Chirped pulse velocity interferometer
A technology of chirped pulses and interferometers, applied in the use of devices that measure the time required to move a certain distance, the re-radiation of electromagnetic waves, and the use of re-radiation, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the application range of the system and the high construction cost of VISAR , to achieve the effect of obvious price advantage and control of construction cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
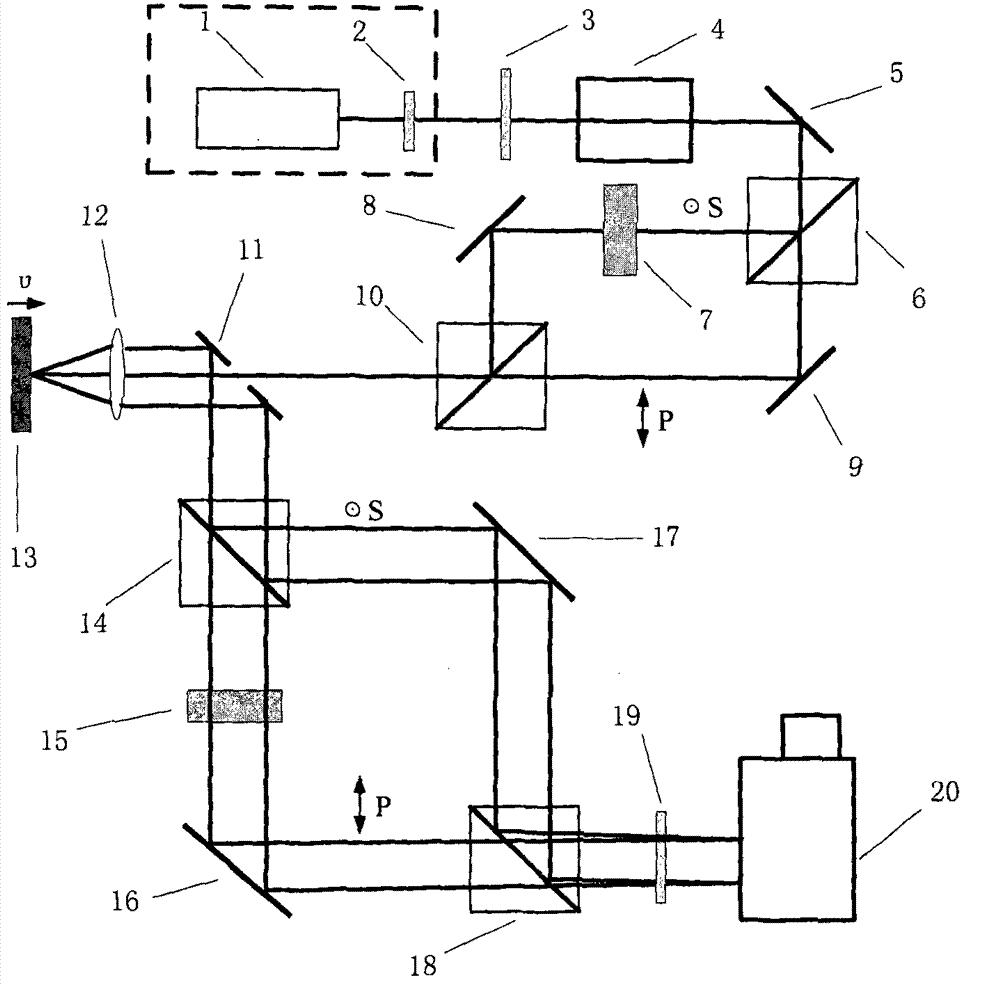
[0033] figure 1Shown, a kind of chirped pulse velocity interferometer of the present invention, supercontinuum pulse laser 1 outputs the supercontinuum laser pulse of certain central wavelength, filters into the laser pulse of required bandwidth after passing through broadband filter 2, utilizes polarizer again 3 and pulse stretcher 4 to change it into a linearly polarized linearly chirped pulse. After the chirped pulse passes through the reflector 5, it is divided into S-polarized light and P-polarized light by the polarization beam splitter 6 with the polarization directions perpendicular to each other, wherein the S-polarized light reaches the polarization beam-splitter prism 10 through the time delay device 7 and the mirror 8, and the P-polarized light After the light is reflected by the mirror 9, it is combined with the S-polarized light through the polarization beam splitter 10, and the time delay device 7 makes the combined S-polarized light lag behind the P-polarized l...
