Near-surface modeling method using tomography inversion of two-step method
A technology of tomographic inversion and modeling method, which is applied in the field of two-step tomographic inversion near-surface modeling to achieve the effects of ensuring reliability, improving imaging quality, and eliminating human errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
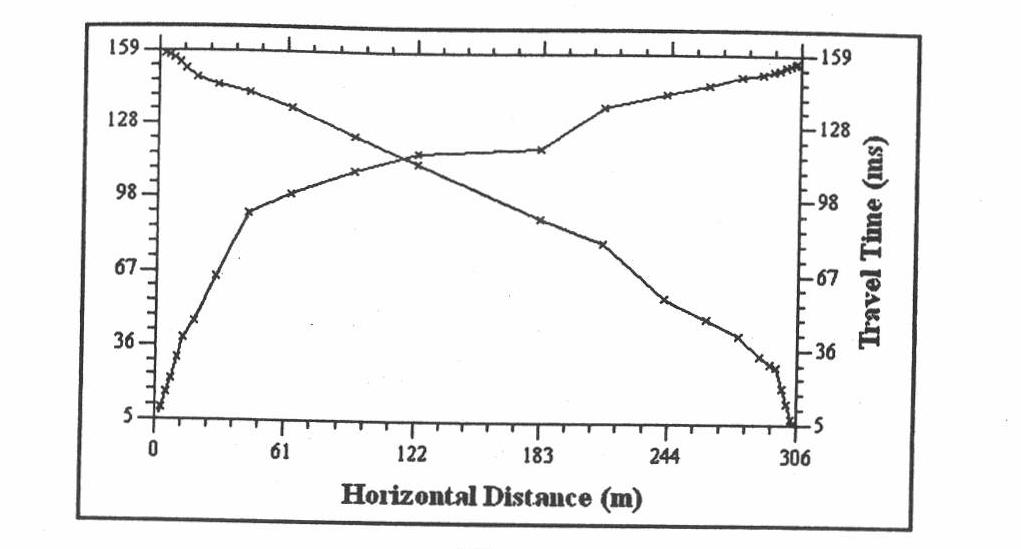
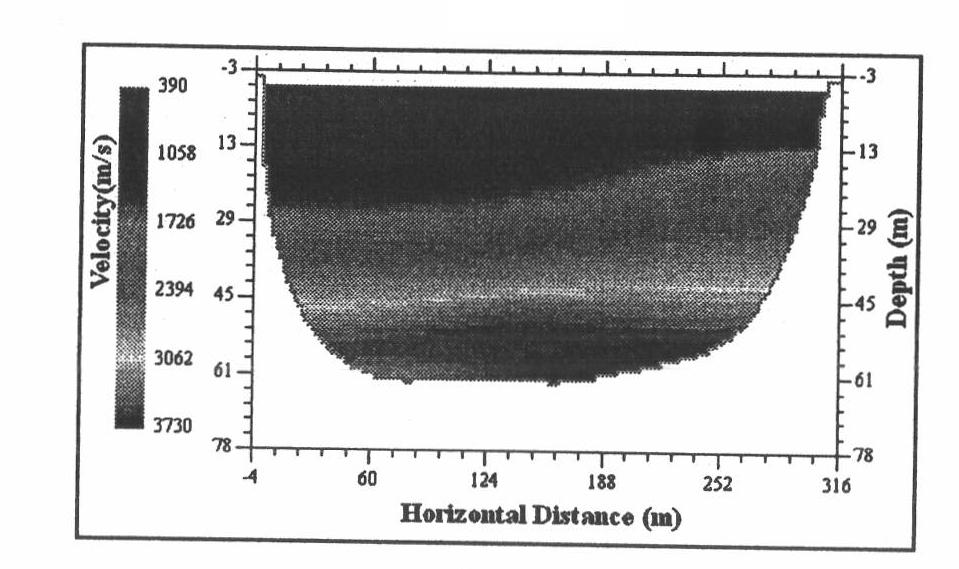
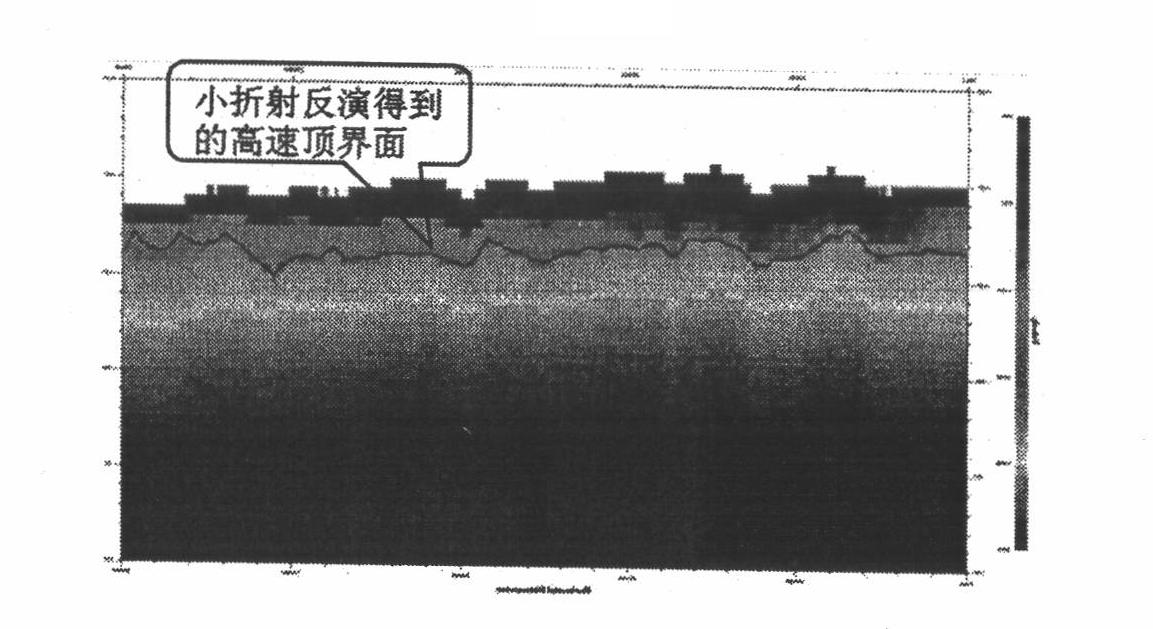
[0035] The two-step tomographic inversion near-surface modeling method is used for actual data processing and application in the L6 work area in the hinterland of the Junggar Basin. The work area is composed of three contiguous blocks constructed in different years. Covered by steep slopes and semi-fixed deserts, the dunes are nearly north-south, and there are honeycomb sand dunes in some parts, with a maximum height difference of 50 meters. The ground altitude is between 593.7 meters and 369.6 meters, and the height difference reaches 224 meters. Between 50 meters and 200 meters; most of the original single shots are distorted at the first arrival, and the static correction problem is very serious. The traditional static correction method does not work well in this area.
[0036] We used the two-step tomographic inversion near-surface modeling method in this work area to carry out near-surface modeling and static correction calculation applications. The implementation steps of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com