Patents
Literature
132 results about "Pulse stretcher" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
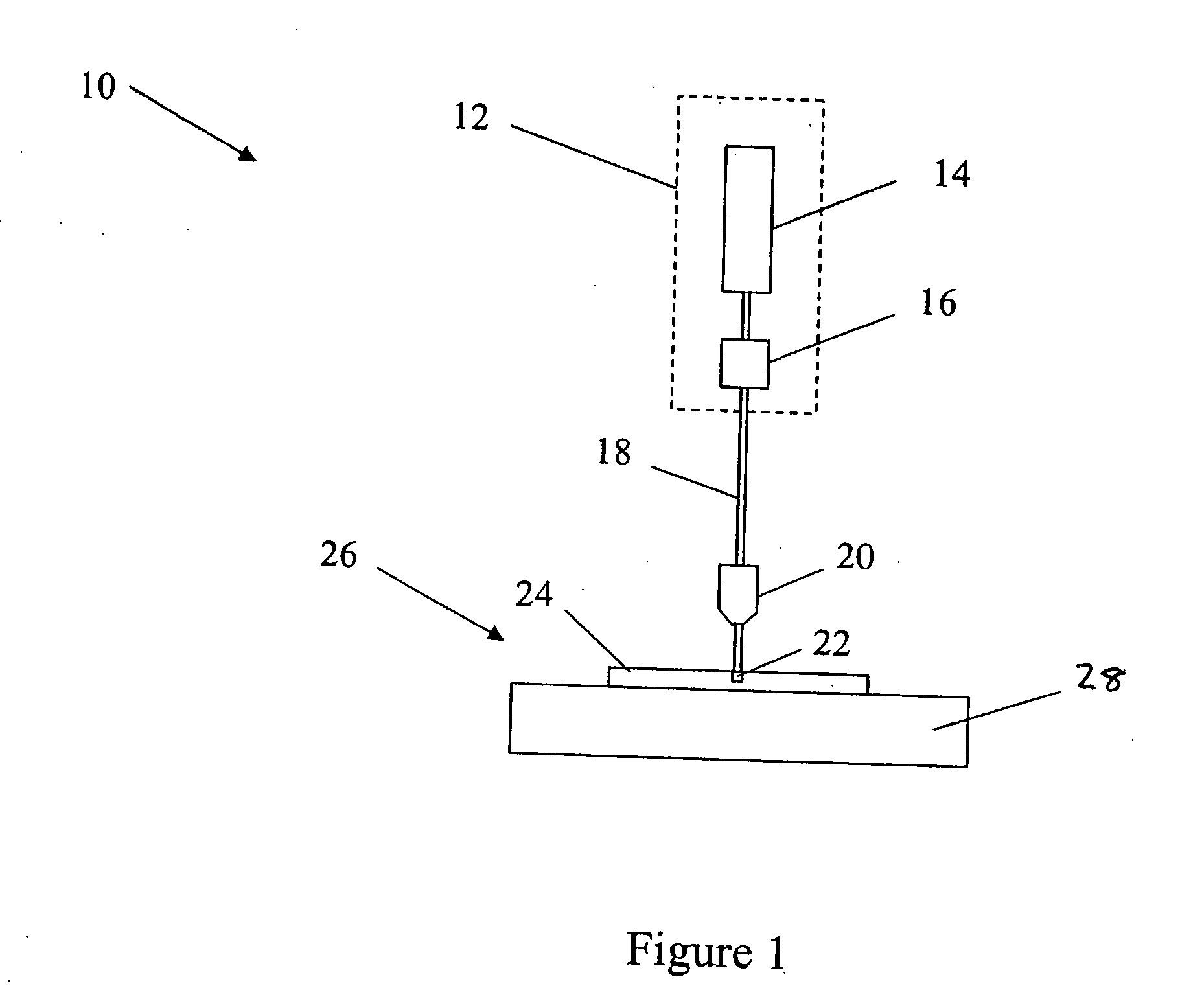
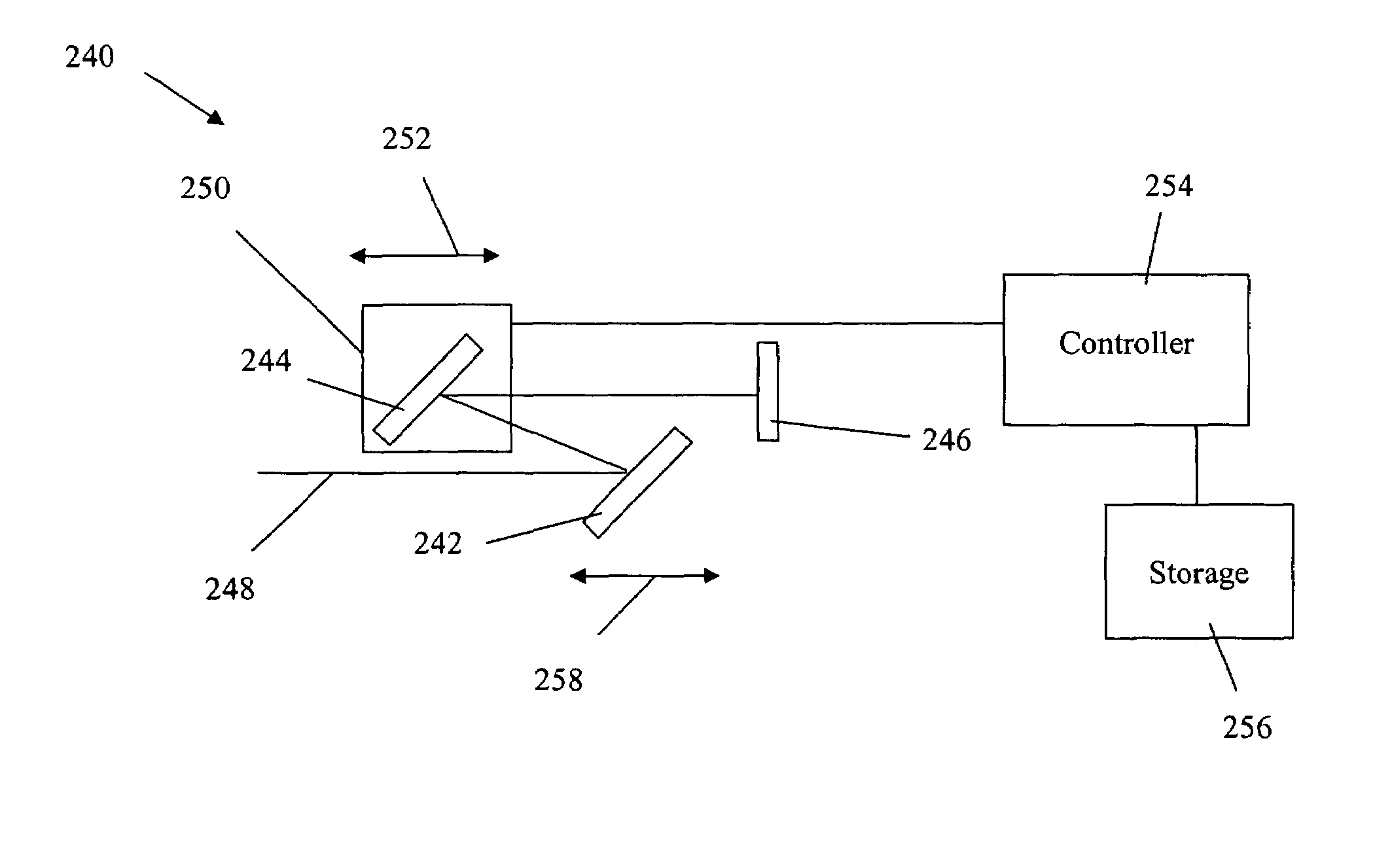
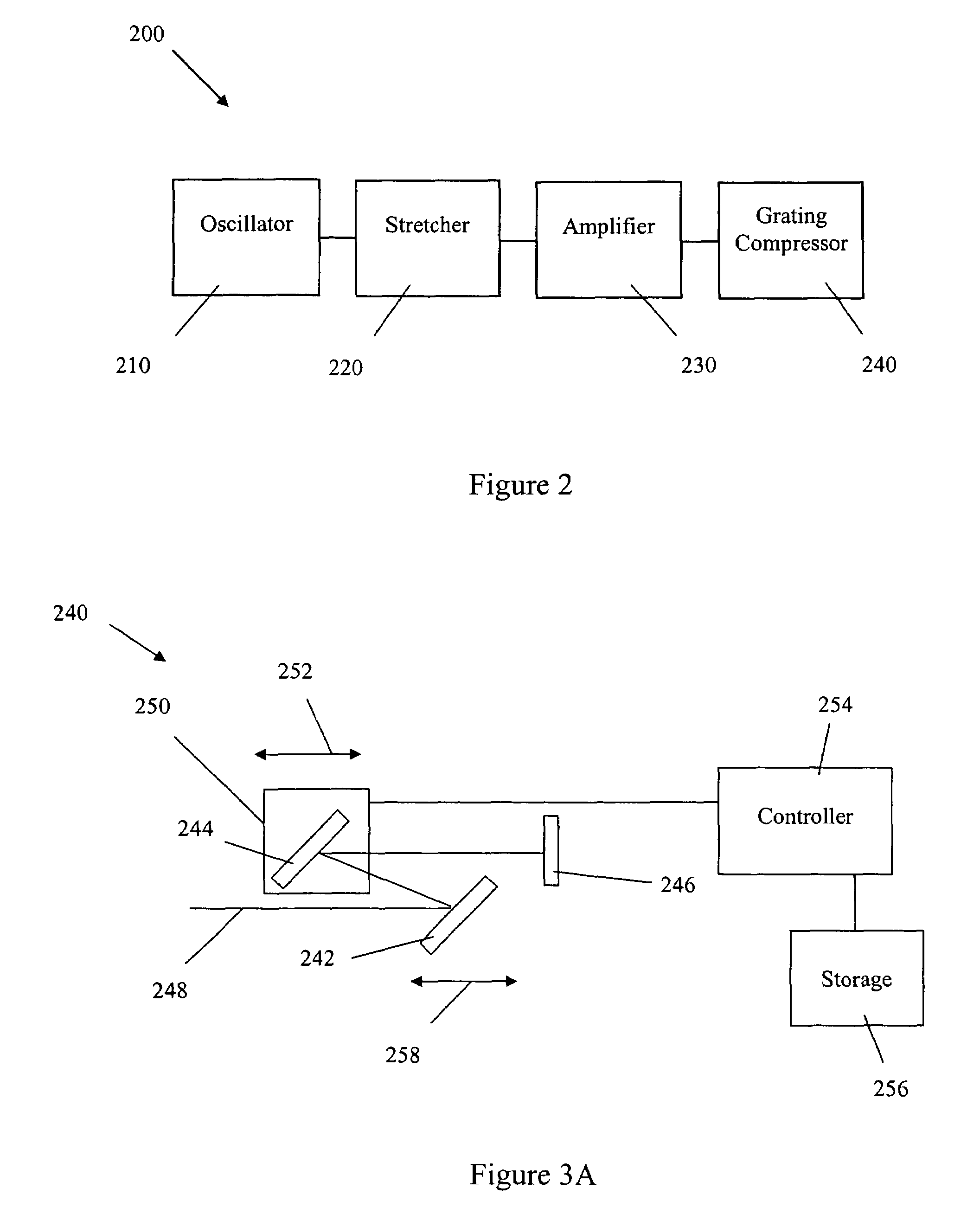
Long delay and high TIS pulse stretcher
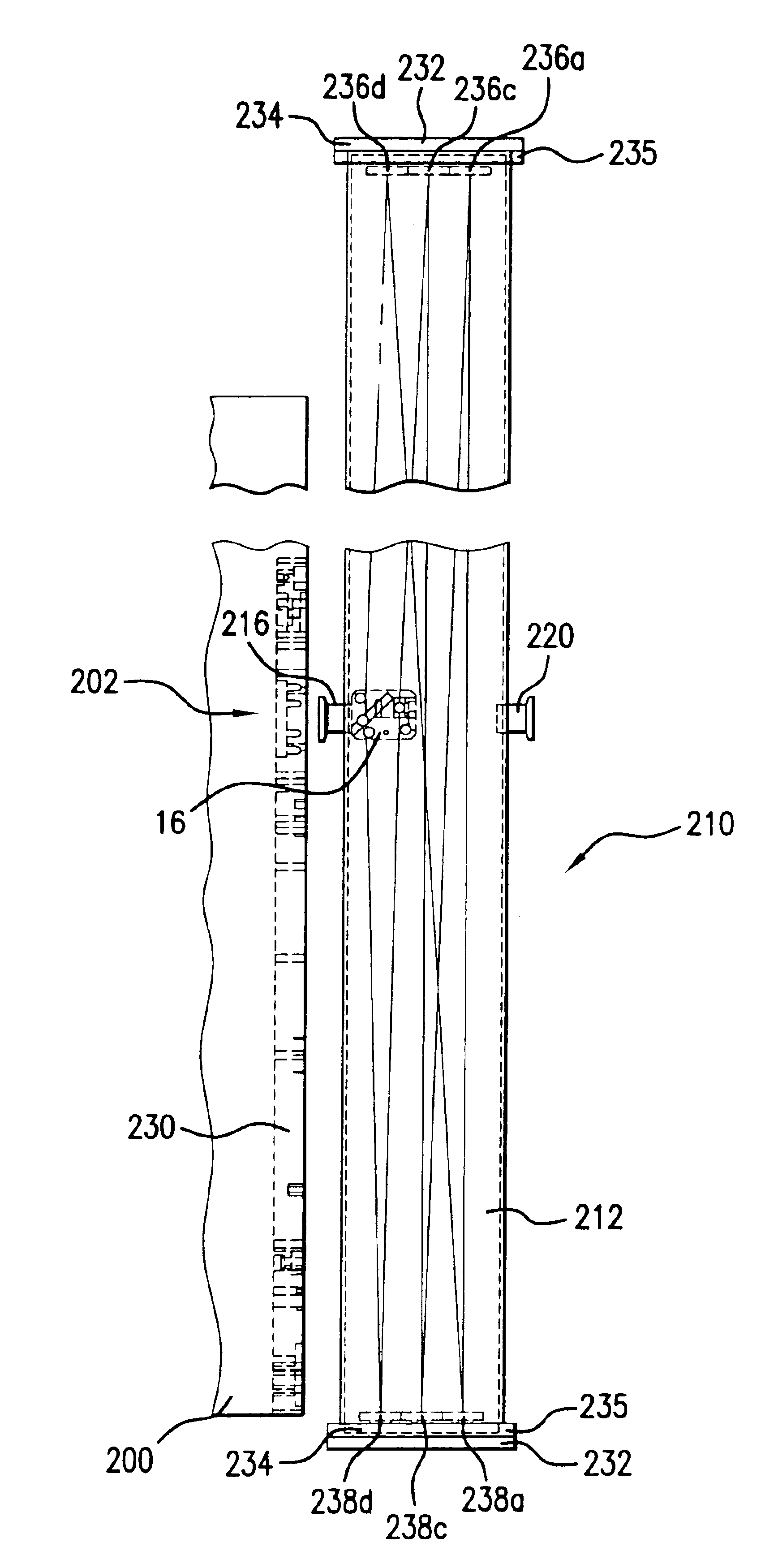
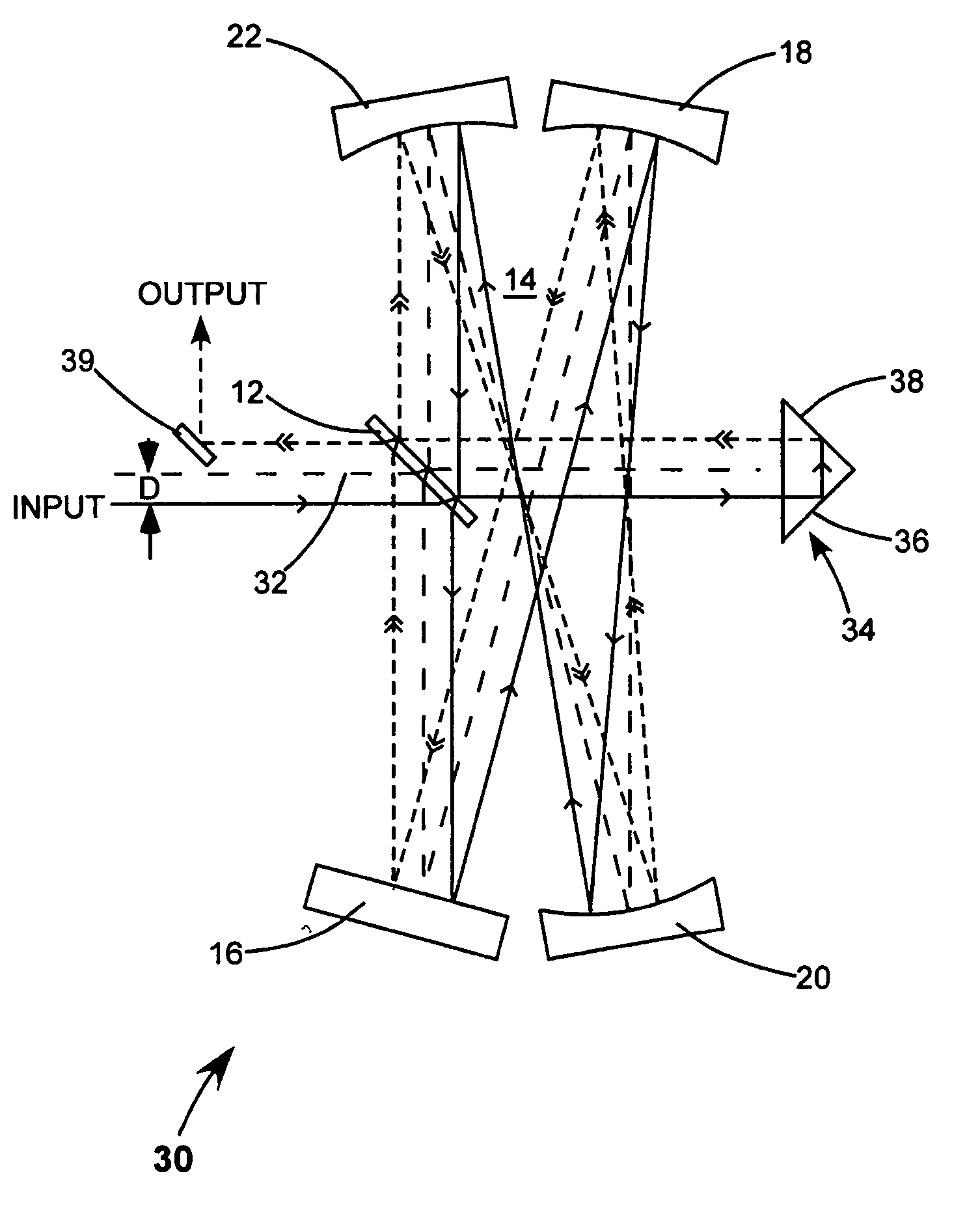
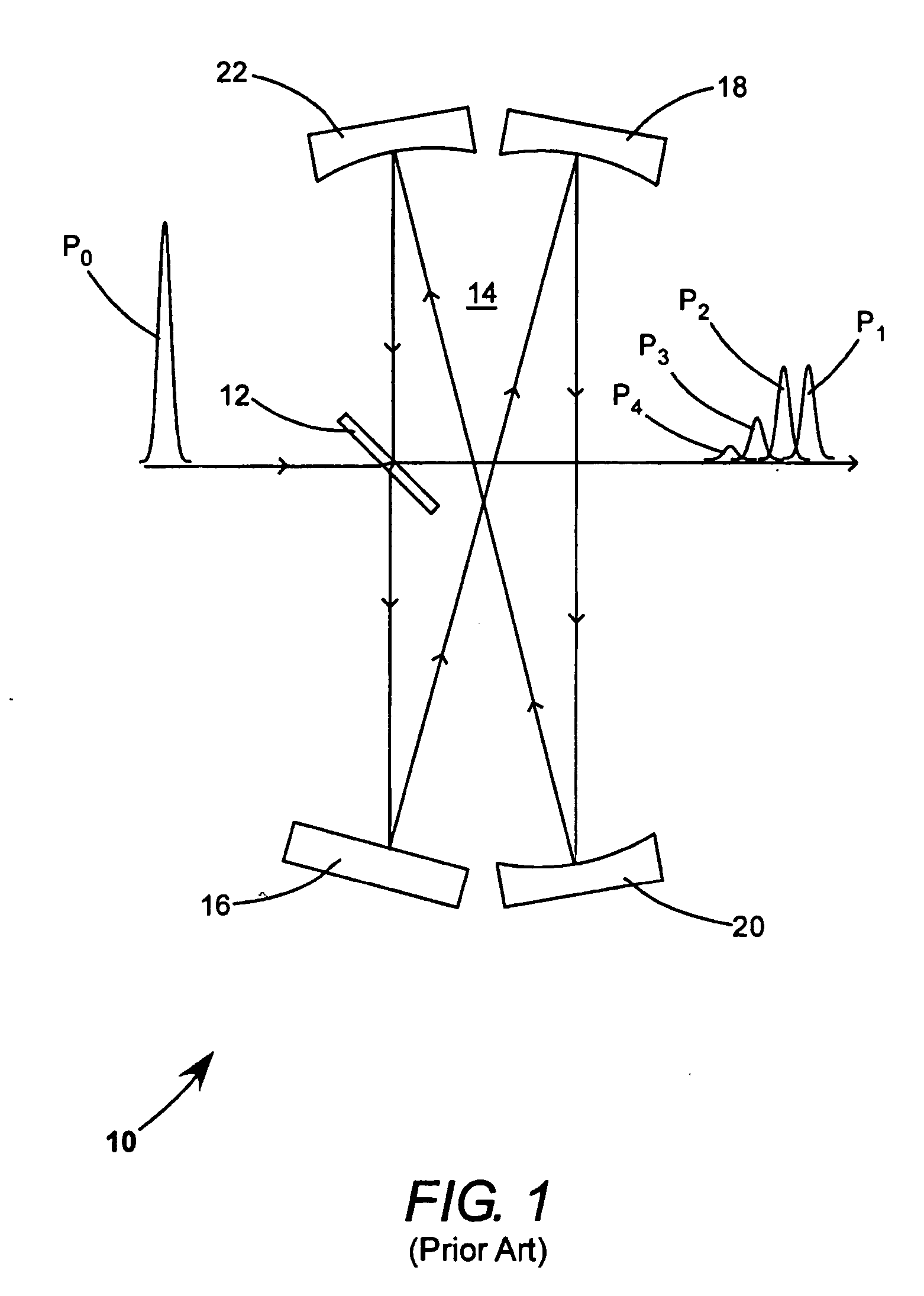
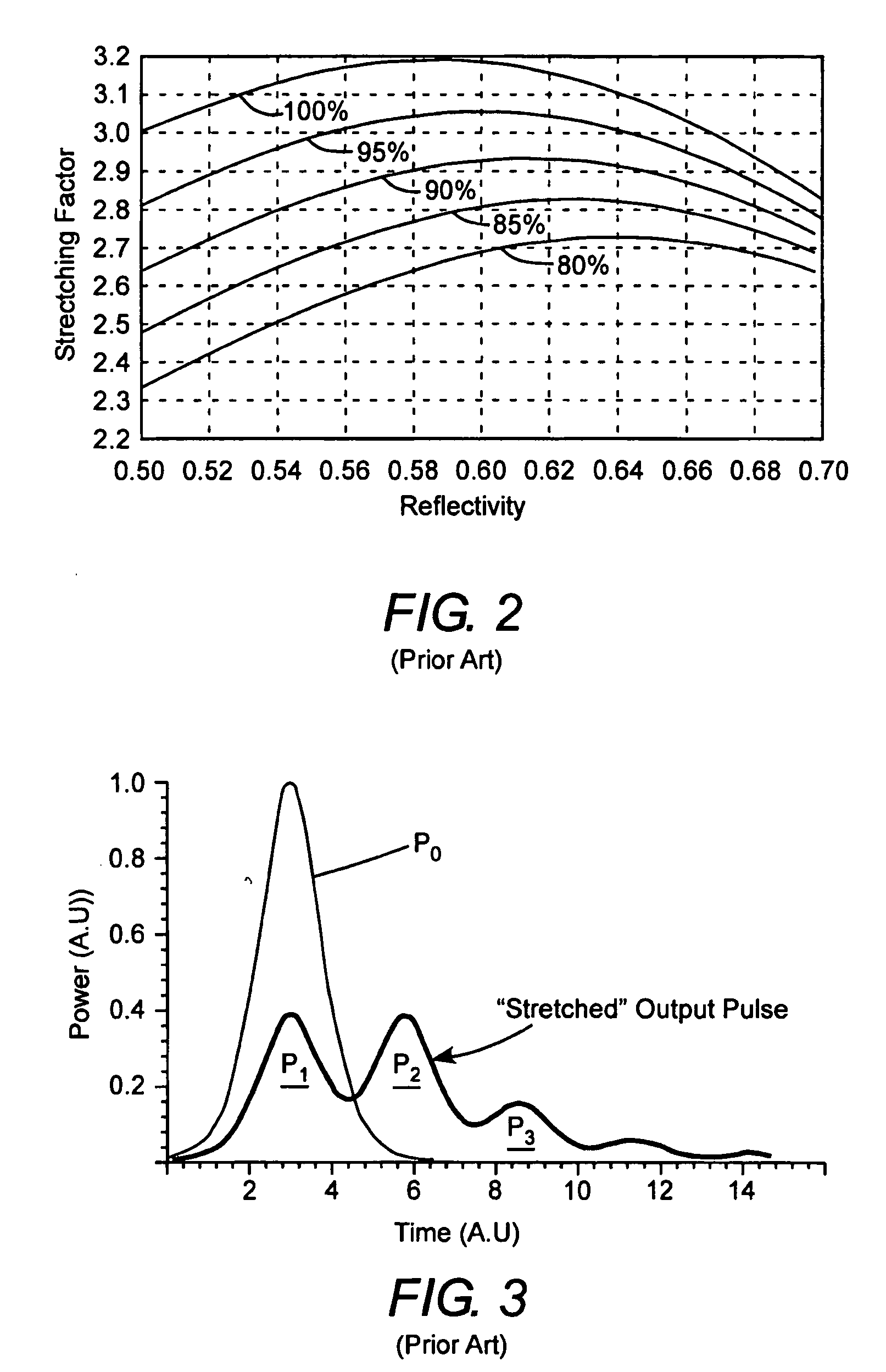
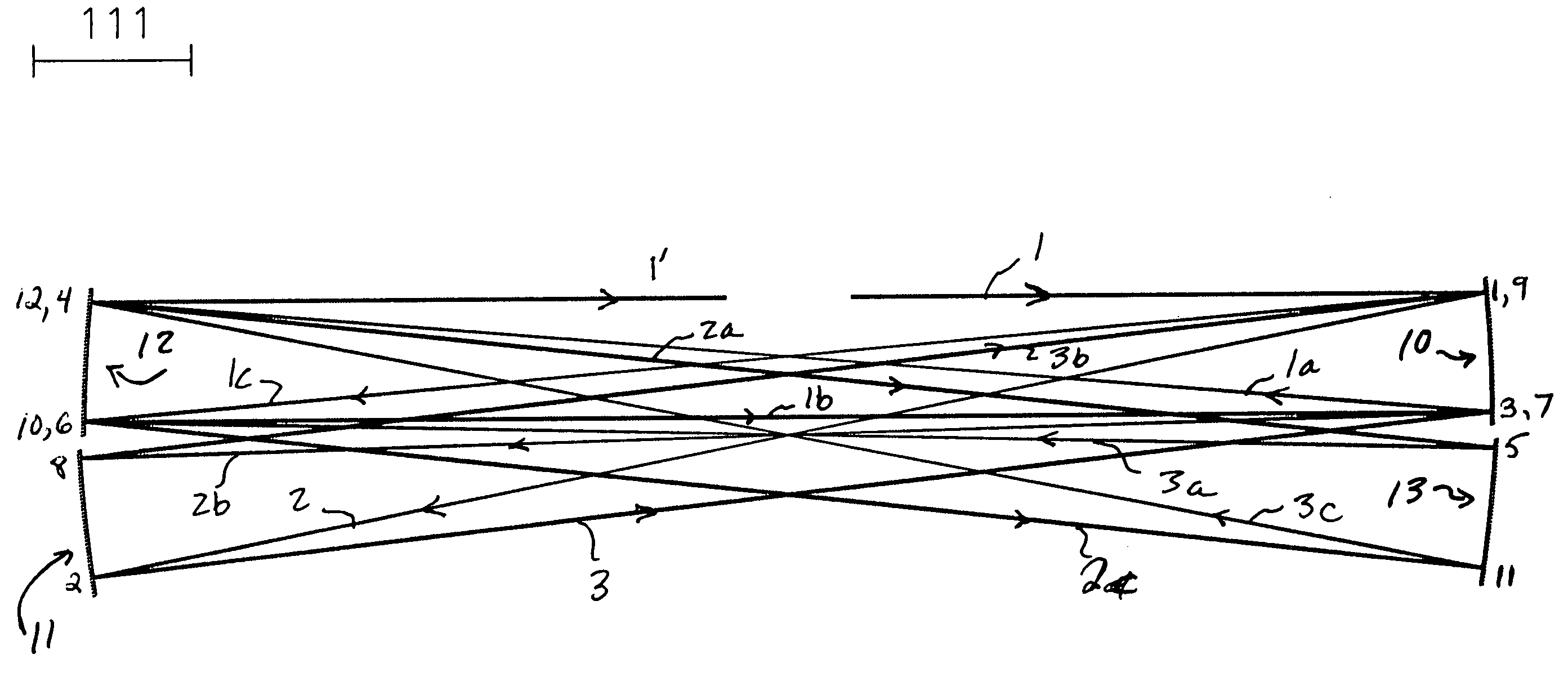
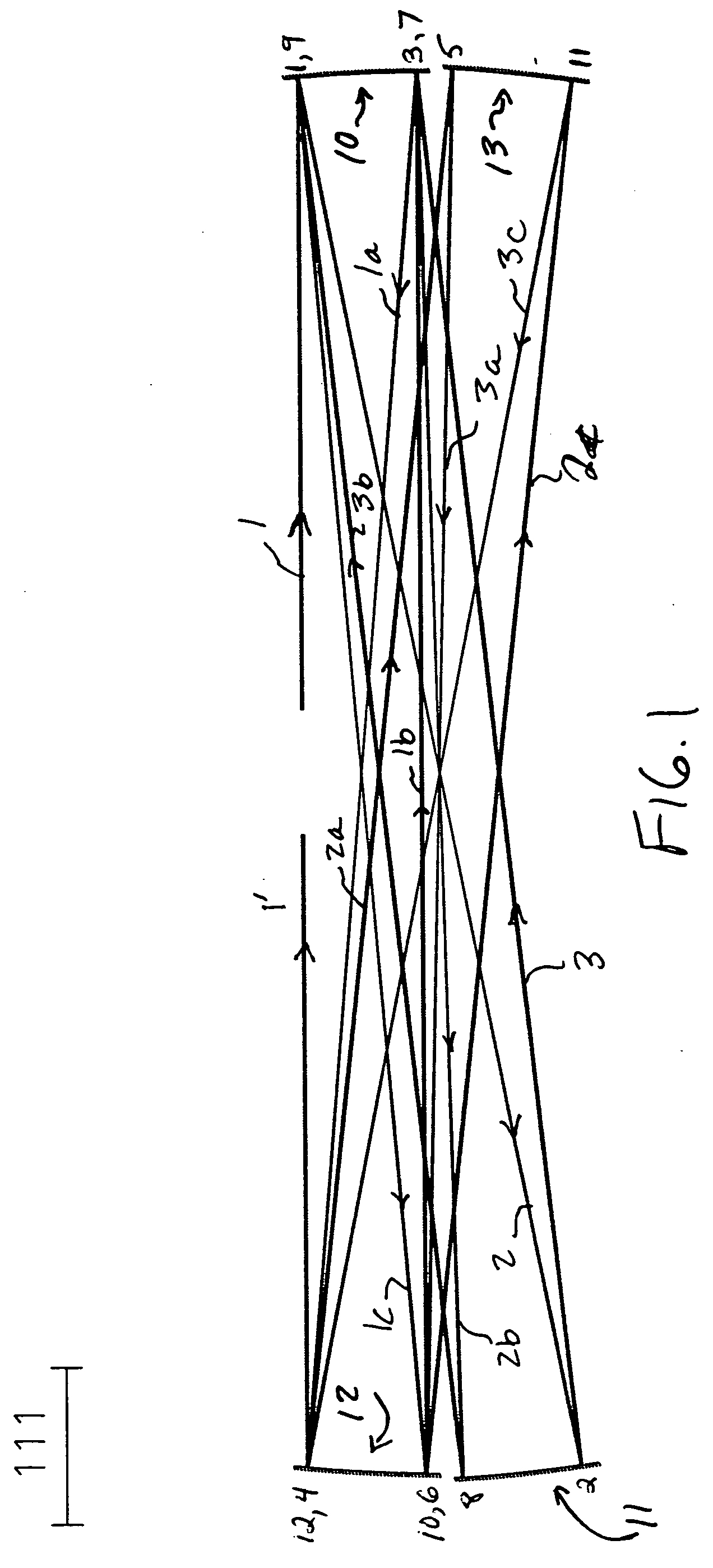
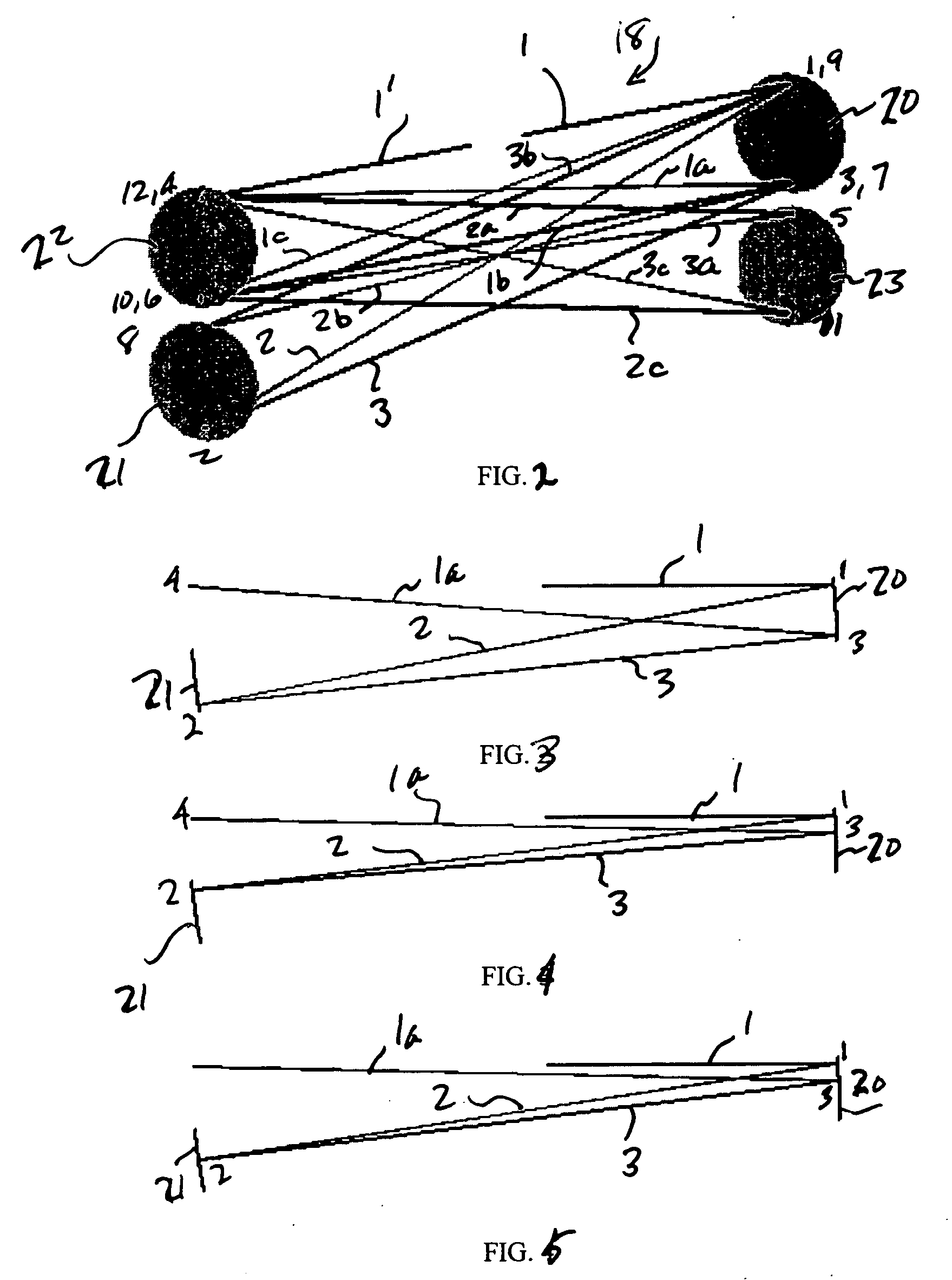
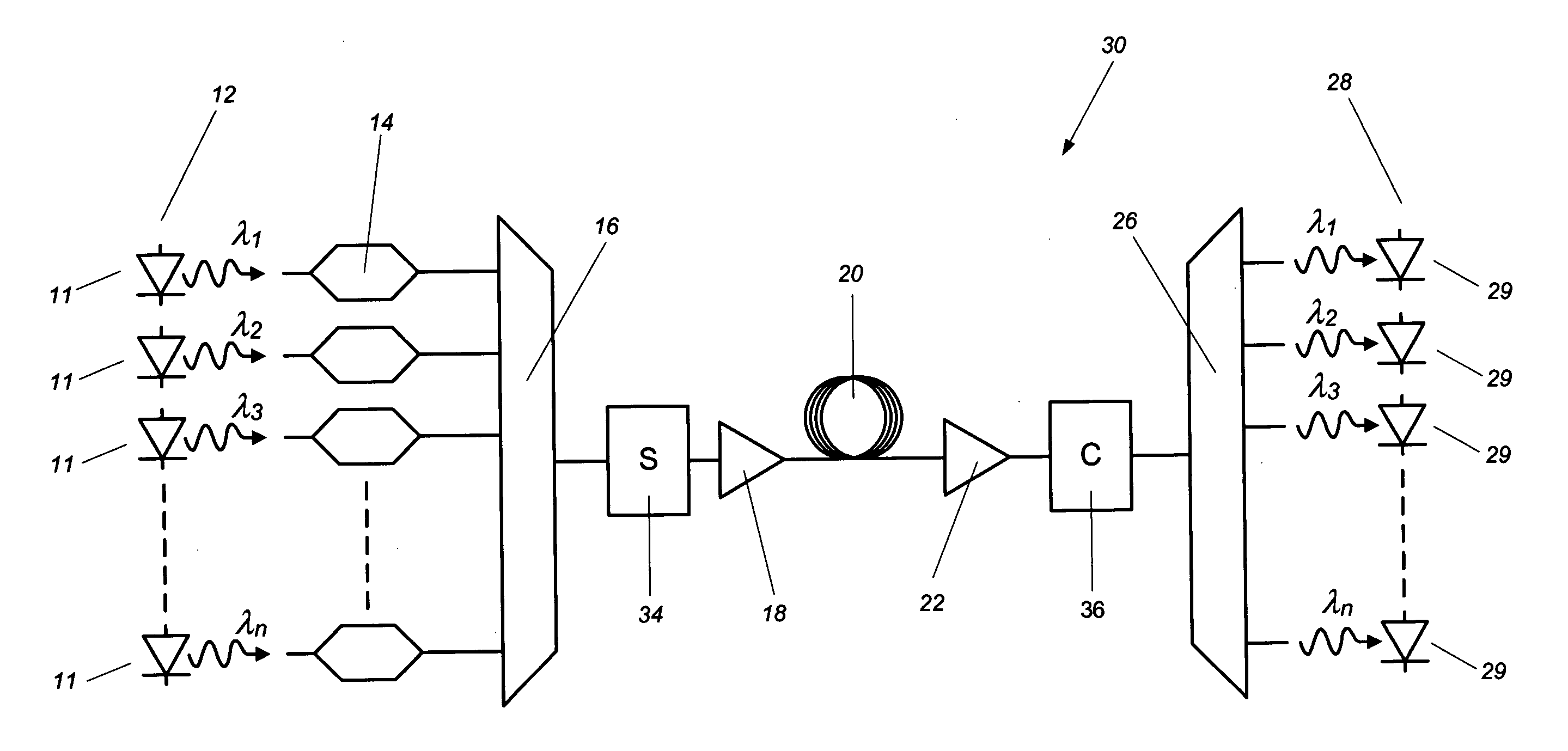
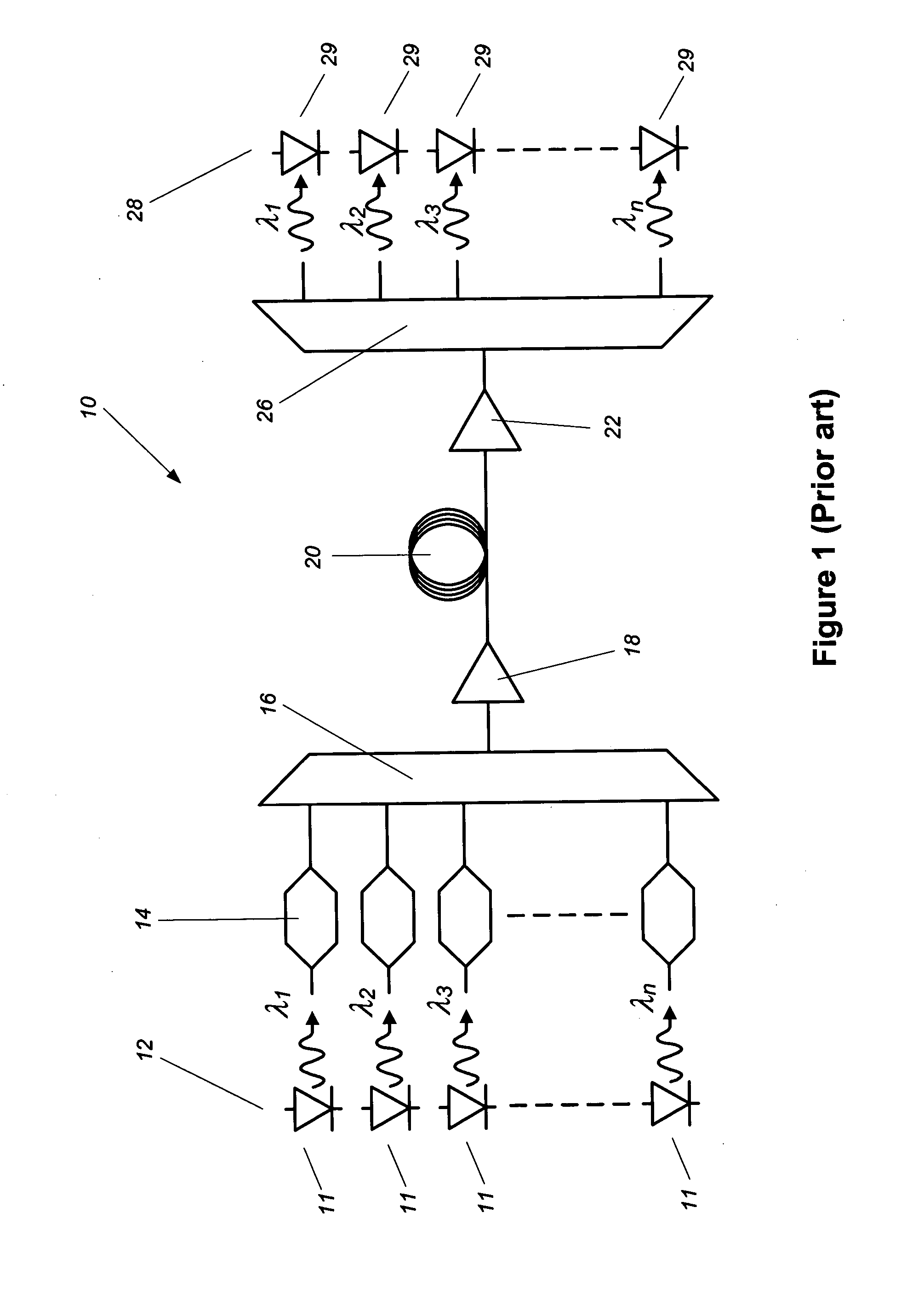
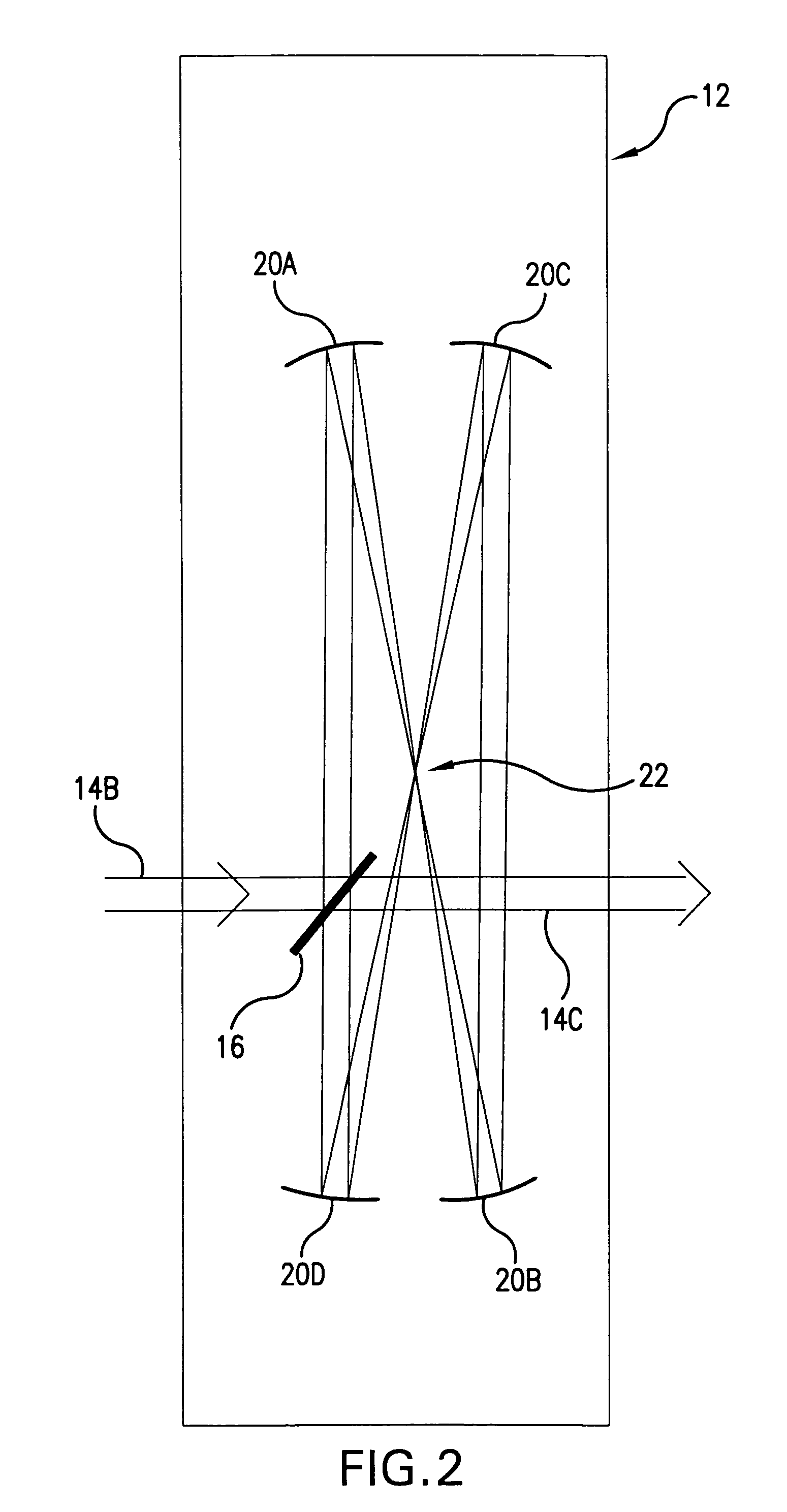
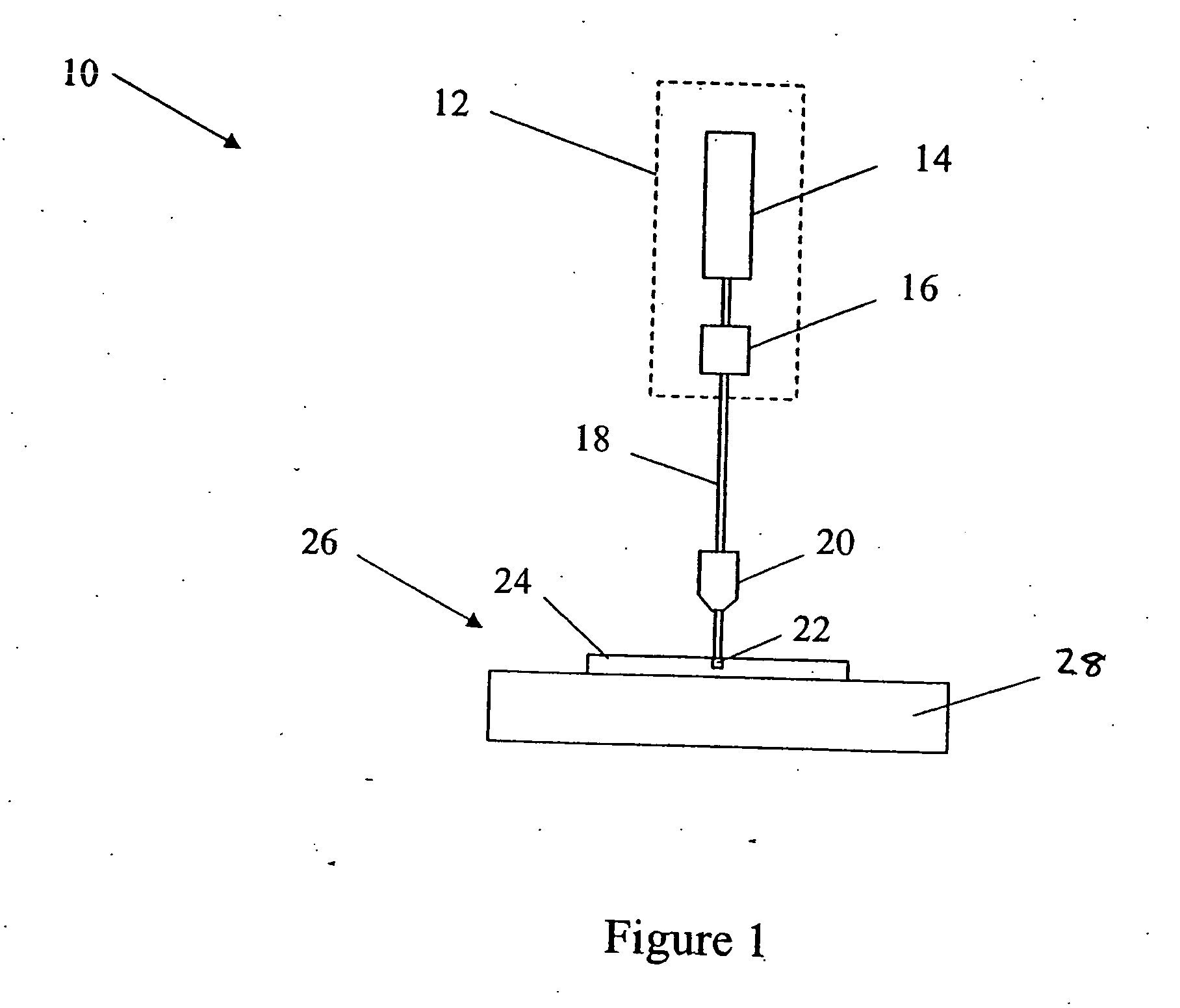
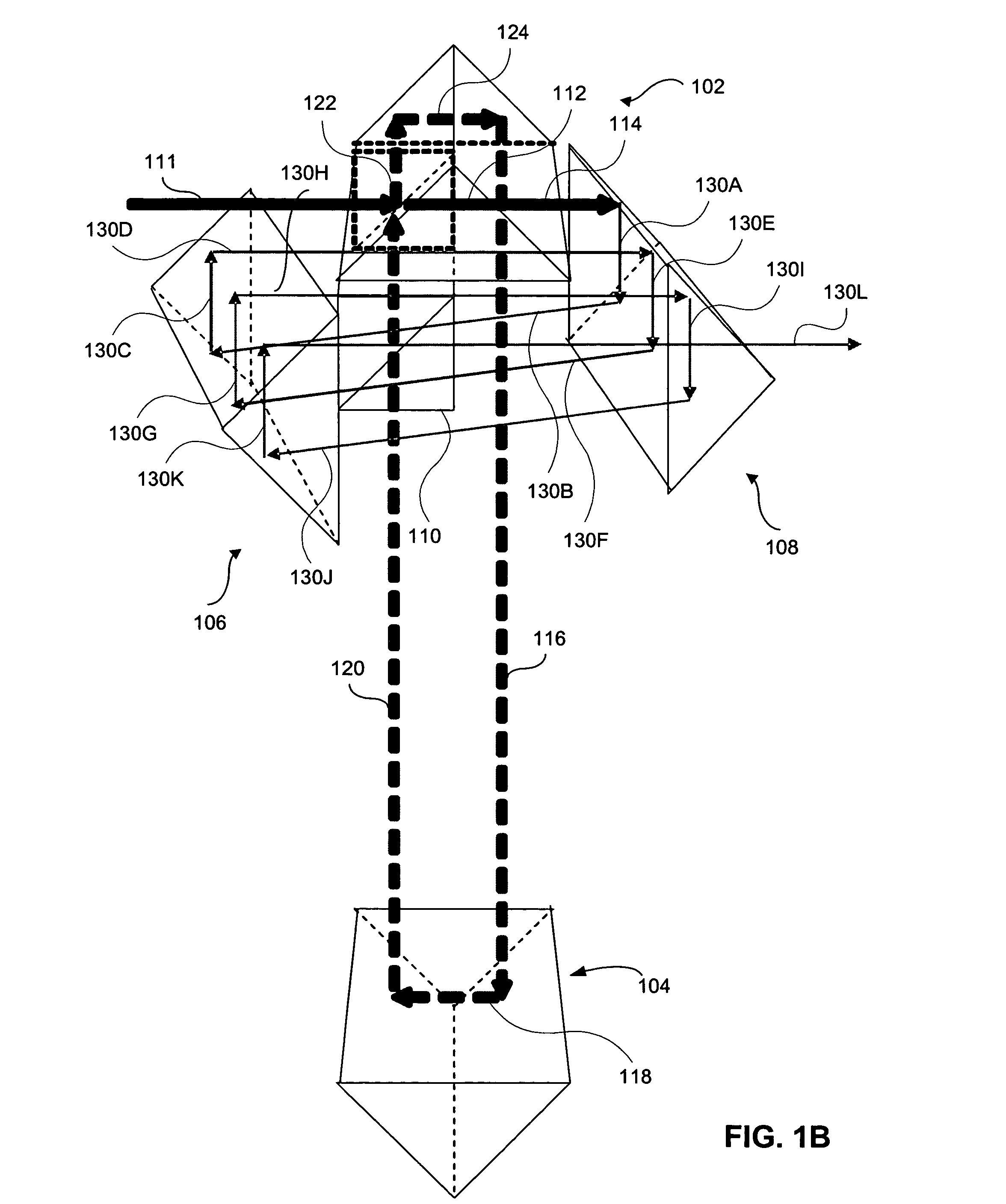
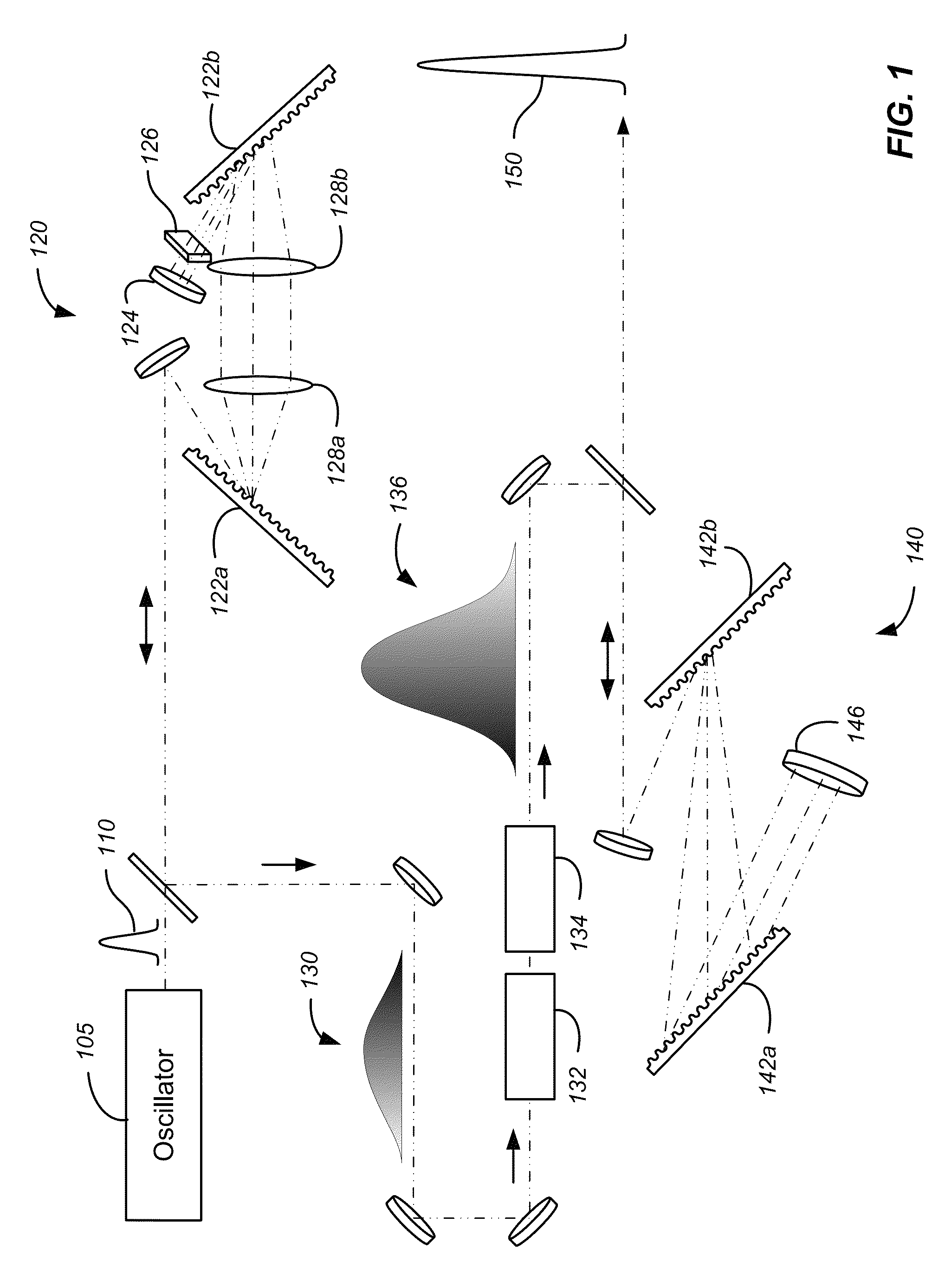
A method and apparatus for laser light pulse stretching is disclosed which may comprise a beam splitter in the path of a laser output light pulse beam; selected to pass a first percent of the energy of a first input pulse of the laser output light pulse beam along a laser output light pulse beam output path as a first output pulse and to reflect a second percent of the energy of the laser output light pulse beam into a first delayed beam; an optical delay path receiving the first delayed beam and returning the first delayed beam to the beam splitter in an orientation such that a third percent of the first delayed beam is reflected into the output path as a second output pulse and a fourth percent is passed into the optical delay path as a second delayed beam; the optical delay path receiving the second delayed beam and returning the second delayed beam to the beam splitter in an orientation such that the third percent of the second delayed beam is reflected into the output path as a third output pulse and the fourth percent of the second delayed beam is passed into the optical delay path as a third delayed beam; the optical delay path receiving the third delayed beam and returning the third delayed beam to the beam splitter in an orientation such that the third percent of the third delayed beam is reflected into the output path as a fourth output pulse; the first input pulse being a first pulse in a plurality of pulses output from a prior pulse stretcher, each of a plurality of succeeding input pulses comprising the output of the prior pulse stretcher resulting from the stretching of a narrow band laser light output pulse, forming successive first, second, third and fourth output pulses, the combination of which forms a pulse stretcher having an output with TIS of at least 200 ns. The optical delay path may be formed of a plurality of at least eight reflecting mirrors and contained in an elongated enclosure having first and second end plates mounting a first group of at least four of the at least eight reflecting mirrors mounted on the first mounting surface symmetrically about a center axis of the optical delay path and a second group of at least four of the at least eight reflecting mirrors mounted on the second mounting surface symmetrically about the center axis. The mirrors may be staggered in a predefined pattern, e.g., a circular pattern. The delay path may lie in a plurality of planes. The apparatus may be part of a laser system, part of a beam delivery system or an interface between the two.
