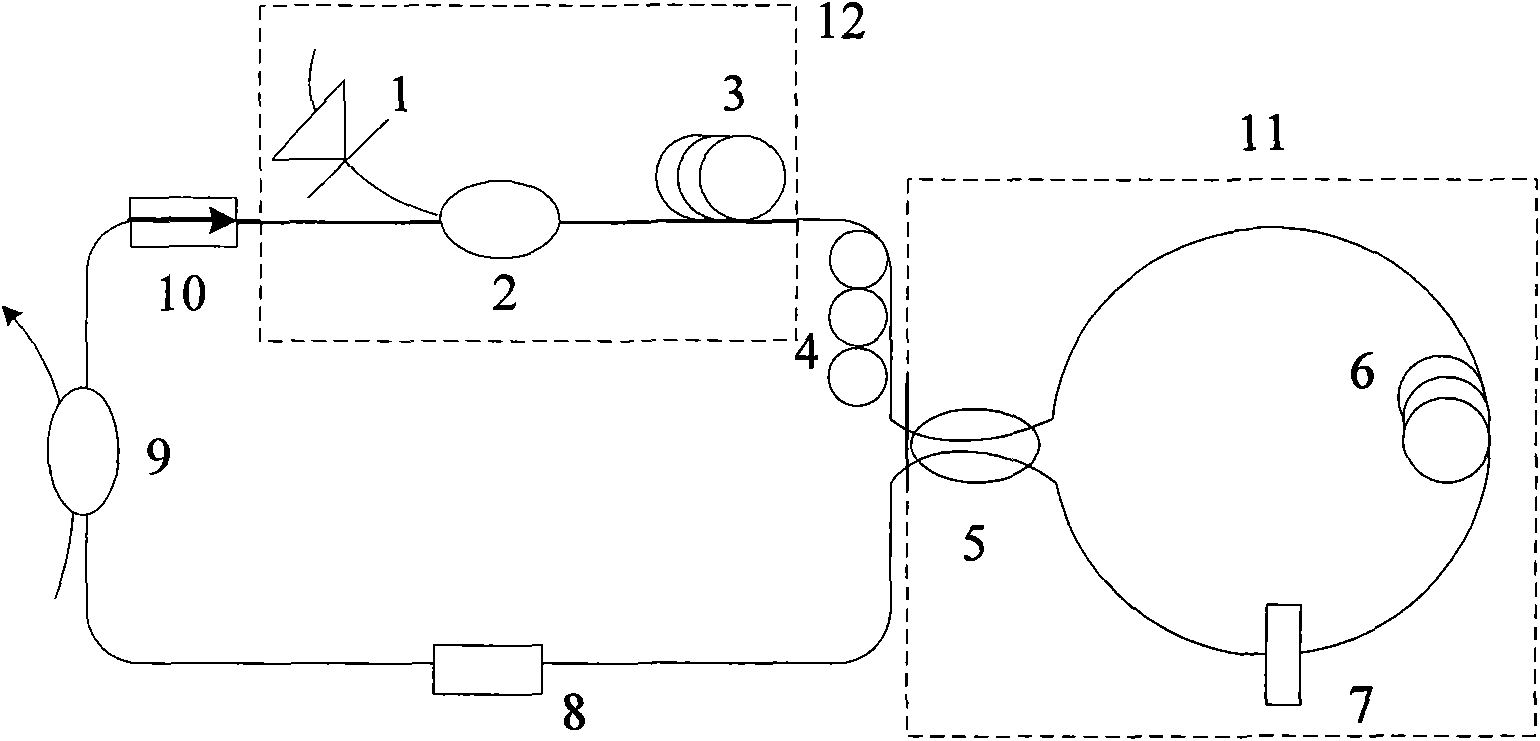
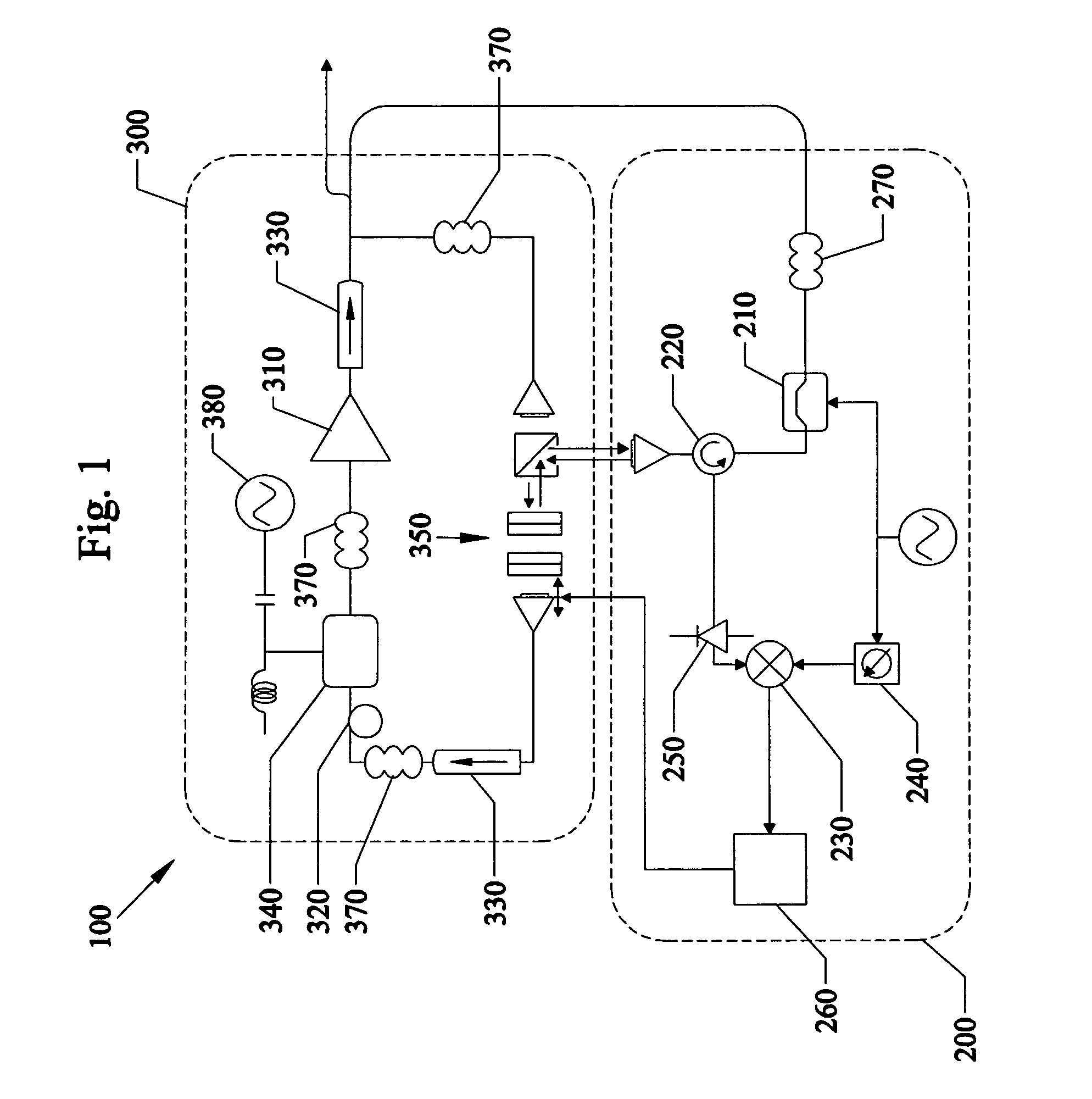
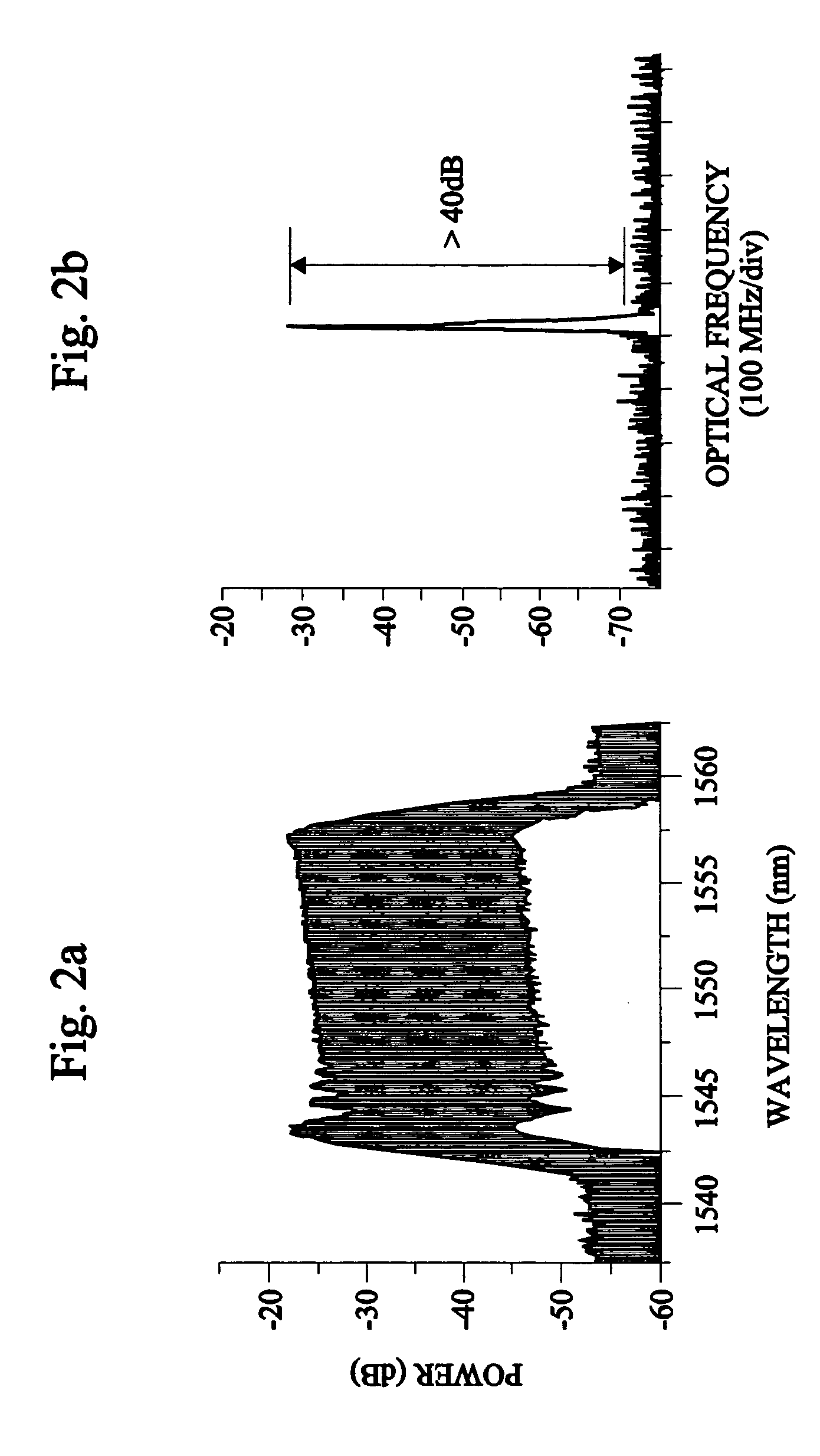
Mode locking methods and apparatus
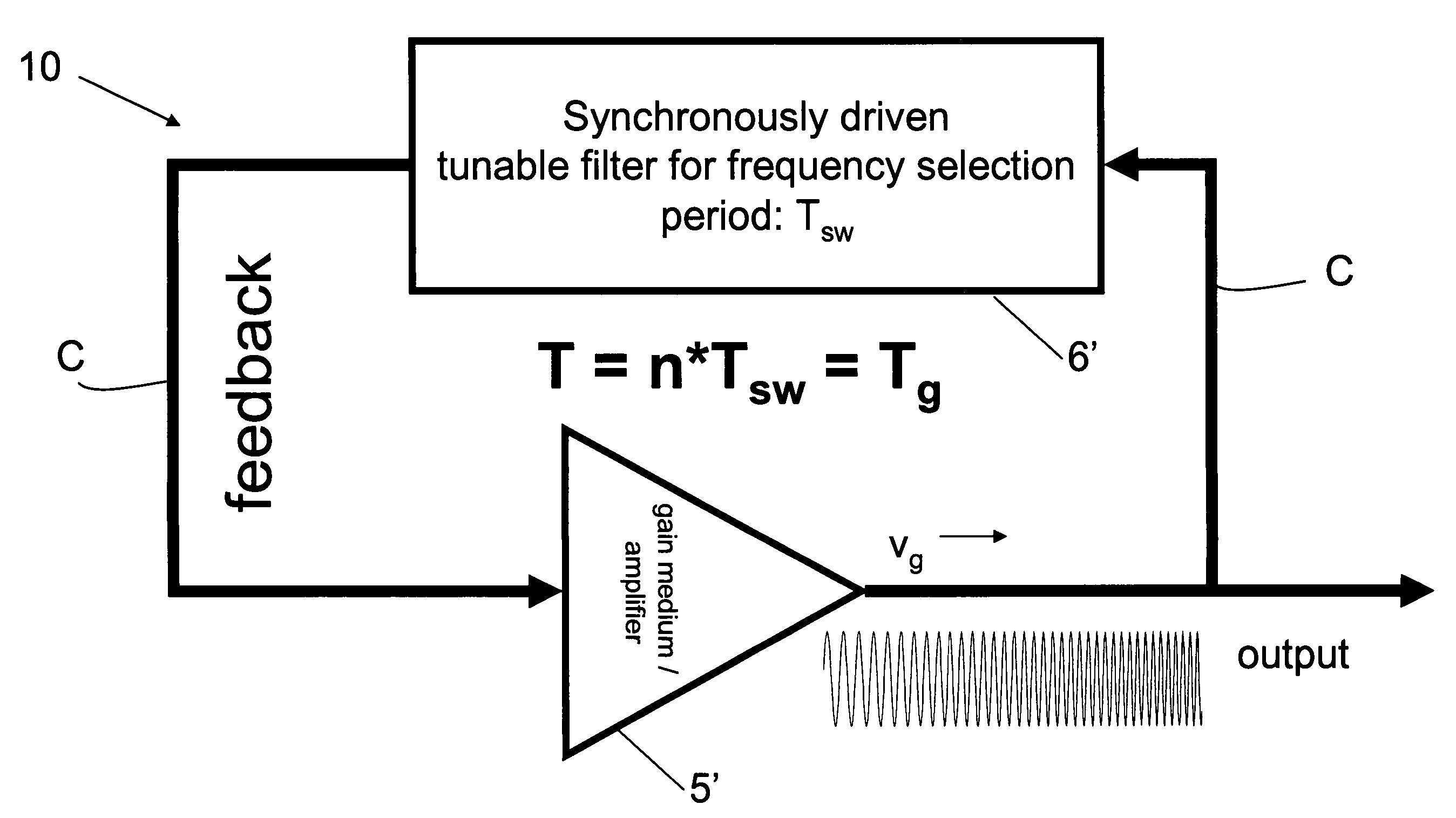
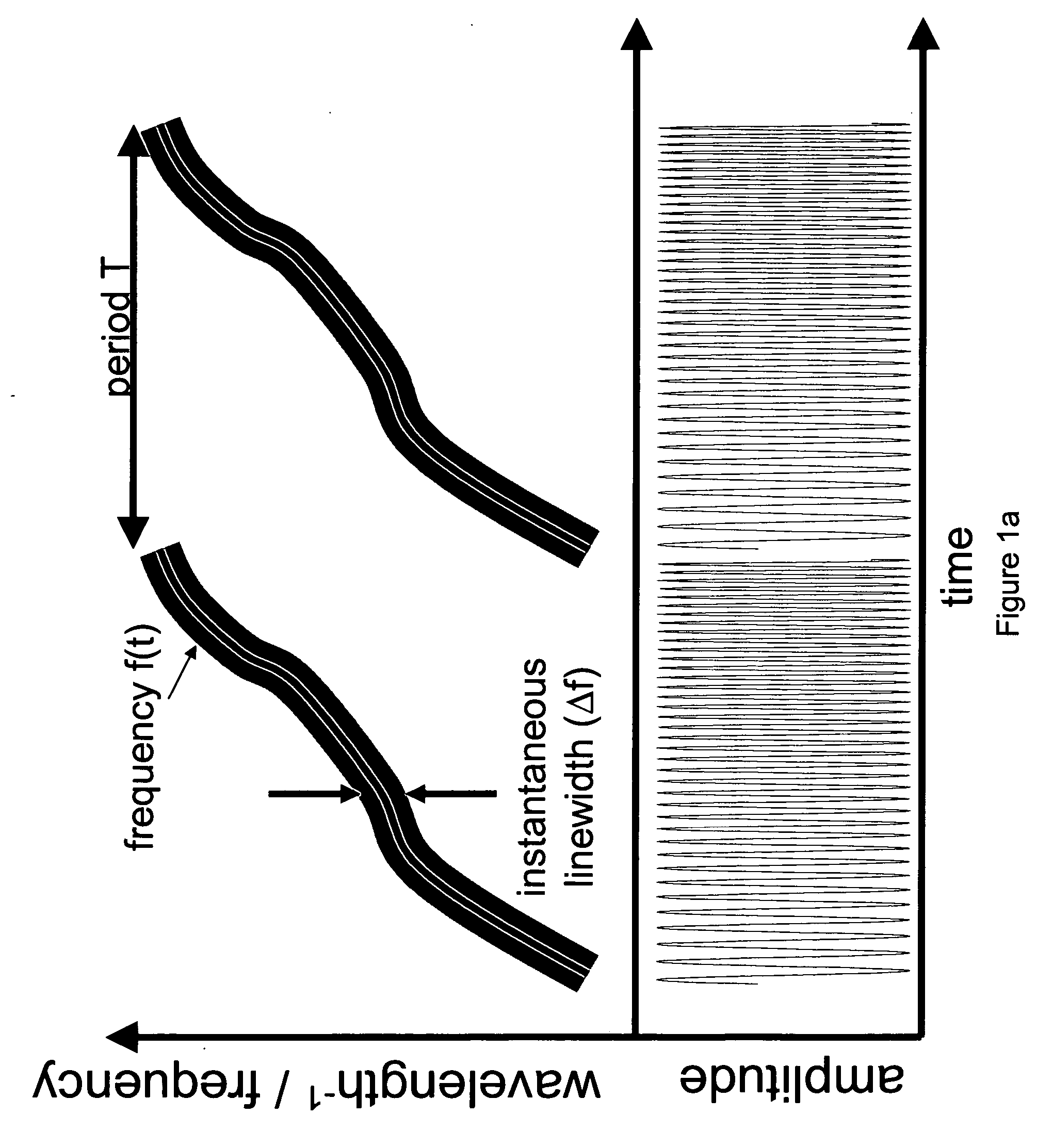
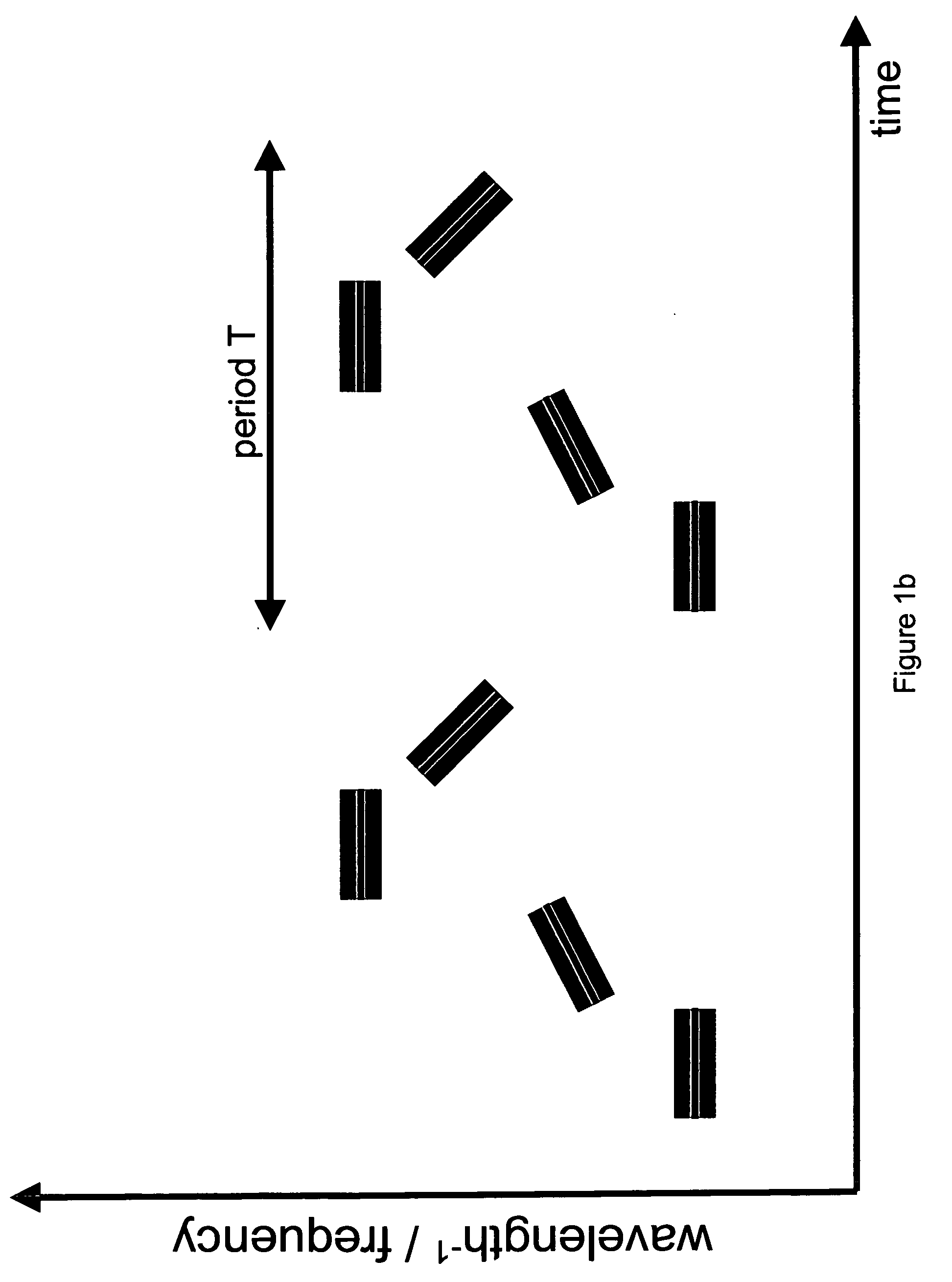
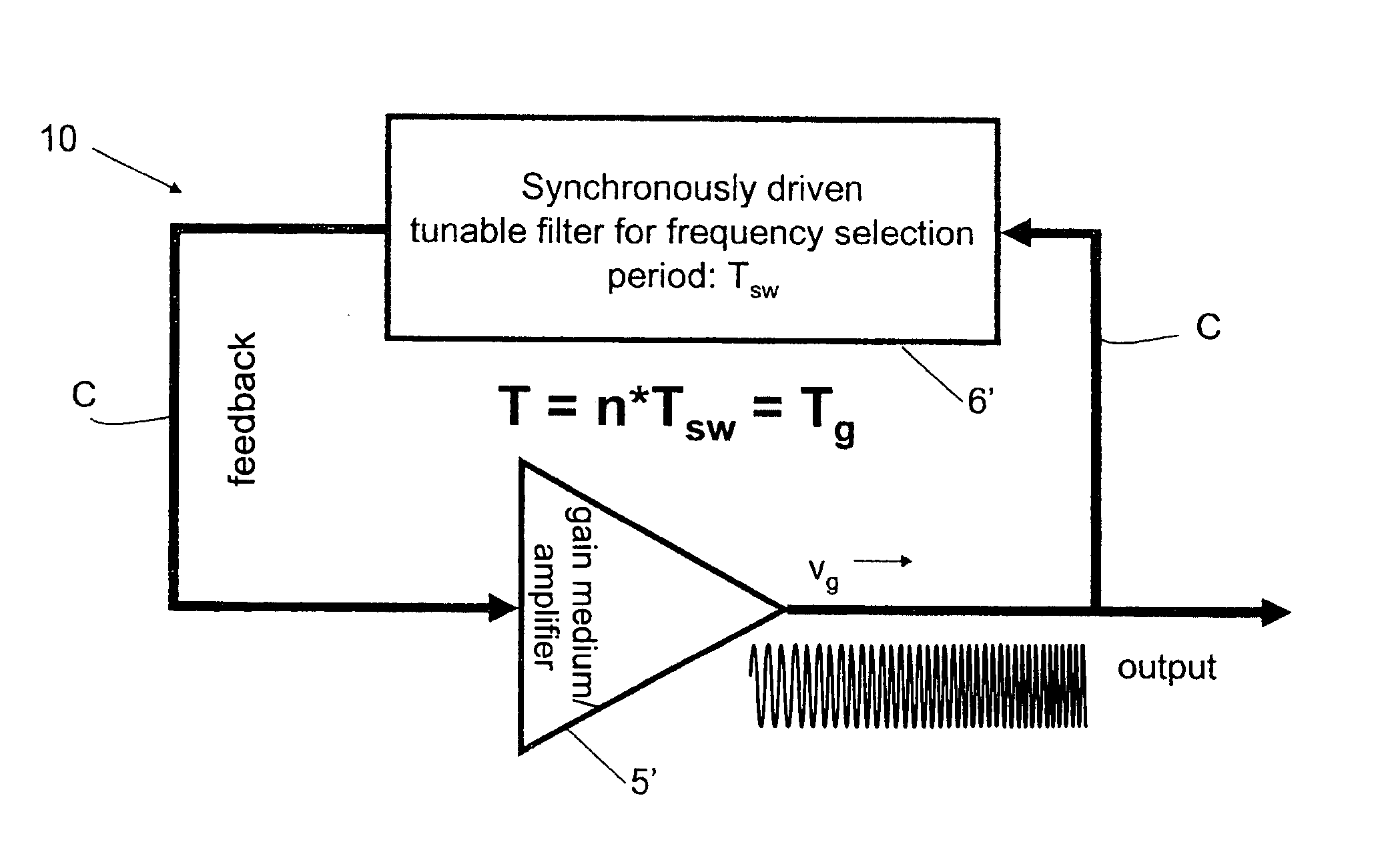
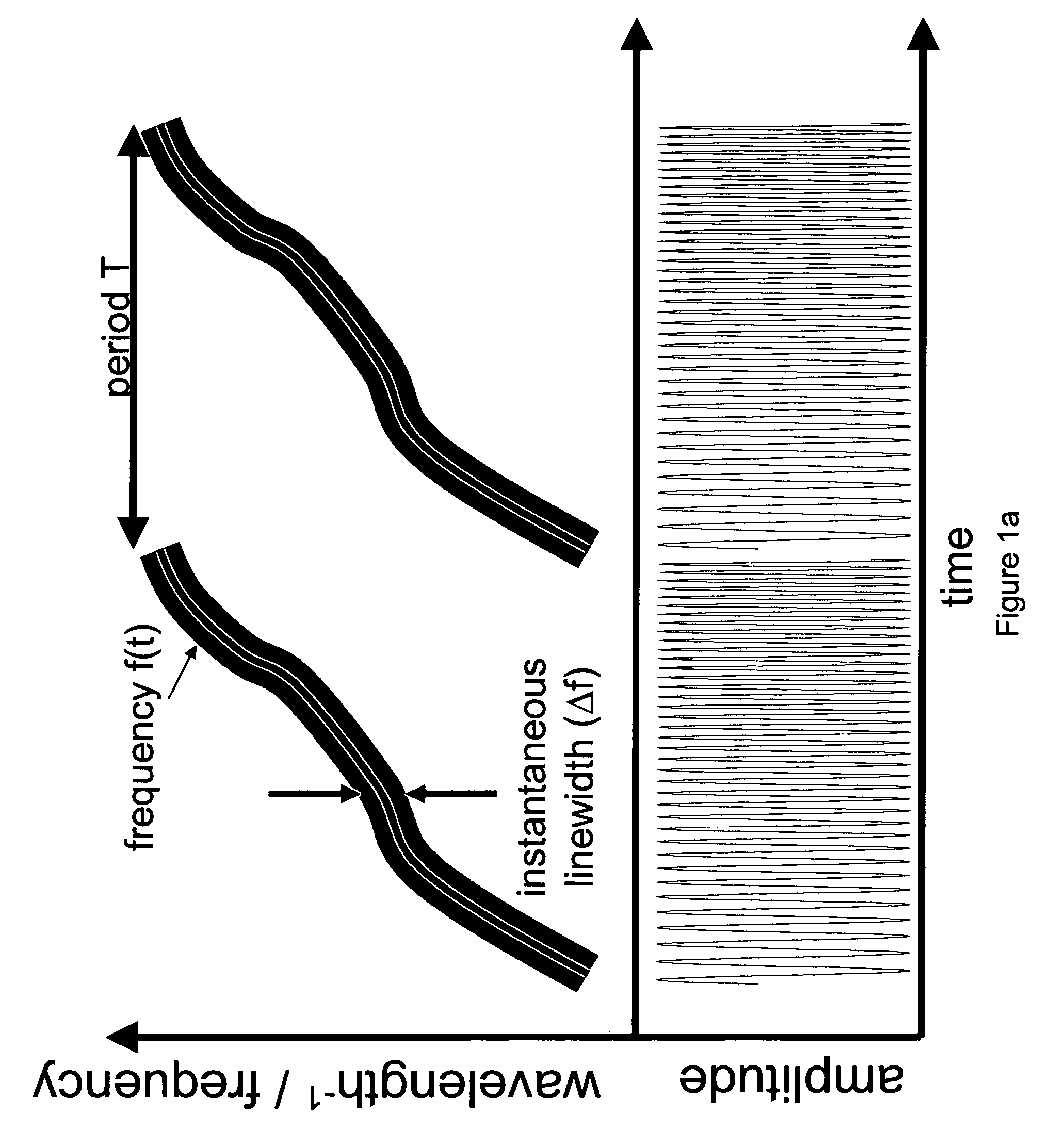
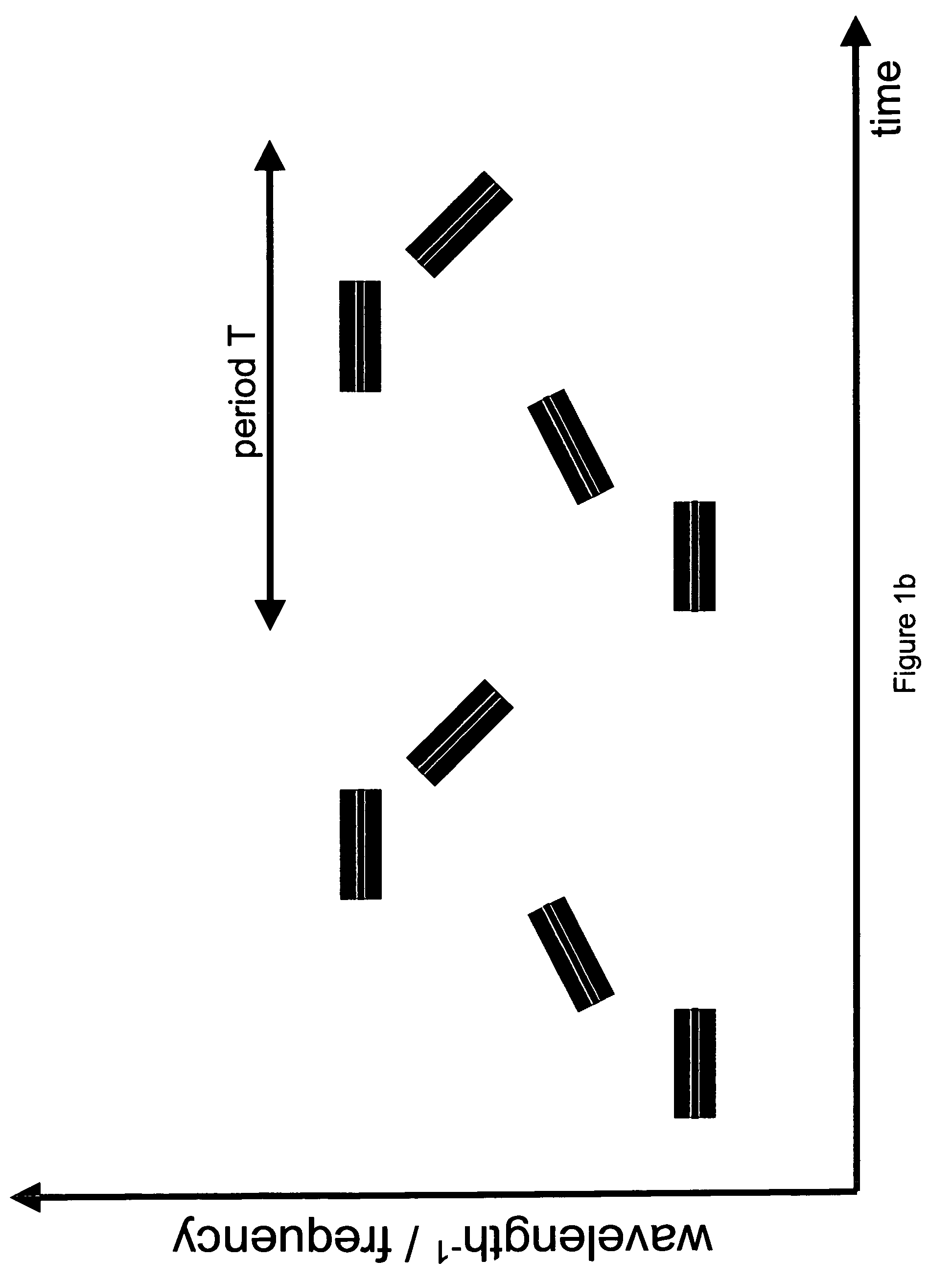
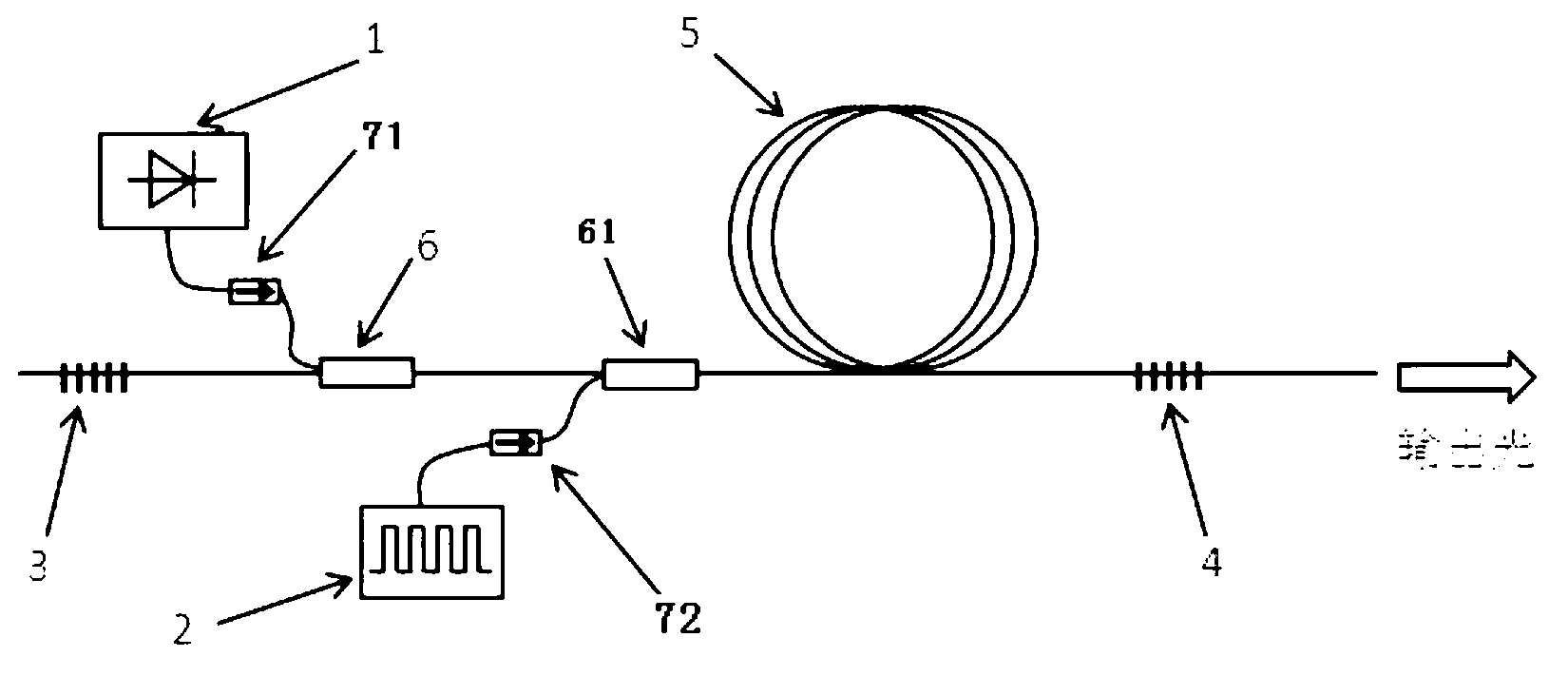
In one aspect the invention relates to a frequency varying wave generator. The generator includes a gain element adapted to amplify a wave having a wavelength; a time varying tunable wavelength selective filter element in communication with the gain element, the tunable filter element adapted to selectively filter waves during a period T; and a feedback element in communication with the tunable filter element and the gain element, wherein the tunable wavelength selective filter element, the gain element and the feedback element define a circuit such that the roundtrip time for the wave to propagate through the circuit is substantially equal to a non-zero integer multiple of the period T.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Mode locking methods and apparatus
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
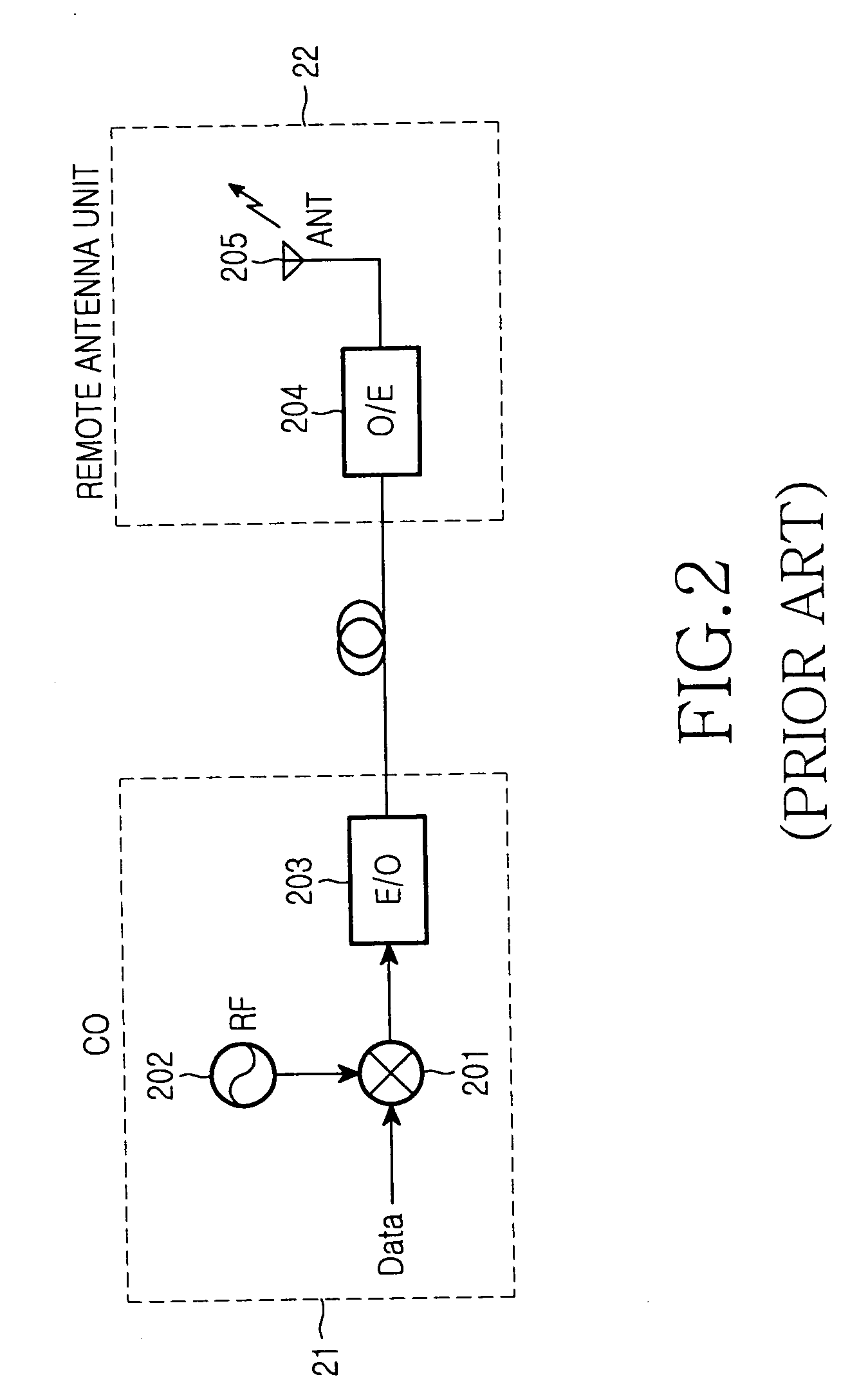
Integrated wired and wireless WDM PON apparatus using mode-locked light source
InactiveUS20060182446A1Low costEfficient wireless integrationIndoor gamesWavelength-division multiplex systemsMode-lockingBroadband
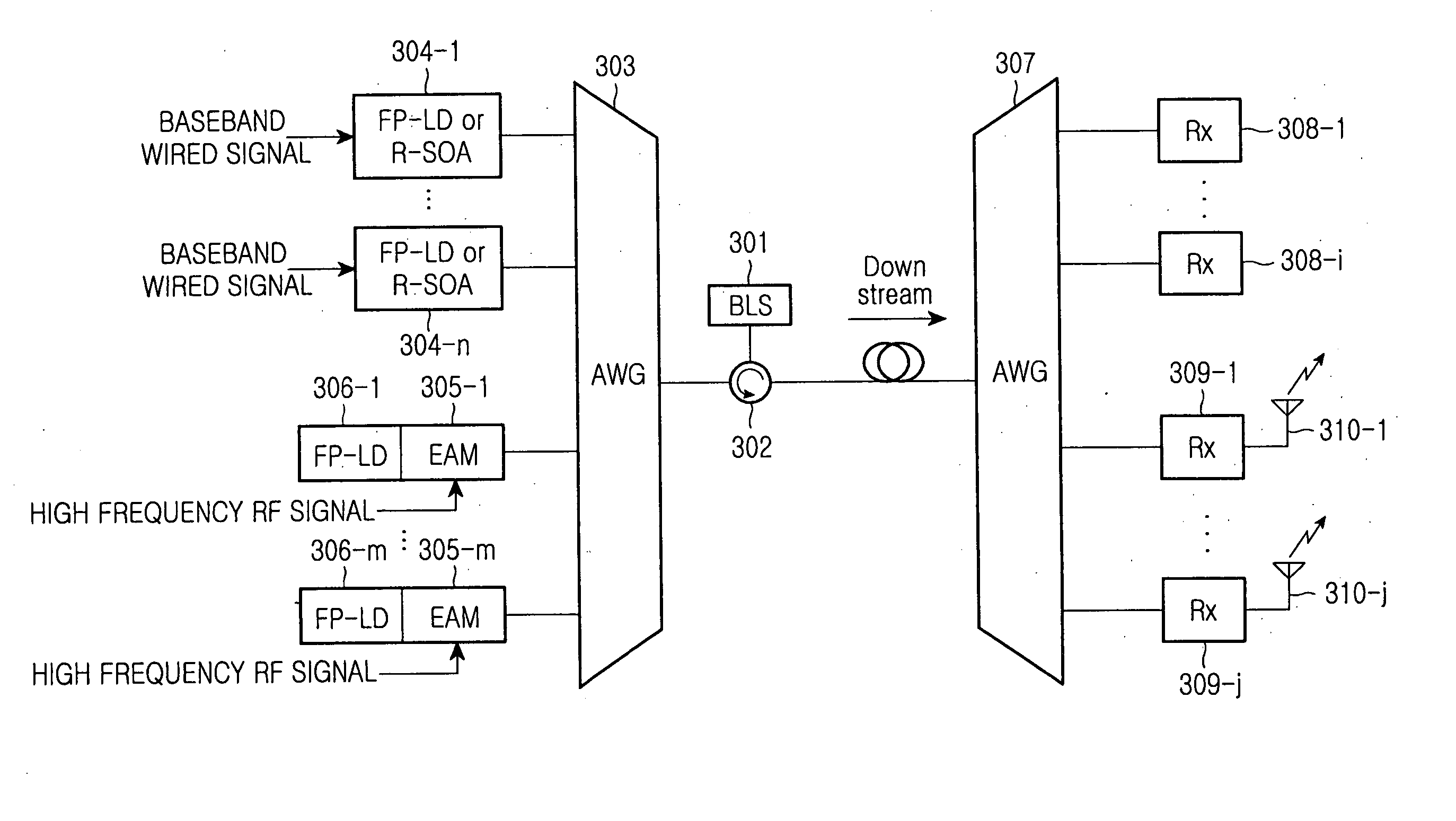
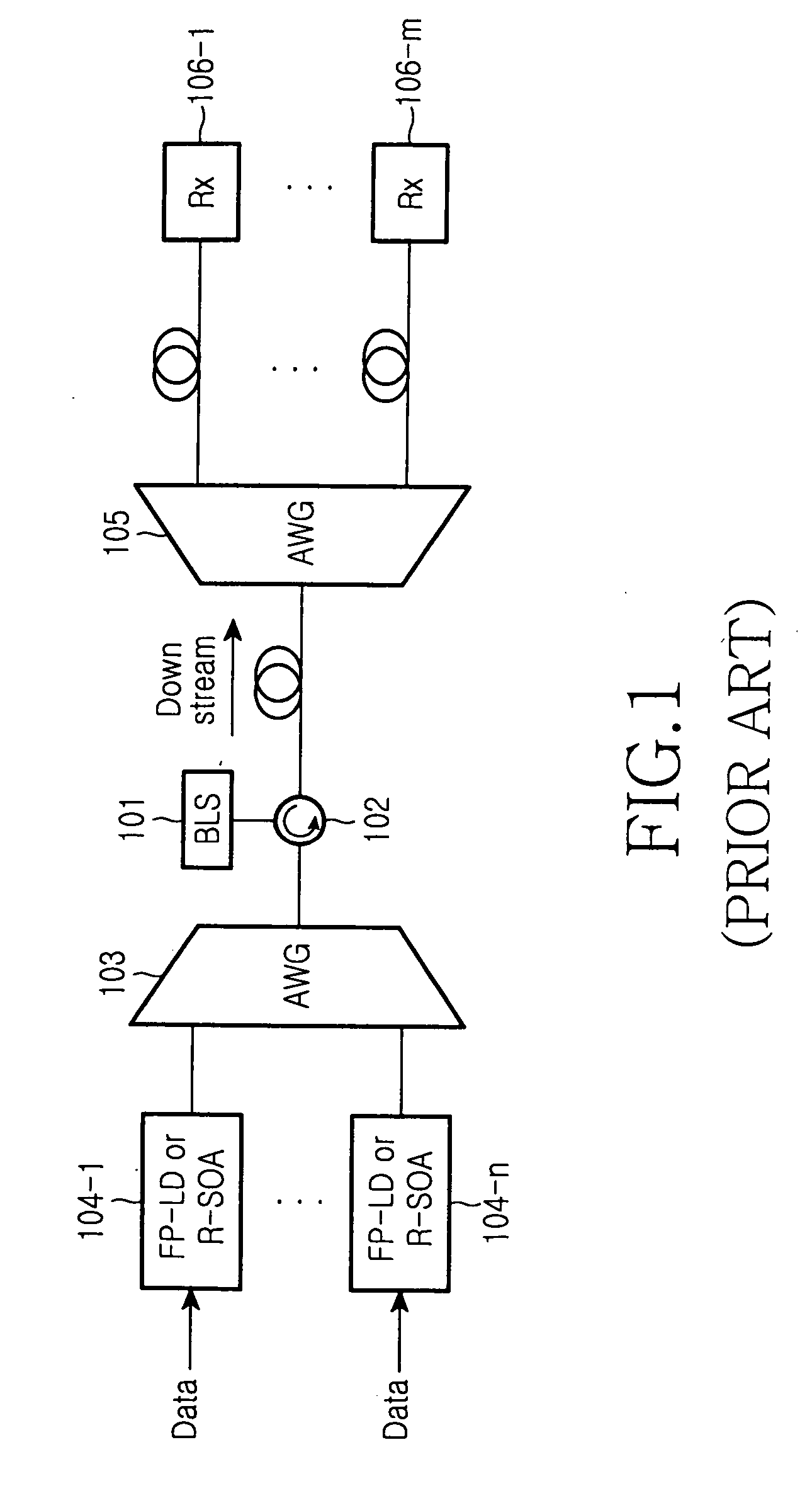
Integrated wired and wireless wavelength division multiplexing passive optical network (WDM PON) apparatus using a light source mode-locked to fed incoherent light includes: a fed light generator for providing fed light for up / downstream signals via a broadband light source emitting an incoherent optical signal; a central office (CO) for receiving, mode-locking, and downstream-optical-transmitting the incoherent optical signal generated by the fed light generator and receiving and optical-detecting an upstream optical signal transmitted from a subscriber unit; and the subscriber unit for receiving, mode-locking, and upstream-optical-transmitting the incoherent optical signal generated by the fed light generator and receiving and optical-detecting a downstream optical signal transmitted from the CO, wherein a wired optical transmitter for transmitting a baseband wired signal and a wireless optical transmitter for transmitting a high frequency radio frequency (RF) signal are comprised for up / downstream optical transmission of the CO and the subscriber unit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Mode-locked multi-mode fiber laser pulse source
