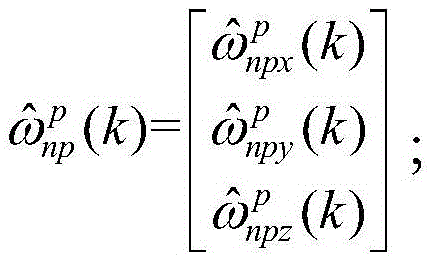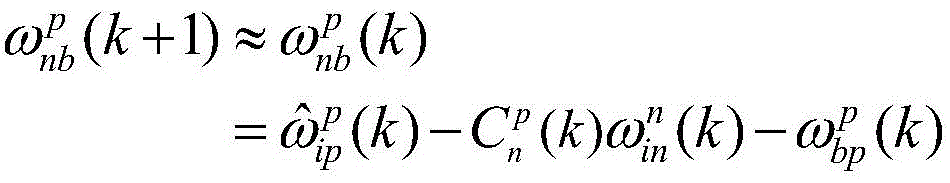Patents
Literature
181 results about "Constant angular velocity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
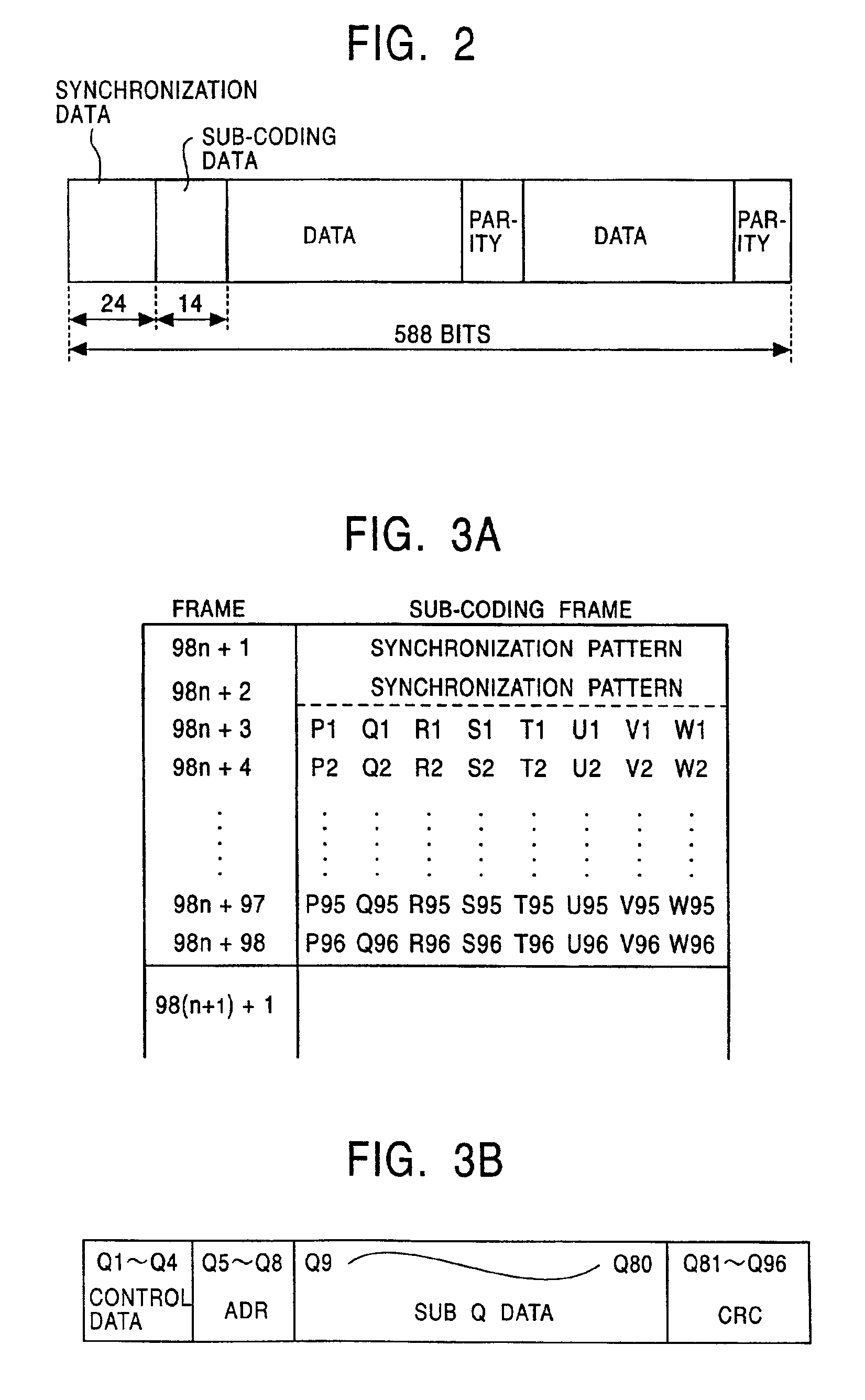
In optical storage, constant angular velocity (CAV) is a qualifier for the rated speed of any disc containing information, and may also be applied to the writing speed of recordable discs. A drive or disc operating in CAV mode maintains a constant angular velocity, contrasted with a constant linear velocity (CLV).
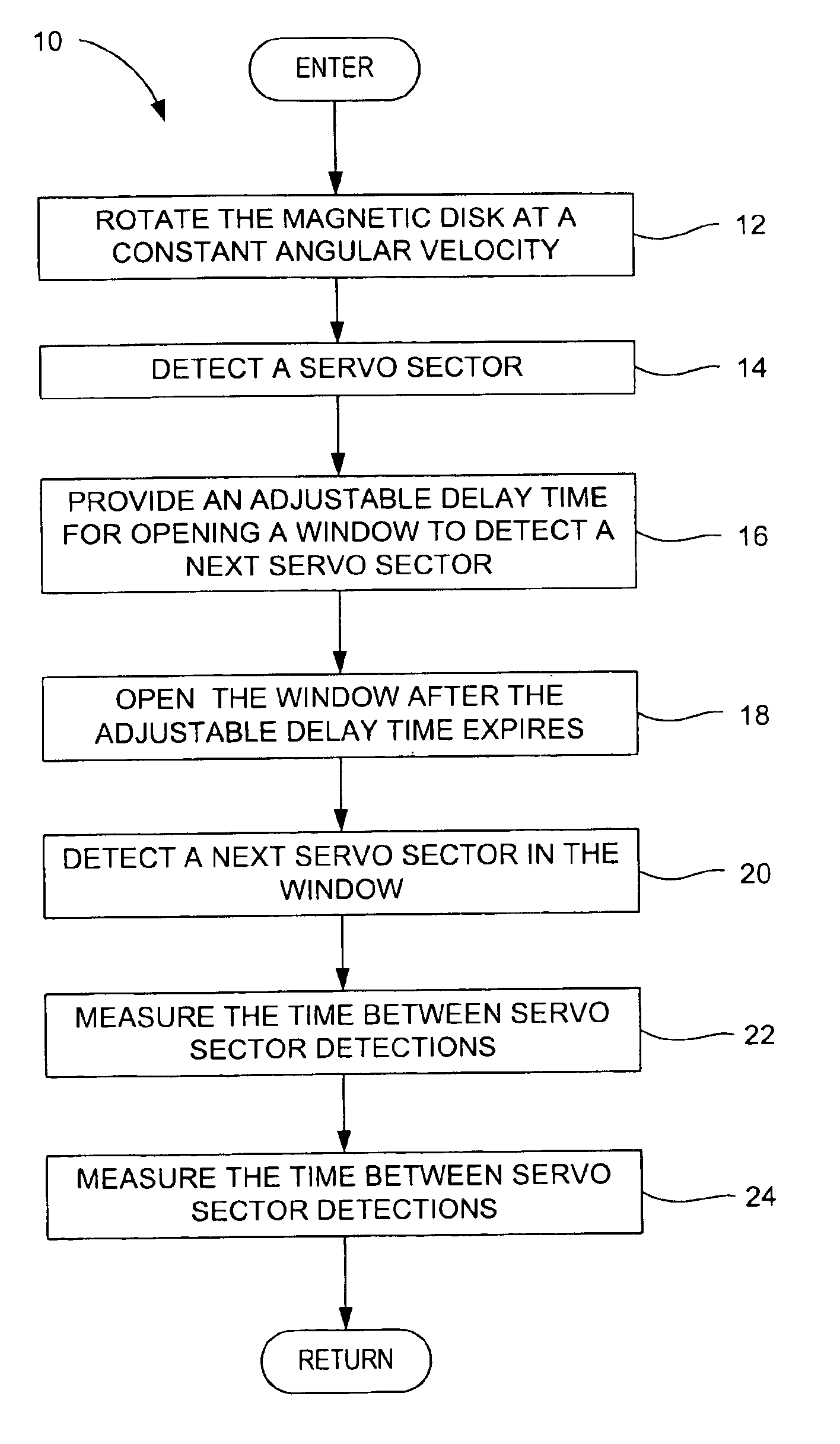
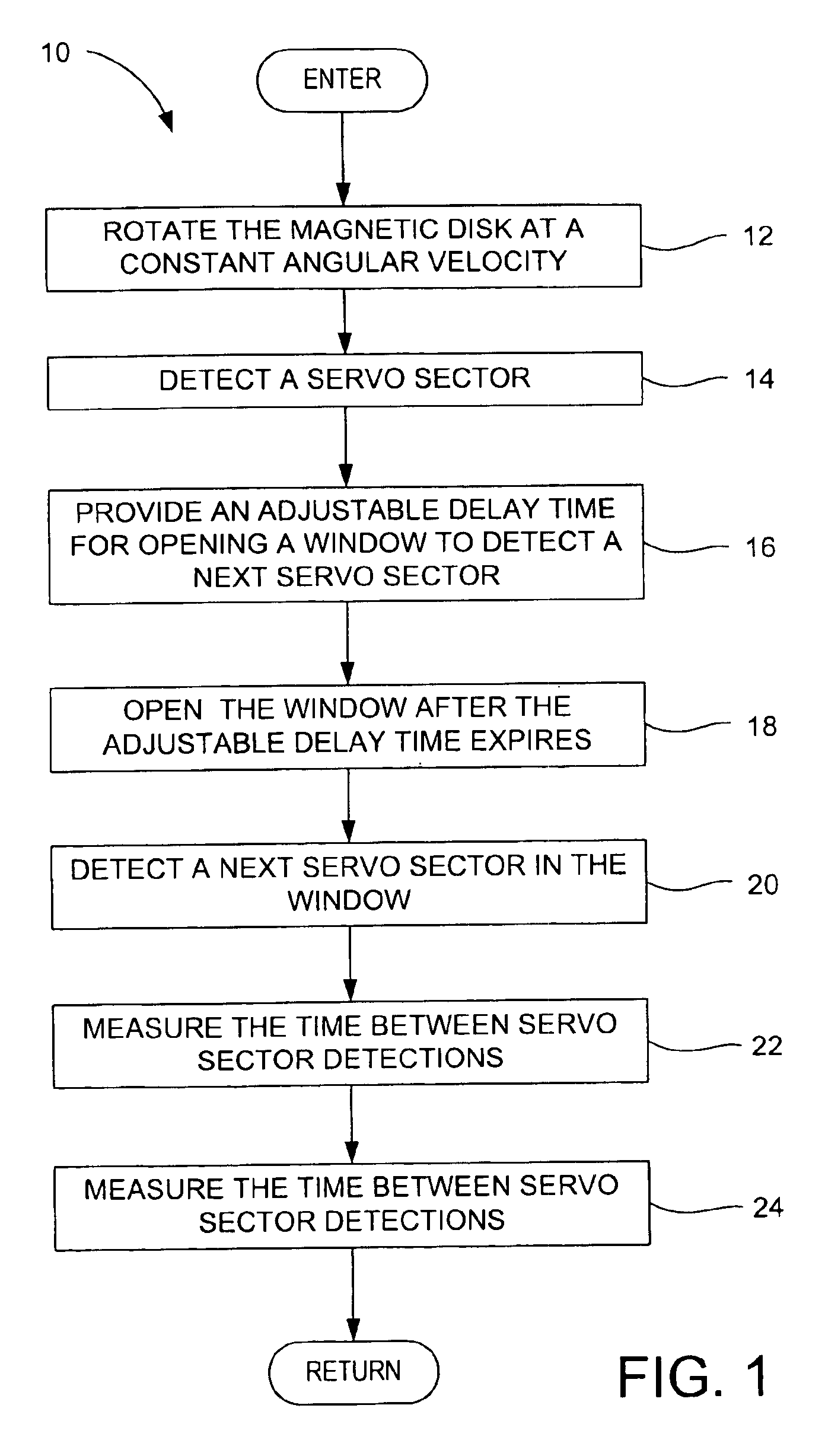
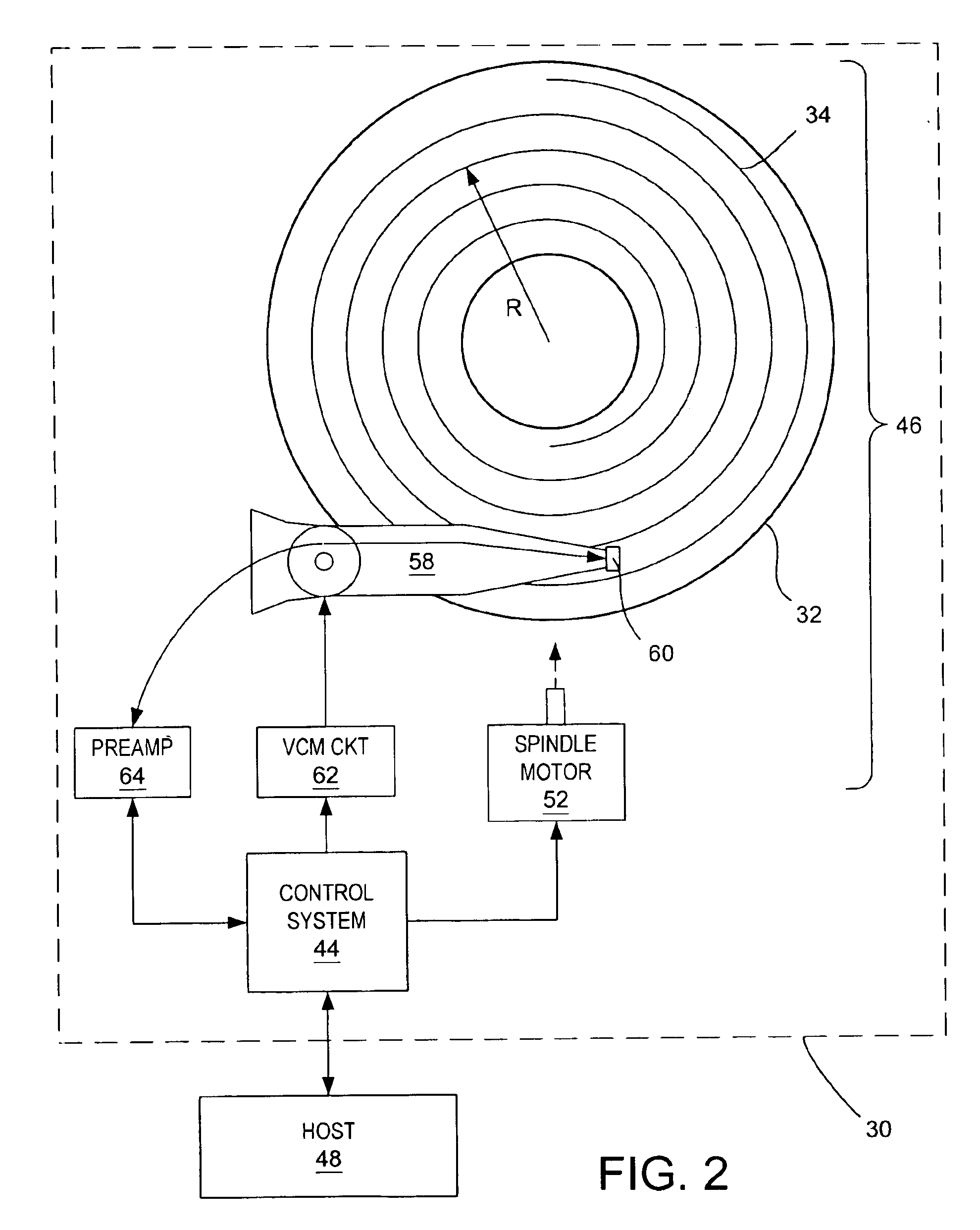
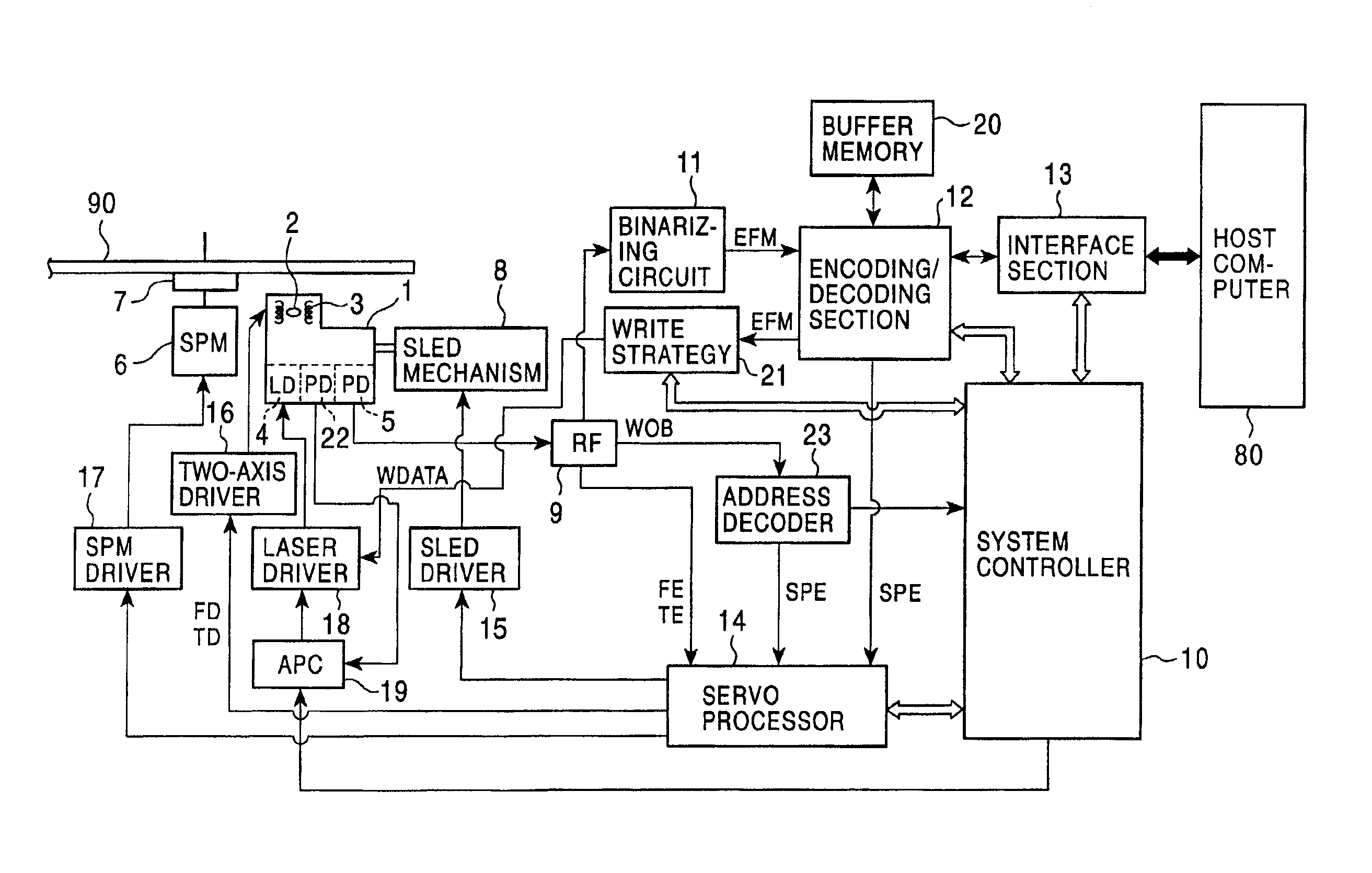
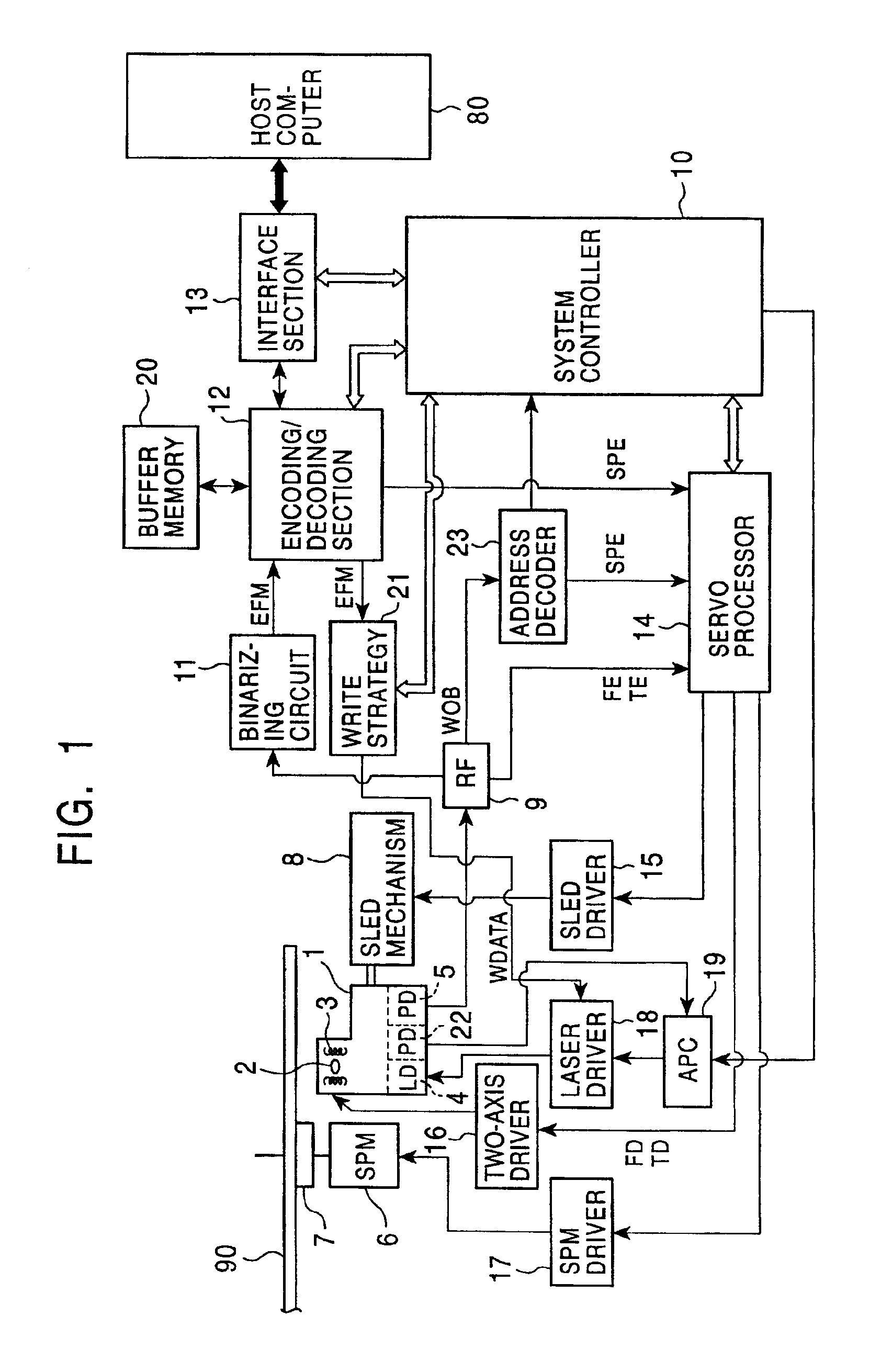
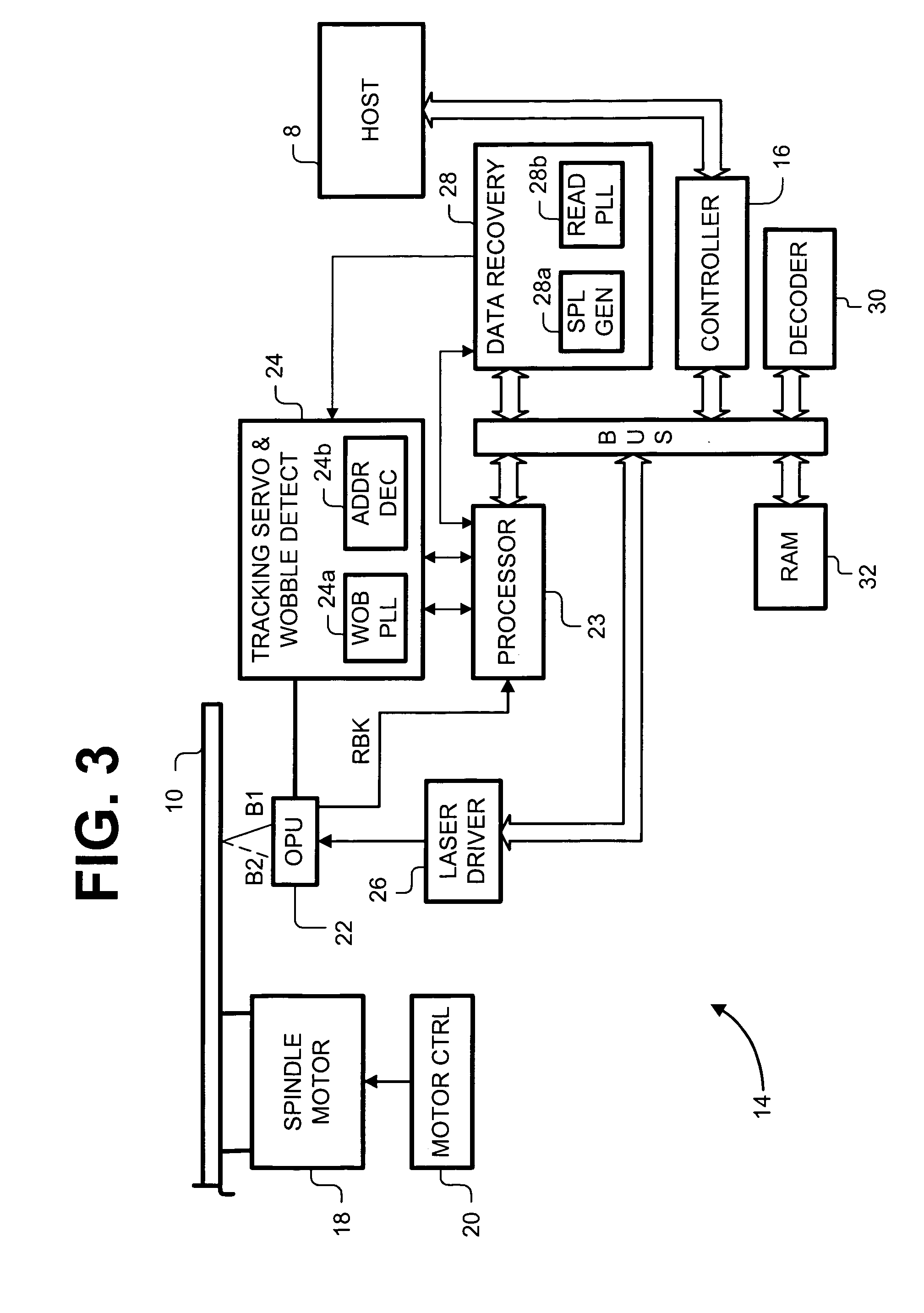
Method for adjusting a delay time for opening a servo sector detection window in a disk drive having a spiral track
InactiveUS6920004B1Disc-shaped record carriersRecord information storageLinear densityControl theory
The present invention may be embodied in a method for adjusting a servo sector detection delay time between detection windows in a disk drive. The disk drive includes a magnetic disk with a spiral track having contiguous storage segments. Each storage segment has a servo sector and a predetermined number of uniformly-sized data sectors. The storage segments are written at a relatively constant linear density along the spiral track. In the method, the magnetic disk is rotated at a constant angular velocity. A servo sector is detected. An adjustable delay time is provided for opening a window to detect a next servo sector. The window is opened after the adjustable delay time expires. A next servo sector is detected in the window. A time between the servo sector detections is measured and the adjustable delay time is adjusted based on the measured time.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
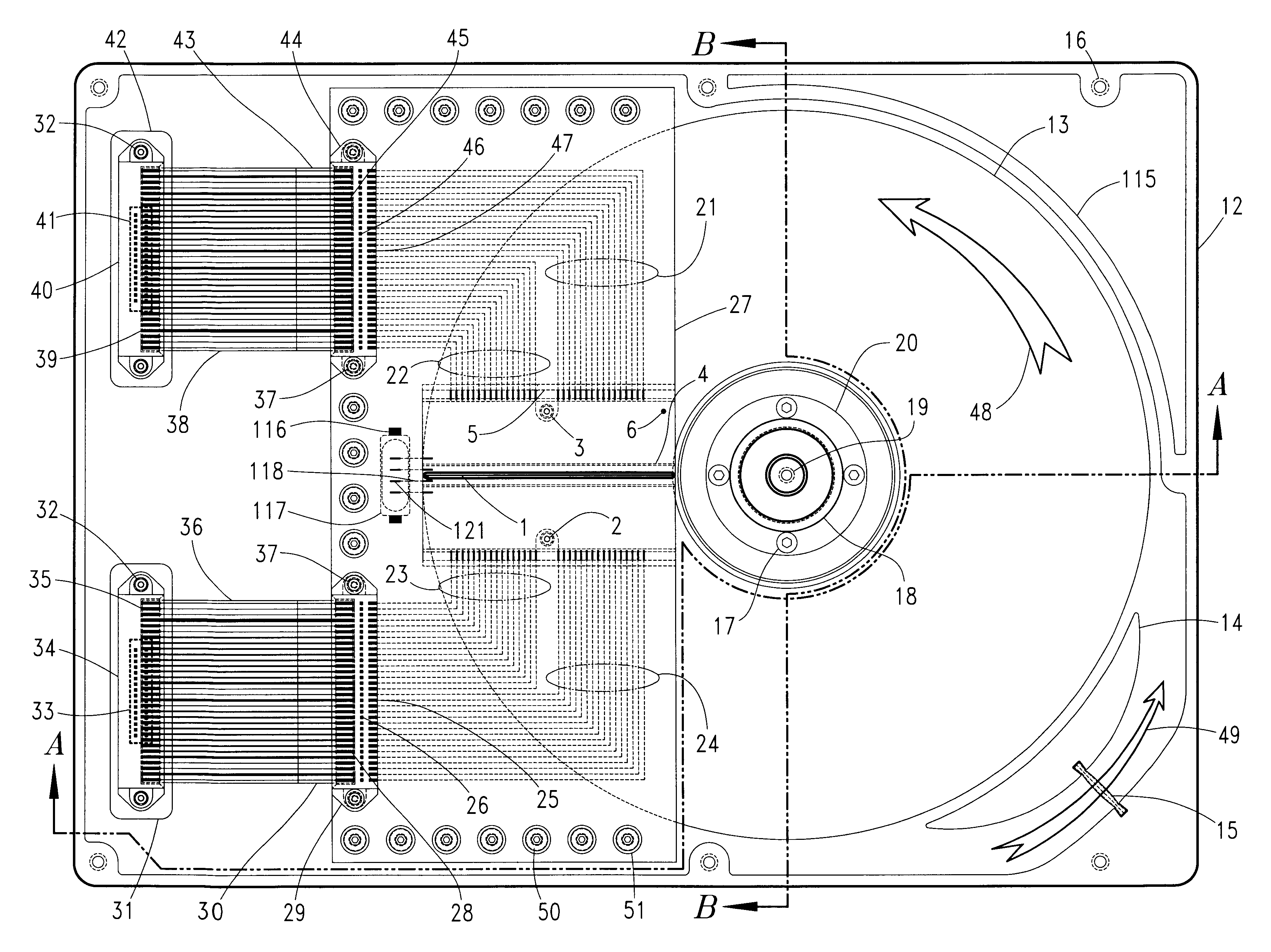
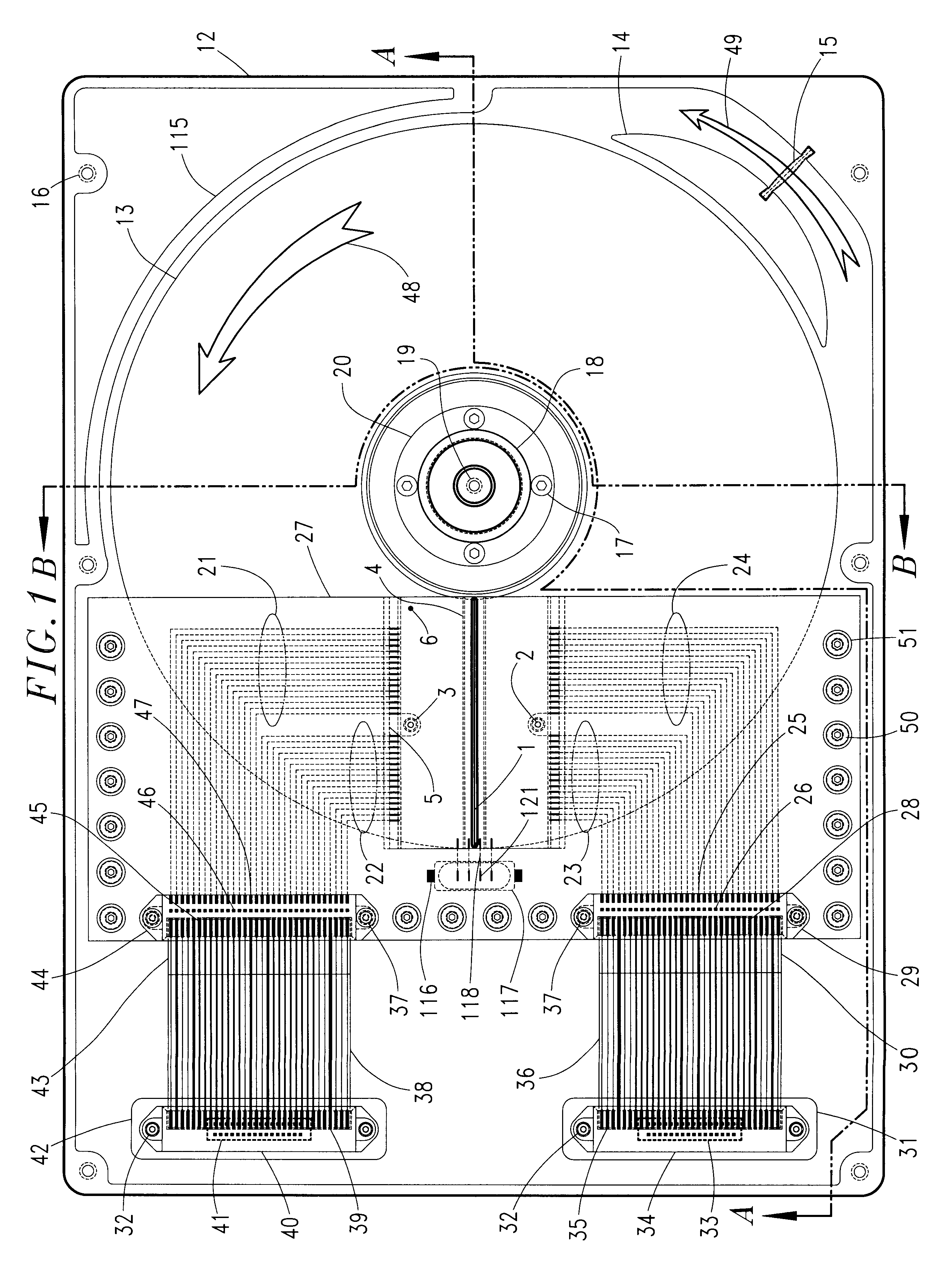
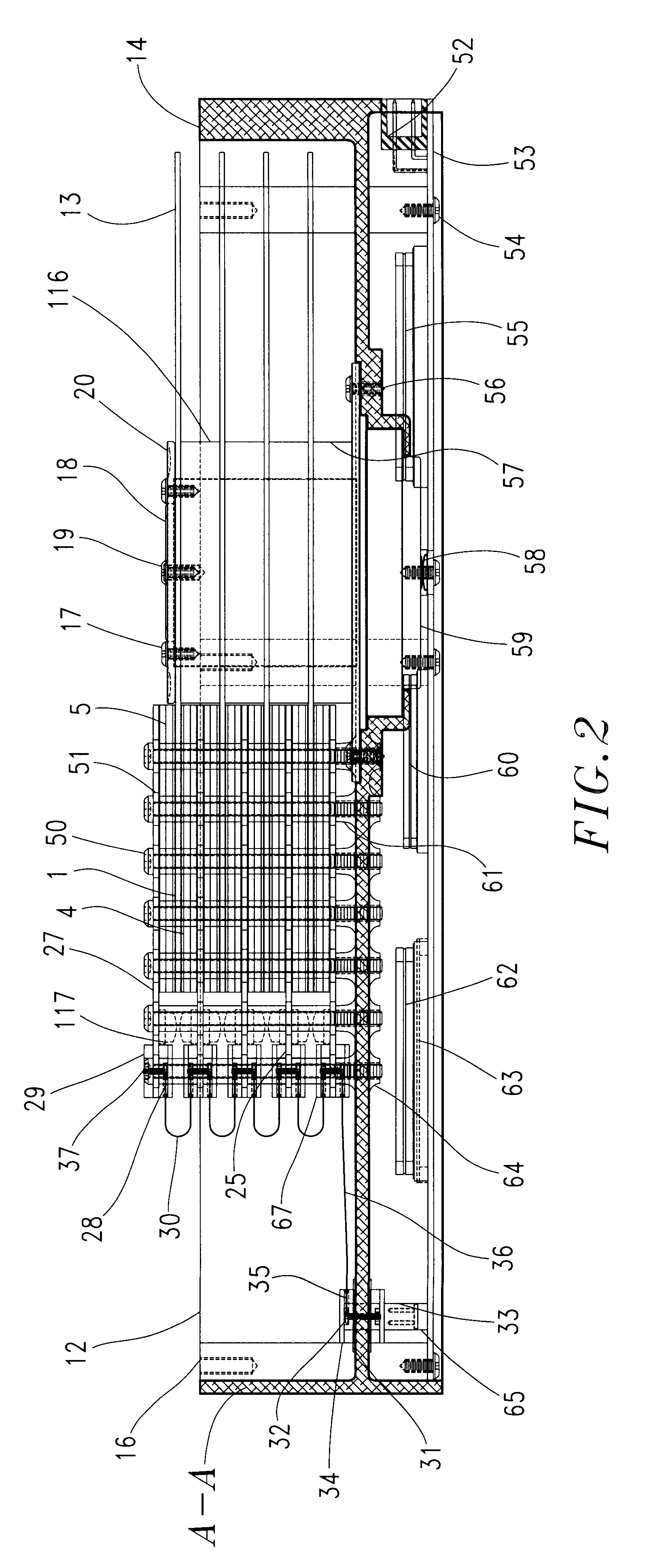
Magnetic data storage fixed hard disk drive using stationary microhead array chips in place of flying-heads and rotary voice-coil actuators
InactiveUS6249824B1Input/output to record carriersApparatus modification to store record carriersHard disc driveTransducer
