Patents
Literature
208 results about "Surface velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
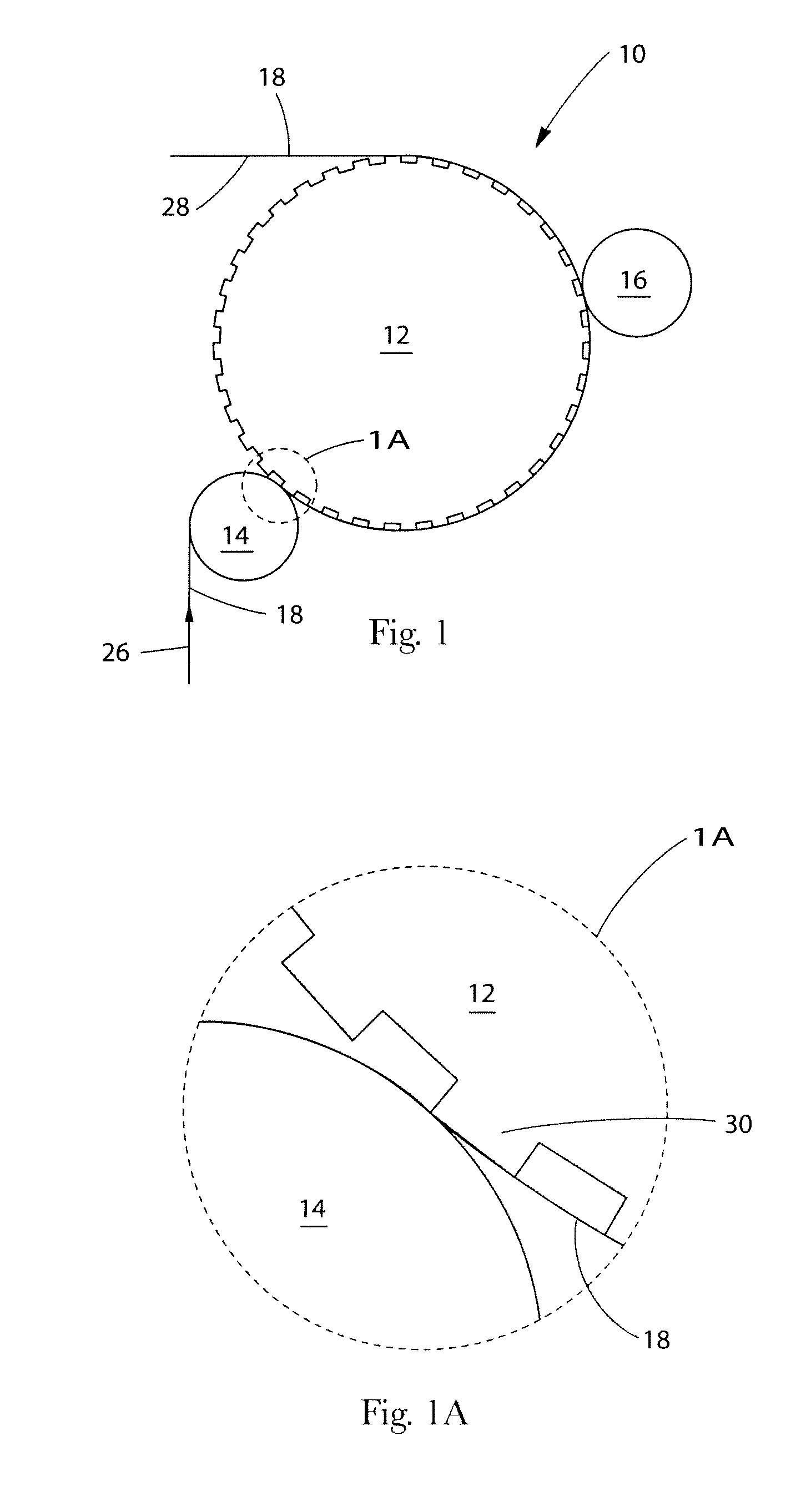
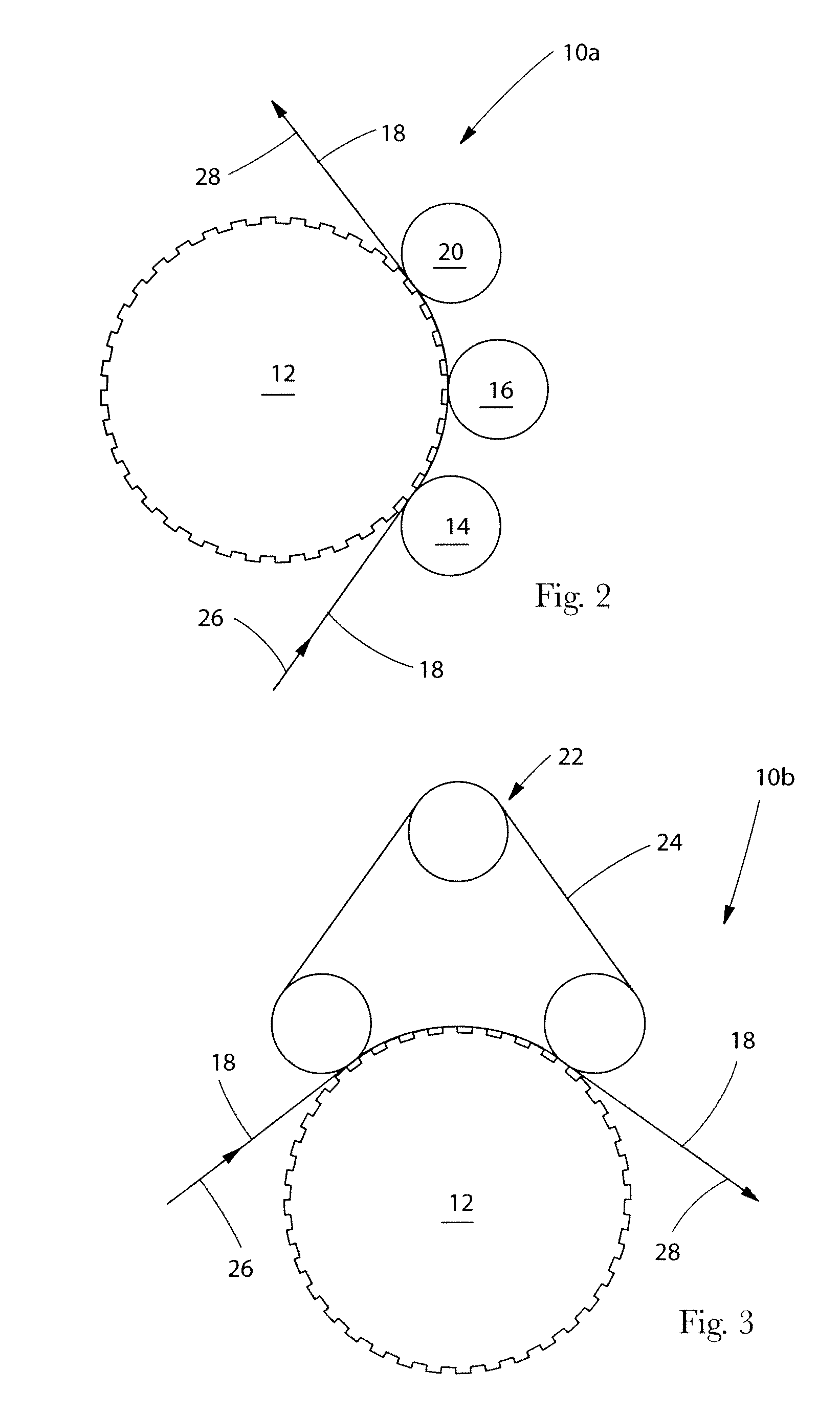
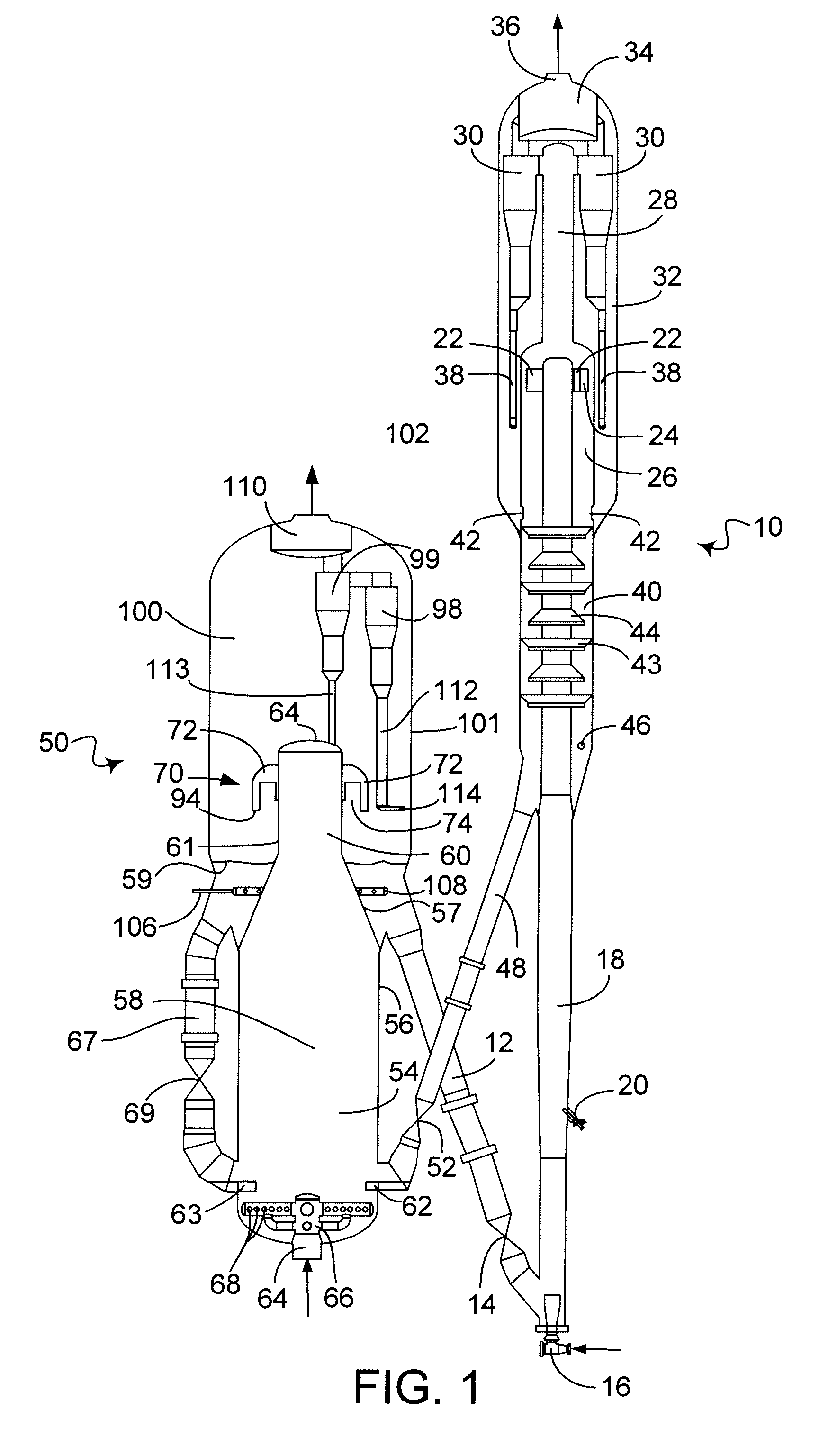
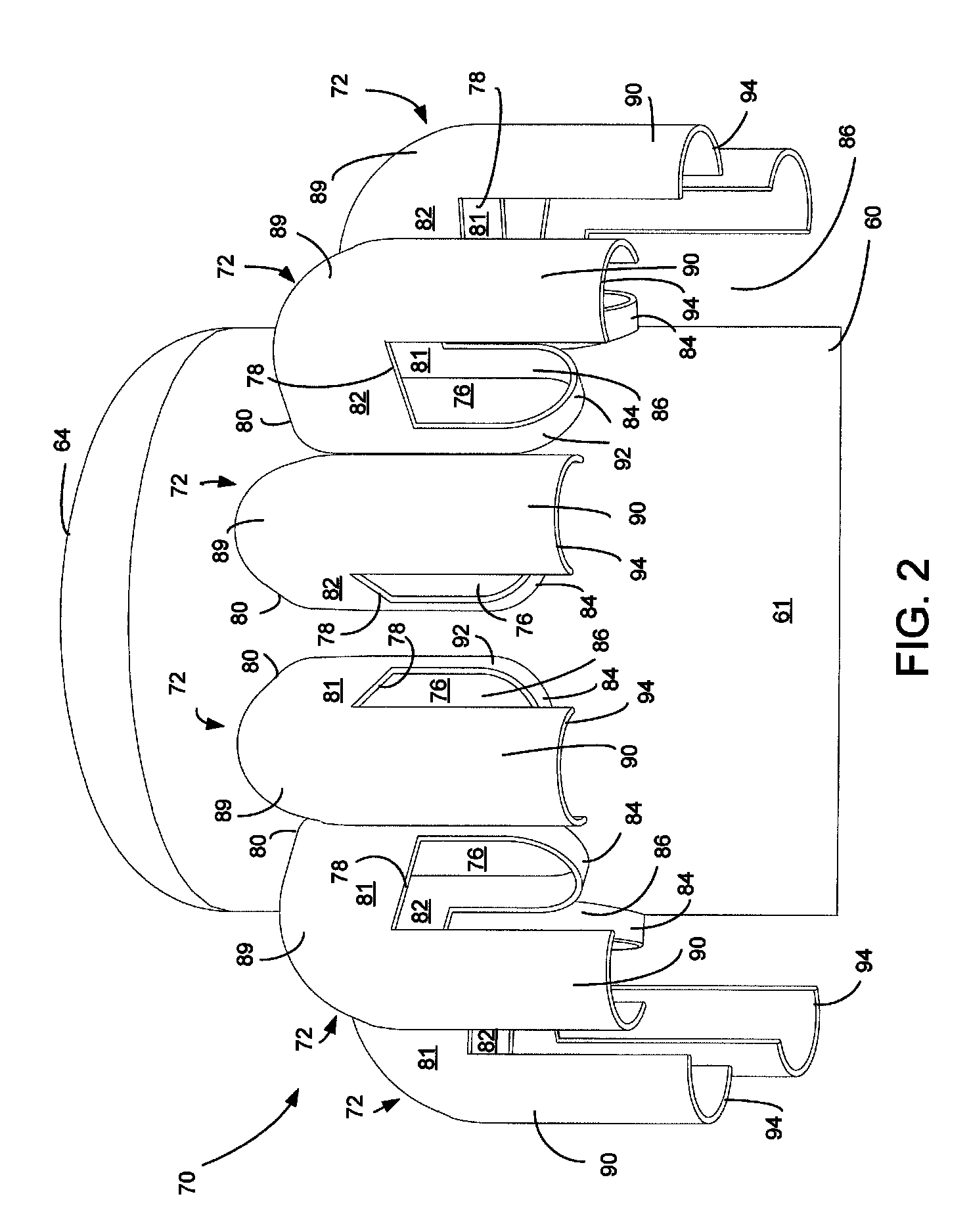
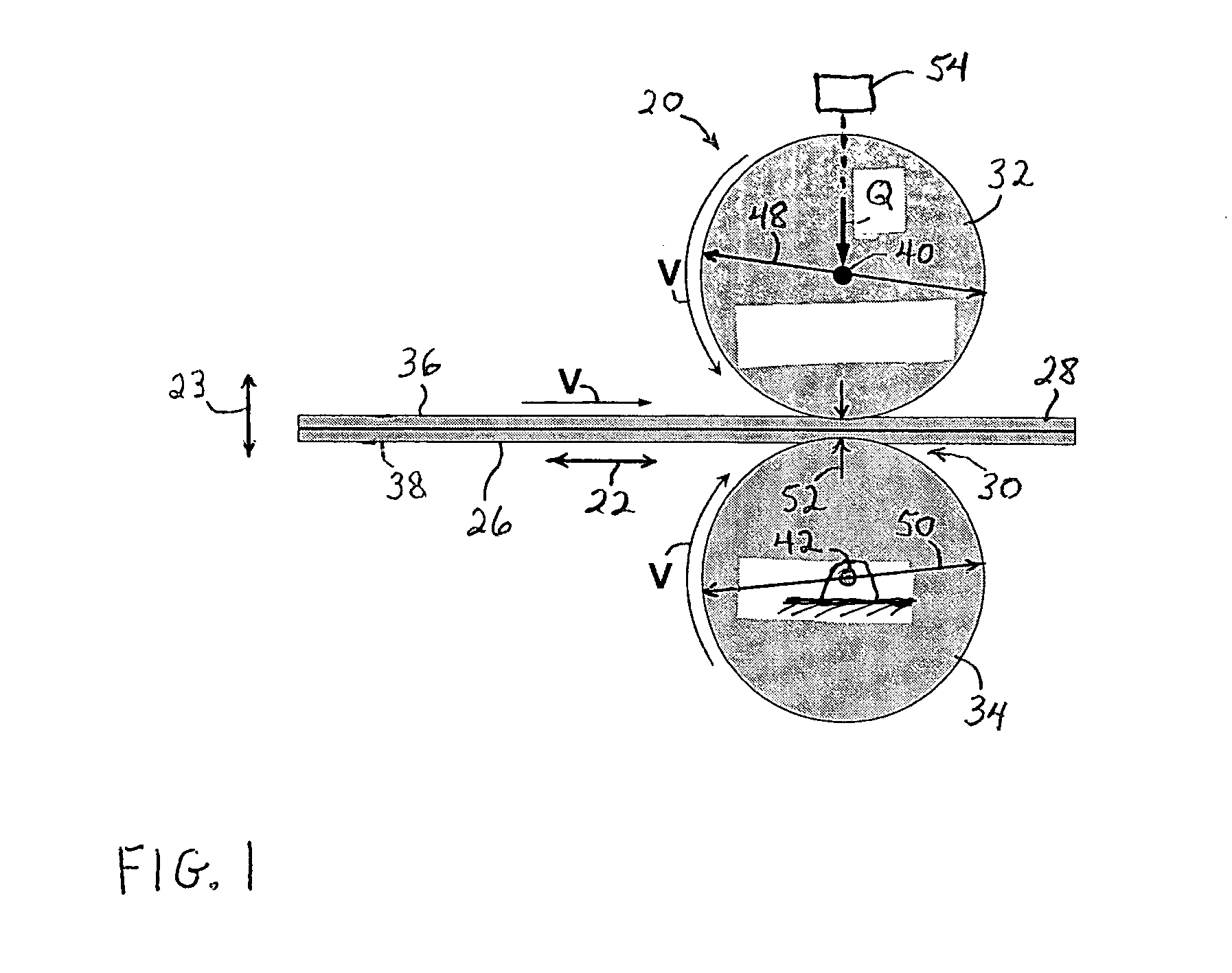
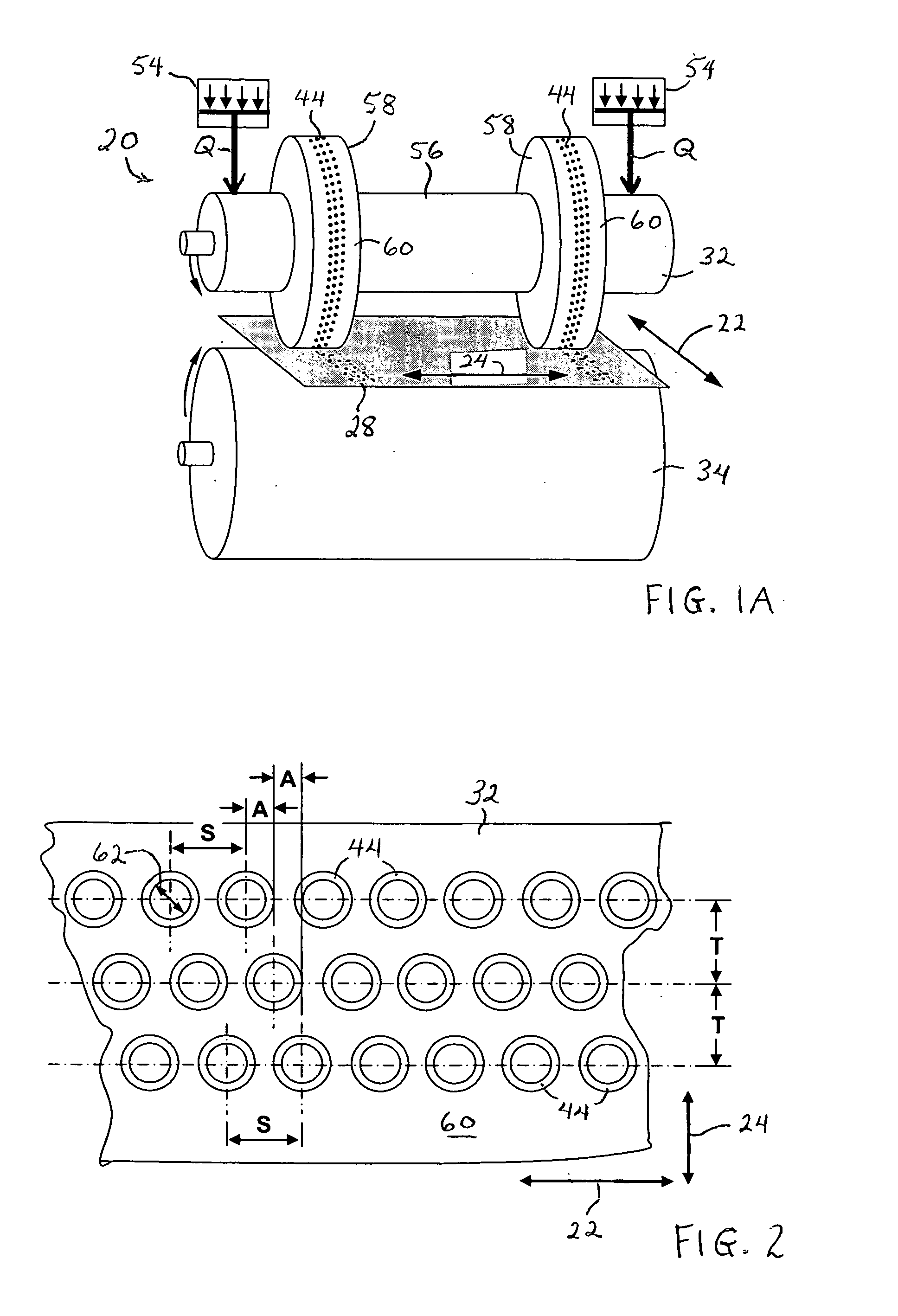
Methods and apparatus for intermittent rotary ultrasonic bonding system
InactiveUS6123792AAvoids deleterious bounceExtended service lifeLaminationLamination apparatusFiberSurface velocity
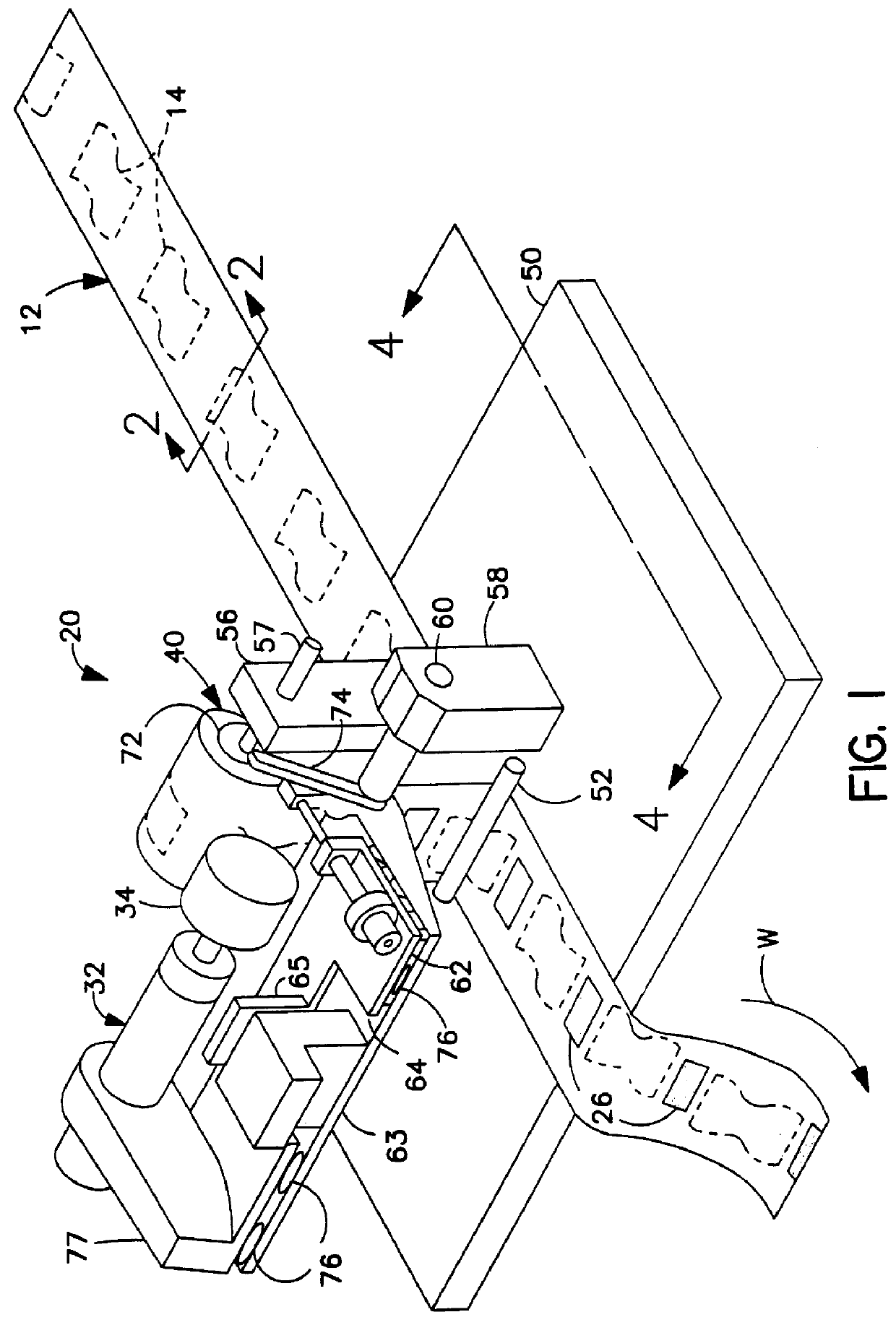
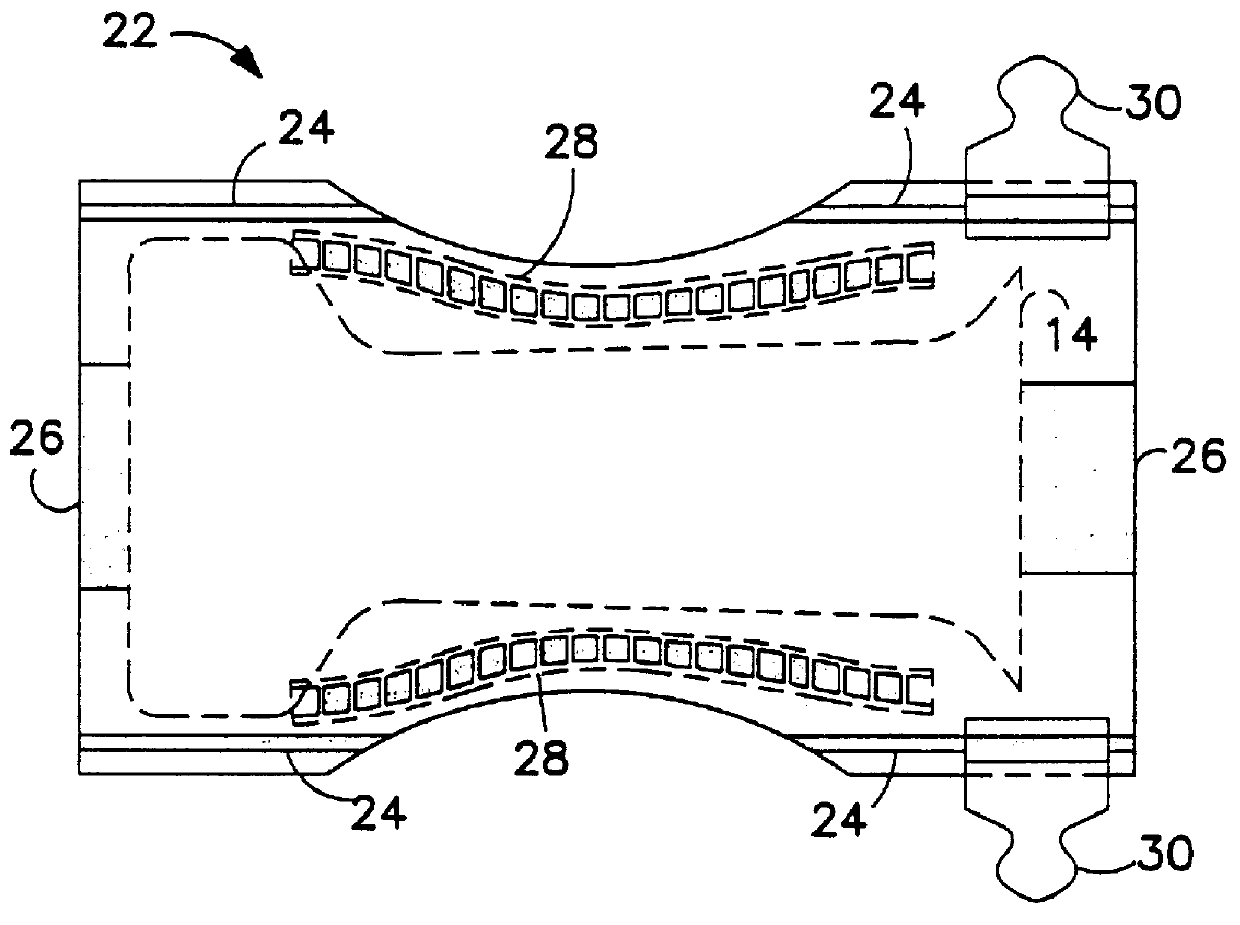
This invention relates to apparatus and methods for intermittently bonding a substrate web in fabricating a blank subassembly for an absorbent article. The invention comprises ultrasonic bonding apparatus including an anvil roll, a substrate web thereon, and at least one rotary ultrasonic horn. The substrate web can comprise at least first and second layers of material. The rotary ultrasonic horn, in combination with the anvil roll, ultrasonically bonds intermittent segments of the first and second layers of the substrate web to each other. Such intermittent bonds can comprise end seals for the absorbent articles. The ultrasonic horn and anvil roll are periodically separated from each other to provide the intermittent bonding of the substrate web. An actuator apparatus periodically moves the anvil roll and ultrasonic horn from engaging contact with each other preventing bond formation. The actuator apparatus can include a cam mechanism moving one of the anvil roll and ultrasonic horn from engaging contact with the other during rotation of the rotary ultrasonic horn. The cam mechanism can create a physical gap between the ultrasonic horn and the anvil roll. The cam mechanism moves either the ultrasonic horn and the anvil roll toward the other of the ultrasonic horn and anvil roll at a velocity of no more than about 80 millimeters / second to prevent bounce or impact loading when the horn and anvil roll are in engaging contact. The anvil roll comprises a substrate-receiving surface generally moving the substrate web through the nip at a surface speed of at least 300 meters per minute. The ultrasonic system generally creates bonds between the first and second layers of the substrate web at least about 600 times per minute.
Owner:DUKANE IAS LLC
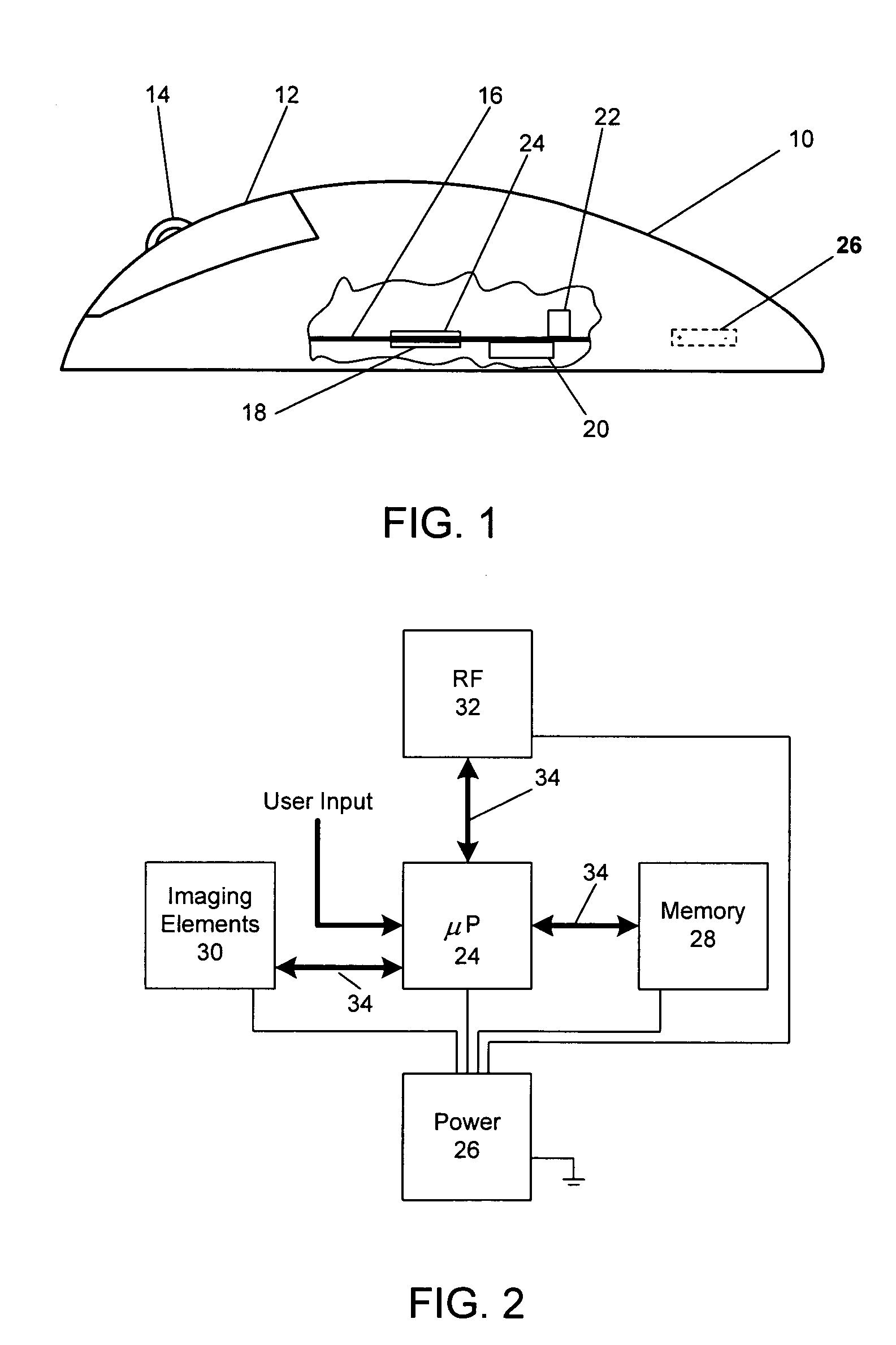
Dynamically adjusting operation of one or more sensors of a computer input device