InactiveUS20050008044A1High energy storageIncrease the sectionCoupling light guidesActive medium shape and constructionHigh power lasersPeak value
A laser utilizes a cavity design which allows the stable generation of high peak power pulses from mode-locked multi-mode fiber lasers, greatly extending the peak power limits of conventional mode-locked single-mode fiber lasers. Mode-locking may be induced by insertion of a saturable absorber into the cavity and by inserting one or more mode-filters to ensure the oscillation of the fundamental mode in the multi-mode fiber. The probability of damage of the absorber may be minimized by the insertion of an additional semiconductor optical power limiter into the cavity. To amplify and compress optical pulses in a multi-mode (MM) optical fiber, a single-mode is launched into the MM fiber by matching the modal profile of the fundamental mode of the MM fiber with a diffraction-limited optical mode at the launch end, The fundamental mode is preserved in the MM fiber by minimizing mode-coupling by using relatively short lengths of step-index MM fibers with a few hundred modes and by minimizing fiber perturbations. Doping is confined to the center of the fiber core to preferentially amplify the fundamental mode, to reduce amplified spontaneous emission and to allow gain-guiding of the fundamental mode. Gain-guiding allows for the design of systems with length-dependent and power-dependent diameters of the fundamental mode. To allow pumping with high-power laser diodes, a double-clad amplifier structure is employed. For applications in nonlinear pulse-compression, self phase modulation and dispersion in the optical fibers can be exploited. High-power optical pulses may be linearly compressed using bulk optics dispersive delay lines or by chirped fiber Bragg gratings written directly into the SM or MM optical fiber. High-power cw lasers operating in a single near-diffraction-limited mode may be constructed from MM fibers by incorporating effective mode-filters into the laser cavity. Regenerative fiber amplifiers may be constructed from MM fibers by careful control of the recirculating mode. Higher-power Q-switched fiber lasers may be constructed by exploiting the large energy stored in MM fiber amplifiers.