A magnetic data storage fixed hard disk drive using stationary Microhead Array Chips in place of conventional Flying-Heads and Rotary Voice-Coil Actuators or other Servo-Tracking mechanisms. Every Microhead Array Chip has a minimum of one thousand or maximum of four billion individual and addressable microhead read and write data-transducers built into it. The hard disk drive unit assembly that uses the Microhead Array Chip approach will have within its assembly as few as two or as many as twenty-eight installed Microhead Array Chips. The Microhead Array Chip hard disk drive unit assemblies will have at least one storage disk-platter with two disk-platter data-surfaces containing a multiplicity of concentric data-tracks that rotates at a substantially constant angular velocity. While Microhead Array Chips are made stationary by specially designed circuit boards, that positions a Microhead Array Chip over each of two data-surfaces of every disk-platter within the hard disk drive assembly. The total number of microheads within a stationary positioned Microhead Array Chip's Microhead Array is what determines the total number of available tracks on and across a data-platter's data-surface (i.e., 65,000 microheads would equal 65,000 cylinder / tracks).
Owner:OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
Method of recording and reproducing information and apparatus for recording and reproducing information using the method
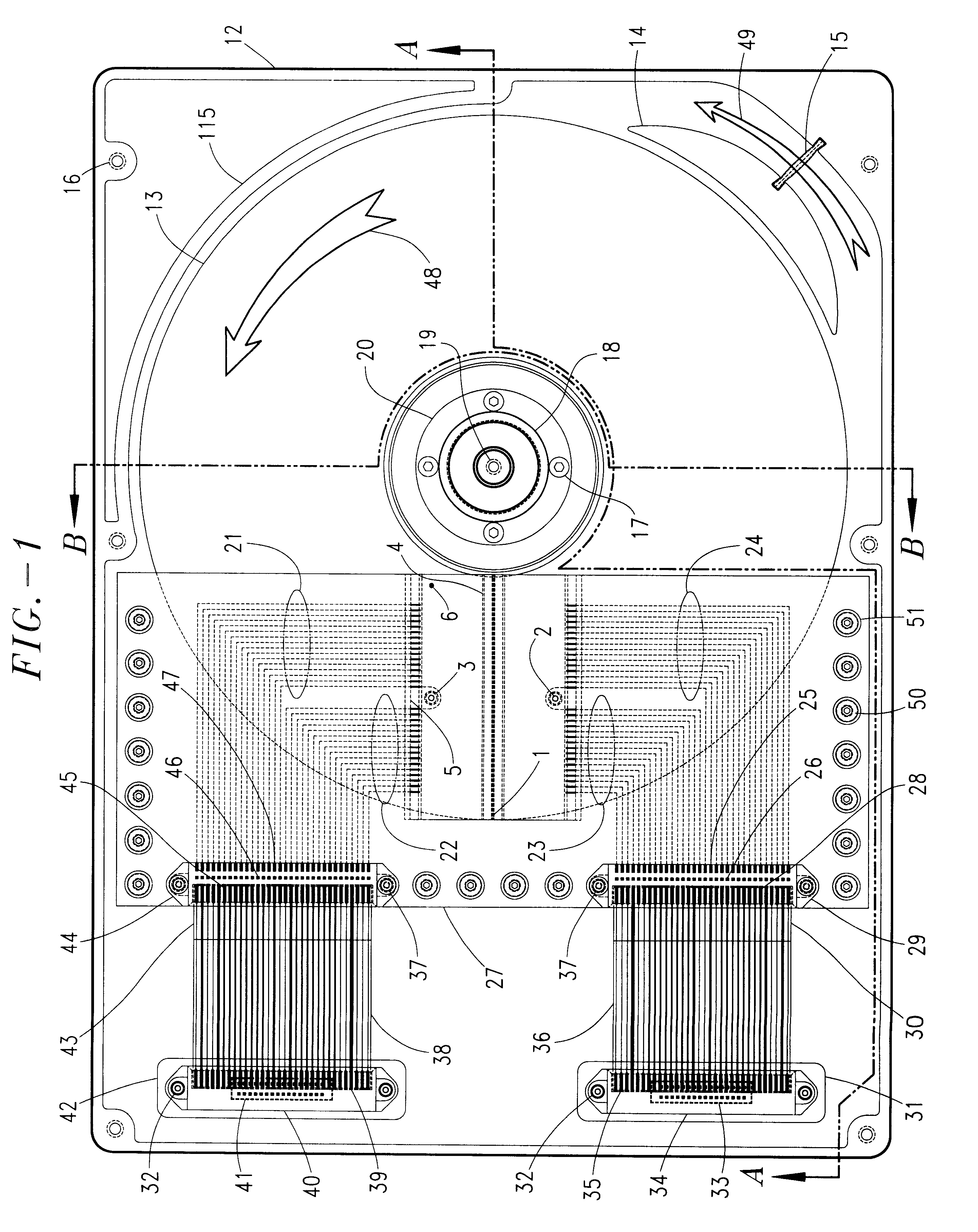
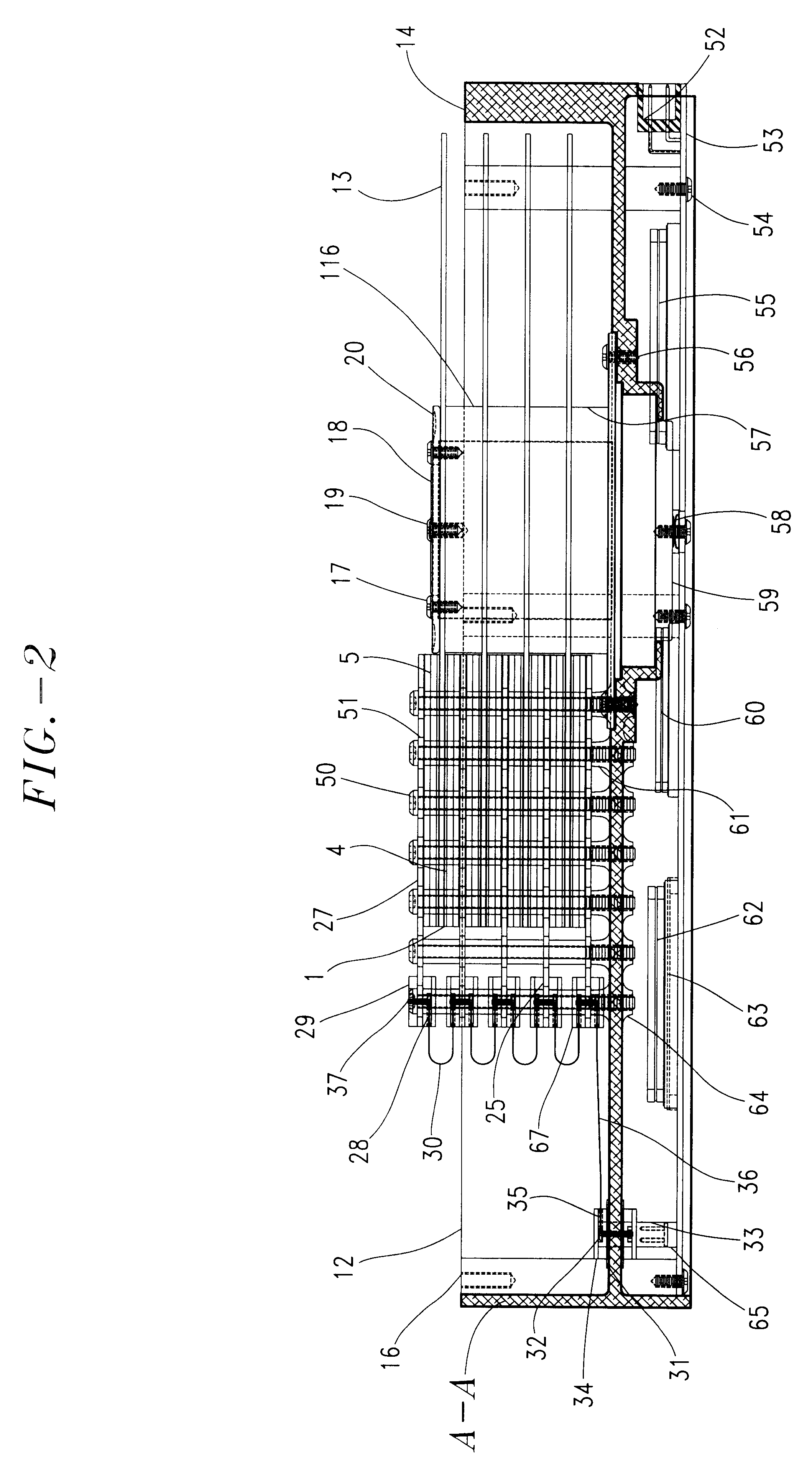
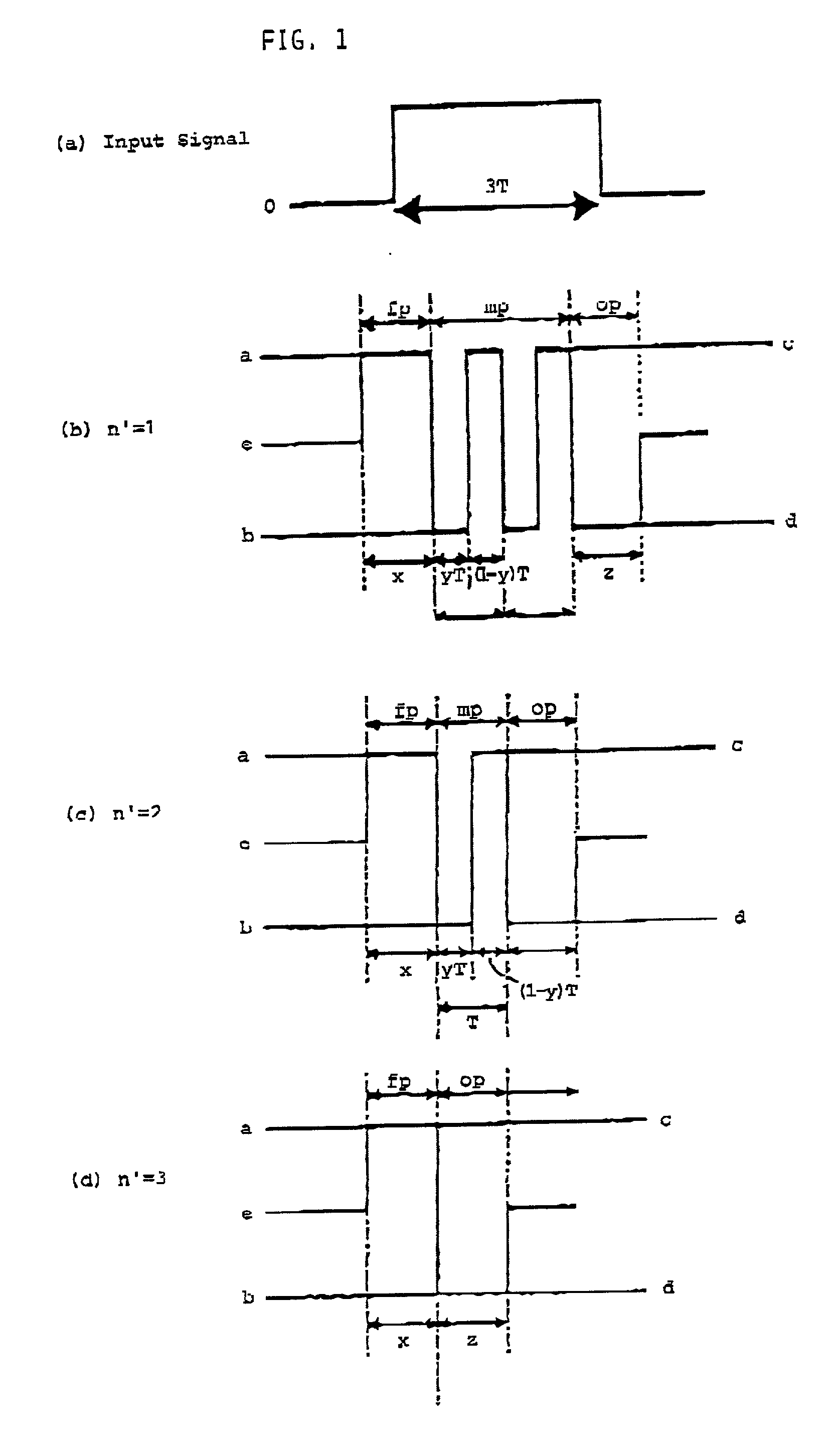
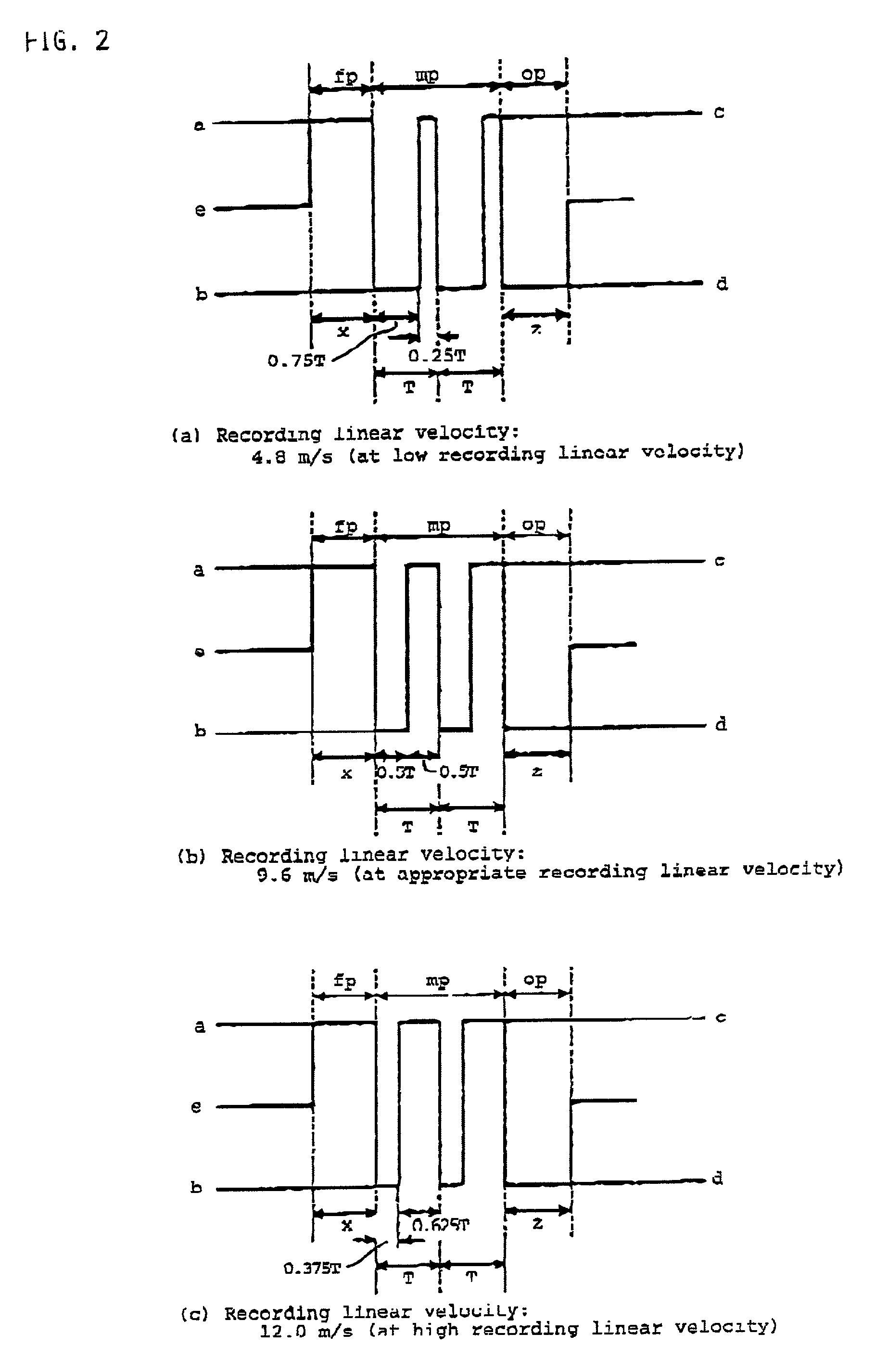
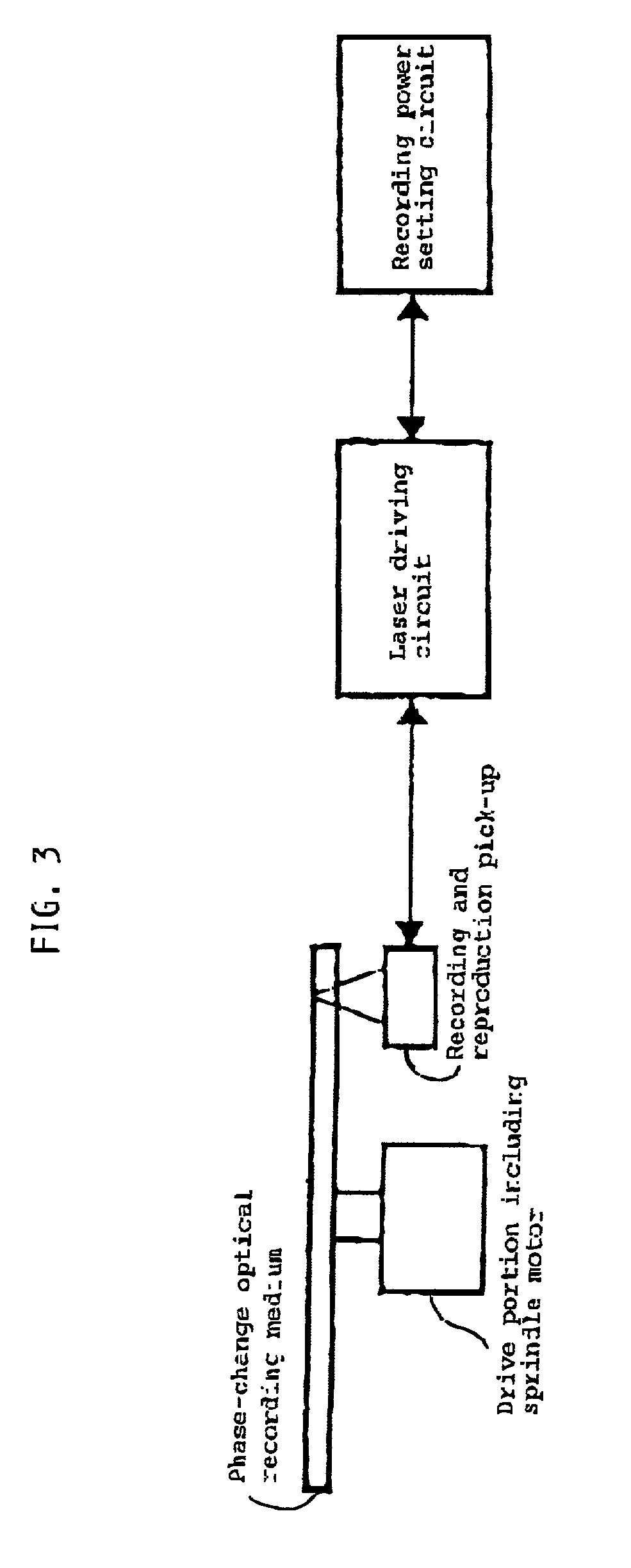
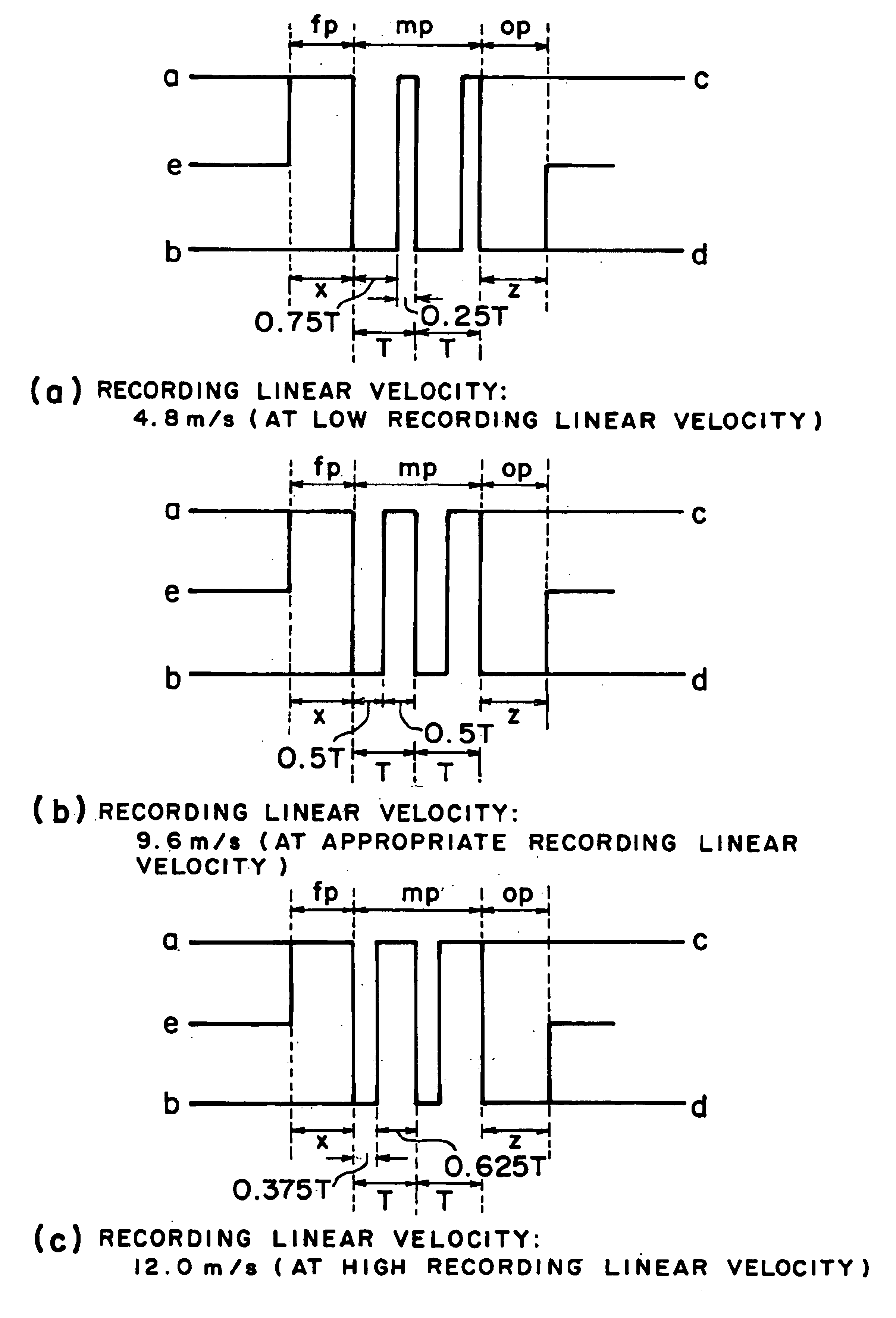
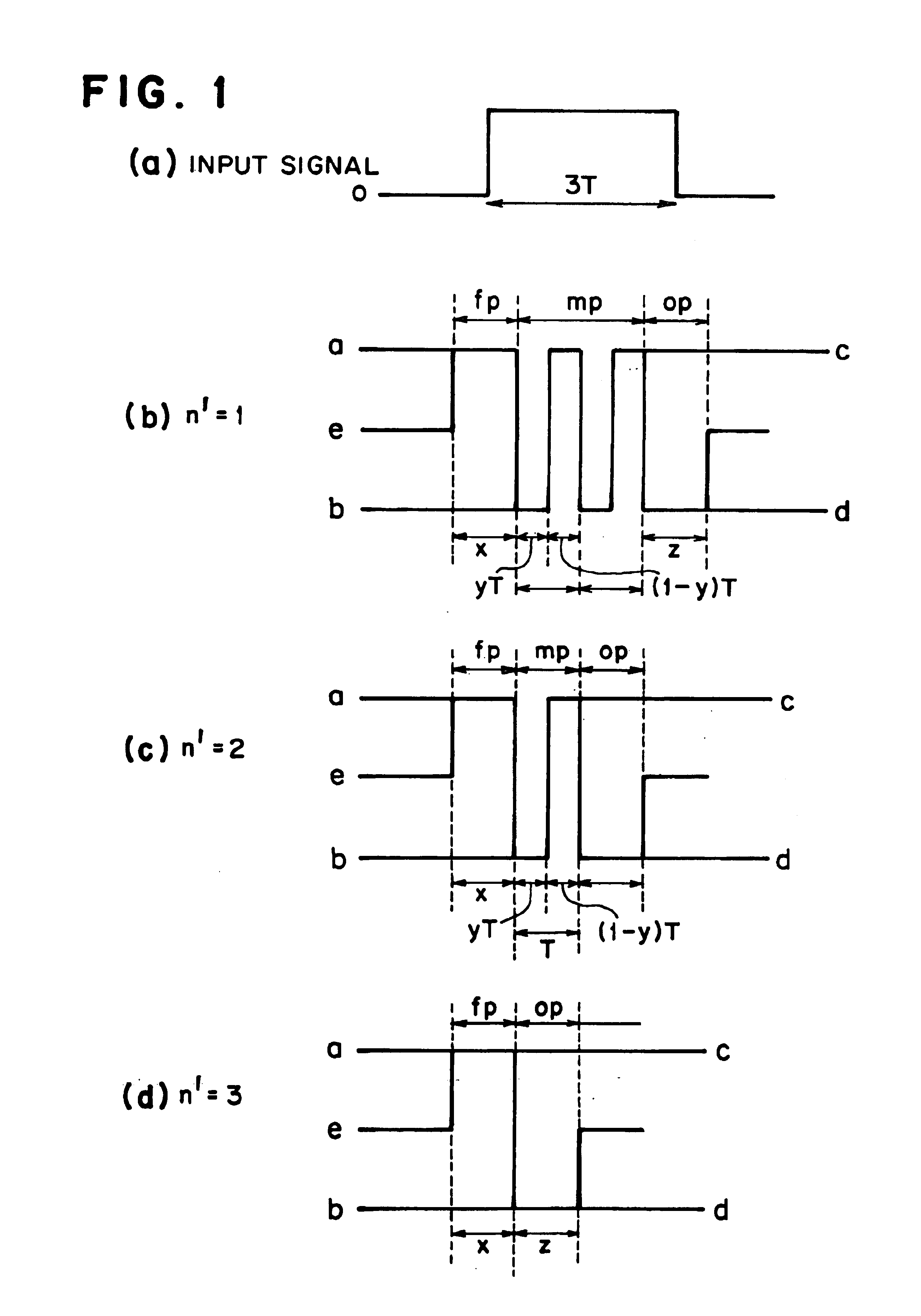
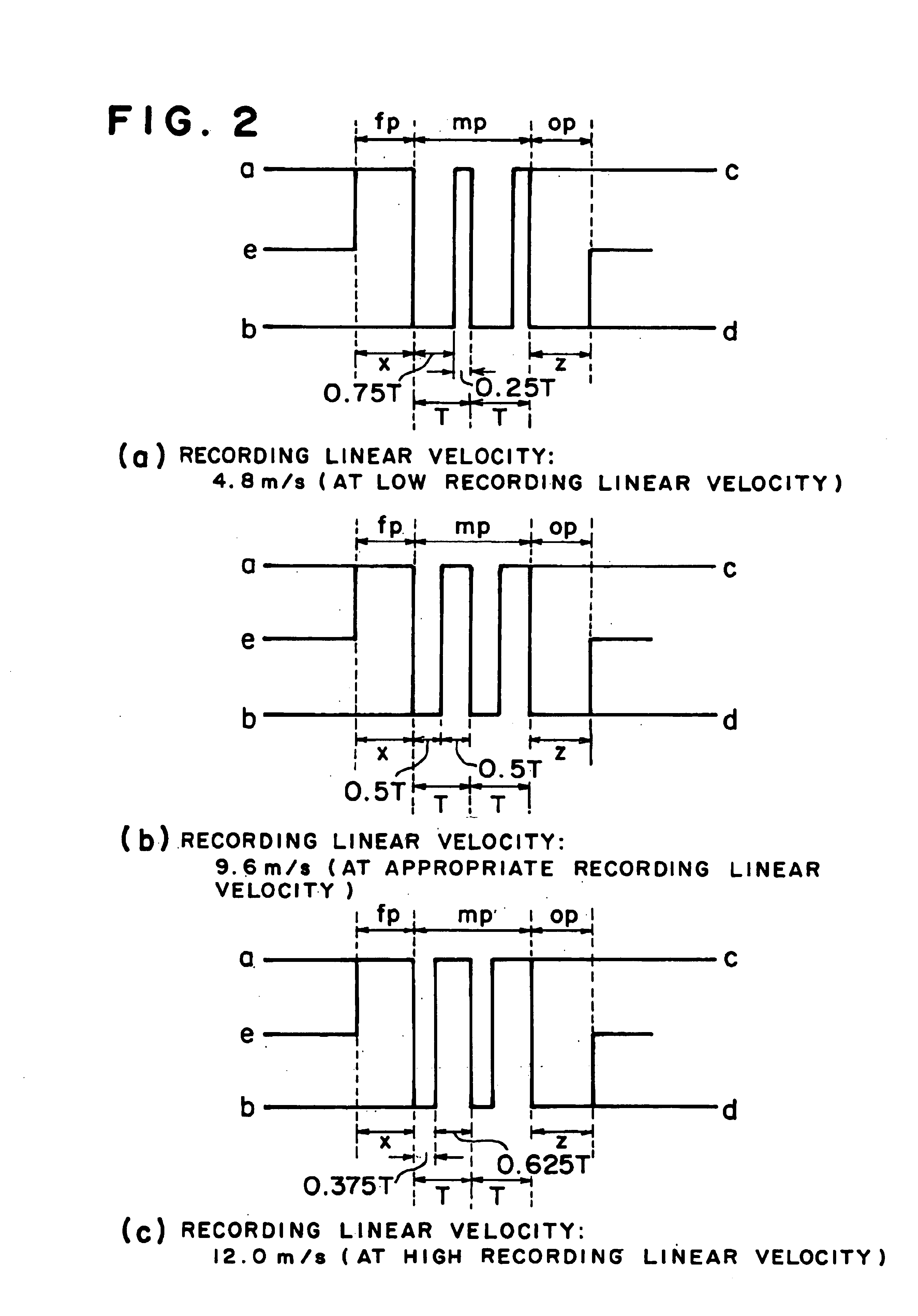
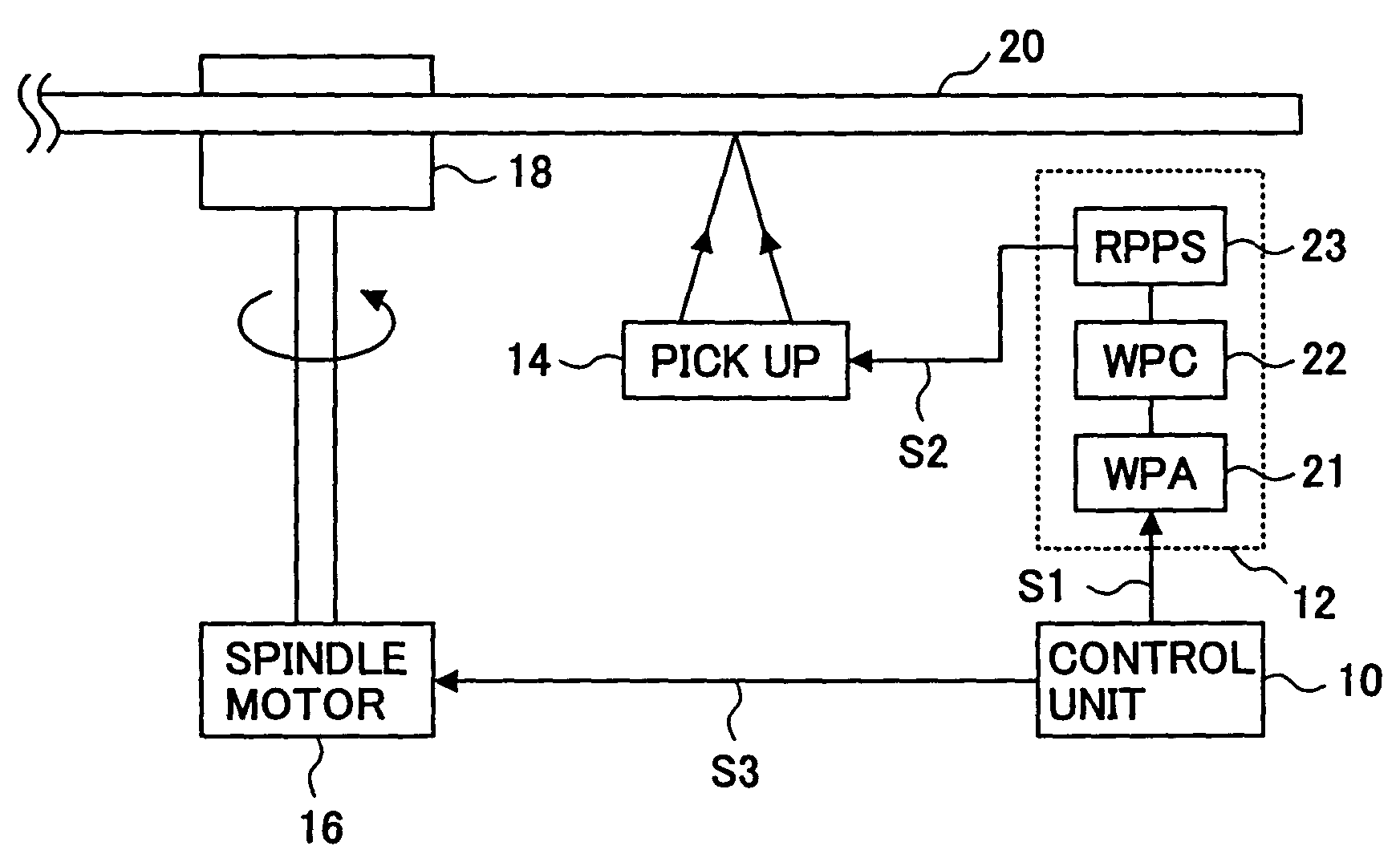
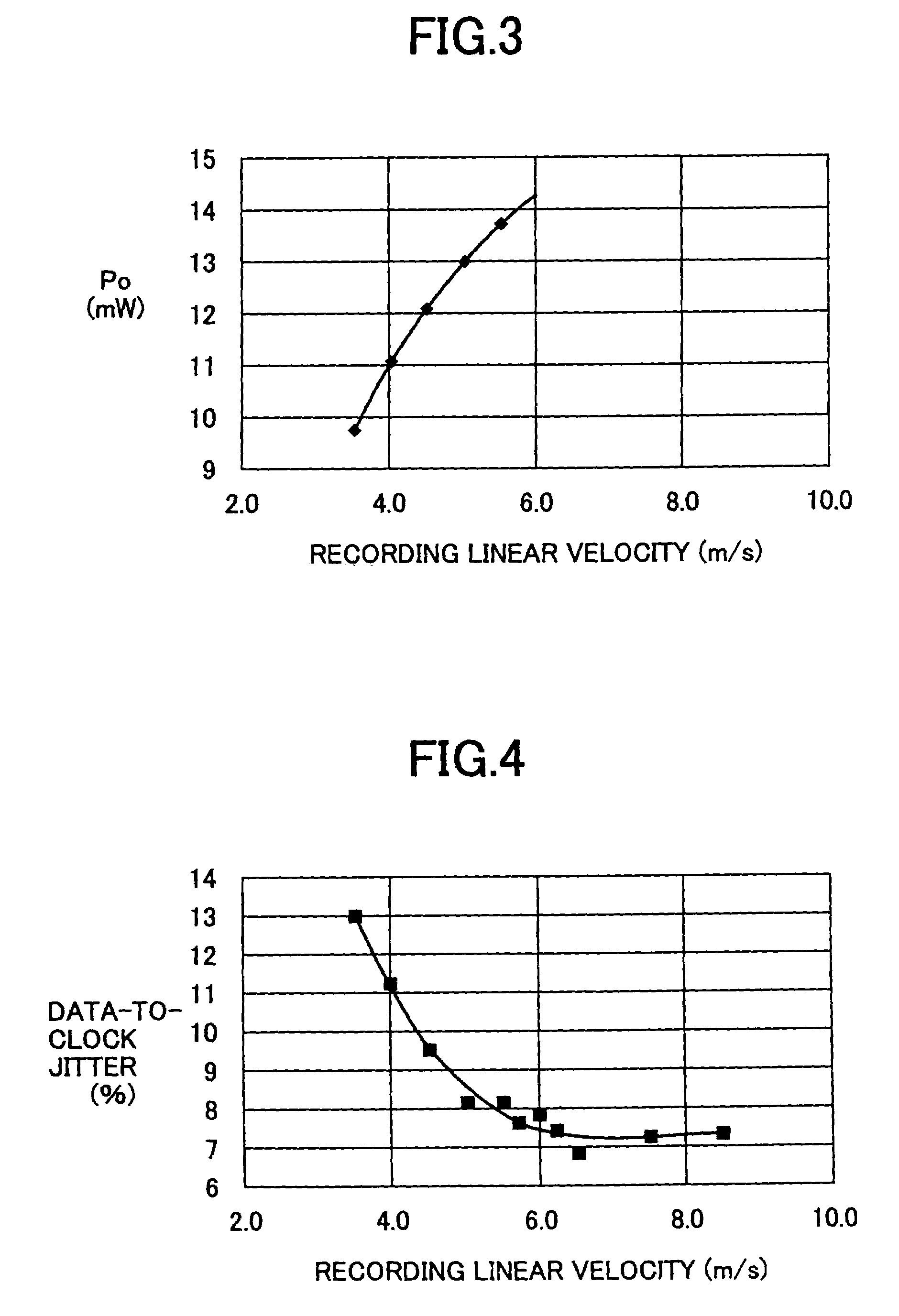
A method of recording and reproducing information in a phase-change optical recording medium by irradiation of an electromagnetic wave for recording, reproducing and / or rewriting information is proposed, wherein when information is recorded in the phase-change optical recording medium by modulating an input signal and conducting pulse width modulation recording, a recording pulse string for recording and rewriting is a continuous electromagnetic