InactiveUS20050190158A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingRelative displacementSurface velocity
A computer input device controller dynamically adjusts the rate at which an illumination source is activated, and may also adjust the rate at which other optical tracking system components are activated. As the velocity of optical tracking system movement relative to a tracked surface increases, the controller increases the activation rate(s). As the velocity of relative movement decreases, the controller decreases the activation rate(s). Future displacements of a tracking system relative to a tracked surface are also estimated. In particular, relative tracking system / tracked surface velocity is calculated based on a series of images. Relative displacement is then estimated based on the calculated velocity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Near-surface modeling method using tomography inversion of two-step method
InactiveCN102590864ASolve detailed modeling challengesImprove image qualitySeismic signal processingGeophoneOffset distance
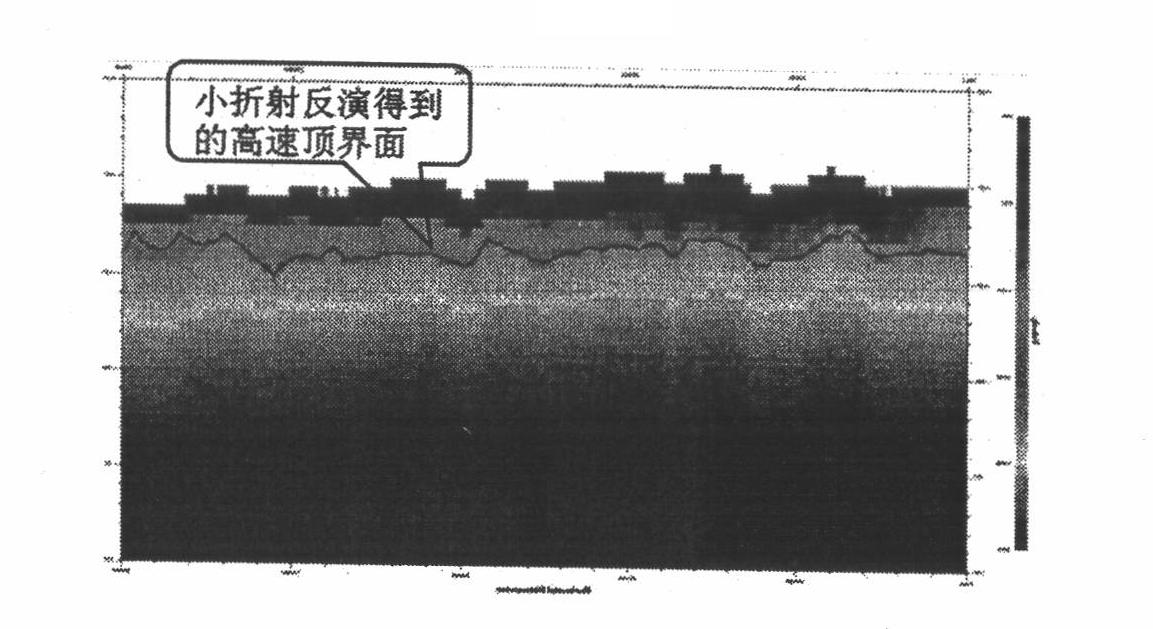
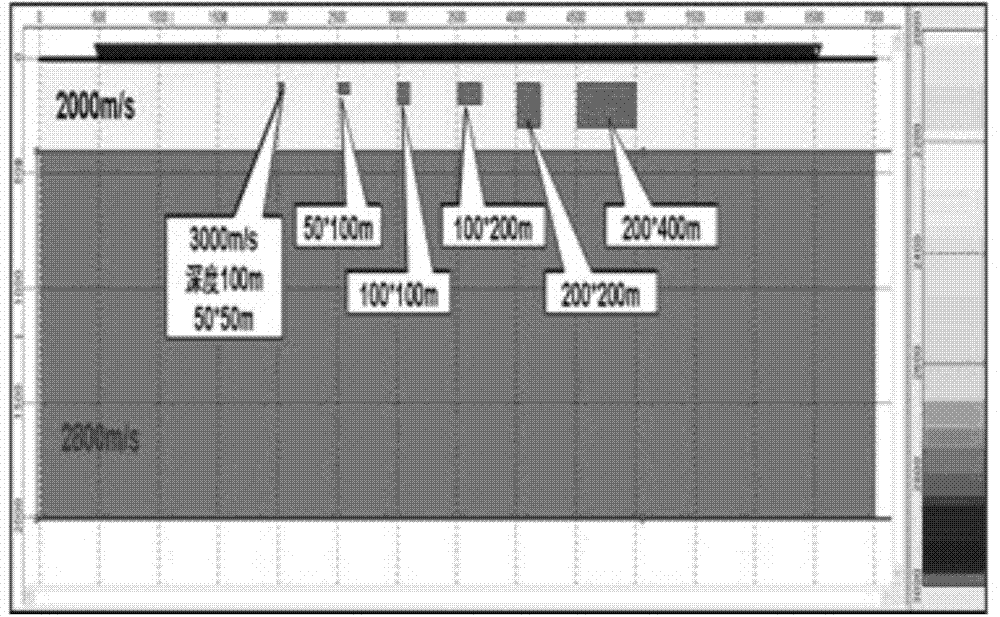
The invention relates to a near-surface modeling method using tomography inversion of a two-step method. The near-surface modeling method specifically comprises the following steps of: (1) picking and inputting short-refraction first-break; (2) carrying out tomography inversion on the short-refraction first-break and outputting explanation results capable of reflecting fine velocity change in an extremely shallow stratum as shown in picture 2; (3) picking a big shot and recording first-break time; (4) interpolating short-refraction inversion results in combination with explanation results of a microlog in a work area by using a kriging method and building near-surface velocity body of the extremely shadow stratum; (5) meshing and constraining inversion initial-velocity modeling, replacing a near-surface velocity body at the extremely shallow stratum obtained in the last step into the shallow stratum part of the initial model generated at the big-shot first-break, replenishing the velocity loss of the extremely shallow stratum resulting from the excessive minimum offset distance of the big shot; (6) constraining generation of a weight field; and (7) inversing the near-surface velocity model by using a constrained chromatography method, picking the top interface of a high-speed layer on the basis of a velocity-depth model obtained by tomography inversion, and calculating static correcting values of a shot point and a geophone position.