Owner:CYMER INC
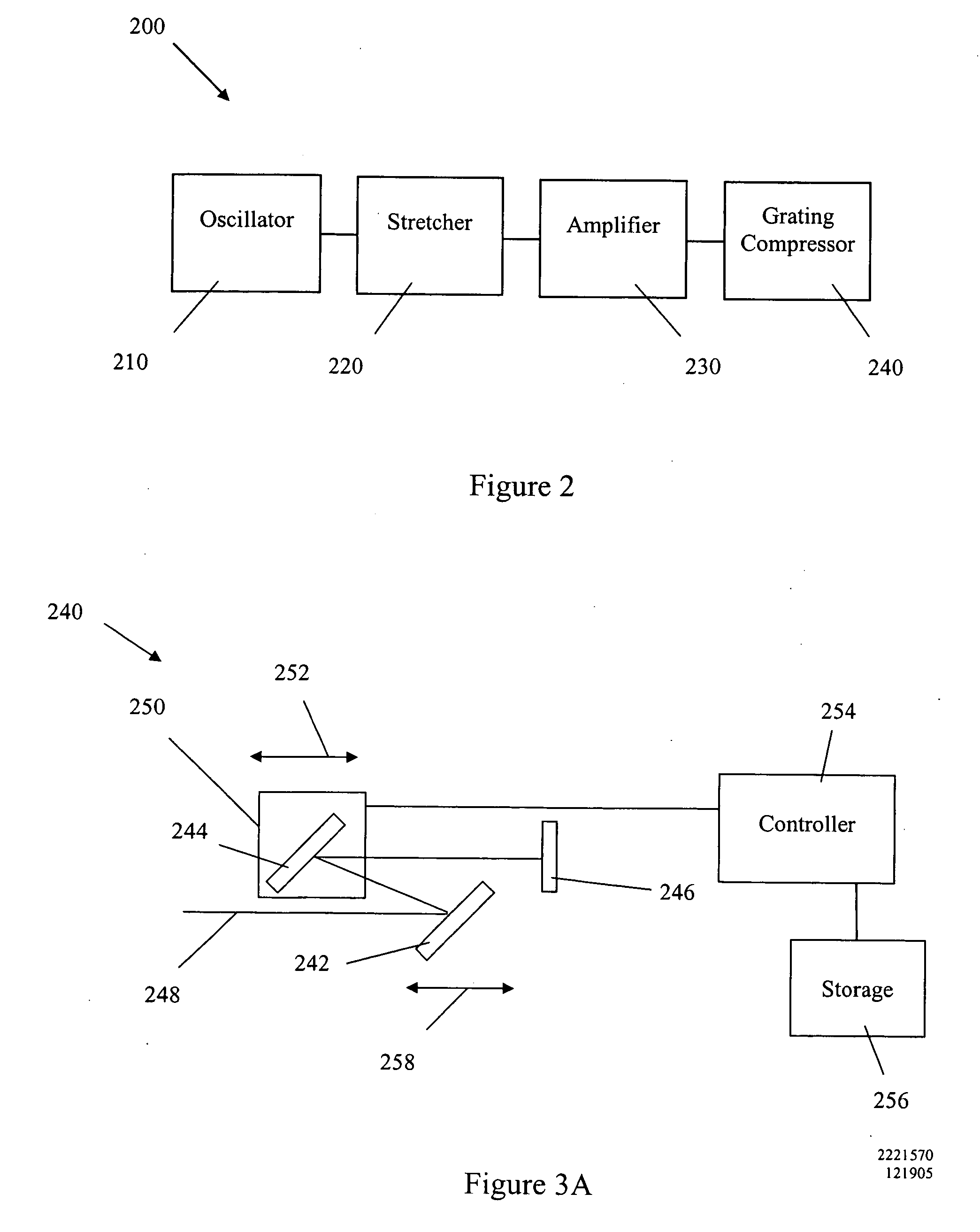
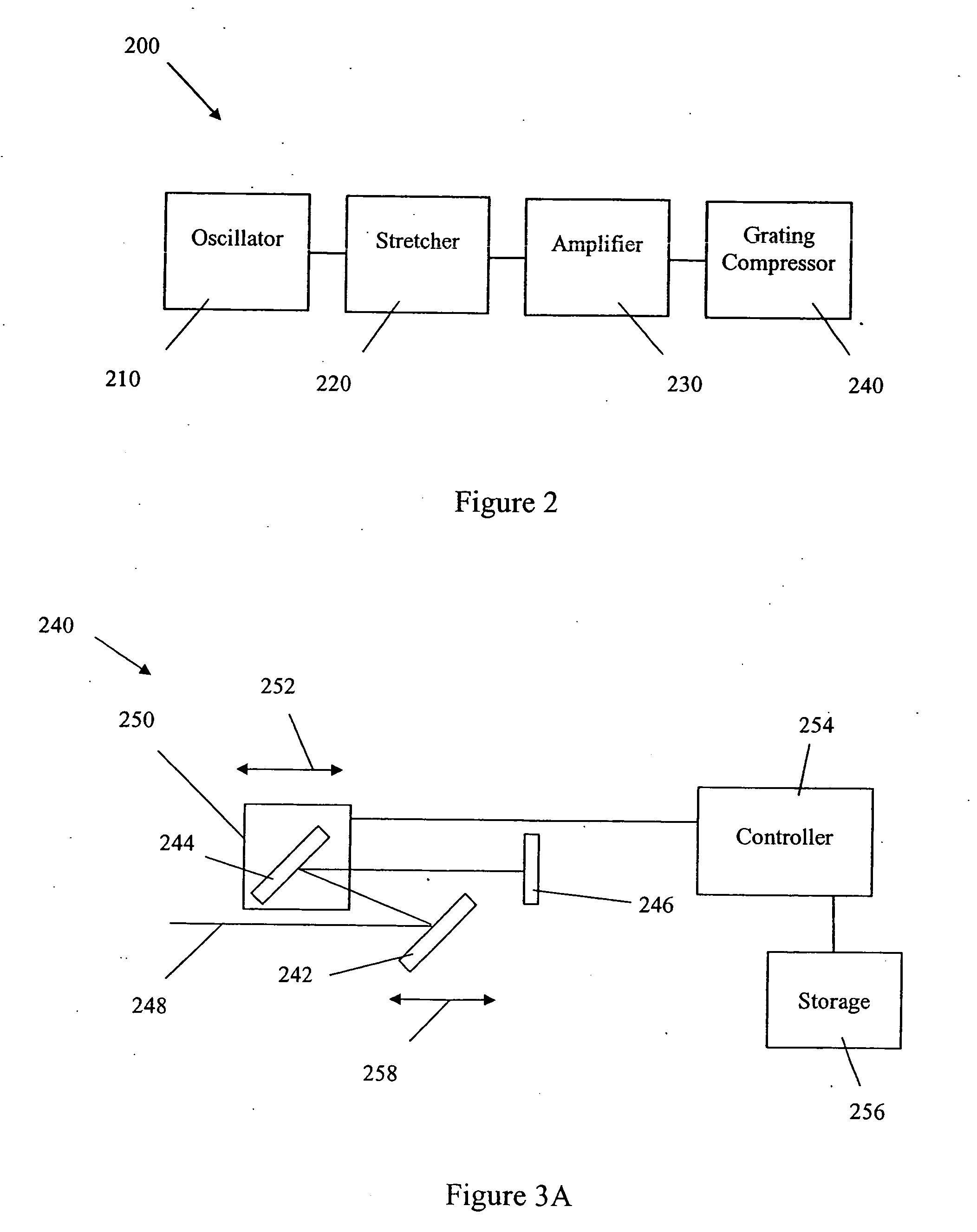
Pulsed laser source with adjustable grating compressor
ActiveUS20060159137A1Optimal pulse compressionOptical resonator shape and constructionOptical waveguide light guideFiberGrating
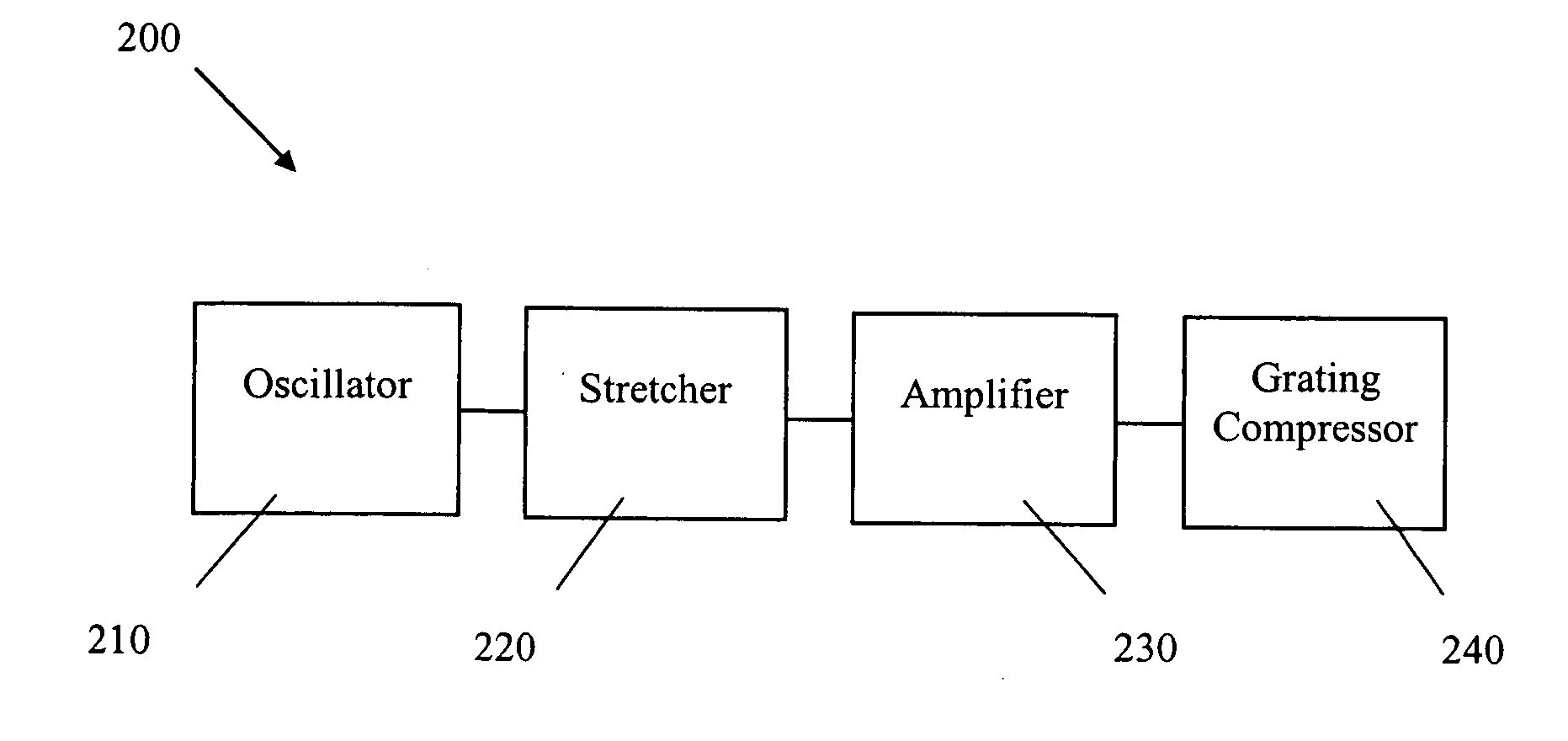
Various embodiments described herein relate to a laser source for producing a pulsed laser beam comprising a plurality of ultrashort optical pulses having a variable repetition rate. In one embodiment, the laser source comprises a fiber oscillator, which outputs optical pulses and a pulse stretcher disposed to receive the optical pulses. The optical pulses have an optical pulse width. The pulse stretcher has dispersion that increases the optical pulse width yielding stretched optical pulses. The laser source further comprises a fiber amplifier disposed to receive the stretched optical pulses. The fiber optical amplifier has gain so as to amplify the stretched optical pulses. The laser source includes an automatically adjustable grating compressor having dispersion that reduces the optical pulse width. The grating compressor automatically adjusts this dispersion for different repetition rates.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
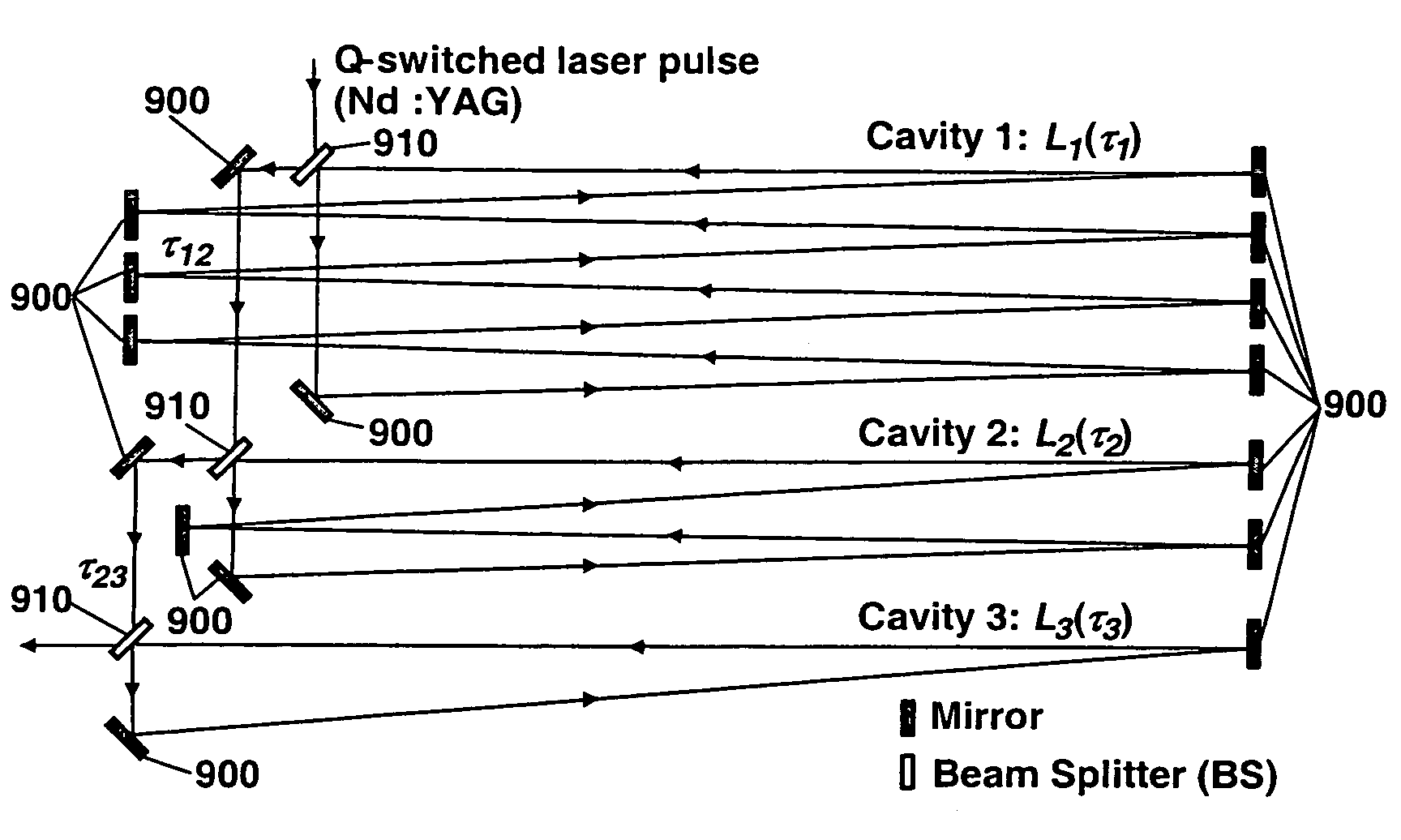
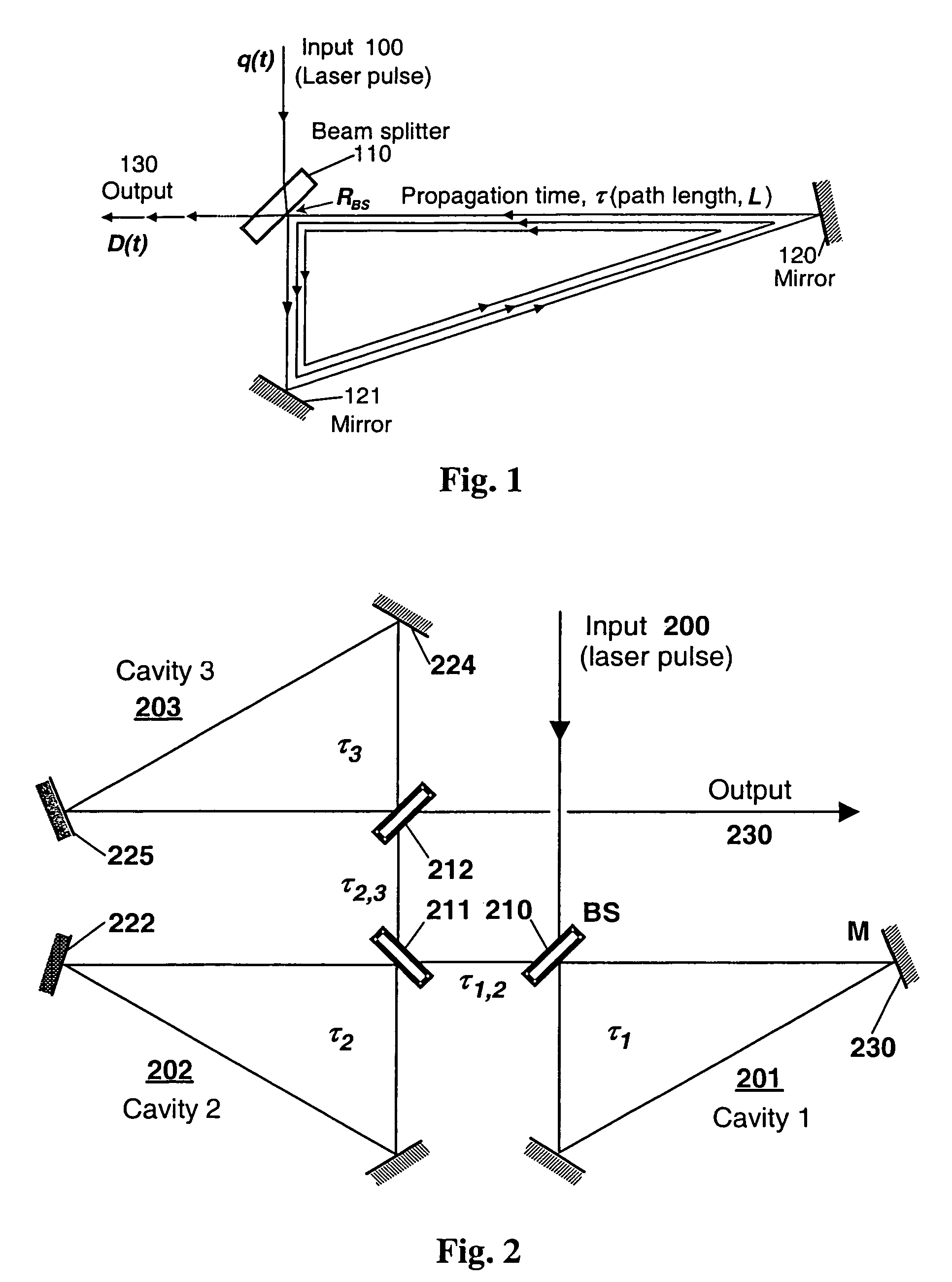
Temporal laser pulse manipulation using multiple optical ring-cavities
An optical pulse stretcher and a mathematical algorithm for the detailed calculation of its design and performance is disclosed. The optical pulse stretcher has a plurality of optical cavities, having multiple optical reflectors such that an optical path length in each of the optical cavities is different. The optical pulse stretcher also has a plurality of beam splitters, each of which intercepts a portion of an input optical beam and diverts the portion into one of the plurality of optical cavities. The input optical beam is stretched and a power of an output beam is reduced after passing through the optical pulse stretcher and the placement of the plurality of optical cavities and beam splitters is optimized through a model that takes into account optical beam divergence and alignment in the pluralities of the optical cavities. The optical pulse stretcher system can also function as a high-repetition-rate (MHz) laser pulse generator, making it suitable for