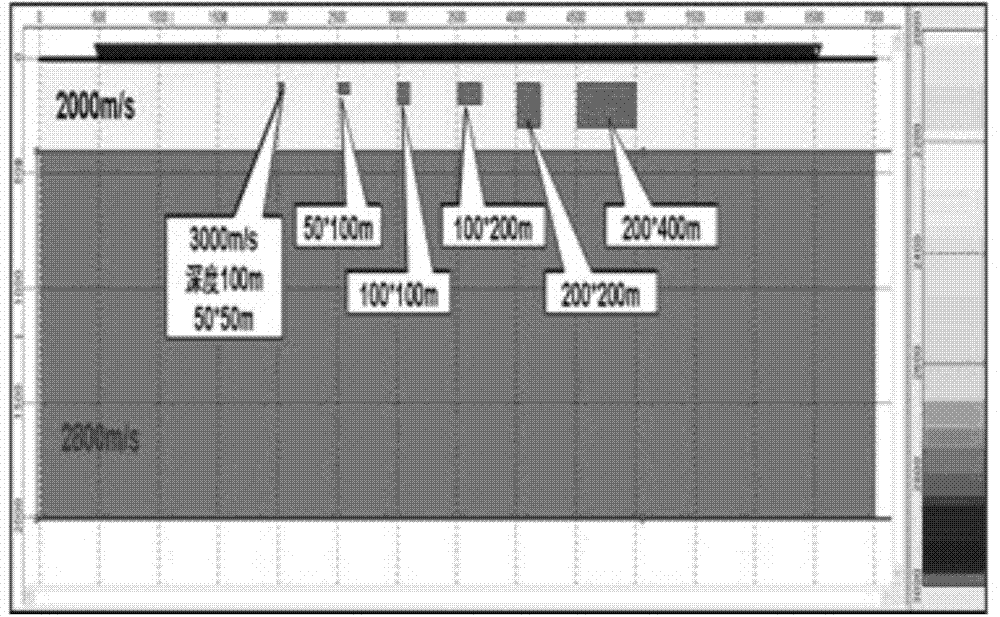
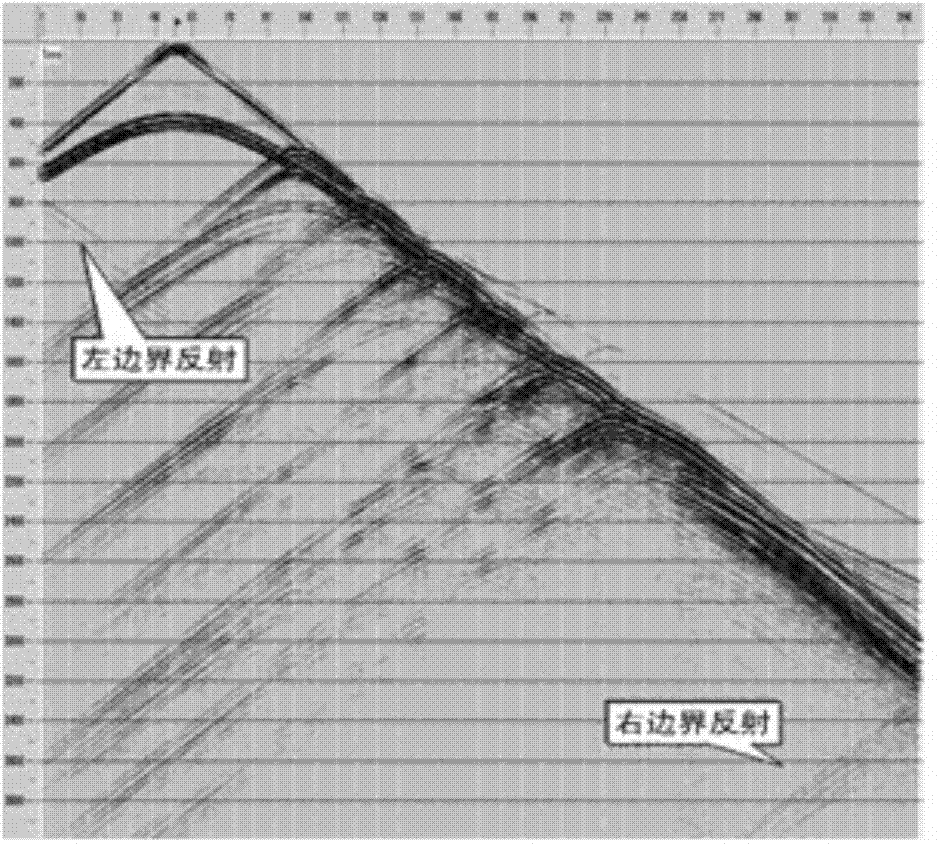
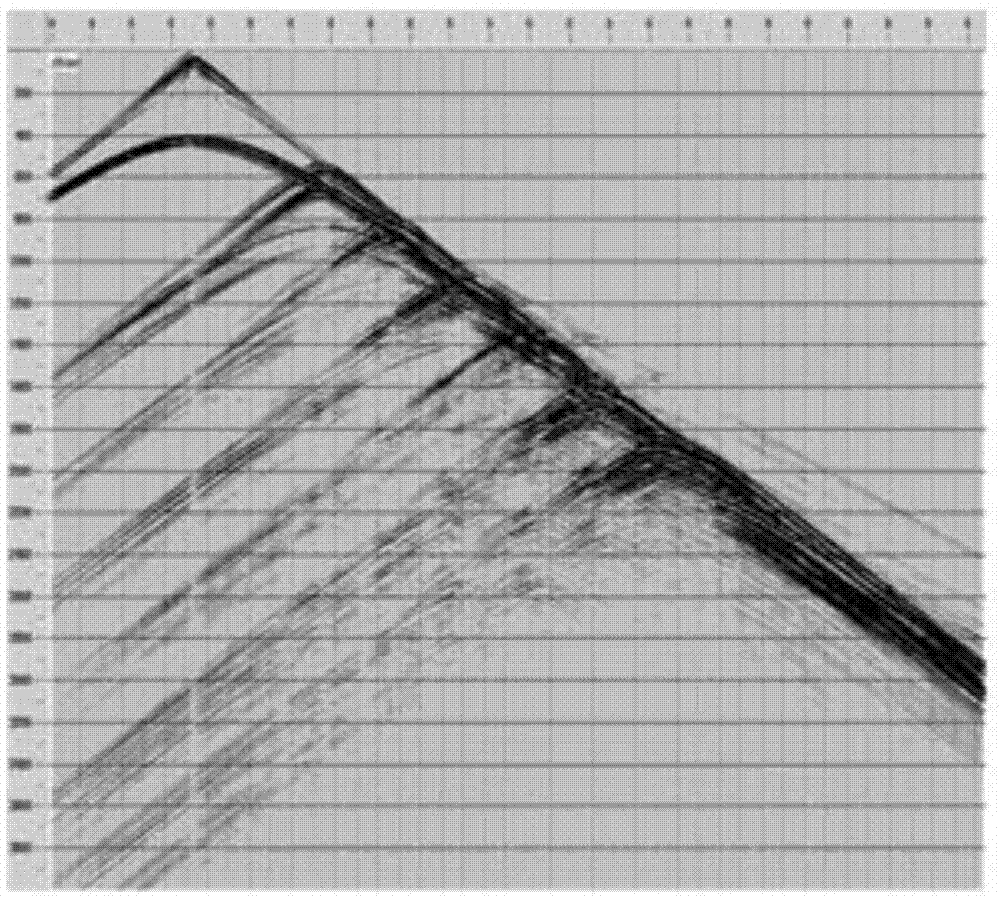
Method for inverting near-surface velocity model by utilizing preliminary waveforms
A waveform inversion and velocity model technology, applied in seismic signal processing and other directions, can solve problems such as practical application limitations, limited data SNR inversion methods, multiple solutions and computational efficiency, and velocity model resolution limitations. The effect of reducing polysolution, improving stability and computational efficiency, and improving accuracy and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and example this technical scheme is further described
[0036] The near-surface velocity model method of first-arrival waveform inversion, this method includes two technologies: acoustic wave equation staggered grid finite-difference forward modeling and steepest descent method waveform inversion. The method steps of the implementation process are as follows:
[0037] (1) Extract the time-domain first-arrival waveform record Pobs and initial velocity model;
[0038] ⑵Using the staggered grid finite difference forward modeling of the acoustic wave equation to calculate the simulated wave field P cal , and calculate the wave field residual δp=P obs -P cal ;
[0039] (3) Back propagation of the wave field residual to obtain the return wave field P′;
[0040] (4) Calculate the gradient of the objective function by using the return wave field and the forward propagation wave field, that is, the update direction of the veloc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com