Owner:FERMANN MARTIN E +1
High-repetition rate passively mode-locked solid-state laser
InactiveUS6393035B1Simple designOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersOptical probingMode-locking
A passively mode-locked solid-state laser for emitting a continuous-wave train of electromagnetic-radiation pulses, the fundamental repetition rate of the emitted pulses exceeding 1 GHz, without Q-switching has an optical resonator, a solid-state laser gain element placed inside the optical resonator, an exciter for exciting said laser gain element to emit electromagnetic radiation having the effective wavelength, and a saturable absorber for passive mode locking. The laser gain element preferably consists of a laser material with a stimulated emission cross section exceeding 0.8x10-18 cm-2 at the effective wavelength. Typically, the laser gain element is made of Nd:vanadate. The saturable absorber is preferably a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror device. The laser is simple, robust, compact, efficient, and low-cost. It generates a relatively large average power of 100 mW and higher, which is useful for a number of optical probing and detection applications, in a beam which is substantially a fundamental spatial mode.
Owner:LUMENTUM SWITZERLAND AG
Optical pulse lasers
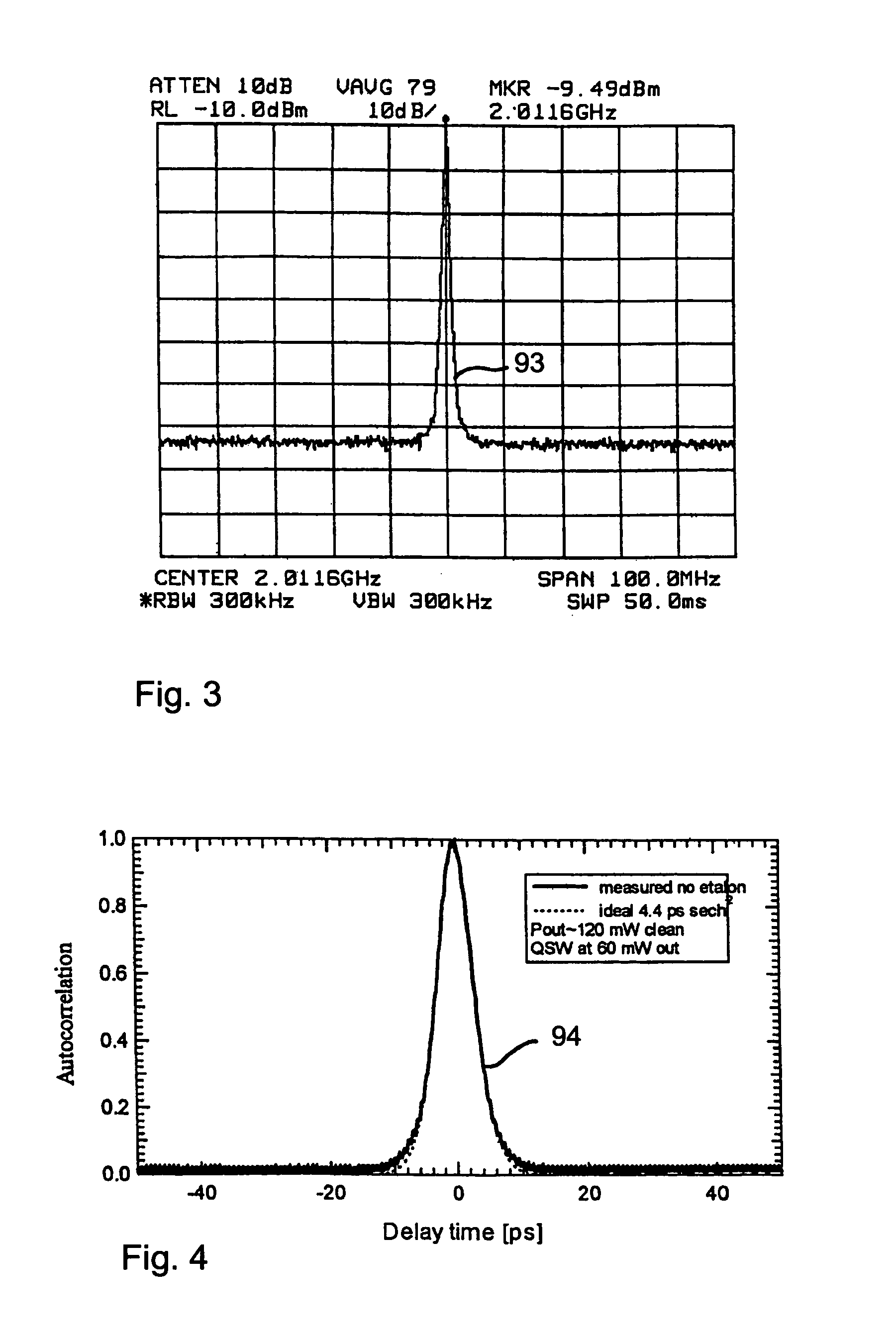
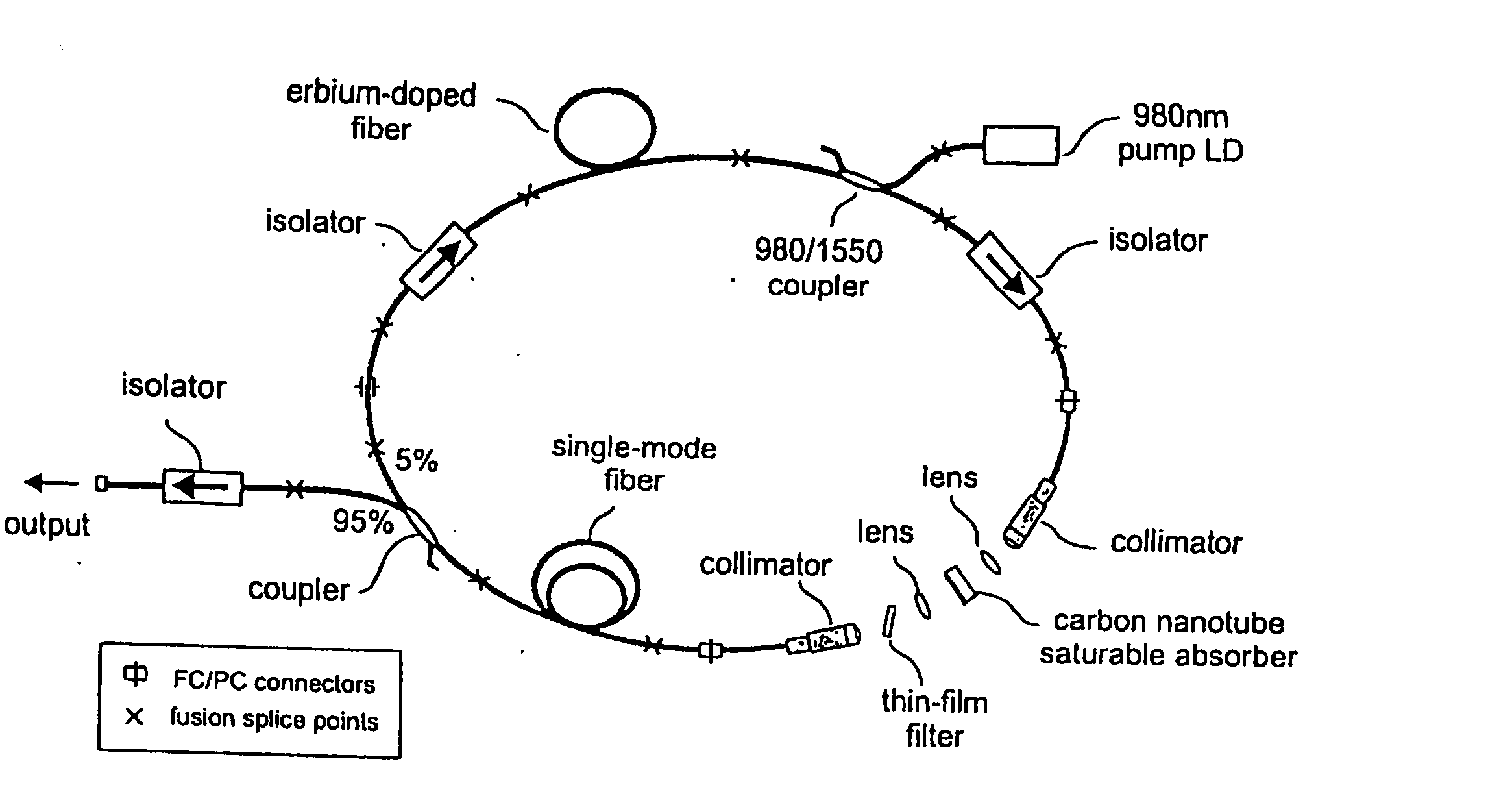
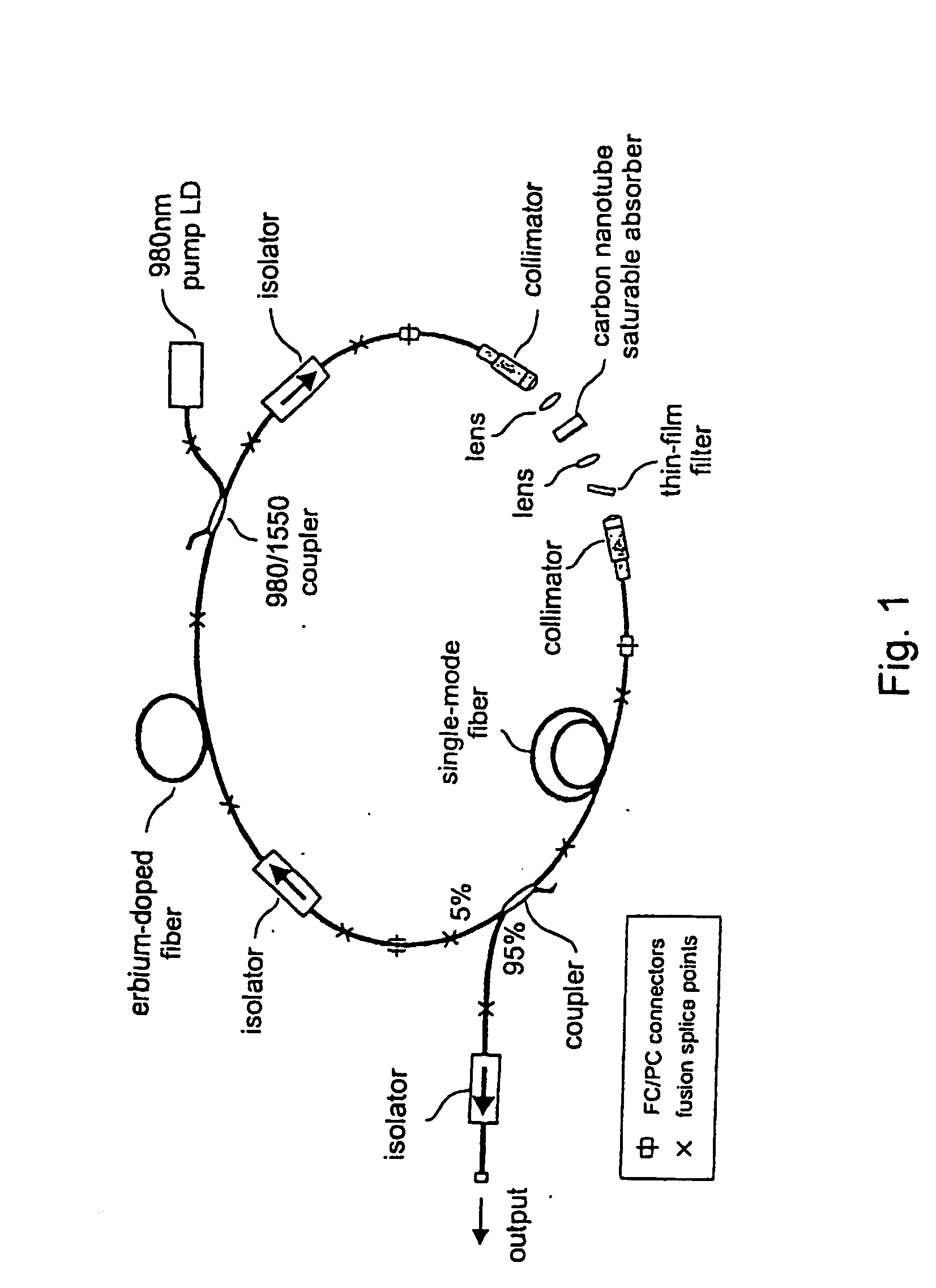
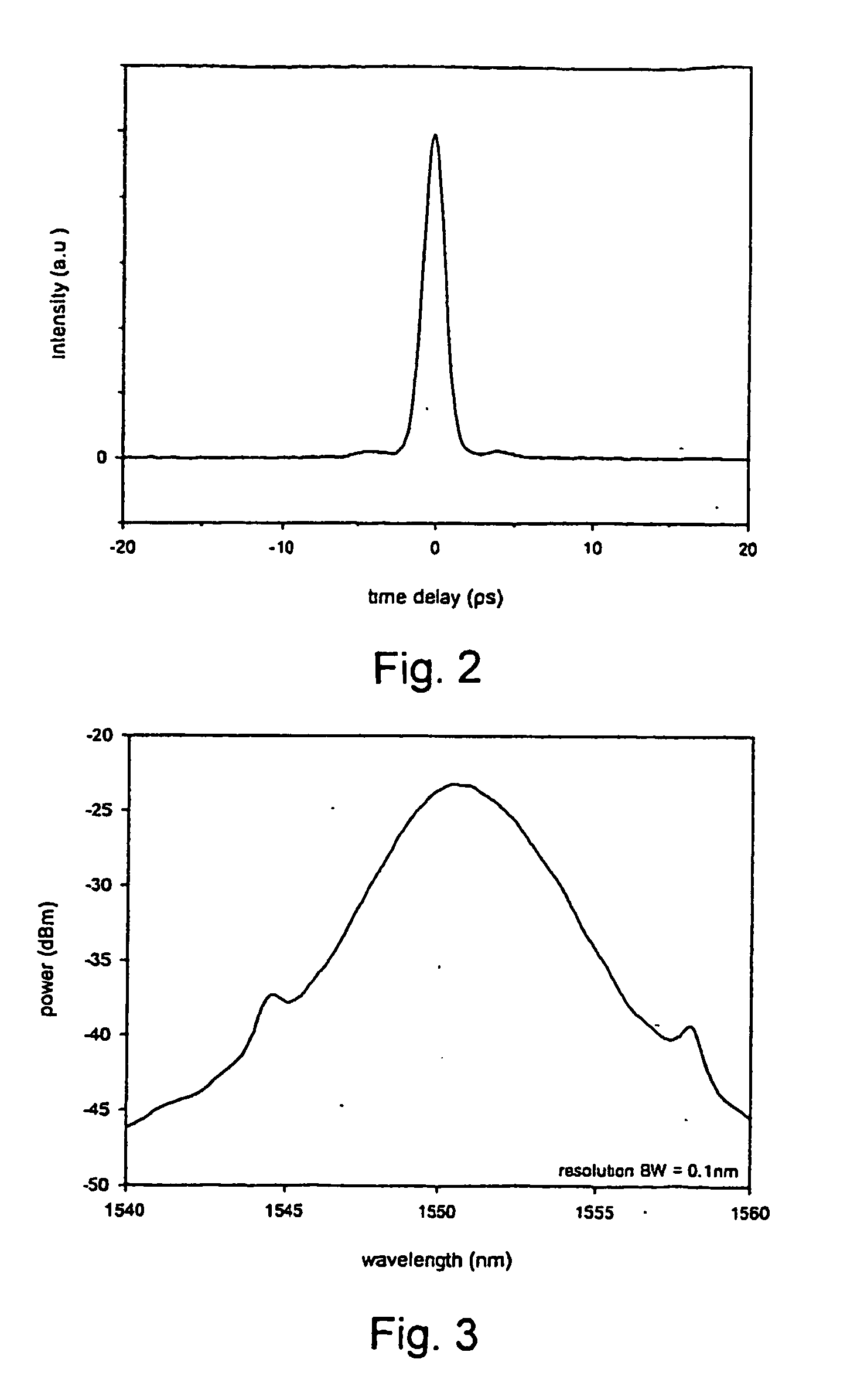
InactiveUS7372880B2Fast recovery timeHigh optical damage thresholdMirrorsNanoinformaticsCarbon nanotubeMode-locking
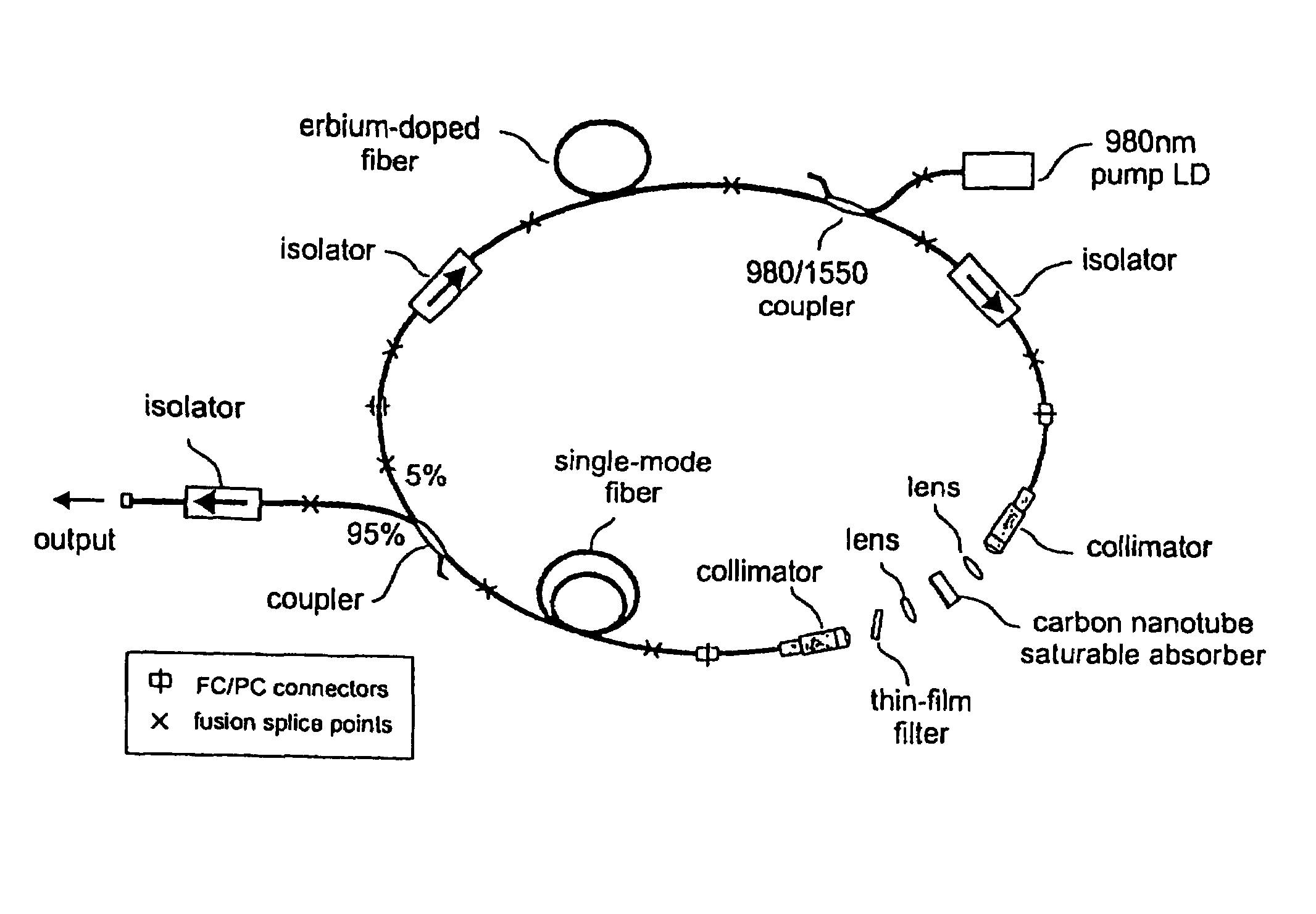
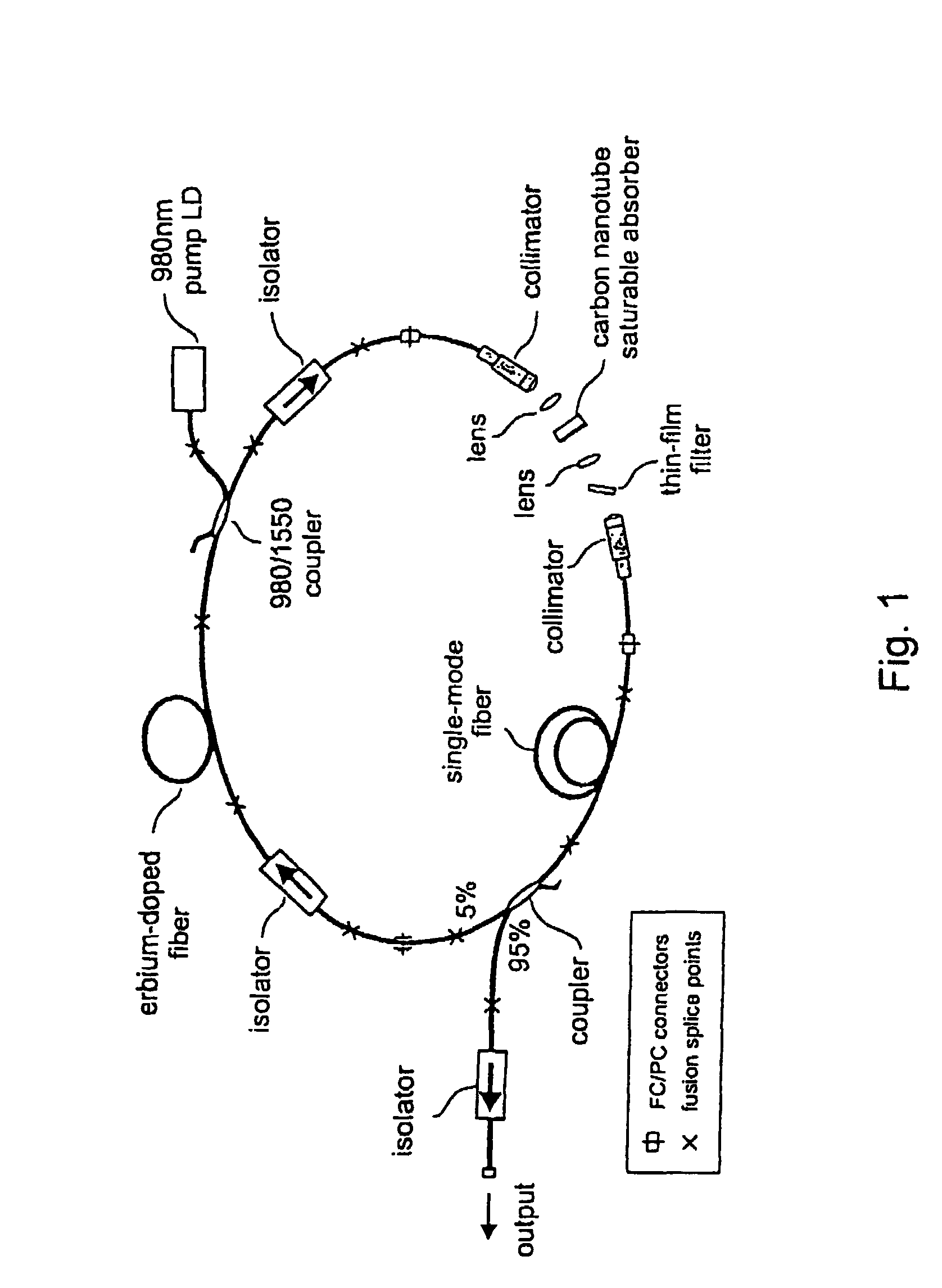
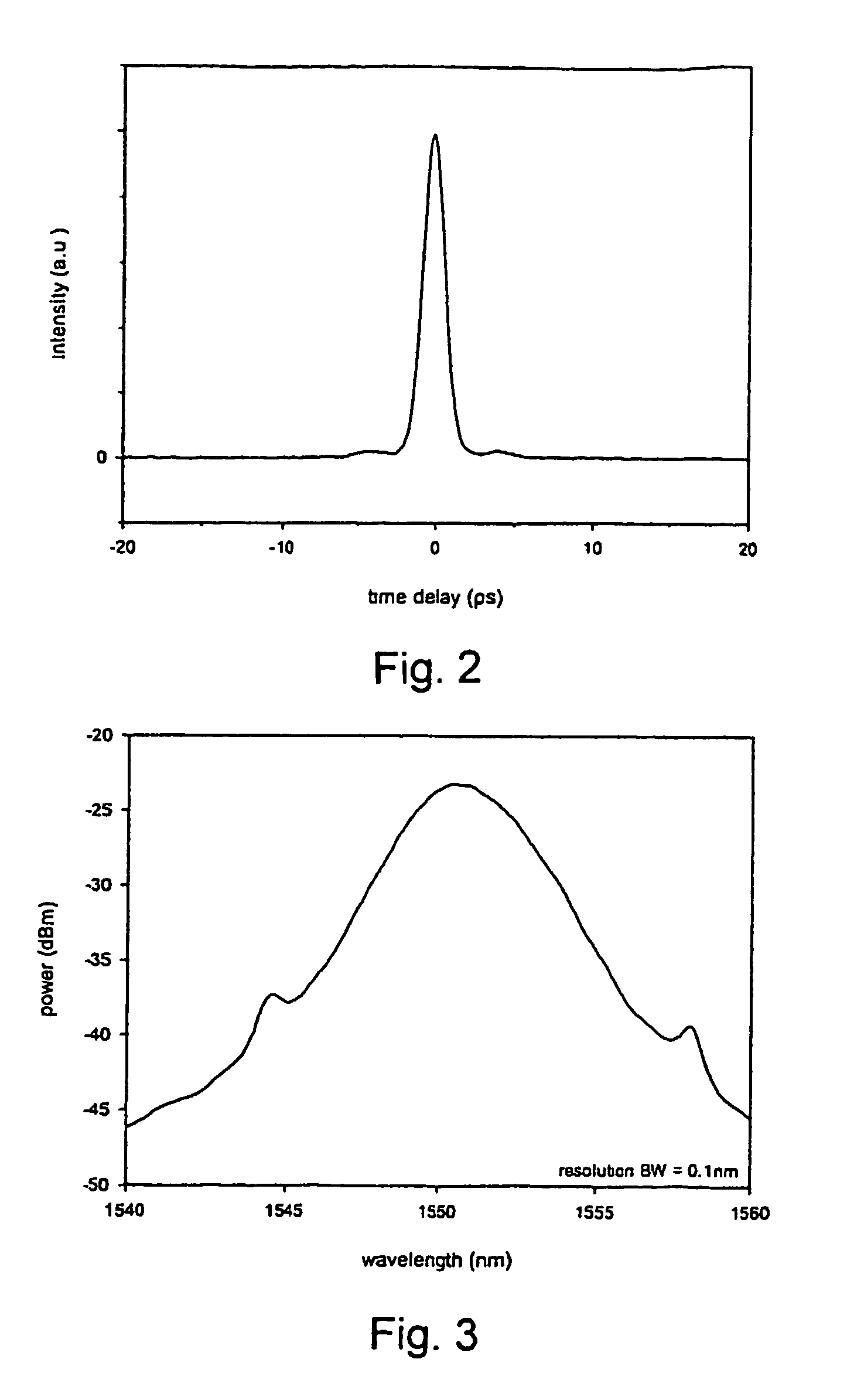
The present invention provides pulsed lasers which employ carbon nanotubes, particularly layers of carbon nanotubes, as saturable absorbers, mode lockers or for Q-switching elements. The present invention also provides methods and materials for mode-locking and Q-switching of lasers in which carbon nanotubes are employed as non-linear optical materials and / or saturable absorbers which facilitate mode-locking and / or Q-switching. The invention further provides mode locker and Q-switching elements or devices which comprise one or more layers containing carbon nanotubes which layer or layers function for mode locking and / or Q-switching.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
High-repetition-rate passively mode-locked solid-state laser
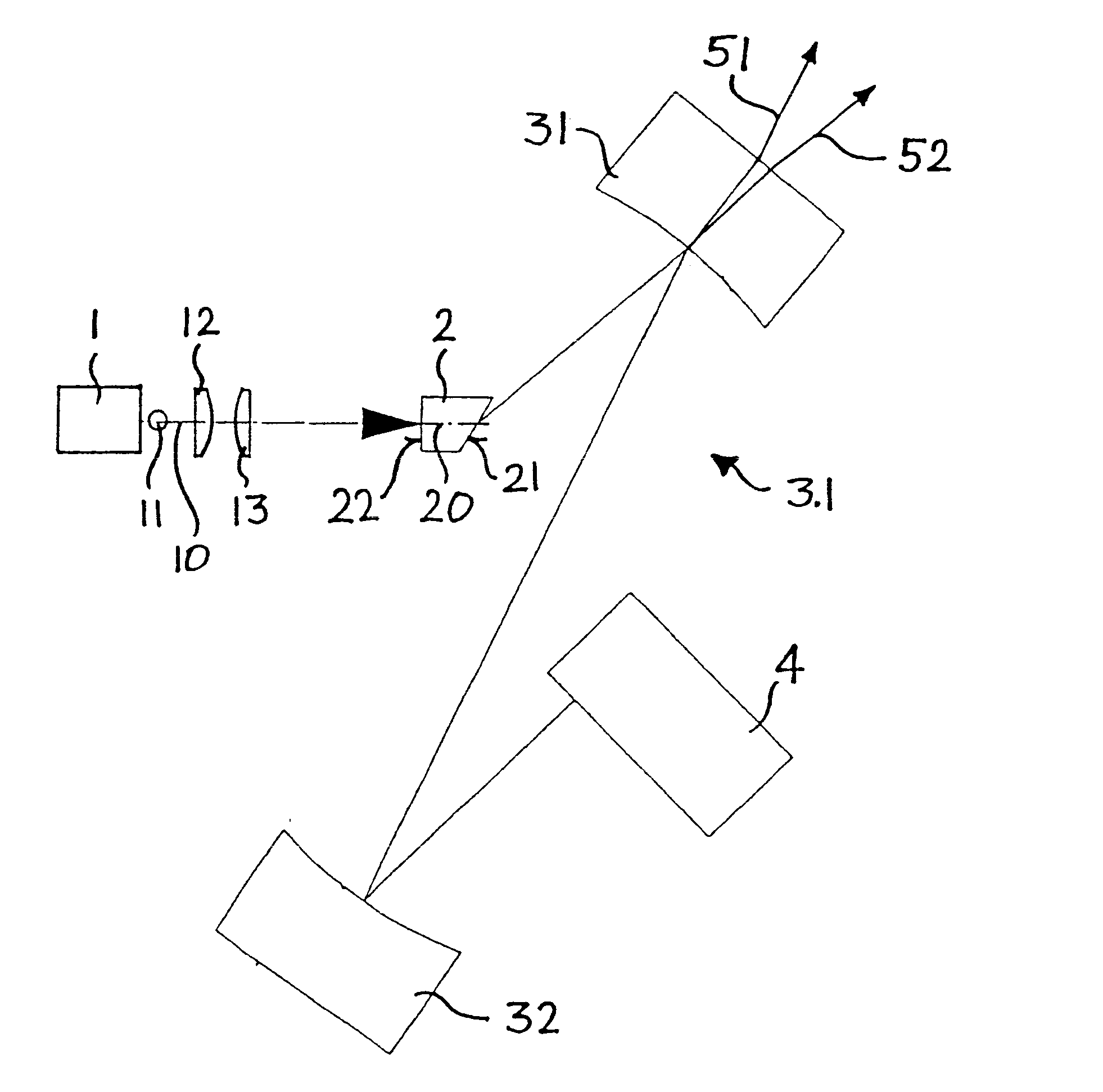
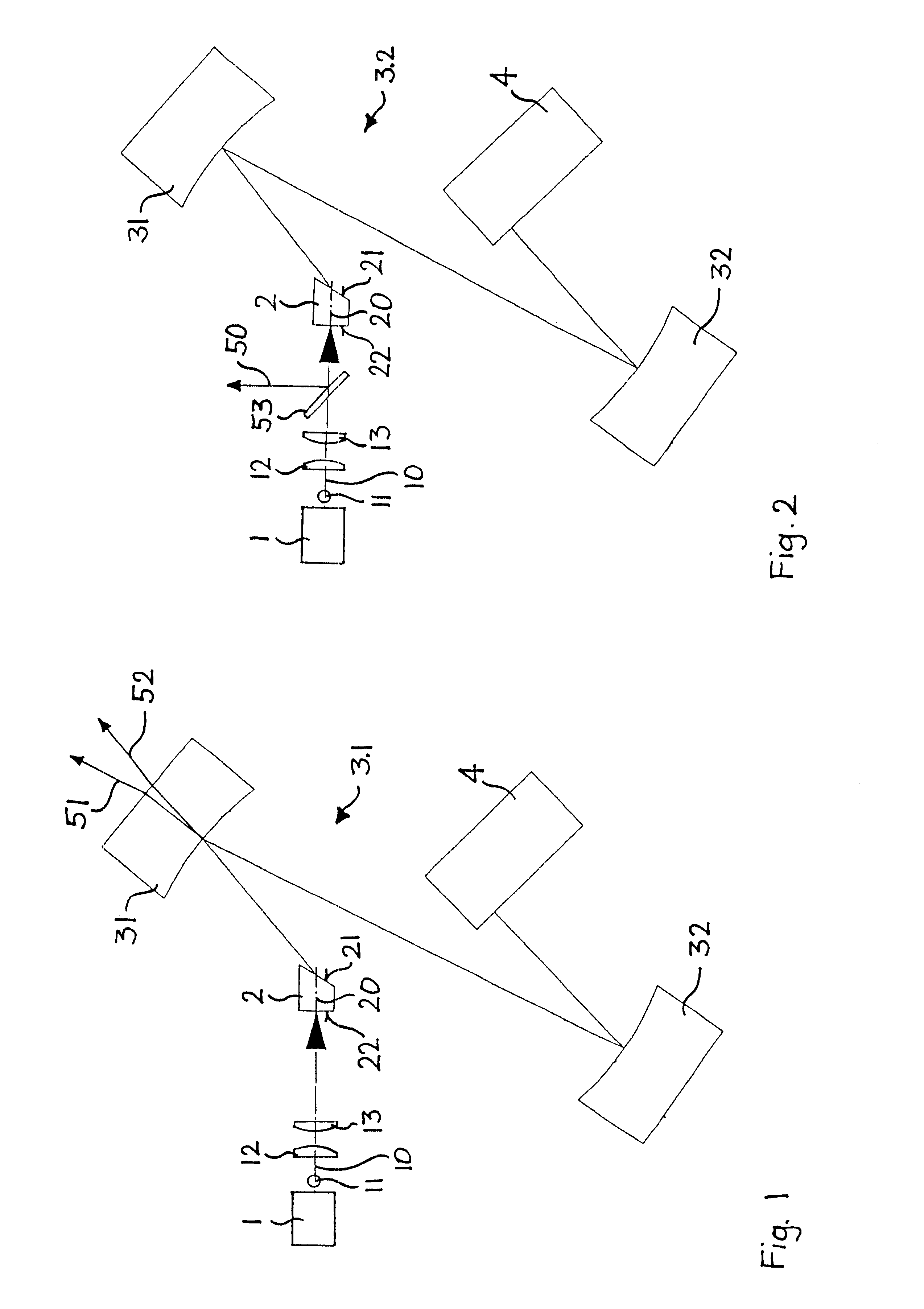
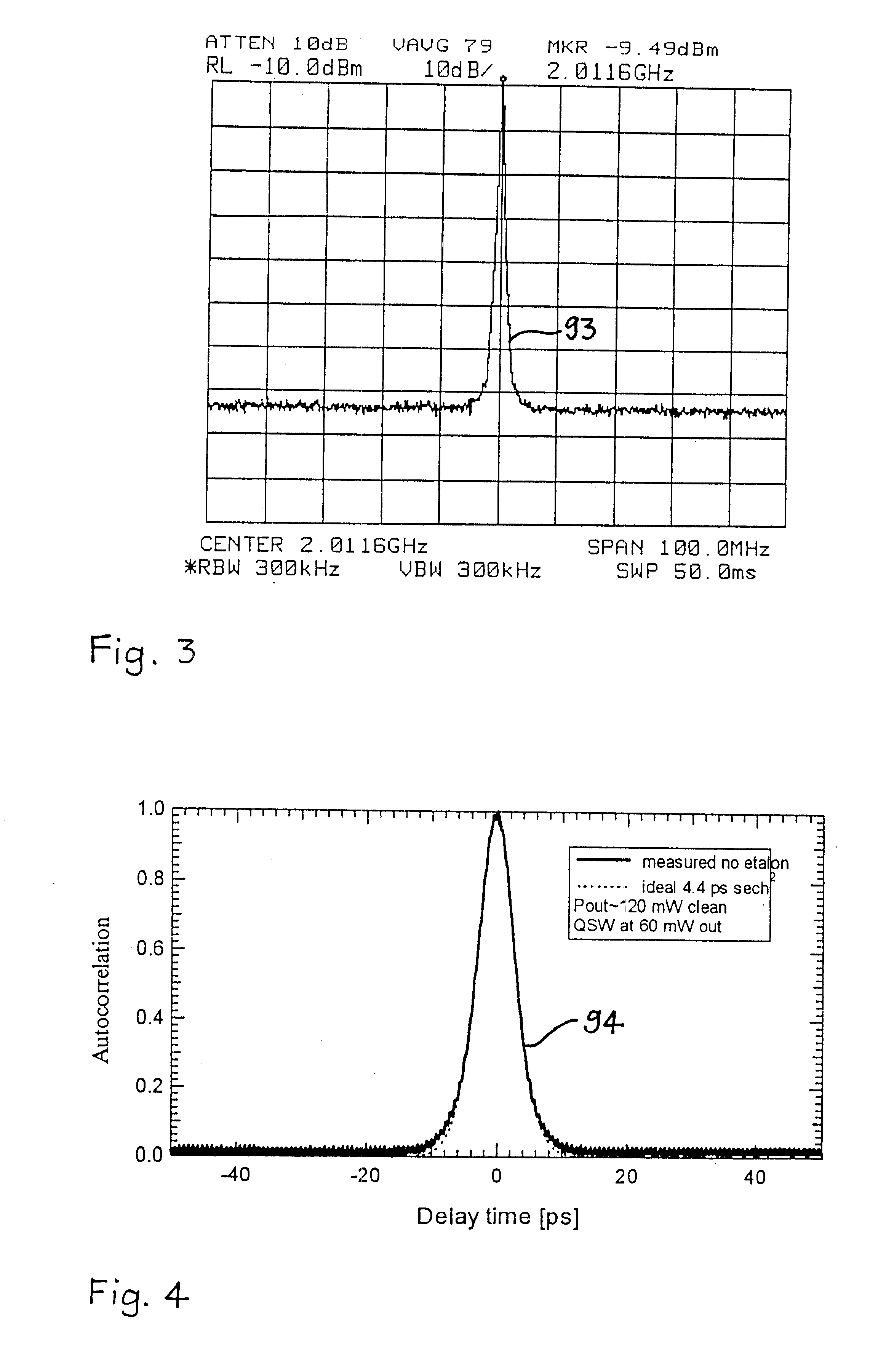
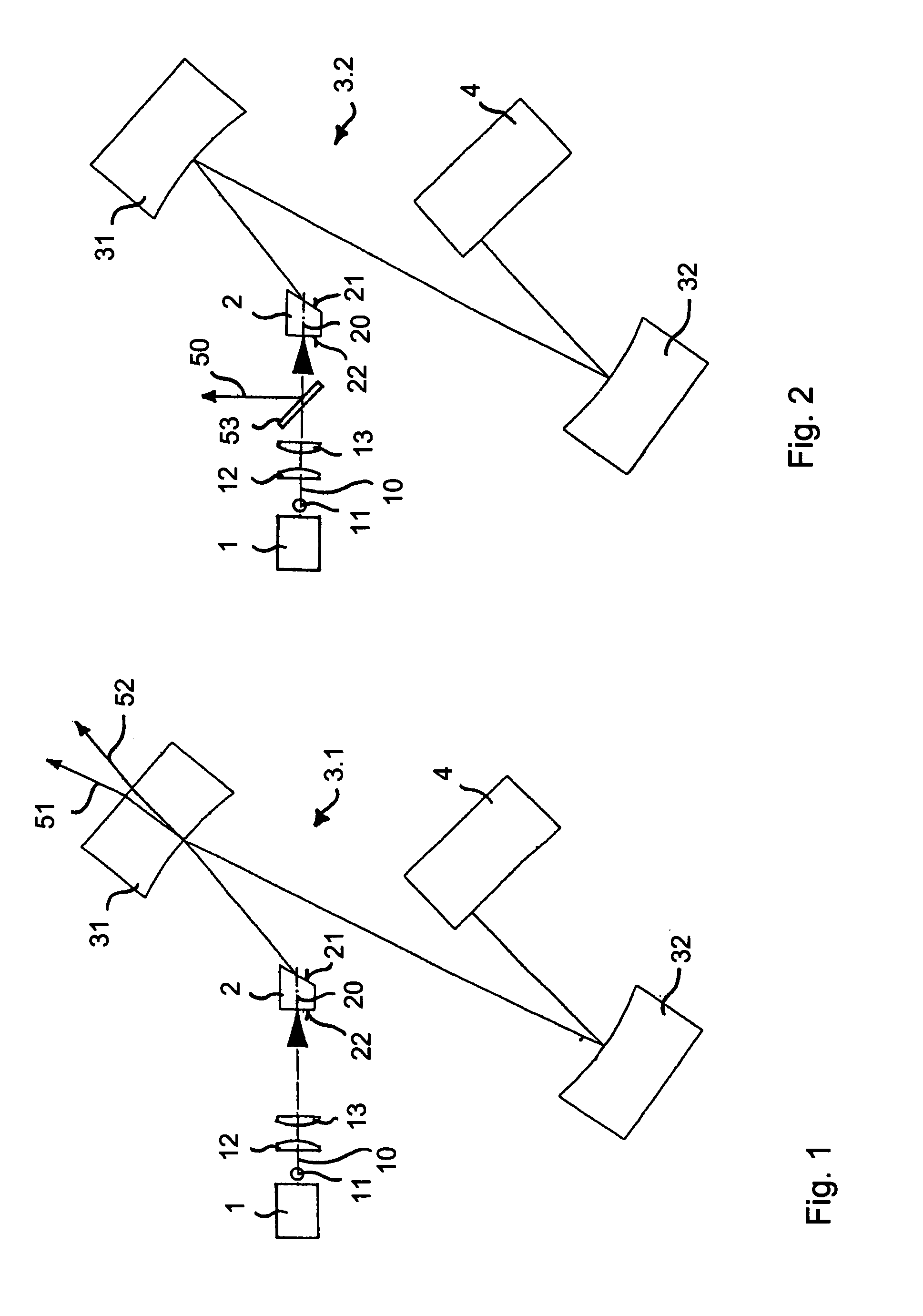