Owner:中国石油集团西北地质研究所有限公司
Velocity determination of the near-surface layers in the earth using exploration 2D or 3D seismic data
InactiveUS20050256648A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime structureSeismic survey
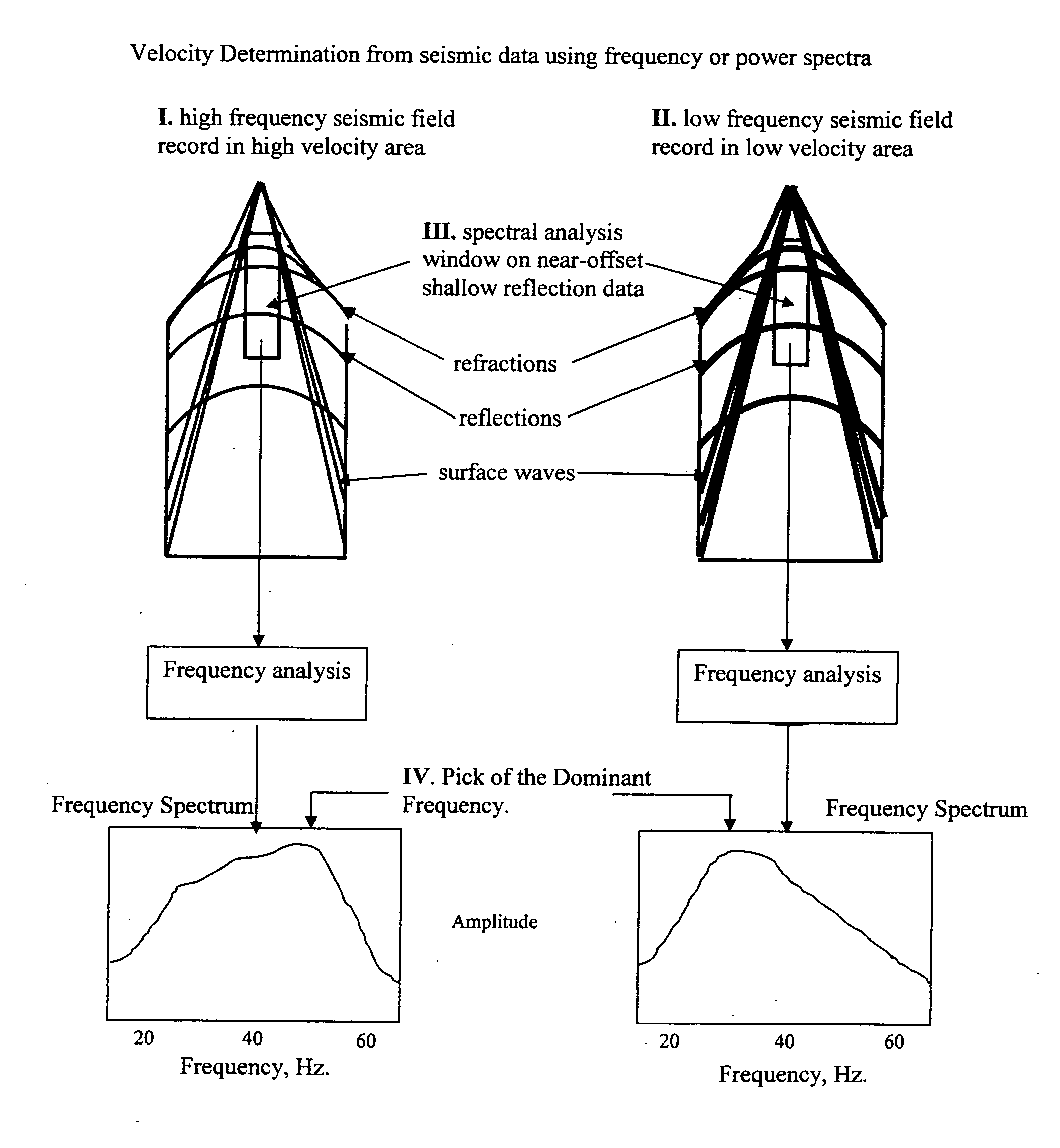
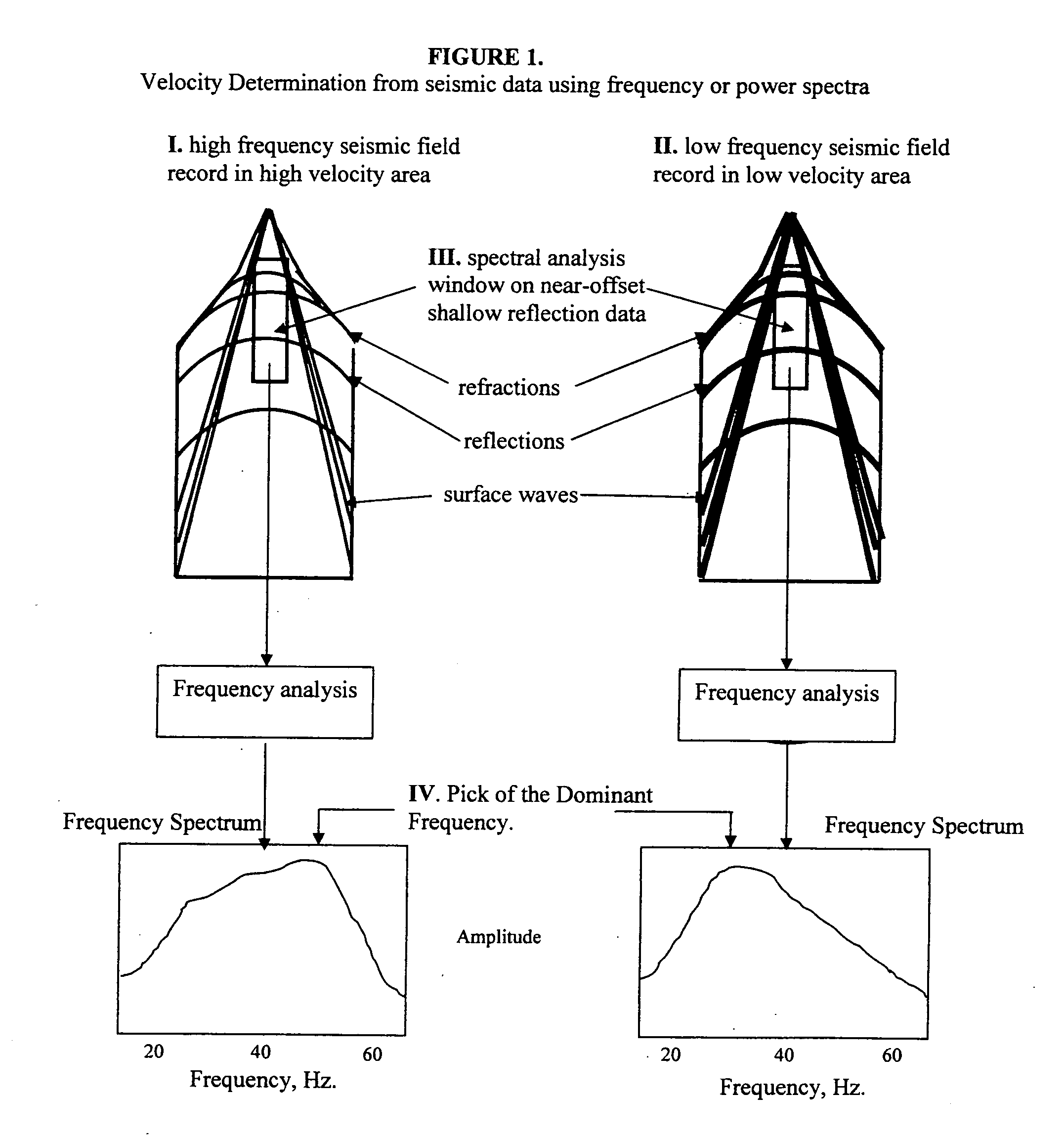
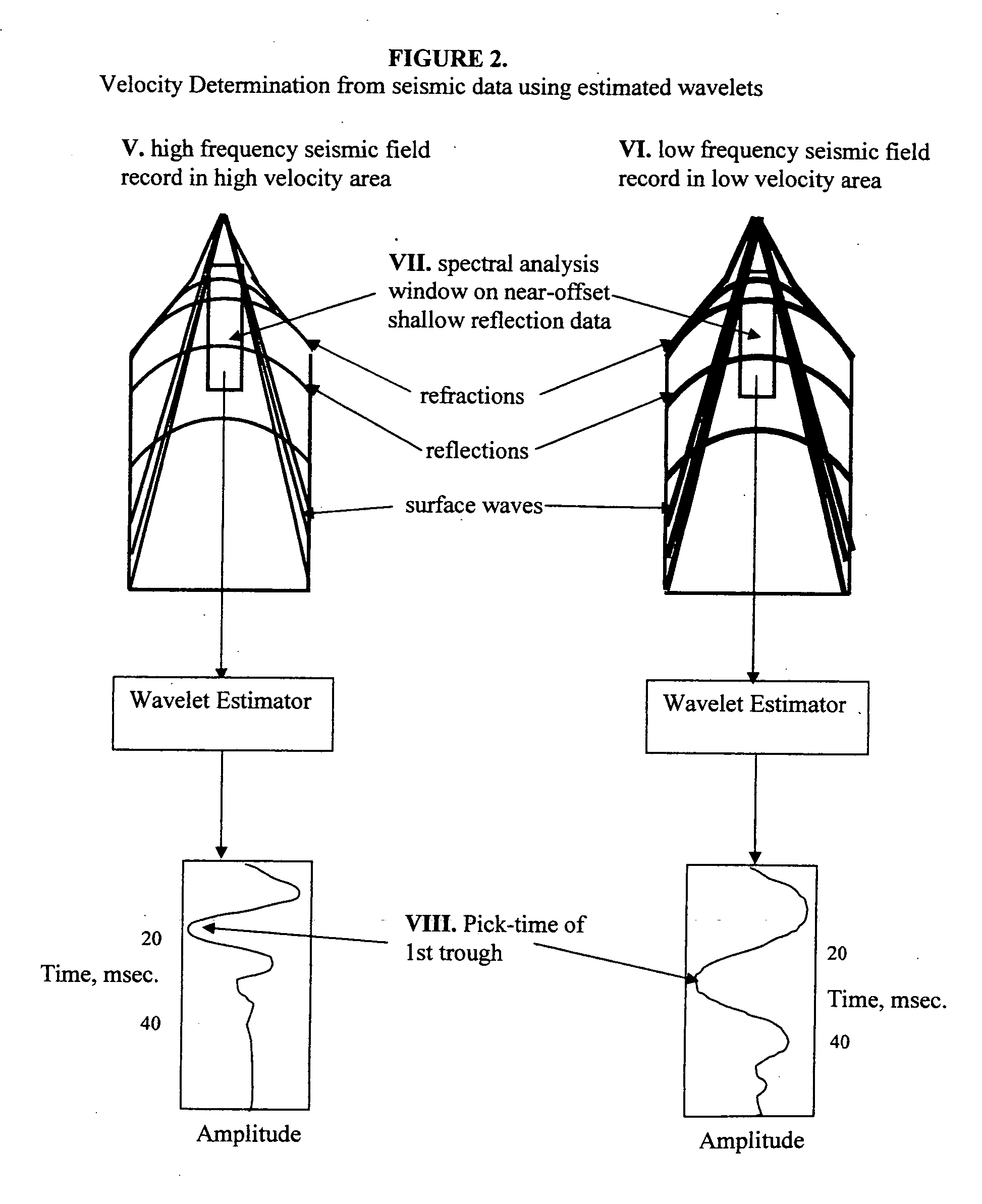
Several methods for determining the near-surface layer velocity in the earth (can include the weathering layer velocity) from exploration seismic 2D or 3D data are presented. These velocity measurements are to be used in time-correcting seismic data during data processing in refraction statics, datum statics, elevation statics derivation and application or any other data processing scheme wherein the near-surface velocity is required. They can also be used as the near-surface velocity model for depth-migration of seismic data. The velocity of the near-surface is directly related to the character of the shot records themselves. By statistically measuring this character from the shot records in an automated fashion, a large amount of data can be processed and the character measurement numerically converted to a velocity measurement using benchmark velocities. A complete near-surface velocity field for the seismic survey can be created in this way and used to correct for false time-structure in seismic datasets used for hydrocarbon exploration or any other sub-surface exploration purposes.
Owner:WEST MICHAEL PATRICK
Image forming apparatus, image forming method, and computer program product
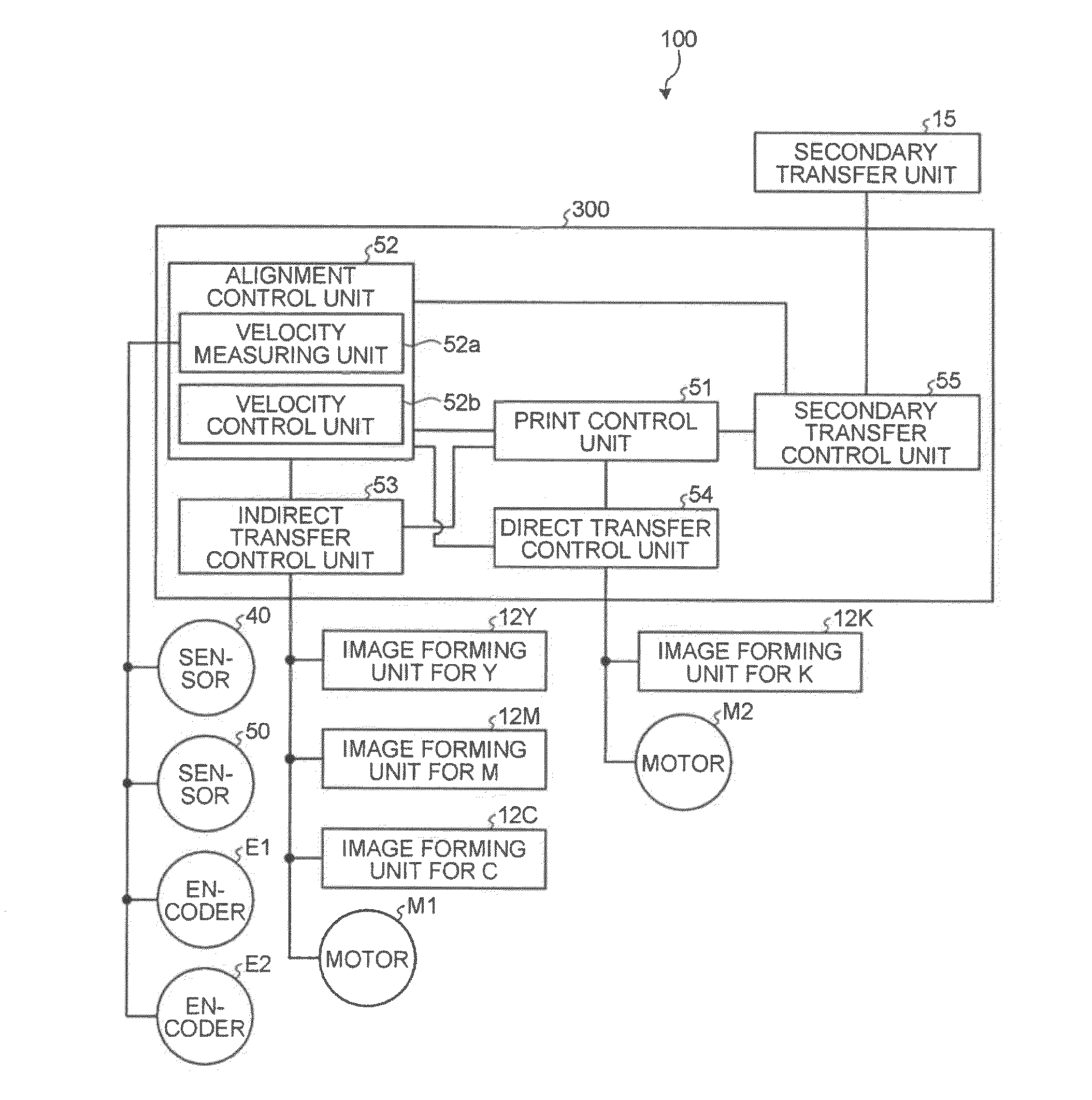
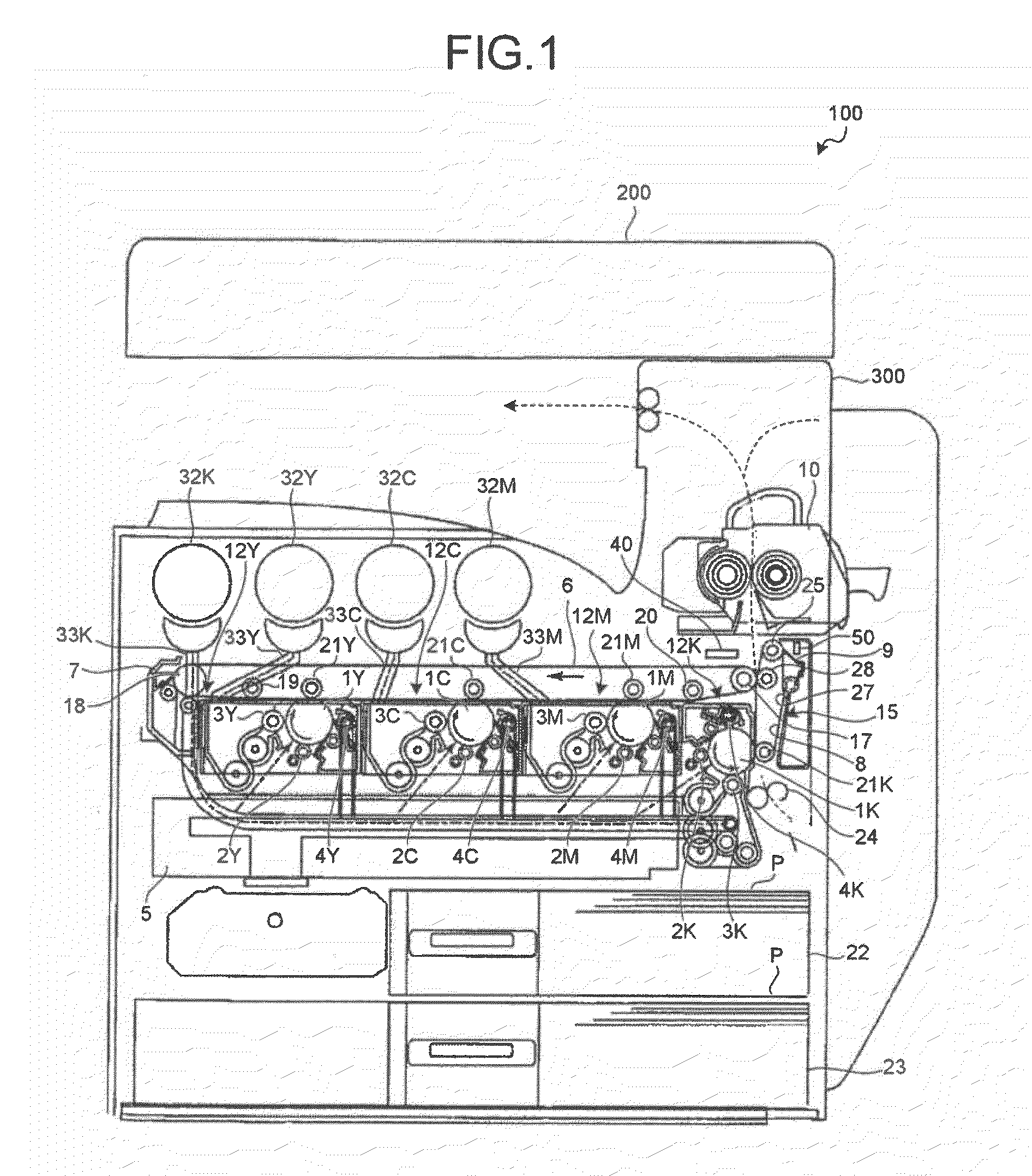
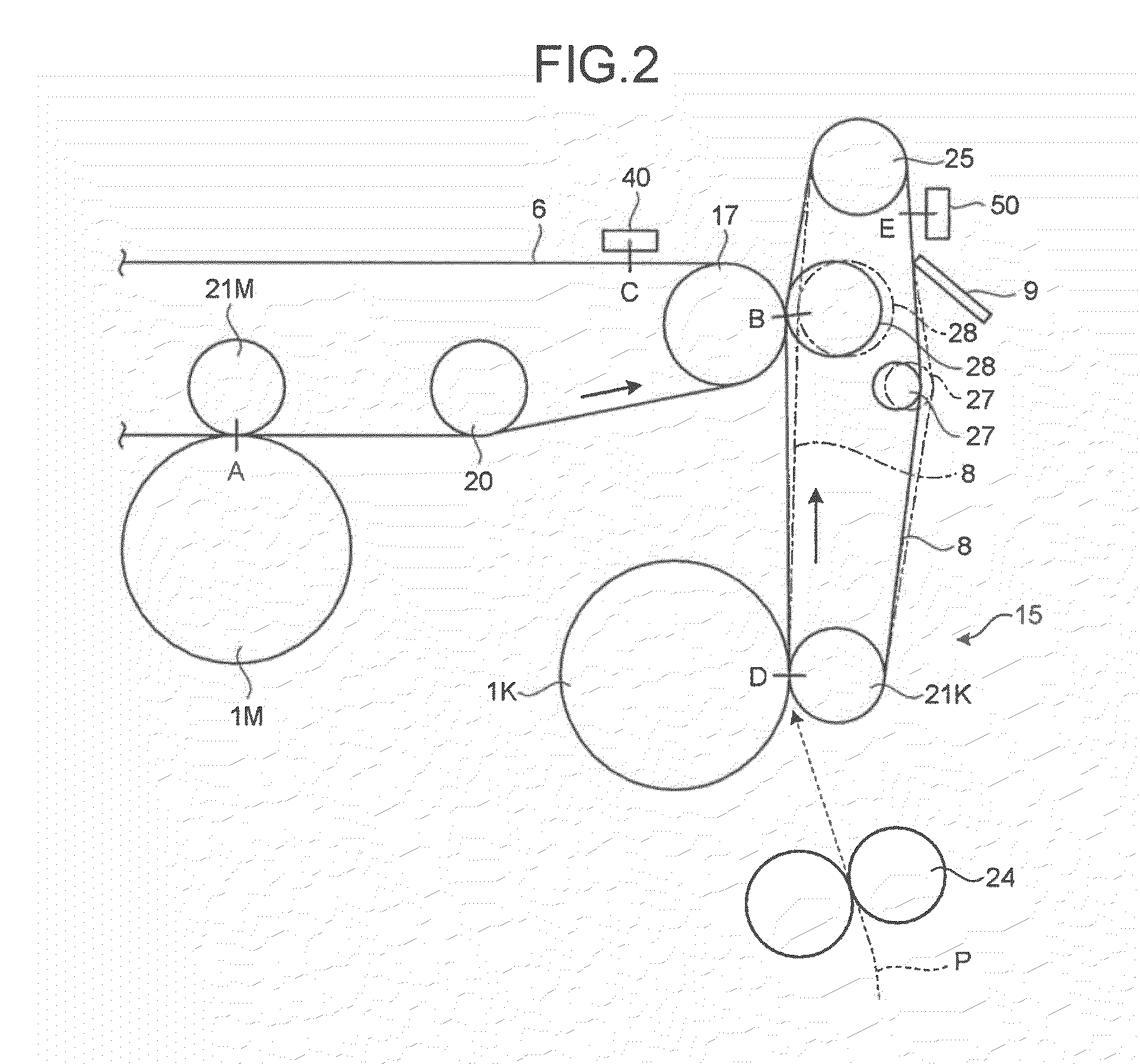
An image forming apparatus includes: a transfer-sheet conveying member that rotates to convey a transfer sheet; a first image forming unit that directly transfers a color image onto the transfer sheet; an intermediate transfer member that rotates while an image is transferred thereon; a second image forming unit that transfers images onto the intermediate transfer member; a secondary transfer unit that transfers the images on the intermediate transfer member onto the transfer sheet; a measuring unit that measures a surface velocity of the transfer-sheet conveying member and the intermediate transfer member; and a control unit that performs phase matching control by accelerating or decelerating the transfer-sheet conveying member or the intermediate transfer member so as to match a phase of fluctuation of the measured surface velocity of the transfer-sheet conveying member and a phase of fluctuation of the measured surface velocity of the intermediate transfer member.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method of manufacturing electro-magnetic wave shielding yarn
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing electromagnetic wave shielding yarn comprising the steps of (1) spinning core yarn with the apparatus for core spun yarn on ring spinning machine, (2) preparing rovings made of natural, synthetic and blended fiber, (3) preparing a twisted wire-filament core, (4) feeding rovings to front rollers through back and middle rollers, (5) supplying said twisted core to the front rollers applying tension on the twisted core by means of drafting the twisted core with suitable draft ratio which is the ratio of surface velocity between core supplying rollers and the front rollers and (6) twisting the delivered core yarn.