wave, and a recording pulse string for input signal, is an electromagnetic wave pulse string having a front-pulse portion fp, a multi-pulse portion mp with a total pulse duration period T and a duty ratio y, and an off-pulse portion op, wherein the duty ratio y is decreased as a recording linear velocity for the phase-change change optical recording medium is increased, whereby multi-speed recording or CAV (constant angular velocity) recording is carried out. An information recording and reproducing apparatus, using the above method, is also proposed.
Owner:RICOH KK
Optical data storage fixed hard disk drive using stationary magneto-optical microhead array chips in place of flying-heads and rotary voice-coil actuators
InactiveUS6266712B1Input/output to record carriersHard disc driveVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
An optical data-storage hard disk drive, which uses stationary Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chips in place of conventional Flying-Heads, Rotary Voice-Coil Actuators and other similar types of Servo-Tracking mechanisms to transcribe or retrieve digital information to or from at least one non-volatile memory medium's data-surface, using an optical magnetic process of recording and reading data. The Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip Hard Disk Drives will have at least one storage disk-platter with two disk-platter data-surfaces containing a multiplicity of concentric data-tracks that rotates at a substantially constant angular velocity. Every Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip will comprise a (VCSEL) "Vertical Cavity Surface Emitting Laser" microhead array having a minimum of one thousand or a maximum of four billion individually addressable VCSELs. Each Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip is placed into a stationary position above each disk platter data-surface using a chip-positioning circuit board. While the number of cylinder / tracks available to each Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip is determined by the number of VCSEL microheads contained within a Magneto-Optical Microhead Array Chip's microhead array (e.g., "325,000" vertical cavity surface emitting laser microheads would therefore equal "325,000" corresponding cylinder / tracks).