A passively mode-locked solid-state laser is designed to emit a continuous-wave train (51, 52) of electromagnetic-radiation pulses, the fundamental repetition rate of the emitted pulses exceeding 1 GHz, without Q-switching instabilities. The laser includes an optical resonator (3.1), a solid-state laser gain element (2) placed inside the optical resonator (3.1), a device (1) for exciting said laser gain element (2) to emit electromagnetic radiation having the effective wavelength, and a device (4) for passive mode locking including a saturable absorber. The laser gain element (2) is a laser material with a stimulated emission cross section exceeding 0.8×10−18 cm2 at the effective wavelength, and is made of Nd:vanadate. The saturable absorber (4) is preferably a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM) device. Even higher repetition rates are achieved by operating the laser in the soliton regime. For use in fiber-optical telecommunication, the laser wavelength is preferably shifted to 1.5 μm by use of an optical parametric oscillator. The laser is simple, robust, compact, efficient, and low-cost. It generates a relatively large average power of 100 mW and higher, which is useful for a number of optical probing and detection applications, in a beam (51, 52) that is substantially a fundamental spatial mode.
Owner:LUMENTUM SWITZERLAND AG
Optical pulse lasers
InactiveUS20060198399A1Easy to operateFast recovery timeMirrorsNanoinformaticsMode-lockingCarbon nanotube
The present invention provides pulsed lasers which employ carbon nanotubes, particularly layers of carbon nanotubes, as saturable absorbers, mode lockers or for Q-switching elements. The present invention also provides methods and materials for mode-locking and Q-switching of lasers in which carbon nanotubes are employed as non-linear optical materials and / or saturable absorbers which facilitate mode-locking and / or Q-switching. The invention further provides mode locker and Q-switching elements or devices which comprise one or more layers containing carbon nanotubes which layer or layers function for mode locking and / or Q-switching.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +1
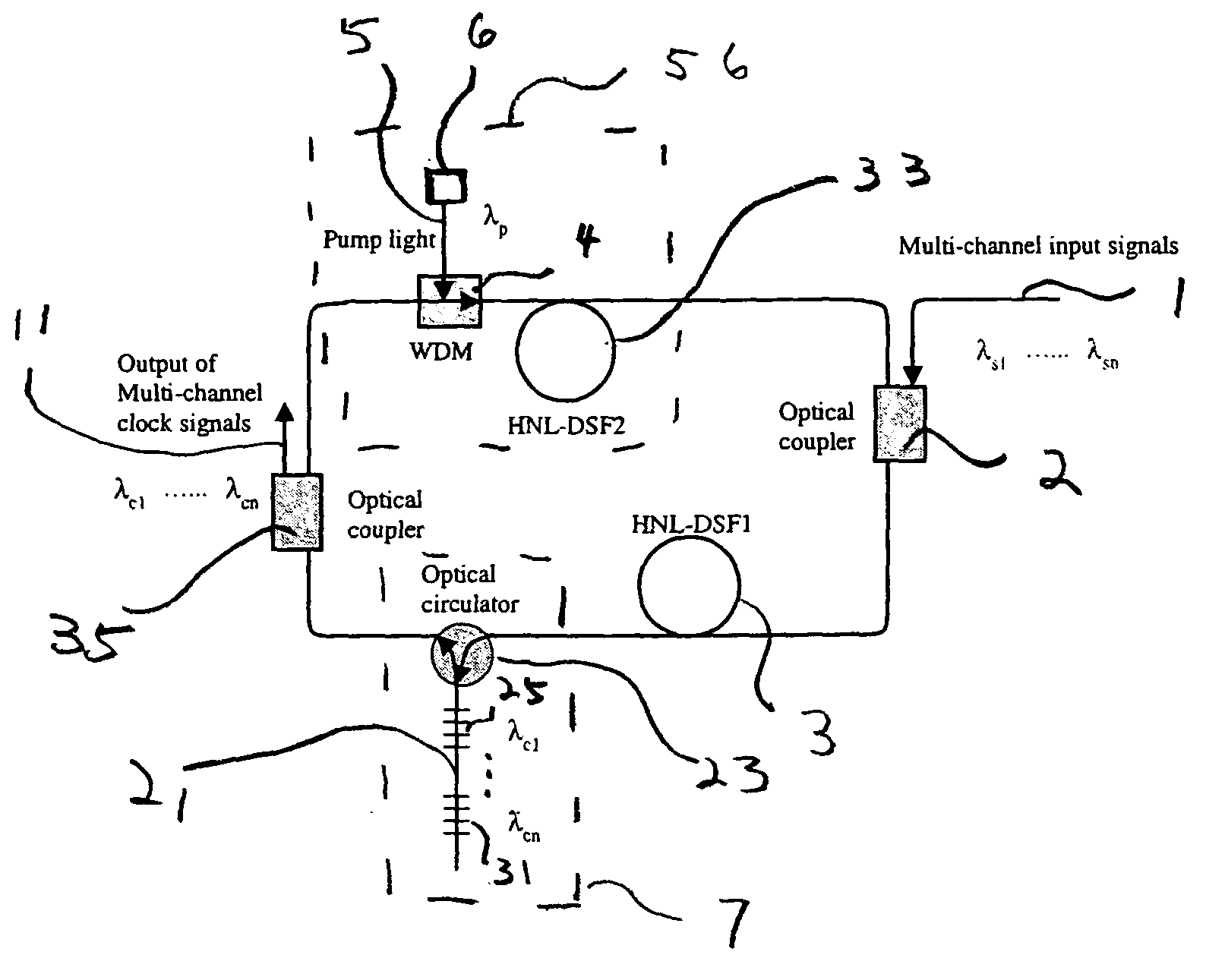
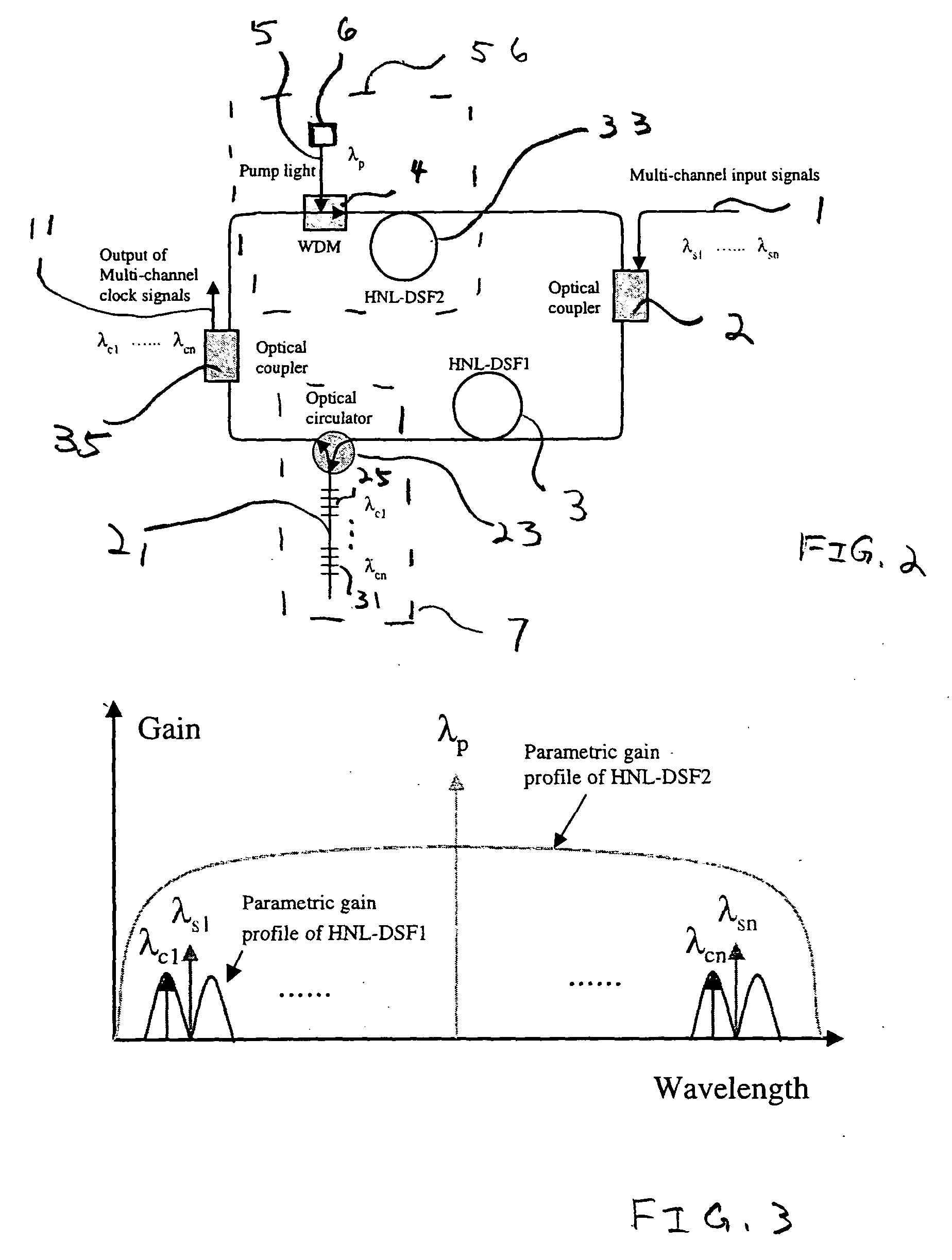
Phase-insensitive recovery of clock pulses of wavelength division multiplexed optical signals
InactiveUS20050063425A1Large dispersionEffective gainLaser using scattering effectsSynchronisation by photonic/optical meansMultiplexingMode-locking
An optically-pumped mode-locked fiber ring laser for optical clock recovery of multiple wavelength division multiplexed optical signals actively mode-locks a plurality of outputs of the laser as a plurality of recovered clocks for a plurality of the multiple wavelength division multiplexed optical signals. The laser cavity has a cavity length corresponding to an integer multiple of bit periods of at least one of the multiplexed optical signals for receiving a pre-amplified version of the plurality of wavelength division multiplexed optical signals to provide gain modulation through a phase-insensitive parametric amplification and recirculating a proportion of the output from the laser cavity back through the laser cavity for spatially mode-locking the output of the laser cavity as a recovered clock.