use as a stroboscopic light source for high speed ballistic projectile imaging studies, or it can be used for high speed flow diagnostics using a laser light sheet with digital particle imaging velocimetry. The optical pulse stretcher system can also be implemented using fiber optic components to realize a rugged and compact optical system that is alignment free and easy to use.
Owner:NASA
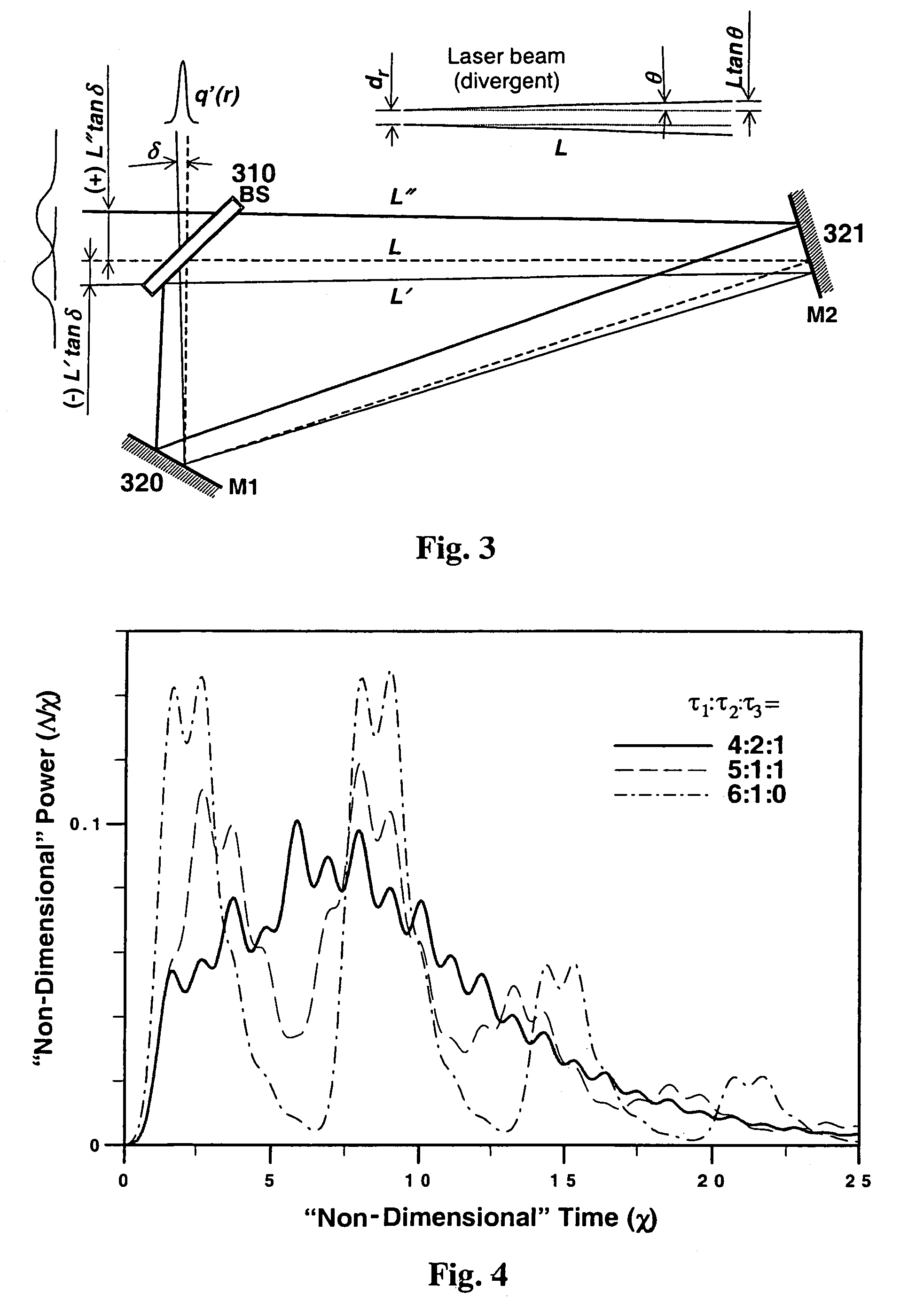
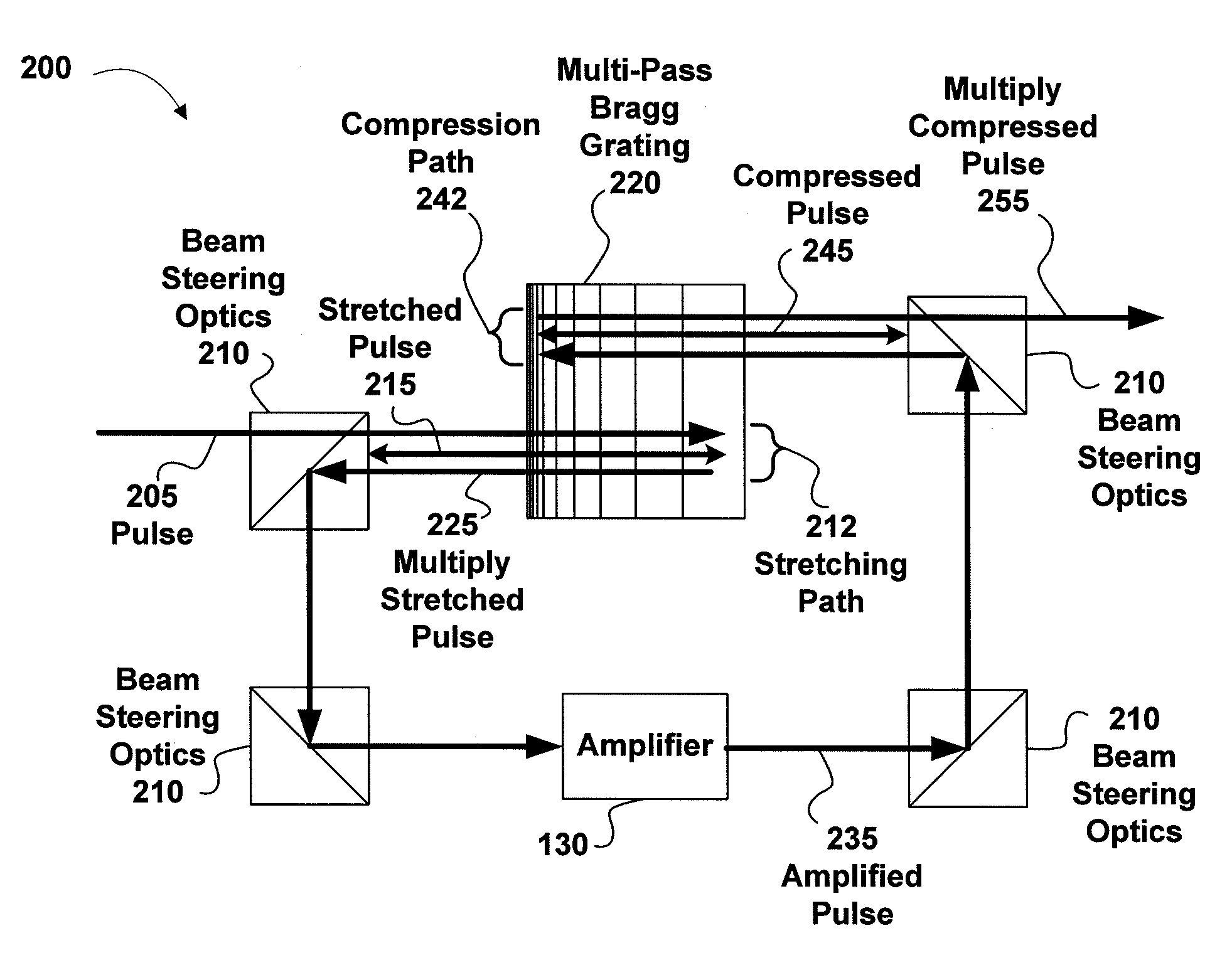
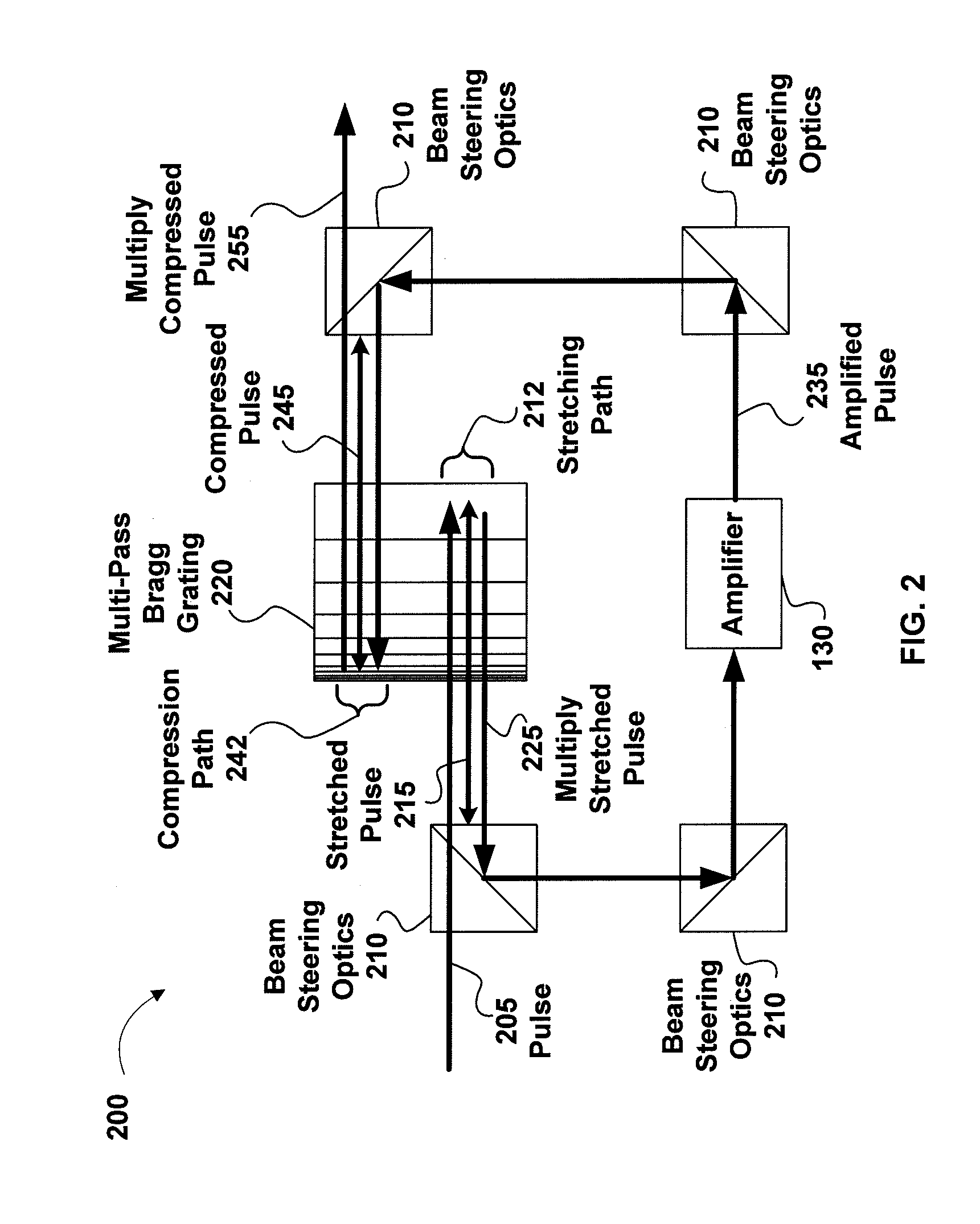
Pulse stretcher and compressor including a multi-pass Bragg grating
A chirped pulse amplification (CPA) system and method is described wherein the pulse is stretched using multiple passes through a Bragg grating or compressed using multiple passes through a Bragg grating. A switch may be used to control the number of passes through the Bragg grating, thus, tuning the compressed or the stretched pulse width. The pulse may be directed through an amplifier between the multiple passes through the Bragg grating to apply amplification to the stretched pulse multiple times. The Bragg grating may include a fiber Bragg grating, a volume Bragg grating, or a Bragg waveguide.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Laser output light pulse stretcher
InactiveUS7369597B2Photomechanical apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionMetrologySpatial coherency
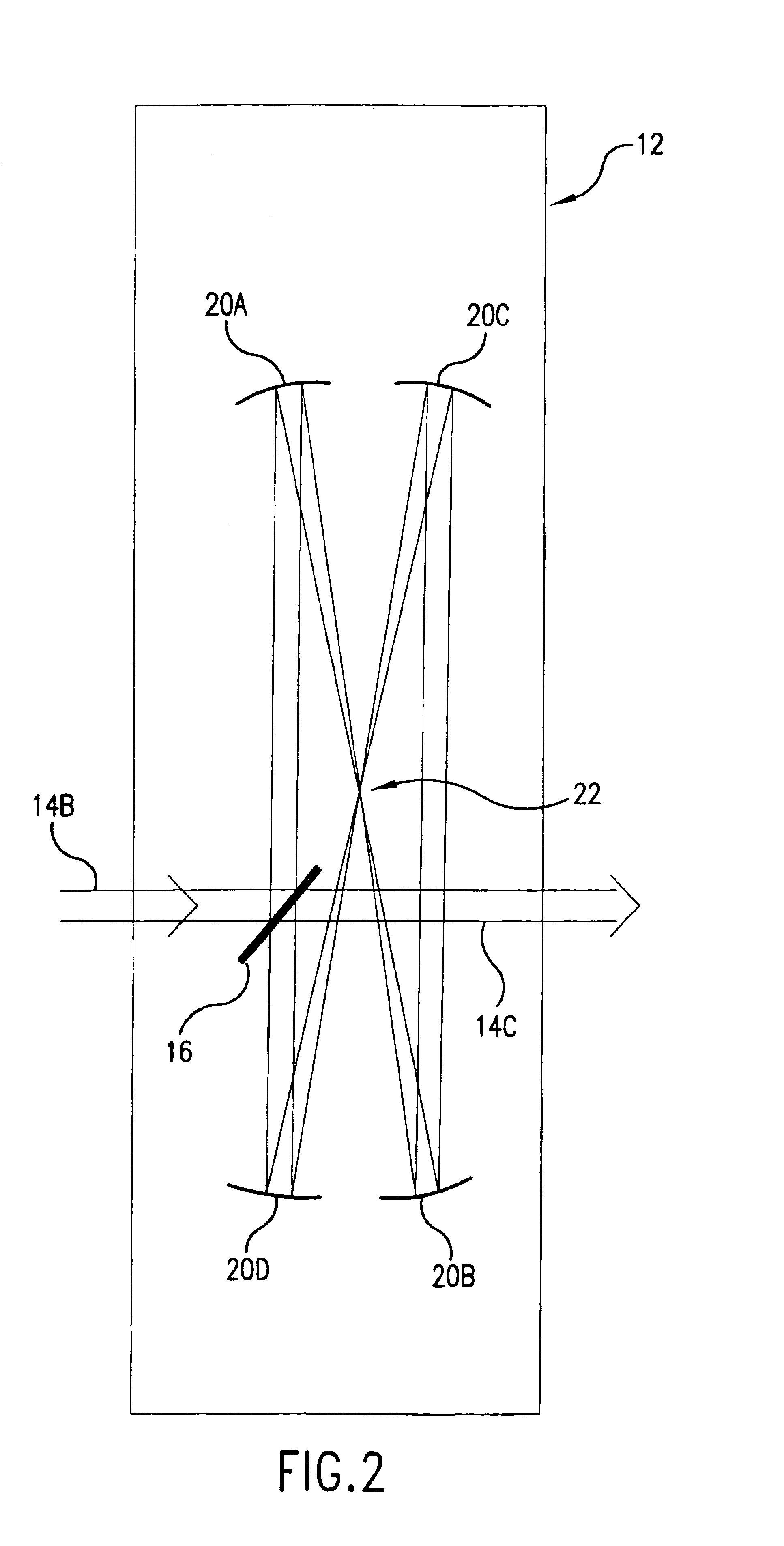
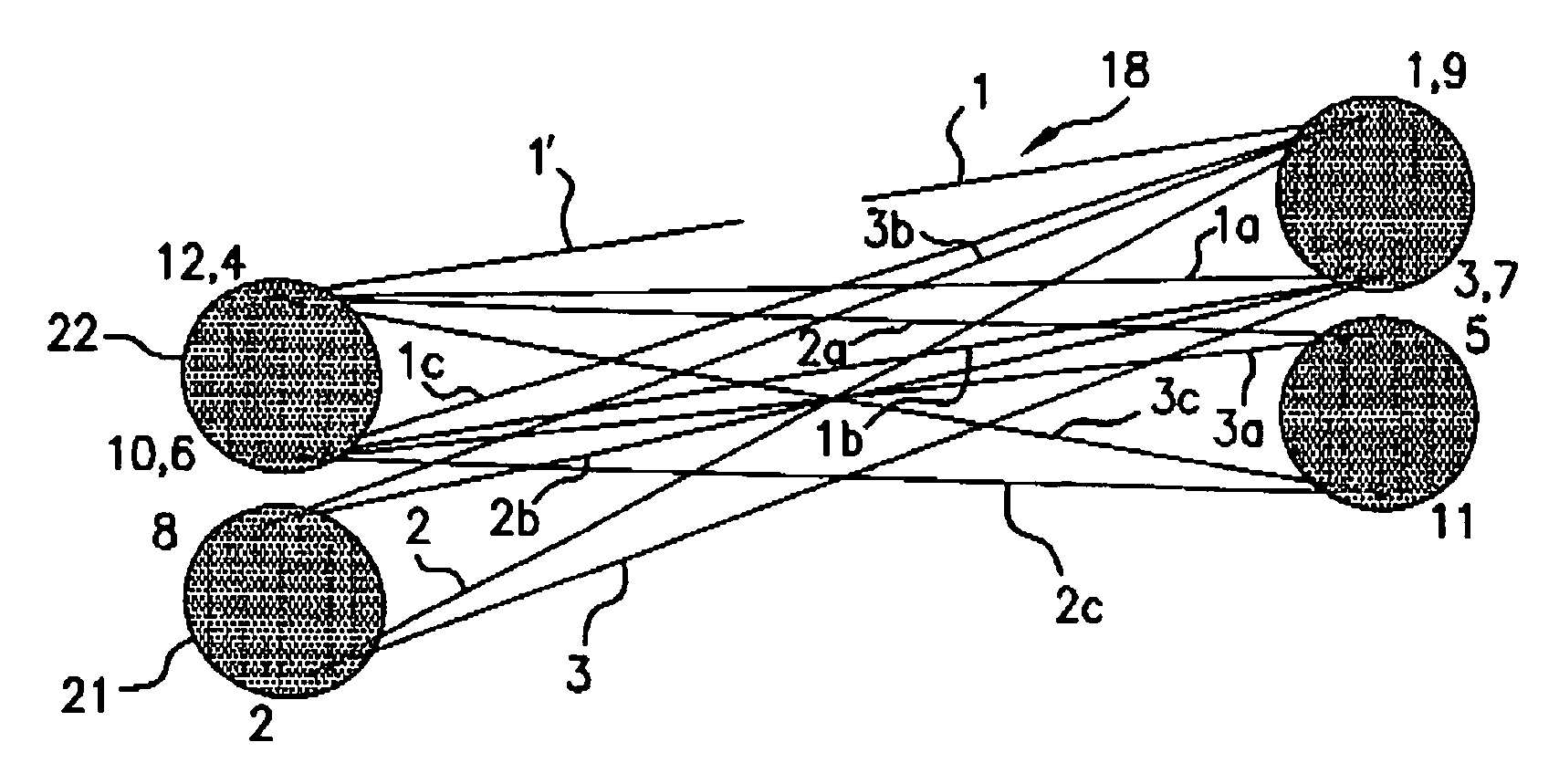
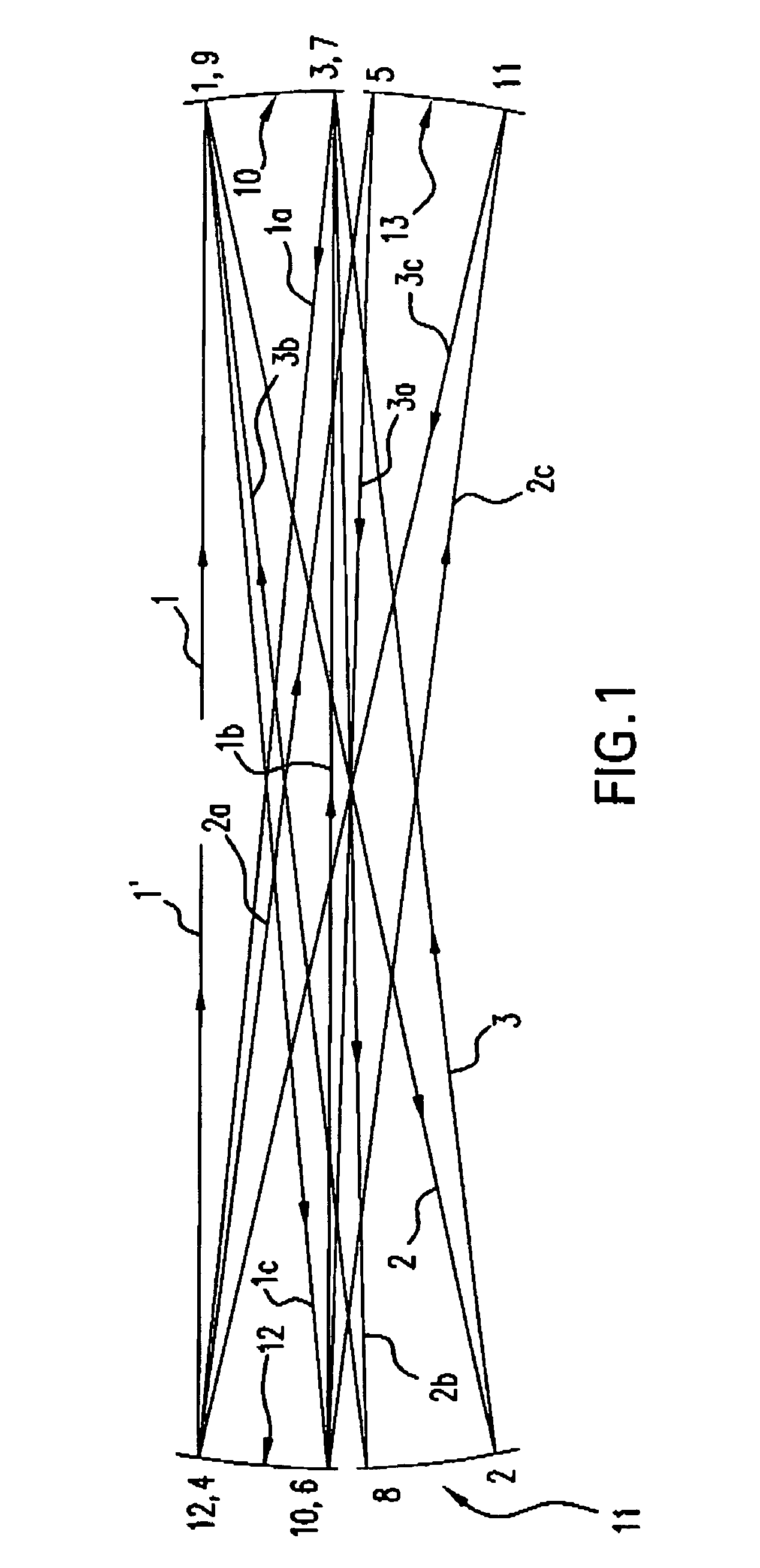
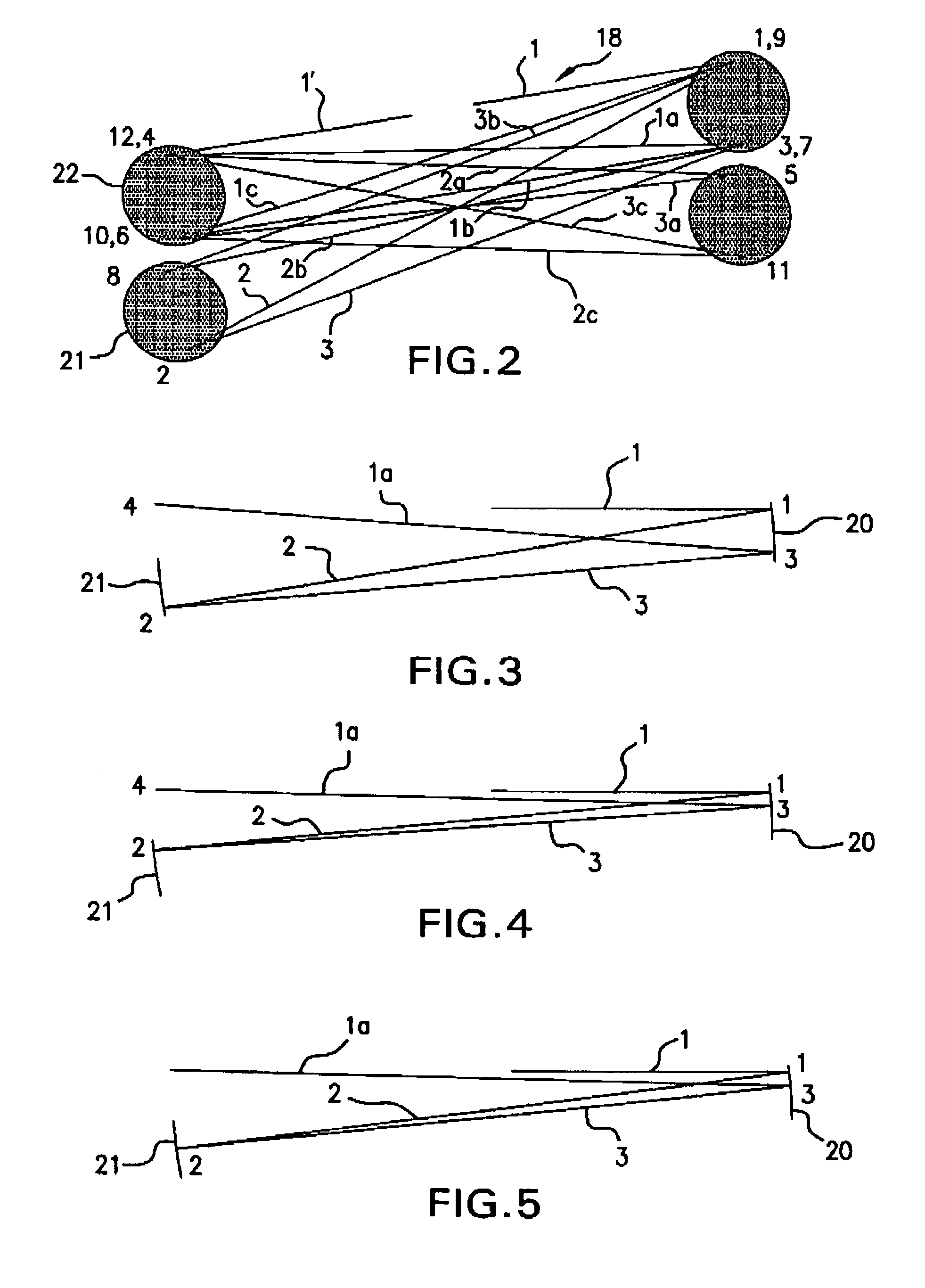
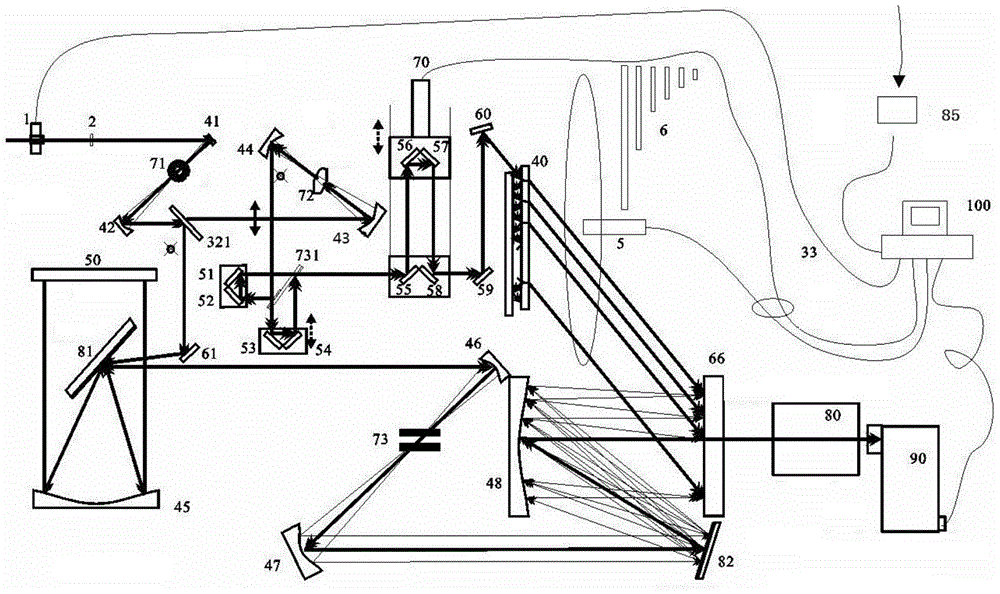
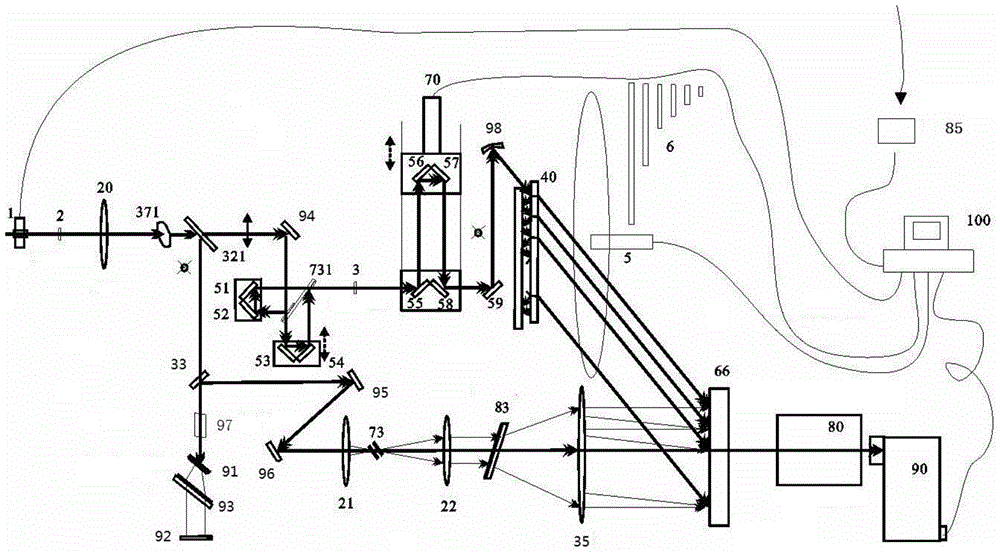
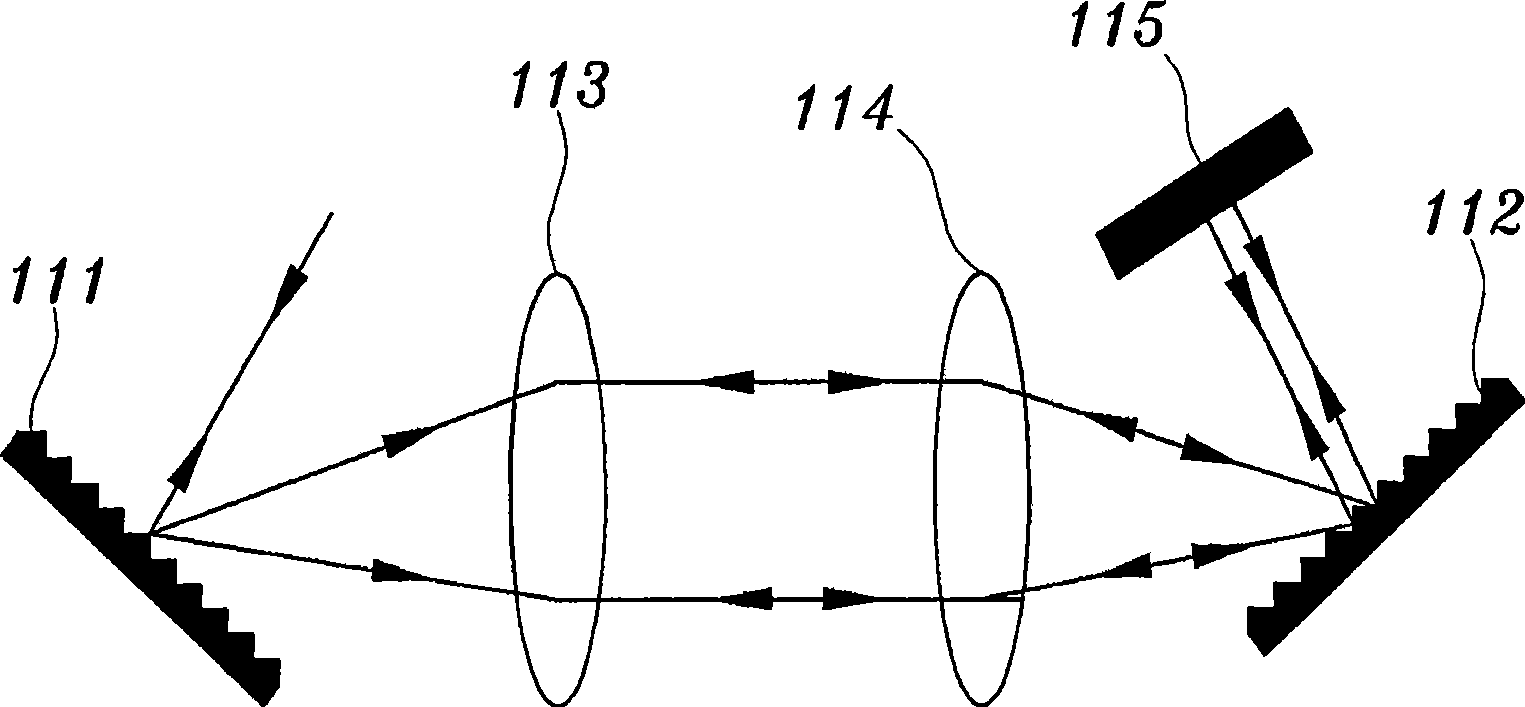
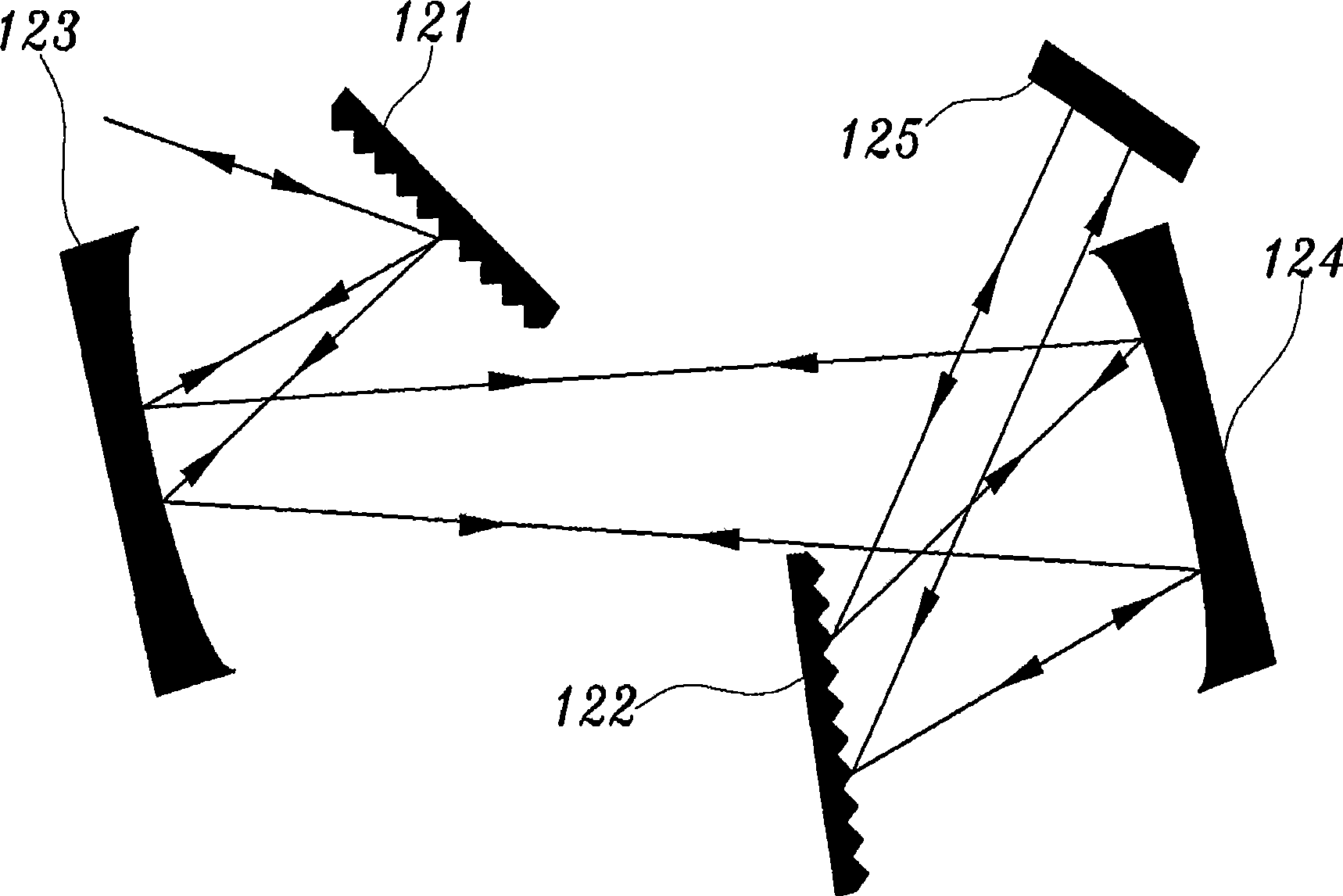
Providing a high peak power short pulse duration gas discharge laser output pulse comprises a pulse stretcher a laser output pulse optical delay initiating optic diverting a portion of the output laser pulse into an optical delay having an optical delay path and comprising a plurality of confocal resonators in series aligned to deliver an output of the optical delay to the laser output pulse optical delay initiating optic. The plurality of confocal resonators comprises four confocal resonators comprising a twelve pass four mirror arrangement. An apparatus and method may comprise a plurality, e.g., two pulse stretchers in series and may include spatial coherency metrology.