Owner:OPTICAL STORAGE DEVICES
Apparatus for and method of driving motor to move object at a constant velocity
ActiveUS6949896B2DC motor speed/torque controlDynamo-electric converter controlDrive motorControl theory
A drive control method includes detecting an angular displacement of a rotor driven by a pulse motor, calculating a difference between the detected angular displacement and a preset target value of the angular displacement, and calculating a drive pulse frequency of a drive pulse signal used to drive the pulse motor. The pulse motor is driven by the drive pulse signal having the drive pulse frequency to allow the rotor at a constant angular velocity.
Owner:RICOH KK
Drill bit tracking apparatus and method
An apparatus is provided for assessing the location of a drill bit underground. The apparatus includes an acoustic sound generator that is driven by the drilling mud supplied to the drill bit. The sound generator a characteristic string of pulses, which may be termed a signature or key. The key is repeated over and over. Monitors (i.e., sensors) at the surface listen for this key. The key is distorted by the inconstant angular velocity of the drill bit. Thus the observed data do not precisely match the key. On the basis of numerical algorithms, a digitally revised reference signal or key, is identified to map the known reference key onto the best fitting observed data. The correction factors are then applied to map the modified reference key onto the data observed at other sensors of an array of sensors mounted on the surface. By determining the phase shift and travel time of the signals at the various sensors, and having determined the speed of wave propagation in the geological media, the position of the bit, or a fairly close approximation thereof, may be obtained. The correction factors applied to the reference key may also tend to permit the actual rotational speed of the drill bit to be determined.
Owner:ATHENA IND TECH
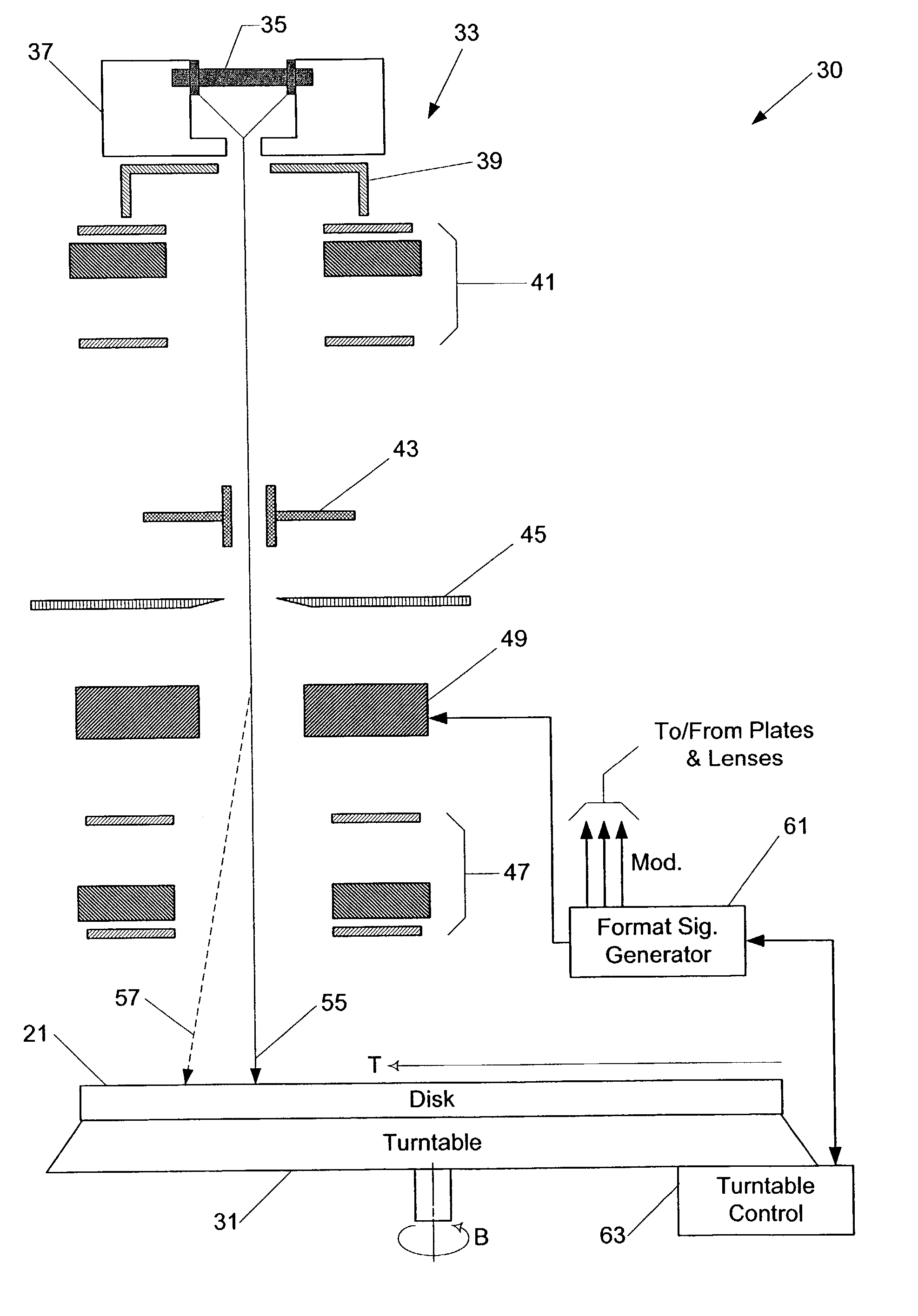
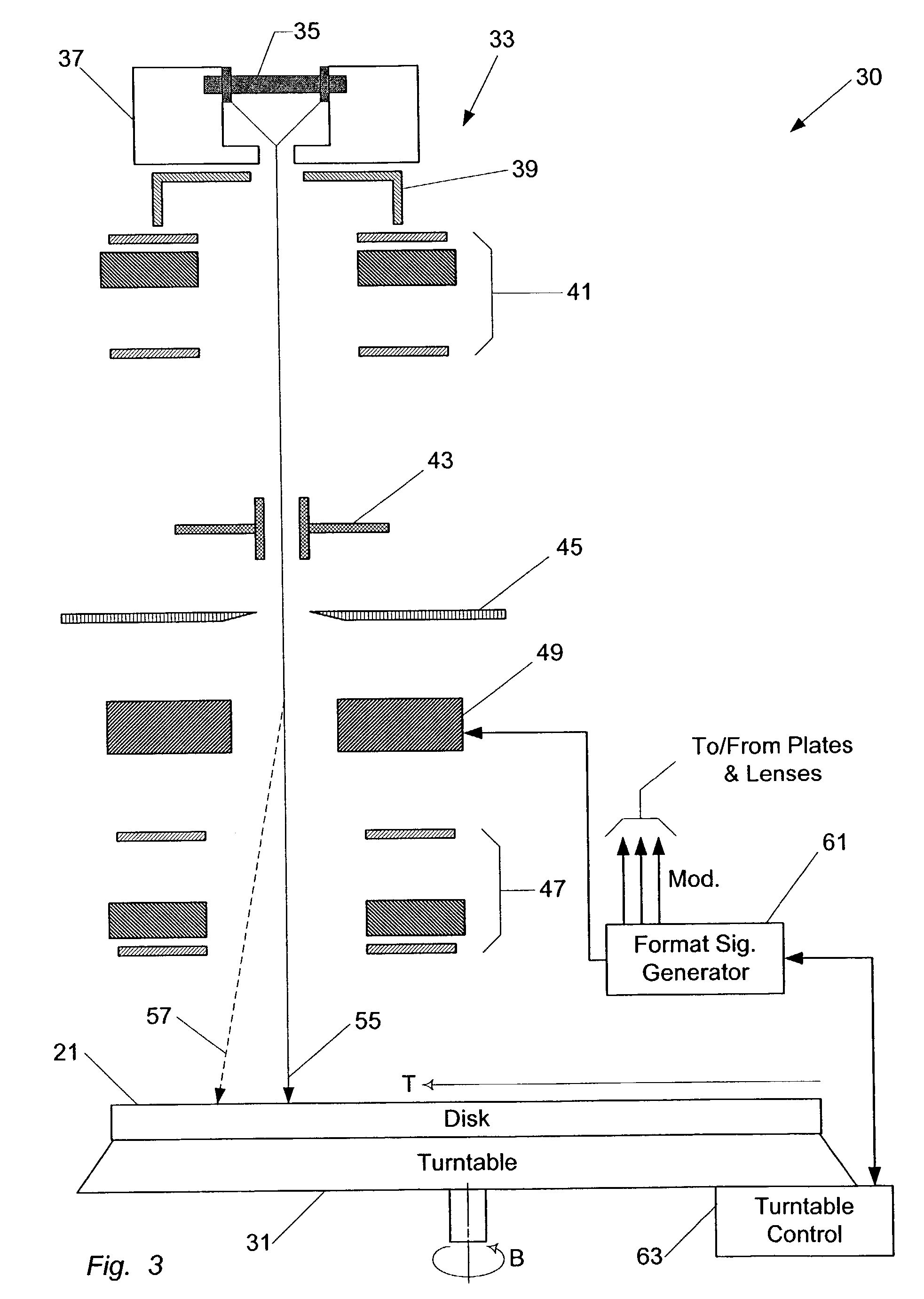
Constant angular velocity disk label printing
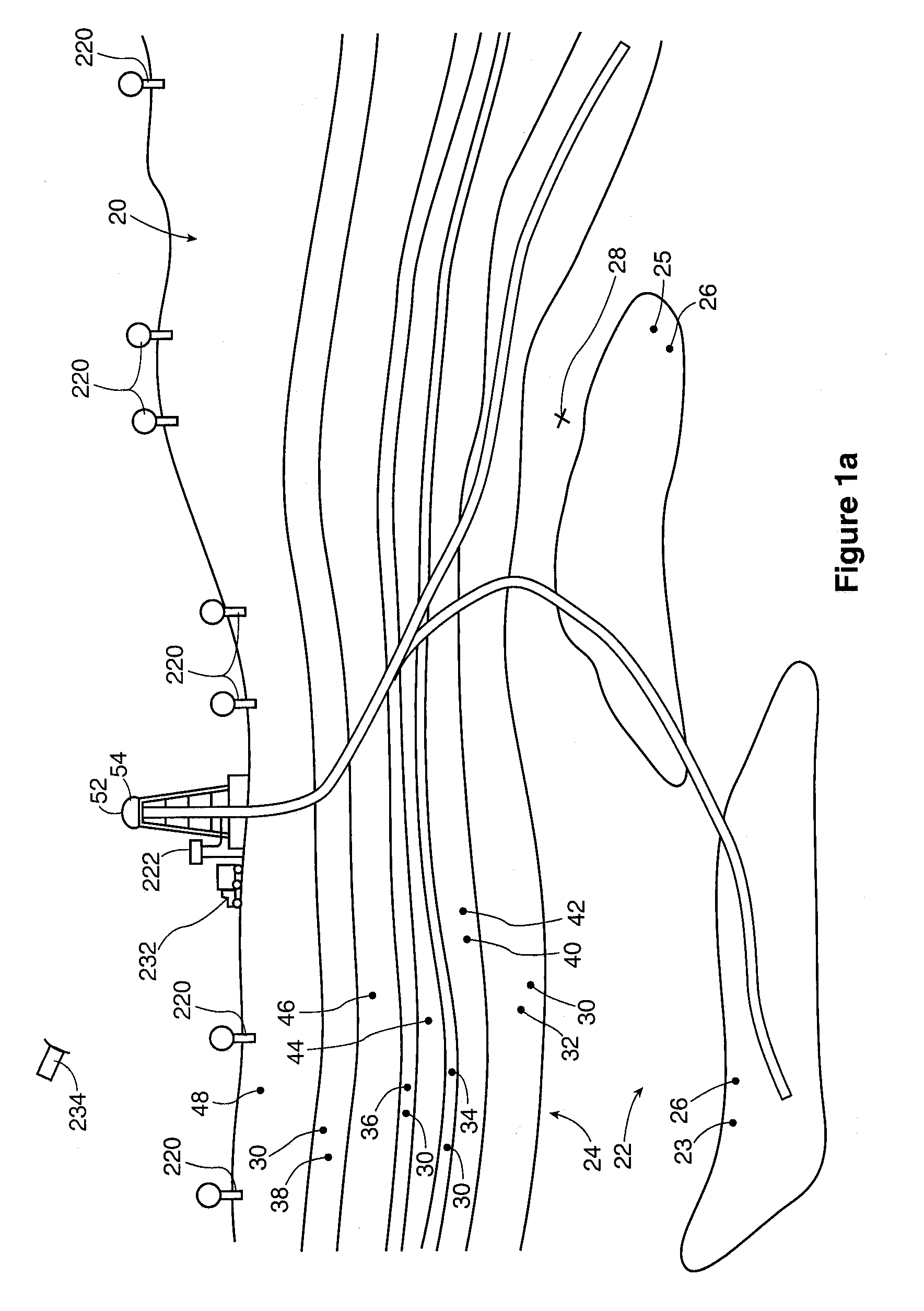
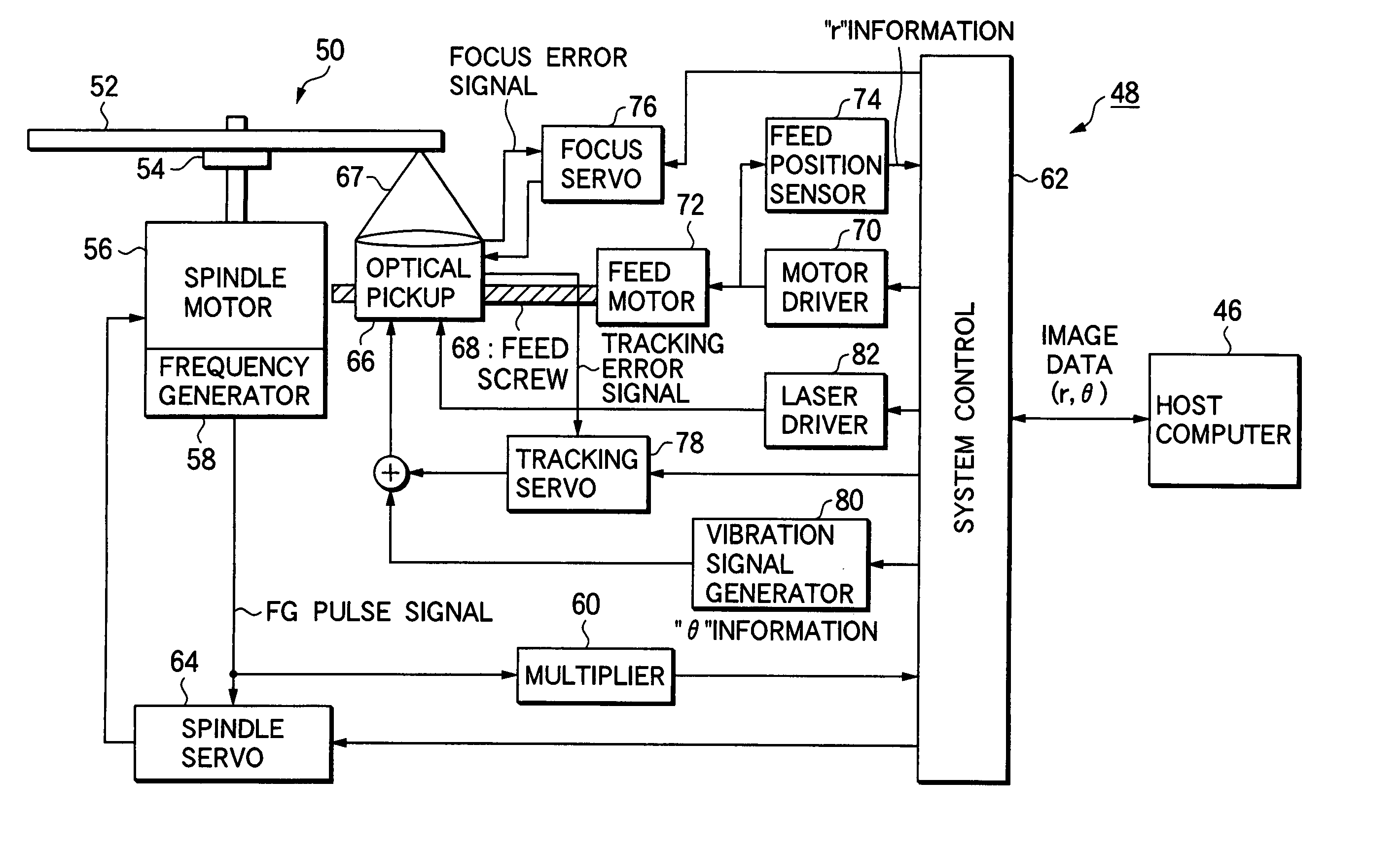
InactiveUS7015939B2Average permeabilityTelevision system detailsFilamentary/web record carriersOptical pickupLight beam
A visible light characteristic changing layer is formed in a location which can be viewed from a part of a label surface of an optical medium. The optical medium is set on a turntable of an optical disk unit, which may be rotated at a constant angular velocity, while the power of a laser beam is modulated in accordance with image data. The optical pickup operates at a first power level when changing a visible light characteristic of the optical medium to form the visible information and the optical pickup operates at a lower power level when not changing a visible light characteristic of the optical medium. As a result, a visible-light reflectivity of the visible light characteristic layer is changed, thereby forming an image corresponding to the image data on the label surface, A tracking servo operation is turned off while the optical pickup forms the visible information.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Recording method and optical disk device
InactiveUS20050286390A1Increase speedDeterioration of data can be preventedRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsDVD-RAMOptoelectronics
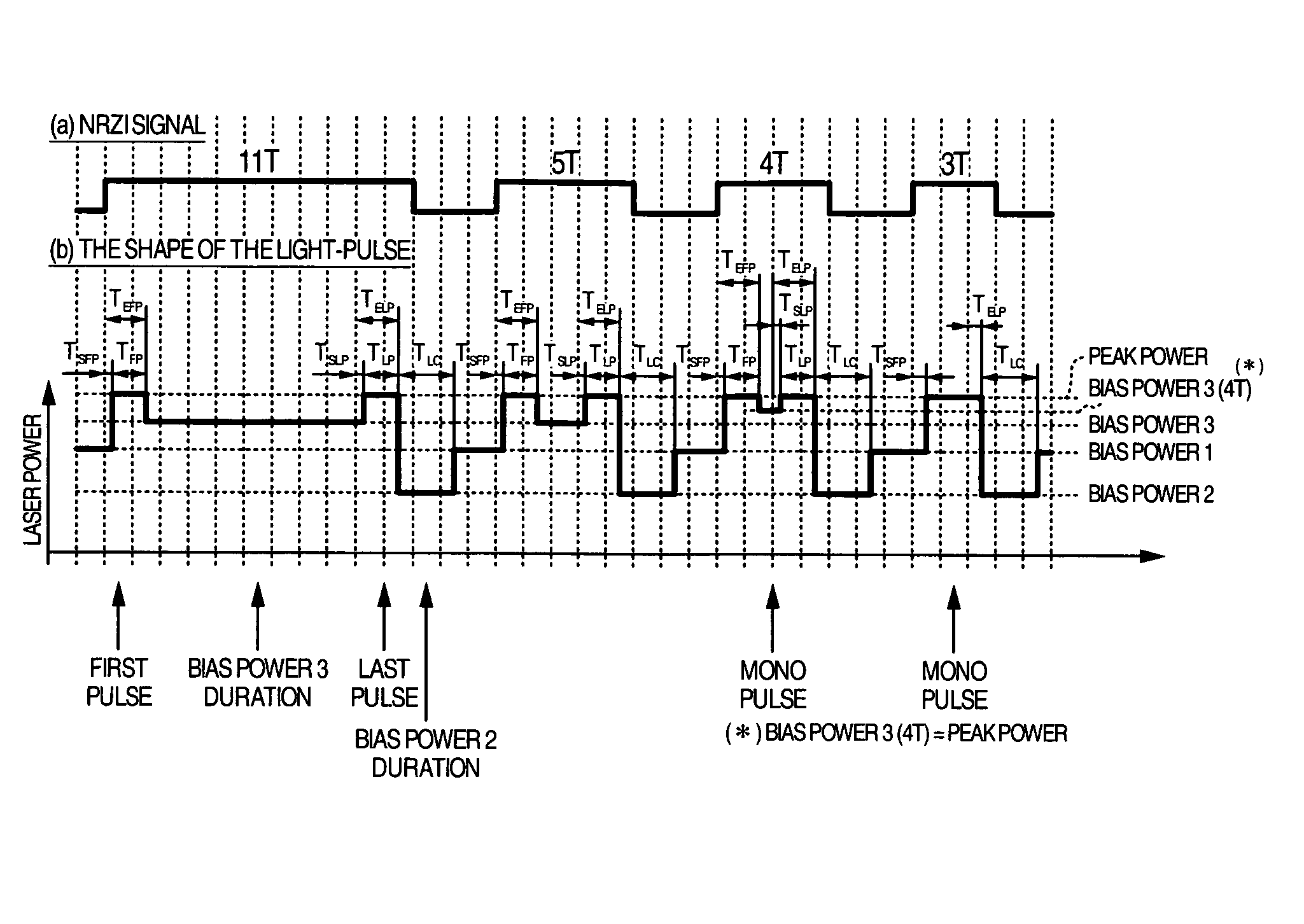
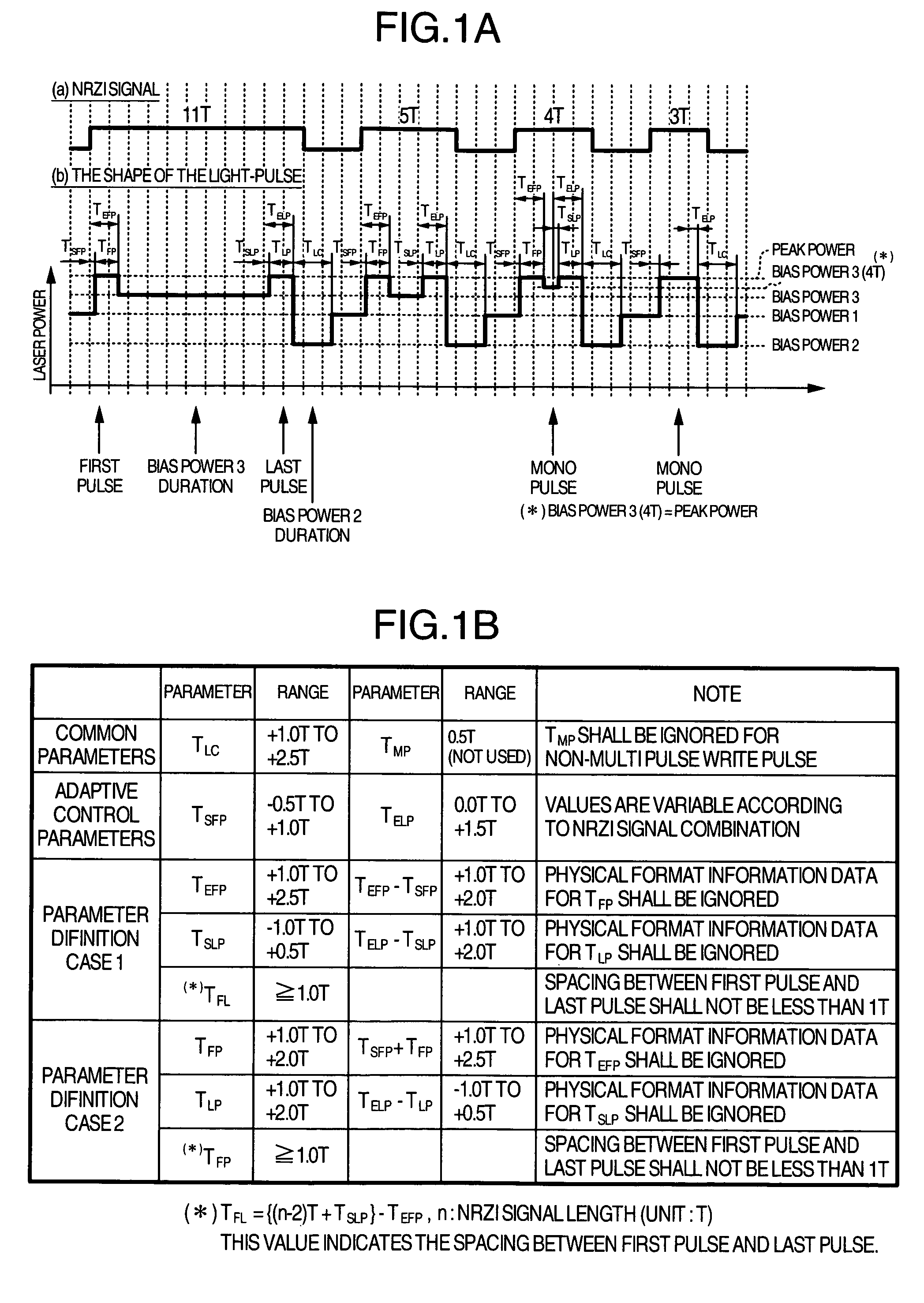
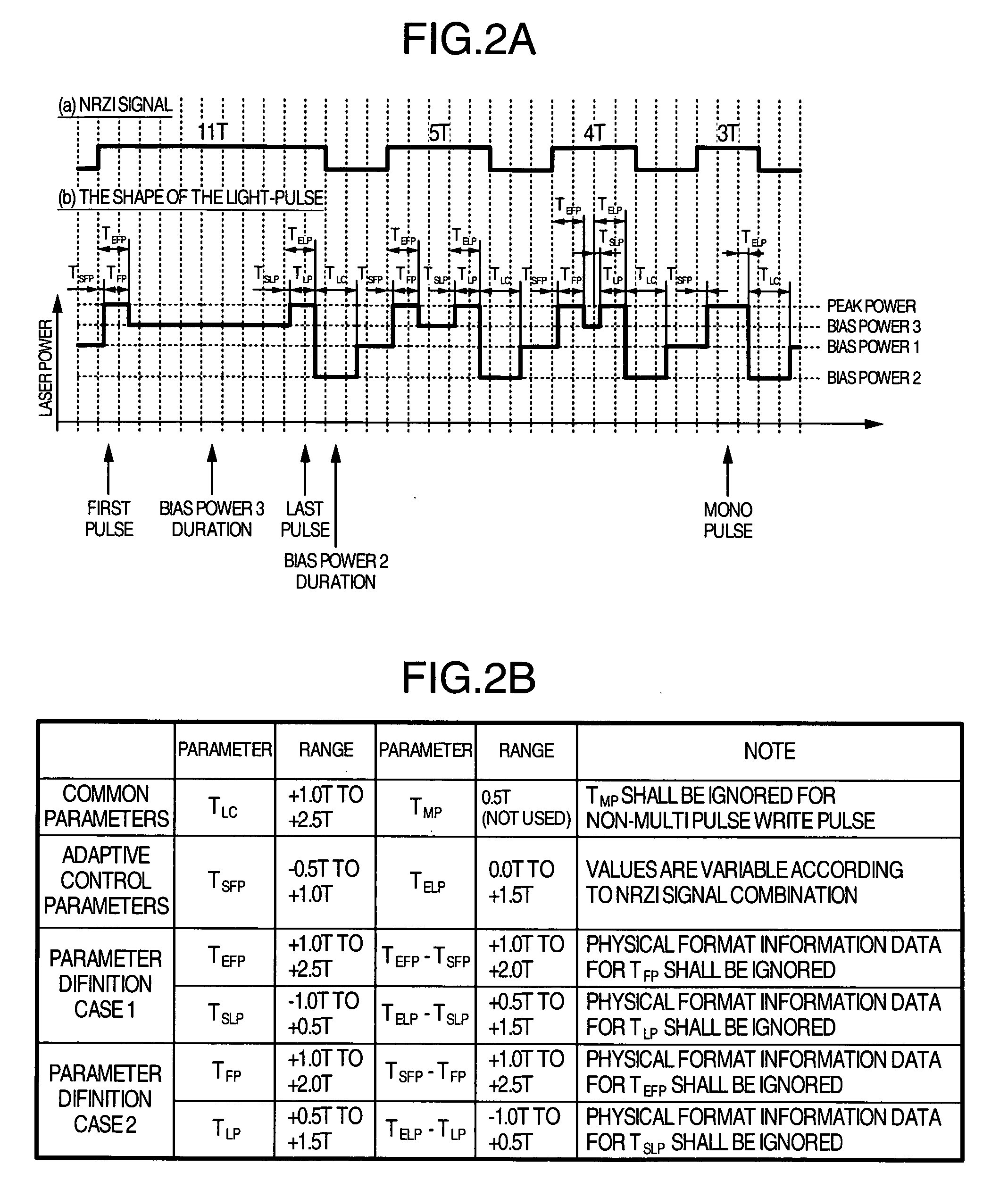
In order that it is realized to put 16× speed DVD-RAM in practice, a recording method coping with CAV (constant angular velocity) and a method for improving S / N ratio are provided and an optical disk device using them is provided. In order that a cutoff phenomenon of pulse in a laser driving circuit may not occur, the shortest pulse width is set at 1 Tw or more where Tw indicates a window width, and a recording pulse in which a 4T mark is recorded with a mono pulse where T indicates a detection window width and the parameter setting range are prescribed. Simultaneously, a reproduction power for 6× speed or more is set at 1.5-2.0 mW, different from a conventional value, and a setup sequence with which deterioration of data in reproducing does not occur is provided. Thereby it becomes possible to put 16× speed DVD-RAM in practice.