Owner:YOUNG NAM TEXTILE
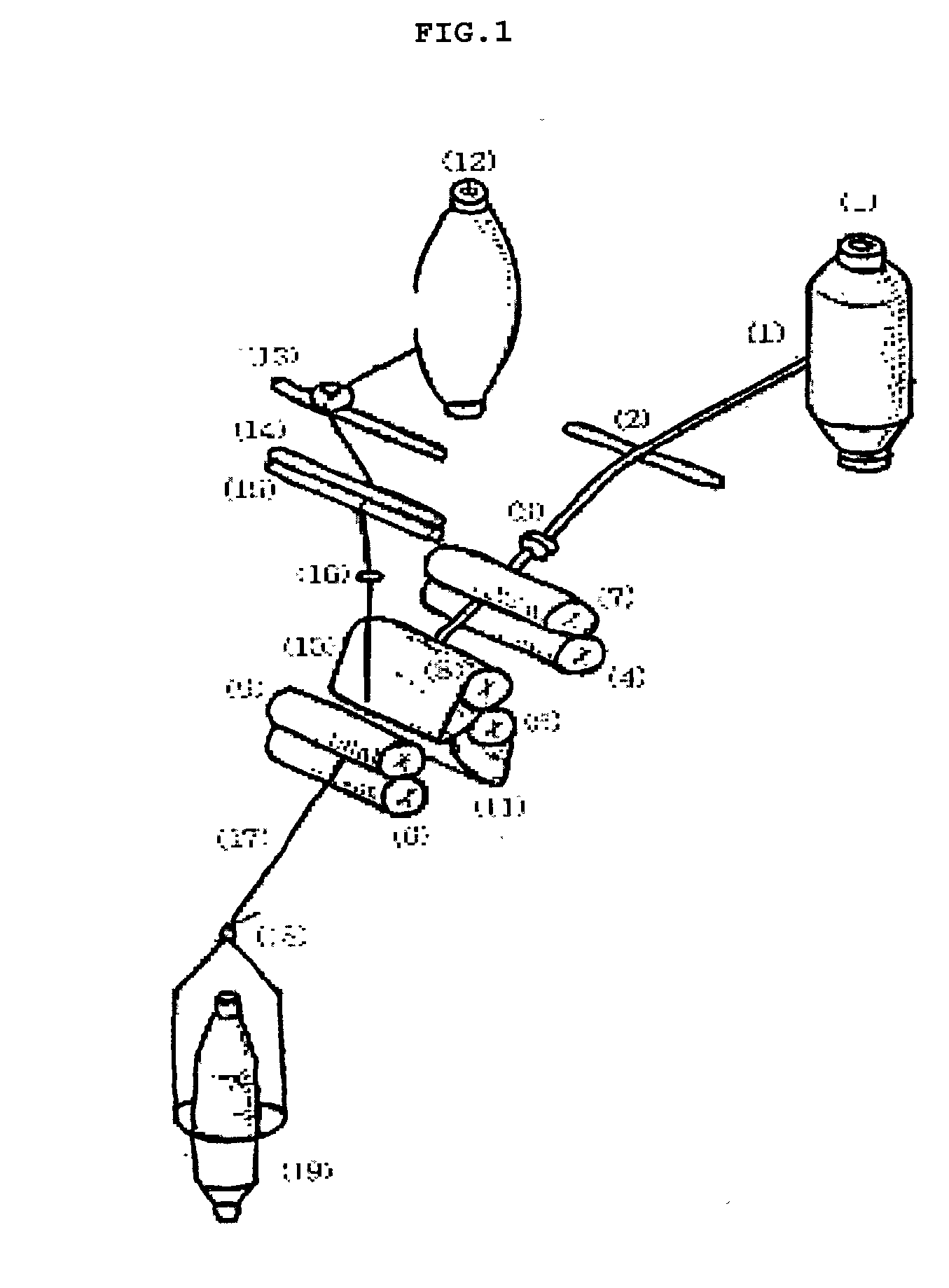
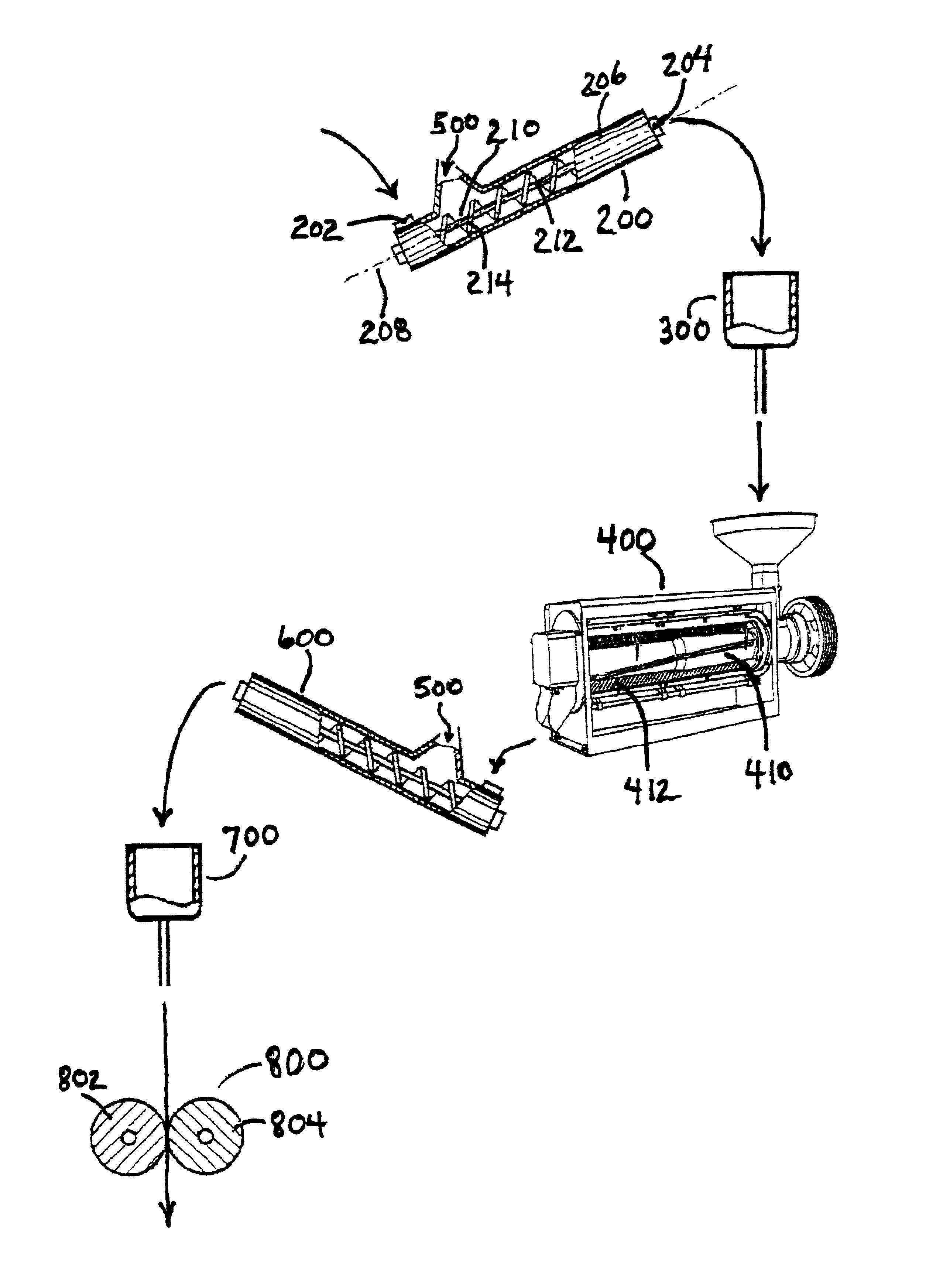
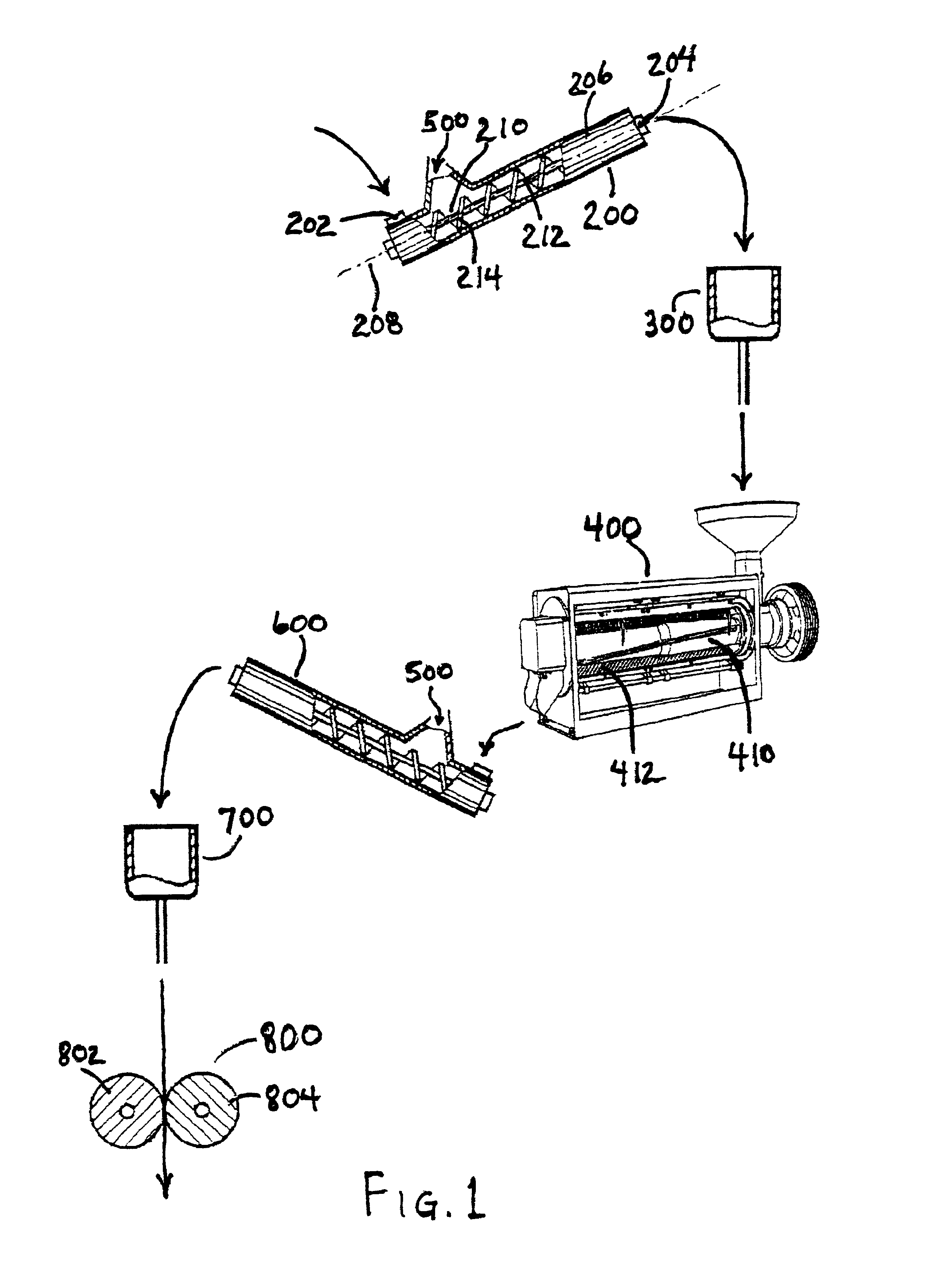
Corn degermination process
InactiveUS6936294B2Increase productionYield maximizationGrain huskingGrain polishingSurface velocityEngineering
Owner:SATAKE USA INC
Method for establishing near-surface velocity model in high-density seismic static correction processing
ActiveCN101980054ASolve the statics problemReduce memory usageSeismic signal processingGeophoneHigh density
The invention belongs to seismic data processing in petroleum geophysical exploration and geological engineering survey, and relates to near-surface velocity modeling and static correction in seismic exploration aiming at research and development of a shallow velocity model required for combined post static correction in a detector chamber of single-point high-density seism. A method for establishing a near-surface velocity model in high-density seismic static correction processing comprises the following steps of: supposing that the near-surface velocity is linearly increased along with the depth, calculating refracted wave velocity of different geophone offset from the travel time difference of primary waves of adjacent detection points of the high-density seism according to the physical property of the primary wave of the near-surface velocity field, establishing a near-surface ramp velocity field parameter according to the relationship between the geophone offset and the refracted wave, and further establishing the near-surface velocity model which can be directly used for static correction quantity calculation in seismic processing and also can be used as an initial model for tomographic inversion of near-surface velocity. The method has high calculation speed, and does not depend on the change of the initial position caused by a seismic focus.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Process for embossing web materials
A process for embossing a web substrate is disclosed. The process comprises the steps of: 1. disposing the web substrate in a circumferentially elongate nip formed between a pattern roll having a circumference and an embossing pattern disposed upon a surface thereof and a continuous belt disposed about at least a portion of the circumference of the pattern roll; 2. providing the continuous belt with a surface speed corresponding to a speed of the web substrate; and, 3. juxtaposing the embossing pattern upon the web substrate while the web substrate is disposed within the elongate nip.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
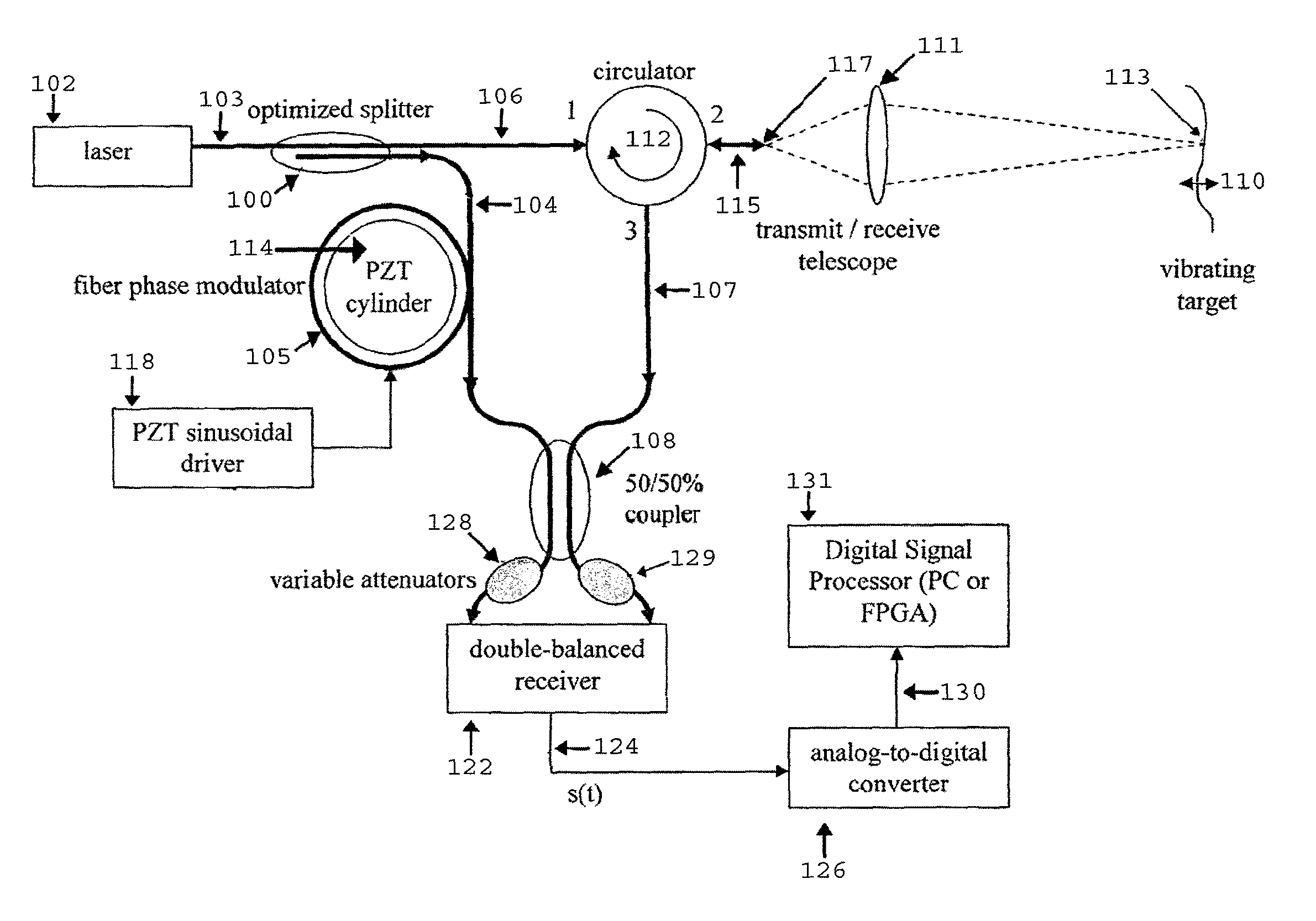
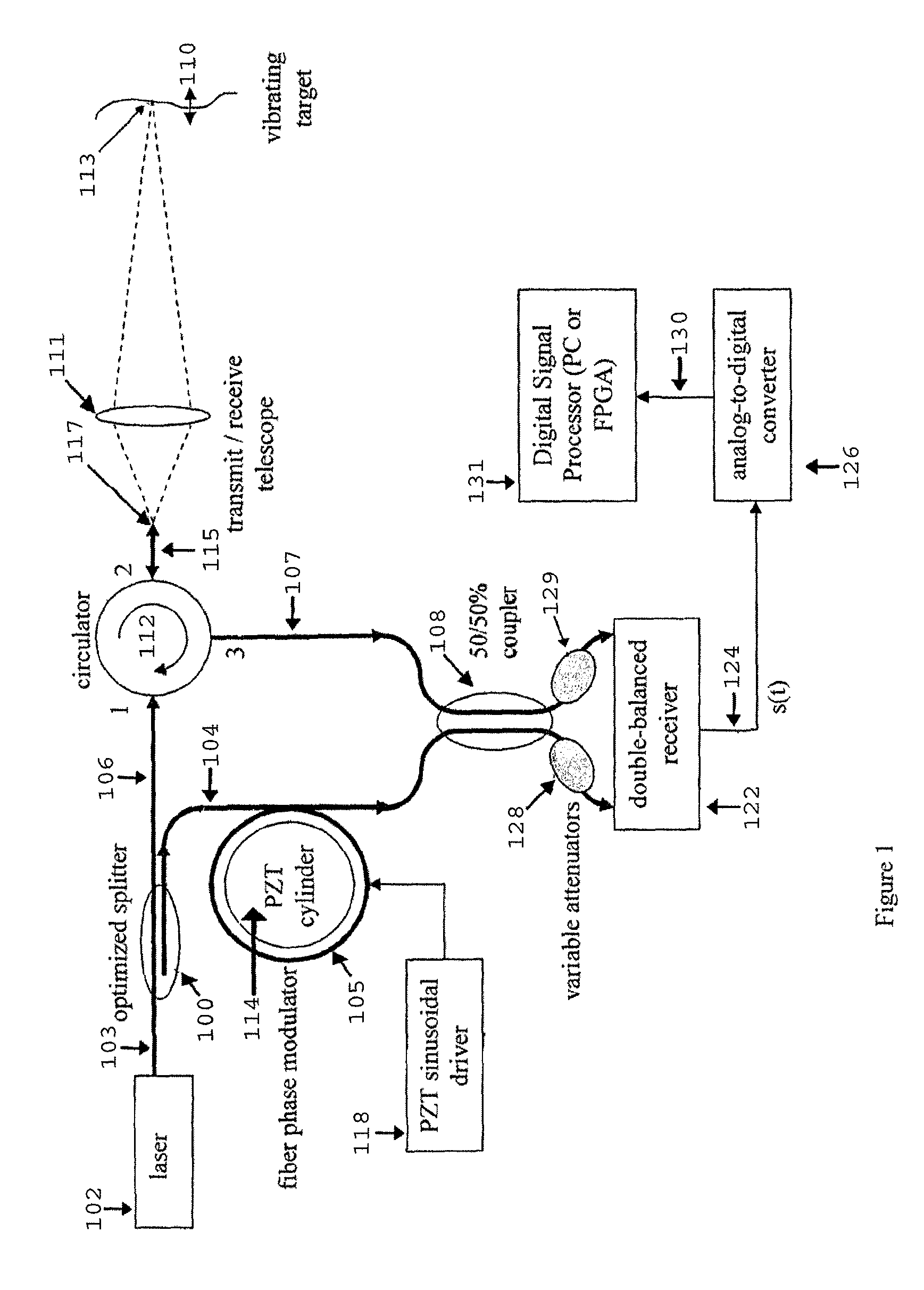
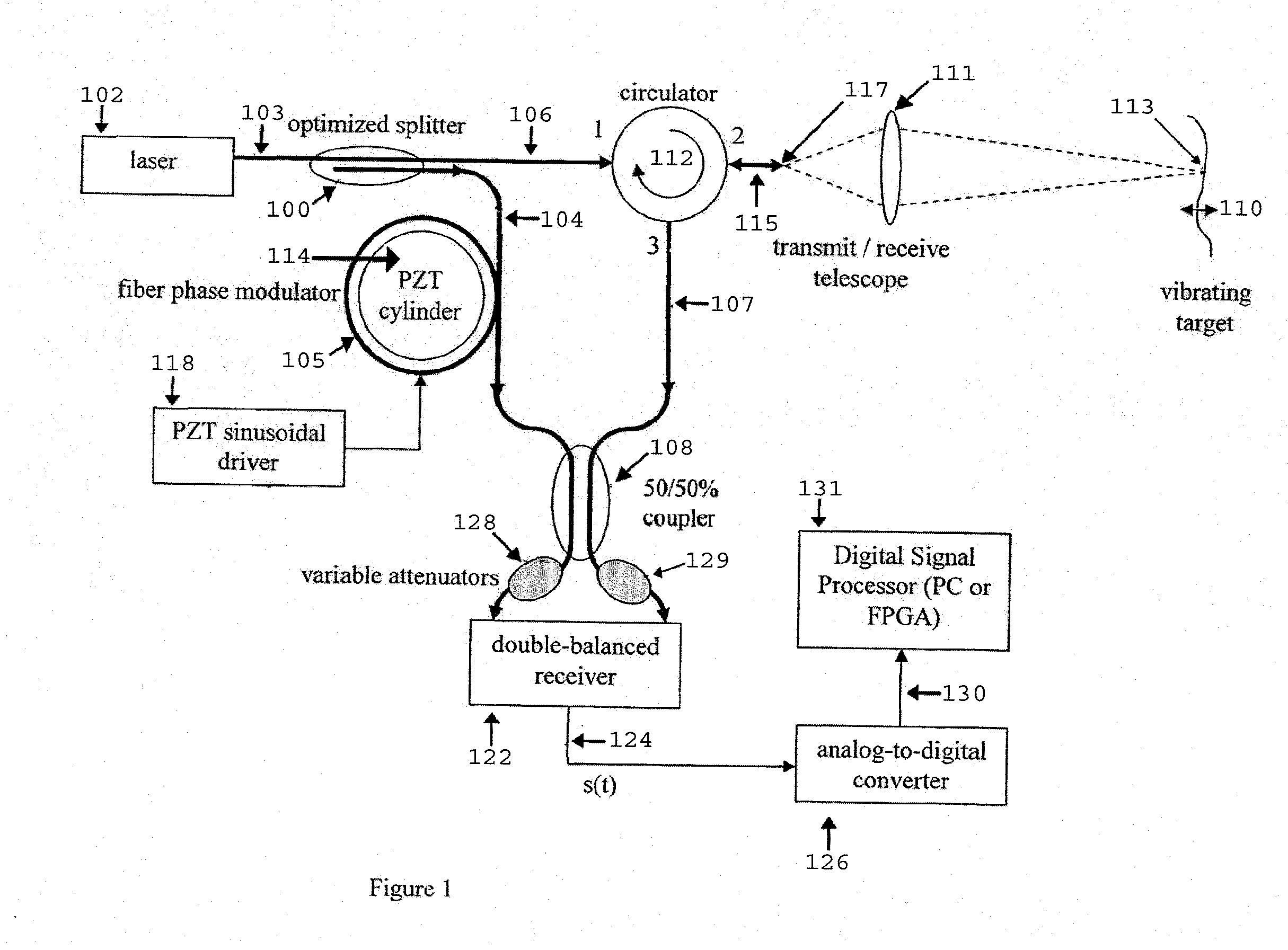
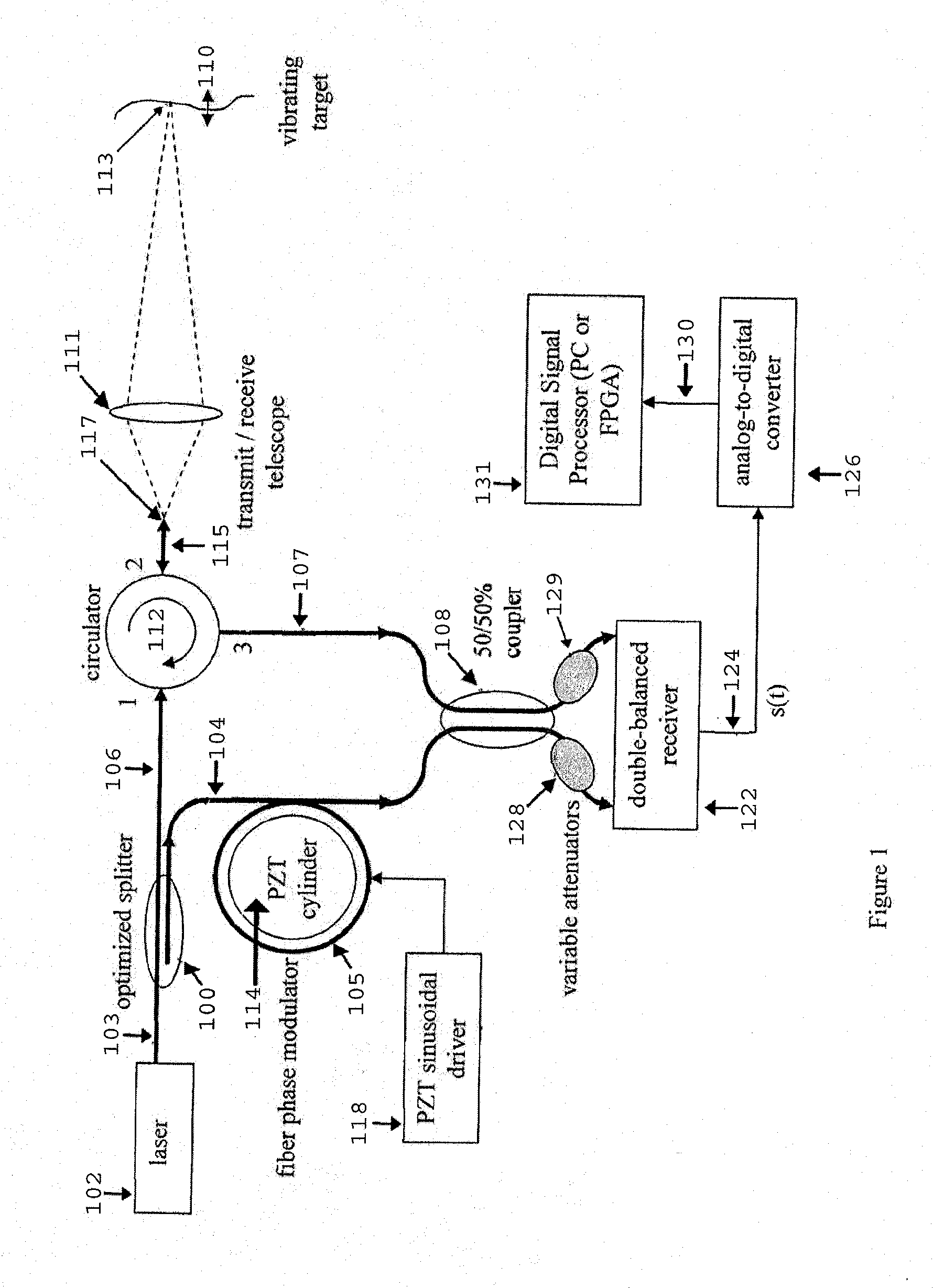
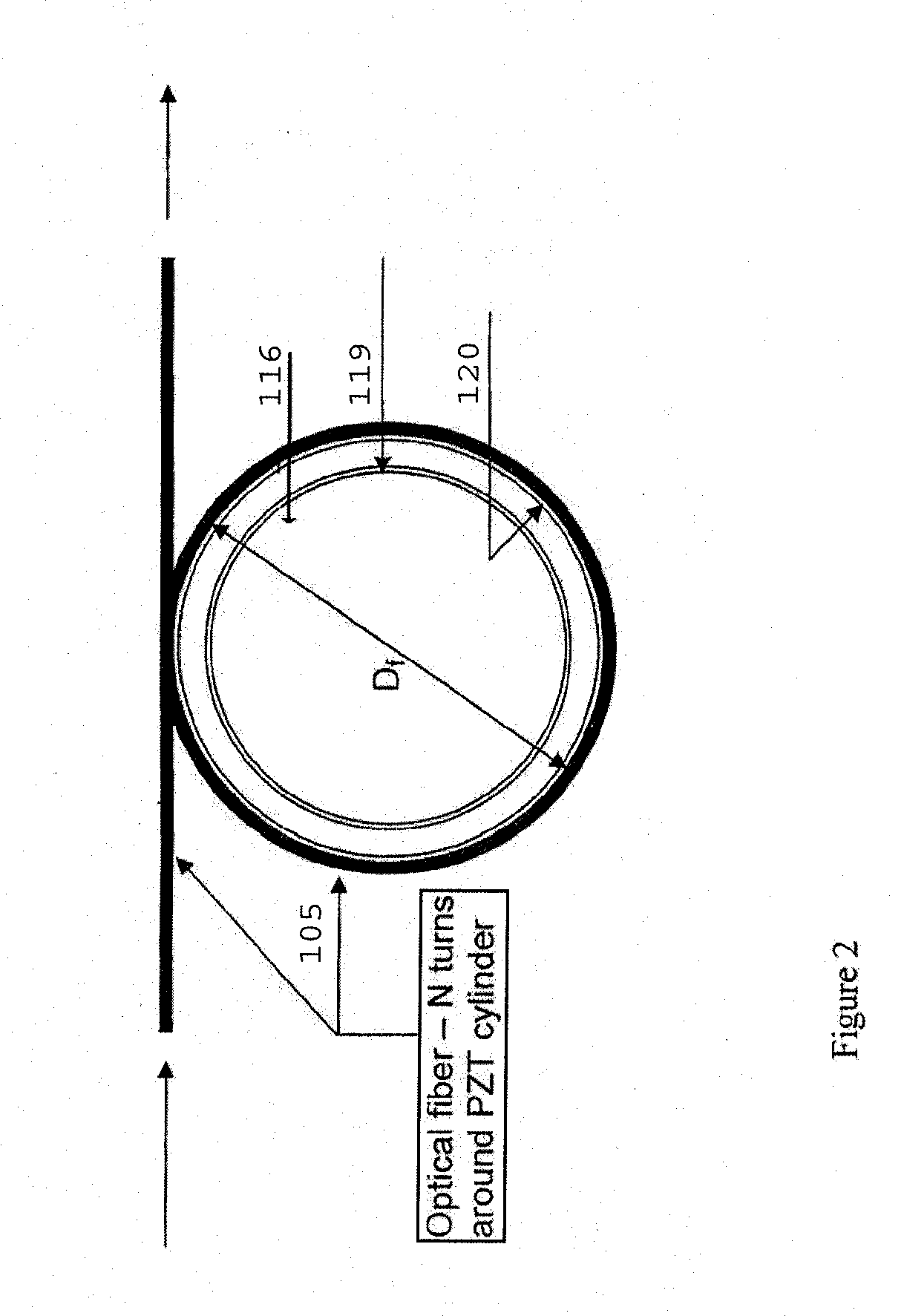
Fiber-optic, digital system for laser Doppler vibrometers (LDVs)
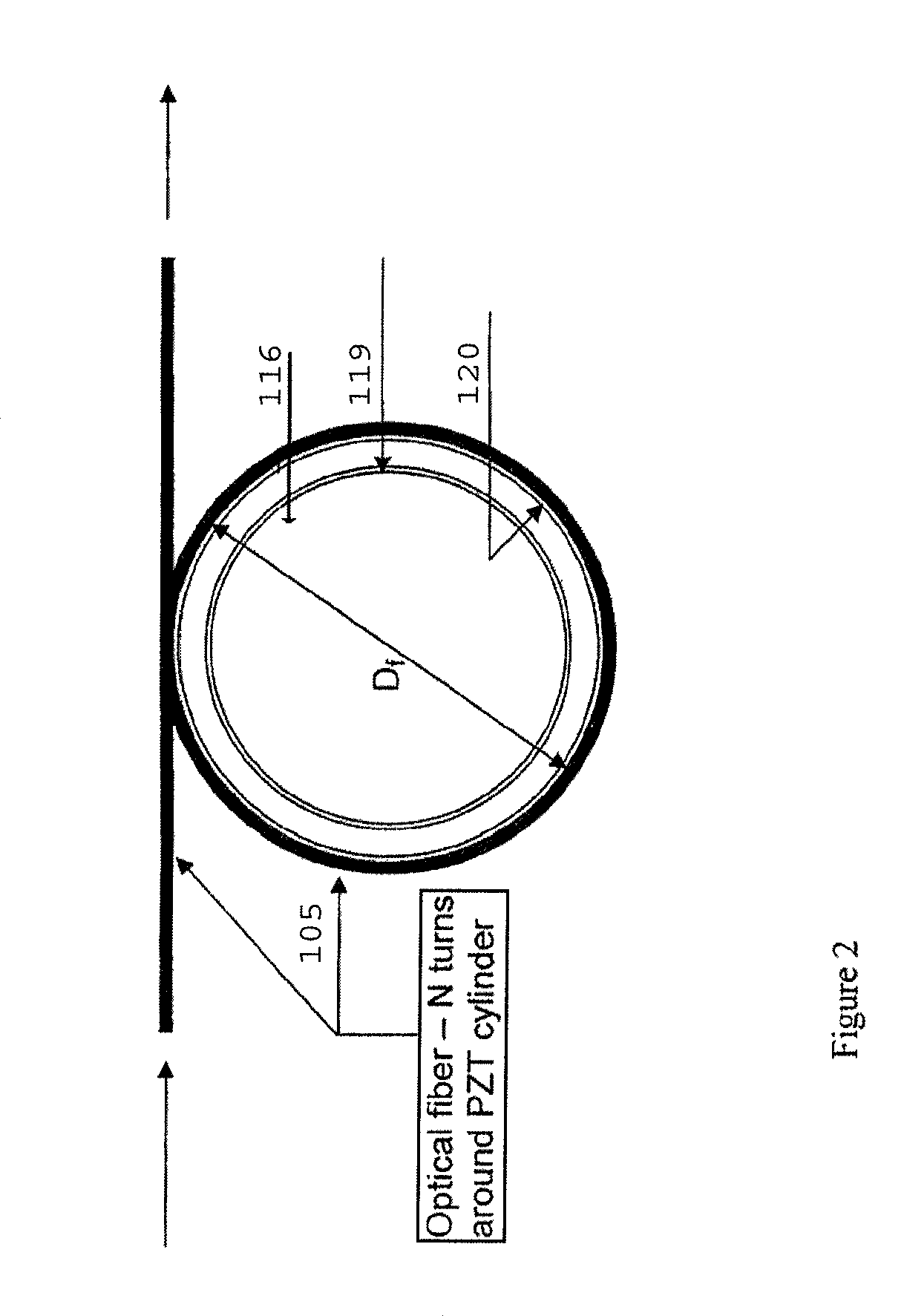
InactiveUS8144334B2Improve efficiencyMaintain efficiencyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementFiberSmall amplitude
An apparatus and method for non-determination of the surface velocity of a target using optical interference and Doppler shifting of the light reflected from the target are disclosed. It may be used to measure small-amplitude, acoustic frequency surface vibrations as well as non-periodic surface vibration.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Direct prestack time migration method for three-dimensional seismic data acquired from irregular surfaces
InactiveCN102193109AAvoid difficultiesReduce processing linksSeismic signal processingLand acquisitionSurface velocity
The invention discloses a direct prestack time migration method for three-dimensional seismic data acquired from irregular surfaces, and the method is applied to the processing on reflected seismic information in seismic exploration. The method can be used for directly carrying out three-dimensional seismic data migration imaging (at different elevations) on shot points and geophone points acquired from irregular surfaces without statically correcting a processing process. In the method, no vertical emergence and incidence assumption is performed on nearsurface seismic wave propagation, therefore, the method can adapt to the situations which have no obvious low velocity region and velocity-reduction region such as high-velocity rock outcropping, and the like. In the method, the seismic wave propagation in near surfaces or stratums is described by using two equivalent speed parameters; and the two equivalent speed parameters can be determined according to the straightness of lineups inmigrated gathers, thereby avoiding the difficulties in near-surface velocity modeling. By using the method disclosed by the invention, the gathers subjected to migration can be subjected to remainingstatic correction, thereby effectively compensating the inherent errors existing in a land acquisition technology. The method has important application value in oil, gas and mineral resource exploration in complex surface areas.