Owner:CYMER INC
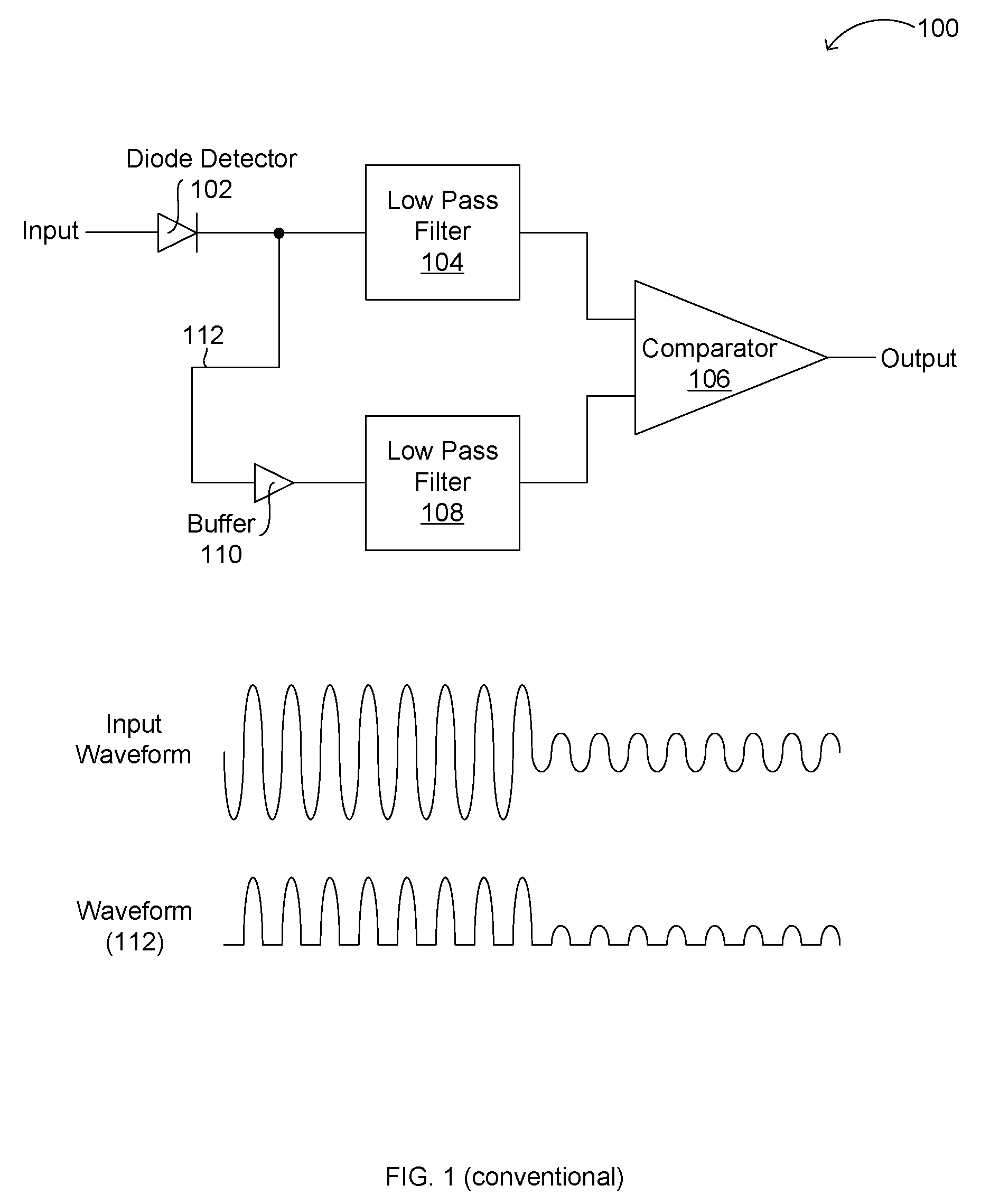
Sampling demodulator for amplitude shift keying (ASK) radio receiver
InactiveUS7885359B2Efficient integrationReliable and simplified ASKAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRadio receiver designRadio reception
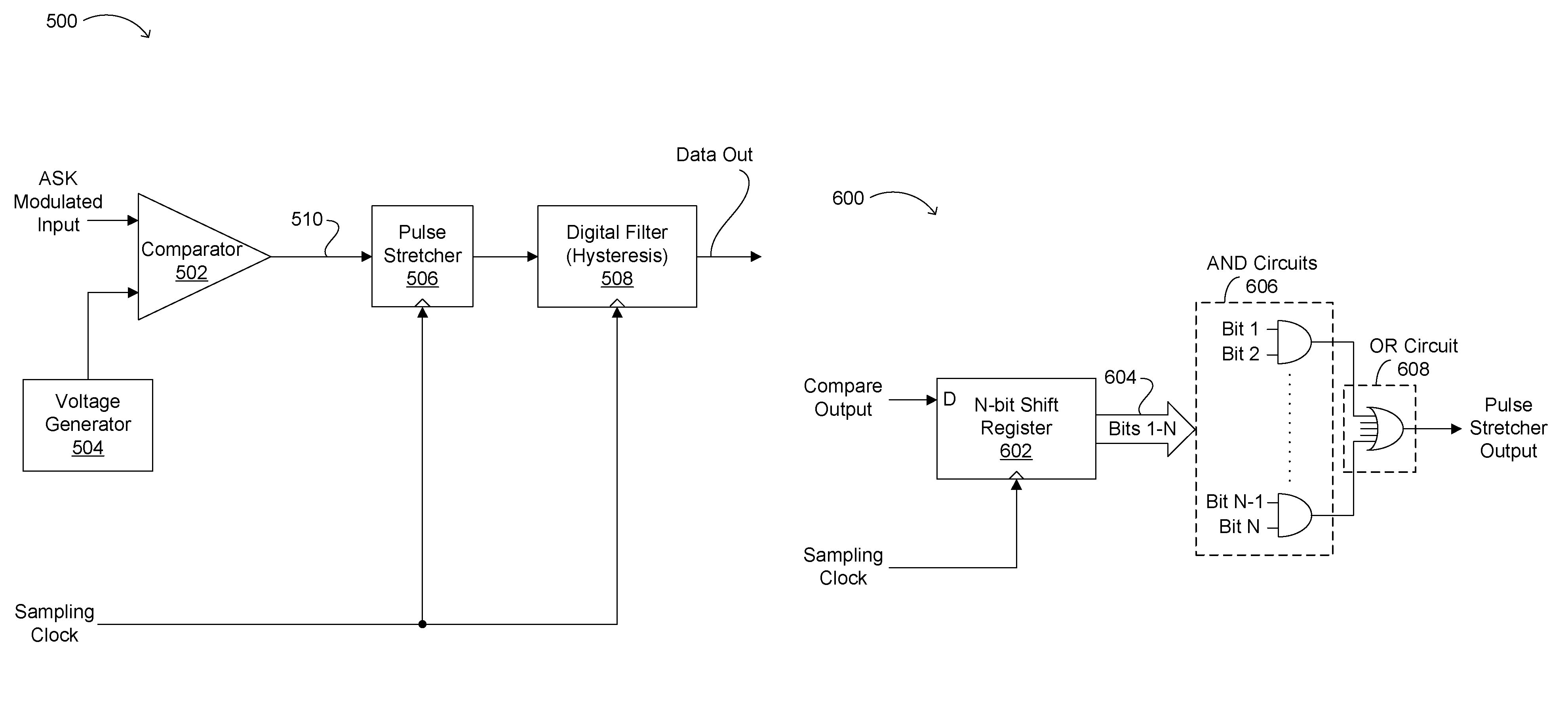
A method, algorithm, circuits, and / or systems for amplitude shift keying (ASK) modulation are disclosed. In one embodiment, a sampling demodulator includes a comparator configured to compare an ASK modulated input to a predetermined voltage level and provide a comparison result, a pulse stretcher with a sampler configured to sample the comparison result a plurality of times for each of a plurality of cycles of the ASK modulated input to generate a bit stream and digital logic configured to determine a value for each data bit in the ASK modulated input from the bit stream, and a digital filter configured to filter an output of the digital logic, thereby providing a demodulated signal.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
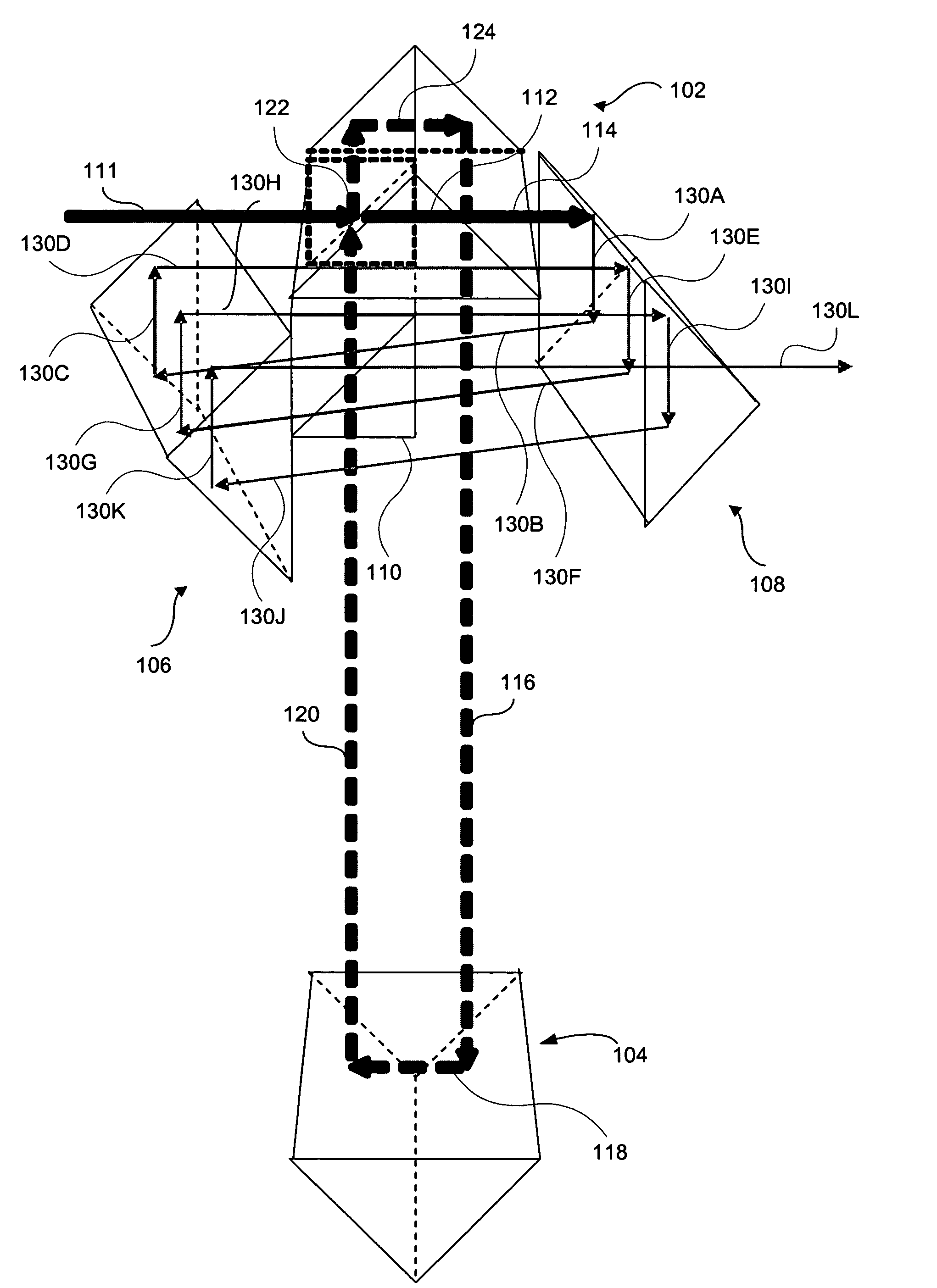
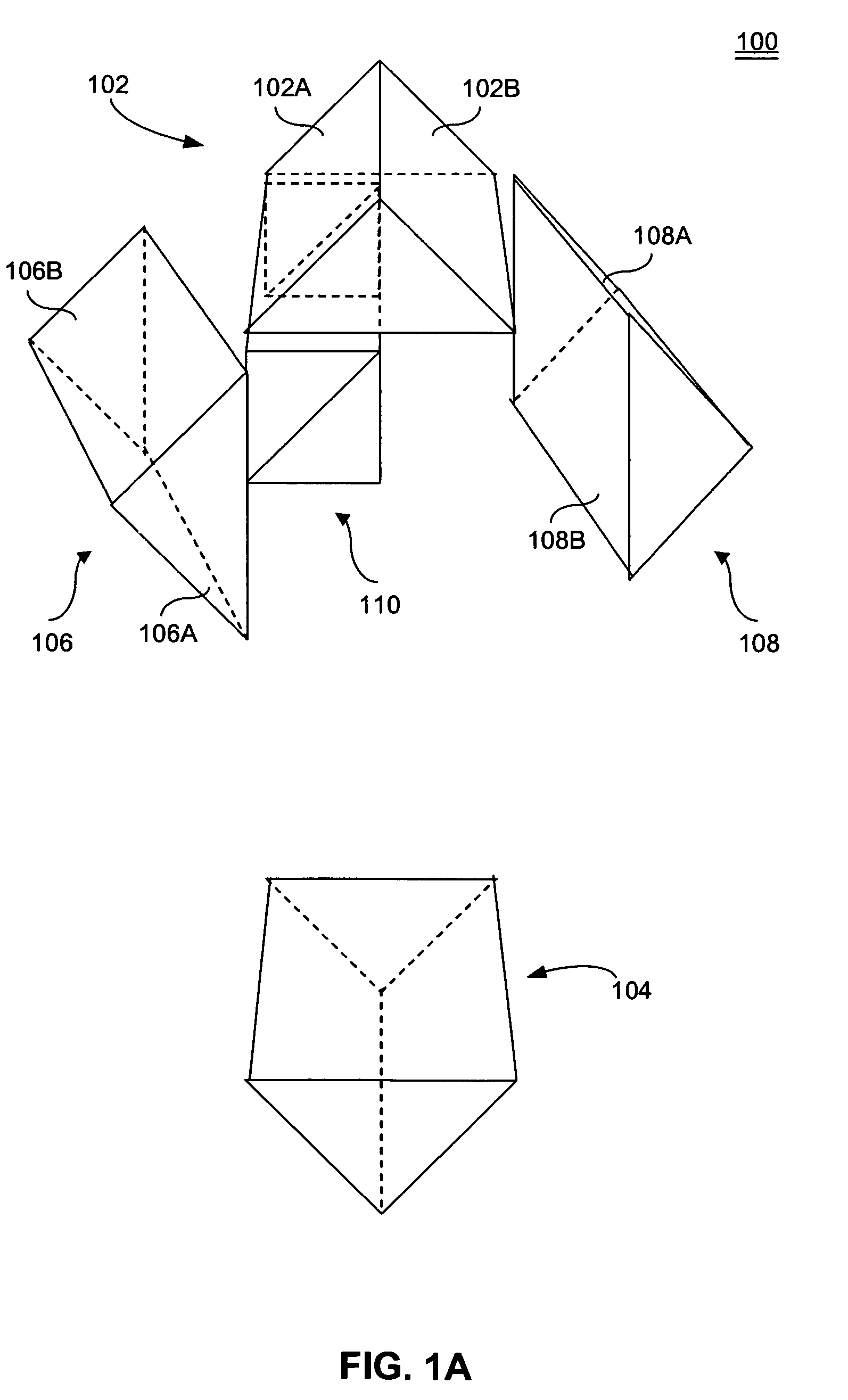
Helical optical pulse stretcher
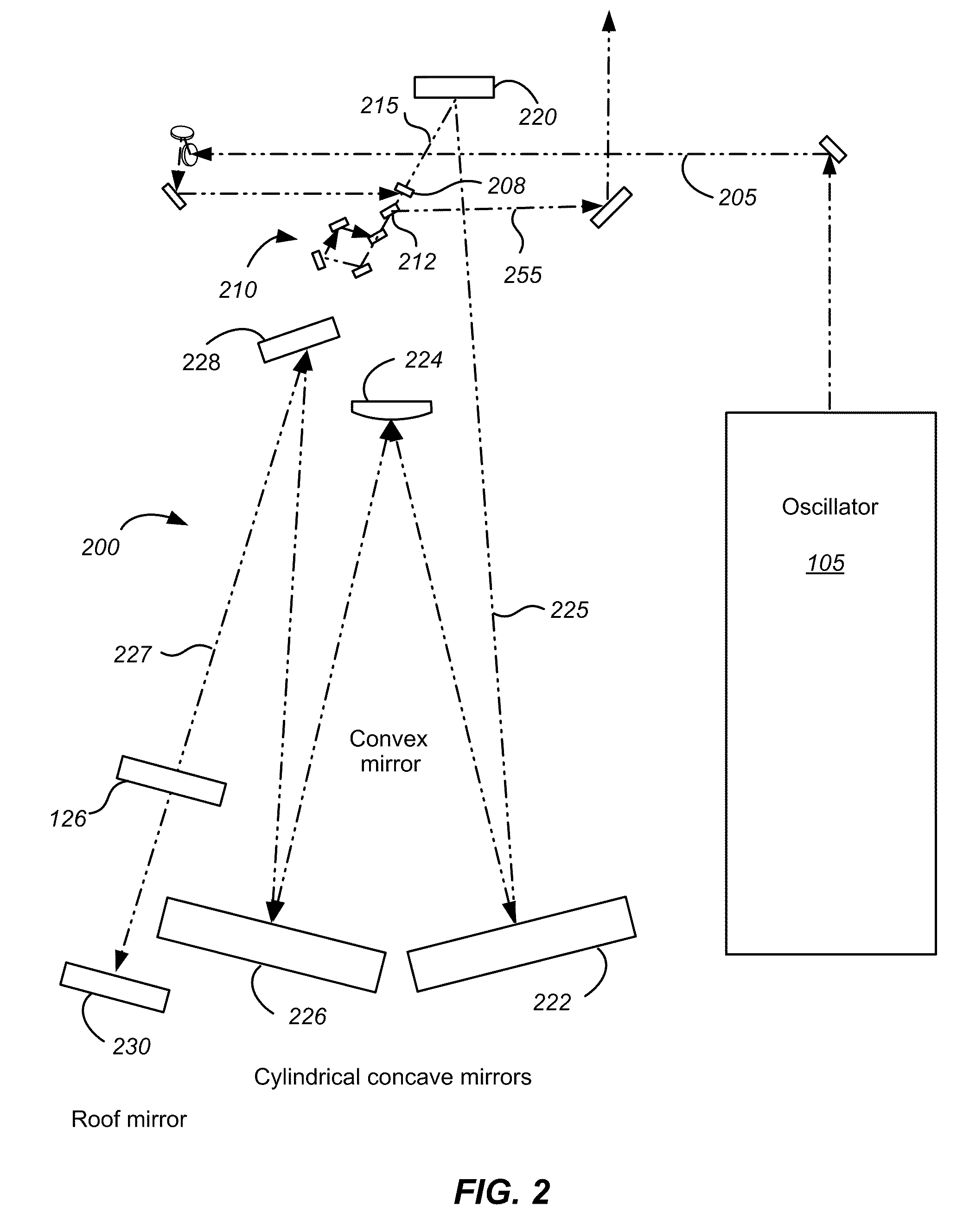
A pulse stretcher includes a single pass pulse stretcher. An optical system is arranged around the single pass pulse stretcher. A beam enters the single pass stretcher and is reflected in a helical path using the optical system for multiple passes through the single pass pulse stretcher. The single pass pulse stretcher can include two 90° prisms, with a beam splitter located therebetween. The optical system can include first and second prisms. At least one of the first and second prisms can be a roof prism. The first and second prisms can have at least one surface oriented so as to direct the beam into the helical path. The optical system can have at least one mirror, or a plurality of mirrors.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Ultrahigh energy short pulse lasers
ActiveUS20070171945A1Improve reliabilityLaser using scattering effectsAudio power amplifierHybrid amplifier
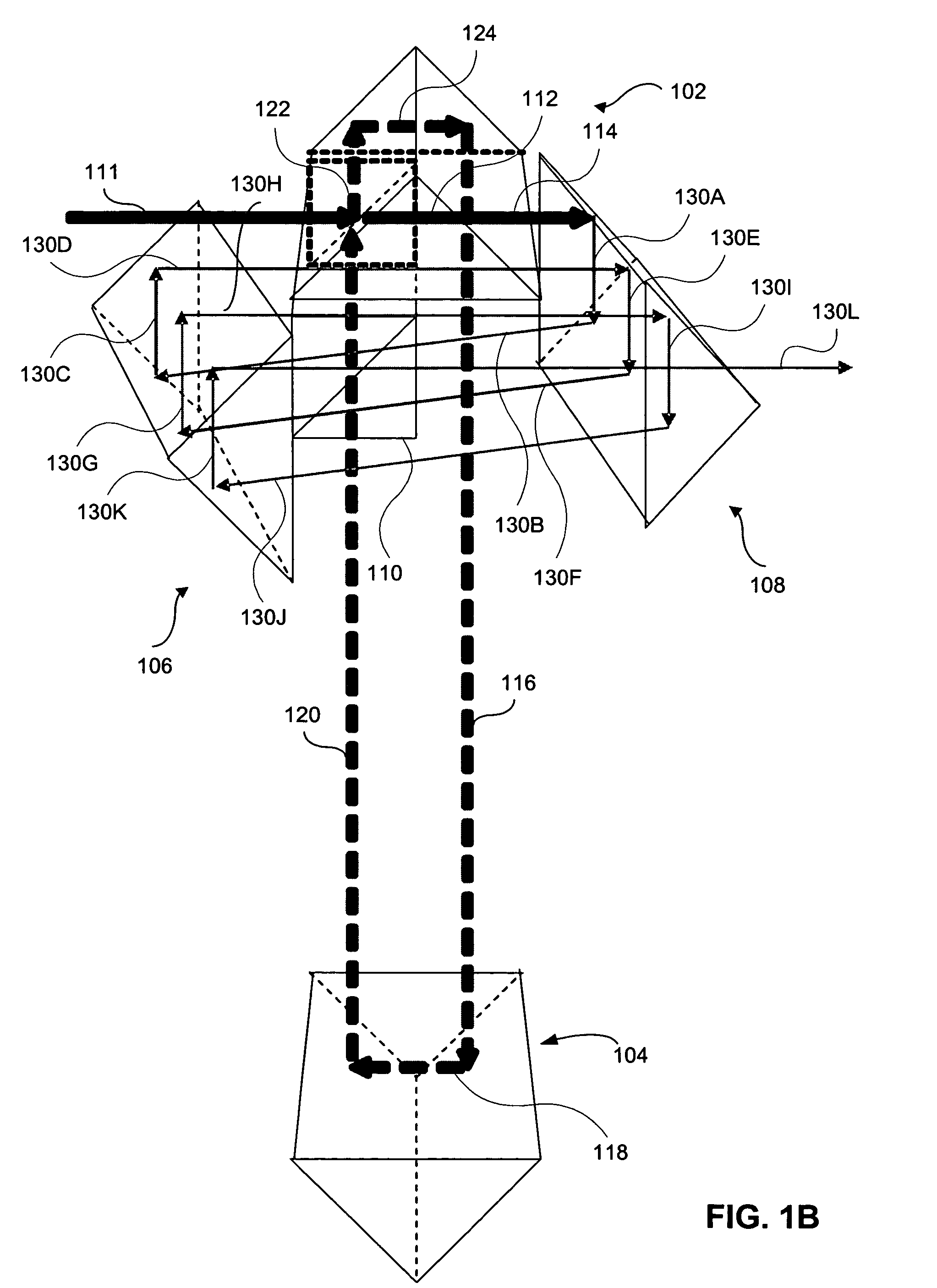
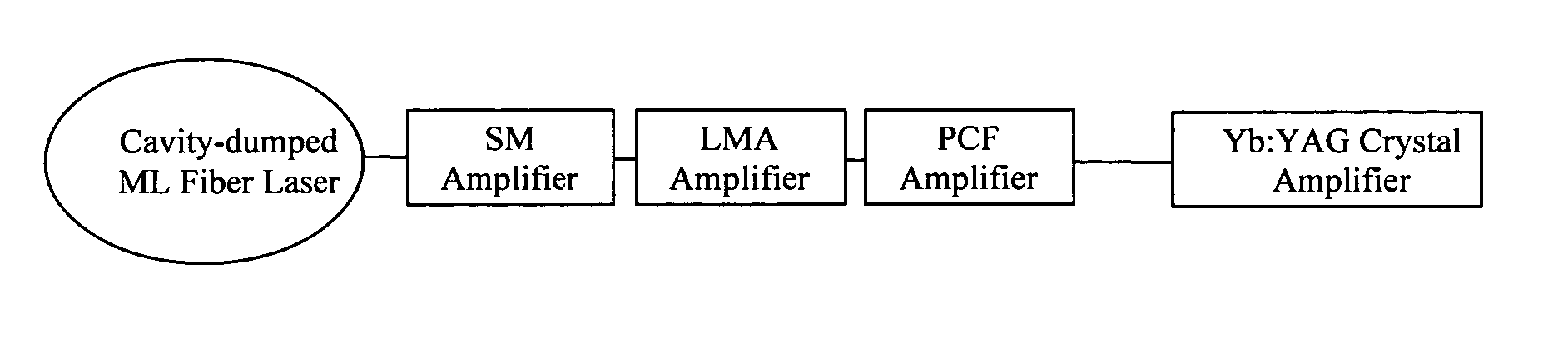
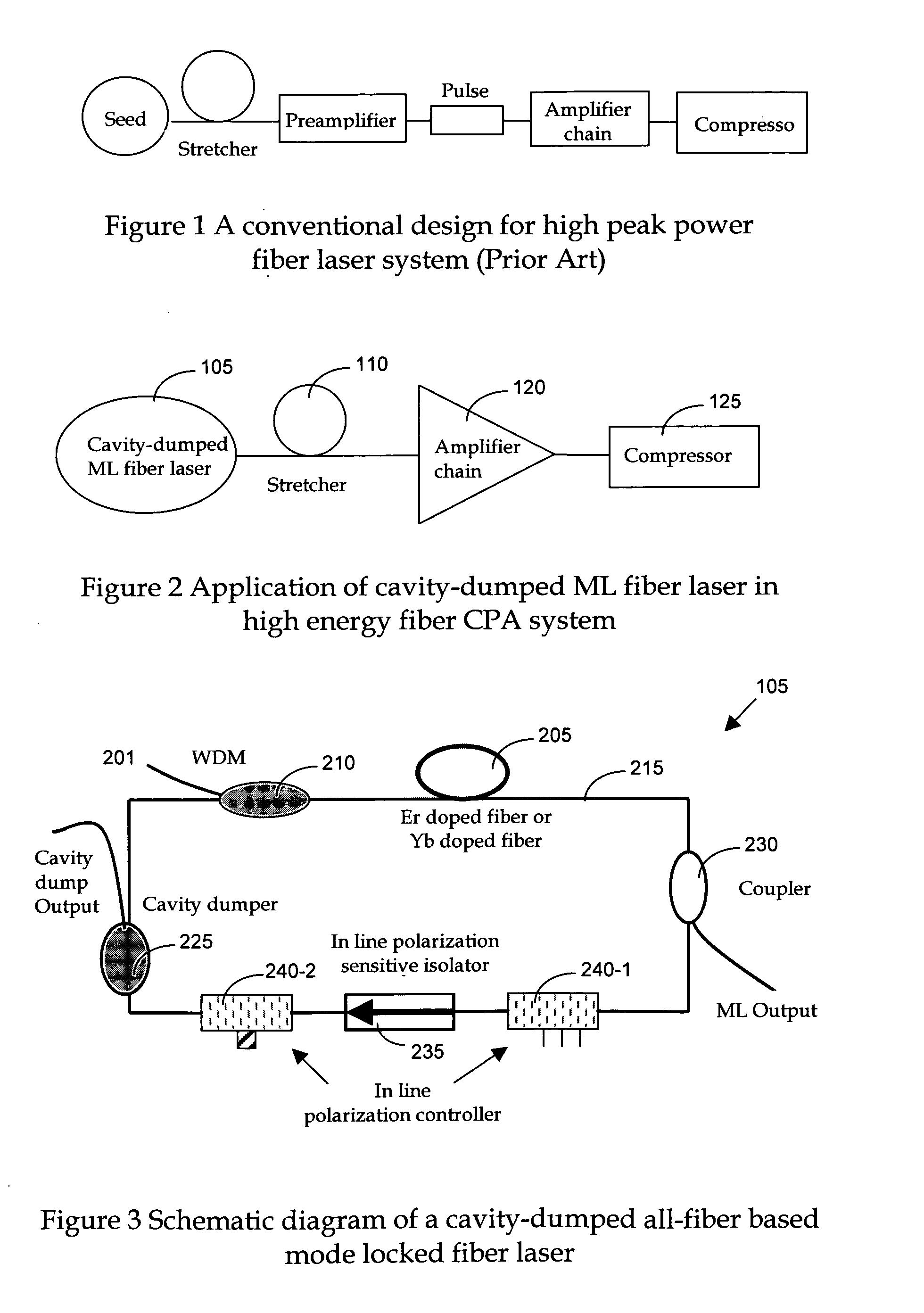
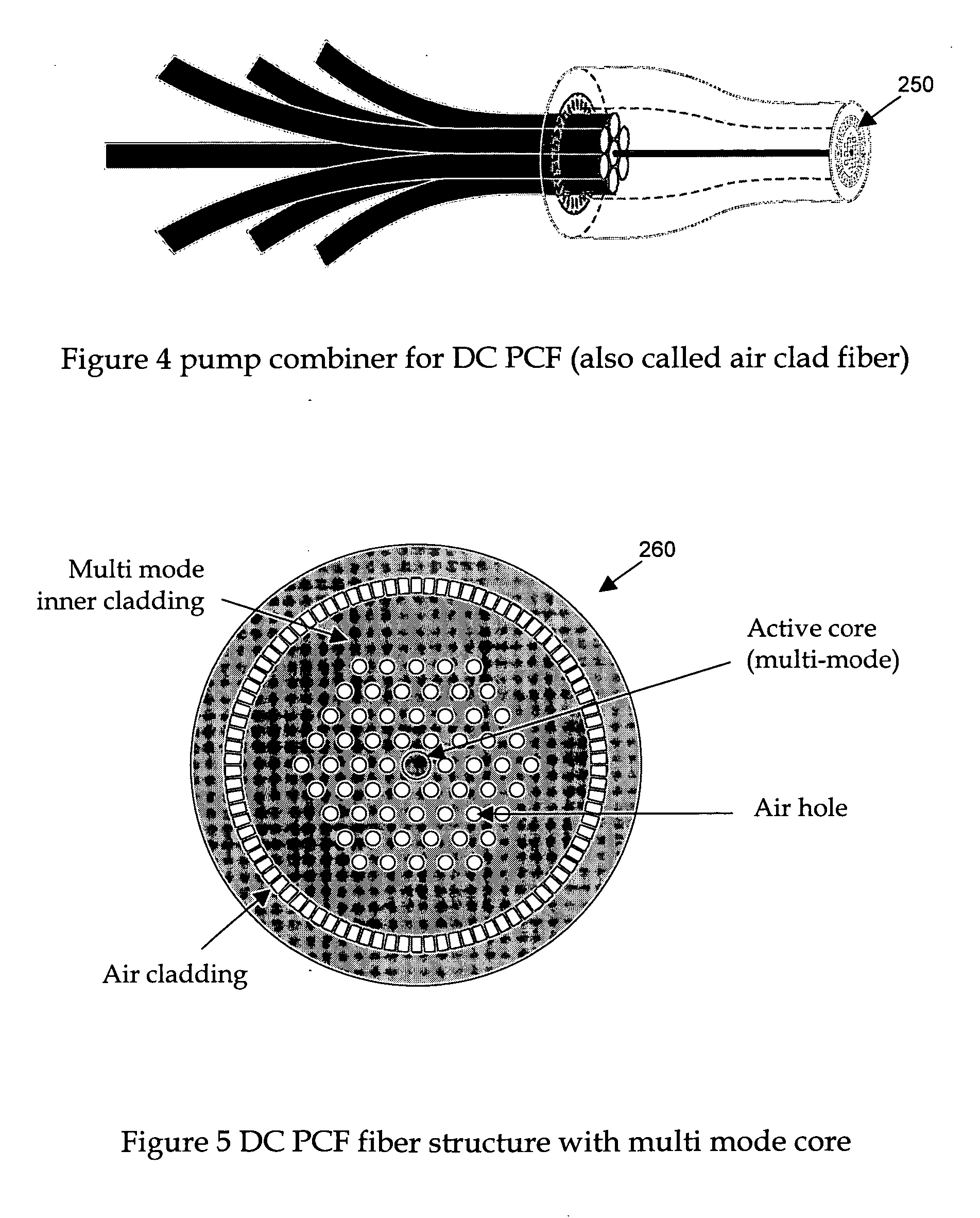
A Chirped pulse amplification (CPA) fiber laser system. The CPA fiber laser system includes a fiber mode-locking (ML) oscillator implemented as a cavity dumped ML oscillator including a cavity dumper for generating a seed laser at a reduced repetition rate to project to a pulse stretcher for stretching a pulse width of the laser. The CPA fiber laser system further includes a multistage amplifier chain for generating an amplified laser to project to a compressor for compressing the amplified laser. The multistage amplifier chain further includes a hybrid amplifier includes a solid-state amplifier to generate a laser of approximately 1˜10 mJ for a 10-100 KHz repetition rate.