Owner:HITACHI CONSUMER ELECTRONICS CORP +1
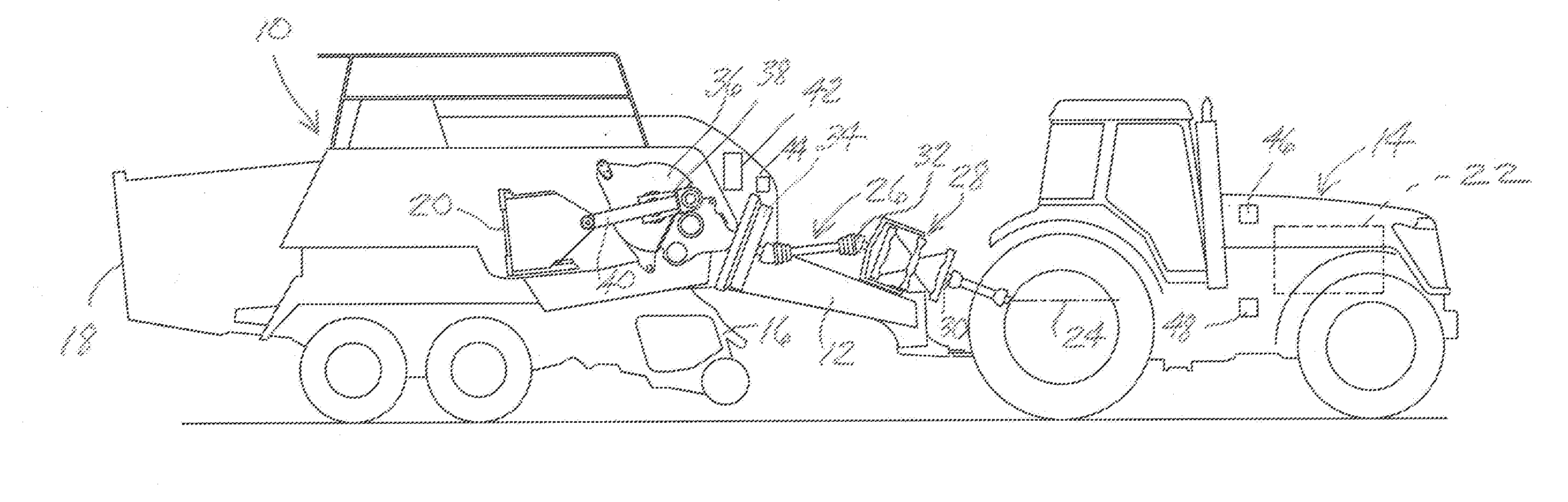
Agricultural implement with power input having continuously variable transmission
A crop baler has a plunger reciprocable through compression and retraction strokes for compressing charges of crop material into bales within the baler. The crop baler also includes a rotatable flywheel operably coupled with the plunger for transferring kinetic energy to the plunger during reciprocation of the plunger. An output shaft is operably coupled with the flywheel for rotating the flywheel and driving the plunger through its compression and retraction strokes and an input shaft is adapted to be coupled with a power takeoff shaft of a towing tractor for receiving driving power from the tractor. The crop baler also includes a continuously variable transmission operably coupled between the input and output shafts for adjusting the ratio of the angular velocities of the shafts in response to changes in the angular velocity of the flywheel while maintaining the input shaft at a substantially constant angular velocity.
Owner:AGCO CORP
Recording apparatus and recording method
InactiveUS6904008B2Reduction in accessibilityReduce data transferTelevision system detailsRecord information storageRecord statusConstant linear velocity
A method and apparatus for recording data wherein the amount of light reflected from a disk is detected, and it is determined according to the amount of reflected light whether the disk is a recordable disk or a rewritable disk. The disk is controlled according to the result of determination such that it is rotated at a constant angular velocity (CAV) or at a constant linear velocity (CLV) and recording is executed. Further, rotation driving control of the disk is selected according to factors other than the type of the disk, such as according to whether random recording is allowed or not, according to a recording state in the disk, according to whether an alternative area is provided or not, according to a recording start position, or according to whether initialization is required or not. CLV control or CAV control is appropriately selected for a disk at recording to suppress a reduction in accessibility and a reduction in data transmission rate.
Owner:SONY CORP
Non-synchronous motor rotary inertia identification method
InactiveCN1354558AHigh accuracy of identification parametersImprove the performance of vector controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsFriction torqueSynchronous motor
The invention relates to a method for recognizing moment of inertia of asynchronous motor. For the purpose, following steps are taken. The electrical motor is controlled to run at constant acceleration from angular velocity omega 1 of no load operation to angular velocity omega 2 and recording the running time delta t by using control method of torque vector. By using control method of speed vector. The motor is controlled to run at constant angular velocity omega 3 of no load operation. The value of electromagnet torque is calculated based on the torque current component It at this time, so as to get the friction torque To of the motor. then based on the running time delta t and the friction torque Io, the moment of inertia Jo of the omtor is calculated. The invented method provides high accuracy for recognizing these parameters, thus improving the performance of the method of vector control.
Owner:SOMER LEROY ELECTRO TECH FUZHOU CO LTD
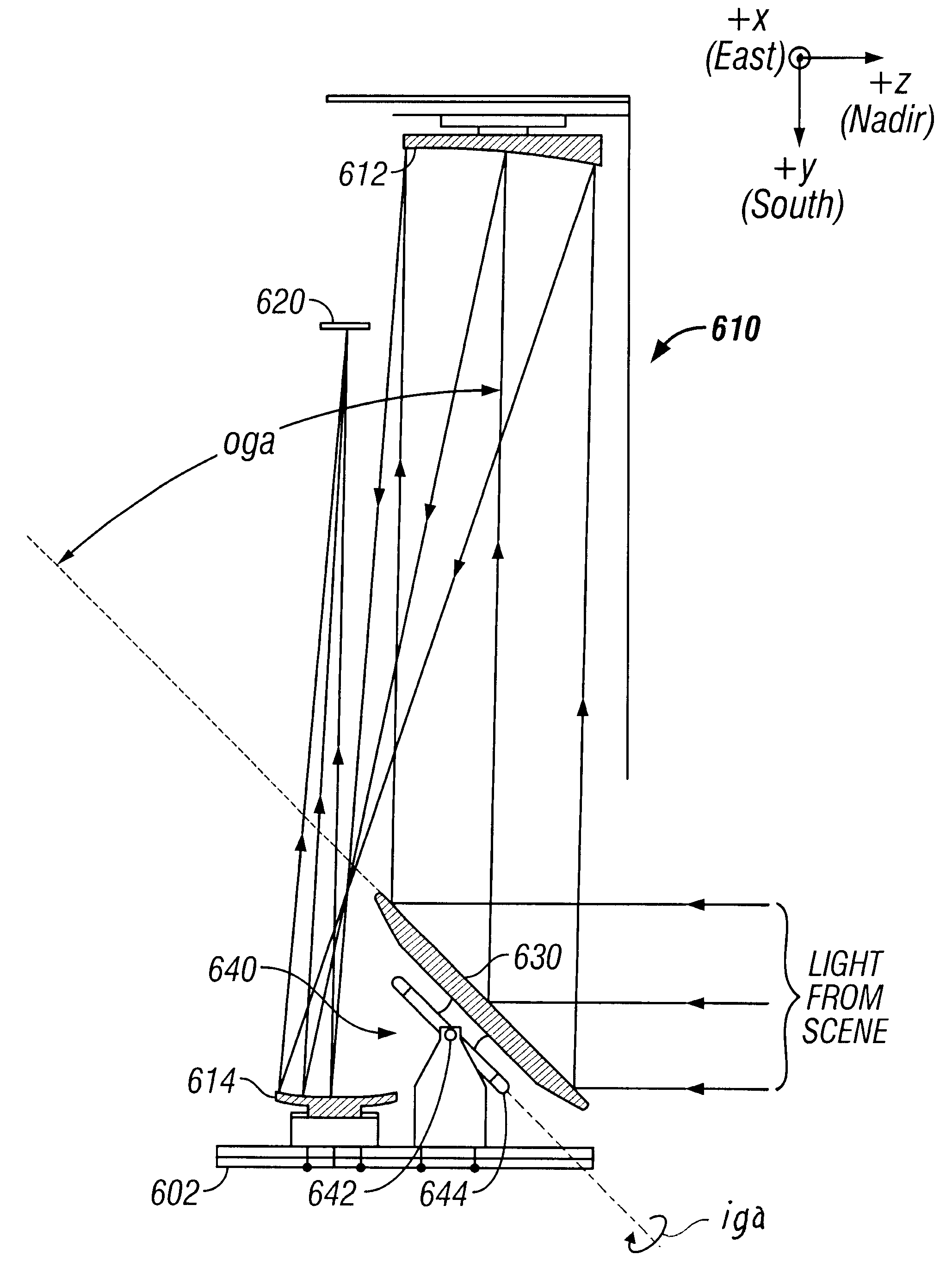
Method and apparatus for imaging a field of regard by scanning the field of view of an imaging electro-optical system in a series of conical arcs to compensate for image rotation
InactiveUS6555803B1Photometry using reference valueBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsConstant linear velocityPlane mirror
A two-dimensional field of regard is scanned with a single plane mirror in the object space of a telescope, maintaining a fixed relationship between the rotational direction of scan and the projection of the telescope's focal plane. The two dimensional field of regard is covered by a series of conical arcs, each arc being scanned by rotation at constant angular velocity about the inner axis of the two-axis system. This scanning system accommodates applications such as TDI that require an opto-mechanical scan with a constant linear velocity (magnitude and direction) in the focal plane. Shading of IR images is mitigated by calibration at the ends of each scan line and by a scan geometry that minimizes changes in reflection angle.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN INNOVATION SYST INC
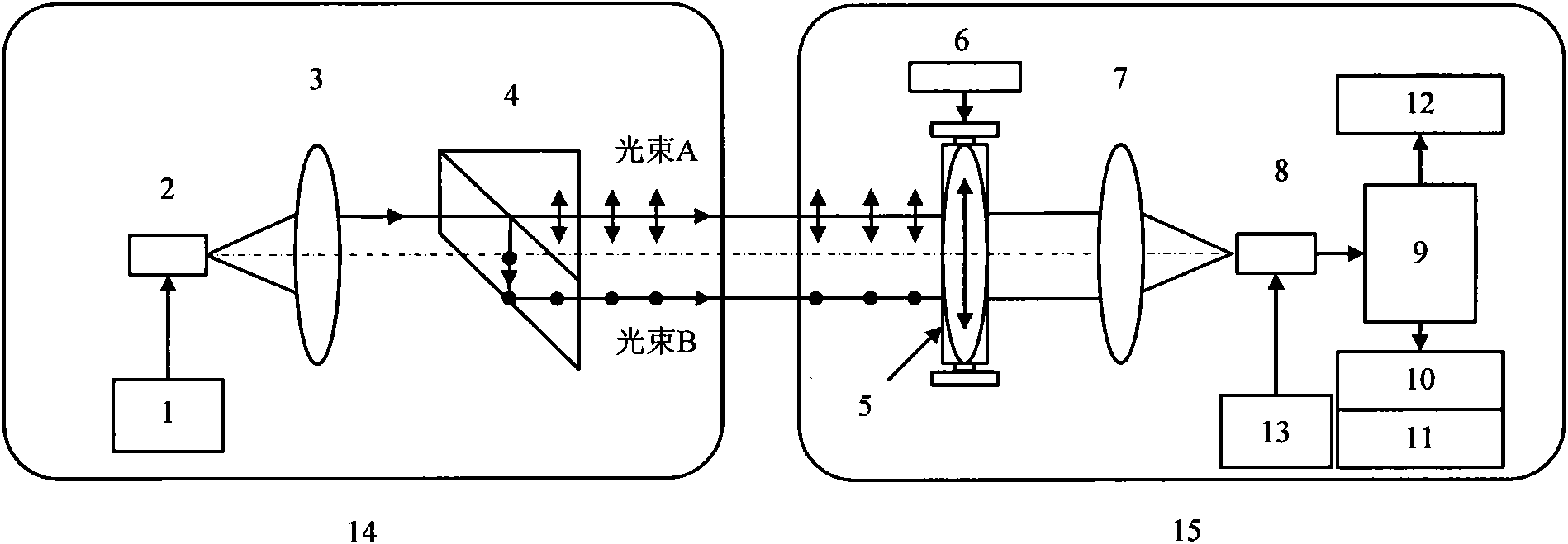
Light beam position and polarization angle common light path detection device and method
The invention discloses a light beam position and polarization angle common light path detection device and method based on a photoelectric position sensor. The method comprises the following steps: utilizing a lateral excursion and polarization dispersion prism to shape an incident light beam, outputting orthogonal parallel polarized lights with proportionable light intensities and realizing the contactless space position attitude transfer function; enabling a receiving system to utilize a rotary motor with a coder to drive an analyzer to detect the beacon light polarization through rotation at a constant angular velocity, utilizing the horizontal photoelectric effect of a PSD (Phase-sensitive Detector) to measure the light spot imaging position of beacon light and reversely pushing a beacon light beam position coordinate according to the imaging principle; utilizing light current generated by gathering incident light intensities on the surface of the PSD to detect the incident light intensities, comparing with an angle instantaneously fed back by the rotary motor, obtaining the synchronous polarization angle information of a beacon light beam after the phase sensitive detection, and achieving the function of simultaneously adjusting and detecting the beacon light track and the base vector angle on a same light path and a device. The light beam position and polarization angle common light path detection device has the benefits of simple structure and simple components and is suitable for the multi-dimensional angle measurement demands.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