Owner:INST OF GEOLOGY & GEOPHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for inverting near-surface velocity model by utilizing preliminary waveforms
The invention discloses a method for inverting a near-surface velocity model by utilizing preliminary waveforms. The method comprises acoustic wave equation-based wave field forward modeling and steepest descent-based waveform inversion technologies, and comprises the following steps of 1, extracting time-domain preliminary waveform records and an initial model; 2, calculating a simulated wave field and a wave field residual by utilizing acoustic wave equation staggered grid finite-difference forward modeling simulation; 3, reversely propagating the wave field residual to obtain a retransmission wave field; 4, calculating a gradient of a target function by utilizing the retransmission wave field and a forward propagation wave field, and calculating an updating step length; 5, updating a speed model; 6, inspecting whether the speed model is consistent with an iteration stopping condition, outputting the speed model if the speed model is consistent with the iteration stopping condition, otherwise returning to the step 2, and continuing iterative updating. According to the method, a wave equation theory-based full-waveform inversion technology is used as reference, and preliminary waves with higher energy and more stable waveforms are used for inversion, so that the multiplicity of solutions of full-waveform inversion is reduced, and the inversion stability and the calculation efficiency are improved; the accuracy of static correction and shallow depth imaging is improved.
Owner:中国石油集团西北地质研究所有限公司
FIBER-OPTIC, DIGITAL SYSTEM FOR LASER DOPPLER VIBROMETERS (LDVs)
InactiveUS20110174078A1Improve efficiencyMaintain efficiencyAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementSmall amplitudeFiber
An apparatus and method for non-determination of the surface velocity of a target using optical interference and Doppler shifting of the light reflected from the target are disclosed. It may be used to measure small-amplitude, acoustic frequency surface vibrations as well as non-periodic surface vibration.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Dynamically adjusting operation of one or more sensors of a computer input device
InactiveUS7629961B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingRelative displacementSurface velocity
A computer input device controller dynamically adjusts the rate at which an illumination source is activated, and may also adjust the rate at which other optical tracking system components are activated. As the velocity of optical tracking system movement relative to a tracked surface increases, the controller increases the activation rate(s). As the velocity of relative movement decreases, the controller decreases the activation rate(s). Future displacements of a tracking system relative to a tracked surface are also estimated. In particular, relative tracking system / tracked surface velocity is calculated based on a series of images. Relative displacement is then estimated based on the calculated velocity.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Image quality by printing frequency adjustment using belt surface velocity measurement
Embodiments described herein are directed to a reflex printing system with improved image quality. A media transport moves a media substrate or an intermediate belt along a media path in a process direction past the two or more print heads, which deposit inks onto the media substrate or the intermediate belt. A velocity measuring device directly measures and transmits the speed of the surface of belt or media that is to receive the image to a controller, which sends print commands to the two or more print heads to control the frequency of the printing. The inks deposited on the media substrate or intermediate belt have a color registration of from 10 to 20 microns.