Owner:CORNING INC
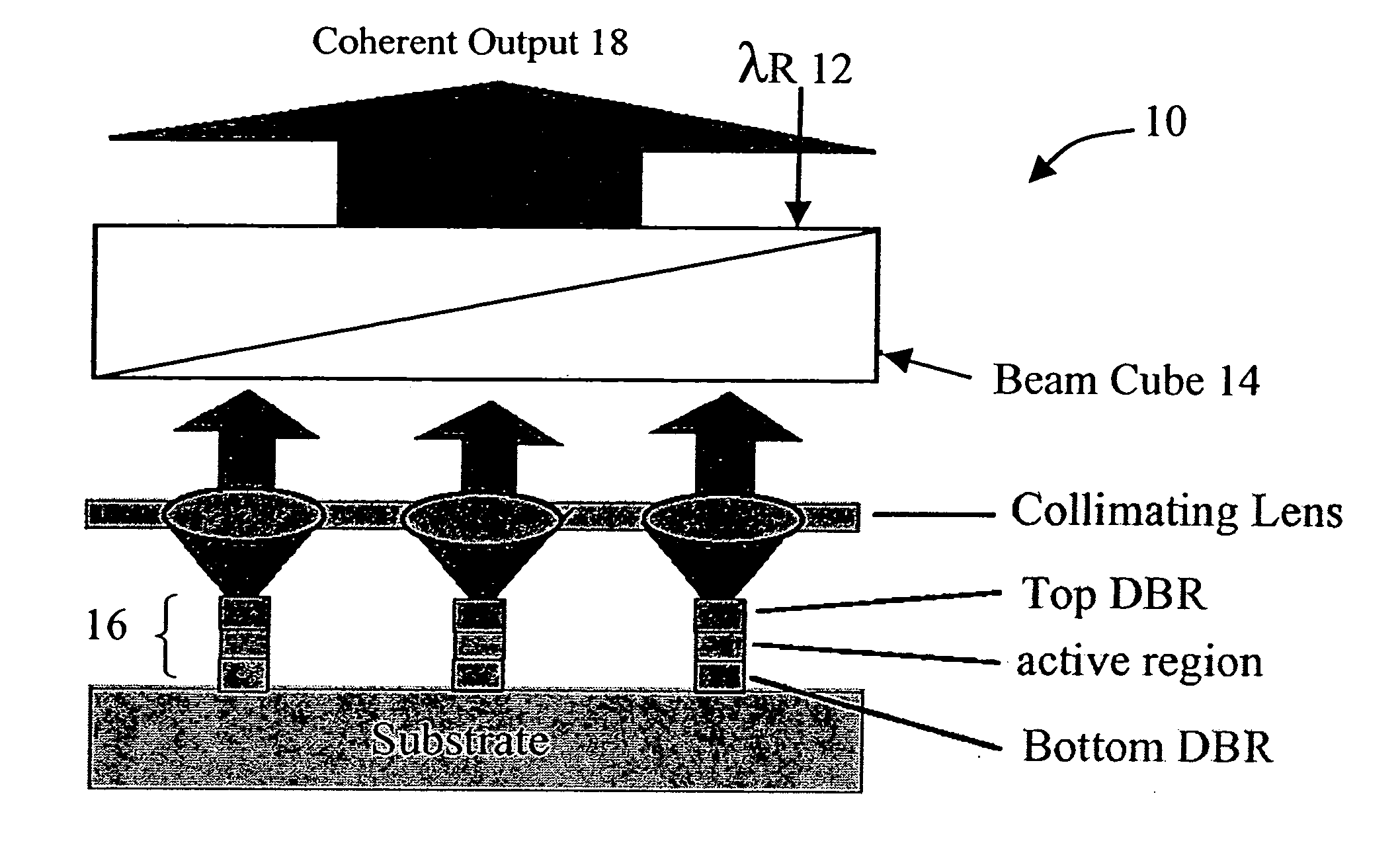
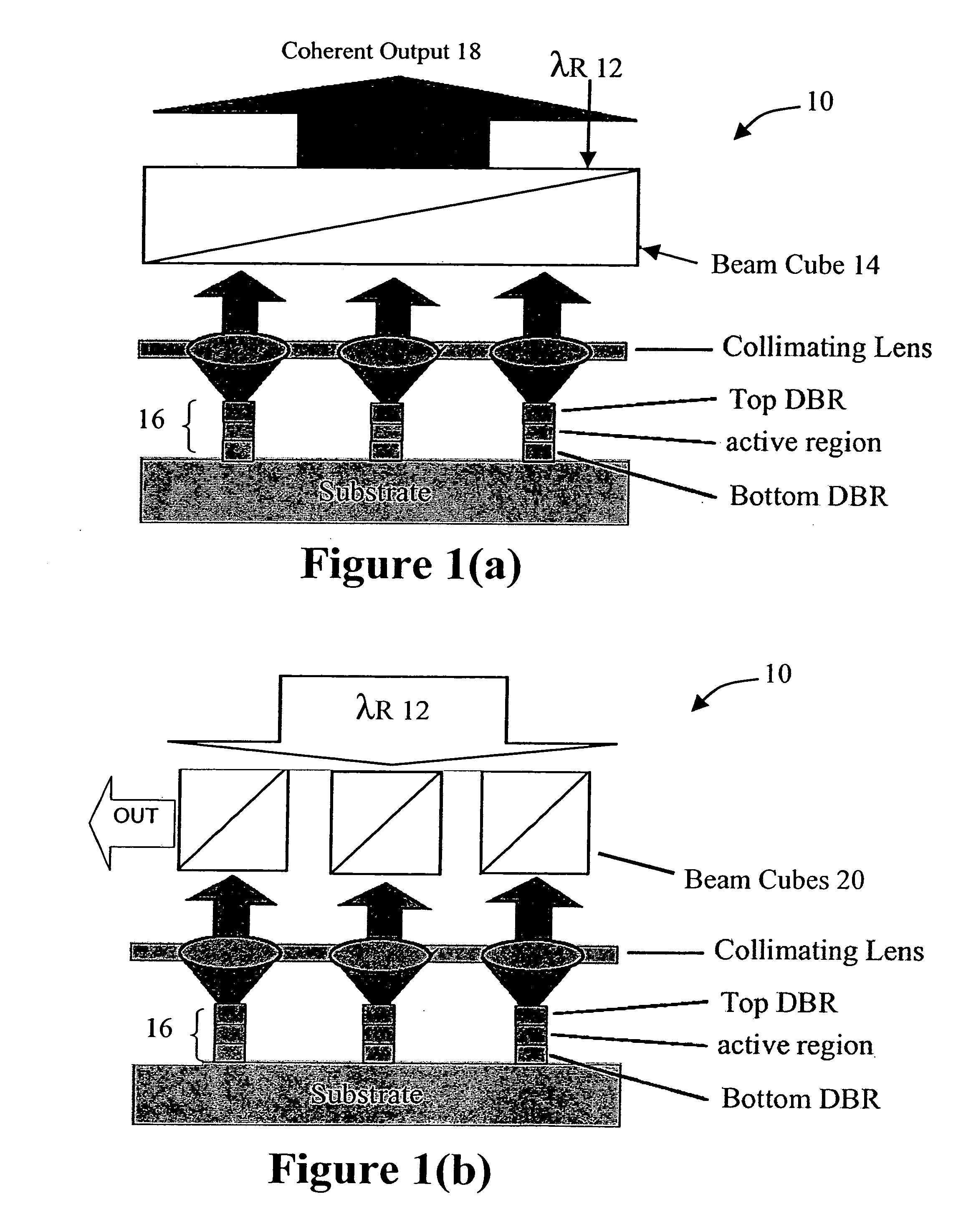
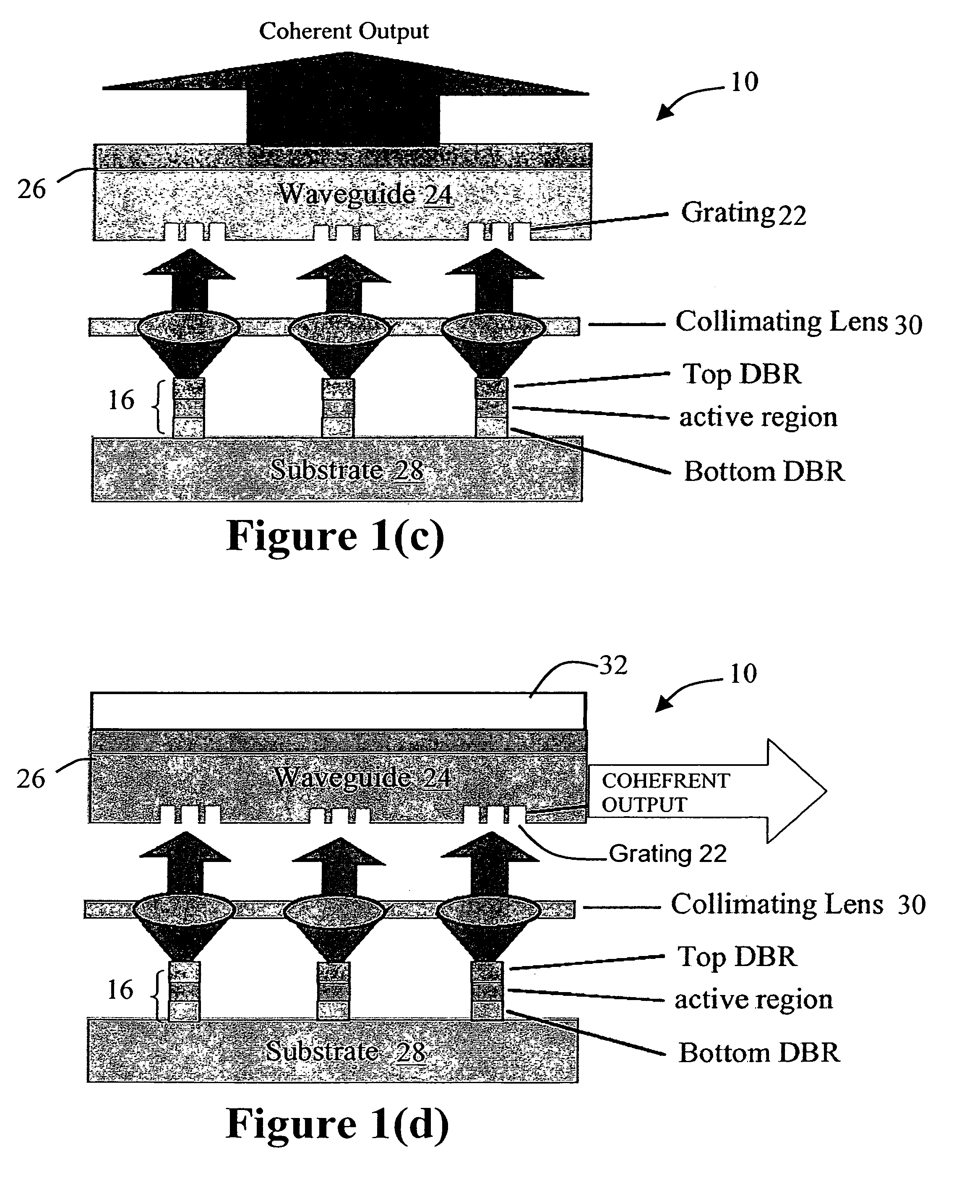
High-power coherent arrays of vertical cavity surface emitting lasers
A high-power coherent array of Vertical Cavity Surface Emitter Lasers is described in which a plurality of Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers (VCSELs) are provided along with a structure which optically couples each of the VCSELs the plurality of VCSELs to one another by a predetermined amount to cause a coherent mode locking condition to occur. The coupling structure can be a beam cube, a plurality of smaller bean cubes, or a waveguide / grating system, for example. A reference source, or controlled coupling among the VCSELs, is used to phase lock the VCSELs to one another.
Owner:OC ACQUISITION CORP
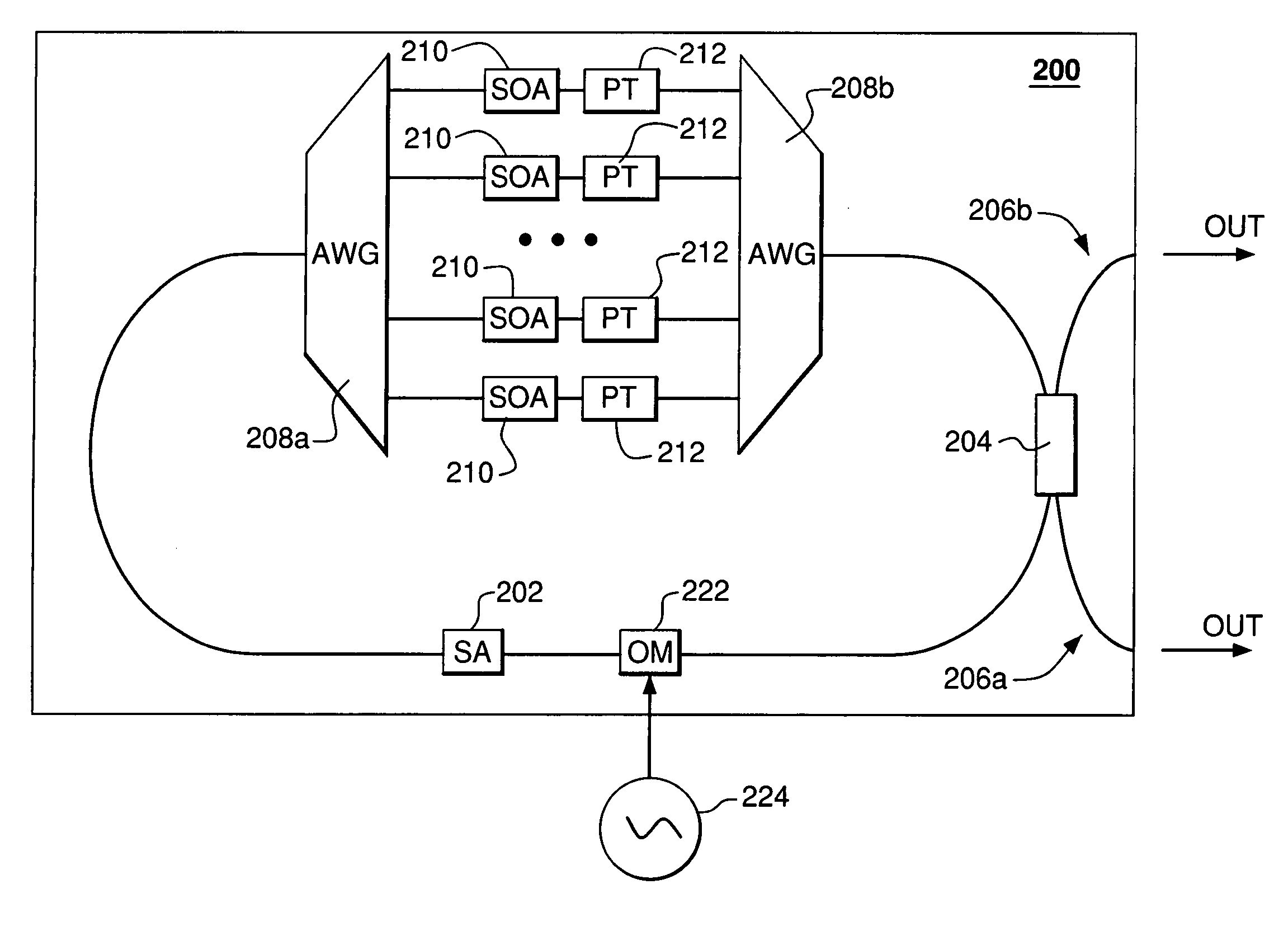
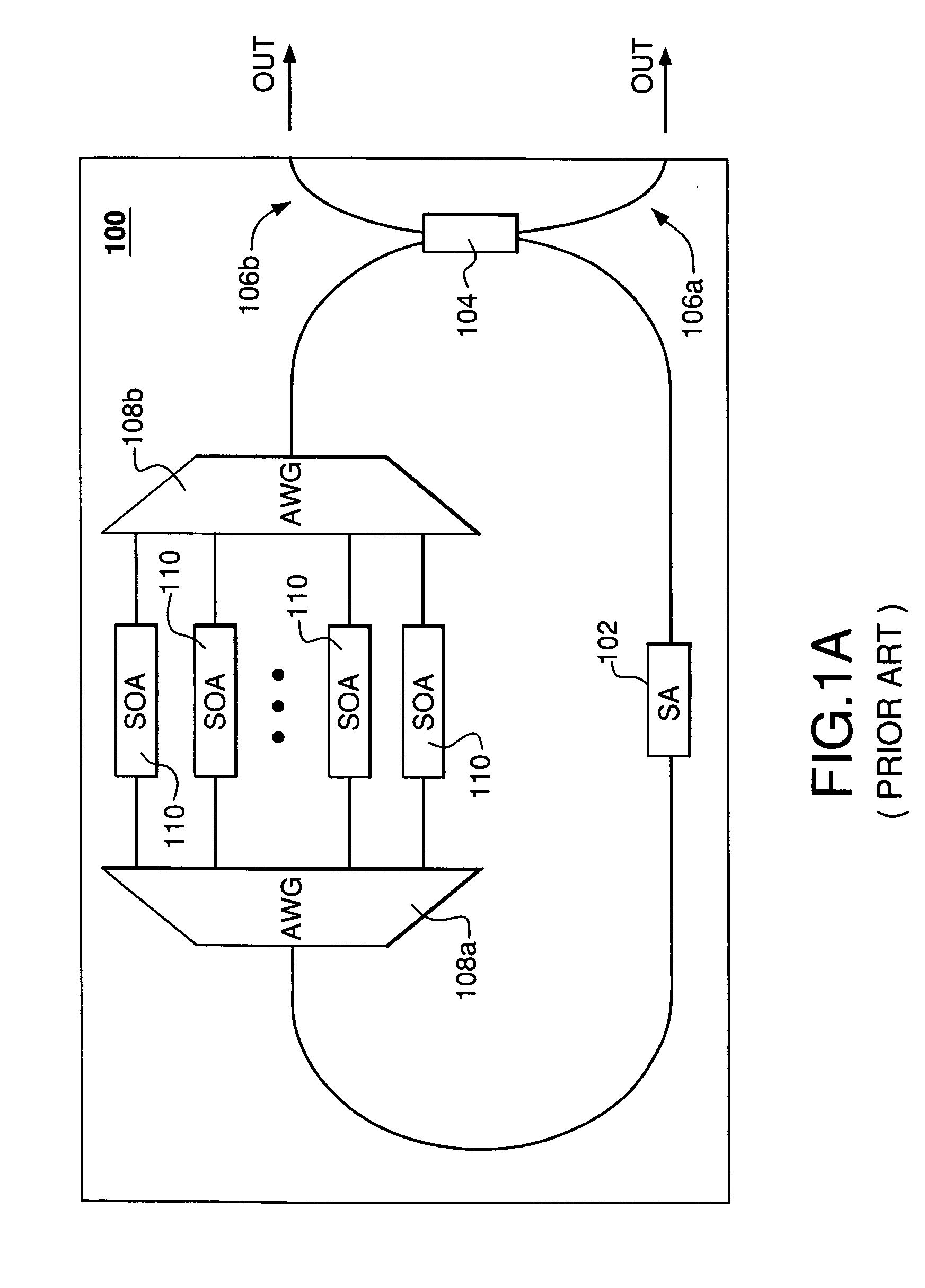
Wide-bandwidth mode-locked laser
InactiveUS20070133632A1Wide combined gain spectrumLaser optical resonator constructionOptical resonator shape and constructionFrequency spectrumGrating
A mode-locked laser that has an optical cavity containing multiple optical amplifiers, each dedicated to a respective spectral portion of an optical signal generated by the laser, wherein the dispersion effects are managed by utilizing a separate intra-cavity phase tuner for each such spectral portion and / or by having appropriately configured waveguides corresponding to different spectral portions. Advantageously, a relatively wide combined gain spectrum provided by the optical amplifiers and the intra-cavity dispersion compensation provided by the phase tuners and / or waveguides enable this laser to realize a mode-locking regime that results in the emission of an optical pulse train having a relatively wide frequency spectrum. In one embodiment, the optical cavity of the mode-locked laser has a perfectly spectrally sampled arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) that is configured to divide the optical signal into the spectral portions and apply these portions to the respective waveguides, optical amplifiers, and phase tuners.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
Mode-locked external-cavity surface-emitting semiconductor laser
A laser resonator includes an OPS gain-structure that is pumped with optical pulses repeatedly delivered at a pulse-repetition frequency corresponding to a resonant frequency of the laser resonator. The laser resonator additionally includes a passive mode-locking arrangement such that the resonator delivers mode-locked optical pulses. In one example the laser resonator further includes a CW optically pumped OPS gain-structure for increasing the power of the mode-locked pulses delivered from the resonator.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Carrier-suppressed optical pulse train generation method and mode-locked semiconductor laser diode for realizing this method
InactiveUS20080025358A1Small sizePrevented from reachingOptical resonator shape and constructionSemiconductor lasersMode-lockingCarrier signal
A CS optical pulse train generation method, which is able to change the half width of an optical pulse constituting a CS optical pulse train, and which is compact and has low power consumption. A distributed Bragg reflector semiconductor laser utilized in this method is one which is constituted comprising an optical modulation region, a gain region, a phase control region, and a distributed Bragg reflector region. Current is injected into the gain region by way of a p-side electrode and a n-side common electrode by a constant current source, forming the population inversion required for laser oscillation. Optical modulation required to manifest mode locking is carried out in the optical modulation region. A diffraction grating is formed in the distributed Bragg reflector region. A CS optical pulse train with a repetitive frequency of frep is generated by adjusting the effective indices of both the phase control region and the distributed Bragg reflector region such that, of the longitudinal modes of the mode-locked semiconductor laser diode, the two longitudinal modes close to the frequency f0, which is the Bragg wavelength of the distributed Bragg reflector region converted to a frequency, become f0+(frep / 2) and f0−(frep / 2).