Owner:POLARONYX
Double-pass imaging pulse-stretcher
InactiveUS20060216037A1Reduce peak powerLong durationLaser detailsElectromagnetic transmissionLight beamPrism
A pulse-stretcher has an optical delay loop including a beamsplitter. The beamsplitter divides an input pulse into a temporal sequence of pulse replicas, a first of which is transmitted by the beamsplitter and the remainder of which are reflected by the beamsplitter along the path of the transmitted replica. The sequence of replicas form an initially stretched pulse having a longer duration and lower peak power than the input pulse. A prism cooperative with the delay loop reflects the initially stretched pulse back into the delay loop along a path laterally displaced from the replica path. The beamsplitter divides the initially stretched pulse into a temporal sequence of pulse replicas propagating along a common path to form a finally stretched pulse, having a longer duration and a lower peak power than the initially stretched pulse. The finally stretched pulse has a sequence of power peaks. Peak power in the pulse is minimized when the beamsplitter reflectivity is selected such that the power of the first two of these peaks is equal.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Laser output light pulse stretcher
ActiveUS20050105579A1Photomechanical apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionMetrologyLithographic artist
An apparatus and method for providing a high peak power short pulse duration gas discharge laser output pulse is disclosed which may comprise a pulse stretcher which may comprise a laser output pulse optical delay initiating optic diverting a portion of the output laser pulse into an optical delay having an optical delay path and comprising; a plurality of confocal resonators in series aligned to deliver an output of the optical delay to the laser output pulse optical delay initiating optic. The plurality of confocal resonators comprises four confocal resonators comprising a twelve pass four mirror arrangement. Each of the plurality of confocal resonators may comprise a first concave spherical mirror having a radius of curvature and a second concave spherical mirror having the same radius of curvature and separated by the radius of curvature. The pulse stretcher may comprise a first confocal resonator cell which may comprise: a first concave spherical mirror having a radius of curvature receiving an input beam from the laser output pulse optical delay initiating optic comprising the portion of the output laser pulse at a first point on a face of the first concave spherical mirror and generating a first reflected beam; a second concave spherical mirror having the same radius of curvature and separated from the first concave spherical mirror by the radius of curvature and receiving the first reflected beam at a first point on a face of the second concave spherical mirror and generating a second reflected beam incident on a second point on the face of the first concave spherical mirror, the second reflected beam being reflected by the first concave spherical mirror from the second point on the first mirror to form an output beam from the first confocal resonator cell; and, a second confocal resonator cell receiving the output beam of the first confocal resonator cell as an input beam of the second confocal resonator cell. The apparatus and method may form part of a beam delivery unit and may be part of an integrated circuit lithography lights source or an integrated circuit lithography tool. The apparatus and method may comprise a plurality, e.g., two pulse stretchers in series and may include spatial coherency metrology.
Owner:CYMER INC
Novel method and device for measuring ultra-short optical pulse spectrum phase
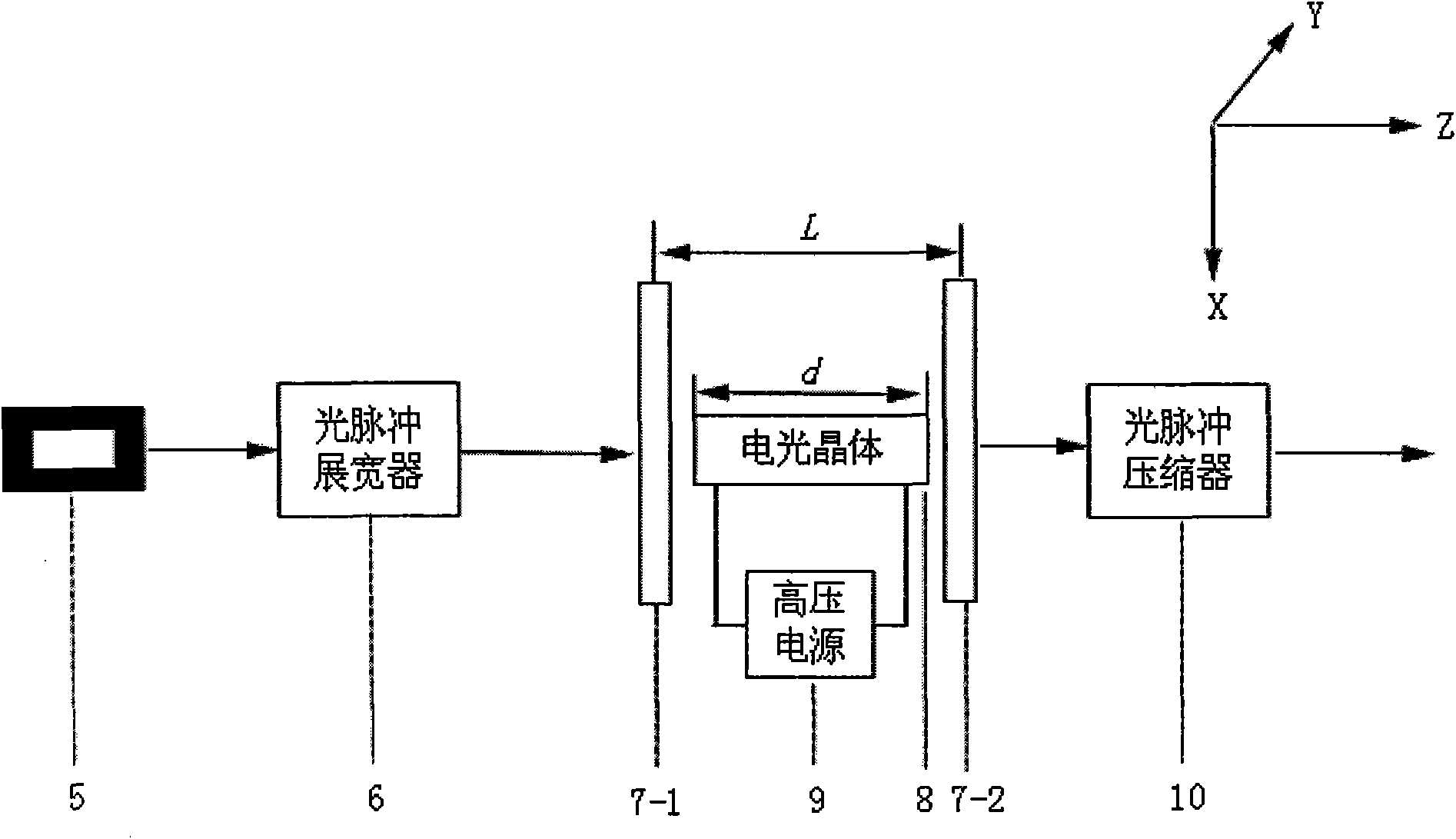
InactiveCN101294850AAvoid restrictionsEliminate the phase difference problemOptical measurementsFrequency spectrumPhase difference
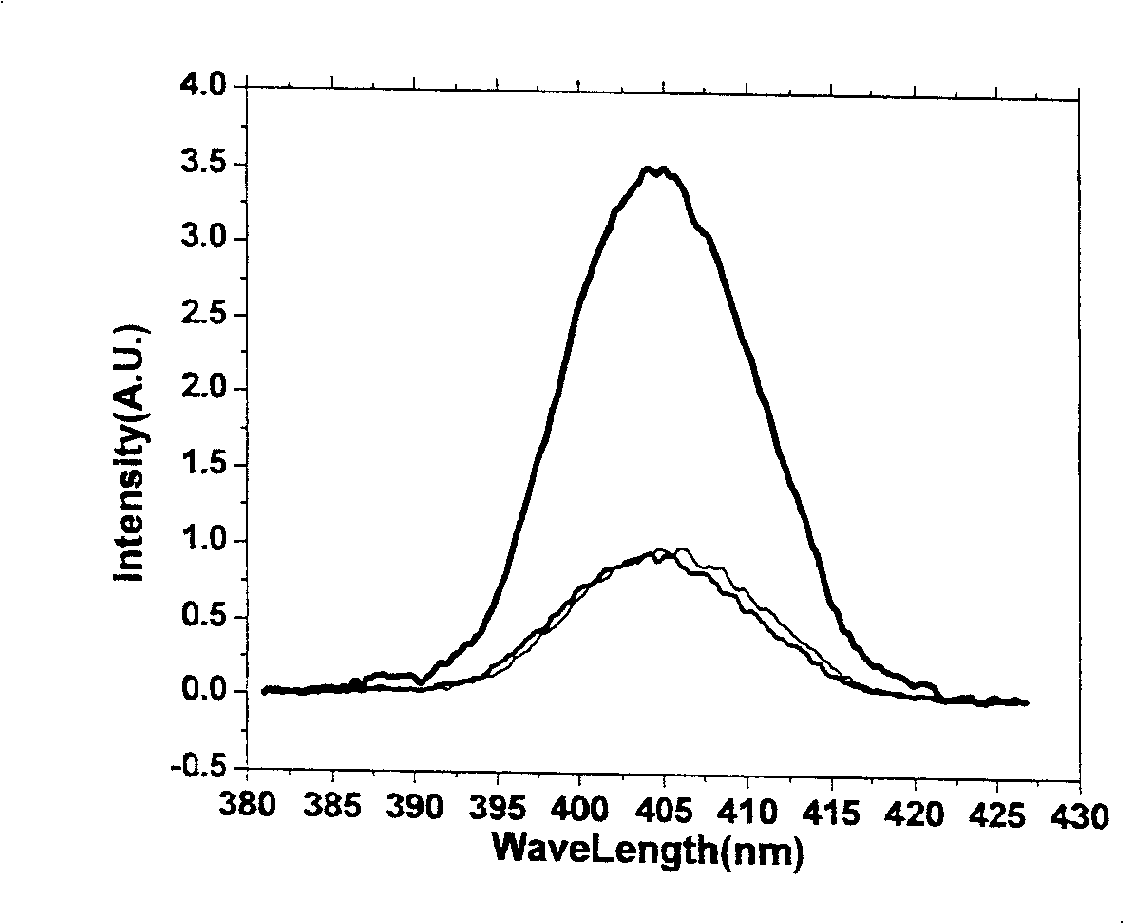
The invention relates to a new method for measuring an ultrashort light pulse spectral phase in the field of information optoelectronics and a device thereof. According to the method, a time delay minus T with polarity is introduced between two quasi-monochromatic light components with frequency Omega generated by the chirped stretching of a pulse to be detected; an additional time delay plus T, which is introduced between two quasi-monochromatic light components due to a pulse stretcher, is compensated to be in synchronization with the pulse to be measured and generate two sum frequency lights together with the pulse through a sum frequency crystal; respective power spectra and coherent spectra without interference fringe are acquired through a spectrometer. The phase difference between the two sum frequency lights is calculated by the three spectra through formulae. A spectrum phase curve of the pulse to be measured is calculated by adopting a concatenated method. The method can accurately determine the phase difference polarity of the pulse spectrum, and provide the simple, real-time, rapid and accurate measurement method and the device thereof for measuring the ultrashort optical pulse spectral phase.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
All fiber chirped pulse amplification system and method
InactiveUS7486436B1Minimize distortionOptical connection lossLaser detailsFibre transmissionPhotonic bandgapRare earth ions
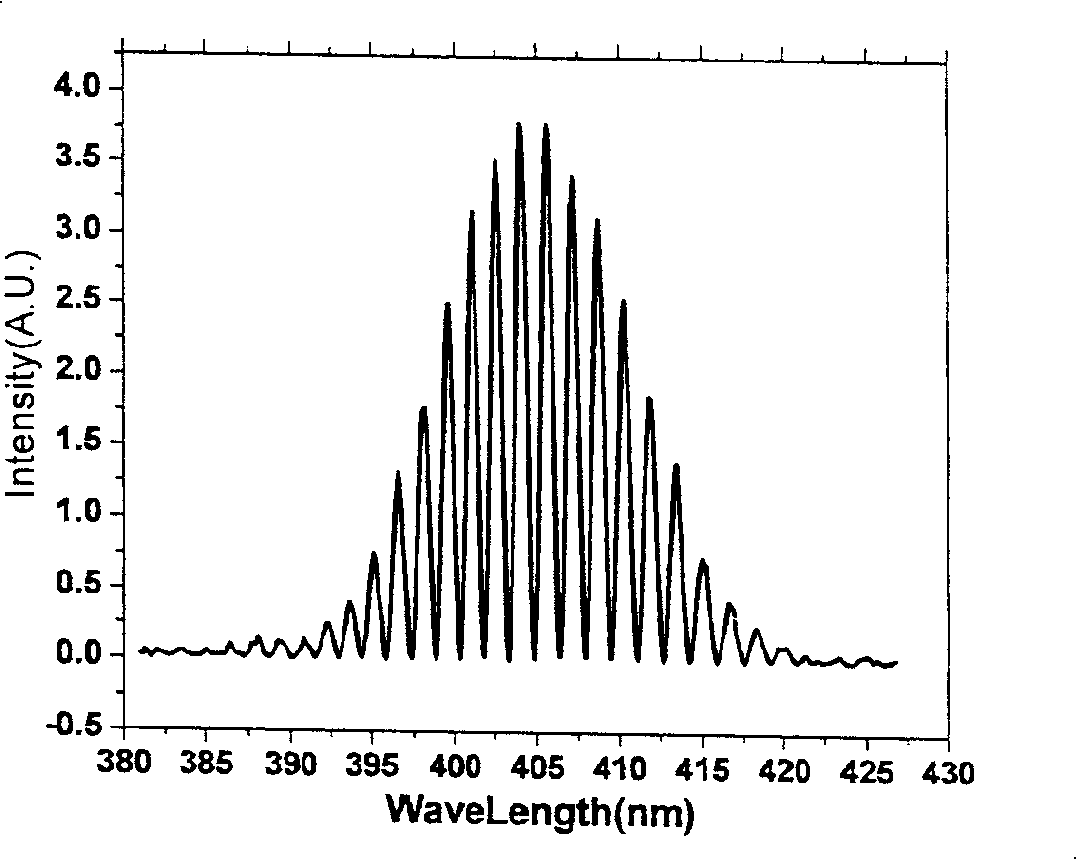
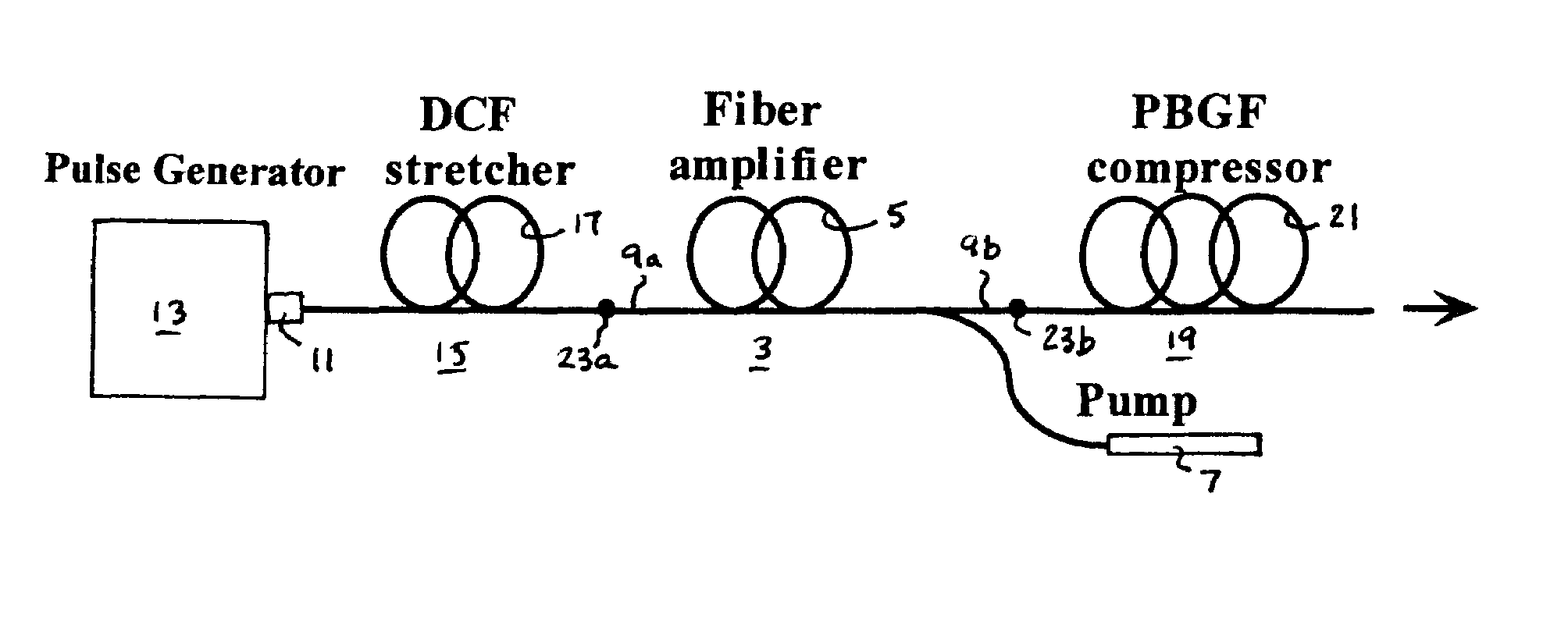
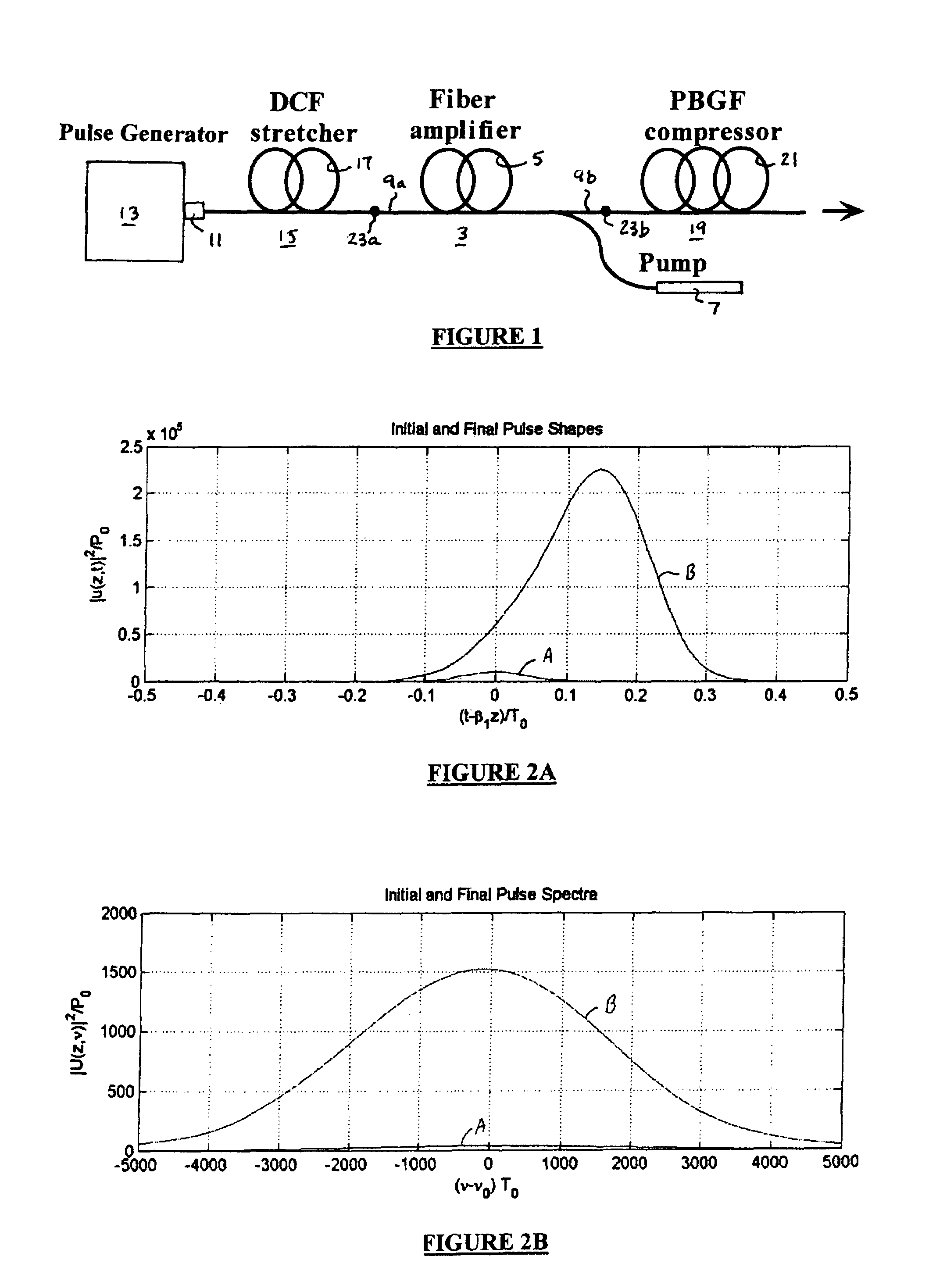
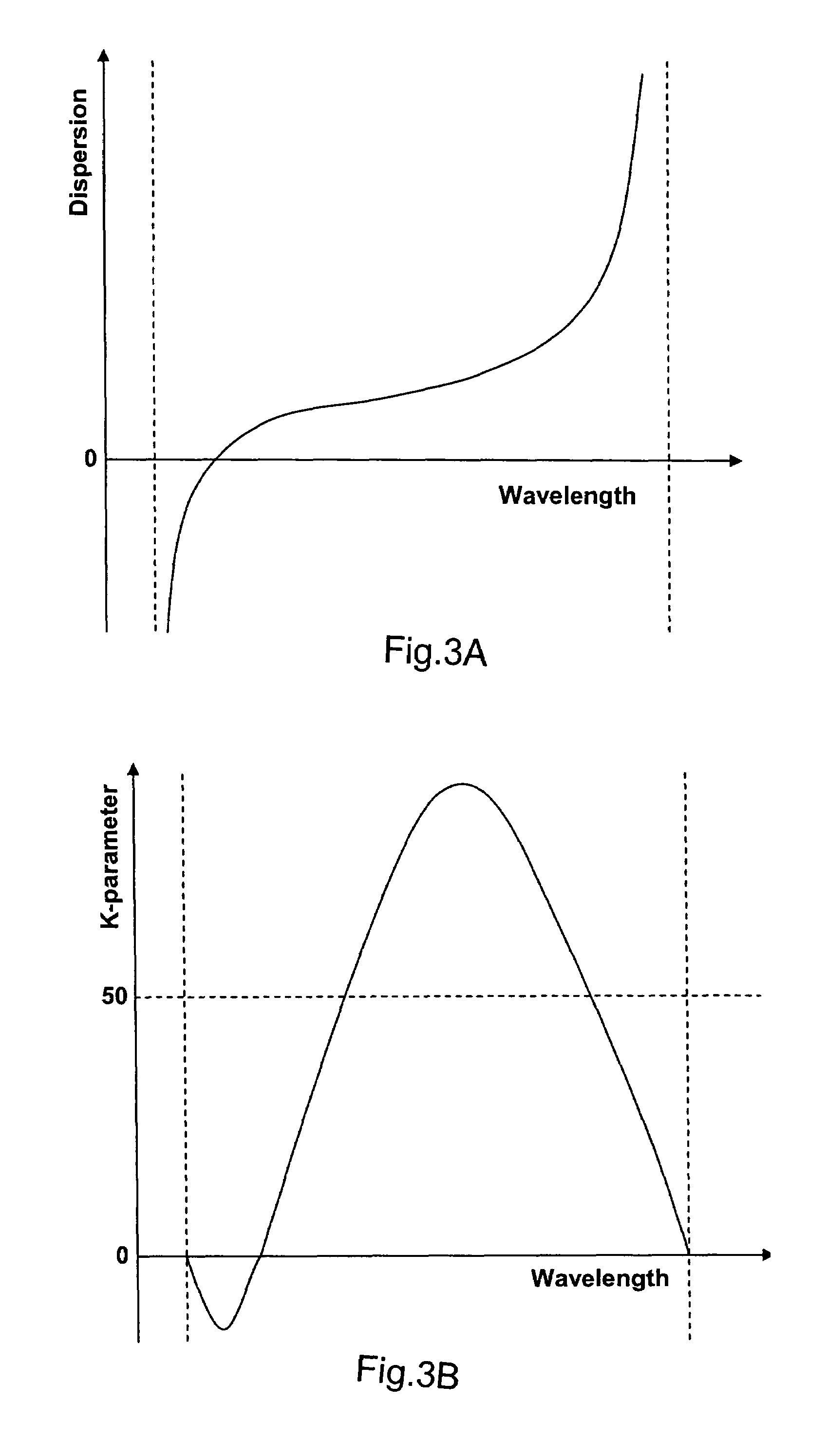
An all-fiber chirped pulse amplification (CPA) system and method is provided that utilizes a hollow core photonic bandgap fiber as a pulse compressor and a dispersion compensating optical fiber as a pulse stretcher that are matched with respect to both the amount and slope of dispersion to avoid peak power-limiting pulse distortion. The CPA system includes a rare earth ion-doped optical fiber amplifier having an input and an output that amplifies optical pulses having a center wavelength of λc, a pulse compressing length L1 of hollow core photonic bandgap fiber having a dispersion value D1 and a dispersion slope S1 that varies over a wavelength λ of the pulses that is optically connected to the output of the fiber amplifier and having a k-parameter defined by a ratio of D1 over the slope of the function D1(λ) that is larger than about 50, and a pulse stretching length L2 of dispersion compensating optical fiber connected to the input of the fiber amplifier having a dispersion value D2 and dispersion slope S2. The lengths are selected such that L1D1=−L2D2, and the center wavelength λc of the inputted optical pulses is preferably close to the center wavelength of the bandgap of the photonic bandgap fiber.