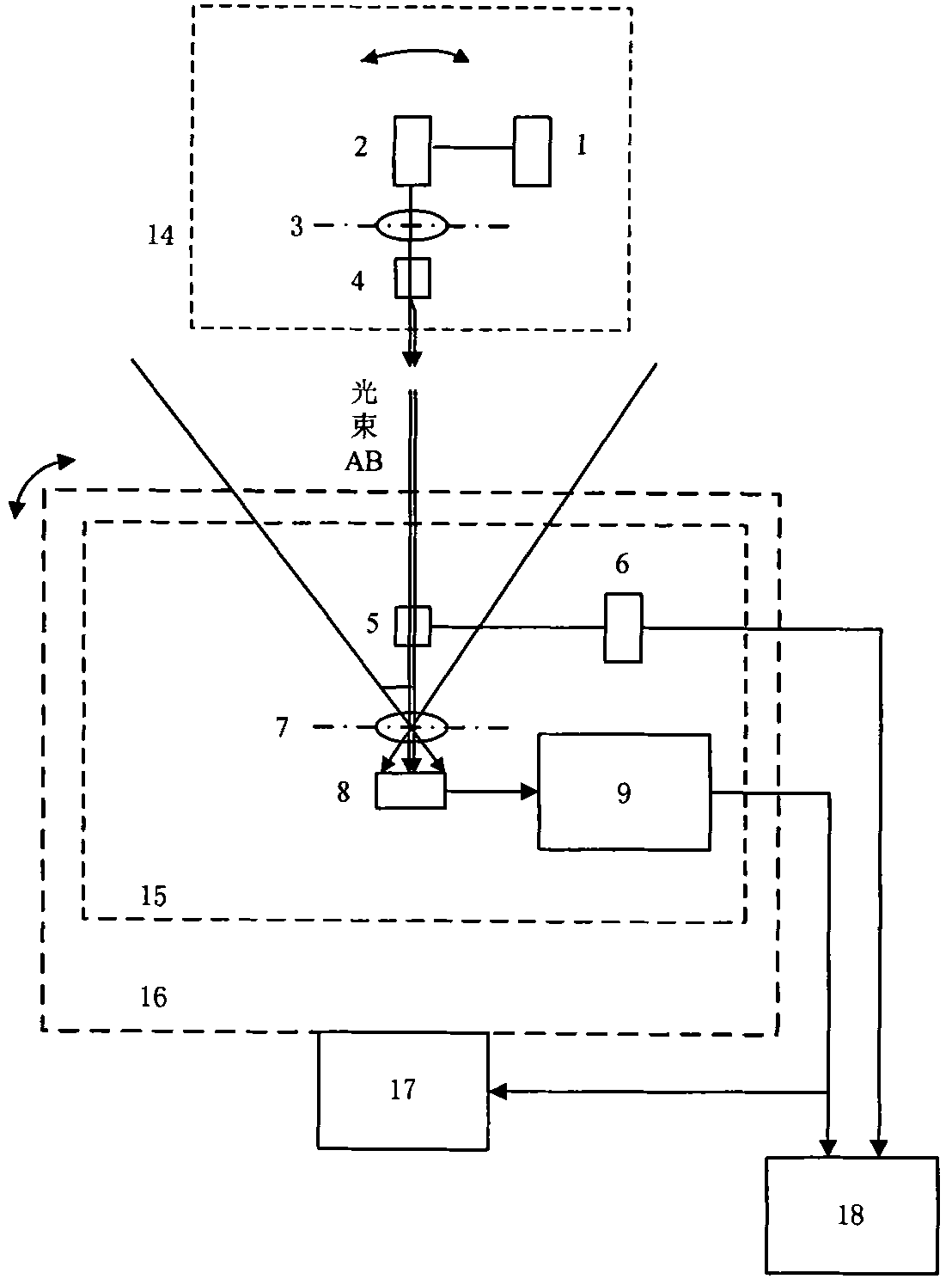
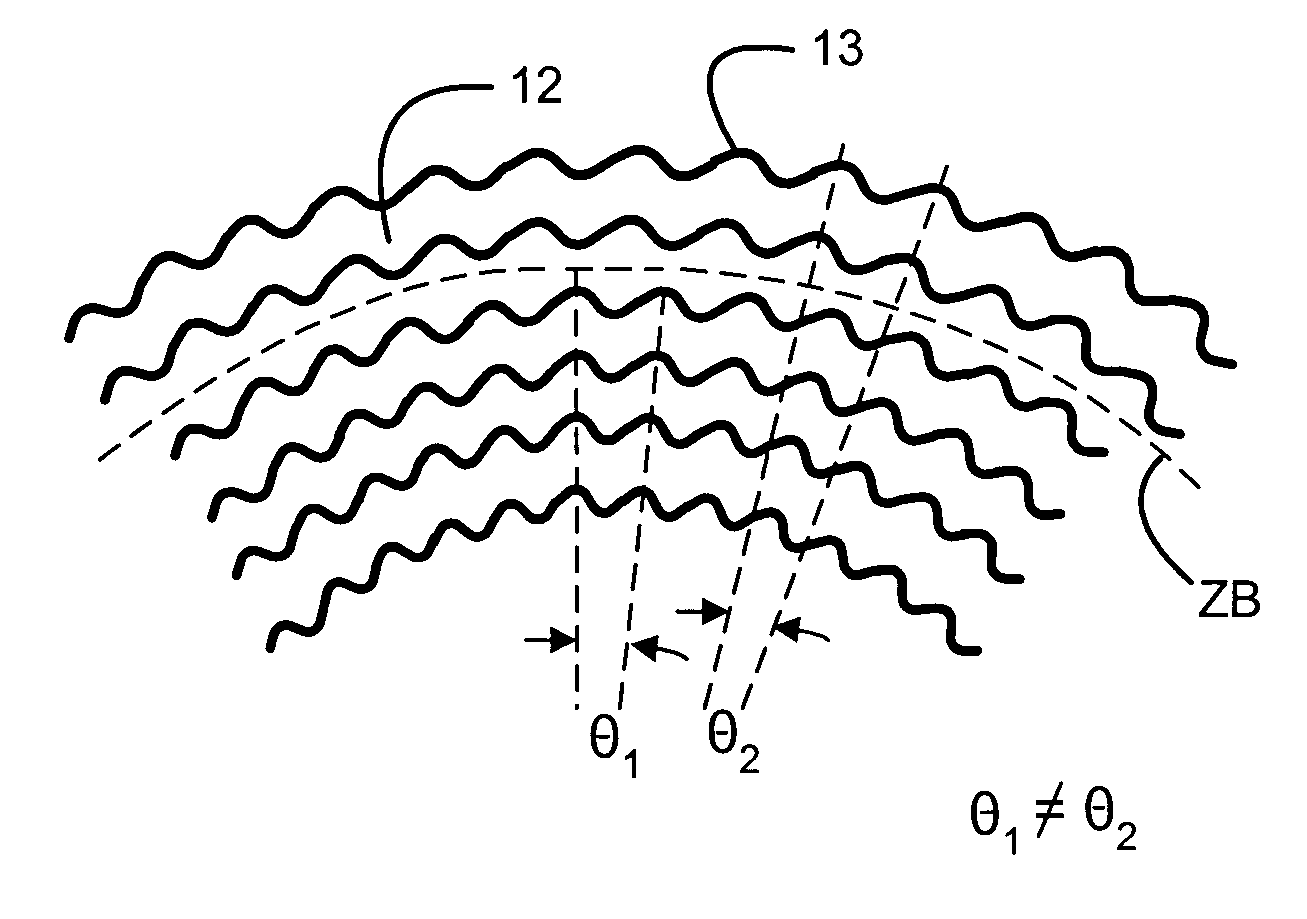
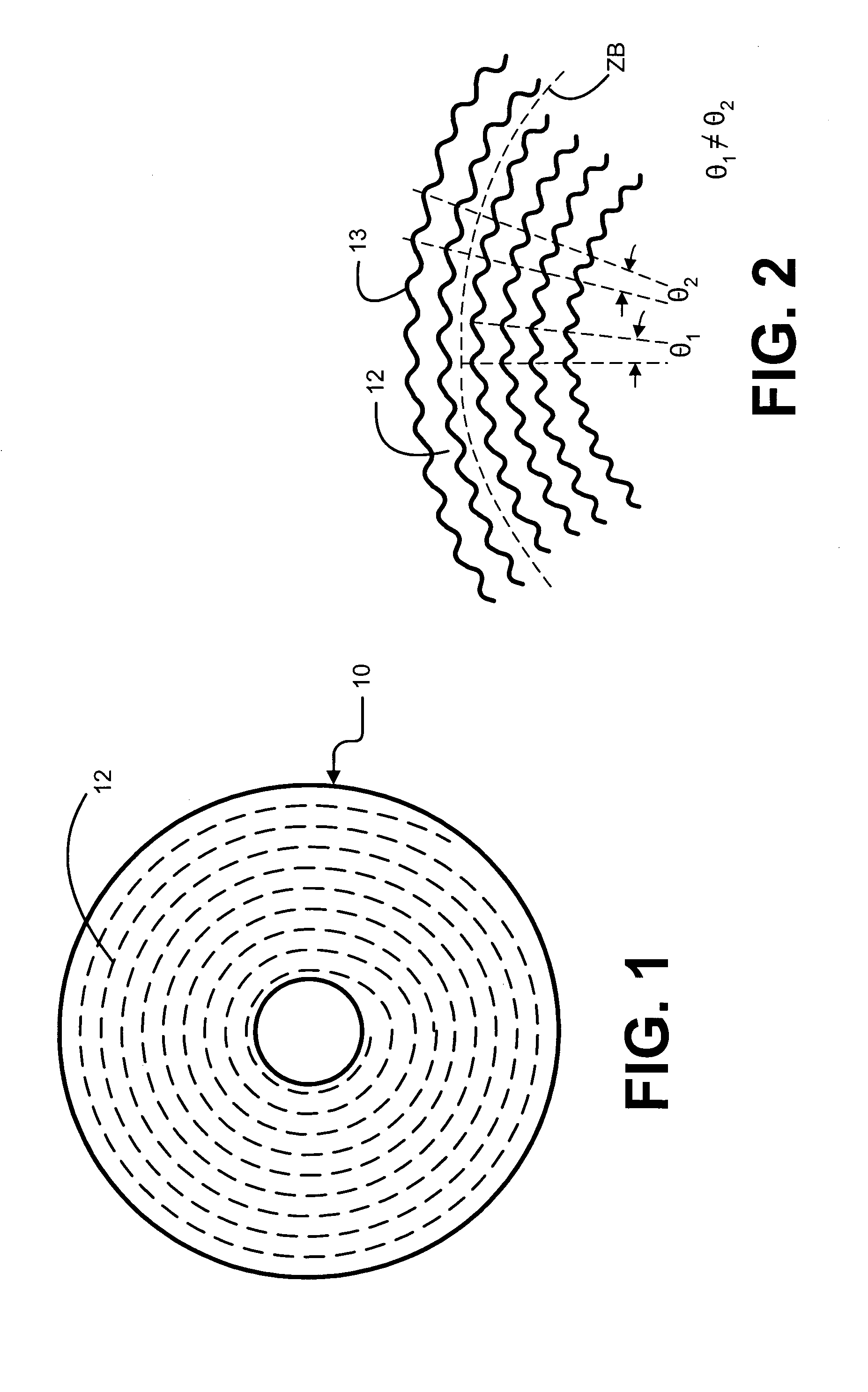
Optical disk having zone constant angular velocity wobble
InactiveUS7002895B1Reduce jitterConstant angular velocity wobbleInformation arrangementRecord information storageClassical mechanicsBpsk modulation
An optical disk has a groove in a recordable medium. The groove has a constant angular velocity wobble that is BPSK-modulated. Such a wobble provides timing and address information.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Liquid Metal Rotating Anode X-Ray Source For Semiconductor Metrology
ActiveUS20190115184A1Effectively self-healingIncrease brightnessMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMetrologyX-ray
Methods and systems for realizing a high brightness, liquid based x-ray source suitable for high throughput x-ray metrology are presented herein. A high brightness x-ray source is produced by bombarding a rotating liquid metal anode material with a stream of electrons to generate x-ray radiation. A rotating anode support structure supports the liquid metal anode material in a fixed position with respect to the support structure while rotating at the constant angular velocity. In another aspect, a translational actuator is coupled to the rotating assembly to translate the liquid metal anode in a direction parallel to the axis of rotation. In another aspect, an output window is coupled to the rotating anode support structure. Emitted x-rays are transmitted through the output window toward the specimen under measurement. In another further aspect, a containment window maintains the shape of the liquid metal anode material independent of rotational angular velocity.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
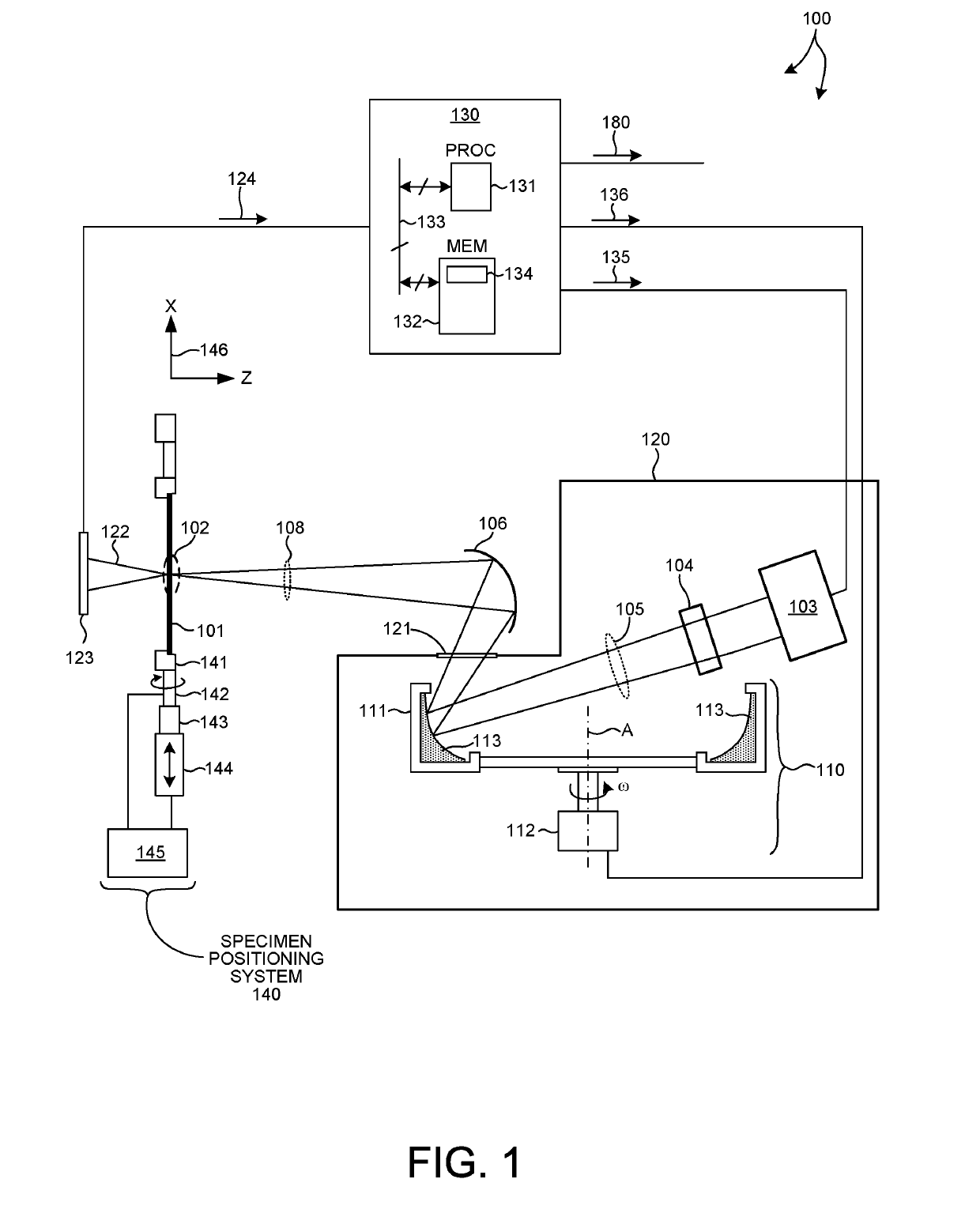
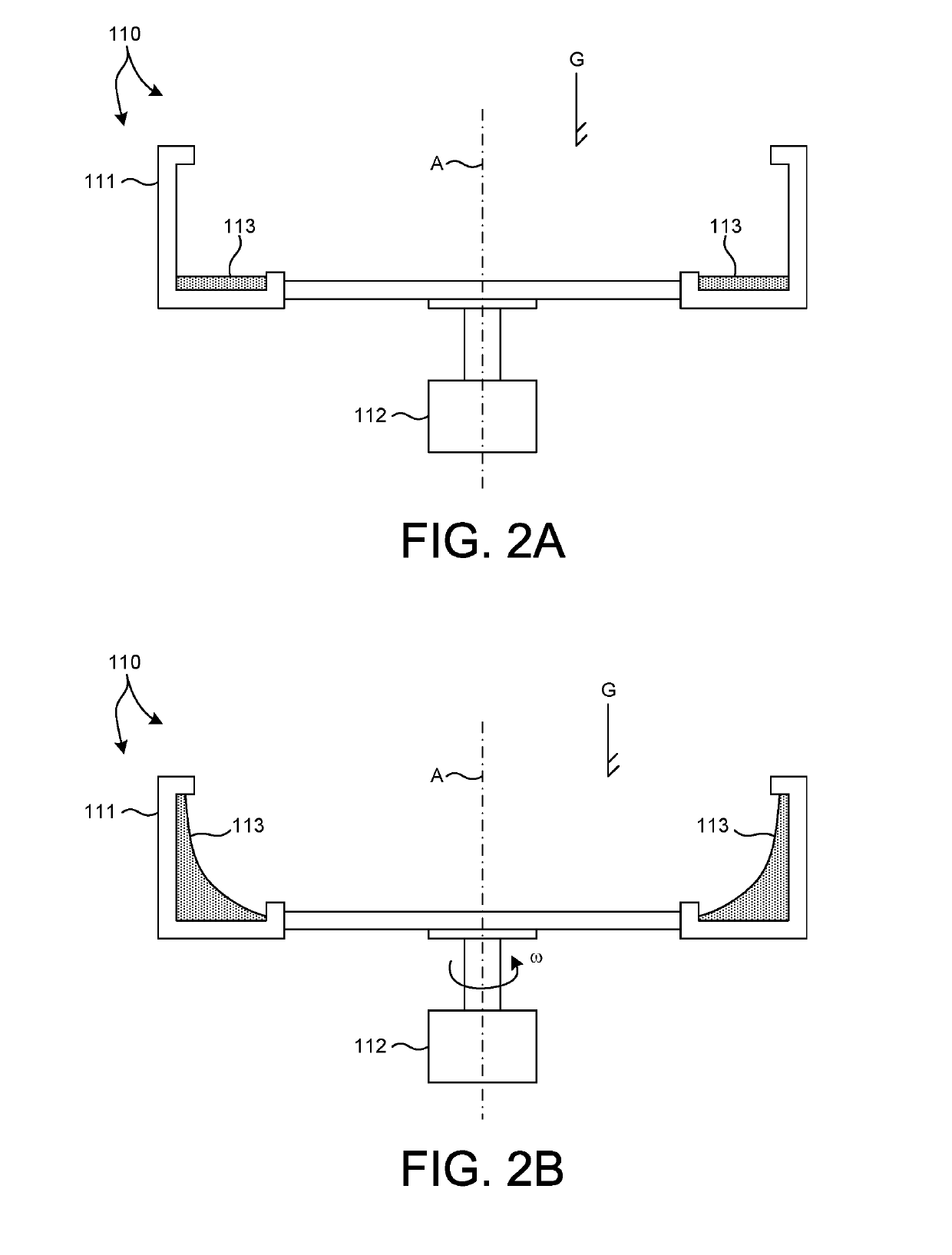
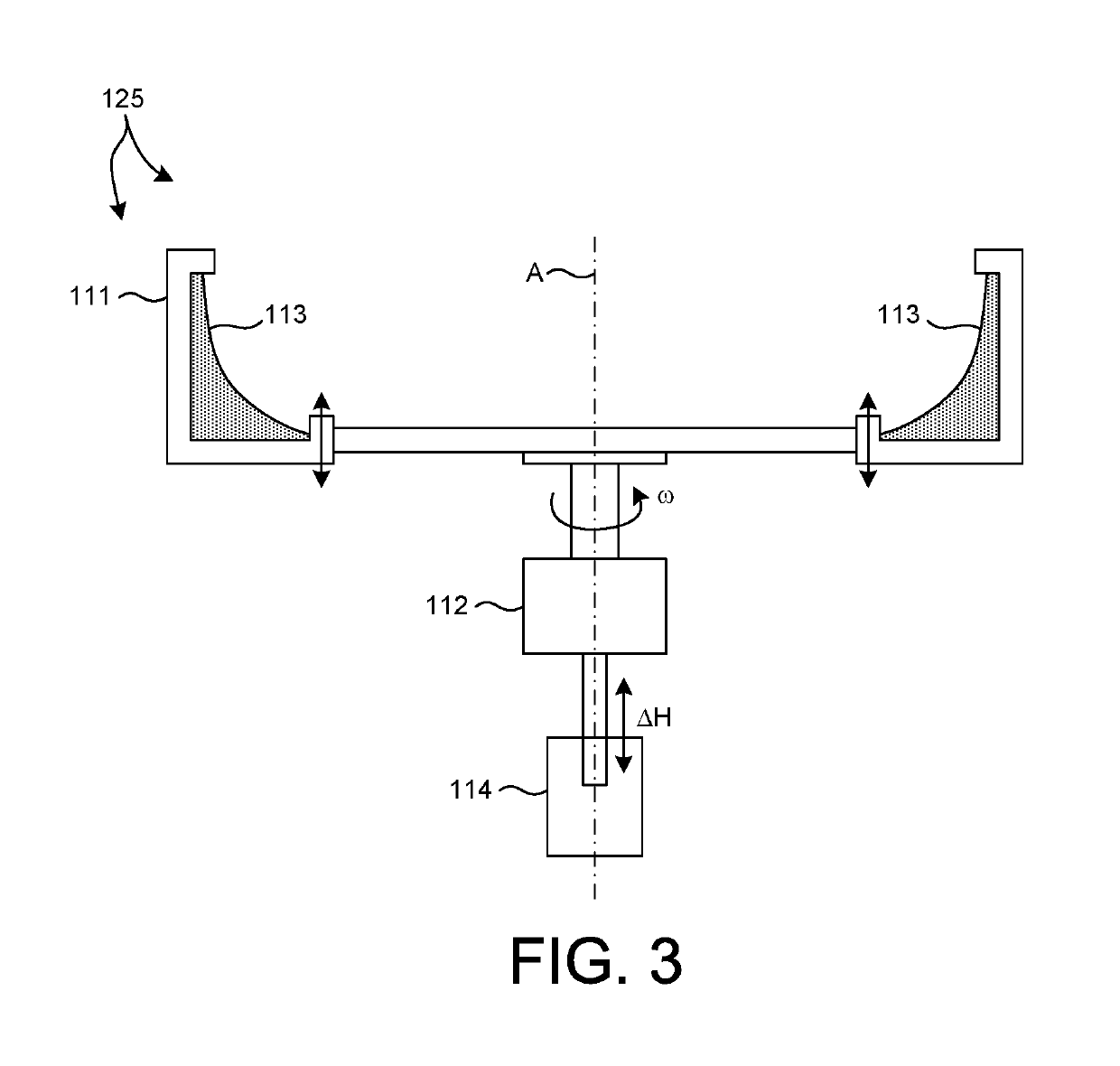
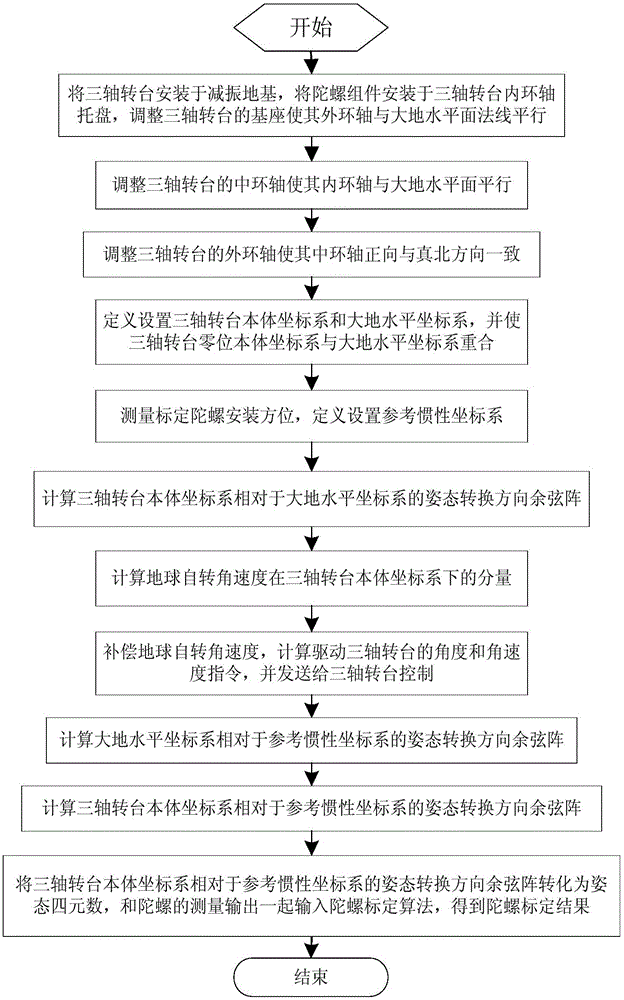
Inertial space gyro calibration test method based on three-shaft turntable
ActiveCN106525073AThe result is validHigh precisionMeasurement devicesSpace constantEarth's rotation
The invention relates to an inertial space gyro calibration test method based on a three-shaft turntable; while a gyro assembly attitude rotation is provided by the three-shaft turntable, the compensation dosage of the earth autorotation angular velocity is calculated according to the real-time rotating angle output of three rotating shafts of the three-shaft turntable, so that the influence of earth autorotation on the gyro measurement output is eliminated, and the inertial space constant angular velocity required for a gyro calibration algorithm is ensured. At the same time, based on attached rotation characteristics of the three rotation shafts of the three-shaft turntable, the method defines a rotation sequence rule of the three rotation shafts and a three-shaft turntable body coordinate system and a reference inertial coordinate system having the initial zero coinciding with the ground horizontal coordinate system, and provides a reference benchmark for determining the inertial system angle increment according to the gyro output and for determining the inertial system attitude according to the rotation angle output of the three rotation shafts of the three-shaft turntable. The method can significantly improve the precision of a ground gyro calibration test, can guarantee the ground to perform effective calibration and test result calibration on a gyro assembly, can establish a good foundation for performing relevant calibration tests of satellites in orbit, and improves the determination precision of the gyro attitude.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
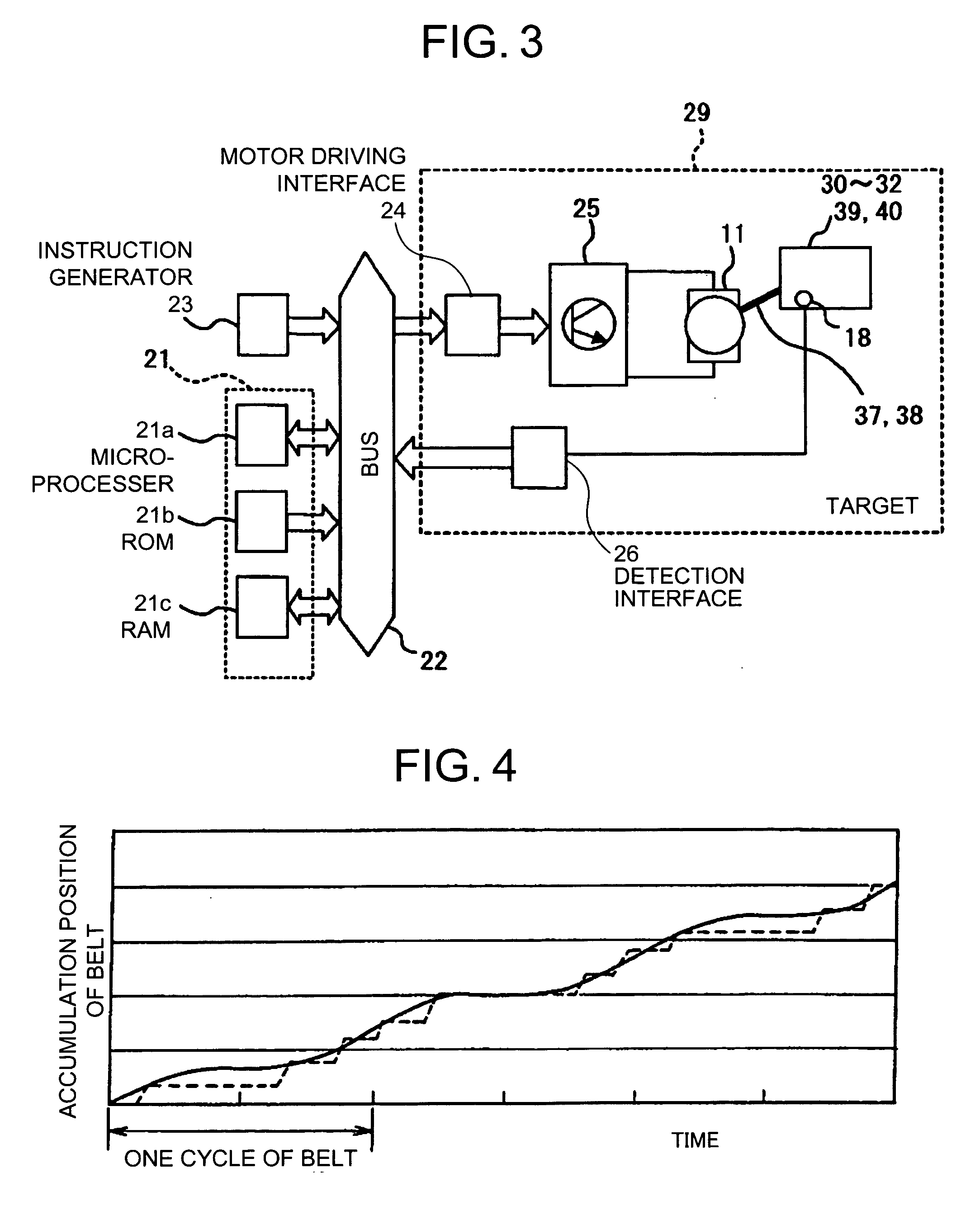
Belt drive controlling method, belt drive controlling apparatus, belt apparatus, image forming apparatus, and computer product
An endless belt is spanned around at least one driving member and at least one supporting member. The driving member is driven by a pulse motor. An angular displacement of the driving member is detected, a difference between detected angular displacement and a target angular displacement is calculated, a frequency of a driving pulse used to drive the pulse motor is calculated based on the difference and a reference driving pulse frequency, and the pulse motor is controlled based on a driving pulse with calculated frequency. The target angular displacement is set so as to cancel a specific velocity fluctuation component of a surface velocity of the belt produced when the drive member is rotated at a constant angular velocity and that is smaller than amount of surface movement of the belt in one driving pulse.
Owner:RICOH KK
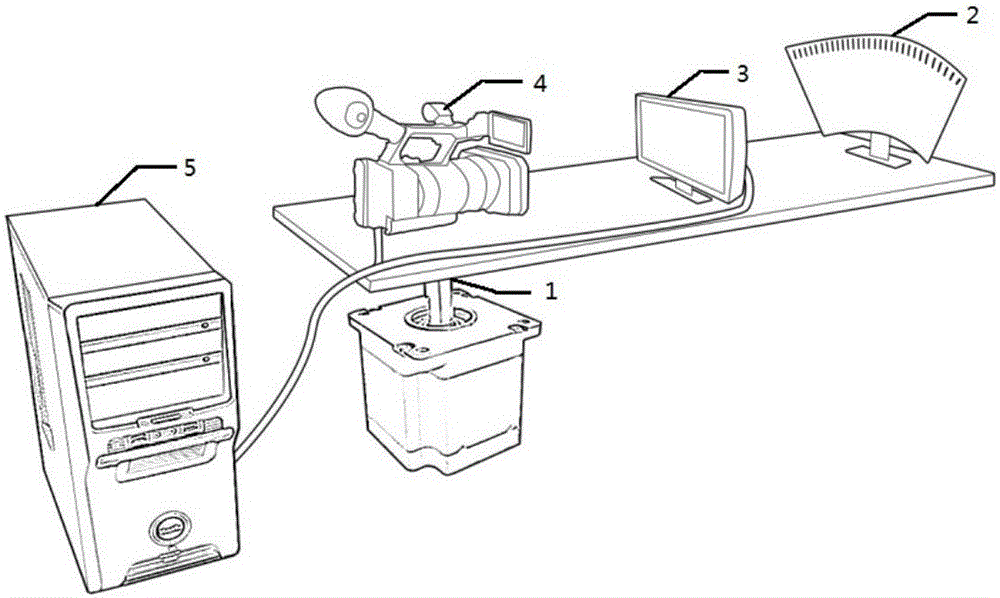
Time delay test system and method used for virtual reality helmet acceleration motion
InactiveCN105954007AHigh control precisionTest results are accurate and reliableOptical apparatus testingTotal delayMotor drive
The present invention discloses a time delay test system and method used for virtual reality helmet acceleration motion. The time delay test system used for the virtual reality helmet acceleration motion is characterized in that an arc-shaped scale, a virtual reality helmet and a camera are arranged orderly at intervals along a straight line and are fixedly arranged on a controllable rotating disc, a servo motor is arranged below one side of the controllable rotating disc, and the output shaft of the servo motor is fixedly connected with the controllable rotating disc; a display screen of the virtual reality helmet displays a virtual scale, the servo motor drives the controllable rotating disc to rotate at a constant angular velocity, and the camera shoots the arc-shaped scale and the virtual reality helmet on the controllable rotating disc; the interface of the virtual scale of the display screen of the virtual reality helmet in an image is analyzed to obtain the measurement amount, and further the delay amount of the virtual reality helmet is calculated. According to the present invention, a time delay test of the virtual reality helmet acceleration motion is realized, the total delay of the system is measured accurately, a view angle error brought by shooting can be avoided, the system accuracy is improved, and a final test result is accurate and reliable.