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber and production method thereof
InactiveCN104218443AWide wavelength rangeReduce absorption lossActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionMode-lockingWavelength
The invention relates to a two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber and a production method thereof, and belongs to the field of saturable absorbers of lasers. The two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber comprises a substrate, a high-reflection layer, a saturable absorption layer and a functional layer. One end face of the functional layer is connected with the saturable absorption layer, one end face of the saturable absorption layer is connected with the high-reflection layer, and one end face of the high-reflection layer is connected with the substrate. By the two-dimensional stratified material based practical saturable absorber and the production method thereof, application of the lasers, such as Q-switching, mode locking and optical signal processing, is realized. By the high-reflection layer formed by composite materials, absorption loss is reduced and reflection rate is increased, and optimal material combinations can be found in terms of different wave lengths.
Owner:鲍小志
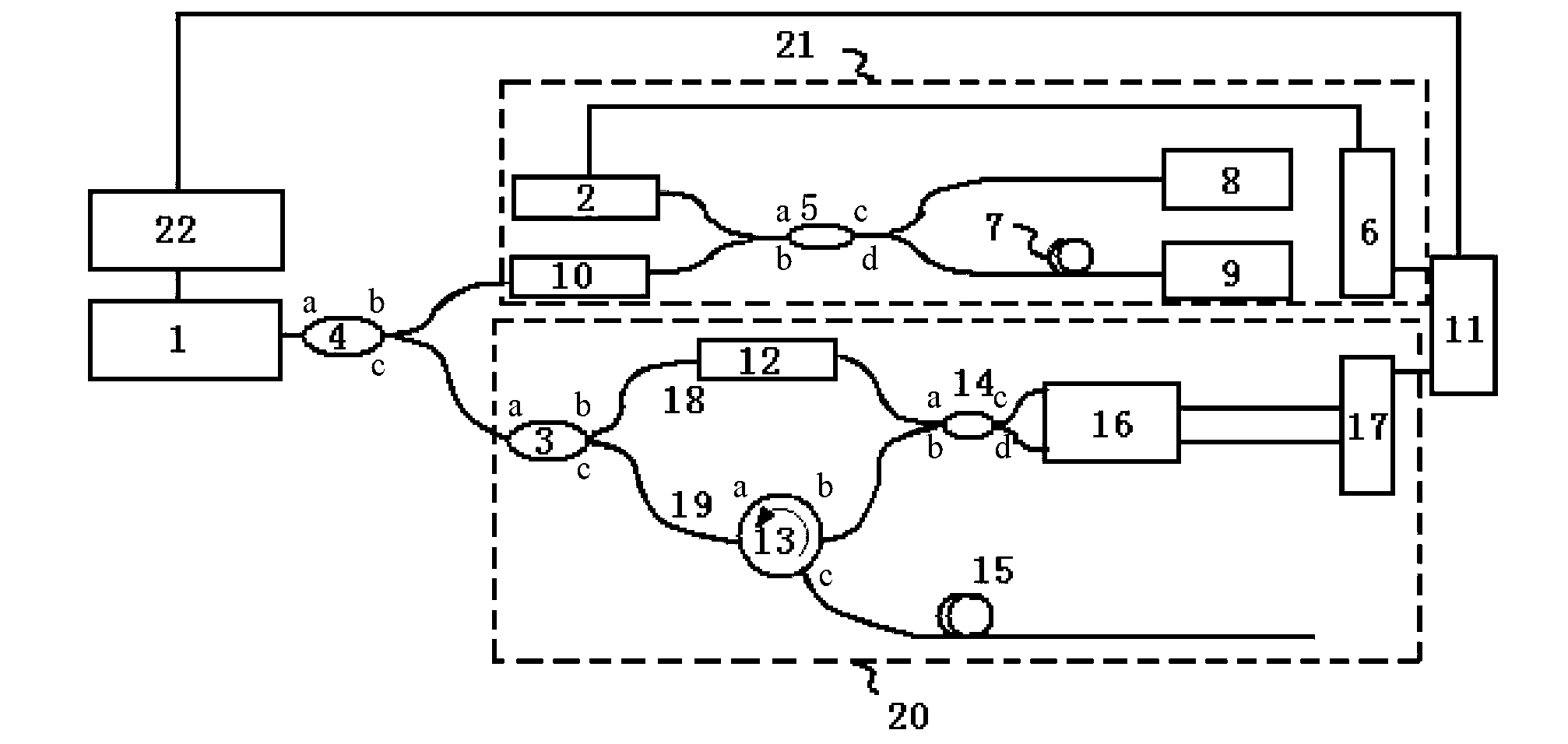
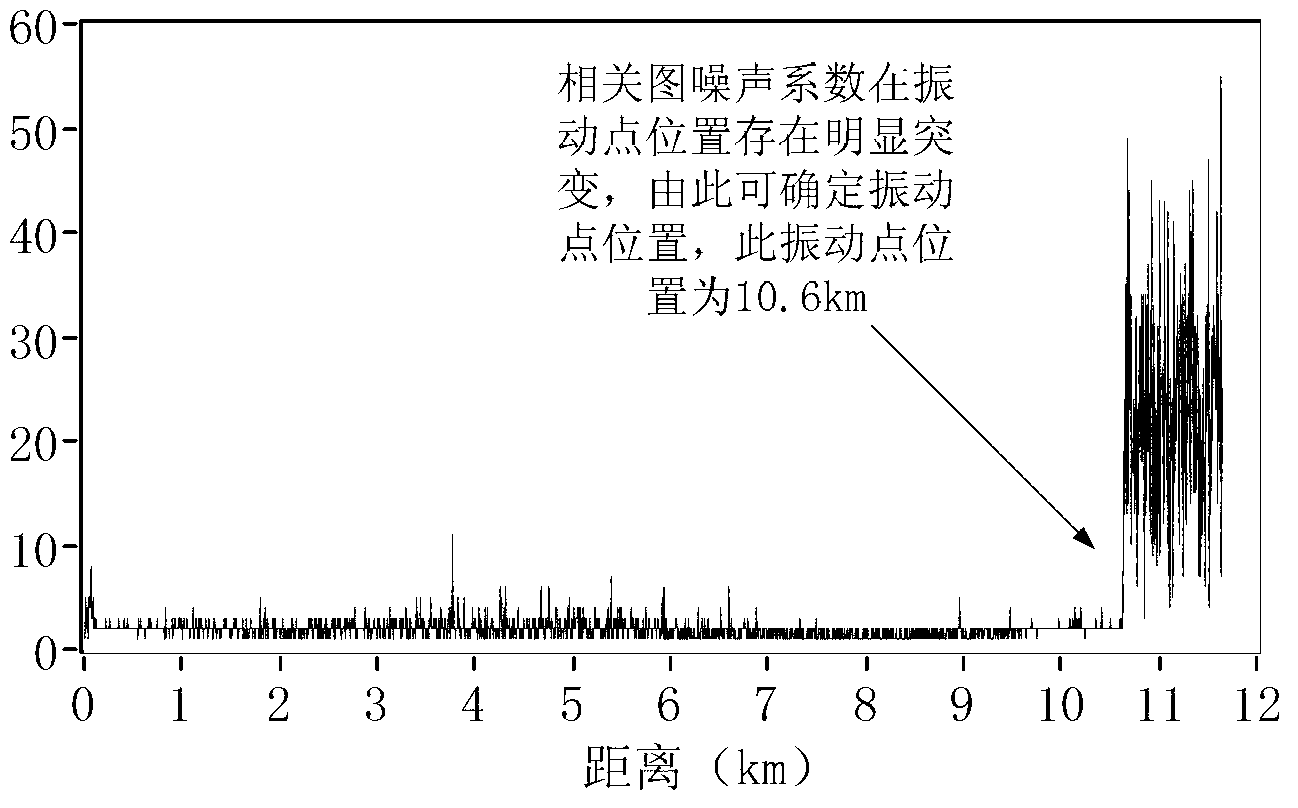
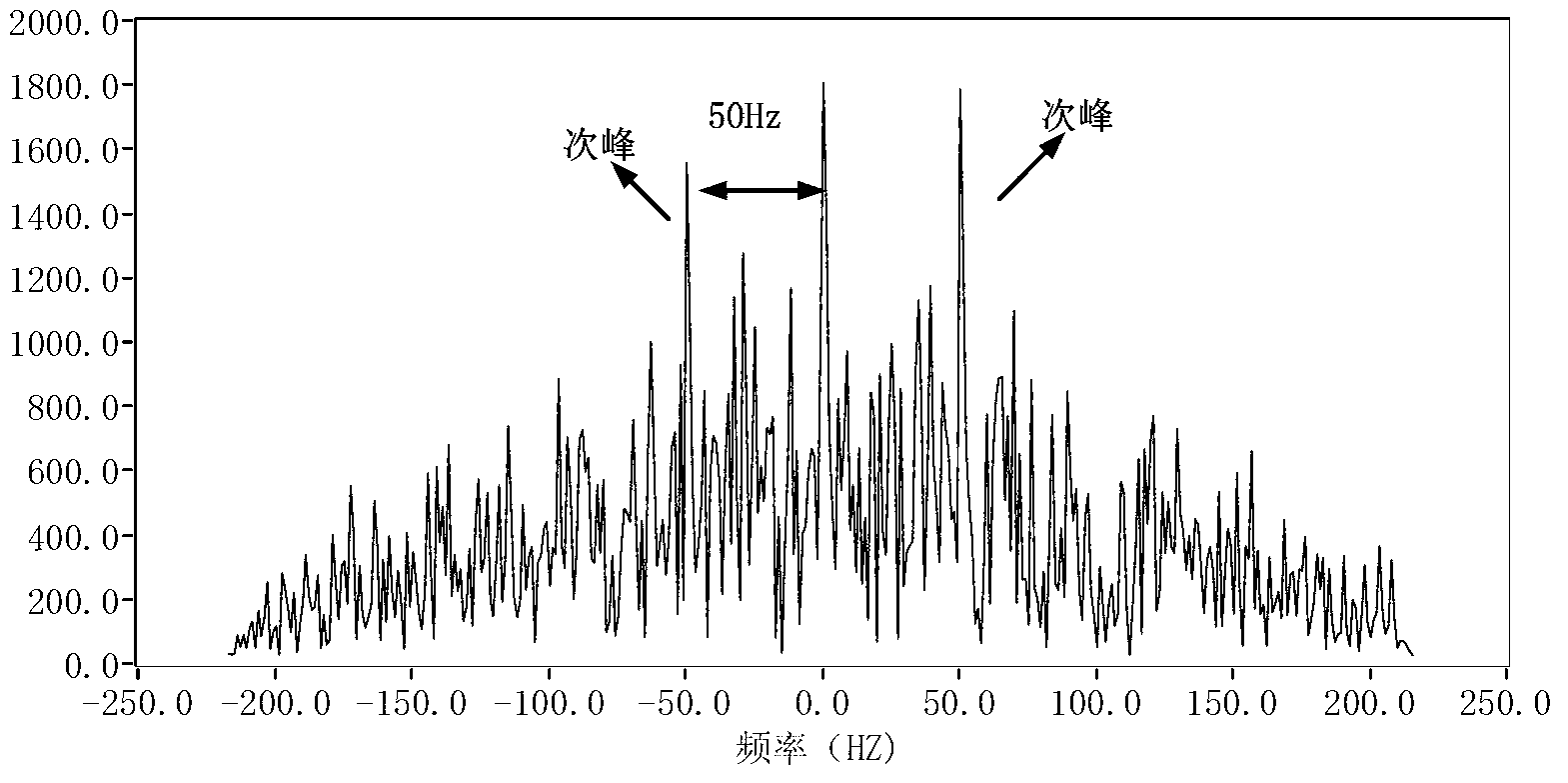
Optical frequency domain reflection-distributed vibration frequency sensing and locating device and demodulation method
ActiveCN102840909ASubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFast Fourier transformWhispering gallery
The invention discloses an optical frequency domain reflection-distributed vibration frequency sensing and locating device and a demodulation method. A technical method of optical frequency domain reflection beat frequency interference of a self-injective mode locking laser of a linear turning ultra-narrow linewidth whispering gallery mode is adopted in the optical frequency domain reflection-distributed vibration frequency sensing and locating device. The optical frequency domain reflection-distributed vibration frequency sensing and locating device comprises a main interferometer which is used to obtain a sensing signal and an auxiliary interferometer of a clock trigger signal. The demodulation method comprises that wavelength domain information is obtained by the main interferometer, fast Fourier transform is used to transform the wavelength domain information, and then distance domain information is obtained. A group of static reference signals and a group of vibration signals are collected. The distance domain information, namely local distance domain information, is selected in sequence by moving windows. Complex number cross correlation is used on the static signals and the vibration signals of the local distance domain information on each position. According to a noise coefficient of the complex number cross correlation, a position of a vibration point is obtained. A subsidiary summit position of the complex number cross correlation of the local distance domain information on the position of the vibration is picked up, and the subsidiary summit position is vibration frequency information.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Electrically-Pumped Semiconductor Zigzag Extended Cavity Surface Emitting Lasers and Superluminescent Leds
ActiveUS20090207873A1High power amplificationInsufficient optical gainLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionAudio power amplifierDistributed Bragg reflector
A semiconductor surface emitting optical amplifier chip utilizes a zigzag optical path within an optical amplifier chip. The zigzag optical path couples two or more gain elements. Each individual gain element has a circular aperture and includes a gain region and at least one distributed Bragg reflector. In one implementation the optical amplifier chip includes at least two gain elements that are spaced apart and have a fill factor no greater than 0.5. As a result the total optical gain may be increased. The optical amplifier chip may be operated as a superluminescent LED. Alternately, the optical amplifier chip may be used with external optical elements to form an extended cavity laser. Individual gain elements may be operated in a reverse biased mode to support gain-switching or mode-locking.
Owner:PHILIPS LUMILEDS LIGHTING CO LLC +1
Practical saturable absorption device based on black phosphorus
InactiveCN104466646AWide wavelength rangeFlexible adjustment of modulation depthLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersMode-lockingBlack phosphorus
The invention relates to a practical saturable absorption device based on black phosphorus and belongs to the field of saturable absorption devices of laser devices. The practical saturable absorption device based on the black phosphorus is formed by combining four layers of materials or mutual combining three layers of the four layers of materials or combining the four layers of materials combined mutually and functional insertion layers added on the upper portion and the lower portion of the four layers of materials at will or combining the saturable absorption layers and any one layer of materials or combining the saturable absorption layers, and each saturable absorption layer comprises at least one of a black phosphorus film, black phosphorus nano lamella particles, black phosphorus ramifications and functionalization black phosphorus. According to the practical saturable absorption device based on the black phosphorus, the application of Q regulation and mode locking of the laser device, optical signal processing and the like is achieved, and more importantly, the effect that the modulation depth can be flexibly regulated by giving play to the property of the black phosphorus is achieved.
Owner:鲍小志
Small-size optical fiber femtosecond laser with wide repetition frequency tuning range
The invention provides a small-size optical fiber femtosecond laser with a wide repetition frequency tuning range. The small-size optical fiber femtosecond laser comprises a repetition frequency adjustable erbium-doped optical fiber laser based on a mixing mode-locking mechanism, a repetition frequency locking system and a computer control system, wherein the erbium-doped optical fiber laser is provided with an annular cavity, an automatically controlled optical delay line is added into the cavity, the repetition frequency of the laser can realize the large-range tuning, and in order to realize the repetition frequency stabilization, on one hand, piezoelectric ceramics are used for controlling the length of the gain optical fiber, so that the short period fluctuation of the repetition frequency is inhibited; on the other hand, the large-range long-period fluctuation of the repetition frequency can be compensated through regulating an optical delay line. The femtosecond laser has the advantages that the size is small, the stability is high, the repetition frequency tuning performance is realized, the repetition frequency can be controlled, and the like. The work potential in industrial environment is realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Passive mode-locking ultrashort pulse all-fiber laser with waveband of 2.0 microns
InactiveCN102368584AGood environmental stabilityEasy to realize industrial applicationActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionGratingNonlinear optics
The invention relates to a passive mode-locking ultrashort pulse all-fiber laser with a waveband of 2.0 microns and belongs to the field of a laser technology and nonlinear optics. The passive mode-locking ultrashort pulse all-fiber laser with the waveband of 2.0 microns mainly comprises a laser pumping source, a pumping combiner, thulium-doped or thulium-holmium-codoped rear earth doped fibers, a circulator, a saturable absorber, a laser beam splitter, an isolator, a fiber bragg grating, a polarization controller and the like. The thulium-doped or thulium-holmium-codoped rear earth doped fibers are used as a gain medium; the saturable absorber is used as a passive mode-locking device; and the output of an ultrashort laser pulse which is in the waveband of 2.0 microns and has high pulse energy is realized. Due to the adoption of the all-fiber structure design, the passive mode-locking ultrashort pulse all-fiber laser with the waveband of 2.0 microns has the advantages of simple structure, high environment stability and the like, and the industrialization application is easy to realize.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Erbium doped fiber laser with convertible multi-wavelength and mode locking and realization method thereof
InactiveCN101557071AMeet needsSwitchable wavelength tunableActive medium shape and constructionMode-lockingLaser light
The invention relates to an erbium doped fiber laser with multi-wavelength and mode locking functions and convertible working state and a realization method thereof, in particular to a laser which can realize switching conversion between multi-wavelength and mode locking, has adjustable output wavelength position of multi-wavelength, and can stably work at room temperature and a realization method thereof. The laser comprises: a gain amplification unit, a polarization control unit, an output coupling unit, a comb filtering unit, an optical isolation unit and a nonlinear fiber loop mirror. The realization method of the laser includes the following steps: incident polarization state and double refraction are adjusted to lead the nonlinear fiber loop mirror inserted in the cavity of the laser to be in different working states, and the multi-wavelength and mode locking functions of the laser are respectively realized according to the different working conditions of the nonlinear fiber loop mirror. The invention has the advantages of convenient toning, low cost, being capable of realizing the two functions of stable multi-wavelength continuous output and mode locking pulse output, and the like, and can satisfy the demand for multifunctional laser light sources of optical time division multiplex / wavelength division multiplex communication technology.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Optical parameter chirp impulse amplification laser system
InactiveCN101055968AStable ultrashort pulse outputLow conversion efficiencyLaser detailsNon-linear opticsMode-lockingFrequency multiplier
A optical parameter chirp pulse amplification laser system, includes a titanium gem femtosecond mode-locking pulse oscillator, a first splitting film, a CEP steady signal pulse source, an OPCPA synchronous pumping source, an OPCPA amplifier stage and compressor. In the output beam direction of the titanium gem femtosecond mode-locking pulse oscillator is the first splitting film, which divides a laser beam into a transmission light beam and a reflection light beam, and in the said transmission light beam is said CEP steady signal pulse source, OPCPA amplifier stage and compressor in order. The said CEP steady signal pulse source comprises a photonic crystal optical fiber, a chirp mirror, a period polarization lithium niobate crystal and a stretcher; said OPCPA amplifier stage comprises a first two-tone mirror, a first nonlinear crystal, a second two-tone mirror and a second nonlinear crystal; said OPCPA synchronous pumping source comprises a Q-tuning frequency-multiplier YAG laser, a narrowband titanium gem regenerating amplifier and a second splitting film, and a holophote. The invention apparatus may get a near-infrared ultrashort laser pulse output with a pulse width less than 30 femtoseconds.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ultrahigh energy short pulse lasers
ActiveUS20070171945A1Improve reliabilityLaser using scattering effectsAudio power amplifierHybrid amplifier
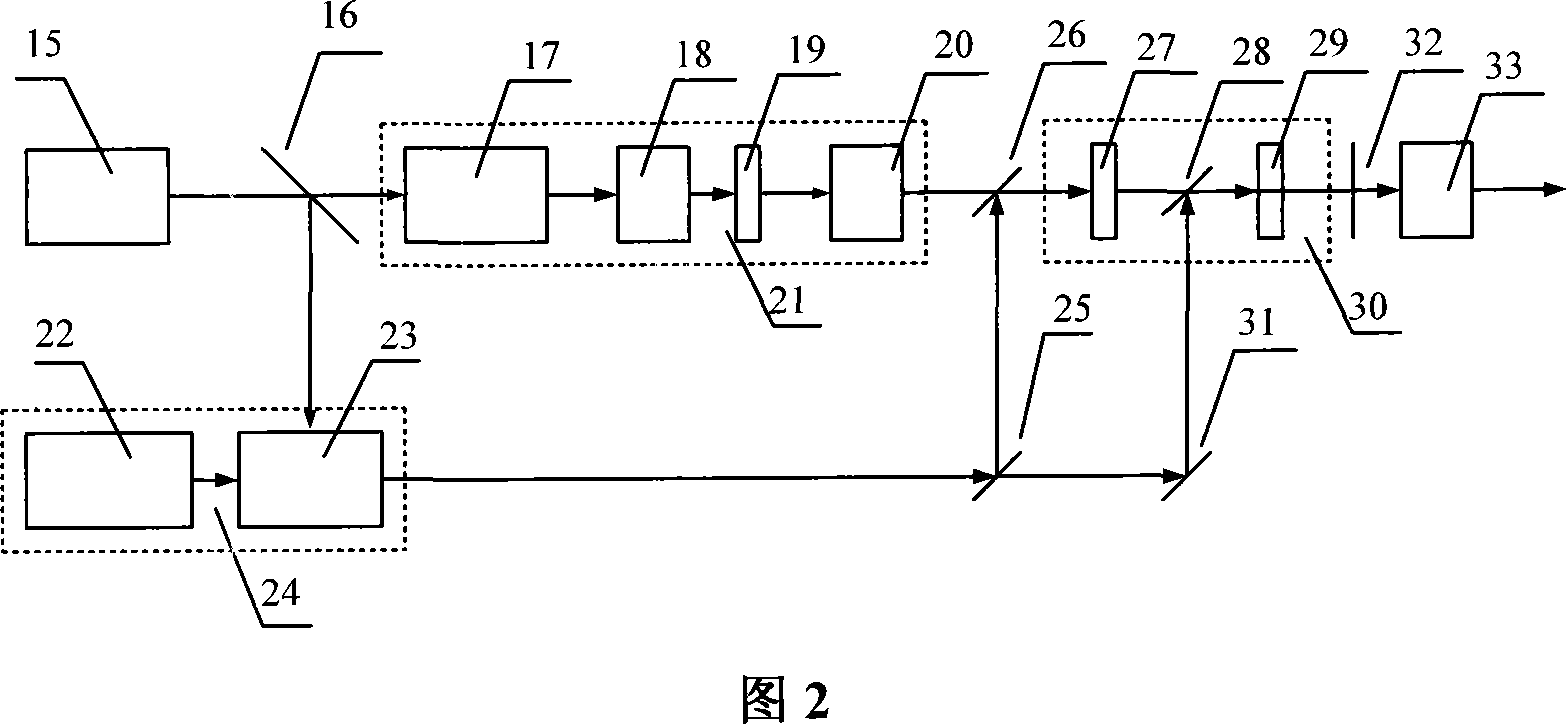
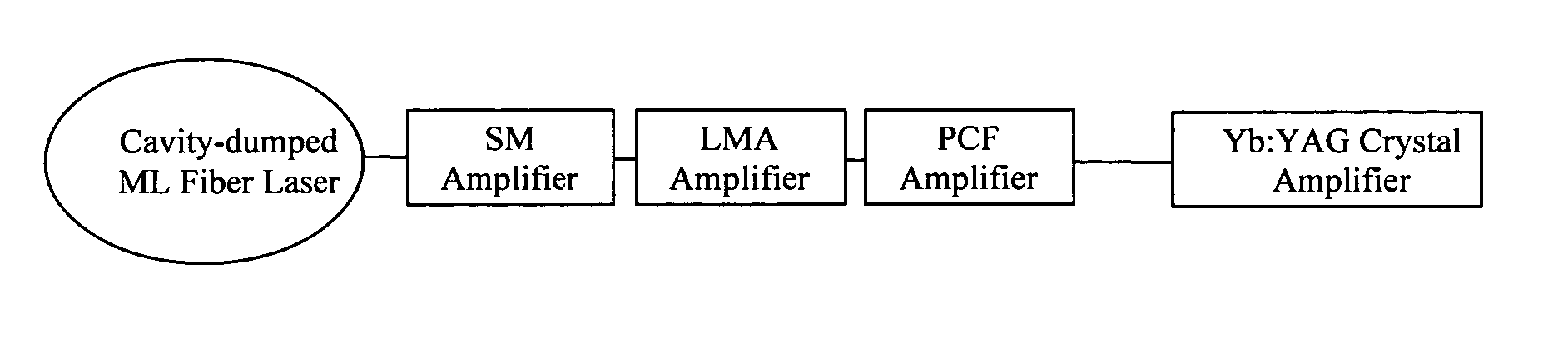
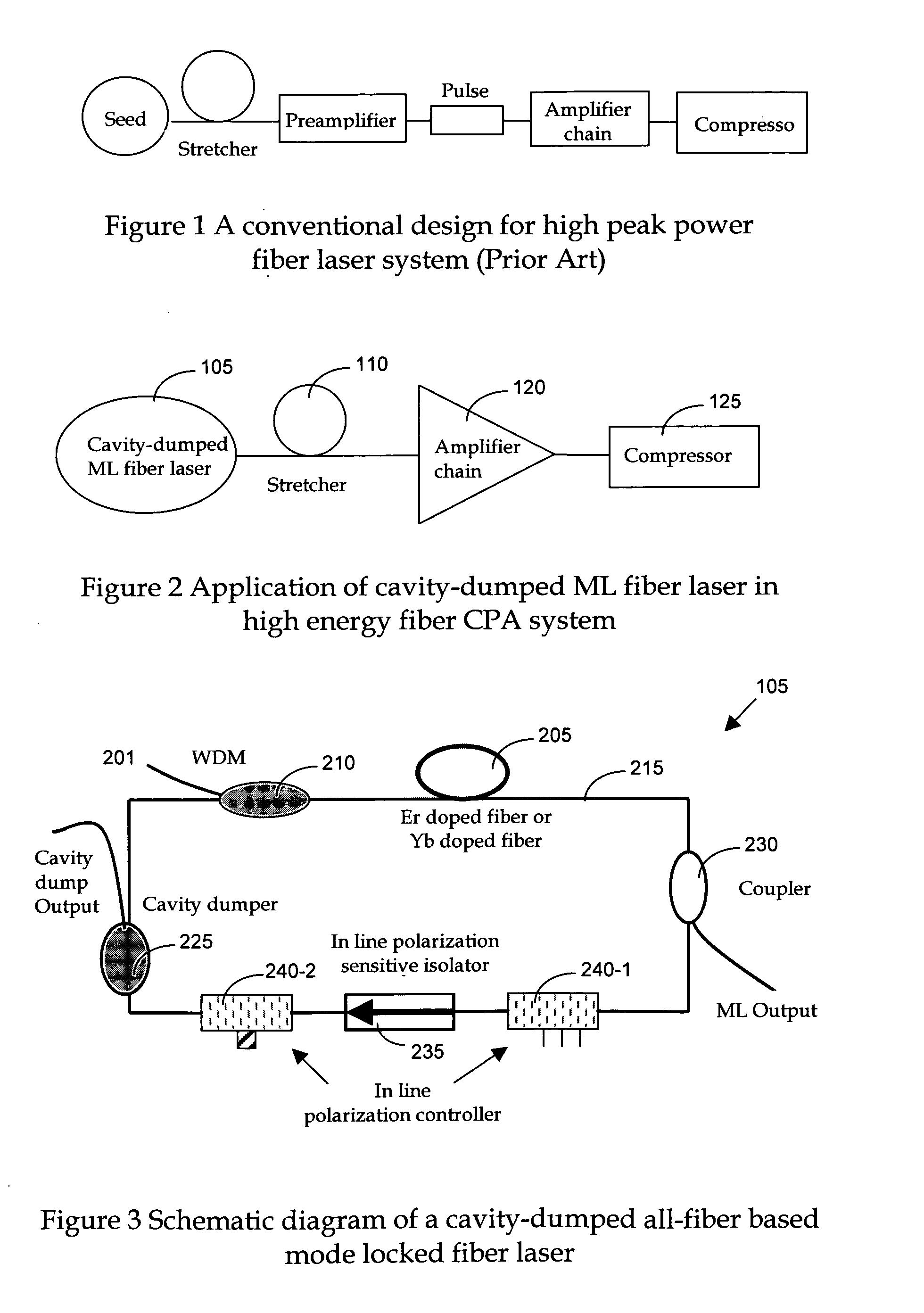
A Chirped pulse amplification (CPA) fiber laser system. The CPA fiber laser system includes a fiber mode-locking (ML) oscillator implemented as a cavity dumped ML oscillator including a cavity dumper for generating a seed laser at a reduced repetition rate to project to a pulse stretcher for stretching a pulse width of the laser. The CPA fiber laser system further includes a multistage amplifier chain for generating an amplified laser to project to a compressor for compressing the amplified laser. The multistage amplifier chain further includes a hybrid amplifier includes a solid-state amplifier to generate a laser of approximately 1˜10 mJ for a 10-100 KHz repetition rate.