Owner:XEROX CORP
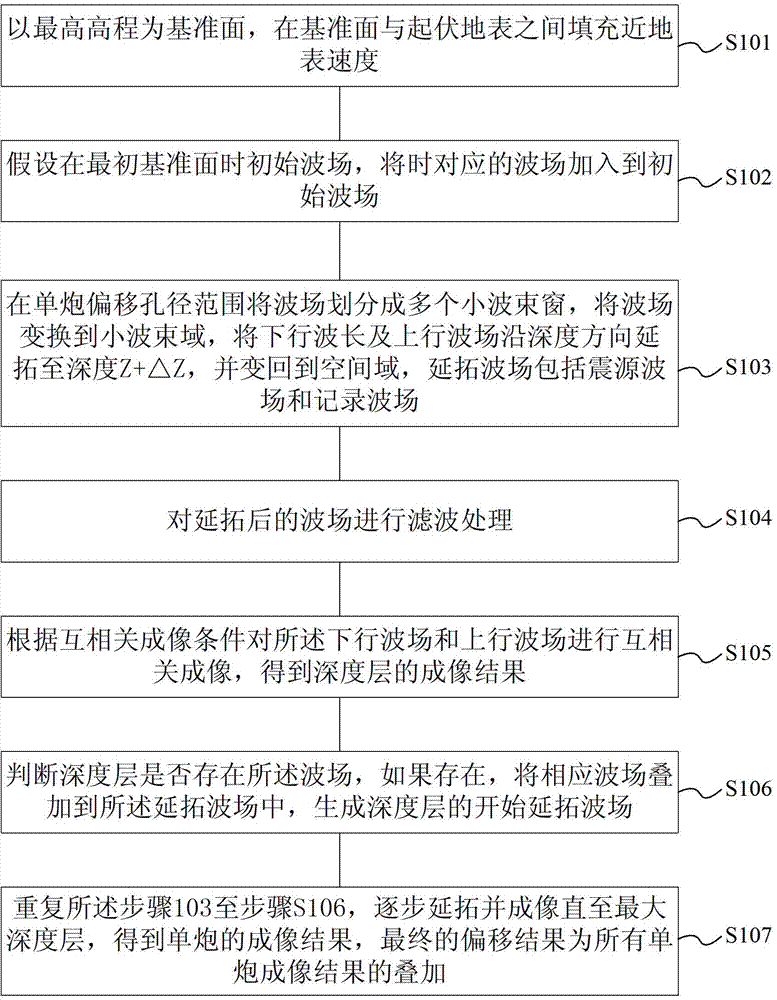
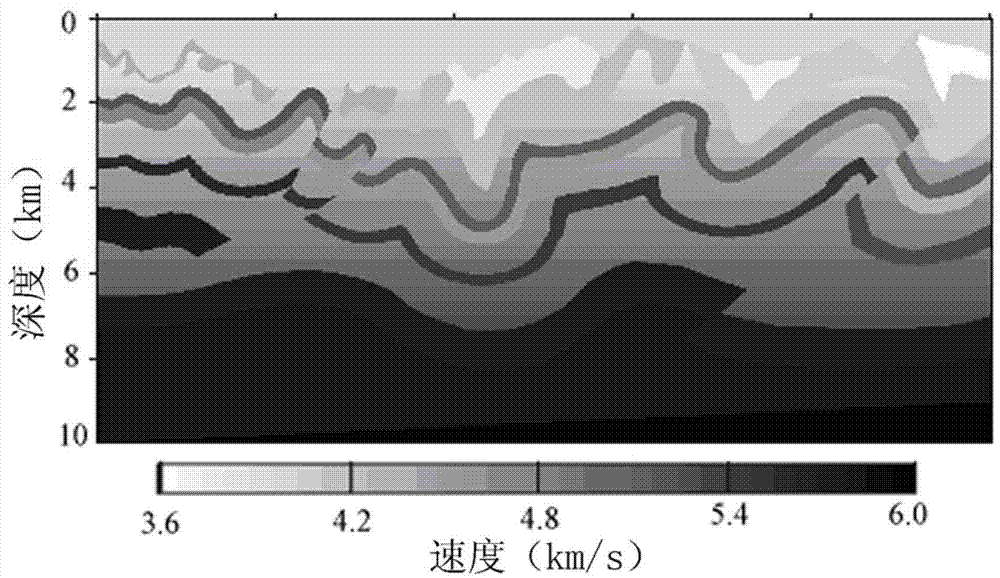
Prestack depth migration method under condition of undulating surface
ActiveCN102890290AImproving Prestack Depth Migration AccuracyImprove image qualitySeismic signal processingHigh elevationImaging condition
The invention discloses a prestack depth migration method under a condition of an undulating surface. The prestack depth migration method under the condition of the undulating surface comprises the follows: a step 1 of filling a near-surface velocity between a reference surface and the undulating surface by regarding the highest elevation as a reference surface zbeg=0; a step 2 of adding a corresponding when the wave field zbeg=z=0 into an initial wave field providing that the initial reference surface zbeg=0; a step 3 of dividing the wave field in a range of a single-shot migration aperture into multiple small wave beam windows, converting the multiple wave beam windows to small wave beam regions, and respectively extending a downlink wave field and an uplink wave field to a depth z+deltaz along a depth direction; a step 4 of performing filtration treatnmetn on the extended wave fields; a step 5 of performing cross-correlation imaging by applying the downlink wave field and the uplink wave field based on the cross-correlation imaging condition to obtain an imaging result of the depth layer z+deltaz; a step 6 of judging if a wave field exists in the depth layer z+deltaz, if so, adding a corresponding wave field to the extended wave field to generate an initial extension wave field of the depth layer z+deltaz; and a step 7 of repeating the step 3 to step 6 and gradually extending and imaging until reaching a maximum depth layer zmax so as to obtain an imaging result of the single shot.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method and device for researching near-surface three-dimensional velocity field of physical geography
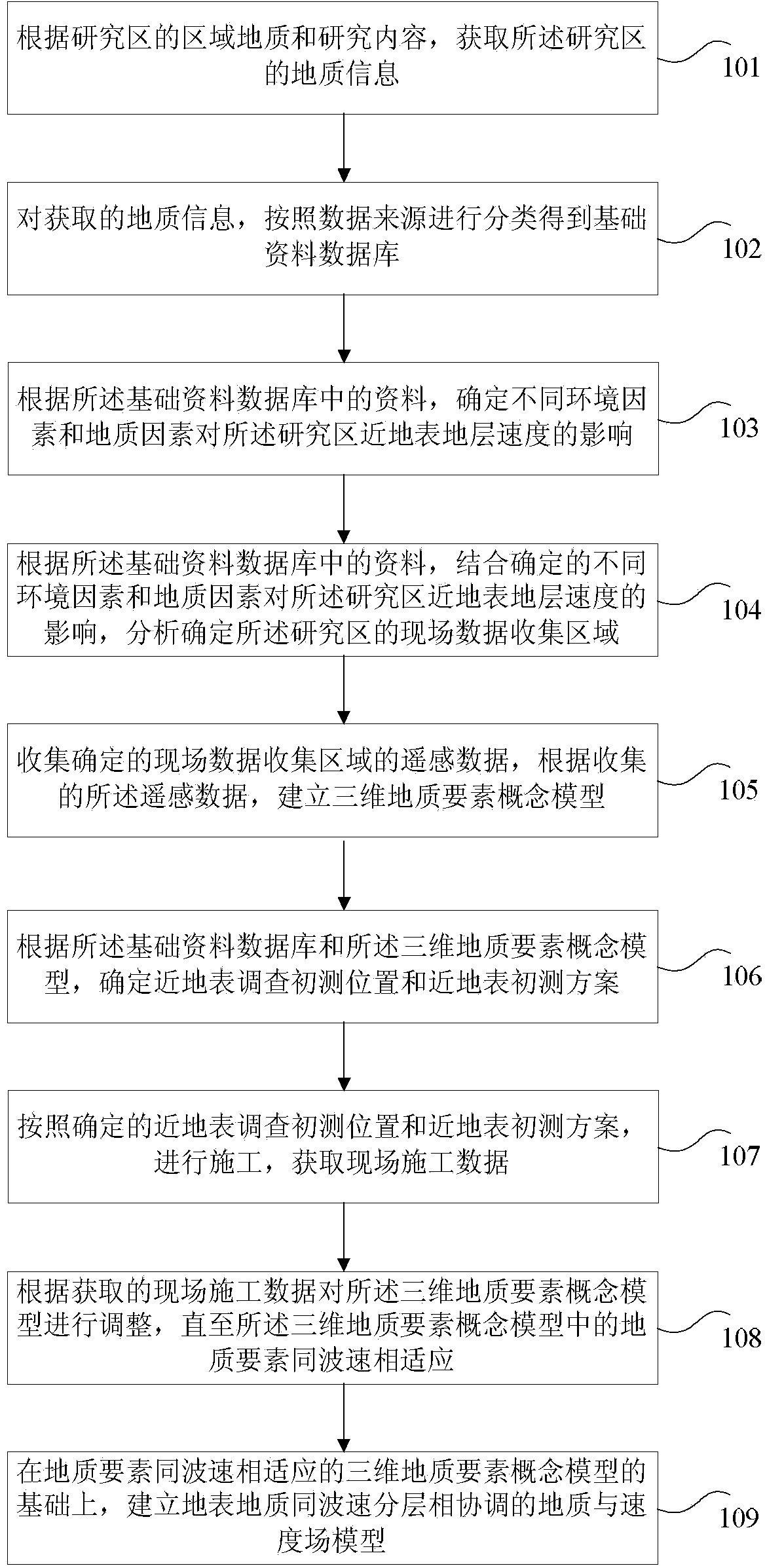
ActiveCN104316978ATroubleshoot technical issues with low accuracyImprove accuracyGeological measurements3D modellingSurface velocityStudy methodology
The invention provides a method and device for researching a near-surface three-dimensional velocity field of physical geography. The method comprises the steps of obtaining geological information of a research area according to the areal geology of the research area and research content; establishing a three-dimensional geological element conceptual model according to collected data; determining the preliminary survey position of a near-surface survey and a near-surface preliminary survey scheme, carrying out construction according to the determined preliminary survey position of the near-surface survey and the determined near-surface preliminary survey scheme, and obtaining site construction data; adjusting the three-dimensional geological element conceptual model according to the obtained site construction data until the geological elements in the three-dimensional geological element conceptual model are adaptive to wave velocity; establishing a geology and speed field model with the surficial geology coordinated with wave velocity layers on the basis of the three-dimensional geological element conceptual model with the geological elements adaptive to the wave velocity. According to the method and device for researching the near-surface three-dimensional velocity field of physical geography, the technical problem that in the prior art, a near-surface velocity model is not accurate is solved, and the effect of effectively improving the accuracy of the near-surface velocity model is achieved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Belt drive controlling method, belt drive controlling apparatus, belt apparatus, image forming apparatus, and computer product
An endless belt is spanned around at least one driving member and at least one supporting member. The driving member is driven by a pulse motor. An angular displacement of the driving member is detected, a difference between detected angular displacement and a target angular displacement is calculated, a frequency of a driving pulse used to drive the pulse motor is calculated based on the difference and a reference driving pulse frequency, and the pulse motor is controlled based on a driving pulse with calculated frequency. The target angular displacement is set so as to cancel a specific velocity fluctuation component of a surface velocity of the belt produced when the drive member is rotated at a constant angular velocity and that is smaller than amount of surface movement of the belt in one driving pulse.
Owner:RICOH KK
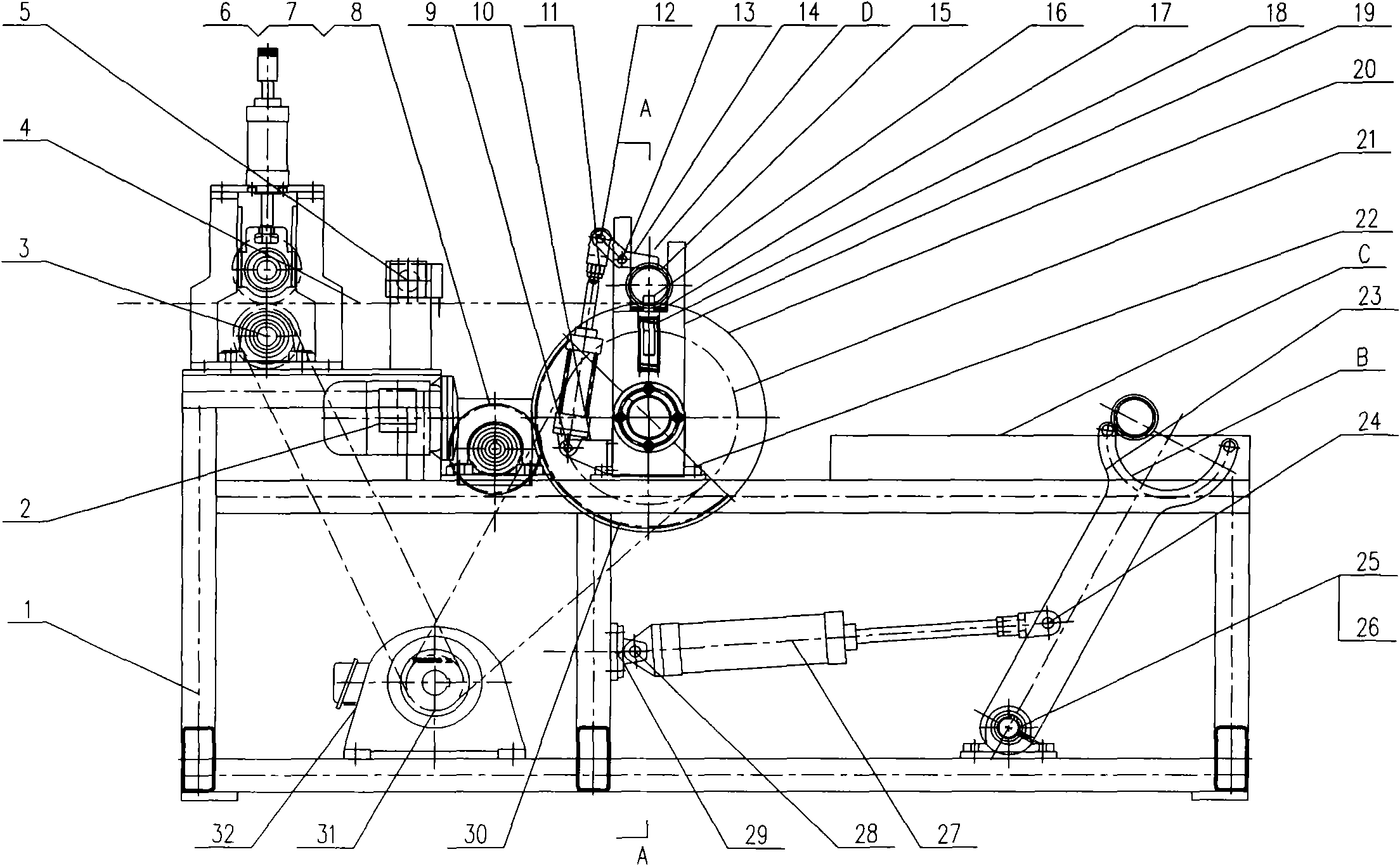
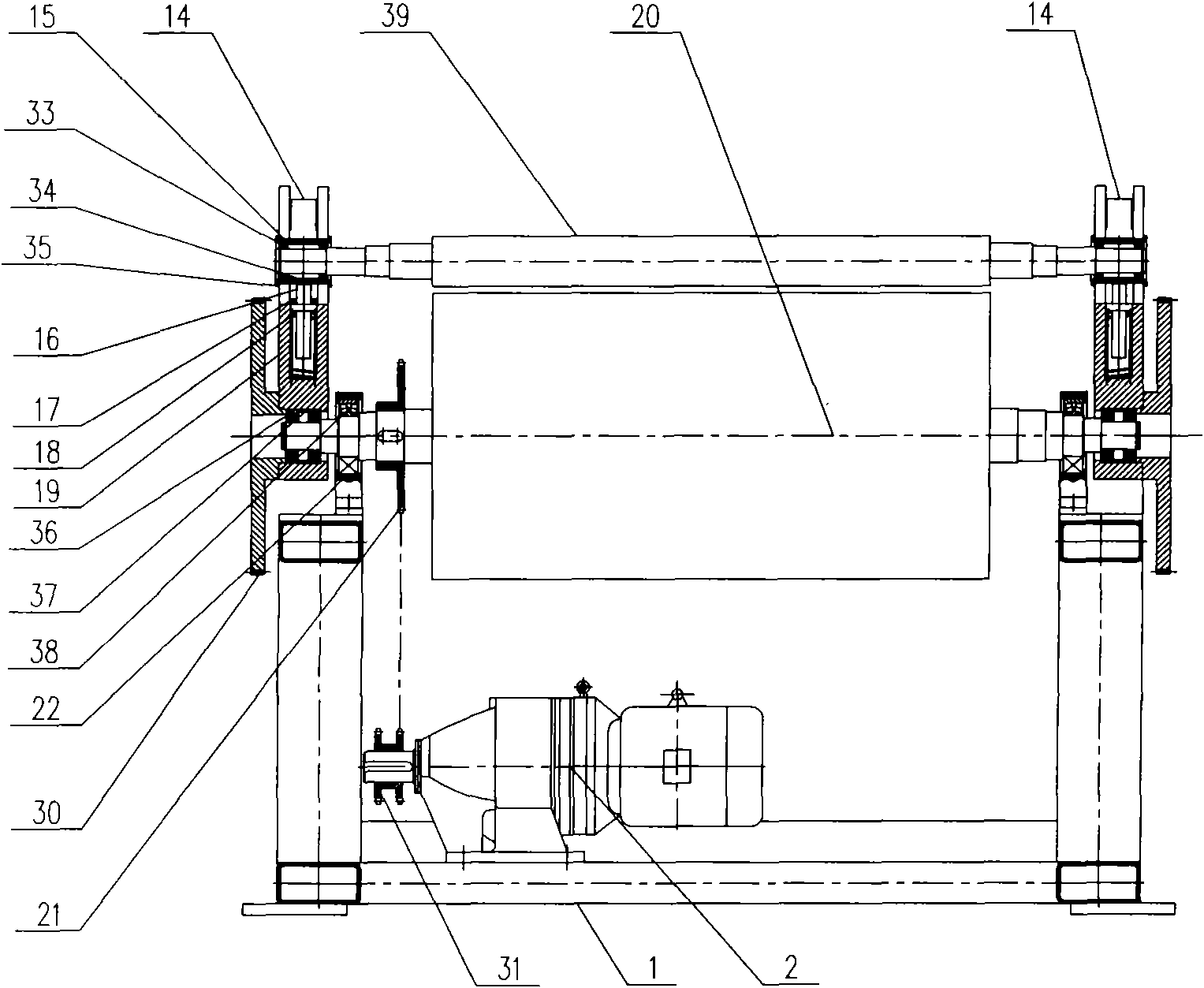
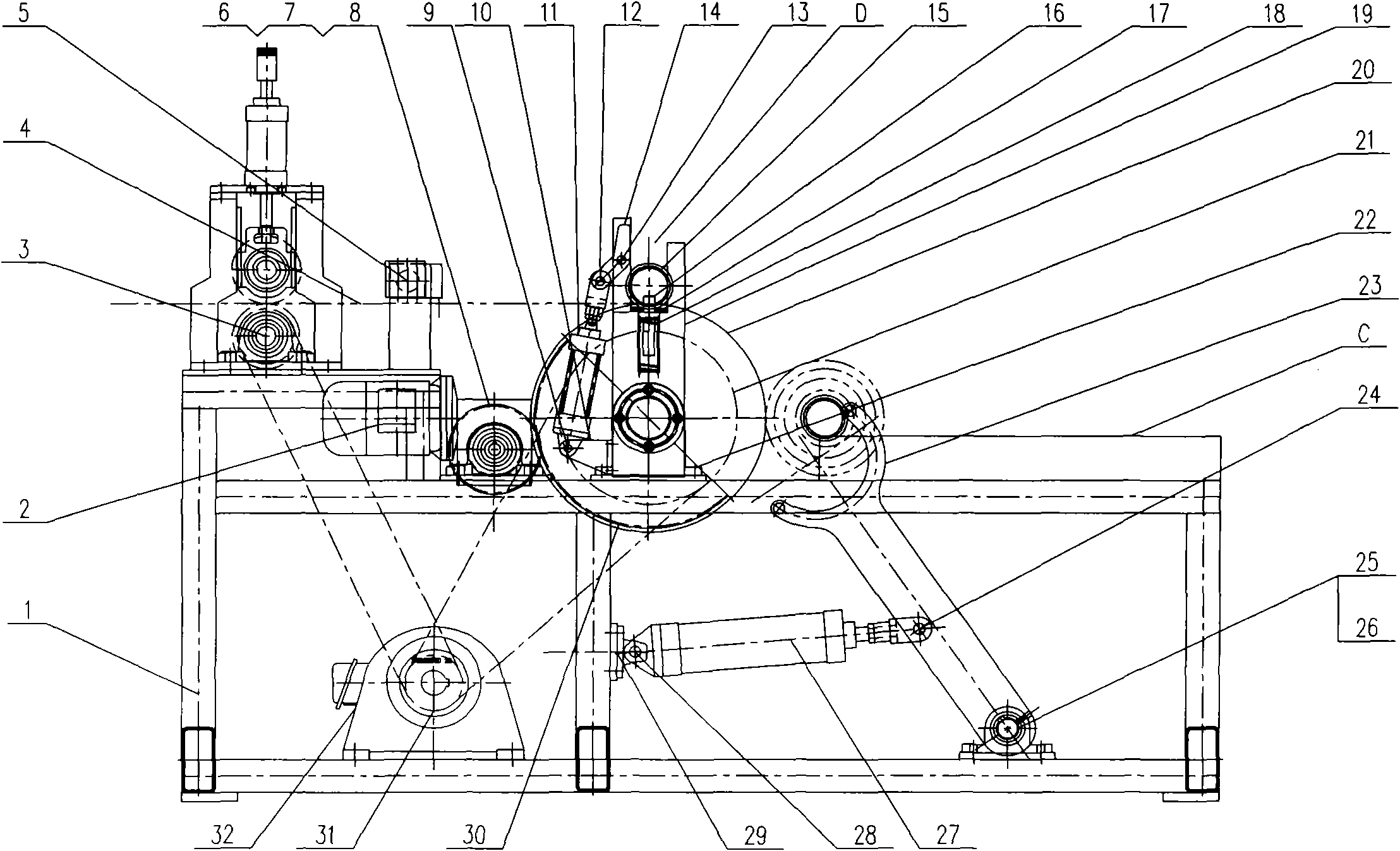
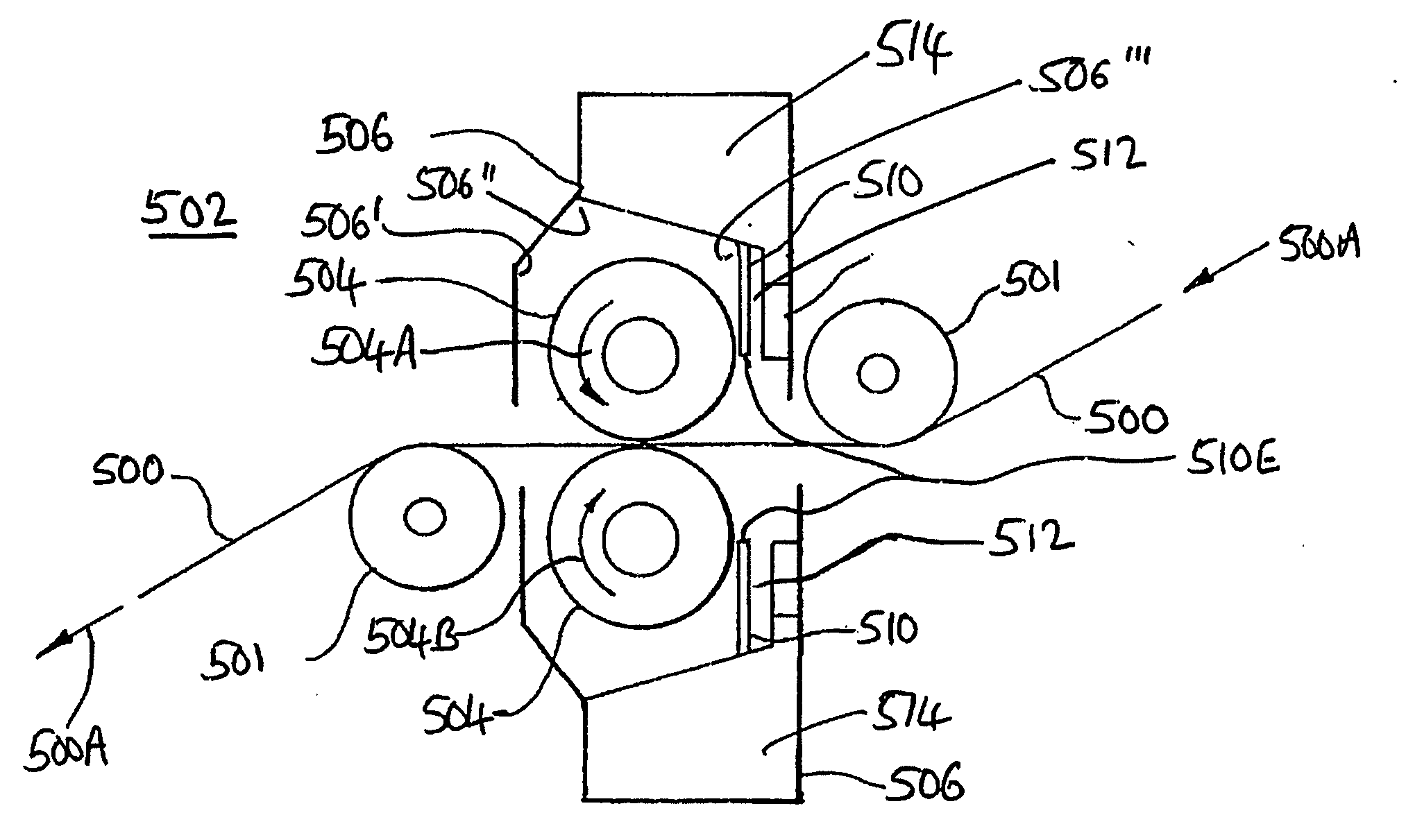
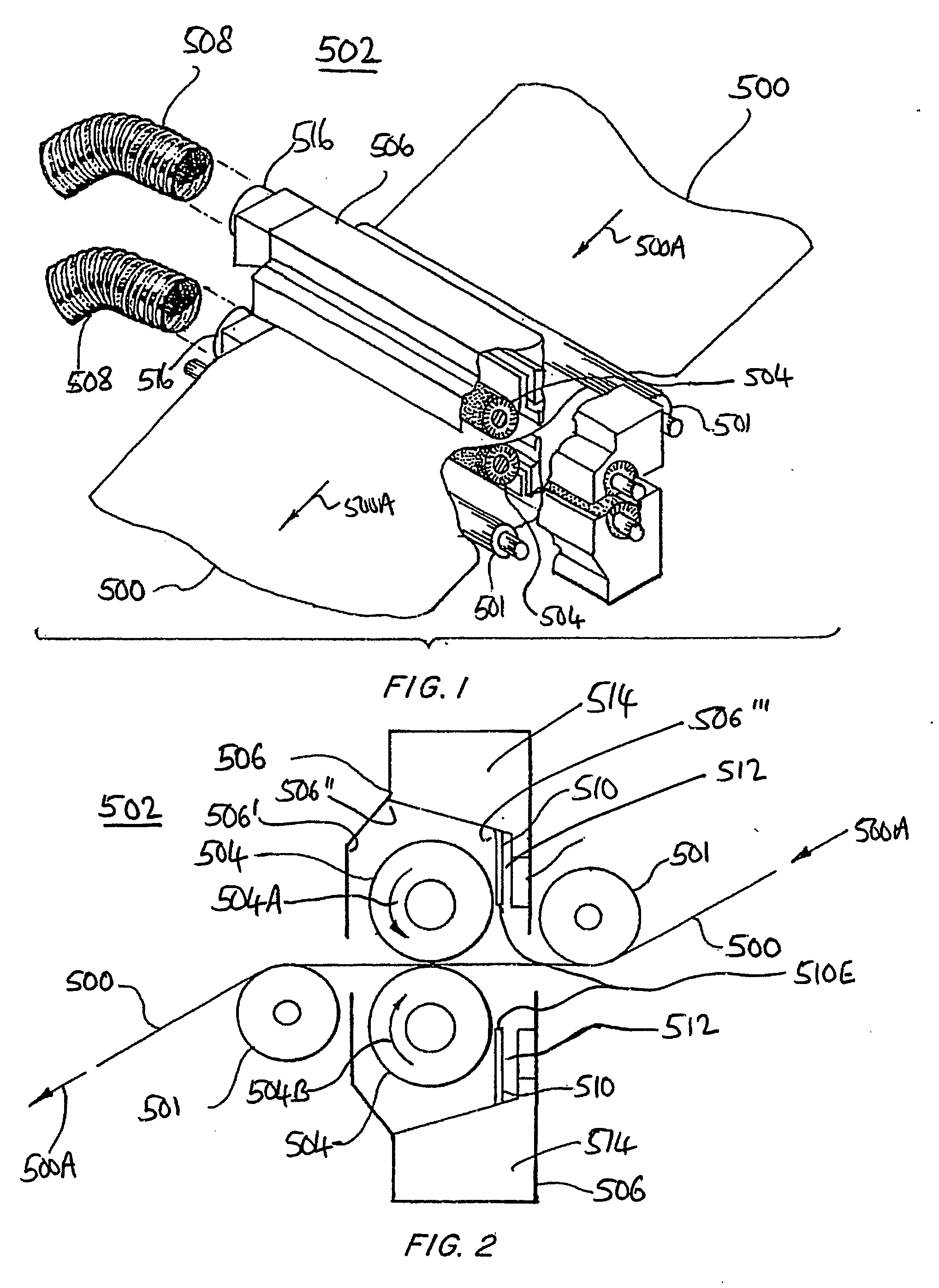
Automatic lap changing winder
The invention provides an automatic lap changing winder which comprises a frame, a drawing mechanism, a cross cutting mechanism, an air expanding shaft assembly, a large roller synchronous winding mechanism, a turnover mechanism, a pressing claw mechanism and a swing arm mechanism. The automatic lap changing winder is characterized in that the linear surface velocity of the drawing mechanism is equal to that of a large roller when the drawing mechanism and the large roller synchronous winding mechanism are under the action of a main driving motor and a sprocket pair, rotatable air expanding shaft guide wheels are mounted at two ends of an air expanding shaft, guide rails are arranged on the frame, a U-shaped groove in a turnover seat can function in guiding, the air expanding shaft can linearly move in winding, a gear is fixed onto the turnover seat, the turnover seat is supported on the large roller and can turn over around the large roller, the pressing claw mechanism is arranged on the turnover seat to automatically change laps, an arc-shaped head is arranged above a swing arm, and the air expanding shaft guide wheels can be tightly pressed to realize winding and can also be pushed away to discharge coiled materials. The automatic lap changing winder is reasonable in structure and simple to operate, manual lap changing is omitted, continuous production of winding is realized, and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU KUNTAI MACHINERY
Apparatus and process for regenerating catalyst
ActiveUS7799287B2Increased disengager discharge velocityMinimizing any tendencyCatalytic crackingOther chemical processesFlue gasSurface velocity
Owner:UOP LLC
Web cleaner
The invention is relates a web cleaning apparatus including: a pair of operatively rotating cleaning rollers operatively disposed on opposite sides of the web; a housing surrounding a major part of the surface of each roller; a vacuum chamber substantially co-extensive with each roller; a longitudinal slot extending parallel to each roller and substantially co-extensive therewith, the slot having an inlet proximate the roller surface and an outlet in communication with the vacuum chamber and operatively providing an air flow path from adjacent the roller into the vacuum chamber, wherein the air flow speed at each inlet is not less than the surface speed of the rollers, and a method of using such apparatus. Another apparatus of the invention includes a housing surrounding the roller and spaced therefrom with a gap of about 0.5 mm to about 5 mm. Further embodiments of the invention provide a shutter for controlling the air flow around the rollers in a cleaning step. Further embodiments of the invention provide a valve controlled bypass line whereby a given portion of a web cleaning apparatus can communicate with the atmosphere such that it is not under vacuum.