Owner:杭州映墨科技有限公司
Method of recording and reproducing information and apparatus for recording and reproducing information using the method
A method of recording and reproducing information in a phase-change optical recording medium by irradiation of an electromagnetic wave for recording, reproducing and / or rewriting information is proposed, wherein when information is recorded in the phase-change optical recording medium by modulating an input signal and conducting pulse width modulation recording, a recording pulse string for recording and rewriting is a continuous electromagnetic wave, and a recording pulse string for input signal, is an electromagnetic wave pulse string having a front-pulse portion fp, a multi-pulse portion mp with a total pulse duration period T and a duty ratio y, and an off-pulse portion op, wherein the duty ratio y is decreased as a recording linear velocity for the phase-change optical recording medium is increased, whereby multi-speed recording or CAV (constant angular velocity) recording is carried out. An information recording and reproducing apparatus, using the above method, is also proposed.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method and apparatus for directional boring
InactiveUS6199643B1Improved directional stabilityEarth drilling toolsDirectional drillingEngineeringOrbit
Owner:TRACTO TECHN PAUL SCHMIDT SPEZIALMASCHEN
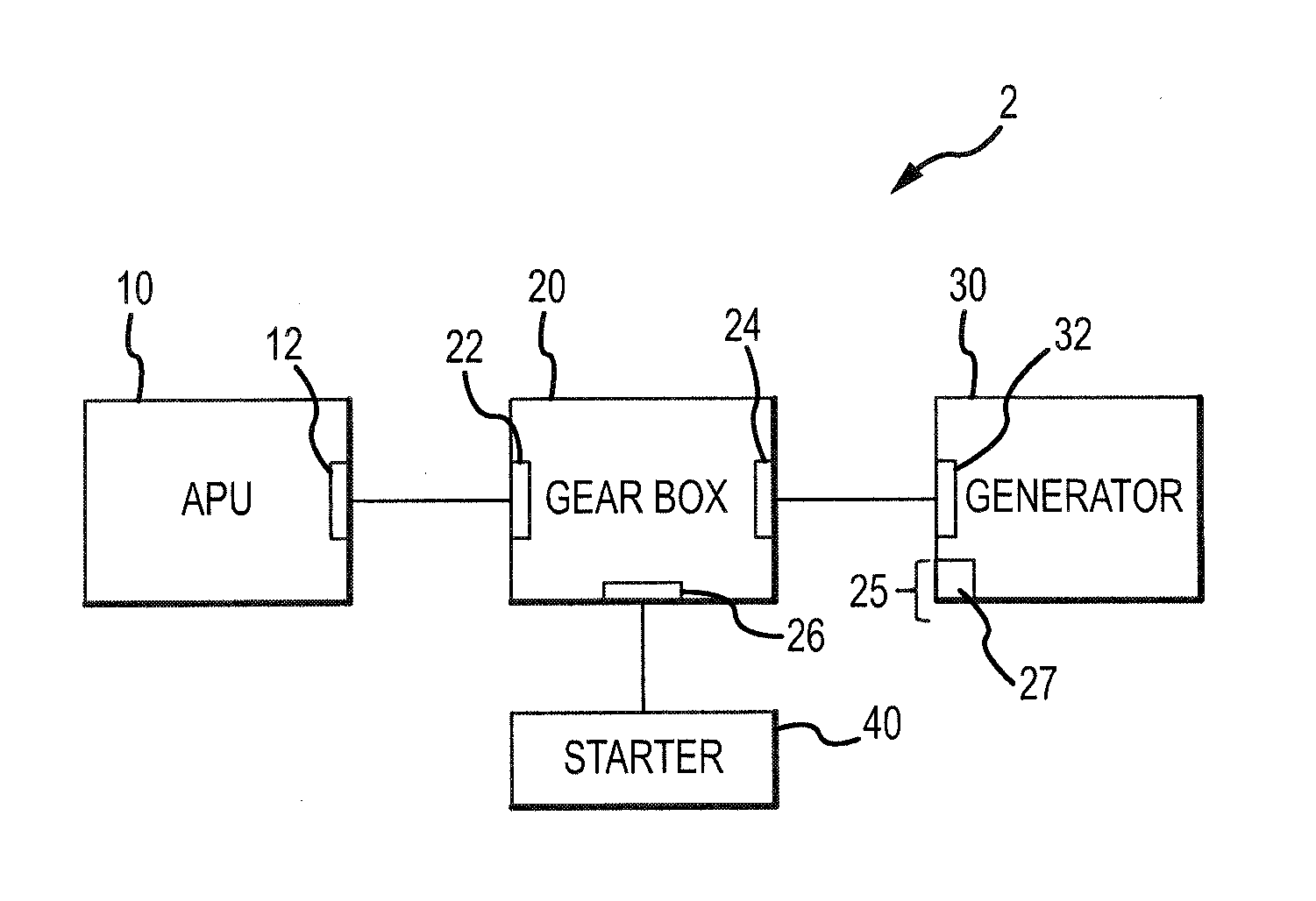
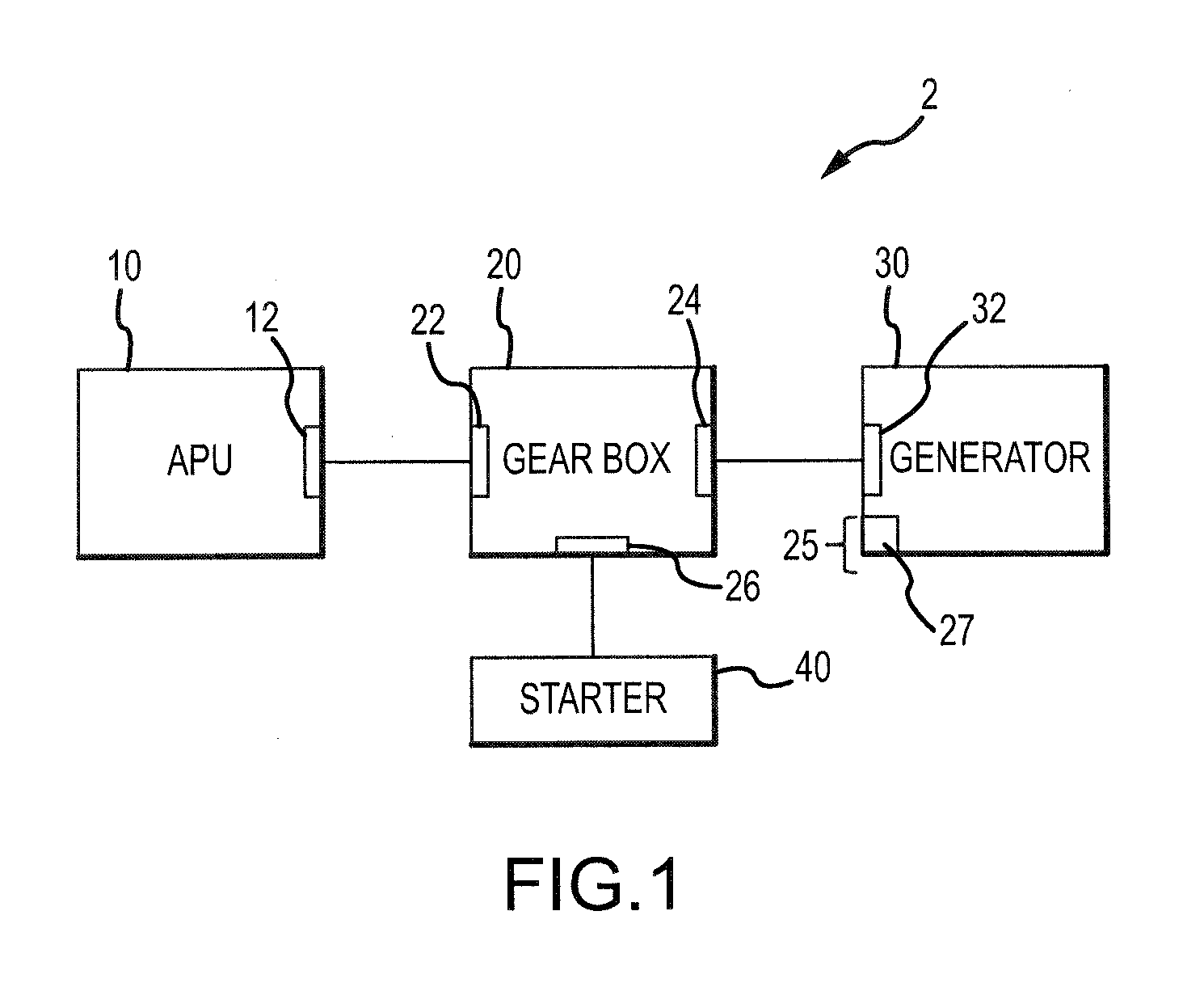
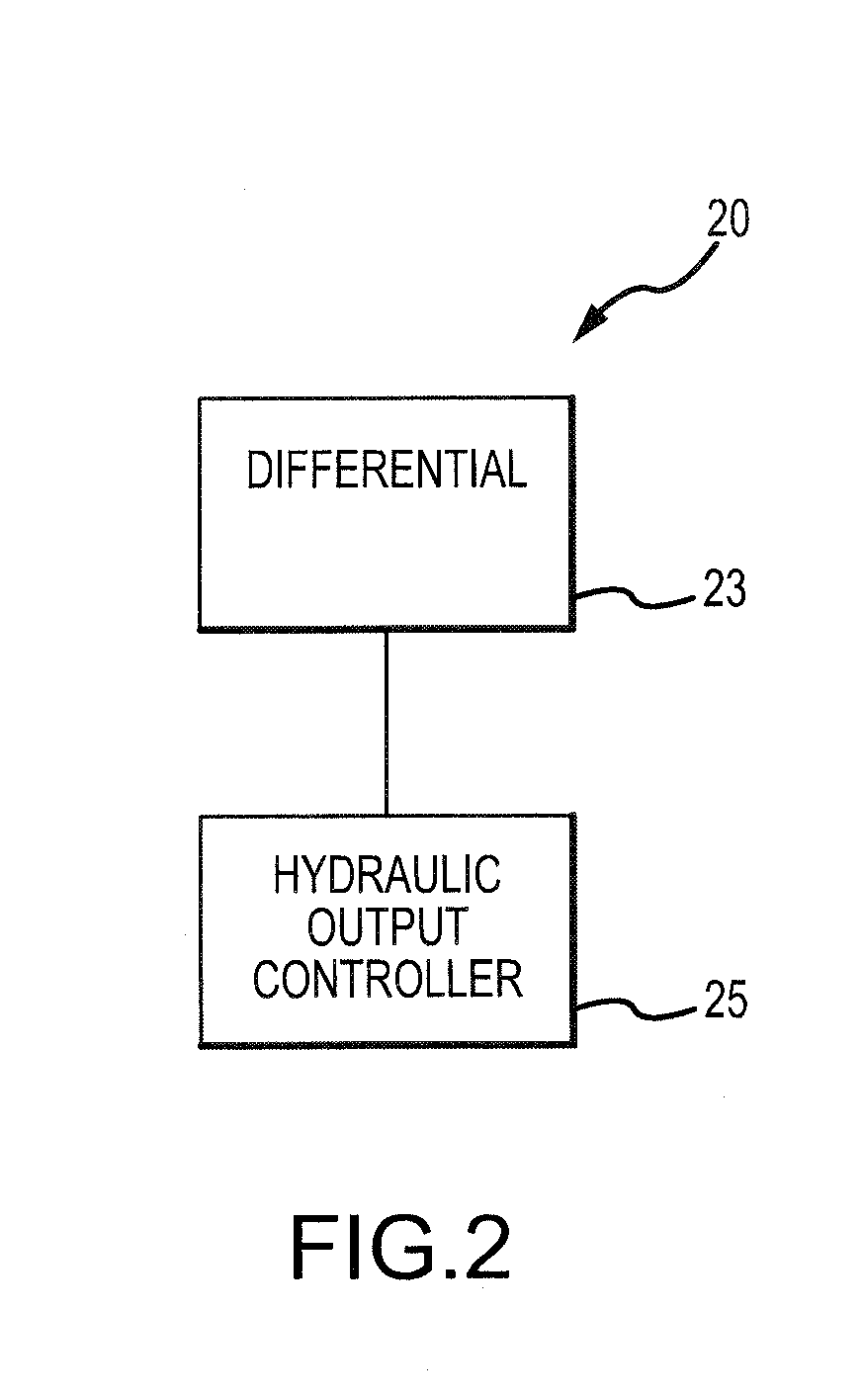
Integrated APU Generator Constant Speed Drive
An integrated APU-generator constants speed drive system having various features is disclosed. The system may have a gearbox having a differential with a constant speed gearbox output and a hydraulic output controller control shaft. The system may have a hydraulic output speed controller that adjusts the angular velocity of the hydraulic output controller control shaft of the differential. In response, the differential may adjust the angular velocity of the constant speed gearbox output. In this manner, the angular velocity of the constant speed gearbox output may be maintained at a substantially constant angular velocity. A generator may be driven by the constant speed gearbox output. By maintaining the constant speed gearbox output at a substantially constant angular velocity, an alternating current generated by the generator may be maintained at a substantially constant frequency.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
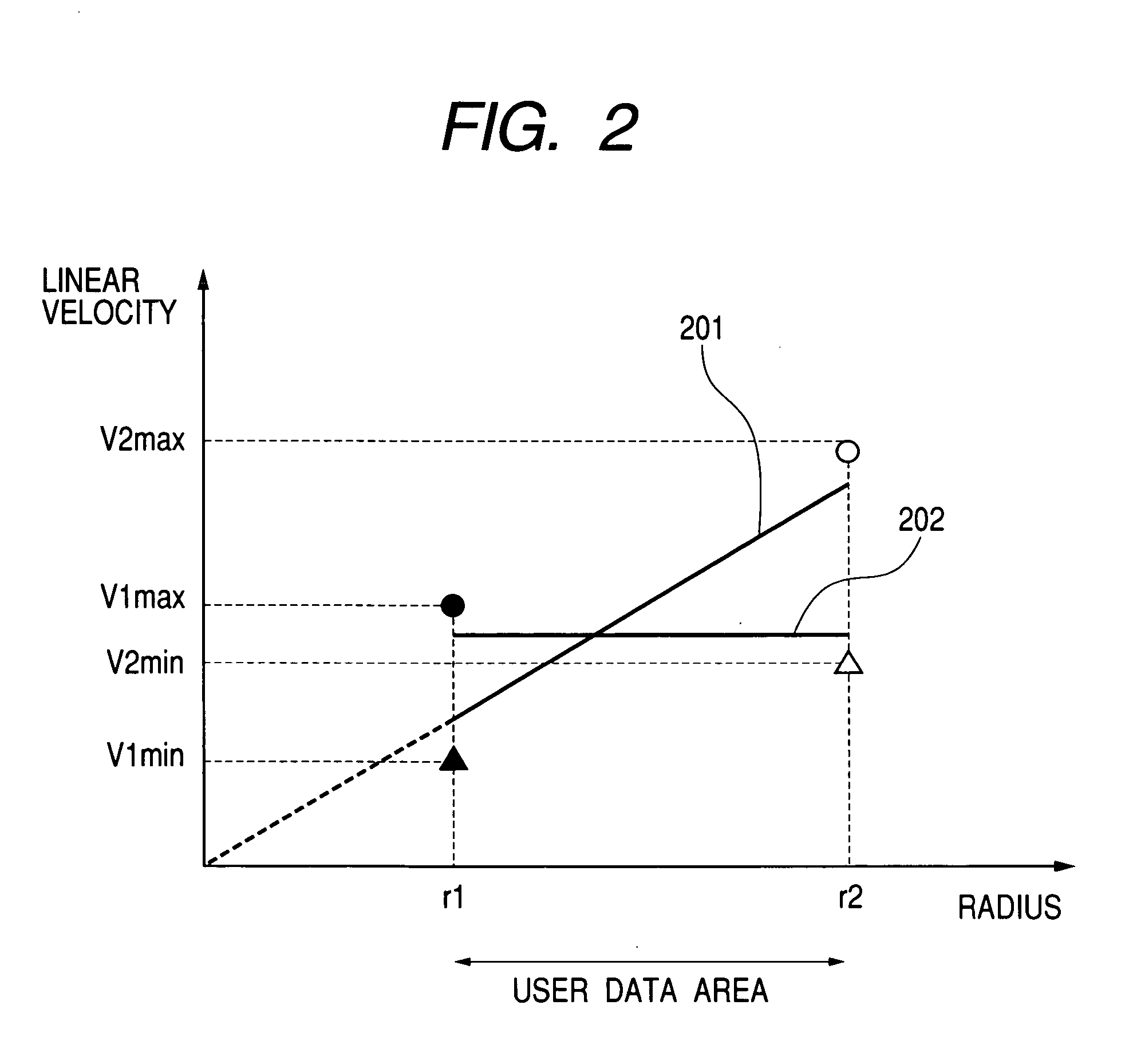
Information recording medium and its control method and information recording/reproducing method
InactiveUS20050063264A1Reduce manufacturing costImprove signal qualityFilamentary/web record carriersRecord information storageConstant linear velocityComputer science
An information recording medium includes data concerning a maximum linear velocity (V1max) and a minimum linear velocity (V1min) at a first location on the medium and a maximum linear velocity (V2max) and a minimum linear velocity (V2min) at a second location on the medium, are recorded at a predetermined location on said medium, and at the first and second locations both of which are located at different locations on the medium, performing selectively CLV / CAV (Constant Linear Velocity / Constant Angular Velocity) control or alternatively a CLV / CAV-hybrid control.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Locating information on an optical media disc to maximize the rate of transfer
InactiveUS7321539B2Improve data transfer rateIncrease speedTelevision system detailsOptical re-recordingCD-ROMControl data
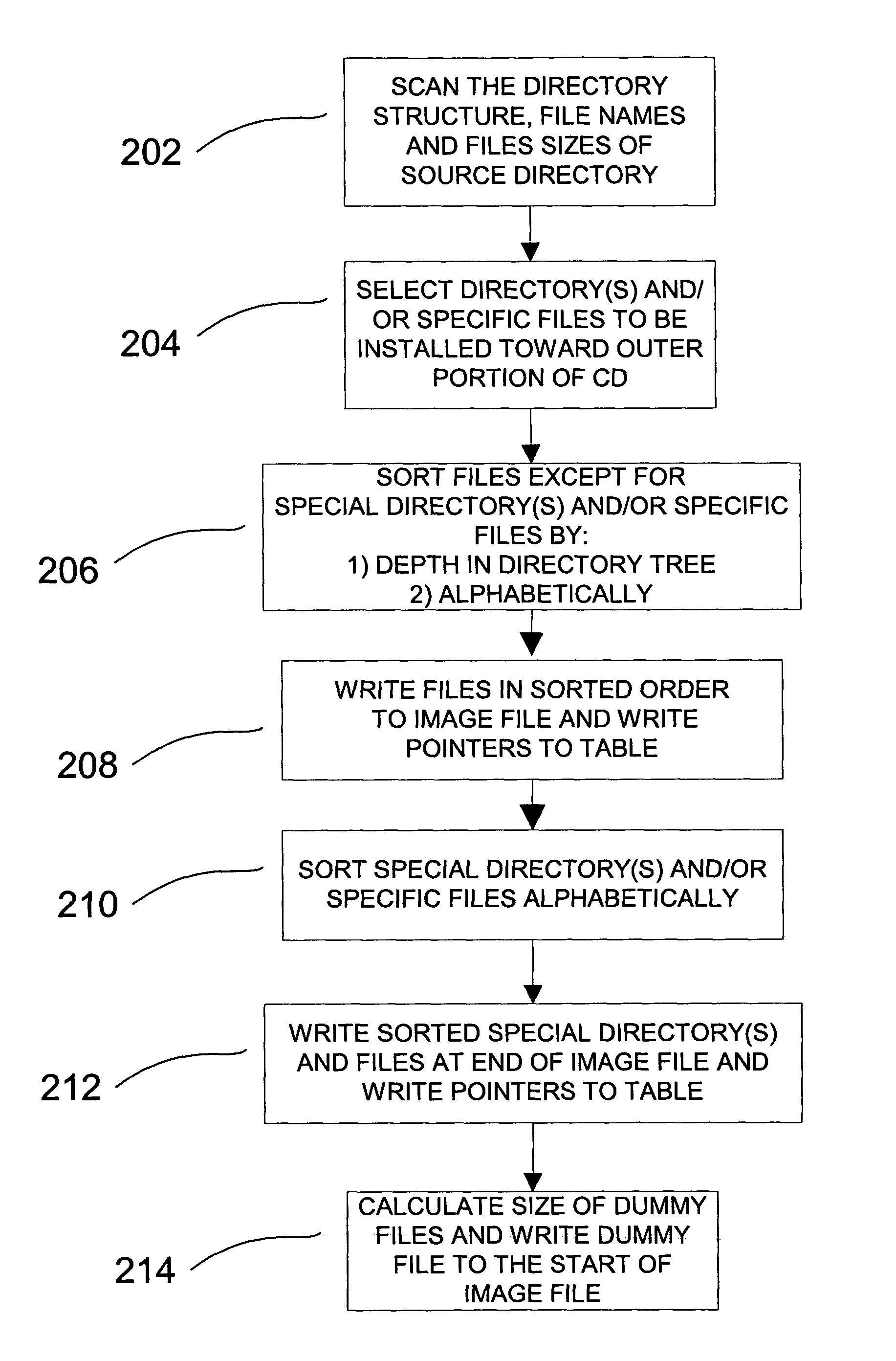
A user-interactive program assists a user in locating files on optical media discs such as CD-ROMs and DVDs to enhance file-transfer rates and program installation times in computers with a Constant Angular Velocity (CAV) optical media disc drive. In addition, an application program calculates an optimal location for files and / or directories on an optical media disc so that the files are located near the location with the highest data transfer rate. This program may be used to compute an image file that defines where data will be located on an optical disc, or may be used to control transfer of data to the optical media disc.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
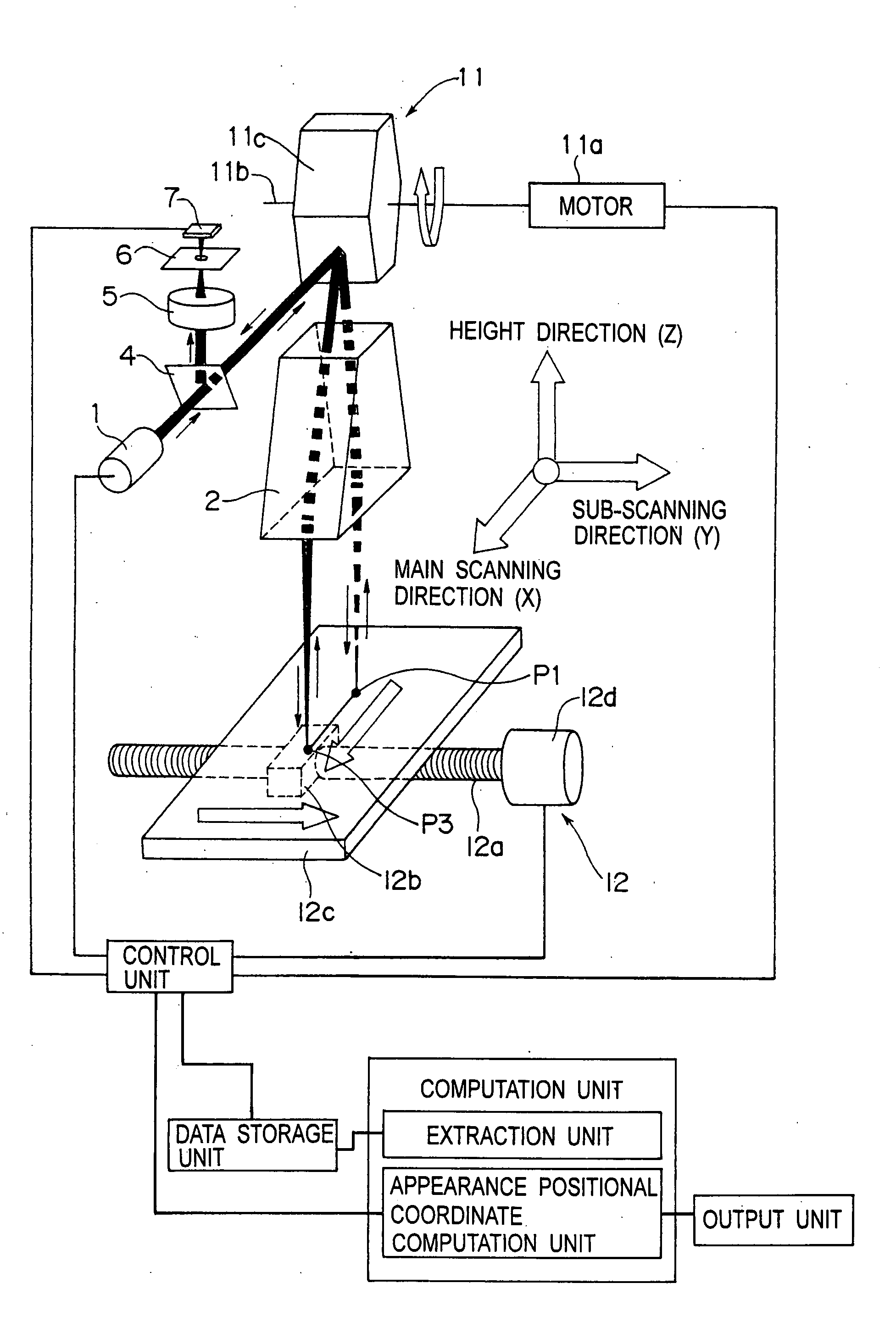
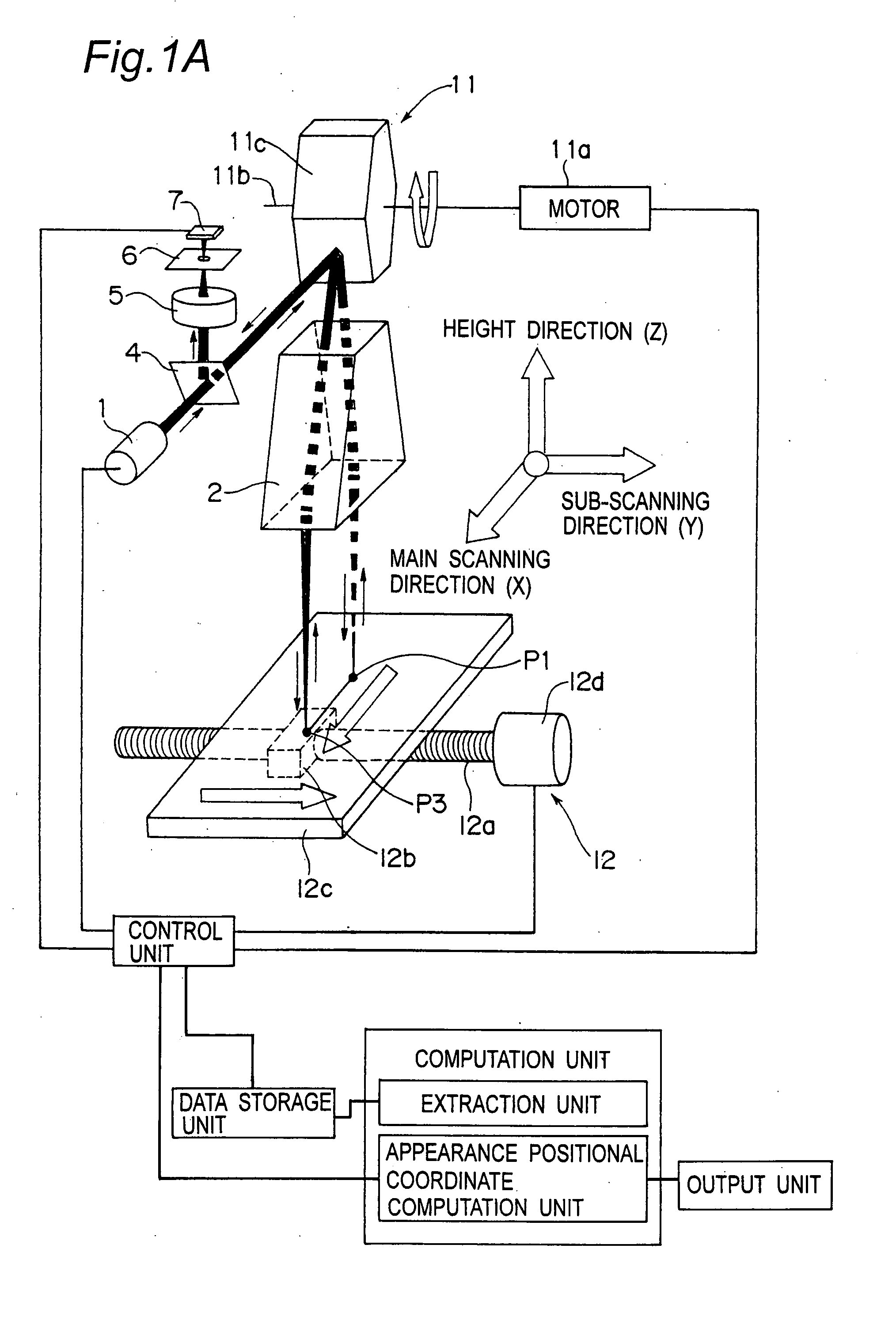
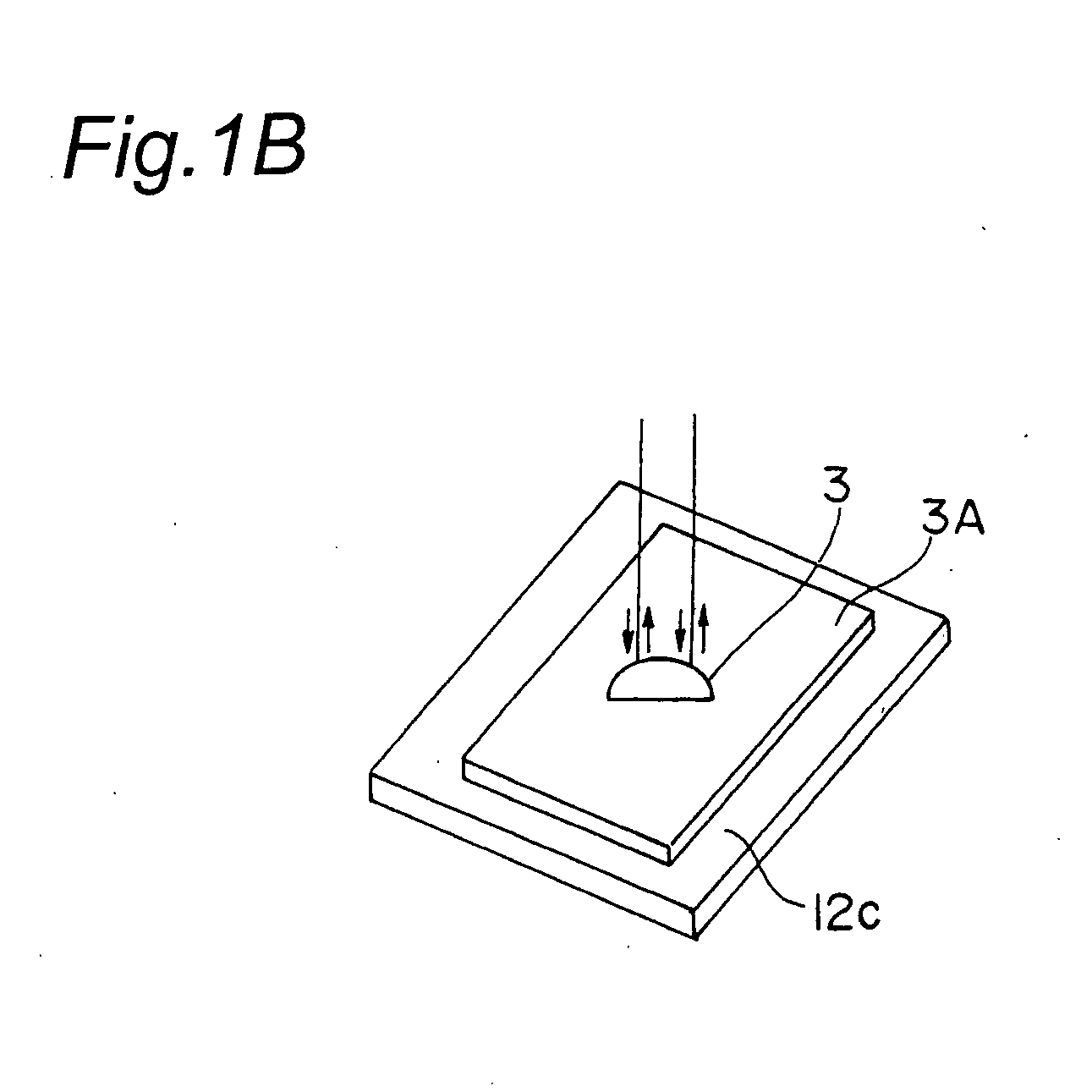
Apparatus and Method for Appearance Inspection
InactiveUS20080225299A1High resolutionDecrease inspection accuracyMirrorsScattering properties measurementsLight fluxLight beam
Rotating polygon mirrors are configured such that angles formed by a rotation axis and mirror surfaces differs from one another in the mirror surfaces in order to shift a collecting point of a scanning light flux in a sub-scanning direction in association with rotation at constant angular speed. A collecting point position forming optical system is configured such that the collecting point is moved in an inspection range Zr in a height direction Z. The XYZ scanning is performed by moving the inspection object in the sub-scanning direction such that the collecting point shifted in the sub-scanning direction and the height direction is linearly scanned in the height direction of the inspection object in synchronization with the rotation of the rotating polygon mirror at the constant angular speed, and the an appearance positional coordinate of the inspection object is determined by a confocal method to perform the appearance inspection.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for modulating angular movement of isolation carrier in inertial navigation system through rotation
InactiveCN105588562AHigh precisionGuarantee the effect of rotation modulationNavigational calculation instrumentsNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsNavigation systemConstant angular velocity