Owner:POLARONYX
Compression design for high energy short pulse fiber laser
ActiveUS20070014317A1Quality improvementIncrease flexibilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingHigh energy
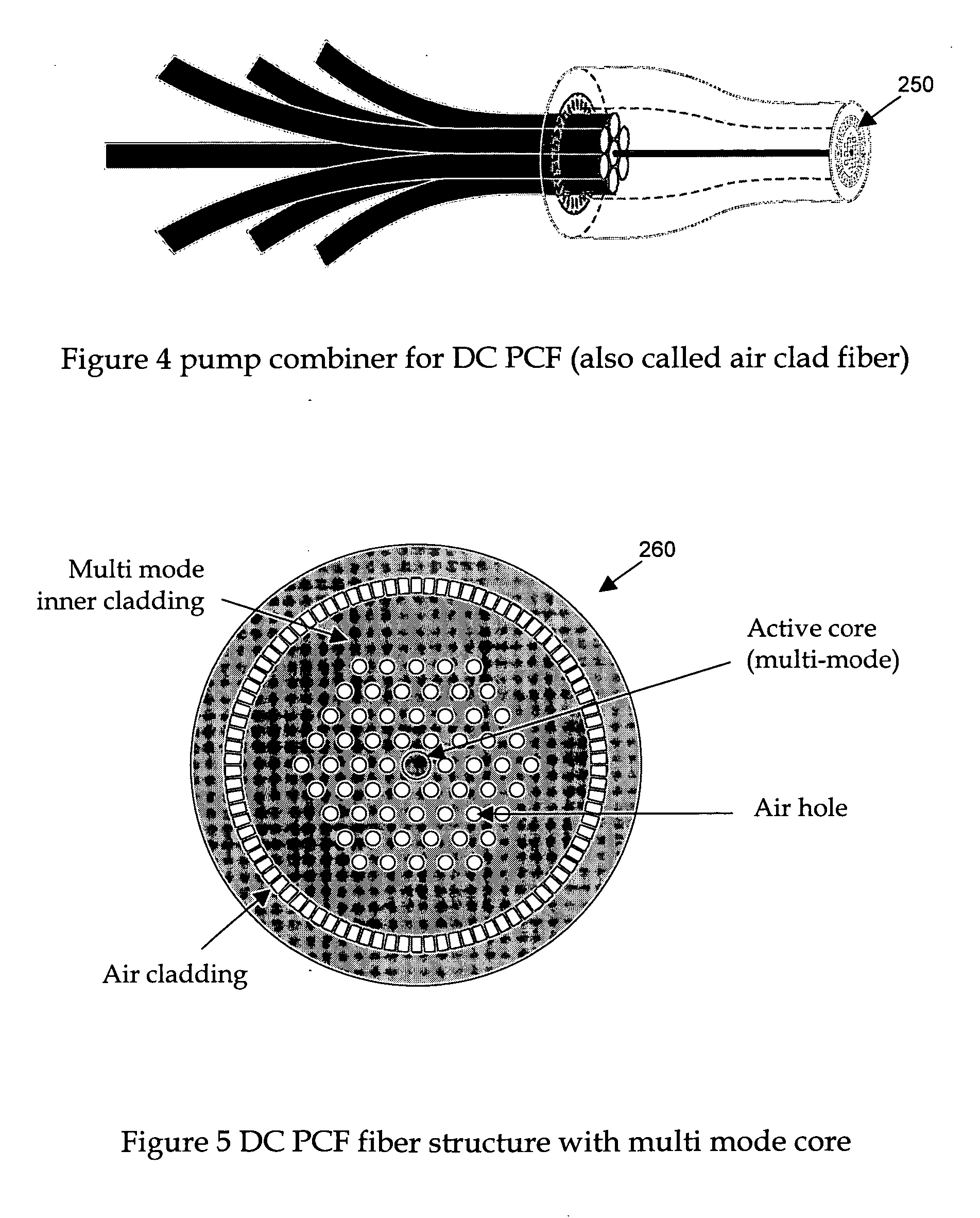
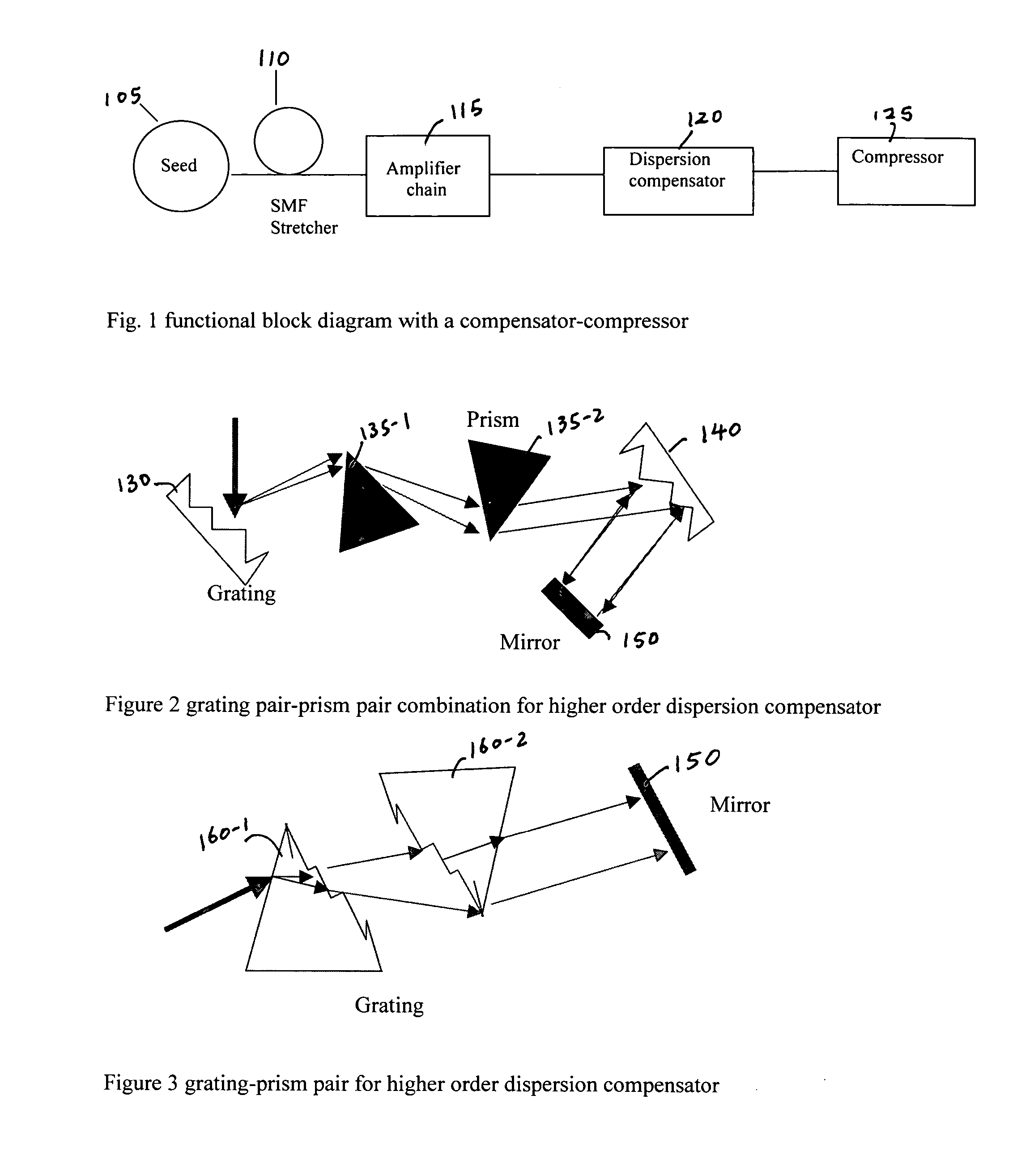
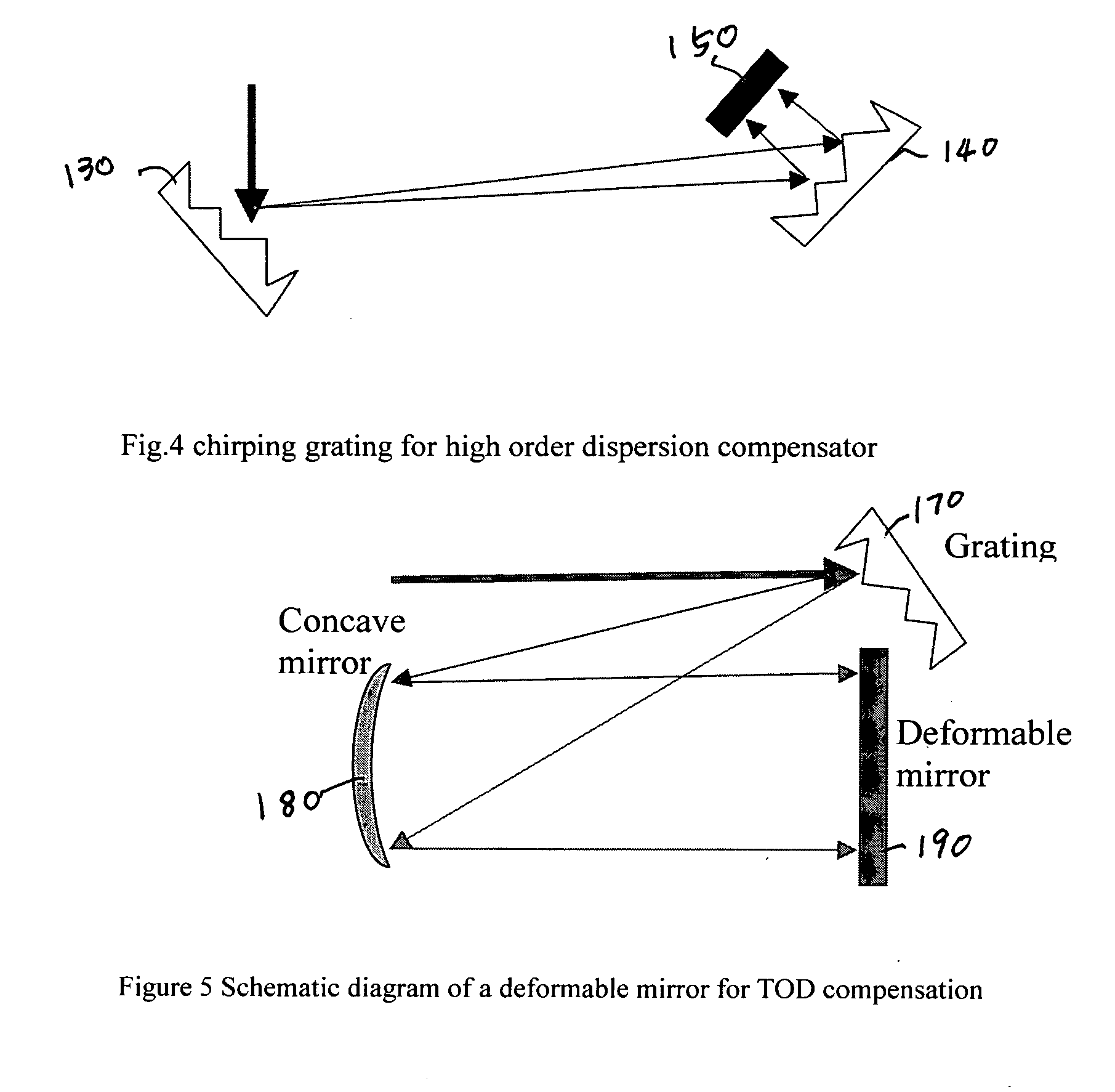
A fiber Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA) laser system includes a fiber mode-locking oscillator for generating a laser for projecting to a fiber stretcher for stretching a pulse width of the laser. The fiber CPA laser system further includes a multistage amplifier for amplifying the laser and a high-order dispersion compensating compressor for compensating high order dispersions and compressing the pulse width of the laser. The high-order dispersion compensating compressor further includes a pair of gratings coupled with a pair of prisms, a grating pair engraved on the surfaces of a pair of prisms, a chirped grating pair and a phase modulator consists of a grating and a deformable mirror, for generating a negative group velocity dispersion (GVD) and a negative third order dispersion (TOD) for the laser.
Owner:POLARONYX
Laser device with kerr effect based mode-locking and operation thereof
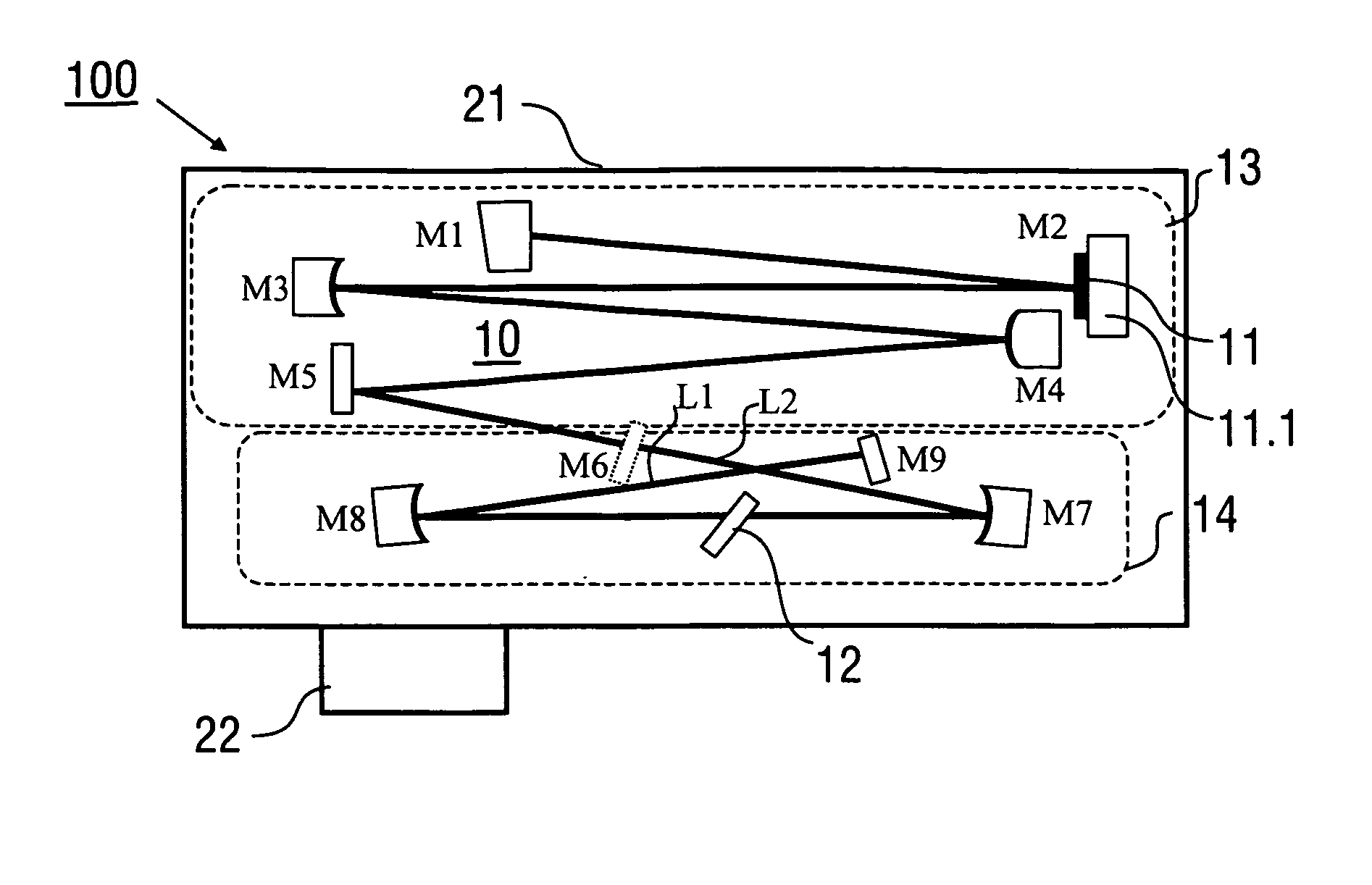
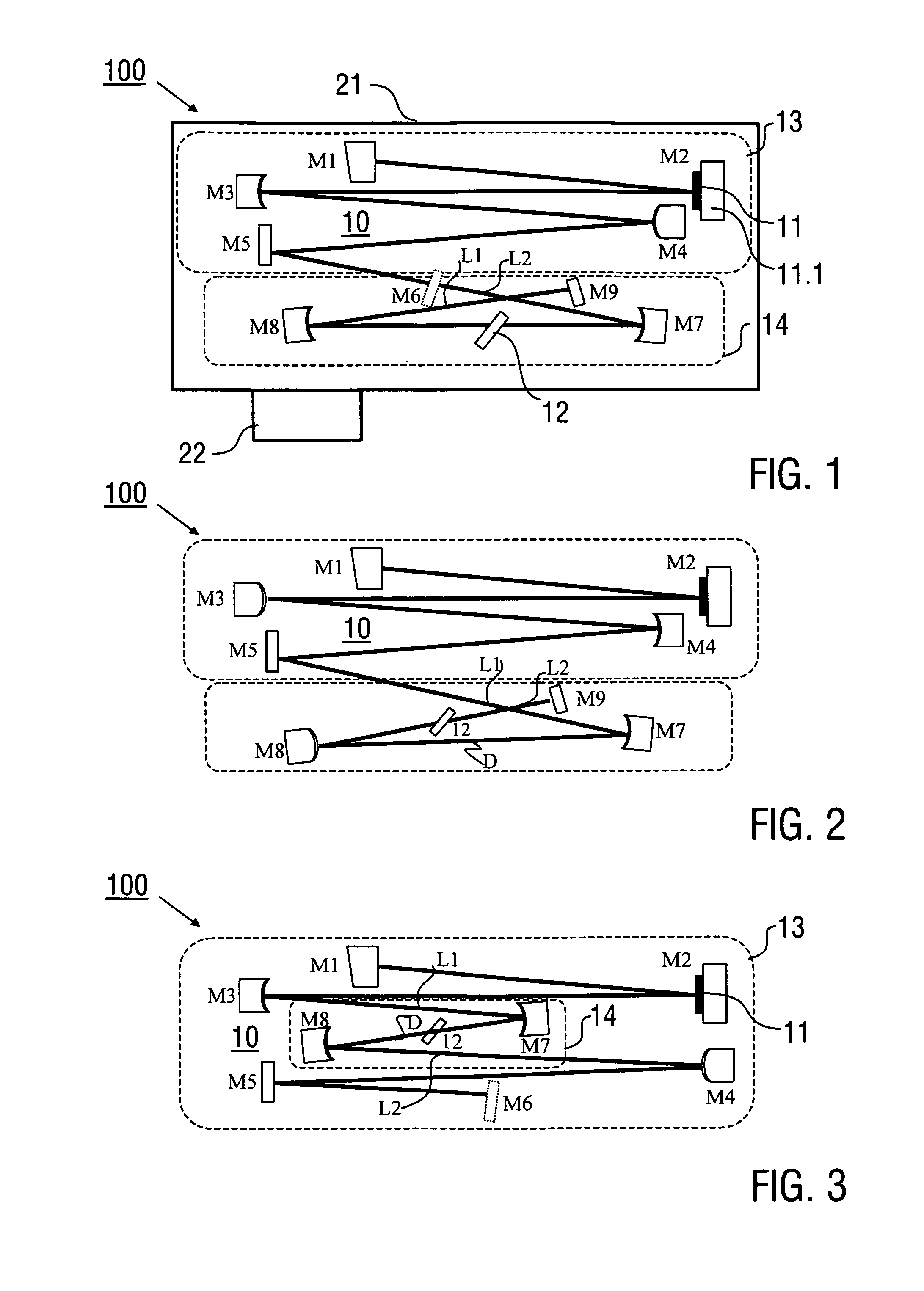
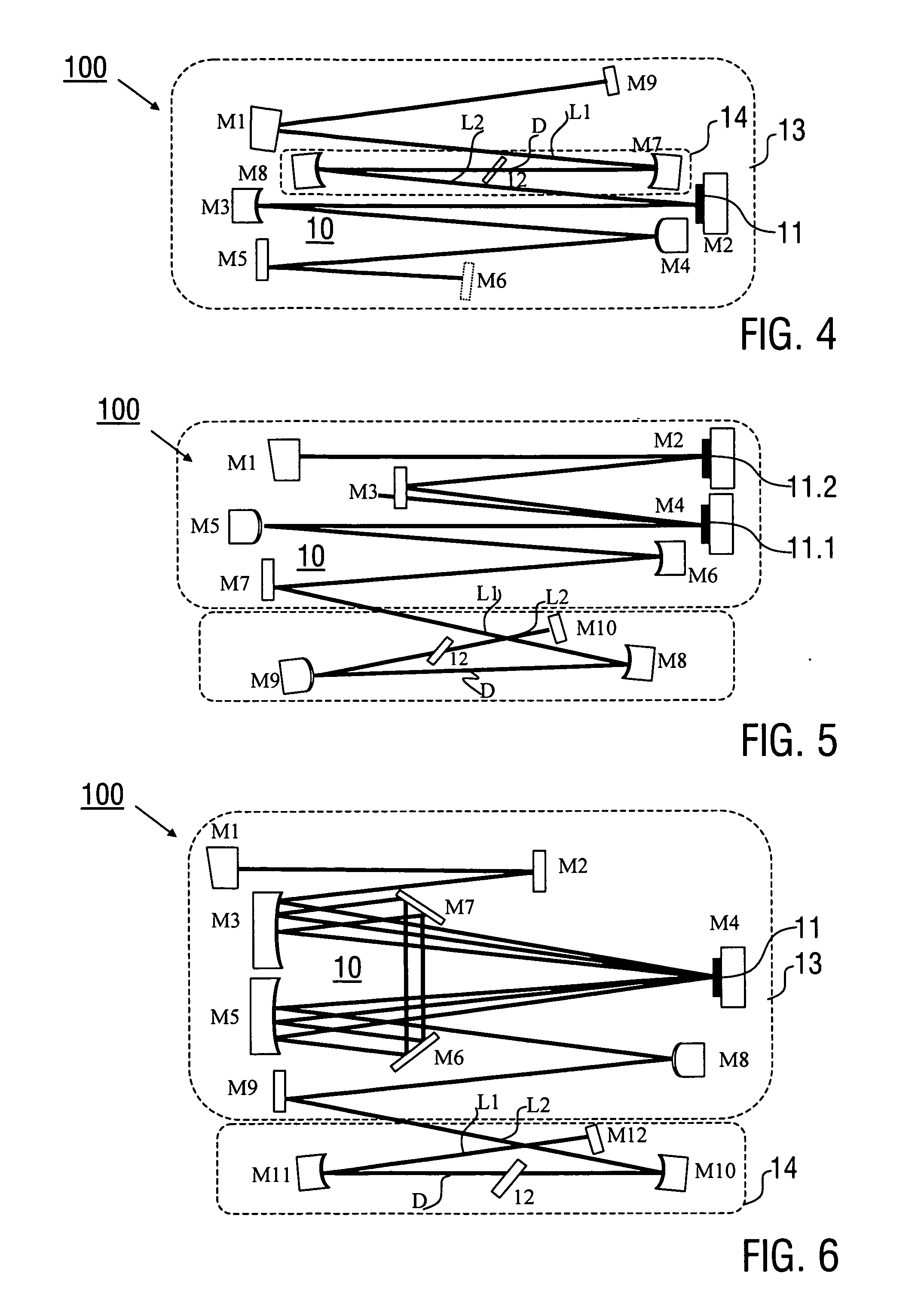
ActiveUS20140286364A1Easy to adjust independentlyCompactOptical resonator shape and constructionSolid state laser constructional detailsMode-lockingResonator
A laser device (100), configured for generating laser pulses, has a laser resonator (10) with a gain disk medium (11) and a Kerr medium (12). The laser resonator (10) includes a first mode shaping section (13) which is adapted for shaping a circulating electric field coupled into the gain disk medium (11), and a second mode shaping section (14), which is adapted for shaping the circulating electric field coupled into the Kerr medium (12) independently of the electric field shaping in the first mode shaping section (13). Furthermore, a method of generating laser pulses (1) using a laser resonator (10) with a gain disk medium (11) and a Kerr medium (12) is described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV +1
2-micrometer high-pulse energy thulium-doped optical fiber laser of hybrid pump
InactiveCN103078243ALower threshold energyHigh energyActive medium shape and constructionGratingHigh energy
The invention discloses a 2-micrometer high-pulse energy thulium-doped optical fiber laser of a hybrid pump. The 2-micrometer high-pulse energy thulium-doped optical fiber laser comprises a first fiber grating, a first fiber beam combiner, a second fiber beam combiner, a gain fiber and a second fiber grating, which are connected in sequence, wherein a first pumping source is connected with a second input end of the first fiber beam combiner through a first optical isolator, a second pumping source is connected with a second input end of the second fiber beam combiner through a second optical isolator, the first fiber gating and the second fiber gating form a laser resonance cavity, the first pumping source is a continuous laser diode, the second pumping source is a pulsed laser, and the gain fiber is a thulium-doped fiber. The 2-micrometer high-pulse energy thulium-doped optical fiber laser is reduced in the threshold valve energy of a pumping pulsed light in a gain switch technology, is capable of obtaining pulse with higher energy compared with other laser pulse producing technologies such as regulating Q and mode locking, has the characteristics of full-fiber connection, simple structure and the like, and brings convenience for application and popularization.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Double cladding large mode field area Yb-doped photon crystal optical fiber femtosecond laser
InactiveCN101101427AGood Polarization Maintaining PropertiesImprove stabilityCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideFrequency spectrumNonlinear optics
The invention discloses a double-coating large-mode-area photon crystal flysecond laser directly obtaining micro joule-level single pulse energy, belonging to the field of laser technique and nonlinear optics, where the laser main body is based on double-coating large-mode-area photon crystal optical fiber of polarization-protection structure and adopts high-power LD laser to directly pump; the laser uses grating pair to compensate dispersion, starts mode locking with the help of semiconductor saturable absorber mirror (SESAM), and controls polarization by wave plate and polarization beam splitter and implements tunable output; laser resonant cavity keeps net positive dispersion inside and runs in self-similar mode locking mode and outside-cavity dispersion compensation is made on the output pulse and the pulse is 100-200fs wide. And the advantages: the laser has good stability, and the output pulse has high energy and high repeating frequency. And the invention can effectively avoid split of pulse running at high energy.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
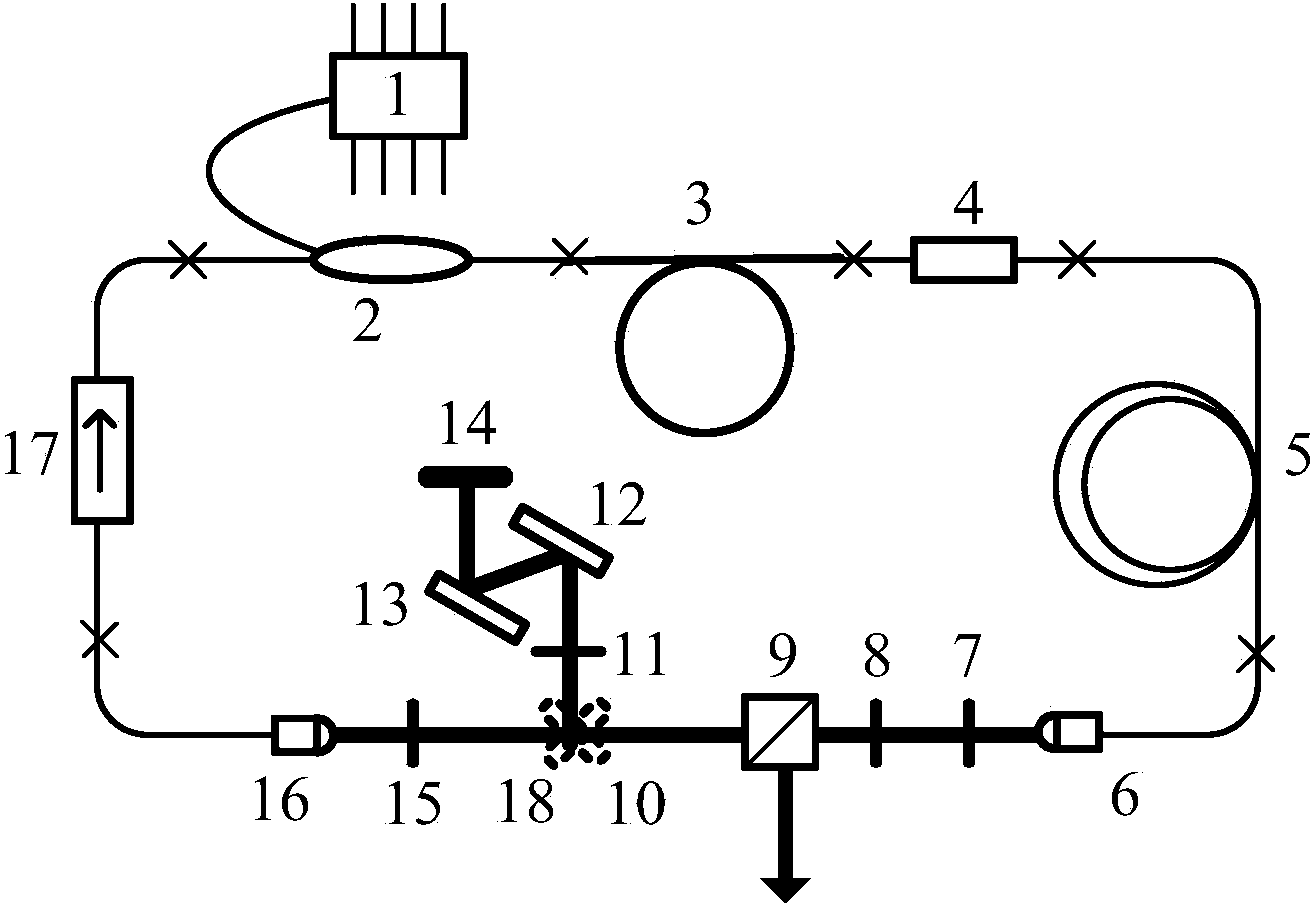
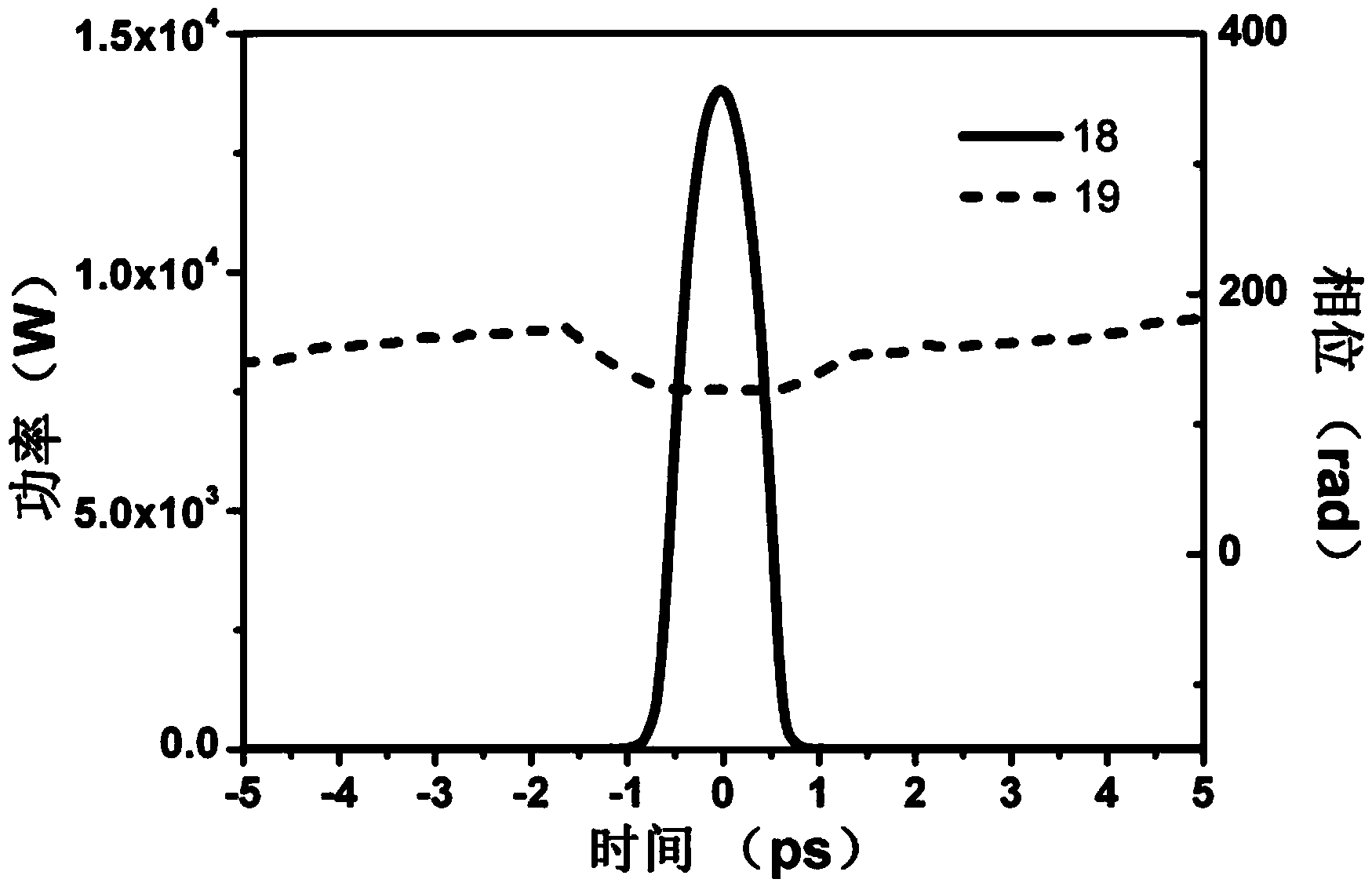
Resonant cavity for outputting mode-locking picosecond laser and mode-locking picosecond laser device