Embodiment 2
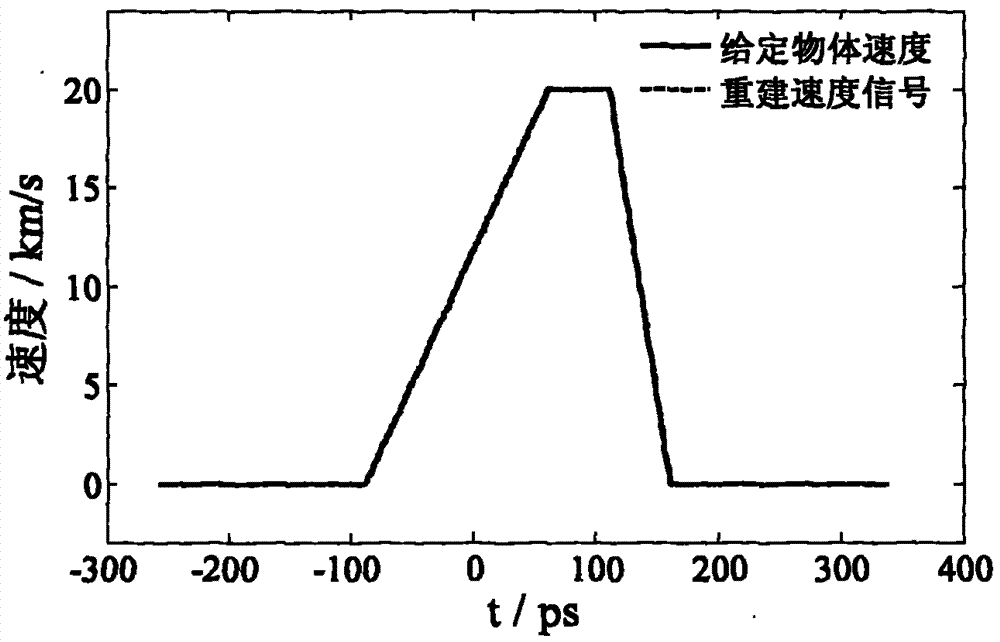
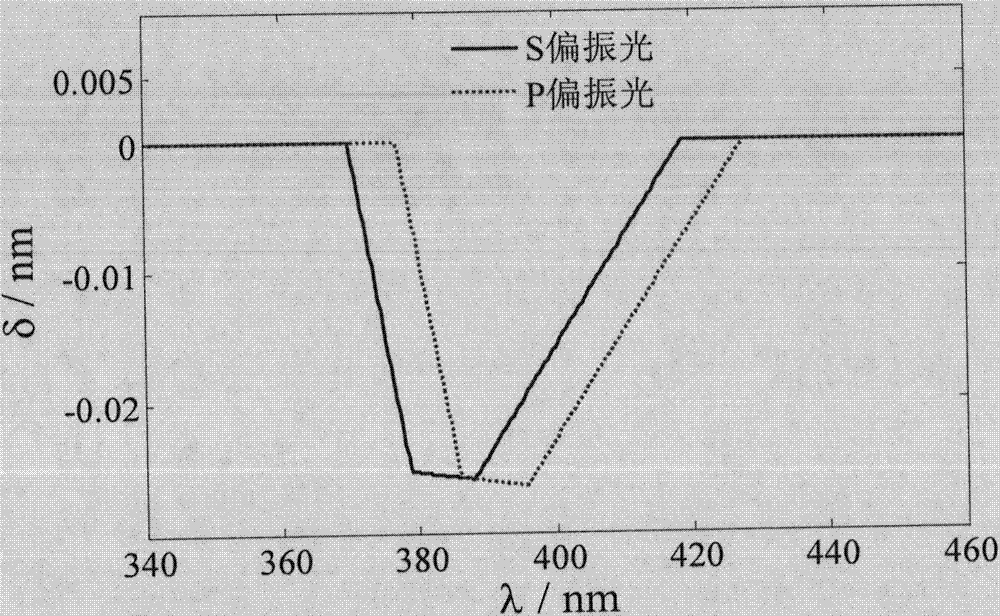
[0041] The broadband pulsed laser light source in this embodiment is a femtosecond laser. When measuring the free surface velocity of the sample when the femtosecond laser-driven shock wave is unloaded, it is more convenient to use the femtosecond laser as the broadband pulsed laser source of the chirped pulse velocity interferometer. The pulse output by the femtosecond laser is divided into two beams by the beam splitter 2. The reflected beam is used as the pump light. After passing through the delay optical path formed by the mirrors 3 and 4, it is reflected by the mirrors 5 and 6 and focused by the convex lens 7 in front of the sample. Surface, so as to drive the shock wave in the material, when the shock wave propagates to the rear interface of the sample for unloading, the rear interface starts to move; another beam passing through the beam splitter 2 is reflected by the mirror 8 and used as a chirped pulse velocity interferometer The incident broadband laser pulse is use...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Center wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com