The invention discloses a method for modulating angular movement of an isolation carrier in an inertial navigation system through rotation. The method comprises the steps of calculating rotation angular velocity, relative to a navigation coordinate system, of a rotating platform at the k control moment according to the rotating scheme of the rotating platform; controlling the rotating platform to rotate, so that an IMU coordinate system p coincide with a carrier coordinate system b; modulating the inertial navigation system to enter the navigation state through rotation, so that control angular velocity of an inner ring shaft and control angular velocity of an outer ring shaft in the rotating platform within the first control cycle are obtained; predicting movement angular velocity, relative to the navigation coordinate system, of the carrier within the (k+1) control cycle and rotation control angular velocity, relative to the carrier coordinate system, of the rotating platform; obtaining the control angular velocity of inner ring shaft and the control angular velocity of the outer ring shaft in the rotating platform; controlling the control angular velocity of inner ring shaft and the control angular velocity of the outer ring shaft, and eliminating influence of the angular movement of the carrier, so that isolation of angular movement of the carrier is achieved. By means of the method for modulating angular movement of the isolation carrier in the inertial navigation system through rotation, the rotation modulation effect is guaranteed, and precision of the navigation system is improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Optical scanning device and image forming apparatus
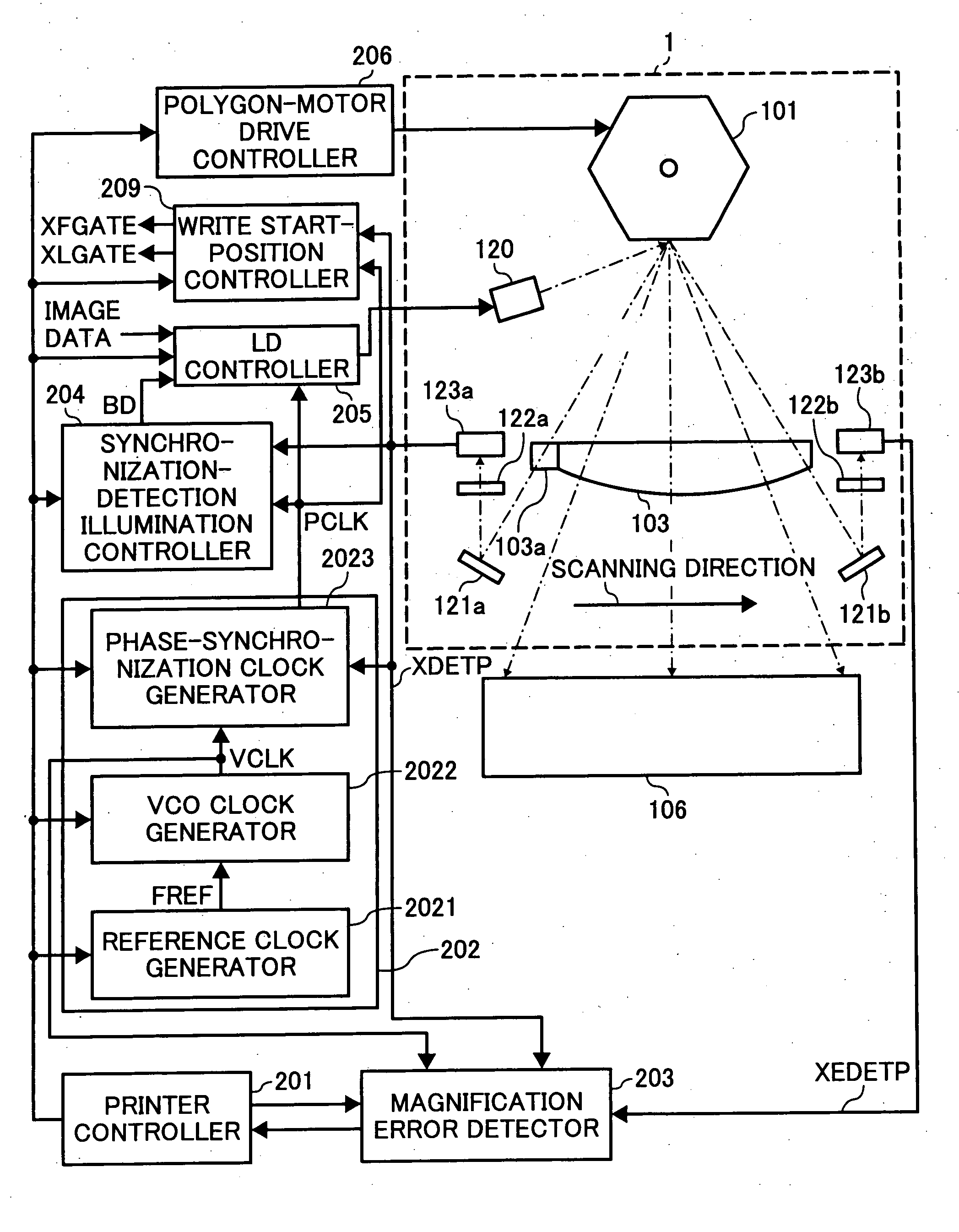
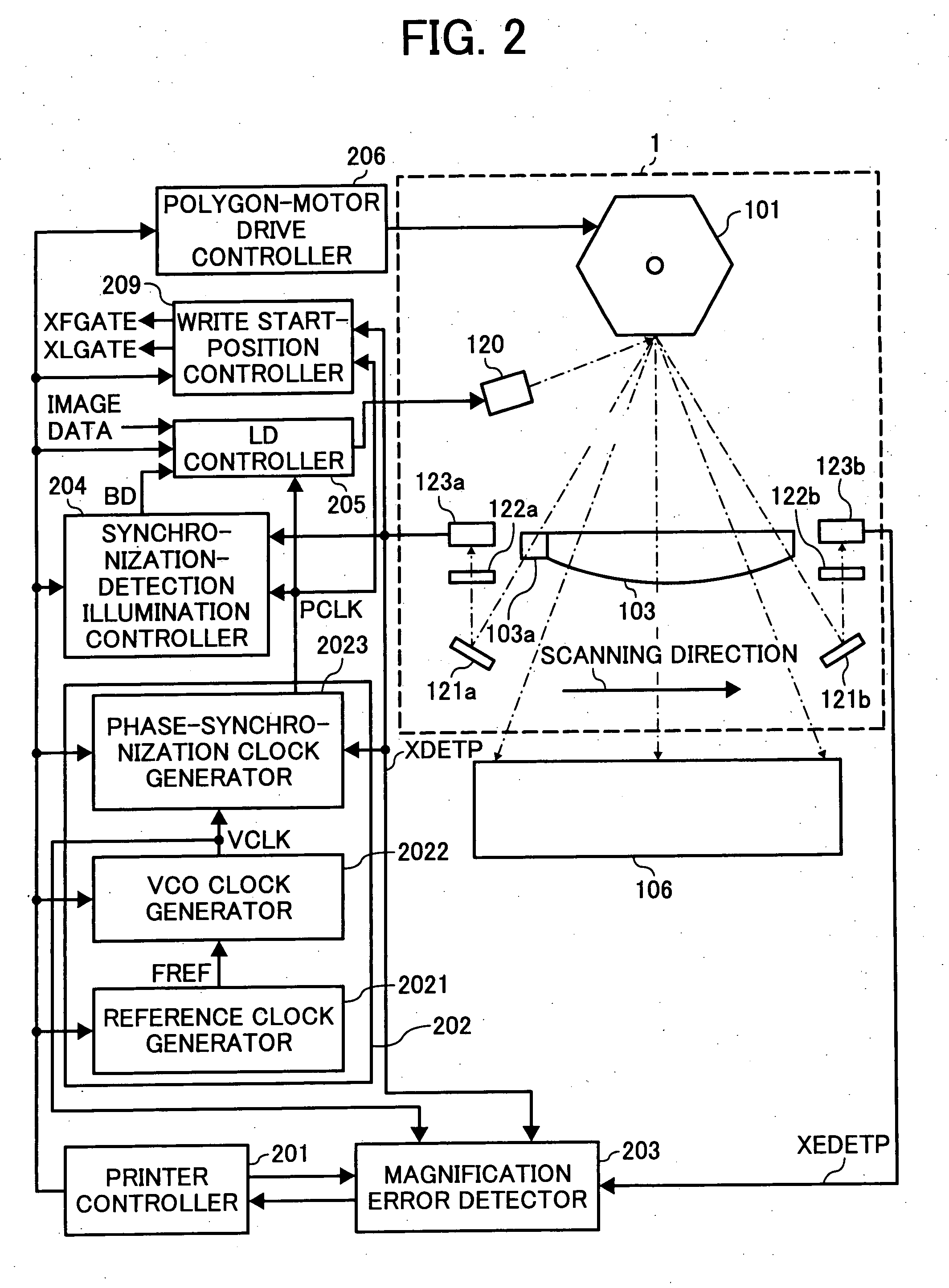
InactiveUS20070210245A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamImage formation
Image forming apparatus and optical scanning apparatus each includes a light source, a deflector, an fθ lens, and first and second light-beam detectors. The light source outputs light beams, and is turned on and is controlled in accordance with image data. The deflector deflects the output light beams in a main-scanning direction. The fθ lens corrects the deflected light beams from constant-angular-velocity scanning to constant-velocity scanning. The first and second light-beam detector detect the deflected light beams at two spots along the main-scanning direction. The first light-beam detector is located at a scanning-start side, and the second light-beam detector is located at a scanning-end side. The light beam that is incident on the first light-beam detector is not transmitted through the fθ lens, and the light beam that is incident on the second light-beam detector is transmitted through the fθ lens.
Owner:RICOH KK
Exposure dose control of rotating electron beam recorder
InactiveUS7218470B2Uniform exposure dosageUniform exposureDriving/moving recording headsElectric discharge tubesLithographic artistSurface velocity
In a beam lithography operation the relative motion between a work piece and the exposure beam produces variations in linear speed at different regions of the work piece surface. For example, if a disk work piece rotates with a constant angular velocity (CAV) relative to the beam, the linear surface speed relative to the beam impact point increases in proportion to increasing radial distance of that point from the center of the disk. To provide uniform exposure dose, the duty cycle of pulses of the exposure beam are varied in accord with radial distance.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Seat supporting assembly and wheelchair including same
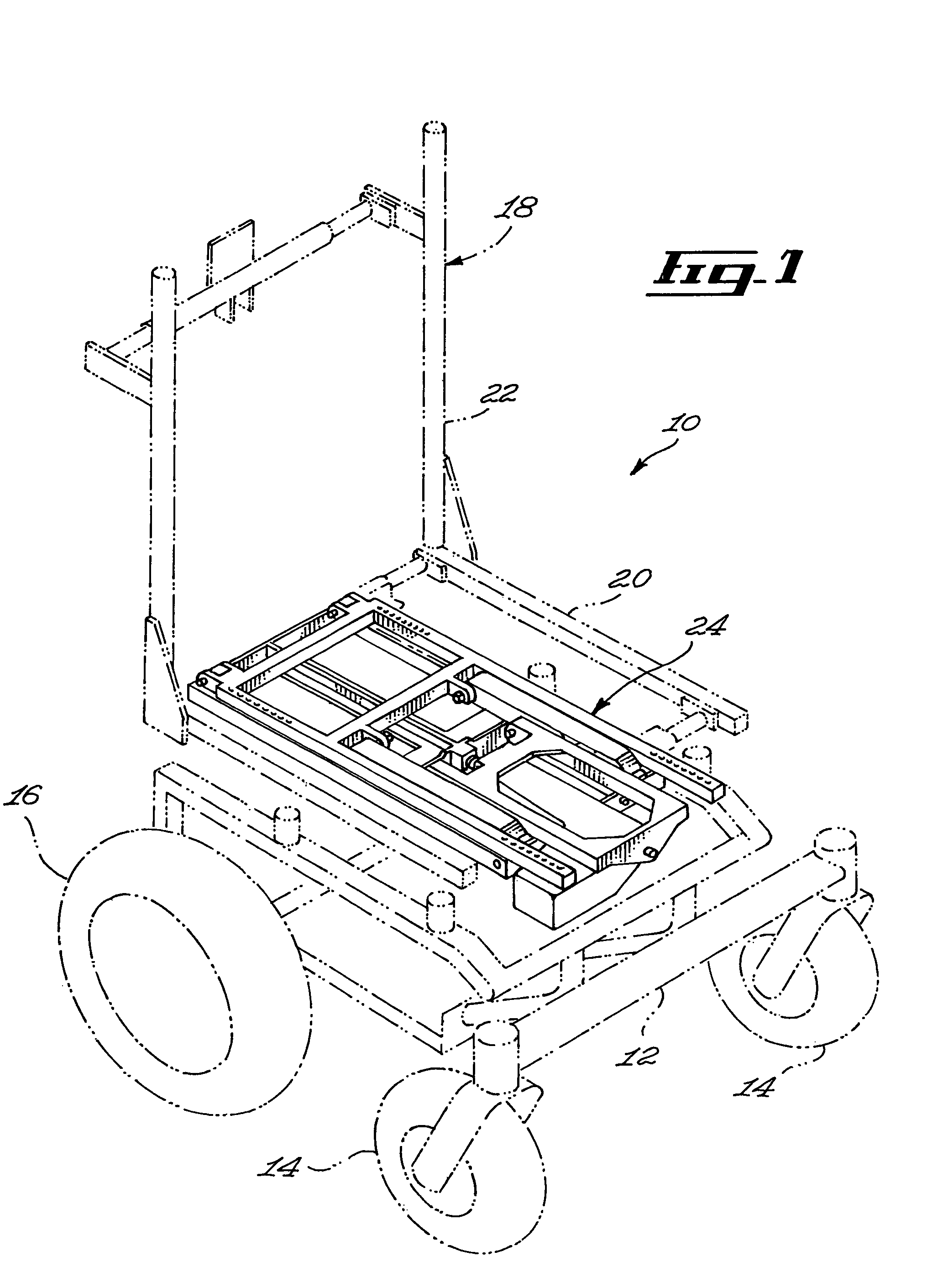
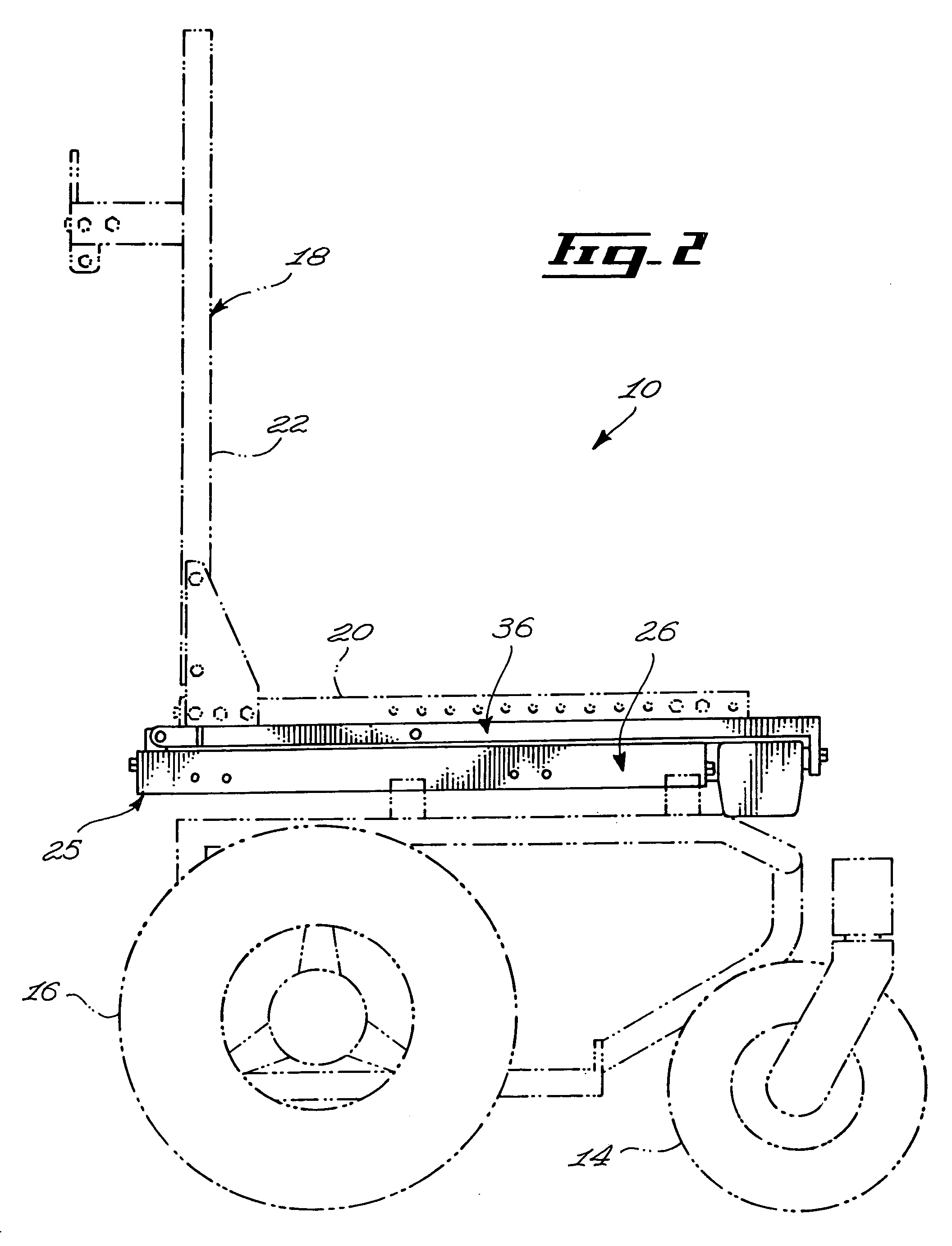
ActiveUS8297641B2Reduce needDecrease shiftCarriage/perambulator accessoriesOperating chairsWheelchairEngineering
A seat supporting assembly (24) for supporting a seat (18), the assembly comprising a base (25) including a substantially elongated guiding rod (58), a seat support (36), a seat support-to-base linking member (56) pivotally coupled to the seat support (36) and sliding on the base guiding rod (58), a substantially elongated tilting member (60) having a guiding groove (66) and being pivotally attached to the seat support (36) and to the base (25). An actuating assembly (44) is coupled to the base (25) and includes a motion transmitting member (68) mounted within the guiding groove (60). The force from the actuating assembly moves the tilting member (60) according to the geometry of the guiding groove (66), which causes the seat supporting assembly (24) to move between tilted and upright configurations by pivoting the tilting member (60) relative to the seat support (36) and the base (25) and substantially simultaneously moving the seat support-to-base linking member (56) longitudinally relative to the guiding rod (58). The assembly is designed to maintain the location of the center of gravity of a user as the seat tilts rearwardly by automatically moving the seat forwardly during tilting. The guiding groove (66) in the tilting member (60) may be curved such that the tilting motion occurs with a constant angular velocity The seat assembly is particularly useful for wheelchairs.
Owner:AMYLIOR
Optical recording method and apparatus for an optical storage medium
InactiveUS7061847B2Simple power controlEasy to implementRecording strategiesTelevision system detailsLight beamEngineering
In an optical recording method and apparatus for an optical storage medium, a recording pulse pattern having a sequence of multiple pulses is used to record one of plural kinds of marks with different lengths on the storage medium through a variable-linear-velocity recording process or a constant-angular-velocity recording process. Two or more discrete write powers are individually allocated to the respective pulses of the recording pulse pattern. Each of the write powers, allocated to the respective pulses of the recording pulse pattern, is linearly varied in proportion with a change of one of the recording linear velocity and a recording position of the storage medium. The resulting recording pulse pattern is supplied to a pickup, and the pickup emits a light beam to the storage medium in accordance with the recording pulse pattern having the linearly varied write powers allocated to the respective pulses, so that one of the plural kinds of marks is recorded on the storage medium.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method and apparatus for ultra-fast aperture exposure
InactiveUS6850351B1Lower performance requirementsMinimize dynamic loadShuttersOptical elementsOptical axisUltra fast
An apparatus and method for extremely fast opening and closing of an exposure path or optical axis. Two disk-shaped shutters are coaxially rotated in opposite directions at an initial synchronous speed so as to dynamically align openings in the discs at an angular position offset from the exposure path. The angular speeds of two of the disks are selectively increased and decreased to dynamically align the openings with the exposure path. A third masking disk may be provided, which rotates coaxially with the other two at a constant angular speed less than the angular speeds of the other two disks, to permit the invention to rapidly open and close two or more separate optical paths.
Owner:TEAM SPECIALTY PROD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com