InactiveCN102832536APeak power controlMeet the requirements of different applicationsOptical resonator shape and constructionPicosecond laserResonant cavity
The invention provides a resonant cavity for outputting mode-locking picosecond laser and a mode-locking picosecond laser device. The mode-locking picosecond laser device comprises a pumping source, a focusing lens and the resonant cavity for outputting the mode-locking picosecond laser, and the pumping source, the focusing lens and the resonant cavity are sequentially arranged along a light path. The resonant cavity is characterized that a laser crystal, a focusing device, a Fabry-Perot etalon and a semiconductor saturable absorber mirror are arranged in the resonant cavity, and the energy density of light beams acting on the semiconductor saturable absorber mirror can be sufficient to realize continuous mode-locking owing to the focusing device. Peak power of the picosecond laser device can be accurately controlled, so that different application requirements can be effectively met advantageously. Besides, pulse width of the picosecond laser device can be controlled, so that different application requirements can be effectively met advantageously. In addition, picosecond pulse width can be tuned, operation is easy, and mode-locking stability is unaffected. A pulse width tunable device is small in size and is beneficial to saving space.
Owner:ACAD OF OPTO ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Optical frequency self stabilization in a coupled optoelectronic oscillator
Methods and devices for a coupled optoelectronic oscillator having optical frequency stabilization. The coupled optoelectronic oscillator includes a harmonically mode-locked laser cavity having a Mach-Zehnder modulator for mode-locking and an intracavity Fabry-Perot etalon to allow only one single supermode to lase, a stabilization loop coupled with the Fabry-Perot etalon to detect changes in the laser cavity optical frequency and generate an error signal to compensate for the frequency change to stabilize the mode-locking of the laser frequency stabilization, and an electrical loop between the laser cavity and the stabilization loop for driving the Mach-Zehnder modulator with the coupled optoelectronic oscillator signal.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Self-similarity mode locking optical fiber femtosecond laser device based on spectrum compression and amplification
InactiveCN104242025AImprove efficiencyAchieving nonlinear phase balanceActive medium shape and constructionFrequency spectrumGrating
A self-similarity mode locking optical fiber femtosecond laser device based on spectrum compression and amplification is composed of an optical fiber coupling output laser diode, a wavelength division multiplexing coupler, a ytterbium-mixed monomode optical fiber, an optical fiber frequency spectrum filter, a monomode optical fiber, an optical fiber collimator, a quarter-wave plate, a half-wave plate, a polarization splitting prism, a 45-degree reflector, a grating and an optical fiber isolator. Spectrum is compressed by using the self-phase modulation generated when negative chirp pulses are amplified in the ytterbium-mixed monomode optical fiber, narrow-band chirp-free picosecond pulses are formed, the optical fiber frequency spectrum filter is used for eliminating residual side lobes in nonlinear spectrum compression, self-similarity evolution is completed in the monomode optical fiber, broadband linear chirp parabola pulses are output directly, and Fourier transformation extremity femtosecond lasers are output after chirps are eliminated. The self-similarity mode locking optical fiber femtosecond laser device is high in efficiency, large in self-similarity evolution spectrum widening amount, capable of obtaining Fourier transformation extremity femtosecond laser pulses high in energy and narrow in pulse width, compact in structure and easy to operate.
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
All-fiber pulsed laser
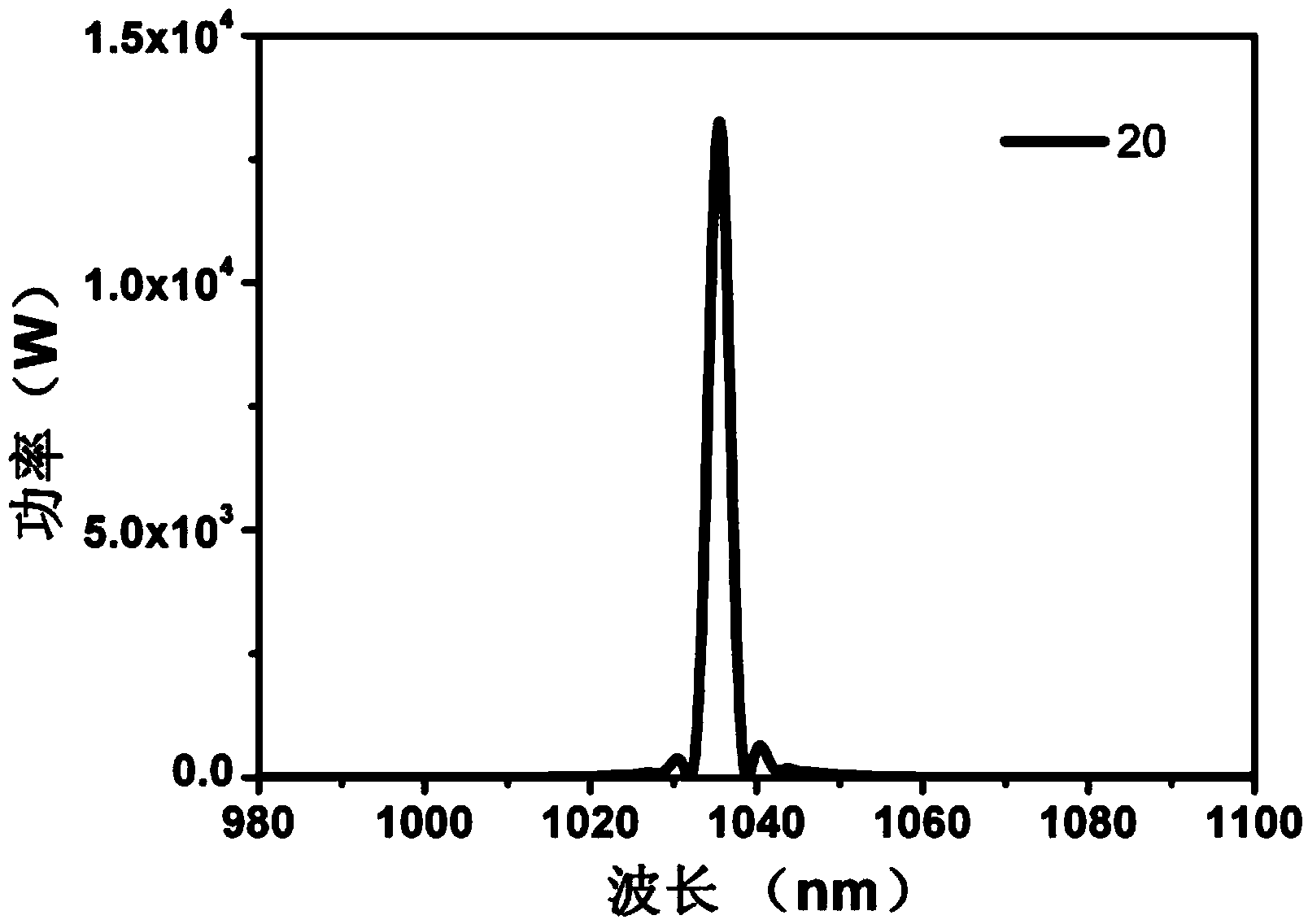
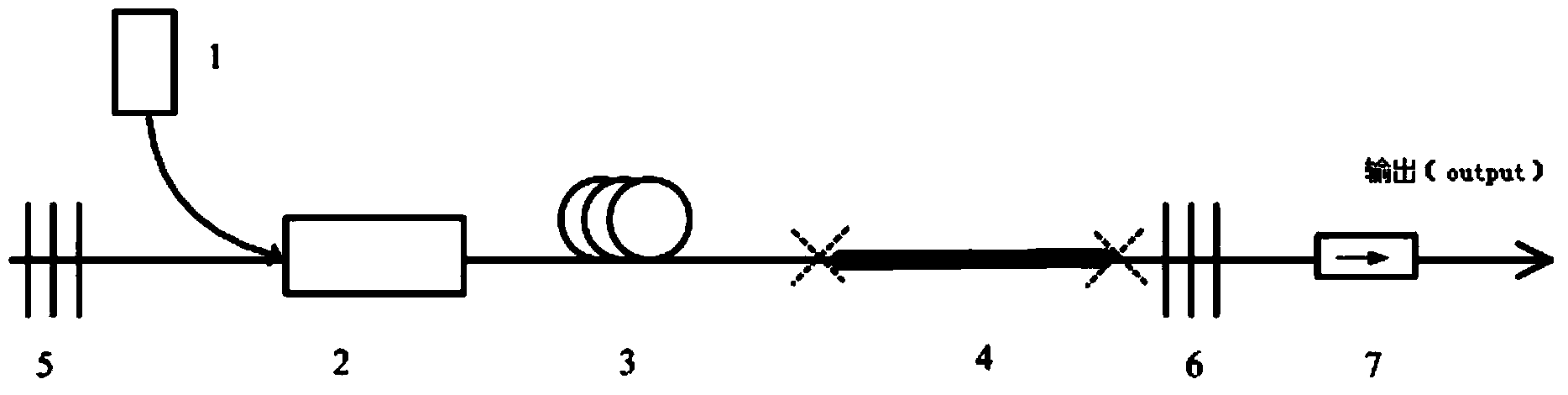
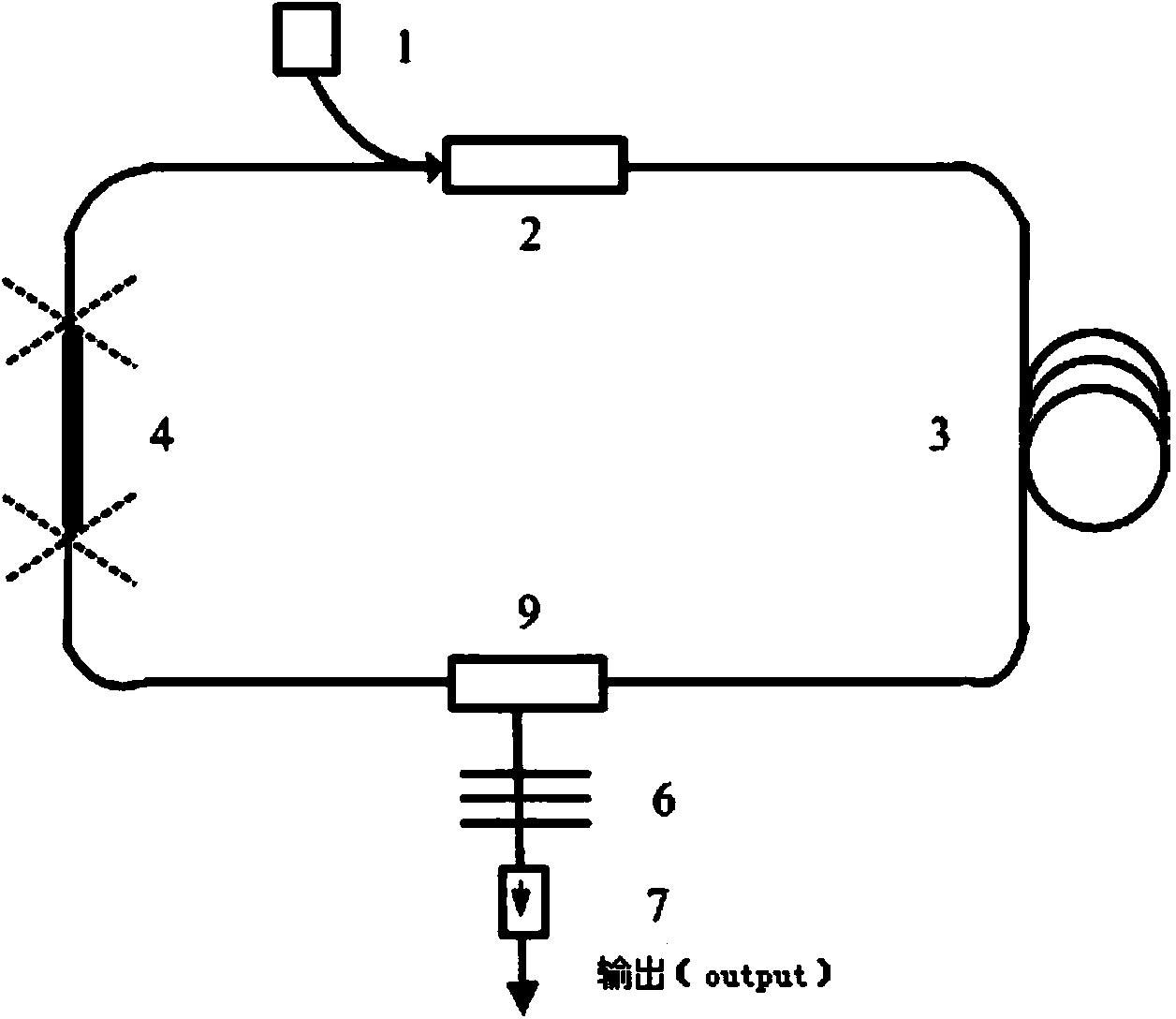
ActiveCN103414093AReduce manufacturing costReduce processing difficultyActive medium shape and constructionFiberNonlinear optics
The invention discloses an all-fiber pulsed laser, and belongs to the field of laser technology and nonlinear optics. The all-fiber pulsed laser includes a pump source (1), an optical combiner (2), a first gain fiber (3), a second gain fiber (4), a first reflective fiber Bragg grating (5), a second reflective fiber Bragg grating (6), an optical isolator (7), a full reflection mirror (8) and a circulator (9), and adopts a structure of linear cavity or annular cavity. By use of the rare earth-doped gain fibers as a laser modulator, with no additional external modulation source and an all-fiber structure, ultrashort pulse laser output of high stability, high power, high energy and high efficiency is achieved. Compared with a semiconductor saturable absorption mirror (SESAM) and graphene (Graphene) modulation Q, mode-locking technology, the all-fiber pulsed laser employs gain fiber for direct pulse modulation, has the advantages of simple design, compact structure and high stability, and is easier to industrialize.
Owner:BWT BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com