Owner:PDM
Non-contact flow measurement method for measuring high flood based on flow velocity of representative vertical line points
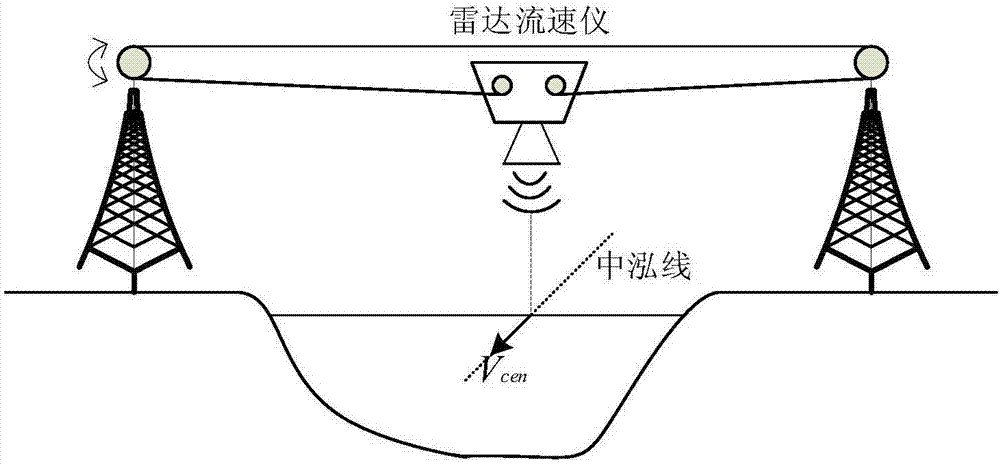
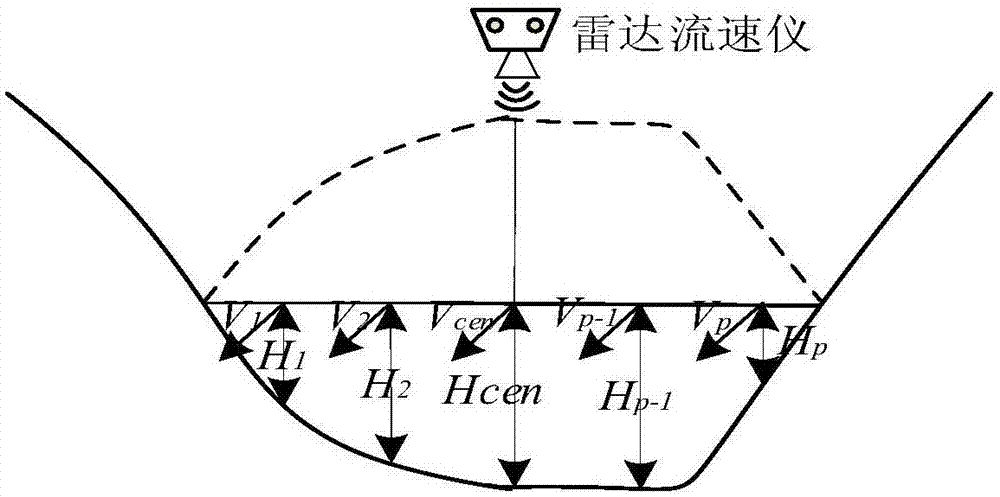
ActiveCN107490410AQuick calculationEasy to calculateVolume/mass flow measurementRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadarSurface velocity
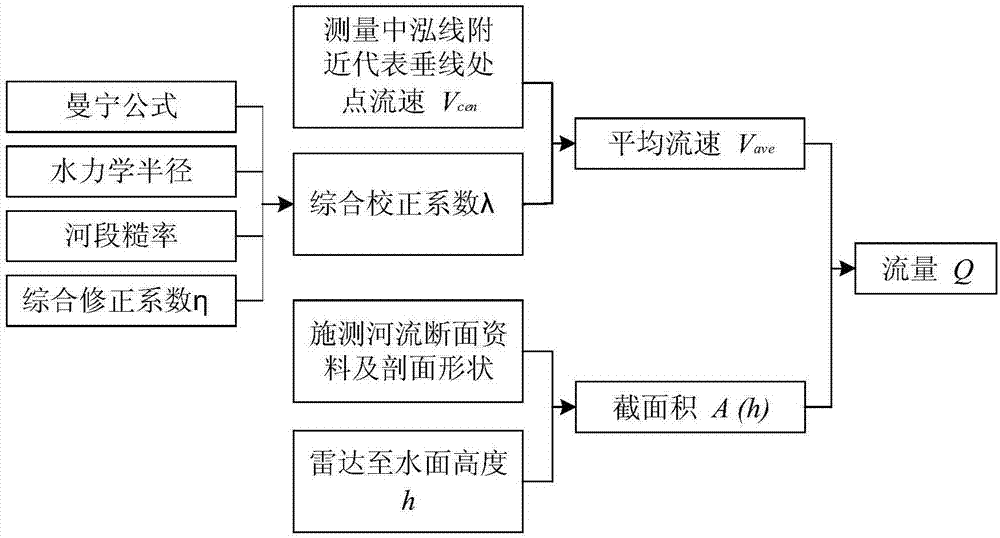
The invention discloses a non-contact flow measurement method for measuring a high flood based on the flow velocity of representative vertical line points. The method includes the following steps of (1) determining the positions of one or more vertical lines according to river section data, and using a radar flow velocity meter to measure the flow velocity of a river surface point below a measured vertical line; (2) calculating the flow velocities V1-Vp (the surface point flow velocity of P vertical lines) of the surface points of multiple vertical lines according to the surface point flow velocity of the measured vertical line; (3) conducting arithmetic average on the section surface point flow velocity of the multiple vertical lines, and obtaining the average flow velocity Vsur of the river surface; according to the empirical formula of hydraulics, making the average flow velocity of the river surface multiplied by the surface velocity coefficient lambda to obtain the average flow velocity Vave of the section; (4) according to the river section data, obtaining the river water passing section area corresponding to the set water depth, and making the area multiplied by the average flow velocity of the section to obtain a river flow value. The method can calculate the flow of artificial and natural rivers quickly, conveniently and accurately, and is especially suitable for unattended heavy rain, high flood and other complex disastrous environments.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
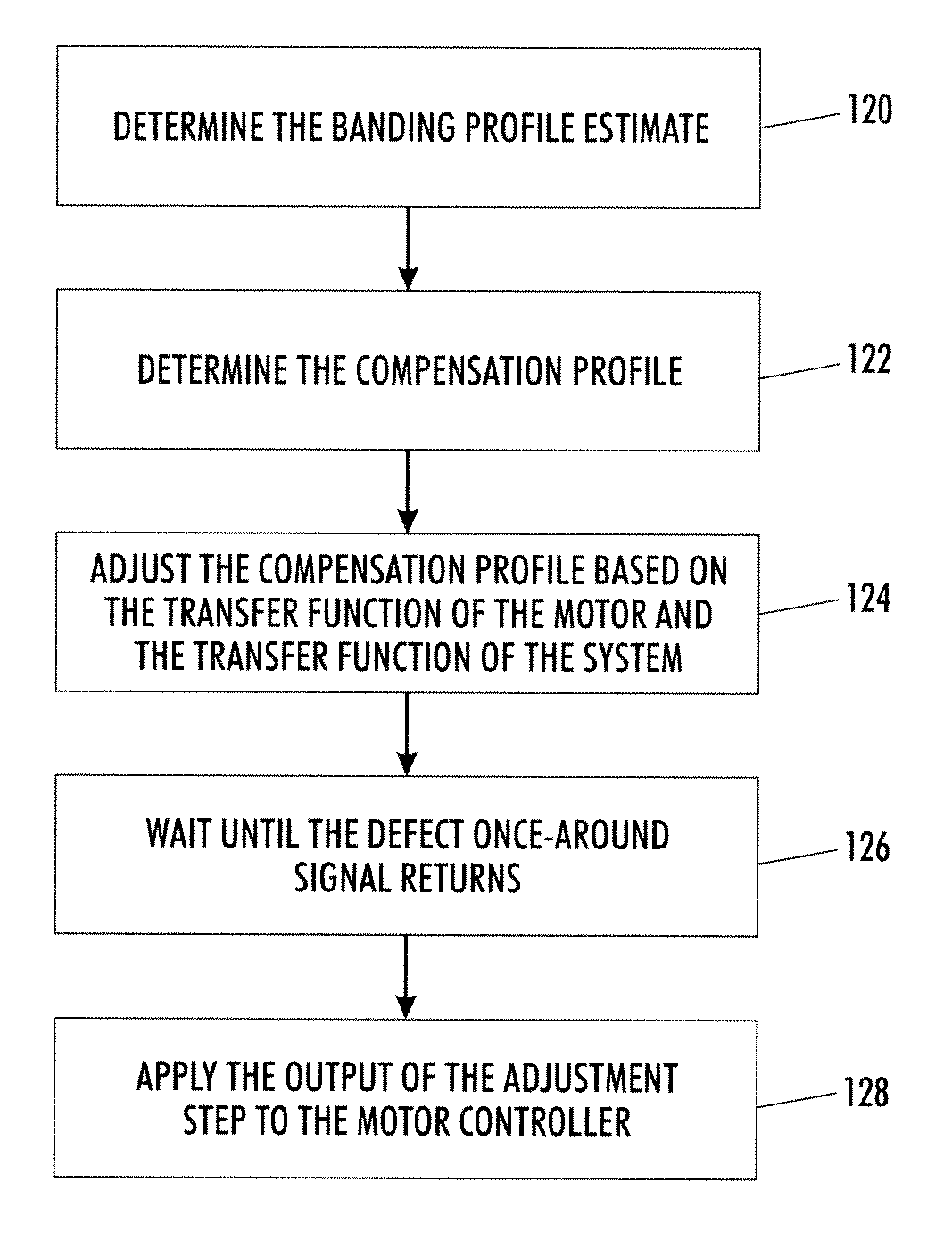
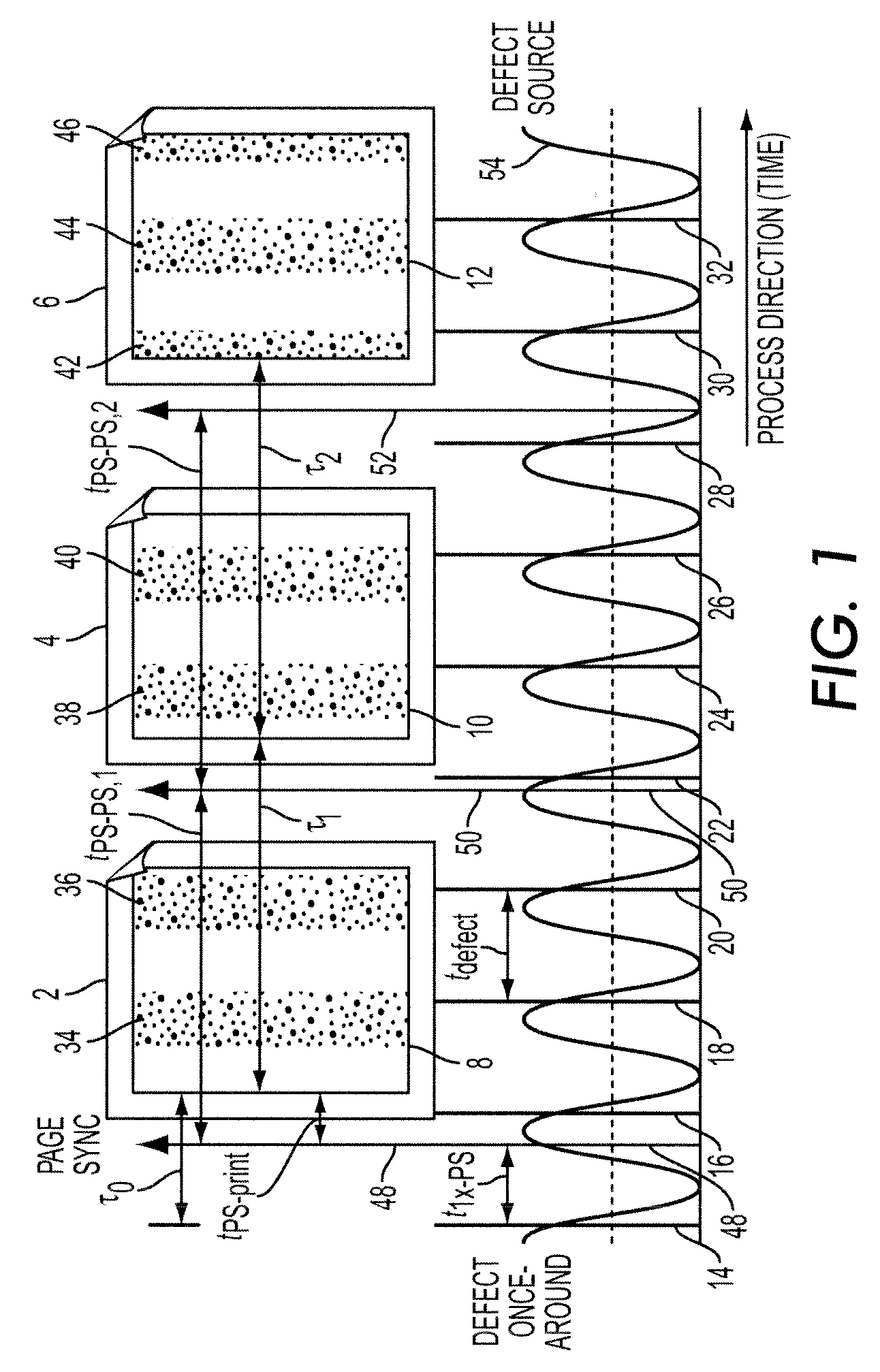
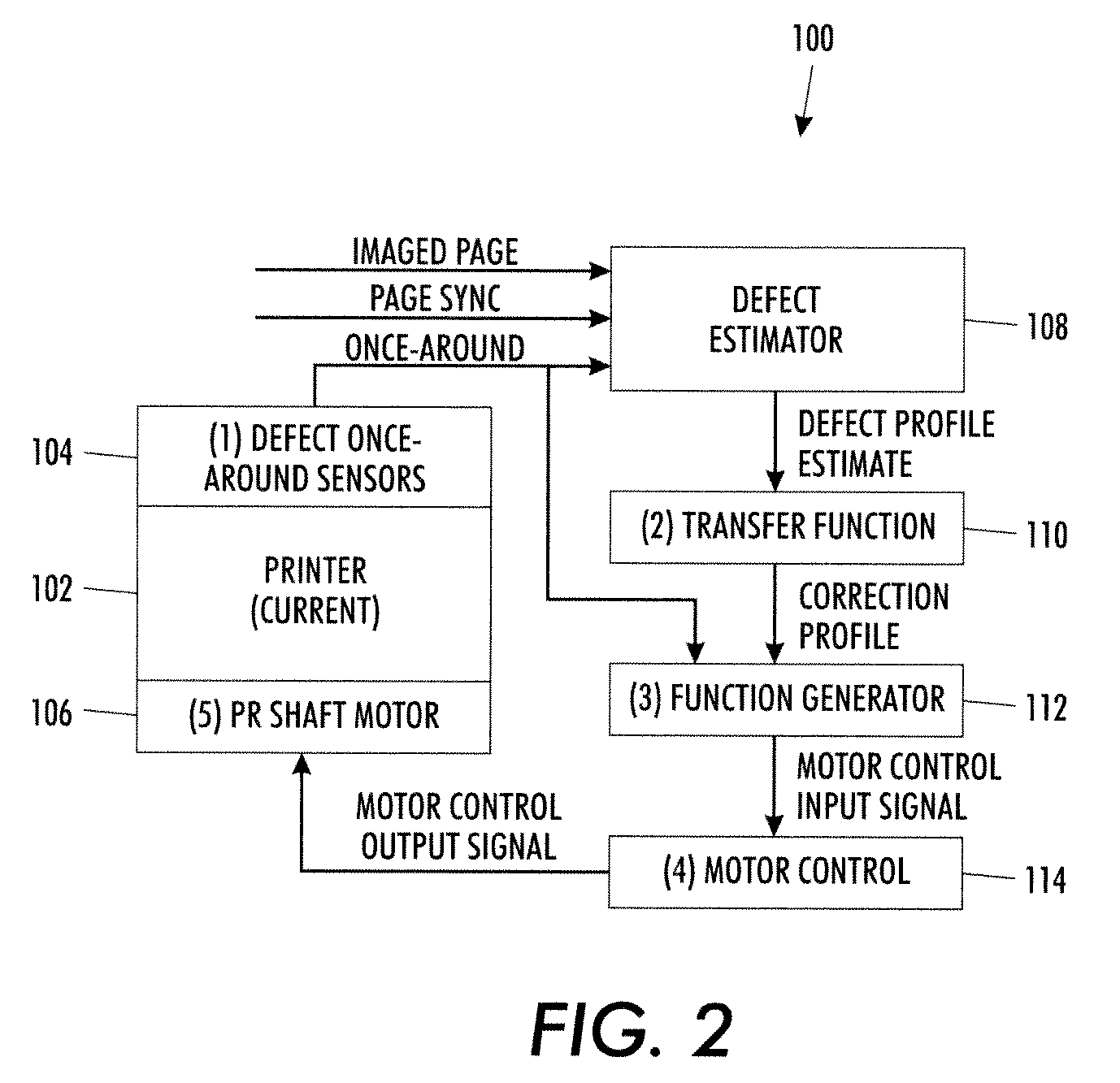
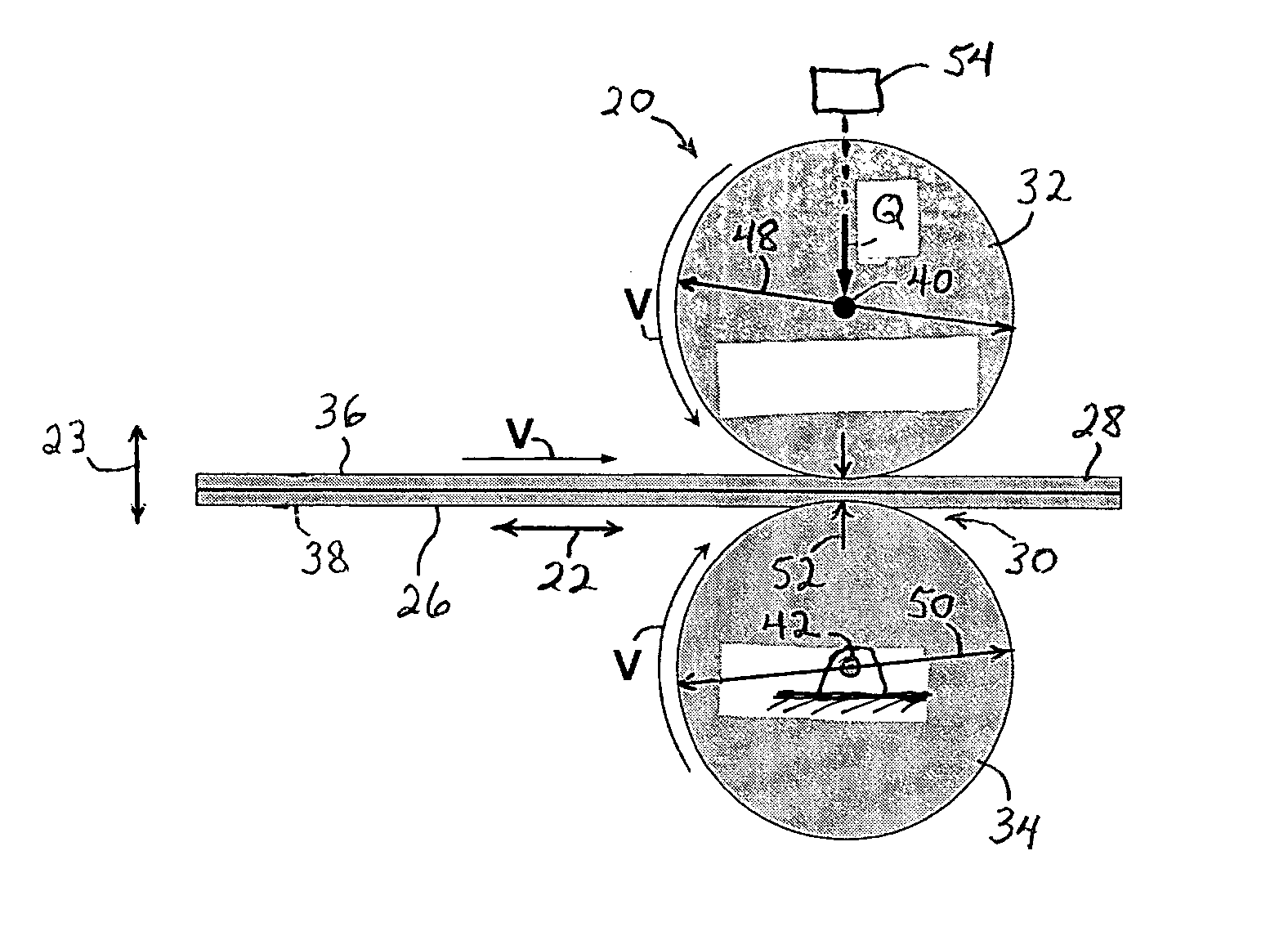
Method and system to compensate for banding defects
A method of correcting periodic banding defects in a printing system is provided. The method comprises: determining a banding profile estimate; determining a compensation profile; adjusting the compensation profile based on the transfer function of a motion system and the transfer function of a printing system; waiting until a defect once-around signal returns; and applying the output of the adjustment step to a controller controlling the speed of an imaging surface.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Bonding by induced high-rate of shear deformation
InactiveUS20060266473A1High surface speedLow pressure valueMechanical working/deformationLaminationHigh rateSurface velocity
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Laser-based method of detecting underwater sound through an ice layer
ActiveUS8599649B1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansLight beamSurface velocity
A sensor system is provided comprising a Laser Doppler Vibrometer (LDV) that senses underwater sound via vibrations on an ice surface. In operation, a beam of the LDV measures a surface velocity and therefore an associated pressure signal from the ice surface due to an impinging underwater sound. The beam reflected from the surface carries the acoustic information back to the LDV. Using interferometry to derive the acoustic signal carried on the reflected beam; the LDV provides acoustic signal data in the form of a voltage signal. A computer processes the voltage signal as data that estimates a sound pressure level of the underwater source.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
NMR MAS inflow bernoulli bearing
ActiveUS20060082371A1Improve stabilityIncrease stiffnessMagnetic circuit rotating partsMagnetic measurementsAxial pressureSurface velocity
Owner:DOTY SCI
Seismic data processing method and device for keeping kinematics characteristics of seismic wave field
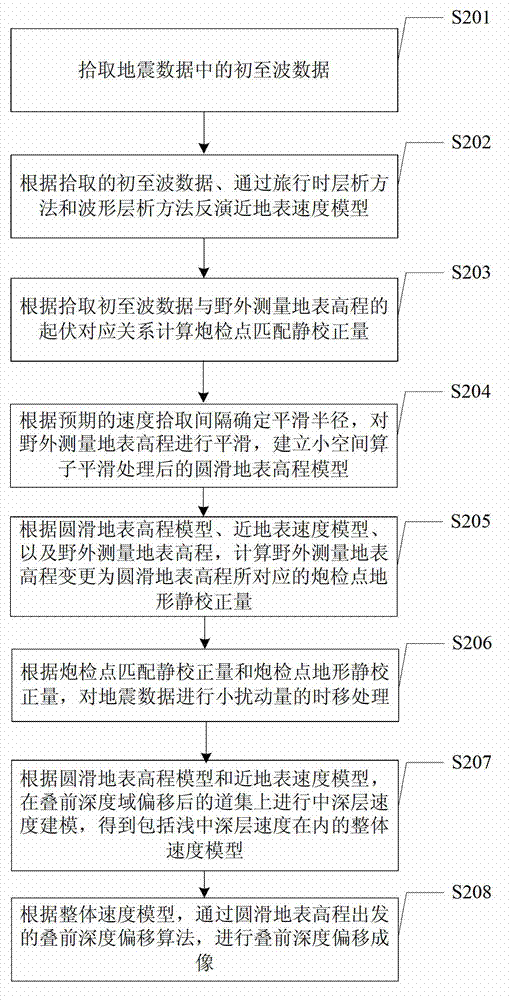
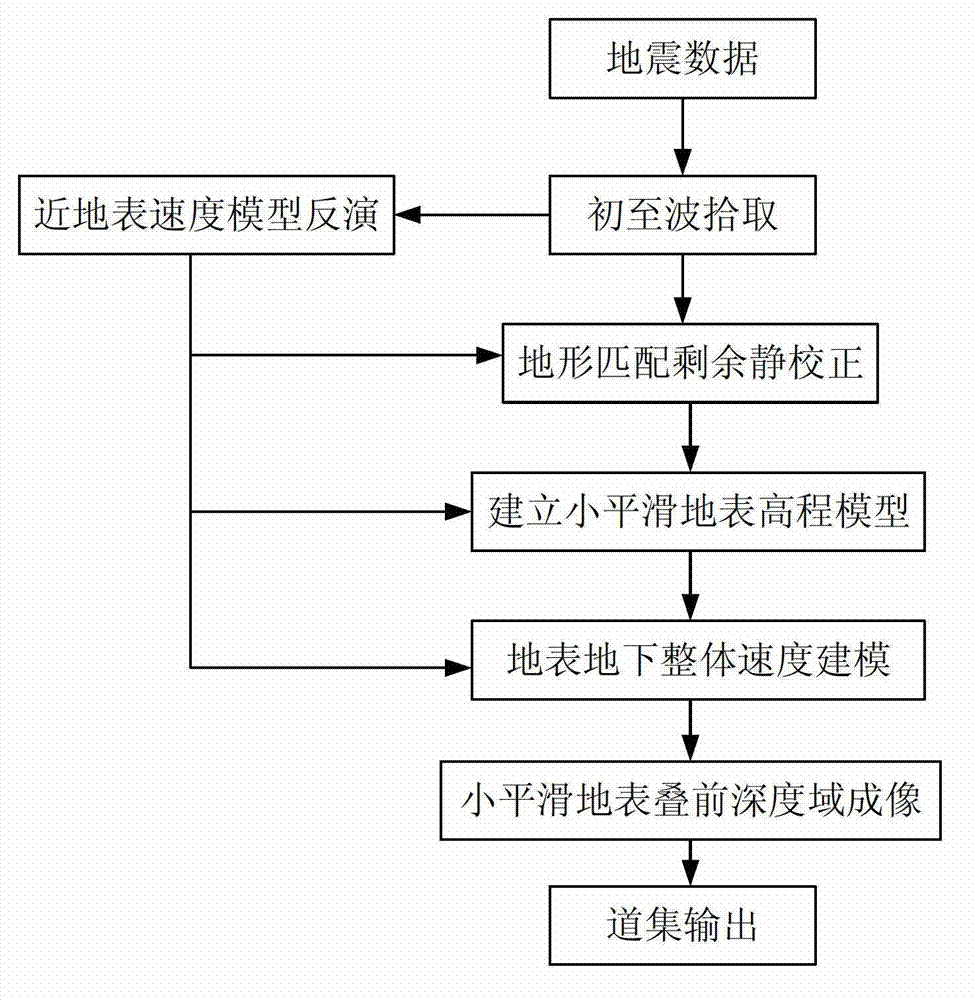