Owner:CORNING INC
Pulsed laser source with adjustable grating compressor
Various embodiments described herein relate to a laser source for producing a pulsed laser beam comprising a plurality of ultrashort optical pulses having a variable repetition rate. In one embodiment, the laser source comprises a fiber oscillator, which outputs optical pulses and a pulse stretcher disposed to receive the optical pulses. The optical pulses have an optical pulse width. The pulse stretcher has dispersion that increases the optical pulse width yielding stretched optical pulses. The laser source further comprises a fiber amplifier disposed to receive the stretched optical pulses. The fiber optical amplifier has gain so as to amplify the stretched optical pulses. The laser source includes an automatically adjustable grating compressor having dispersion that reduces the optical pulse width. The grating compressor automatically adjusts this dispersion for different repetition rates.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
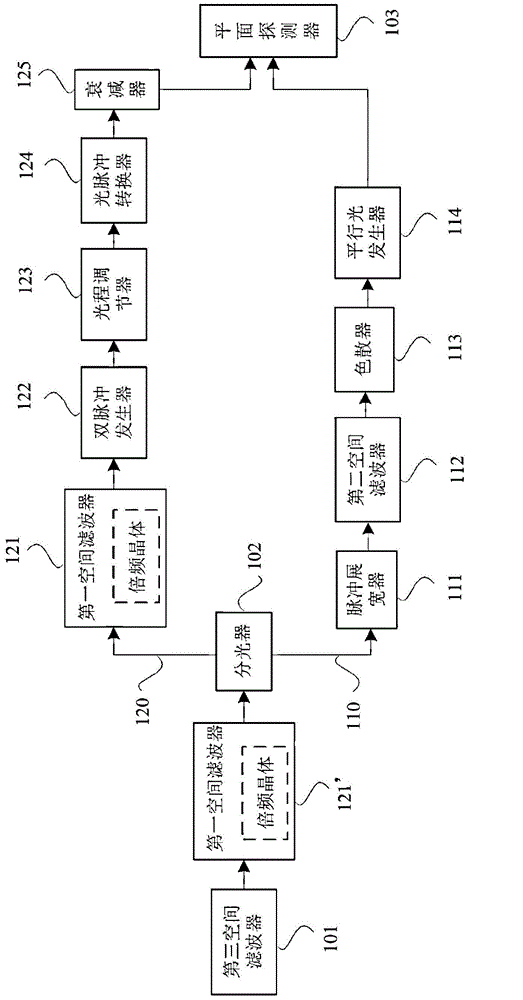
Single-shot laser pulse detection device
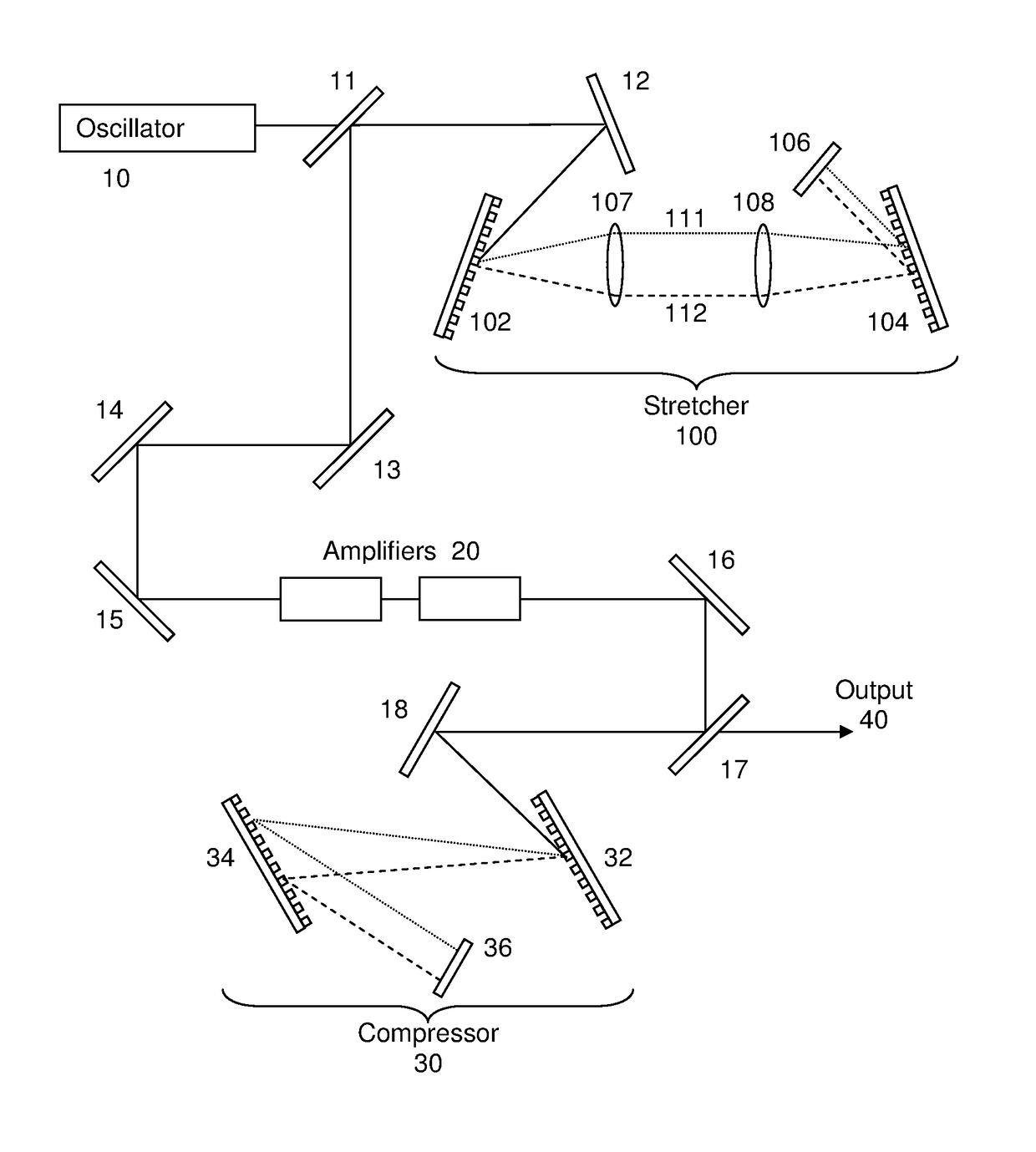
ActiveCN104697649AAvoid the problem of high beam quality requirements and large aperture laserAvoid the problem of high quality requirements and large aperture laserInstrumentsTime delaysOptoelectronics
The invention provides a single-shot laser pulse detection device. The single-shot laser pulse detection device comprises a detection light path for transmitting baseband detection light pulses, a reference light path for transmitting frequency-doubled reference light pulses, a dual-pulse generator for obtaining dual-pulses having a first time delay and transmitted collinearly along the reference light path, a light pulse converter for converting the dual-pulses into a series of dual-pulse form sub-pulses mutually delayed in time, separated from each other in space and propagated in parallel basically, a pulse stretcher for translating each frequency component of the baseband detection light pulses so as to stretch in the time domain, a dispersor for separating the frequency components in the baseband detection light pulses in space, and a plane detector for generating third-order mutual-correlation pulse signals from the baseband detection light pulses and the sub-pulses from the dispersor. The single-shot laser pulse detection device is capable of accurately measuring the waveform of the femtosecond petawatt lase pulses and solving the problem of difficult diagnosis of ultrafast and ultrastrong pulses large in dynamic range.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
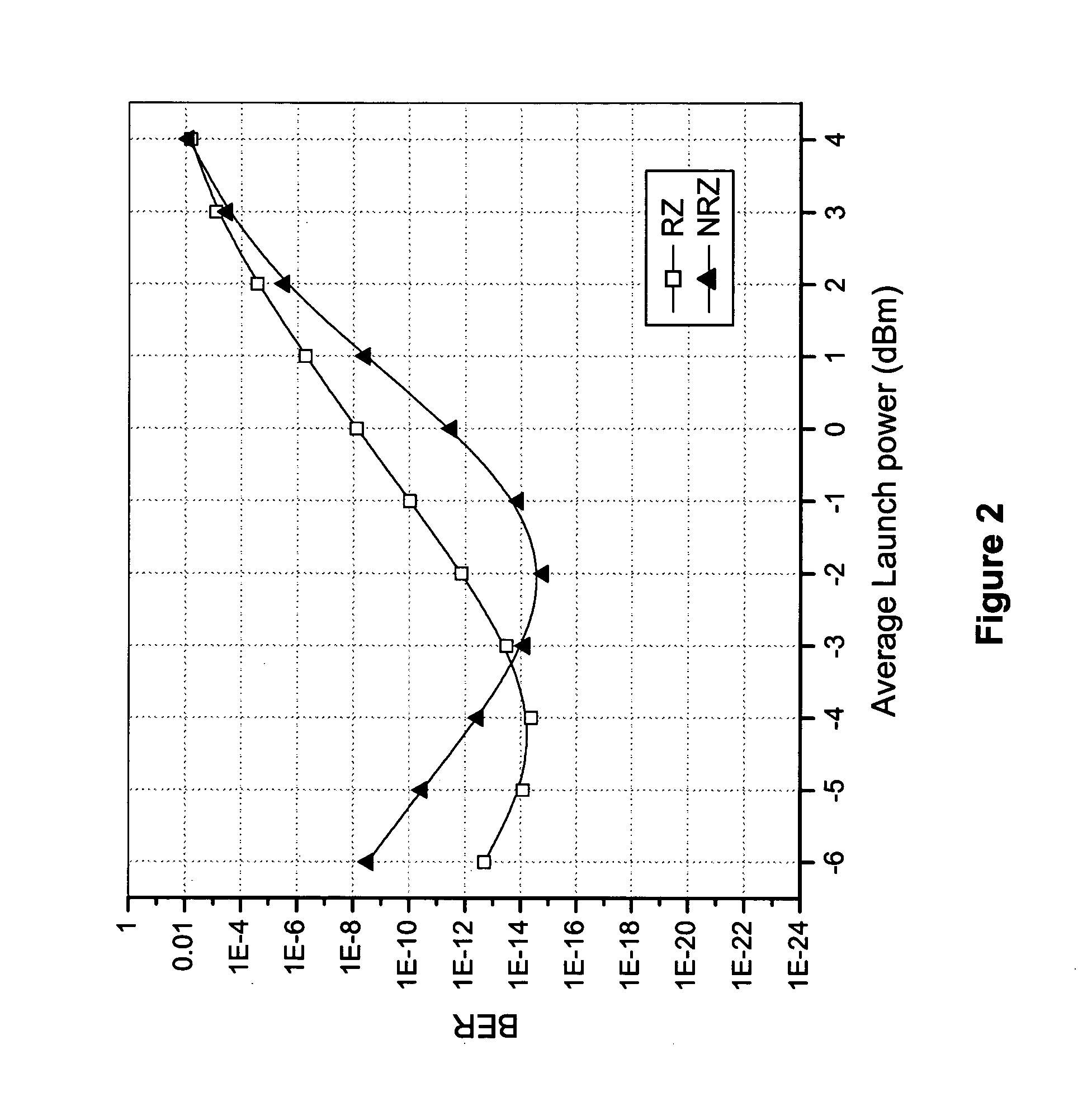
Transmission format for supression of four-wave mixing in optical networks
InactiveUS20050058462A1Improve performanceIncrease system capacityElectromagnetic transmittersReturn-to-zeroFrequency spectrum
Owner:NOVX SYST CANADA
Method for improving signal-to-noise ratio of femtosecond laser by using chirp matched optical parametric chirped pulse amplification
InactiveCN101814689AImprove signal-to-noise ratioEfficient amplificationActive medium materialNonlinear optical crystalLaser light
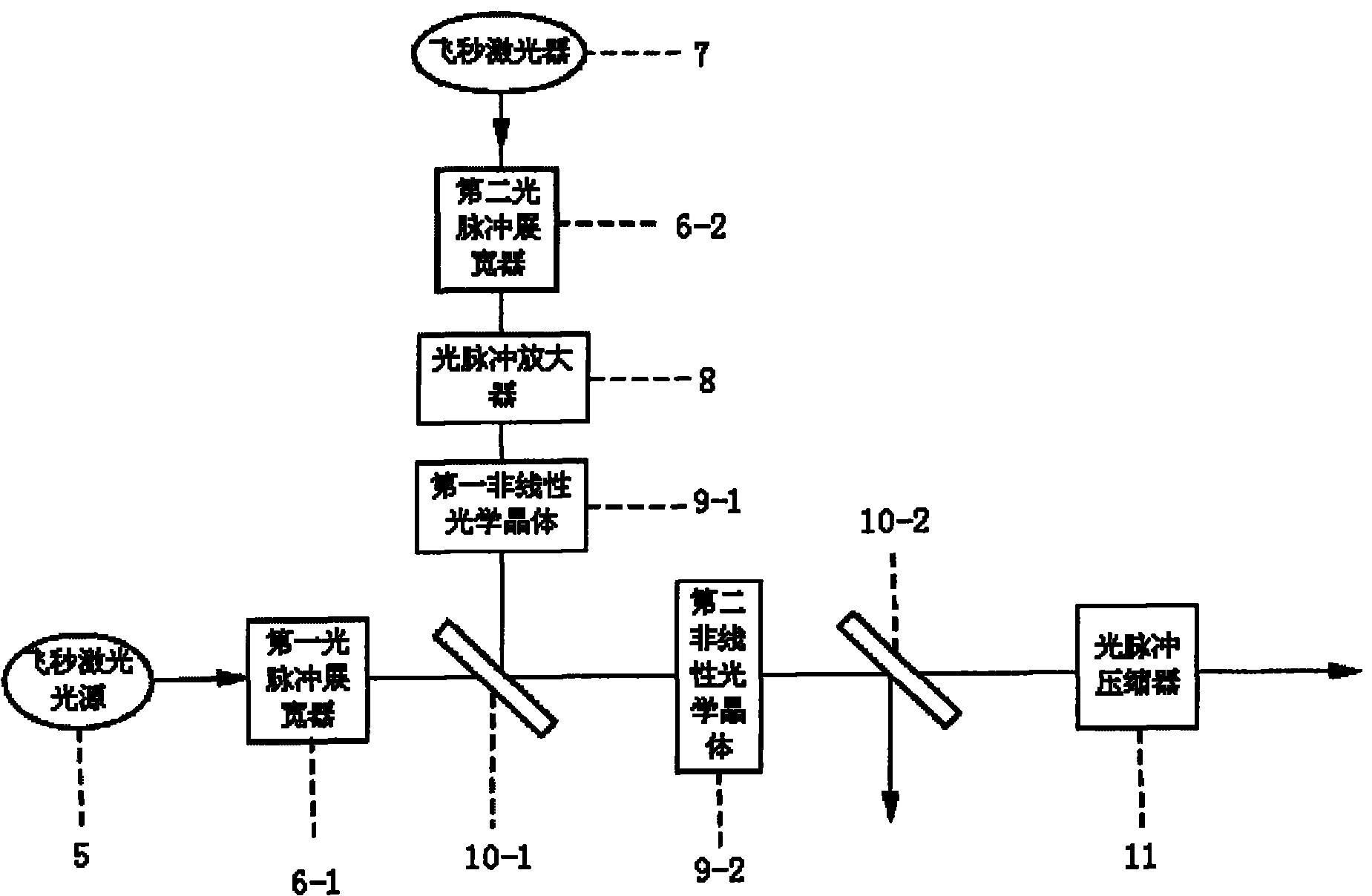
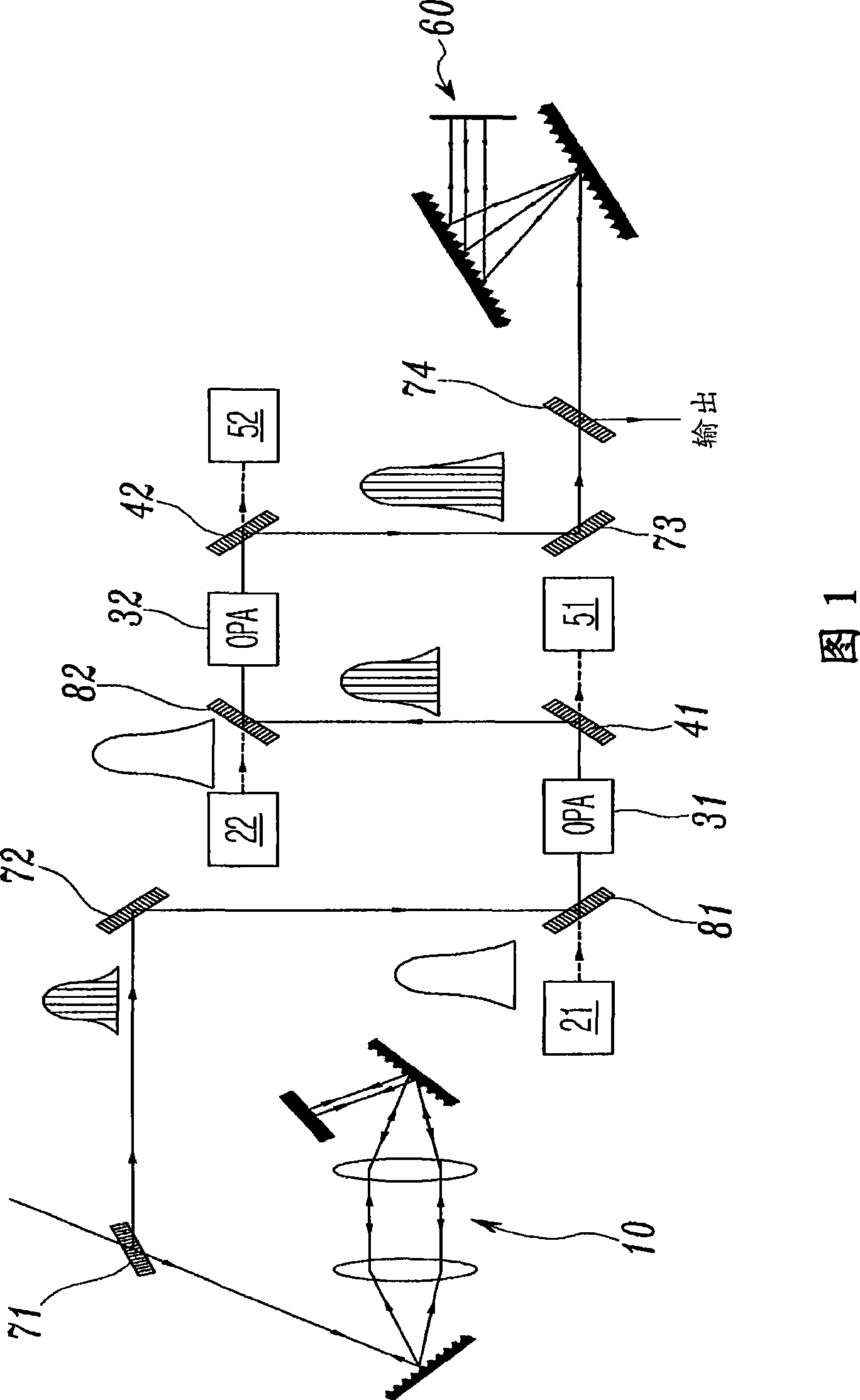
The invention discloses a method for improving a signal-to-noise ratio of femtosecond laser by using chirp matched optical parametric chirped pulse amplification and a device thereof, which belong to the technical field of ultra-short pulses. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, stretching the femtosecond laser with a signal-to-noise ratio to be improved output by a femtosecond laser light source into chirp signal light; secondly, performing high magnification on a signal and performing low magnification on a noise by using the chirp matched optical parametric chirped pulse amplification so as to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the chirp signal light; and finally, compressing the chirp signal light into femtosecond laser with a high signal-to-noise ratio by using an optical pulse compressor. The device for implementing the method comprises a femtosecond laser light source, a femtosecond laser, a first non-linear optical crystal, a second non-linear optical crystal, a first light pulse stretcher, a second light pulse stretcher, an optical pulse amplifier, an optical pulse compressor, a first dichroic mirror and a second dichroic mirror. The method and the device of the invention can not only improve the signal-to-noise ratio of the femtosecond laser effectively, but also realize high-efficient amplification of the femtosecond laser.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
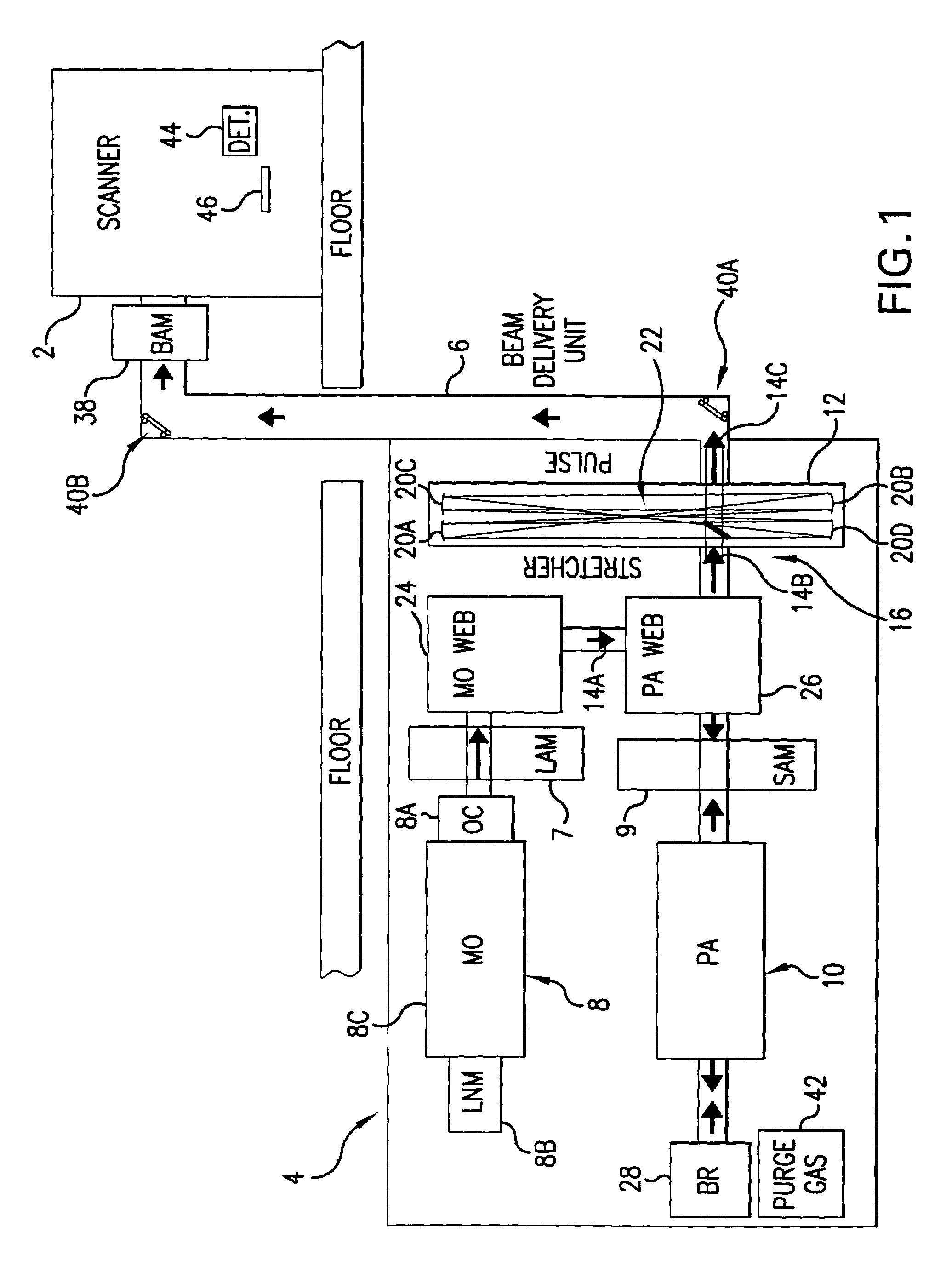
Lithography laser with beam delivery and beam pointing control
InactiveUS7230964B2Output powerBeam quality specificationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser arrangementsUltravioletLaser light
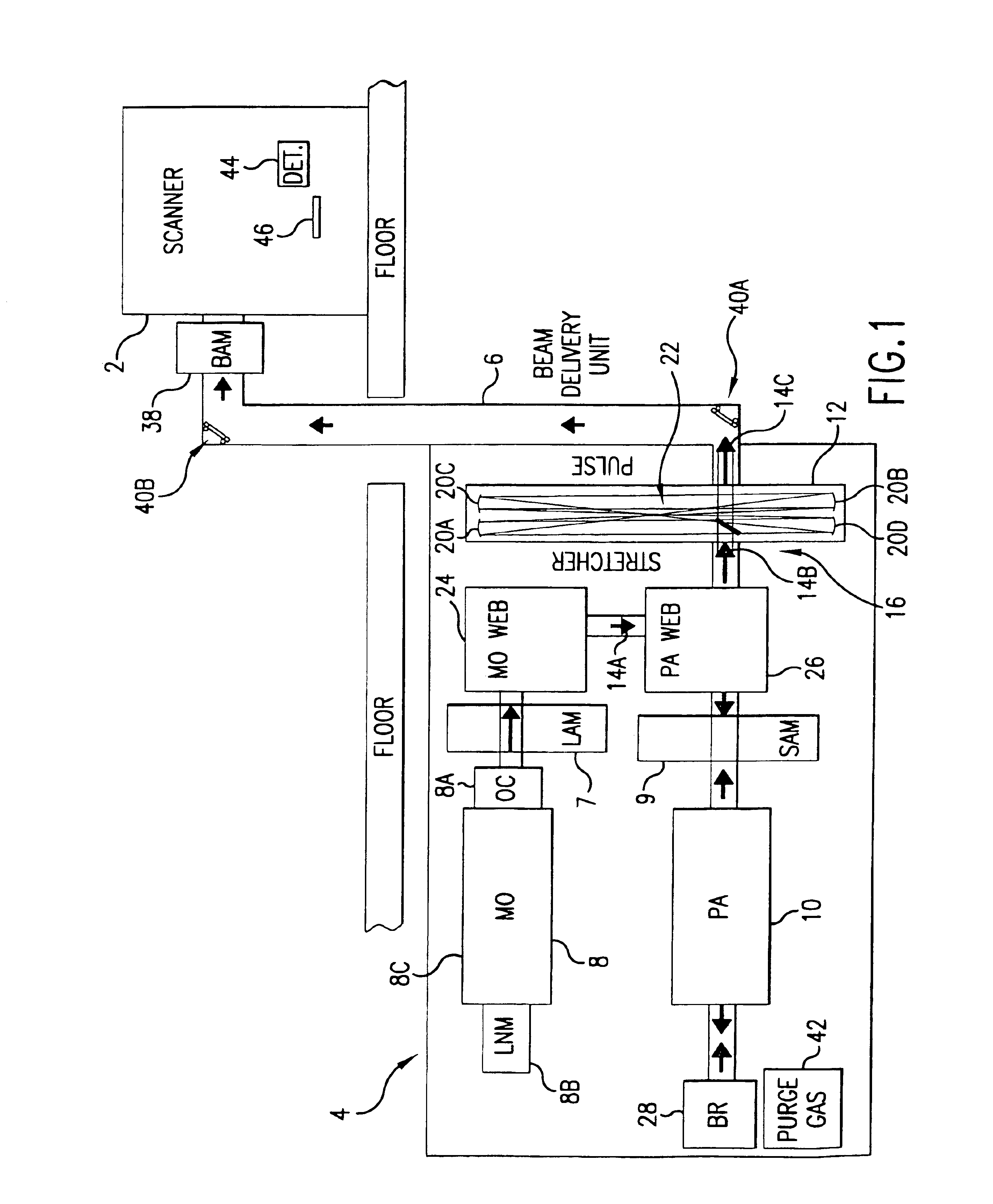
The present invention provides a modular high repetition rate ultraviolet gas discharge laser light source with a beam delivery to a production line machine. The system includes an enclosed and purged beam path with beam pointing control for delivery the laser beam to a desired location such as the entrance port of the production line machine. Preferred embodiments include equipment for beam attenuation, equipment for automatic feedback beam alignment and equipment for accurate optics module positioning at installation and during maintenance. In preferred embodiments, the production line machine is a lithography machine and two separate discharge chambers are provided, one of which is a part of a master oscillator producing a very narrow band seed beam which is amplified in the second discharge chamber. This MOPA system is capable of output pulse energies approximately double the comparable single chamber laser system with greatly improved beam quality. A pulse stretcher more than doubles the output pulse length resulting in a reduction in pulse power (mJ / ns) as compared to prior art laser systems. This preferred embodiment is capable of providing illumination at a lithography system wafer plane which is approximately constant throughout the operating life of the lithography system, despite substantial degradation of optical components.
Owner:CYMER INC
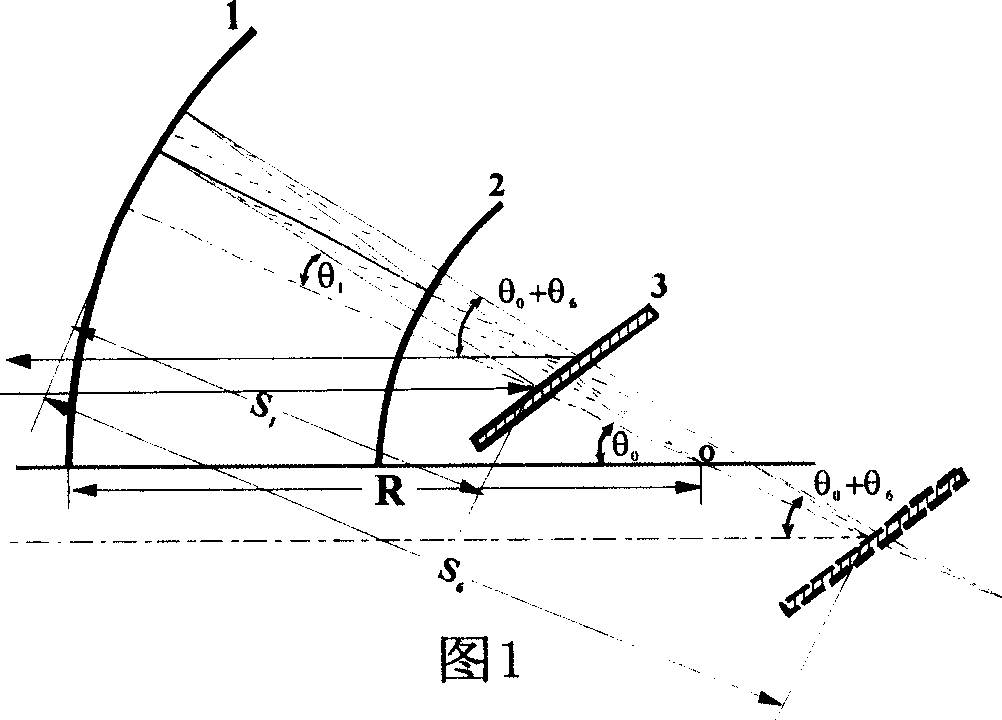
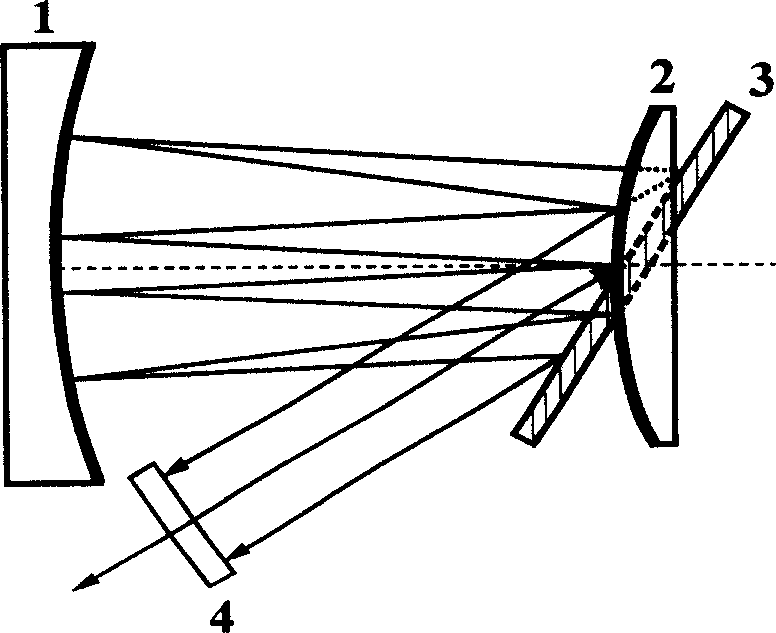
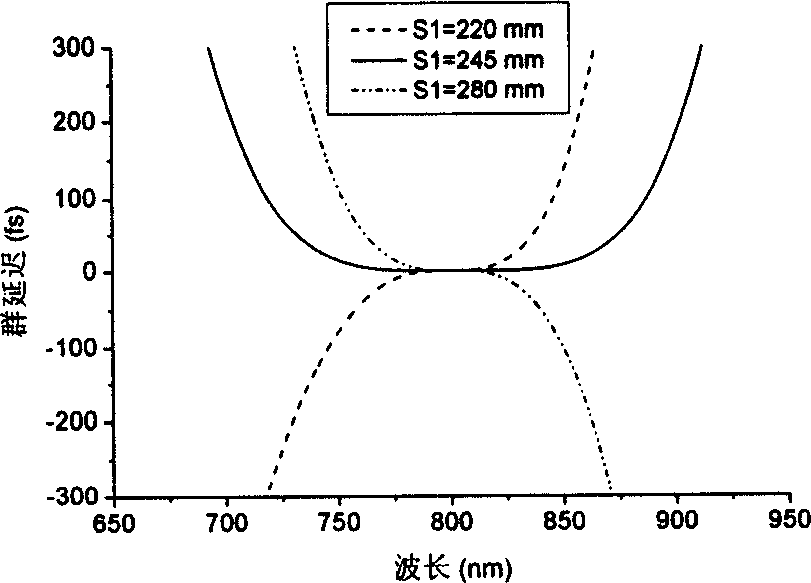
Miniaturization pulse stretcher design method for compensating high material dispersion of regenerative amplifier
InactiveCN1595272AGood collimationSmall spatial dispersionNon-linear opticsGratingAudio power amplifier
This invention discloses a design method for small femtosecond laser impulse stretcher used in regenerative amplifier high-dispersion material compensation, which belongs to the femtosecond impulse amplify technique. This method adopts concave spherical lens, convex spherical lens, grating and plane lens to design structure according to the phase Phi and grating position S1 of the stretcher. This method is characterized by the following: If the curvature radius of spherical lens is R, the distance between the grating and the concave spherical lens varies between zero to R; the convex spherical lens overlapped with the grating; if the stretching spectrum of the incidence light is larger than the lens width of the concave spherical lens, then it needs to reduce with equal proportion the curvature radium of the concave spherical lens and convex spherical lens and reduces the spectrum stretching width and keeps the original stretching degree.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device
ActiveCN104391416AReduce usageEliminate third order dispersionNon-linear opticsPicosecond laserBeam splitter
The invention discloses a mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device. The mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device comprises a femtosecond laser, a synchronous narrowband picosecond laser, a beam splitter, a near-infrared pulse stretcher, a non-linear frequency converter, an optical parametric chirped pulse amplier and a mid-infrared pulse compressor. Due to the fact that grism pairs and grating pairs are matched with each other to serve as the pulse stretcher and the pulse compressor, usage of a mid-infrared pulse stretcher is avoided, residual third-order dispersion in compression pulses in the process that the grating pairs serve as the pulse stretcher and the pulse compressor is eliminated, and the mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device is particularly suitable for generation of mid-infrared ultra-short ultra-strong pulse lasers with the frequency lower than hundreds of femtoseconds.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Pulsed laser source with adjustable grating compressor
Owner:TORONTO UNIV OF THE GOVERNING COUNCIL OF THE +1
Helical optical pulse stretcher
A pulse stretcher includes a single pass pulse stretcher. An optical system is arranged around the single pass pulse stretcher. A beam enters the single pass stretcher and is reflected in a helical path using the optical system for multiple passes through the single pass pulse stretcher. The single pass pulse stretcher can include two 90° prisms, with a beam splitter located therebetween. The optical system can include first and second prisms. At least one of the first and second prisms can be a roof prism. The first and second prisms can have at least one surface oriented so as to direct the beam into the helical path. The optical system can have at least one mirror, or a plurality of mirrors.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
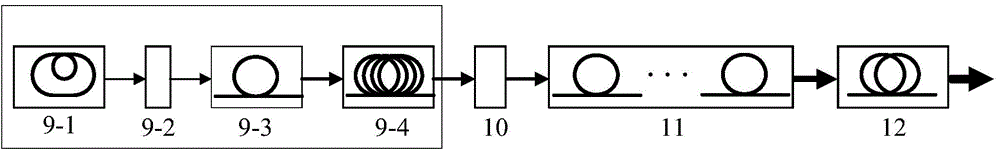
Super Gaussian pulse generation method and device on basis of gain reshaping
InactiveCN104158075AIncrease powerImprove signal-to-noise ratioActive medium shape and constructionFrequency spectrumGain coefficient
A super Gaussian pulse generation method on the basis of gain reshaping includes the following steps: firstly, a wideband linear chirp laser pulse is generated, and the central wavelength of the wideband linear chirp laser pulse is adjusted to be longer than the intrinsic emission line peak wavelength of the doped gain ion of an optical fiber amplifier; secondly, the gain-narrowed lower triangular chirp laser pulse is obtained after the linear chirp laser pulse is gain amplified by a pre-amplifier selected with the gain coefficient spectral lines all presenting triangular shapes; finally, the super Gaussian pulse is formed by injecting the lower triangular chirp pulse into a main amplifier selected with the gain optical fiber length being 1 to 3 times of that of the pre-amplifier and the central wavelength of the gain spectrum lines being longer than the pre-amplifier. The device capable of realizing the method comprises an optical fiber femtosecond laser oscillator (9-1), a dispersion compensator (9-2), an optical fiber self-similarity pulse amplifier (9-3), a positive dispersion optical fiber pulse stretcher (9-4), a frequency spectrum filter (10), and a front optical fiber amplifier (11) with at least one stage and a main optical fiber amplifier (12).