The invention provides a seismic data processing method and a device for keeping kinematics characteristics of a seismic wave field. The method comprises the steps as follows: carrying out inversion on a near-surface velocity model according to preliminary wave data; calculating matching static correction values of shot detection points according to fluctuation corresponding relation of the preliminary wave data and field measurement ground surface elevation; carrying out smoothing on the field measurement ground surface elevation and establishing a smooth ground surface elevation model; calculating corresponding terrain static correction values of the shot detection points when the field measurement ground elevation is changed into the smooth ground surface elevation, and combining the terrain static correction values of the shot detection points to carry out small disturbance time shifting processing on seismic data; embedding the near-surface velocity model into a whole velocity model to obtain a shallow velocity model; carrying out depth domain medium-deep velocity modeling based on the smooth ground surface elevation model and the shallow velocity model; establishing a new common imaging point or a common reflection angle set; establishing iteration of the common imaging point or the common reflection angle set to obtain the whole velocity model including shallow and medium-deep velocities; and carrying out prestack depth migration imaging through a prestack depth migration algorithm from the smooth ground surface elevation.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for simulation of multiphase fluid flow in pipelines
ActiveUS20150286755A1Robust methodFunction increaseComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationDimensional simulationFluid phase
This invention relates to a method for one dimensional simulation of multiphase fluid flow in pipelines enabling determination of pressure drop, fluid volume fractions, and heat and mass transfer coefficients in multiphase pipeline flows, wherein the method comprises providing real world values of the superficial velocities of each of the continuous fluid phases, the pipe diameter, and the inclination angle of the pipeline relative to the horizontal plane, providing initial values describing the flow geometry of the multiphase flow, where the initial values at least comprises the axial pressure gradient and the positions of the large scale interfaces separating the continuous fluid phases, employing a one-dimensional numerical model based on Eulerian formulated transport equations of the multiphase flow in the pipeline, solving the numerical model with the set of input values from step a) and b) to determine the flow parameters of the multiphase flow, and displaying one or more of the determined flow parameters.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO +1
Powder filling processes
ActiveUS20100229859A1Suitable for useFacilitate prevention of formationRespiratorsPowder deliverySurface velocityEngineering
A method for filling a plurality of microdepressions in a major surface of a web with finely divided powder in which the web is fed continuously to and through a powder filling stage including a driven roller. At the powder filling stage, the powder, which is fed either onto the web upstream of the roller or to the roller of the powder filling stage, is filled into the microdepressions of the web using the driven roller, wherein said roller is rotating about an axis generally transverse to the direction of web, while the surface speed of the roller and the web speed are different and wherein the roller and web are positioned relative to one another, such that between the upper surface of the web and the outer surface of the roller there is a gap. A method of manufacturing an elongate carrier with microdepressions containing finely divided powder comprising steps filling a plurality of microdepressions in a major surface of a web as described, removing from upper surface of the web excess powder not filled within the microdepressions and remaining on areas of the surface between the depressions, and optionally slitting and / or cutting the web in width and / or length.
Owner:ADAMIS PHARMA
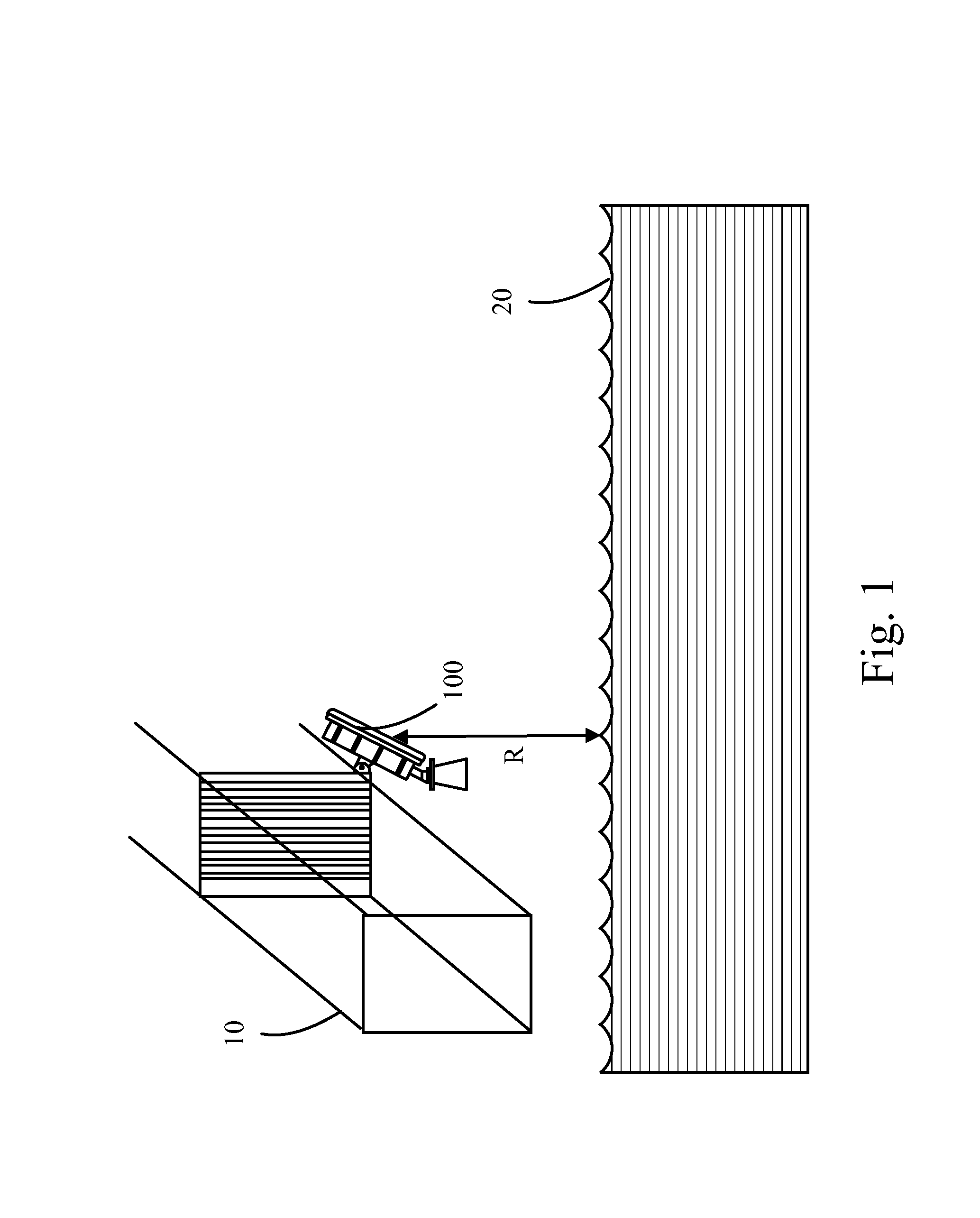
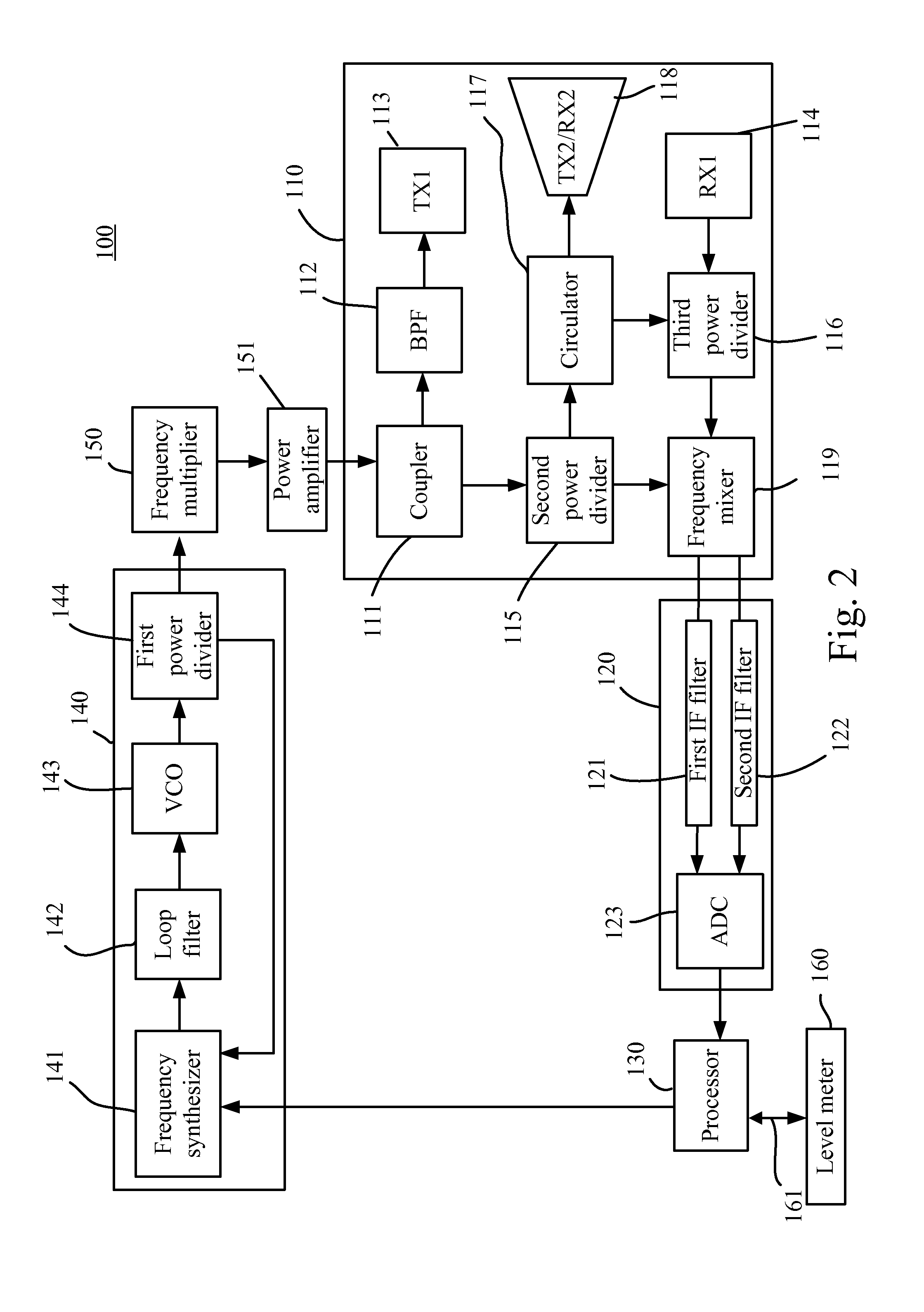
Device for Measuring Surface Speed and Liquid Level of Fluid
InactiveUS20170016984A1Convenient data synchronizationVolume/mass flow measurementMachines/enginesSurface velocityData transmission
A device for measuring a surface speed and a liquid level of a fluid is disclosed. The device includes a RF transceiving module for alternatively transmitting a first FMCW signal and a first CW signal to the fluid, and receiving a second FMCW signal and a second CW signal reflected from the fluid. A processor is used for calculating the liquid level of the fluid based on a frequency difference between the first FMCW signal and the second FMCW signal, and for calculating the surface speed of the fluid based on a frequency difference between the first CW signal and the second CW signal. Since the device integrates functions of measuring the surface speed and the liquid level of a fluid, it reduces an occupied room and facilitates a synchronization of data transmission.
Owner:U&U ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com