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY
Chirped pulse velocity interferometer
InactiveCN104730279AReduce construction costsObvious price advantagePhase-affecting property measurementsDevices using time traversedBroadband pulseDelayed time
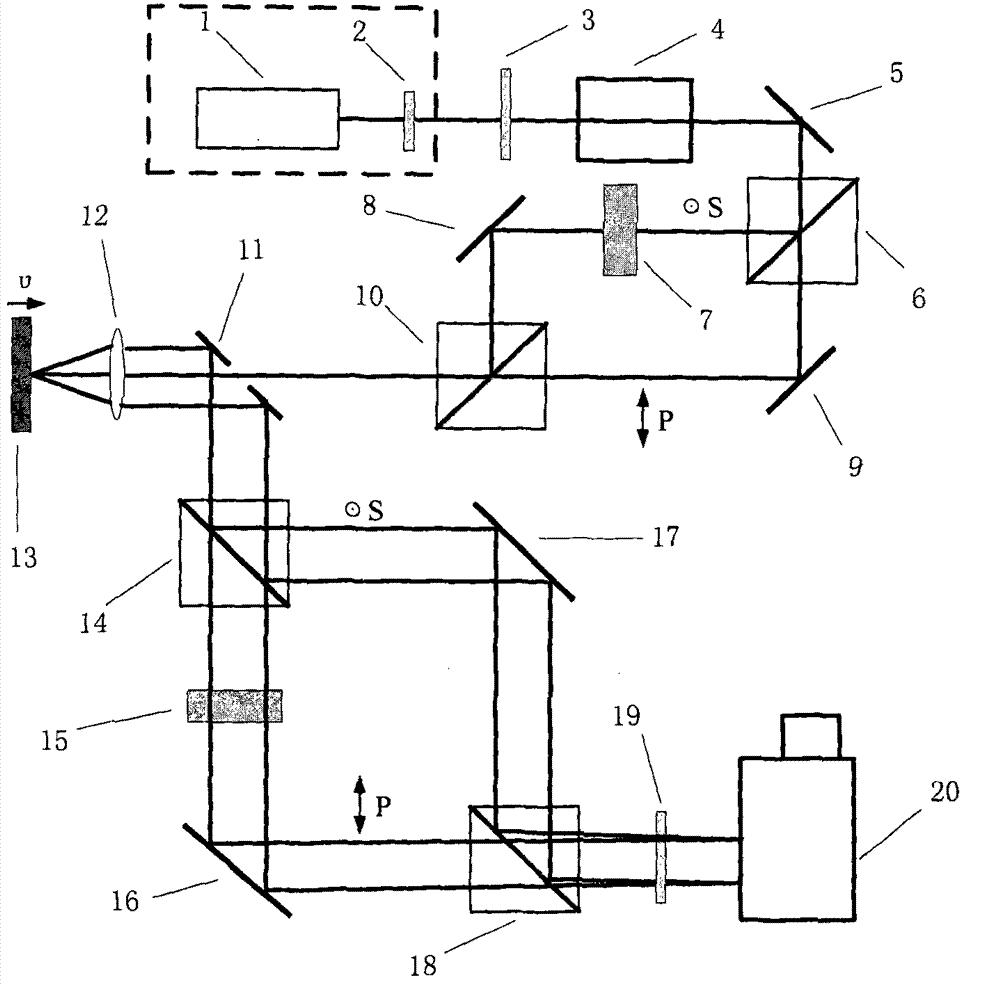
The invention discloses a chirped pulse velocity interferometer. In the chirped pulse velocity interferometer, broadband laser pulses output by a broadband pulse laser light source are changed into linear polarization linear chirped pulses after passing through a polarizer and a pulse stretcher; polarization light S and polarization light P which are perpendicular in polarization direction are produced after the linear chirped pulses pass through a polarization splitting prism, and then the polarization light S and the polarization light P are successively emitted into the surface of a tested sample; the beat-wave interferometry is conducted on reflected light at a certain included angle, and produced beat-wave interferometric fringes are recorded through an imaging type spectrometer. A certain delay time difference exists before the polarization light S and the polarization light P are emitted into the surface of the sample, and synchronous transmission is achieved through optical path compensation after the polarization light S and the polarization light P are reflected by the surface of the sample. The oscillation penetrating direction of the polarizer is perpendicular to that of an analyzer. By means of the chirped pulse velocity interferometer, the time distinguishing of sub-picosecond scale can be achieved, the imaging type spectrometer serves as the corresponding recording system, an expensive streak camera recording system is avoided, and therefore the cost of a test system is effectively controlled.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Dispersion compensation in chirped pulse amplification systems
ActiveUS8780440B2Improving lifetimeImprove performanceFibre transmissionSpecial data processing applicationsAudio power amplifierChirped pulse amplification
A chirped pulse amplification system includes a laser source providing an input laser pulse along an optical path. The input laser pulse is characterized by a first temporal duration. The system also includes a multi-pass pulse stretcher disposed along the optical path. The multi-pass pulse stretcher includes a first set of mirrors operable to receive input light in a first plane and output light in a second plane parallel to the first plane and a first diffraction grating. The pulse stretcher also includes a second set of mirrors operable to receive light diffracted from the first diffraction grating and a second diffraction grating. The pulse stretcher further includes a reflective element operable to reflect light diffracted from the second diffraction grating. The system further includes an amplifier, a pulse compressor, and a passive dispersion compensator disposed along the optical path.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
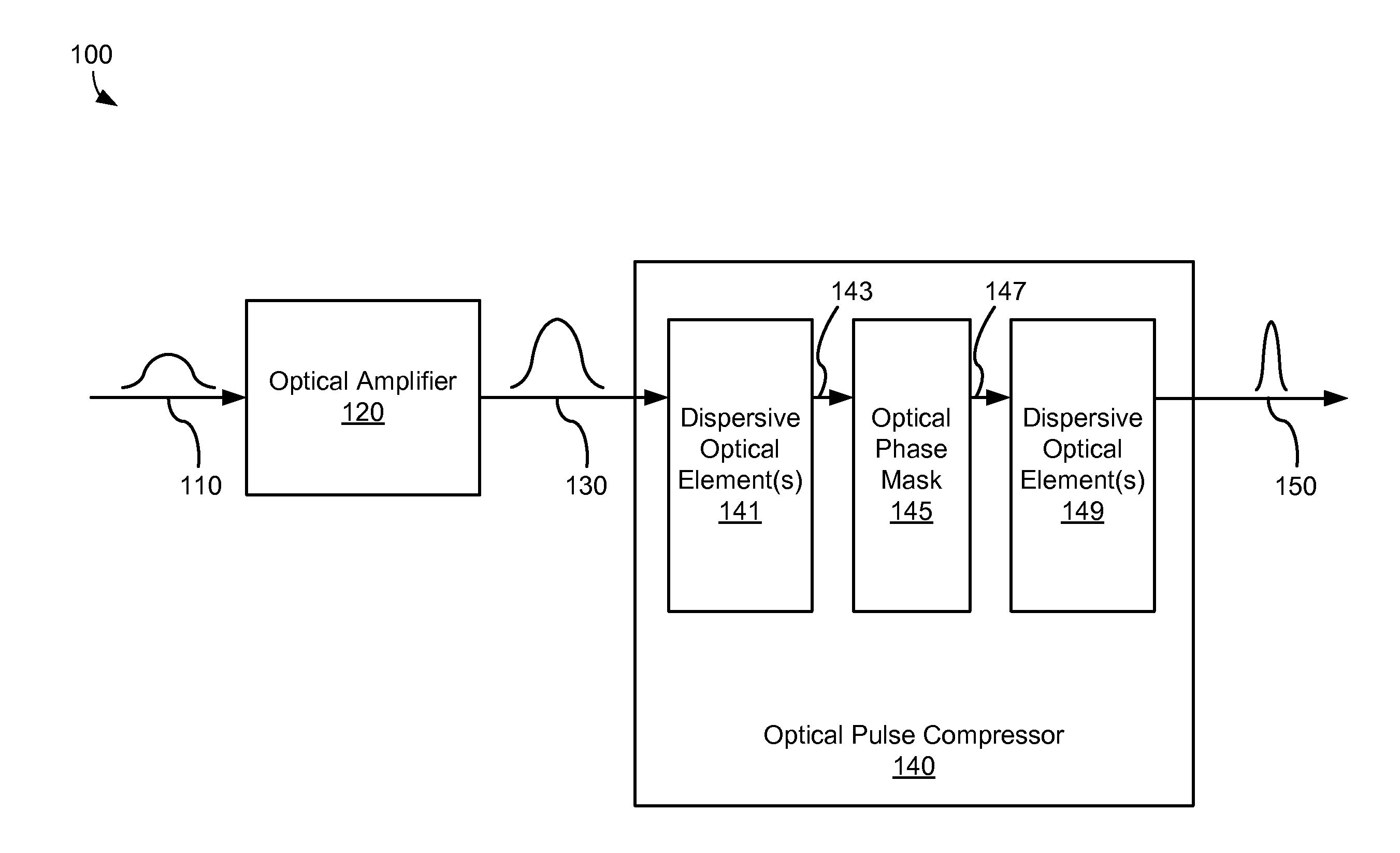
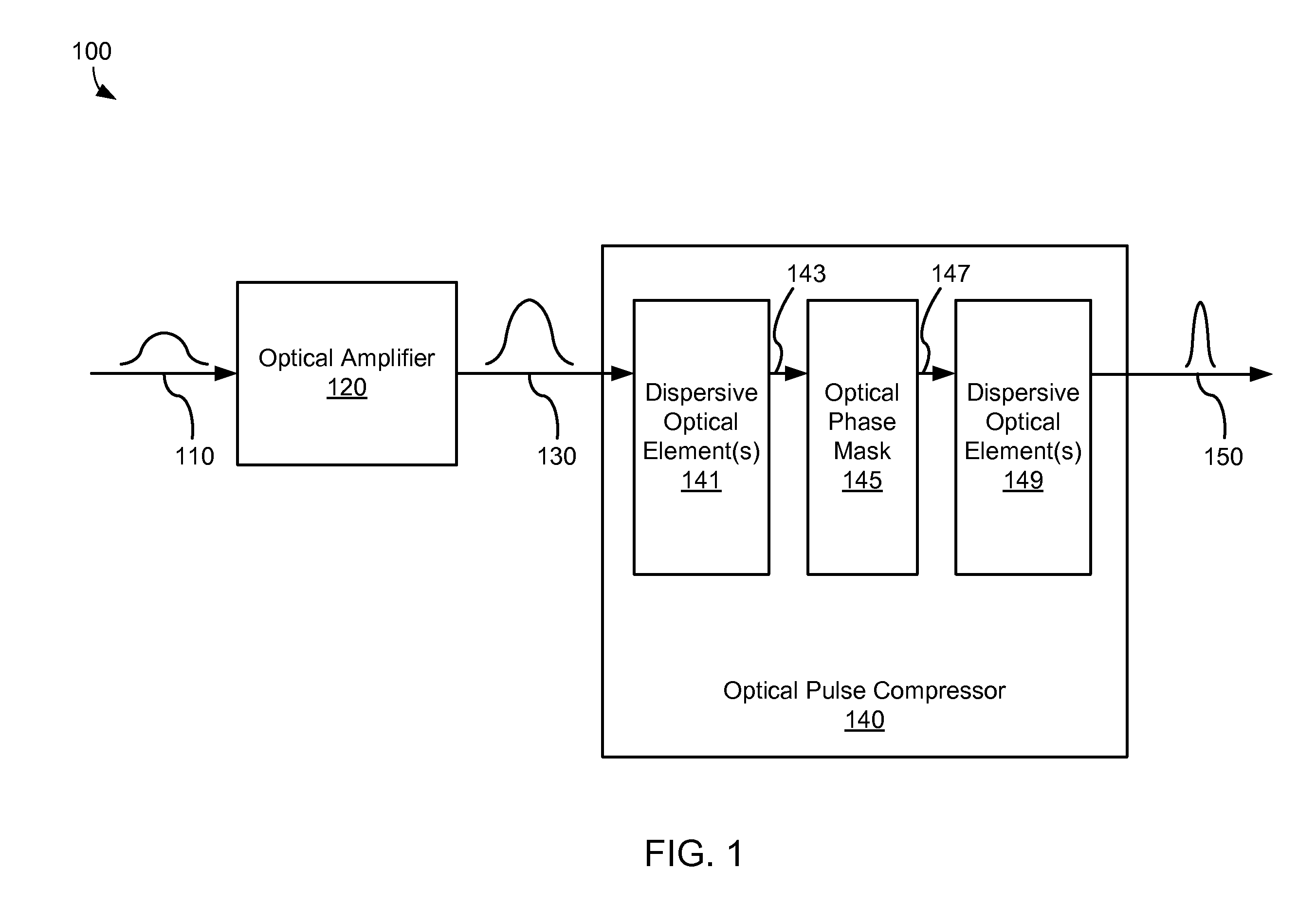
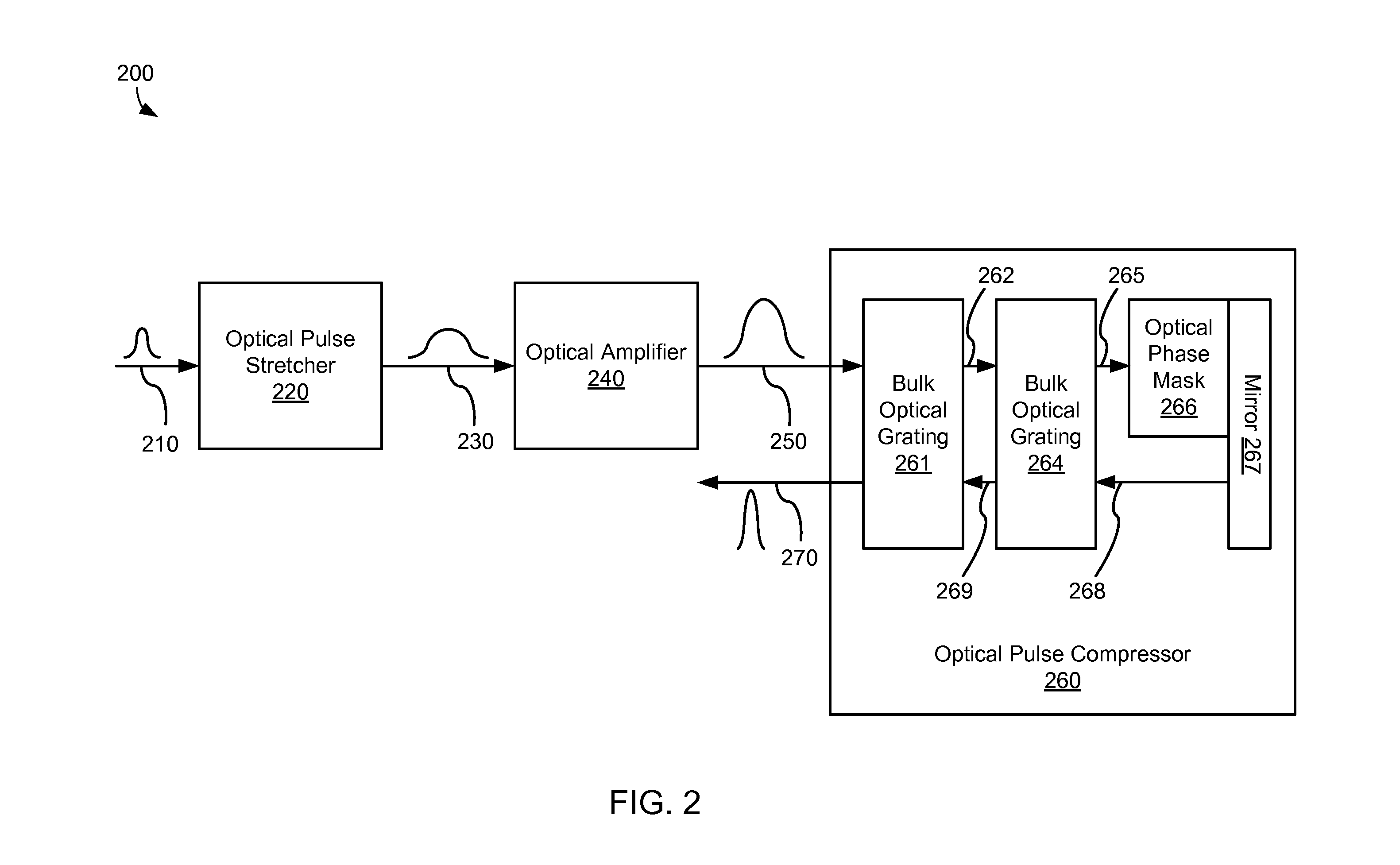
Static phase mask for high-order spectral phase control in a hybrid chirped pulse amplifier system
A chirped pulse amplification (CPA) system comprises an optical pulse stretcher and an optical pulse compressor that are mismatched in that the optical pulse compressor includes a bulk optical grating while the optical pulse stretcher does not. High order dispersion compensation is provided by an optical phase mask disposed within the optical pulse compressor.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Apparatus and method for producing ultrashort, super strong laser pulse sequence in high repetition rate
A device generating supershort-superhigh laser pulse line of highly repeated frequency consists of self mode locking iiwaarite laser oscillator of mode locking pulse line, Faraday light isolator, aberration free laser pulse stretcher, regeneration amplifier of iiwaaeite, quantity selector of laser pulse, multistroke iiwaarite laser amplifier chain, gating pair pulse compressor in pumping laser and vacuum chamber. It is featured as exerting the first and the second DC high voltage signals on electrodes of Pochels box on amplifier, using a synchronous signal to control the first and the second DC high voltage source to work separately.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical parameter chatter pulses amplification laser system
InactiveCN1431740ASimple AlignmentSimple and adjustableLaser detailsNon-linear opticsGratingBeam splitter
The system is composed of the laser oscillator in femtosecond level, the pulse stretcher of grating pair, the pulse shortener of grating pair, the beam splitter, the first stage OPA amplifier, the back stage OPA amplifier, the prime amplifier of pump source system, the first double frequency crystal, the dichroism spectroscopic plate etc. the characters of the invention are that the signal light and the pump light source are come from the same laser oscillator. The accurate time synchronization between the signal light pulse and the pump light pulse can be realized and the time jitted is reduced without need of the additional collimation light source. That is to say the signal light of each optical parameter amplification stage and the pump light can be collimated and synchronous adjusted.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for increasing signal to noise ratio of femtosecond laser through F-P (Fabry-Perol) etalon internally installed with electro-optic crystal
InactiveCN101867145AGreat filtrationImprove signal-to-noise ratioLaser detailsSignal lightLaser light
The invention relates to a method for increasing the signal to noise ratio of a femtosecond laser through an F-P (Fabry-Perol) etalon internally installed with an electro-optic crystal and a device thereof, which belong to the technical field of ultrashort pulses. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, stretching a femtosecond laser pulse to be increased in the signal to noise ratio, which is output from a femtosecond laser light source, into chirp signal light; enabling an instaneous spectral filtering function output by the F-P etalon to be consistent with the chirp size of the chirp signal light by modulating the voltages of both ends of the electro-optic crystal internally installed in the F-P etalon, and thereby, a chirp signal pulse efficiently pass, whereas noise is filtered off to achieve the goal of increasing the signal to noise ratio of the chirp pulse; finally, compressing the chirp signal light into the femtosecond laser with higher signal to noise ratio. The device for realizing the method comprises the femtosecond laser light source, a laser pulse stretcher, the F-P etalon, the electro-optic crystal, a high-voltage pulse power supply, a laser pulse compressor and the like. The signal to noise ratio of the femtosecond laser can be effectively increased by adopting the method and the device. Moreover, the device has simple structure and convenient adjustment.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
High power laser with chirped pulse amplification
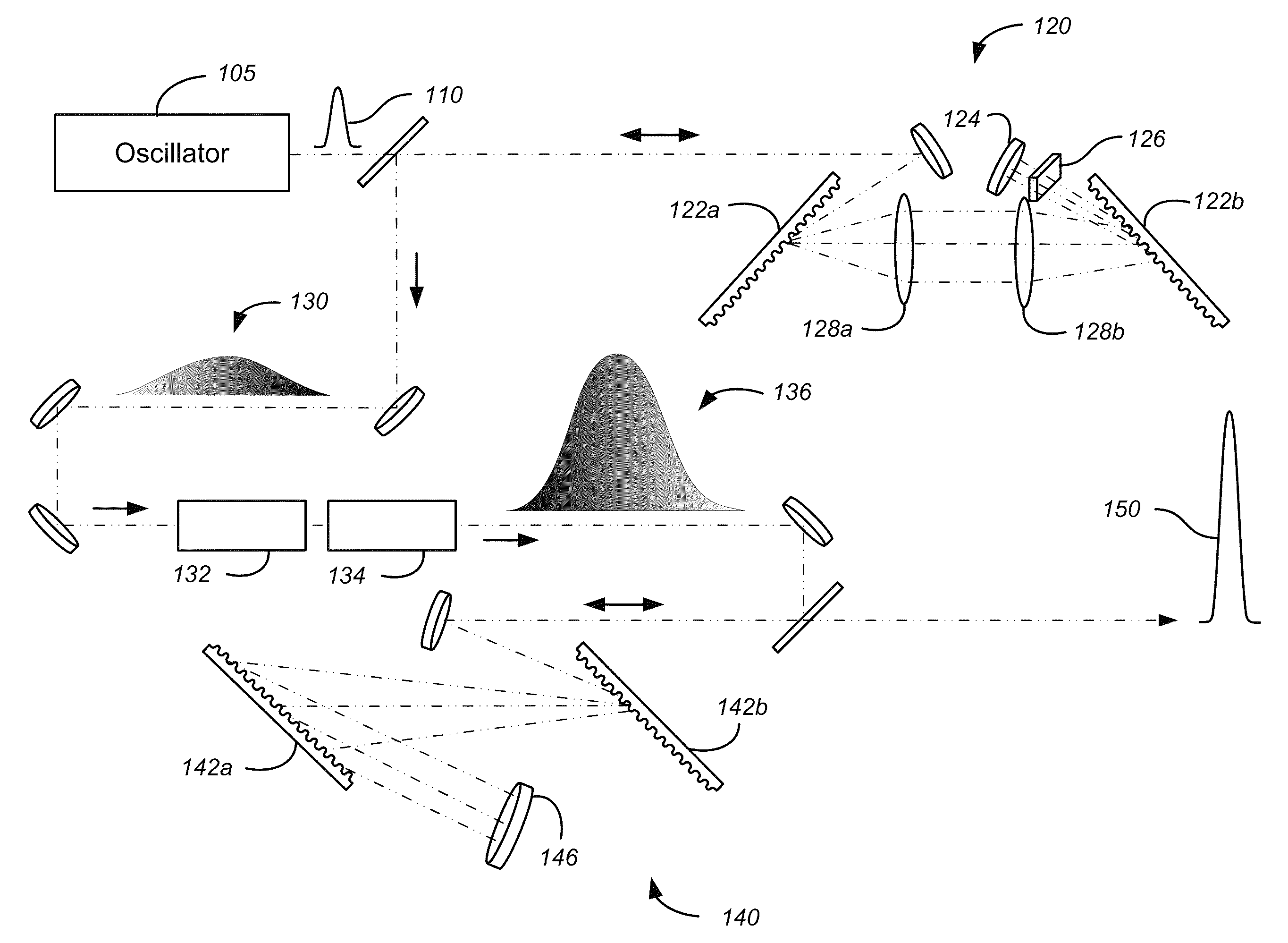
InactiveUS20170093111A1Improve Phase Noise PerformanceImprovements in pulse stretchersLaser arrangementsHigh power lasersPhase noise
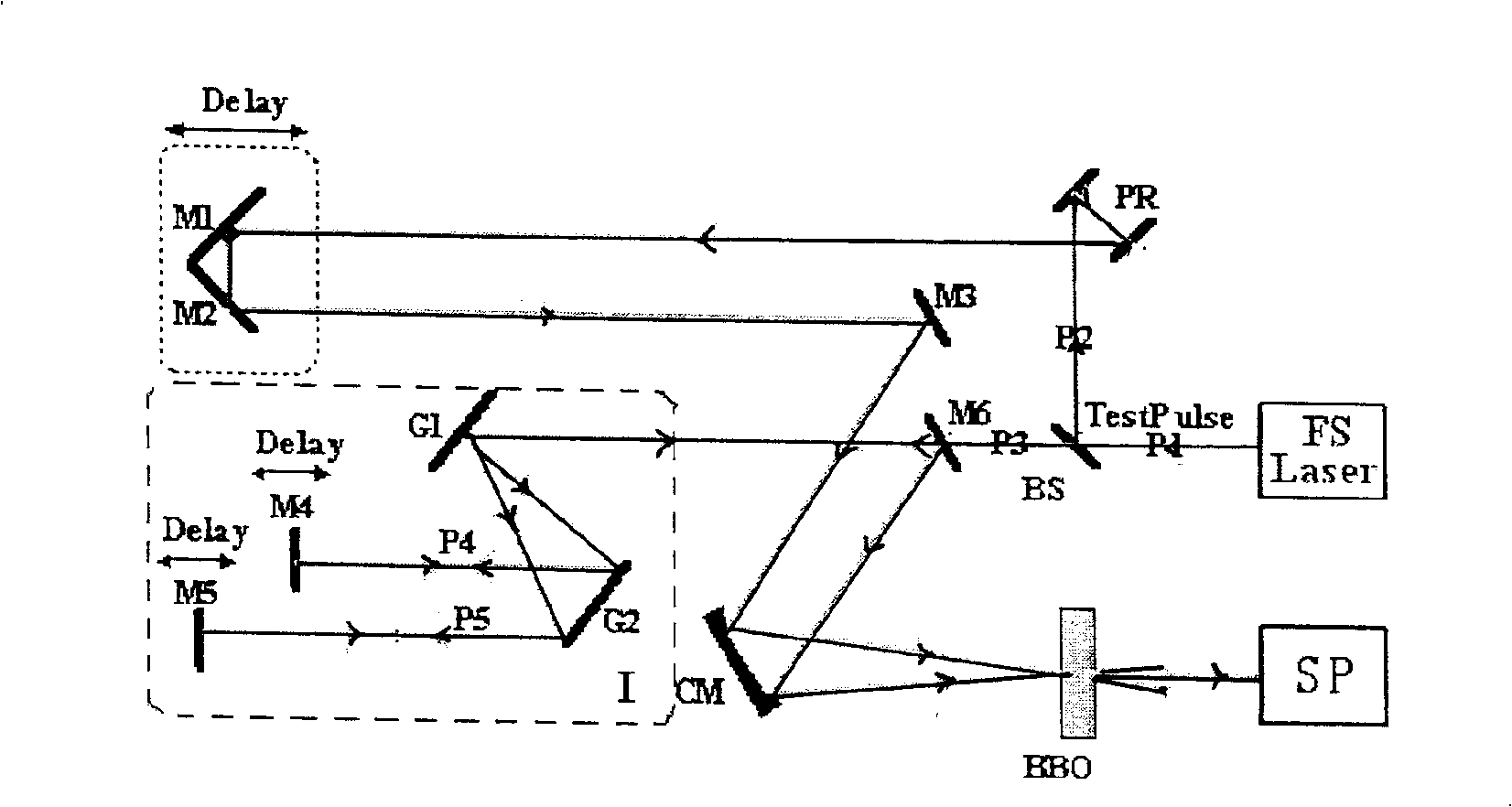
A high power laser with chirped pulse amplification to produce extremely high power ultrashort pulses is disclosed. A pulse stretcher and methods of stretching a laser pulse are also disclosed. The pulse stretcher comprises: a first diffraction grating (G1) arranged to receive and disperse a seed laser pulse; transfer optics (CM) arranged to collect the dispersed pulse and direct it to a transmission diffraction grating (G2) which is either the first diffraction grating or a second diffraction grating; the transmission diffraction grating arranged to collimate the collected pulse to a reflector (BM), the reflector arranged such that the pulse is reflected back through the pulse stretcher via the transmission diffraction grating. The pulse stretcher provides better phase noise performance of the output pulse, and therefore a reduction in the noise floor to improve contrast pedestal.
Owner:UK RES & INNOVATION LTD
Apparatus for optical parametric chirped pulse amplification (opcpa) using inverse chirping and idler
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com